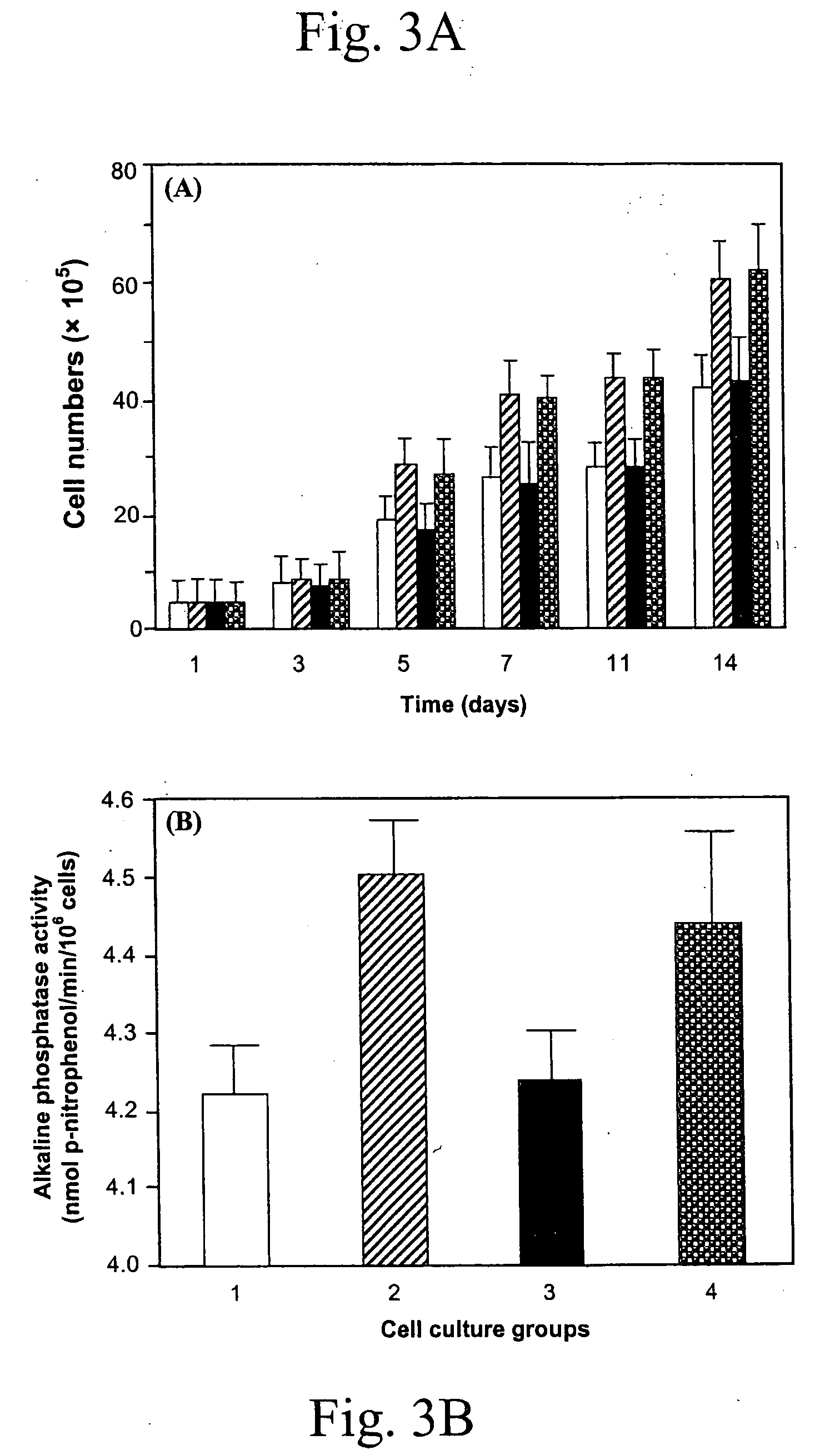
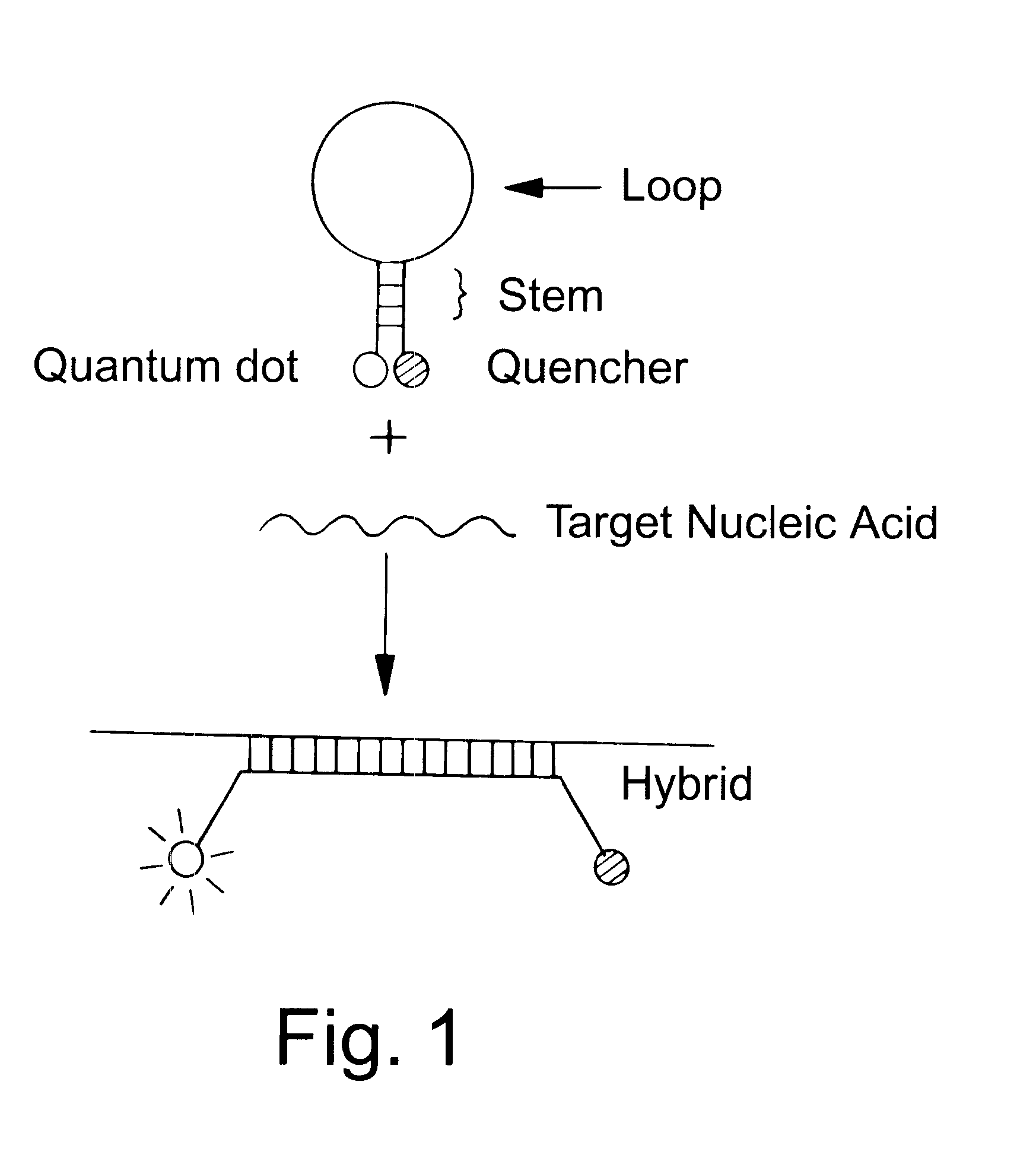
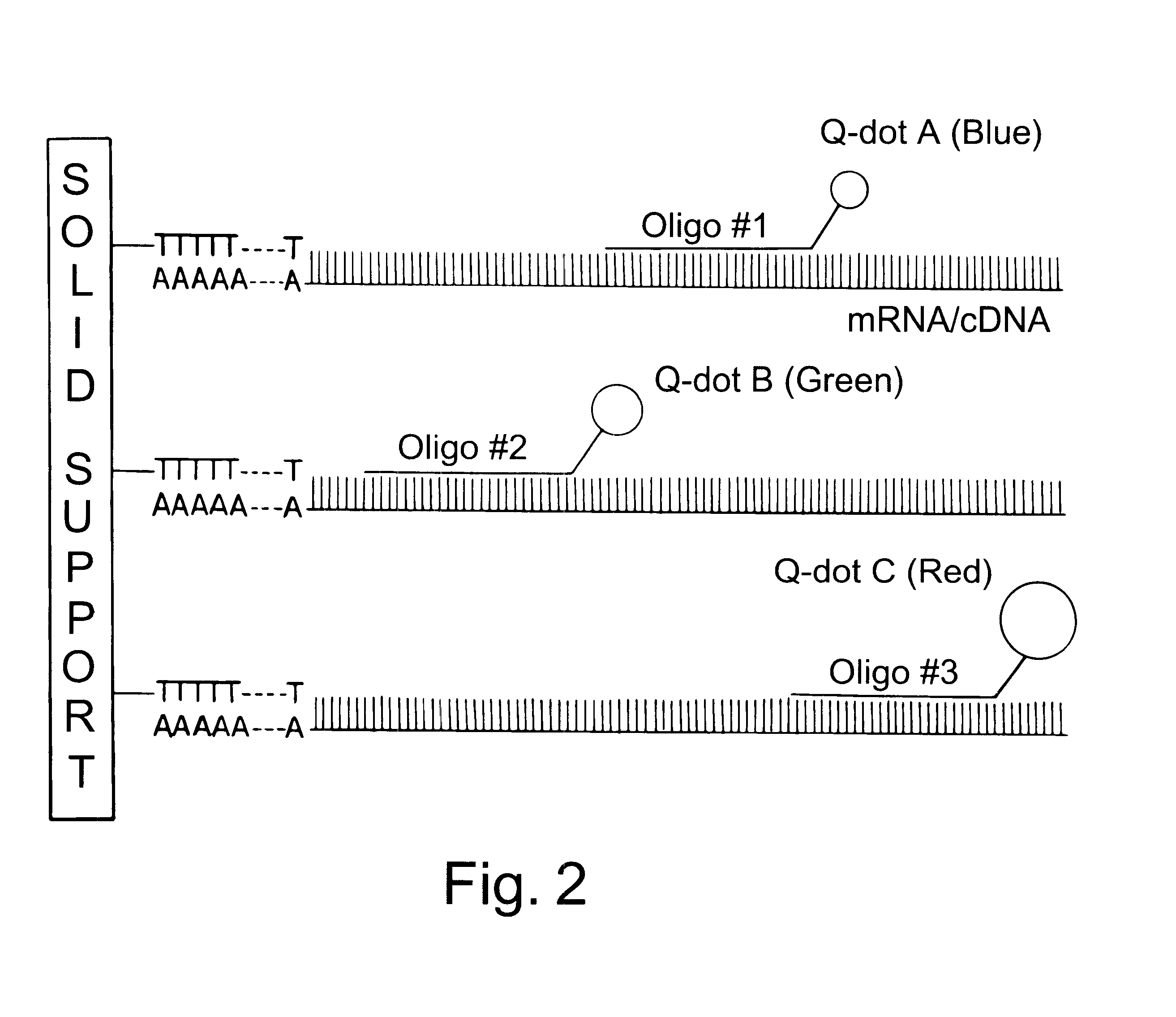
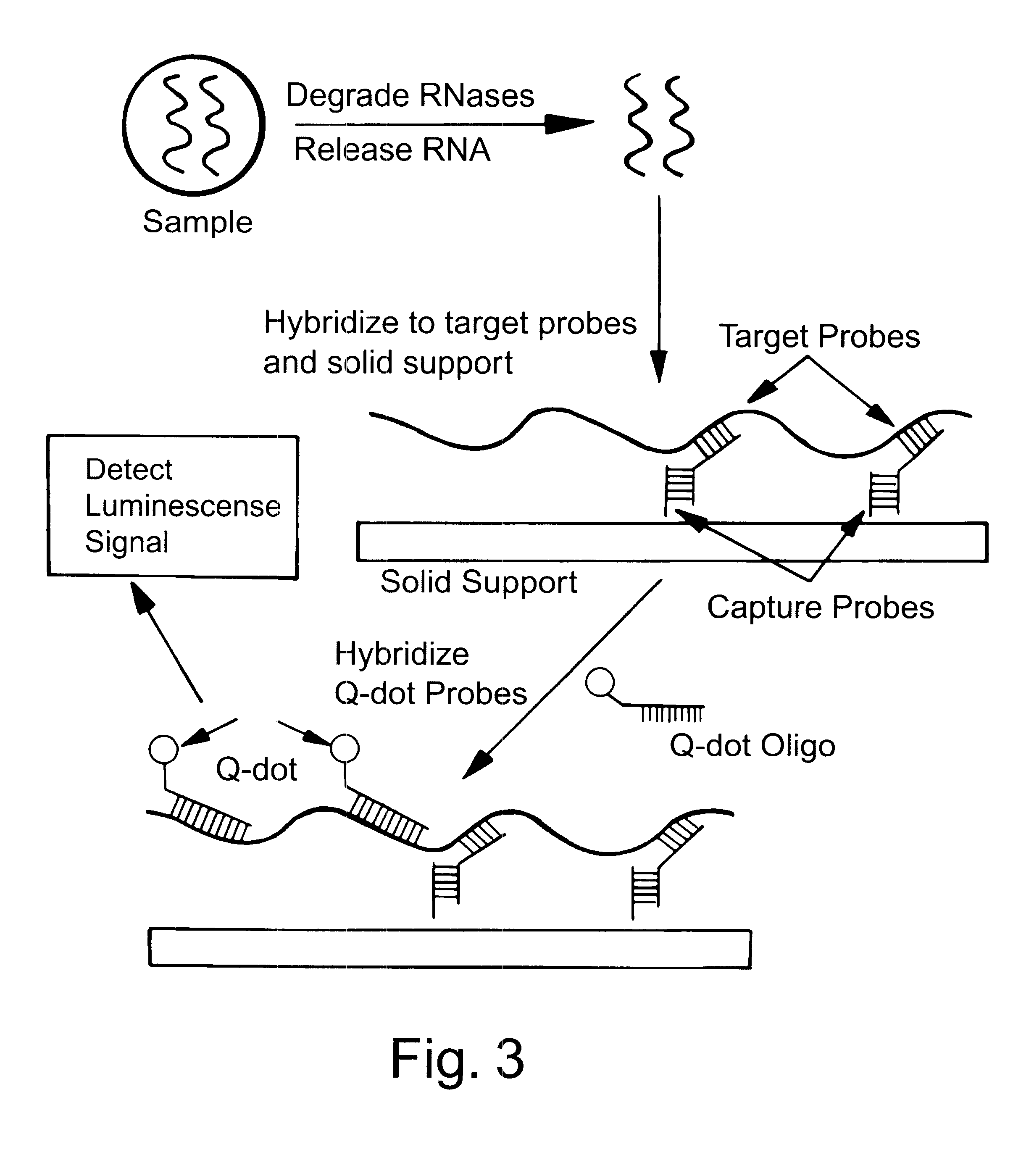
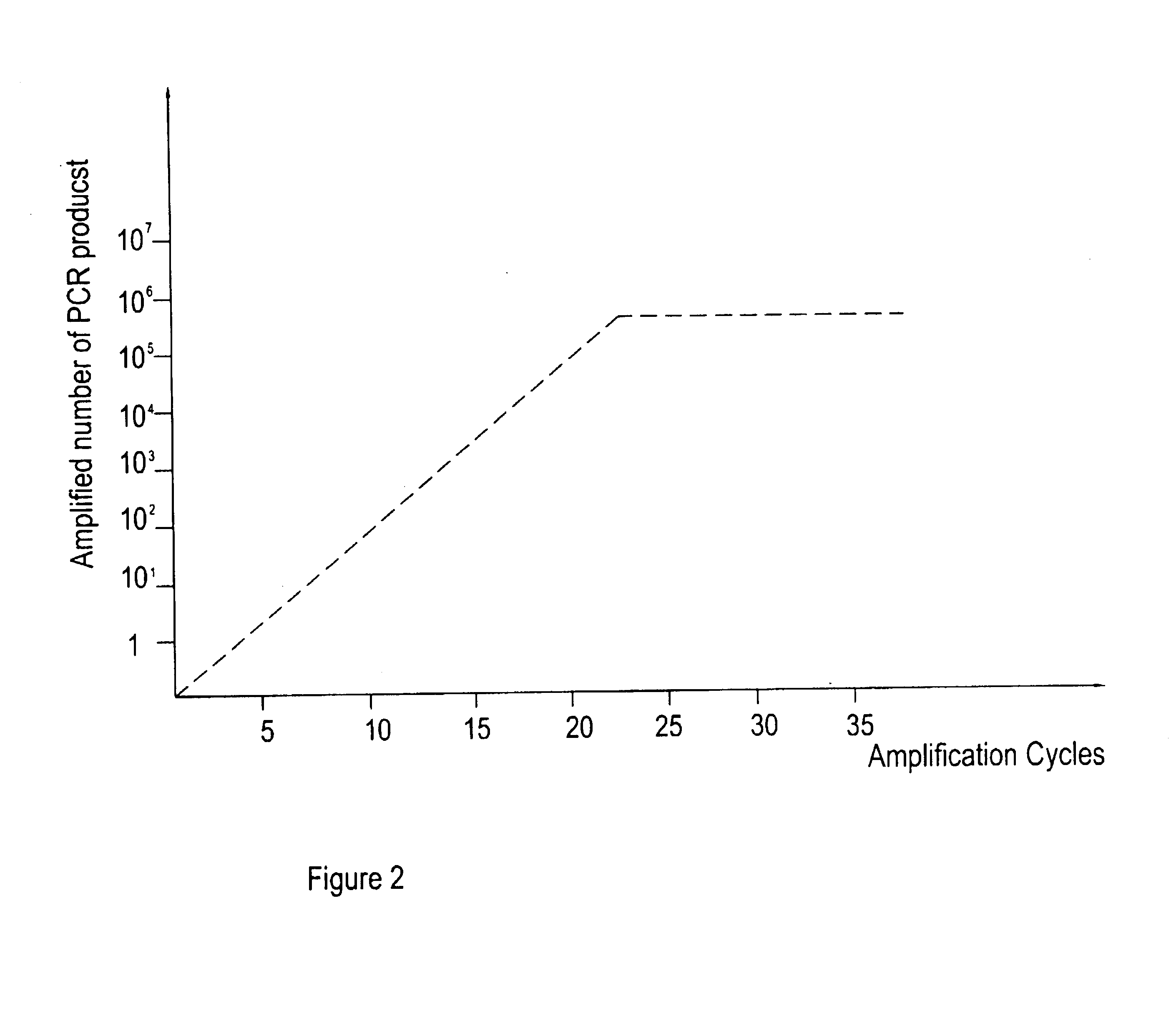Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4927 results about "Biomolecule" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A biomolecule or biological molecule is a loosely used term for molecules and ions present in organisms that are essential to one or more typically biological processes, such as cell division, morphogenesis, or development. Biomolecules include large macromolecules (or polyanions) such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids, as well as small molecules such as primary metabolites, secondary metabolites, and natural products. A more general name for this class of material is biological materials. Biomolecules are usually endogenous, produced within the organism but organisms usually need exogenous biomolecules, for example certain nutrients, to survive.
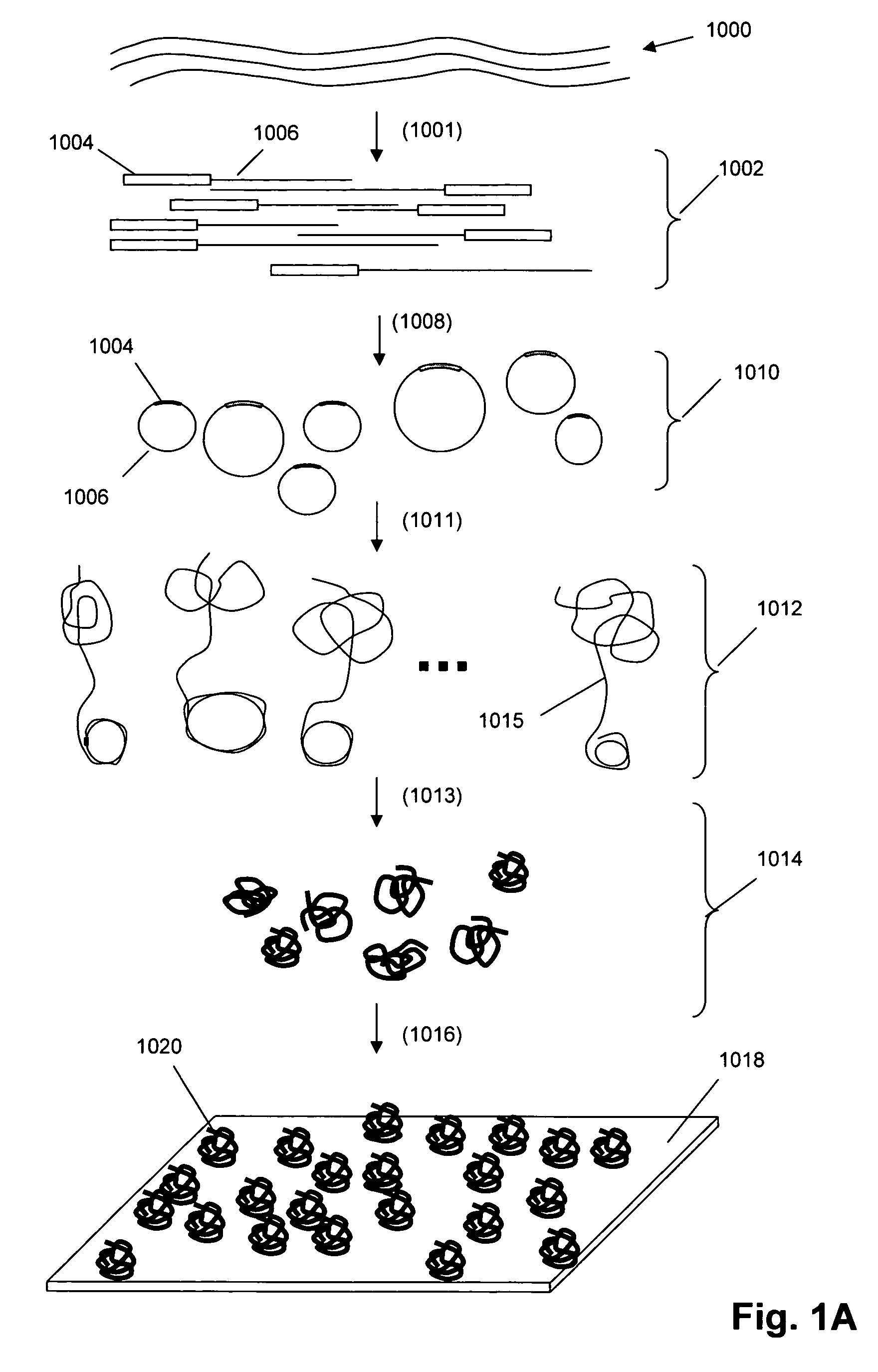
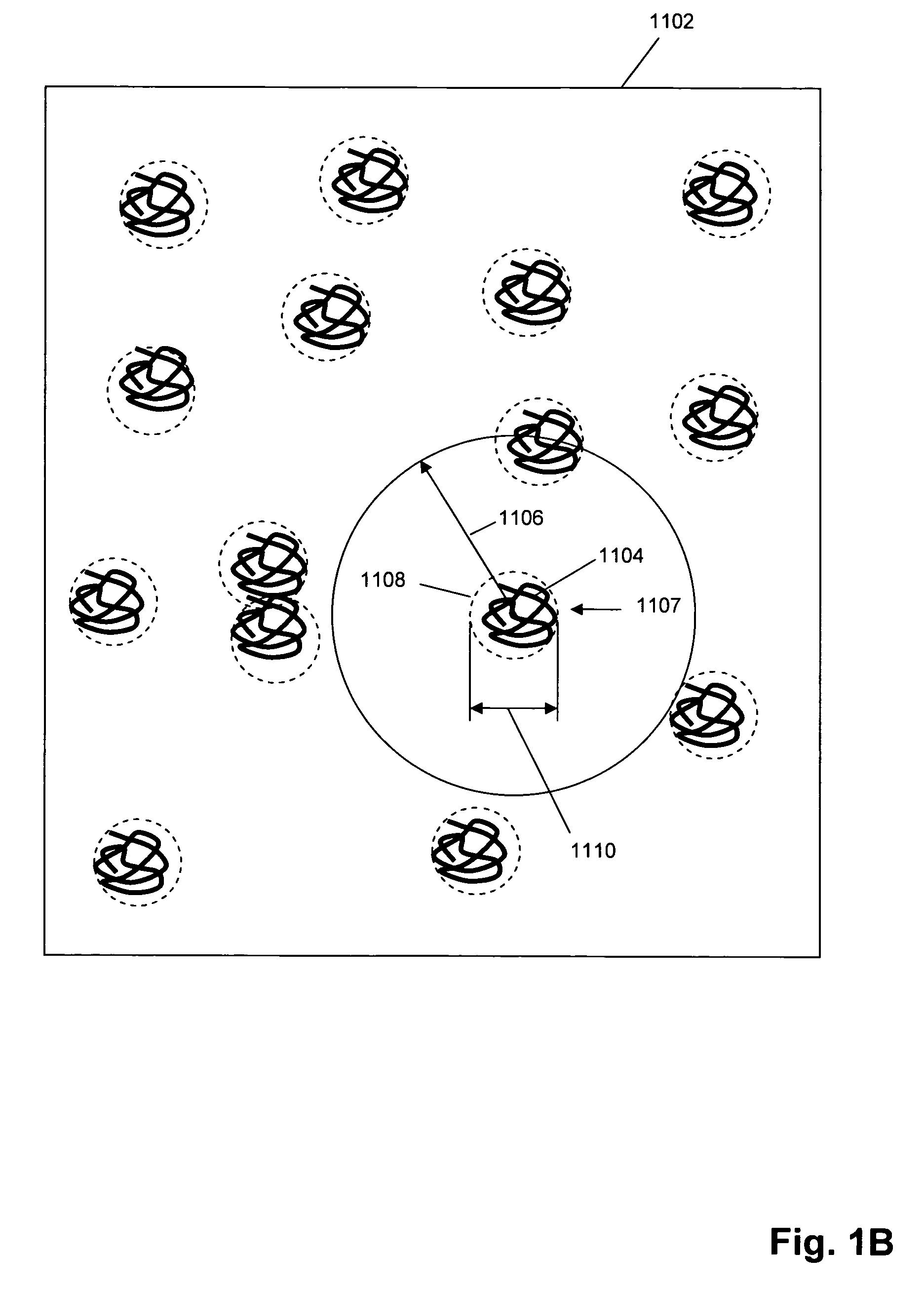
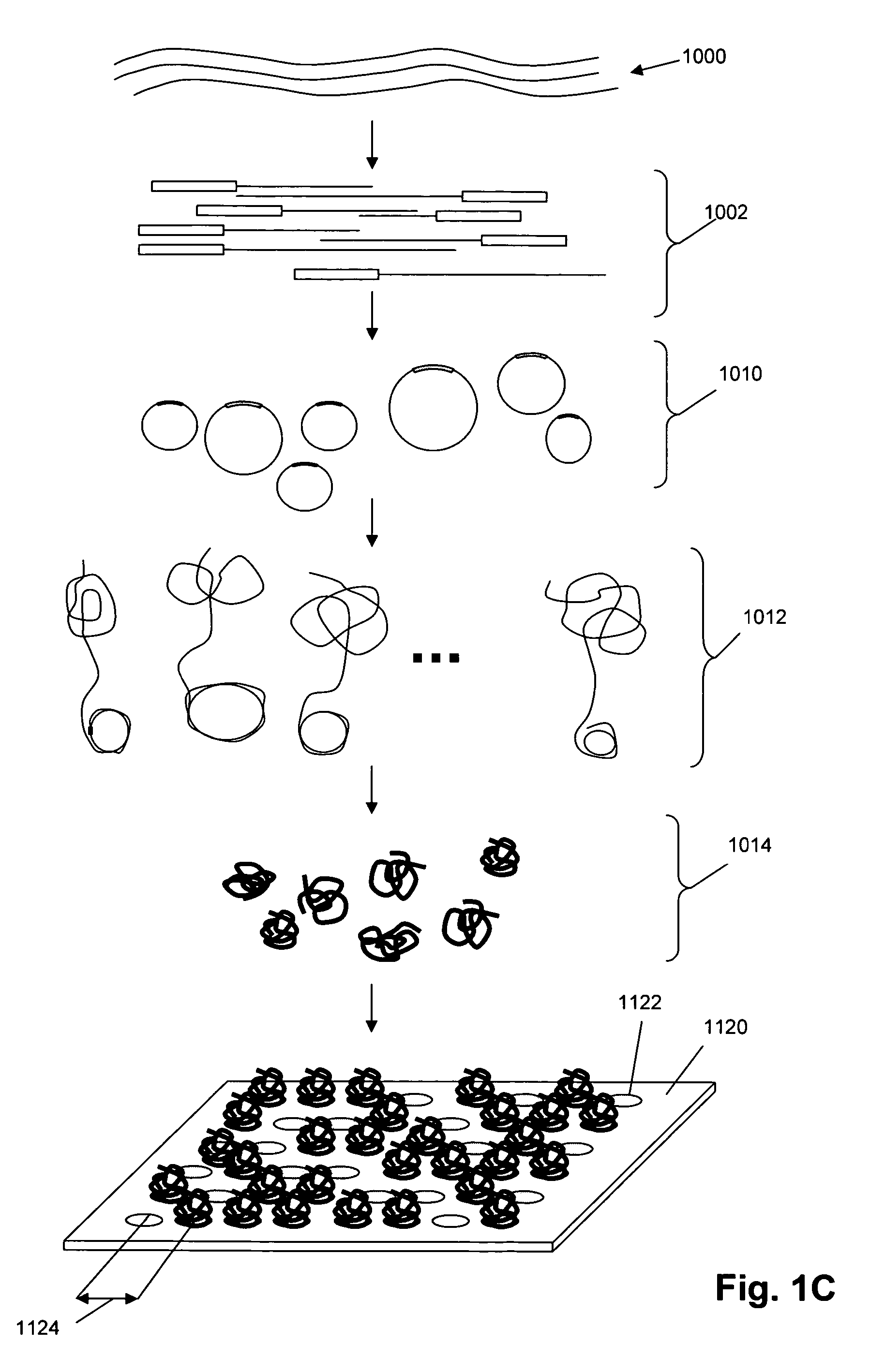
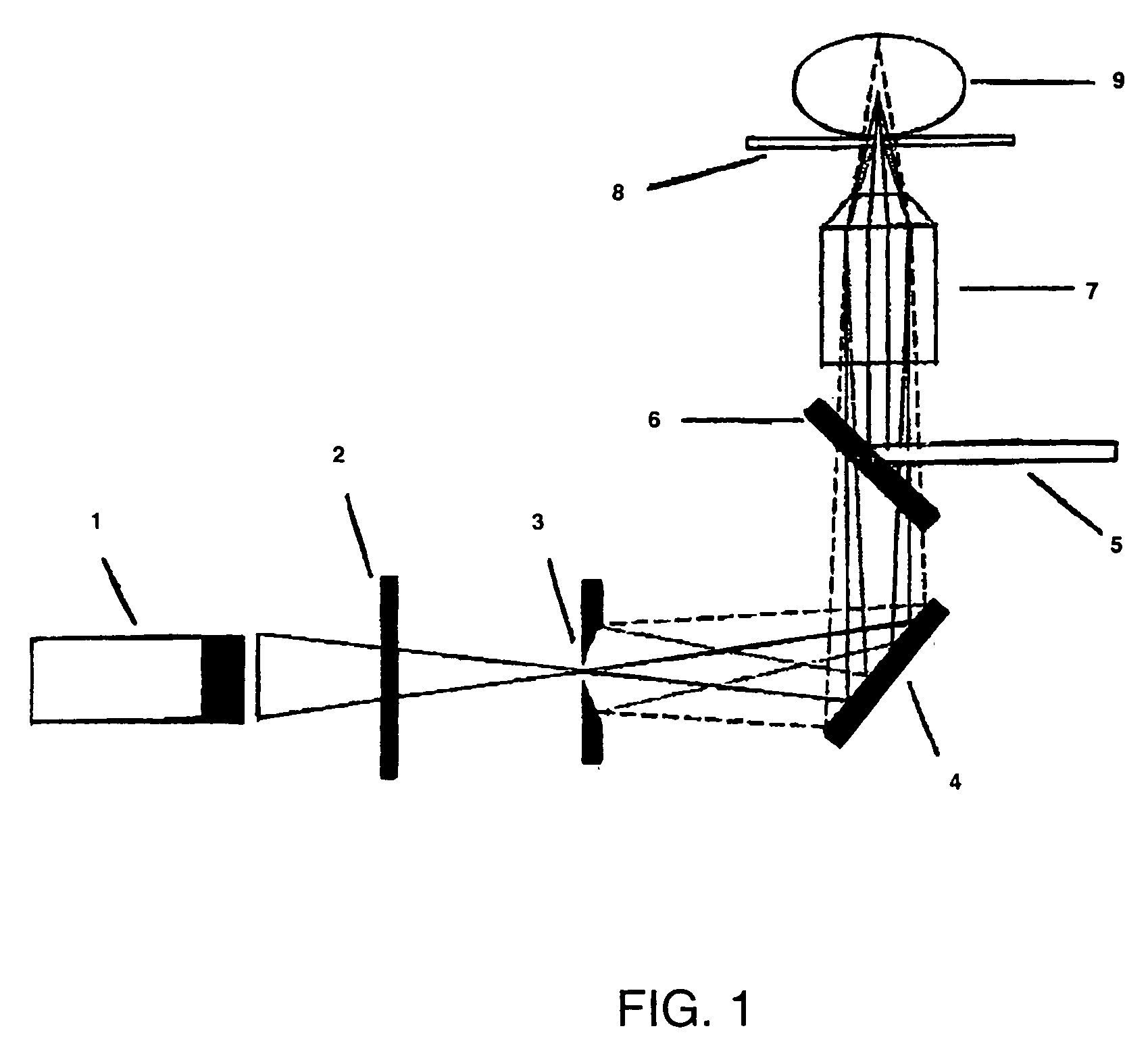
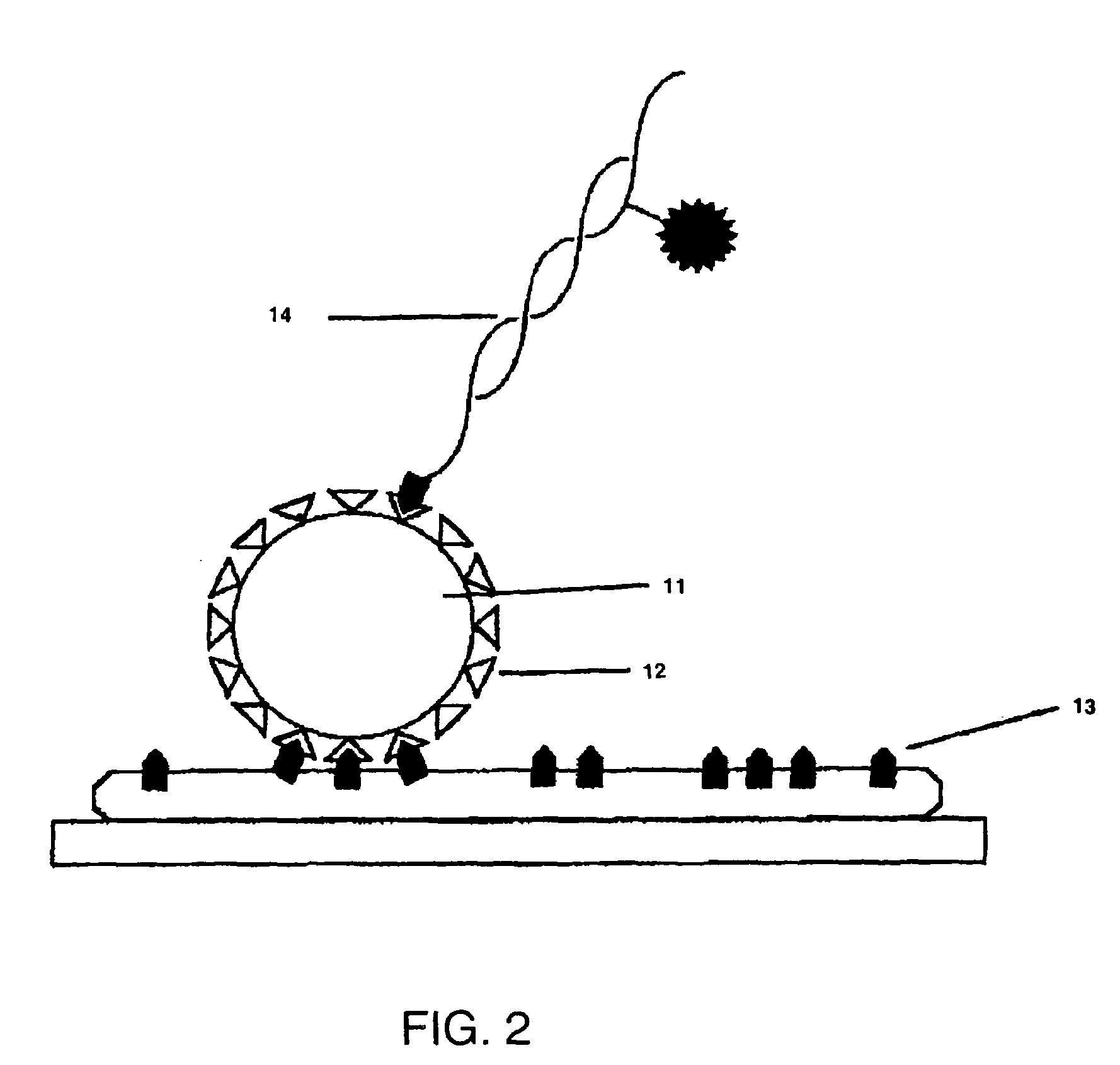
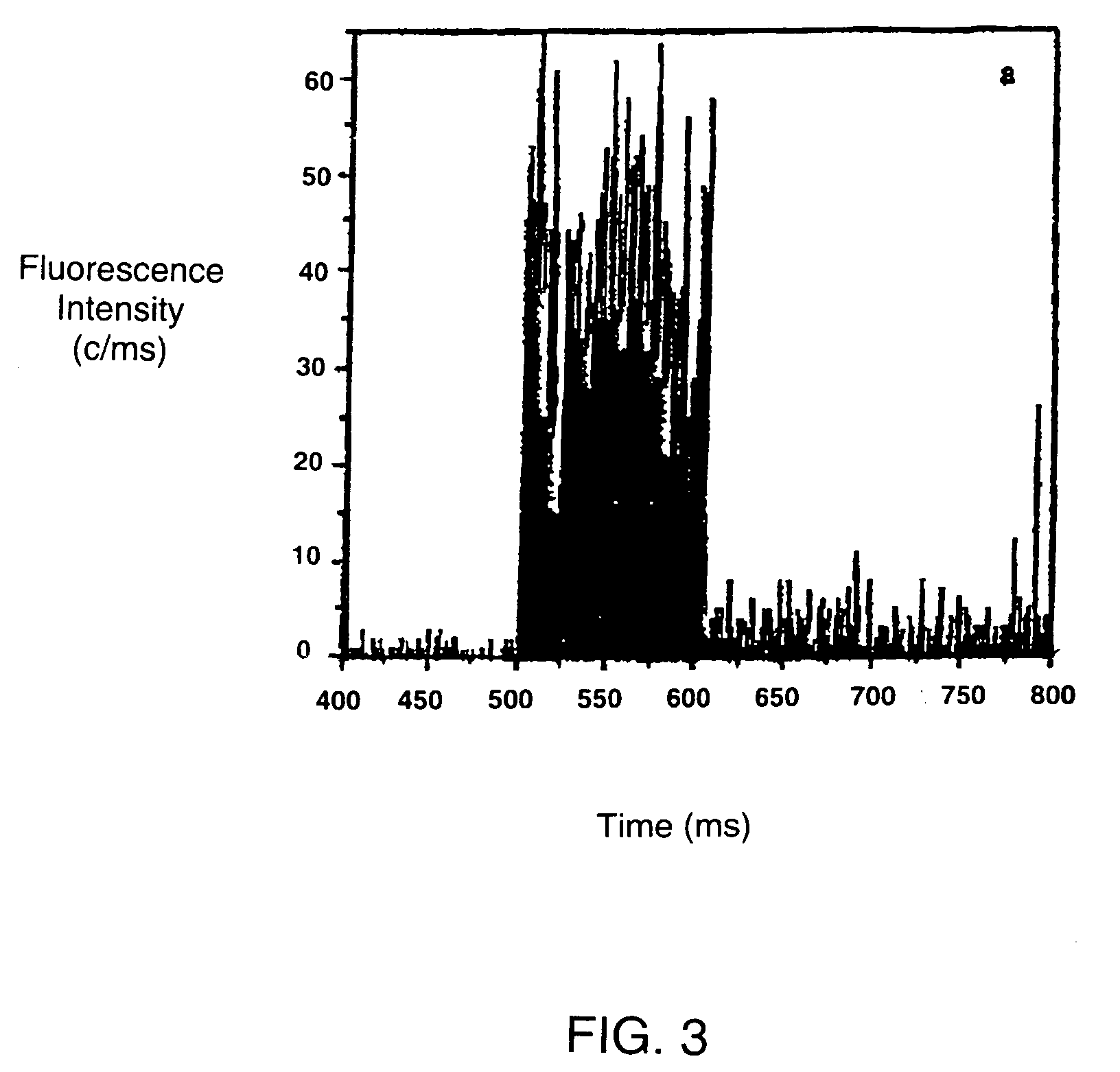
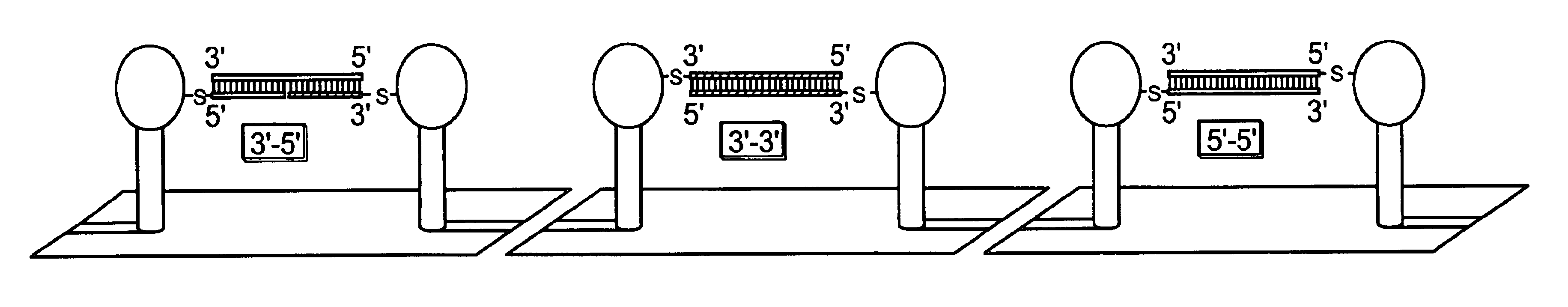
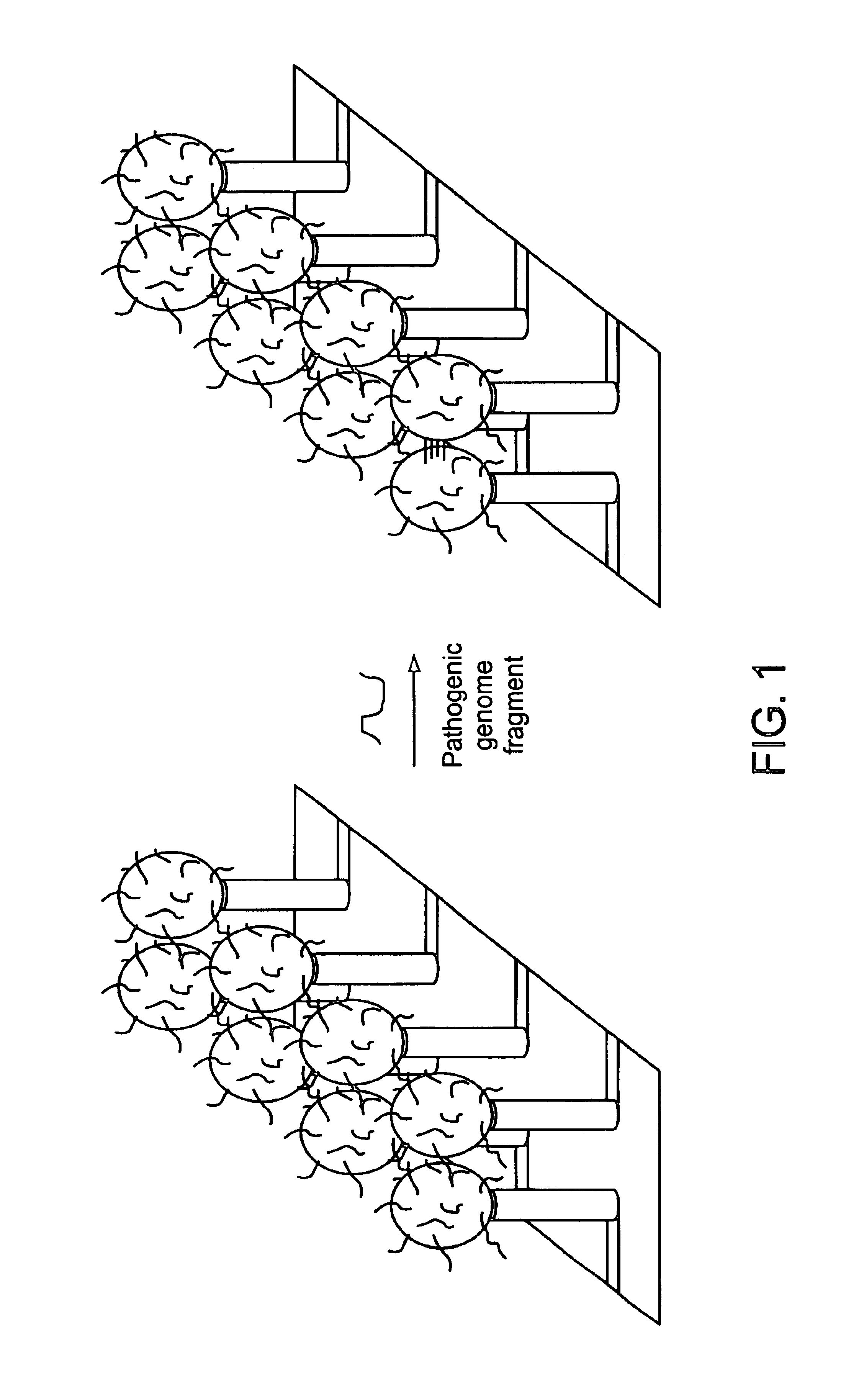
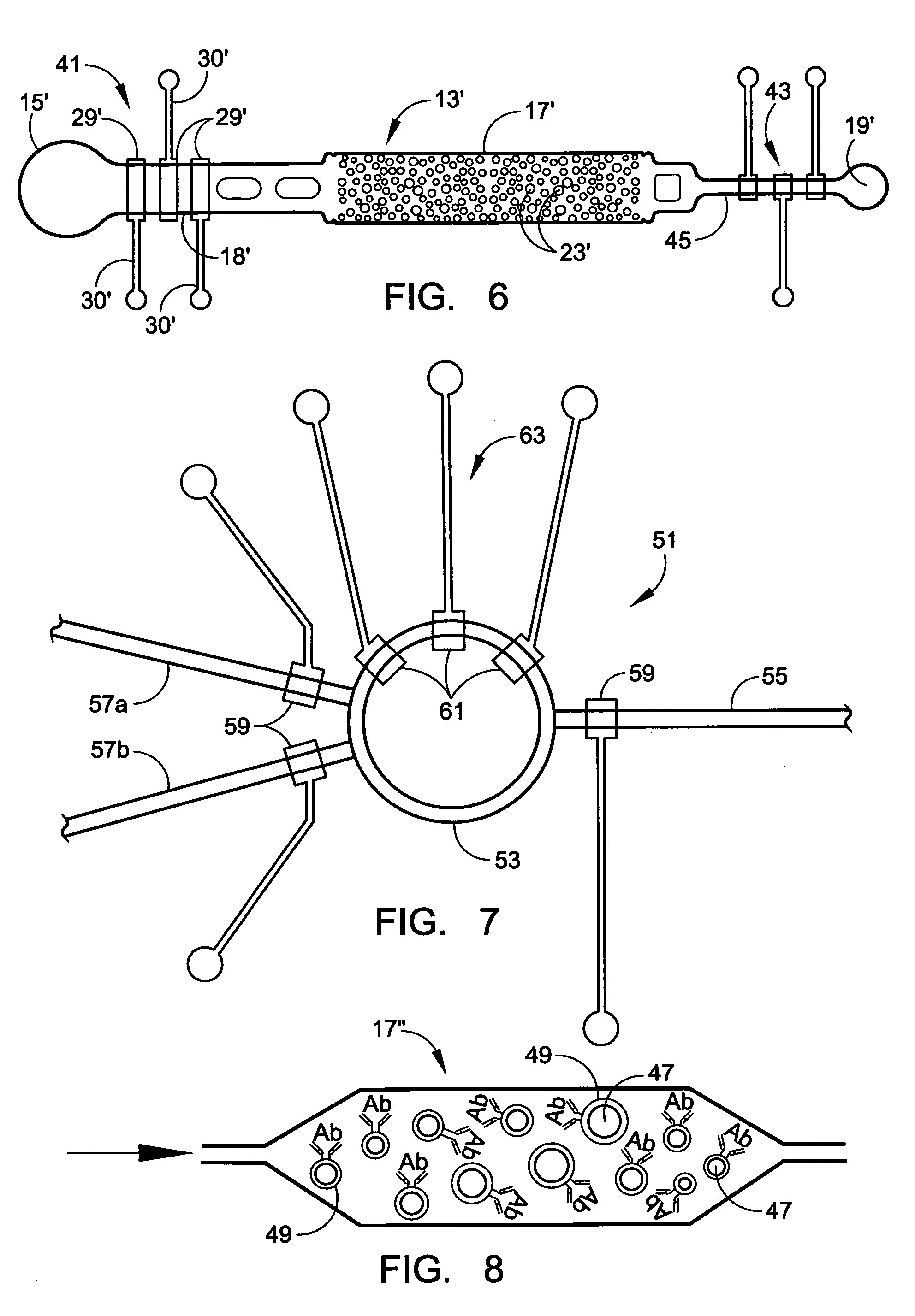
Single molecule arrays for genetic and chemical analysis
ActiveUS20070099208A1Efficient high resolution analysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanotechImage resolutionRandom array
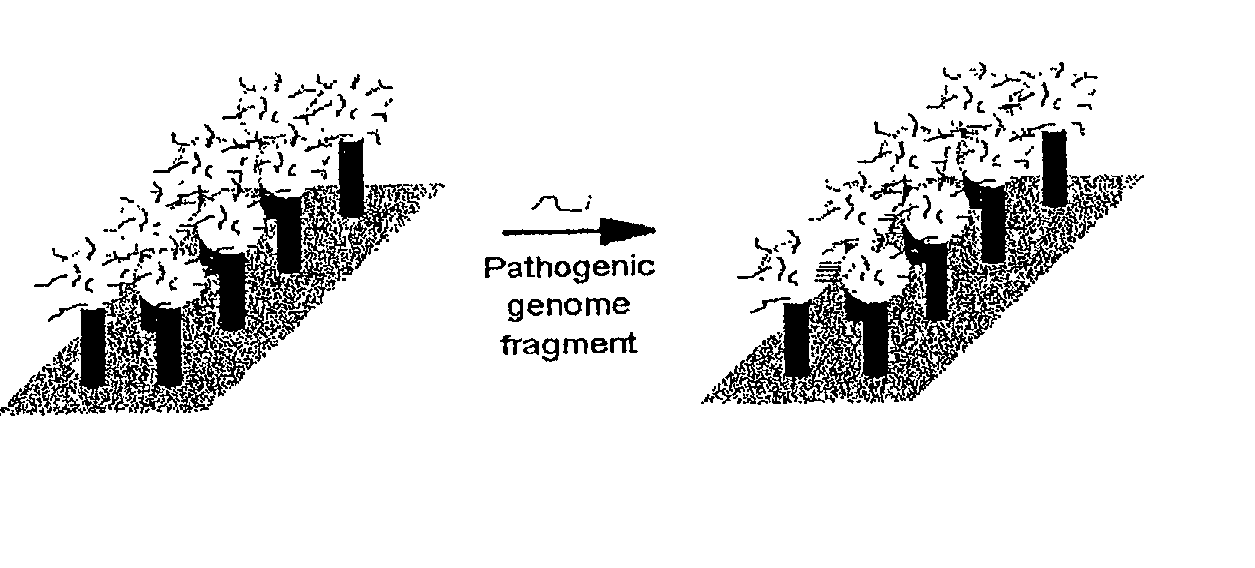
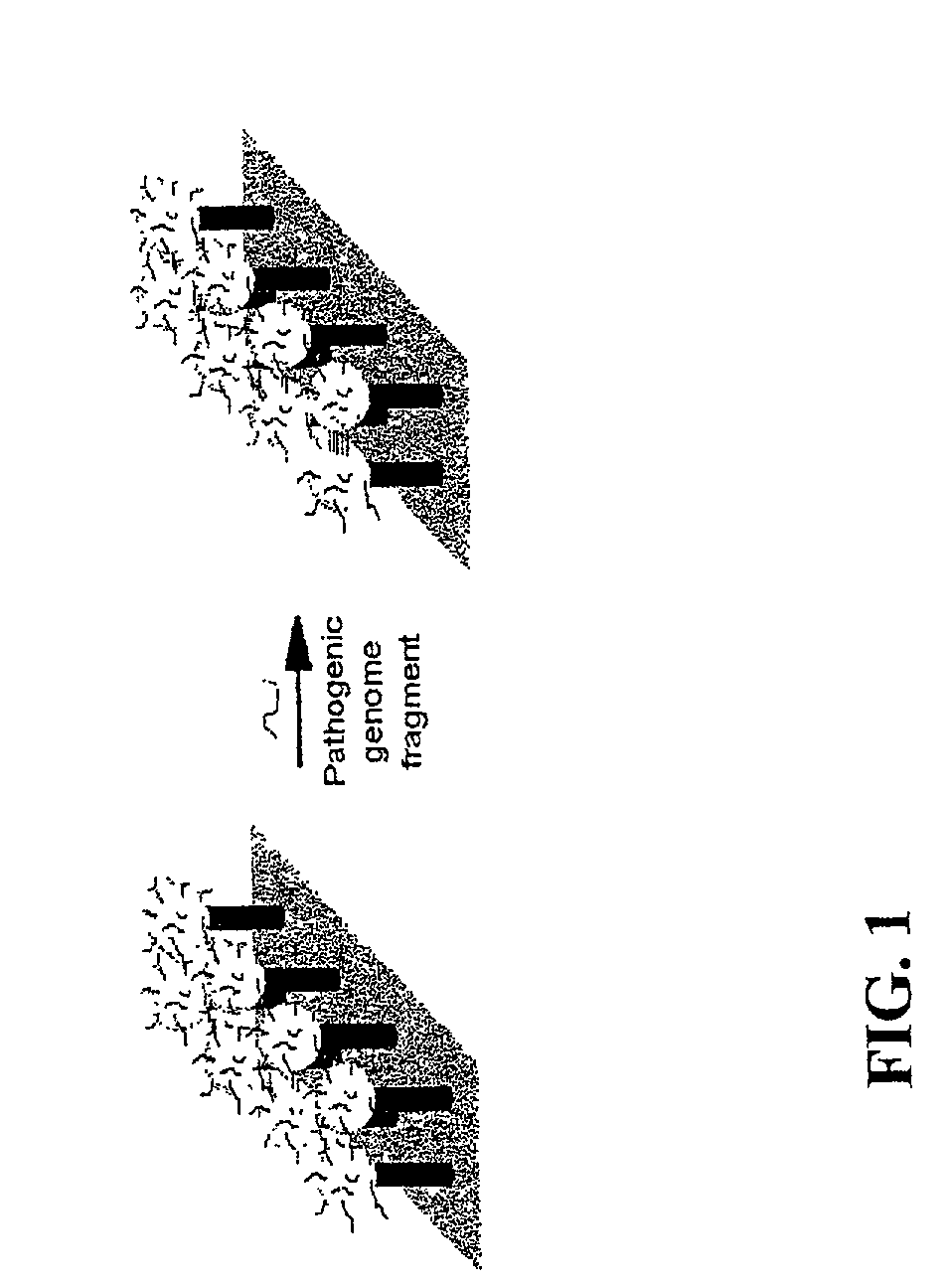
Random arrays of single molecules are provided for carrying out large scale analyses, particularly of biomolecules, such as genomic DNA, cDNAs, proteins, and the like. In one aspect, arrays of the invention comprise concatemers of DNA fragments that are randomly disposed on a regular array of discrete spaced apart regions, such that substantially all such regions contain no more than a single concatemer. Preferably, such regions have areas substantially less than 1 μm2 and have nearest neighbor distances that permit optical resolution of on the order of 109 single molecules per cm2. Many analytical chemistries can be applied to random arrays of the invention, including sequencing by hybridization chemistries, sequencing by synthesis chemistries, SNP detection chemistries, and the like, to greatly expand the scale and potential applications of such techniques.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
Support for high performance affinity chromatography and other uses
Multilayered particulate materials are formed by coating a particulate substrate with a metal and adsorbing an organic layer comprising a recognition moiety onto the metal film. The recognition moiety interacts with an analyte of interest allowing for its detection, purification, etc. Suitable recognition moieties can be selected from a range of species including, small molecules, polymers and biomolecules and the like. The novel particulate materials of the invention can be utilized in an array of methods including, ion-exchange, ion-selective ion-exchange, assays, affinity dialysis, size exclusion dialysis, as supports in solid phase synthesis, combinatorial synthesis and screening of compound libraries and the like.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
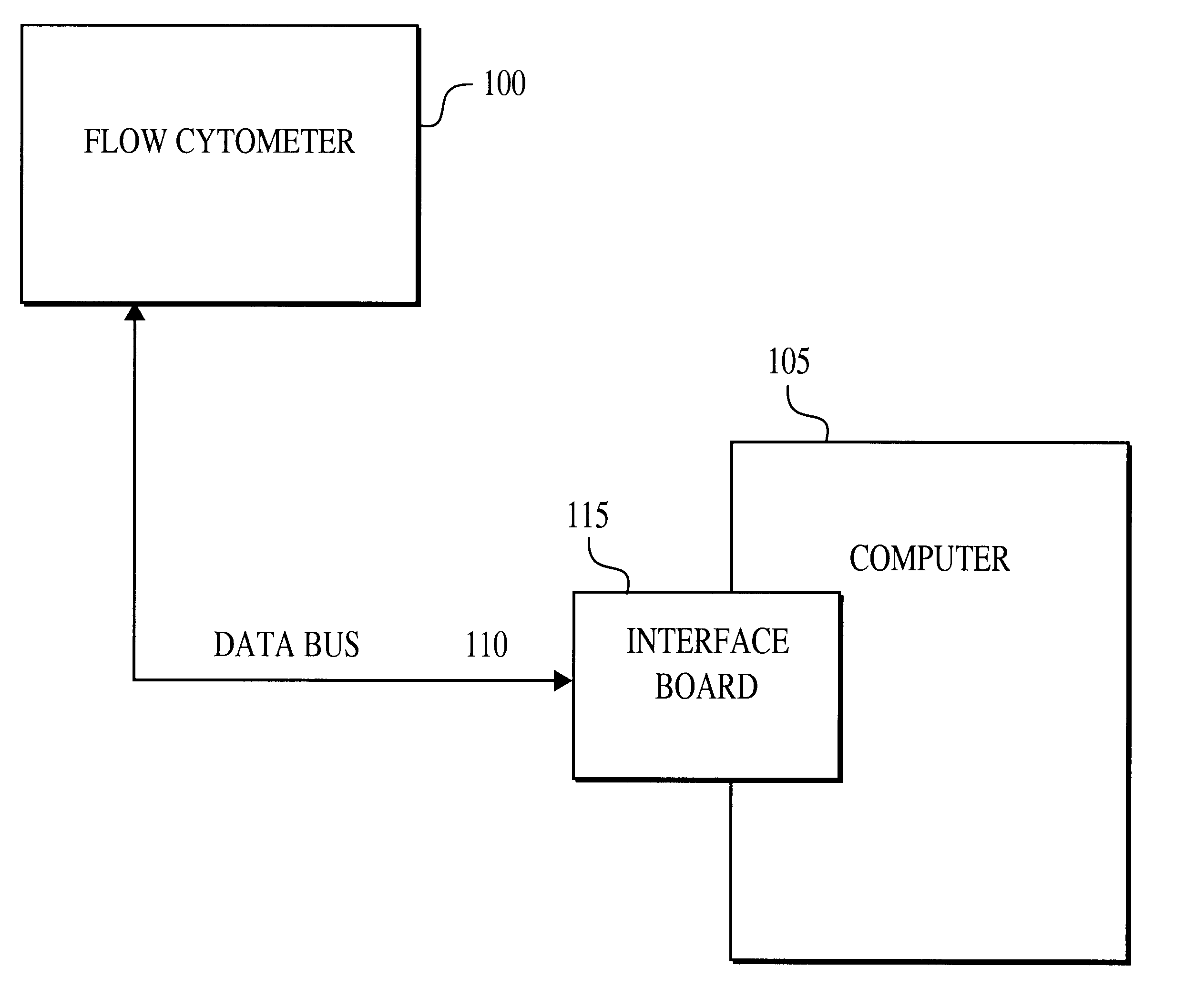
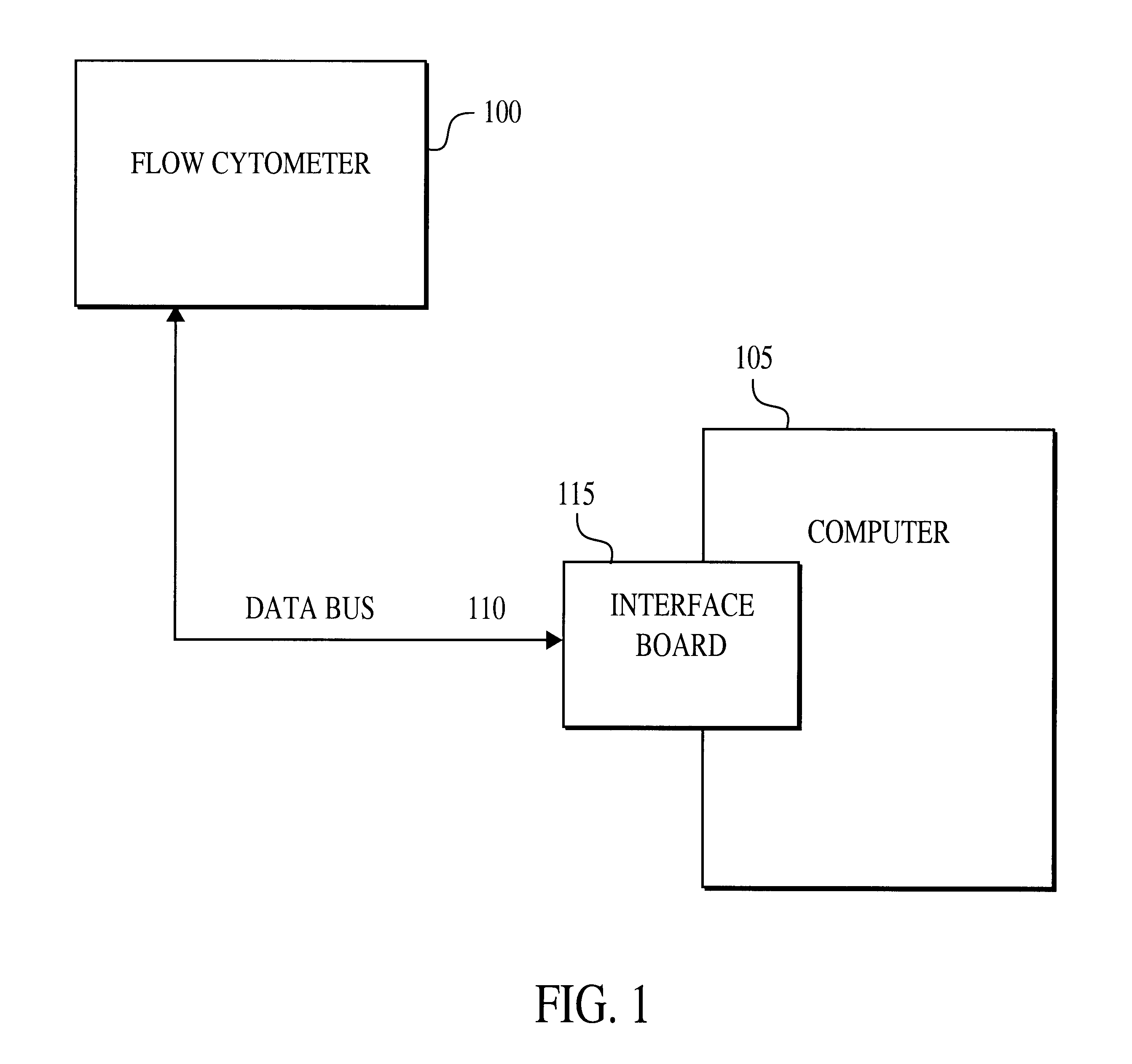
Multiplexed analysis of clinical specimens apparatus and method
InactiveUS6524793B1Simple methodSure easyMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymologyReal time analysisDNA fragmentation
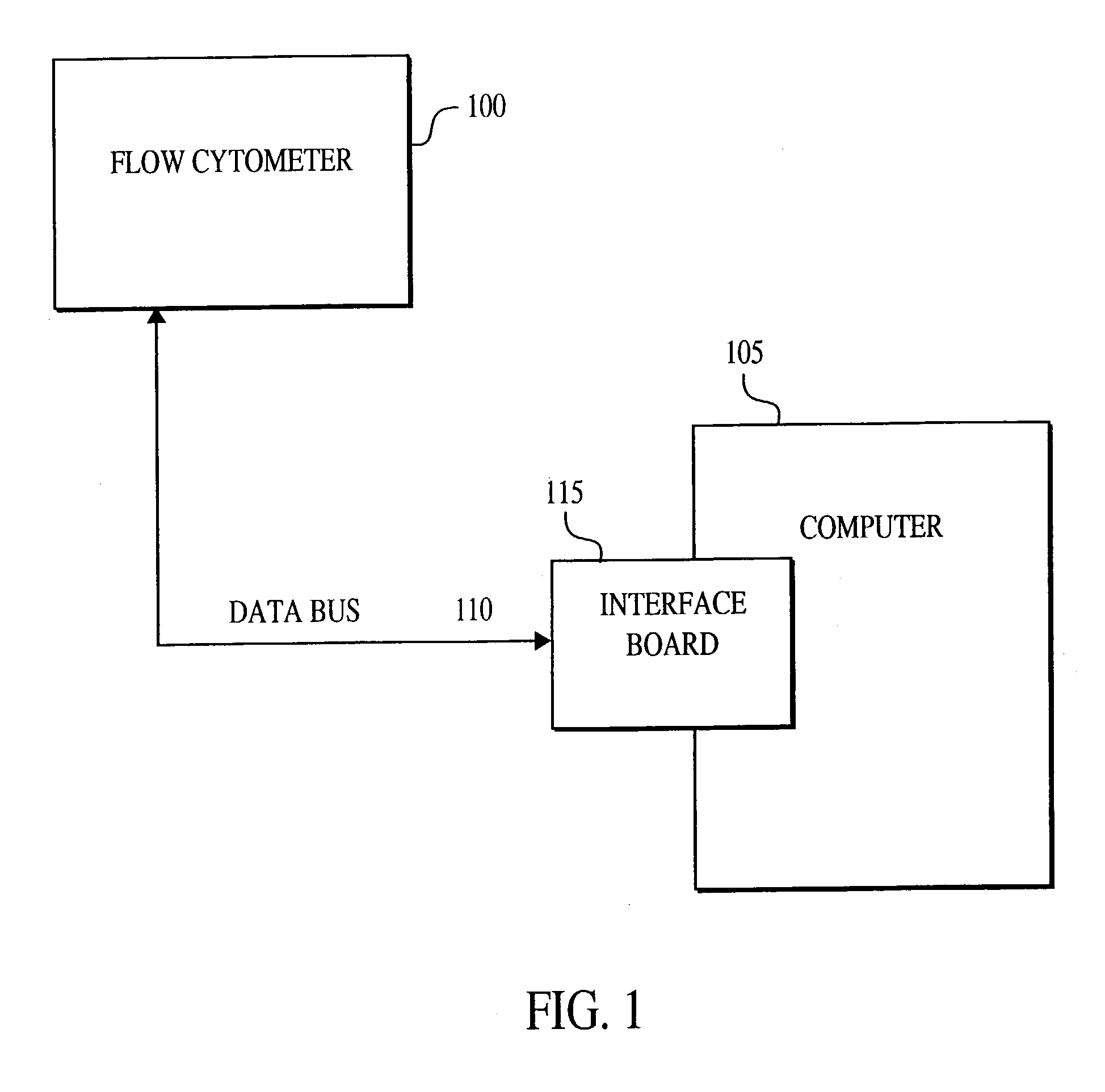
A method for the multiplexed diagnostic and genetic analysis of enzymes, DNA fragments, antibodies, and other biomolecules comprises the steps of constructing an appropriately labeled beadset, exposing the beadset to a clinical sample, and analyzing the combined sample / beadset by flow cytometry. Flow cytometric measurements are used to classify, in real-time, beads within an exposed beadset and textual explanations, based on the accumulated data obtained during real-time analysis, are generated for the user. The inventive technology enables the simultaneous, and automated, detection and interpretation of multiple biomolecules or DNA sequences in real-time while also reducing the cost of performing diagnostic and genetic assays.
Owner:LUMINEX
Methods and systems for annotating biomolecular sequences
A method of annotating biomolecular sequences. The method comprises (a) computationally clustering the biomolecular sequences according to a progressive homology range, to thereby generate a plurality of clusters each being of a predetermined homology of the homology range; and (b) assigning at least one ontology to each cluster of the plurality of clusters, the at least one ontology being: (i) derived from an annotation preassociated with at least one biomolecular sequence of each cluster; and / or (ii) generated from analysis of the at least one biomolecular sequence of each cluster thereby annotating biomolecular sequences.
Owner:COMPUGEN
Biocompatible implant and use of the same
InactiveUS20060252981A1Good biological affinityStrong enoughImpression capsEye implantsRough surfaceBiological body
The present invention provides an implant capable of being cellularized in treatment of an injured organ or tissue in organisms. The present inventors found that a biocompatible implant comprising a biological molecule and a support is capable of being cellularized. The implant can be used instead of conventional implants which essentially comprise cells. The present invention provides a biocompatible implant comprising A) a biological molecule and B) a support. The present invention also provides A) a first layer having a rough surface, B) a rough surface; B) a second layer having a strength which allows the support to resist in vivo shock. The first layer is attached to the second layer via at least one point.
Owner:CARDIO
Arrayed biomolecules and their use in sequencing
InactiveUS7232656B2Reduce interferencePermit resolutionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsGenome variationComputational biology
The invention is directed to a method for analysing genome wide variation in an individual. The method comprises randomly fragmenting the individual's genome and generating sequence reads of multiple bases on all fragments of the individual's genome, aligning the sequence reads generated with a known genomic reference sequence, and analysing variations between the sequence reads derived from the individual's genome and the known genomic reference sequence.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
DNA-bridged carbon nanotube arrays
InactiveUS20020172963A1High precisionHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyChemical ligationElectron transfer reactions
A class of biological sensing devices that include a substrate comprising an array of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) to which are chemically attached biological molecules is disclosed. The attached biological molecules are capable of electrical conductivity that is responsive to chemical changes occurring as a result of their interaction with target species. A means for means for using DNA as a material of potential in molecular electronic sensor devices, being primarily based on molecular electron-transfer reaction processes between DNA-binding donors and acceptors is also disclosed, including composition, method of manufacture and their use are described.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON COLLEGE THE
Multiplexed analysis of clinical specimens apparatus and method
InactiveUS6939720B2Sure easyMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymologyReal time analysisDNA fragmentation
A method for the multiplexed diagnostic and genetic analysis of enzymes, DNA fragments, antibodies, and other biomolecules comprises the steps of constructing an appropriately labeled beadset, exposing the beadset to a clinical sample, and analyzing the combined sample / beadset by flow cytometry. Flow cytometric measurements are used to classify, in real-time, beads within an exposed beadset and textual explanations, based on the accumulated data obtained during real-time analysis, are generated for the user. The inventive technology enables the simultaneous, and automated, detection and interpretation of multiple biomolecules or DNA sequences in real-time while also reducing the cost of performing diagnostic and genetic assays.
Owner:LUMINEX
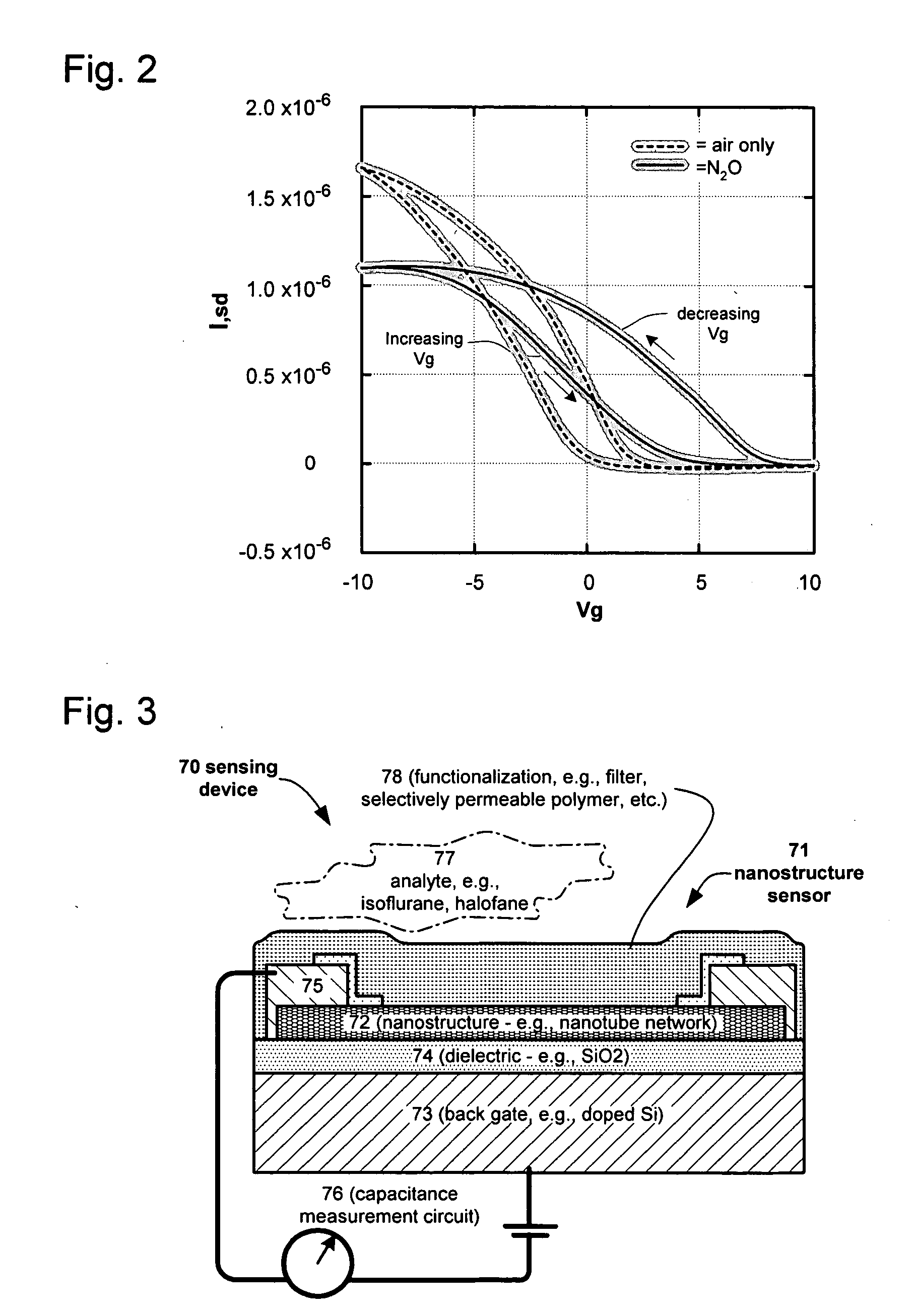
Nano-electronic sensors for chemical and biological analytes, including capacitance and bio-membrane devices
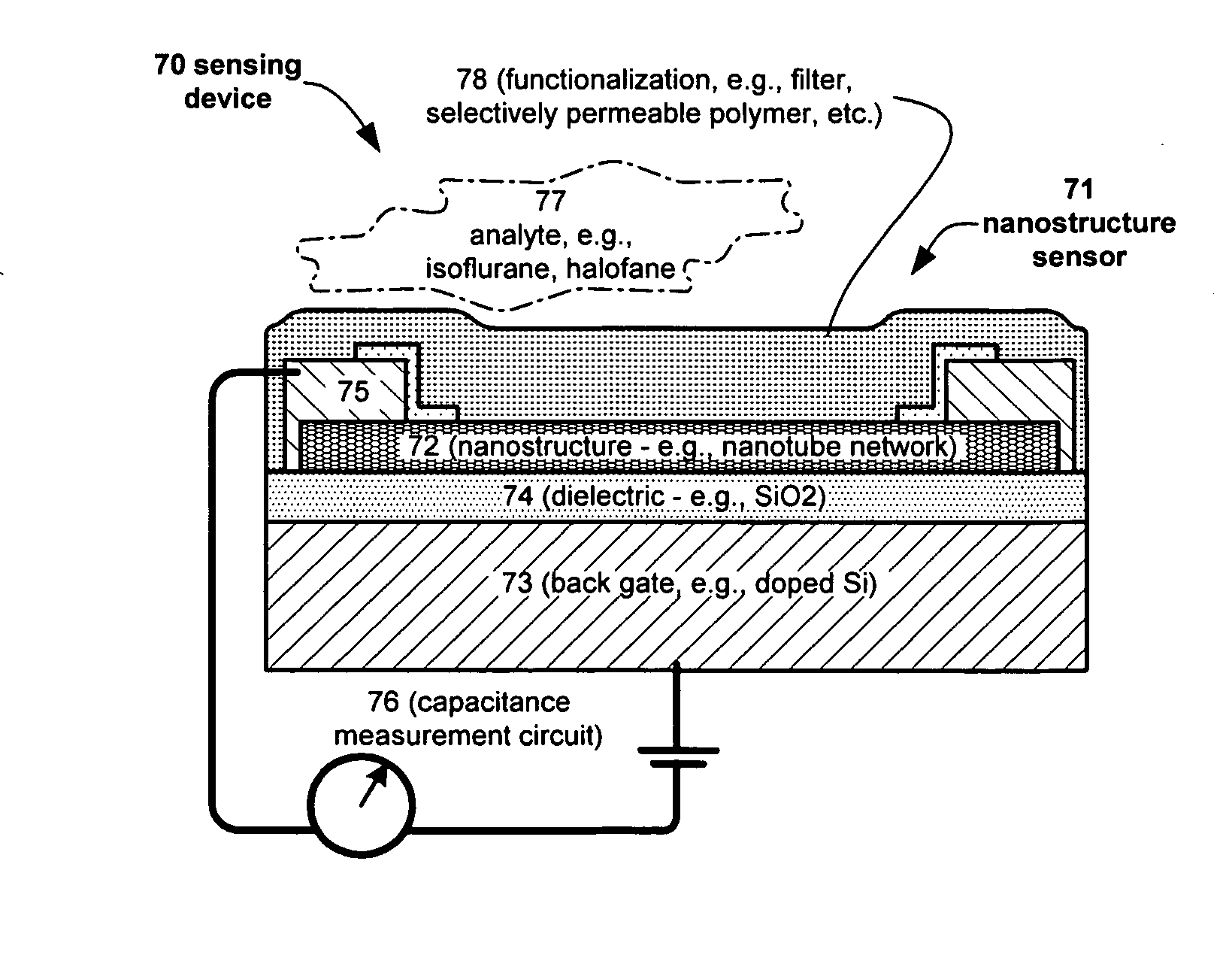
InactiveUS20070132043A1Enhanced signalSmall sizeNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesAnalyteCell membrane
Embodiments of nanoelectronic sensors are described, including sensors for detecting analytes inorganic gases, organic vapors, biomolecules, viruses and the like. A number of embodiments of capacitive sensors having alternative architectures are described. Particular examples include integrated cell membranes and membrane-like structures in nanoelectronic sensors.
Owner:NANOMIX
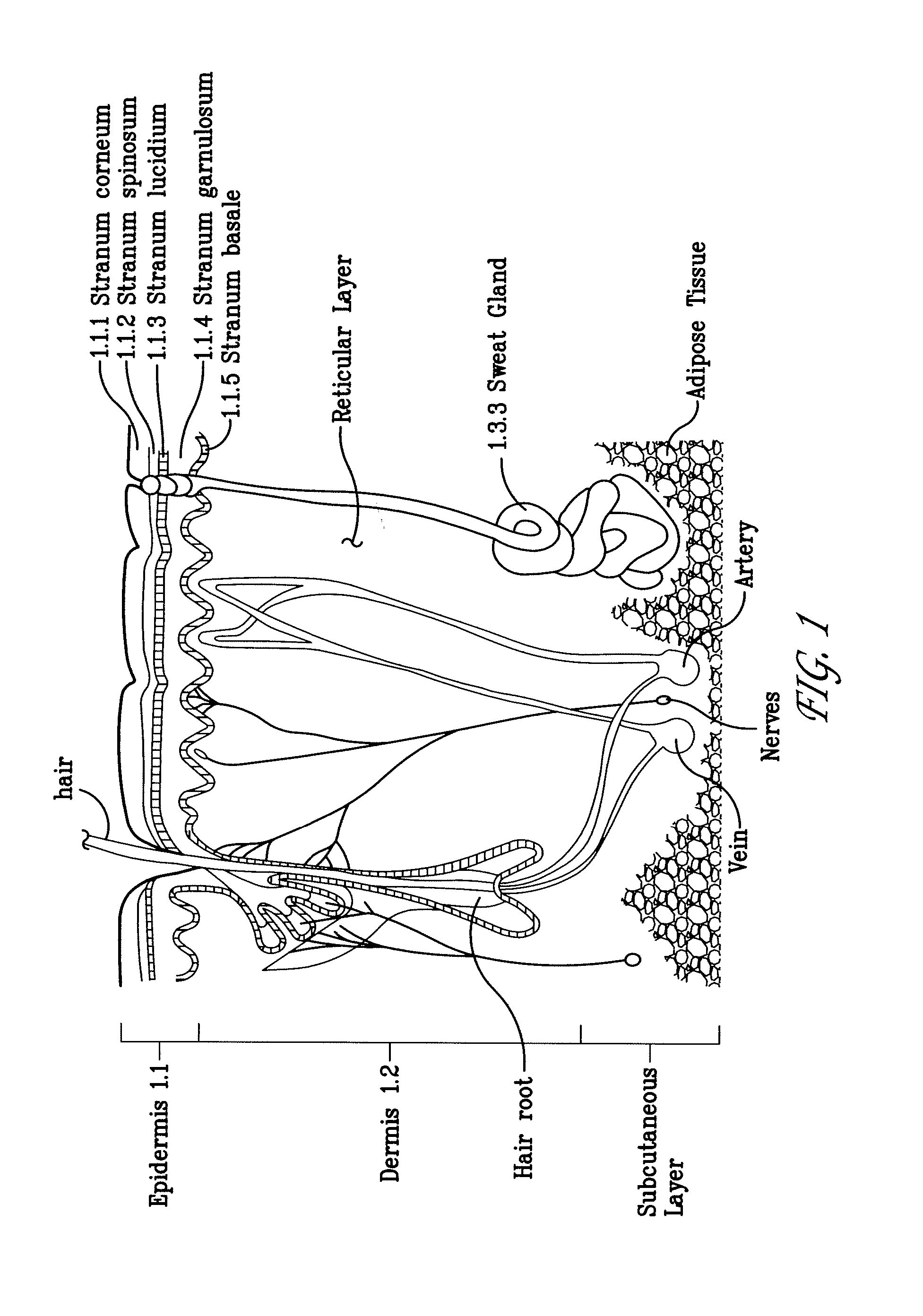
Devices and methods for enhanced microneedle penetration of biological barriers
InactiveUS20050137531A1Easy to transportEnhanced interactionAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurgerySkin surfacesTissue skin
Microneedle devices and methods of use thereof are provided for the enhanced transport of molecules, including drugs and biological molecules, across tissue by improving the interaction of microneedles and a deformable, elastic biological barrier, such as human skin. The devices and methods act to (1) limit the elasticity, (2) adapt to the elasticity, (3) utilize alternate ways of creating the holes for the microneedles to penetrate the biological barrier, other than the simply direct pressure of the microneedle substrate to the barrier surface, or (4) any combination of these methods. In preferred embodiments for limiting the elasticity of skin, the microneedle device includes features suitable for stretching, pulling, or pinching the skin to present a more rigid, less deformable, surface in the area to which the microneedles are applied (i.e. penetrate). In a preferred embodiments for adapting the device to the elasticity of skin, the device comprising one or more extensions interposed between the substrate and the base end of at least a portion of the microneedles.
Owner:VALERITAS LLC (US) +1
Methods and apparatus for application of micro-mechanical forces to tissues
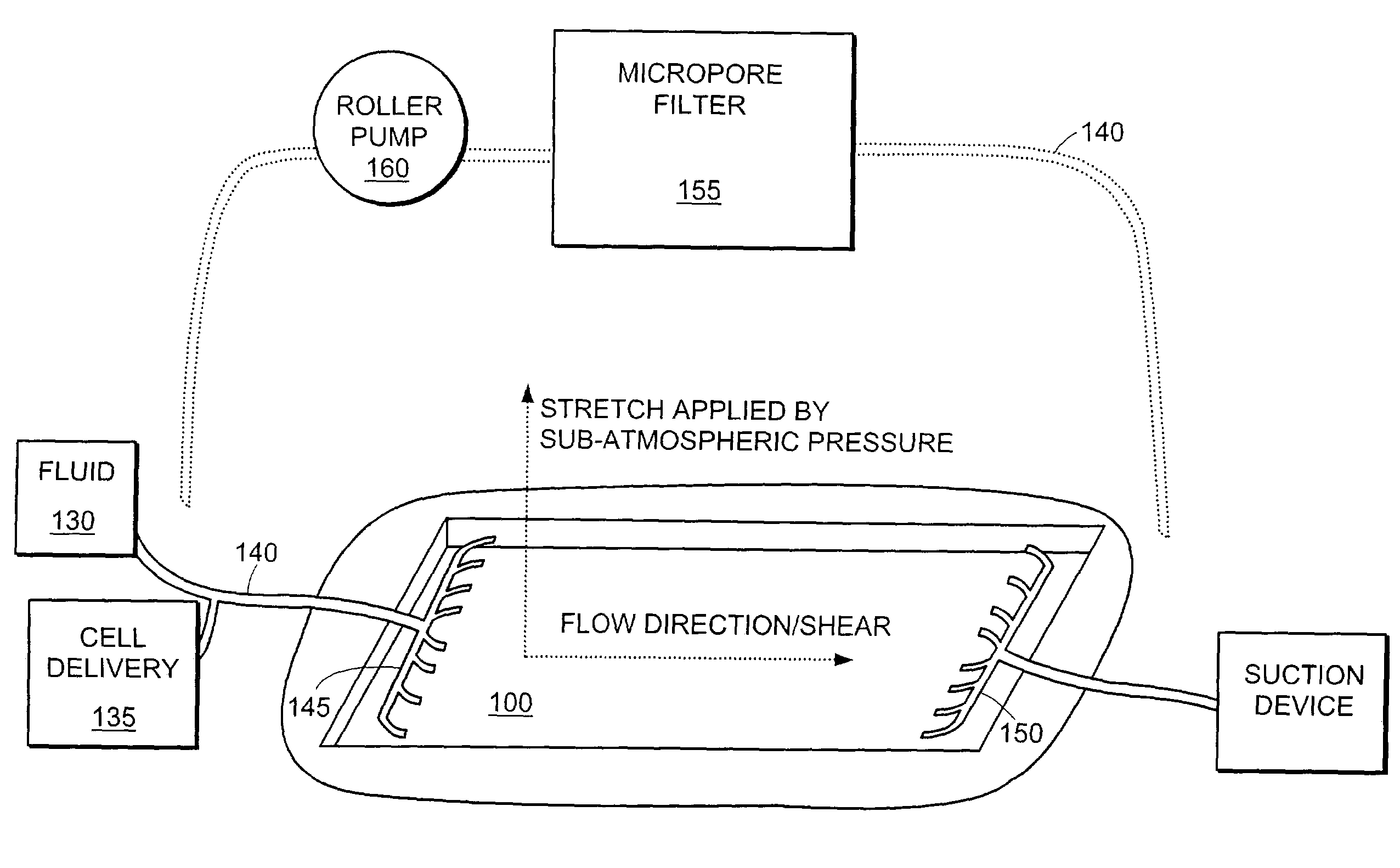
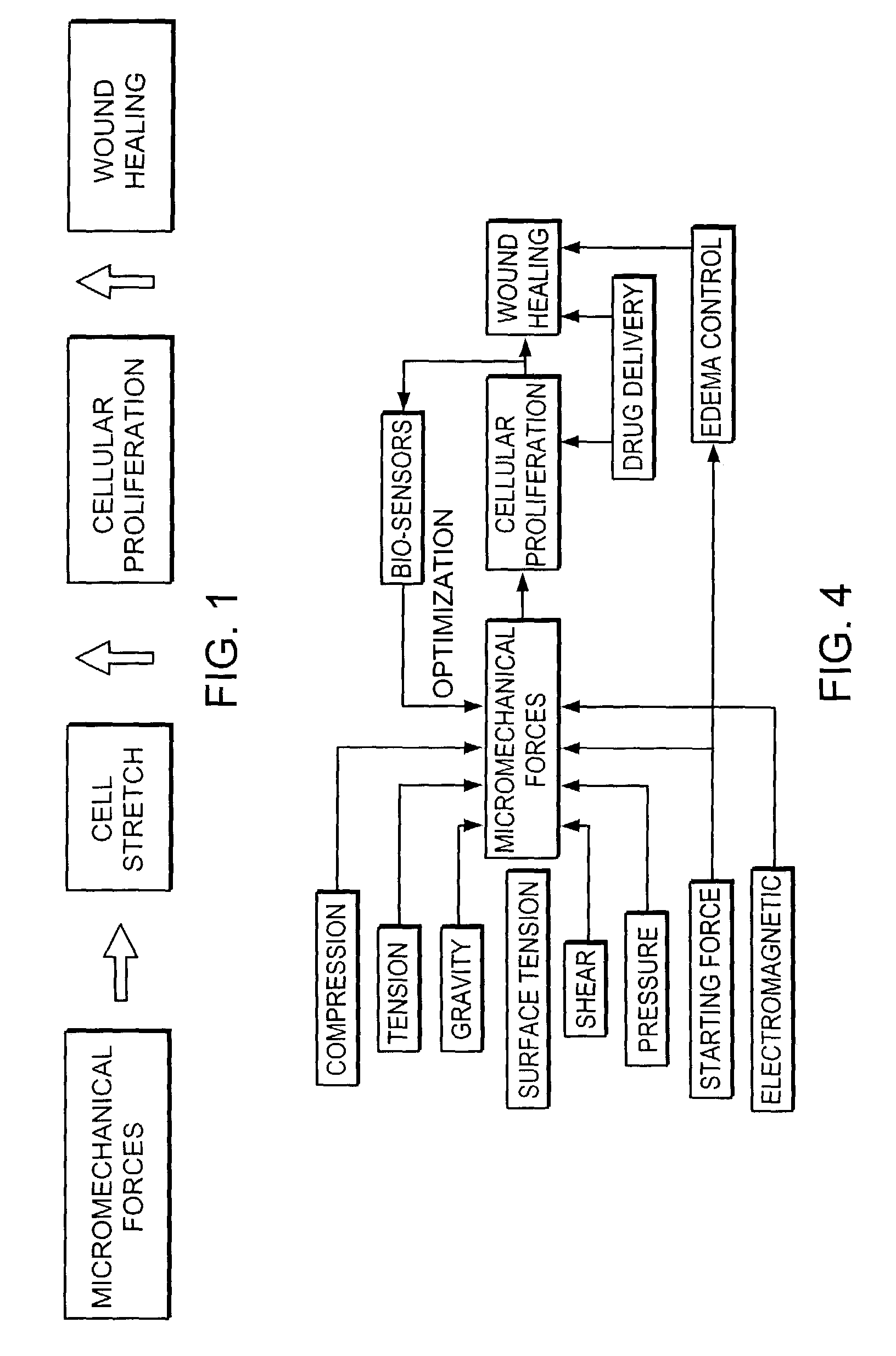
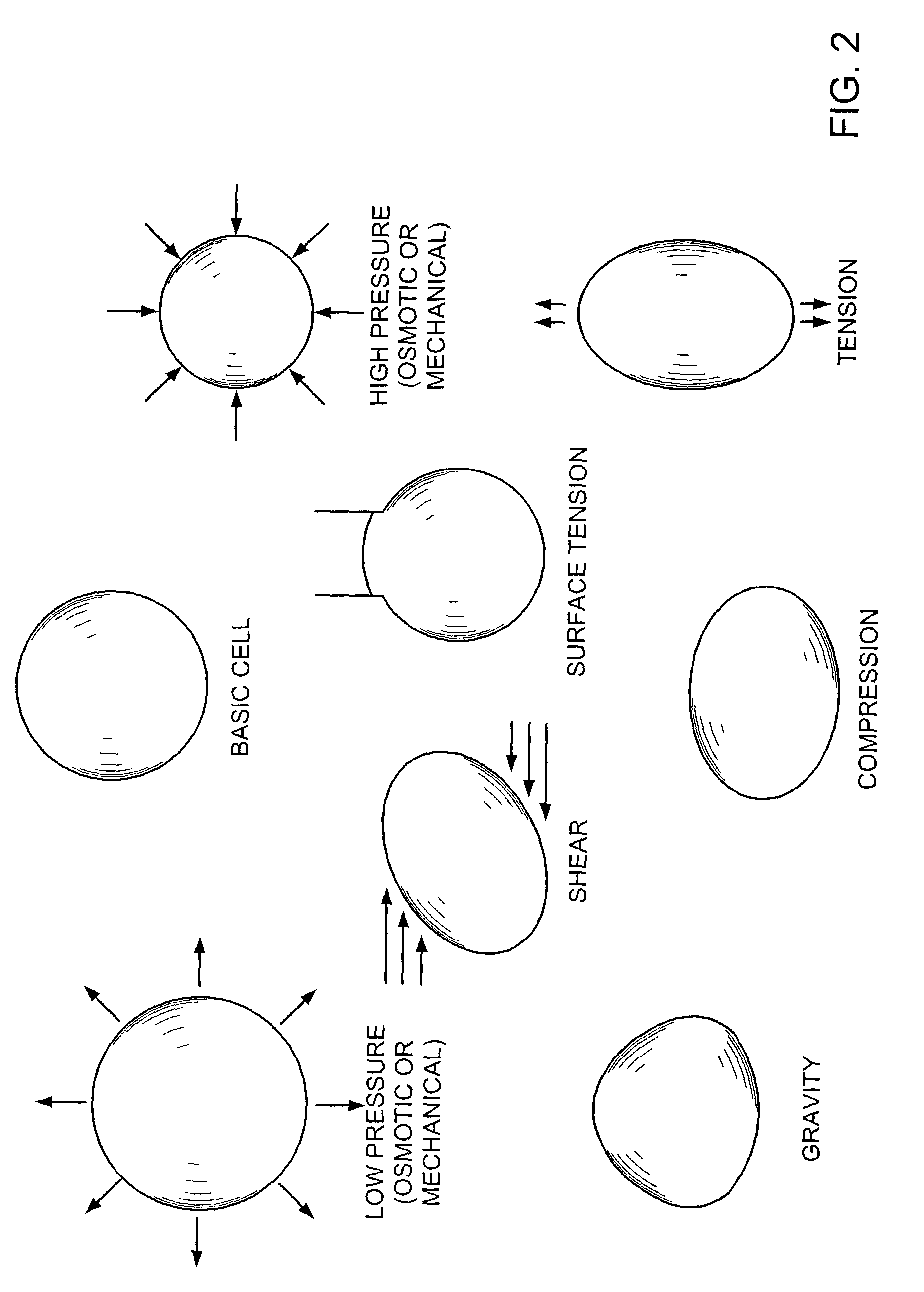
InactiveUS7494482B2Accelerate tissue ingrowthEnhancing tissue repairNon-adhesive dressingsBone implantMicron scaleCell-Extracellular Matrix
Methods and devices for transmitting micromechanical forces locally to induce surface convolutions into tissues on the millimeter to micron scale for promoting wound healing are presented. These convolutions induce a moderate stretching of individual cells, stimulating cellular proliferation and elaboration of natural growth factors without increasing the size of the wound. Micromechanical forces can be applied directly to tissue, through biomolecules or the extracellular matrix. This invention can be used with biosensors, biodegradable materials and drug delivery systems. This invention will also be useful in pre-conditioned tissue-engineering constructs in vitro. Application of this invention will shorten healing times for wounds and reduce the need for invasive surgery.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +2
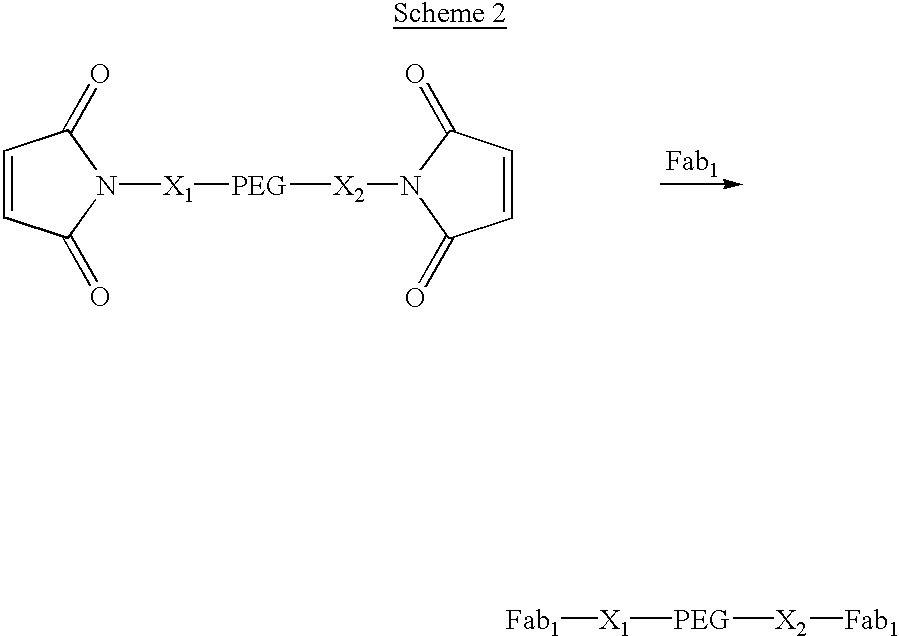
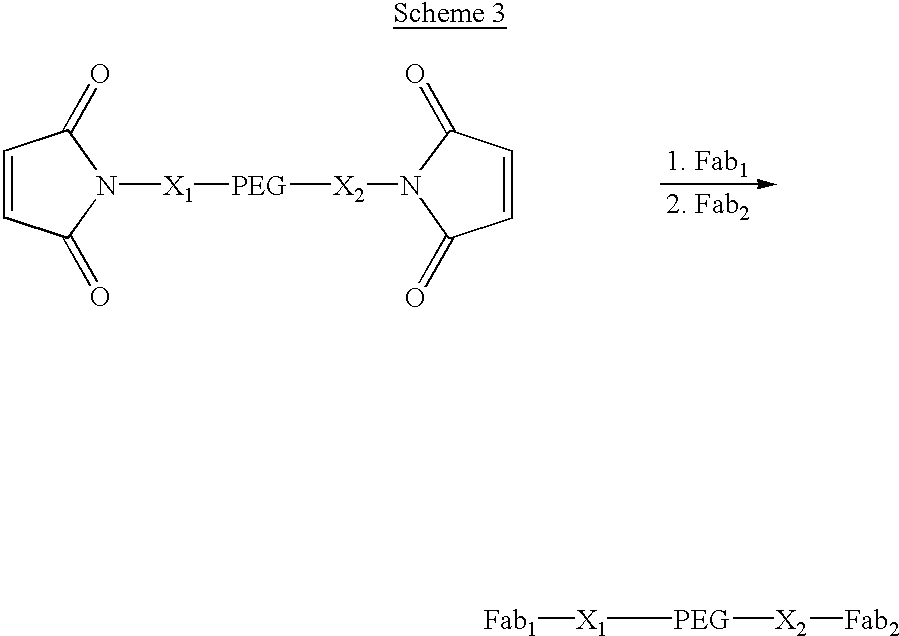
Pseudo-antibody constructs
InactiveUS20030211078A1Reduce productionInhibit synthesisOrganic active ingredientsBiocideHalf-lifeIn vivo
This invention relates to novel pharmaceutically useful compositions that bind to a biological molecule, having improved circulatory half-life, increased avidity, increased affinity, or multifunctionality, and methods of use thereof. The present invention provides a pseudo-antibody comprising an organic moiety covalenty coupled to at least two target-binding moieties, wherein the target-binding moieties are selected from the group consisting of a protein, a peptide, a peptidomimetic, and a non-peptide molecule that binds to a specific targeted biological molecule. The pseudo-antibody of the present invention may affect a specific ligand in vitro, in situ and / or in vivo. The pseudo-antibodies of the present invention can be used to measure or effect in an cell, tissue, organ or animal (including humans), to diagnose, monitor, modulate, treat, alleviate, help prevent the incidence of, or reduce the symptoms of, at least one condition.
Owner:CENTOCOR
DNA-bridged carbon nanotube arrays
InactiveUS6958216B2High sensitivityImprove portabilityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsChemical ligationElectron transfer reactions
A class of biological sensing devices that include a substrate comprising an array of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) to which are chemically attached biological molecules is disclosed. The attached biological molecules are capable of electrical conductivity that is responsive to chemical changes occurring as a result of their interaction with target species. A means for means for using DNA as a material of potential in molecular electronic sensor devices, being primarily based on molecular electron-transfer reaction processes between DNA-binding donors and acceptors is also disclosed, including composition, method of manufacture and their use are described.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON COLLEGE THE
Graphitic nanotubes in luminescence assays
Graphitic nanotubes, which include tubular fullerenes (commonly called "buckytubes") and fibrils, which are functionalized by chemical substitution, are used as solid supports in electrogenerated chemiluminescence assays. The graphitic nanotubes are chemically modified with functional group biomolecules prior to use in an assay. Association of electrochemiluminescent ruthenium complexes with the functional group biomolecule-modified nanotubes permits detection of molecules including nucleic acids, antigens, enzymes, and enzyme substrates by multiple formats.
Owner:MESO SCALE TECH LLC
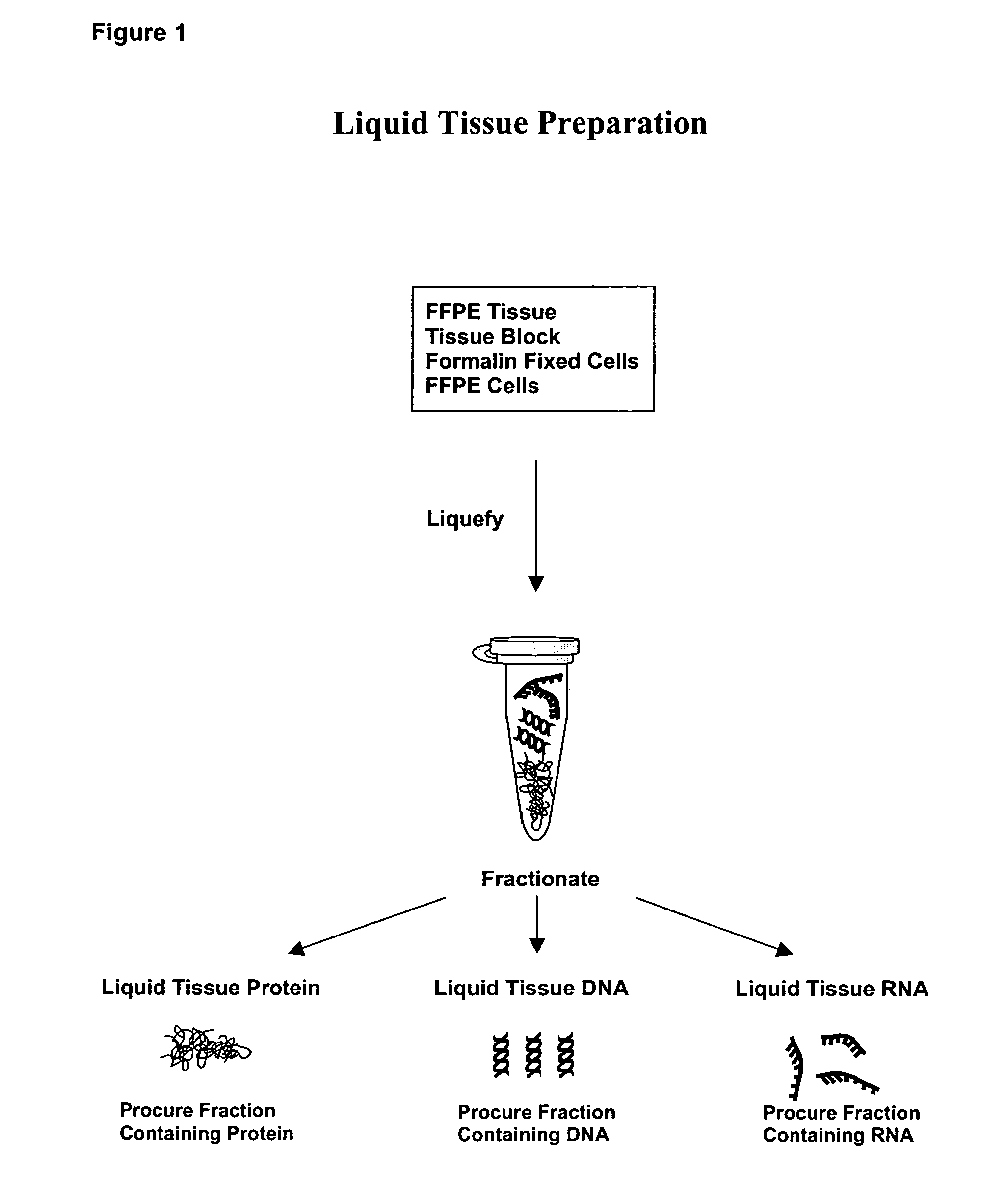
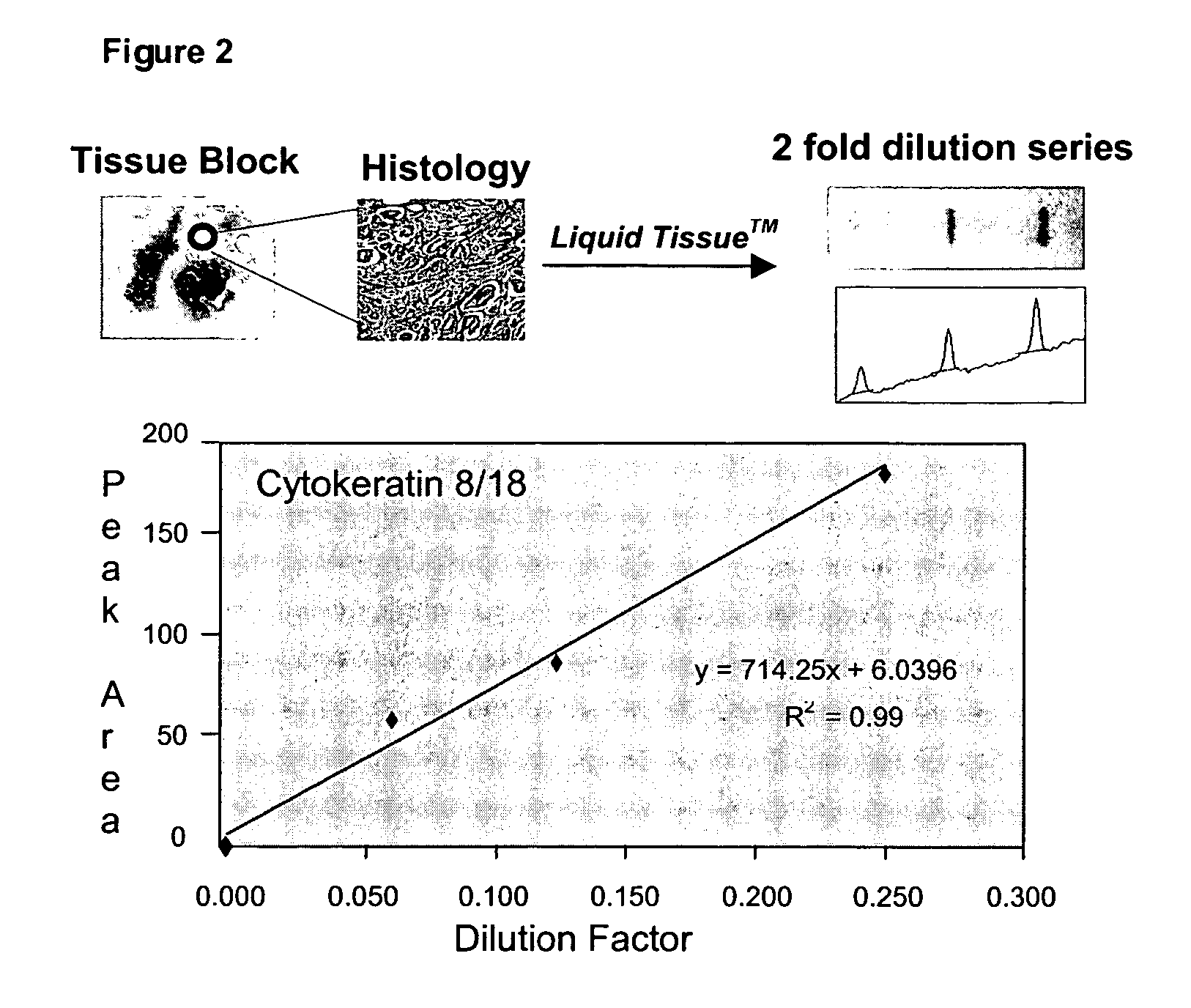
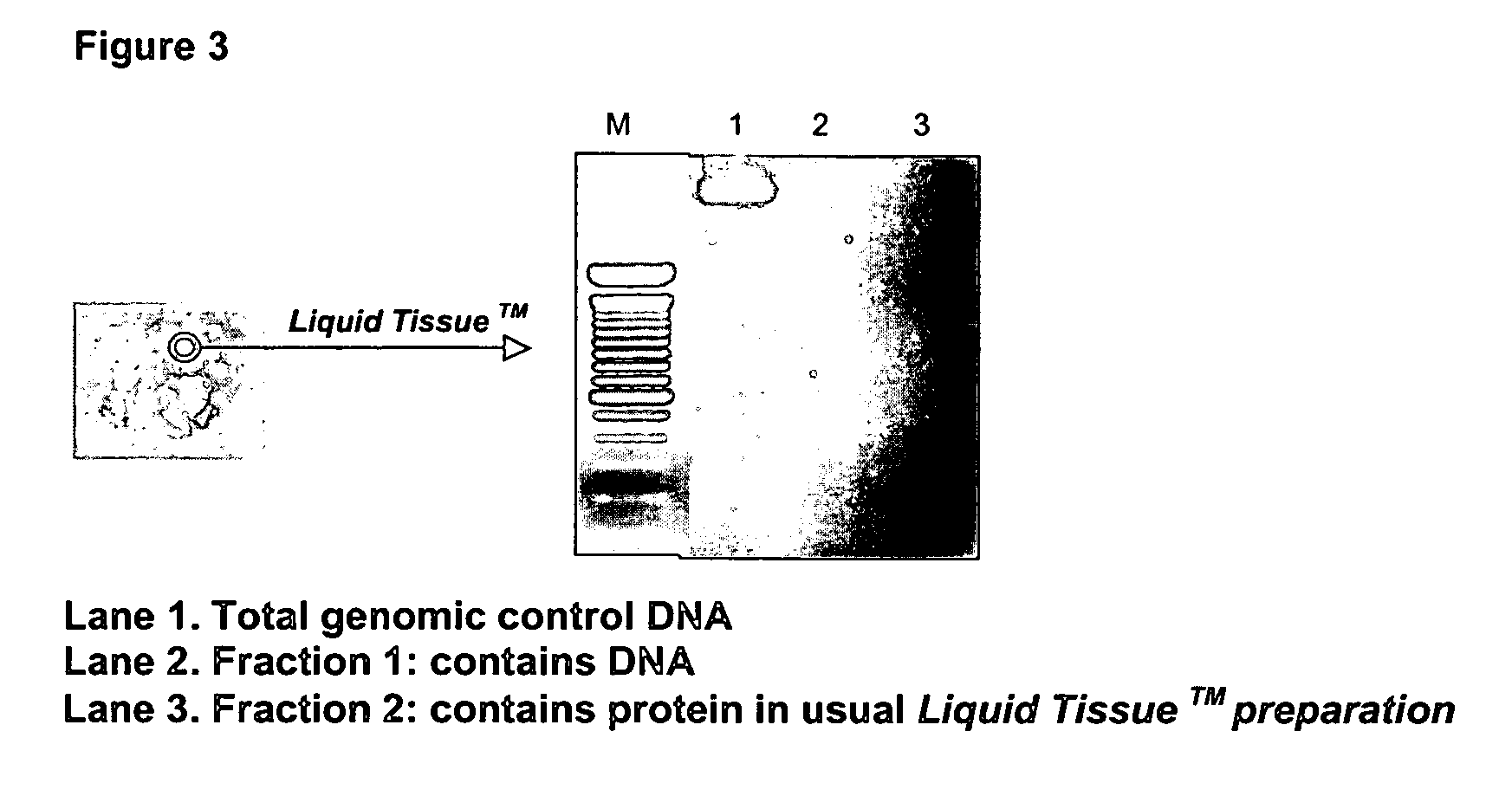
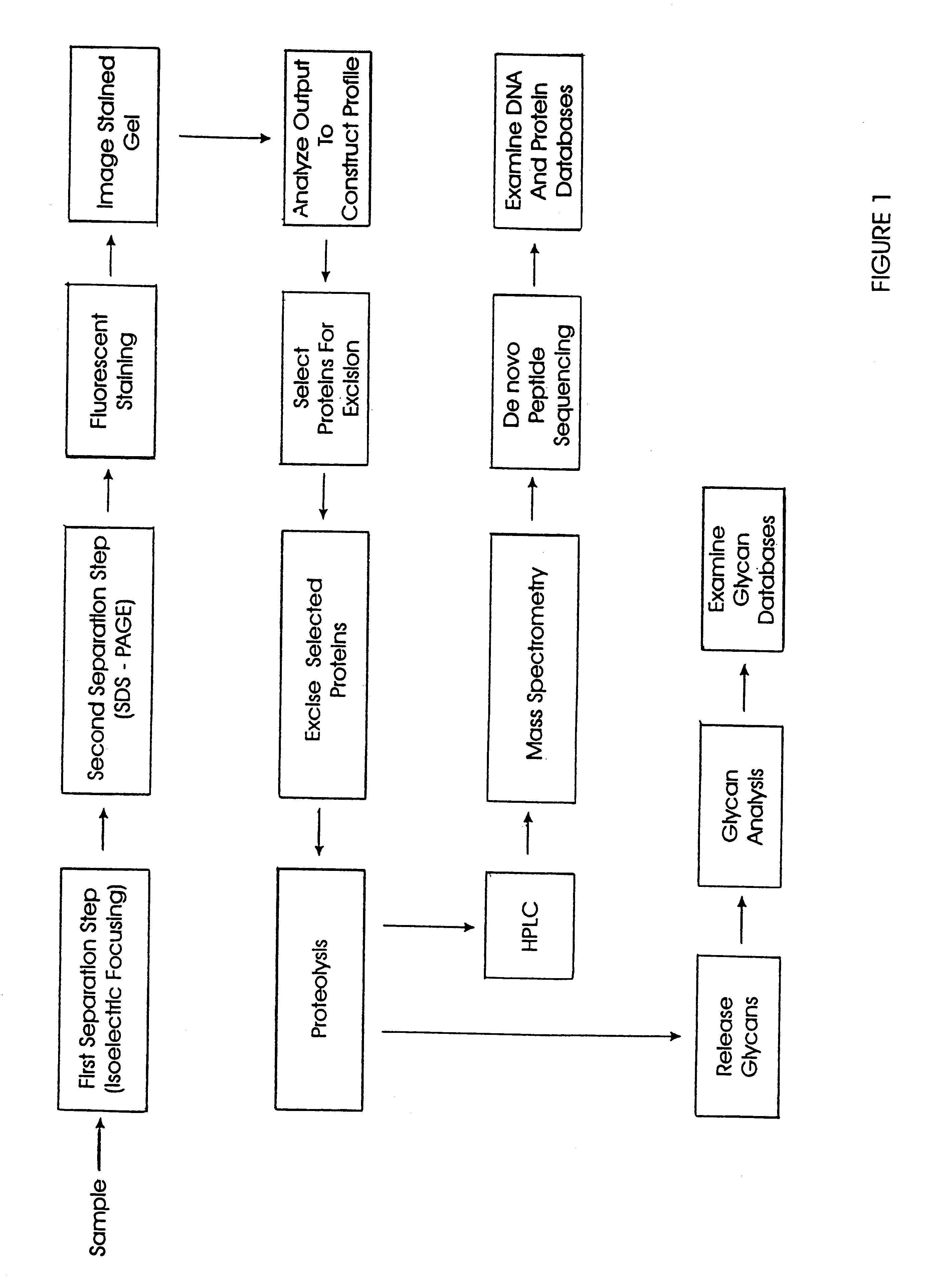
Liquid tissue preparation from histopathologically processed biological samples, tissues and cells
The current invention provides a method for directly converting histopathologically processed biological samples, tissues, and cells into a multi-use biomolecule lysate. This method allows for simultaneous extraction, isolation, solublization, and storage of all biomolecules contained within the histopathologically processed biological sample, thereby forming a representative library of said sample. This multi-use biomolecule lysate is dilutable, soluble, capable of being fractionated, and used in any number of subsequent experiments.
Owner:EXPRESSION PATHOLOGY
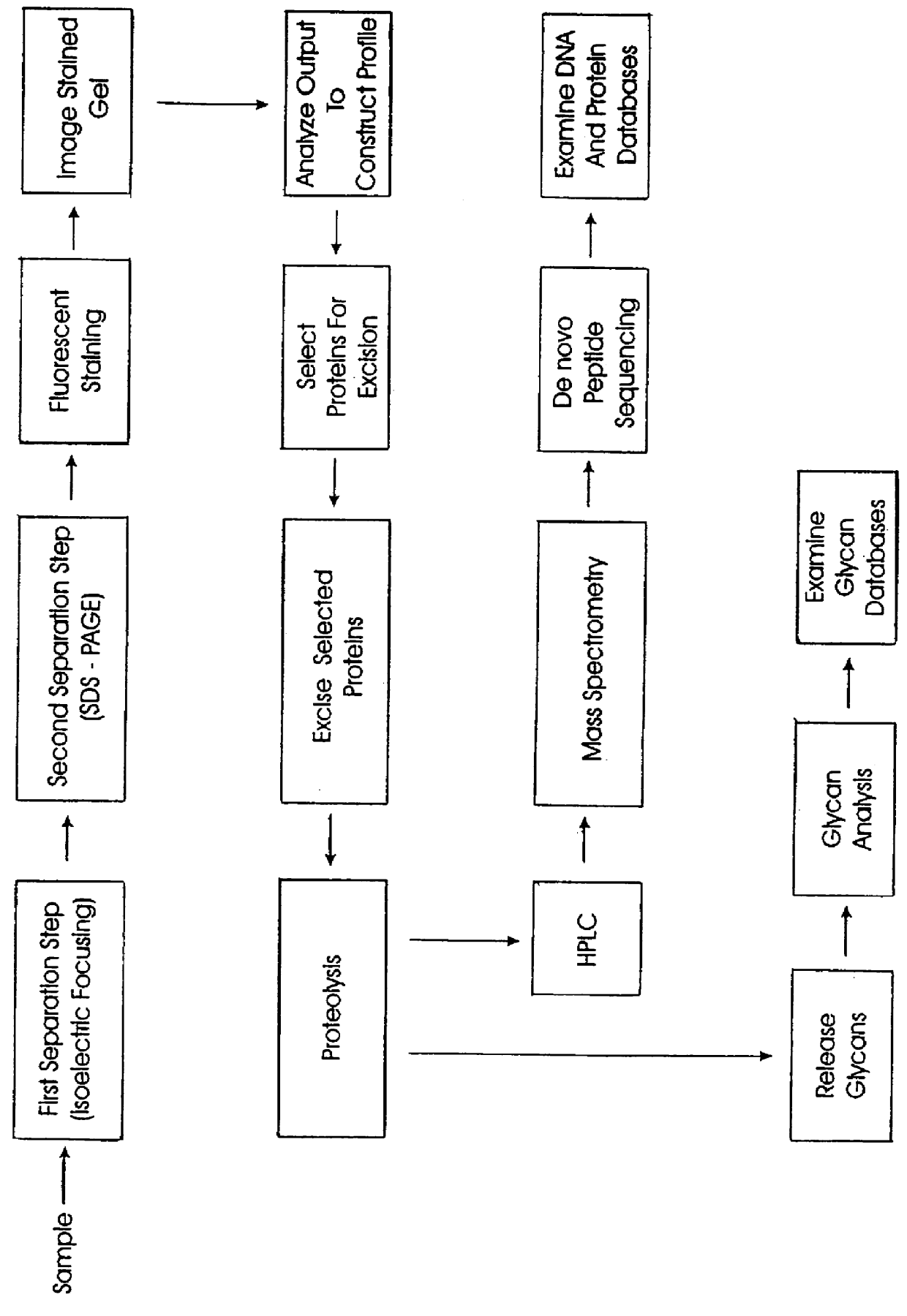
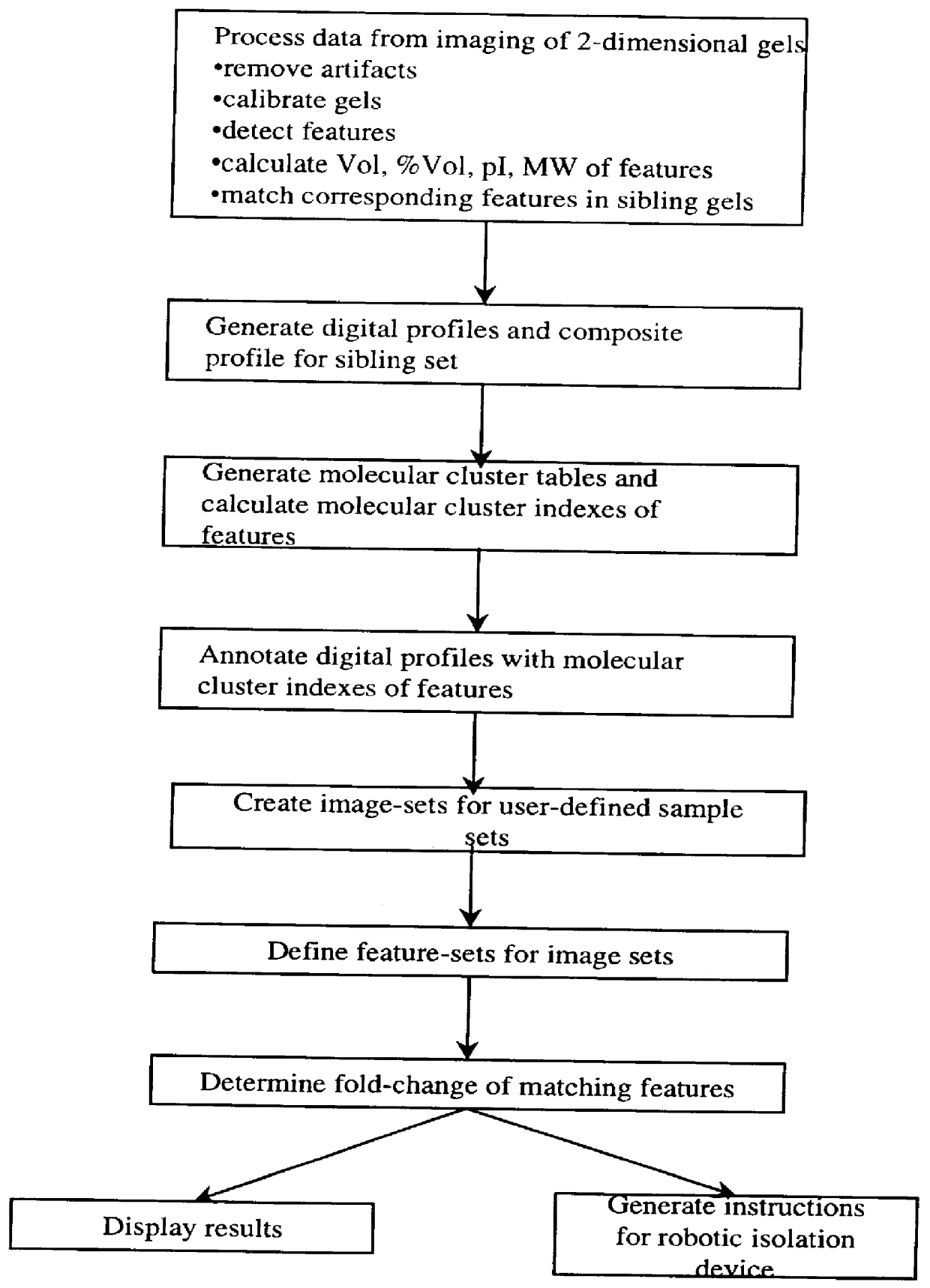
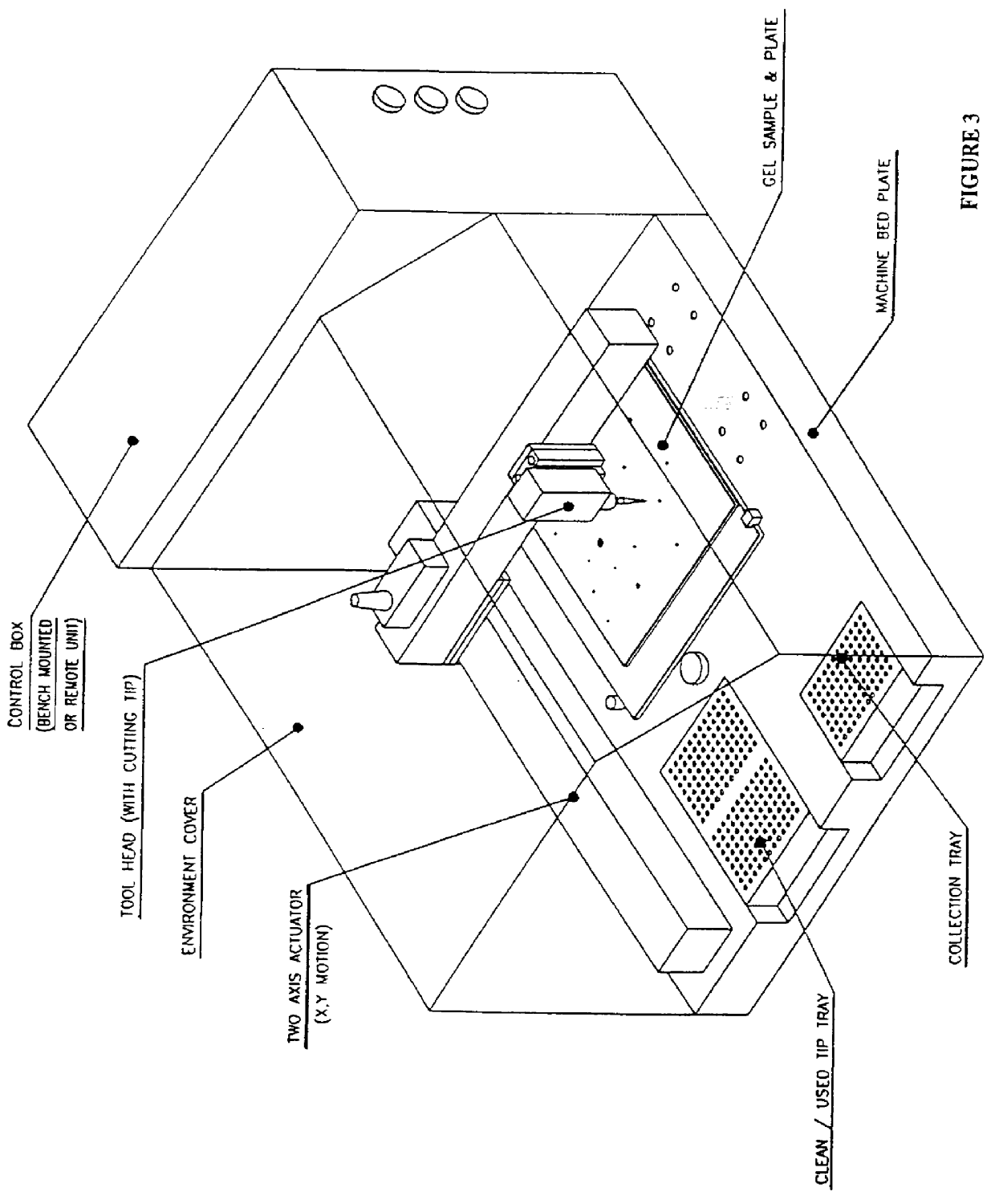
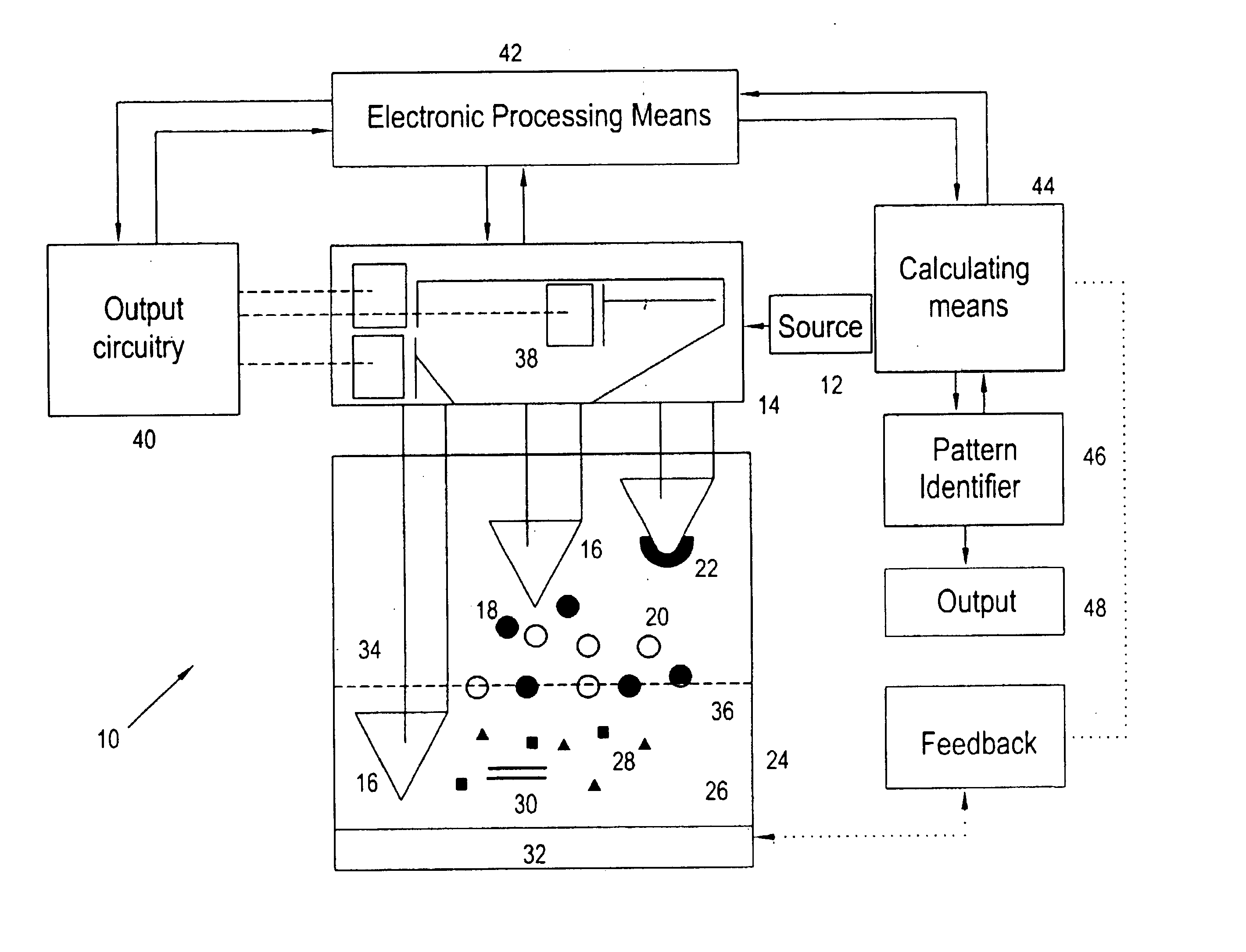
Computer-assisted methods and apparatus for identification and characterization of biomolecules in a biological sample
InactiveUS6064754ARapid and efficient identificationPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrophoresisComputer-aided
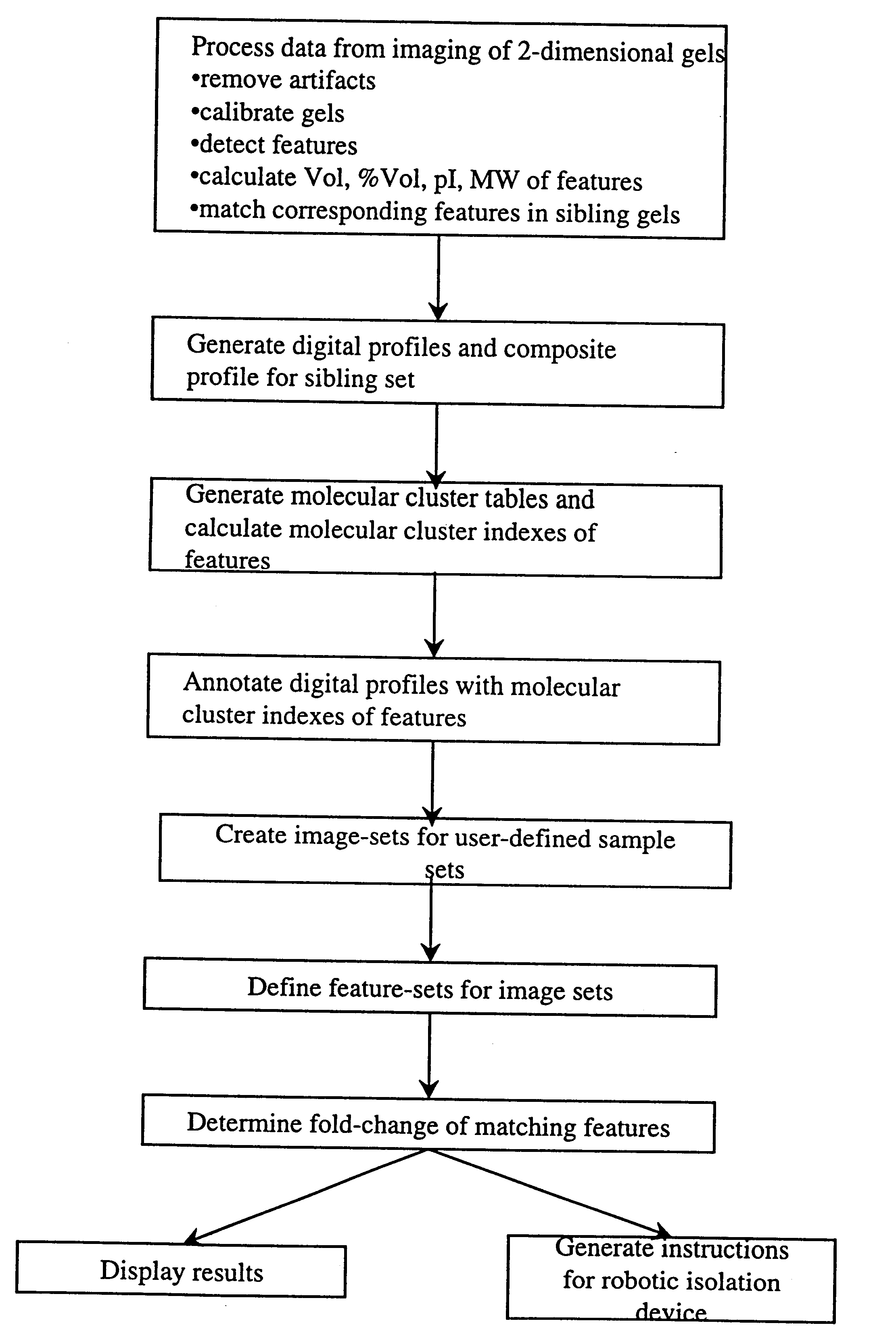
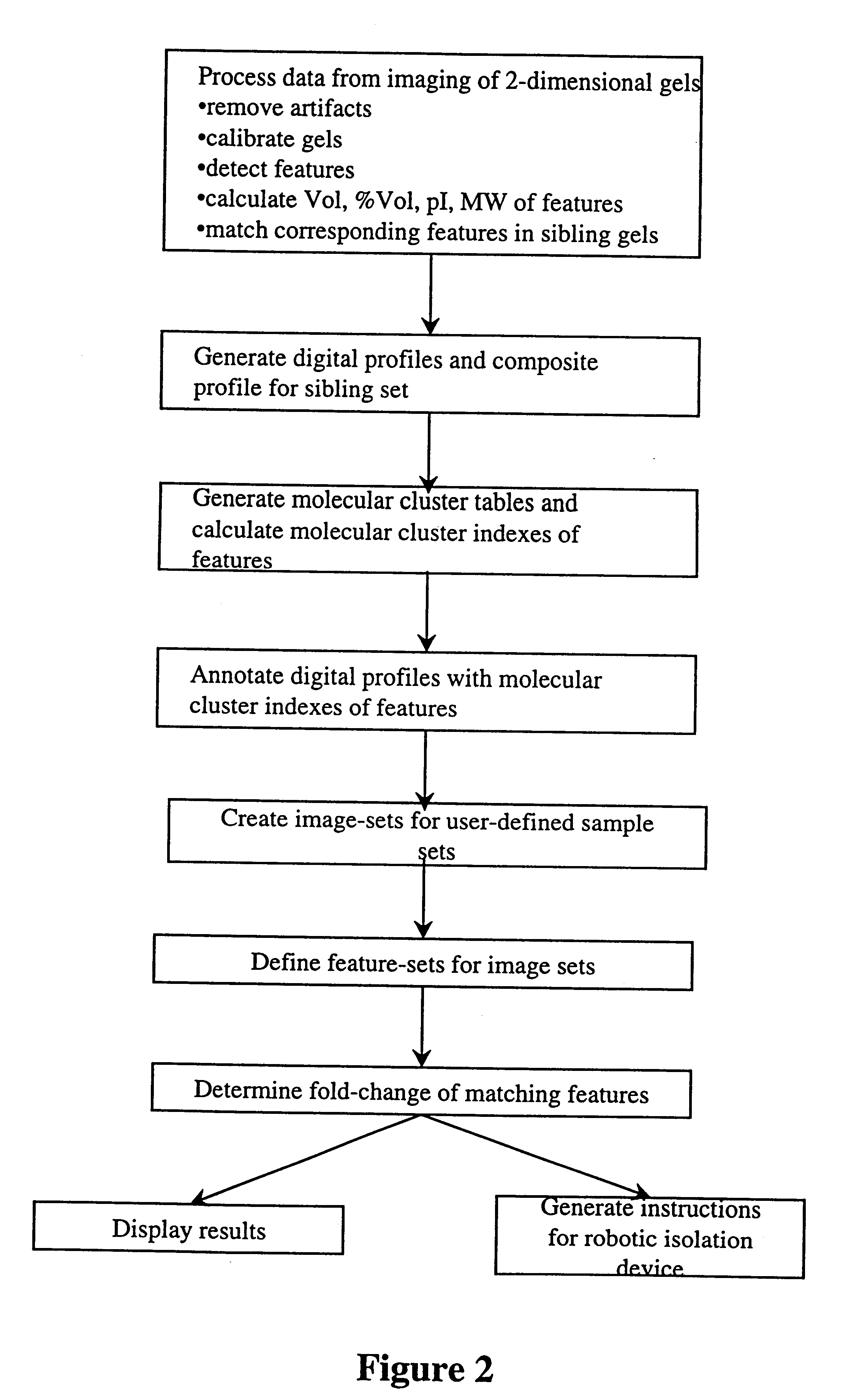
The present invention provides computer-assisted methods and apparatus for identifying, selecting and characterizing biomolecules in a biological sample. A two-dimensional array is generated by separating biomolecules present in a complex mixture. A computer-readable profile is constructed representing the identity and relative abundance of a plurality of biomolecules detected by imaging the two dimensional array. Computer-mediated comparison of profiles from multiple samples permits automated identification of subsets of biomolecules that satisfy pre-ordained criteria. Identified biomolecules can be automatically isolated from the two dimensional array by a robotic device in accordance with computer-generated instructions. A supported gel suitable for electrophoresis is provided that is bonded to a solid support such that the gel has two-dimensional spatial stability and the solid support is substantially non-interfering with respect to detection of a label, such as a fluorescent label, associated with one or more biomolecules in the gel.
Owner:OXFORD GLYCOSCI UK
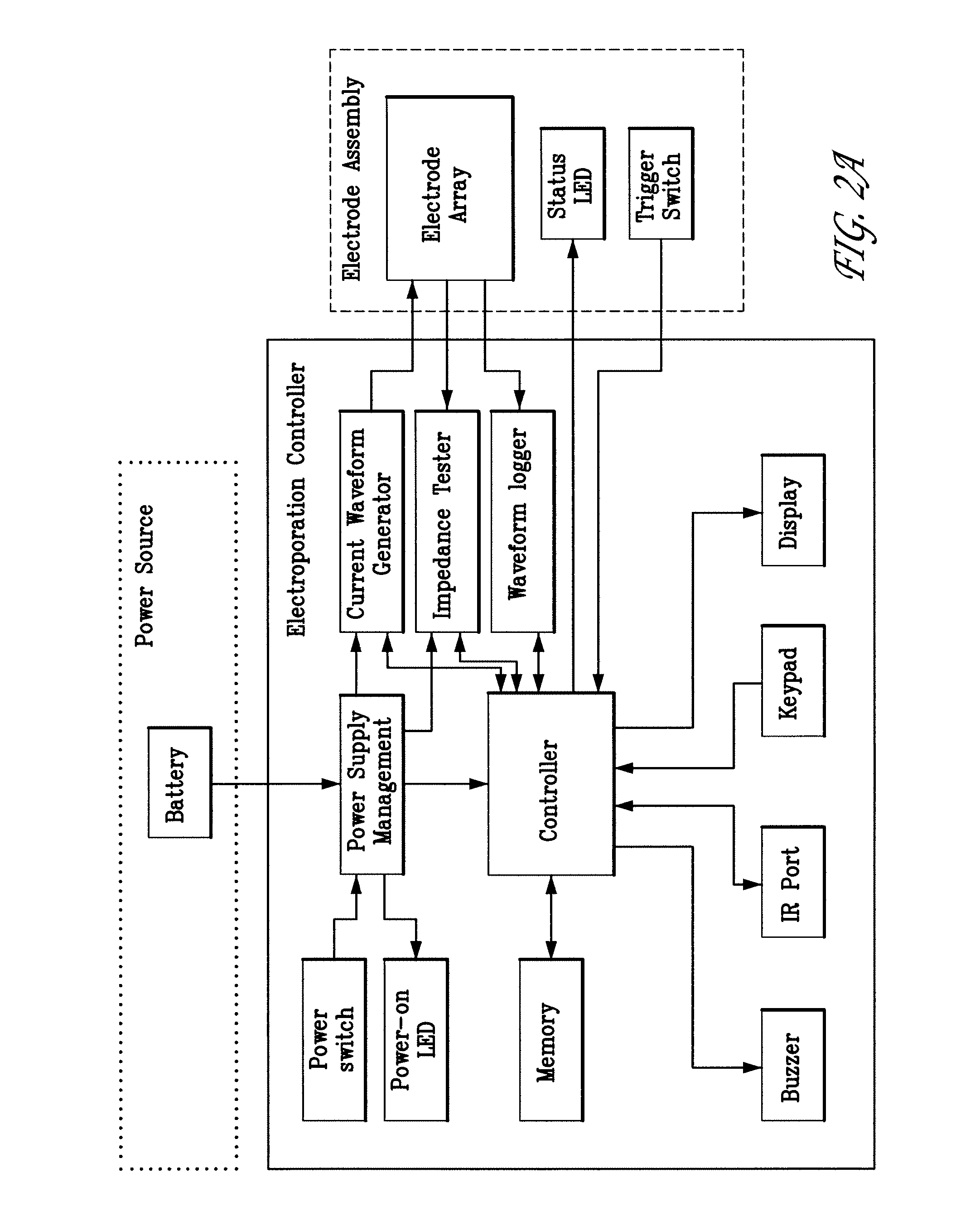
Electroporation devices and methods of using same for electroporation of cells in mammals
Aspects of the present invention relate to electroporation devices and methods of using same to effectively facilitate the introduction of a biomolecule into cells of a selected tissue in a body, in particular skin such as intradermic or subcutaneous tissue. In some aspects, the present invention is a skin EP device, which produces a pulse of energy and delivers same to the skin tissue using a skin electrode array and maintains a constant current in the same skin tissue based on user input, including a preset current, and allows the storage and acquisition of current waveform data.
Owner:INOVIO PHARMA
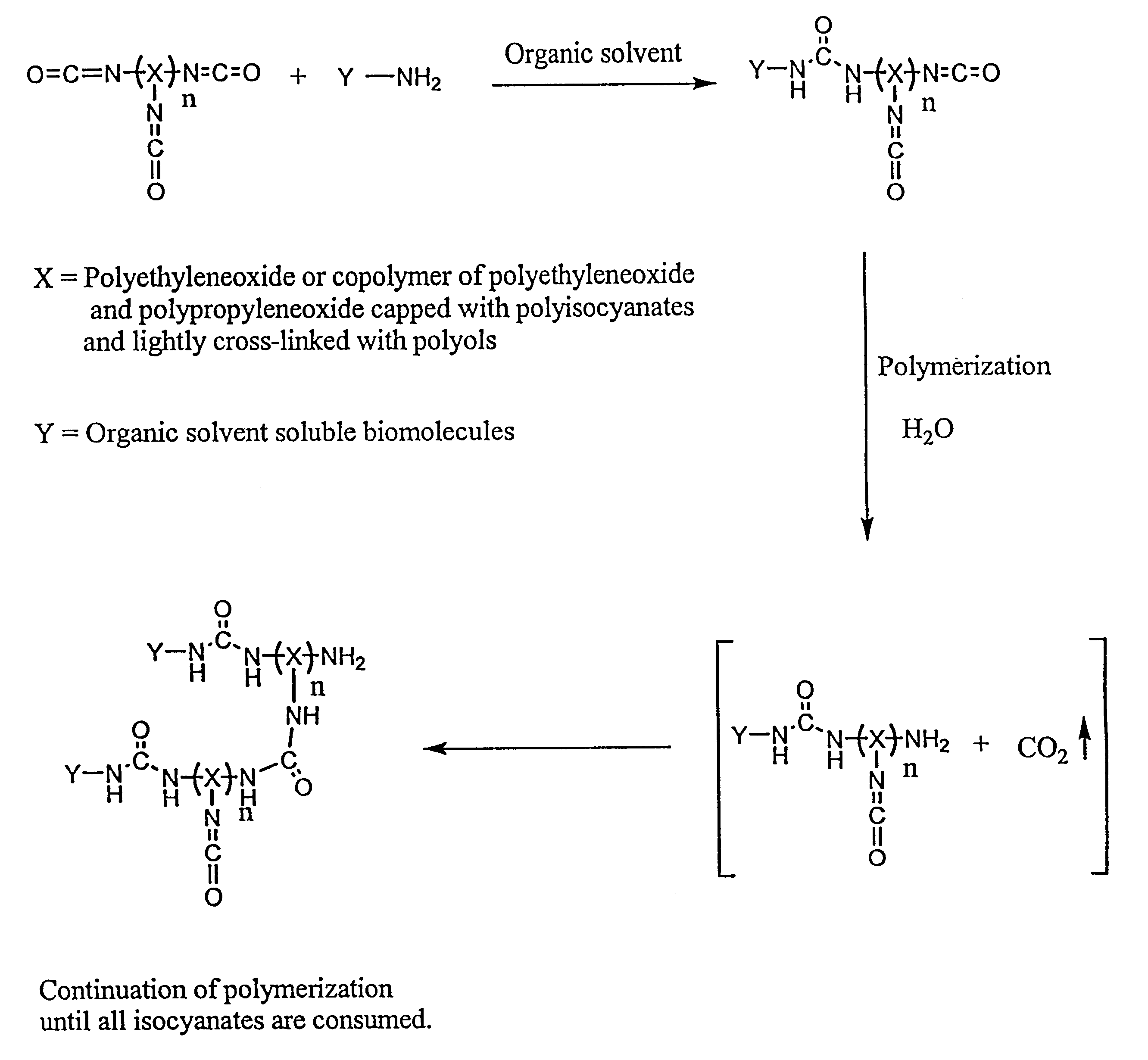
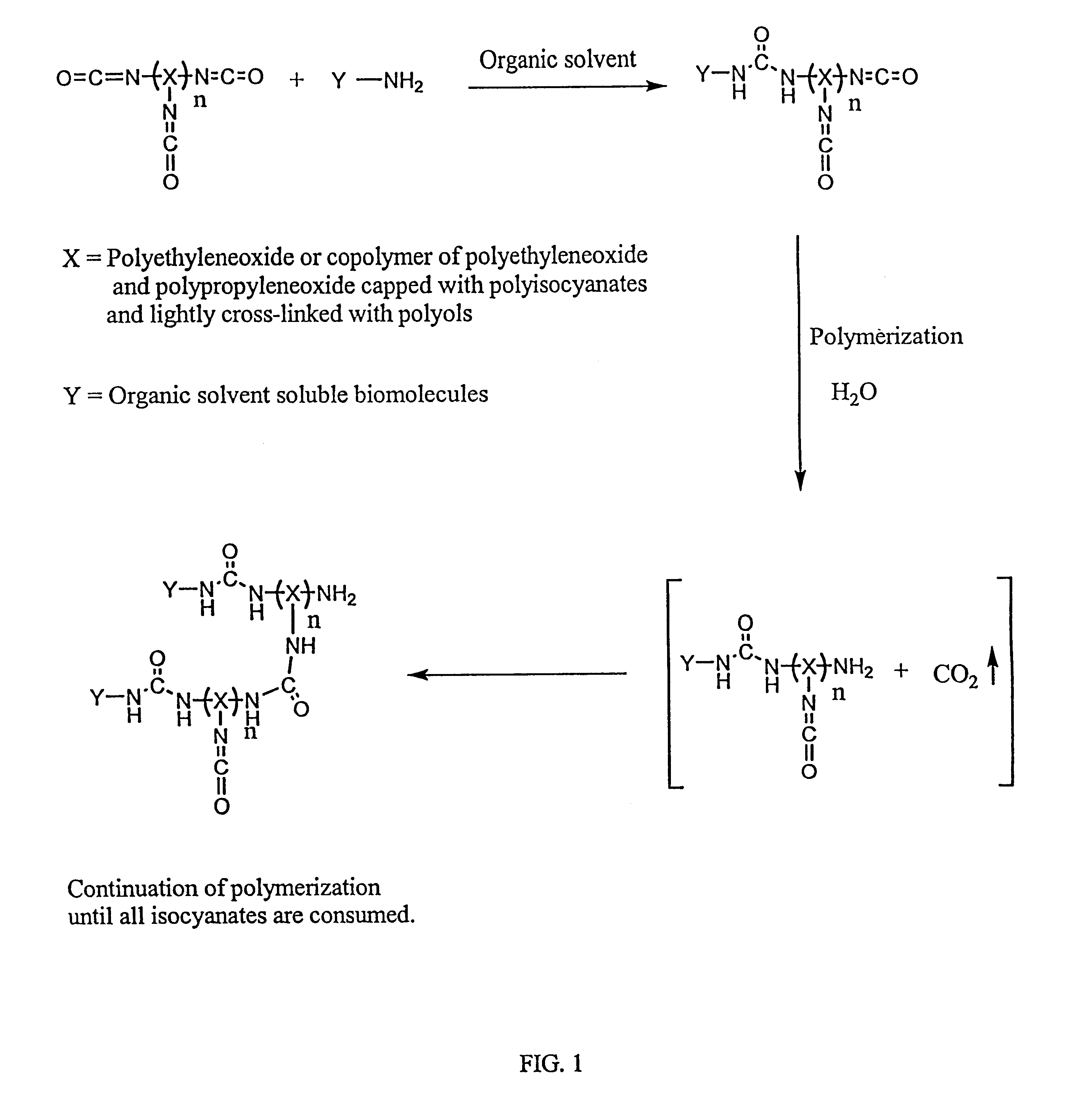
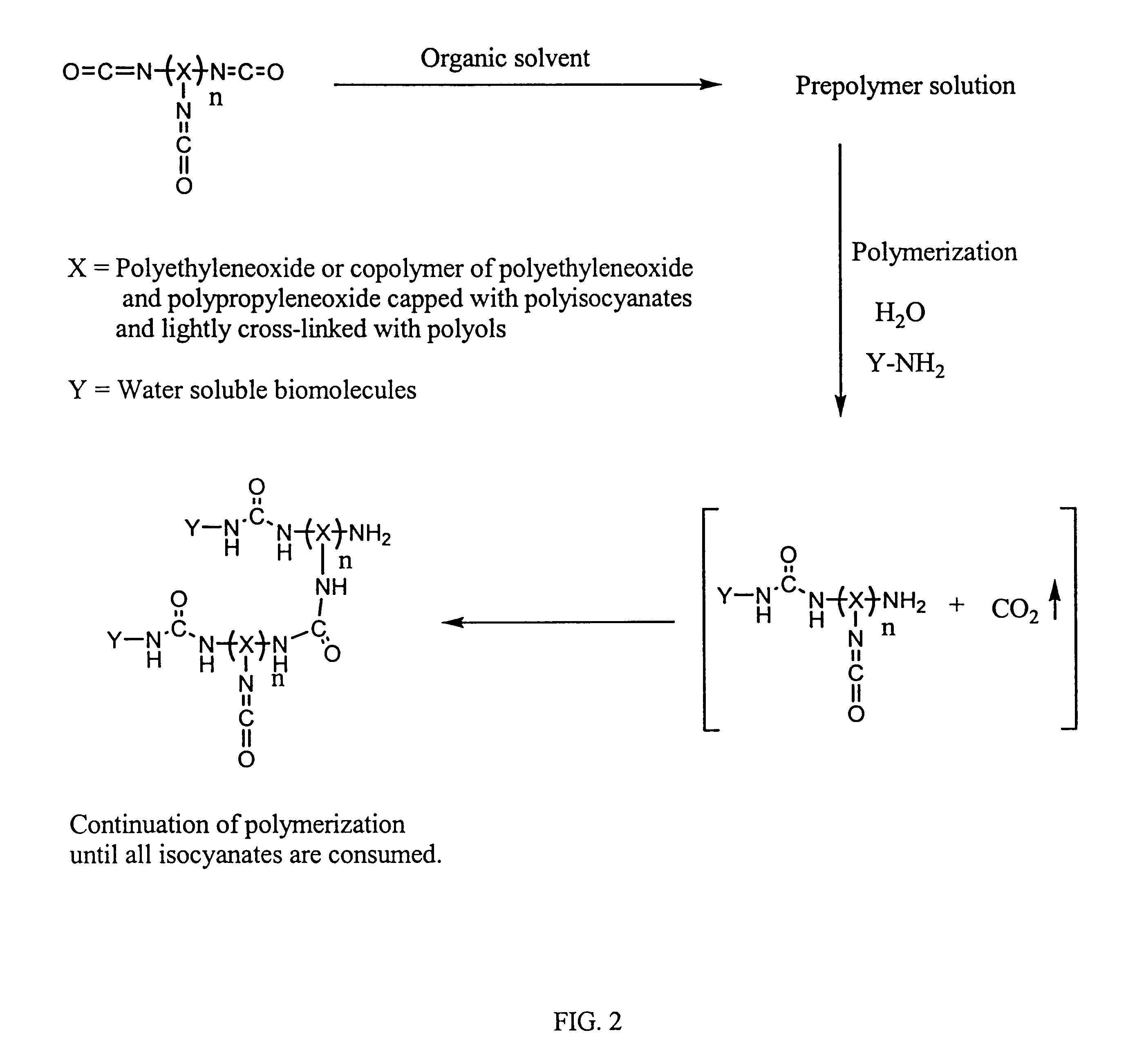
Method of making biochips and the biochips resulting therefrom
InactiveUS6174683B1Rapid and simple and cost-effective methodHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSodium bicarbonateSolid substrate
Methods for preparing a biochip are provided herein wherein the biomolecular probe to be used with the biochip is alternatively bound to a hydrogel prepolymer prior to or simultaneously with polymerization of the prepolymer. In particularly preferred embodiments, a polyurethane-based hydrogel prepolymer is derivatized with an organic solvent soluble biomolecule, such as a peptide nucleic acid probe in aprotic, organic solvent. Following derivatization of the prepolymer, an aqueous solution, for example sodium bicarbonate, preferably buffered to a pH of about 7.2 to about 9.5, is added to the derivatized prepolymer solution to initiate polymerization of the hydrogel. Alternatively, a water soluble biomolecule, such as DNA or other oligonucleotide, is prepared in an aqueous solution and added to the polyurethane-based hydrogel prepolymer such that derivatization and polymerization occur, essentially, simultaneously. While the hydrogel is polymerizing, it is microspotted onto a solid substrate, preferably a silanated glass substrate, to which the hydrogel microdroplet becomes covalently bound. Most preferably the hydrogel microdroplets are at least about 30 mum thick, for example about 50 mum to about 100 mum thick. The resulting biochips are particularly useful for gene discovery, gene characterization, functional gene analysis and related studies.
Owner:BIOCEPT INC
Detection of molecular interactions using a field effect transistor
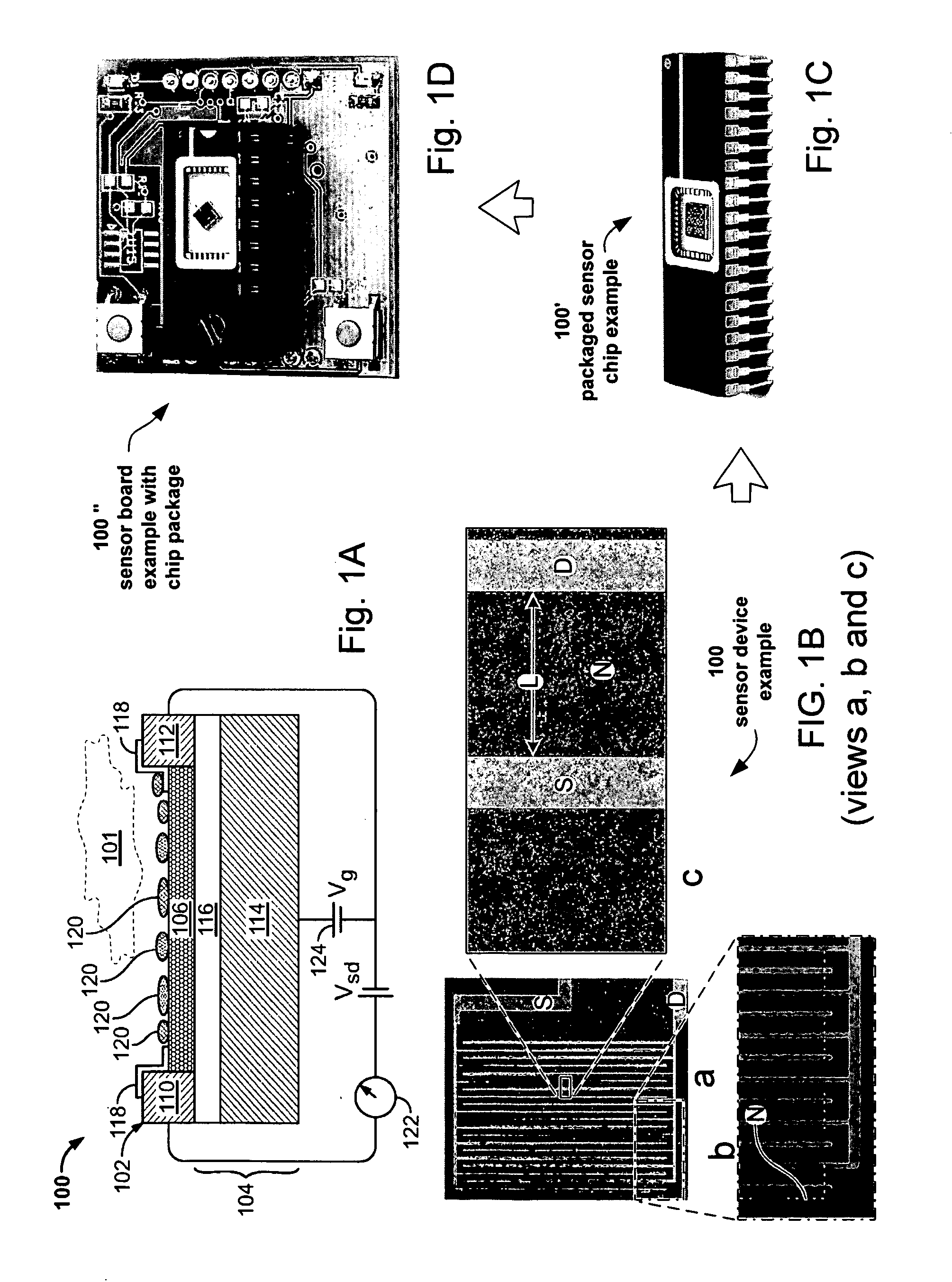
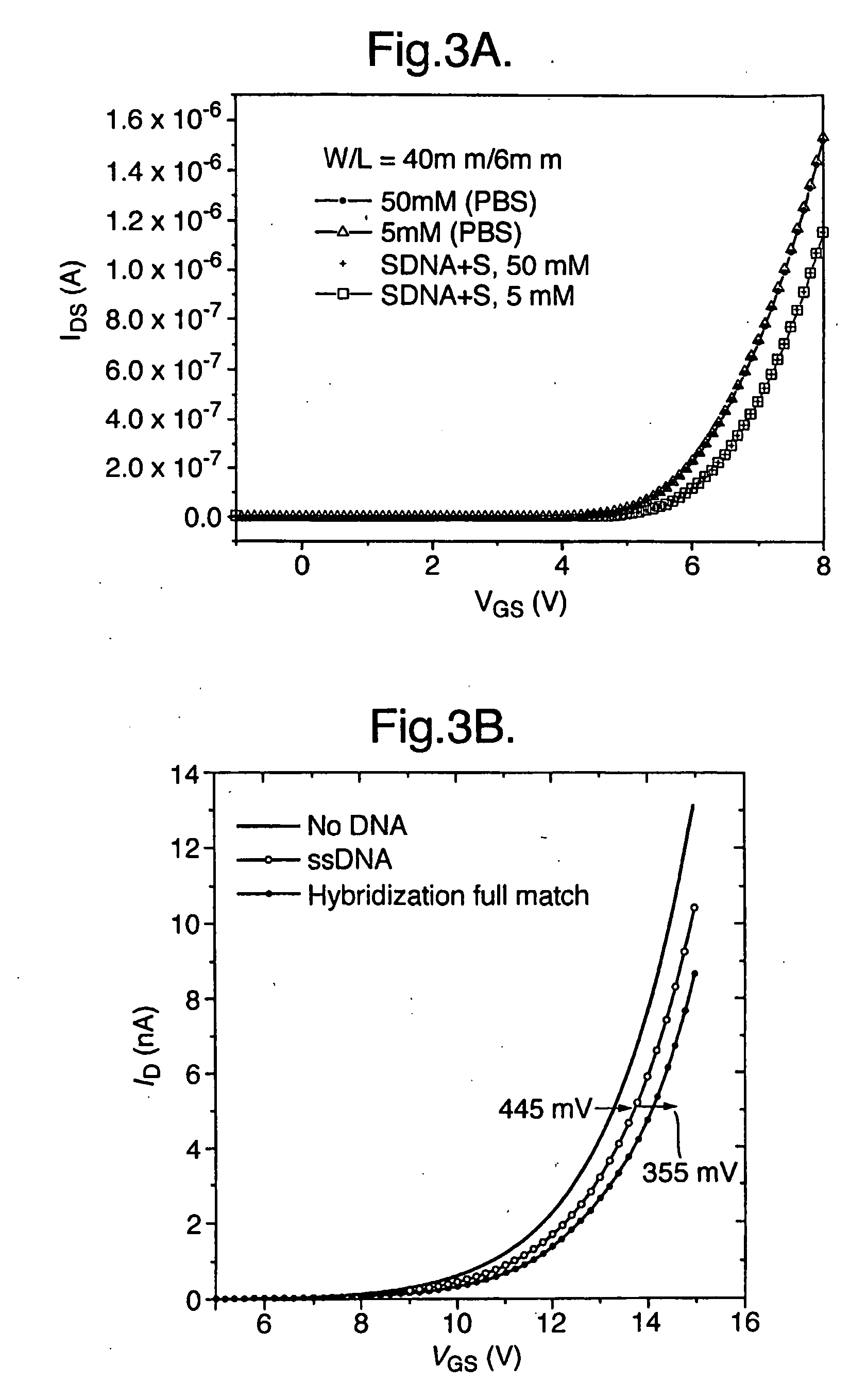
InactiveUS20060197118A1Operation may changeHigh impedanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesField-effect transistorDNA
A sensor for use in the detection of a molecular interaction comprises a field effect transistor (FET) having a core structure and an extended gate structure, the core structure and the extended gate structure being located on substantially separate regions of a substrate, the extended gate structure including an exposed metal sensor electrode on which probe molecules can be immobilized, wherein, in use, the sensor is operative to produce a change in an electrical characteristic of the FET in response to molecular interaction at the exposed surface of the metal sensor electrode. The sensor is particularly suitable for detecting biomolecular interactions such as the hybridization of DNA, when the sensor is prepared with suitable probe molecules immobilized on the exposed gate metal.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENTERPRISE LTD
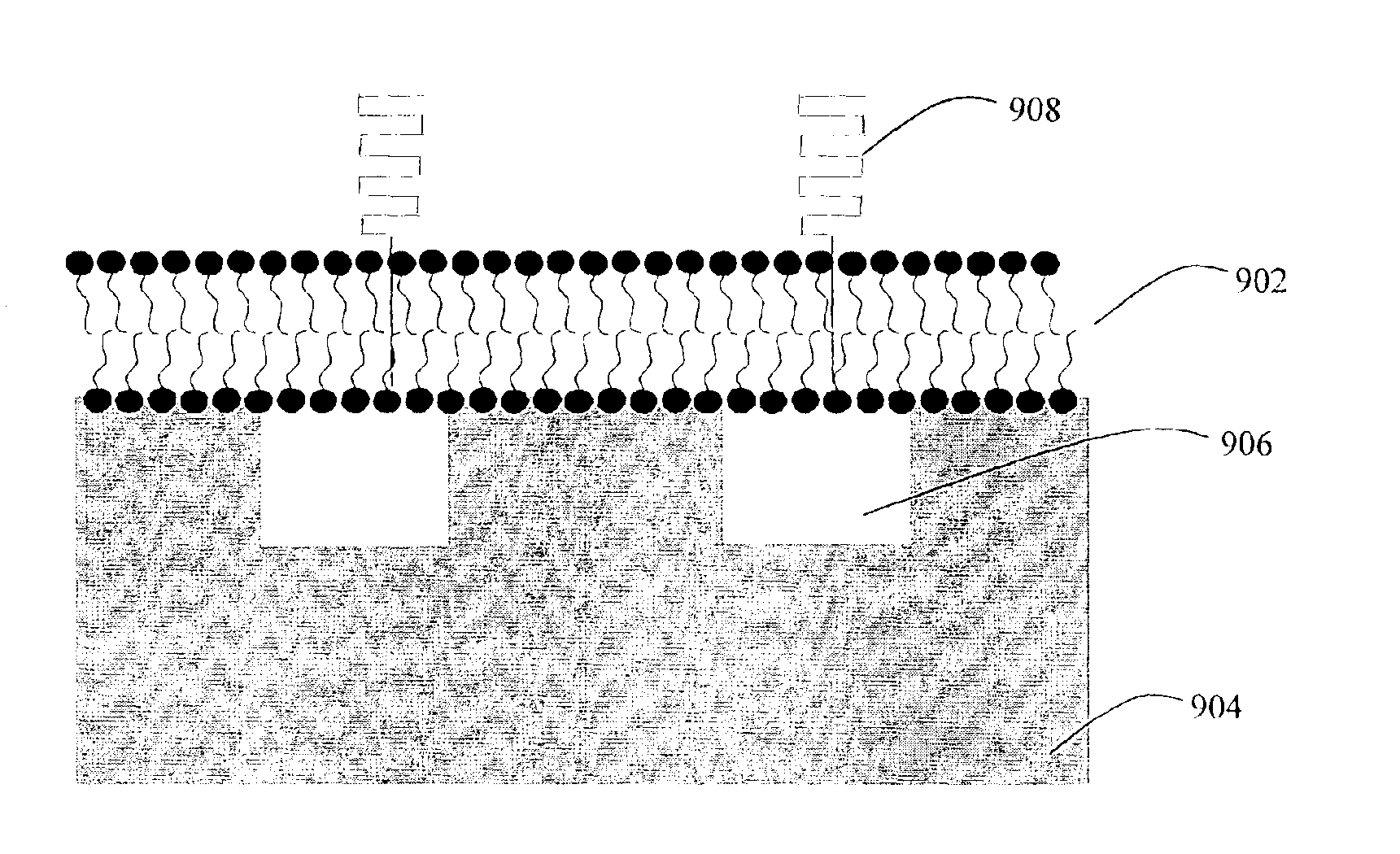
Nanostructured separation and analysis devices for biological membranes
InactiveUS6913697B2Ion-exchanger regenerationVolume/mass flow measurementBiological membraneNanostructure
The present invention provides a nanostructured device comprising a substrate including nanotroughs therein; and a lipid bilayer suspended on or supported in the substrate. A separation method is also provided comprising the steps of supporting or suspending a lipid bilayer on a substrate; wherein the substrate comprises nanostructures and wherein the lipid bilayer comprises at least one membrane associated biomolecule; and applying a driving force to the lipid bilayer to separate the membrane associated biomolecule from the lipid bilayer and to drive the membrane associated biomolecule into the nanostructures.
Owner:STC UNM
Biodegradable polyurethanes and use thereof
InactiveUS20050013793A1Improve responseIncrease ratingsCell culture supports/coatingSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPolymer scienceDrug biological activity
A biodegradable and biocompatible polyurethane composition synthesized by reacting isocyanate groups of at least one multifunctional isocyanate compound with at least one bioactive agent having at least one reactive group —X which is a hydroxyl group (—OH) or an amine group (—NH2). The polyurethane composition is biodegradable within a living organism to biocompatible degradation products including the bioactive agent. Preferably, the released bioactive agent affects at least one of biological activity or chemical activity in the host organism. A biodegradable polyurethane composition includes hard segments and soft segments. Each of the hard segments is preferably derived from a diurea diol or a diester diol and is preferably biodegradable into biomolecule degradation products or into biomolecule degradation products and a biocompatible diol. Another biodegradable polyurethane composition includes hard segments and soft segments. Each of the hard segments is derived from a diurethane diol and is biodegradable into biomolecule degradation products.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV +1
Water-soluble luminescent quantum dots and biomolecular conjugates thereof and related compositions and method of use
InactiveUS6468808B1Material nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsQuantum dotWater soluble
The present invention provides a water-soluble luminescent quantum dot, a biomolecular conjugate thereof and a composition comprising such a quantum dot or conjugate. Additionally, the present invention provides a method of obtaining a luminescent quantum dot, a method of making a biomolecular conjugate thereof, and methods of using a biomolecular conjugate for ultrasensitive nonisotopic detection in vitro and in vivo.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
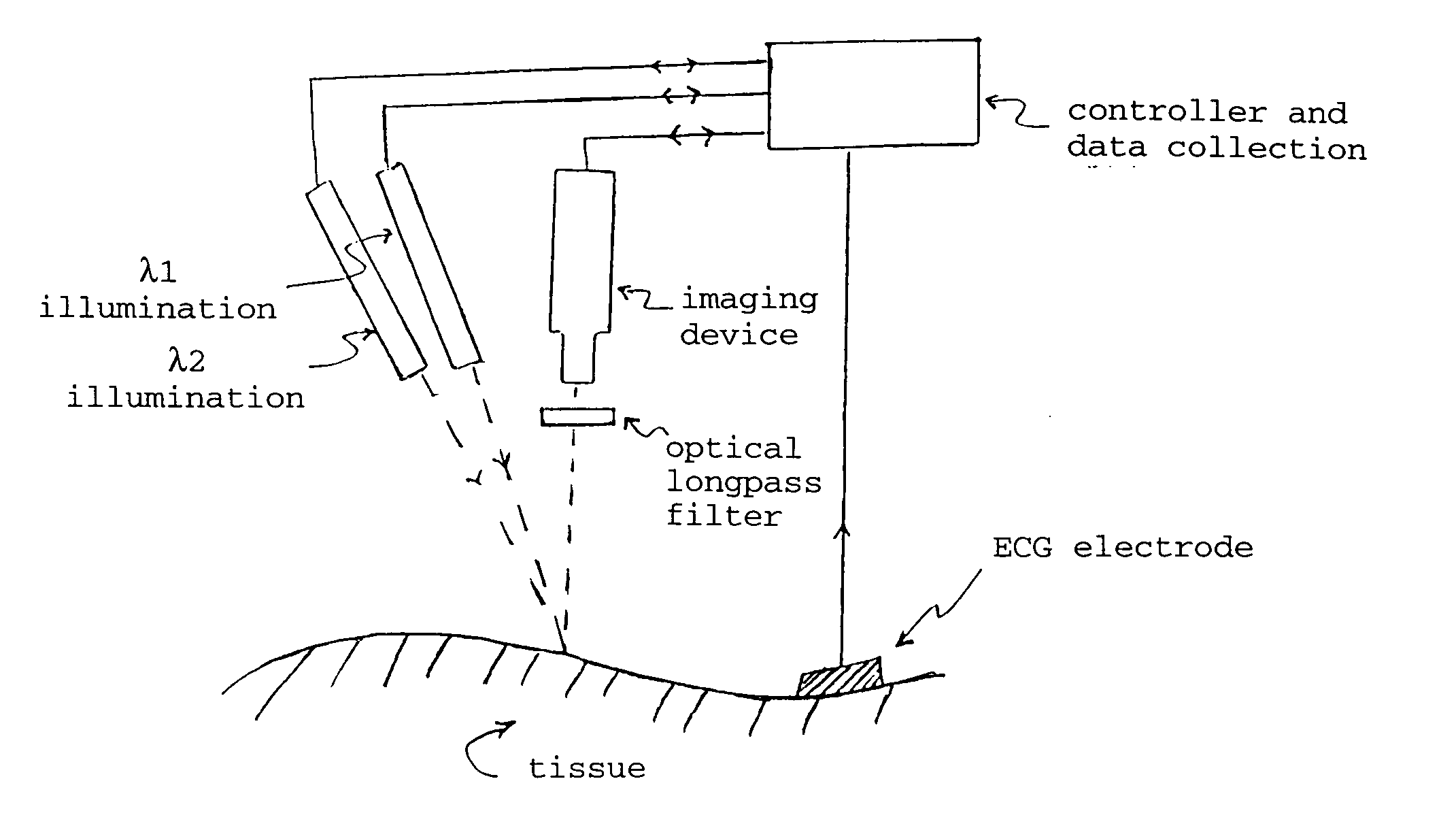
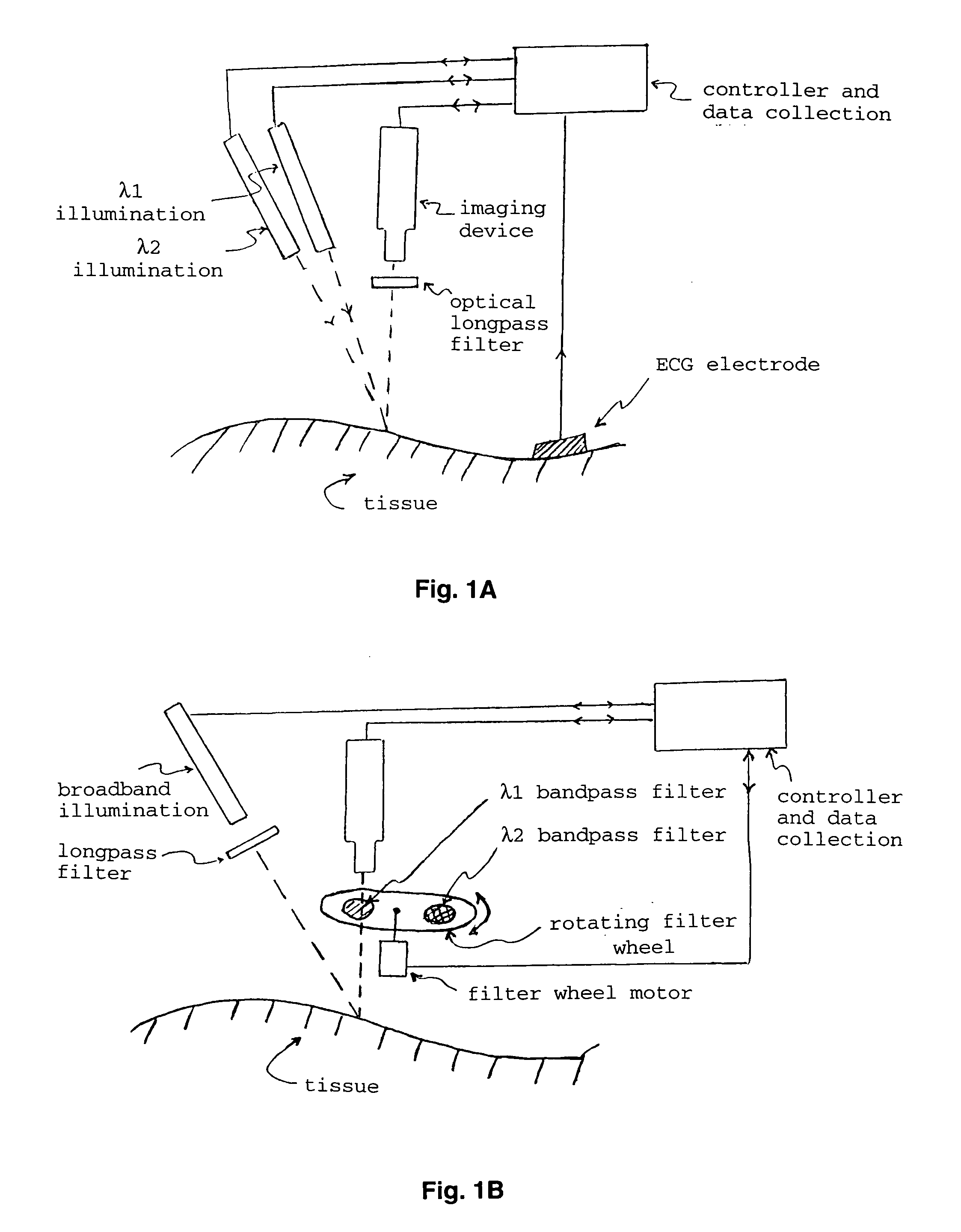
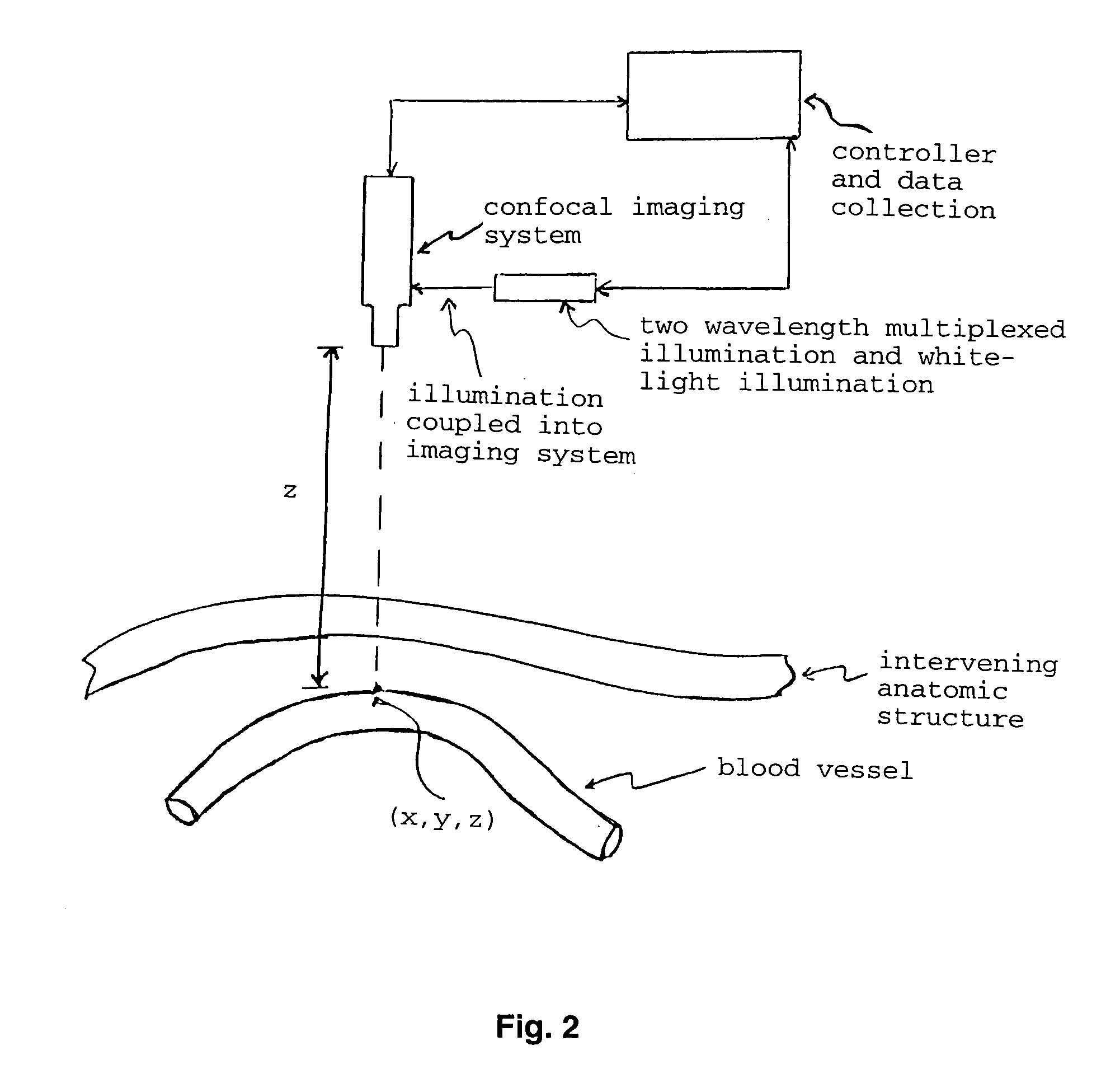
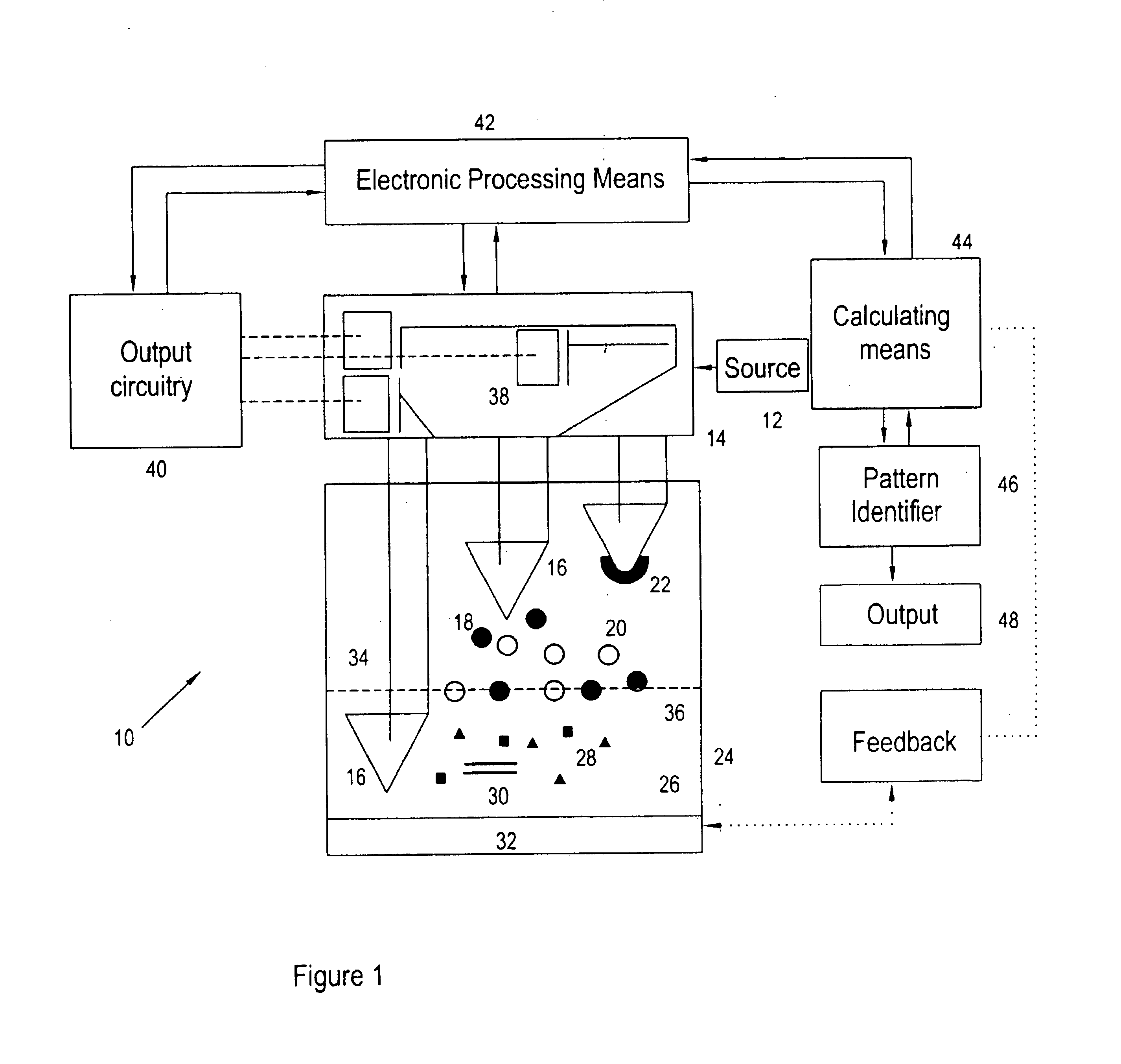
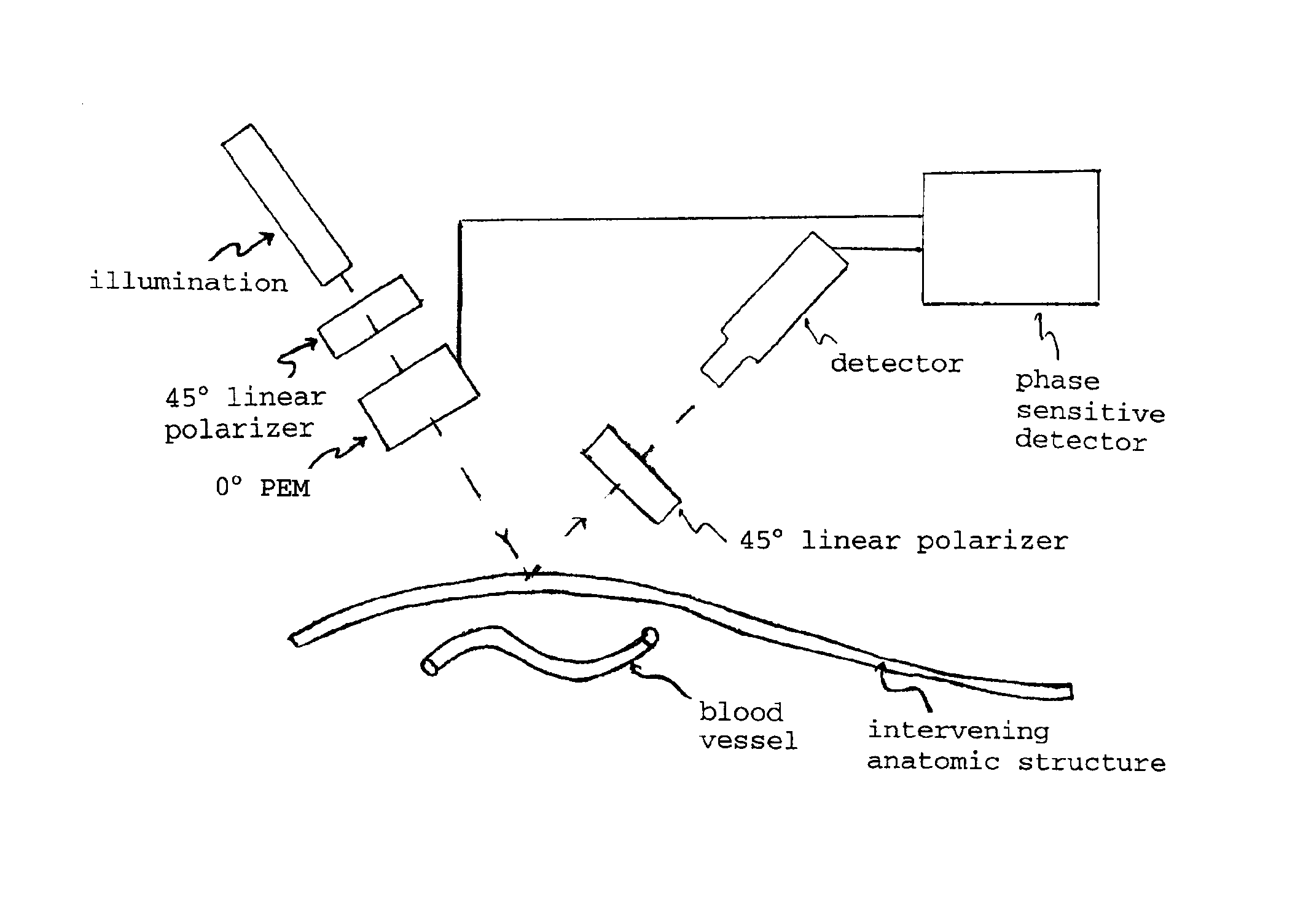
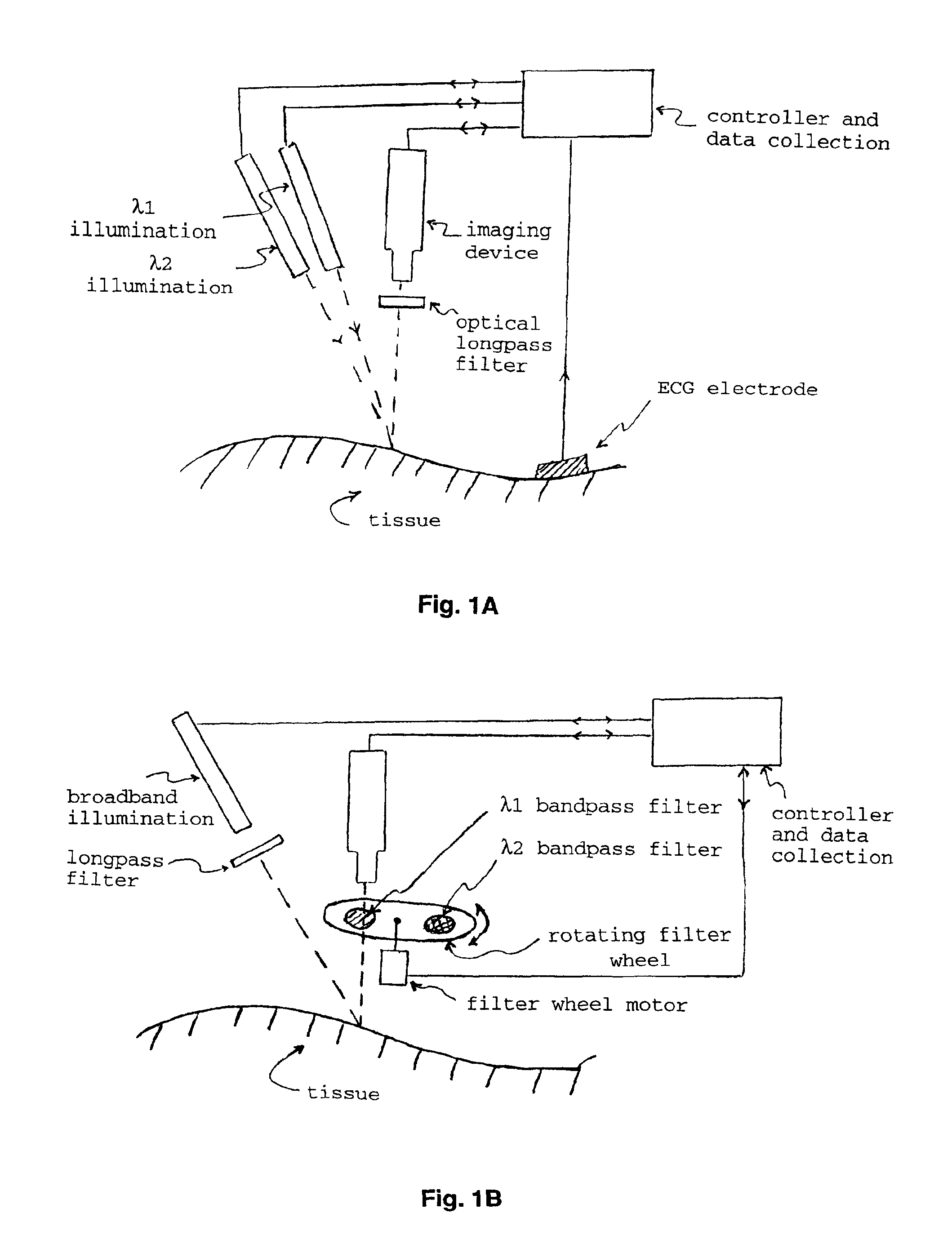
Optical imaging of subsurface anatomical structures and biomolecules
InactiveUS20050143662A1Increase contrastLow costElectrocardiographySurgeryAnatomical structuresMedical diagnosis
The present invention provides various methods / systems of optical imaging of subsurface anatomical structures and biomolecules utilizing red and infrared radiant energy. Also provided are various applications of such methods / systems in medical diagnosis and treatment.
Owner:ROCKY MOUNTAIN BIOSYST
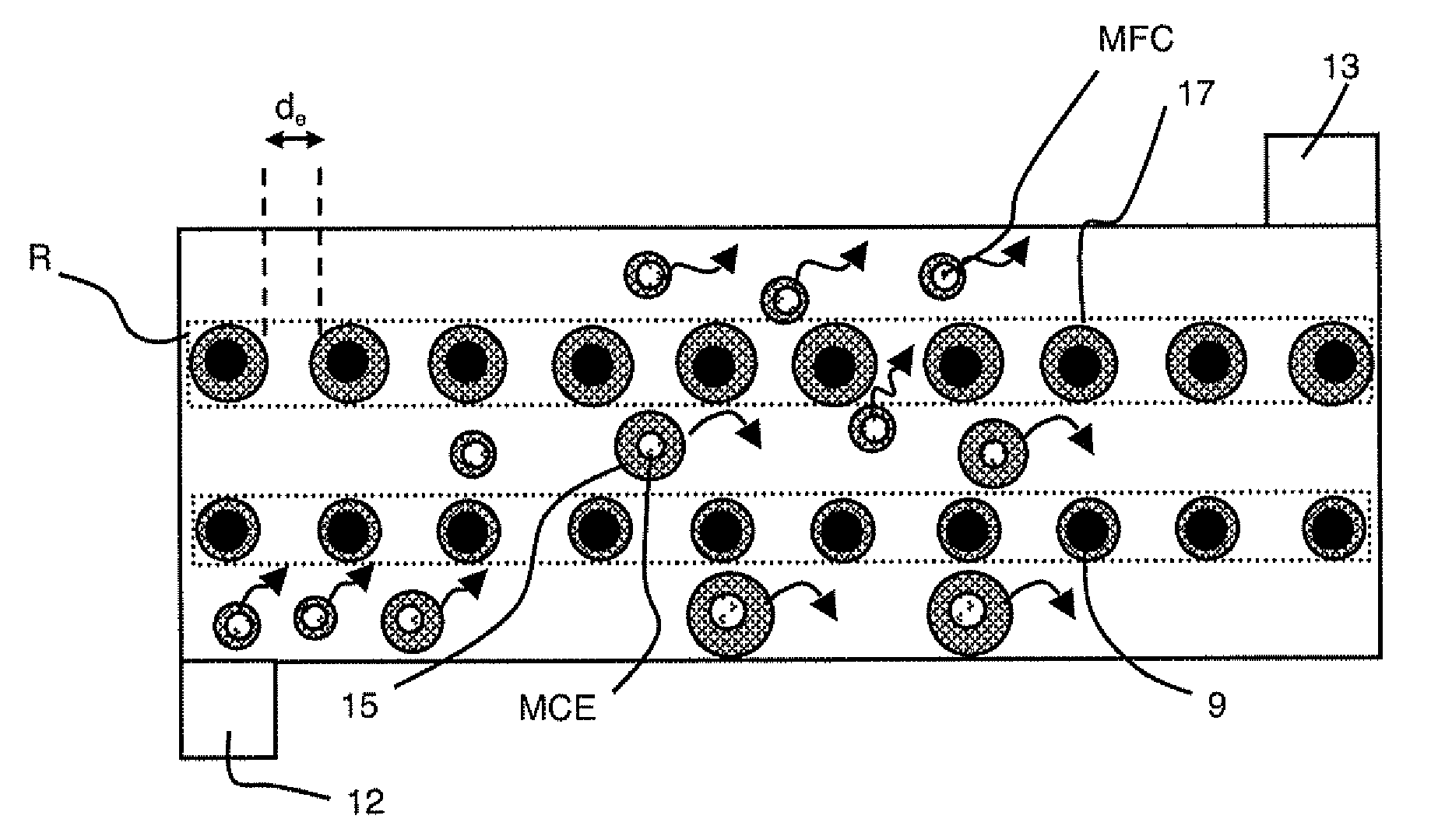
Device for separating biomolecules from a fluid
The device for separating biomolecules from a fluid comprises a microfluidic component provided with at least one microchannel having at least one of the walls supporting a plurality of nanotubes or nanowires. The component comprises at least one electrode electrically connected to at least a part of the nanotubes or nanowires and the device comprises means for applying a voltage between the electrode and the fluid. The nanotubes or nanowires are divided into several active areas in which the nanotubes or nanowires have a different density.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Recovery of rare cells using a microchannel apparatus with patterned posts
ActiveUS20060160243A1Flow interruptionEfficient captureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHydrophilic coatingFlow disruption
A microflow apparatus for separating or isolating cells from a bodily fluid or other liquid sample uses a flow path where straight-line flow is interrupted by a pattern of transverse posts. The posts are spaced across the width of a collection region in the flow path, extending between the upper and lower surfaces thereof; they have rectilinear surfaces, have arcuate cross-sections, and are randomly arranged so as to disrupt streamlined flow. Sequestering agents, such as Abs, are attached to all surfaces in the collection region via a hydrophilic coating, preferably a hydrogel containing isocyanate moieties or a PEG or polyglycine of substantial length, and are highly effective in capturing cells or other targeted biomolecules as a result of such streamlined flow disruption.
Owner:BIOCEPT INC
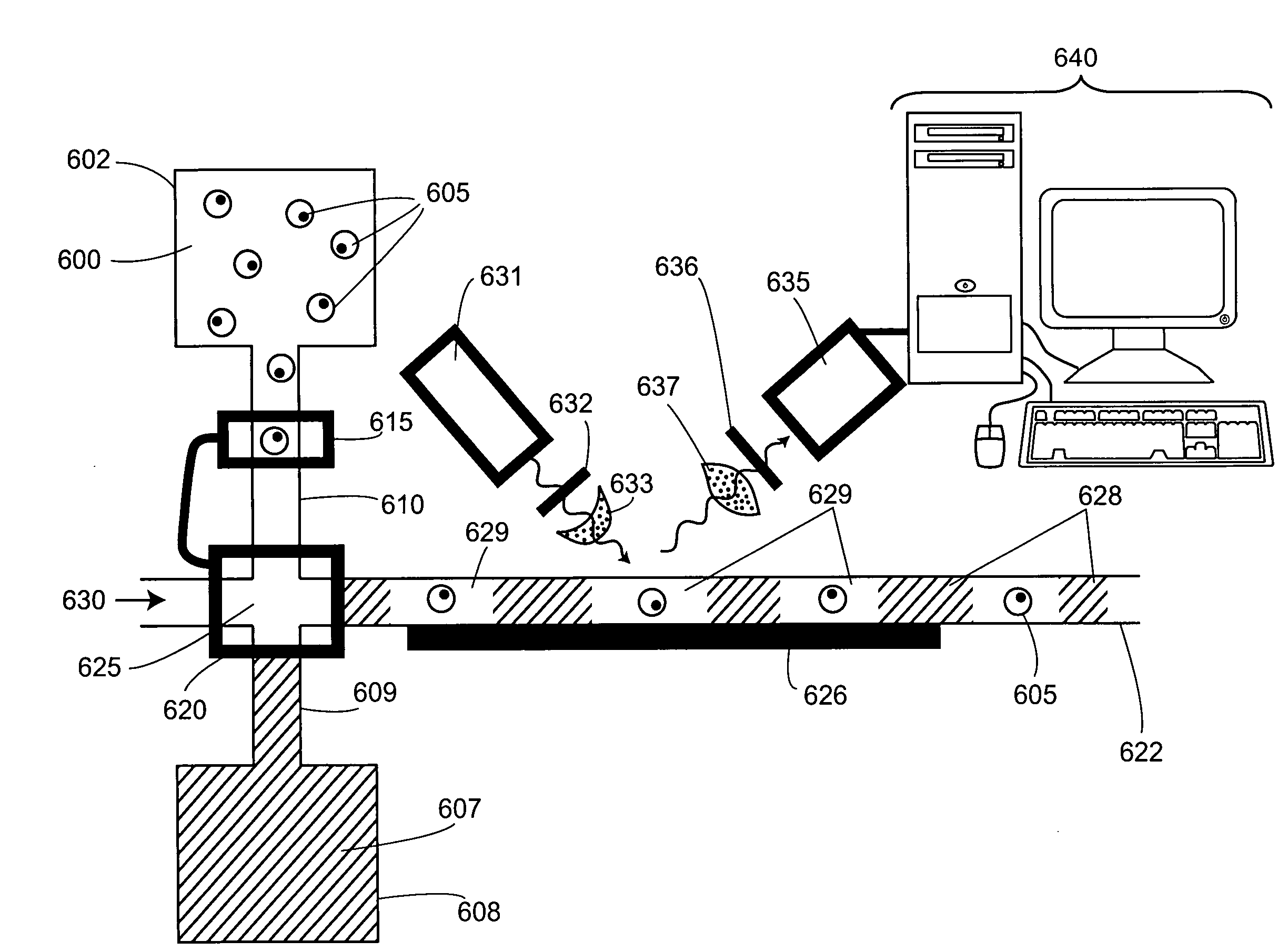
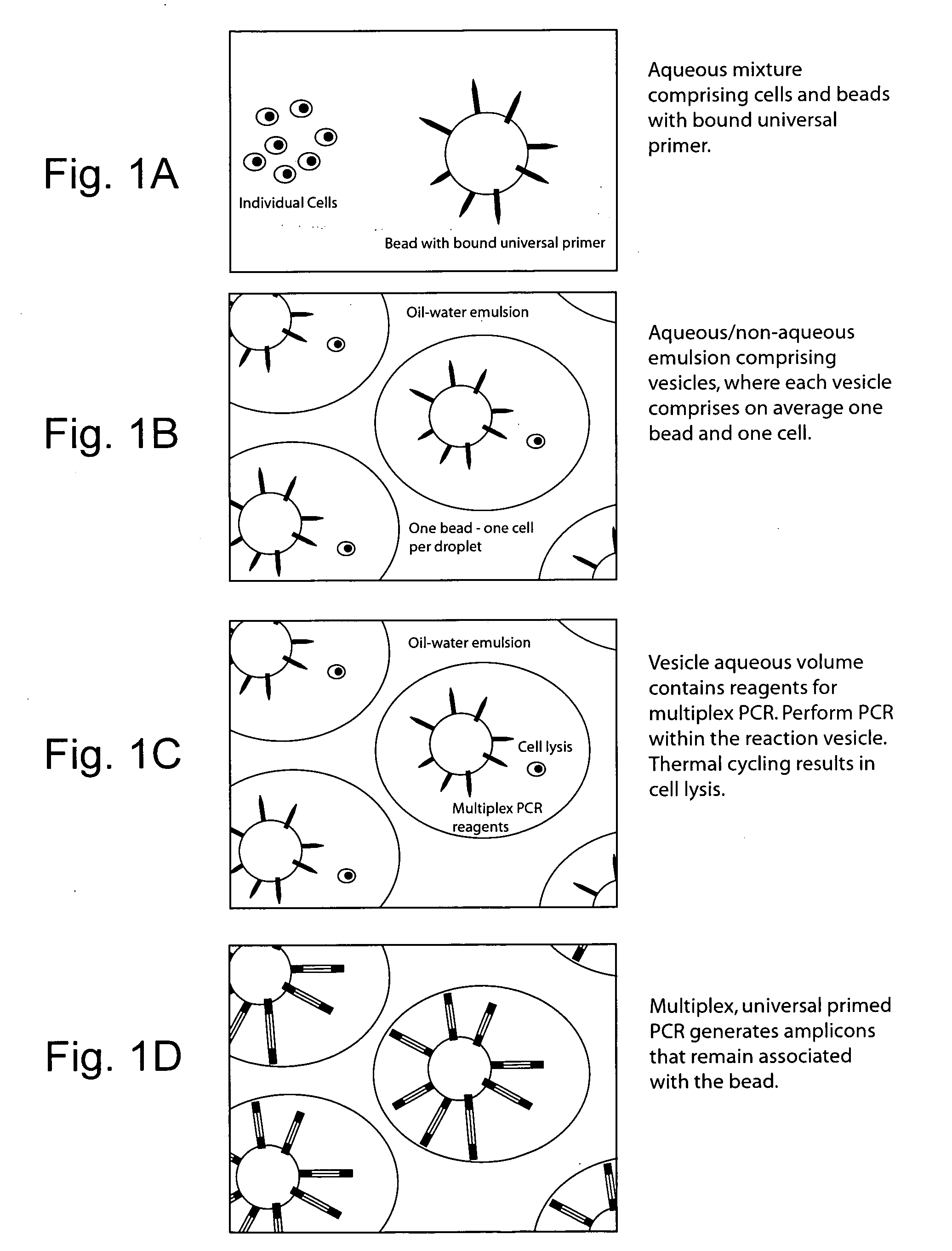
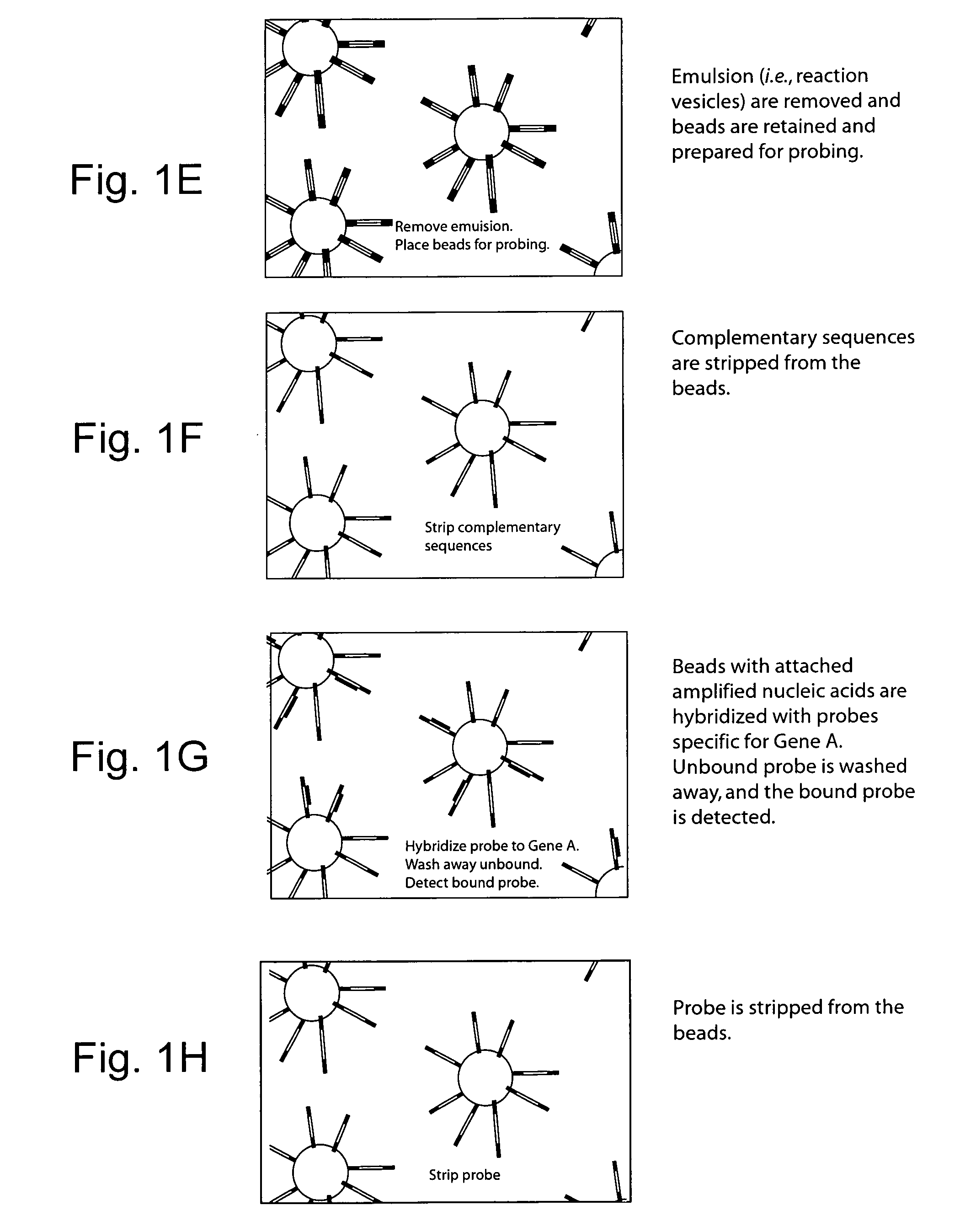
Biochemical analysis of partitioned cells
InactiveUS20080124726A1Avoid mixingFacilitate methodBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusGene expressionThroughput
The invention relates to compositions and methods for the analysis of biomolecules associated with cells, where the presence or absence of a particular biomolecule (e.g., an expressed protein or a nucleic acid gene expression product) associated with the cells is examined. The invention provides methods for single cell biochemical analysis, as well as instrumentation for the single-cell biochemical analysis. Most advantageously, the invention affords methods and instrumentation for high-throughput biochemical analysis of large numbers of single cells.
Owner:ALTHEADX
Computer-assisted isolation and characterization of proteins
InactiveUS6278794B1Rapid and efficient identificationPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrophoresisComputer-aided
The present invention provides computer-assisted methods and apparatus for identifying, selecting and characterizing biomolecules in a biological sample. A two-dimensional array is generated by separating biomolecules present in a complex mixture. A computer-readable profile is constructed representing the identity and relative abundance of a plurality of biomolecules detected by imaging the two dimensional array. Computer-mediated comparison of profiles from multiple samples permits automated identification of subsets of biomolecules that satisfy pre-ordained criteria. Identified biomolecules can be automatically isolated from the two dimensional array by a robotic device in accordance with computer-generated instructions. A supported gel suitable for electrophoresis is provided that is bonded to a solid support such that the gel has two-dimensional spatial stability and the solid support is substantially non-interfering with respect to detection of a label, such as a fluorescent label, associated with one or more biomolecules in the gel.
Owner:OXFORD GLYCOSCI UK
Method for monitoring molecular species within a medium
InactiveUS7097973B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSensor arrayGas phase
Apparatus and methods for monitoring, analyzing, and / or discriminating molecular species, preferably a biomolecule, within a medium using a multisensor array (MSA) and multivariate processing. Biological compounds such as nucleotides and polynucleotides can be detected and analyzed. A reaction process such as an accumulation cycle of nucleic acids can be monitored, analyzed, and controlled using a multisensor array (MSA) and multivariate processing. Monitoring a biomolecule includes interrogating the medium, and preferably its gas phase, by coupling a sensor responsive to any changes of the medium and or biomolecule and its secondary products when, for example, an amplification reaction is proceeded. It is also a scope of the present invention to use direct detection and monitoring of biomolecular reactions in real-time without radioactive or fluorescent labeling. A preferred application is real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) detection.
Owner:ALPHA MOS
Optical imaging of subsurface anatomical structures and biomolecules
InactiveUS6889075B2Increase contrastLow costElectrocardiographyDiagnostics using spectroscopyAnatomical structuresMedical diagnosis
The present invention provides various methods / systems of optical imaging of subsurface anatomical structures and biomolecules utilizing red and infrared radiant energy. Also provided are various applications of such methods / systems in medical diagnosis and treatment.
Owner:ROCKY MOUNTAIN BIOSYST
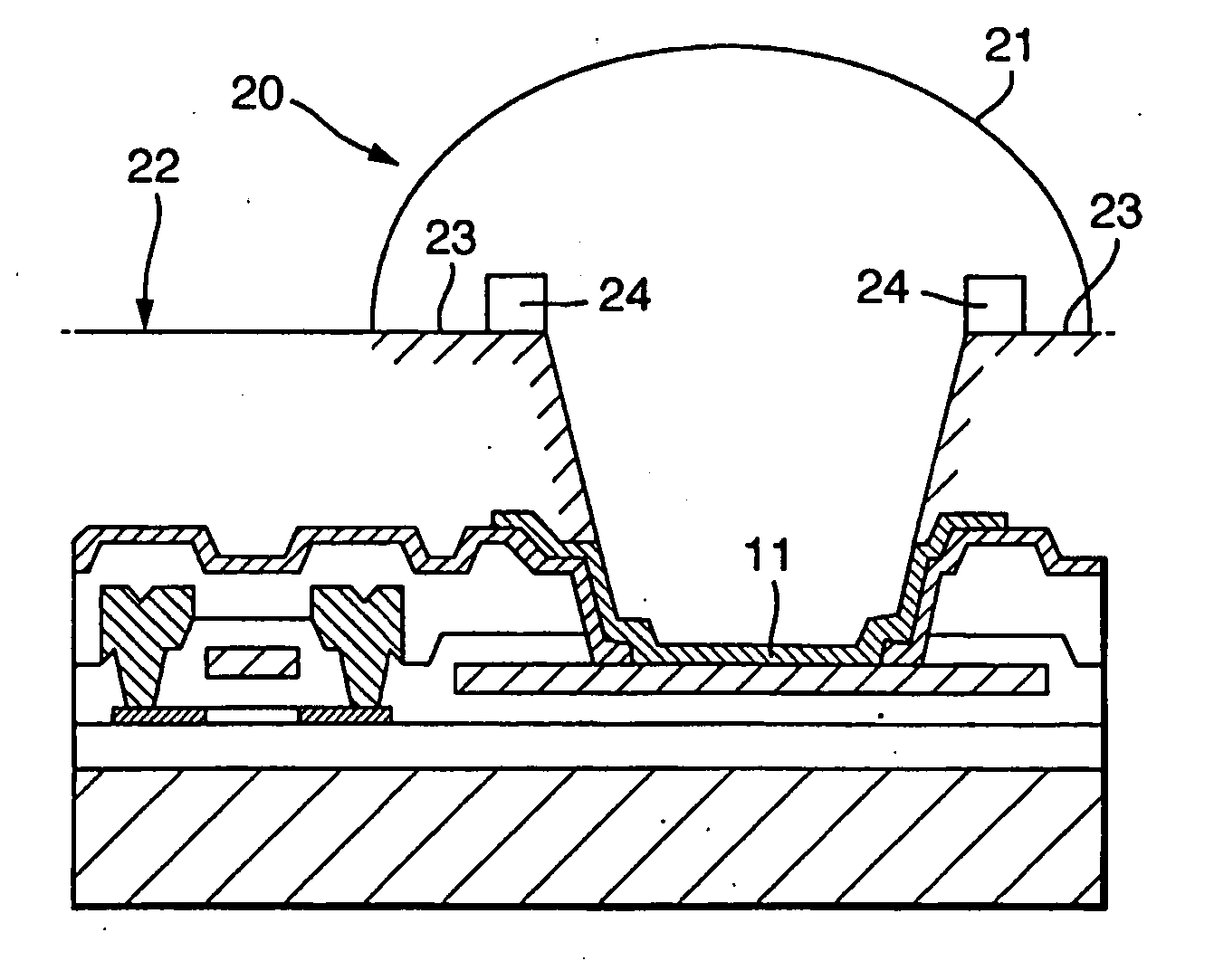
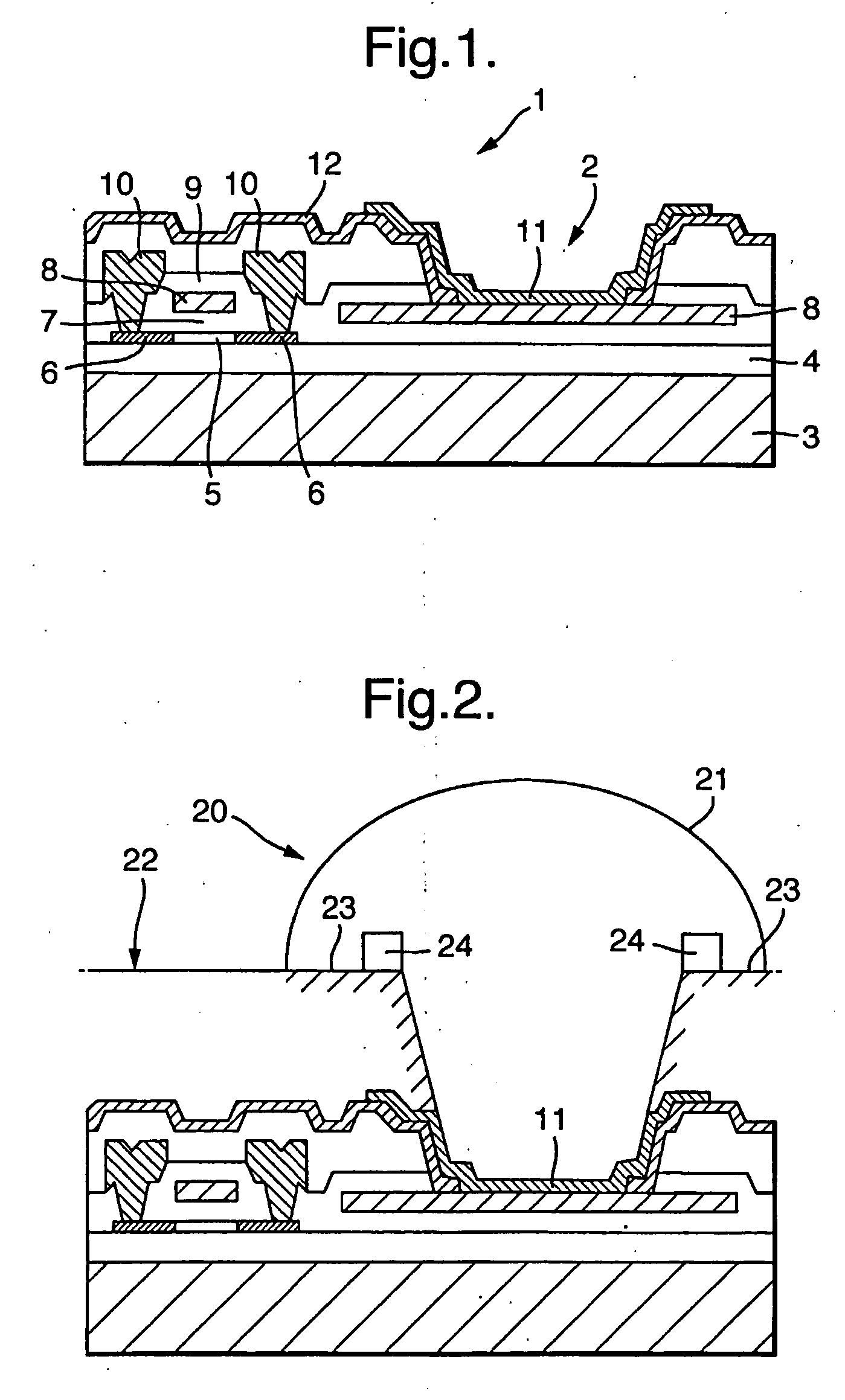
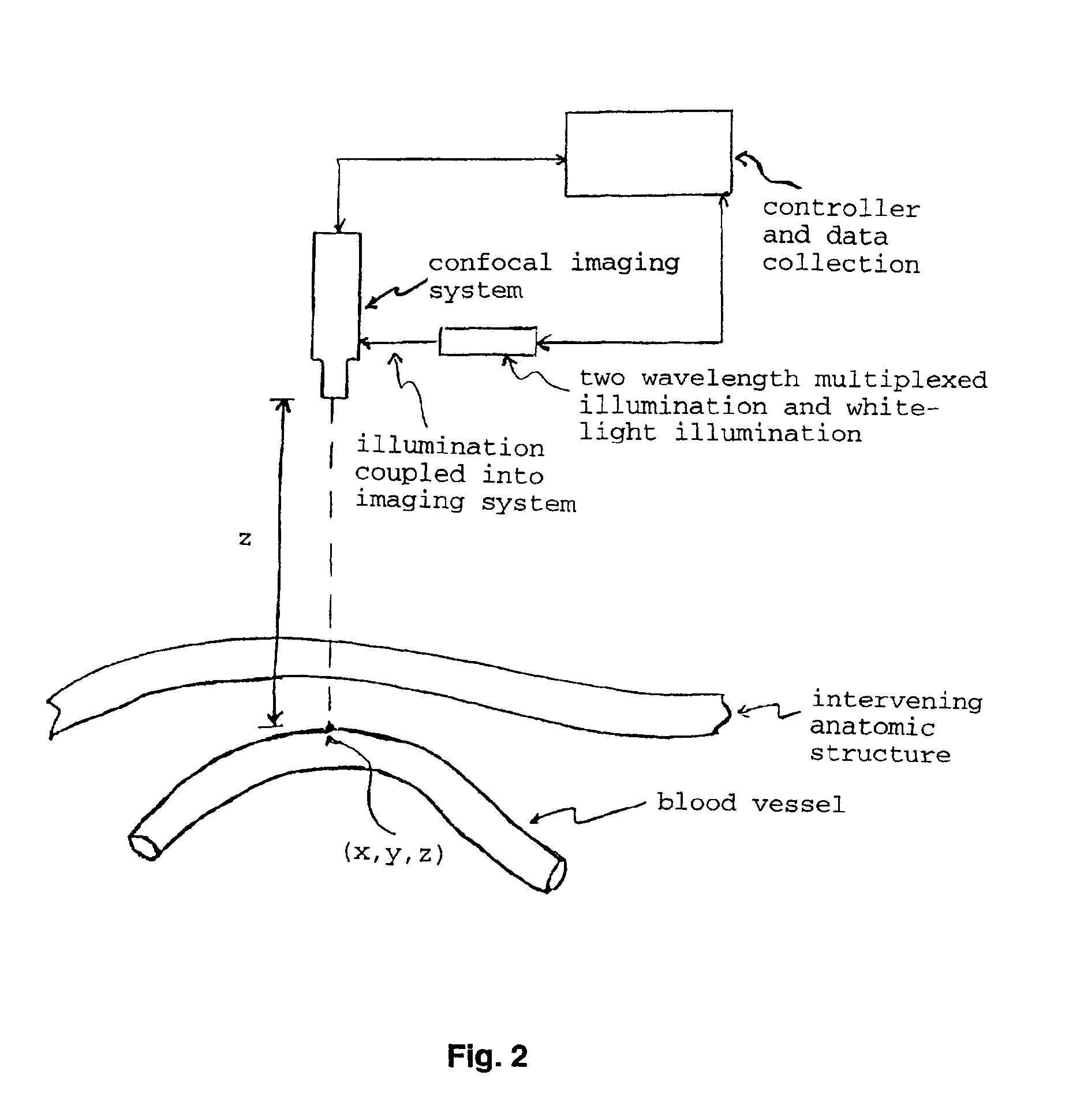
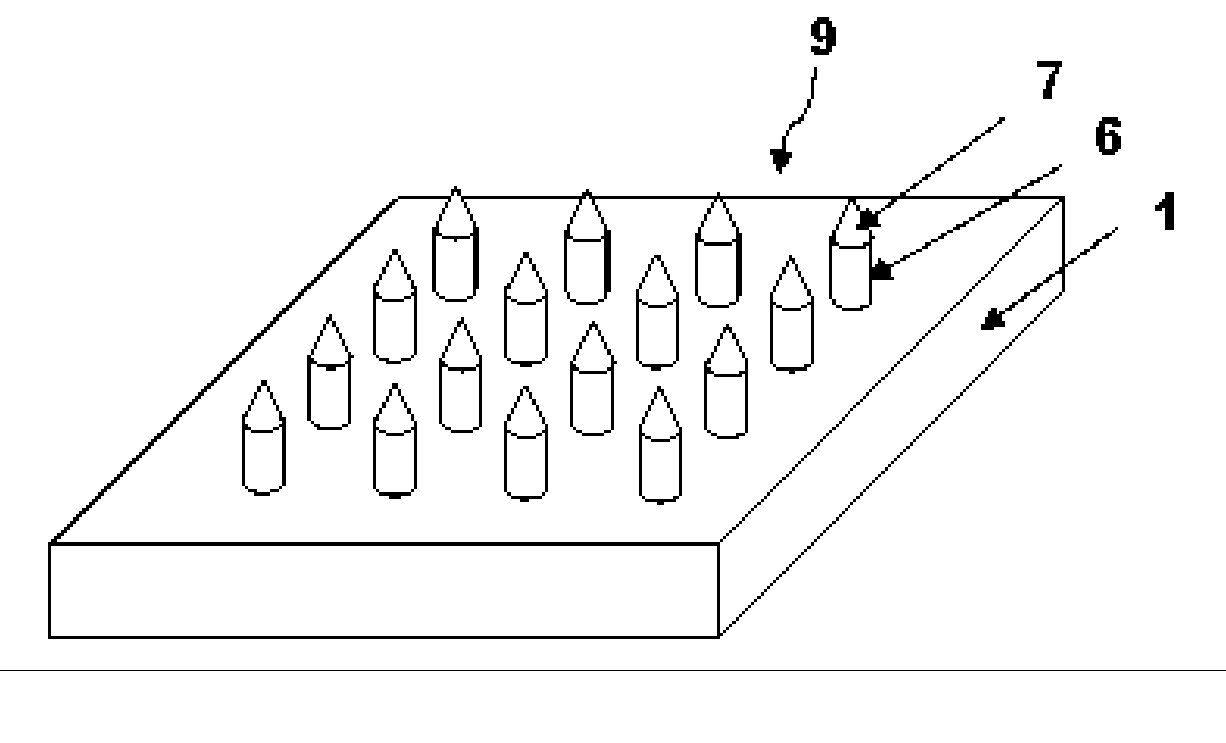
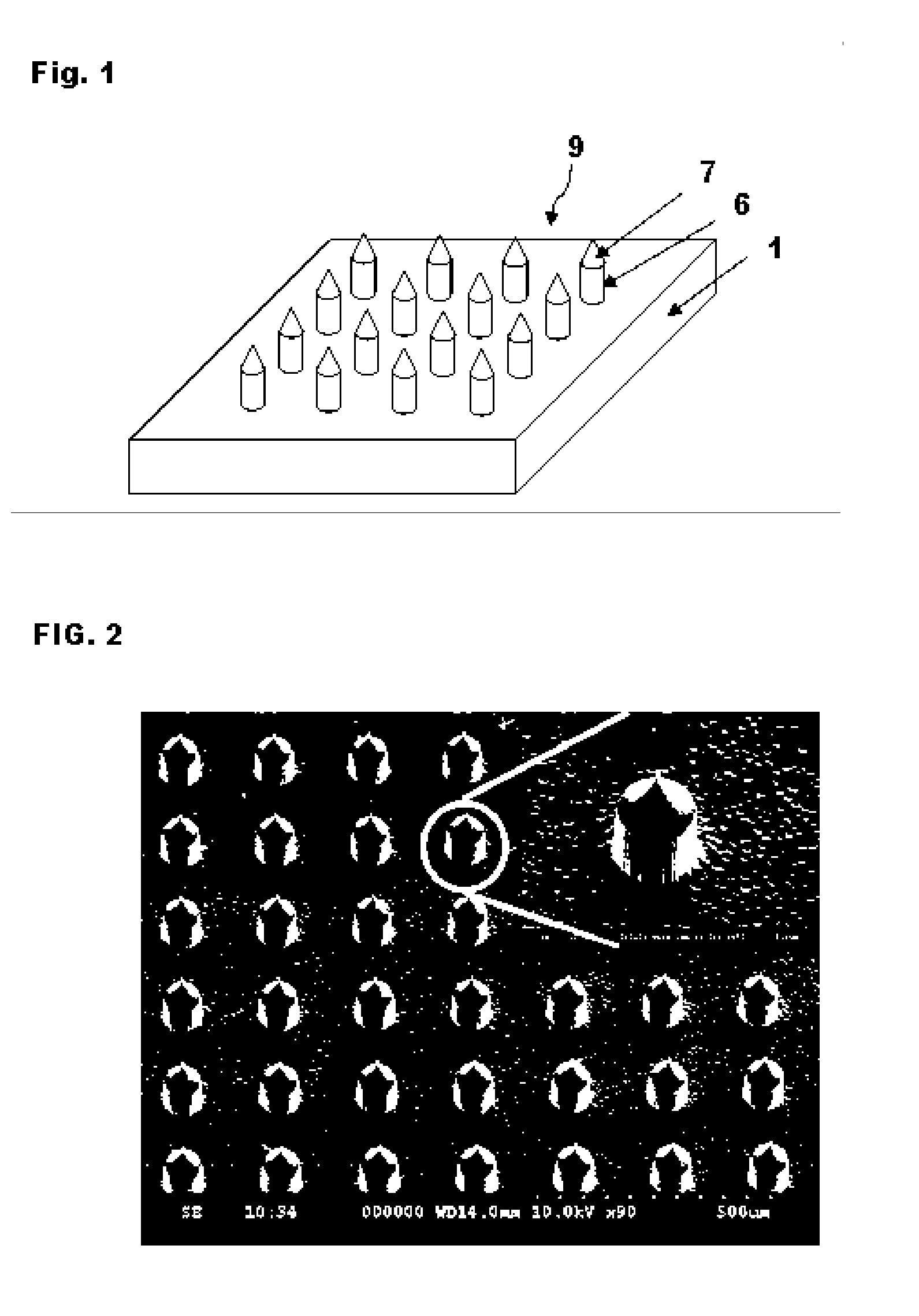
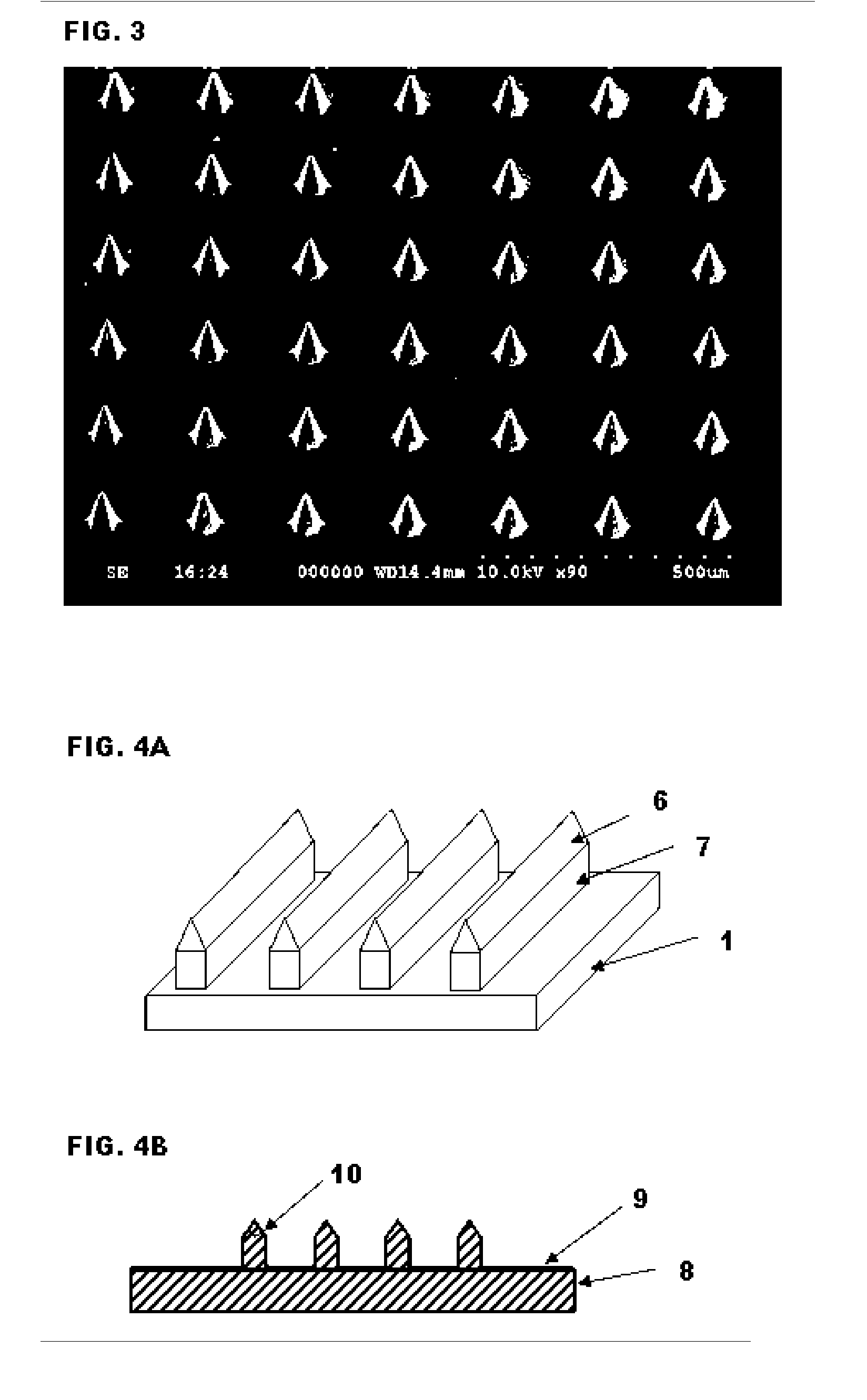
High-Aspect-Ratio Microdevices and Methods for Transdermal Delivery and Sampling of Active Substances
ActiveUS20050261632A1Increased needle lengthHigh selectivityNanoinformaticsMicroneedlesSensor arrayBody fluid
High-aspect-ratio microdevices comprising microneedles, microknives and microblades and their manufacturing methods are disclosed. These devices can be used for the delivery of therapeutic agents across the skin or other tissue barriers to allow chemical and biological molecules getting into the circulation systems. The microneedles can also be used to withdraw body fluids for analysis of clinically relevant species when the device has an integrated body fluid sensor or sensor array in the vicinity of microneedles.
Owner:XU BAI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com