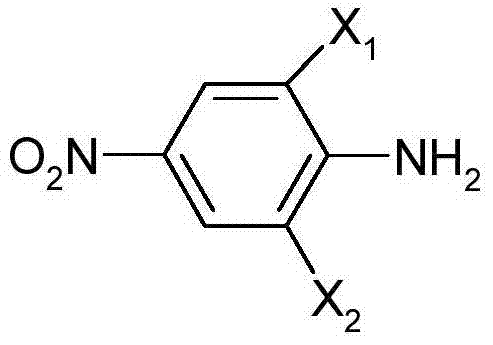
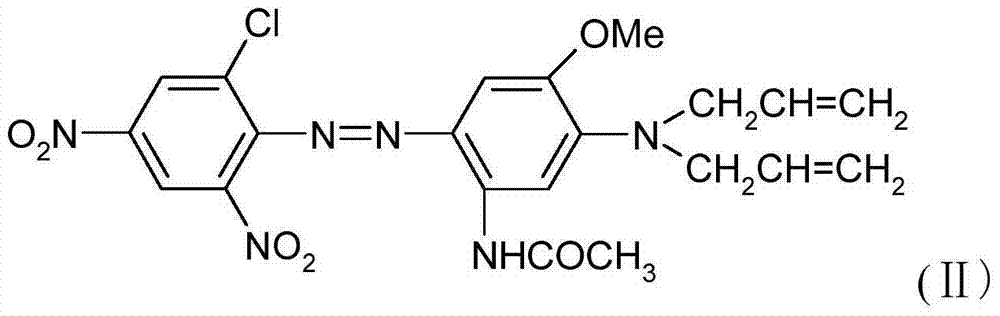
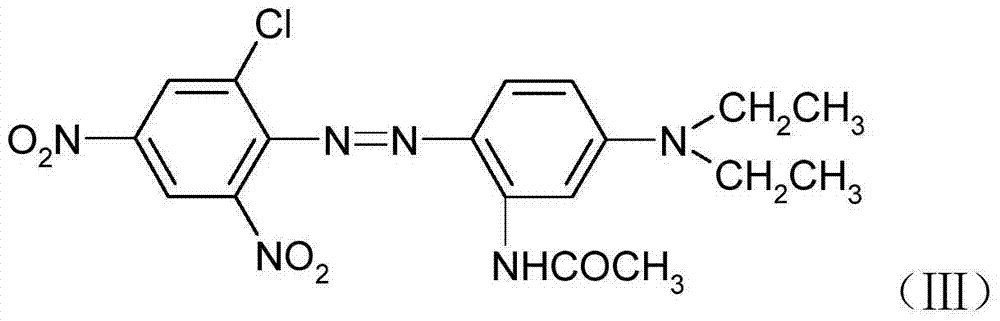
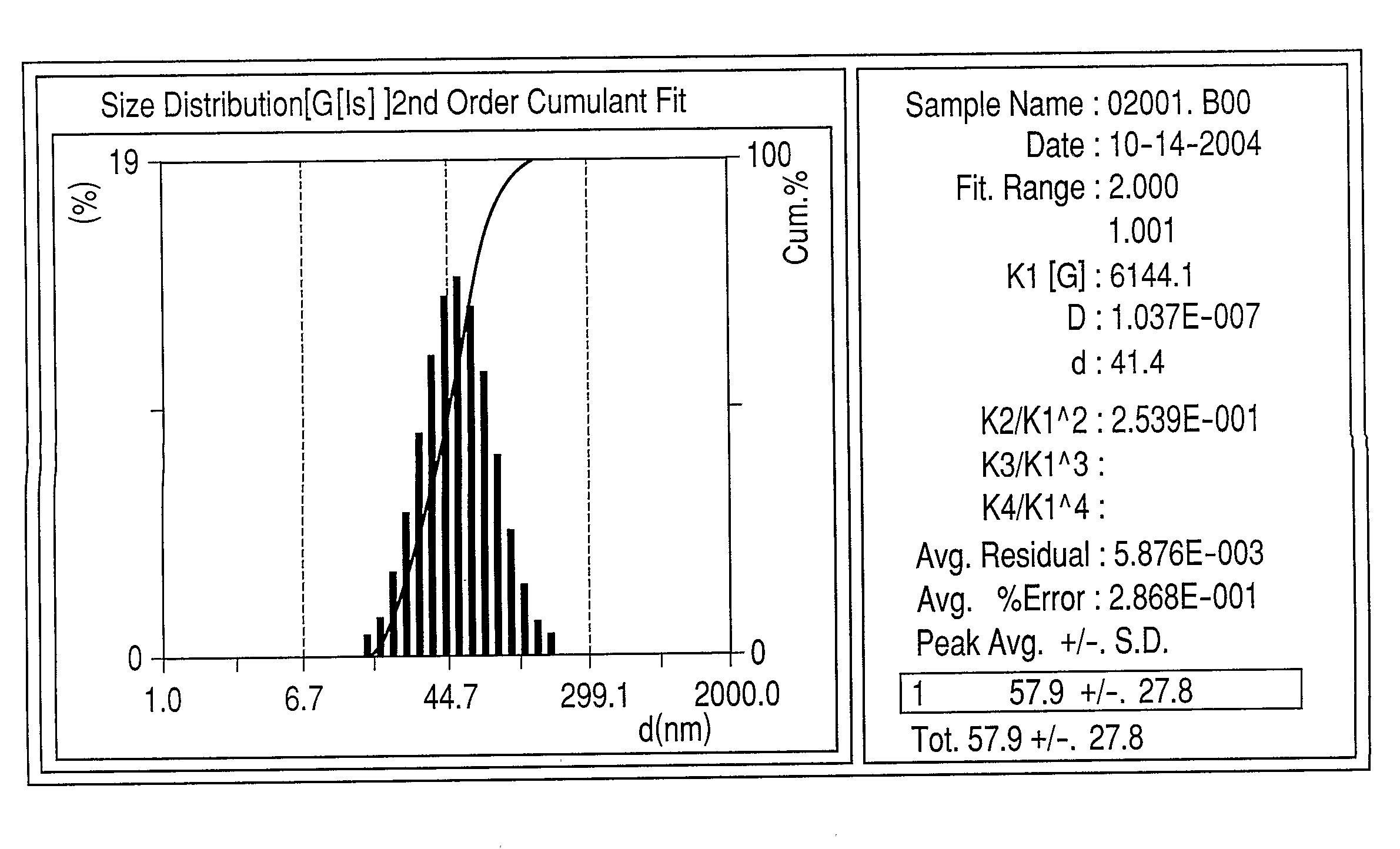
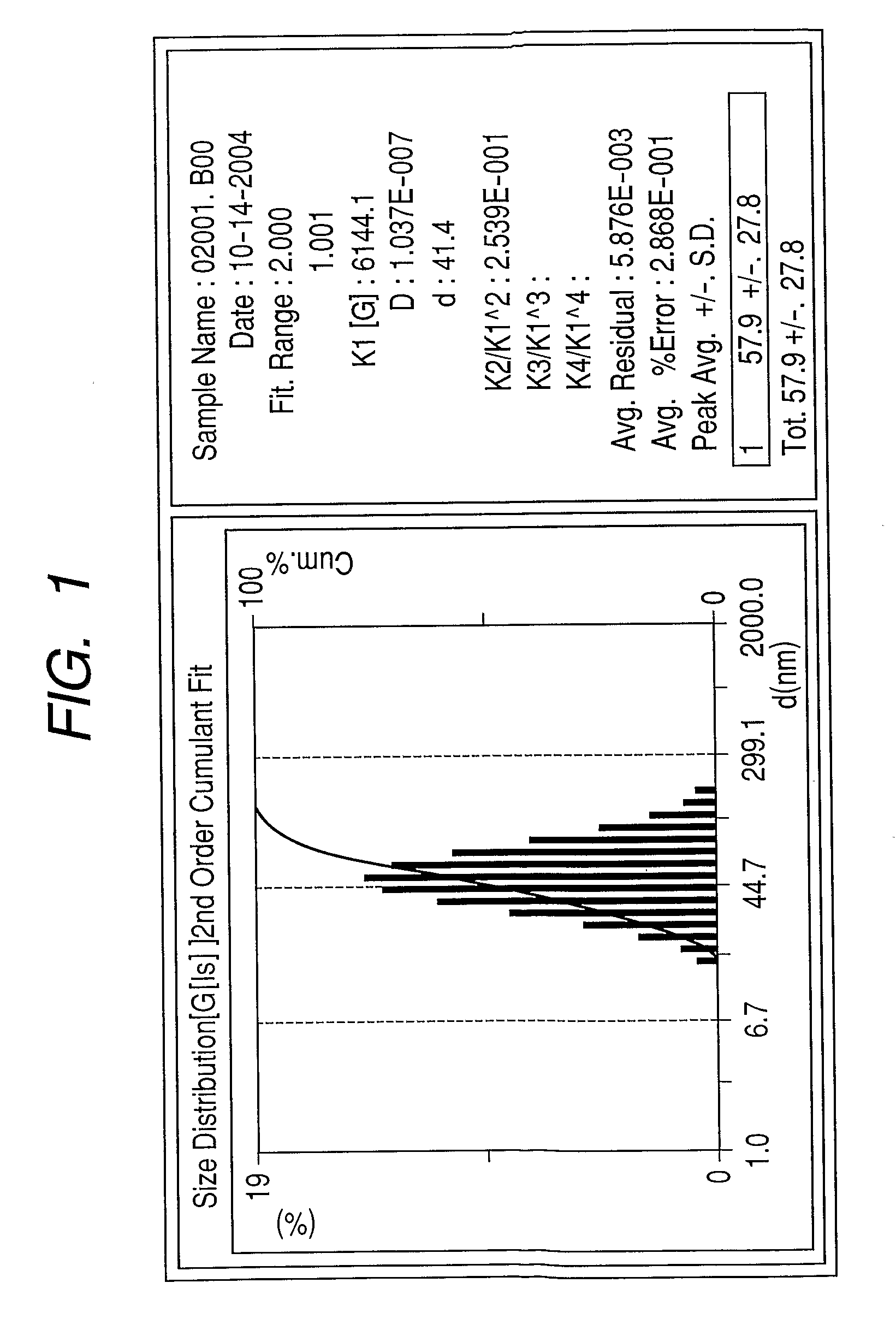
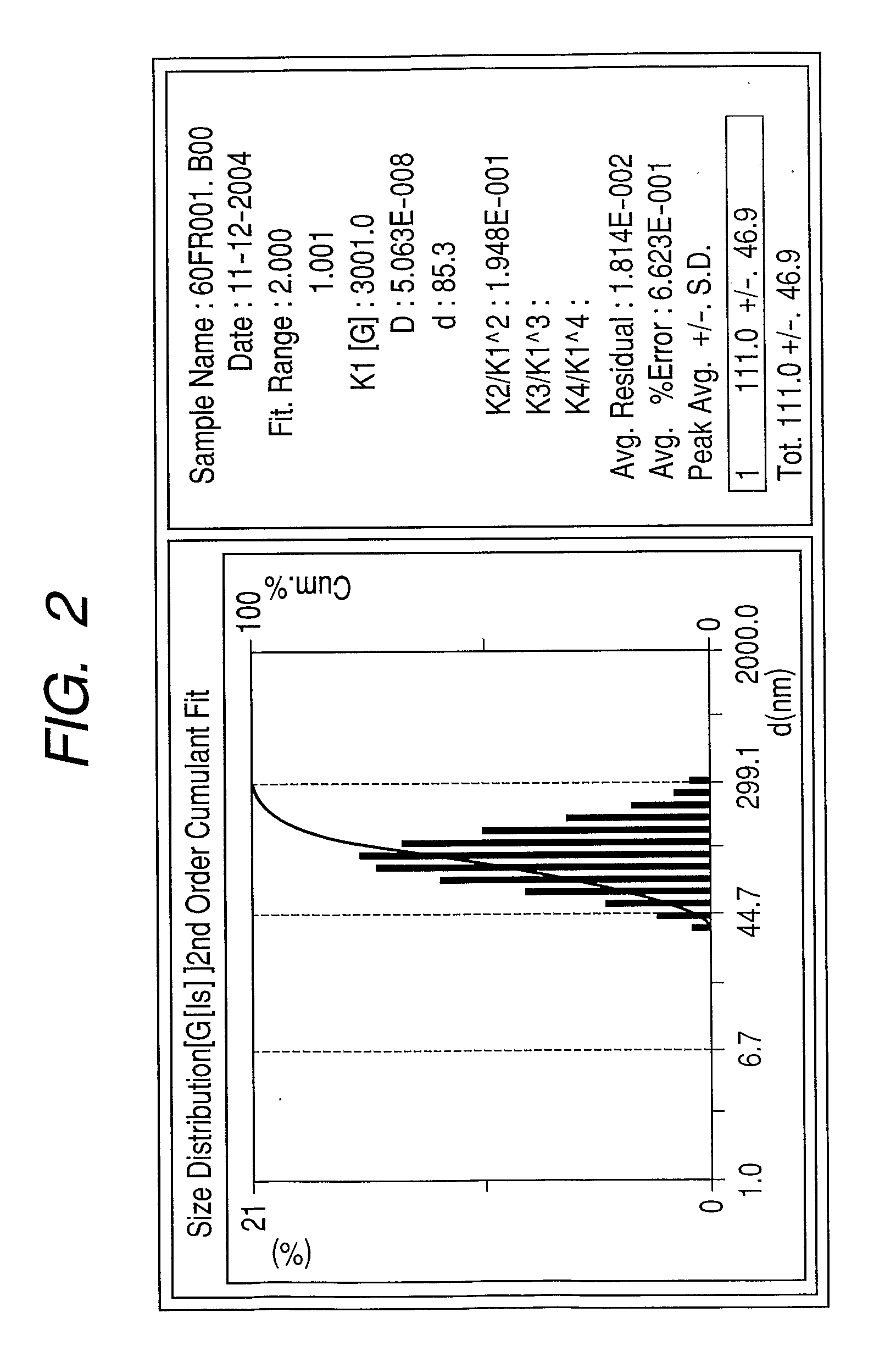
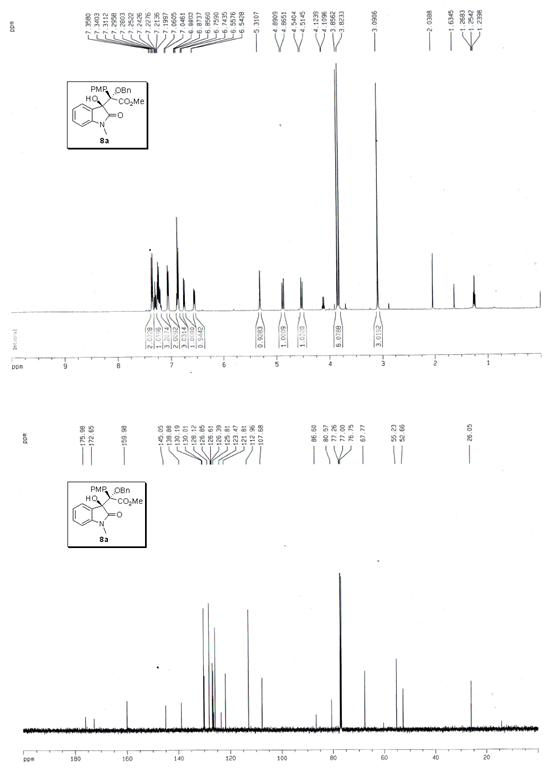
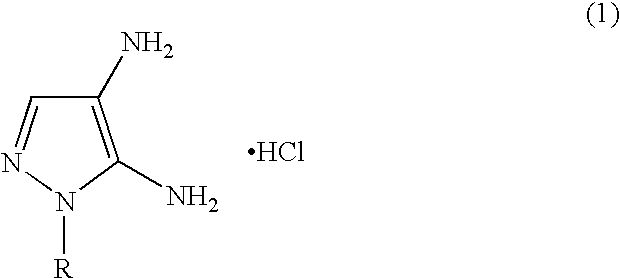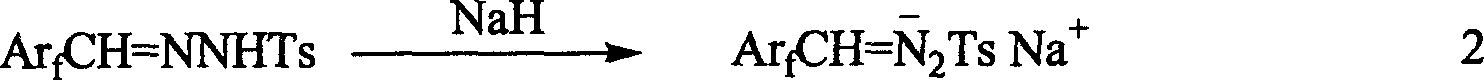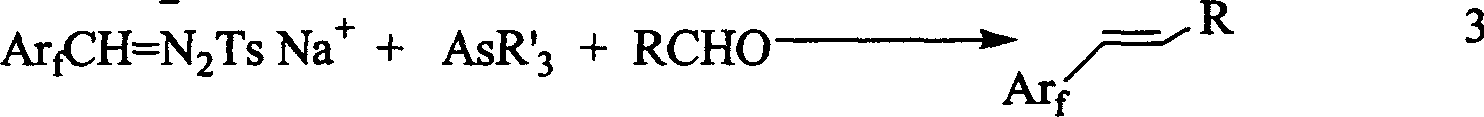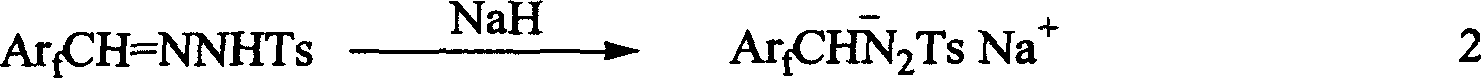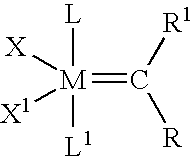Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
172 results about "Diazonium Compounds" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Diazonium compounds or diazonium salts are a group of organic compounds sharing a common functional group R−N⁺₂X⁻ where R can be any organic group, such as an alkyl or an aryl, and X is an inorganic or organic anion, such as a halogen.
Method and apparatus for detection of a controlled substance
InactiveUS6558956B1Many of techniqueRaise the ratioRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringChemical reactionAnalyte
Techniques and devices for detecting and analyzing controlled substances and the like are discussed including highly reactive sensor molecules which are coated on a spectroscopic sample surface (4) and which may chemically react with a given analyte to form a covalently bonded adduct with spectral characteristics unique to the new adduct. The techniques provide the basis of a detection system with high sensitivity and high specificity in which the surface can even be washed to remove interfering or nonreactive compounds. The sensor molecules which comprise the coating (8) may have three major components: a central molecular scaffold ("CMS"), a "tether" terminated by a surface attachment group "SAG," and a reactive functional group "RFG" which may be highly reactive towards certain classes of molecules. One or more modifiers or modifier groups "Z" which may serve to increase or decrease the reactivity of the RFG towards target analytes, or to modify the spectral characteristics of the adduct may also be included. Some sensor molecules include diazonium compounds, activated acyls, and nitrosos.
Owner:WYOMING UNIV OF THE
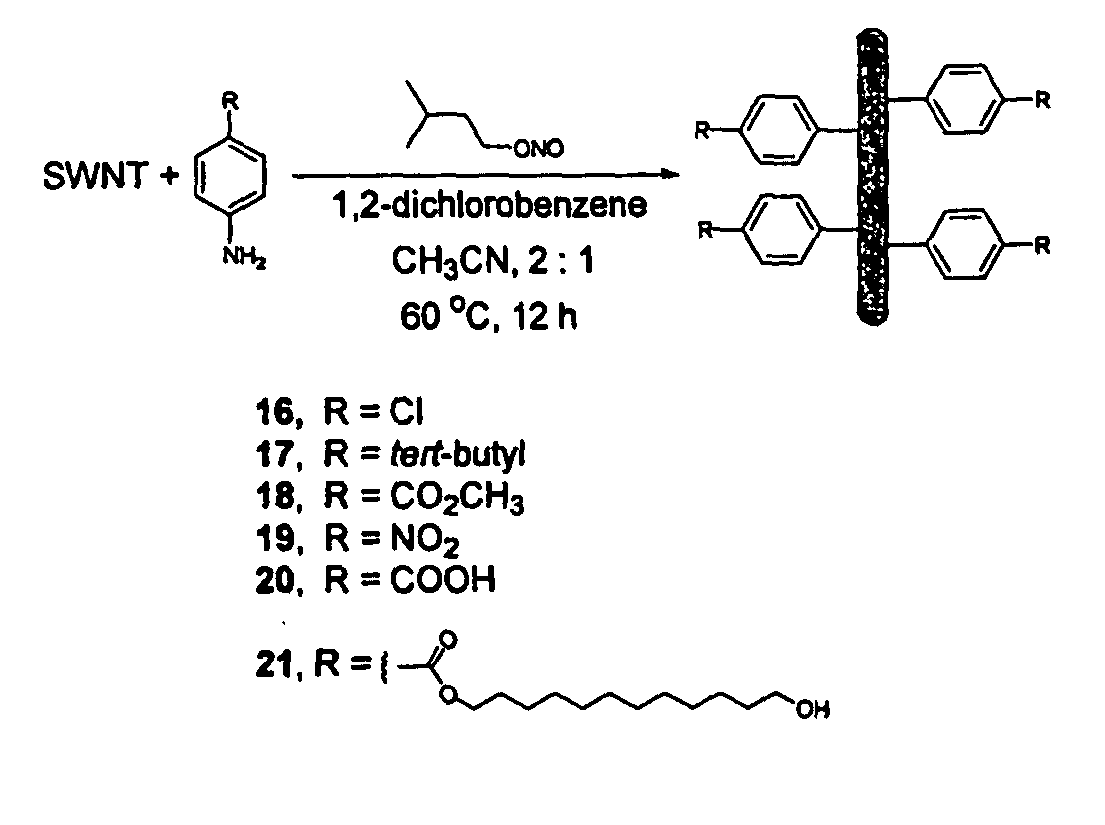
Carbon nanotubes derivatized with diazonium species
InactiveUS20050207963A1Advantage of scalabilityMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentElectrochemistryOrganic compound
Owner:RICE UNIV
Positive photosensitive resin composition
ActiveCN1536442AGood shading propertiesQuality improvementPhotomechanical apparatusQuinoneLiquid-crystal display
Disclosed is a positive-type photosensitive resin composition comprising: (a) an alkali-soluble resin; (b) a quinone diazide compound; (c) a heatsensitive compound which colors upon being heated and which shows an absorption maximum at a wavelength of not less than 350 nm and not more than 700 nm; and (d) a compound which does not have an absorption maximum at a wavelength of not less than 350 nm to less than 500 nm, and has an absorption maximum at a wavelength of not less than 500 nm and not more than 750 nm. The composition is preferably used for forming light-blocking separators or black matrices of organic electroluminescent devices and liquid crystal display elements.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Process for attaching molecular wires and devices to carbon nanotubes and compositions thereof
InactiveUS20050074613A1Advantage of scalabilityPigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologyElectrochemistryOrganic compound
The invention incorporates new processes for the chemical modification of carbon nanotubes. Such processes involve the derivatization of multi- and single-wall carbon nanotubes, including small diameter (ca. 0.7 nm) single-wall carbon nanotubes, with diazonium species. The method allows the chemical attachment of a variety of organic compounds to the side and ends of carbon nanotubes. These chemically modified nanotubes have applications in polymer composite materials, molecular electronic applications, and-sensor devices. The methods of derivatization include electrochemical induced reactions, thermally induced reactions (via in-situ generation of diazonium compounds or pre-formed diazonium compounds), and photochemically induced reactions. The derivatization causes significant changes in the spectroscopic properties of the nanotubes. The estimated degree of functionality is ca. 1 out of every 20 to 30 carbons in a nanotube bearing a functionality moiety. Such electrochemical reduction processes can be adapted to apply site-selective chemical functionalization of nanotubes. Moreover, when modified with suitable chemical groups, the derivatized nanotubes are chemically compatible with a polymer matrix, allowing transfer of the properties of the nanotubes (such as, mechanical strength or electrical conductivity) to the properties of the composite material as a whole. Furthermore, when modified with suitable chemical groups, the groups can be polymerized to form a polymer that includes carbon nanotubes.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Process for making polymers comprising derivatized carbon nanotubes and compositions thereof
InactiveUS20050074390A1Advantage of scalabilityMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentElectrochemistryOrganic compound
The invention incorporates new processes for the chemical modification of carbon nanotubes. Such processes involve the derivatization of multi- and single-wall carbon nanotubes, including small diameter (ca. 0.7 nm) single-wall carbon nanotubes, with diazonium species. The method allows the chemical attachment of a variety of organic compounds to the side and ends of carbon nanotubes. These chemically modified nanotubes have applications in polymer composite materials, molecular electronic applications, and sensor devices. The methods of derivatization include electrochemical induced reactions, thermally induced reactions (via in-situ generation of diazonium compounds or pre-formed diazonium compounds), and photochemically induced reactions. The derivatization causes significant changes in the spectroscopic properties of the nanotubes. The estimated degree of functionality is ca. 1 out of every 20 to 30 carbons in a nanotube bearing a functionality moiety. Such electrochemical reduction processes can be adapted to apply site-selective chemical functionalization of nanotubes. Moreover, when modified with suitable chemical groups, the derivatized nanotubes are chemically compatible with a polymer matrix, allowing transfer of the properties of the nanotubes (such as, mechanical strength or electrical conductivity) to the properties of the composite material as a whole. Furthermore, when modified with suitable chemical groups, the groups can be polymerized to form a polymer that includes carbon nanotubes.
Owner:RICE UNIV
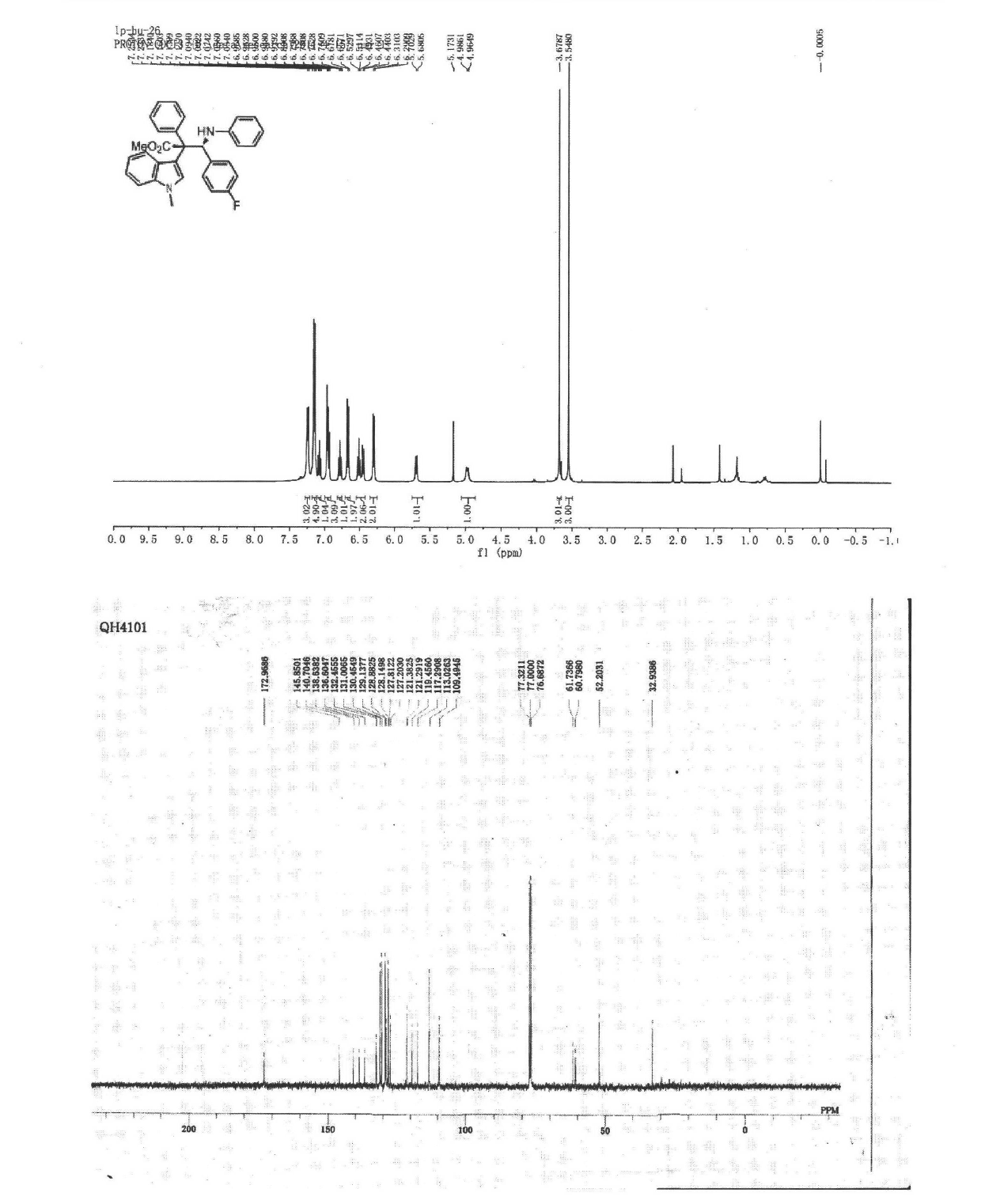
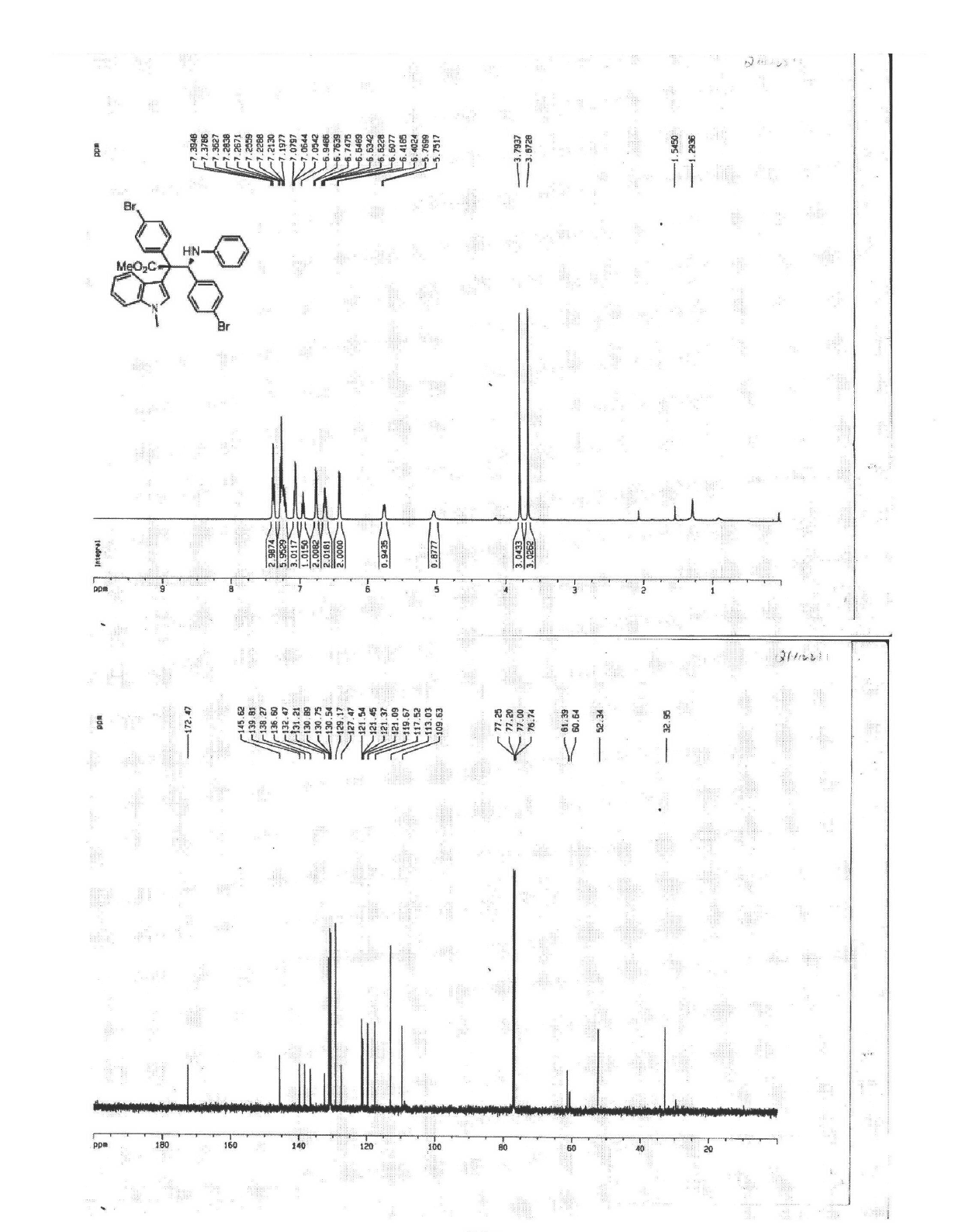
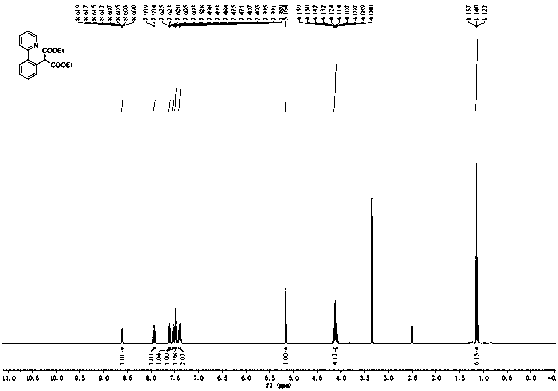
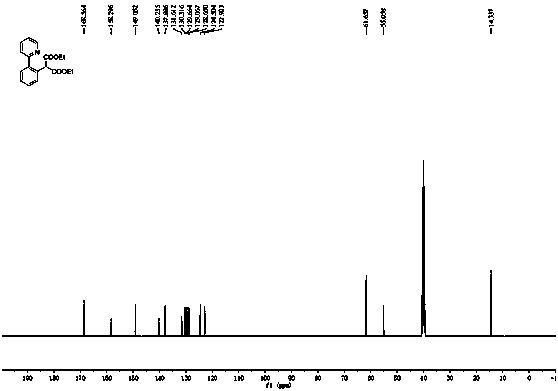
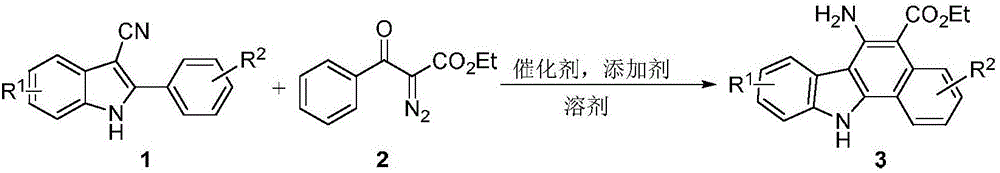
Synthetic method for aromatic[a]carbazole compounds
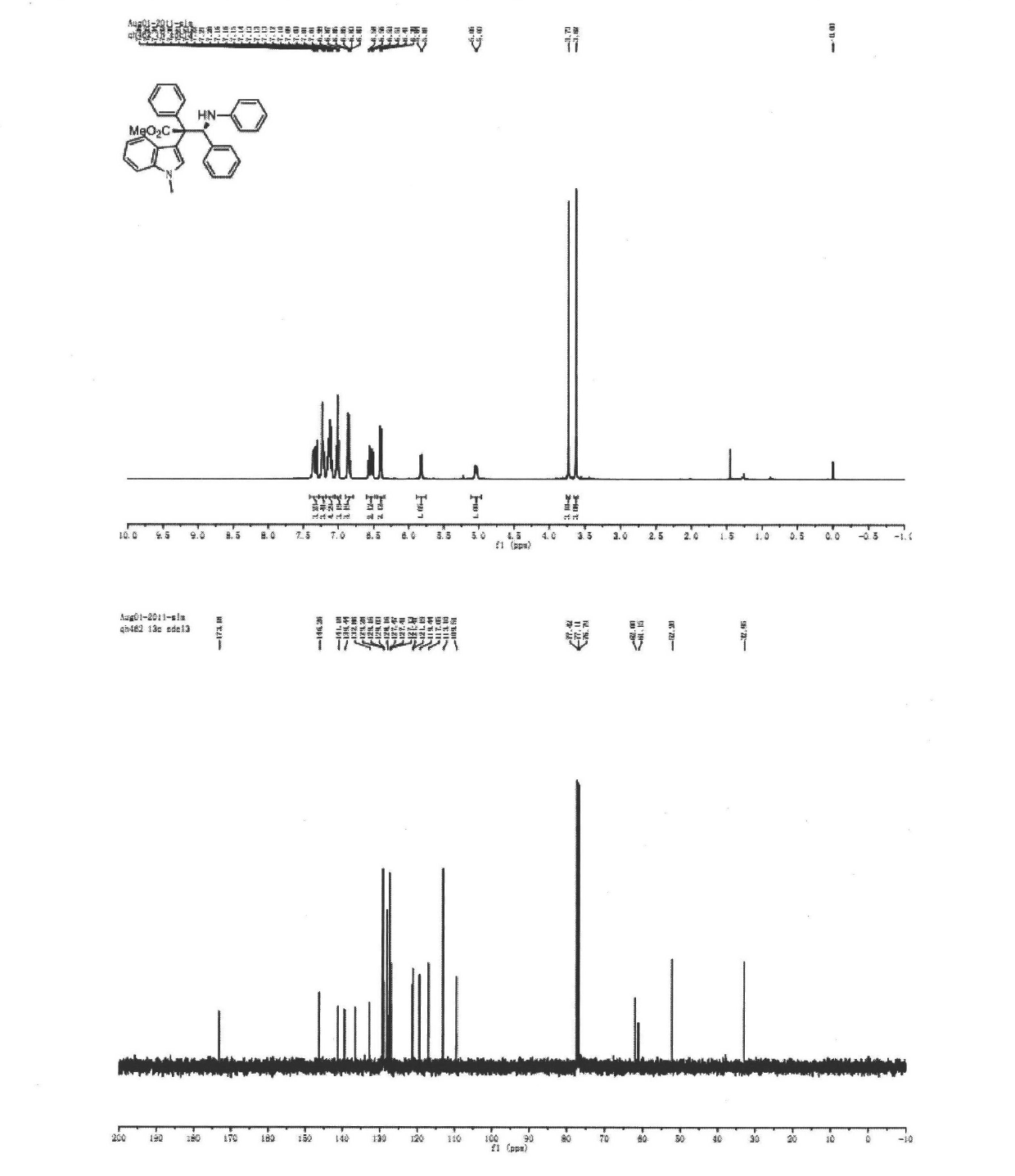
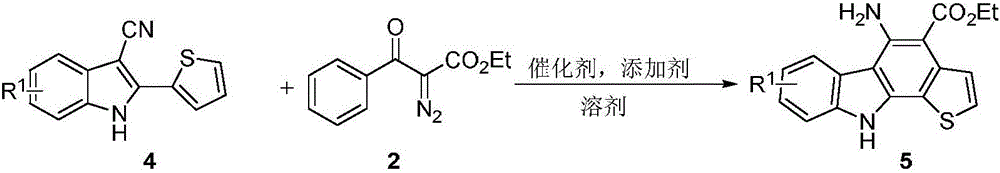
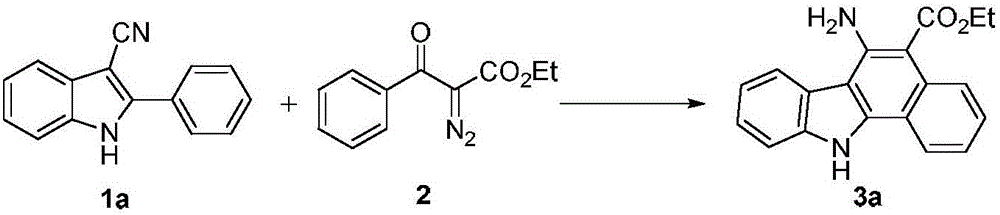
The invention discloses a synthetic method for aromatic[a]carbazole compounds, belonging to the technical field of organic synthesis. According to a technical scheme in the invention, the synthetic method comprises the following steps: dissolving a 2-phenylindole compound, 2-(naphth-1-yl)indole compound or 2-(thiazol-1-yl)indole compound and a diazo compound in a solvent together; then adding a catalyst and an additive; and carrying out a reaction at 100 to 140 DEG C so as to prepare a benzo[a]carbazole compound, naphtho[a]carbazole compound or thiazolo[a]carbazole compound. According to the invention, 2-substituted indole compounds and the diazo compound are used as raw materials and subjected to a one-pot cascade reaction so as to directly obtain the aromatic[a]carbazole compounds; and the synthetic method is simple and convenient in process, mild in conditions, wide in a substrate adaptability range and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Dilute sulfuric acid diazotization process of substituted phenylamine
The invention discloses a dilute sulfuric acid diazotization process of substituted phenylamine, which comprises the steps of adding substituted phenylamine into 40-95% of dilute sulfuric acid by mass, adding a nitrosyl sulfuric acid solution at a temperature of 0-40 DEG C, and keeping at the temperature for 1-3 hours to obtain a diazonium compound of substituted phenylamine. In the process disclosed by the invention, the original production process and feed amount are not changed when dilute sulfuric acid is used for diazotization, a positive effect is realized on the consumption of sulfuric acid, the energy consumption in coupling and the wastewater treatment, the heat generated by the dilution of concentrated sulfuric acid can be effectively utilized, and the energy consumption of a unit industrial production value is reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU JIHUA CHEMICAL CO LTD
Optical sensing elements for nitrogen dioxide (NO2) gas detection, a sol-gel method for making the sensing elements and fiber optic sensors incorporating nitrogen dioxide gas optical sensing elements
InactiveUS20050089260A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorCoupling reagentDiazo
A sensing element, a method of making a sensing element, and a fiber optic sensor incorporating the sensing element are described. The sensor can be used for the quantitative detection of NO2 in a mixture of gases. The sensing element can be made by incorporating a diazotizing reagent which reacts with nitrous ions to produce a diazo compound and a coupling reagent which couples with the diazo compound to produce an azo dye into a sol and allowing the sol to form an optically transparent gel. The sensing element changes color in the presence of NO2 gas. The temporal response of the absorption spectrum at various NO2 concentrations has also been recorded and analyzed. Sensors having different design configurations are described. The sensing element can detect NO2 gas at levels of parts per billion.
Owner:MISSISSIPPI STATE UNIVERSITY
Process for derivatizing carbon nanotubes with diazonium species and compositions thereof
InactiveUS20080093224A1Advantage of scalabilityElectrolysis componentsElectrolytic organic coupling reactionsChemical groupsElectrochemistry
The invention incorporates new processes for the chemical modification of carbon nanotubes. Such processes involve the derivatization of multi- and single-wall carbon nanotubes, including small diameter (ca. 0.7 nm) single-wall carbon nanotubes, with diazonium species. The method allows the chemical attachment of a variety of organic compounds to the side and ends of carbon nanotubes. These chemically modified nanotubes have applications in polymer composite materials, molecular electronic applications, and sensor devices. The methods of derivatization include electrochemical induced reactions, thermally induced reactions (via in-situ generation of diazonium compounds or preformed diazonium compounds), and photochemically induced reactions. The derivatization causes significant changes in the spectroscopic properties of the nanotubes. The estimated degree of functionality is ca. 1 out of every 20 to 30 carbons in a nanotube bearing a functionality moiety. Such electrochemical reduction processes can be adapted to apply site-selective chemical functionalization of nanotubes. Moreover, when modified with suitable chemical groups, the derivatized nanotubes are chemically compatible with a polymer matrix, allowing transfer of the properties of the nanotubes (such as, mechanical strength or electrical conductivity) to the properties of the composite material as a whole. Furthermore, when modified with suitable chemical groups, the groups can be polymerized to form a polymer that includes carbon nanotubes.
Owner:RICE UNIV
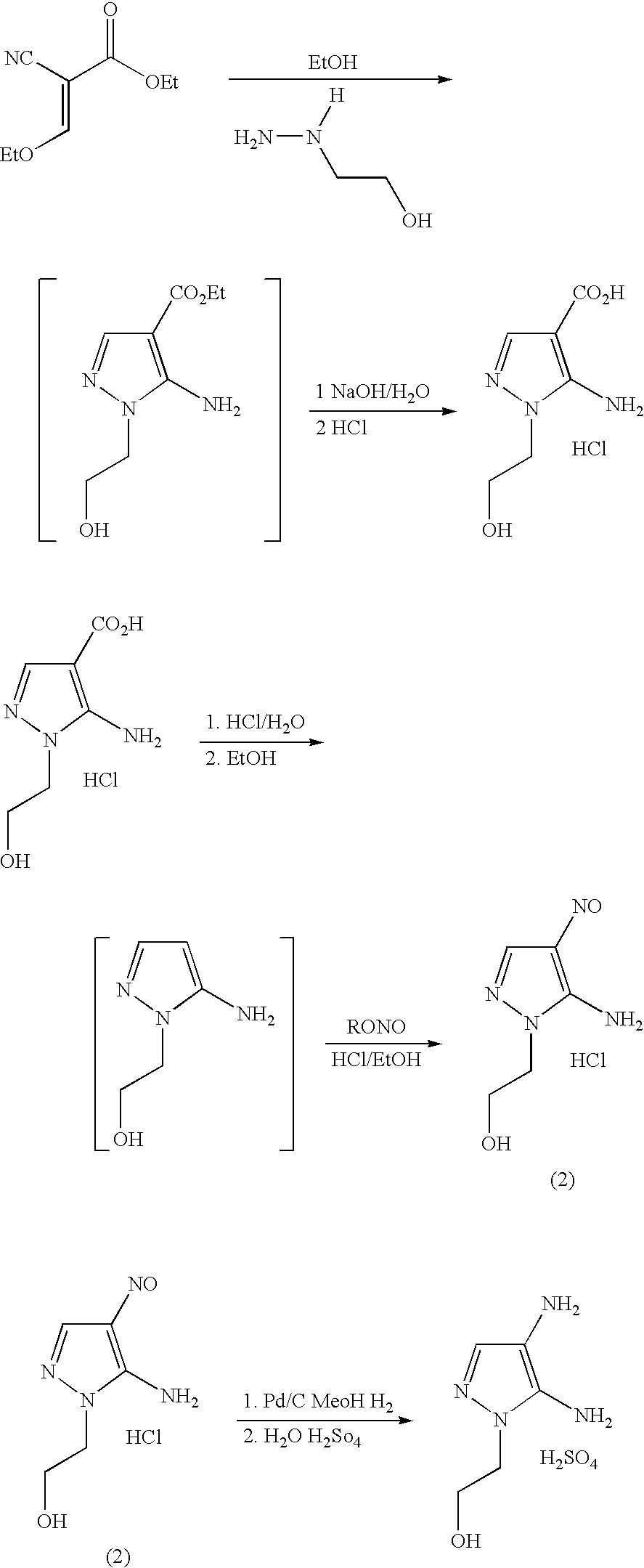
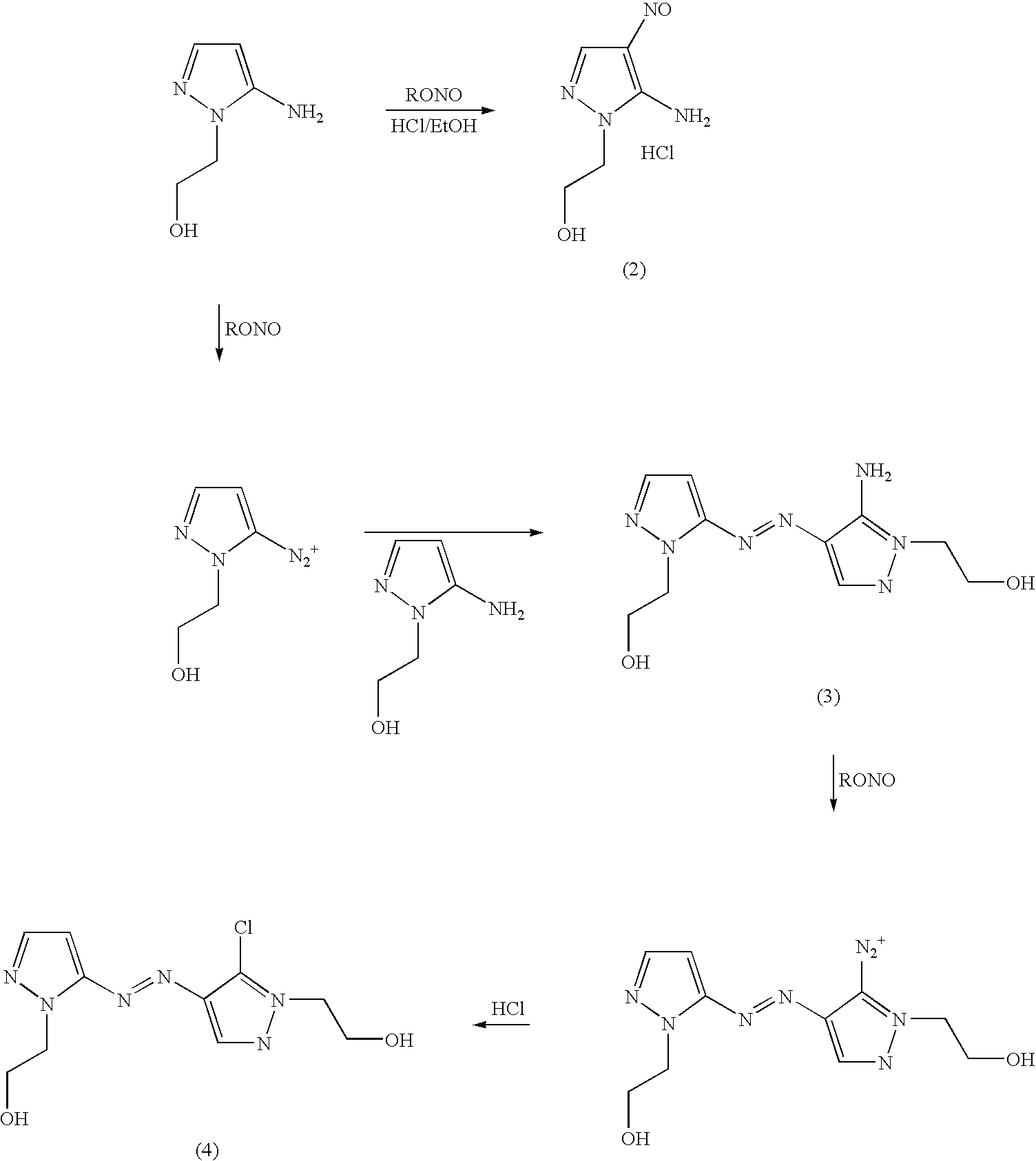
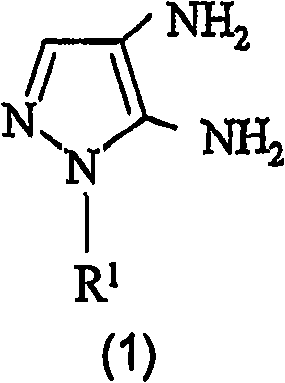
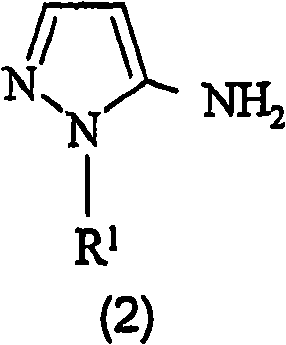
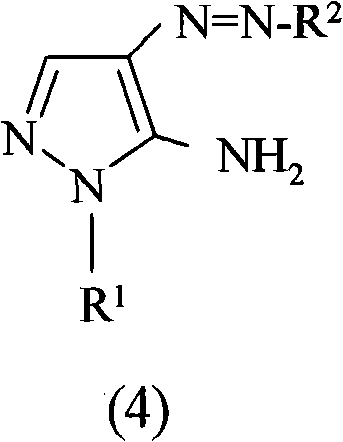
Preparation of 4,5-diamino-1-(substituted)-pyrazole and acid addition salts thereof
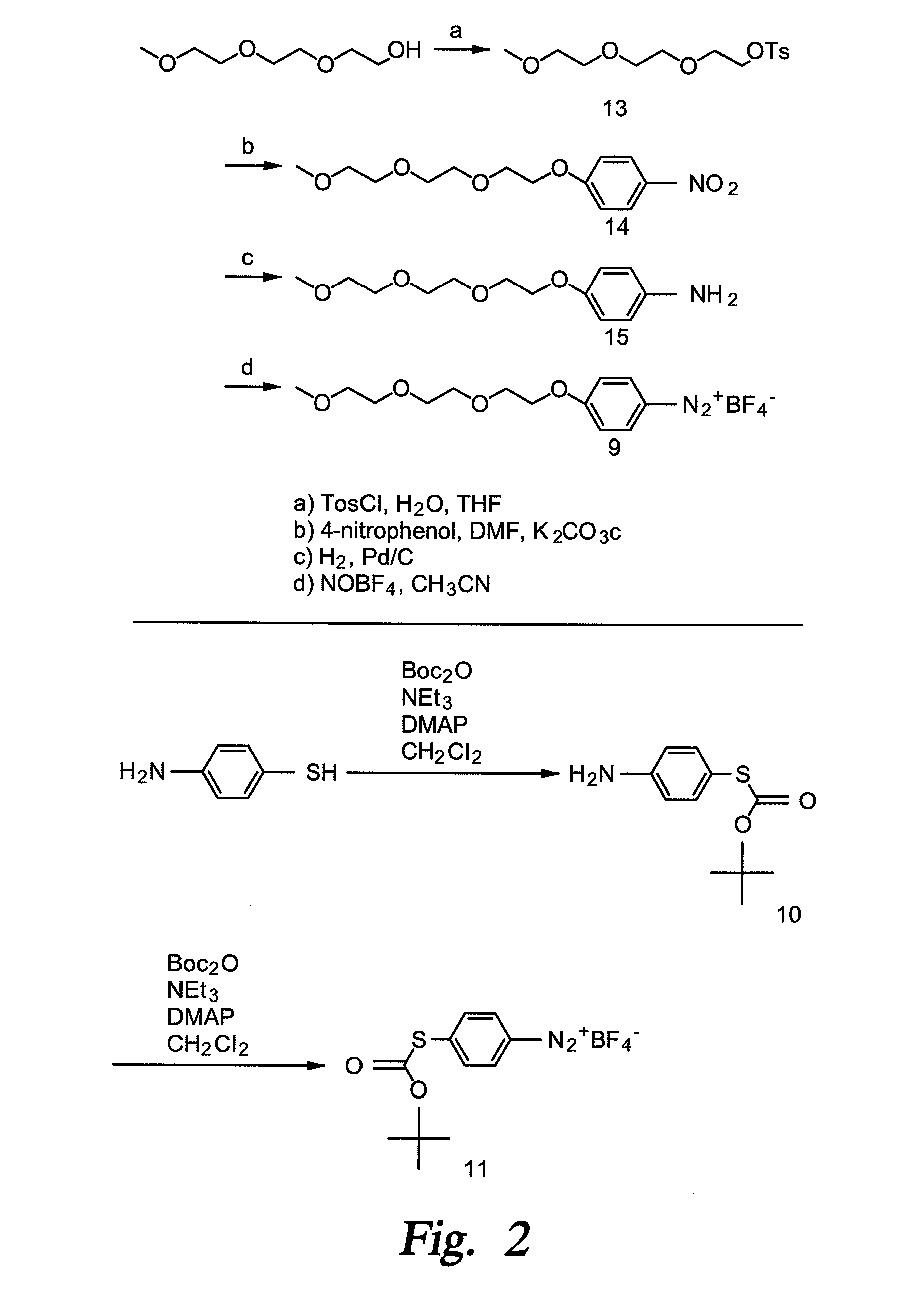
Disclosed is an improved process for the preparation of 4,5-diamino-1-(substituted)pyrazoles and acid addition salts thereof by coupling the corresponding 5-amino-1-(substituted)pyrazole with an aromatic diazonium compound to produce an intermediate azo compound and contacting the intermediate azo compound with hydrogen in the presence of a hydrogenation catalyst to produce 4,5-diamino-1-(substituted)pyrazoles. Also disclosed is a decarboxylation process for the preparation of a 5-amino-1-(substituted)pyrazole by heating a solution comprising a 5-amino-4-carboxy-1-(substituted)pyrazole, an inorganic acid and an inert solvent.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
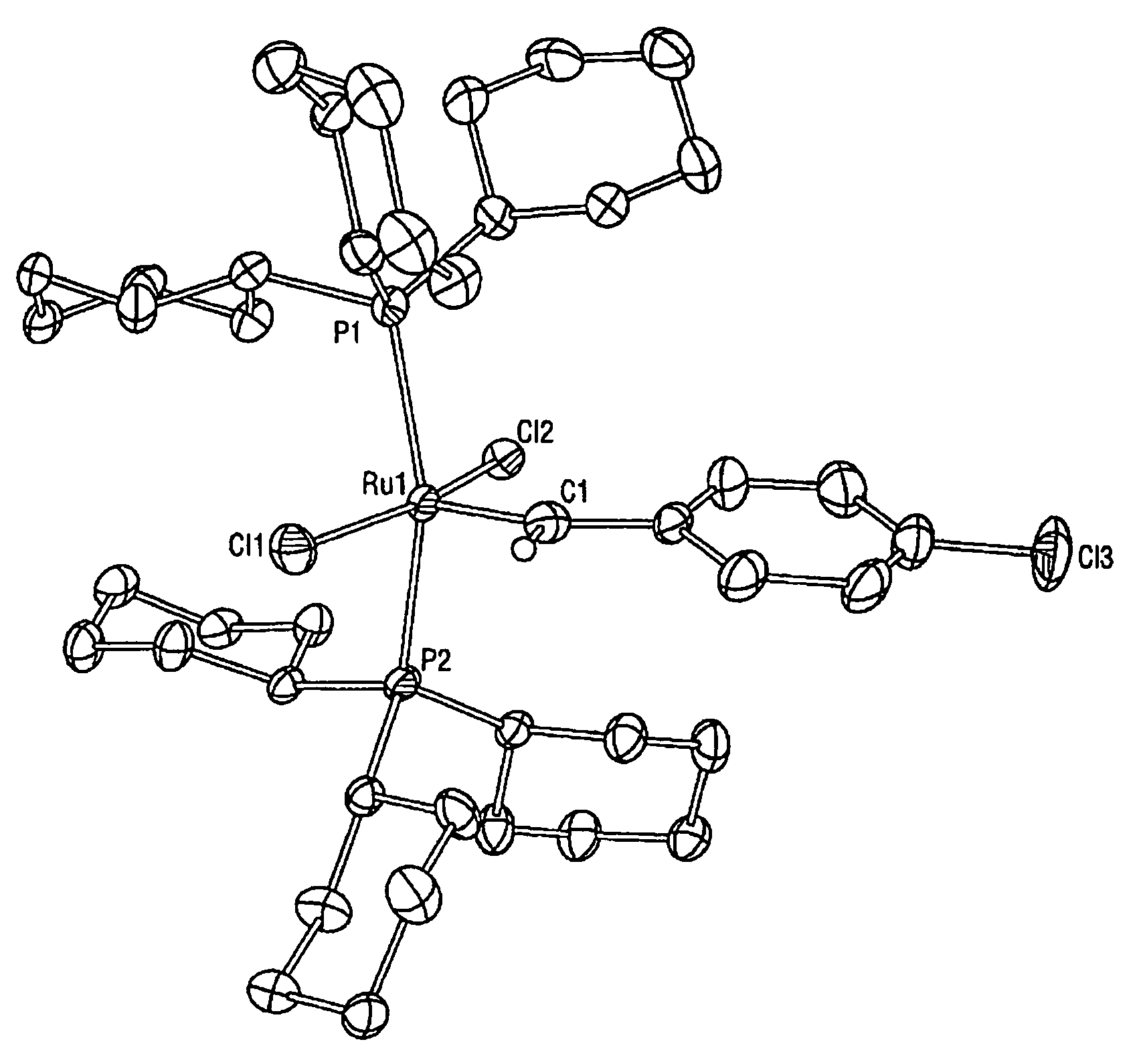
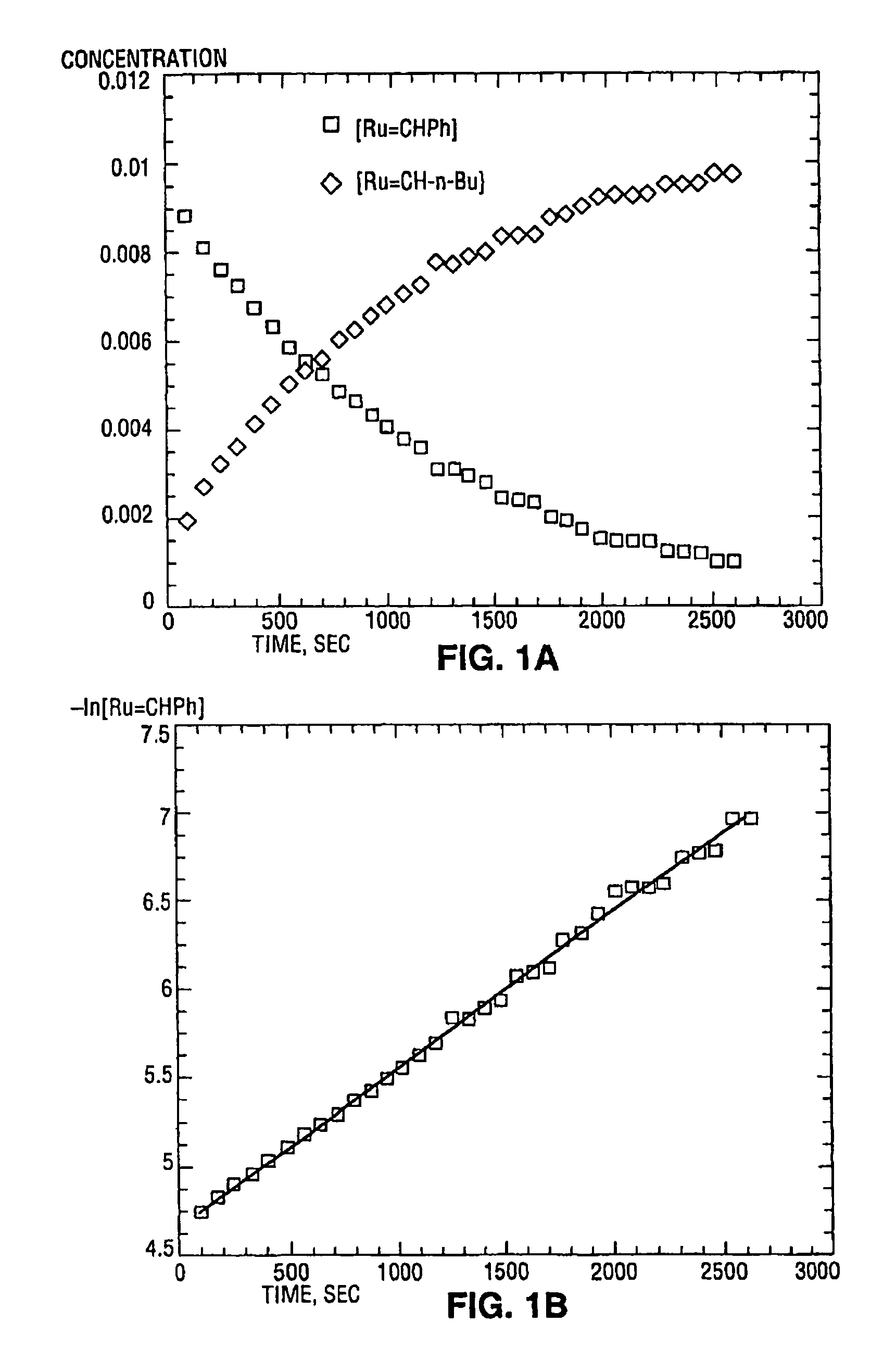
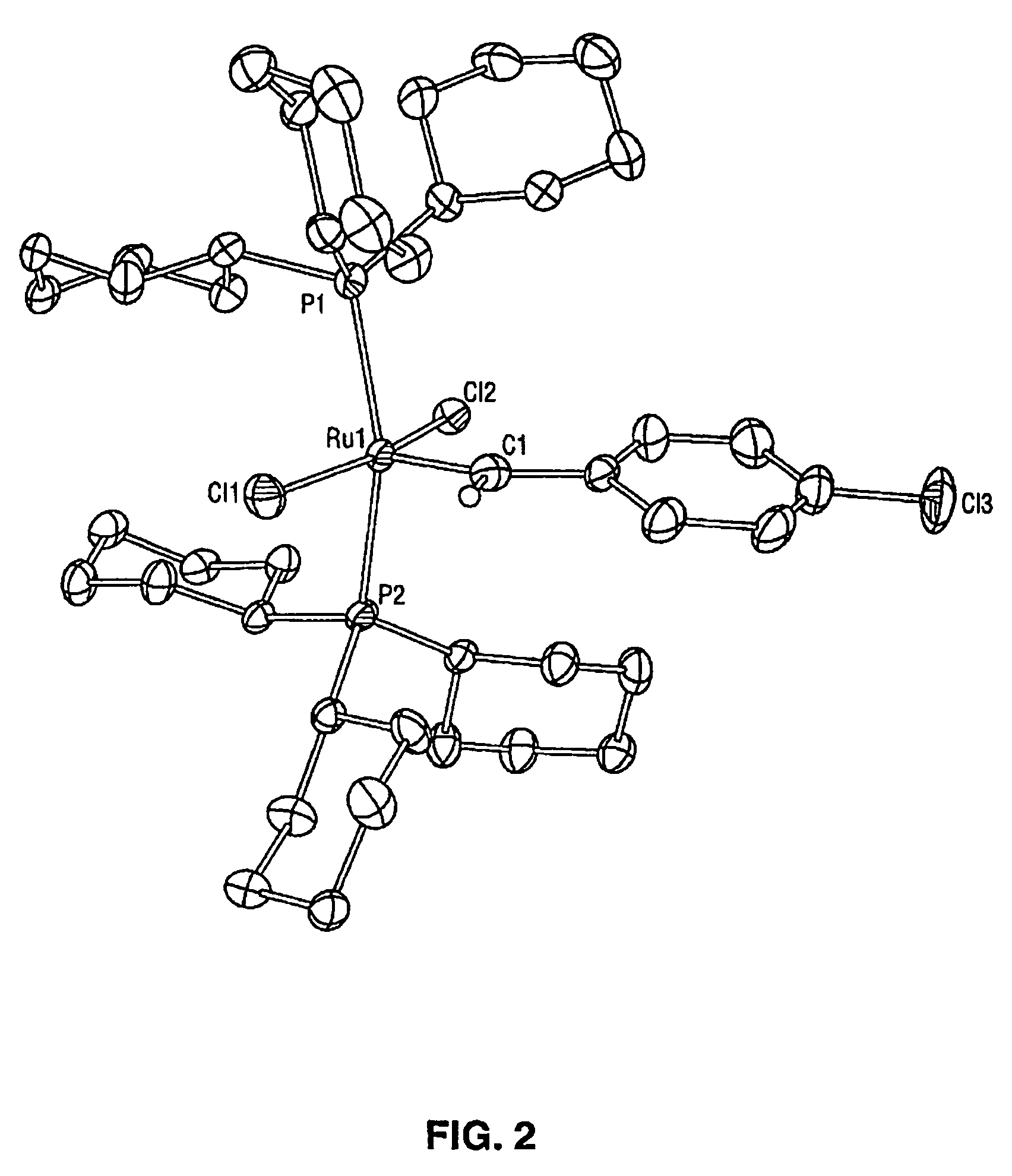
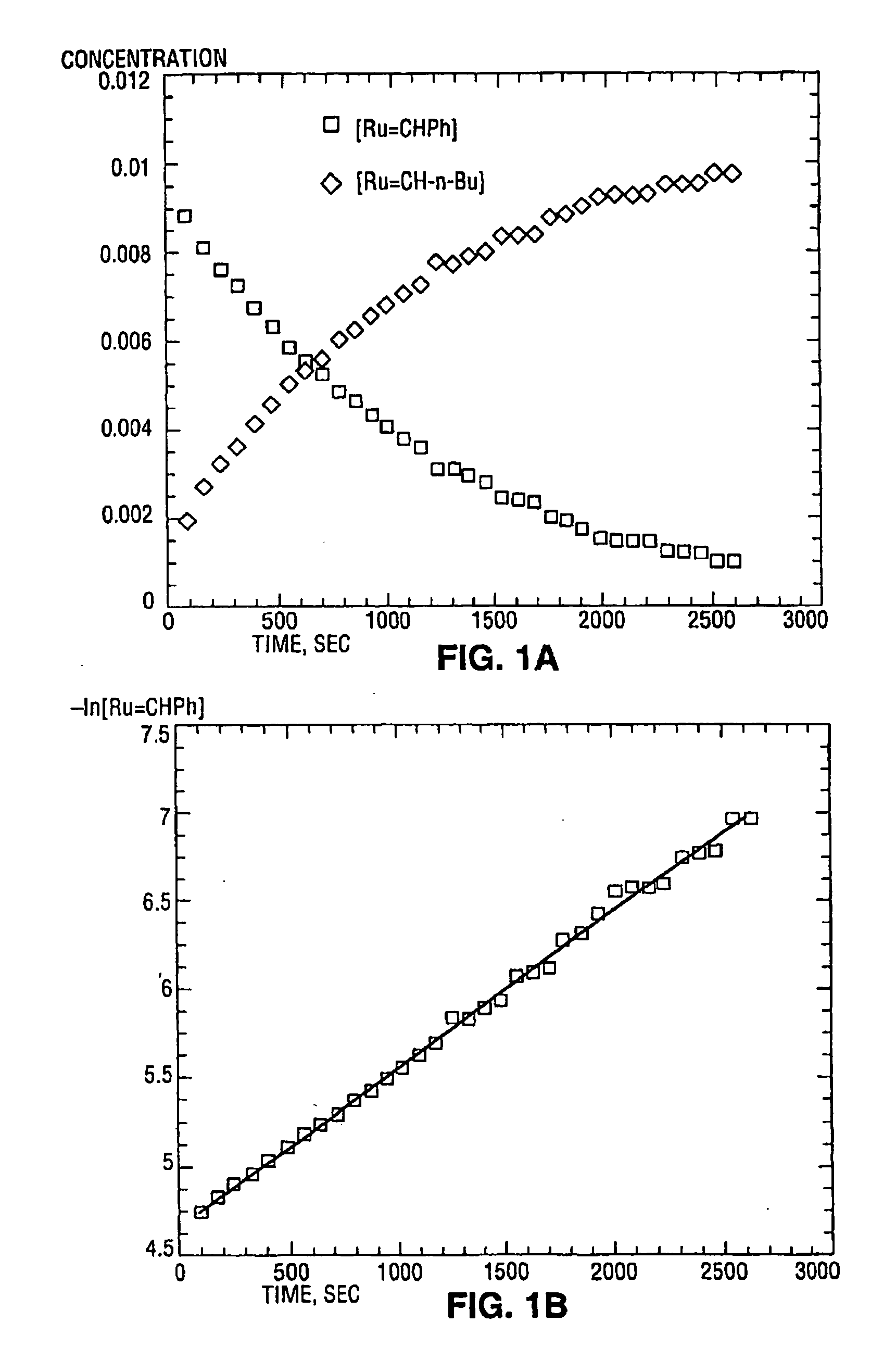
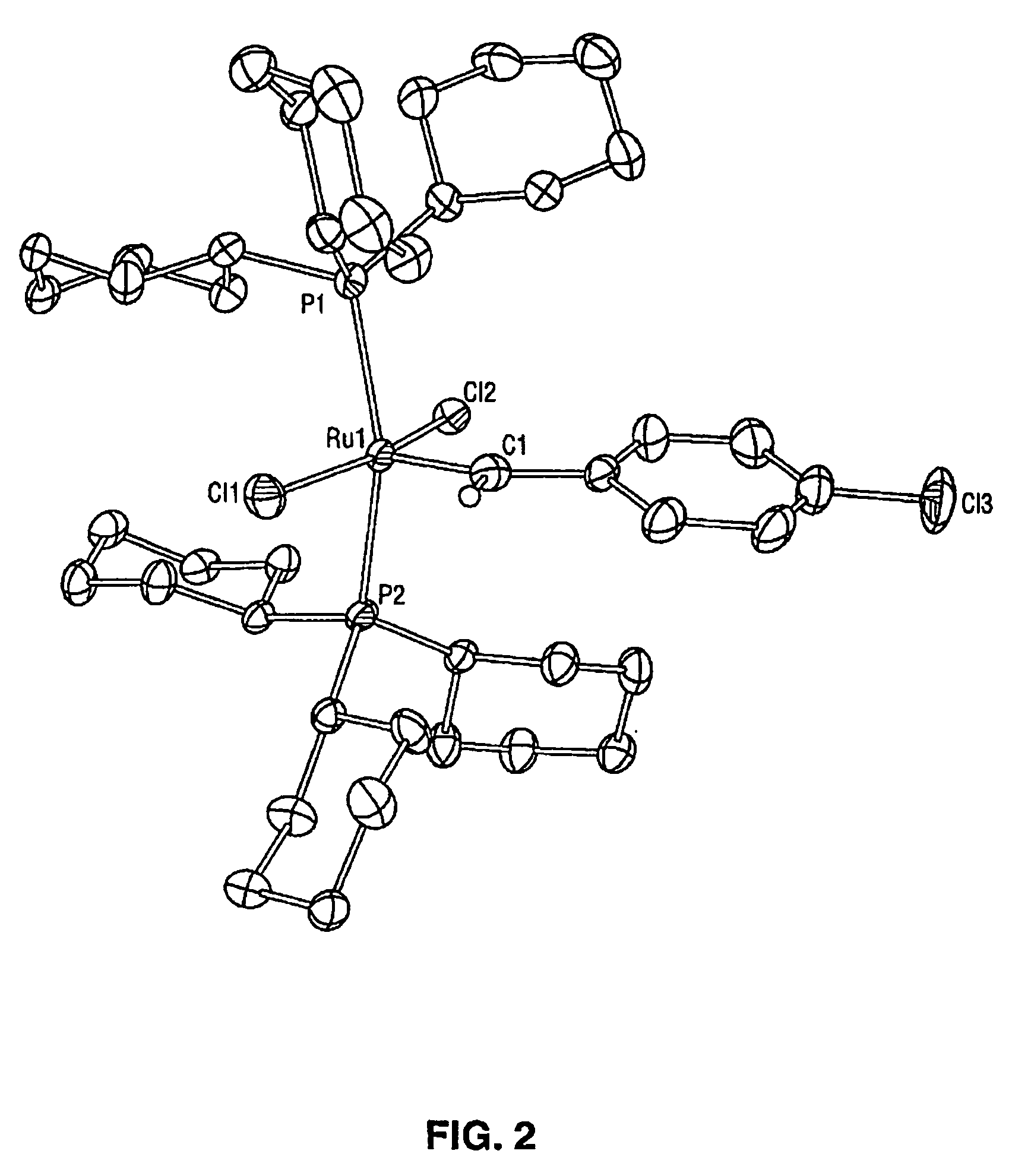
High metathesis activity ruthenium and osmium metal carbene complexes
InactiveUS7288666B2Increase the probability of activationHighly active andRuthenium organic compoundsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsDepolymerizationElectron donor
Ruthenium and osmium carbene compounds that are stable in the presence of a variety of functional groups and can be used to catalyze olefin metathesis reactions on unstrained cyclic and acyclic olefins are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods of making the carbene compounds. The carbene compounds are of the formulawhere M is Os or Ru; R<1> is hydrogen; R is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, substituted or unsubstituted alkyl, and substituted or unsubstituted aryl; X and X<1> are independently selected from any anionic ligand; and L and L<1> are independently selected from any neutral electron donor. The ruthenium and osmium carbene compounds of the present invention may be synthesized using diazo compounds, by neutral electron donor ligand exchange, by cross metathesis, using acetylene, using cumulated olefins, and in a one-pot method using diazo compounds and neutral electron donors. The ruthenium and osmium carbene compounds of the present invention may be used to catalyze olefin metathesis reactions including, but not limited to, ROMP, RCM, depolymerization of unsaturated polymers, synthesis of telechelic polymers, and olefin synthesis.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
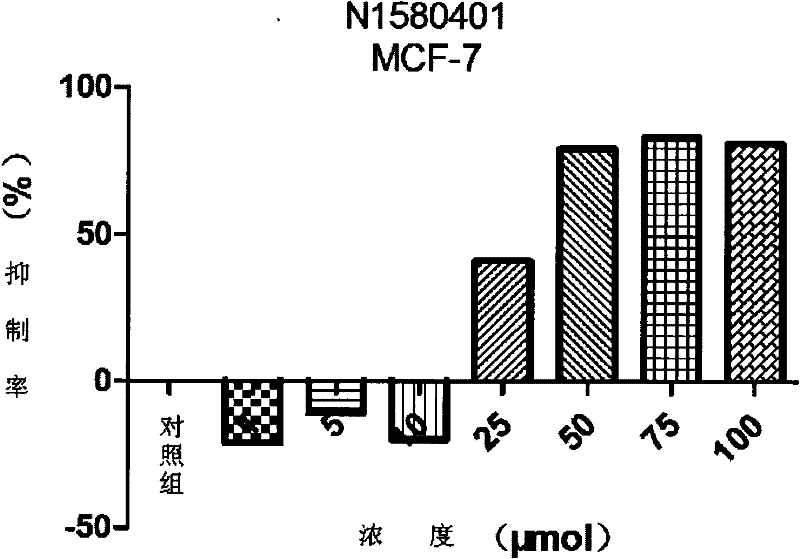
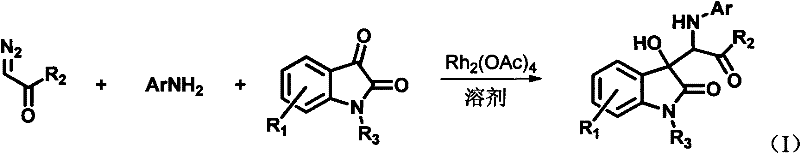
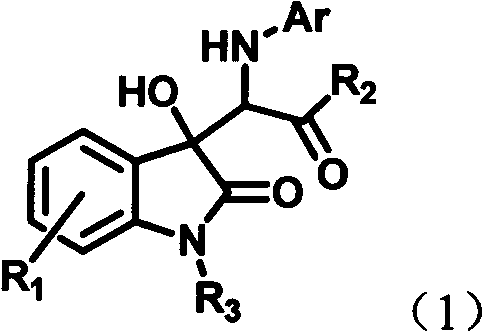
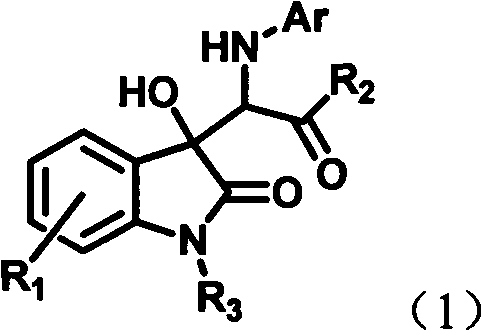
3-substituted indolone derivative and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102491931AHigh atomic economyHigh selectivityOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsPhosphoric acidSolvent
The invention discloses a preparation method for 3-substituted indolone derivative. The preparation method comprises the steps of: using imine and diazo compound as materials, rhodium acetate and chiral phosphoric acid as catalysts and organic solvent as solvent, performing one-step reaction to acquire the 3-substituted indolone derivative. The preparation method has the advantages of high-efficiency atom economy, high selectivity, high yield, simple and safe operation and the like. With high diastereomeric selectivity and enantioselectivity, and bioactivity, the 3-substituted indolone derivative prepared by the method is applicable to the preparation application of anti-tumour medicines.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
3-substituted-3-hydroxyindazolone derivatives, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102516151AHigh atomic economyHigh selectivityOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsSolventDrug biological activity
The invention discloses 3-substituted-3-hydroxyindazolone derivatives, and a preparation method and application thereof. Isatin, amine and diazo compound are used as raw materials, rhodium acetate is used as a catalyst, and an organic solvent is used as a solvent, a one-step reaction is carried out to obtain the product 3-substituted-3-hydroxyindazolone derivatives. The preparation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high atom economical efficiency, high selectivity, high yield and the like, and is simple and safe to operate. The 3-substituted-3-hydroxyindazolone derivatives have bioactivity, and are applicable to preparing antineoplastic drugs.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Fluorinated elastomers with low glass transition temperatures based on vinylidene fluoride and free of tetrafluoroethylene or siloxane group
Owner:HYDRO QUEBEC CORP
Optically active tryptamine derivative and synthetic method and application thereof
InactiveCN102503881AEfficient atom economyHigh selectivityOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsChemical industryPhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a synthetic method of an optically active trytamine derivative. The optically active trytamine derivative is obtained by taking a diazo compound, imine and an indole derivative as raw materials, taking rhodium acetate and chiral phosphoric acid as catalysts, taking an organic solvent as a solvent, taking a molecular sieve as a water absorbent and undergoing a one-step reaction at the temperature of -10 DEG C to 50 DEG C. The synthetic method of the optically active trytamine derivative has the advantages of efficient atom economy, high selectivity, high yield, low catalyst using amount, easiness and safety for operating, and the like. The optically active trytamine derivative obtained with the method has high antitumor activity, and can be widely applied in the field of chemical industry.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Preparation of 4,5-diamino-1-(substituted)-pyrazole and acid addition salts thereof
InactiveCN101287710AOvercoming the problem of by-product formationOperational securityOrganic chemistryHydrogenSolvent
Disclosed is an improved process for the preparation of 4,5-diamino- 1-(substituted)pyrazoles and acid addition salts thereof by coupling the corresponding 5-amino-1-(substituted)pyrazole with an aromatic diazonium compound to produce an intermediate azo compound and contacting the intermediate azo compound with hydrogen in the presence of a hydrogenation catalyst to produce 4,5-diamino-1-(substituted)pyrazoles. Also disclosed is a decarboxylation process for the preparation of a 5-amino-1-(substituted)pyrazole by heating a solution comprising a 5-amino-4-carboxy-1-(substituted)pyrazole, an inorganic acid and an inert solvent.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
1-aryl-2 perluoro or polyfluoro phenyl ethylene and its derirative, its synthesis and application
InactiveCN1475471ACarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationTosylhydrazoneCarbene
A 1-aryl-2 perfluoro (or polyfluoro) phenylethene and its derivative used as fluoric organic luminescent material or electrically conductive polymer is prepared from perfluoro (or polyfluoro) phenylformaldehyde through condensating with toluenesulfonyl diamine, dehydrogenating by sodium hydride, reacting on phase-transfer catalyst to generate perfluoro (or polyfluoro) phenyldiazo, catalytic decomposing by catalyst to generate metal carbene, capturing it by triphenyl (or trialkyl) arsenic, and condensating reaction on aldehide.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Novel green method of synthesizing C-C bond and N heterocycle derivatives through transition metal catalyzed C-H carbenoid coupling reaction
InactiveCN109336808AAvoid pollutionReduce production finished productGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsChemical recyclingSynthesis methodsCarbenoid
The invention relates to a novel green synthesis method of efficiently synthesizing C-C bond and N heterocycle derivatives through a transition metal catalyzed C-H active carbene coupling reaction. The method takes N1,N3-di-substituted imidazole ionic liquid as a solvent and takes a diazonium compound as a carbene donor. Compared with the prior art, the method is safer, simpler, and more convenient, efficient and environmentally friendly; functional group tolerance and a yield are high; the solvent and a catalyst can be recycled; the cost is greatly lowered; a byproduct is only nitrogen; the generation of a large amount of waste is avoided; an atom utilization ratio is increased; pre-activation of a substrate is not required; reaction conditions are mild; the operation difficulty is reduced.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
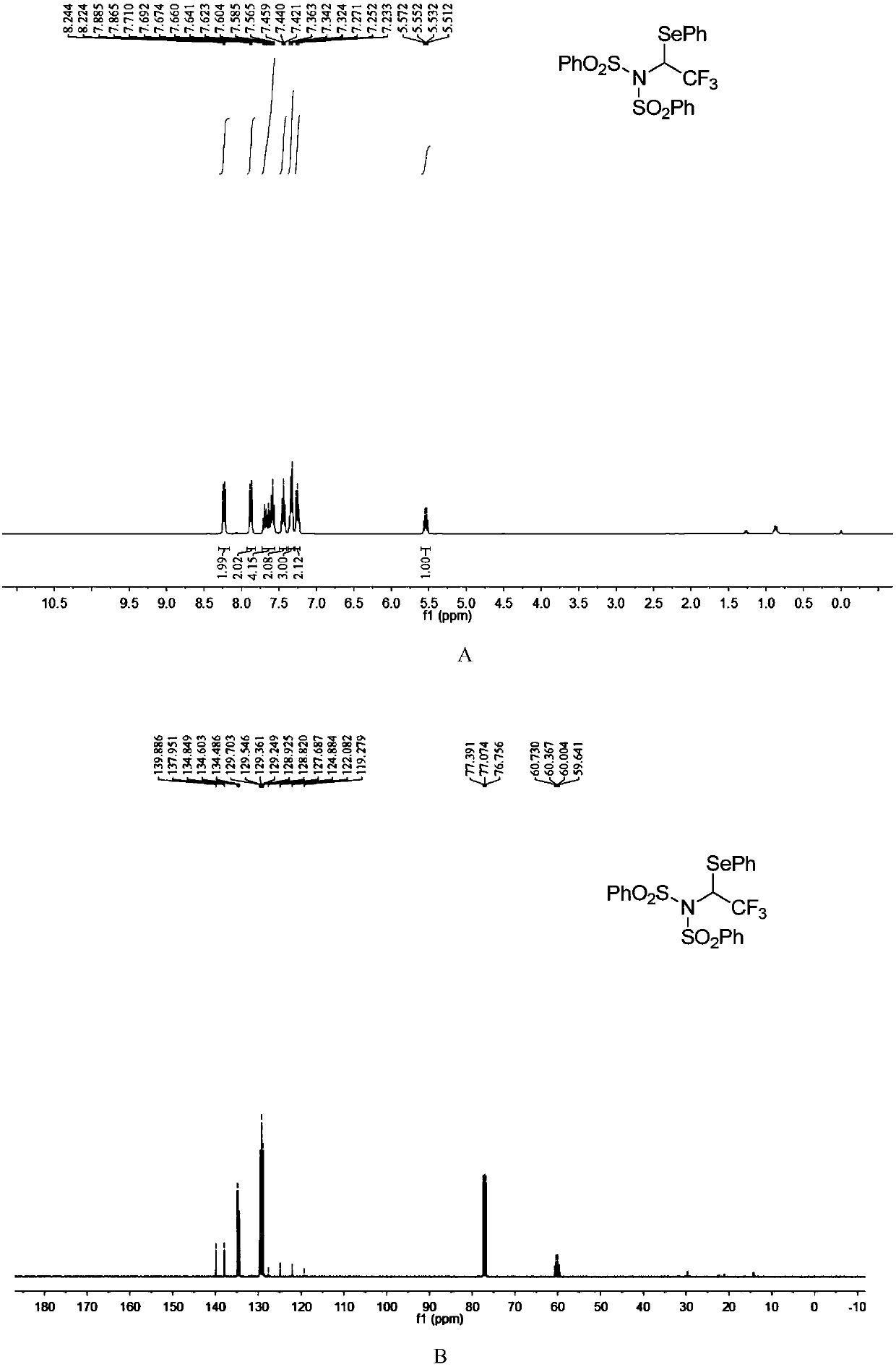
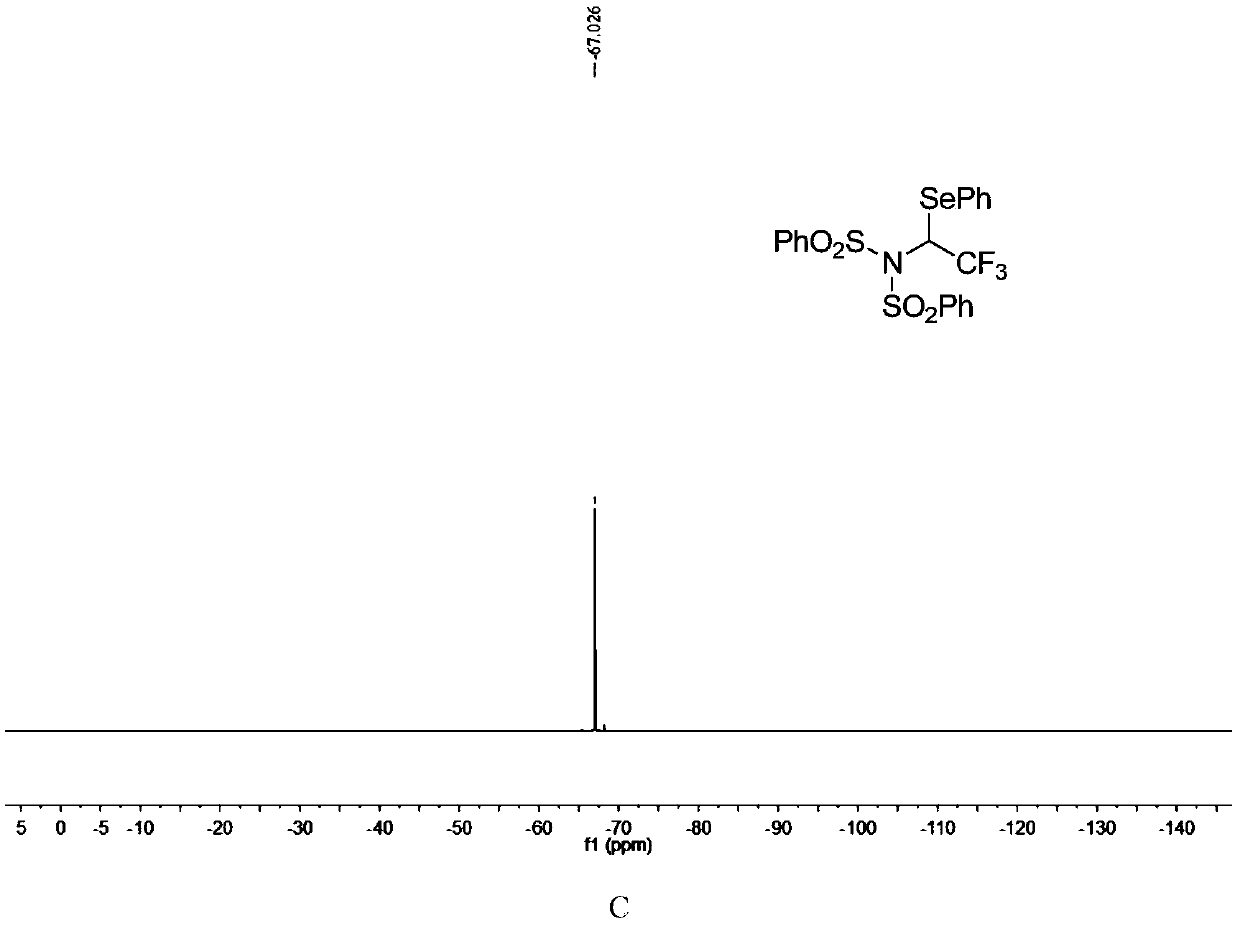
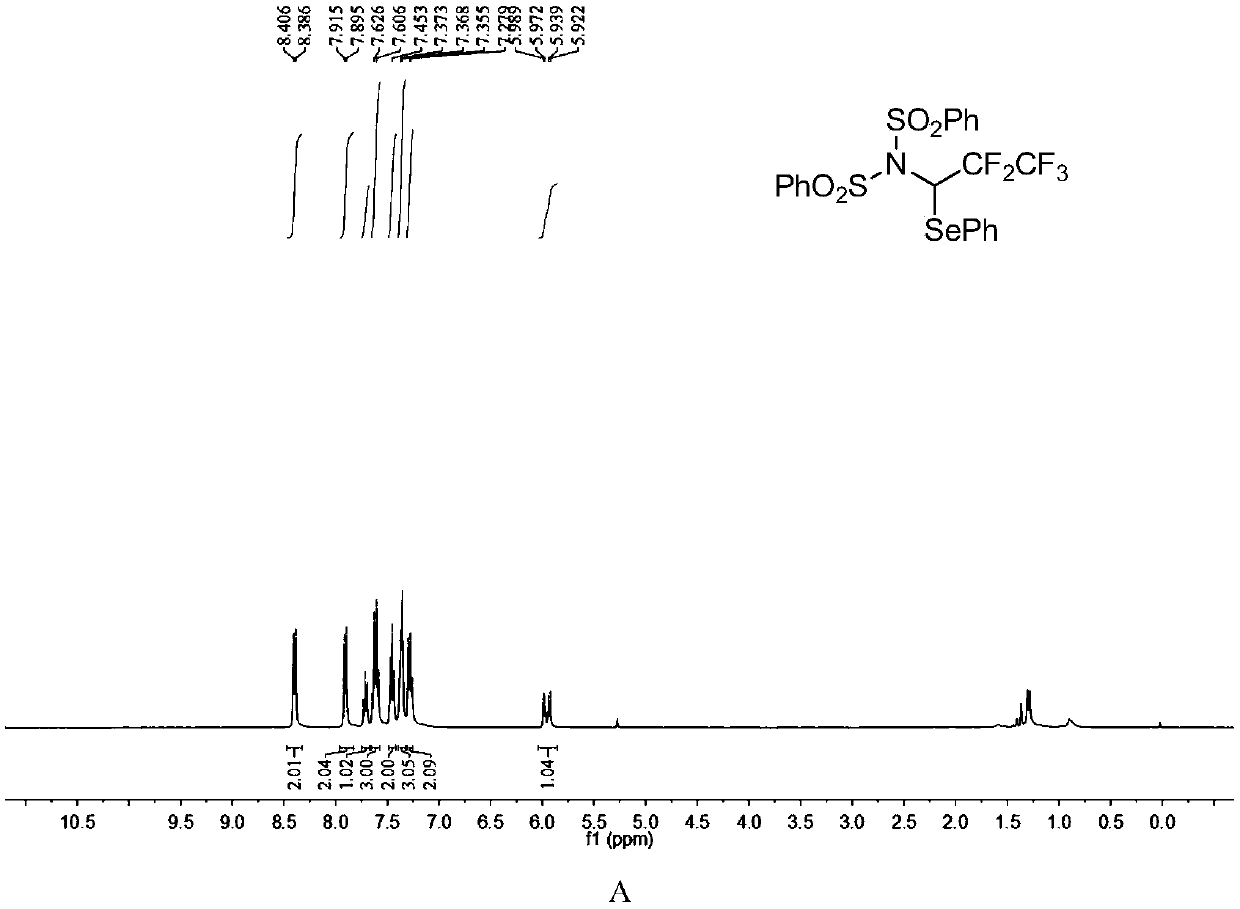
N-bisbenzenesulfonyl-1-phenylseleno trifluoroethane derivative, synthesis method and applications thereof
ActiveCN110857281AEfficient atom economyRaw materials are easy to obtainGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPtru catalystOrganic synthesis
The invention discloses an N-bisbenzenesulfonyl-1-phenylseleno trifluoroethane derivative synthesis method, which comprises: carrying out a one-step reaction by using a diazo compound, a diether compound and N-fluorobisbenzenesulfonyl imide as raw materials and using an organic solvent as a solvent in the absence of a catalyst to obtain the N-bisbenzenesulfonyl-1-phenylseleno trifluoroethane derivative. According to the invention, the synthesis method has efficient atom economy, does not need any organic catalysts or metal catalysts, and is simple and safe to operate, and the synthesized N-bisbenzenesulfonyl-1-phenylseleno trifluoroethane derivative is an important organic synthesis and medical intermediate.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
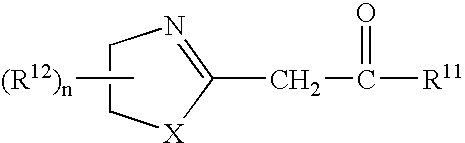
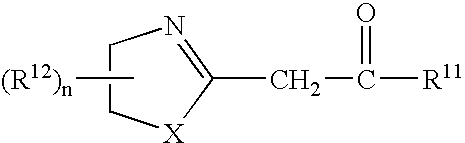
Azolinyl acetic acid derivative and azolinyl acetic acid derivative containing recording material
A recording material having, on a support, a recording layer containing an azolinyl acetic acid derivative and a diazo compound. The azolinyl acetic acid derivative is preferably is a compound represented by the following general formula (1): General formula (1) wherein X represents an oxygen atom or a sulfur atom; R<11 >represents an alkyl group, an aryl group, a heterocyclic group, -OR<13 >or -NR<14>R<15>; R<12 >represents a substituent; R<13 >represents an alkyl group, an aryl group or a heterocyclic group; R<14 >and R<15 >each independently represents a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group, an aryl group or a heterocyclic group; n represents an integer from 0 to 4; and, when n is an integer of 2 or greater, two or more R<12>s may be linked with each other to form a ring.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
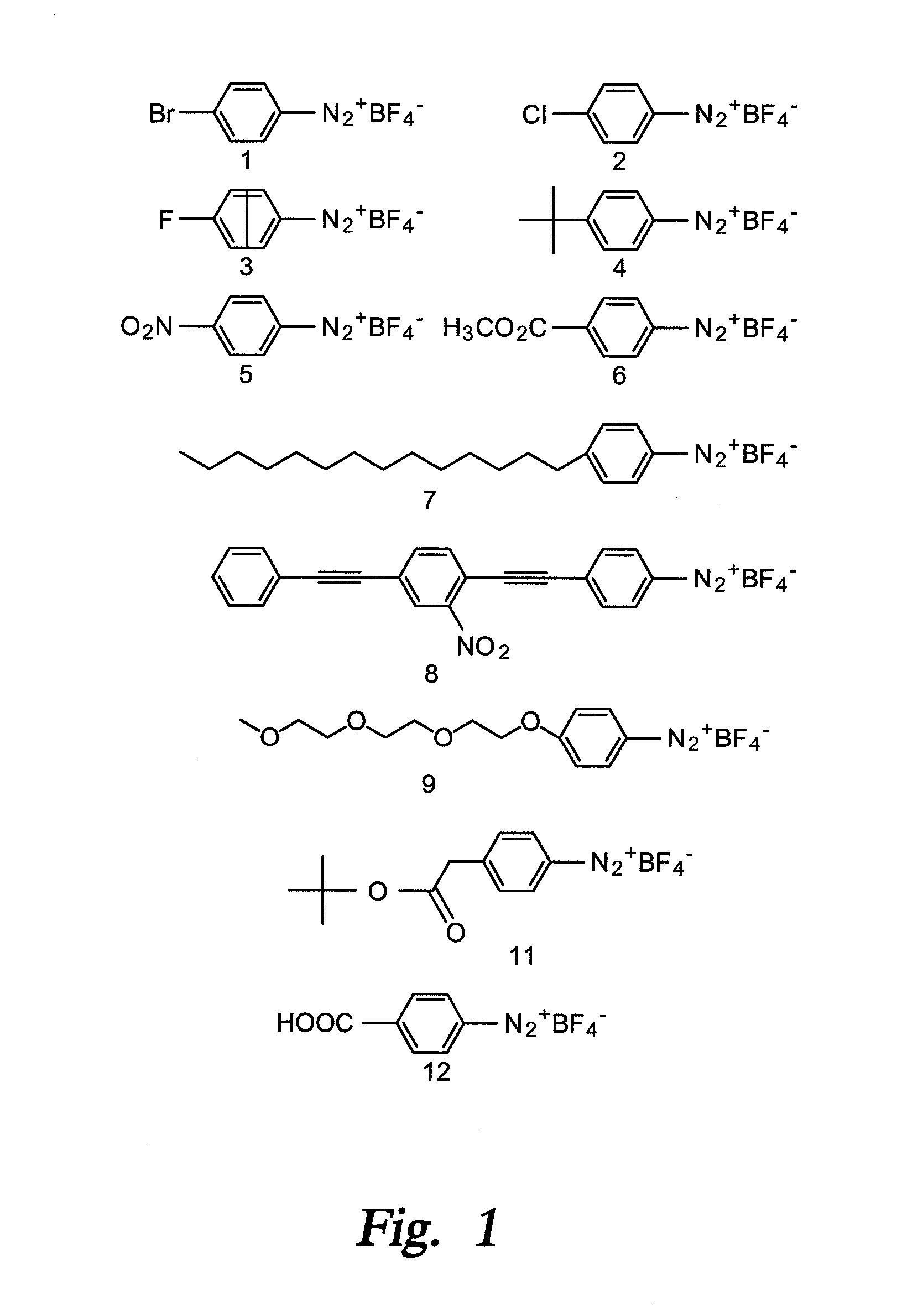
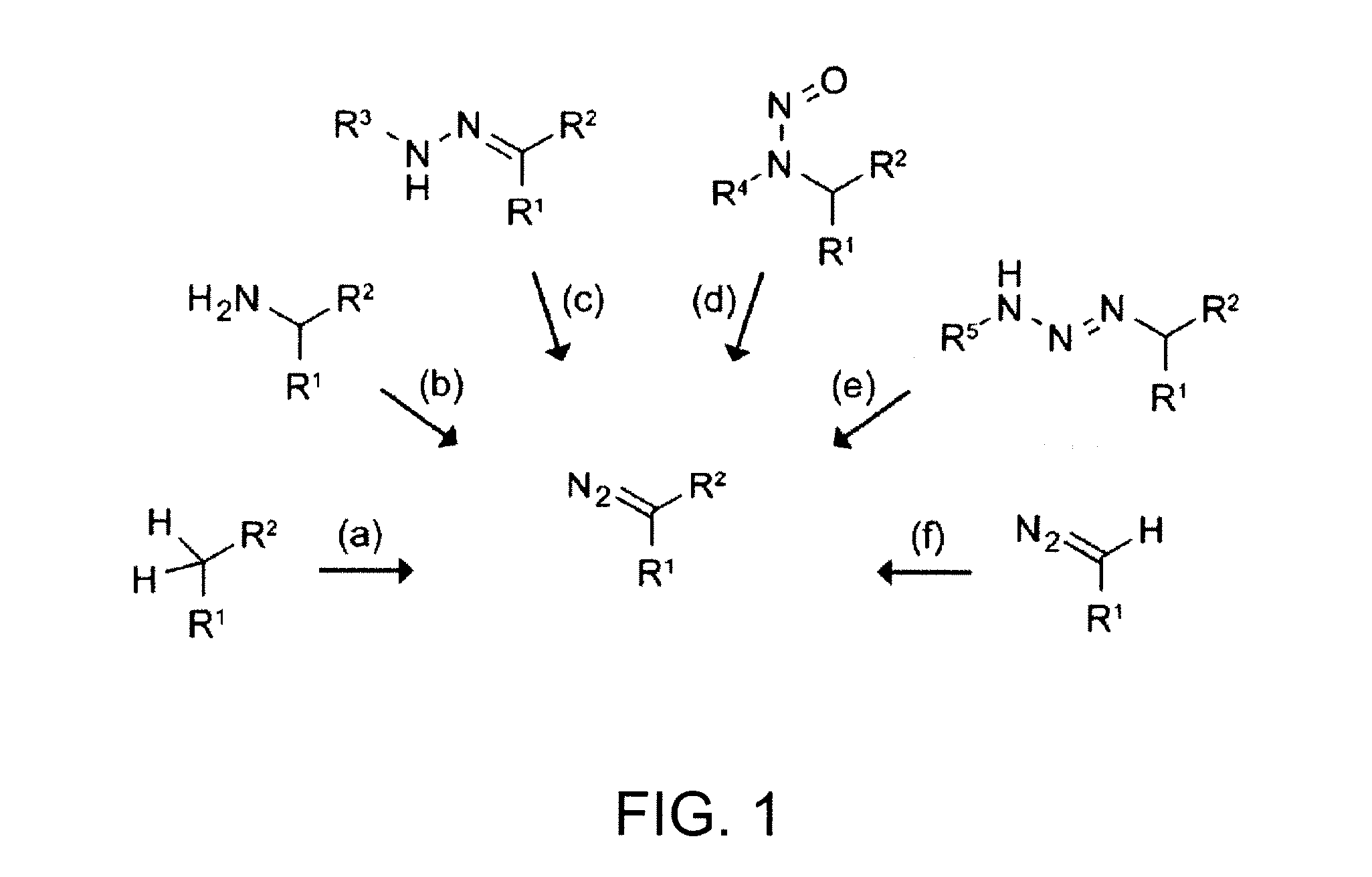
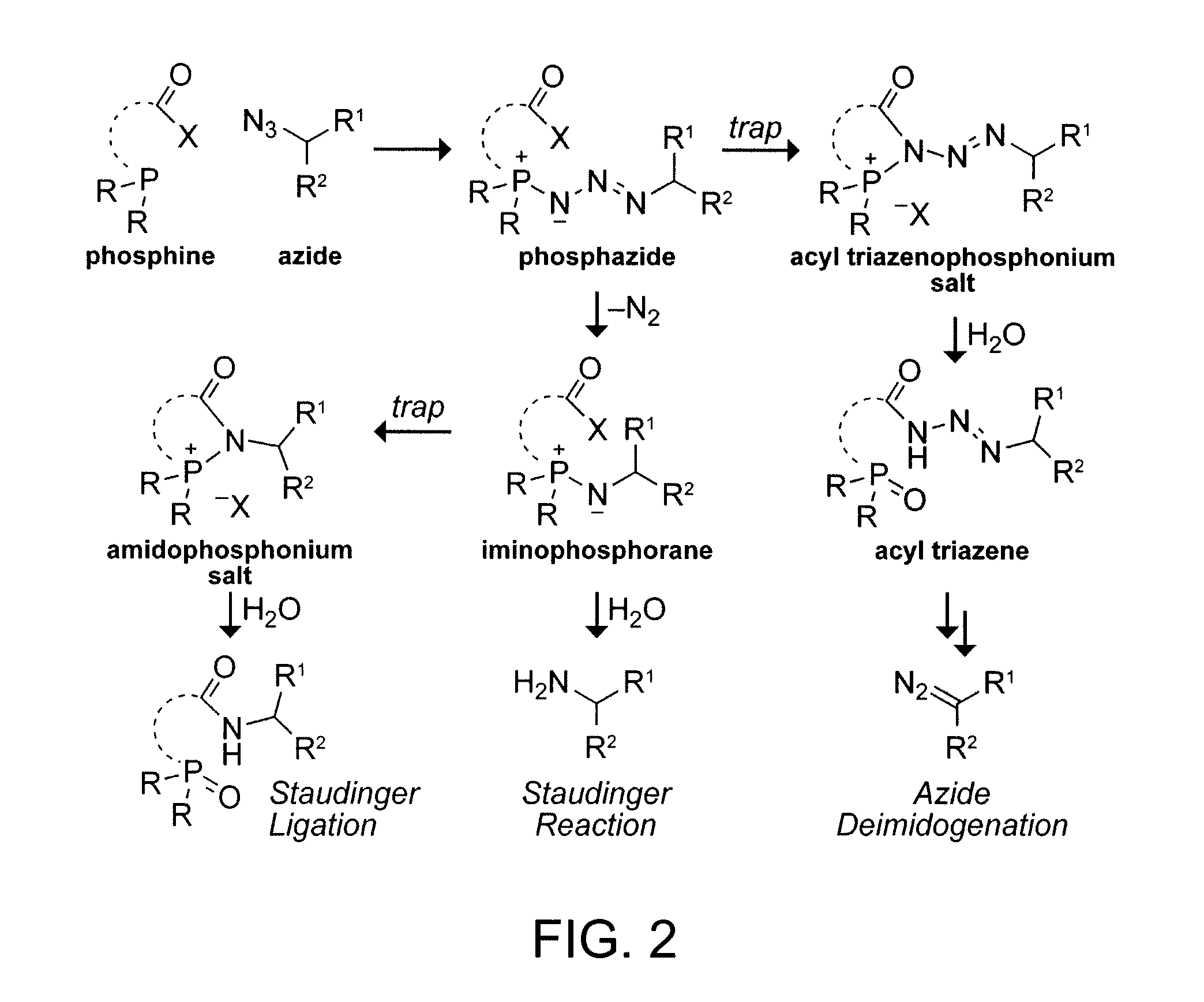
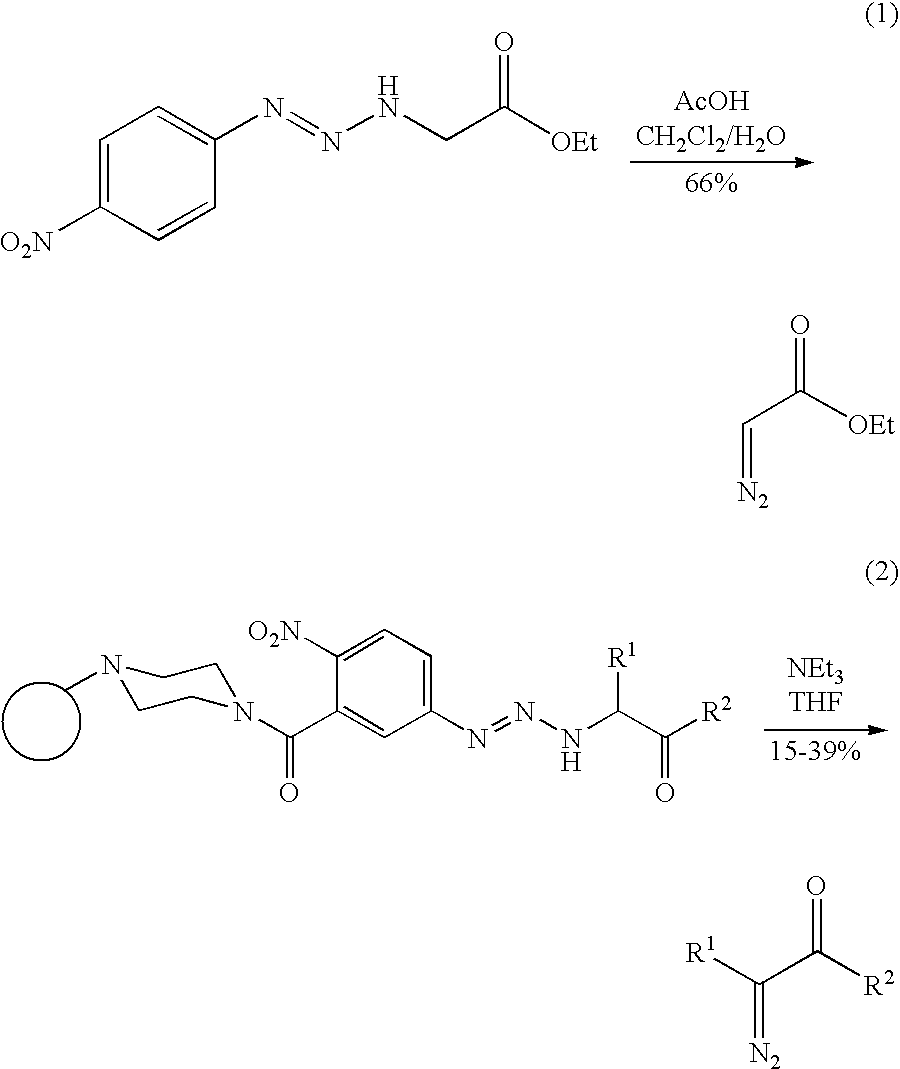
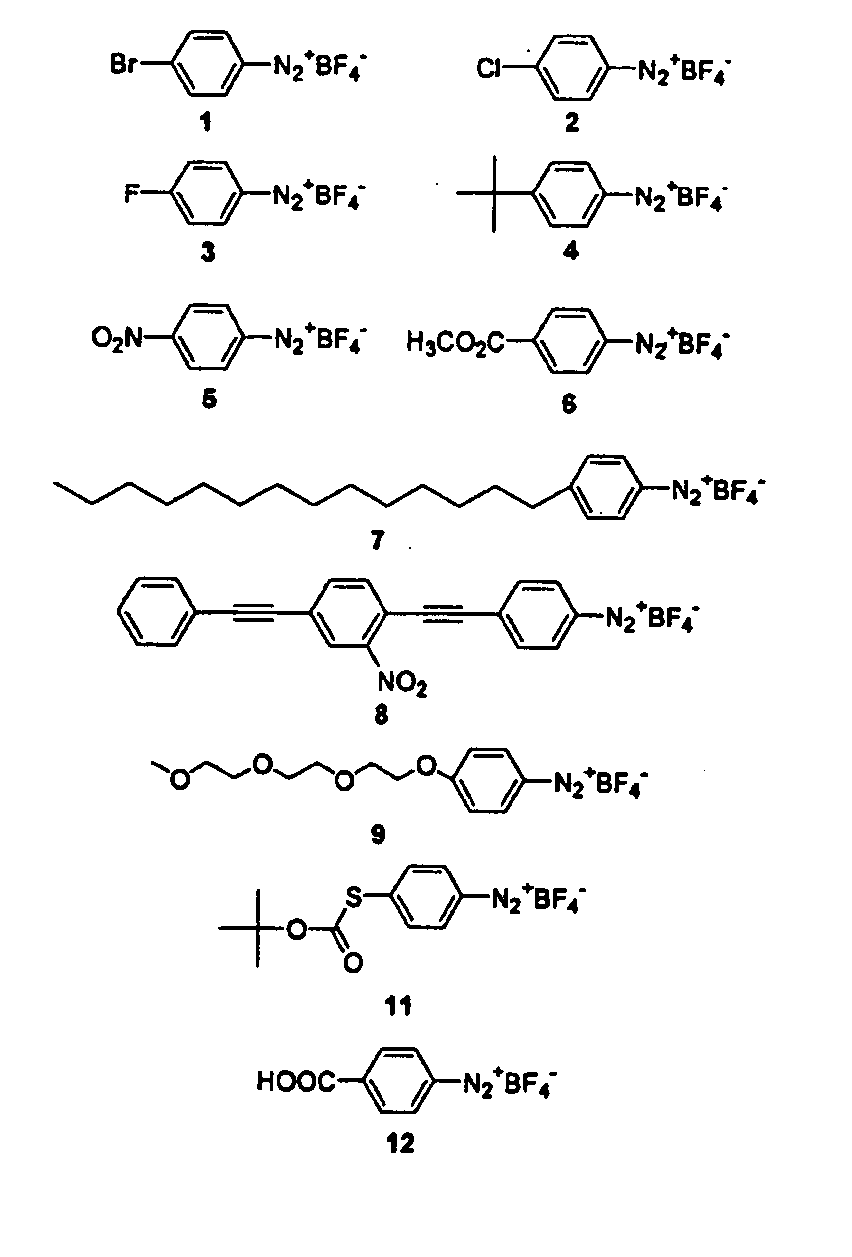
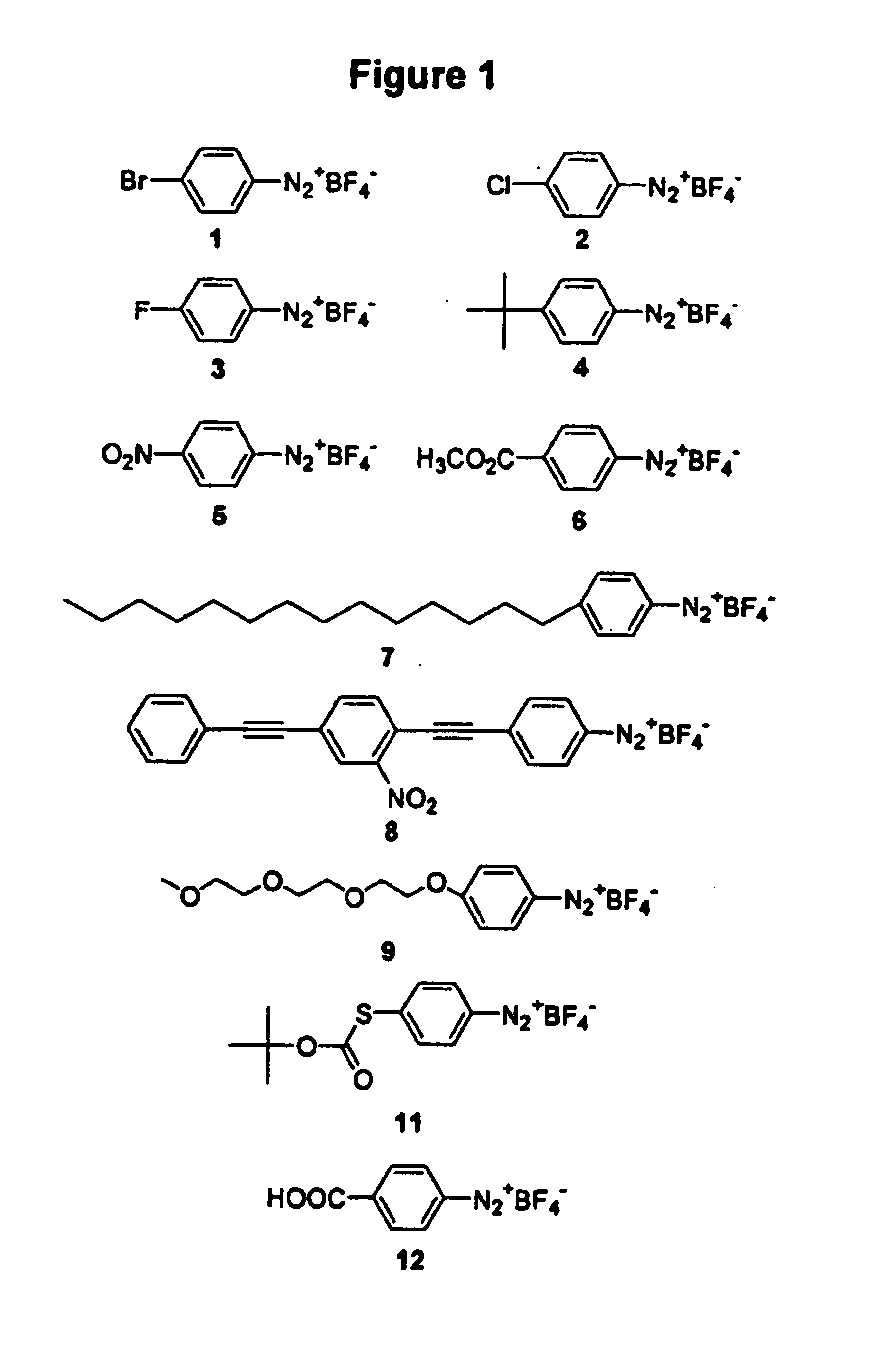
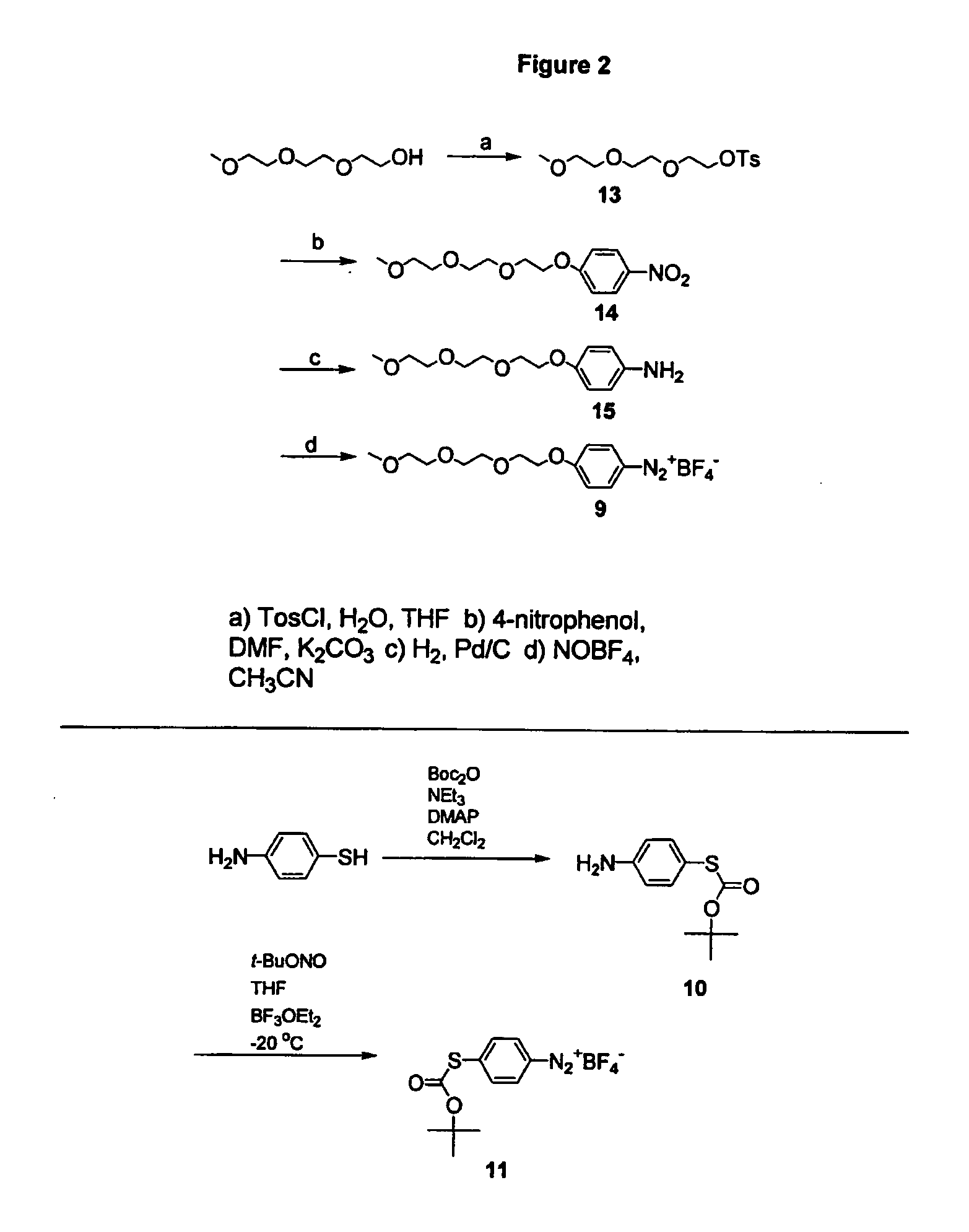
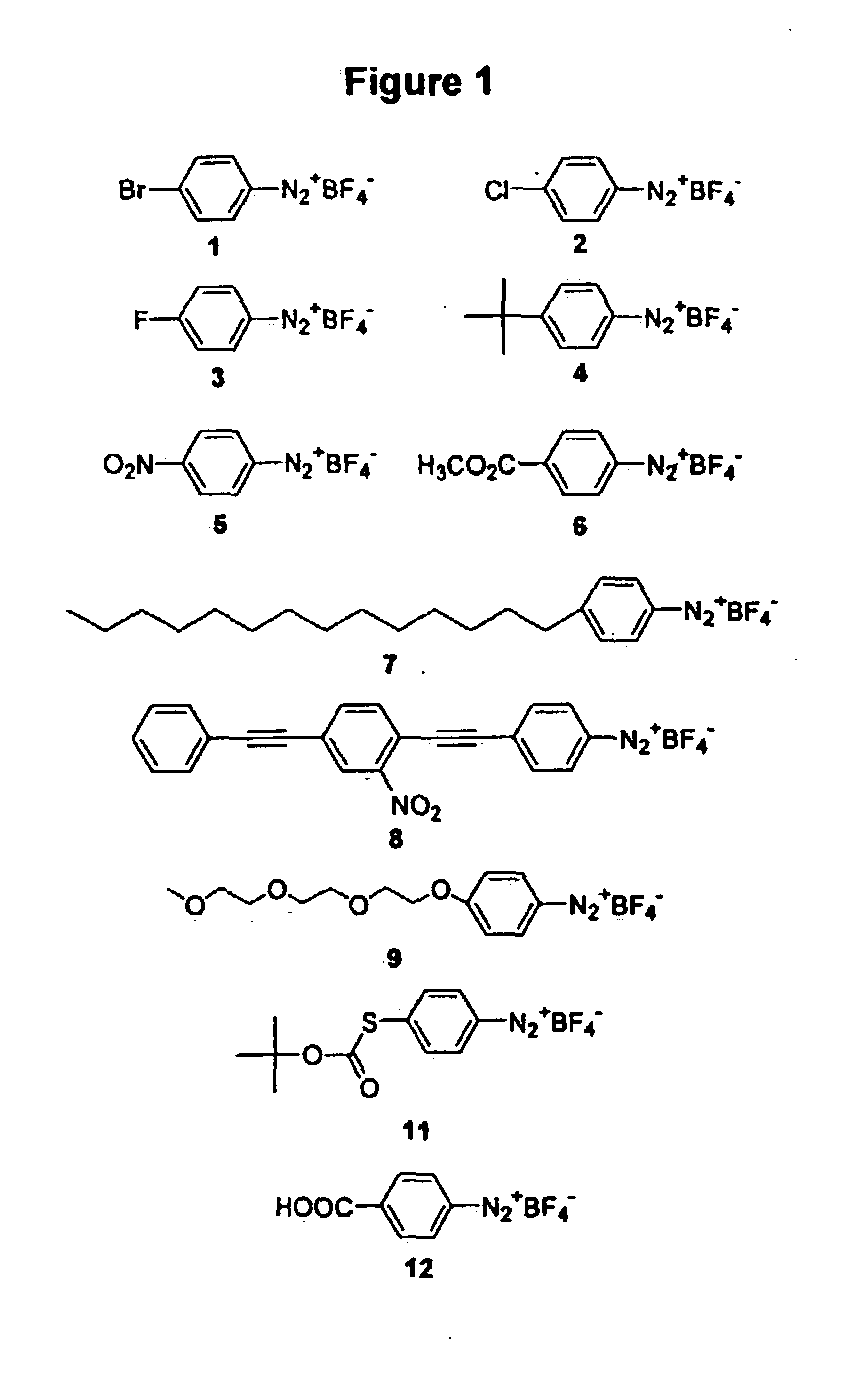
Preparation of diazo and diazonium compounds
A method for making diazo-compounds, diazonium salts thereof and other protected forms of these compounds. Diaz-compounds are prepared by reaction of a tertiary phosphine reagent carrying a reactive carbonyl group with an azide. The reaction can also generate an acyl triazene which can be converted thermally or by addition of base to form the diazo-compound or the acyl triazene can be isolated. The method is particularly useful for conversion of azides carrying one or more electron withdrawing groups to diazo-compounds. The method can be carried out in aqueous medium under mild conditions and is particularly useful for conversion of azido sugars to diazo-compound and diazonium salts thereof under physiological conditions. Tertiary phosphine reagents, particularly those that are water-soluble, and precursors for preparation of the reagents are provided.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
High metathesis activity ruthenium and osmium metal carbene complexes
InactiveUS20060241317A1Increase the probability of activationHighly active andRuthenium organic compoundsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsDepolymerizationElectron donor
Ruthenium and osmium carbene compounds that are stable in the presence of a variety of functional groups and can be used to catalyze olefin metathesis reactions on unstrained cyclic and acyclic olefins are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods of making the carbene compounds. The carbene compounds are of the formula where M is Os or Ru; R<1> is hydrogen; R is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, substituted or unsubstituted alkyl, and substituted or unsubstituted aryl; X and X<1> are independently selected from any anionic ligand; and L and L<1> are independently selected from any neutral electron donor. The ruthenium and osmium carbene compounds of the present invention may be synthesized using diazo compounds, by neutral electron donor ligand exchange, by cross metathesis, using acetylene, using cumulated olefins, and in a one-pot method using diazo compounds and neutral electron donors. The ruthenium and osmium carbene compounds of the present invention may be used to catalyze olefin metathesis reactions including, but not limited to, ROMP, RCM, depolymerization of unsaturated polymers, synthesis of telechelic polymers, and olefin synthesis.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method for synthesizing amino-substituted carbazole compound
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing an amino-substituted carbazole compound, belonging to the technical field of organic synthesis. According to key points of the technical scheme, the method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: dissolving 2-phenyl-3-cyanoindole compounds or 2-(thiazole-2-yl)-3-cyanoindole compounds and diazo compounds in a solvent; adding catalysts and additives, reacting at the temperature of 100-140 DEG C so as to obtain 6-aminobenzo[a]carbazole compounds or 5-aminothieno[a]carbazole compounds. The method disclosed by the invention starts from simple and easily prepared raw materials, the amino-substituted carbazole compounds are directly obtained by virtue of a one-pot cascade reaction, the synthetic process is easy and convenient to operate, the conditions are mild, and the method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Process for derivatizing carbon nanotubes with diazonium species and compositions thereof
The present invention specifically describes a new method for chemical modification of carbon nanotubes. Such methods involve the derivatization of multiwalled and single-walled carbon nanotubes, including small-diameter (about 0.7 nm) single-walled carbon nanotubes derivatized with diazo compounds. This method allows various organic compounds to be chemically attached to the sidewalls and ports of carbon nanotubes. Such chemically modified carbon nanotubes are used in polymer composites, molecular electronics and sensor elements. Derivatization methods include electrochemically induced reactions, thermally induced reactions (via in situ or pre-generated diazo compounds) and photochemically induced reactions. Derivatization significantly changes the spectral properties of the nanotubes. The functionality is estimated to be approximately one functional moiety for every 20-30 carbon atoms in the nanotube. Such electrochemical reduction methods can be used for site-selective chemical functionalization of nanotubes, and, after modification with appropriate chemical groups, derivatized nanotubes are chemically compatible with the polymer matrix, enabling nanotube properties (e.g., mechanical strength or conductivity) essentially translates into composite properties. Moreover, after modification of appropriate chemical genes, these chemical groups can be polymerized into polymers including carbon nanotubes.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Preparation Process Of Azo Pigment Dispersion
InactiveUS20080108736A1Reduce in quantityEasy to makeCoupling reaction in azo dyesInksPh bufferingSolvent
A process for preparing an azo pigment dispersion, comprising the step of causing a solution containing a diazonium compound to react with a solution containing a coupling agent to prepare an azo pigment dispersion in which an azo pigment is dispersed, wherein the reaction is carried out in the presence of a dispersing agent for dispersing the azo pigment in a solvent and a pH buffering agent having a buffering action under alkaline conditions.
Owner:CANON KK
3-hydroxyindole derivatives and synthesis method and use thereof
InactiveCN102070510AHigh selectivityAtom economy is highOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsOrganosolvEthyl acetate
The invention relates to 3-hydroxyindole derivatives, a synthesis method thereof and use thereof. The synthesis method of the 3-hydroxyindole derivatives comprises: dissolving alcohol, an isatin derivative, indiumbromide and a 4-angstrom molecular sieve in an organic solvent, refluxing at 40 DEG C, dripping organic solvent solution of a diazo compound, stirring, removing solvent to obtain a coarse product, and obtaining the 3-hydroxyindole derivatives by column chromatography in solution of ethyl acetate and petroleum ether in a volume ratio of 1:20 to 1:5. In the method, the molar ratio of the diazo compound to the alcohol to the isatin derivative, to the indiumbromide is 2:2:1:0.2, and the added amount per millimol of the 4-angstrom molecular sieve is 4 grams. The synthesis method for preparing the series of 3-hydroxyindole derivatives with diastereoselectivity by one step has the advantages of high atom economy, high selectivity and high yield, the cost of a catalyst is low, and the operation is simple and safe. The 3-hydroxyindole derivatives prepared in the invention has high anticancer activity and can be widely used in medical and chemical fields.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Recording layer with organic dye-in-polymer (DIP) medium for write-once-read-many (WORM) optical discs with fluorescent reading
InactiveUS7094517B1High densityIncrease speedRadiation applicationsLayered productsCelluloseQuantum yield
High sensitive organic dye-in-polymer (DIP) medium for write-once-read-many (WORM) optical discs with fluorescent reading. The medium consists of a fluorescent color means, capable of absorbing writing radiation produced by a laser, a compound capable of generating free radicals upon influence of heat produced by the writing radiation and a polymer capable of producing a translucent film enabling high quantum yield of the fluorescence induced in the color means. The color means can be selected from xanthene dyes of the eosine and rhodamine groups, acridine, oxazine, azine, peylene, violanthrone, cyanine, phtalocyanine, indigoide colors and porphyries. The free radicals generating compound can be chosen from the group of compounds comprising azo and diazoi compounds or peroxyde compounds. The film producing polymer can be selected from the group of compounds comprising cellulose ethers, vinyl resins or acrylic resins.
Owner:D DATA
Azo and diaza derivatives and uses thereof in phototherapy
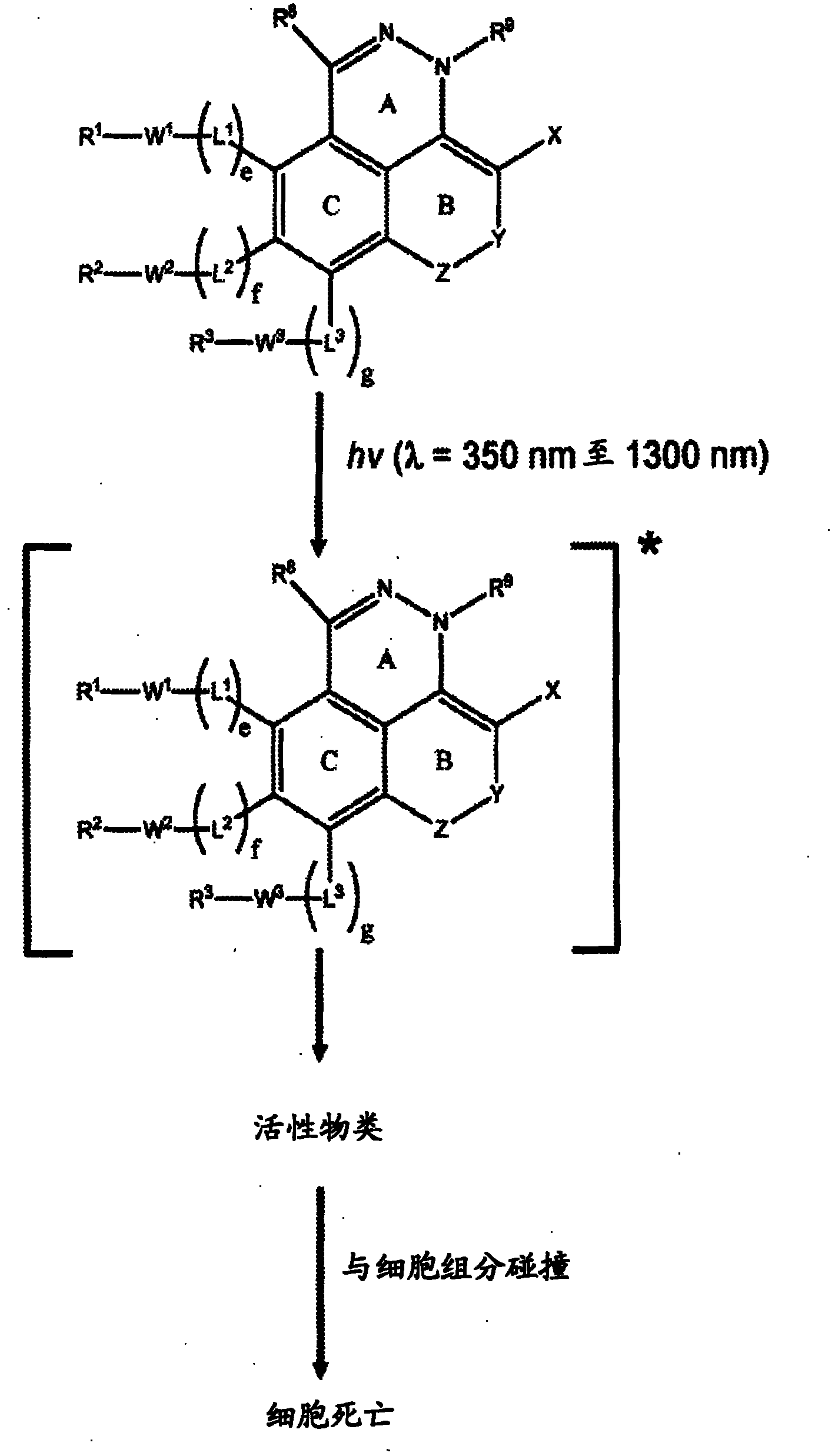
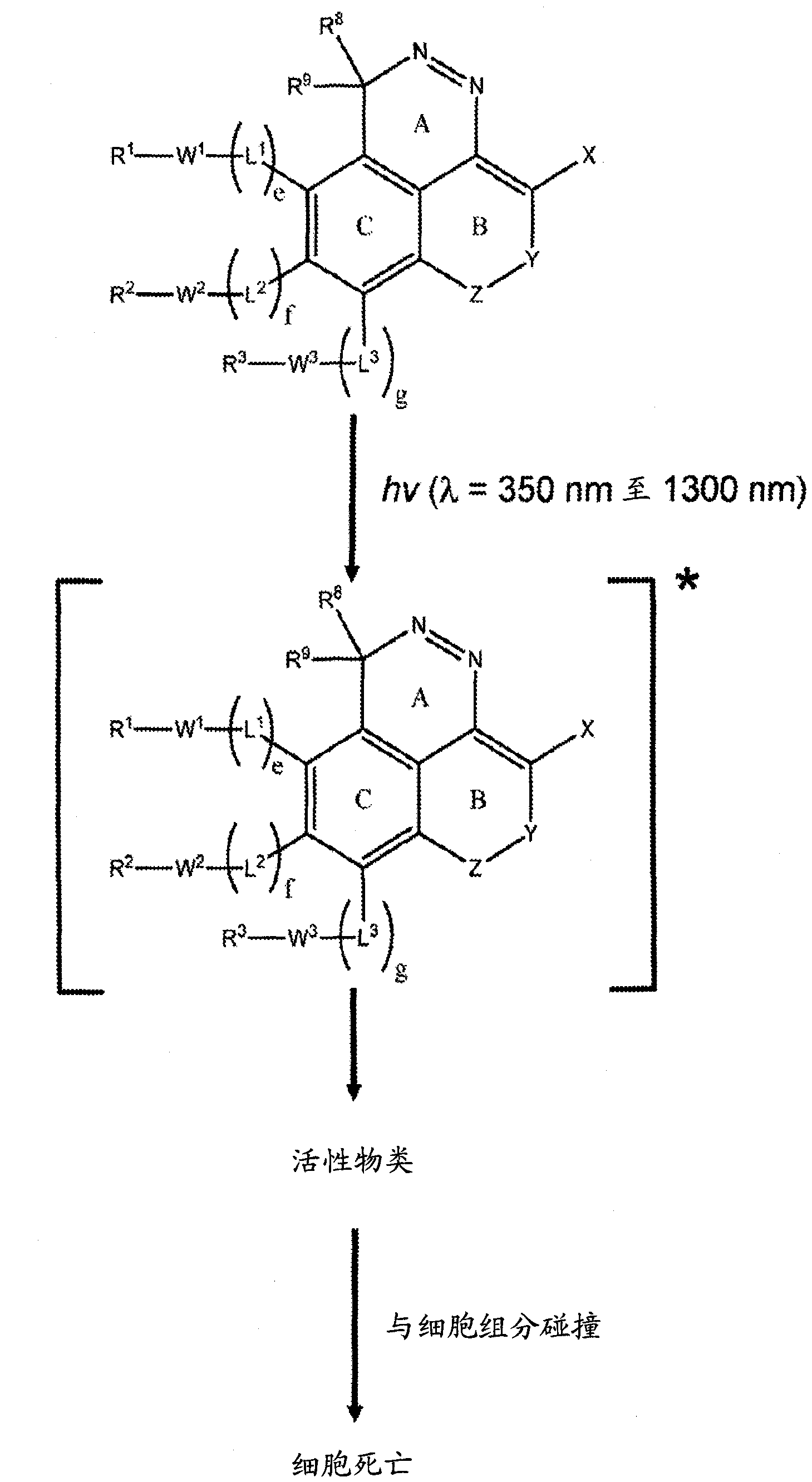
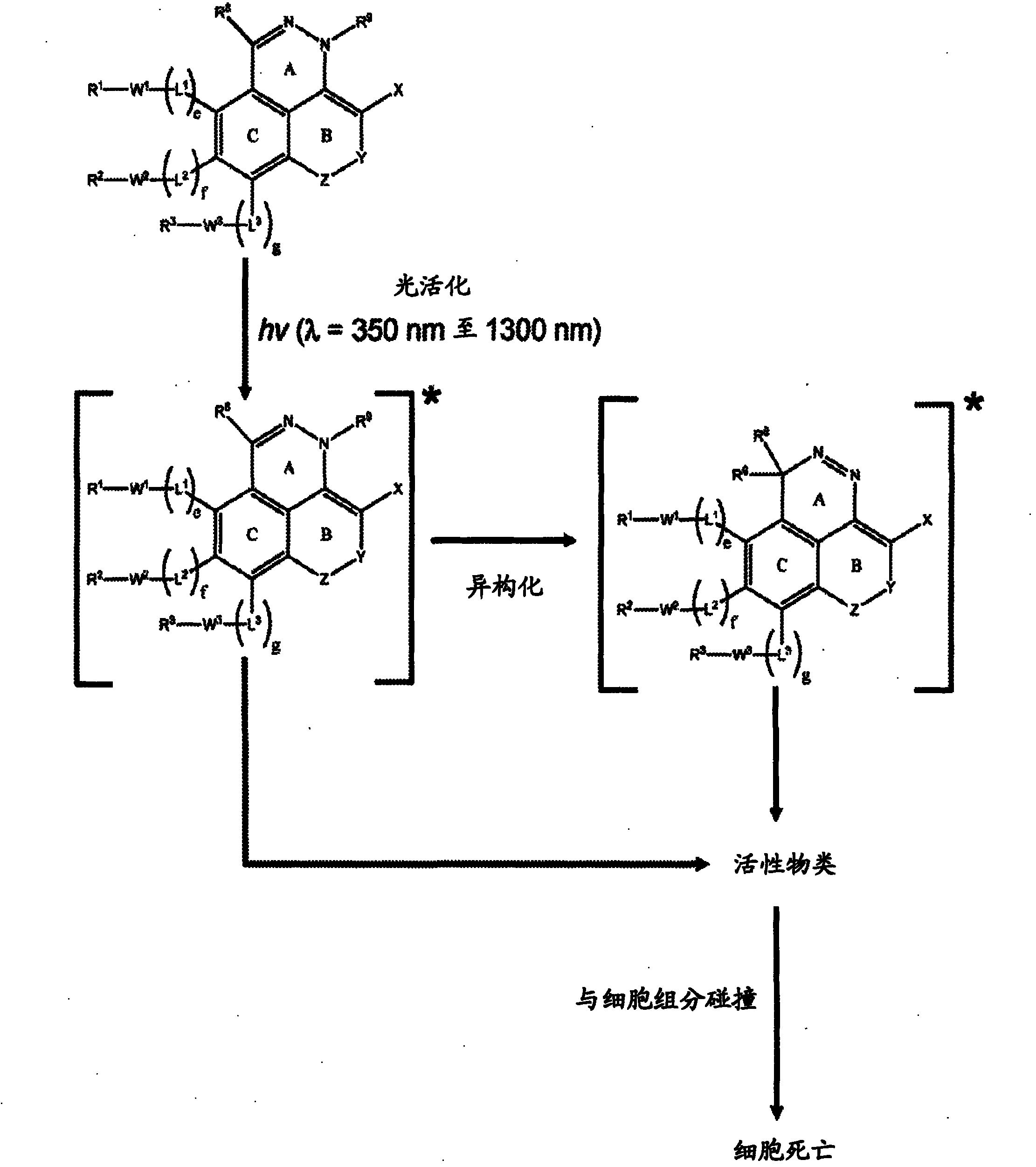
InactiveCN102046632AOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryElectromagnetic spectrumElectromagnetic radiation
The invention relates generally to optical agents, including Type 1 phototherapeutic agents, for biomedical applications, such as phototherapy. Provided are fused ring azo and diaza compounds comprising a plurality of fused rings including a first ring having an intra-ring azo or intra-ring diaza group capable of activation upon exposure to electromagnetic radiation in visible and / or infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Optical agents of the invention enable a versatile phototherapy platform for treatment of a range of pathological conditions, including the treatment of cancers, stenosis and inflammation. The invention further provides preparations and formulations comprising the fused ring azo and diaza compounds and methods of making and using the fused ring azo and diaza compounds as optical agents in in vivo or ex vivo biomedical procedures.
Owner:MALLINCKRODT INC
Reagents and methods for esterification
ActiveUS9790483B2Facilitate labeling and cell targeting and cell penetrationCarbamic acid derivatives preparationThiol preparationHydrogenOrganic group
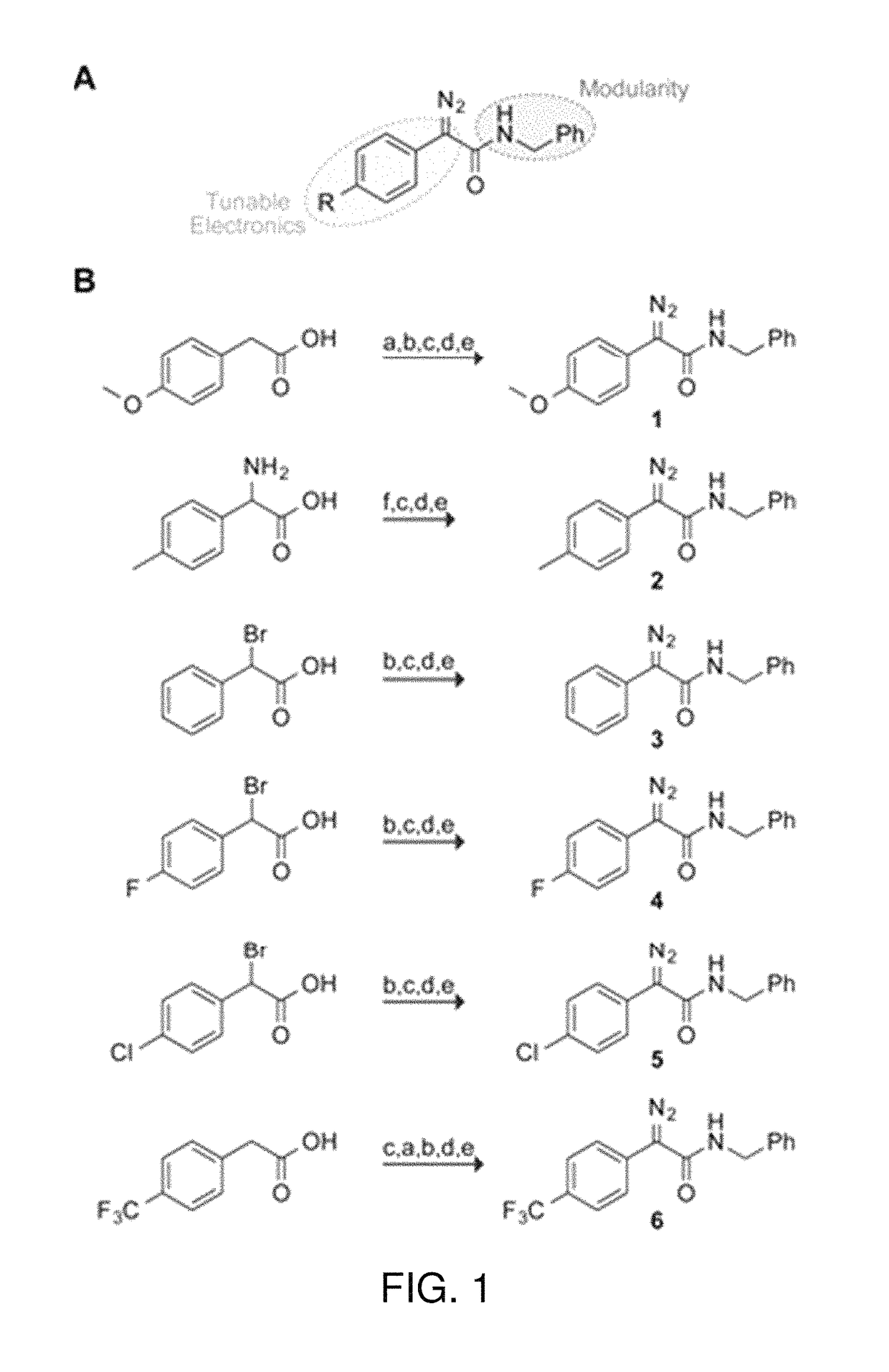
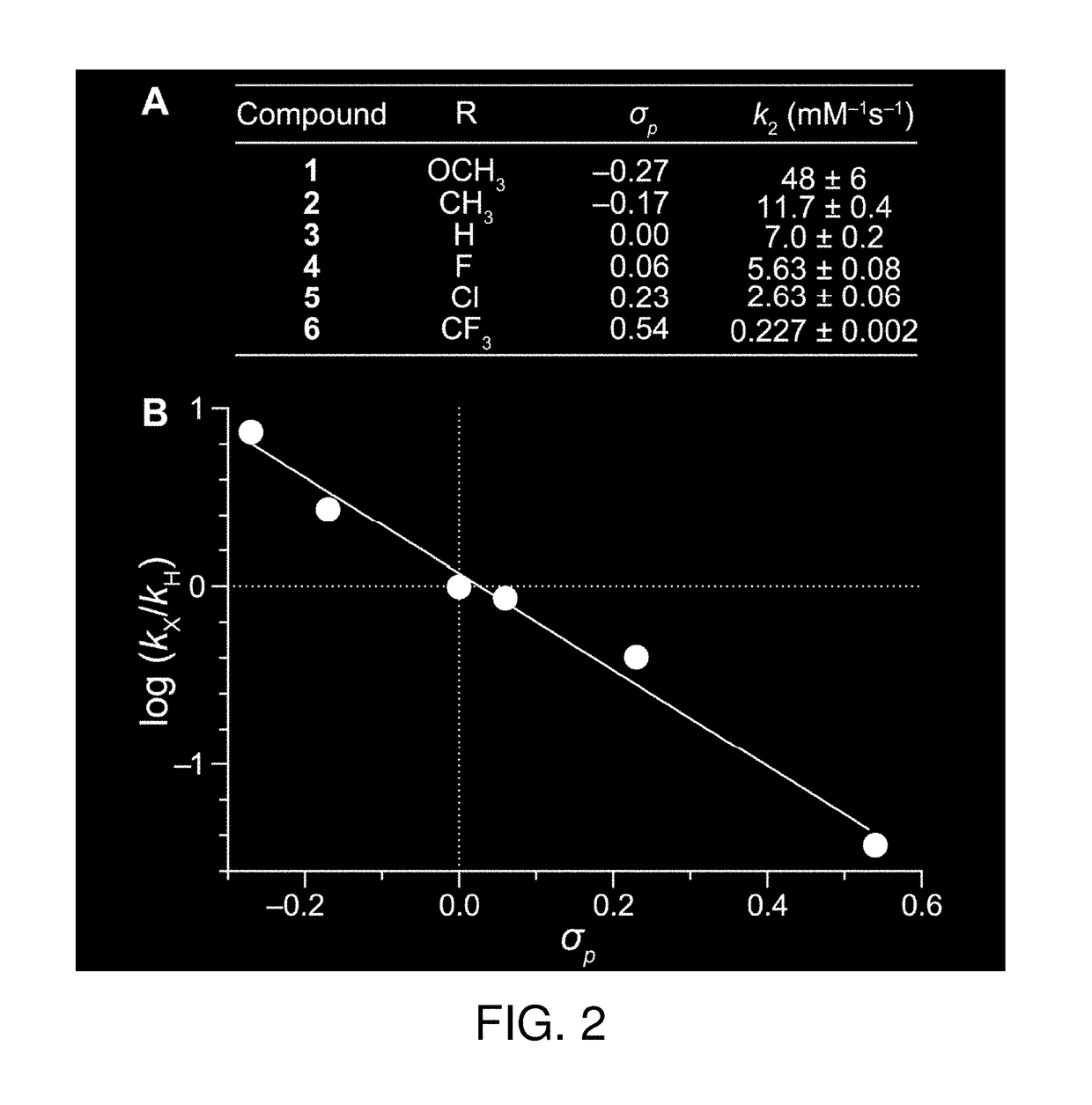
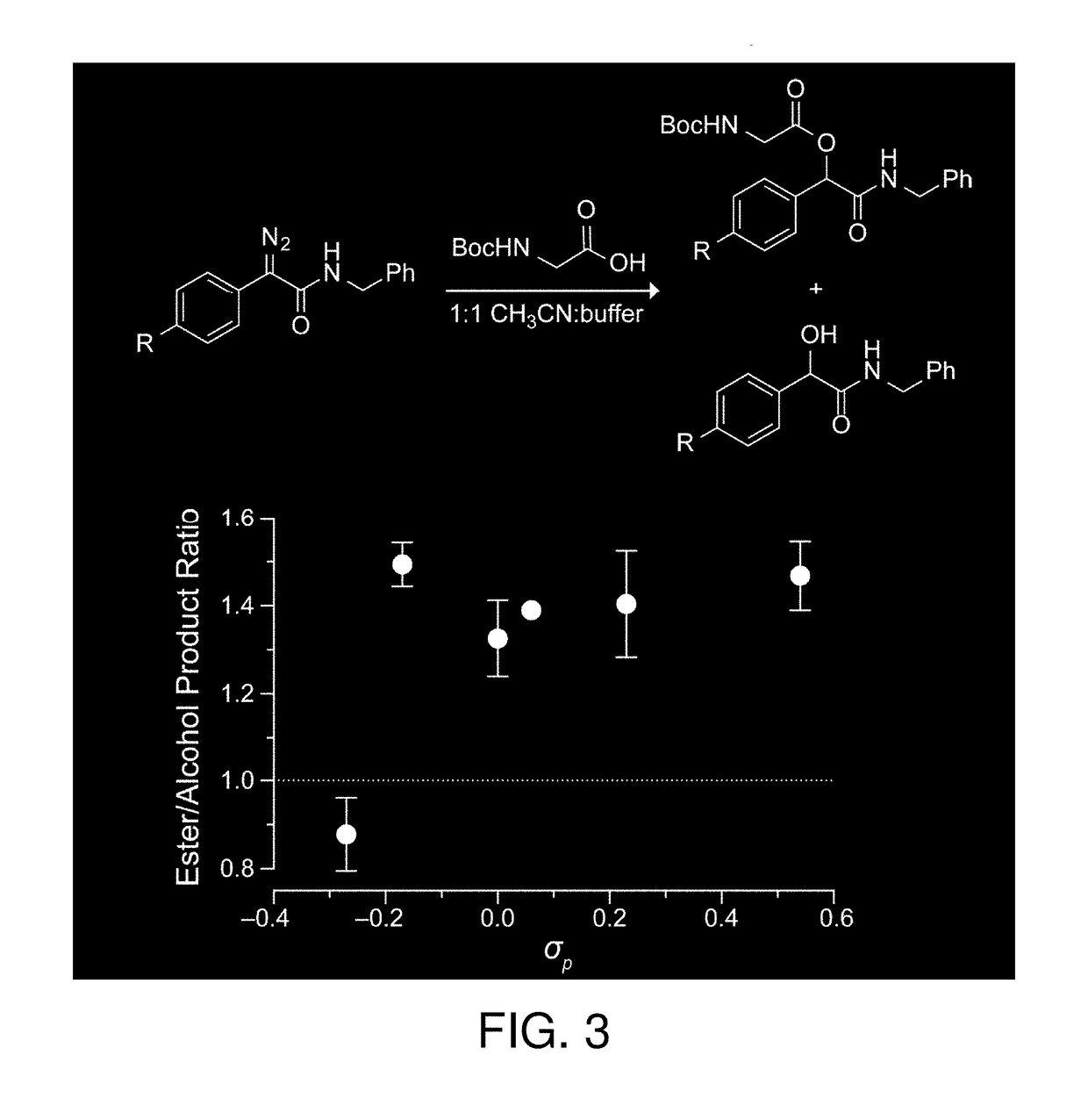
Methods and reagents for esterification of biological molecules including proteins, polypeptides and peptides. Diazo compounds of formula I:where R is hydrogen, an alkyl, an alkenyl or an alkynyl, RA represents 1-5 substituents on the indicated phenyl ring and RM is an organic group, which includes a label, a cell penetrating group, a cell targeting group, or a reactive group or latent reactive group for reaction to bond to a label, a cell penetrating group, or a cell targeting group, among other organic groups are useful for esterification of biological molecules. Also provided are diazo compounds which are bifunctional and trifunctional coupling reagents as well as reagents for the synthesis of compounds of formula I.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Isoquinoline compound as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN113698399AAntiproliferative activityThe reaction system is simple and safeOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsBenzoic acidChemical synthesis
The invention discloses an isoquinoline compound as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and relates to the technical field of chemical synthesis. The isoquinoline compound is an indolo [2, 1-a] isoquinoline compound or a benzimidazo [2, 1-a] isoquinoline-6 (5H) ketone compound, and the preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving a 1-(2, 3-diphenyl-1H-indole-1-yl)-2-methyl propenyl-1-ketone compound or a 1-methyl acryloyl-2-aryl-benzimidazole compound and an S-phenyl phenyl thiosulfonate compound in an organic solvent, adding tert-butyl benzoate oxide and a catalytic amount of copper bromide, and reacting at 110 DEG C to obtain the isoquinoline compound. The synthesis process does not need diazo compounds, has the characteristics of cheap and easily available raw materials, mild reaction conditions, simplicity and convenience in operation, high regioselectivity and high yield, and is beneficial to industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG PROVINCIAL PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com


![Synthetic method for aromatic[a]carbazole compounds Synthetic method for aromatic[a]carbazole compounds](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/1ceef379-c79e-4323-87be-5b6f2e922b79/BDA0001160801260000011.png)
![Synthetic method for aromatic[a]carbazole compounds Synthetic method for aromatic[a]carbazole compounds](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/1ceef379-c79e-4323-87be-5b6f2e922b79/BDA0001160801260000021.png)
![Synthetic method for aromatic[a]carbazole compounds Synthetic method for aromatic[a]carbazole compounds](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/1ceef379-c79e-4323-87be-5b6f2e922b79/BDA0001160801260000022.png)