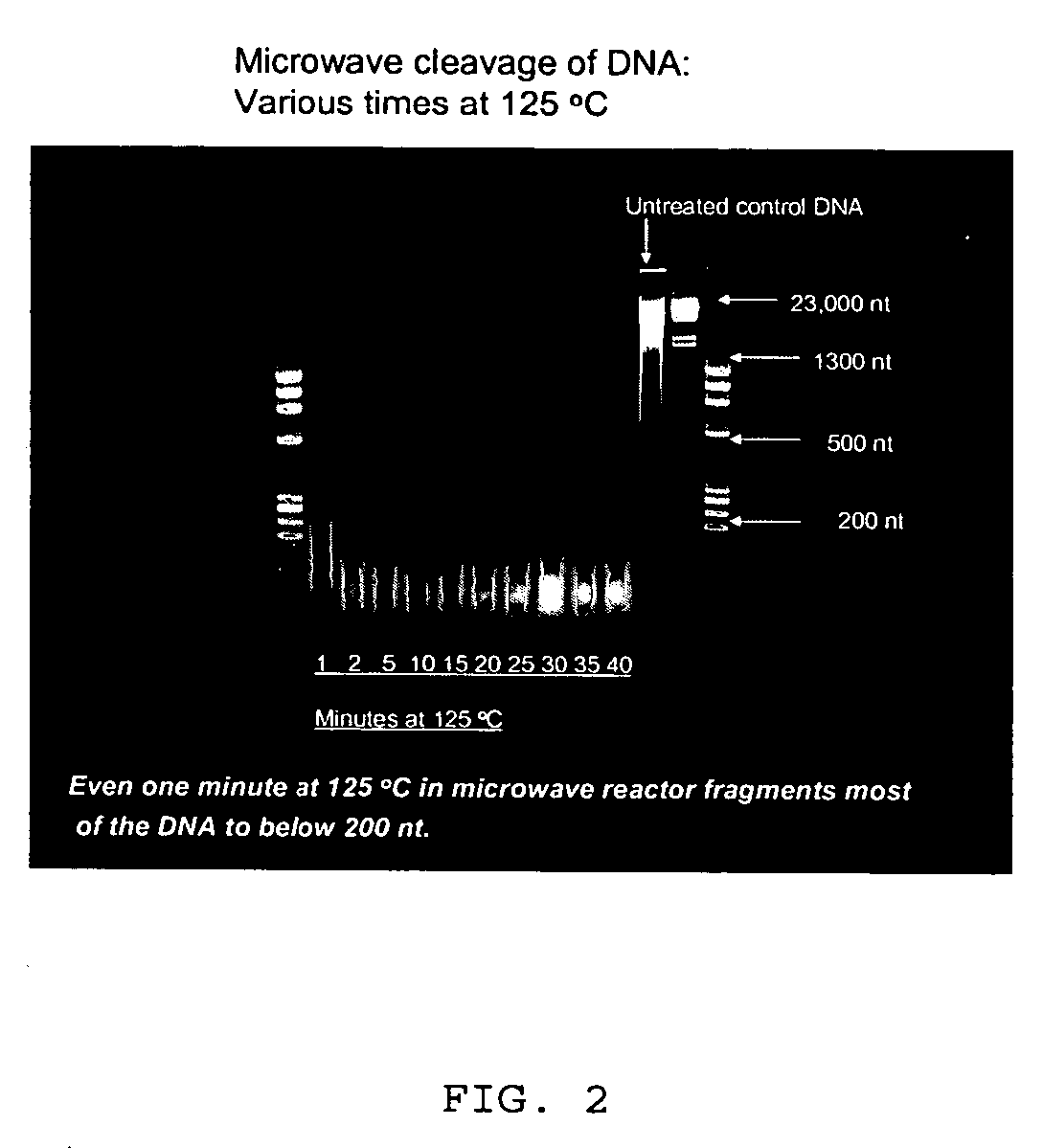
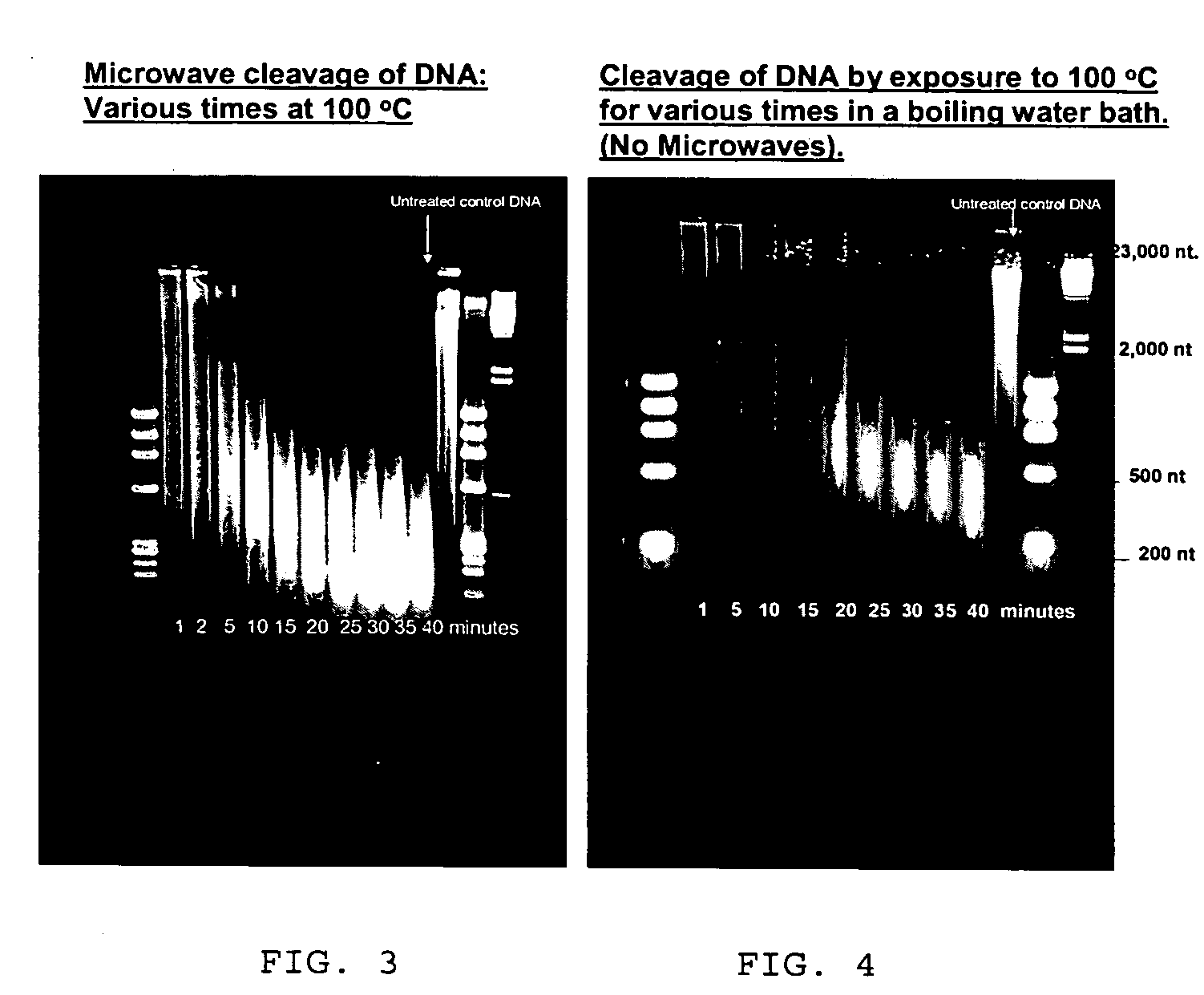
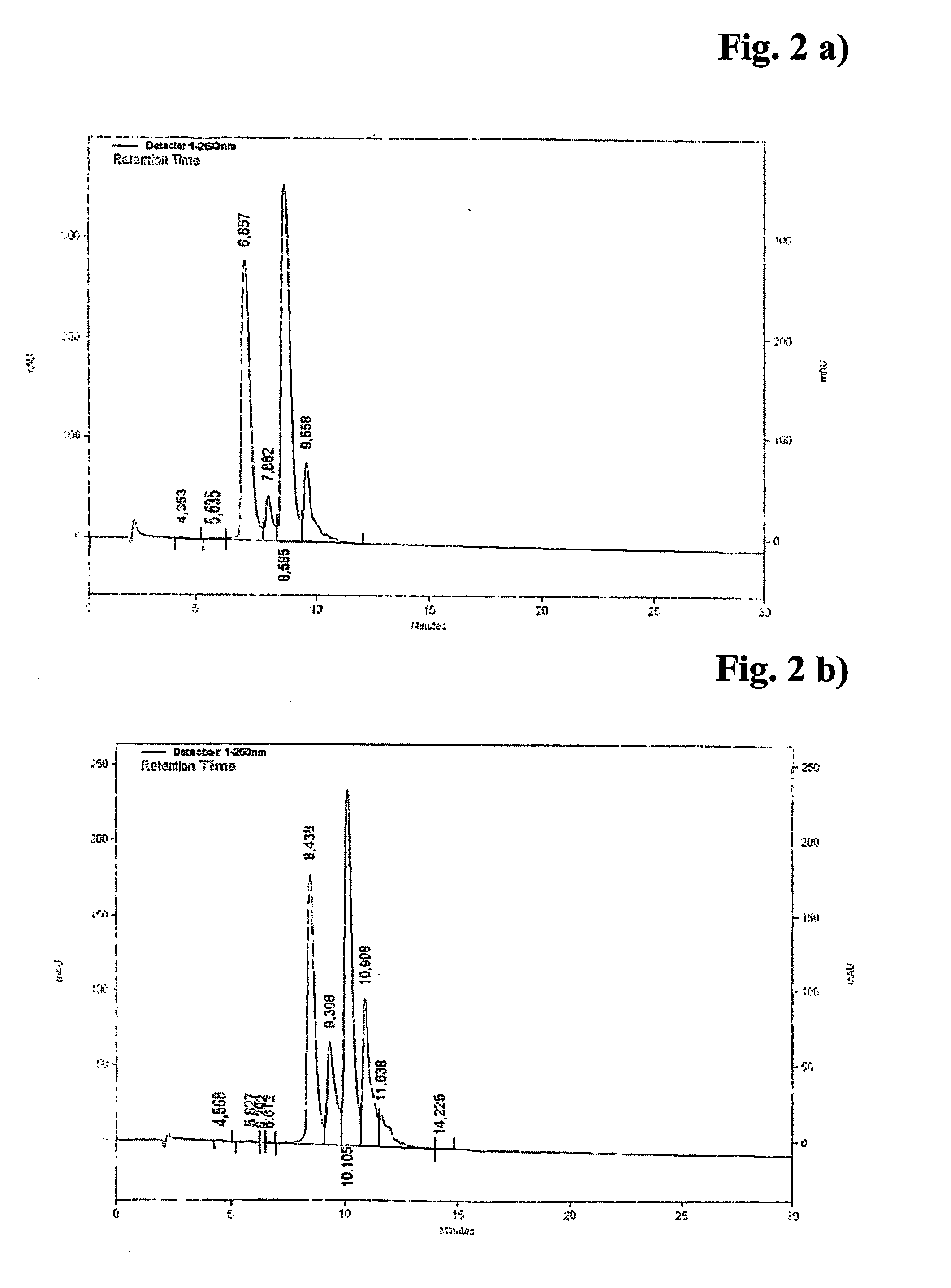
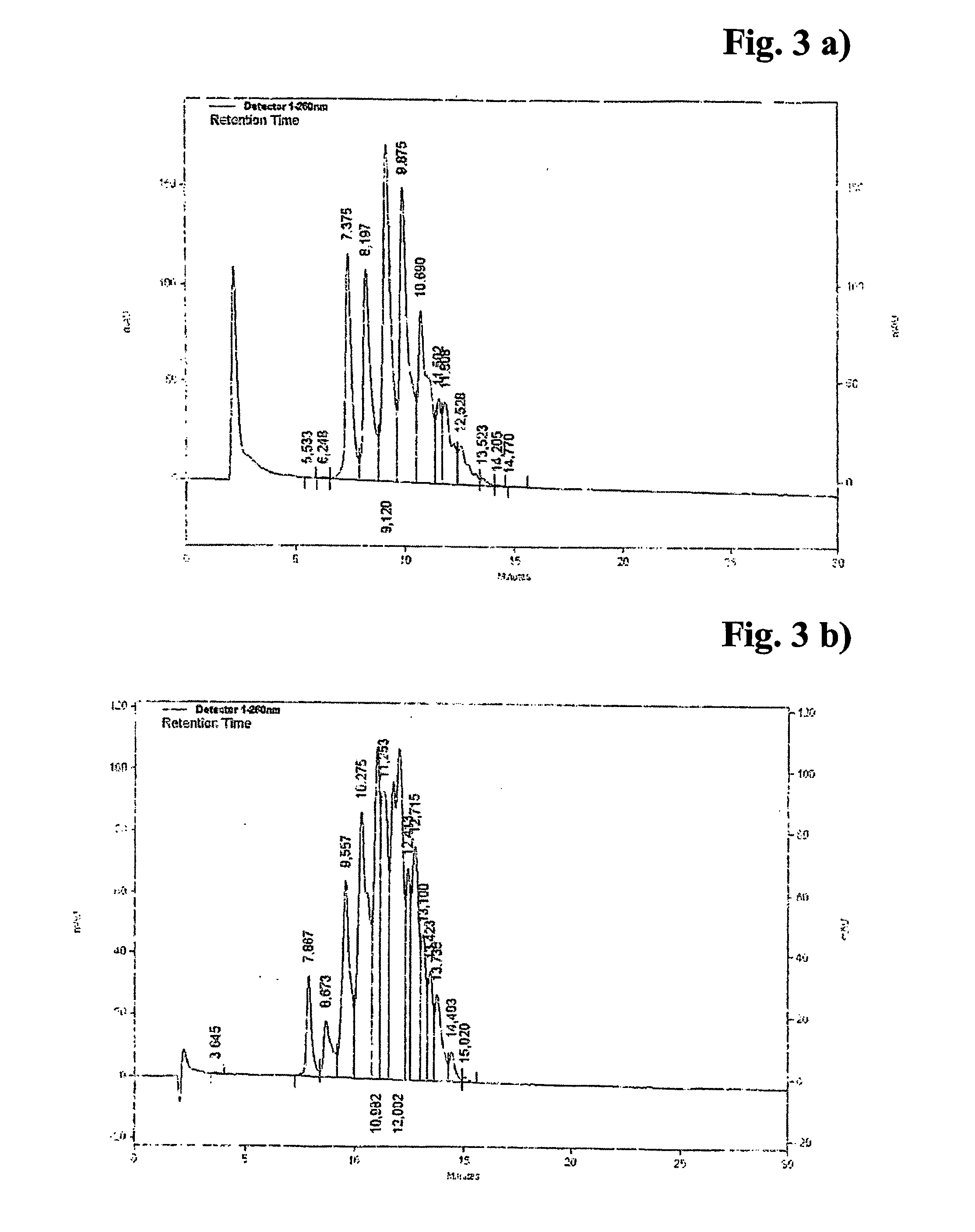
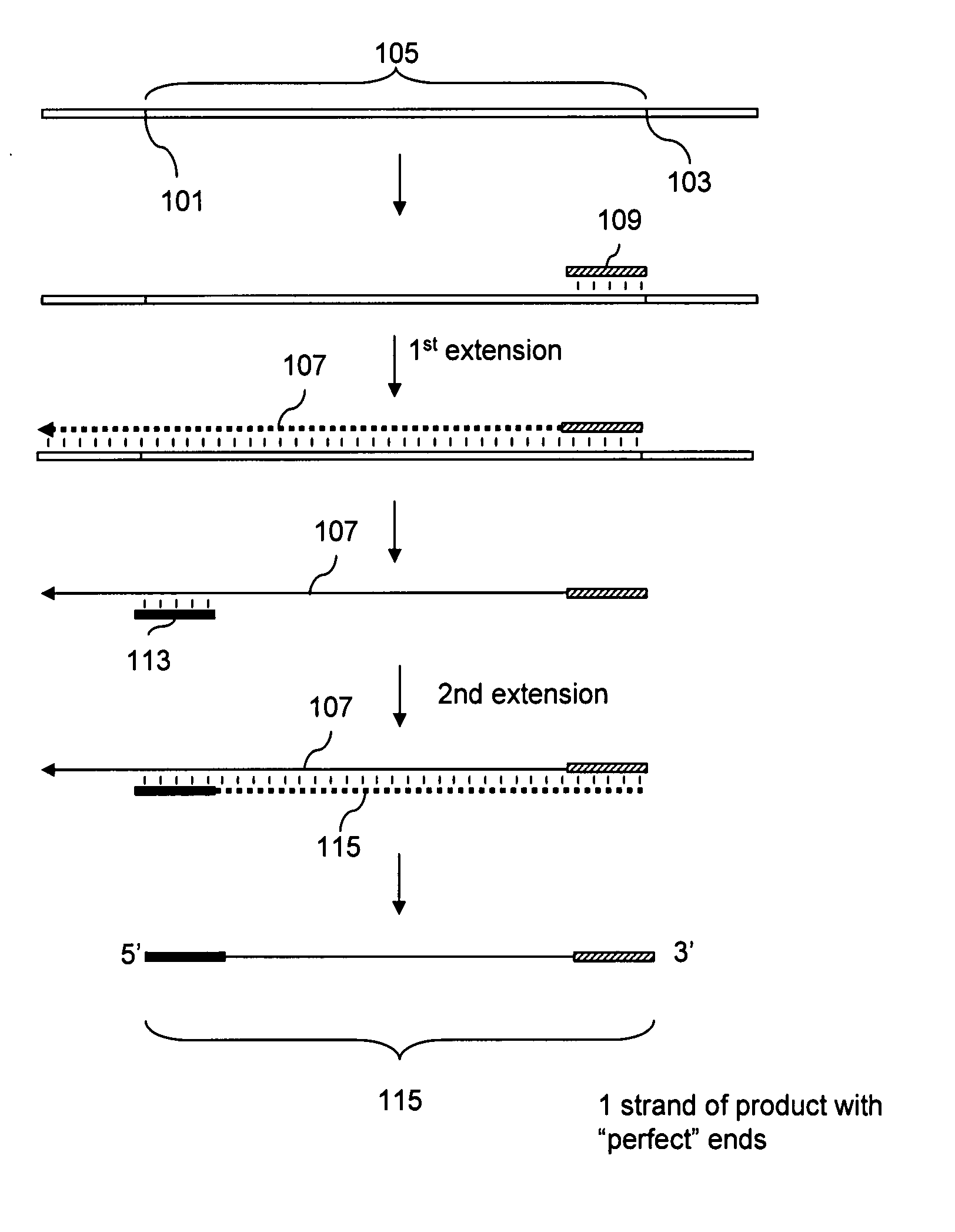
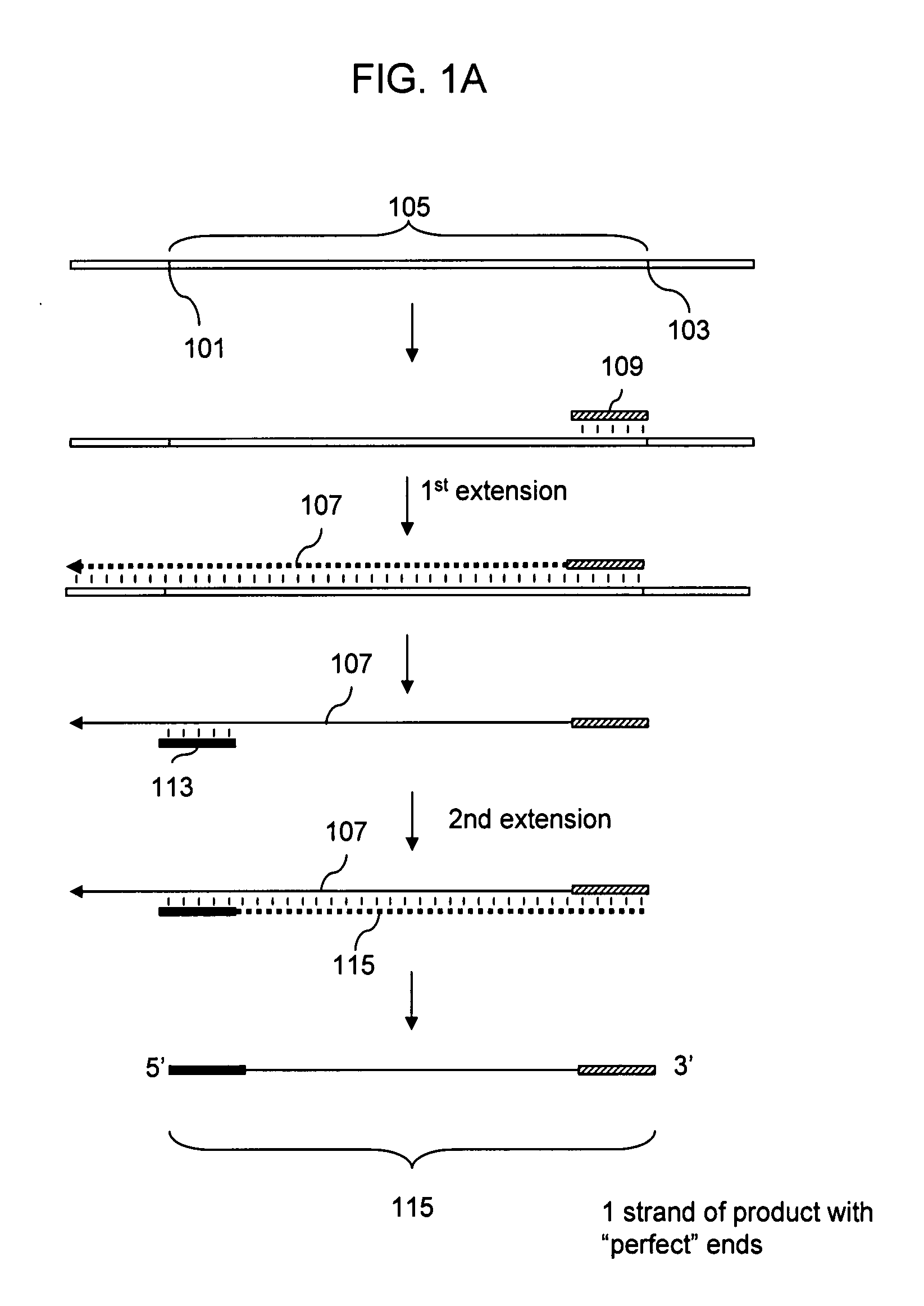
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
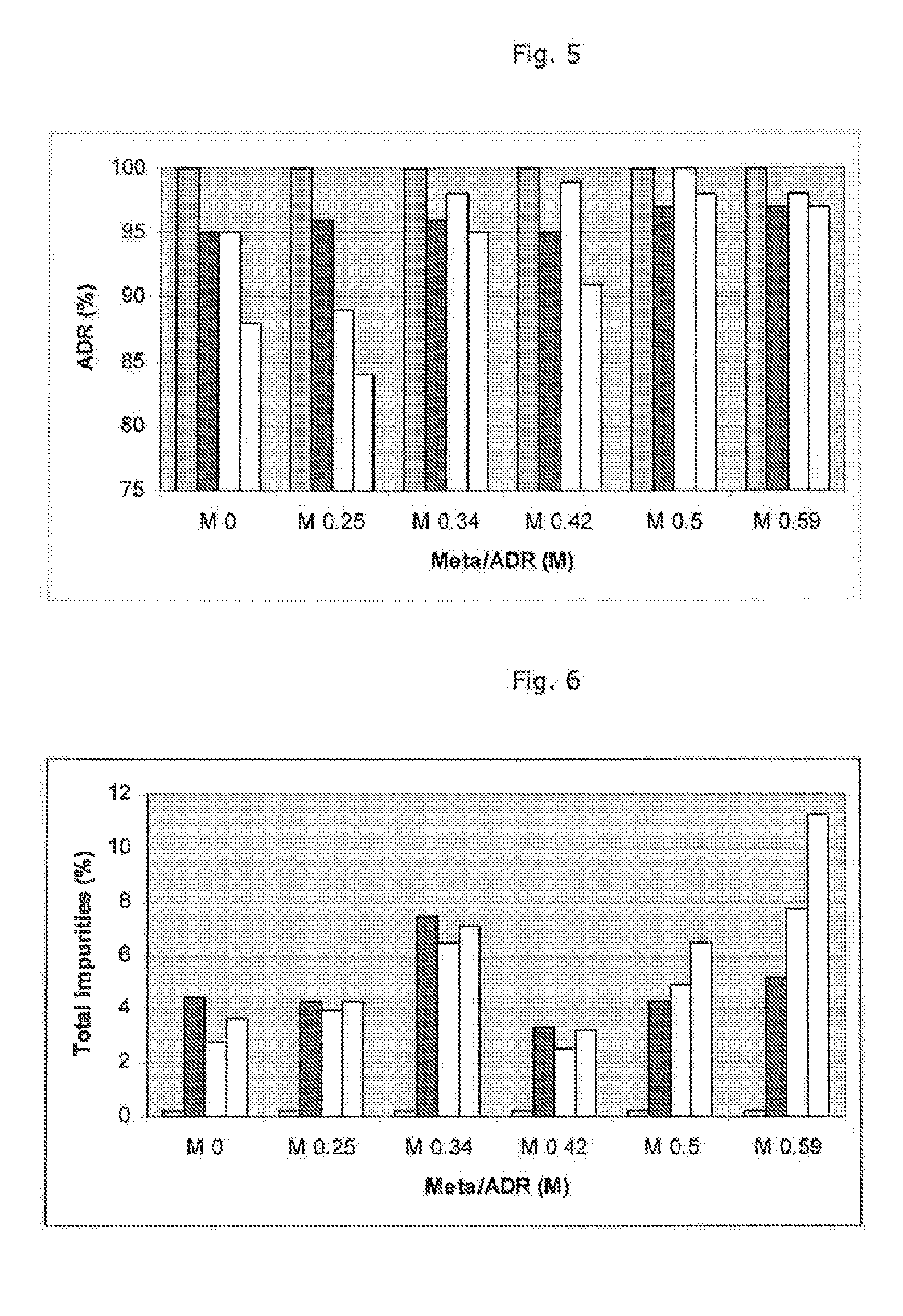
403 results about "Bisulfite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
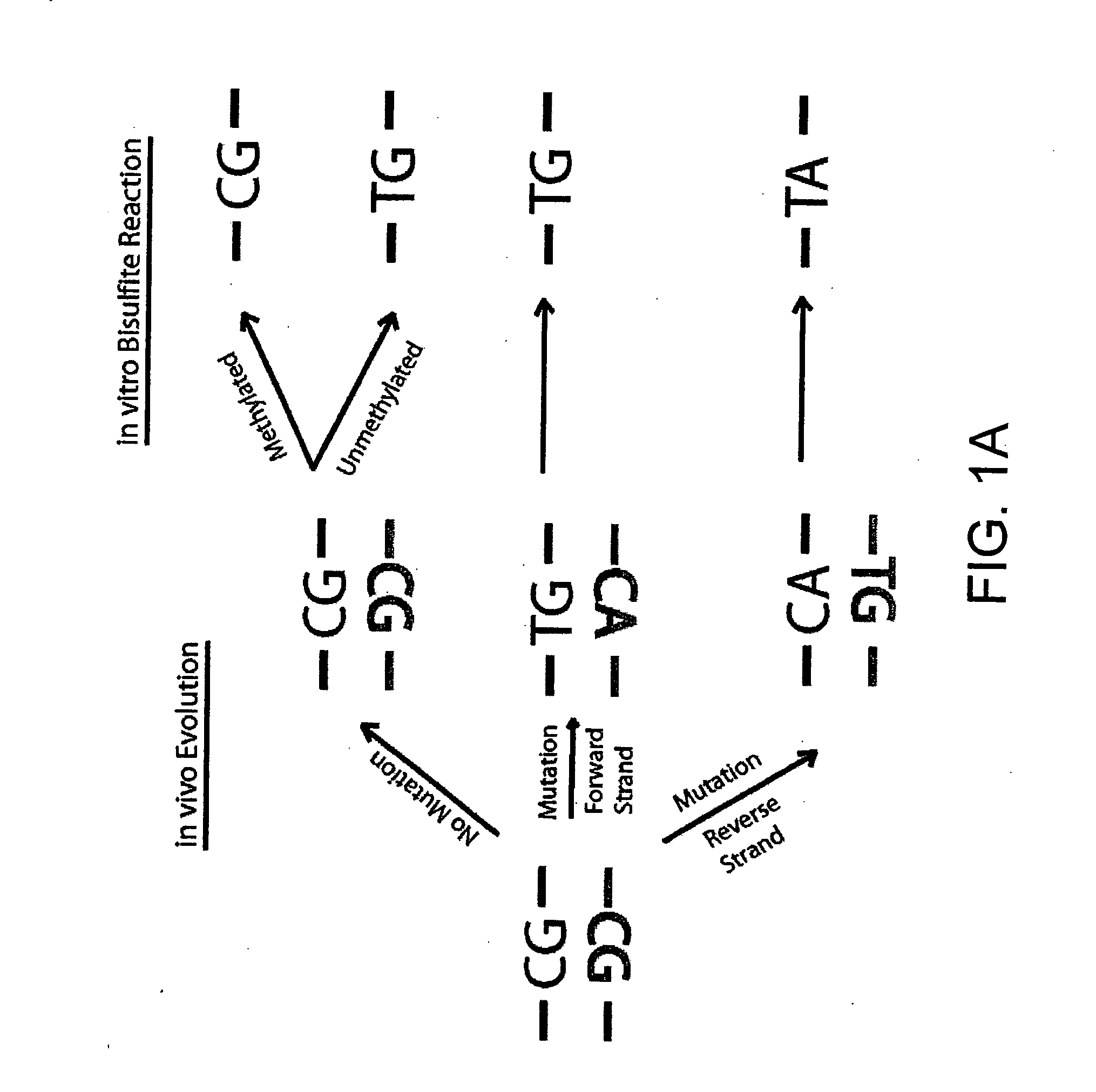
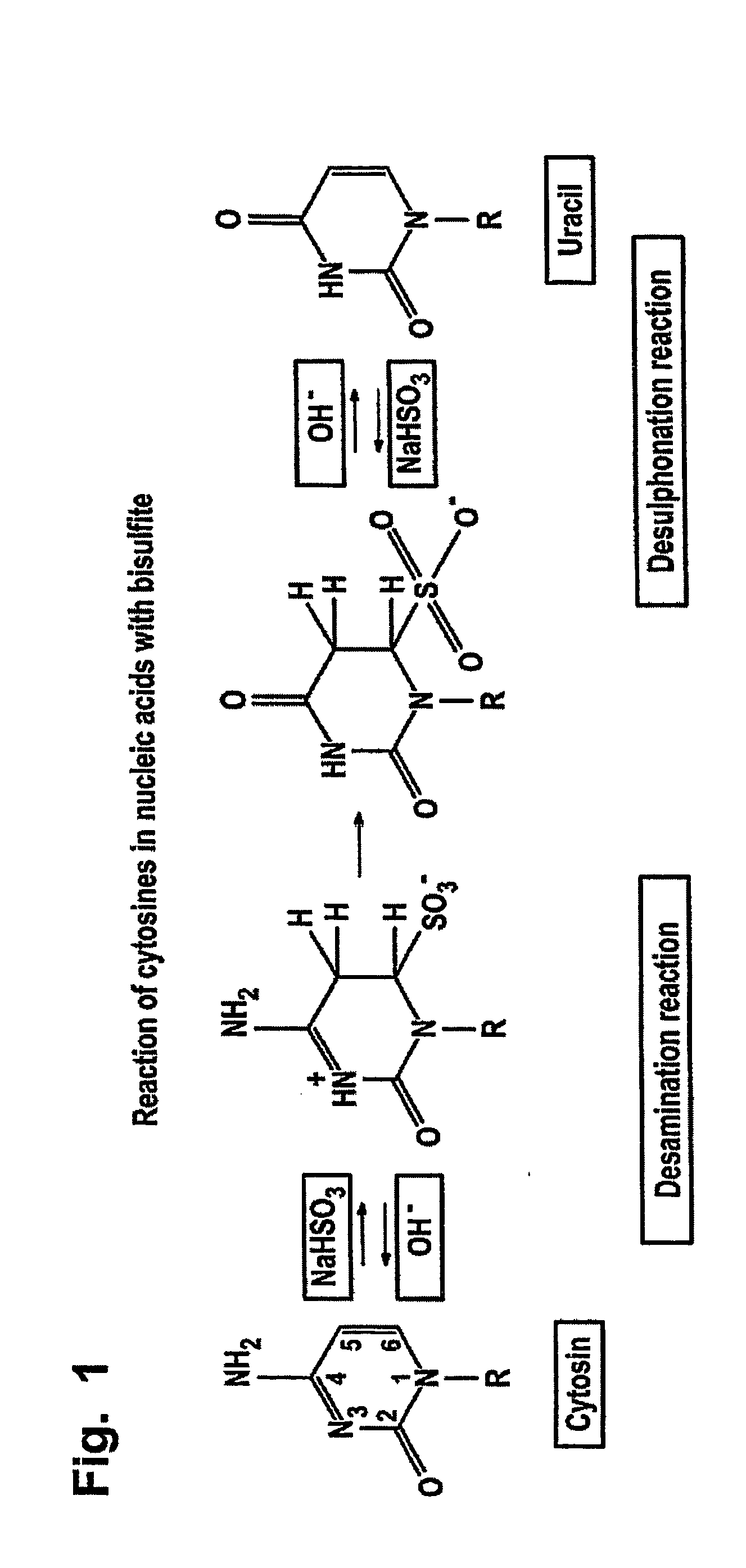
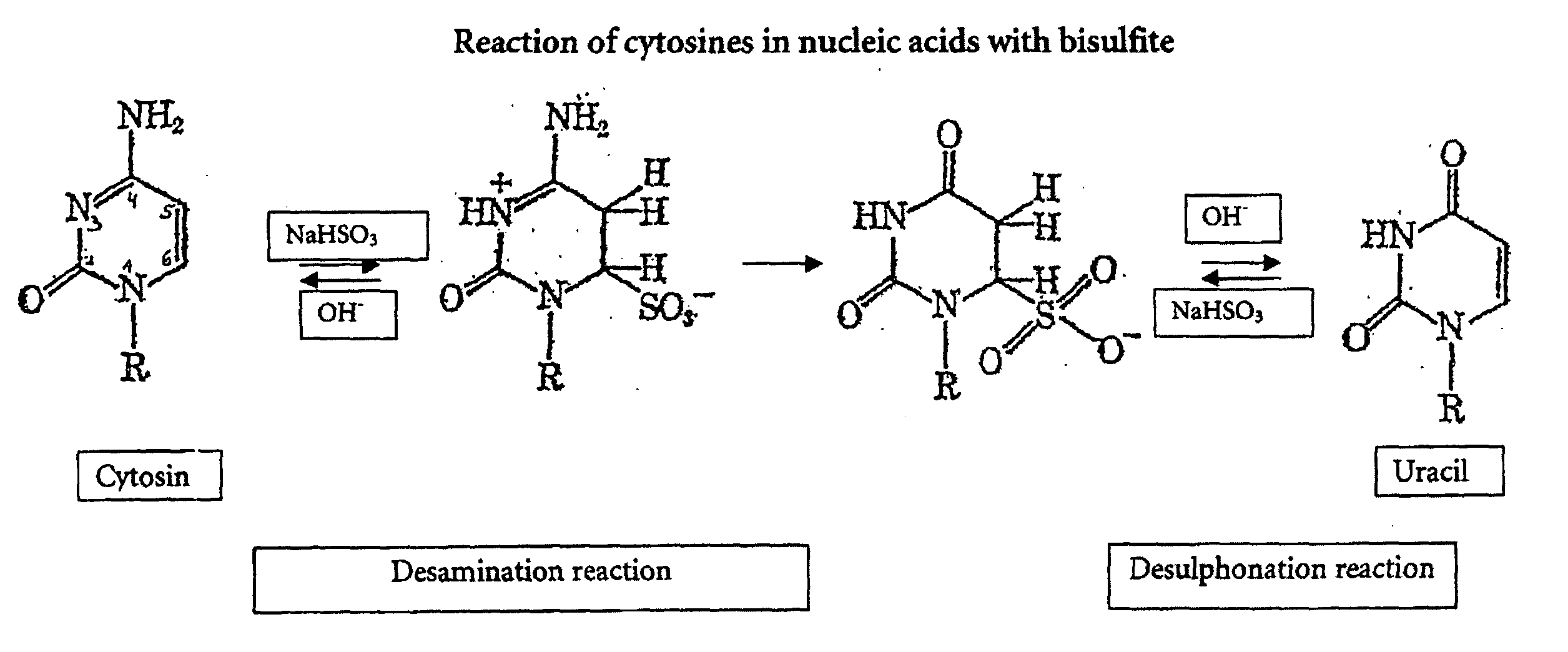
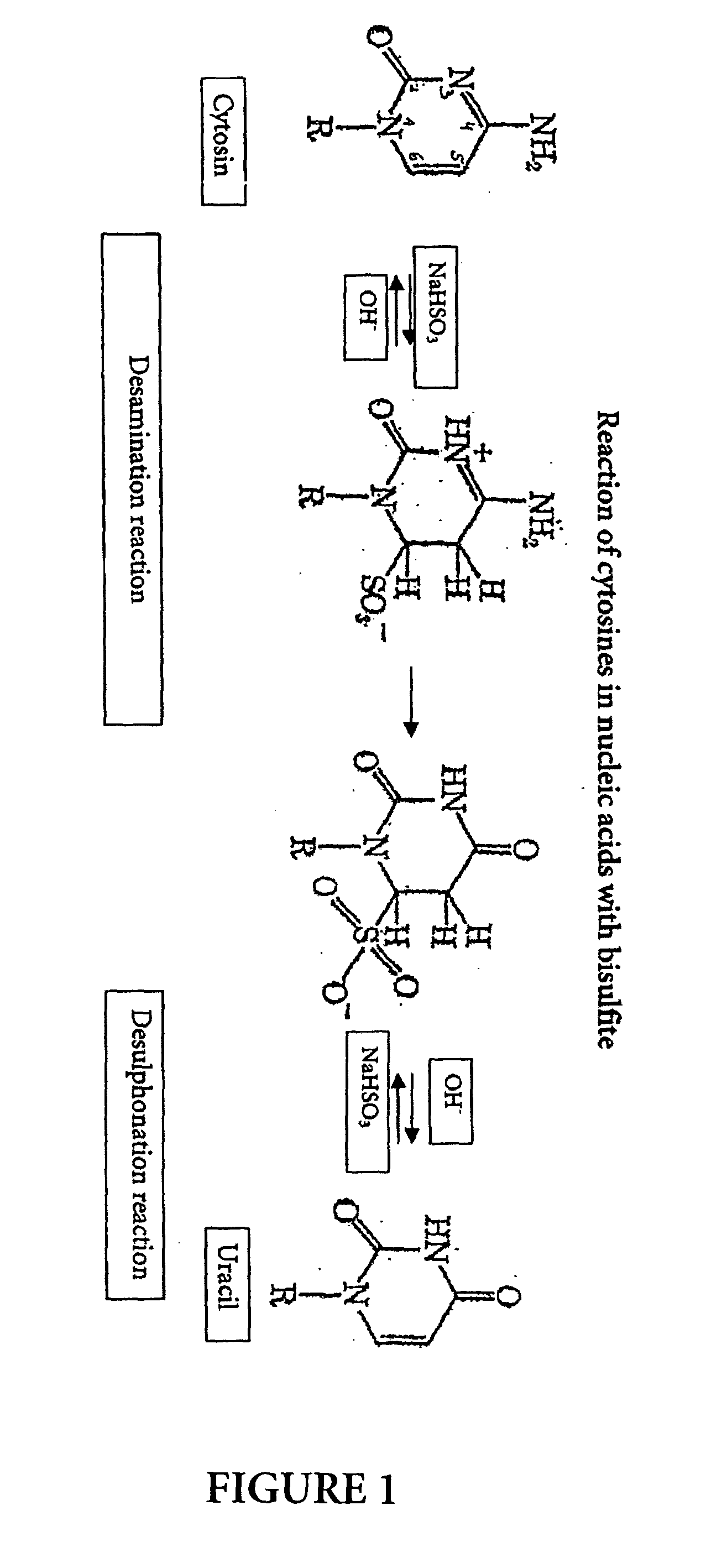
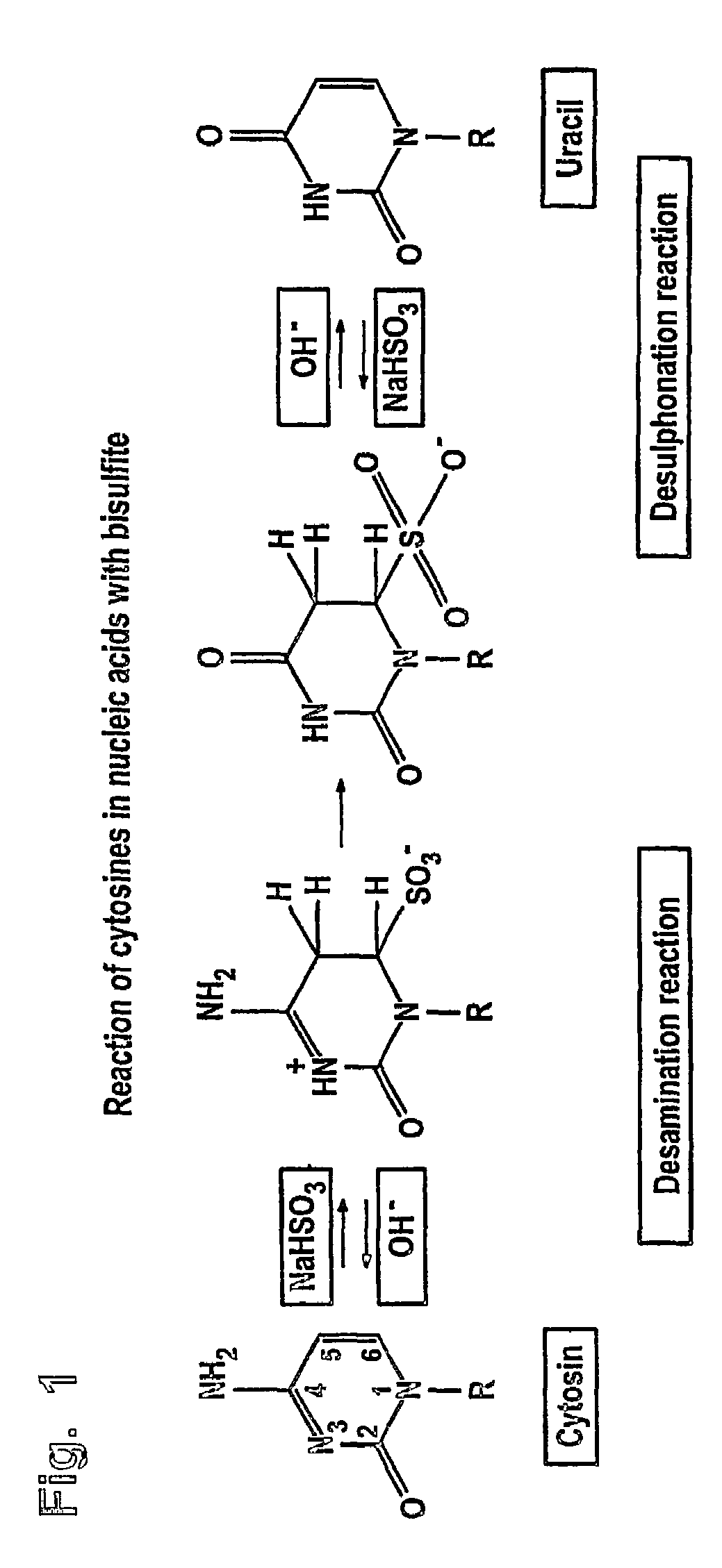
The bisulfite ion (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogen sulfite) is the ion HSO₃⁻. Salts containing the HSO₃⁻ ion are termed bisulfites also known as sulfite lyes. For example, sodium bisulfite is NaHSO₃.
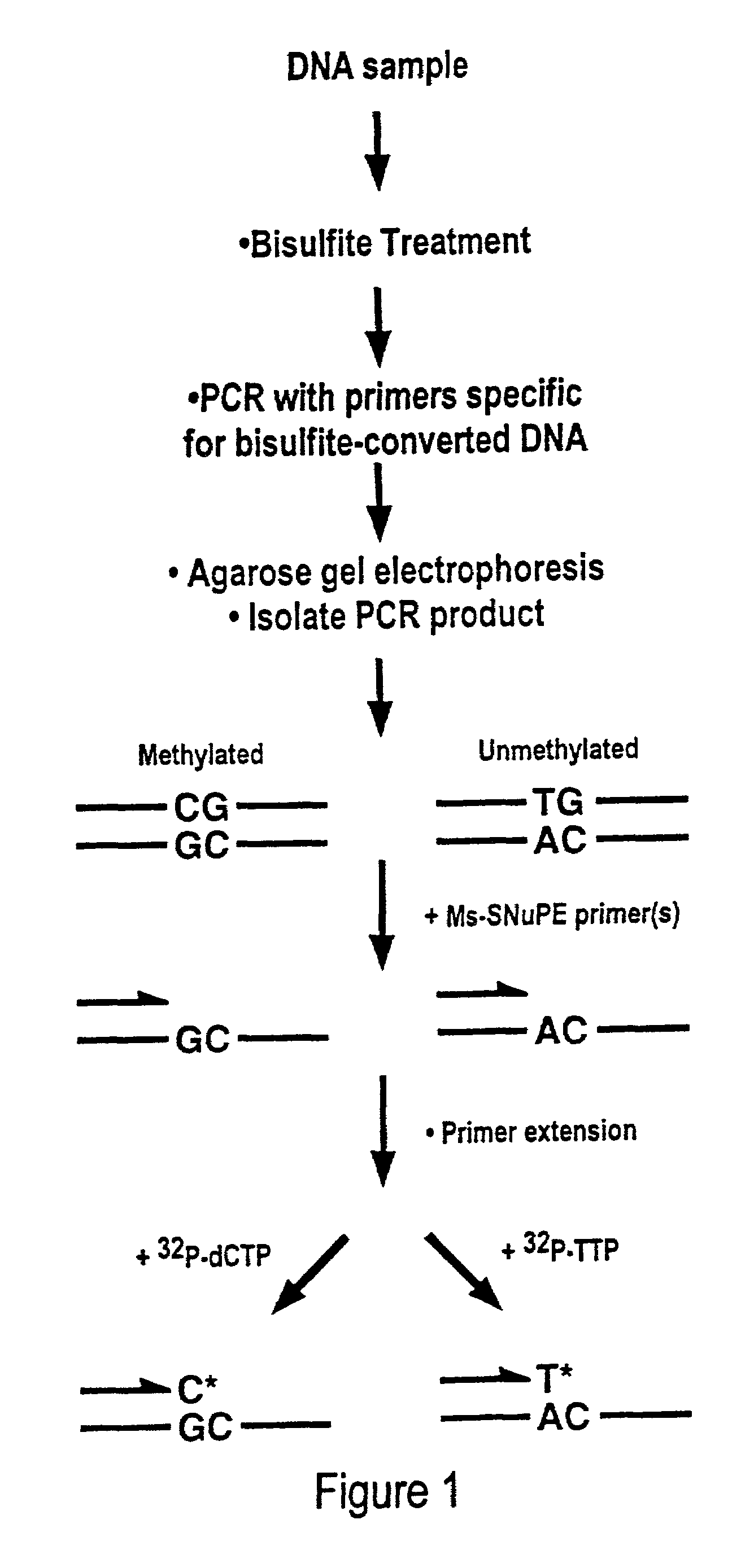
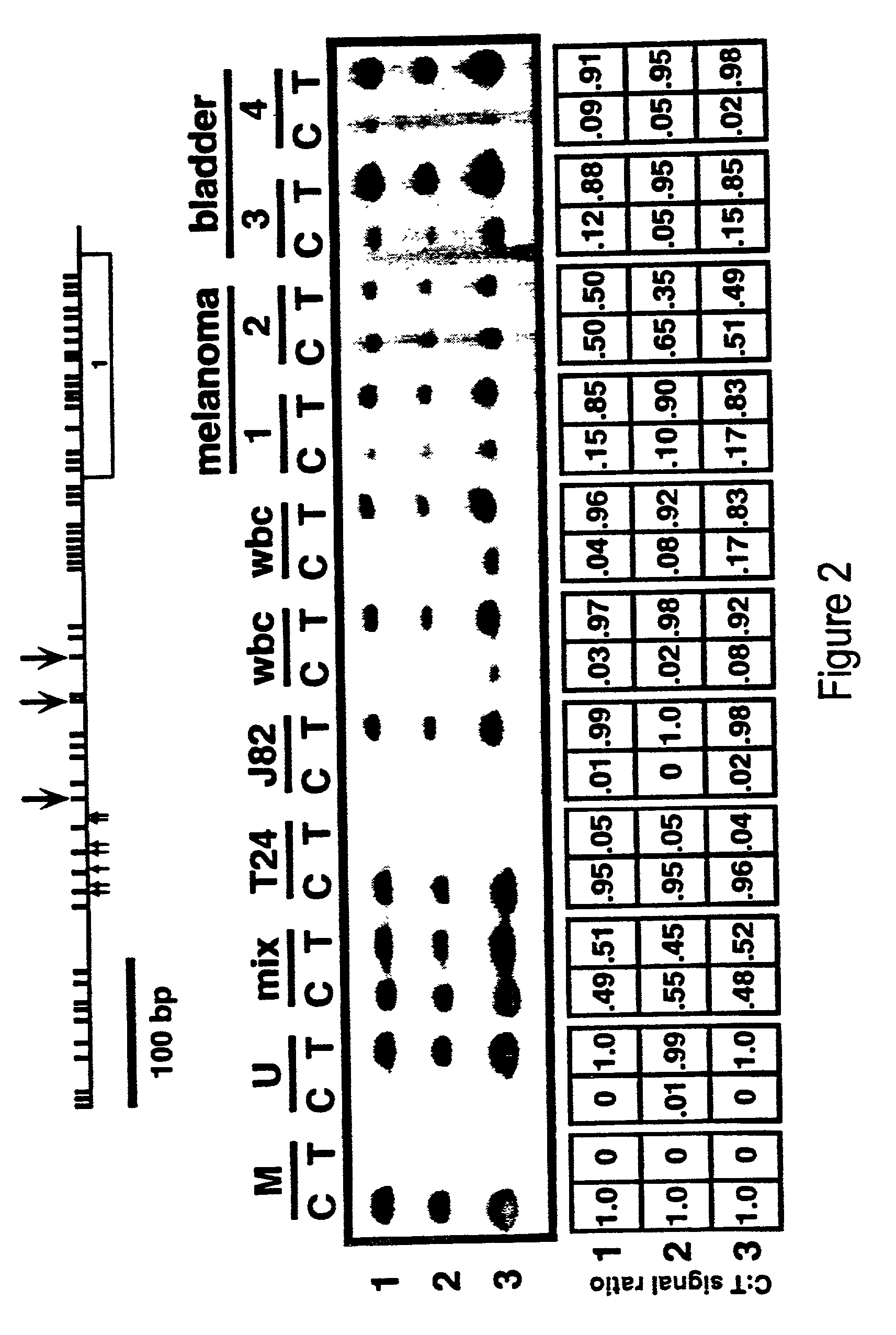
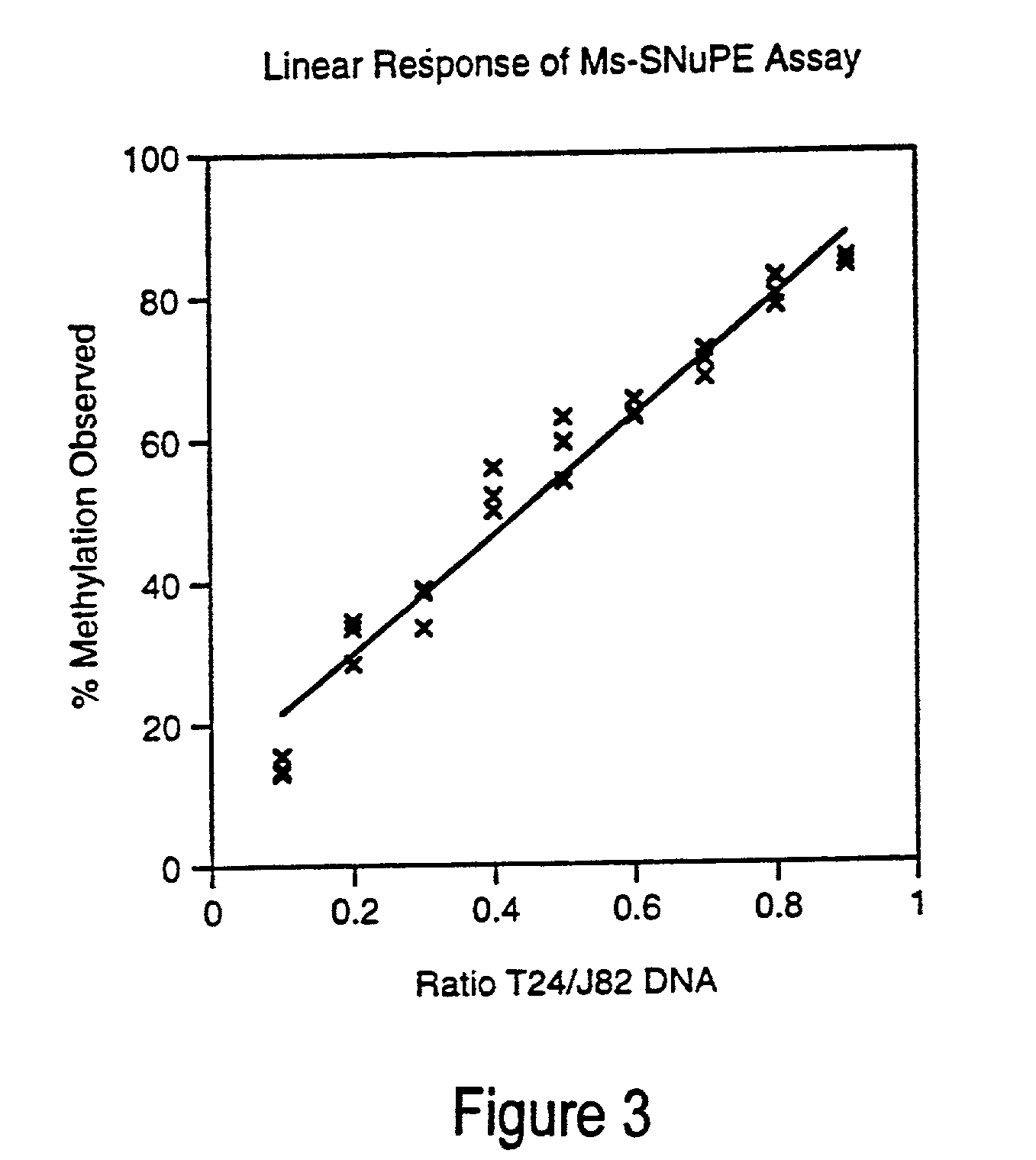
Cancer diagnostic method based upon DNA methylation differences
There is disclosed a cancer diagnostic method based upon DNA methylation differences at specific CpG sites. Specifically, the inventive method provides for a bisulfite treatment of DNA, followed by methylation-sensitive single nucleotide primer extension (Ms-SNuPE), for determination of strand-specific methylation status at cytosine residues.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Microwave mediated synthesis of nucleic acid probes
A method for preparing a nucleic acid probe is provided. The method comprises forming an activated cytosine or cytidine by a bisulfite catalyzed reaction; and covalently linking a reporter molecule to the activated cytosine or cytidine, wherein said activating step, said covalently linking step, or both are conducted in the presence of microwave energy. Also provided by the invention are nucleic acid probes.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Construction method and application of high-throughout sequencing library
InactiveCN103806111AEfficient constructionEfficiently obtainedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCytosineDNA fragmentation
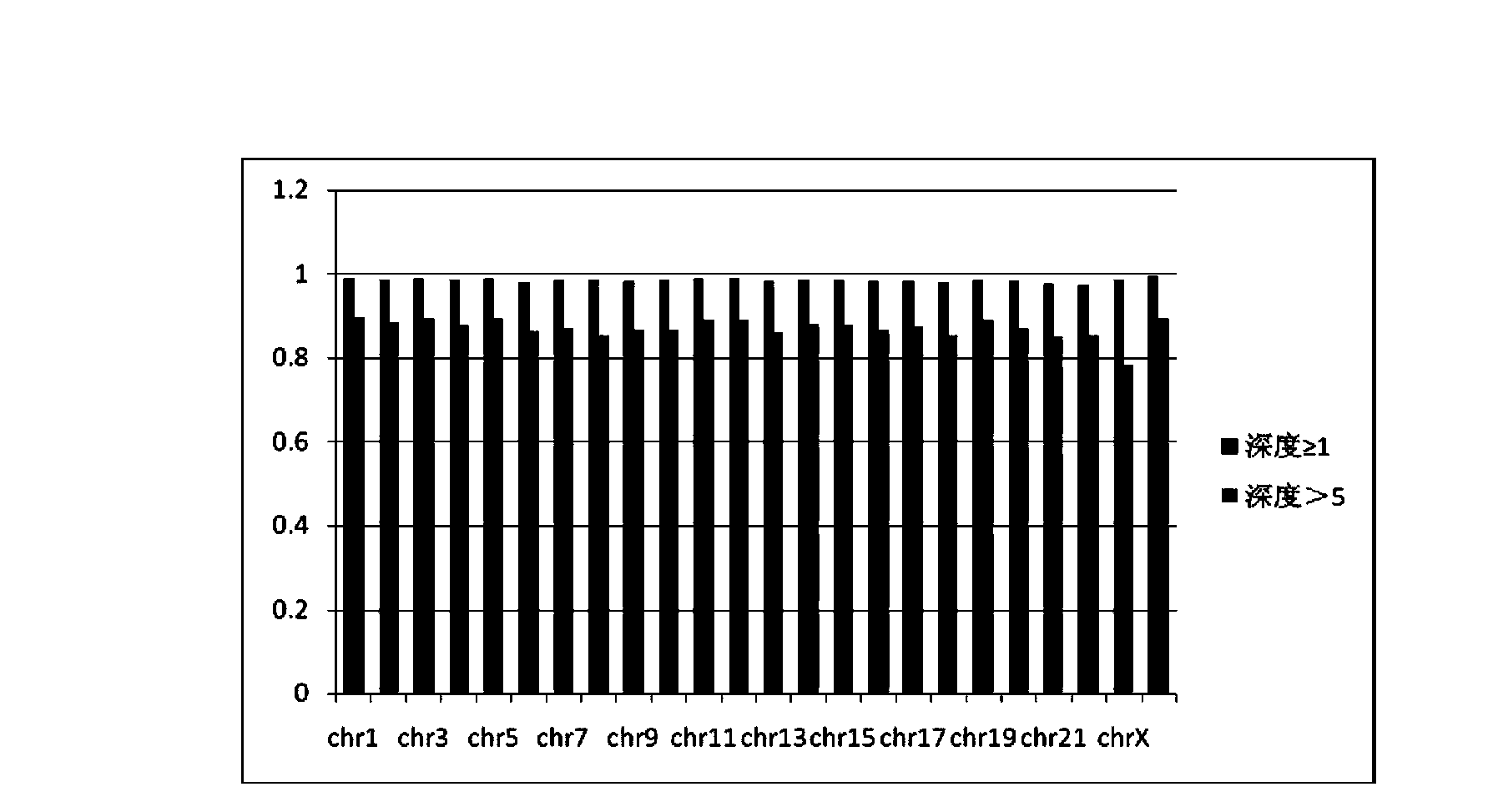
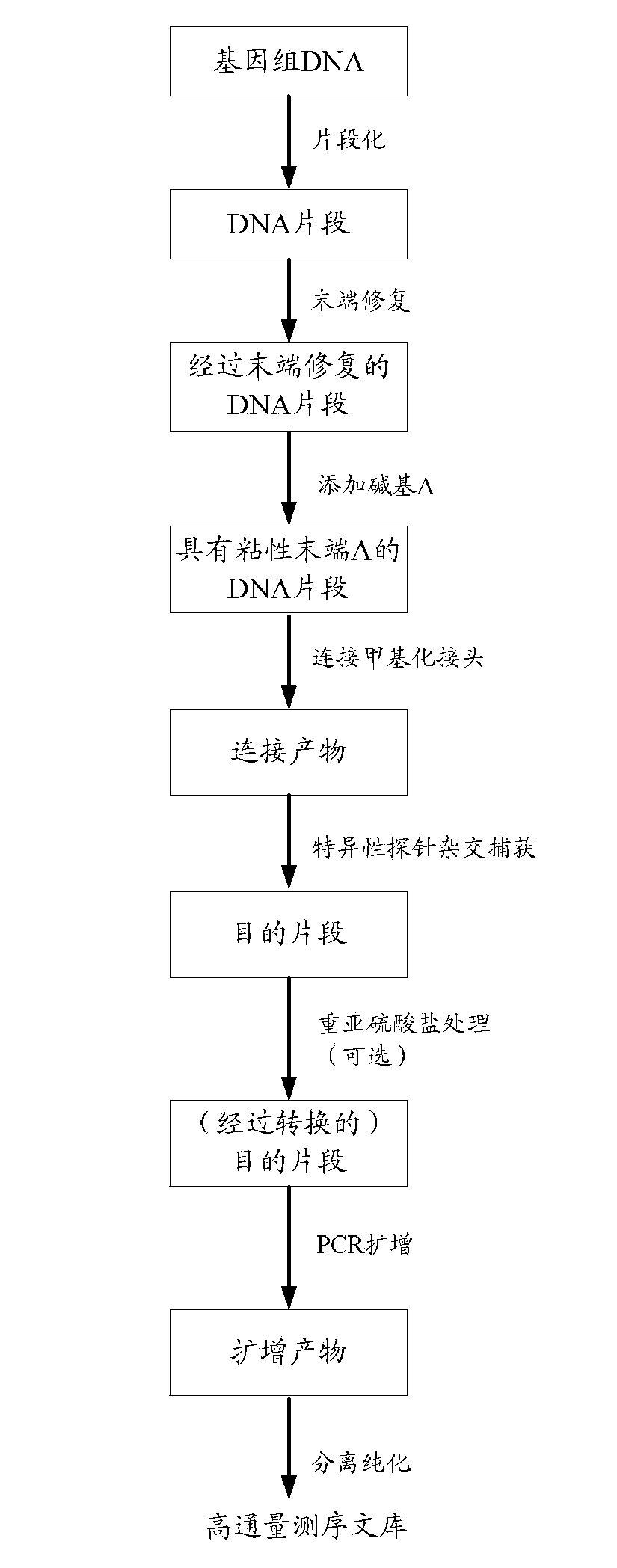
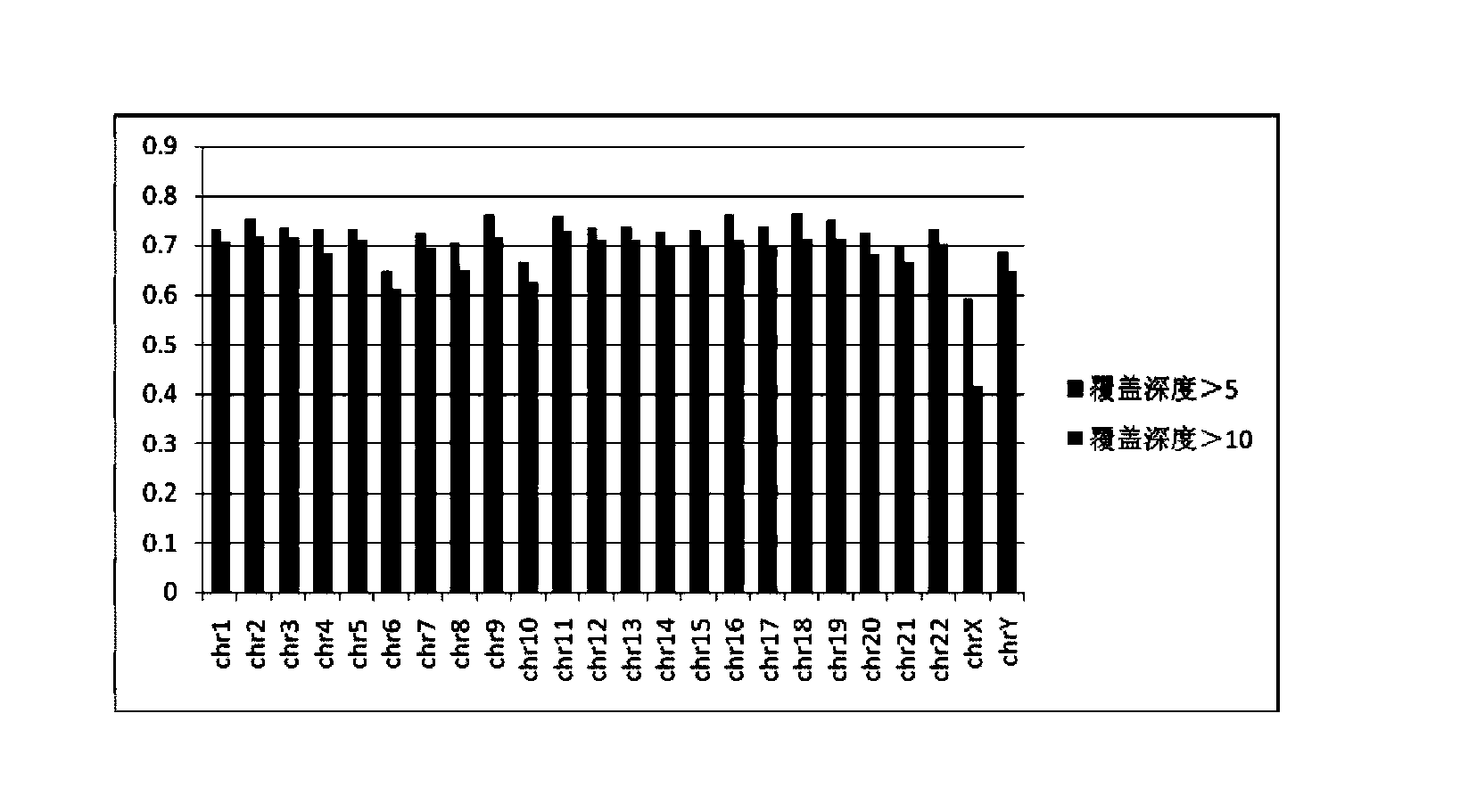
The invention discloses a construction method and an application of a high-throughout sequencing library. The construction method of the high-throughout sequencing library comprises the following steps: fragmenting genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid); repairing terminals of DNA fragments; adding a base A to 3' terminals of the DNA fragments with the repaired terminals; connecting the DNA fragments with sticky ends A to methylation linkers; carrying out hybrid capture on connecting products by using a specificity probe so as to obtain target fragments; carrying out bisulfite treatment on the target fragments so as to convert non-methylated cytosine in the target fragments to uracil; carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on the converted target fragments; separating and purifying amplification products which form the high-throughout sequencing library. According to the method and application of the high-throughout sequencing library, the high-throughout sequencing library of a genome specific zone of a sample can be conveniently and efficiently constructed.
Owner:BGI SHENZHEN CO LTD +1
Construction method and application of genome-wide methylation high-throughput sequencing library and
ActiveCN103088433AEfficient constructionEfficiently obtainedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCytosineDNA fragmentation
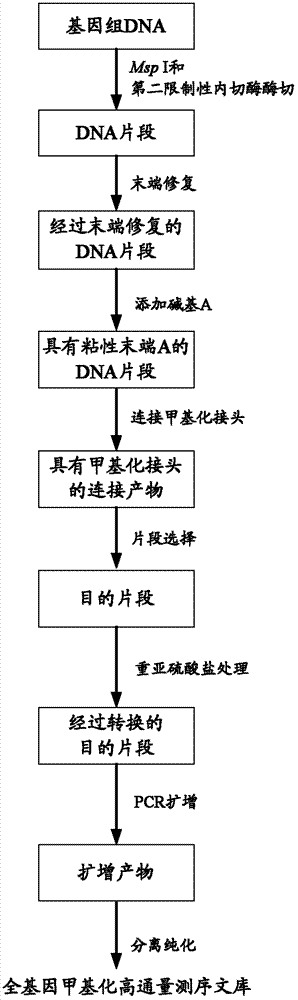
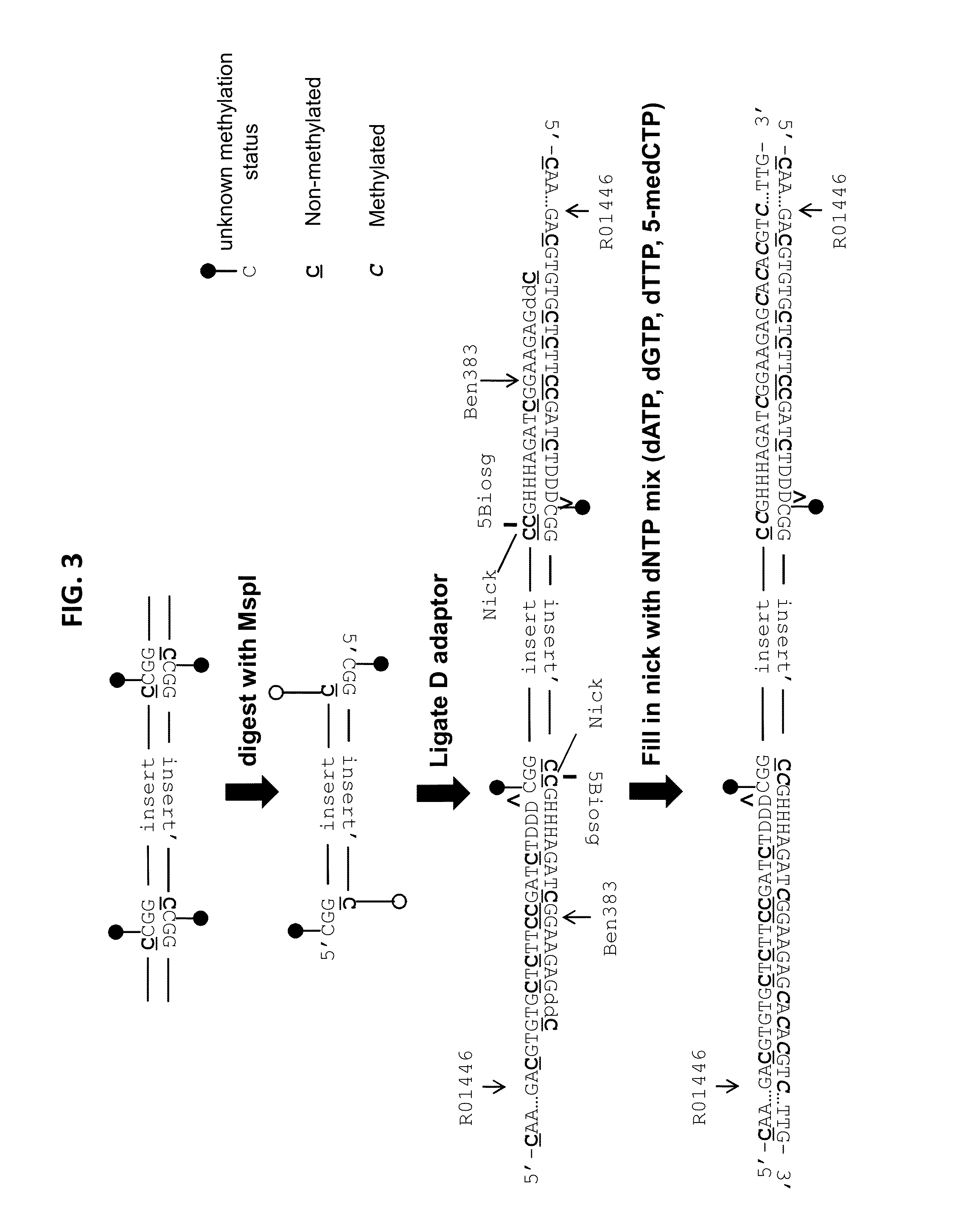
The invention provides a construction method and application of a genome-wide methylation high-throughput sequencing library. The construction method of the genome-wide methylation high-throughput sequencing library comprises steps of: conducting digestion on a genome DNA with Msp I and a second restriction endonuclease; conducting end repair on DNA fragments; adding a basic group A on a 3'terminal of the DNA fragment subjected to end repair; connecting a DNA fragment with a cohesive end A to a methylation joint; conducting fragment selection on the connect products with the methylation joint, in order to obtain a target fragment; subjecting the target fragment to a bisulfite treatment, in order to convert unmethylated cytosine in the target fragment to uracil; subjecting the converted target fragment to PCR amplification; and separating and purifying the amplification products, wherein the amplification products form the genome-wide methylation high-throughput sequencing library. The construction method and application of the genome-wide methylation high-throughput sequencing library provided by the invention can conveniently and effectively construct the genome-wide methylation high-throughput sequencing library of the genome DNA sample.
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL LAB BGI
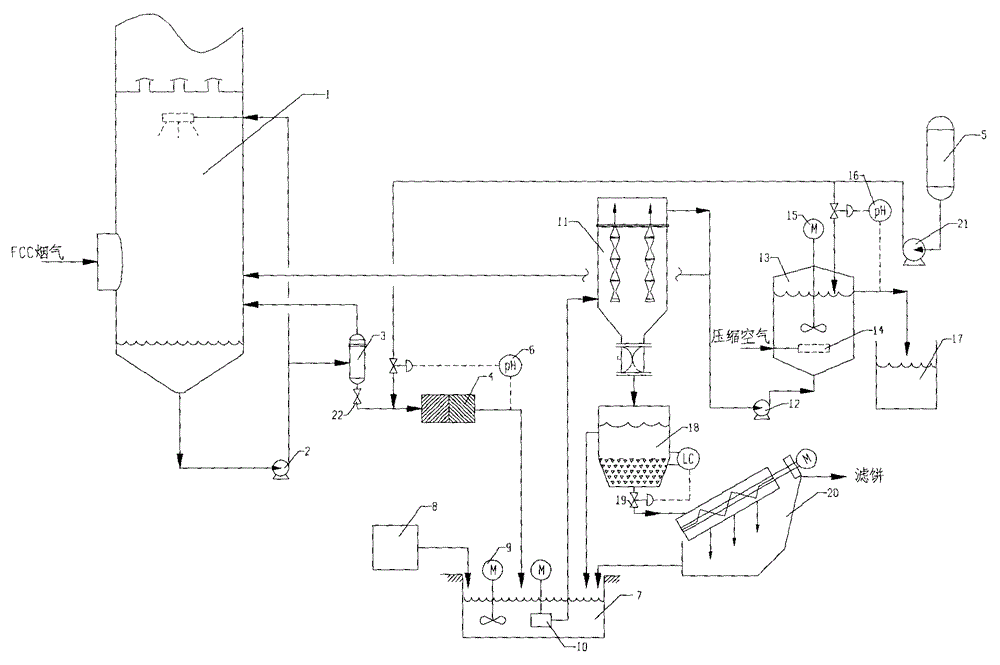
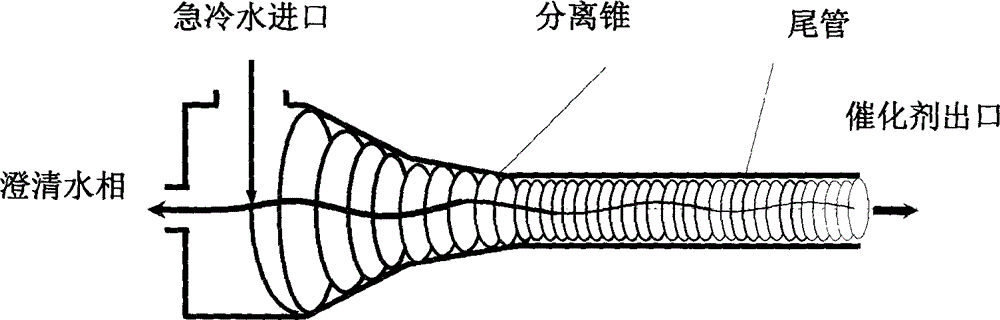
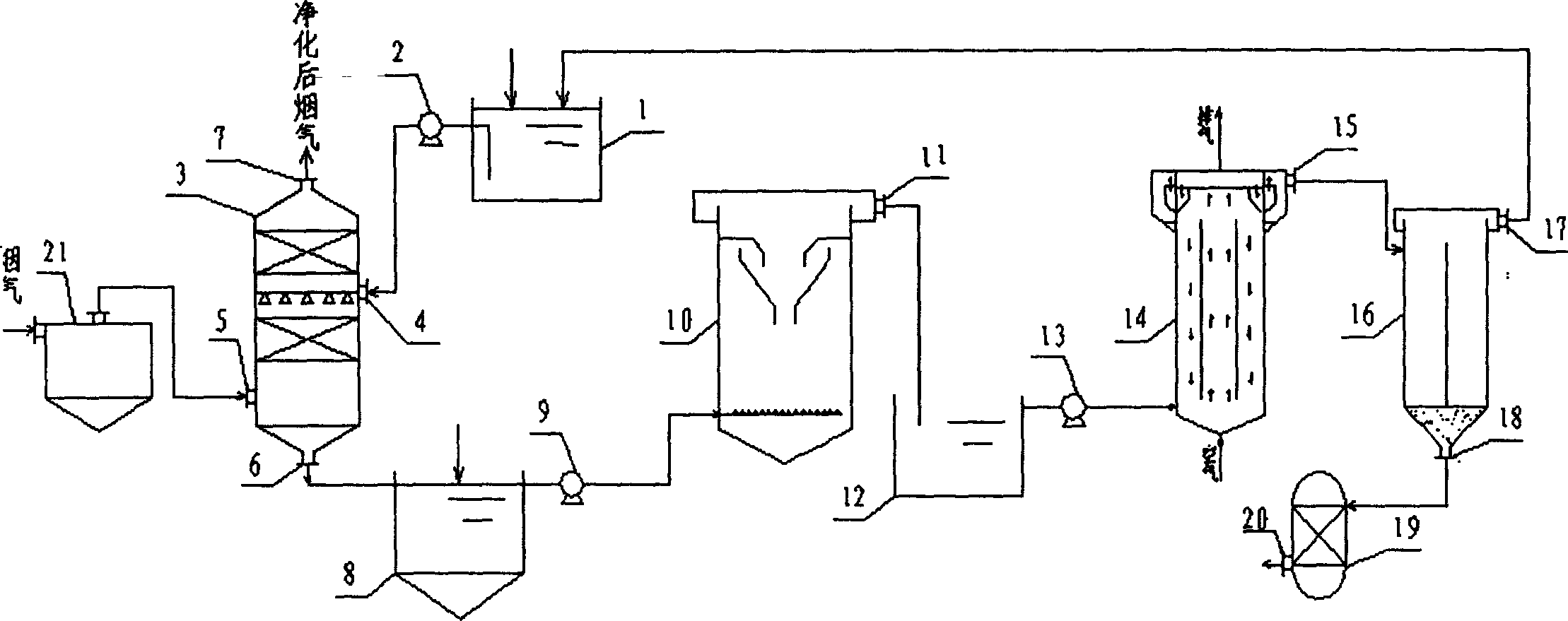
Catalytic cracking fume desulfuration wastewater treatment process
ActiveCN102815808AImprove effluent qualityEasy to operateMultistage water/sewage treatmentParticulatesChemical oxygen demand
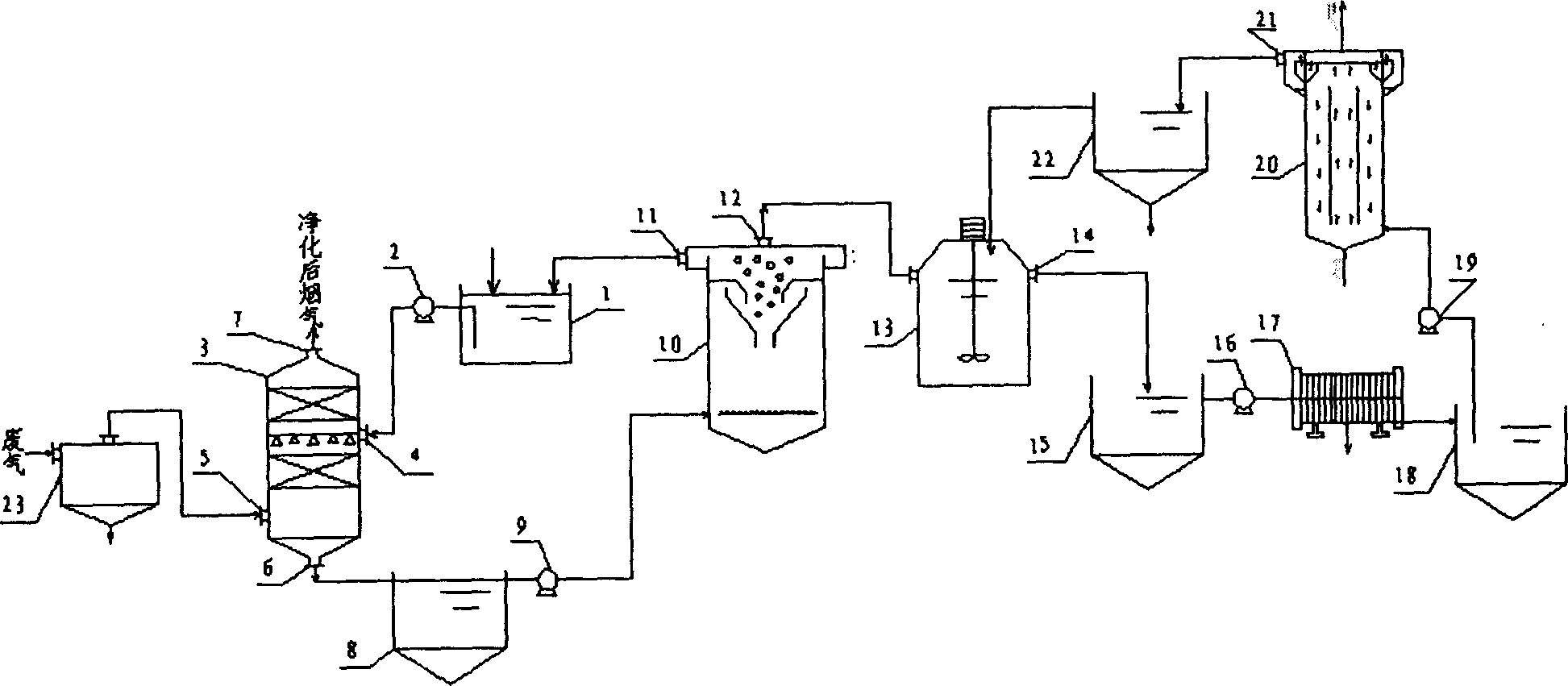
A catalytic cracking fume desulfuration wastewater treatment process is characterized in that wastewater is discharged to a slurry pool and is mixed with a flocculating agent, a stirrer is used for stirring the wastewater and the flocculating agent, the wastewater and the flocculating agent are mixed evenly, the wastewater after being mixed is discharged to an expansion tube type filter and is subjected to the coagulation reaction at the lower end of the expansion tube type filter, small particulate matters in the wastewater are flocculated, large flocculating bodies are formed, the solid-liquid separation is achieved through the filtration of a filtering film, thick slag and supernatant fluid are obtained, the supernatant fluid is discharged to an oxidation tank further, the thick slag is subjected to back washing and enters a subsequent filtering box, the thick slag is concentrated and dewatered in the filtering box, mud cakes which are concentrated are transported outwards, the water of dehydration returns to the slurry pool again, is mixed with the wastewater and is processed again, the false chemical oxygen demand (COD) which contains sulfite and bisulfite is oxidized and removed by the supernatant fluid in the oxidation tank, and the sewage which meets standards is discharged. Compared with the prior art, the process has the advantages that the area occupied by devices is small, the operation cost is low, the solid and the liquid can be separated completely, the working environment of workers is good, device parameters can be set in accordance with parameters of different materials, and the application is wide.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +3
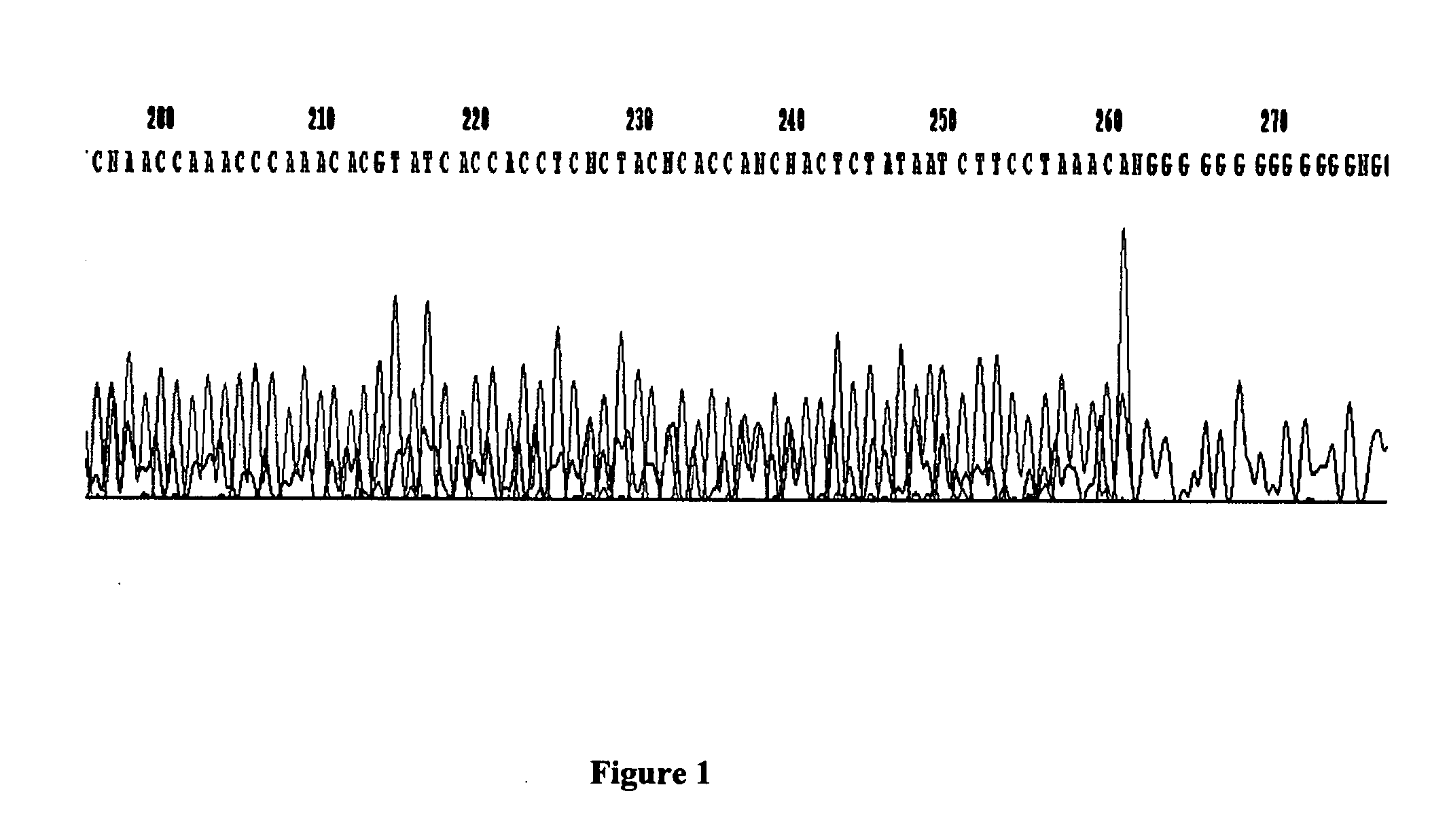
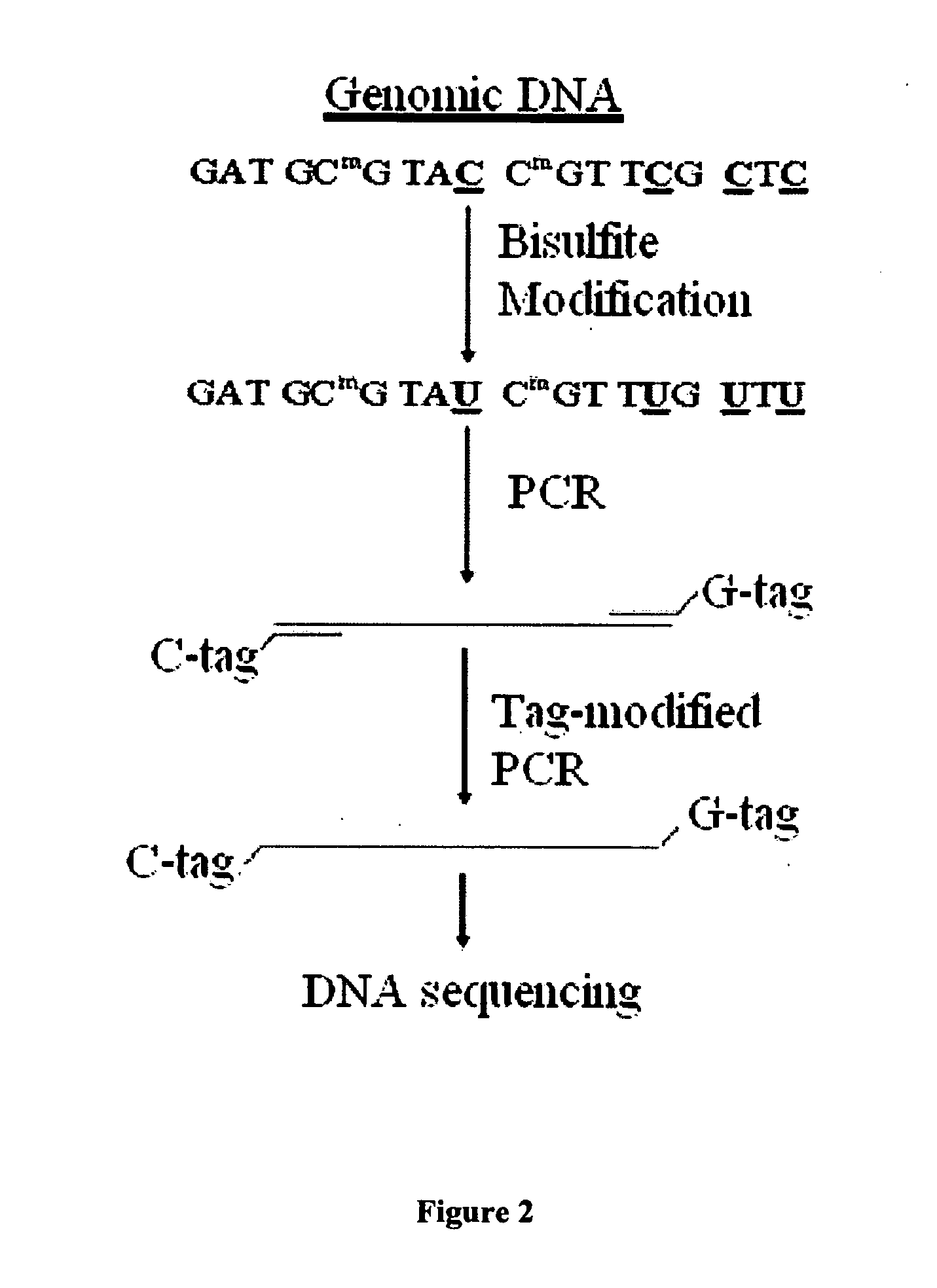
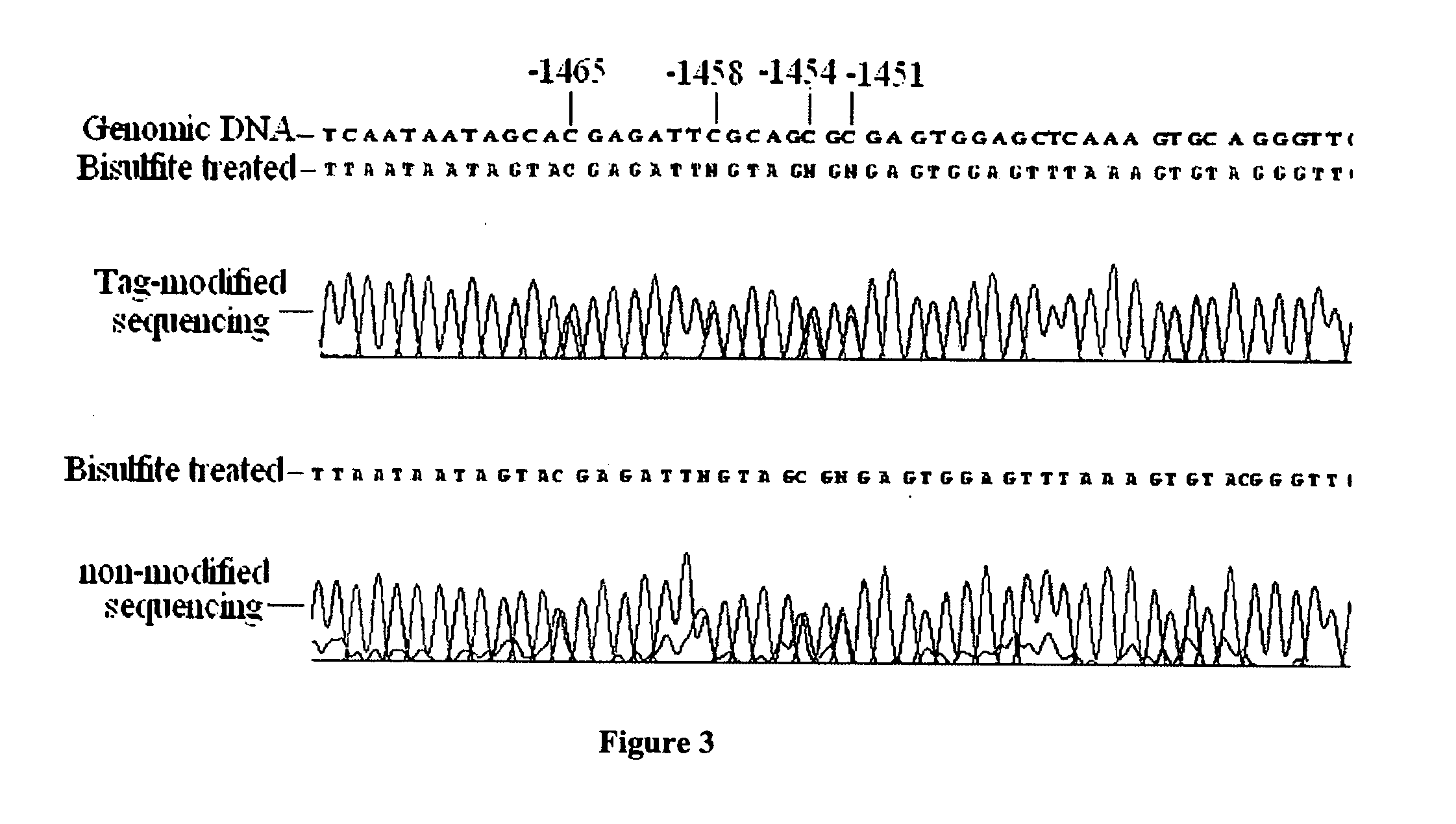
GC tag-modified bisulfite genomic DNA sequencing for continuous methylation spectra
InactiveUS20070054295A1Avoid the needMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGenomic sequencingCycle sequencing
The present invention relates to a tag-modified bisulfite genomic sequencing (tBGS) method developed for simplified evaluation of DNA methylation sites. The method employs direct cycle sequencing of PCR products at kilobase scale, without conventional DNA fragment cloning. The method entails subjecting bisulfite-modified genomic DNA to a second-round PCR amplification employing GC-tagged primers. The invention also relates to a method for identifying a patient at risk for lung cancer using the tBGS technique disclosed.
Owner:SPIVACK SIMON DANIEL +2
Impregnated filter element, and methods
InactiveUS20060130451A1High molecular weightCombination devicesGas treatmentKetoneAldehyde formation
A contaminant-removal filter for removing carbonyl-containing compounds from a gas stream, such as air. Examples of common airborne carbonyl-containing compounds include ketones, including acetone, and aldehydes, including formaldehyde. The filter has a porous or fibrous body that includes a plurality of passages extending from a first, inlet face to a second, outlet face, the passages providing flow paths. The body has a reactant material impregnated throughout the substrate. The reactant material is a sulfite, bisulfite, oxidant, or derivative of ammonia, specifically high molecular weight and stable amines. Strong alkali (basic) materials are particularly suitable for aldehyde removal. The filter is free of any humectants.
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
Method for removing organic pollutants in water at ultrahigh speed
ActiveCN104609597AObvious superiorityEasy to transportMultistage water/sewage treatmentBisulfiteHydroxyl radical
The invention relates to a method for removing organic pollutants in water at an ultrahigh speed. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, adding a reducing agent to water to be treated; secondly, adjusting the pH value of the water to be treated to be within the range of 3-7; thirdly, adding an oxidizing agent to the water to be treated. According to the method, bisulfite radicals are utilized for reacting with potassium permanganate or manganese dioxide, the removal of the organic pollutants in the water at the ultrahigh speed is realized by quickly generating a highly active oxidizing agent Mn(III) (at a non-complexing state), the rate of removing the pollutants by potassium permanganate and manganese dioxide can be improved by one thousand to one million times and is ten thousand times higher than the apparent oxidation rate of a general advanced oxidation technology, and the degradation for the pollutants can be completed in ten seconds or several seconds. According to the method, the pollutants incapable of being oxidized by potassium permanganate and manganese dioxide can also be oxidized, and even nitrobenzene capable of being oxidized by hydroxyl radicals only in traditional meanings can be oxidized, so that the oxidizing capacity of potassium permanganate and manganese dioxide is greatly improved, and the application range of potassium permanganate and manganese dioxide is expanded.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV +1
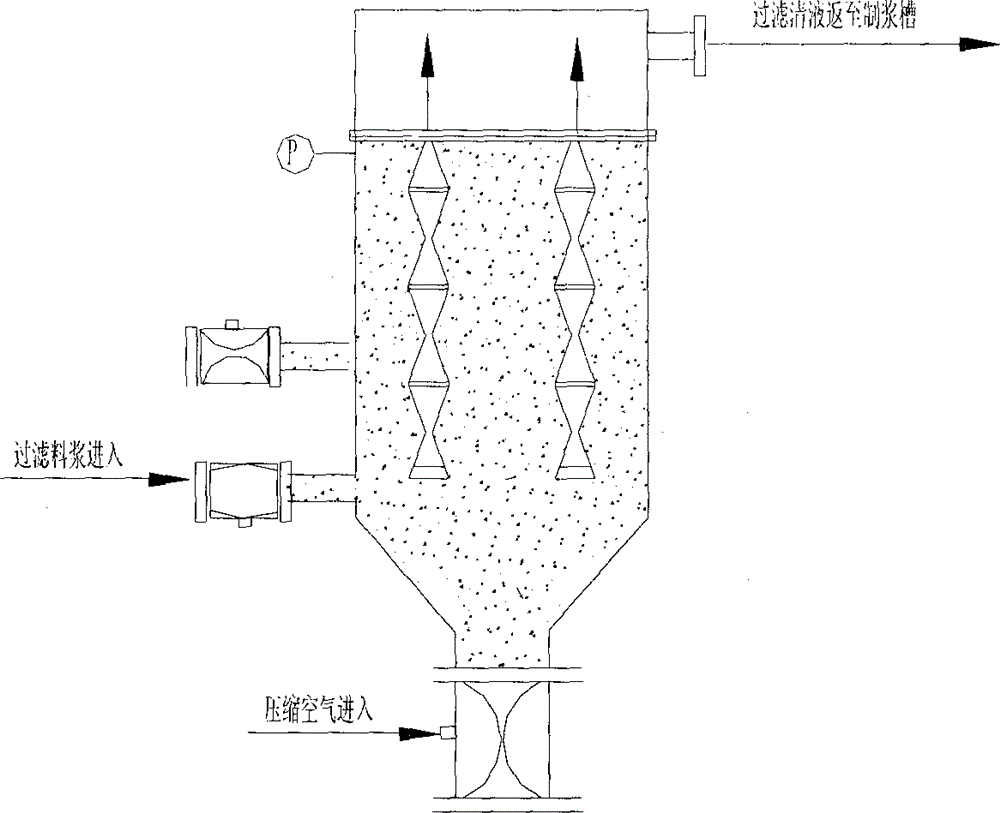
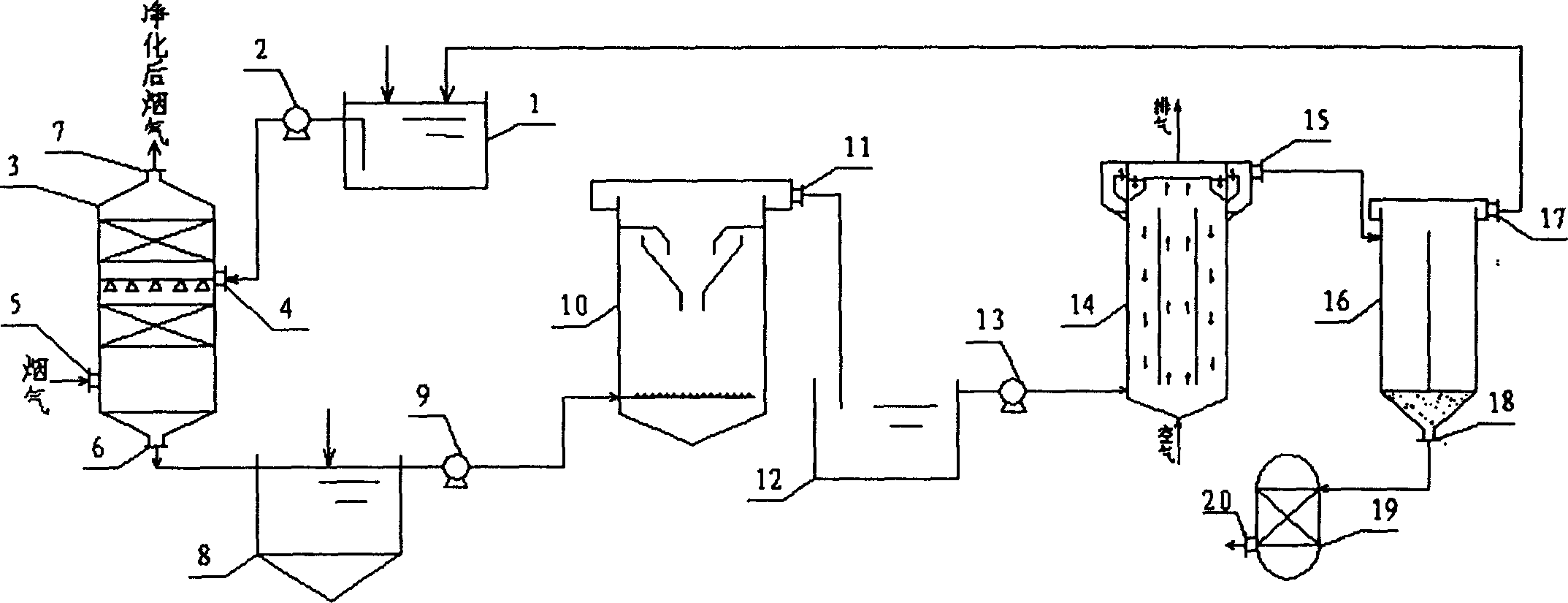
Process for treating waste liquid from catalytic cracking flue gas desulfurization
InactiveCN104418447AReduce dust concentrationReduce wearWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationSludge treatmentLiquid wasteSlurry
The invention provides a process for treating waste liquids from catalytic cracking flue gas desulfurization. The process comprises the following steps: enabling a part of waste liquids from a quenching washing tower to enter a hydraulic cyclone separator so as to be subjected to solid-liquid separation, returning the thin liquids to the quenching washing tower so as to be recycled, enabling the thick liquids to enter a neutralization reactor so as to be subjected to neutralization reaction, enabling the neutralized waste liquids to enter a slurry pond so as to be mixed with a flocculating agent uniformly, and enabling the mixture to enter an expansion-drum type filter so as to be subjected to solid-liquid separation with a thick slurry and a supernatant being obtained; returning part of the supernatant to the quenching washing tower so as to be recycled, discharging the remaining supernatant into an oxidation tank, removing the pseudo-COD containing sulfite roots and bisulfite roots by oxidizing, and directly discharging the qualified sewage; enabling the thick slurry to enter a settling pond from the bottom of the expansion-drum type filter so as to be further settled, feeding the thick slurry subjected to settlement into a dewatering machine so as to be concentrated and dewatered, directly transporting the filter cakes obtained by dewatering the thick slurry, returning the filtrate from the dewatering of the thick slurry to the slurry pond, and mixing the filtrate with the waste liquids so as to be retreated. The process provided by the invention has the advantages of a stable and efficient treatment effect, strong shock resistance, low investment and small floor area occupation and convenience of operation.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Global DNA methylation assessment using bisulfite PCR
The present invention provides a method and assay for determining global methylation using the methylation status of repetitive DNA elements as a surrogate marker. Also provided by the invention is a method for determining efficacy of a DNA methylation inhibiting drug by using changes in repetitive DNA methylation as a marker for drug efficacy. Additionally, the invention provides nucleic acid compositions for performing the method.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method for bisulfite treatment
InactiveUS20070190530A1Increase speedImprove accuracySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCytosineHydrogen
The invention is related to the detection of a methylated cytosine in a nucleic acid wherein guanidinium hydrogen sulfite is used for the preparation of a solution containing guanidinium ions and sulfite ions and subsequent modification of the nucleic acid. Thereby, a non-methylated cytosine is converted to uracil. The invention further discloses kits for performing the methods of the invention.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Method for accurate detection of whole genome methylation sites by utilizing trace genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
ActiveCN102409408AHigh amplification efficiencyImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationFragment sizeExogenous DNA
According to the invention, based on Illumina common tag library sequencing and methylation normal sequencing and combining a common library tag sequencing method, a new method for accurate detection of whole genome methylation sites by utilizing trace genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is built. According to the method, in the construction of a methylation library by using trace genome DNA, exogenous DNA is innovatively added to carry out bisulfite high-efficiency co-treatment; and at the same time, fragment size selection is not needed, and PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification is directly carried out after bisulfite treatment. By the method, the defects that in the common methylation sequencing, samples can not be mixed, the PCR amplification efficiency is low and the trace DNAsample can not be researched are overcome.
Owner:BGI TECH SOLUTIONS
Methods of Analysis of Methylation
InactiveUS20080108073A1Uniformly amplifyStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMultiplexCytosine
Methods for determining the methylation status of a plurality of cytosines are disclosed. In some aspects genomic DNA target sequences containing CpGs are targeted for analysis by multiplex amplification using target specific probes that can be specifically degraded prior to amplification. The targets may be modified with bisulfite prior to amplification. In another aspect targets are cut with methylation sensitive or insensitive restriction enzymes and marked with a tag using the target specific probes. The presence or absence of methylation may be determined using methylation sensitive restriction enzyme or bisulfite treatment. Detection in many embodiments employs hybridization to tag arrays, genotyping arrays or resequencing arrays.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
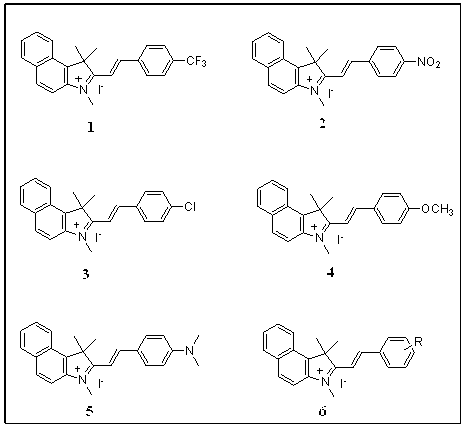
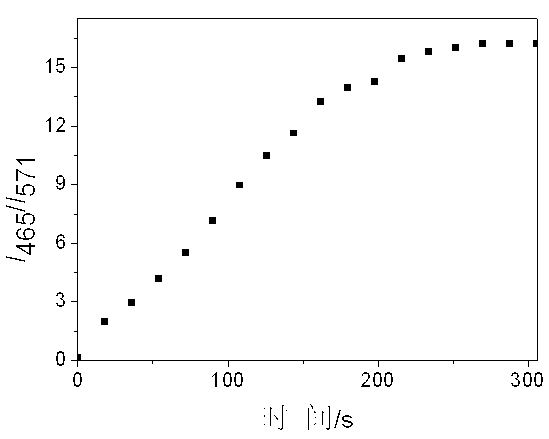
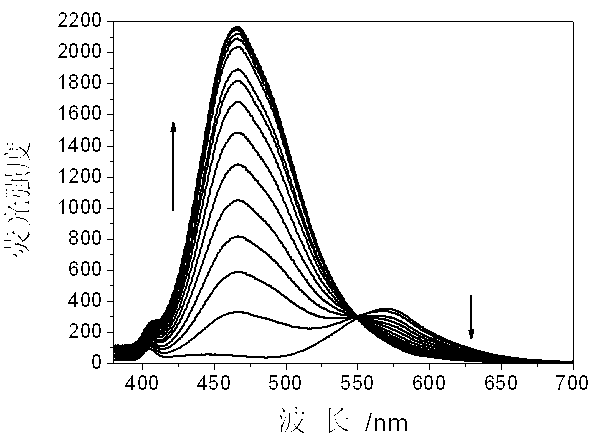
Ratio-dependent bisulfite ion fluorescent probes and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103275698AHigh detection sensitivitySimple post-processingOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluoProbesFluorescence ratio
The invention relates to preparation and application methods of ratio-dependent bisulfite ion fluorescent probes, belonging to the technical field of anion detection. The probe molecules have recognition specificity for bisulfite ions in a neutral aquatic environment, generate fluorescence ratio variations, have very high sensitivity, and meanwhile, cause obvious color and fluorescent color variations. The fluorescent probes do not generate obvious variations for other ions, free radicals or molecules. The invention implements recognition specificity of the probe molecules for the bisulfite ions, provides the fluorescent probes with color comparison sensing function, and thus, has wide application prospects in the fields of biology and ion detection.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
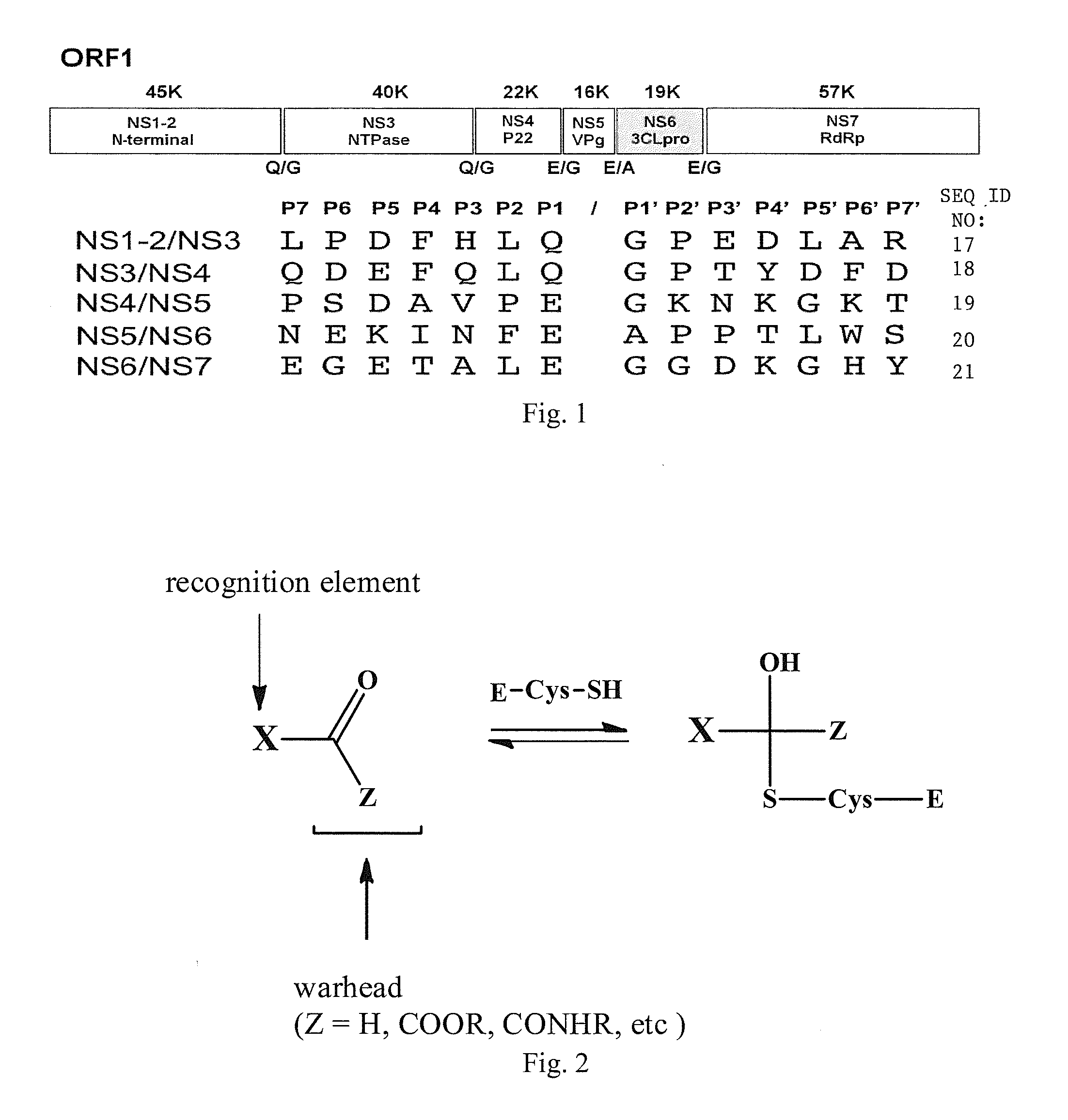
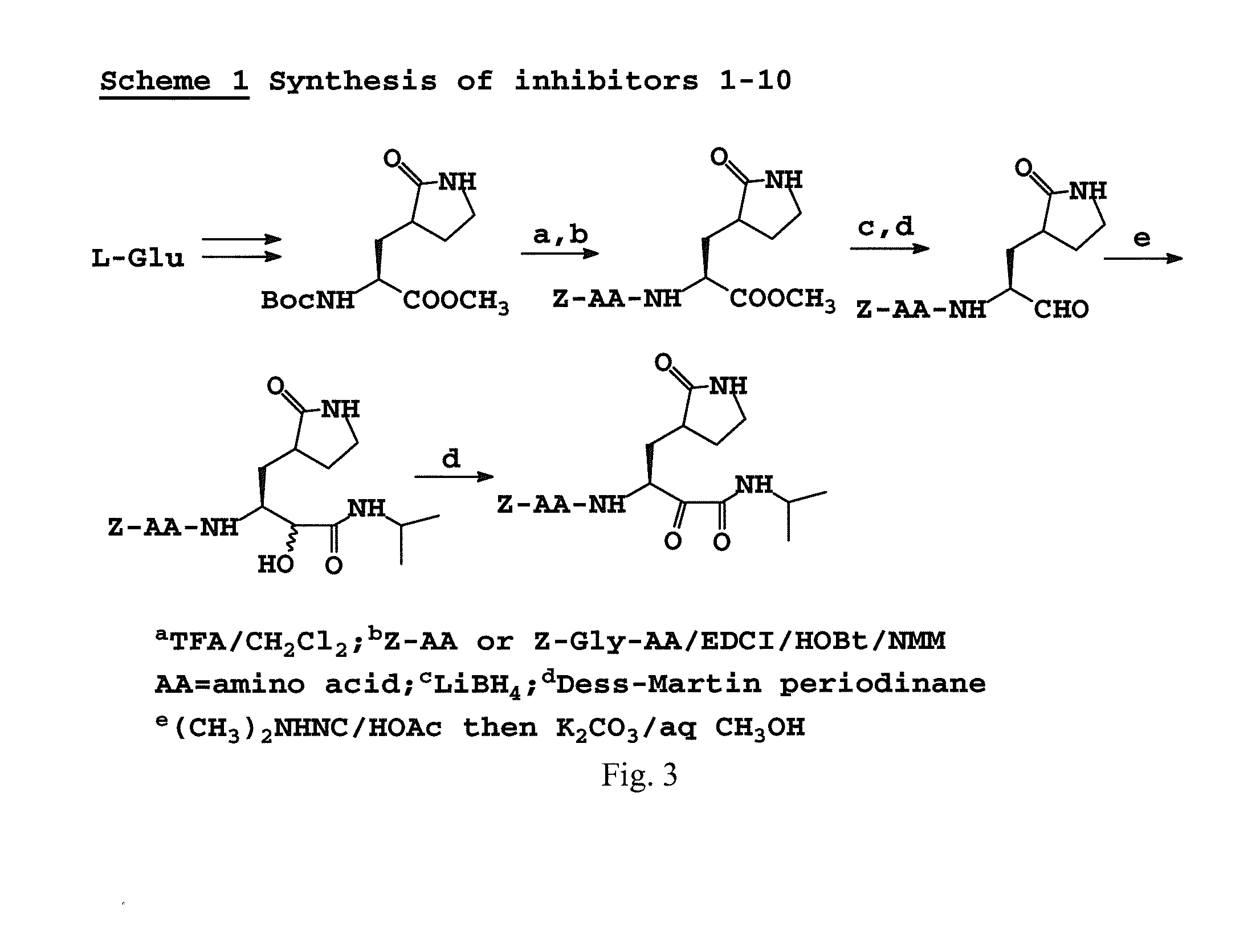
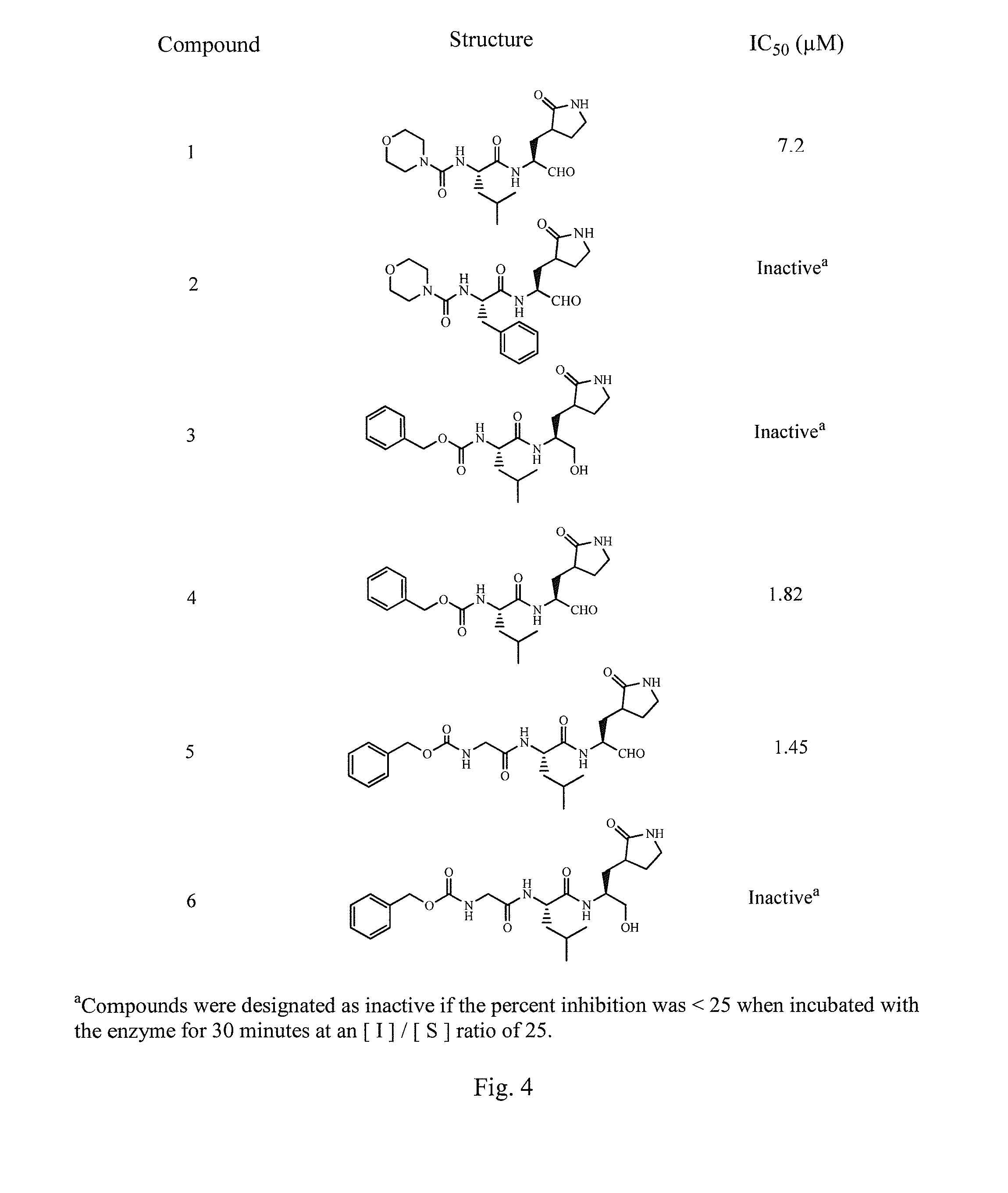
Broad-spectrum antivirals against 3c or 3c-like proteases of picornavirus-like supercluster: picornaviruses, caliciviruses and coronaviruses
ActiveUS20140243341A1Preventing and inhibiting replicationBiocideSsRNA viruses positive-senseEnterovirusDisease
Antiviral protease inhibitors, including peptidyl aldehydes, peptidyl α-ketoamides, peptidyl bisulfite salts, and peptidyl heterocycles, are disclosed, along with related antiviral compounds, and methods of using the same to treat or prevent viral infection and disease. The compounds possess broad-spectrum activity against viruses that belong to the picornavirus-like supercluster, which include important human and animal pathogens including noroviruses, enteroviruses, poliovirus, foot-and-mouth disease virus, hepatitis A virus, human rhinovirus (cause of common cold), human coronavirus (another cause of common cold), transmissible gastroenteritis virus, murine hepatitis virus, feline infectious peritonitis virus, and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus.
Owner:WICHITA STATE UNIVERSITY +2
Method for bisulfite treatment
ActiveUS20040241704A1Increase speedImprove accuracySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGlass fiberCytosine
The present application is directed to a method for performing a bisulfite reaction to determine methylation positions in a nucleic acid, i.e. methylated and non-methylated cytosines, whereby the nucleic acid is bound to a solid phase during the deamination and / or desulfonation step of the bisulfite reaction. The solid phase is preferably a material comprising glass or silica, more preferably a glass fleece, glass membrane or a magnetic glass particle. Further, the use of a solid phase for binding a nucleic acid during the deamination and / or desulfonation step of the bisulfite reaction is disclosed and a kit containing a bisulfite reagent and a solid phase.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Method for bisulfite treatment
InactiveUS7413855B2Short reaction timeReduce processSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCytosineBisulfite
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Electroless gold plating method and electronic parts
ActiveUS20080277140A1Efficient and effective mannerSimplify procedureNon-insulated conductorsSolid-state devicesGold CompoundsChemistry
Part or whole of an electroless gold plating film of a plated film laminate including an electroless nickel plating film, an electroless palladium plating film and an electroless gold plating film is formed by an electroless gold plating using an electroless gold plating bath including a water-soluble gold compound, a completing agent, formaldehyde and / or a formaldehyde-bisulfite adduct, and an amine compound represented by the following general formula R1—NH—C2H4—NH—R2 or R3—(CH2—NH—C2H4—NH—CH2)n—R4. The method of the invention does not need two types of baths, a flash gold plating bath and a thick gold plating bath for thickening. Gold plating films of different thicknesses suited for solder bonding or wire bonding can be formed using only one type of gold plating bath. Especially, an electroless gold plating film having a thickness of not smaller than 0.15 μm can be efficiently, effectively formed by use of one plating bath in one step, thereby enabling the process to be simplified along with an attendant advantage in cost.
Owner:C UYEMURA & CO LTD
Litchi and longan antistaling agent and methods of use
InactiveCN1541543AEliminate browningFew stepsFruit and vegetables preservationDithionous acidSulfate
The present invention discloses one kind of lichi and longan preservative with high preserving effect, no toxicity, no environmental pollution and low cost and suitable for industrial production. The preservative consists of queensland arrowroot powder and bisulfite, pyrosulfite or dithionite capable of releasing SO2 when reacting with water and air. When the preservative is used, it is packed into non-woven polypropylene pocket, the pocket is set inside non-woven polypropylene bag for holding lichi or longan, and the bag is sealed and set into some packing box, with the amount of the preservative being 3.1-8.6 % of the weight of lichi or longan.
Owner:黄海雄
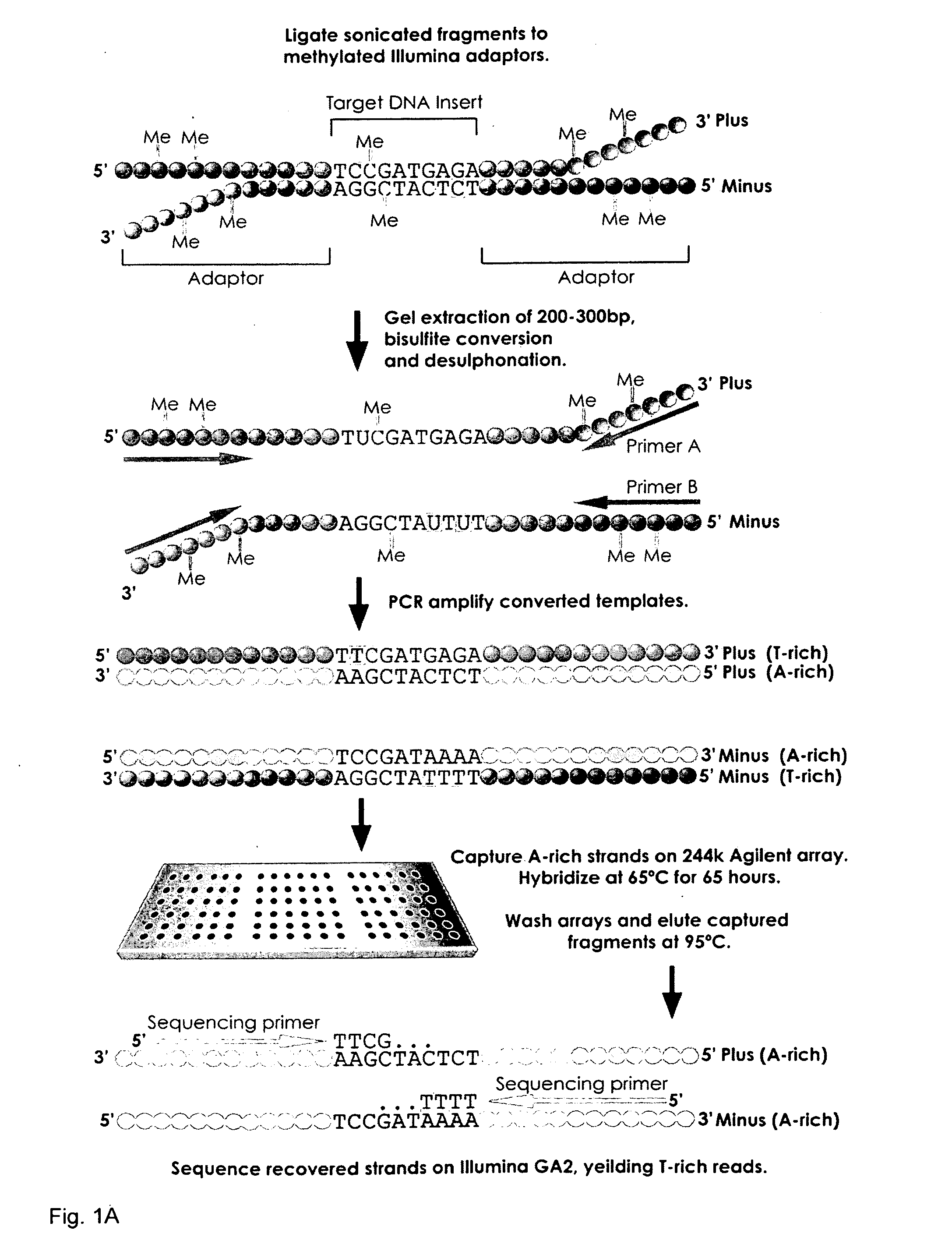
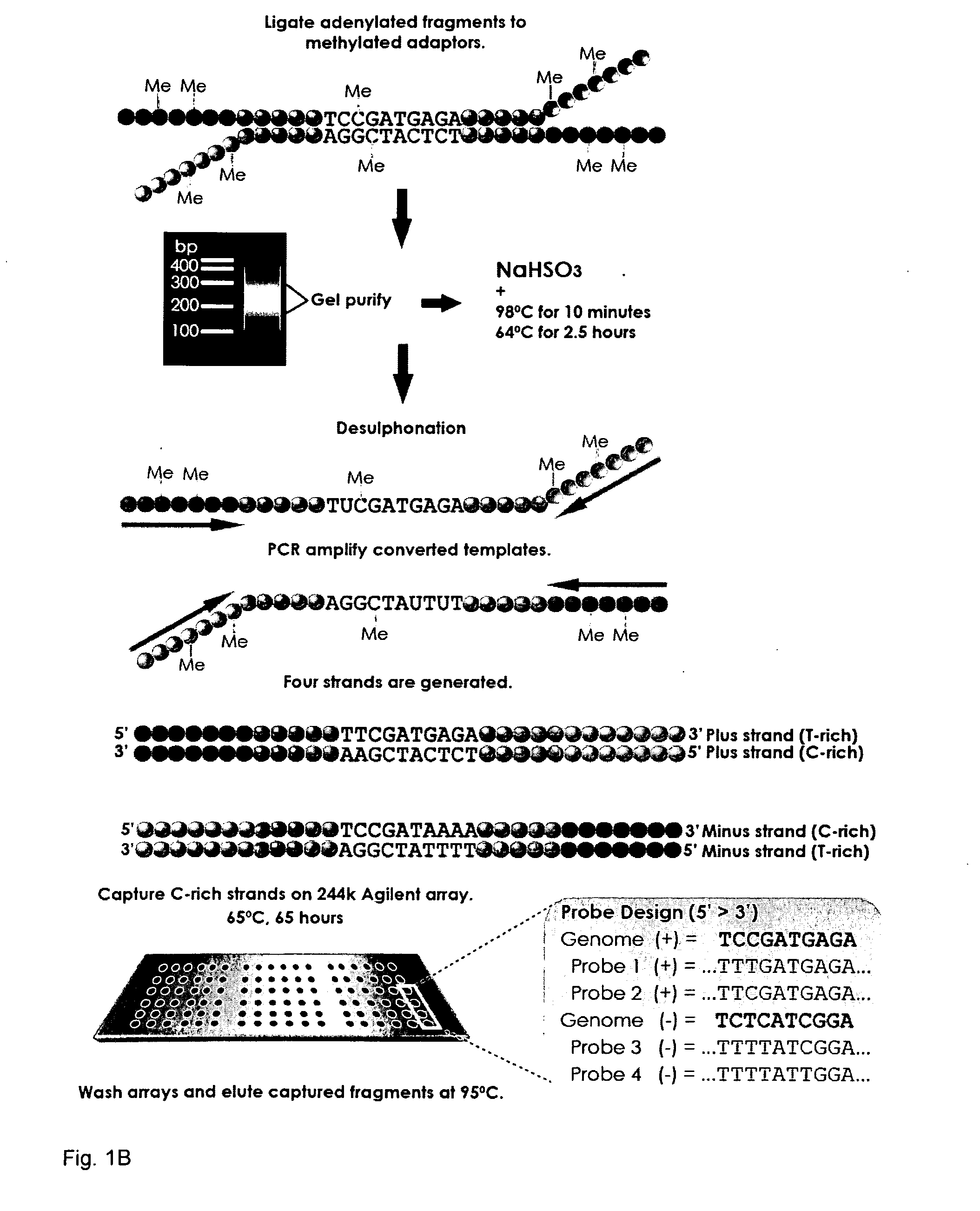
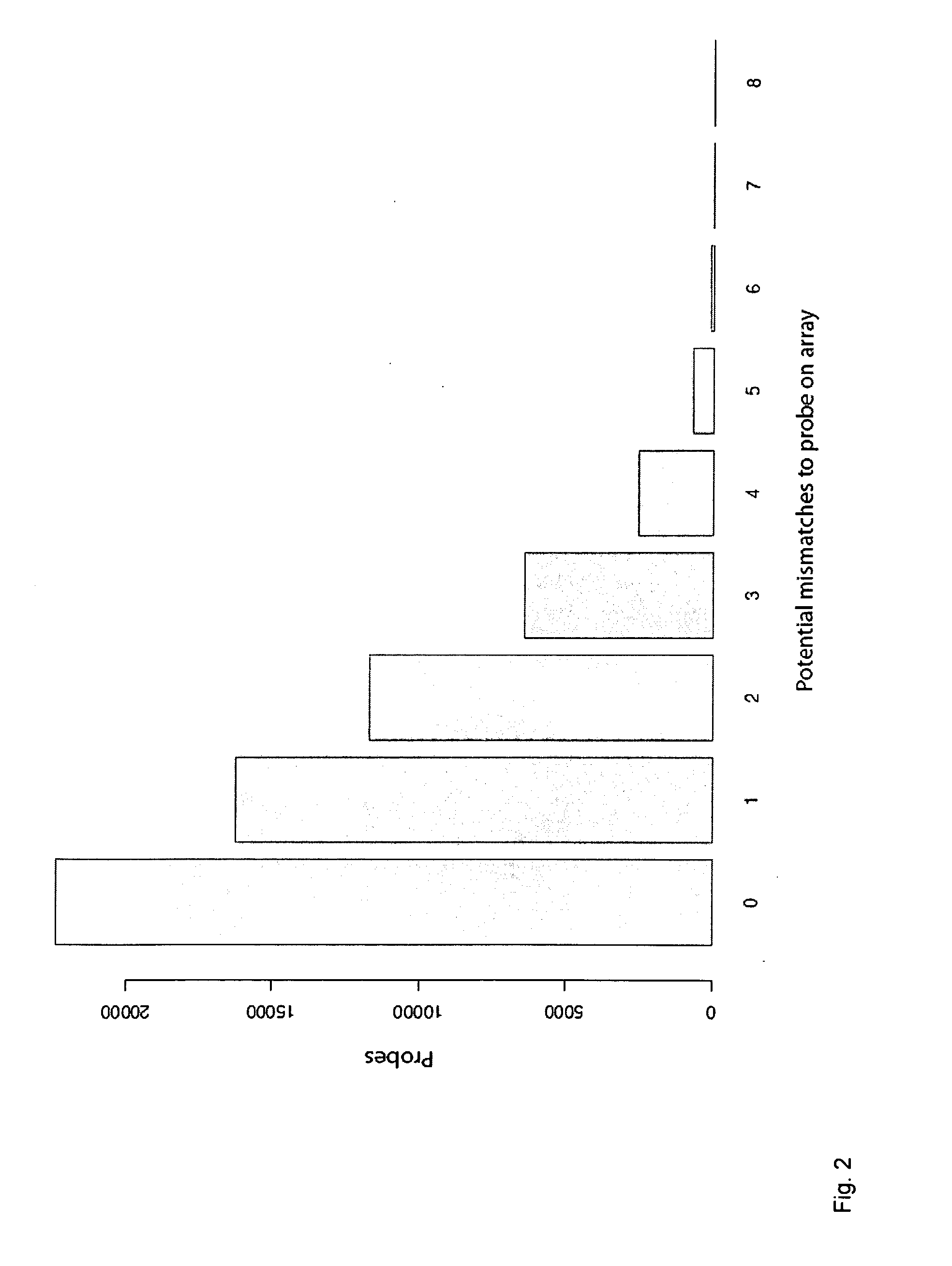
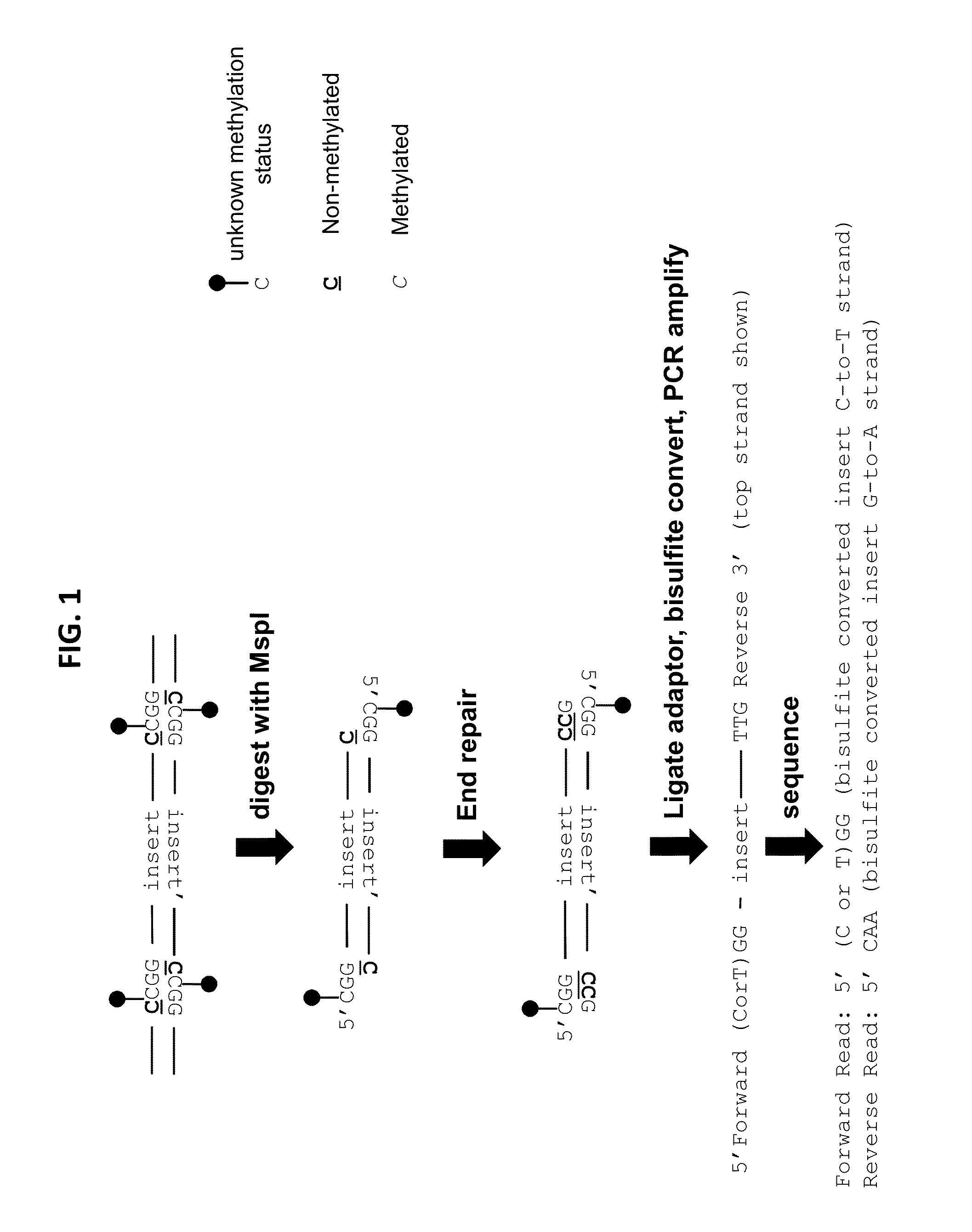
Methods and arrays for profiling DNA methylation
This invention provides methods and arrays for determination of the methylation patterns at single-nucleotide resolution by array-based hybrid selection and next-generation sequencing of bisulfite-treated DNA.
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC
Reduced representation bisulfite sequencing with diversity adaptors
ActiveUS20150284769A1Increase diversityEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationGeneticsReduced representation bisulfite sequencing
Described herein are methods, compositions and kits for the generation of bisulfite-converted libraries useful for conducting reduced representation bisulfite sequencing (RRBS). The methods described herein can be employed to generate RRBS libraries in a manner that is easier and more cost-efficient than conventional RRBS methods, and can be efficiently sequenced with next generation sequencing (NGS) techniques without the need for genomic, higher diversity sequencing controls such as PhiX spike-ins.
Owner:NUGEN TECH
Whole-genome methylation non-bisulfite sequencing library, construction and applications thereof
InactiveCN110820050ASolve the defect of low usage rateReduce usageNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementDihydrouracilPhosphoric acid
The invention relates to the technical field of bioinformatics, particularly to a whole-genome methylation non-bisulfite sequencing library, a construction and applications thereof, wherein the sequencing library comprises a TET enzyme reaction solution, the TET enzyme reaction solution comprises the following independently packaged components: a TET enzyme oxidation buffer solution, and the TET enzyme oxidation buffer solution comprises, by micromole, (20-167)*10<3> parts of HEPES or Tris-Cl, (100-333)*10<3> parts of NaCl, 3.3*10<3> parts of alpha-KG or 2-oxoglutarate, 6.67*10<3> parts of ascorbic acid and 4*10<3> parts of adenosine triphosphate. According to the invention, by combining the kit, Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2 and TET enzyme, 5mc can be oxidized into 5cac, the 5cac is reduced into dihydrouracil under the action of a reducing agent, and T is identified through PCR sequencing, so that the the DNA methylation C-to-T conversion under the non-bisulfite condition is achieved, the defects ofbase imbalance and low sequencing data use rate of the existing methylation sequencing library constructed based on the bisulfite conversion are solved; and the formula further has effects of simplecomponents, extremely low TET enzyme use amount and significant cost reducing.
Owner:BEIJING GENEPLUS TECH +1
Waste gas control method by removing sulfur dioxide for resource utilization
InactiveCN1736557AReasonable workmanshipMild desulfurization reaction conditionsDispersed particle separationResource utilizationSulfur
The invention provides a method for desulfurization of SO2 waste gas. A basic absorption liquid neutralizes the SO2- laden waste gas to eliminate SO2, discharge the purified gas when the content of SO2 reaches the standard; microbe reduces the desulfurizing absorption tail liquid (containing sulfite group, bisulphate group, or sulfuric group), then microbe oxygenizes the liquid, and the SO2 contained is recovered as a existent of elemental sulfur. The liquid treated by microbe is basic, and it can return directly to the desulfurizing absorption unit and be reused as a basic absorption liquid. And it realizes the aim of eliminating waste and recycling sulfur resource. The method for waste gas treatment is easy to operate and leads to none secondary pollution.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Stabilized composition comprising at least one adrenergic compound
ActiveUS20120129944A1Improve stabilityExtended shelf lifeBiocideOrganic active ingredientsCompound aBisulfide
A stabilised composition comprising at least one adrenergic compound and at least one antioxidant selected from the group consisting of a bisulfite, a metabisulfite and a sulfite compound.
Owner:ALK ABELLO SA
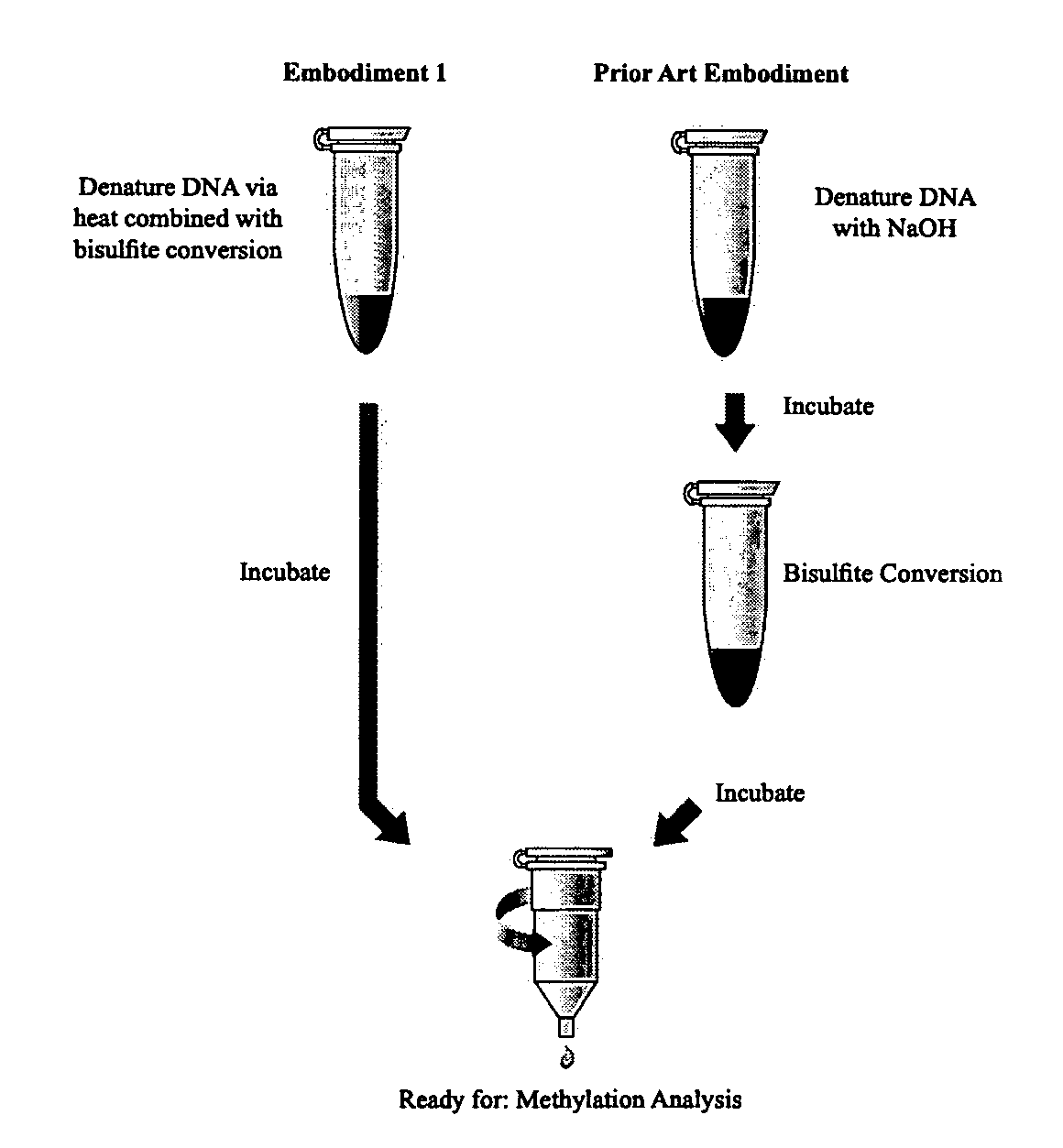
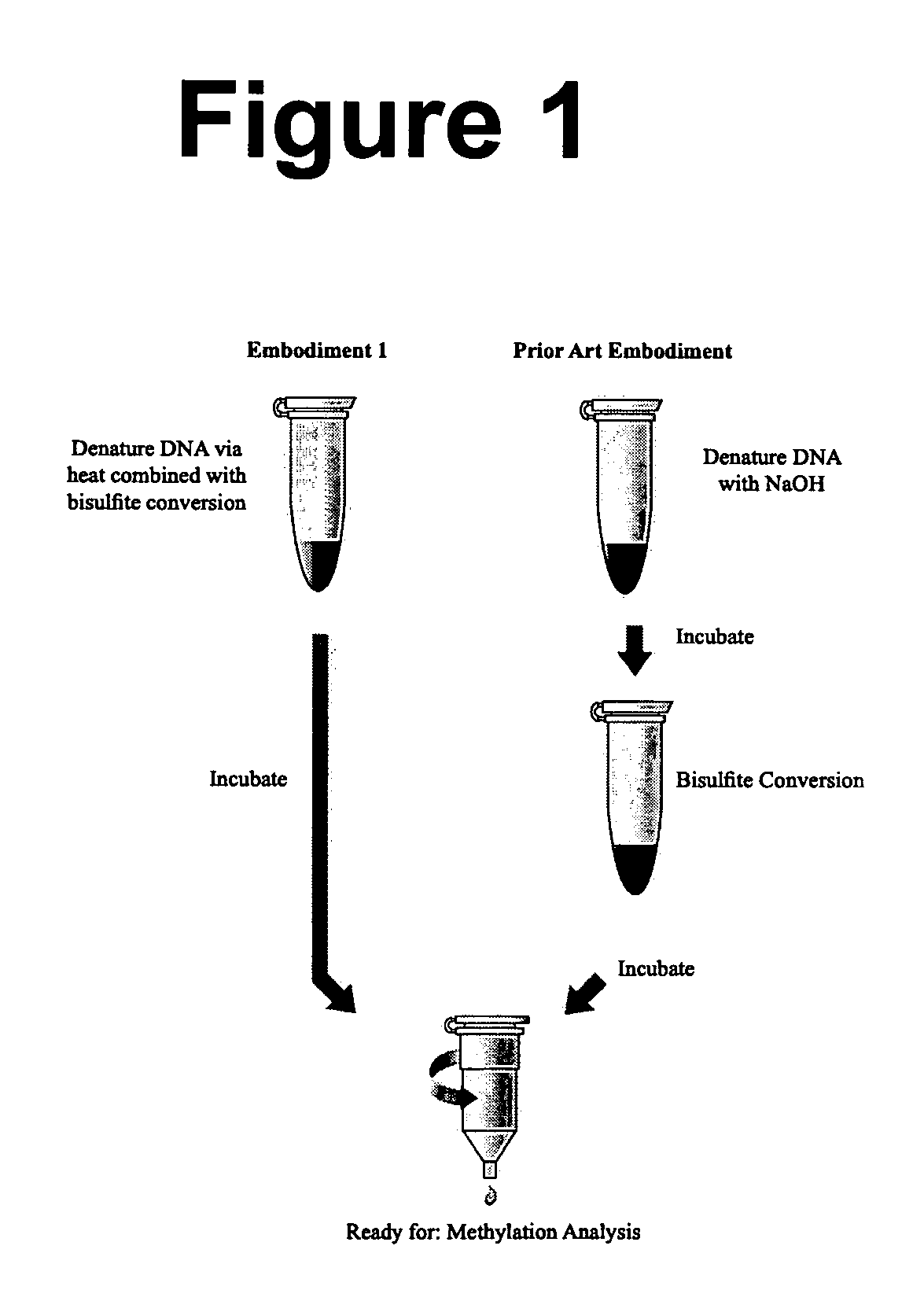
Methods for detection of methylated DNA
InactiveUS20060286577A1Save a lot of timeImprove efficiencySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCurrent technologyBiology
The present invention provides methods for improving the efficiency of methylation detection. The present invention provides improvements from current technologies via increased efficiency of template denaturation and bisulfite conversion reaction, also significant time savings in sample preparation, recovery, as well as increased efficiency of desulfonation. These methods facilitate rapid analysis of research and clinical samples and enhance the ability to process high-through put sample preparations. The methods are applicable to essentially all methylation detection procedures and also to the analysis of methylation patterns from various species.
Owner:JIA XIYU
Construction method, kit and application of plasma free DNA methylation detection library
InactiveCN107541791AImprove recycling efficiencyReduce the initial amount of conventional trace methylation library constructionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationMagnetic beadSmall fragment
The invention discloses a construction method, a kit and application of a plasma free DNA methylation detection library. The construction method comprises the following steps: S1 of extracting plasmafree DNA from a blood sample; S2 of performing tail end repair and 3' terminal A base addition on the plasma free DNA; S3 of connecting the tail ends of the plasma free DNA obtained in the S2 with C methylation modified connectors; S4 of performing bisulfite conversion on a product obtained in S3 and performing PCR expansion; S5 of performing magnetic bead purification on the PCR product of S4 andremoving small-fragment DNA which is not amplified in a non-specific mode and primer dimer; S6 of performing PCR amplification on a product of S5 and performing magnetic bead purification to obtain aplasma free DNA methylation detection library. By means of the technical scheme of the construction method disclosed by the invention, an initial amount of general microscale methylation library construction is reduced, library construction steps are simplified, library recycling efficiency is improved, and a foundation is established for sequentially screening tumor diagnosis markers through plasma free DNA methylation difference locus.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION
Method for desulfurizing waste gas and reutilizing sulfur source
InactiveCN1736556AAchieve recyclingAvoid effluxDispersed particle separationChemical treatmentSulfur
The invention provides a method for desulfurization from a SO2- laden waste gas and for recovery of the sulfur resource. A basic absorption liquid neutralizes the SO2- laden waste gas, discharge the purified gas when the content of SO2 reaches the standard; microbe reduces the desulfurizing absorption tail liquid (containing bisulphate group), and then the liquid is oxygenized with chemical treatment to recover elemental sulfur. The desulfurizing absorption tail liquid treated by microbe is basic, and it can return directly to the desulfurizing absorption unit and be reused as a basic absorption liquid; the chemical oxidant is oxygenized by microbe to revive. The invention realizes the aim of eliminating waste and recycling sulfur resource. And it is easy to operate and leads to none secondary pollution.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Process for producing methanesulfonic acid
ActiveCN101219975AEfficient use ofEasy to produceSulfuric acid esters preparationAlkaline earth metalEvaporation
The invention discloses a preparation method for methanesulfonic acid. A water liquor or a solid mixture of a sulfite or a mixture of the sulfite and a bisulfite is reacted with a dimethyl sulfate to generate a methylsulfonate and a sulfate, and the mixture liquor of the reaction directly cools and precipitates a sulfate salt crystallization through concentration by adding a salting-out agent or a concentrated liquor; filtering and removing a dilute-methyl sulfonate liquor of the sulfate; a soluble alkaline earth salt can also be reused as a precipitant for further removing the remained sulfate ion; finally, the purified methylsulfonate liquor is concentrated to pulpiness or dry powder to be acidified by excess concentrated hydrochloric acid or excess hydrogen chloride gas is directly pumped in the purified methylsulfonate liquor to precipitate a sodium chloride crystallization. After filtering, the mixed acid liquor of hydrochloride and methanesulfonic acid can be gotten, which can get the highly-purified methanesulfonic acid after evaporation concentration, vacuum distillation and distillation. The materials of the invention can be gotten easily and the invention has simple techniques and low cost, which does no harm to the environment and is suitable to be used in industry.
Owner:HEBEI YANUO CHEM IND
Cyanide-free monovalent copper eletroplating solutions
A substantially cyanide-free plating solution for depositing copper from the monovalent ionic state, which includes a source of copper ions, a reducing agent capable of reducing divalent copper ions to monovalent copper ions, an alkali material in an amount sufficient to maintain the pH of the solution in the range of about 7 to about 10, and a complexing agent of an imide, such as succinimide, 3-methyl-3-ethyl succinimide, 3-methyl succinimide, 3-ethyl succinimide, 3,3,4,4-tetramethyl succinimide, or 3,3,4-trimethyl succinimide, or a hydantoin, such as dimethyl hydantoin. The substantially cyanide-free plating solutions may also include at least one of a conductivity salt, an additive to promote brightness, or an alloying metal. The reducing agent may be an alkali sulfite, alkali bisulfite, hydroxylamine, or hydrazine. The copper is typically provided in the form of CuC1, CuC12, CuSO4, or Cu20 in an amount sufficient to provide a copper ion concentration of from about 2 to about 30 grams per liter of solution, and the complexing agent is present in an amount sufficient to provide a molar ratio of copper ions to complexing agent of from about 1:1 to about 1:5, preferably about 1:4. The alkali material is typically NaOH, KOH, NH4OH, or Na2CO3, and the conductivity salt is typically NaC1, KC1, Na2SO4, K4P2O7, Na3PO4, C6H5Na3O7, C6H11NaO7, NH4C1, or KNaC4H4O6. Useful additives include organic amines or oxyalkyl polyamines, such as triethylene tetramine, tetraethylene pentamine, and polyoxypropyl-triamine. Methods for preparing such a solution for plating copper onto a substrate, and of plating copper onto a substrate with such a solution are also disclosed.
Owner:LEARONAL
Process for the desulfurization of sulfur dioxide-containing gases
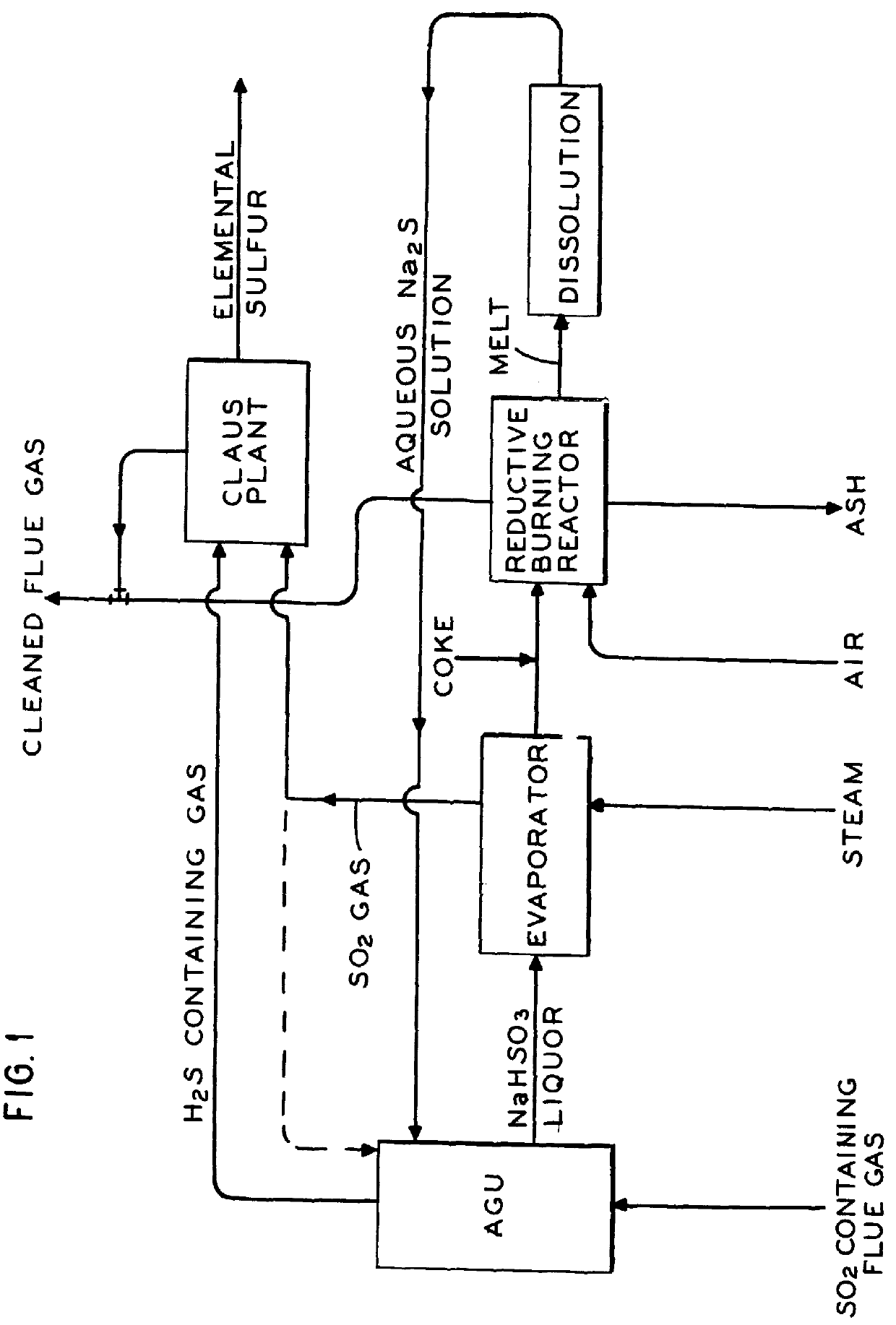
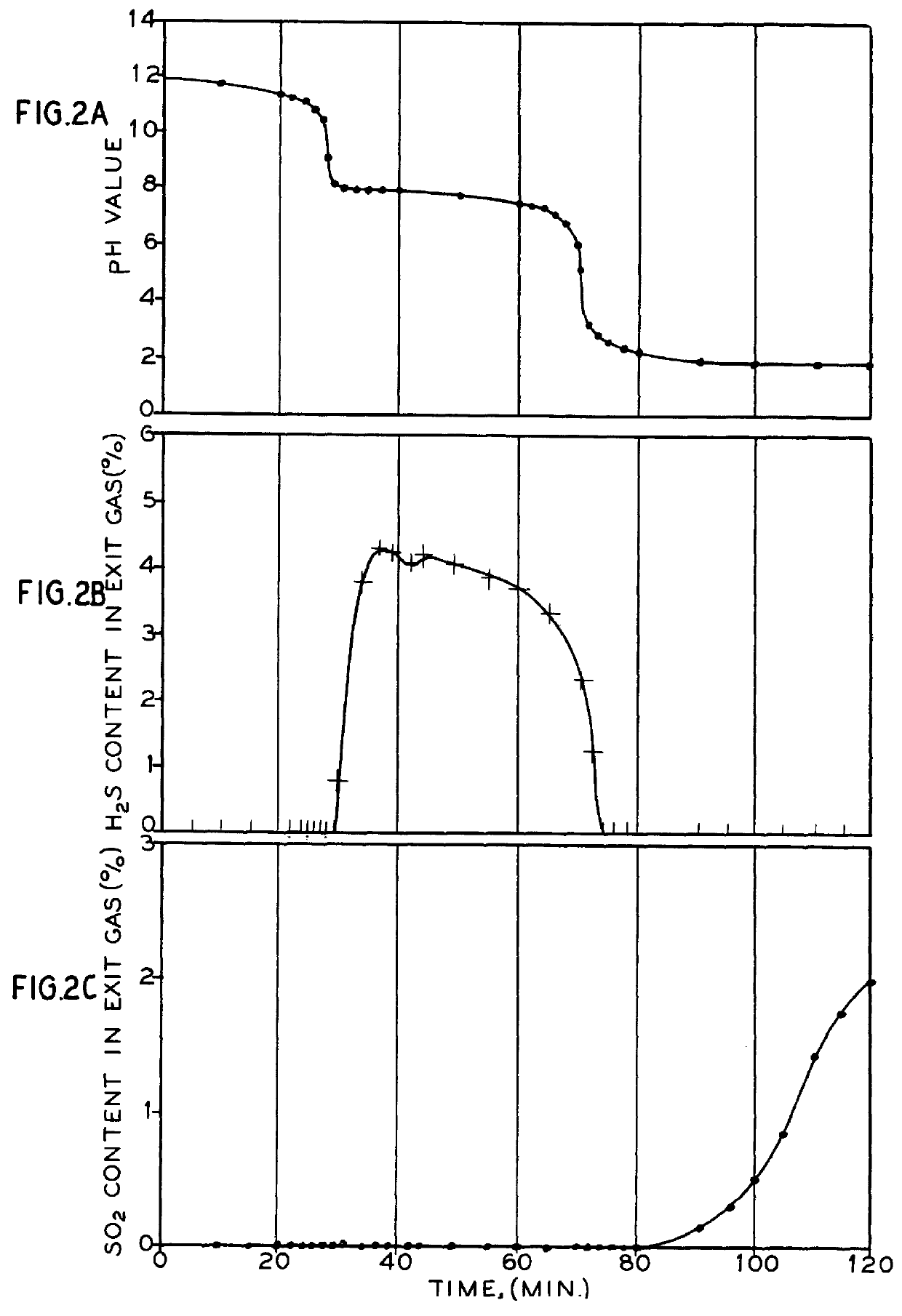
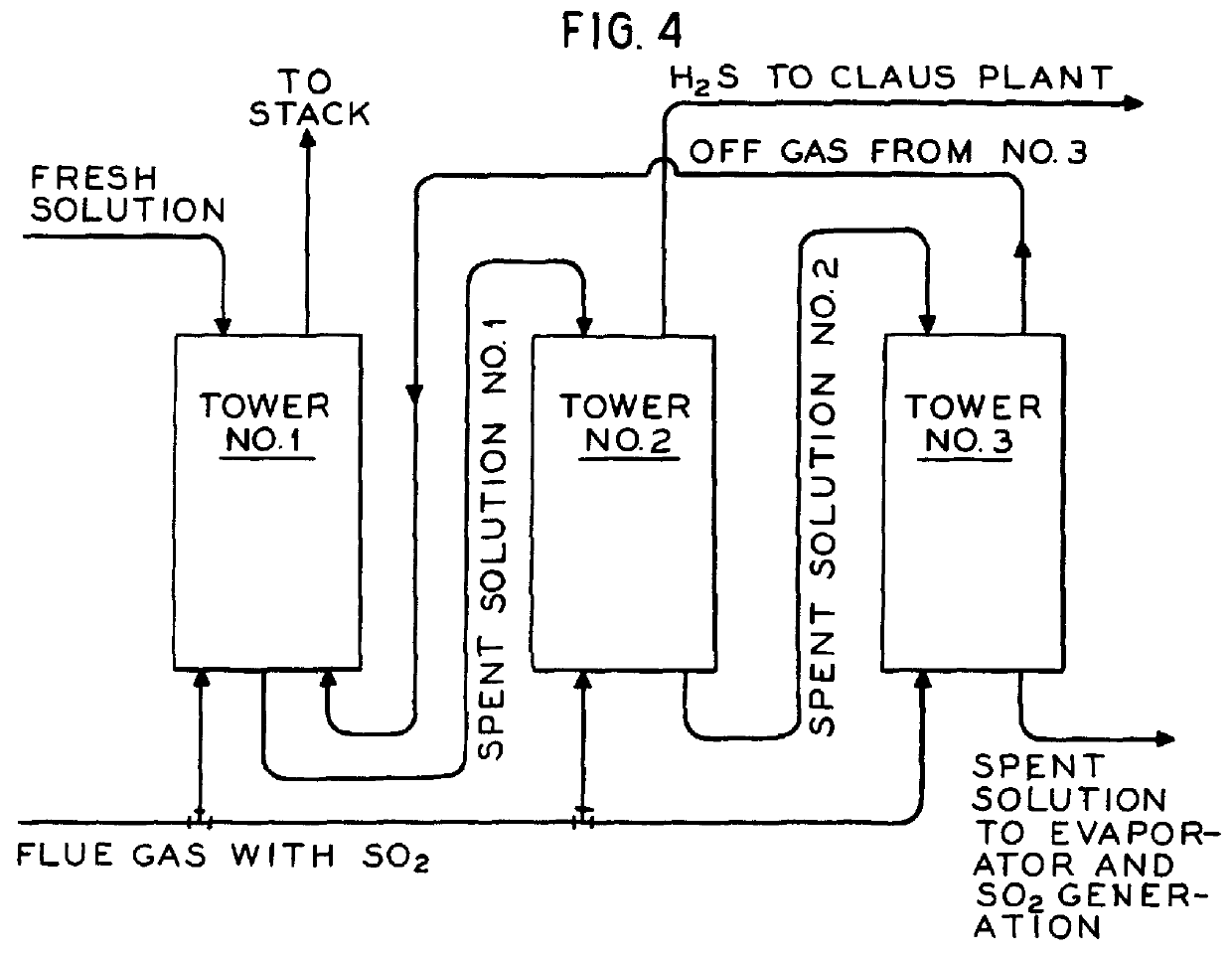
The process of invention provides a simplified conversion of sulfur dioxide gas into hydrogen sulfide gas. First, sulfur dioxide gas is absorbed into an aqueous sulfide solution to form sulfite and bisulfide ions. Second, additional sulfur dioxide gas is absorbed into the aqueous solution to form hydrogen sulfide. Third, another portion of the sulfur dioxide is absorbed and reacts in the aqueous solution to form bisulfite. Most advantageously, the bisulfite is decomposed into sulfur dioxide and sulfite. The sulfite is then reduced to sulfide and returned for use in the absorption process. The hydrogen sulfide may then be reacted with SO2 via the Claus reaction to form elemental sulfur.
Owner:INCO +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com