Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
931 results about "Lignocellulosic biomass" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Lignocellulose refers to plant dry matter (biomass), so called lignocellulosic biomass. It is the most abundantly available raw material on the Earth for the production of biofuels, mainly bio-ethanol. It is composed of carbohydrate polymers (cellulose, hemicellulose), and an aromatic polymer (lignin). These carbohydrate polymers contain different sugar monomers (six and five carbon sugars) and they are tightly bound to lignin. Lignocellulosic biomass can be broadly classified into virgin biomass, waste biomass and energy crops. Virgin biomass includes all naturally occurring terrestrial plants such as trees, bushes and grass. Waste biomass is produced as a low value byproduct of various industrial sectors such as agriculture (corn stover, sugarcane bagasse, straw etc.) and forestry (saw mill and paper mill discards). Energy crops are crops with high yield of lignocellulosic biomass produced to serve as a raw material for production of second generation biofuel; examples include switch grass(Panicum virgatum) and Elephant grass.
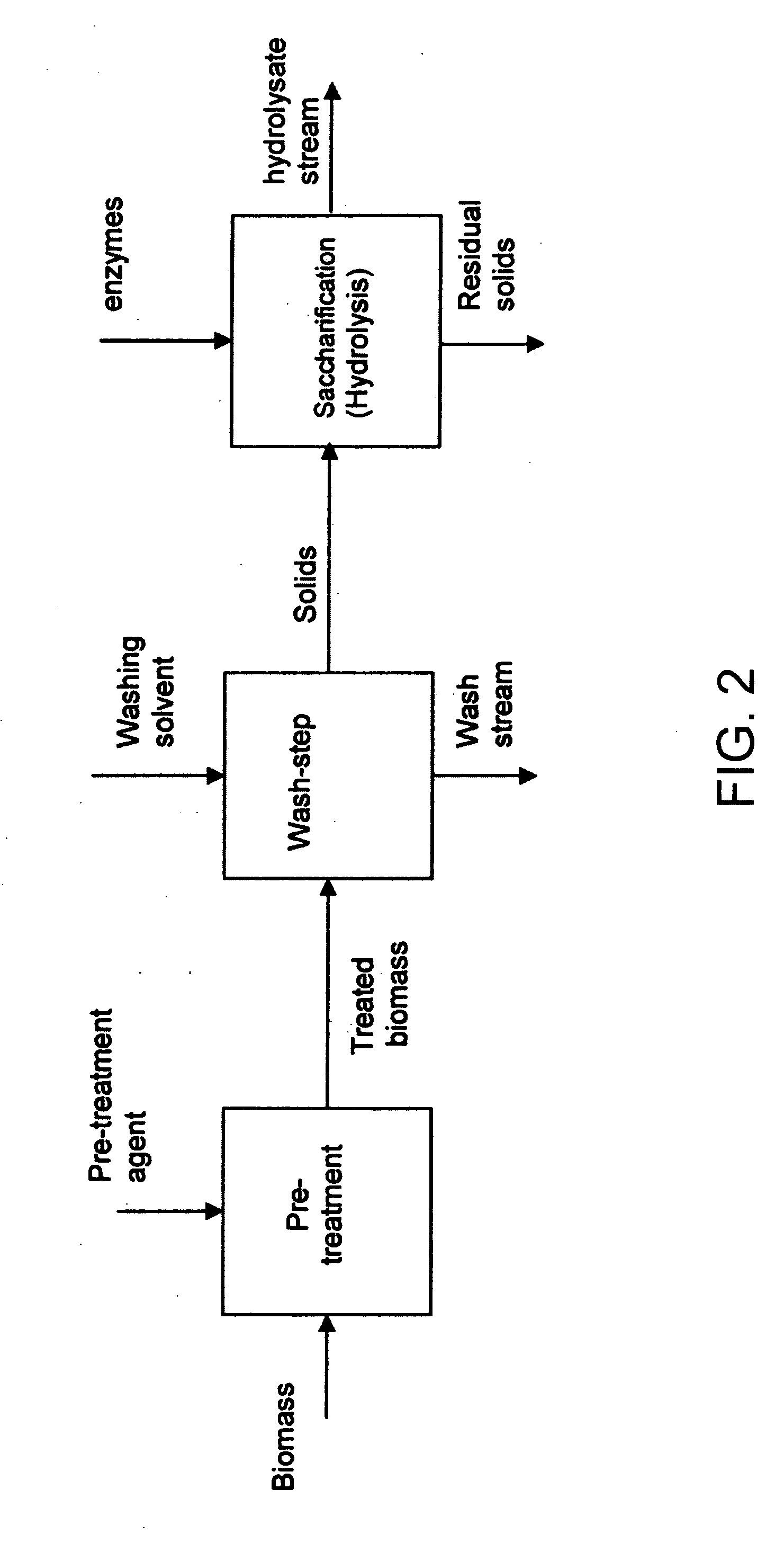
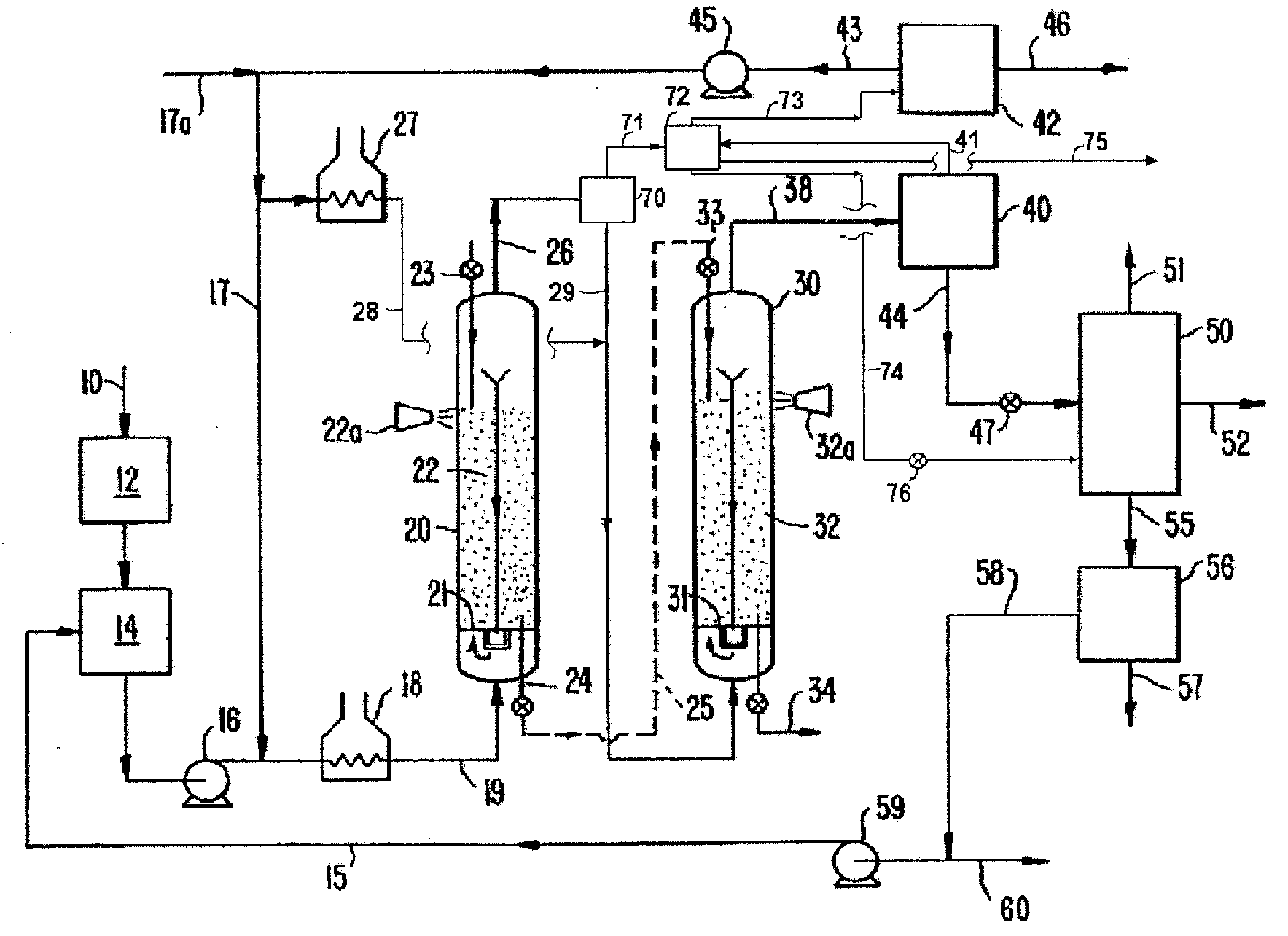
Method for processing lignocellulosic material
InactiveUS6555350B2High degreeReduce water consumptionSludge treatment by oxidationBiofuelsCelluloseWater flow
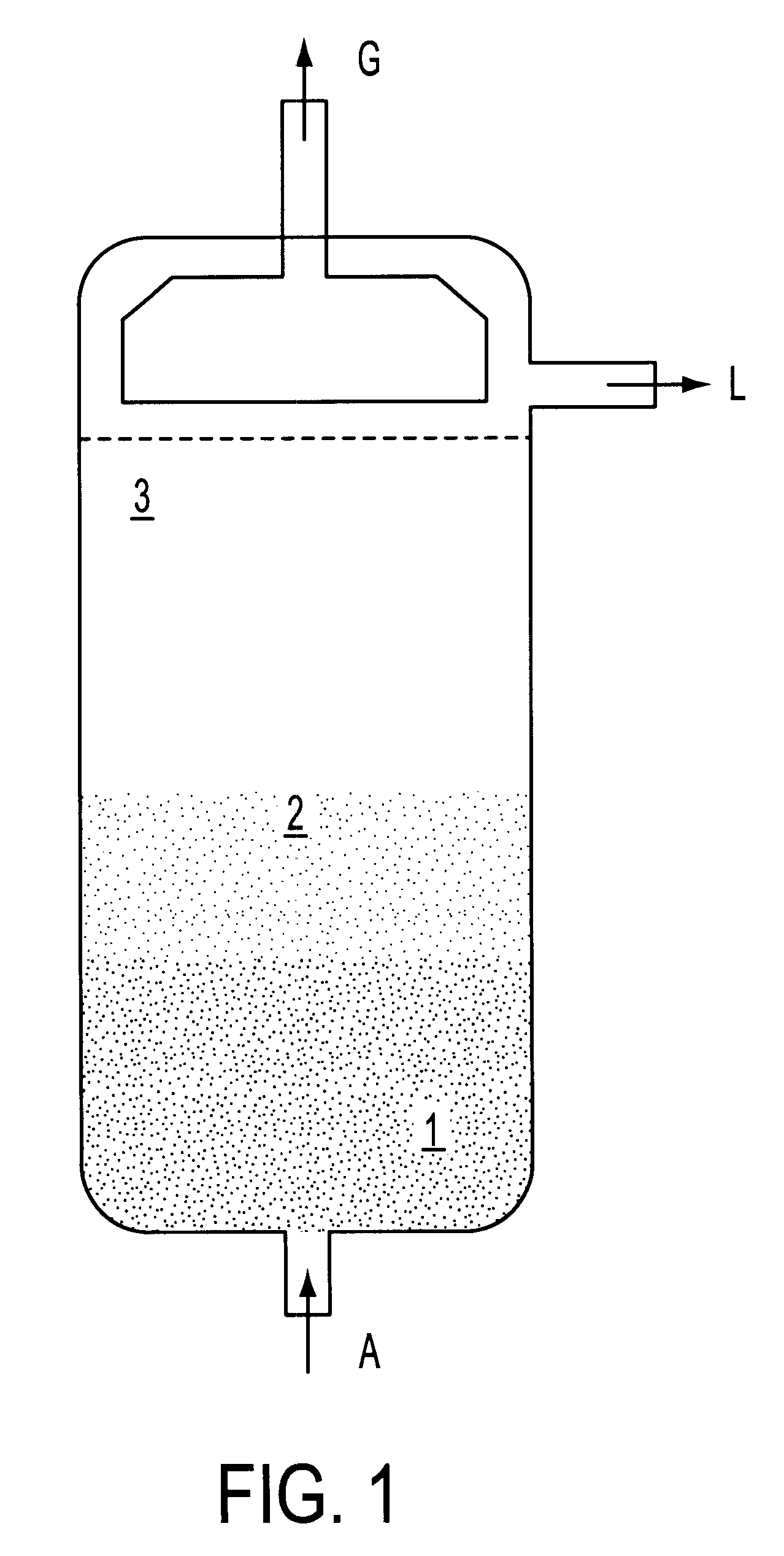
A method wherein lignocellulosic biomass materials are converted into combustible fuel products. In particular, the method is a continuous process, involving wet oxidation or steam explosion, for fermentatively converting such biomass materials into ethanol using a process design that permits all or part of the process water from the ethanol fermentation process to be recycled to reduce the consumption of process water. The effluent from the ethanol fermentation step may be subjected to an anaerobic fermentation step generating methane and a water effluent in which the amount of potentially inhibitory substances is at a sub-inhibitory level, which in turn permits all or part of the effluent water from the anaerobic fermentation step to be recycled into the process.
Owner:POET RES INC
Integrated process for separation of lignocellulosic components to fermentable sugars for production of ethanol and chemicals
InactiveUS20080057555A1Robust and cost-effectiveImprove responseChemical industryBiofuelsChemical treatmentButanediol
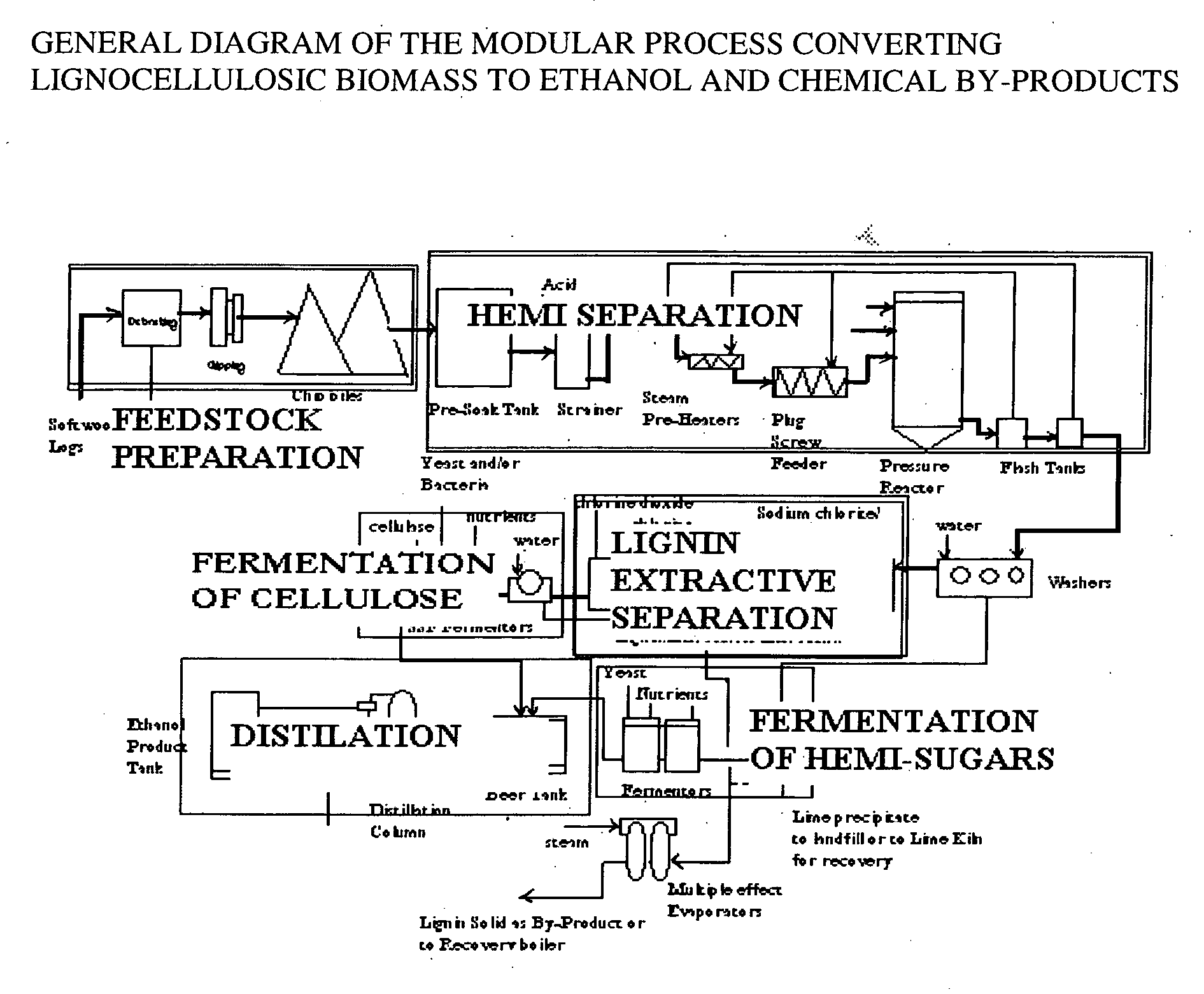
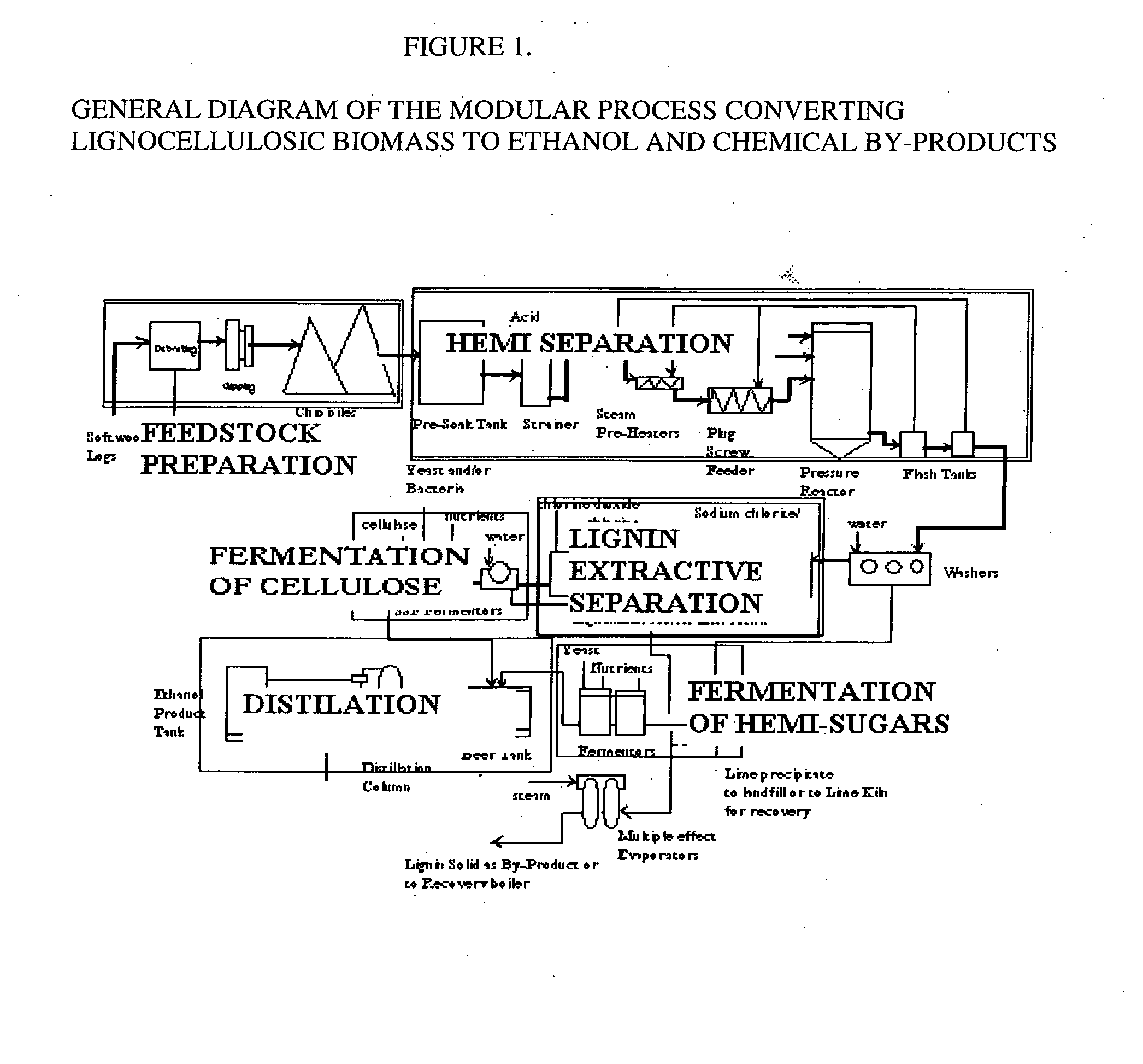
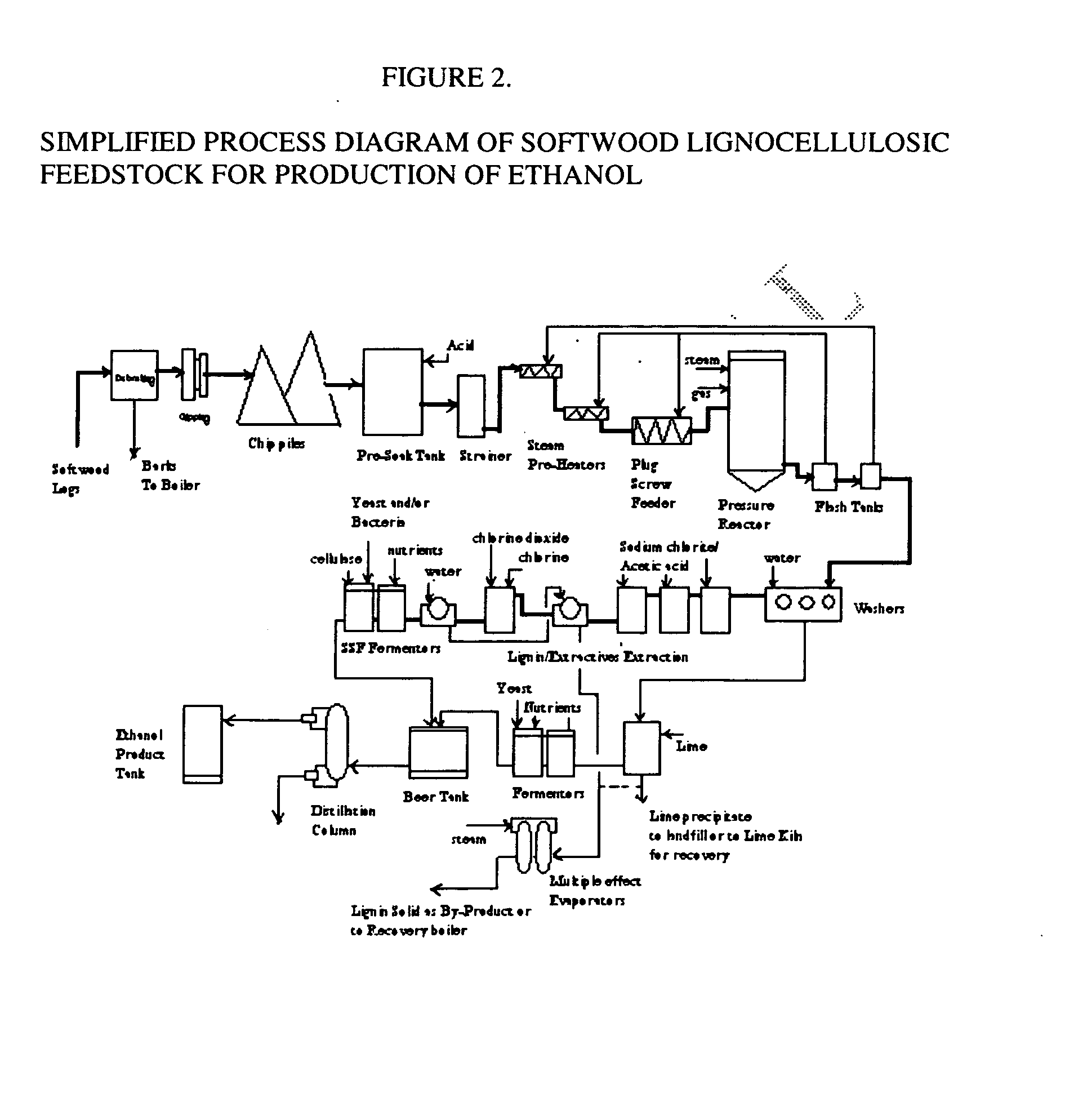
A continuous and modular process converts lignocellulosic materials for the production of ethanol principally and / or chemicals such as methanol, butanediol, propanediol, hydrocarbon fuel, etc. Renewable lignocellulosic biomass such as but not all inclusive hardwoods (gum, beech, oak, sweet gum, poplar, eucalyptus, etc.), soft woods (pines, firs, spruce, etc.), corn stovers, straws, grasses, recycled papers, waste products from pulp and paper mills, etc can be used as feedstock. The process is designed to be modular and the feed entry point can be selected to adapt to different biomass feedstock. Lignocellulosic biomass such as hardwood and softwood are subjected to chemical / pressure treatment stages using potent and selective chemicals such as sodium chlorite / acetic acid (anhydrous) and chlorine / chlorine dioxide to separate the main components—lignin, cellulose (glucose) and hemicelluloses (xylose, arabinose, galactose)—into three process streams. The separated carbohydrates are further subjected to washing, cleaning, neutralization, and / or mild hydrolysis and subsequently fermented to produce ethanol. Residual lignin and extractives remained with the cellulose are removed by chemical treatment steps to enhance the fermentations of cellulose. Pre-hydrolysate after neutralization to neutralize and remove toxic components such as acetic acid, furfural, phenolics, etc. containing (xylose, arabinose, galactose) and hexoses (glucose) can be either separately or together with the purified cellulosic fraction fermented to produce ethanol. Approximately 100 gallons of ethanol, suitable to be used as a fuel, can be produced from one dried ton of wood. Significant amount of lignin are separated as a by-product and can be converted to hydrocarbon fuel, surfactant, drilling aid, or can be incinerated for generation of power and steam.
Owner:NGUYEN XUAN NGHINH
Procedure for the production of ethanol from lignocellulosic biomass using a new heat-tolerant yeast
InactiveUS20050069998A1Low conversion rateReduce yieldFungiBiological substance pretreatmentsFiltrationSolid fraction
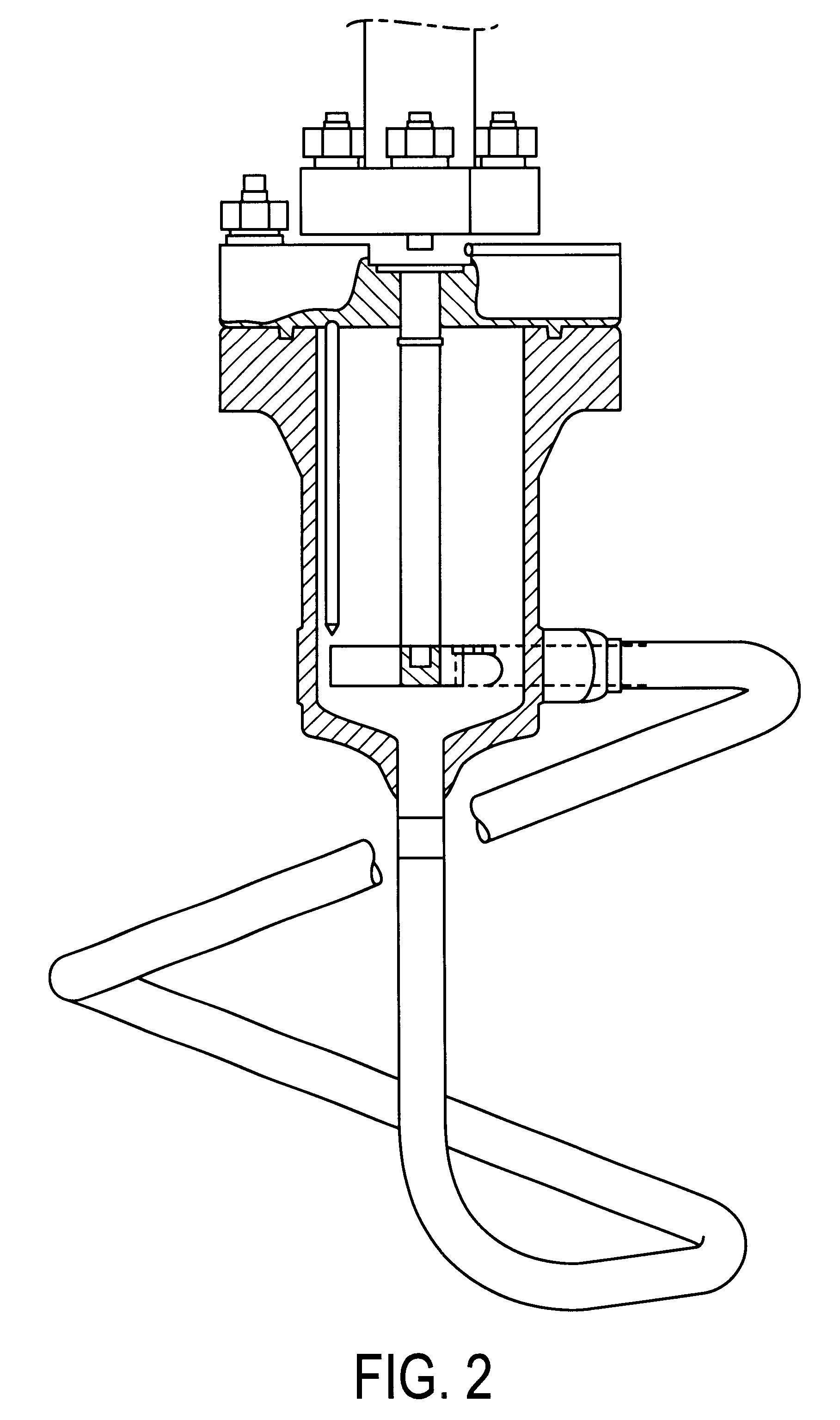
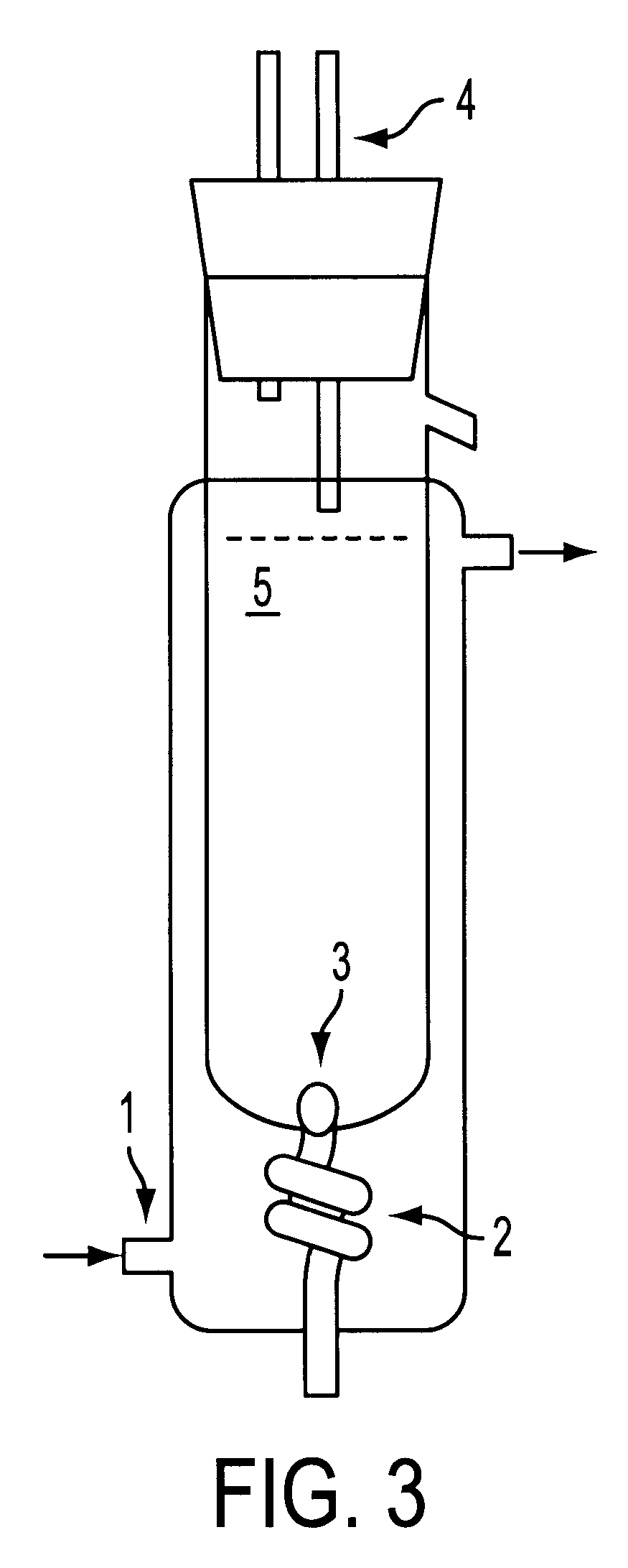
It includes the stages of grinding the lignocellulosic biomass to a size of 15-30 mm, subjecting the product obtained to steam explosion pre-treatment at a temperature of 190-230° C. for between 1 and 10 minutes in a reactor (2), collecting the pre-treated material in a cyclone (3) and separating the liquid and solid fractions by filtration in a filter press (9), introducing the solid fraction in a fermentation deposit (10), adding a cellulase at a concentration of 15 UFP per gram of cellulose and 12.6 International Units of β-glucosidase enzyme dissolved in citrate buffer pH 4.8, inoculating the fermentation deposit (10) with a culture of the heat-tolerant bacteria Kluyveromyces marxianus CECT 10875, obtained by chemical mutagenesis from strain DER-26 of Kluyveromyces marxianus and shaking the mixture for 72 hours at 42° C.
Owner:CENT DE INVESTIGACIONES ENERGETICAS MEDIO AMBIENTALLES Y TECNOLOGICAS (C I E M A T)
Biomass pretreatment
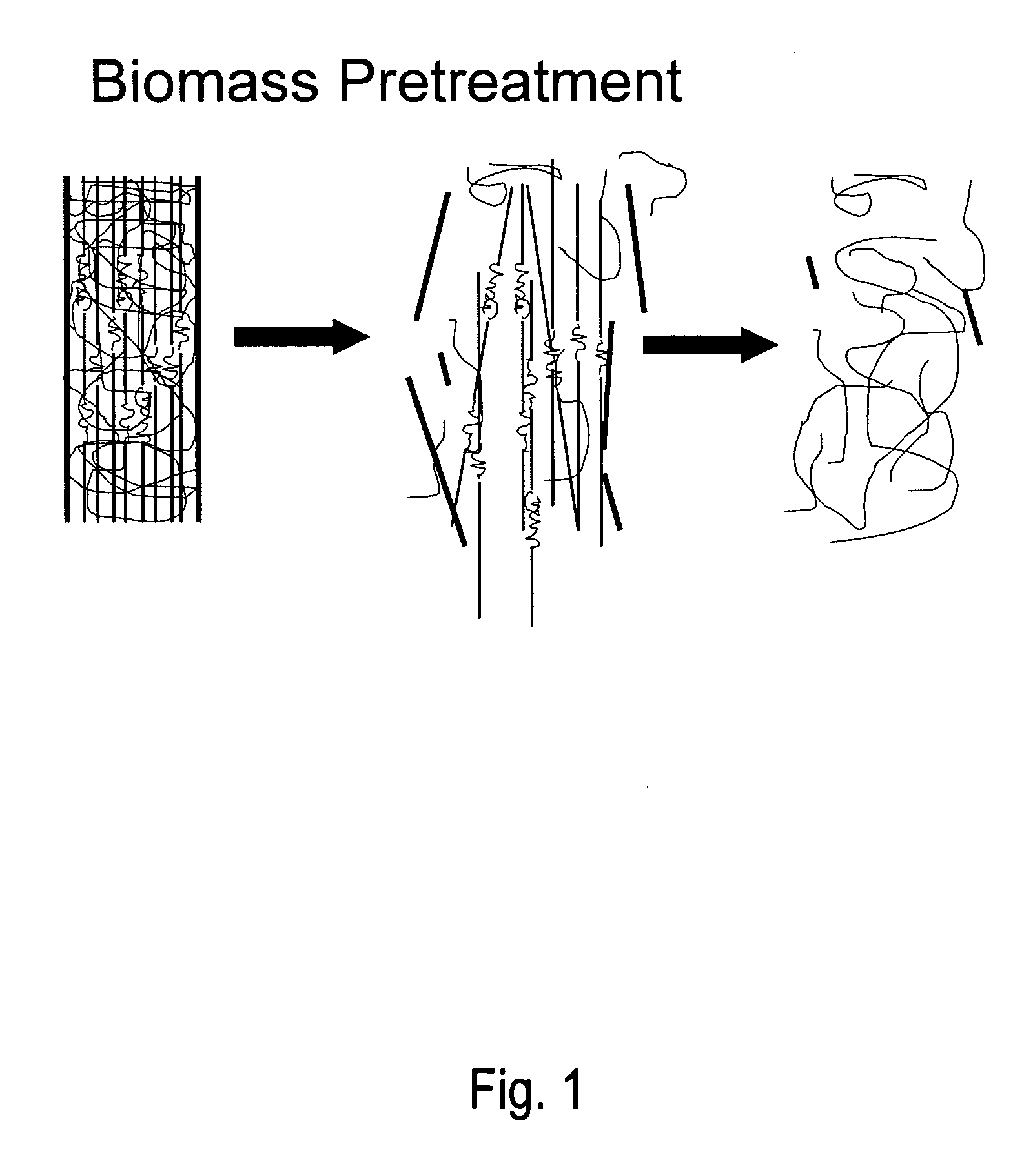
A method for lignocellulose conversion to sugar with improvements in yield and rate of sugar production has been developed by using ionic liquid pretreatment. This new pretreatment strategy substantially improves the efficiency (in terms of yield and reaction rates) of saccharification of lignocellulosic biomass. Cellulose and hemicellulose, when hydrolyzed into their sugars, can be converted into ethanol fuel through well established fermentation technologies. These sugars also form the feedstocks for production of variety of chemicals and polymers. The complex structure of biomass requires proper pretreatment to enable efficient saccharification of cellulose and hemicellulose components to their constituent sugars. Current pretreatment approaches suffer from slow reaction rates of cellulose hydrolysis (by using the enzyme cellulase) and low yields.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO +1
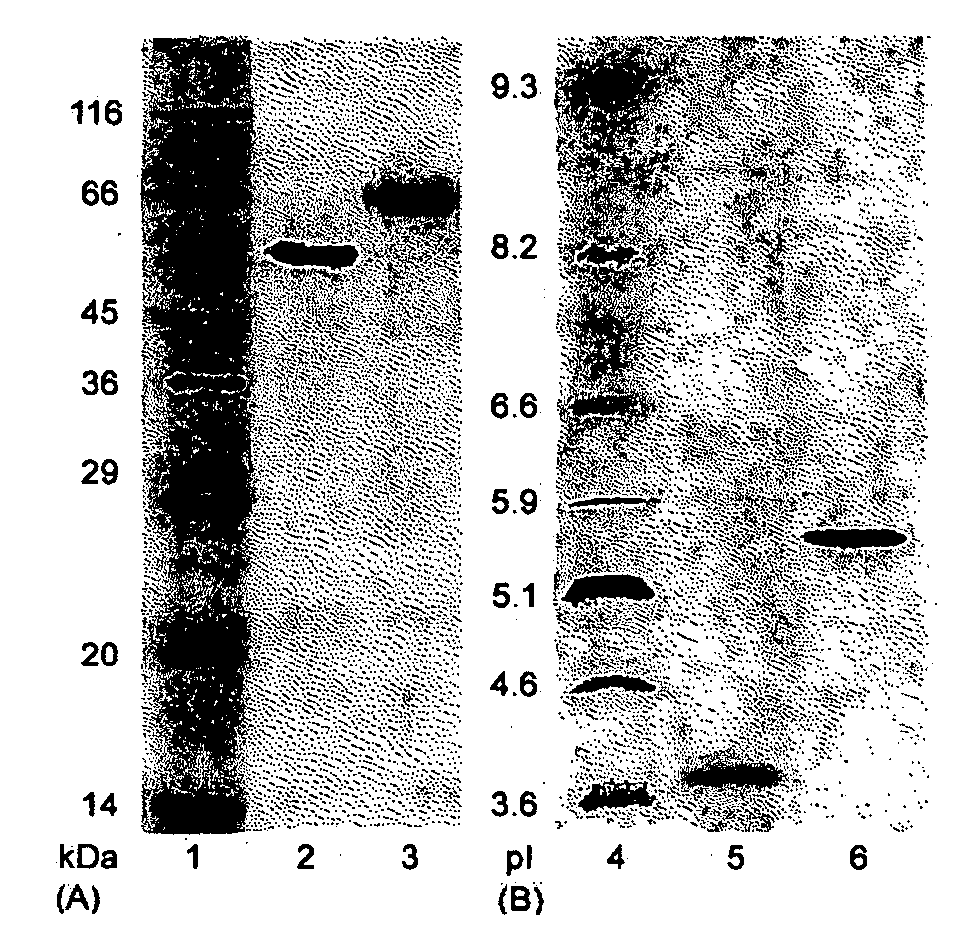
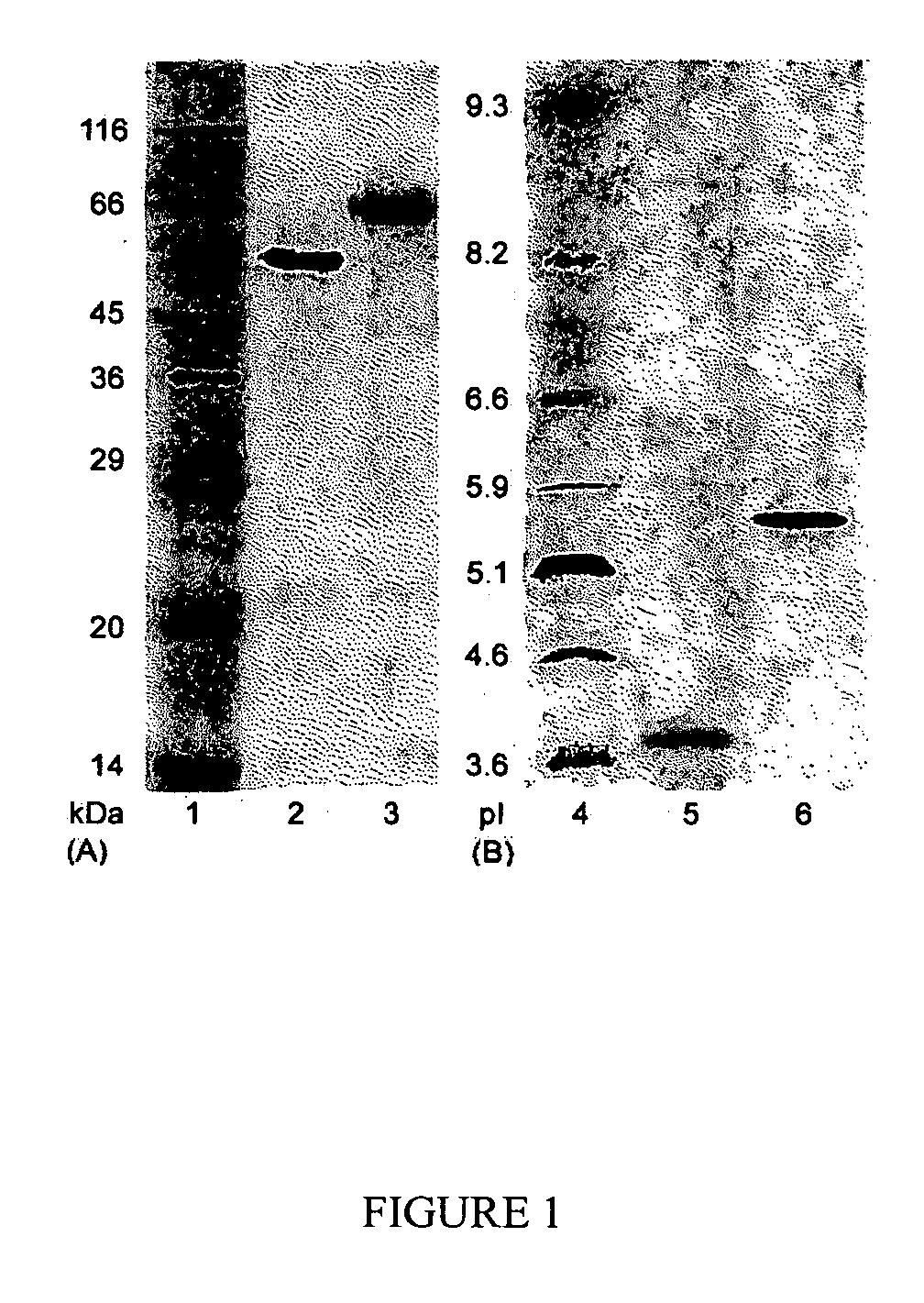
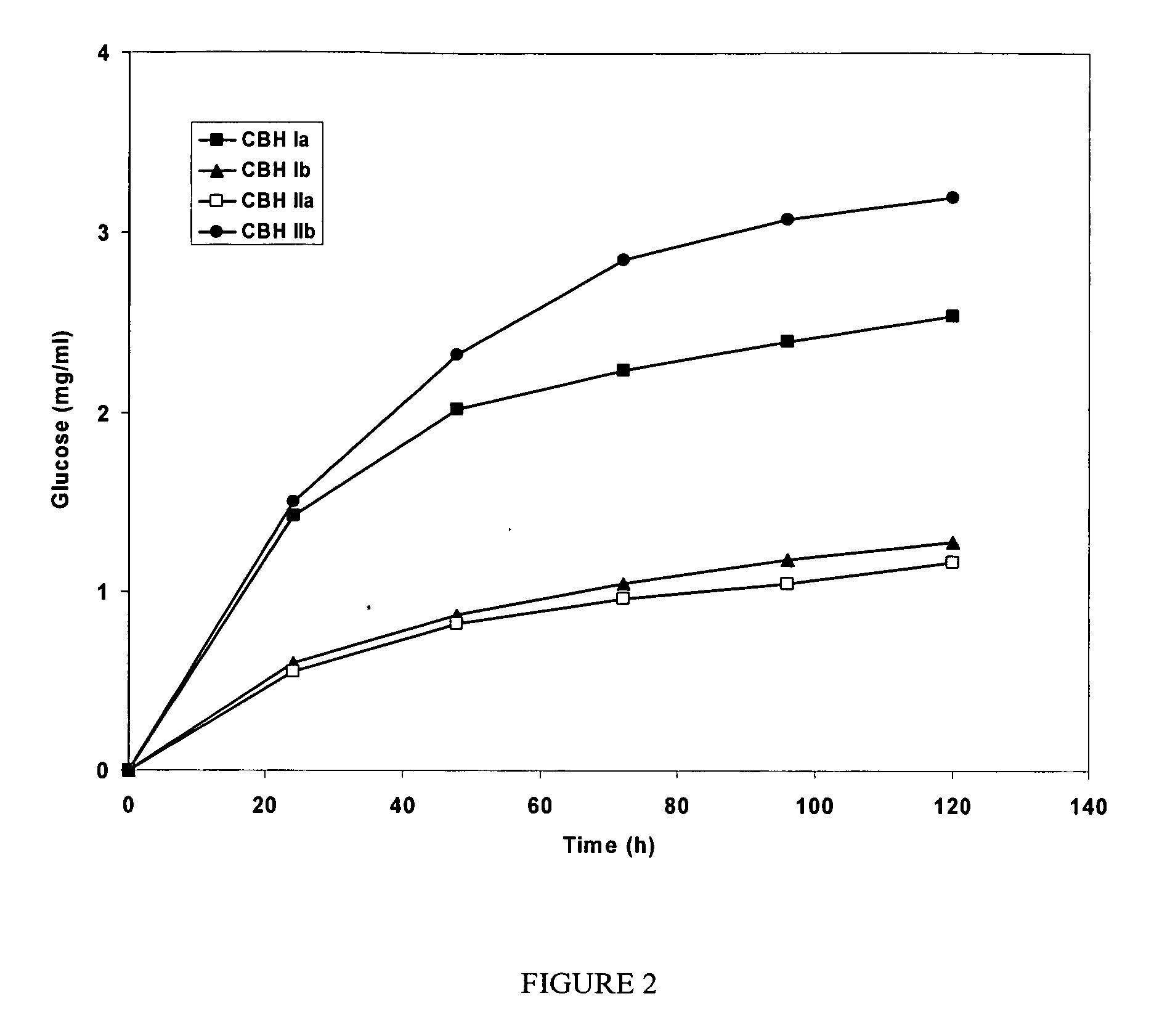
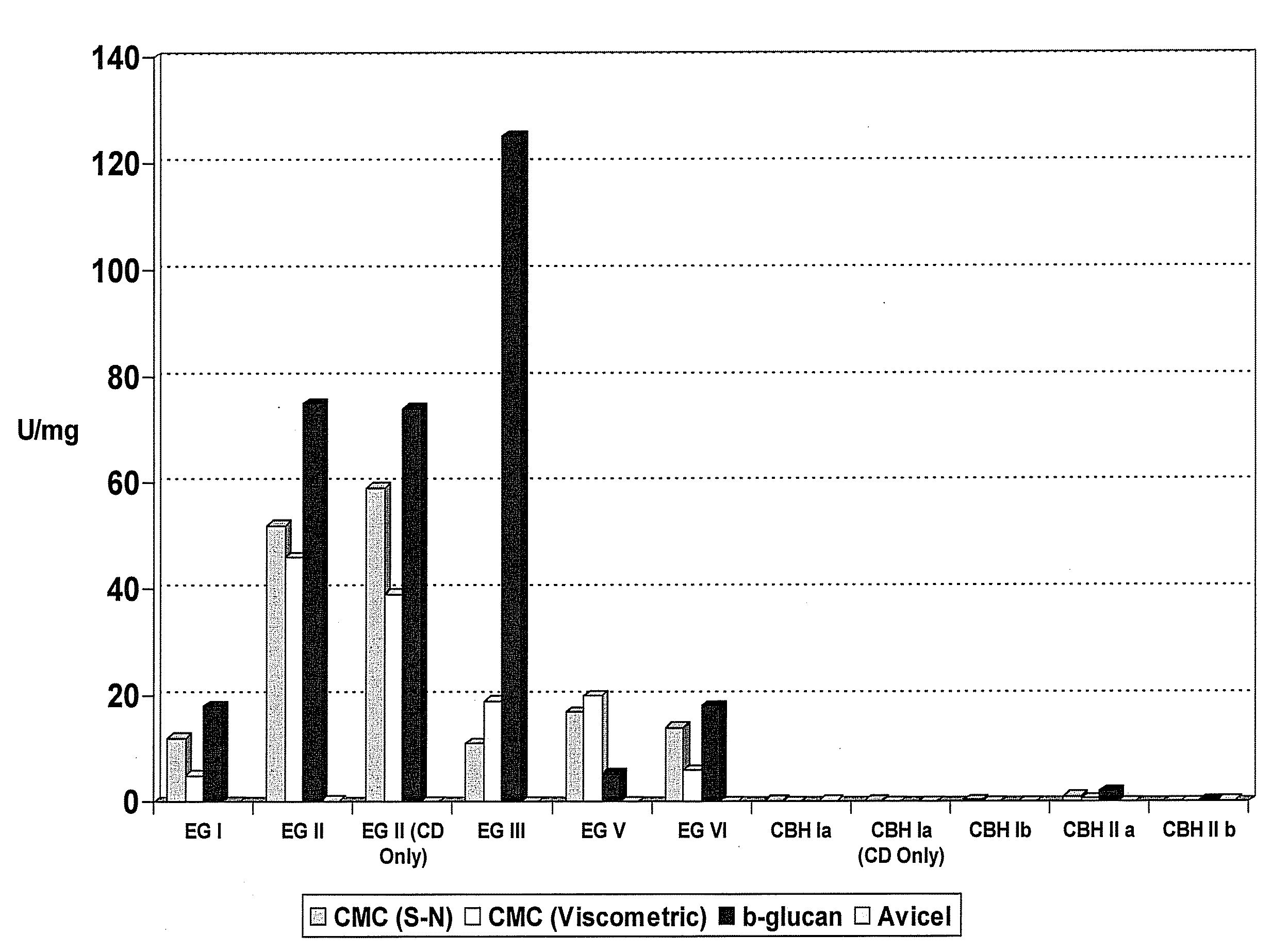
Construction of highly efficient cellulase compositions for enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose
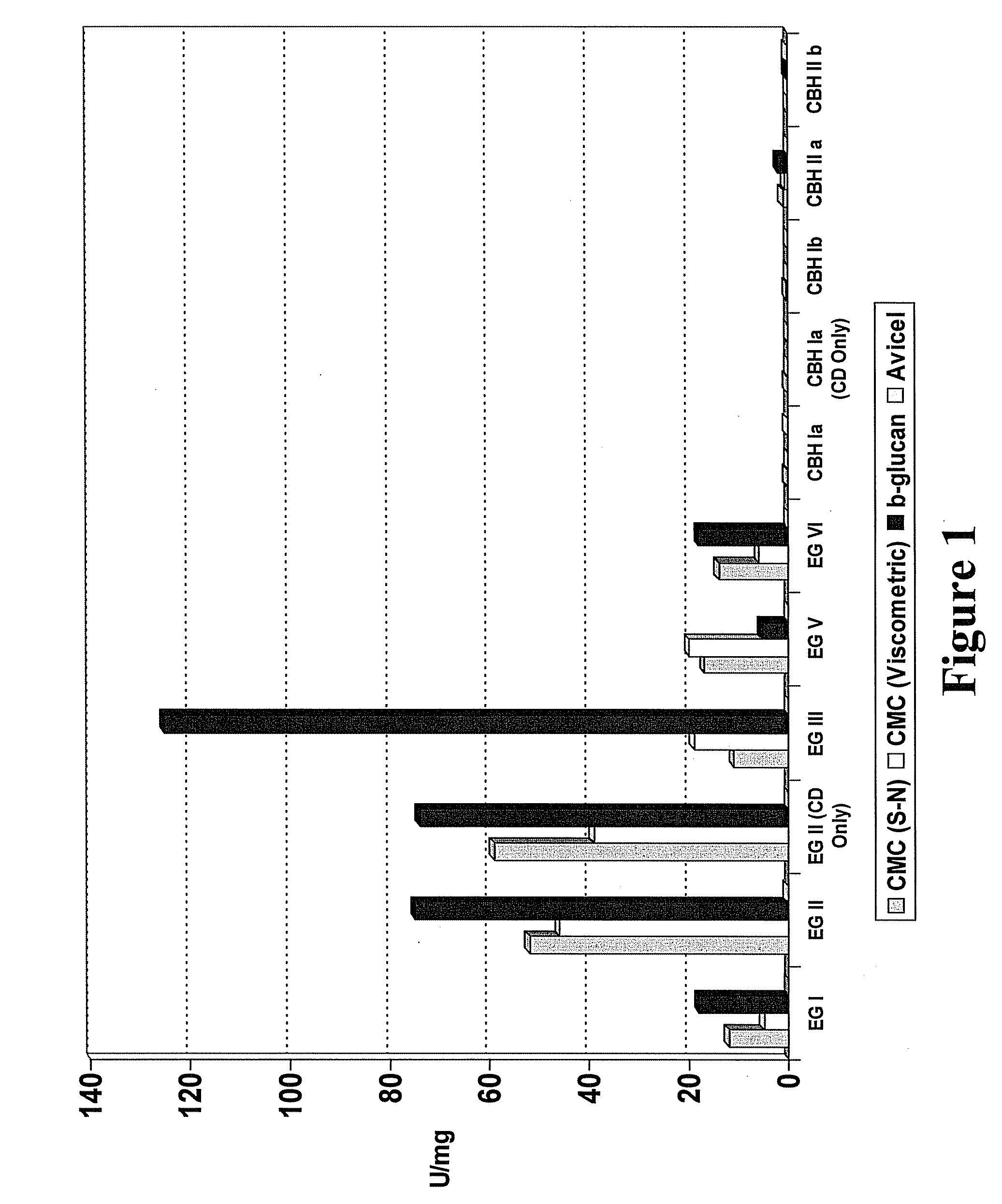
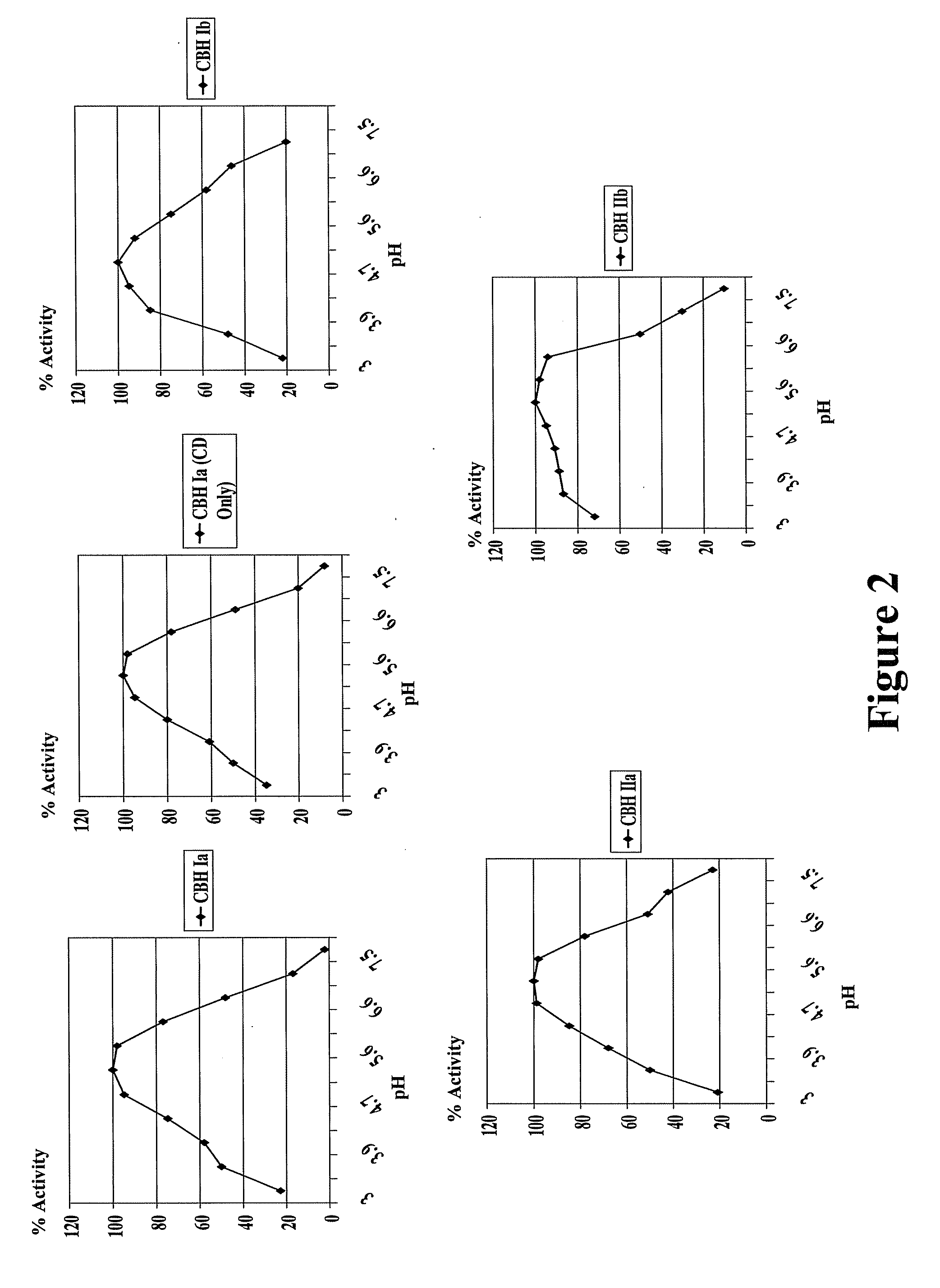
This invention provides novel enzyme compositions using newly identified and isolated C. lucknowense enzymes, including CBH Ib CBH IIb, EG II, EG VI, β-glucosidase, and xylanase II in conjunction with previously identified enzymes CBH Ia, CBH IIa (previously described as Endo 43), and EG V. These enzyme compositions demonstrate an extremely high ability to convert lignocellulosic biomass (e.g., Avicel, cotton, Douglas fir wood pretreated by organosolv) to glucose. CBH Ia and IIb, which both have a cellulose-binding module (CBM) displayed a pronounced synergism with three major endoglucanases (EG II, EG V, EG VI) from the same fungus in hydrolysis of cotton as well as a strong synergy with each other. The enzyme compositions are effective in hydrolysis of the lignocellulosic biomass.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Novel Fungal Enzymes
This invention relates to novel enzymes and novel methods for producing the same. More specifically this invention relates to a variety of fungal enzymes. Nucleic acid molecules encoding such enzymes, compositions, recombinant and genetically modified host cells, and methods of use are described. The invention also relates to a method to convert lignocellulosic biomass to fermentable sugars with enzymes that degrade the lignocellulosic material and novel combinations of enzymes, including those that provide a synergistic release of sugars from plant biomass. The invention also relates to a method to release cellular content by degradation of cell walls. The invention also relates to methods to use the novel enzymes and compositions of such enzymes in a variety of other processes, including washing of clothing, detergent processes, biorefining, deinking and biobleaching of paper and pulp, and treatment of waste streams.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
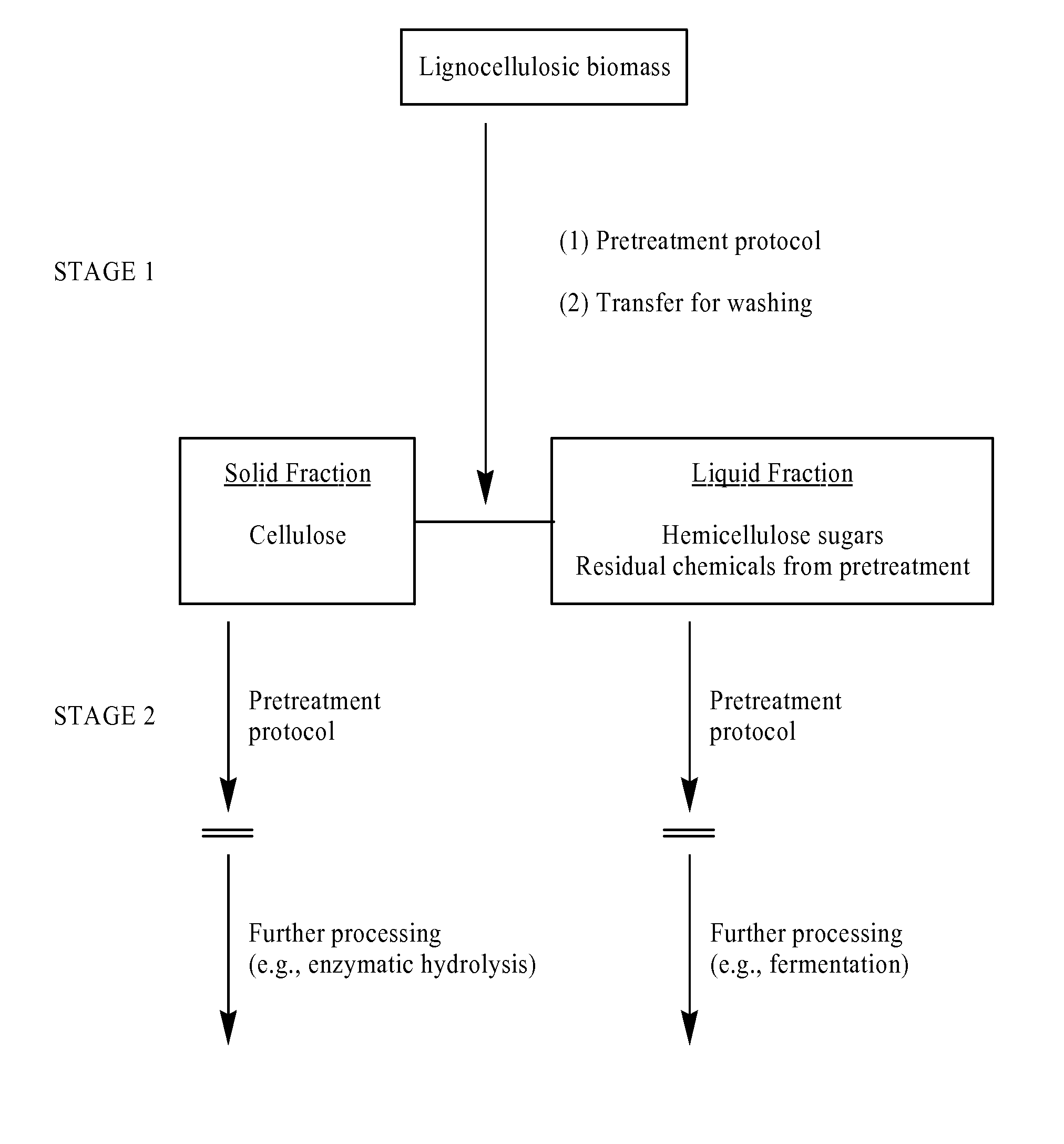
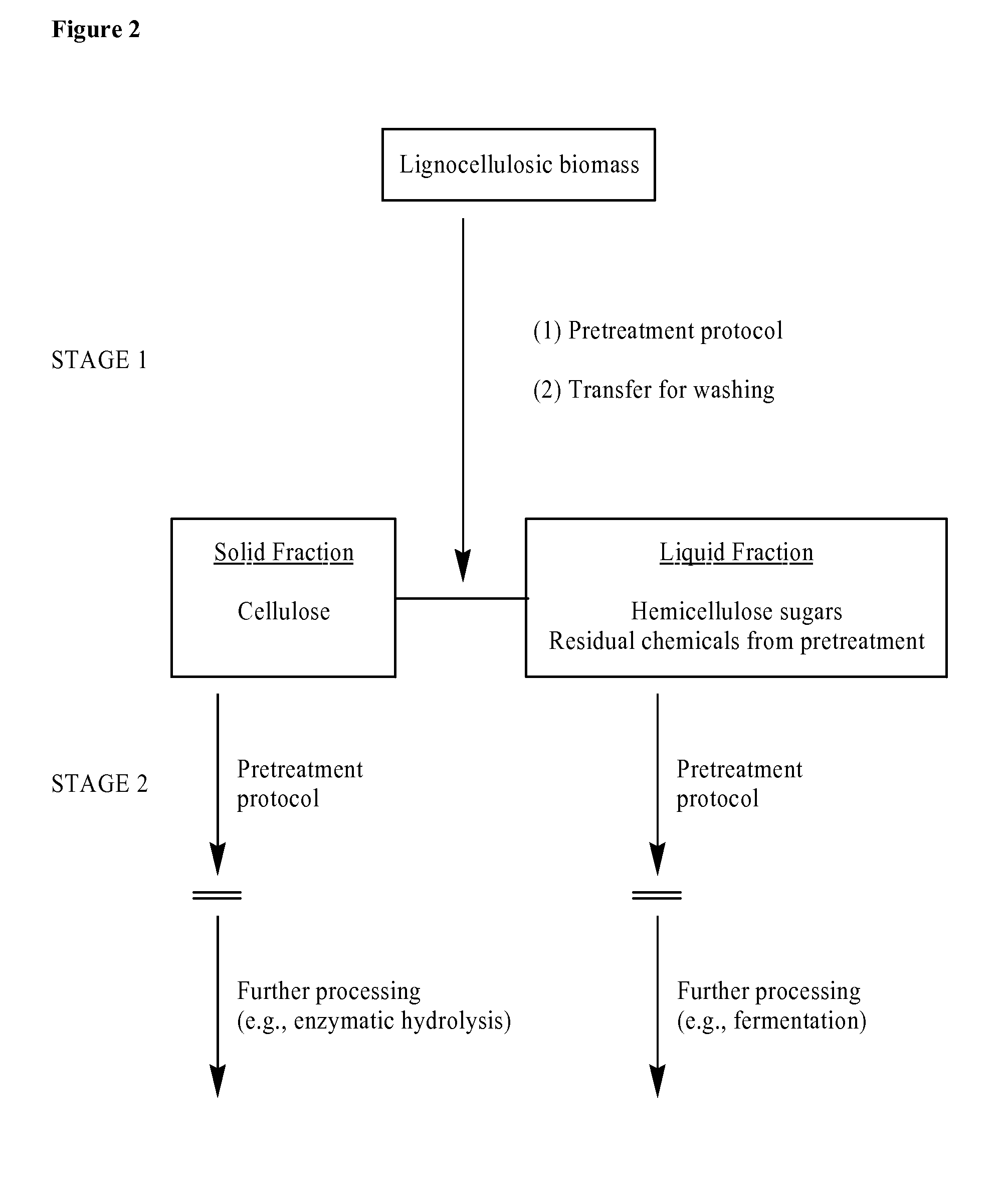
Two-stage method for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass
InactiveUS20100279361A1Reduce decreaseMaximize efficiencyOrganic compound preparationFood processingCelluloseFiber
One aspect of the invention relates to a process, comprising treating lignocellulosic biomass according to a first pretreatment protocol, thereby generating a first product mixture; separating the first product mixture into a first plurality of fractions; and treating at least one fraction of said first plurality of fractions according to a second pretreatment protocol, thereby generating a second product mixture. In one embodiment, the lignocellulosic biomass is selected from the group consisting of grass, switch grass, cord grass, rye grass, reed canary grass, miscanthus, sugar-processing residues, sugarcane bagasse, agricultural wastes, rice straw, rice hulls, barley straw, corn cobs, cereal straw, wheat straw, canola straw, oat straw, oat hulls, corn fiber, stover, soybean stover, corn stover, forestry wastes, recycled wood pulp protocol protocol fiber, paper sludge, sawdust, hardwood, softwood, and combinations thereof.
Owner:MASCOMA CORPORATION
Ethanol production with dilute acid hydrolysis using partially dried lignocellulosics
InactiveUS20030199049A1Increase sugar yieldImprove digestibilityBiofuelsWaste based fuelCelluloseGrowth phase
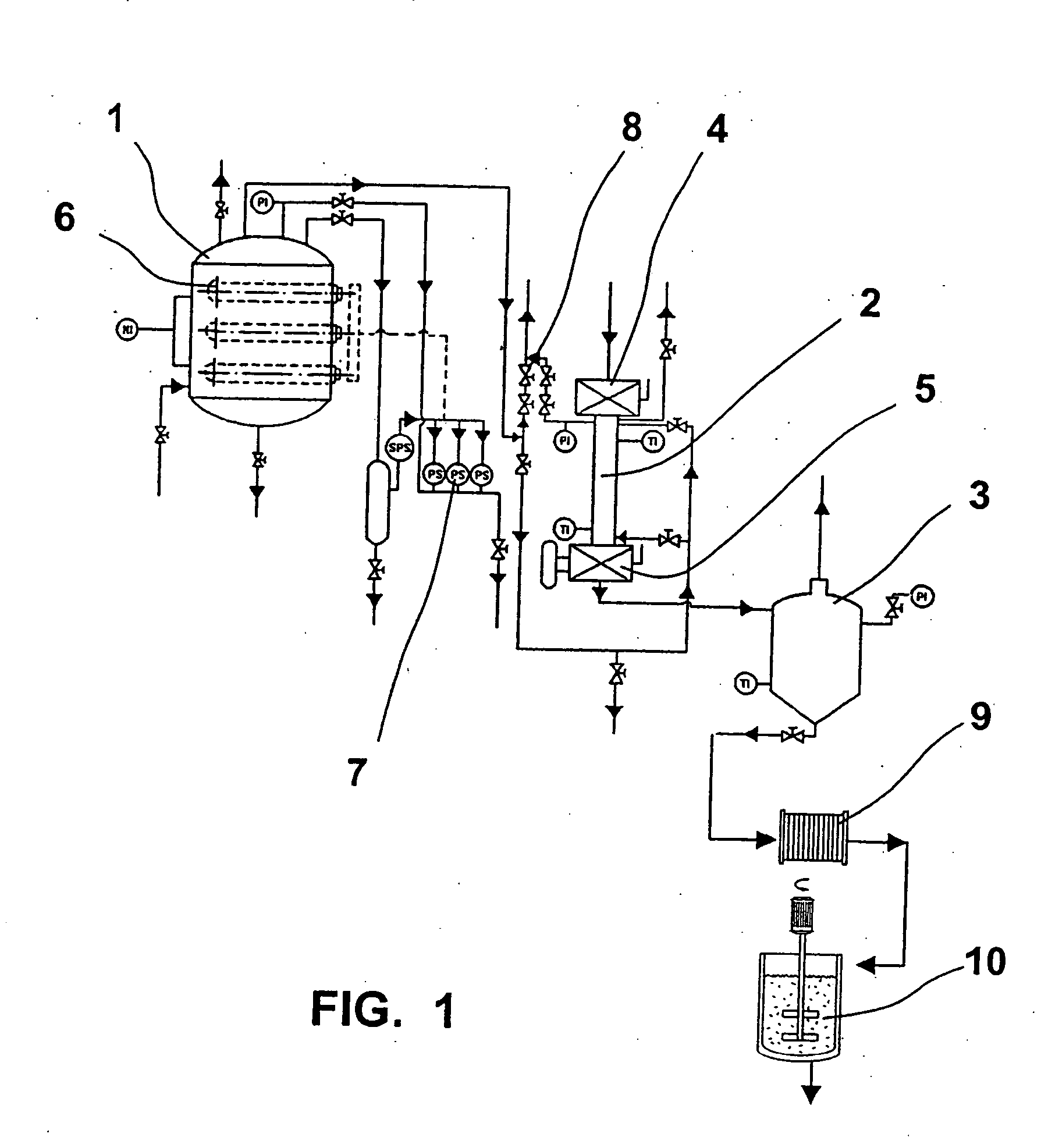
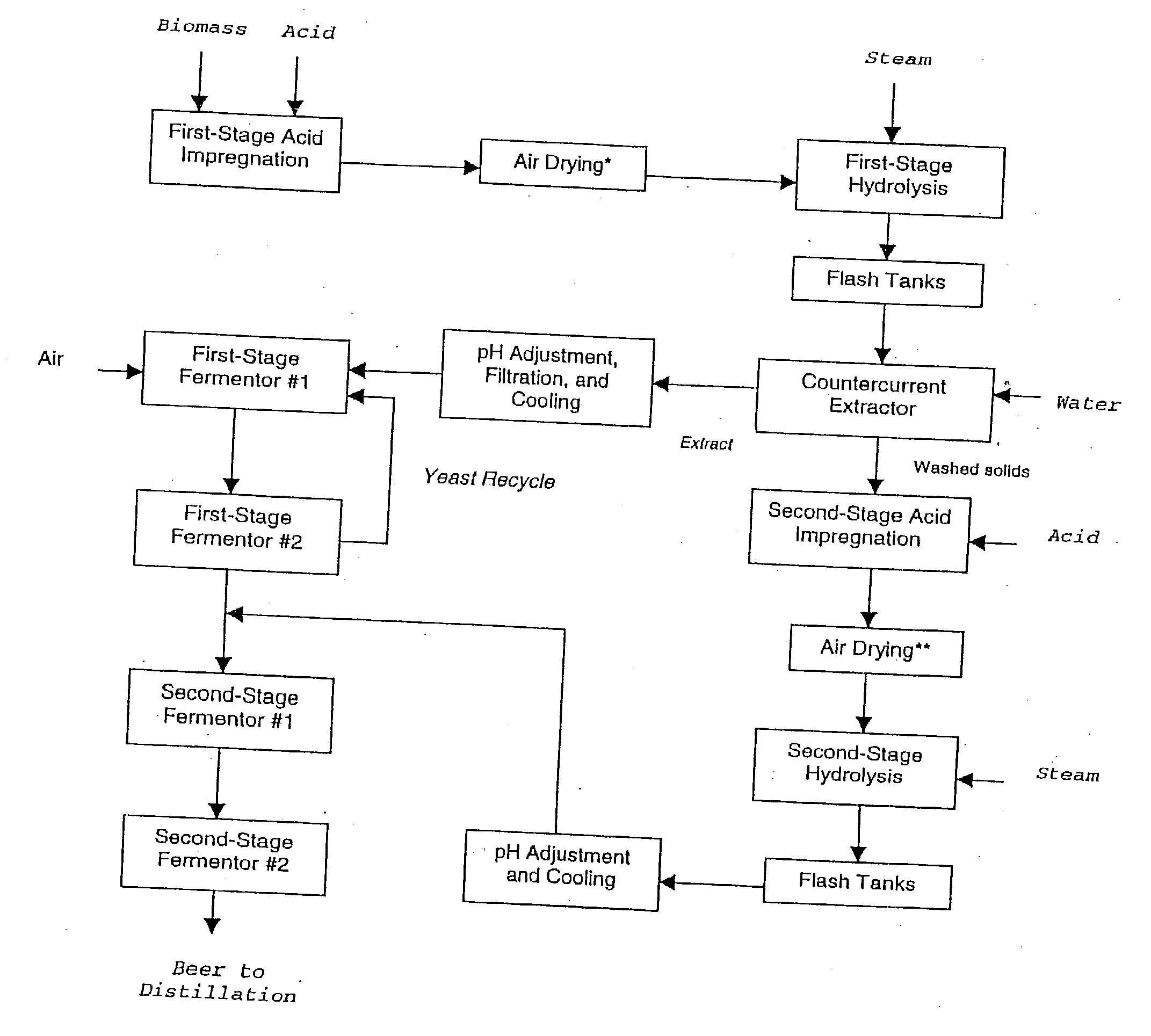
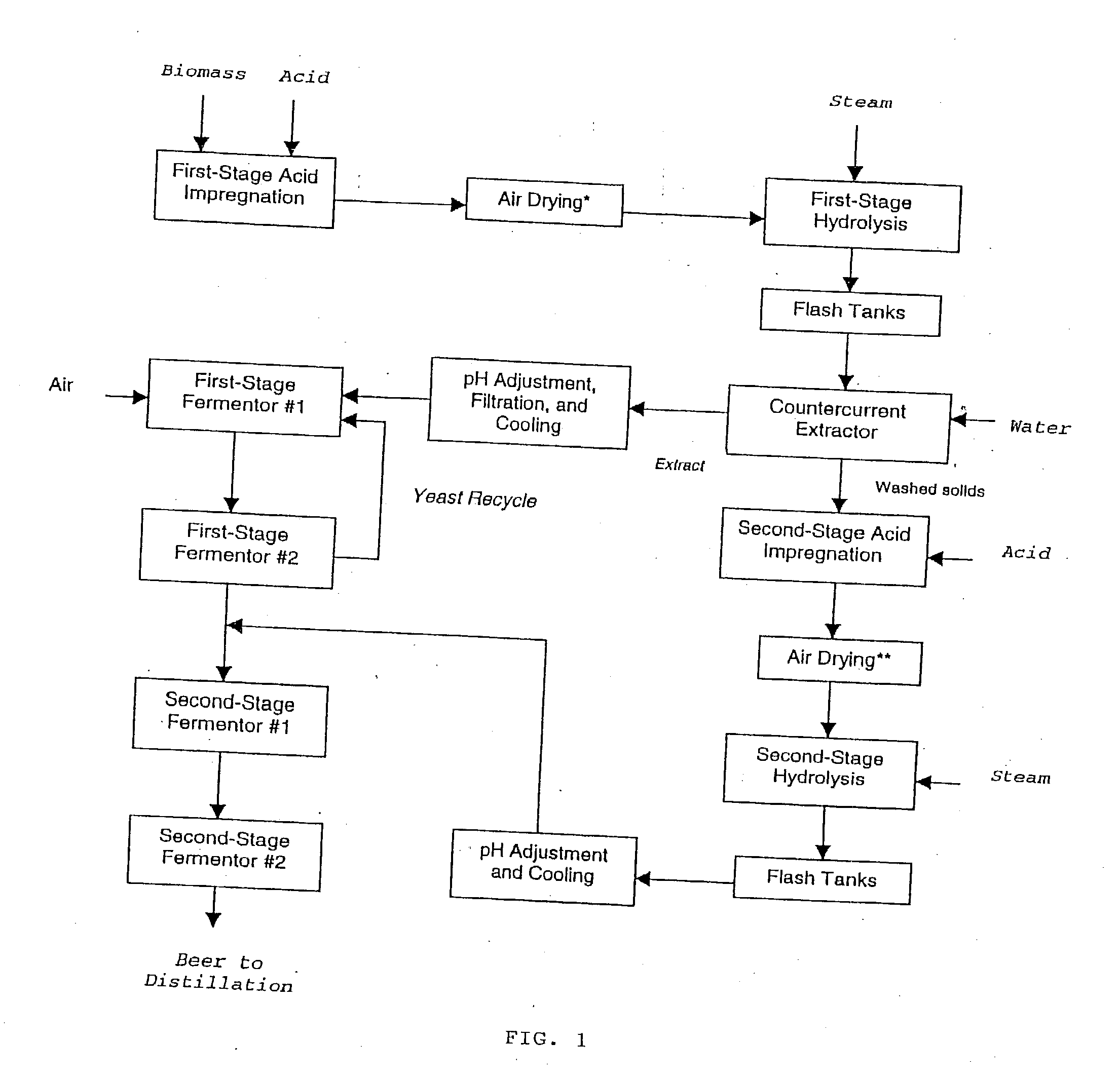
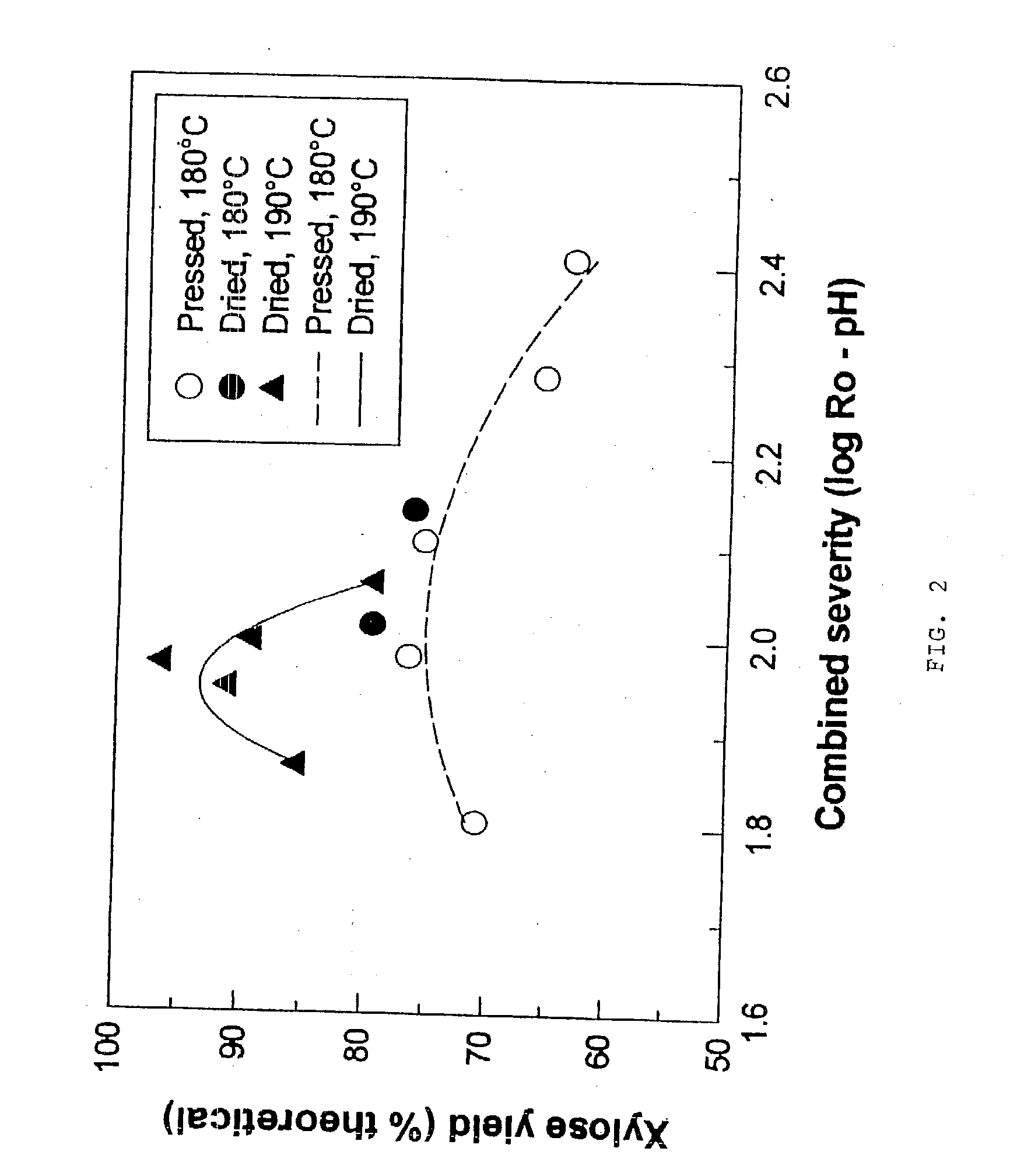
In a process for converting lingnocellulosic biomass to ethanol, the improvement of obtaining higher fermentable soluble sugar yields by drying acid impregnated biomass particles, comprising: a) feeding moist lignocellulosic biomass into an acid impregnator to render it acid-soaked and draining the acid-soaked biomass to about 30% to 35% by weight solids; b) dewatering the acid-soaked biomass by drying or centrifugation to prevent compaction of the biomass and arrive at about 40% to 60% by weight solids; c) subjecting the acid-impregnated biomass to a first-stage hydrolysis reactor at a temperature of from 130° C. to 220° C. and discharging formed hydrolysate into a flash tank at about 120° C. to 140° C. to hydrolyze most of the remaining soluble oligosaccharides to monomeric sugars, and flashing remaining hydrolysate to a second flash tank at a lower temperature than the first flash tank-the second flash tank serving as a feed surge tank for a counter-current extractor; d) washing the hydrolysate, adjusting the pH of the sugar extract to about 5, and recovering more than 95% of the soluble sugars in the first-stage hydrolysate slurry by a counter-current extractor; e) subjecting remaining washed-first stage solids of pretreated biomass to a second-stage acid and metal salt impregnator and dewatering by drying or centrifugation to prevent compaction of biomass to arrive at 40% to 60% by weight solids; f) subjecting the acid and metal salt-impregnated biomass to a second-stage hydrolysis reactor at a temperature from 190° C. to 240° C. and discharging formed hydrolysate into a flash tank, at about 120° C. to 140° C. to hydrolyze most of the remaining soluble oligosaccharides to monomeric sugars and flashing remaining hydrolysate to a second flash tank at a lower temperature than the first flash tank, the second flash tank serving as a feed surge tank for second-stage fementors; g) cooling pH-adjusted extract from the counter-current extractor, feeding the extract to a first-stage fermentor and air sparging the first-stage fermentor at a rate sufficient to promote enough yeast growth to compensate for loss through second-stage fermentors; h) pH adjusting second-stage hydrolysate slurry to 4.5, cooling the slurry and adding it into the top of the first fermentor of a two-fermentor train in the second stage fermentors, pumping broth from the bottom of the first stage fermentors to the second stage fermentors while the yeast is in the growth phase for a period sufficient to consume over 95% of fermentable sugars; and i) recovering ethanol.
Owner:MIDWEST RES INST
Method for processing lignocellulosic material
InactiveUS20020192774A1High degreeReduce water consumptionSludge treatment by oxidationBiofuelsCelluloseEnvironmental engineering
A method wherein lignocellulosic biomass materials are converted into combustible fuel products. In particular, the method is a continuous process. involving wet oxidation or steam explosion, for fermentatively converting such biomass materials into ethanol using a process design that permits all or part of the process water from the ethanol fermentation process to be recycled to reduce the consumption of process water. The effluent from the ethanol fermentation step may be subjected to an anaerobic fermentation step generating methane and a water effluent in which the amount of potentially inhibitory substances is at a sub-inhibitory level, which in turn permits all or part of the effluent water from the anaerobic fermentation step to be recycled into the process.
Owner:POET RES INC
Cellulose-solvent-based lignocellulose fractionation with modest reaction conditions and reagent cycling
InactiveUS20100170504A1Lower cost of capitalReduce operating costsBiofuelsChemical recyclingFractionationProcessing cost
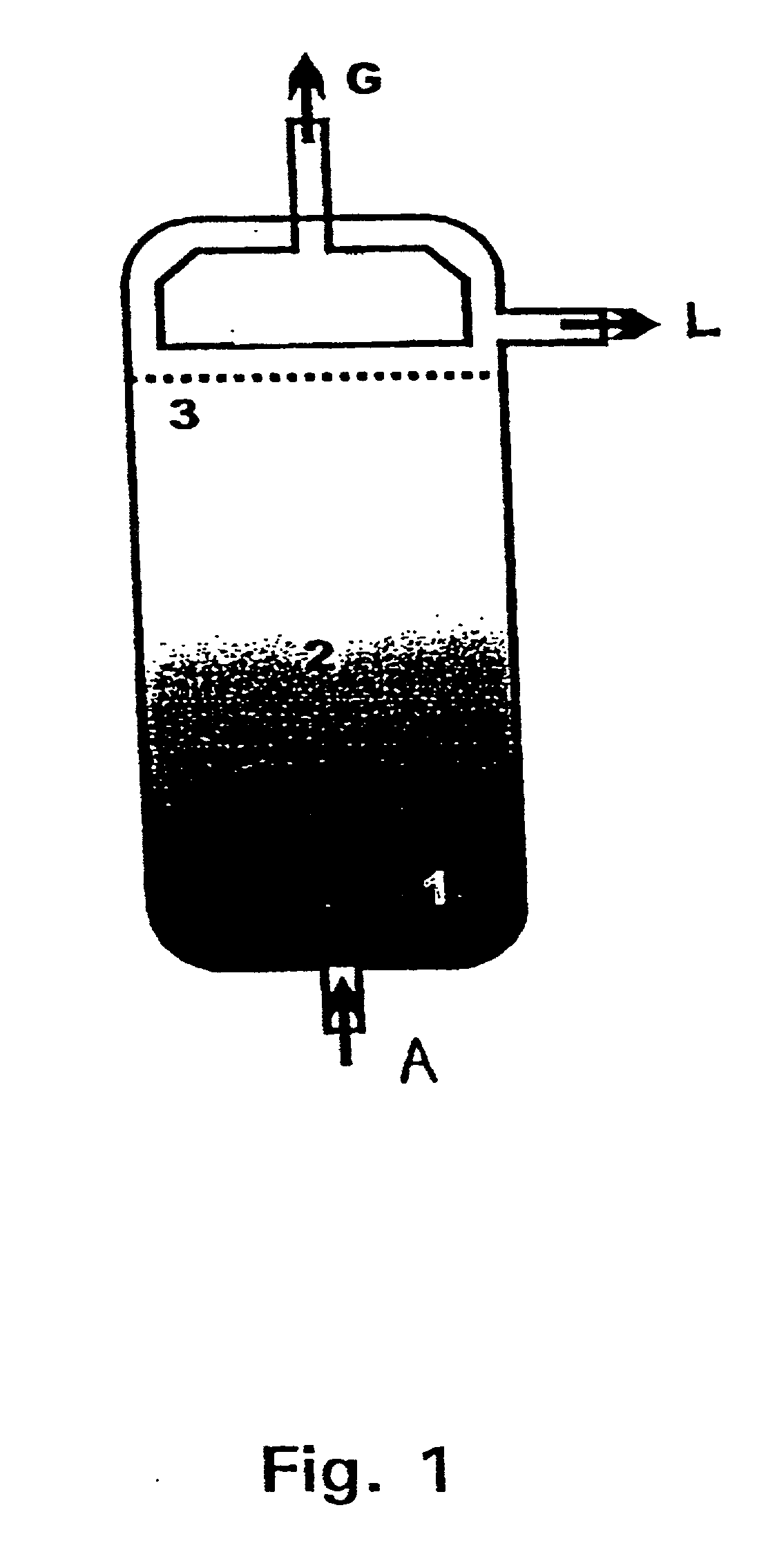
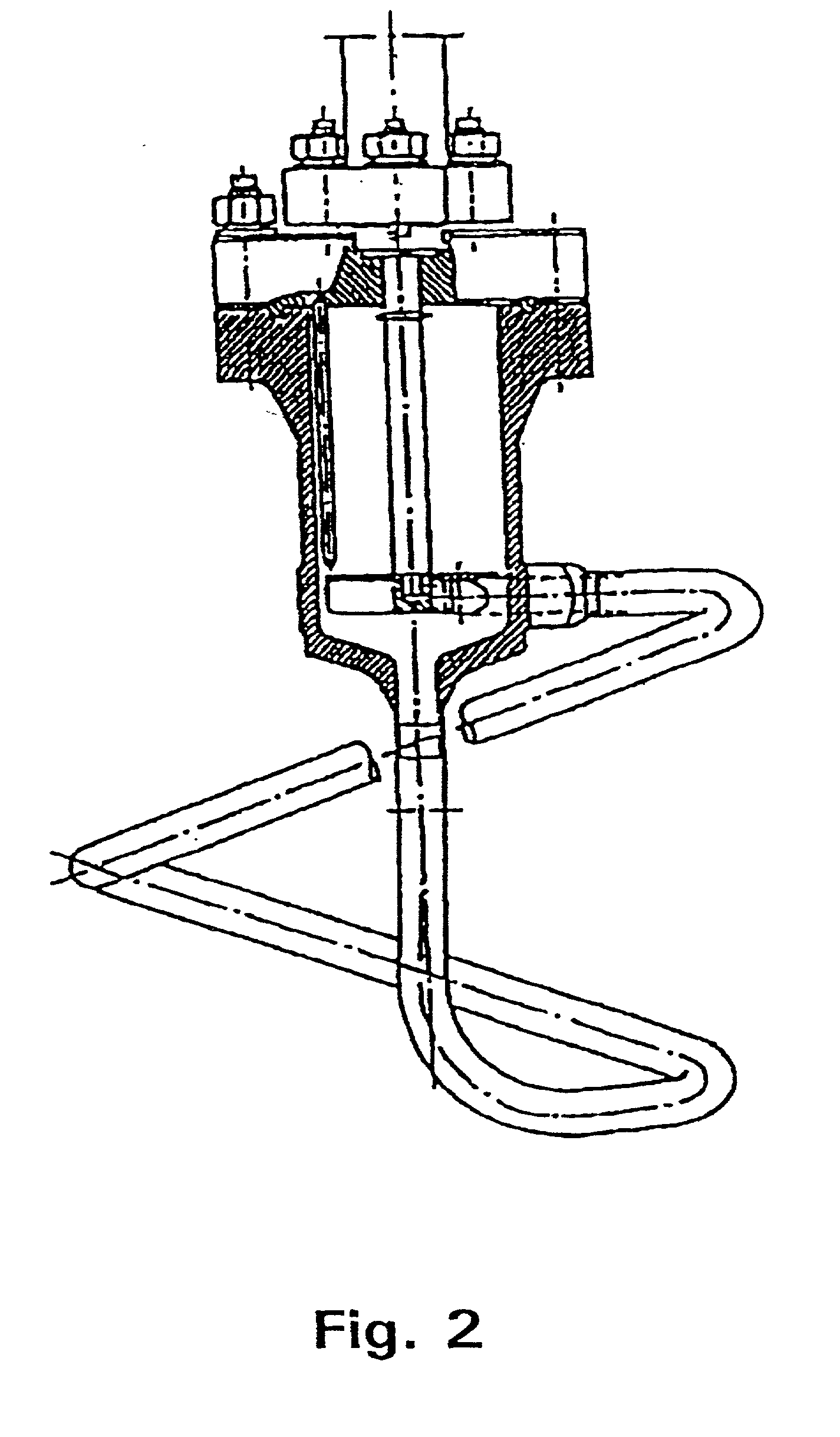
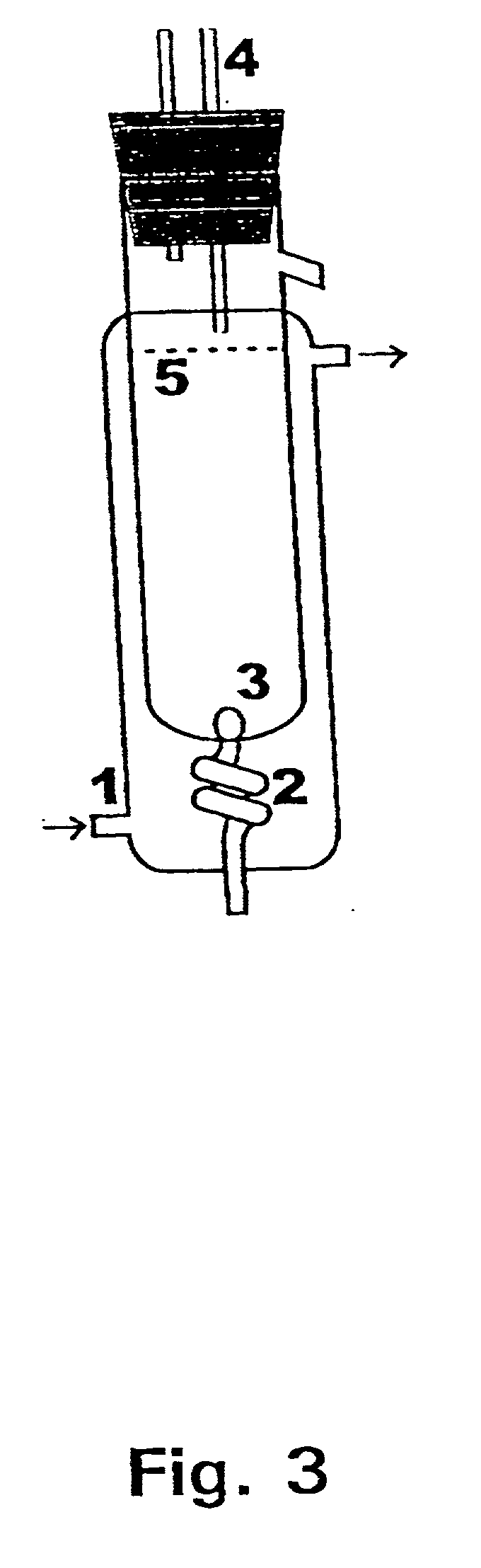
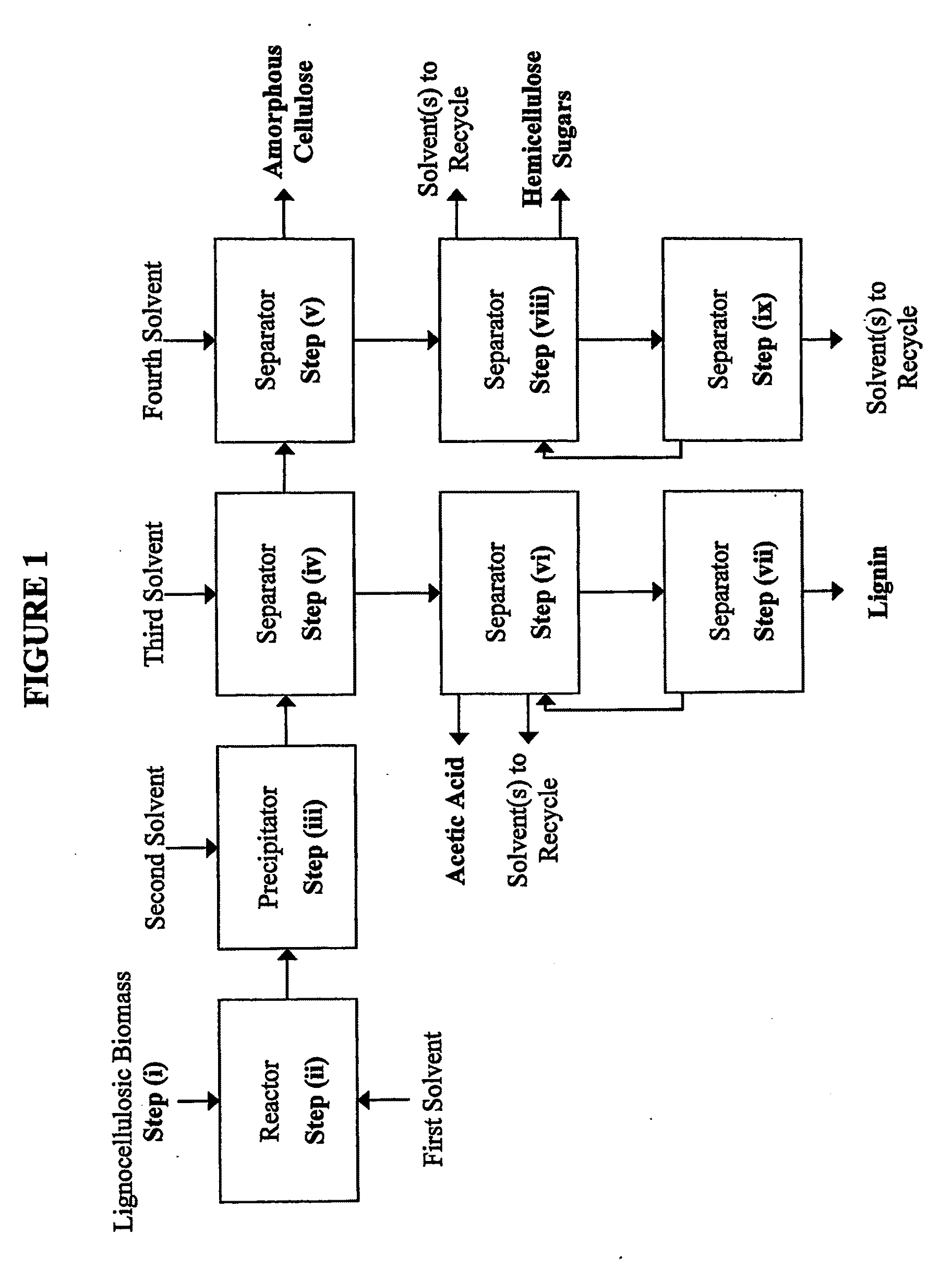
Embodiments of the present invention overcome the well-known recalcitrance of lignocellulosic biomass in an economically viable manner. A process and system are provided for the efficient fractionation of lignocellulosic biomass into cellulose, hemicellulose sugars, lignin, and acetic acid. The cellulose thus obtained is highly amorphous and can be readily converted into glucose using known methods. Fermentable hemicellulose sugars, low-molecular—weight lignin, and purified acetic acid are also major products of the process and system. The modest process conditions and low solvent / solid ratios of some embodiments of the invention imply relatively low capital and processing costs.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Separation of reactive cellulose from lignocellulosic biomass with high lignin content
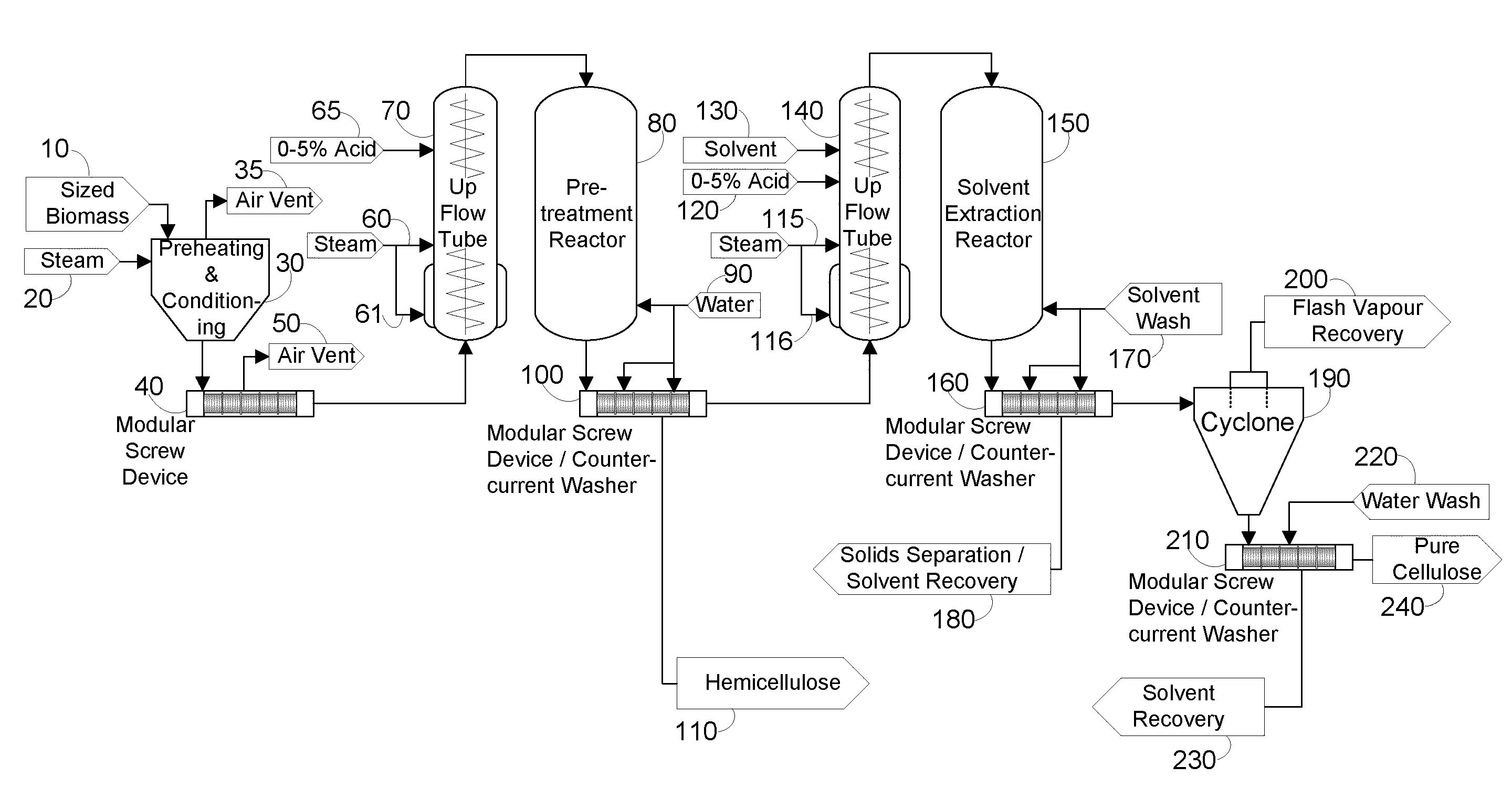
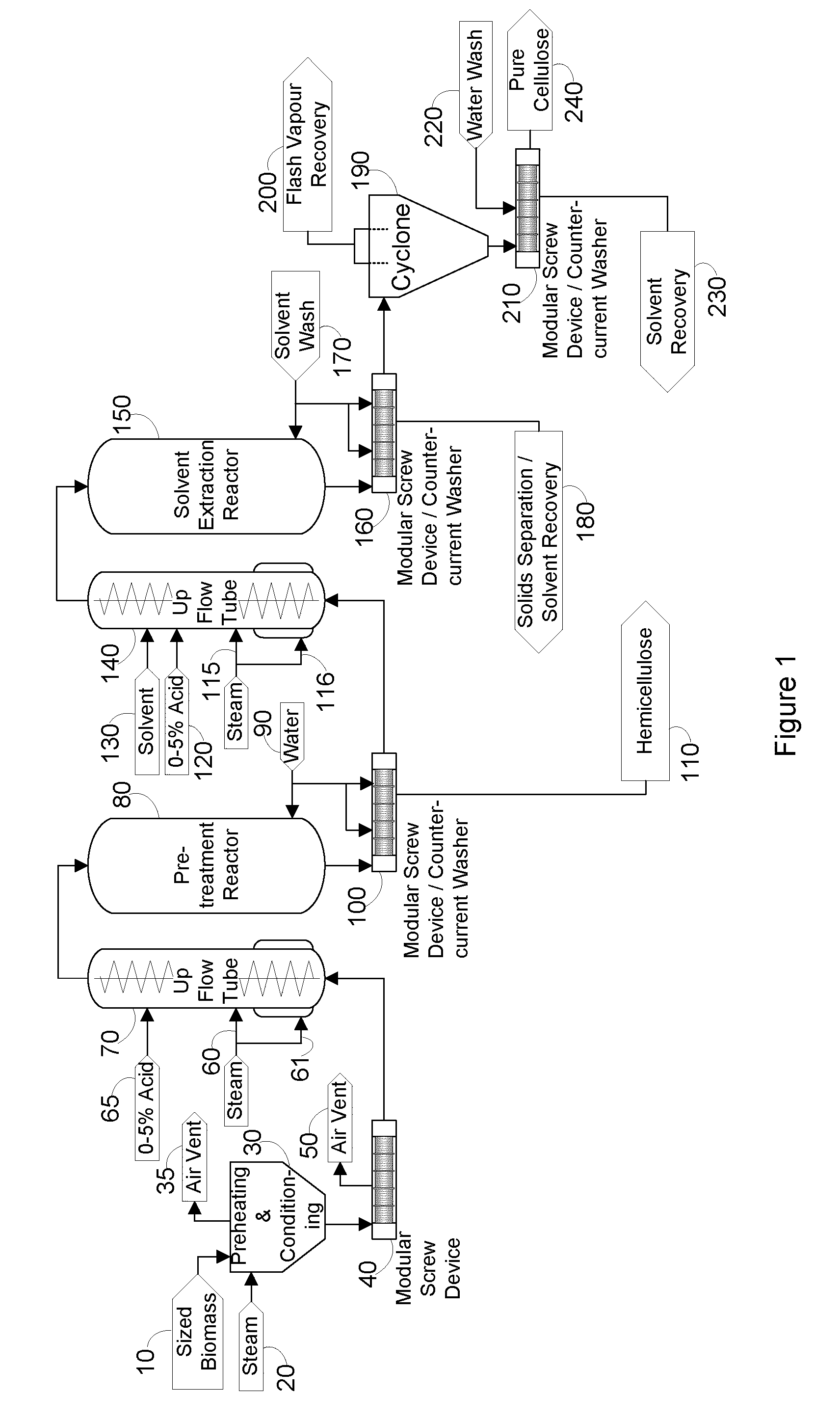
InactiveUS20100269990A1Reduce inhibitionReduce extractionCellulosic pulp after-treatmentBiofuelsFiberLignocellulosic biomass
A process for separating the components of lignocellulosic biomass for the purpose of producing a pure reactive cellulose is disclosed. The process has two stages. In the first stage, the lignocellulosic biomass is pretreated with steam, with or without an acid catalyst, and then pressed, with or without the presence of an eluent, to remove hemicellulose and other impurities. In the second stage, the pretreated biomass is extracted with a solvent such as ethanol with or without acid catalysts in order to remove lignin and release a purified cellulose stream. The extracted cellulose is then rapidly decompressed to rupture the fibrous structure. The process provides a purified cellulose stream that is relatively easy to hydrolyze with enzymes and ferment to biofuels and other chemicals such as ethanol.
Owner:GREENFIELD SPECIALTY ALCOHOLS
Moving bed biomass fractionation system and method
InactiveUS20080029233A1Improve production yieldIncrease pressureWashing/displacing pulp-treating liquorsDigestersChemical reactionFiltration
Countercurrent extraction of lignocellulosic biomass such as trees, grasses, shrubs, and agricultural residues or waste involves the separation of cellulose fibers from other constituents, for subsequent use in the manufacture of paper, plastics, ethanol, and other industrial chemicals. Systems and methods involve continuous, multiple processing steps that may include chemical reactions with mixing at elevated temperature and / or pressure, efficient reagent or solvent utilization, filtration at elevated temperature and / or pressure, controlled discharge of liquid and solid products, and energy recuperation.
Owner:PUREVISION TECH
Methods for enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulose
Compositions and methods for biomass conversion are provided. Compositions comprise novel enzyme mixtures that can be used directly on lignocellulose substrate. Methods involve converting lignocellulosic biomass to free sugars and small oligosaccharides with enzymes that break down lignocellulose. Novel combinations of enzymes are provided that provide a synergistic release of sugars from plant biomass. Also provided are methods to identify enzymes, strains producing enzymes, or genes that encode enzymes capable of degrading lignocellulosic material to generate sugars.
Owner:ATHENIX
Direct biomass hydroliquefaction process comprising two ebullated bed hydroconversion steps
ActiveCN102127462AExtend your lifeEasy to operateBiofuelsWaste based fuelHydrogen pressureLignocellulosic biomass
A process for direct hydroliquefaction of biomass selected from algae, lignocellulosic biomass and / or of one or more constituents of lignocellulosic biomass selected from the group comprising cellulose, hemicellulose and / or lignin for producing fuel bases comprising two successive hydroconversion stages under high hydrogen pressure in ebullating bed reactors. Hydroconversion takes place in the presence of a supported catalyst of the type for hydroconversion of petroleum residue and a suspension composed of the biomass and a solvent, preferably a hydrogen donor solvent and preferably recycled from the process. The biomass can undergo a pretreatment of drying and / or roasting and / or grinding and / or demineralization prior to hydroliquefaction.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Hydrothermal hydrocatalytic treatment of biomass
A method of hydrothermal hydrocatalytic treating biomass is provided. Lignocellulosic biomass is treated with a digestive solvent to form a pretreated biomass containing soluble carbohydrates. The pretreated biomass is contacted, with hydrogen at a temperature in the range of 150° C. to less than 300° C. in the presence of a pH buffering agent and a supported hydrogenolysis catalyst containing (a) sulfur, (b) Mo or W, and (c) Co, Ni or mixture thereof, incorporated into a suitable support, to form a plurality of oxygenated hydrocarbons.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Method for producing ethanol and co-products from cellulosic biomass
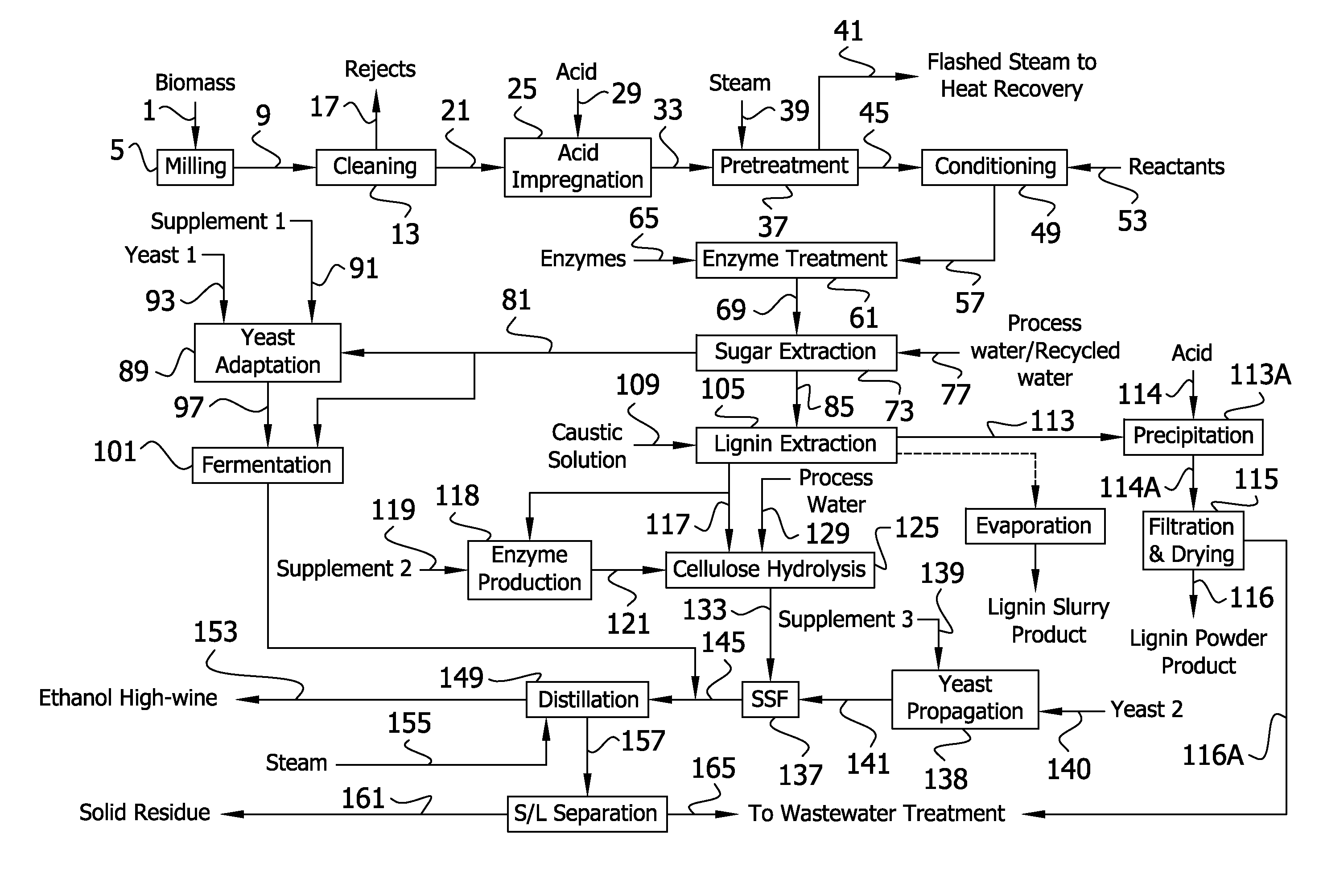
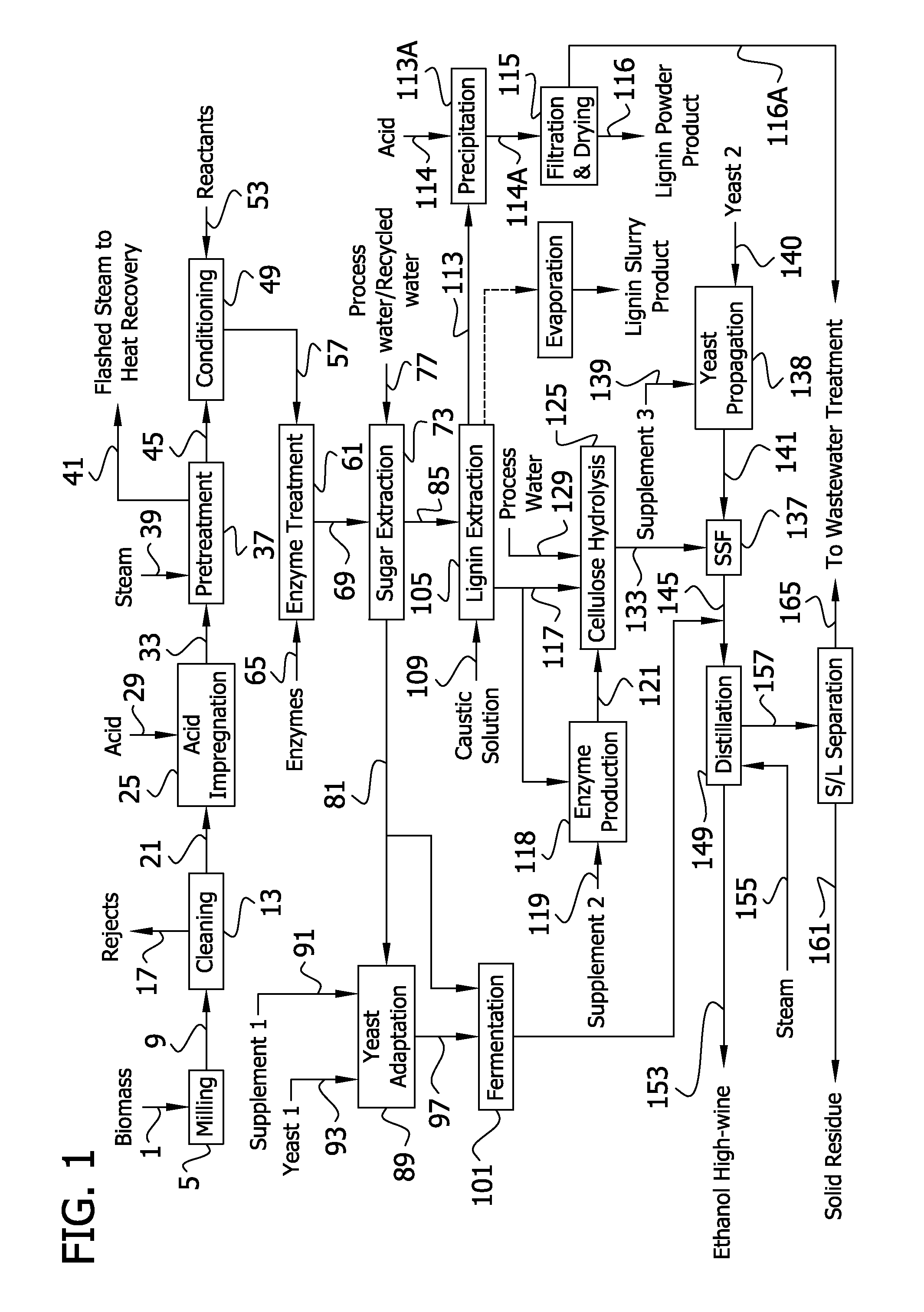
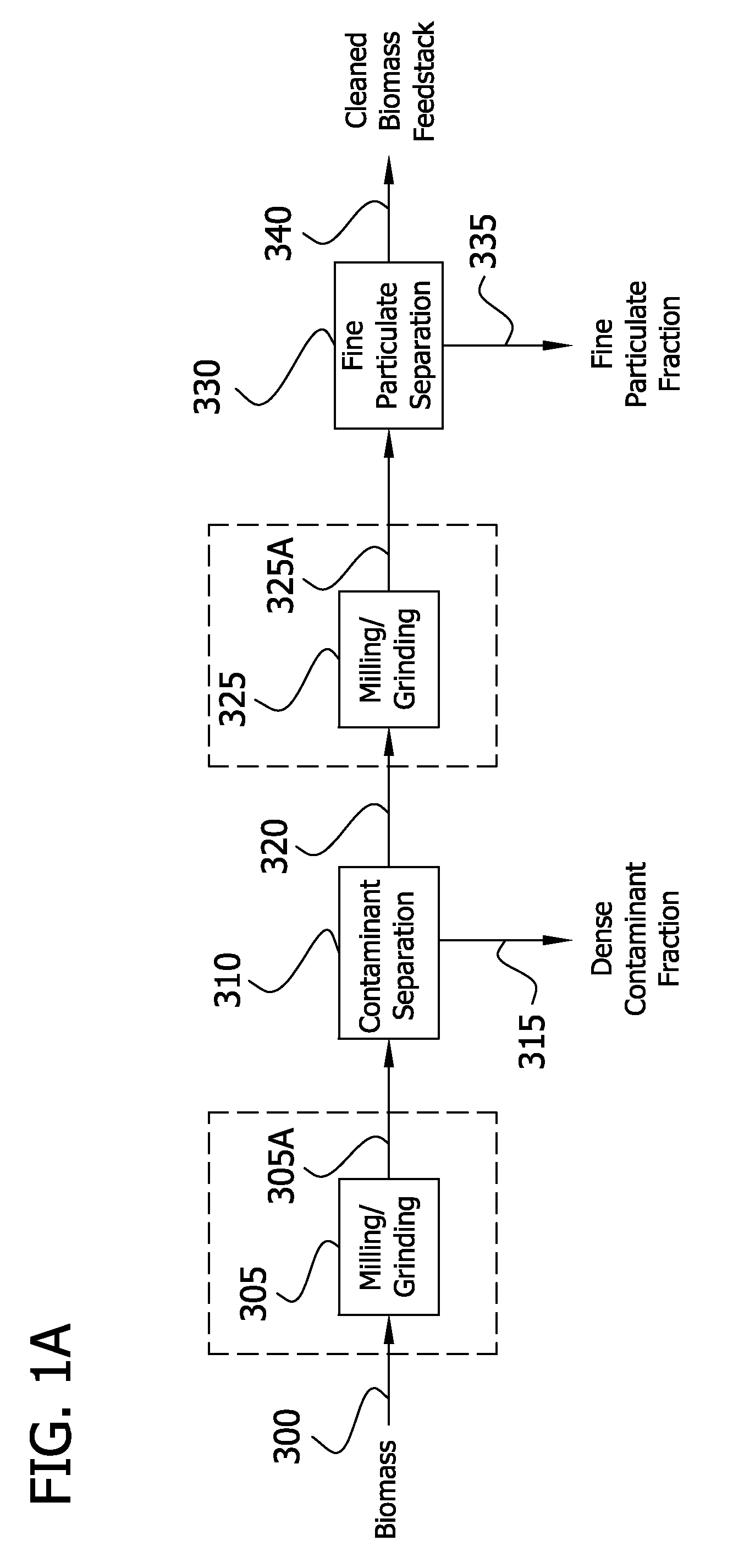
InactiveUS20120006320A1Increased ethanol productionImproved co-productsFuel supply regulationPretreatment with acid reacting compoundsCelluloseLignocellulosic biomass
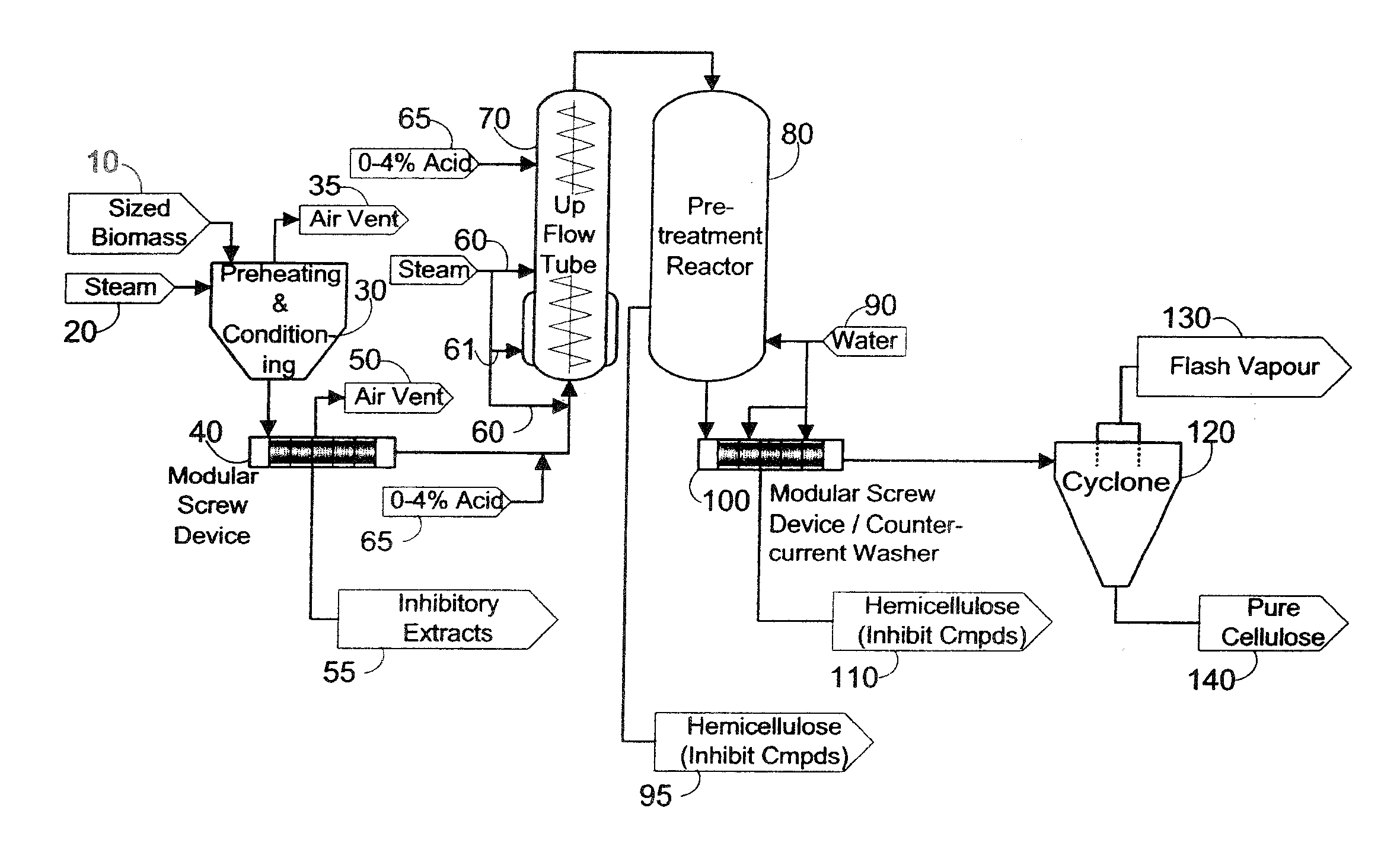
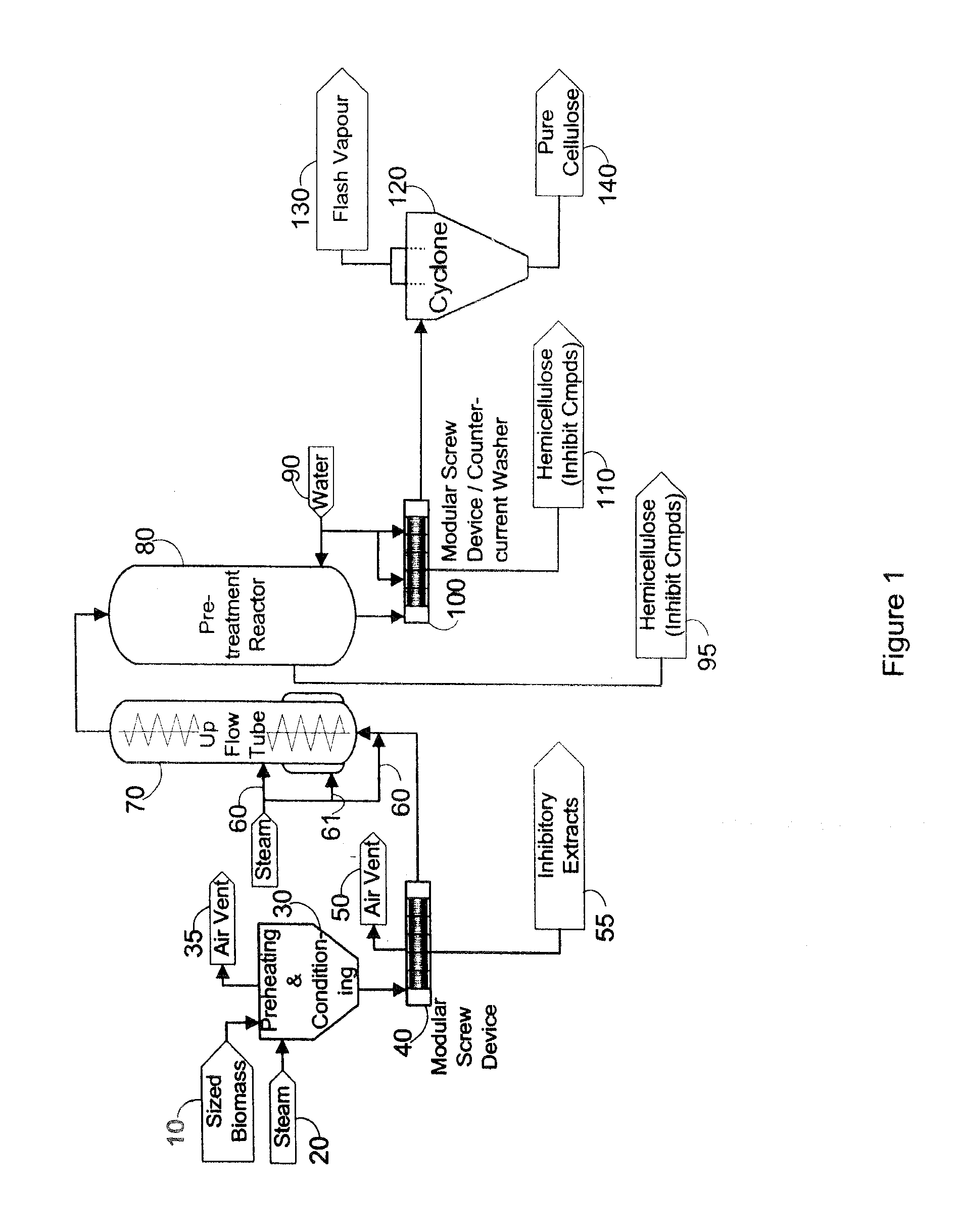
The present invention generally relates to processes for production of ethanol from cellulosic biomass. The present invention also relates to production of various co-products of preparation of ethanol from cellulosic biomass. The present invention further relates to improvements in one or more aspects of preparation of ethanol from cellulosic biomass including, for example, improved methods for cleaning biomass feedstocks, improved acid impregnation, and improved steam treatment, or “steam explosion.”
Owner:ABENGOA BIOENERGY NEW TECH
Lignin blockers and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060088922A1High efficiency in cellulose conversionLess of advantageProtein composition from vegetable seedsBiofuelsLignin degradationLignocellulosic biomass
Disclosed is a method for converting cellulose in a lignocellulosic biomass. The method provides for a lignin-blocking polypeptide and / or protein treatment of high lignin solids. The treatment enhances cellulase availability in cellulose conversion and allows for the determination of optimized pretreatment conditions. Additionally, ethanol yields from a Simultaneous Saccharification and Fermentation process are improved 5-25% by treatment with a lignin-blocking polypeptide and / or protein. Thus, a more efficient and economical method of processing lignin containing biomass materials utilizes a polypeptide / protein treatment step that effectively blocks lignin binding of cellulase.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Production of chemicals from lignocellulose, biomass or sugars
InactiveUS20050250192A1High yieldLow costBacteriaUnicellular algaeBiological bodyCompound (substance)
The subject invention relates to newly isolated organisms from nature that produce L(+)-lactic acid high yield from hexose and pentose sugars found in biomass. Organisms and processes or methods for the production of lactic acid and other industrially important chemicals from cellulose and hemicellulose are also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA
Process for the treatment of lignocellulosic biomass
ActiveUS20080008783A1Lower the volumeIncreasing fractionBiofuelsAnimal feeding stuffCelluloseEnergy source
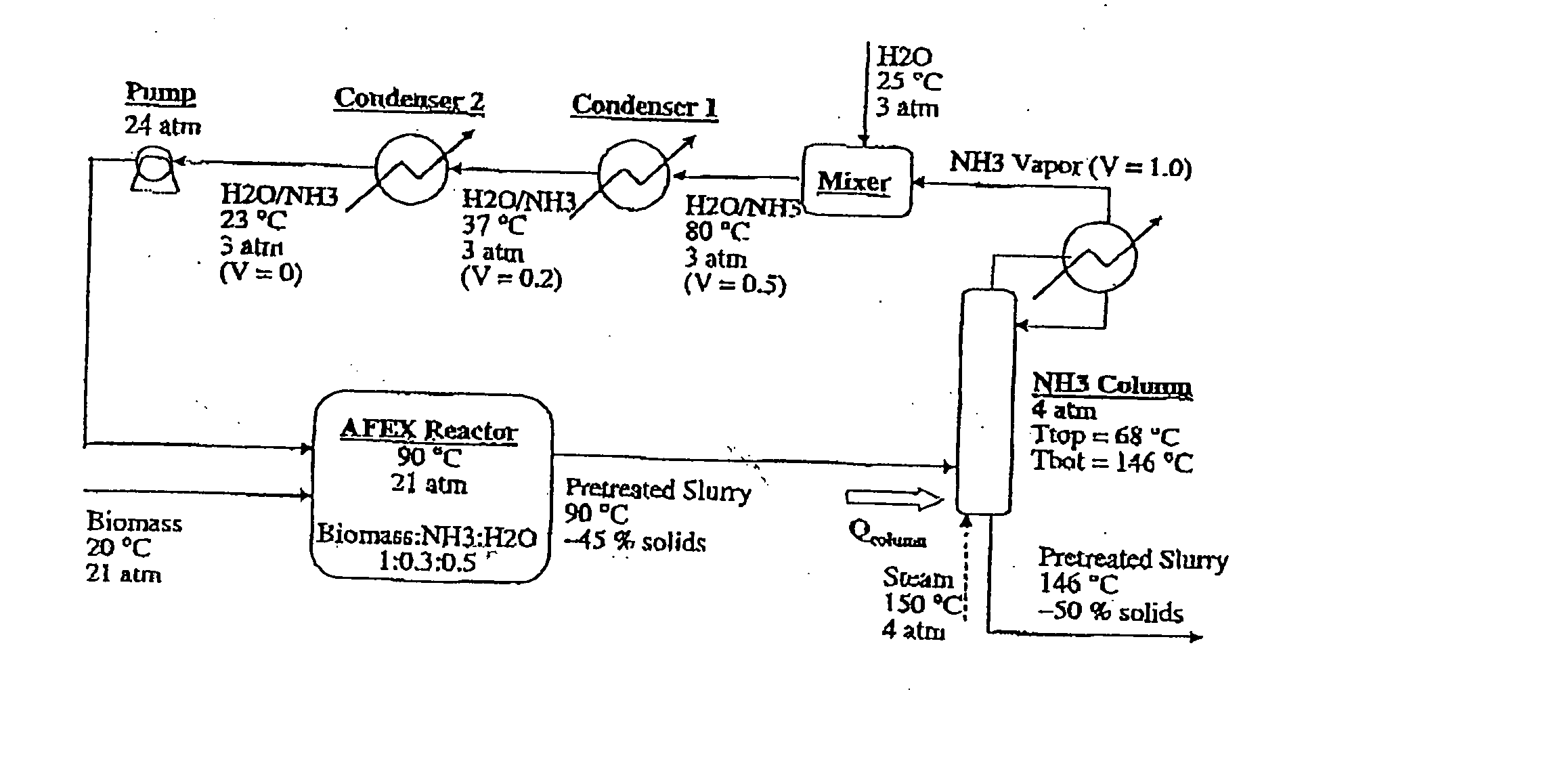
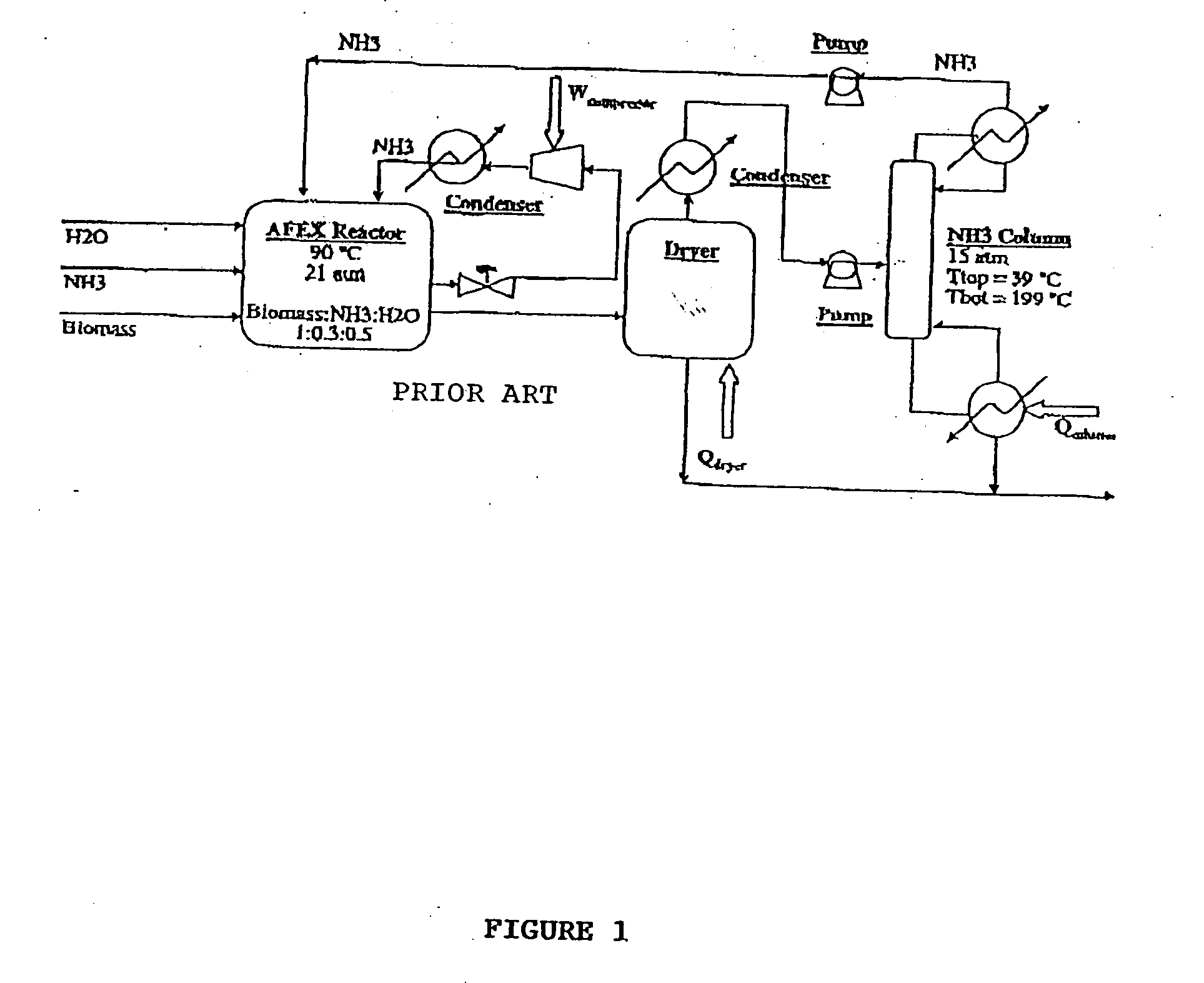
A process for the treatment of biomass to render structural carbohydrates more accessible and / or digestible using concentrated ammonium hydroxide with or without anhydrous ammonia addition, is described. The process preferably uses steam to strip ammonia from the biomass for recycling. The process yields of monosaccharides from the structural carbohydrates are good, particularly as measured by the enzymatic hydrolysis of the structural carbohydrates. The monosaccharides are used as animal feeds and energy sources for ethanol production.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Process for enzymatically converting a plant biomass
The present invention describes a process for at least a 90% conversion of a plant biomass preferably by a reduction of the units of cellulase needed and by using a xylanase which acts synergistically with the cellulase to improve the yield of xylose and glucose as sugars. The process enables greater conversion of a lignocellulosic plant biomass to glucose and xylose for use as animal feeds and as fermentation as medium for producing ethanol.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Method and apparatus for lignocellulose pretreatment using a super-cellulose-solvent and highly volatile solvents
InactiveUS20090229599A1Overcome shortcomingReduce solvent usagePressurized chemical processBiofuelsAlcoholGram
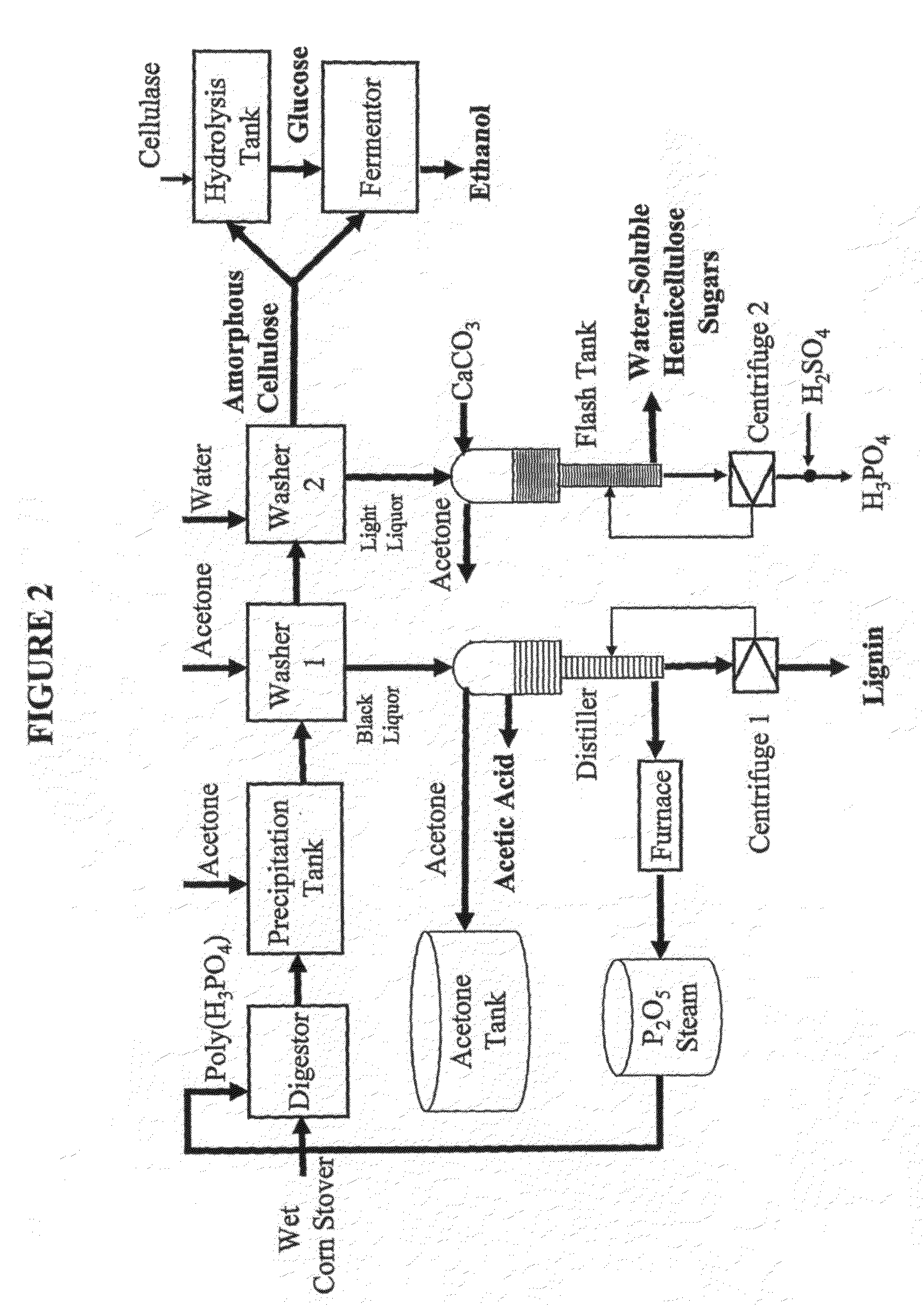
Embodiments of the present invention overcome the well-known recalcitrance of lignocellulosic biomass in an economically viable manner. A process and a system are provided for the efficient fractionation of lignocellulosic biomass into cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin. The cellulose and hemicellulose thus obtained are highly amorphous and can be readily converted into highly concentrated mixtures of five and six carbon sugars using known methods. Typical yields of sugars exceed 100 grams of sugars per liter of sugar solution. Other products, such as alcohols, can easily be prepared according to methods of the invention. The modest process conditions and low solvent / solid ratios of some embodiments of the invention require relatively low capital and processing costs.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Recyclable buffer for the hydrothermal hydrocatalytic treatment of biomass
InactiveUS20140166221A1Minimal lossMaintain activityPulp bleachingLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionCelluloseHydrogen
A method of hydrothermal hydrocatalytic treating biomass is provided. Lignocellulosic biomass solids is provided to a hydrothermal digestion unit in the presence of a digestive solvent, at least one of ammonia or a source of ammonia, and a supported hydrogenolysis catalyst containing (a) sulfur, (b) Mo or W, and (c) Co, Ni or mixture thereof, incorporated into a suitable support. The lignocellulosic biomass solids and digestive solvent are heated in the presence of hydrogen, supported hydrogenolysis catalyst and the at least one of ammonia or a source of ammonia forming a product solution containing plurality of oxygenated hydrocarbons and ammonia. At least a portion of ammonia is separated and recycled to the hydrothermal digestion unit.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Conversion of Lignocellulosic Biomass to Chemicals and Fuels
InactiveUS20080312346A1Pulp liquor regenerationOther chemical processesCelluloseLignocellulosic biomass
A method for preparing biomass for slurry processing. The method includes solubilizing the solid material into either a dissolved state or a suspended solid in a liquid phase, and treating the liquid phase to produce chemicals and fuels.
Owner:UOP LLC +1
Chemical Transformation of Lignocellulosic Biomass into Fuels and Chemicals
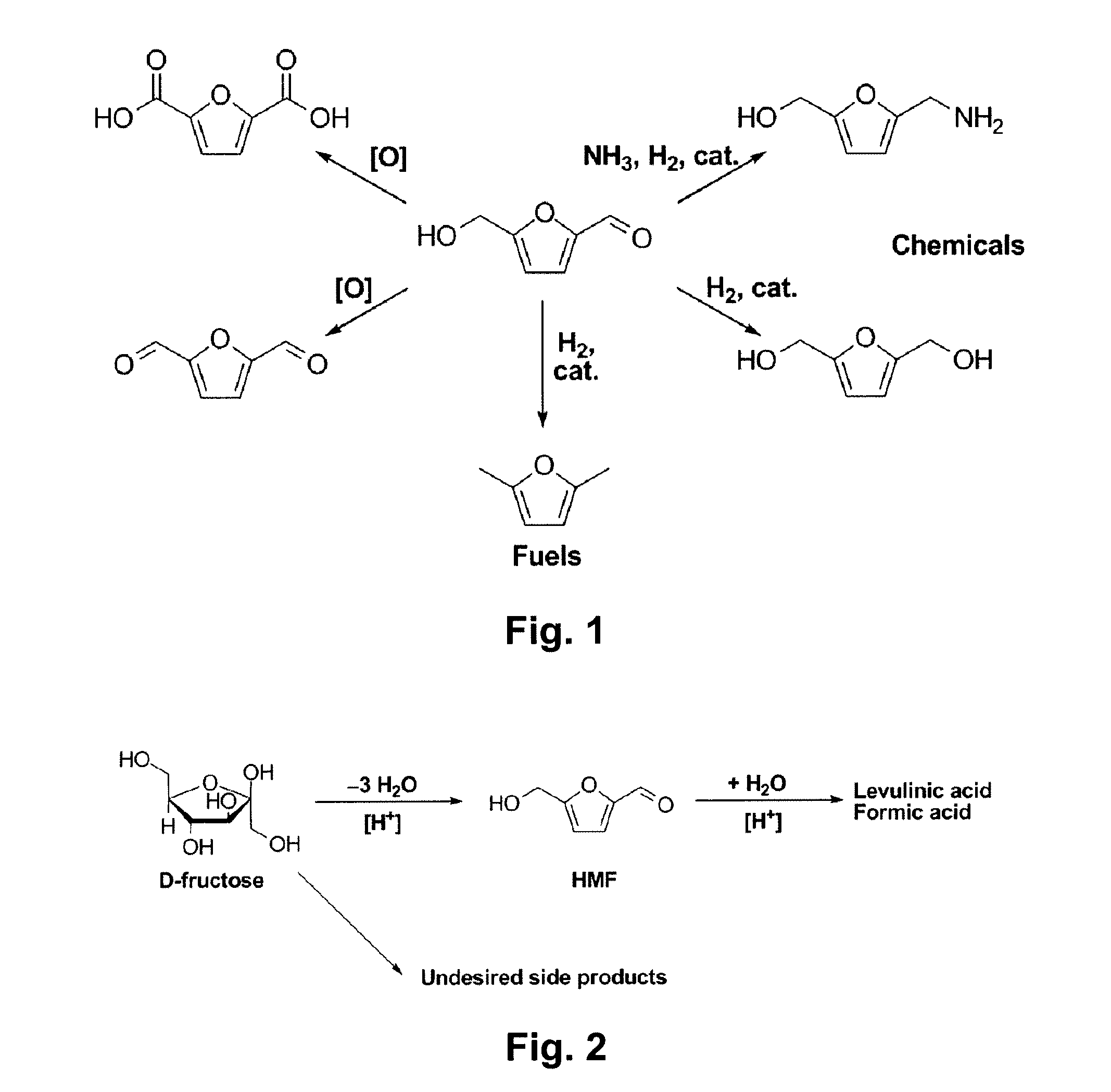
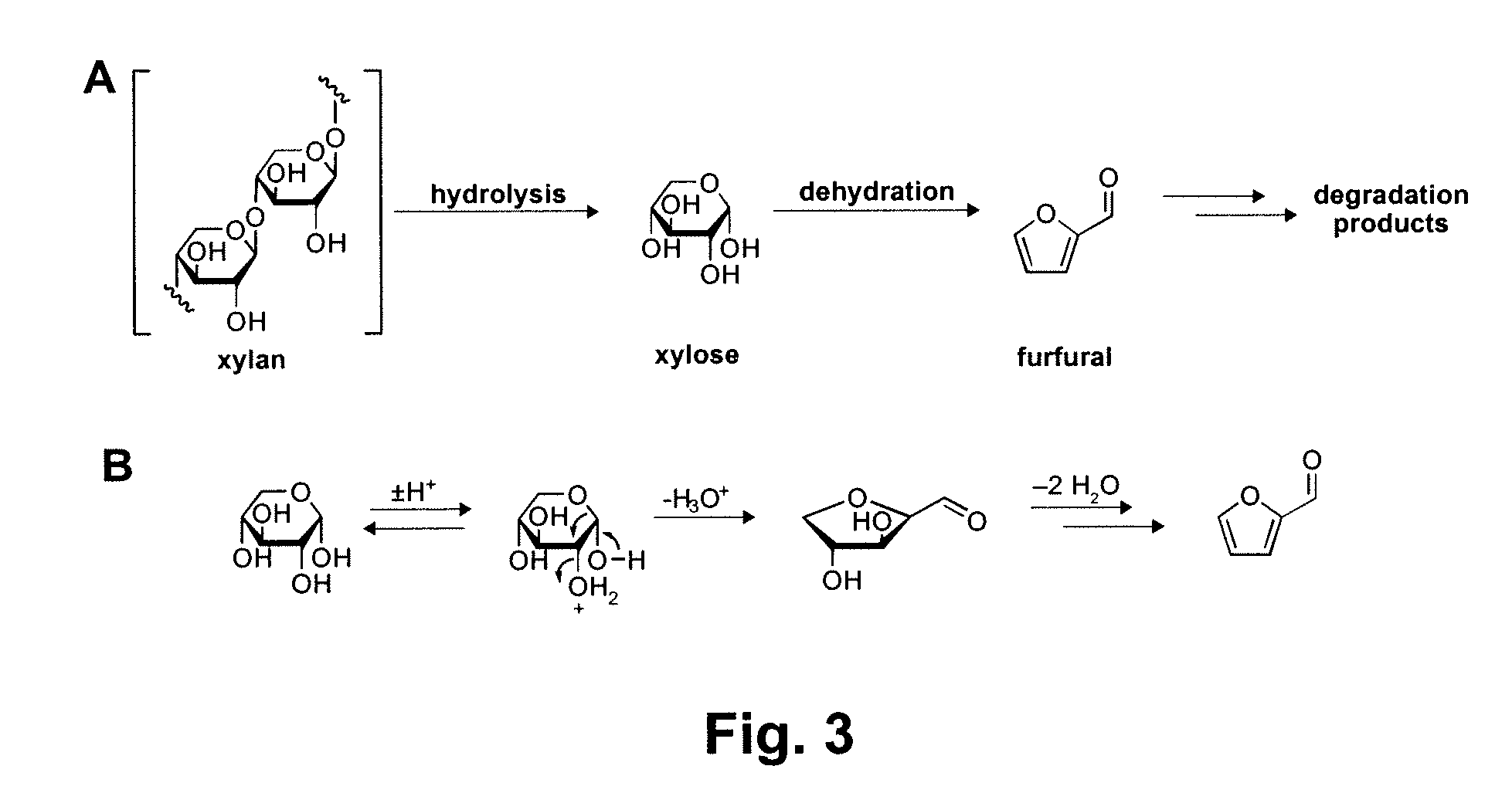
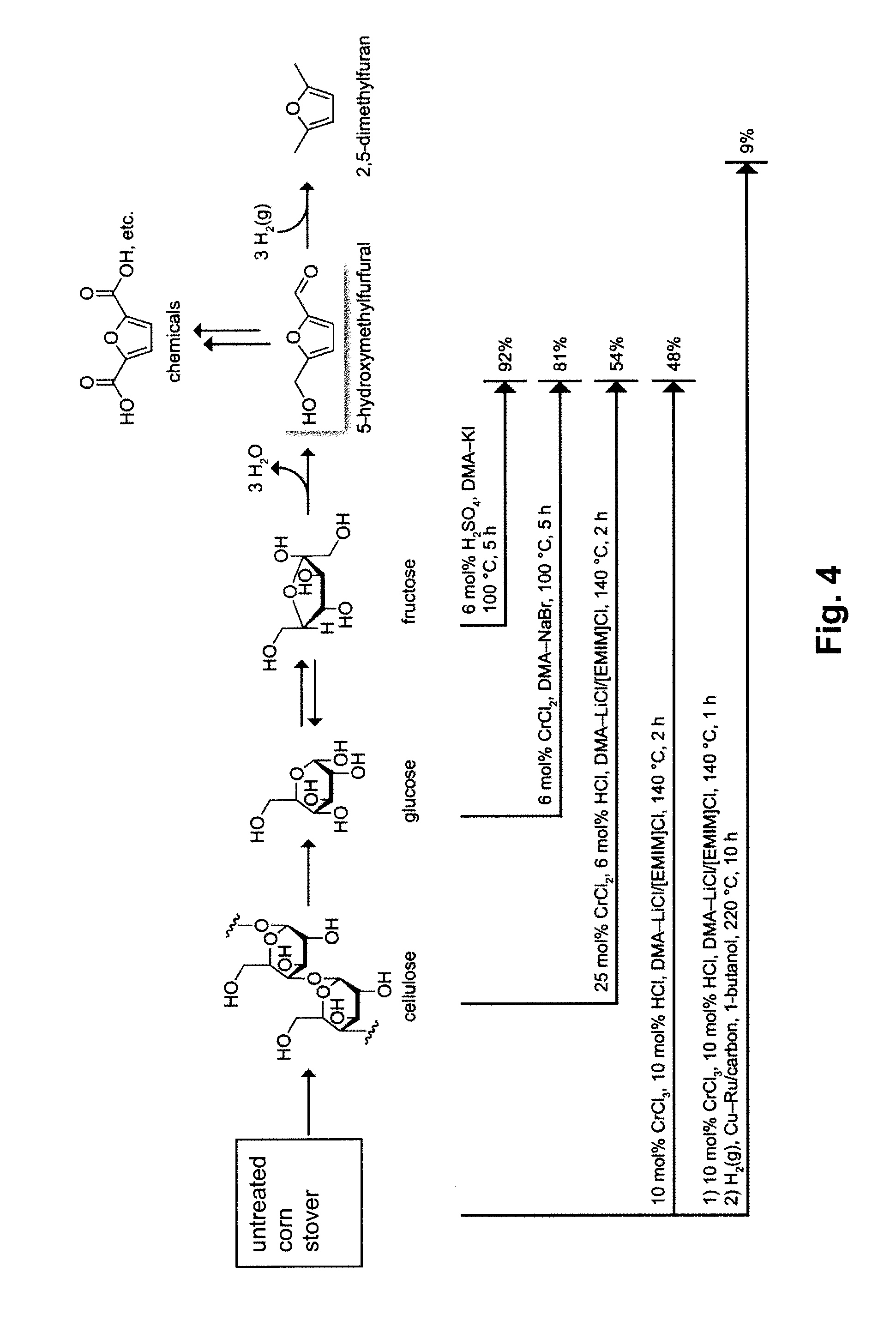
A method for converting a carbohydrate to a furan in a polar aprotic solvent in the presence of a chloride, bromide, or iodide salt or a mixture thereof and optionally in the presence of an acid catalyst, a metal halide catalyst and / or an ionic liquid (up to 40 wt %). The method can be employed in particular to produce furfural or 5-hydroxymethylfurfural.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Novel Fungal Enzymes
InactiveUS20090280105A1Easy to cleanOrganic active ingredientsNon-fibrous pulp additionCelluloseWaste stream
This invention relates to novel enzymes and novel methods for producing the same. More specifically this invention relates to a variety of fungal enzymes. Nucleic acid molecules encoding such enzymes, compositions, recombinant and genetically modified host cells, and methods of use are described. The invention also relates to a method to convert lignocellulosic biomass to fermentable sugars with enzymes that degrade the lignocellulosic material and novel combinations of enzymes, including those that provide a synergistic release of sugars from plant biomass. The invention also relates to methods to use the novel enzymes and compositions of such enzymes in a variety of other processes, including washing of clothing, detergent processes, deinking and biobleaching of paper and pulp, and treatment of waste streams.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
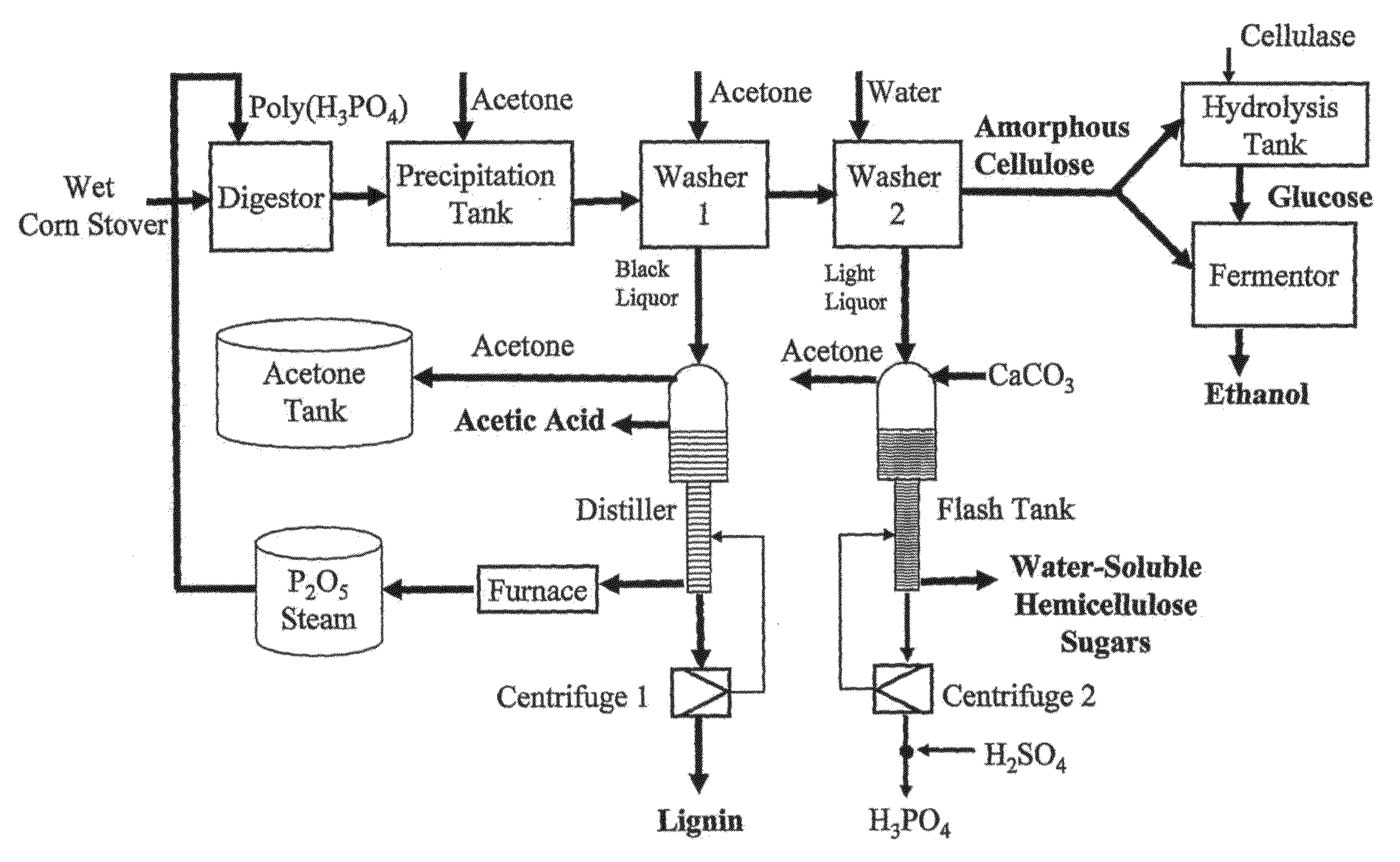
Process for preparing multicomponent liquid glucose and lignose while effectively hydrolyzing lignocellulosic biomass
InactiveCN101285106ASimple recycling processNot volatileSulfate preparationLignin derivativesLiquid glucoseFiltration
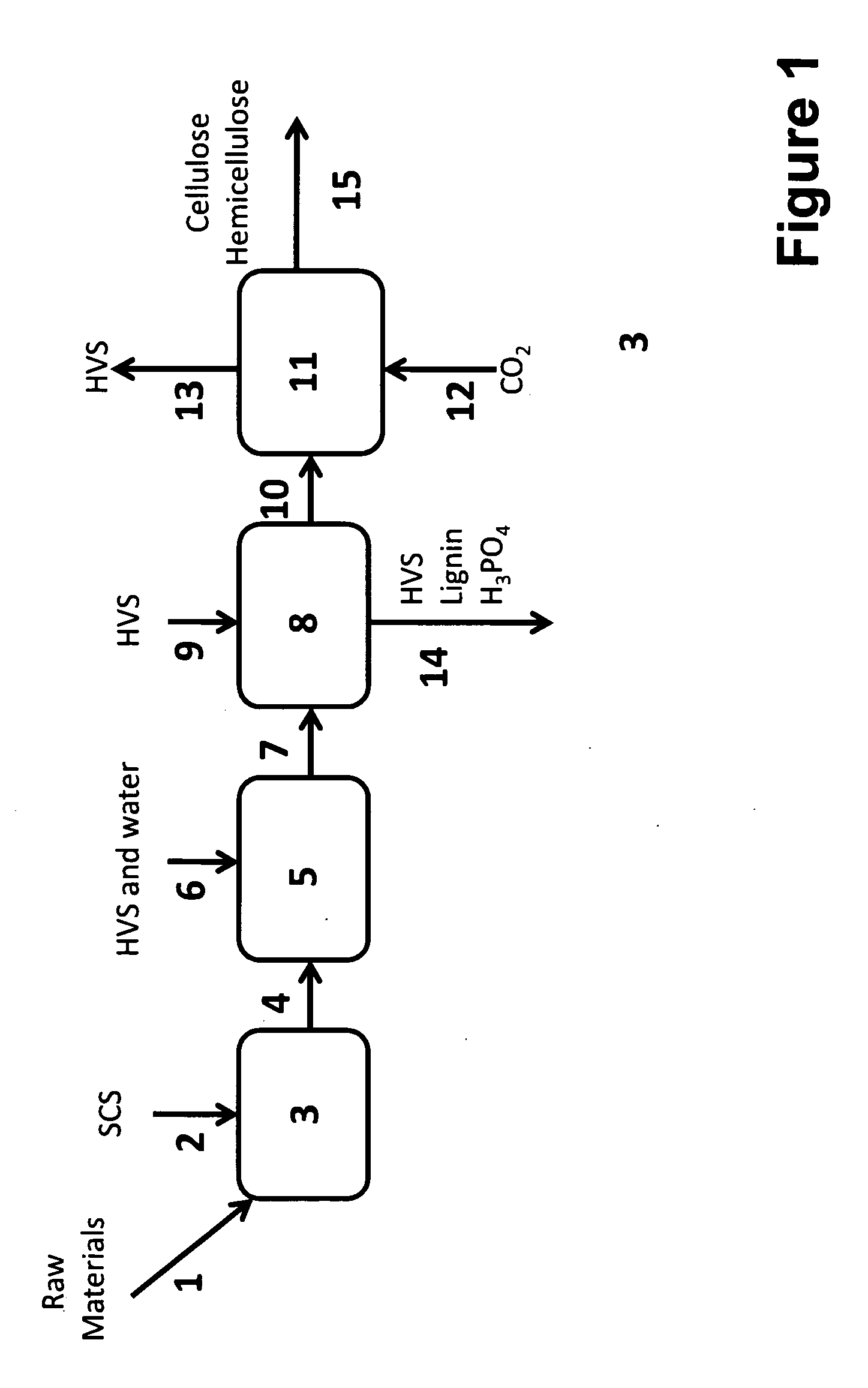
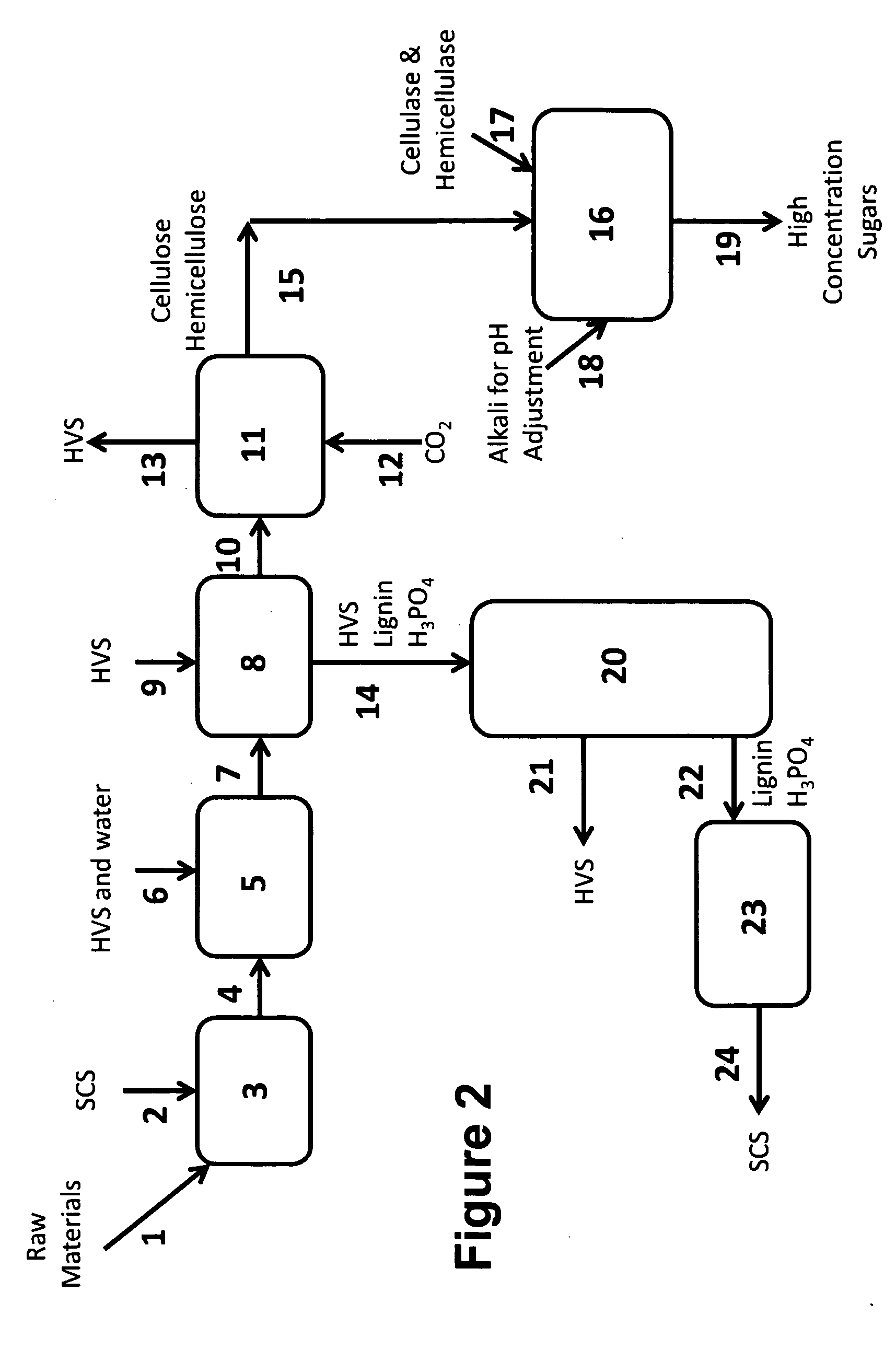
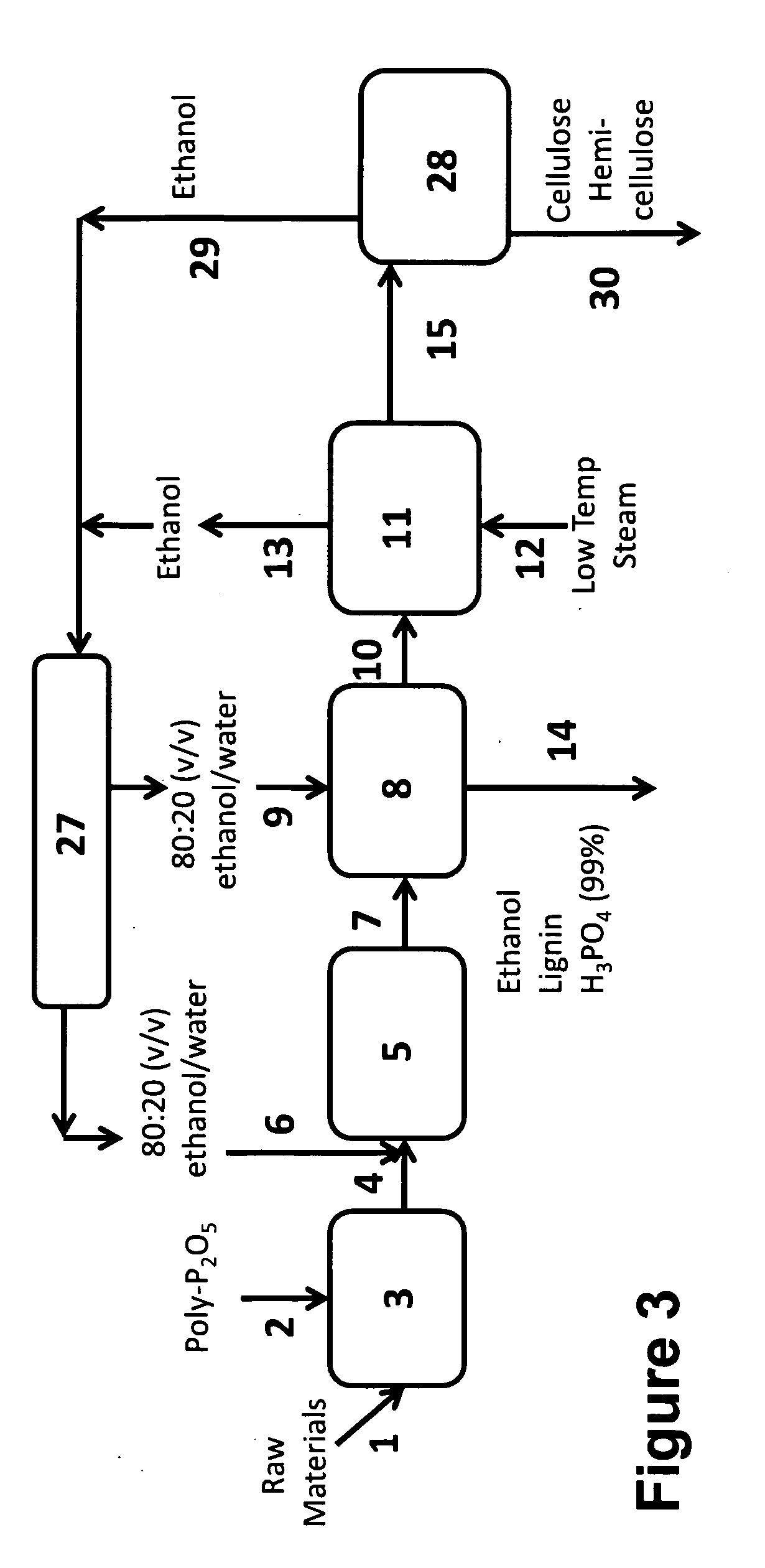
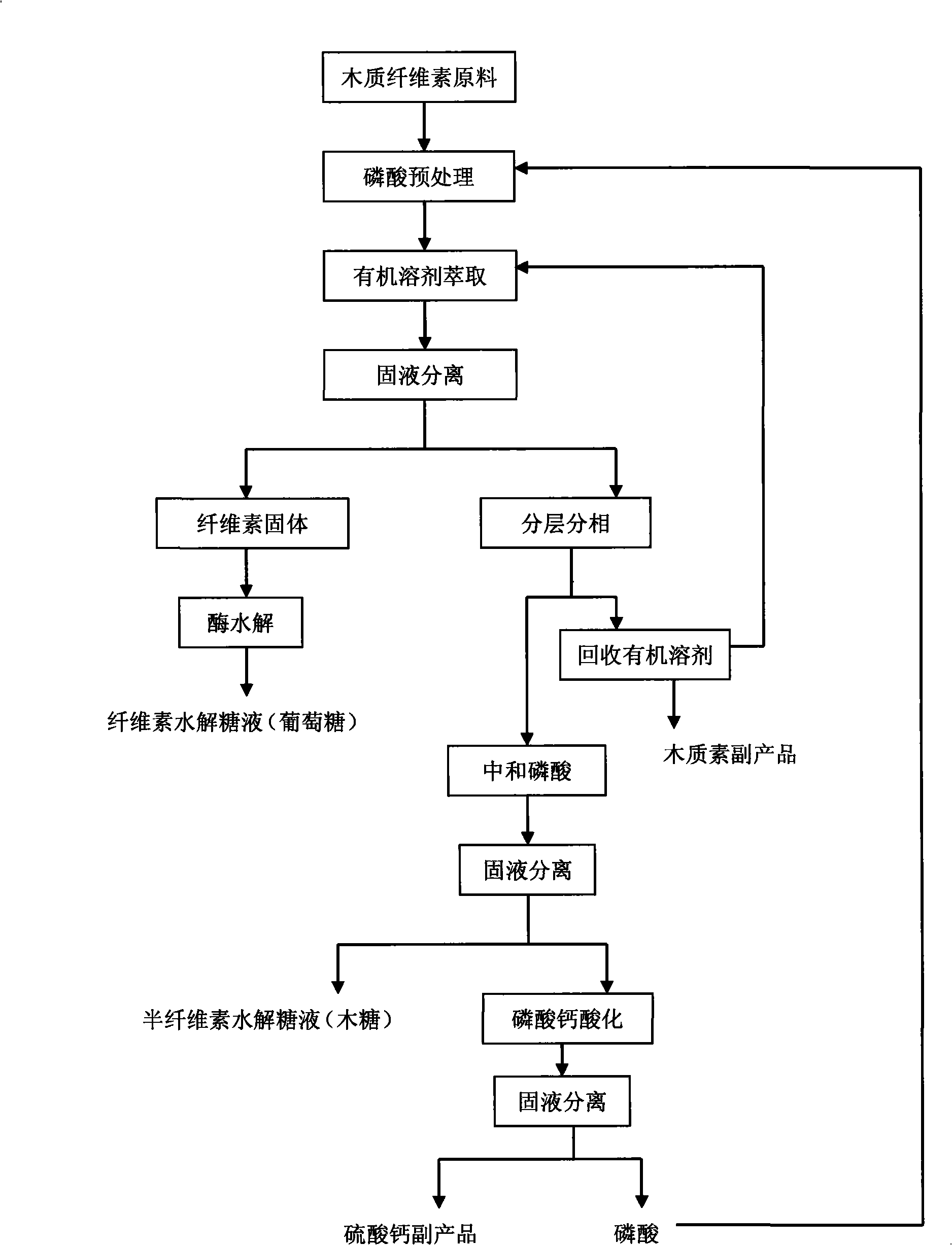
The invention discloses a method for efficiently hydrolyzing lignocellulosic biomass and synchronously preparing multi-component liquid glucose and lignin. The method comprises the steps that: the lignocellulosic biomass through physical crushing is added with phosphoric acid to perform acid hydrolysis; then organic solvent is added to extract the lignin, the layering and the phase separation are performed, then the lignin is extracted out while the organic solvent is reclaimed under the condition of pressure reduction and distillation; phosphoric acid can be reclaimed through steps such as neutralization, filtration, acidification and so on, hemicellulose hydrolyzed liquid glucose is obtained at the same time; and the remained cellulose undergoes the zymohydrolysis to prepare cellulosic hydrolyzed liquid glucose. The method can separate lignin, hemicellulose and cellulose, remarkably decreases the degree of crystallinity of the cellulose hydrolyzed by phosphoric acid, and remarkably improves the zymohydrolysis efficiency; and the prepared hydrolyzed liquid glucose does not contain fermentation inhibitors. The method has mild treatment conditions, simple process and less side reactions; the phosphoric acid and the organic solvent can both be reclaimed and circularly used; and the method is environment-friendly, and has broad social and economic benefits.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method of obtaining a product sugar stream from cellulosic biomass
InactiveUS20090023187A1Improve performanceHigh yieldSugar derivativesBiofuelsInorganic saltsAcetic acid
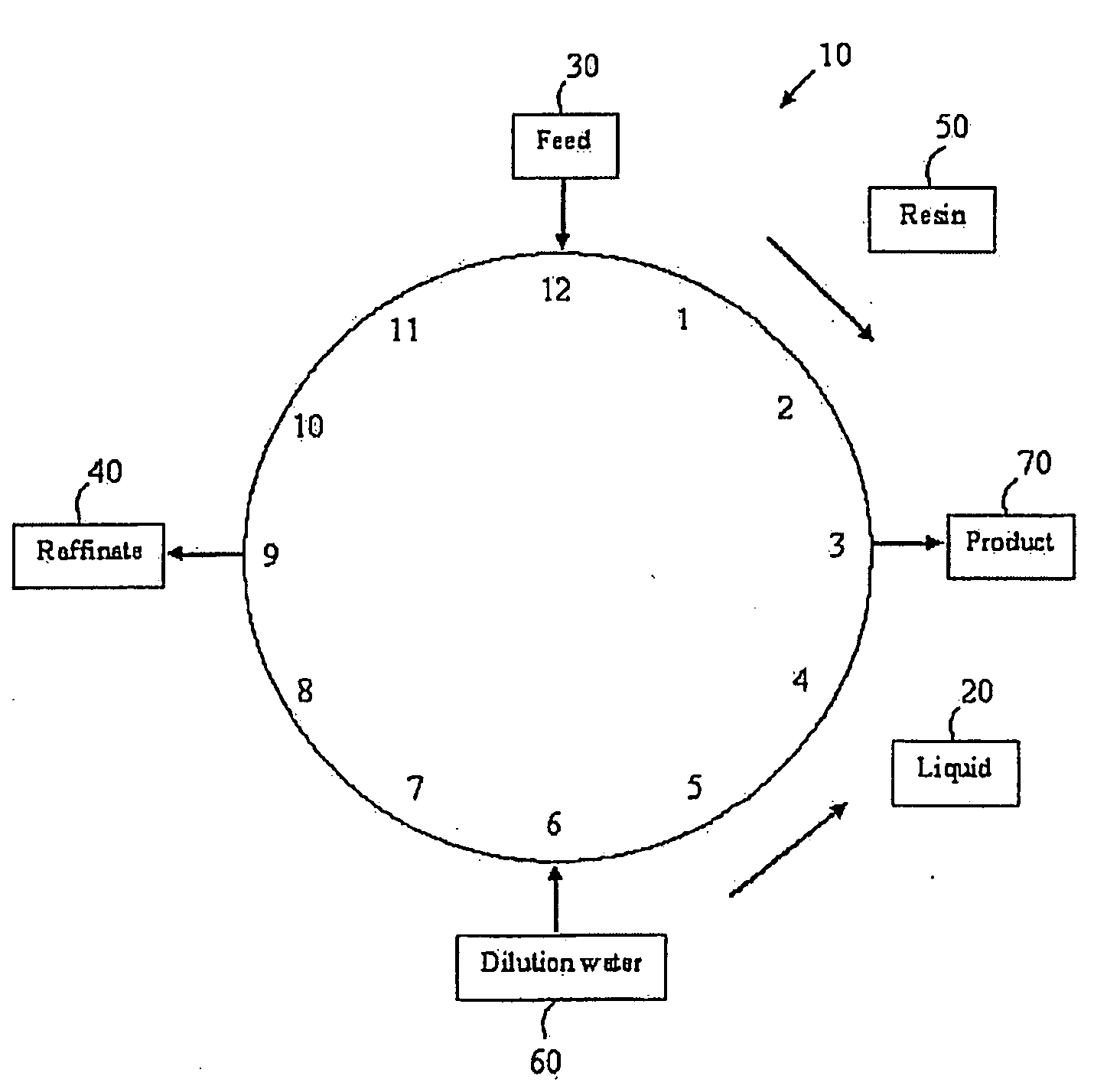
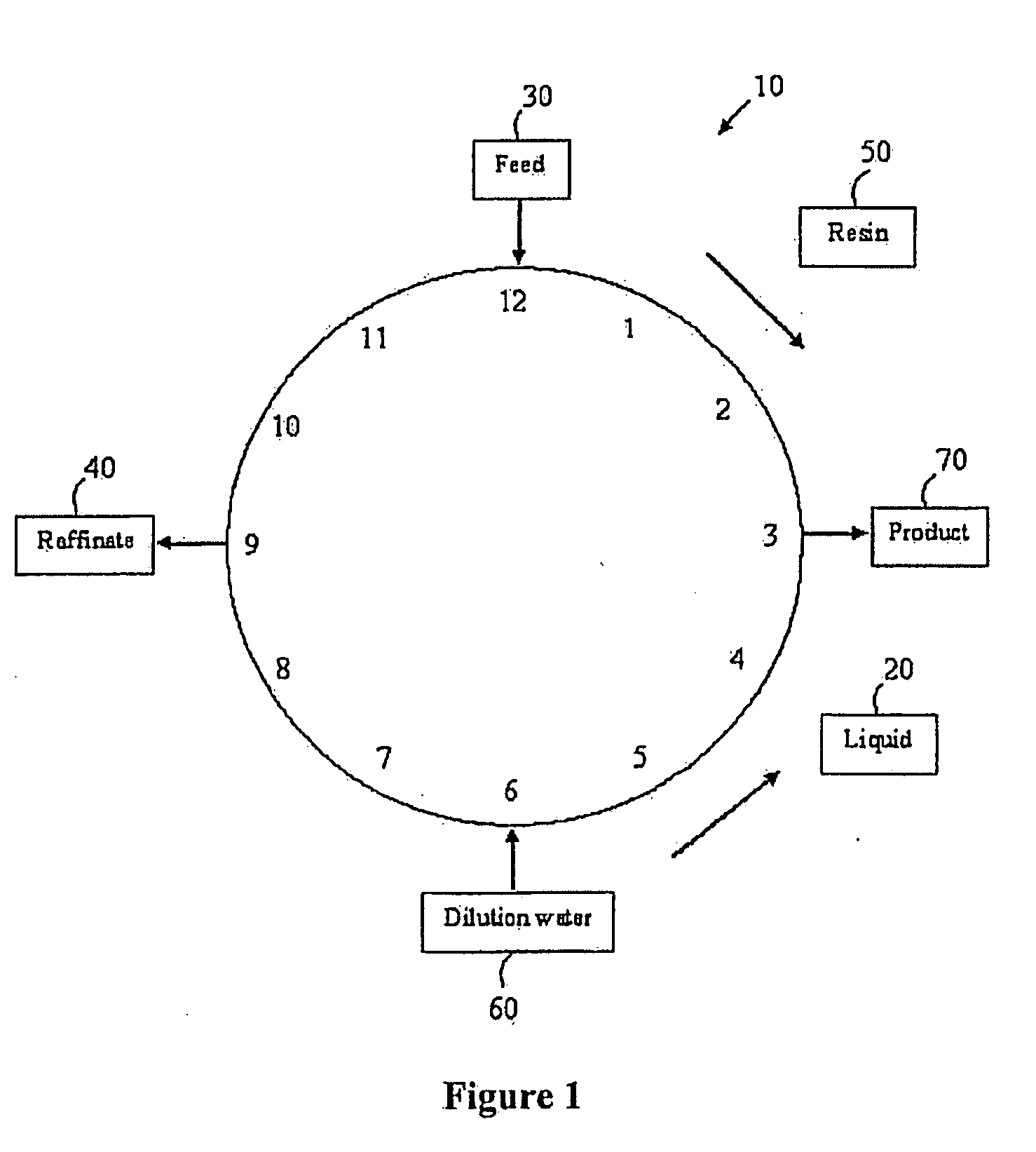
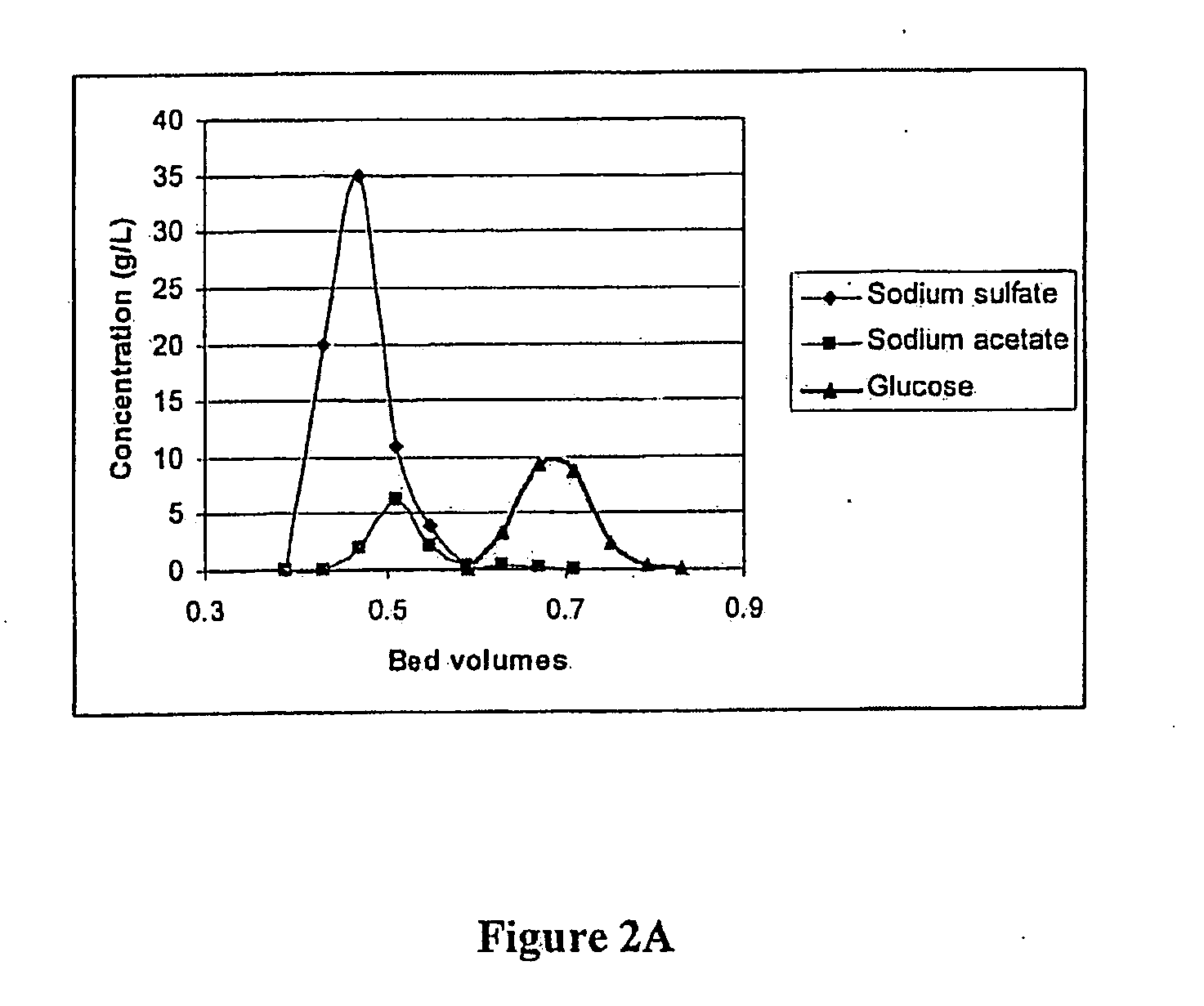
A process for obtaining a product sugar stream from cellulosic biomass is disclosed. In one process, the cellulosic biomass is pretreated at a pH between about 0.4 to 2.0 by adding one or more than one acid to produce a pretreated cellulosic biomass comprising acetic acid. One or more than one base is then added to the pretreated cellulosic biomass to adjust the pretreated cellulosic biomass to a pH of about 4.0 to about 6.0 to produce a neutralized cellulosic biomass comprising inorganic salt and acetate salt. The neutralized biomass is then hydrolyzed by cellulase enzymes to produce a crude sugar stream. Insoluble residue is separated from the crude sugar stream and the resulting clarified sugar stream is treated using ion exclusion chromatography at about pH 5.0 to about 10.0 to produce one or more raffinate streams and a product stream. The raffinate stream comprises inorganic salts and acetate salts, and the product stream comprises sugar. The product stream may then be fermented or otherwise further processed. In an alternate process, a product sugar stream is obtained from a crude sugar stream that is produced from conversion of cellulosic biomass to sugar. The cellulosic biomass may be produced using any suitable method. In this process the crude sugar stream is treated using ion exclusion chromatography at about pH 5.0 to about 10.0 to produce one or more than one raffinate stream comprising sulfate and acetate salts, and a product stream comprising sugar, and the product sugar stream is obtained.
Owner:IOGEN ENERGY CORP
Fractionation of biomass for cellulosic ethanol and chemical production
InactiveUS20100313882A1Reduce inhibitionMore cost-effectivelyBiofuelsGlucose productionFractionationFermentation
A process is defined for the continuous steam pretreatment and fractionation of corn cobs and low lignin lignocellulosic biomass to produce a concentrated cellulose solid stream that is sensitive to enzymatic hydrolysis. Valuable chemicals are recovered by fractionating the liquid and vapor stream composed of hydrolysis and degradation products of the hemicellulose. Cellulosic derived glucose is produced for fermentation to biofuels. A hemicellulose concentrate is recovered that can be converted to value added products including ethanol.
Owner:GREENFIELD SPECIALTY ALCOHOLS
Method for producing furfural from lignocellulosic biomass material
InactiveUS20110144359A1The process is simple and effectiveEasy to useOrganic chemistryOrganic acidLignocellulosic biomass
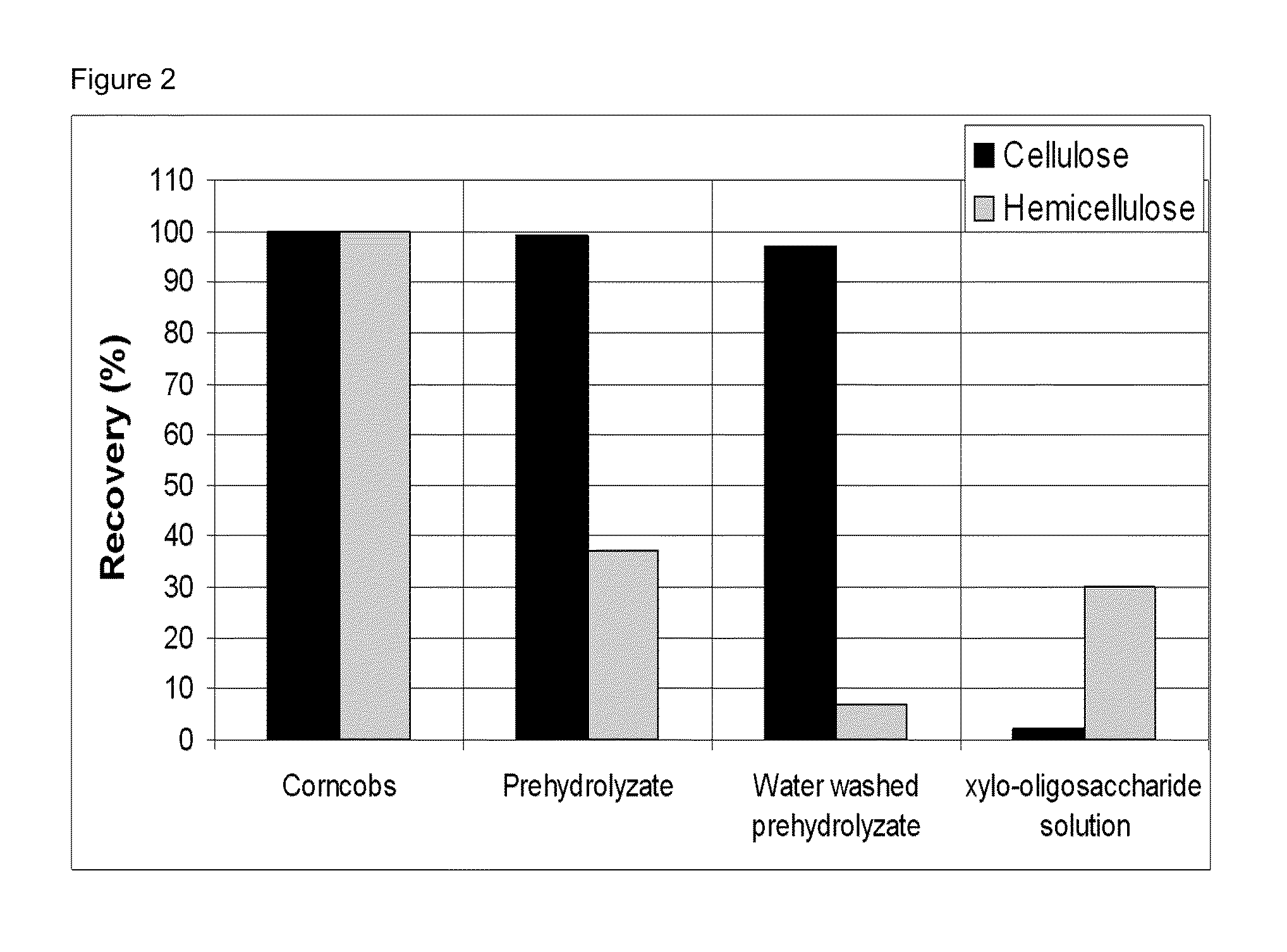
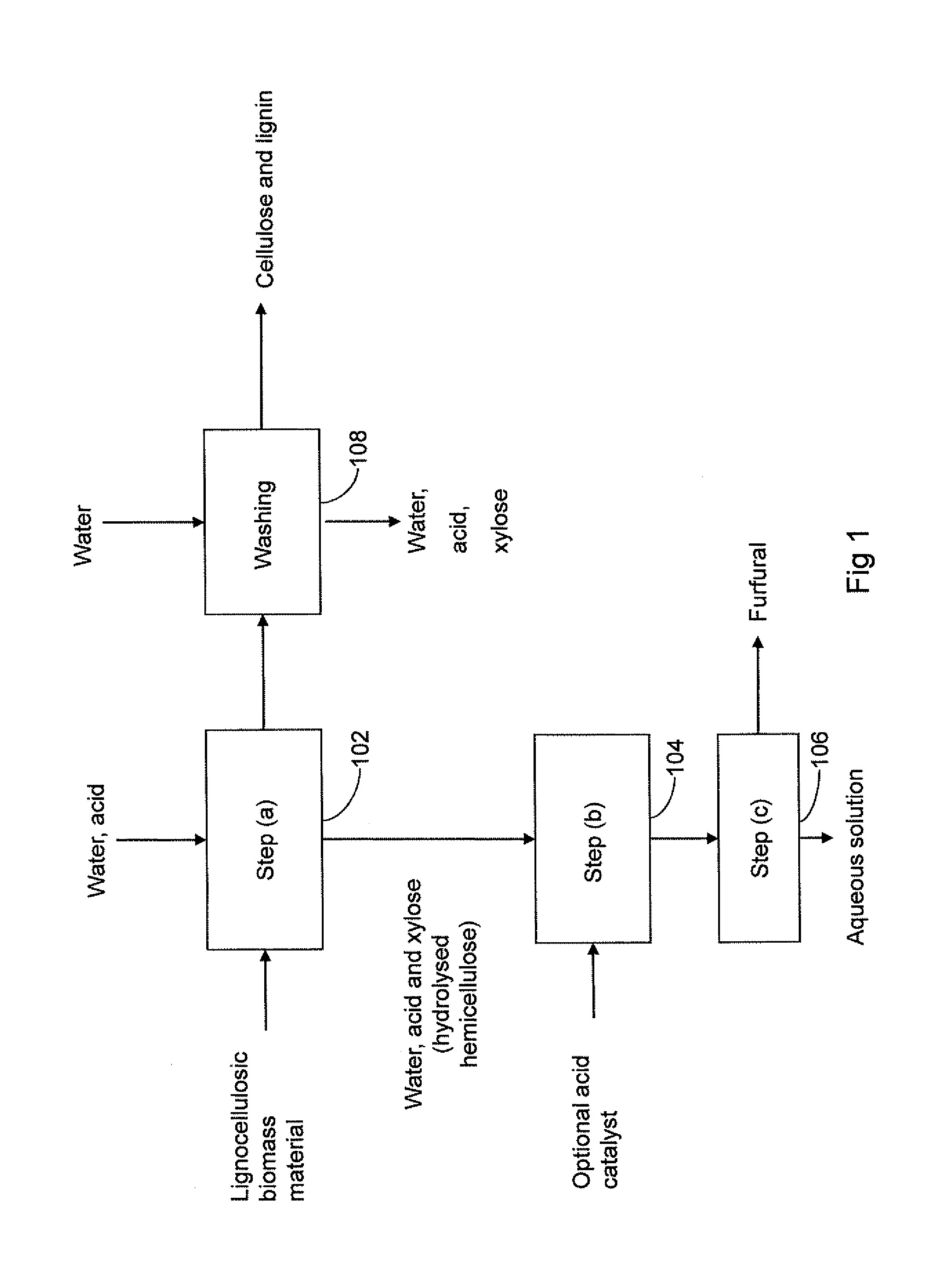
A method for producing furfural from lignocellulosic biomass material is provided, comprising (a) contacting the lignocellulosic biomass material with a mixture comprising water and an organic acid at a temperature of at least 100° C. and a pressure of at most 10 bar (absolute) to obtain a first liquid stream comprising hydrolysed hemicellulose and a second stream comprising lignin and cellulose; (b) maintaining the first liquid stream comprising hydrolysed hemicellulose at a temperature of at least 130° C. to obtain a second liquid stream comprising furfural; and (c) separating the furfural obtained in step b) from the second liquid stream.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Ozone treatment of biomass to enhance enzymatic saccharification
InactiveUS20100159521A1Reduce yieldReduction in yieldSugar derivativesBiofuelsCelluloseFermentable sugar
Methods for treating lignocellulosic biomass to produce readily saccharifiable carbohydrate-enriched biomass are provided. In one method, lignocellulosic biomass comprising lignin is treated with aqueous ammonia, then contacted with a gas comprising ozone at a temperature of about 0° C. to about 50° C. In another method, lignocellulosic biomass comprising lignin is contacted with a gas comprising ozone at a temperature of about 0° C. to about 50° C., then treated with aqueous ammonia. The readily saccharifiable carbohydrate-enriched biomass may be saccharified with an enzyme consortium to produce fermentable sugars.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com