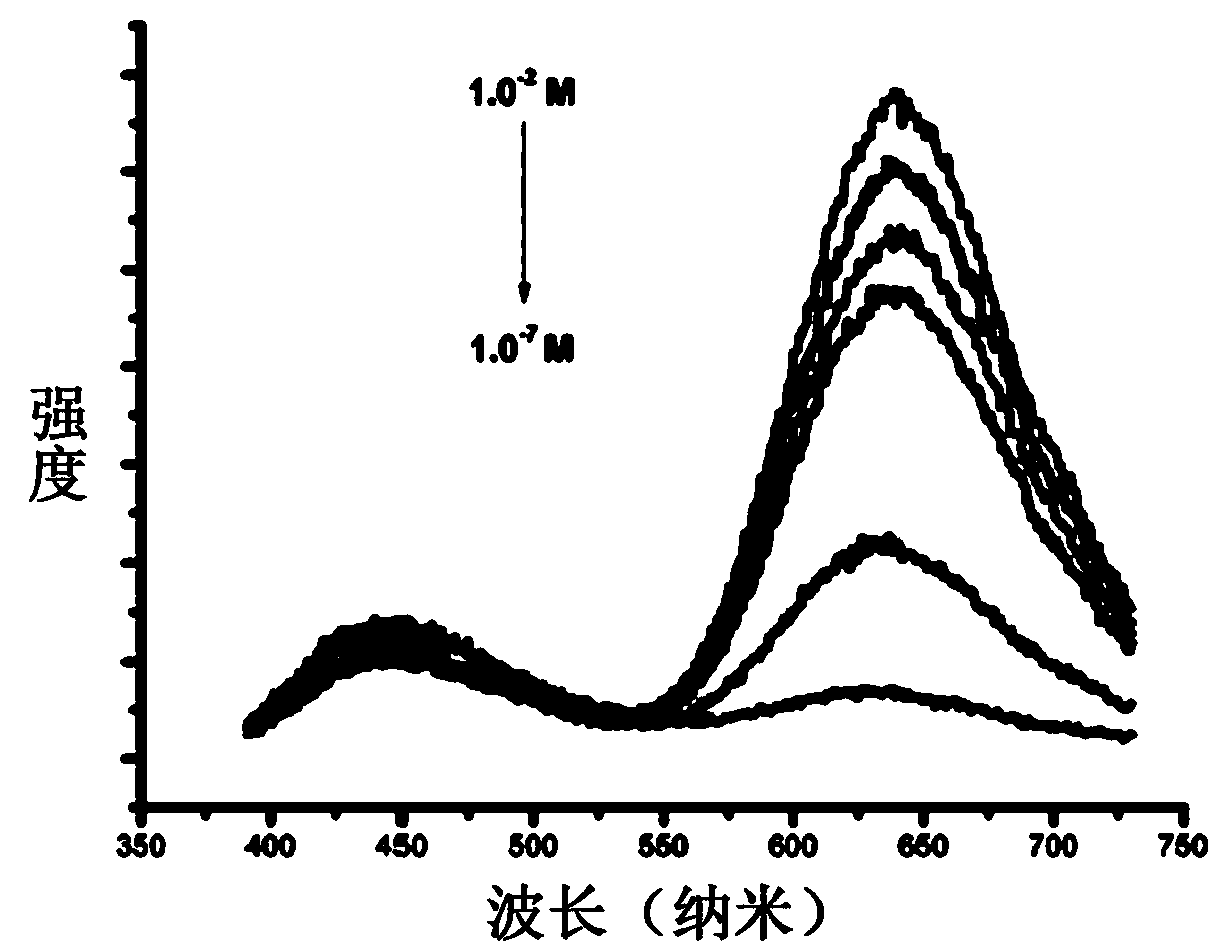
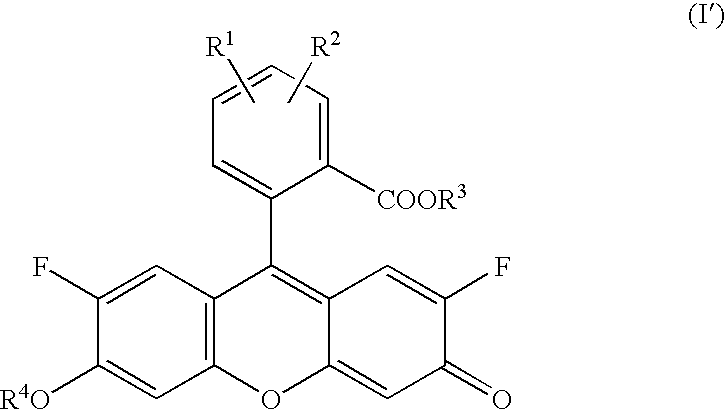
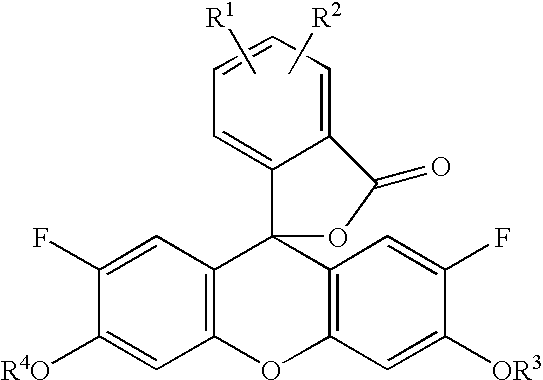
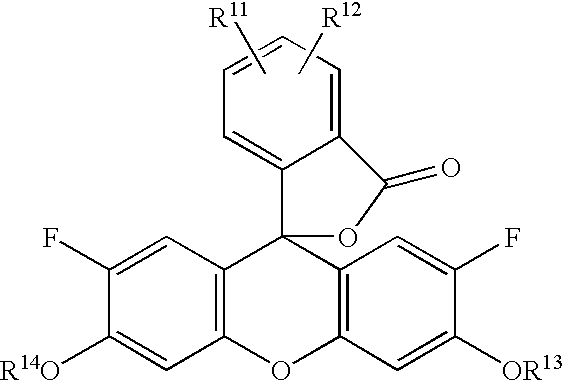
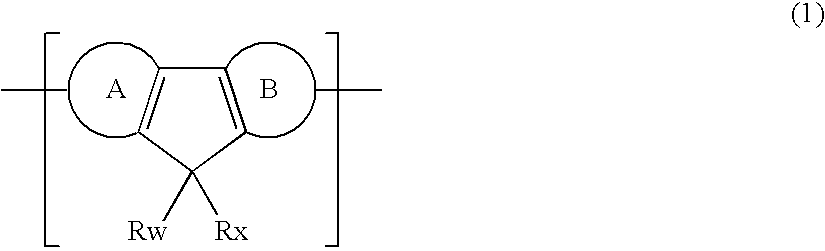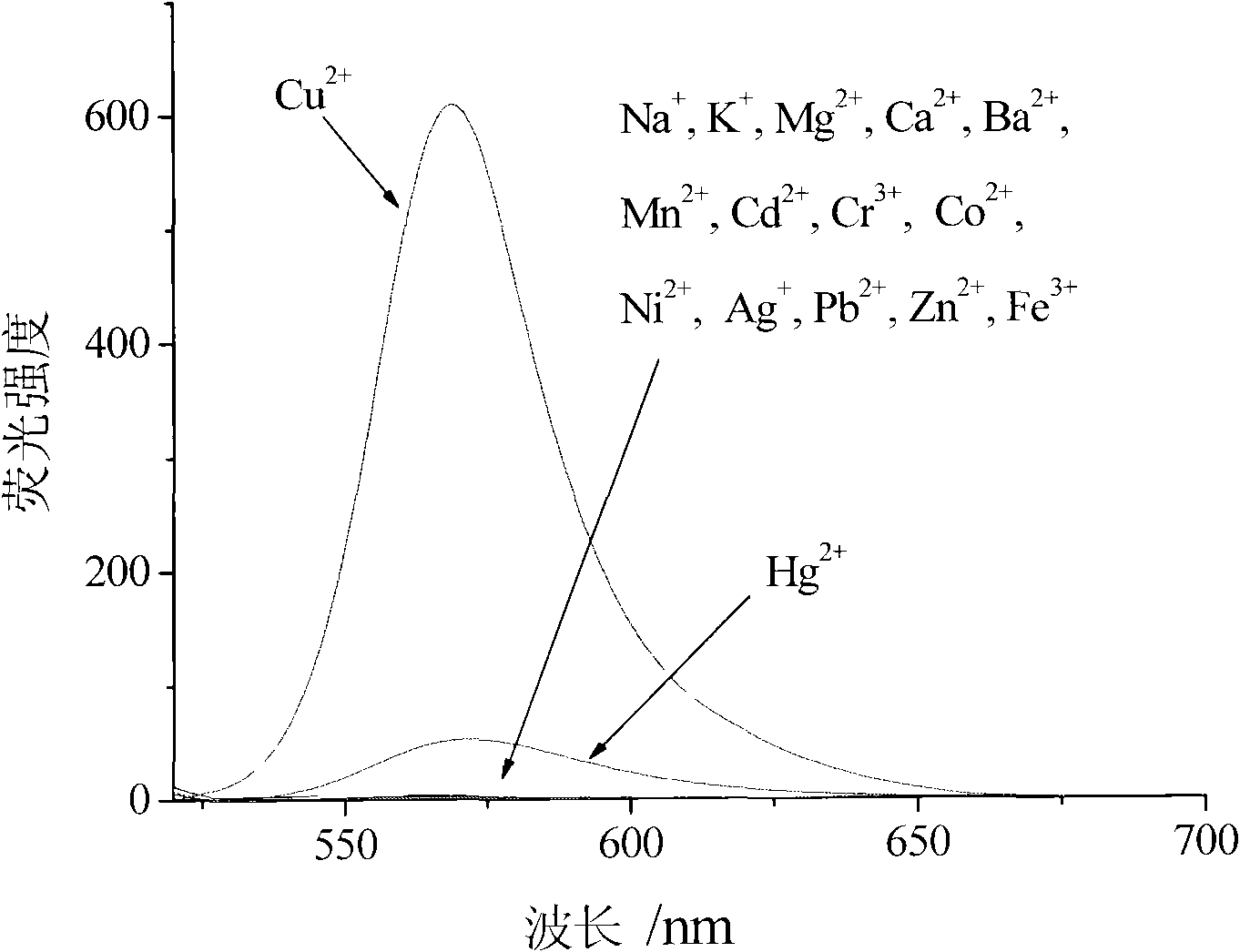Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1941results about How to "High fluorescence intensity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cell-based fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) assays for clostridial toxins
InactiveUS7183066B2Increase in fluorescence intensityDecrease in fluorescence intensityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaFörster resonance energy transferCell based
The present invention provides a method of determining clostridial toxin activity by (a) contacting with a sample a cell containing a clostridial toxin substrate that includes a donor fluorophore; an acceptor having an absorbance spectrum overlapping the emission spectrum of the donor fluorophore; and a clostridial toxin recognition sequence containing a cleavage site that intervenes between the donor fluorophore and the acceptor, where resonance energy transfer is exhibited between the donor fluorophore and the acceptor under the appropriate conditions; (b) exciting the donor fluorophore; and (c) determining resonance energy transfer of the contacted cell relative to a control cell, where a difference in resonance energy transfer of the contacted cell as compared to the control cell is indicative of clostridial toxin activity.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Modified nucleosides and nucleotides and uses thereof
ActiveUS7592435B2Increase brightnessHigh fluorescence intensitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePurine
The invention is directed to modified guanine-containing nucleosides and nucleotides and uses thereof. More specifically, the invention relates to modified fluorescently labelled guanine-containing nucleosides and nucleotides which exhibit enhanced fluorophore intensity by virtue of reduced quenching effects.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
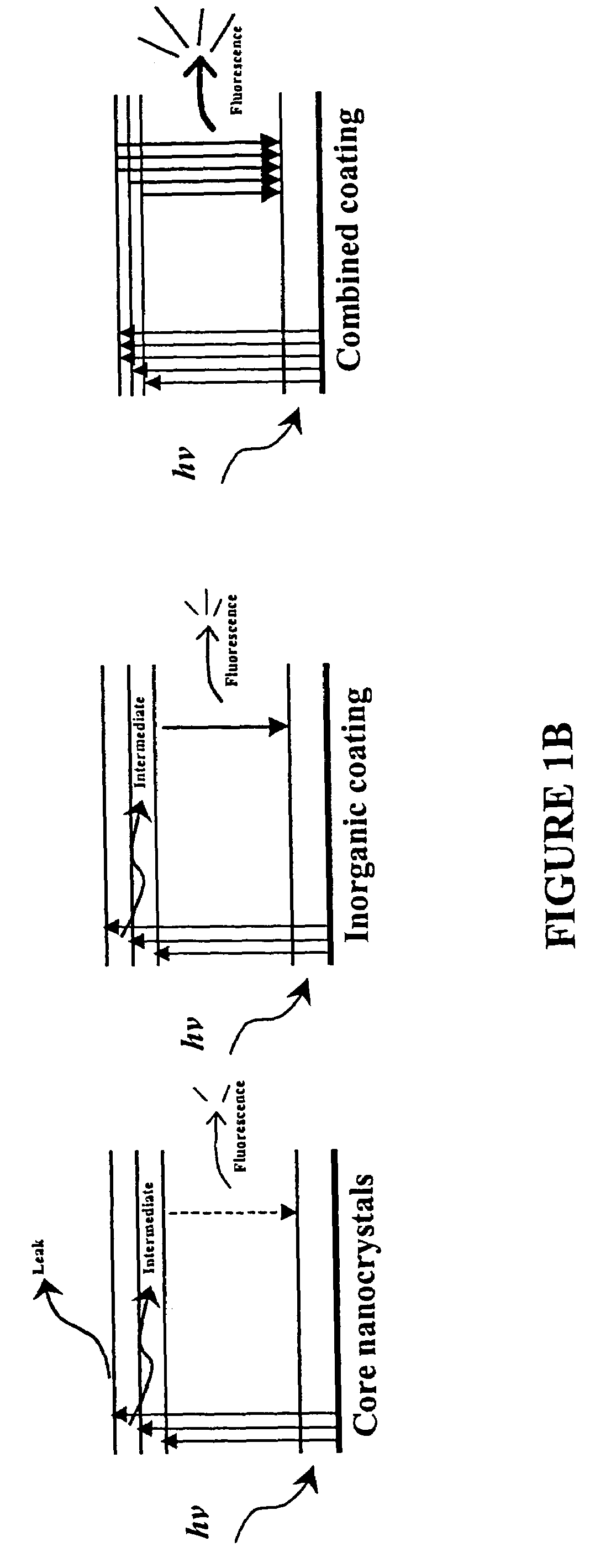
Functionalized fluorescent nanocrystal compositions and methods of making
InactiveUS7205048B2Improve efficiencyImprove solubilityInksRecord information storageSolubilityQuantum yield
The present invention provides for functionalized fluorescent nanocrystal compositions and methods for making these compositions. The compositions are fluorescent nanocrystals coated with at least one material. The coating material has chemical compounds or ligands with functional groups or moieties with conjugated electrons and moieties for imparting solubility to coated fluorescent nanocrystals in aqueous solutions. The coating material provides for functionalized fluorescent nanocrystal compositions which are water soluble, chemically stable, and emit light with a high quantum yield and / or luminescence efficiency when excited with light. The coating material may also have chemical compounds or ligands with moieties for bonding to target molecules and cells as well as moieties for cross-linking the coating. In the presence of reagents suitable for reacting to form capping layers, the compounds in the coating may form a capping layer on the fluorescent nanocrystal with the coating compounds operably bonded to the capping layer.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Ocular analyte sensor
InactiveUS6681127B2Increase rangeIncrease sensitivityNanotechMedical devicesInterstitial fluidIntracellular Fluid
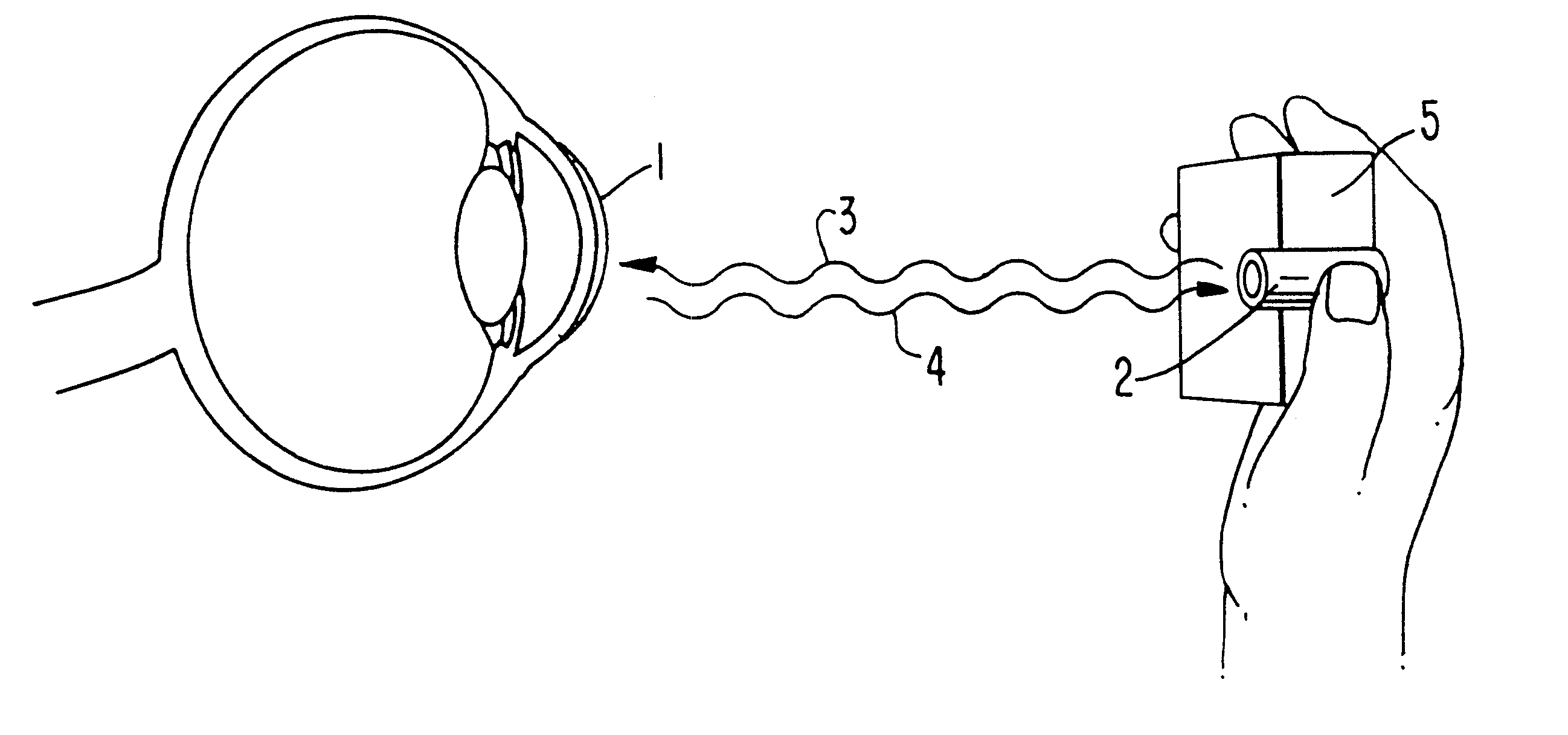
An ophthalmic lens comprising a receptor moiety can be used to determine the amount of an analyte in an ocular fluid. The receptor moiety can bind either a specific analyte or a detectably labeled competitor moiety. The amount of detectably labeled competitor moiety which is displaced from the receptor moiety by the analyte is measured and provides a means of determining analyte concentration in an ocular fluid, such as tears, aqueous humor, or interstitial fluid. The concentration of the analyte in the ocular fluid, in turn, indicates the concentration of the analyte in a fluid or tissue sample of the body, such as blood or intracellular fluid.
Owner:EYESENSE AG
Polymer Compound And Polymer Light-Emitting Device Using The Same
ActiveUS20080138651A1High luminous intensityHigh fluorescence intensityConductive layers on insulating-supportsOrganic chemistryCompound (substance)Polystyrene
High-molecular compounds comprising repeating units represented by the general formula (1) or (2) and having number-average molecular weights of 103 to 108 in terms of polystyrene: (1) [wherein Ar1 and Ar2 are each independently a trivalent aromatic hydrocarbon group or a trivalent heterocyclic group; and X1 and X2 are each independently O, S, C(═O), S(═O), SO2, C(R1)(R2), Si(R3)(R4), N(R5), B(R6), P(R7), or P(═O)(R8), with the provisos that X1 and X2 must not be the same and that X1 and Ar2 are bonded respectively to the adjacent carbon atoms constituting the aromatic ring of Ar1, and X2 and Ar1 are bonded respectively to the adjacent carbon atoms constituting the aromatic ring of Ar2] (2) [wherein Ar3 and Ar4 are each independently a trivalent aromatic hydrocarbon group or a trivalent heterocyclic group; and X3 and X4 are each independently N, B, P, C(R9), or Si(R10), with the provisos that X3 and X4 must not be the same and that X3 and Ar4 are bonded respectively to the adjacent carbon atoms constituting the aromatic ring of Ar3, and X4 and Ar3 are bonded respectively to the adjacent carbon atoms constituting the aromatic ring of Ar4].
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Method for detecting quantum dot mark fast immune chromatographic test paper bar
InactiveCN1811449ARealize detectionGood luminous stabilityFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceChemistry
The present invention relates to a detection method of quantum point labeled quick immunochromatographic test paper strip, belonging to the field of detection technology. Said invention is characterized by that the antibody of quantum point labeled objective material can be coated on the glass fibre membrane, another antibody of objective material and second antibody are respectively coated on the nitrocellulose membrane or nitrocellulose / acetyl cellulose mixed membrane to form detection band and quality control band, on the polyester or plastic plate the glass fibre membrane and nitrocellulose membrane can be made into the immunochromatographic test paper strip. Said invention also provides the concrete steps of said detection method by utilizing said test paper strip and the concrete application range of said test paper strip.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
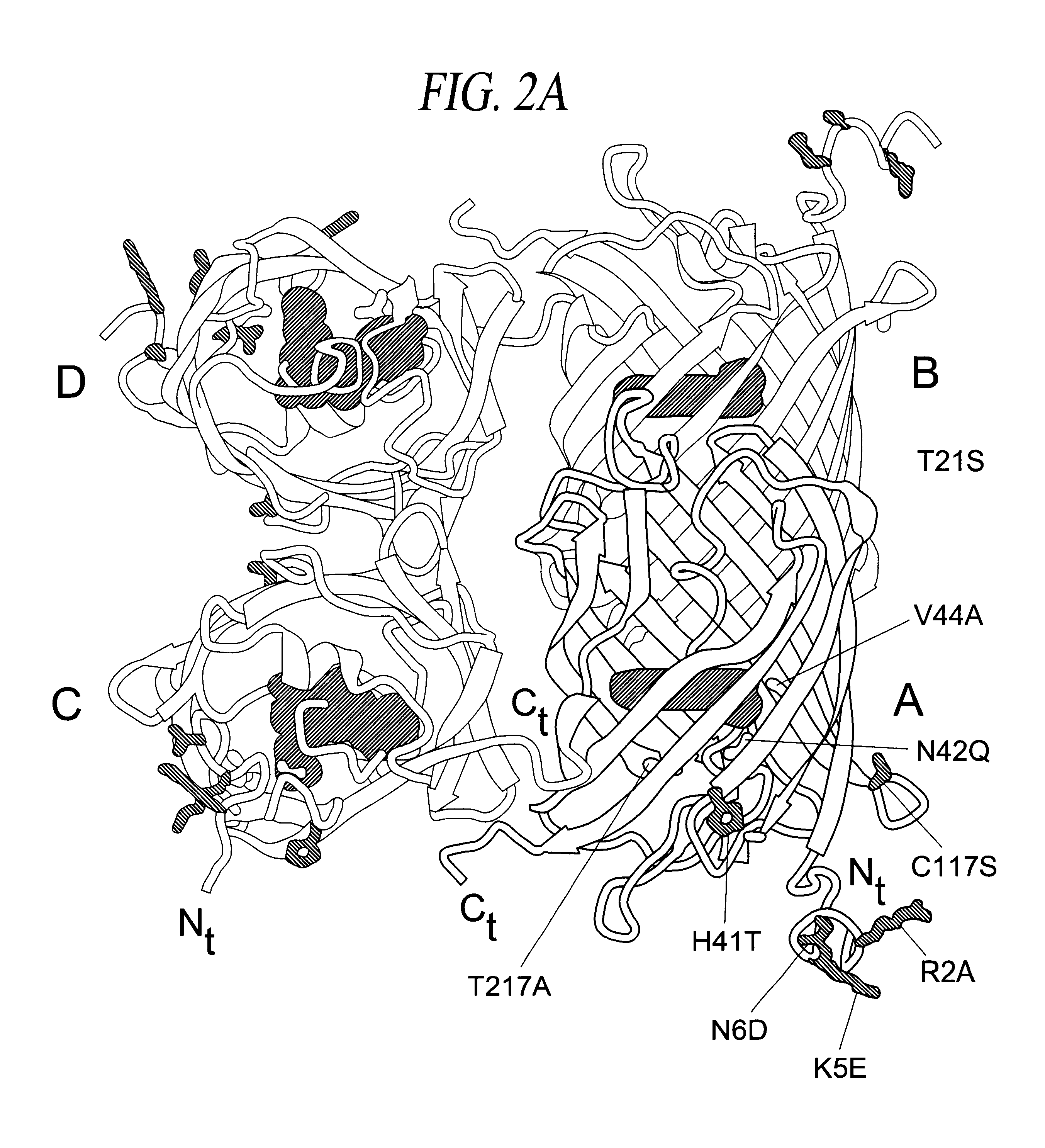
Monomeric and dimeric fluorescent protein variants and methods for making same
InactiveUS7157566B2Reduced propensity to oligomerizeReduces or eliminates the degree of oligomerization of said fluorescent proteinUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsFungiCrystallographyFluorescence
The present invention relates generally to variant fluorescent proteins, and more specifically to monomeric and dimeric forms of Anthozoan fluorescent proteins. In one aspect, the present invention provides variants of fluorescent proteins, where the variants have a reduced propensity to tetramerize, and form dimeric or monomeric structures. The invention also relates to methods of making and using such fluorescent protein monomers and dimers.
Owner:HOWARD HUGHES MEDICAL INST +1
Print ink containing a plurality of fluorescent coloring materials and inkjet recording method
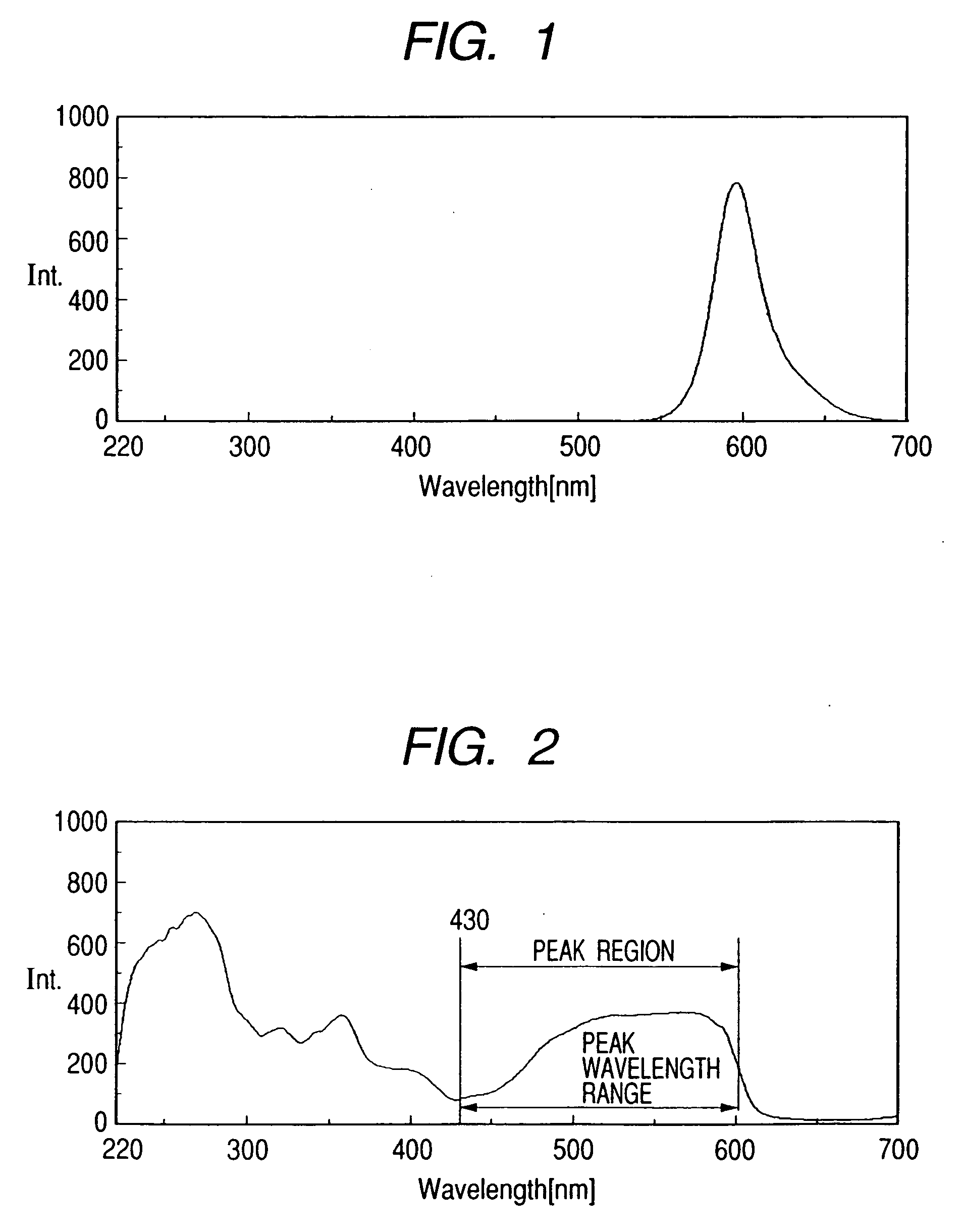
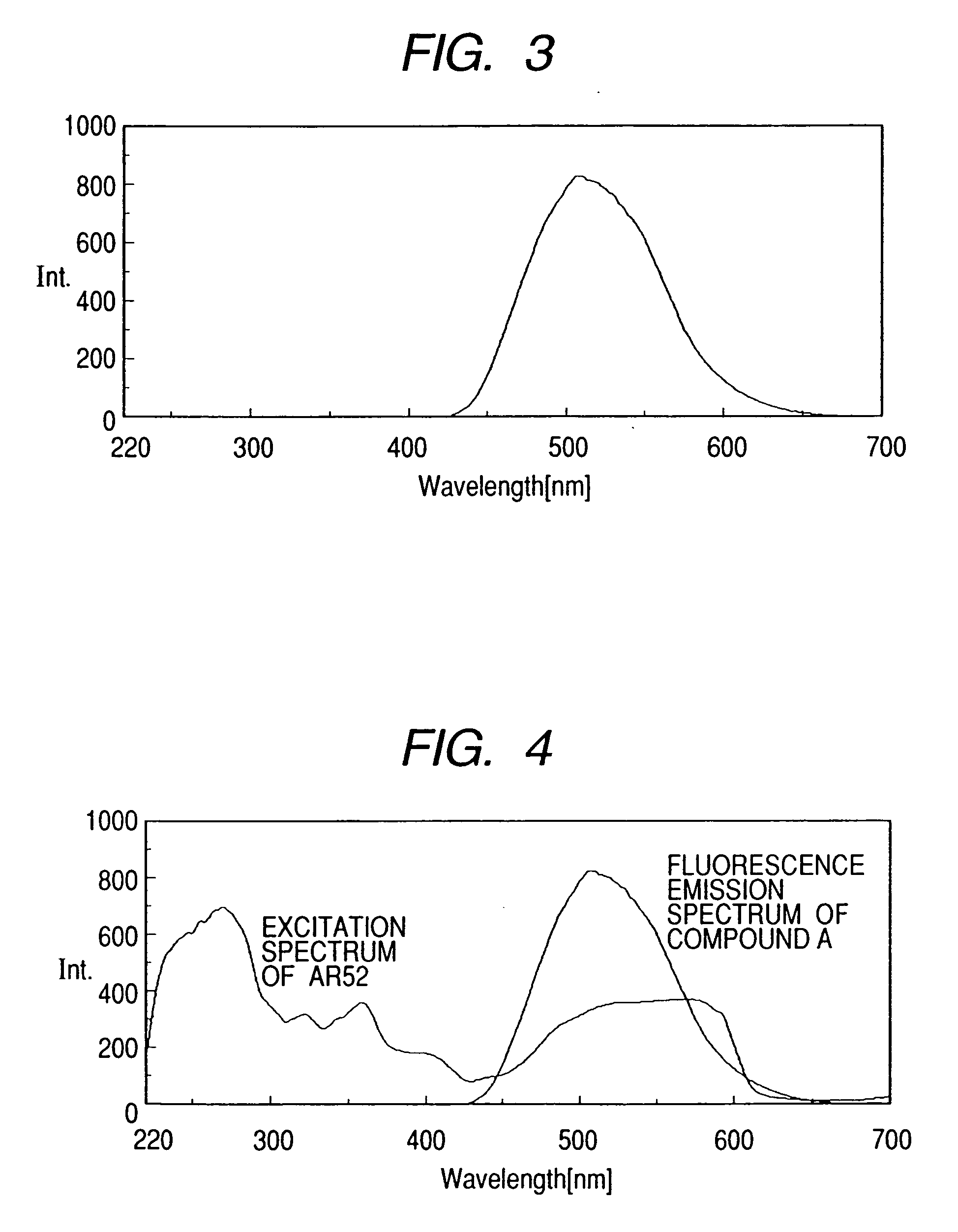
ActiveUS7144449B2High solubilityIncrease in fluorescence intensityDuplicating/marking methodsPattern printingExcitation wavelengthPrinting ink
The present invention provides a fluorescence ink having a high fluorescence intensity, and an ink jet recording method using the same. The ink contains a first fluorescent coloring material that emits fluorescence at a predetermined fluorescence wavelength to be used for measurement or determination with excitation at a predetermined excitation wavelength, a second fluorescent coloring material that emits fluorescence on excitation at the predetermined excitation wavelength, where the excitation spectrum of the first coloring material in the ink to obtain the fluorescence at the predetermined emission wavelength has a peak wavelength range next to the predetermined fluorescence wavelength, and the emission fluorescence spectrum of the second coloring material has an emission wavelength region substantially including at least the above peak wavelength range.
Owner:CANON KK
Nanoparticle-doped porous bead and fabrication method thereof
InactiveUS20100224831A1Improved photo-stabilityIncreased durabilityBleaching apparatusElectrostatic spraying apparatusMetal oxide nanoparticlesPhotoluminescence
Disclosed are a nanoparticle-doped porous bead with a highly enhanced photoluminescence without wavelength shift and improved durability, and a fabrication method thereof, the nanoparticle-doped porous bead comprising porous beads, and nanoparticles radially bonded onto homocentric spheres of the porous beads by an electrostatic attractive force, the homocentric sphere located inside the porous bead near a surface thereof, wherein the nanoparticles are photoluminescent nanoparticles or mixed nanoparticles of photoluminescent nanoparticles and another nanoparticles, wherein the another nanoparticle is one or more than two mixed, selected from a group consisting of magnetic nanoparticle, metallic nanoparticle and metal oxide nanoparticle.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Method for detecting by using quantum dot fluorescence immunochromatographic test strips
ActiveCN103048460AHigh fluorescence intensityOperational securityMaterial analysisFluorescenceQuantum dot
The invention provides a method for detecting by using quantum dot fluorescence immunochromatographic test strips. The method comprises the following specific steps: (1) preparing a quantum dot labeled protein liquid; (2) preparing a quantum dot labeled protein detecting liquid; (3) preparing a reaction film coated with a detection index; (4) bonding a sample pad, the reaction film prepared in the step (3) and a water absorbing pad on a PVC backing in sequence so as to obtain a test paper board; cutting the test paper board into test strips; and loading the test strips into a test paper clip; and (5) qualitatively or quantitatively detecting. The method for detecting by using the quantum dot fluorescence immunochromatographic test strips, provided by the invention, is a rapid detecting method using the quantum dot fluorescence immunochromatographic test strips, which is featured by high sensitivity, synchronicity in multi-index detection, simplicity, convenience, intuitive nature, low price and wide application.
Owner:WUHAN JIAYUAN BIOMEDICAL ENG
Recording method, ink cartridge, printing device and information recording apparatus
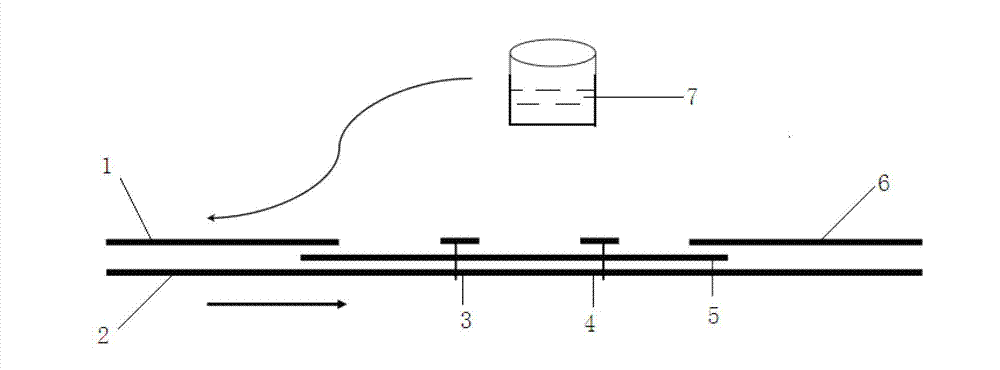
InactiveUS7185978B2High fluorescence intensityImprove printing qualityMeasurement apparatus componentsInksRecording headPolyolefin
A recording method including the step of providing an ink from a recording head to a recording medium through a gap provided between the recording head and the recording medium, the ink being supplied to the recording head from an ink tank including an ink contact member and the ink contacting the ink contact member, wherein the ink comprises:(i) a fluorescent coloring material;(ii) a nonionic surfactant;(iii) a compound which is not compatible with (ii); and(iv) a liquid medium for dissolving or dispersing (i), (ii) and (iii),and wherein the ink contact member comprises at least one compound selected from the group consisting of polyacetate and polyolefin.
Owner:CANON KK
Cell-based fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) assays for clostridial toxins
InactiveUS20070122858A1Decreased acceptor fluorescence intensityHigh fluorescence intensityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaClostridial toxinEnergy transfer
The present invention provides a method of determining clostridial toxin activity by (a) contacting with a sample a cell containing a clostridial toxin substrate that includes a donor fluorophore; an acceptor having an absorbance spectrum overlapping the emission spectrum of the donor fluorophore; and a clostridial toxin recognition sequence containing a cleavage site that intervenes between the donor fluorophore and the acceptor, where resonance energy transfer is exhibited between the donor fluorophore and the acceptor under the appropriate conditions; (b) exciting the donor fluorophore; and (c) determining resonance energy transfer of the contacted cell relative to a control cell, where a difference in resonance energy transfer of the contacted cell as compared to the control cell is indicative of clostridial toxin activity.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Polymer Compound and Polymer Light-Emitting Device Using the Same
InactiveUS20080233429A1Improve heat resistanceHigh fluorescence intensityElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesFluorescenceBenzene
A polymer compound comprising a repeating unit of the following formula (1) and which is useful as a light emitting material or charge transporting material and excellent in heat resistance, fluorescent intensity and the like:(wherein, ring A and ring B represent each independently an aromatic hydrocarbon ring optionally having a substituent, at least one of ring A and ring B is an aromatic hydrocarbon ring composed of a plurality of condensed benzene rings, Rw and Rx represent each independently a hydrogen atom, alkyl group, alkoxy group or the like, and Rw and Rx may mutually bond to form a ring).
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Print ink containing a plurality of fluorescent coloring materials and inkjet recording method
InactiveUS20070029522A1High fluorescence intensityImprove solubilityDuplicating/marking methodsPattern printingFluorescence spectrometryPrinting ink
The present invention provides a fluorescence ink having a high fluorescence intensity, and an ink jet recording method using the same. The ink contains a first fluorescent coloring material that emits fluorescence at a predetermined fluorescence wavelength to be used for measurement or determination with excitation at a predetermined excitation wavelength, a second fluorescent coloring material that emits fluorescence on excitation at the predetermined excitation wavelength, where the excitation spectrum of the first coloring material in the ink to obtain the fluorescence at the predetermined emission wavelength has a peak wavelength range next to the predetermined fluorescence wavelength, and the emission fluorescence spectrum of the second coloring material has an emission wavelength region substantially including at least the above peak wavelength range.
Owner:CANON KK
Optically fluorescent nanoparticles
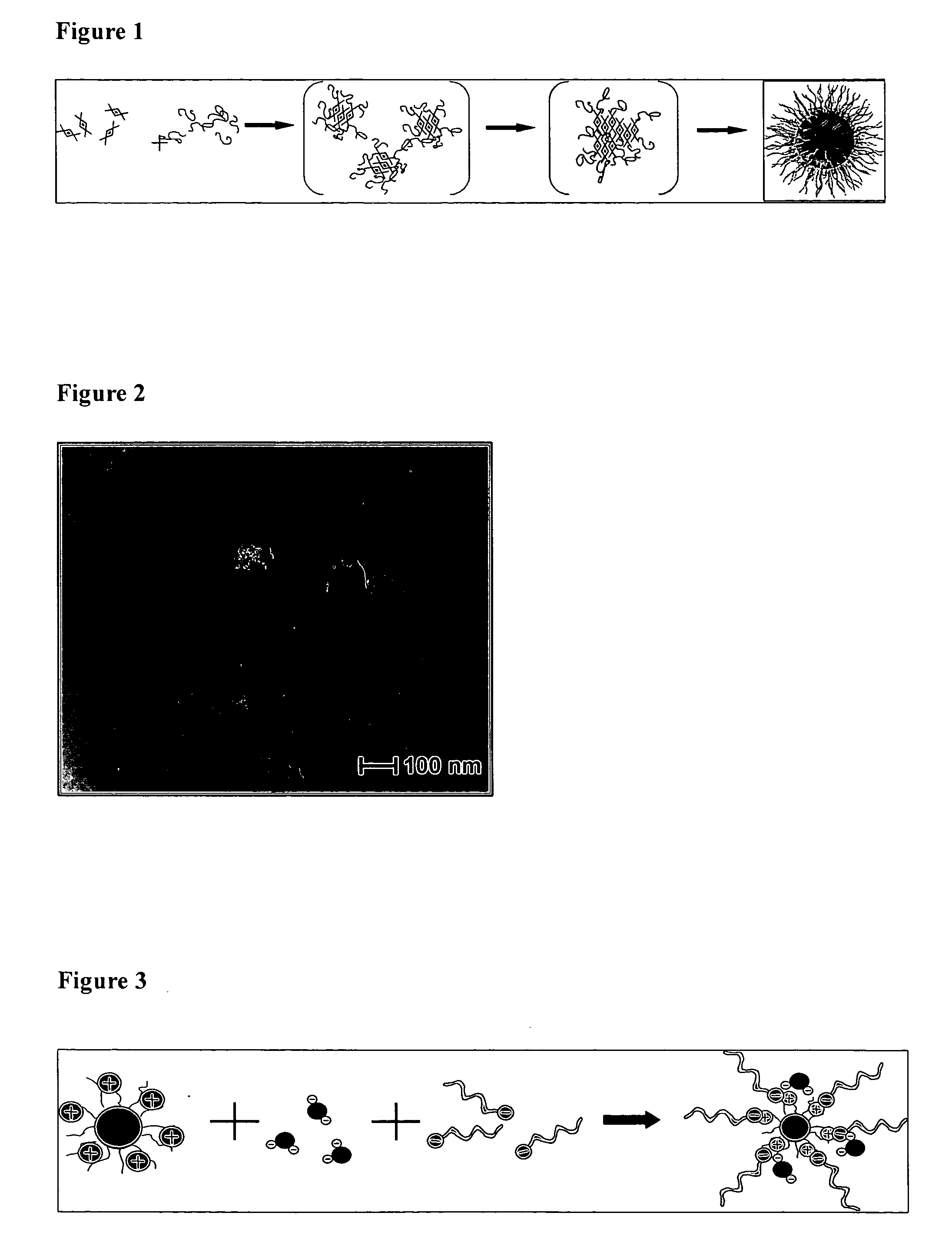
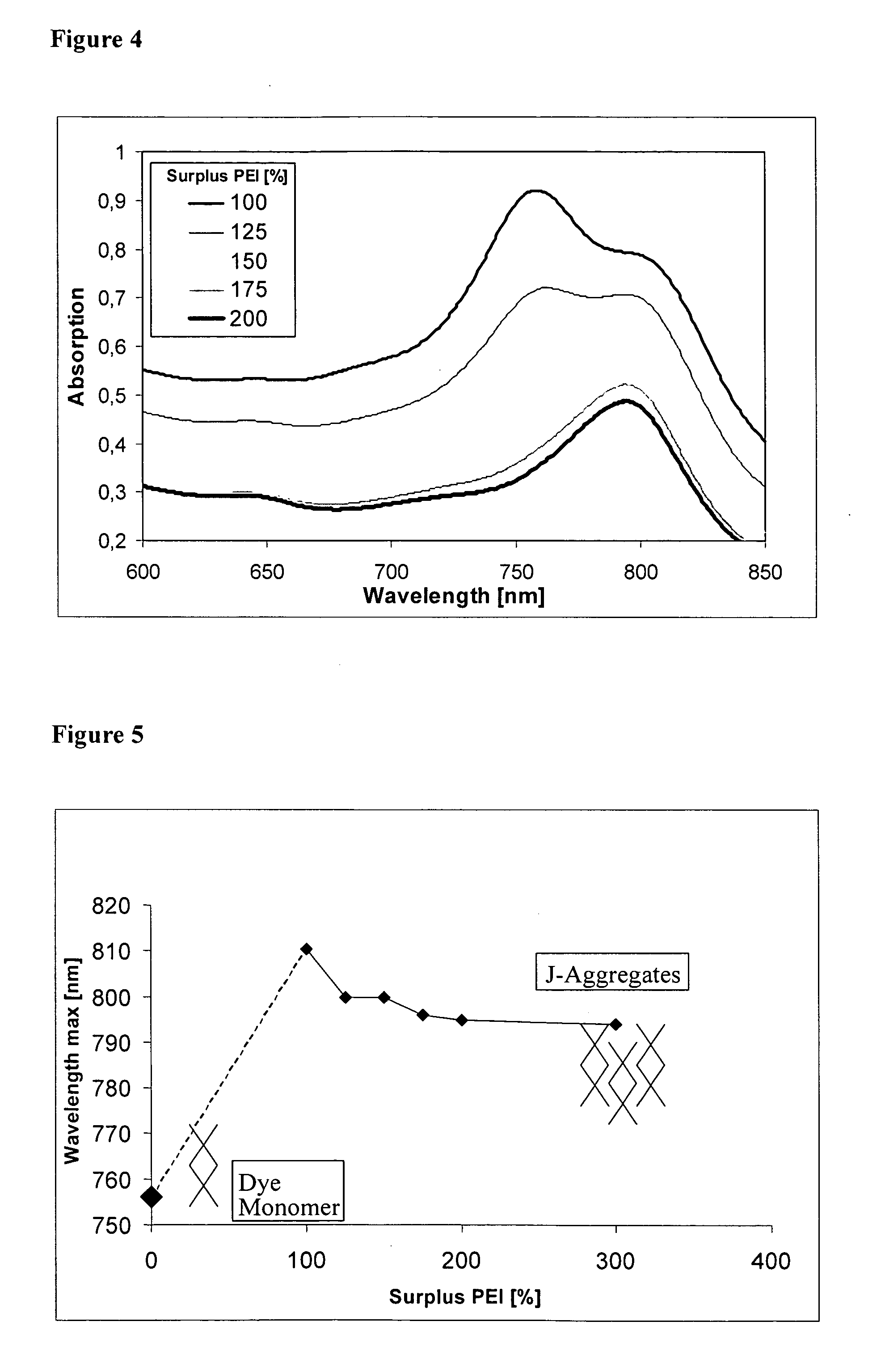
InactiveUS20070104649A1Simple processHigh dye concentrationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPowder deliveryPolyelectrolyteActive agent
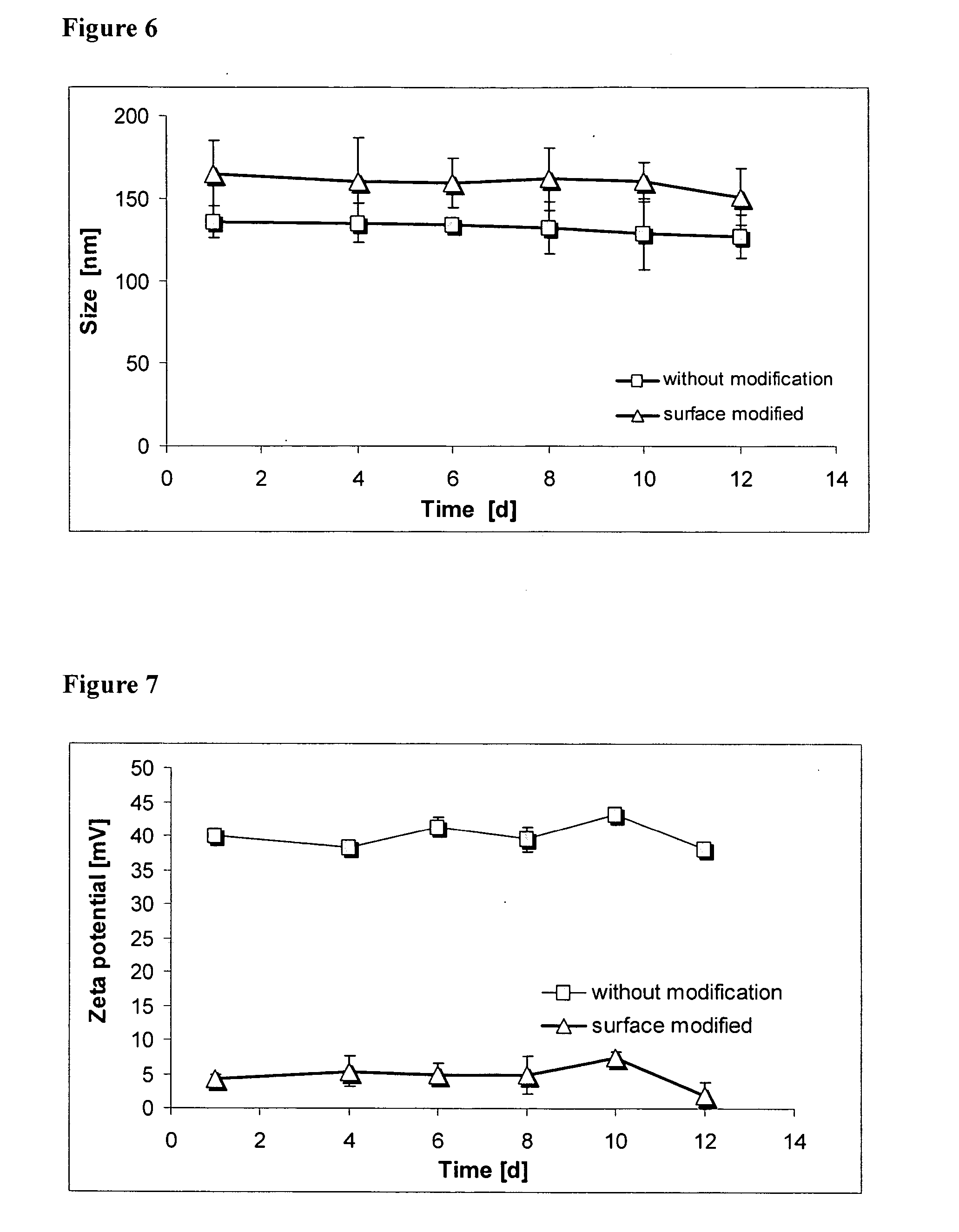
The present invention refers to nanoparticles having optically fluorescent activity. In more detail, the invention refers to a nanoparticle matrix comprising a co-aggregate of at least one charged polyelectrolyte and at least one oppositely charged active agent, wherein the active agent is a hydrophilic optically fluorescent agent, and the invention further refers to a nanoparticle comprising said nanoparticle matrix. Optionally, the nanoparticle is surface modified. The invention also refers to a method for preparing said nanoparticle, and to a method of surface modification. Furthermore, the invention refers to uses of said nanoparticle in vitro and in vivo, and to methods for in vitro and in vivo diagnosis.
Owner:SCHERING AG
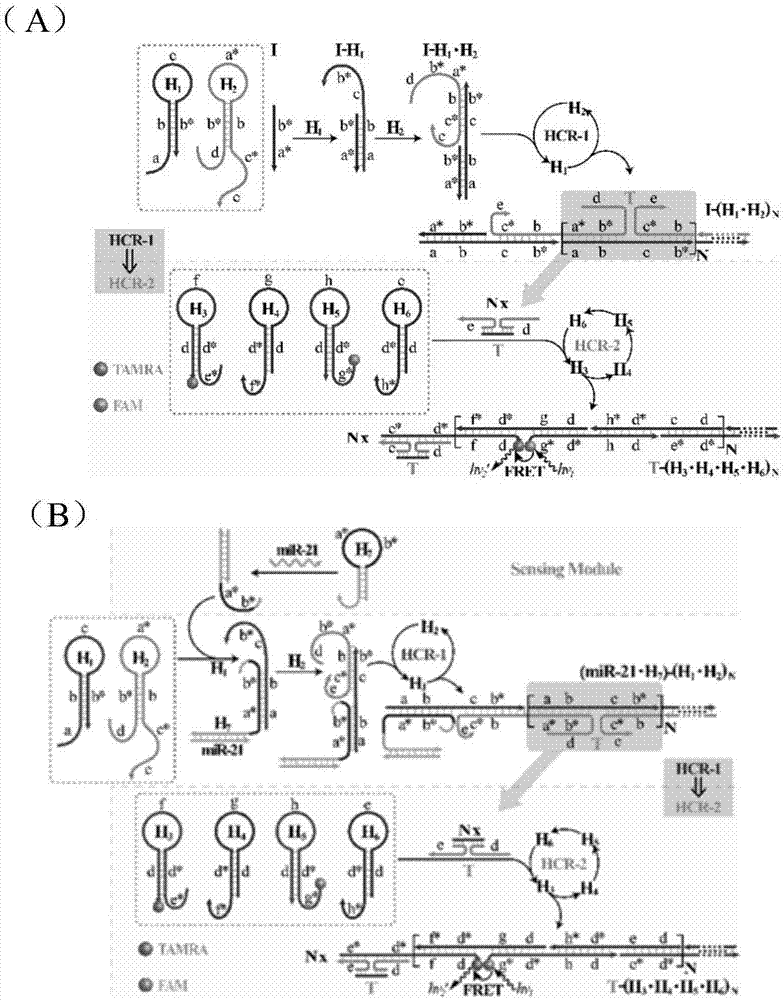
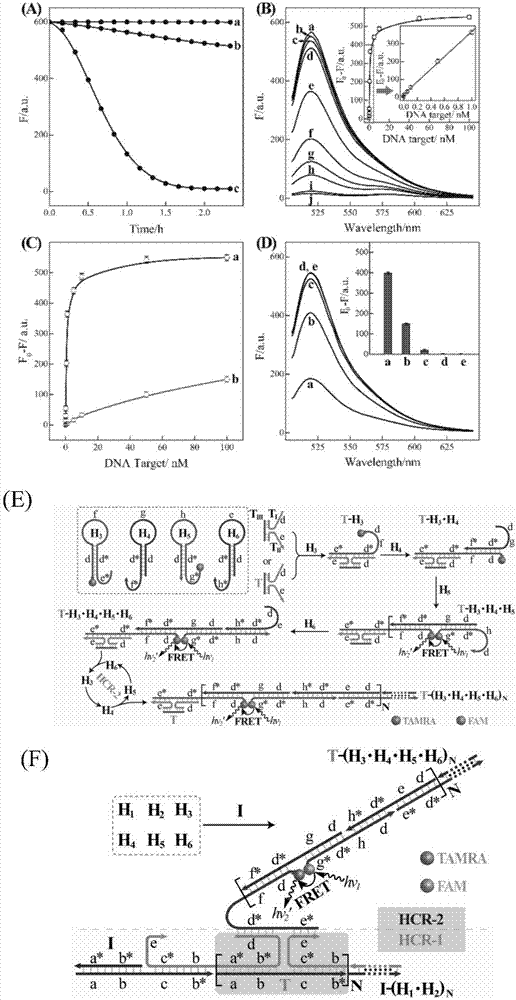
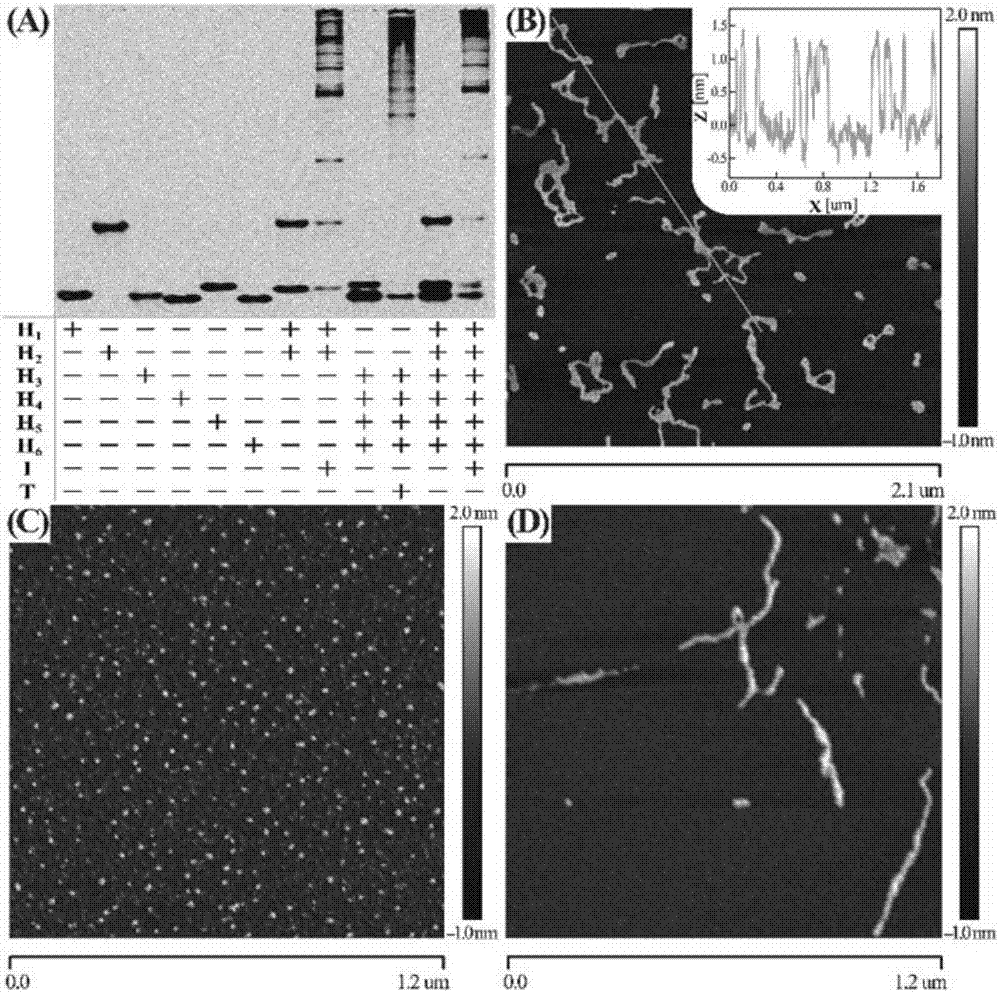
Nucleic acid analyzing method based on cascade HCR (hybridization chain reaction)
ActiveCN107574227AHigh detection sensitivityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementEnergy transferImaging analysis
The invention discloses a nucleic acid analyzing method based on cascade HCR (hybridization chain reaction), and belongs to the field of molecule detection. The nucleic acid analyzing method is characterized in that on the basis of single HCR, two stages of HCR reaction are designed, and the signals can be further amplified on the basis of single HCR; the hairpin nucleic acid probes marked with multiple different fluorescent dyes can be alternatively hybridized by a final target product, so as to form a branched DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) nanometer structure; the signal output is provided bythe fluorescent resonance energy transfer, and the concentration of the target nucleic acid can be judged according to the change value of the fluorescence intensity of fluorophore. The nucleic acid analyzing method has the advantages that the nucleic acid analyzing method can be used for in-vitro detection of DNA and miRNA (miniature ribonucleic acid), the specificity is good, and the sensitivityis high; the nucleic acid analyzing method can be used for the imaging analysis of miRNA in cells, and be favorable for the early diagnosis on cancers.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
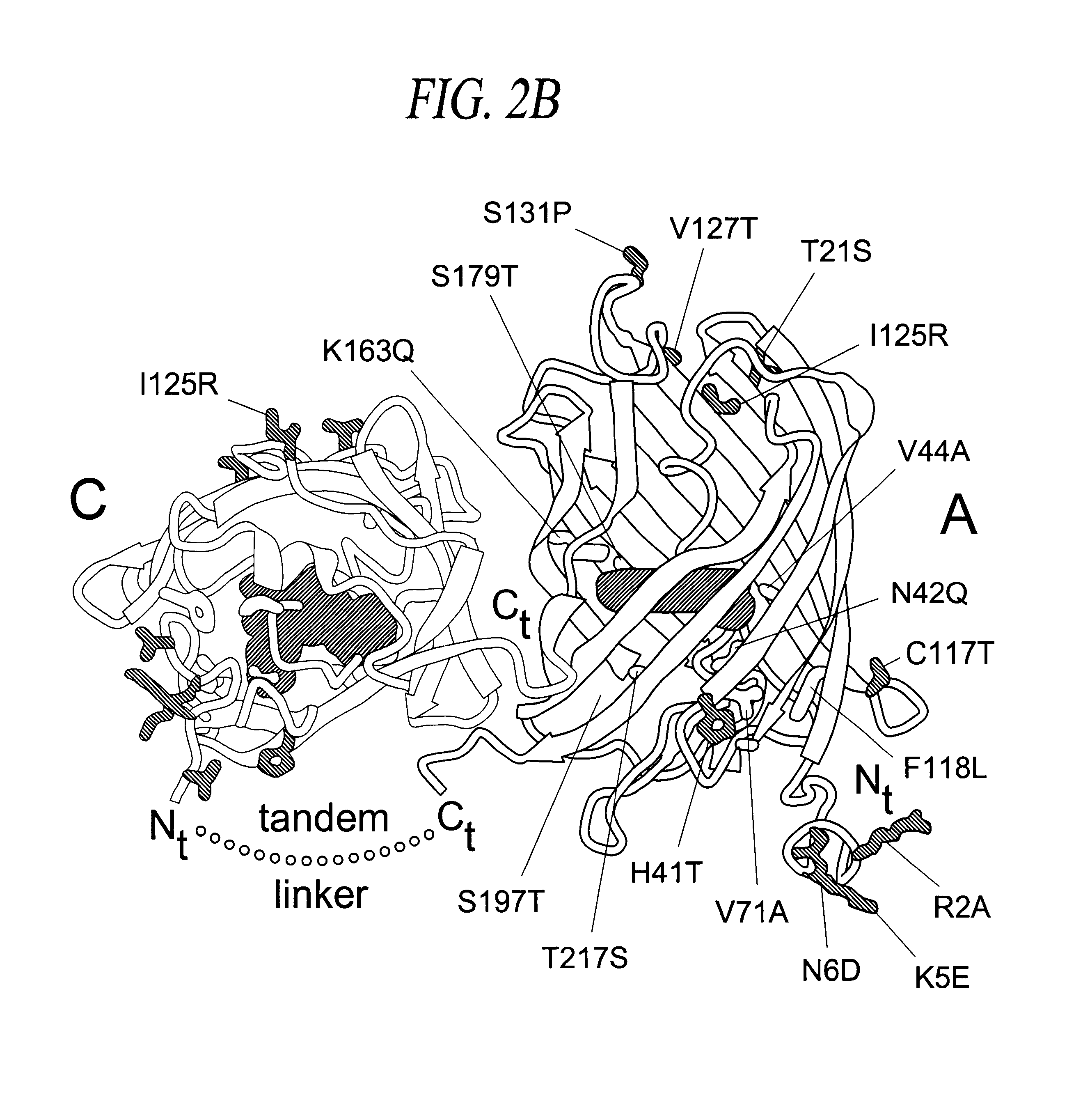
Monomeric and dimeric fluorescent protein variants and methods for making same
InactiveUS20050196768A1Improve efficiencyReduction tendencyCompound screeningApoptosis detectionDimerBiochemistry
The present invention relates generally to fluorescent proteins and fluorescent protein variants, and more specifically to monomeric and dimeric forms of Anthozoan fluorescent proteins. In one aspect, the present invention provides variants of fluorescent proteins, where the variants have a reduced propensity to tetramerize, and form dimeric or monomeric structures. In a further aspect, the present invention provides variants of fluorescent proteins, the variants being characterized by more efficient maturation than corresponding fluorescent proteins from which they are derived. The invention also relates to methods of making and using such fluorescent proteins and fluorescent protein variants, including fluorescent protein monomers and dimers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
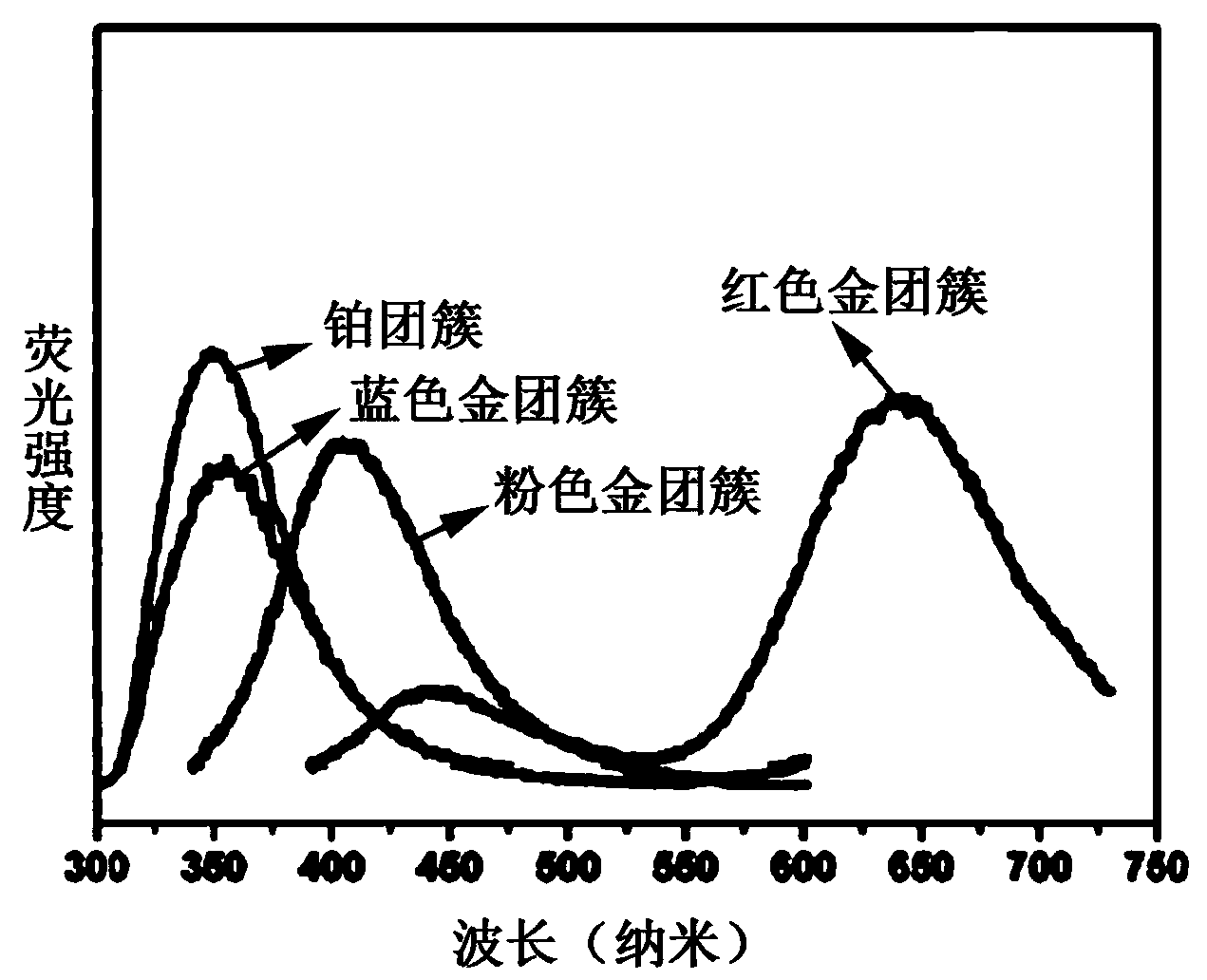
Preparation method for noble metal nanoclusters of fluorescent sensor
The invention relates to a preparation method for noble metal nanoclusters of a fluorescent sensor. The preparation method comprises the following steps: sucking egg white from a fresh egg, diluting by purified water, and uniformly mixing; finally fully and uniformly mixing the diluted egg white with chloroauric acid (HAuCl4), uniformly mixing a mixture with sodium hydroxide, and standing to prepare red fluorescent gold nanoclusters. A preparation method for silver and platinum nanoclusters is similar to that for the gold nanoclusters, and silver nitrate and chloroplatinic acid (H2PtCl6) are added into the diluted egg white respectively in the preparation method for the silver and platinum nanoclusters. The clusters prepared by the method are uniform in size, uniform in surface appearance, very strong in fluorescence and ultra-low in detection sensitivity. The method is simple, novel, simple in materials, small in equipment number, low in energy consumption and convenient to popularize, and has a wide application prospect in the fields of disease detection, gas adsorption, chemical catalysis, food safety, photoelectronic devices and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT FORNANOTECH
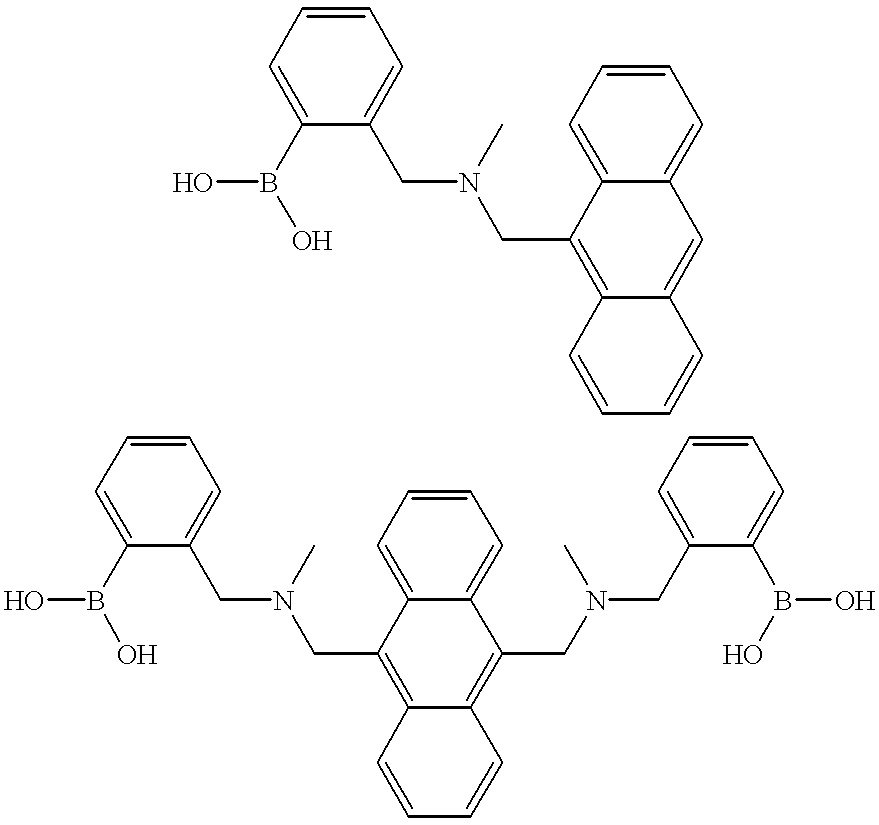
Diaminofluorescein derivatives
InactiveUS6569892B2Accurate measurementHigh fluorescence intensityBiocideOrganic chemistryNitrogen monooxideAmino radical
Owner:SEKISUI MEDICAL CO LTD
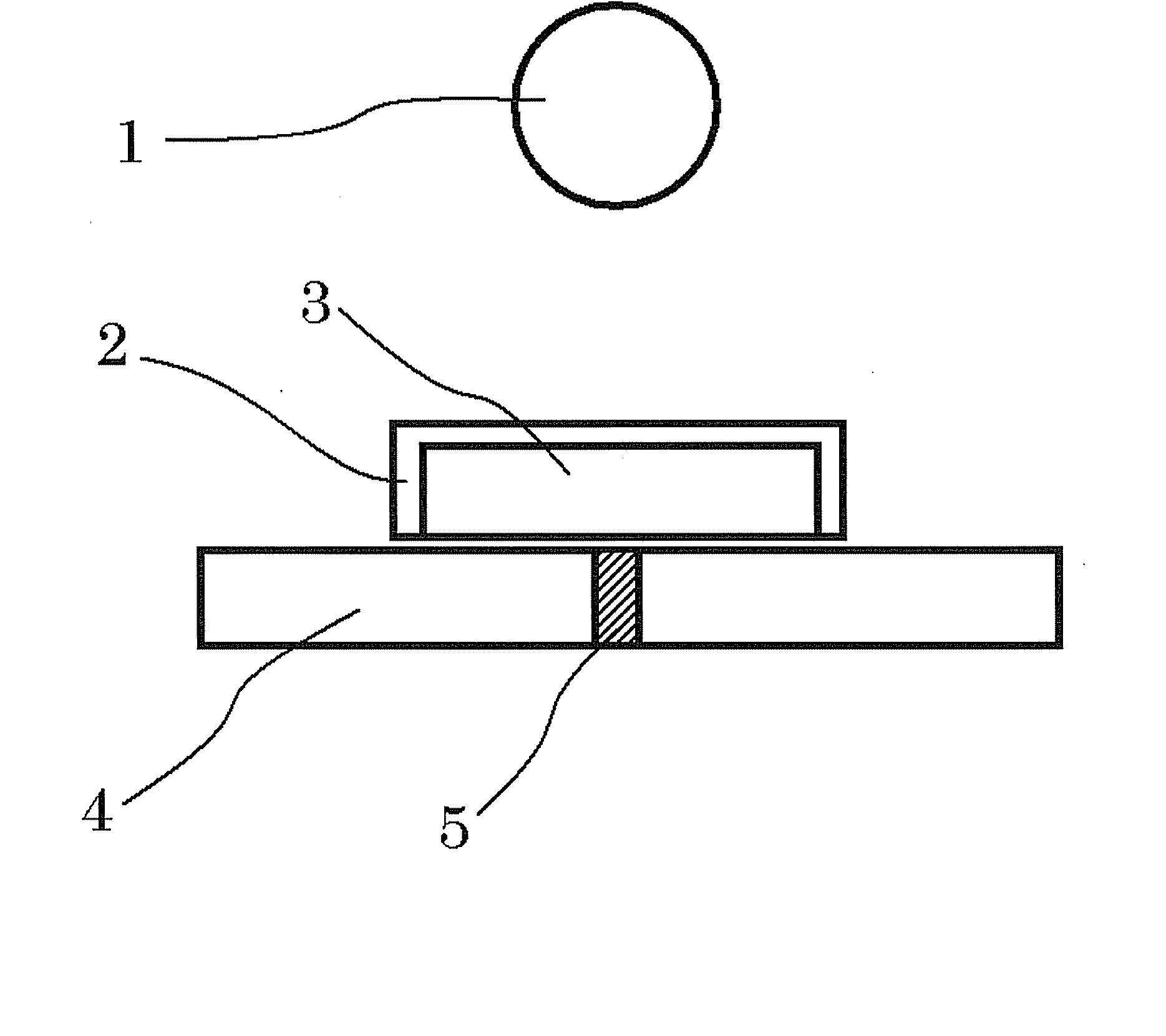
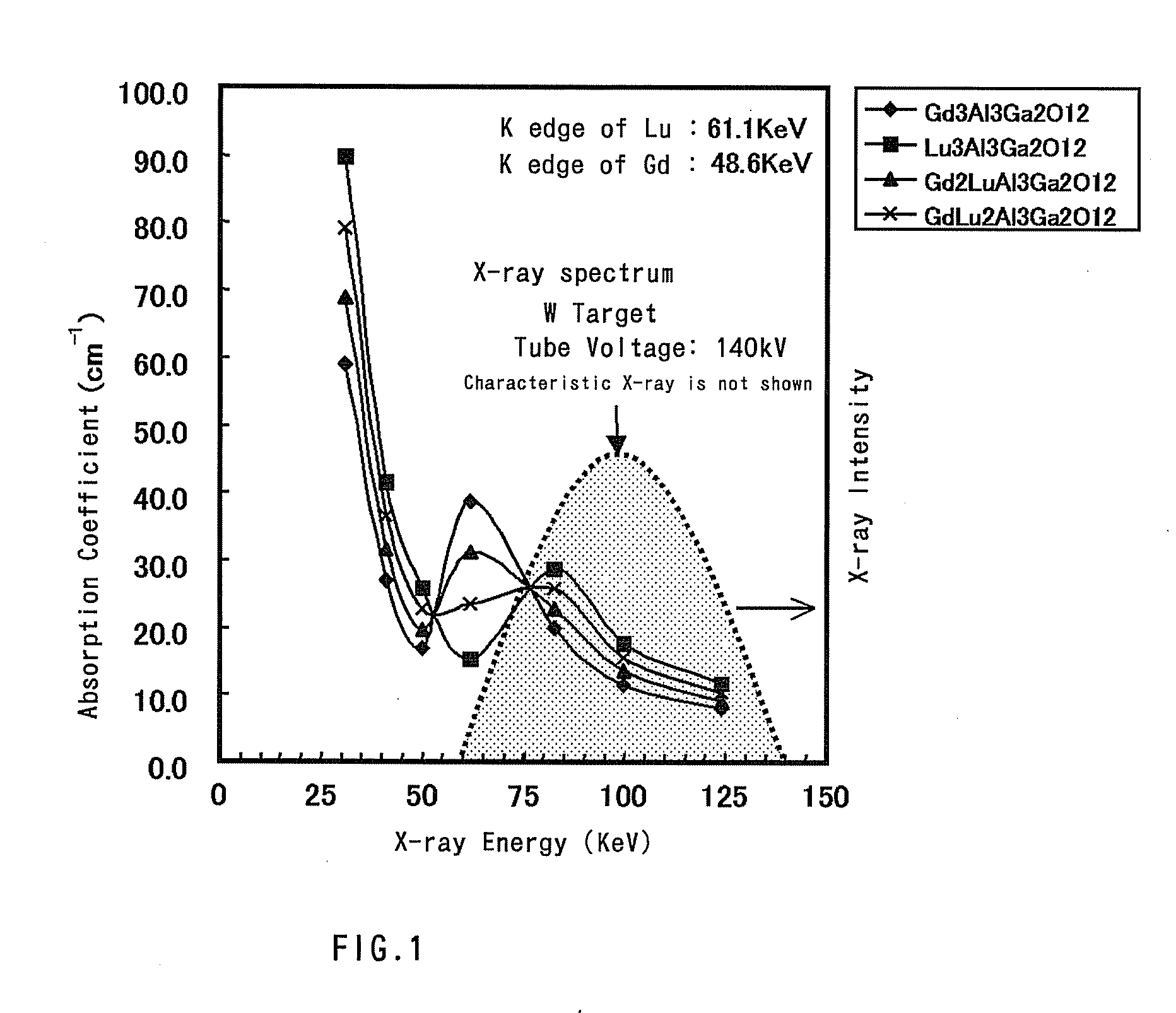
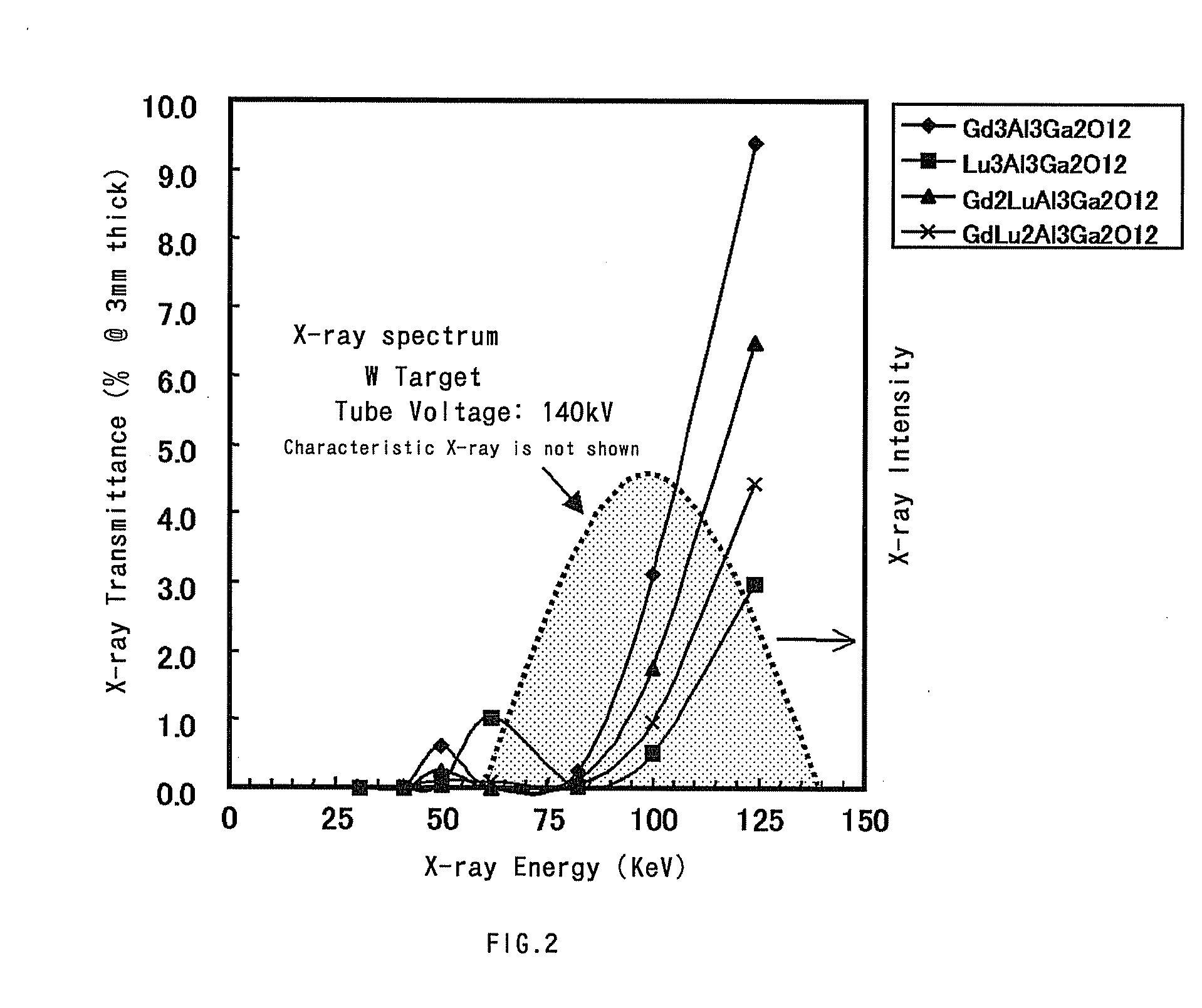
Fluorescent Material, a Method of Manufacturing the Fluorescent Material, a Radiation Detector Using the Fluorescent Material, and an X-Ray Ct Scanner
ActiveUS20080017802A1High fluorescence intensityWeak afterglowPolycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsCt scannersX-ray
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
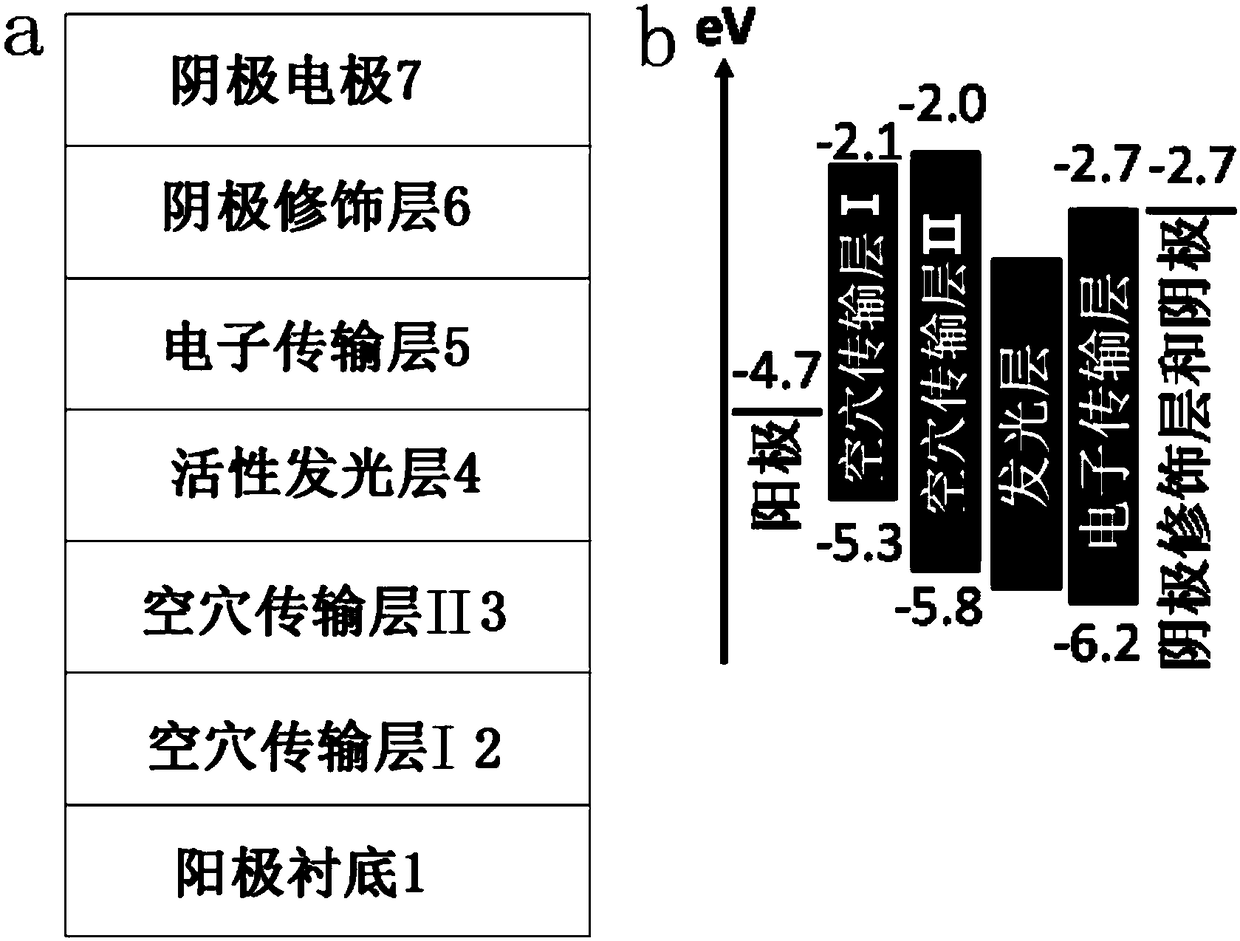
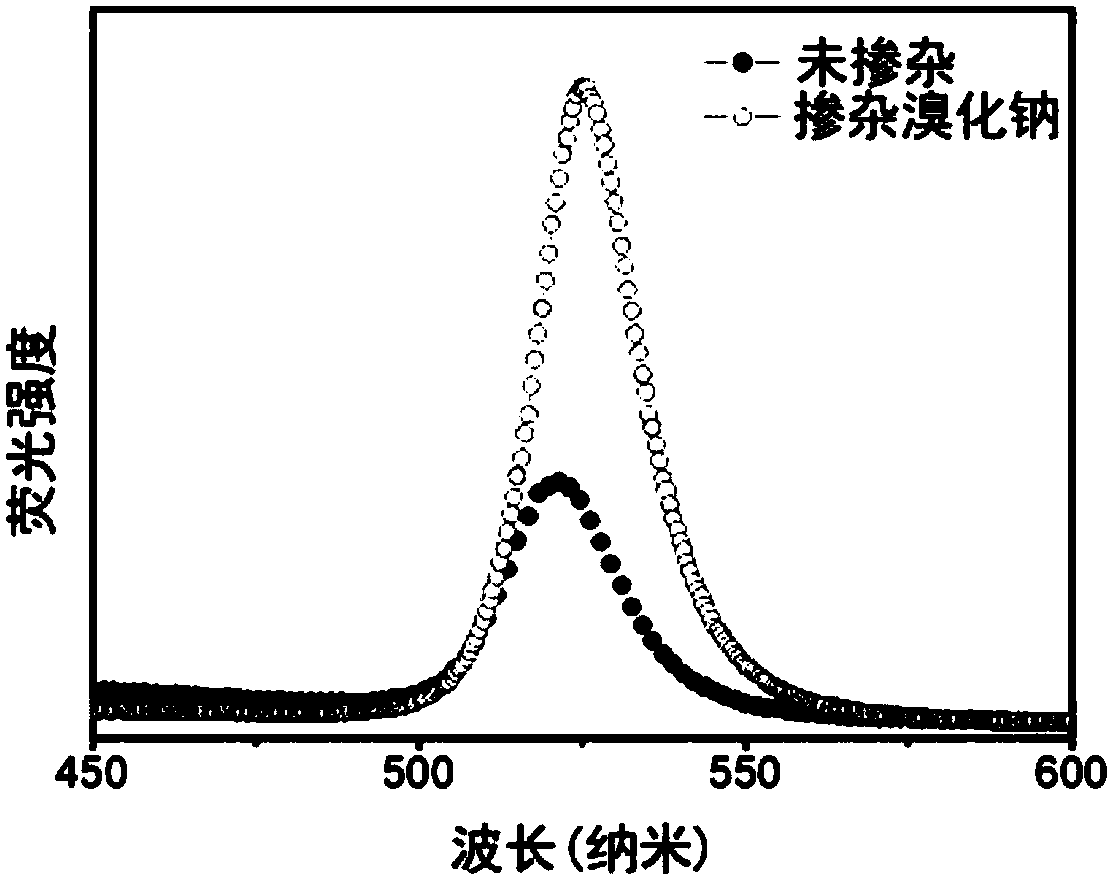
Alkali halide-doped perovskite light-emitting diode and fabrication method thereof
InactiveCN108269940ALow costSimple preparation processSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHole transport layerAlkali metal halide
The invention relates to an alkali halide-doped perovskite light-emitting diode. The alkali halide-doped perovskite light-emitting diode comprises a substrate, a hole transmission layer, an active light-emitting layer, an electron transmission layer, an electrode modification layer and an electrode, wherein the thickness of the active light-emitting layer is 5-100 nanometers, the active light-emitting layer comprises perovskite and an alkali halide doped in the perovskite, the molecular formula of the perovskite is one or more of CsPbCl<x>Br<3-x>, CsPbBr<x>I<3-x>, MAPbCl<x>Br<3-x>, MAPbBr<x<I<3-x>, FAPbCl<x>Br<3-x> and FAPbBr<x>I<3-x>, x is equal to 0, 1, 2 or 3, and the alkali halide is one or more of LiCl, NaCl, KCl, RbCl, LiBr, NaBr, KBr, RbBr, LiI, NaI, KI and RbI. The invention also provides a fabrication method of the alkali halide-doped perovskite light-emitting diode. The fabrication method comprises the steps of forming the hole transmission layer or the electron transmissionlayer o the substrate; modifying an alkali halide-containing perovskite precursor solution used as the active light-emitting layer on the hole transmission layer of the electron transmission layer; sequentially forming the electron transmission layer, a negative electrode modification layer and a negative electrode on the active light-emitting layer or sequentially forming the hole transmission layer, a positive electrode modification layer and a positive electrode on the active light-emitting layer; and performing package.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
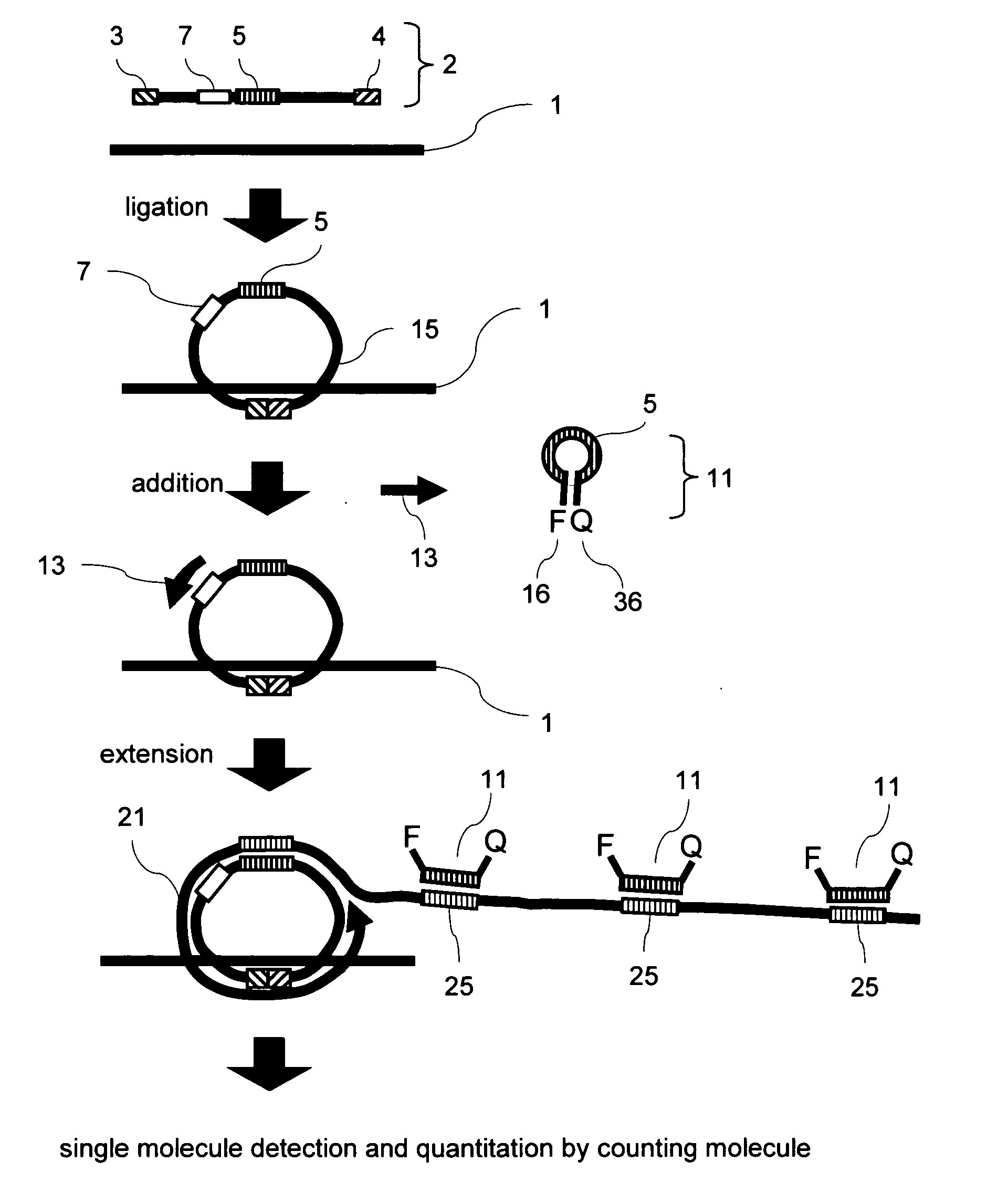
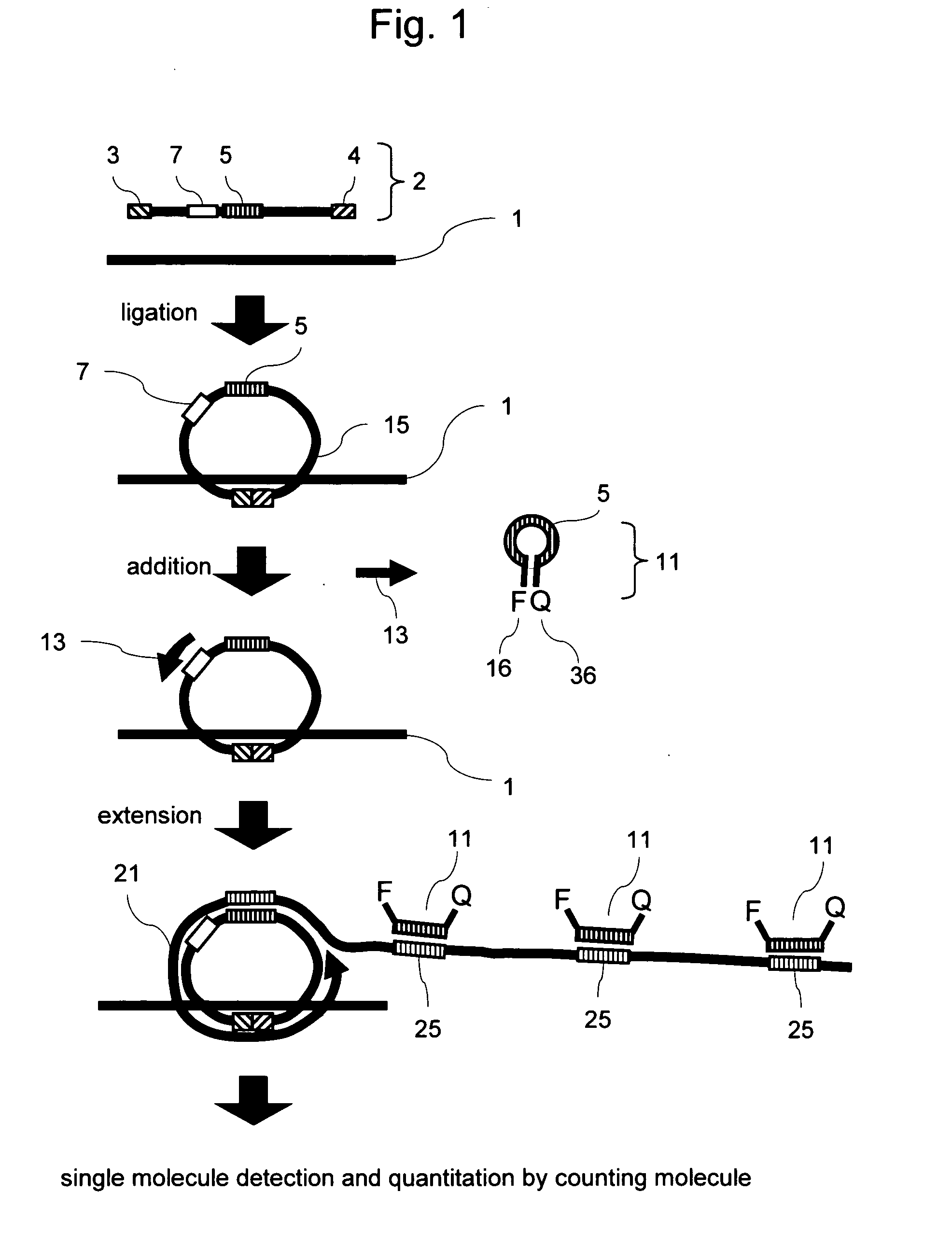
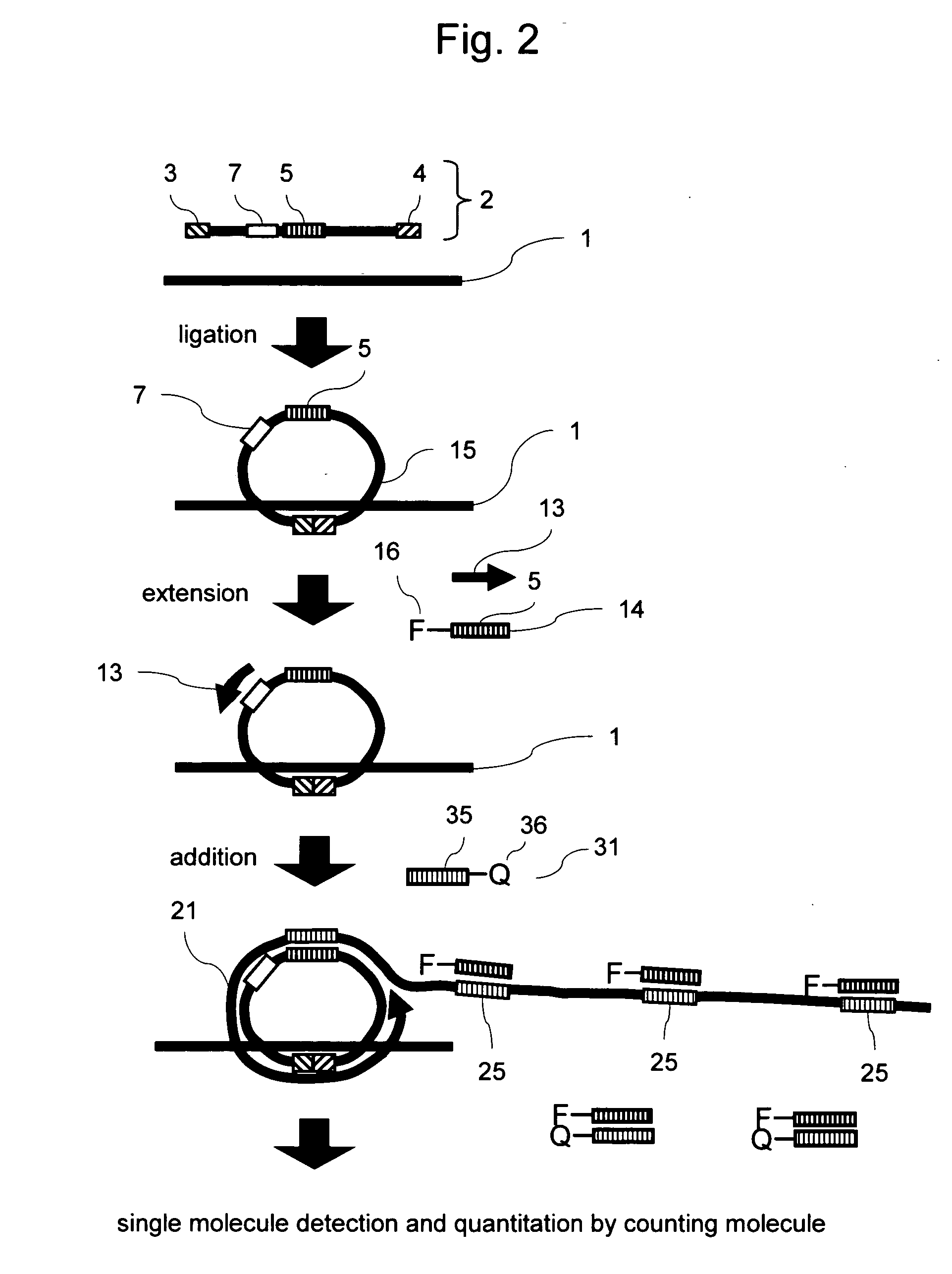
Methods of nucleic acid analysis by single molecule detection
InactiveUS20070231808A1Improve accuracyAccurate and sensitive quantitationMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideSingle strand
This invention provides a method of nucleic acid analysis that enables highly accurate and sensitive quantitation by counting the number of molecules among a plurality of types of genes without amplifying specific genes and that enable reduction of quantitation limits. This method comprises steps of: allowing a polynucleotide comprising a first region having a sequence complementary to the target gene at the 3′ end, a second region having a sequence complementary to the target gene at the 5′ end, and a third region corresponding to a detection probe to hybridize to the target gene; allowing the 3′ end of the first region hybridized to the target gene to ligate to the 5′ end of the second region so as to obtain a circularized polynucleotide; with the use of the circularized polynucleotide as a template, performing a primer extension reaction using a primer having a sequence complementary to part of the circularized polynucleotide and a strand-displacement DNA polymerase; allowing a detection probe containing a sequence identical to the third region to hybridize to a sequence complementary to the third region that iteratively appears in a single-stranded portion of the extension product; and optically detecting the quantity of the detection probe hybridized to the extension product to thereby quantitate the target gene.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
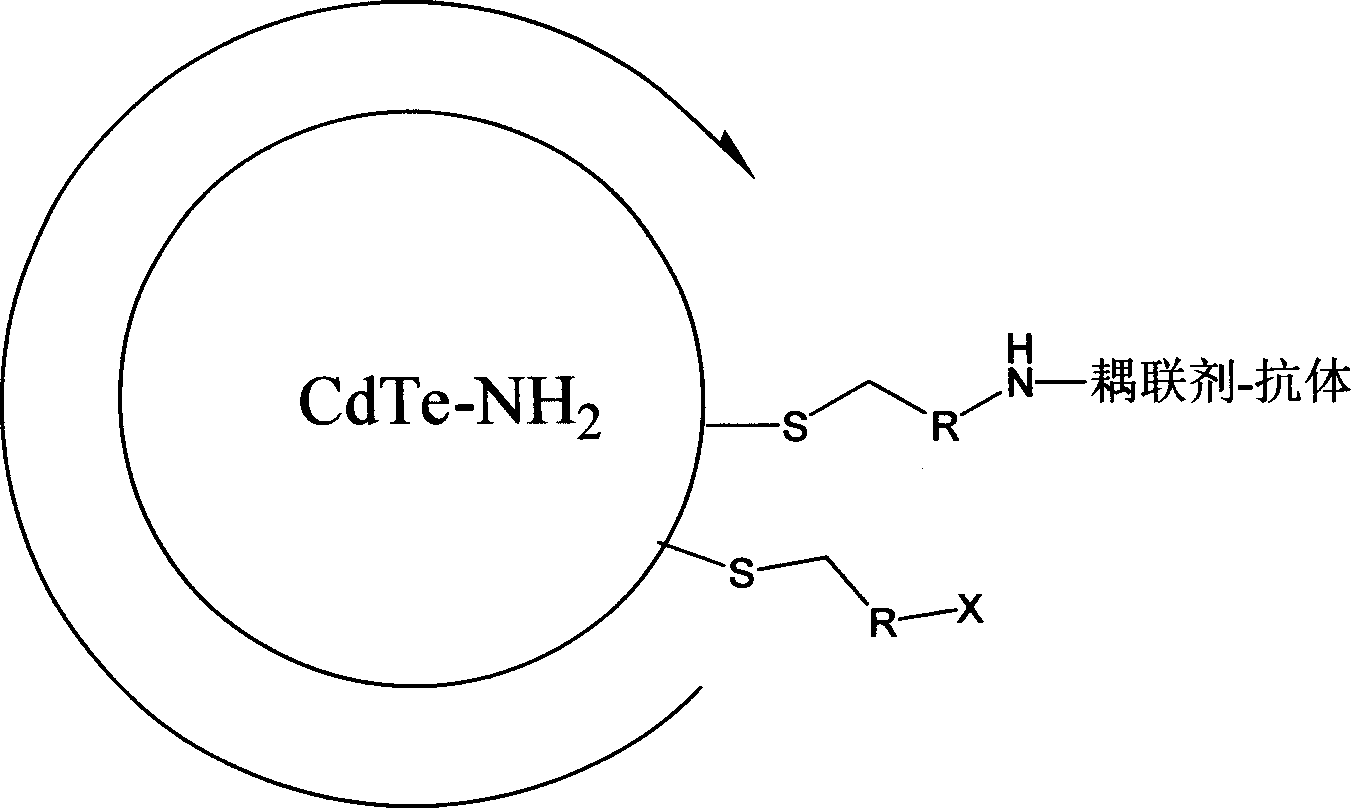
Prepn. and application of nano particle, nano microballoon and biological fuorescent probe
InactiveCN1389539AEasy to makeSimple and fast operationLuminescent compositionsFluorescenceMicrosphere
There is a kind of nano particle and micro-sphere biological fluorescence probem and the manufacturing method. The method mainly includes: 1) hydrosulphenyl compound with amidocyanogen is used as stabilizing agent in particle synthesis, water-soluble fluorescence nano particle whose surface is bedecked with amidocyanogen is directly prepared under mild condition, then it takes advantages of the amidocyanogen on the surface of particle to couple with biological system directly, further nano-particle biological fluorescence probe is acquired; 2) said fluorescence nano particle whose surface is bedecked with radical dumpling with different functions is compounded into micro-sphere is inorganic silicon dioxide or organic polymer by various means, fluorescence micro-sphere which can be dispersed equably in aqueous solution is acquired.
Owner:高明远
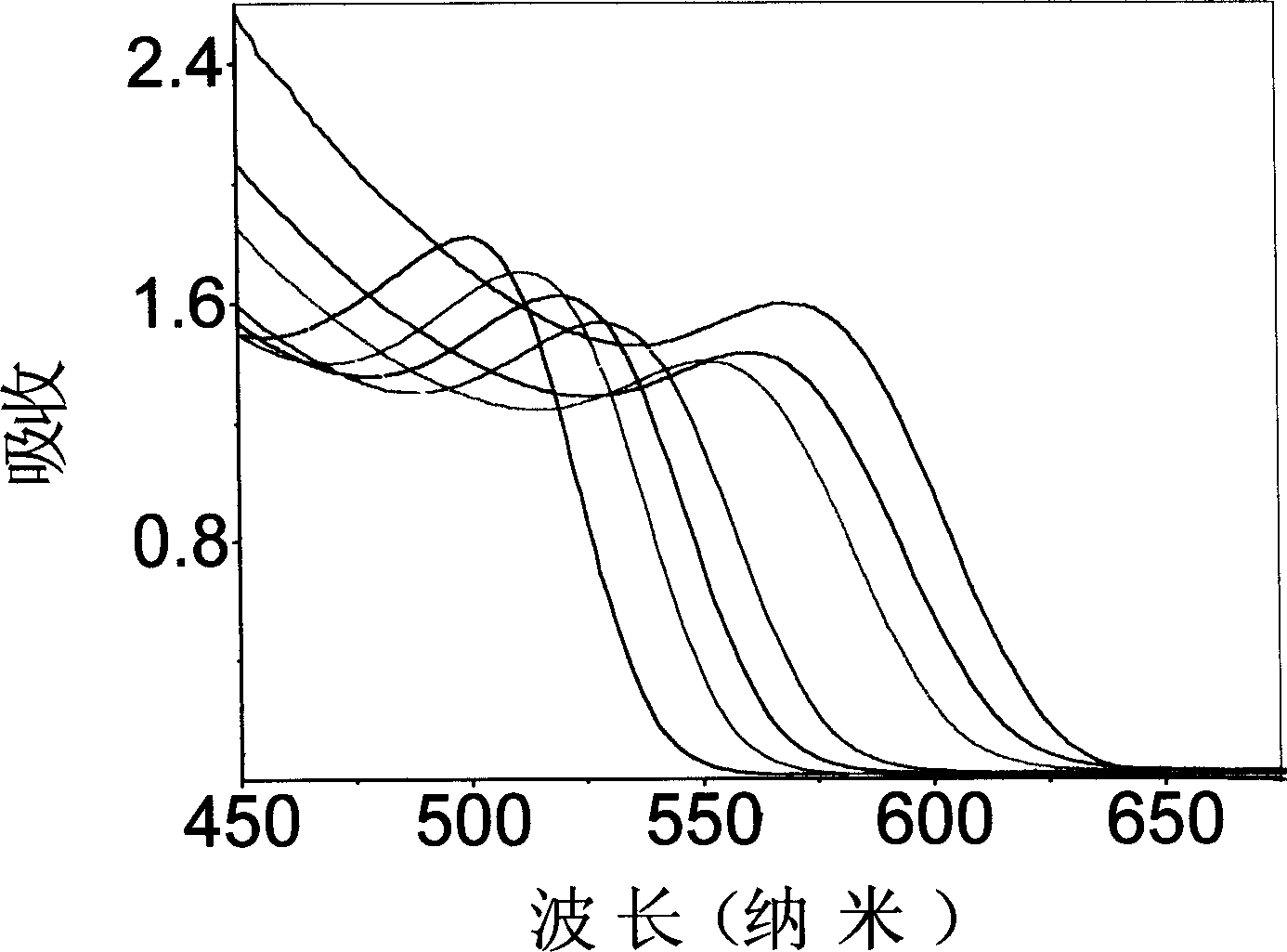
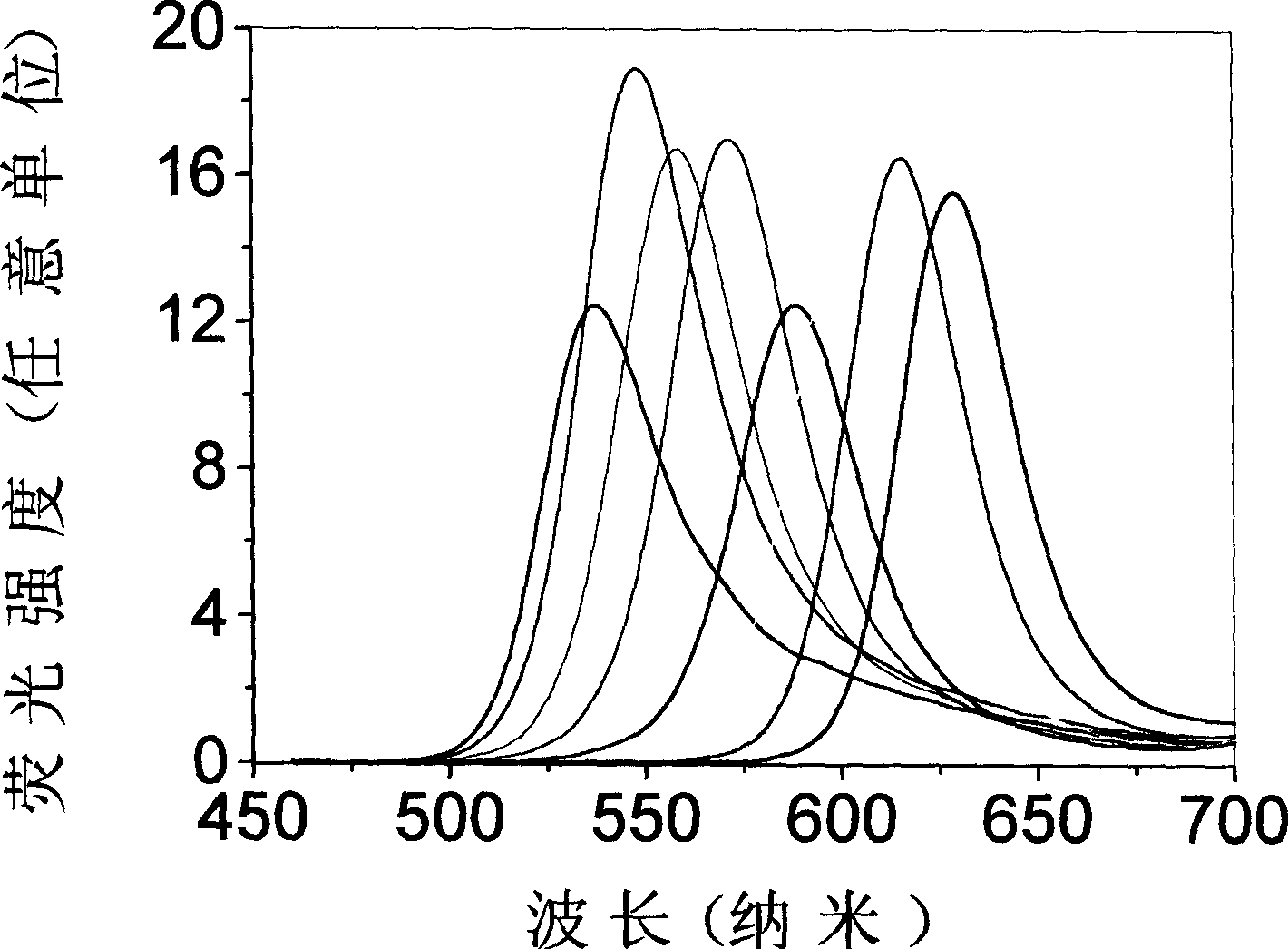
Semiconductor-Nanoparticle-Dispersed Small Glass Particles and Process for Preparing the same
InactiveUS20090108235A1Improve long-term stabilityHigh fluorescence intensityRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationQuantum yieldGlass particle
The present invention provides semiconductor-nanoparticle-dispersed small silica glass particles that emit bright fluorescent light with high fluorescence quantum yield and high density, compared to the conventional semiconductor-nanoparticle-dispersed small glass particles, and that have excellent fluorescence intensity stability over time; and a process for preparing the same. The semiconductor-nanoparticle-dispersed silica glass particles have a mean particle size of not less than 10 nanometers and not more than 5 micrometers, and contain a hydrolyzed alkoxide and semiconductor nanoparticles at a concentration of not less than 2×10−5 mol / l and not more than 1×10−2 mol / l. The particles emit fluorescent light with a fluorescence quantum yield (quantum yield) of 25% or more (and 60% or more), when dispersed in a solution.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Gold nano-star @ quantum dot composite cell probe with photothermal and fluorescence enhancement dual-functions and preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN103205258AEffective targeted killHigh fluorescence intensityMaterial nanotechnologyEnergy modified materialsToxicitySeed crystal
The invention provides a gold nano-star @ quantum dot composite cell probe with photothermal and fluorescence enhancement dual-functions, which sequentially comprises a gold nano-star, a silica layer, quantum dots and a silica nano-shell layer from inside to outside. The cell probe is prepared by using a chemical layer-by-layer growth method implemented through the following steps of: firstly, preparing a gold nano-star by using a seed crystal growth method; coating a silica layer on the outside of the gold nano-star by means of hydrolysis so as to form a silica sphere coated with the gold nano-star; then, linking quantum dots on the surface of the silica sphere through a crosslinking reaction so as to form a silica sphere composite material internally coated with the gold nano-star and externally linked with the quantum dots; and finally, coating a silica nano-shell layer on the surface of the composite material. Compared with traditional probes, the probe integrates the functions of photothermal treatment and fluorescence labeling; the fluorescence intensity of the quantum dots is enhanced, and the biological toxicities of the gold nano-star and the quantum dots are effectively avoided; and in addition, the cell probe has extremely good biological compatibility.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Spirulina phycocyanin and extraction method thereof
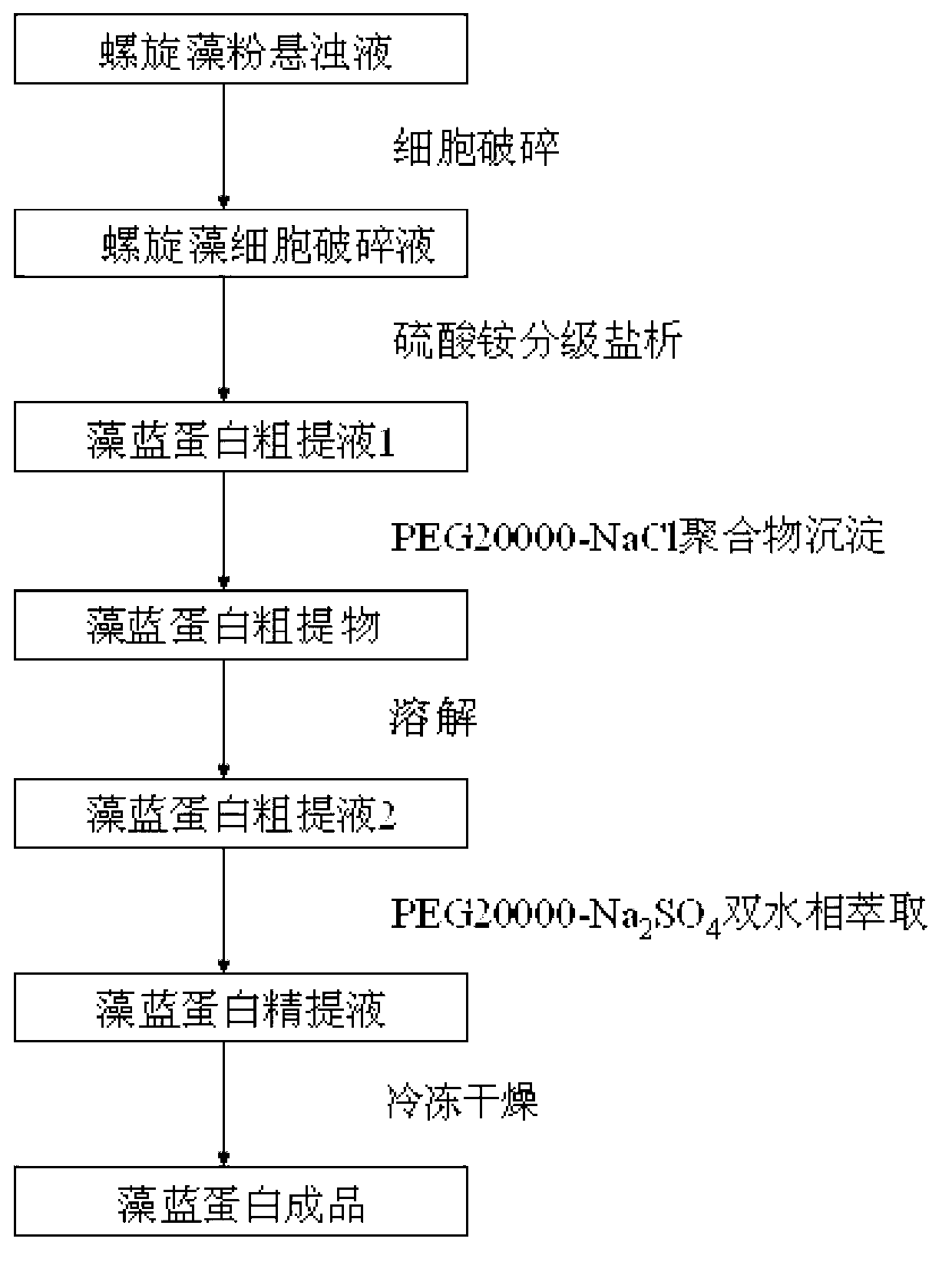
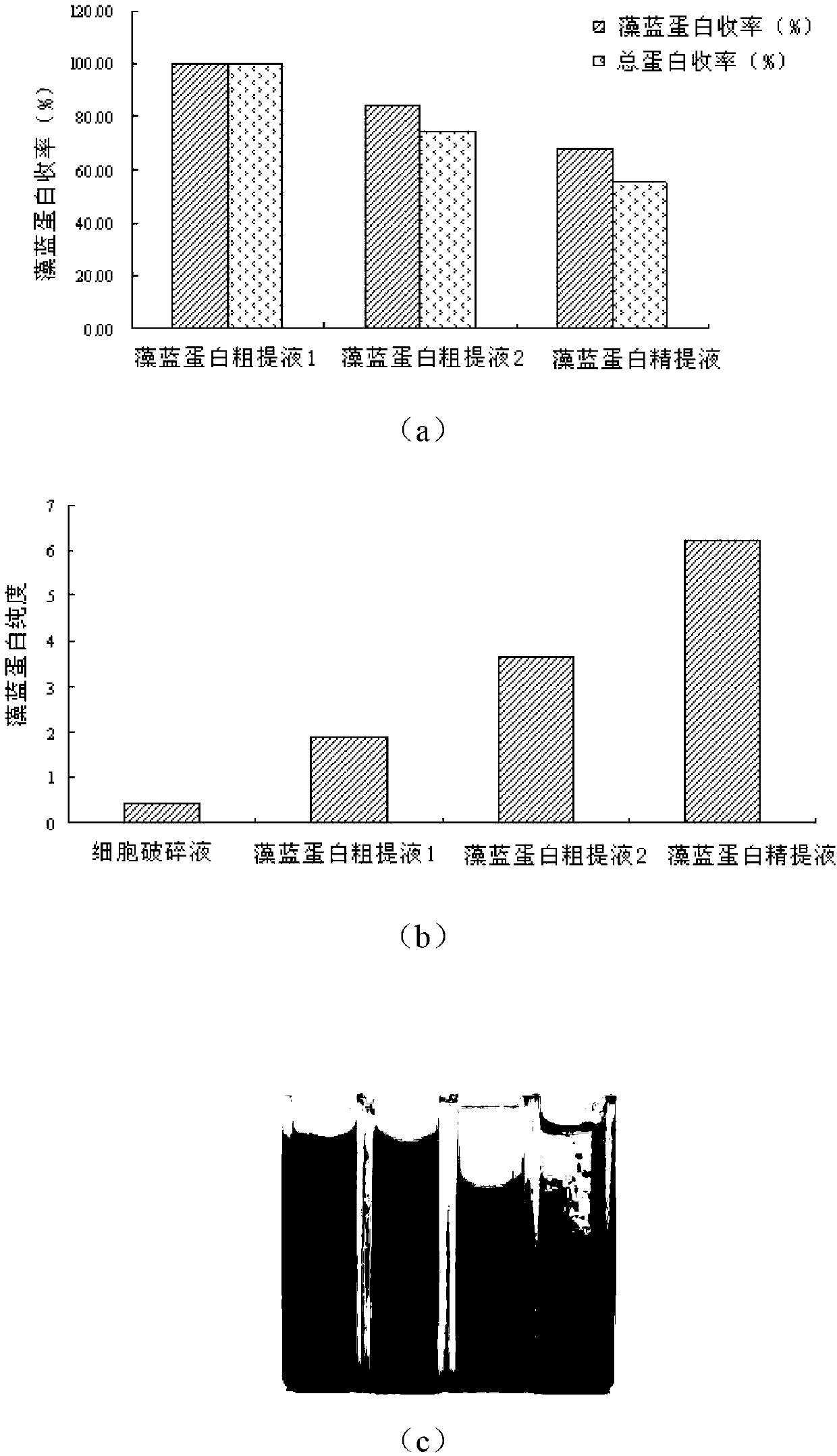
The invention relates to an extraction method of spirulina phycocyanin. The method comprises the following steps of: processing spirulina powder suspension by adopting a freeze thaw method and a machine crushing process to obtain spirulina cell disruption liquid; performing fractional salting out to precipitate the spirulina cell disruption liquid with 30 percent ammonium sulfate liquid and 50 percent ammonium sulfate liquid to obtain phycocyanin coarse extract liquid 1; adding PEG 20000 (polyethylene glycol 20000) and NaCl to further precipitate out phycocyanin coarse extract with higher purity; dissolving the phycocyanin coarse extract with phosphate buffer to prepare phycocyanin coarse extract liquid 2; and extracting the phycocyanin coarse extract liquid with PEG 20000 / Na2SO4 aqueous two-water-phase system, and desalting extracted lower phase by dialysis to obtain phycocyanin fine extract liquid, and lyophilizing to prepare a phycocyanin finished product. The method is simple in extraction process and low in cost, and is suitable for intermittent and scale production processing of high-purity and high-yield spirulina phycocyanin finished product. The phycocyanin coarse extract can be stored for a long time, and the phycocyanin finished product which is prepared by further purification has excellent antioxidant free radical scavenging effect and fluorescent strength.
Owner:丽江美之源食品有限公司
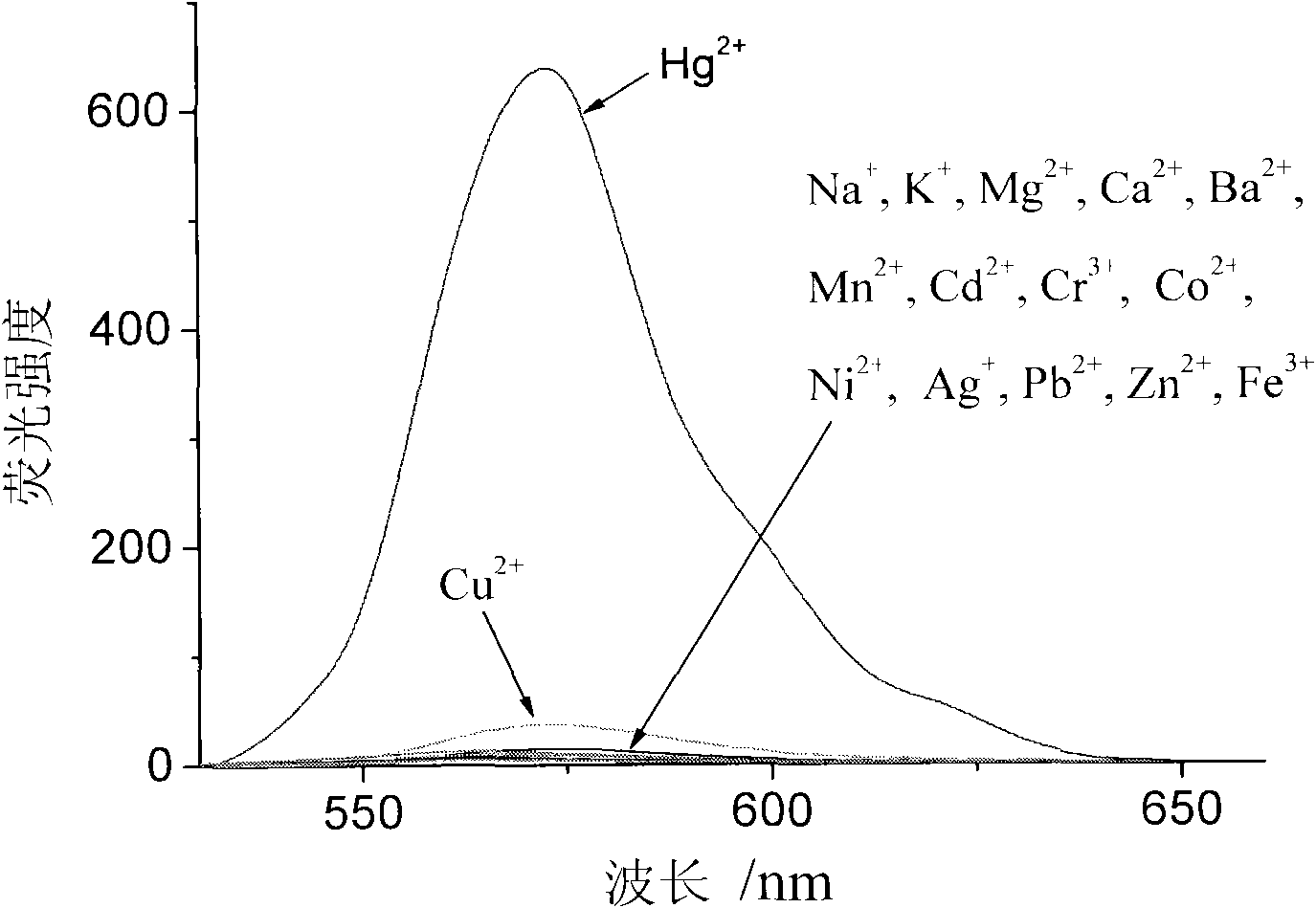
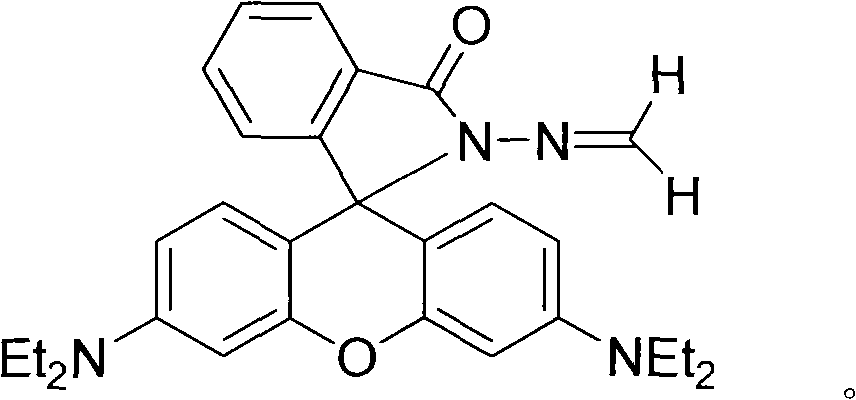
Copper ion/mercury ion fluorescence molecular probe, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102127421AHigh fluorescence quantum yieldPolarity insensitiveOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceChromatographic separationQuantum yield
The invention relates to a copper ion / mercury ion fluorescence molecular probe, and a preparation method and application thereof. The invention mainly aims to solve the problem of single detection ion in the fluorescence molecular probe for detecting copper ions or mercury ions in the prior art, and the problems of low sensitivity, poor selectivity, high sensitivity to pH value, and the like in most fluorescence molecular probes. The preparation method of the fluorescence molecular probe comprises the following steps: (1) dissolving 1 part of rhodamine B in ethanol, adding 2-5 parts of hydrazine hydrate at room temperature, stirring under reflux for 1-2 hours, cooling, and filtering to obtain a precipitate; and (2) adding 1 part of precipitate into 50-500 parts of mixed solvent composed of methanol and dichloromethane in a volume ratio of 3:1, adding 2-6 parts of 40-60wt% formalin, stirring at room temperature in a nitrogen atmosphere for 6-8 hours, evaporating under reduced pressure to remove the solvent, and carrying out silica gel chromatographic separation to obtain the fluorescence molecular probe. The invention has the advantages of high fluorescence quantum yield, low sensitivity to solvent polarity, high chemical / light stability and the like.
Owner:SHANXI DATONG UNIV
Flourescence observation equipment
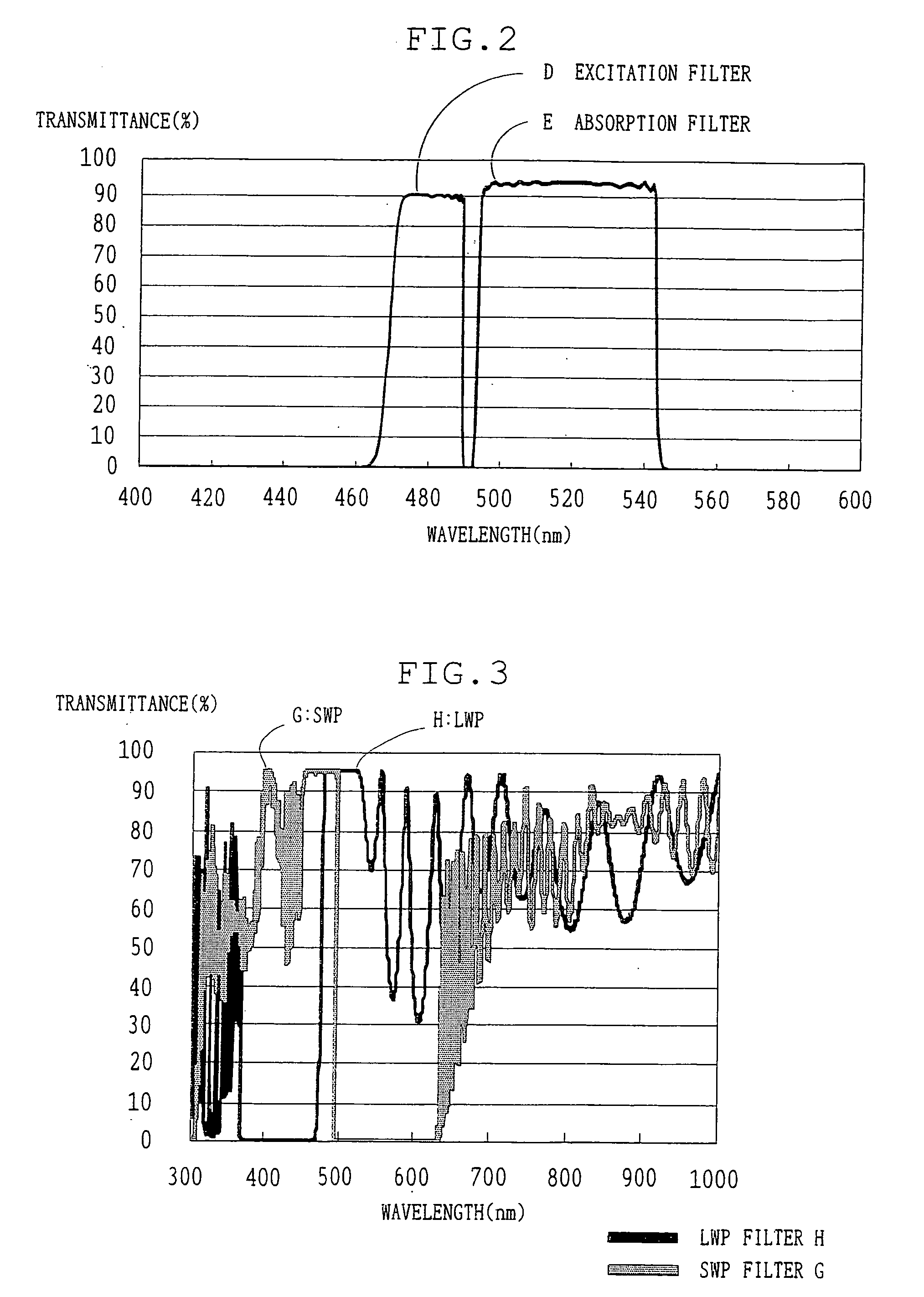
ActiveUS20060017913A1High fluorescence intensityWeakOptical radiation measurementForce measurement by measuring optical property variationPhysicsFluorescence
An apparatus for fluorescence observation includes an excitation filter which transmits only exciting light of an specific wavelength among illumination light, and an absorption filter which blocks the exciting light and transmits only fluorescence generated from a specimen when the exciting light is irradiated to the specimen. Here, an interval of a half-value wavelength at a long-wavelength side of the excitation filter and a half-value wavelength at a short-wavelength side of the absorption filter is in a width between 1 nm to 6 nm, and change of the half-value wavelength of the excitation filter and the absorption filter when humidity changes from 10% to 95%, is 0.5 nm or less.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
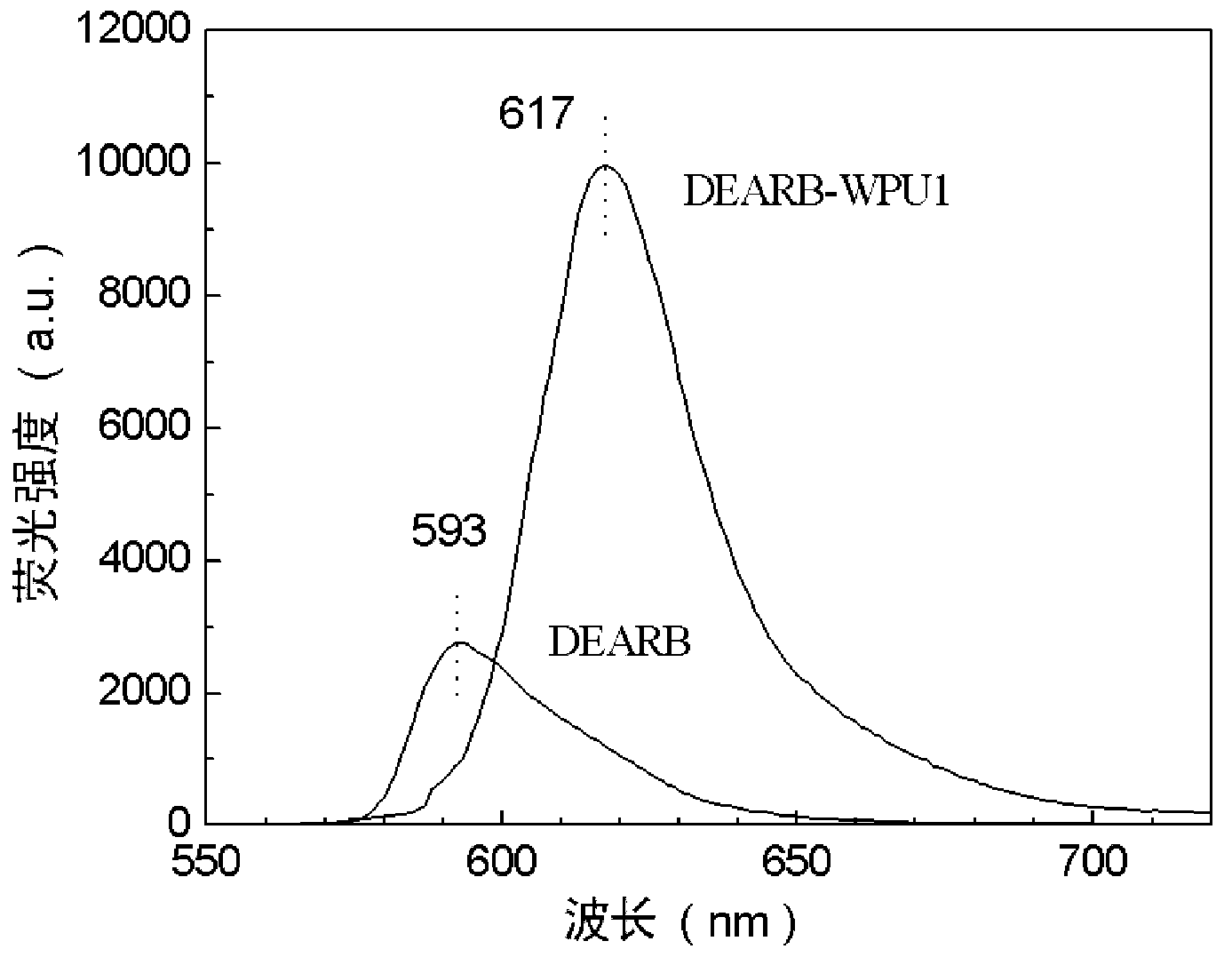
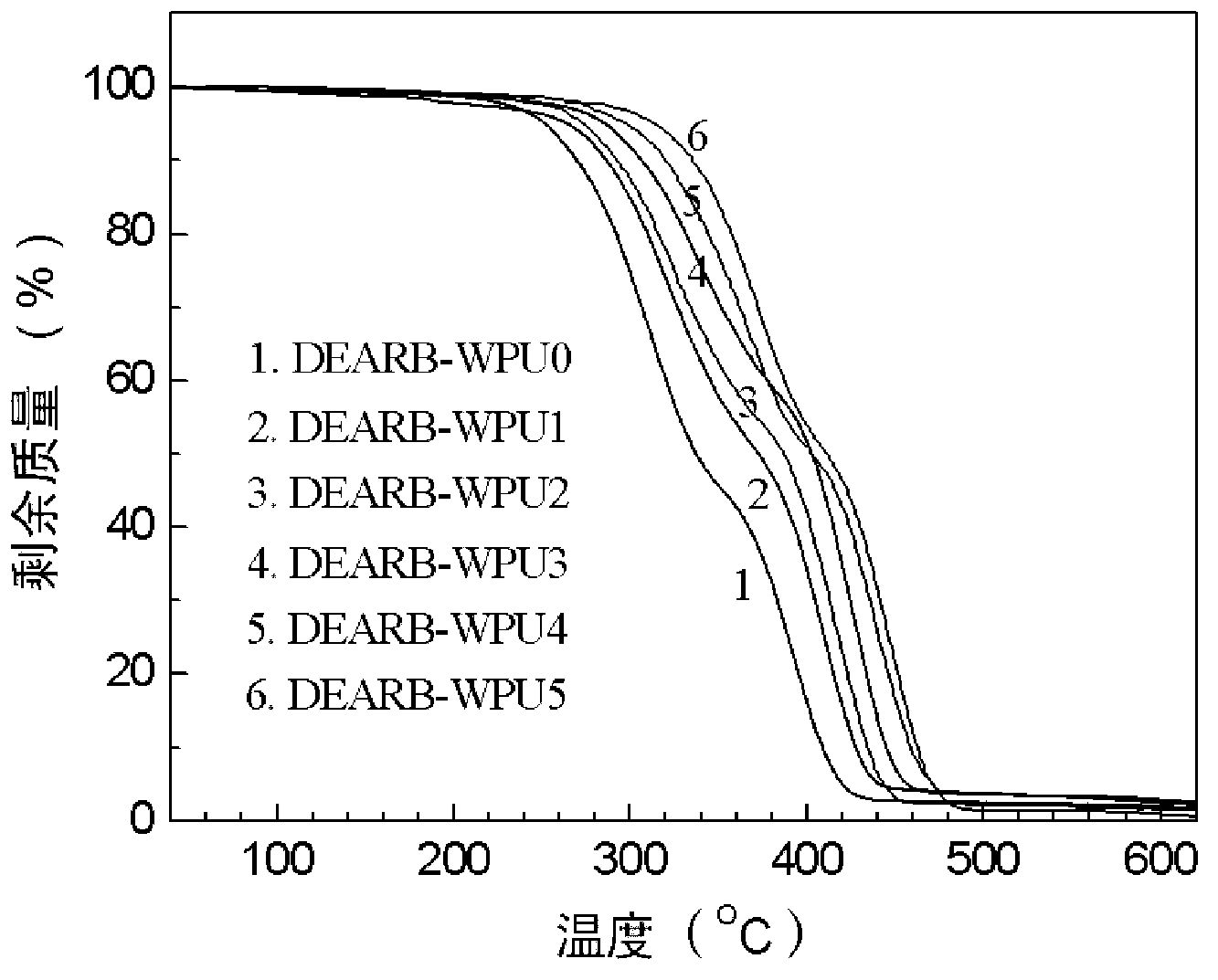
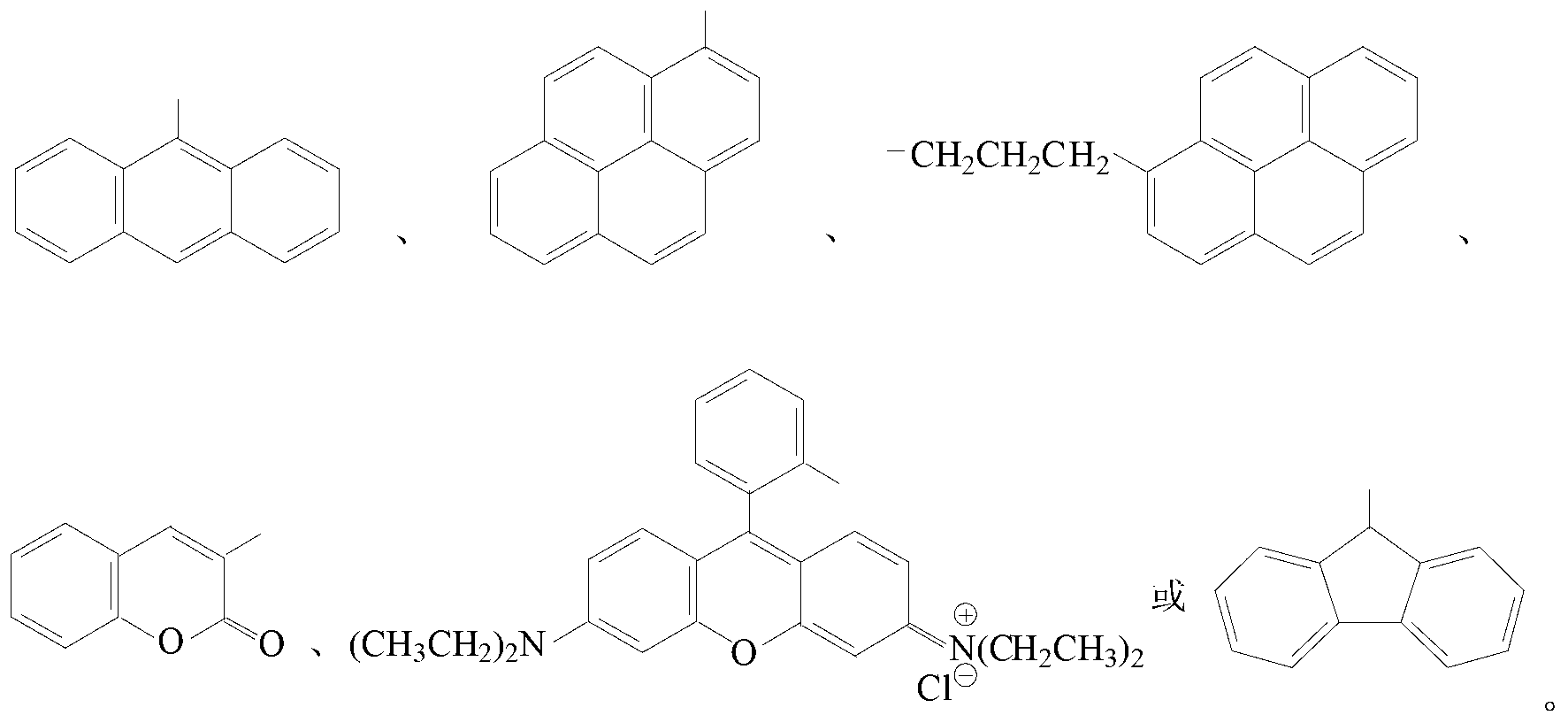
Fluorescent waterborne polyurethane based on chromophore in dihydric alcohol and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103254396AEvenly distributedNot easy to migrateLuminescent compositionsAlcoholOrganic solvent
The invention discloses fluorescent waterborne polyurethane based on chromophore in dihydric alcohol and a preparation method thereof. The fluorescent waterborne polyurethane is generated by utilizing the fluorescent dihydric alcohol containing the fluorescent chromophore to be reacted with diisocyanate and hydrophilic chain-extender. When the dihydric alcohol containing the fluorescent chromophore forms the fluorescent waterborne polyurethane latex, since the fluorescent chromophore is already chemically keyed into a polyurethane molecular chain, the fluorescent intensity is greatly enhanced, and a typical fluorescent enhanced effect can be displayed. The fluorescent chromophore is uniformly distributed in the polyurethane, the content is controllable, the chromophore is difficult to migrate, the fluorescence can be stored for a long time, the generated fluorescent waterborne polyurethane adopts the water as a solvent, so that safety in transportation and use can be realized, the environment is not polluted, only the low-boiling-point organic solvent such as acetone and butanone is used in the production process, and the solvent is easy to recover.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
Method for preparing nano silver and titanium dioxide thin films on surfaces of hollow glass beads
ActiveCN103007931AImprove photocatalytic activityHigh fluorescence intensityMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsChemical platingPhotocatalytic degradation
The invention discloses a method for preparing nano silver and titanium dioxide thin films on the surfaces of hollow glass beads, which comprises the following steps of: I, firstly coating a nano silver thin film on the surface of a hollow glass bead by using a chemical plating method; and II, then directly coating a layer of nano titanium dioxide thin film on the surface of the hollow glass bead coated with the nano silver thin film by using a hydrothermal method. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of raw material saving, simplicity and convenience in operation, good binding strength, higher photocatalytic activity and the like, and endows hollow glass beads with a photocatalytic degradation property for dyes and organic pollutants.
Owner:JIAXING HENENG TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com