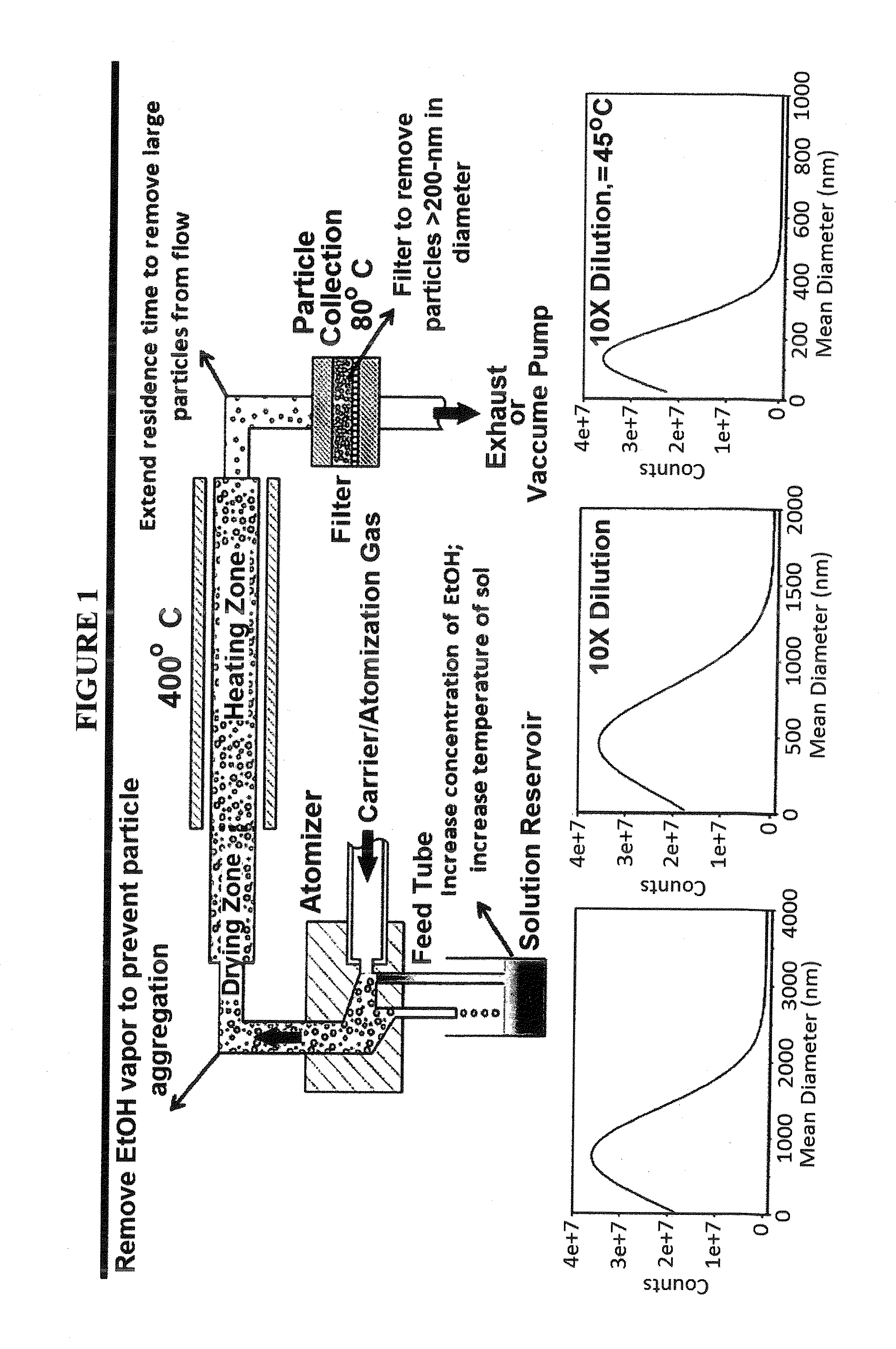
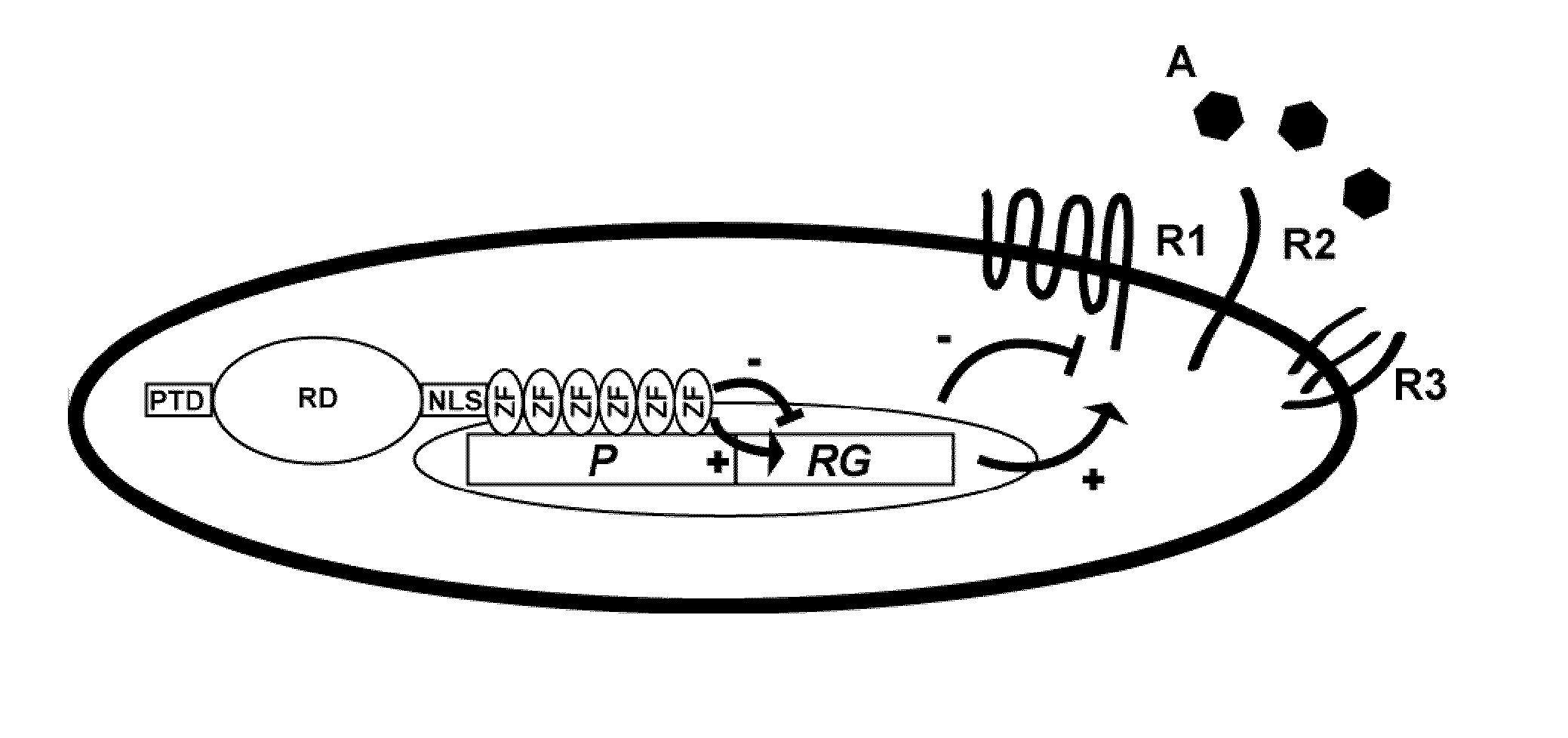
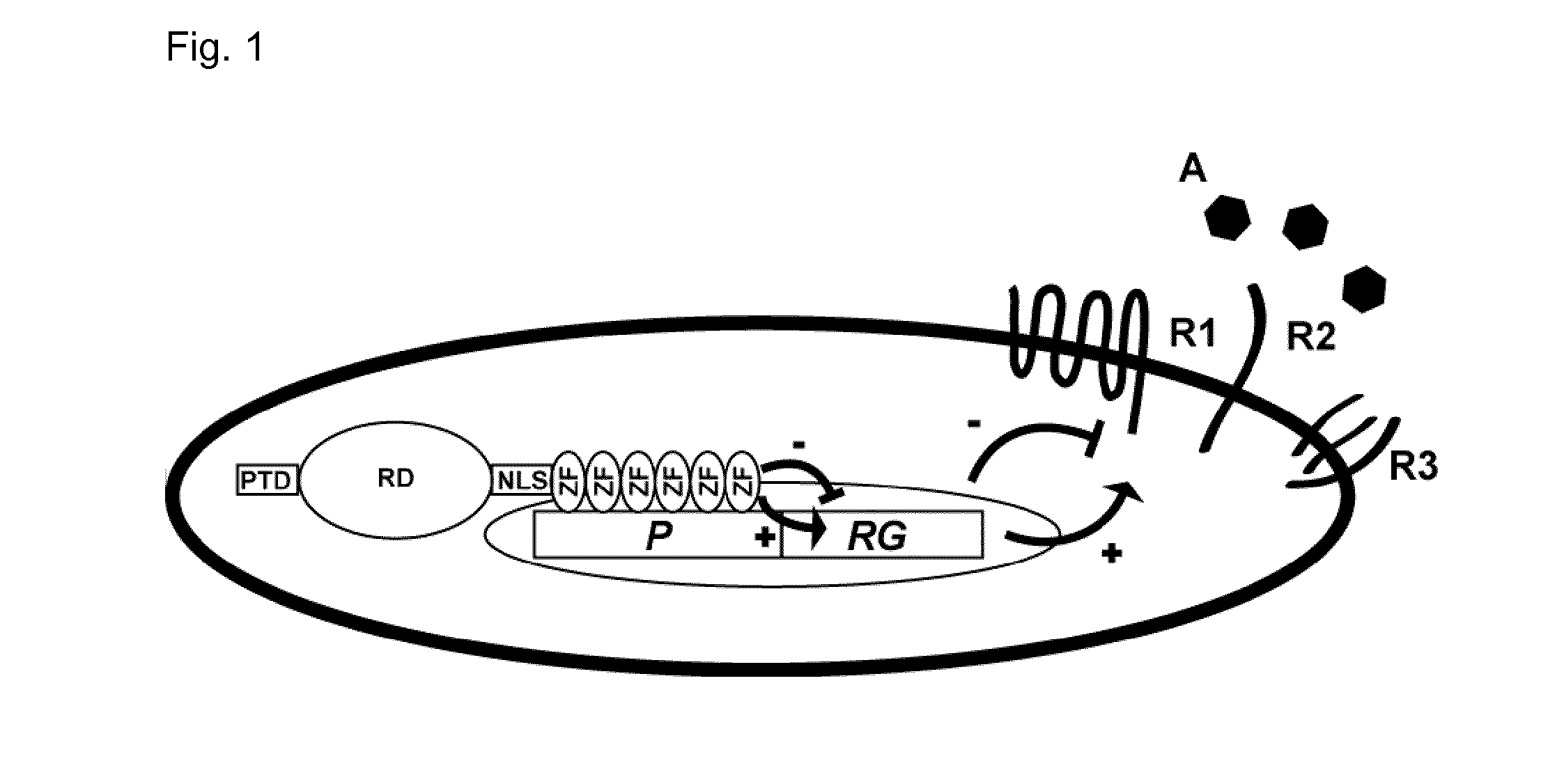
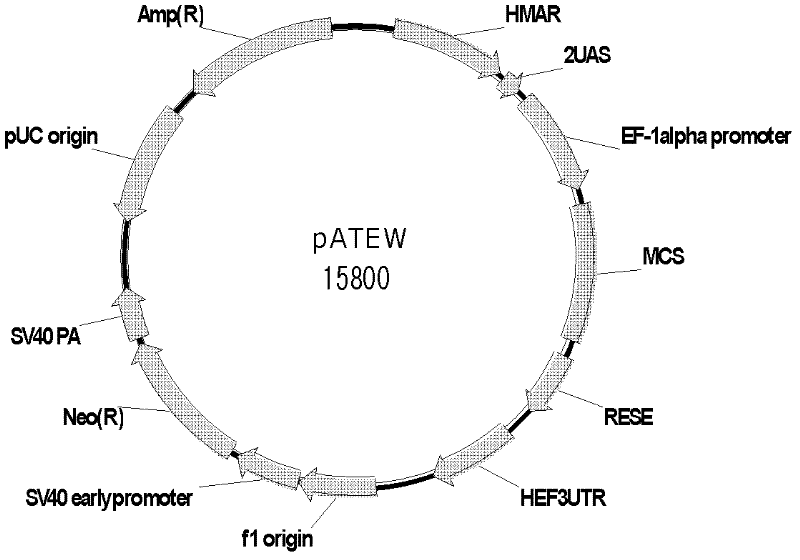
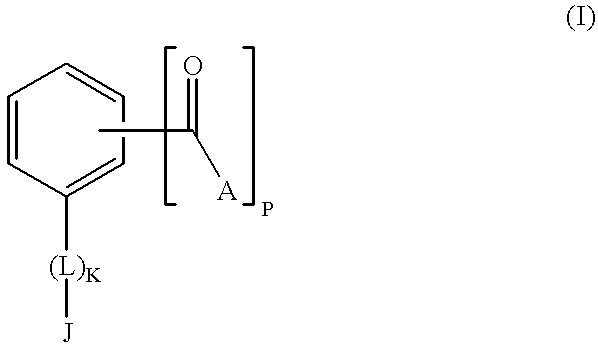Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
59 results about "Nuclear localization sequence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A nuclear localization signal or sequence (NLS) is an amino acid sequence that 'tags' a protein for import into the cell nucleus by nuclear transport. Typically, this signal consists of one or more short sequences of positively charged lysines or arginines exposed on the protein surface. Different nuclear localized proteins may share the same NLS. An NLS has the opposite function of a nuclear export signal (NES), which targets proteins out of the nucleus.
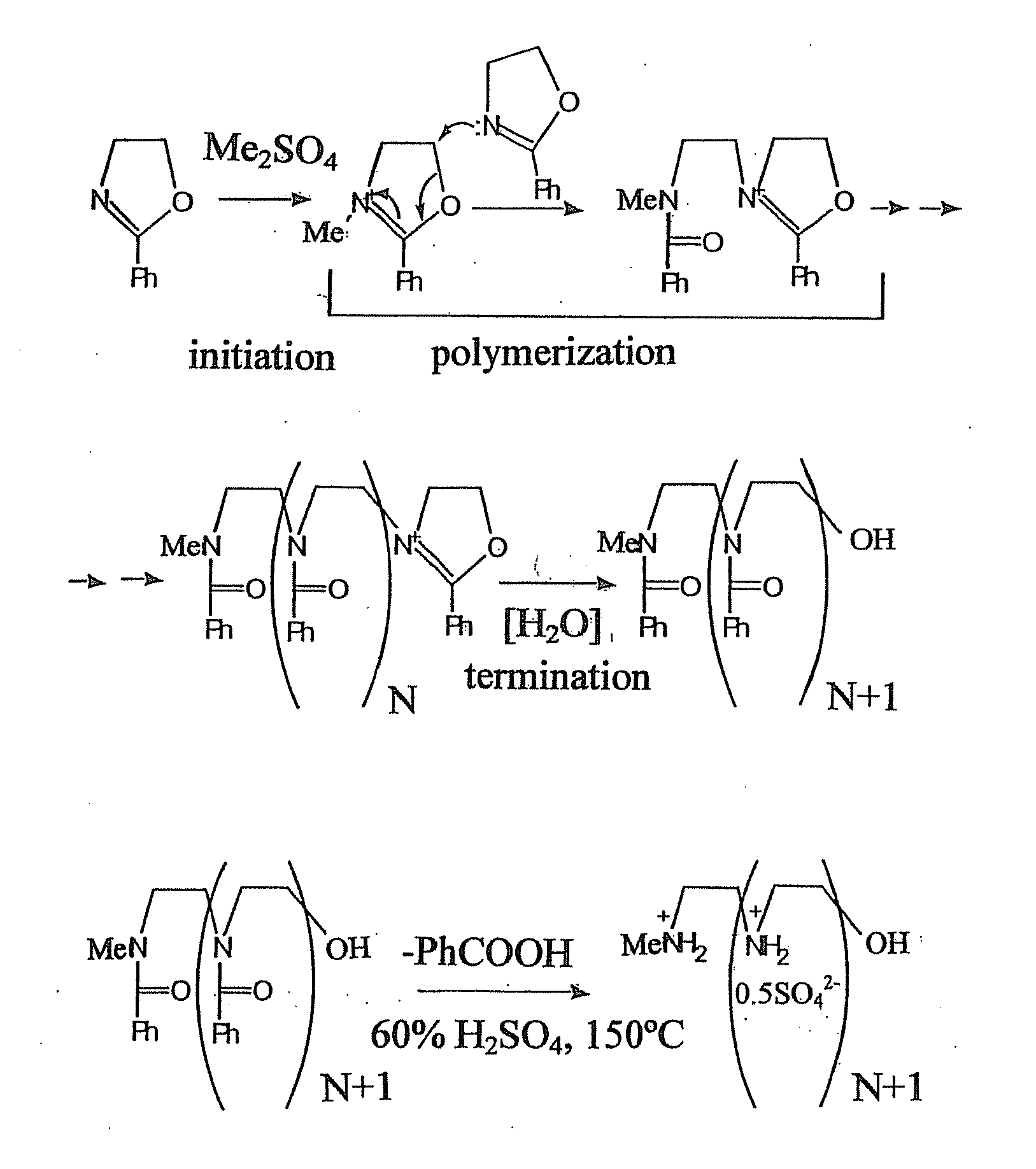
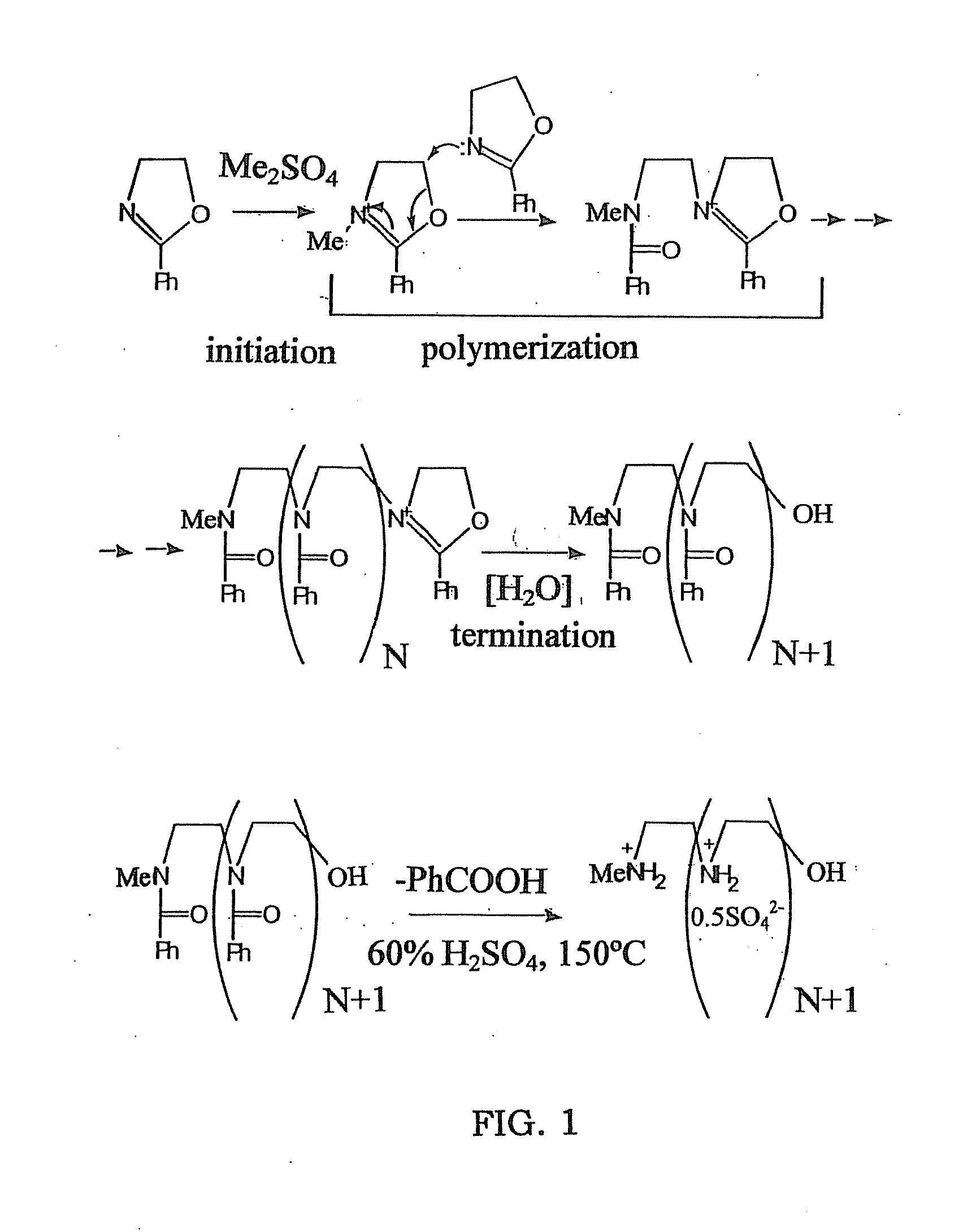
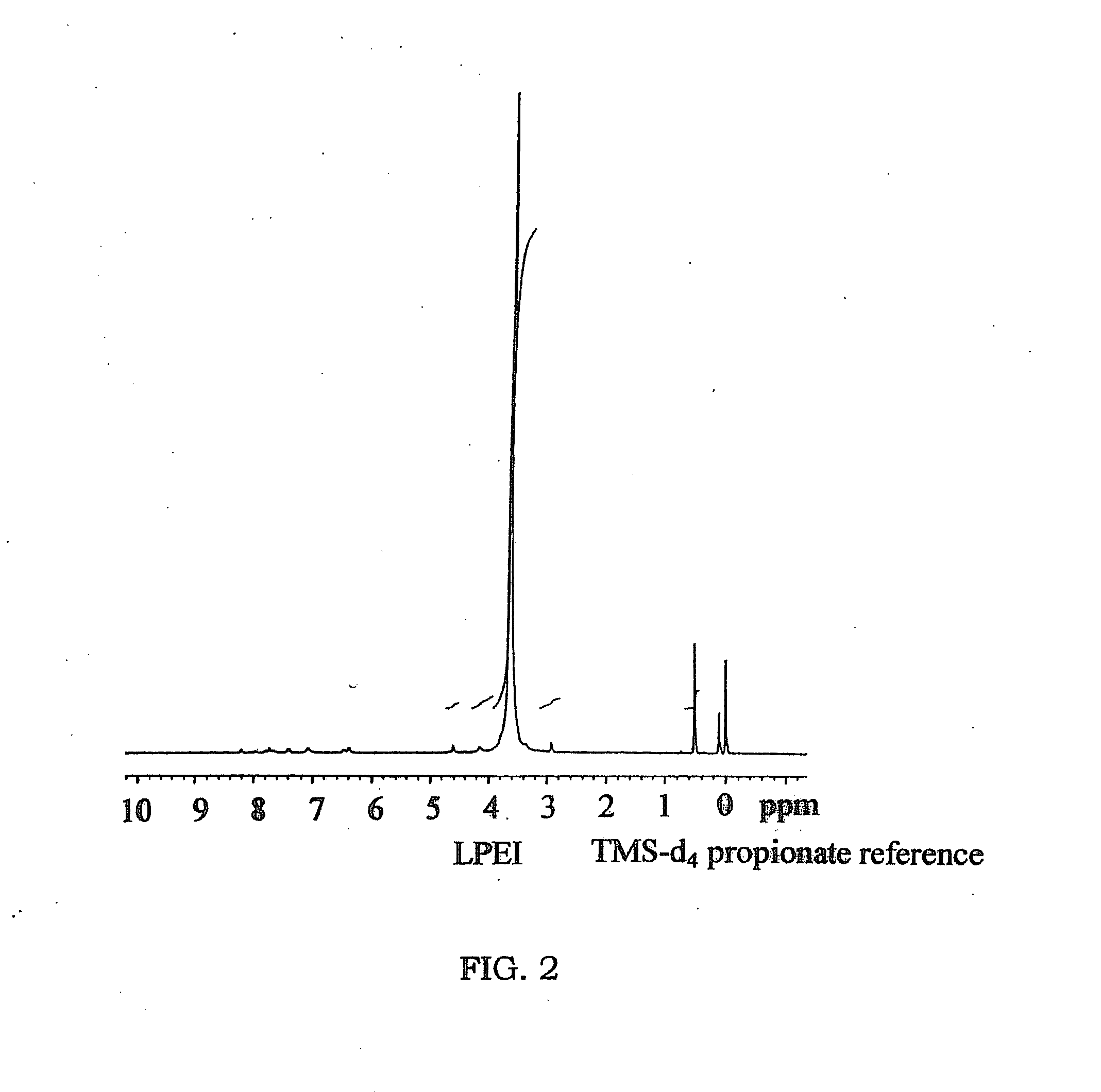
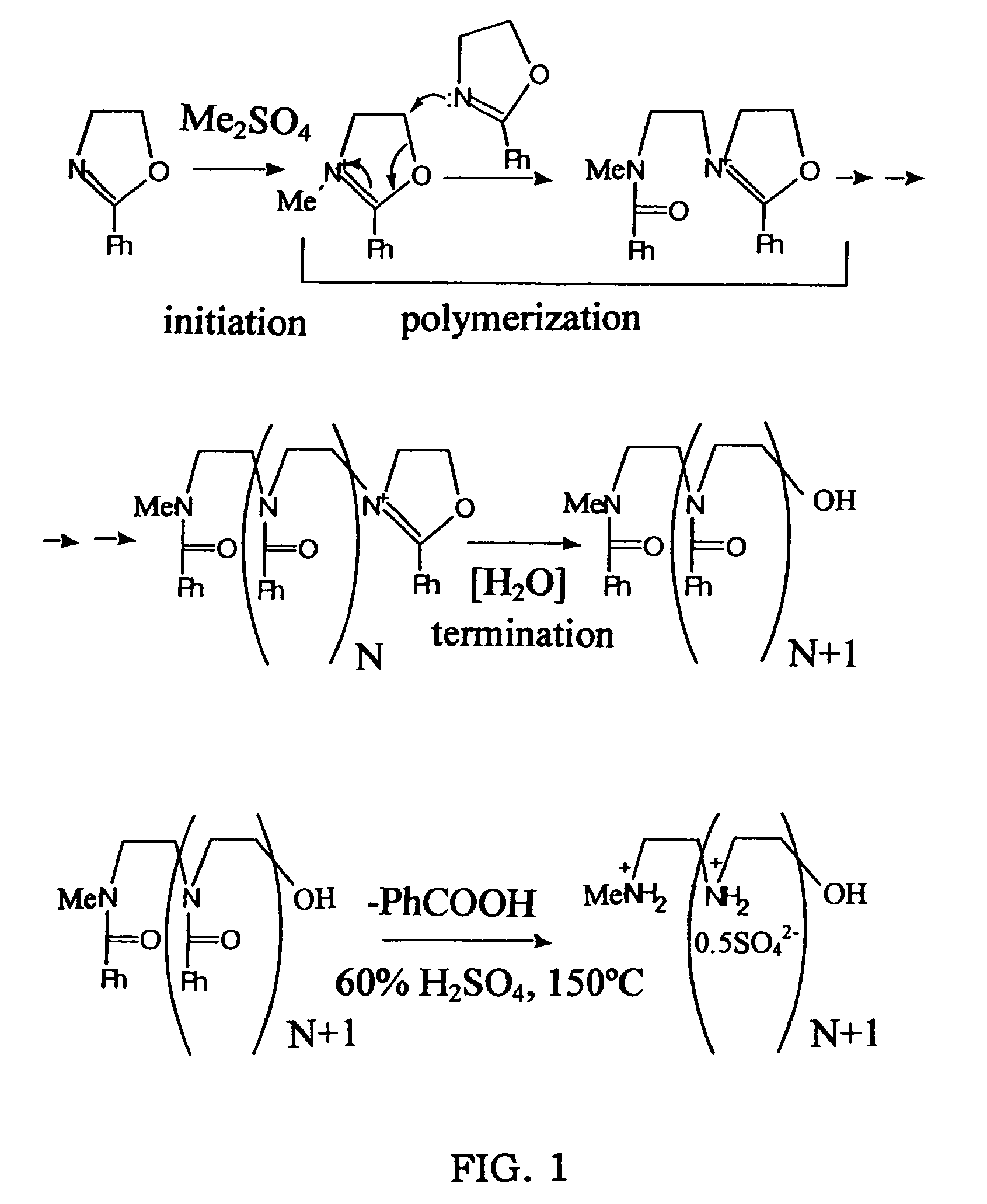
Biodegradable Cross-Linked Cationic Multi-block Copolymers for Gene Delivery and Methods of Making Thereof
ActiveUS20120009145A1Easy to controlGuaranteed effective sizeCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsCross-linkGene delivery
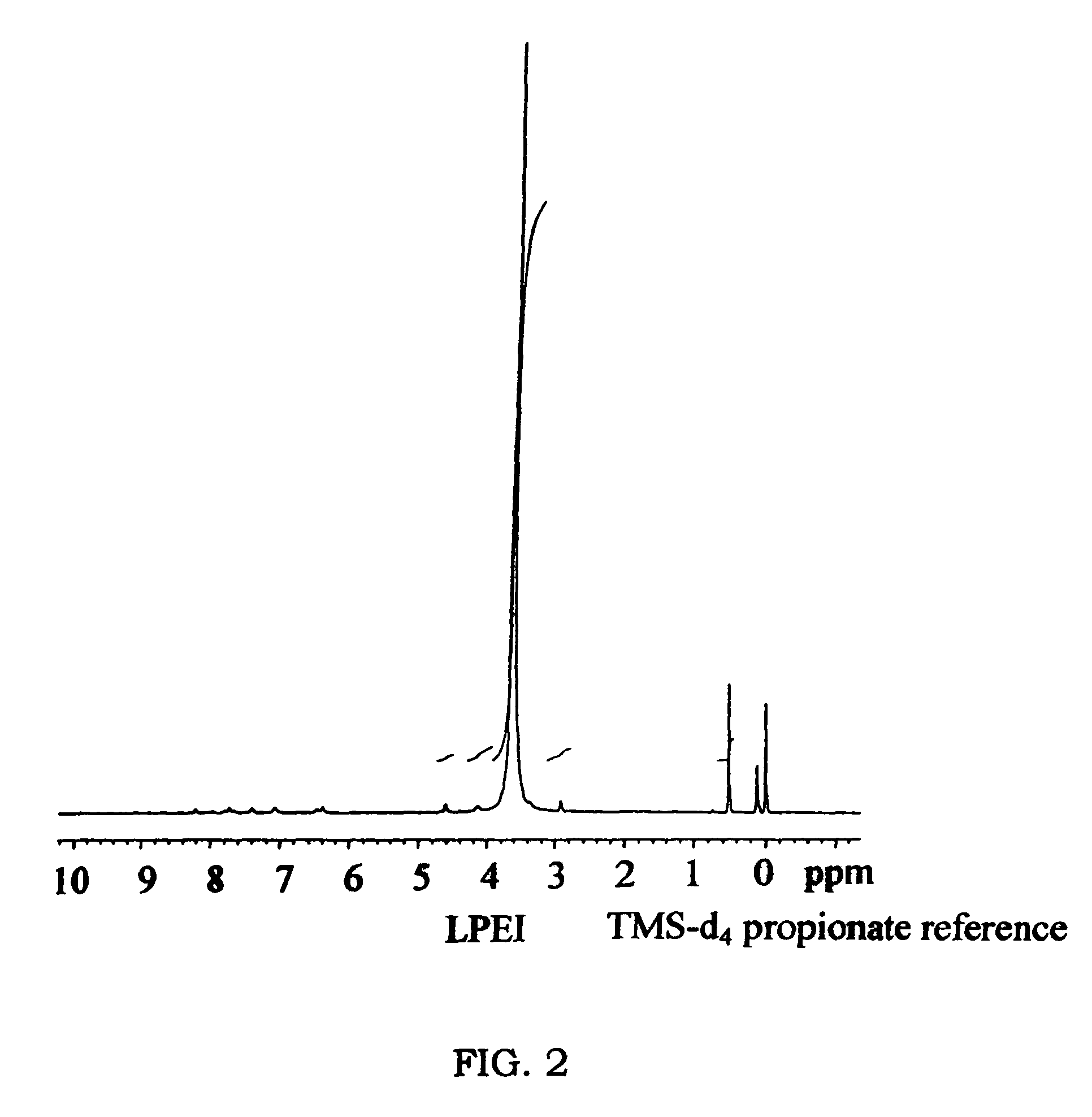
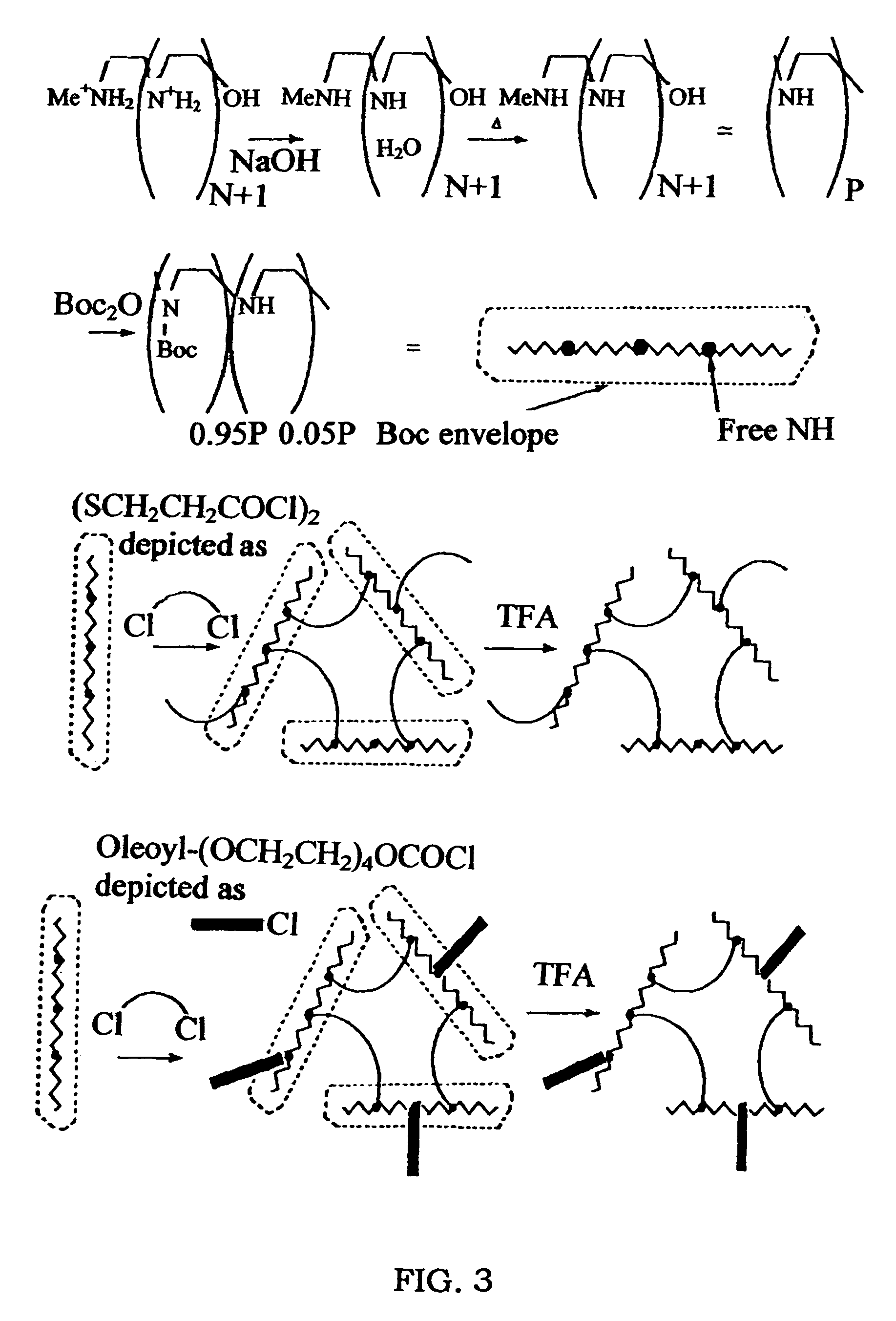
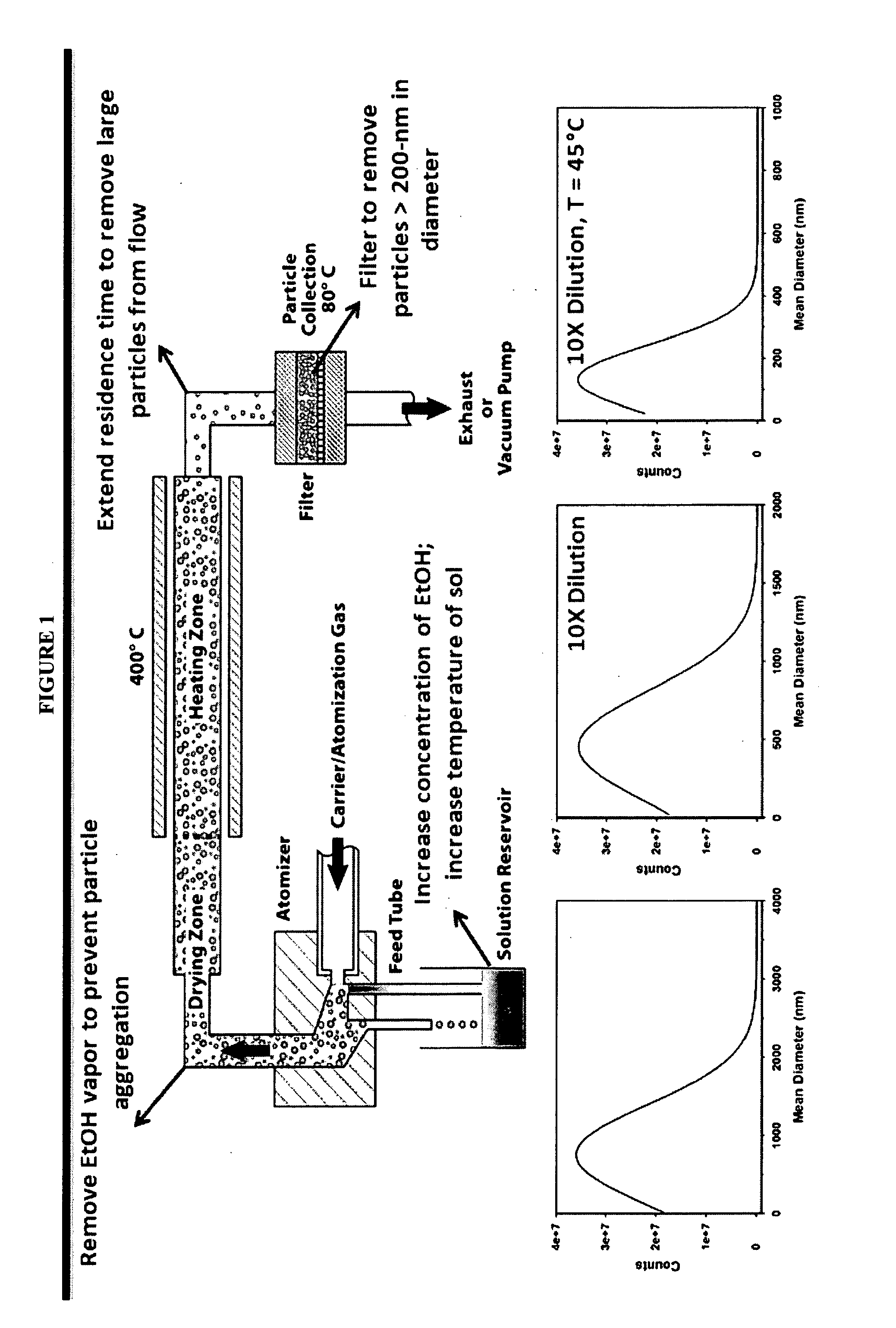
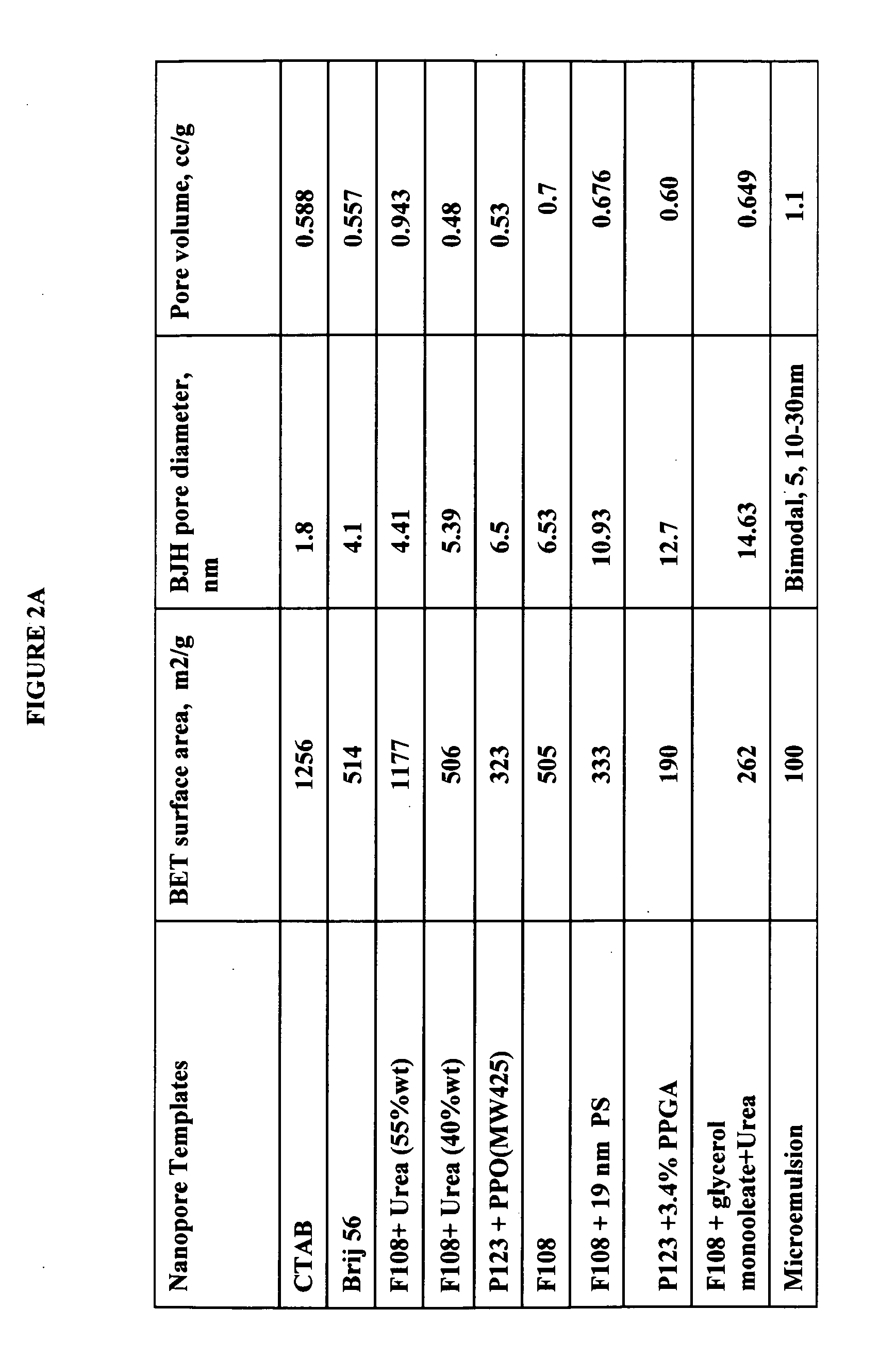
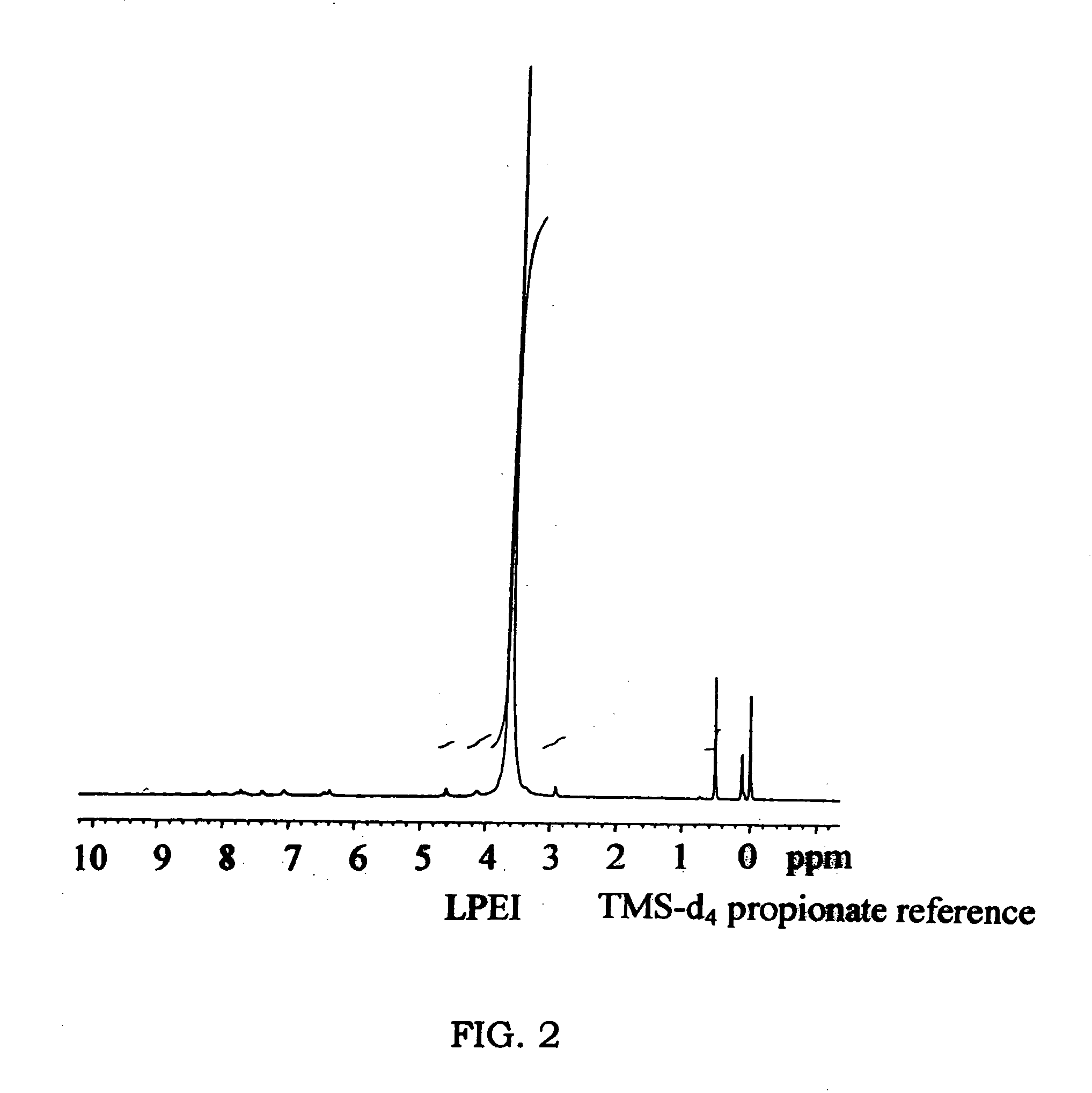
A biodegradable cross-linked cationic multi-block copolymer of linear polyethylenimine (LPEI) wherein the LPEI blocks are linked together by hydrophilic linkers with a biodegradable disulfide bond and methods of making thereof. The biodegradable cross-linked cationic multi-block copolymer may also contain pendant functional moieties which are preferably receptor ligands, membrane permeating agents, endosomolytic agents, nuclear localization sequences, pH sensitive endosomolytic peptides, chromogenic or fluorescent dyes.
Owner:CLSN LAB
Biodegradable cross-linked cationic multi-block copolymers for gene delivery and methods of making thereof
ActiveUS8057821B2Easy to controlGuaranteed effective sizePowder deliveryGenetic material ingredientsCross-linkGene delivery
A biodegradable cross-linked cationic multi-block copolymer of linear polyethylenimine (LPEI) wherein the LPEI blocks are linked together by hydrophilic linkers with a biodegradable disulfide bond and methods of making thereof. The biodegradable cross-linked cationic multi-block copolymer may also contain pendant functional moieties which are preferably receptor ligands, membrane permeating agents, endosomolytic agents, nuclear localization sequences, pH sensitive endosomolytic peptides, chromogenic or fluorescent dyes.
Owner:CLSN LAB
Porous nanoparticle-supported lipid bilayers (protocells) for targeted delivery and methods of using same
ActiveUS20140079774A1Promoting death of cancer cellEfficient packagingBiocideSpecial deliveryLipid formationBinding peptide
The present invention is directed to protocells for specific targeting of hepatocellular and other cancer cells which comprise a nanoporous silica core with a supported lipid bilayer; at least one agent which facilitates cancer cell death (such as a traditional small molecule, a macromolecular cargo (e.g. siRNA or a protein toxin such as ricin toxin A-chain or diphtheria toxin A-chain) and / or a histone-packaged plasmid DNA disposed within the nanoporous silica core (preferably supercoiled in order to more efficiently package the DNA into protocells) which is optionally modified with a nuclear localization sequence to assist in localizing protocells within the nucleus of the cancer cell and the ability to express peptides involved in therapy (apoptosis / cell death) of the cancer cell or as a reporter, a targeting peptide which targets cancer cells in tissue to be treated such that binding of the protocell to the targeted cells is specific and enhanced and a fusogenic peptide that promotes endosomal escape of protocells and encapsulated DNA. Protocells according to the present invention may be used to treat cancer, especially including hepatocellular (liver) cancer using novel binding peptides (c-MET peptides) which selectively bind to hepatocellular tissue or to function in diagnosis of cancer, including cancer treatment and drug discovery.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC +1
Nanoparticle delivery vehicle
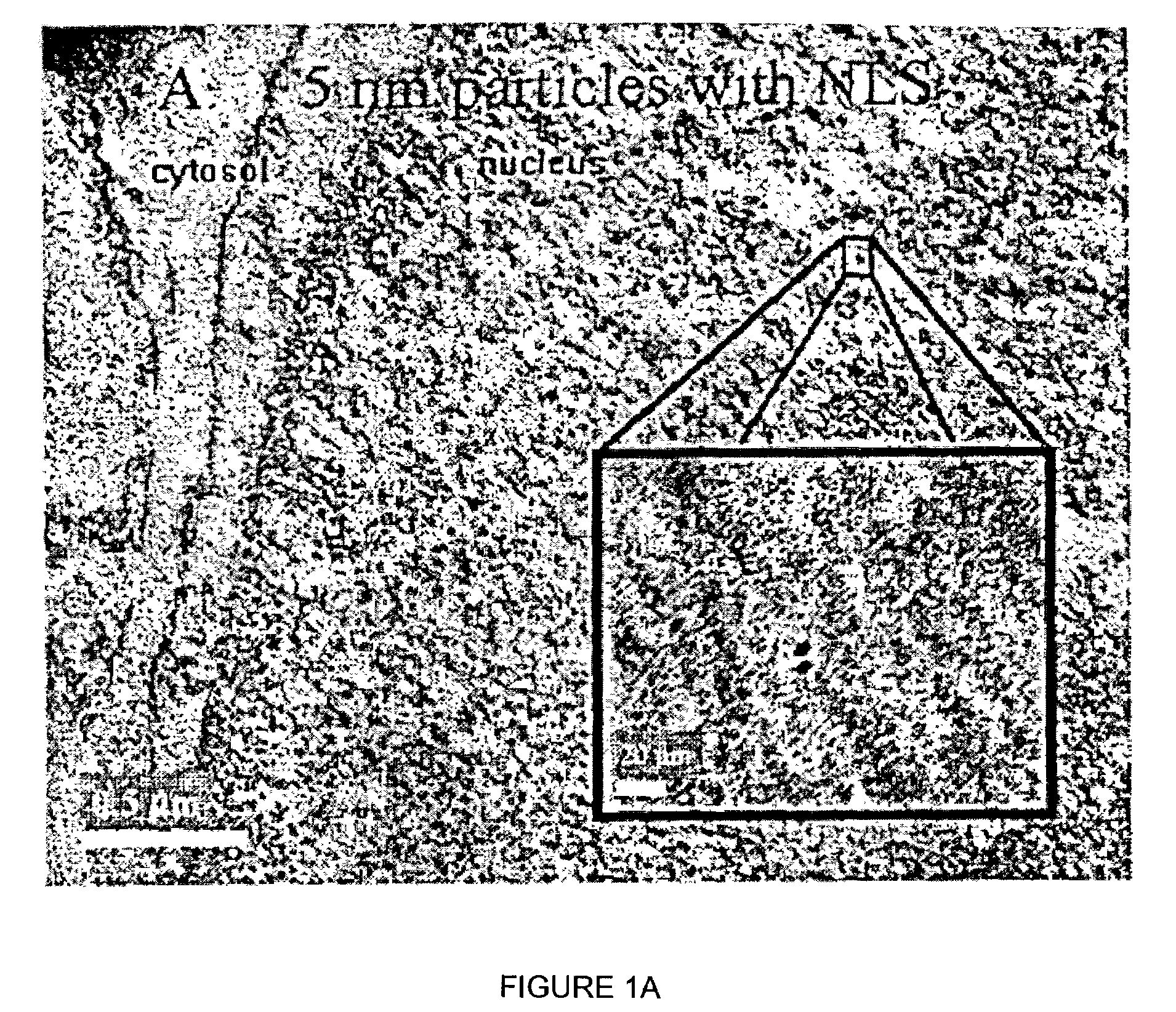
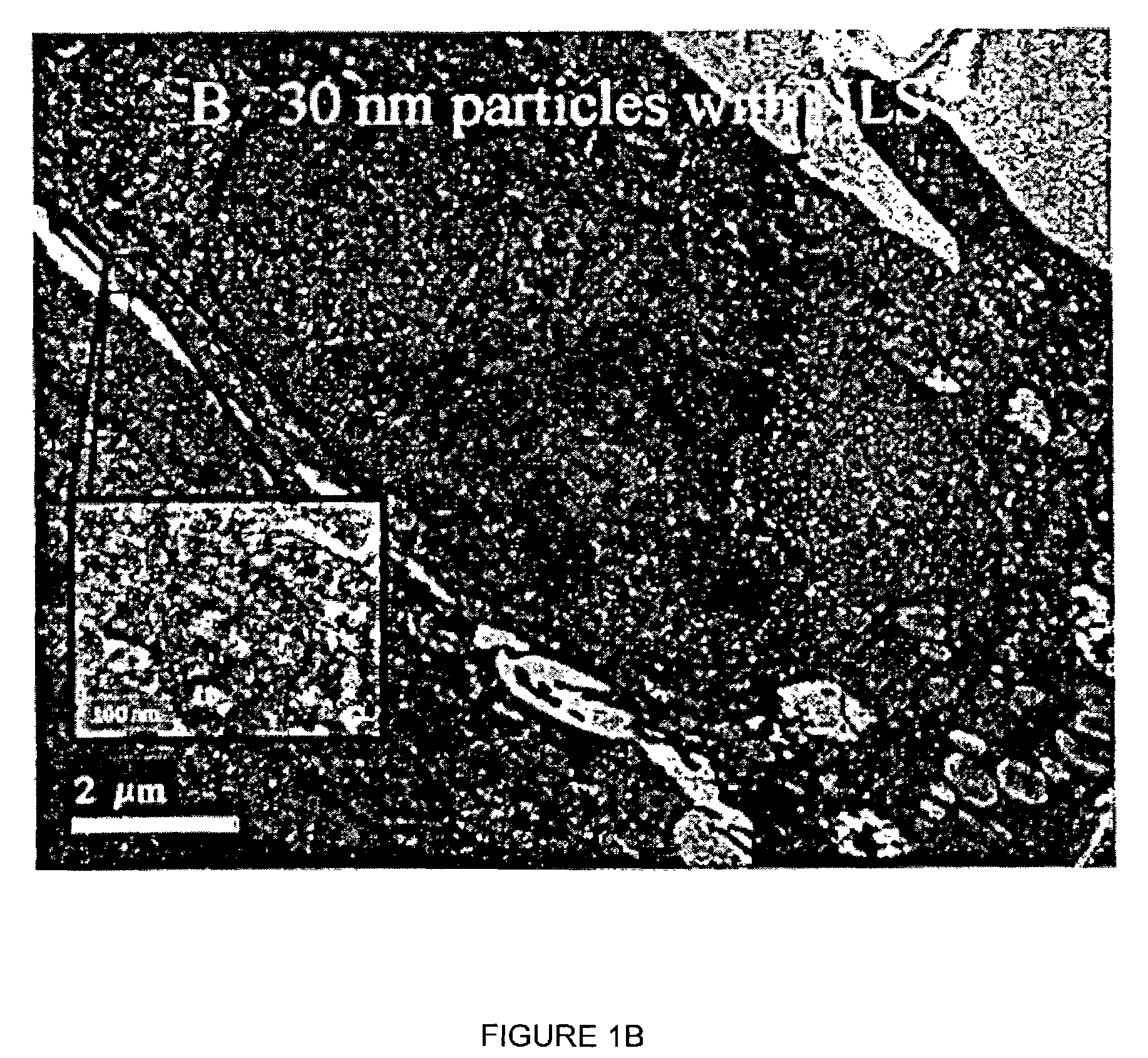
A nanoparticle delivery vehicle, comprising a nanoparticle, an active agent and a nuclear localization signal and methods of modulating gene expression and protein expression employing the nanoparticle delivery vehicle. A representative method includes providing a nanoparticle delivery vehicle comprising a nanoparticle having a diameter of about 30 nm or less, an active agent and a nuclear localization signal; and contacting a target cell with the nanoparticle delivery vehicle, whereby an active agent is delivered to the nucleus of a target cell. Another representative method includes providing a nanoparticle delivery vehicle comprising a nanoparticle having a diameter greater than or equal to about 30 nm, an active agent and a nuclear localization signal; and contacting a target cell with the nanoparticle delivery vehicle, whereby an active agent is delivered to the cytoplasm of a cell.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Biodegradable cross-linked cationic multi-block copolymers for gene delivery and methods of making thereof
ActiveUS20060093674A1Effective particle sizeSafe and efficientPowder deliveryGenetic material ingredientsGene deliveryCross-link
A biodegradable cross-linked cationic multi-block copolymer of linear polyethylenimine (LPEI) wherein the LPEI blocks are linked together by hydrophilic linkers with a biodegradable disulfide bond and methods of making thereof. The biodegradable cross-linked cationic multi-block copolymer may also contain pendant functional moieties which are preferably receptor ligands, membrane permeating agents, endosomolytic agents, nuclear localization sequences, pH sensitive endosomolytic peptides, chromogenic or fluorescent dyes.
Owner:CLSN LAB
Porous nanoparticle-supported lipid bilayers (protocells) for targeted delivery including transdermal delivery of cargo and methods thereof
InactiveUS20150272885A1Large specific surface areaAmenable to high capacity loadingOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryCancers diagnosisBinding peptide
The present invention is directed to protocells for specific targeting of hepatocellular and other cancer cells which comprise a nanoporous silica core with a supported lipid bilayer; at least one agent which facilitates cancer cell death (such as a traditional small molecule, a macromolecular cargo (e.g. siRNA or a protein toxin such as ricin toxin A-chain or diphtheria toxin A-chain) and / or a histone-packaged plasmid DNA disposed within the nanoporous silica core (preferably supercoiled in order to more efficiently package the DNA into protocells) which is optionally modified with a nuclear localization sequence to assist in localizing protocells within the nucleus of the cancer cell and the ability to express peptides involved in therapy (apoptosis / cell death) of the cancer cell or as a reporter, a targeting peptide which targets cancer cells in tissue to be treated such that binding of the protocell to the targeted cells is specific and enhanced and a fusogenic peptide that promotes endosomal escape of protocells and encapsulated DNA. Protocells according to the present invention may be used to treat cancer, especially including hepatocellular (liver) cancer using novel binding peptides (c-MET peptides) which selectively bind to hepatocellular tissue or to function in diagnosis of cancer, including cancer treatment and drug discovery.
Owner:STC UNM +1
PiggyBac transformation system
The present invention is directed to a transformation system for making transgenic organisms that includes a vector containing a modified piggyBac transposon into which is inserted an enhanced green fluorescent protein gene linked to a polyubiquitin promoter sequence and a nuclear localizing sequence; and a helper transposase vector that includes an hsp7O promoter sequence upstream of the putative piggyBac promoter that increases the transformation frequency of this system.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Genetic assay for protein nuclear transport
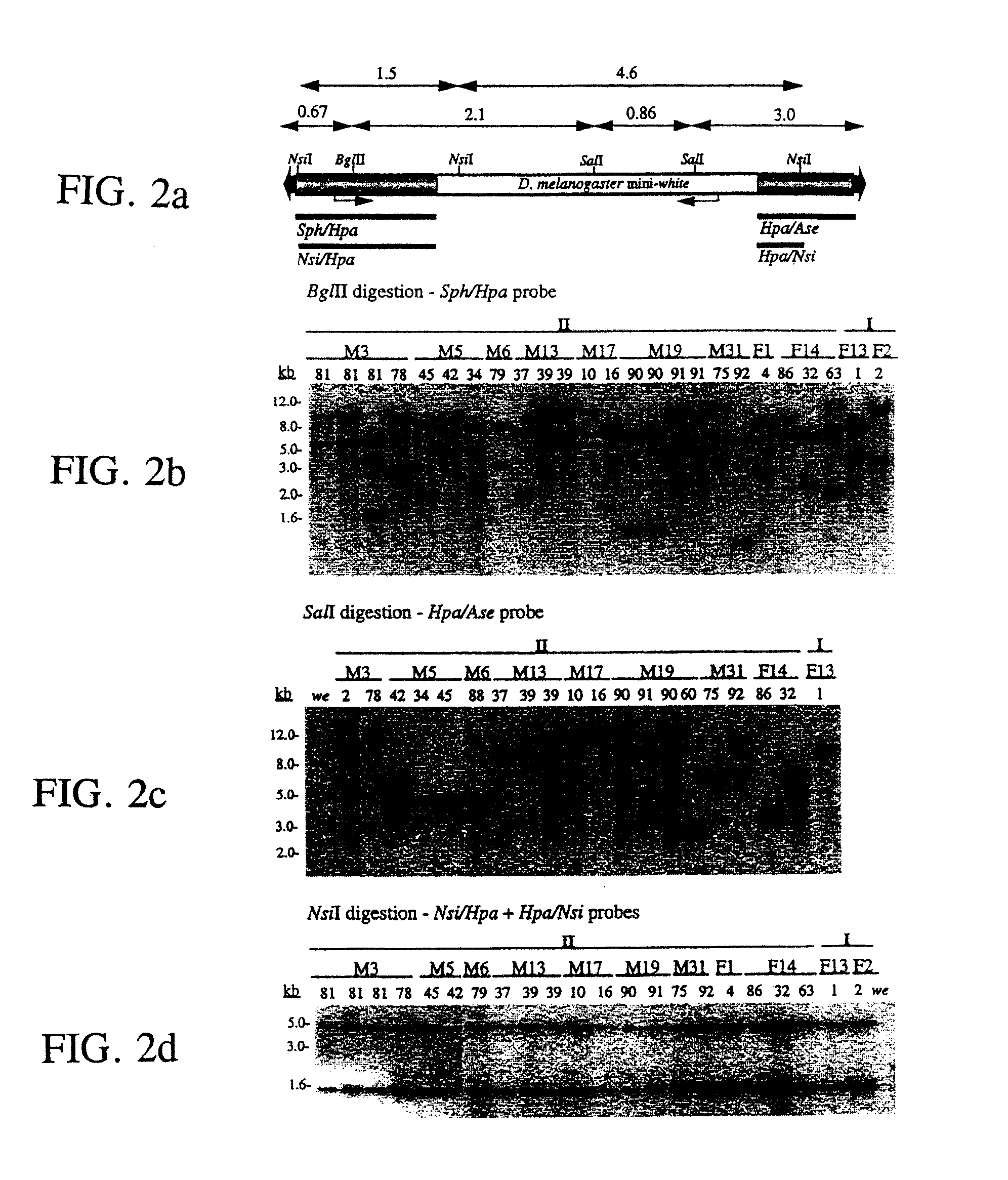
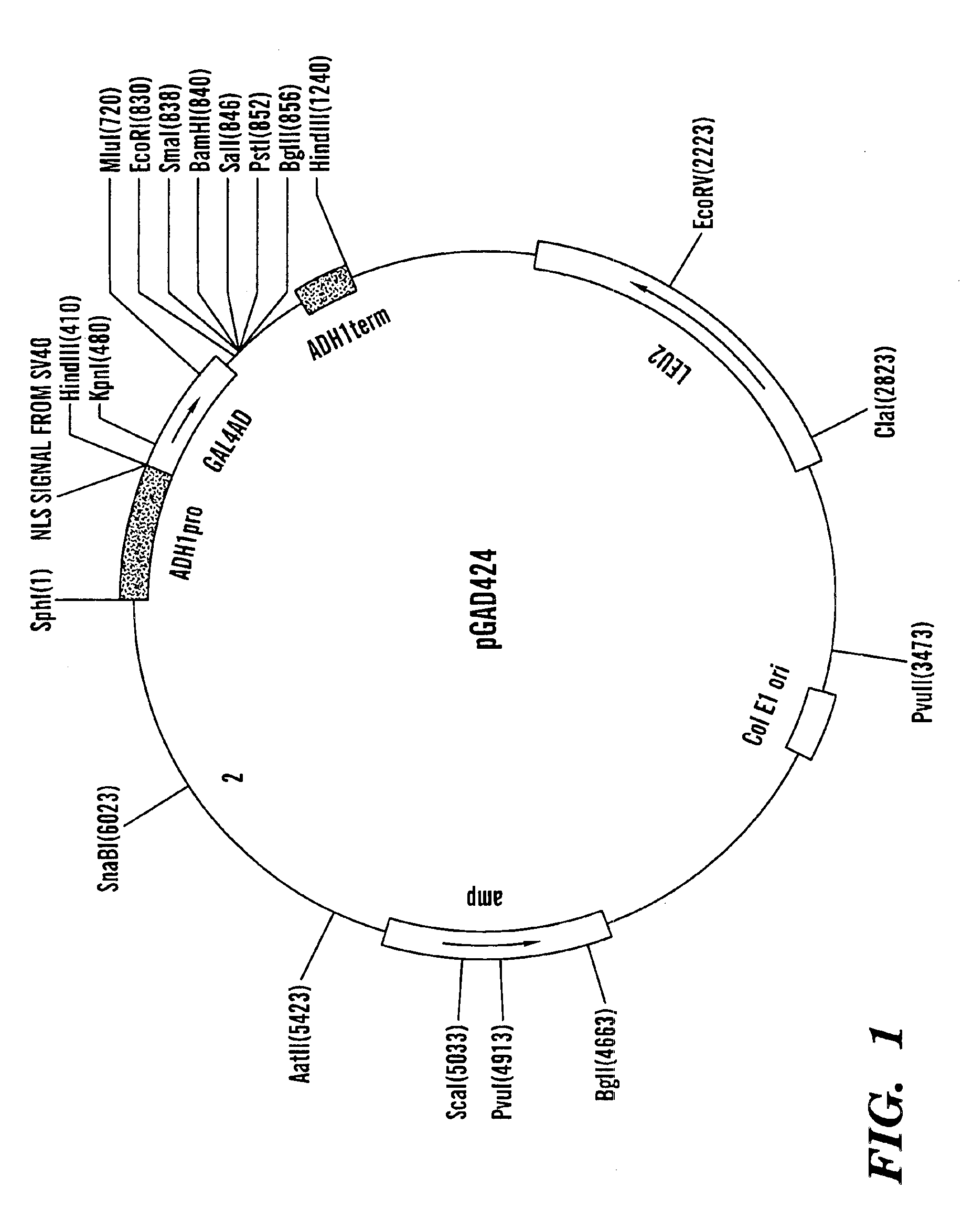
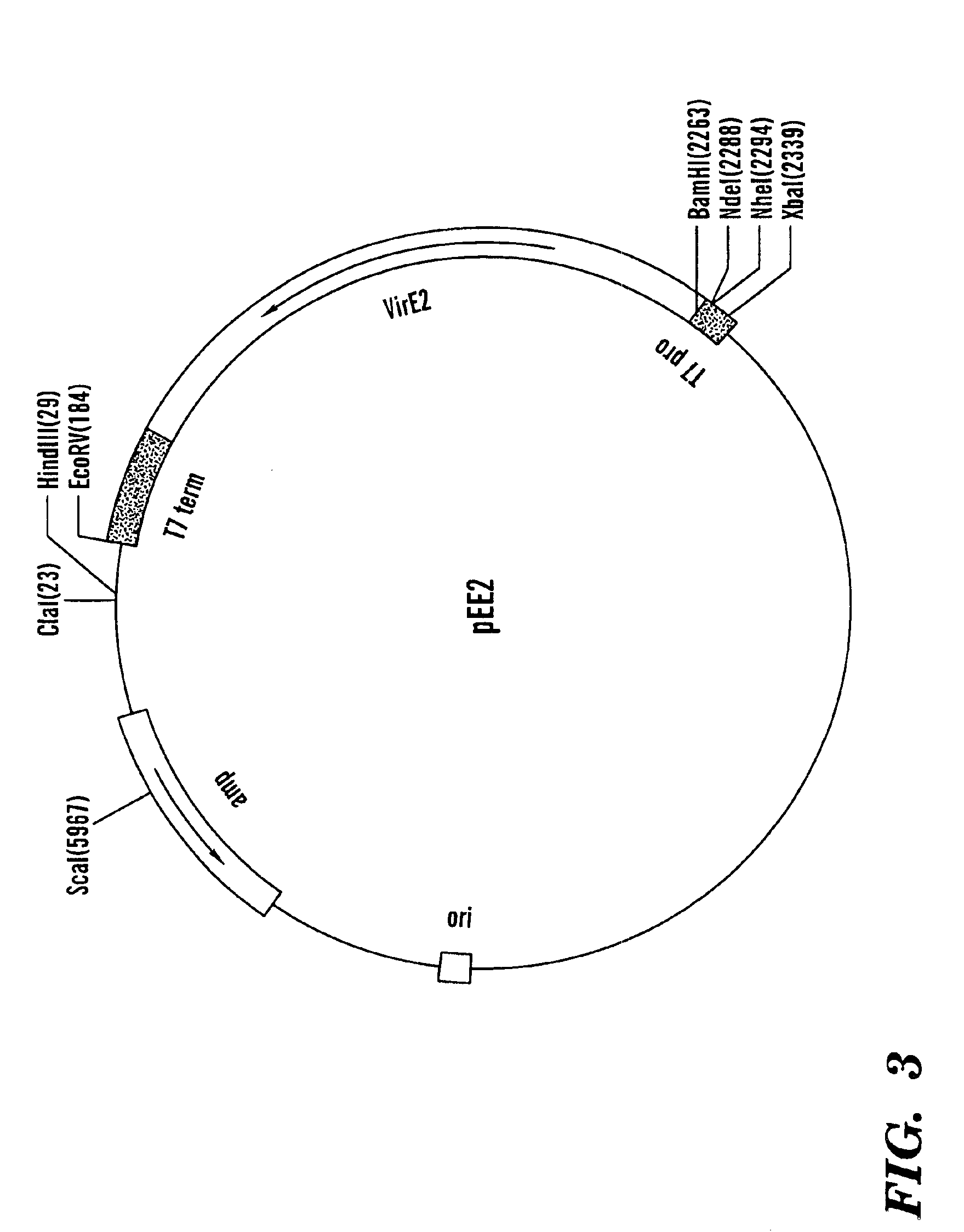
InactiveUS6902886B1Decreasing reporter gene expression levelFunction increaseSugar derivativesMicroorganismsProtein insertionNuclear transport
The invention provides methods of determining the presence of a nuclear localization signal and / or the presence of a nuclear export signal in a protein of interest. The invention further provides chimeric nucleic acids and recombinant host cells for use in such methods. Additionally provided is a nucleic acid molecule encoding a modified LexA protein, wherein the modified LexA protein has no nuclear localization signal, as well as the modified LexA protein itself. In the nuclear import assay, if a protein of interest fused to a mLexA-Gal4AD hybrid contains a functional NLS, the fusion product will enter the yeast cell nucleus and activate the expression of reporter genes. In the nuclear export assay, if a protein of interest fused to a mLexA-SV40 NLS-Gal4AD hybrid contains a functional NES, the fusion product localized to the cell nucleus will exit into the cytoplasm, decreasing the reporter gene expression levels.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Porous nanoparticle-supported lipid bilayers (protocells) for targeted delivery including transdermal delivery of cargo and methods thereof
The present invention is directed to protocells for specific targeting of hepatocellular and other cancer cells which comprise a nanoporous silica core with a supported lipid bilayer; at least one agent which facilitates cancer cell death (such as a traditional small molecule, a macromolecular cargo (e.g. siRNA or a protein toxin such as ricin toxin A-chain or diphtheria toxin A-chain) and / or a histone-packaged plasmid DNA disposed within the nanoporous silica core (preferably supercoiled in order to more efficiently package the DNA into protocells) which is optionally modified with a nuclear localization sequence to assist in localizing protocells within the nucleus of the cancer cell and the ability to express peptides involved in therapy (apoptosis / cell death) of the cancer cell or as a reporter, a targeting peptide which targets cancer cells in tissue to be treated such that binding of the protocell to the targeted cells is specific and enhanced and a fusogenic peptide that promotes endosomal escape of protocells and encapsulated DNA. Protocells according to the present invention may be used to treat cancer, especially including hepatocellular (liver) cancer using novel binding peptides (c-MET peptides) which selectively bind to hepatocellular tissue or to function in diagnosis of cancer, including cancer treatment and drug discovery.
Owner:STC UNM +1
Porous nanoparticle-supported lipid bilayers (protocells) for targeted delivery and methods of using same
InactiveUS20160106671A1Inhibit growthBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsLipid formationBinding peptide
The present invention is directed to protocells for specific targeting of hepatocellular and other cancer cells which comprise a nanoporous silica core with a supported lipid bilayer; at least one agent which facilitates cancer cell death (such as a traditional small molecule, a macromolecular cargo (e.g. siRNA or a protein toxin such as ricin toxin A-chain or diphtheria toxin A-chain) and / or a histone-packaged plasmid DNA disposed within the nanoporous silica core (preferably supercoiled in order to more efficiently package the DNA into protocells) which is optionally modified with a nuclear localization sequence to assist in localizing protocells within the nucleus of the cancer cell and the ability to express peptides involved in therapy (apoptosis / cell death) of the cancer cell or as a reporter, a targeting peptide which targets cancer cells in tissue to be treated such that binding of the protocell to the targeted cells is specific and enhanced and a fusogenic peptide that promotes endosomal escape of protocells and encapsulated DNA. Protocells according to the present invention may be used to treat cancer, especially including hepatocellular (liver) cancer using novel binding peptides (c-MET peptides) which selectively bind to hepatocellular tissue or to function in diagnosis of cancer, including cancer treatment and drug discovery.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC +1
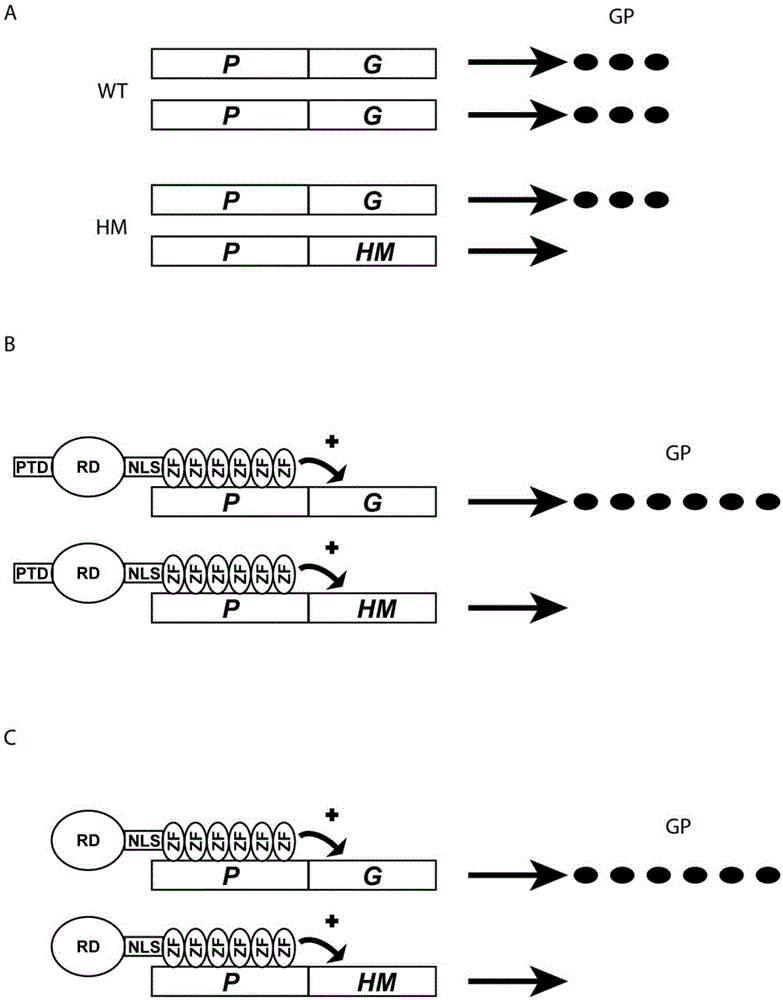
Regulation of receptor expression through delivery of artificial transcription factors
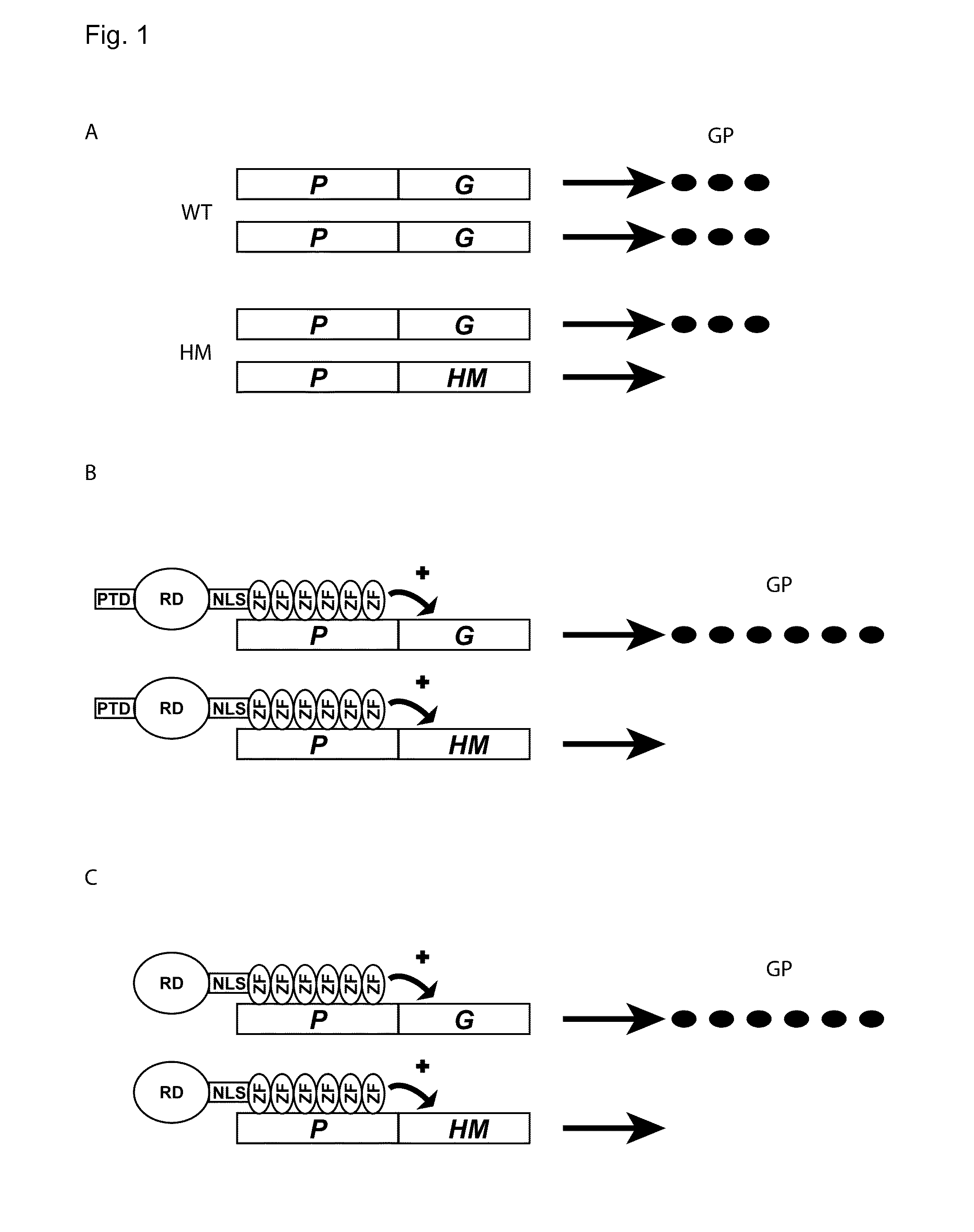
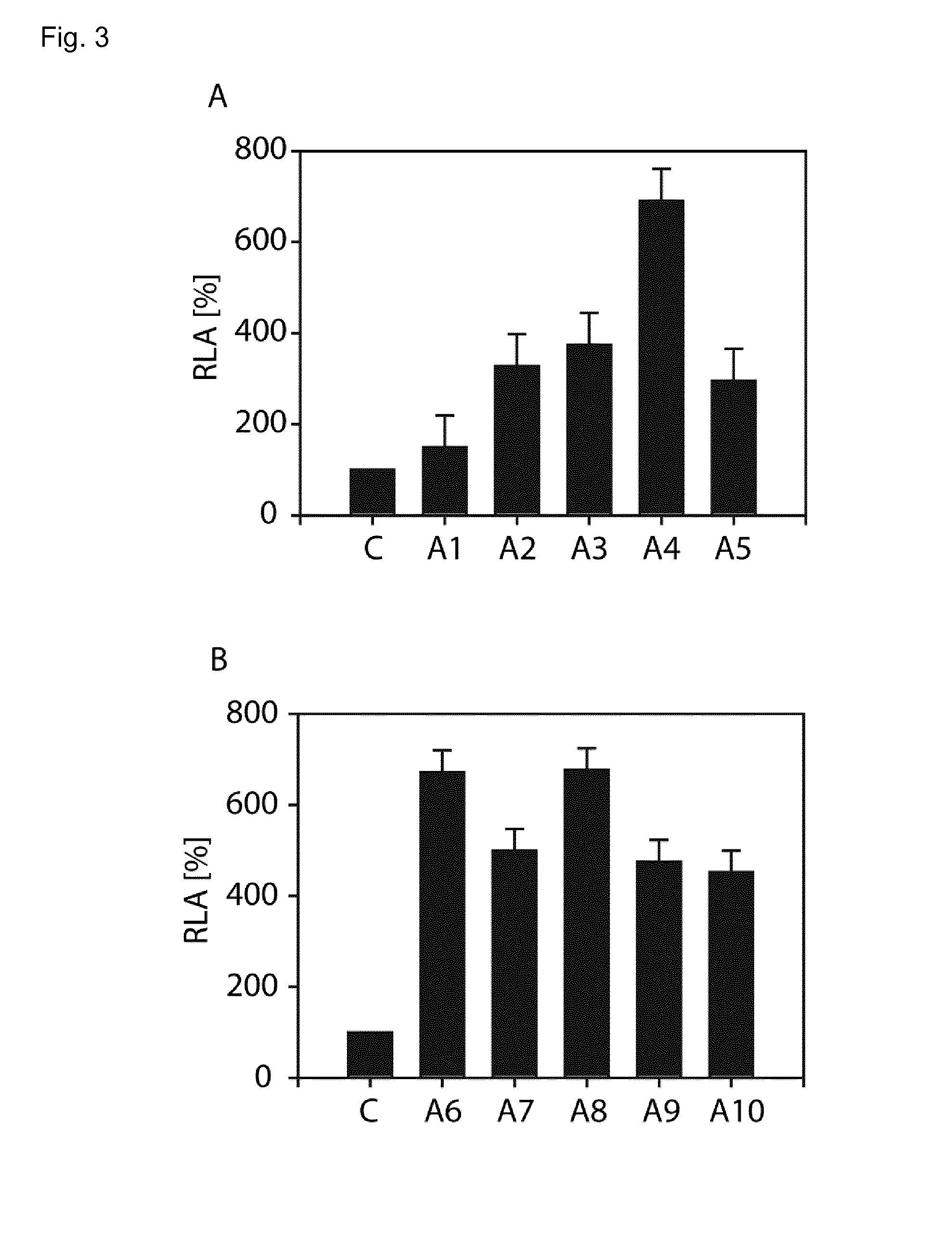
The invention relates to an artificial transcription factor comprising a polydactyl zinc finger protein targeting specifically a receptor gene promoter fused to an inhibitory or activatory protein domain, a nuclear localization sequence, and a protein transduction domain. In particular examples these receptor gene promoters regulate the expression of the endothelin receptor A, the endothelin receptor B, the Toll-like receptor 4 or the high-affinity IgE receptor. Artificial transcription factors directed to the endothelin A or B receptors are useful in the treatment of diseases modulated by endothelin, such as cardiovascular diseases, and, in particular, eye diseases, e.g. retinal vein occlusion, retinal artery occlusion, macular edema, optic neuropathy, central serous chorioretinopathy, retinitis pigmentosa, Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy, and the like. Artificial transcription factors directed to the Toll-like receptor 4 or the IgE receptor are useful for the treatment of autoimmune disorders, and the like, and allergic disorders, respectively.
Owner:ALIOPHTHA
Vector for mediating high-efficiency expression of exogenous gene in cells of mammal and use thereof
InactiveCN102250952AImprove output efficiencyImprove output stabilityVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsBeta globinMammal
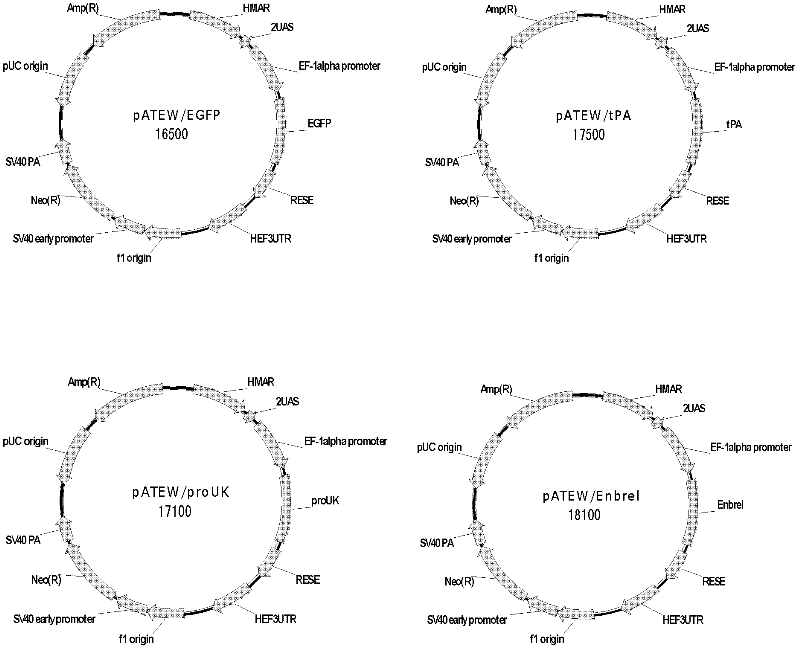
The invention discloses a combined vector for mediating the high-efficiency expression of an exogenous gene in cells of a mammal, which comprises an exogenous gene high-efficiency expression vector pATEW and an artificial transcription factor pcDNA3.1(+) / Hy / GVP4. The exogenous gene high-efficiency expression vector pATEW combines gene expression regulatory elements including a human beta-globin MAR sequence, a hEF-1a genetic transcription regulatory sequence, an after-transcription regulatory element WPRE and the like and an artificial transcription factor combined site sequence. The artificial transcription factor expression vector (pcDNA3.1(+) / Hy / GVP4 is an artificial transcription factor GVP4 which is formed by connecting two parts: four tandem repeats of 12 peptides (DALDDFDLDMLG) in VP16, which serves as the functional structural region of the artificial transcription factor; and the nuclear localization sequence of SV40. By co-transfecting cells of the mammal with the pATEW carrying the exogenous gene and the pcDNA3.1(+) / Hy / GVP4, the high-efficiency expression of the exogenous gene in the cells of the mammal can be realized.
Owner:INST OF BIOENG ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE CHINESE
Porous nanoparticle-supported lipid bilayers (protocells) for targeted delivery including transdermal delivery of cargo and methods thereof
InactiveUS20170232115A1Amenable to high capacity loadingPorosity adjustableOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryCancer cellApoptosis
The present invention is directed to protocells for specific targeting of hepatocellular and other cancer cells which comprise a nanoporous silica core with a supported lipid bilayer; at least one agent which facilitates cancer cell death (such as a traditional small molecule, a macromolecular cargo (e.g. siRNA or a protein toxin such as ricin toxin A-chain or diphtheria toxin A-chain) and / or a histone-packaged plasmid DNA disposed within the nanoporous silica core (preferably supercoiled in order to more efficiently package the DNA into protocells) which is optionally modified with a nuclear localization sequence to assist in localizing protocells within the nucleus of the cancer cell and the ability to express peptides involved in therapy (apoptosis / cell death) of the cancer cell or as a reporter, a targeting peptide which targets cancer cells in tissue to be treated such that binding of the protocell to the targeted cells is specific and enhanced and a fusogenic peptide that promotes endosomal escape of protocells and encapsulated DNA. Protocells according to the present invention may be used to treat cancer, especially including hepatocellular (liver) cancer using novel binding peptides (c-MET peptides) which selectively bind to hepatocellular tissue or to function in diagnosis of cancer, including cancer treatment and drug discovery.
Owner:STC UNM +1
PiggyBac transformation system
The present invention is directed to a transformation system for making transgenic organisms that includes a vector containing a modified piggyBac transposon into which is inserted an enhanced green fluorescent protein gene linked to a polyubiquitin promoter sequence and a nuclear localizing sequence; and a helper transposase vector that includes an hsp70 promoter sequence upstream of the putative piggyBac promoter that increases the transformation frequency of this system.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF AGRI THE
Compounds and methods of use to treat infectious diseases
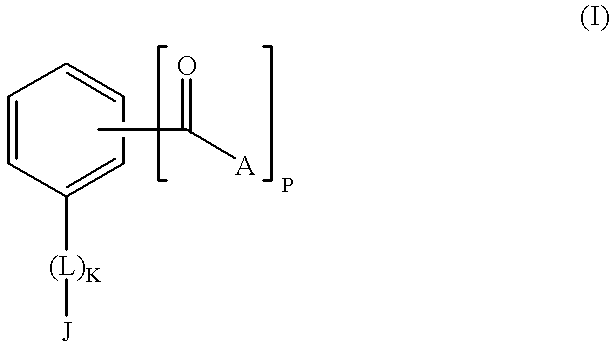
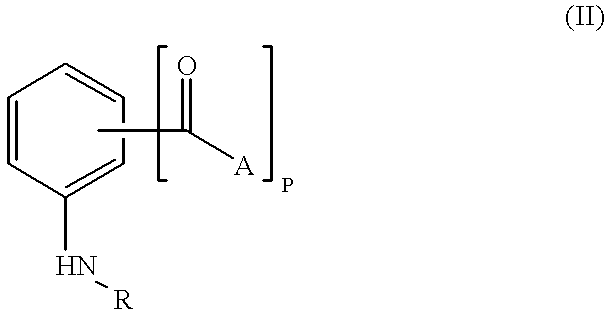
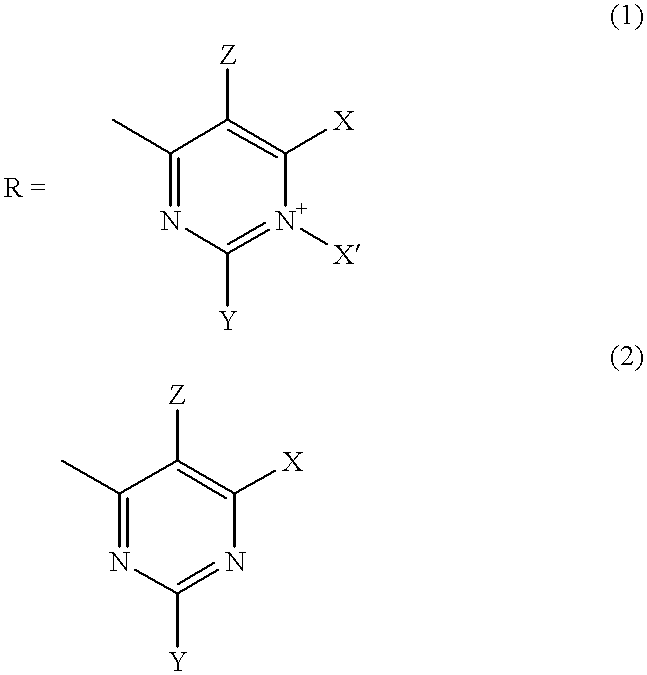
The present invention concerns alkyl aryl carbonyl compounds that possess anti-infective activity. The compounds of the invention can be used to target specific nuclear localization signal, thereby blocking importation of specific proteins or molecular complex into the nucleus of a cell. The invention encompasses methods of use of such compounds for treatment or prevention of infectious diseases, such as parasitic and viral diseases, including, for example, malaria and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. The use of the compounds to detect certain specific protein structures which are present in nuclear localization sequences is also taught.
Owner:FERRING BV
Antibacterial polypeptide conjugate with multiple target points and synthesis method and application of biopolymer of antibacterial polypeptide conjugate
ActiveCN104961801APrevent proliferationHigh antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBiopolymerSynthesis methods
The invention provides an antibacterial polypeptide conjugate Acr3-NLS (nuclear localization sequence) as well as a bipolymer (Acr3-NLS)2 of the antibacterial polypeptide conjugate, and belongs to the field of medicinal chemistry. The antibacterial polypeptide conjugate Acr3-NLS is formed by connecting acridine molecules to an N end of NLS, and the biopolymer (Acr3-NLS)2 is formed by connecting Acr3-NLS molecules by virtue of a disulfide bond. The activity test shows that the antibacterial activity of the antibacterial polypeptide conjugate Acr3-NLS and (Acr3-NLS)2 is remarkably improved compared with that of the NLS, and the bacteria can be killed by virtue of the action mechanism of multiple target points. The action mechanism of the multiple target points can enable the Acr3-NLS and (Acr3-NLS)2 to kill the traditional antibiotics drug-fastness bacteria; moreover, the bacteria is unlikely to have drug fastness. The Acr3-NLS and (Acr3-NLS)2 as an active ingredient have a potential application value in preparing the antibacterial drugs.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Non-viral gene vector constructed on basis of N-terminal octadecane acylated antibacterial peptide
InactiveCN102719477AEasily biodegradableLow cytotoxicityAnimals/human peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionCytotoxicityPlasmid dna
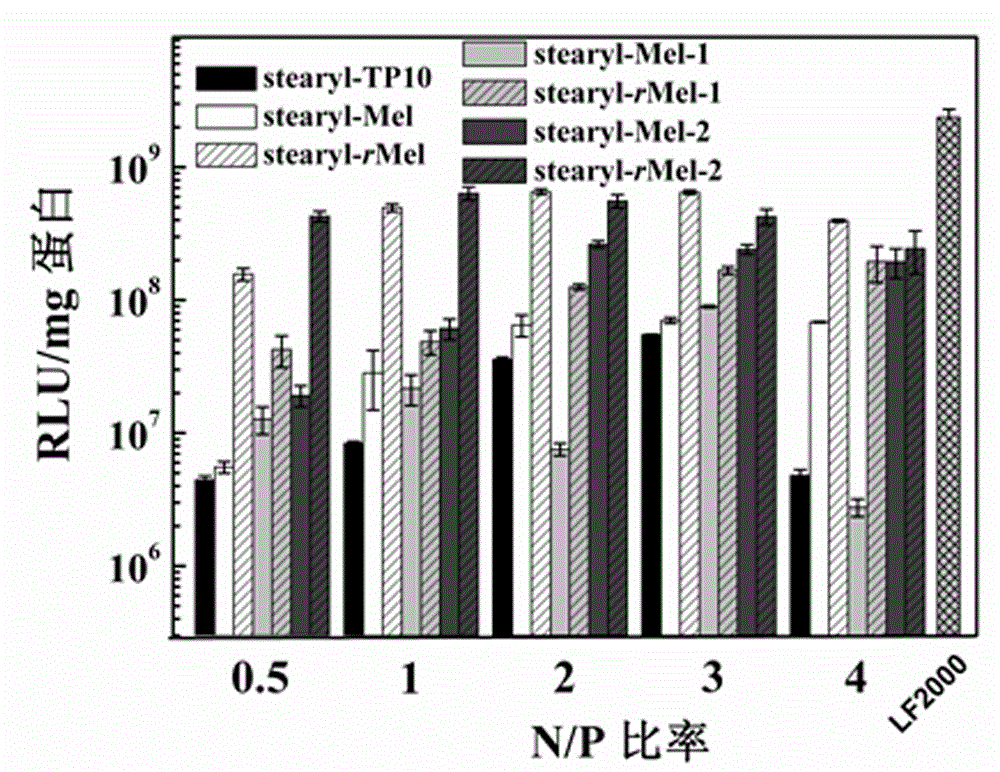
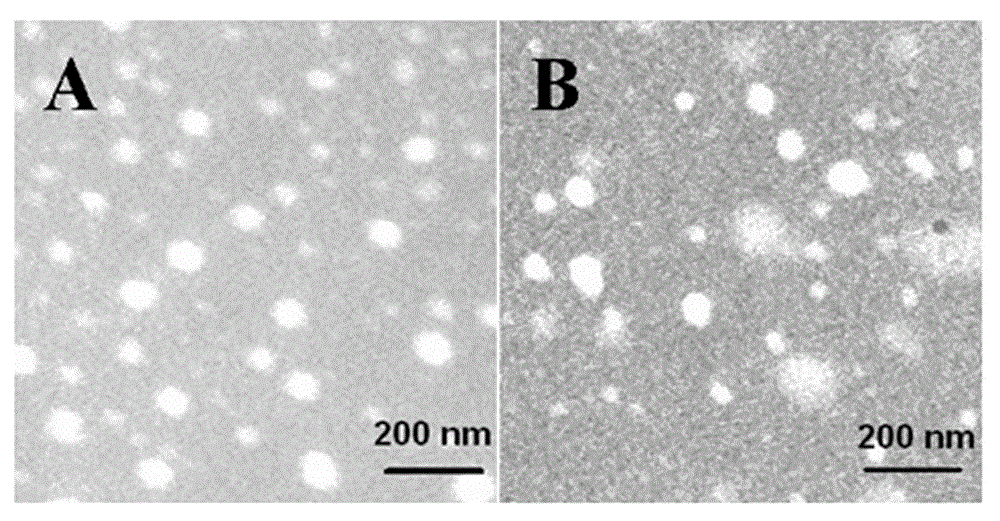
The invention discloses a non-viral gene vector constructed on the basis of N-terminal octadecane acylated antibacterial peptide. The vector utilizes the characteristics of melittin, i.e. endosome-destroying activity and membrane penetrating activity, moreover, a nuclear localization sequence and a polyarginine sequence are added into the melittin sequence, and then a series of forward and reverse analogues are synthesized, and octadecanoic acid is connected with the N terminals of the obtained analogues, so that the analogues and plasmid DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) form stable nano-particles. An experiment result shows that because the non-viral gene vector constructed on the basis of N-terminal octadecane acylated antibacterial peptide has higher transfection efficiency and lower cytotoxicity and the polypeptide vector is easy to biodegrade, the non-viral gene vector is more suitable for application in vivo.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Non-viral vector
InactiveUS20150307897A1High expressionImprove expression levelChemokinesGenetic material ingredientsNucleotide sequencingViral vector
The present invention provides a non-viral vector which comprises a sequence encoding an RNA replicase and a nuclear localisation sequence. The vector may also comprise a nucleotide sequence of interest (NOI). The vector may be used to deliver an NOI to a target cell.
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE CORK NAT UNIV OF IRELAND CORK
Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria with low-yielding ethyl carbamate, and building method and application of saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria
InactiveCN103571765AImprove utilizationReduce formationFungiMicroorganism based processesAdditive ingredientBacterial strain
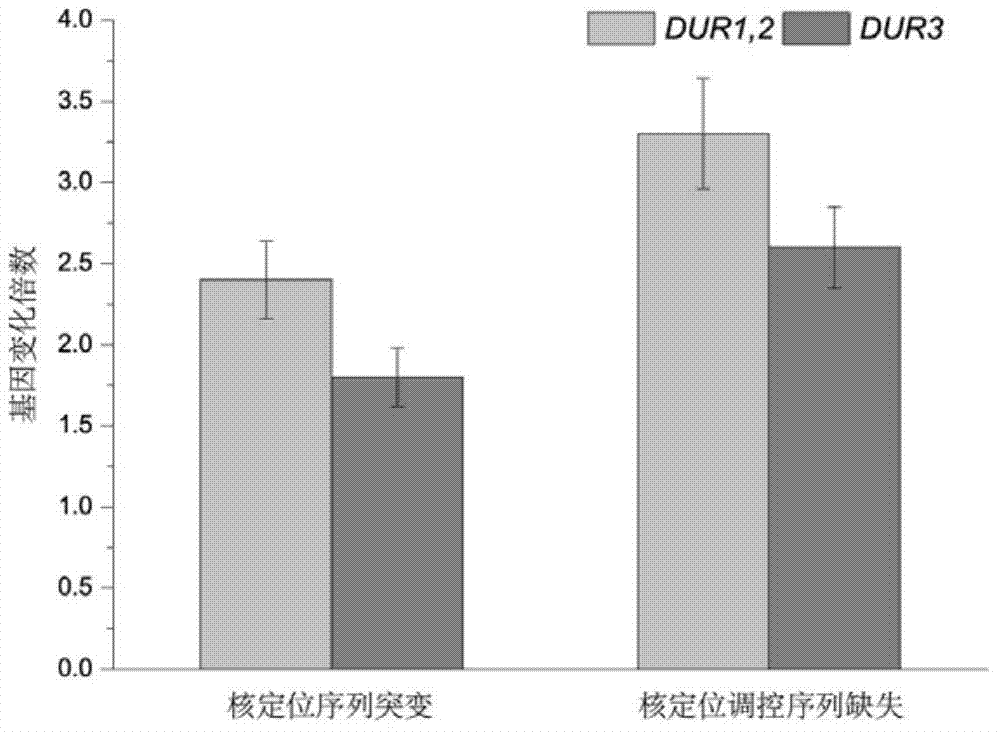
The invention discloses saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria with low-yielding ethyl carbamate. A regulatory factor G1n3p in saccharomyces cerevisiae is transformed through engineering bacteria. The concrete strategy is that a phosphorylation site on a G1n3p nuclear localization sequence is subjected to mutation to form three phosphorylation sites on the G1n3p nuclear localization sequence; the three phosphorylation sites respectively are the 344th, 347th and 355th serine. In order to obtain a better technical effect, a nuclear localization regulatory region of combining G1n3p with an upstream regulatory factor can be further removed; the G1n3p of a regulatory sequence at the tail end of C is removed by truncated expression, wherein an expression sequence is 1-653. The EC yield of the engineering bacteria disclosed by the invention is reduced by 62% by detection of a yellow rice wine simulation system. In addition, the content of main ingredients is not significantly changed, and the fermentation characteristics and the growth characteristics of a bacterial strain are not affected after the content of other ingredients in a fermentation liquor after fermentation is detected.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Nuclear localization signal of lentiviral integrase and method of use thereof
InactiveUS20100099162A1Preventing proviral nuclearPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifVirus peptidesGene deliveryIntegrases
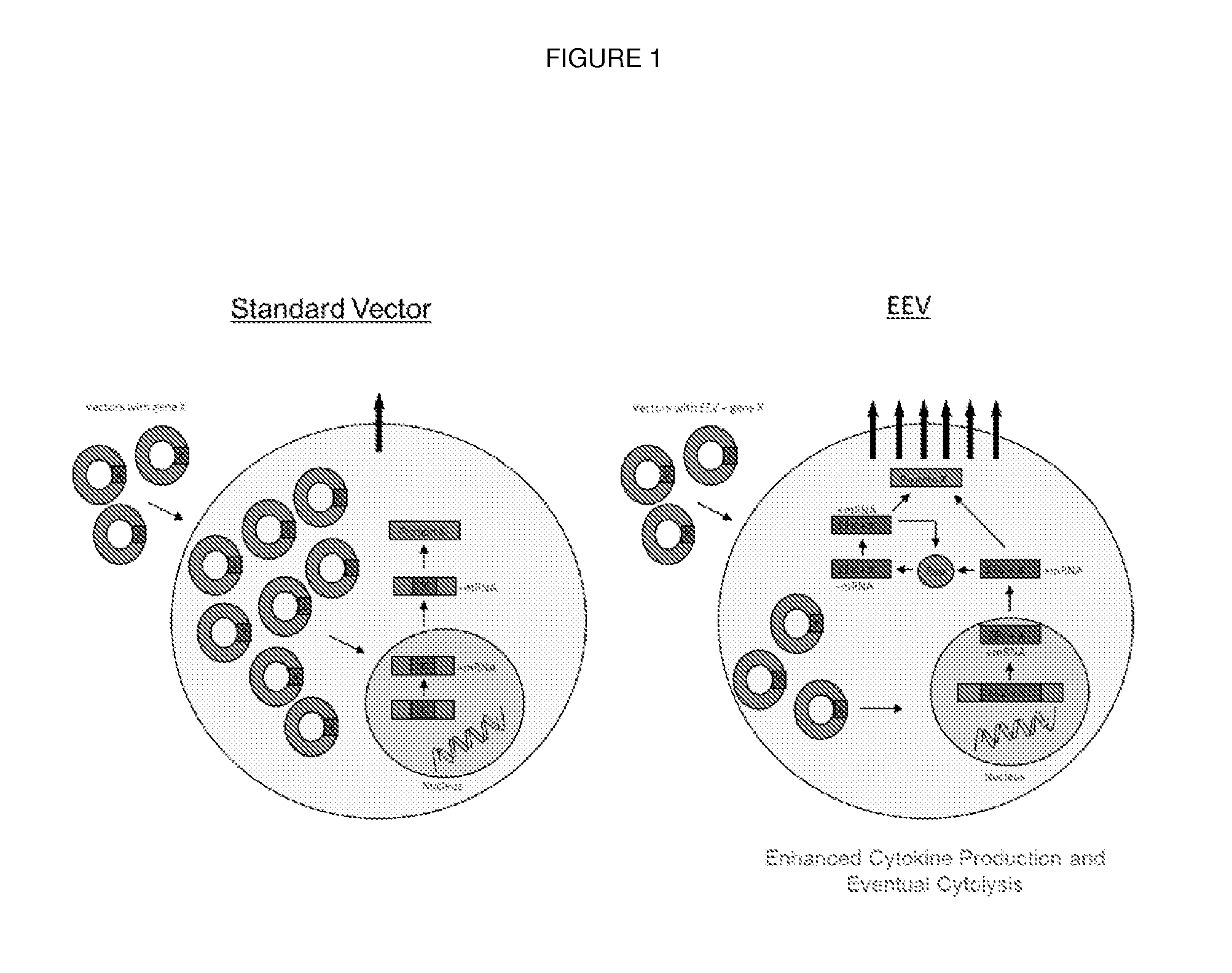
The present invention provides novel peptides, nucleic acids, vectors, compounds, compositions and methods for regulating nuclear import The present invention also relates to a lentiviral NLS, and methods of use thereof for inhibiting HIV pathogenesis and disease progression, and for gene delivery methods
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Artificial transcription factors for the treatment of diseases caused by opa1 haploinsufficiency
InactiveCN105358568APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSenses disorderHaploinsufficiencyFactor ii
The invention relates to an artificial transcription factor comprising a polydactyl zinc finger protein targeting specifically the OPA1 promoter fused to an activatory protein domain, and a nuclear localization sequence. Artificial transcription factors directed against the OPA1 promoter are useful for the treatment of diseases associated with OPA1 haploinsufficiency, such as autosomal dominant optic atrophy, syndromic autosomal dominant optic atrophy plus and normal tension glaucoma.
Owner:ALIOPHTHA
Method with function of reducing accumulation of ethyl carbamate in rice wine fermentation
InactiveCN105273918AMeet production requirementsReduce contentFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicrobial genetics
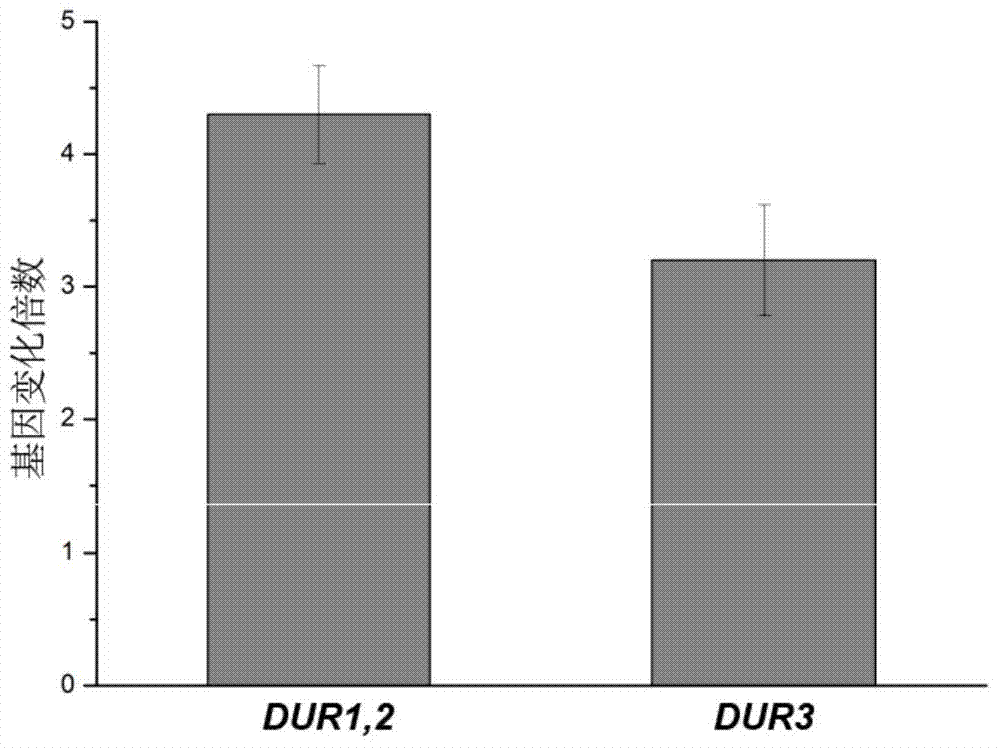
The invention belongs to the field of microbial genetics and molecular biology and discloses a method with a function of reducing accumulation of ethyl carbamate in rice wine fermentation. Genetically engineered bacteria modified by nitrogen catabolite repression regulation factors are adopted for rice wine fermentation, and engineered saccharomyces cerevisiae eliminates nuclear localization regulatory sequences of the regulation factors Gln3p and Gat1p and mutates phosphorylation sites of the nuclear localization sequences. In a simulated rice wine fermentation system, compared with rice wine with wild strains for fermentation, rice wine fermented with the genetically engineered bacteria has the advantages that contents of carbamide and ethyl carbamate in the rice wine are decreased by 63% and 72% respectively, the content of the ethyl carbamate in the rice wine is decreased to about 55.53 microgram / L, and contents of major nutrient substances and characteristic flavor substances are less in difference. Therefore, the method has a huge potential of application to rice wine production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
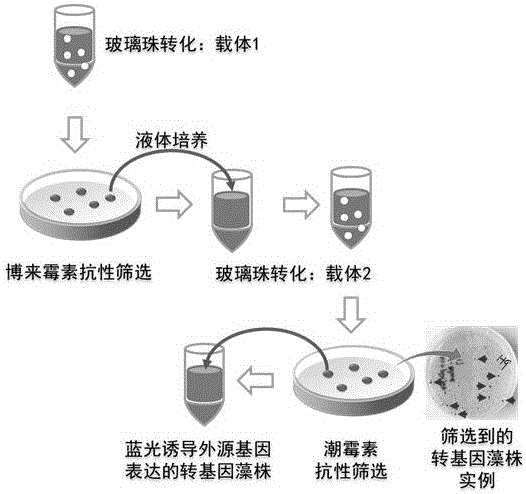
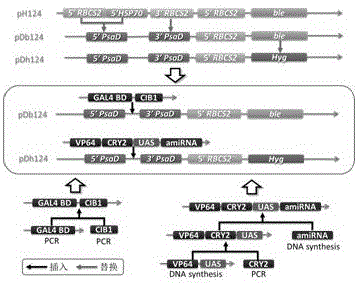
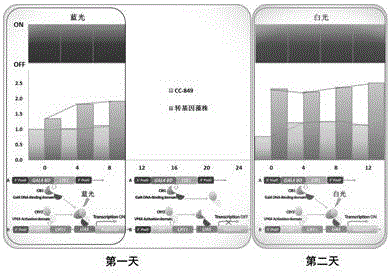
Chlamydomonas exogenous gene expression system based on blue light induction and application thereof
ActiveCN106591349AAvoid harmOvercoming the effects of metabolismVector-based foreign material introductionBiological activationSystem element
The invention discloses a chlamydomonas exogenous gene expression system based on blue light induction and an application thereof. Expression system elements include a light receptor cryptochrome CRY2 gene and an interacting protein CIB1 gene, a GAL4 DNA binding structural domain BD and an activation domain VP64 having transcriptional activation of an active herpes simplex virus, a nuclear localization sequence NLS, a UAS sequence which can be combined with the GAL4 transcription factor DNA binding structural domain BD, and an exogenous gene, wherein CRY2-BD, CIB1-VP64-NLS and a UAS-exogenous gene are connected together and are integrated into a nuclear genome of chlamydomonas through genetic transformation. Single color light-blue light is used as an inducing factor for inducing the expression of the exogenous gene, and the damage of algae cells caused by heat shock induction is overcome, and the influence of various chemical inducers on the metabolism of the algae cells is overcome.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Functionalized peptide transporters for cellular uptake
Disclosed are novel cell-penetrating transporters for enhancing cellular uptake of peptide fusion proteins into live cells. The cell-penetrating transporters comprise a functionalized peptide construct comprising a cell importation peptide covalently bound to a cargo, the cell importation peptide in an unreactive monomeric form, and a pharmaceutical carrier. In certain embodiments, the cargo further comprises a nuclear localization sequence (NLS) allowing the cargo to be transported across the nuclear membrane.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Tonoplast localization sequence and its application
The invention relates to a tonoplast localization sequence and its application. The inventor, for the first time, separates a segment of signal sequence for specific location of cell tonoplast, i.e. a tonoplast targeting sequence (TTS). The sequence can lead accurate and efficient location of protein on intracellular tonoplast. The sequence can be utilized to perform localization transformation on target protein, and expression of the target protein at other sites other than the tonoplast can be reduced or prevented.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Regulation of receptor expression through delivery of artificial transcription factors
InactiveCN103998609APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSenses disorderPromoterHigh affinity receptor
The invention relates to an artificial transcription factor comprising a polydactyl zinc finger protein targeting specifically a receptor gene promoter fused to an inhibitory or activatory protein domain, a nuclear localization sequence, and a protein transduction domain. In particular examples these receptor gene promoters regulate the expression of the endothelin receptor A, the endothelin receptor B, the Toll-like receptor 4 or the high-affinity IgE receptor. Artificial transcription factors directed to the endothelin A or B receptors are useful in the treatment of diseases modulated by endothelin, such as cardiovascular diseases, and, in particular, eye diseases, e.g. retinal vein occlusion, retinal artery occlusion, macular edema, optic neuropathy, central serous chorioretinopathy, retinitis pigmentosa, Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy, and the like. Artificial transcription factors directed to the Toll-like receptor 4 or the IgE receptor are useful for the treatment of autoimmune disorders, and the like, and allergic disorders, respectively.
Owner:ALIOPHTHA
Porcine circovirus type 2 Cap gene modified recombinant antigen and application thereof
ActiveCN105541976ARaise antibody levelsEasy to saveViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesDiseaseVirus inactivation
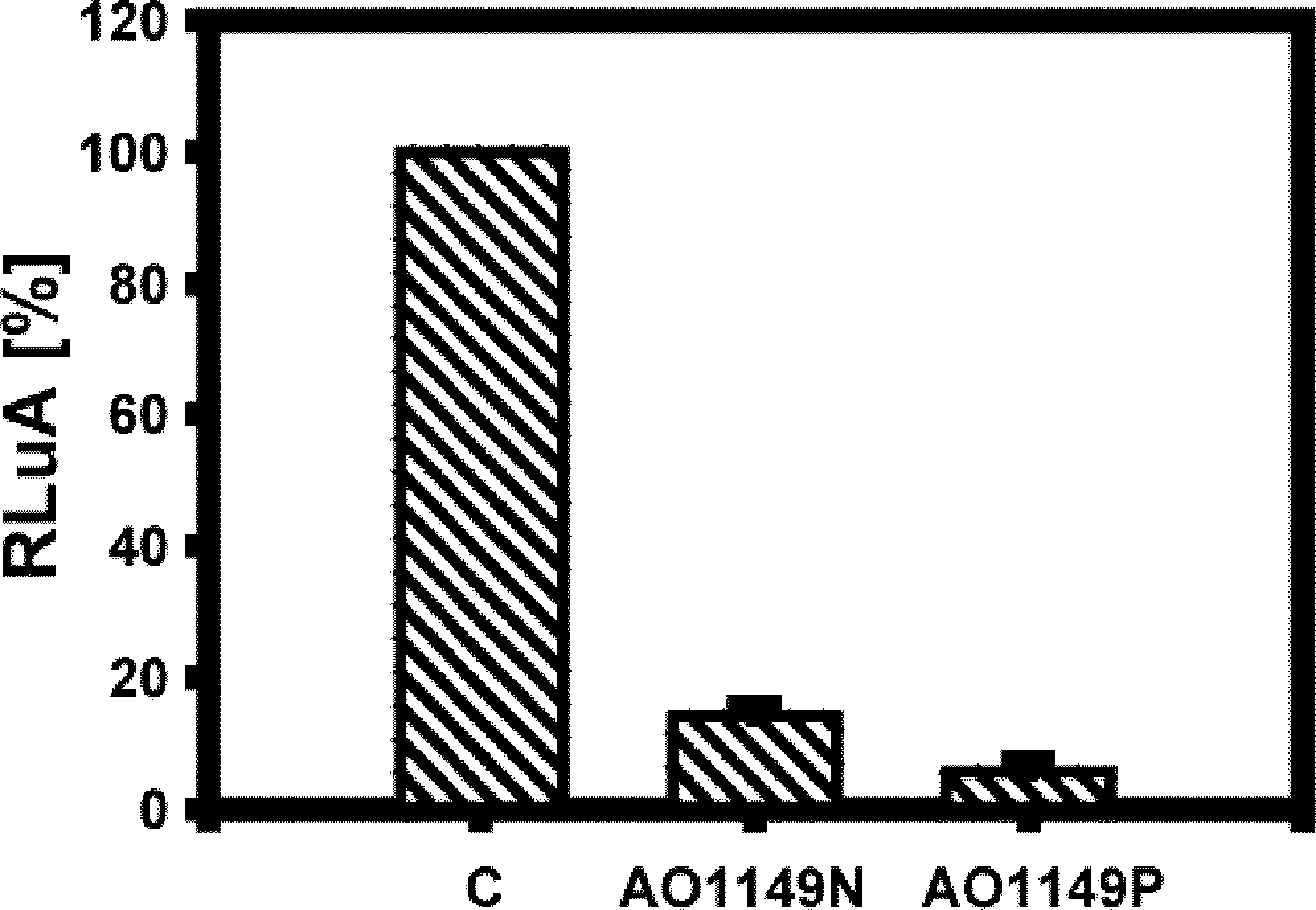
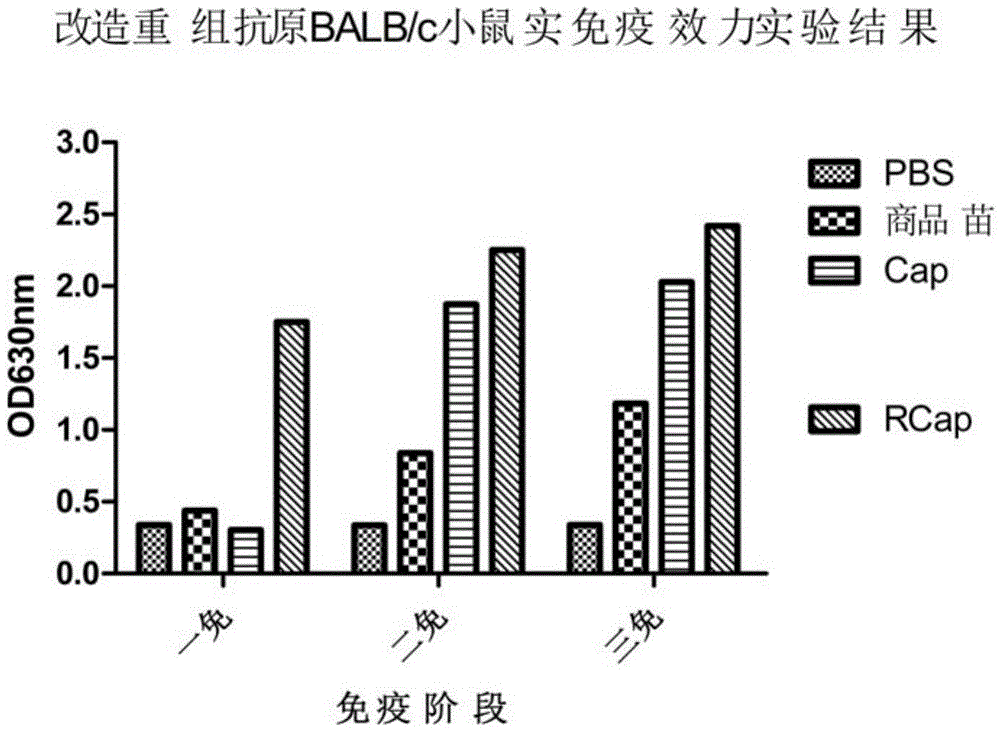
The invention discloses a porcine circovirus type 2 Cap gene modified recombinant antigen and an application thereof, and belongs to the field of veterinary vaccine researches. The modified recombinant antigen is obtained by modification and construction of a Cap gene after a nuclear localization sequence of a porcine circovirus type 2 LG strain widely prevalent in swinery in China at present is deleted. A vaccine prepared from the modified recombinant antigen can stimulate organisms to produce high-level neutralizing antibodies, is superior to commercially available inactivated influenza virus vaccines and separate Cap protein immunization groups after nuclear localization sequences are deleted, has a highest antibody level, is safe and harmless to immunized animals after inoculation, has the advantages of low price, safety, stability, high yield and easiness in preservation and application, and has great significance to related diseases caused by porcine circovirus type 2 infection in China, so that the porcine circovirus type 2 Cap gene modified recombinant antigen has a good application prospect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Artificial transcription factors for the treatment of diseases caused by opa1 haploinsufficiency
InactiveUS20160039893A1High expressionIncrease generationSenses disorderNervous disorderDiseaseHaploinsufficiency
The invention relates to an artificial transcription factor comprising a polydactyl zinc finger protein targeting specifically the OPA1 promoter fused to an activatory protein domain, and a nuclear localization sequence. Artificial transcription factors directed against the OPA1 promoter are useful for the treatment of diseases associated with OPA1 haploinsufficiency, such as autosomal dominant optic atrophy, syndromic autosomal dominant optic atrophy plus and normal tension glaucoma.
Owner:ALIOPHTHA
Compounds and methods of use to treat infectious diseases
The present invention concerns alkyl aryl carbonyl compounds that possess anti-infective activity. The compounds of the invention can be used to target specific nuclear localization signal, thereby blocking importation of specific proteins or molecular complex into the nucleus of a cell. The invention encompasses methods of use of such compounds for treatment or prevention of infectious diseases, such as parasitic and viral diseases, including, for example, malaria and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. The use of the compounds to detect certain specific protein structures which are present in nuclear localization sequences is also taught.
Owner:FERRING BV
Detection method for retinoic acid receptor alpha protein with nuclear localization signal
ActiveCN103412131ABiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceRetinoic acid receptor betaLaser scanning
Owner:AFFILIATED YONGCHUAN HOSPITAL OF CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com