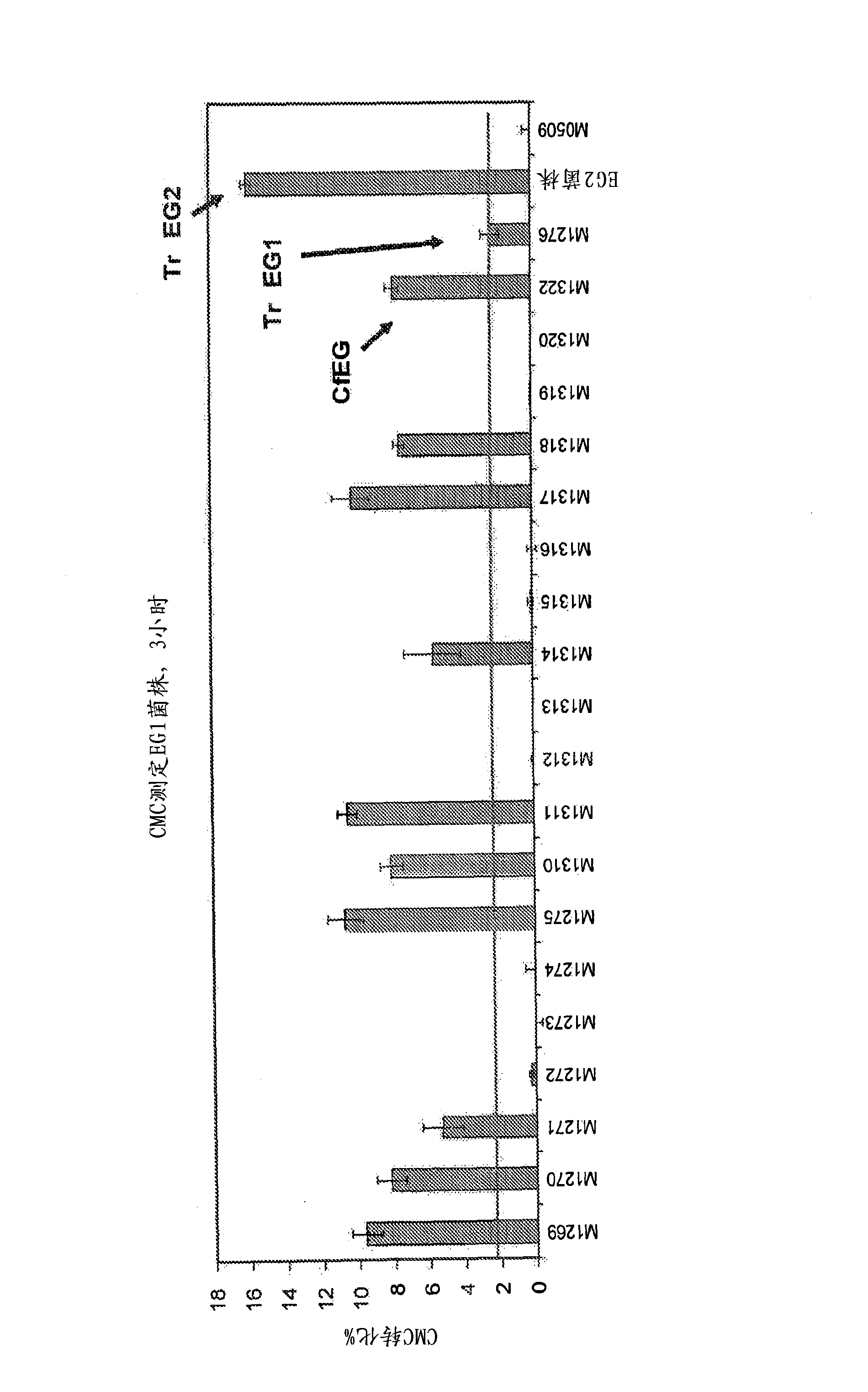
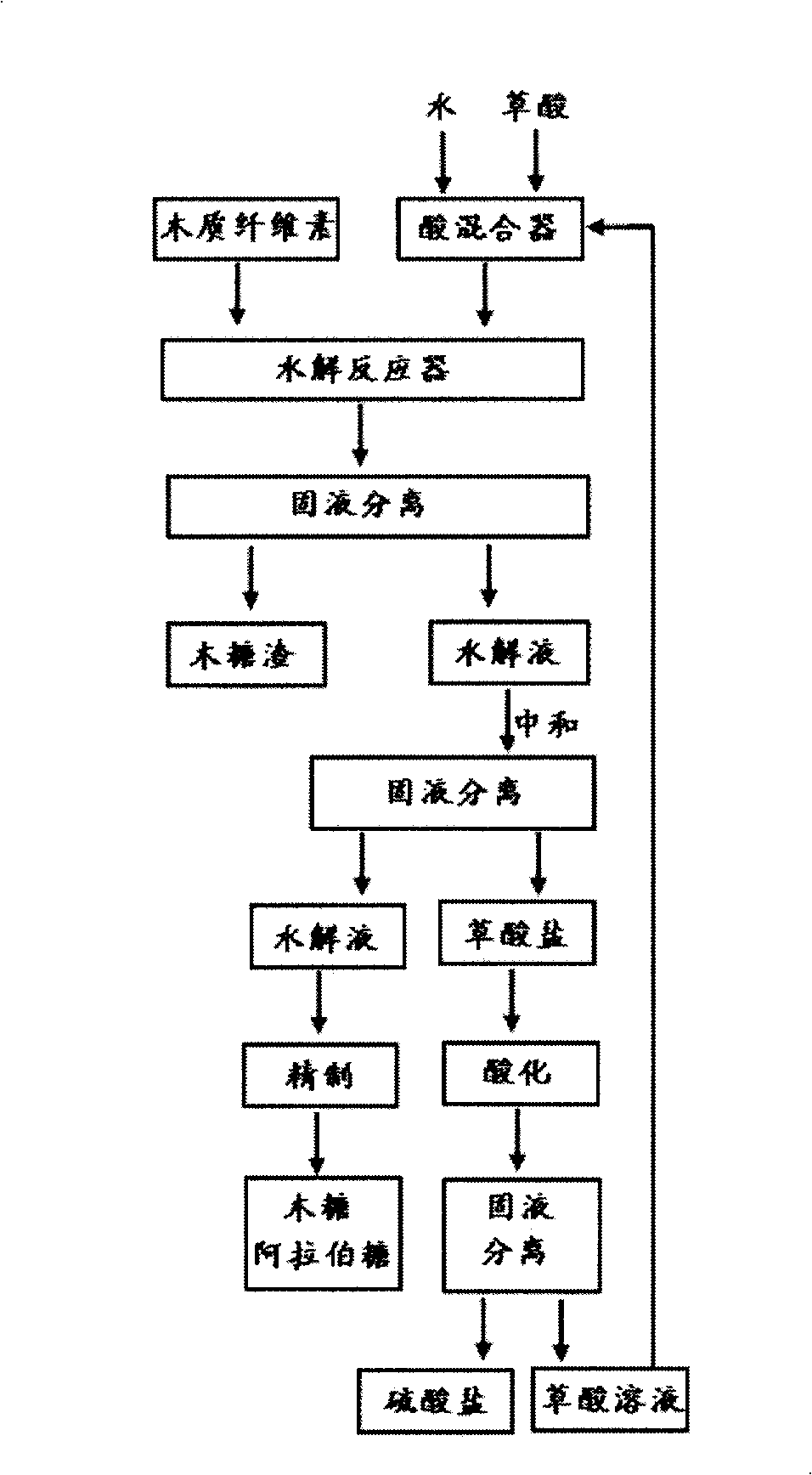
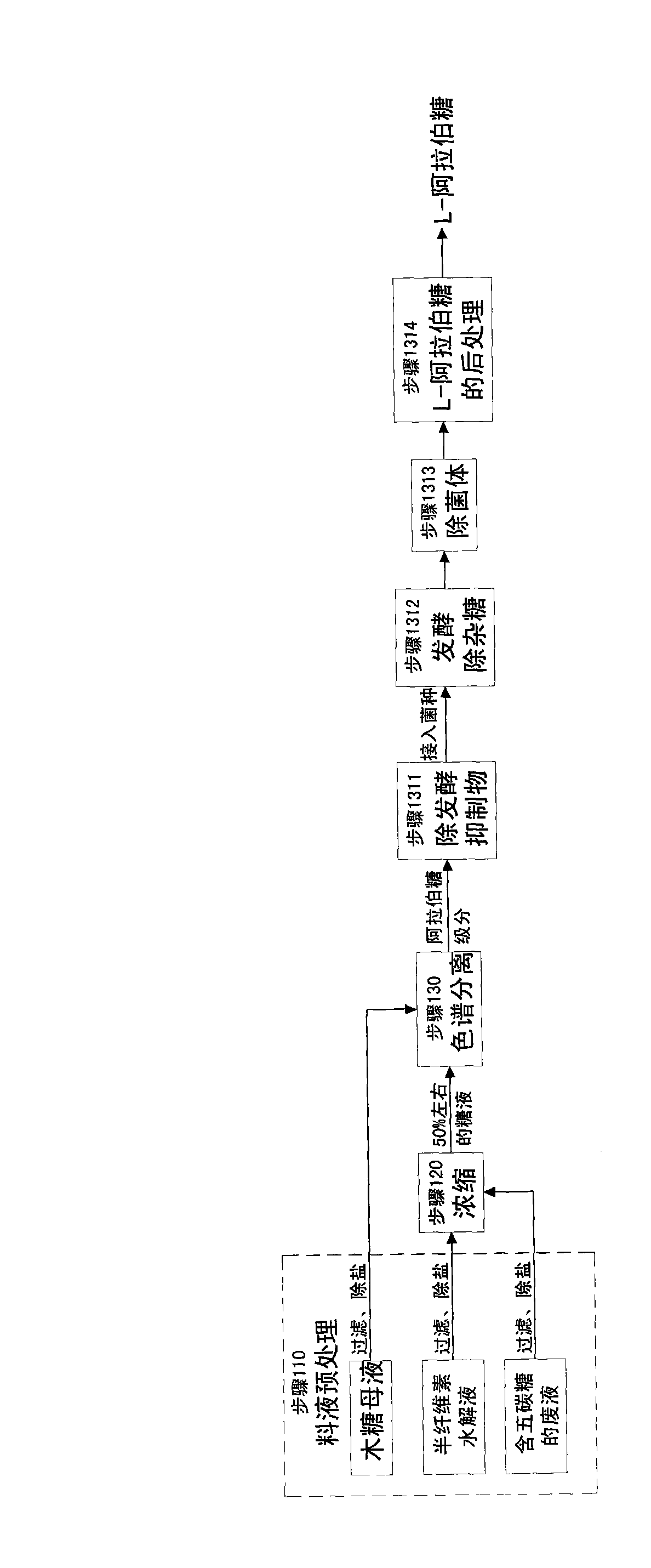
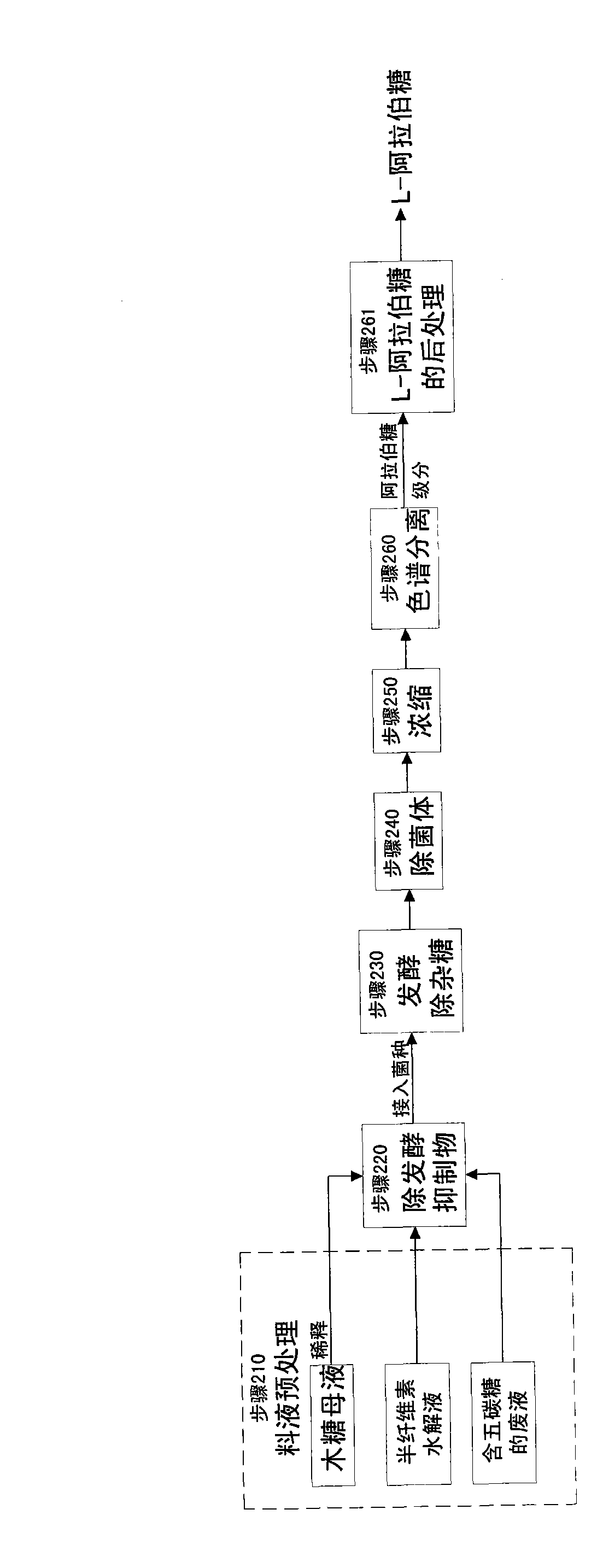
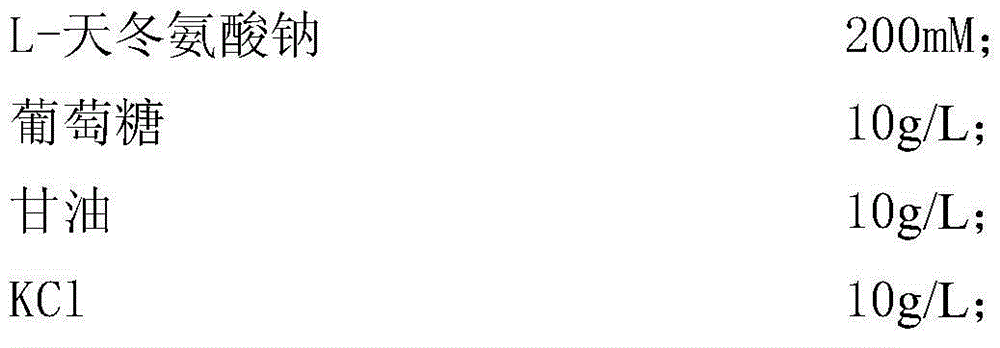Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1244 results about "Arabinose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
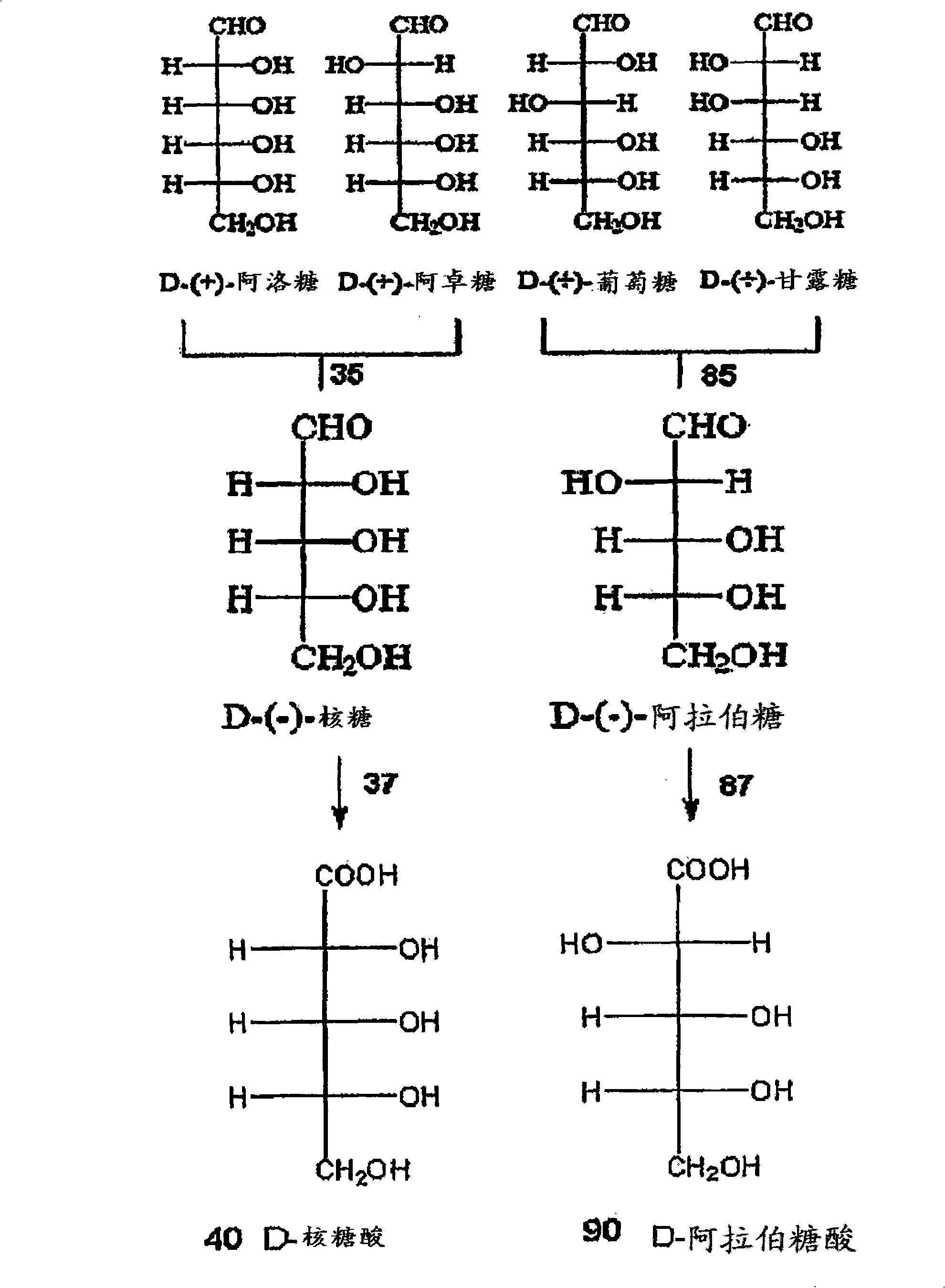
Arabinose is an aldopentose – a monosaccharide containing five carbon atoms, and including an aldehyde (CHO) functional group. For biosynthetic reasons, most saccharides are almost always more abundant in nature as the "D"-form, or structurally analogous to D-glyceraldehyde. However, L-arabinose is in fact more common than D-arabinose in nature and is found in nature as a component of biopolymers such as hemicellulose and pectin.
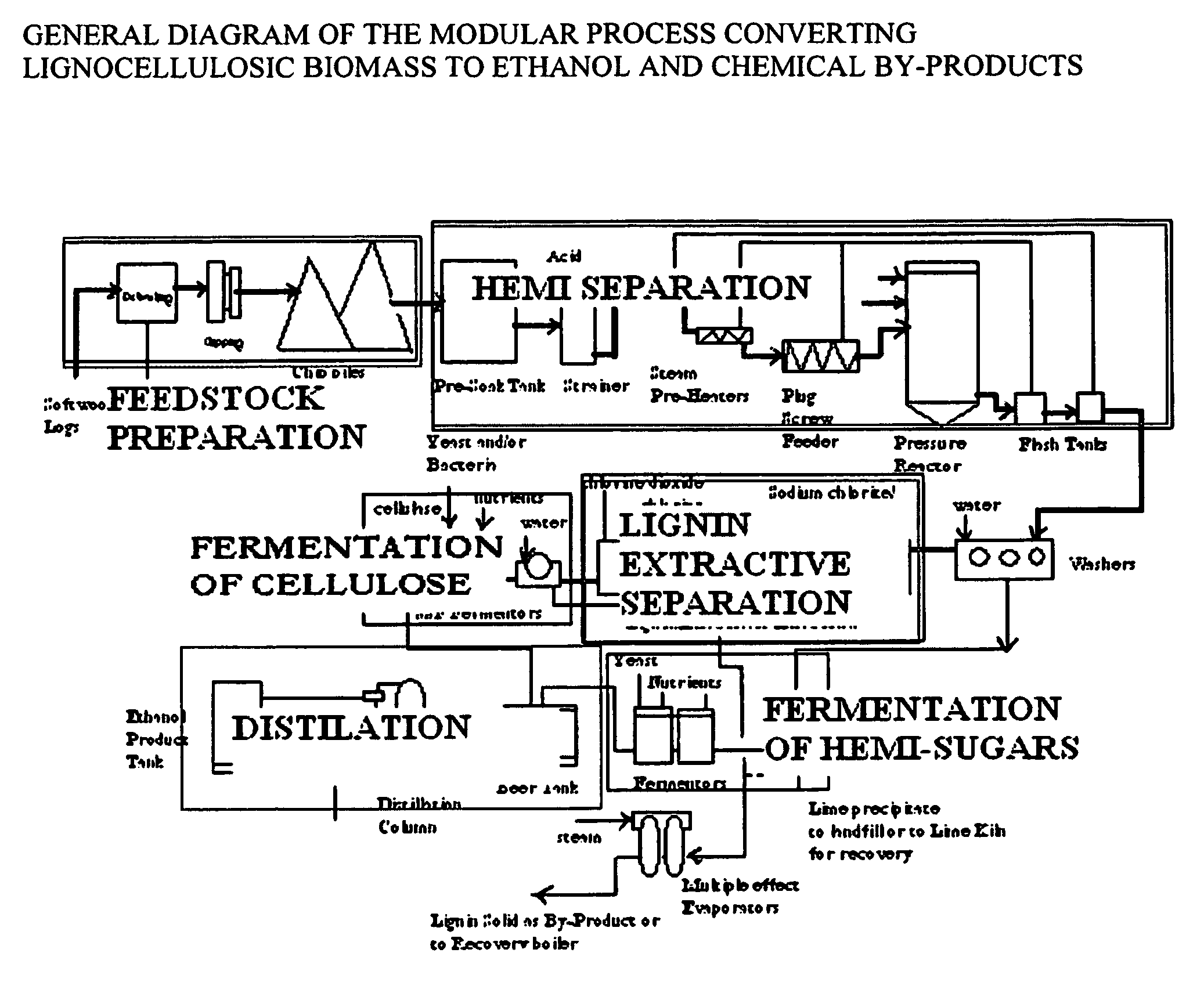
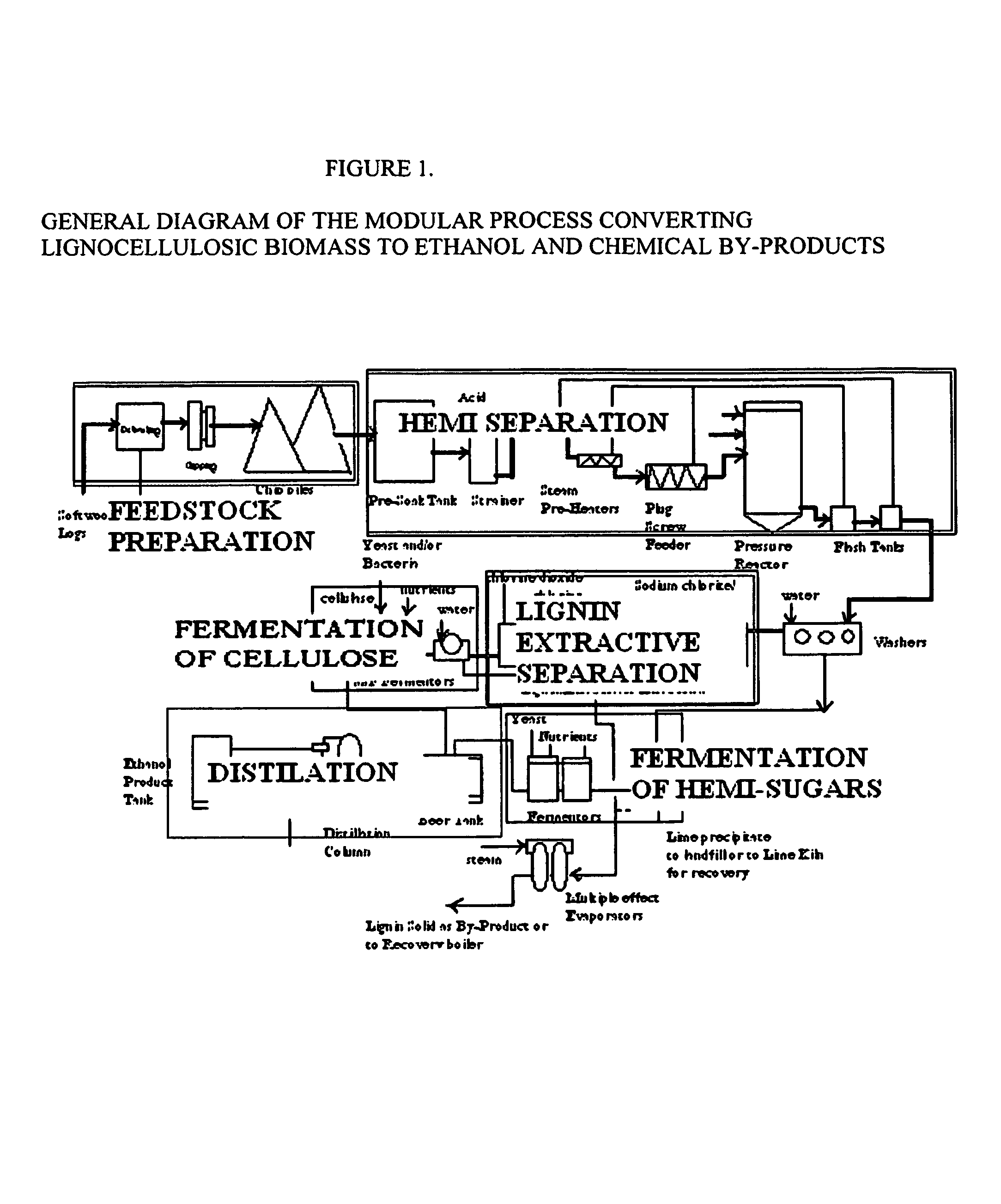
Integrated process for separation of lignocellulosic components to fermentable sugars for production of ethanol and chemicals
InactiveUS20080057555A1Robust and cost-effectiveImprove responseChemical industryBiofuelsChemical treatmentButanediol
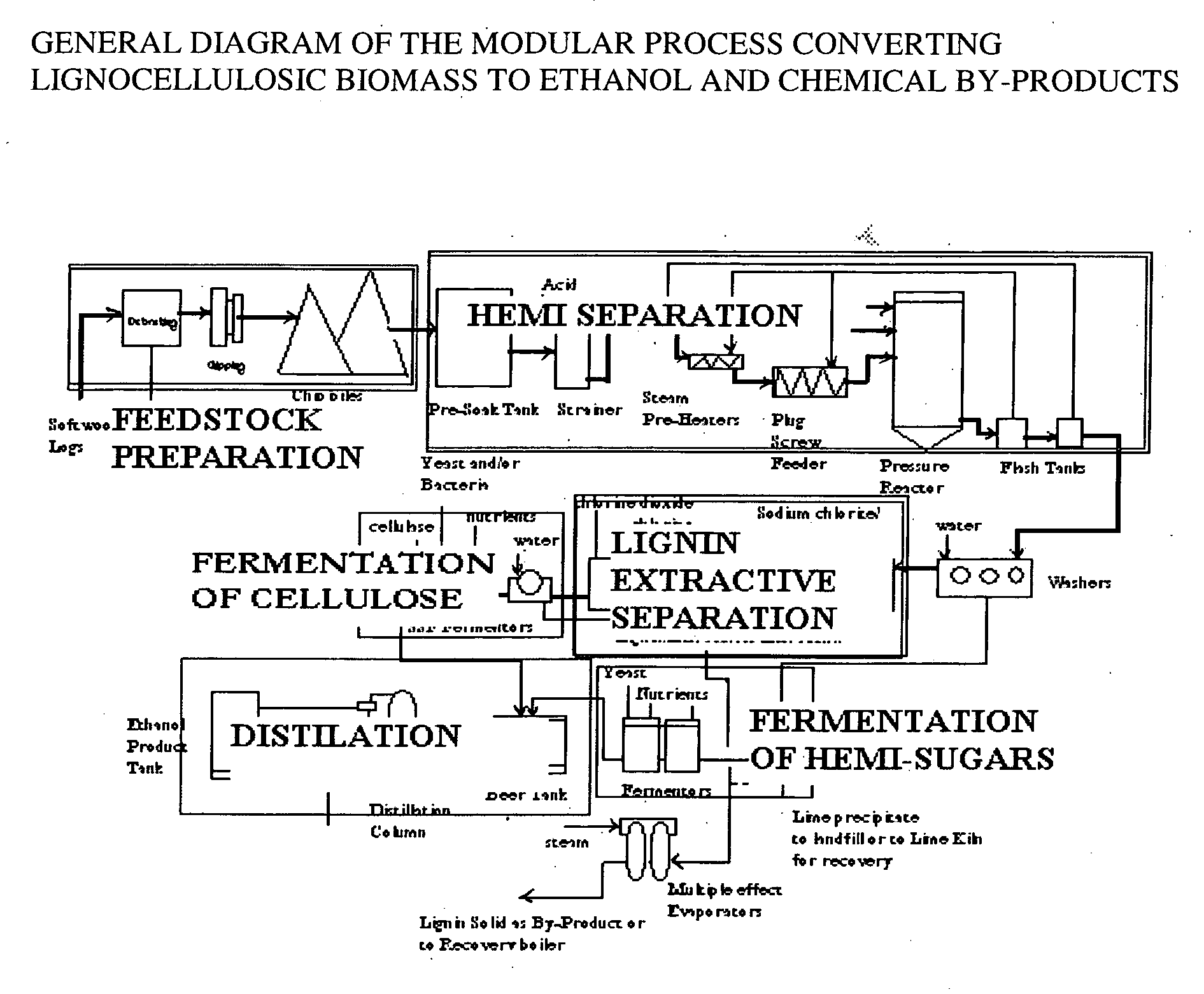
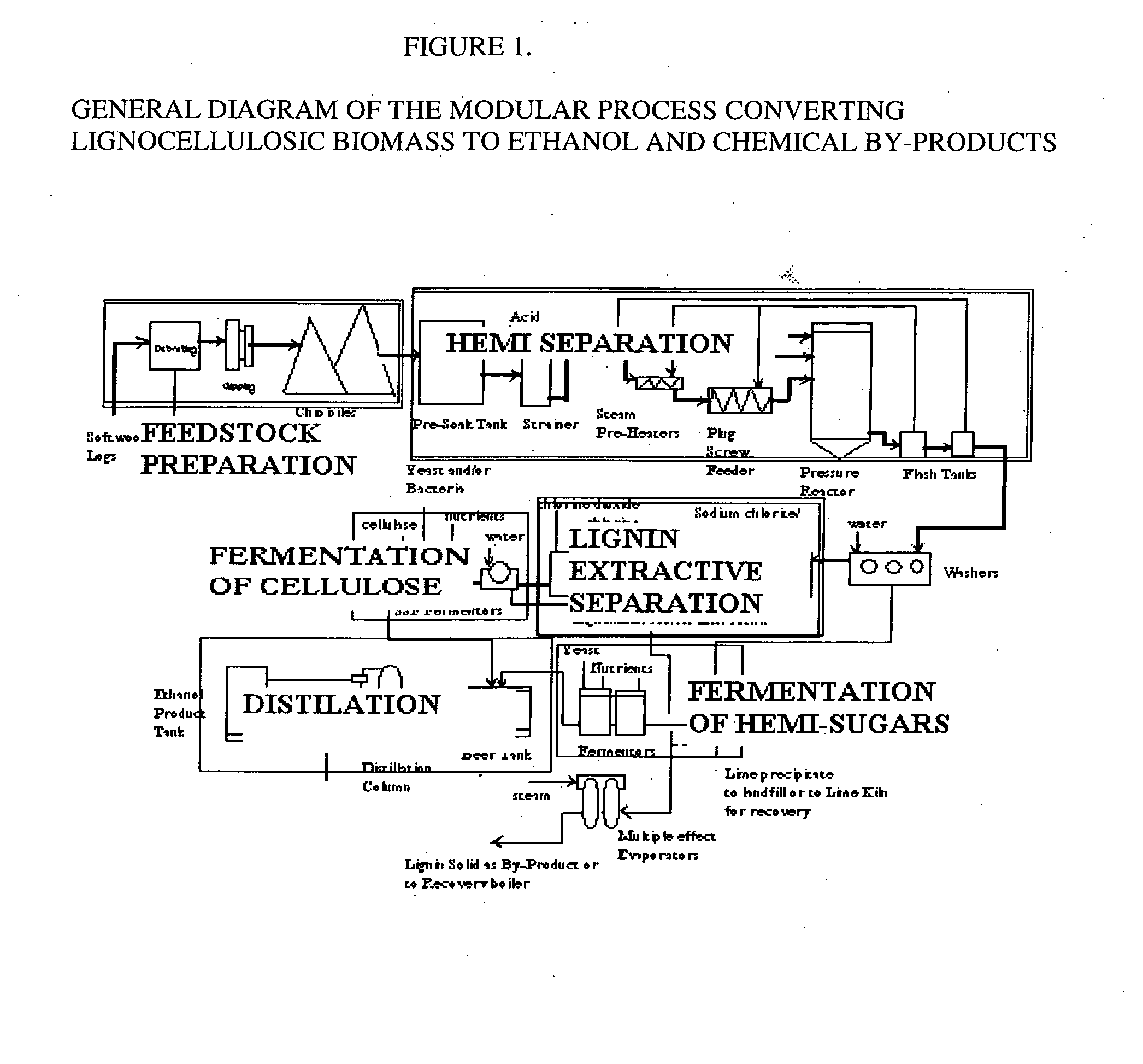
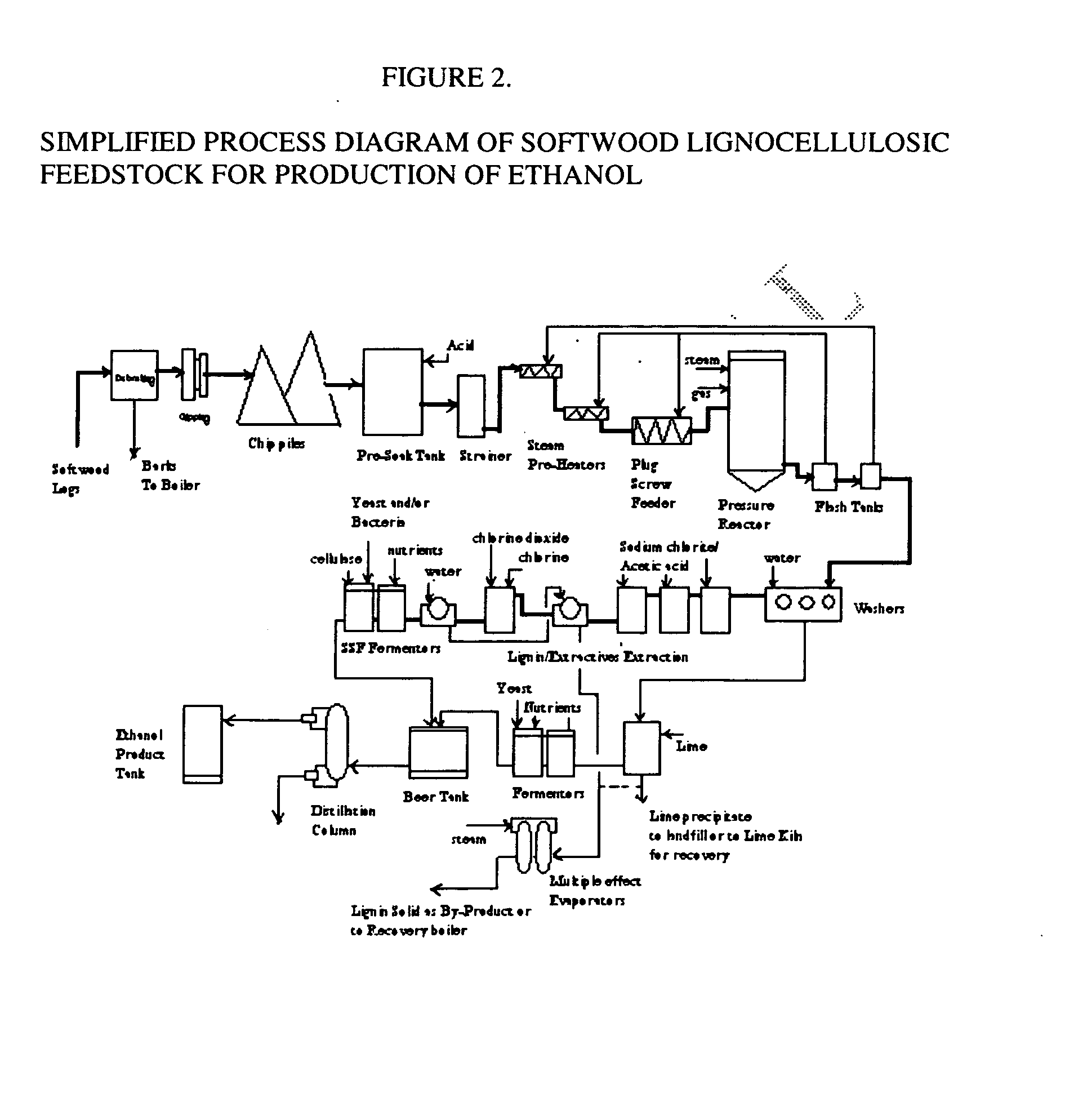
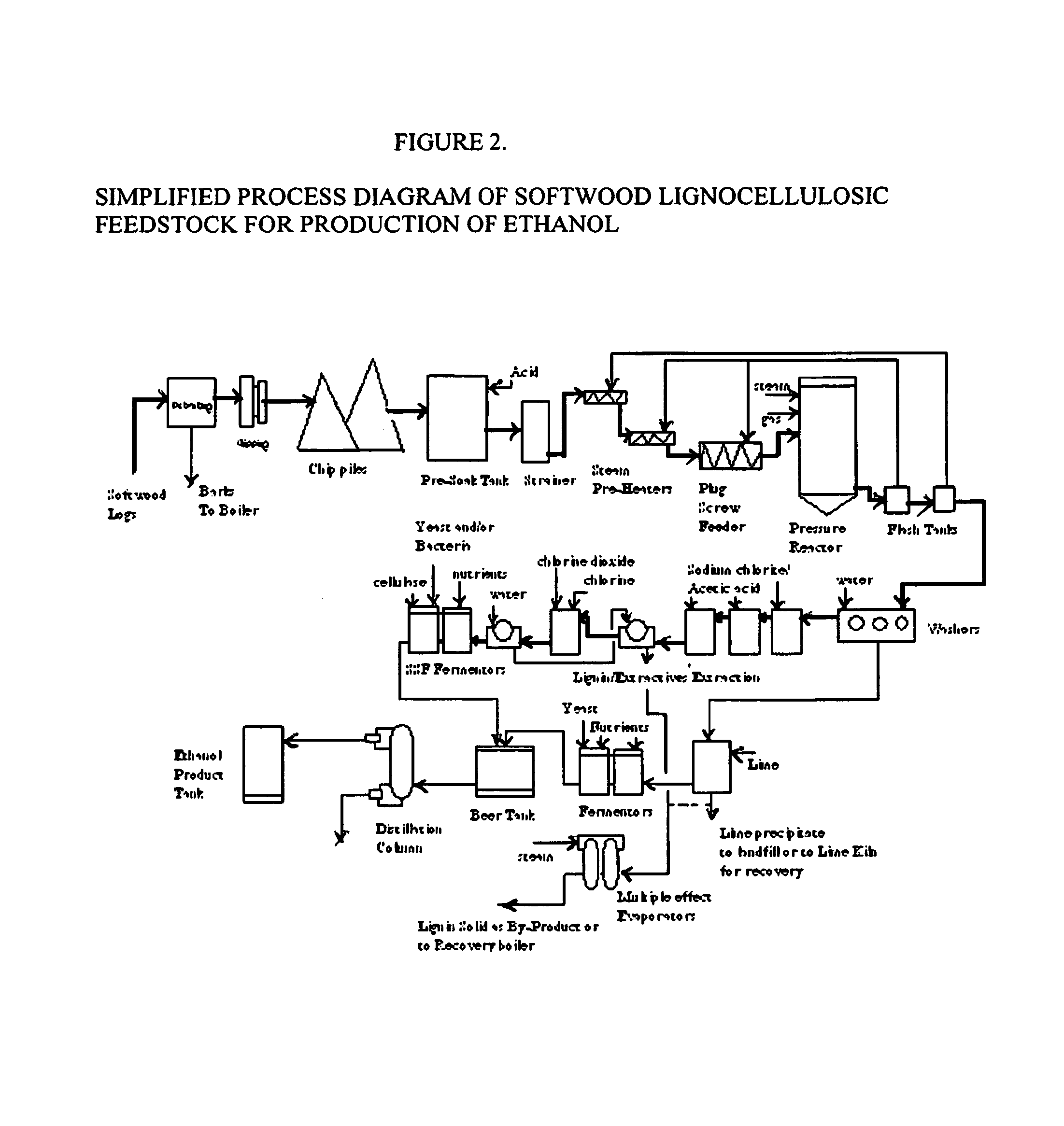
A continuous and modular process converts lignocellulosic materials for the production of ethanol principally and / or chemicals such as methanol, butanediol, propanediol, hydrocarbon fuel, etc. Renewable lignocellulosic biomass such as but not all inclusive hardwoods (gum, beech, oak, sweet gum, poplar, eucalyptus, etc.), soft woods (pines, firs, spruce, etc.), corn stovers, straws, grasses, recycled papers, waste products from pulp and paper mills, etc can be used as feedstock. The process is designed to be modular and the feed entry point can be selected to adapt to different biomass feedstock. Lignocellulosic biomass such as hardwood and softwood are subjected to chemical / pressure treatment stages using potent and selective chemicals such as sodium chlorite / acetic acid (anhydrous) and chlorine / chlorine dioxide to separate the main components—lignin, cellulose (glucose) and hemicelluloses (xylose, arabinose, galactose)—into three process streams. The separated carbohydrates are further subjected to washing, cleaning, neutralization, and / or mild hydrolysis and subsequently fermented to produce ethanol. Residual lignin and extractives remained with the cellulose are removed by chemical treatment steps to enhance the fermentations of cellulose. Pre-hydrolysate after neutralization to neutralize and remove toxic components such as acetic acid, furfural, phenolics, etc. containing (xylose, arabinose, galactose) and hexoses (glucose) can be either separately or together with the purified cellulosic fraction fermented to produce ethanol. Approximately 100 gallons of ethanol, suitable to be used as a fuel, can be produced from one dried ton of wood. Significant amount of lignin are separated as a by-product and can be converted to hydrocarbon fuel, surfactant, drilling aid, or can be incinerated for generation of power and steam.
Owner:NGUYEN XUAN NGHINH
Isolated polynucleotides encoding d-arabino-3-hexulose-6-phosphate synthases from Methylophilus methylotrophus
Owner:POLYNUCLEOTIDES ENCODING POLYPEPTIDES INVOLVED IN ONE CARBON COMPOUNDS METABOLISM IN METHYLOPHILUS METHYLOTROPHUS +1
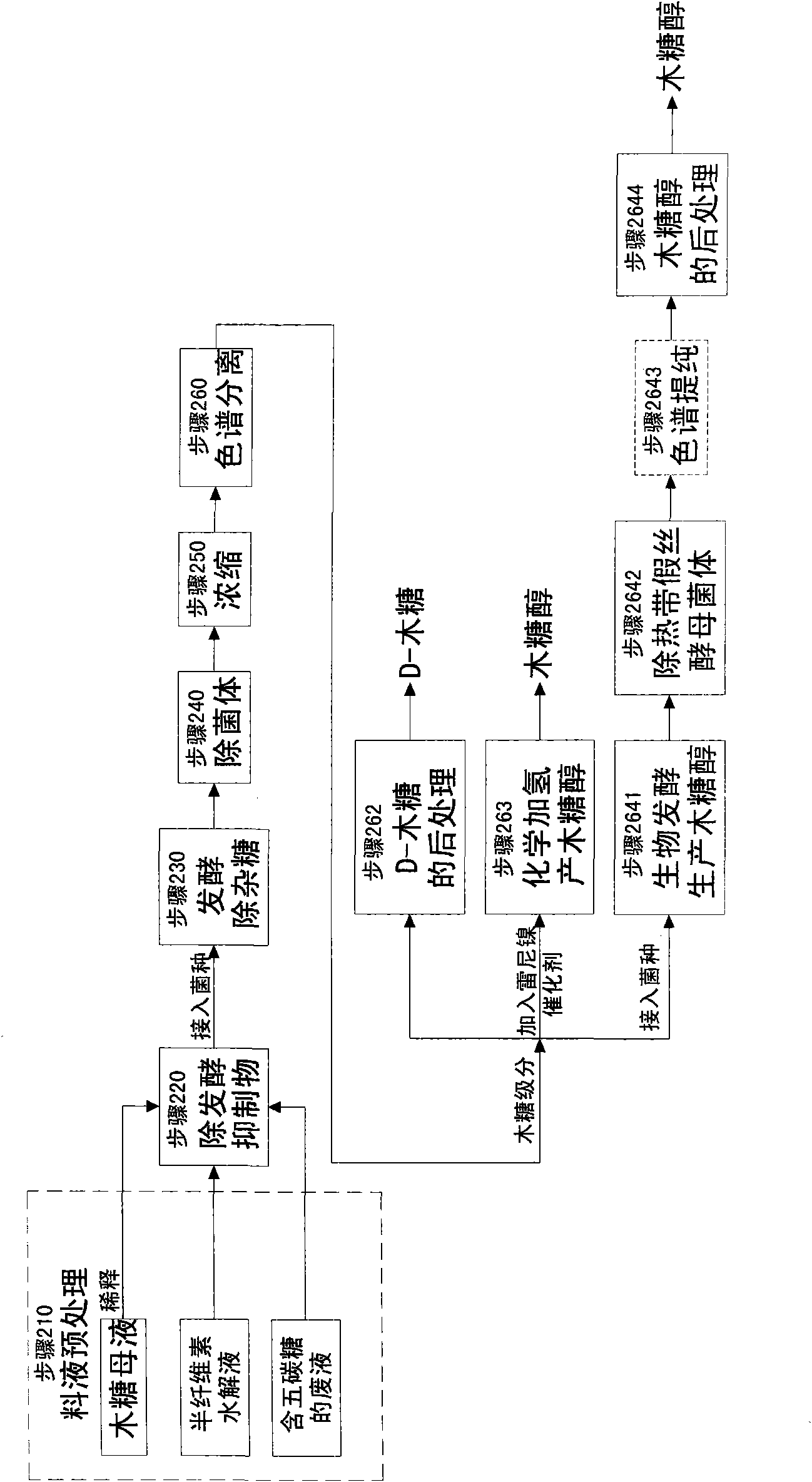
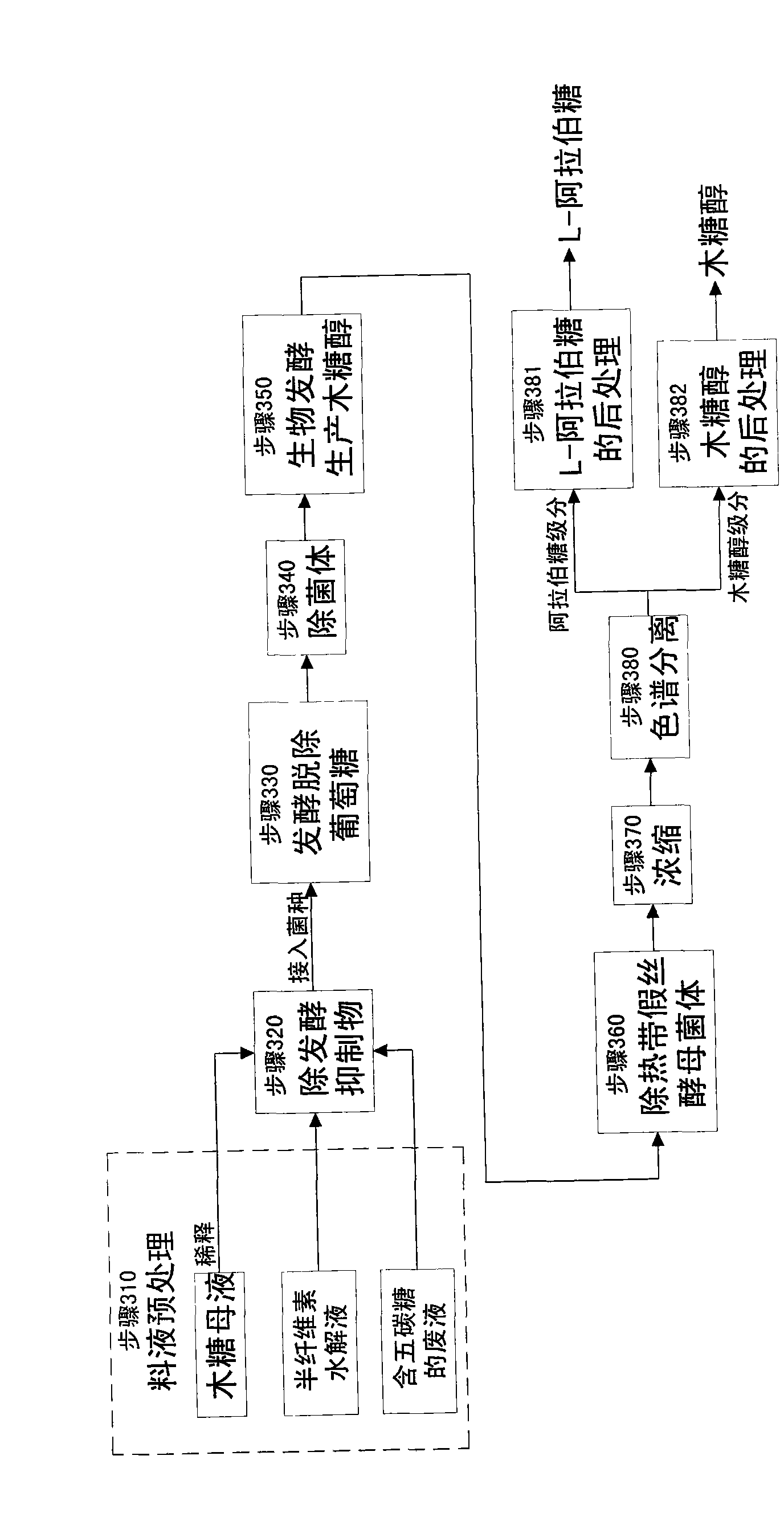
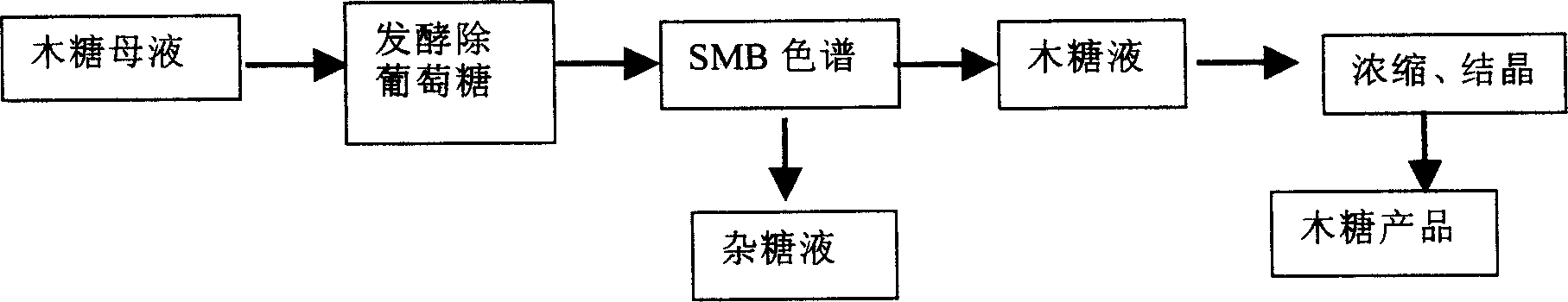
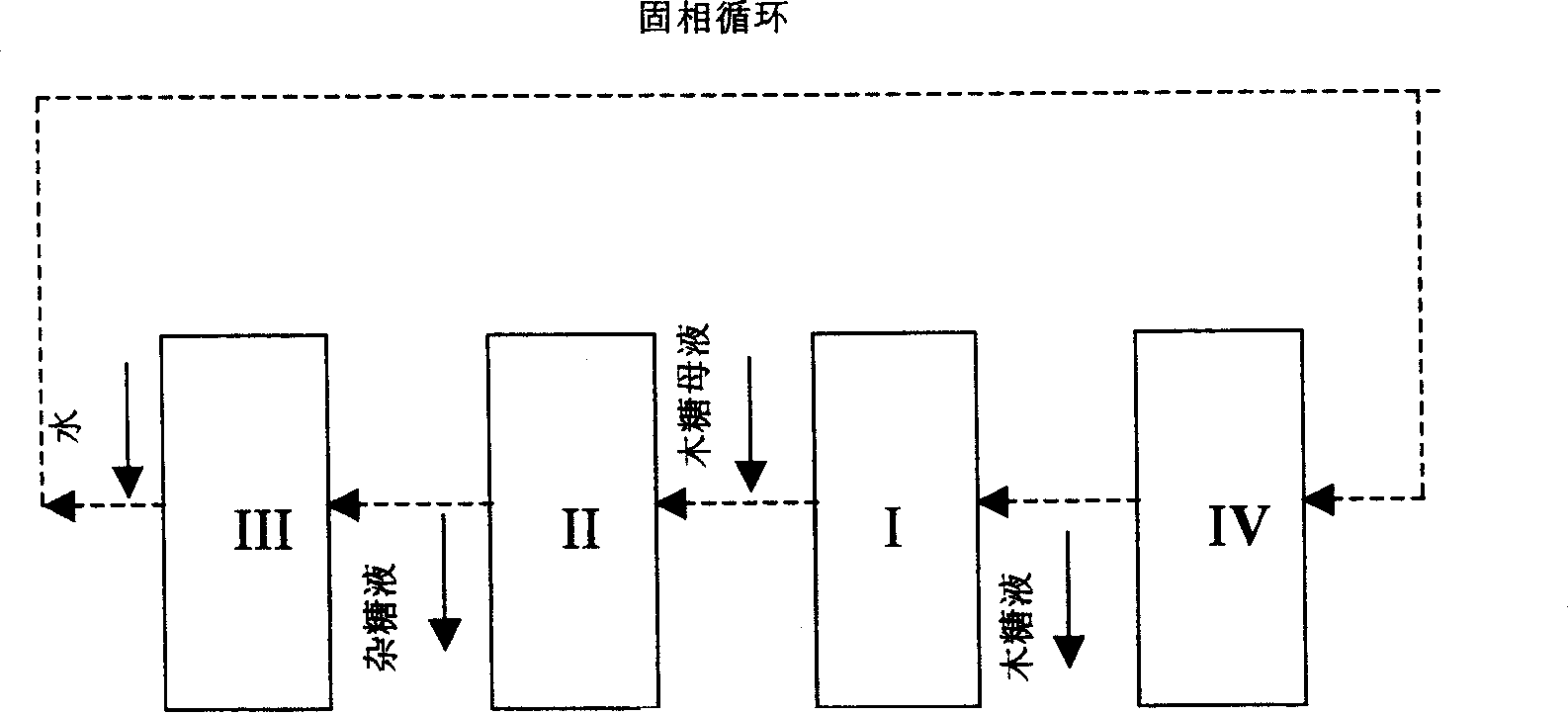
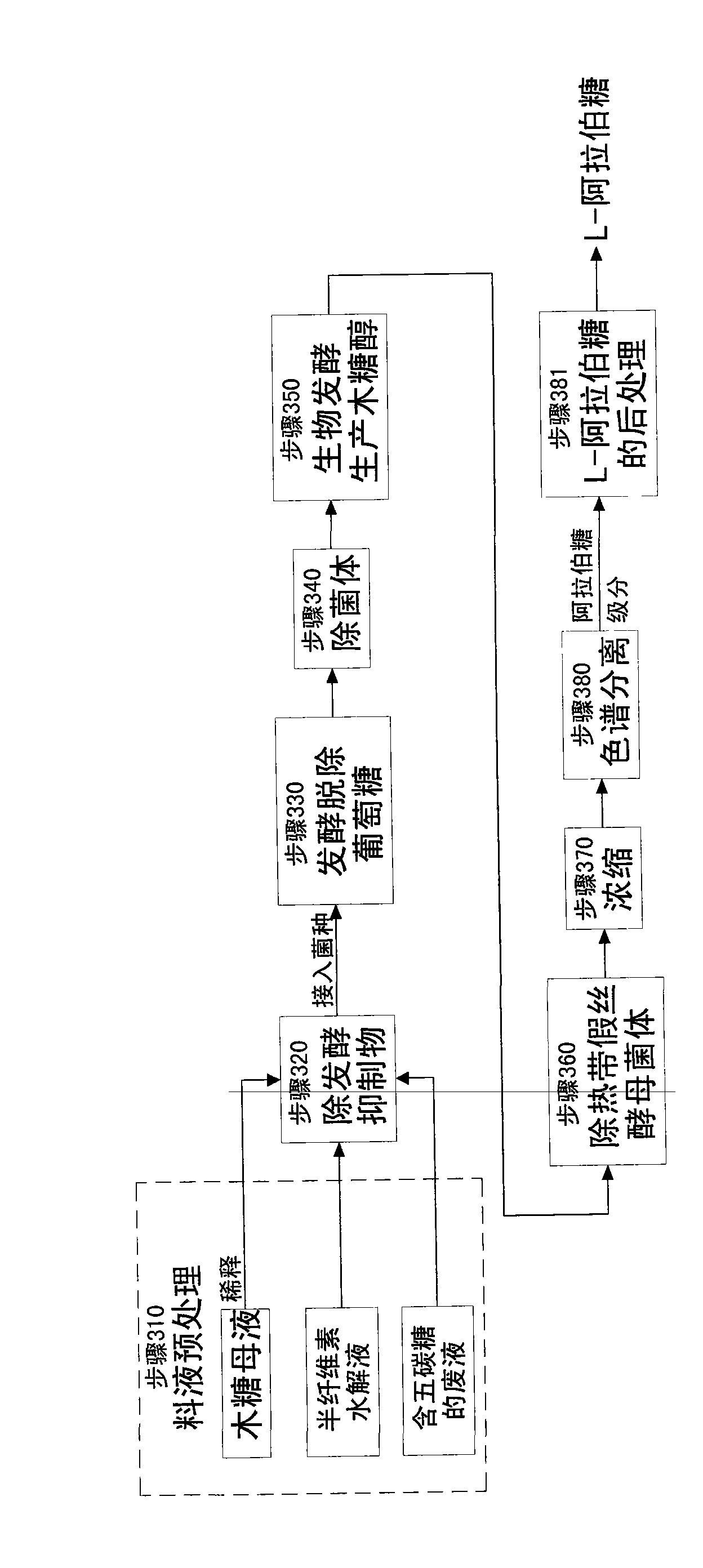
Method for producing wood sugar product
ActiveCN101659681AHigh purityFermentation went wellIon-exchange process apparatusSugar derivativesChromatographic separationHydrolysis
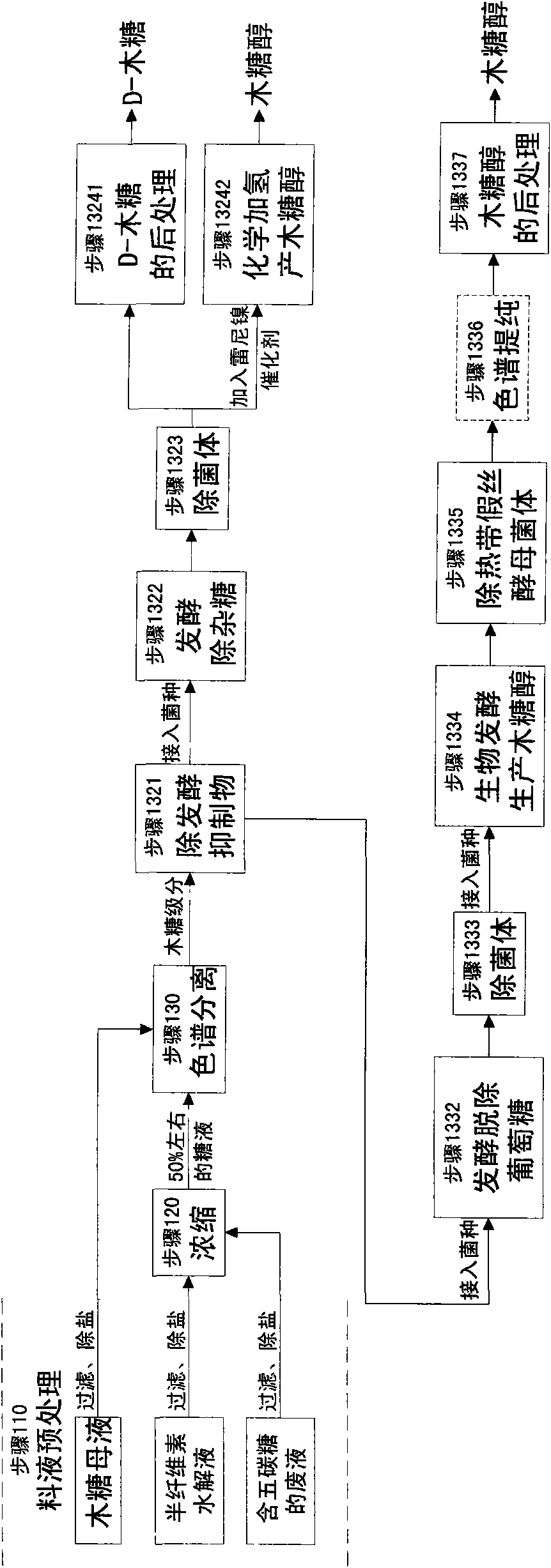
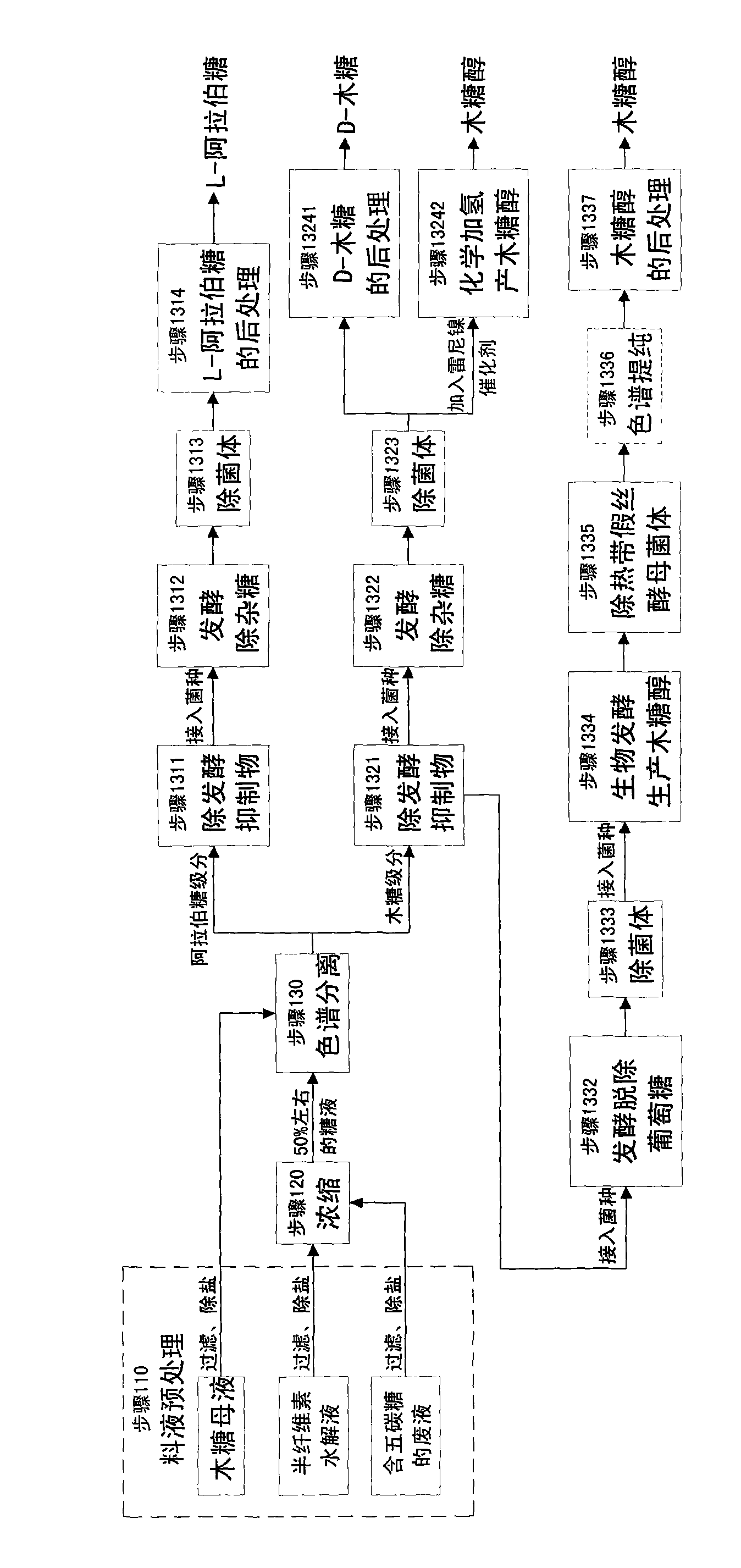
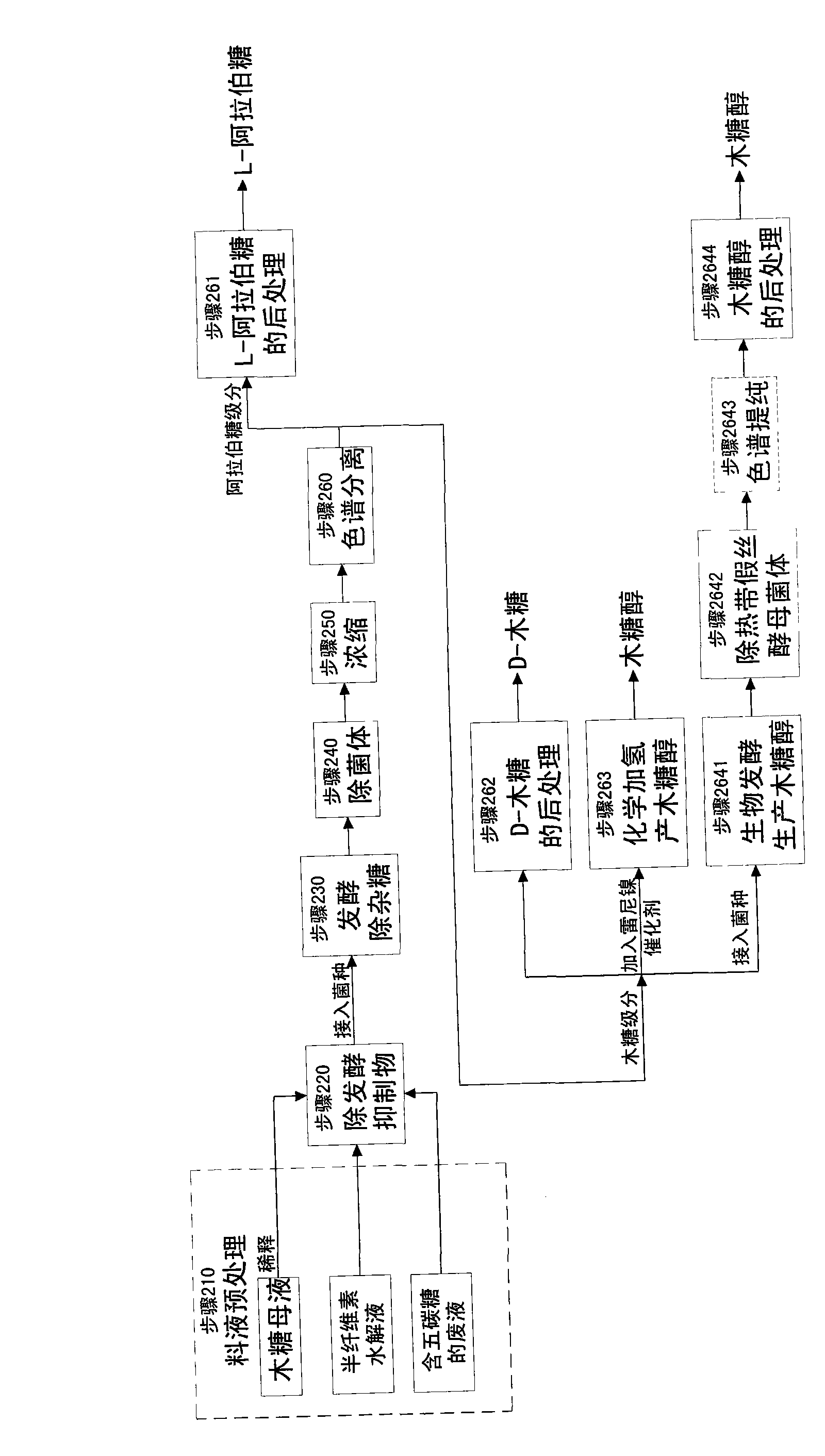
The invention relates to a method for producing a wood sugar product and a byproduct of ethanol or D-ribose or citric acid. The method takes hydrolysis liquid, wood sugar mother liquor and / or production waste liquid containing pentose of agricultural or forestry waste as the raw materials, comprising the following steps: (a) preprocessing feed liquid; (b) colour spectrum separation: separating thefeed liquid into arabinose fraction feed liquid and wood sugar fraction feed liquid; (c) removing mixed sugar at least containing glucose and galactolipin; and (d) carrying out aftertreatment on thewood sugar fraction feed liquid to obtain the wood sugar product. The wood sugar product comprises xylitol and D-wood sugar. The invention has low production cost and high efficiency and is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:SHENGQUAN HEALTANG
Integrated process for separation of lignocellulosic components to fermentable sugars for production of ethanol and chemicals
InactiveUS7666637B2Robust and cost-effectiveImproving biological reactivity of celluloseChemical industryBiofuelsChemical treatmentHydrolysate
The invented process separates main components in lignocellulosic biomass, specifically hardwoods, softwoods into lignin and fractions of high purity sugars which are used for ethanol production. The invented process comprises of treatment stages at high temperature and high pressure with hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid. Residual lignin and extractives in the cellulosic solid fraction are selectively removed by chemical treatments of sodium chlorite, anhydrous acetic acid, chlorine and chlorine dioxide to enhance the purity and biological conversion of cellulose to ethanol. The pre-hydrolysate generated from the acid treatment stage, containing xylose, arabinose, galactose, glucose and the purified cellulosic fraction are enzymatically hydrolyzed and fermented to produce ethanol. Significant amount of lignin from the process is recovered as a by-product.
Owner:NGUYEN XUAN NGHINH
Modification of xylan
InactiveUS20130233501A1Low water solubilityReduce solubilityNon-fibrous pulp additionSpecial paperSolubilityCellulose
The invention provides a method of modifying soluble xylan which contains glucuronic acid and / or arabinose side chains so that it can be adsorbed onto other substrates. The method includes the steps of enzymatically modifying the xylan by selectively removing glucuronic acid and / or arabinose side chains from the xylan with α-D-glucuronidase and / or α-L-arabinofuranosidase, and allowing the modified xylan to adsorb onto the substrate. The substrate may be a cellulosic substrate like pulp or paper or a non-cellulosic substrate. The enzymes are able to remove a sufficient number of the xylan side chains so as to decrease water solubility of the xylan, induce xylan precipitation and allow adsorption of the xylan onto other substrates. A pulping process which incorporates modification of xylan and adsorption onto cellulosic material is also provided, as are products which contain the modified xylan.
Owner:STELLENBOSCH UNIVERSITY
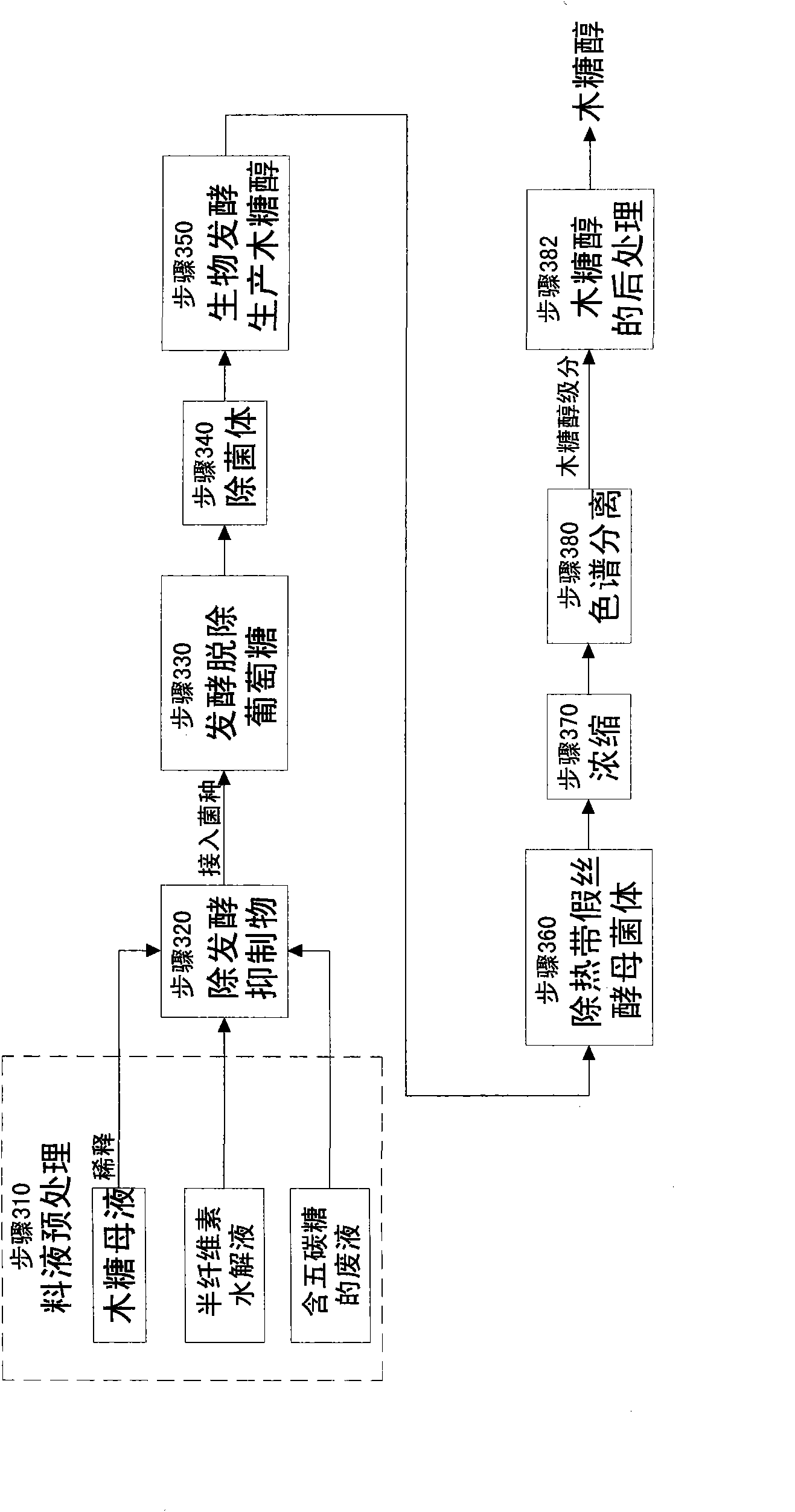
Method for producing L-arabinose and D-xylose
ActiveCN101665523AHigh purityFermentation went wellIon-exchange process apparatusSugar derivativesBiotechnologyChromatographic separation
The invention relates to a method for producing L-arabinose and D-xylose, which can simultaneously produce ethanol or D-ribose or citric acid as a byproduct. The method utilizes a hydrolyzate of agricultural waste, a xylose mother liquor and / or a production waste liquor containing pentose as the raw materials and comprises the following steps: (1) pretreating the raw materials; (b) carrying out the chromatographic resolution to separate the raw materials into an arabinose-stage liquor and a xylose-stage liquor; (c1) removing fermentation inhibitors which are impurities and unwanted bacteria, which have an inhibiting effect on the fermentation; (c2) fermenting to remove unwanted saccharides at least comprising glucose and galactose; (d) and finally, respectively carrying out the post treatment on the arabinose-stage liquor and the xylose-stage liquor to obtain the L-arabinose and the D-xylose. Steps (c1) and (c2) are arranged before the chromatographic resolution in step (b) or after step (b). The method has the advantages of low production cost and high efficiency, and is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:SHENGQUAN HEALTANG
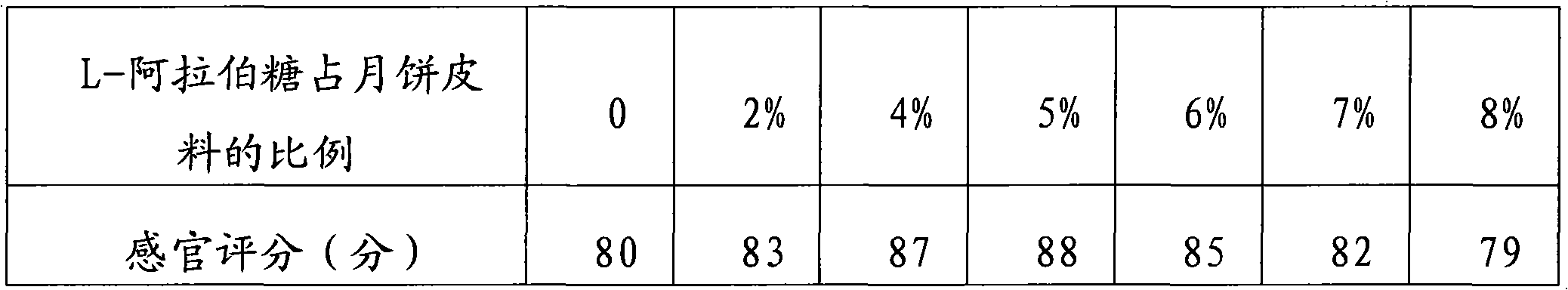
Moon cake
ActiveCN101889600AEasy to shapeImprove plasticityDough treatmentBakery productsAlkaline waterVegetable oil
The invention discloses a moon cake. The moon cake comprises a moon cake cladding and a moon cake filling, wherein the moon cake cladding comprises the following raw materials: 40 to 70 percent of wheat flour, 20 to 45 percent of sugar alcohol, 2 to 8 percent of L-arabinose, 5 to 20 percent of animal and vegetable oil or hydrogenated animal and vegetable oil and 0.2 to 2 percent of alkaline water. The technical problems of soft cladding and poor plasticity caused by the low viscosity of a sugar-free moon cake which takes maltitol solution as a cladding in the prior art are solved. Therefore, the moon cake has the characteristics of easily-shaped cladding, high plasticity and stable texture in baking process.
Owner:SHENGQUAN HEALTANG
Process for extracting xylose and xylitol from a xylose mother liquor or a xylose digest
InactiveCN1699587AImprove physical stabilityImprove adsorption capacitySugar derivativesFermentationForeign matterHydrolysate
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Alkylpolyglucosides containing disinfectant compositions active against pseudomonas microorganism
An antiseptic cleansing composition comprising an antimicrobial agent, an effective amount of an alkylpolysaccharide surfactant, at least one alkyl alcohol and at least one aryl alcohol. Suitable surfactant alkylpolysaccharides may contain one or more sugar units selected from the group consisting of maltose, arabinose, xylose, mannose, galactose, gulose, idose, talose, allose, altrose, sucrose, fructose, sorbose, levulose, lactose, allulose, tagatose, alloheptulose, sedoheptulose, glucoheptulose, mannoheptulose, guloheptulose, idoheptulose, galactoheptulose, taloheptulose and derivatives thereof. Suitable antimicrobial agents include chlorhexidine, chlorhexidine salt, chlorophenol derivative, octenidindihydrochloride (CH3—(CH2)7—NHON—(CH2)10—NO—NH(CH2)7—CH2 or any other salt thereof, and quaternary ammonium compounds.
Owner:NOVAPHARM RES AUSTRALIA
Compositions comprising a polysaccharide component and one or more coating layers
The present disclosure provides compositions comprising a plurality of agglomerates comprising a polysaccharide component comprising xylose and arabinose, wherein the ratio of xylose to arabinose is at least about 3:1, by weight; wherein the compositions further comprise:(i) optionally, a first surrounding layer which surrounds the agglomerate, wherein the first surrounding layer is a hydrophobic layer; and(ii) optionally, a second surrounding layer which surrounds the agglomerate, wherein the second surrounding layer is a hydrophilic layer;wherein the compositions comprise at least one of the first surrounding layer and the second surrounding layer, and wherein when the agglomerate comprises the first surrounding layer and the second surrounding layer then the first surrounding layer is a preceding layer relative to the second surrounding layer.In another embodiment, the disclosure provides compositions comprising a plurality of polysaccharide particles, wherein the polysaccharide particles comprise a polysaccharide component comprising xylose and arabinose, wherein the ratio of the xylose to the arabinose is at least about 3:1, by weight, and wherein the polysaccharide particles have a mean particle size distribution of from about 0.001 microns to about 150 microns, wherein the polysaccharide particles each, independently, comprise:(i) optionally, a first surrounding layer which surrounds the particle, wherein the first surrounding layer is a hydrophobic layer; and(ii) optionally, a second surrounding layer which surrounds the particle, wherein the second surrounding layer is a hydrophilic layer;wherein the polysaccharide particles each, independently, comprise at least one of the first surrounding layer and the second surrounding layer, and wherein when the particle comprises the first surrounding layer and the second surrounding layer then the first surrounding layer is a preceding layer relative to the second surrounding layer.The present compositions are useful for the treatment of a variety of benefits, including providing treatment for gastrointestinal conditions or providing other gastrointestinal benefits.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Method for recovering products
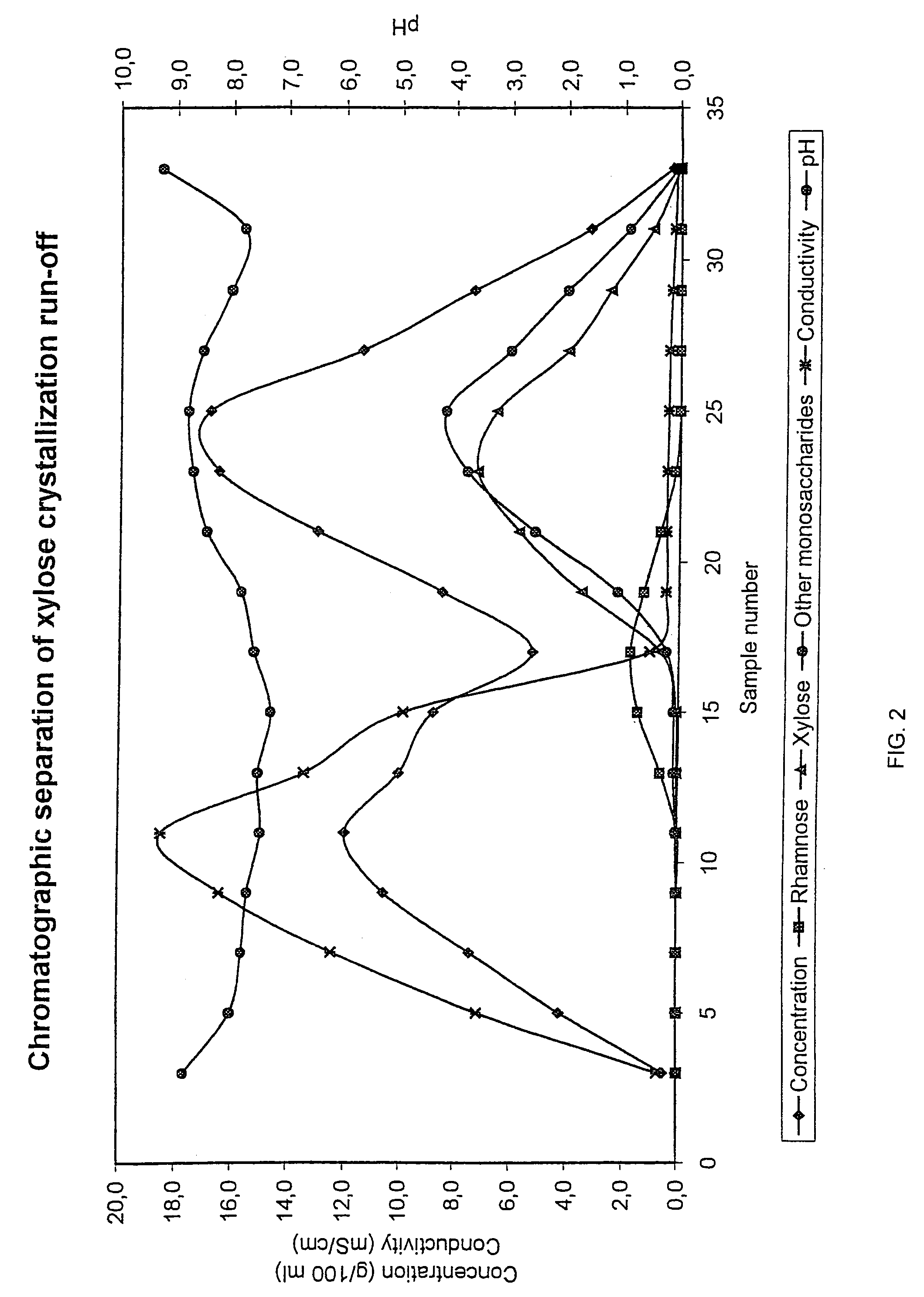
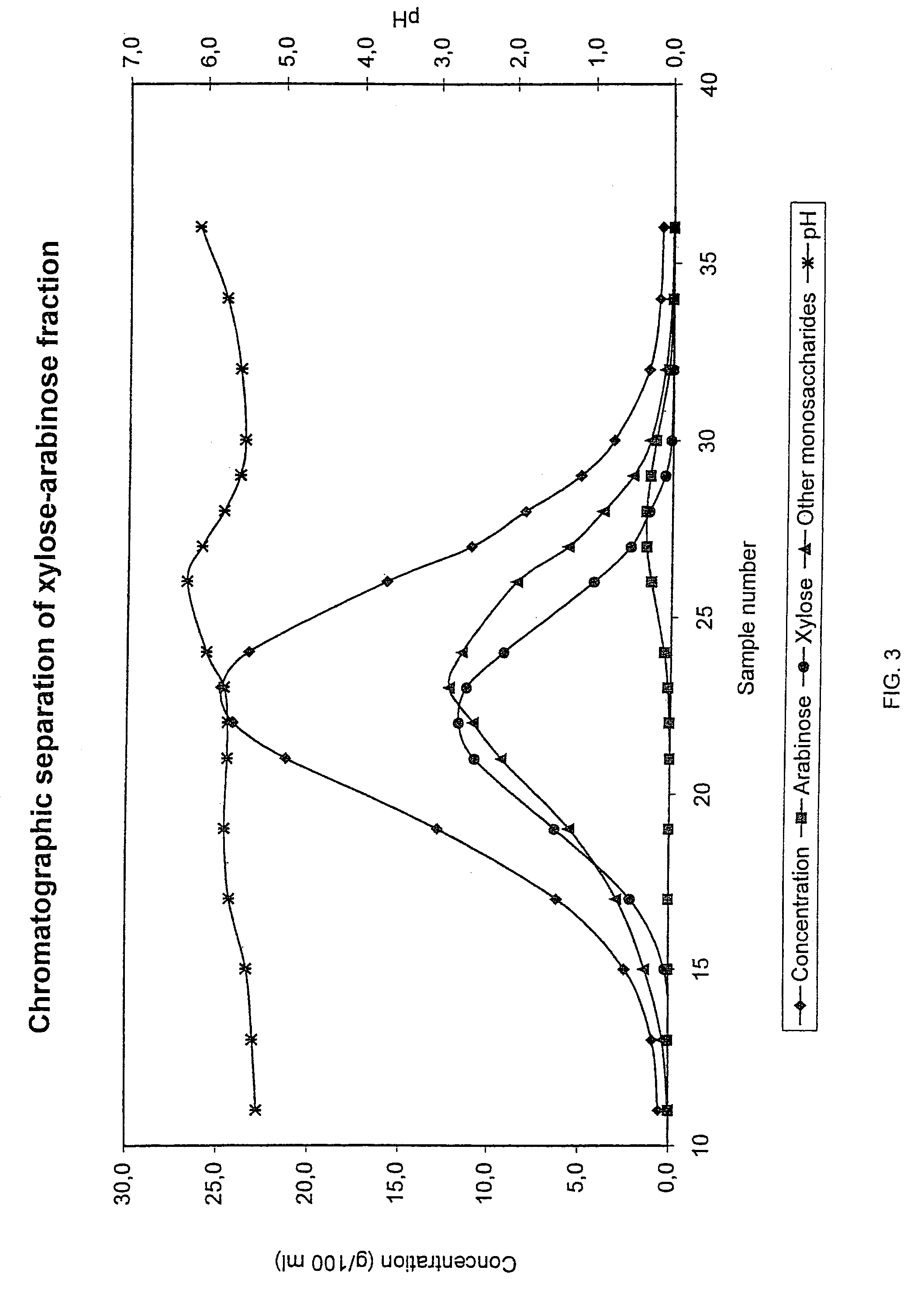
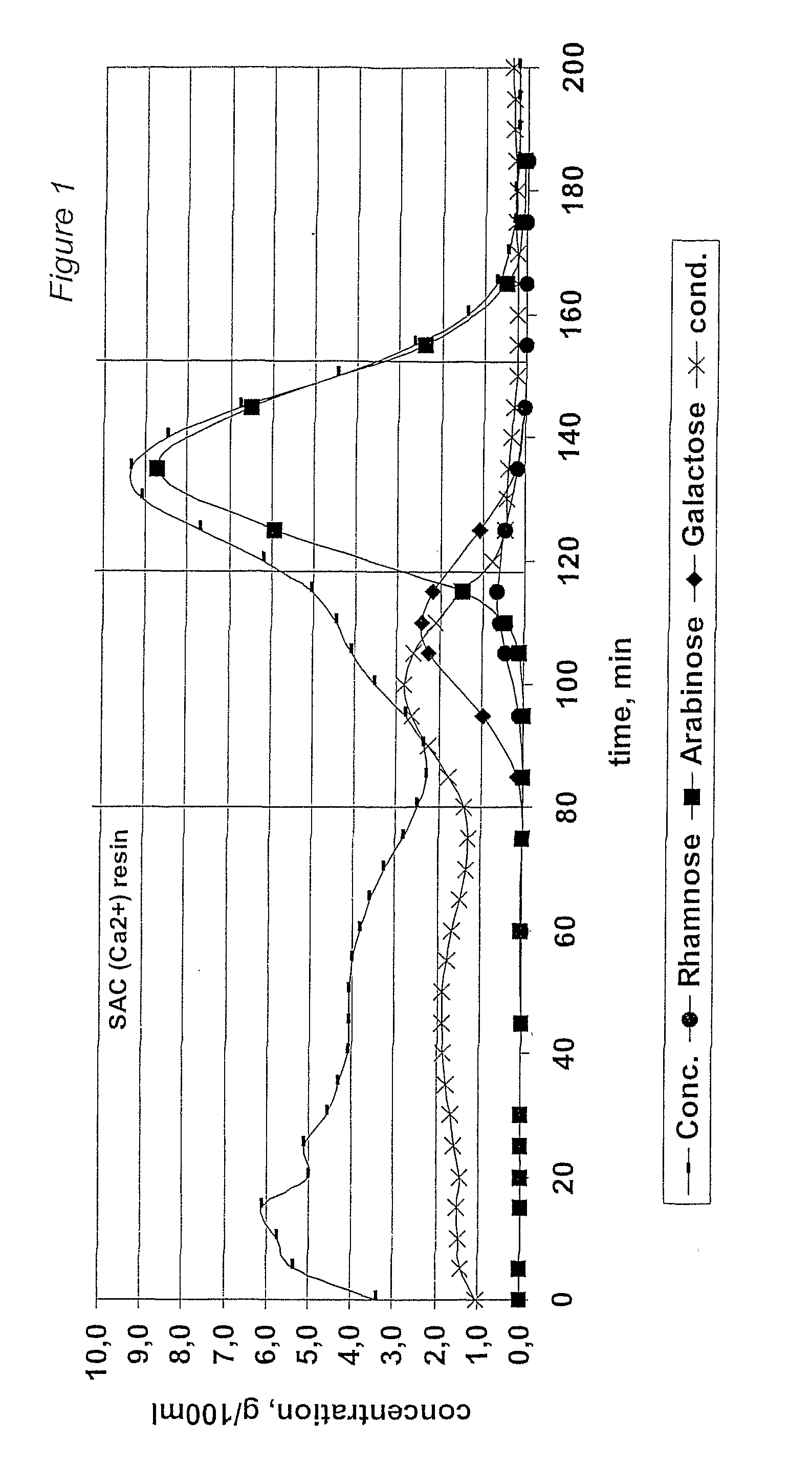
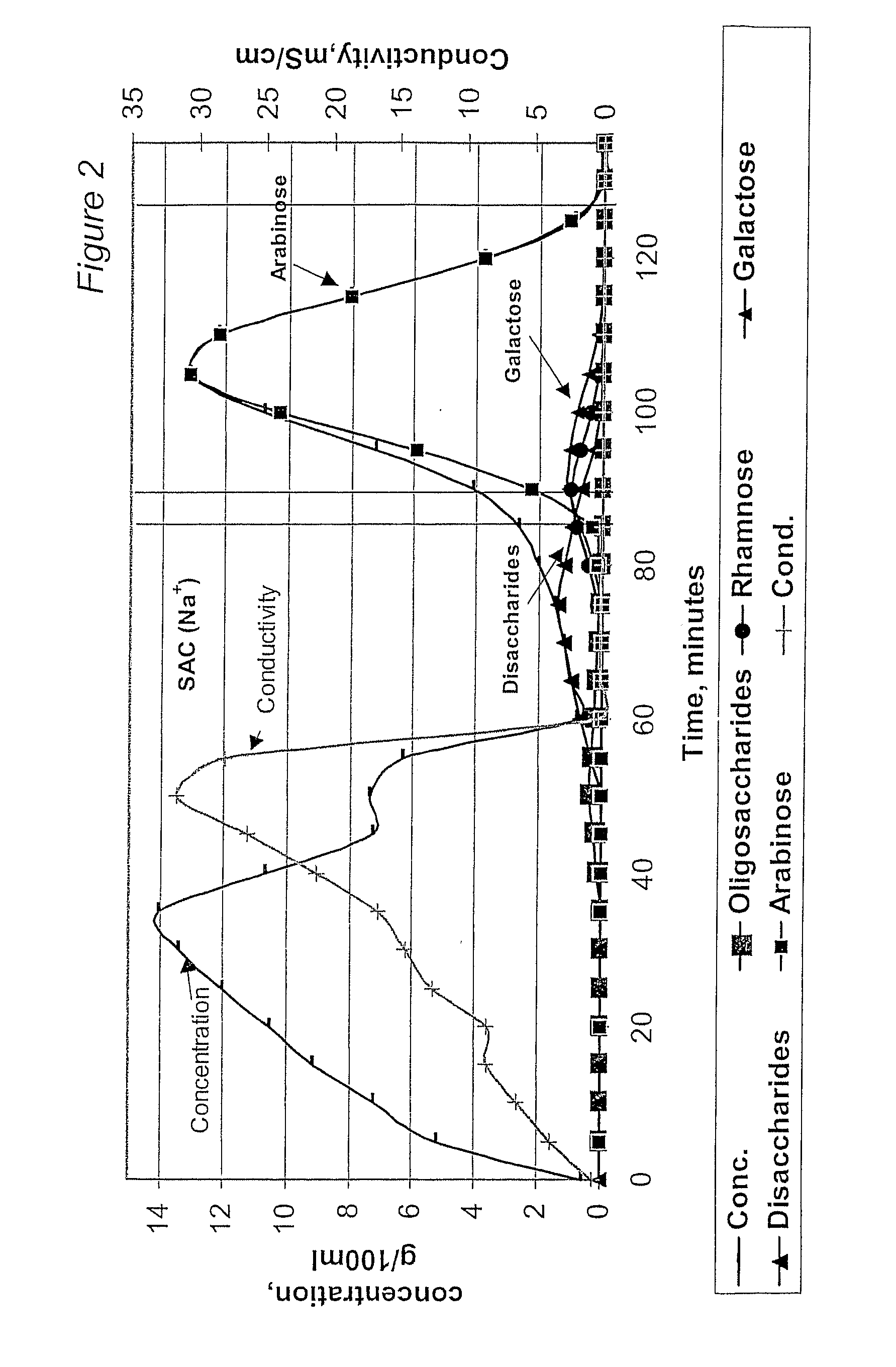
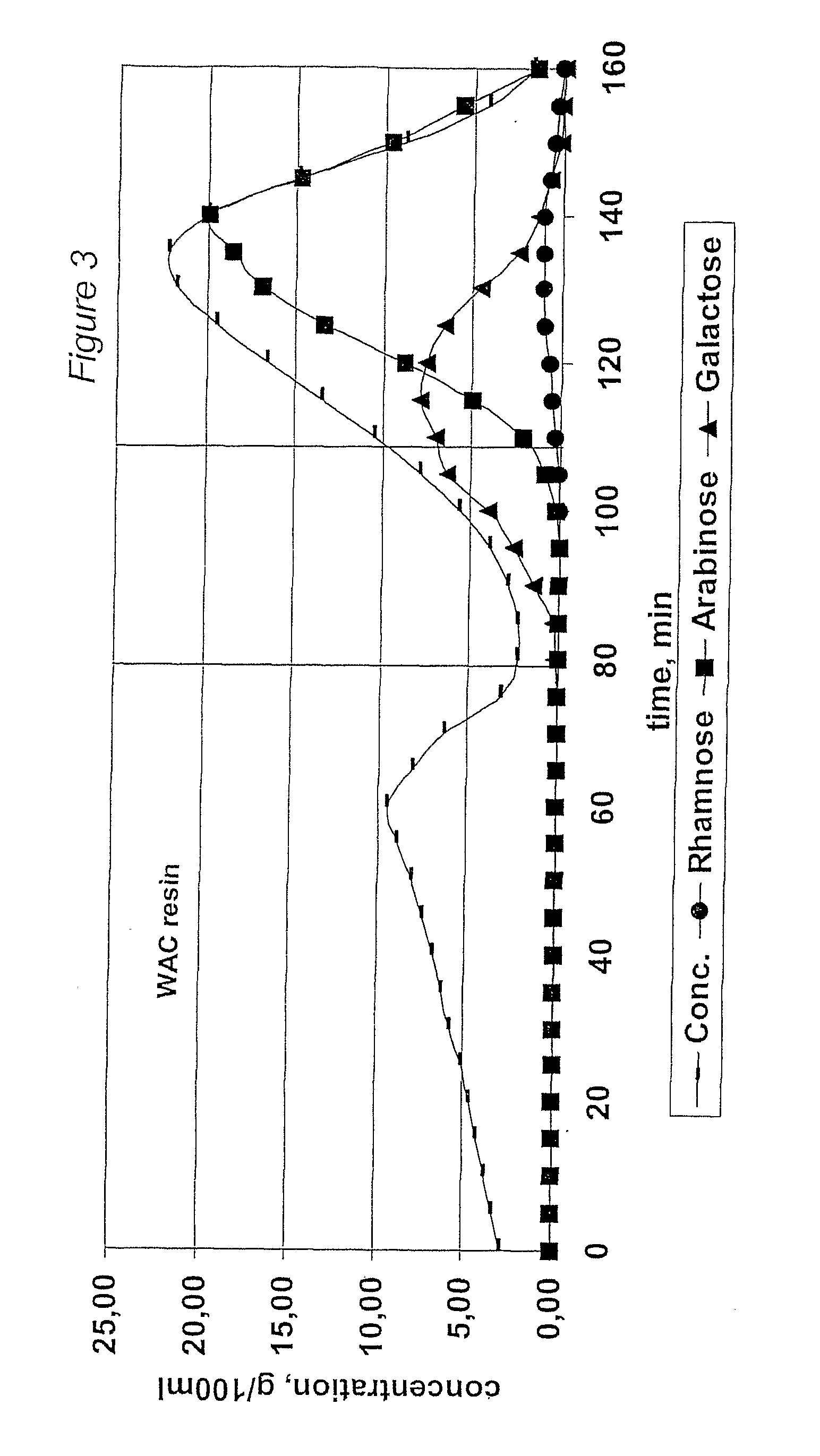
InactiveUS6987183B2Ion-exchanger regenerationSugar crystallisationChromatographic separationArabinose
The present invention is directed to a method comprising a multistep process for recovering one or more monosaccharides from a solution containing at least two monosaccharides selected from the group consisting of rhamnose, arabinose, xylose and mixtures thereof by using chromatographic separation comprising at least one step, where a weak acid cation exchange resin is used for the chromatographic separation.
Owner:DANISCO SWEETENERS
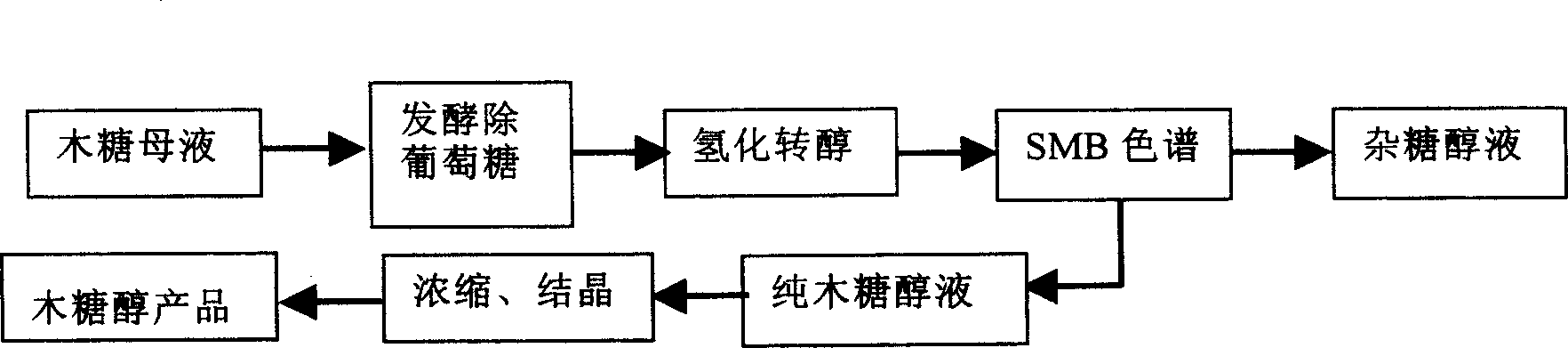
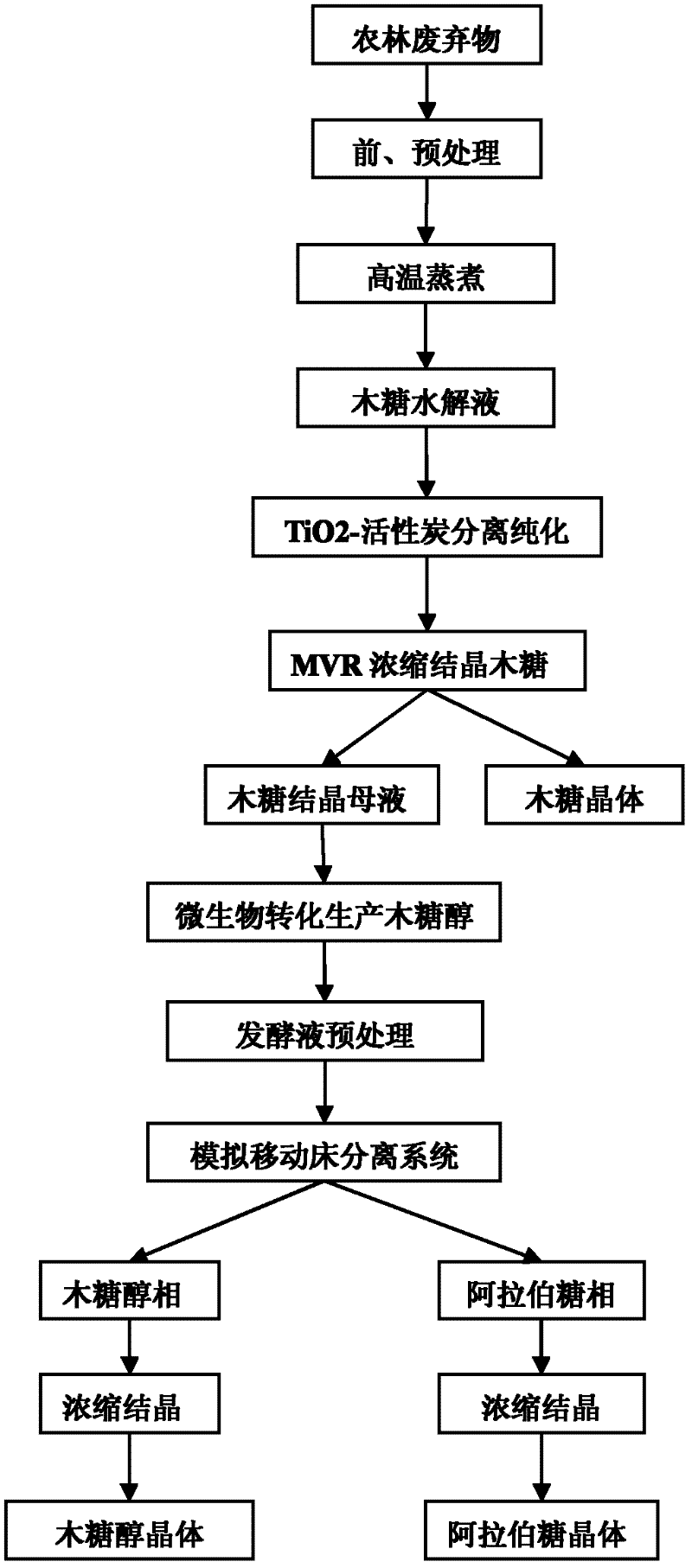
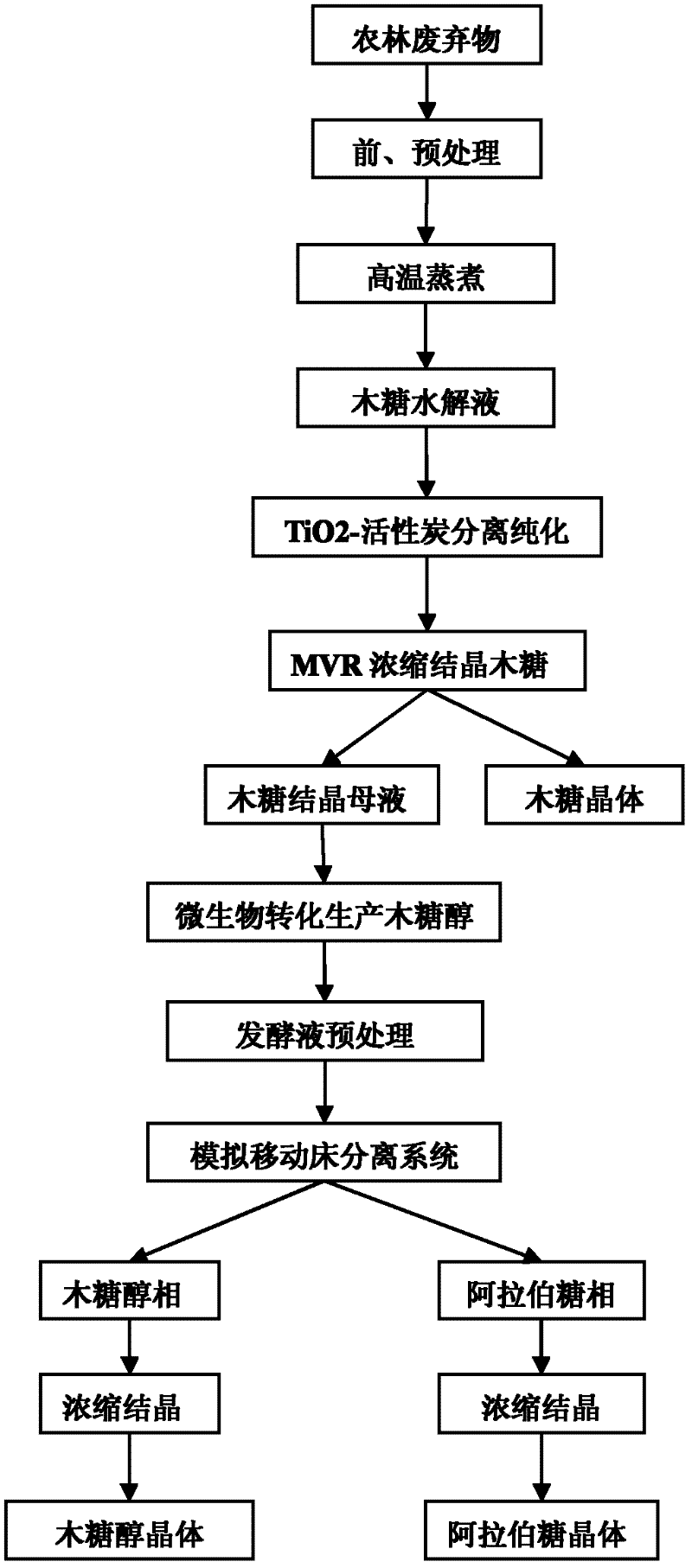
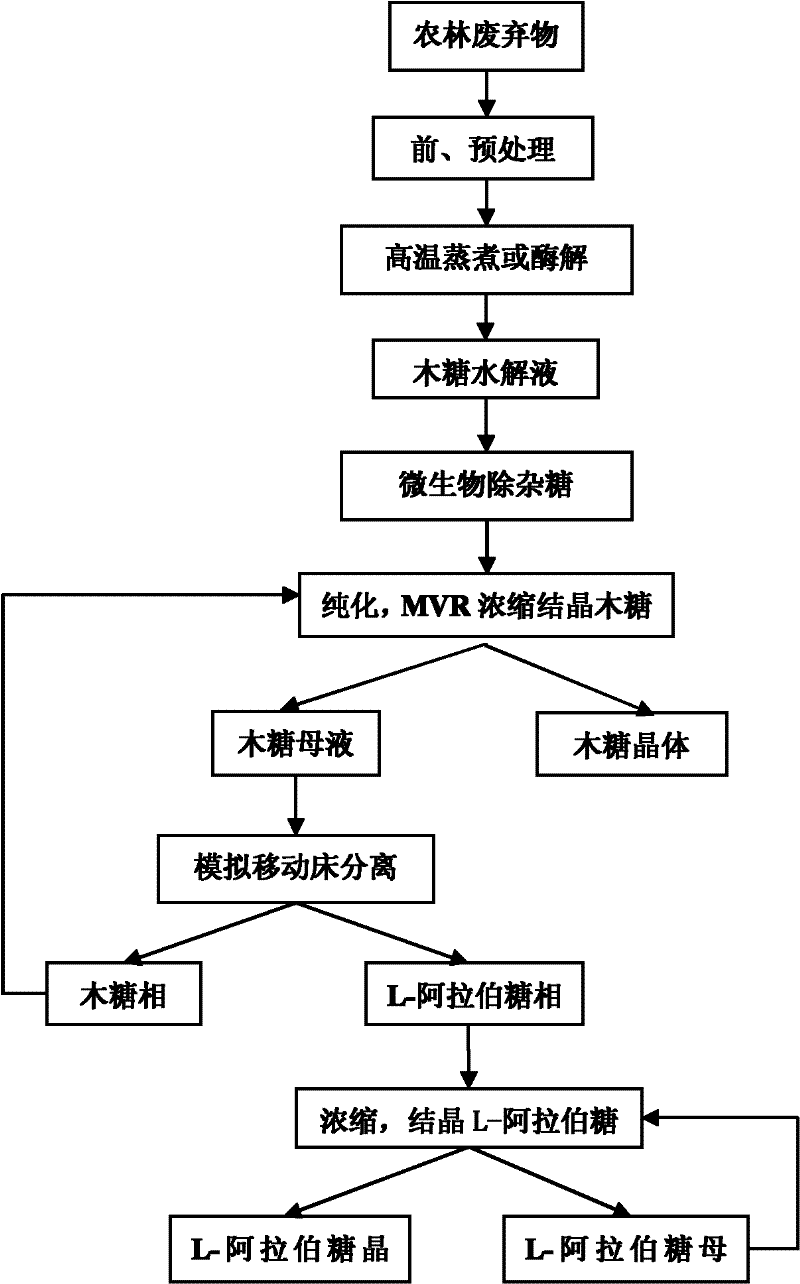
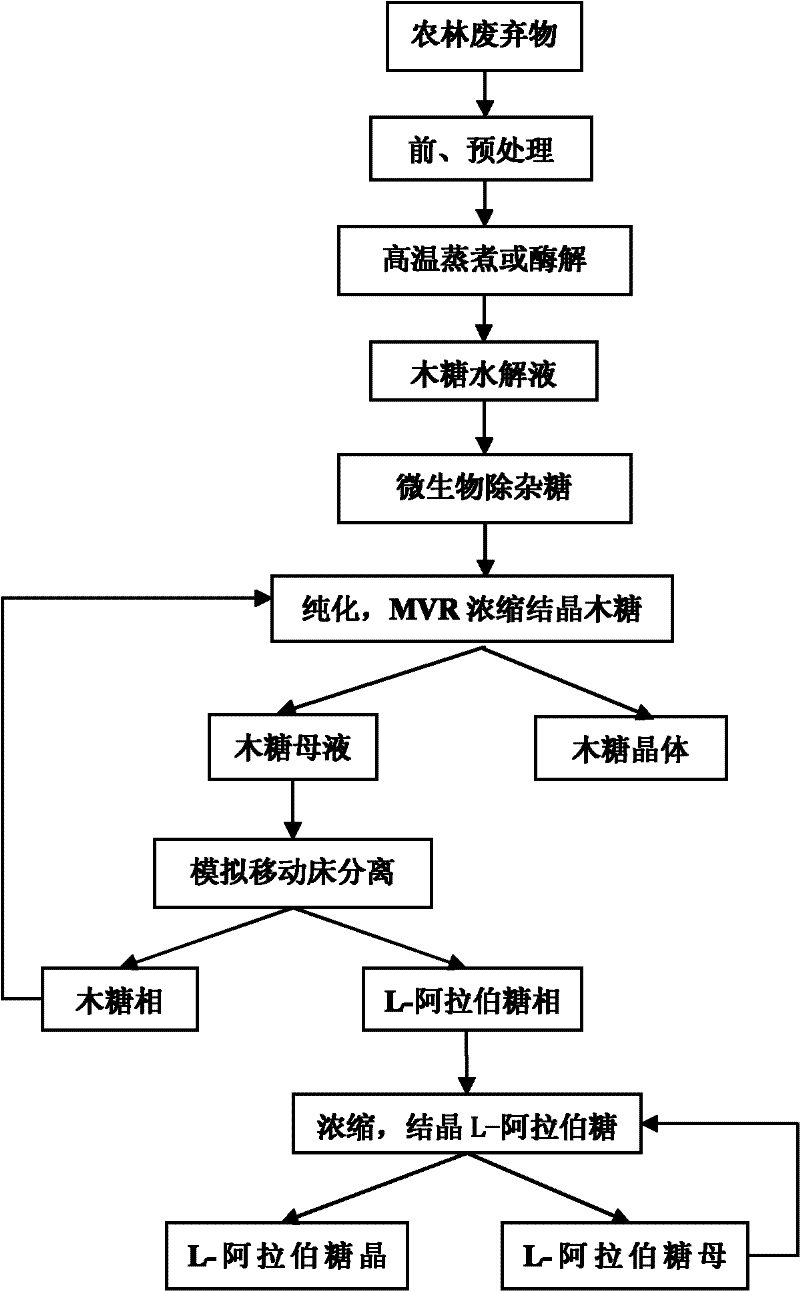
Co-production of xylose, xylitol and arabinose from agricultural and forestry wastes
ActiveCN102268490AEmission reductionReduce salt contentMicroorganism based processesFermentationChromatographic separationHydrolysate
The invention relates to a clean technique for co-producing xylose, xylitol and arabinose from agricultural and forestal waste, belonging to the field of utilization of agricultural and forestal waste. The technique comprises the following steps: pretreating and preprocessing the raw material, and hydrolyzing in a thermophilic digestion mode to prepare a hemicellulose hydrolysate; after centrifugalizing to remove solid residues, carrying out TiO2-loaded activated carbon photocatalysis or ion exchange resin decolorization and detoxification treatment on the hydrolysate; carrying out MVR (mechanical vapor recompression) concentration treatment and gradient-cooling crystallization to obtain a xylose product and a xylose mother solution; fermenting L-arabinose unconverted xylitol fermentationhigh-yield strain xylitol by using the xylose mother solution as the medium to produce the xylitol; centrifugalizing to remove thalli, and carrying out decolorization and desalting treatment by membrane-process or resin adsorption; separating by using a simulated moving bed or chromatographic separation technology to obtain a xylitol phase and an L-arabinose phase; and carrying out MVR or vacuum concentration treatment on the two phases, and crystallizing in a gradient programmed cooling mode to respectively obtaining a xylitol product and an L-arabinose product, wherein the two mother solutions can be recycled.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Method for synthesizing nelarabine
This invention discloses a method for synthesizing nelarabine. The method comprises: utilizing 6-chloroguanosine as the raw material, and performing chemical synthesis to convert ribofuranose configuration into arabinofuranosyl configuration and obtain nelarabine. The method has such advantages as abundant raw materials, simple process, easy operation and high yield, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:CHIA TAI TIANQING PHARMA GRP CO LTD
Enhanced soluble c5 saccharide yields
ActiveUS20120282655A1Improve the level ofOxygen-containing compound preparationSugar derivativesCelluloseLignocellulosic biomass
Methods are disclosed for increasing the level of soluble C5 saccharides produced from lignocellulosic biomass comprising acidifying fractionated lignocellulosic biomass to prevent the recondensation of soluble C5 saccharides, including C5 oligosaccharides and xylose and arabinose monomers, to insoluble higher molecular weight C5 oligosaccharides.
Owner:RENMATIX INC
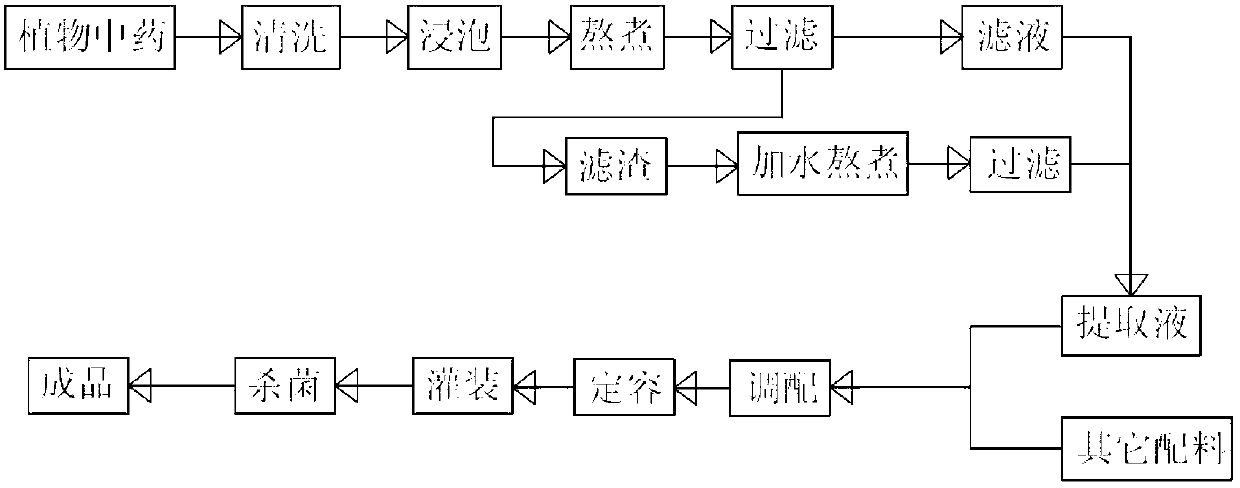
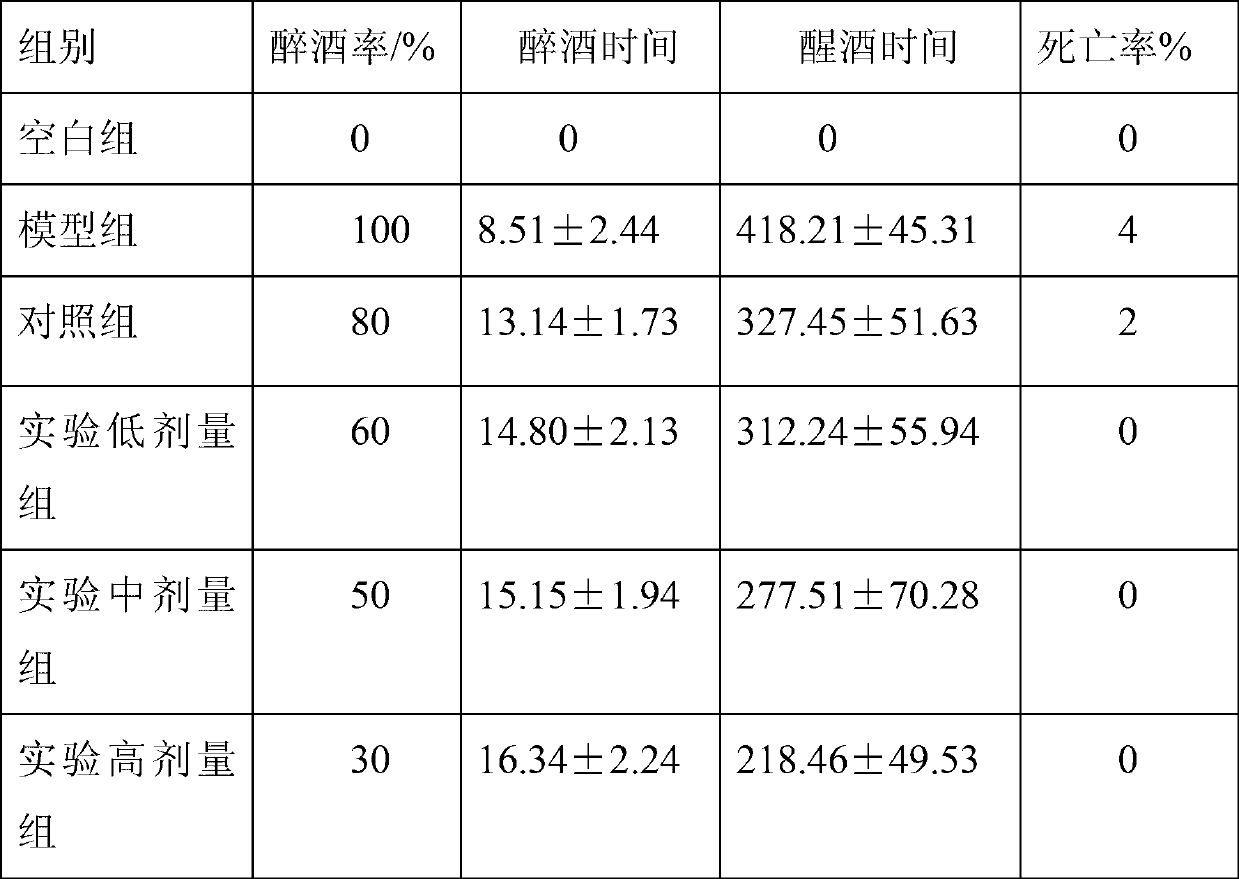
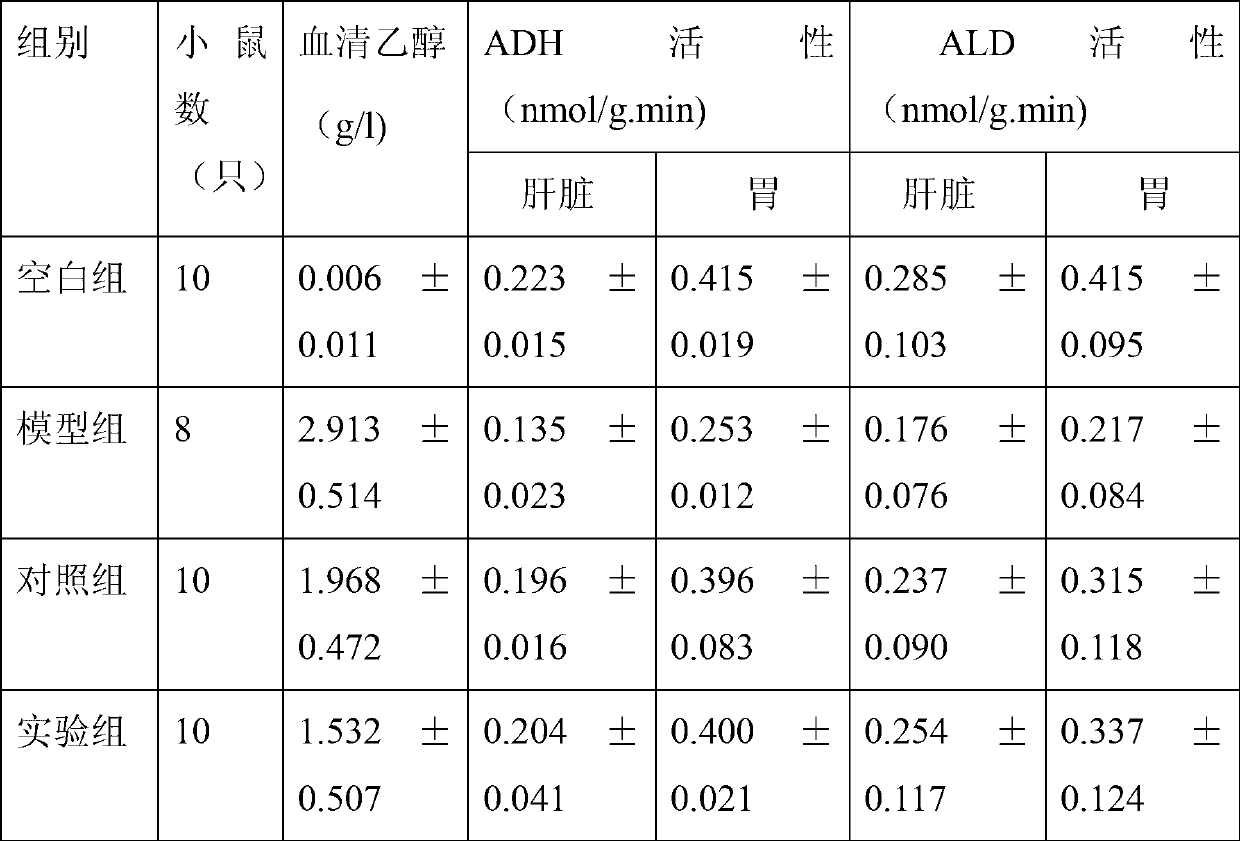
Oral liquid for alleviating hangover and protecting liver, and preparation method thereof
The invention provides oral liquid for alleviating a hangover and protecting a liver, and a preparation method thereof. The oral liquid is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 5-15 parts of root of kudzu vine, 5-15 parts of semen hoveniae, 0.5-5 parts of ginseng, 2-10 parts of lalang grass rhizome, 0-5 parts of hawthorn, 0-3 parts of sealwort, 0-15 parts of pueraria flower, 3-20 parts of glucose, 1-10 parts of xylitol, 1-5 parts of L-arabinose, 0.2-1.0 part of taurine, 0-0.5 parts of glutamine, 0-5 parts of resistant dextrin, 0-1 part of decavitamin, and 0-2 parts of compound amino acid. The oral liquid has the beneficial effects of good hangover alleviating efficacy and good flavor and mouthfeel; the problems of dizzy giddy and scattered attention after excessive drinking are solved; damages to the liver and kidney caused by alcohol are reduced; and gastrointestinal mucosa is protected.
Owner:JINDA BIOENG BIOTECH DEV FUZHOU
Composition and method for reducing the colonization of animal intestines by salmonella and other bacterial pathogens
InactiveUS6126961AReducing human pathogen colonizationSafe and economical reductionBiocideAnimal feeding stuffIntestinal structureBacteroides
An animal feed composition for reducing colonization of animal intestines by Salmonella and other bacterial pathogens, includes a polysaccharide containing cis-hydroxy sugar units or a derivative thereof, or the monosaccharide ribose or rhamnose, or a derivative thereof, and an animal feed. The polysaccharide cis-hydroxy sugar units may be one or more of mannose, a mannose derivative, galactose, a galactose derivative, galactomannans, galactosamine, fucose and arabinose. The polysaccharides may be incorporated into an animal feed in the form of a food gum or other biolpolymer.
Owner:AURUM CERTUS
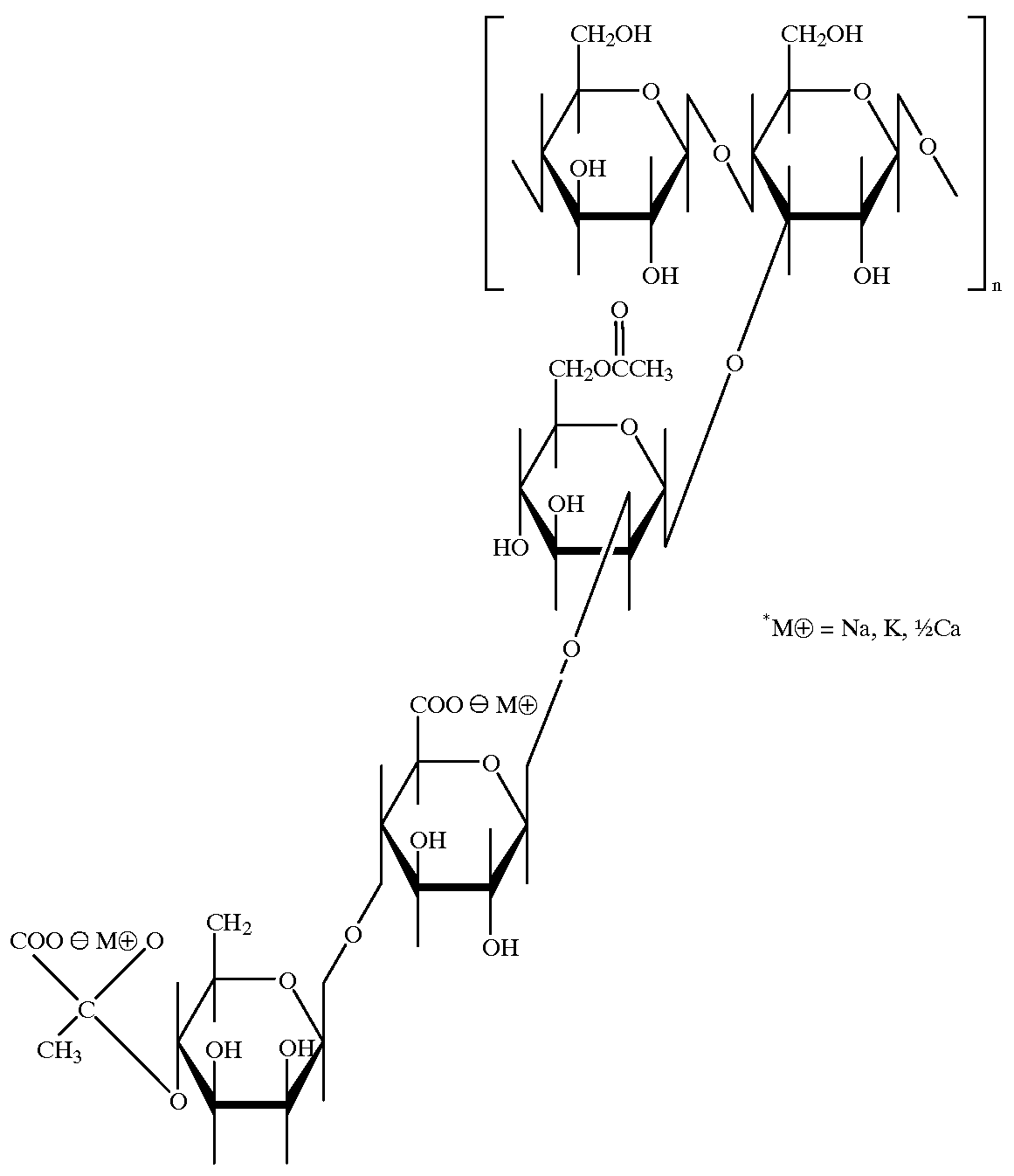
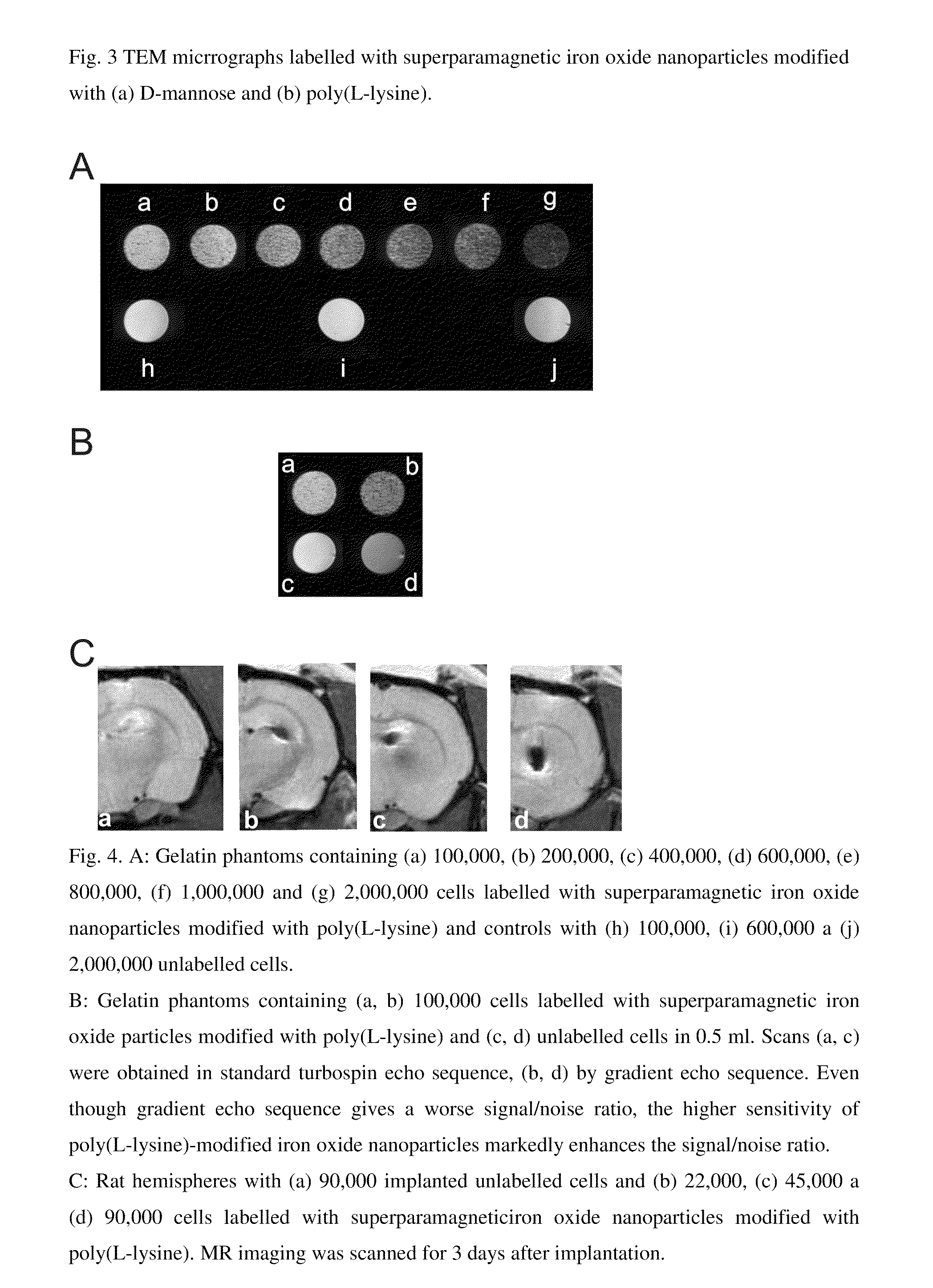
Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles Based on Iron Oxides with Modified Surface, Method of Their Preparation and Application
InactiveUS20090309597A1Less loadImprove abilitiesPigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologyArginineDextran
The subject of the invention is superparamagnetic nanoparticle probes based on iron oxides, to advantage magnetite or maghemite, with modified surface, coated with mono-, di- or polysaccharides from the group including D-arabinose, D-glucose, D-galactose, D-mannose, lactose, maltose, dextrans and dextrins, or with amino acids or poly(amino acid)s from the group including alanine, glycine, glutamine, asparagine, histidine, arginine, L-lysine, aspartic and glutamic acid or with synthetic polymers based on (meth)acrylic acid and their derivatives selected from the group containing poly(N,N-dimethylacrylamide), poly(N,N-dimethylmethacrylamide), poly(N,N-diethylacrylamide), poly(N,N-diethylmethacrylamide), poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), poly(N-isopropylmethacrylamide), which form a colloid consisting of particles with narrow distribution with polydispersity index smaller than 1.3, the average size of which amounts to 0.5-30 nm, to advantage 1-10 nm, the iron content is 70-99.9 wt. %, to advantage 90 wt. %, the modification agent content 0.1-30 wt. %, to advantage 10 wt. %.The particles of size smaller than 2 nm with polydispersity index smaller than 1.1 can be obtained by a modified method of preparation.Superparamagnetic nanoparticle probes according to the invention are prepared by pre-precipitation of colloidal Fe(OH)3 by the treatment of aqueous 0.1-0.2M solution of Fe(III) salt, to advantage FeCl3, with less than an equimolar amount of NH4OH, at 21° C., under sonication, to which a solution of a Fe(II) salt, to advantage FeCl2, is added in the mole ratio Fe(III) / Fe(II)=2 under sonication and the mixture is poured into five- to tenfold, to advantage eightfold, molar excess of 0.5M NH4OH. The mixture is left aging for 0-30 min, to advantage 15 min, and then the precipitate is repeatedly, to advantage 7-10 times, magnetically separated and washed with deionized water. Then 1-3 fold amount, to advantage 1.5 fold amount, relative to the amount of magnetite, of 0.1 M aqueous solution of sodium citrate is added and then, dropwise, 1-3 fold amount, to advantage 1.5 fold amount, relative to the amount of magnetite, of 0.7 M aqueous solution of sodium hypochlorite. The precipitate is repeatedly, to advantage 7-10 times, washed with deionized water under the formation of colloidal maghemite to which, after dilution, is added dropwise, to advantage under 5-min sonication, an aqueous solution of a modification agent, in the weight ratio modification agent / iron oxide=0.1-10, to advantage 0.2 for amino acids and poly(amino acid)s and 5 for saccharides.The particles smaller than 2 nm with polydispersity index smaller than 1.1 are prepared by mixing at 21° C. 1 volume part of 10-60 wt. %, to advantage 50 wt. %, of an aqueous solution of a saccharide, disaccharide or polysaccharide, such as D-arabinose, D-glucose, D-galactose, D-mannose, lactose, maltose, dextran and dextrins, and 1 volume part of aqueous solution of a Fe(II) and Fe(III) salt, to advantage FeCl2 and FeCl3, where the molar ratio Fe(III) / Fe(II)=2. A 5-15%, to advantage 7.5%, solution of NH4OH is added until pH 12 is attained and the mixture is heated at 60° C. for 15 min. The mixture is then sonicated at 350 W for 5 min and then washed for 24 h by dialysis in water using a membrane with molecular weight cut-off 14,000 until pH 7 is reached. The volume of solution is reduced by evaporation so that the final dry matter content is 50-100 mg / ml, to advantage 80 mg per 1 ml.Superparamagnetic nanoparticle probes according to the invention can be used for labelling cells used in magnetic resonance imaging for monitoring their movement, localization, survival and differentiation especially in detection of pathologies with cell dysfunction and of tissue regeneration and also for labelling and monitoring cells administered for cell therapy purposes, in particular embryonal stem cells, fetal stem cells, stem cells of an adult human including bone marrow stem cells, olfactory glial cells, fat tissue cells, in the recipient organism by magnetic resonance.The preparation of labelled cells proceeds by adding to the complete culture medium 5-20 μl, to advantage 10 μl, of a colloid containing 0.05-45 mg iron oxide per ml, to advantage 1-5 mg iron oxide per ml of the medium, and culturing the cells for a period of 1-7 days, to advantage for 1-3 days, at 37° C. and 5% of CO2.
Owner:INST OF MACROMOLECULAR CHEM ASCR V V I +1
Yeast expressing saccharolytic enzymes for consolidated bioprocessing using starch and cellulose
The present invention is directed to a yeast strain, or strains, secreting a full suite, or any subset of that, full suite, of enzymes to hydrolyze com starch, corn fiber, lignocellulose, (including enzymes that hydrolyze linkages in cellulose, hemicelhiiose, and between lignin and carbohydrates) and to utilize pentose sugars (xylose and arabinose). The invention is also directed to the set of proteins that are well expressed in yeast for each category of enzymatic activity. The resulting strain, or strains can be used to hydrolyze starch and cellulose simultaneously. The resulting strain, or strains can be also metabolically engineered to produce less glycerol and uptake acetate. The resulting strain, or strains can also be used to produce ethanol from granular starch without liquefaction.; The resulting strain, or strains, can be further used to reduce the amount of external enzyme needed to hydrolyze a biomass feedstock during an Simultaneous Saccharification and Fermentation (SSF) process, or to increase the yield of ethanol during SSF at current saccharolytic enzyme loadings. In addition, multiple enzymes of the present invention can be co-expressed in cells of the invention to provide synergistic digestive action on biomass feedstock. In some aspects, host cells expressing different heterologous saccharolytic enzymes can also be co-cultured togetherand used to produce ethanol from biomass feedstock.
Owner:LALLEMAND HUNGARY LIQUIDITY MANAGEMENT LLC +1
Method for preparing xylose and arabinose by hydrolyzing lignocellulose
InactiveCN101525355ALess side effectsLess corrosiveSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationHydrolysateBio engineering
The invention discloses a method for preparing xylose and arabinose by hydrolyzing lignocelluloses in the technical field of biological engineering. In the method, aqueous oxalate solution is used for carrying out catalytic hydrolysis on crushed lignocelluloses; lignocelluloses hydrolysate solution and xylose resides are obtained by solid-liquid separation after the reaction; the hydrolysate solution is neutralized to obtain oxalate sediment and obtain solid oxalate by solid-liquid separation again; the oxalate reacts with sulfate in an acidizing tank for regeneration to obtain the aqueous oxalate solution; the oxalate solution is used repeatedly to catalyze next batch of lignocelluloses raw material. The invention uses oxalic acid as organic acid catalyst and has the advantages of high conversion rate, strong selectivity, less side reaction, being capable of recycling, and the like, the oxalic acid can replace regular inorganic acid catalyst, and the invention solves the problem thatthe traditional technology has equipment erosion, evaporating equipment scaling, serious pollution and the like and can be used for hydrolyzing the hemicellulose in lignocelluloses raw material and used for preparing the xylose and the arabinose.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for producing L-arabinose
ActiveCN101665524AHigh purityFermentation went wellIon-exchange process apparatusSugar derivativesChromatographic separationImpurity
The invention relates to a method for producing L-arabinose, which can simultaneously produce ethanol, D-ribose and citric acid as byproducts. The method utilizes a hydrolyzate of agricultural waste, a xylose mother liquor and / or a production waste liquor containing pentose as the raw materials and comprises the following steps: (a) pretreating the raw materials; (b) carrying out the chromatographic resolution to separate the raw materials into an arabinose-stage liquor and a xylose-stage liquor; (c) removing impurities and unwanted bacteria, which have an inhibiting effect on fermentation, as well as unwanted saccharides at least comprising glucose and galactose; (d) and carrying out the post treatment on the arabinose-stage liquor to obtain the L-arabinose. Steps (c1) and (c2) are arranged before the chromatographic resolution in step (b) or after step (b). The invention has the advantages of low production cost and high efficiency, and is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:SHENGQUAN HEALTANG
A clean and efficient production process for preparing xylose and l-arabinose
ActiveCN102286571AAddressing the effects of crystallizationHigh yieldSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationChromatographic separationYeast
The invention relates to a clean and high-efficiency production process for preparing xylose and L-arabinose and belongs to the field of application of wastes of agriculture and forestry. The production process comprises the following steps of: performing pretreatment on raw materials; hydrolyzing the raw materials in a high-temperature cooking mode; performing neutralizing treatment and performing centrifugal separation on solid slag to obtain xylose or xylooligosaccharide hydrolyzate; adding coarse enzyme solution into xylooligosaccharide solution to hydrolyze to obtain xylose solution; treating the hydrolyzate by Angle yeast; purifying by using active carbon and resin; performing recompression and concentration treatment on the purified hydrolyzate by using a mechanical vapor recompression (MVR) machine; crystallizing the concentrated solution in a gradient program cooling mode to obtain xylose products and xylose mother solution; separating the xylose mother solution by a simulated moving bed or a chromatographic separation technology to obtain a xylose phase and an L-arabinose phase; returning the xylose phase to the xylose solution to concentrate and recrystallize; reusing the xylose mother solution; performing MOVR concentration treatment on the L-arabinose phase and crystallizing in a gradient program cooling mode to obtain L-arabinose products; and reusing the L-arabinose mother solution.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
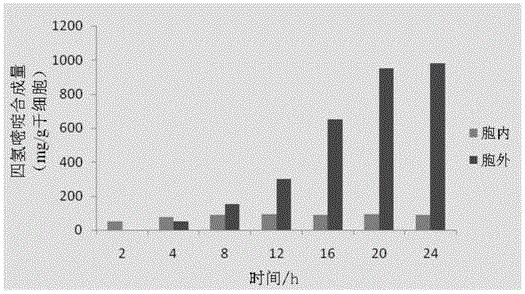
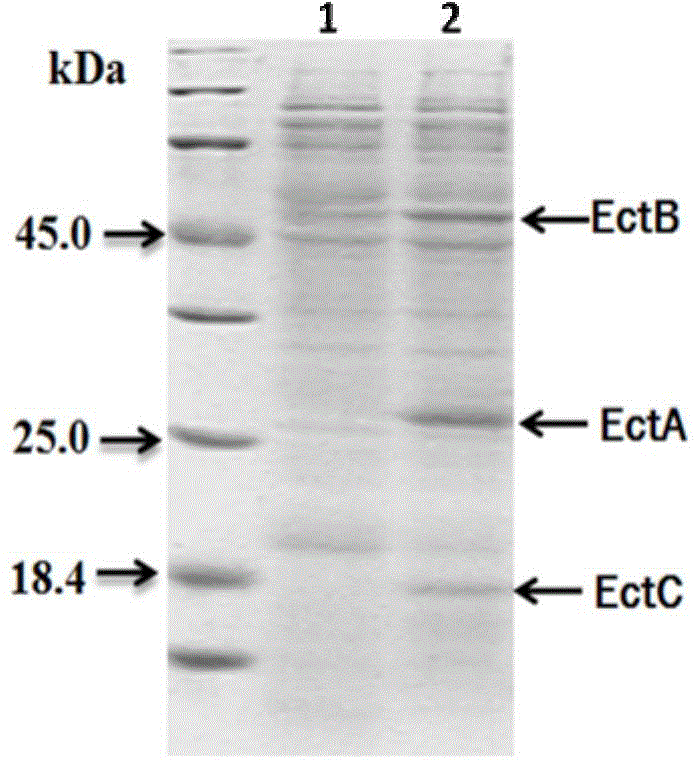
Escherichia coli engineering bacterium for high-yield tetrahydropyrimidine and applications of escherichia coli engineering bacterium
ActiveCN104560844AHigh synthesis efficiencyFacilitate downstream purification and separationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliRecombinant escherichia coli
The invention provides a recombinant escherichia coli for high-yield tetrahydropyrimidine and a method for preparing tetrahydropyrimidine by using the recombinant escherichia coli. The recombinant escherichia coli provided by the invention is prepared by importing Halomonas elongate EctABC containing recombinant plasmids into escherichia coli. The recombinant escherichia coli disclosed by the invention realizes the soluble expression of three key enzymes synthesized by tetrahydropyrimidine under the adjustment and control of an arabinose promoter. Thalli subjected to induced expression implements the efficient secretory expression of tetrahydropyrimidine by taking sodium aspartate as a precursor through a bioconversion method. Thalli per gram can synthesize 1.1 grams of tetrahydropyrimidine, and more than 90% of tetrahydropyrimidine is secreted to extracellular receptors. The method for preparing tetrahydropyrimidine by using the recombinant escherichia coli provided by the invention facilitates the downstream purification and separation of products, and has great significance on the industrial production and large-scale application of tetrahydropyrimidine.
Owner:南京众惠生物材料科技有限公司
Methods for the electrolytic production of erythrose or erythritol
Owner:DFI USA LLC
Conditioning powder and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104432084AInhibition of secretionPromote excretionFood ingredient functionsFood preparationNutrientDiabetic complication
The invention provides conditioning powder suitable of being eaten by a diabetic patient. The conditioning powder comprises 6-12 parts of water-soluble dietary fiber extractive, 0.1-1 part of wheat germ extractive, 0.1-1.5 parts of soybean protein isolate, 1-3 parts of secalin, 0.5-2 part of vegetable fat powder, 0.2-1.5 parts of Chinese yam extractive, 0.2-1 part of sealwort extractive, 0.2-1 part of mulberry leaf extractive, 0.2-1 part of polygonatum odoratum extractive, 0.1-1 part of medlar extractive, 0.1-0.3 part of flaxseed gum, 0.5-2 parts of L-arabinose, 0.09-0.3 part of yeast and 0.001-0.006 part of zinc gluconate. The conditioning powder is low in carbohydrate content, has abundant nutrients, is particularly suitable for serving as food of the diabetic patent, has the remarkable hypoglycemic effect and the conditioning function, has the prevention and treatment functions on various diabetic complications, and particularly has the good conditioning effect on a diabetes type nephropathy patient. The nutrients of the conditioning powder are easy to digest and absorb. The conditioning powder is convenient to eat and good in taste.
Owner:东方百草堂国际科贸(北京)有限公司
Extraction process and application of peach gum polysaccharide
ActiveCN105061617AHigh purityThe preparation method is fineMetabolism disorderGlucose degradationPrecipitation
The invention discloses an extraction process and application of peach gum polysaccharide (PGPSD). The process includes: water extraction and alcohol precipitation, protein removal by a Sevage reagent, dialysis, passing of a column with DEAE cellulose as the filler and other steps, thus obtaining finer polysaccharide (PGPSD). The PGPSD can be dissolved in water at room temperature, and is formed by connection of arabinose, mannose and galactose through a glycosidic bond. The peach gum polysaccharide (PGPSD) prepared by the process provided by the invention can reinforce the expression of insulin related transcription factors and glucose degradation key enzyme, has no toxicity to mice, and can significantly lower the blood glucose of diabetic mice.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
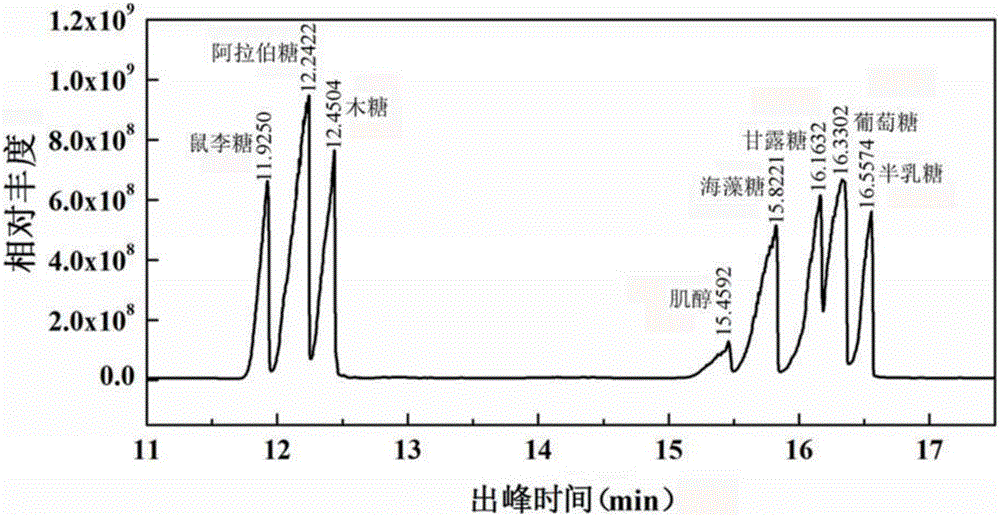
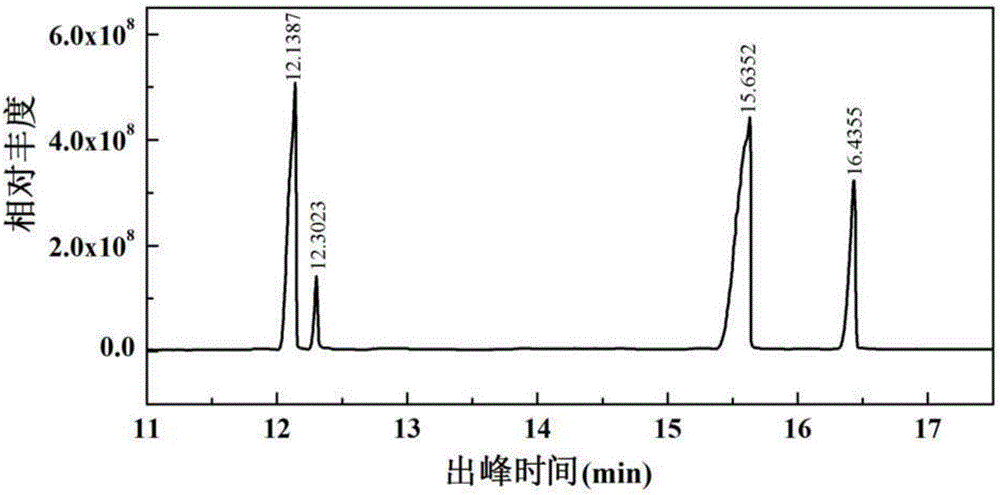
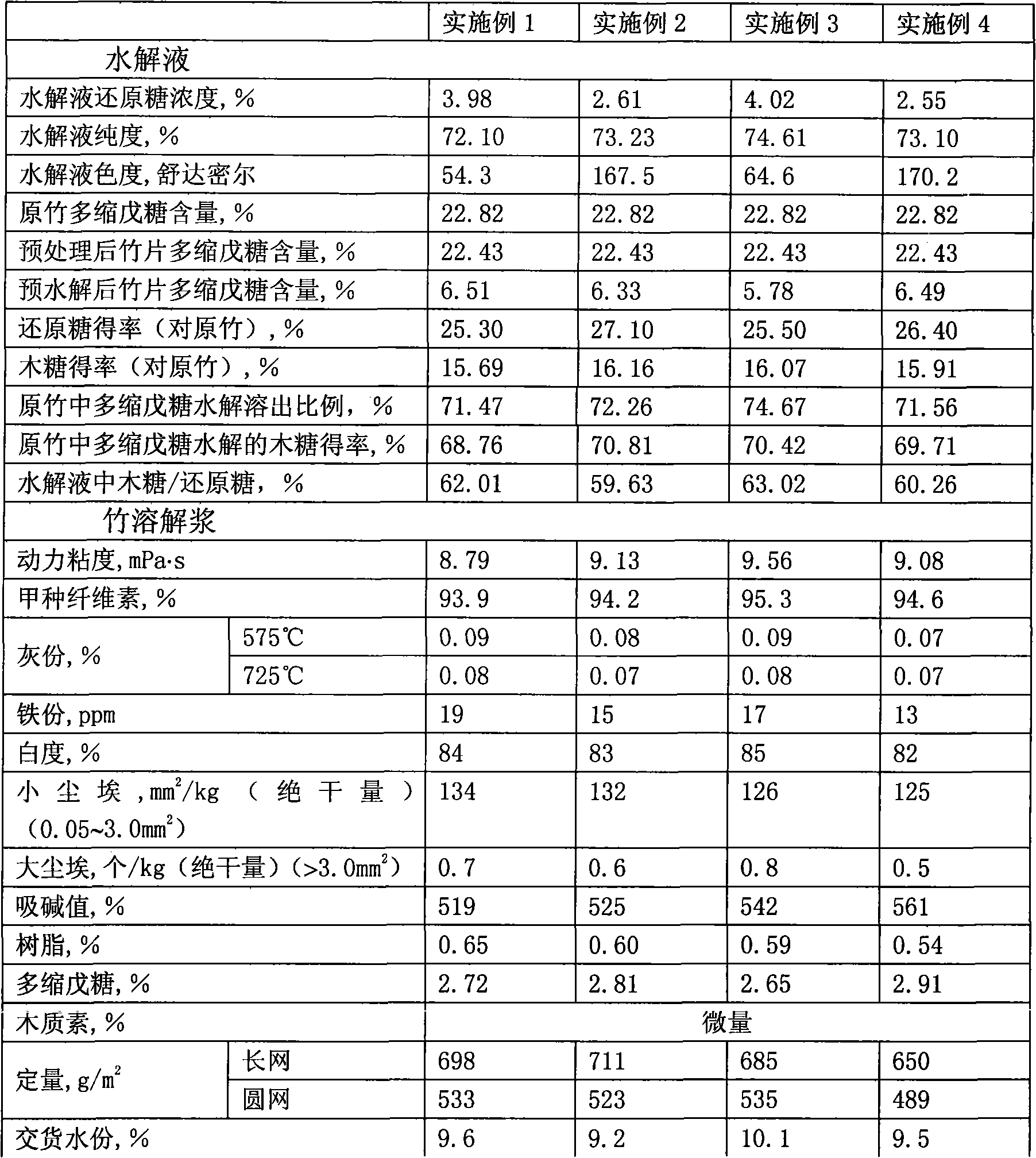
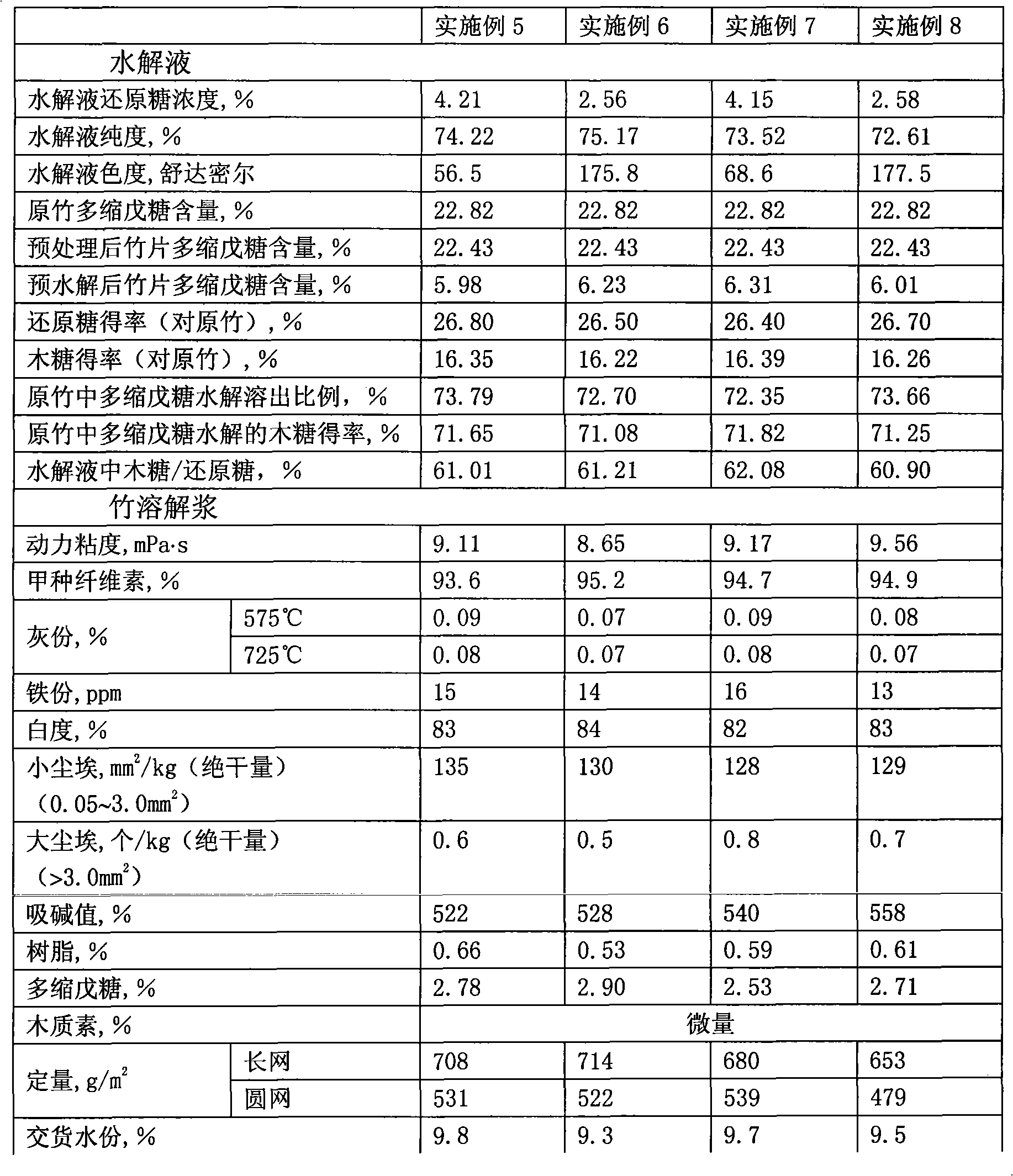
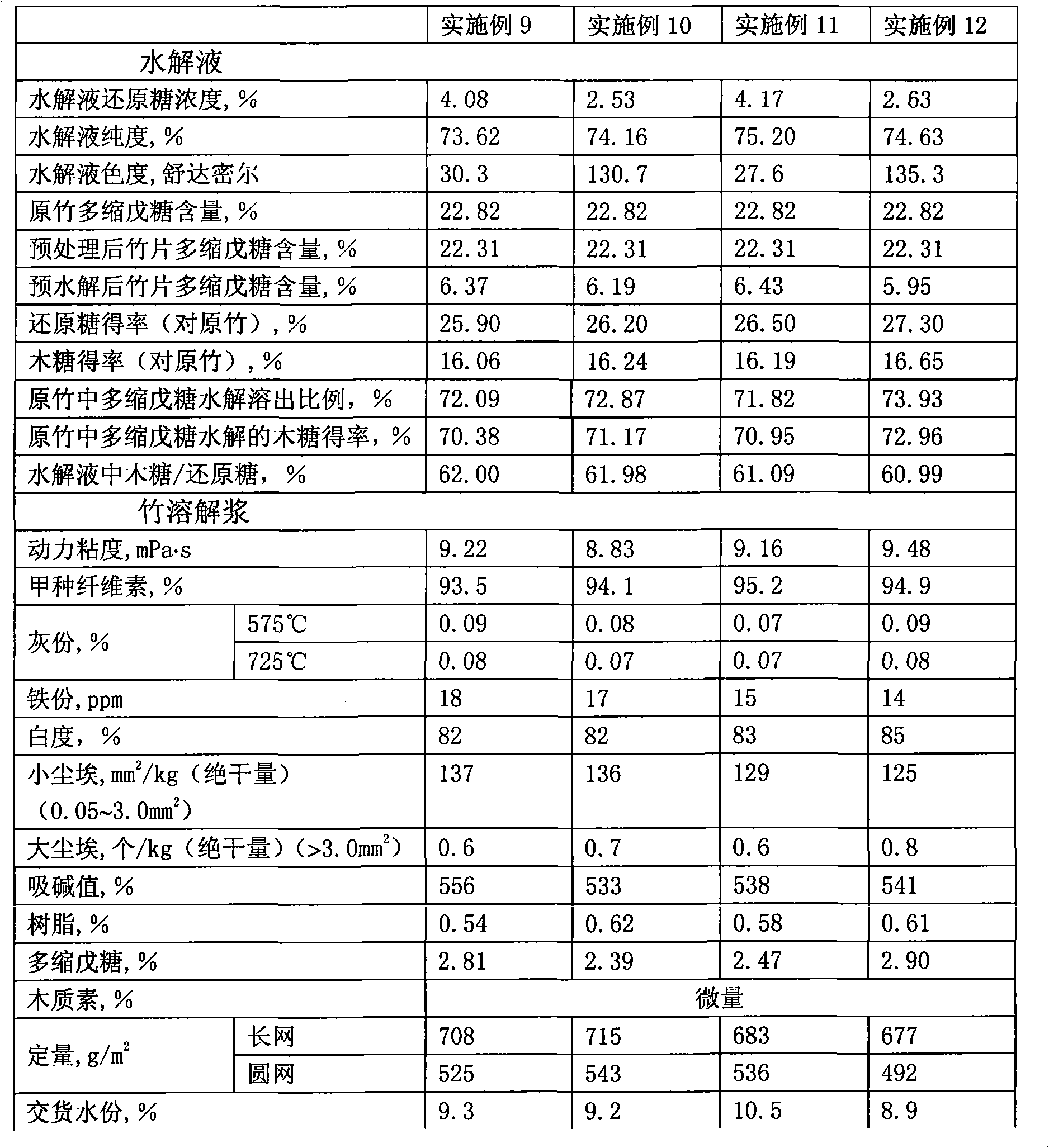
Method for preparing bamboo dissolving pulp by improved prehydrolysis alkaline process and product thereof
InactiveCN101514529AReasonable range of hydrolyzed reducing sugar concentrationReasonable range of purityPretreatment with acid reacting compoundsPulping with inorganic basesHydrolysatePerformance index
The invention relates to a method for preparing bamboo dissolving pulp by improved prehydrolysis alkaline process, which comprises the following steps of: bamboo material preparation, in which bamboo is made into bamboo sheets and bamboo threads, the bamboo sheets and threads are washed to remove impurities and dust; pretreatment, which is for removing more organic and nonorganic impurities, and in which the loss of pentosan is less than 2 percent; prehydrolysis, which is carried out at an acid concentration of sulphuric acid and hydrochloric acid of 0.1 to 10.0 weight percent, a temperature of between 80 and 14 DEG C and a liquor ratio of 1:4-15 for 30 to 400 minutes; and alkaline process. The method has the advantages that: the performance index of the bamboo dissolving pulp meets the requirements of viscose fibre pulp and the like; the improved prehydrolysis process allows the major part of pentosan in the bamboo to be hydrolyzed; the hydrolysate can be used as a raw material for xylose, xylitol, L-Arabinitol, ethanol and other products; the improved prehydrolysis process lays a good foundation for cooking and improving the reaction performance of the dissolving pulp; little production cost is added, the treatment load and cost of waste are reduced with the recovery of the products of the prehydrolysis, and the comprehensive cost is the lowest; and the comprehensive utilization of the components of biomass is realized during the pulping process of the dissolving pump.
Owner:上海士林纤维材料有限公司
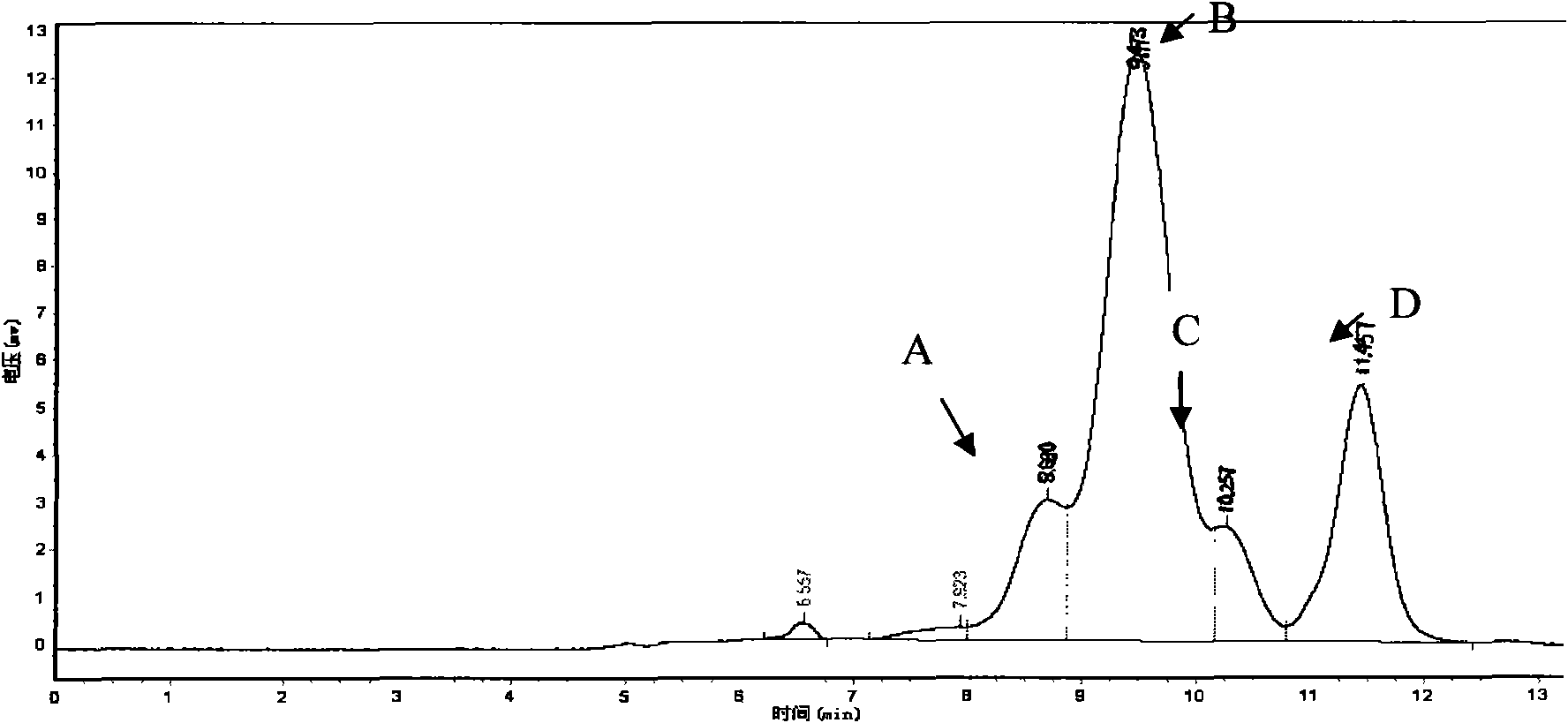
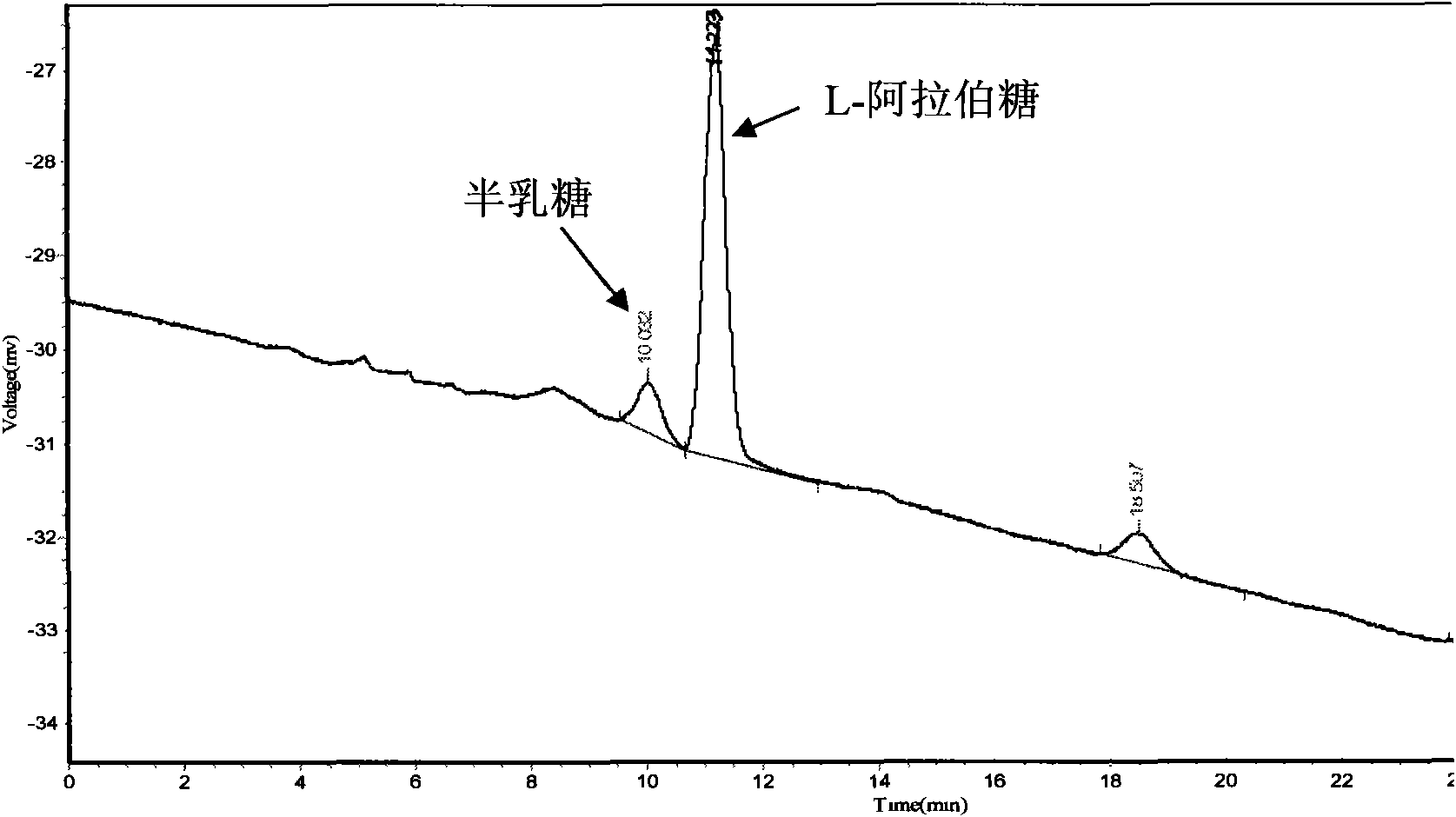
Method for separating and extracting L-arabinose from waste wood sugar mother liquid from wood sugar production
InactiveCN101555503ASolve processing problemsFacilitate subsequent separation and purificationMicroorganism based processesFermentationInorganic saltsIon exchange
The invention provides a method for separating and extracting L-arabinose from wasted wood sugar mother liquid from wood sugar production. The method comprises the following steps: the wood sugar mother liquid is decolorized; the decolorized wood sugar mother liquid is desalted by using ion exchange resin; the desalted defecated wood sugar mother liquid is diluted and added by required nitrogen source and inorganic salt for germicidal treatment; microzyme is inoculated into the sterilized wood sugar mother liquid for fermenting cultivation; the microzyme is removed after the ferment is finished, supernatant is processed with the methods of discolorationt, desaltification, concentration, and the like, to get colorless defecated fermenting liquid; the fermenting liquid is further concentrated, crystallized and dried to get the L-arabinose of high purity. The method has the advantages of no pollution, low energy consumption and low cost, and is suitable for industrial large-scale production.
Owner:上海金杉生物科技有限公司
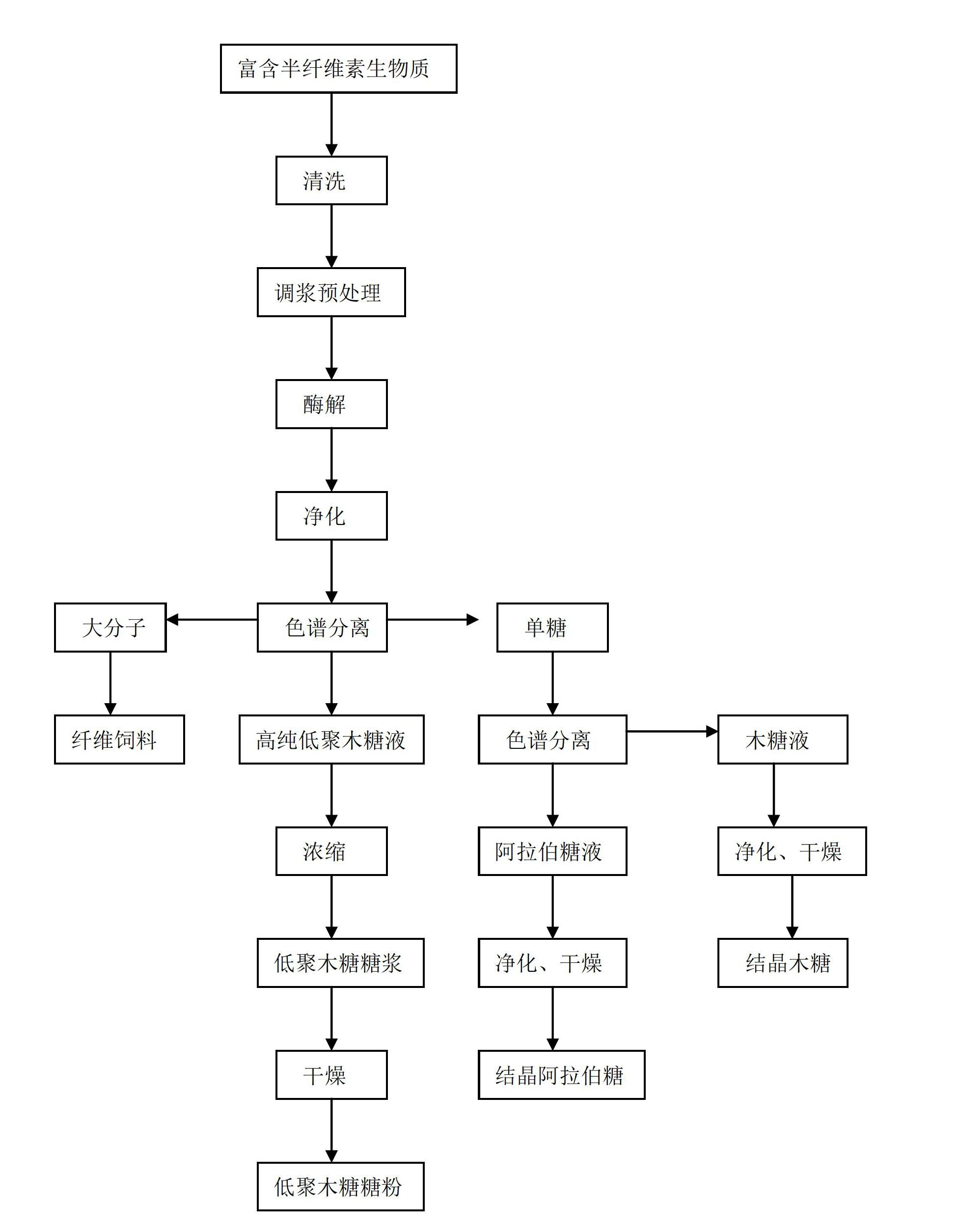
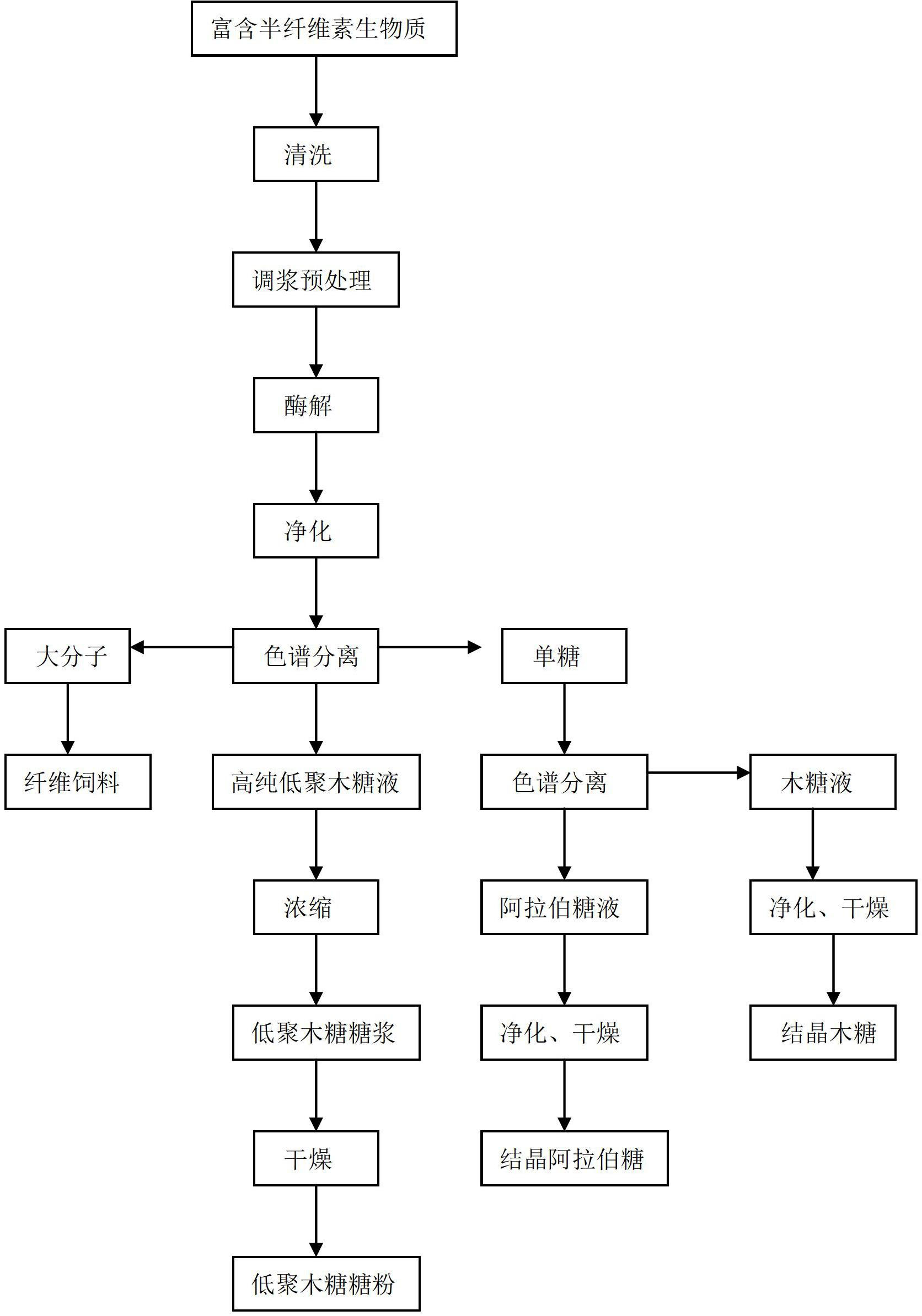
Bio-preparation method for production of high-purity xylo-oligosaccharide and coproduction of arabinose and xylose
ActiveCN102660606AEfficient full value conversionNo churnSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationChromatographic separationFiber
The invention discloses a bio-preparation method for production of high-purity xylo-oligosaccharide and coproduction of arabinose and xylose. The method comprises the following steps of: washing hemicellulose-enriched biomass, performing size mixing pretreatment, adding xylanase, performing enzymolysis, and separating and purifying to obtain mixed liquid glucose; concentrating the mixed liquid glucose until the mass concentration is 50 to 70 percent, and performing chromatographic separation to sequentially obtain AD phase, BD phase, CD phase and BD phase, and concentrating the BD phase to obtain a high-purity xylo-oligosaccharide syrup liquid product; concentrating the CD phase, mixing with cellulosic materials, drying, and crushing to prepare fiber feed; performing yeast fermentation on the AD phase to remove glucose, removing impurities, purifying, concentrating and performing chromatographic separation to obtain the high-purity xylose liquid and arabinose liquid; concentrating the xylose liquid, crystallizing, separating and drying to obtain crystallized xylose; and concentrating arabinose liquid, crystallizing, separating and drying to obtain crystallized arabinose. The invention also provides a bio-preparation method for arabinose and xylose.
Owner:SHANDONG LONGLIVE BIO TECH CO LTD
Hydrolyzed liquid prepared from corn peel, its preparation method and application
InactiveCN1966665AImprove utilizationPromote sustainable developmentMicroorganismsFermentationEcological environmentSocial effects
The invention belongs to the bioengineering field, and discloses digest prepared from corn skin and its production method and application. The digest is prepared by treating the corn skin with physical method, and then treating the crushed corn skin with chemical and / or biological method to obtain the digest containing glucose, xylose, arabinose, galactose and mannose and the total amount of the monosaccharide occupies 54-71.9% wt. of the dry corn skin. The digest can be used for the preparation of medium. The digest of the invention can be used as sugar source for fermentation instead of glucose, lowers the fermentation cost, increases economic returns, makes full use of renewable resources, promotes the integrated usage of corn skin, reduces environmental pollution, improves ecological environment, promotes the sustainable development of national economy, and has wide social effects.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
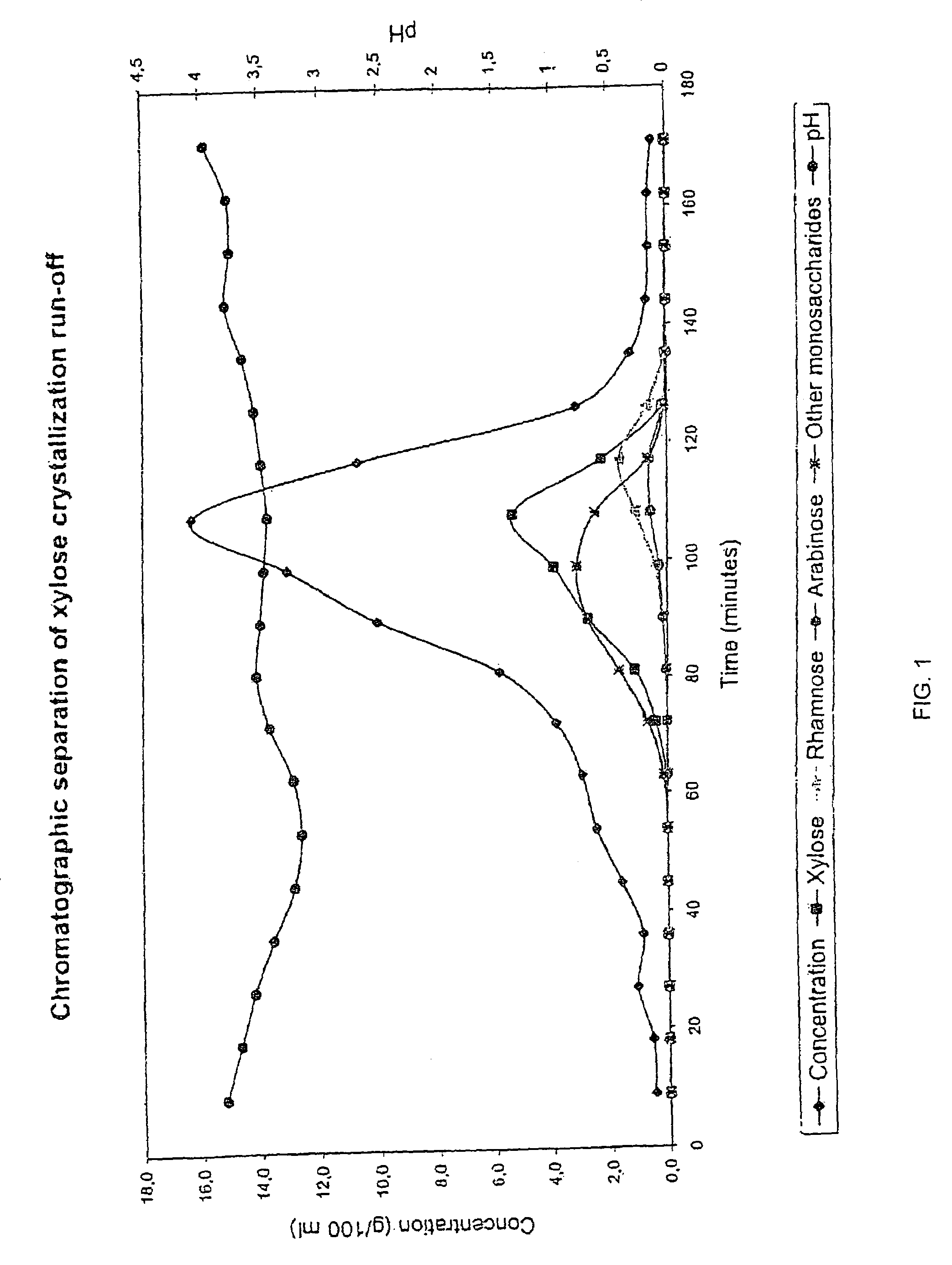
Separation process
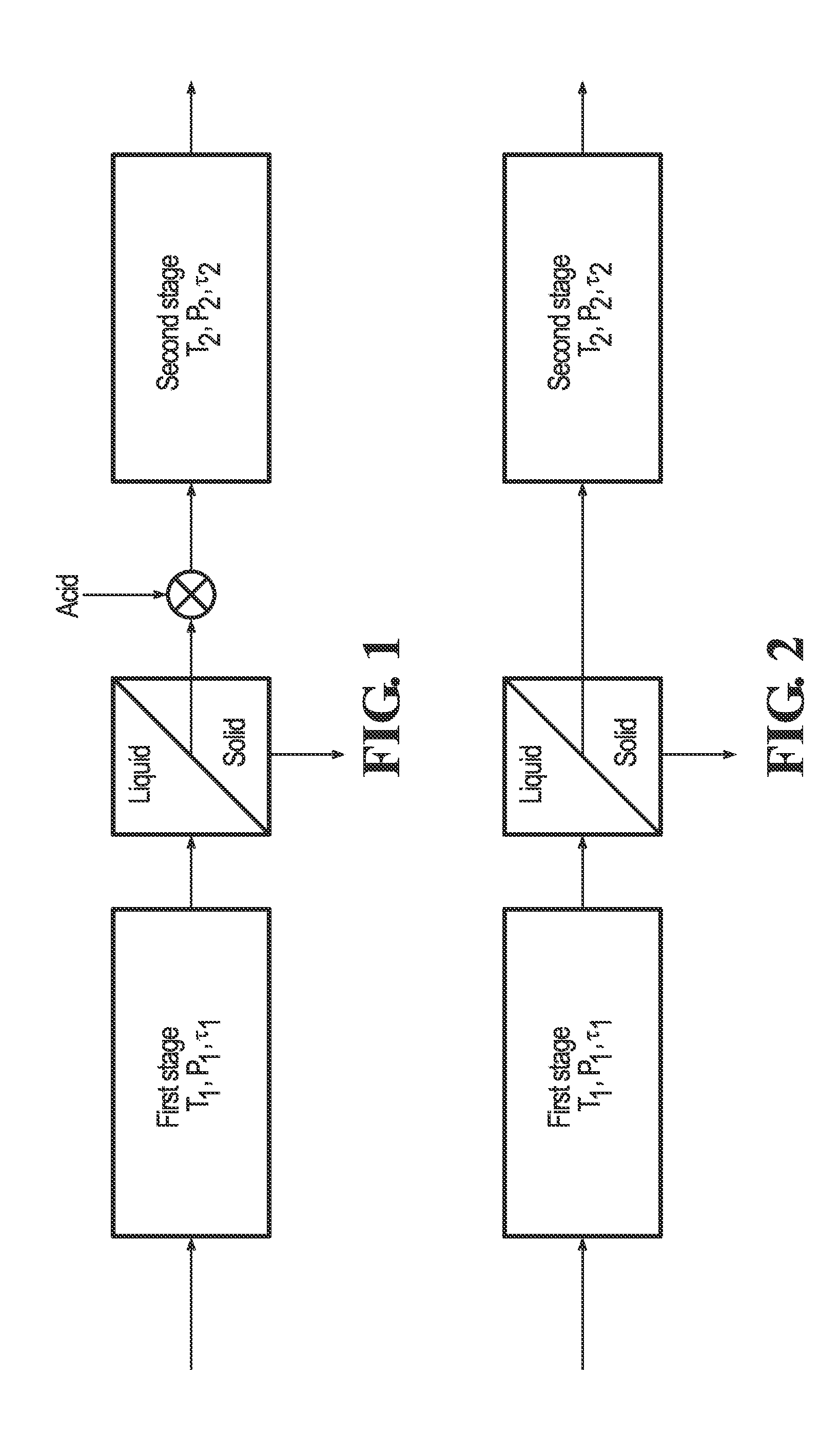
InactiveUS20070112187A1High purityHigh yieldSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationHydrolysateVegetable fibers
The invention relates to a process of recovering arabinose and optionally other monosaccharides from vegetable fiber rich in heteropolymeric arabinose, such as gum arabic. Said other monosaccharides are typically selected from galactose and rhamnose. The process of the invention comprises controlled hydrolysis of the arabinose-rich vegetable fiber and fractionation of the hydrolysis product to obtain a fraction enriched in arabinose and optionally other product fractions followed by crystallization of arabinose. The invention also relates to a novel method of crystallizing arabinose from biomass-derived material. Furthermore, the invention relates to novel crystalline L-arabinose.
Owner:DANISCO SWEETENERS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com