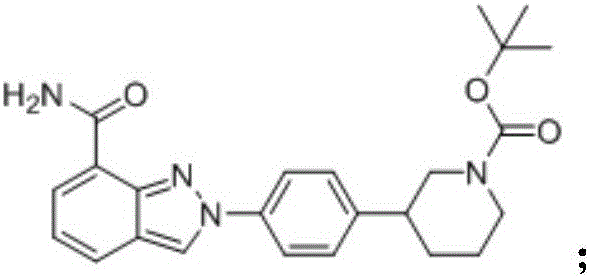
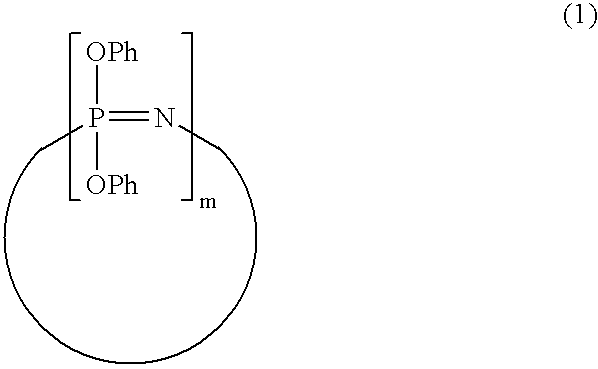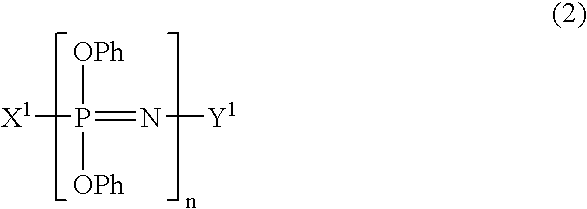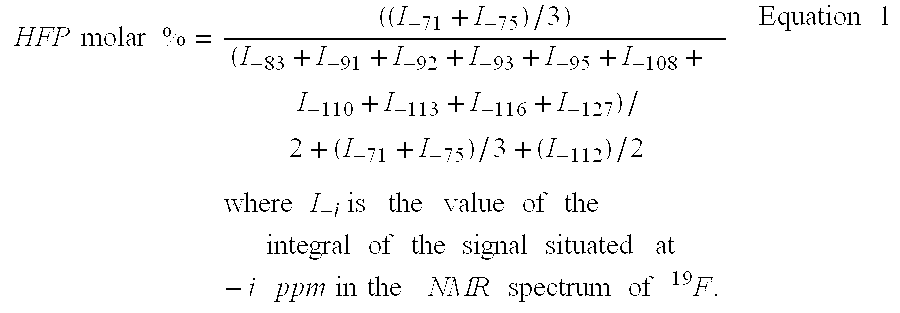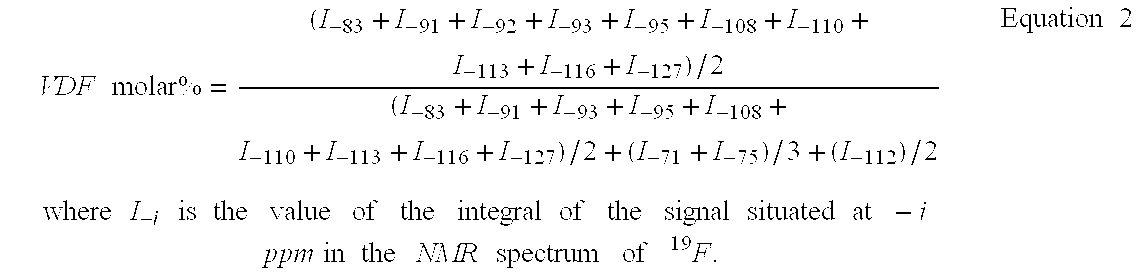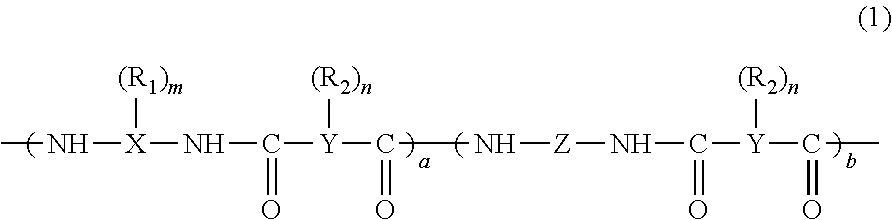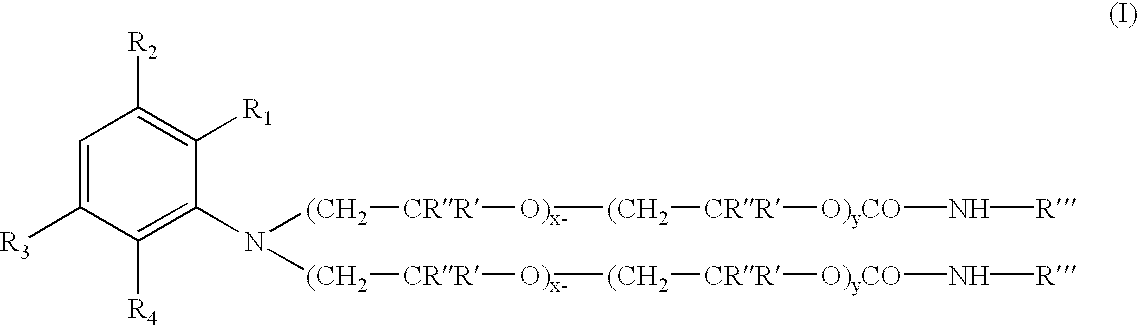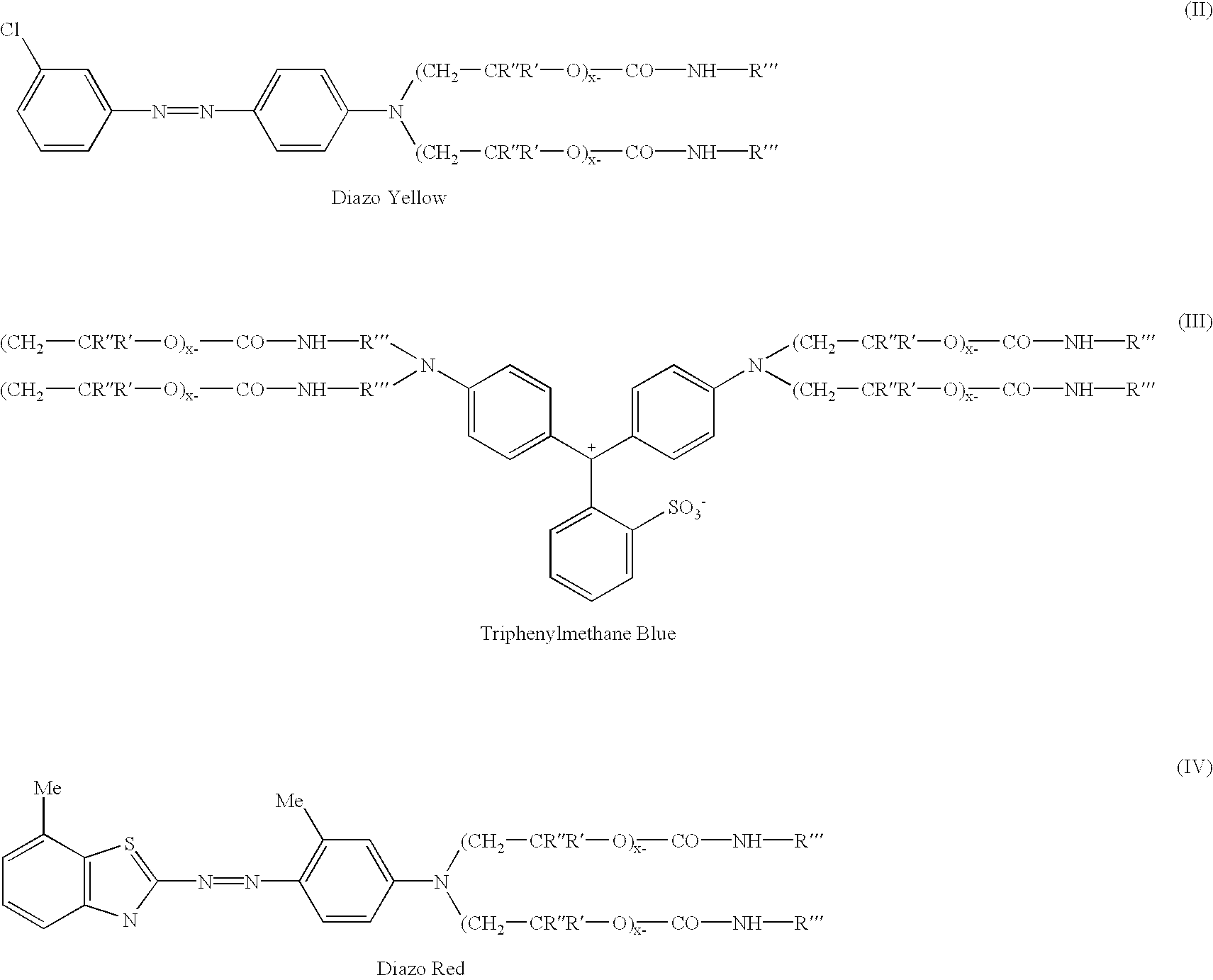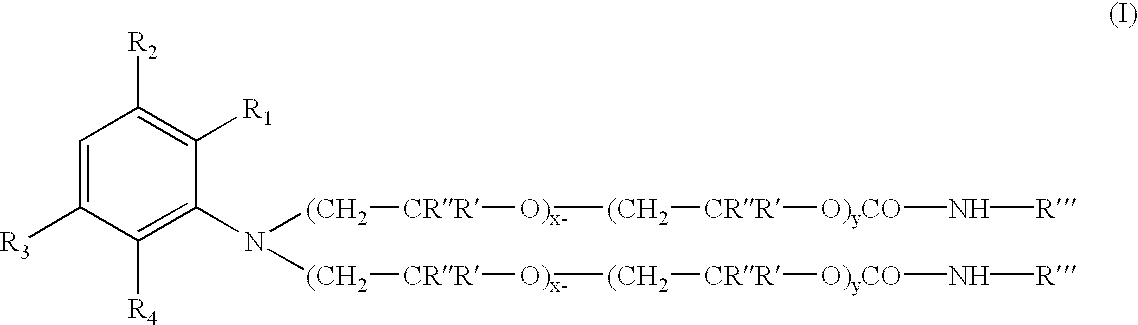Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1737 results about "Diazo" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
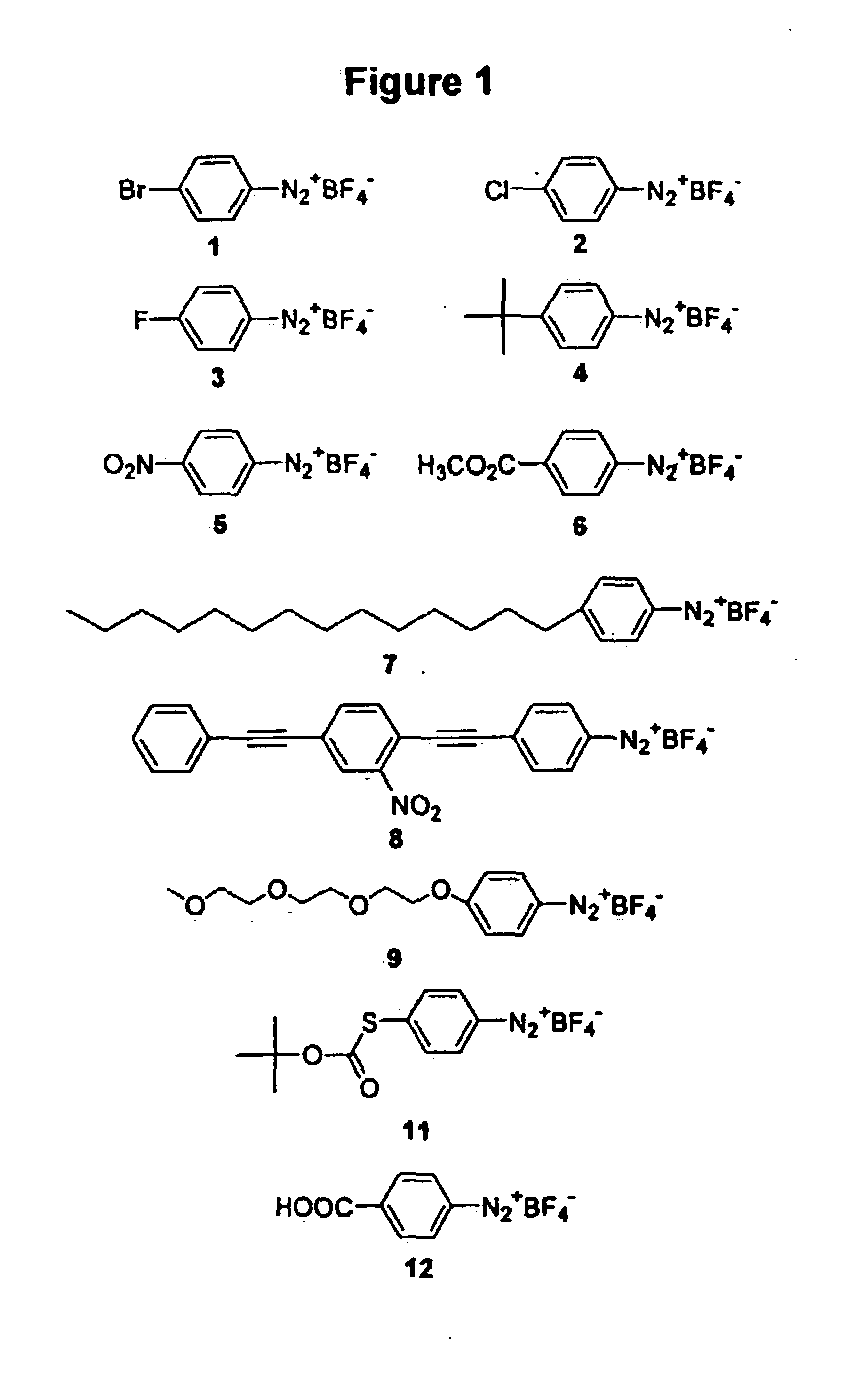
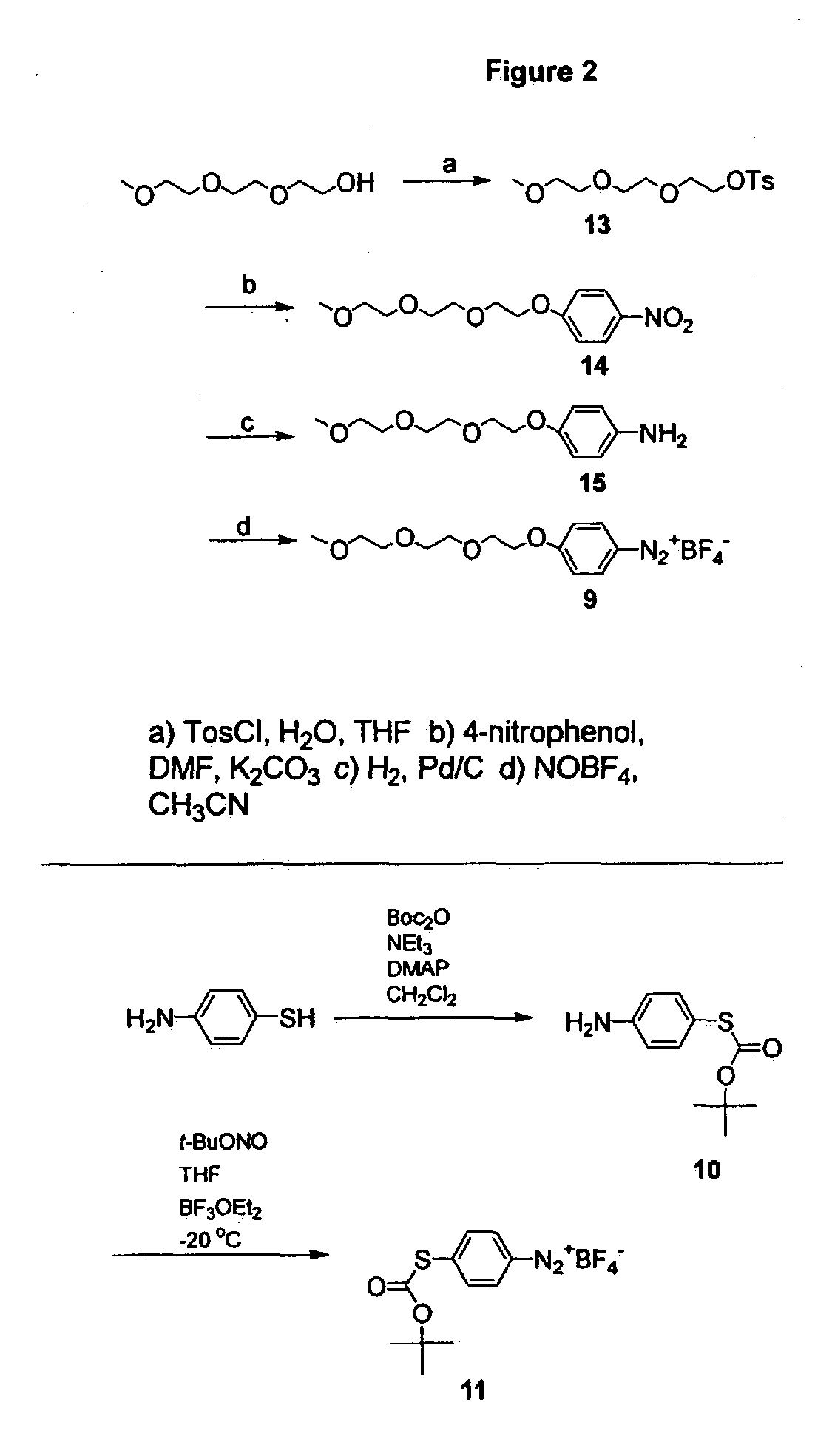
The diazo group is an organic moiety consisting of two linked nitrogen atoms (azo) at the terminal position. Overall charge neutral organic compounds containing the diazo group bound to a carbon atom are called diazo compounds or diazoalkanes and are described by the general structural formula R₂C=N⁺=N⁻, and the simplest example of a diazo compound is diazomethane. Compounds with the diazo moiety should be distinguished from diazonium compounds, which have the same terminal azo group but bear an overall positive charge, and azo compounds in which the azo group bridges two organic substituents. The electronic structure of diazo compounds is characterized by π electron density delocalized over the α-carbon and two nitrogen atoms, along with an orthogonal π system with electron density delocalized over only the terminal nitrogen atoms. Because all octet rule-satisfying resonance forms of diazo compounds have formal charges, they are members of a class of compounds known as 1,3-dipoles. Some of the most stable diazo compounds are α-diazo-β-diketones and α-diazo-β-diesters with the electron density further delocalized into an electron-withdrawing carbonyl group. In contrast, most diazoalkanes without electron-withdrawing substituents, including diazomethane itself, are explosive. A commercially relevant diazo compound is ethyl diazoacetate (N₂CHCOOEt). A group of isomeric compounds with only few similar properties are the diazirines, where the carbon and two nitrogens are linked as a ring.
Pharmaceutical co-crystal compositions
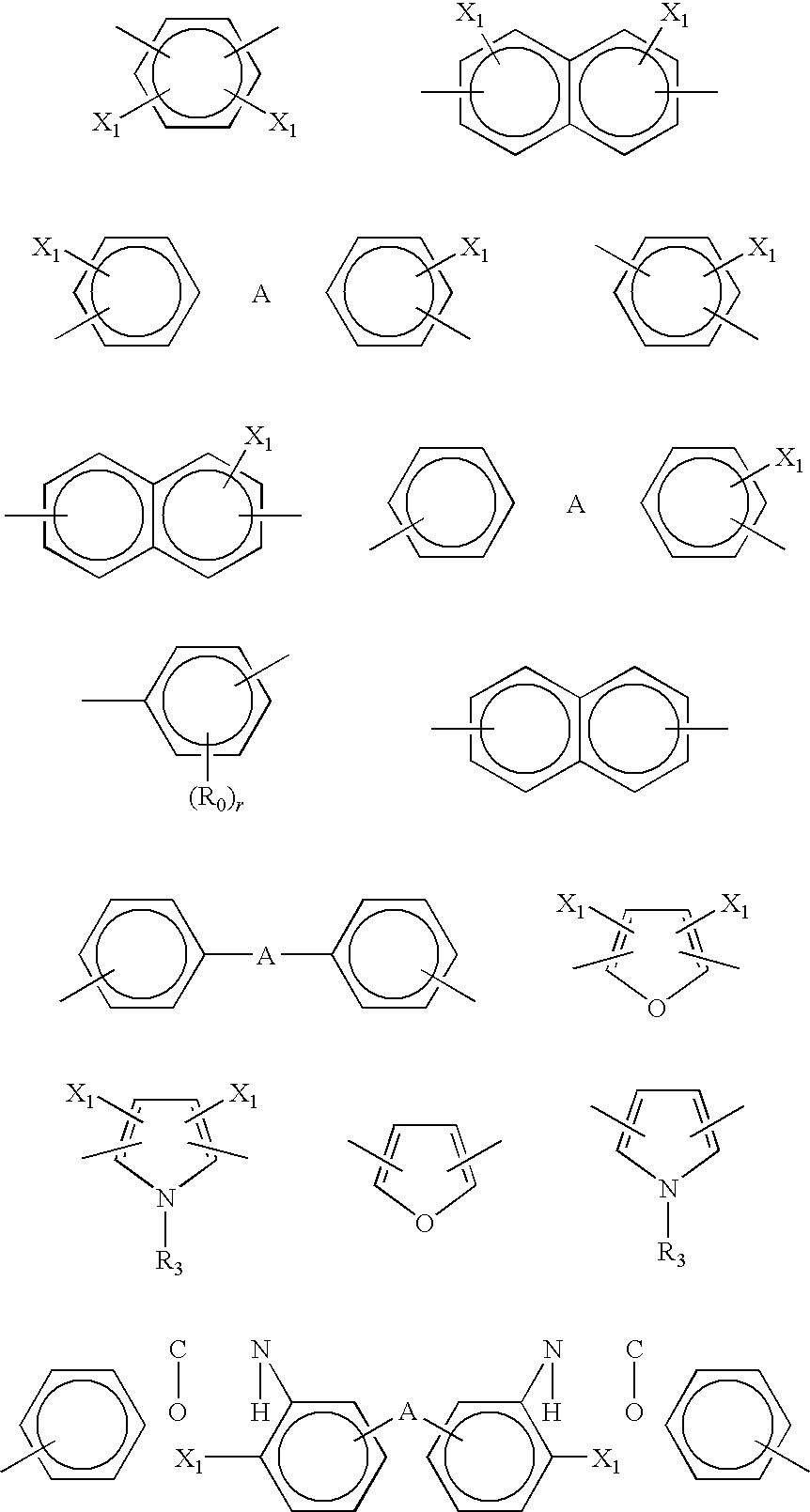
A pharmaceutical composition comprising a co-crystal of an API and a co-crystal former; wherein the API has at least one functional group selected from ether, thioether, alcohol, thiol, aldehyde, ketone, thioketone, nitrate ester, phosphate ester, thiophosphate ester, ester, thioester, sulfate ester, carboxylic acid, phosphonic acid, phosphinic acid, sulfonic acid, amide, primary amine, secondary amine, ammonia, tertiary amine, sp2 amine, thiocyanate, cyanamide, oxime, nitrile diazo, organohalide, nitro, s-heterocyclic ring, thiophene, n-heterocyclic ring, pyrrole, o-heterocyclic ring, furan, epoxide, peroxide, hydroxamic acid, imidazole, pyridine and the co-crystal former has at least one functional group selected from amine, amide, pyridine, imidazole, indole, pyrrolidine, carbonyl, carboxyl, hydroxyl, phenol, sulfone, sulfonyl, mercapto and methyl thio, such that the API and co-crystal former are capable of co-crystallizing from a solution phase under crystallization conditions.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON CONSUMER COPANIES +2
Pharmaceutical co-crystal compositions
InactiveUS20070026078A1Improve solubilityLow hygroscopicityBiocidePowder deliveryThioketoneHydroxamic acid
A pharmaceutical composition comprising a co-crystal of an API and a co-crystal former; wherein the API has at least one functional group selected from ether, thioether, alcohol, thiol, aldehyde, ketone, thioketone, nitrate ester, phosphate ester, thiophosphate ester, ester, thioester, sulfate ester, carboxylic acid, phosphonic acid, phosphinic acid, sulfonic acid, amide, primary amine, secondary amine, ammonia, tertiary amine, sp2 amine, thiocyanate, cyanamide, oxime, nitrile diazo, organohalide, nitro, s-heterocyclic ring, thiophene, n-heterocyclic ring, pyrrole, o-heterocyclic ring, furan, epoxide, peroxide, hydroxamic acid, imidazole, pyridine and the co-crystal former has at least one functional group selected from amine, amide, pyridine, imidazole, indole, pyrrolidine, carbonyl, carboxyl, hydroxyl, phenol, sulfone, sulfonyl, mercapto and methyl thio, such that the API and co-crystal former are capable of co-crystallizing from a solution phase under crystallization conditions.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON CONSUMER COPANIES +2
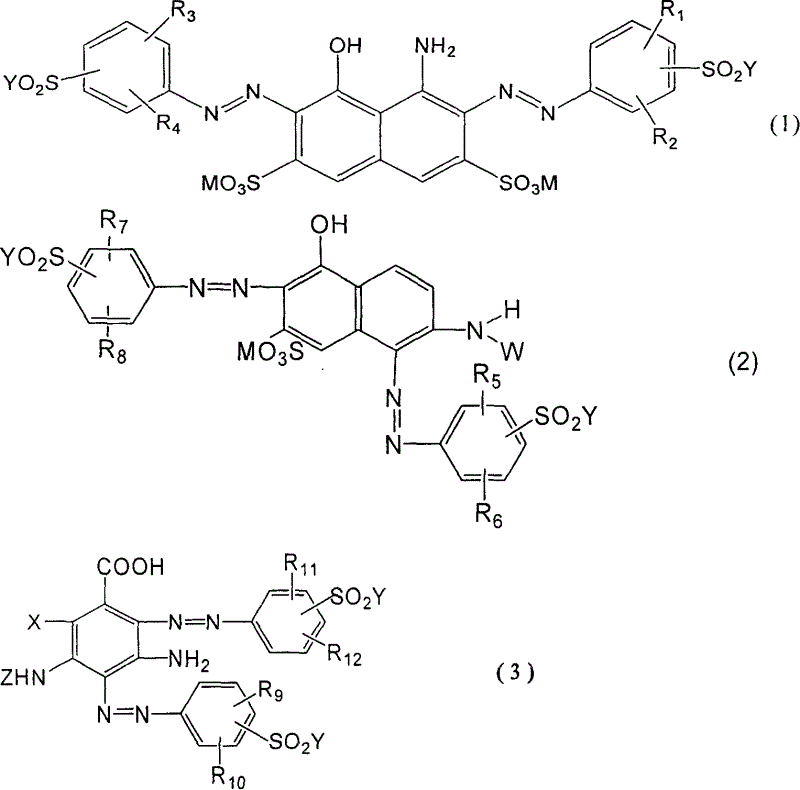
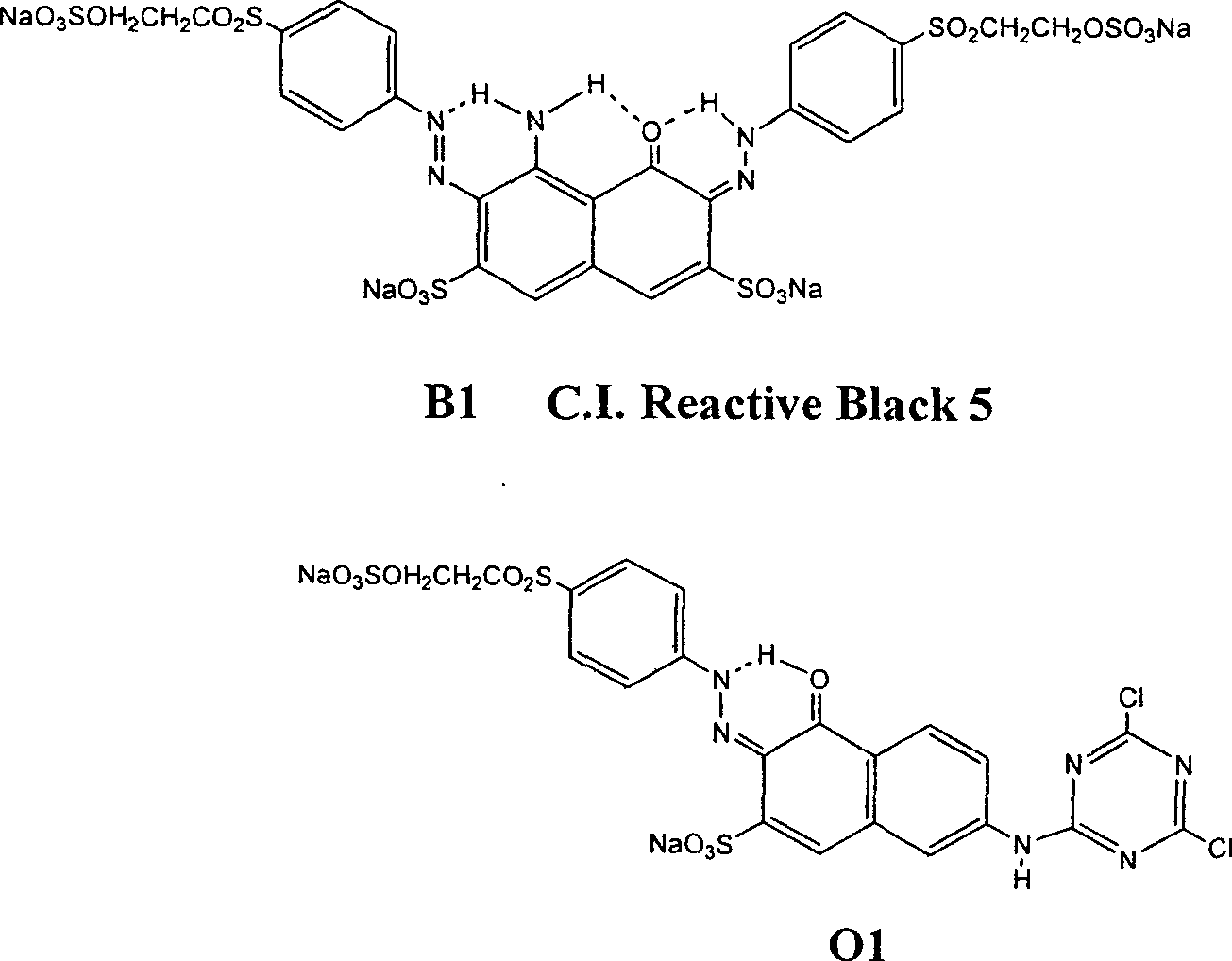
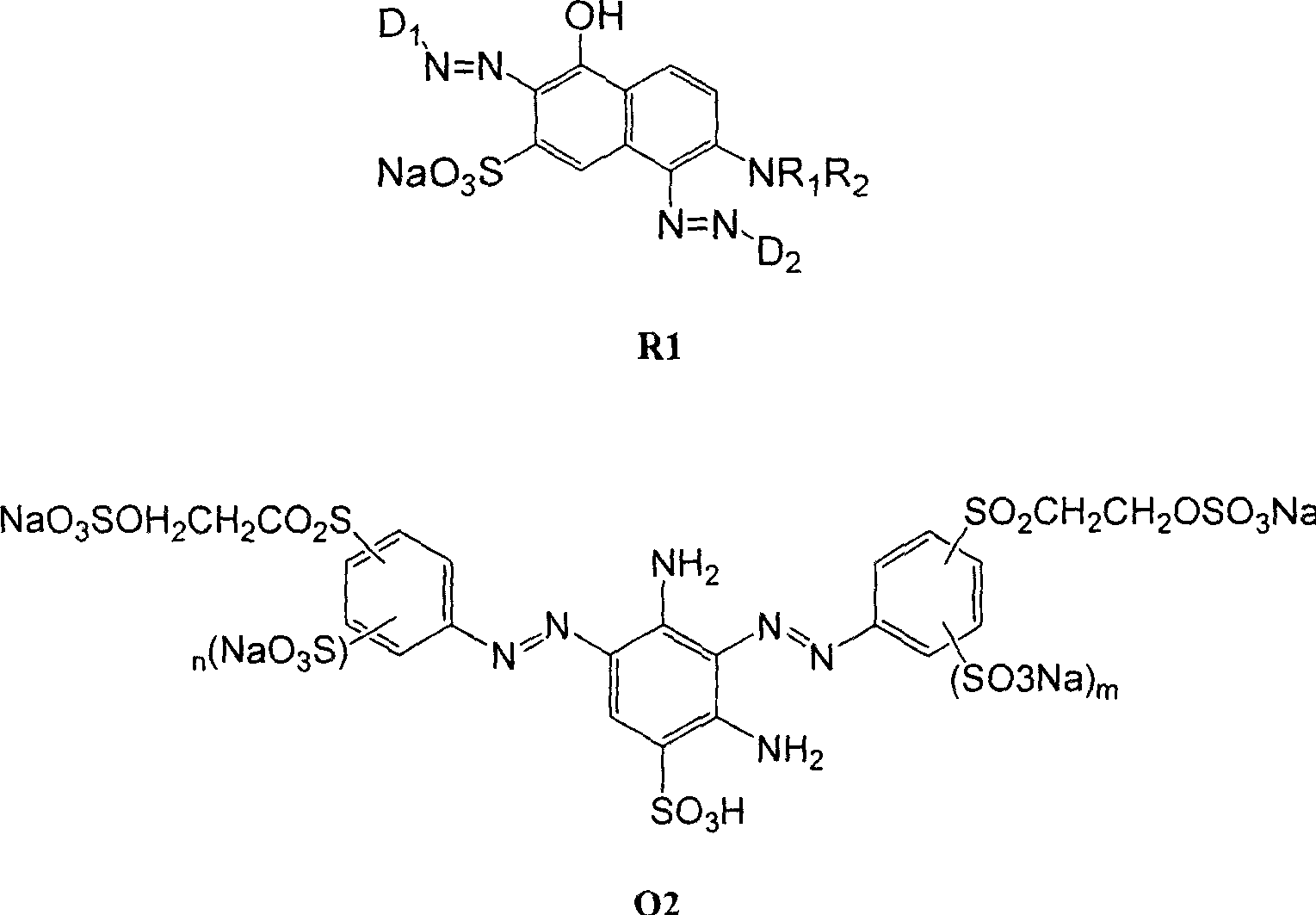
Black and active dye
The invention provides a black composite reactive dye having three primary color constituents comprising, green disazo dye employing ethylene sulfone series arylamine or aniline derivative as diazo component and H acid as coupling component, one ore more red disazo dyes employing sulfoalkyl J acid or carboxymethyl J acid derivatives as coupling components, one ore more yellow bisazo or polyazo dyes employing sulfochlorinated 3,5-diaminobenzoic acid or sulfoalkyl derivatives as coupling components. The dye can be applied to intermittent and continuous dyeing for cellulose fiber, protein fiber, poly nylon and their fiber mixed fabrics.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Pharmaceutical co-crystal compositions of drugs such as carbamazepine, celecoxib, olanzapine, itraconazole, topiramate, modafinil, 5-fluorouracil, hydrochlorothiazide, acetaminophen, aspirin, flurbiprofen, phenytoin and ibuprofen
A pharmaceutical composition comprising a co-crystal of an API and a co-crystal former; wherein the API has at least one functional group selected from ether, thioether, alcohol, thiol, aldehyde, ketone, thioketone, nitrate ester, phosphate ester, thiophosphate ester, ester, thioester, sulfate ester, carboxylic acid, phosphinic acid, phosphonic acid, sulfonic acid, amide, primary amine, secondary amine, ammonia, tertiary amine, imine, thiocyanate, cyanamide, oxime, nitrile diazo, organohalide, nitro, S-heterocyclic ring, thiophene, N-heterocyclic ring, pyrrole, 0-heterocyclic ring, furan, epoxide, peroxide, hydroxamic acid, imidazole, pyridine and the co-crystal former has at least one functional group selected from amine, amide, pyridine, imidazole, indole, pyrrolidine, carbonyl, carboxyl, hydroxyl, phenol, sulfone, sulfonyl, mercapto and methyl thio, such that the API and co-crystal former are capable of co-crystallizing from a solution phase under crystallization conditions.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA +3
N,N-disubstituted diazocycloalkanes
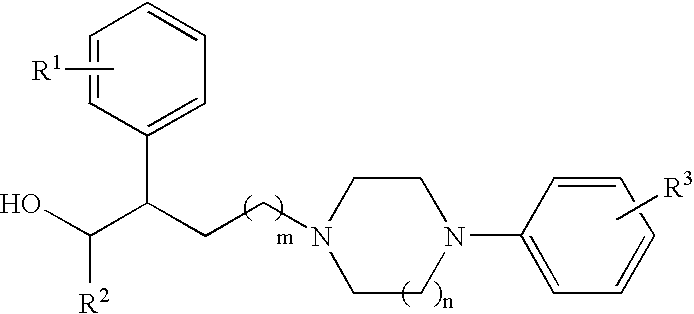
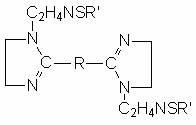
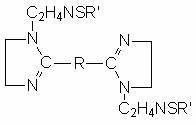
N,N-Disubstituted diazocycloalkanes of the formula I(R1=halogen, R2=(C3–C8)-cycloalkyl, R3=(C1–C4)-alkoxy or (C1–C4)-haloalkoxy group, m is 1 or 2 and n is 1 or 2, have affinity for serotonergic receptors. These compounds and their enantiomers, diastereoisomers, N-oxides, polymorphs, solvates and pharmaceutically acceptable salts are useful in the treatment of patients with neuromuscular dysfunction of the lower urinary tract and diseases related to 5-HT1A receptor.
Owner:RECORDATI SA
Non-fluorescent quencher compounds and biomolecular assays
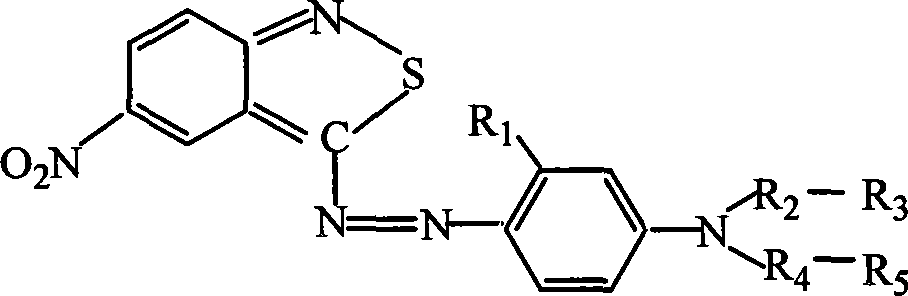
Bis-diazo,triaryl and aryldiazo-N-arylphenazonium quencher moieties, substituted with electron-withdrawing and electron-donating substituents which induce polarity in the delocalized aryl / diazo ring systems, are useful as labels when attached to biomolecules such as polynucleotides, nucleosides, nucleotides, and polypeptides. The quencher moieties are non-fluorescent and accept energy from fluorescent reporter labels by any energy-transfer mechanism, such as FRET. Fluorescence quencher compositions are useful in preparing quencher labelled biomolecules for various molecular biology assays based on fluorescence detection.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Negative photosensitive composition and negative photosensitive lithographic printing plate
InactiveUS7291438B2Less likelyImprove adhesionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiazo compound compositionsOrganoboron compoundsOxygen
There are provided a negative-working photosensitive composition which can be cured by infrared rays and is less likely to suffer polymerization inhibition by oxygen during radical polymerization, and also exhibits high adhesion with a metal, and a negative-working photosensitive lithographic printing plate which is capable of directly forming images by irradiation with infrared rays from a solid or semiconductor laser based on digital signals, and also has high sensitivity and excellent printing durability. The negative-working photosensitive composition contains an infrared absorber (A), an organoboron compound (B) which functions as a polymerization initiator by using in combination with the infrared absorber (A), a compound having a polymerizable unsaturated group (C) and a diazo resin (D), and the negative-working photosensitive lithographic printing plate comprises a support, and a photosensitive layer containing the negative-working photosensitive composition formed on the support.
Owner:KODAK POLYCHROME GRAPHICS +1
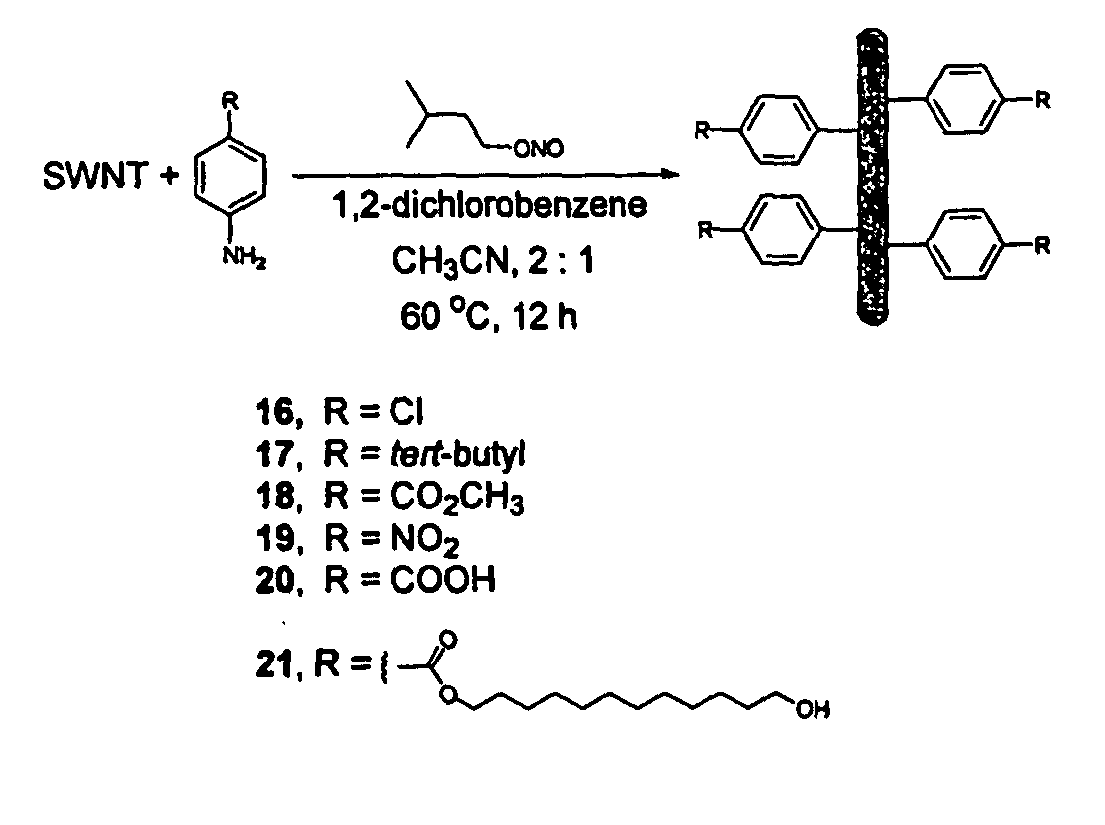
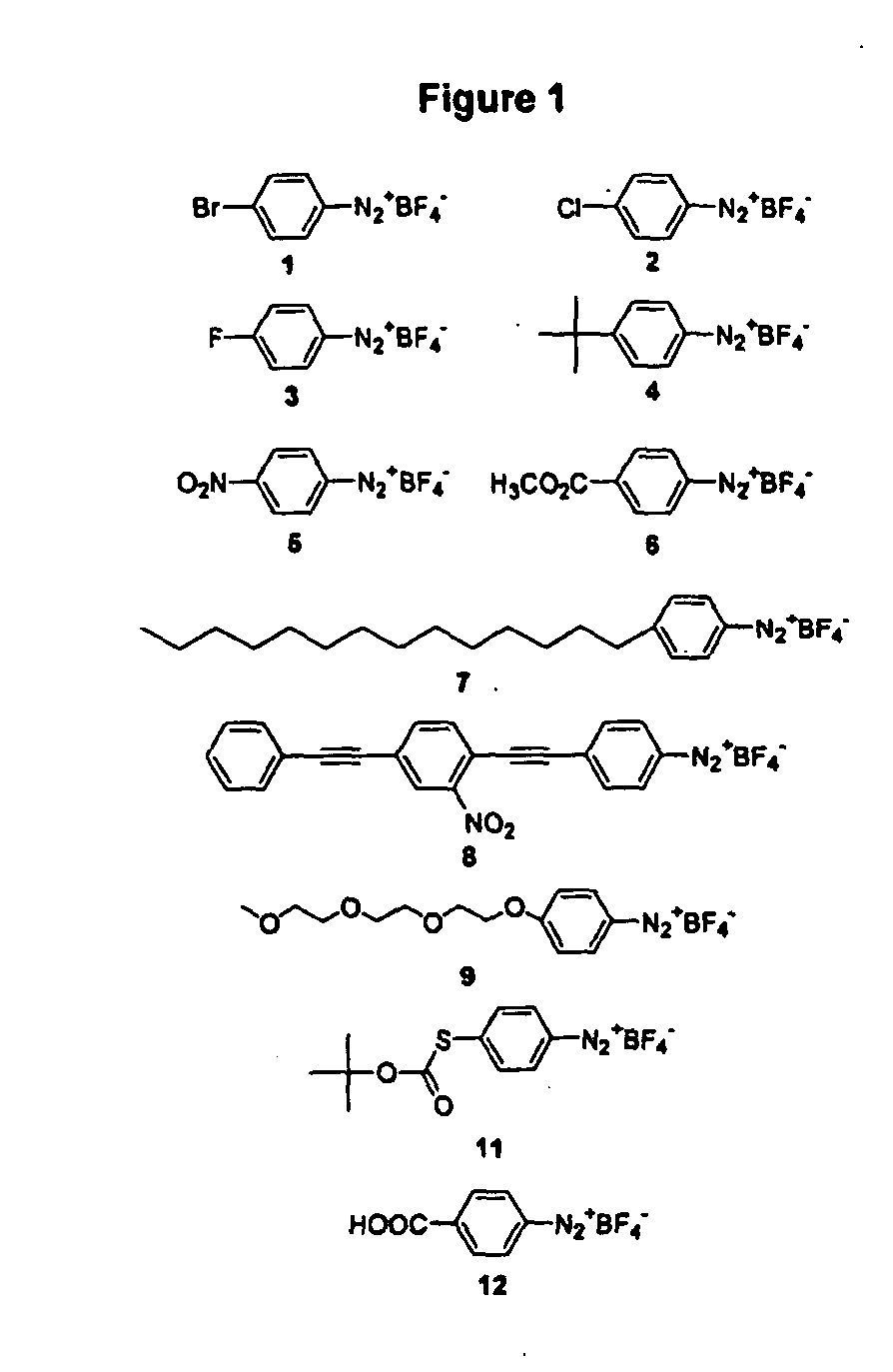
Carbon nanotubes derivatized with diazonium species
InactiveUS20050207963A1Advantage of scalabilityMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentElectrochemistryOrganic compound
Owner:RICE UNIV
Photochromic organic materials
InactiveUS6034193AWithout altering optical quality of materialHigh refractive indexCosmetic preparationsImpression capsRefractive indexSpiropyran
The invention relates to photochromic transparent organic materials presenting an index of refraction of more than 1.55, which are free of optical distortions and are prepared by radical polymerization of a polymerizable composition comprising: a) 80-95 wt % of at least one monomer represented by the general formula (I): ##STR1## where R=H or CH.sub.3, and m and n are independently 1 or 2; b) 5-20 wt % of at least one aromatic monovinyl monomer represented by the general formula (II): ##STR2## c) an effective quantity of at least one dye that imparts photochromic properties to the material, selected from the groups of spiroxazines, spiropyrans and chromenes; d) an effective quantity of a chain transfer agent; and e) an effective quantity of a radical polymerization initiator, characterized in that the chain transfer agent is a linear alkanethiol and the radical polymerization initiator is a diazo compound.
Owner:CORNING INC
Sulfur-containing bis-imidazoline type carbon dioxide corrosion inhibitor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102321463AImprove protectionGood water solubilityOrganic chemistryBorehole/well accessoriesCarbon dioxide corrosionActive agent
The invention discloses a sulfur-containing bis-imidazoline type carbon dioxide corrosion inhibitor and a preparation method thereof. The corrosion inhibitor comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 20-50 percent of sulfur-containing bis-imidazoline quaternary ammonium salt, 1-5 percent of nonionic surfactant, 40-70 percent of low molecular alcohol solvent and 5-10 percent of alkynol, wherein a sulfur-containing bis-imidazoline compound has a general formula of a structure which is shown in the specification; the number of carbon atoms in R of the formula is 5 or 8; the nonionic surfactant is fatty alcohol-polyoxyethylene ether or alkylphenol ethoxylate; the low molecular alcohol solvent is methanol, ethanol, isopropanol or ethylene glycol; and the alkynol is propargyl alcohol or hexynol. In the invention, the sulfur-containing bis-imidazoline compound which is generated through dehydration between dicarboxylic acid and polyamine molecule, dehydration reaction in the molecule and further reaction with the sulfur-containing compound is adopted; the molecule contains a plurality of active adsorption centers such as two diazo five-membered heterocyclic rings, a sulfur-containing group and the like; and a formed organic adsorption membrane has better protection effect on carbon steel.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Process for producing phenoxyphosphazene compound, flame- retardant resin composition, and flame-retardant resin molding
InactiveUS20030040643A1Quality improvementIncrease resistanceGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsAlkanePolymer science
The phenoxyphosphazene compound of the present invention is prepared by treating a phenoxyphosphazene compound with (a) at least one adsorbent selected from activated carbon, silica gel, activated alumina, activated clay, synthetic zeolite and macromolecular adsorbents, (b) at least one reagent selected from metal hydrides, hydrazine, hypochlorites, thiosulfates, dialkyl sulfuric acids, ortho esters, diazoalkanes, lactones, alkanesultones, epoxy compounds and hydrogen peroxide or (c) both the adsorbent and reagent. Incorporation of the phenoxyphosphazene compound prepared by the process of the invention into a synthetic resin achives the following advantages: the synthetic resin can be prevented from discoloration; when the resultant resin composition is stored for a long time, the properties of the synthetic resin, such as heat resistance, weatherability, resistance to discoloration and chemical resistance are not deteriorated; and the resin composition gives a resin composition molded article excellent in properties such as flame retardancy, thermal stability, and moldability.
Owner:OTSUKA CHEM CO LTD
Method for preparing hydrazinobenzene in continuous micro-channel reactor
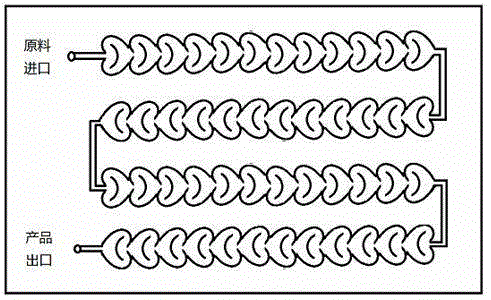
InactiveCN106316879AHigh mixing mass transfer effectImprove thermal conductivityHydrazine preparationToxic gasContinuous flow
The invention relates to a method for preparing highly pure hydrazinobenzene by using continuous flow micro-channel reactor. The method concretely comprises the following steps: preparing aniline hydrochloride from hydrochloric acid and aniline, respectively pumping the aniline hydrochloride and a sodium nitrite solution into the micro-channel reactor by two metering pumps to obtain a diazo salt solution, reducing the obtained reaction solution, carrying out acid separation on the reduced solution, filtering the obtained solution, neutralizing the filtered solution, and distilling the neutralized solution to obtain the highly pure hydrazinobenzene. The diazotization process is a strong exothermic reaction, and the generated diazo salt easily decomposes after standing at a high temperature for a long time, and generates toxic gases which pollute environment and even blast. The mixing effect of the heart-shaped micro-channel reactor is far better than the mass transfer effect generated by stirring, so the aniline conversion rate can reach 99%, the mixing mass transfer effect is good, and heat conduction is fast to avoid local overheating phenomenon; and the reaction can be carried out at constant temperature conditions, so the temperature runaway blast danger of general reactors is eliminated, and the safety is improved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
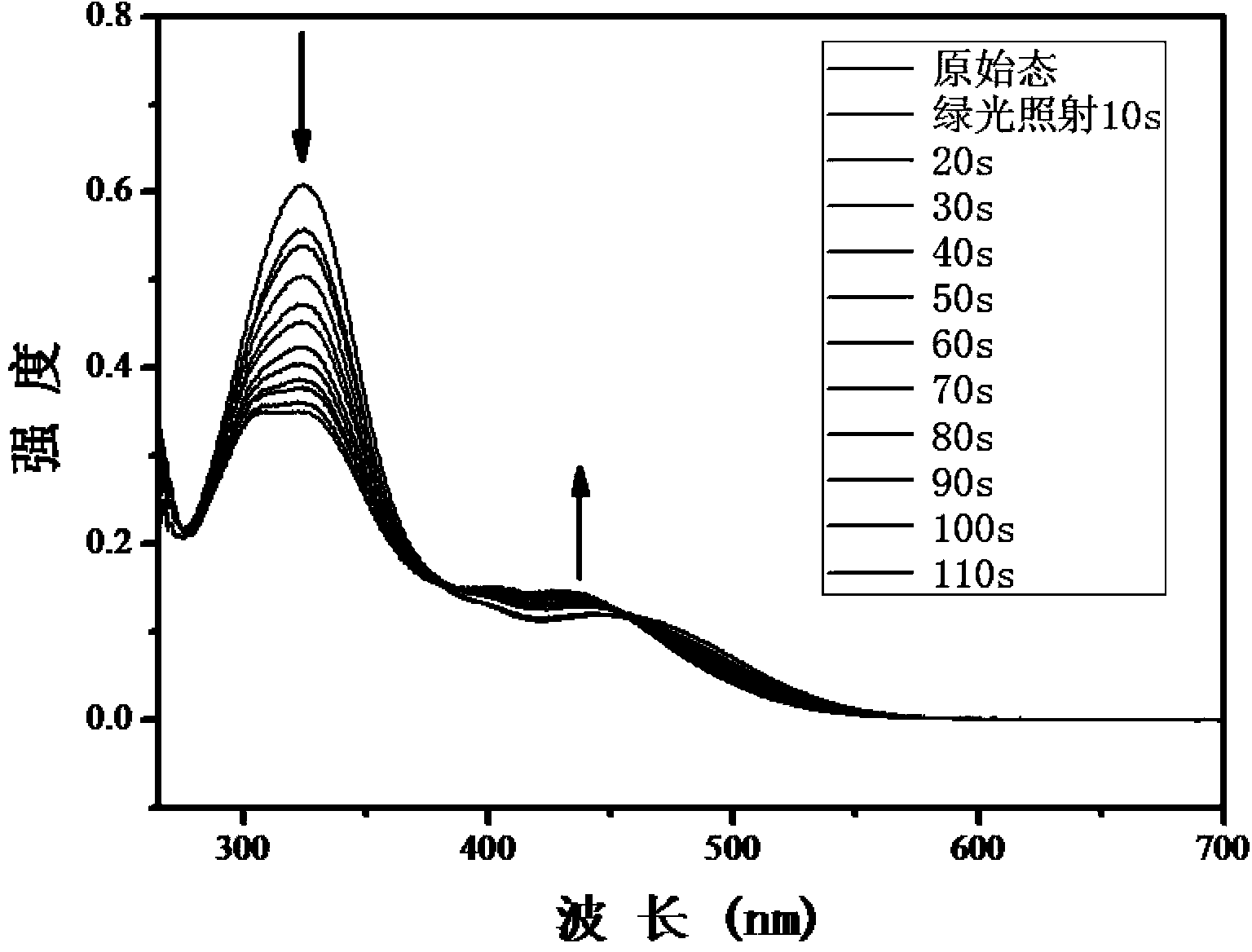
Method for synthesizing visible-light response type azobenzene polymer
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing a visible-light response type azobenzene polymer. The method comprises the following steps: preparing tetramethoxy dihydroxyazobenzene from 2,6-dimethoxyaniline and 3,5-dimethoxy phenol through diazo-reaction, reacting tetramethoxy dihydroxyazobenzene as a raw material with 6-bromohexane alcohol to prepare tetramethoxy-4-ethanol oxyl azobenzene, grafting azobenzene onto a polypropylene acyl chloride framework through alcoholysis reaction of acyl chloride groups, and converting unreacted acyl chloride groups into carboxyl through hydrolysis, thereby finally obtaining the visible-light response type azobenzene polymer, namely, a 2-(2,6,2',6'-tetramethoxy-4-hexyloxy azobenzene phenoxy) crylic acid ethyl ester acrylic copolymer. The method has the advantages that the method is simple and feasible, the synthesized polymer has visible-light response type azobenzene groups, trans / cis-form conversion is achieved under the radiation of green light (520nm), reverse conversion can be achieved under radiation of blue light (420nm), and compared with conventional azobenzene molecules, the azobenzene polymer has the most remarkable advantage that bidirectional conversion of isomer can be achieved without ultraviolet light.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Process for attaching molecular wires and devices to carbon nanotubes and compositions thereof
InactiveUS20050074613A1Advantage of scalabilityPigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologyElectrochemistryOrganic compound
The invention incorporates new processes for the chemical modification of carbon nanotubes. Such processes involve the derivatization of multi- and single-wall carbon nanotubes, including small diameter (ca. 0.7 nm) single-wall carbon nanotubes, with diazonium species. The method allows the chemical attachment of a variety of organic compounds to the side and ends of carbon nanotubes. These chemically modified nanotubes have applications in polymer composite materials, molecular electronic applications, and-sensor devices. The methods of derivatization include electrochemical induced reactions, thermally induced reactions (via in-situ generation of diazonium compounds or pre-formed diazonium compounds), and photochemically induced reactions. The derivatization causes significant changes in the spectroscopic properties of the nanotubes. The estimated degree of functionality is ca. 1 out of every 20 to 30 carbons in a nanotube bearing a functionality moiety. Such electrochemical reduction processes can be adapted to apply site-selective chemical functionalization of nanotubes. Moreover, when modified with suitable chemical groups, the derivatized nanotubes are chemically compatible with a polymer matrix, allowing transfer of the properties of the nanotubes (such as, mechanical strength or electrical conductivity) to the properties of the composite material as a whole. Furthermore, when modified with suitable chemical groups, the groups can be polymerized to form a polymer that includes carbon nanotubes.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Sulfonium salt compound
A compound shown by the general formula [1](wherein R1, R2 and R3 are each independently an aromatic hydrocarbon residual group, Yn− is an anion derived from a carboxylic acid having 3 or more carbon atoms with substituted fluorine atoms, and n is 1 or 2, provided that R1, R2 and R3 each is not a phenyl group having substituents at an ortho and / or a meta position), and a composition consisting of the compound and a diazodisulfone compound are disclosed. Use of the compound or the compound as an acid generator for resists produces the effects of improving the profiles of ultra-fine patterns or diminishing sidewall irregularities in ultra-fine patterns. The compound is also useful as a cationic photopolymerization initiator.
Owner:FUJIFILM WAKO PURE CHEM CORP
Heat sensitive imaging element for providing a lithographic printing plate
InactiveUS6096471AGood ink absorptionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiazo compound compositionsHeat sensitiveEngineering
According to the present invention there is provided a heat-sensitive imaging element for providing a lithographic printing plate, comprising a support and as top layer a heat switchable image forming layer comprising a hardened hydrophilic binder and a heat switchable polymer wherein said top layer or a layer adjacent to said top layer comprises a compound capable of converting light into heat; characterized in that said heat switchable polymer is a polymer containing aryldiazosulphonate units.
Owner:AGFA NV
Synthetic diazonamides
The application discloses novel synthetic compounds, modeled after unique toxins extracted from the marine invertebrate Diazona angulata useful in the treatment abnormal cell mitosis. The application also discloses novel methods for synthesis of these compounds and methods of using these compounds.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method of adopting fluorescence quenching system to potential fingerprint display
InactiveCN103919558AApplication objects are not limitedWon't be disturbedPerson identificationFluorescenceLatent fingerprint
The invention relates to the technical field of trace amount detection, and discloses a method of adopting a fluorescence quenching system to potential fingerprint display. The method is characterized in that potential fingerprint is displayed by utilizing 'turn-on' effect of the fluorescence quenching system to transmit fluorescence once again and includes: firstly, preparing the fluorescence quenching system, wherein the quenching state can be destroyed by fingerprint components; then spraying and painting the fluorescence on various objects with fingerprints, wherein the fingerprint components of chloride ion, amino acid or glucose and the like destroy the quenching state of the fluorescence quenching system to enable the fluorescence to appear to display the fingerprints; taking photos directly through a filter under special light or under natural light. The method is simple and rapid; when fingerprint details are not clear enough, common components like DFO (1.8-diazo-flurene-9-one), IND (indanedione), ninhydrin, silver nitrate and the like are used for continuously displaying the fingerprints, and the method can be further used for 'marking' or 'tracing' the fingerprints.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Process for making polymers comprising derivatized carbon nanotubes and compositions thereof
InactiveUS20050074390A1Advantage of scalabilityMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentElectrochemistryOrganic compound
The invention incorporates new processes for the chemical modification of carbon nanotubes. Such processes involve the derivatization of multi- and single-wall carbon nanotubes, including small diameter (ca. 0.7 nm) single-wall carbon nanotubes, with diazonium species. The method allows the chemical attachment of a variety of organic compounds to the side and ends of carbon nanotubes. These chemically modified nanotubes have applications in polymer composite materials, molecular electronic applications, and sensor devices. The methods of derivatization include electrochemical induced reactions, thermally induced reactions (via in-situ generation of diazonium compounds or pre-formed diazonium compounds), and photochemically induced reactions. The derivatization causes significant changes in the spectroscopic properties of the nanotubes. The estimated degree of functionality is ca. 1 out of every 20 to 30 carbons in a nanotube bearing a functionality moiety. Such electrochemical reduction processes can be adapted to apply site-selective chemical functionalization of nanotubes. Moreover, when modified with suitable chemical groups, the derivatized nanotubes are chemically compatible with a polymer matrix, allowing transfer of the properties of the nanotubes (such as, mechanical strength or electrical conductivity) to the properties of the composite material as a whole. Furthermore, when modified with suitable chemical groups, the groups can be polymerized to form a polymer that includes carbon nanotubes.
Owner:RICE UNIV
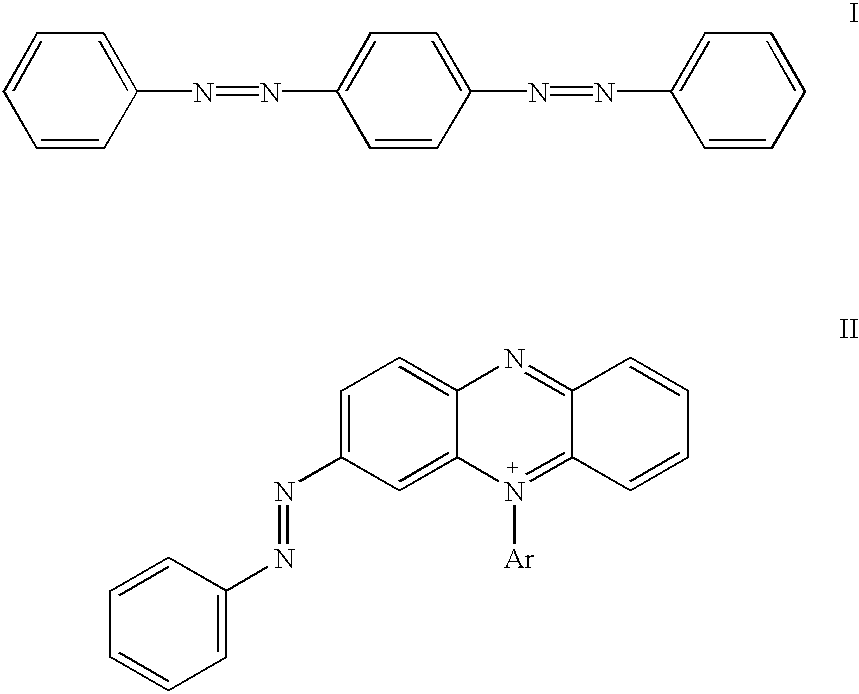
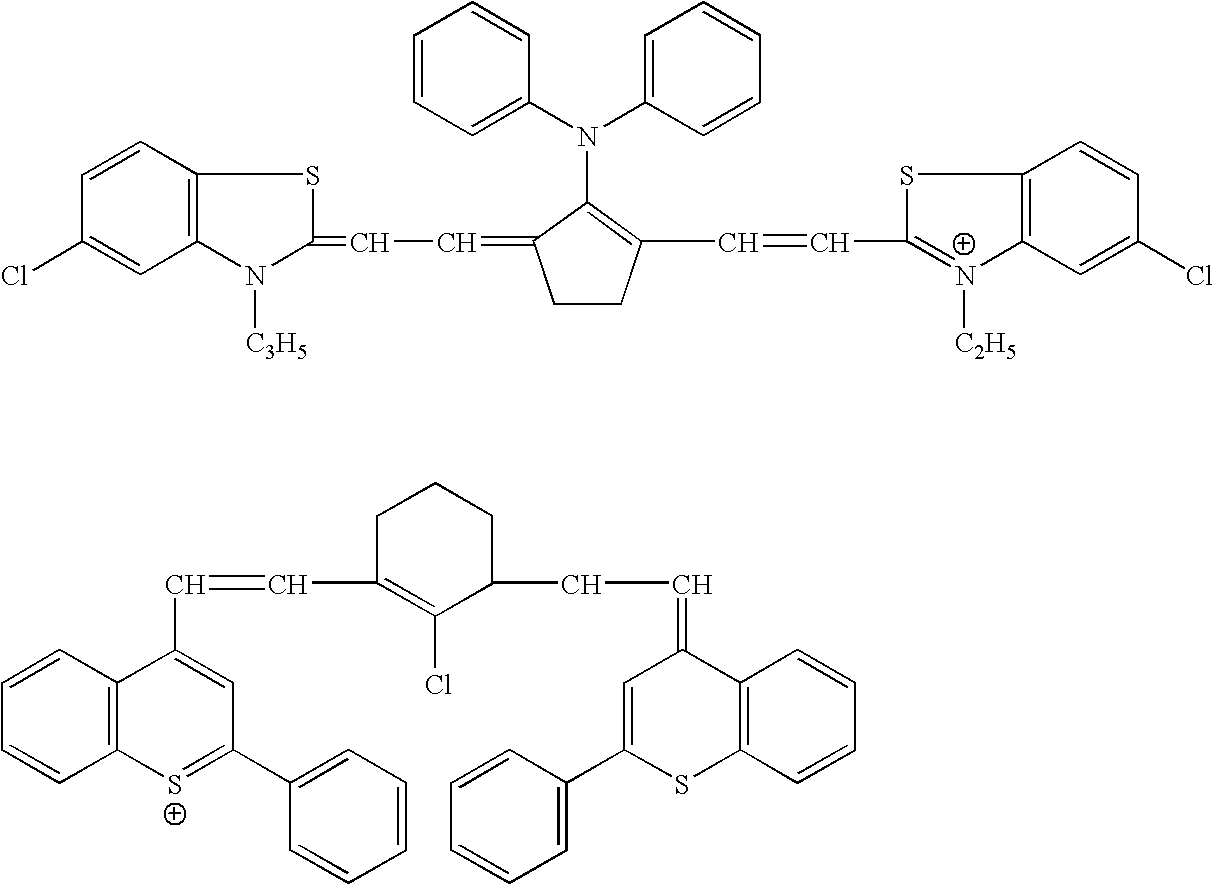
Novel colorants for use within ink systems
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
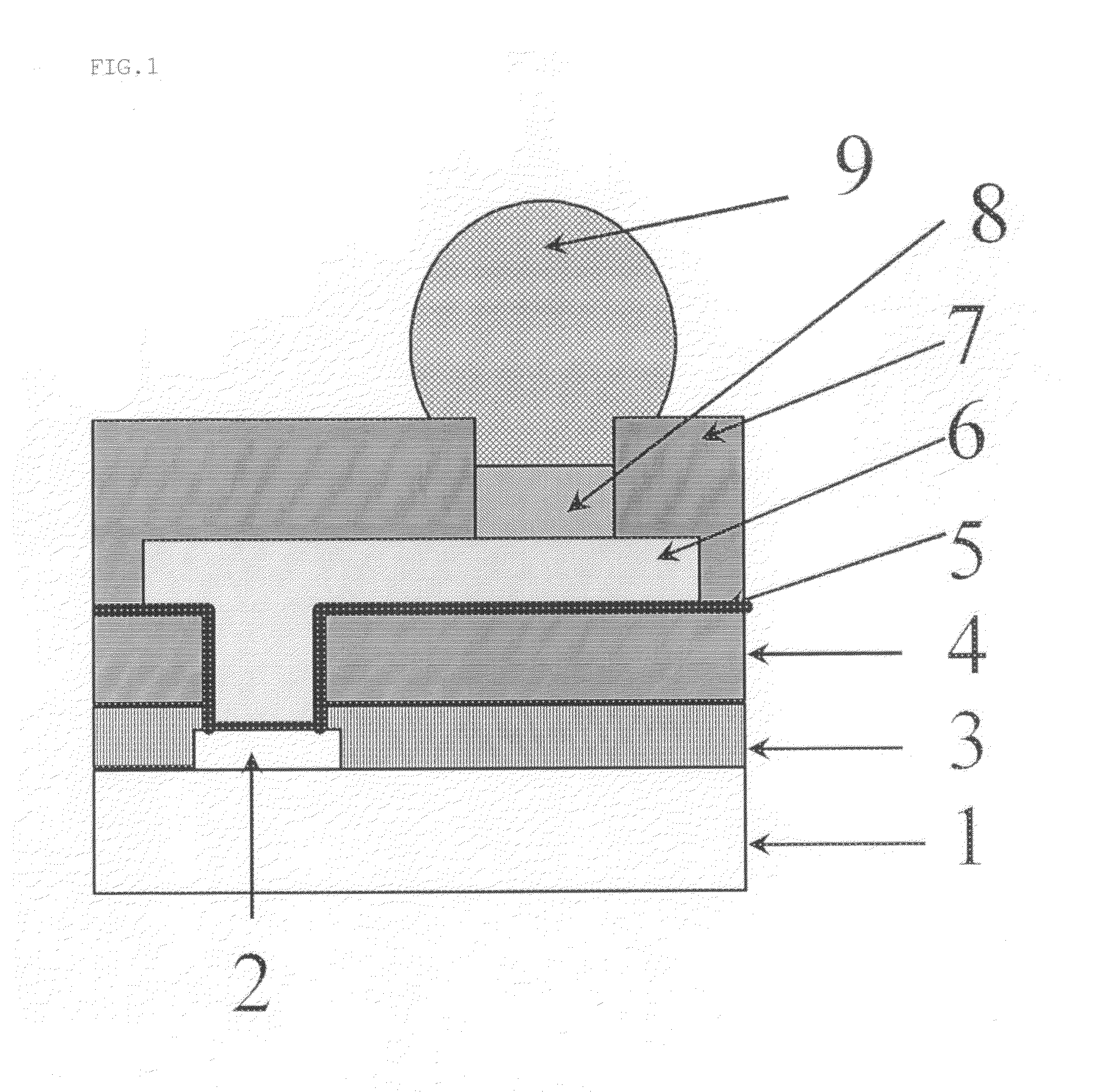
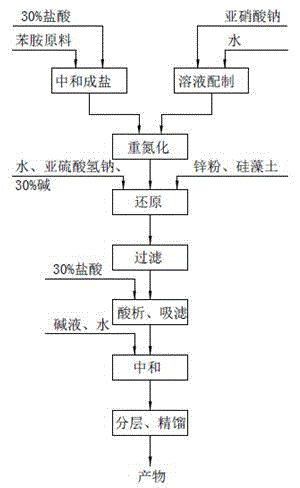
Method for preparing 4-(3-chlorine-4-fluorophenylalanine)-7-methoxy-6-[3-(4-morpholinyl) propoxy] quinazoline
ActiveCN101570516AReduce pollutionReduce manufacturing costOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistry4 FluorophenylalanineNitration
The invention relates to a method for preparing 4-(3-chlorine-4-fluorophenylalanine)-7-methoxy-6-[3-(4-morpholinyl) propoxy] quinazoline (I). The method takes 4-methoxy-2-nitrobenzoic acid as initial material which is subjected to reduction and nitration to obtain 4-methoxy-5-nitryl-2-aminobenzoic acid, is then subjected to cyclization to obtain 7-methoxy-6-nitryl quinazoline-4(3H)-ketone, is again subjected to reduction and diazo reaction hydrolysis to obtain 7-methoxy-6-hydroxy quinazoline-4(3H)-ketone, after etherification reaction is carried out, phosphorus oxychloride is used for preparing 7-methoxy-6-[3-(4-morphjolinyl) propoxy]-4-chloroquinazoline, which is subjected to amination to obtain the compound in the formula (I). The initial material adopted by the preparation method is convenient and accessible, the cost is low, the process route is simple and reasonable, the three wastes produced in the process of preparation generates less pollution, therefore the preparation method can prepare final product with high quality and yield in mass production, and is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:CHONGQING WORLD HAORUI PHARM CHEM
Process for producing phenoxyphosphazene compound, flame-retardant resin composition, and flame-retardant resin molding
InactiveUS6946578B2Reduce molecular weightChange hueGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsPhosphorus organic compoundsHypochloriteHydrazine compound
An improved phenoxyphosphazene compound is produced by treating a phenoxyphosphazene compound with (a) at least one adsorbent selected from activated carbon, silica gel, activated alumina, activated clay, synthetic zeolite and macromolecular adsorbents, (b) at least one reagent selected from metal hydrides, hydrazine, hypochlorites, thiosulfates, dialkyl sulfuric acids, ortho esters, diazoalkanes, lactones, alkanesultones, epoxy compounds and hydrogen peroxide, or (c) both the adsorbent and reagent, thereby reducing the acid value of said phosphazene compound to lower than 0.025 mgKOH / g.
Owner:OTSUKA CHEM CO LTD
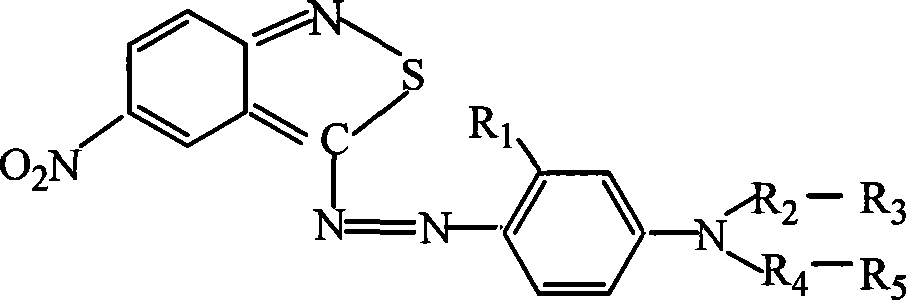
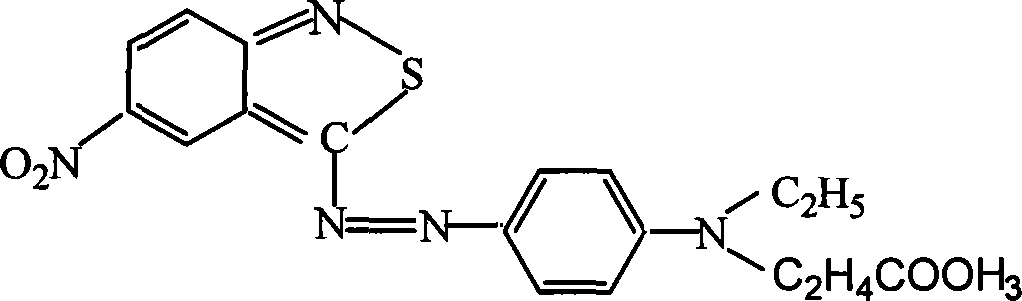
Azo type heterocyclic blue dispersion dyes
The invention provides a class of heterocyclic blue disperse dye and mixed dyes thereof, wherein the general formula of the dye is the formula at right, in the general formula: R1 is hydrogen, C1-4alkyl or C1-4alkoxy; R2, R4 is C1-4 saturated linear or branched alkane; R2 and R4 are the same or different; R3 is hydrogen, hydroxy, C1-4 alkoxy, or phenoxy; R5 is hydrogen, C1-4alkoxy, cyanoethyl or phenoxy; R3 and R5 are the same or different. The preparation of the dye includes that heterocyclic diazo component is diazotized, followed by reaction with different coupling components to get brilliant blue disperse dye. The dye can have a single structure, and also be the dye with mixed structure directly prepared. The class of dyes can give rich and deep color and has high lifting force, and good dye-uptake property, which has the same results of brilliant color light for polyester cellulose dying in acid or basic dye bath. The invention also can dye polyamide, polyurethane and cellulose acetate, and ultra-fine and blended fabric thereof.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUIDELONG CHEM
Hexafluoropropene-based fluorosulfonated elastomers with a low glass transition temperature, containing neither tetrafluoroethylene nor a siloxave group
InactiveUS20030153699A1Easy to operateImprove the immunityThin material handlingElastomerPolymer science
The present invention describes the synthesis of new fluorinated elastomers with very low glass transition temperatures (Tg), a good resistance to bases, gasoline and other carburants and good workability properties, these elastomers contain hexafluoropropene (HFP), perfluoro(4-methyl-3,6-dioxaoct-7-ene) sulfonyl fluoride (PFSO2F), vinylidene fluoride (VDF) and / or at least one fluorinated alkene and / or one vinyl perfluorinated ether. In a precise case, they are prepared by radical polymerisation of HFP and PFSO2F or by radical terpolymerisation HFP, PFSO2F and VDF in the presence of different organic initiator, such as peroxides, peresters or diazo compounds.
Owner:AMEDURI BRUNO MICHEL +3
Positive type photo-sensitive siloxane composition, cured film formed from the composition and device incorporating the cured film
ActiveUS7374856B2Increase photosensitivityLow dielectric constantPhotomechanical apparatusDiazo compound compositionsSolventWaveguide
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Positive type photosensitive resin composition
ActiveCN101727006AHigh resolutionExcellent pattern formationRadiation applicationsPhotomechanical apparatusSilane compoundsPolymer science
Disclosed is a positive photosensitive resin composition that includes (A) a first polybenzoxazole precursor that includes: a repeating unit of Chemical Formula 1 and a thermally polymerizable functional group at least one terminal end; (B) a second polybenzoxazole precursor that includes a repeating unit of Chemical Formula 3; (C) a photosensitive diazoquinone compound; (D) a silane compound; and (E) a solvent.
Owner:CHEIL IND INC
Positive photosensitive resin composition, and semiconductor device and display therewith
InactiveUS8080350B2Reduce corrosionGood physical propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesChemical compoundDisplay device
Disclosed is a positive photosensitive resin composition containing (A) an alkali-soluble resin, (B) a diazoquinone compound, (d1) an activated silicon compound and (d2) an aluminum complex. Also disclosed is a positive photosensitive resin composition containing (A) an alkali-soluble resin, (B) a diazoquinone compound, (C) a compound having two or more oxetanyl groups in one molecule and (D) a catalyst for accelerating the ring-opening reaction of the oxetanyl groups of the compound (C).
Owner:SUMITOMO BAKELITE CO LTD
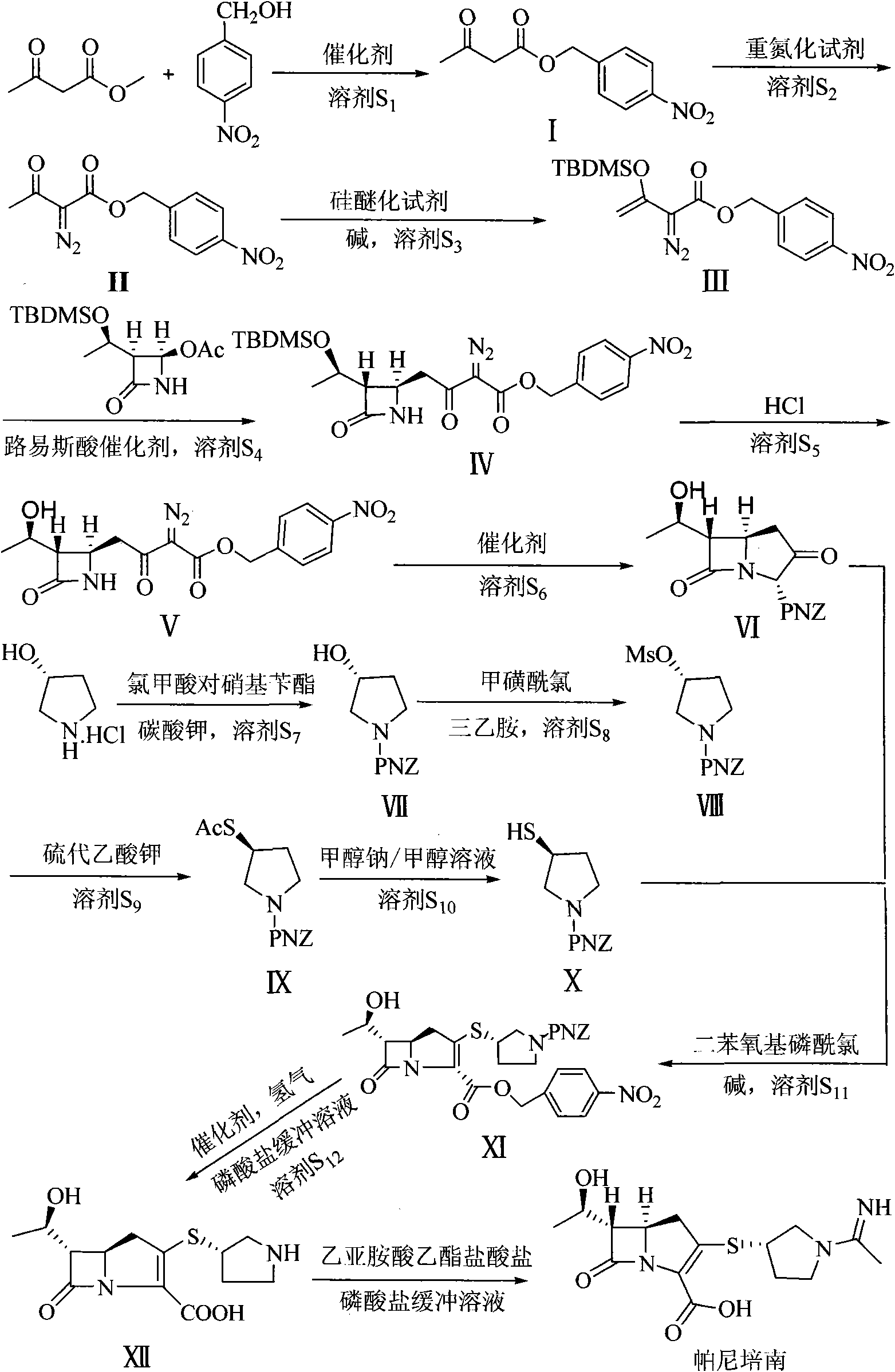
Preparation method of panipenem
The invention relates to a preparation method of panipenem. Firstly, methyl acetoacetate and p-nitrobenzyl alcohol are taken as raw materials to prepare panipenem parent nucleus by six steps of reactions: ester exchange reaction, diazo reaction, enolization reaction, substitution reaction, hydrolysis reaction and ring closing reaction; then, (3R)-3-hydroxy-pyrrolidine hydrochloride, nitrobenzyl chroformate ester are taken as raw materials to prepare panipenem side chain by amidation reaction, sulfonylation reaction, nucleophilic substitution reaction and saponification reaction; finally, the prepared panipenem parent nucleus and panipenem side chain are in butt joint by condensation and are subjected to catalytic hydrolysis and imidization to obtain panipenem. The preparation method of panipenem features simple operation, mild reaction condition, friendly environment, high yield, good product purity, low cost and better industrialized production prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Methods of making novel colorants for use within ink systems
InactiveUS6479647B1Excellent spectral strengthDesired propertyMonoazo dyesOrganic chemistrySolubilityWax
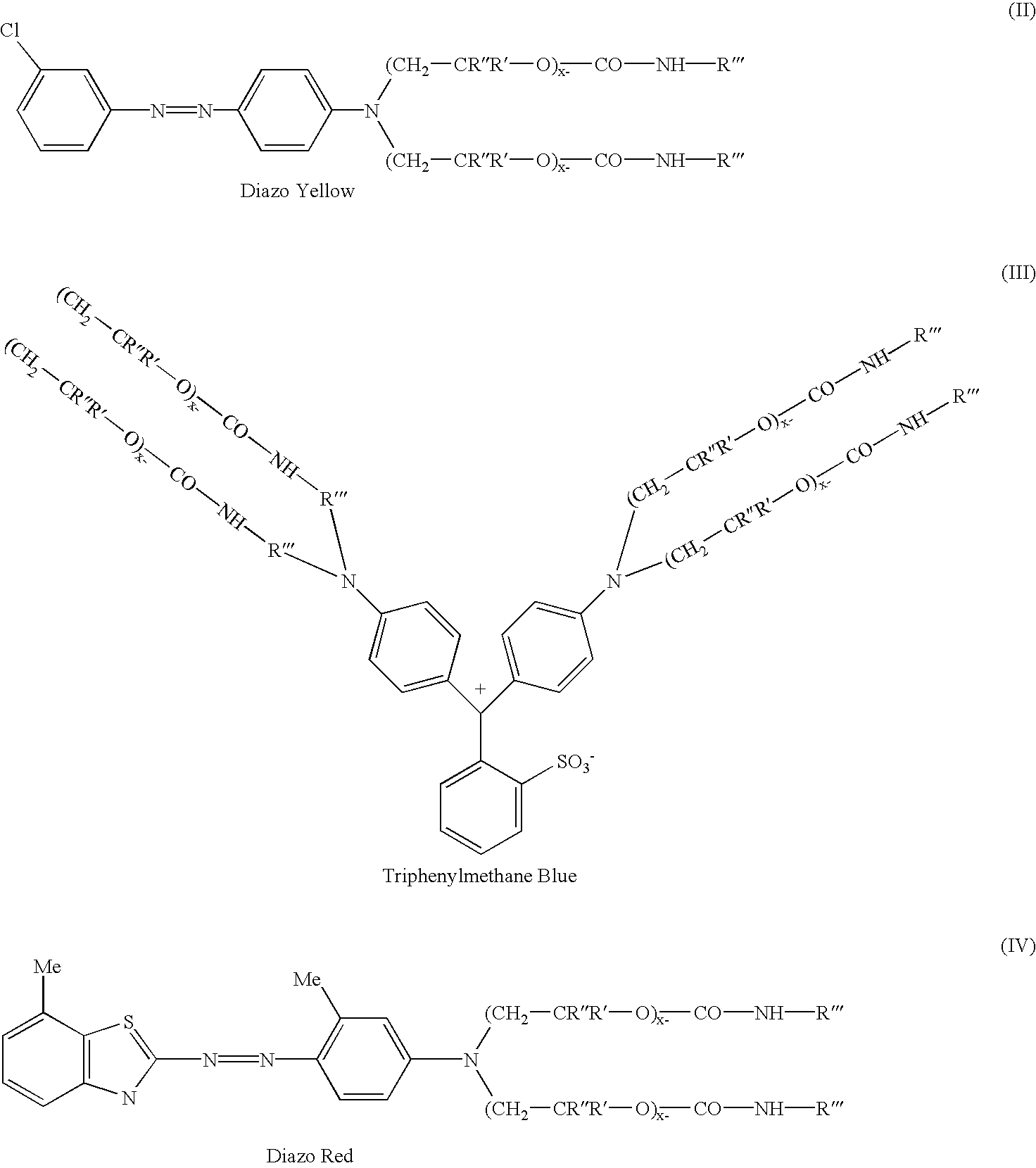
Novel addition products of hydroxyl-protecting groups (such as isocyanates) with oxyalkylene-substituted intermediates, such as poly(oxyalkylenated) aniline compounds, for the eventual production of substituted, and substantially pure, colorants, particularly diazo and triphenylmethane derivatives, through the reaction of such intermediates with certain reactants are provided. These new colorants exhibit improved wax and / or oil solubility and high purity, particularly due to the inability of certain impurities to deleteriously react with the protected hydroxyl groups of either the intermediate or the colorant during and / or after formation thereof. A method for producing such novel colorants through utilization of these novel substantially pure colorant intermediates is also provided.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
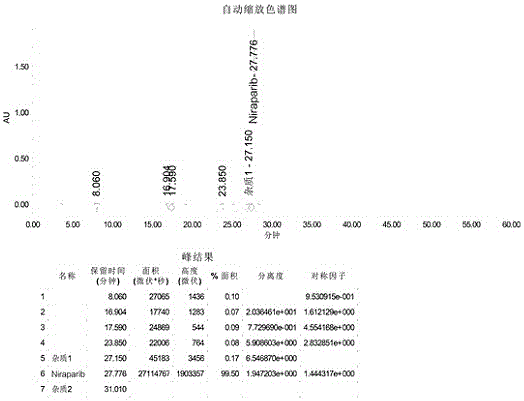
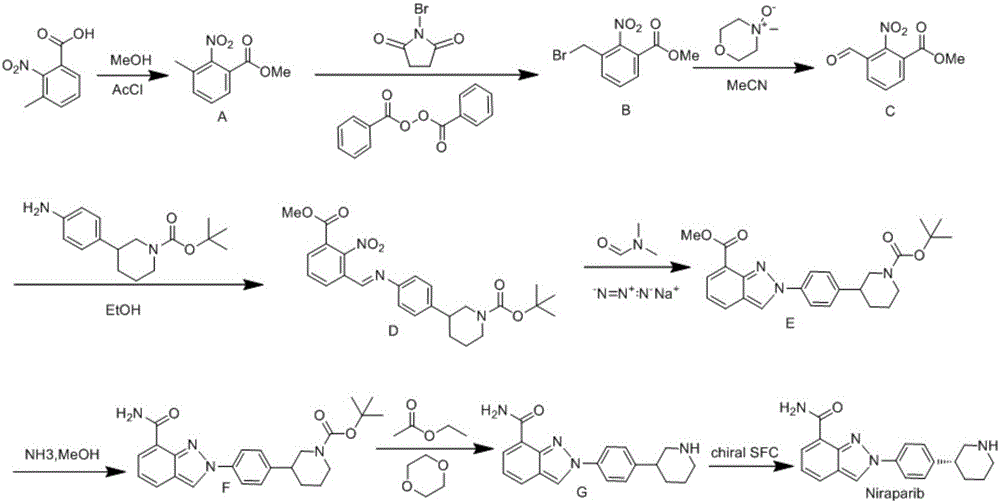
Synthesis method for preparing PARP inhibitor Niraparib
InactiveCN106496187ALow priceEasy to getOrganic chemistryBulk chemical productionSynthesis methodsMethyl anthranilate
The invention provides a novel synthesis method for preparing a PARP inhibitor Niraparib. The method comprises the steps that a starting material methyl anthranilate is subjected to diazo coupling, cyclization, amidation, BOC removal and chiral resolution, and then the Niraparib with the purity reaching 99.5% is obtained. The method is simple, convenient and easy to operate suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
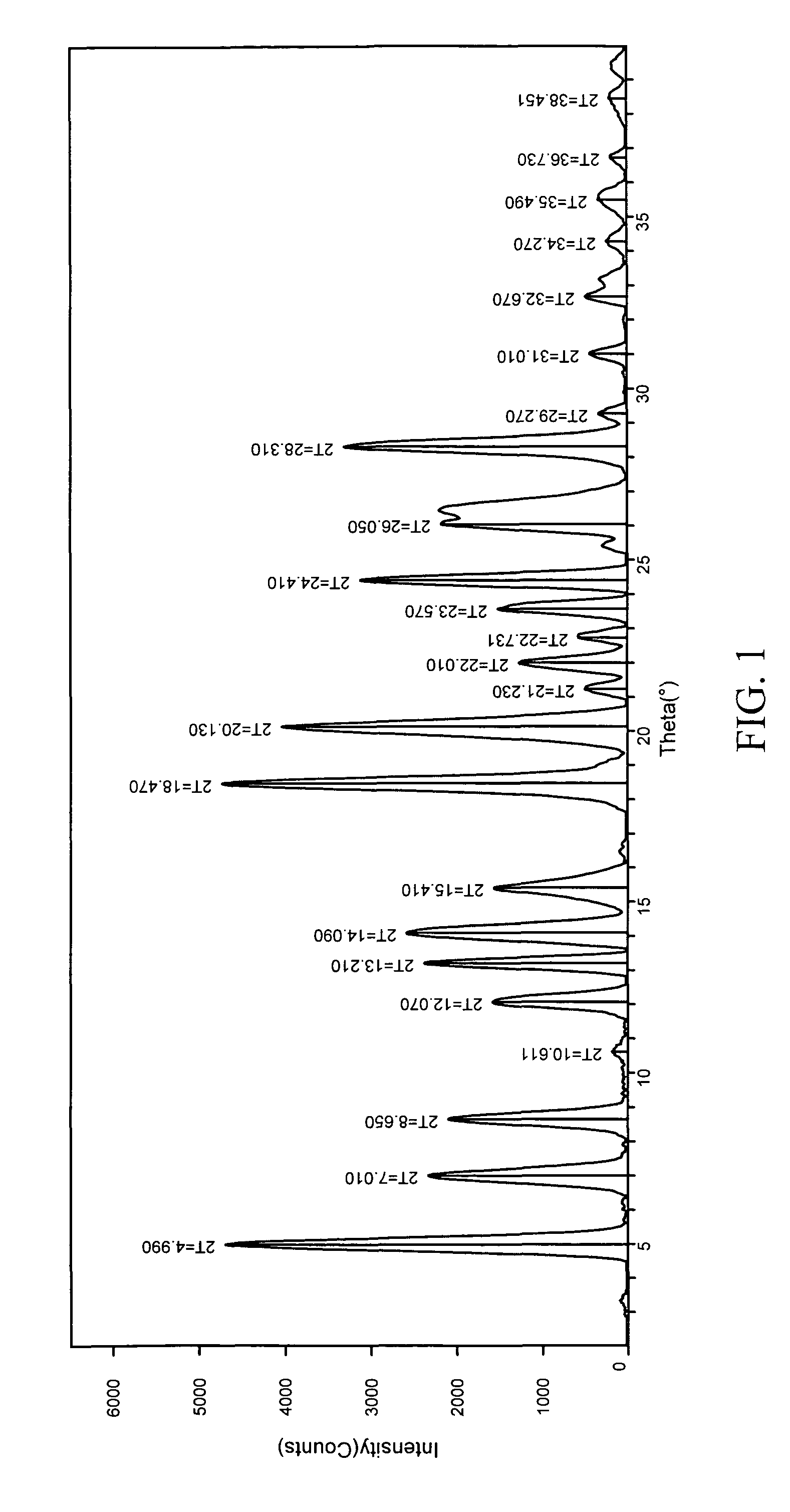

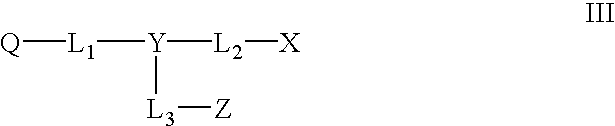

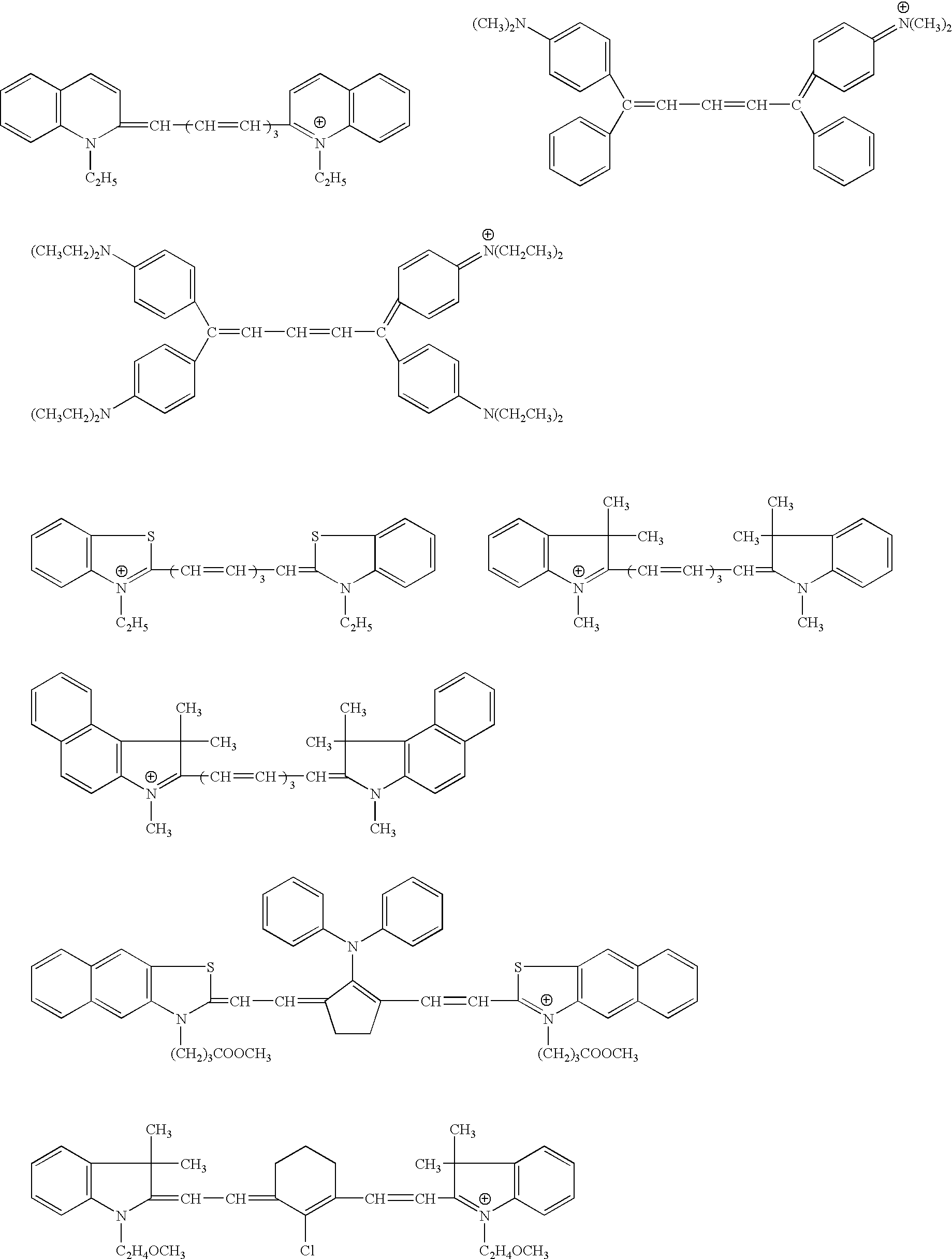

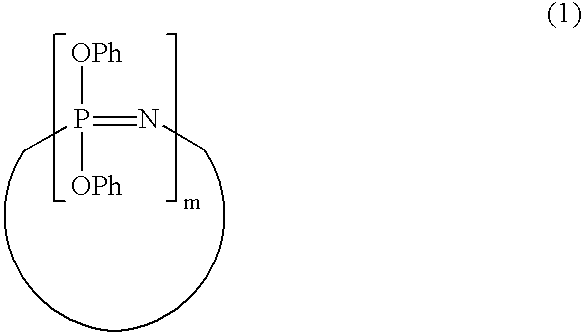

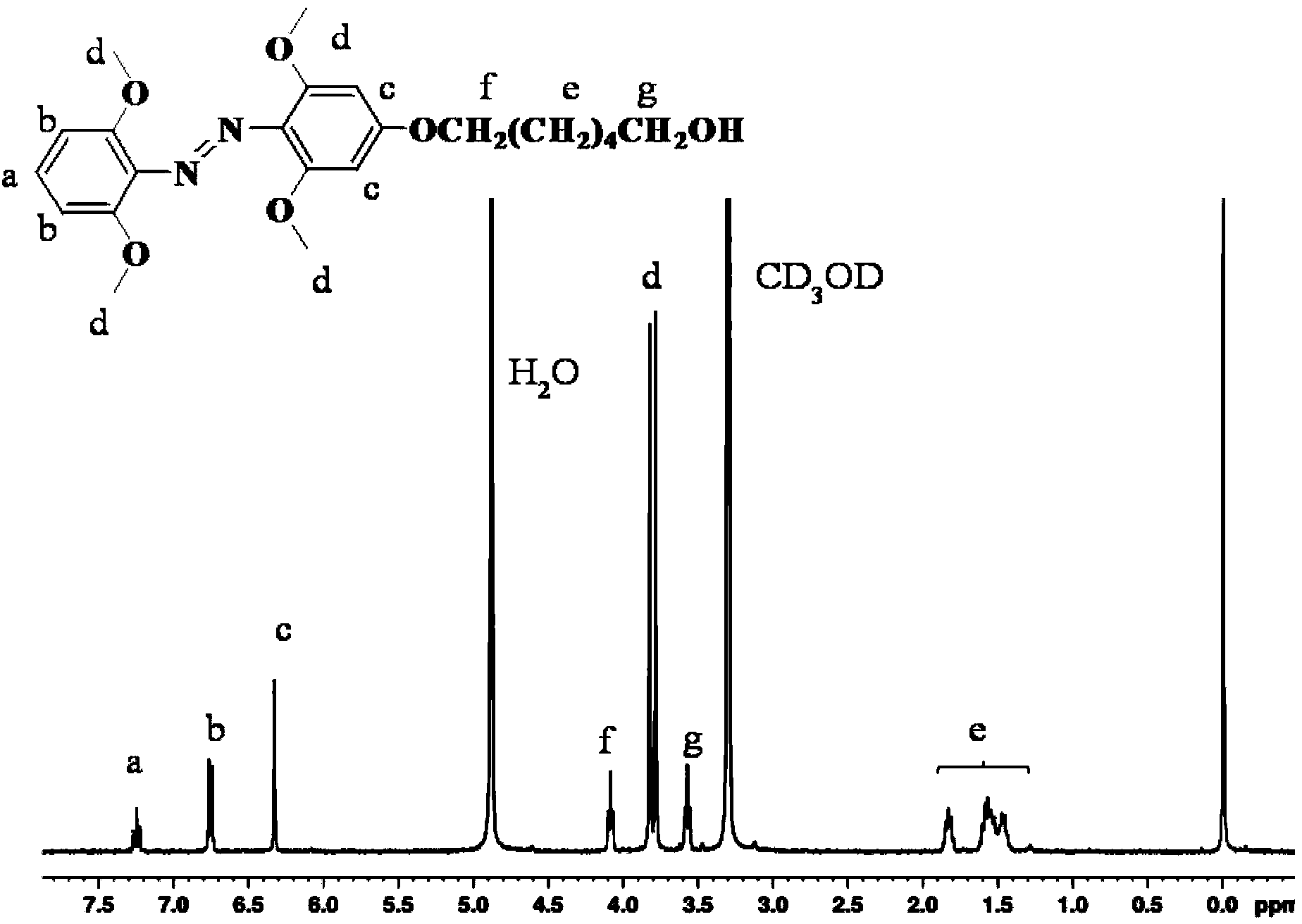










![Method for preparing 4-(3-chlorine-4-fluorophenylalanine)-7-methoxy-6-[3-(4-morpholinyl) propoxy] quinazoline Method for preparing 4-(3-chlorine-4-fluorophenylalanine)-7-methoxy-6-[3-(4-morpholinyl) propoxy] quinazoline](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/ab0c394b-e0e0-4d69-a4b9-9f77c6cd947e/A20091010360500051.PNG)
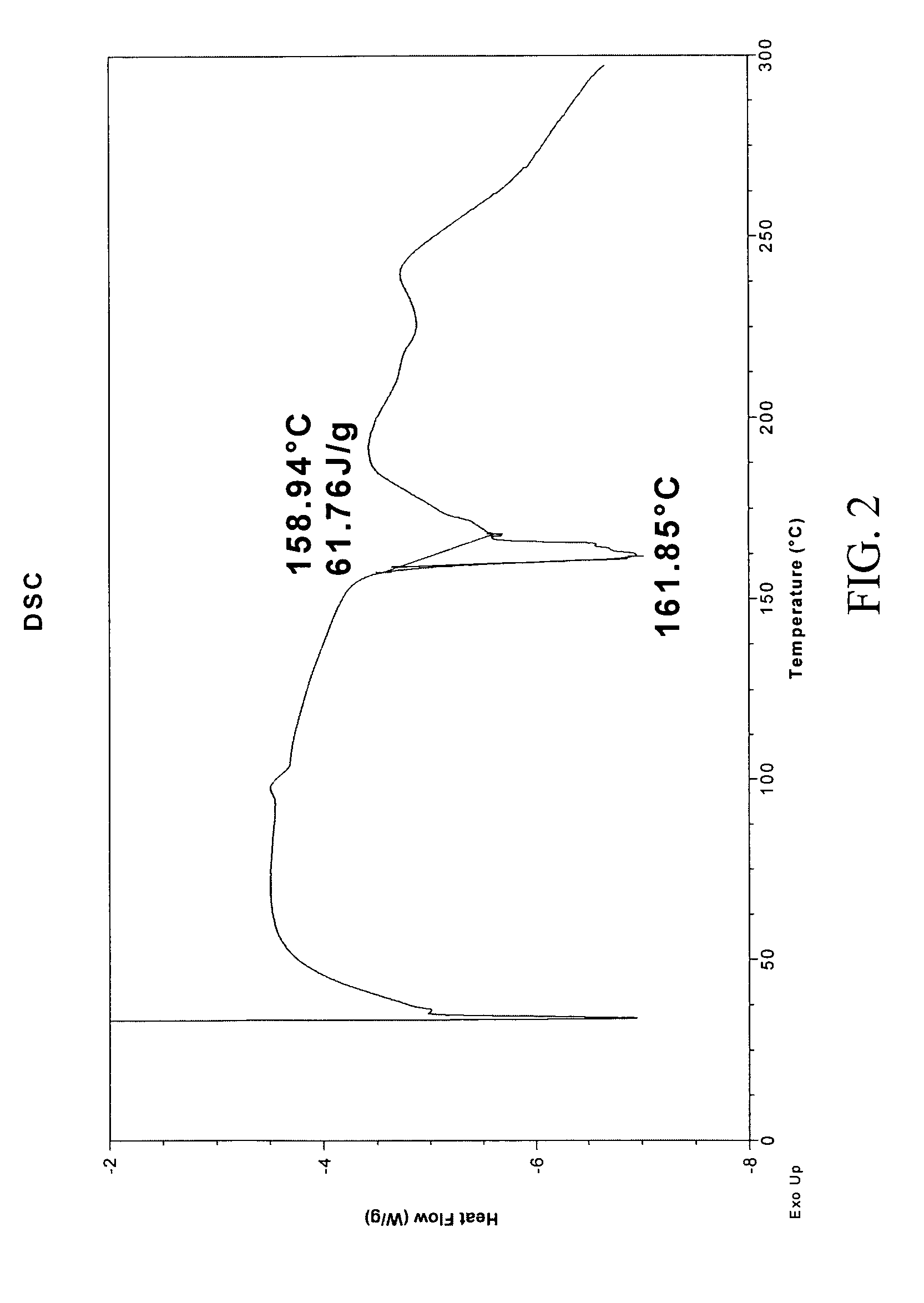
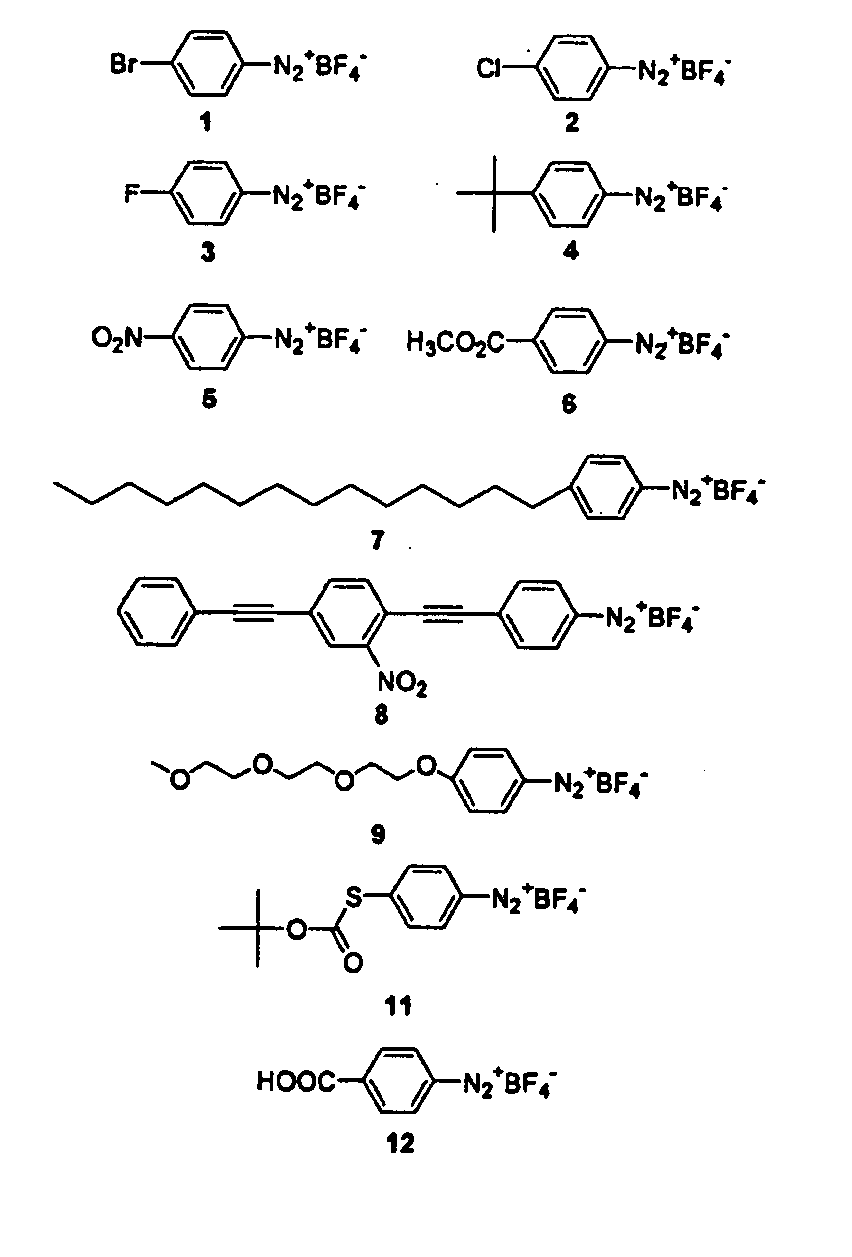
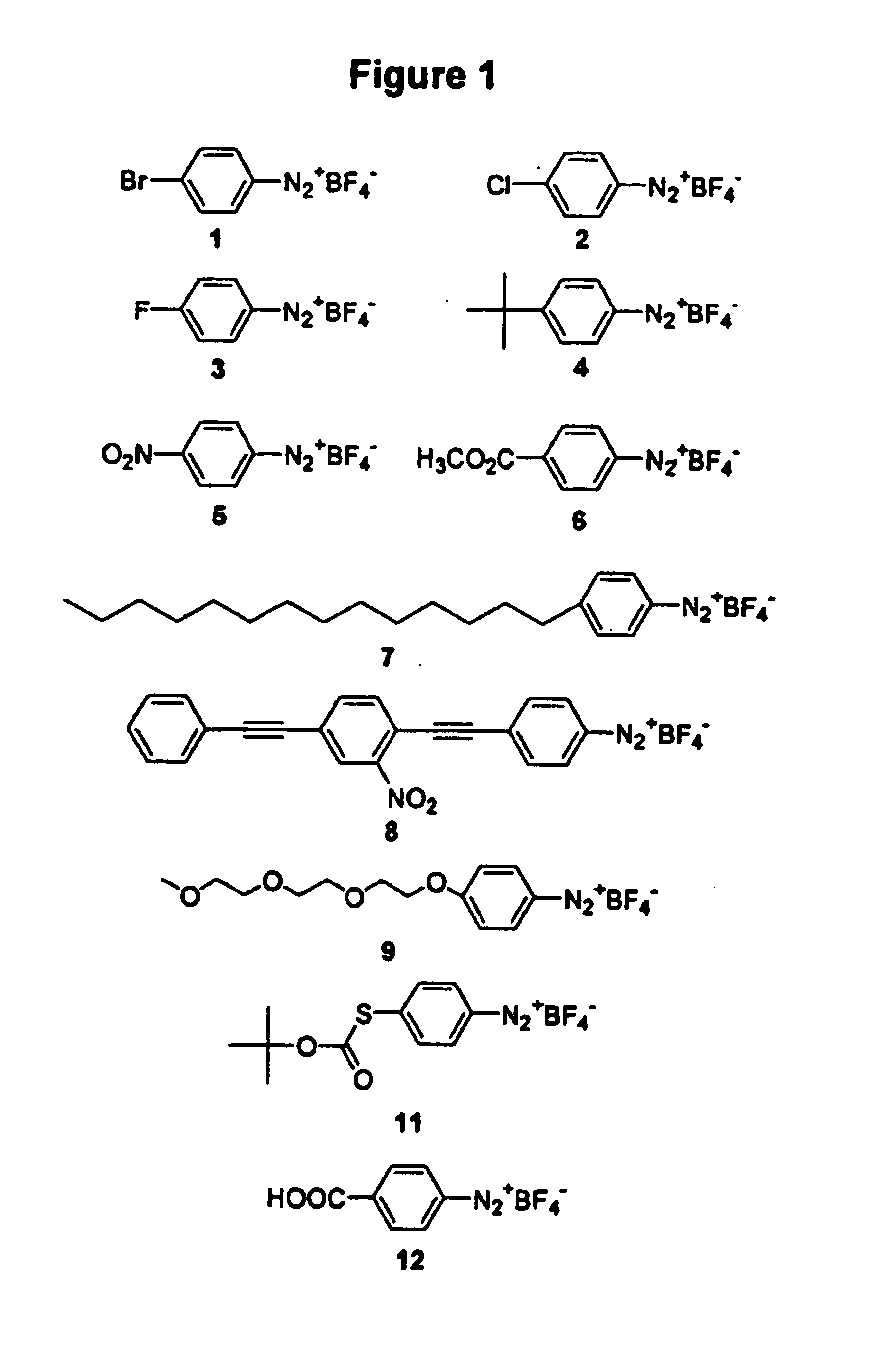
![Method for preparing 4-(3-chlorine-4-fluorophenylalanine)-7-methoxy-6-[3-(4-morpholinyl) propoxy] quinazoline Method for preparing 4-(3-chlorine-4-fluorophenylalanine)-7-methoxy-6-[3-(4-morpholinyl) propoxy] quinazoline](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/ab0c394b-e0e0-4d69-a4b9-9f77c6cd947e/A20091010360500091.PNG)
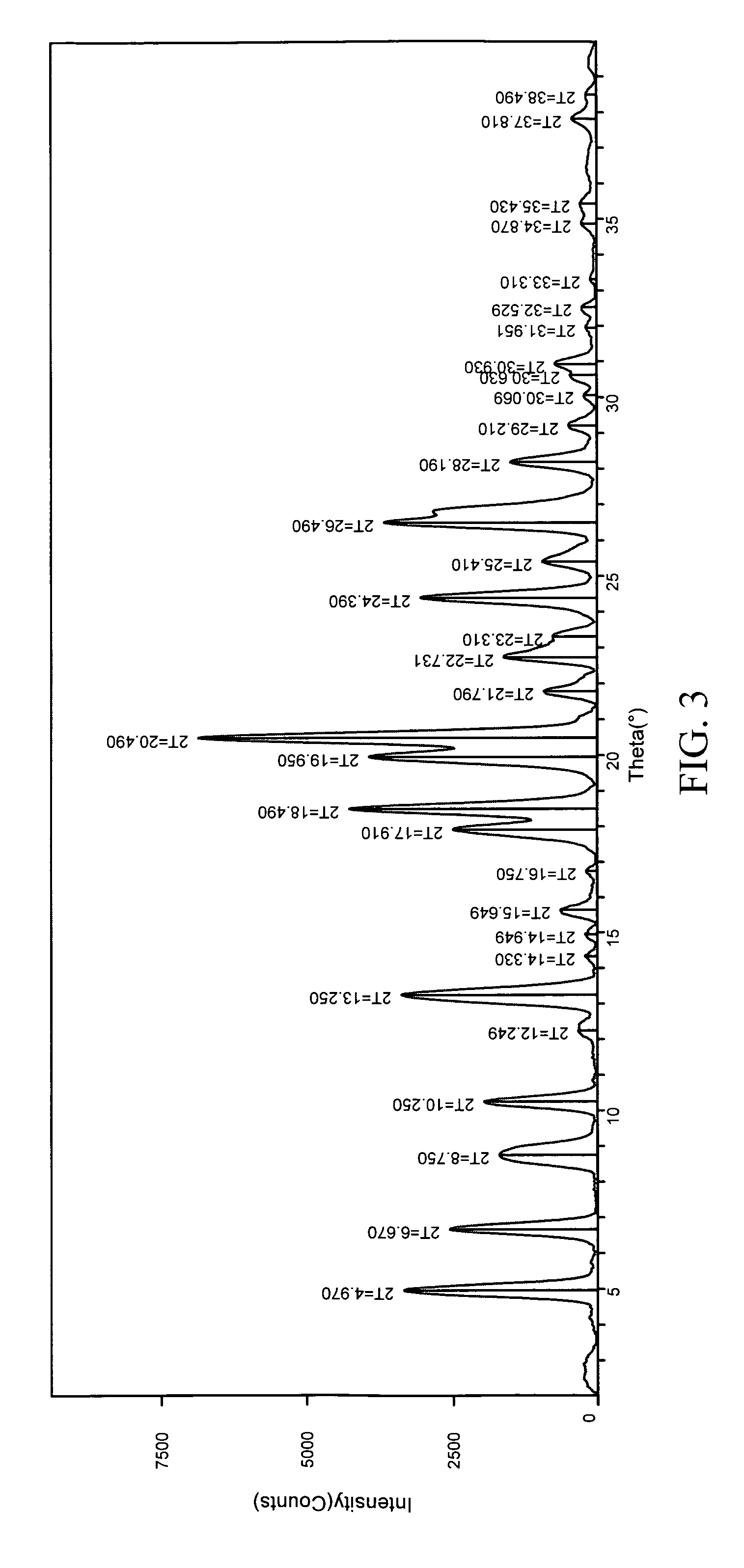
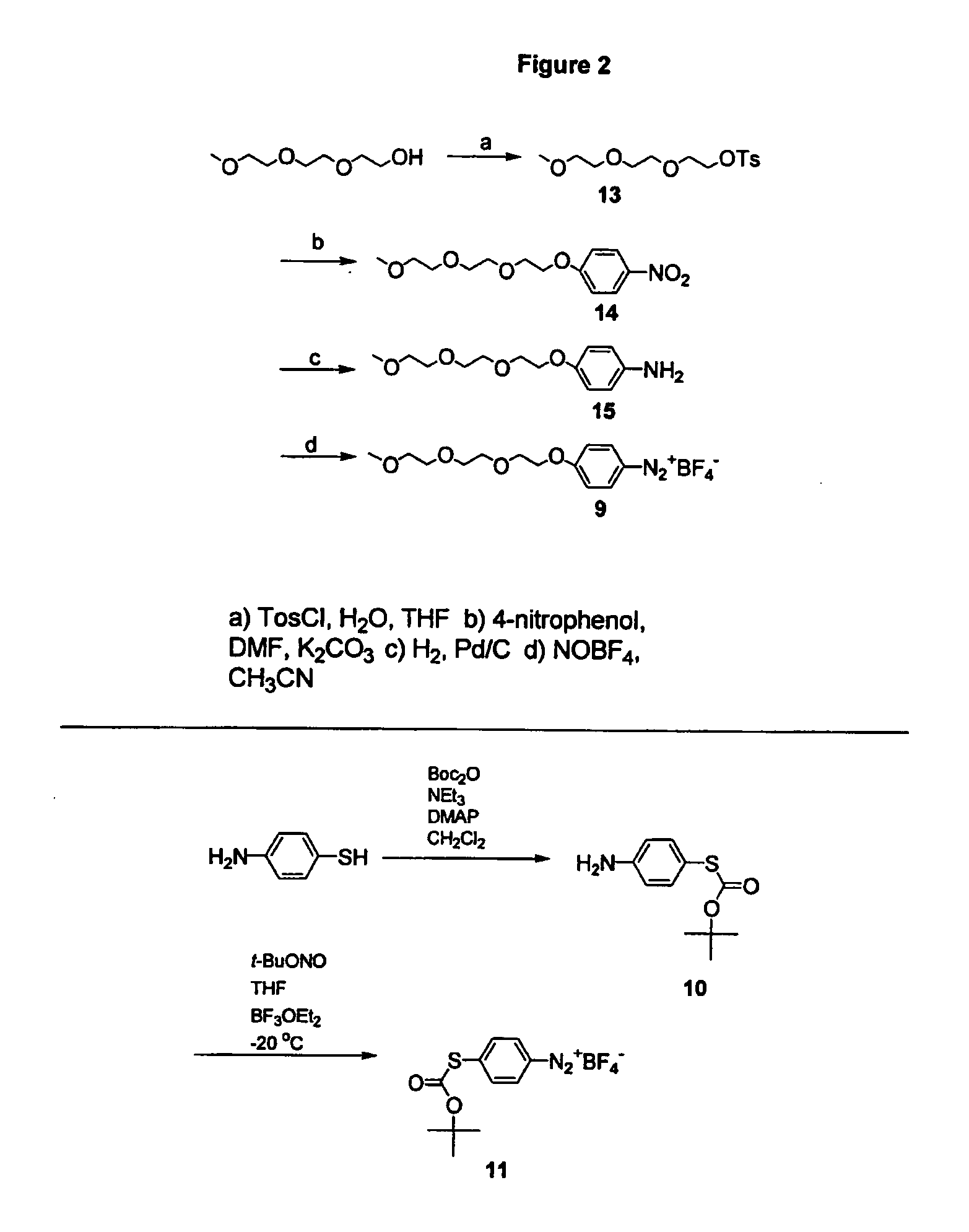
![Method for preparing 4-(3-chlorine-4-fluorophenylalanine)-7-methoxy-6-[3-(4-morpholinyl) propoxy] quinazoline Method for preparing 4-(3-chlorine-4-fluorophenylalanine)-7-methoxy-6-[3-(4-morpholinyl) propoxy] quinazoline](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/ab0c394b-e0e0-4d69-a4b9-9f77c6cd947e/A20091010360500101.PNG)