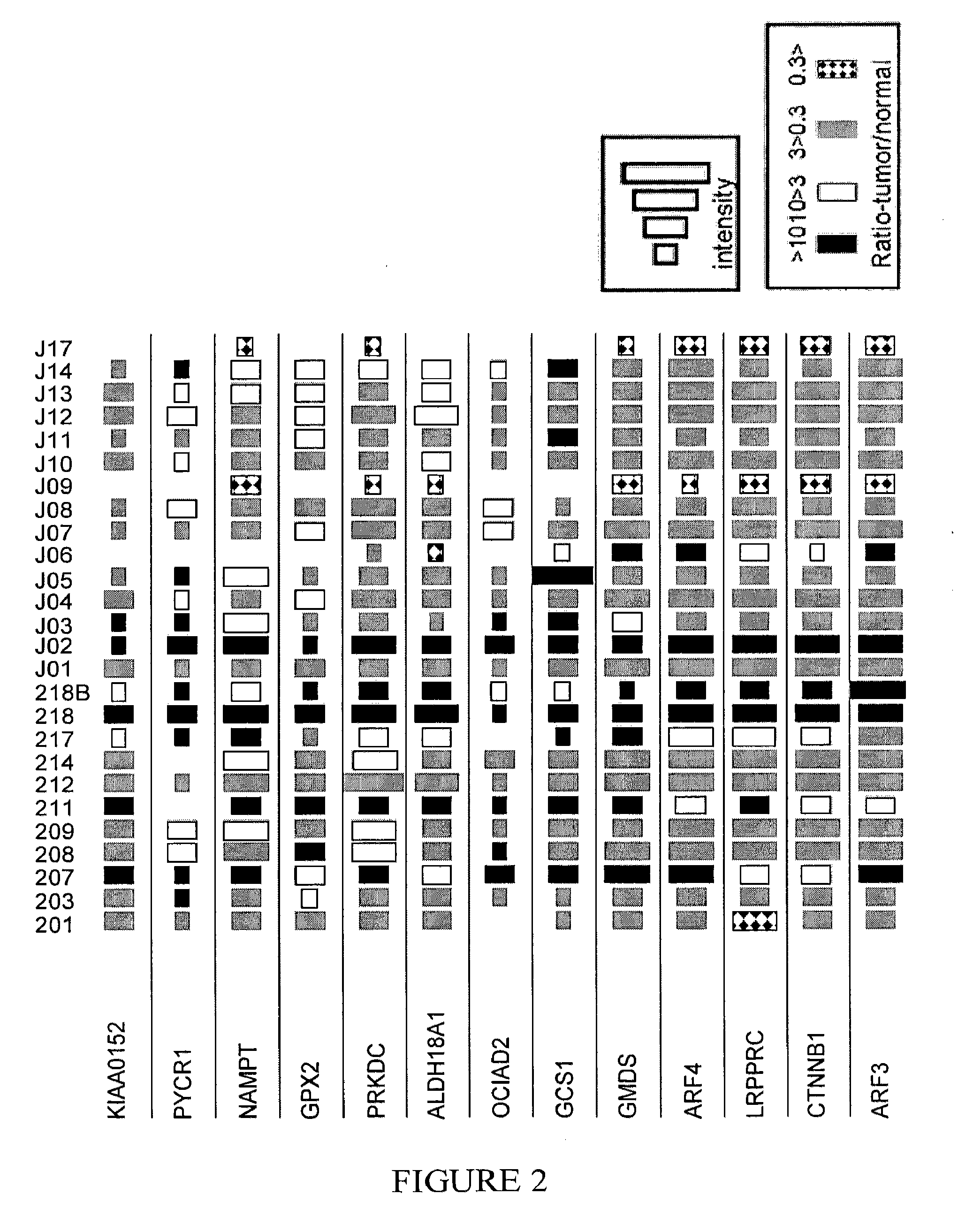
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
955 results about "Specific protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Specific proteins are valuable markers for a variety of diseases including microbial infections, inflammatory response, cardiac risk and even cancer. The complement system is a family of proteins that is integral in the destruction of viruses and bacteria, and is a major part of the immune system.
Organ-specific proteins and methods of their use
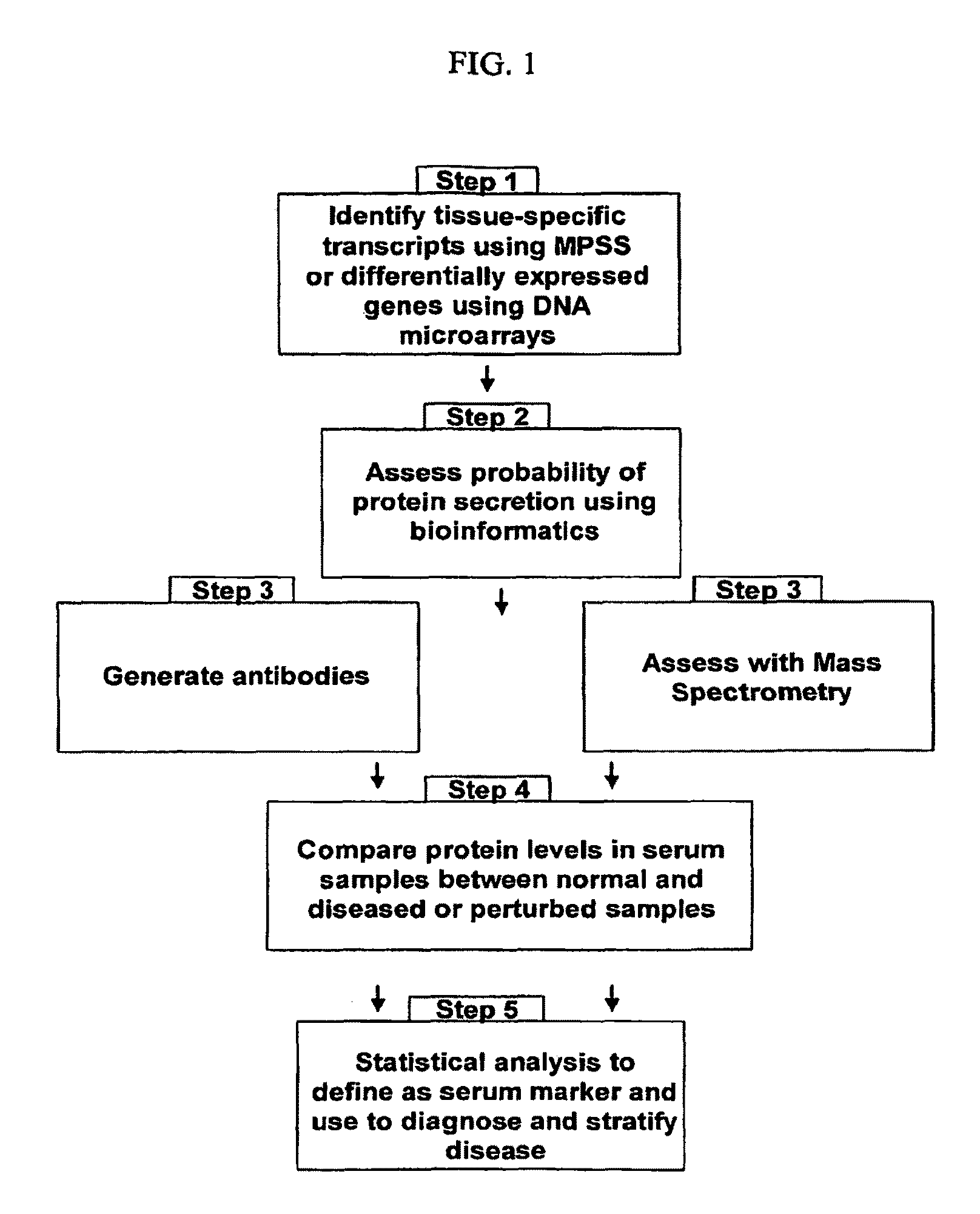
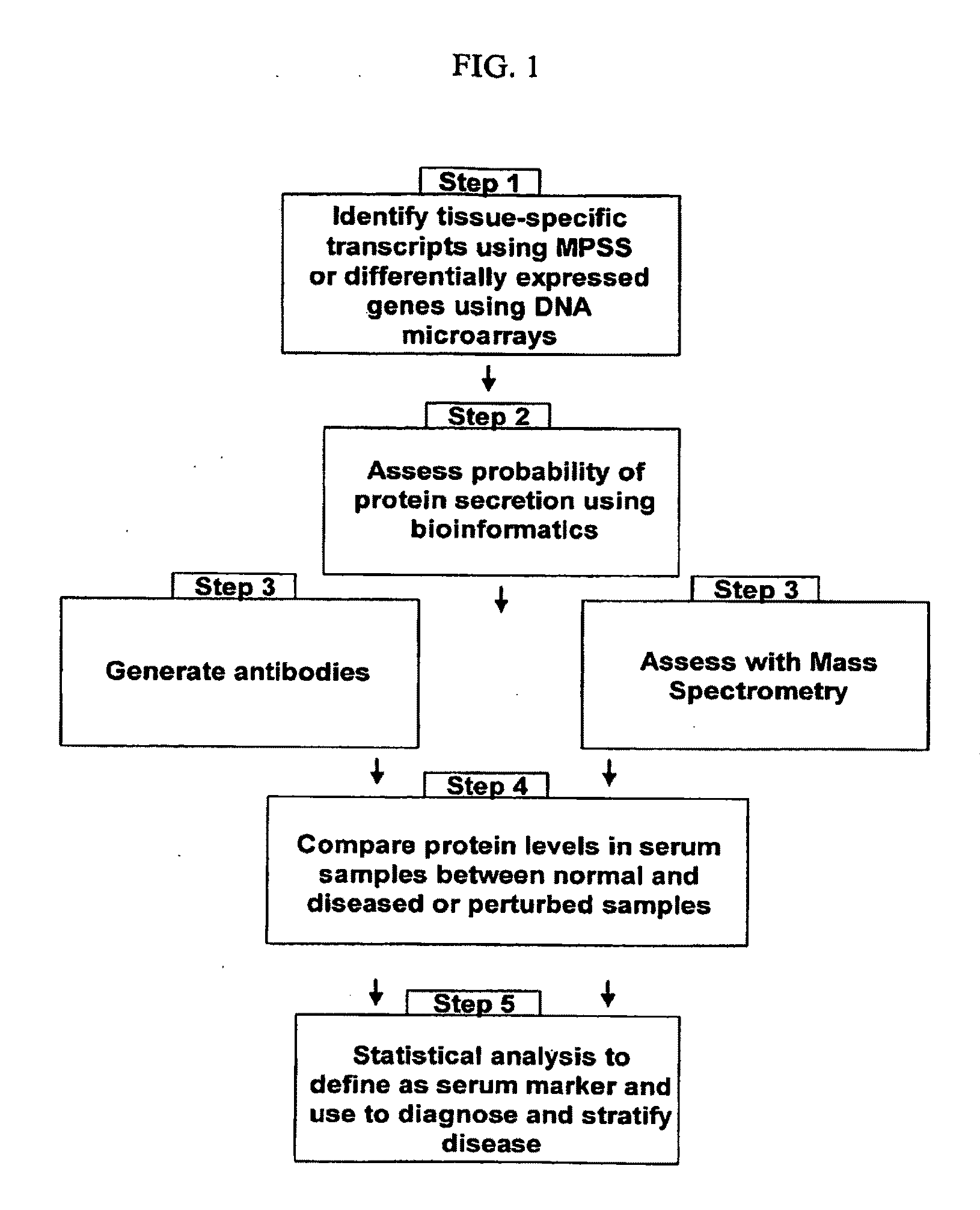
The present invention relates generally to methods for identifying and using organ-specific proteins and transcripts. The present invention further provides compositions comprising organ-specific proteins and transcripts encoding the same, detection reagents for detecting such proteins and transcripts, and diagnostic panels, kits and arrays for measuring organ-specific proteins / transcripts in blood, biological tissue or other biological fluid.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR SYSTEMS BIOLOGY +1
Identification and comparison of protein-protein interactions that occur in populations and identification of inhibitors of these interactors
InactiveUS6057101AEfficient screeningLess experimentally significant and specific indicationMaterial nanotechnologyFungiDiseaseBinding site
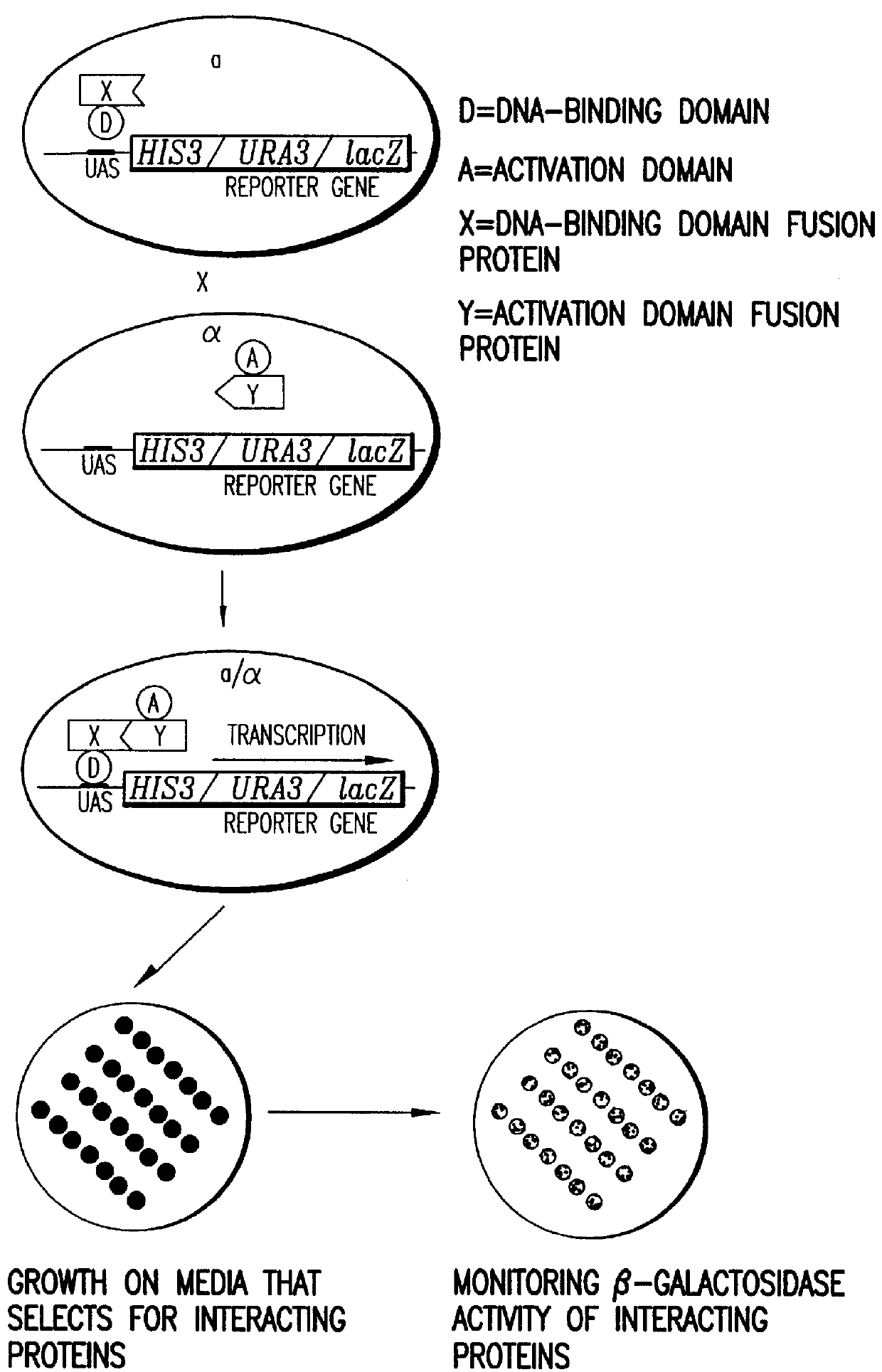
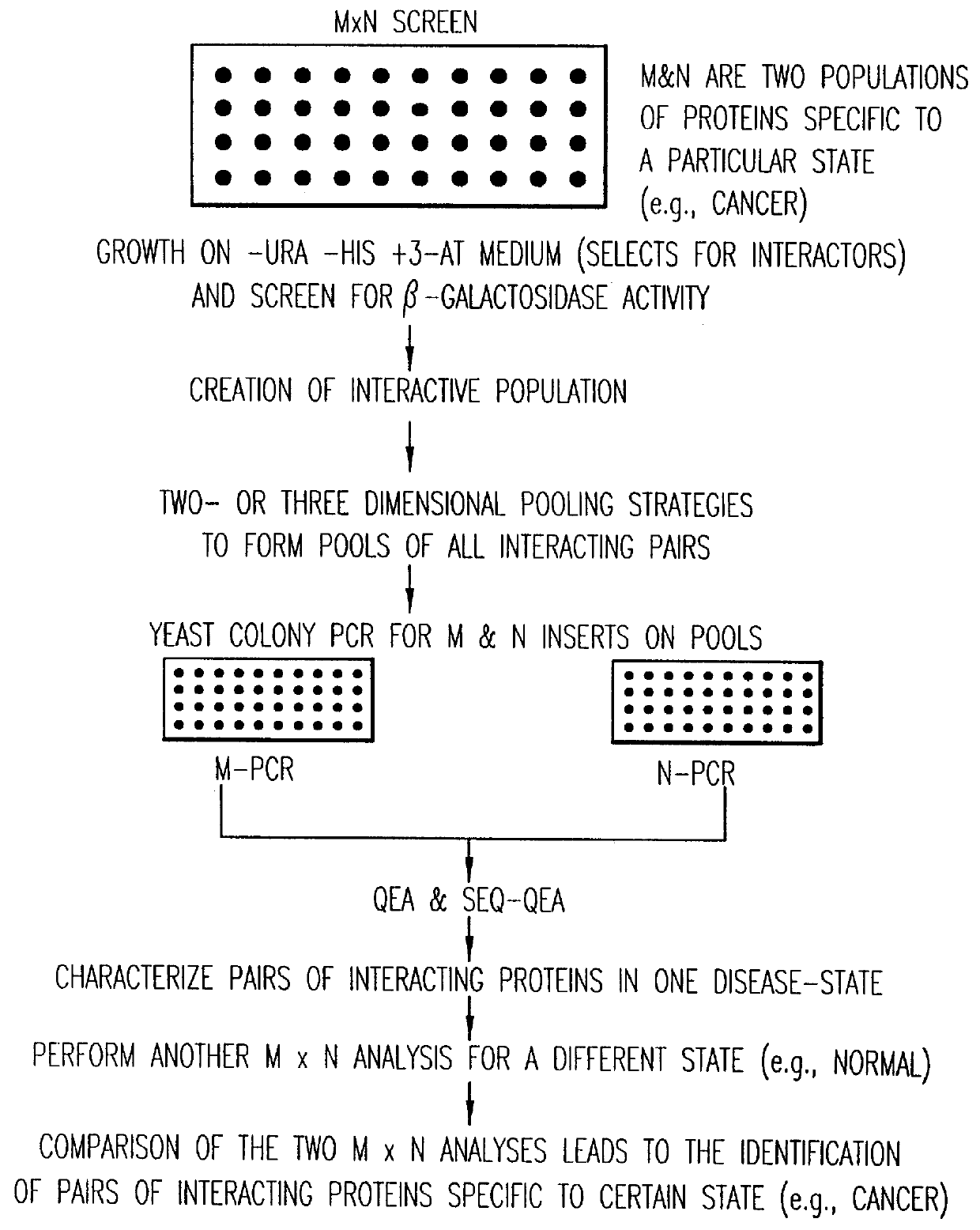
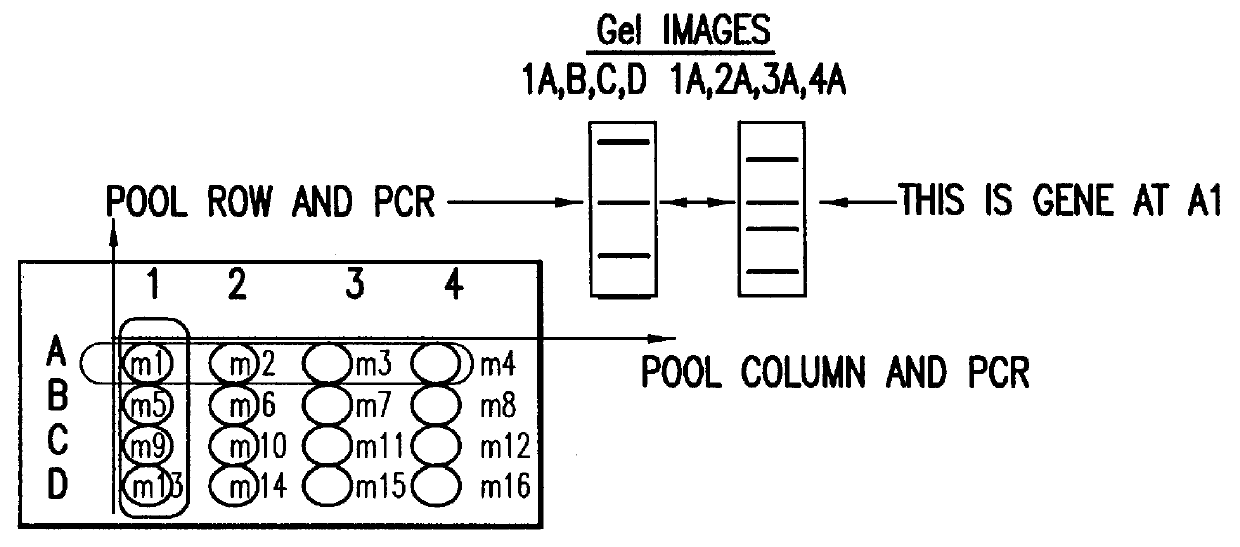
Methods are described for detecting protein-protein interactions, among two populations of proteins, each having a complexity of at least 1,000. For example, proteins are fused either to the DNA-binding domain of a transcriptional activator or to the activation domain of a transcriptional activator. Two yeast strains, of the opposite mating type and carrying one type each of the fusion proteins are mated together. Productive interactions between the two halves due to protein-protein interactions lead to the reconstitution of the transcriptional activator, which in turn leads to the activation of a reporter gene containing a binding site for the DNA-binding domain. This analysis can be carried out for two or more populations of proteins. The differences in the genes encoding the proteins involved in the protein-protein interactions are characterized, thus leading to the identification of specific protein-protein interactions, and the genes encoding the interacting proteins, relevant to a particular tissue, stage or disease. Furthermore, inhibitors that interfere with these protein-protein interactions are identified by their ability to inactivate a reporter gene. The screening for such inhibitors can be in a multiplexed format where a set of inhibitors will be screened against a library of interactors. Further, information-processing methods and systems are described. These methods and systems provide for identification of the genes coding for detected interacting proteins, for assembling a unified database of protein-protein interaction data, and for processing this unified database to obtain protein interaction domain and protein pathway information.
Owner:CURAGEN CORP
Novel liposome complexes for increased systemic delivery
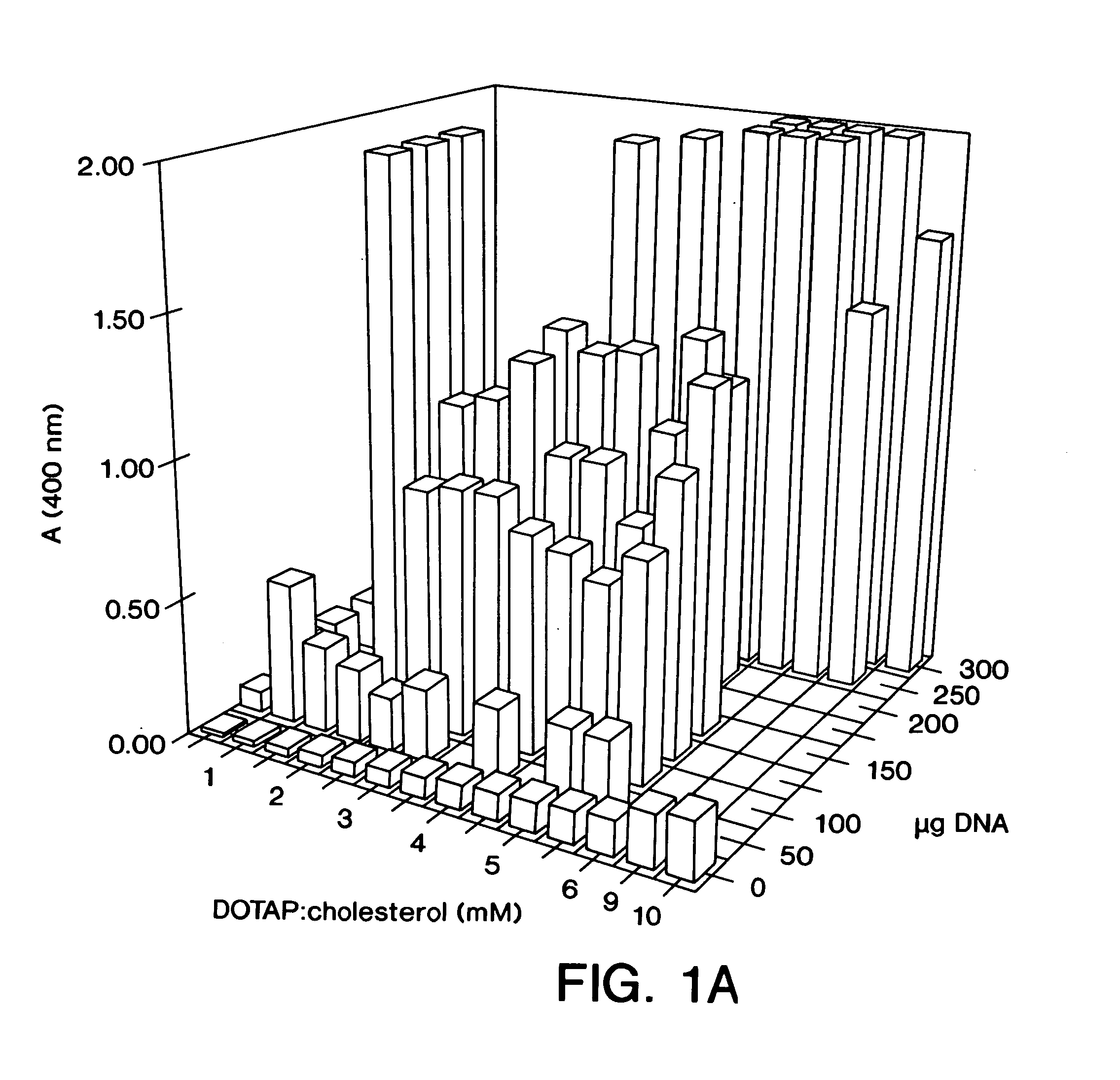
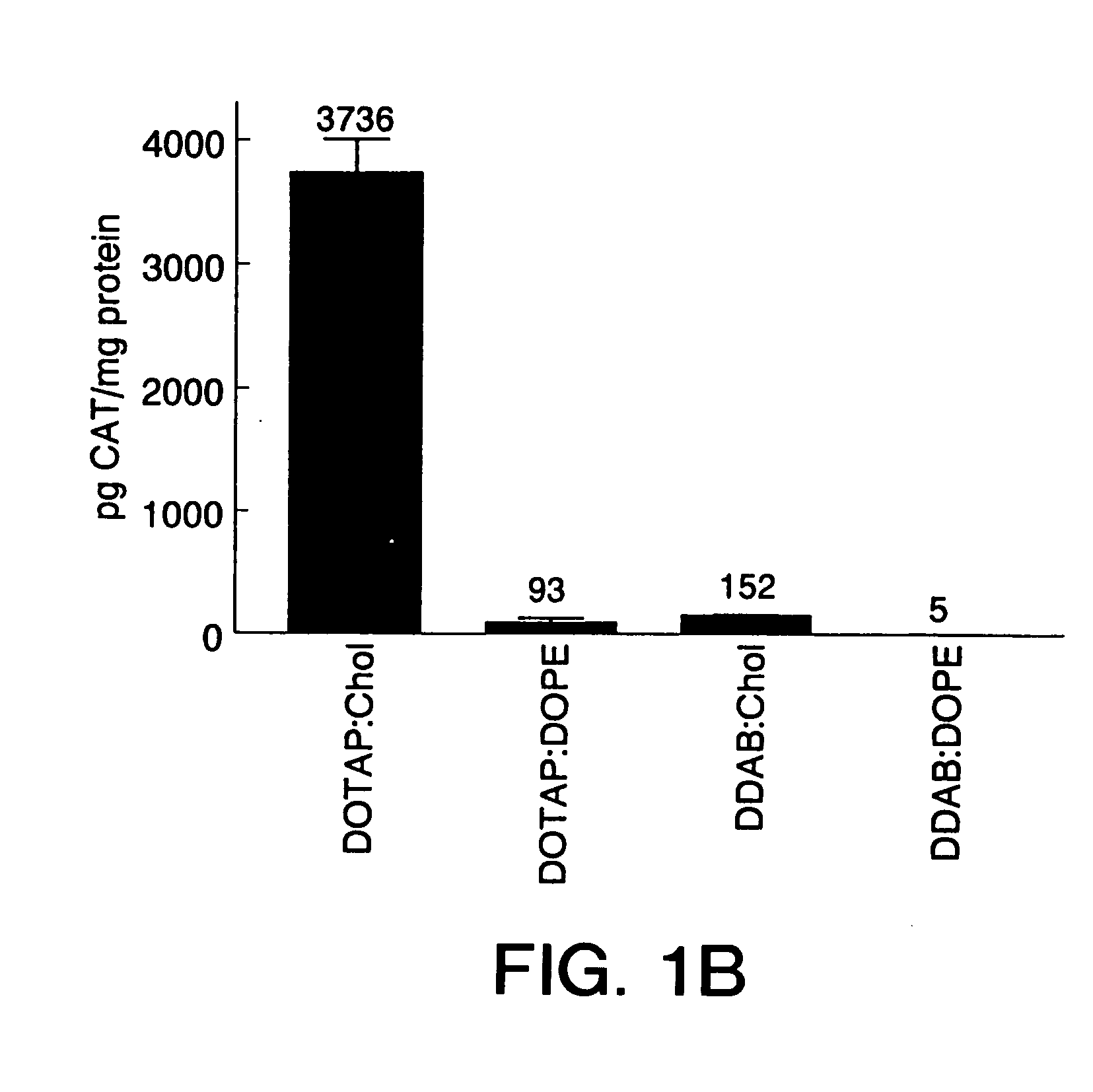
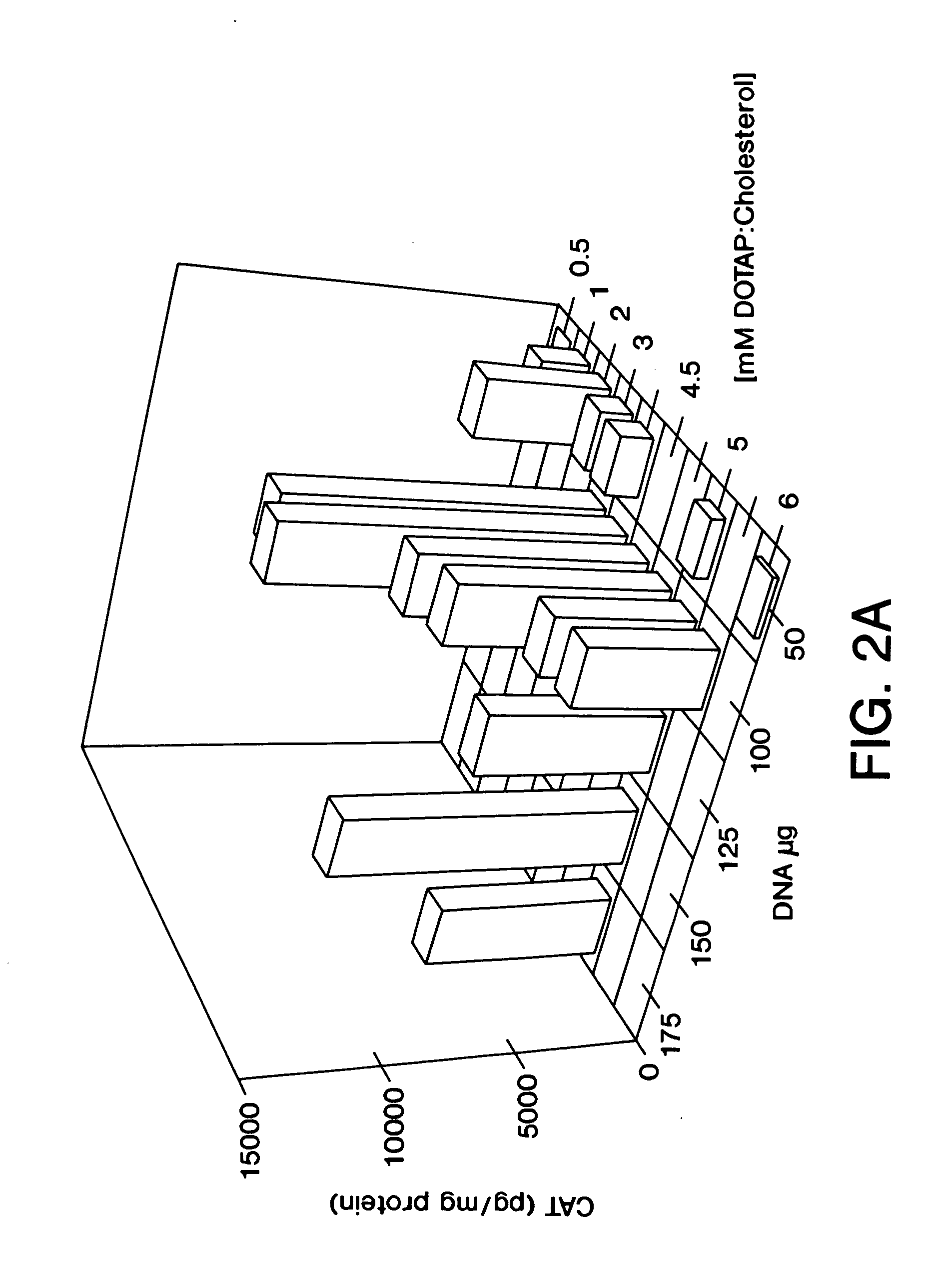
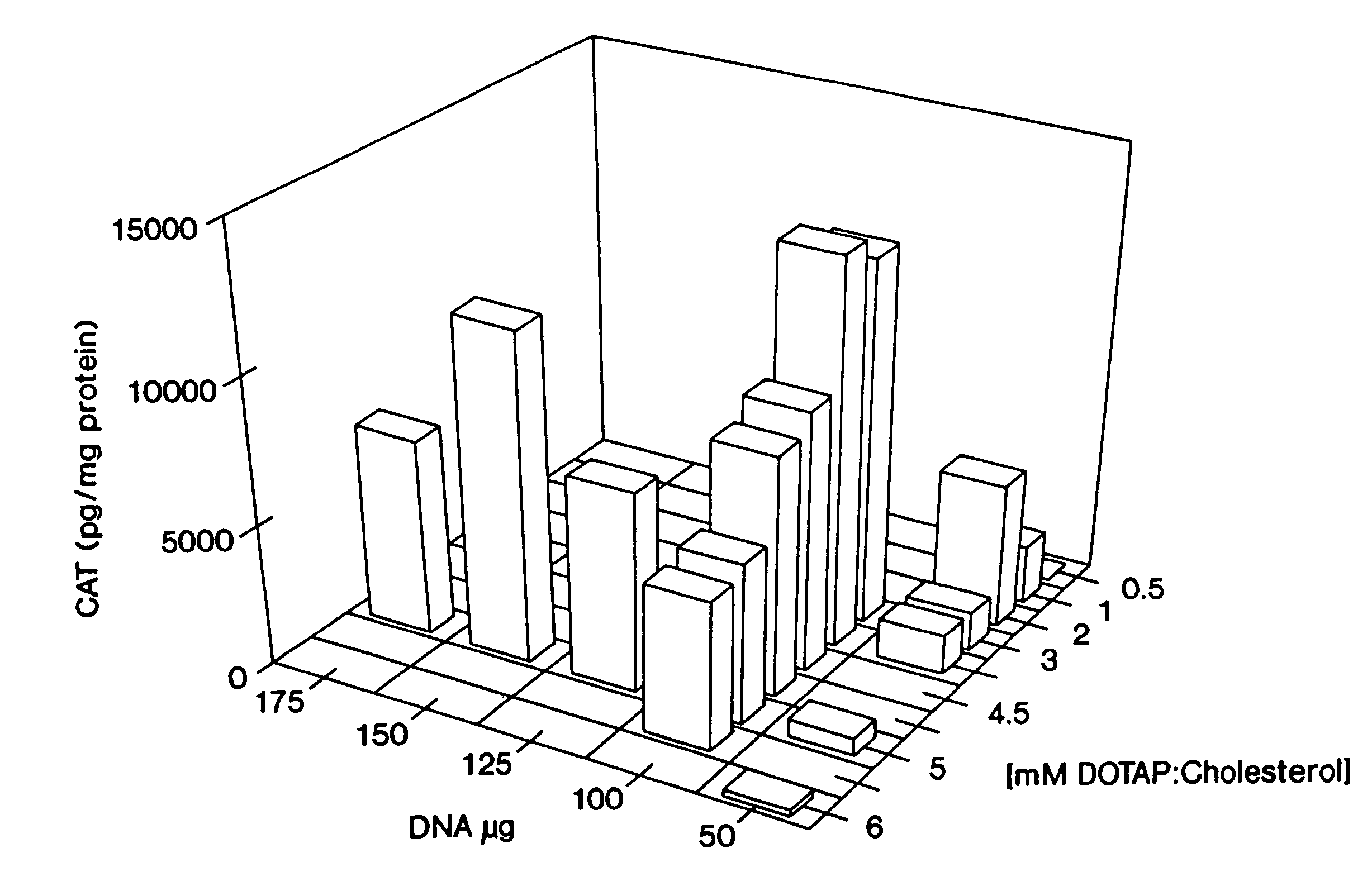
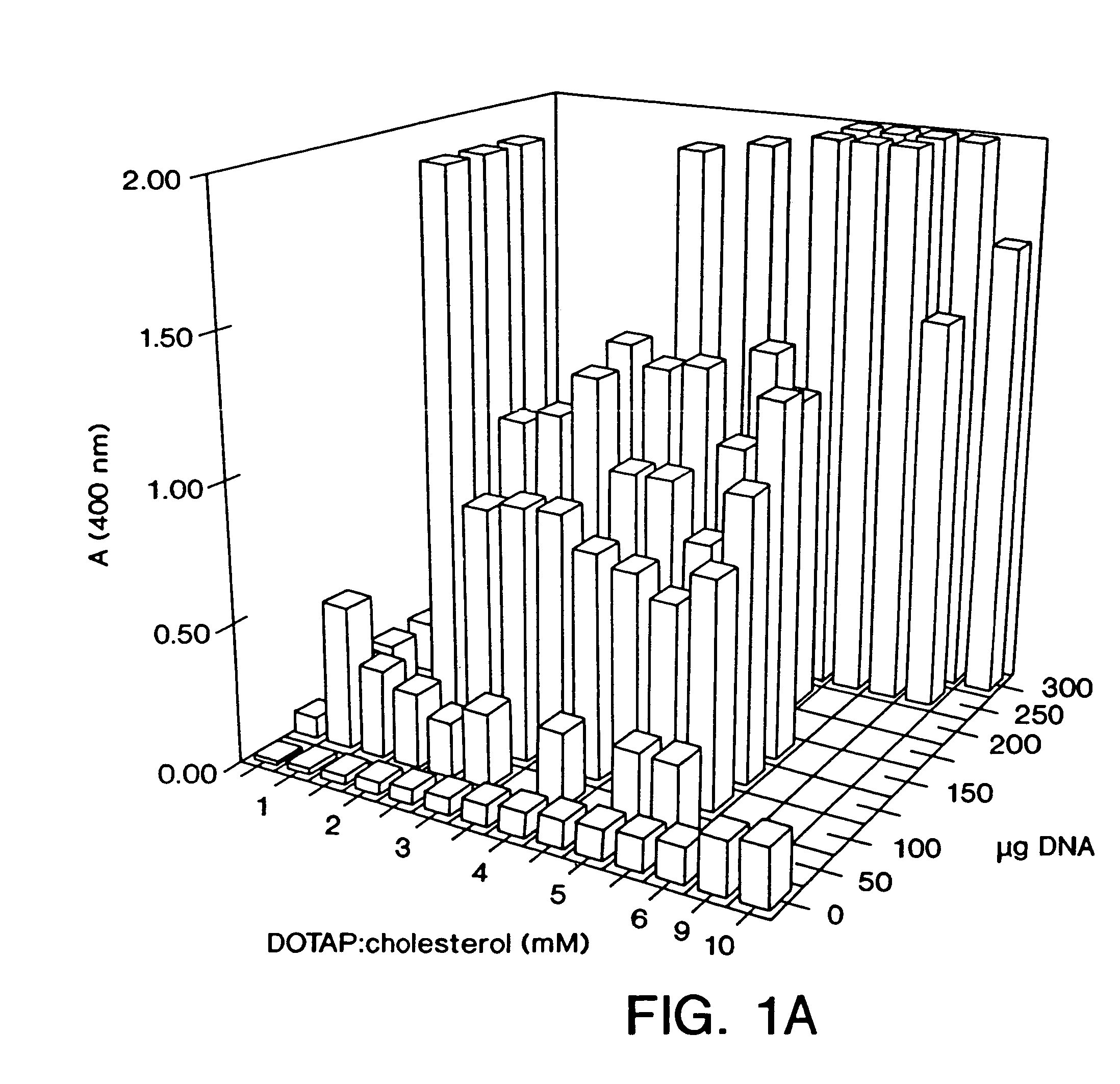
Highly efficient cationic liposomes have been developed as an improved delivery system for biologically-active reagents. A novel structure, the sandwich liposome, is formed and comprises one or more biologically active agents internalized between two bilomellar liposomes. This structure protects the incoming agent and accounts for the high efficiency of in vivo delivery and for the broad tissue distribution of the sandwich liposome complexes. These novel liposomes are also highly efficient carriers of nucleic acids. By using extruded DOTAP:cholesterol liposomes to form complexes with DNA encoding specific proteins, expression has been improved dramatically. Highest expression was achieved in the lung, while increased expression was detected in several organs and tissues.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Organ-specific proteins and methods of their use
The present invention relates generally to methods for identifying and using organ-specific proteins and transcripts. The present invention further provides compositions comprising organ-specific proteins and transcripts encoding the same, detection reagents for detecting such proteins and transcripts, and diagnostic panels, kits and arrays for measuring organ-specific proteins / transcripts in blood, biological tissue or other biological fluid.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR SYSTEMS BIOLOGY +1
Bone matrix compositions and methods
ActiveUS20070154563A1Good osteoinductivityHigh activityHydrolysed protein ingredientsBone implantOsteoblastLine of therapy
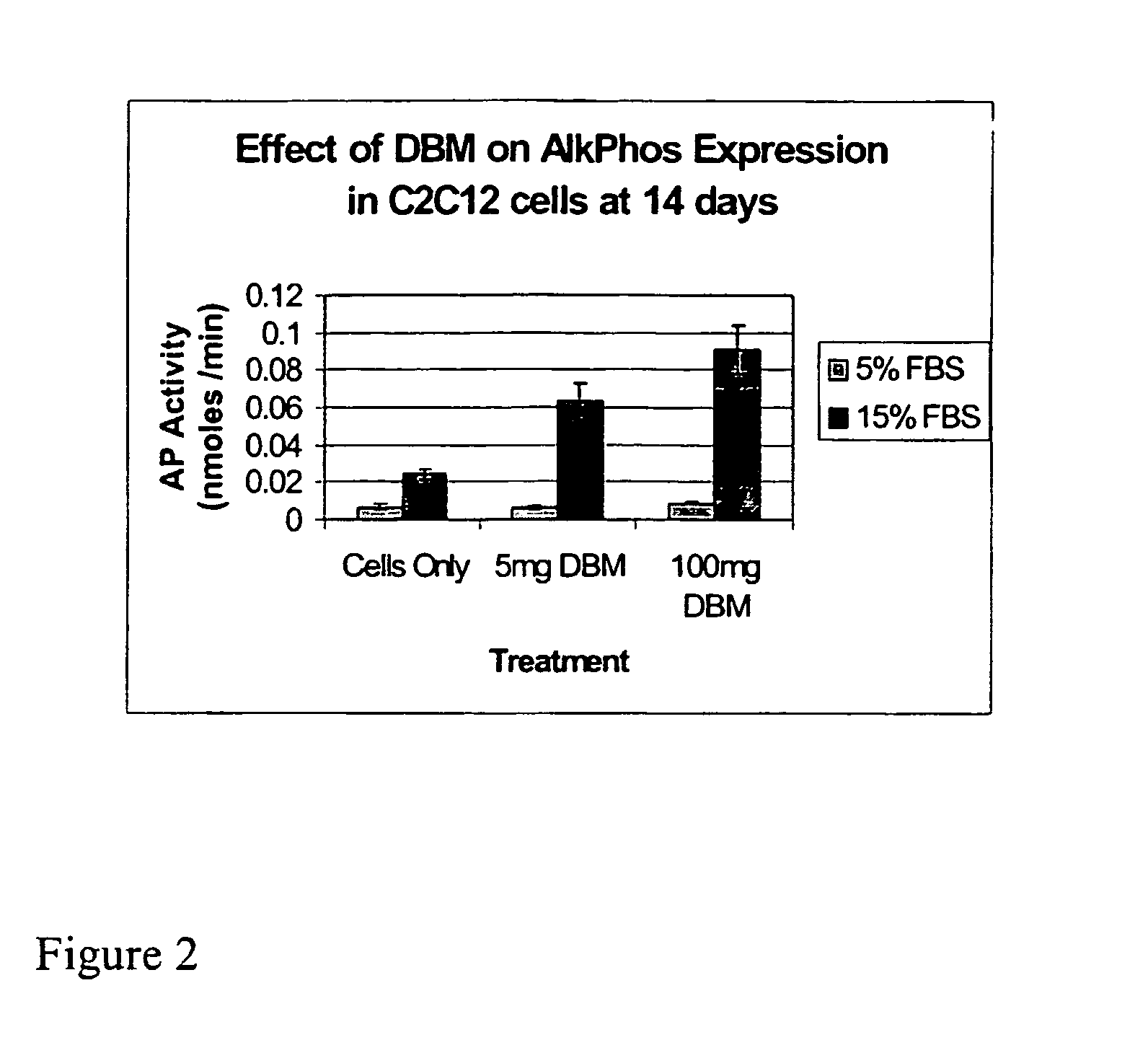
The present invention provides methods of improving the osteogenic and / or chondrogenic activity of a bone matrix, e.g., a dermineralized bone matrix (DBM), by exposing the bone matrix to one or more treatments or conditions. In preferred embodiments the bone matrix is derived from human bone. The treatment or condition may alter the structure of the bone matrix and / or cleave one or more specific proteins. Cleavage may generate peptides or protein fragments that have osteoinductive, osteogenic, or chondrogenic activity. Preferred treatments include collagenase and various other proteases. The invention further provides improved bone and cartilage matrix compositions that have been prepared according to the inventive methods and methods of treatment using the compositions. The invention further provides methods of preparing, testing, and using the improved bone matrix compositions. Ona assay comprises exposing relatively undifferentiated mesenchymal cells to a bone matrix composition and measuring expression of a marker characteristic of osteoblast or chondrocyte lineage(s). Increased expression of the marker relative to the level of the marker in cells that have been exposed to a control matrix (e.g., an inactivated or untreated matrix) indicates that the treatment or condition increased the osteogenic and / or chondrogenic activity of the bone matrix. Suitable cells include C2C12 cells. A suitable marker is alkaline phosphatase. The inventive methods increase the osteogenic and / or chondrogenic activity of human DBM when tested using this assay system.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
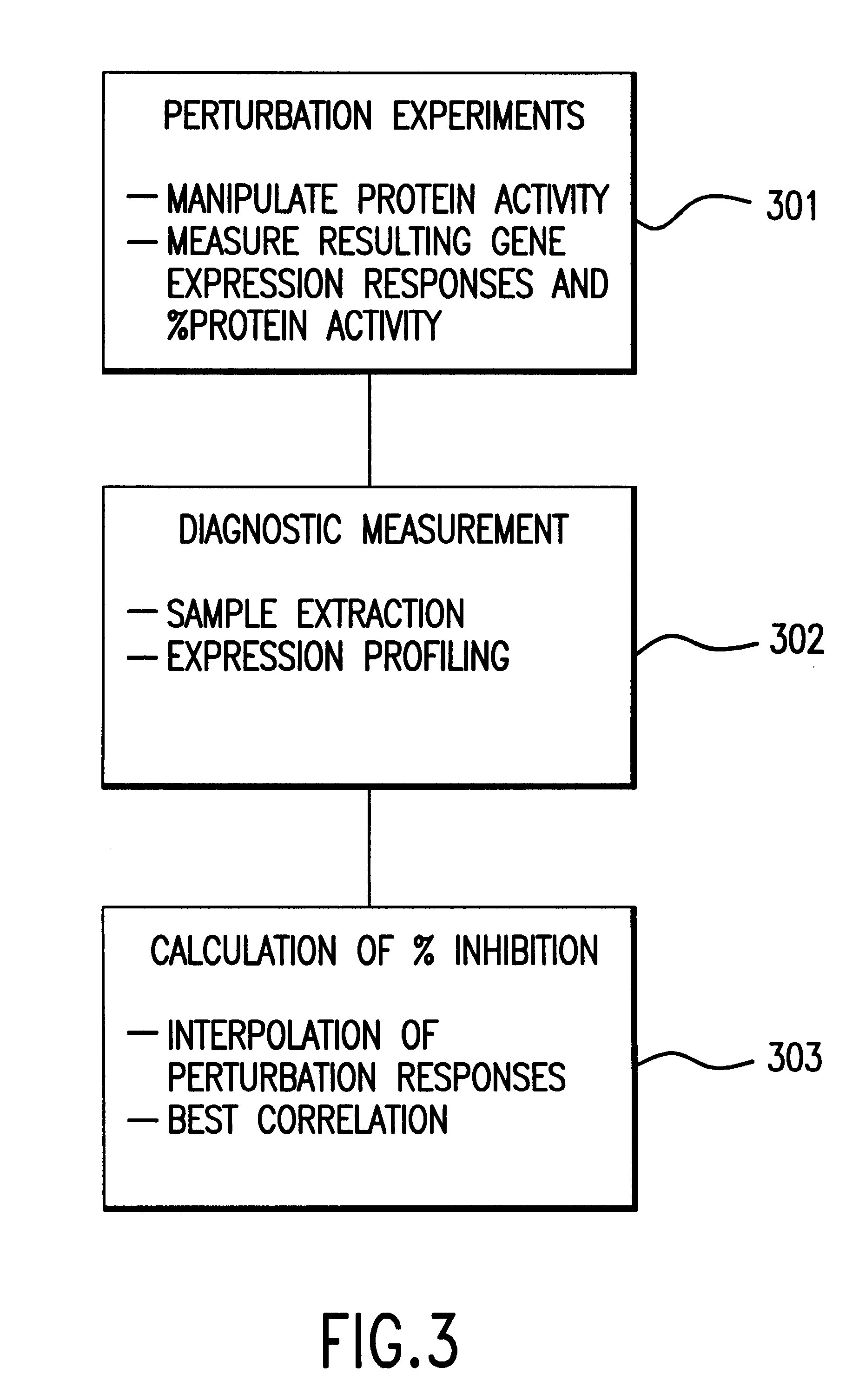
Methods of determining protein activity levels using gene expression profiles
InactiveUS6324479B1High similaritySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsProtein insertionDrug activity
The present invention provides methods for determining the level of protein activity in a cell by: (i) measuring abundances of cellular constituents in a cell in which the activity of a specific protein is to be determined so that a diagnostic profile is thus obtained; (ii) measuring abundances of cellular constituents that occur in a cell in response to perturbations in the activity of said protein to obtain response profiles and interpolating said response profiles to generate response curves; and (iii) determining a protein activity level at which the response profile extracted from the response curves best fits the measured diagnostic profile, according to some objective measure. In alternative embodiments, the present invention also provides methods for identifying individuals having genetic mutations or polymorphisms that disrupt protein activity, and methods for identifying drug activity in vivo by determining the activity levels of proteins which interact with said drugs.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
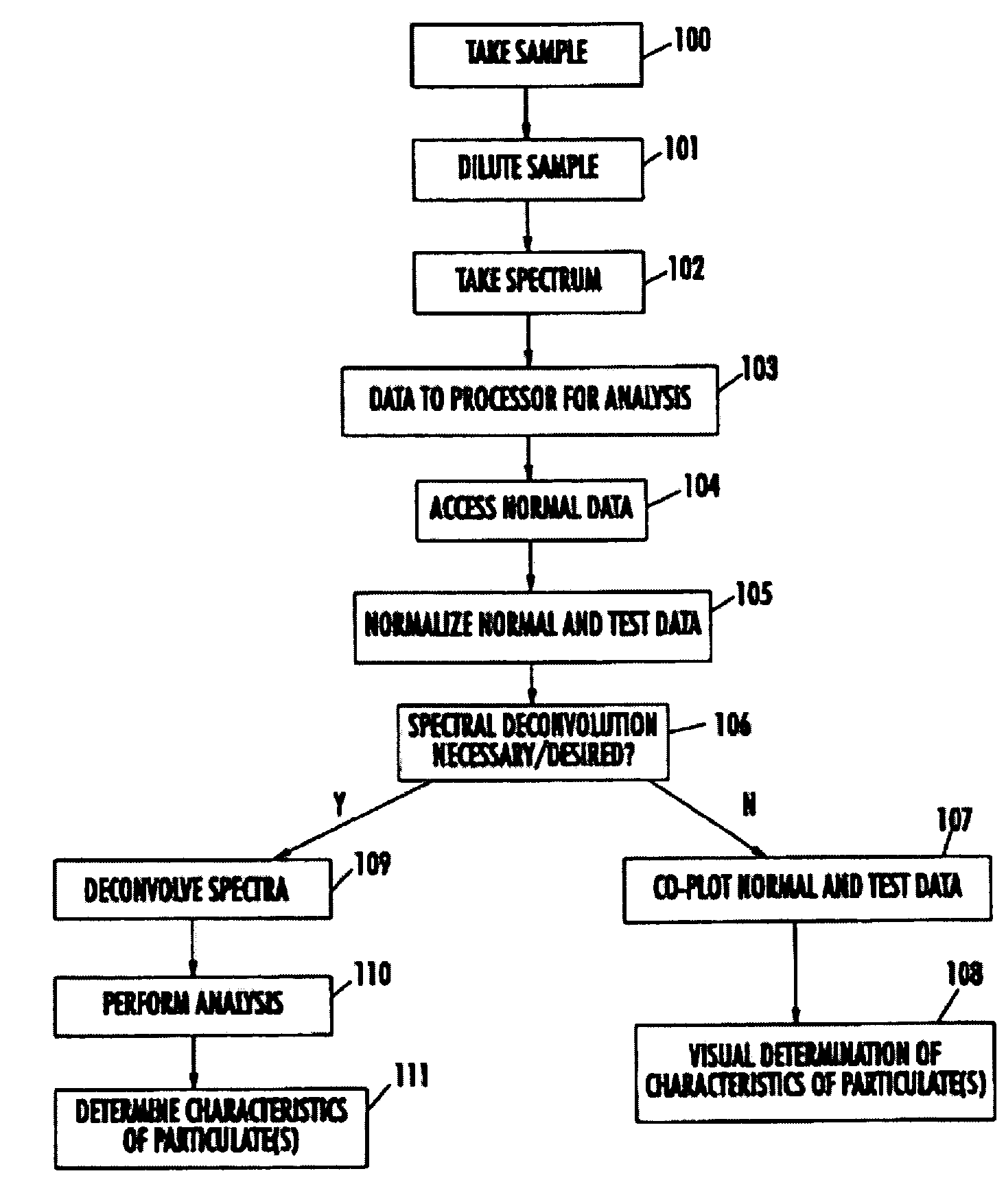
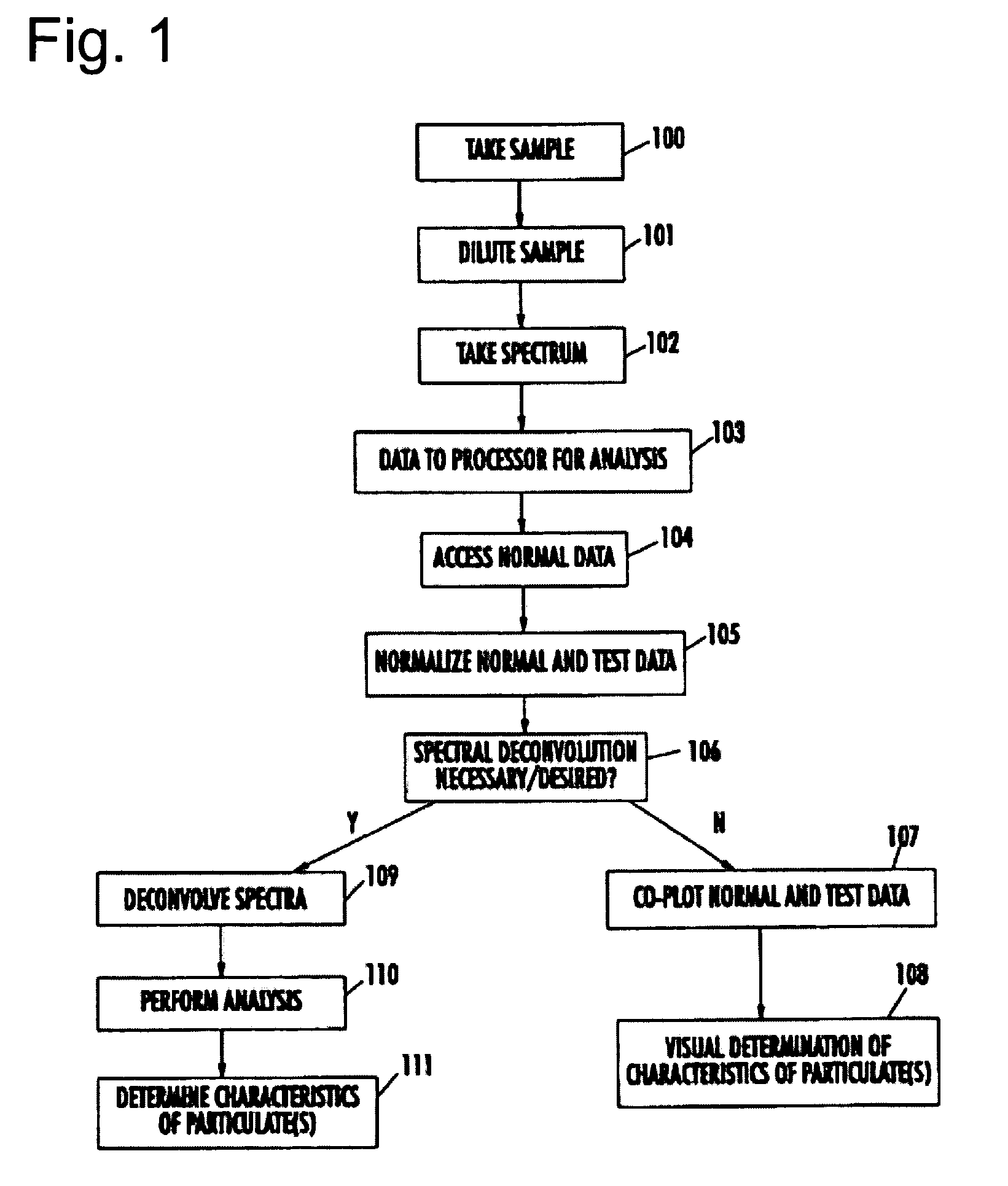
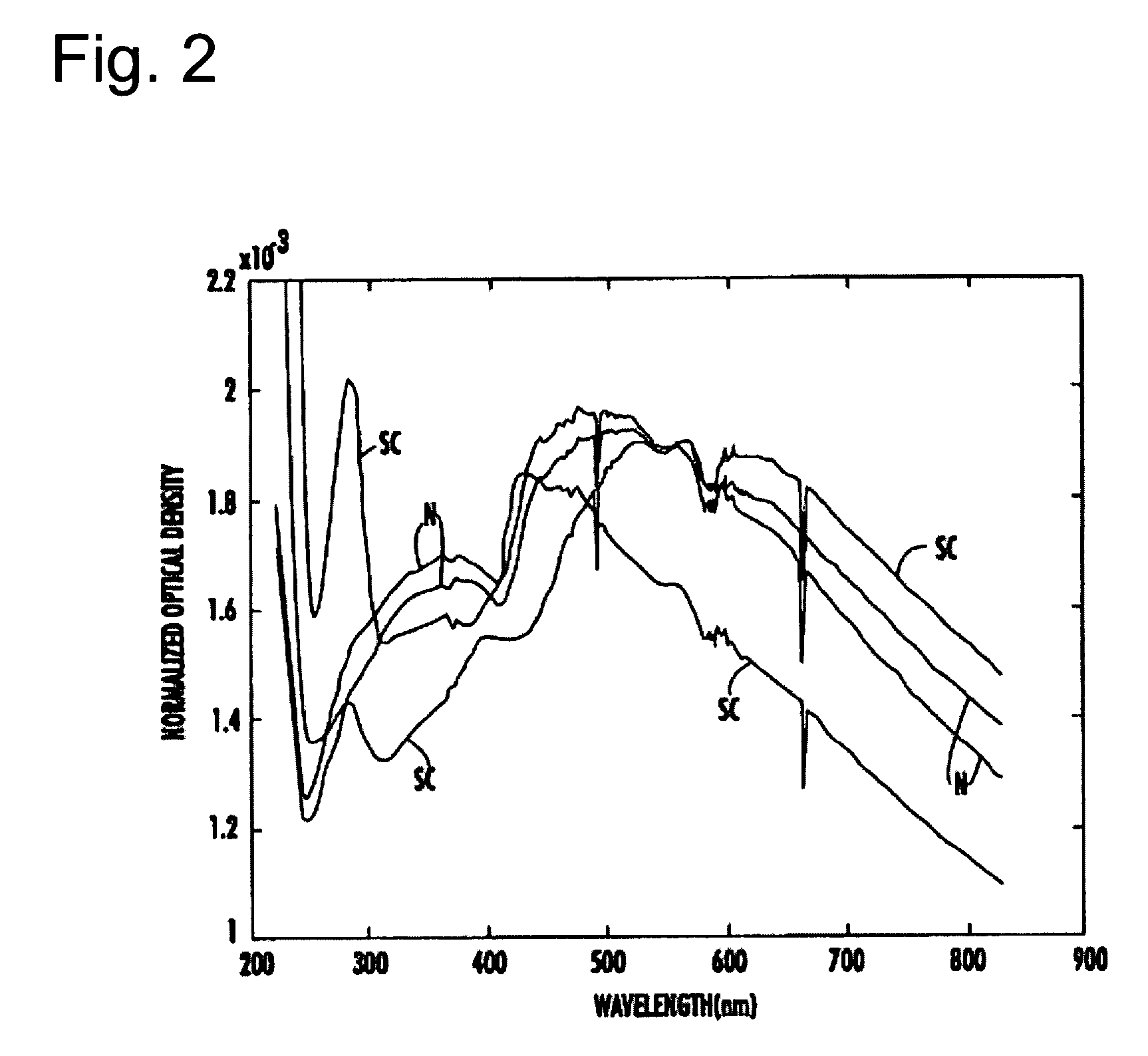
Spectrophotometric system and method for the identification and characterization of a particle in a bodily fluid
InactiveUS7027134B1Rapid and inexpensive and convenient for diagnosisRapidly and inexpensively disease diagnosisScattering properties measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringTurbidimetryWavelength
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for the detection of an infectious disease or disorder in a fluid, such as a mammalian blood sample, the detection of a specific protein in a urine sample, or the detection of a particle in a plasma. The identification of the particles of interest is enable by taking a transmission spectrum of a test sample in at least a portion of the ultraviolet, visible, near-infrared portion of the spectrum and comparing the spectrum with a standard sample spectrum. From the comparison it is then determined whether the fluid from the test sample contains an particle of interest, and an identity of the particle of interest is determined. Spectroscopic and multiwavelength turbidimetry techniques provide a rapid, inexpensive, and convenient means for diagnosis. The comparison and determination steps may be performed visually or by spectral deconvolution.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Peptide sequences specific for the hepatic stages of P. falciparum bearing epitopes capable of stimulating the T lymphocytes
The present invention relates to an in vitro diagnostic method for malaria in an individual comprising placing a tissue or a biological fluid taken from an individual in contact with a molecule or polypeptide composition, wherein said molecule or polypeptide composition comprises one or more peptide sequences bearing all or part of one or more T epitopes of the proteins resulting from the infectious activity of P. falciparum, under conditions allowing an in vitro immunological reaction to occur between said composition and the antibodies that may be present in the tissue or biological fluid, and in vitro detection of the antigen-antibody complexes formed. The invention further relates to a polypeptide comprising at least one T epitope from a liver-stage specific protein produced by P. falciparum and a vaccine composition directed against malaria comprising a molecule having one or more peptide sequences bearing all or part of one or more T epitopes resulting from the infectious activity of P. falciparum in the hepatic cells.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
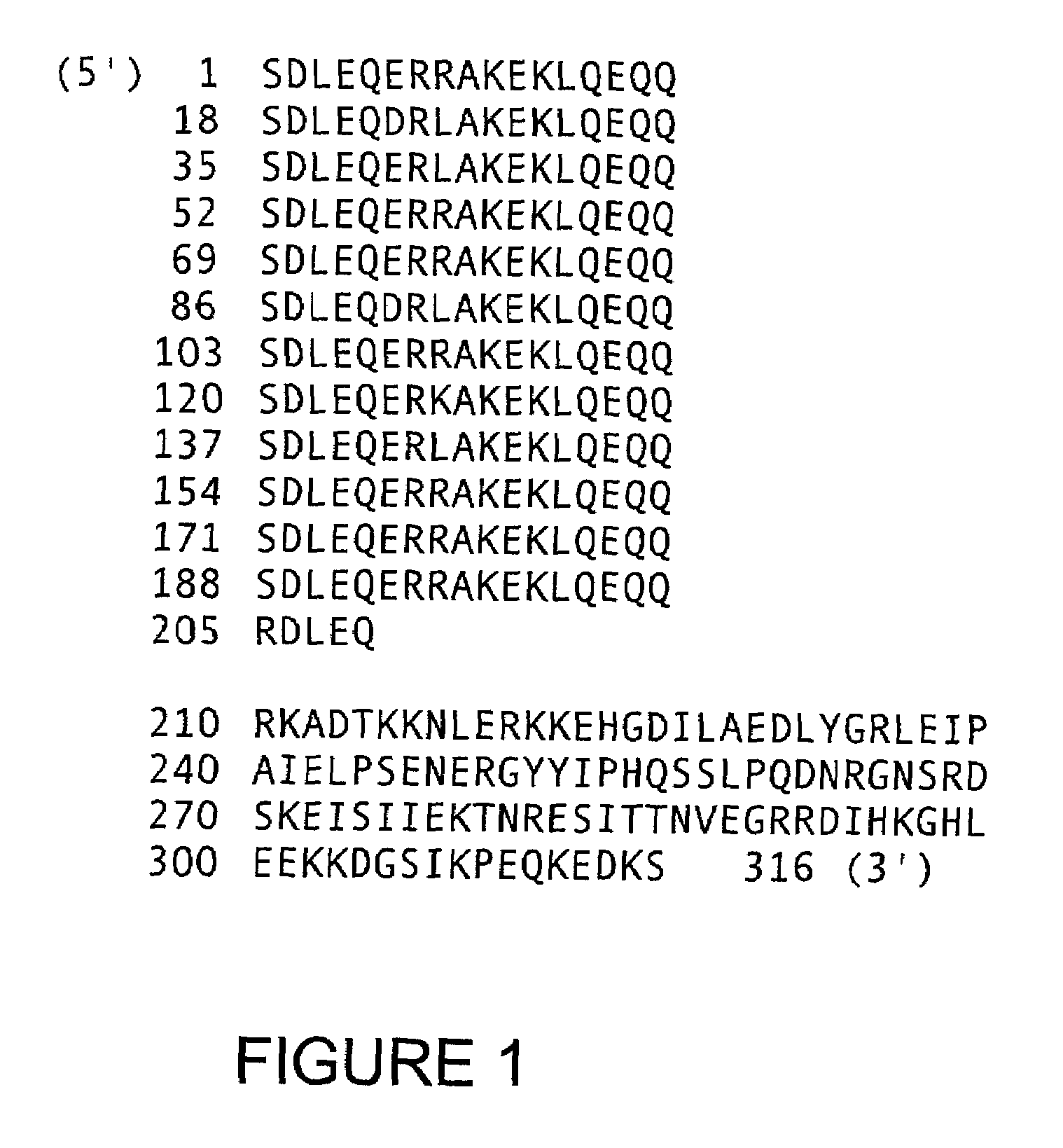
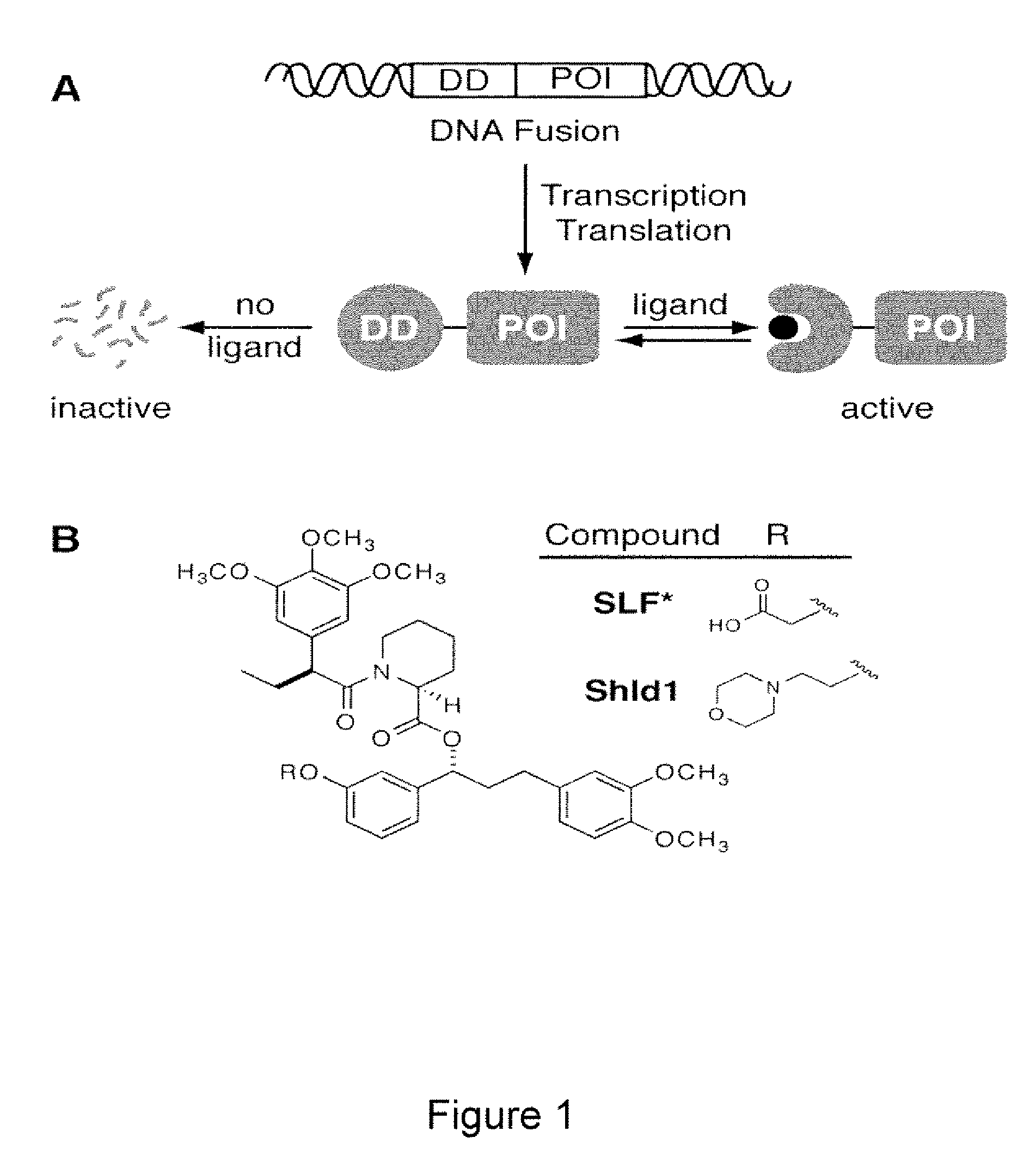
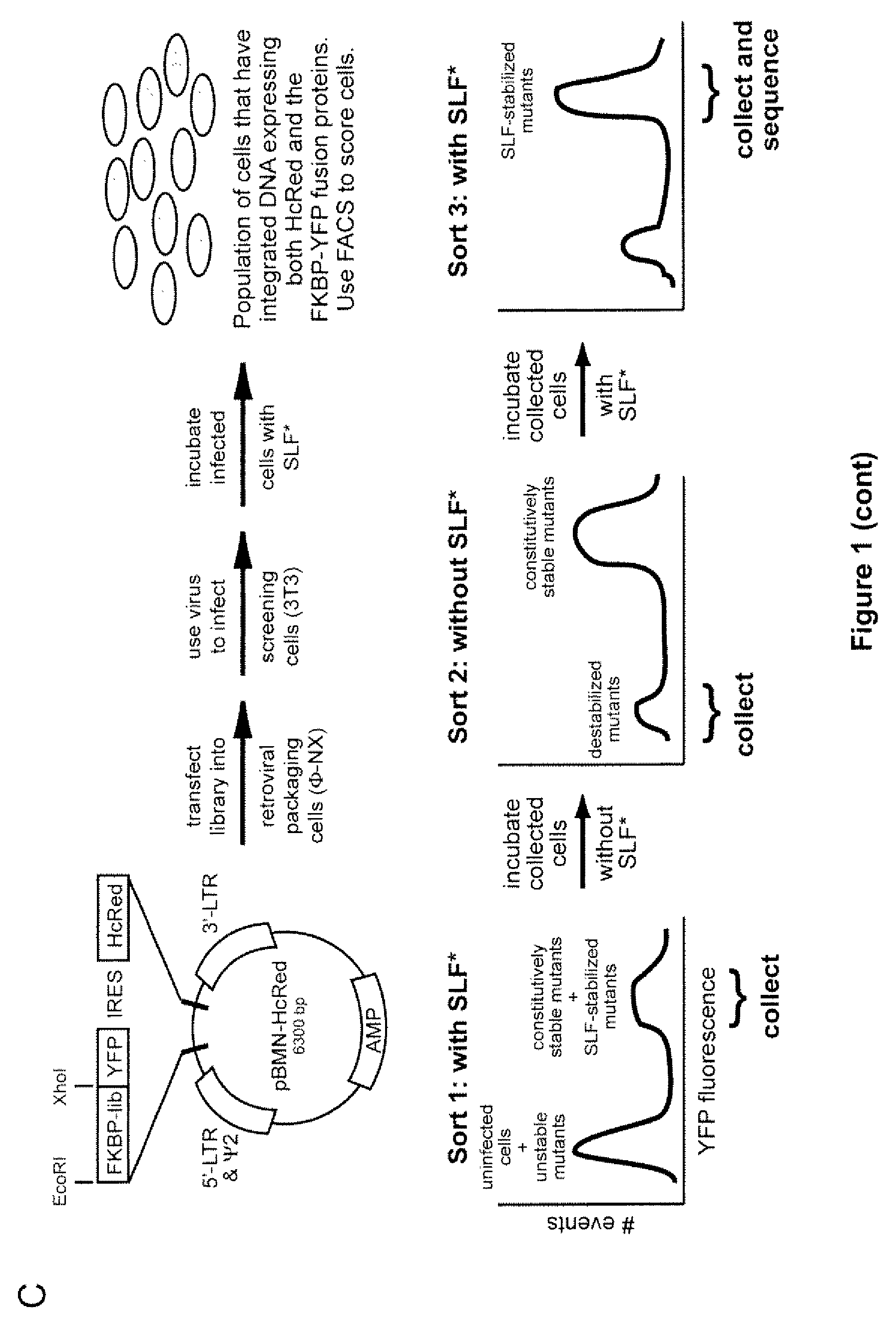
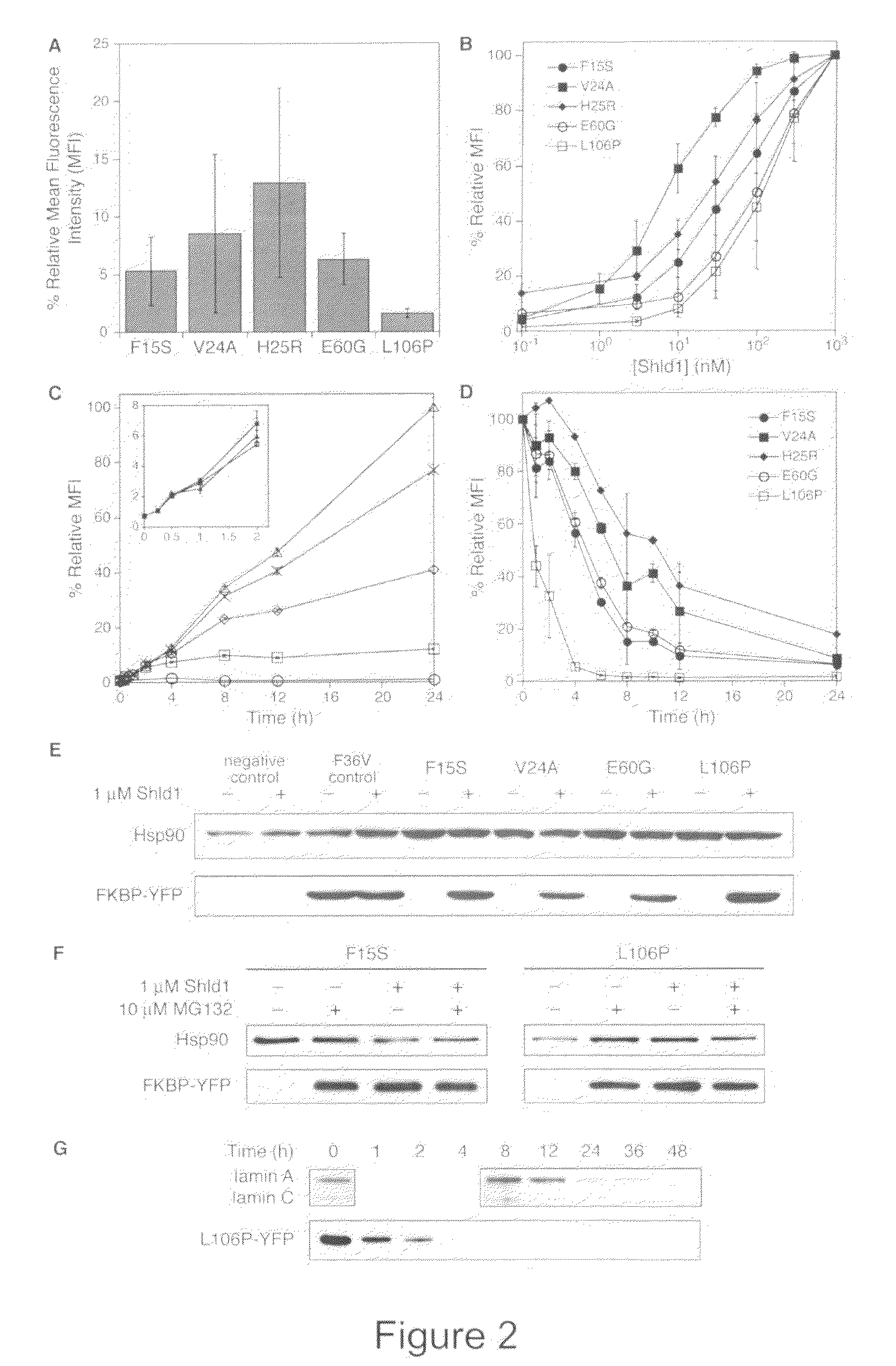
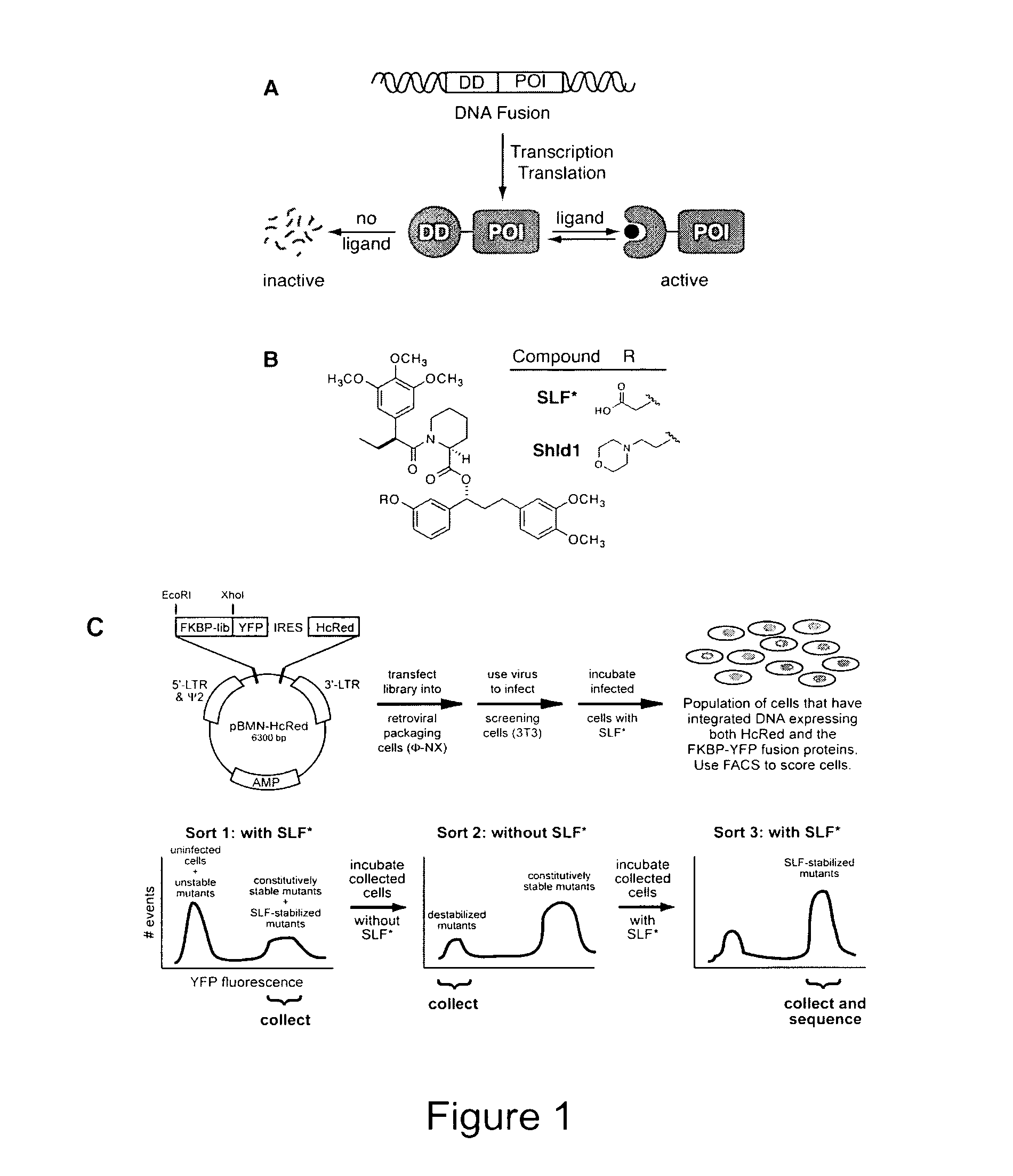
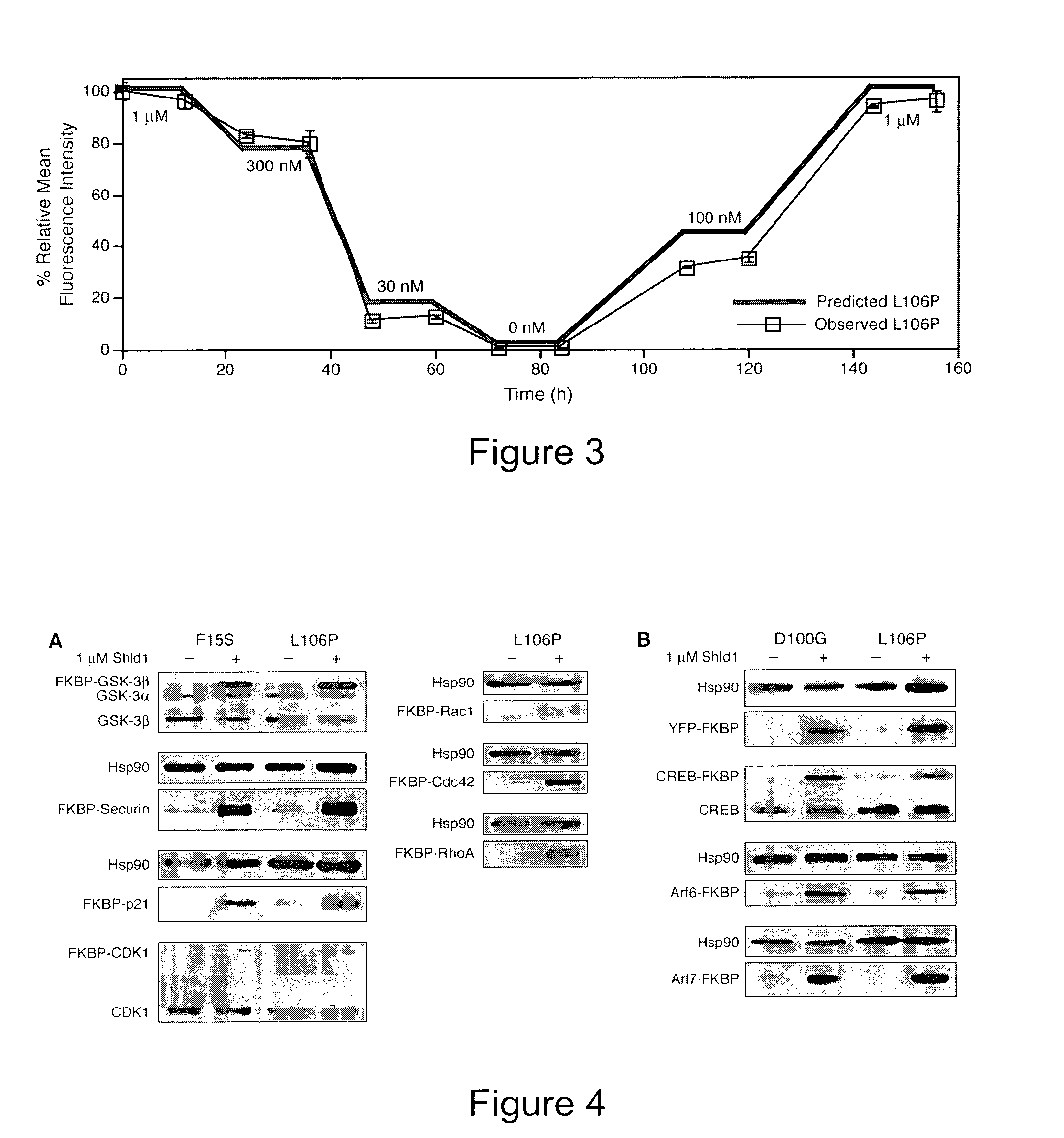
Method for regulating protein function in cells using synthetic small molecules
Methods and compositions for the rapid and reversible destabilizing of specific proteins using cell-permeable, synthetic molecules are described. Stability-affecting proteins, e.g., derived from FKBP and DHFR proteins are fused to a protein of interest and the presence or absence of the ligand is used to modulate the stability of the fusion protein.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
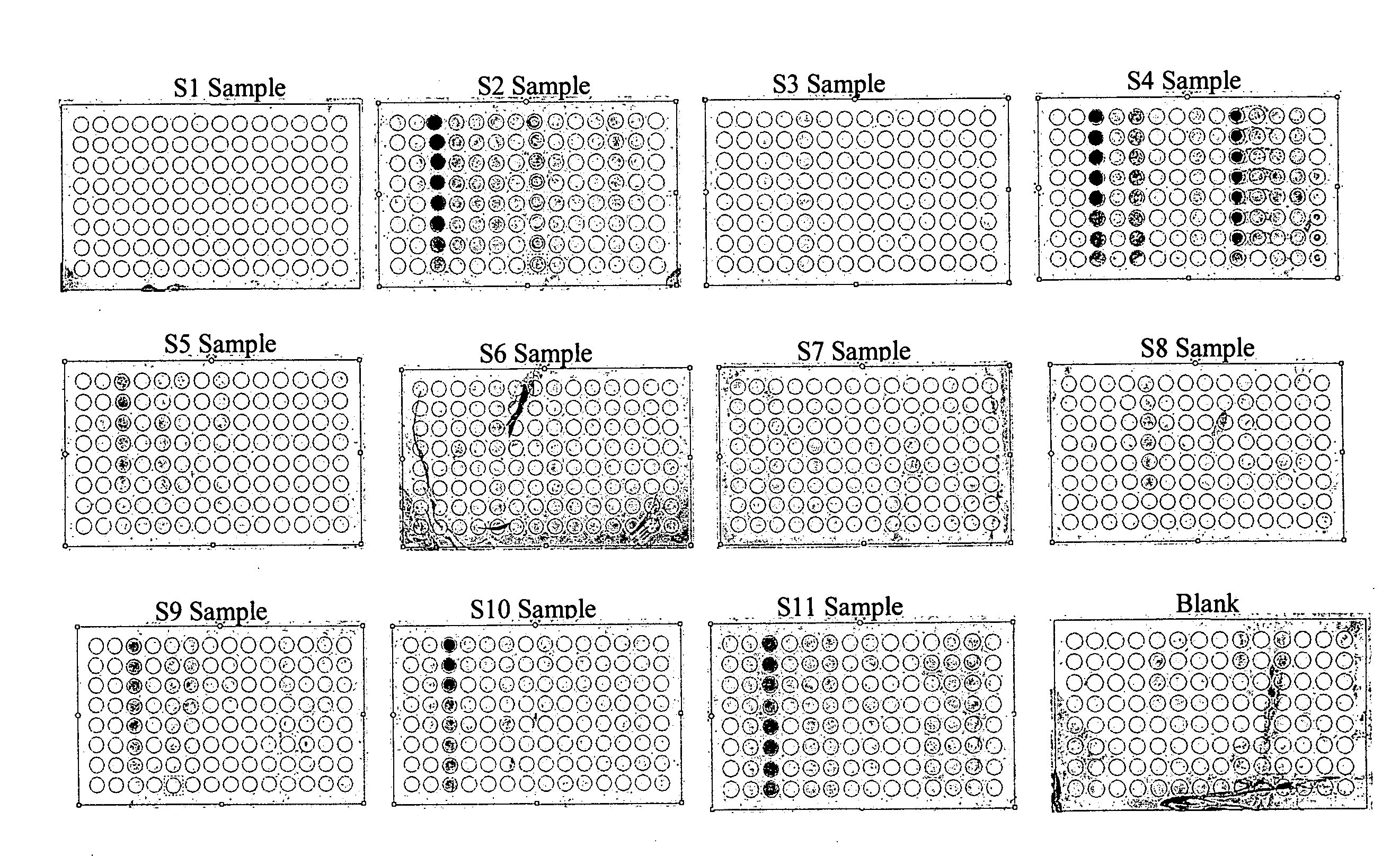
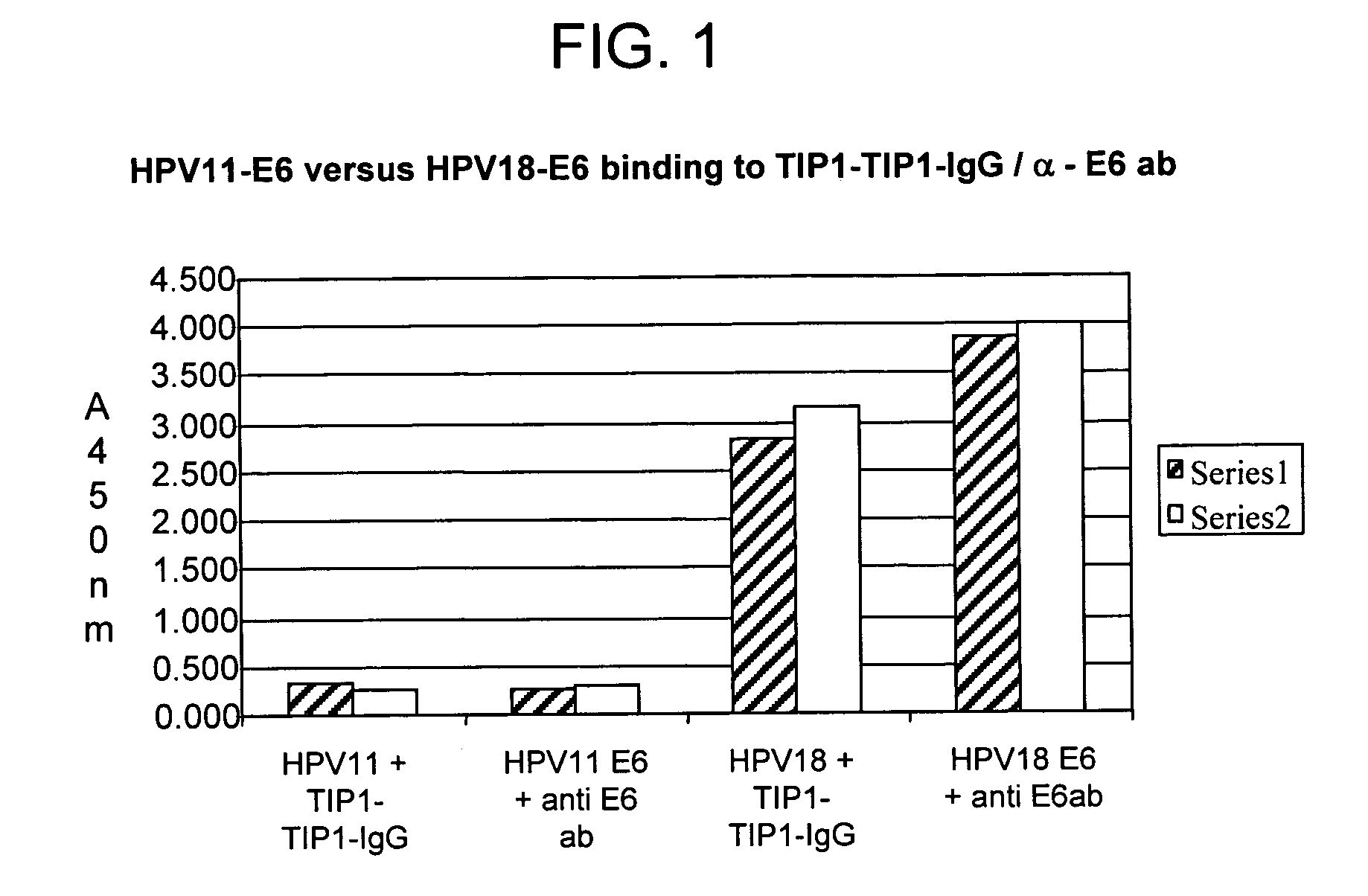
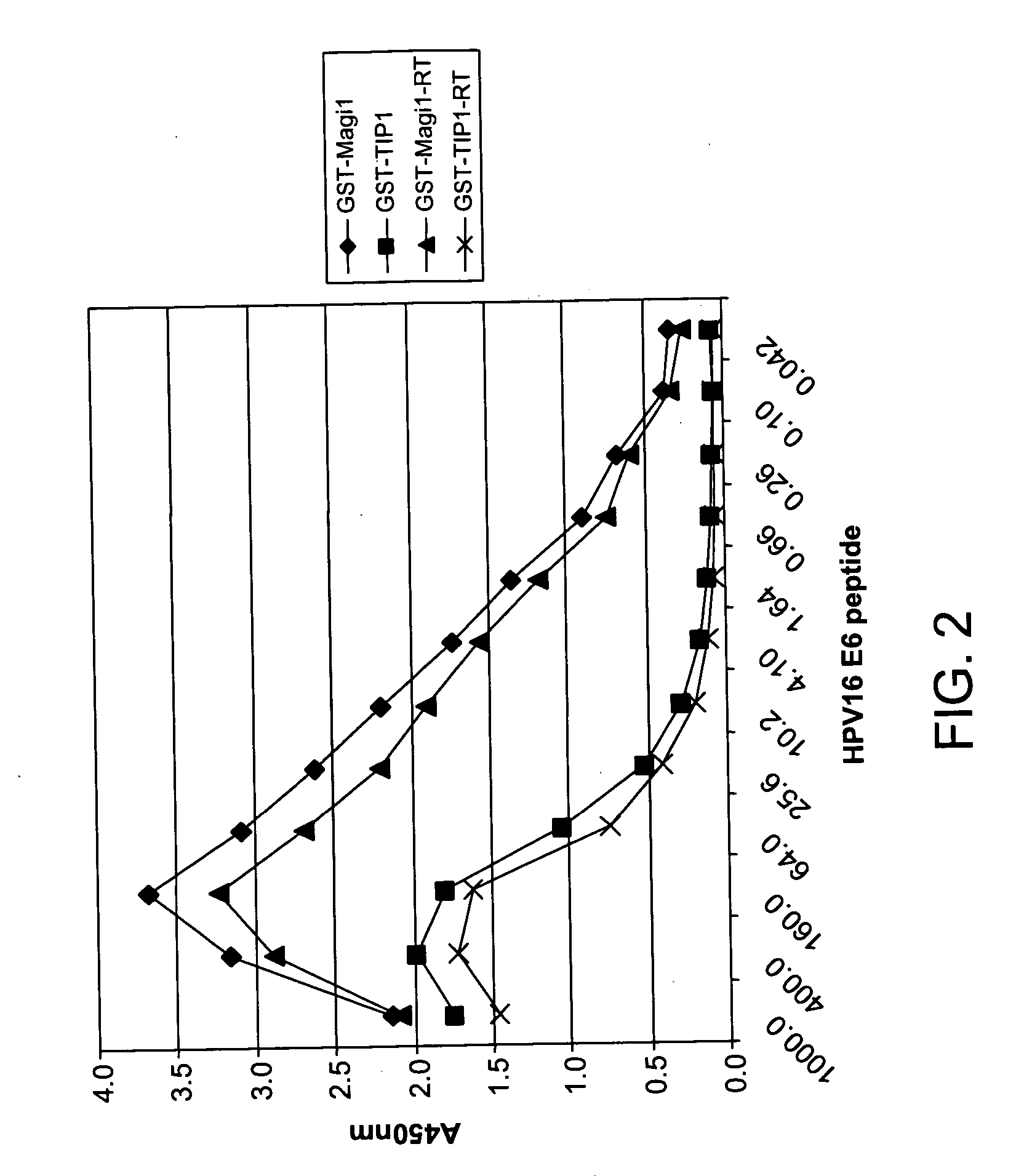
Protein chips for HPV detection
Embodiments of the invention provide methods, assays, and kits for detecting HPV infection, including infection by various HPV genotypes, early and / or late HPV-associated or HPV-specific proteins or antibodies. Detection of HPV DNAs, genomes, and / or oncoproteins by protein chips immunological assays can be used in early clinical screening for HPV infection and general diagnosis for cervical cancer and can be advantageous performed in a multiplexed test. Comparative detection of altered levels of HPV proteins and host proteins can performed in one or more assays. The polypeptides, recombinant proteins, antibodies, nucleic acids, and various detection methods thereof are particularly useful for diagnosing carcinomas of the uterine cervix and those at risk of developing cervical cancer.
Owner:HEER MEDICAL TECH DEV CO LTD
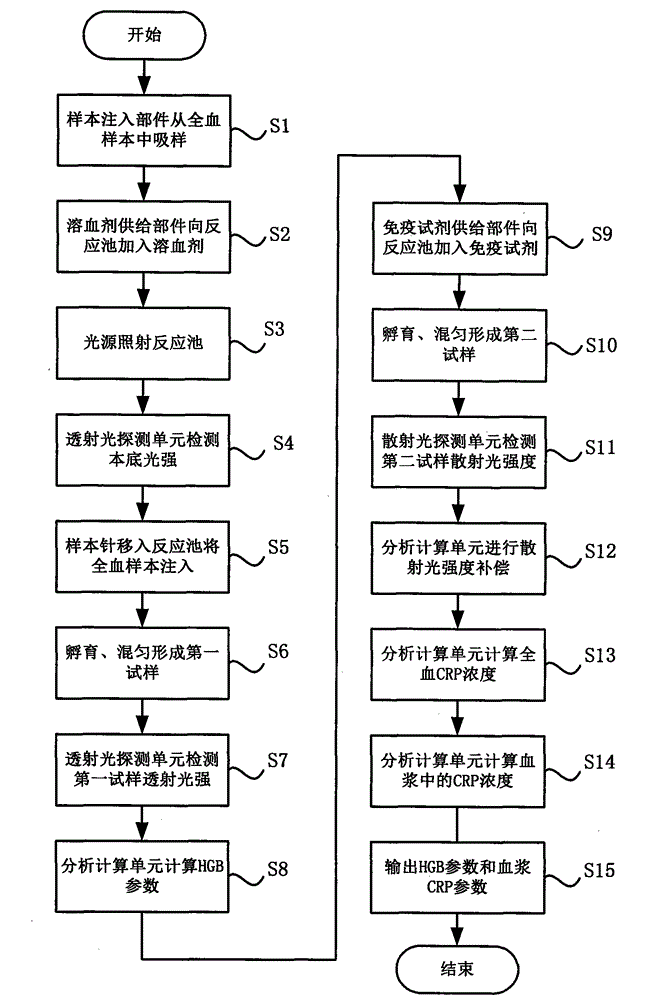
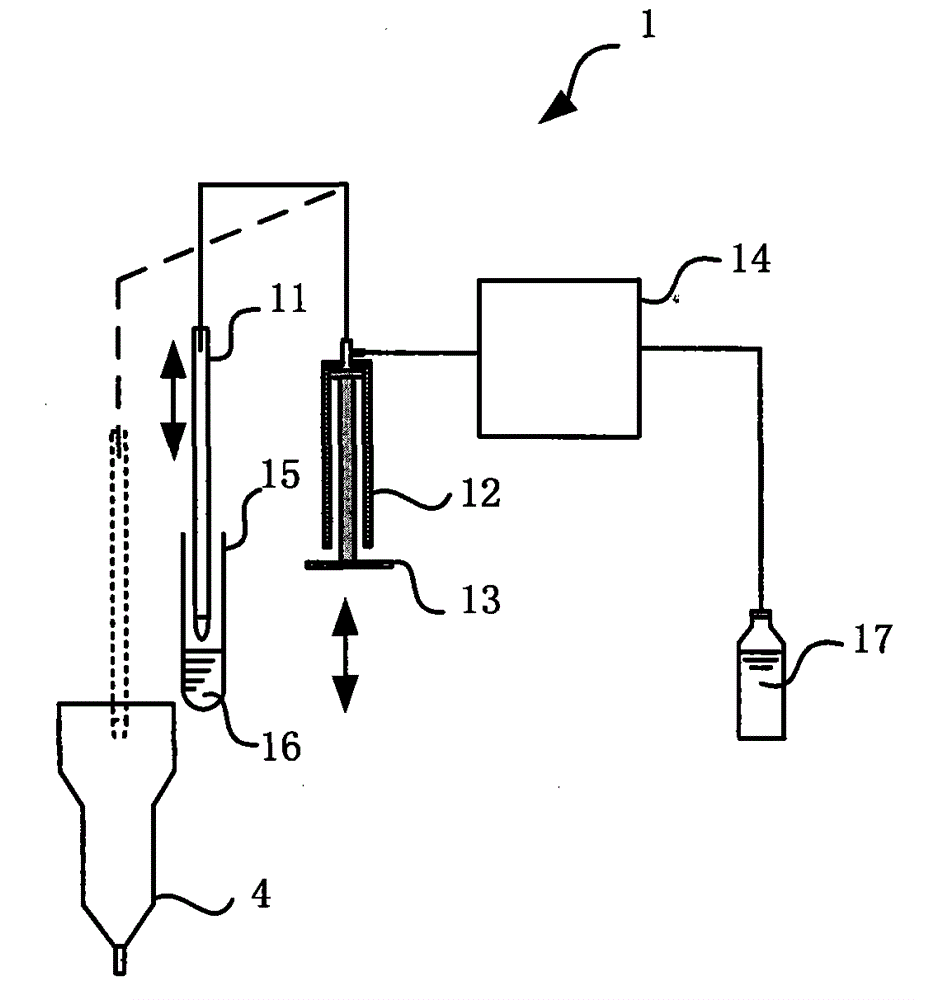
Whole-blood immunoassay device and blood analyzer with same
ActiveCN103336130AFast implementation of joint inspectionSimplify the cumbersome inspection processColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingAbsorbanceControl unit
The invention provides a device and a method for simultaneously carrying out immune measurement and blood cell measurement on whole blood. The device comprises a reaction tank, a hemolytic reagent supplying part, a sample injection part, an immune reagent supplying part, a light irradiation unit, a control unit, a transmission light detection unit, a scattered light detection unit and an analytical calculation unit, wherein the reaction tank is used for reaction and measurement of a hemolytic agent, an immune reagent and a whole blood test sample; the hemolytic reagent supplying part is used for injecting the hemolytic agent into the reaction tank; the sample injection part is used for injecting the whole blood test sample into the reaction tank to form a first test sample; the immune reagent supplying part is used for adding the immune reagent into the first test sample to form a second test sample; the light irradiation unit provides irradiation light; the control unit is used for controlling the temperature of the reaction tank and controlling the hemolytic reagent supplying part, the sample injection part and the immune reagent supplying part to act according to a certain sequence; the transmission light detection unit is used for detecting absorbance of the first test sample; the scattered light detection unit is used for detecting the strength of scattered light of the second test sample; the analytical calculation unit is used for carrying out analytical calculation on the absorbance and the strength of the scattered light to obtain blood routine parameters and specific protein parameters.
Owner:MACCURA MEDICAL INSTR CO LTD
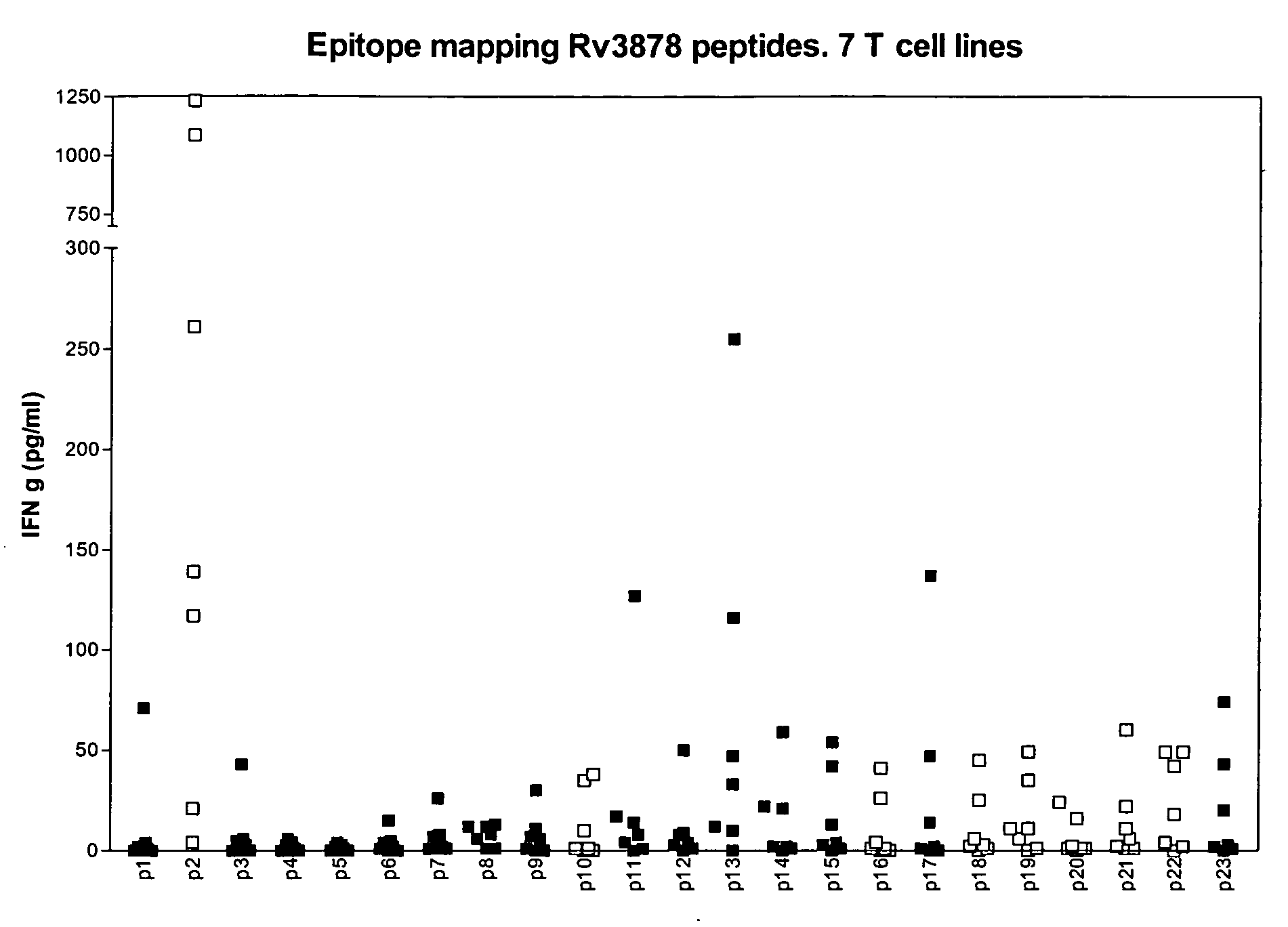
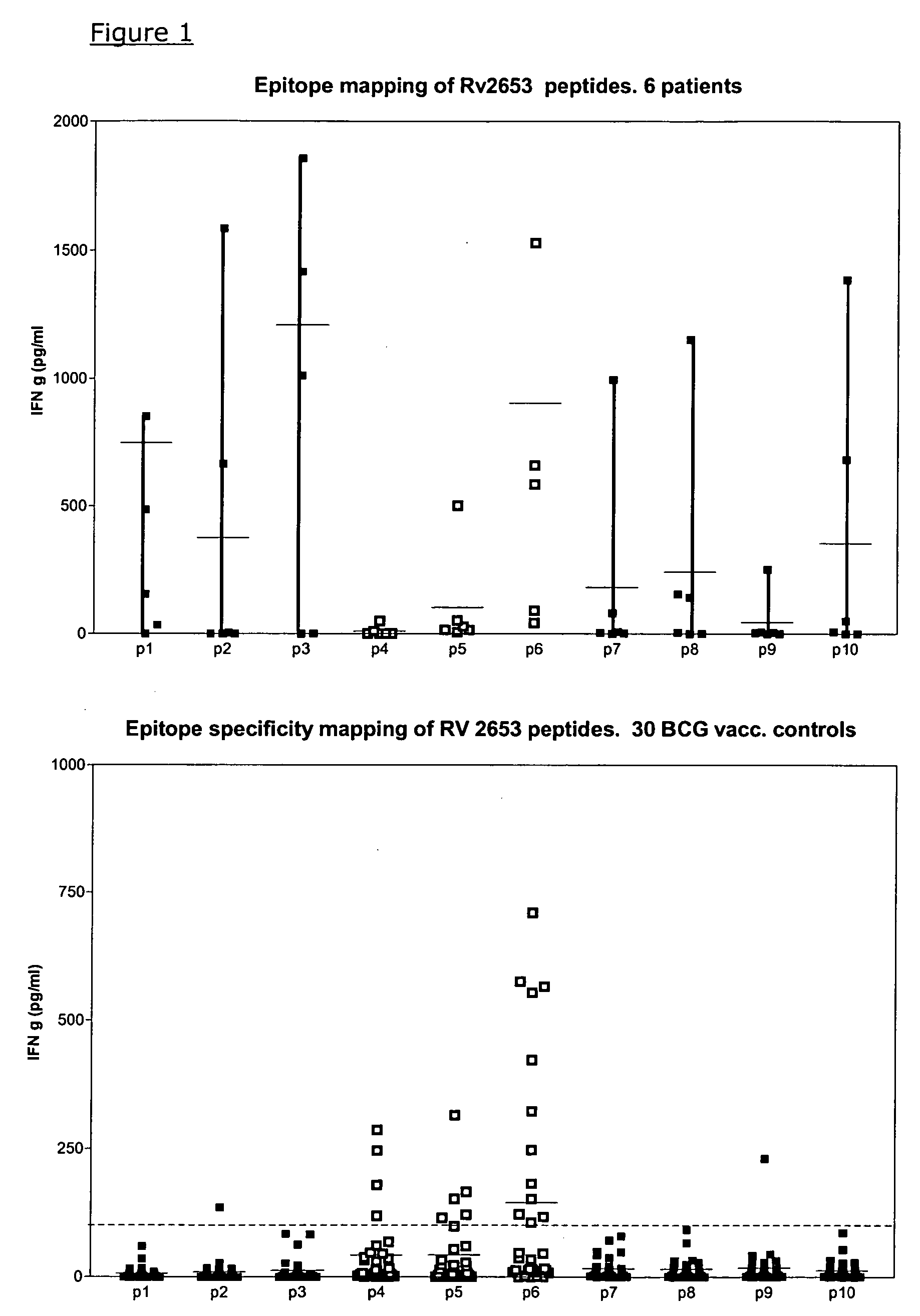
Specific epitope based immunological diagnosis of tuberculosis
ActiveUS20060115847A1Easy to identifyTesting is superfluousBacterial antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementSkin allergy testPeripheral blood mononuclear cell
The currently used method for immunological diagnosis of tuberculosis infection, the tuberculin skin test, is problematic for a number of reasons; it has low specificity in BCG vaccinated individuals, a high interobserver variance and requires skill to be read and interpreted. Furthermore it requires an extra visit to the clinic to have the test read. Both people vaccinated with BCG and those exposed to non-tuberculosis mycobacteria give a positive skin test result similar to that seen in a TB infected individual. This also applies for purified protein derivative (PPD) when used in a blood cell based test. The present invention discloses the development of an immunological TB diagnostic tool based on a combination of epitopes from proteins encoded by regions of the M. Tuberculosis (M. tub.) genome, that are not present in the BCG vaccine strain or in the most common non-tuberculosis mycobacteria. Four recently characterized proteins with this diagnostic potential were selected. Peptides from these proteins were tested one by one with peripheral blood mononuclear cells from microscopy or culture confirmed TB patients as well as from healthy BCG vaccinated controls. Some combinations of peptides showed a sensitivity level comparable to the level seen with the two wellknown M. tuberculosisspecific proteins ESAT 6 and CFP 10. An epitope combination with these peptides combined with ESAT 6 and CFP 10 gave a sensitivity of 93%, representing a raise in sensitivity of about 26-33% compared to using ESAT6 or CFP 10 alone. The results from a panel of TB patients, using a collection of the new specific epitopes clearly demonstrates, that addition of other specific epitopes to the already known specific antigens, increases the sensitivity of a diagnostic assay based on cell mediated immune response.
Owner:STATENS SERUM INST
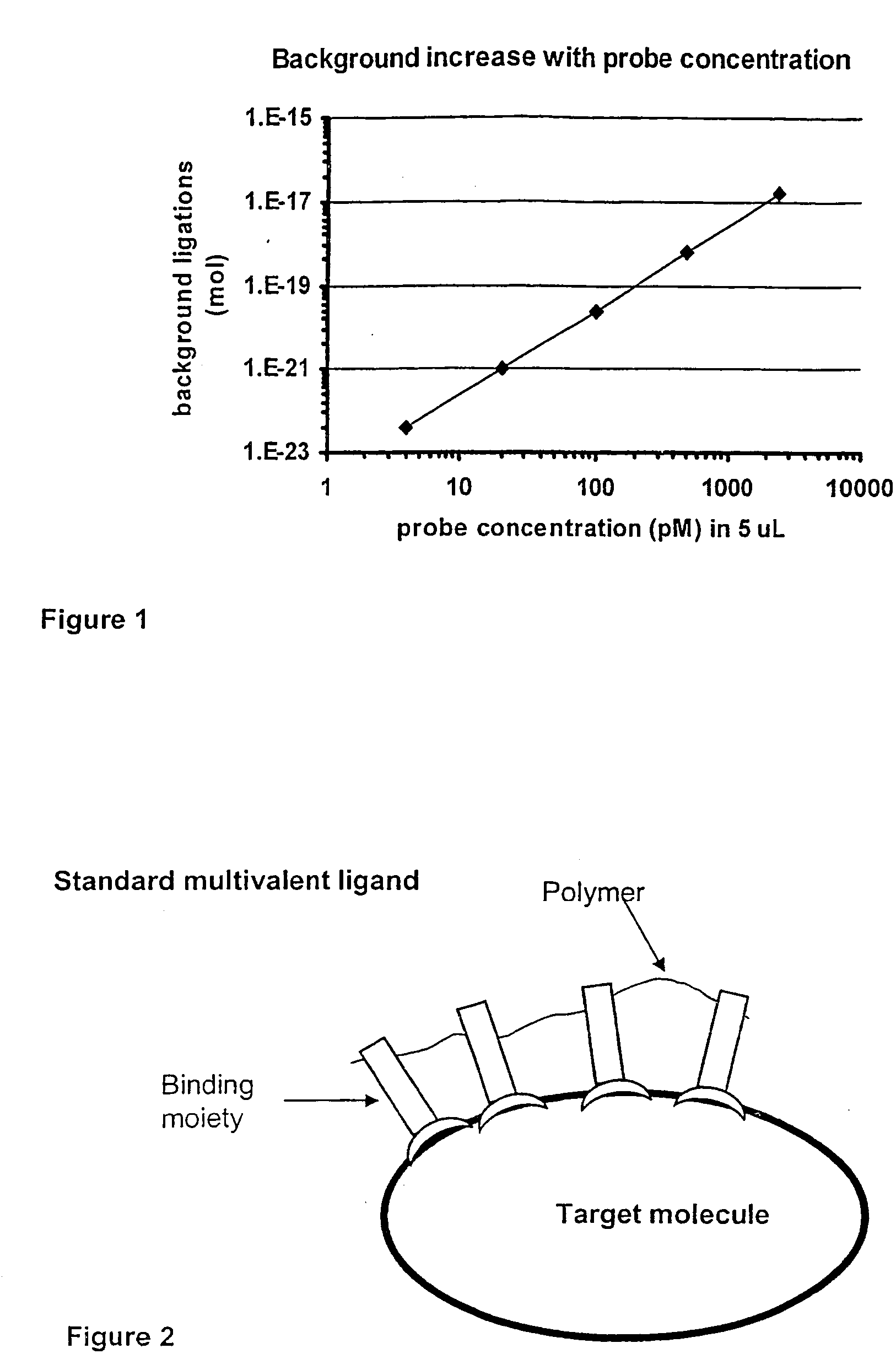
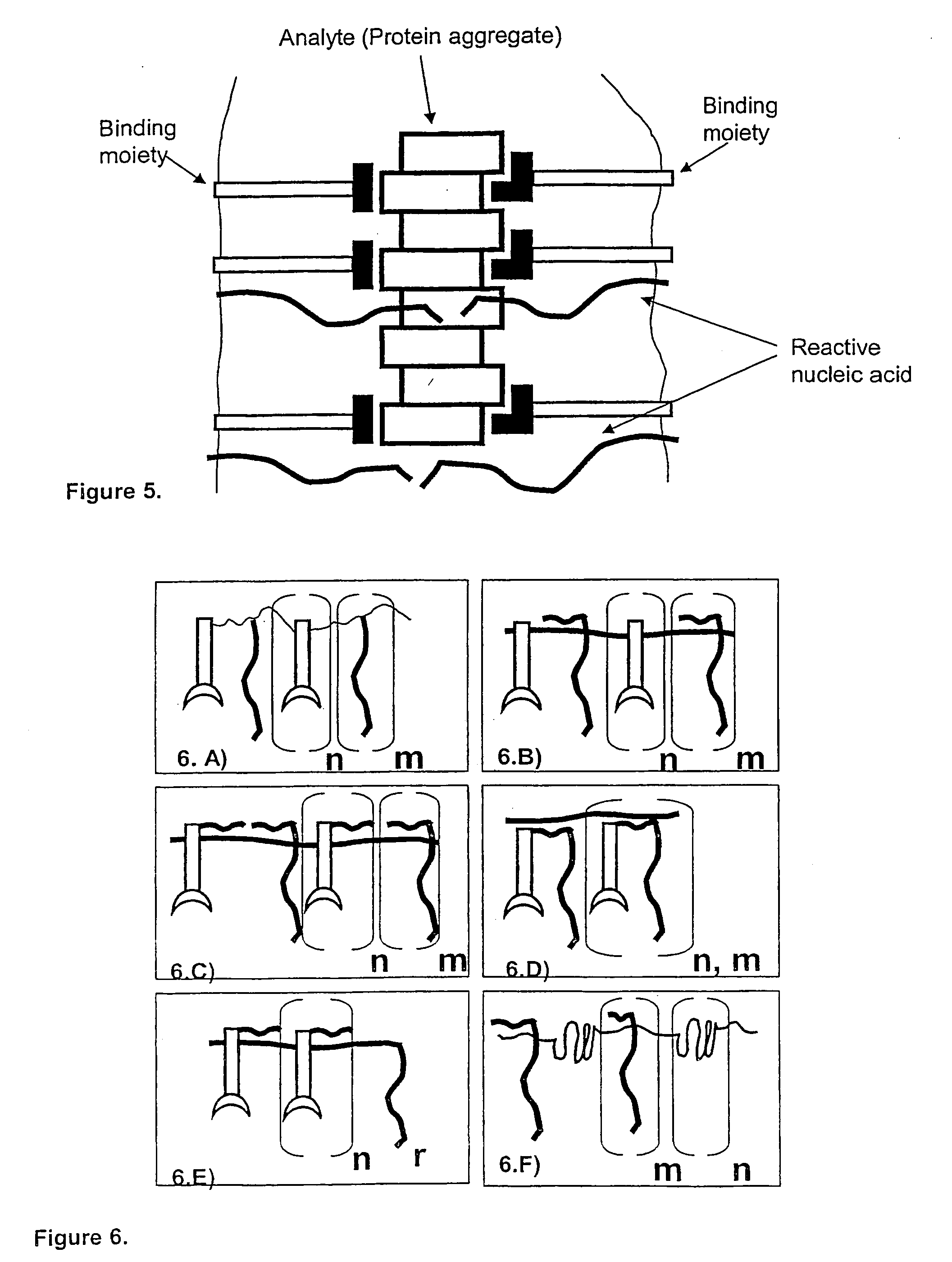
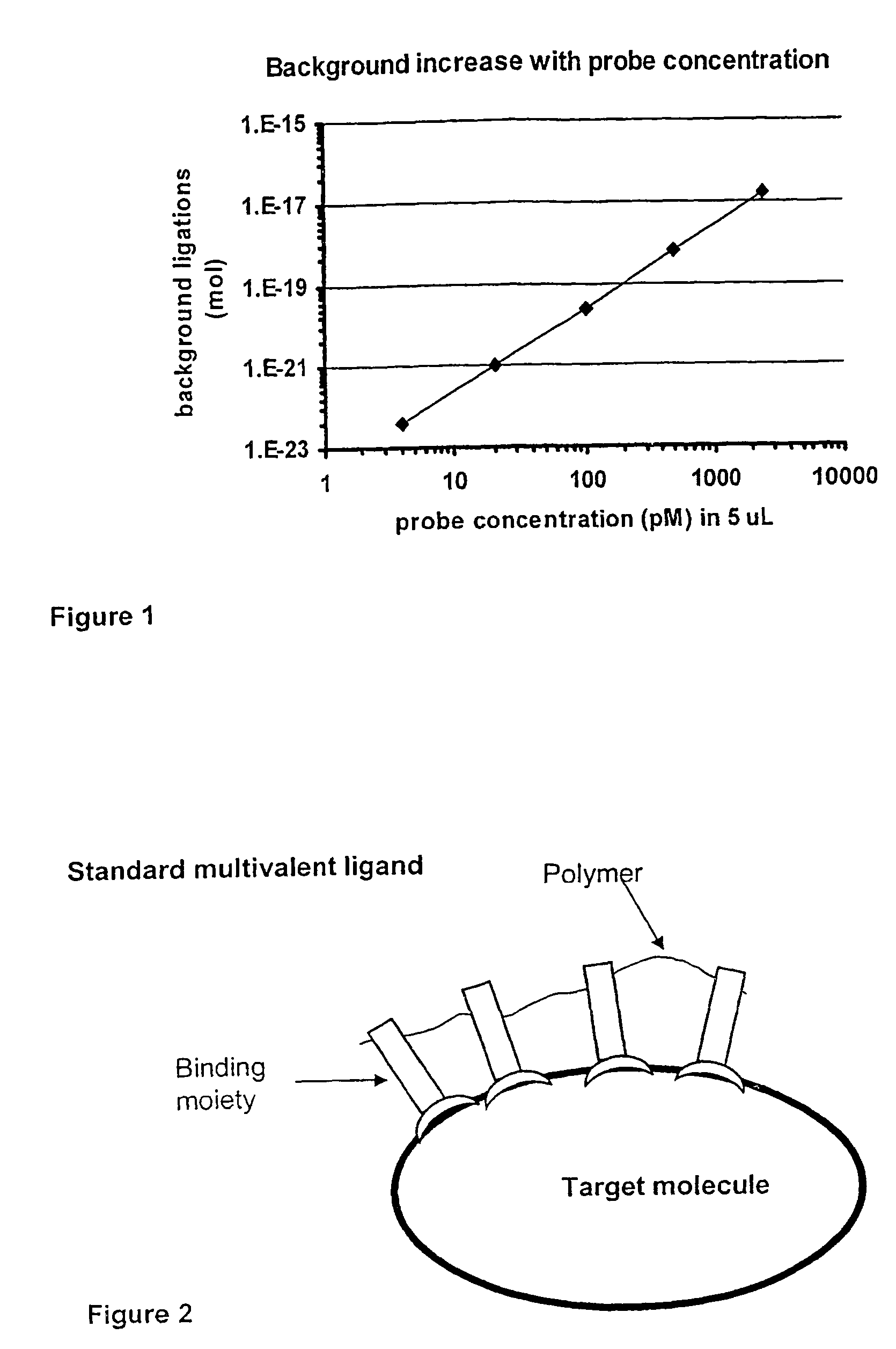
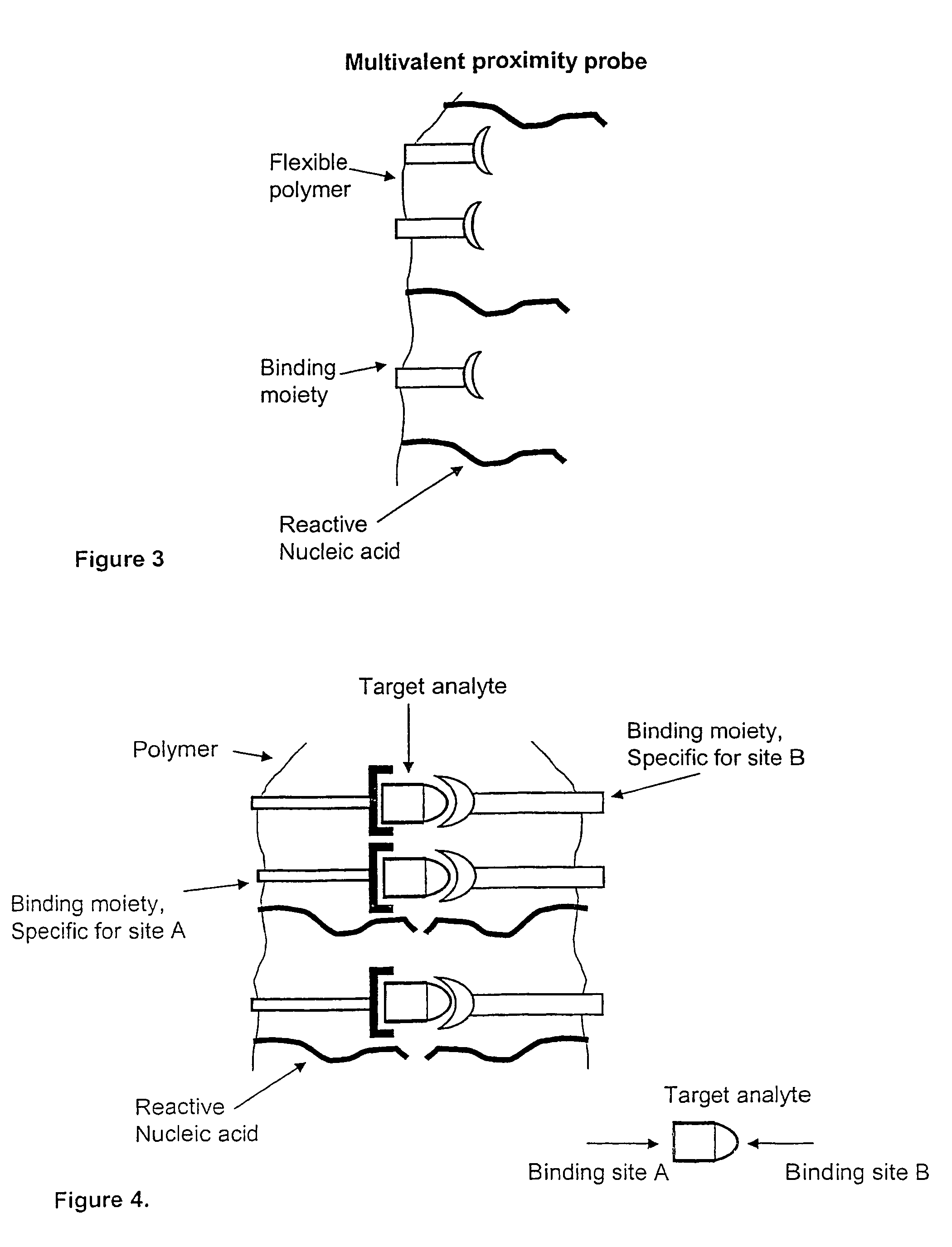
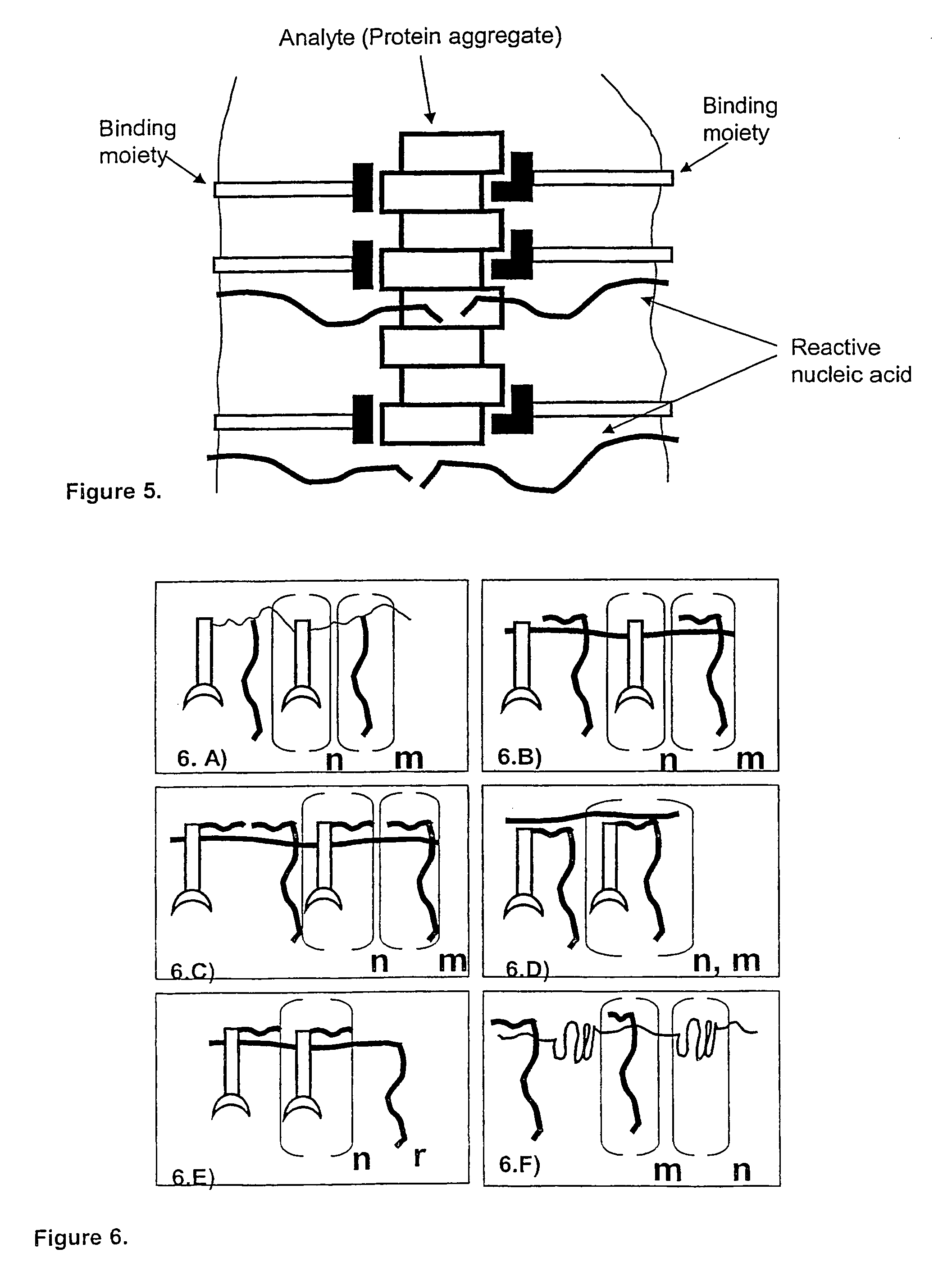
Method and kit for proximity probing with multivalent proximity probes
ActiveUS20050003361A1Reduce signalingHigh affinitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteAntibody
The present invention relates to sensitive, rapid and convenient assays for detection and or quantification of one or more analyte(s) in solution using multivalent proximity probes. The proximity probes each comprise several binding moieties, such as antibodies, and associated nucleic acid(s). When the binding moieties have bound to their analyte(s), the nucleic acids on opposite proximity probes interact with each other and a signal is generated based on this interaction. The multivalent proximity probes are especially valuable for highly sensitive and specific protein detection.
Owner:OLINK PROTEOMICS AB
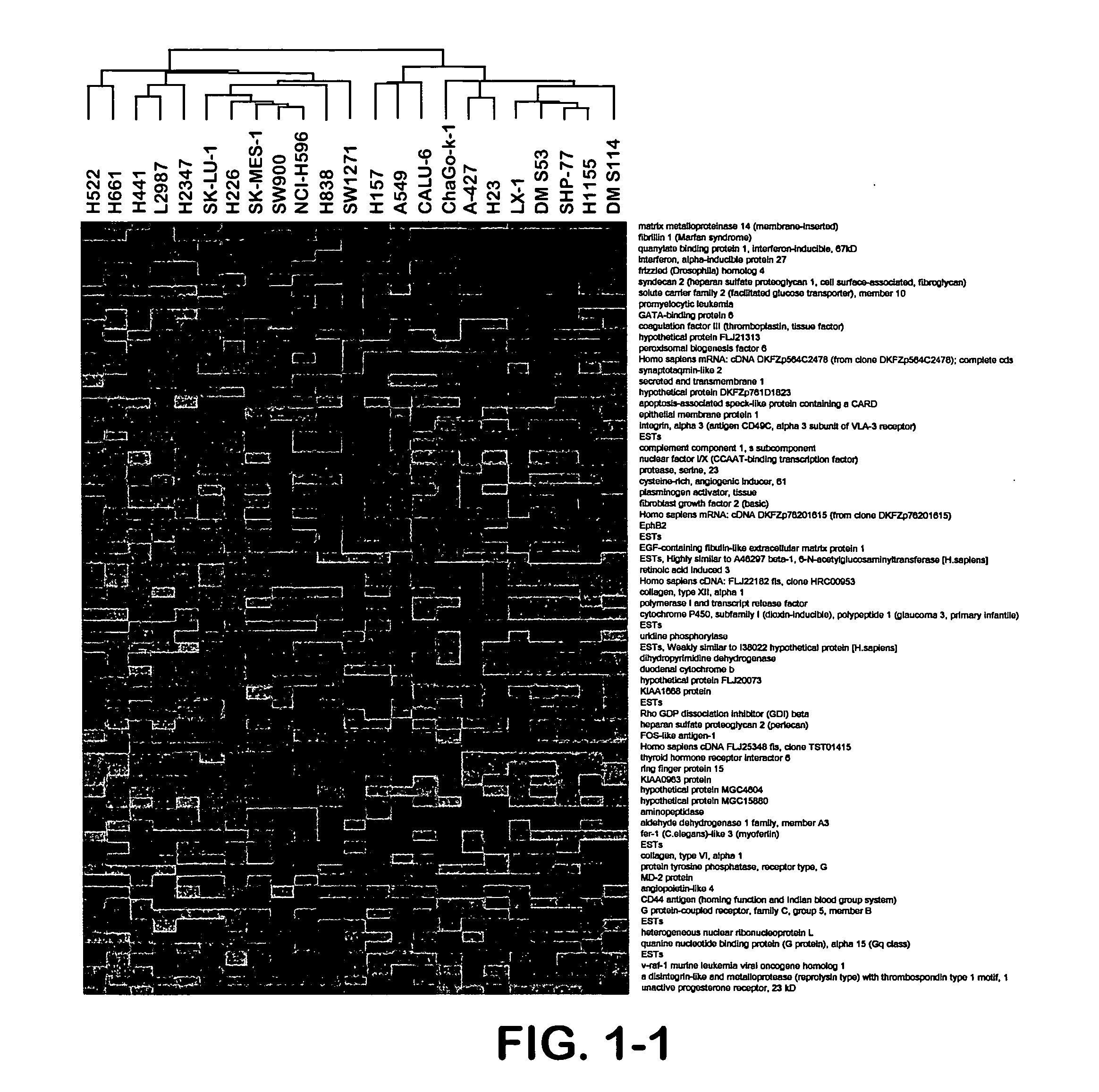
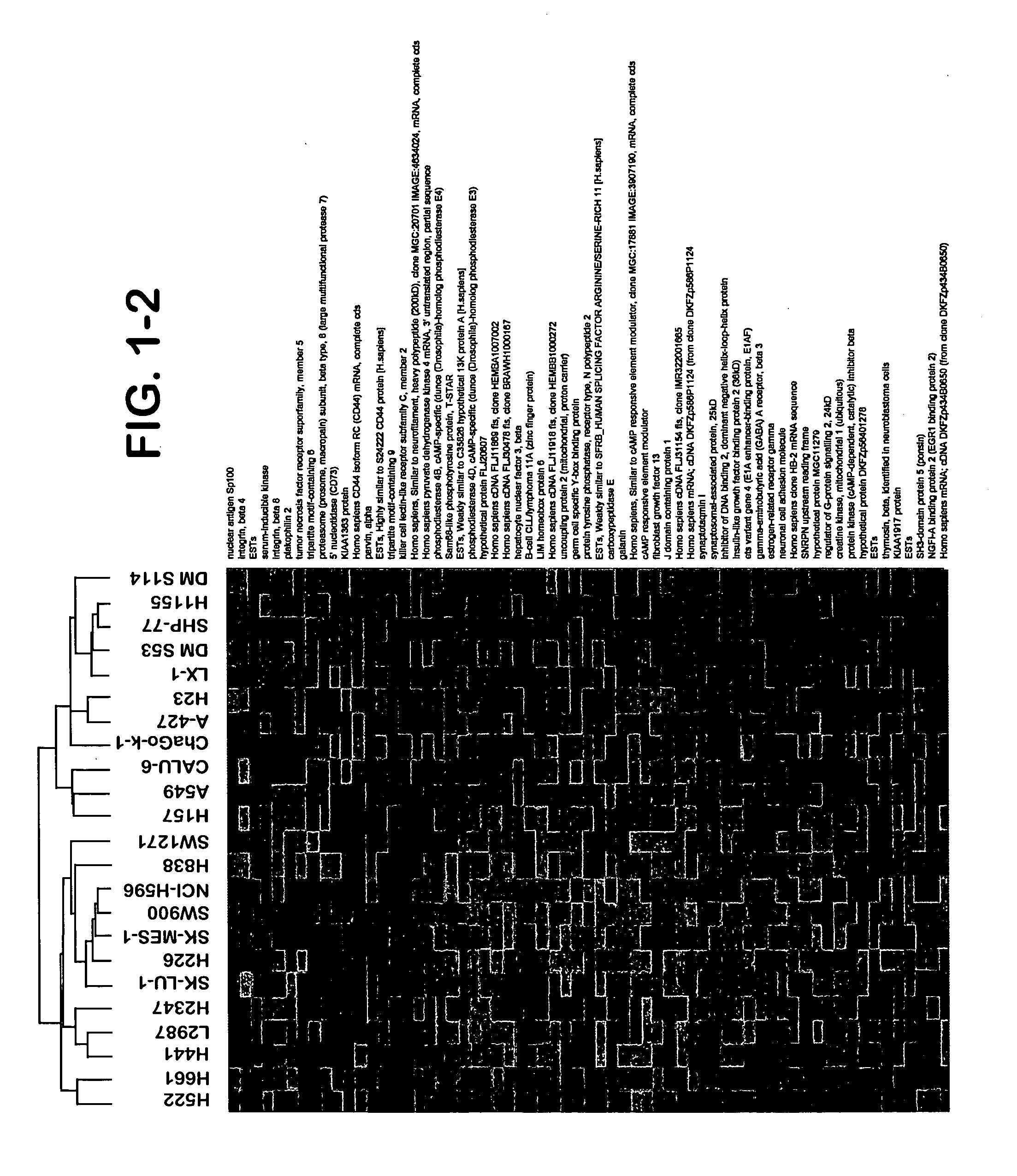
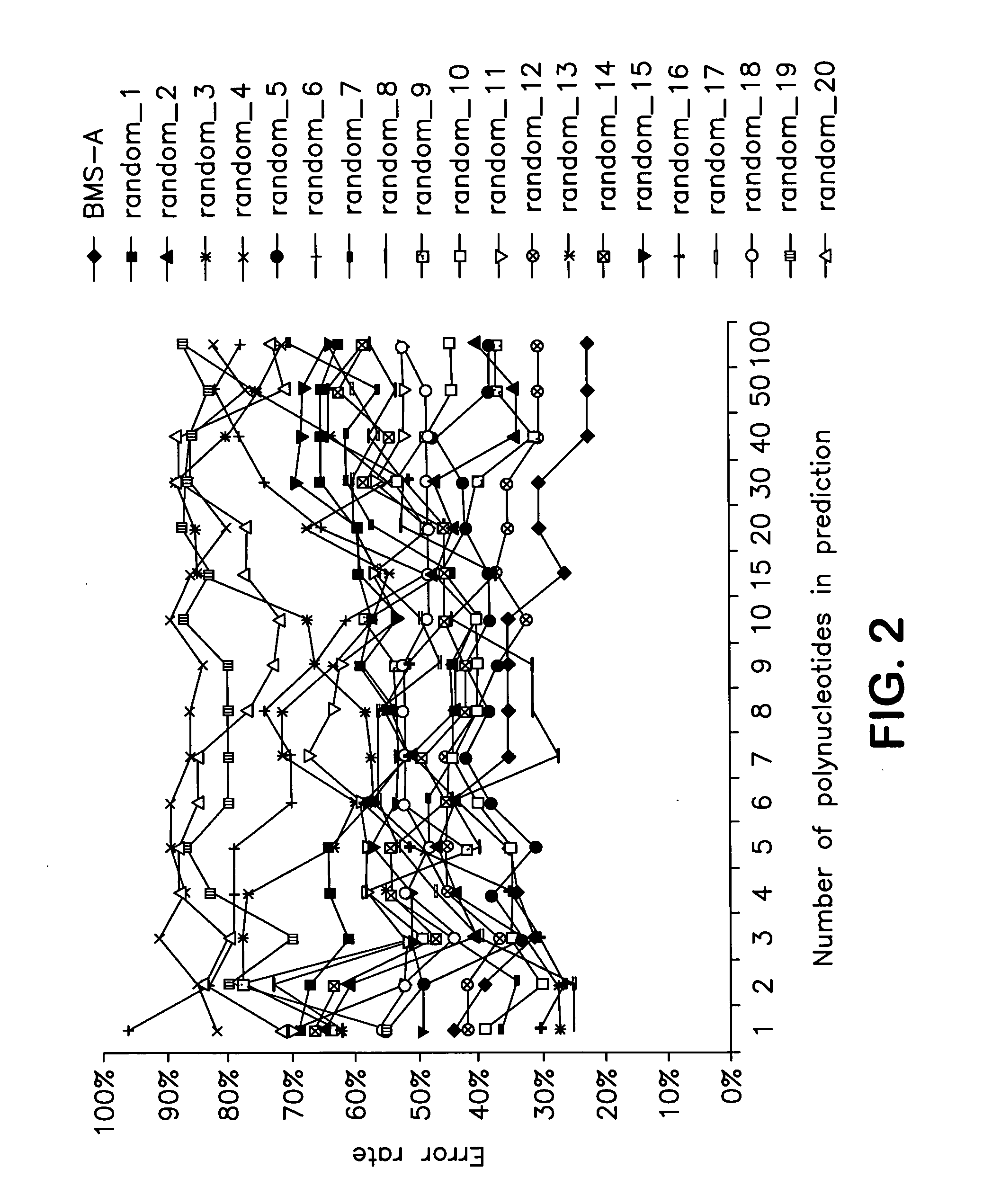
Identification of polynucleotides for predicting activity of compounds that interact with and/or modulate protein tyrosine kinases and/or protein tyrosine kinase pathways in lung cancer cells
InactiveUS20060019284A1Improved prognosisContinue treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementTumor/cancer cellsDisease areaProtein-Tyrosine Kinases
The present invention describes polynucleotides that have been discovered to correlate to the relative intrinsic sensitivity or resistance of cells, e.g., lung cell lines, to treatment with compounds that interact with and modulate, e.g., inhibit, protein tyrosine kinases, such as, for example, members of the Src family of tyrosine kinases, e.g., Src, Fgr, Fyn, Yes, Blk, Hck, Lck and Lyn, as well as other protein tyrosine kinases, including, Bcr-abl, Jak, PDGFR, c-kit and Ephr. These polynucleotides have been shown, through a weighted voting cross validation program, to have utility in predicting the resistance and sensitivity of lung cell lines to the compounds. The expression level of some polynucleotides is regulated by treatment with a particular protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor compound, thus indicating that these polynucleotides are involved in the protein tyrosine kinase signal transduction pathway, e.g., Src tyrosine kinase. Such polynucleotides, whose expression levels correlate highly with drug sensitivity or resistance and which are modulated by treatment with the compounds, comprise polynucleotide predictor or marker sets useful in methods of predicting drug response, and as prognostic or diagnostic indicators in disease management, particularly in those disease areas, e.g., lung cancer, in which signaling through the protein tyrosine kinase pathway, such as the Src tyrosine kinase pathway, is involved with the disease process.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Markers for cancer detection
InactiveUS20120039811A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningGastrointestinal Tract CancersOncology
The present invention relates to methods for detecting, prognosing and staging cancers, in particular cancers of the gastrointestinal tract. The methods of the invention comprise detecting specific protein markers in a tissue of interest, wherein the detected levels thereof may be indicative of pre-cancerous or cancerous tissue, or the stage or prognosis of a cancer. Further provided are methods of treating cancer, and cancer detection kits.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
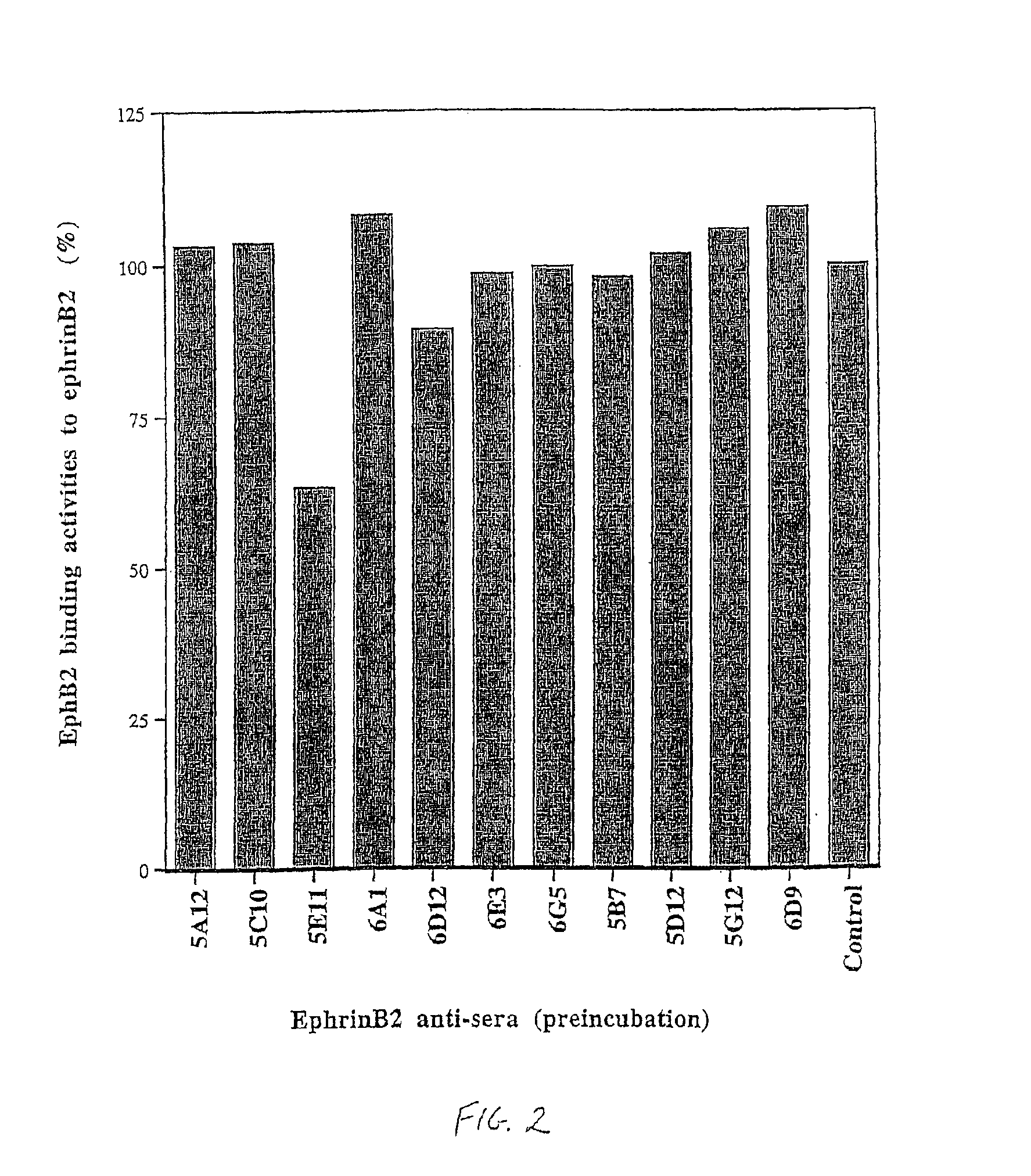
Artery- and vein-specific proteins and uses therefor
InactiveUS6887674B1Enhancing and inhibiting effectCompounds screening/testingPeptide/protein ingredientsBlood vesselReceptor for activated C kinase 1
Arterial and venous endothelial cells are molecularly distinct from the earliest stages of angiogenesis. This distinction is revealed by expression on arterial cells of a transmembrane ligand, called EphrinB2 whose receptor EphB4 is expressed on venous cells. Targeted disruption of the EphrinB2 gene prevents the remodeling of veins from a capillary plexus into properly branched structures. Moreover, it also disrupts the remodeling of arteries, suggesting that reciprocal interactions between pre-specified arterial and venous endothelial cells are necessary for angiogenesis. This distinction can be used to advantage in methods to alter angiogenesis, methods to assess the effect of drugs on artery cells and vein cells, and methods to identify and isolate artery cells and vein cells, for example.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Kit for proximity probing with multivalent proximity probes
ActiveUS8013134B2Reduce signalingHigh affinitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteTrue positive rate
The present invention relates to sensitive, rapid and convenient assays for detection and or quantification of one or more analyte(s) in solution using multivalent proximity probes. The proximity probes each comprise several binding moieties, such as antibodies, and associated nucleic acid(s). When the binding moieties have bound to their analyte(s), the nucleic acids on opposite proximity probes interact with each other and a signal is generated based on this interaction. The multivalent proximity probes are especially valuable for highly sensitive and specific protein detection.
Owner:OLINK PROTEOMICS AB
Direct, externally imposed control of polypeptides
InactiveUS6953656B2Altering functional propertyAltering structuralMicrobiological testing/measurementCell componentsEnergy transferProtein structure and function
Methods and compositions for rendering proteins directly responsive to an external signal utilizing modulators that themselves respond to the external signal and are associated with the proteins. In response to the external signal, the modulator alters physical properties of the specific protein molecule(s) with which it is associated, thereby altering the structural and functional properties thereof. The modulator may, for example, transfer applied energy to a protein, or to a portion of the protein, thereby changing the protein structure and function.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method for regulating protein function in cells using synthetic small molecules
Methods and compositions for the rapid and reversible destabilizing of specific proteins using cell-permeable, synthetic molecules are described. Stability-affecting proteins, e.g., derived from FKBP and DHFR proteins are fused to a protein of interest and the presence or absence of the ligand is used to modulate the stability of the fusion protein.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
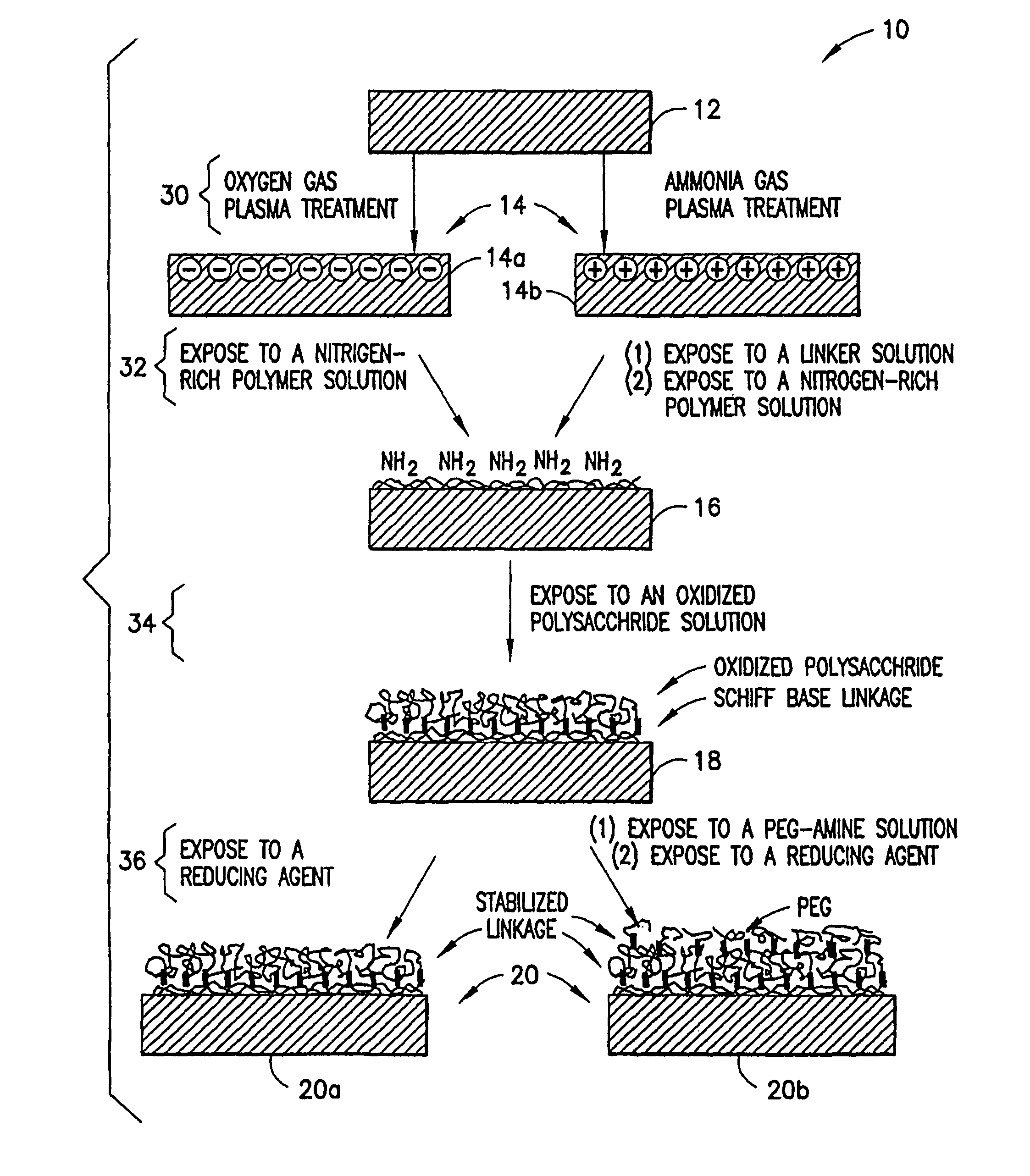
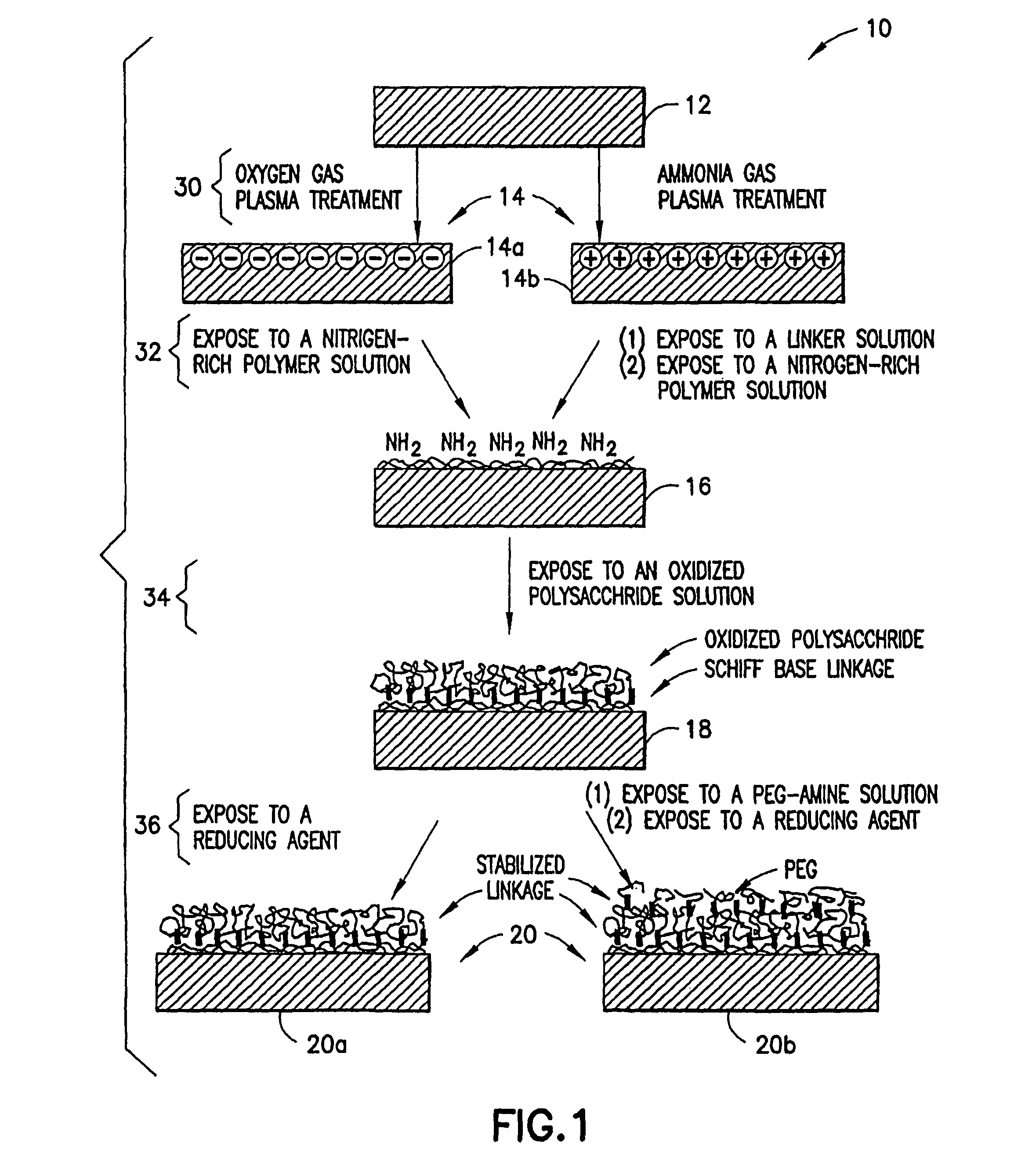
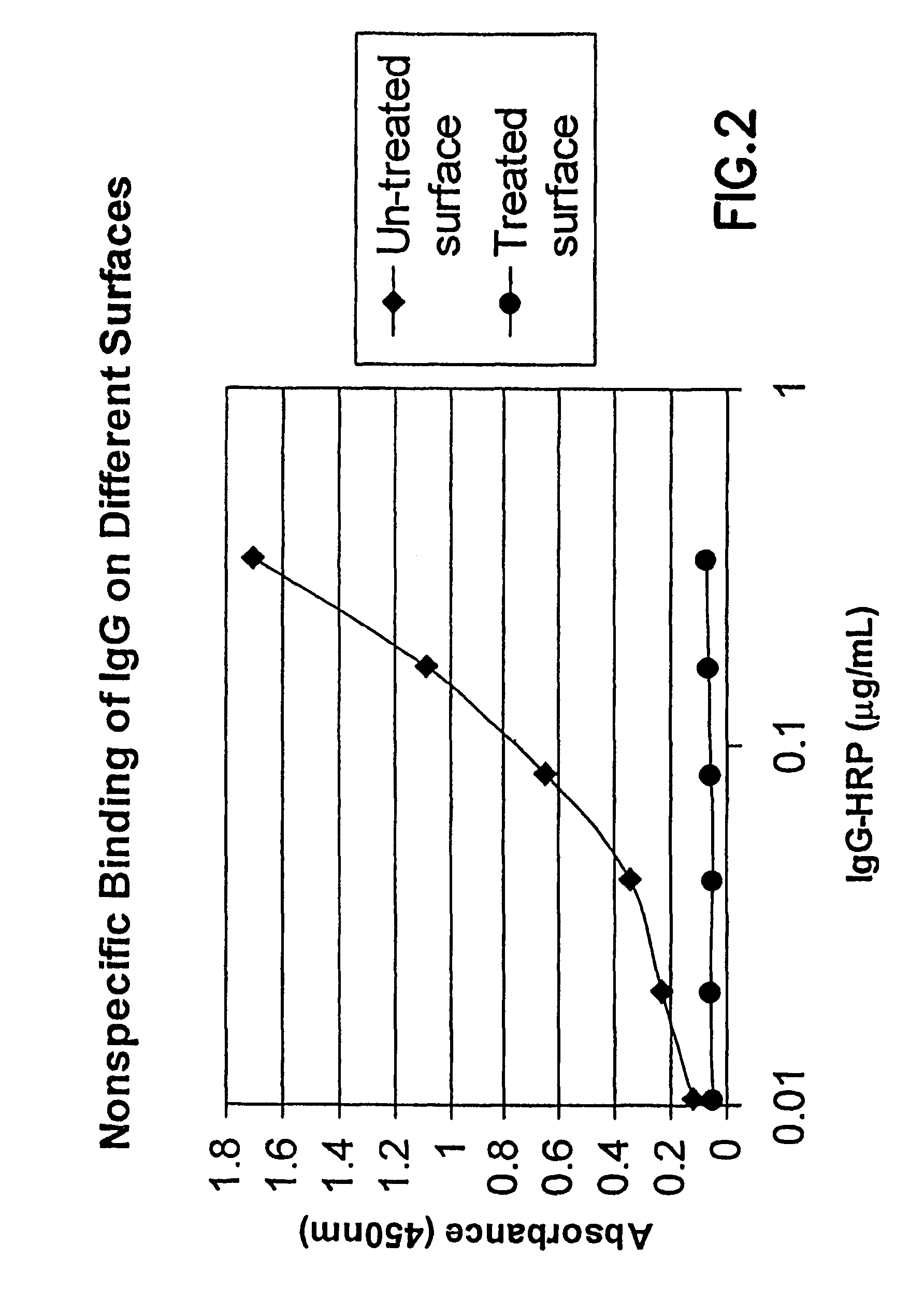
Methods for producing surfaces that resist non-specific protein binding and cell attachment
ActiveUS8475886B2Preparing sample for investigationSynthetic resin layered productsPolymeric surfaceChemical reaction
A method is disclosed herein for treating a polymeric surface to resist non-specific binding of biomolecules and attachment of cells. The method includes the steps of: imparting a charge to the polymeric surface to produce a charged surface; exposing the charged surface to a nitrogen-rich polymer to form a polymerized surface; exposing the polymerized surface to an oxidized polysaccharide to form an aldehyde surface; and exposing the aldehyde surface to a reducing agent. Advantageously, a method is provided which produces surfaces that resist non-specific protein binding and cell attachment and that avoids the use of photochemical reactions or prior art specially designed compounds.
Owner:CORNING INC
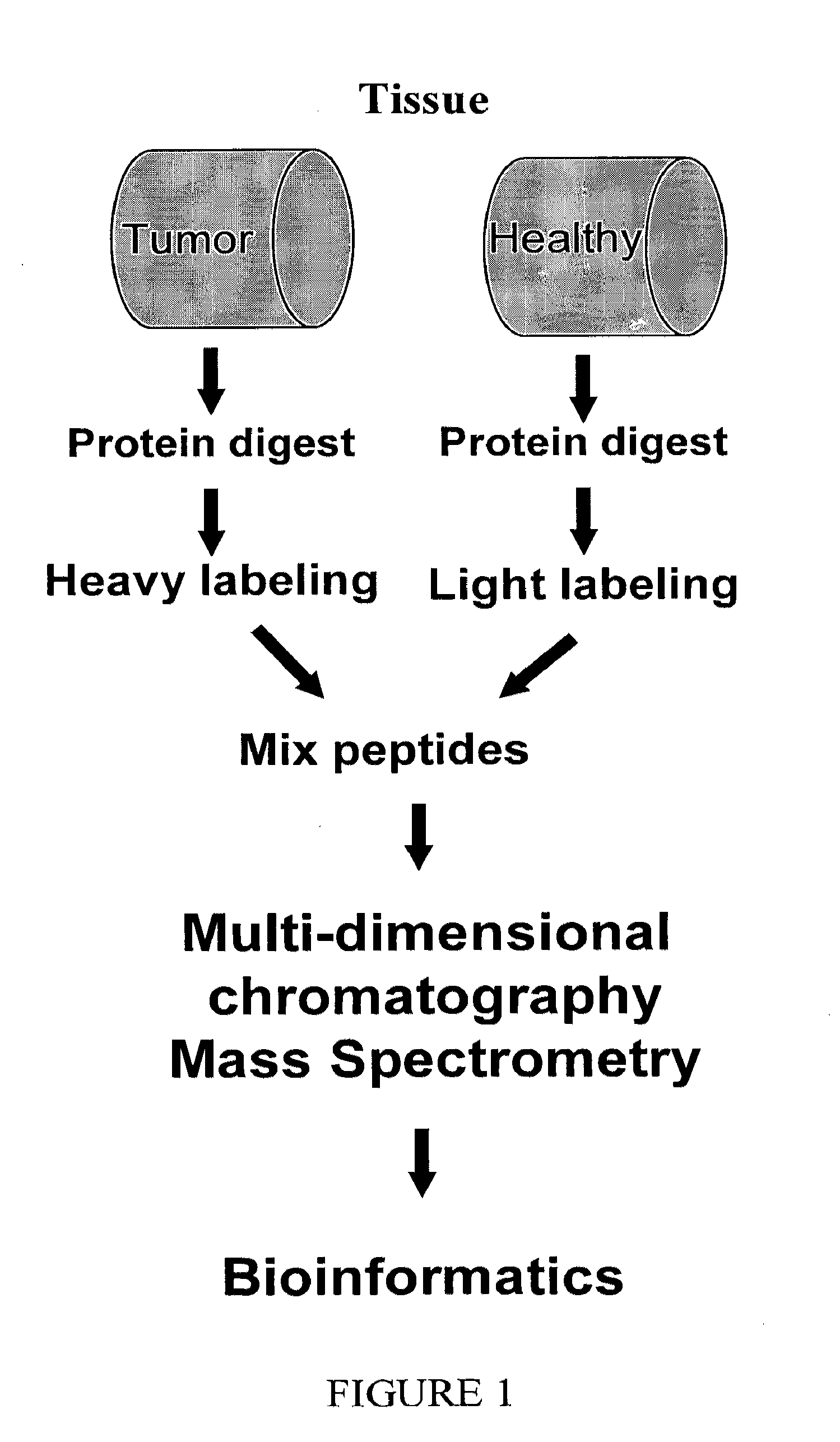
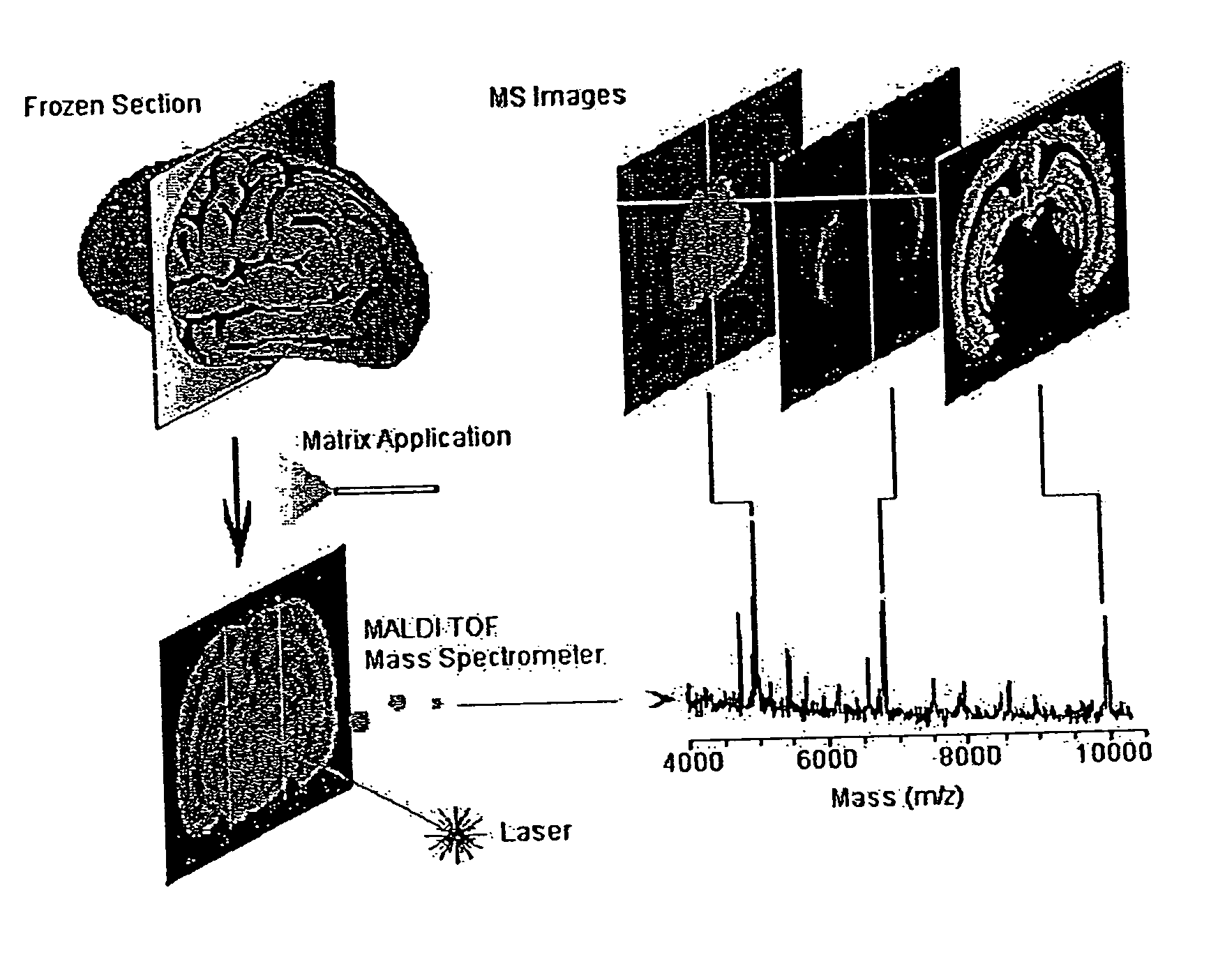
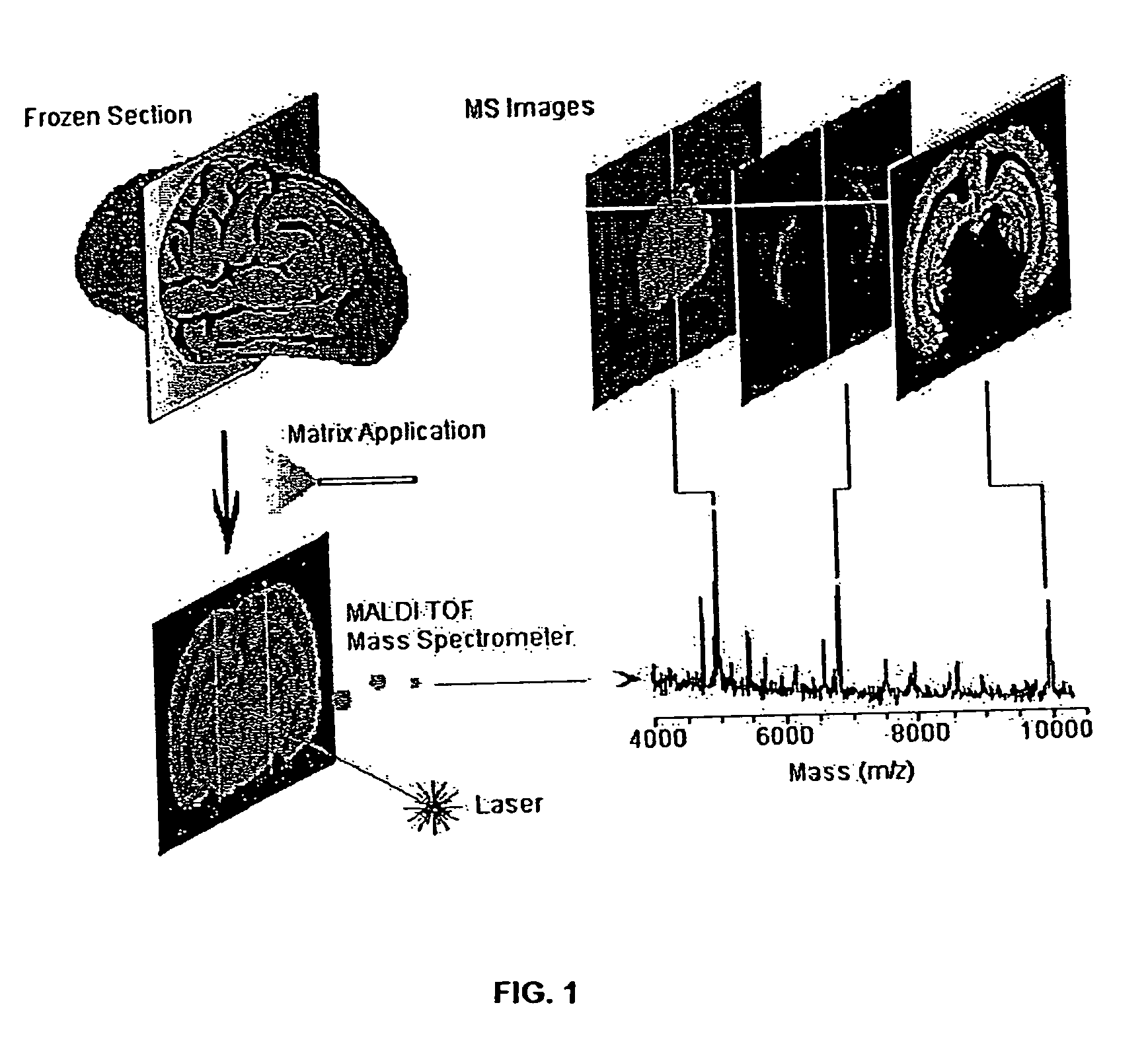
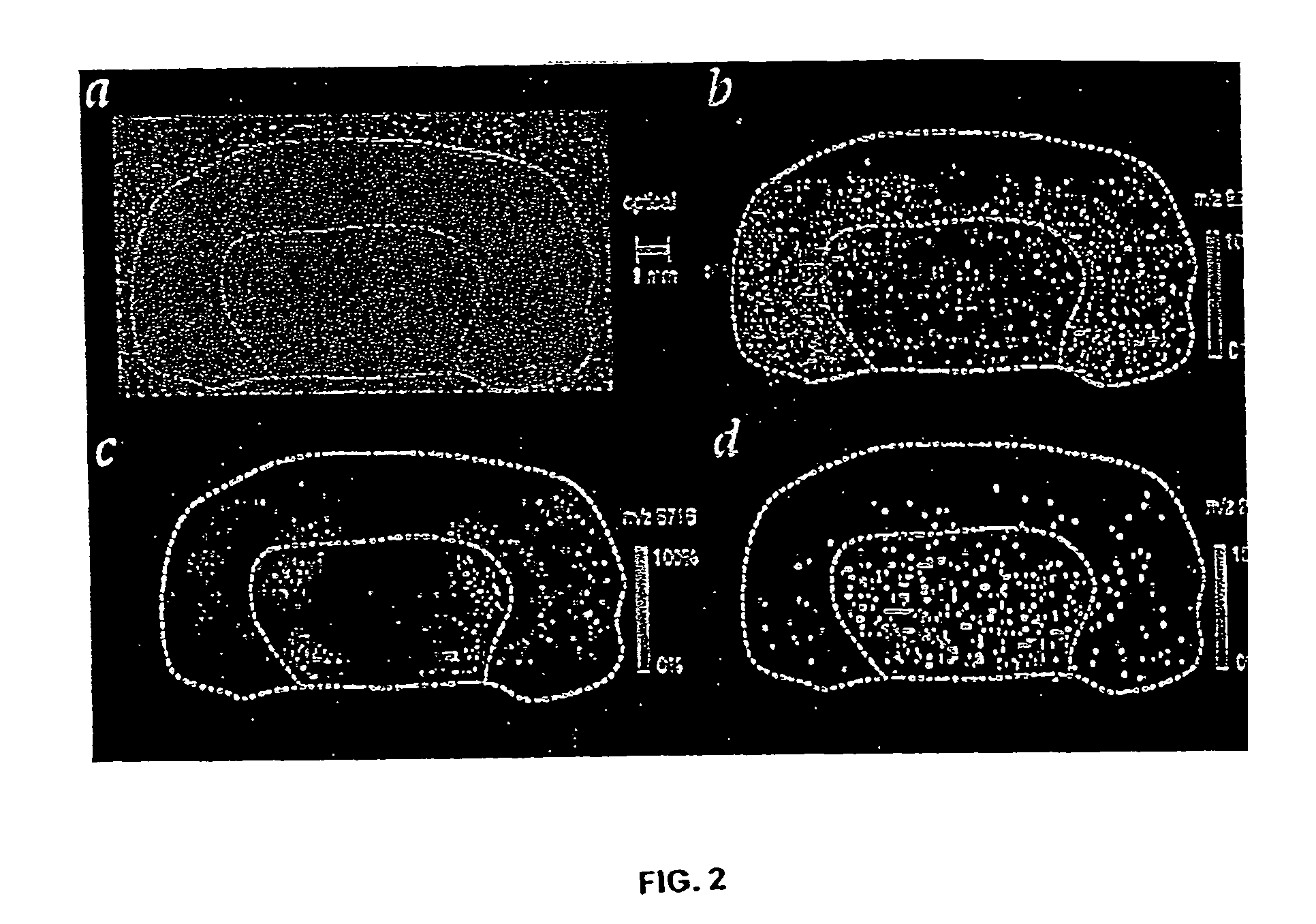
Methods and apparatuses for analyzing biological samples by mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20050029444A1Particle separator tubesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEnergy absorptionXenobiotic degradation
Methods and apparatuses for analyzing proteins and other biological materials and xenobiotics within a sample. A specimen is generated, which may include an energy absorbent matrix. The specimen is struck with laser beams such that the specimen releases proteins. The atomic mass of the released proteins over a range of atomic masses is measured. An atomic mass window of interest within the range of atomic masses is analyzed to determine the spatial arrangement of specific proteins within the sample, and those specific proteins are identified as a function of the spatial arrangement. By analyzing the proteins, one may monitor and classify disease within a sample.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Biochemical method for specific protein labeling
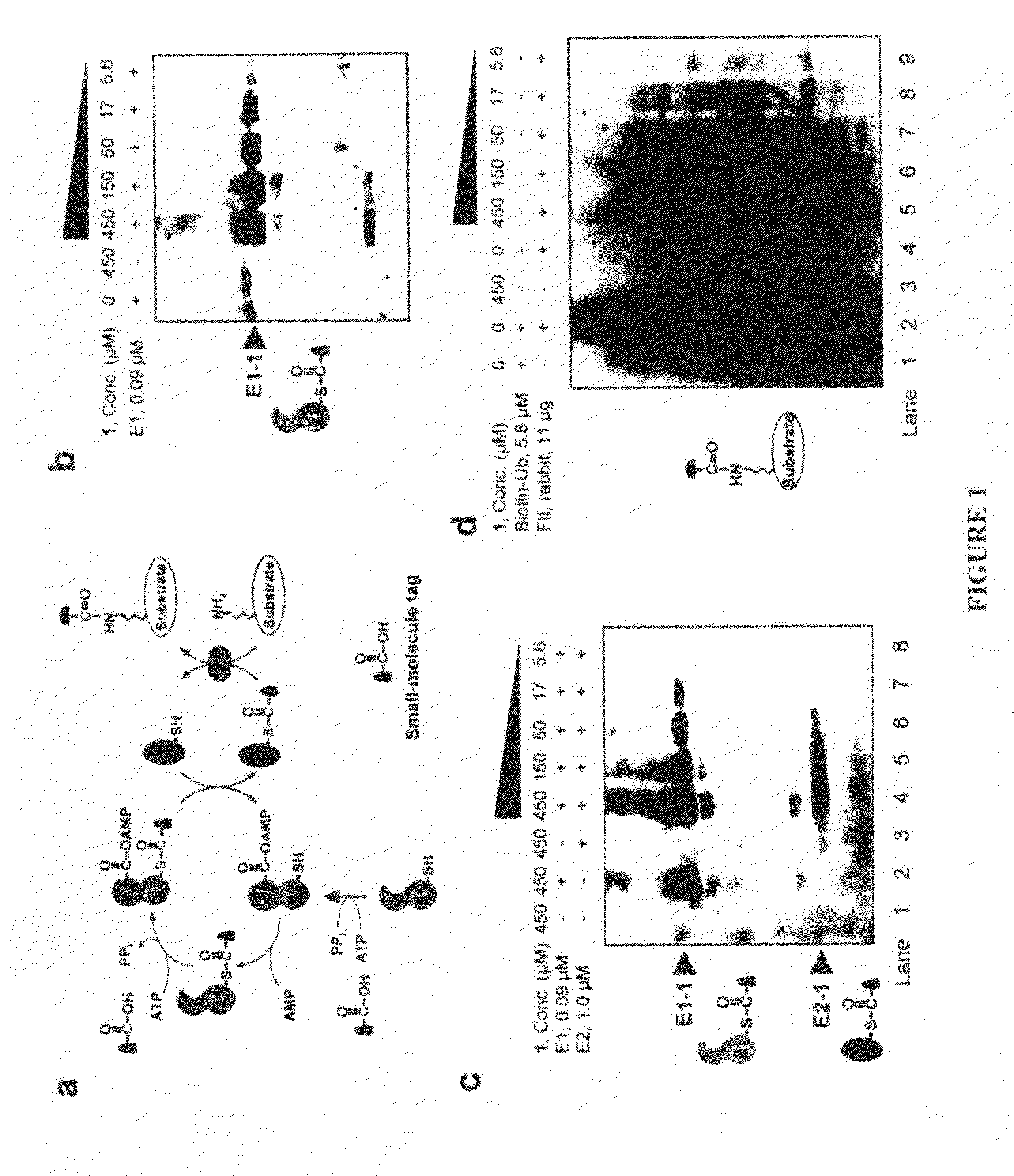
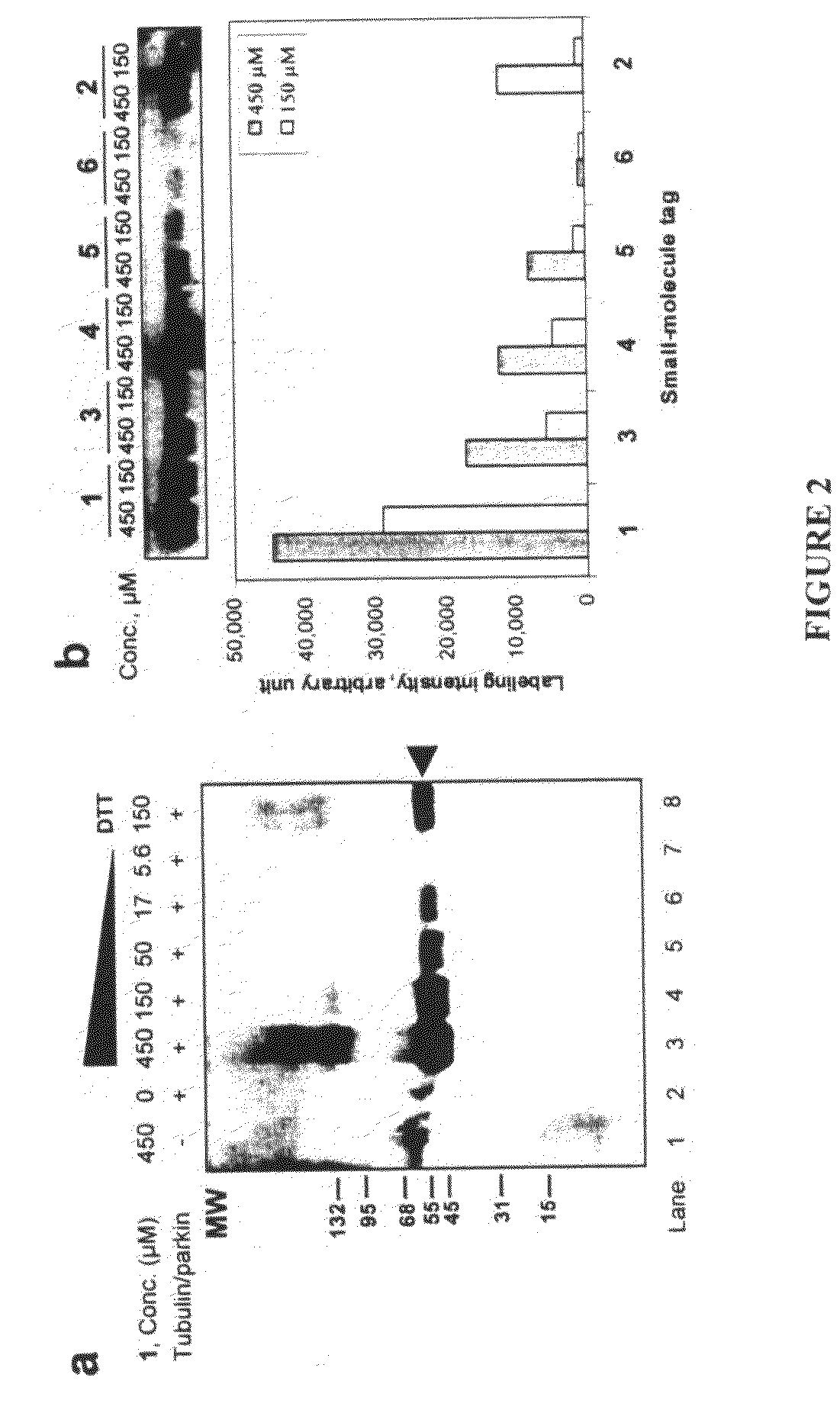
InactiveUS20080305519A1Easy to operatePeptide sourcesTripeptide ingredientsProtein targetProtein insertion
An improved method for protein labeling comprising the steps of providing a synthetic small molecule tag, providing a target protein to be tagged, providing at least two enzymes for catalyzing a conjugation reaction between the tag and the target protein, incubating the tag, the protein and the enzyme, and allowing the tag to conjugate to the target protein. The tag may embody at least one structural feature of an ubiquitin C-terminus, and the structural feature may comprise a recognition sequence that is recognizable by an ubiquitin activating enzyme.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
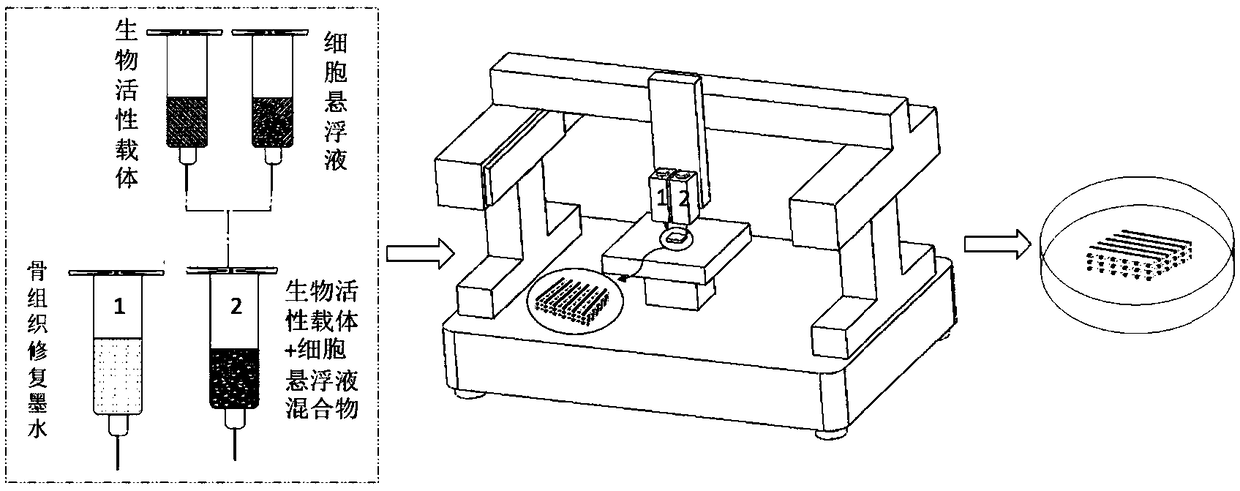
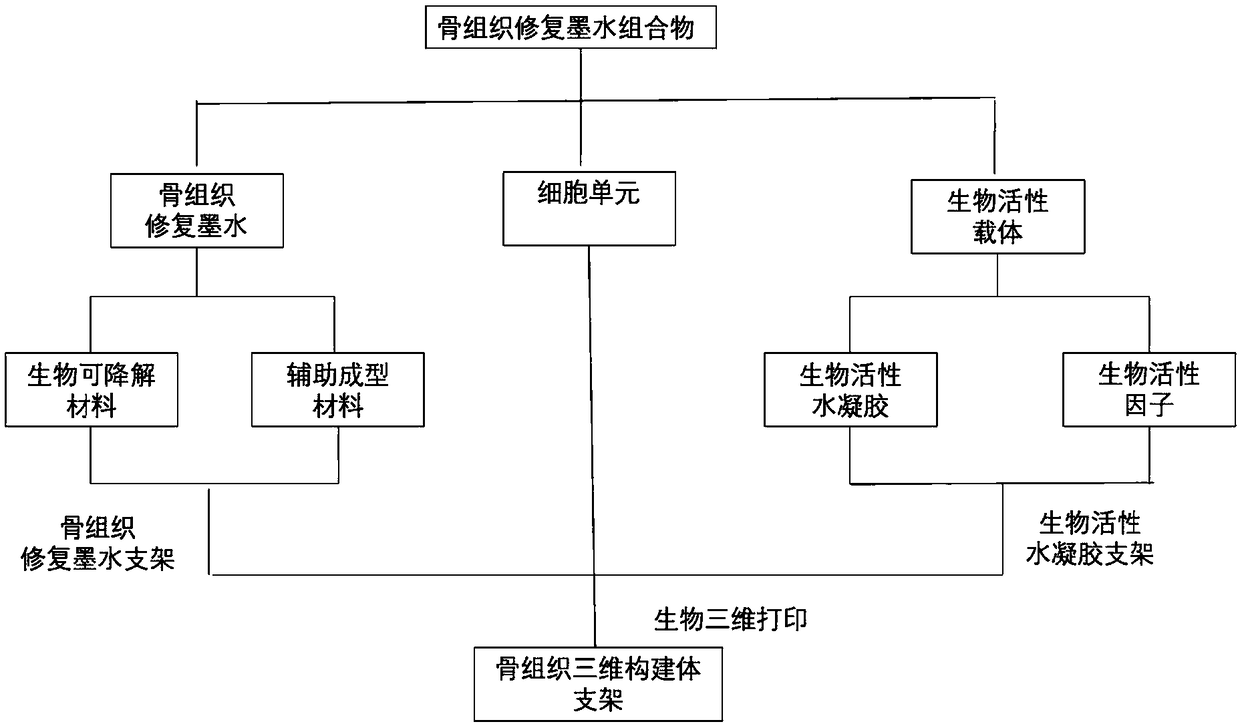
Bone tissue repair ink, composition and bracket, and preparation methods thereof as well as kit
ActiveCN109381749APromote proliferationPromote directed differentiationAdditive manufacturing apparatusTissue regenerationBone tissueBone tissue engineering
The invention relates to the field of bone tissue engineering, in particular to bone tissue repair ink, a bone tissue repair composition and a bone tissue repair bracket, and preparation methods thereof as well as a kit. The bone tissue repair ink and a bioactive carrier wrapping cells are used as raw materials, and the bone tissue repair bracket is printed according to a preset three-dimensionalstructure by adopting a biological printer. Meanwhile, living cell printing is realized by adopting the bone tissue repair ink and the bioactive carrier as the raw materials. The cells are uniformly distributed on a bracket model formed by the bone tissue repair ink and difficultly slide down to the bottom of the bracket, so that the problem that the expression of some characteristic proteins of the cells is easily lost in the prior art is effectively solved. The growth of the cells on the bracket is facilitated. A human body bone cell growth environment is better simulated, the cell proliferation, the directional differentiation and the specific protein expression are promoted, the extension and the migration of the cells in the bone tissue bracket and the cell junction establishment arefacilitated, and an organic construction body is formed.
Owner:REGENOVO BIOTECH
Methods and apparatuses for analyzing biological samples by mass spectrometry
InactiveUS8778695B2Particle separator tubesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDiseaseMass spectrometry imaging
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
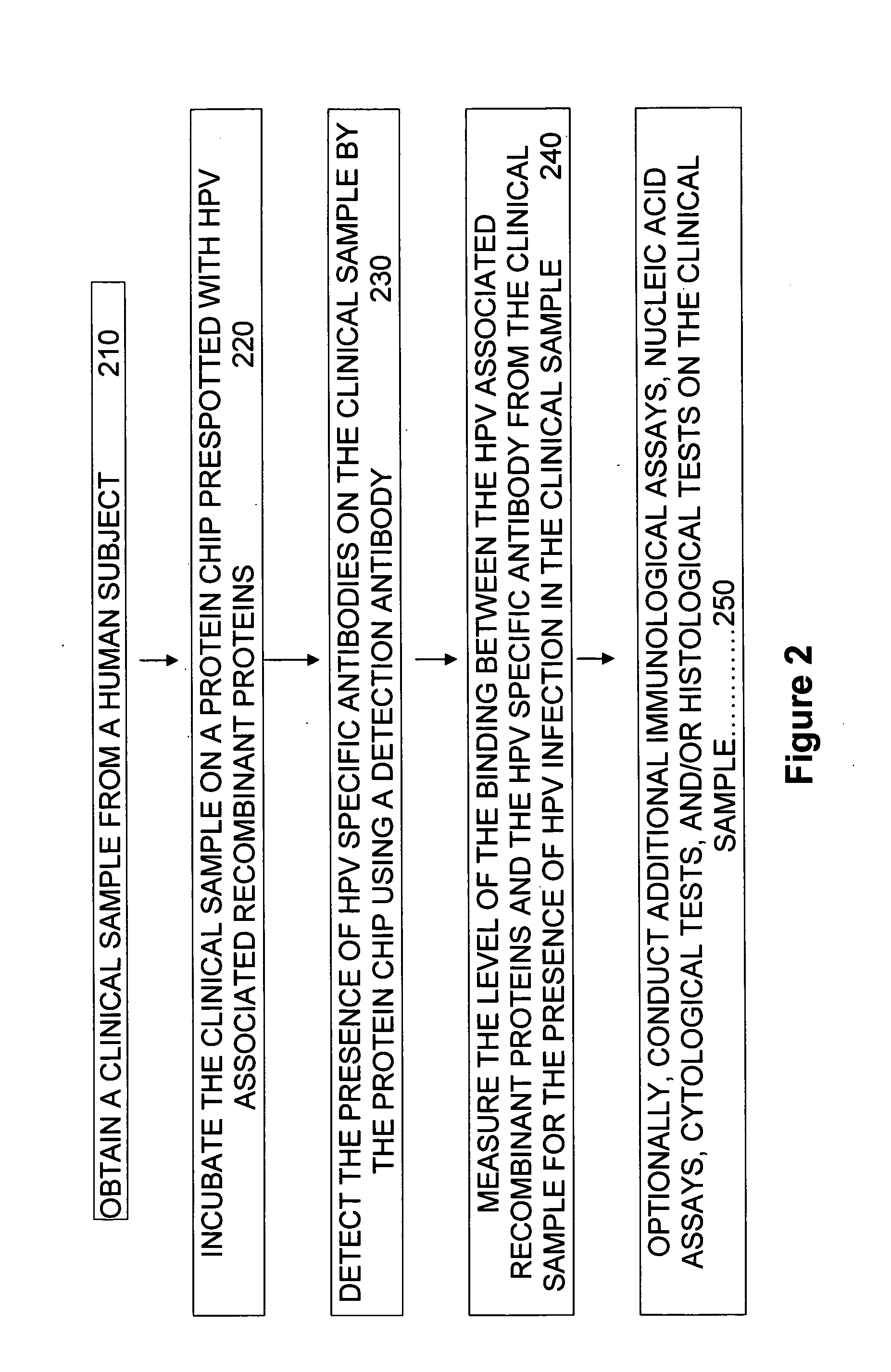
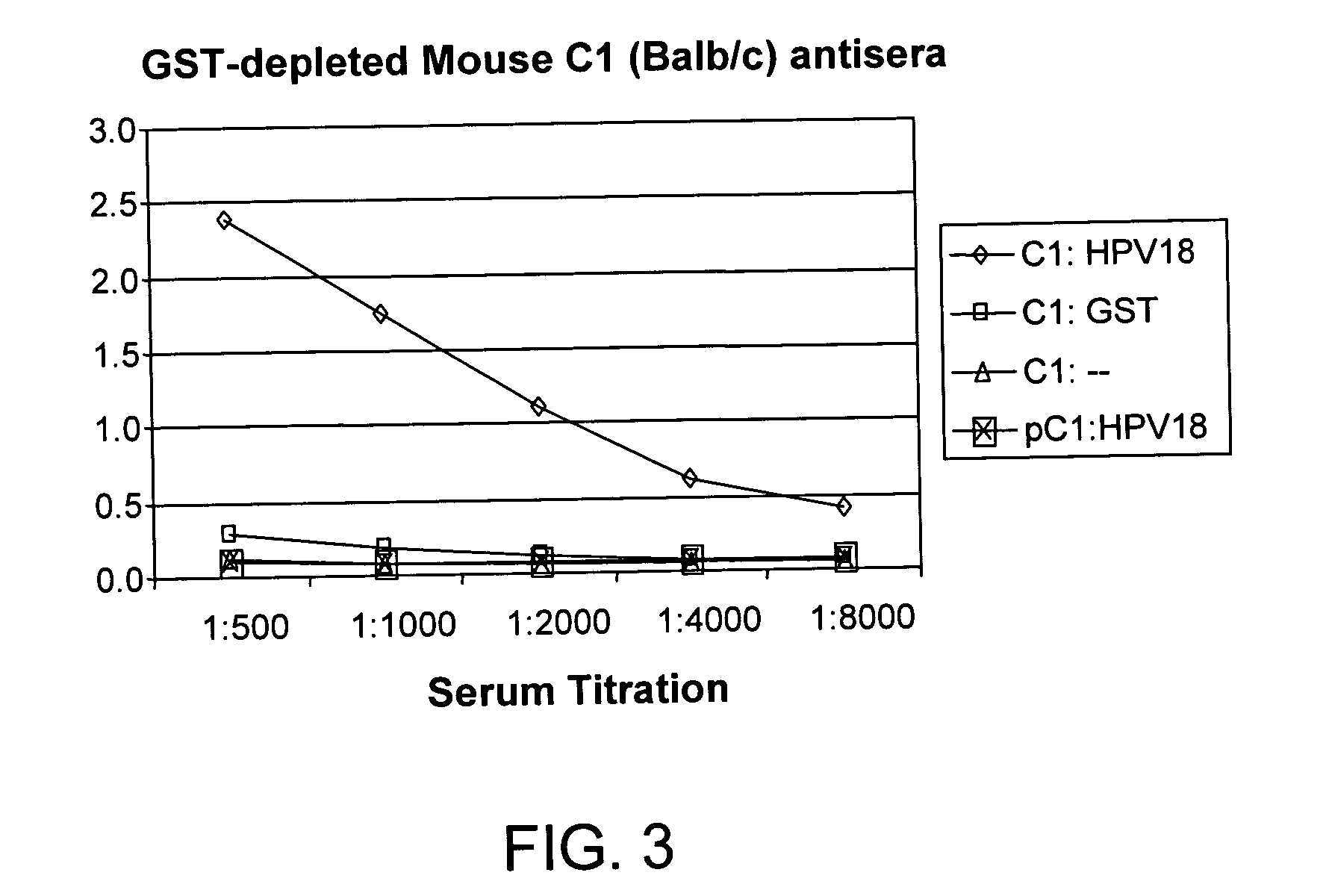
Methods of diagnosing cervical cancer
The invention provides reagents and methods for detecting pathogen infections in human samples. This detection utilizes specific proteins to detect the presence of pathogen proteins or abnormal expression of human proteins resulting from pathogen infections. Specific methods, compositions and kits are disclosed herein for the detection of oncogenic Human papillomavirus E6 proteins in clinical samples.
Owner:ARBOR VITA CORP
Efficient culture of stem cells for the production of hemoglobin
InactiveUS6361998B1Efficiently transfectedExtend your lifeBlood/immune system cellsFermentationSerum free mediaSerum ige
The present invention describes a serum-free medium that promotes the growth and differentiation of erythroid cells, cells that are highly transducible by a non-viral method and genes which increase the growth of erythroid cells and decrease their dependency on Epo. This invention can be used in the expansion of hematopoietic stem cells to produce cultures of erythroid cells as a source of erythroid-specific proteins such as hemoglobin. Hematopoietic stem cells are cultured ex vivo in a serum-free culture medium with the addition of IL-3, SCF and EPO. Cells transfected with the gene described in the present invention can be cultured in the serum-free culture medium with decreased dependency on Epo and other cytokines, thereby reducing the cost of the production of hemoglobin.
Owner:THERAPURE BIOPHARMA INC
Liposome complexes for increased systemic delivery
Highly efficient cationic liposomes have been developed as an improved delivery system for biologically-active reagents. A novel structure, the sandwich liposome, is formed and comprises one or more biologically active agents internalized between two bilomellar liposomes. This structure protects the incoming agent and accounts for the high efficiency of in vivo delivery and for the broad tissue distribution of the sandwich liposome complexes.These novel liposomes are also highly efficient carriers of nucleic acids. By using extruded DOTAP:cholesterol liposomes to form complexes with DNA encoding specific proteins, expression has been improved dramatically. Highest expression was achieved in the lung, while increased expression was detected in several organs and tissues.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Artery- and vein-specific proteins and uses therefor
InactiveUS6916625B2Peptide/protein ingredientsGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsTargeted disruptionVenous endothelium
Arterial and venous endothelial cells are molecularly distinct from the earliest stages of angiogenesis. This distinction is revealed by expression on arterial cells of a transmembrane ligand, called EphrinB2 whose receptor EphB4 is expressed on venous cells. Targeted disruption of the EphrinB2 gene prevents the remodeling of veins from a capillary plexus into properly branched structures. Moreover, it also disrupts the remodeling of arteries, suggesting that reciprocal interactions between pre-specified arterial and venous endothelial cells are necessary for angiogenesis.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Microencapsulation method for preparing hydrotropic substance serving as core material by using complex coacervation method
InactiveCN102580638AEnsure safetyImprove permeabilityMicroballoon preparationMicrocapsule preparationMass ratioFreeze-drying
The invention relates to a microencapsulation method for preparing a hydrotropic substance serving as a core material by using a complex coacervation method. The method is simple in process and low in cost, and the product has high encapsulation rate. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) weighing specific protein and polysaccharide in a certain ratio, stirring and dissolving in hot water to form a wall material solution; (2) weighing a certain mass of hydrotropic core material substance, adding an oil phase substance and an emulsifier in a certain mass ratio, and performing high-speed dispersion to form water / oil (W / O) emulsion; (3) directly pouring the emulsion into the wall material solution, stirring at the constant temperature of 45 DEG C, regulating pH by using 10 percent acid, and reacting for 15 minutes; (4) cooling to the temperature of below 15 DEG C, regulating the pH to 6.0, and adding glutamine transaminase for solidifying; and (5) filtering to obtain a wet capsule product. A dry microcapsule product can be obtained by freeze drying or spray drying.
Owner:山东省万兴食品有限公司 +1
Nucleic acid and corresponding protein entitled 161P2F10B useful in treatment and detection of cancer
InactiveUS20030165505A1Quick filterOvercome difficultiesHydrolasesGenetic material ingredientsSpecific proteinDisease
A protein obtainable from a non pathogenic microorganism, said protein having mucosa binding promoting activity and a molecular weight of 20-40 kD is disclosed. Application of such a protein or a peptide derived therefrom in a method of screening non pathogenic microorganisms for a microorganism capable of specifically binding mucosa, said method comprising detection in a manner known per se of the presence of a particular protein on or in a microorganism or in a culture of microorganisms, said particular protein being the already defined protein. Kits suitable for such a screening method are also disclosed. Use of a component selected from the group of components comprising a protein or peptide as defined an expression vector comprising nucleic acid encoding such protein or peptide a recombinant microorganism or a part of said microorganism expressing such protein or peptide, said part expressing mucosa binding promoting activity a non pathogenic microorganism capable of expressing such protein or peptide or a part of said microorganism, said part expressing mucosa binding promoting activity as pharmaceutically active component in a pharmaceutical composition for prophylaxis and / or treatment of disease or illness associated with a mucosa colonising pathogenic microorganism. Use of such components as food additive and compositions comprising such components are described.
Owner:AGENSYS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com