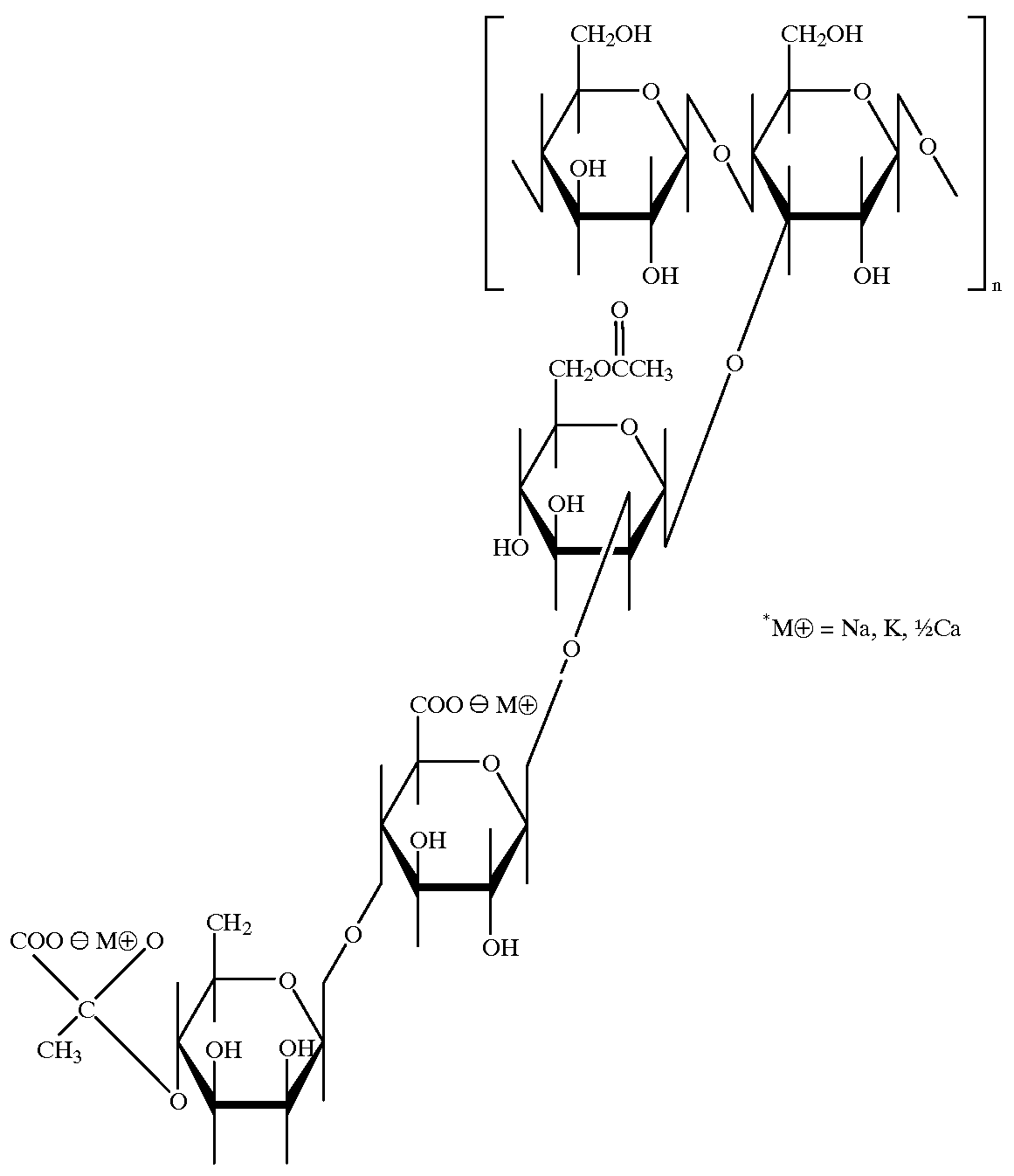
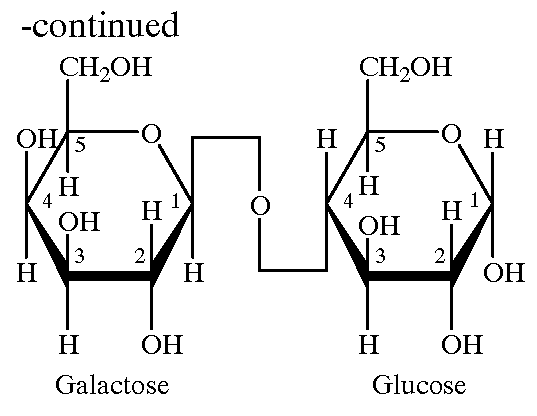
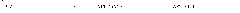Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
199 results about "Galactosamine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Galactosamine is a hexosamine derived from galactose with the molecular formula C₆H₁₃NO₅. This amino sugar is a constituent of some glycoprotein hormones such as follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). Other sugar constituents of FSH and LH include glucosamine, galactose and glucose.
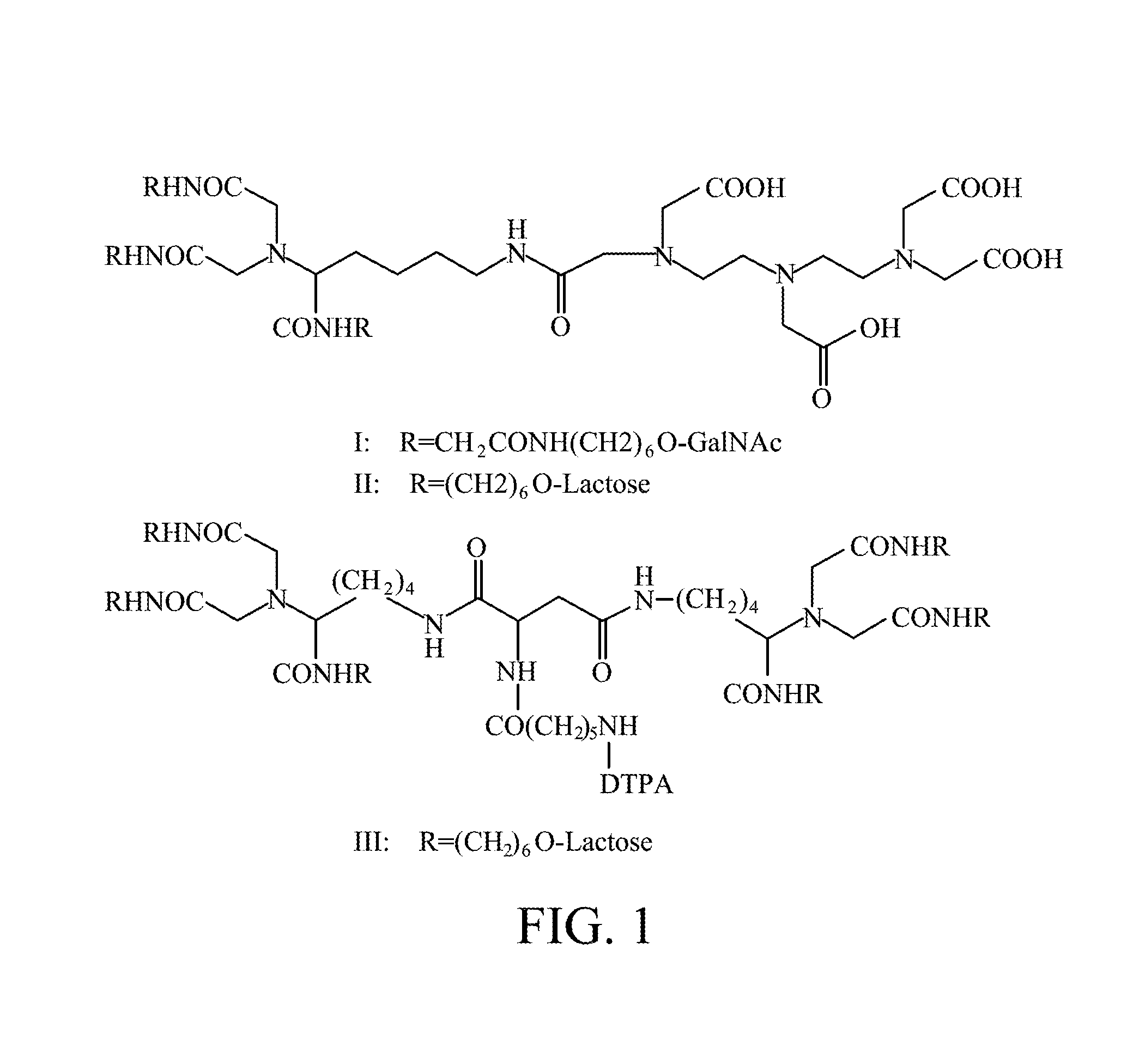
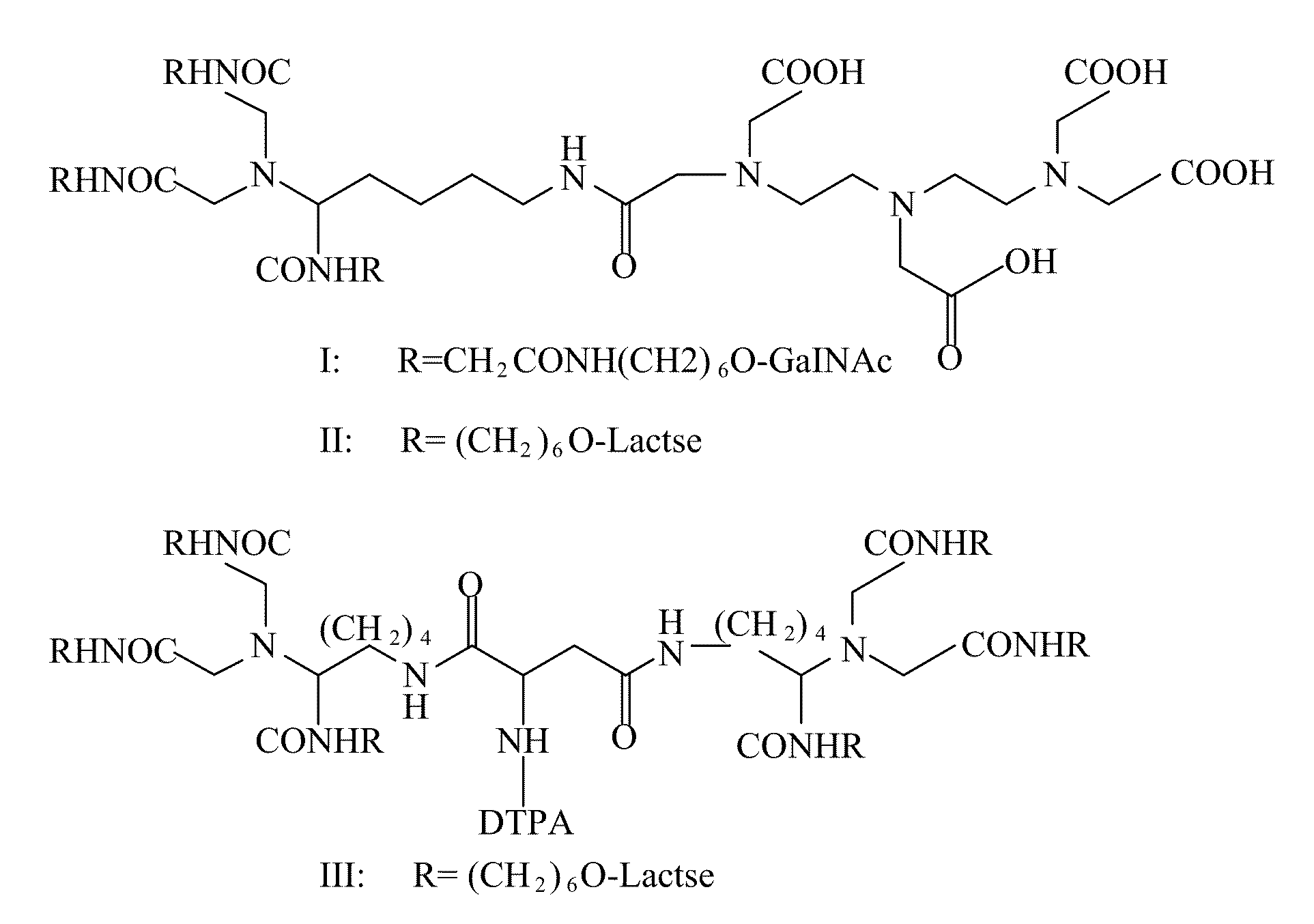
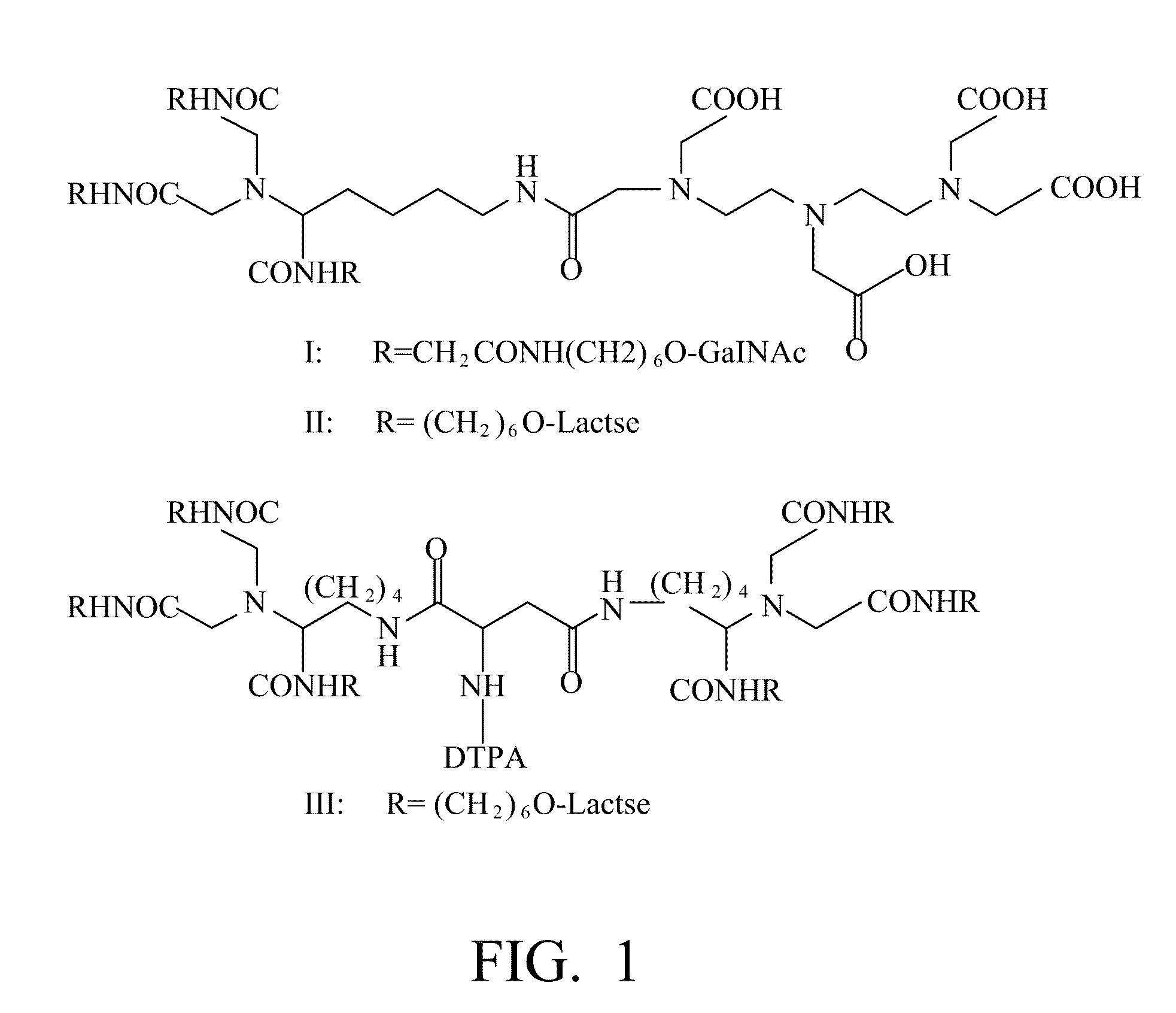
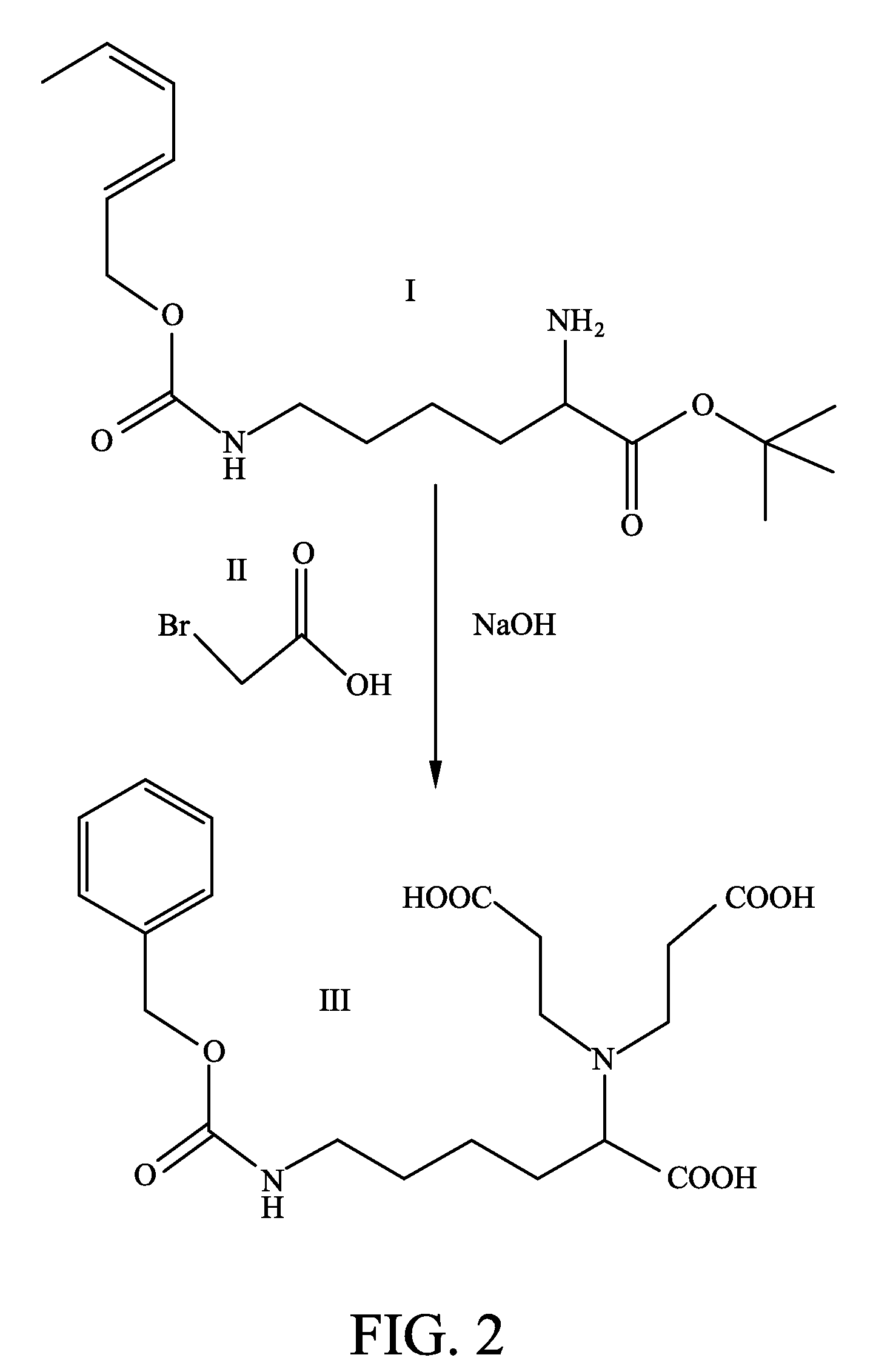
Liver-targeting agents and their synthesis
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
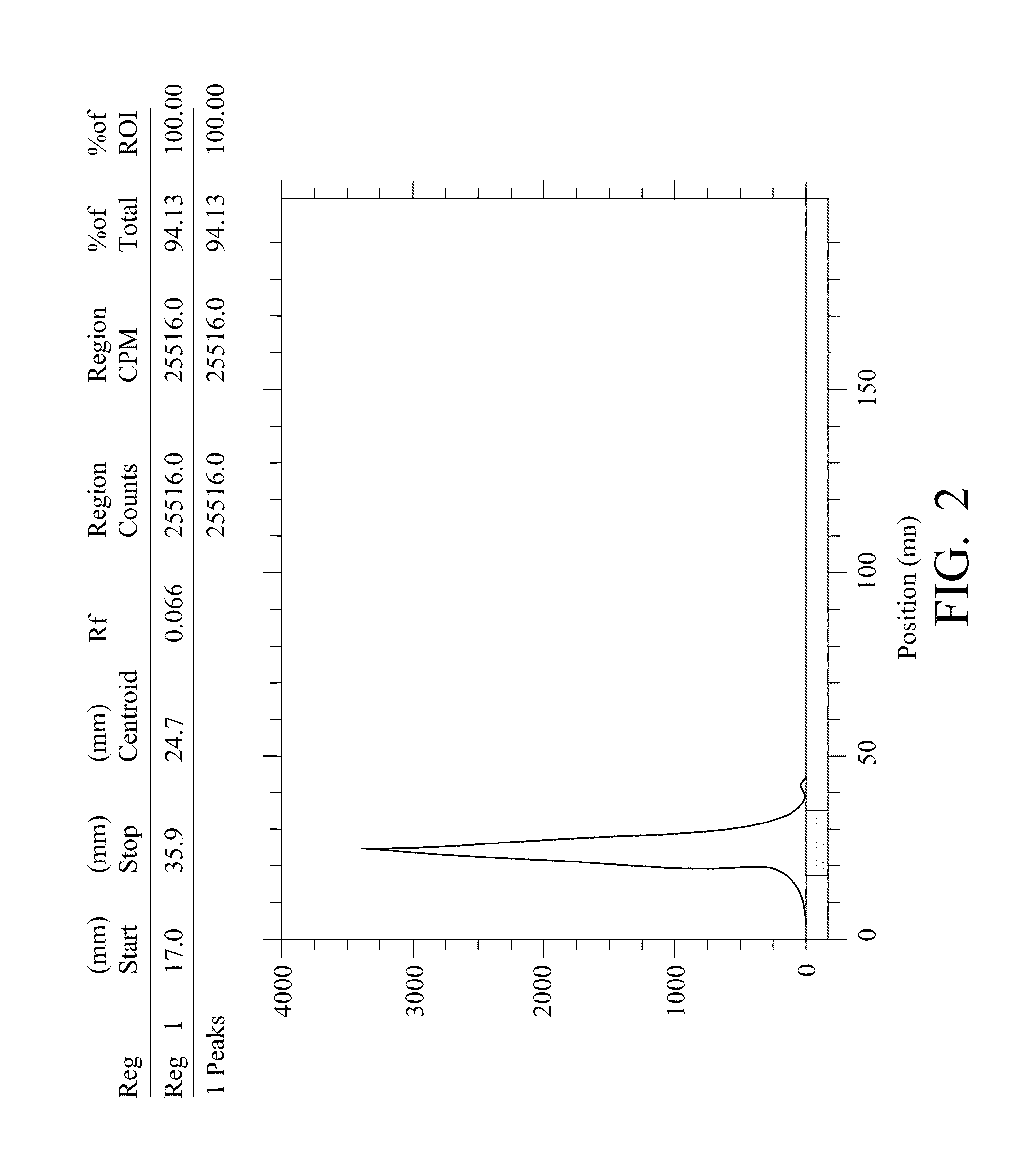
Radiolabeling method using multivalent glycoligands as hepatic receptor imaging agent
InactiveUS20110097264A1Low toxicityImprove securityRadioactive preparation carriersSaccharide peptide ingredientsImaging agentClinical trial
A radiolabeling method using a multivalent glycoligand as hepatic receptor imaging agent is provided. The multivalent glycoligand-DTPA derivatives (In-111-DTPA-hexa lactoside and In-111-DTPA-tri-galactosamine glycoside) labeled with In-111 are used as hepatic receptor imaging agent. The effects of imaging of a hepatic receptor in different species are evaluated, the lowest specific radioactivity values of hepatic receptor imaging required in different species are discovered. Since the specificity of the human ASGPR closely resembles that of the mouse. This kind of radiolabelling method, agent and related study about specific radioactivity could be used in clinical trial in the future.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
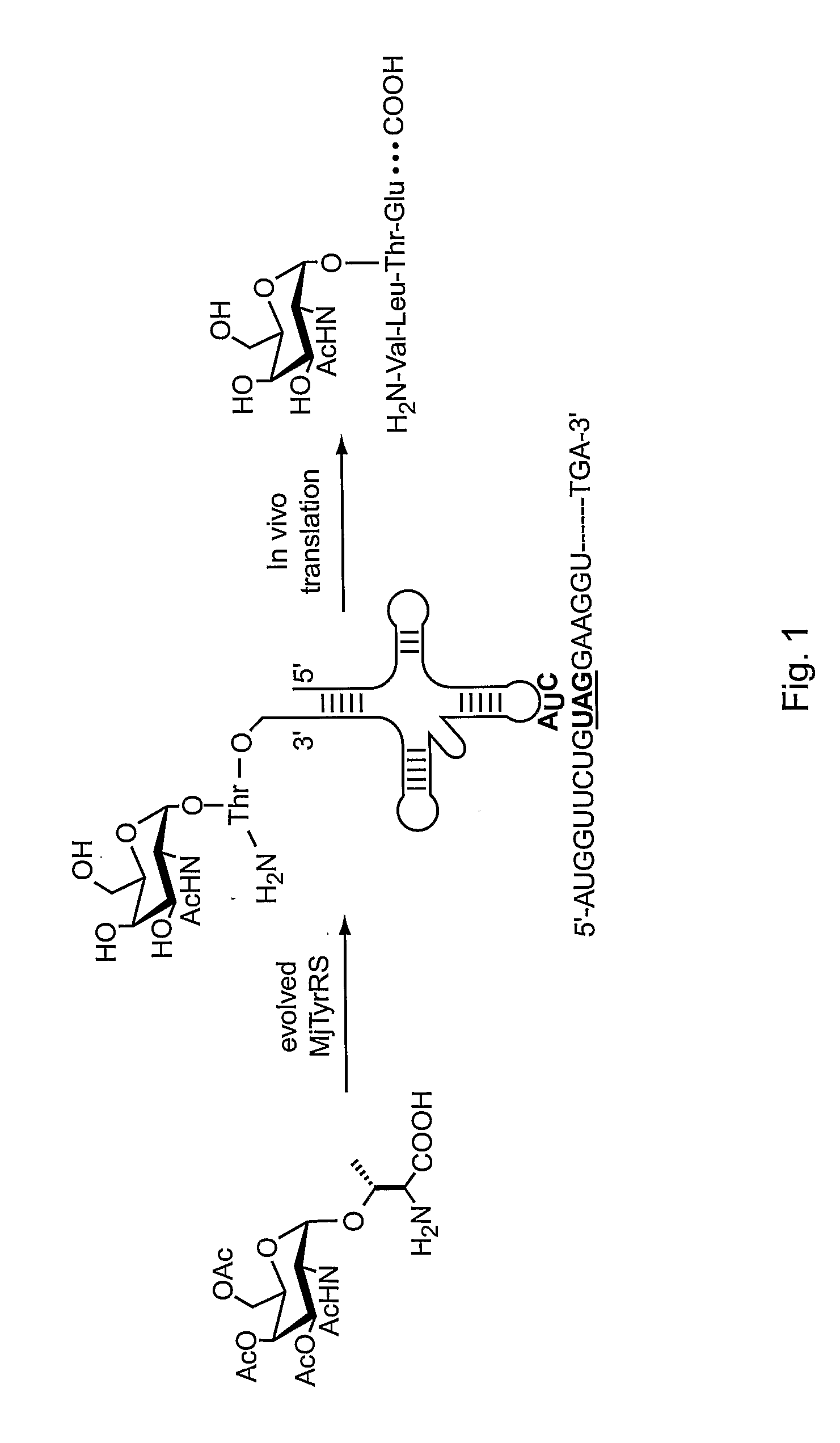
In vivo site-specific incorporation of N-acetyl-galactosamine amino acids in eubacteria
Methods and compositions for making glycoproteins, both in vitro and in vivo, are provided. One method involves incorporating an unnatural amino acid having a N-acetylgalactosamine moiety into a protein; optionally, the N-acetylgalactosamine-containing unnatural amino acid can be further modified with additional sugars.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
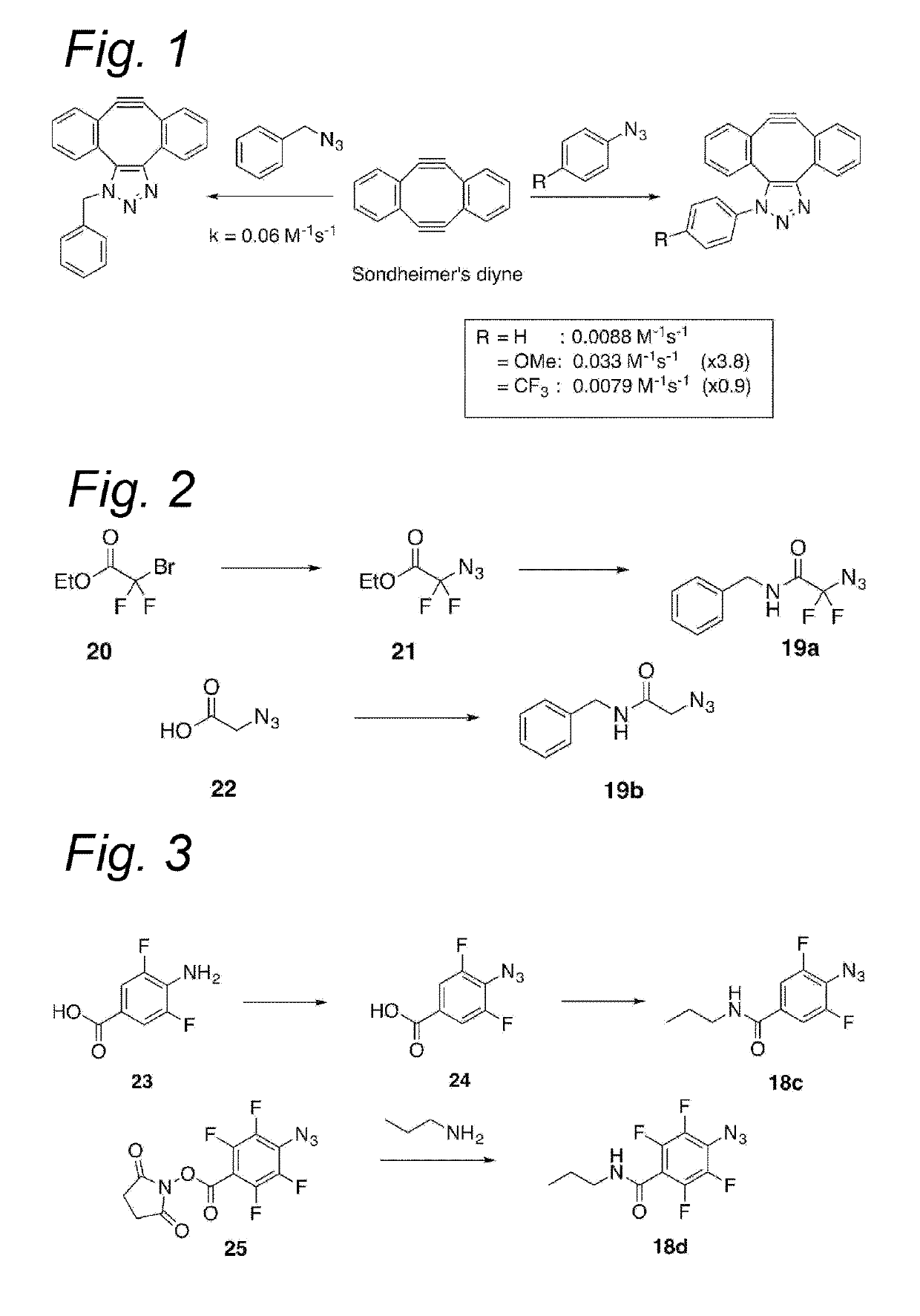
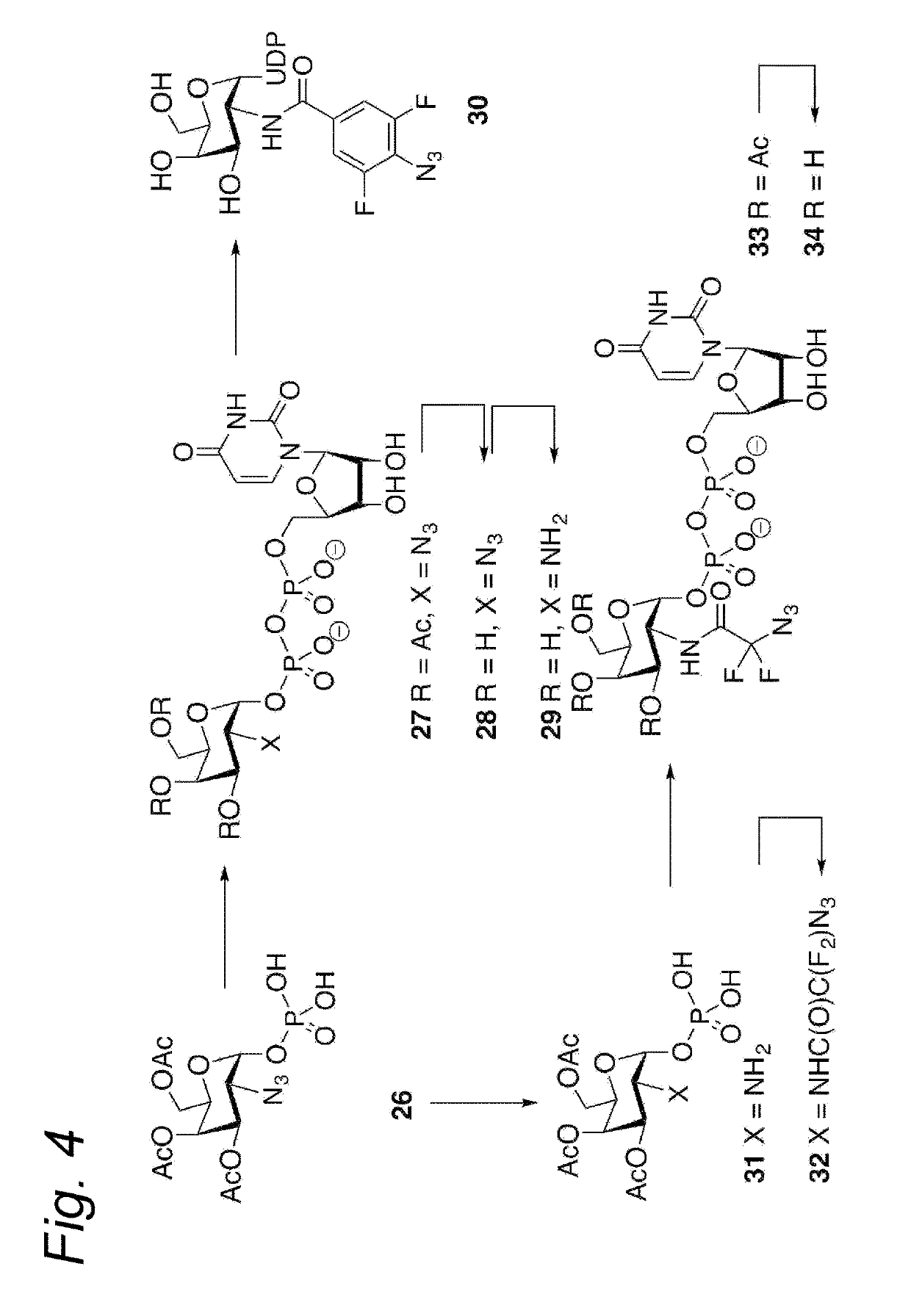
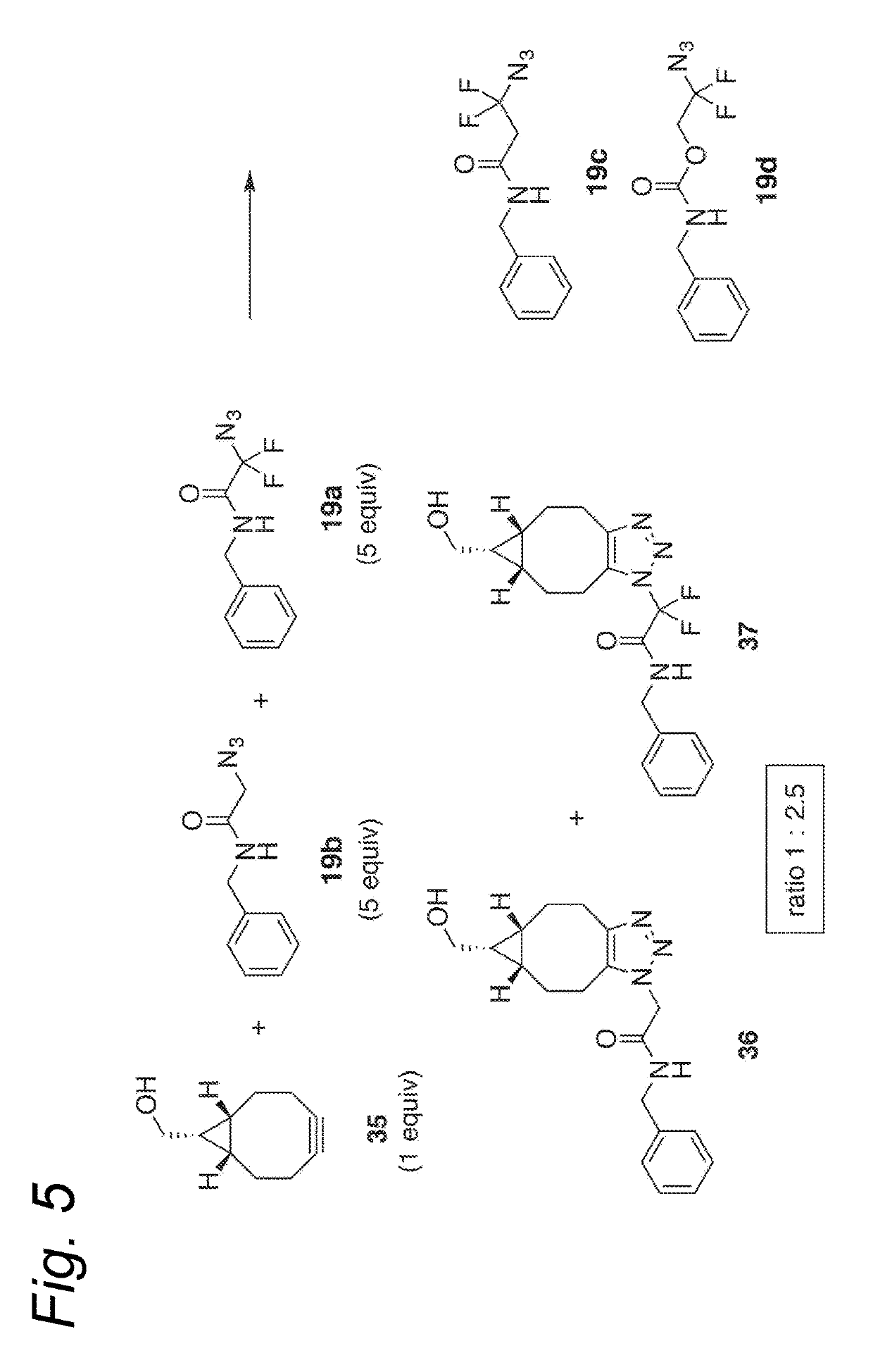
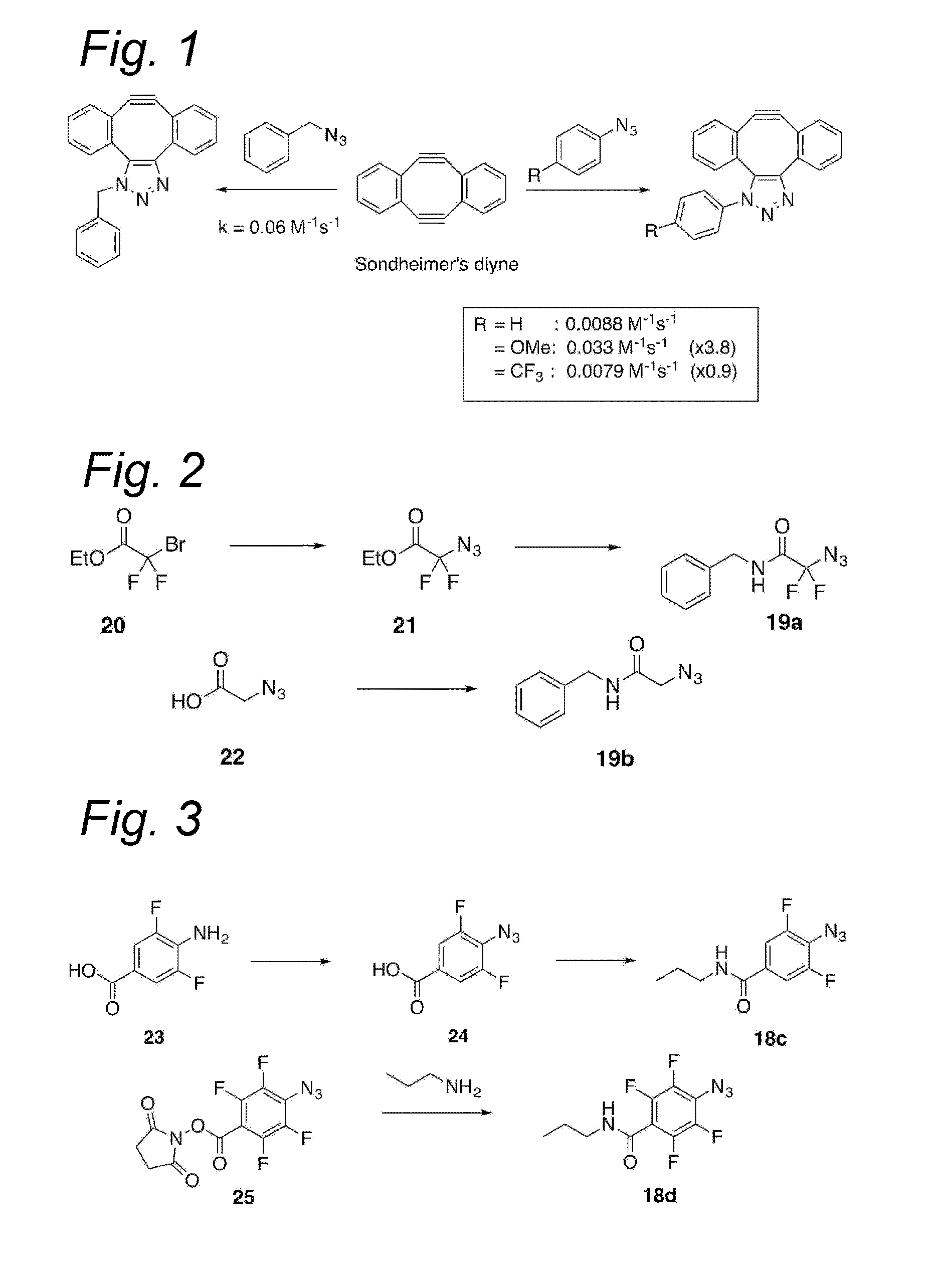
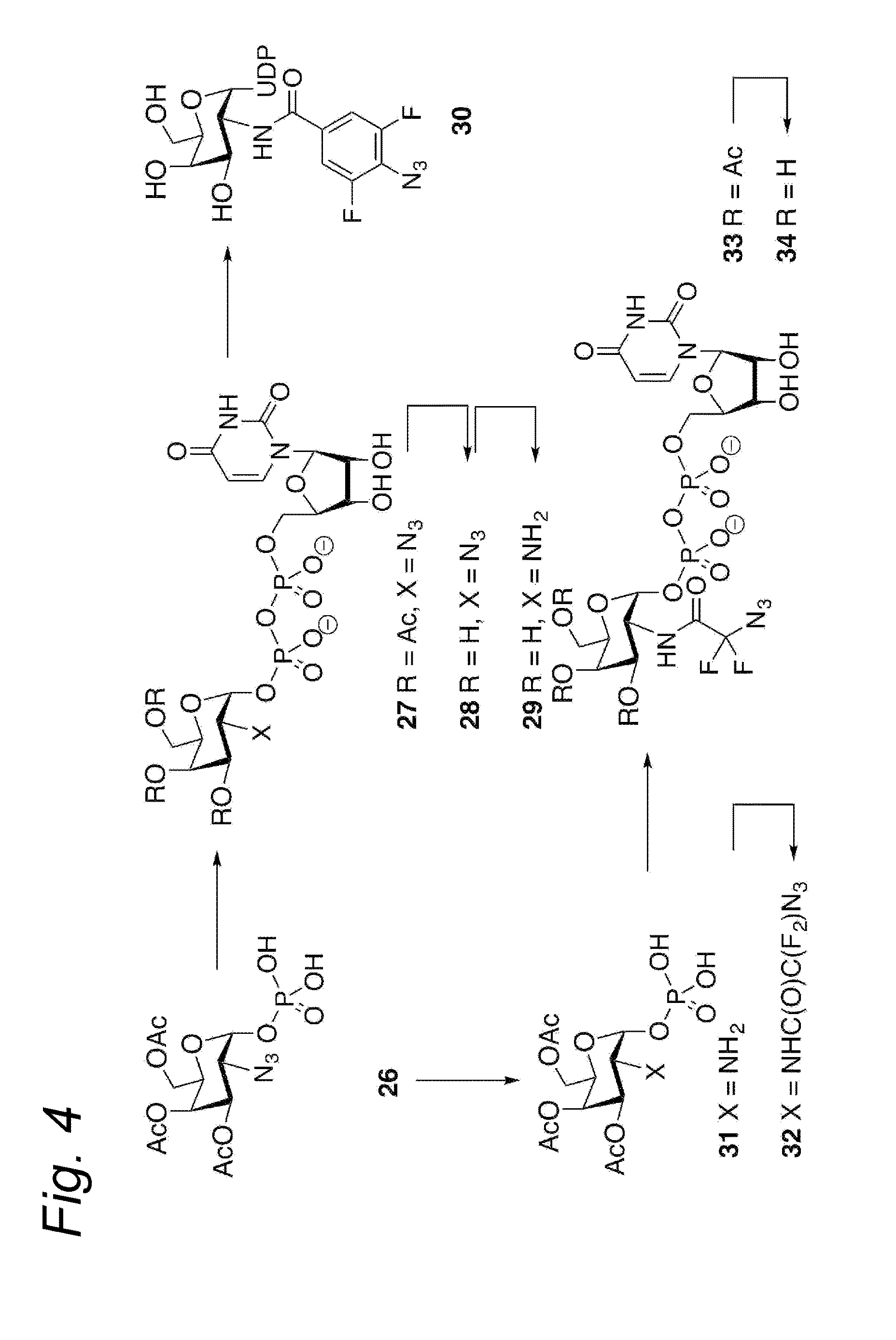
Process for the cycloaddition of a halogenated 1,3-dipole compound with a (hetero)cycloalkyne
ActiveUS10266502B2Esterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesNeuraminic acidN-Acetylglucosamine
Owner:SYNAFFIX
Novel liver-targeting agents and their synthesis
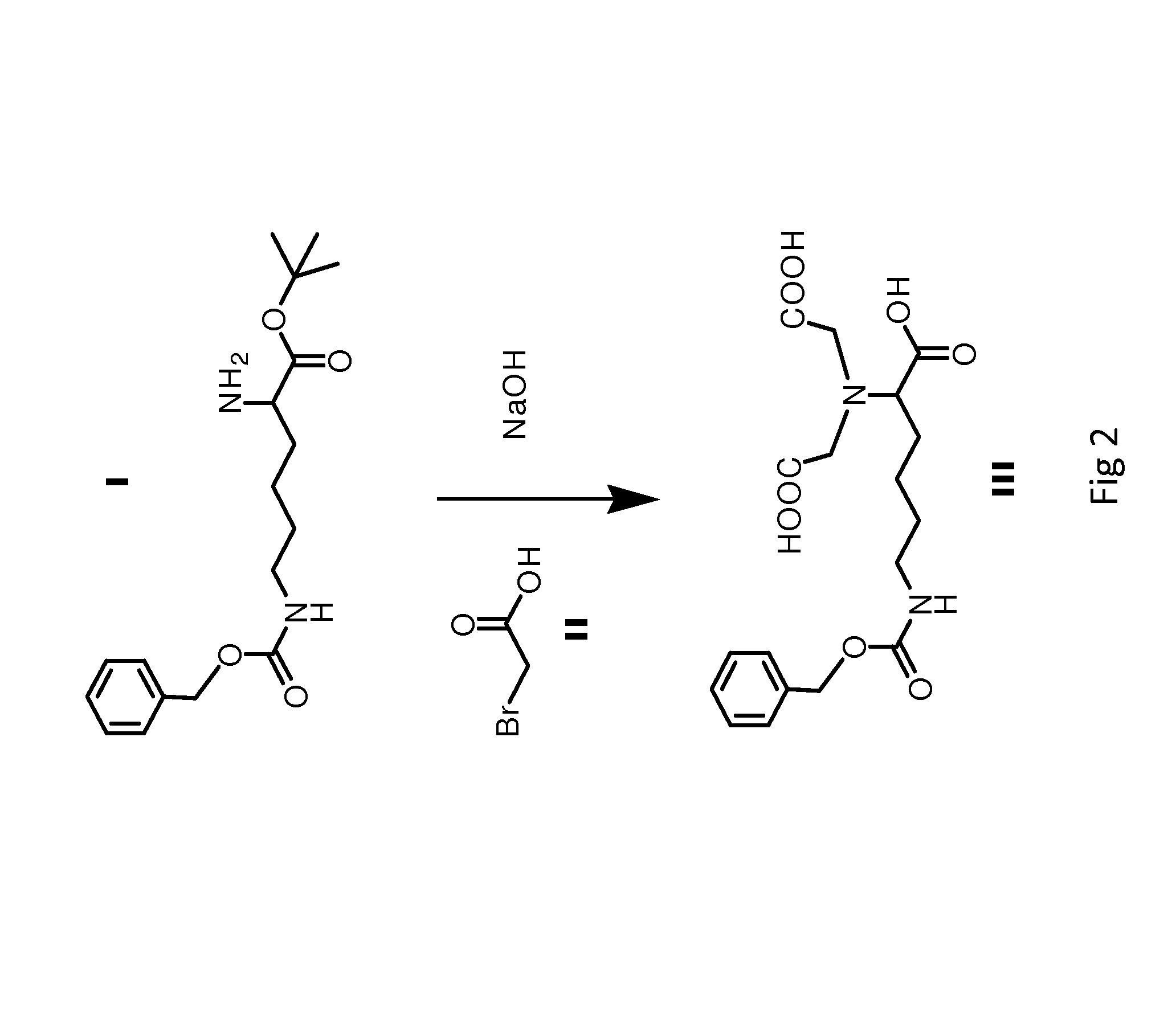
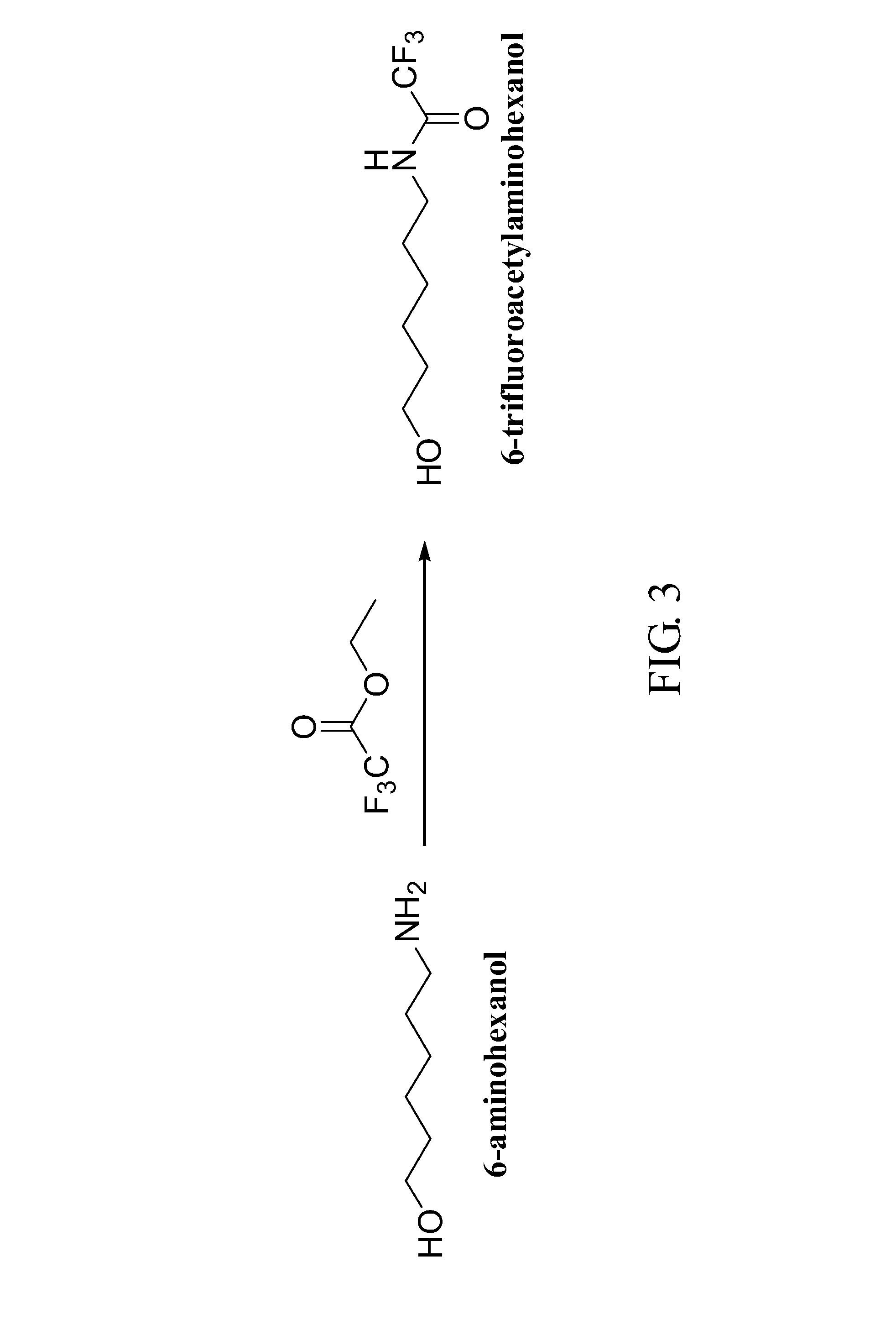
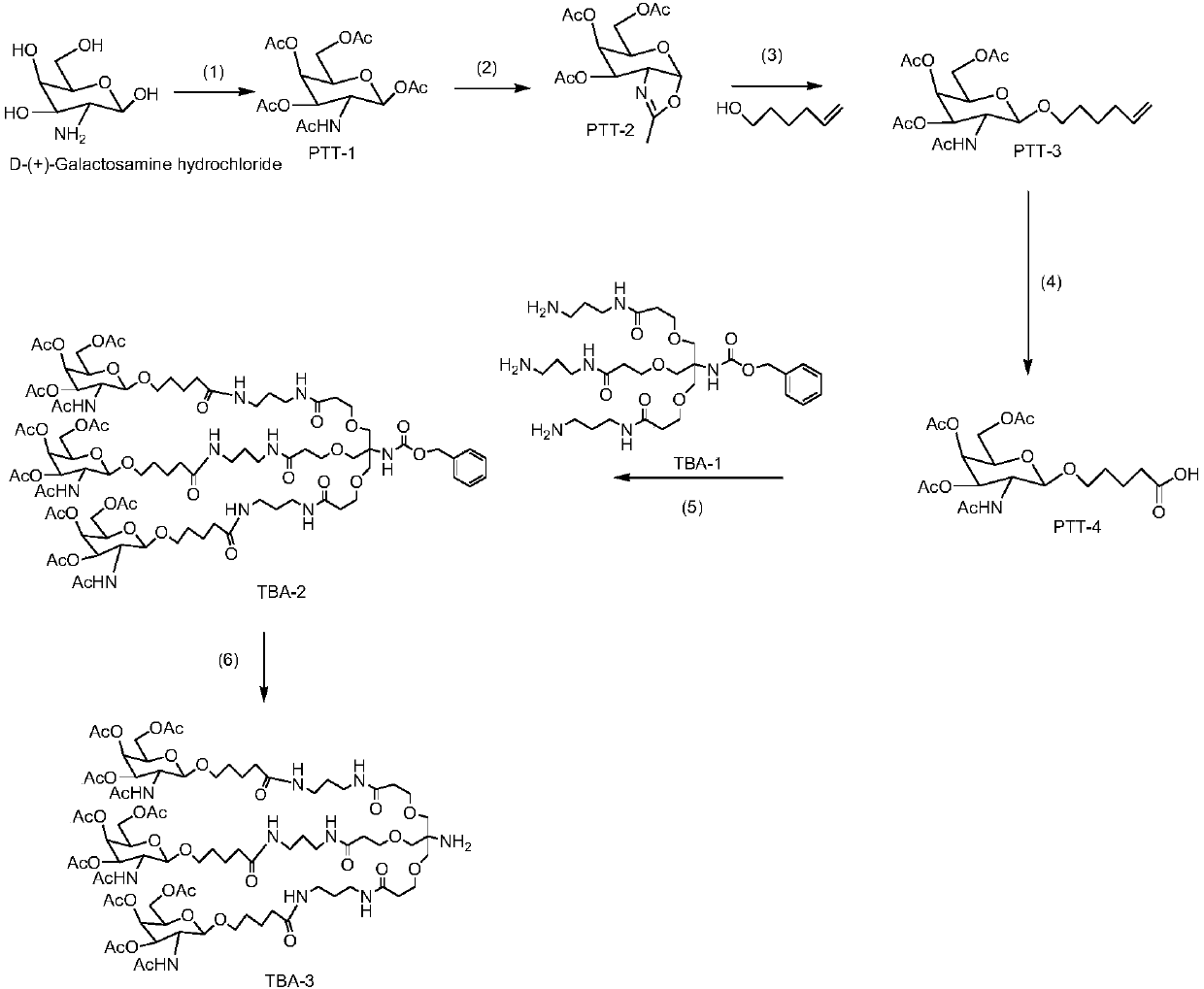
This invention provides novel liver targeting agents and their synthetic methods. A liver targeting agent, with a lysine based nitrilo triacetic acid structure as backbone which acquires multivalency with saccharide groups, to bind with a galactosamine chain or lactose chain is disclosed. In particular, only one amino acid L-lysine is involved to provide trivalency. All carboxyl groups in Nε-benzyloxycarbonyl-Nα-dicarboxymethyl-L-lysine can be conjugated with three glycosides of ahGalNAc or ahLac in one step. This invention also provides a hexa-lactoside. In particular, the TFA-AHA-Asp was used to conjugate 2 moles of NTA(ahLac)3. This invention also provides a method for adding a spacer between NTA and DTPA. The extended hepatocyte-specific glyco-ligand has higher 111In-radiolabelling yield than those non-extended.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Composition and method for reducing the colonization of animal intestines by salmonella and other bacterial pathogens
InactiveUS6126961AReducing human pathogen colonizationSafe and economical reductionBiocideAnimal feeding stuffIntestinal structureBacteroides
An animal feed composition for reducing colonization of animal intestines by Salmonella and other bacterial pathogens, includes a polysaccharide containing cis-hydroxy sugar units or a derivative thereof, or the monosaccharide ribose or rhamnose, or a derivative thereof, and an animal feed. The polysaccharide cis-hydroxy sugar units may be one or more of mannose, a mannose derivative, galactose, a galactose derivative, galactomannans, galactosamine, fucose and arabinose. The polysaccharides may be incorporated into an animal feed in the form of a food gum or other biolpolymer.
Owner:AURUM CERTUS
Nutritional compositions
InactiveUS20060073186A1Suppress in productionSuppression of inflammatory cytokine productionOrganic active ingredientsSugar food ingredientsInterleukin 6Hydrolysate
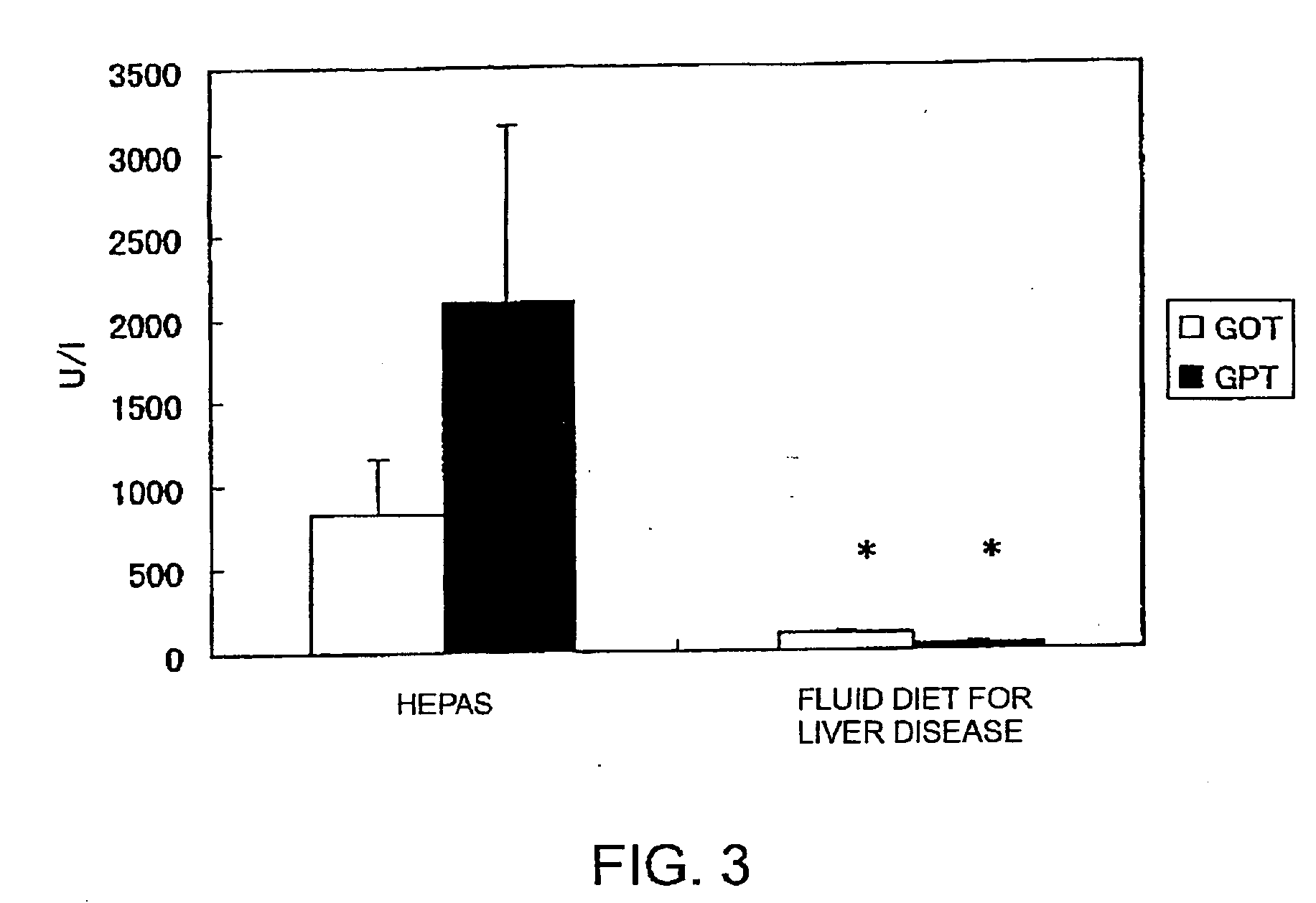
The present inventors discovered that the onset of galactosamine hepatopathy is suppressed by nutritional compositions comprising as essential ingredients: whey protein hydrolysates; lecithin and oils and fats high in oleic acid, which are able to improve the lipid metabolism; and palatinose having an insulin-sparing effect. Furthermore, the whey protein hydrolysate included in the nutritional compositions was found to suppress endotoxin-induced TNF-a and interleukin 6 (IL-6) production in macrophages.
Owner:MEIJI CO LTD
In Vivo Site-Specific Incorporation of N-Acetyl-Galactosamine Amino Acids in Eubacteria
Methods and compositions for making glycoproteins, both in vitro and in vivo, are provided. One method involves incorporating an unnatural amino acid having a N-acetylgalactosamine moiety into a protein; optionally, the N-acetylgalactosamine-containing unnatural amino acid can be further modified with additional sugars.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
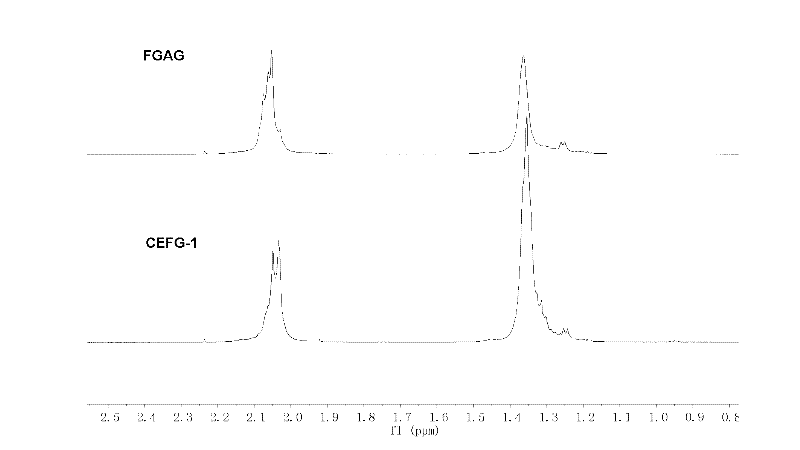
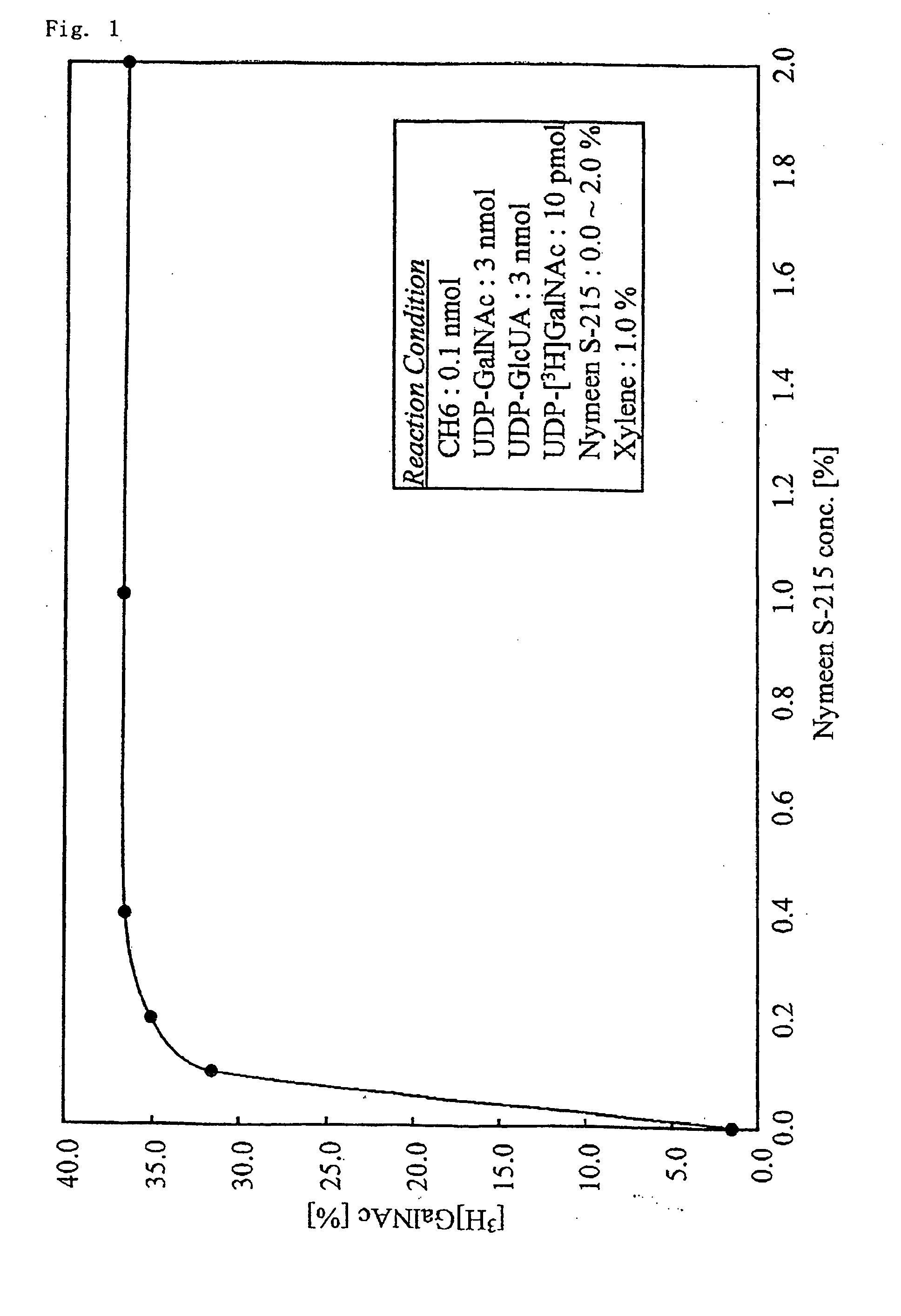
Fucosylated glycosaminoglycan derivative and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102329397APotent anticoagulant activityOrganic active ingredientsBlood disorderOrganosulfateCarboxylic ester
The invention discloses a carboxylic ester of fucosylated glycosaminoglycan (CEFG) with anticoagulation activity, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, a preparation method of the CEFG and the pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, a pharmaceutical composition containing the CEFG or the salt thereof, and application of the pharmaceutical composition in preparation of anticoagulants. The monosaccharides for preparing the CEFG comprise D-glucuronic acid or D-glucuronate (D-GlcU), D-2-deoxy-2-acetyl galactosamine sulfate (D-GalNAcS) and L-fucose sulfate (L-FucS), wherein the molar ratio of D-GlcU to D-GalNAc to L-Fuc to -OSO3<-> is 1:(1+ / -0.3):(1+ / -0.3):(3.5+ / -0.5); the esterification degree of the D-GlcU is not lower than 20%; and the weight average molecular weight of the CEFG is 3000-20000 Da. The glycosylated chondroitin sulfate esterification derivative has strong anticoagulation activity, and can be applied in preparation of drugs for preventing and / or treating thrombotic diseases.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Long-chain chondroitin sugar chain and method for producing the same and method for promoting synthesis of chondroitin
ActiveUS20090263867A1Efficient productionEasy to produceBacteriaSugar derivativesFiltrationChondroitinase ABC
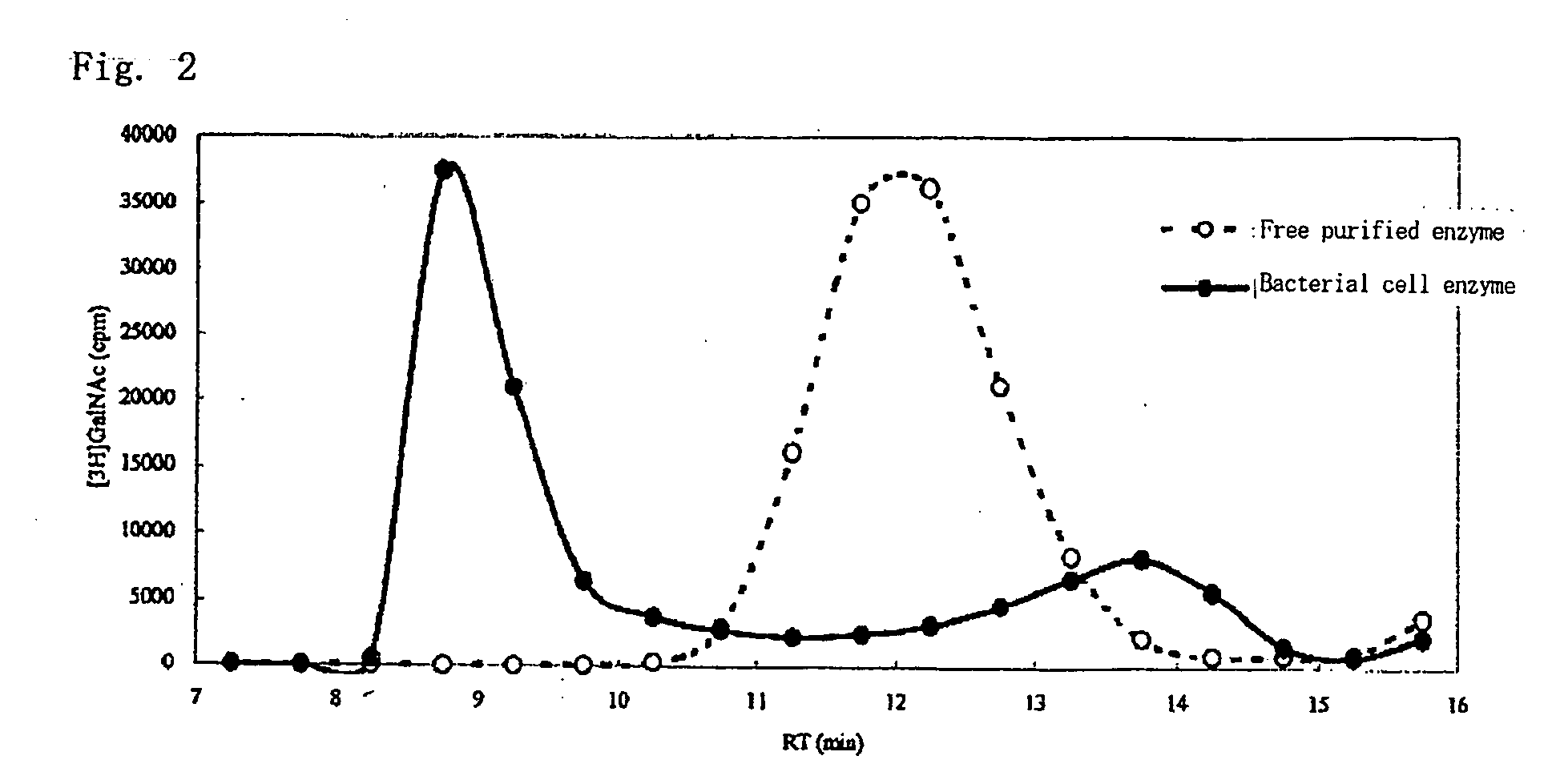
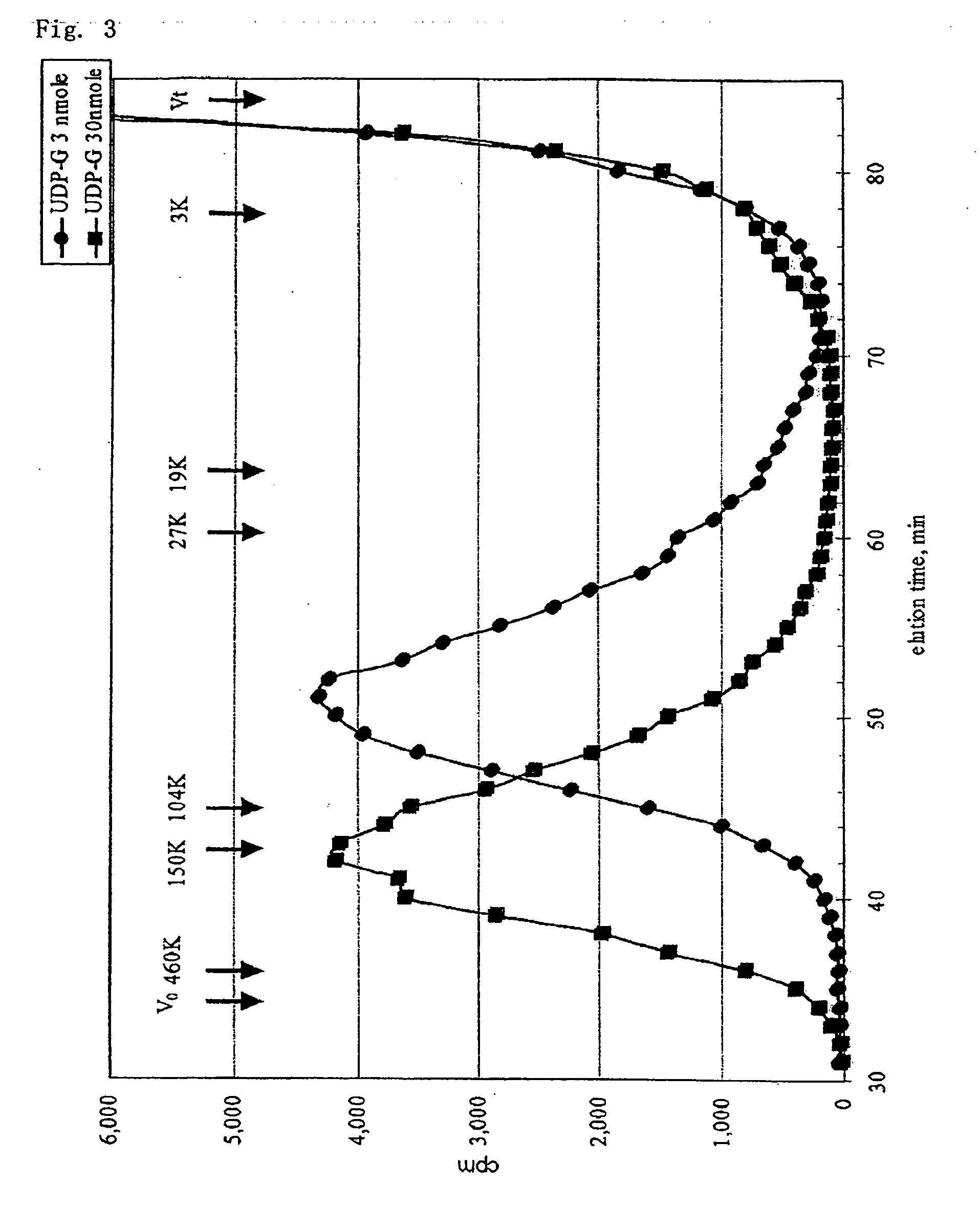
A method for producing a chondroitin sugar chain comprises at least the following step: a step of allowing “a glucuronic acid donor”, “an N-acetyl galactosamine donor”, “a sugar receptor” and “a bacterial cell enzyme which synthesizes chondroitin” to coexist in a reaction system in the presence of a surfactant. Here, the surfactant is preferably selected from n-nonyl-β-D-thiomaltopyranoside, sucrose monocaproate and sucrose monolaurate. The chondroitin sugar chain has all the following properties 1) to 3): 1) a weight average molecular weight: 50,000 or more when it is measured by gel filtration chromatography, 2) it is completely degraded to disaccharides with chondroitinase ABC, 3) when the sugar chain is decomposed with chondroitinase ABC and the decomposed products are subjected to a disaccharide analysis, substantially all of them correspond to an unsaturated disaccharide unit of chondroitin.
Owner:SEIKAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD
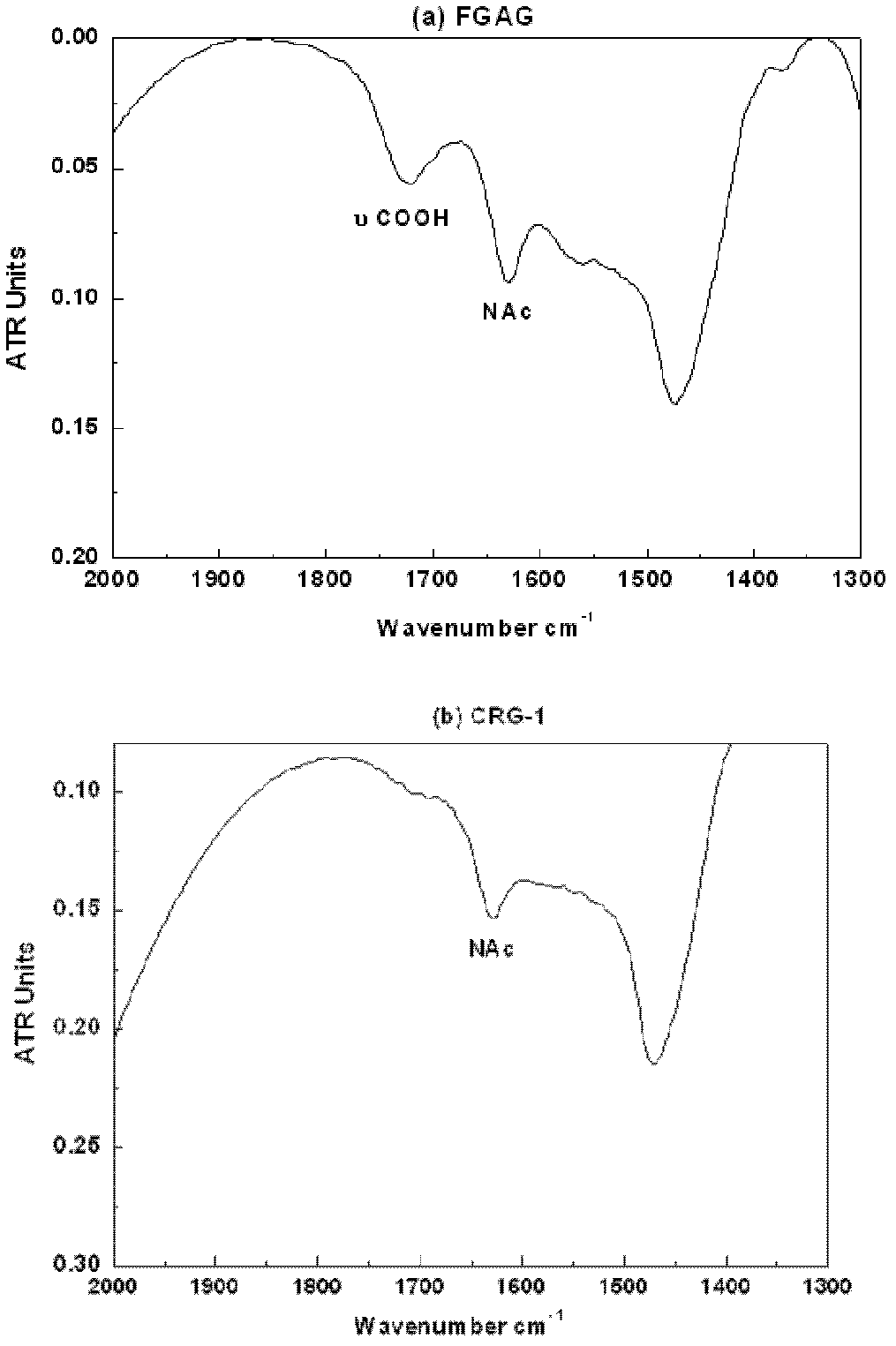
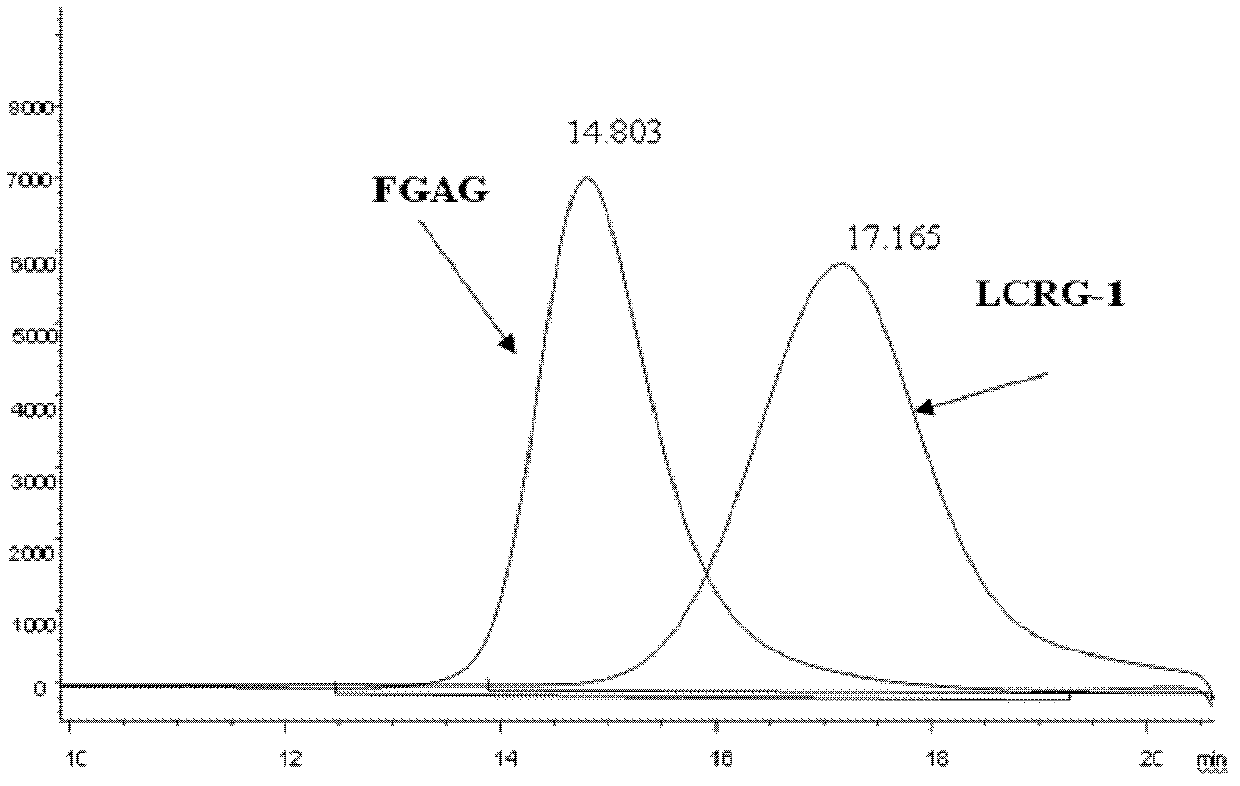
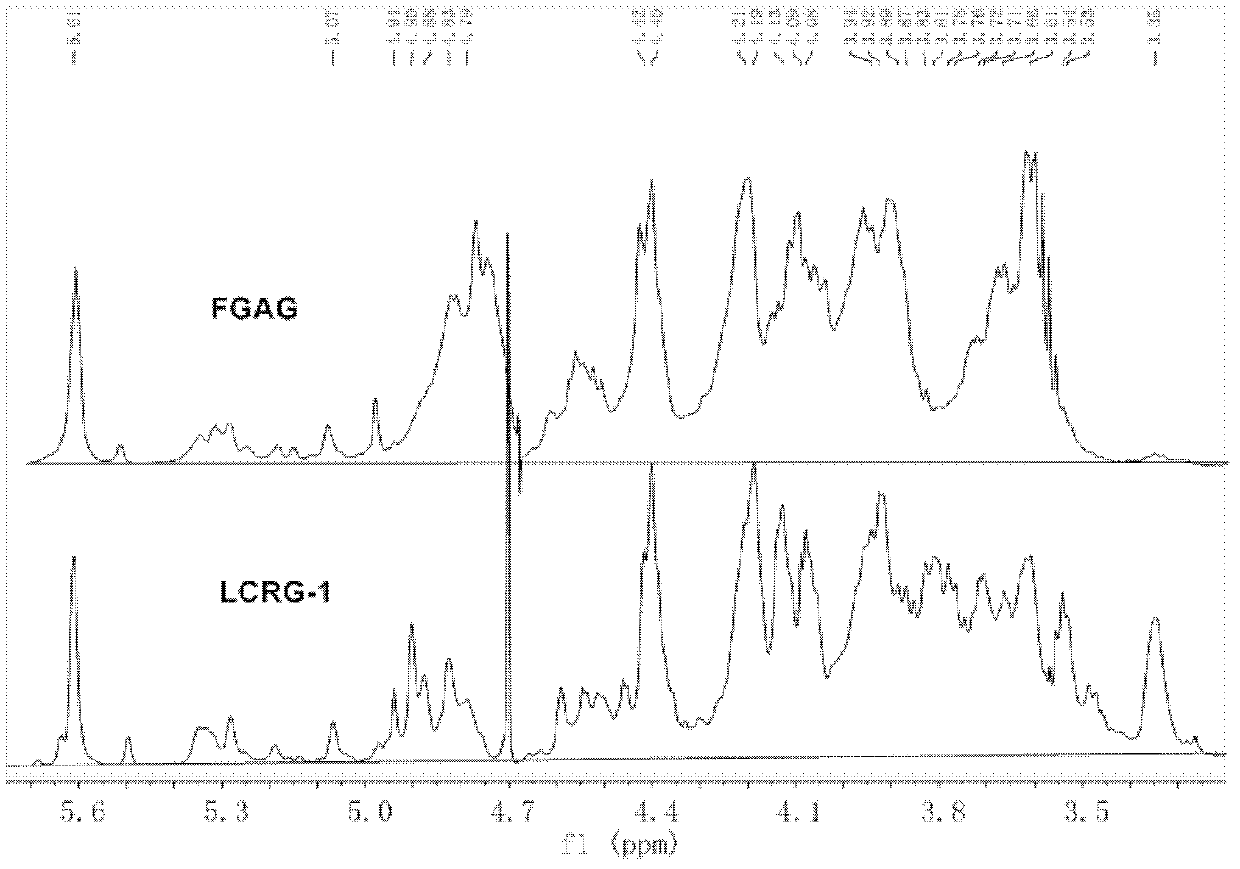
Low molecular weight carboxyl-reduced derivatives of fucosylated glycosaminoglycans and preparation method and applications of low molecular weight carboxyl-reduced derivatives
The invention discloses low molecular weight carboxyl-reduced derivatives of fucosylated glycosaminoglycans (LCRG). The extent of carboxyl reduction is not less than 20%. Weight-average molecular weight of the LCRG is about 3000-20000Da, and monosaccharides comprise acetyl galactosamine (GalNAc), glucose (Glc) or glucuronic acid (GlcUA) and fucose (Fuc) or sulfates of fucose (shown as -OSO3-). The mole ratio of GalNAc, Glc (containing GlcUA), Fuc and -OSO3- is about 1: (1+-0.3): (1+-0.3): (3.0+-1.0). The LCRG is a potent human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) Type 1 entry inhibitor which acts on conserved regions and has the advantages of high activity against HIV Type 1, high therapeutic index and no-drug-resistance, and the LCRG can be used for preventing or curing HIV. The invention further provides a preparation method of the LCRG. The carboxyl-reduced derivatives of fucosylated glycosaminoglycans and medicinal compositions of the carboxyl-reduced derivatives can be prepared into injection agents, lyophilized powder or suppository and the like.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Process for the cycloaddition of a halogenated 1,3-dipole compound with a (hetero)cycloalkyne
ActiveUS20170008858A1Esterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesNeuraminic acidN-Acetylglucosamine
The present invention relates to a cycloaddition process comprising the step of reacting a halogenated aliphatic 1,3-dipole compound with a (hetero)cycloalkyne according to Formula (1): Preferably, the (hetero)cycloalkyne according to Formula (1) is a (hetero)cyclooctyne. The invention also relates to the cycloaddition products obtainable by the process according to the invention. The invention further relates to halogenated aliphatic 1,3-dipole compounds, in particular to halogenated aliphatic 1,3-dipole compounds comprising N-acetylgalactosamine-UDP (GalNAc-UDP), and to halogenated 1,3-dipole compounds comprising (peracylated) N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc), N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc), N-acetylmannosamine (ManNAc) and N-acetyl neuraminic acid (NeuNAc).
Owner:SYNAFFIX
Interfacing Nanostructures to Biological Cells
Disclosed herein are methods and materials by which nanostructures such as carbon nanotubes, nanorods, etc. are bound to lectins and / or polysaccharides and prepared for administration to cells. Also disclosed are complexes comprising glycosylated nanostructures, which bind selectively to cells expressing glycosylated surface molecules recognized by the lectin. Exemplified is a complex comprising a carbon nanotube functionalized with a lipid-like alkane, linked to a polymer bearing repeated α-N-acetylgalactosamine sugar groups. This complex is shown to selectively adhere to the surface of living cells, without toxicity. In the exemplified embodiment, adherence is mediated by a multivalent lectin, which binds both to the cells and the α-N-acetylgalactosamine groups on the nanostructure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Cholesterol Sulfate And Amino Sugar Compositions For Enhancement Of Stratum Corneum Function
InactiveUS20100247692A1Enhances protective barrierImprove skinCosmetic preparationsBiocideWrinkle skinSkin barrier function
The present invention provides compositions containing a mixture of cholesterol sulfate and an exfoliant. The exfoliant can be N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, N-acetylgalactosamine, or a combination thereof. The combination of cholesterol sulfate with the exfoliant surprisingly enhances the skin barrier even though the activity of each of the components is opposite the other. In addition, because of the ability to enhance or repair the skin barrier function, methods of maintaining or improving a healthy skin barrier are included in the present invention by apply to the skin an effective amount of the mixture of cholesterol sulfate with the exfoliant. The mixture can also be useful in treating or preventing damage to the skin, where the damage is caused by a comprised skin barrier function. As a result of improved skin barrier function, the appearance of lines and wrinkles is generally reduced; rough and dry skin conditions are also improved.
Owner:MAES DANIEL H +1
Application of fructus forsythiae aglycone in preparing medicament for preventing or treating liver injury or liver failure
InactiveCN103989668ASignificant preventionGood treatment effectDigestive systemHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsSide effectAglycone
The invention discloses application of fructus forsythiae aglycone in preparing a medicament for preventing or treating liver injury or liver failure, and belongs to the medical field. The fructus forsythiae aglycone is a traditional Chinese medicine monomer obtained by extracting from the conventional fructus forsythiae, and is shown to have better treatment effect for the liver injury caused by acetaminopben, the livery injury caused by anti-tumor drug cis-platinum, acute or chronic livery injury caused by carbon tetrachloride, the livery injury caused by D-galactosamine and the liver failure caused by the D-galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide according to an animal test, has effect, which is better than that of fructus forsythiae and fructus forsythiae aglycone, in treating liver injury or liver failure. The fructus forsythiae aglycone is exact in curative effect and low in side effect for treating the liver injury and the liver failure, and has wide medical application prospect.
Owner:LUNAN PHARMA GROUP CORPORATION
Liver targeted medicine
InactiveCN107929273AImproved Liver TargetingGood curative effectDigestive systemPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsDiseaseCitrulline
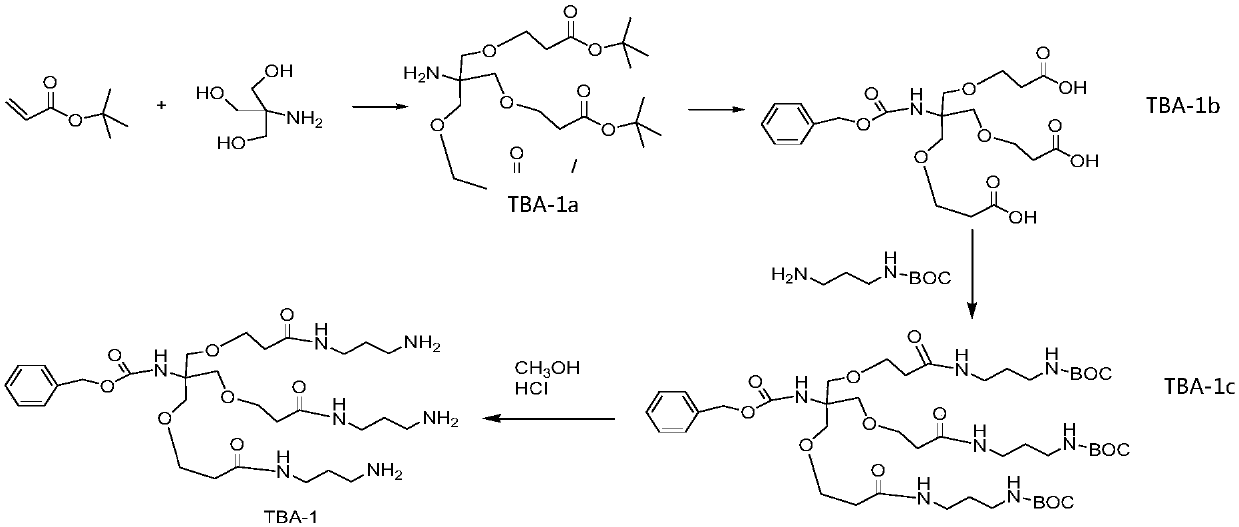
The invention relates to the field of biological medicine, and in particular relates to liver targeted medicine. The medicine is chemical micromolecular medicine connecting galactosamine. The chemicalmicromolecular medicine is medicine for treating liver diseases or liver-related diseases. The chemical micromolecular medicine is prepared from but not limited to thyroxine T3, sorafenib, taxol, regorafenib, lamivudine, entecavir, telbivudine, statins, fibrates, niacin, bile acid sequestrants, other hepatitis virus DNA (RNA) polymerase inhibition compounds and the like. The galactosamine is tervalent acetylgalactosamine. The connection is the direct connection of the galactosamine and the chemical micromolecular medicine or the connection through linking fragments; the linking fragments comprise but not limited to carbon chains, disulfide bonds, pyrophosphate diester, cysteic acid, polypeptide and thioether or valine-citrulline. The medicine provided by the invention has the advantages that the liver targeted performance is improved; the medicine curative effect is enhanced; the toxic and side reactions on other non-targeted tissues are few.
Owner:崔坤元
Nanoparticles for targeting hepatoma cells
InactiveUS7348030B1High fluorescence intensityExtended durationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideMedicineNanoparticle
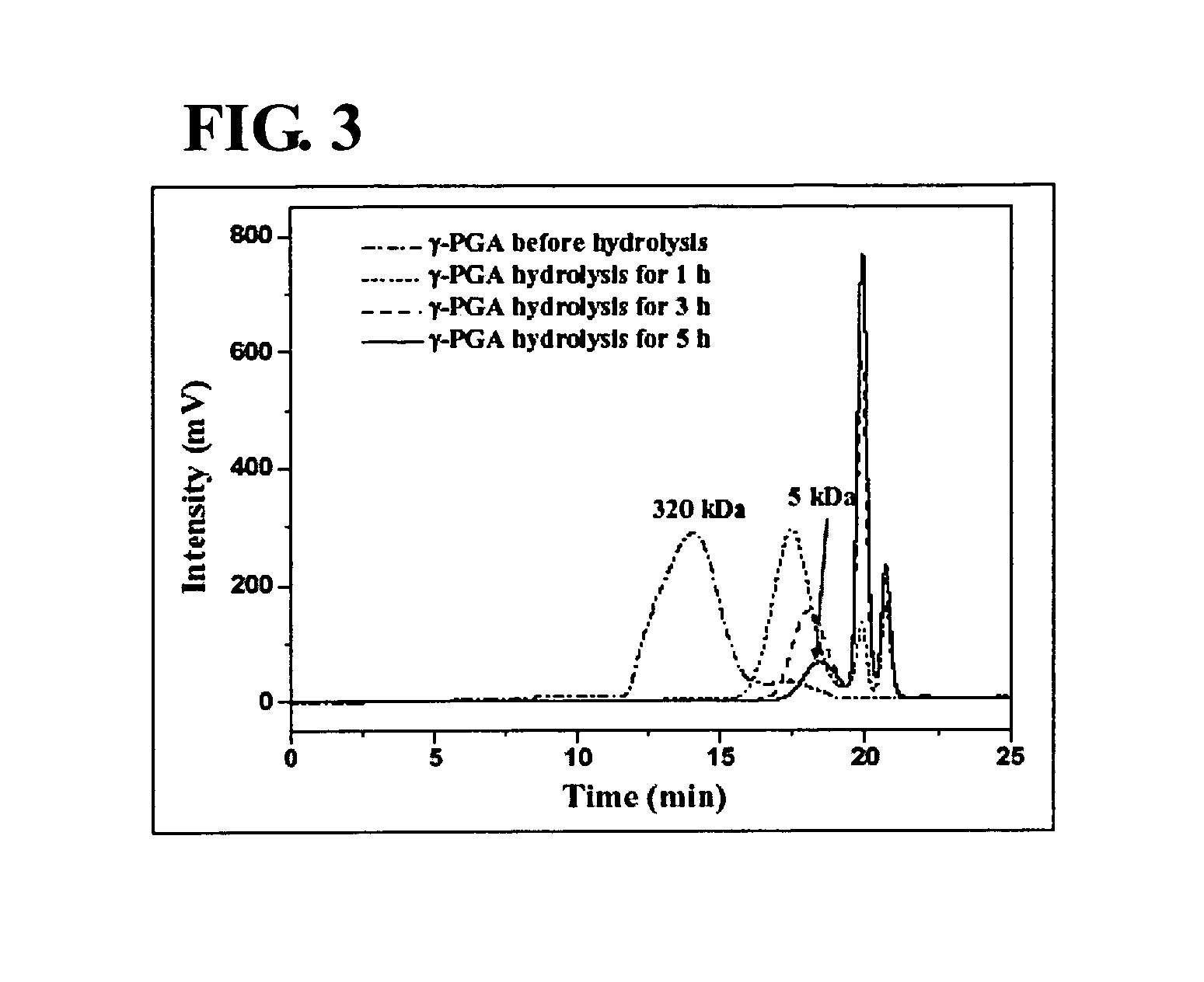
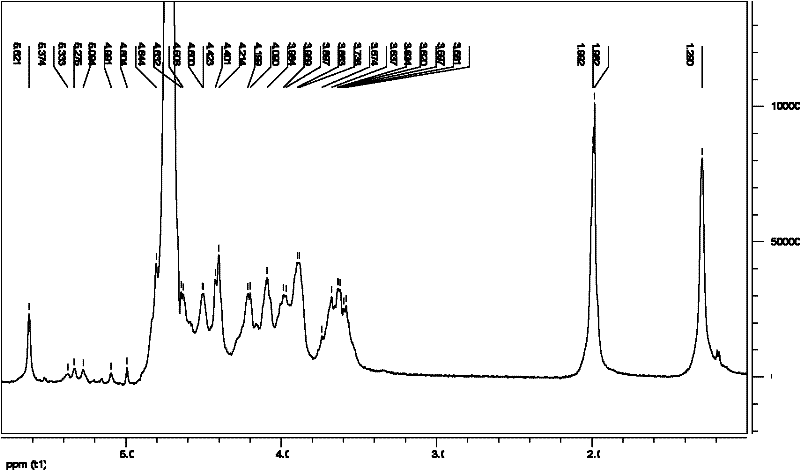
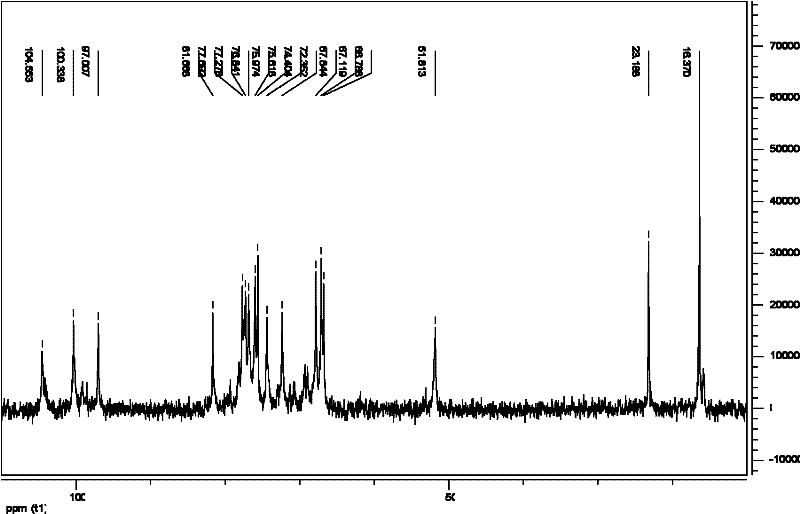
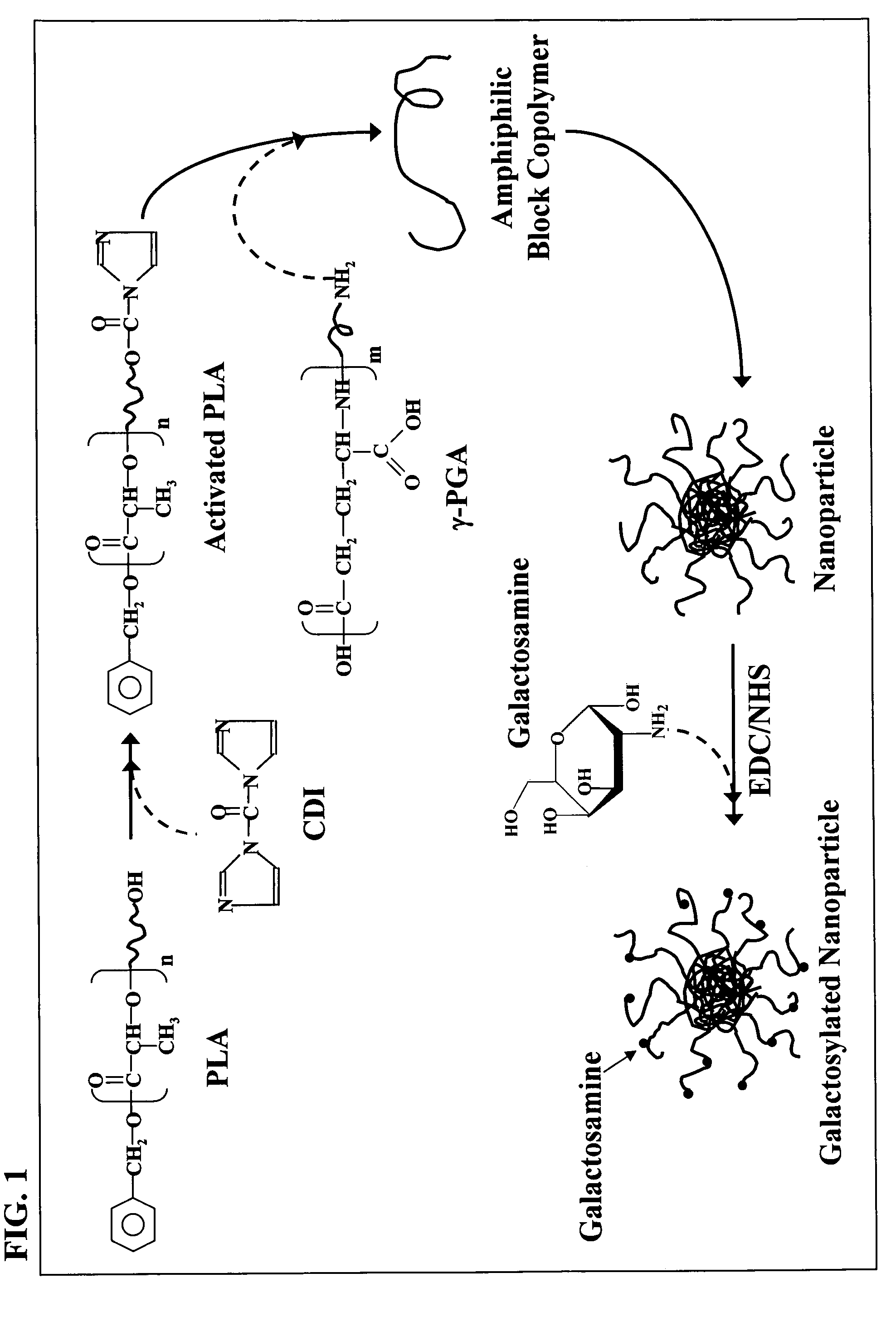
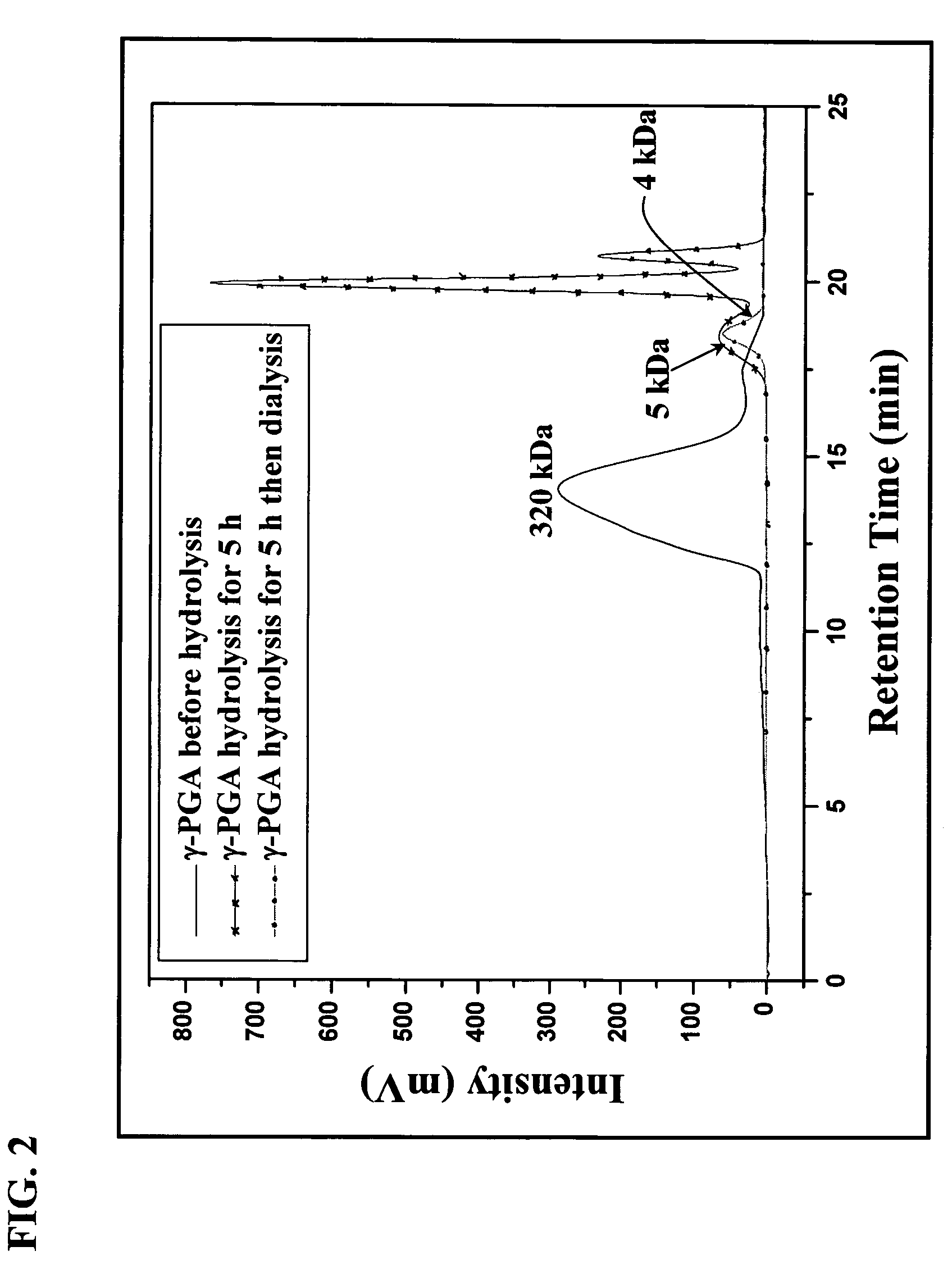
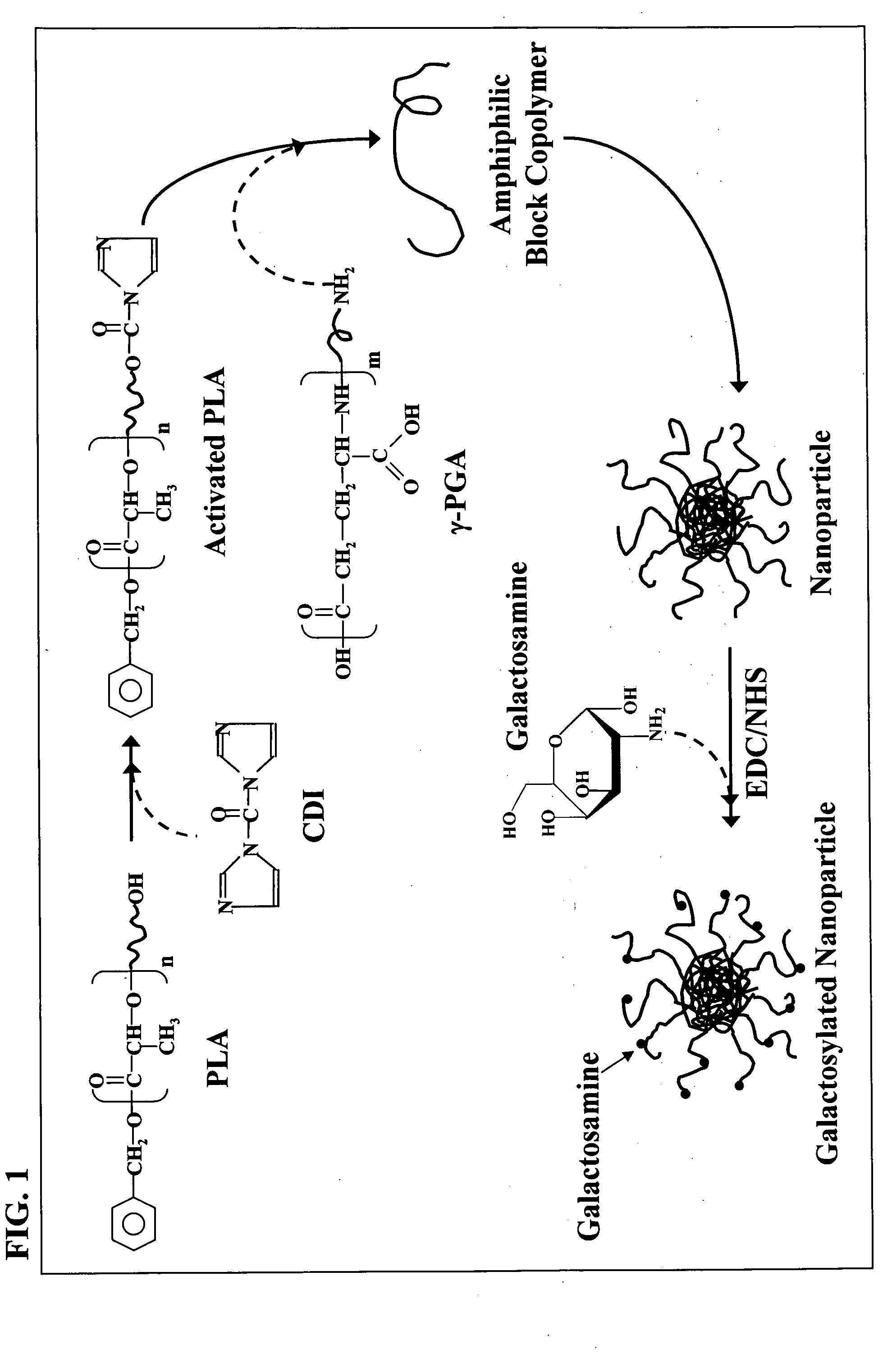
The nanoparticles composed of γ-PGA-PLA block copolymers that are conjugated with galactosamine as a potential drug delivery system and loaded with anticancer drugs for treating liver cancers.
Owner:GP MEDICAL
Chemical synthesis of low molecular weight polyglucosamines and polygalactosamines
A process for the synthesis of beta linked low molecular weight polymers of galactosamine and glucosamine has been developed. Through the use of high amounts of activating agents, efficient coupling of stable monomers is achieved. Using this process, chain extension is through the addition of single monomers, providing populations of single chain length polyhexosamines.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Low molecular weight glycosylated chondroitin sulfate and its purpose in preparation of anti-HIV-1 medicament
InactiveCN102247401AAvoid drug resistanceDepolymerization speed is stableOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsMonosaccharide compositionUltrafiltration
The invention discloses a low molecular weight glycosylated chondroitin sulfate, whose weight average molecular weight is 3000-15000Da. The monosaccharide composition comprises acetyl galactosamine (D-GalNAc), glucuronic acid (D-GlcUA), fucose (L-Fuc), or its sulfuric ester (expressed in -OS03<->), wherein the mole ratio of D-GalNAc to D-GlcUA to L-Fuc to -OS03<-> is 1: (1+ / -0.3): (1+ / -0.3): (3.5+ / -0.5). The low molecular weight glycosylated chondroitin sulfate has a strong anti-HIV-1 virus activity, is a gp120 entry inhibitor, and can be used for preventing and / or treating AIDS. The invention also provides a method for preparing the low molecular weight glycosylated chondroitin sulfate and its composition preparation. Glycosylated chondroitin sulfate is depolymerized by the peroxide method to obtain a low molecular weight product, and then low molecular and / or high-molecular impurities of the product are removed by gel separation or ultrafiltration method. The low molecular weight glycosylated chondroitin sulfate and its medicinal composition can be prepared in the form of an injection, a lyophilized powder or a suppository.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Nanoparticles for targeting hepatoma cells
Owner:GP MEDICAL
Methods and materials for reducing cardiac xenograft rejection
ActiveUS20130111614A1Reducing cardiac xenograft rejectionIncreased durabilityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenGlycan
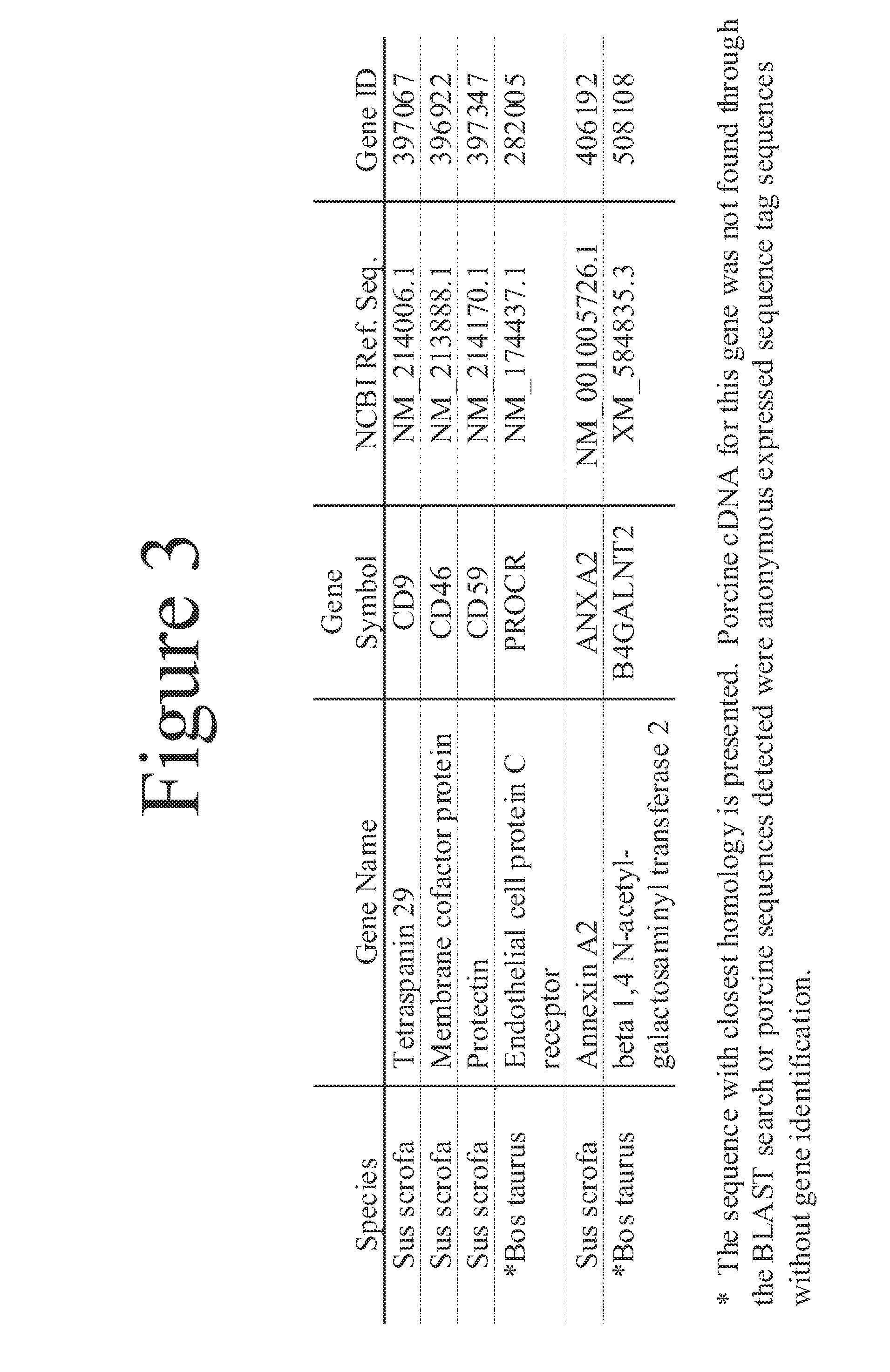
This document provides methods and materials involved in reducing cardiac xenograft rejection. For example, methods and materials for preparing transgenic pigs expressing reduced or no endogenous Sda or SDa-like glycans derived from the porcine β1,4 N-acetyl-galactosaminyl transferase 2 (B4GALNT2) glycosyltransferase and / or reduced or no endogenous α-Gal antigens, methods and materials for modifying the xenograft recipient's immunological response to non-Gal antigens (e.g. CD46, CD59, CD9, PROCR, and ANXA2) to reduce cardiac xenograft rejection, and methods and materials for monitoring the progress of xenotransplant immunologic rejection are provided.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Tumor targeting metal complex, synthetic method and application
ActiveCN106866743AImprove utilizationSmall toxicityRuthenium organic compoundsOrganic active ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthApoptosis
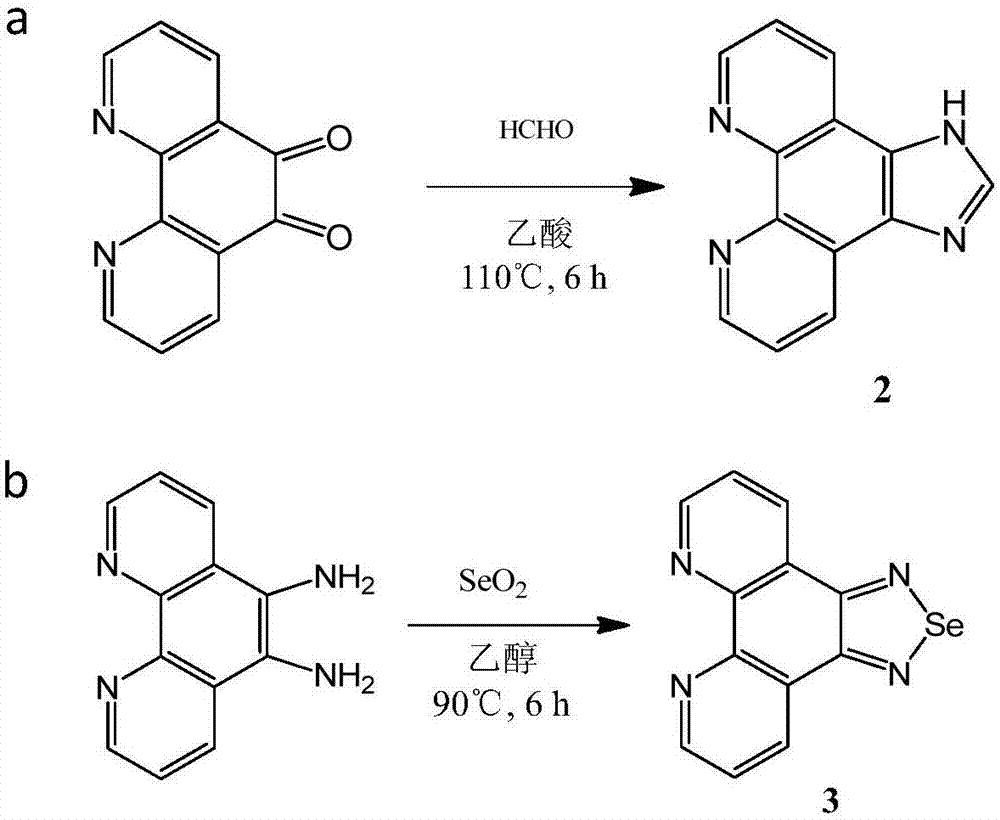
The invention discloses a tumor targeting metal complex, a synthetic method and application. The synthetic method comprises the steps of connecting a ligand with a substituent group and a targeting molecule, complexing the ligand and metal ions, and synthesizing to obtain the tumor targeting metal complex, wherein the ligand is one of a phenanthroline derivative, a dipyridyl derivative, a benzimidazole derivative, a phenyl-pyridine derivative and a thiophene-pyridine derivative; the targeting molecule is one of biotin, folic acid, integrin, transferrin, cell-penetrating peptide, octa-poly-L-arginine, MUC-1 attached membrane protein, galactosamine, neovascular targeting peptide and a granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; the metal ions are ruthenium, osmium, rhodium or iridium ions. The complex obtained by the method provided by the invention can be selectively absorbed by tumor cells, and induces apoptosis of the tumor cells. In a nude mouse tumor-bearing model, the tumor targeting metal complex can image and treat tumors, and the toxicity of organs and tissues is reduced.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Nanoparticles for targeting hepatoma cells
A dual-particle tumor targeting system comprising a first ligand-mediated targeting nanoparticle conjugated with galactosamine and a second EPR-mediated targeting nanoparticle, wherein said first and second nanoparticles are mixed in a solution configured for delivering to a target liver tumor.
Owner:GP MEDICAL
Gene encoding chondroitinase ABC and uses therefor
Nucleic acid sequences coding for the chondroitinase ABC gene and isolated chondroitinase ABC protein produced in a host cell transformed with a nucleic acid vector directing the expression of a nucleotide sequence coding for chondroitinase ABC protein are described. Chondroitinase ABC prepared by chemical synthesis is also described. Monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies which are specifically reactive with chondroitinase ABC protein are disclosed. The isolated chondroitinase ABC can be used in methods of treating intervertebral disc displacement, promoting neurite regeneration, and detecting galactosaminoglycans.
Owner:MARUHA NICHIRO
Galactosamine and polydopamine modified liver cancer targeting nanoparticles as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104666251AEasy to prepareStrong targetingOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryTreatment effectFreeze-drying
The invention discloses galactosamine and polydopamine modified liver cancer targeting nanoparticles as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of the galactosamine and polydopamine modified liver cancer targeting nanoparticles comprises the following steps: taking polymer and a hydrophobic medicine, dissolving the polymer and the hydrophobic medicine into an organic solvent, stirring, dropwise adding the obtained solution into TPGS aqueous solution, stirring, carrying out reduced pressure volatilization, centrifuging, and abandoning supernate, so that polymer initial nanoparticles carrying the hydrophobic medicine are obtained; resuspending the initial nanoparticles in Tris buffer solution, adding dopamine hydrochloride for reacting, and centrifuging, so that hydrophobic-medicine-carrying nanoparticles wrapped by polydopamine are obtained; dispersing the hydrophobic-medicine-carrying nanoparticles wrapped by polydopamine into weakly alkaline aqueous solution, adding a liver cancer targeting ligand galactosamine, reacting, centrifuging, and carrying out freeze drying, so that the galactosamine and polydopamine modified liver cancer targeting nanoparticles are obtained. The preparation method of the galactosamine and polydopamine modified liver cancer targeting nanoparticles is simple and pollution-free; and the galactosamine and polydopamine modified liver cancer targeting nanoparticles have good liver targeting property, biological compatibility and biological degradability, can be used for targeting liver cancer and has treatment effect.
Owner:SHENZHEN BAINUO KANTAI BIOTECH CO LTD
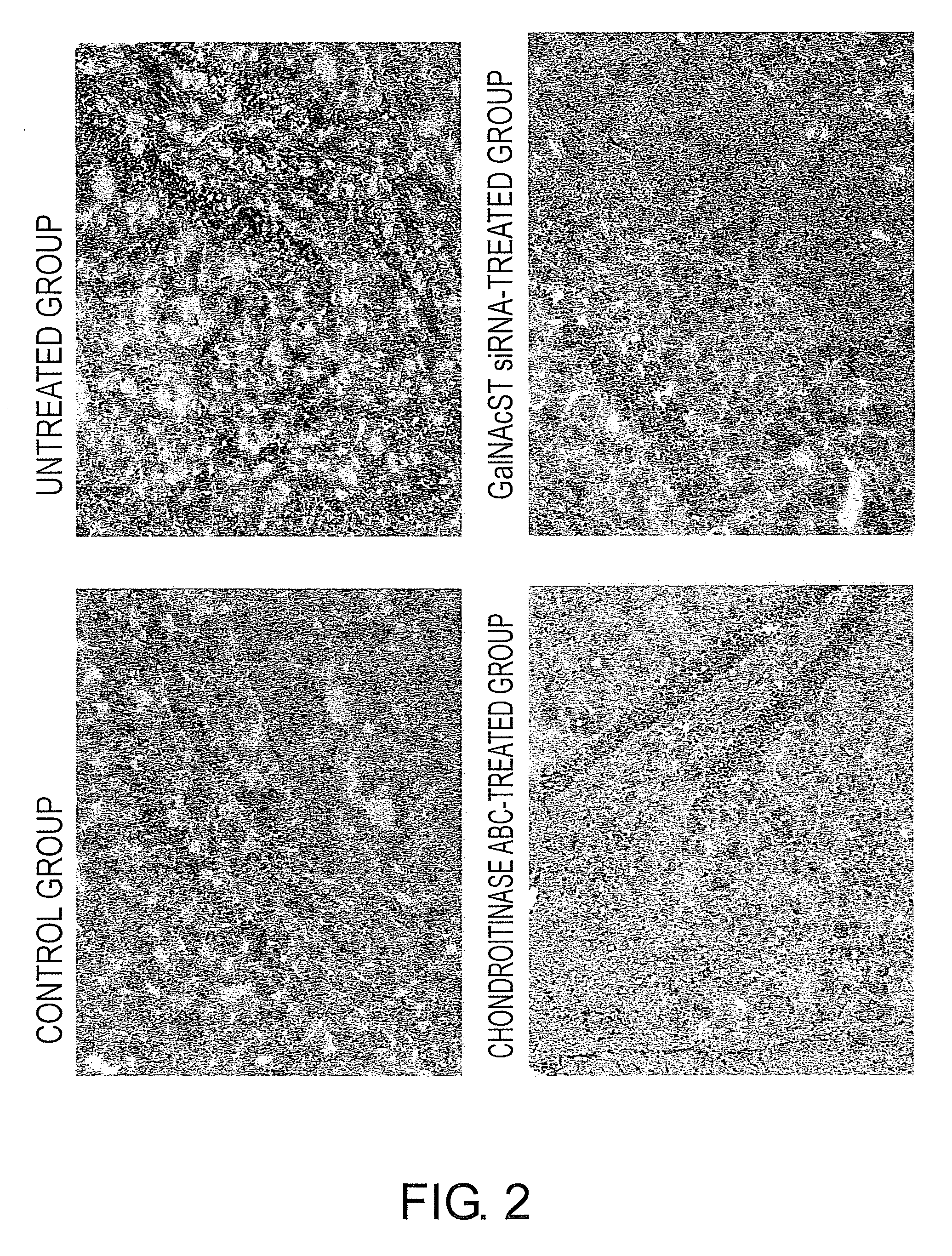
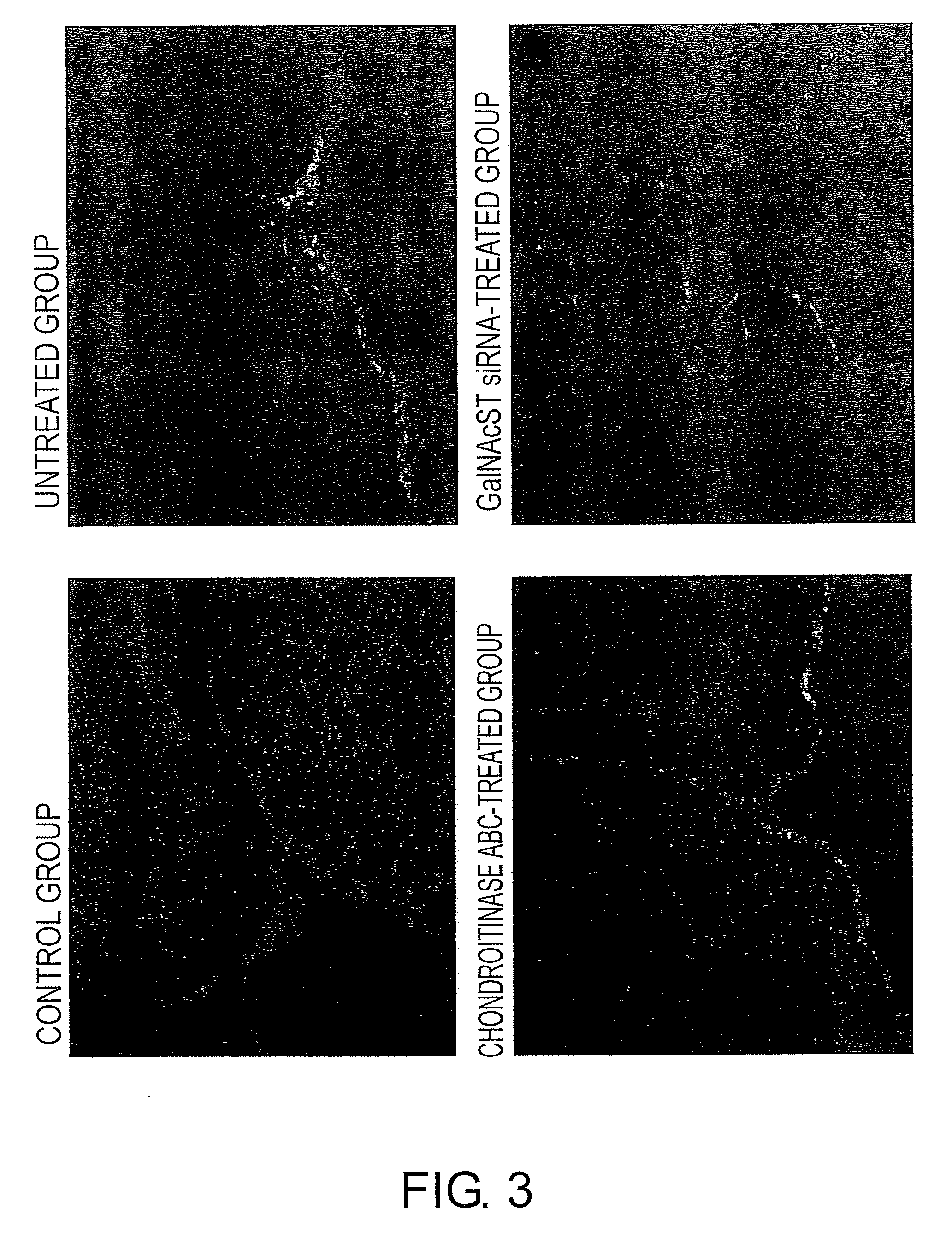
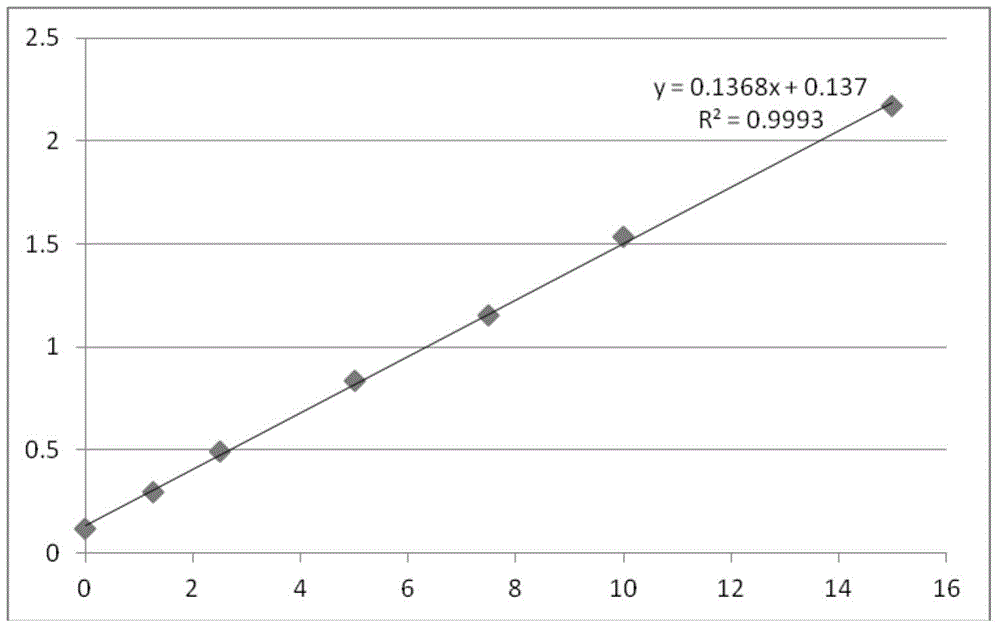
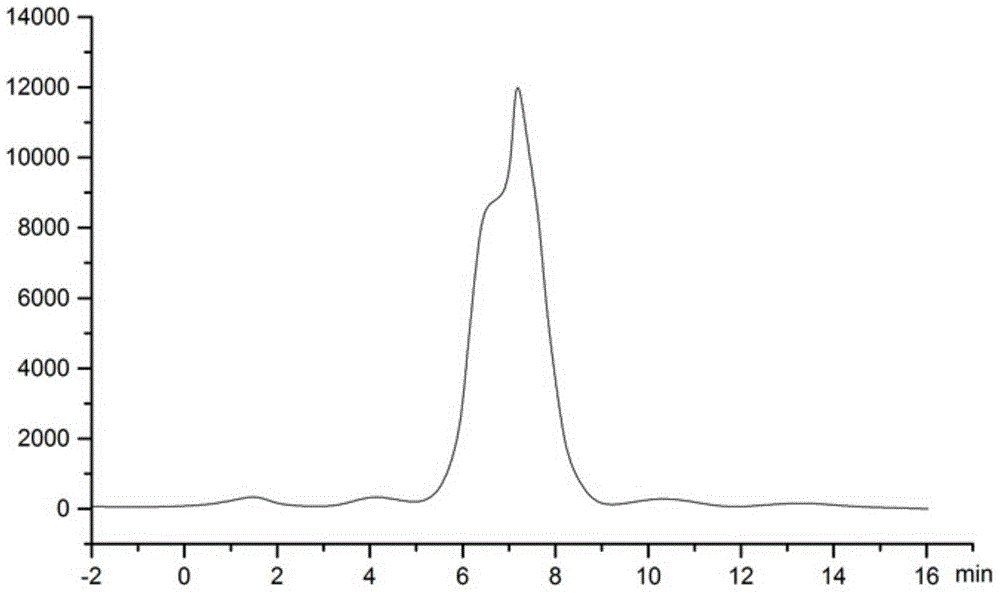
Agents for suppressing neural fibrotic degeneration
InactiveUS20090202515A1Suppress neural fibrotic degenerationGreat medical and industrial significanceOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderSide chainNeural cell
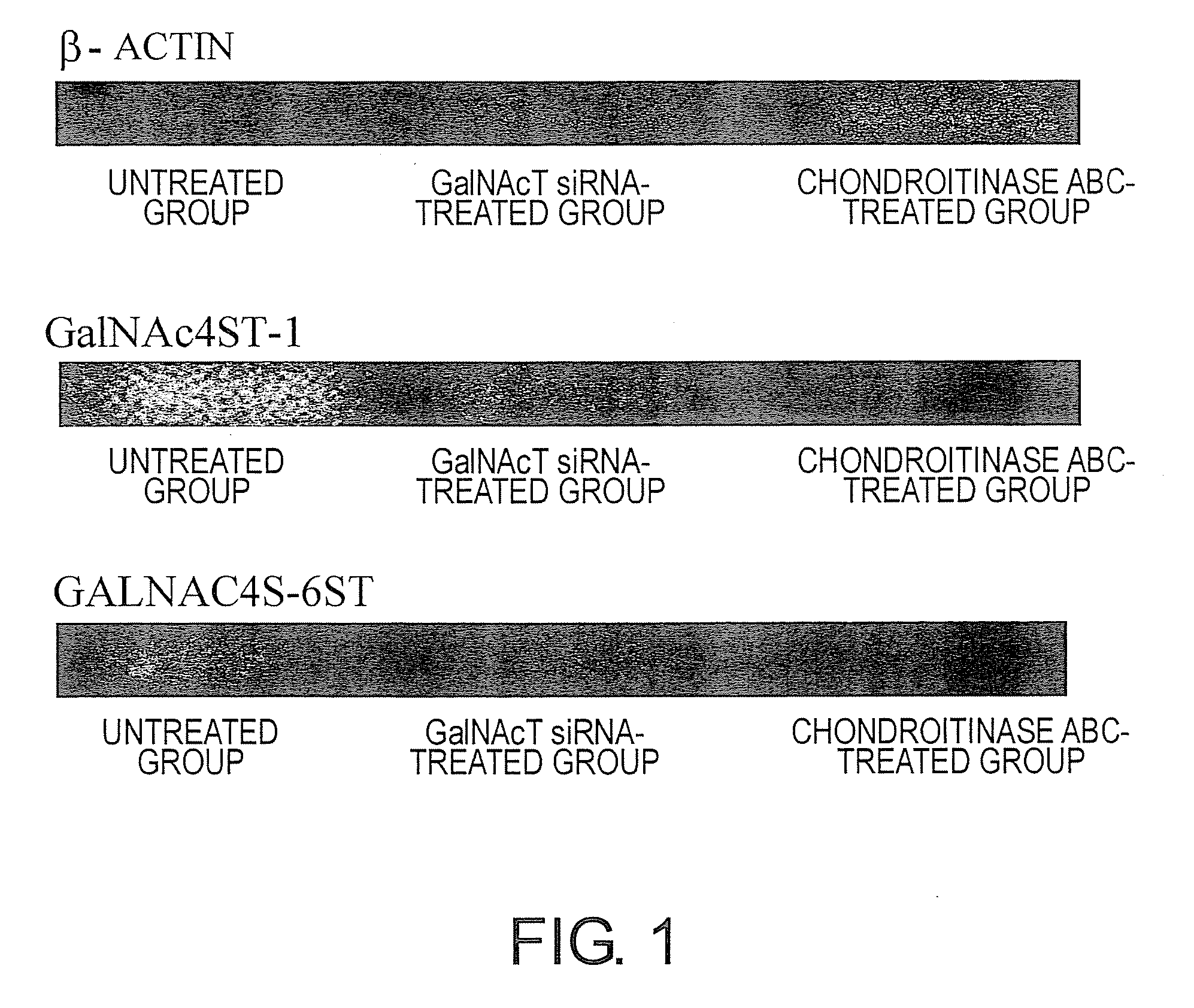
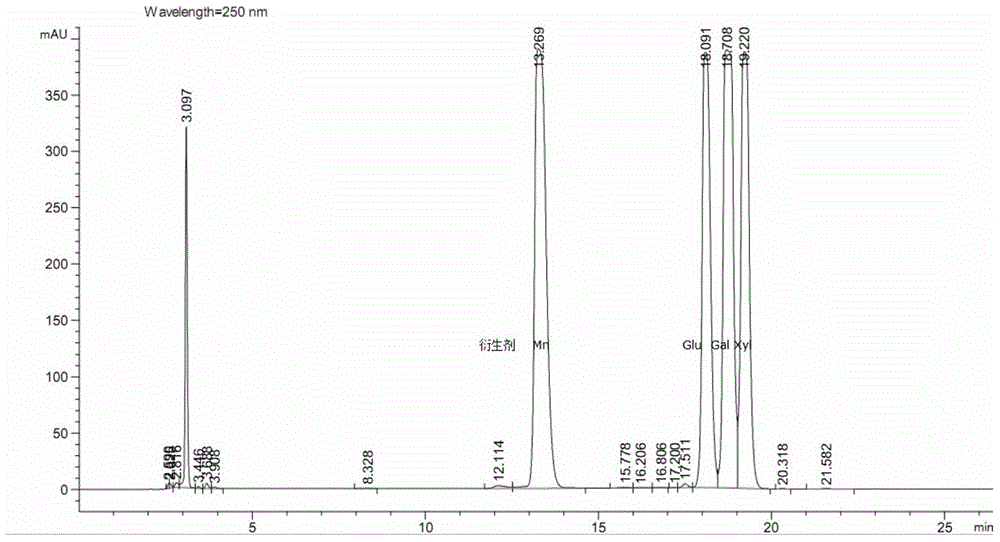
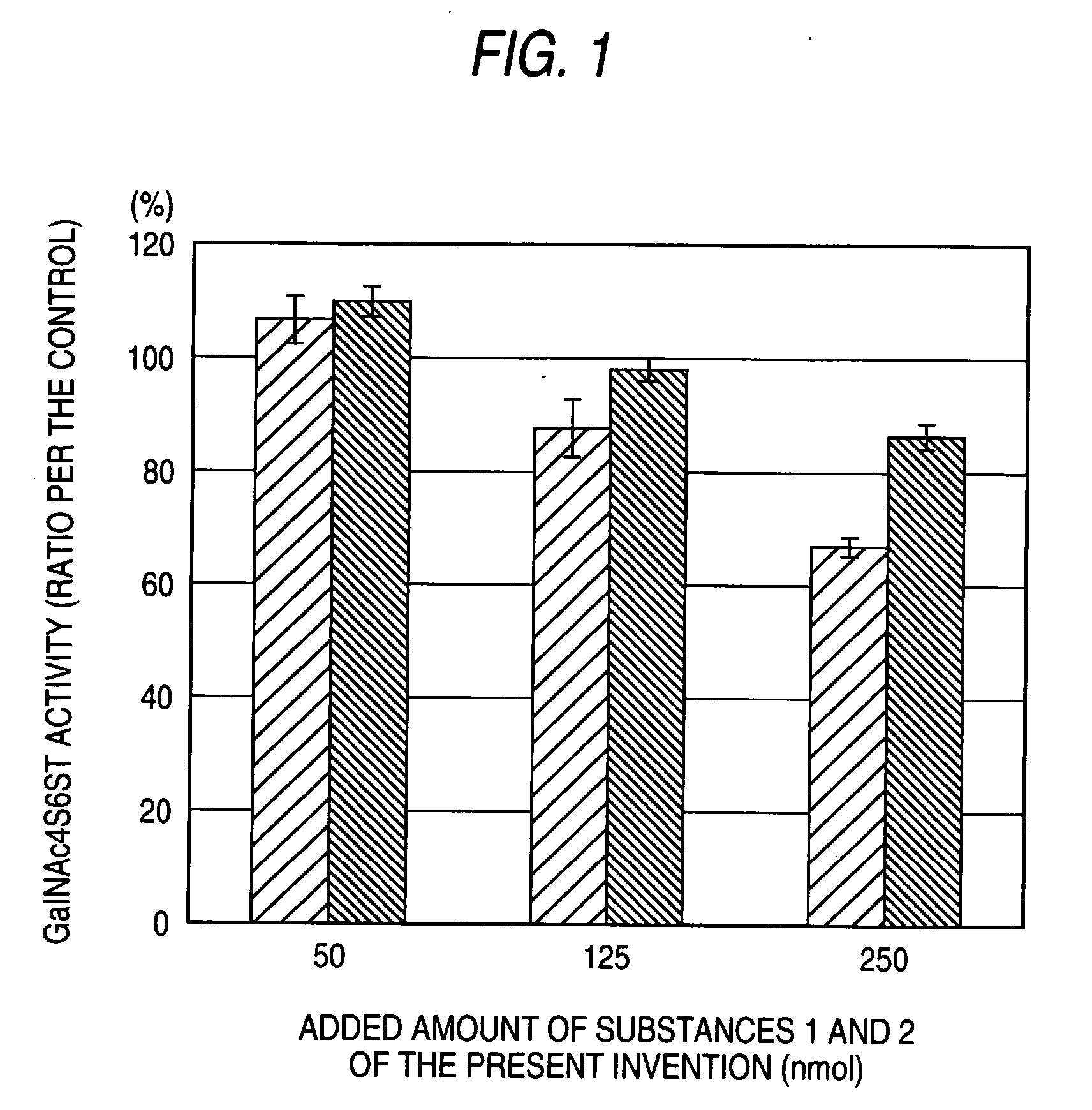
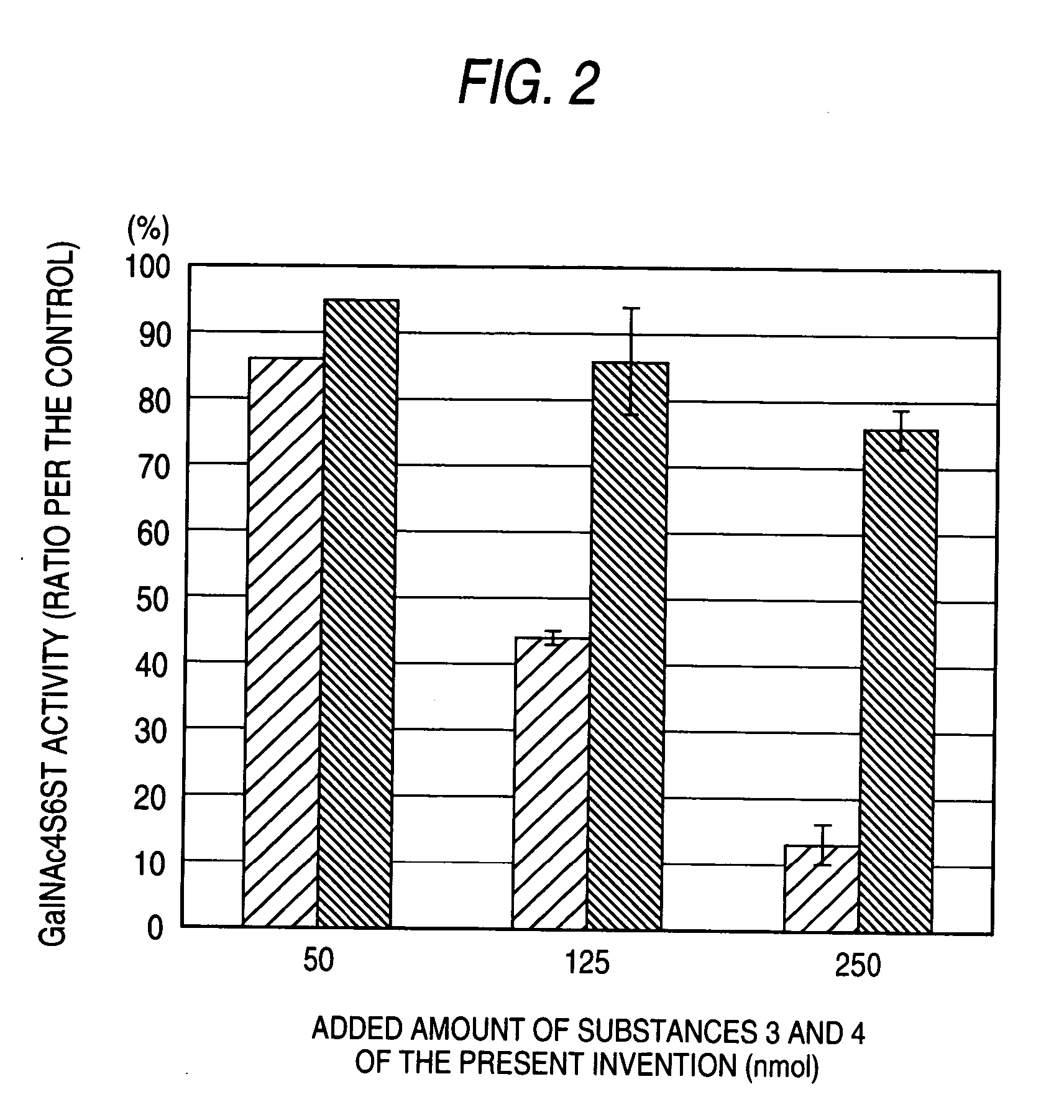
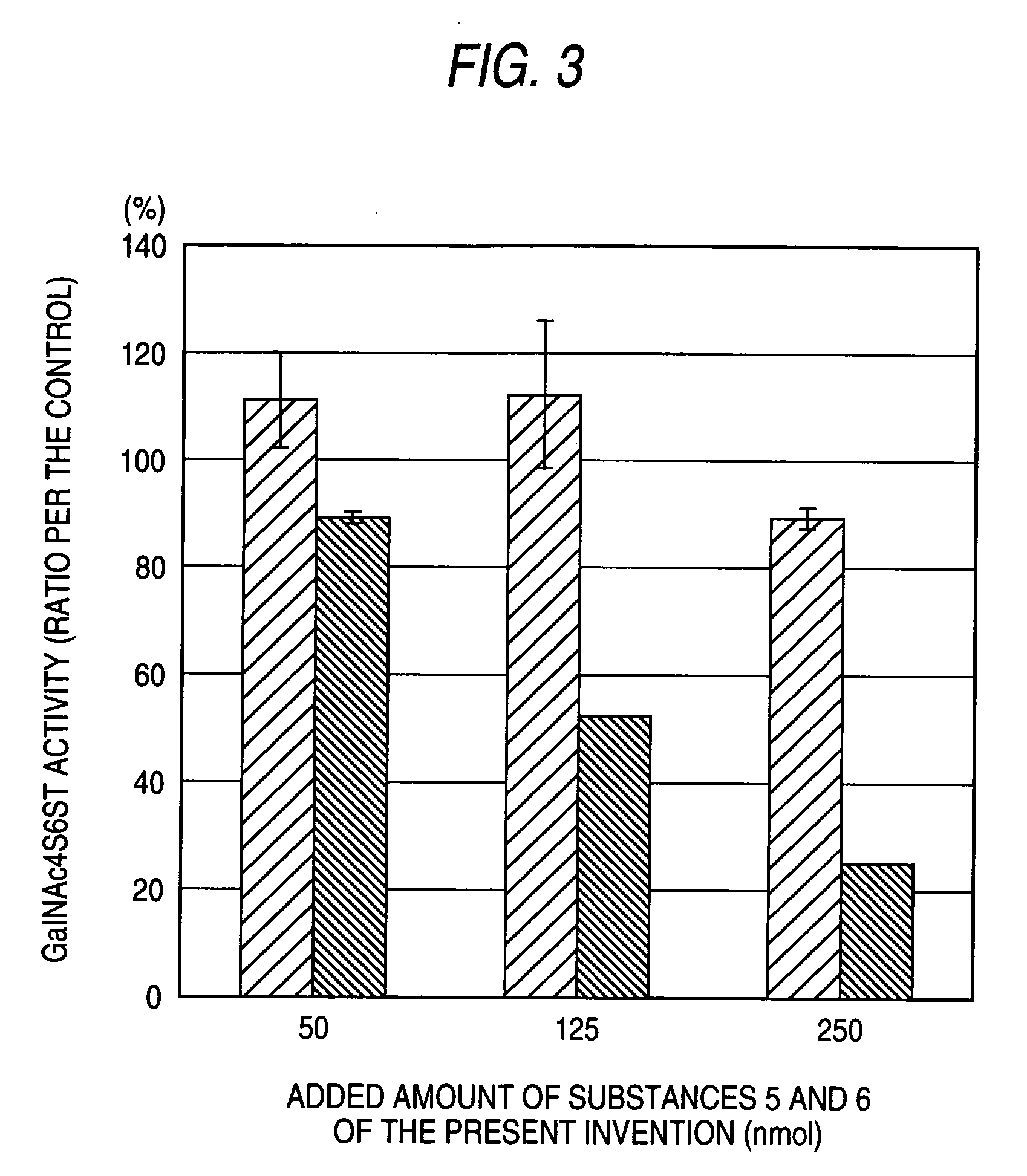
The present invention examined the accumulation of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans (CSPGs). The present invention relates to neurodegeneration-suppressing agents that are suitable for gene therapy or prevention of neural fibrotic degenerative diseases which induce neural cell death due to an accumulation of abnormal proteins, where the therapies are based on siRNAs against N-acetylgalactosamine-4-O-sulfotransferases (N-acetylgalactosamine-4-O-sulfotransferase-1, N-acetylgalactosamine-4-O-sulfotransferase-2, and N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfate 6-O-sulfotransferase (GalNAc4ST-1, GalNAc4ST-2, and GALNAC4S-6ST, respectively)), which are sulfotransferases for acetylgalactosamine, a CSPG side chain, and chondroitinase ABC, an enzyme that degrades chondroitin sulfate, another CSPG side chain.
Owner:STELIC INST OF REGENERATIVE MEDICINE STELIC INST
Galactomannan antigen and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104945527AHigh antigen purityEliminate distractionsAspergillus fumigatus AntibodyIon exchange
The invention relates to a preparation method of a galactomannan antigen. The method comprises the steps that breaking, centrifugation, alcohol precipitation, washing and drying are carried out on a living body rich in galactomannan, and galactomannan crude extract is obtained through separation; hydrazinolysis and hydrolysis are carried out on the obtained galactomannan crude extract in sequence; an enzyme is added to a hydrolysis product for enzymolysis, and the enzyme and small molecular substances in an enzymolysis product are removed; a product is purified through an ion exchange column, an affinity column and gel chromatography, and the pure galactomannan antigen is obtained; the obtained pure galactomannan antigen is identified. The galactomannan antigen obtained through the preparation method is high in purity, the inference of galactosamine, protein, miscellaneous sugar possibly included in the galactomannan crude extract is eliminated, and the preparation method can be used for preparing aspergillus fumigatus antibodies.
Owner:DYNAMIKER BIOTECH TIANJIN
Nanoparticles for targeting hepatoma cells
InactiveUS20060073209A1High fluorescence intensityExtended durationBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsMedicineNanoparticle
The invention discloses the nanoparticles composed of γ-PGA-PLA block copolymers conjugated with galactosamine as a potential drug delivery system for treating liver cancers.
Owner:GP MEDICAL
Sulfotransferase inhibitors
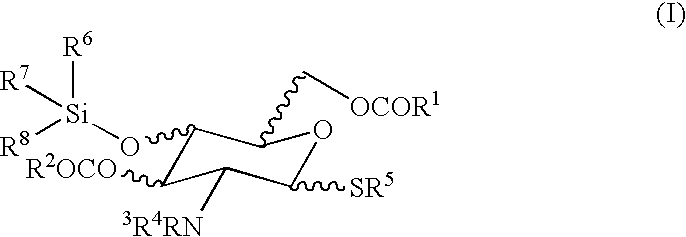
A galactosamine derivative represented by the following formula (1): wherein R1, R2 and R5 each independently represents SO3− or H, and at least one of them represents SO3−; R3 represents H, acetyl or SO3−; R4 represents H, a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkynyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted acyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, or a substituted or unsubstituted aralkyl group; X represents O, S, NH or CH2; and represents an α bond or a β bond, and a sulfotransferase inhibitor comprising the derivative.
Owner:SEIKAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD
Thomsen-Friedenreich (TF) antigen and TF antigen analogue and their chemoenzymatic synthesis method and use
InactiveCN102796144AImprove pharmacokinetic propertiesSugar derivativesCarrier-bound antigen/hapten ingredientsAntigenChemical synthesis
The invention discloses a Thomsen-Friedenreich (TF) antigen and a TF antigen analogue and their chemoenzymatic synthesis method and use. The chemoenzymatic synthesis method comprises the following steps of 1, carrying out chemosynthesis of fluorogalactose and a fluoro-galactosamine analogue, 2, carrying out enzymatic synthesis of a fluoro-TF antigen, and 3, carrying out enzymatic synthesis of a sialyl TF antigen. The preparation method has flexibility of a chemosynthesis method, and high regioselectivity and high efficiency of an enzymatic synthesis method, creatively realizes enzymatic synthesis of the fluoro-TF antigen, and solves the problem that the existing fluoro-TF antigen chemosynthesis method has low substrate reactivity, complex synthesis steps and a low yield. A tumor-associated fluoro-carbohydrate antigen is superior to a natural carbohydrate antigen in pharmacokinetic properties and thus the preparation method has wide application prospects in development of a novel anti-tumor vaccine.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com