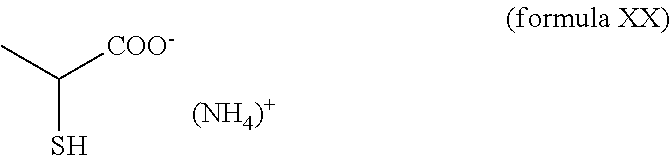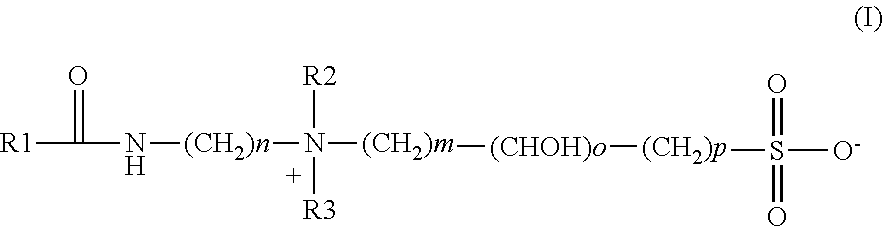Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38 results about "Dithionite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The dithionite anion ([S₂O₄]²⁻), is an oxoanion of sulfur. It is commonly encountered as colorless salts.
Decolorization of dyed keratin fibers
The invention relates to agents for the reductive decolorization of dyed keratin fibers, in particular human hair, containing in an aqueous cosmetic carrier (a) one or more reduction agents from the group consisting of sodium dithionite, zinc dithionite, potassium dithionite, sodium sulfite, sodium hydrogen sulfite, potassium sulfite, potassium hydrogen sulfite, ammonium sulfite, sodium thiosulfate, potassium thiosulfate, ammonium thiosulfate, hydroxymethanesulfinic acid, aminomethanesulfinic acid, cysteine, thiolactic acid, sulfanylacetic acid (thioglycolic acid), and / or ascorbic acid, and (b) one or more zwitterionic surfactants, each of which has at least one quaternary ammonium group and a grouping of —SO3— as structural units.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
Method for preparing corn protein foaming powder by enzymatic hydrolysis of com gluten meal
ActiveCN102630801AHigh in proteinGood foaming effectVegetable proteins working-upNeutral proteaseAlpha-amylase
The invention discloses a method for preparing corn protein foaming powder by enzymatic hydrolysis of com gluten meal. The method comprises the following steps of: pre-treating the com gluten meal by adopting enzymolysis of double enzymes, namely cellulase and alpha-amylase, centrifuging and washing to obtain corn protein concentrate; dissolving the corn protein concentrate into water, and performing thermal denaturation treatment at the temperature between 80 and 90 DEG C; adding sulfite or meta-disulfite for chemical modification; and adding neutral protease or alkali protease for hydrolysis, filtering, drying the clear solution, and thus obtaining a corn foaming protein product. The corn protein foaming powder prepared by pre-treating the com gluten meal by adopting enzymolysis of the double enzymes has high protein content, good foaming effect and high foaming stability; and the application range of the com gluten meal is further widened, the additional value of the deep processing products of the com gluten meal is improved, and the technological content and the quality of the deep processing products of the com gluten meal are greatly improved.
Owner:山东盛泰生物科技有限公司 +1
Remediation of sulfur-containing pollutants with hydrocarbon-utilizing bacteria
InactiveUS7329532B2Reducing sulfur-containing compoundEncouraging growthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAlkaneSulfolane
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for remediating sulfur-containing pollutants with a hydrocarbon that is used to stimulate the growth of hydrocarbon-utilizing bacteria. The hydrocarbon is preferably an alkane such as butane. The sulfur-containing pollutant may comprise sulfate, sulfite, sulfide, disulfides, mercaptans, alkanesulfonates, dialkyl sulfides, thiosulfate, thiofurans, thiocyanates, isothiocyanates, thioureas, thiols, thiophenols, thioethers, thiophene, tetrathionate, dithionite, dialkyl disulfides, sulfones, sulfoxides, sulfolanes, sulfonic acid, dimethylsulfoniopropionate, sulfonic esters, hydrogen sulfide, sulfate esters, sulfur dioxide and any other sour gases, elemental sulfur and any other sulfur-containing material considered to be a contaminant or pollutant.
Owner:GLOBAL BIOSCI
Enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic material in the presence of sulfite, dithionite and/or dithiothreitol
ActiveUS8871475B2Improve efficiencyImprove enzymatic hydrolysis efficiencyBiofuelsFermentationCelluloseDithionous acid
A method is provided for improving enzymatic hydrolysis in saccharification of a lignocellulosic material. The method is comprising pretreating the lignocellulosic material to obtain a slurry of pretreated lignocellulosic material; adding at least one reducing agent to the slurry of pretreated lignocellulosic material or the liquid fraction thereof to decrease the enzymatic hydrolysis inhibitory properties of slurry of the pretreated lignocellulosic material or the liquid fraction thereof; and subjecting the slurry of pretreated lignocellulosic material or the liquid fraction thereof to enzymatic hydrolysis in the presence of the at least one reducing agent.
Owner:SEKAB E TECH
Method of removal of carbonyl compounds along with acid gases from cracked gas in ethylene process
InactiveUS20050224394A1Reduce concentrationPreventing plugging and foulingThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingCaprolactamCaproic Acid
A method for mitigating fouling in a wash unit used in a hydrocarbon cracking process wherein the fouling is due to the presence of polymers and deposits thereof formed by condensation of carbonyl compounds contained within a feed stream of the wash unit. In one embodiment, the invention provides a method of mitigating fouling in a wash unit by introducing into the feed stream an effective amount of an additive including: an inorganic salt of dithionite; and an epsilon caprolactam or a 6-amino caproic acid derivable therefrom. The additive scavenges the carbonyl compounds contained within the feed stream and dissolves deposits of the polymers to thereby mitigate fouling in the wash unit.
Owner:DORF KETAL CHEM
Use of an aqueous neutral cleaning solution and method for removing rouging from stainless steel surfaces
ActiveUS8192550B2Avoid pollutionNon-surface-active detergent compositionsDetergent mixture composition preparationAcid groupDithionite
The invention relates to a method for removing films and deposits from stainless surfaces, especially from stainless metallic surfaces such as they are used in process stations and production units in the pharmaceutical, food and biotechnological industries, and to an aqueous cleaning solution comprising a reducing agent, in particular dithionite and / or disulfite, and at least two different complexing agents, wherein one of these complexing agents is a compound comprising diacetic acid groups or a salt thereof, for removing rouging on surfaces of stainless steels that come into contact with media selected from the group of chromium / nickel and chromium / nickel / molybdenum steels in the neutral pH range.
Owner:ATECO SERVICES
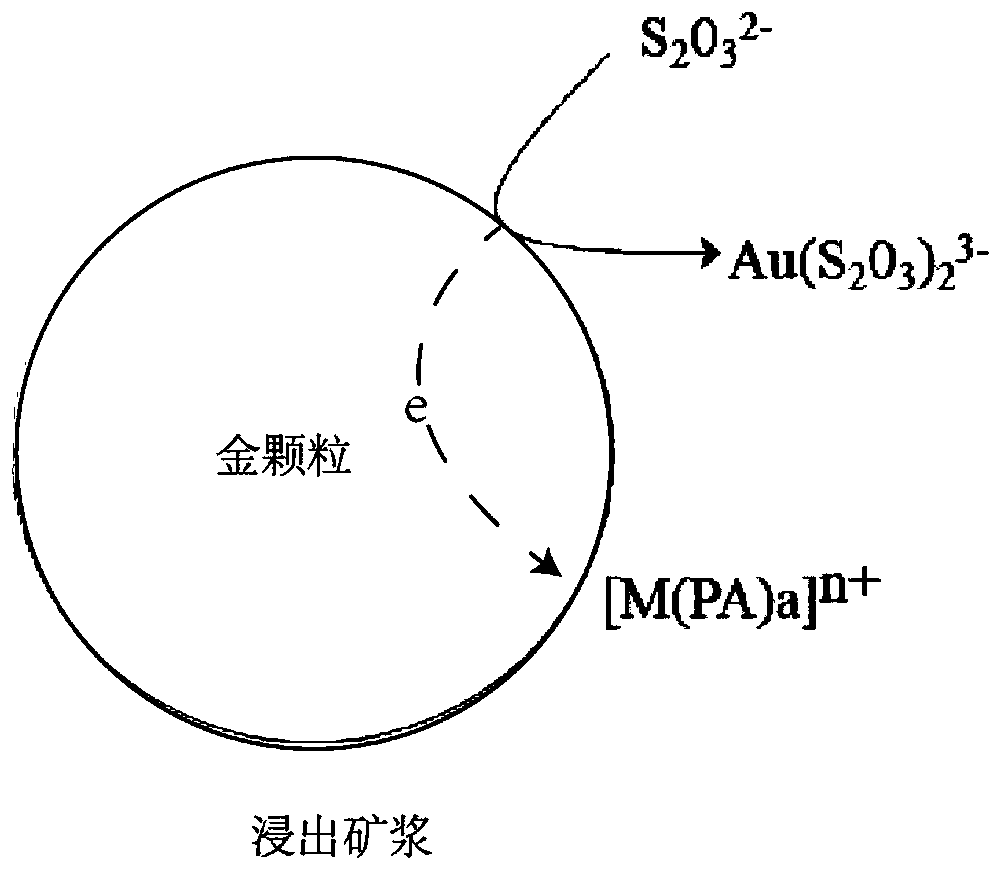
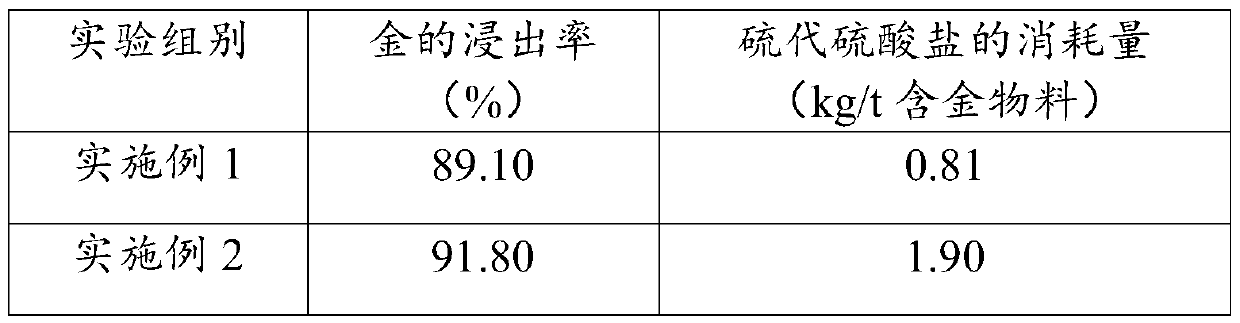
Thiosulfate gold leaching method and application
ActiveCN111471858AImprove the defect of excessive consumptionImprove gold leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementThio-Carboxylic acid
The invention provides a thiosulfate gold leaching method and application, and relates to the technical field of hydrometallurgy. The thiosulfate gold leaching method comprises the steps of adding metal salt, a polycarboxylic acid additive and thiosulfate into gold-containing ore pulp for leaching, wherein a large number of acid radical groups distributed on a hydrocarbon chain of the polycarboxylic acid additive and positive ions generated through hydrolysis of the metal salt in a solution can be subjected to a multi-tooth chelation effect to generate complex ions, thereby replacing Cu (NH3)4 < 2 + > in a traditional thiosulfate gold leaching process, and the defect of large thiosulfate consumption due to the fact that Cu (NH3) 4 < 2 + > has oxidability can be overcome on the premise that the high gold leaching rate is obtained. The concentration of harmful ions such as dithionite in decomposition products of S2O3 < 2-> in the leaching solution is remarkably reduced, and recycling ofthe leaching solution and recycling of gold in the solution are facilitated; and meanwhile, the thiosulfate gold leaching method also avoids the problems of safety and environmental influence causedby the use of ammonia water.
Owner:BEIJING MINING & METALLURGICAL TECH GRP CO LTD
Method for treating refractory organic pollutants in wastewater by dithionite-activated persulfates
PendingCN109987693AReduce energy consumptionNo health riskWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsDithionous acidExternal energy
The invention relates to a method for treating refractory organic pollutants in wastewater by dithionite-activated persulfates, which comprises the following steps: sequentially adding a dithionite and a persulfate into wastewater containing therefractory organic pollutants, and conducting reacting to obtain treated wastewater, wherein the molar ratio of the persulfate to the refractory organic pollutants in the wastewater is 1:1 to 500:1. The method has the characteristics that the method is carried out under the conditions of normal temperature, normal pressure, acidity or neutrality, no external energy is used, the risk of secondary pollution to the environment is avoided, the operation is simple, the degradation effect on the refractory organic pollutants in the environment is good, and the method has great application potential in the field of environmental pollution treatment.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
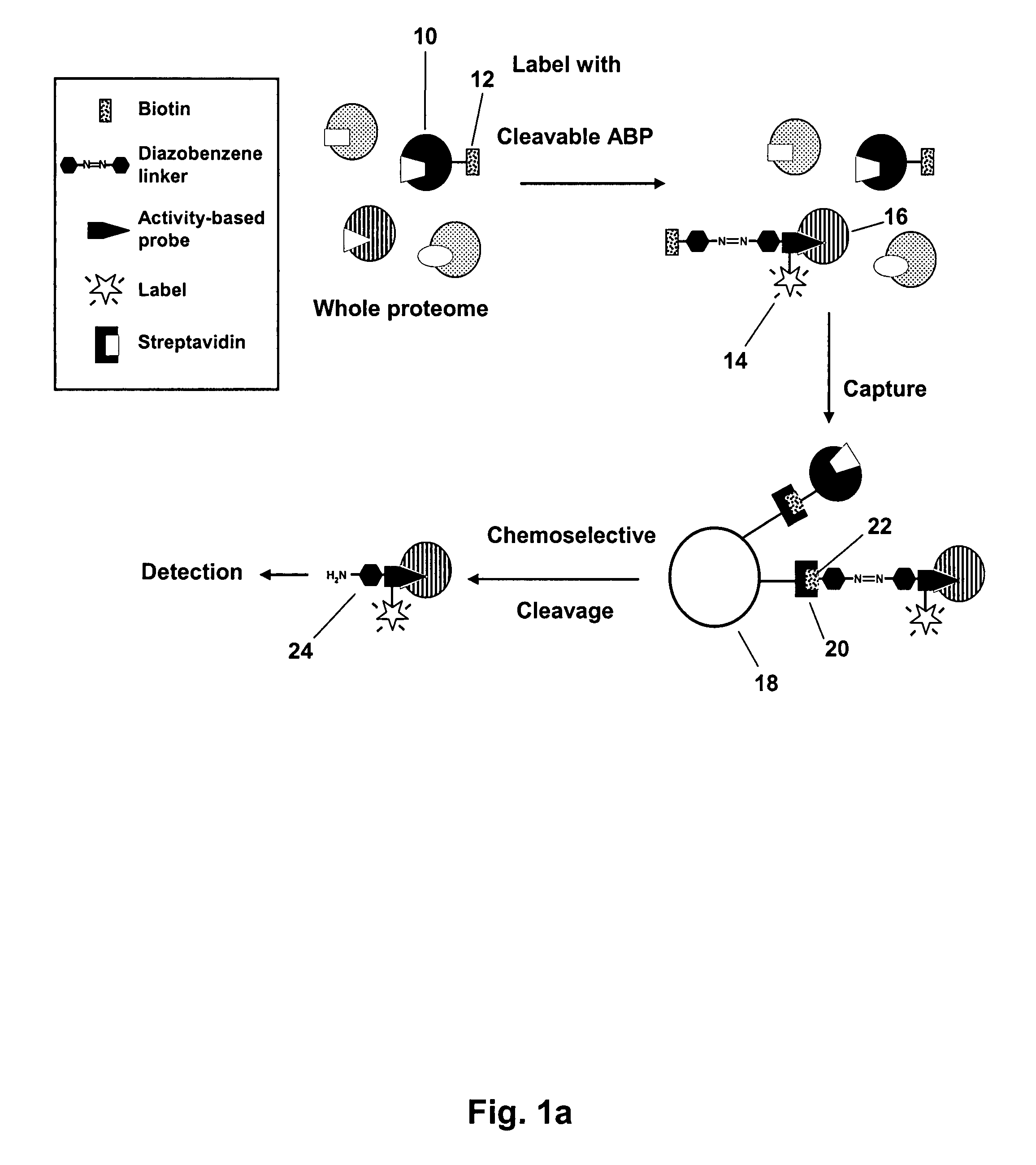
Mild Chemically Cleavable Linker System
A linker system is provided where a small molecule reactive group, e.g., an activity based probe which binds to certain enzymes at the active site, is linked through an aryl diazo linker to an affinity molecule such as biotin. The reactive group may comprise a number of functionalities known to react with a specific target to be studied. This enables the probe to be exposed to analytes, such as proteins and bind specifically to them to form a complex having an affinity molecule allowing immobilization of the bound analyte on an affinity column or other support, e.g. with streptavidin. Then, the linker is cleaved without causing removal of the affinity group or dissociation of the probe from the analyte. The linker is cleaved under mild reducing conditions, e.g., dithionite. The probe is synthesized along with the linker on a solid support.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Decolorization of colored keratinic fibers
ActiveUS10456606B2Good decolorization effectCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsPotassium bisulfiteSodium sulfate
A multi-component packaging unit and related method for the reductive decolorization of colored keratinic fibers comprising, packaged separately from one another,(I) a container (A) containing a cosmetic agent (a),(II) a container (B) containing a cosmetic agent (b), and(III) a container (C) containing a cosmetic, aqueous agent (c), withthe agent (b) in container (B) containing(a1) one or more reducing agents from the group of sodium dithionite, zinc dithionite, potassium dithionite, sodium sulfite, sodium hydrogen sulfite, potassium sulfite, potassium hydrogen sulfite, ammonium sulfite, sodium thiosulfate, potassium thio sulfate, ammonium thio sulfate, hydroxymethane sulfinic acid, aminomethane sulfinic acid, cysteine, thiolactic acid, sulfanylacetic acid (thioglycolic acid) and / or ascorbic acid, andagent (c) in container (C) including(c1) one or more acids from the group of the inorganic and / or organic acids and(c2) one or more zwitterionic and / or amphoteric surfactants.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
Method of brightness enhancement
InactiveUS20070131365A1Increase brightnessNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperPapermakingSulfite
A method of enhancing brightness of paper made from mechanical pulps or recycled pulps that comprise: adding an effective amount of one or more chelants and one or more surfactants to a bleaching stage of a papermaking process that involves the addition of hydrosulfite is disclosed.
Owner:NALCO CO
Mild chemically cleavable linker system
A linker system is provided where a small molecule reactive group, e.g., an activity based probe which binds to certain enzymes at the active site, is linked through an aryl diazo linker to an affinity molecule such as biotin. The reactive group may comprise a number of functionalities known to react with a specific target to be studied. This enables the probe to be exposed to analytes, such as proteins and bind specifically to them to form a complex having an affinity molecule allowing immobilization of the bound analyte on an affinity column or other support, e.g. with streptavidin. Then, the linker is cleaved without causing removal of the affinity group or dissociation of the probe from the analyte. The linker is cleaved under mild reducing conditions, e.g., dithionite. The probe is synthesized along with the linker on a solid support.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
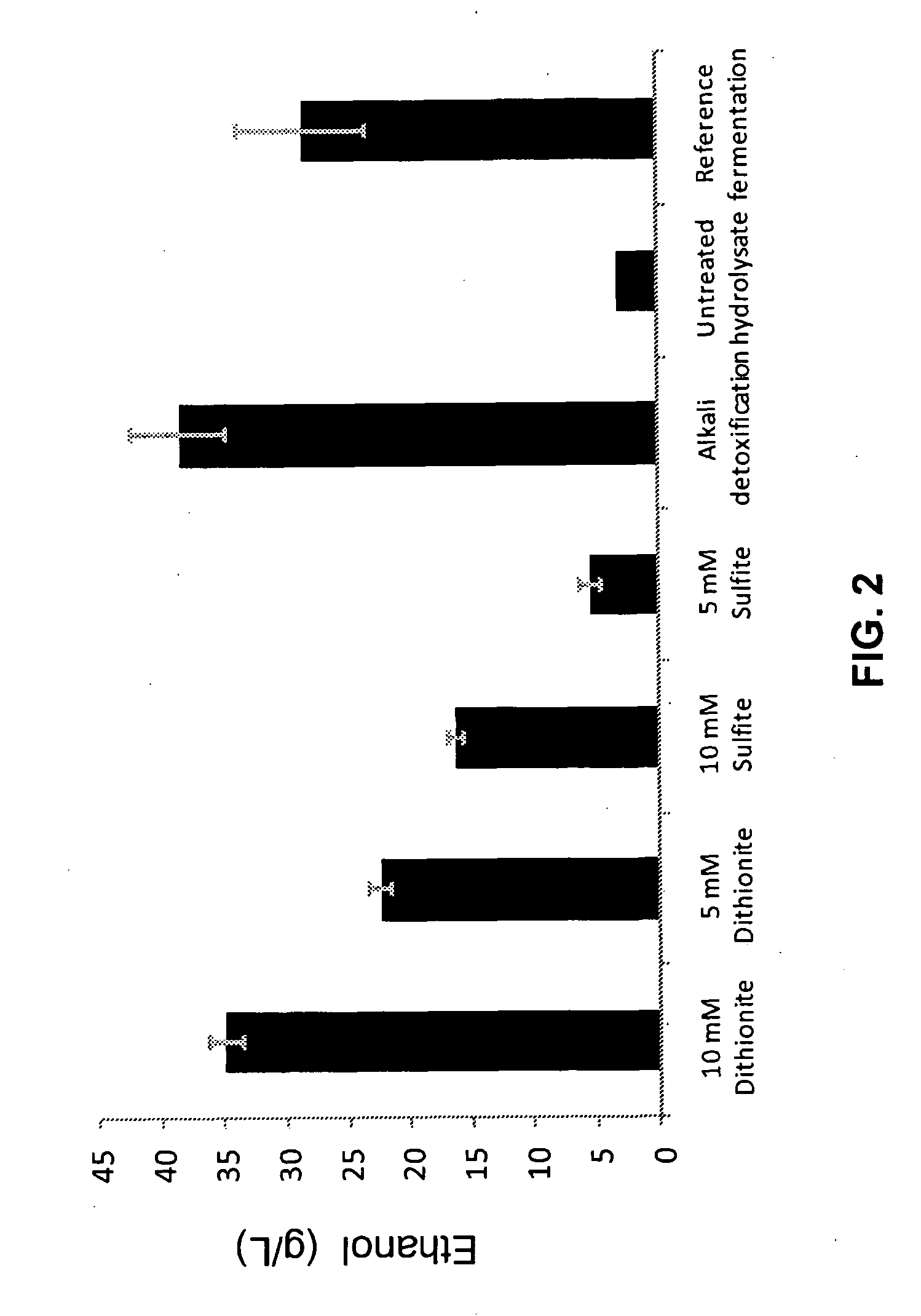
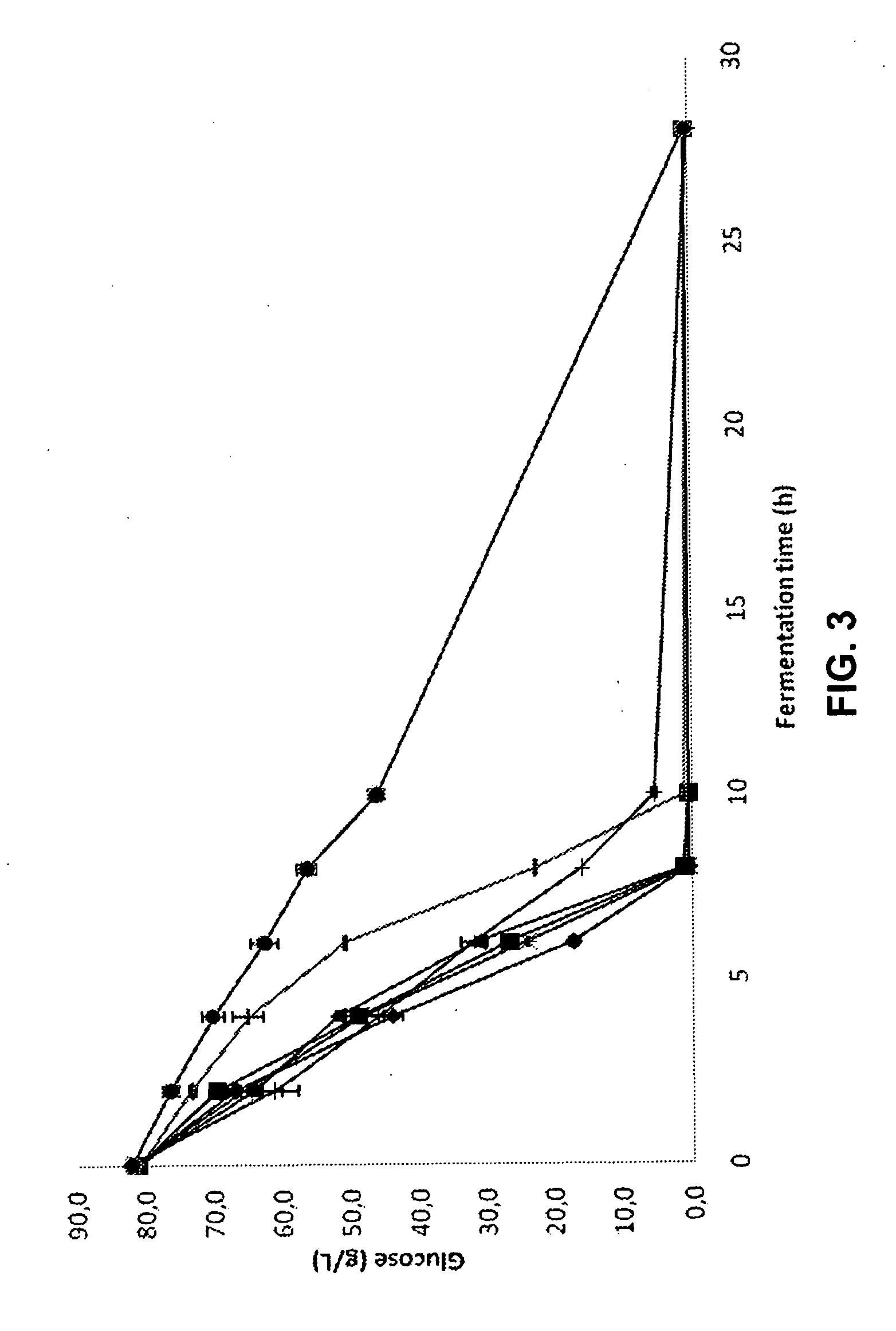
Detoxification with reducing agents
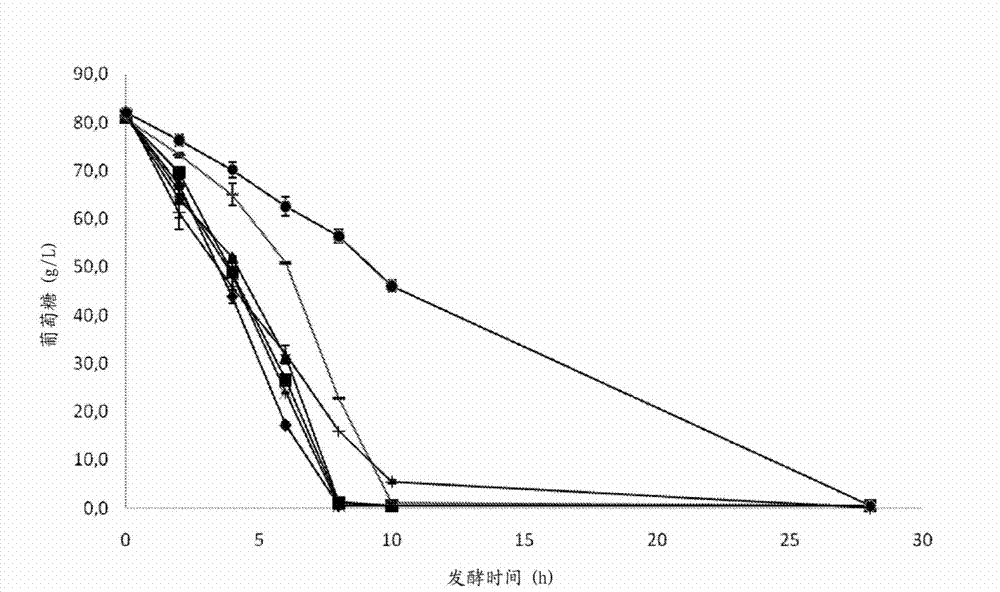
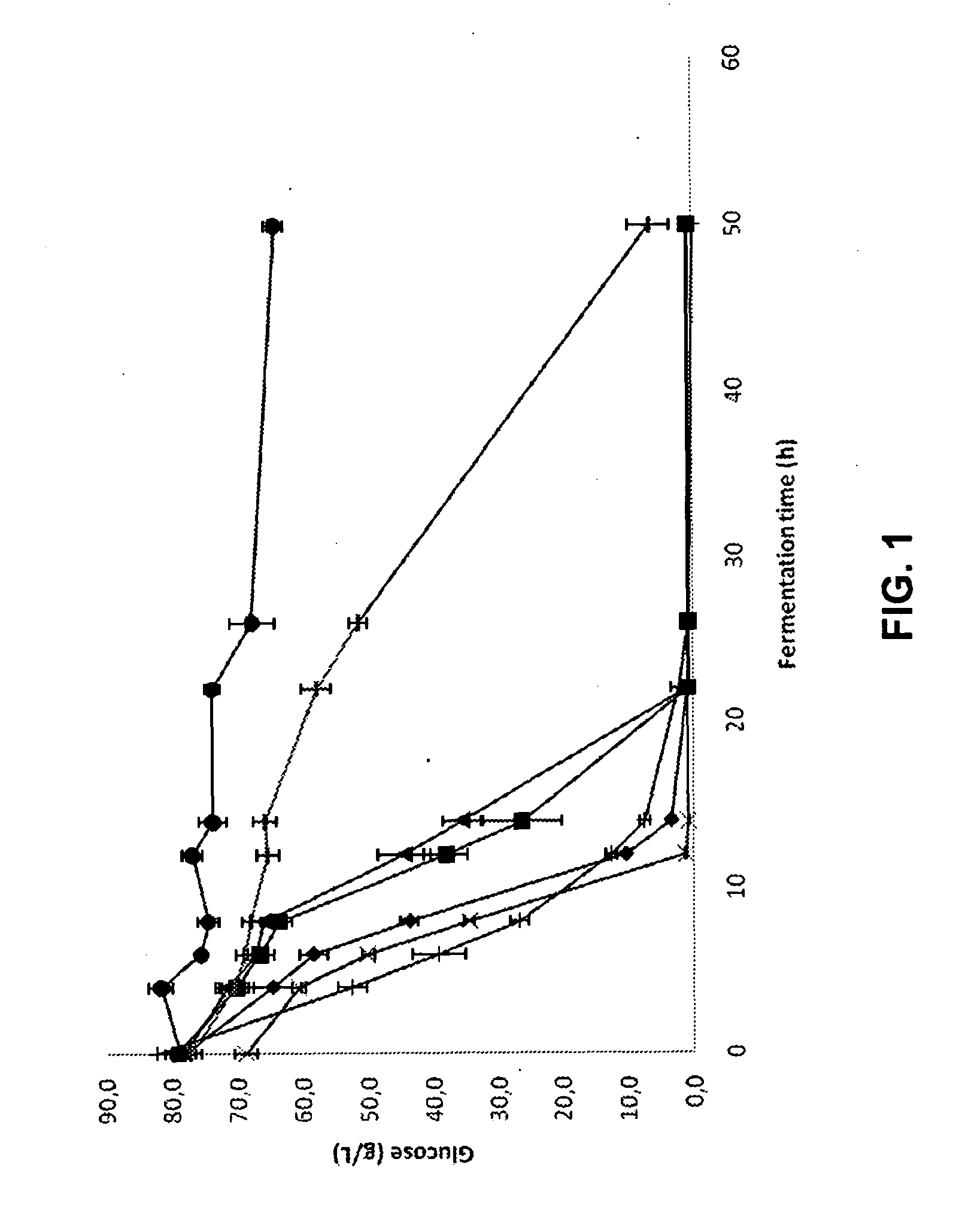
The present invention provides a method for decreasing the fermentation inhibition in a process for producing a target chemical from a pretreated cellulosic material, the process comprising enzymatic hydrolysis of the pretreated cellulosic material and fermentation of hydrolysed material, wherein the fermentation inhibitory properties of the material subjected to fermentation is decreased by an addition of at least one reducing agent to the pretreated material or hydrolysed material. Moreover, the present invention provides the use of dithionite for decreasing the fermentation inhibitory properties of a material being subjected to simultaneous enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation.
Owner:SEKAB E TECH
Method of removal of carbonyl compounds along with acid gases from cracked gas in ethylene process
InactiveUS7575669B2Reduce concentrationPreventing plugging and foulingThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingInorganic saltsDithionous acid
A method for mitigating fouling in a wash unit used in a hydrocarbon cracking process wherein the fouling is due to the presence of polymers and deposits thereof formed by condensation of carbonyl compounds contained within a feed stream of the wash unit. In one embodiment, the invention provides a method of mitigating fouling in a wash unit by introducing into the feed stream an effective amount of an additive including: an inorganic salt of dithionite; and an epsilon caprolactam or a 6-amino caproic acid derivable therefrom. The additive scavenges the carbonyl compounds contained within the feed stream and dissolves deposits of the polymers to thereby mitigate fouling in the wash unit.
Owner:DORF KETAL CHEM
Method for removing organic matters in water
ActiveCN110372048AWide temperatureWide pH rangeWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatmentDithionous acidWastewater
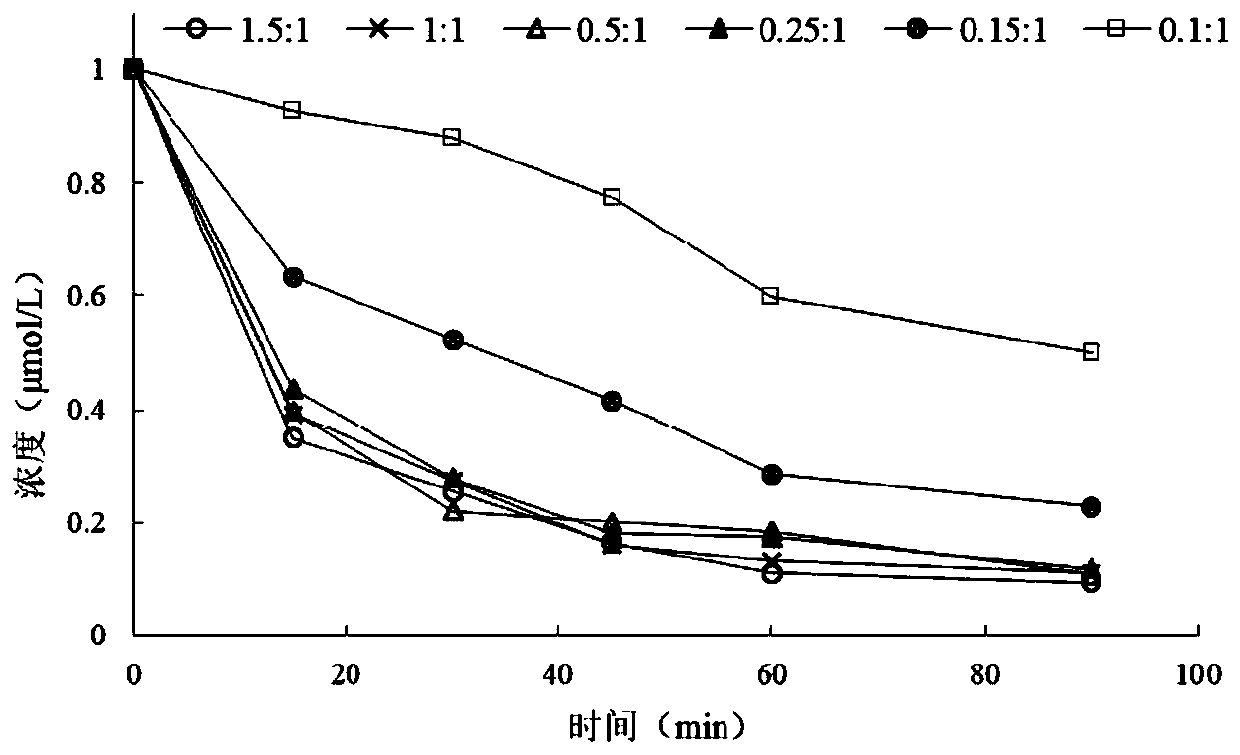
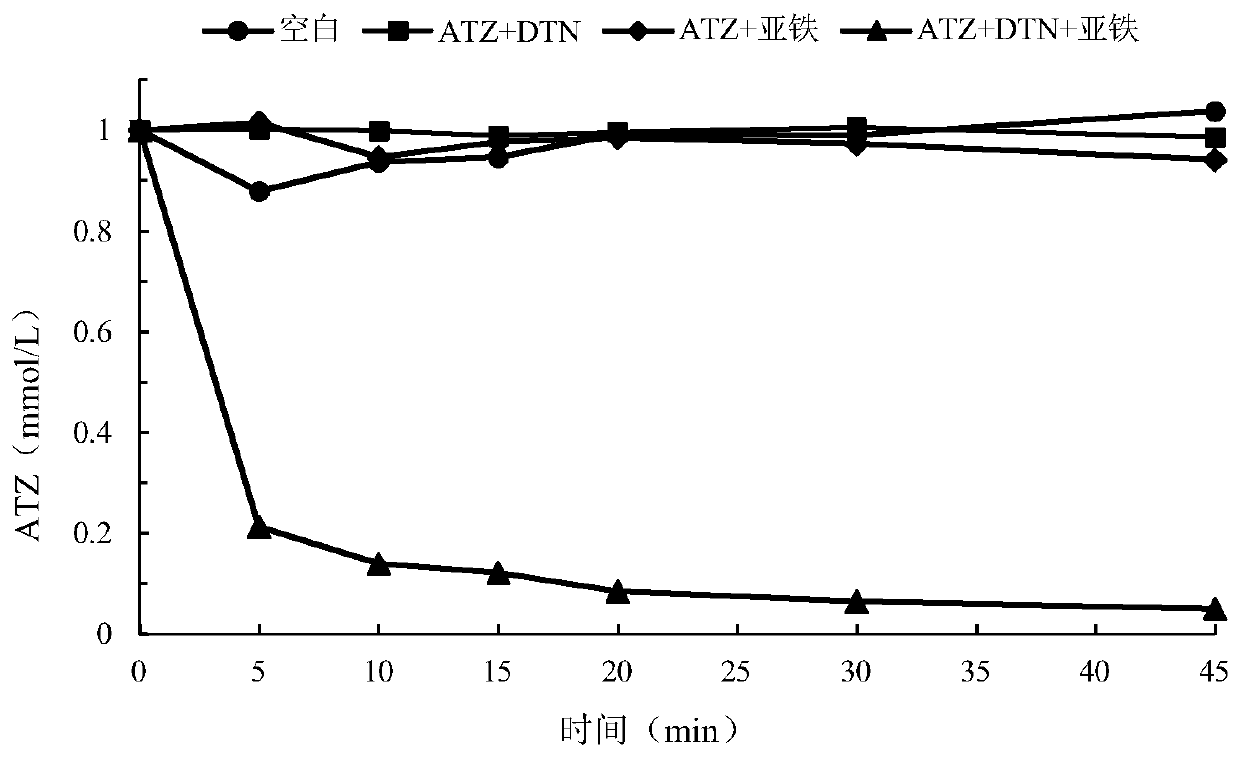
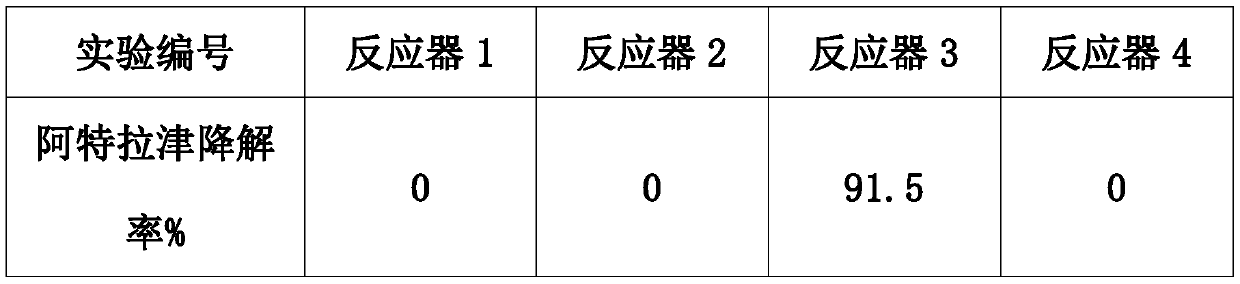
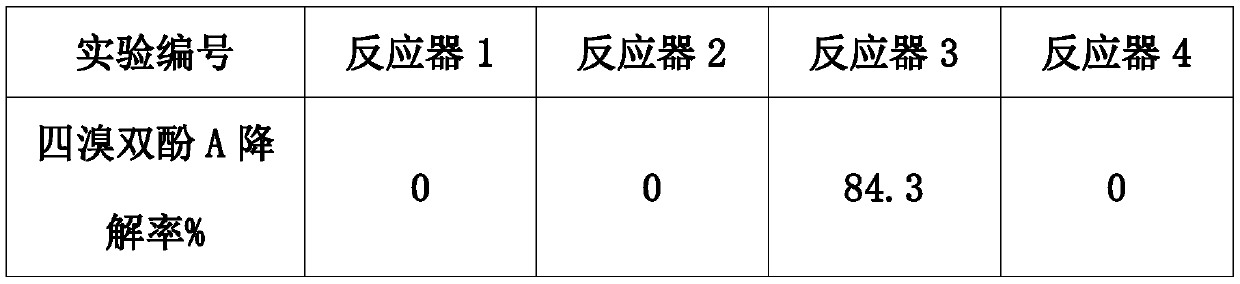
The invention discloses a method for removing organic matters in water, in particular to a method for degrading degradation-resistantorganic pollutants by using iron ions to activate dithionite. The method for degrading thedegradation-resistantorganic pollutants by using the iron ions to activate the dithionitecomprises the following steps that a water body containing the degradation-resistantorganic matters is selected,the dithionite and the iron ions are added,after temperature and the pH value are adjusted, the degradation-resistantorganic matters in the water body are treated. According tothemethod for degrading thedegradation-resistantorganic pollutants by using the iron ions to activate the dithionite,degradation-resistantorganic matters in organic wastewater can be efficiently andconveniently treated, and the method for degrading thedegradation-resistantorganic pollutants by using the iron ions to activate the dithionite has great application potential in organic wastewater treatment.
Owner:深圳市慧创源环保科技有限公司
Method for preparing dithionite
InactiveUS20100181531A1Reduce usageLow costCellulosic pulp after-treatmentLiquid degasificationDithionous acidSodium borohydride
The present invention relates to a method for preparing dithionite solution with a reaction wherein sodium bisulfite is reduced with sodium borohydride solution to obtain dithionite, wherein the rise of the pH of the solution is prevented by adjusting the pH with carbon dioxide.
Owner:KEMIRA OY
Detoxification with Reducing Agents
ActiveUS20130011894A1Reduce inhibitionLow material performance requirementsBiofuelsFermentationCelluloseDithionous acid
The present invention provides a method for decreasing the fermentation inhibition in a process for producing a target chemical from a pretreated cellulosic material, the process comprising enzymatic hydrolysis of the pretreated cellulosic material and fermentation of hydrolysed material, wherein the fermentation inhibitory properties of the material subjected to fermentation is decreased by an addition of at least one reducing agent to the pretreated material or hydrolysed material. Moreover, the present invention provides the use of dithionite for decreasing the fermentation inhibitory properties of a material being subjected to simultaneous enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation.
Owner:SEKAB E TECH
Bleaching method
InactiveUS20110203485A1Reduce conductivityResidual highPigmenting treatmentNatural cellulose pulp/paperCelluloseDithionous acid
Methods for treating lignocellulosic material or pigment with a reductive bleaching solution generally include washing the lignocellulosic material or pigment with a reducing agent of magnesium dithionite. The method includes at least one reductive stage and at least one peroxide stage. Also disclosed are methods for preparing dithionite solution wherein magnesium bisulfite is reduced with borohydride solution to obtain dithionite. Bleached lignocellulosic material or pigment obtained with the treatment methods are also disclosed.
Owner:KEMIRA OY
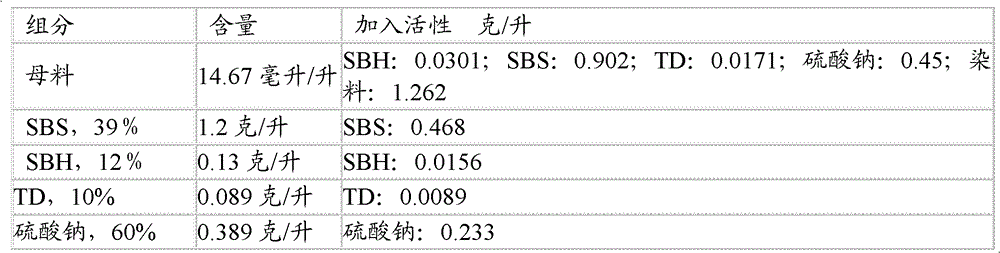
A method for printing and dyeing fabrics with vat dyes
ActiveCN102409561BGood level dyeingImprove wash resistanceDyeing processDithionous acidPresent method
The invention discloses a method for dyeing fabrics by using borohydride, bisulfite and thiourea dioxide (TD) as composite reducing agents. Wherein, bisulfite and borohydride are used to prepare dithionite, and its consumption is half of that when not mixed with thiourea dioxide, and the consumption of thiourea dioxide is about one-tenth of that of dithionite. Compared with the dyeing method using only dithionite as reducing agent, the method has no obvious difference in dyeing effect, but the reducing agent used is relatively safer, more stable, has higher utilization rate, and has greater economic value. At the same time, the fabric dyed by this method has good level dyeing property and washing resistance, and is an ideal dyeing method.
Owner:南通凡百信新材料有限公司
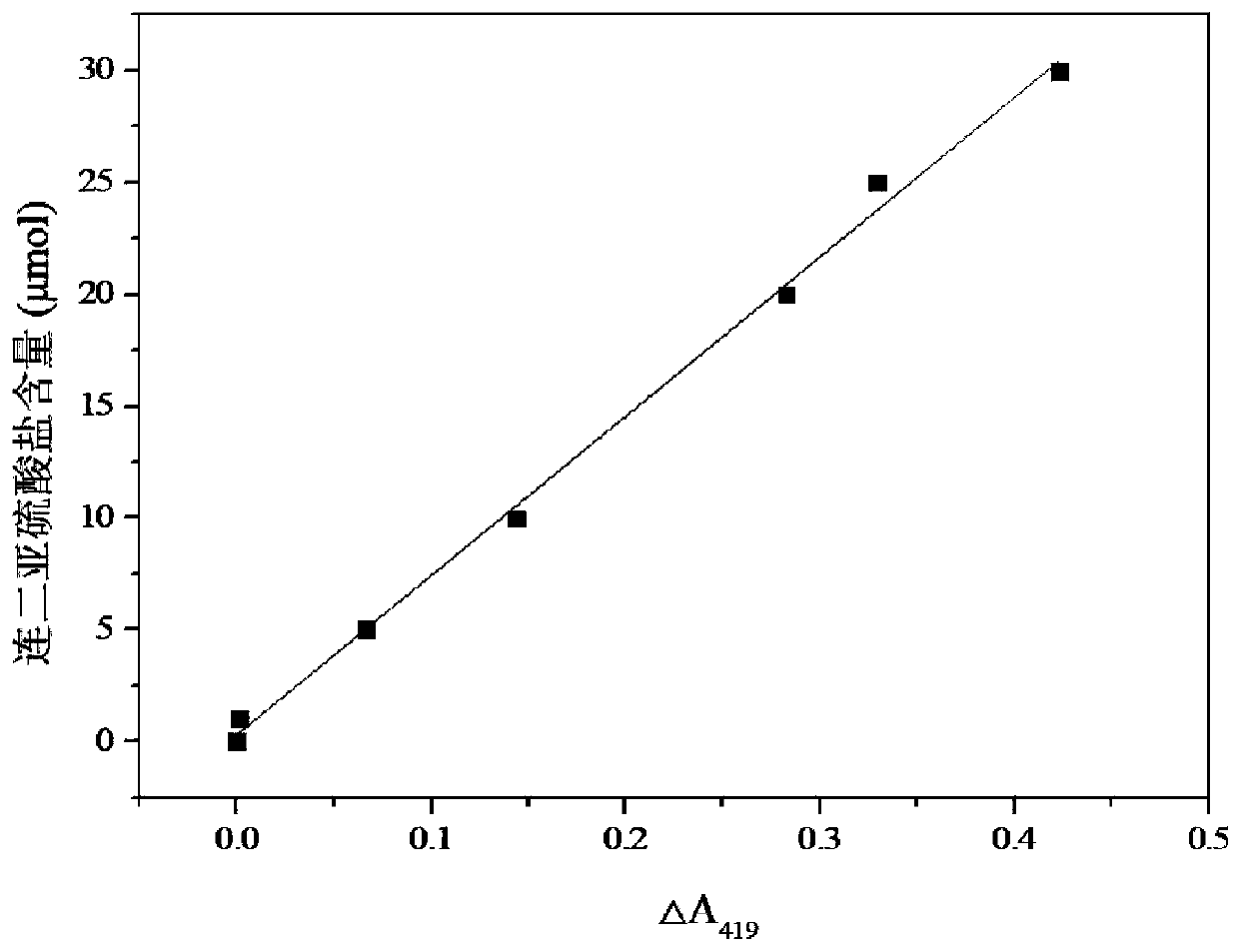
Method for measuring dithionite by potassium ferricyanide differential spectrophotometry
InactiveCN110793925AImprove accuracyReduce mistakesColor/spectral properties measurementsDithionous acidPotassium cyanide
The invention discloses a method for measuring dithionite by potassium ferricyanide differential spectrophotometry, which aims at the problems that in the prior art, when the content of dithionite ismeasured by use of a potassium ferricyanide differential titration method, the detection limit is high, and the detection requirement of low-concentration dithionite cannot be met. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adding an alkaline substance to enable a reaction to occur under an alkaline condition; (2) sequentially adding a potassium ferricyanide solution and a dithionite sample tobe measured into the alkaline substance, oscillating and shaking to enable the substances to react fully; and (3) detecting a difference value between absorbance values before and after the sample tobe measured is added through spectrophotometry, substituting the difference value into a standard curve equation, and calculating to obtain the content of the dithionite in the sample to be measured.According to the method of the invention, the content of the sample to be measured is reflected through the absorbance change of the potassium ferricyanide after being reduced and consumed by the dithionite under alkaline conditions, thus the method has accurate measurement result, wide detection range and small instrument limiting factor, and is convenient for conventional laboratories to use.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Cosmetic Or Dermatological Preparations Containing 4-n-butylresorcinol Combined With One Or More Sulfites, Especially Hydrogen Sulfites And/or Disulfites
Cosmetic or dermatological preparations containing 4-n-butylresorcinol combined with one or more sulfites, especially hydrogen sulfites and / or disulfites.
Owner:BEIERSDORF AG
Sodium dithionite colorimetric fluorescent probe as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110452687AThe synthesis steps are simpleHigh yieldOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceSodium dithioniteFluorescence
The invention provides a colorimetric fluorescent bifunctional molecular probe, a preparation method of the probe and an application of the probe in detection of illegal additivesodium dithionite in food samples, and belongs to the technical field of analytical chemistry. The probe has a molecular formula of C29H31N4O<+> and a structural formula represented by a formula I shown in the description.The sodium dithionite colorimetric fluorescent bifunctional molecular probe designed by the invention has a simple preparation method and a mature synthetic route, can realize direct detection of thesodium dithionite, and has the characteristics of good selectivity, a fast detection speed, high sensitivity and obvious color change; and the method provided by the invention has original innovationand good social value, and is expected to be applied to the detection of illegal additives such as the sodium dithionite in food.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Self-heating agent for the reductive decoloration of dyed keratinous fibers
Kit-of-parts for the reductive decoloration of dyed keratinous fibers comprising, packaged separately from one another(I) a first container (A) containing a cosmetic agent (a) and(II) a second container (B) containing a cosmetic agent (b),wherein the agent (a) in the first container (A)(a1) contains one or more reducing agents from the group of formamidine sulphinic acids, sodium dithionite, zinc dithionite, potassium dithionite, hydroxymethane sulphinic acid, aminomethan sulphinic acid, cysteine, thiolactic acid, sulfanyl acetic acid, and / or ascorbic acid, and the agent (b) in container (B)(b1) contains one or more oxidants from the group of hydrogen peroxide, potassium sulphate, sodium persulphate and / or ammonium persulphate, andwherein the weight ratio of the total quantity of all reducing agents (a1) to the total quantity of all oxidants (b1)—relative to the total weight of agents (a) plus (b)—is a value of 50.0 to 4.0.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
Process for producing sulfinate with low content exogenous salt
InactiveCN1636974AInhibition formationOrganic chemistryElectrolysis componentsDithionous acidAlkaline earth metal
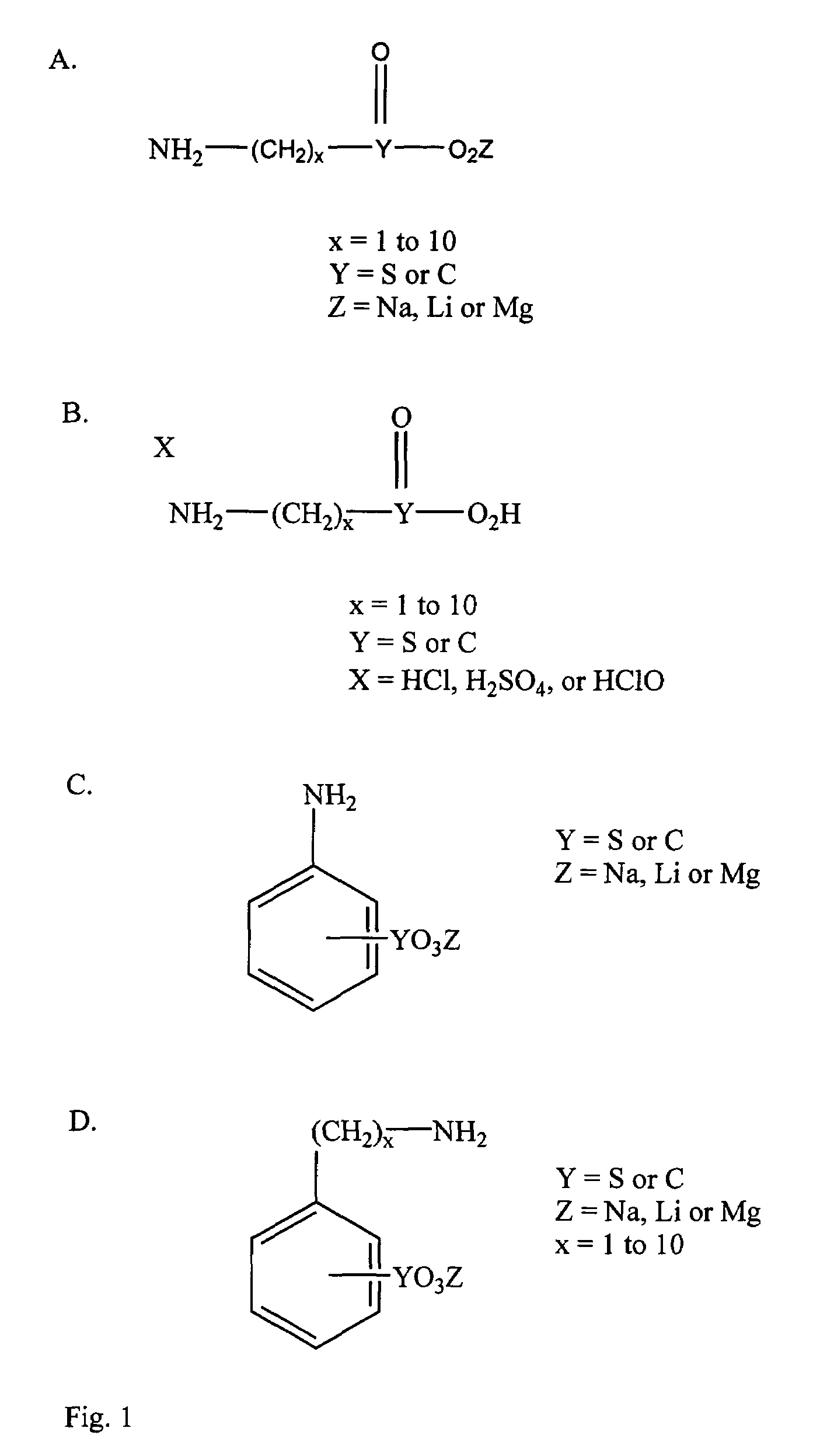
The present invention relates to a process for the preparation of sulfinate salts with low levels of foreign salts by reducing alkali metal or alkaline earth metal or ammonium dithionite salts using carbonyl compounds or imines at pH > 6. The molar ratio of dithionite to carbonyl or imine compound is preferably in the range of 0.75-1.3. The present method provides a sulfinate product with low levels of foreign salts. If desired, the foreign salts formed can be further removed using conventional techniques. The method is particularly useful for the preparation of hydroxymethyl sulfinate.
Owner:BASF AG
Stabilized urea fertilizer compositions and methods for preparing same
PendingUS20210309583A1Good effectLower requirementAgriculture gas emission reductionUrea compound fertilisersThio-Nitration
Provided in the invention is a stabilized fertilizer composition (I) suitable for use in fertilizers and comprising: Urea (a), One or more compounds (b), One or more urease inhibitors (c1) and / or one or more nitrification inhibitors (c2), optionally provided in one or more carriers (d), said compounds (c) being different from compounds (b), Optionally one or more additives (e) different from any of the above, and Water (f) in an amount less than about 10 wt % and preferably less than about 5 wt %; wherein compounds (b) are selected from thiosulfates (b1) and / or from polysulfides (b2) and / or from (bi)sulfites (b3); and wherein the ratio of urea (a) to compounds (b) is from 1:99 to 99:1, preferably from 2:98 to 98:2. Products of the invention can be made in various forms and in different ways. All of the materials of the invention are suitable for use in fertilizers and blend well with solid and liquid fertilizers standardly used. They have excellent shelf life and provide good urea-N protection.
Owner:TESSENDERLO CHEM
Method for advanced oxidation treatment of refractory organic matters in wastewater by utilizing combination of ferrous ions and dissolved oxygen to activate dithionite
PendingCN111573814ADevelopment of Advanced Oxidation TechnologyEasy to transportWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsExternal energyFerrous salts
The invention relates to a method for advanced oxidation treatment of refractory organics in wastewater by utilizing combination of ferrous ions and dissolved oxygen to activate dithionite. The methodcomprises the following steps: under the condition of normal temperature, adding ferrous salt into wastewater containing refractory organic pollutants, then adding dithionite, and conducting a reaction under the condition that a certain amount of dissolved oxygen is contained, wherein a molar ratio of the dithionite to the refractory organic pollutants in the wastewater is 50: 1 to 500: 1. The method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of implementation at normal temperature and normal pressure, mild reaction, no external energy, environment friendliness, easiness in operationand convenience in transportation of a treatment agent, has good effect on removing refractory organic pollutants in water, and presents great application potential in the field of environmental pollution treatment.
Owner:HARBIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SHENZHEN (INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY INNOVATION HARBIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SHENZHEN) +2
Tin plating bath and a method for depositing tin or tin alloy onto a surface of a substrate
PendingCN113891958AIncrease plating rateNo lossSolid-state devicesLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingMetallurgyThio-
The present invention concerns a tin plating bath comprising tin ions; titanium ions as reducing agent suitable to reduce tin ions to metallic tin; and at least one compound selected from the group consisting sulfites, dithionites, thiosulfates, tetrathionates, polythionates, disulfites, sulfides, disulfide, polysulfide, elemental sulfur or mixtures thereof. The present invention further discloses a method of depositing tin or a tin alloy onto a surface of a substrate. The tin plating bath is particularly suitable to be used in the electronics and semiconductor industry.
Owner:ATOTECH DEUT GMBH
Anolyte for indirect electrochemical dyeing of vat dyes
ActiveCN109826023BGood electrical conductivityStrong ability to conduct electronsElectrolysis componentsDyeing processElectrolytic agentStaining
The invention relates to the technical field of vat dye dyeing, in particular to an anolyte for indirect electrochemical dyeing of vat dyes, the electrolyte of which includes sulfite, pyrosulfite, dithionite or thiocyanate at least one. The present invention adopts an electrolyte with excellent electrical conductivity and less side reactions and weak reducibility, and selects sulfite, pyrosulfite, dithionite or thiocyanate as the anode electrolyte, which has a strong ability to conduct electrons, and can be used on the anode. The reaction is fast, the product is sulfate, clean and environmentally friendly, the dyeing process under this system is simple, the reduction time is shortened, and the current efficiency is high, which is conducive to the realization of industrial production and has good application prospects. It solves the traditional anolyte such as sulfuric acid and other electrode corrosion Serious, poor safety, long recovery time, low current efficiency and other problems.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Self-heating agents for reductive decolorization of dyed keratinous fibers
Multi-component package unit (kit-of-parts), ready-to-use agent, and methods for reductive decolorizing of dyed keratinous fibers are provided herein. In an embodiment, a multi-component package unit includes, separately packaged, a first container (A), a second container (B), and a third container (C). The first container (A) includes a cosmetic agent (a) that includes (a1) one or multiple reducing agents chosen from the group of formamidine sulfinic acid, sodium dithionite, zinc dithionite, potassium dithionite, hydroxymethanesulfinic acid, aminomethanesulfinic acid, cysteine, thiolactic acid, sulphanylacetic acid (thioglycolic acid) and / or ascorbic acid. The second container (B) includes a cosmetic agent (b) that includes one or multiple oxidizing agents. The third container (C) includes a cosmetic agent (c) that includes (c1) one or multiple alkalizing agents. The weight ratio of the total amount of all reducing agents (a1) to the total amount of all oxidants (b1) has a value from about 50.0 to about 4.0.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Lignocellulosic Material in the Presence of Sulfite, Dithionite and/or Dithiothreitol
ActiveUS20130210088A1Improve processing efficiencyImprove efficiencyBiofuelsFermentationCelluloseDithionous acid
A method is provided for improving enzymatic hydrolysis in saccharification of a lignocellulosic material. The method is comprising pretreating the lignocellulosic material to obtain a slurry of pretreated lignocellulosic material; adding at least one reducing agent to the slurry of pretreated lignocellulosic material or the liquid fraction thereof to decrease the enzymatic hydrolysis inhibitory properties of slurry of the pretreated lignocellulosic material or the liquid fraction thereof; and subjecting the slurry of pretreated lignocellulosic material or the liquid fraction thereof to enzymatic hydrolysis in the presence of the at least one reducing agent.
Owner:SEKAB E TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com