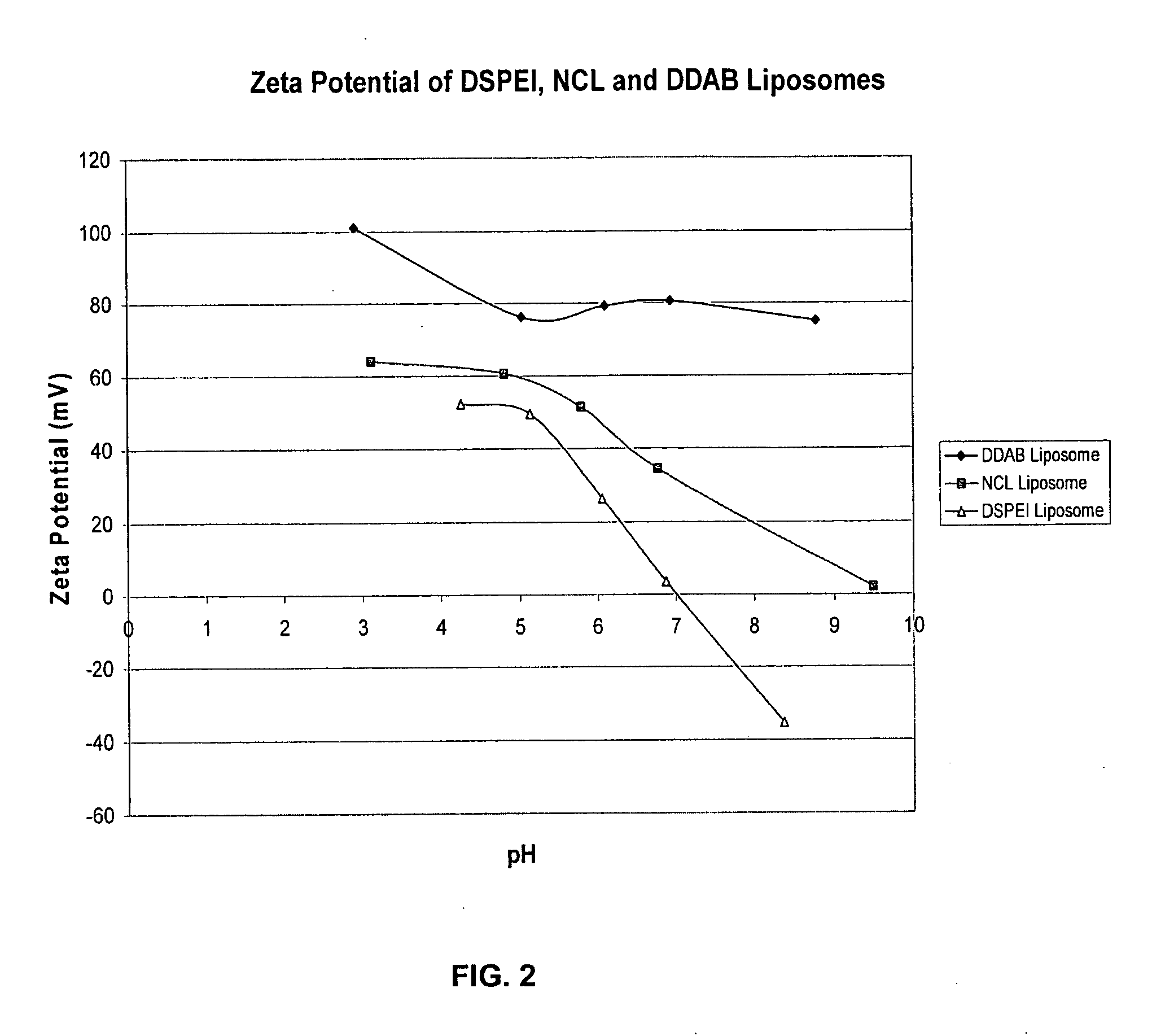
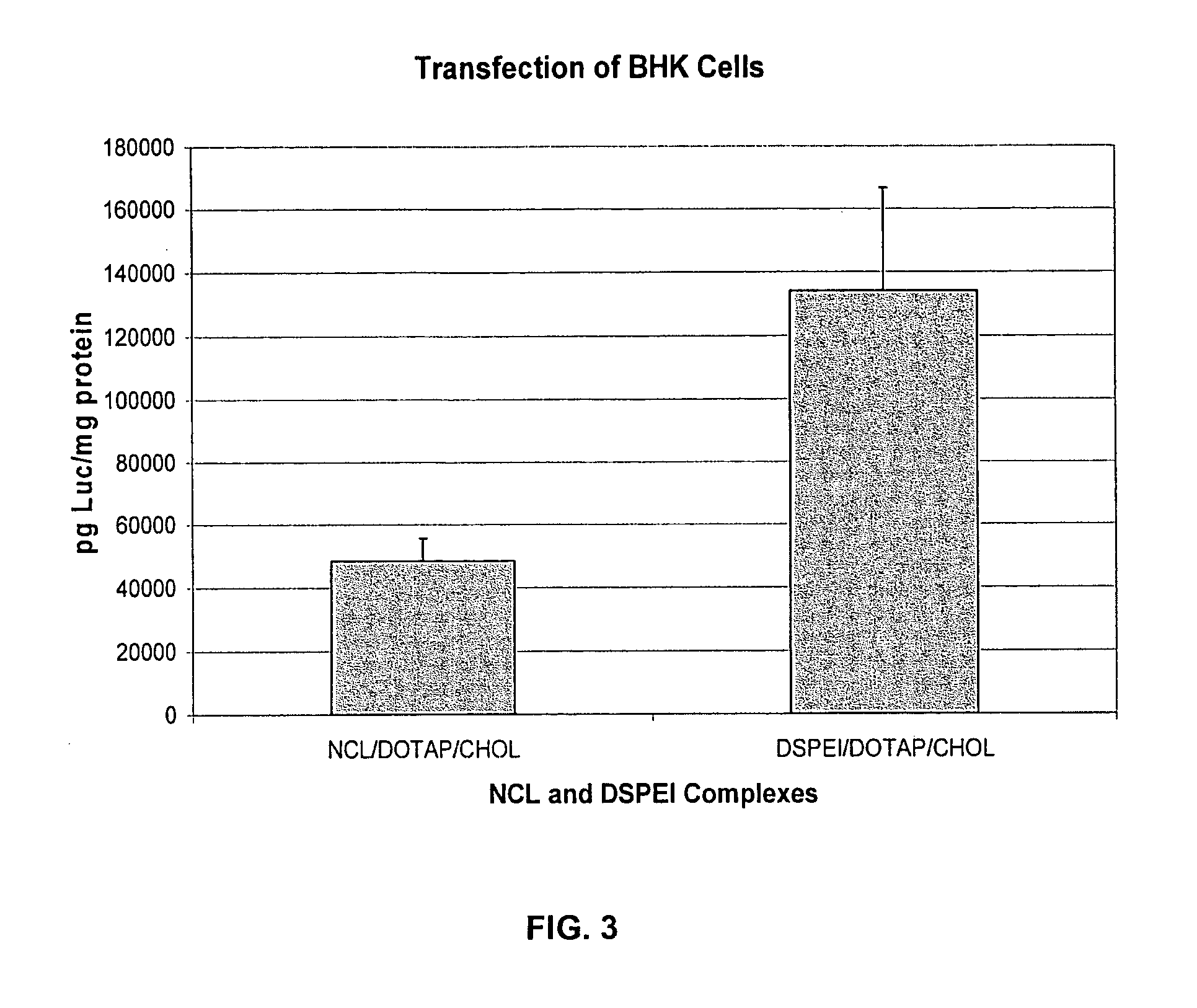
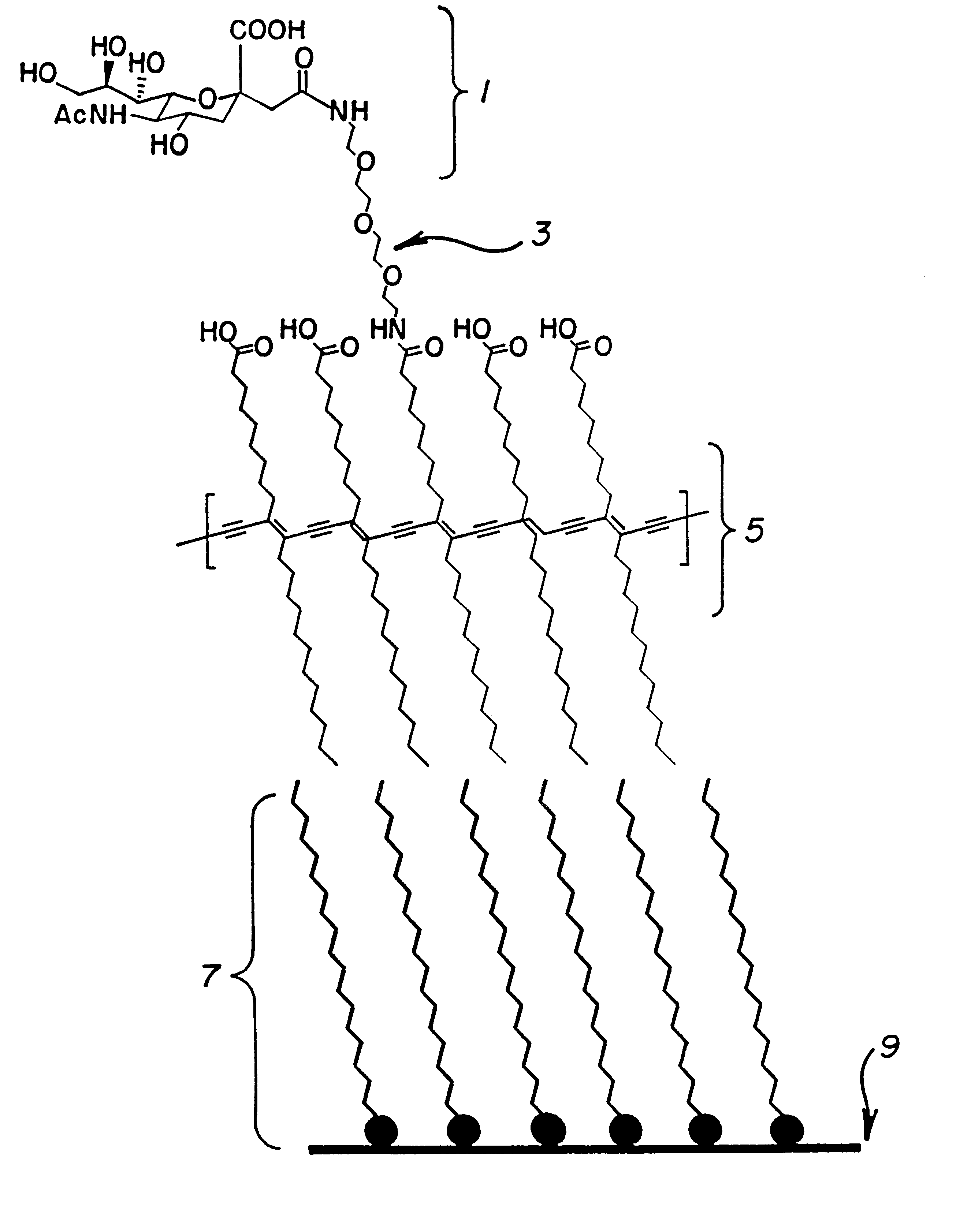
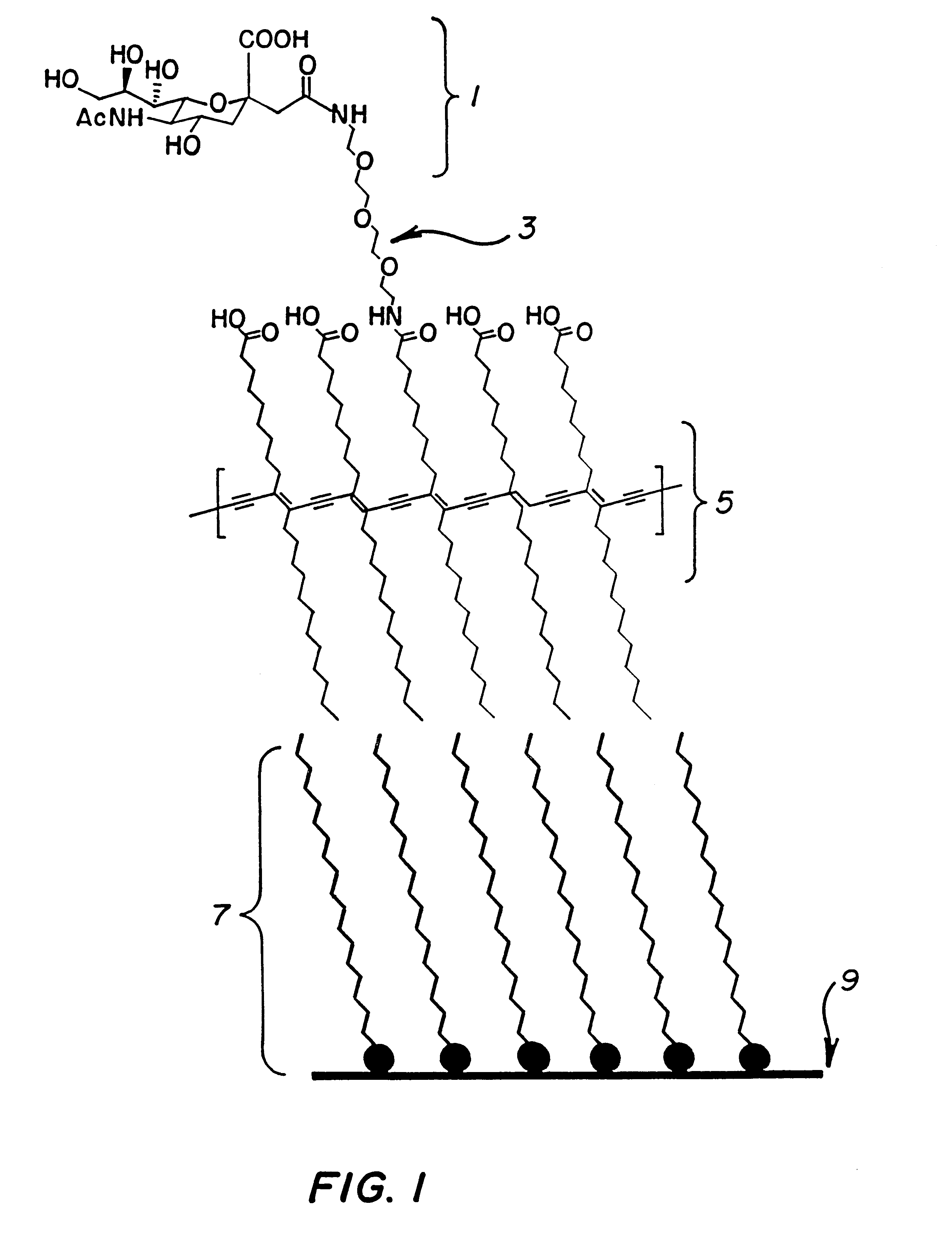
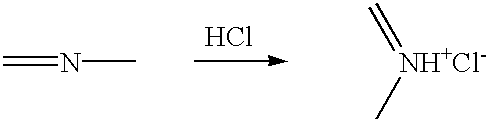Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
486 results about "Lipid bilayer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
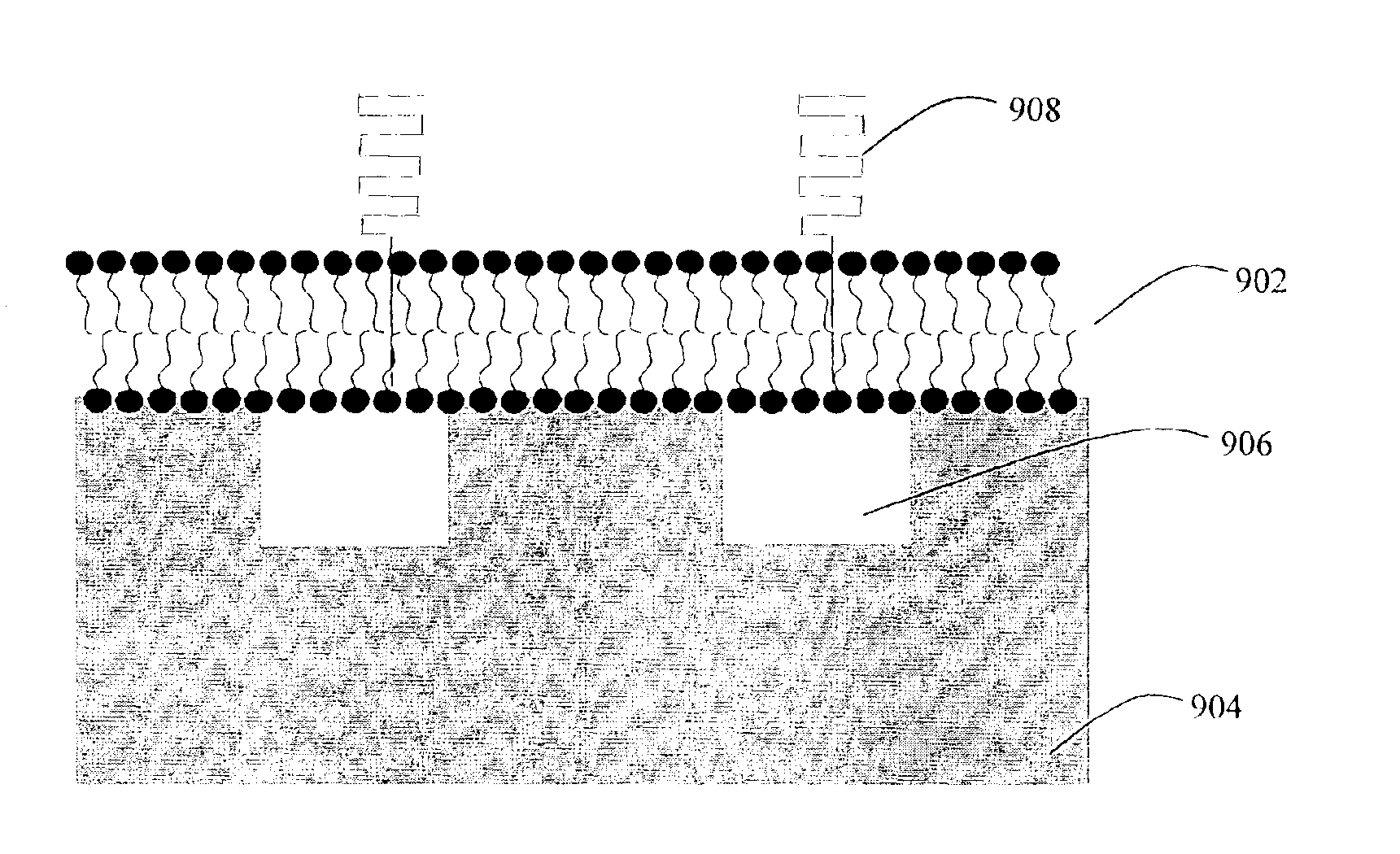
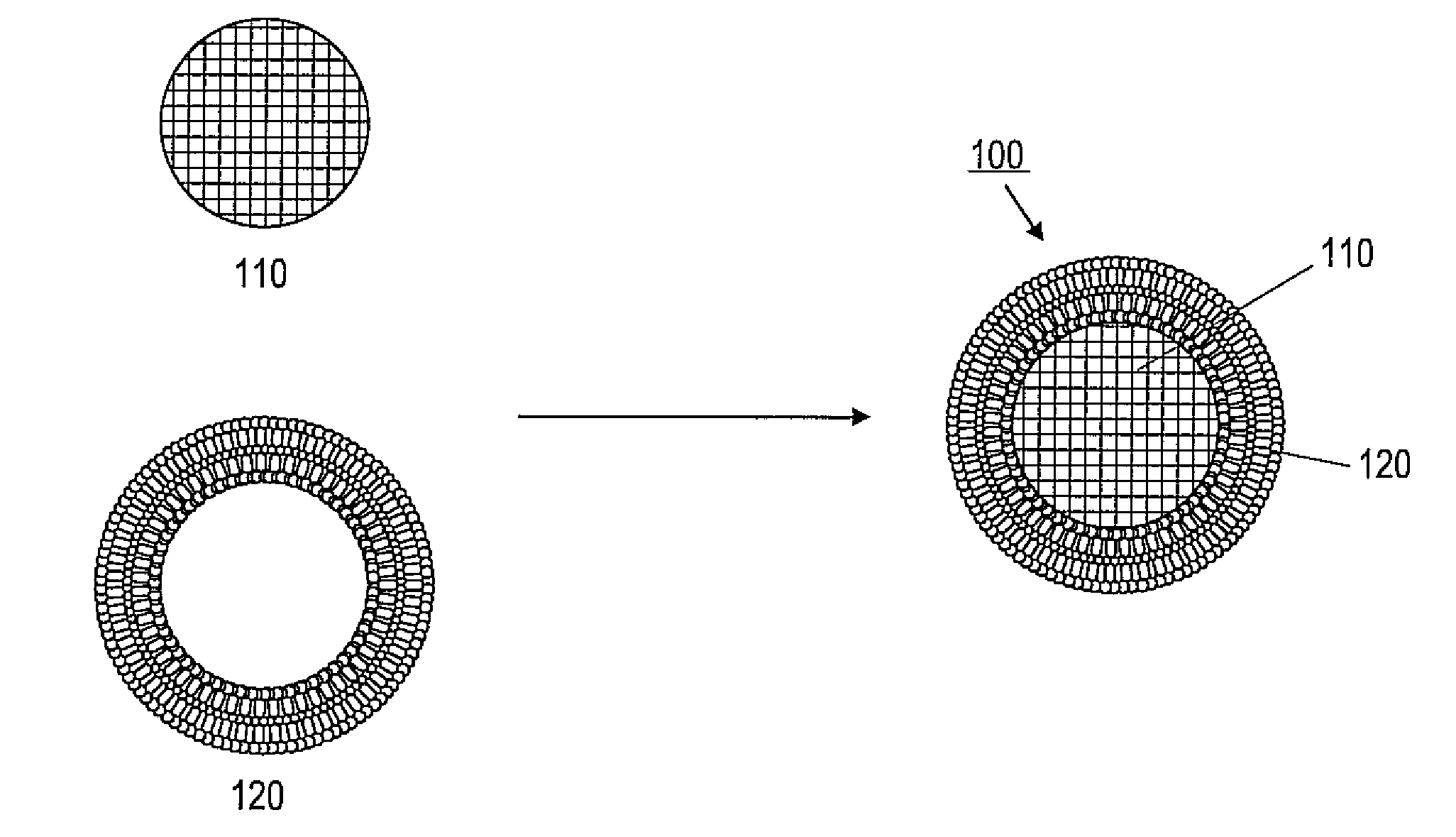
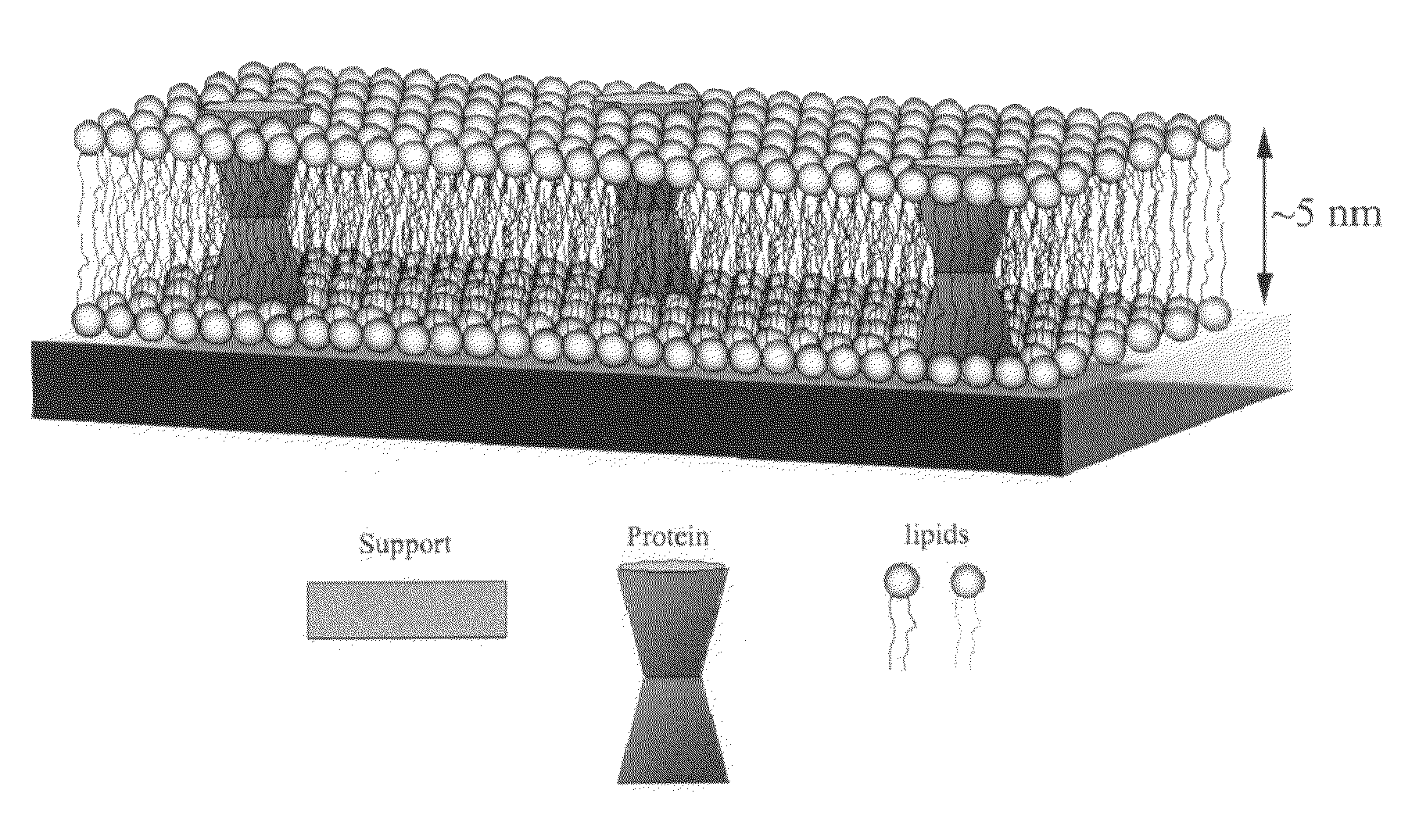
The lipid bilayer (or phospholipid bilayer) is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules. These membranes are flat sheets that form a continuous barrier around all cells. The cell membranes of almost all organisms and many viruses are made of a lipid bilayer, as are the nuclear membrane surrounding the cell nucleus, and other membranes surrounding sub-cellular structures. The lipid bilayer is the barrier that keeps ions, proteins and other molecules where they are needed and prevents them from diffusing into areas where they should not be. Lipid bilayers are ideally suited to this role, even though they are only a few nanometers in width, they are impermeable to most water-soluble (hydrophilic) molecules. Bilayers are particularly impermeable to ions, which allows cells to regulate salt concentrations and pH by transporting ions across their membranes using proteins called ion pumps.
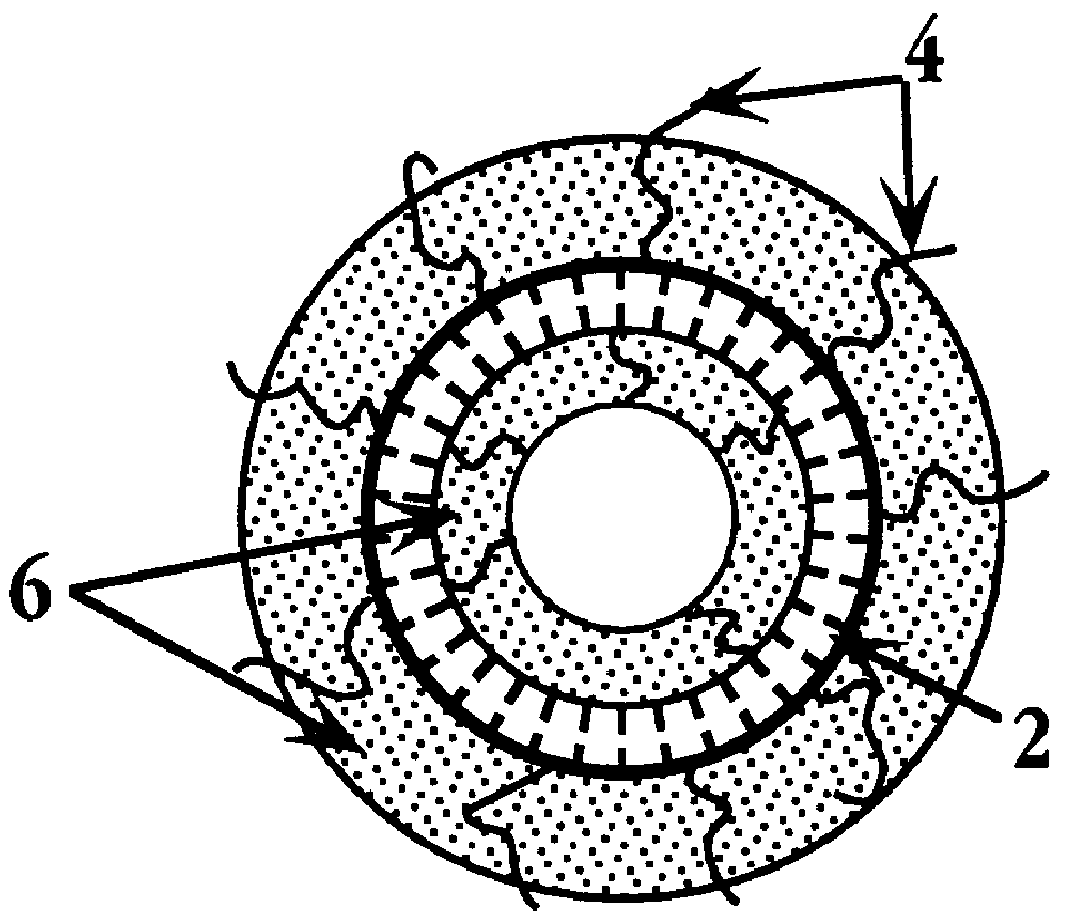
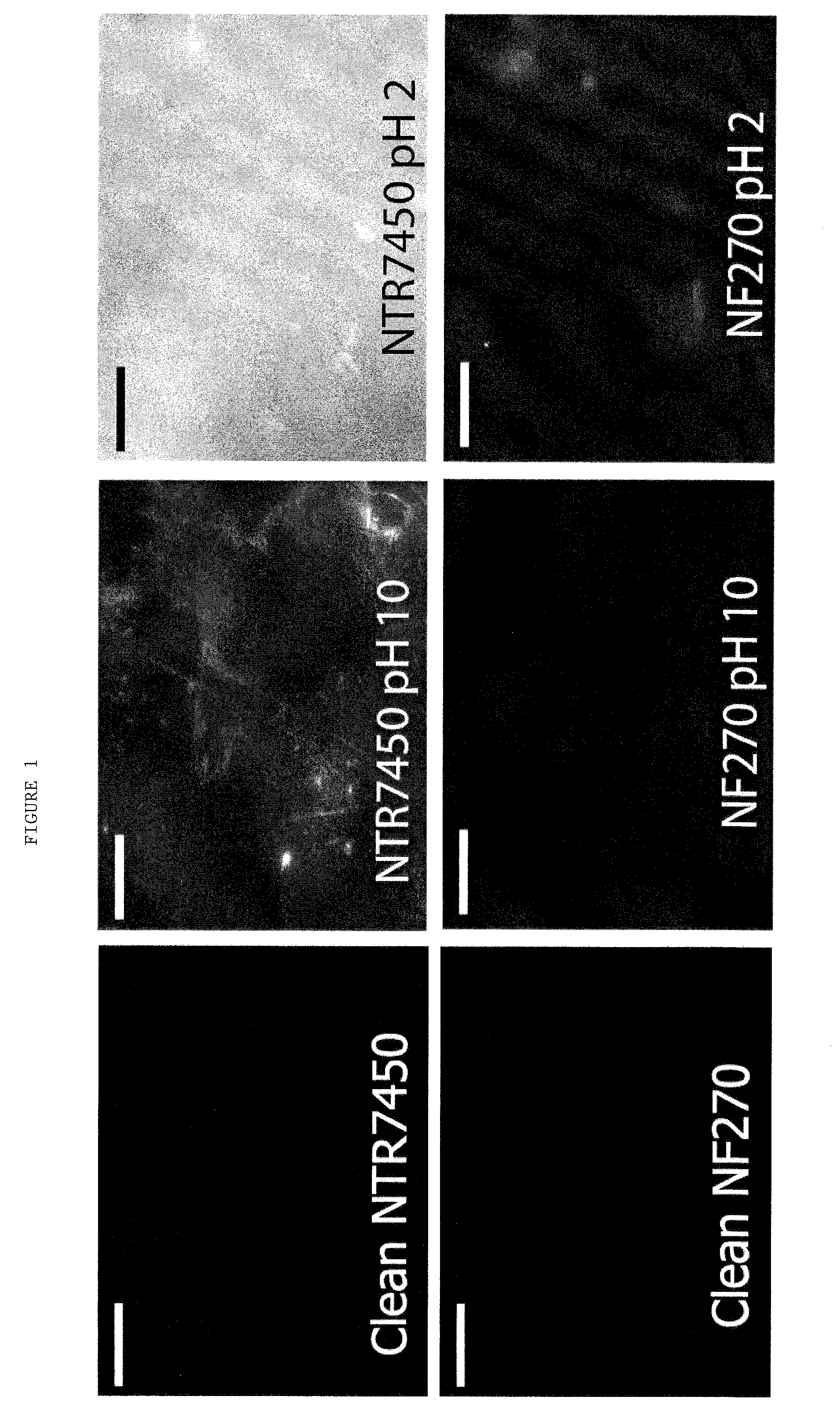
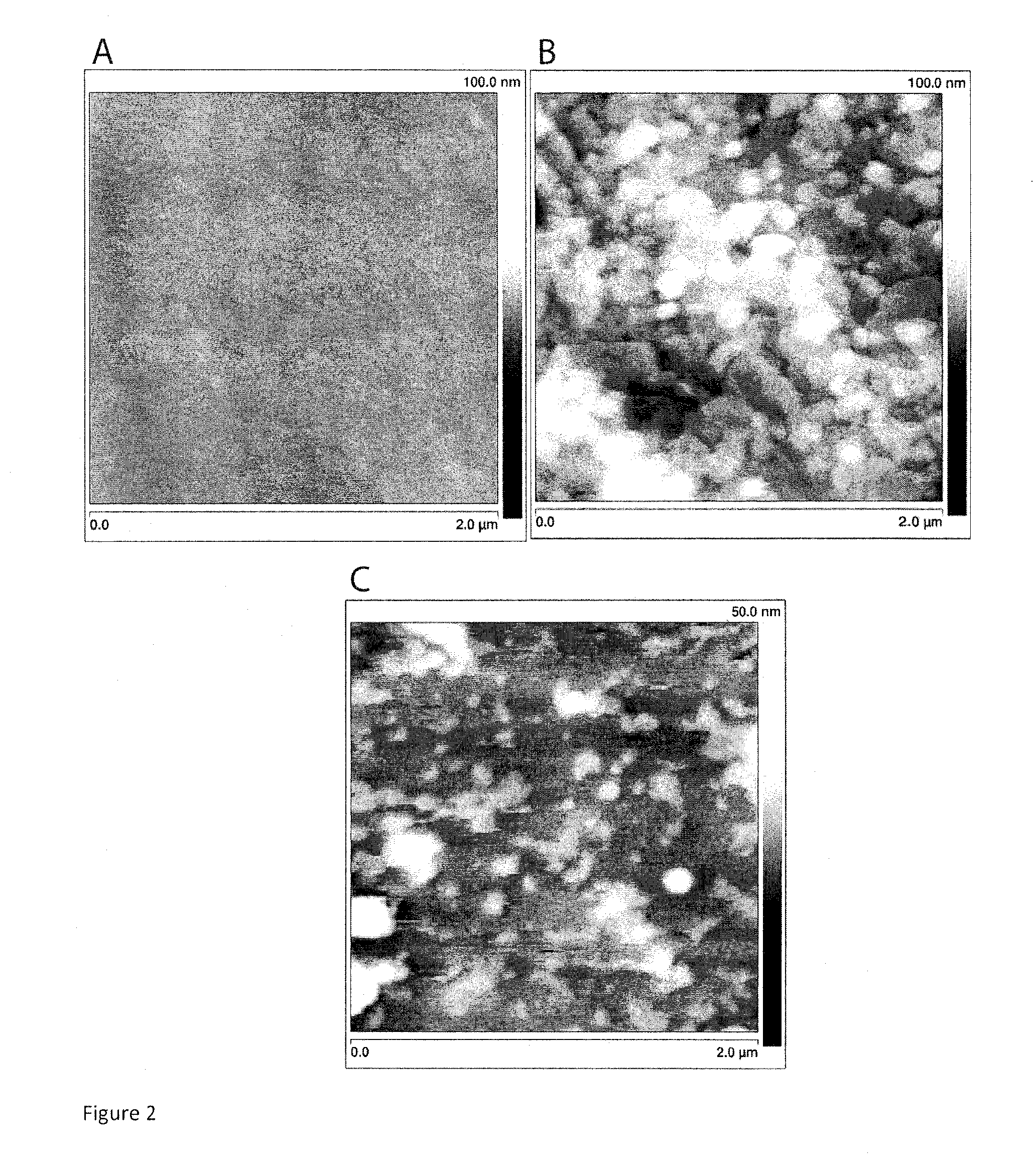
Nanostructured separation and analysis devices for biological membranes
InactiveUS6913697B2Ion-exchanger regenerationVolume/mass flow measurementBiological membraneNanostructure
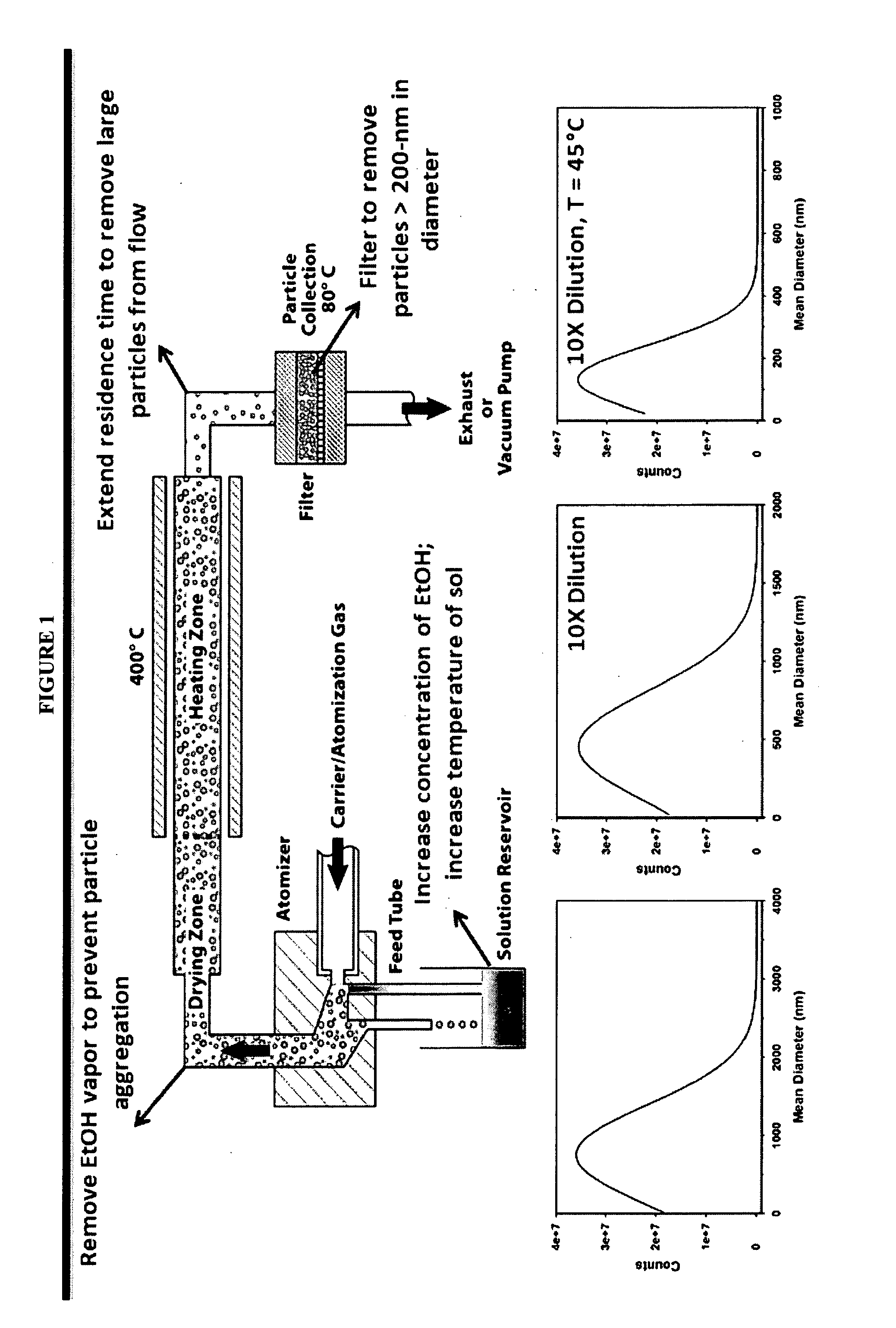
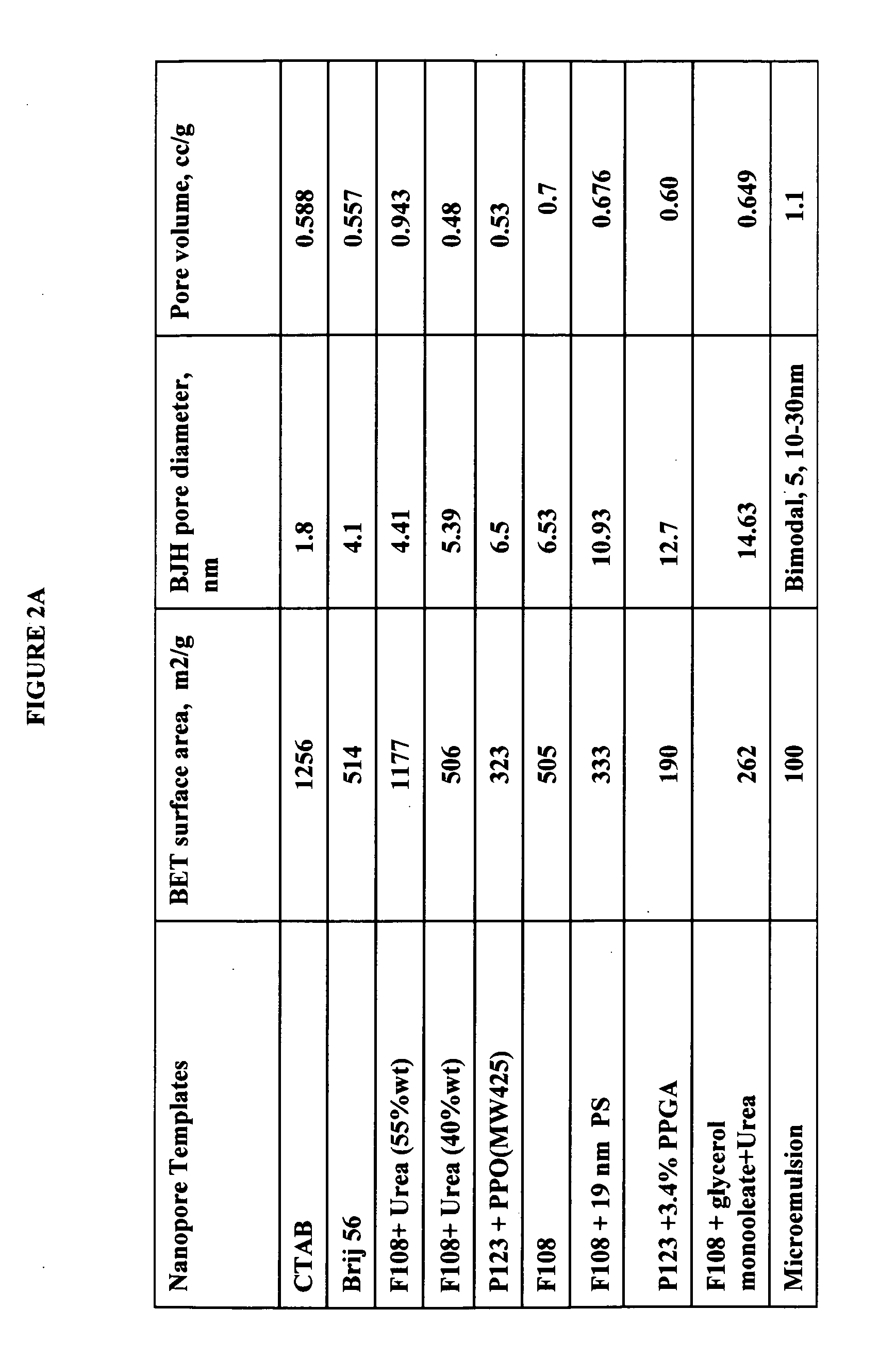
The present invention provides a nanostructured device comprising a substrate including nanotroughs therein; and a lipid bilayer suspended on or supported in the substrate. A separation method is also provided comprising the steps of supporting or suspending a lipid bilayer on a substrate; wherein the substrate comprises nanostructures and wherein the lipid bilayer comprises at least one membrane associated biomolecule; and applying a driving force to the lipid bilayer to separate the membrane associated biomolecule from the lipid bilayer and to drive the membrane associated biomolecule into the nanostructures.
Owner:STC UNM
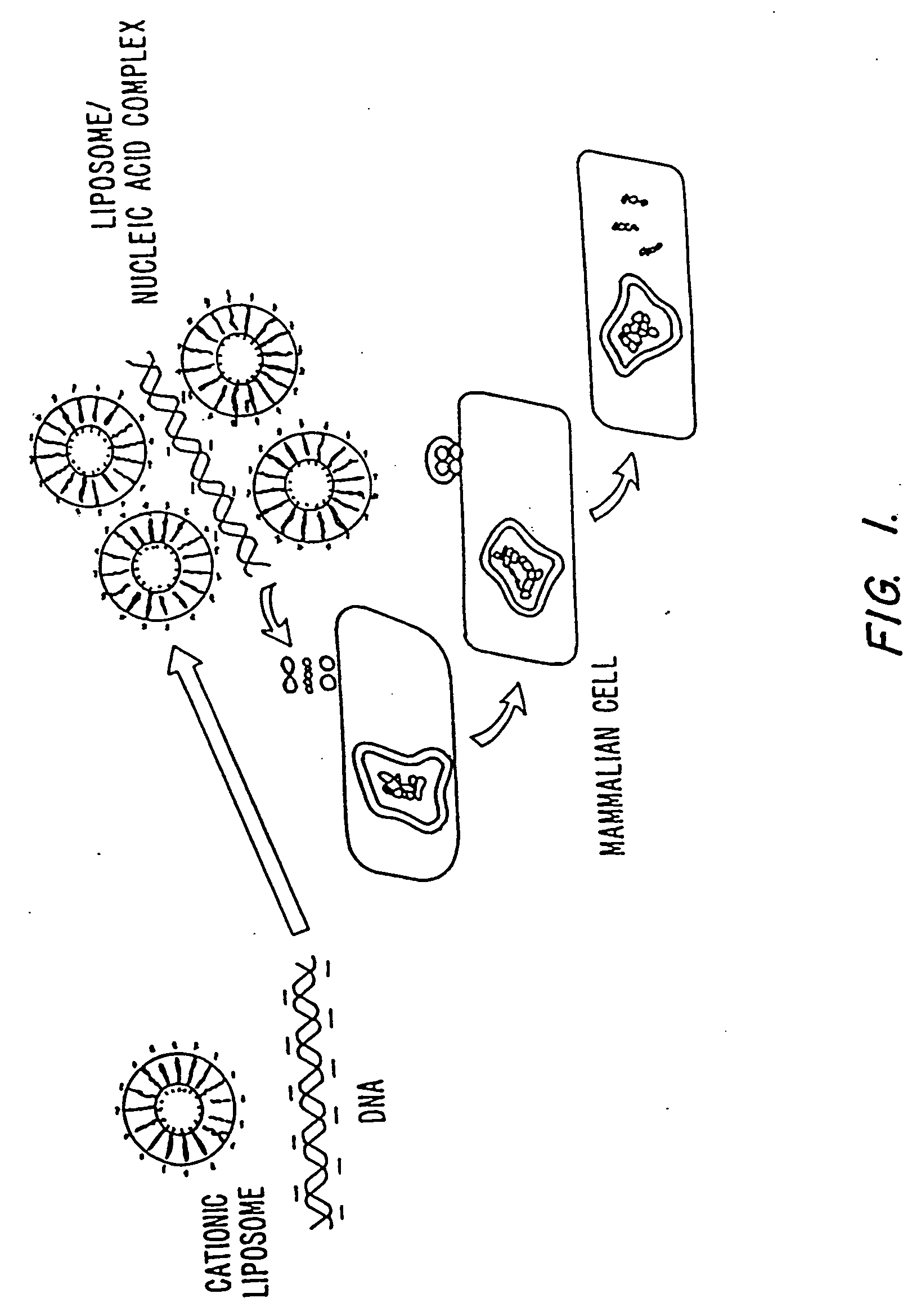
Modular targeted liposomal delivery system
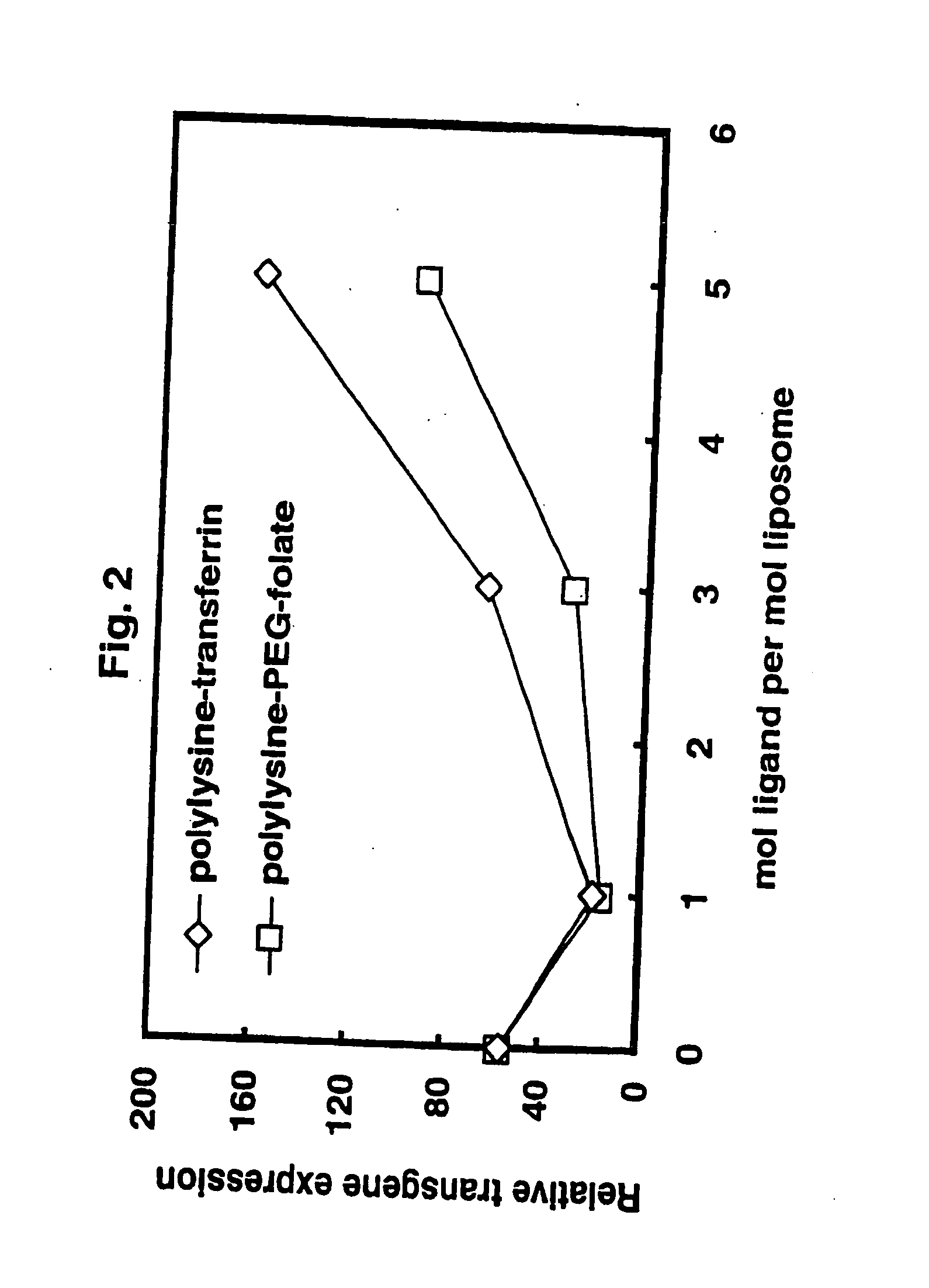
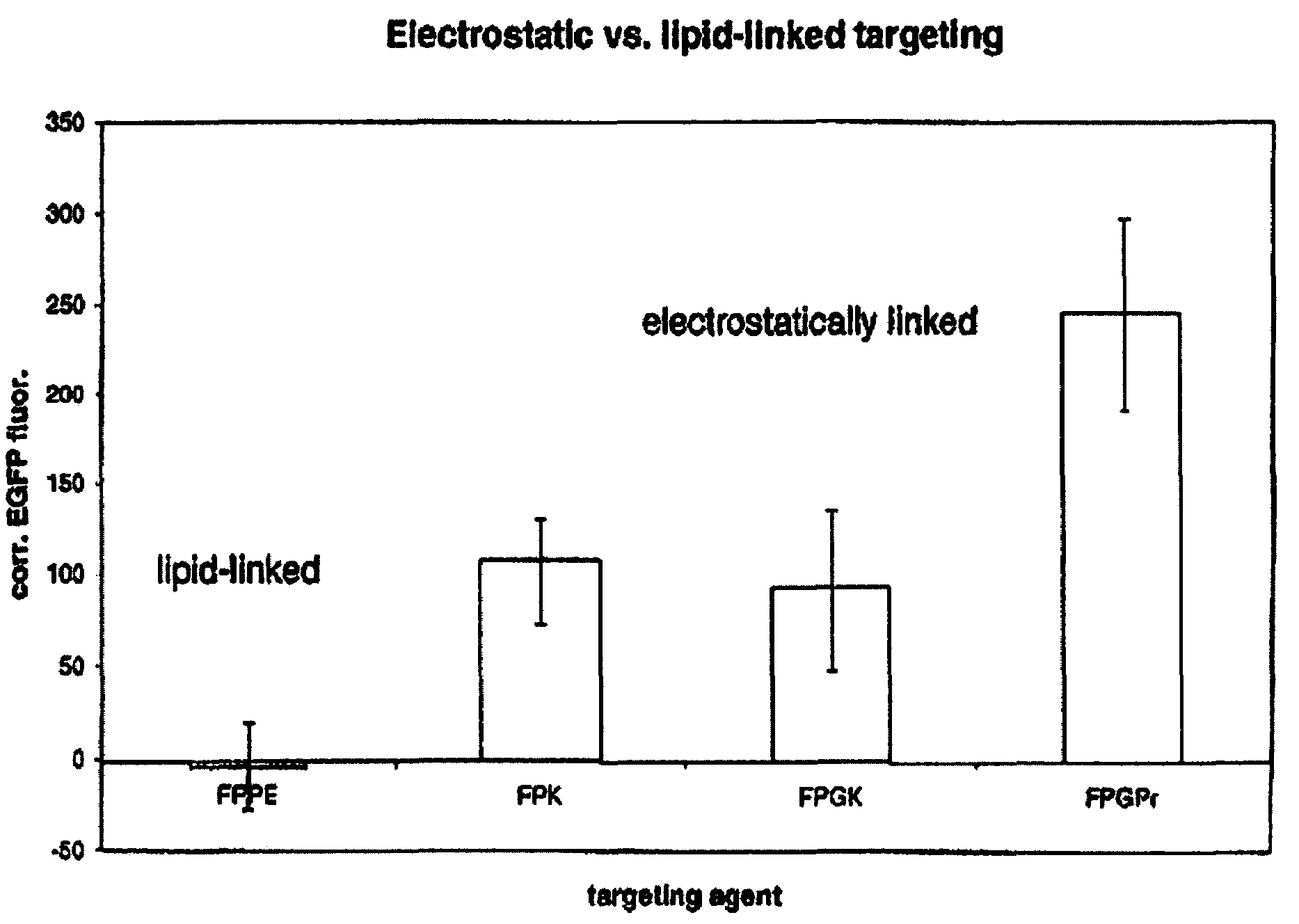
A liposome including a fusogenic liposome, a linking moiety and a targeting moiety. The fusogenic liposome is a lipid bilayer encapsulating contents. The linking moiety is electrostatically bound to the lipid bilayer, and the targeting moiety is covalently bound to the linking moiety. The liposome may also include a stabilizing moiety interposed between the linking and targeting moieties, and covalently bound to both. Alternatively, the stabilizing and targeting moieties may be covalently bound to separate linking moieties, the linking moieties being electrostatically bound to the lipid bilayer.
Owner:TRANSAVE
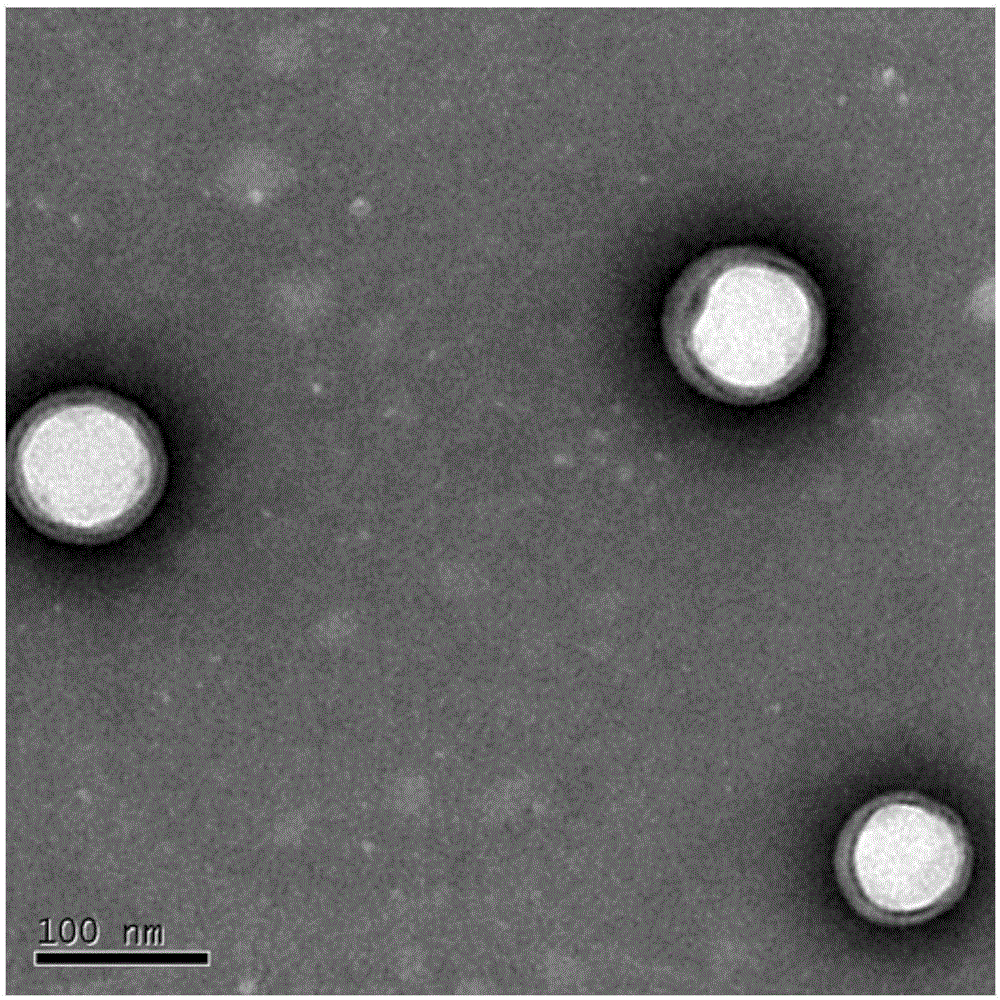
Porous nanoparticle-supported lipid bilayers (protocells) for targeted delivery and methods of using same
ActiveUS20140079774A1Promoting death of cancer cellEfficient packagingBiocideSpecial deliveryLipid formationBinding peptide
The present invention is directed to protocells for specific targeting of hepatocellular and other cancer cells which comprise a nanoporous silica core with a supported lipid bilayer; at least one agent which facilitates cancer cell death (such as a traditional small molecule, a macromolecular cargo (e.g. siRNA or a protein toxin such as ricin toxin A-chain or diphtheria toxin A-chain) and / or a histone-packaged plasmid DNA disposed within the nanoporous silica core (preferably supercoiled in order to more efficiently package the DNA into protocells) which is optionally modified with a nuclear localization sequence to assist in localizing protocells within the nucleus of the cancer cell and the ability to express peptides involved in therapy (apoptosis / cell death) of the cancer cell or as a reporter, a targeting peptide which targets cancer cells in tissue to be treated such that binding of the protocell to the targeted cells is specific and enhanced and a fusogenic peptide that promotes endosomal escape of protocells and encapsulated DNA. Protocells according to the present invention may be used to treat cancer, especially including hepatocellular (liver) cancer using novel binding peptides (c-MET peptides) which selectively bind to hepatocellular tissue or to function in diagnosis of cancer, including cancer treatment and drug discovery.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC +1
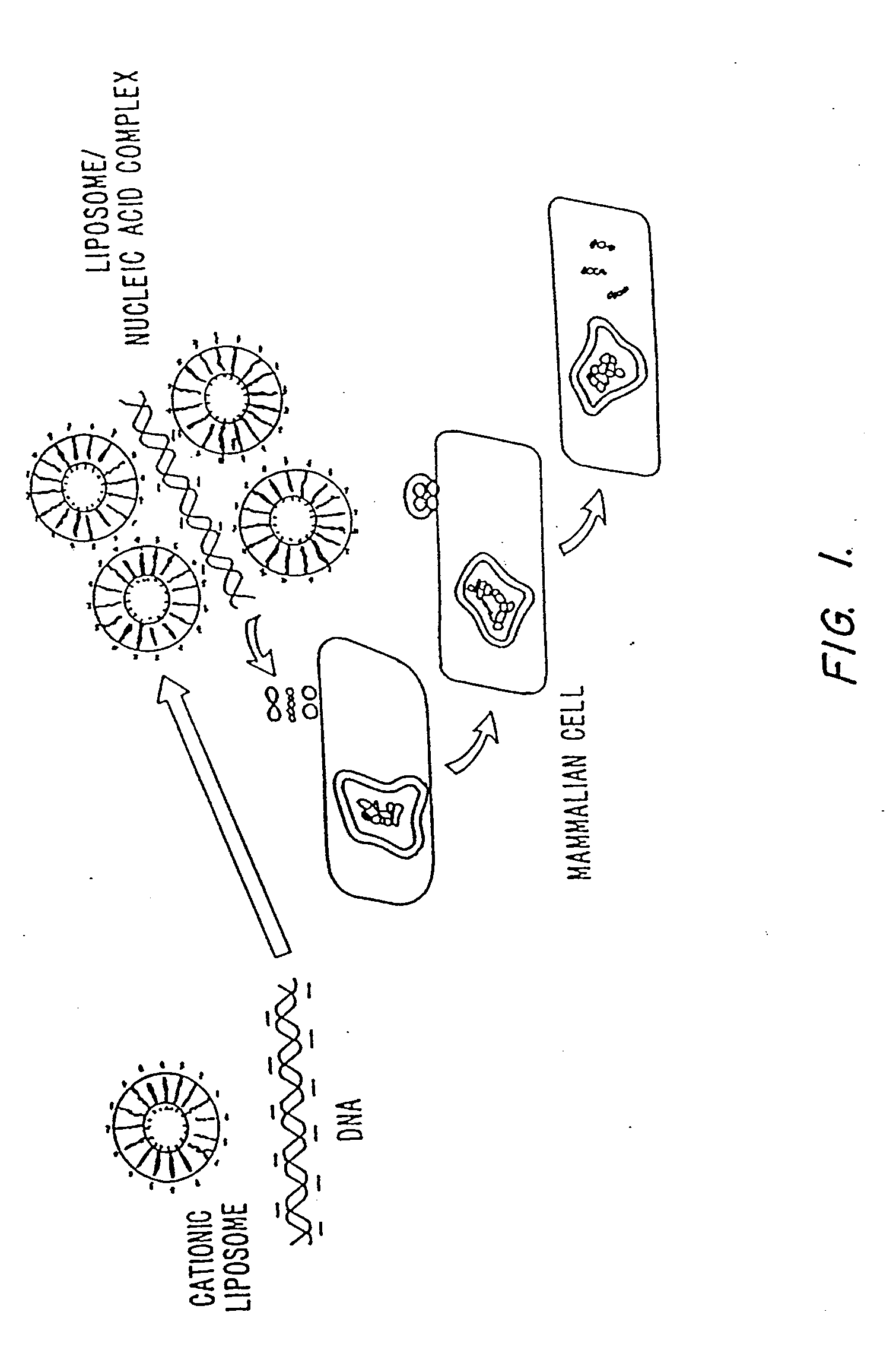
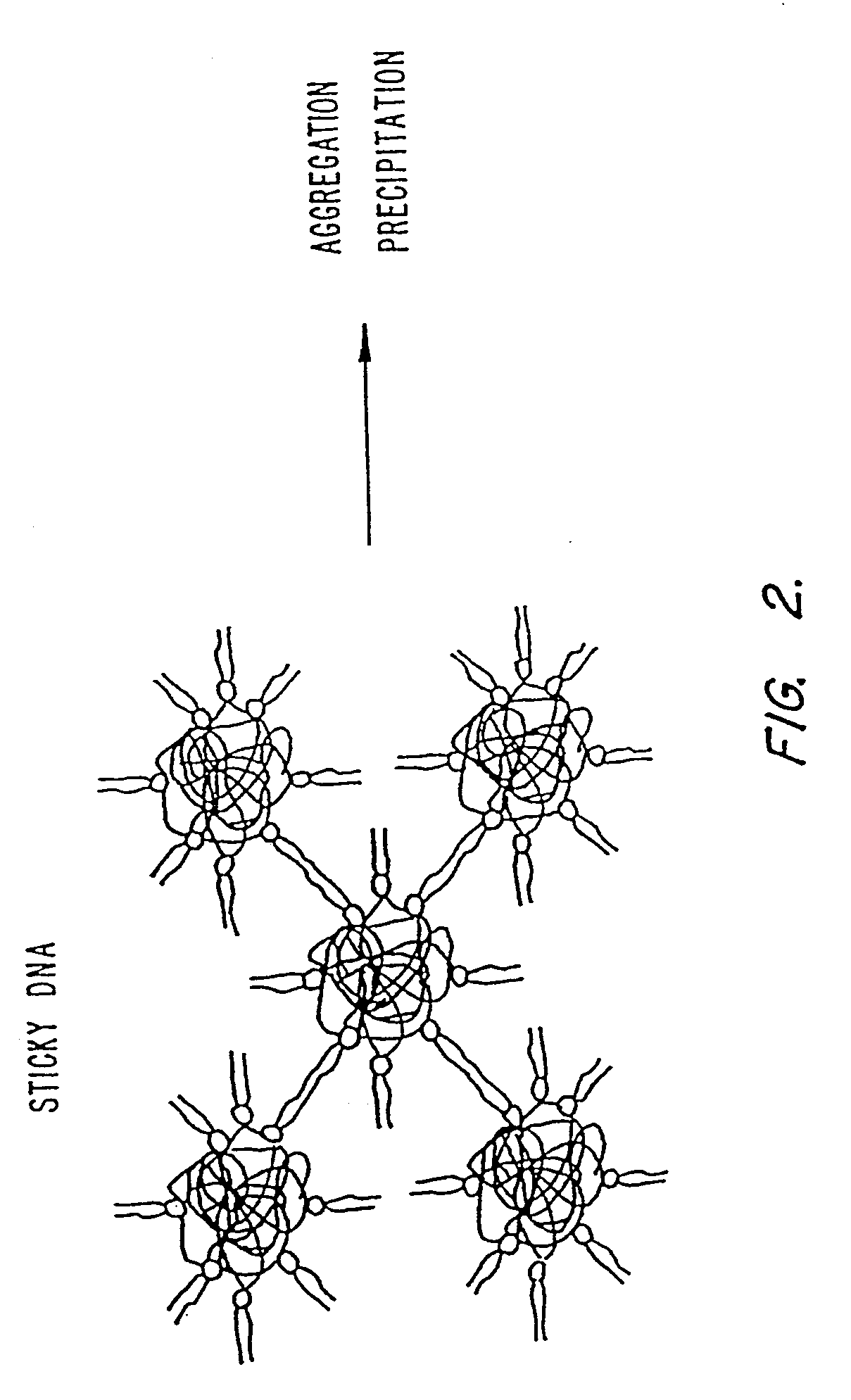
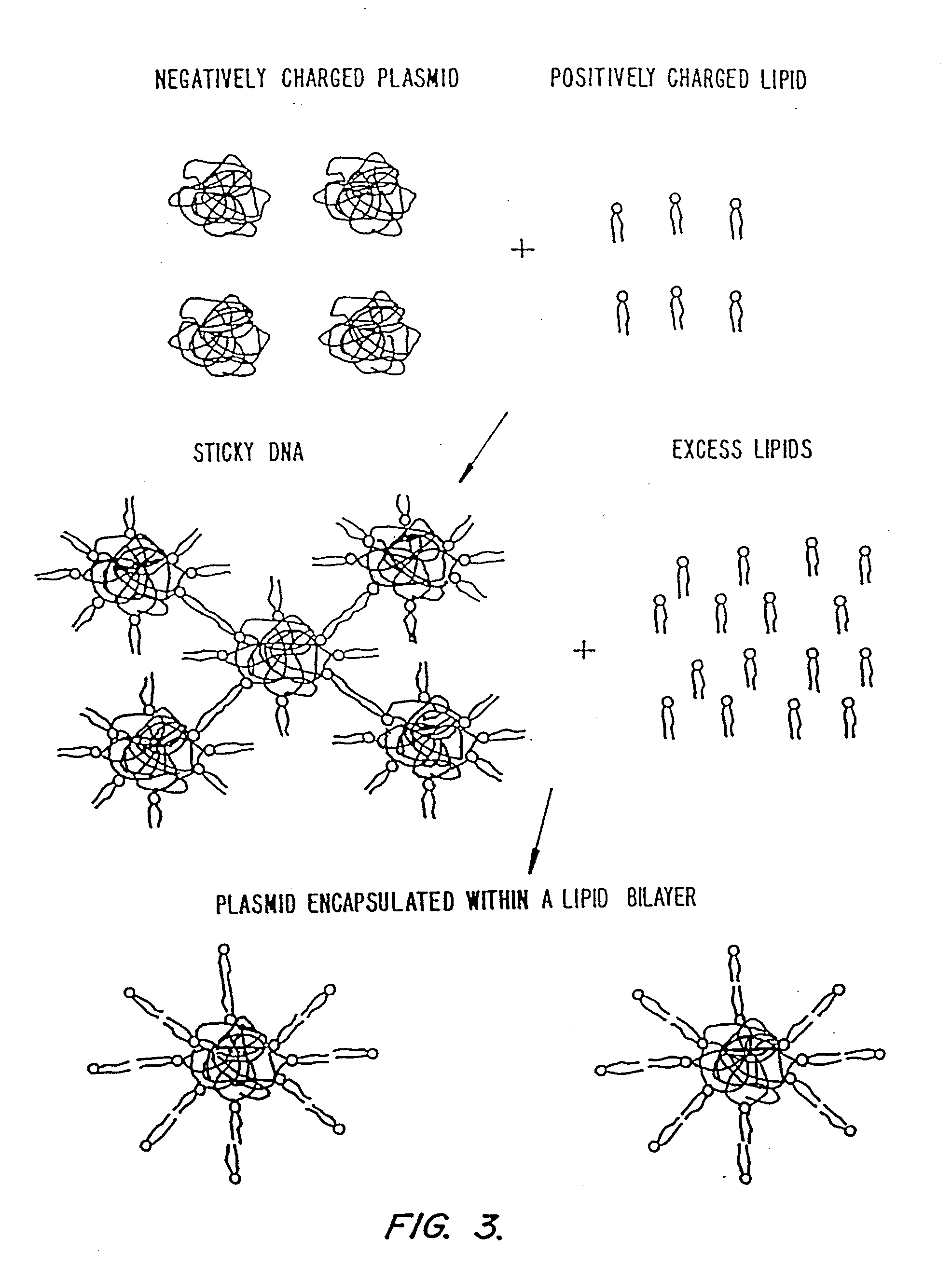
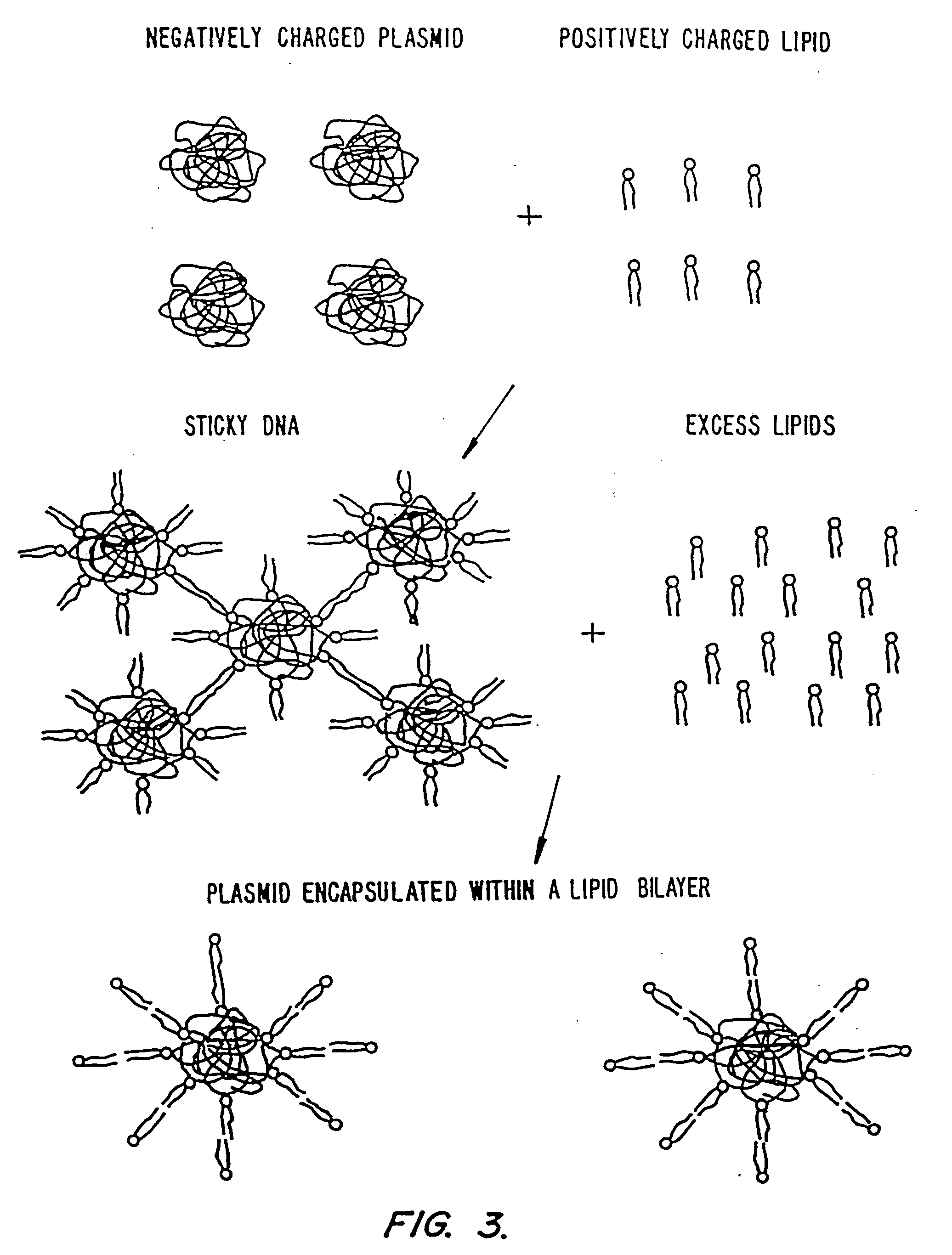
Methods for encapsulating plasmids in lipid bilayers
Plasmid-lipid particles which are useful for transfection of cells in vitro or in vivo are described. The particles can be formed using either detergent dialysis methods or methods which utilize organic solvents. The particles are typically 65-85 nm, fully encapsulate the plasmid and are serum-stable.
Owner:TEKMIRA PHARMA CORP +1
Radiation-protective phospholipid and method
InactiveUS6165501AImprove Oxidation StabilityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsLipid formationEther
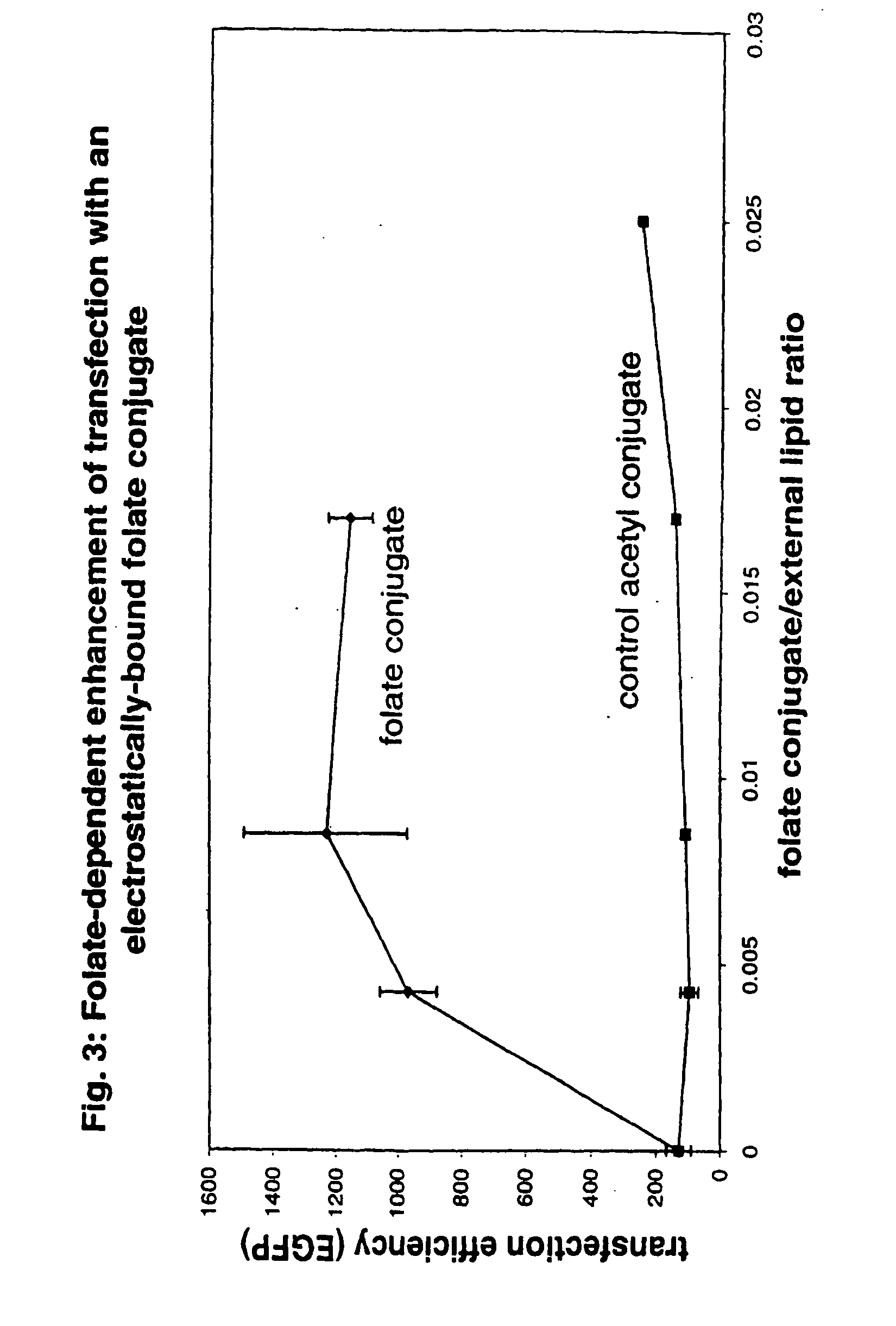
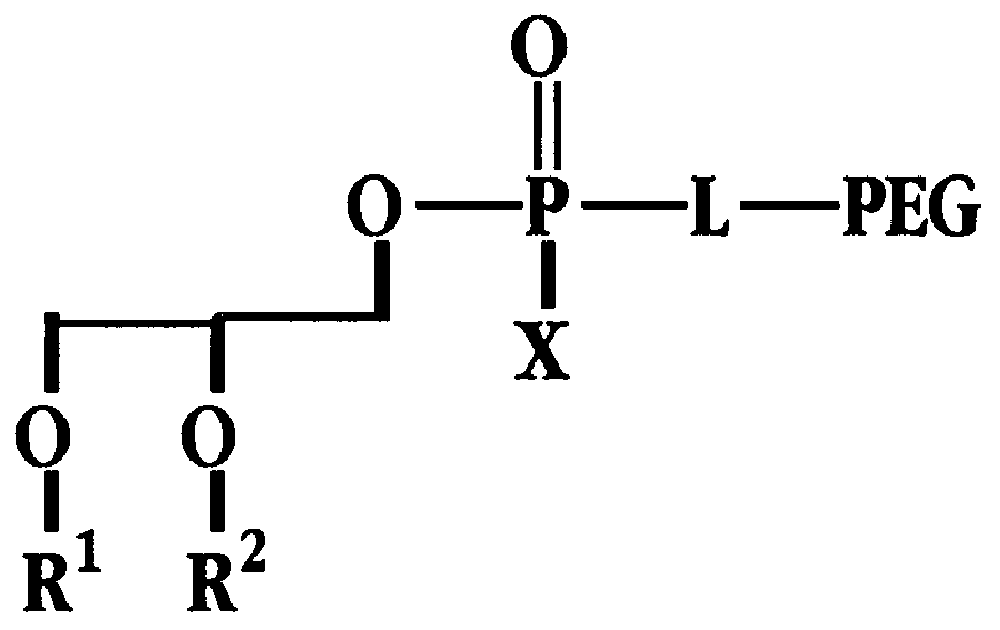
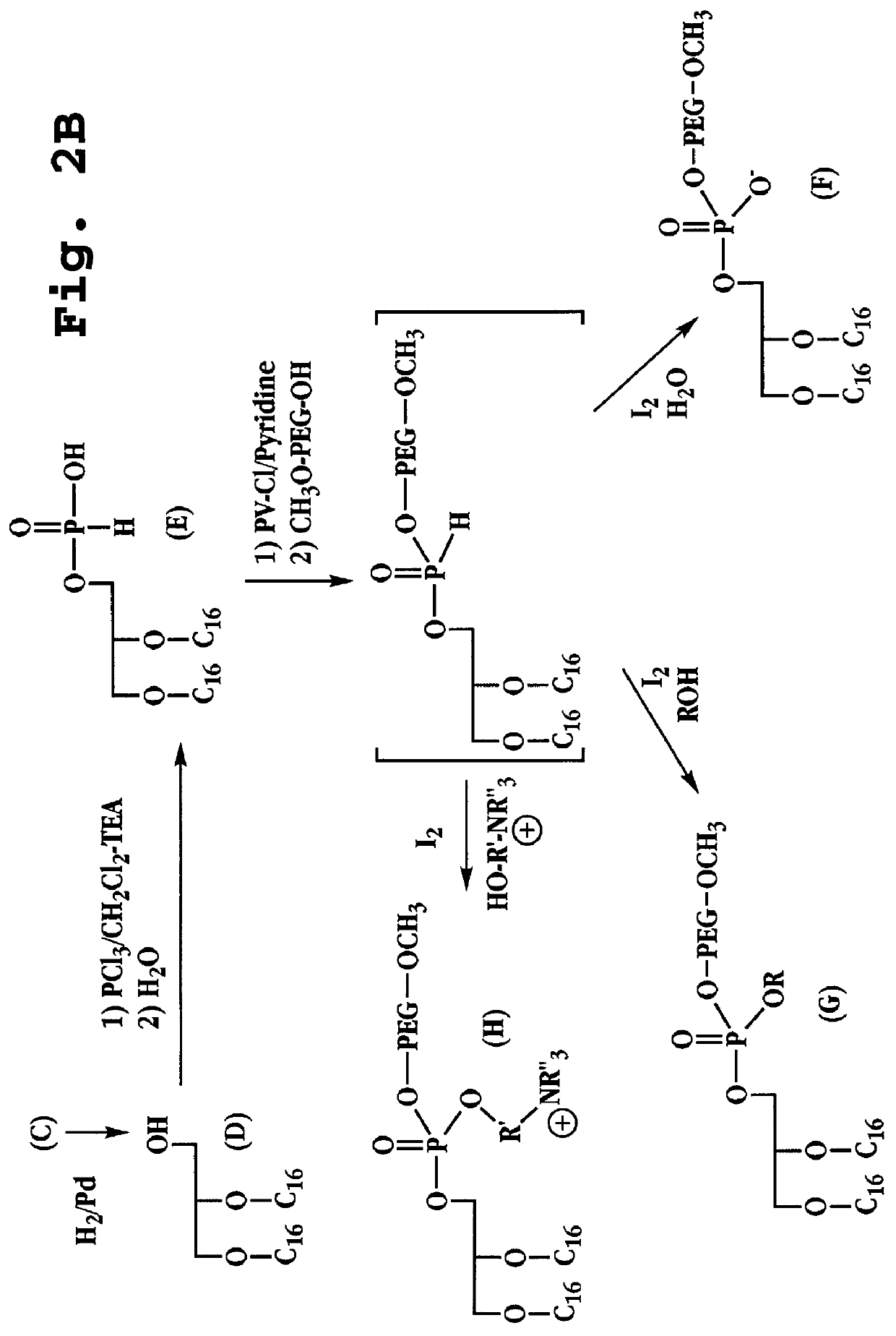
Ether-linked phospholipids, derivatized at the polar head group with polyethylene glycol chains having molecular weights greater than 2,000 daltons, are disclosed. Lipid bilayers containing these phospholipids show high oxidative stability. Also disclosed is the use of PEG-derivatized ether-linked lipids in moisturizing and radiation-protective cosmetic compositions.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
Methods for encapsulating plasmids in lipid bilayers
Plasmid-lipid particles which are useful for transfection of cells in vitro or in vivo are described. The particles can be formed using either detergent dialysis methods or methods which utilize organic solvents. The particles are typically 65-85 nm, fully encapsulate the plasmid and are serum-stable.
Owner:TEKMIRA PHARMA CORP +1
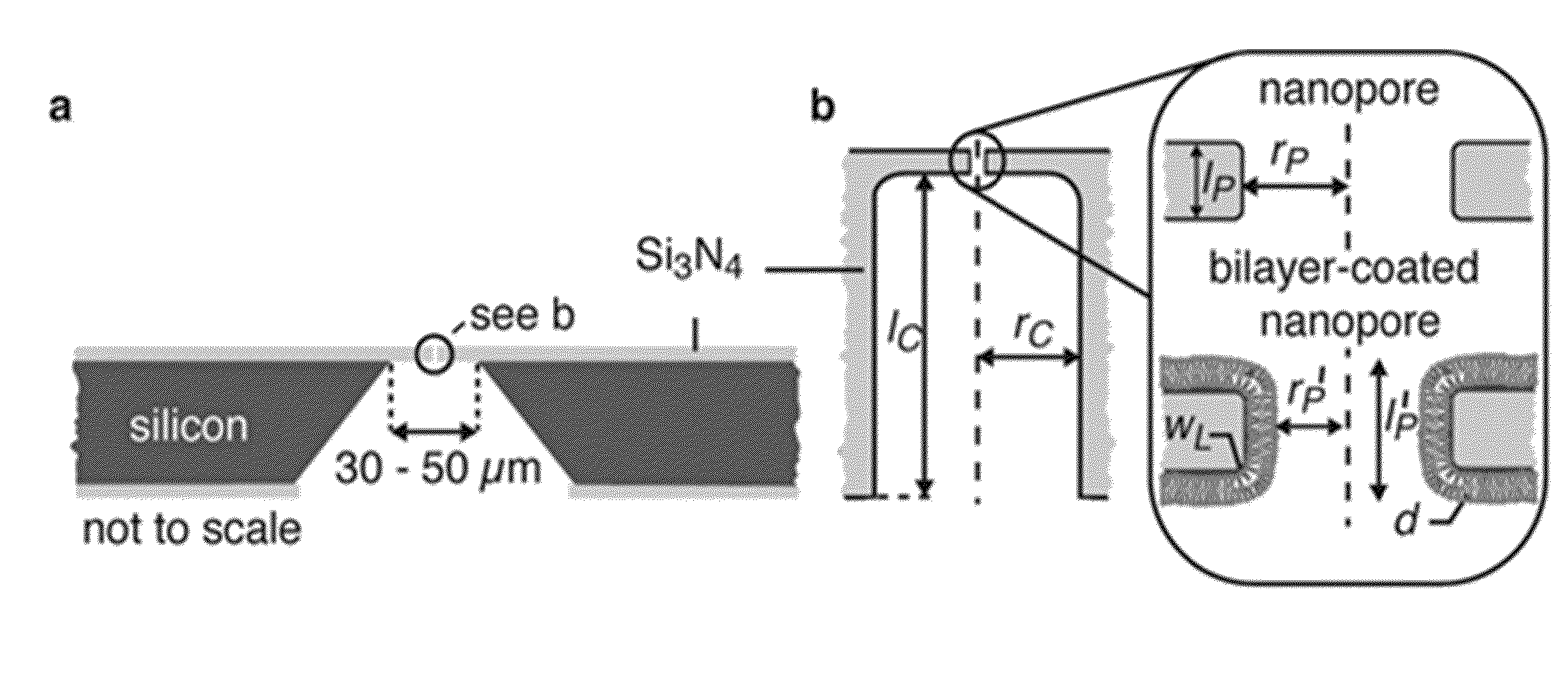
Controlling translocation through nanopores with fluid wall
ActiveUS20130048499A1Improved resolution and detectionPrevents clogged poresMaterial nanotechnologySludge treatmentLipid formationNanoparticle
Improved resolution and detection of nanoparticles are achieved when a nanopore connecting liquid compartments in a device running on the Coulter principle is provided with fluid lipid walls. The fluid lipid walls are made of a lipid bilayer, and preferably include lipid anchored mobile ligands as part of the lipid bilayer. By varying the nature and concentration of the mobile ligand in the lipid bilayer, multifunctional coatings of lipids are provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Hybrid phosphoinositide phospholipids: compositions and uses
InactiveUS20050148042A1Facilitate recruitment of PtdlnsPPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementLipid formationChemical Moiety
The methods and compositions disclosed herein concern the synthesis of a novel class of “two-headed” phospholipid-phosphoinositide hybrids possessing a carbon backbone, such as 2,3-diacylthreitol, erythritol or a synthetic module. The second phospholipid head group allows introduction of a biochemical or chemical moiety in a position orthogonal in space to those occupied by the phosphoinositide head group and the two acyl chains. The diacyl moieties allow for the incorporation of Pea-PIP2 into a lipid bilayer, while the Ptdlns(4,5)P2 moiety in the aqueous layer is specifically recognized by lipid binding proteins. In alternative embodiments of the invention, reporters, for example biotin, fluorophores and / or spin labels, are attached to the free amino group of the head groups of such molecules to specifically target the reporters to the lipid-water interface.
Owner:PRESTWICH GLENN +5
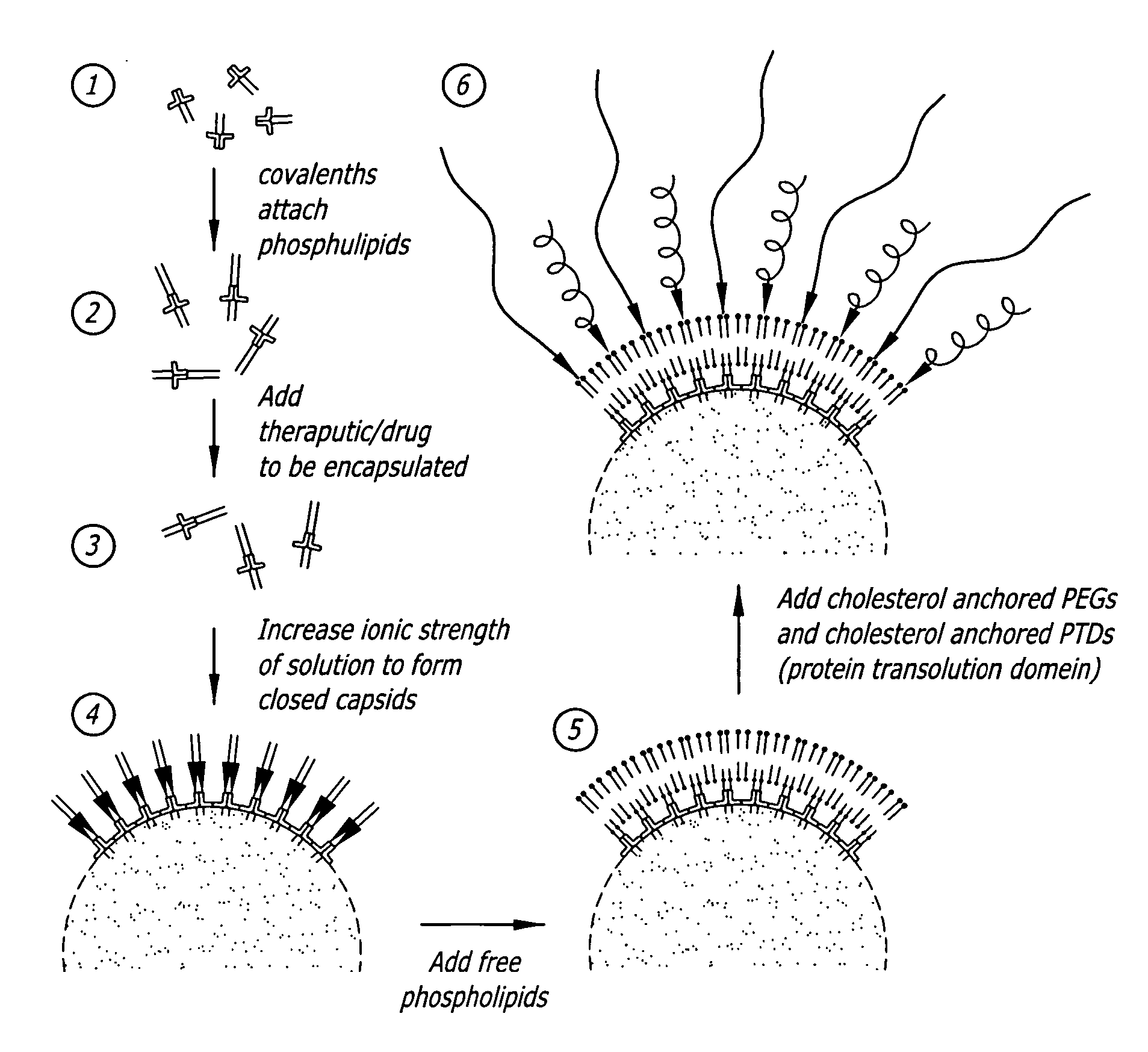
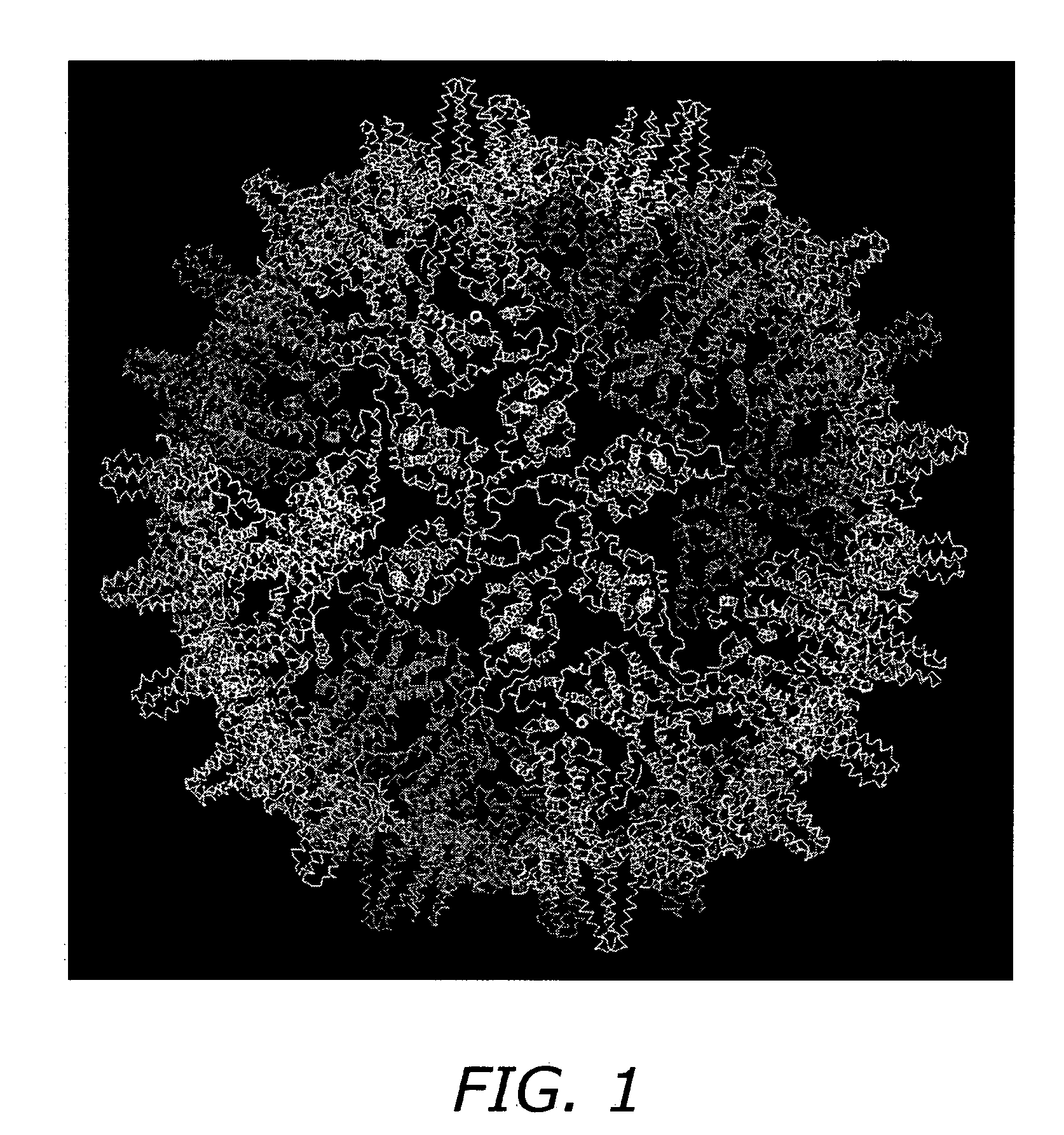
Self-assembling nanoparticle drug delivery system
InactiveUS20060292174A1Facilitate membrane transductionFacilitate transductionAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsLipid formationMedicine
A self-assembling nanoparticle drug delivery system for the delivery of drugs including peptides, proteins, nucleic acids or synthetic chemical drugs is provided. The self-assembling nanoparticle drug delivery system described herein includes viral capsid proteins, such as Hepatitis B Virus core protein, encapsulating the drug, a lipid bi-layer envelope and targeting or facilitating molecules anchored in the lipid bilayer. A method for construction of the self-assembling nanocparticle drug delivery system is also provided.
Owner:CHIMEROS
Cell Transport Compositions and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20090232891A1Enhance intracellular deliveryReduce deliveryPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsDiketopiperazinesImmune Stimulation
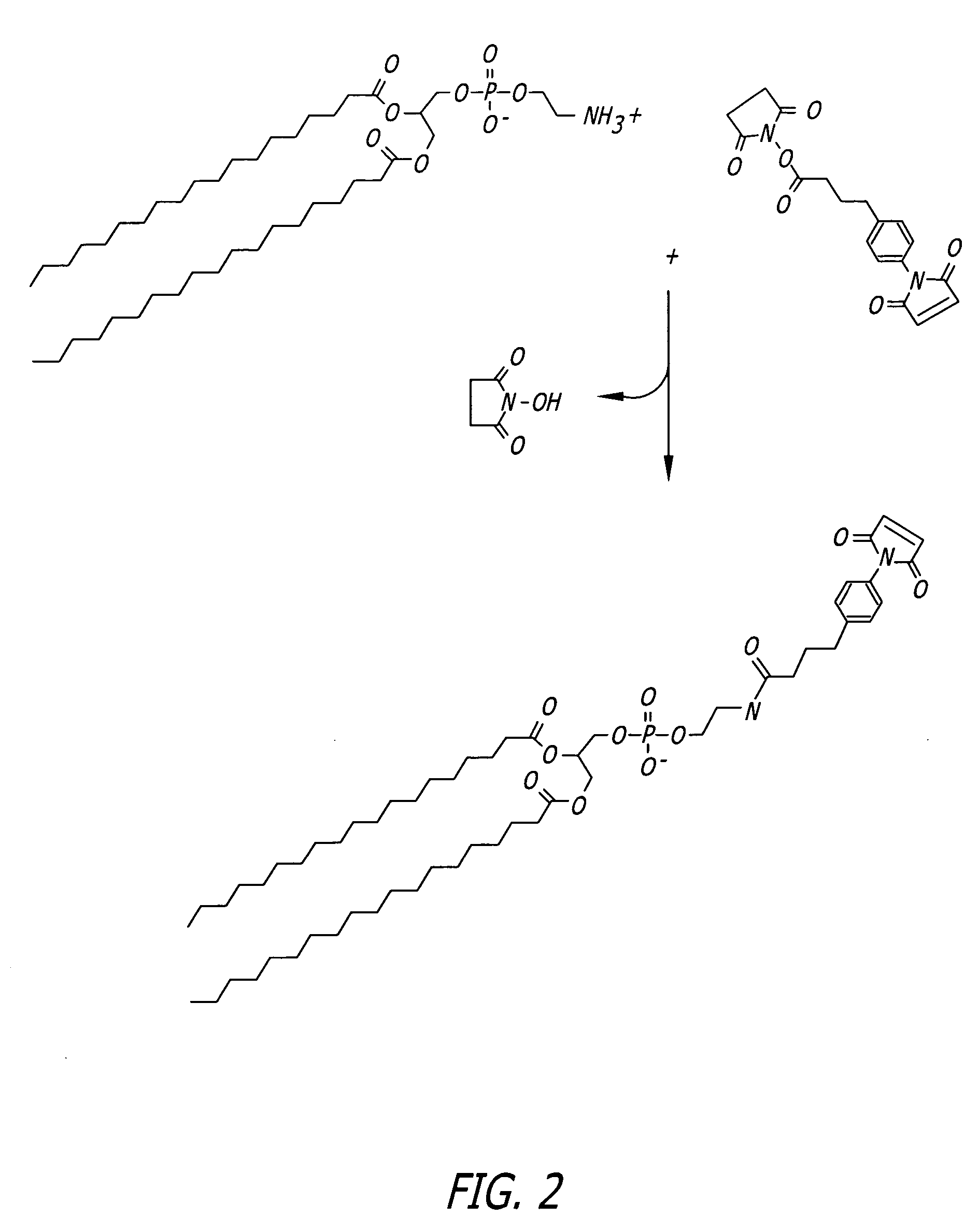
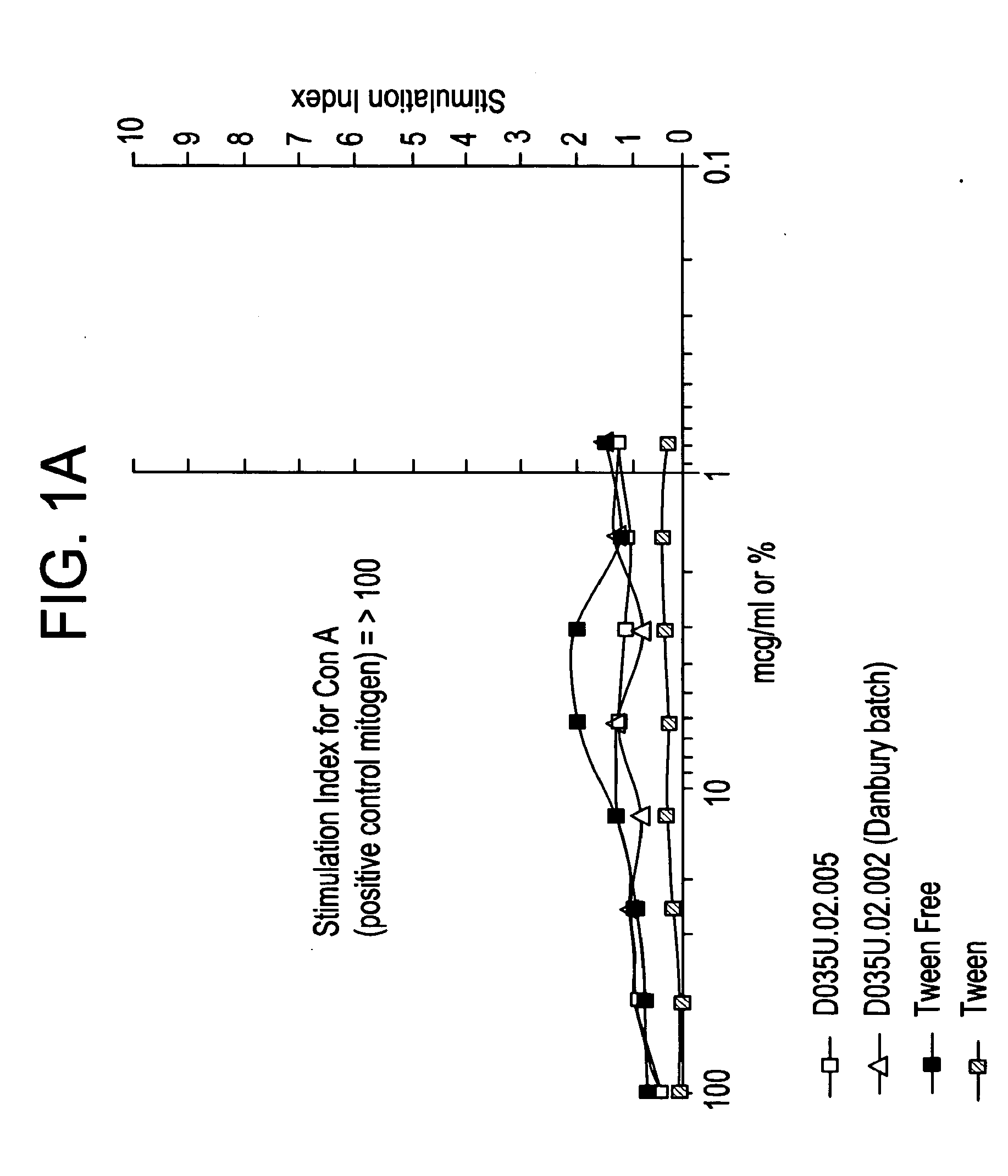
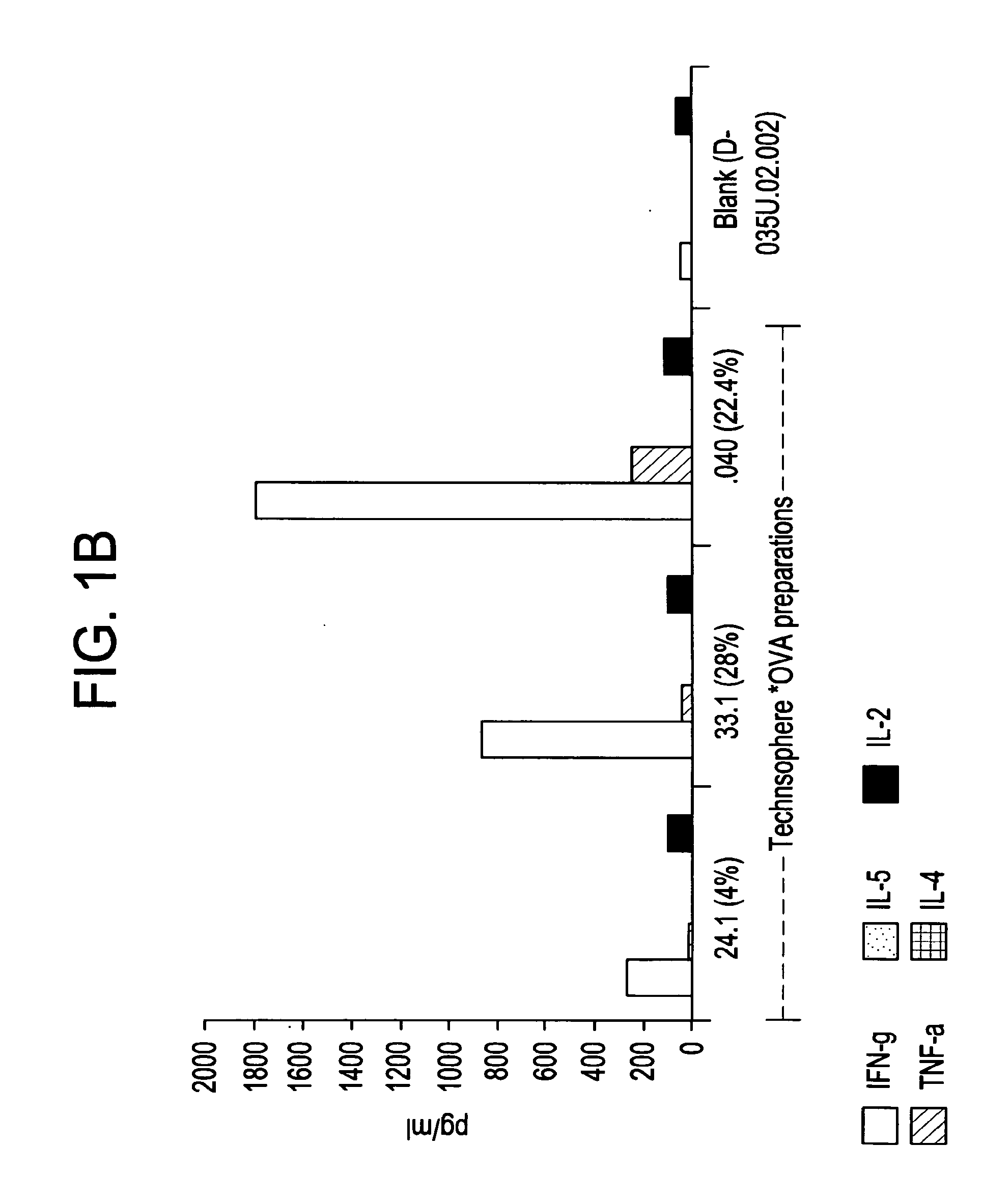
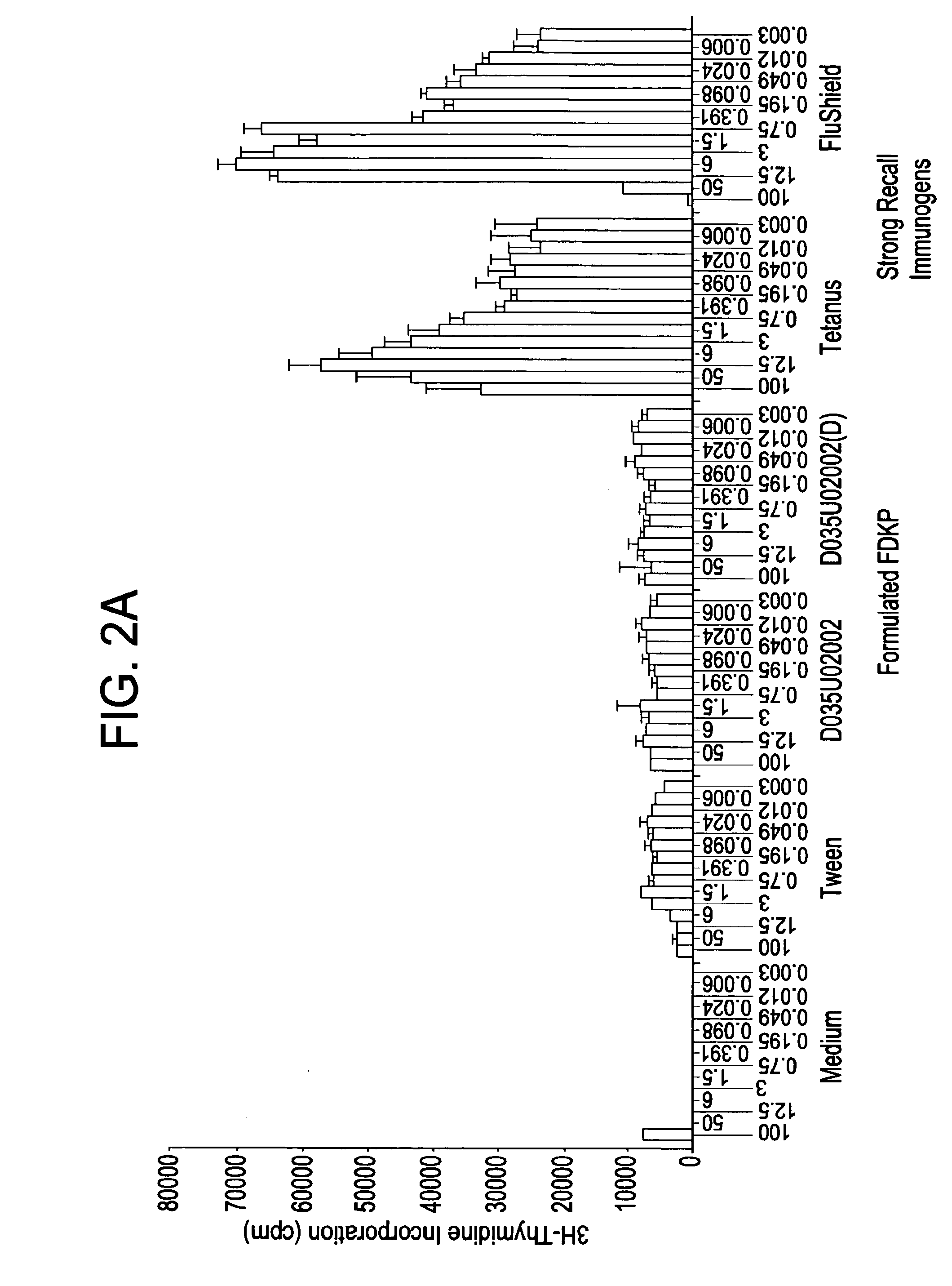
Compositions and methods have been developed for transporting compounds across membranes with little or no toxicity and, when targeted through the appropriate routes of administration (i.e., lung, gastrointestinal (GI) tract), little or no immune stimulation. The compositions can mediate cellular delivery of compounds that would otherwise not enter cells and enhance the intracellular delivery of compounds that would otherwise enter cells inefficiently. The methods are carried out by contacting a proximal face of a lipid bilayer or membrane (e.g. the surface of an intact cell) with a complex containing a compound (e.g., a therapeutic agent) and a diketopiperazine (DKP). DKP and the compound are non-covalently associated with each other or covalently bound to each other.
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
Systems and methods for assembling a lipid bilayer on a substantially planar solid surface
InactiveUS20120052188A1Microbiological testing/measurementPretreated surfacesLipid bilayerSolid surface
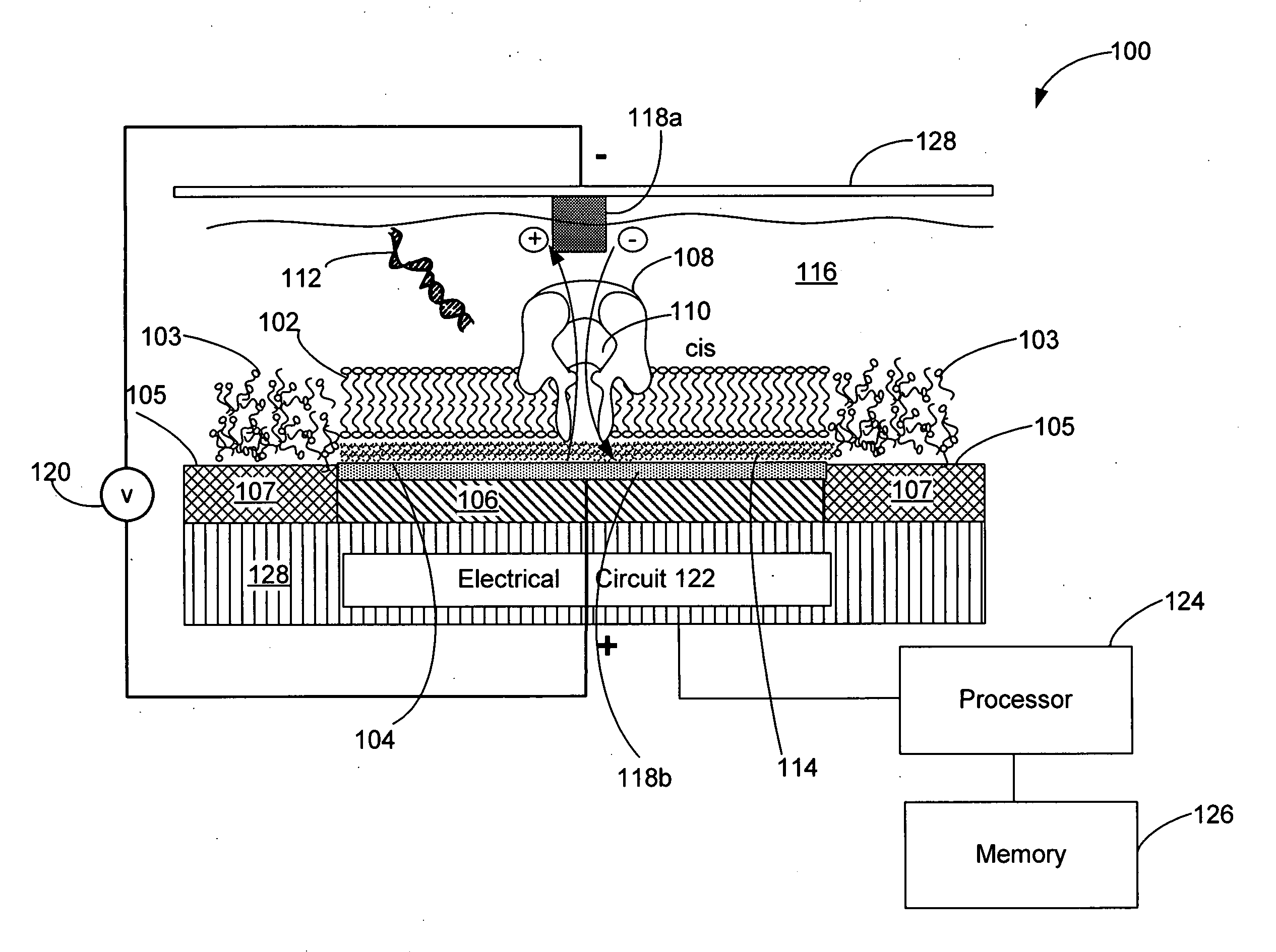
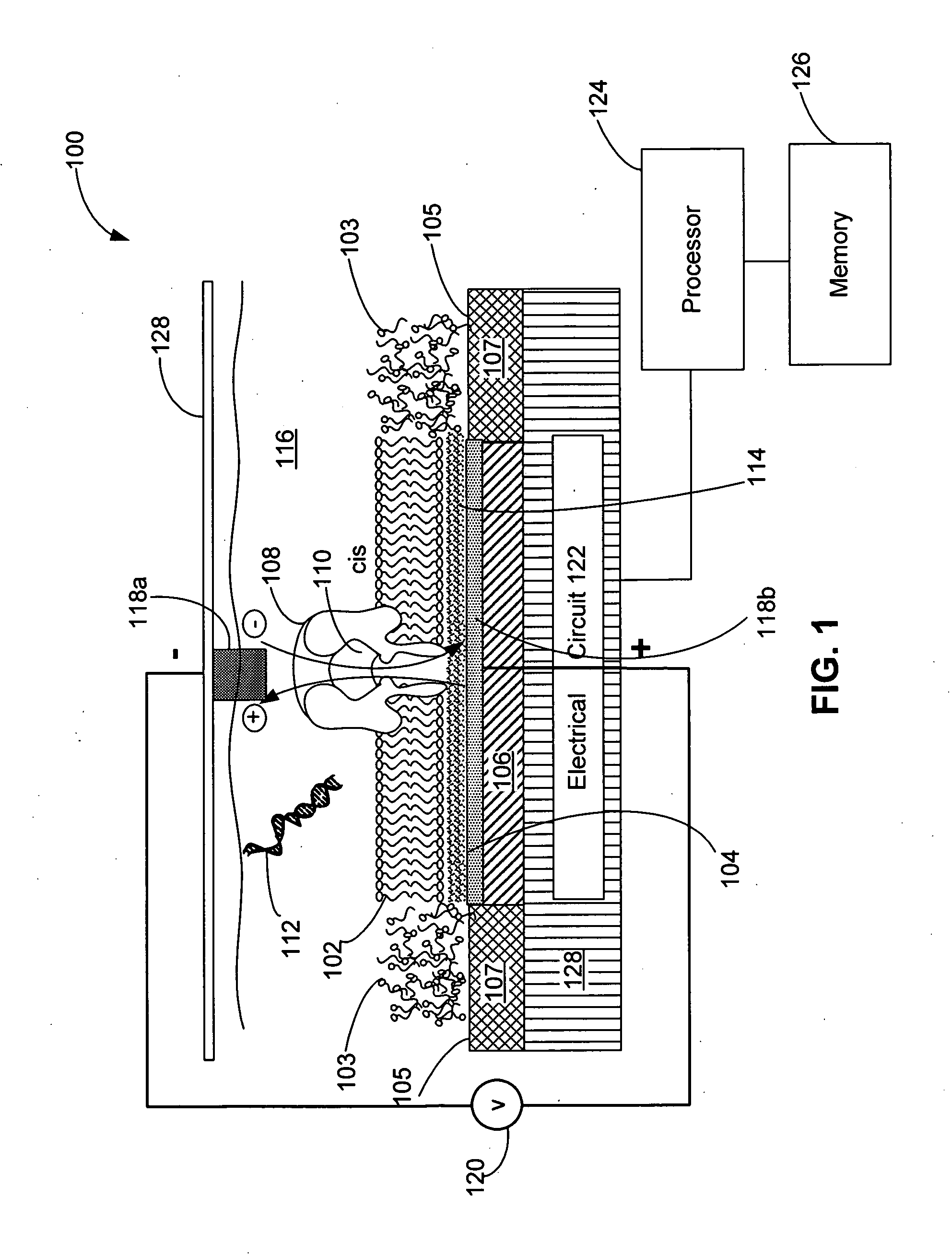
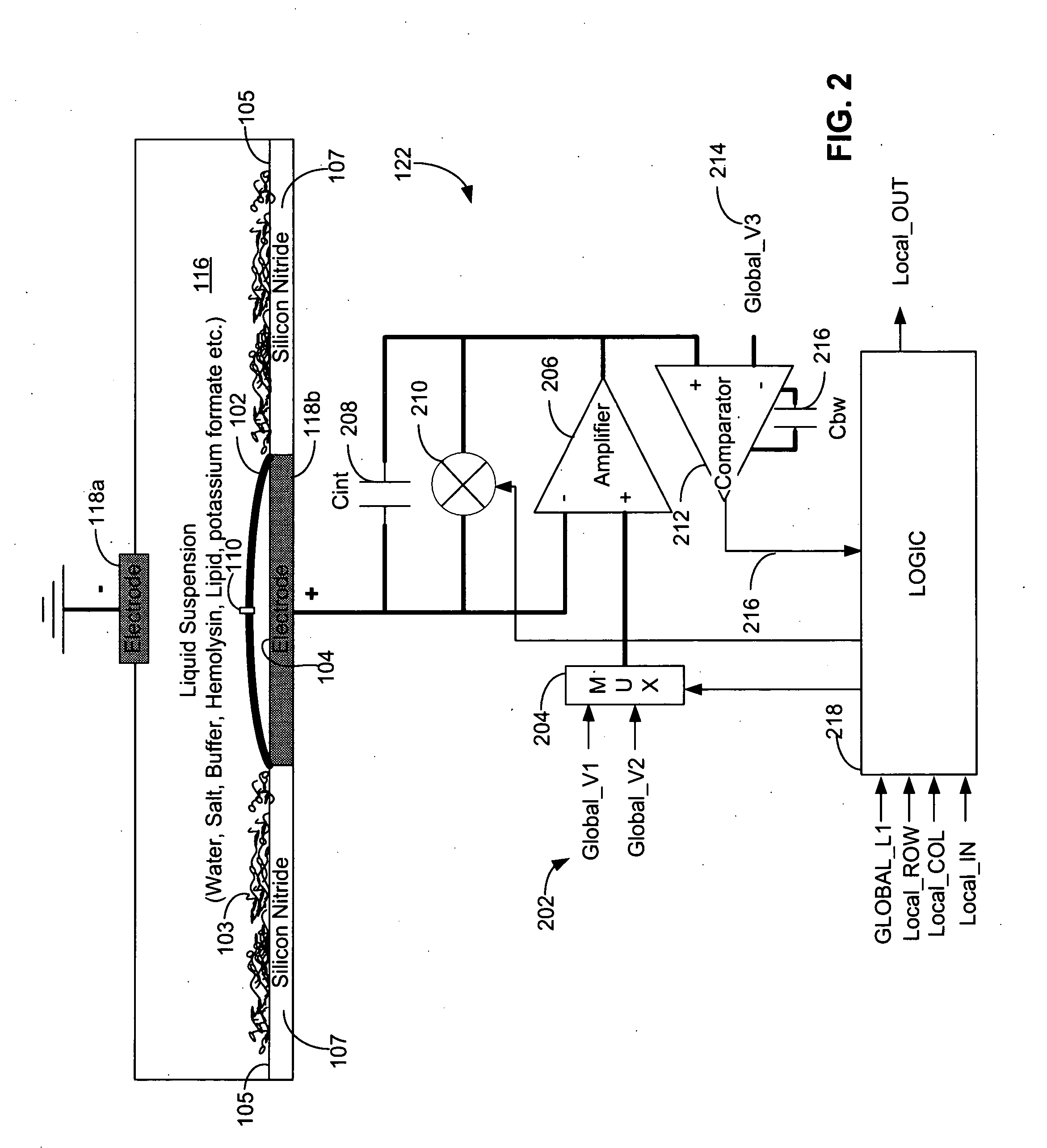
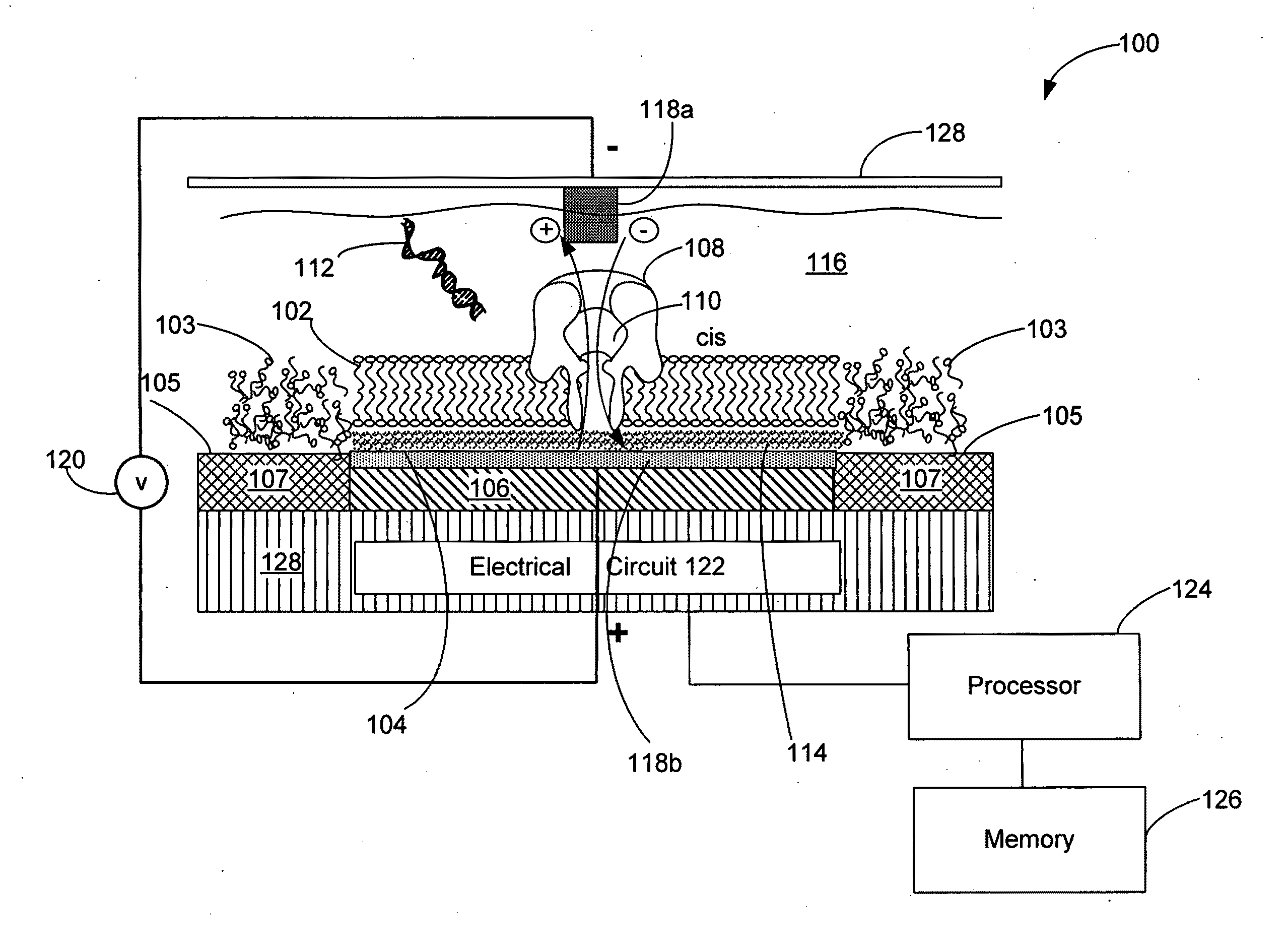
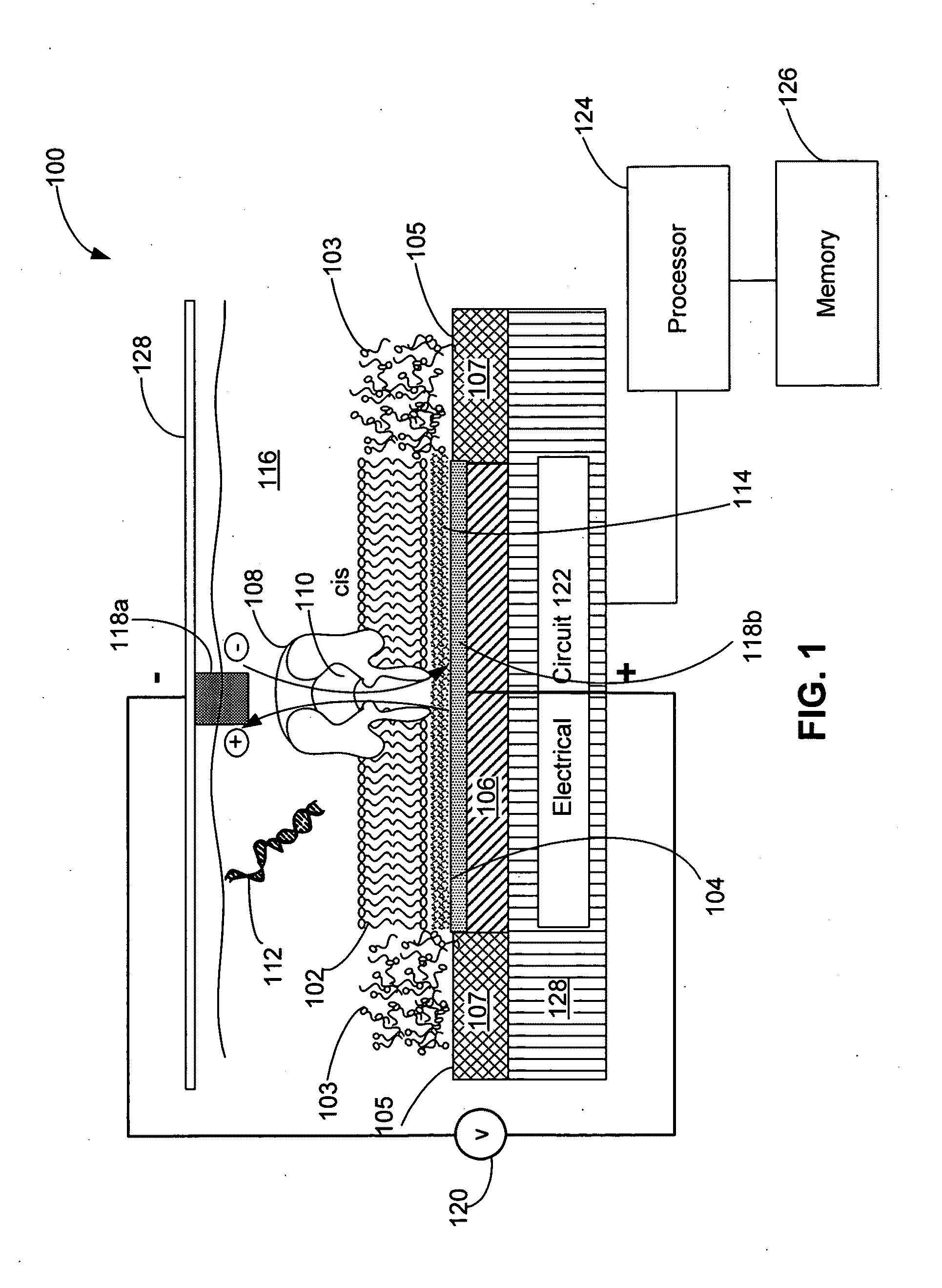
Techniques for assembling a lipid bilayer on a substantially planar solid surface are described herein. In one example, a lipid material such as a lipid suspension is deposited on a substantially planar solid surface, a bubble filled with fast diffusing gas molecules is formed on the solid surface, and the gas molecules are allowed to diffuse out of the bubble to form a lipid bilayer on the solid surface.
Owner:GENIA TECH
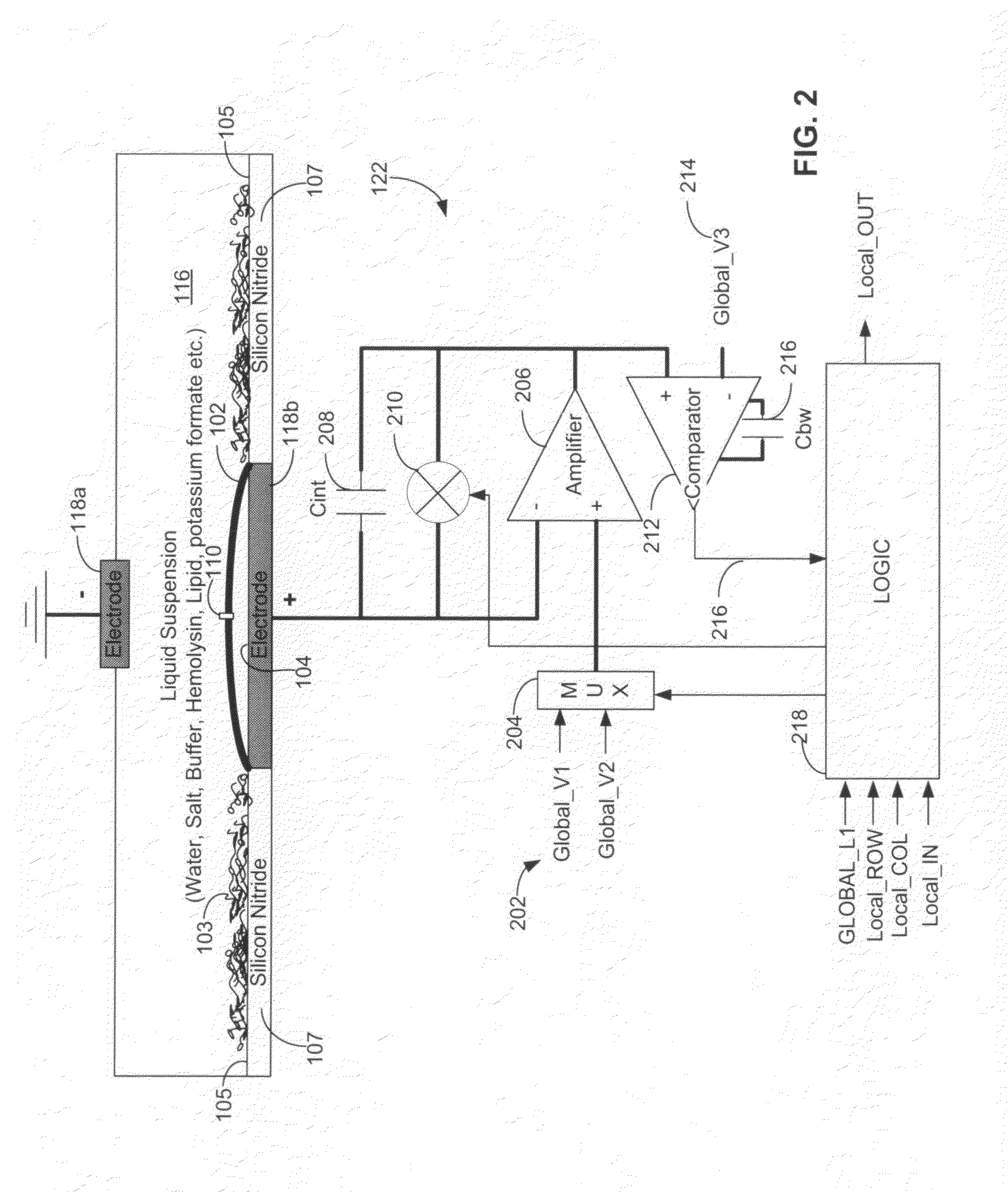
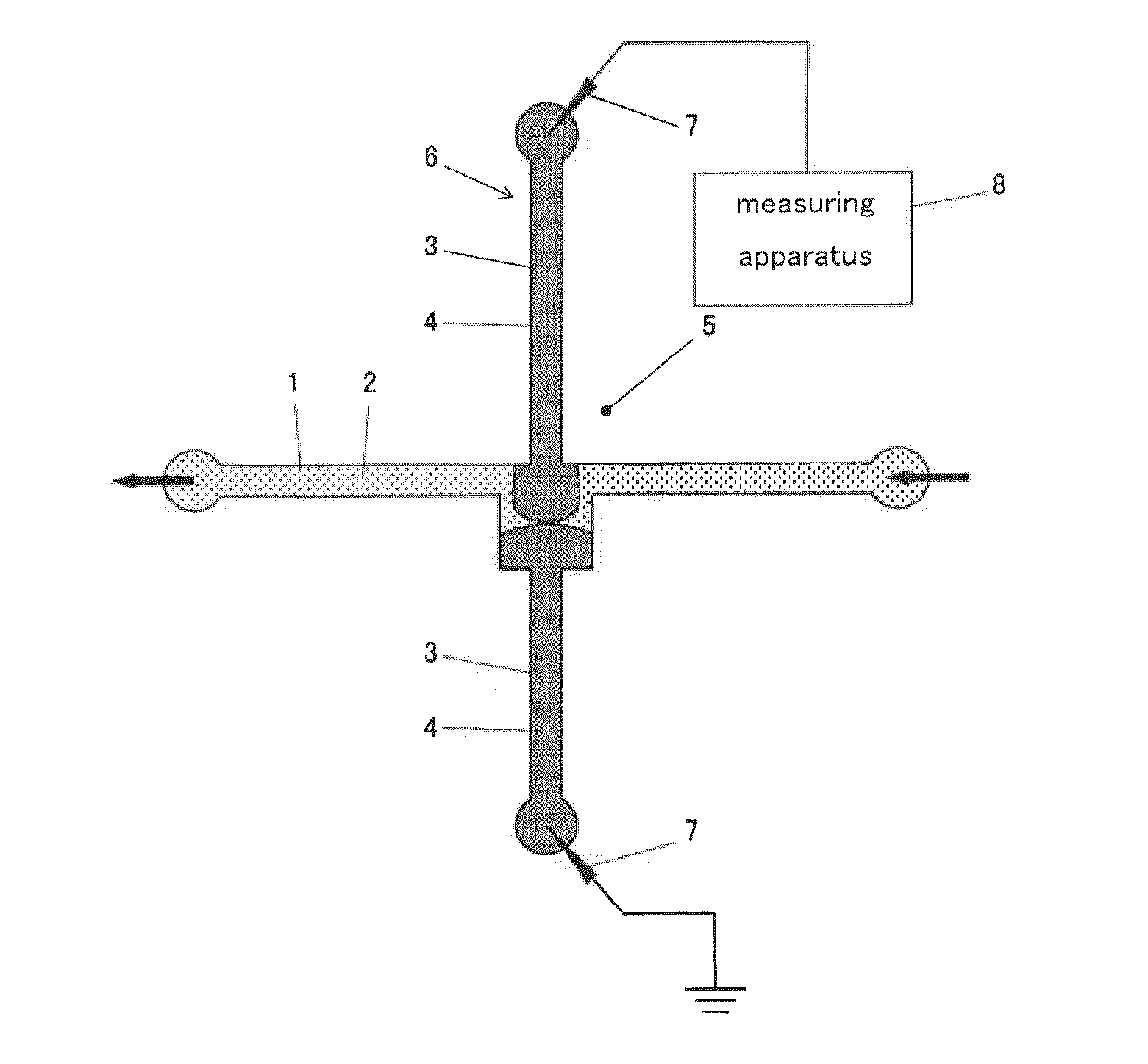
Systems and methods for forming a nanopore in a lipid bilayer
Techniques for forming a nanopore in a lipid bilayer are described herein. In one example, an agitation stimulus level such as an electrical agitation stimulus is applied to a lipid bilayer wherein the agitation stimulus level tends to facilitate the formation of nanopores in the lipid bilayer. In some embodiments, a change in an electrical property of the lipid bilayer resulting from the formation of the nanopore in the lipid bilayer is detected, and a nanopore has formed in the lipid bilayer is determined based on the detected change in the lipid bilayer electrical property.
Owner:GENIA TECH
Membrane for filtering of water
InactiveUS20090120874A1Efficient desalinationEfficient purificationCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsGeneral water supply conservationLipid formationHydrophobic polymer
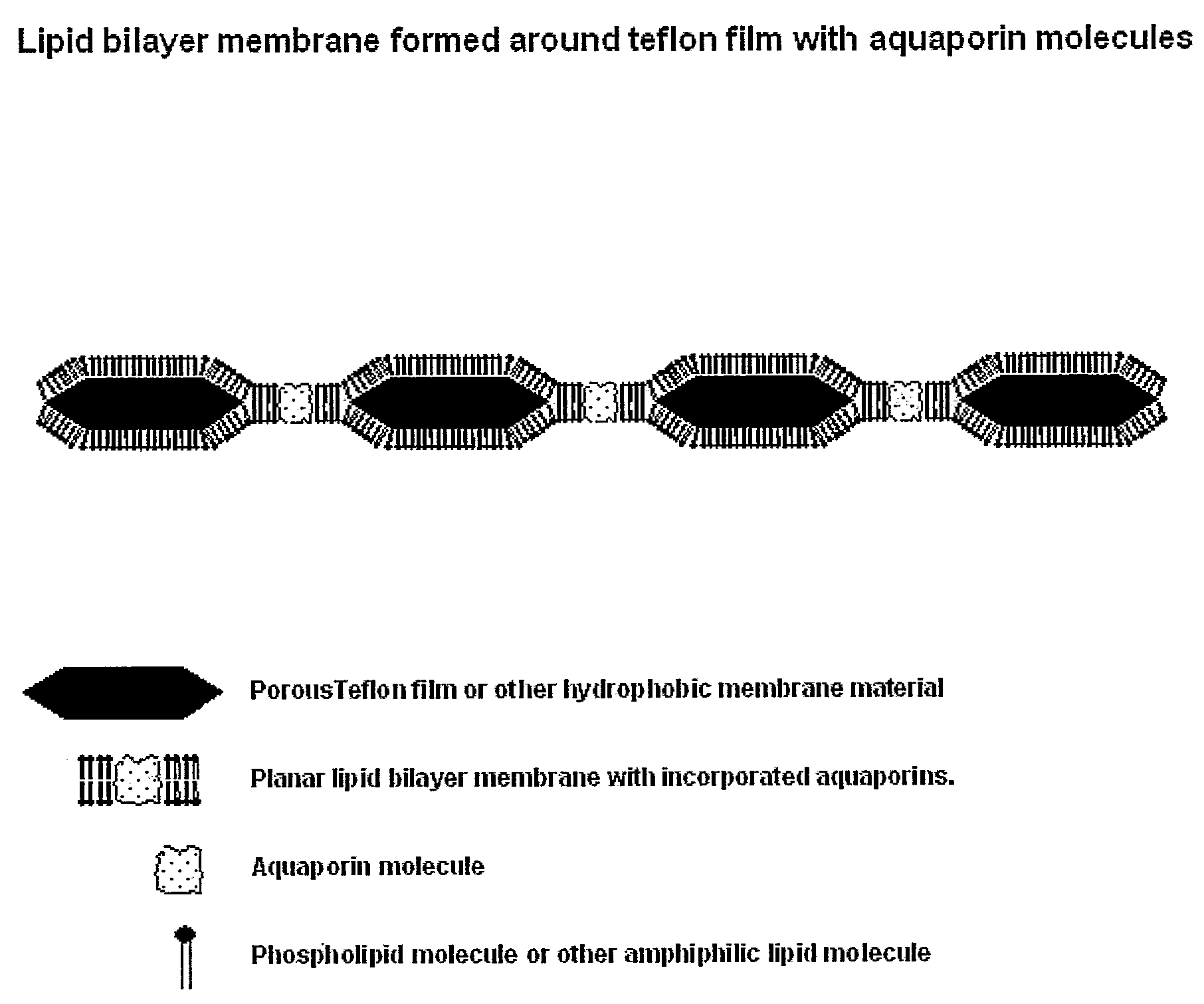
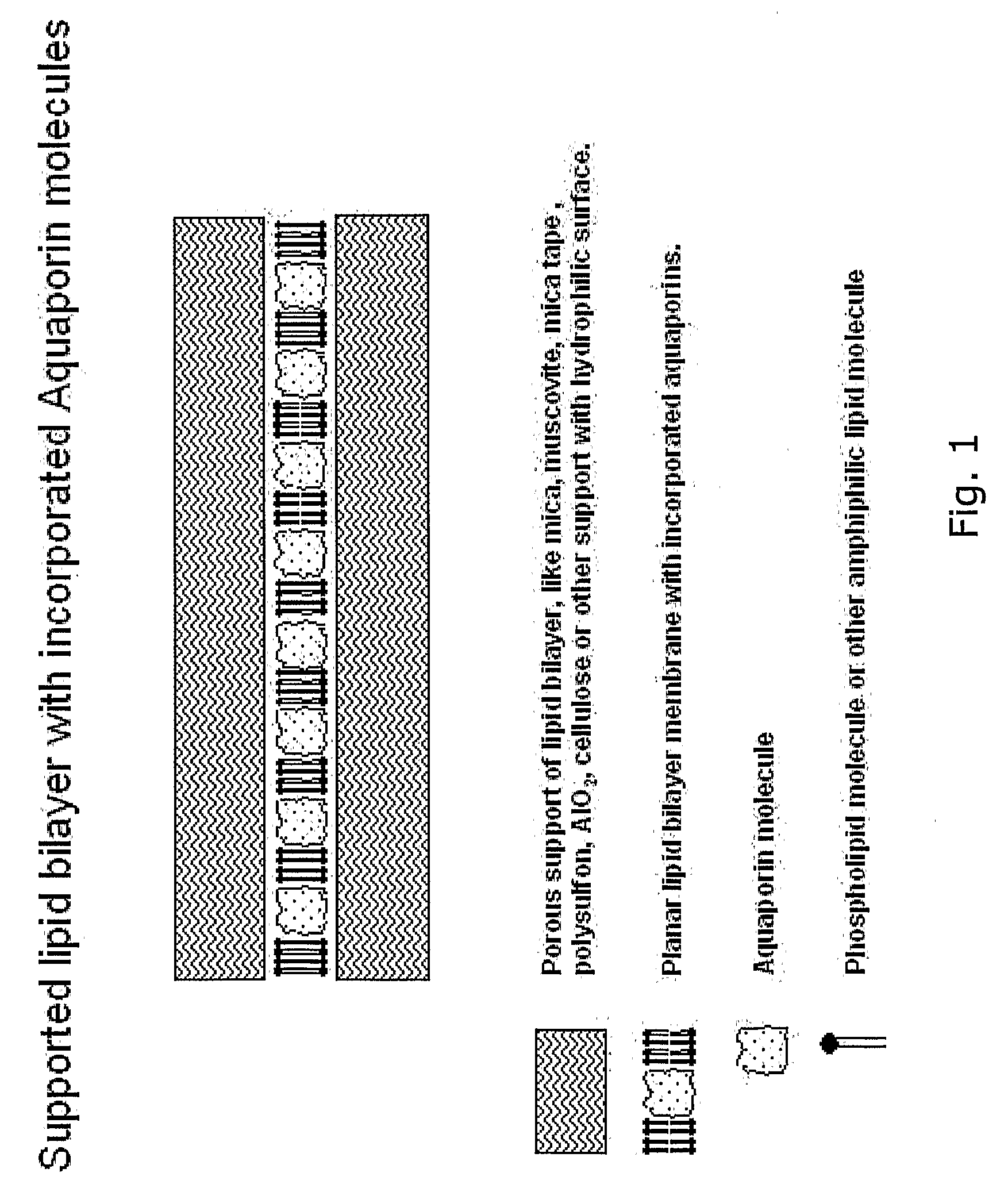
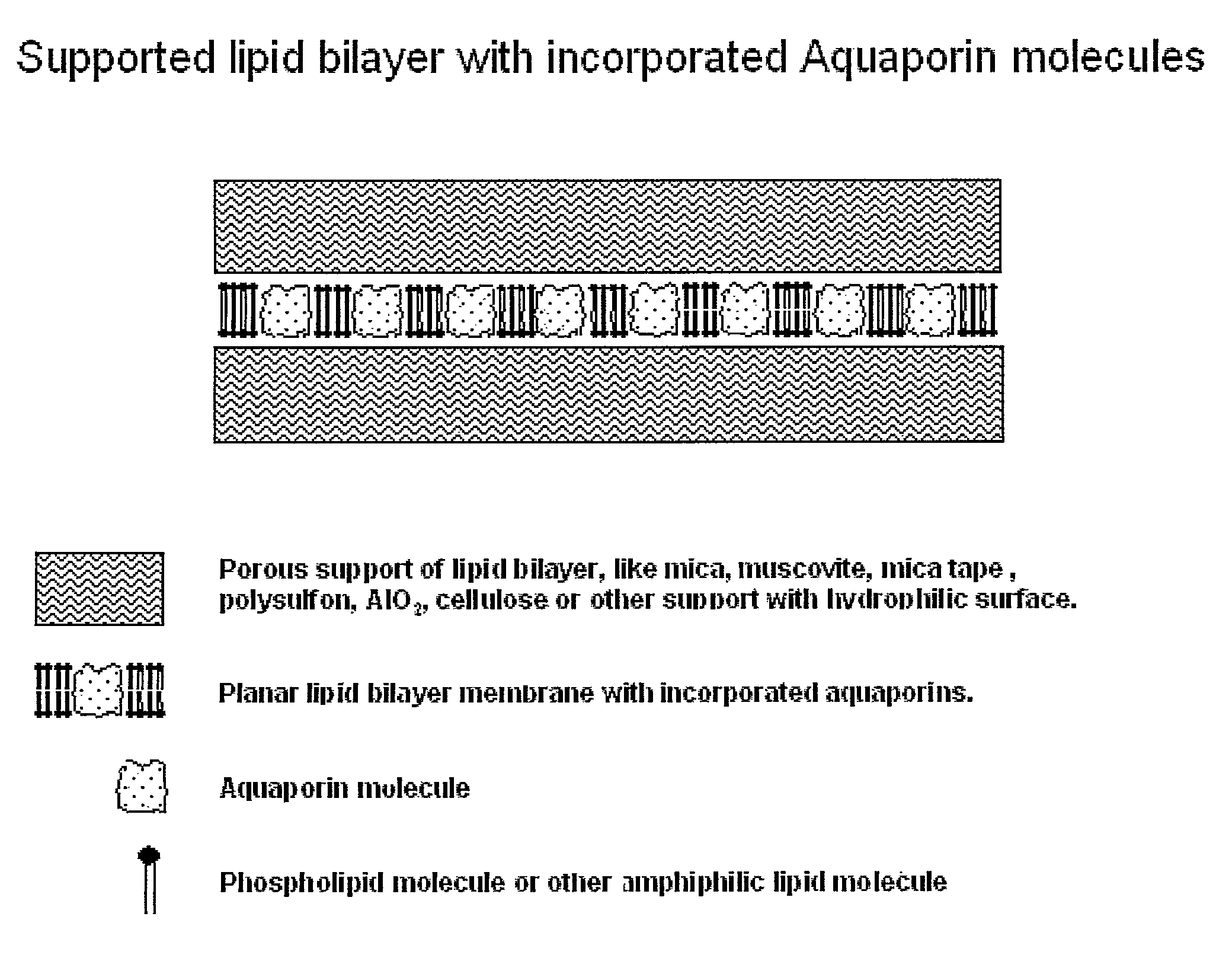
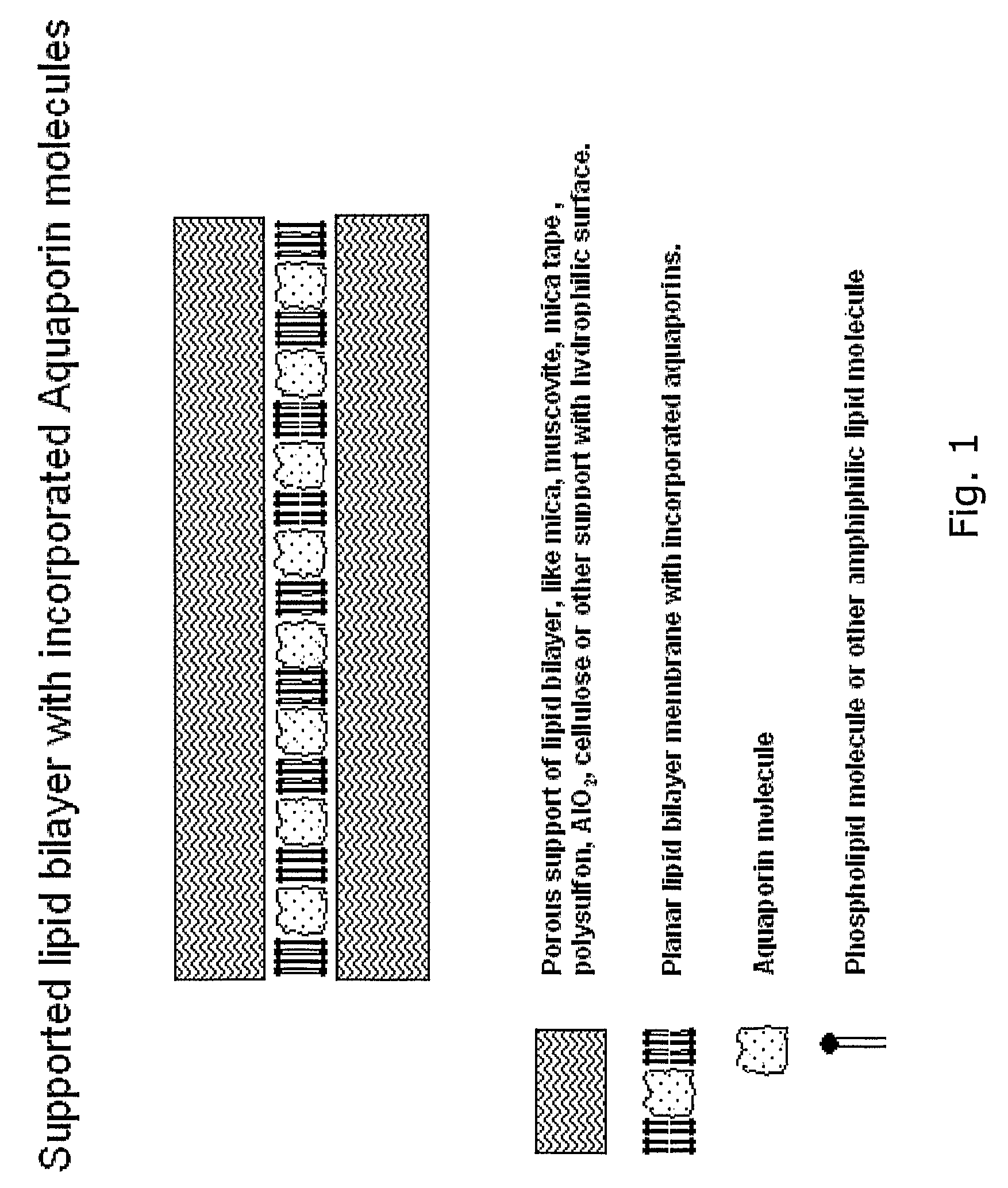
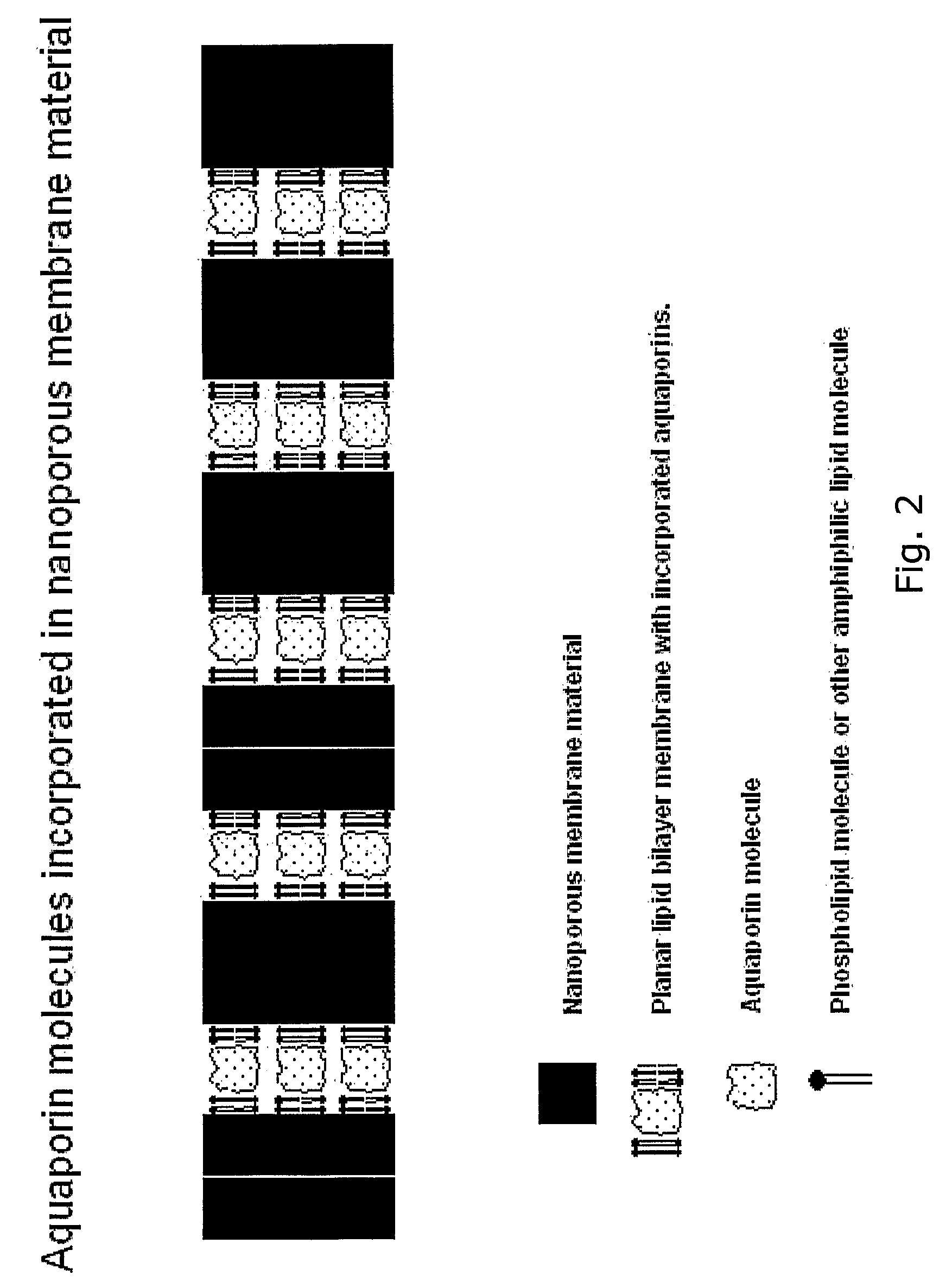
Disclosed are novel water membranes comprising lipid bilayers incorporating functional aqua-porins. The lipid bilayers are arranged in sandwich structures including hydrophilic or hydro-phobic support materials. Also disclosed are water purification devices / systems, including reverse osmosis filtering devices that include membranes having functional aquaporins. Methods of water purification and methods of preparing the membranes are also disclosed. Further, the invention provides for a new type of perforated, hydrophobic polymer film and to membranes containing lipid bilayers having other transmembrane proteins than aquaporins introduced.
Owner:AQUAPORIN AS
Lipid bilayer carrier for drugs or imaging agents
InactiveUS20130108551A1Better addressMaximize MR contrast enhancementOrganic active ingredientsDispersion deliveryChain lengthImaging agent
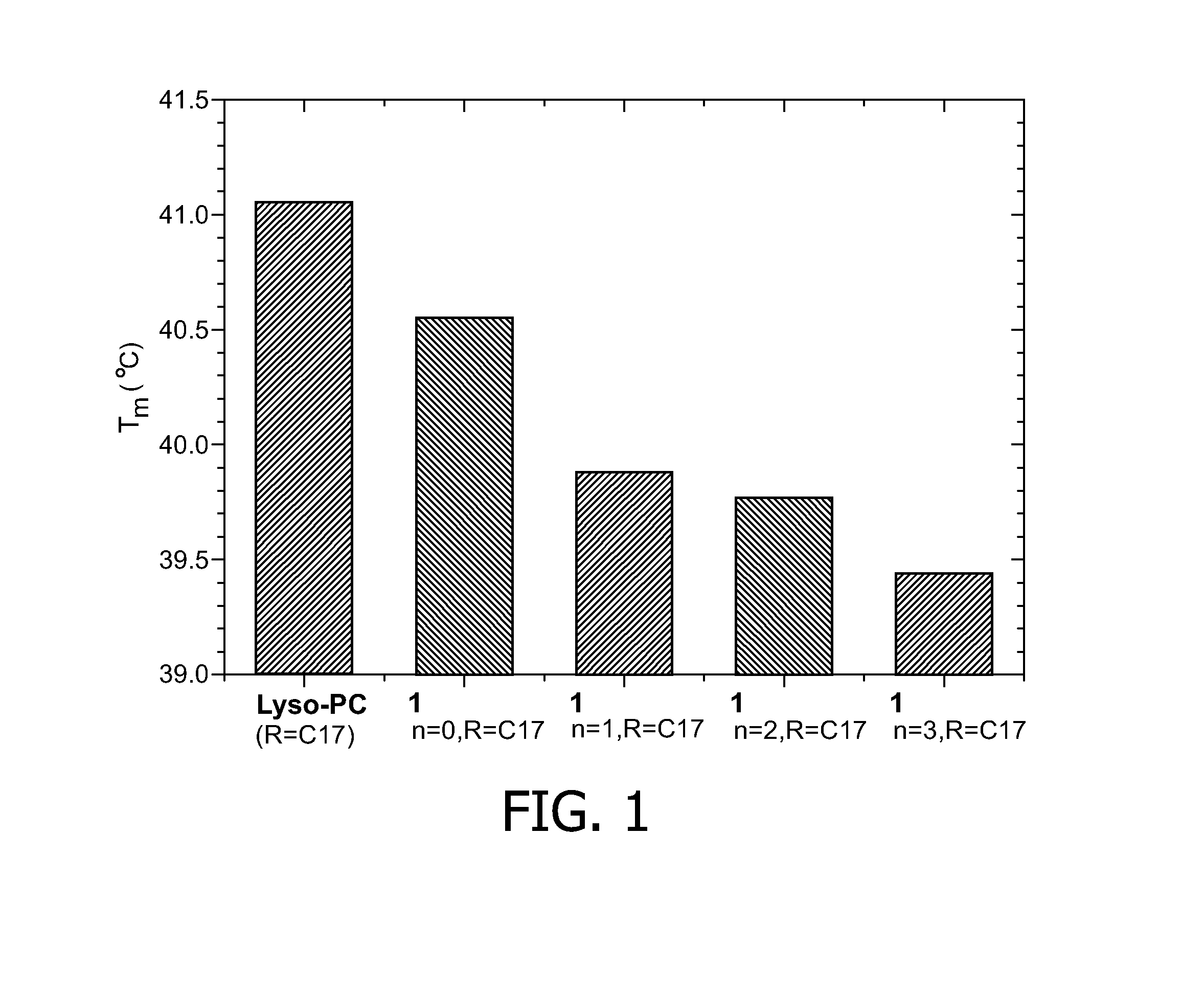
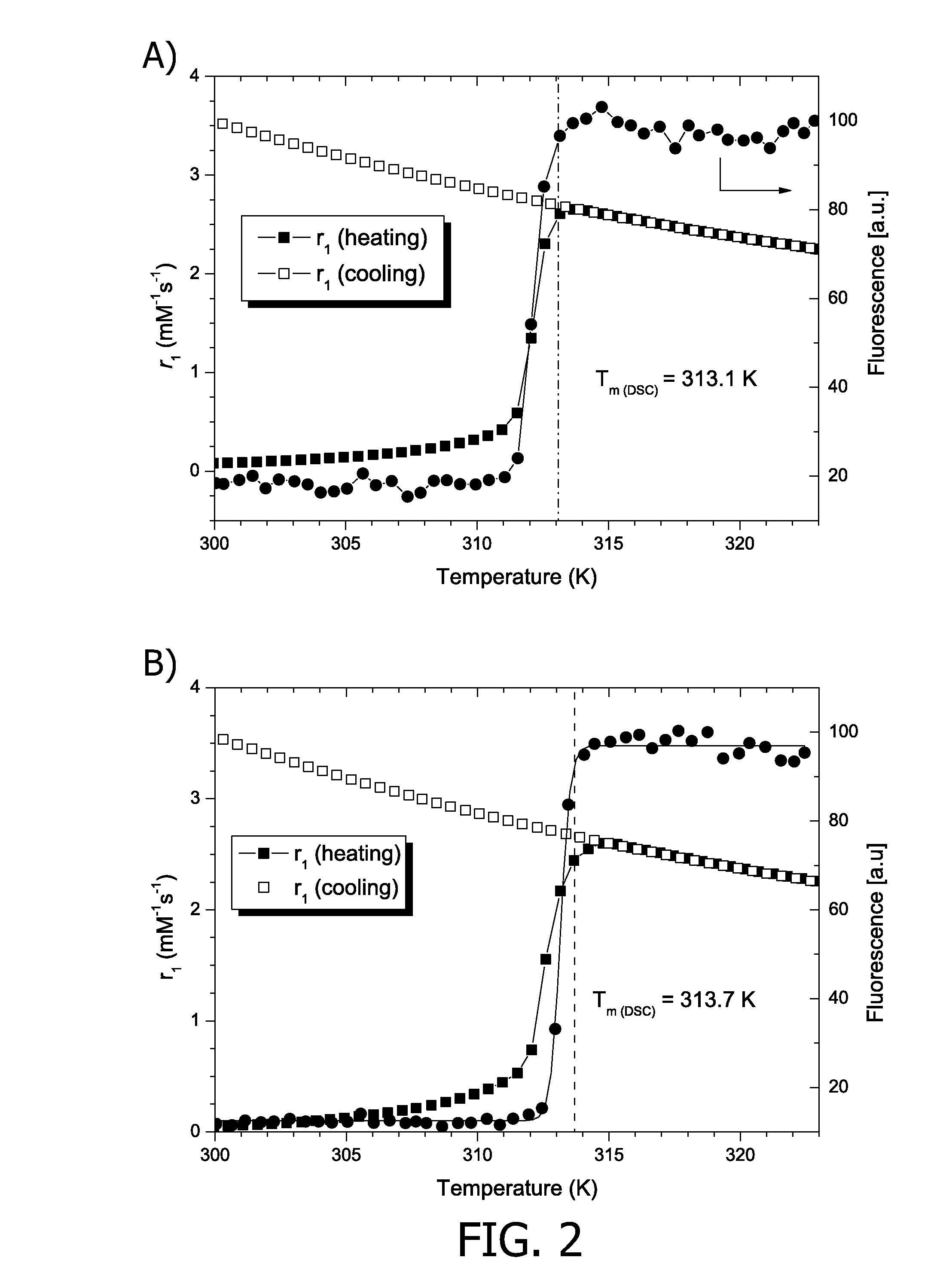
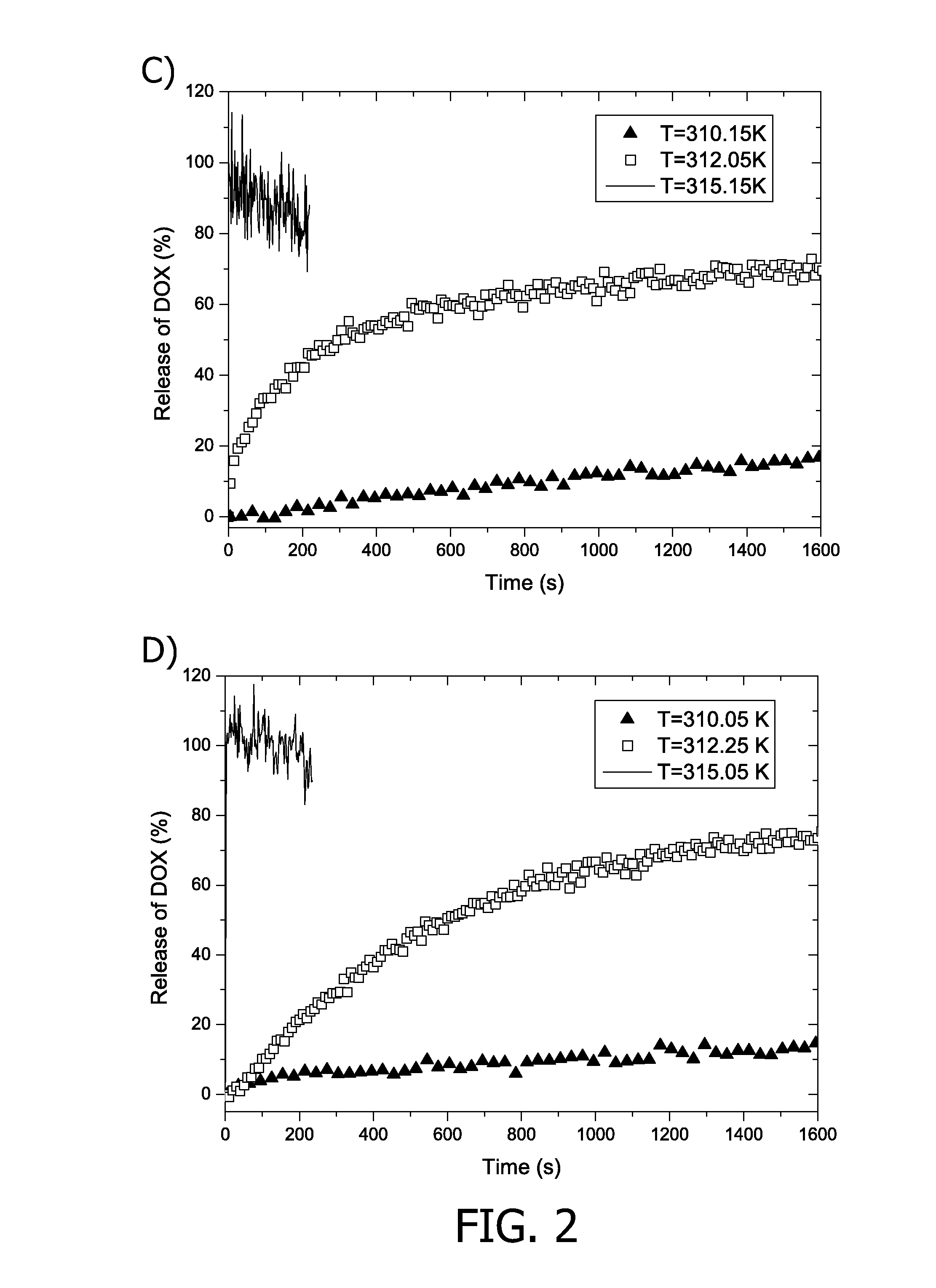
Disclosed are carriers for drugs and / or MR imaging agents having a lipid bilayer shell comprising a phospholipid having two terminal alkyl chains, one being a short chain having a chain length of at most seven carbon atoms, the other being a long chain having a chain length of at least fifteen carbon atoms. The mixed long / short chain phospholipids serve to tune the release properties of the carrier. Preferred phospholipids are phosphatidylcholines.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Coatings for implantable medical devices for liposome delivery
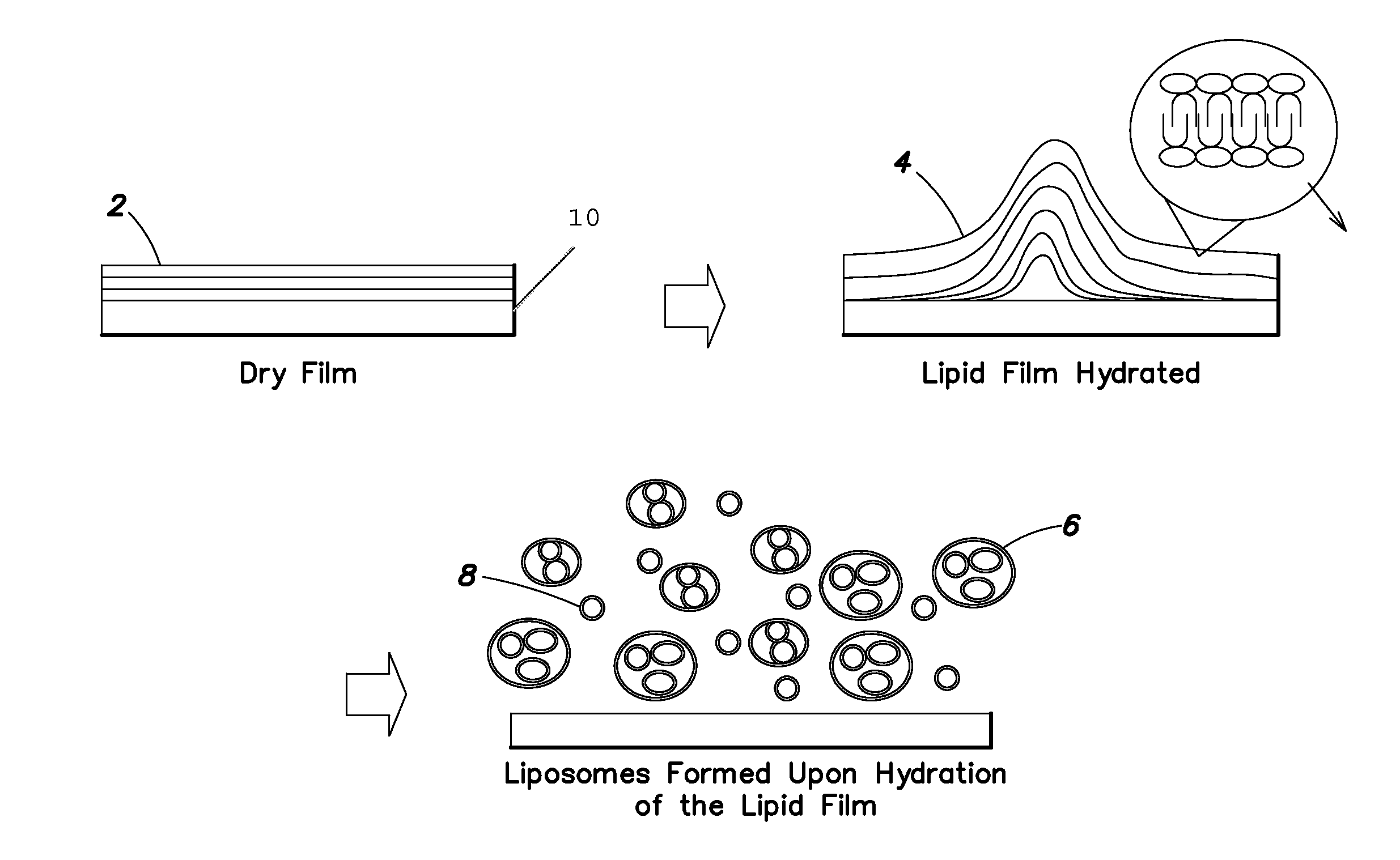
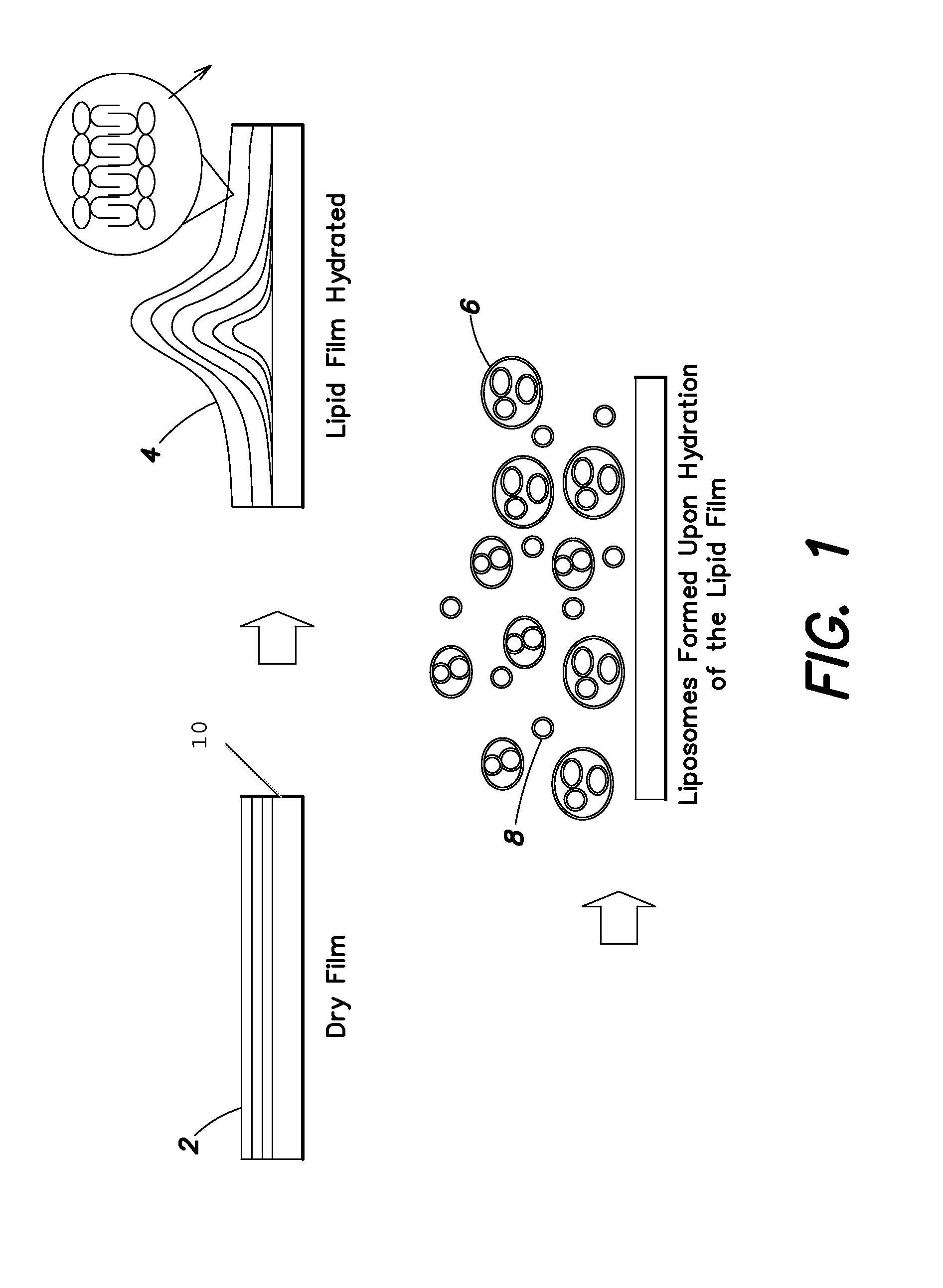
Disclosed herein are medical devices, such as implantable medical devices (e.g., stents), comprising at least one coating covering at least a portion of the device comprising dry film. The dry film comprises at least one lipid bilayer and at least one pharmaceutically effective agent. Upon exposure to an aqueous fluid, liposomes are released comprising lipids from the dry film encapsulating the pharmaceutically effective agent. The film can contact the device directly or can be coated on a substrate, such as a ceramic.
Owner:MIV SCI HLDG
Modular targeted liposomal delivery system
InactiveUS7060291B1Improve abilitiesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBiocideLipid bilayerOrganic chemistry
A liposome including a fusogenic liposome, a linking moiety and a targeting moiety. The fusogenic liposome is a lipid bilayer encapsulating contents. The linking moiety is electrostatically bound to the lipid bilayer, and the targeting moiety is covalently bound to the linking moiety. The liposome may also include a stabilizing moiety interposed between the linking and targeting moieties, and covalently bound to both. Alternatively, the stabilizing and targeting moieties may be covalently bound to separate linking moieties, the linking moieties being electrostatically bound to the lipid bilayer.
Owner:TRANSAVE
Porous nanoparticle supported lipid bilayer nanostructures
ActiveUS20110268791A1Low release rateFacilitated releaseOrganic active ingredientsHeavy metal active ingredientsNanoparticleLipid bilayer
Various exemplary embodiments provide protocell nanostructures and methods for constructing and using the protocell nanostructures. In one embodiment, the protocell nanostructures can include a core-shell structure including a porous particle core surrounded by a shell of lipid bilayer(s). The protocell can be internalized in a bioactive cell. Various cargo components, for example, drugs, can be loaded in and released from the porous particle core of the protocell(s) and then delivered within the bioactive cell.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC +1
Lactobacillus plantarum ZJ316, procreant antibiotic peptides, preparation and use thereof
ActiveCN101353633ABroad-spectrum antibacterialHigh potential for application developmentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFecesAntibiotic Y
The invention provides a lactobacillus plantarum ZJ316 which is separated from excrement of infants and anti-bacterial peptide which is produced by the fermentation of the lactobacillus plantarum ZJ316, namely plantaricin ZJ316, and preparation and application thereof; the plantaricin ZJ316 is a novel lactobacillus anti-bacterial peptide with high efficiency and small molecular; the anti-bacterial peptide has bacteriostatic action of broad spectrum; due to small molecular weight, a lipid bilayer is hard to be crossed so as to form a complex body with small holes to be different from the action mode of nisin; but the anti-bacterial peptide also has sterilizing capacity with high efficiency, is a lantibiotic anti-bacterial peptide with superhigh application and development potential and can be applied to preparing the alternative medicine of feed additives, food preservatives and antibiotic, etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
Cell Transport Compositions and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20150290132A1Reduce deliveryPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsDiketopiperazinesImmune Stimulation
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
Lipidosome-polymer drug-loaded nanoparticle and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106177986AImprove tumor targetingImprove anti-tumor effectAntibody ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsPlatelet inhibitorsBlood vessel
The invention provides a lipidosome-polymer drug-loaded nanoparticle and a preparation method and application thereof. The lipidosome-polymer drug-loaded nanoparticle comprises a three-layer structure, wherein the innermost layer is the drug-loaded nanoparticles formed by taking an amphiphilic cationic polymer as a carrier-coated chemotherapeutic drug; the intermediate layer is a platelet inhibitor layer adsorbed onto the surface of the drug-loaded nanoparticles; and the outermost layer is a lipid bilayer connected with tumor microenvironment responsiveness polypeptides. The lipidosome-polymer drug-loaded nanoparticle disclosed by the invention is capable of specifically targeting tumor tissues, has tumor microenvironment responsiveness, and can achieve the effects of improving tumor vascular permeability without influencing functions of blood vessels at normal tissue or cell parts, enhancing permeability and retention of the drug-loaded nanoparticles to tumor cells, enhancing the EPR effect, improving enrichment of the drug-loaded nanoparticles at tumor location and realizing high tumor killing efficiency.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Liposome composition for delivery of therapeutic agents
InactiveUS20050191344A1Extended circulation timeProlong blood circulation timePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsNon-active genetic ingredientsLipid formationSolubility
A neutral cationic lipid and liposomes prepared from the neutral cationic lipid are described. Liposomes comprised of the lipid are suitable for delivery of a polyanionic compound, such as a nucleic acid. The delivery can be performed in vivo or ex vivo. The neutral cationic lipid, which is neutral in charge at physiologic pH and positively charged at pH values less than physiologic pH, contains a polar head group that imparts solubility of the lipid and permits its packing into a liposomal lipid bilayer.
Owner:ALZA CORP
Polymeric assay film for direct colorimetric detection
InactiveUS6395561B1Limited applicabilityMaintain its infectivityMaterial nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteDrug development
A lipid bilayer with affinity to an analyte, which directly signals binding by a changes in the light absorption spectra. This novel assay means and method has special applications in the drug development and medical testing fields. Using a spectrometer, the system is easily automated, and a multiple well embodiment allows inexpensive screening and sequential testing. This invention also has applications in industry for feedstock and effluent monitoring.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Porous nanoparticle-supported lipid bilayers (protocells) for targeted delivery including transdermal delivery of cargo and methods thereof
InactiveUS20150272885A1Large specific surface areaAmenable to high capacity loadingOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryCancers diagnosisBinding peptide
The present invention is directed to protocells for specific targeting of hepatocellular and other cancer cells which comprise a nanoporous silica core with a supported lipid bilayer; at least one agent which facilitates cancer cell death (such as a traditional small molecule, a macromolecular cargo (e.g. siRNA or a protein toxin such as ricin toxin A-chain or diphtheria toxin A-chain) and / or a histone-packaged plasmid DNA disposed within the nanoporous silica core (preferably supercoiled in order to more efficiently package the DNA into protocells) which is optionally modified with a nuclear localization sequence to assist in localizing protocells within the nucleus of the cancer cell and the ability to express peptides involved in therapy (apoptosis / cell death) of the cancer cell or as a reporter, a targeting peptide which targets cancer cells in tissue to be treated such that binding of the protocell to the targeted cells is specific and enhanced and a fusogenic peptide that promotes endosomal escape of protocells and encapsulated DNA. Protocells according to the present invention may be used to treat cancer, especially including hepatocellular (liver) cancer using novel binding peptides (c-MET peptides) which selectively bind to hepatocellular tissue or to function in diagnosis of cancer, including cancer treatment and drug discovery.
Owner:STC UNM +1
Membrane for filtering of water
InactiveUS7857978B2Improve concentrationCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsGeneral water supply conservationLipid formationHydrophobic polymer
Owner:AQUAPORIN AS
Compound polypeptide nanometer vesicles with skin repair function and preparing method and application thereof
InactiveCN109875910AWith skin repair functionImproves anti-inflammationCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsSkin penetrationCholesterol
The invention provides compound polypeptide nanometer vesicles with a skin repair function, and belongs to the technical field of cosmetics. The compound polypeptide nanometer vesicles are prepared from, by weight, 0.01-1 part of regenerated repairing active peptide, 0.01-1 part of antioxidant active peptide, 0.1-5 parts of natural moisturizing active factors, 0.01-1 part of microcirculation-promoting active ingredients, 5-20 parts of lipoid wall materials, 0.1-5 parts of cholesterol, 10-45 parts of polyhydric alcohols and 30-98 parts of water. According to the compound polypeptide nanometer vesicles, repairing components acting on different target spots are provided aiming at different repair mechanisms of the skin barrier; meanwhile, the nanometer vesicles are adopted for covering various hydrophilic and lipophilic active ingredients, a unique closed lipid bilayer structure of the vesicles is utilized, the stability of the repairing compound is significantly improved, the skin penetration amount is increased, slow release of the active ingredients is effectively controlled, and the repairing effect is improved.
Owner:WUHAN BEST CARRIER NANO TECH
Liposomes comprising a calcium phosphate-containing precipitate
ActiveUS20120201872A1Improve efficiencyMinimize ToxicityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseCalcium biphosphate
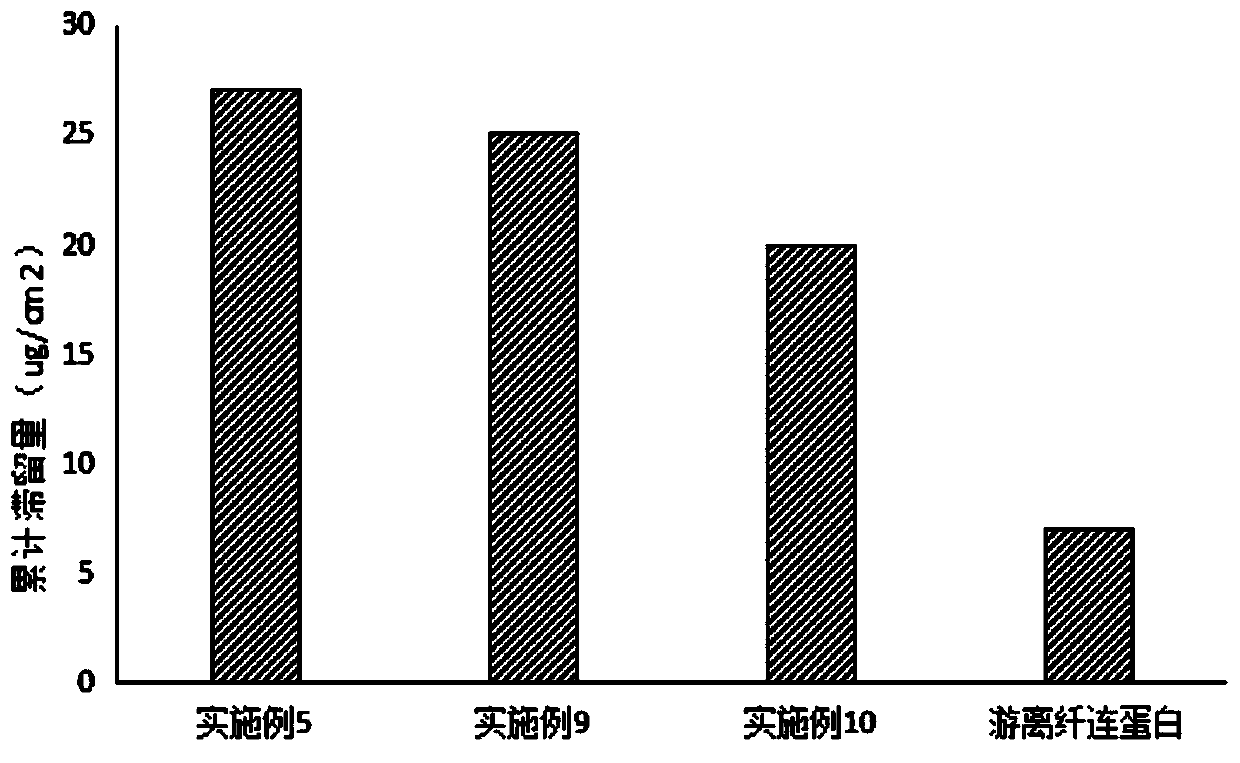
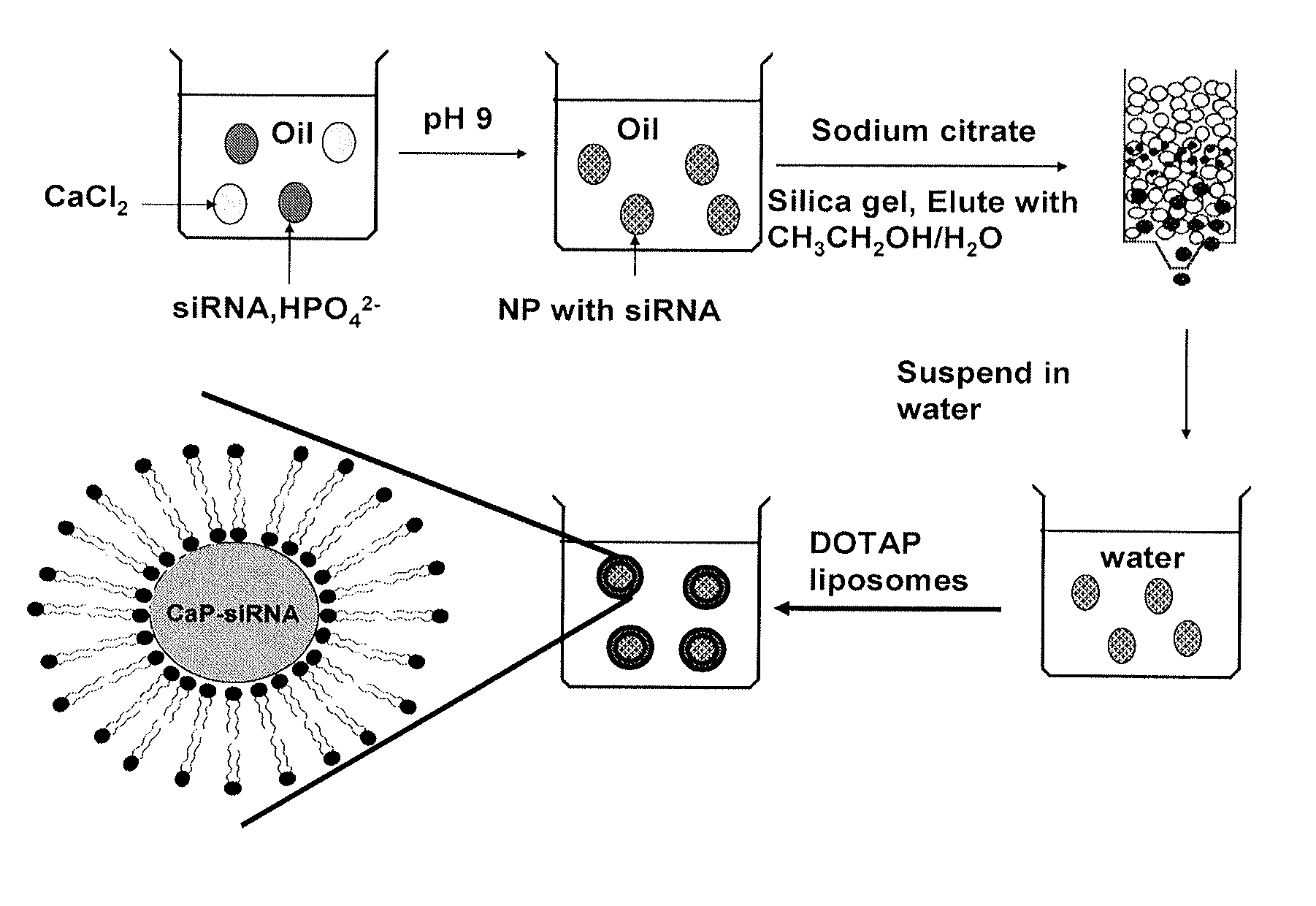
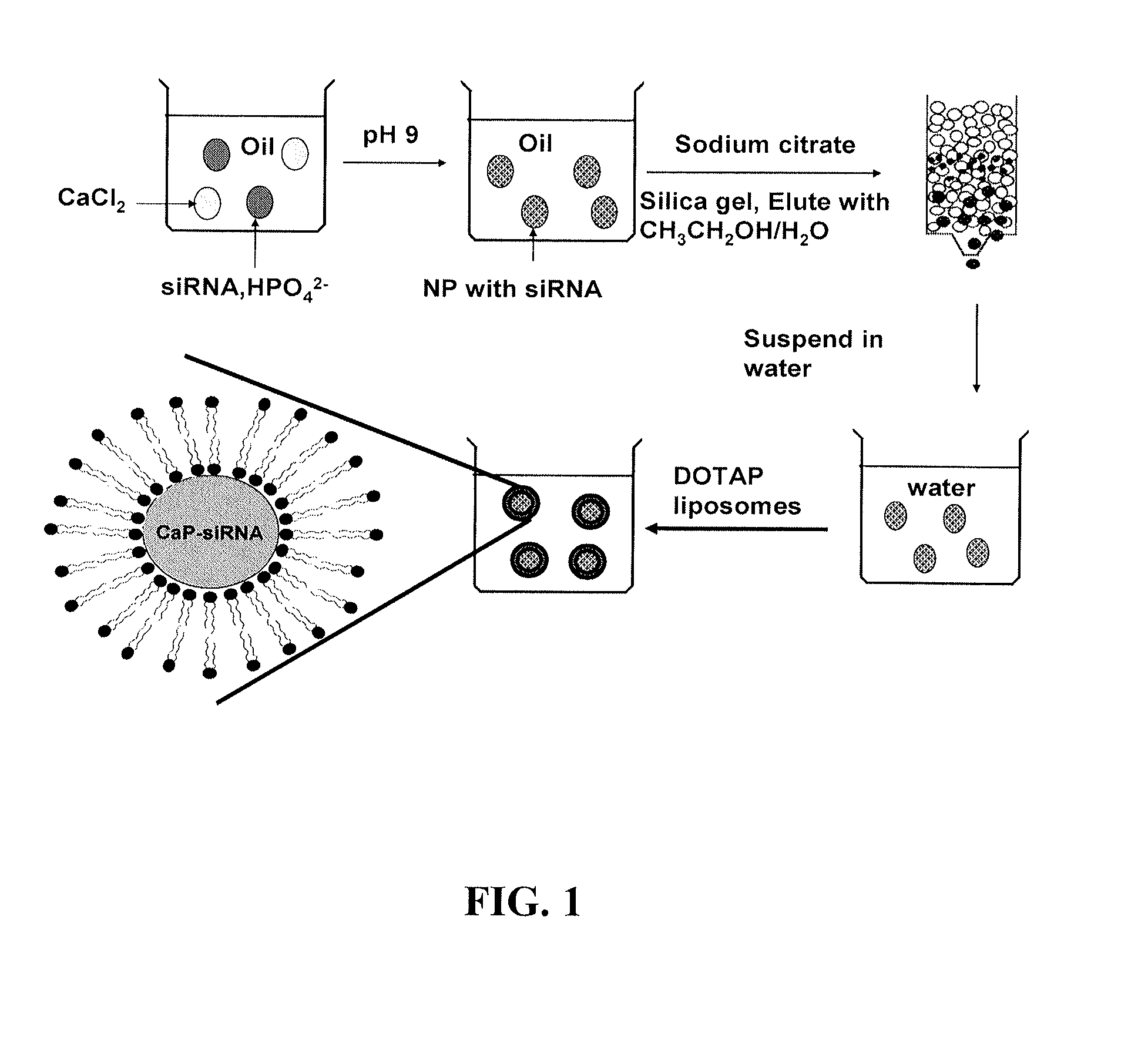
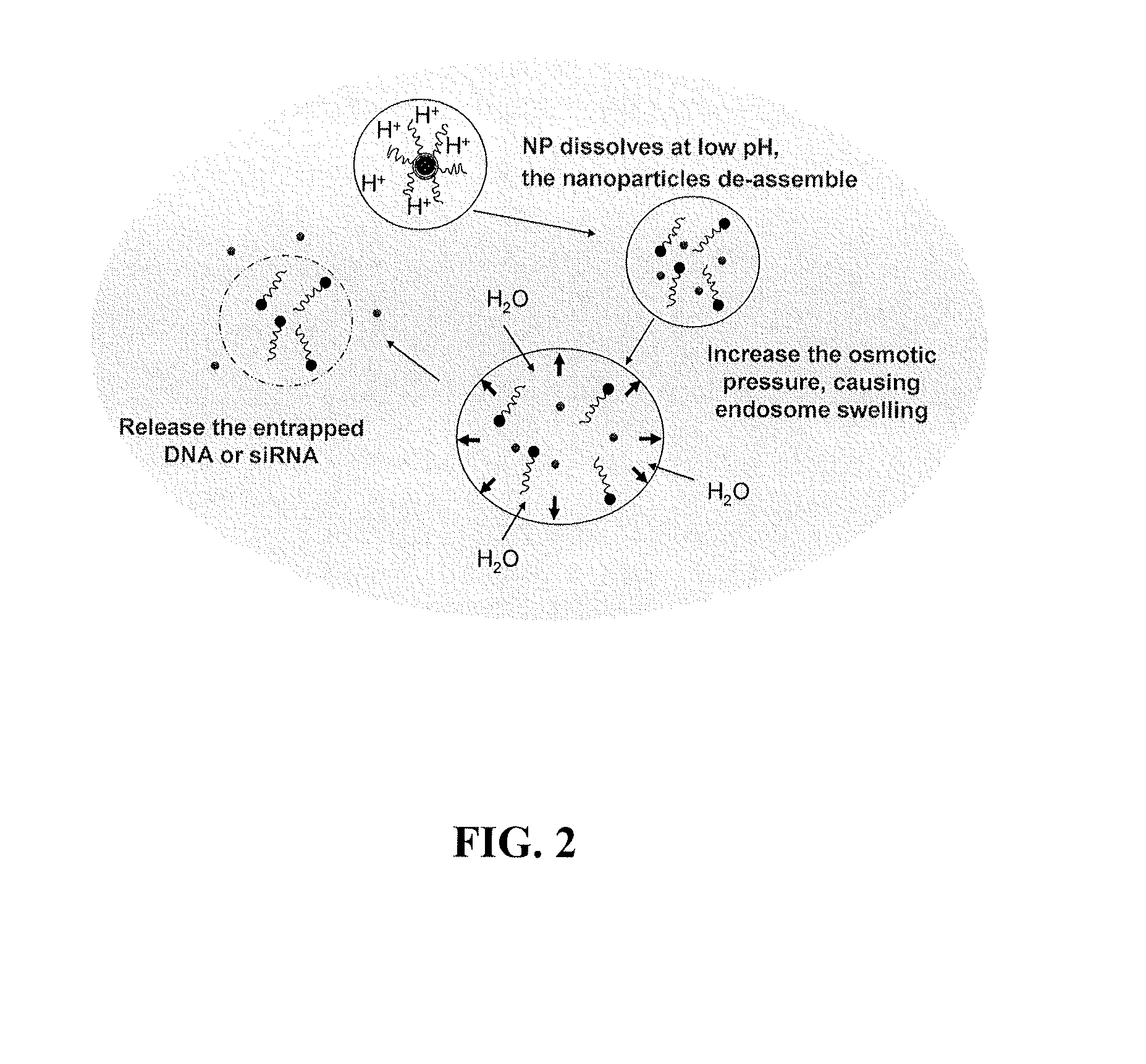
Provided herein are methods and compositions for the delivery of bioactive compounds to a cell, tissue, or physiological site. The compositions comprise delivery system complexes comprising liposomes encapsulating a biodegradable ionic precipitate having incorporated therein a bioactive compound and delivery system complexes comprising a biodegradable ionic precipitate ionically bound to a surrounding lipid bilayer, wherein the biodegradable ionic precipitate comprises a bioactive compound. Also provided herein are methods for the treatment of a disease or an unwanted condition in a subject, wherein the methods comprise administering the delivery system complexes comprising bioactive compounds that have therapeutic activity against the disease or unwanted condition to the subject.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Nanogels and their production using liposomes as reactors
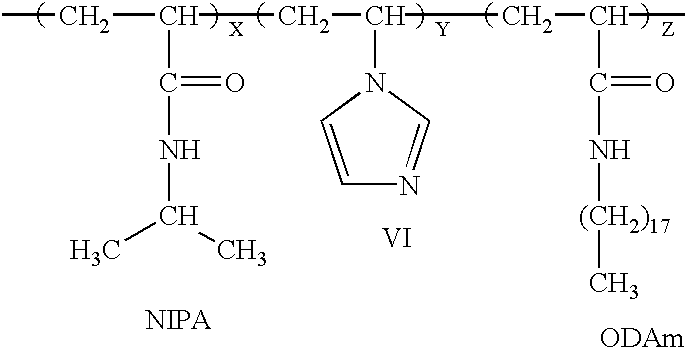
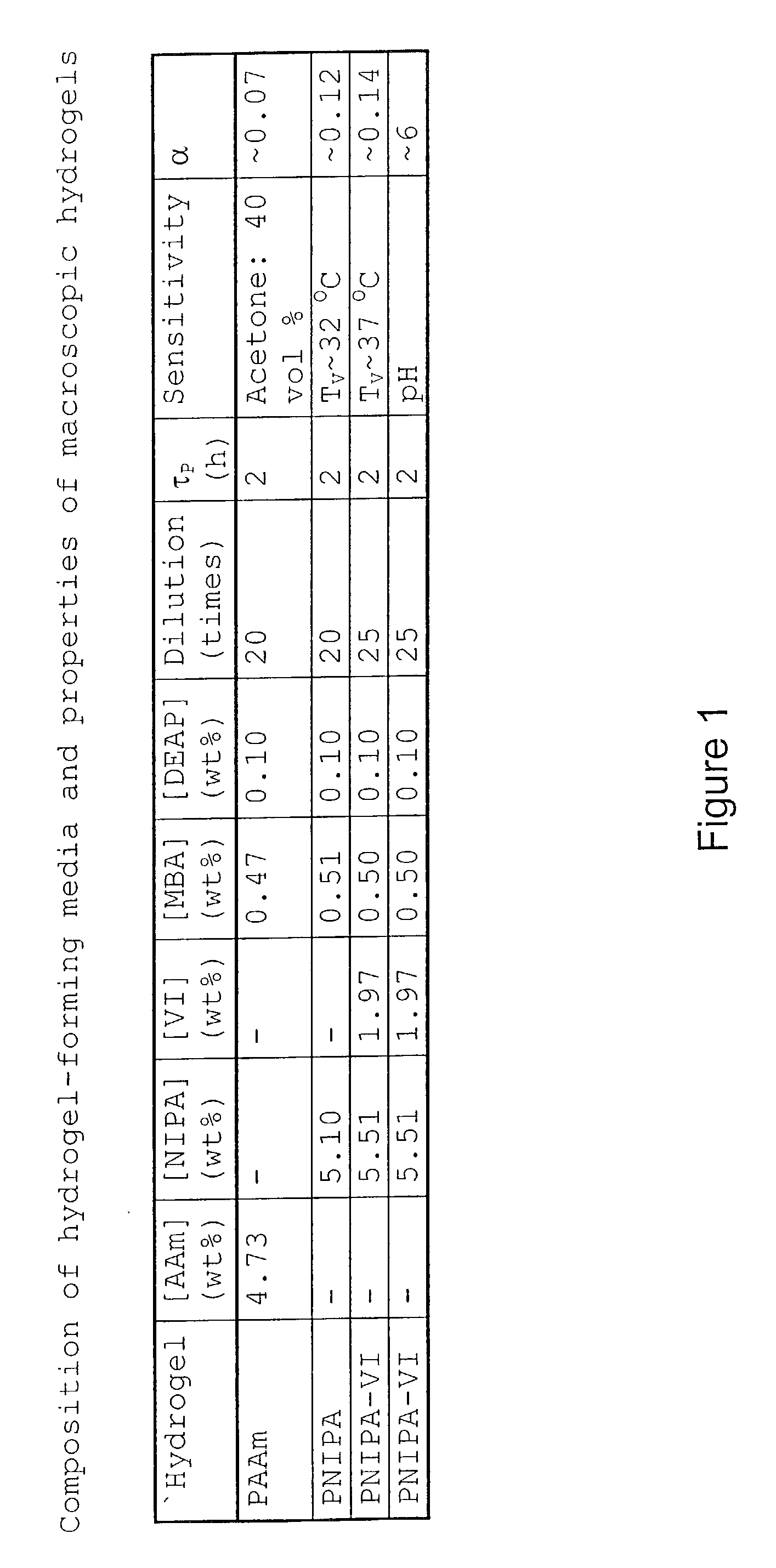
The present invention includes a method for preparing polymer hydrogel spherical particles on a nanometer scale (nanogels). The method includes encapsulating hydrogel-forming components into liposomes, diluting the large unilamellar liposomes suspension to prevent polymerization outside the liposomes, and polymerizing the encapsulated hydrogel-forming components. The lipid bilayer may be solubilized with detergent. The phospholipid and detergent molecules and their micelles may then be removed by dialysis. The resulting nanogels may then be dried by evaporation in a temperature gradient. Poly(acrylamide), poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), and poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-1-vinylimidazole) hydrogel particles with a diameter from 30 to 300 nm were detected and characterized by dynamic light scattering technique. The solvent, temperature, pH, and ionic sensitivities of the nanogels were studied.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Biomimetic membranes, their production and uses thereof in water purification
InactiveUS20110084026A1Prevent crashPromote fermentationSemi-permeable membranesGeneral water supply conservationLipid formationFiltration
The present invention discloses a water membrane comprising a lipid bilayer supported on a single side thereof on a water permeable dense support layer, this lipid bilayer being composed of one or more lipids and aquaporin proteins are embedded therein, further wherein the water permeable dense support layer is impermeable to the lipids and to the aquaporin proteins. Also are provided a method for the preparation of these membranes and uses thereof in water filtration applications.
Owner:B G NEGEV TECH & APPL LTD
Method of forming bilayer membrane by contact between amphipathic monolayers and apparatus therefor
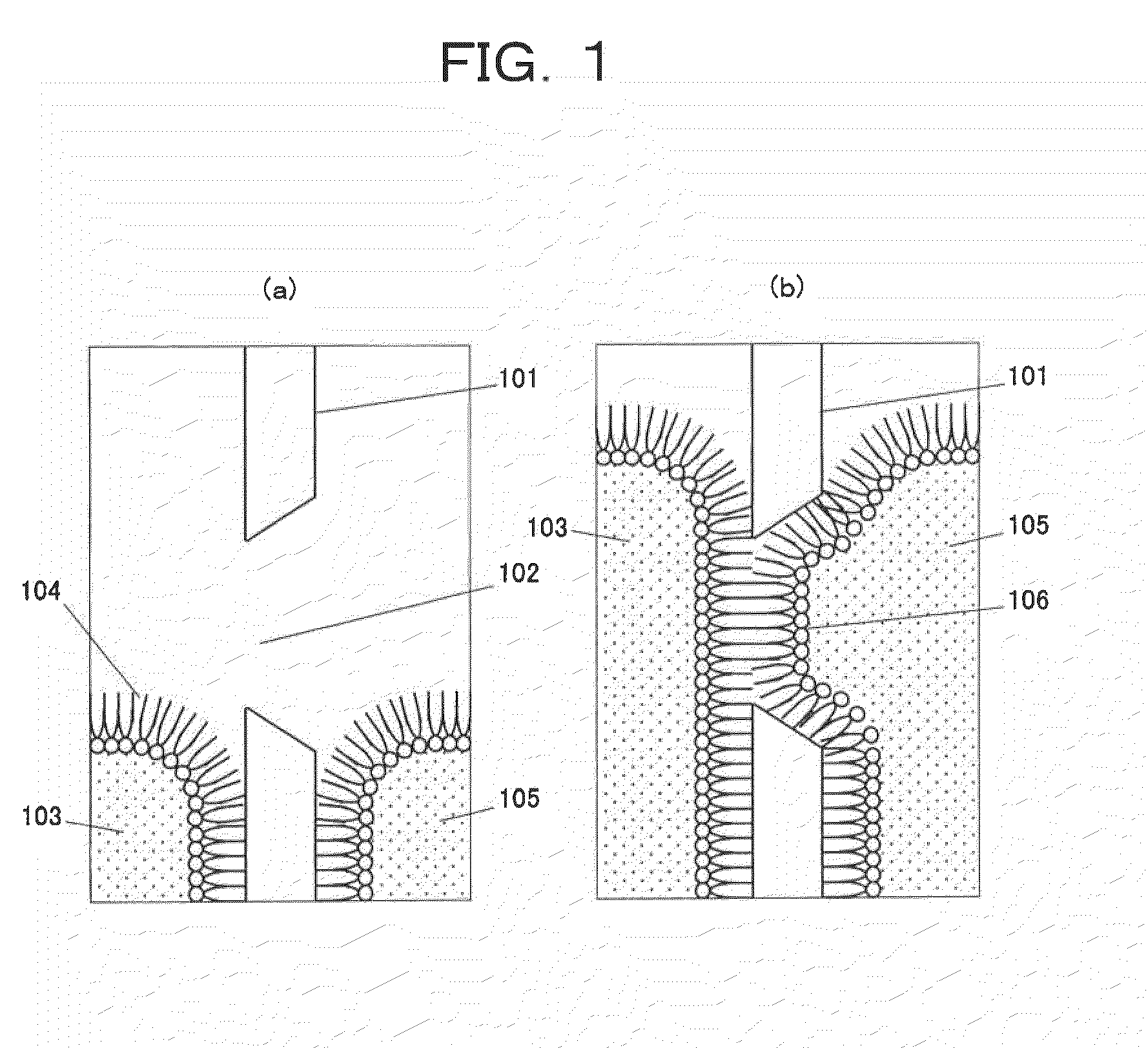
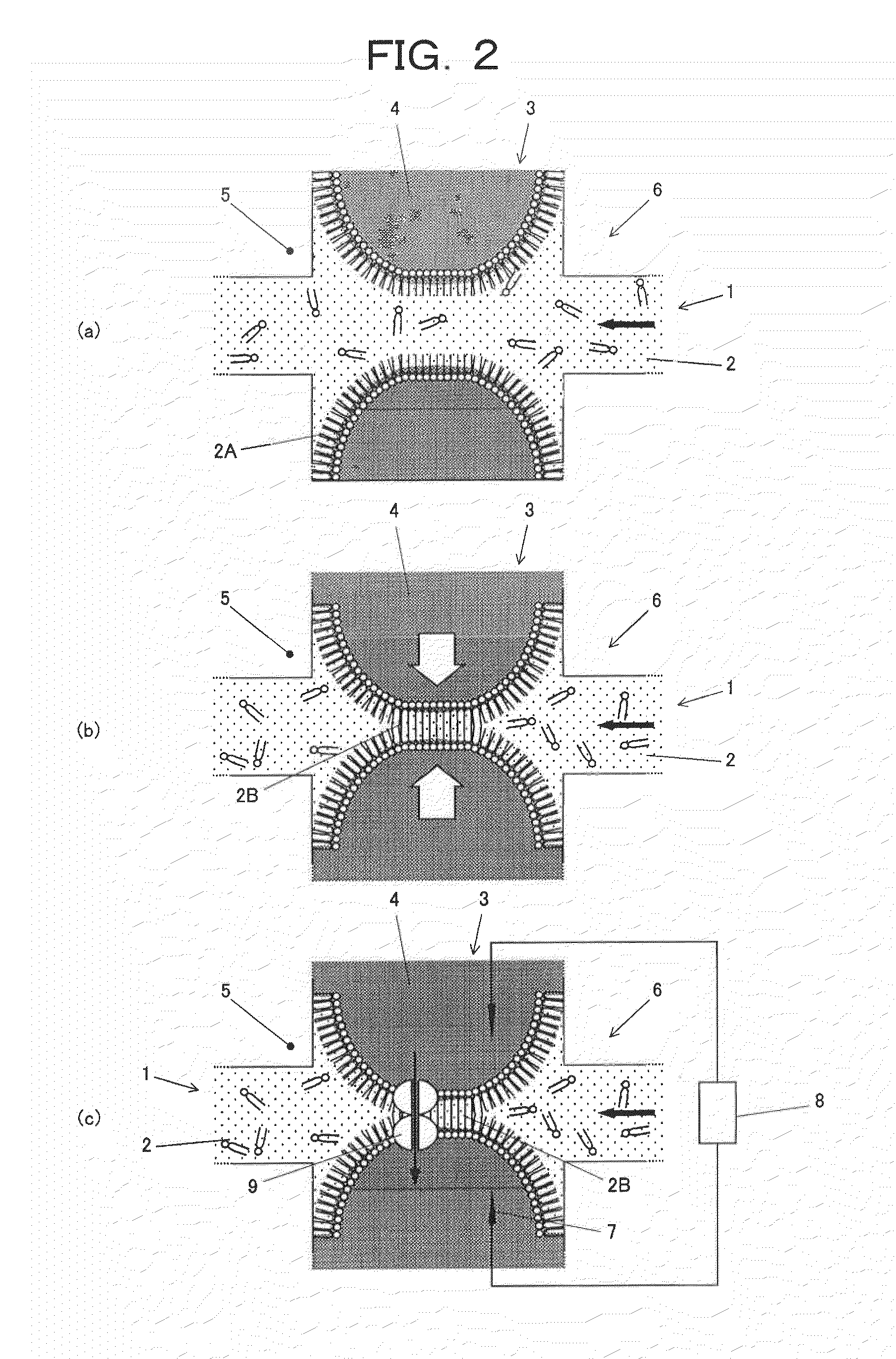
ActiveUS20100147450A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsContact formationLipid formation
The present invention provides a simple and an accurate method of forming a bilayer membrane by the contact of amphipathic monolayers and an apparatus therefor. The method is characterized in that the organic solvent (2) containing lipid molecules is introduced into a first microchannel (1) formed on a substrate (5). A liquid (4) immiscible with the organic solvent (2) containing lipid molecules is introduced into a second microchannel (3), which crosses the first microchannel (1) from both sides to form an intersection, from both ends of the second microchannel (3) toward the intersection. Amphipathic monolayers (2A) opposing each other are formed at the interfaces between the liquid (4) and the organic solvent (2), and finally a lipid bilayer membrane (2B) is obtained by bringing the amphipathic monolayers (2A) into contact and fusing, by the contact of the interfaces of the liquid (4) introduced from the both ends of the second microchannel (3) with the control of the pressure of the liquid (4) using syringe pumps.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com