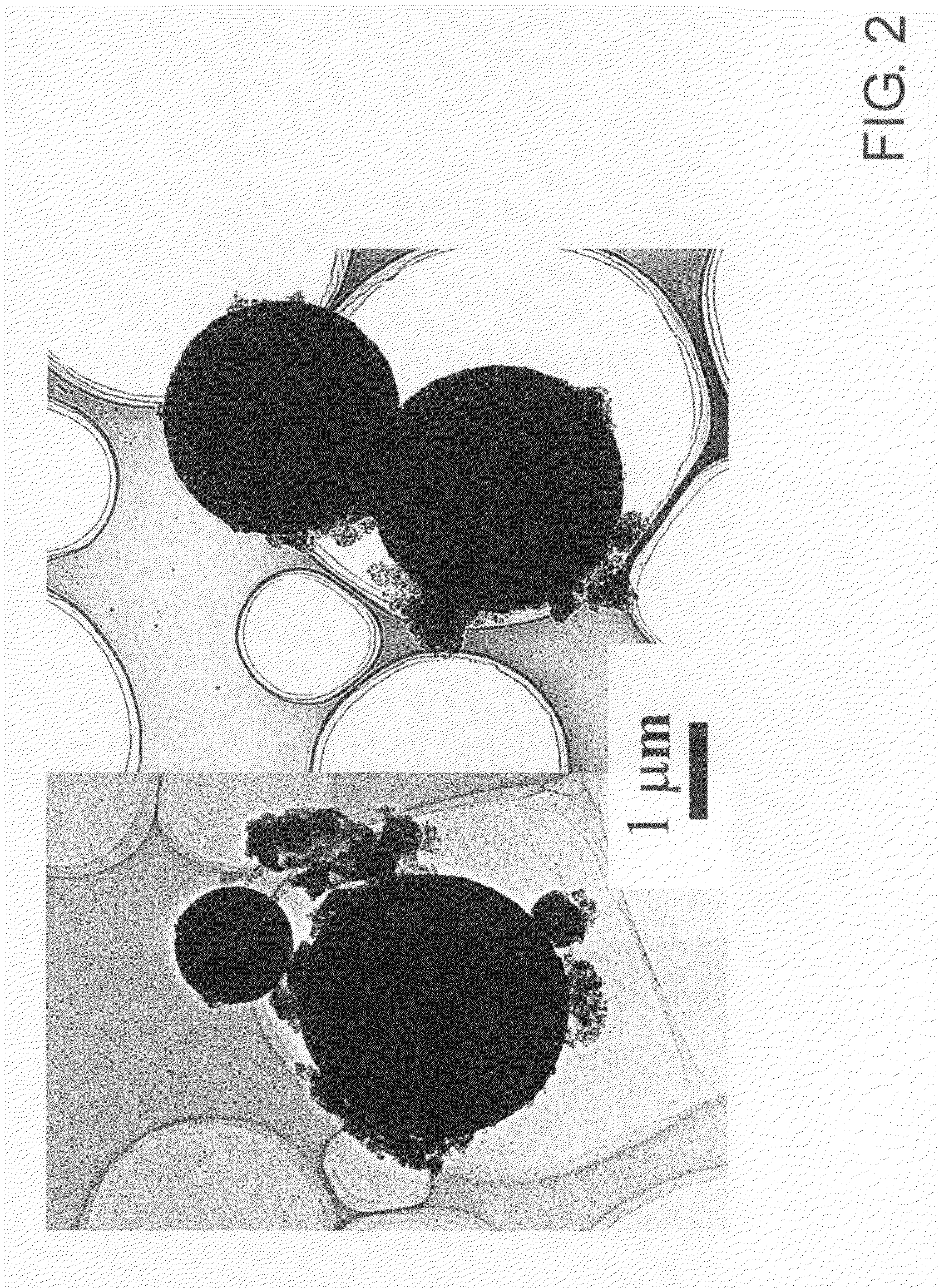
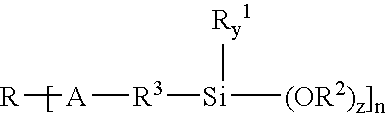
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
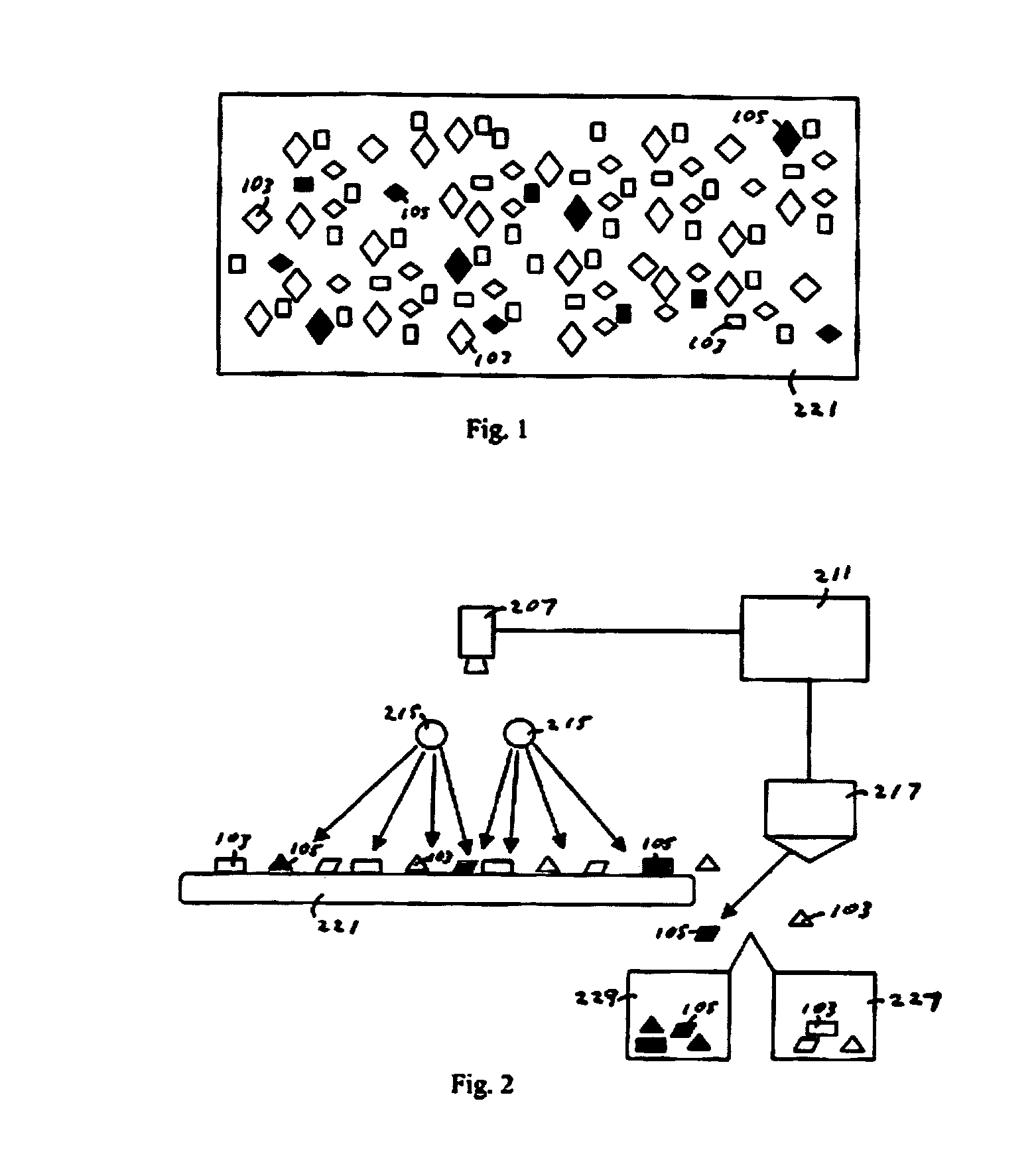
769 results about "Glass particle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
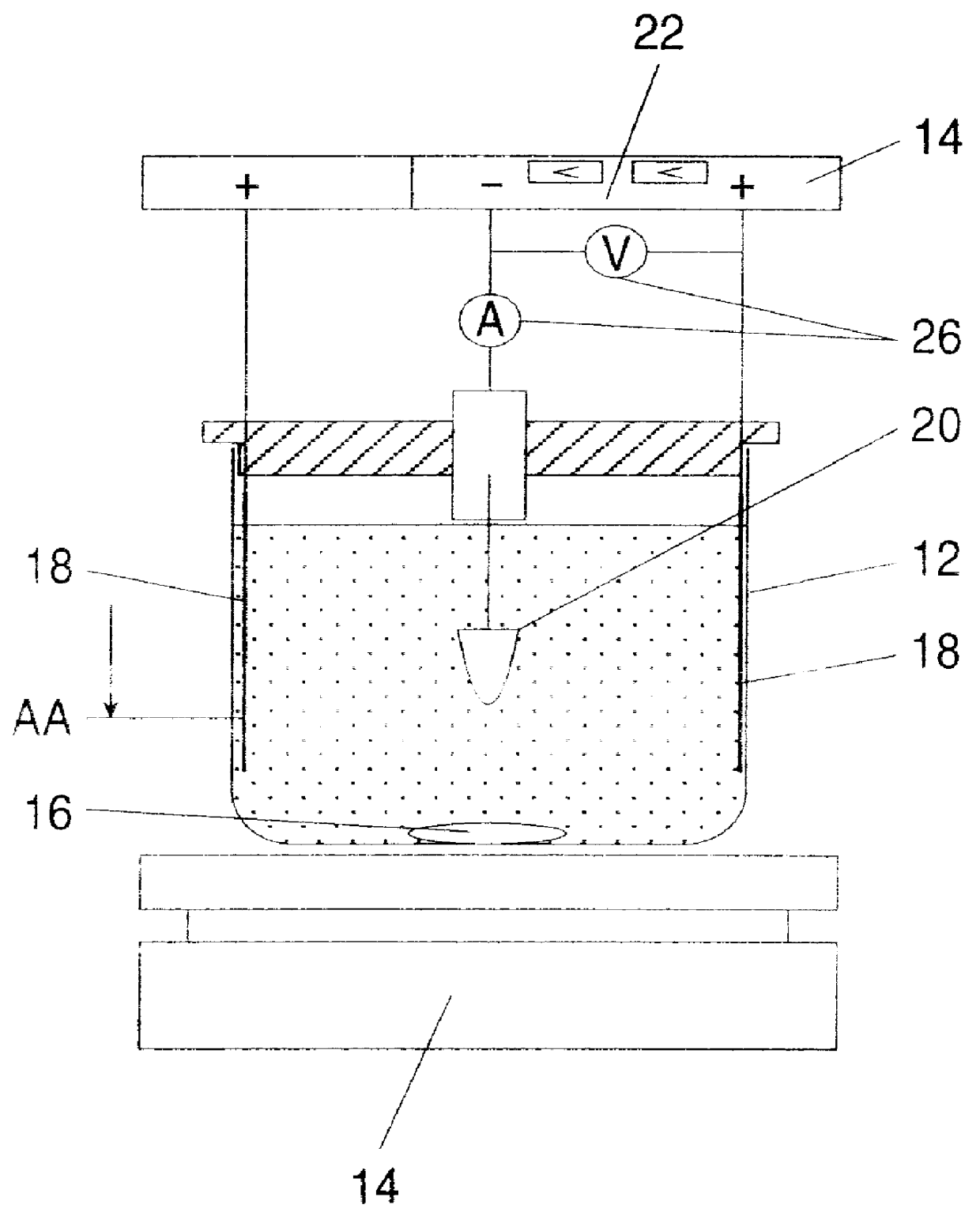
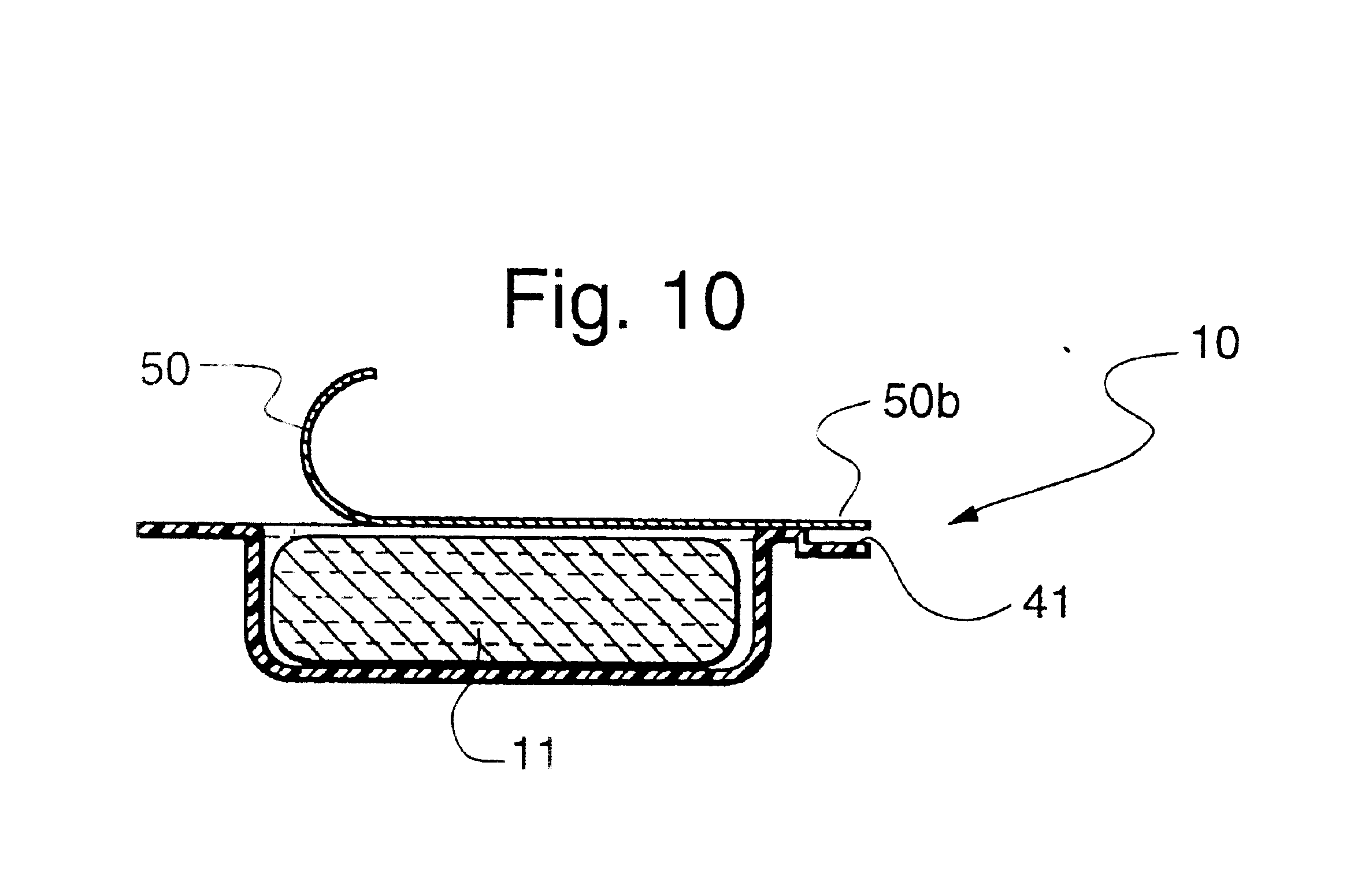
Method of electrophoretic deposition of ceramic bodies for use in manufacturing dental appliances
InactiveUS6059949AHigh strengthImprove toughnessElectrolysis componentsTeeth fillingMetallurgyElectrophoresis
A method for electrophoretic deposition of ceramic particles as a green body shaped as a dental appliance, the method comprising the steps of (a) forming a suspension of the ceramic particles in a first polar solvent, the ceramic particles constituting at least about 5% of the first suspension by weight; (b) passing a direct electrical current through the first suspension, using a deposition electrode shaped as the dental appliance to form a green body; (c) coating the green body with glass particles; and (d) sintering the resultant coated body for obtaining a glass coated all-ceramic dental appliance.
Owner:CEREL CERAMIC TECH
Paste composition for electrode and photovoltaic cell
InactiveUS20110209751A1Prevent oxidationLow resistivityConductive materialNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialMetal particleGlass particle
The paste composition for an electrode according to the present invention includes metal particles containing copper as a main component, a flux, glass particles, a solvent, and a resin. Further, a photovoltaic cell according to the present invention has an electrode formed by using the paste composition for an electrode.
Owner:HITACHI CHEM CO LTD
Paste composition for electrode and photovoltaic cell
InactiveUS20110180137A1Low resistivityPrevent oxidationConductive materialNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialGlass particleMetal particle
Owner:HITACHI CHEM CO LTD
Hot melt conductor paste composition
InactiveUS6814795B2Freeze fastHigh densitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsConductive materialScreen printingWire gauze
The present invention provides a hot melt conductor paste composition that includes conductive particles and glass particles dispersed in a thermoplastic polymer system. The hot melt conductor paste composition according to the invention is a solid at room temperature, but melts at a temperature of from about 35.degree. C. to about 90.degree. C. to form a flowable liquid that can be applied to a silicon substrate by screen printing. The hot melt conductor paste composition is particularly suitable for use in the fabrication of photovoltaic cells.
Owner:HERAEUS PRECIOUS METALS NORTH AMERICA CONSHOHOCKEN
Electroconductive thick film composition, electrode, and solar cell formed therefrom
InactiveUS20060231802A1Conductive materialNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialGlass particleSolar cell
The electroconductive thick film paste of the present invention is a silver electroconductive paste, which includes silver particles, glass particles, and an organic vehicle, and is used in an electrode for connecting a back face terminal on the silicon substrate of a solar cell, and is characterized by the fact that the average particle diameter of said silver particles is 3.0-15.0 μm. The present invention is further directed to an electrode formed from the composition as detailed above and a solar cell comprising said electrode.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Dental composite restorative material and method of restroring a tooth
InactiveUS20030060532A1Highly packableCosmetic preparationsImpression capsMicrometerDental composite
A dental composite material includes a hardenable resin matrix and a filler component. The filler component includes (a) a first plurality of preferably glass particles having an average particle size of from about 1 to about 10 micrometers; (b) a second plurality of preferably glass particles having an average particle size of from about 0.1 to about 1 micrometers; and, (c) a plurality of filler particles having an average particle size of from about 0.01 to about 0.04 micrometers. A method according to the invention includes compacting a dental composite material into a prepared tooth cavity, wherein the material has a packability index above about 300 g / mm2.
Owner:DENTSPLY RES DEVMENT
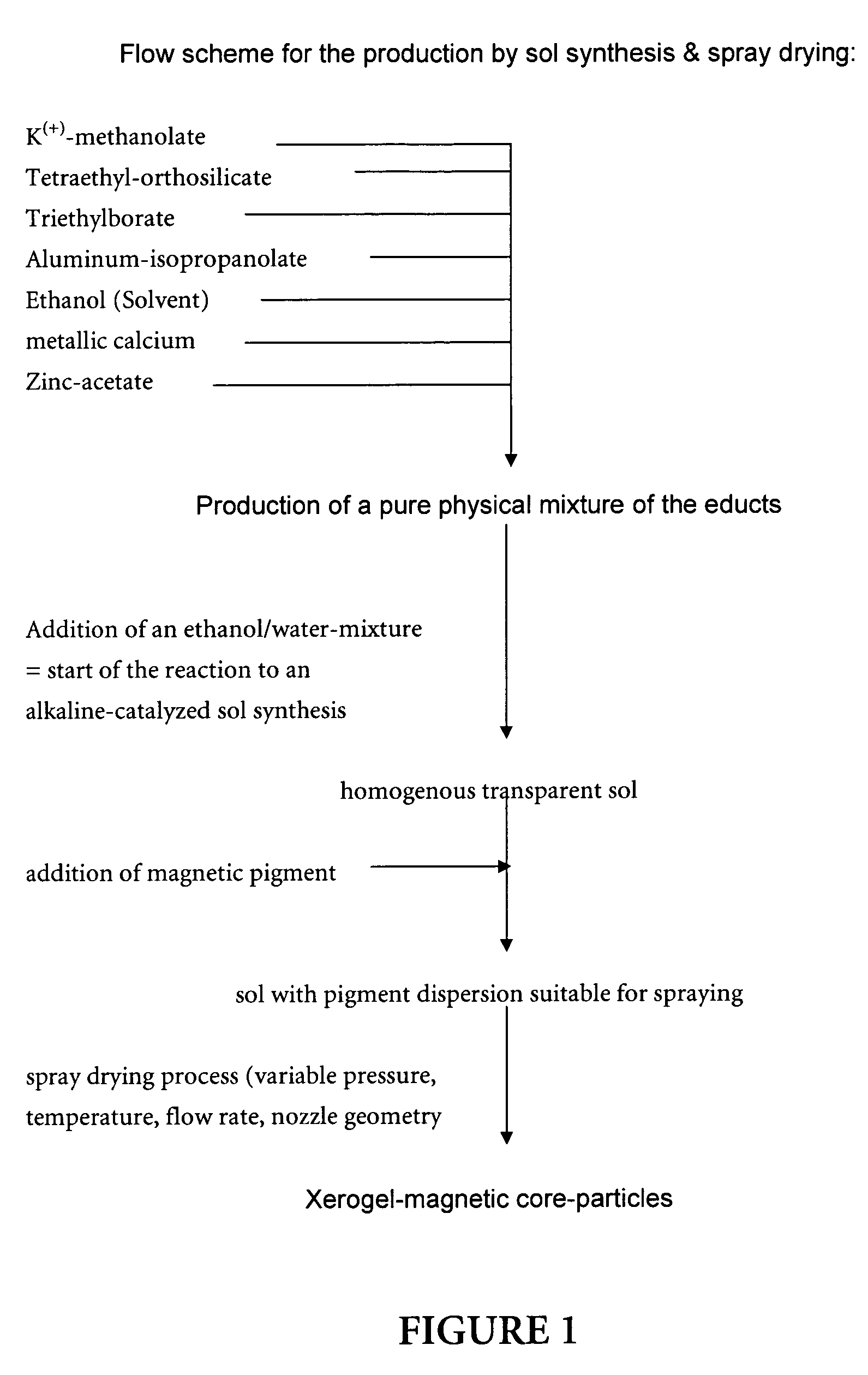
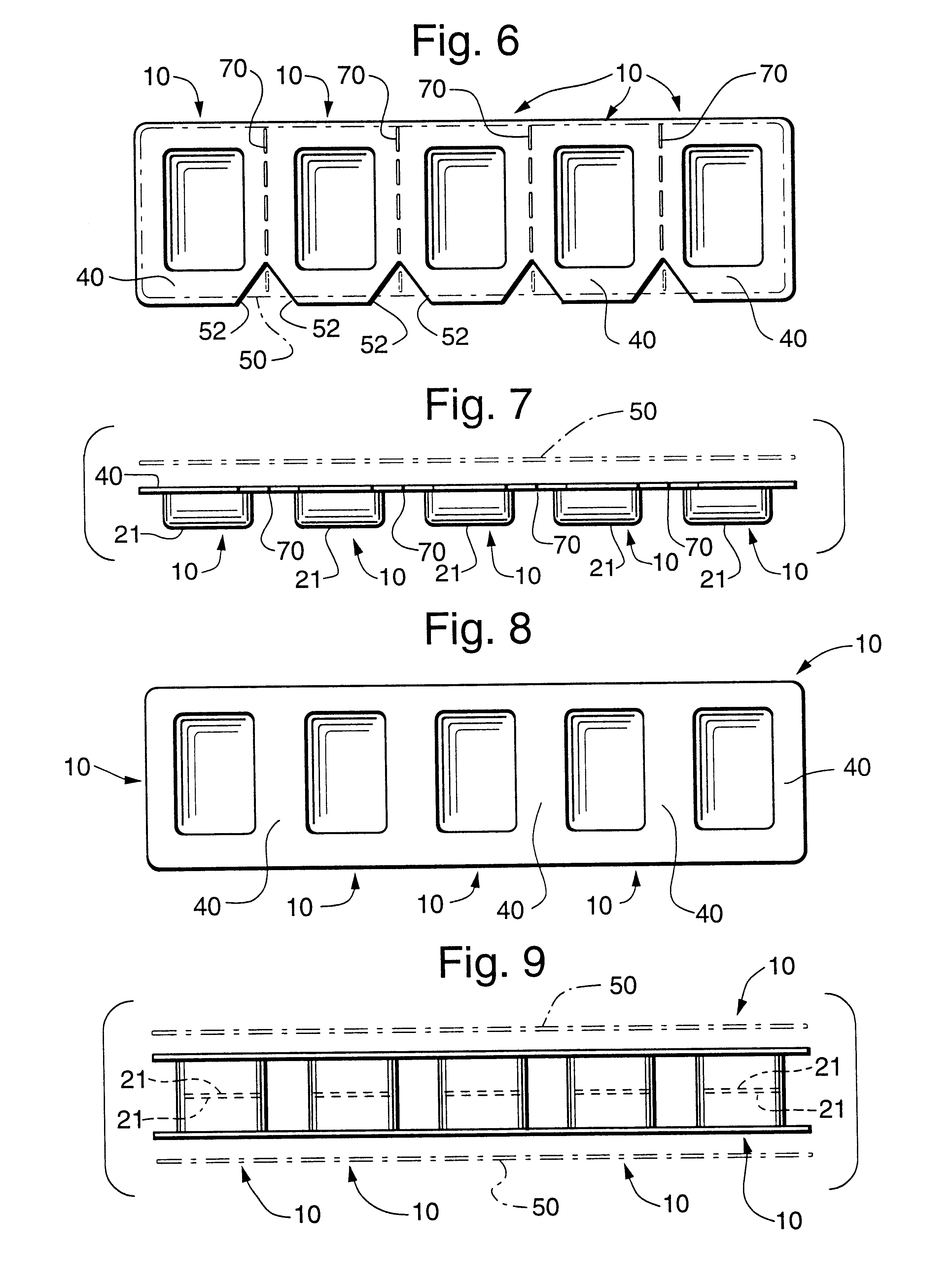
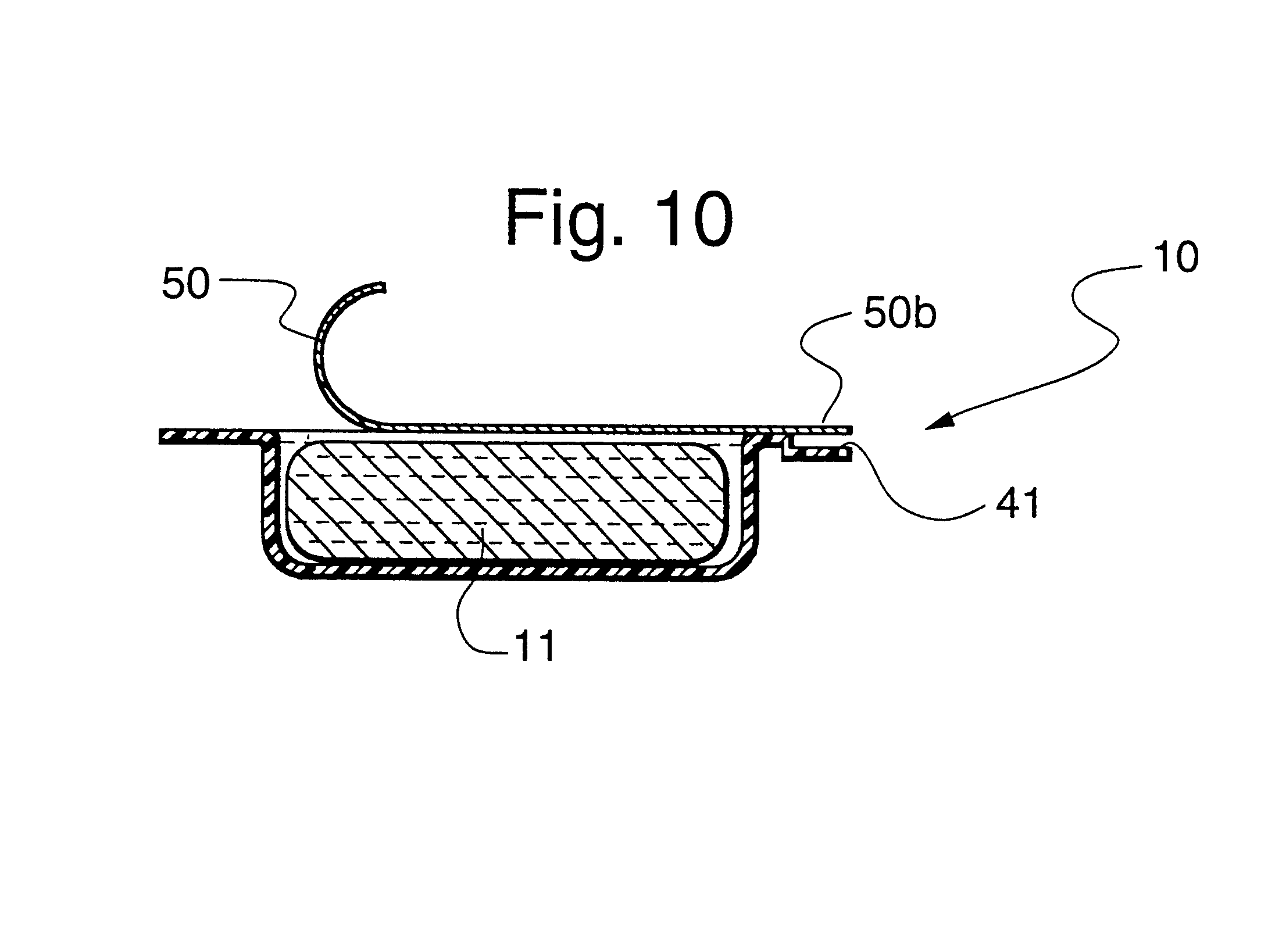
Magnetic glass particles, method for their preparation and uses thereof
InactiveUS8129118B2Promote resultsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanomagnetismGlass particleCombinatorial chemistry
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
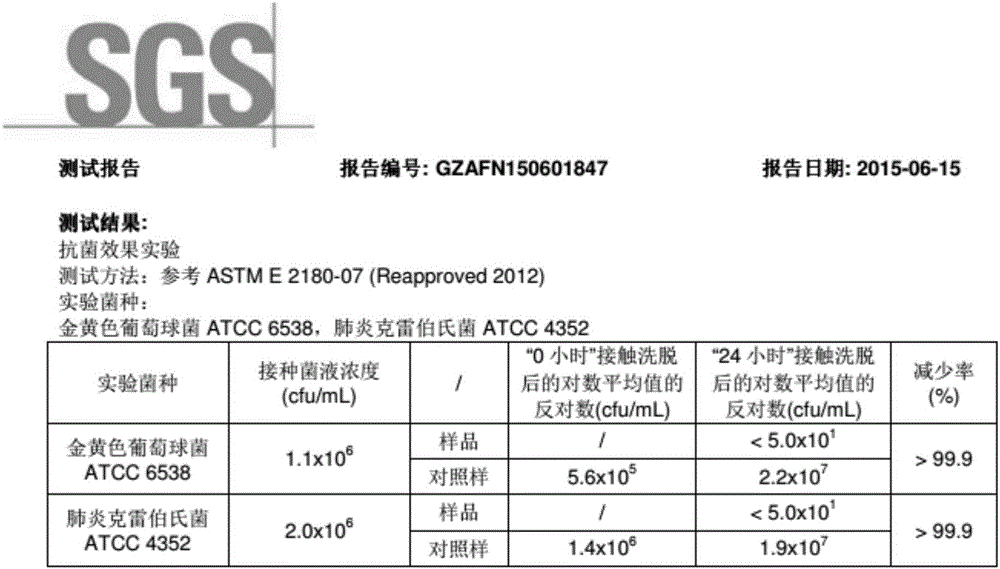
Anti-bacterial artificial quartzite board and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an anti-bacterial artificial quartzite board. The anti-bacterial artificial quartzite board is prepared from 55-65% of particulate raw materials with the diameter ranging from 0.075 mm to 5 mm, 20-30% of quartz powder with the diameter ranging from 0.005 mm to 0.045 mm, 0.01-10% of colored pigment, 0.1-1% of a silane coupling agent, 8-14% of unsaturated polyester resin, 0.8-1.4% of a curing agent and 0.01-0.1% of an anti-bacterial agent, wherein the particulate raw materials are quartz particles or glass particles or a mixture of quartz particles and glass particles. Anti-bacterial performance of the anti-bacterial artificial quartzite board reaches 99.9% or above, and basically no bacterium exists.
Owner:GUANGDONG BANNER NEW MATERIAL TECH
Scraped glass smashing device
The invention discloses a scraped glass smashing device which comprises a vibration breaking device which comprises a vibration hammer, a vibration generator and a breaking platform. The vibration generator is used for driving the vibration hammer to vibrate up and down, and the breaking platform is arranged below the vibration hammer and used for bearing scraped glass. Glass substrates are smashed through up and down vibration of the vibration hammer of the vibration breaking device, and scraped glass substrates with larger size are quickly decomposed into small broken glass particles for convenience for transport and subsequent treatment; in addition, the vibration hammer of the vibration smashing device during vibration enables the glass substrates to generate multiple cracks to be smashed into multiple blocks, efficiency is greatly improved when compared with the cutting mode, the vibration hammer can smash the glass substrates into smaller fragments, but more time is needed to obtain fragments identical in size by means of cutting; and moreover, the scraped glass smashing device is free of manual direct operation, only the vibration is needed to operate for vibration, so that safety is also greatly improved.
Owner:TCL CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
High-impact toughness man-made quartzite slab and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a high-impact toughness man-made quartzite slab and a preparation method thereof. The man-made quartzite slab comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 58-75 percent of particle raw materials, 15-33 percent of quartz powder, 0.01-10 percent of paint, 0.1-1 percent of coupling agent, 8-12 percent of adhesive and 0.8-2 percent of curing agent, wherein the particle raw materials are quartz particles, glass particles, or a mixture of the two. The man-made quartzite slab provided by the invention has the characteristics of low probability of cracking and deformation, and the like.
Owner:GUANGDONG BANNER NEW MATERIAL TECH
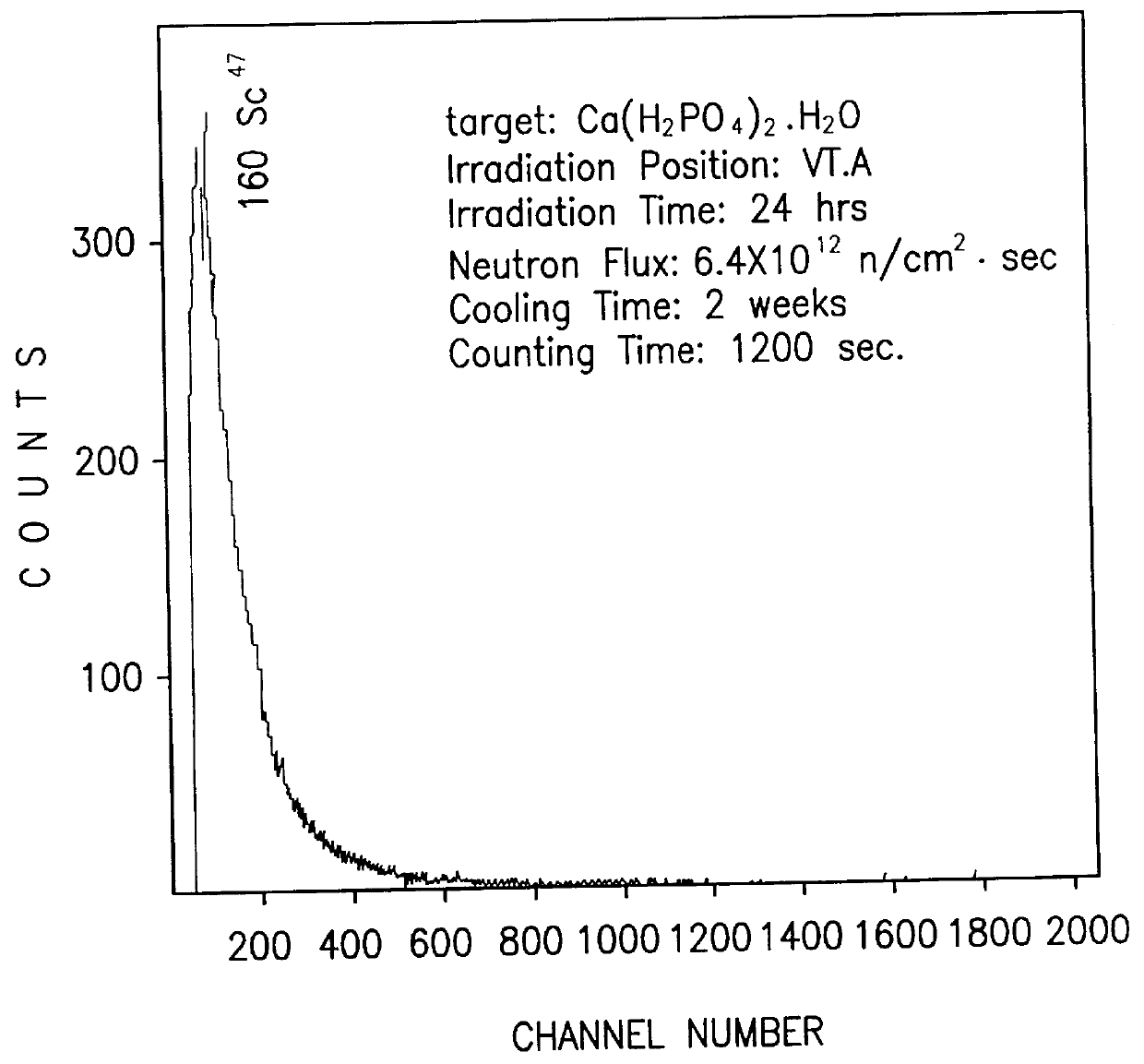
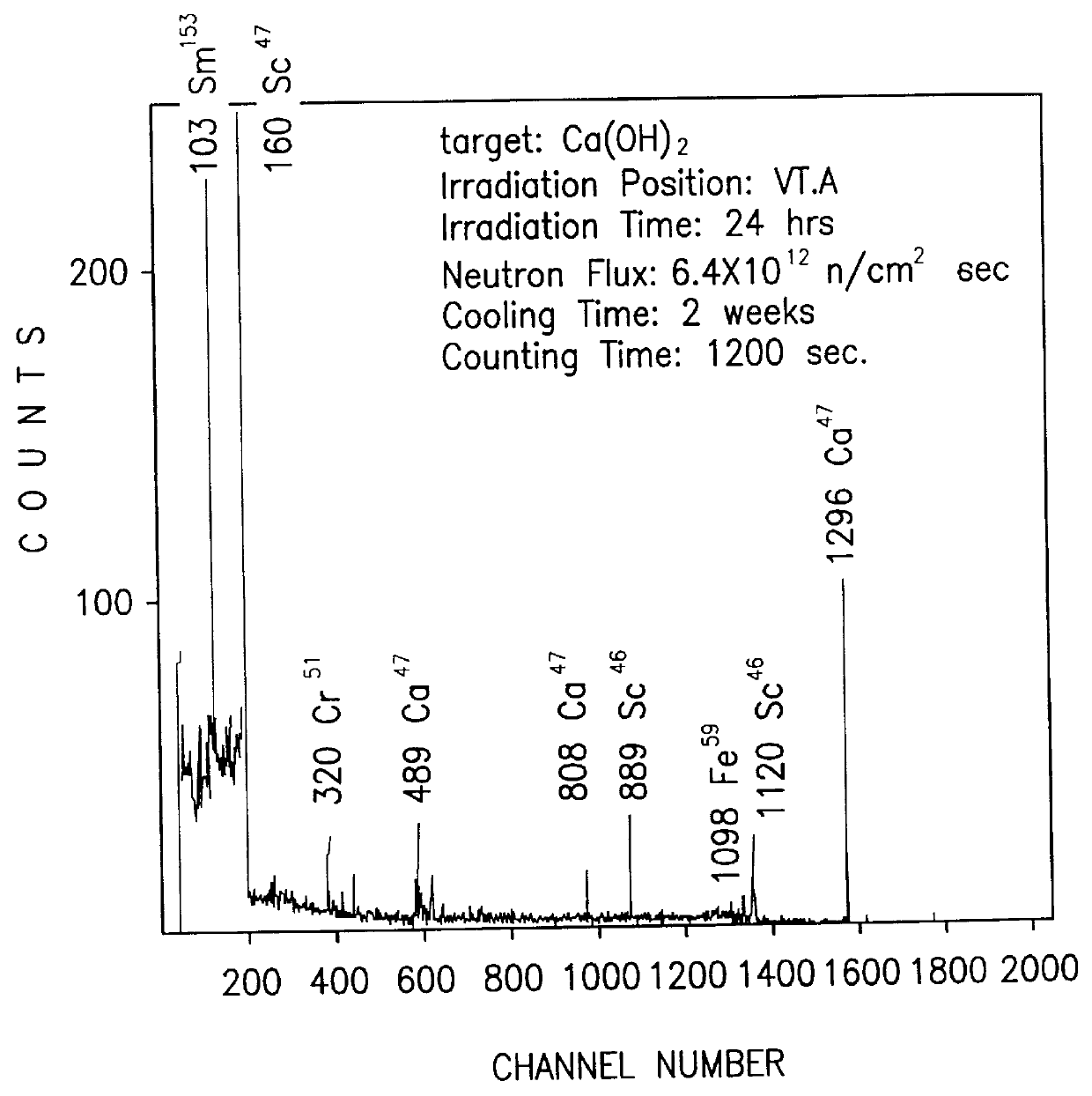
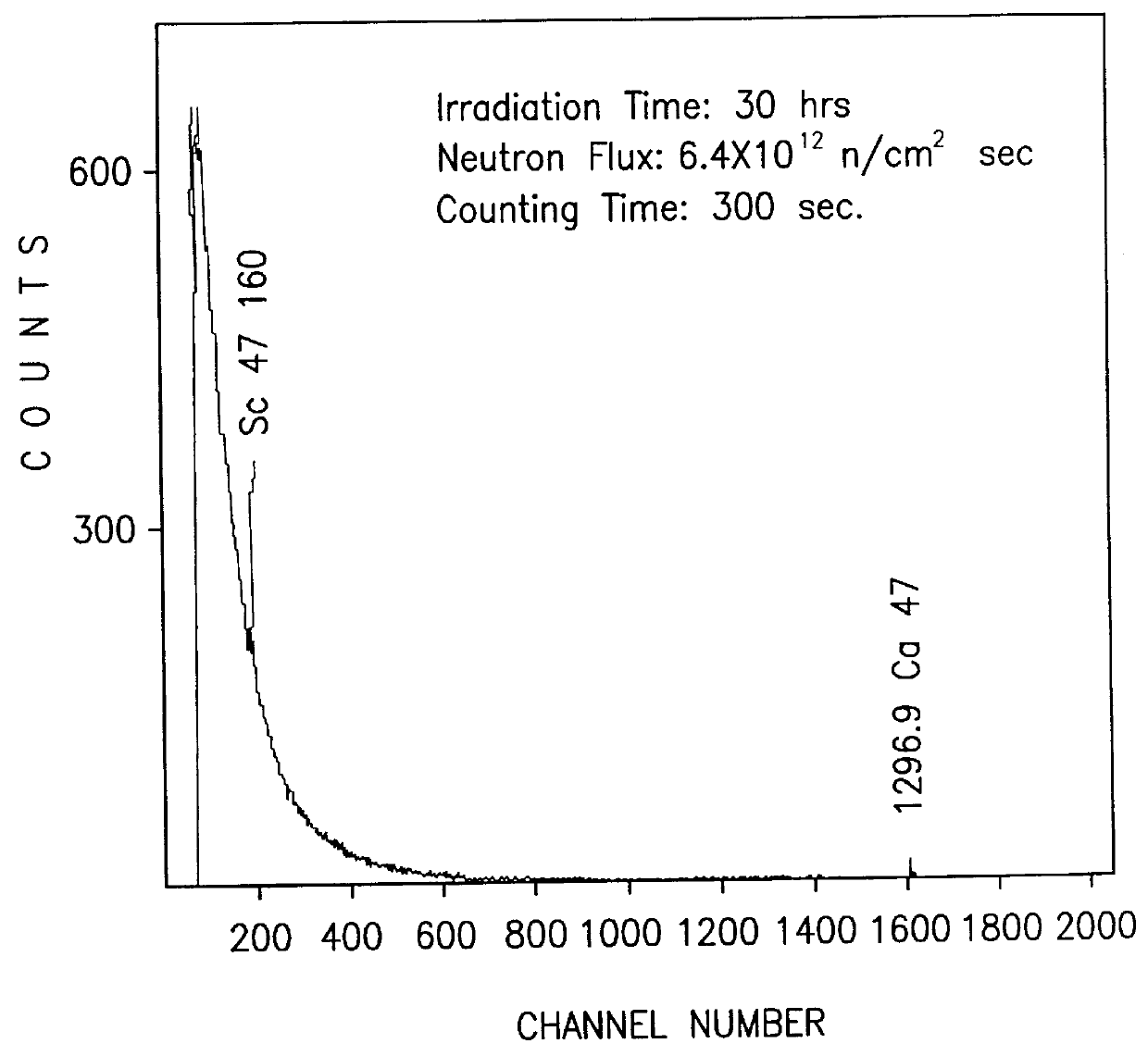
Radioactive particles and methods for preparing same
InactiveUS6149889AMinimizing damageLong lastingPowder deliveryRadioactive preparation carriersGlass particleRadioactive decay
A nuclear medical drug for localize radiotheraphy of a tumor and methods for its preparation. The drug includes a radioactive ceramic or glass particle having biocompatiblity. Ceramic or glass particles prepared by traditional processes become radioactive particles with pure beta -particle-emitting radionuclides after being irradiated with an appropriate flux of neutrons. The radioactive particle with suitable particle size can then be dispersed into a contrast medium for injection or can be implanted by operation.
Owner:DEPT OF HEALTH THE EXECUTIVE YUAN REPUBLIC OF CHINA
Dental composite restorative material and method of restoring a tooth
InactiveUS6353040B1Highly packableCosmetic preparationsImpression capsRestorative materialDental composite
A dental composite material includes a hardenable resin matrix and a filler component. The filler component includes (a) a first plurality of preferably glass particles having an average particle size of from about 1 to about 10 micrometers; (b) a second plurality of preferably glass particles having an average particle size of from about 0.1 to about 1 micrometers; and, (c) a plurality of filler particles having an average particle size of from about 0.01 to about 0.04 micrometers. A method according to the invention includes compacting a dental composite material into a prepared tooth cavity, wherein the material has a packability index above about 300 g / mm2.
Owner:DENTSPLY RES DEVMENT
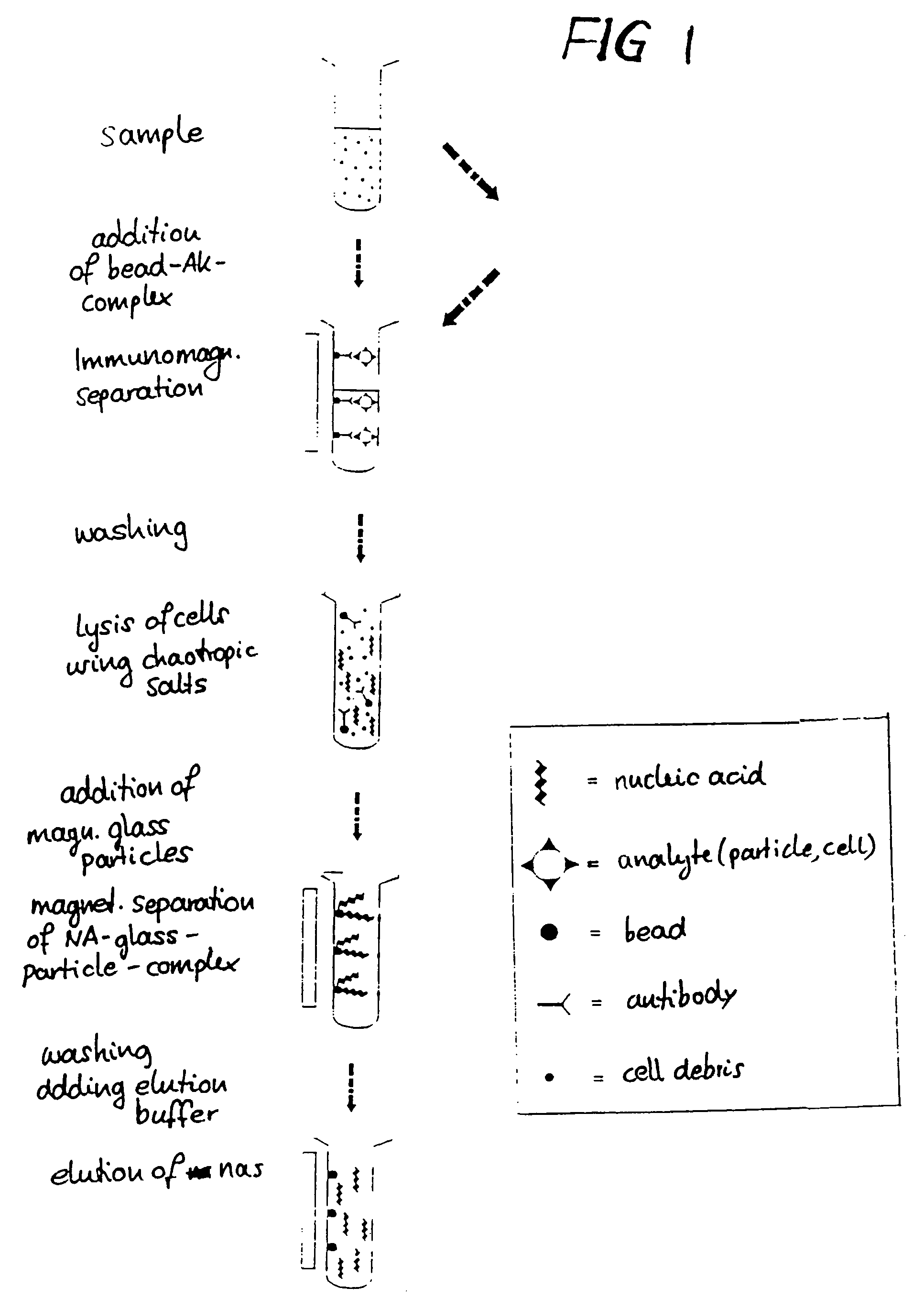
Method for separating biological material from a fluid using magnetic particles
InactiveUS7371830B2Simple procedureSimple materialImmobilised enzymesMicroorganism separationAlcoholMagnetite
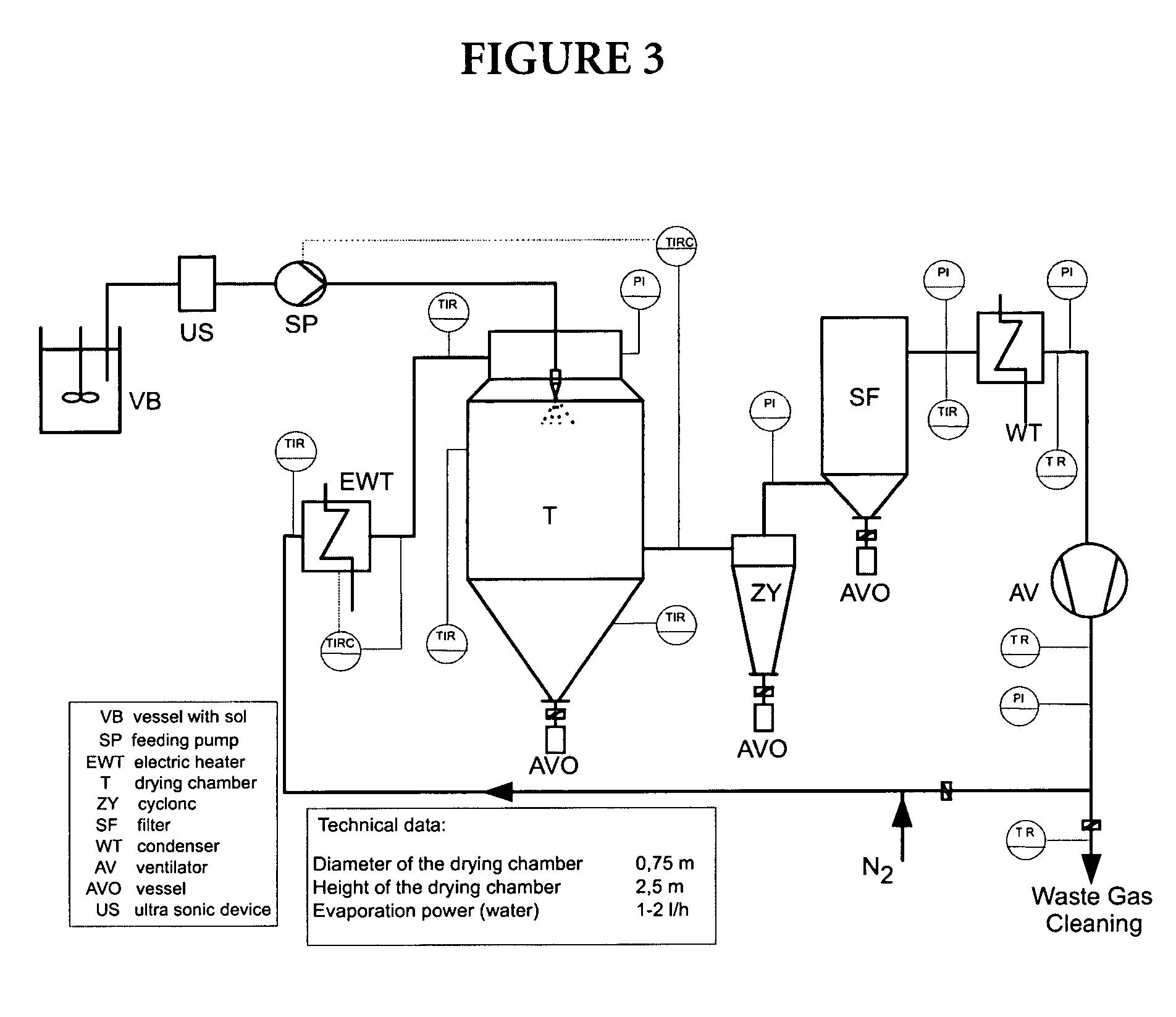
Magnetic particles are prepared containing a magnetic core coated with a glass layer having a substantially pore-free glass surface or having pores with a diameter of less than 10 nm. The particles are used for separating biological material such as nucleic acids. A preferred process of preparing the particles is by forming a mixture of magnetic cores with a sol formed from an alcohol and a metal alkoxide, spray-drying the mixture to coat the cores with a layer of gelled sol, and heating the coated cores to obtain the magnetic glass particles. Preferably, the particles have an average particle size of less than 100 μm. The magnetic core may be a composite material containing a mica core and magnetite particles immobilized on the mica core, and the glass layer may contain boron oxide. Magnetic core materials include magnetite (Fe3O4) and Fe2O3.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
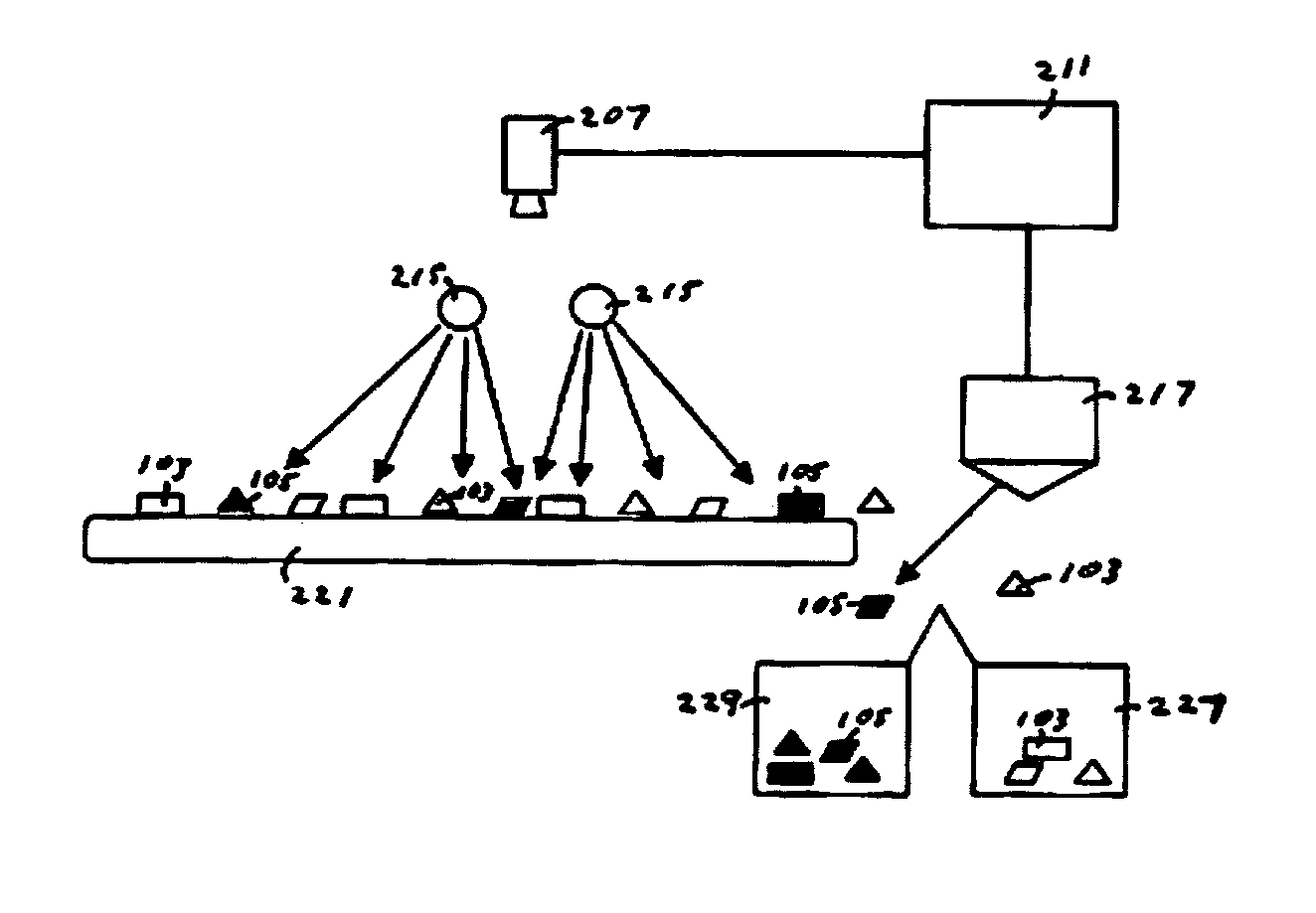
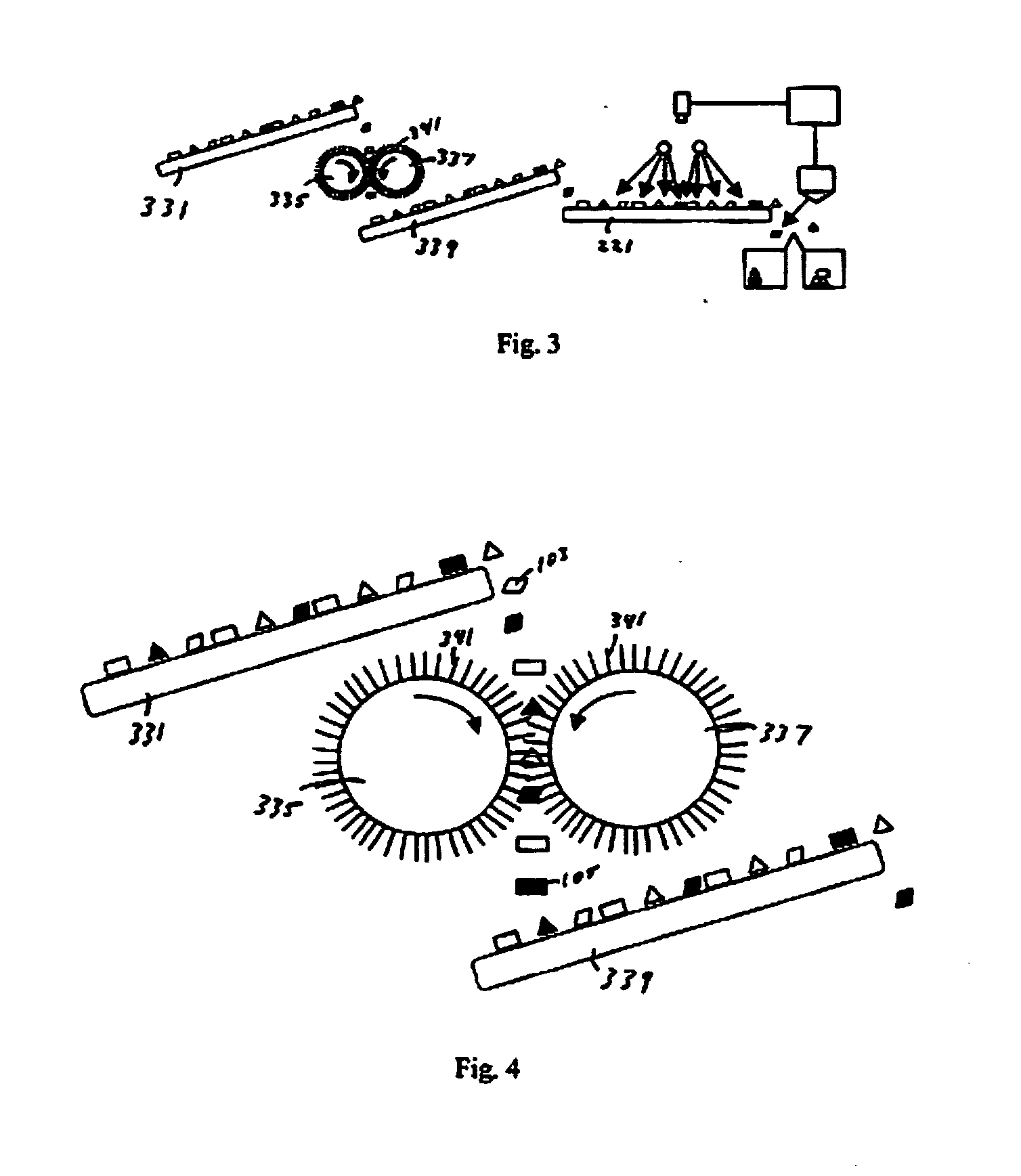
Method and apparatus for sorting contaminated glass
A method, apparatus and system for sorting contaminated glass from a stream of glass particles used light of a wavelength suited to inducing fluorescence in the contaminated glass pieces. Automatic cleaning mechanisms are included in some embodiments to facilitate removal of coatings which would prevent the contaminated particles from fluorescing. The identified particles are then automatically separated from the remaining particles.
Owner:MTD AMERICA
Semiconductor-Nanoparticle-Dispersed Small Glass Particles and Process for Preparing the same
InactiveUS20090108235A1Improve long-term stabilityHigh fluorescence intensityRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationQuantum yieldGlass particle
The present invention provides semiconductor-nanoparticle-dispersed small silica glass particles that emit bright fluorescent light with high fluorescence quantum yield and high density, compared to the conventional semiconductor-nanoparticle-dispersed small glass particles, and that have excellent fluorescence intensity stability over time; and a process for preparing the same. The semiconductor-nanoparticle-dispersed silica glass particles have a mean particle size of not less than 10 nanometers and not more than 5 micrometers, and contain a hydrolyzed alkoxide and semiconductor nanoparticles at a concentration of not less than 2×10−5 mol / l and not more than 1×10−2 mol / l. The particles emit fluorescent light with a fluorescence quantum yield (quantum yield) of 25% or more (and 60% or more), when dispersed in a solution.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Furnace for heating particles
InactiveUS20070275335A1Reduce heat lossEnergy efficiencyBurnersGlass shaping apparatusCombustorMicrosphere
A bottom-up cocurrent combustion furnace for the production of synthetic microspheres by thermal expansion of glass particles is provided having improved characteristics with regard to anti-fouling, process efficiency, and yield. The disclosed furnace uses preheated combustion air to preheat the feed material and to convey the feed material in a dilute phase transport regime to a burner. The combustion air, fuel, and feed material are premixed prior to being injected though the burner. The feed material rapidly expands as it is ejected through the burner and through a flame and then rapidly cools to solidify the microspheres. Additional features are provided to prevent the furnace from fouling by keeping the feed material away from the furnace walls, removing feed material that adheres to the furnace walls, and collecting feed material that agglomerates or does not expand.
Owner:JAMES HARDIE INT FINANCE BV
Adhesives, sealants and coatings containing glass particles as a filler
InactiveUS20080287574A1Improve technical effectNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesSpecial tyresAdhesiveGlass particle
The invention relates to chemically or physically curable compositions suitable as adhesives or sealants or coating materials, which compositions contain at least one binding agent selected from the group comprising crosslinkable or polymerizable monomers, prepolymers, or polymers, as well as at least one filler. The filler proportion is 0.2 to 70 wt % based on the total weight of the compositions, and at least a portion of the filler is made up of glass particles having a particle size from 100 nm to 20 μm, which have been obtained by comminuting foamed neutral or acid glass.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
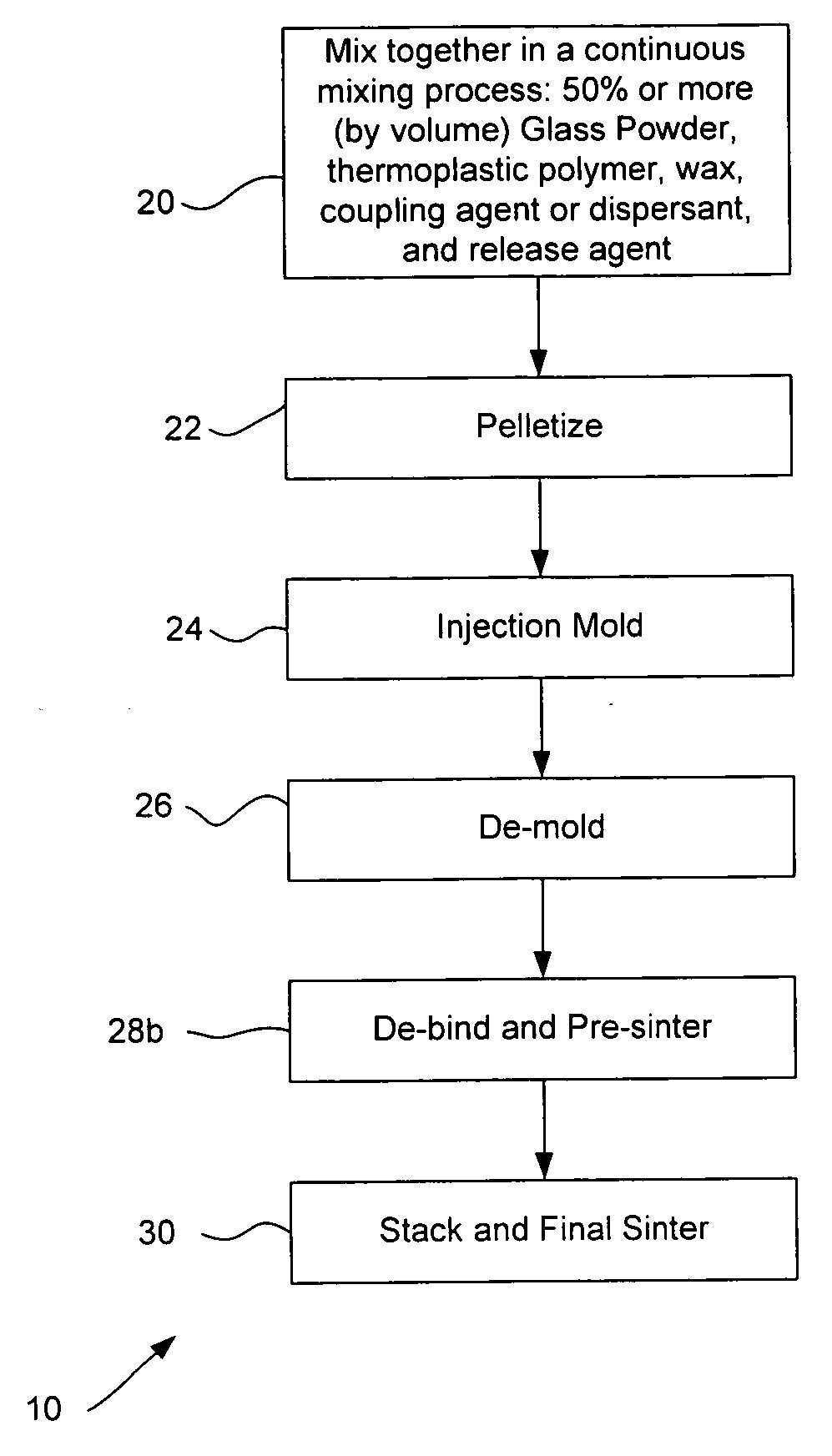
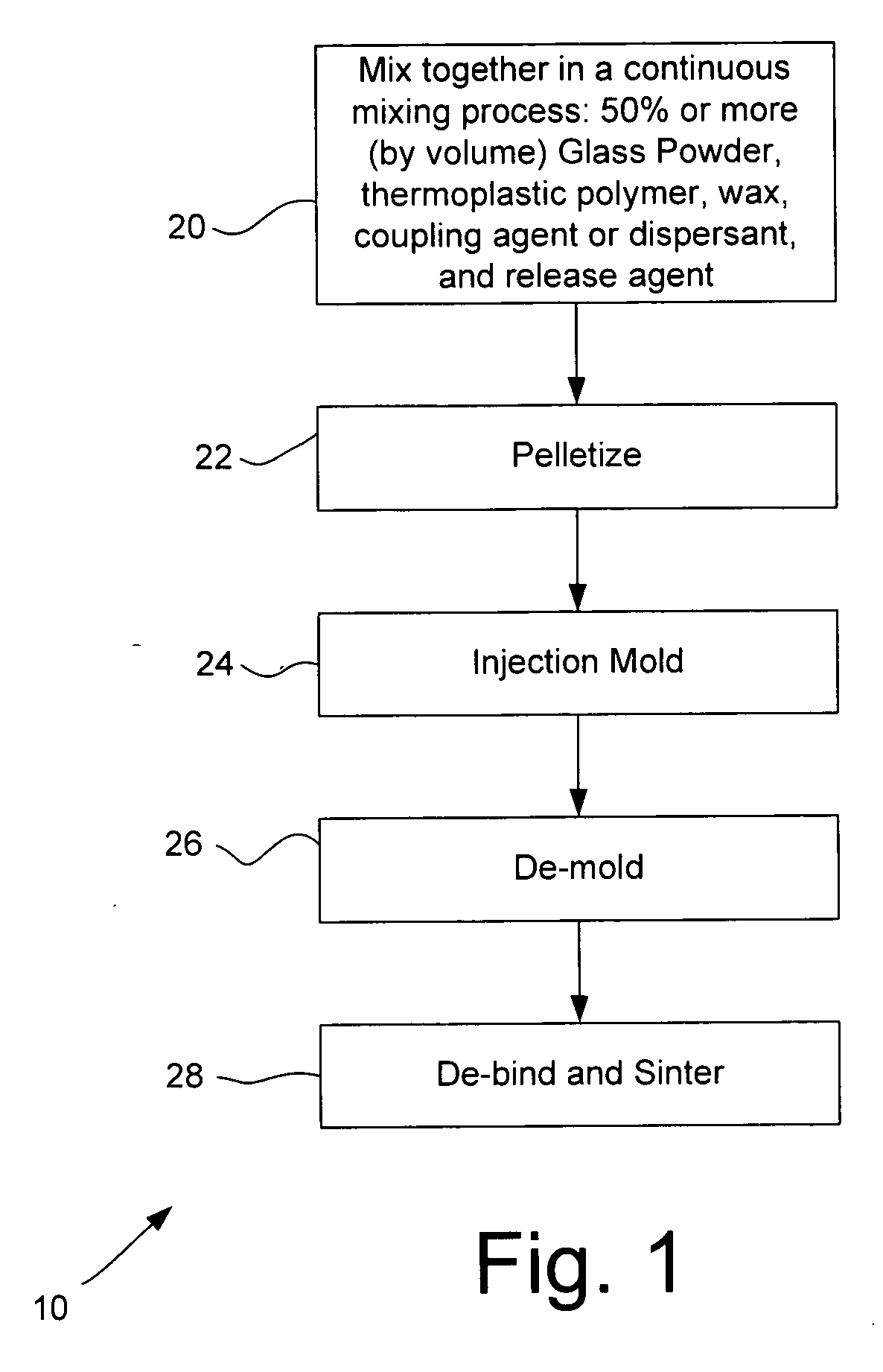
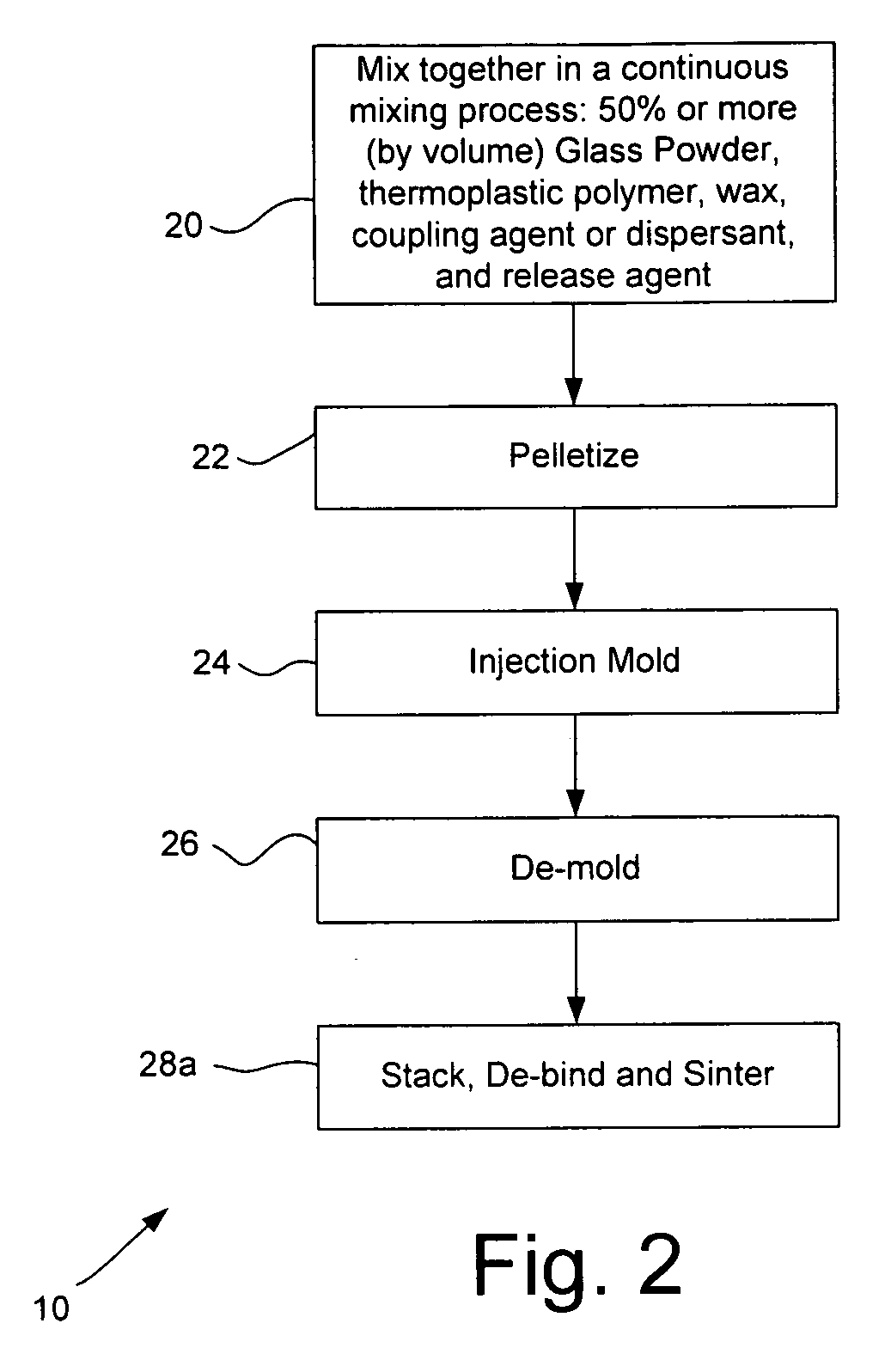
Powder injection molding of glass and glass-ceramics
InactiveUS20070154666A1Good shape retentionImprove surface propertiesLayered productsGlass shaping apparatusMetallurgyAdditive ingredient
A method for producing glass or glass ceramic articles by powder injection molding of glass powder includes mixing together, in a continuous mixing process, ingredients to form a mixture comprising a glass powder and a binder, where the ingredients include a glass powder in a relative amount sufficient to equal at least 50% by volume of the resulting mixture and a binder comprising a thermoplastic polymer, desirably a thermoplastic elastomer, and a wax; forming the mixture into a formed structure; and de-binding and sintering the formed structure. The method desirably involves mixing via a high intensity mixing process, desirably by mixing in a twin-screw extruder. The forming process may include pelletizing the mixture and injection molding the pelletized mixture to form the formed structure. The ingredients of the mixture desirably comprise a glass powder in a relative amount sufficient to equal at least 70% by volume of the resulting mixture. The glass powder desirably includes at least some glass particles having irregular shapes.
Owner:CORNING INC
Antimicrobial glass and glass ceramic surfaces
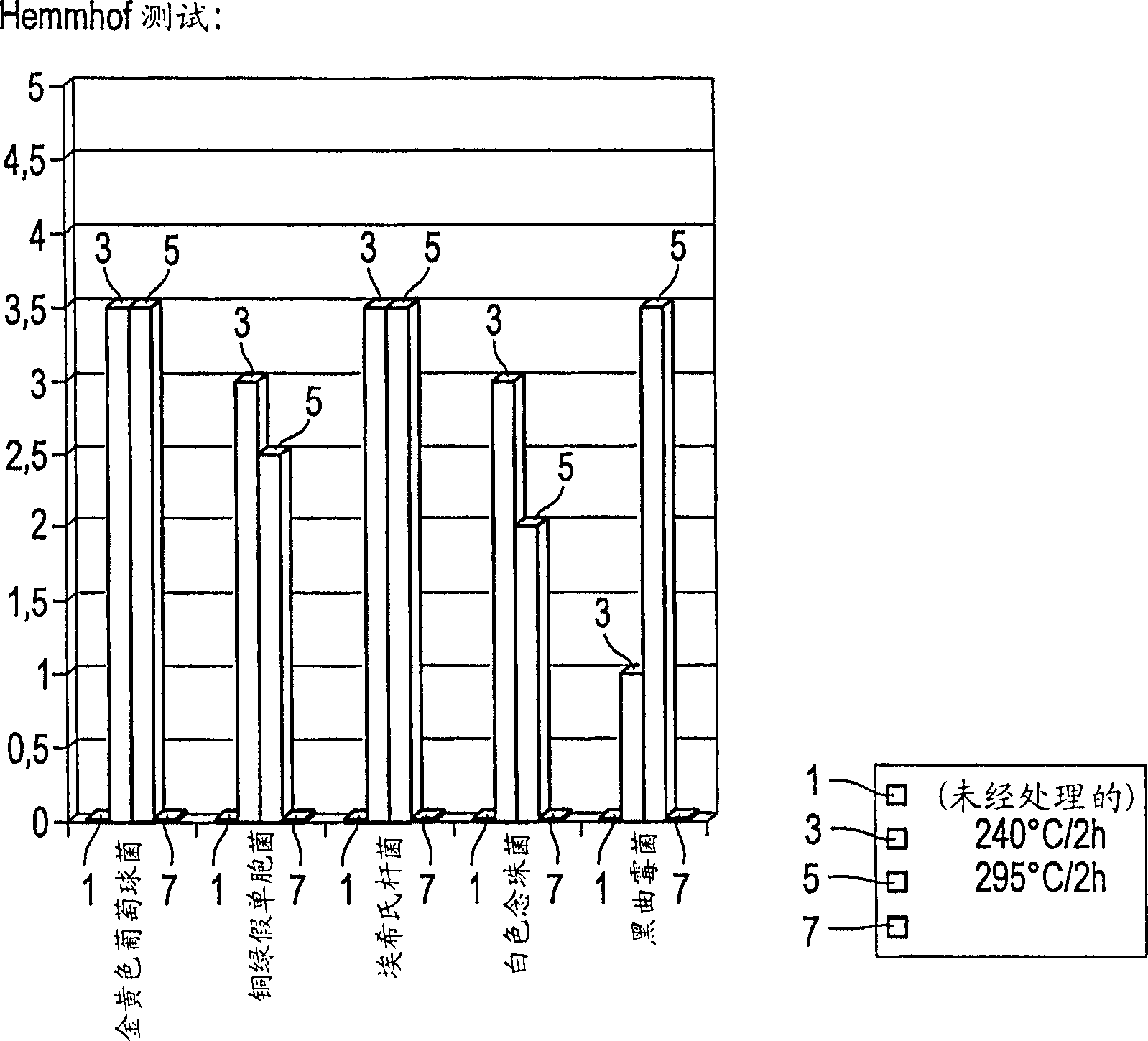
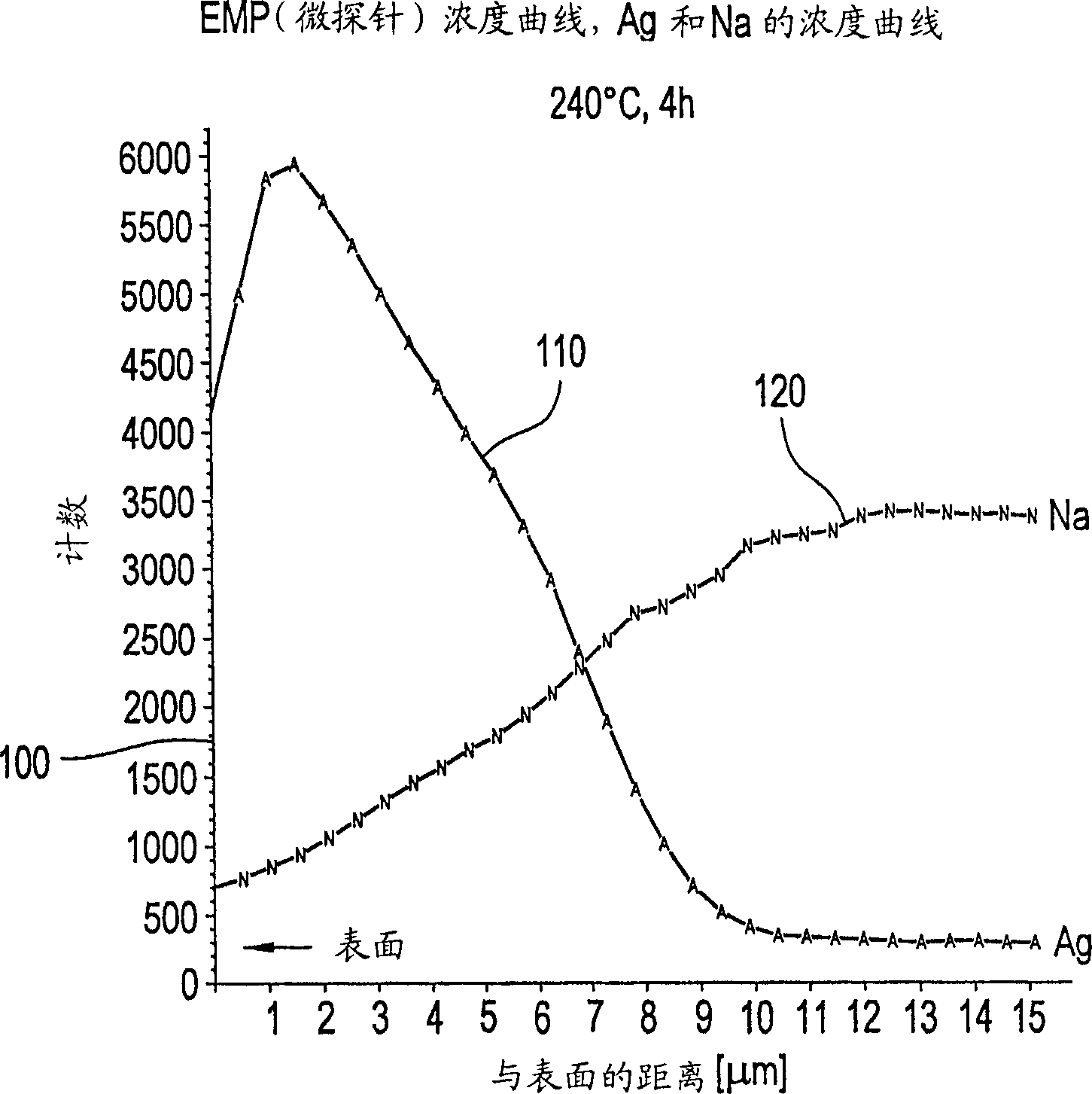
The invention relates to a water-insoluble silicate glass powder comprising glass particles that have the following composition (in wt. % on an oxide basis): SiO2 20-80; Na2O 5-30; K2O 0-5; P2O5 0-15; B2O3 0-10; CaO 4-30; MgO 0-8; AI2O3 0-7; Fe2O3 0-2; and common quantities of standard refining agents. The invention is characterized in that the glass particles contain at least one of the components ZnO, AgO, CuO, CeO2, GeO2, and TeO2, said components being concentrated in the subsurface of the glass particles.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Black micro-crystalline glass plate made of gold ore tailings and manufacturing method thereof
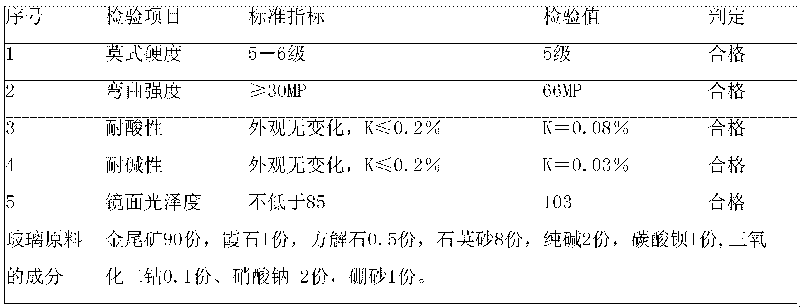
The invention discloses a black micro-crystalline glass plate made of gold ore tailings, which is prepared from the following raw materials in part by mass: gold ore tailings 60-90, quartz sand 8-20, calcite 0.5-2, nepheline 1-2, sodium carbonate 2-5, borax 1-2, barium carbonate 1-8, sodium nitrate 2-6 and cobalt oxide 0.1-0.5. A manufacturing method comprises: crushing and screening the gold ore tailings, the quartz sand, the calcite and the nepheline; removing cyanides from the gold ore tailings by an iron exchange method; weighing the raw materials in proportion and preparing a mixed material; melting the mixed material at 1,250 to 1,350 DEG C to form vitreous humour; allowing molten vitreous humour directly to flow into water to be quenched by water into glass grains; flatly spreading the glass grains in a refractory mould for crystallization; and grinding and cutting an obtained black crystalline glass sample. Compared with the traditional black crystalline glass, the product has more higher quality, and has the advantages of high Mohs' hardness, high bending strength, high chemical stability and pure color.
Owner:君达环保科技(宝鸡)有限公司
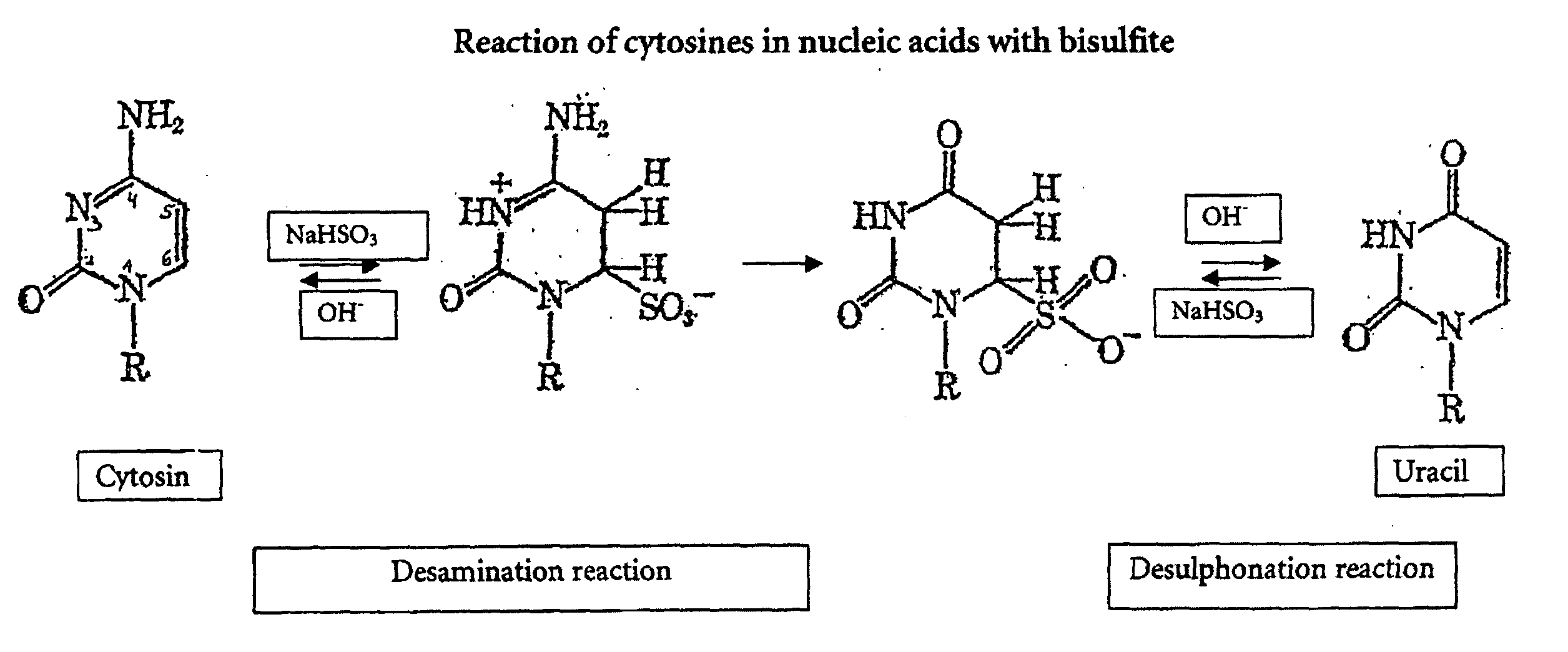
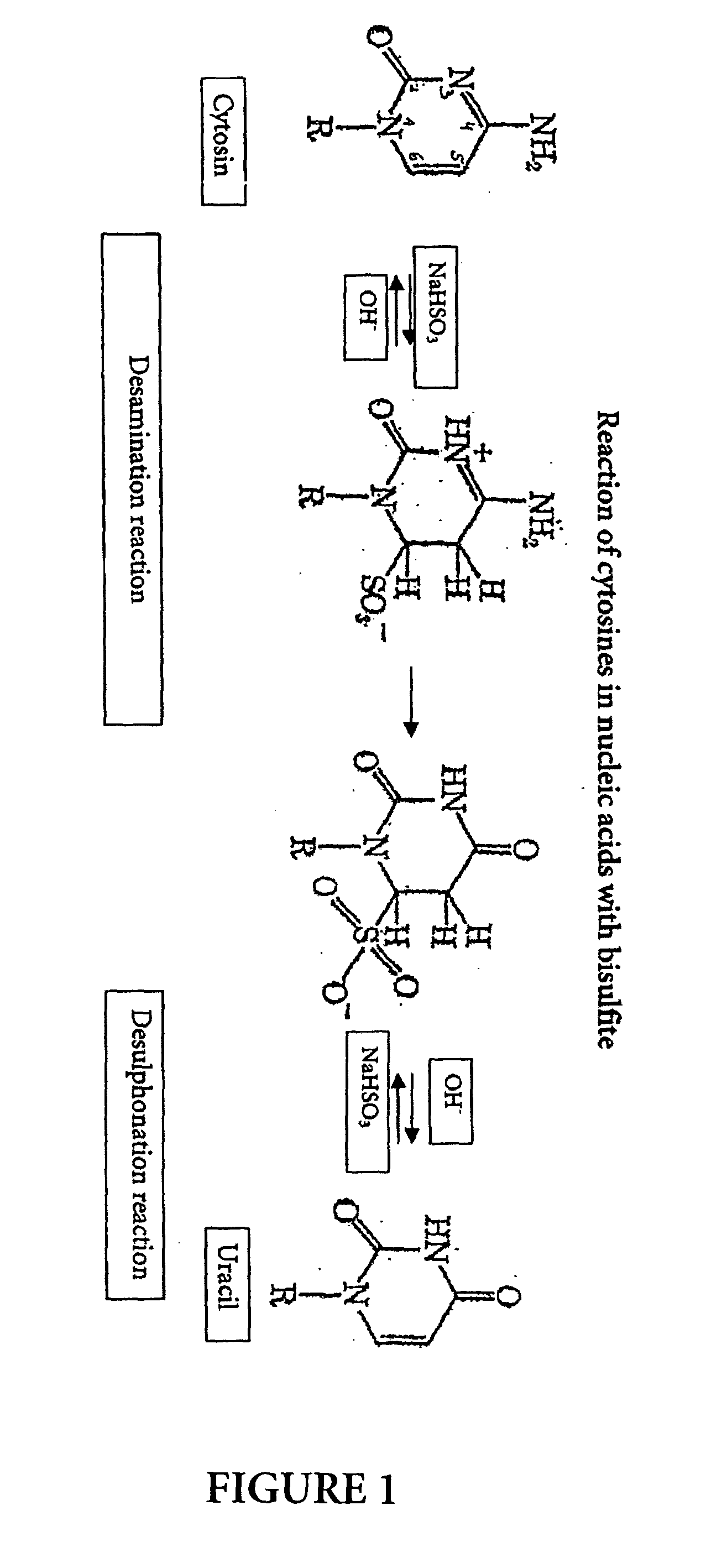
Method for bisulfite treatment
ActiveUS20040241704A1Increase speedImprove accuracySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGlass fiberCytosine
The present application is directed to a method for performing a bisulfite reaction to determine methylation positions in a nucleic acid, i.e. methylated and non-methylated cytosines, whereby the nucleic acid is bound to a solid phase during the deamination and / or desulfonation step of the bisulfite reaction. The solid phase is preferably a material comprising glass or silica, more preferably a glass fleece, glass membrane or a magnetic glass particle. Further, the use of a solid phase for binding a nucleic acid during the deamination and / or desulfonation step of the bisulfite reaction is disclosed and a kit containing a bisulfite reagent and a solid phase.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Sintering process method and device for producing microcrystalline glass by using blast furnace slag
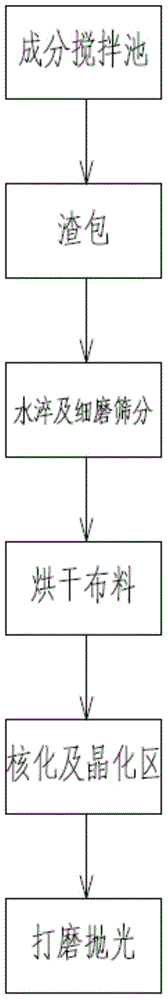
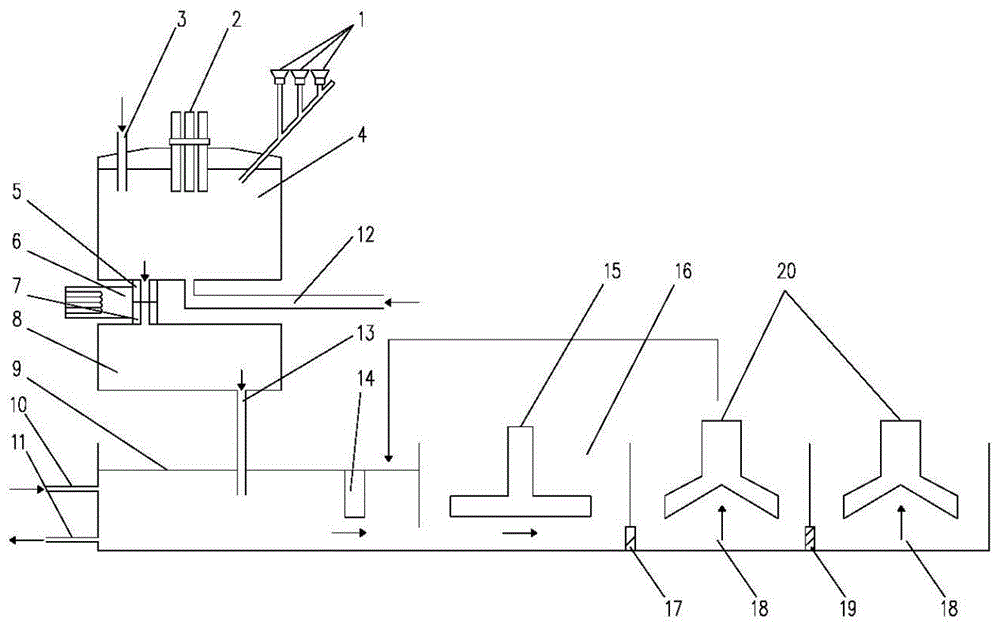
The invention discloses a sintering process method and device for producing microcrystalline glass by using blast furnace slag, belonging to the field of metallurgical and inorganic non-metallic materials. The process method comprises the following main steps that: (1) blast furnace slag is transferred to a composition hardening, tempering and stirring tank, a modifier, a coloring agent and a nucleating agent are added into the tank, the obtained mixture is uniformly stirred, and the temperature of the slag is ensured; (2) the slag enters a water quenching pond through a slag inlet and is quenched with water so as to form glass particles; (3) after the glass particles are finely ground and screened, qualified glass particles are dried; (4) the dried glass particles are distributed on a shelf board and enter a nucleating area; (5) after the temperature of the nucleating area arises to 700-800 DEG C, the glass particles are subjected to heat preservation; (6) after entering a crystallization area, the glass particles are heated to 900-1100 DEG C and then subjected to heat preservation; and (7) the glass particles enter a cooling area to be cooled, thus obtaining products; and then the qualified products are subjected to surface grinding and polishing, thus obtaining a finished product microcrystalline glass. According to the invention, blast furnace slag and solid waste resources are fully used, and the product microcrystalline glass has the advantages of high strength, corrosion resistance, multiple colors and the like and has remarkable economic benefits and environmental protection benefits.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Lithium disilicate glass-ceramics composite material using ZrO2 as reinforcing phase and method for making same
InactiveCN101139170AGuaranteed densificationGood mechanical propertiesGlass particleMechanical property
The present invention relates to a lithium disilicate glass-ceramic composite material with ZrO2 as the reinforcing phase and thepreparation method, which solve the problems that the production cycle is long, the cost is high, the products can be easily formed and the mechanical properties of the lithium disilicate glass-ceramic is lower. The present invention is composed of the lithium disilicate base glass and zirconia powders. The preparation method goes in that the ball milling is carried out according to the components of the original glass; the desiccated raw materials are placed in a corundum crucible so as to be melted under high temperature; the glass solution is poured into the distilled water to go into water quenching so as to be changed into 1 to 2mm glass particles; the ball milling is applied to the glass particles after going into the water quenching so as to obtain the glass powders; the lithium disilicate glass powder is taken to be mixed with the zirconia powders and the ball milling is applied to the lithium disilicate glass powder and the zirconia powders with the alcohol as the medium; the vacuum heating-press sintering is implemented and then the lithium disilicate glass-ceramic composite material with ZrO2 as the reinforcing phase is prepared. The present invention is uneasily deformed, has short production cycle and low cost and has excellent bending strength and fracture toughness indexes.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Electroconductive Paste Compositions and Solar Cell Electrodes and Contacts Made Therefrom
InactiveUS20140026953A1Conductive materialNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialMetal particleGlass particle
Electroconductive paste compositions, particularly for solar cells, contain electroconductive metal particles, glass particles, and an organic vehicle. The electroconductive metal particles are provided as a mixture of silver powder particles and at least one selected from nickel powder, tin (IV) oxide powder, and core-shell particles having a silver shell and a core of nickel and / or tin (IV) oxide. The pastes may be used in the manufacture of contacts or electrodes for the front side or back side of solar cells.
Owner:HERAEUS PRECIOUS METALS NORTH AMERICA CONSHOHOCKEN
Porous ceramic-microcrystalline glass composite insulation decorative plate and preparation method thereof
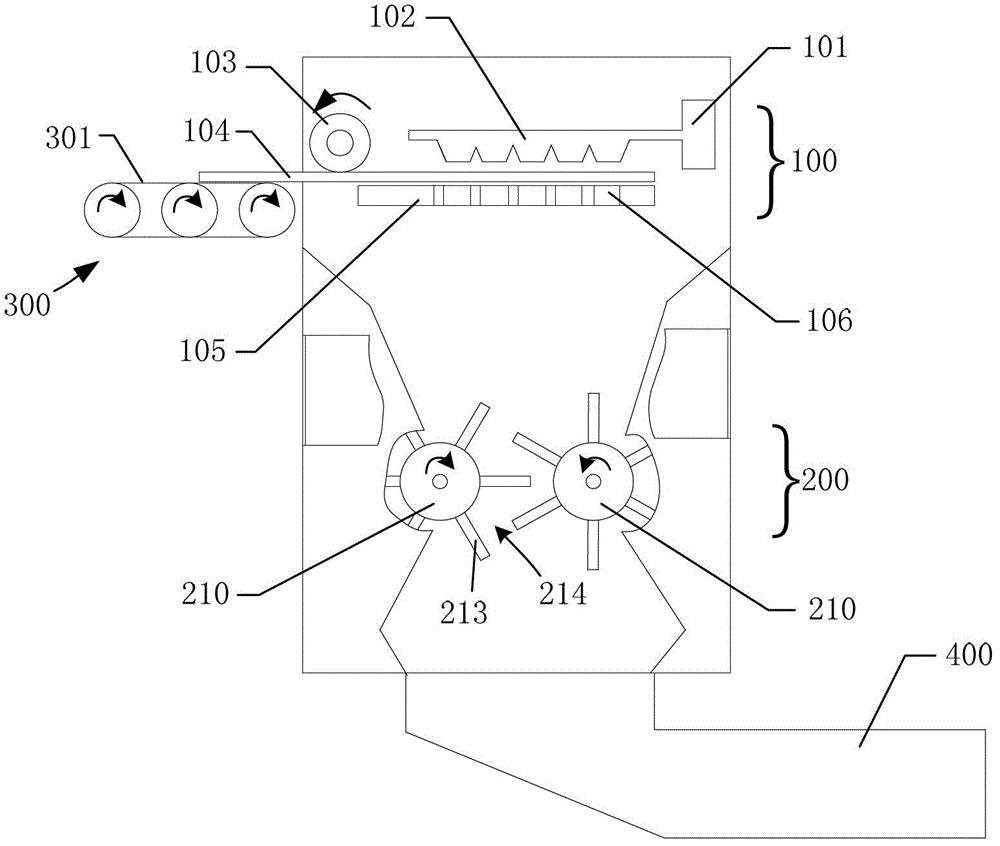
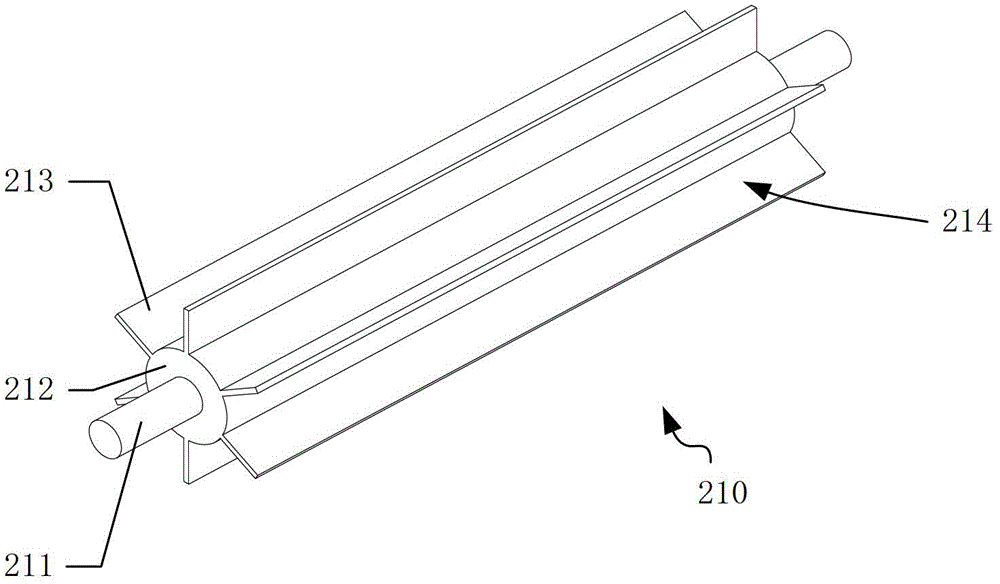
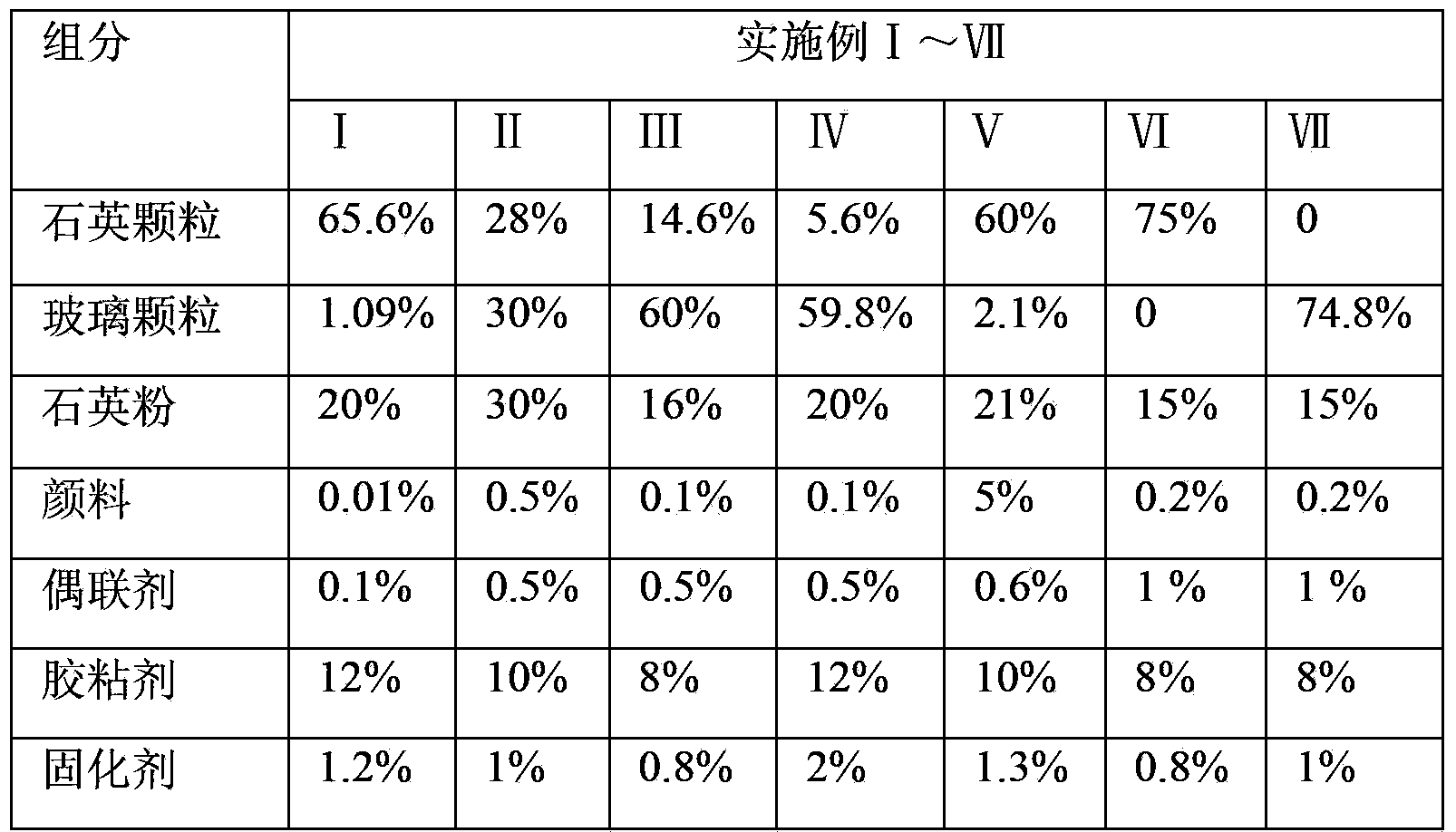
InactiveCN102942383AImprove insulation effectImprove waterproof performanceCeramicwareSlurryGlass particle
The invention discloses a porous ceramic-microcrystalline glass composite insulation decorative plate and a preparation method thereof. The porous ceramic comprises ceramic tile raw material, additive, pore forming agent and foaming agent, and the microcrystalline glass comprises SiO2, CaO, ZnO, Al2O3, Na2O, K2O, etc. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly uniformly mixing ceramic tile raw material, additive, pore forming agent and foaming agent, and conducting ball milling to obtain an ultrafine powder slurry; then granulating, drying, and conducting compression molding; drying the green ware body and then sintering in a roller kiln or a shuttle kiln; then, melting quartz sand, limestone, soda ash and other minerals or chemical raw materials to obtain a glass melt, carrying out water quenching on the glass melt to obtain glass particles; screening the dried glass particles and then classifying, paving on the surface of a porous ceramic plate, then pushing into a crystallization kiln to sinter, crystallize, anneal and cool the glass particles to form a microcrystalline glass layer; in the process, simultaneously compounding the microcrystalline glass with the porous ceramic plate to form the porous ceramic-microcrystalline glass composite insulation decorative plate.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
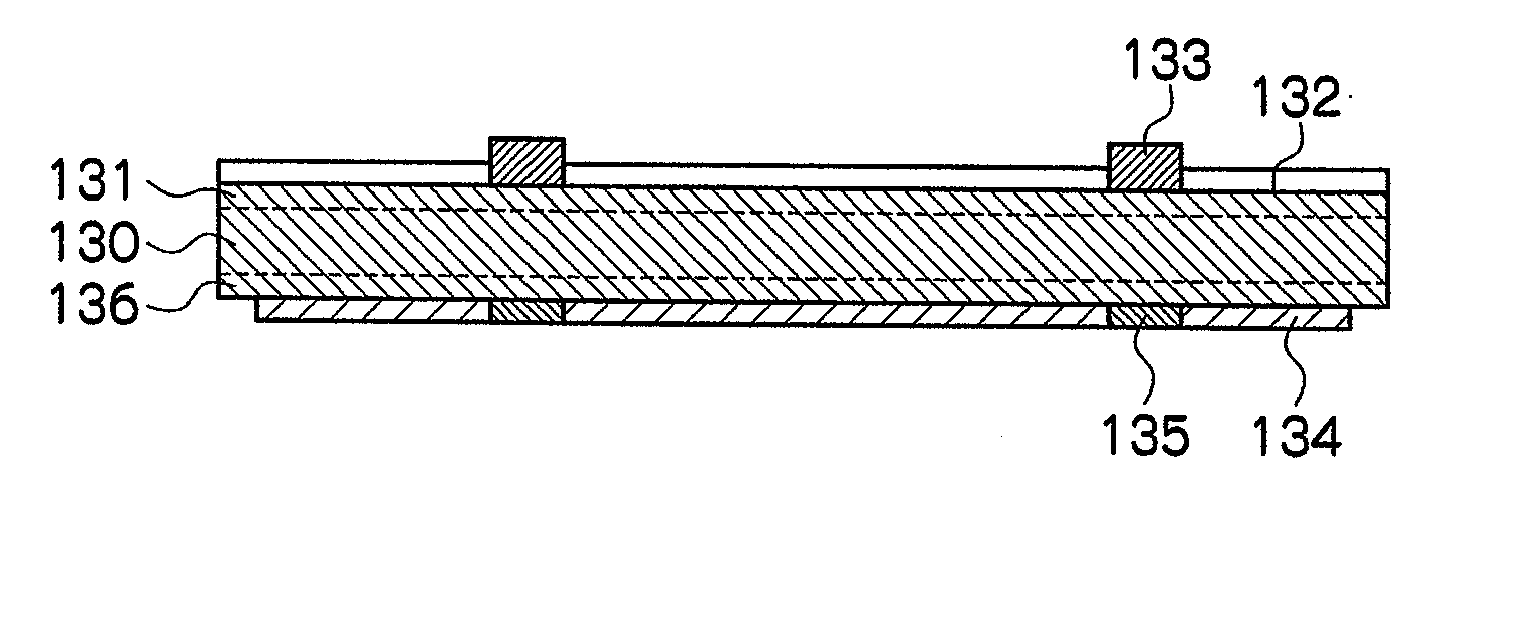
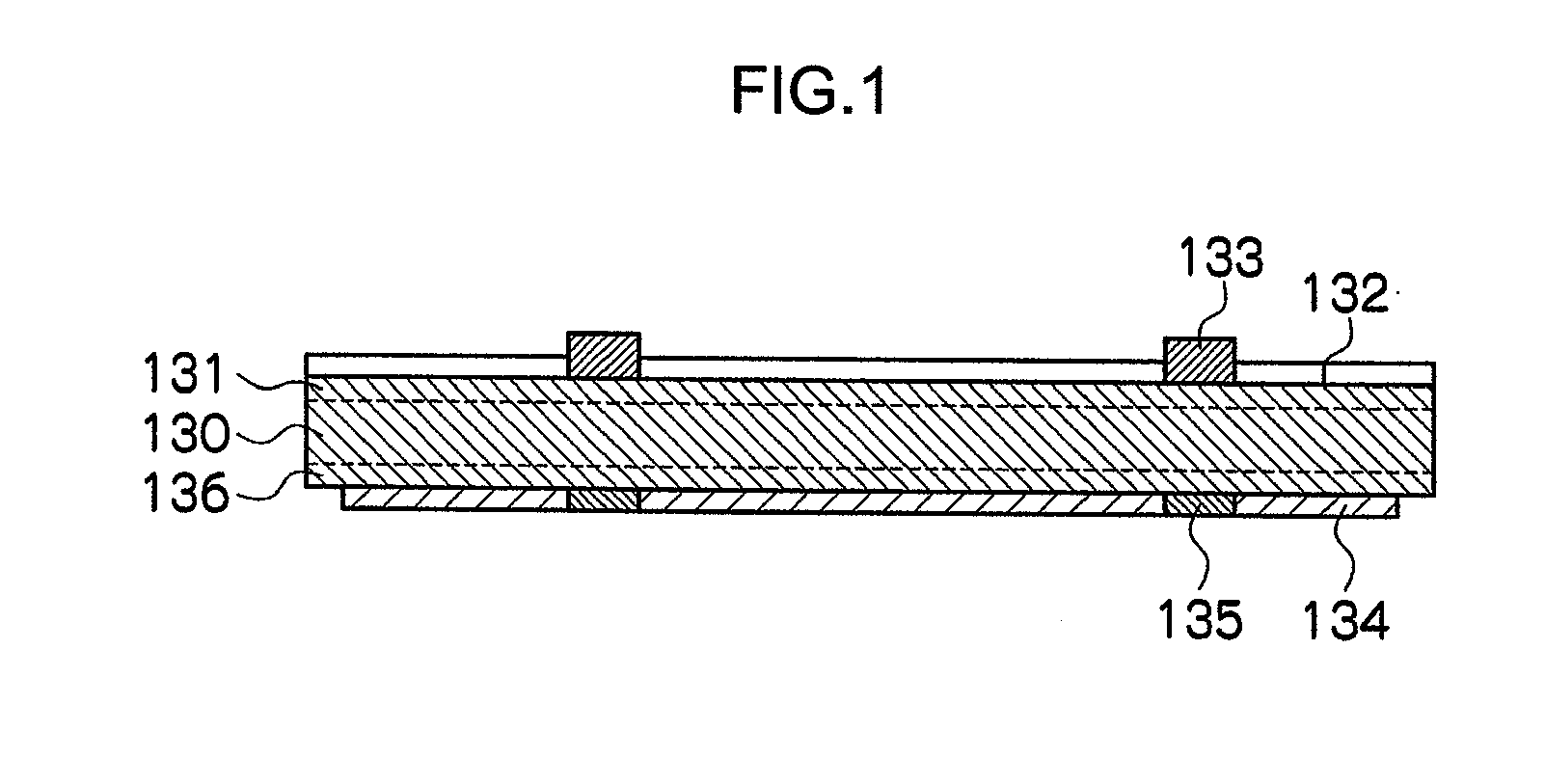
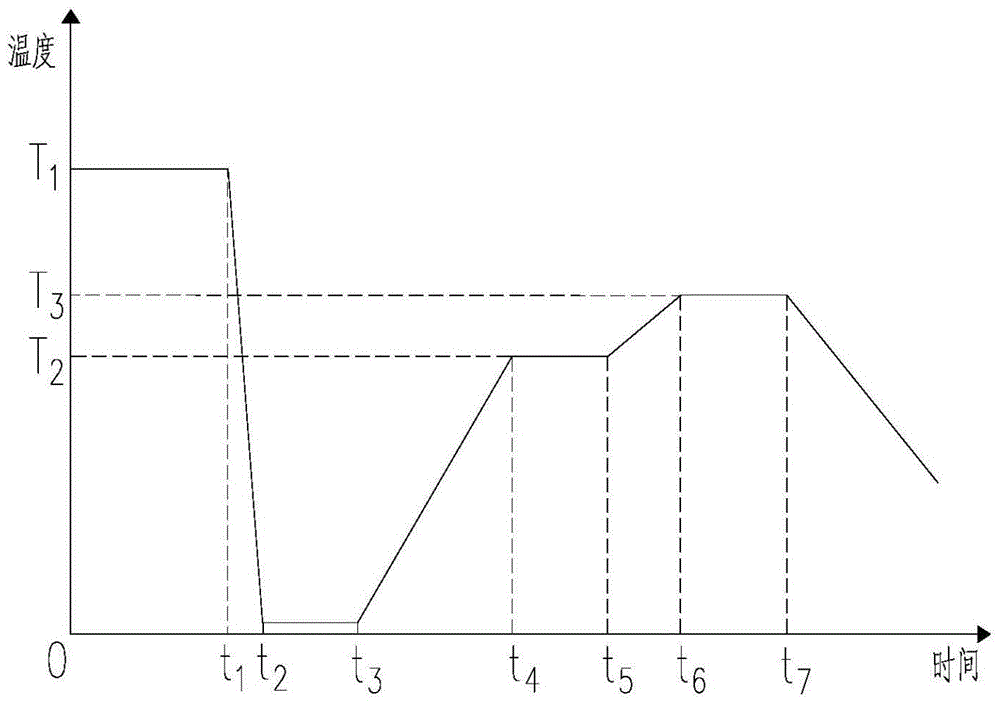
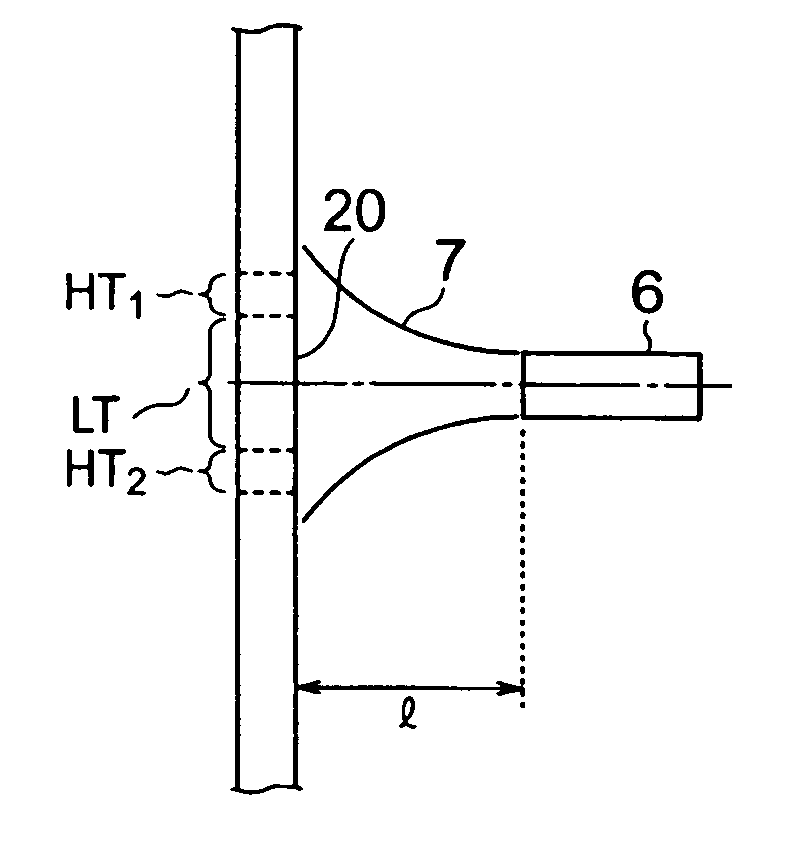
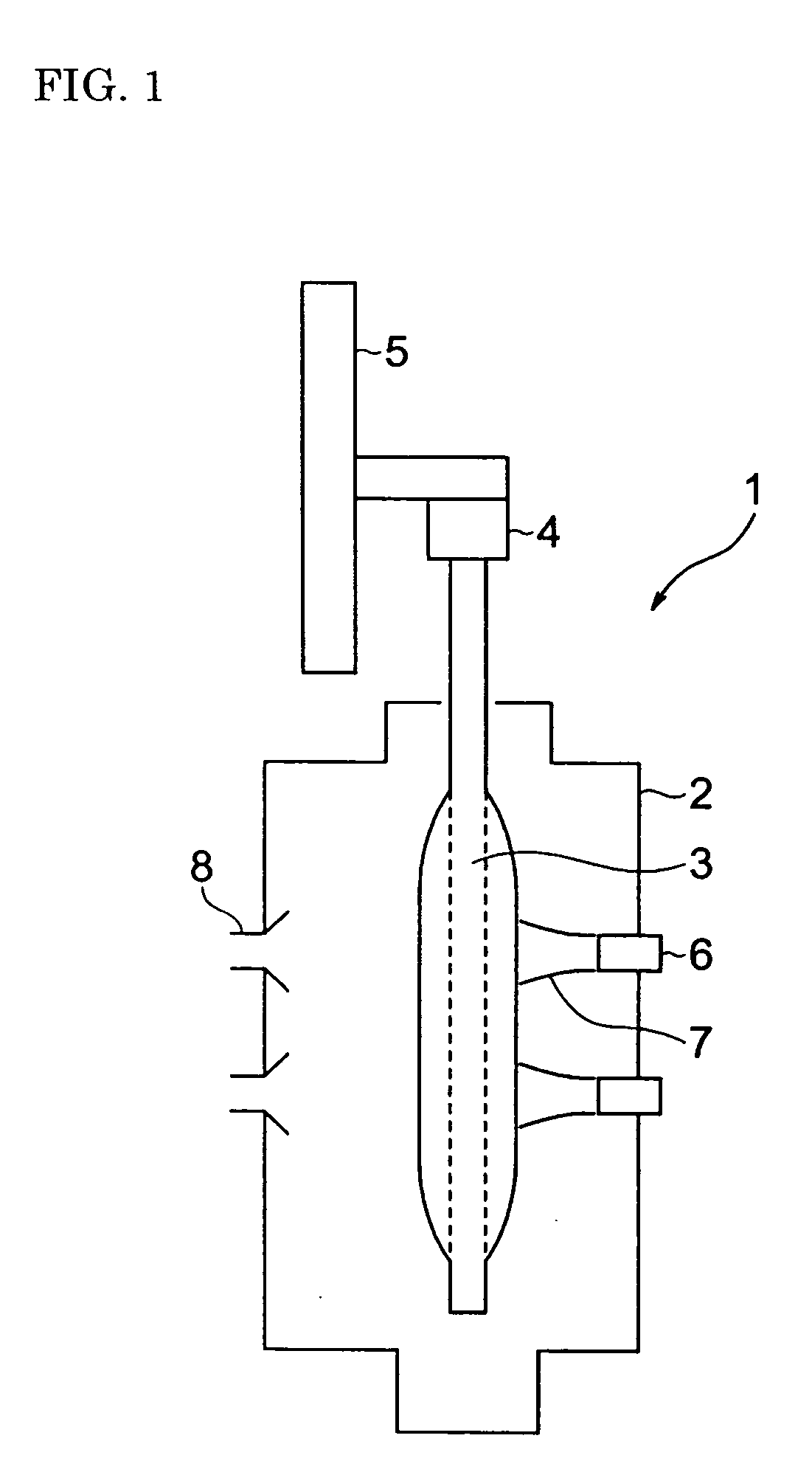
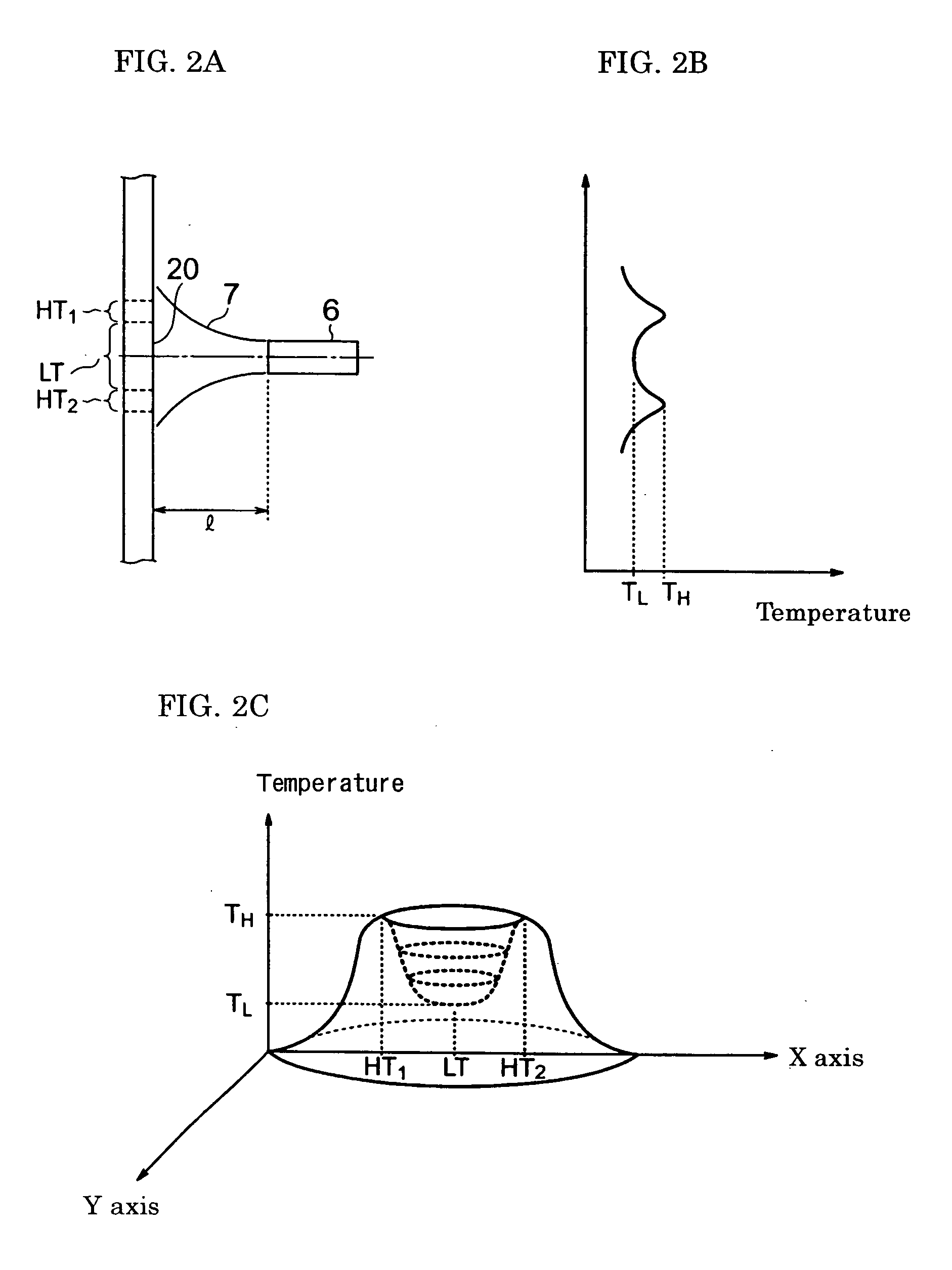
Method of producing porous glass-particle-deposited body and burner for synthesizing glass particles
InactiveUS20040182114A1Efficiency of the deposition of the glass particles on the surface of the starting member isImprove efficiencyGlass shaping apparatusGlass deposition burnersCombustorGlass particle
A method of producing a porous glass-particle-deposited body by effectively depositing the glass particles synthesized by a burner for synthesizing glass particles on a starting member with increased bonding strength between the deposited glass particles and decreased possibility of developing cracks and other problems, and a burner to be used for the production method. In the method of producing the deposited body by depositing the glass particles synthesized by a burner on the surface of the starting member, the glass particle deposition surface has (a) a region that is hit by the center portion of the flame issuing from the burner and (b) another region that has a temperature higher than that of the region hit by the center portion of the flame and that is located at the outside of the region hit by the center portion of the flame.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Transparent resin concrete and preparation method thereof
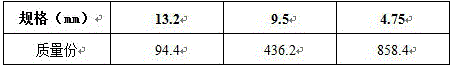
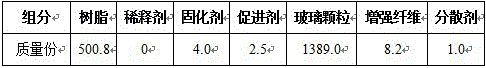
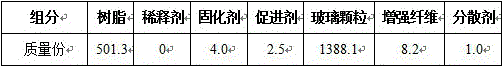
The invention discloses transparent resin concrete. The transparent resin concrete is prepared from the following raw materials: a resin component, a curing agent component, aggregate and a reinforcing material component. The transparent resin concrete is characterized in that the resin component is prepared from resin and a diluent; the curing agent component is prepared from a resin curing agent and a resin accelerant; the aggregate is glass particles; the reinforcing material component is prepared from reinforced fibers and a reinforced fiber dispersing agent. The glass particles are taken as the aggregate, the strength of the concrete is improved by using the reinforced fibers, and the novel transparent concrete is prepared by using the cementing action of resin. The invention aims at providing a building material with good transparence; the building material effectively improves the day-lighting performance of a house and reduces the use of indoor lamp light, thus saving energy.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
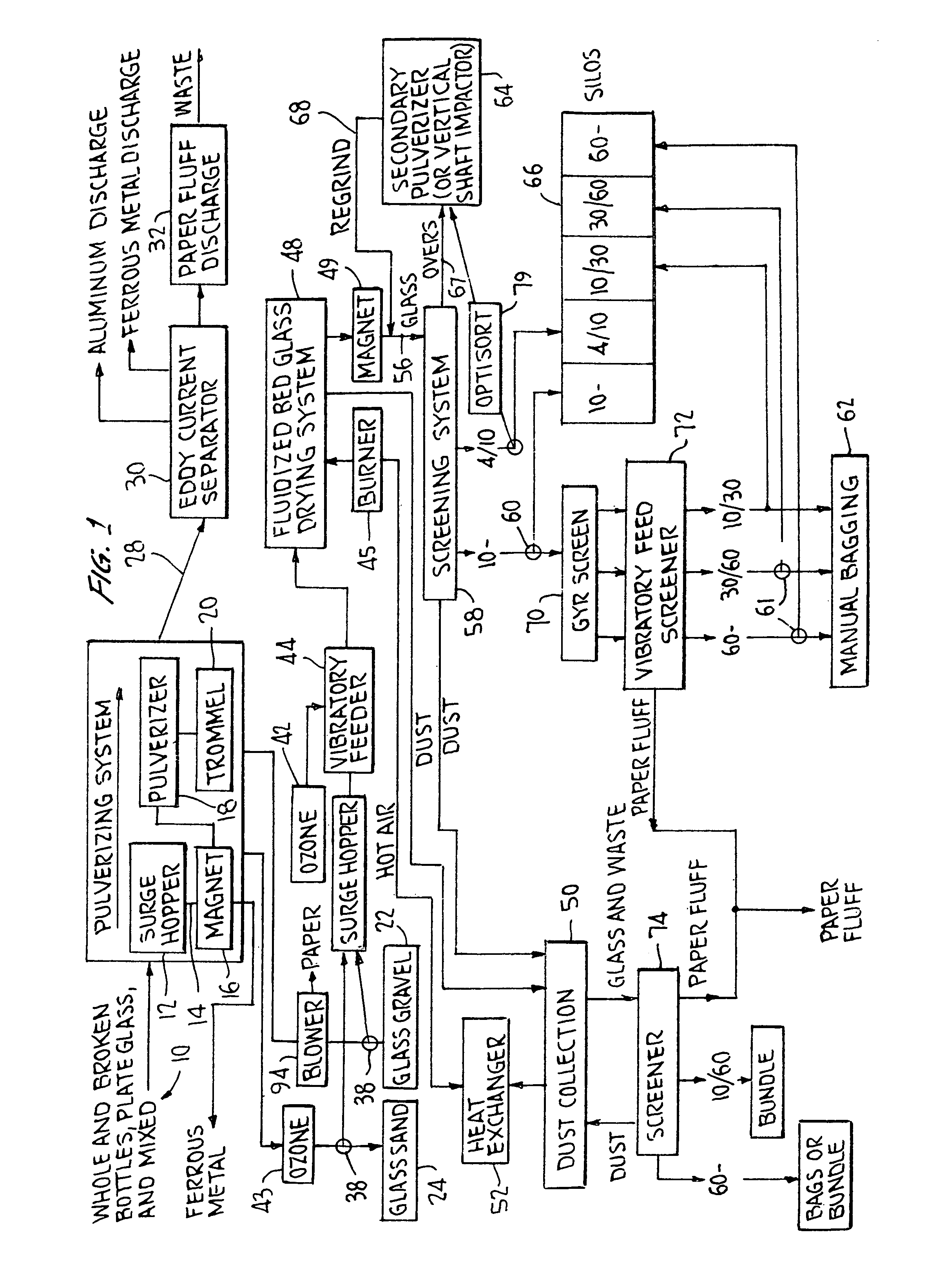
Production of clean glass particles from post-consumer waste
ActiveUS8146841B2Separate cleanInhibit productionMechanical working/deformationGlass recyclingWaste streamPost-consumer waste
Owner:GLASS PROCESSING SOLUTIONS
Apparatus and method for comminuting glass fibers
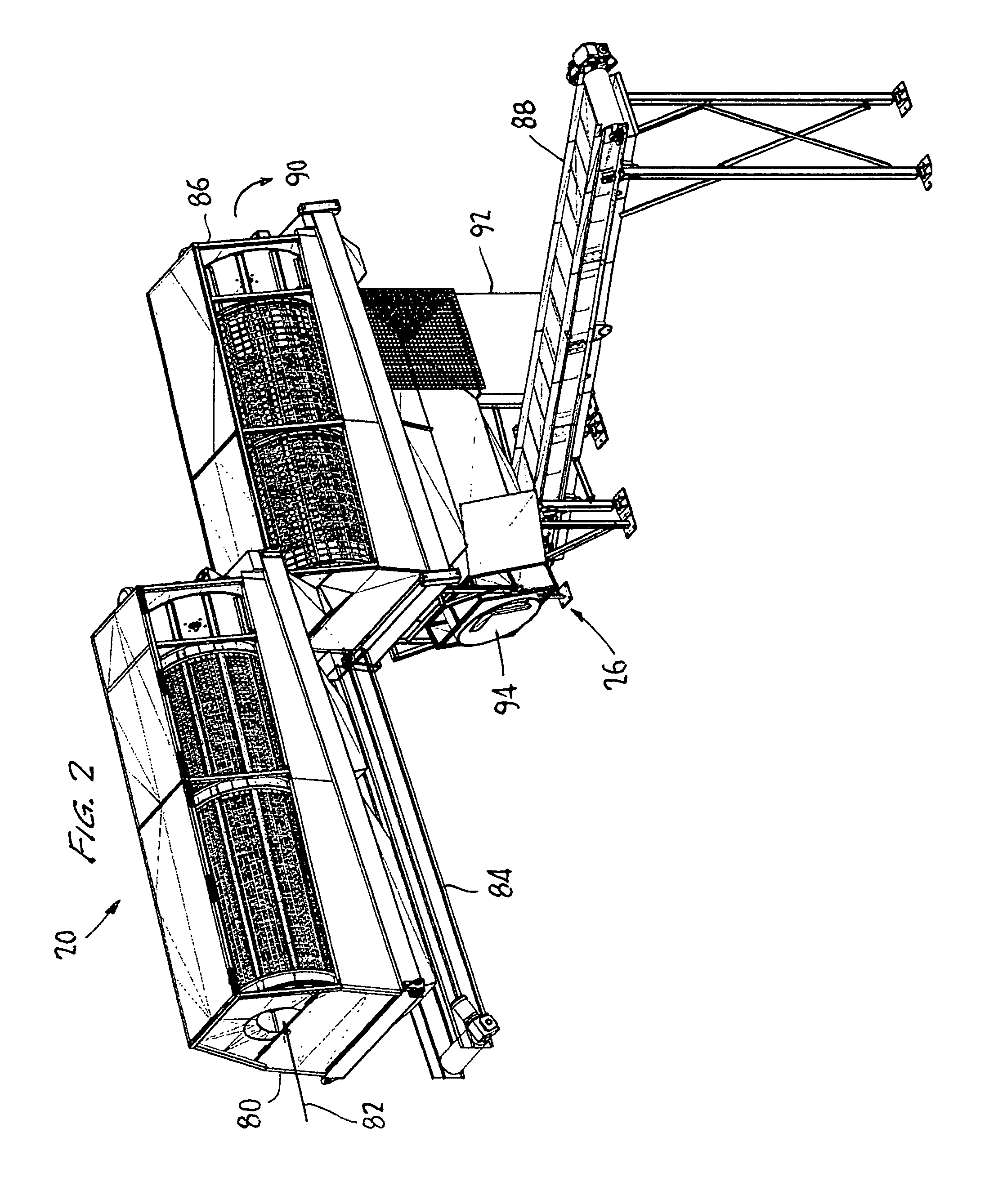
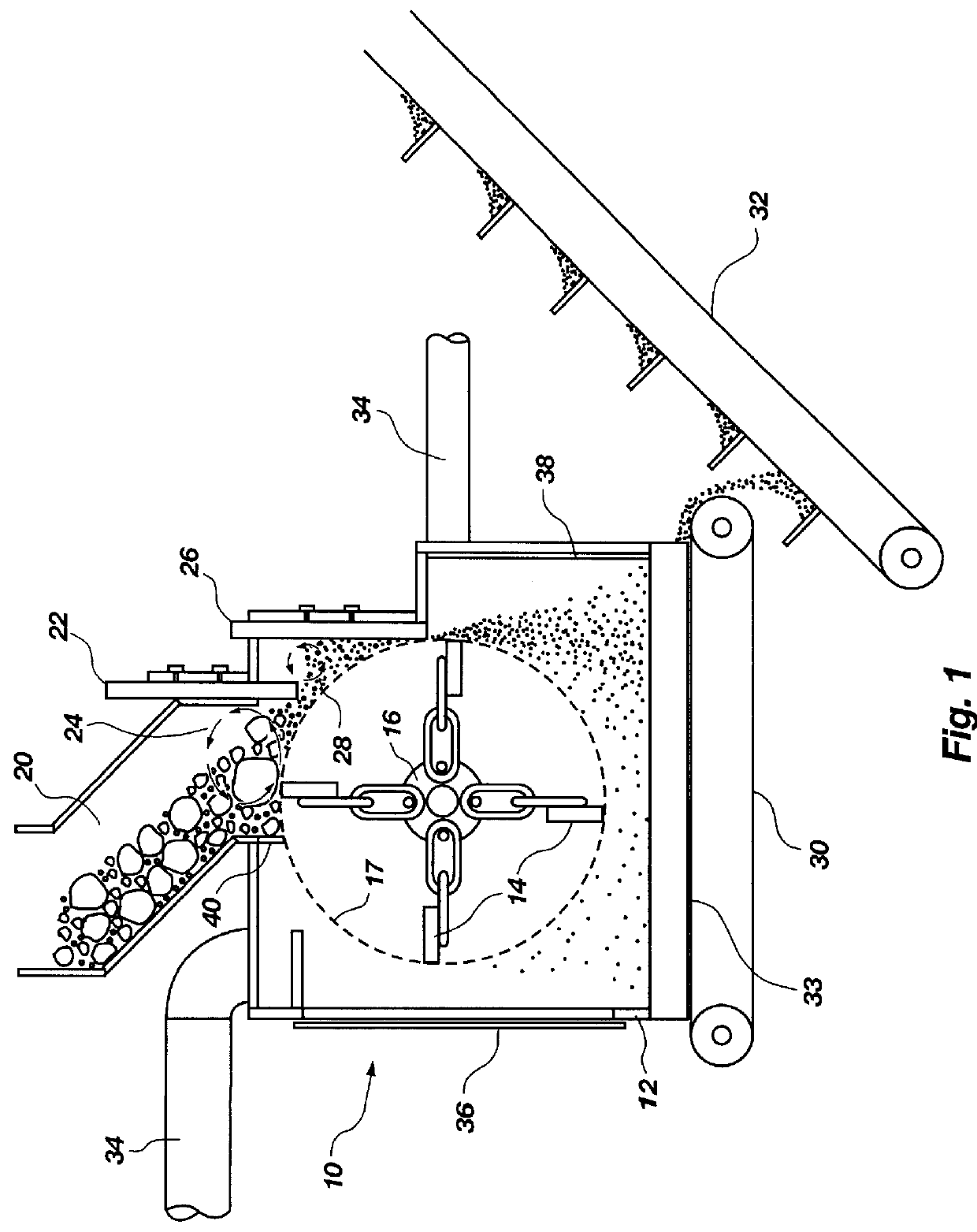
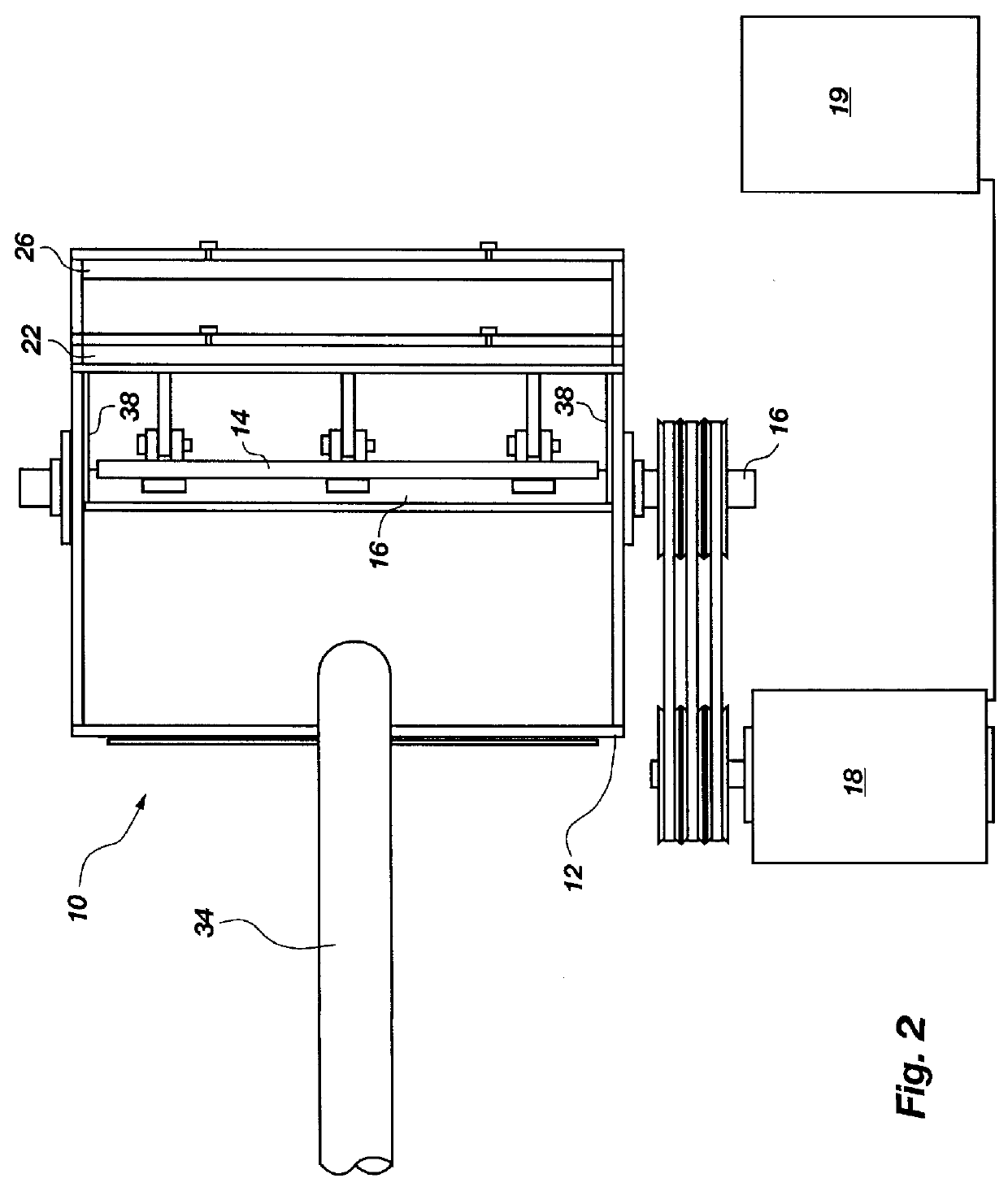
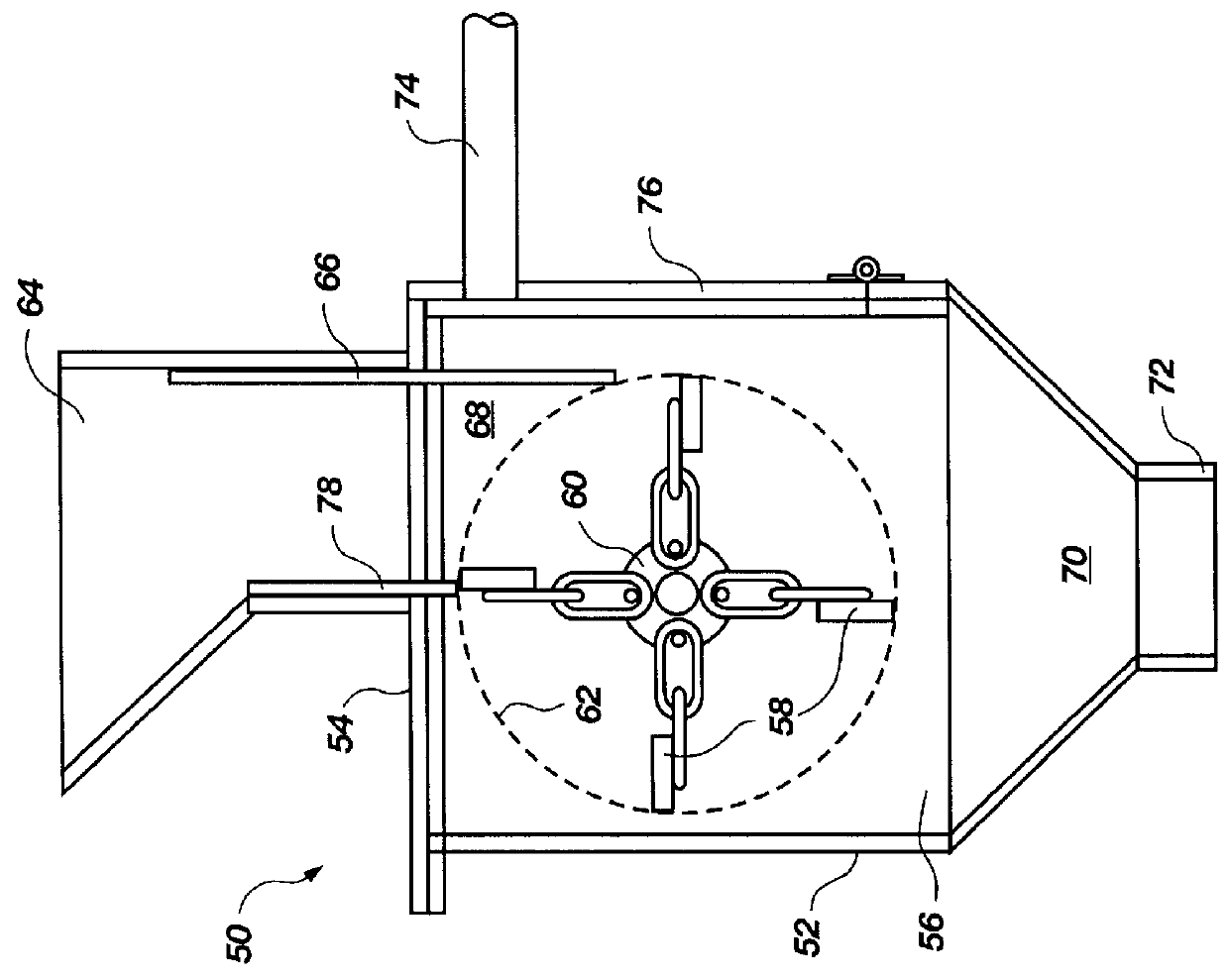
An apparatus for comminuting glass fibers is disclosed. Within a housing are a plurality of weighted members or hammers, flexibly connected to and spaced about a rotatable shaft. A drive member rotates the hammers about the shaft to define a rotation circumference. A glass intake opening located at the top portion of the housing is provided to introduce glass fibers and carrier material into the apparatus. A first adjustable plate is located adjacent the glass intake opening and positioned to provide a space between the first adjustable plate and the hammers' rotation circumference. A first glass suspension chamber is defined by the glass intake opening, the first adjustable plate, and the rotation circumference of the hammers. In operation, a quantity of glass fibers and carrier material is introduced into the apparatus, and spinning weighted members contact the glass, causing the glass to strike the first adjustable plate and other glass particles. Adjusting the space between the first adjustable plate the weighted members' rotation circumference helps control the resulting particle size of the comminuted glass. Controlling the shaft rotation speed affects the resulting particle size of the comminuted glass.
Owner:R & J HANSEN L L C
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com