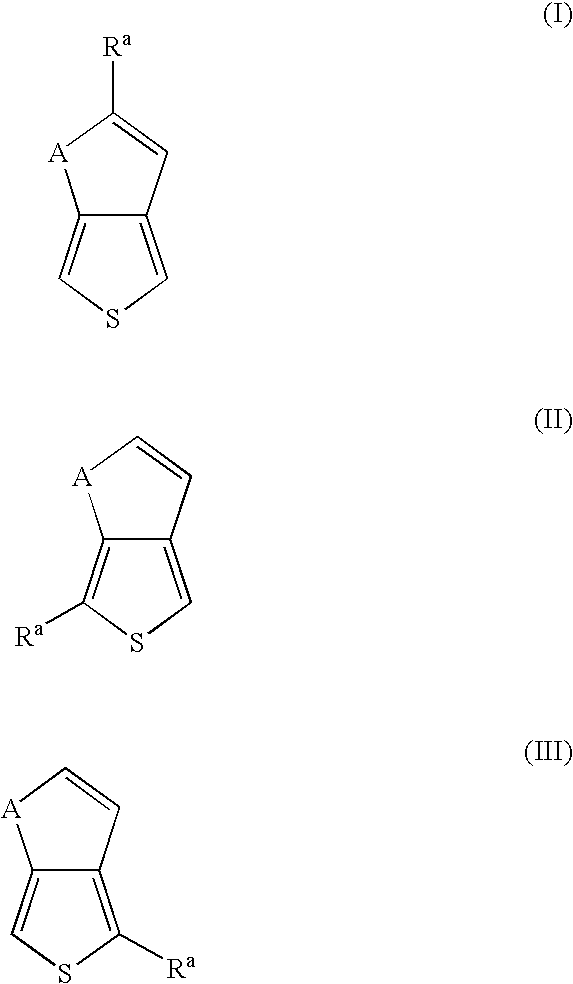
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
647 results about "Electromagnetic spectrum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
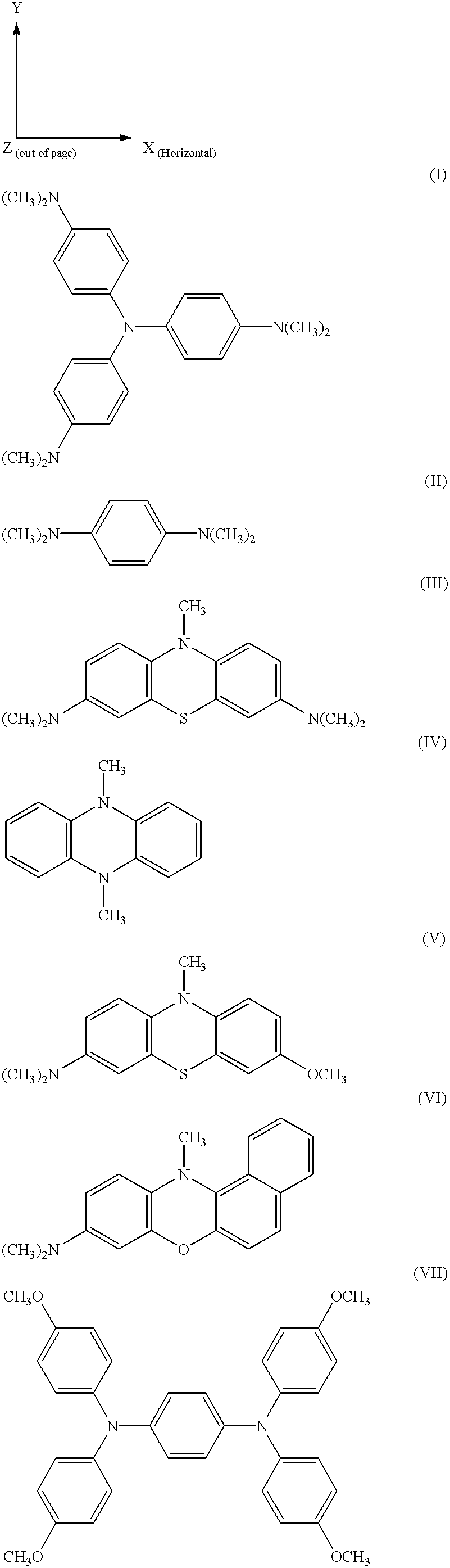
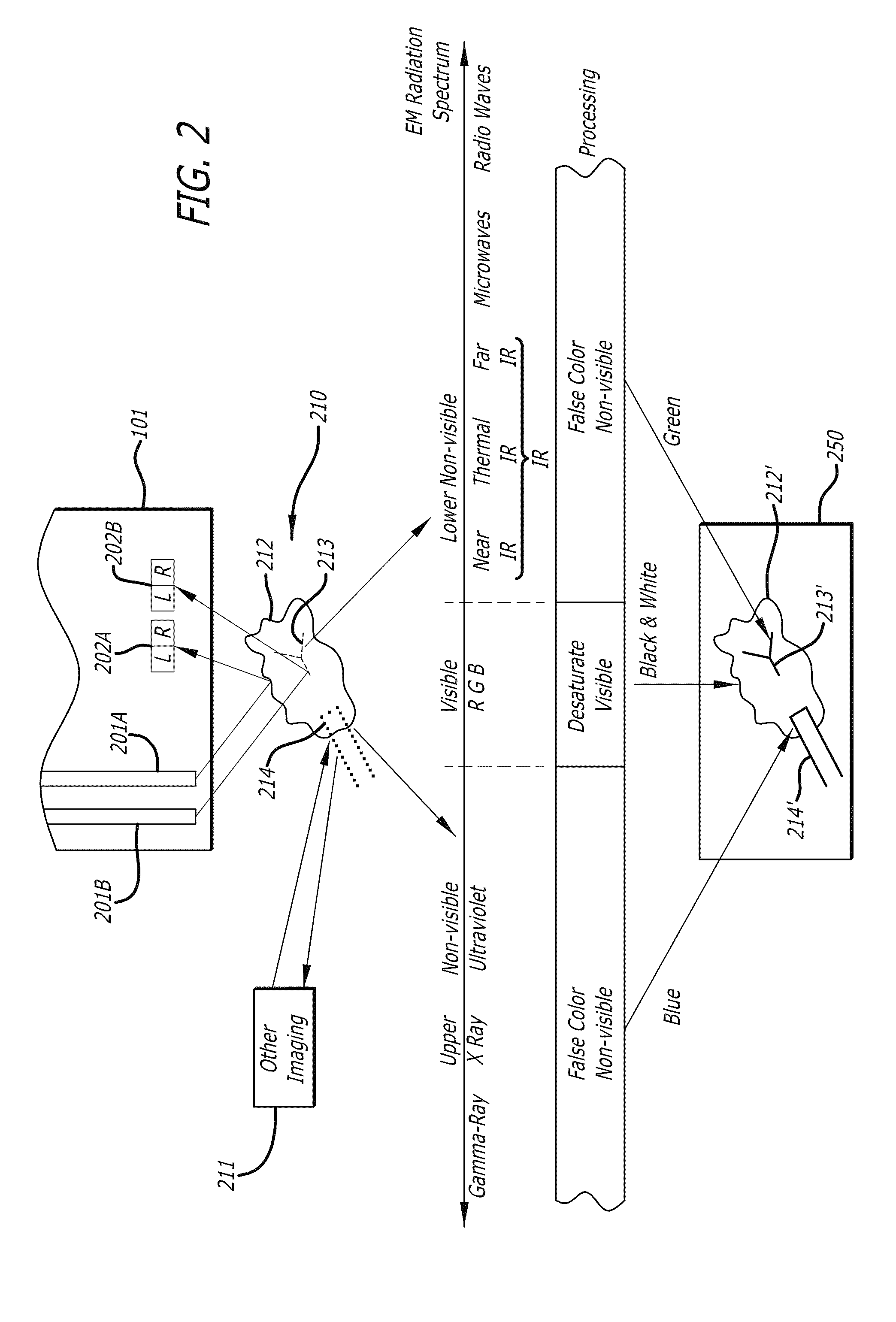
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of frequencies (the spectrum) of electromagnetic radiation and their respective wavelengths and photon energies. The electromagnetic spectrum covers electromagnetic waves with frequencies ranging from below one hertz to above 10²⁵ hertz, corresponding to wavelengths from thousands of kilometers down to a fraction of the size of an atomic nucleus. This frequency range is divided into separate bands, and the electromagnetic waves within each frequency band are called by different names; beginning at the low frequency (long wavelength) end of the spectrum these are: radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays at the high-frequency (short wavelength) end. The electromagnetic waves in each of these bands have different characteristics, such as how they are produced, how they interact with matter, and their practical applications. The limit for long wavelengths is the size of the universe itself, while it is thought that the short wavelength limit is in the vicinity of the Planck length. Gamma rays, X-rays, and high ultraviolet are classified as ionizing radiation as their photons have enough energy to ionize atoms, causing chemical reactions.
Photoluminescent fibers, compositions and fabrics made therefrom
Disclosed are photoluminescent fibers containing photoluminescent phosphorescent materials and photoluminescent fluorescent materials whose emission signature lies partly or fully in the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum. Also disclosed are the use of the inventive fibers, fabrics made therefrom, and objects containing the fiber.
Owner:PERFORMANCE INDICATOR LLC
Near infrared-absorbing electrochromic compounds and devices comprising same
InactiveUS6193912B1Efficient NIR absorberImproved and more intense NIR activityTenebresent compositionsNon-linear opticsElectricityNear infrared absorption
Electrochromic compounds capable of reversibly attenuating the transmittance of the near infrared portion of the electromagnetic spectrum are provided. These compounds exhibit an energy difference between the singly occupied molecular orbital (SOMO) energy and the highest doubly occupied molecular orbital (HDOMO) energy (ESOMO-EHDOMO) of less than about 3.6 eV. In addition, these compounds have a transition moment of the configuration made up of the HDOMO and SOMO that is "long axis polarized".
Owner:GENTEX CORP
Driver health and fatigue monitoring system and method using optics
Method and arrangement for optically monitoring a driver of a vehicle in which a portion of the driver is illuminated with electromagnetic radiation in an infrared portion of the electromagnetic spectrum using at least one illumination device, images of the illuminated driver are obtained using at least one image obtaining device and the images are analyzed to derive a measure of flow of blood in at least one blood vessel, capillary and vein in the face of the occupant. The blood flow over time is analyzed to determine whether the driver has lost the ability to continue to control the vehicle. The loss of ability to continue to control the vehicle exemplifies the driver becoming drowsy, falling asleep or otherwise being incapable of controlling the vehicle after initially having been awake or otherwise capable of controlling the vehicle.
Owner:AMERICAN VEHICULAR SCI
Processing multi-aperture image data
InactiveUS20130033579A1Provide controlFunction increaseTelevision system detailsImage enhancementElectromagnetic spectrumComputer science
A method and a system for processing multi-aperture image data is described wherein the method comprises: capturing image data associated of one or more objects by simultaneously exposing an image sensor in an imaging system to spectral energy associated with at least a first part of the electromagnetic spectrum using at least a first aperture and to spectral energy associated with at least a second part of the electromagnetic spectrum using at least a second aperture; generating first image data associated with said first part of the electromagnetic spectrum and second image data associated with said second part of the electro-magnetic spectrum; and, generating depth information associated with said captured image on the basis of first sharpness information in at least one area of said first image data and second sharpness information in at least one area of said second image data.
Owner:DUAL APERTURE INT
Systems and methods for combining virtual and real-time physical environments
Systems, methods and structures for combining virtual reality and real-time environment by combining captured real-time video data and real-time 3D environment renderings to create a fused, that is, combined environment, including capturing video imagery in RGB or HSV / HSV color coordinate systems and processing it to determine which areas should be made transparent, or have other color modifications made, based on sensed cultural features, electromagnetic spectrum values, and / or sensor line-of-sight, wherein the sensed features can also include electromagnetic radiation characteristics such as color, infra-red, ultra-violet light values, cultural features can include patterns of these characteristics, such as object recognition using edge detection, and whereby the processed image is then overlaid on, and fused into a 3D environment to combine the two data sources into a single scene to thereby create an effect whereby a user can look through predesignated areas or “windows” in the video image to see into a 3D simulated world, and / or see other enhanced or reprocessed features of the captured image.
Owner:BACHELDER EDWARD N +1
Multispectral data acquisition system and method
InactiveUS7298869B1Increase speedEasy to analyzeInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlTerrainGyroscope
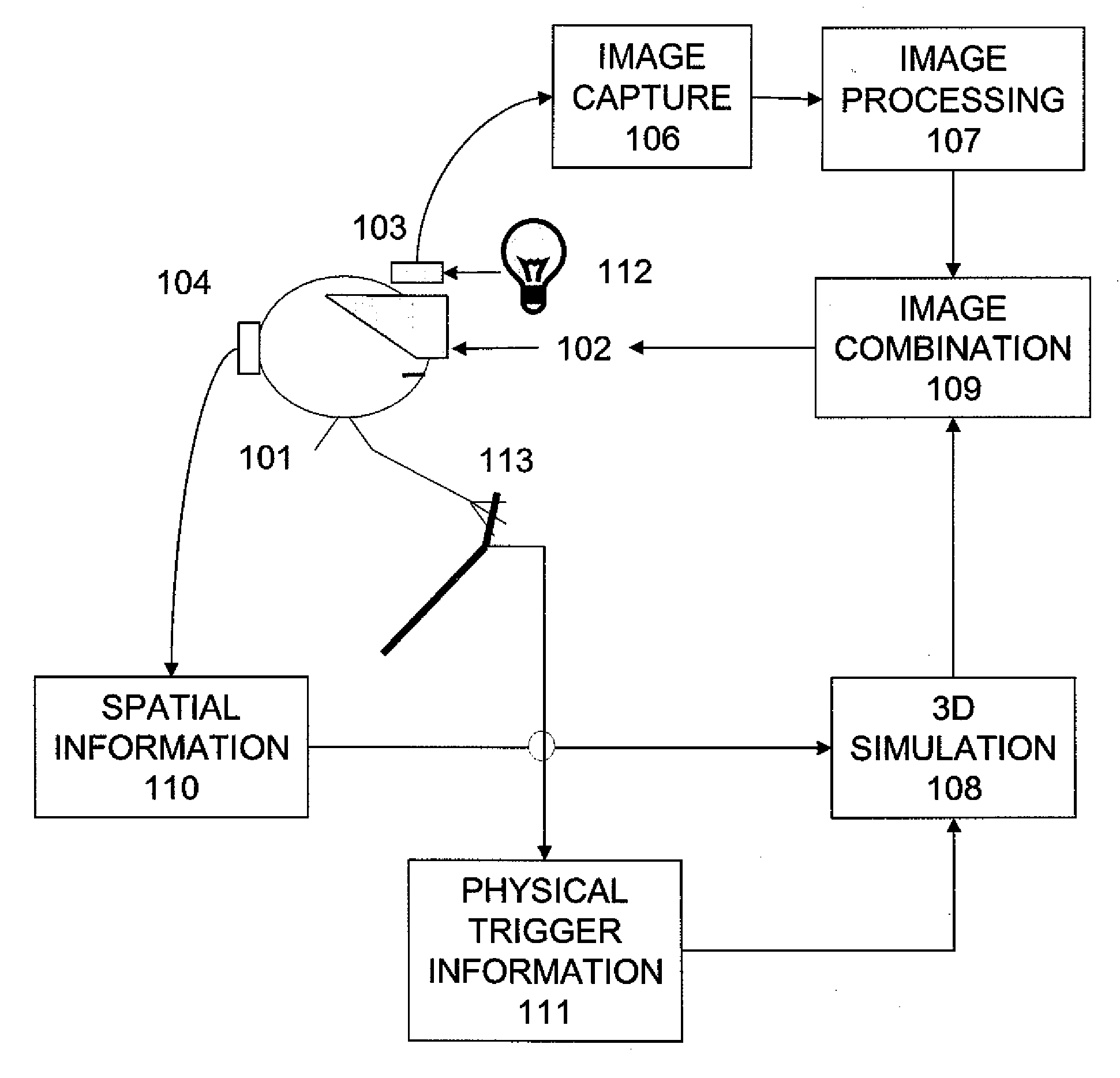
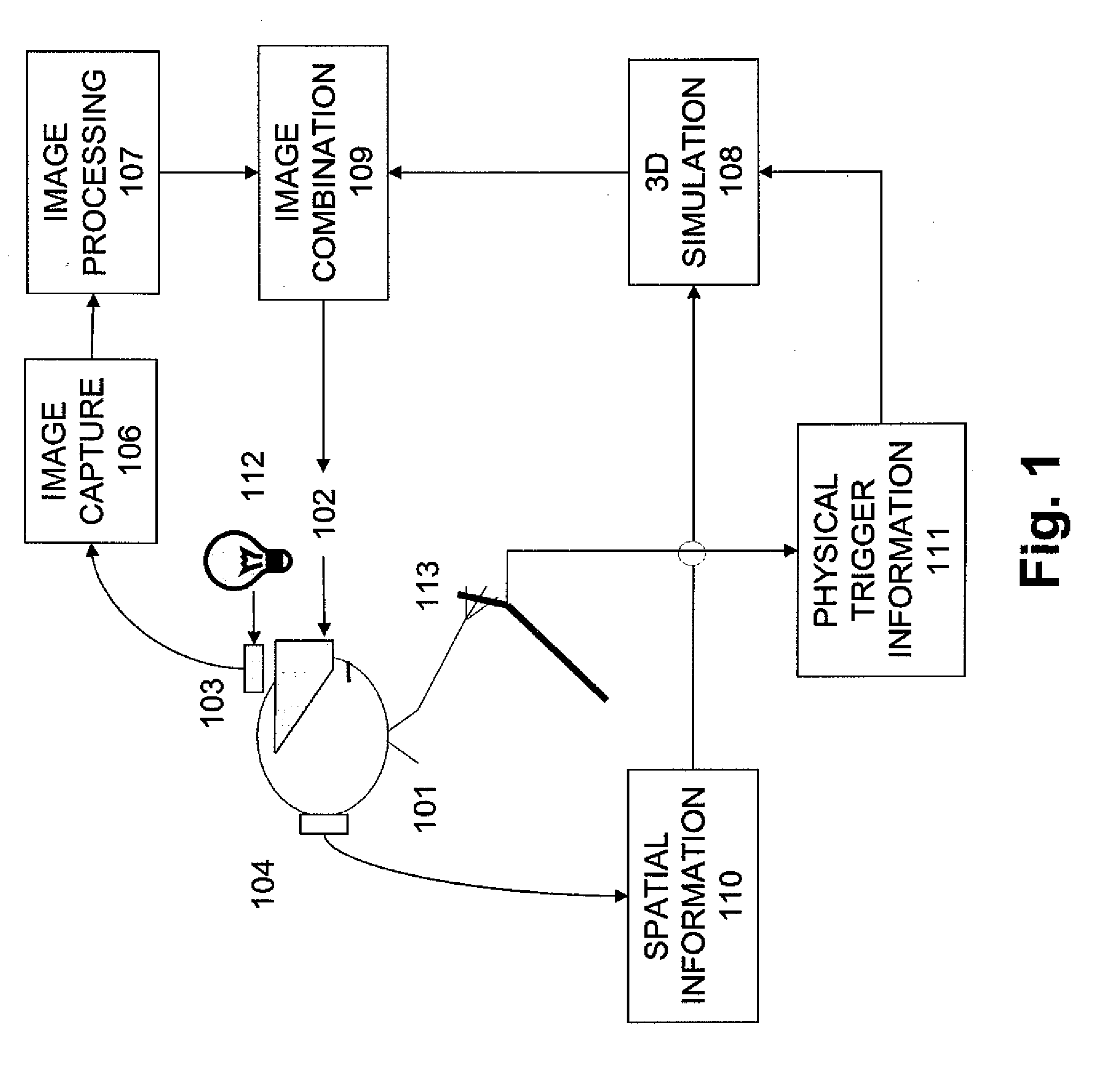
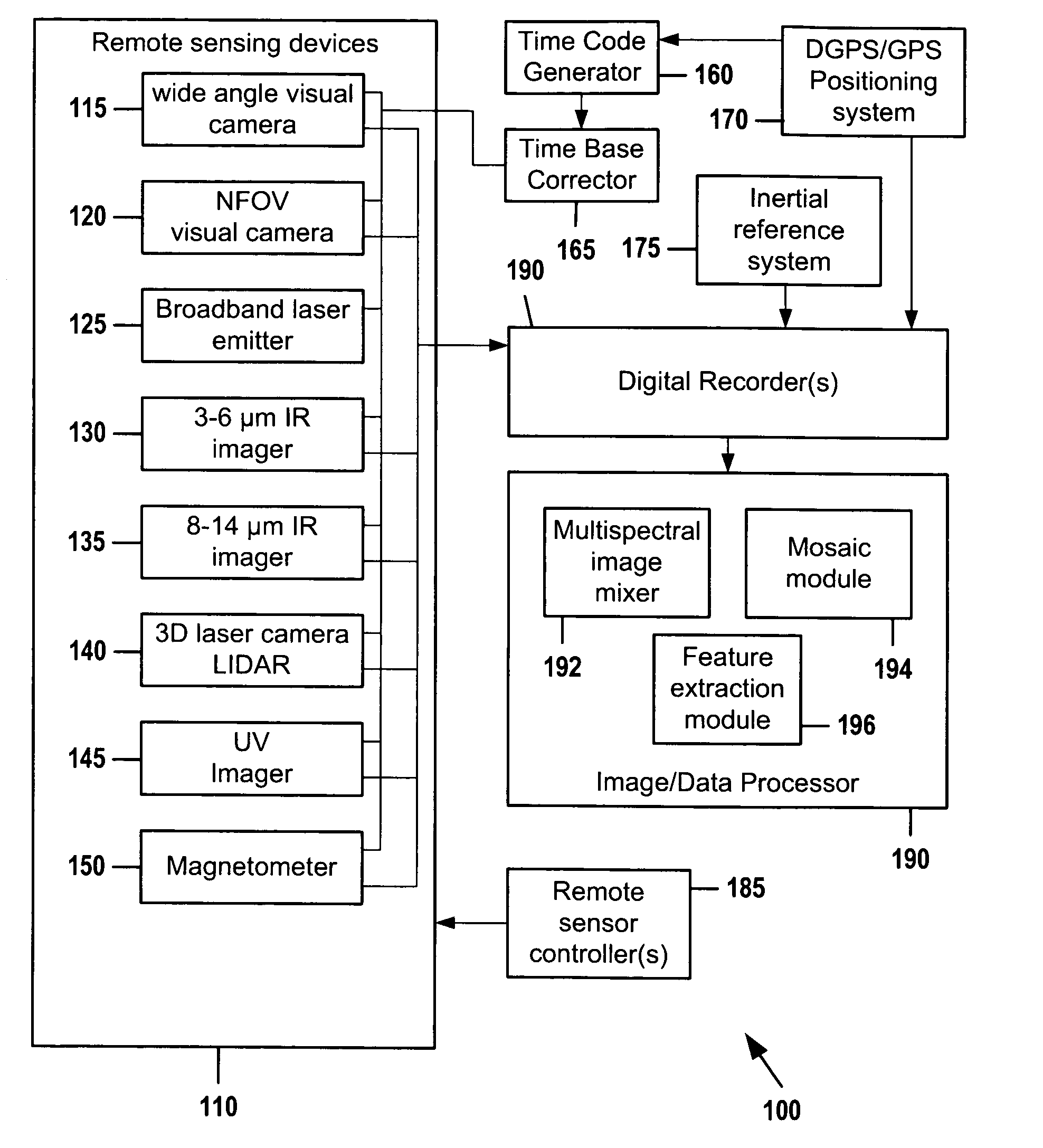
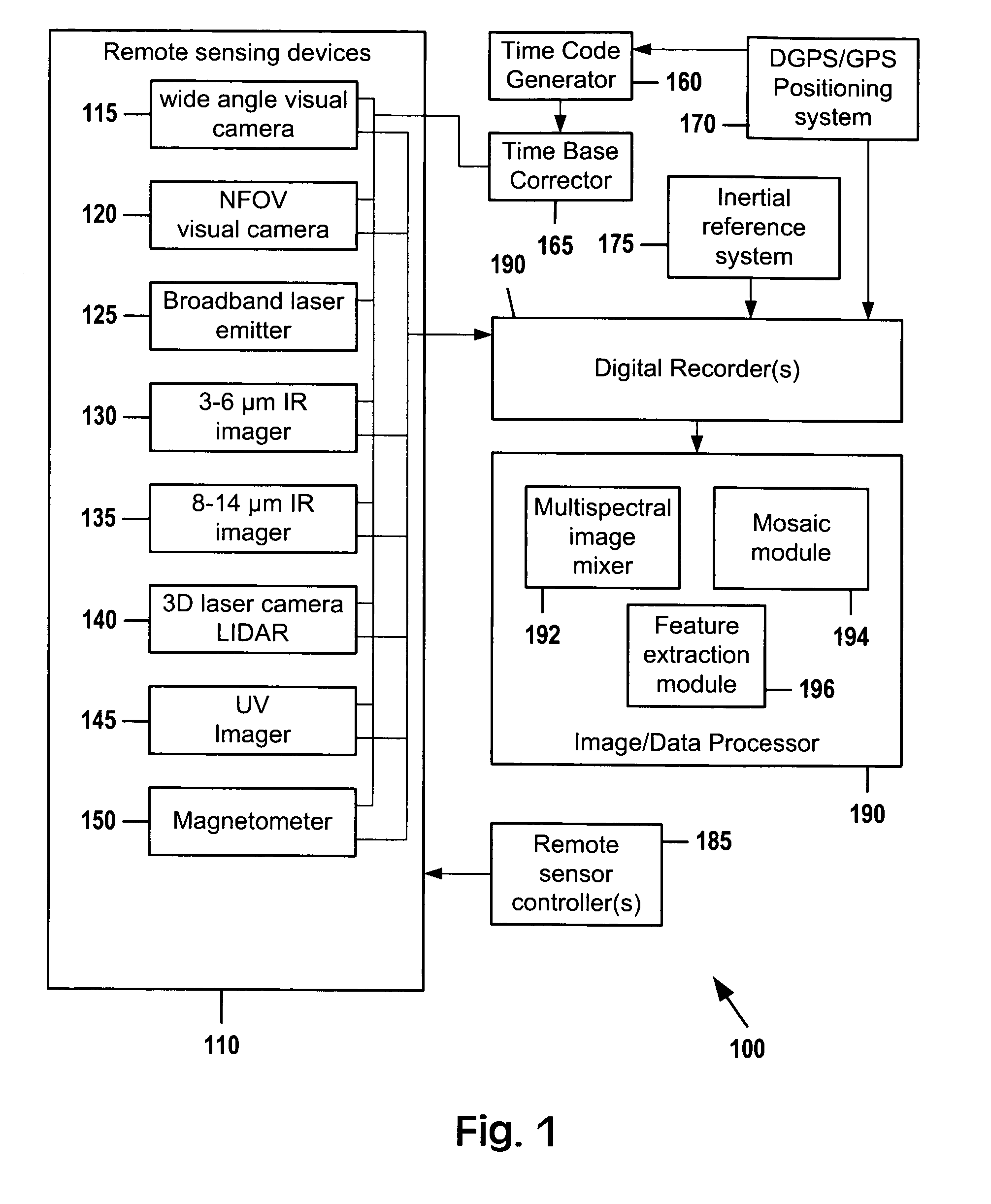
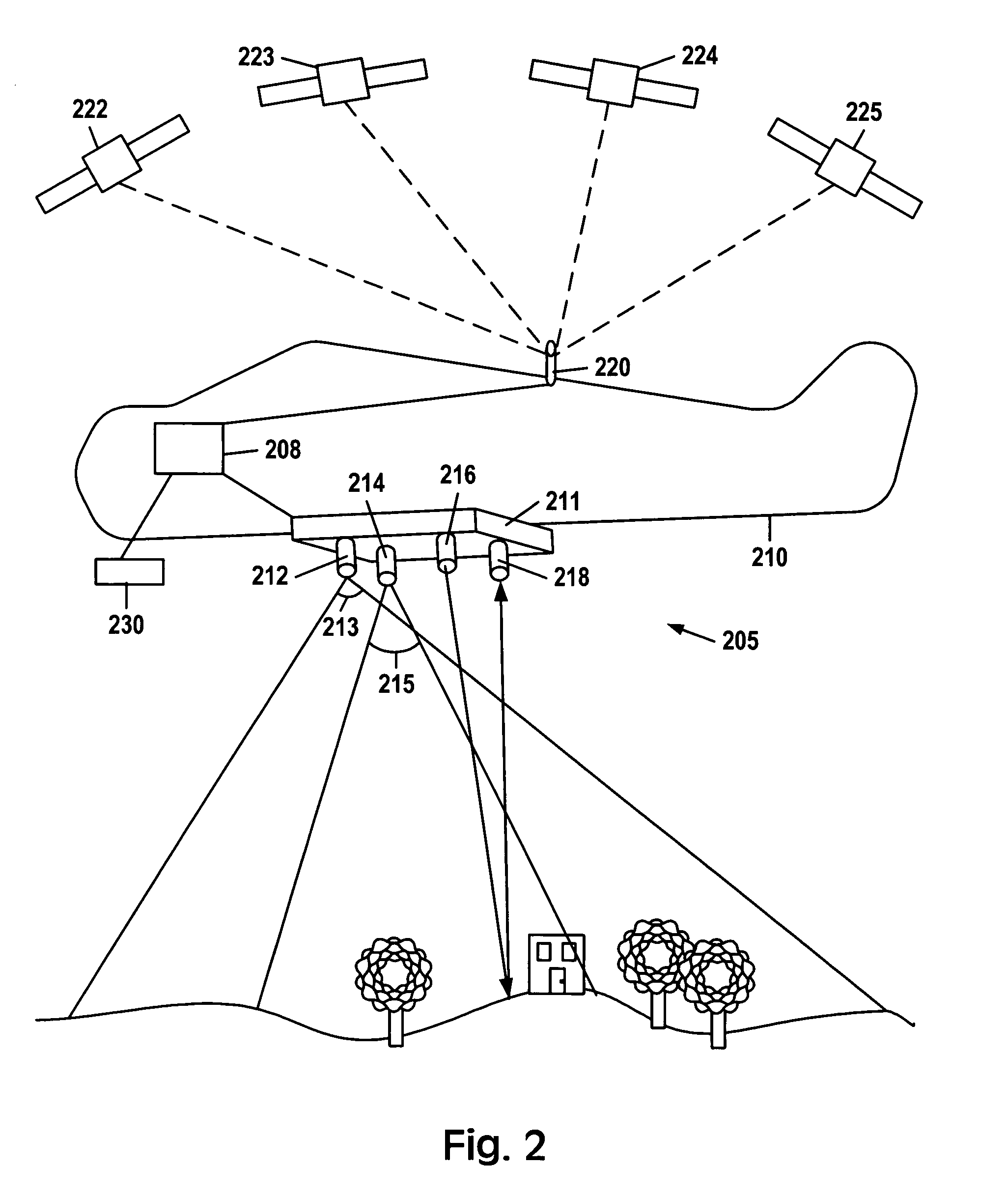
A portable multispectral data acquisition system for use on a vehicle such as an aircraft comprises a plurality of gyroscope-stabilized remote sensing devices synchronized to simultaneously capture images of a common spatial area in both visible and invisible bands of the electromagnetic spectrum, a computer and digital recorder to record and correlate the captured images with temporospatial reference information, image processing software to stack or layer the images and to extract and compare the images in order to identify and filter hidden or subsurface anomalies that are invisible to the naked eye, and additional image processing software to orthorectify the images to a three-dimensional digital terrain map and to stitch adjacent images together into a mosaic. Methods for using the portable multispectral data acquisition system are also provided.
Owner:ABERNATHY DONALD A
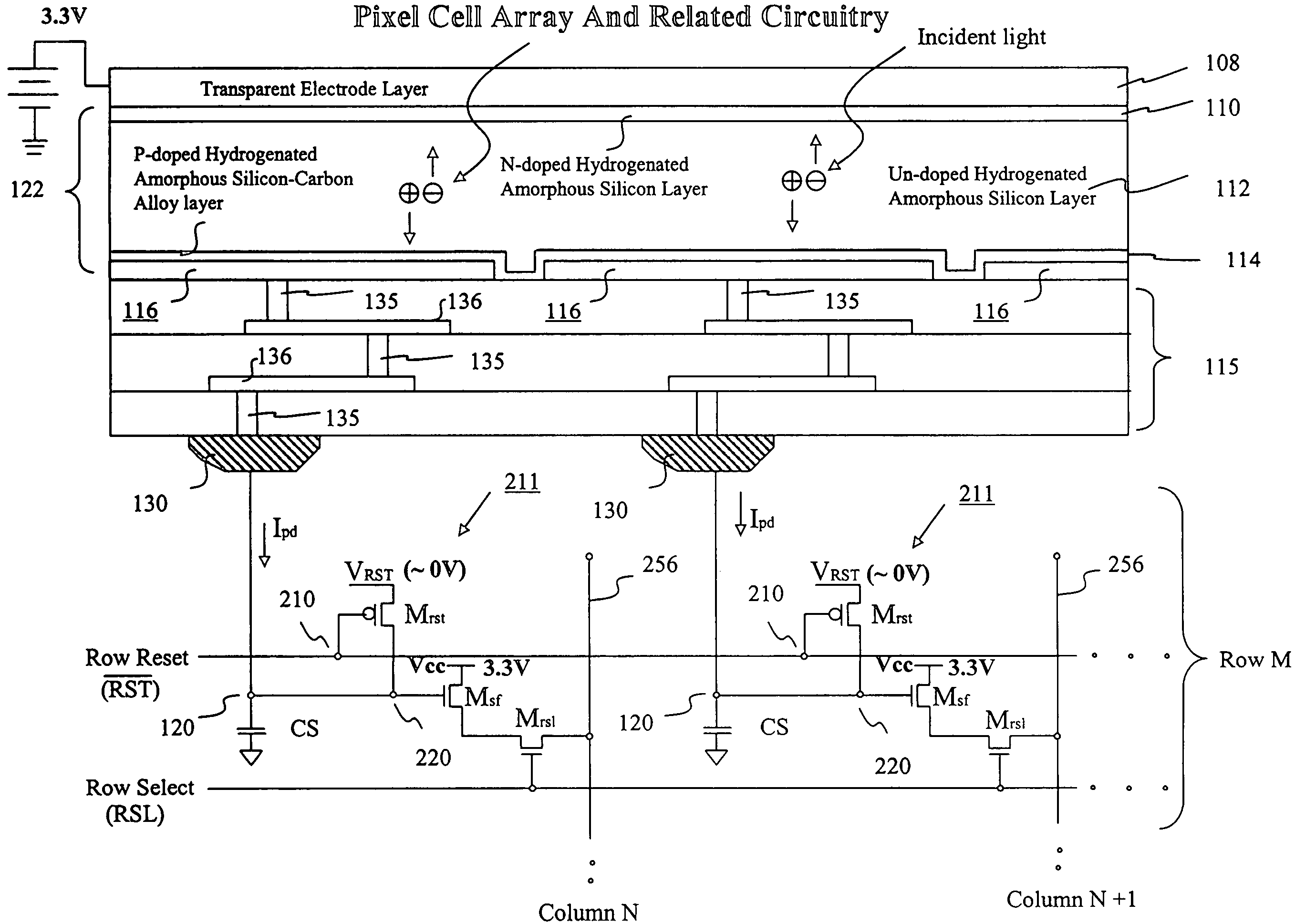
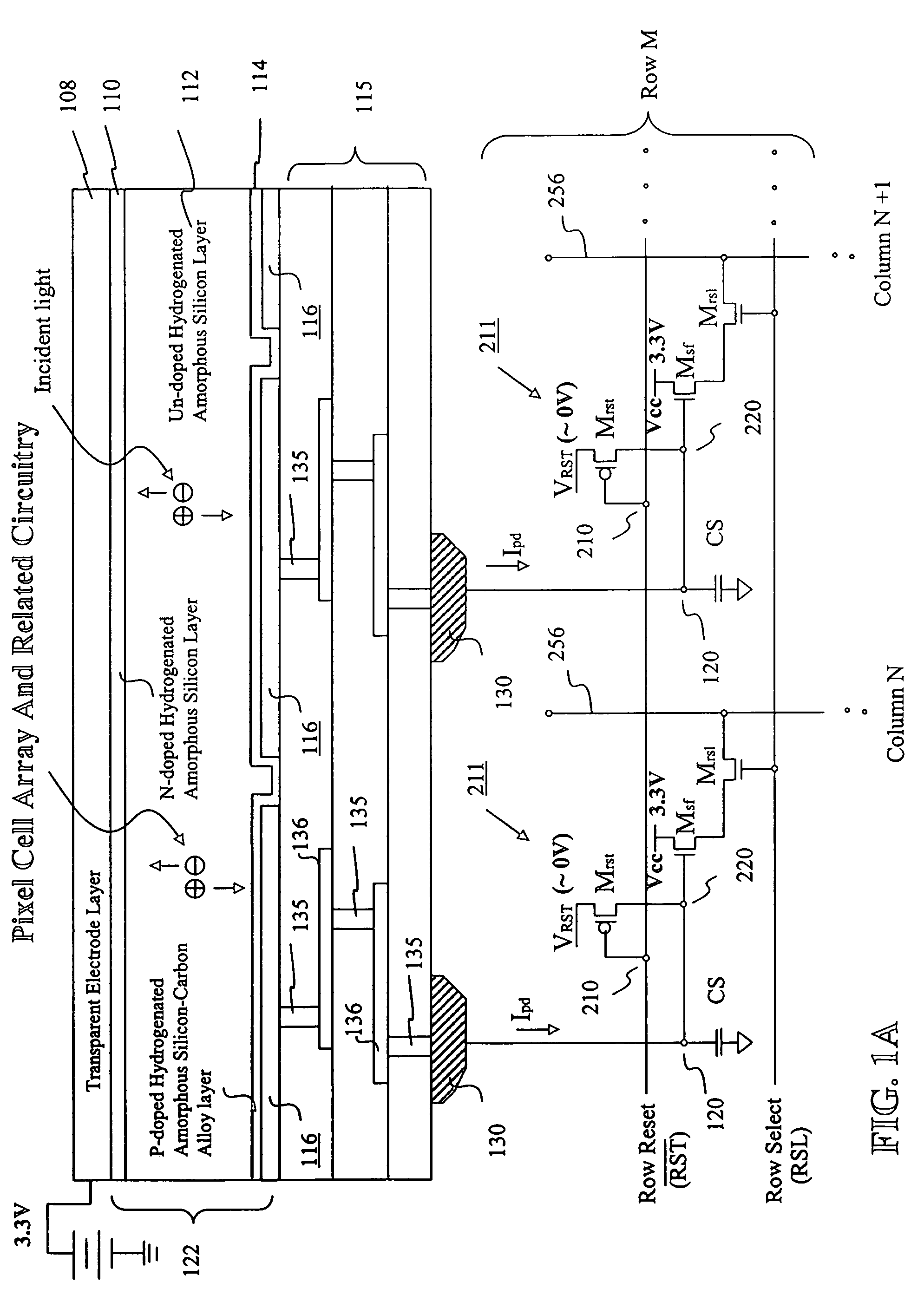
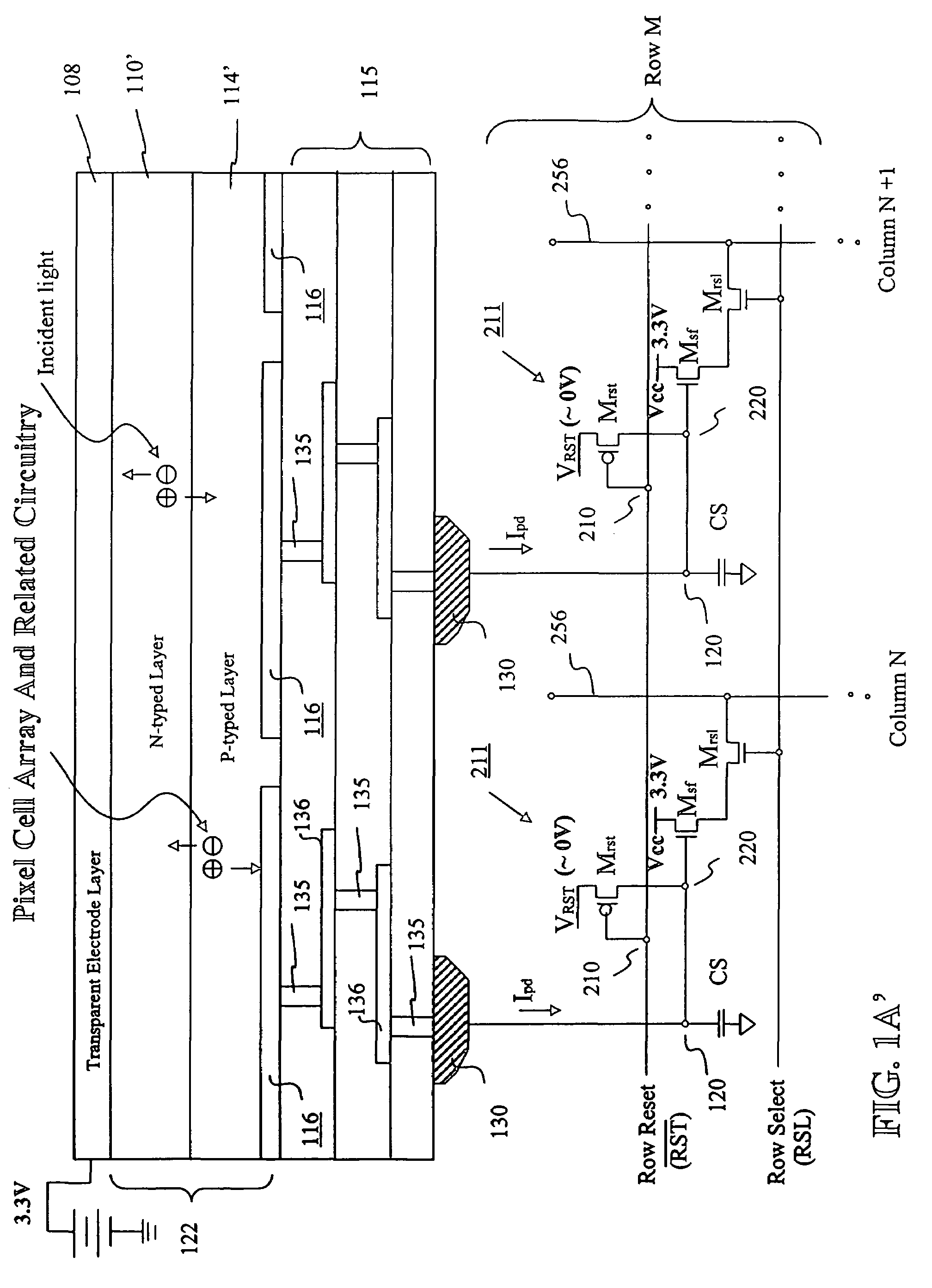
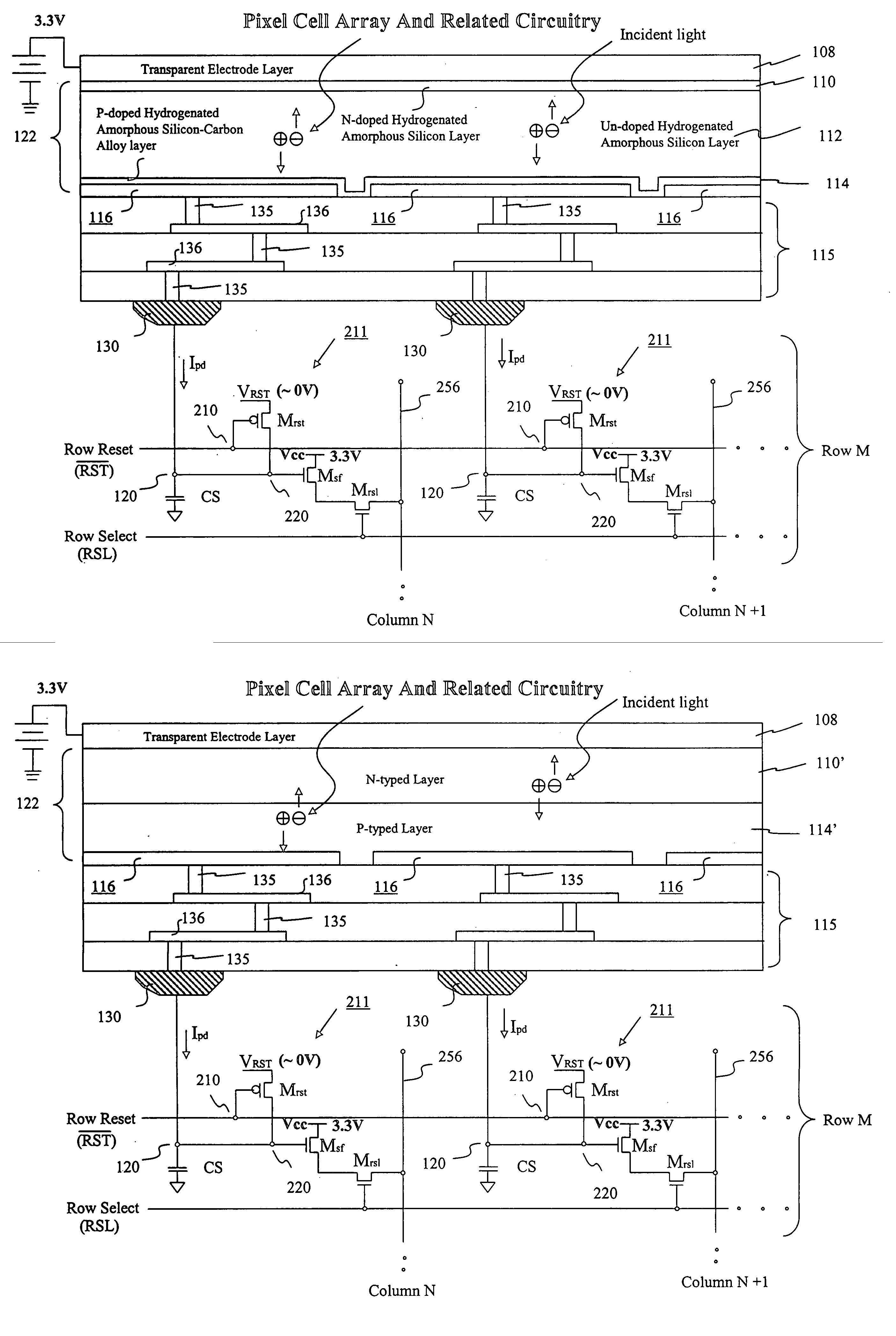
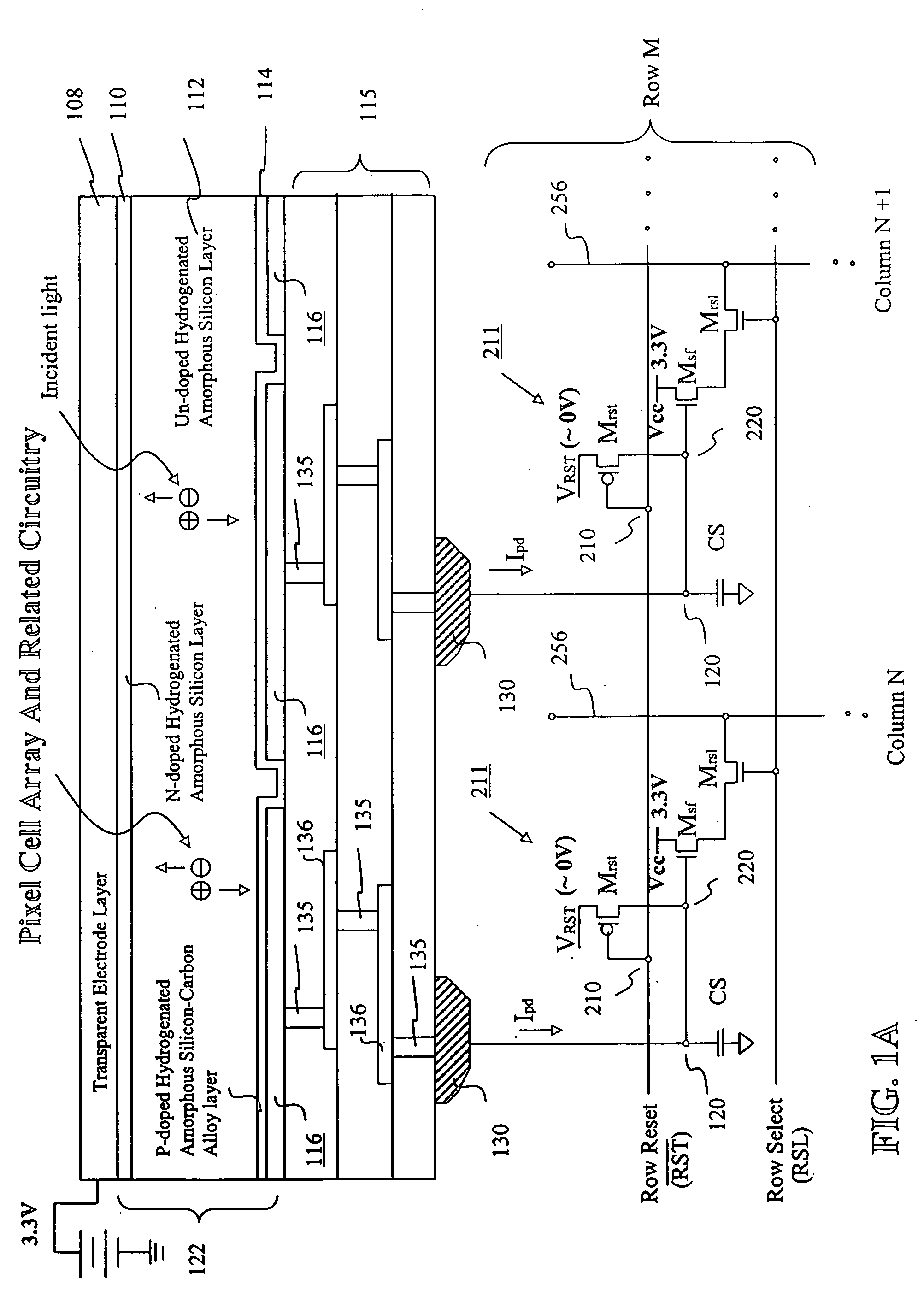
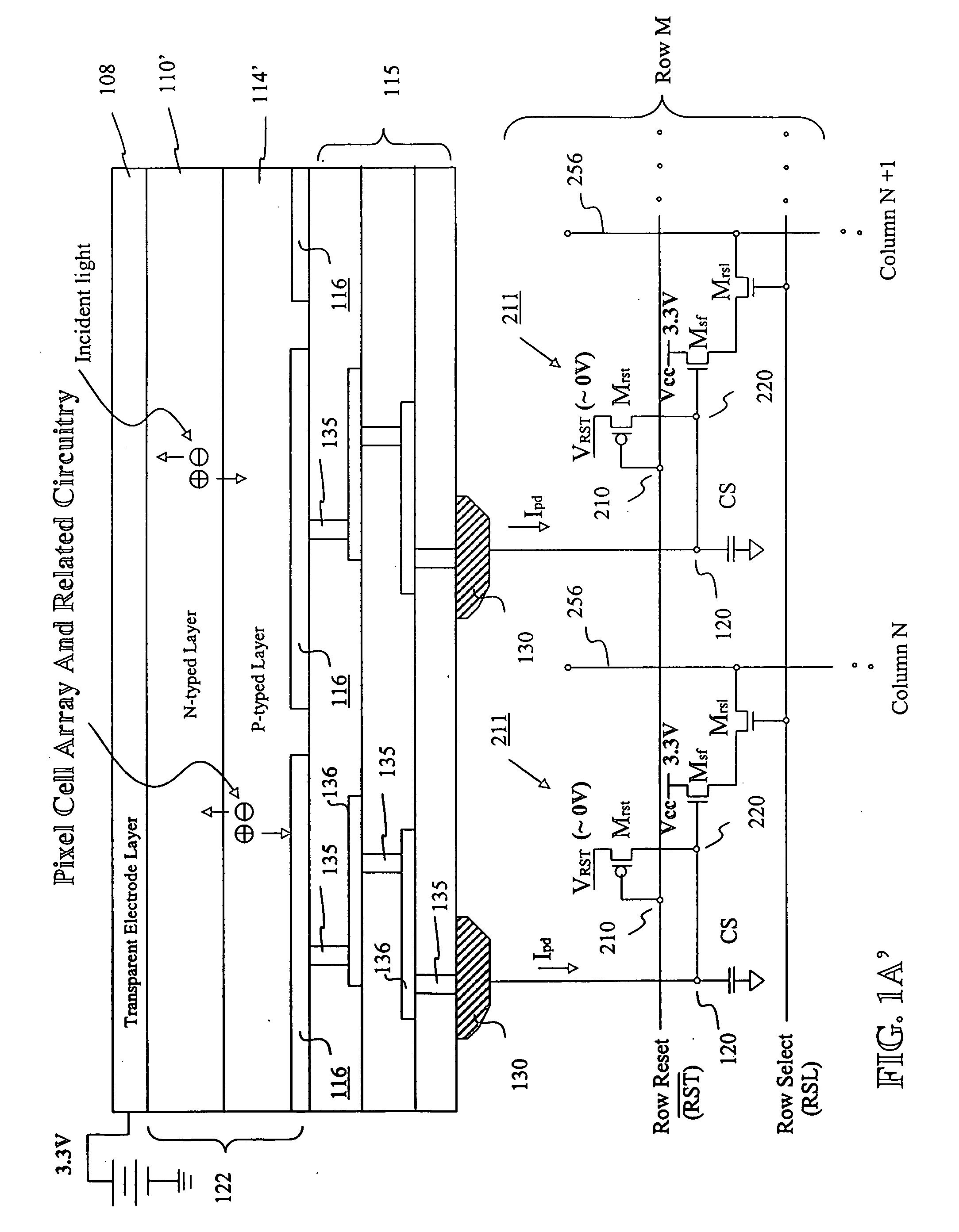
Image sensor with microcrystalline germanium photodiode layer
InactiveUS7276749B2Improve performanceRaise countTransistorSolid-state devicesSensor arrayElectromagnetic radiation
A microcrystalline germanium image sensor array. The array includes a number of pixel circuits fabricated in or on a substrate. Each pixel circuit comprises a charge collecting electrode for collecting electrical charges and a readout means for reading out the charges collected by the charge collecting electrode. A photodiode layer of charge generating material located above the pixel circuits convert electromagnetic radiation into electrical charges. This photodiode layer includes microcrystalline germanium and defines at least an n-layer, and i-layer and a p-layer. The sensor array also includes and a surface electrode in the form of a grid or thin transparent layer located above the layer of charge generating material. The sensor is especially useful for imaging in visible and near infrared spectral regions of the electromagnetic spectrum and provides imaging with starlight illumination.
Owner:E PHOCUS
Image sensor with microcrystalline germanium photodiode layer
InactiveUS20060267054A1High sensitivityEnhanced pixel size pixelTransistorSolid-state devicesSensor arrayElectromagnetic spectrum
A microcrystalline germanium image sensor array. The array includes a number of pixel circuits fabricated in or on a substrate. Each pixel circuit comprises a charge collecting electrode for collecting electrical charges and a readout means for reading out the charges collected by the charge collecting electrode. A photodiode layer of charge generating material located above the pixel circuits convert electromagnetic radiation into electrical charges. This photodiode layer includes microcrystalline germanium and defines at least an n-layer, and i-layer and a p-layer. The sensor array also includes and a surface electrode in the form of a grid or thin transparent layer located above the layer of charge generating material. The sensor is especially useful for imaging in visible and near infrared spectral regions of the electromagnetic spectrum and provides imaging with starlight illumination.
Owner:E PHOCUS
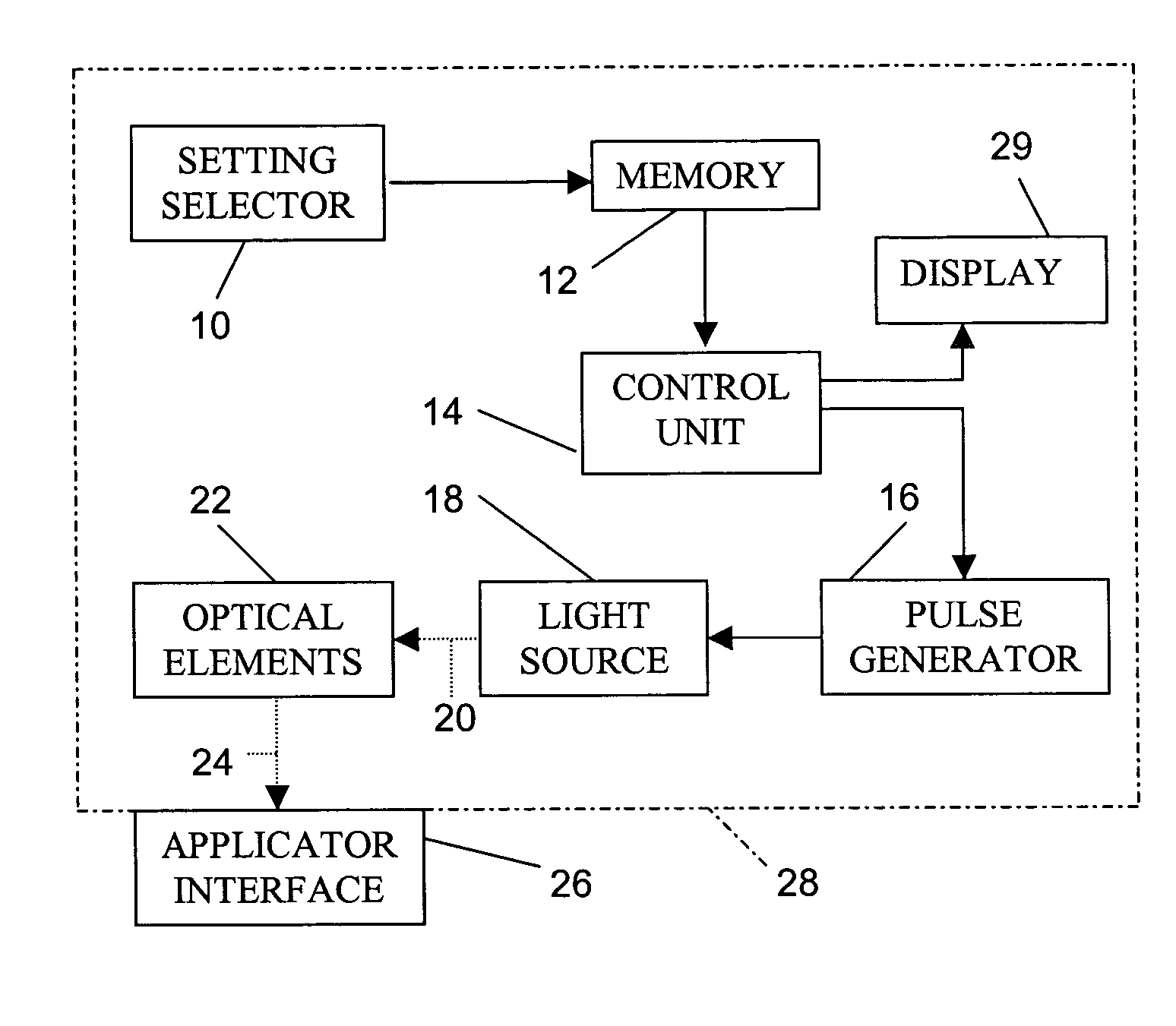
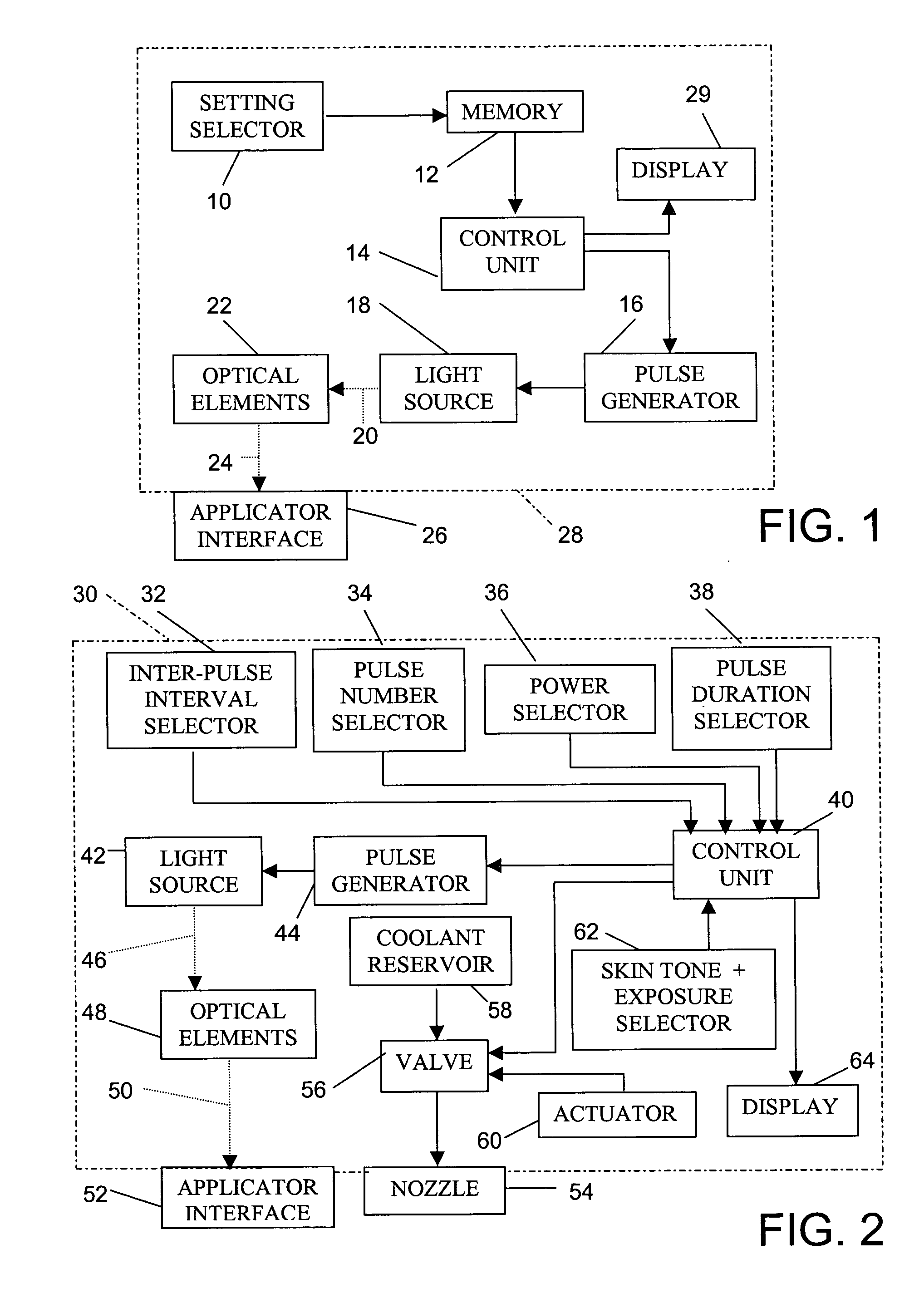
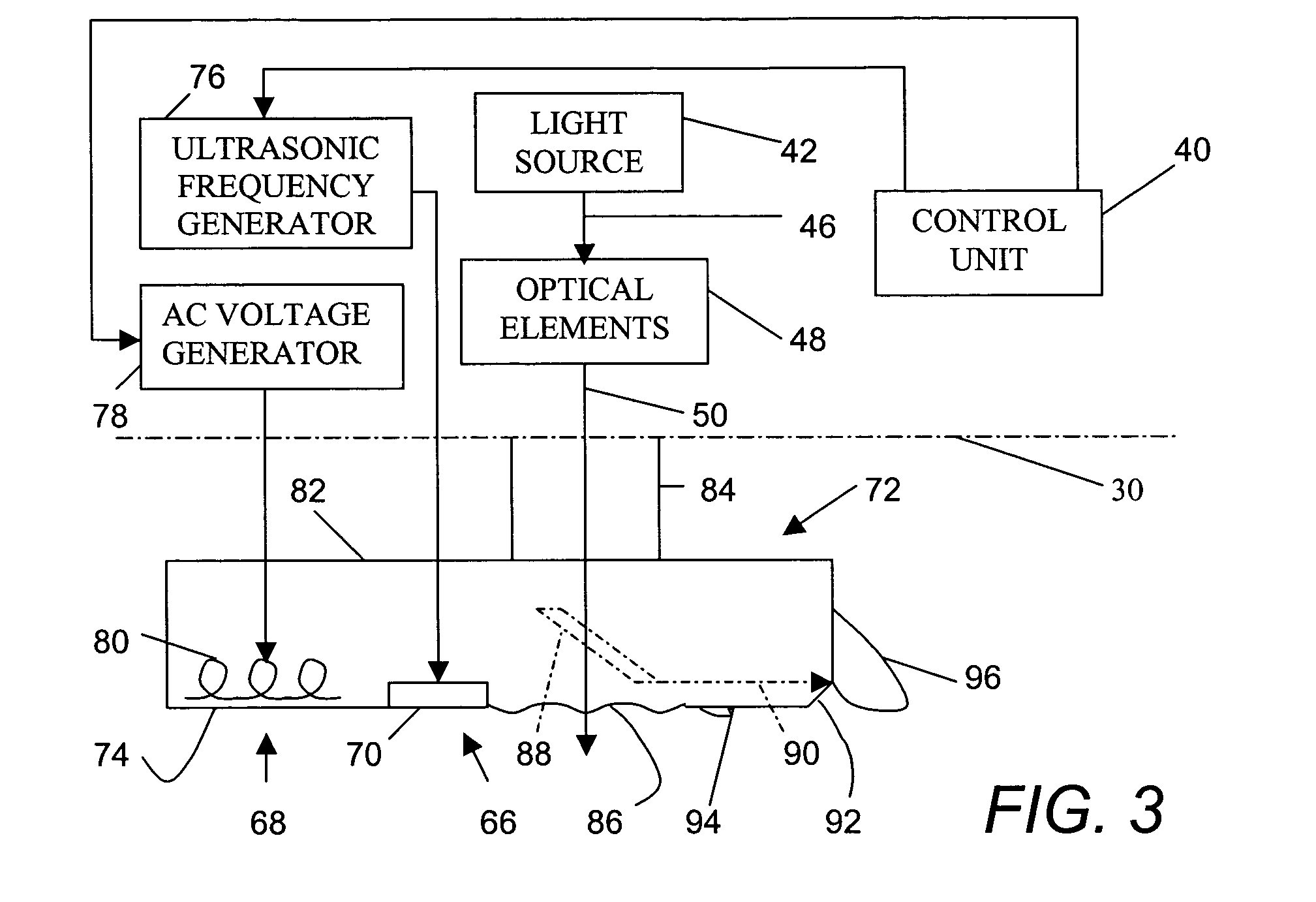
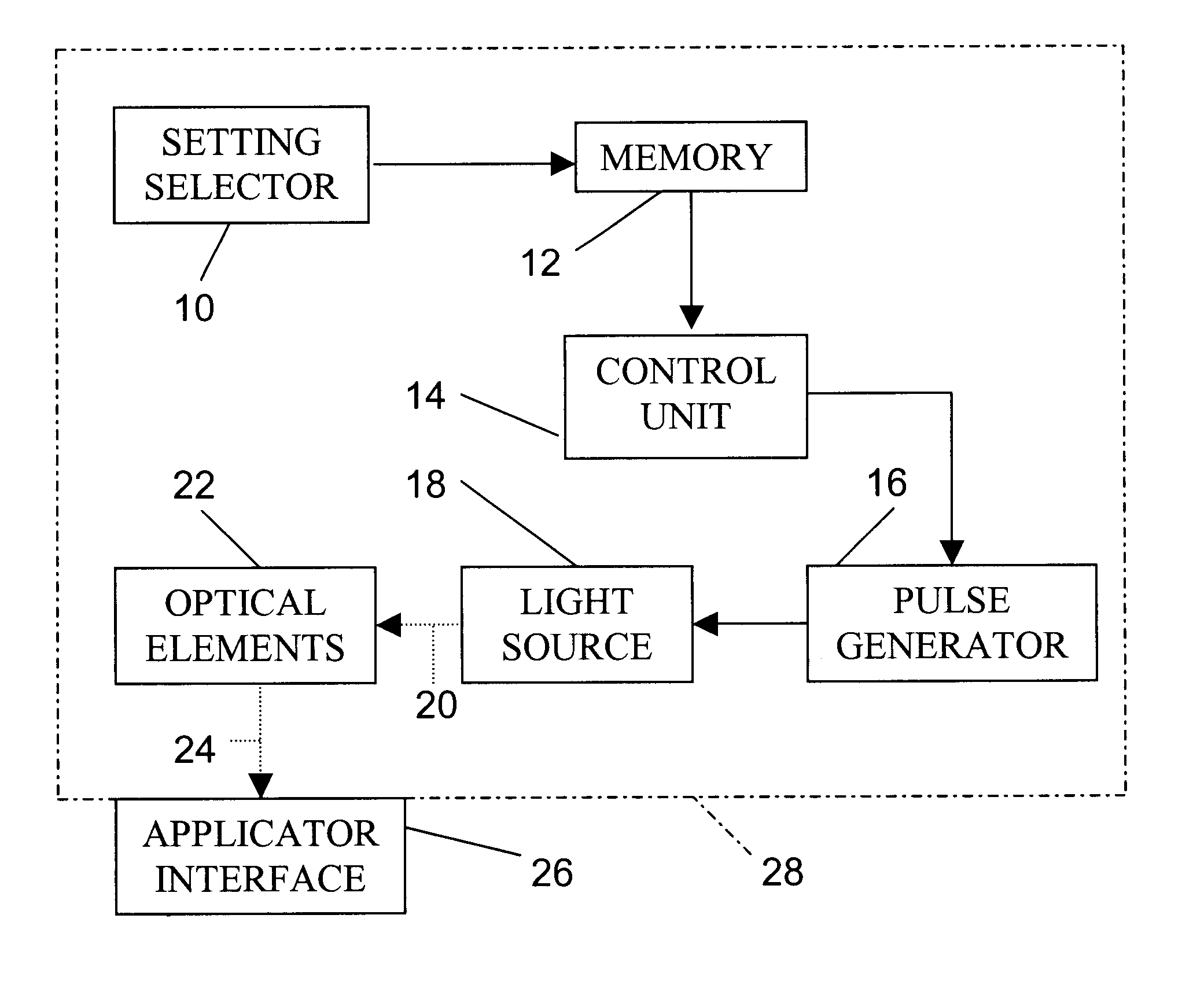
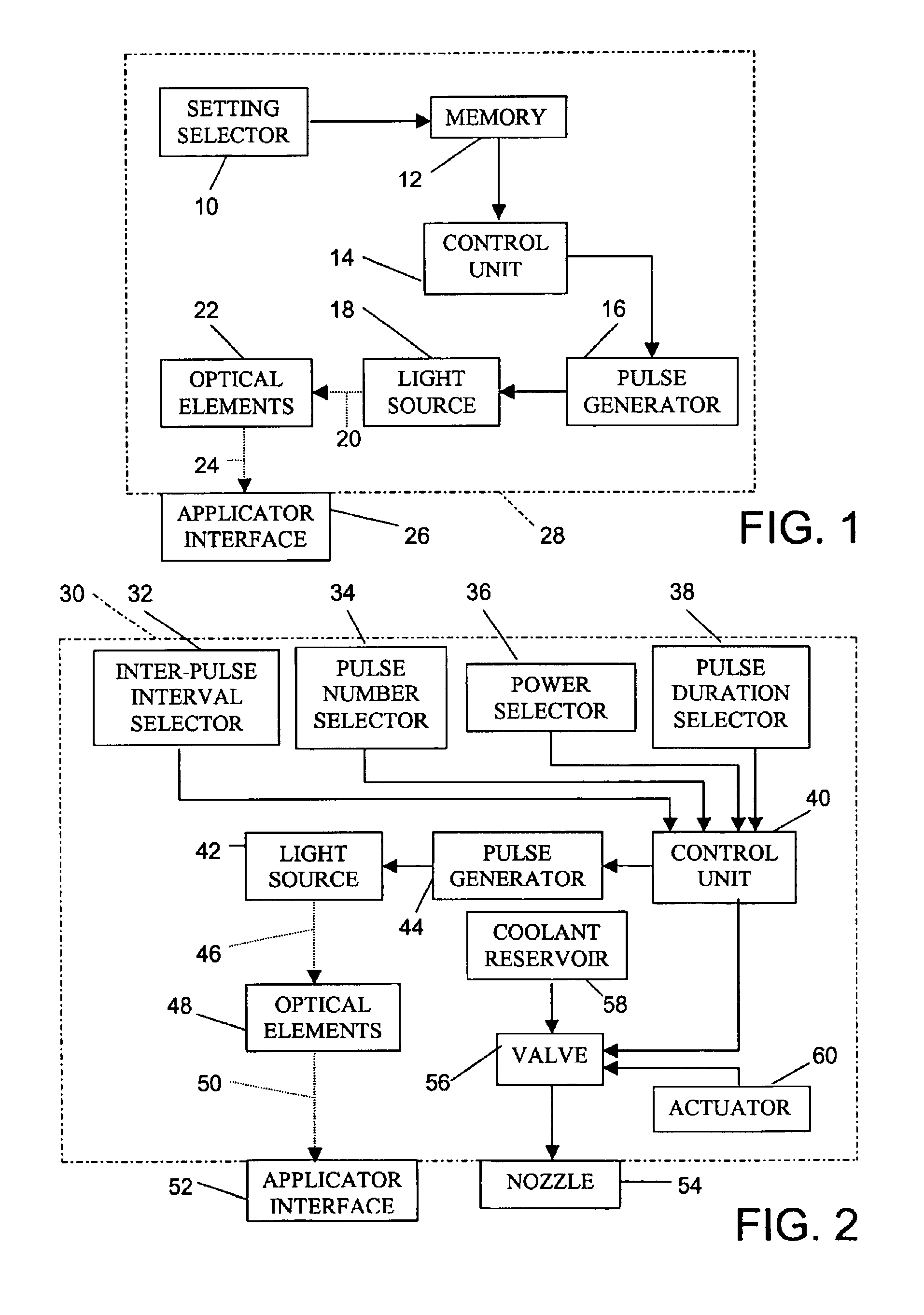
Skin treatment with optical radiation
InactiveUS20050045189A1Promote protect healthReduces and inhibits tissue damageElectrotherapyDiagnostics using lightOptical radiationFrequency spectrum
A hand held device generates a predetermined number of pulses of electromagnetic radiation having a predetermined electromagnetic spectrum, a predetermined duration, a predetermined inter-pulse interval, and a predetermined total energy. The pulse sequence is delivered to a skin surface to reduce or eliminate Xray or ultraviolet radiation damage to the skin surface.
Owner:JAY HARVEY H
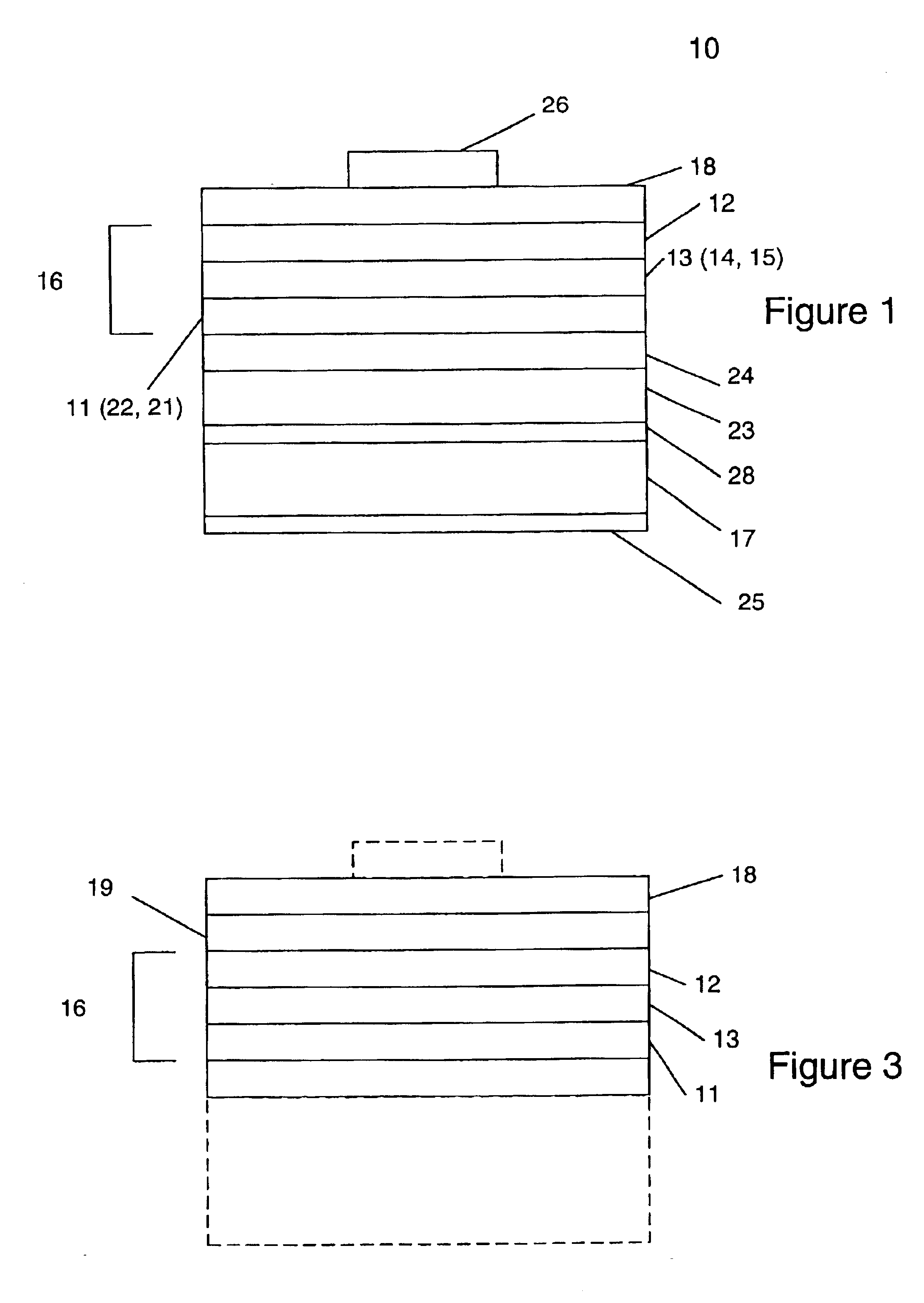
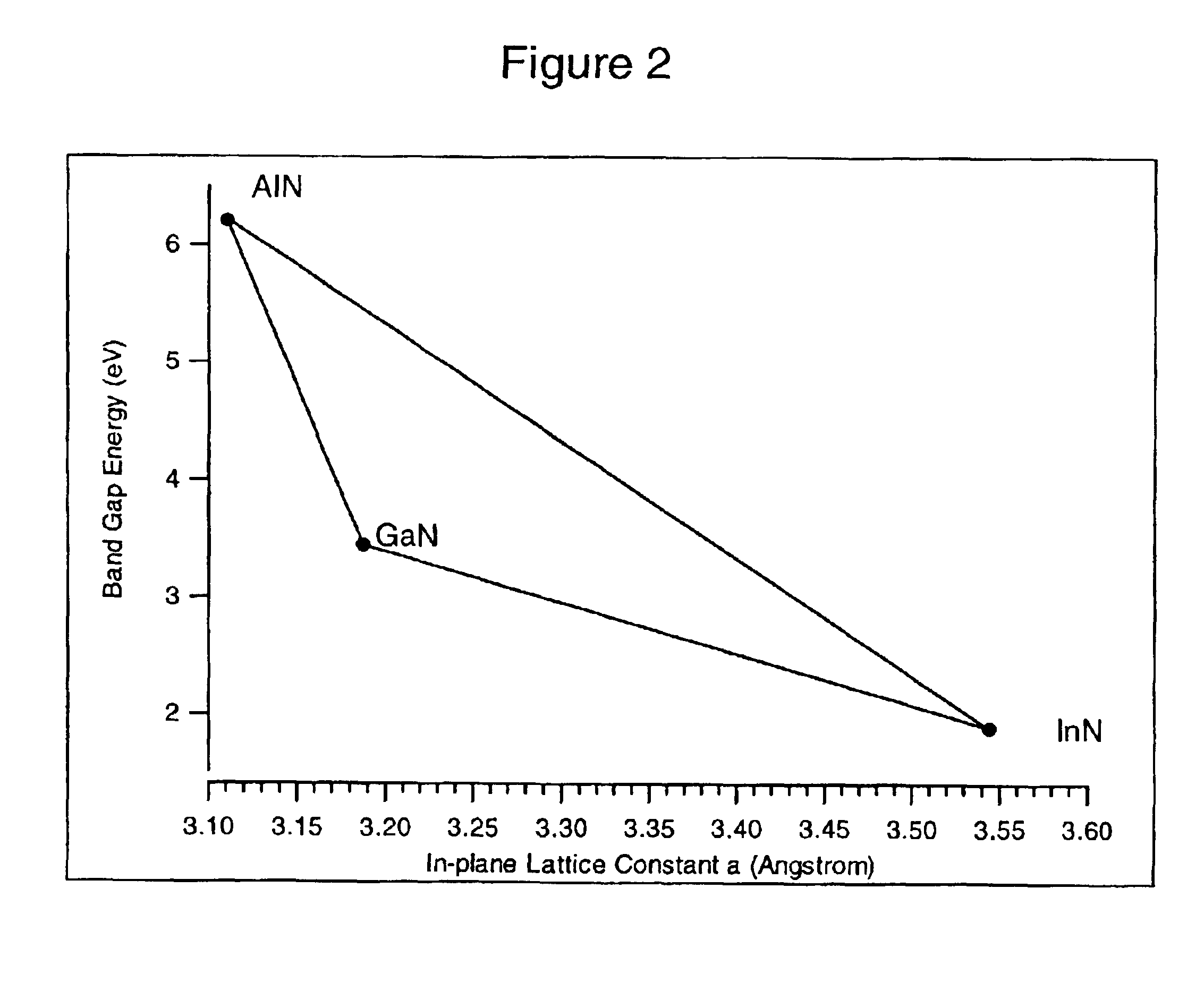
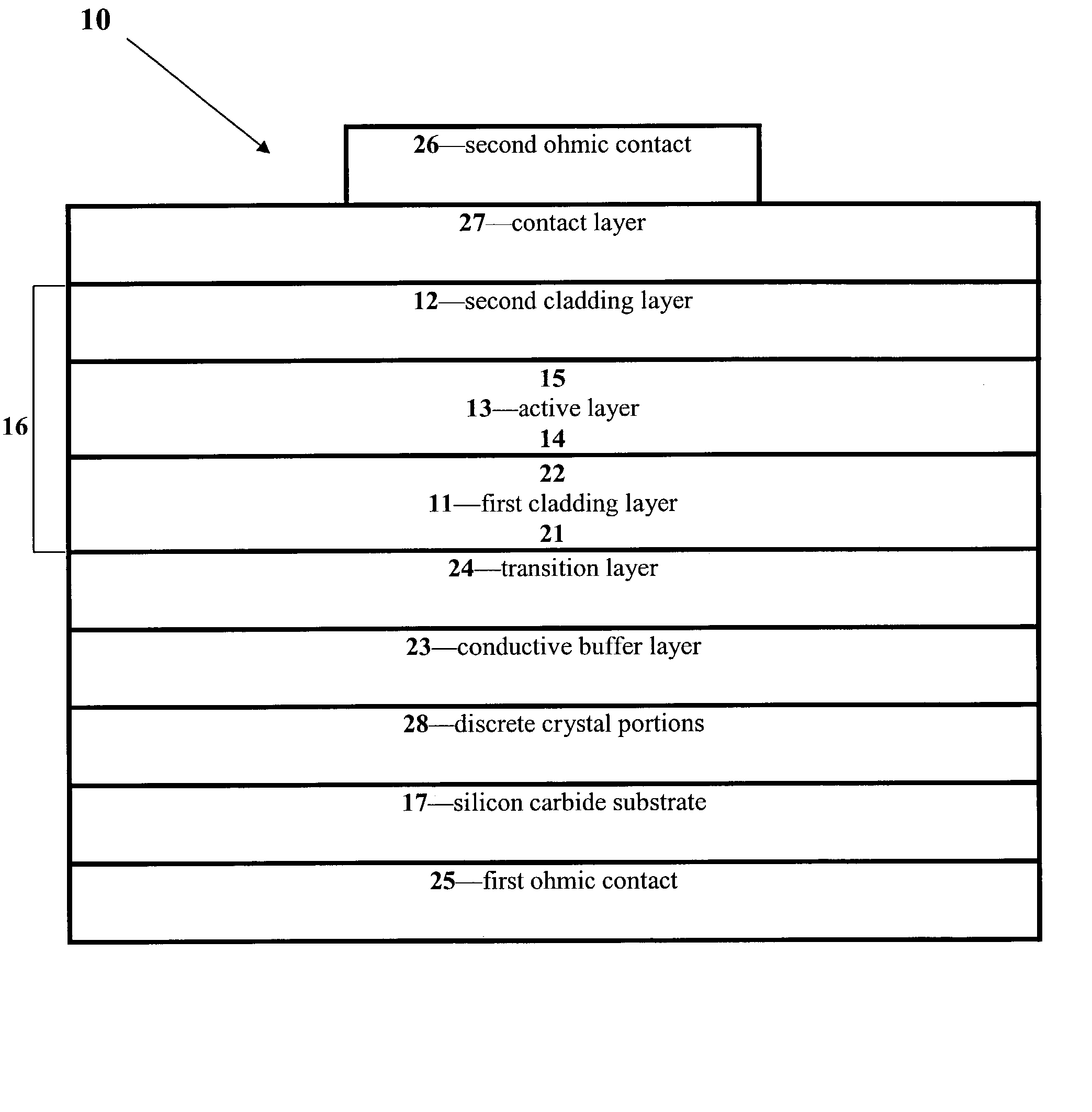
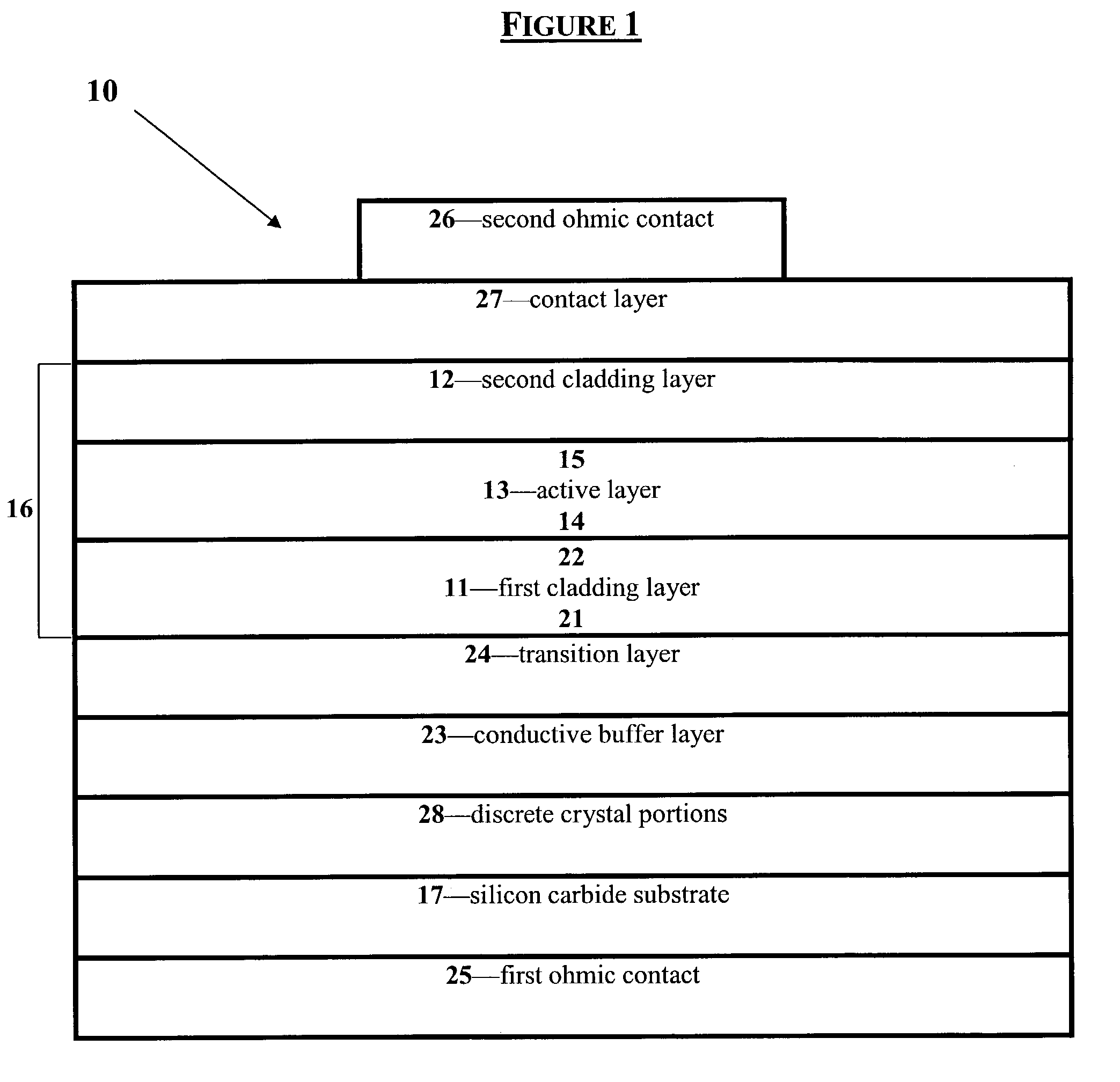
Group III nitride LED with undoped cladding layer and multiple quantum well
InactiveUS6906352B2Maintain good propertiesEasy to manufactureLaser detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor structureElectromagnetic spectrum
The present invention is a semiconductor structure for light emitting devices that can emit in the red to ultraviolet portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. The structure includes a first n-type cladding layer of AlxInyGa1−x−yN, where 0≦x≦1 and 0≦y<1 and (x+y)≦1; a second n-type cladding layer of AlxInyGa1−x−yN, where 0≦x≦1 and 0≦y<1 and (x+y)≦1, wherein the second n-type cladding layer is further characterized by the substantial absence of magnesium; an active portion between the first and second cladding layers in the form of a multiple quantum well having a plurality of InxGa1−xN well layers where 0<x<1 separated by a corresponding plurality of AlxInyGa1−x−yN barrier layers where 0≦x≦1 and 0≦y≦1; a p-type layer of a Group III nitride, wherein the second n-type cladding layer is positioned between the p-type layer and the multiple quantum well; and wherein the first and second n-type cladding layers have respective bandgaps that are each larger than the bandgap of the well layers. In preferred embodiments, a Group III nitride superlattice supports the multiple quantum well.
Owner:CREE INC
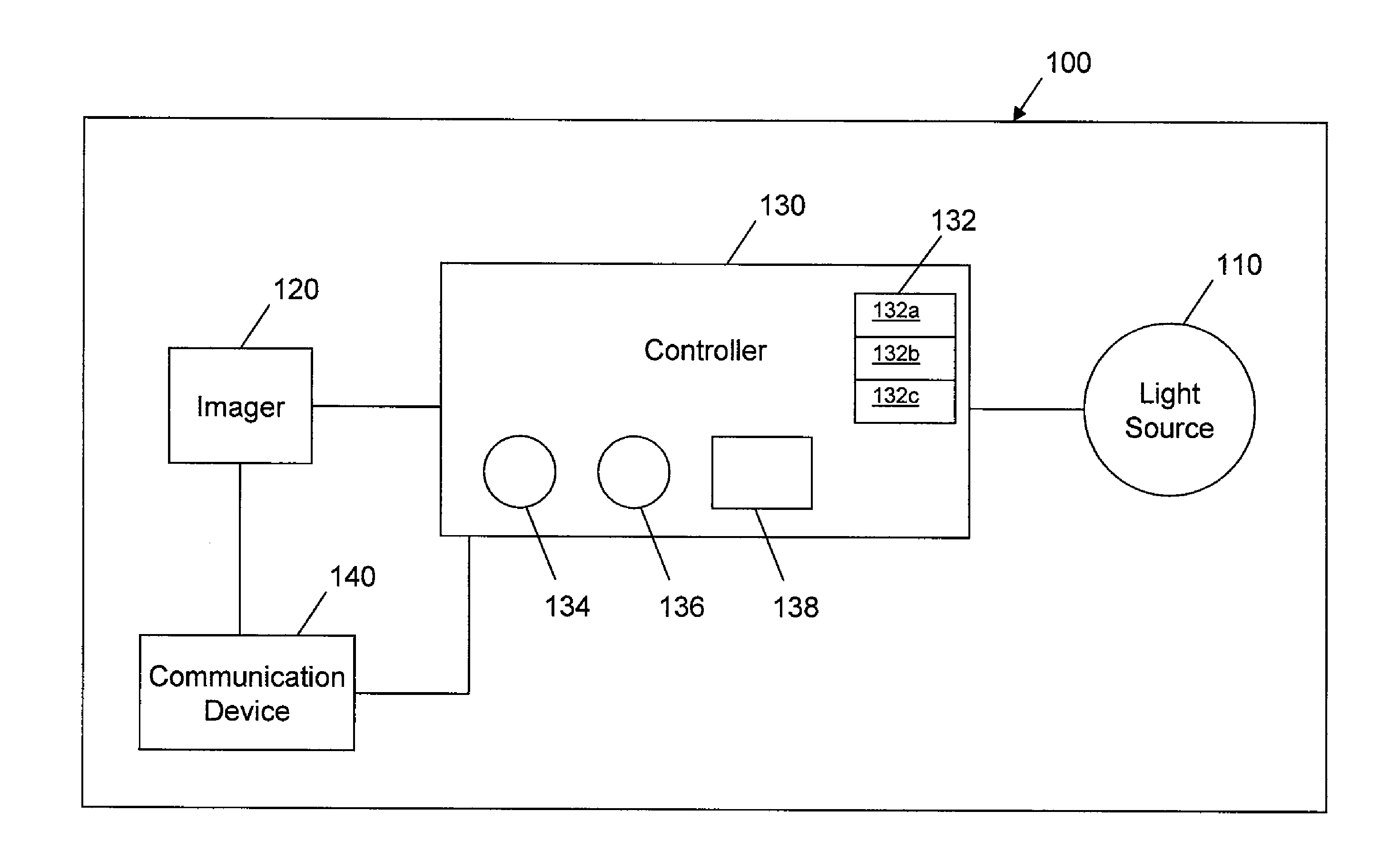
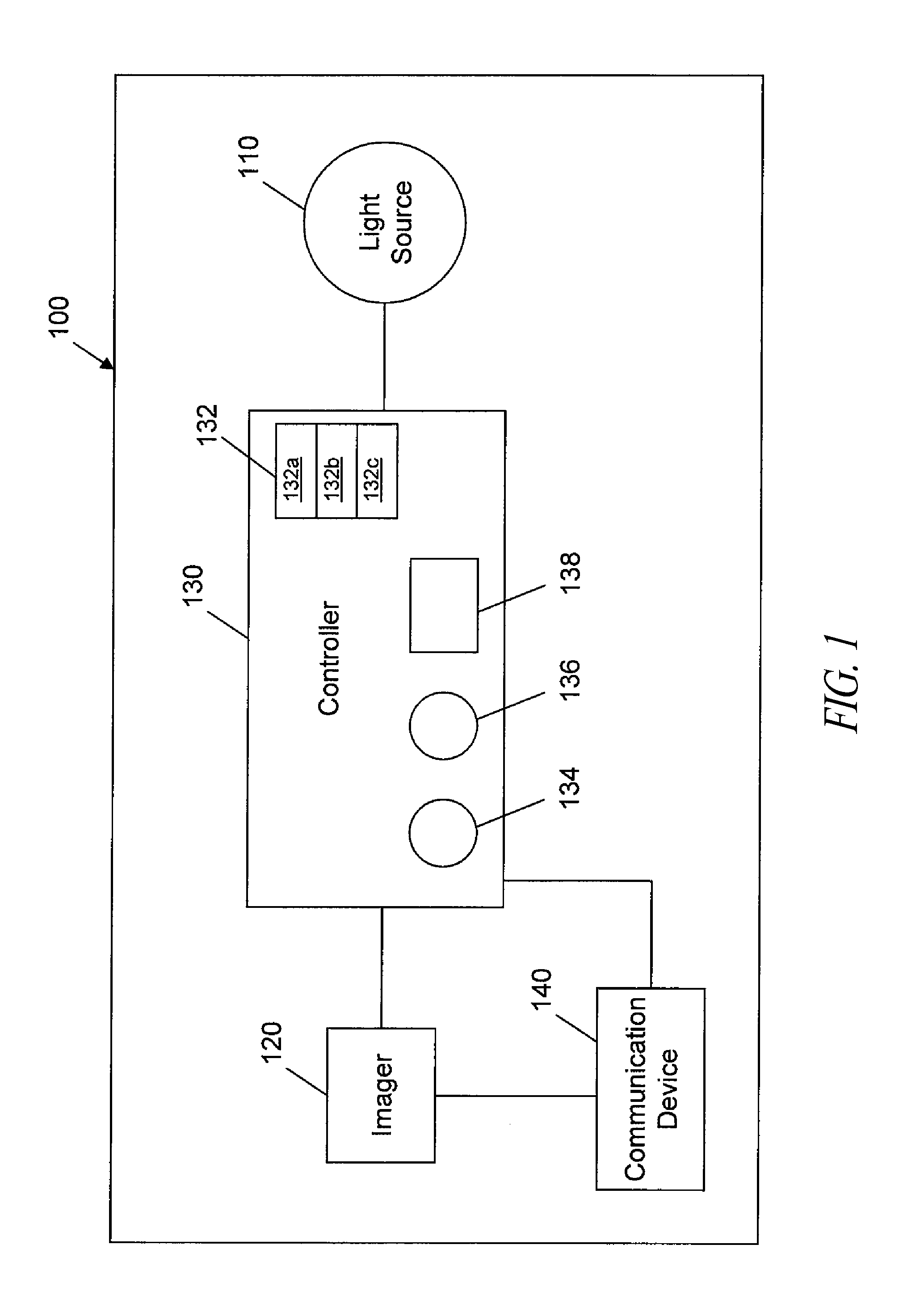
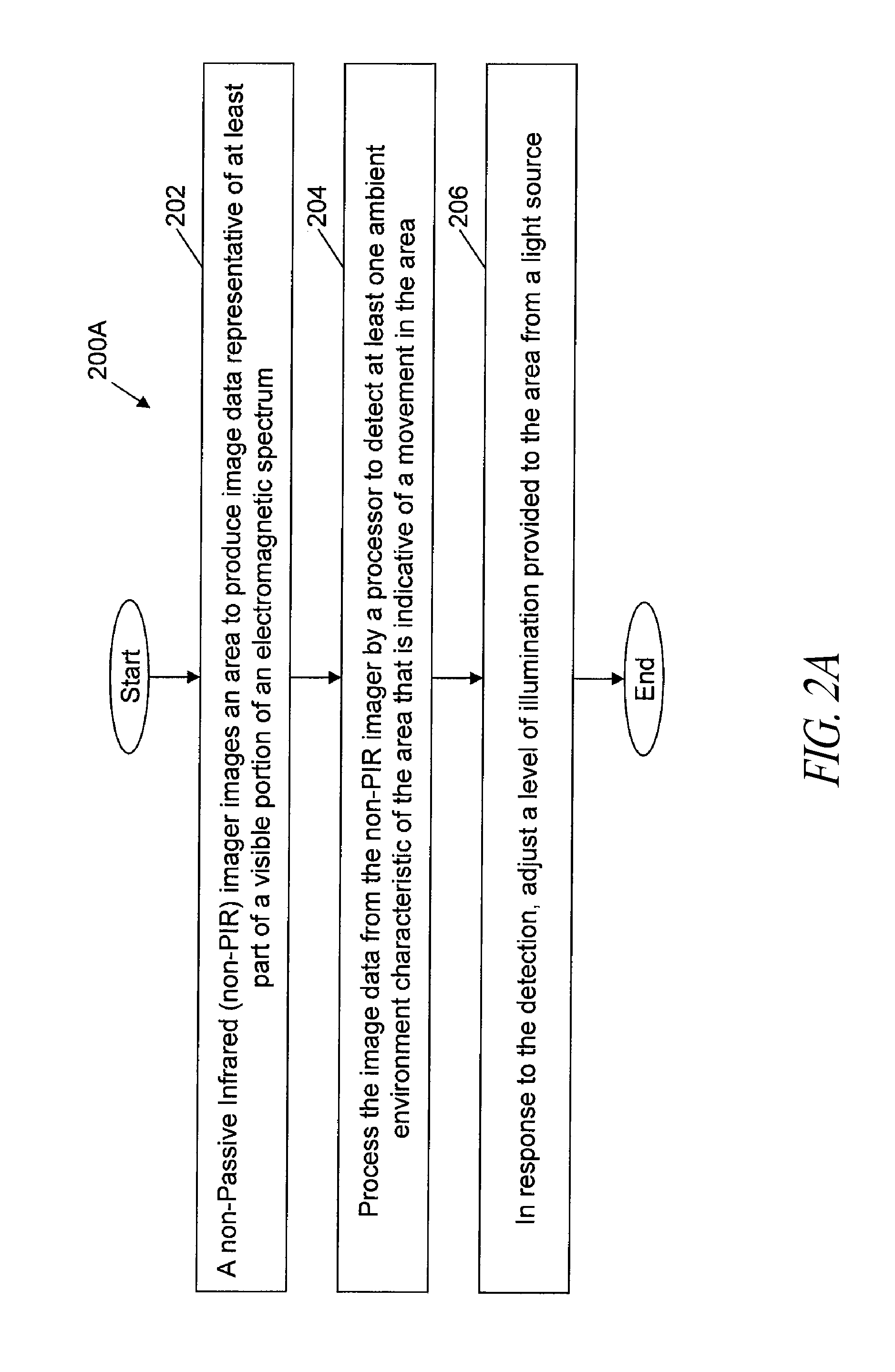
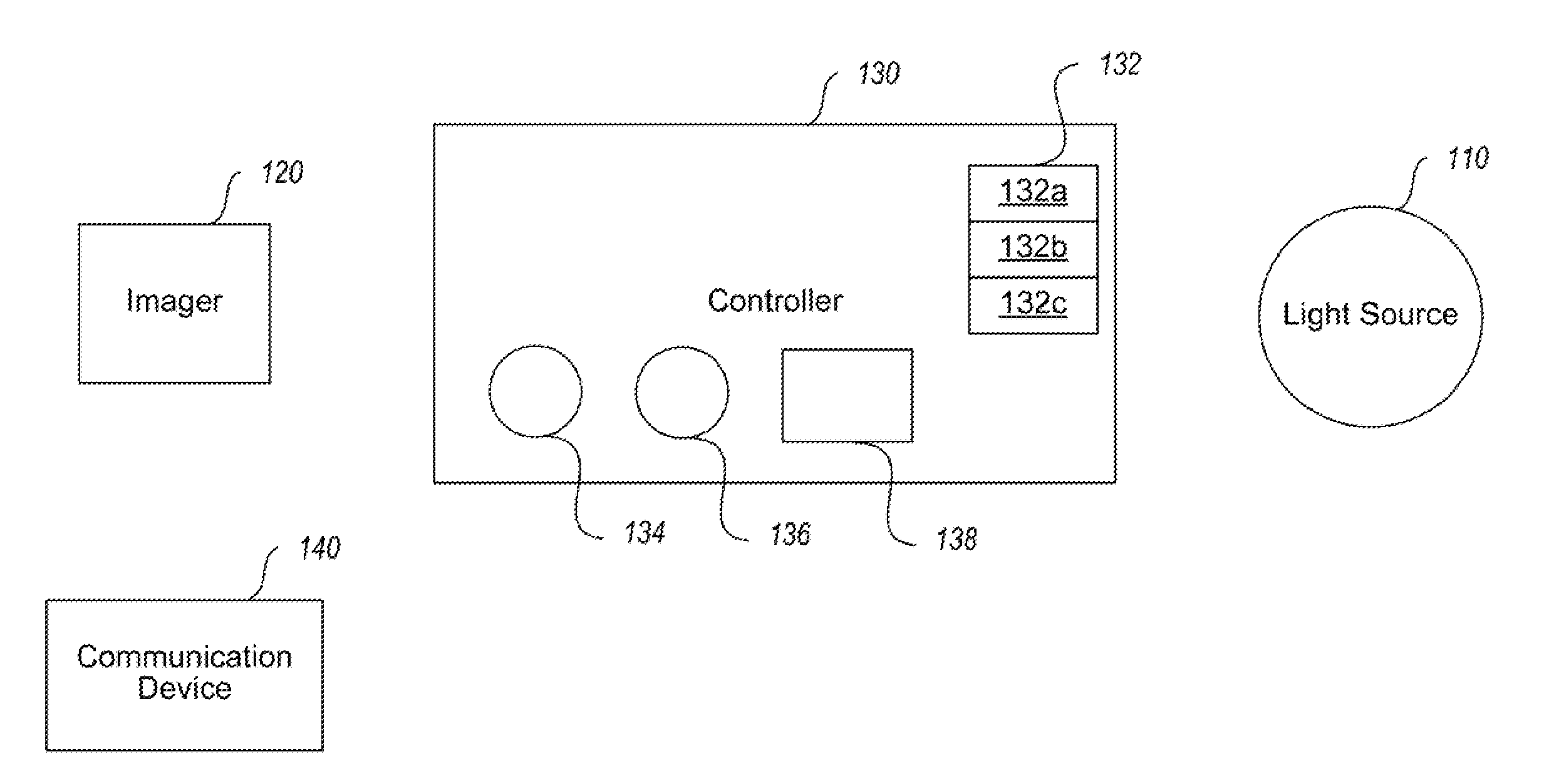
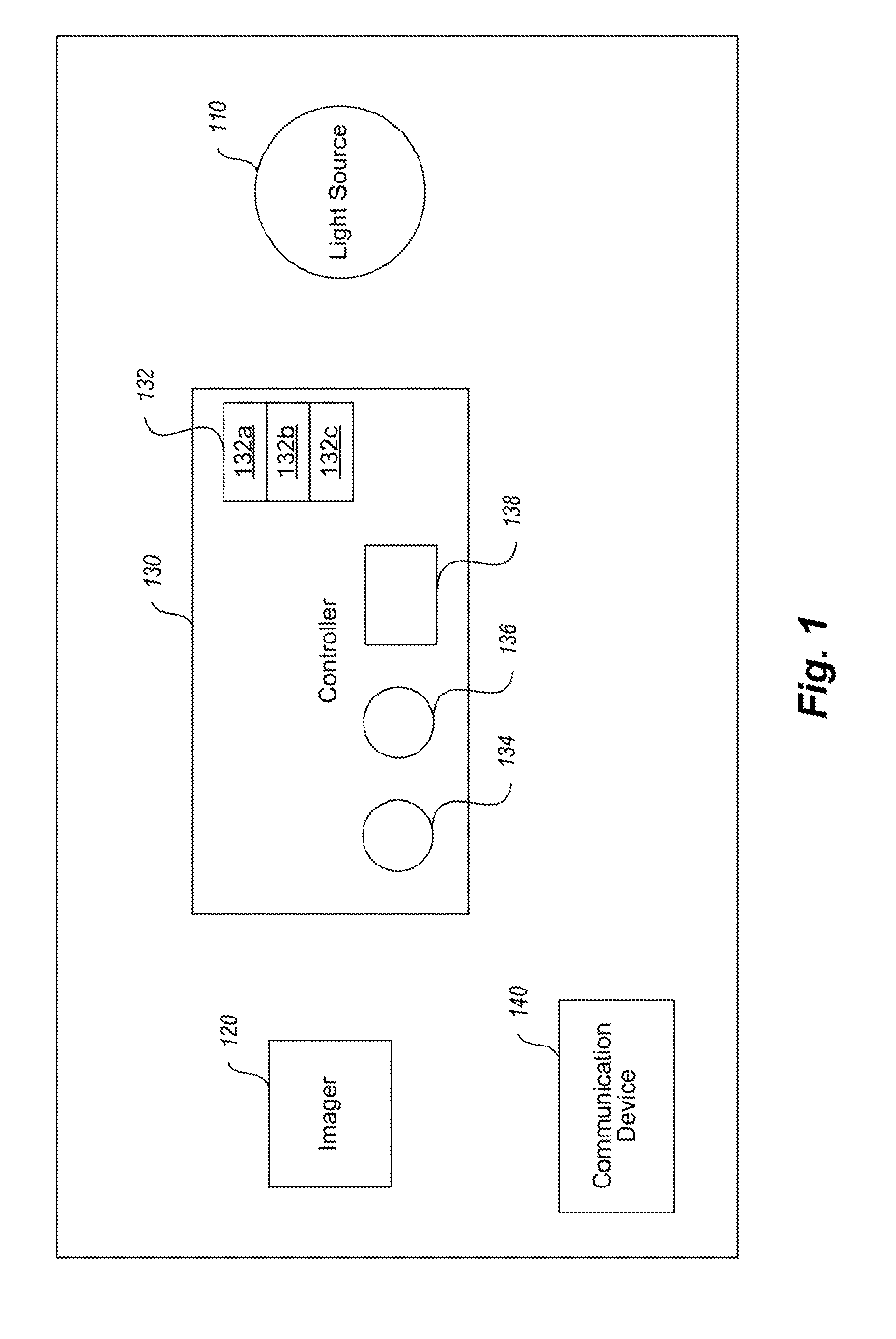
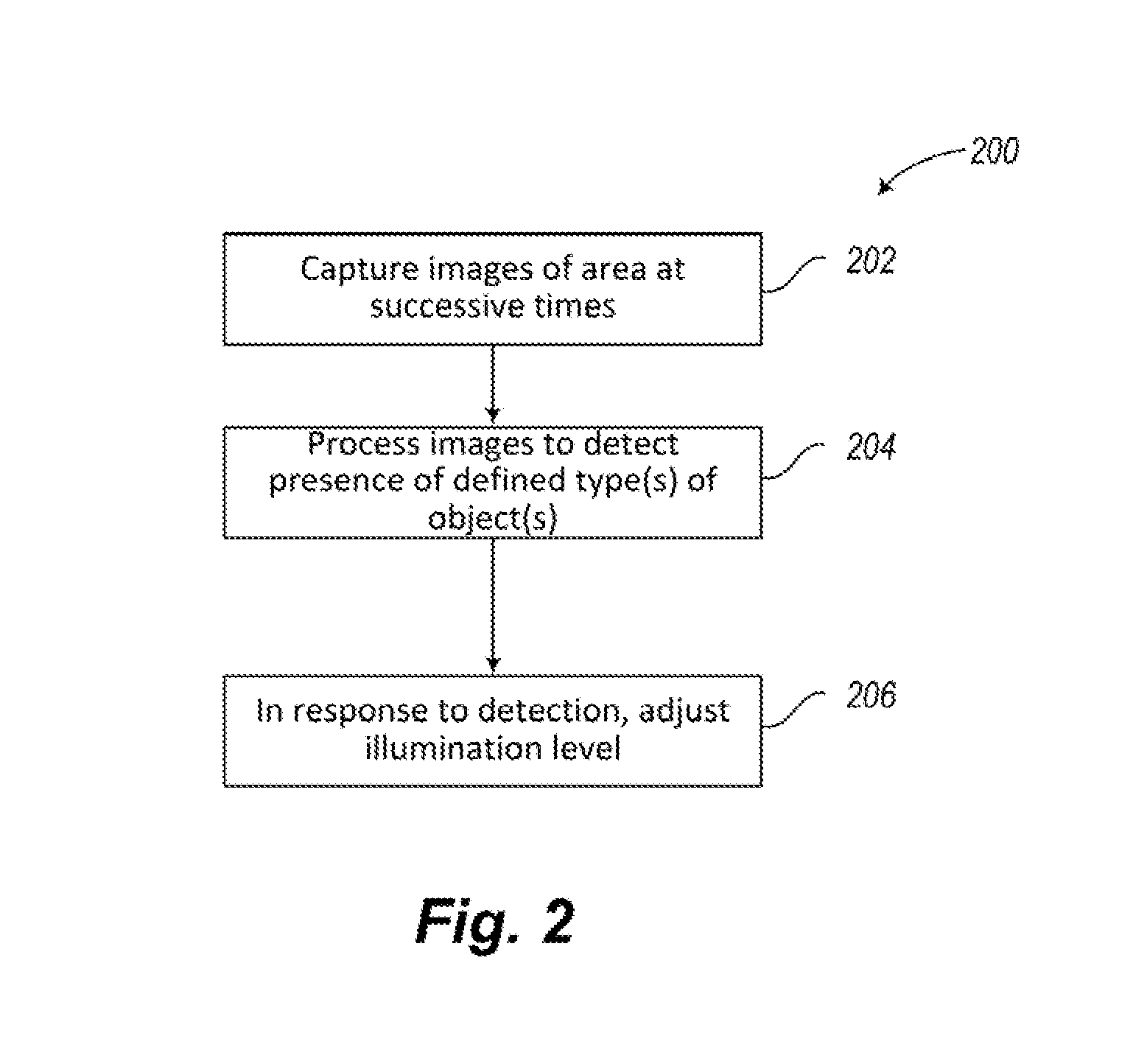
Long-range motion detection for illumination control
ActiveUS20100295946A1Television system detailsColor television detailsElectromagnetic spectrumLighting system
An illumination system and methods to control a light source are provided. An illumination system includes a light source, a two-dimensional non-Passive Infrared (non-PIR) imager, and a controller. The light source provides at least two levels of illumination. The non-PIR imager images an area and to produce image data representative of images across at least part of a visible portion of an electromagnetic spectrum. The controller is communicatively coupled to receive the image data from the non-PIR imager and process the received image data to detect at least one ambient environmental characteristic of the area in the part of the visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, where the ambient environmental characteristic is indicative of a presence or imminent presence of a body in the area. The controller is also coupled to control operation of the light source based on, at least in part, detection of the ambient characteristic of the environment.
Owner:EXPRESS IMAGING SYST
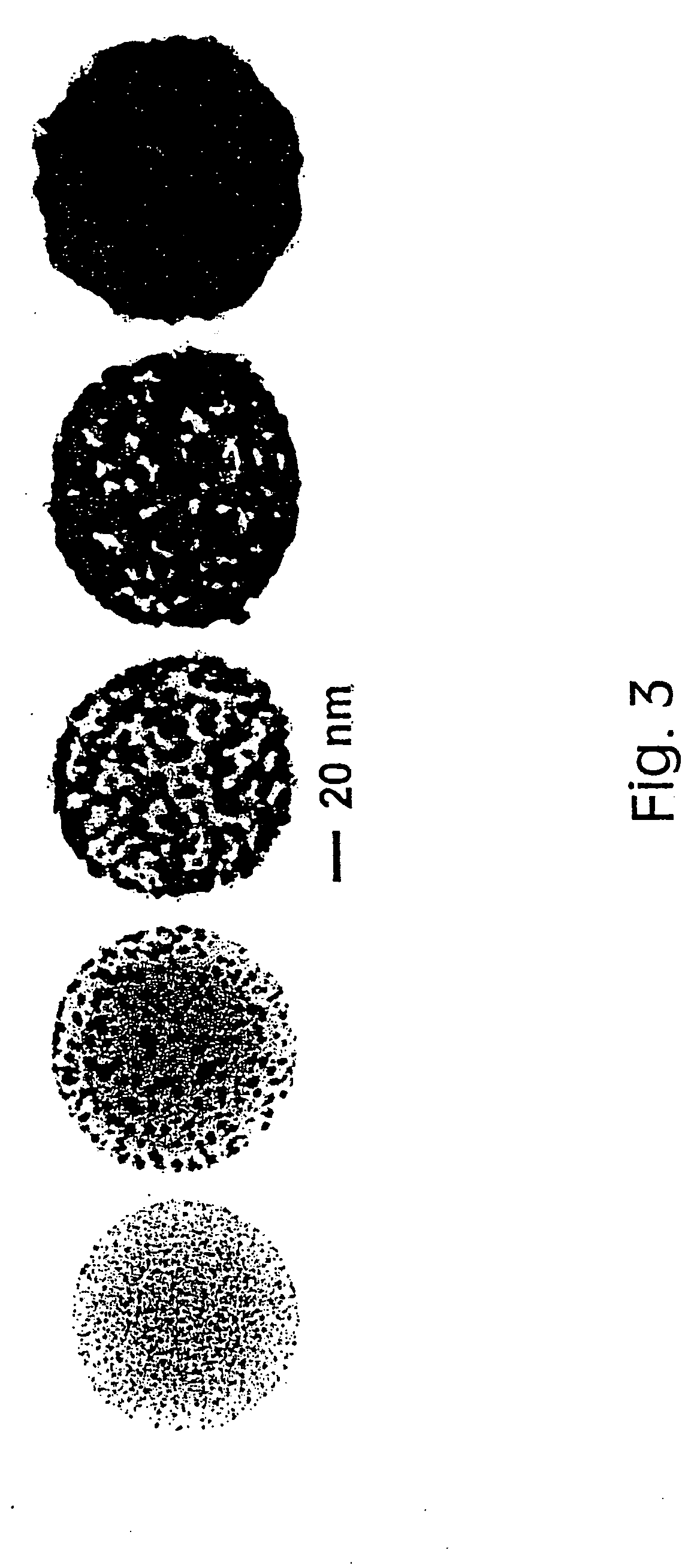
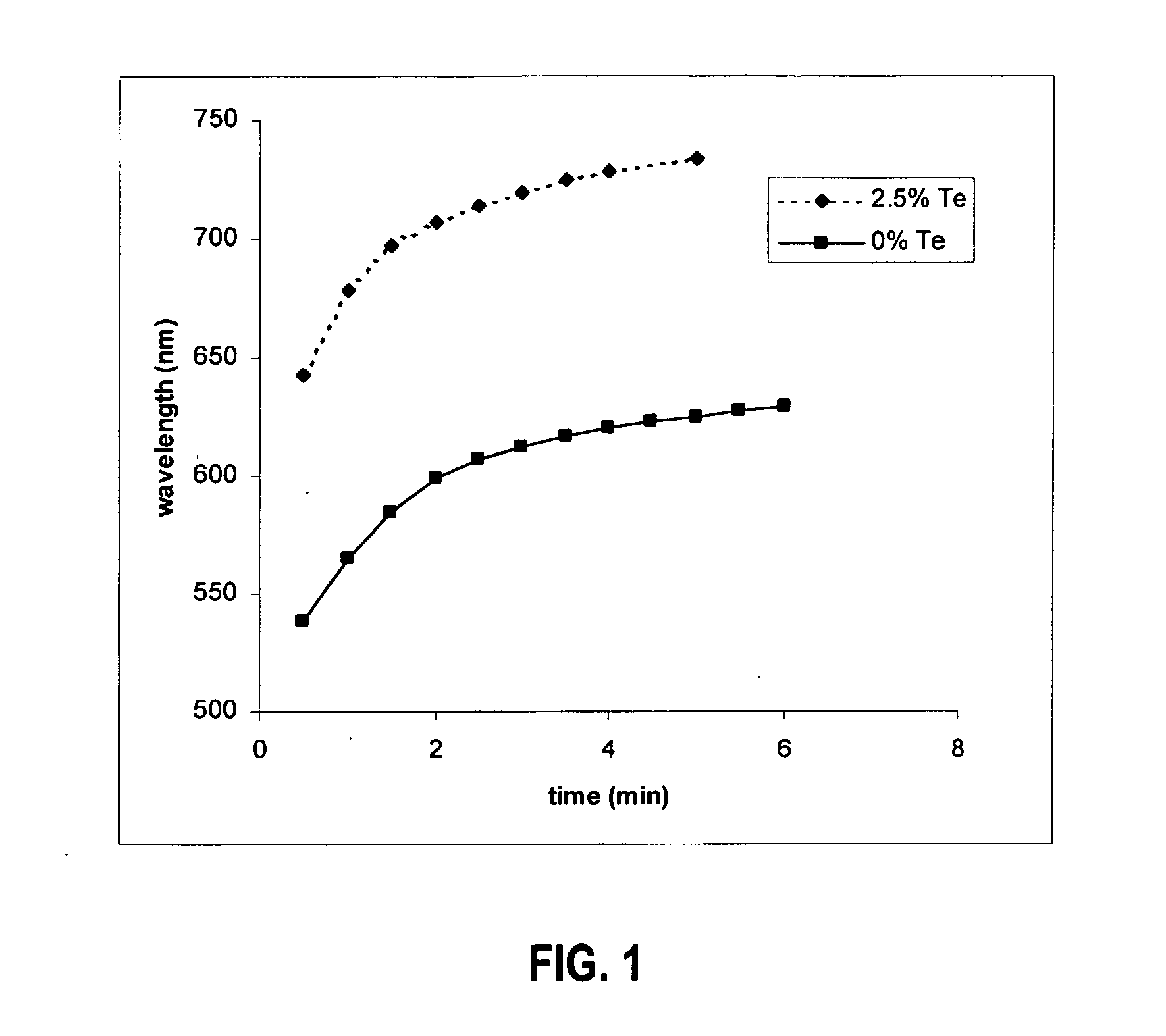
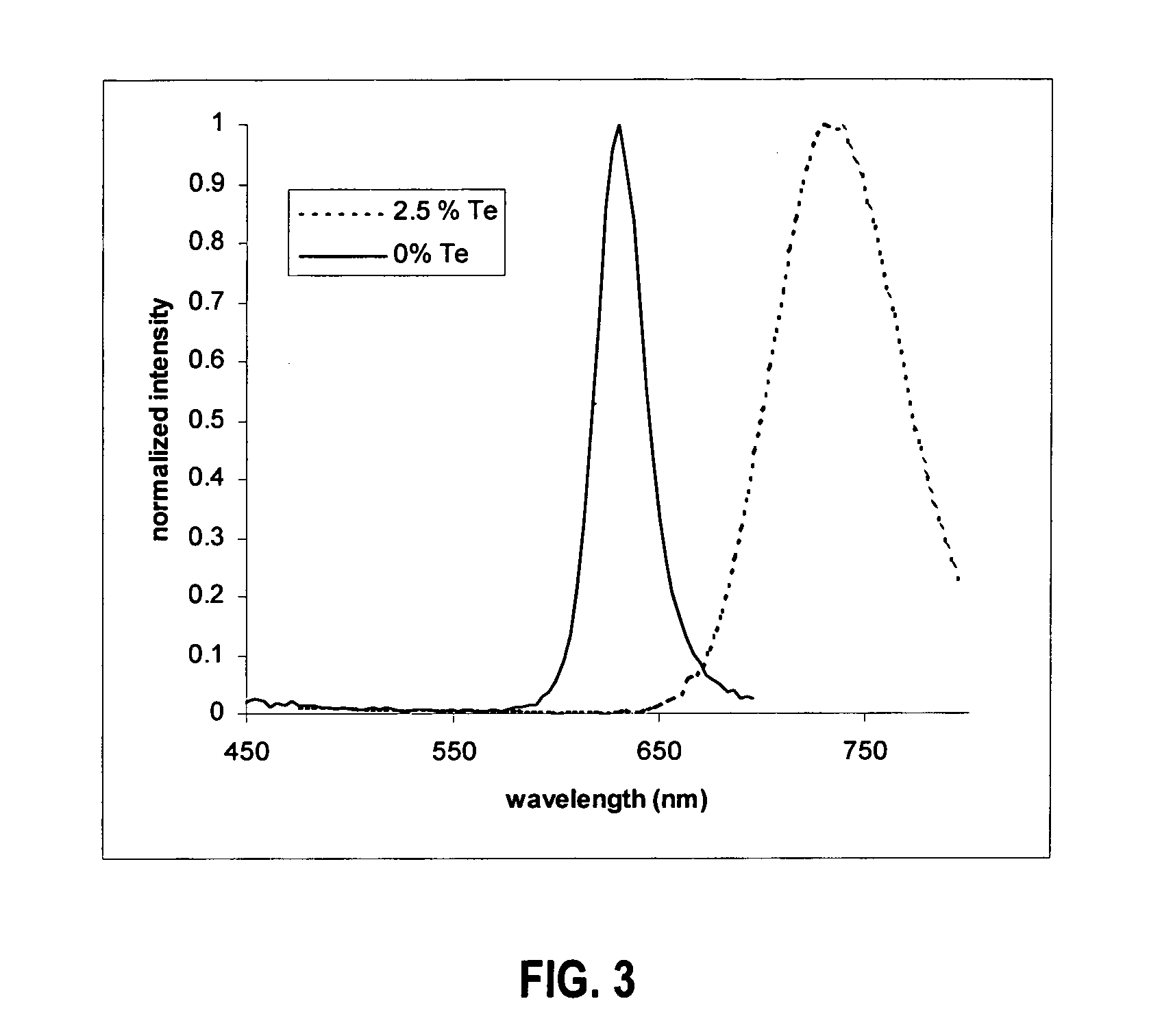
Preparation of stable, bright luminescent nanoparticles having compositionally engineered properties
ActiveUS20050214536A1Reduce compositionSmall sizeMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentElectromagnetic spectrumSemiconductor Nanoparticles
A method is provided for preparing luminescent semiconductor nanoparticles composed of a first component X, a second component A, and a third component B, wherein X, A, and B are different, by combining B with X and A in an amount such that the molar ratio B:(A+B) is in the range of approximately 0.001 to 0.20 and the molar ratio X:(A+B) is in the range of approximately 0.5:1.0 to 2:1. The characteristics of the thus-prepared nanoparticles can be substantially similar to those of nanoparticles containing only X and B while maintaining many useful properties characteristic of nanoparticles containing only X and A. The nanoparticles so prepared can additionally exhibit emergent properties such as a peak emission energy less than that characteristic of a particle composed of XA or XB alone; this method is particularly applicable to the preparation of stable, bright nanoparticles that emit in the red to infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Luminescent semiconductor nanoparticles having exemplary properties are also provided.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Solar cell and its spectrum converter
InactiveUS20090151785A1Increases electric parameterImprove efficiencyPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesPhotoluminescencePhosphor
A solar cell is disclosed to include a single crystal silicon chip, an electrode system, a glass plate cover, a polymer film set between the single crystal silicon chip and the glass plate cover, and a spectrum converter containing an inorganic phosphor, which absorbs radiation in purple, blue and green light of the Sun's solar radiation and converts the absorption into a photoluminescent light in yellow, orange-yellow and infrared area in the electromagnetic spectrum. The architecture characteristic of the solar cell increases the efficiency by about 20%.
Owner:LO WEI HUNG
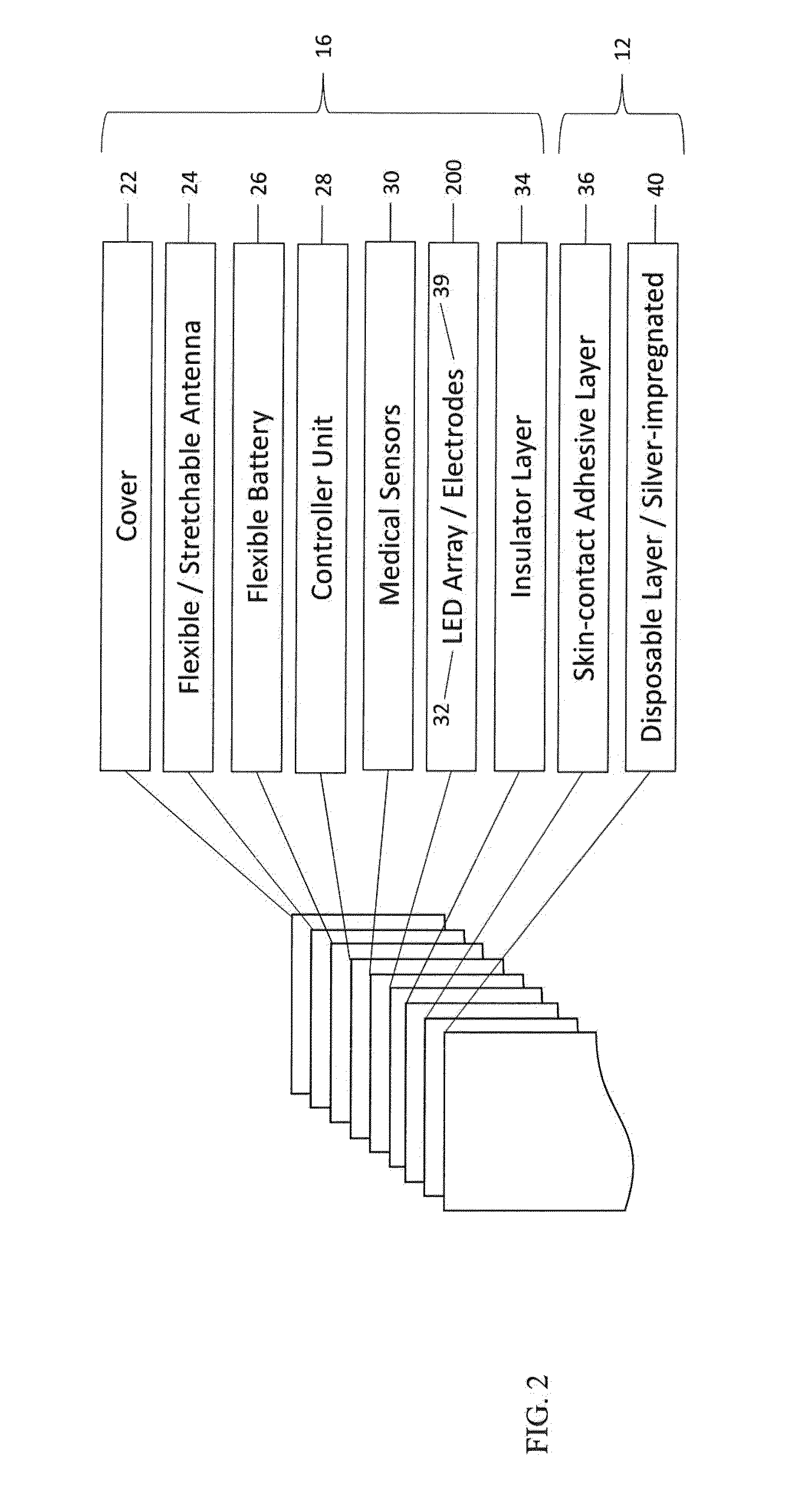
Smart Patch For Wound Management
InactiveUS20160015962A1Accelerate wound healing processEliminate bacterial infectionDiagnostics using lightNon-adhesive dressingsWound healingOperating instruction
A flexible patch is provided that is capable of emitting light in the UV, visible, and / or infrared electromagnetic spectrums. The patch contains a feedback process and system using one or more sensors and a controller on the patch to (1) accelerate the wound healing process by providing adaptable, controlled light exposure and electrical stimulation, (2) monitor the healing process for signs of infection (3) eliminate bacterial infections by sanitizing the infected site and (4) relaying the information wirelessly to a central location for storage and interpretation by a physician as well as by providing the ability to receive feedback and operating instructions from the physician from a remote location.
Owner:SHOKOUEINEJAD MARAGHEH MEHDI +3
Apparatus and method for cooking food with a controlled spectrum
InactiveUS6069345AHigh strengthIncrease temperatureMilk preparationDomestic stoves or rangesLight energyEngineering
A lightwave oven for cooking with light having wavelengths in the visible, near visible, and infra-red spectral ranges uses one or more quartz halogen tungsten lamps or quartz arc bulbs positioned above and below the food item and delivers light energy in select ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum during select portions of the cooking cycle.
Owner:HAIER US APPLIANCE SOLUTIONS INC
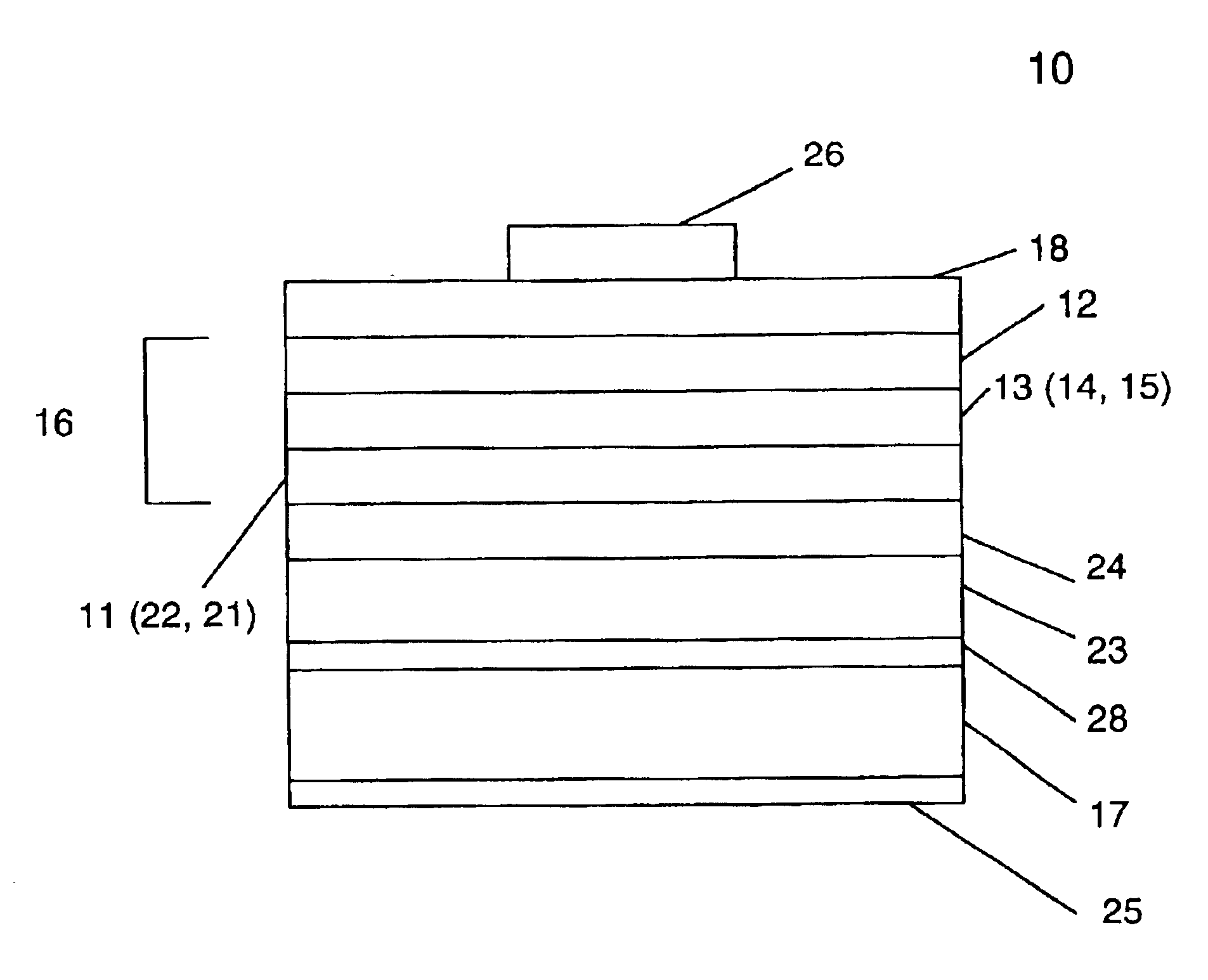
System for Multi- and Hyperspectral Imaging
InactiveUS20080123097A1Improve performanceCost effectiveRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSensor arrayMulti band
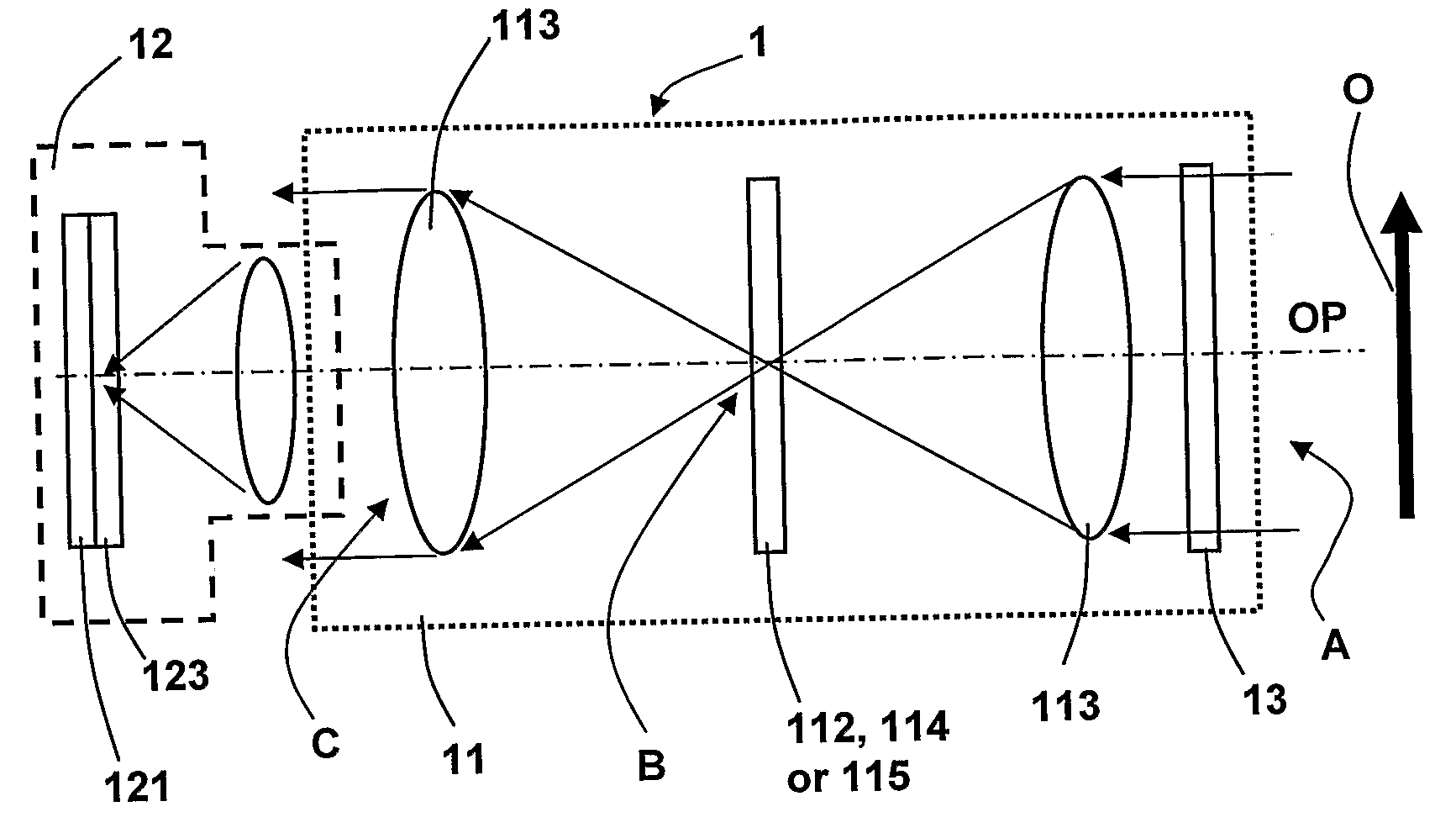
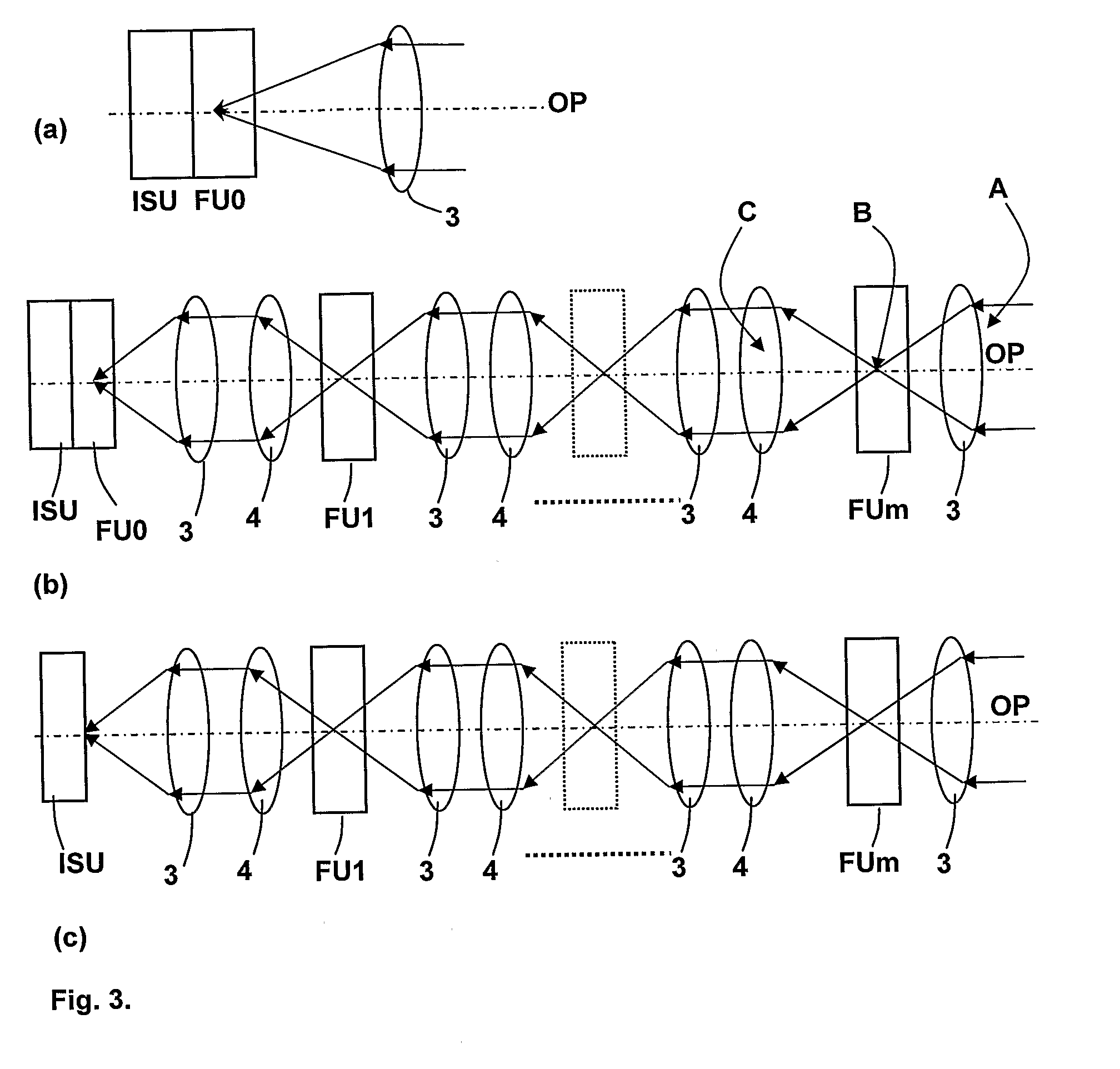
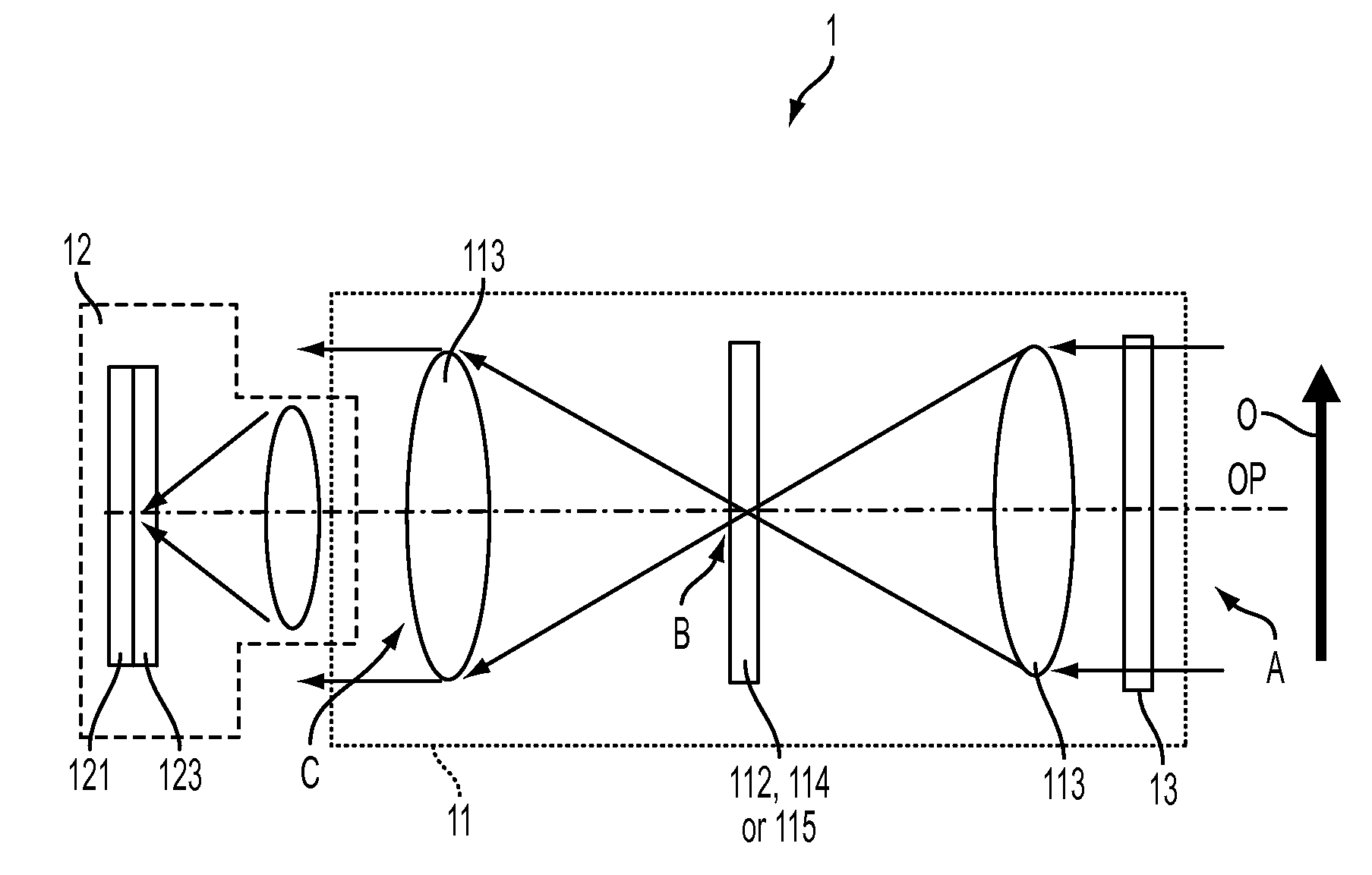
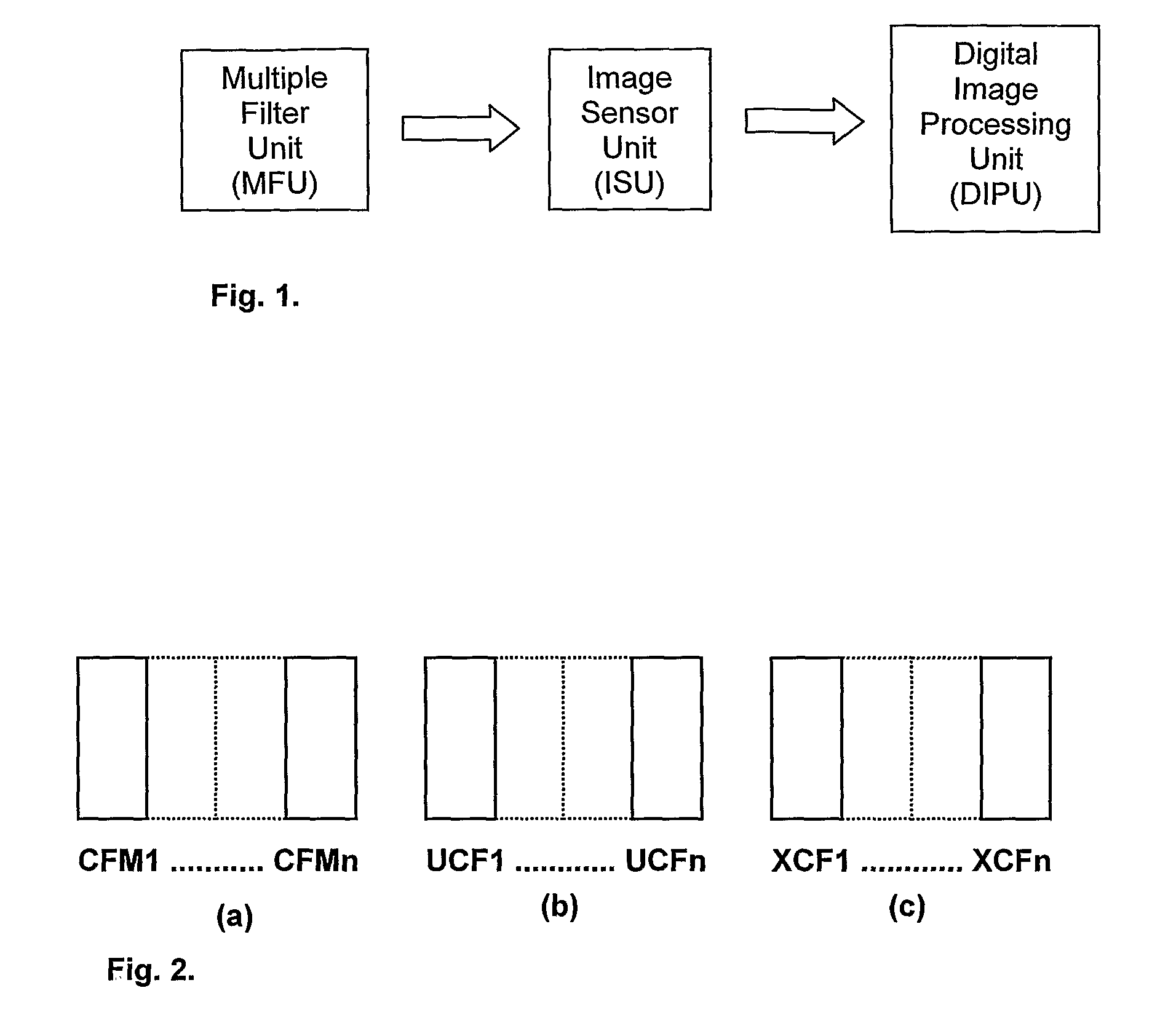
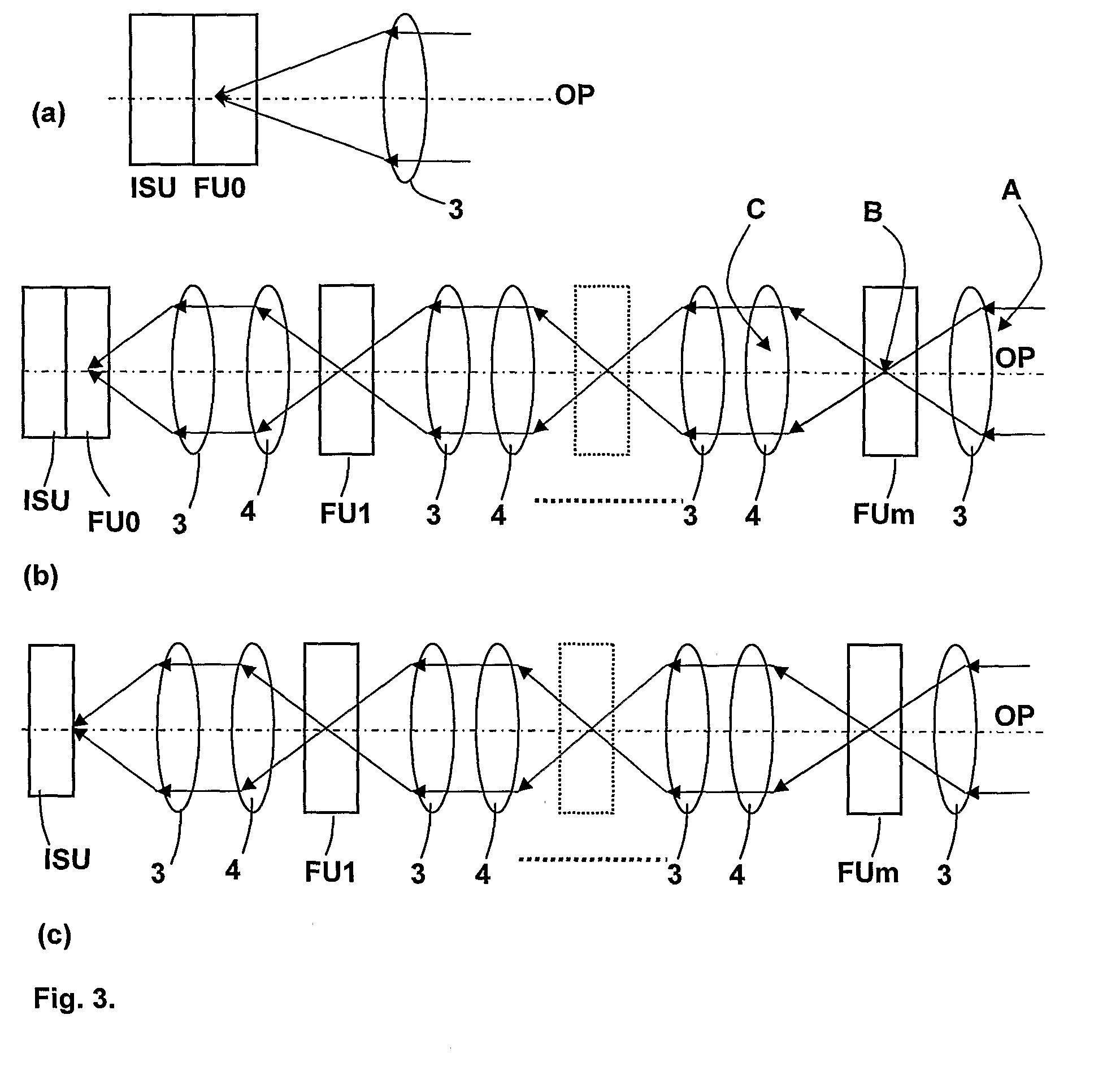
The present invention relates to the production of instantaneous or non-instantaneous multi-band images, to be transformed into multi- or hyperspectral images, comprising light collecting means (11), an image sensor (12) with at least one two dimensional sensor array (121), and an instantaneous colour separating means (123), positioned before the image sensor array (121) in the optical path (OP) of the arrangement (1), and first uniform spectral filters (13) in the optical path (OP), with the purpose of restricting imaging to certain parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. The present invention specifically teaches that a filter unit (FU) comprising colour or spectral filter mosaics and / or uniform colour or spectral filters mounted on filter wheels (114) or displayed by transmissive displays (115), is either permanently or interchangeably positioned before the colour separating means (123) in the optical path (OP) in, or close to, converged light (B). Each colour or spectral filter mosaic consists of a multitude of homogeneous filtering regions. The transmission curves (TC) of the filtering regions of a colour or spectral filter mosaic can be partly overlapping, in addition to overlap between these transmission curves and those belonging to the filtering regions of the colour separating means (123). The transmission curves (TC) of the colour or spectral filter mosaics and the colour separating means (123) are suitably spread out in the intervals of a spectrum to be studied. The combination of the colour separating means (123) and the spectral or colour or spectral filter mosaics produces different sets of linearly independent transmission curves (TC). The multiple-filter image captured by the image sensor (12) is demosaicked by identifying and segmenting the image regions that are affected by the regions of the multiple filter mosaic, and after an optional interpolation step, a multi-band image is obtained. The resulting multi-band image is transformed into a multi- or hyperspectral image.
Owner:RP VENTURES TECH OFFICE
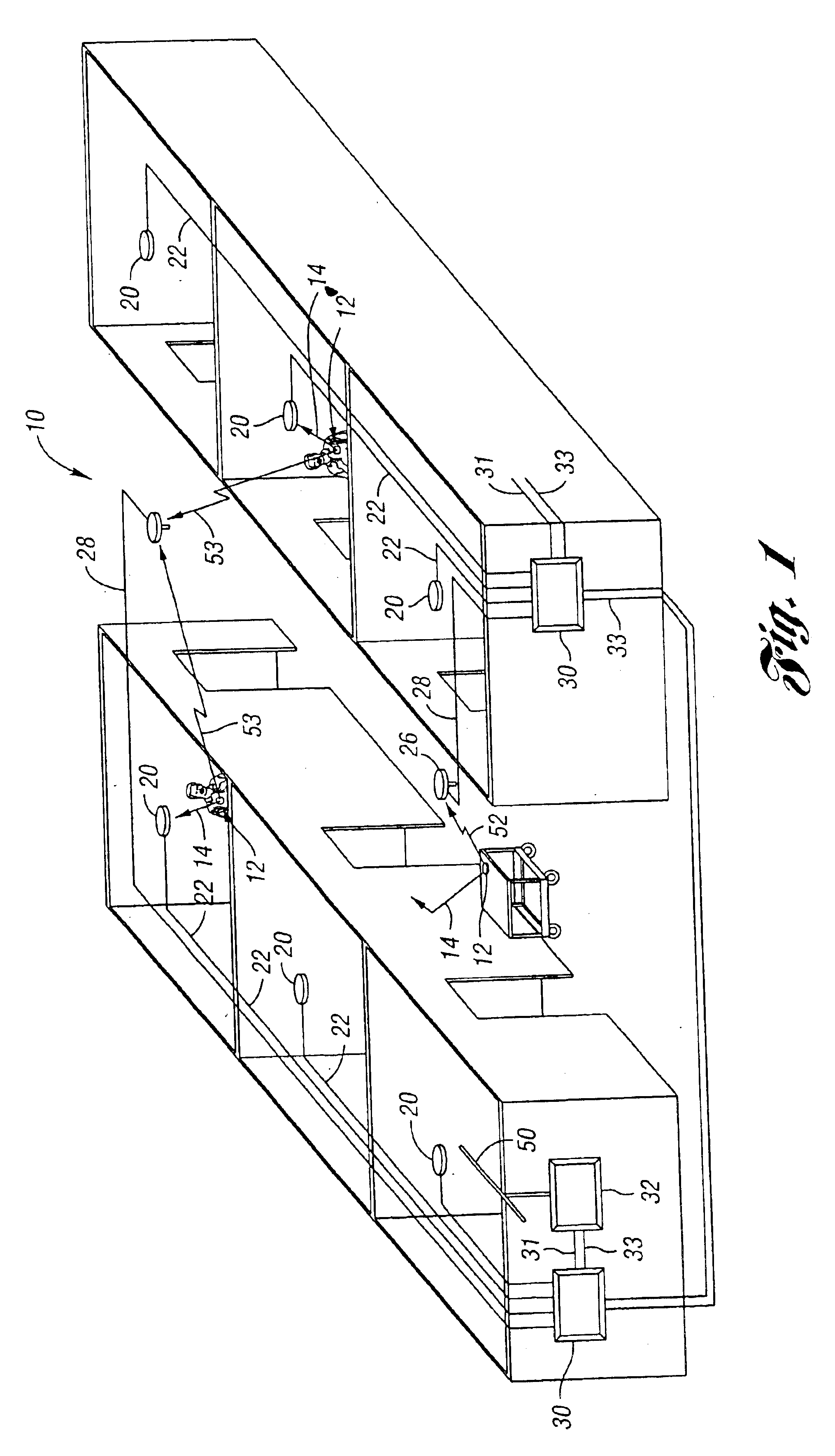
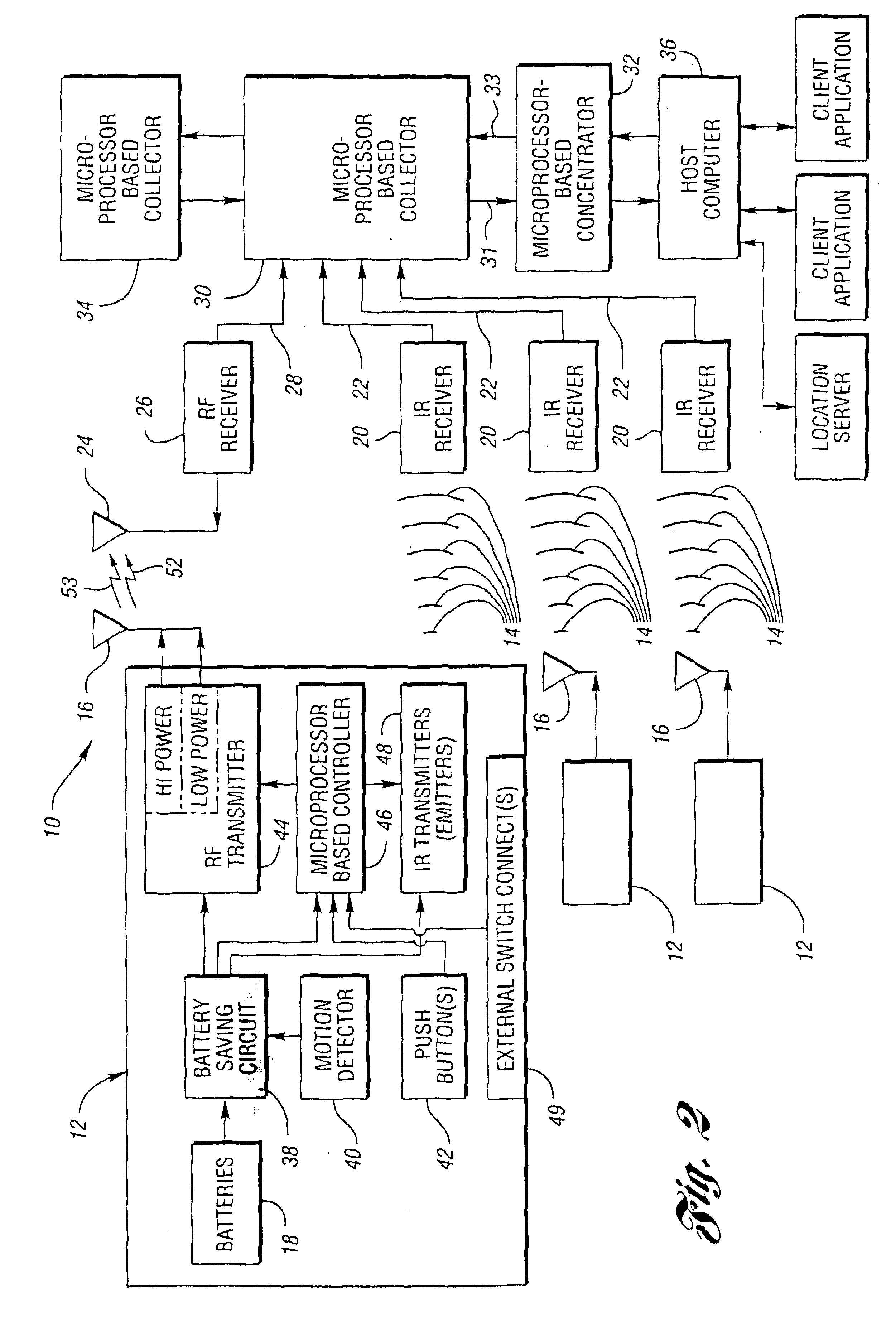
Methods and systems for locating subjects and providing event notification within a tracking environment and badge for use therein
InactiveUS6838992B2Increase powerElectric signal transmission systemsPosition fixationWide areaFrequency spectrum
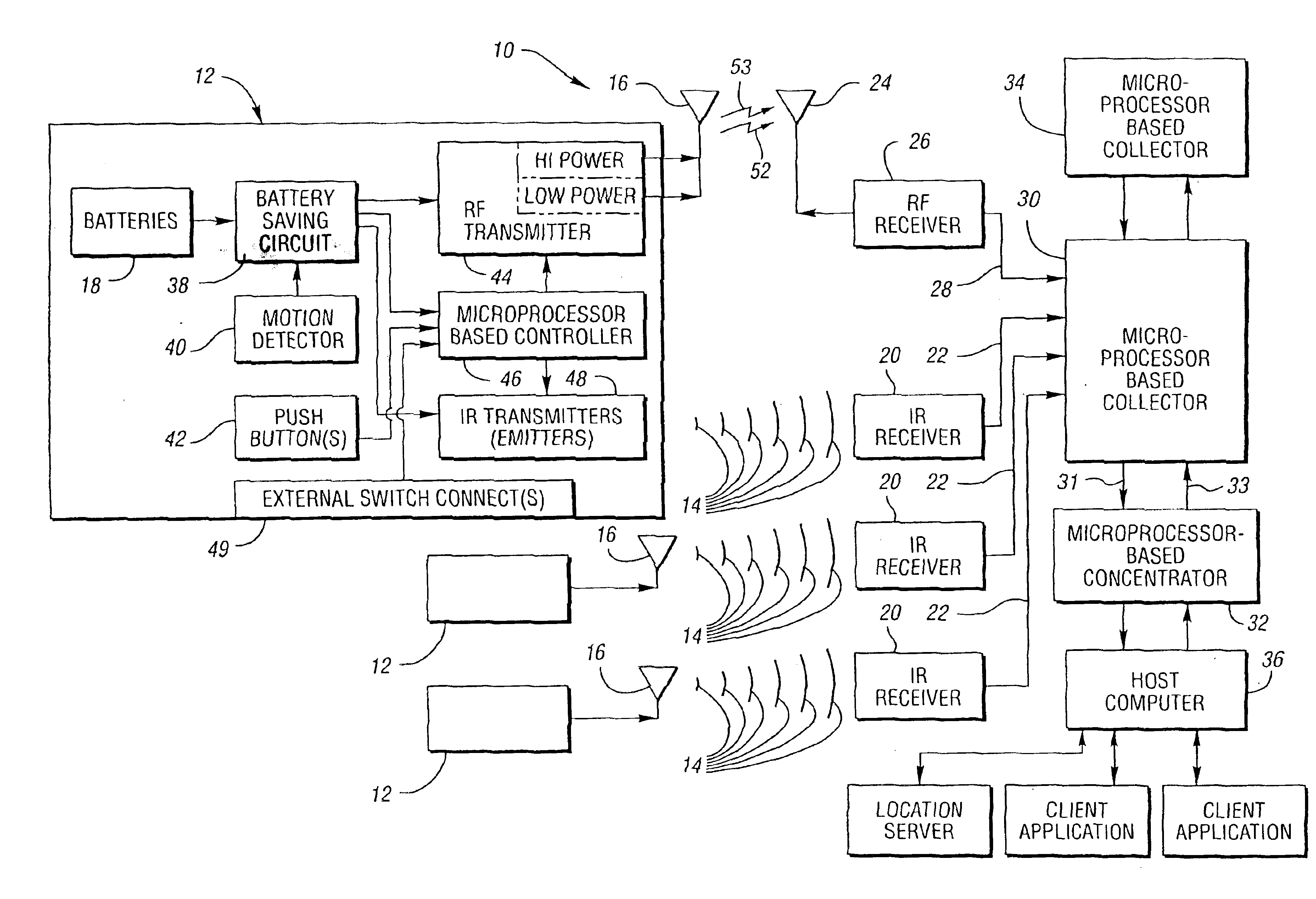
A method, system and a badge utilized therein utilize both the radio frequency (RF) and infrared (IR) parts of the electromagnetic spectrum to locate subjects (i.e. objects and persons) within a tracking environment. The system includes a battery-operated, microprocessor-based badge for each subject to be located. Each badge automatically transmits: (1) shorter interval, digitized, infrared light signals to identify a delimited area zone of its subject's location; (2) shorter interval, digitized, lower power RF signals to provide a local area zone of its subject's location; and (3) longer interval, digitized, higher power RF signals to provide a wide area zone of its subject's location. Each badge transmits uniquely identifiable IR and higher power RF signals upon actuation of one or more push button switches integrated on the badge or a change of state of one or more external switch connections. Each higher power, longer interval, RF signal is a “supervisory” pulse. This pulse informs a host computer that the badge is in range of an RF receiver and is functional.
Owner:VERSUS TECHNOLOGY INC
Systems and methods that employ object recognition
ActiveUS20130229518A1Television system detailsColor television detailsElectromagnetic spectrumLighting system
An illumination system and methods to control a light source are provided. An illumination system includes a light source, a two-dimensional non-Passive Infrared (non-PIR) imager, and a controller. The light source may provide at least two levels of illumination. The non-PIR imager images an area and to produce image data representative of images across at least part of a visible portion of an electromagnetic spectrum. The controller is communicatively coupled to receive the image data from the non-PIR imager and process the received image data to detect at least one object in the area of a defined type of object. The controller is also coupled to control operation of the light source based on, at least in part, detection of the ambient characteristic of the environment. Alternatively, one or more components of a system may be used to monitor traffic, with or without active illumination.
Owner:EXPRESS IMAGING SYST
Temporary hair removal method
InactiveUS6824542B2Stable removalEasy to operateDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsPR intervalSkin surface
A hand held device generates a predetermined number of pulses of light having a predetermined electromagnetic spectrum, a predetermined duration, a predetermined inter-pulse interval, and a predetermined total energy. The pulse sequence is delivered to a skin surface to temporarily remove hair. A period of time for reappearance of hair on the selected skin surface after the using of the device to remove hair from the selected skin surface is determined by counting the days to hair reappearance after a test light application. Subsequently, the device is used periodically to apply the pulses of light to the selected skin surface at intervals of shorter length than the determined period of hair regeneration, thereby temporarily maintaining the selected skin surface free of visible hair.
Owner:JAY HARVEY H
System and methods for detection and identification of chemical substances
InactiveUS20050077476A1MinimizesHigh sensitivityRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationAnesthetic AgentSpectrograph
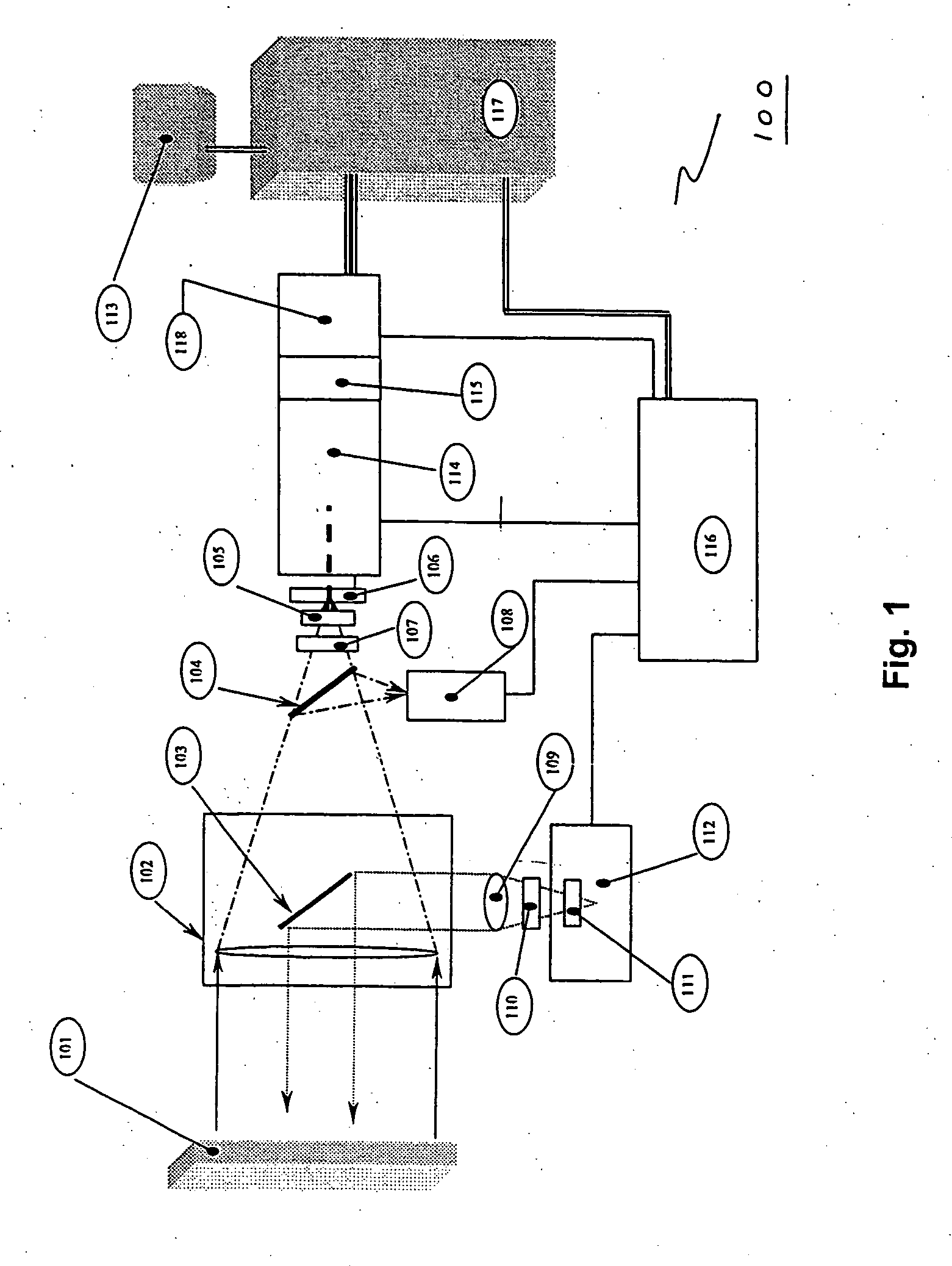
The invention provides a system and method utilizing, among other things, fluorescence spectroscopy in the ultraviolet portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to determine chemical species and concentrations. The basic measuring system includes optics, a spectrograph, a detector, and an energy source (“head” components), along with a computer and control electronics and power source capable of generating and detecting unique fluorescence signatures for individual and unique mixtures of chemical substances including, for example, prescribed and / or compounded medications, alcohol products, food types, synthetic drugs, narcotics, perfumes, liquids, and the like.
Owner:CDEX
System for multi- and hyperspectral imaging
InactiveUS7835002B2Improve performanceCost effectiveRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSensor arrayElectromagnetic spectrum
Owner:RP VENTURES TECH OFFICE
Copy protected display screen
InactiveUS20040091110A1Quality improvementInternal/peripheral component protectionTelevision systemsComputer graphics (images)Radiology
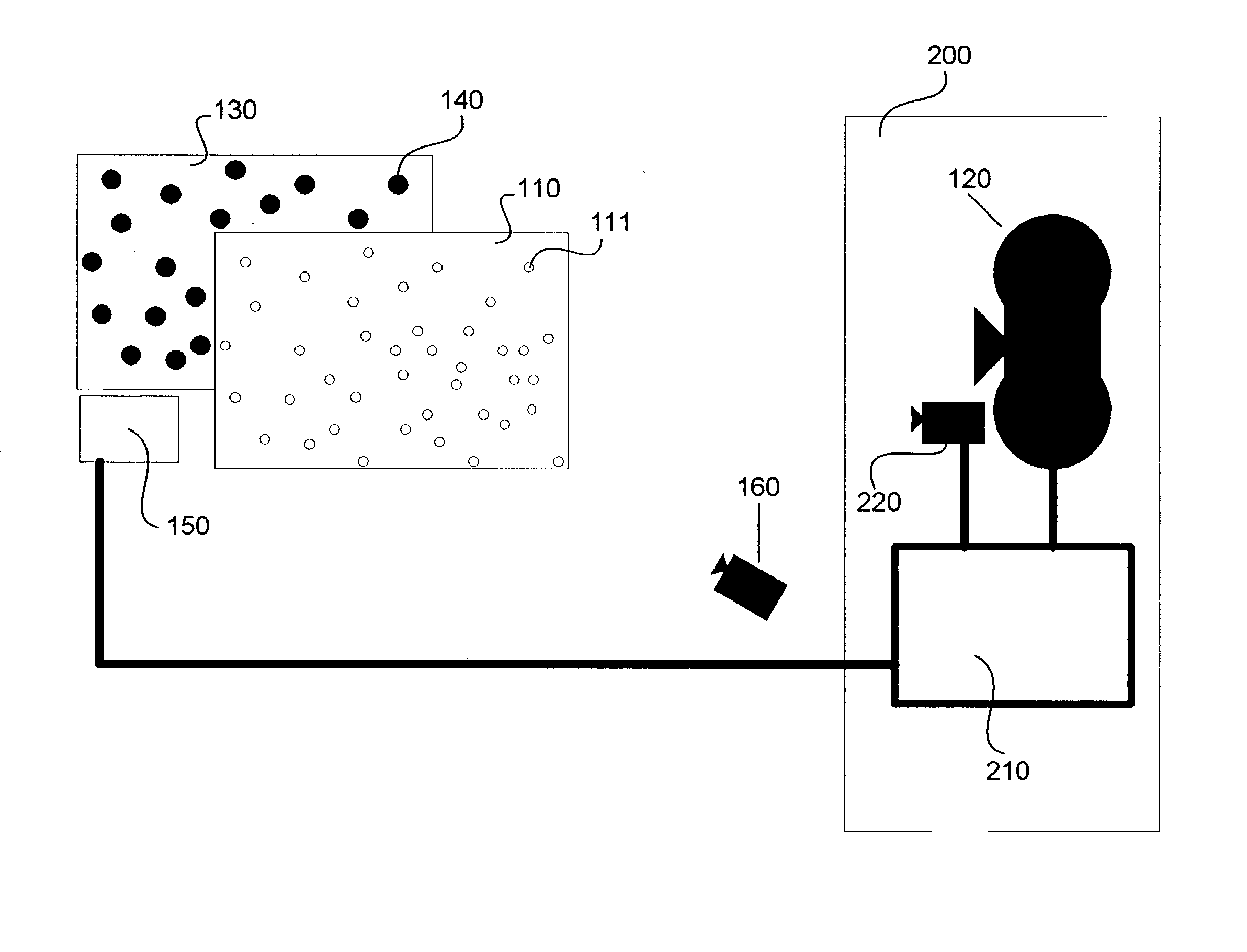
A display system capable of displaying an image is modified with one or more elements that emit energy (140) that is outside the range of human perception, but within the range that is detected by the sensors used in a mechanical recording device (160). This energy could be in the infrared range of the electromagnetic spectrum. With this modification the display screen (110) will produce two simultaneous, or near simultaneous, images. The first image, seen by a human observer, will differ from the second image captured by the sensors of a recording device, such as a video camera.
Owner:BARKANS ANTHONY CHRISTIAN
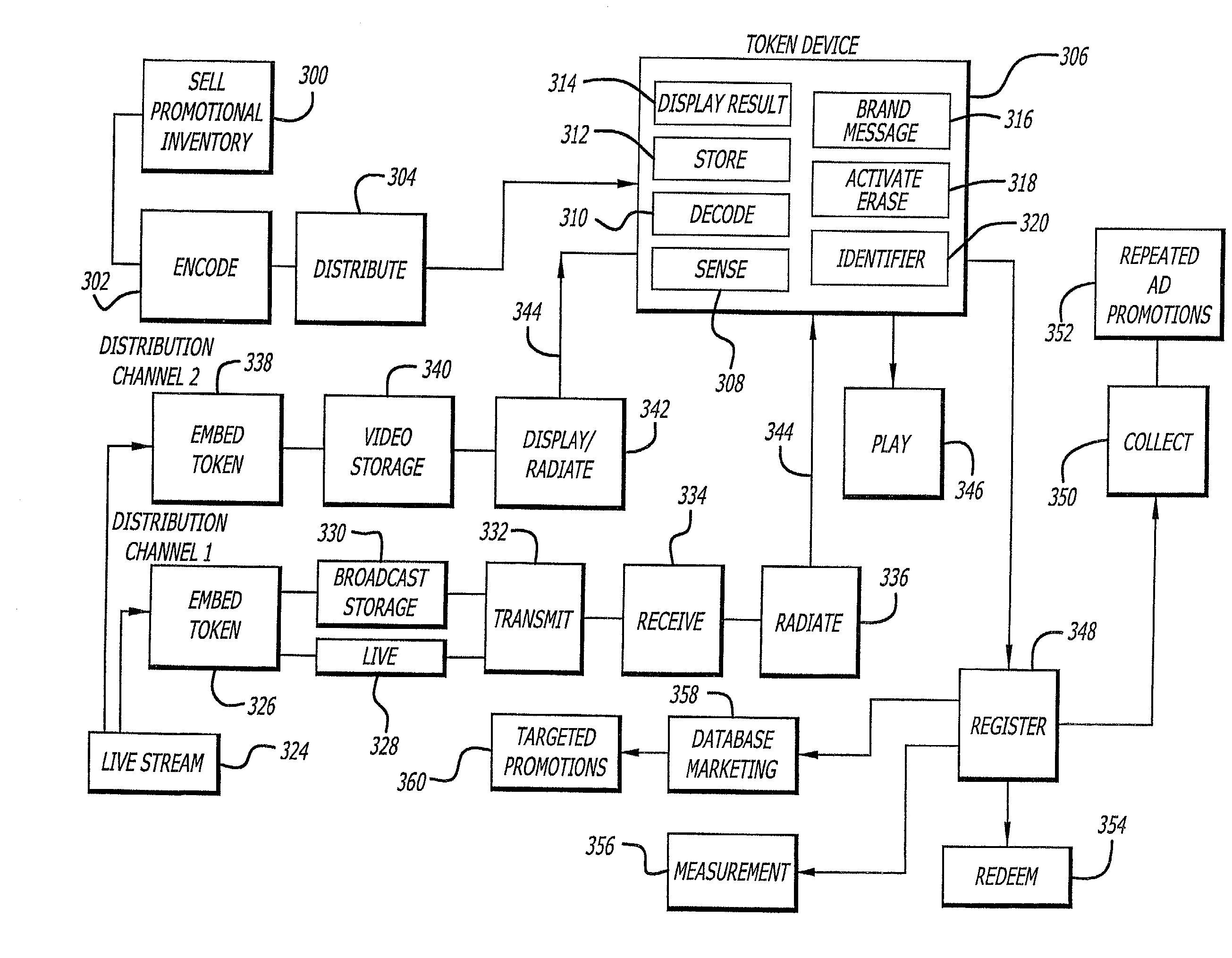
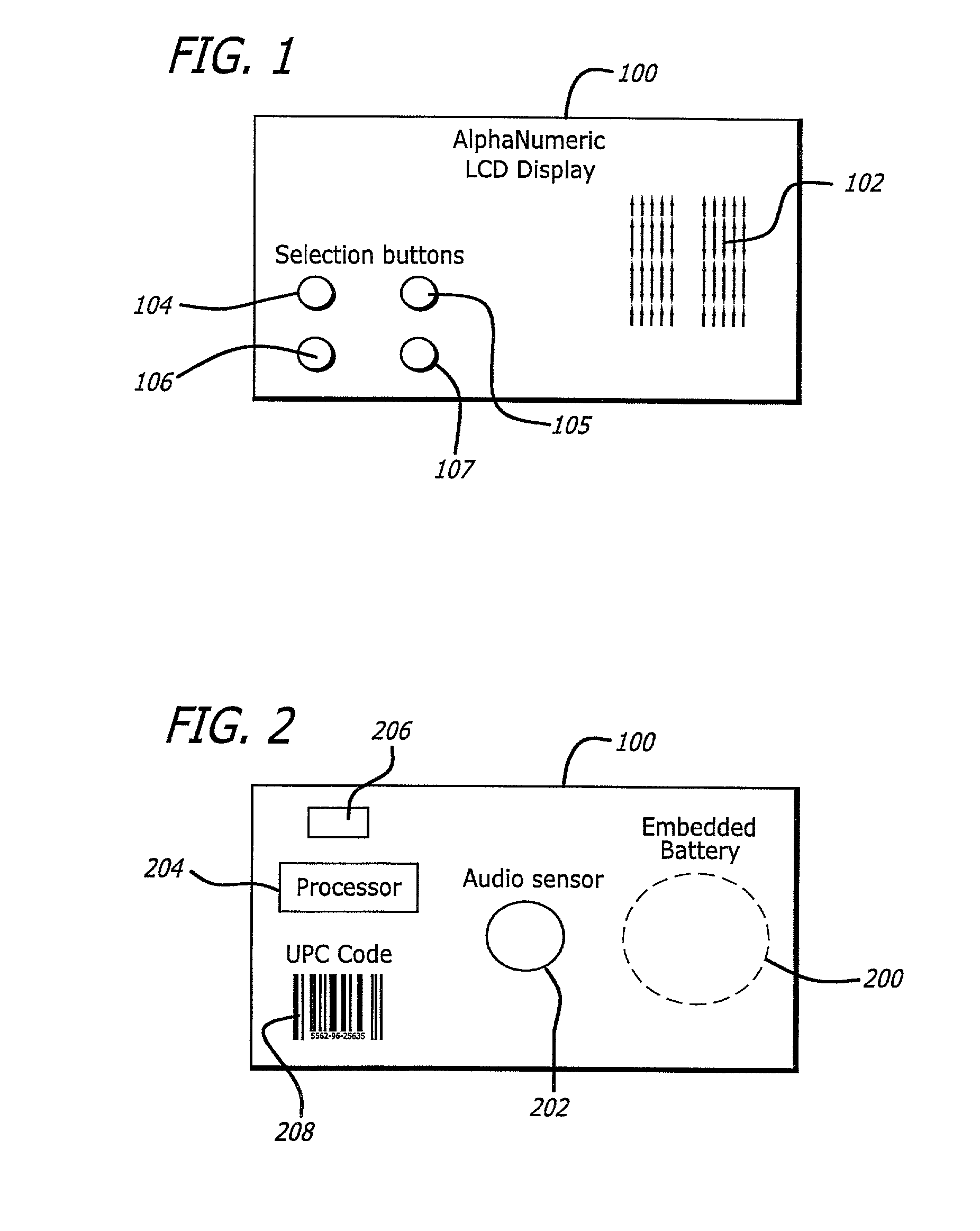
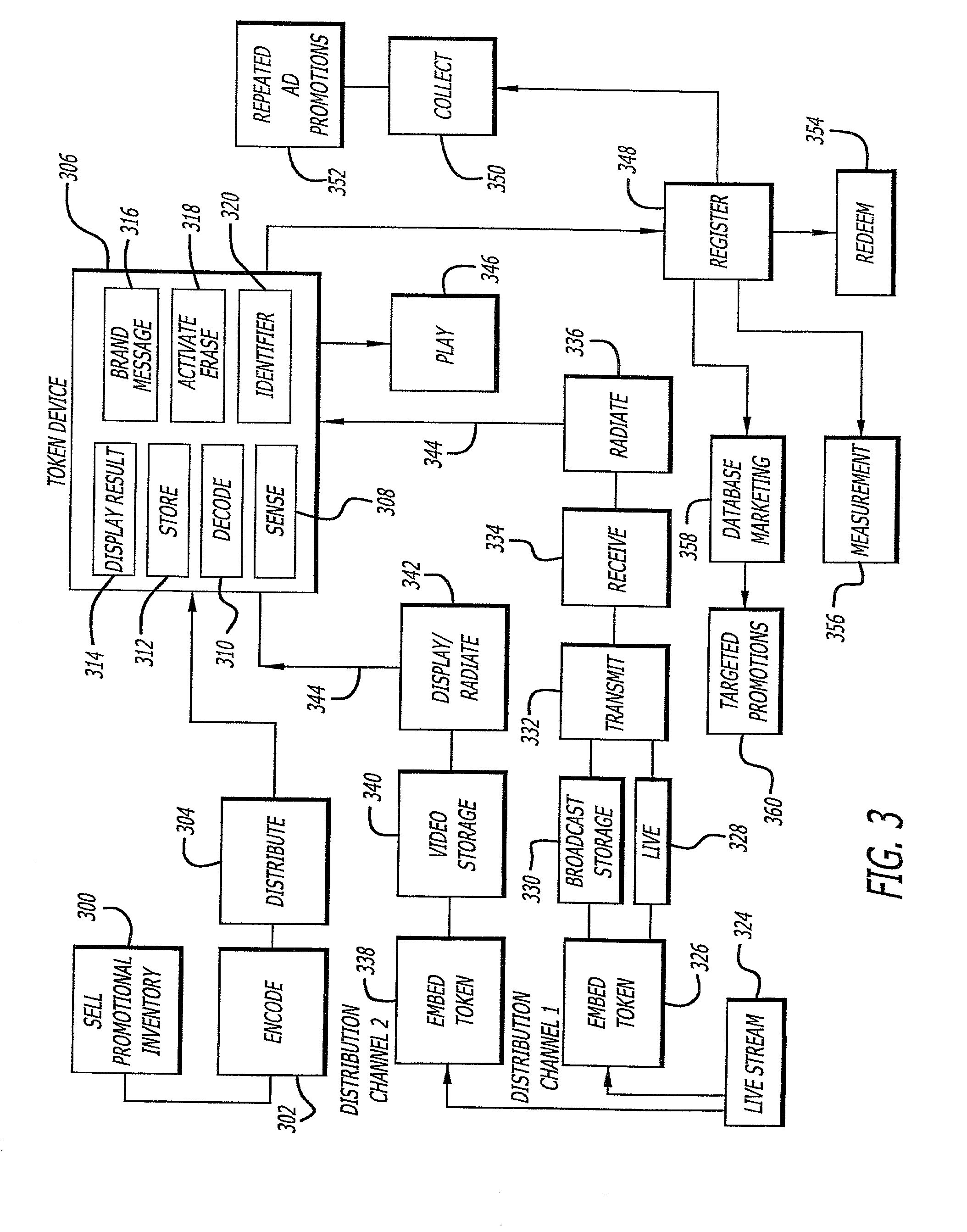
Processes for exploiting electronic tokens to increase broadcasting revenue
InactiveUS20020049967A1Low costEasy to collectTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsFrequency spectrumElectromagnetic spectrum
A system and method for utilizing electronic tokens to increase broadcasting tokens is disclosed. Electronic tokens comprise encoded data that are embedded within broadcasting content and radiated from broadcast appliances, such as in the inaudible ranges of an acoustic spectrum or in an electromagnetic spectrum. The radiated tokens are then captured by a token capture device (TCD) possessed by a consumer. Upon receipt of the token from the broadcast, the TCD processes the token and becomes of value to the consumer. For example, the token may cause the TCD to light up, indicating that the consumer has won a prize. A TCD having indication of token receipt thereon may then be redeemed by the consumer for a prize, thus generating incentive for viewing the broadcast and using the TCD to capture the tokens embedded therein.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
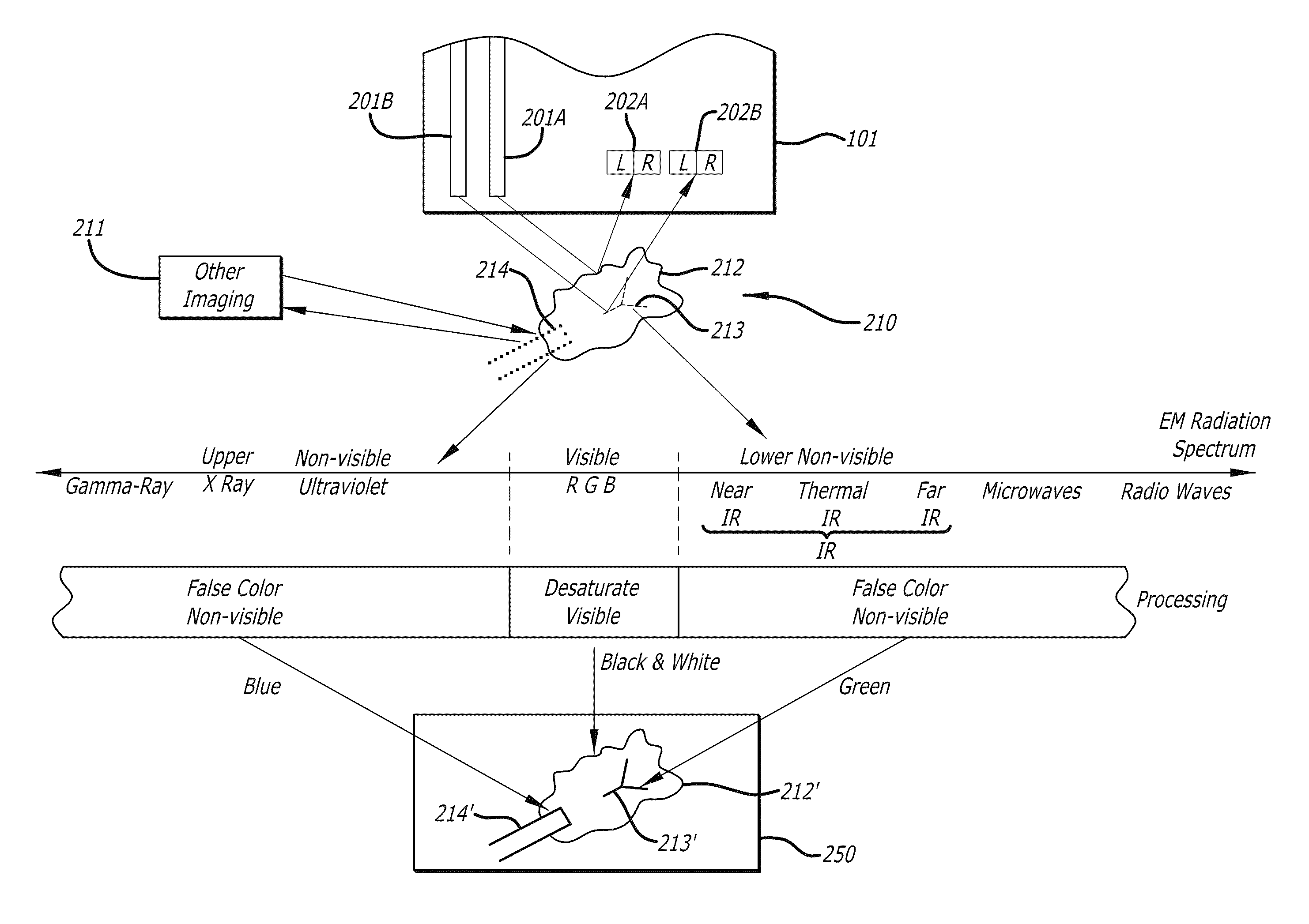
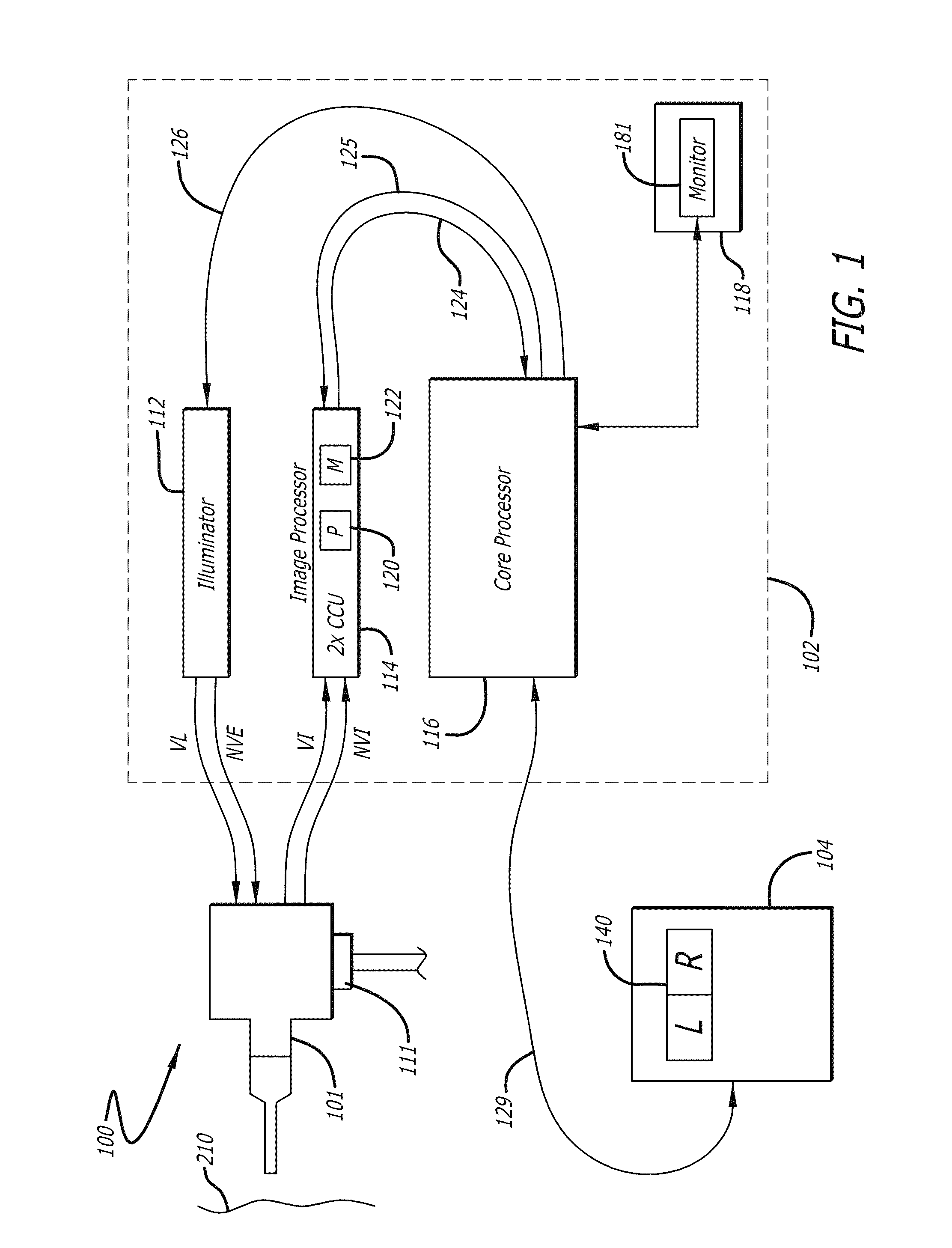
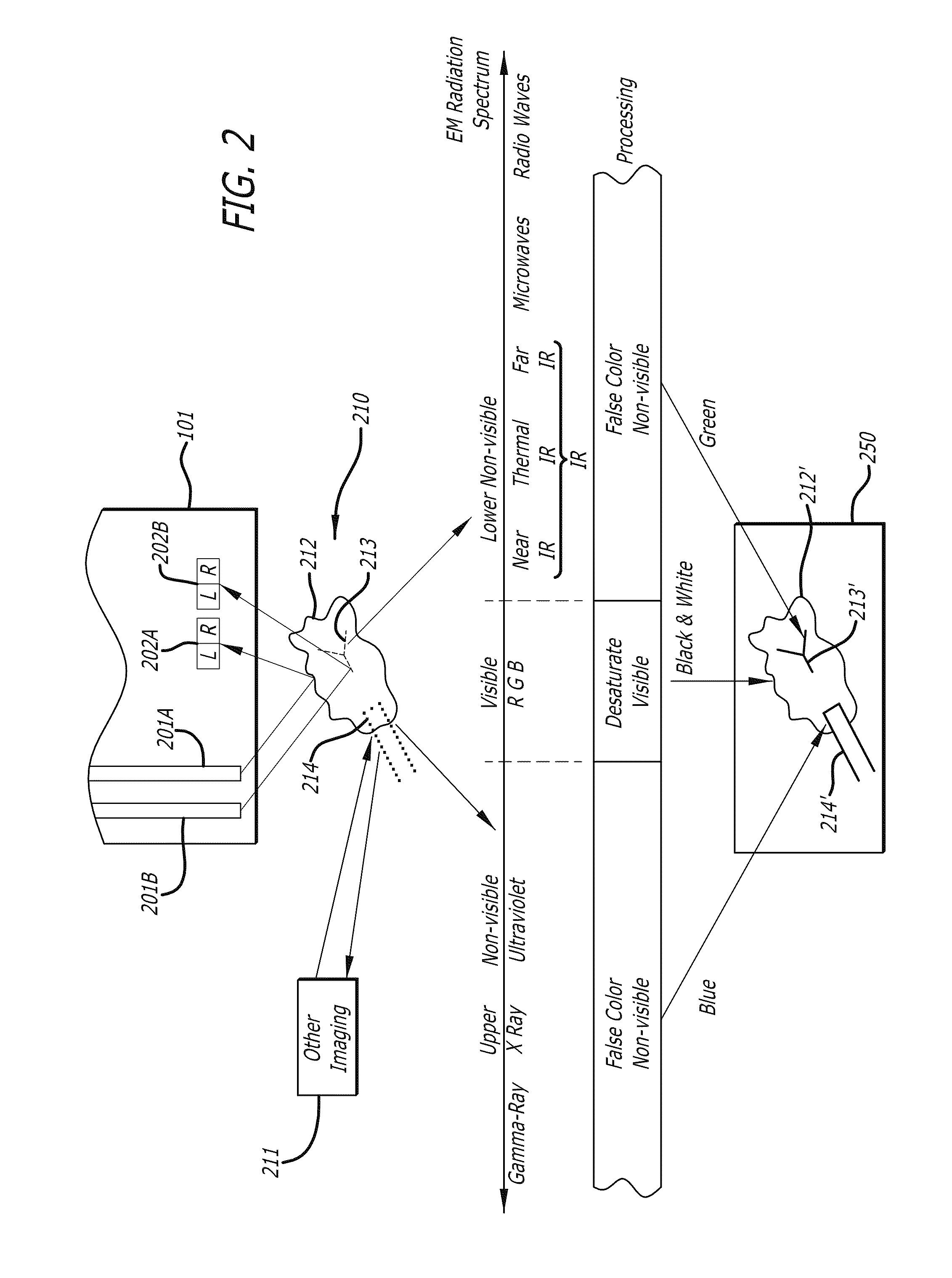
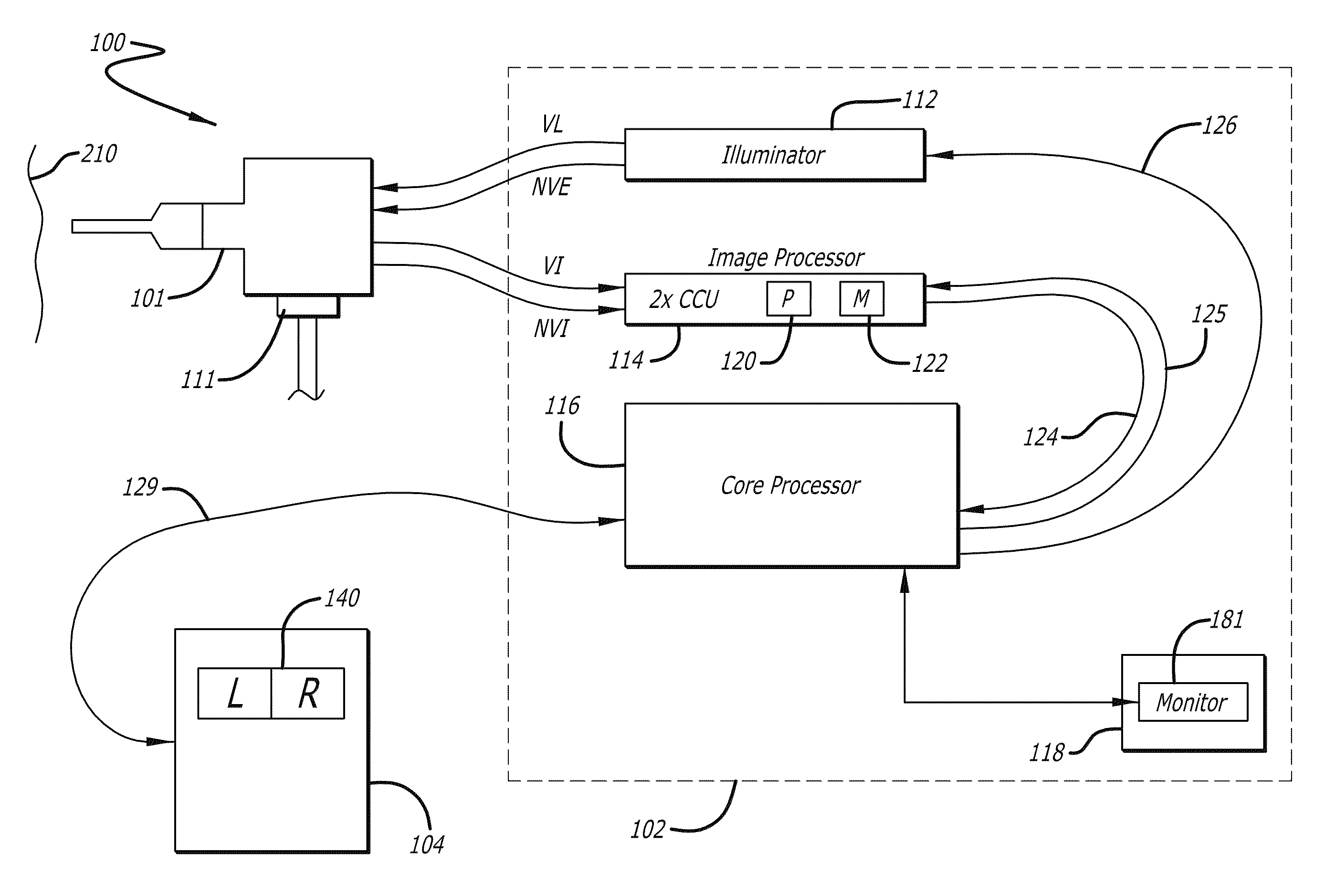
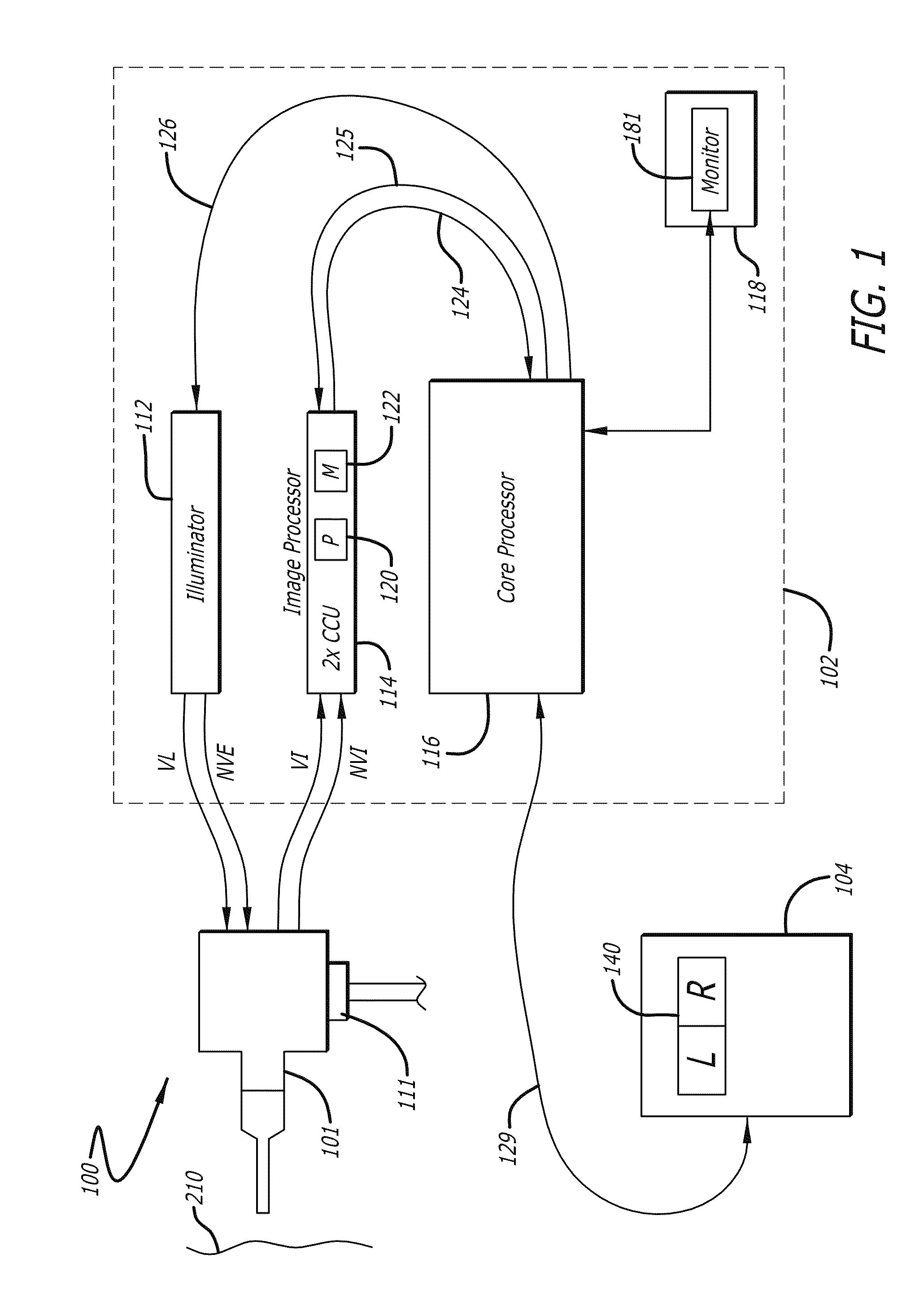
Methods and apparatus for displaying enhanced imaging data on a clinical image
In one embodiment of the invention, an apparatus includes a display device. The display device displays a desaturated image of tissue captured in the visible electro-magnetic (EM) spectrum from a body cavity; and a first color enhanced image combined with the desaturated image. The first color enhanced image represents the first data captured from the body cavity outside the visible electromagnetic spectrum. The relative brightness between the desaturated image and the first color enhanced image is set to emphasize the first data over the tissue captured in the visible electromagnetic spectrum to provide improved information content.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Electrochromic devices utilizing very low band gap conjugated counter electrodes: preparation and use
ActiveUS20070008603A1Tenebresent compositionsNon-linear opticsElectromagnetic spectrumMolecular physics
Disclosed herein are electrochromic devices using a very low band-gap conjugated polymer having a band gap (Eg) of less than or equal to about 1.5 eV, and having little or no electrochromism in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Group III nitride light emitting devices with progressively graded layers
InactiveUS20030164507A1Improve emission efficiencyReduce non-radiative recombinationLaser detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor structureElectromagnetic spectrum
The present invention is a semiconductor structure for light emitting devices that can emit in the red to ultraviolet portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. The semiconductor structure includes a first cladding layer of a Group III nitride, a second cladding layer of a Group III nitride, and an active layer of a Group III nitride that is positioned between the first and second cladding layers, and whose bandgap is smaller than the respective bandgaps of the first and second cladding layers. The semiconductor structure is characterized by the absence of gallium in one or more of these structural layers.
Owner:CREE INC
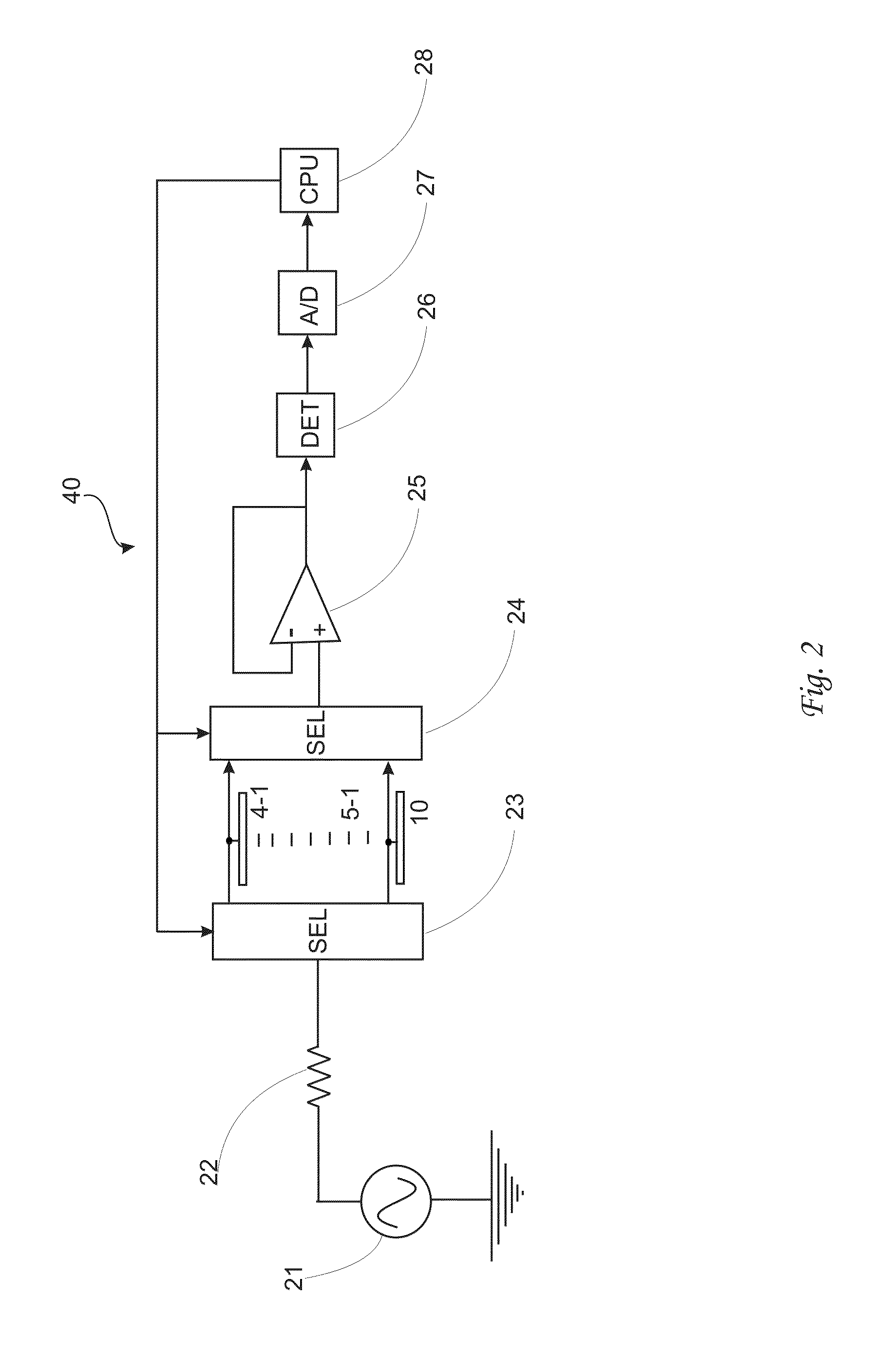
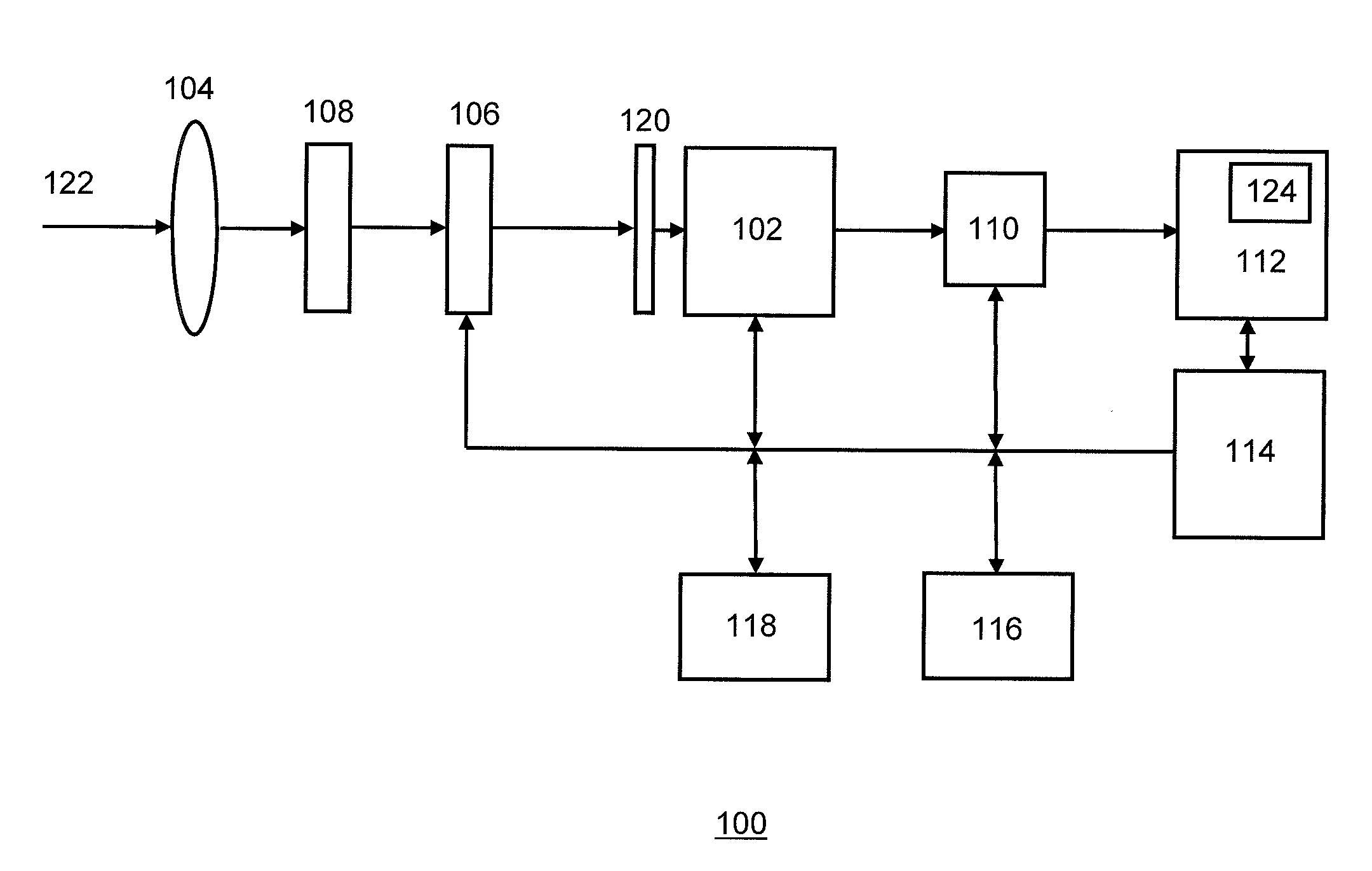
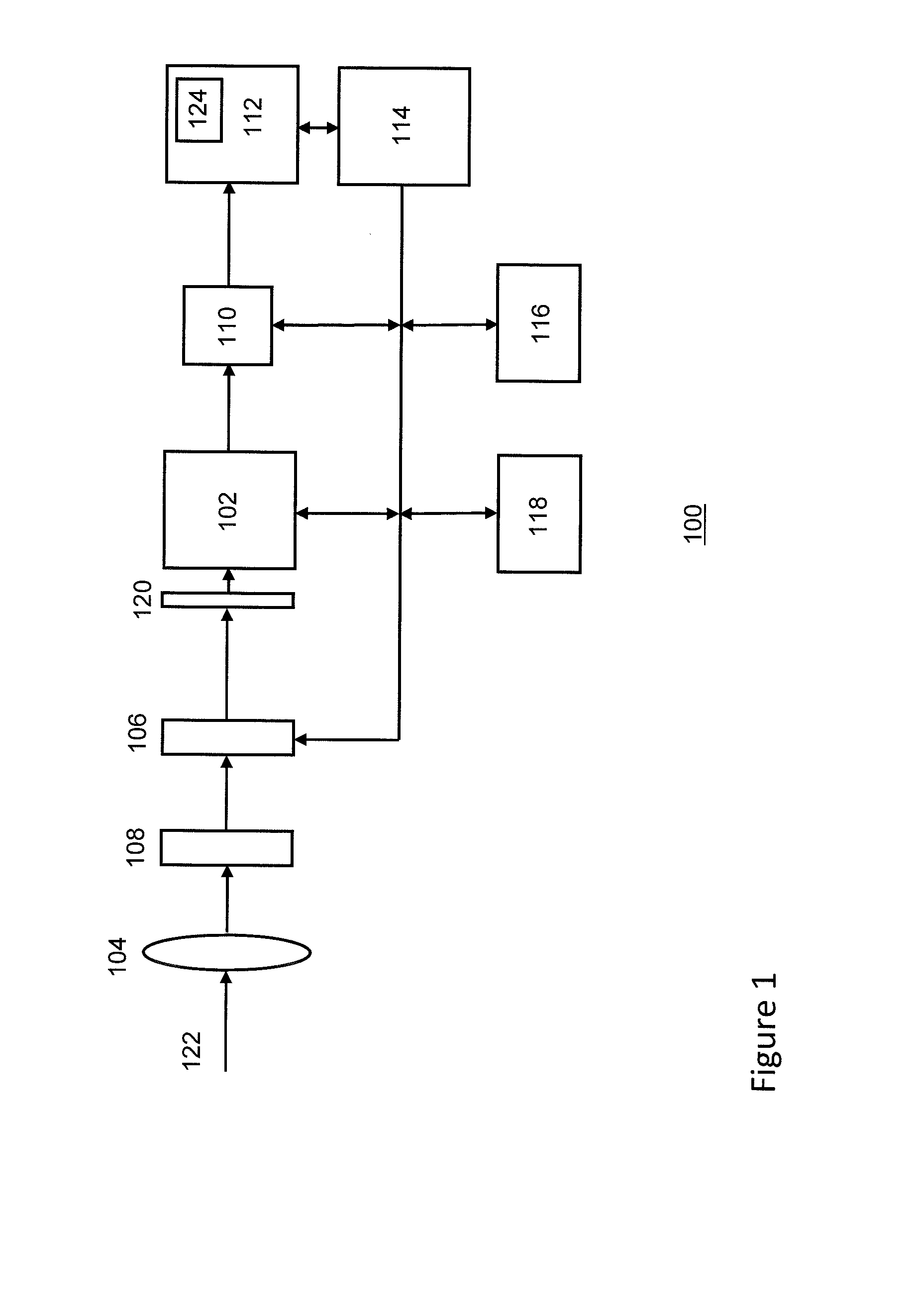
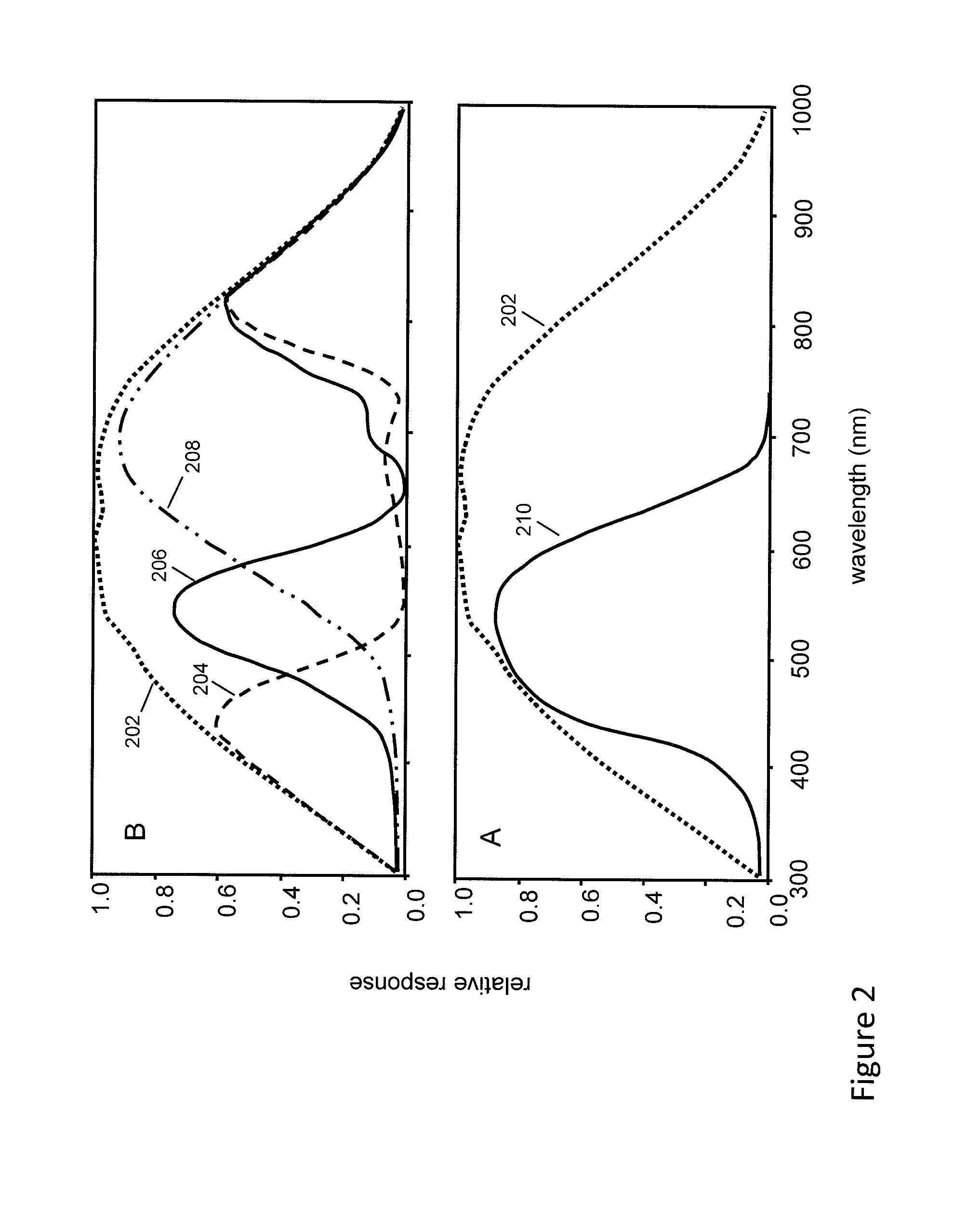
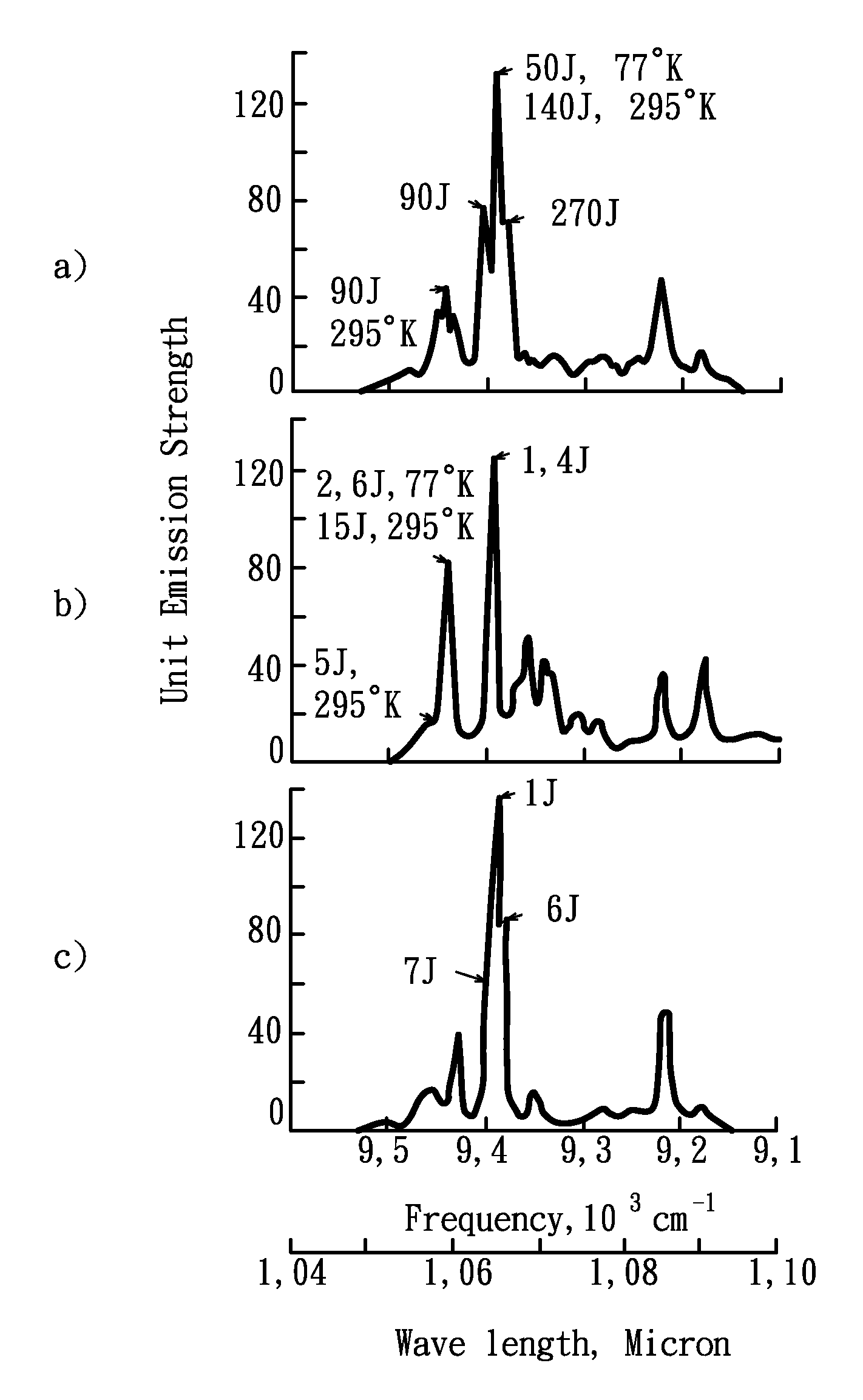
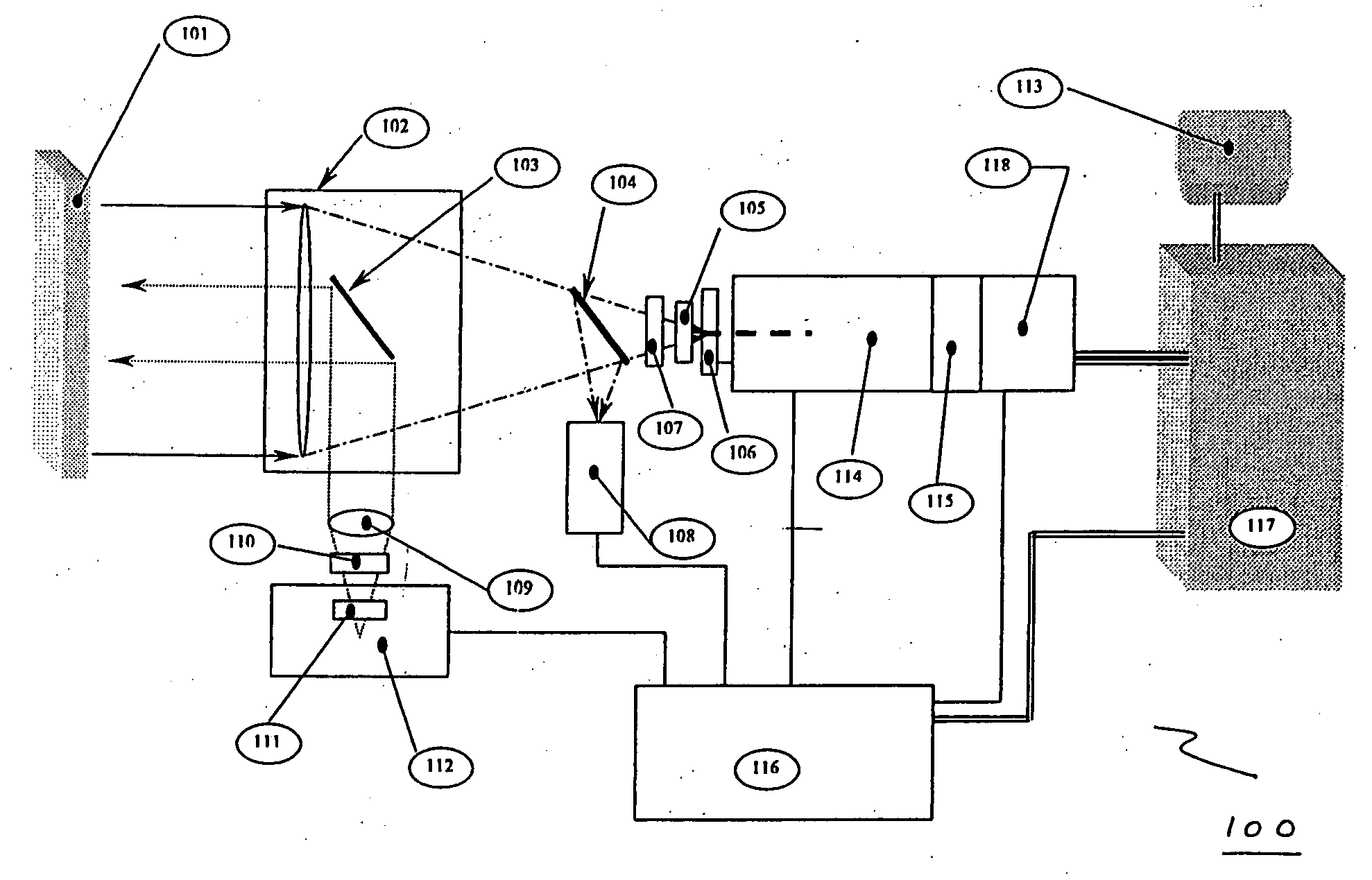
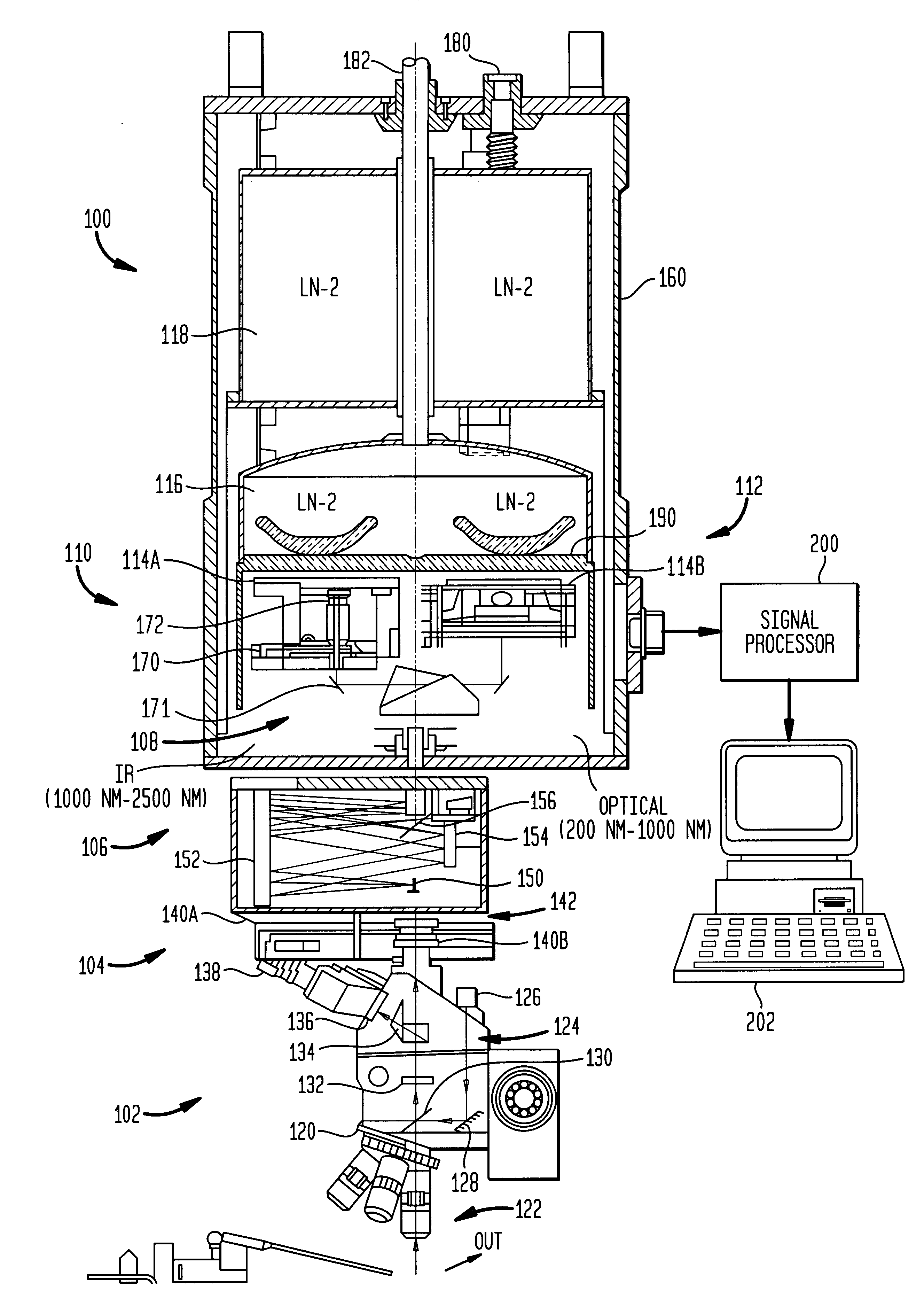
Multiwavelength imaging and spectroscopic photoemission microscope system
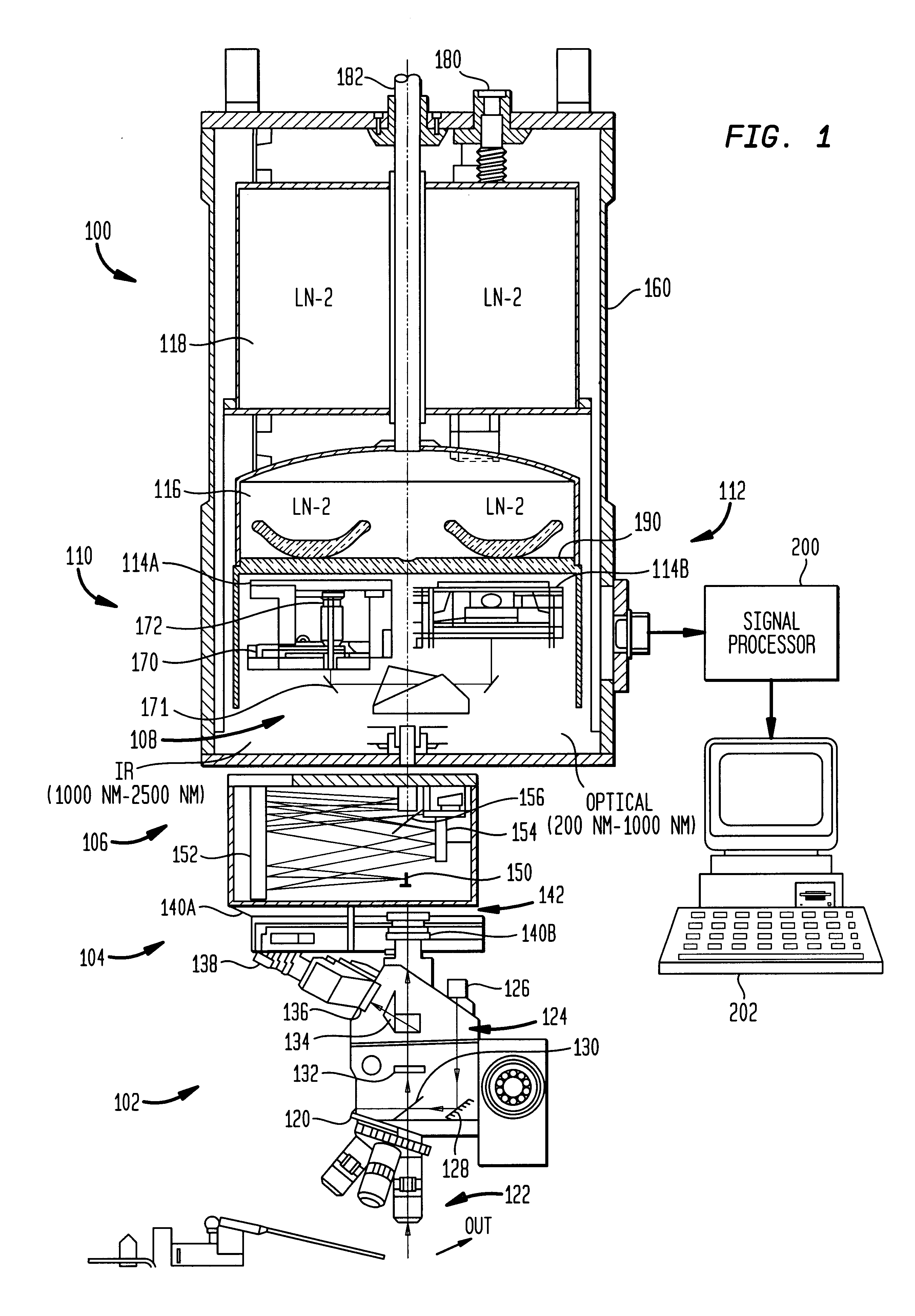
InactiveUS6222187B1Wide of electromagnetic emissionReduce the temperatureEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryBeam splitterSpectrograph
A multiwavelength imaging and spectroscopic photoemission microscope system (100) which simultaneously provides images in a broad range of the electromagnetic spectrum, such as between 200 nm-1000 nm (optical or visible light) and 1000 nm-500 nm (infrared light). The multiwavelength imaging and spectroscopic photoemission microscope system comprises a microscope (102), a spectrometer (106), a beam splitter (108), a first spectrum focal plane array (110) including an appropriate photodiode (114A), a second spectrum focal plane array (120) including an appropriate photodiode (114B), and a cryogenic vessel (160) to maintain relevant portions of the system at a very low temperature. The invention may be used in failure analysis of integrated circuits and in semiconductor and low temperature physics.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
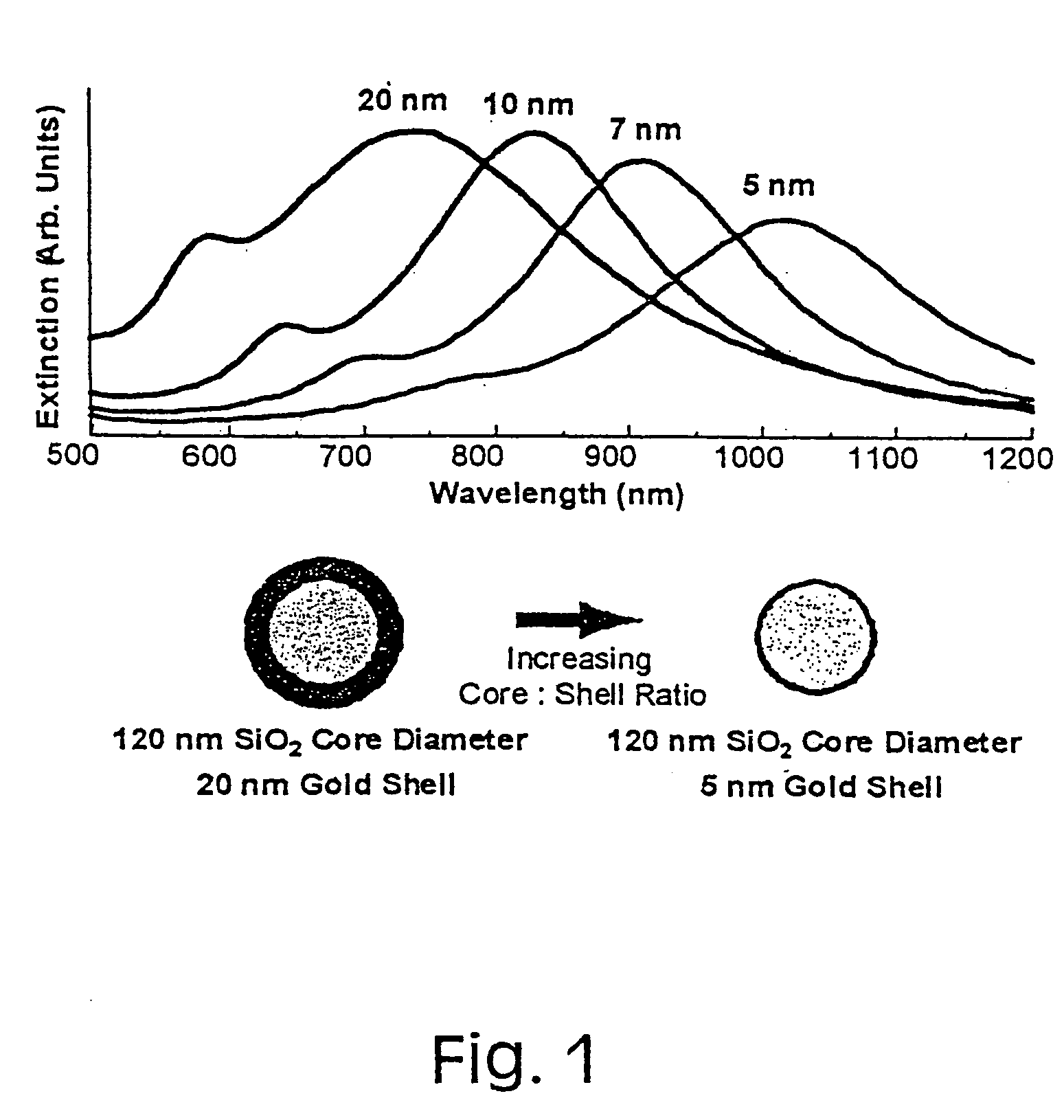
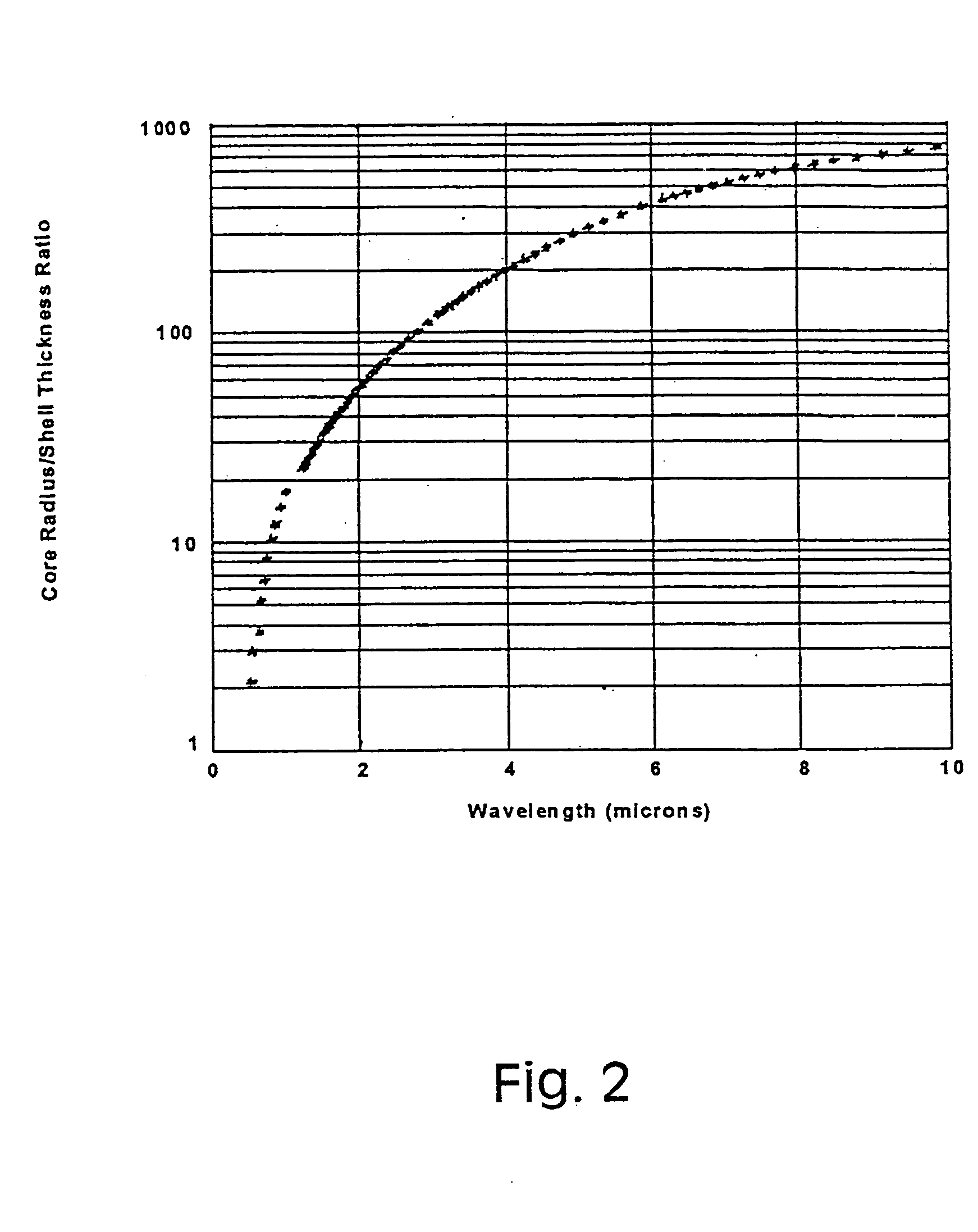
Metal nanoshells for biosensing applications
InactiveUS20050130324A1Eliminate needBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPigmenting treatmentUltravioletIn vivo
The present invention provides nanoshell particles (“nanoshells”) for use in biosensing applications, along with their manner of making and methods of using the nanoshells for in vitro and in vivo detection of chemical and biological analytes, preferably by surface enhanced Raman light scattering. The preferred particles have a non-conducting core and a metal shell surrounding the core. For given core and shell materials, the ratio of the thickness (i.e., radius) of the core to the thickness of the metal shell is determinative of the wavelength of maximum absorbance of the particle. By controlling the relative core and shell thicknesses, biosensing metal nanoshells are fabricated which absorb light at any desired wavelength across the ultraviolet to infrared range of the electromagnetic spectrum. The surface of the particles are capable of inducing an enhanced SERS signal that is characteristic of an analyte of interest. In certain embodiments a biomolecule is conjugated to the metal shell and the SERS signal of a conformational change or a reaction product is detected.
Owner:RICE UNIV
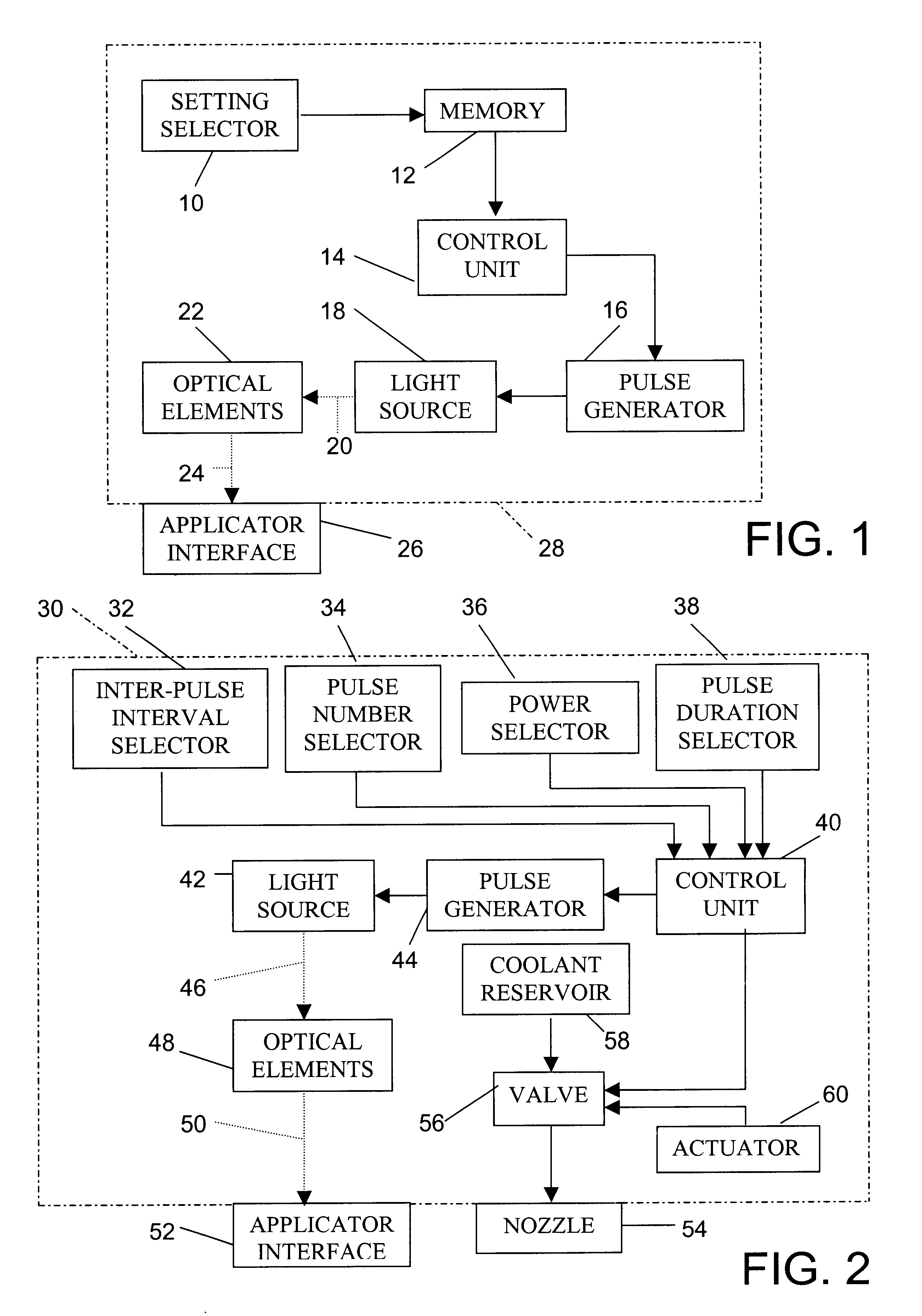
Hair treatment method
InactiveUS6916316B2Easy to useClean evenlyRotary piston pumpsSurgical instrument detailsPR intervalLight energy
A hand held device generates a predetermined number of pulses of light having a predetermined electromagnetic spectrum, a predetermined duration, a predetermined inter-pulse interval, and a predetermined total energy. The pulse sequence is delivered to a skin surface to temporarily remove hair through the absorption of light energy only by endogenous chromophores of the hair. Exogenous chromophores for light absorpotion are not applied to the skin surface at any time. A period of time for reappearance of hair on the selected skin surface after the using of the device to remove hair from the selected skin surface is determined by counting the days to hair reappearance after a test light application. Subsequently, the device is used periodically to apply the pulses of light to the selected skin surface at intervals of shorter length than the determined period of hair regeneration, thereby temporarily maintaining the selected skin surface free of visible hair.
Owner:JAY HARVEY H
Methods and apparatus for displaying enhanced imaging data on a clinical image
ActiveUS8706184B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementElectromagnetic spectrumDisplay device
In one embodiment of the invention, an apparatus includes a display device. The display device displays a desaturated image of tissue captured in the visible electro-magnetic (EM) spectrum from a body cavity; and a first color enhanced image combined with the desaturated image. The first color enhanced image represents the first data captured from the body cavity outside the visible electromagnetic spectrum. The relative brightness between the desaturated image and the first color enhanced image is set to emphasize the first data over the tissue captured in the visible electromagnetic spectrum to provide improved information content.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com