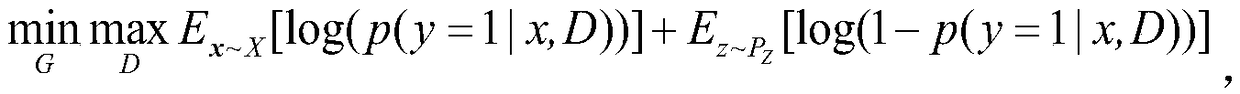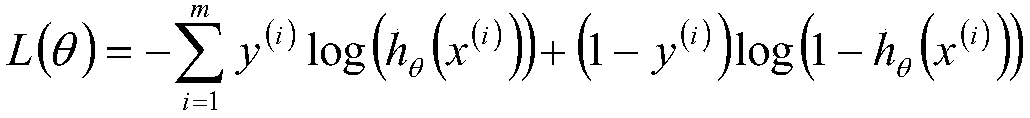Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1987 results about "Deconvolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, deconvolution is an algorithm-based process used to reverse the effects of convolution on recorded data. The concept of deconvolution is widely used in the techniques of signal processing and image processing. Because these techniques are in turn widely used in many scientific and engineering disciplines, deconvolution finds many applications. In general, the objective of deconvolution is to find the solution of a convolution equation of the form: f*g=h Usually, h is some recorded signal, and f is some signal that we wish to recover, but has been convolved with some other signal g before we recorded it.
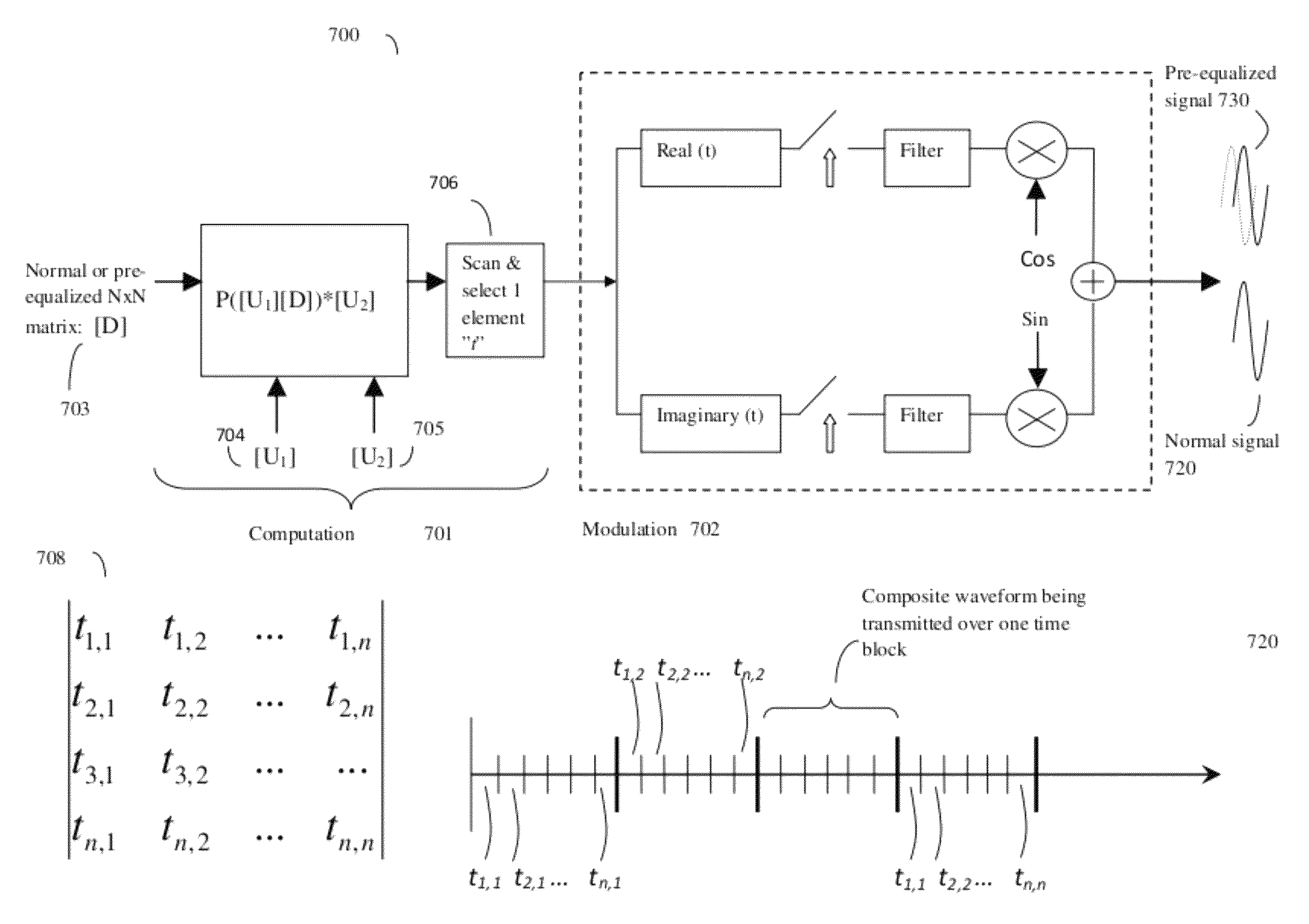
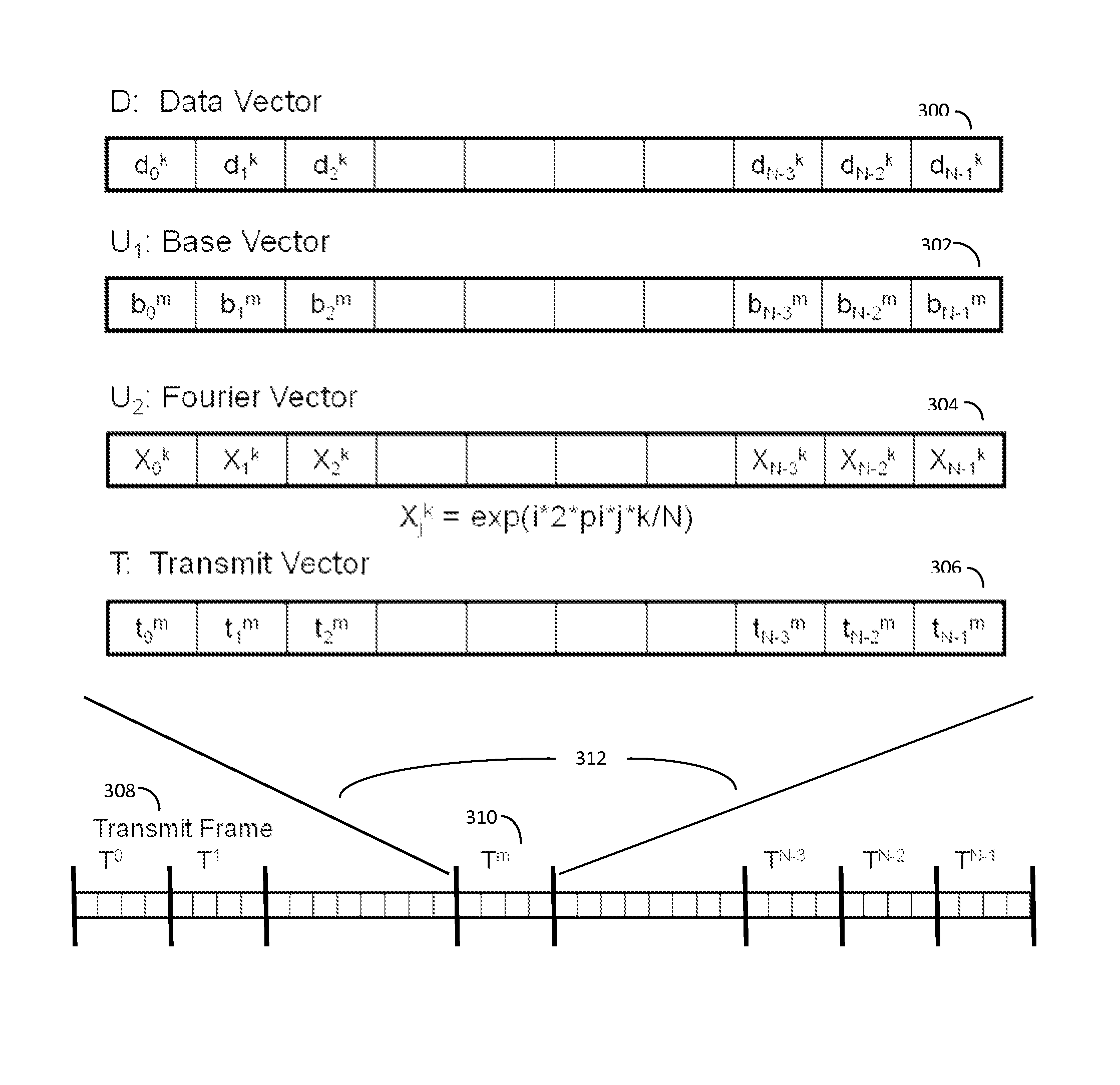
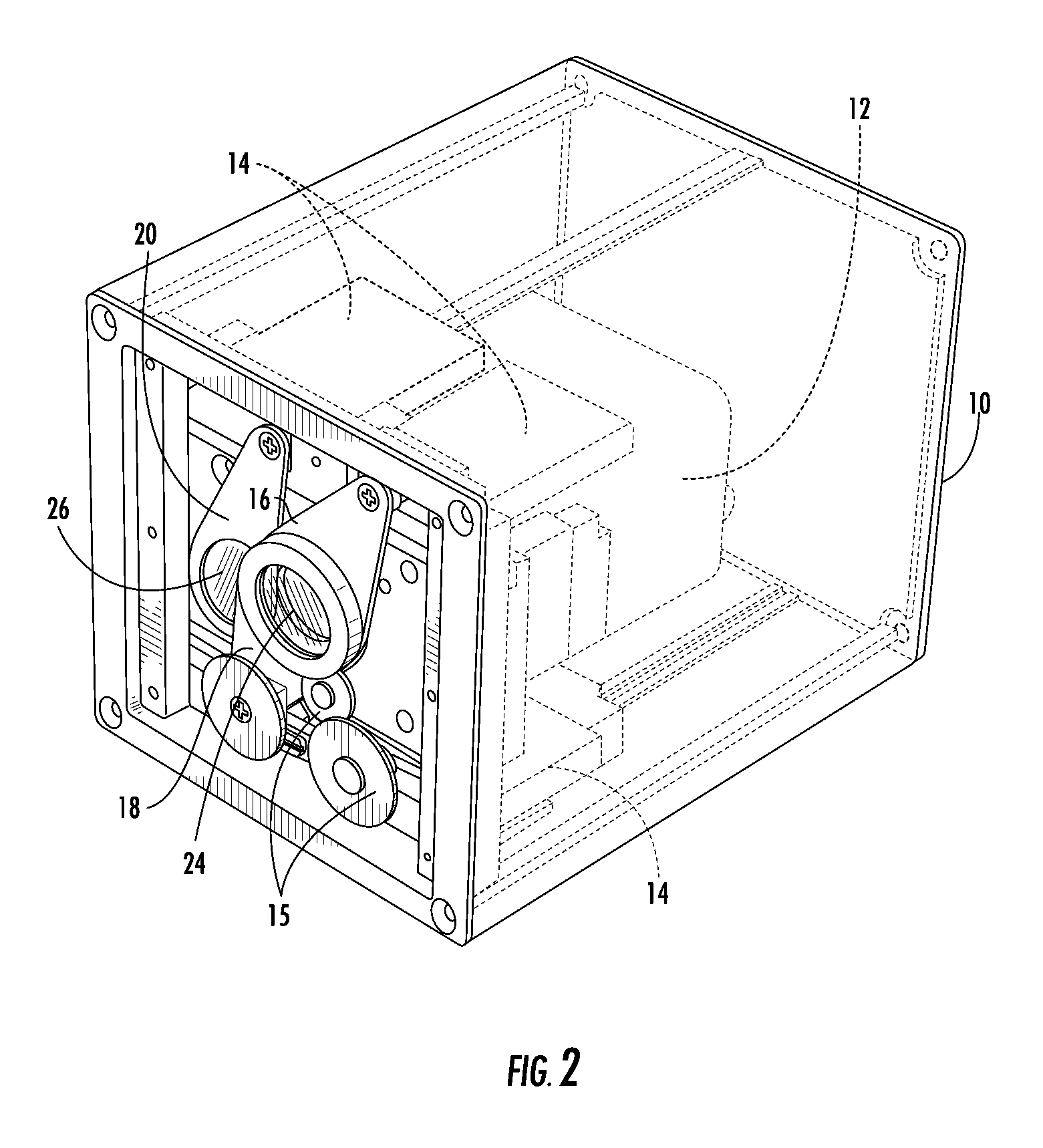
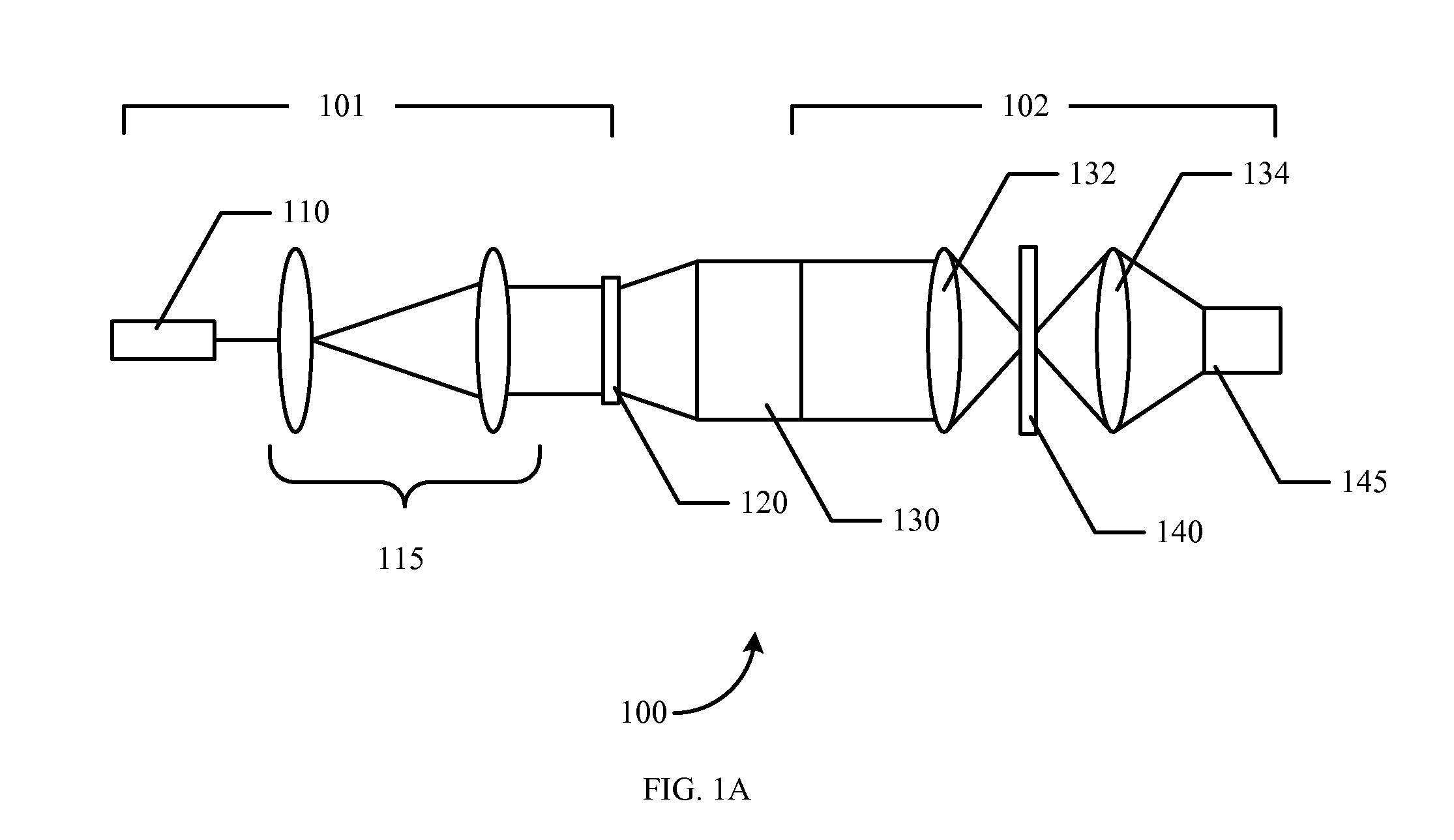
Signal modulation method resistant to echo reflections and frequency offsets
ActiveUS9083595B2Improve performancePromote decompositionNetwork traffic/resource managementMulti-frequency code systemsHigh rateEngineering
A method of modulating communications signals, such as optical fiber, wired electronic, or wireless signals in a manner that facilitates automatic correction for the signal distortion effects of echoes and frequency shifts, while still allowing high rates of data transmission. Data symbols intended for transmission are distributed into N×N matrices, and used to weigh or modulate a family of cyclically time shifted and cyclically frequency shifted waveforms. Although these waveforms may then be distorted during transmission, their basic cyclic time and frequency repeating structure facilitates use of improved receivers with deconvolution devices that can utilize the repeating patterns to correct for these distortions. The various waveforms may be sent in N time blocks at various time spacing and frequency spacing combinations in a manner that can allow interleaving of blocks from different transmitters. Applications to channel sounding / characterization, system optimization, and also radar are also discussed.
Owner:COHERE TECH
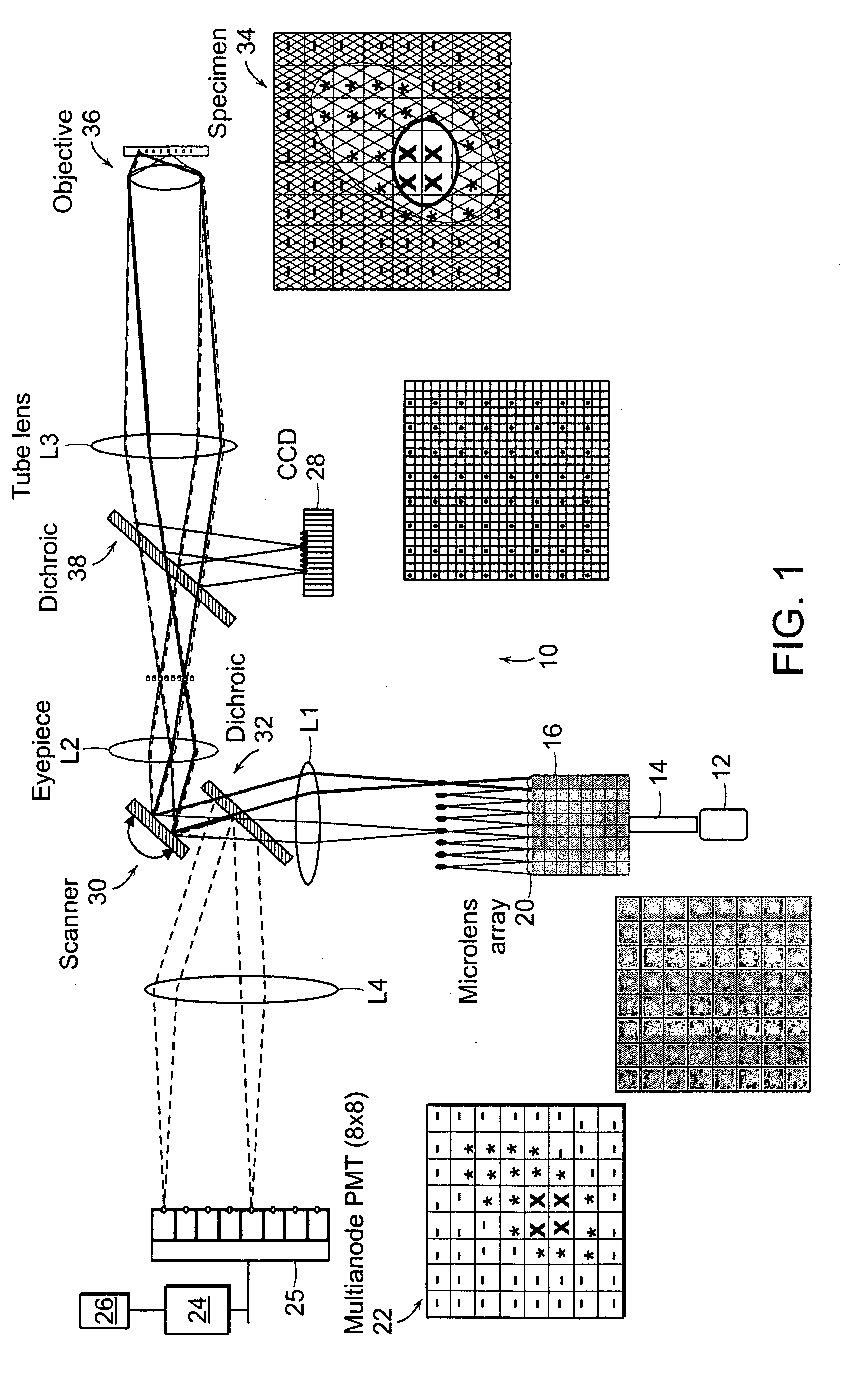
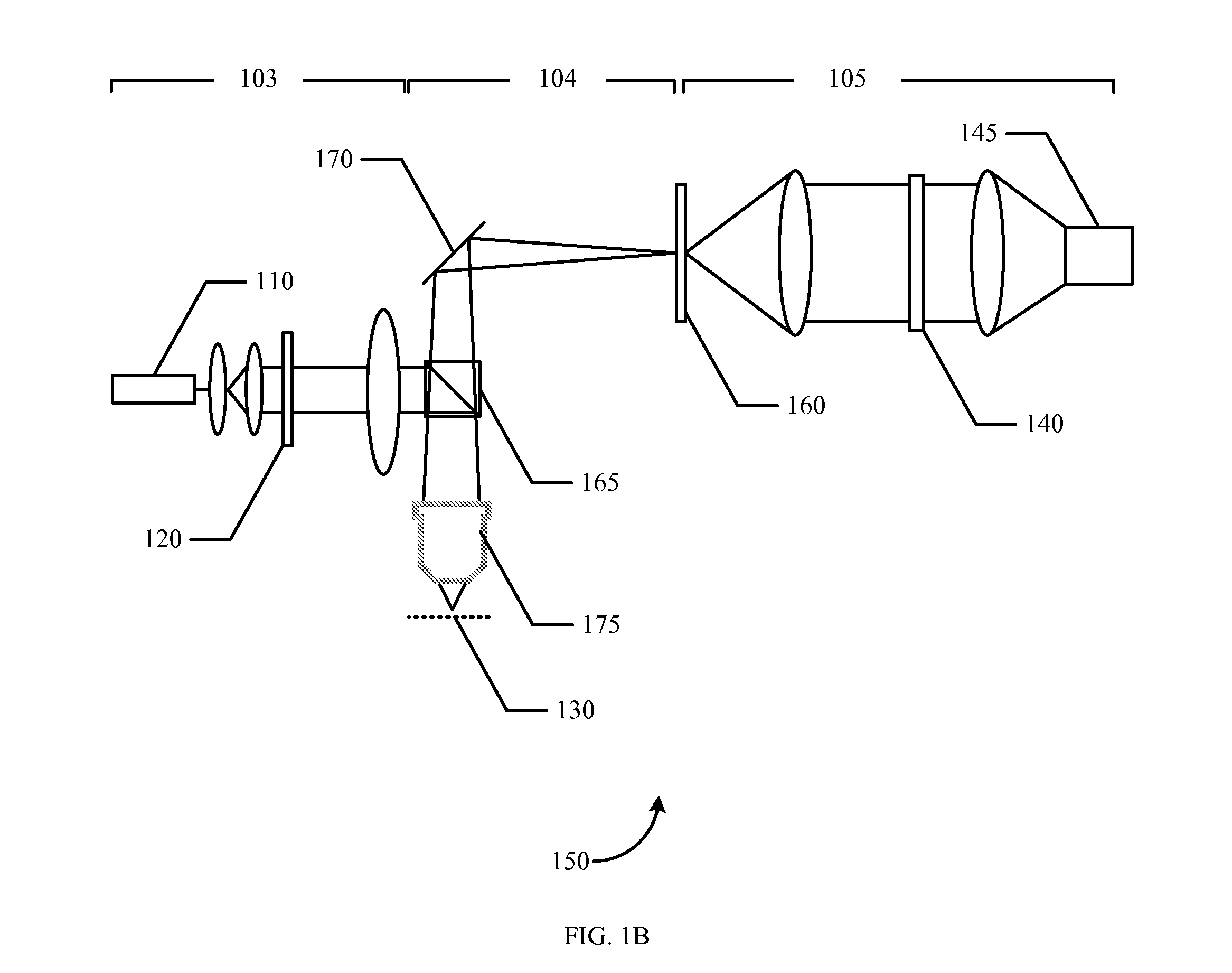
Multifocal imaging systems and method
InactiveUS20070057211A1Fast imagingEfficient collectionMaterial analysis by optical meansColor television detailsLow noiseGrating
In the systems and methods of the present invention a multifocal multiphoton imaging system has a signal to noise ratio (SNR) that is reduced by over an order of magnitude at imaging depth equal to twice the mean free path scattering length of the specimen. An MMM system based on an area detector such as a multianode photomultiplier tube (MAPMT) that is optimized for high-speed tissue imaging. The specimen is raster-scanned with an array of excitation light beams. The emission photons from the array of excitation foci are collected simultaneously by a MAPMT and the signals from each anode are detected using high sensitivity, low noise single photon counting circuits. An image is formed by the temporal encoding of the integrated signal with a raster scanning pattern. A deconvolution procedure taking account of the spatial distribution and the raster temporal encoding of collected photons can be used to improve decay coefficient. We demonstrate MAPMT-based MMM can provide significantly better contrast than CCD-based existing systems.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
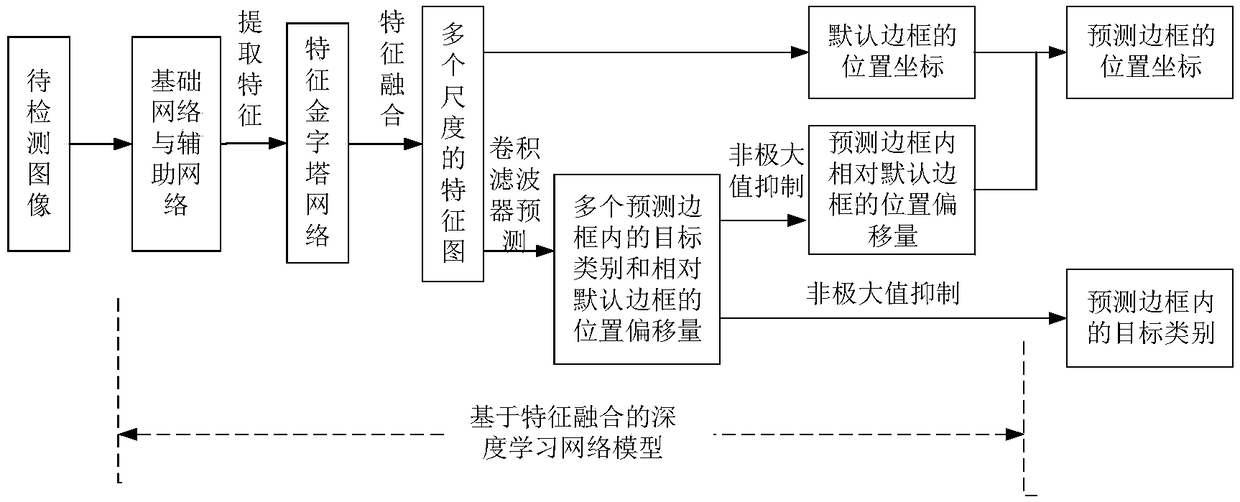
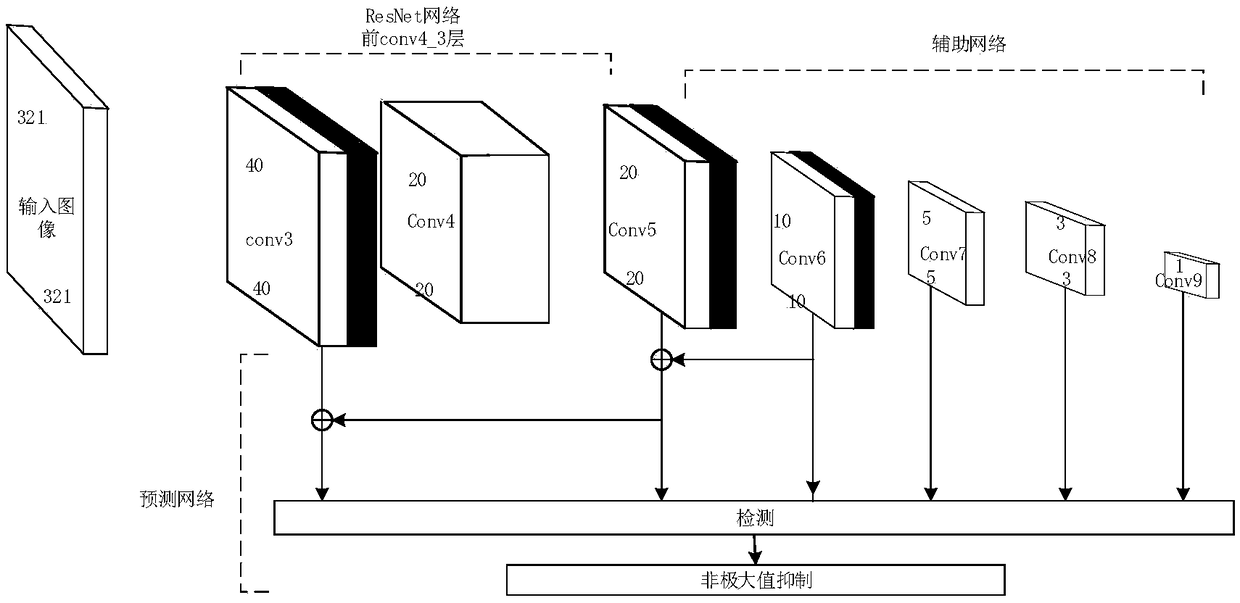
Small target detection method based on feature fusion and depth learning
InactiveCN109344821AScalingRich information featuresCharacter and pattern recognitionNetwork modelFeature fusion
The invention discloses a small target detection method based on feature fusion and depth learning, which solves the problems of poor detection accuracy and real-time performance for small targets. The implementation scheme is as follows: extracting high-resolution feature map through deeper and better network model of ResNet 101; extracting Five successively reduced low resolution feature maps from the auxiliary convolution layer to expand the scale of feature maps. Obtaining The multi-scale feature map by the feature pyramid network. In the structure of feature pyramid network, adopting deconvolution to fuse the feature map information of high-level semantic layer and the feature map information of shallow layer; performing Target prediction using feature maps with different scales and fusion characteristics; adopting A non-maximum value to suppress the scores of multiple predicted borders and categories, so as to obtain the border position and category information of the final target. The invention has the advantages of ensuring high precision of small target detection under the requirement of ensuring real-time detection, can quickly and accurately detect small targets in images, and can be used for real-time detection of targets in aerial photographs of unmanned aerial vehicles.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
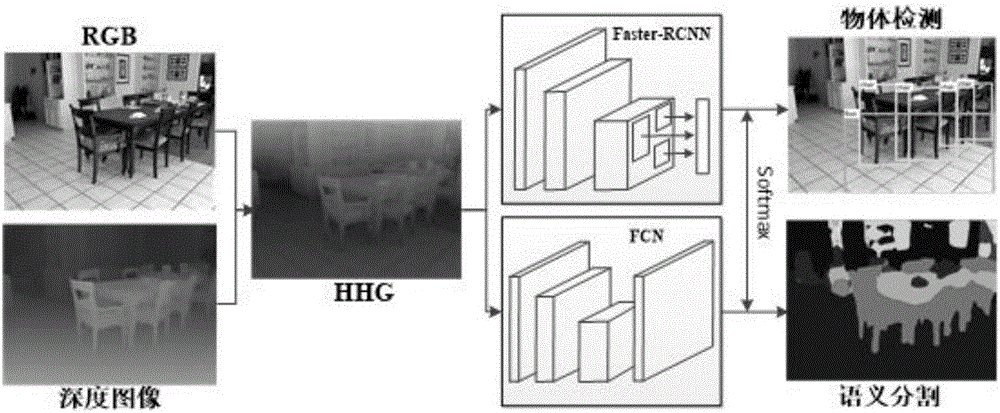
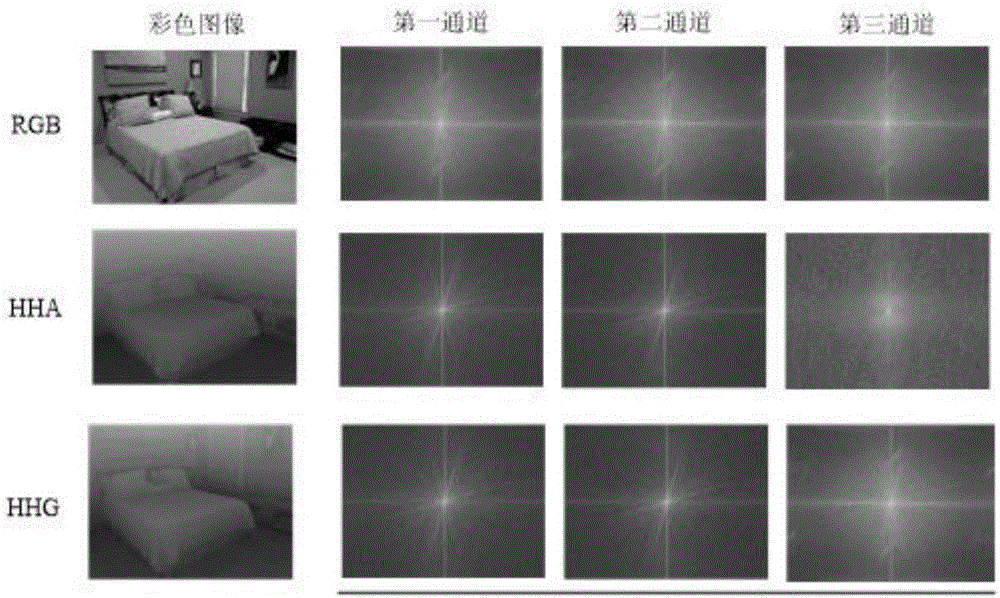
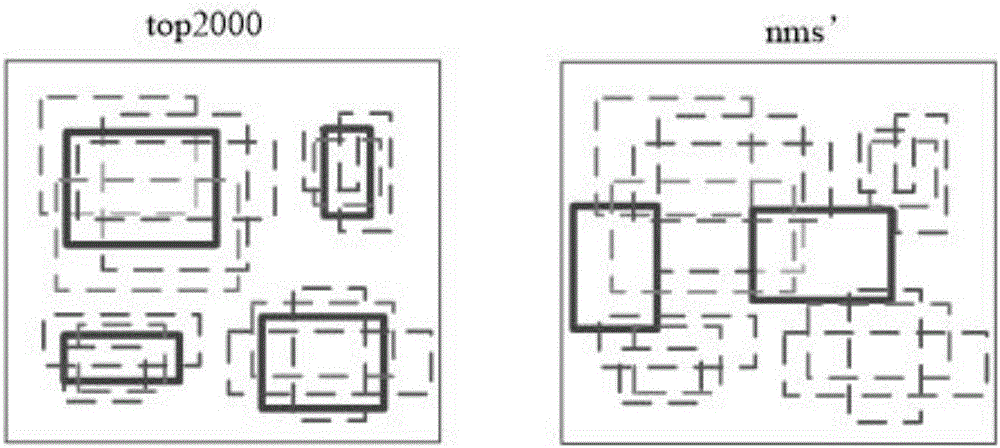
RGB-D image object detection and semantic segmentation method based on deep convolution network
ActiveCN106709568ACharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesMachine visionVisual perception
The invention discloses an RGB-D image object detection and semantic segmentation method based on a deep convolution network, which belongs to the field of depth learning and machine vision. According to the method provided by the technical scheme of the invention, Faster-RCNN is used to replace the original slow RCNN; Faster-RCNN uses GPU, which is fast in the aspect of feature extracting, and at the same time generates a regional scheme in the network; the whole training process is training from end to end; FCN is used to carry out RGB-D image semantic segmentation; FCN uses a GPU and the deep convolution network to rapidly extract the deep features of an image; deconvolution is used to fuse deep features and shallow features of the image convolution; and the local semantic information of the image is integrated into the global semantic information.
Owner:深圳市小枫科技有限公司
Near-eye optical deconvolution displays
ActiveUS20140168035A1Blurring effectCathode-ray tube indicatorsOptical elementsDisplay deviceComputerized system
In embodiments of the invention, an apparatus may include a display comprising a plurality of pixels. The apparatus may further include a computer system coupled with the display and operable to instruct the display to display a deconvolved image corresponding to a target image, wherein when the display displays the deconvolved image while located within a near-eye range of an observer, the target image may be perceived in focus by the observer.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
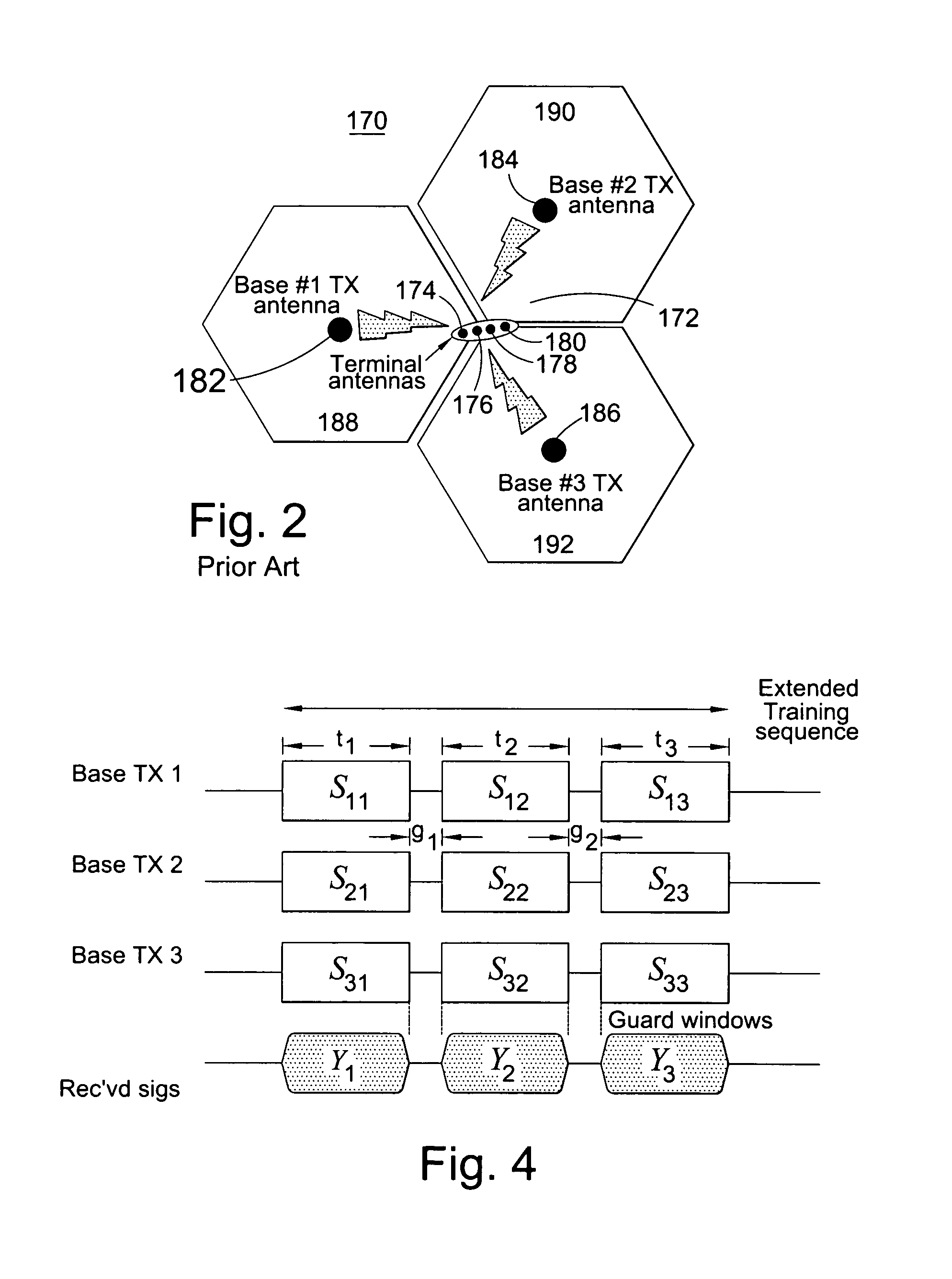
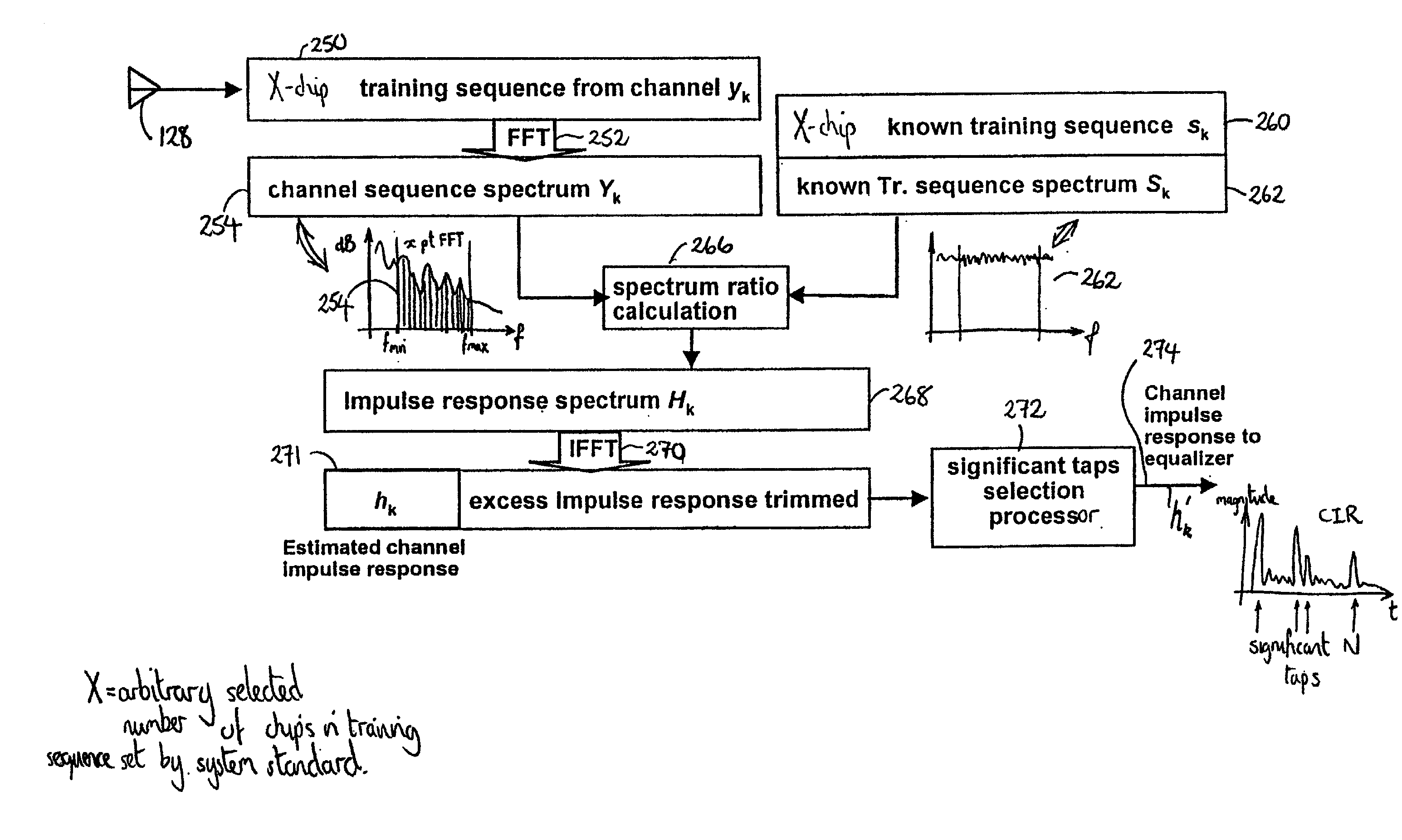
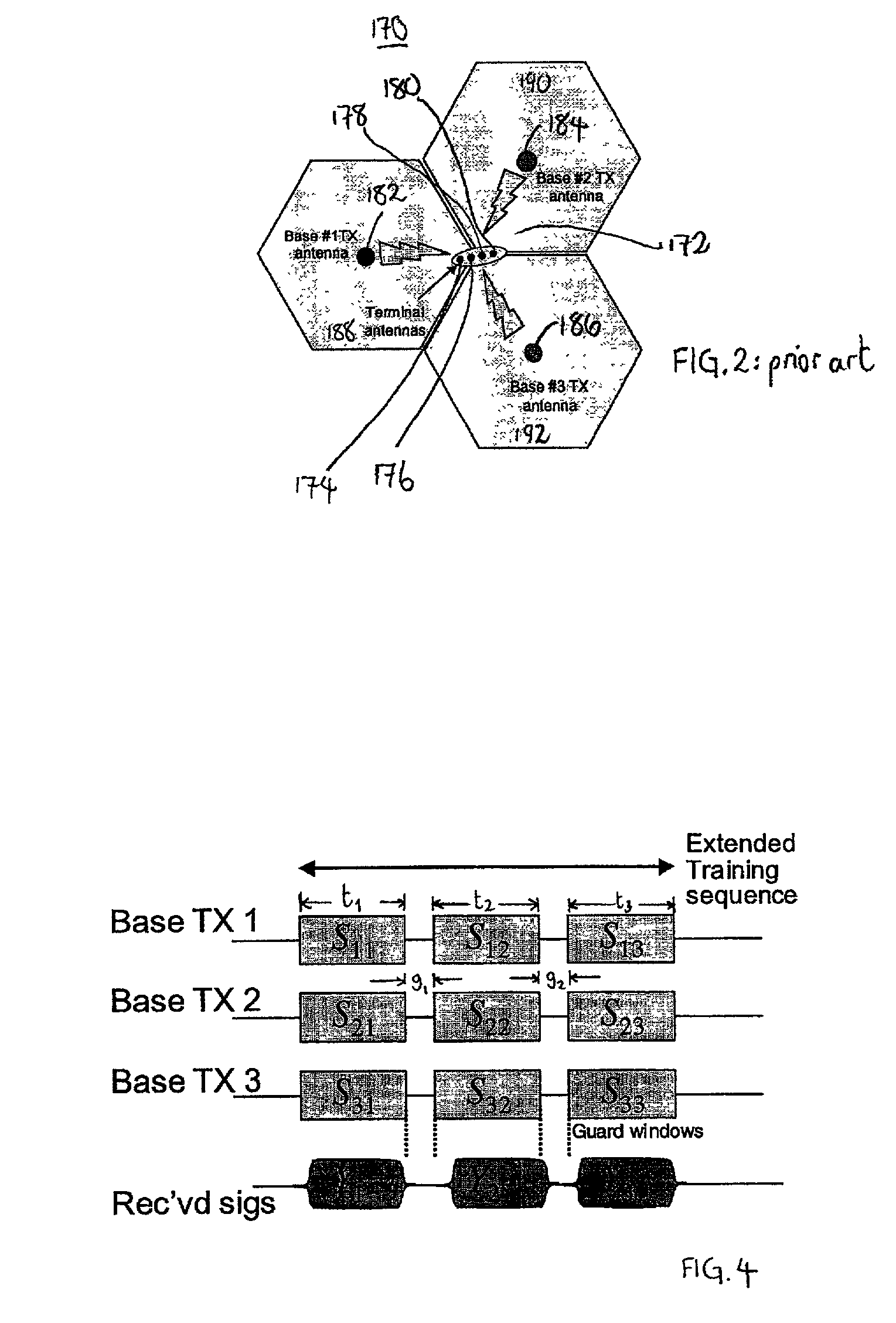
Communication system and methods of estimating channel impulse responses therein
InactiveUS7149239B2Improve interferenceImprove accuracySecret communicationChannel estimationTime transformationEngineering
Multiple Steiner codes are transmitted as bursts from multiple base stations (182, 184, 186) having one or more transmit elements (174, 176, 178, 180), with successive bursts providing an extended training sequence for use in channel estimation at an addressed unit (172), such as a mobile handset. Accurate channel estimation is possible through the use of Wiener frequency domain MMSE deconvolution (518) combined with frequency domain spatial decoupling matrices, with quasi-orthogonal pseudo-noise sequences (502, 504, 520, 522) allocated to base stations and their antenna elements. The use of Steiner codes to supplement Wiener frequency domain MMSE deconvolution and frequency domain spatial decoupling results in the possibility of allocating only a single training sequence to each base station provided that the training sequence is of sufficient length to encompass all multiple time-translated channel impulse responses (H). Estimates may be refined iteratively by minimising the MS error of demodulated pilot symbols. Estimates may also be refined by removing taps from the impulse response which are insignificant based on a relatively long-term power-delay profile for the channel.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
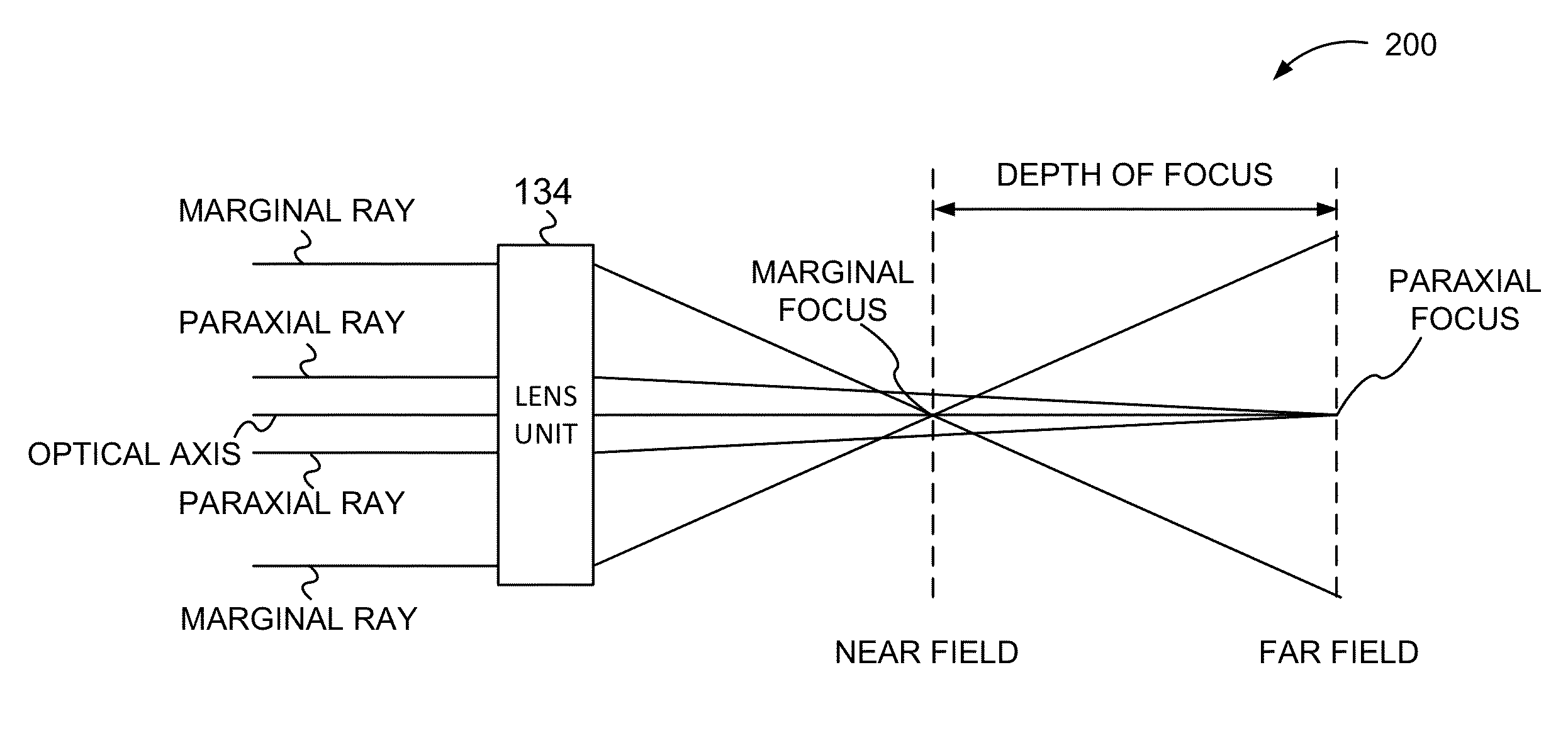
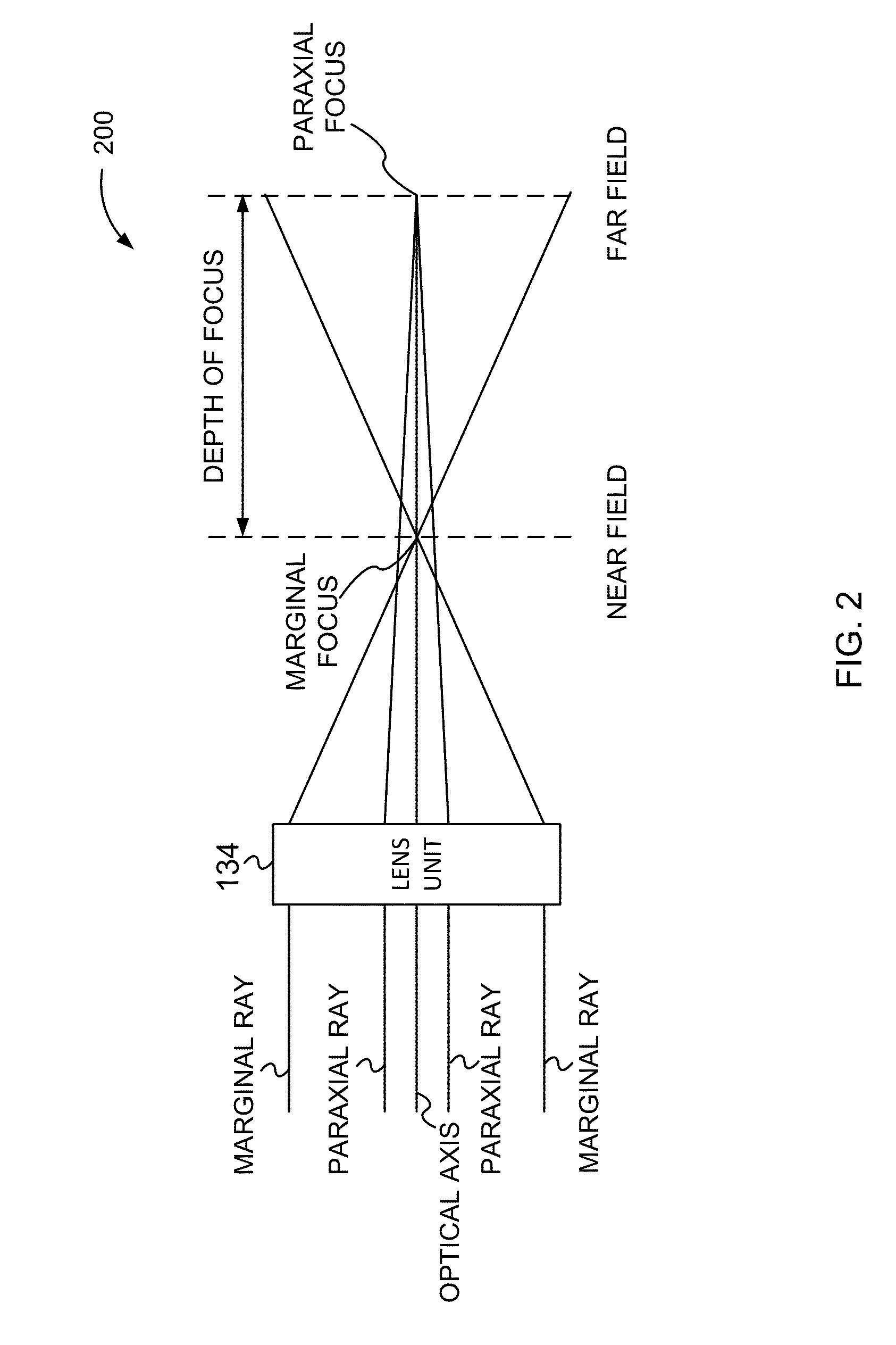
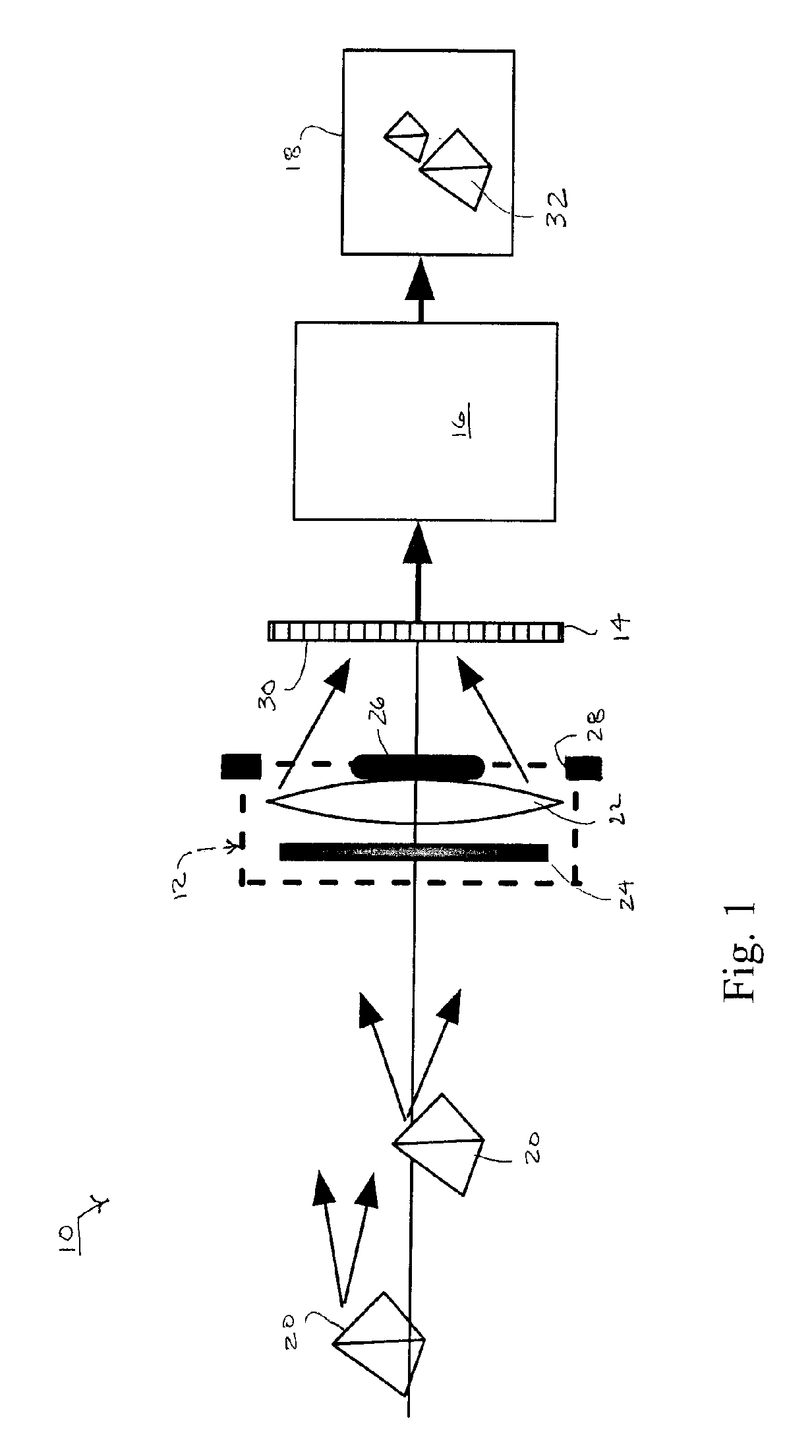
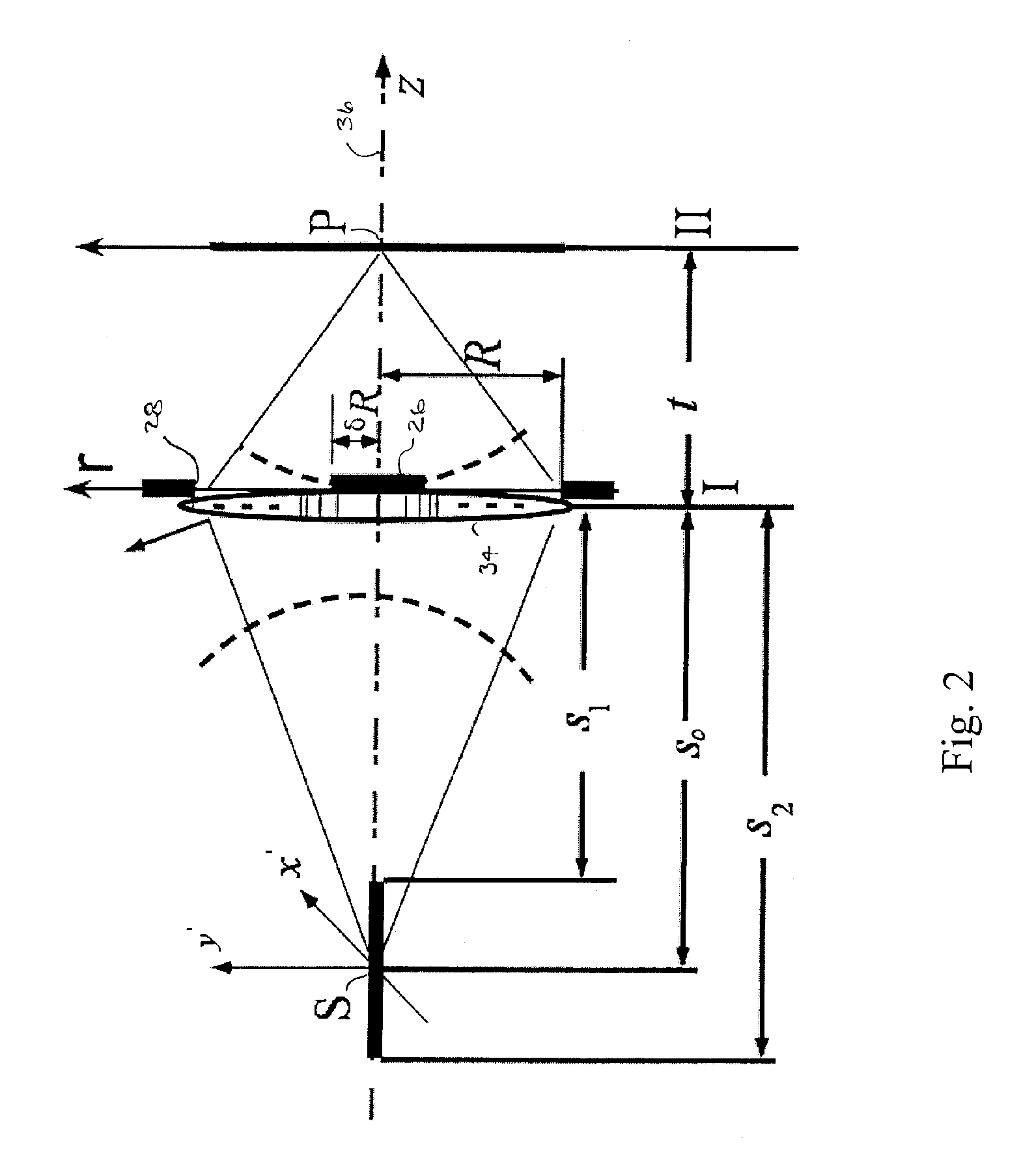
Method and apparatus for scanning with controlled spherical aberration
A reader obtains image data corresponding to an image of optically encoded information that is received via a lens unit that causes controlled spherical aberration blurring that is precisely known. The reader may perform deconvolution processing on the image data to render it decodable. The deconvolution processing may implement a Weiner filter that uses data corresponding to a near-field point spread function of the lens unit. The depth of field of the reader is greater than that of conventional reader in all lighting conditions.
Owner:INTERMEC TECH
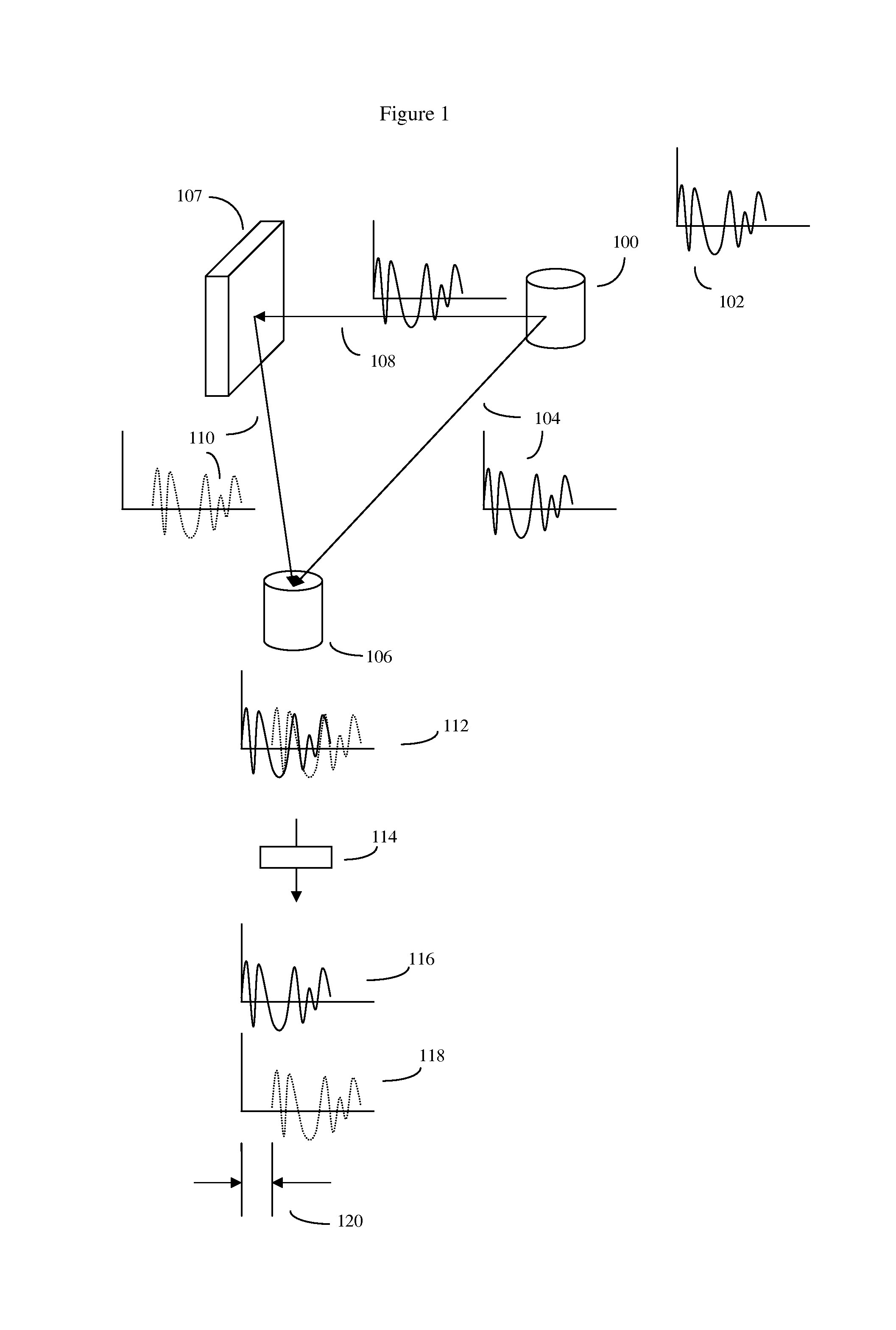
Signal modulation method resistant to echo reflections and frequency offsets
ActiveUS20120201322A1Improve performancePromote decompositionModulated-carrier systemsNetwork traffic/resource managementHigh rateFrequency shift
A method of modulating communications signals, such as optical fiber, wired electronic, or wireless signals in a manner that facilitates automatic correction for the signal distortion effects of echoes and frequency shifts, while still allowing high rates of data transmission. Data symbols intended for transmission are distributed into N×N matrices, and used to weigh or modulate a family of cyclically time shifted and cyclically frequency shifted waveforms. Although these waveforms may then be distorted during transmission, their basic cyclic time and frequency repeating structure facilitates use of improved receivers with deconvolution devices that can utilize the repeating patterns to correct for these distortions. The various waveforms may be sent in N time blocks at various time spacing and frequency spacing combinations in a manner that can allow interleaving of blocks from different transmitters. Applications to channel sounding / characterization, system optimization, and also radar are also discussed.
Owner:COHERE TECH
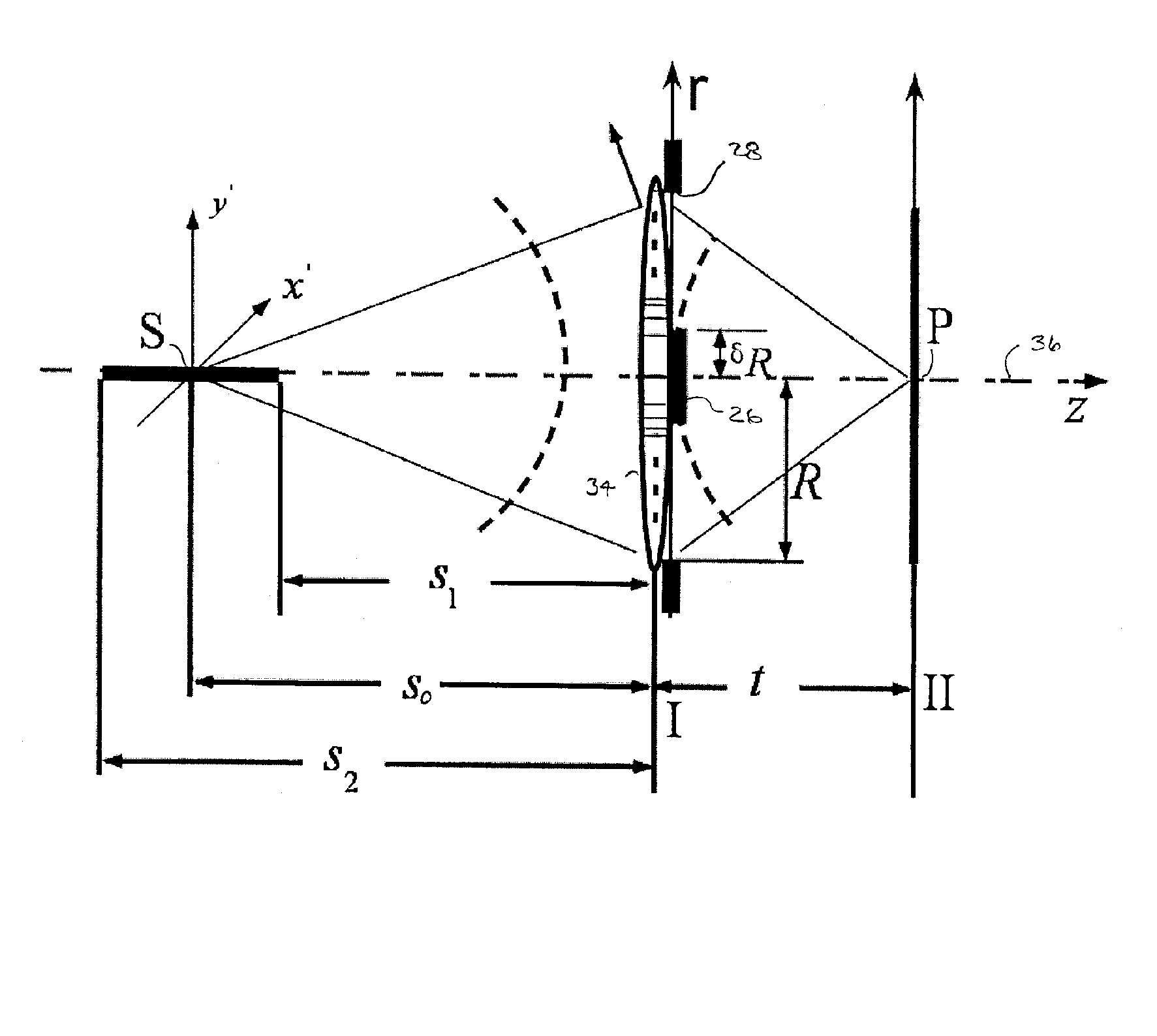
Extended depth of field using a multi-focal length lens with a controlled range of spherical aberration and a centrally obscured aperture
ActiveUS7336430B2Easy to manufactureUniform responseImage enhancementTelevision system detailsIntermediate imageImaging quality
An extended depth of field is achieved by a computational imaging system that combines a multifocal imaging subsystem for producing a purposefully blurred intermediate image with a digital processing subsystem for producing a recovered image having an extended depth of field. The multifocal imaging system preferably exhibits spherical aberration as the dominant feature of the purposeful blur. A central obscuration of the multifocal imaging subsystem renders point-spread functions of object points more uniform over a range of object distances. An iterative digital deconvolution algorithm for converting the intermediate image into the recovered image contains a metric parameter that speeds convergence, avoids stagnations, and enhances image quality.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
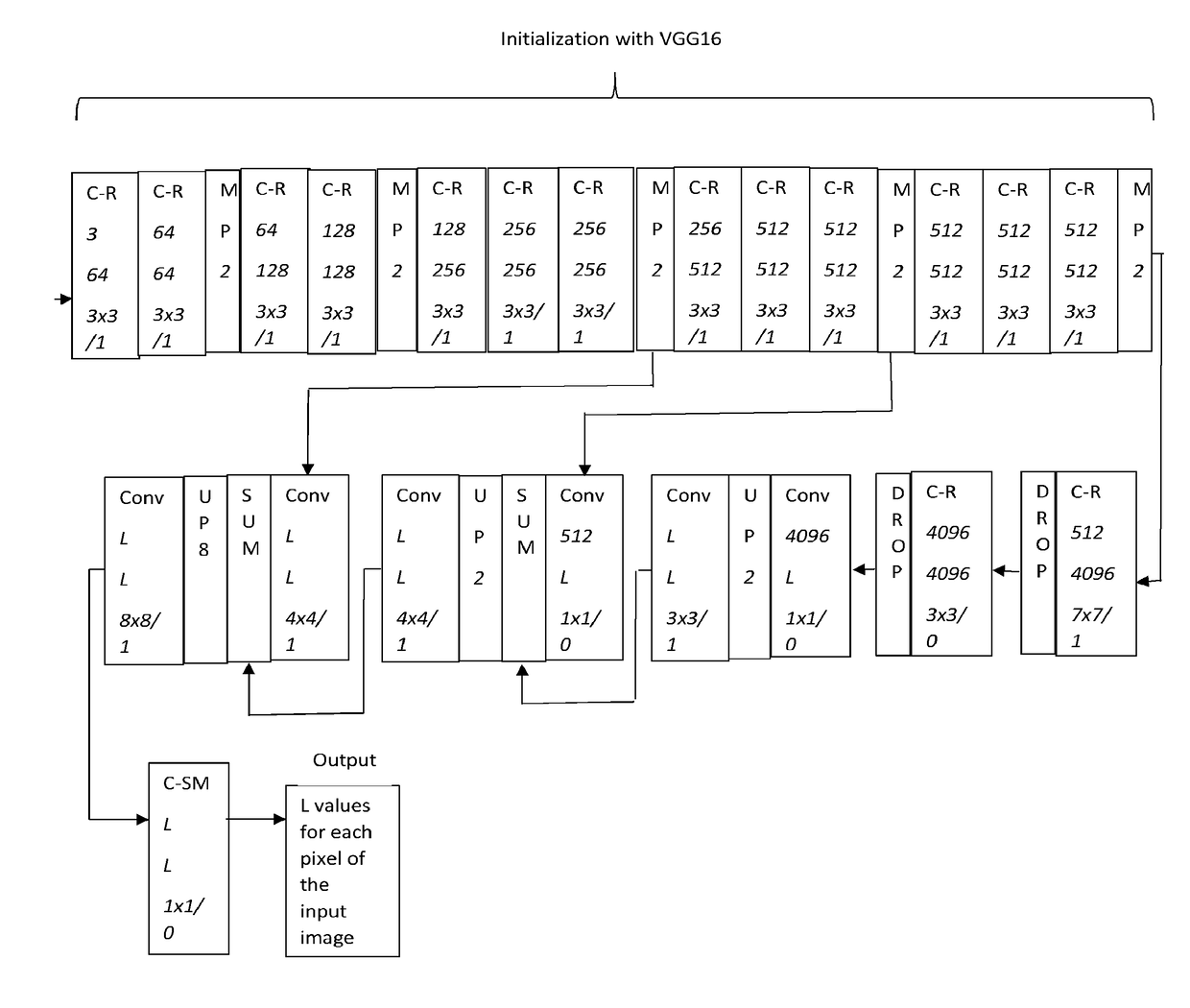
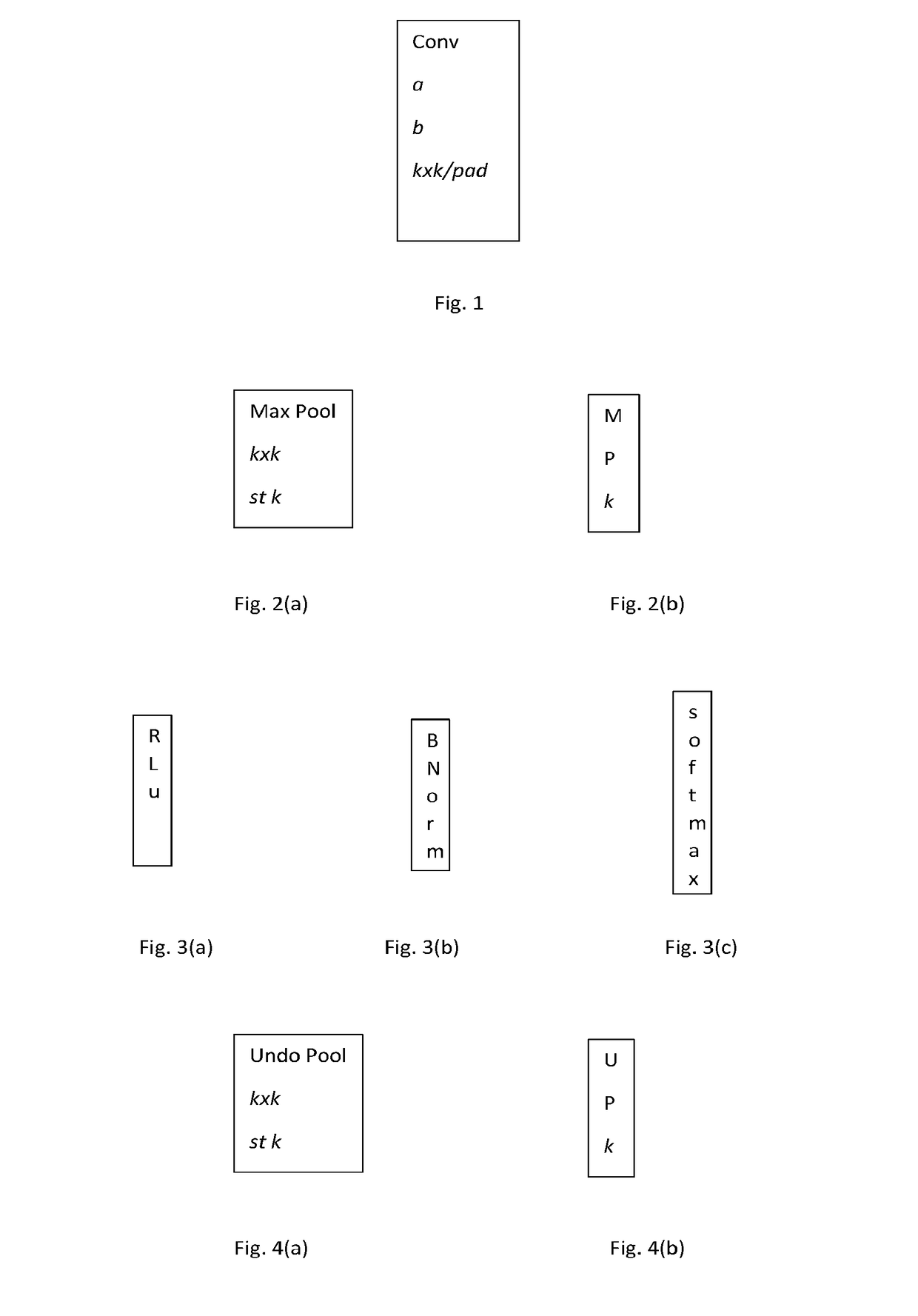
Training constrained deconvolutional networks for road scene semantic segmentation
ActiveUS20170262735A1Image enhancementAutonomous decision making processPattern recognitionComputer vision
A source deconvolutional network is adaptively trained to perform semantic segmentation. Image data is then input to the source deconvolutional network and outputs of the S-Net are measured. The same image data and the measured outputs of the source deconvolutional network are then used to train a target deconvolutional network. The target deconvolutional network is defined by a substantially fewer numerical parameters than the source deconvolutional network.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Multi-scale image semantic segmentation method
ActiveCN110232394AIncrease profitEasy to handleCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesSample imageMinutiae
The invention discloses a multi-scale image semantic segmentation method. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a to-be-segmented image and a corresponding label; constructing a full convolutional deep neural network, wherein the full convolutional deep neural network comprises a convolution module, a hole convolution module, a pyramid pooling module, a 1 * 1 * depth convolution layer and a deconvolution structure; setting hole convolution as channel-by-channel operation, and utilizing low-scale, medium-scale and high-scale characteristics in a targeted mode; training the full convolutional deep neural network, establishing a loss function, and determining parameters of the full convolutional deep neural network by training the sample image; and inputting the to-be-segmentedimage into the trained full convolutional deep neural network to obtain a semantic segmentation result. By means of the method, the image semantic segmentation problem with complex details, holes andlarge targets can be well solved while the calculated amount and the parameter number are reduced, and the consistency of category labels can be reserved while the target edges can be well segmented.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Removing camera shake from a single photograph
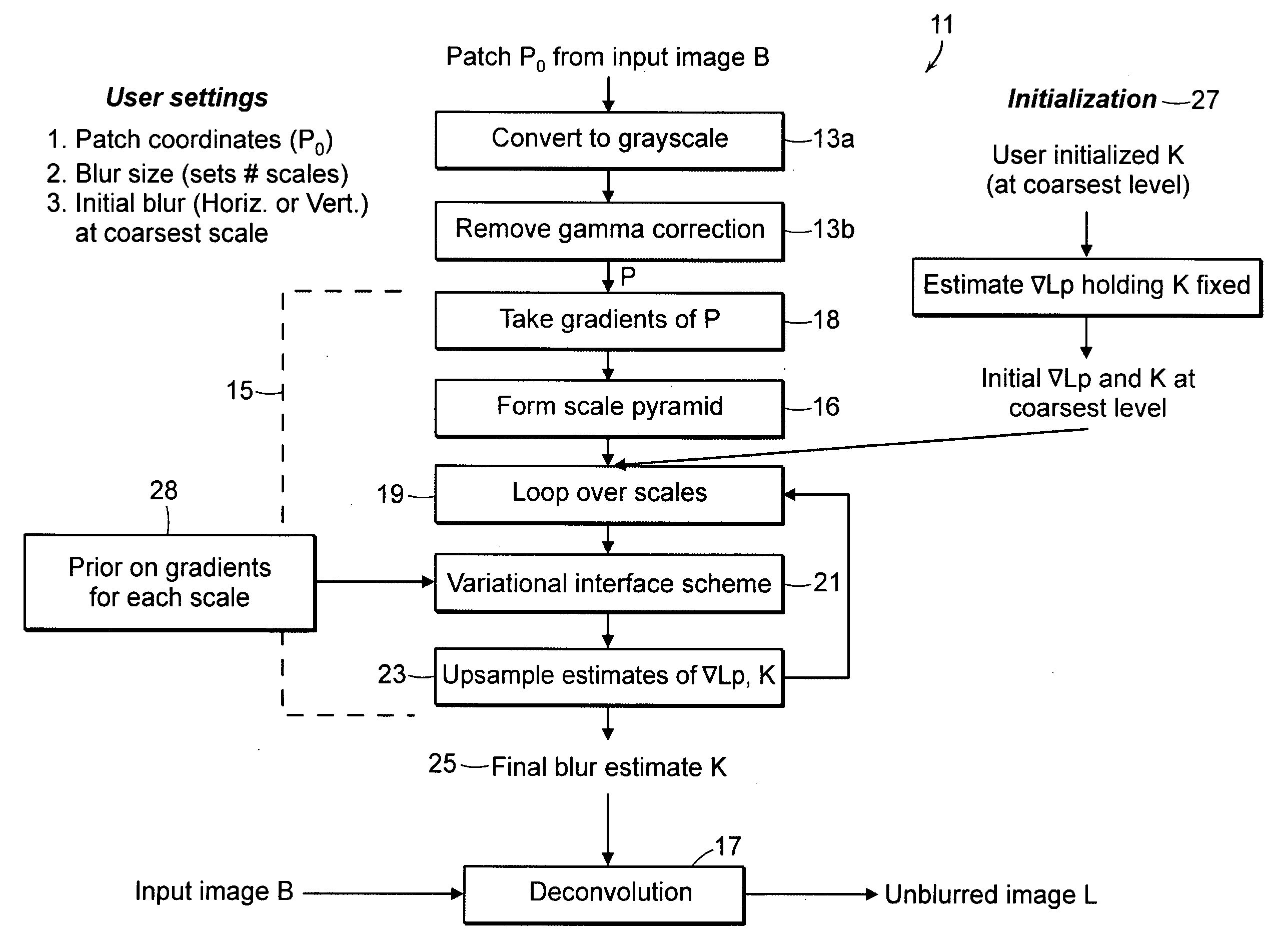
A computer method and system for deblurring an image is provided. The invention method and system of deblurring employs statistics on distribution of intensity gradients of a known model. The known model is based on a natural image which may be unrelated to the subject image to be deblurred by the system. Given a subject image having blur, the invention method / system estimates a blur kernel and a solution image portion corresponding to a sample area of the subject image, by applying the statistics to intensity gradients of the sample area and solving for most probable solution image. The estimation process is carried out at multiple scales and results in a blur kernel. In a last step, the subject image is deconvolved image using the resulting blur kernel. The deconvolution generates a deblurred image corresponding to the subject image.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TORONTO +1
Single-image super-resolution reconstruction method based on symmetric depth network
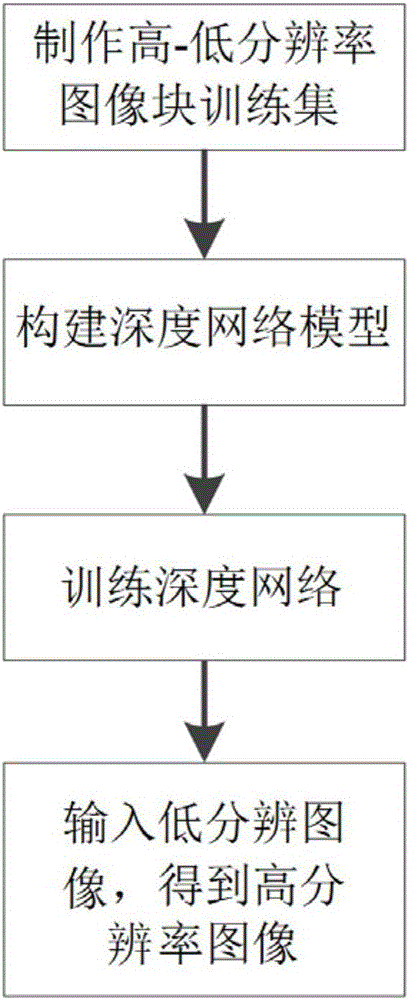
ActiveCN106204449AImprove image qualityImproving the ability of super-resolution reconstruction mapsImage enhancementGeometric image transformationData setSymmetric convolution
The invention discloses a single-image super-resolution reconstruction method based on a symmetric depth network and belongs to the image processing technology field. The method mainly comprises the following steps of 1, making a high resolution image block and low resolution image block training set; 2, constructing a symmetric convolution-deconvolution depth network used for model training; 3, based on the constructed depth network and the made data set, carrying out network model training; and 4, based on a learned model parameter, inputting one low resolution image, wherein acquired output is a reconstructed high resolution image. In the invention, a convolution layer and a deconvolution layer are combined and simultaneously a network depth is increased; the network depth is used to increase network performance; a reconstruction capability of an image detail portion is enhanced and a good image super-resolution reconstruction effect is acquired. The method has a wide application prospect in fields of image high definition displaying, medical imaging, a remote sensing image and the like.
Owner:安徽禾丰牧业有限公司
Extended depth of field using a multi-focal length lens with a controlled range of spherical aberration and a centrally obscured aperture
ActiveUS20060050409A1Increase contrastReduce image contrastImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPoint spreadIntermediate image
An extended depth of field is achieved by a computational imaging system that combines a multifocal imaging subsystem for producing a purposefully blurred intermediate image with a digital processing subsystem for producing a recovered image having an extended depth of field. The multifocal imaging system preferably exhibits spherical aberration as the dominant feature of the purposeful blur. A central obscuration of the multifocal imaging subsystem renders point-spread functions of object points more uniform over a range of object distances. An iterative digital deconvolution algorithm for converting the intermediate image into the recovered image contains a metric parameter that speeds convergence, avoids stagnations, and enhances image quality.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Method and system for high resolution ultrasonic imaging of small defects or anomalies.
InactiveUS6128092ARadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometrySonificationSynthetic aperture focusing
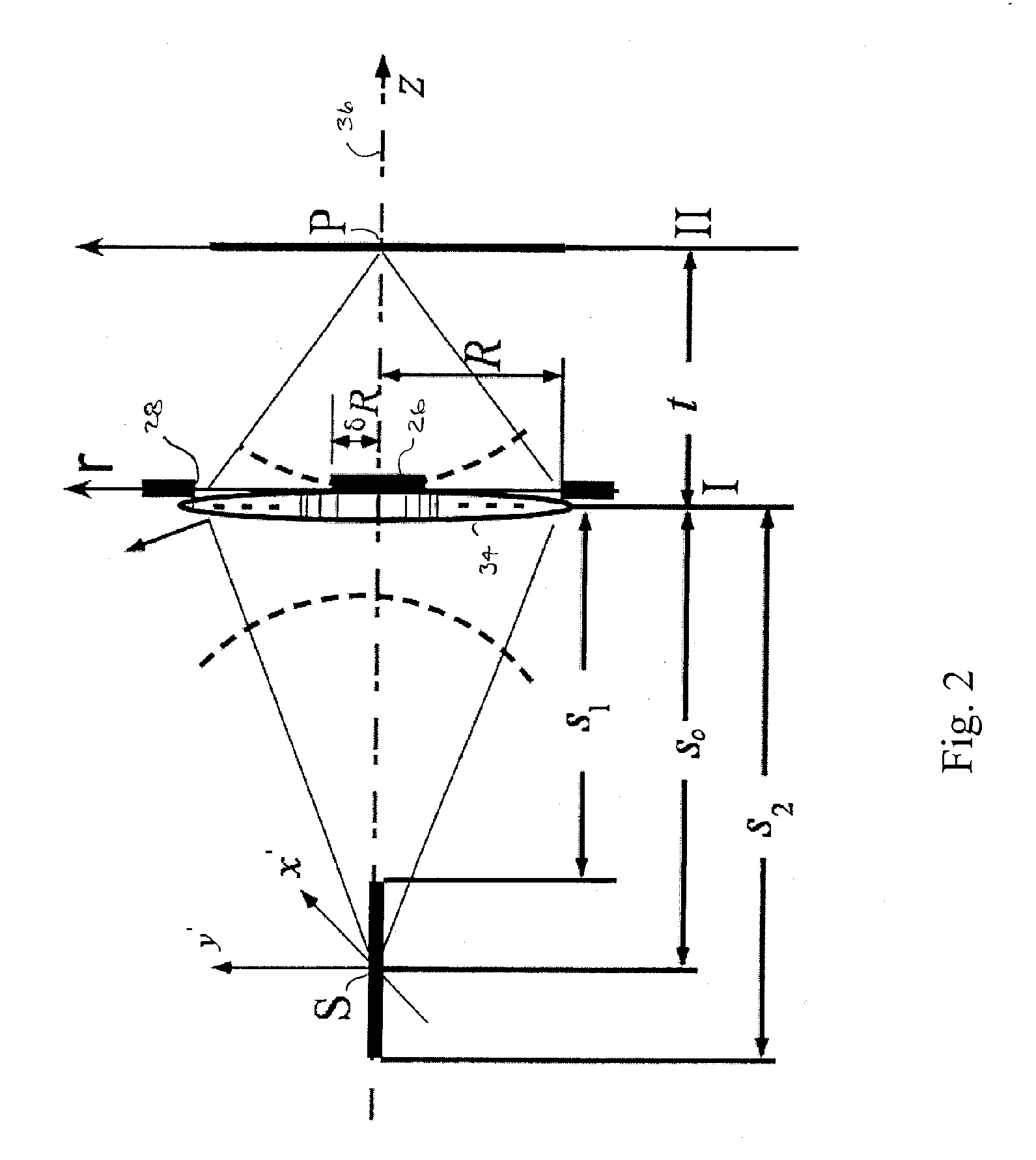
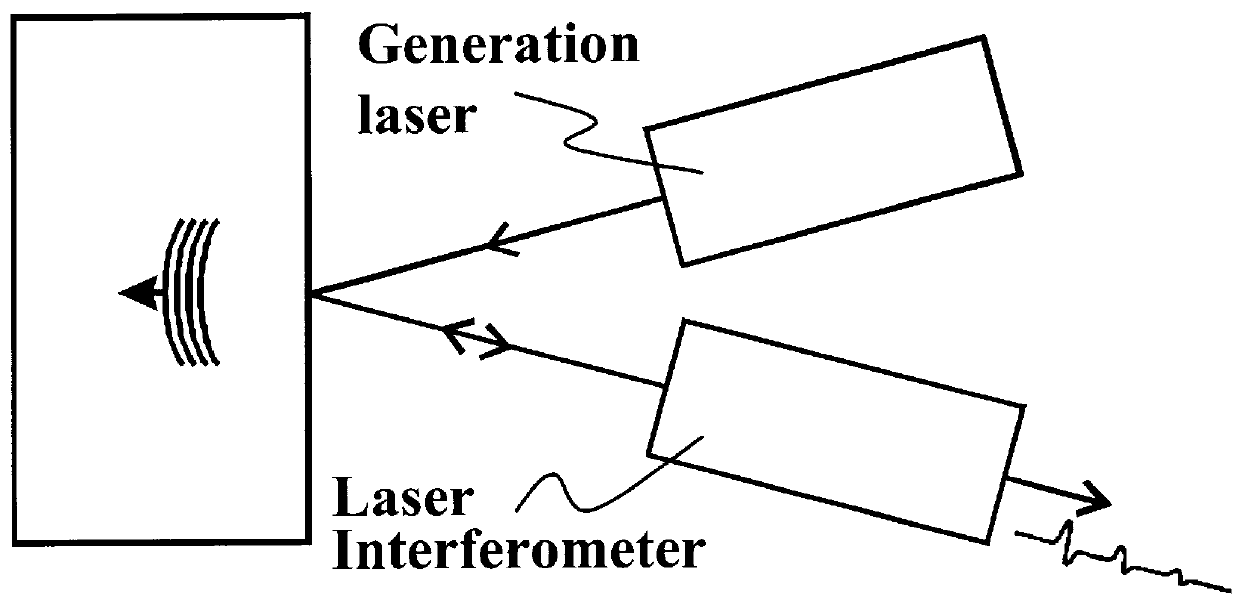
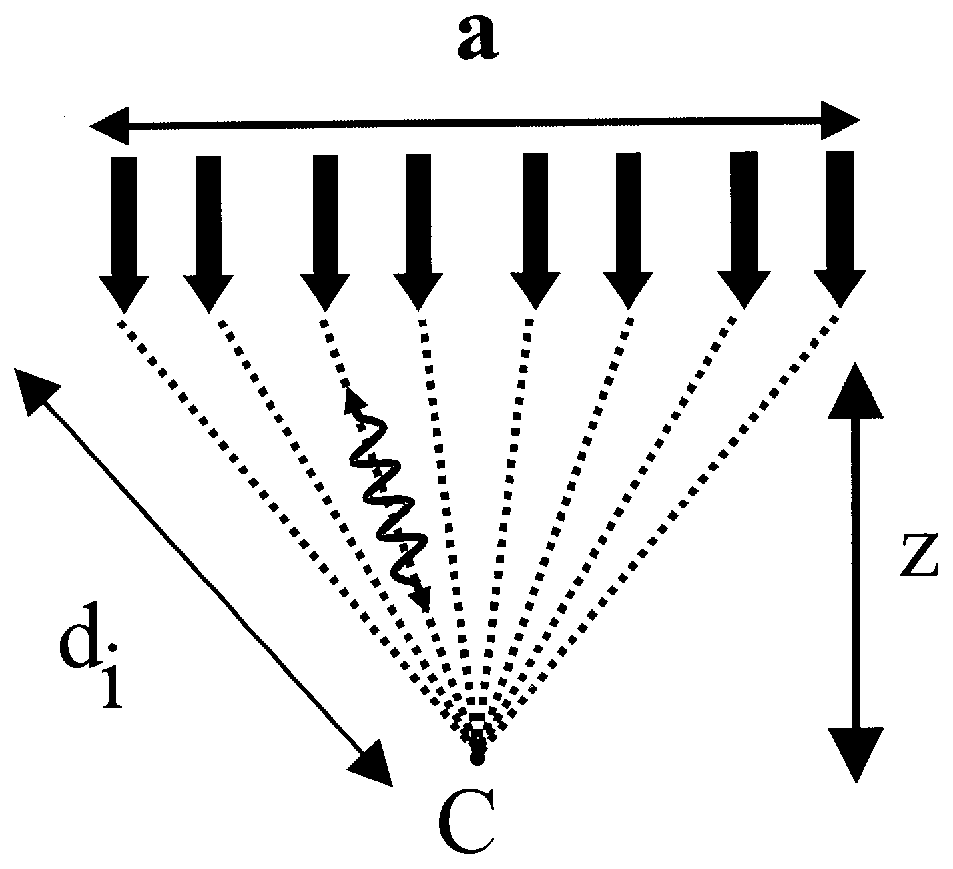
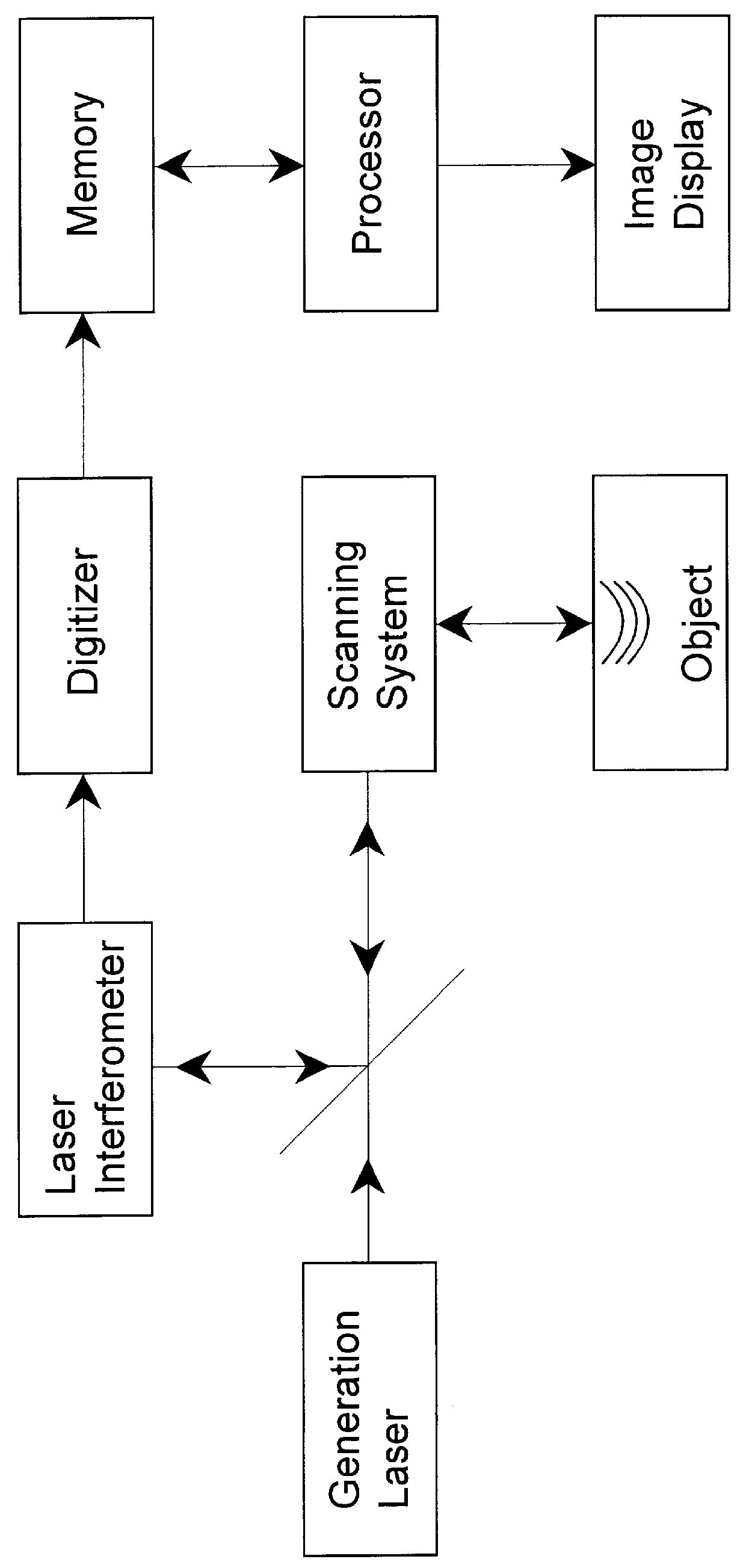
A method and system is provided for enhanced ultrasonic detection and imaging of small defects inside or at the surface of an object. The Synthetic Aperture Focusing Technique (SAFT) has been used to improve the detectability and to enhance images in conventional ultrasonics and this method has recently been adapted to laser-ultrasonics. In the present invention, an improved version of the frequency-domain SAFT (F-SAFT) based on the angular spectrum approach is described. The method proposed includes temporal deconvolution of the waveform data to enhance both axial and lateral resolutions, control of the aperture and of the frequency bandwidth to improve signal-to-noise ratio, as well as spatial interpolation of the subsurface images. All the above operations are well adapted to the frequency domain calculations and embedded in the F-SAFT data processing. The aperture control and the spatial interpolation allow also a reduction of sampling requirements to further decrease both inspection and processing times. This method is of particular interest when ultrasound is generated by a laser and detected by either a contact ultrasonic transducer or a laser interferometer.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
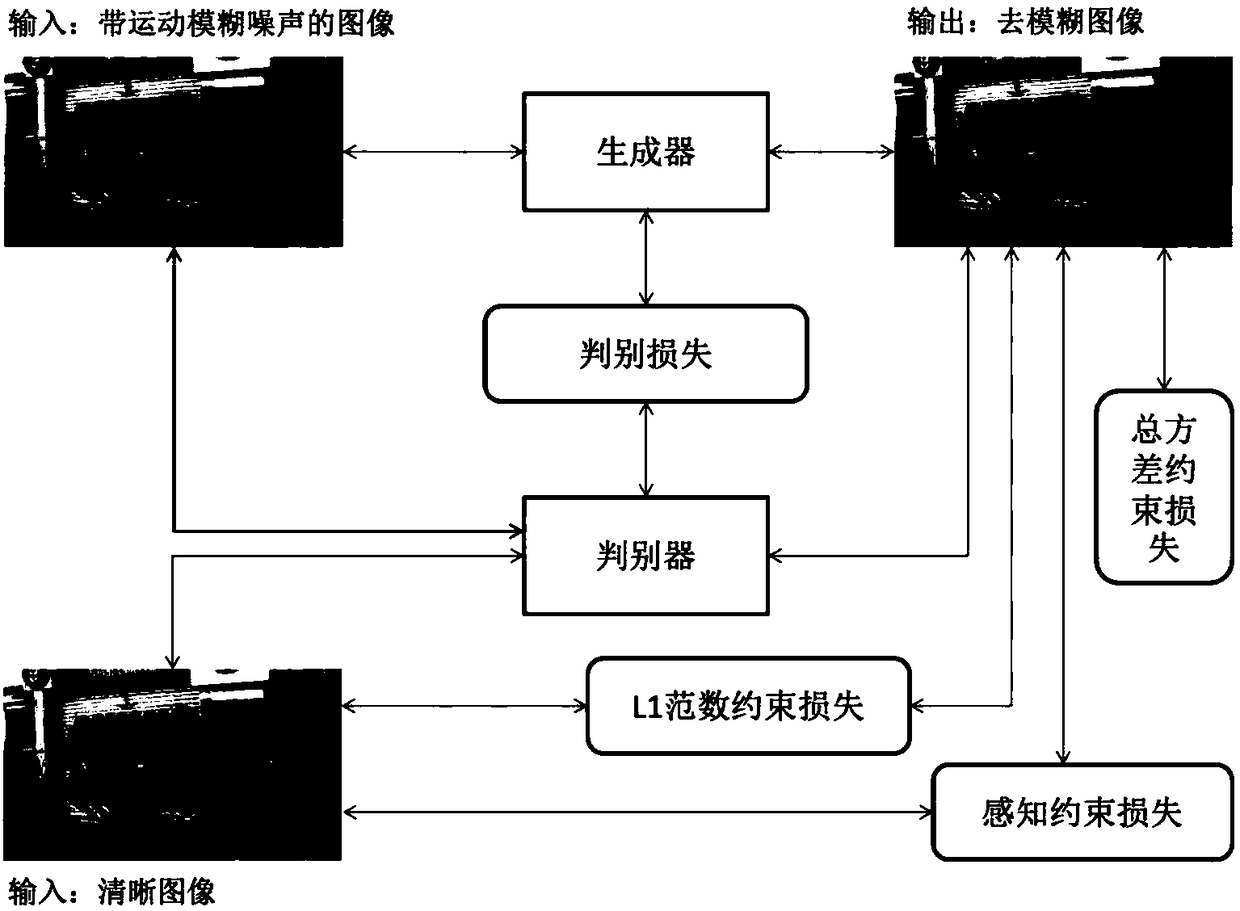
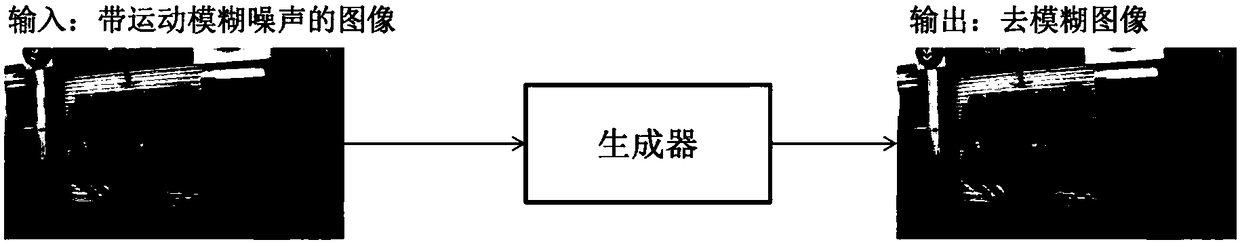
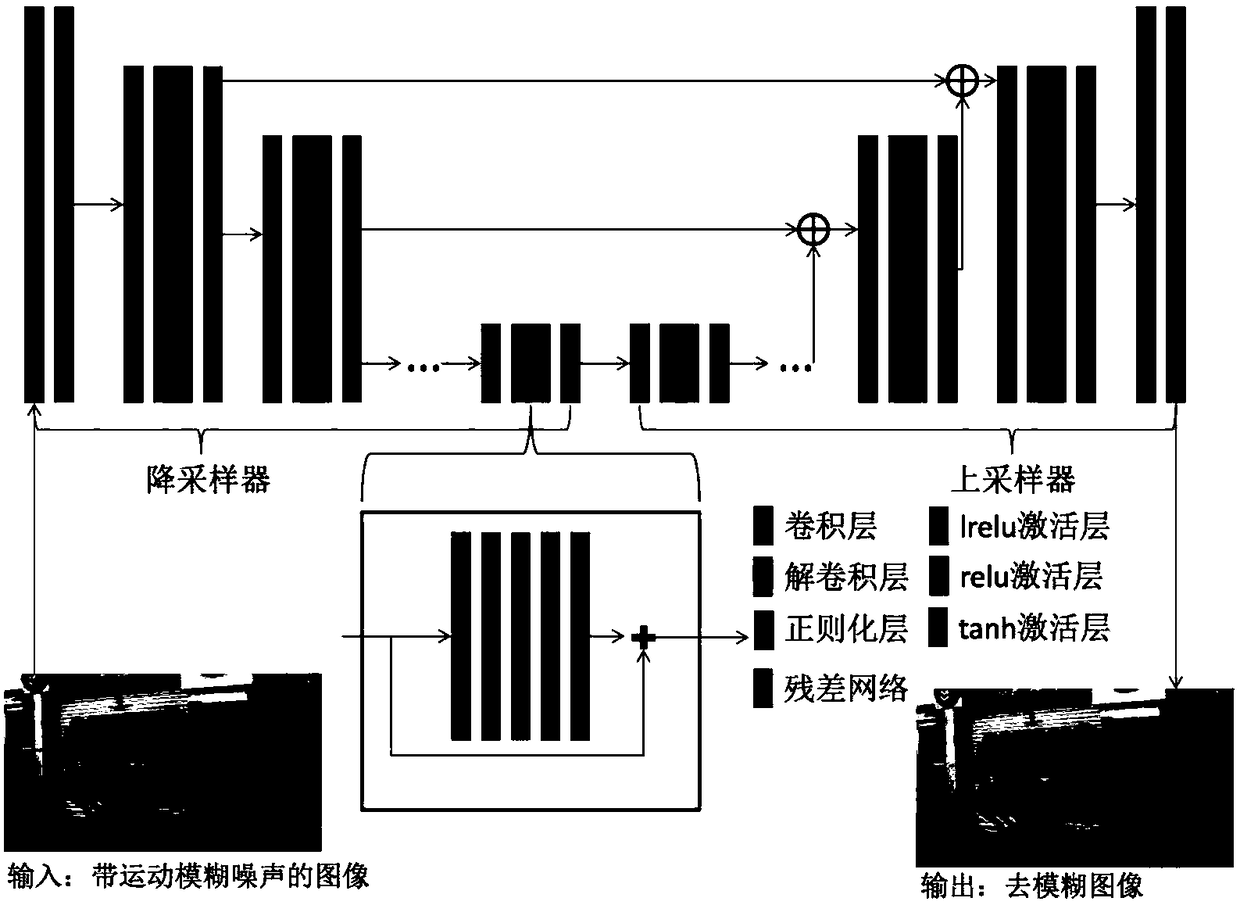
GAN (Generative Adversarial Network) based motion blur removing method of image
ActiveCN108416752AImprove efficiencyEasy to handleImage enhancementImage analysisDiscriminatorGenerative adversarial network
The invention discloses a GAN based motion blur removing method of an image and a motion blur removing GAN model for the method. The method comprises that the GAN model is designed; the model is trained; and in an application phase, the GAN model comprises a generator and a discriminator, the generator optimizes parameters continuously so that a generated image approaches distribution of a clear image, the discriminator optimizes parameters continuously so that whether the image is from fuzziness removing image distribution or clear image distribution can be discriminated more effectively, thegenerator comprises a down-sampling device and an up-sampling device, the down-sampling device carries out convolution on the image and extract semantic information from the image, and the up-sampling device carries out deconvolution on the image by combining the obtained semantic information with structure information of the image. Thus, motion blur of the image can be removed effectively, and the clear image satisfying perception of humans is obtained.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
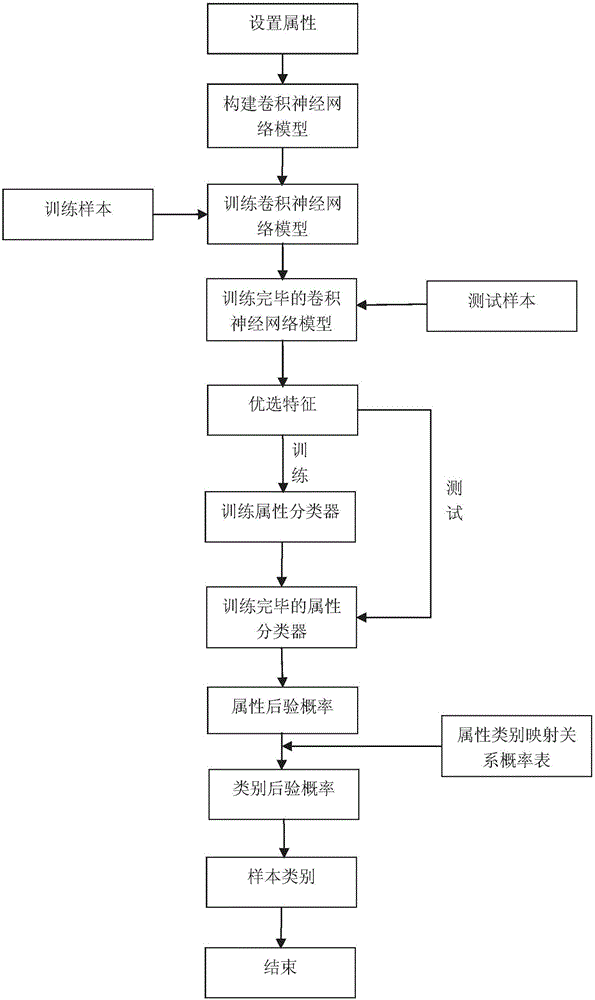
Pedestrian recognition method based on combination of depth learning and property learning
ActiveCN104992142ALow costImprove recognition rateBiometric pattern recognitionPedestrian recognitionDeconvolution
The invention discloses a pedestrian recognition method based on combination of depth learning and property learning. According to the invention, a convolution neural network containing five implicit strata is constructed. Network training is performed by an anti-convolution method and a concept of property learning is combined. Preferred features obtained from the convolution neural network are input to property classifiers, so that the posterior probability of the property of a sample is obtained. Then by combining with a property class mapping relation, the posterior probability of the class is obtained, so that the class of the sample can be judged. The method is good in detection recognition performance and intrinsic features of an image can be extracted. Besides, since the property has better semantic expression performance than low-stratum features and due to the insensitivity to light and view angles, the algorithm has a good recognition effect.
Owner:南京昭视智能科技有限公司
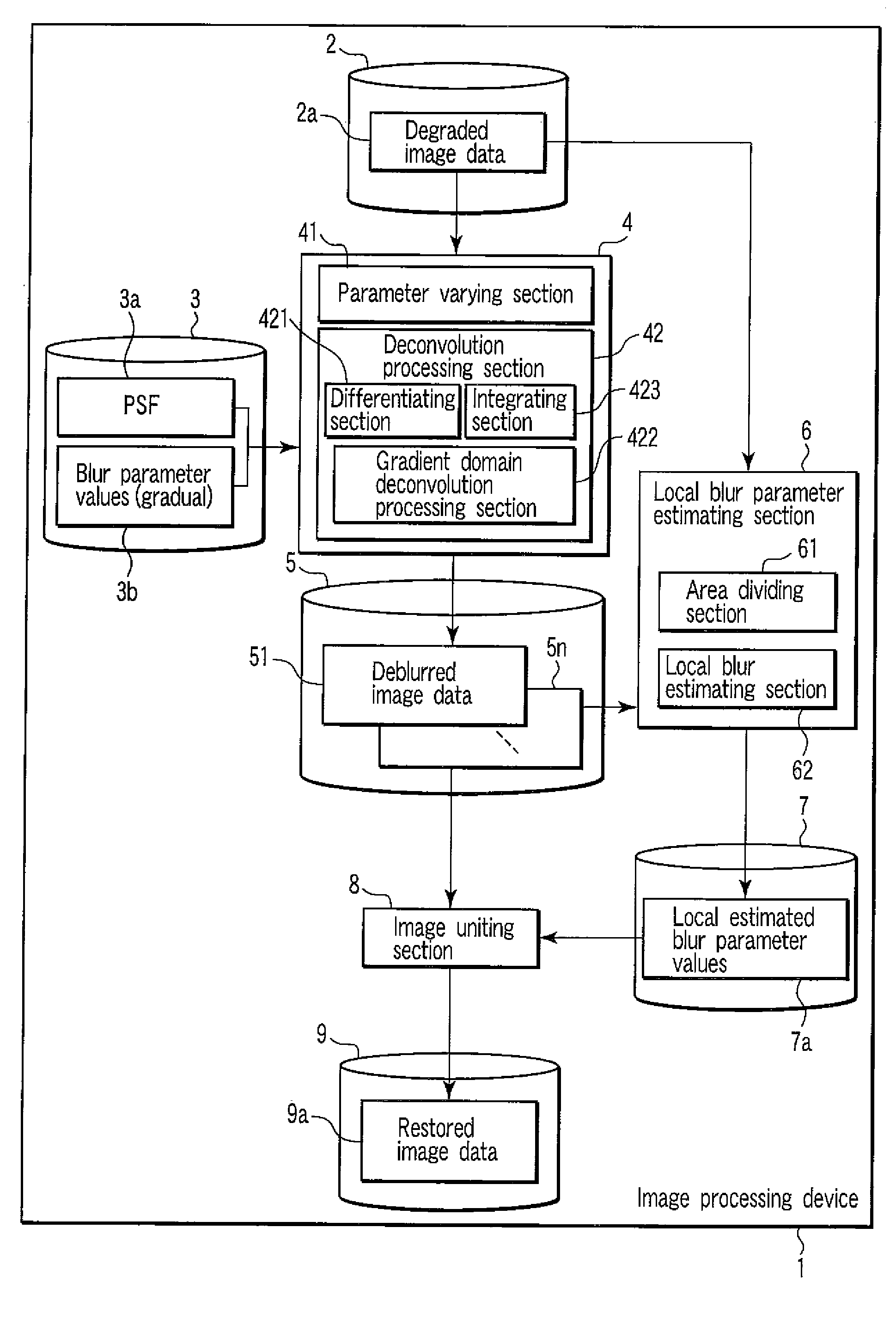
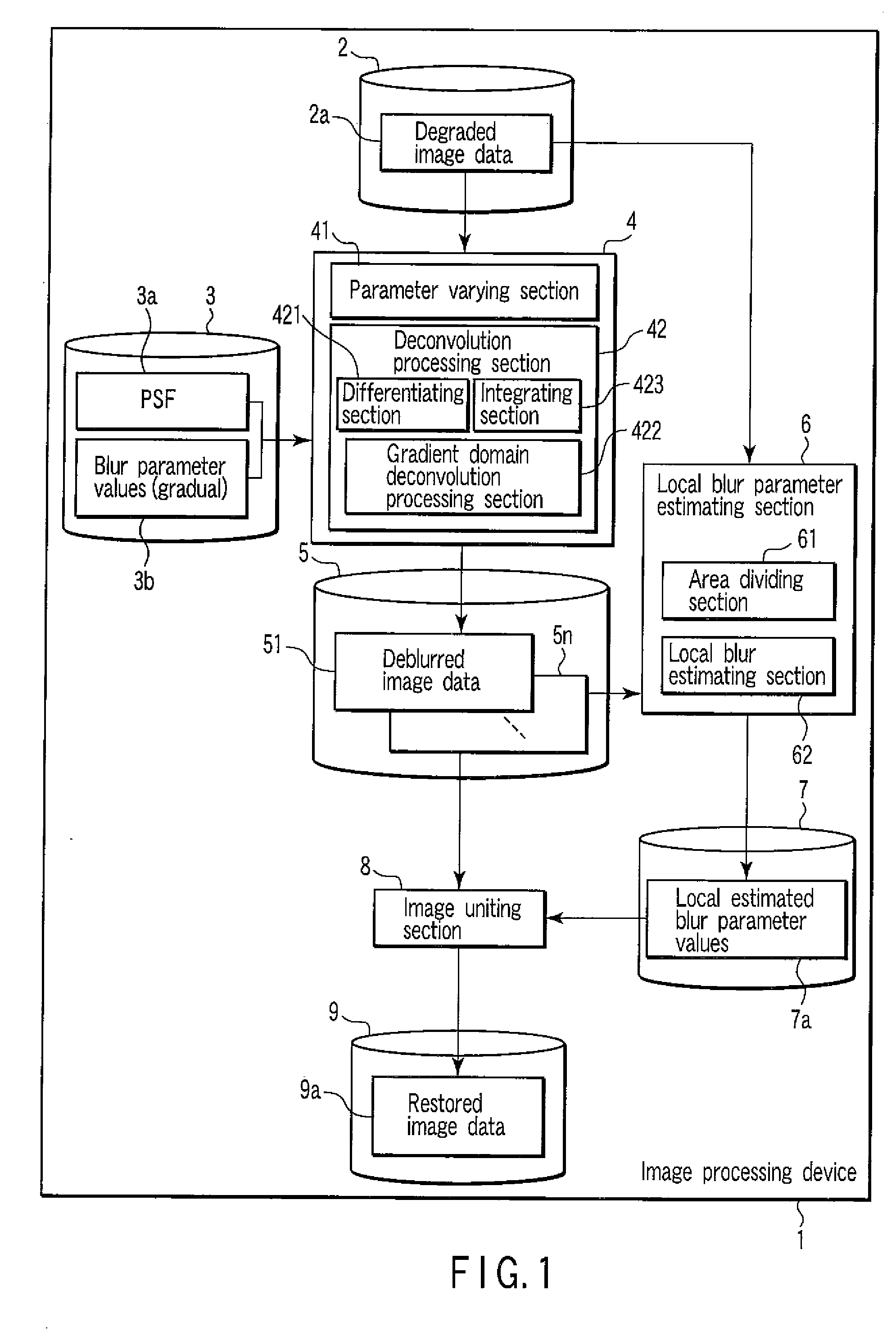
Image Processing Device
InactiveUS20080175508A1Image enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingImage gradient
An image processing device according to an example of the invention comprises a differentiating section which differentiates input image data to generate gradient image data, a gradient domain deconvolution processing section which applies a deconvolution to the gradient image data, the deconvolution performing deblurring corresponding to a prior distribution of an image gradient of an image to generate deconvolved data, and an integrating section which integrates the deconvolved data to generate deblurred image data.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
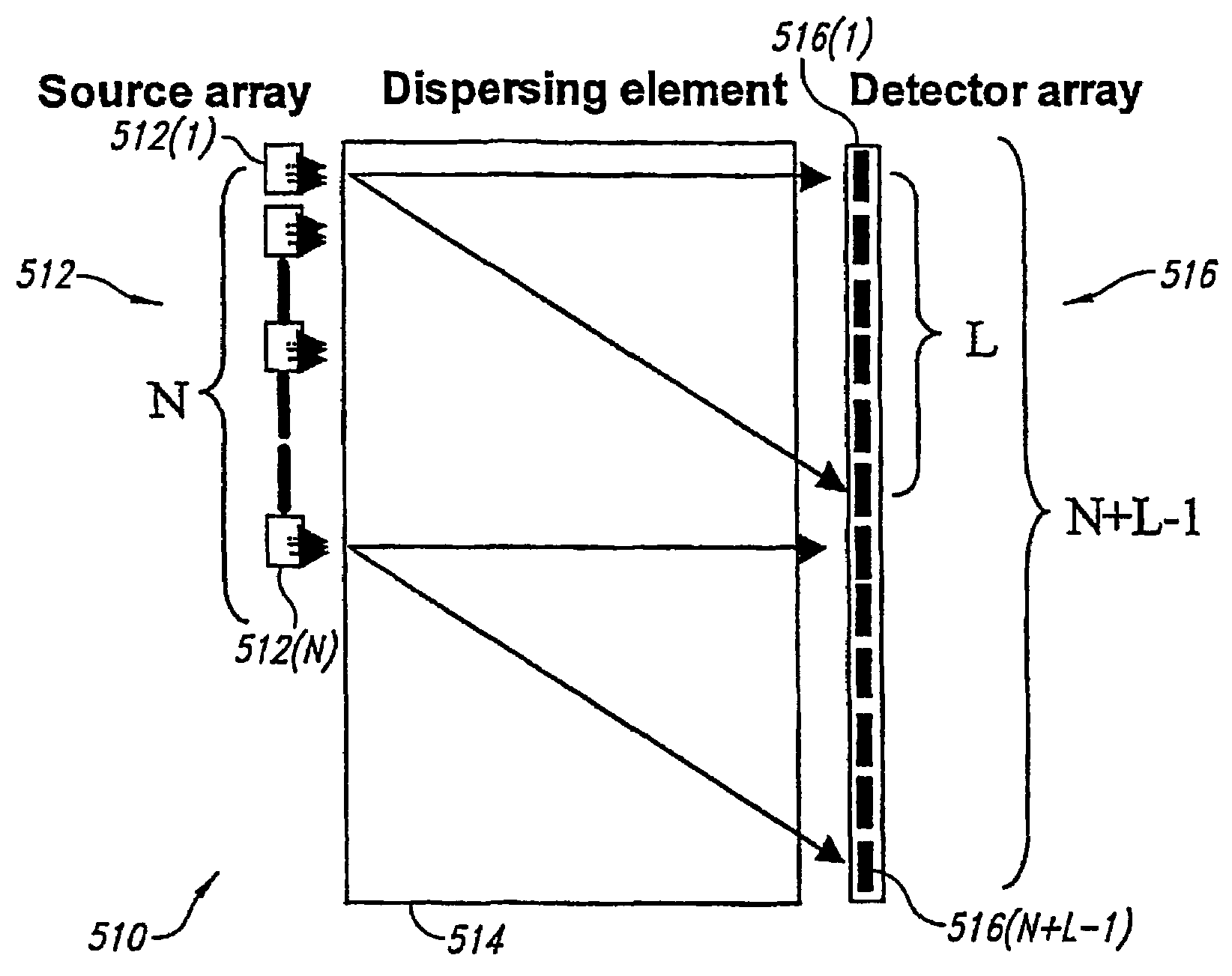
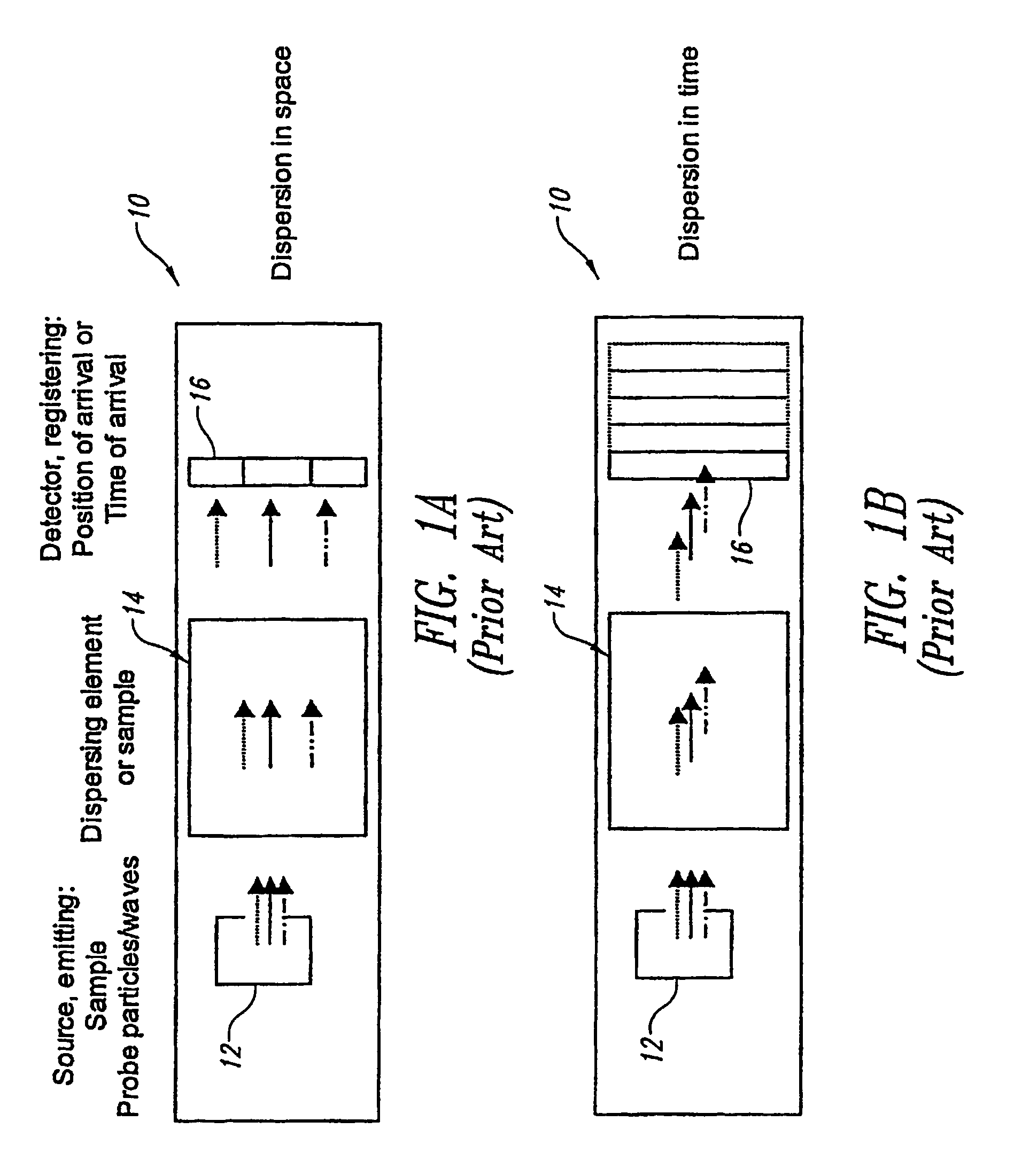
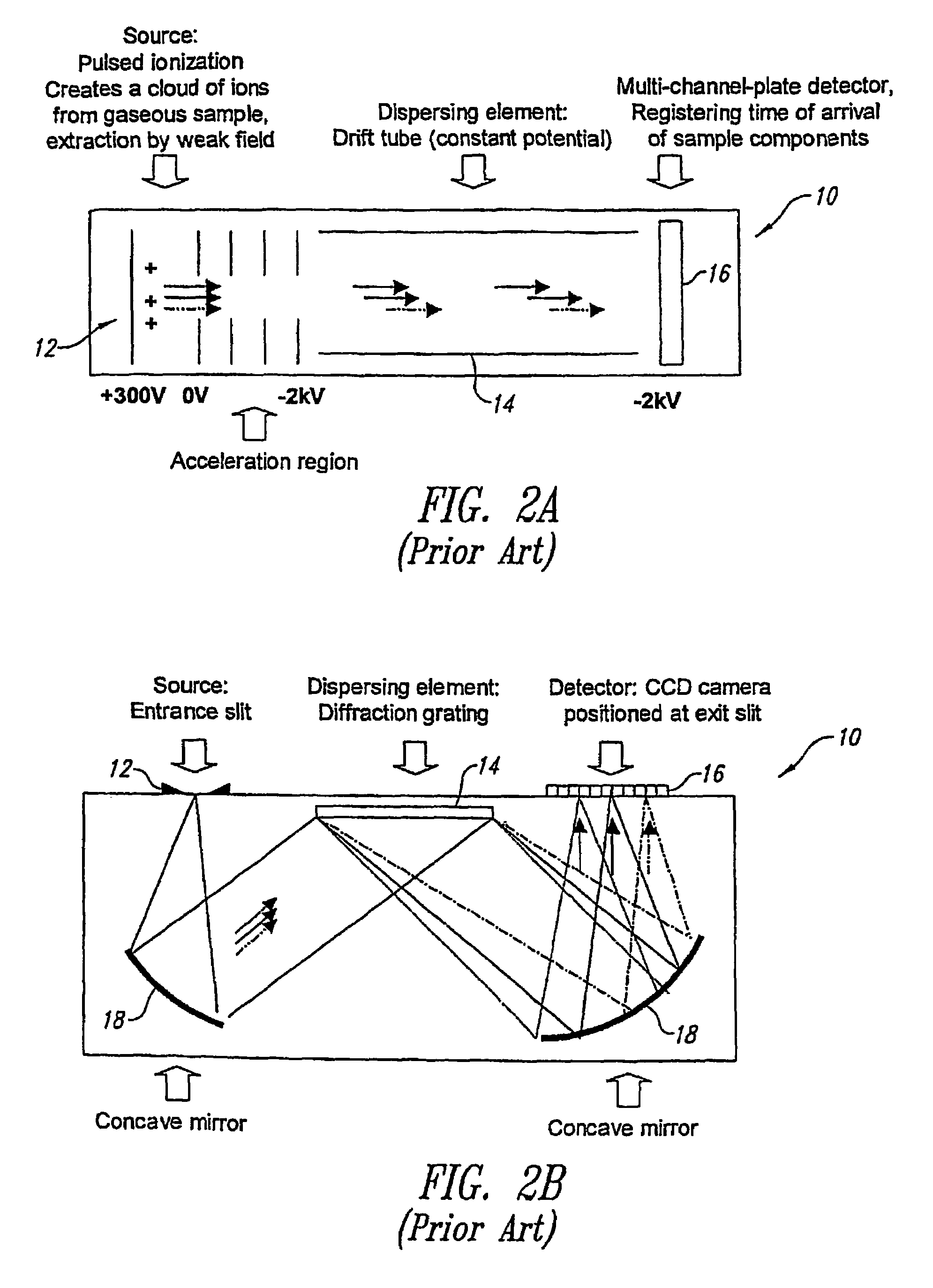
Analytical instruments using a pseudorandom array of sources, such as a micro-machined mass spectrometer or monochromator
InactiveUS7339521B2Maximize signalEnhanced signalParticle separator tubesAntenna arraysSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Signal on
Novel methods and structures are disclosed herein which employ pseudorandom sequences to spatially arrange multiple sources in a pseudorandom source array. The pseudorandom source array can replace the single source in analytical instruments relying on spatial separation of the sample or the probe particles / waves emitted by the sources. The large number of sources in this pseudorandom source array enhances the signal on a position sensitive detector. A mathematical deconvolution process retrieves a spectrum with improved signal-to-noise ratio from the detector signal.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
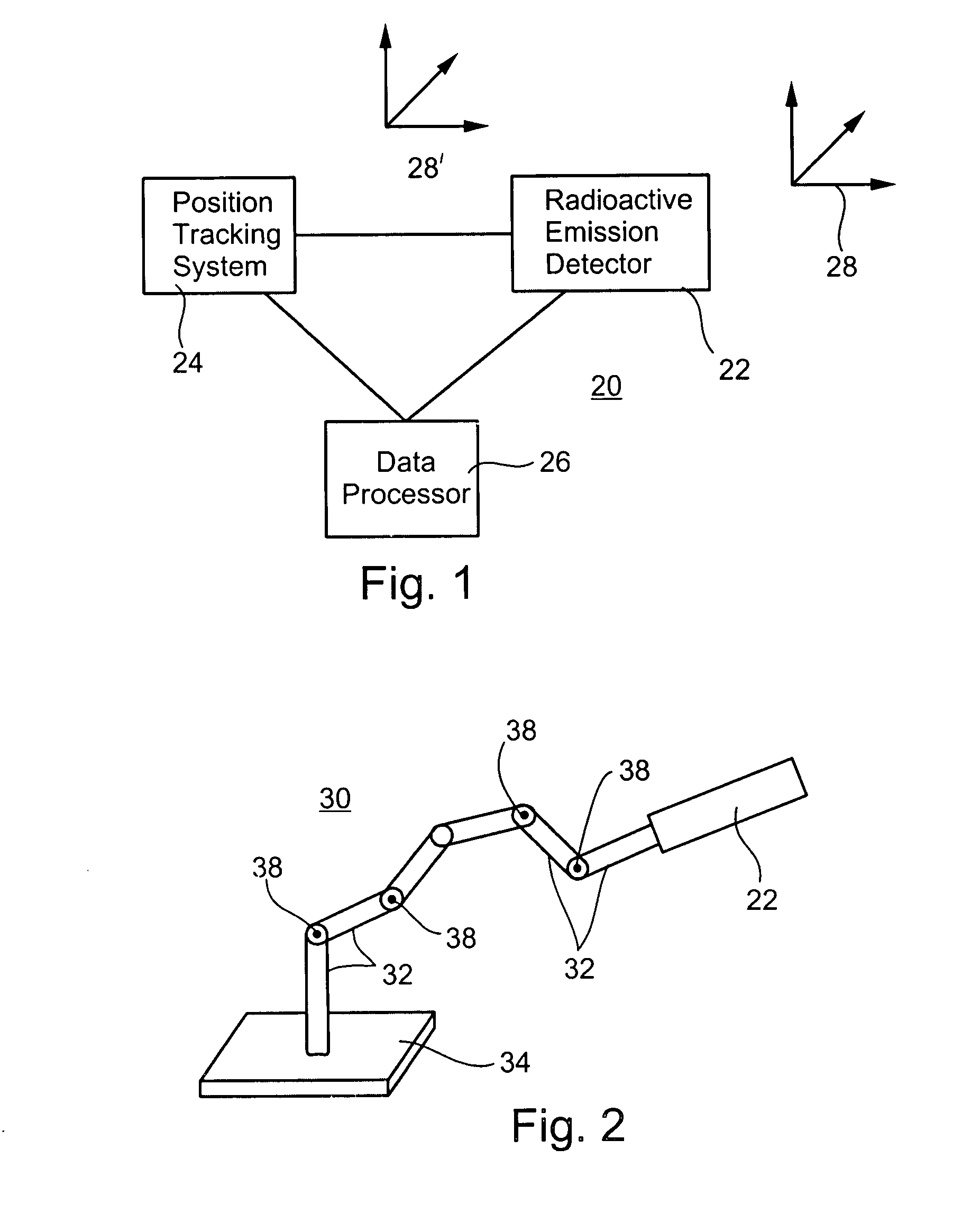
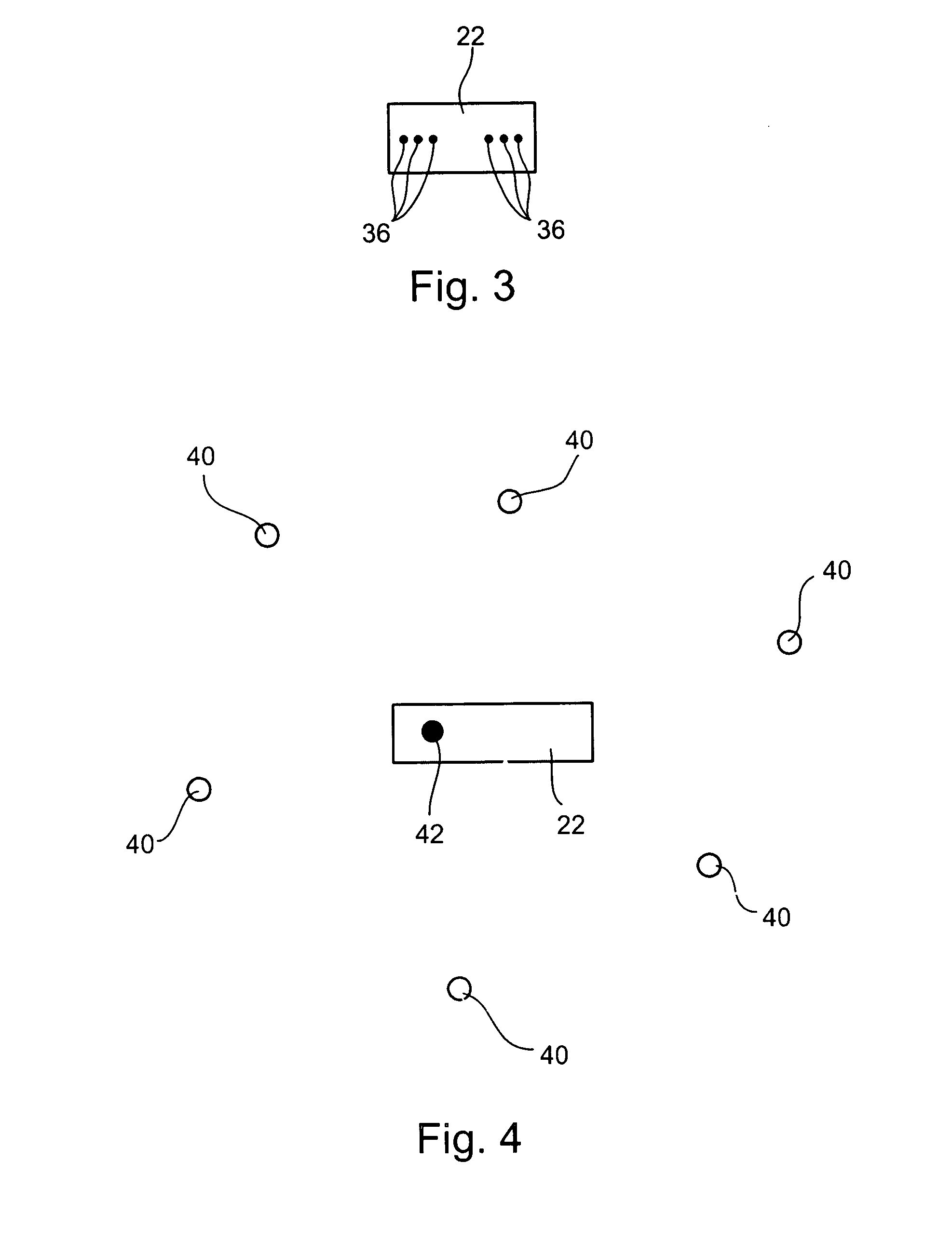
Radioactive emission detector equipped with a position tracking system
ActiveUS8565860B2Successfully addressUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryUltrasound attenuationImage resolution
A radioactive emission probe in communication with a position tracking system and the use thereof in a variety of systems and methods of medical imaging and procedures, are provided. Specifically, wide aperture collimation—deconvolution algorithms are provided, for obtaining a high-efficiency, high resolution image of a radioactivity emitting source, by scanning the radioactivity emitting source with a probe of a wide-aperture collimator, and at the same time, monitoring the position of the radioactive emission probe, at very fine time intervals, to obtain the equivalence of fine-aperture collimation. The blurring effect of the wide aperture is then corrected mathematically. Furthermore, an imaging method by depth calculations is provided, based on the attenuation of photons of different energies, which are emitted from the same source, coupled with position monitoring.
Owner:SPECTRUM DYNAMICS MEDICAL LTD
Post processing of iris images to increase image quality
ActiveUS7869627B2Quality improvementLow resolution imageTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersDiffusion functionImage resolution
A rapid iris acquisition, tracking, and imaging system can be used at longer standoff distances and over larger capture volumes, without the active cooperation of subjects. Light illuminates the subjects' eyes and a high resolution camera captures images of the irises. The images of the irises are processed by a post processing module to improve their quality. In one approach, the point spread function of the image capture subsystem is estimated using glint reflections from the eye, and the estimated point spread function is used in deconvolution to increase the resolution of the iris images. The post processed iris images have sufficient resolution to be used for biometric identification.
Owner:TASCENT INC
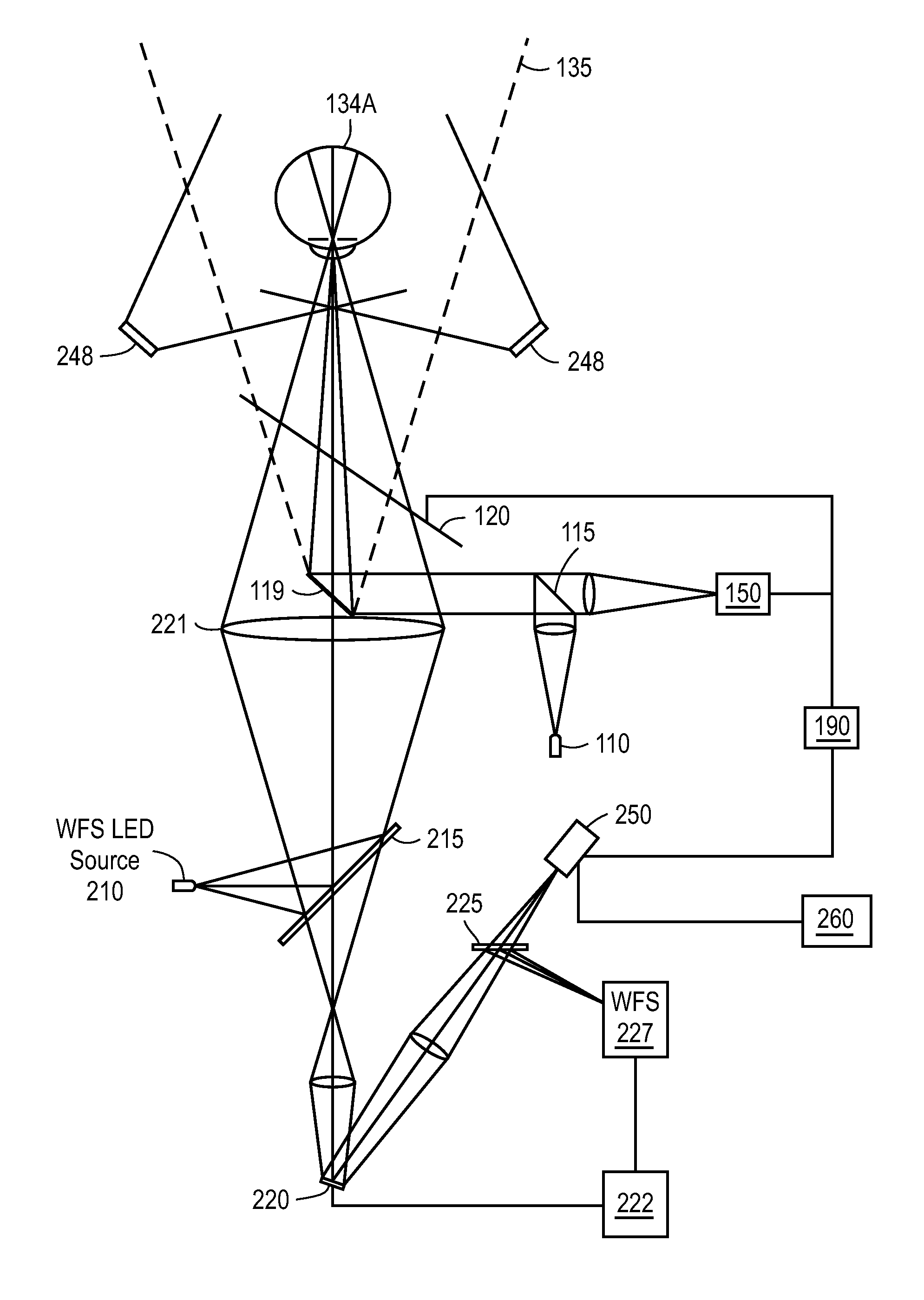
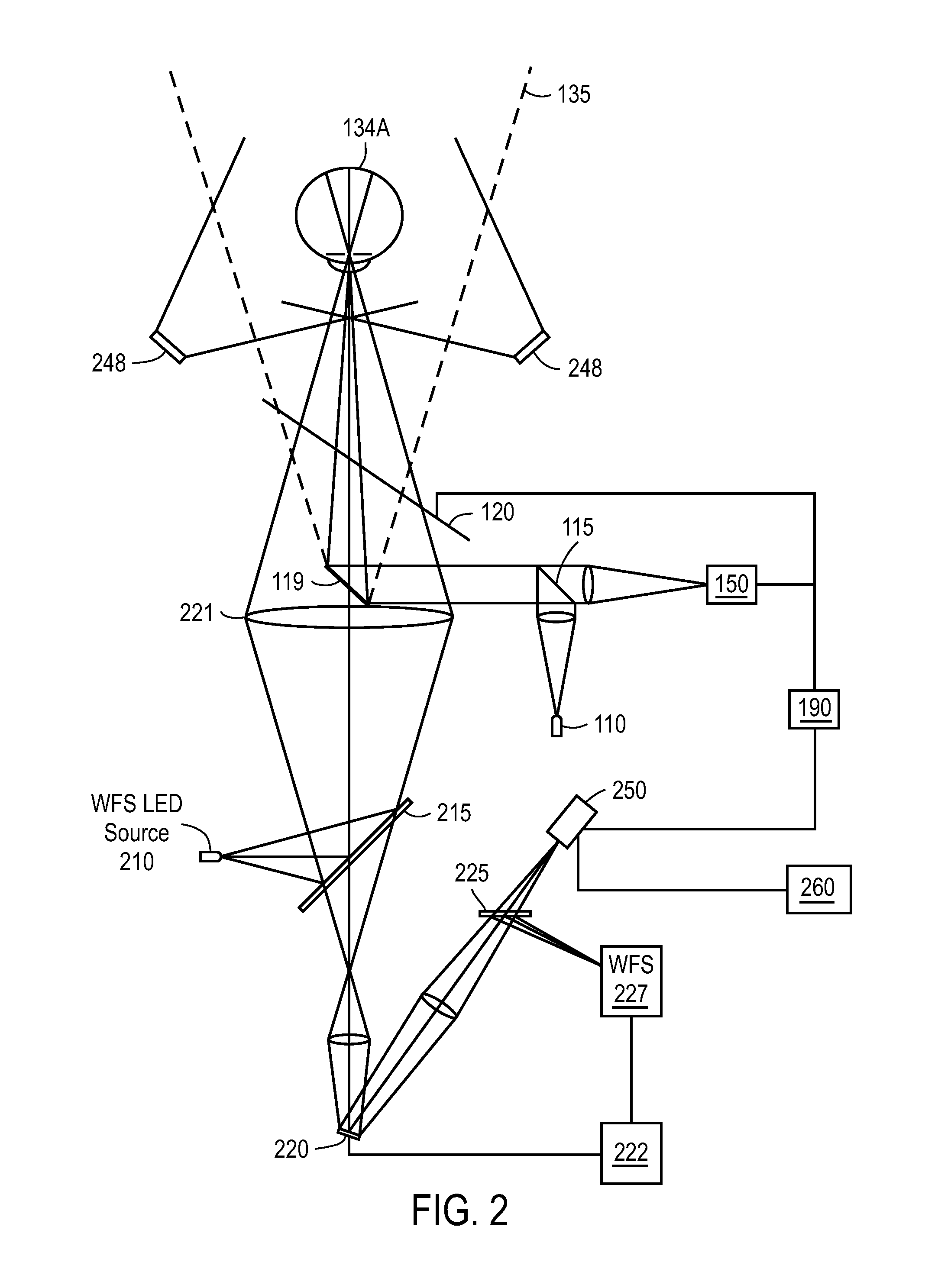
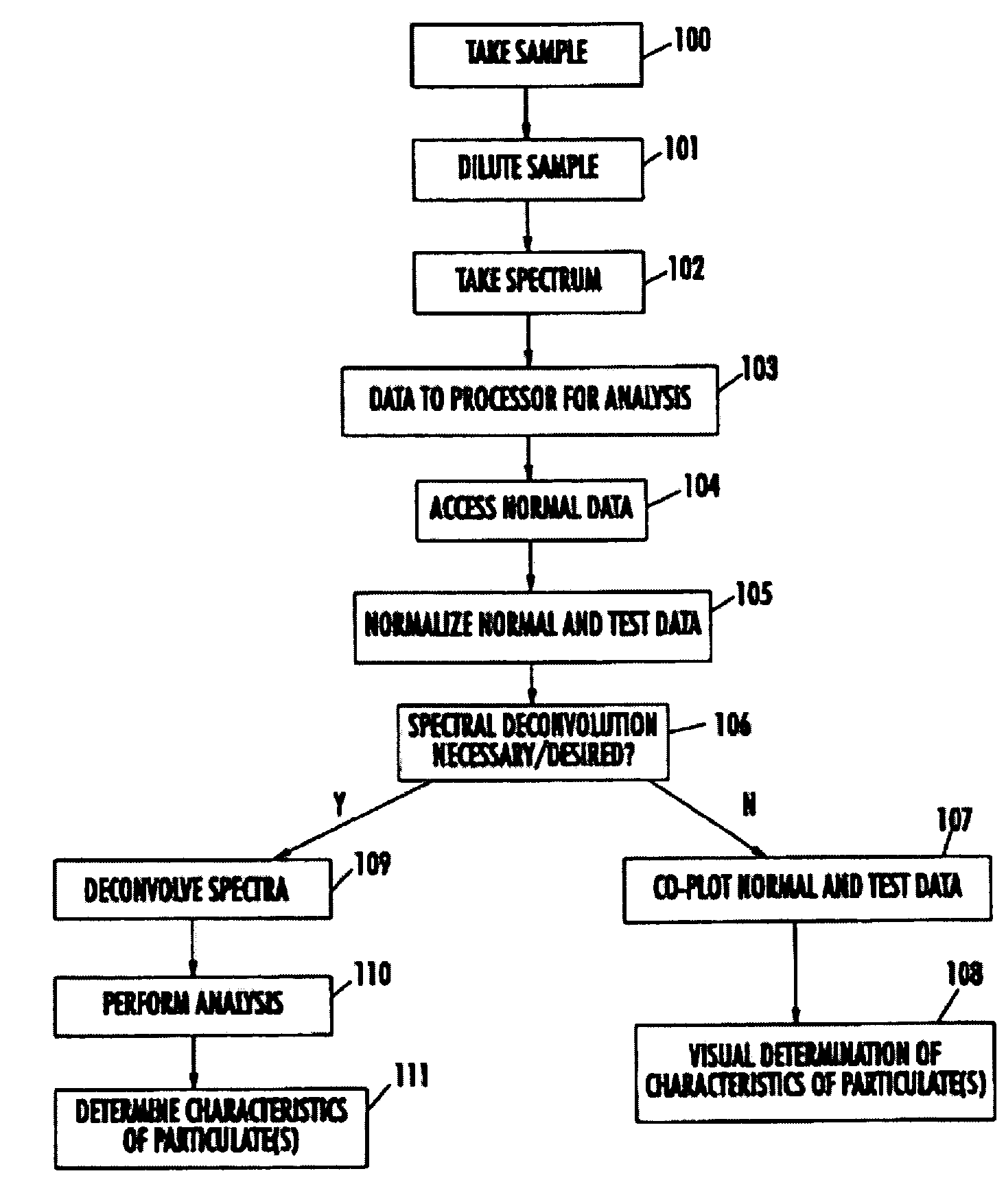
Spectrophotometric system and method for the identification and characterization of a particle in a bodily fluid
InactiveUS7027134B1Rapid and inexpensive and convenient for diagnosisRapidly and inexpensively disease diagnosisScattering properties measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringTurbidimetryWavelength
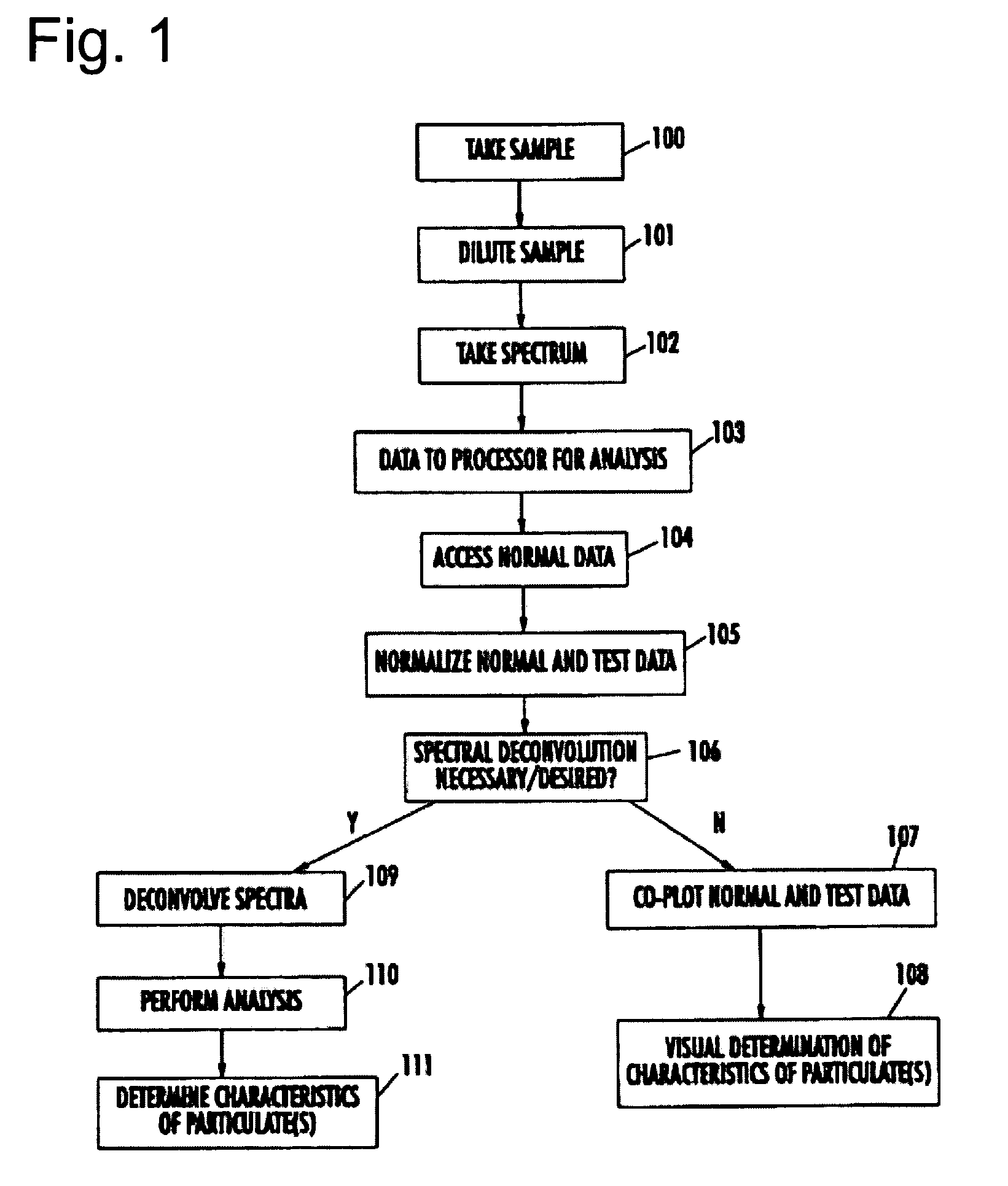
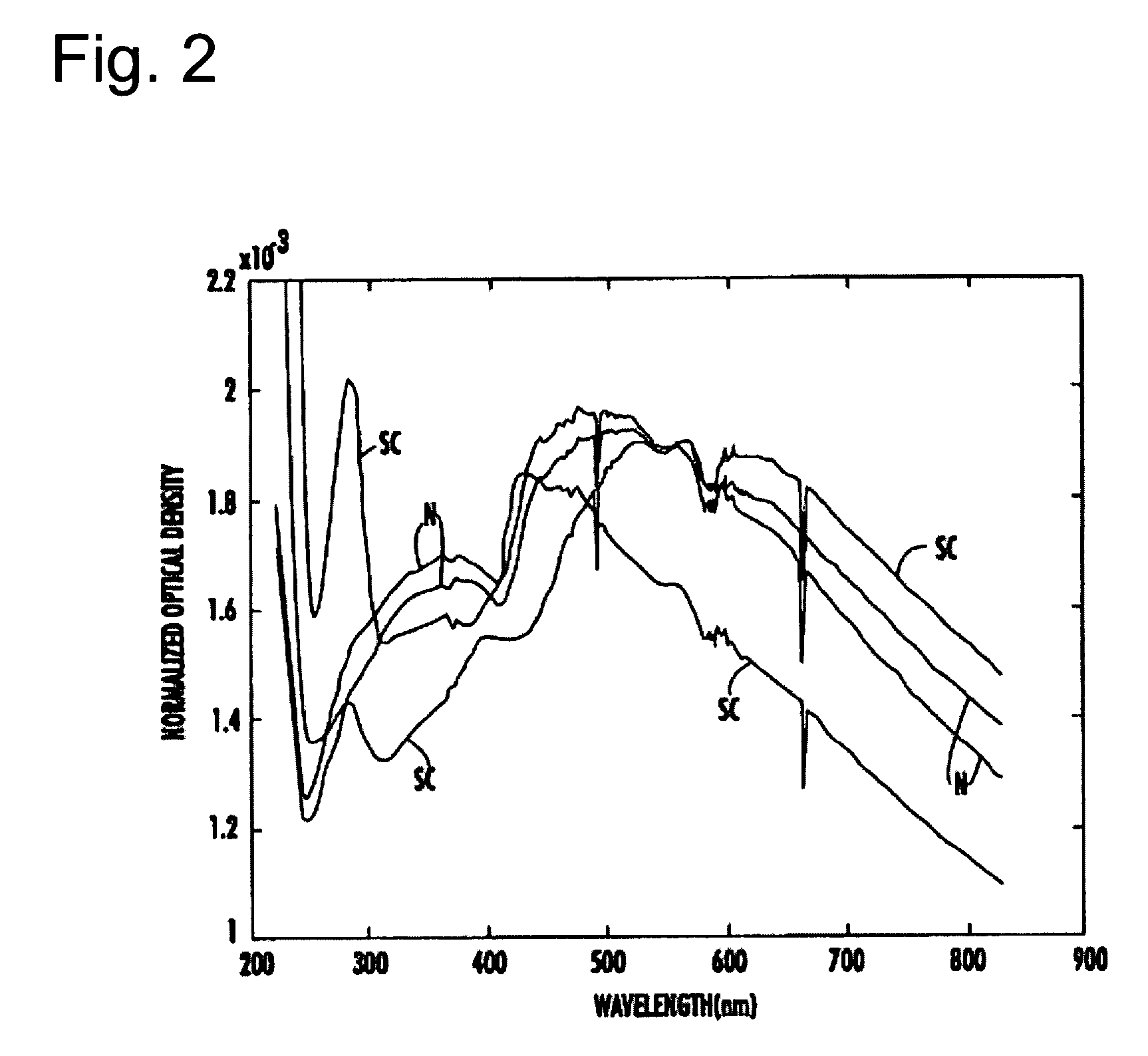
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for the detection of an infectious disease or disorder in a fluid, such as a mammalian blood sample, the detection of a specific protein in a urine sample, or the detection of a particle in a plasma. The identification of the particles of interest is enable by taking a transmission spectrum of a test sample in at least a portion of the ultraviolet, visible, near-infrared portion of the spectrum and comparing the spectrum with a standard sample spectrum. From the comparison it is then determined whether the fluid from the test sample contains an particle of interest, and an identity of the particle of interest is determined. Spectroscopic and multiwavelength turbidimetry techniques provide a rapid, inexpensive, and convenient means for diagnosis. The comparison and determination steps may be performed visually or by spectral deconvolution.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Filter assembly and image enhancement system for a surveillance camera and method of using the same
InactiveUS20080252882A1Reduce glareReduce the amount requiredTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometrySurveillance cameraDeconvolution
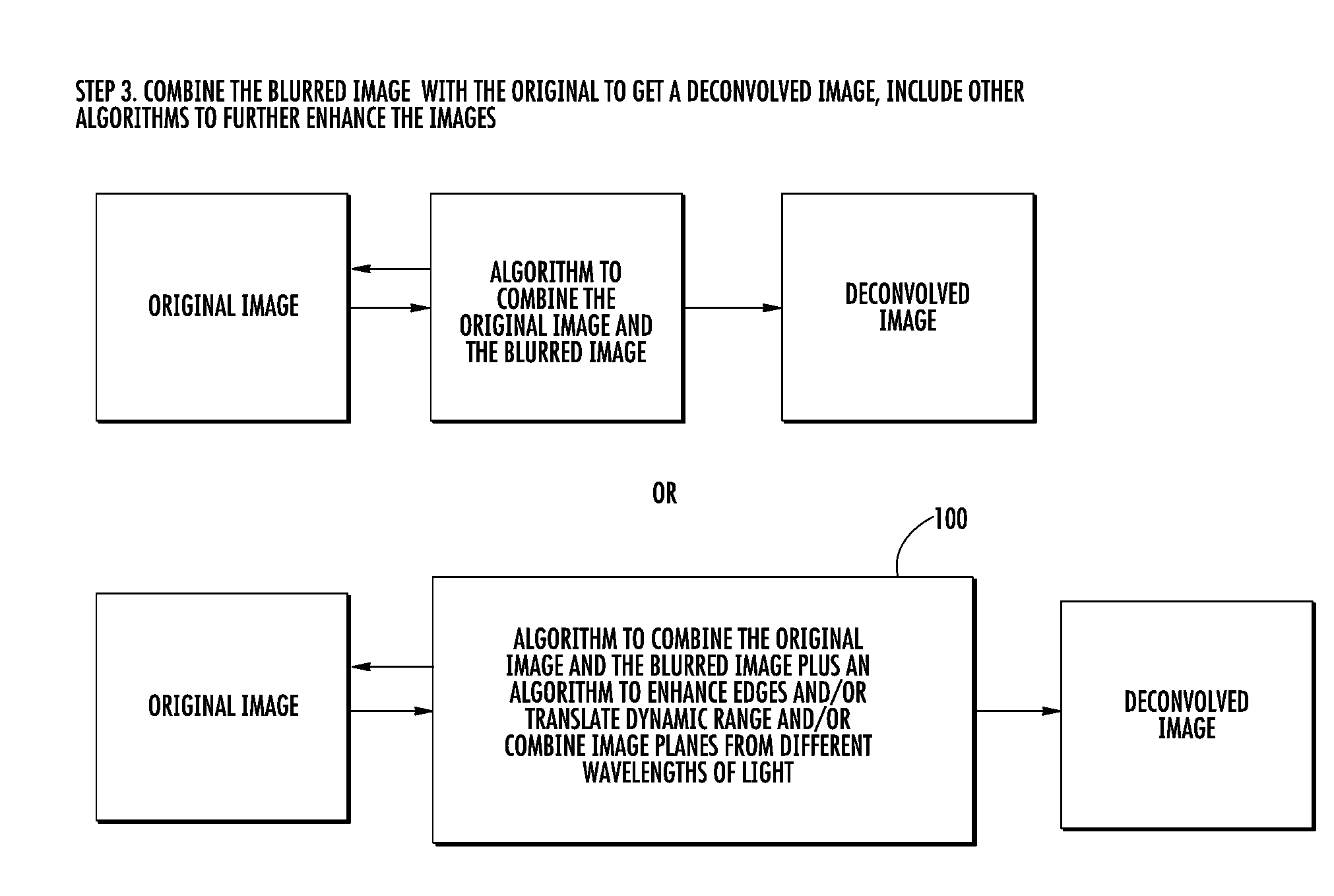
A filter assembly adapted to be used with a camera for selectively controlling the light that reaches the camera's aperture. In one embodiment, the filter assembly comprises three filters adapted to be independently moved between a first position wherein they are not in front of the camera's aperture and a second position wherein they are in front of the camera's aperture. The first and second filters are polarizing filters adapted to block portions of visible light. The third filter is an infrared filter adapted to block infrared light. In addition to moving between its first position and its second position, the second filter is also adapted to rotate up to 360 degrees. The image captured by the camera may be improved using a computer implemented image enhancement system that uses one or more of multi-spectral imaging, deconvolution, edge enhancement, and dynamic range translation.
Owner:KESTERSON JOHN
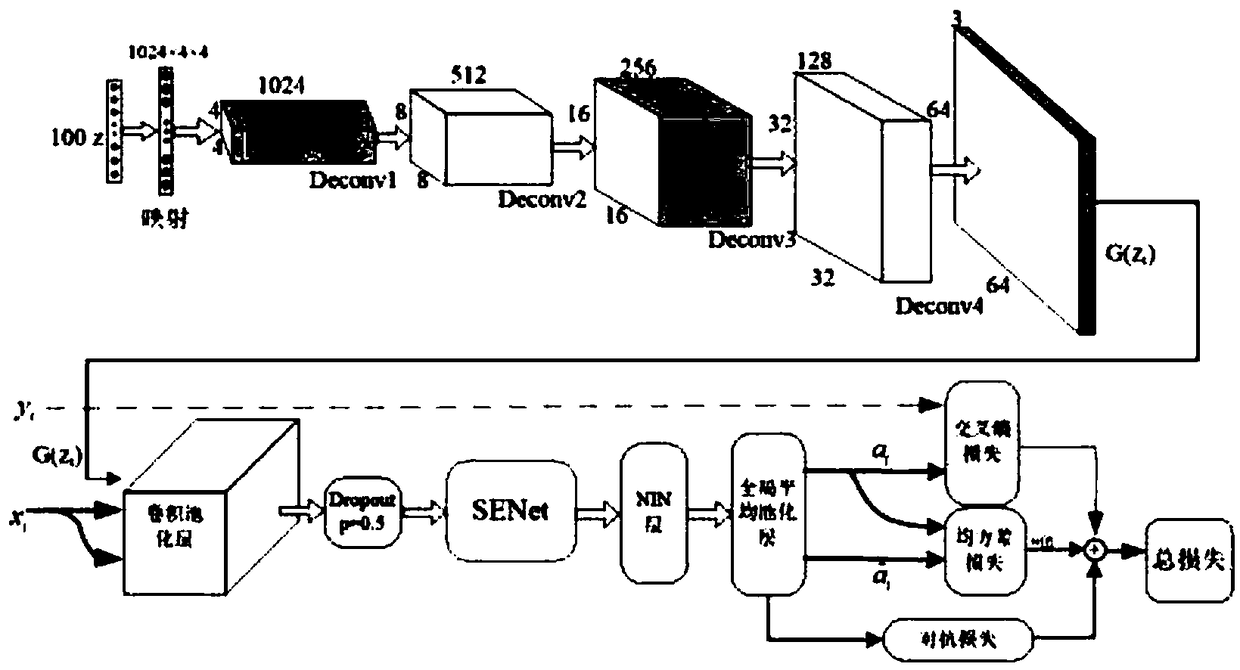
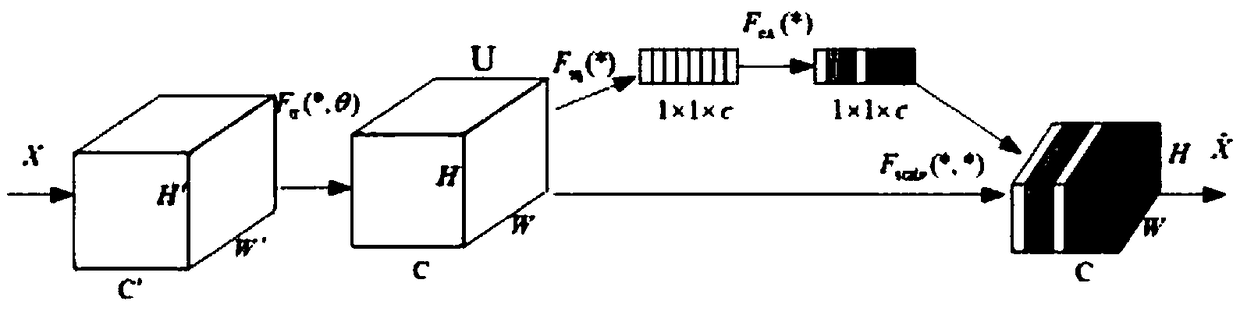
Image classification method based on confrontation network generated through feature recalibration
ActiveCN108805188AImprove generalization abilityClassification task performance improvementCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesGenerative adversarial networkClassification methods
The invention discloses an image classification method based on a confrontation network generated through feature recalibration. The image classification method based on the confrontation network generated through feature recalibration is suitable for the field of machine learning and comprises the steps that to-be-classified image data are input into a confrontation network model for network training; a generator and a discriminator which are constituted by a convolutional network are constructed; random noise is initialized and input into the generator; the random noise is subjected to multilevel deconvolution operation in the generator through the convolutional network, and finally, generated samples are obtained; the generated samples and authentic samples are input into the discriminator; and the input samples are subjected to convolution and pooling operation in the discriminator through the convolutional network, thus a feature graph is obtained, a compressed and activated SENetmodule is imported into an intermediate layer of the convolutional network to calibrate the feature graph, thus the calibrated feature graph is obtained, global average pooling is used, and finally,image data classification is output. The SENet module is imported into the intermediate layer of the discriminator, the importance degree of each feature channel is automatically learned, useful features relevant to a task are extracted, features irrelevant to the task are restrained, and thus semi-supervised learning performance is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU YUNYI ELECTRIC
Multi-cast communication system and method of estimating channel impulse responses therein
InactiveUS20020176485A1Low costImprove efficiencyAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSecret communicationChannel impulse responseCommunications system
Multiple Steiner codes are transmitted as bursts (s11, S12, . . . S33, 560, 524) from multiple base stations (182, 184, 186) having one or more transmit elements (174, 176, 178, 180), with successive bursts providing an extended training sequence for use in channel estimation at an addressed unit (172), such as a mobile handset. Accurate channel estimation is possible through the use of Wiener frequency domain MMSE deconvolution (518) combined with frequency domain spatial decoupling matrices, with quasi-orthogonal pseudo-noise sequences (502, 504, 520, 522) allocated to base stations and their antenna elements. The use of Steiner codes to supplement Wiener frequency domain MMSE deconvolution and frequency domain spatial decoupling results in the possibility of allocating only a single training sequence to each base station provided that the training sequence is of sufficient length to encompass all multiple time-translated channel impulse responses (H).
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD +1
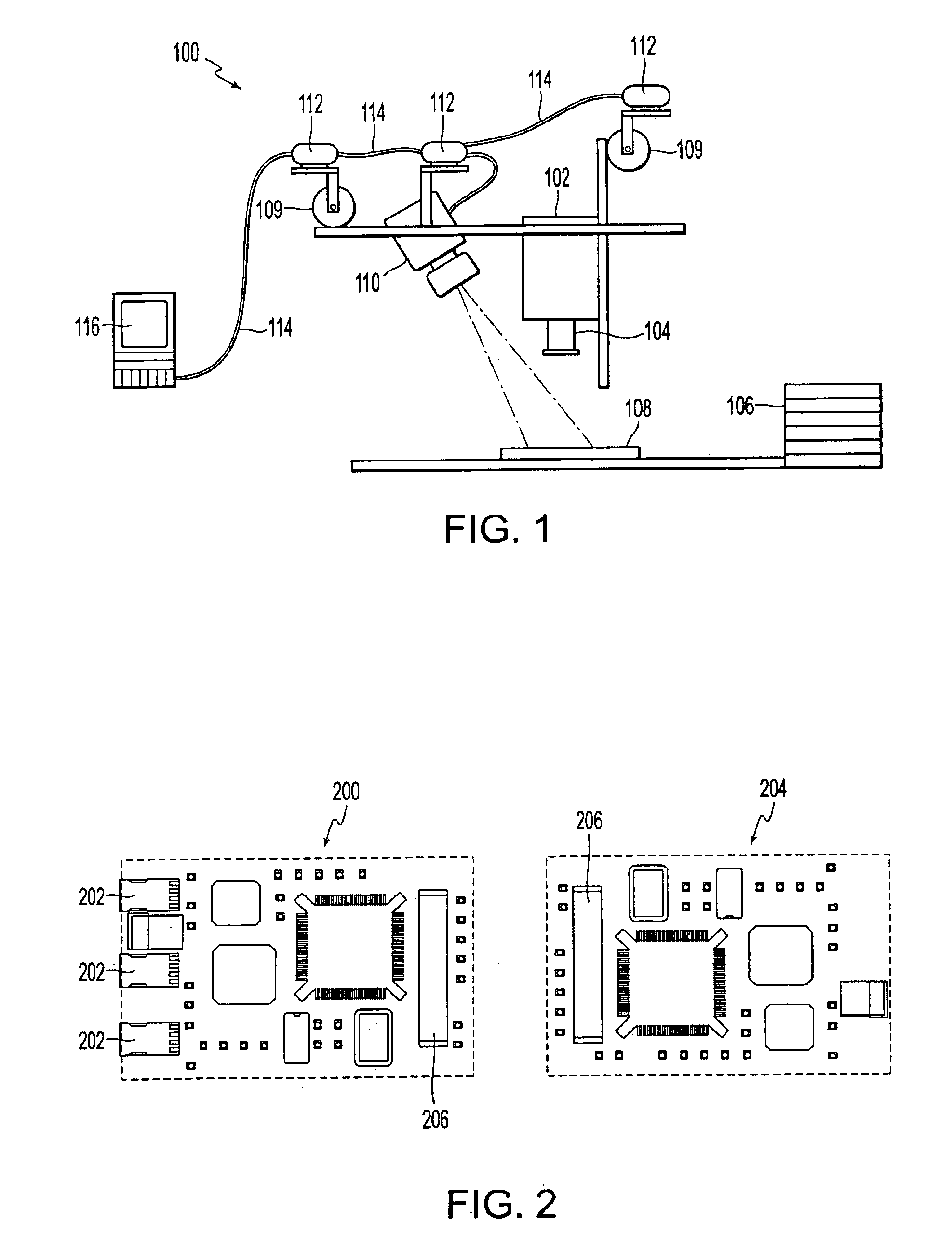
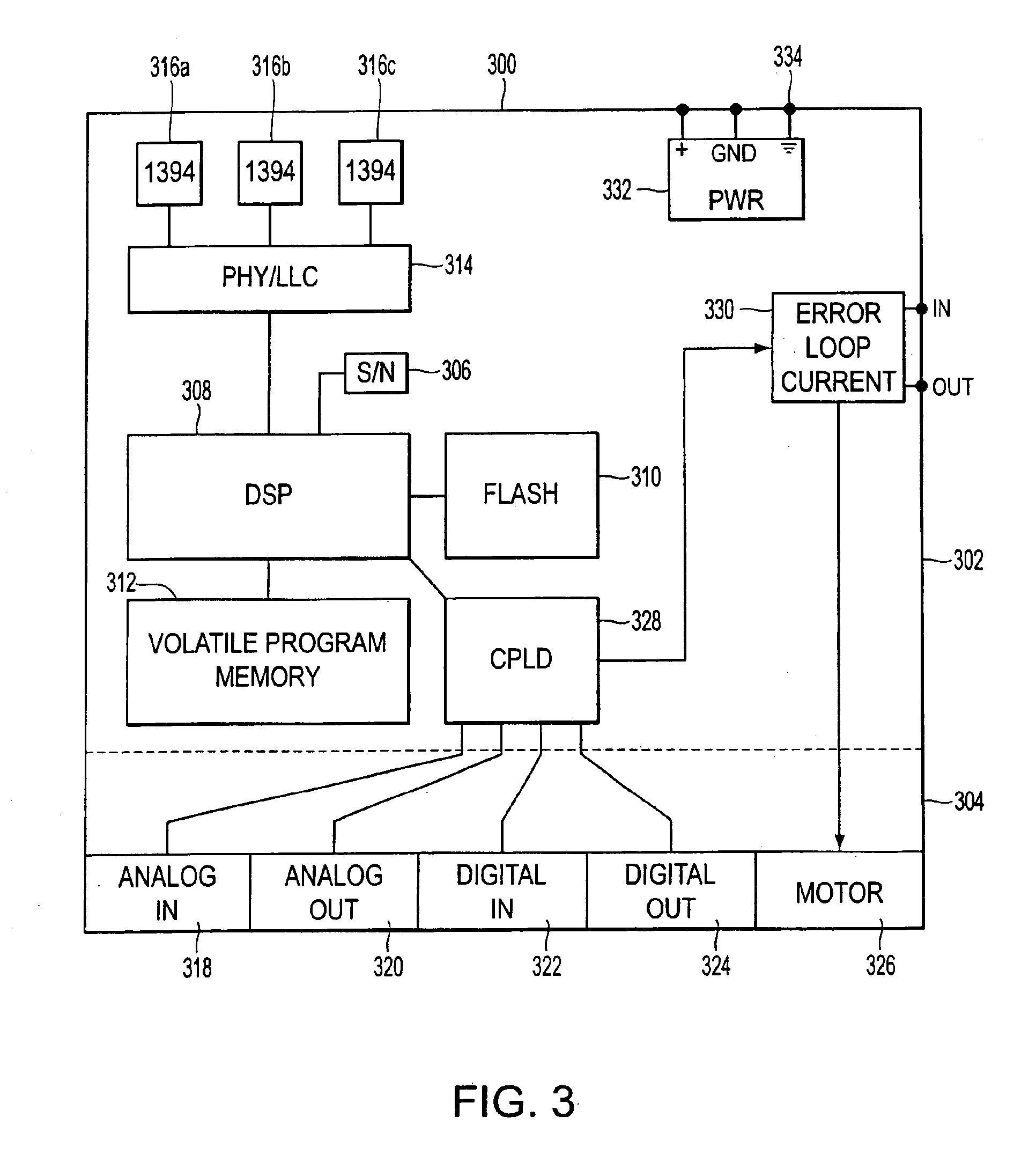
Smart camera
A smart camera system provides focused images to an operator at a host computer by processing digital images at the imaging location prior to sending them to the host computer. The smart camera has a resident digital signal processor for preprocessing digital images prior to transmitting the images to the host. The preprocessing includes image feature extraction and filtering, convolution and deconvolution methods, correction of parallax and perspective image error and image compression. Compression of the digital images in the smart camera at the imaging location permits the transmission of very high resolution color or high resolution grayscale images at real-time frame rates such as 30 frames per second over a high speed serial bus to a host computer or to any other node on the network, including any remote address on the Internet.
Owner:ORMON CORP
Image depth estimation method based on convolutional neural network
ActiveCN107767413AAvoid inaccuraciesAvoid problems such as poor performanceImage analysisEstimation methodsNetwork model
The invention discloses an image depth estimation method based on a convolutional neural network. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a convolution-deconvolution pair neural networkmodel, wherein the convolution-deconvolution pair neural network model comprises a plurality of different convolutional layers, a plurality of convolution-deconvolution layer pairs and an activationlayer; selecting a training set, and setting training parameters of the convolution-deconvolution pair neural network model; according to the convolution-deconvolution pair neural network model and the training parameters thereof, training the convolution-deconvolution pair neural network model with minimizing of a loss function being a target to form an image depth estimation neural network model; and inputting an image to be processed to the image depth estimation neural network model and outputting a corresponding depth image. The grayscale value of the depth image obtained through the image depth estimation method based on the convolution-deconvolution pair neural network is more accurate, and the sense of depth of the depth image is higher.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
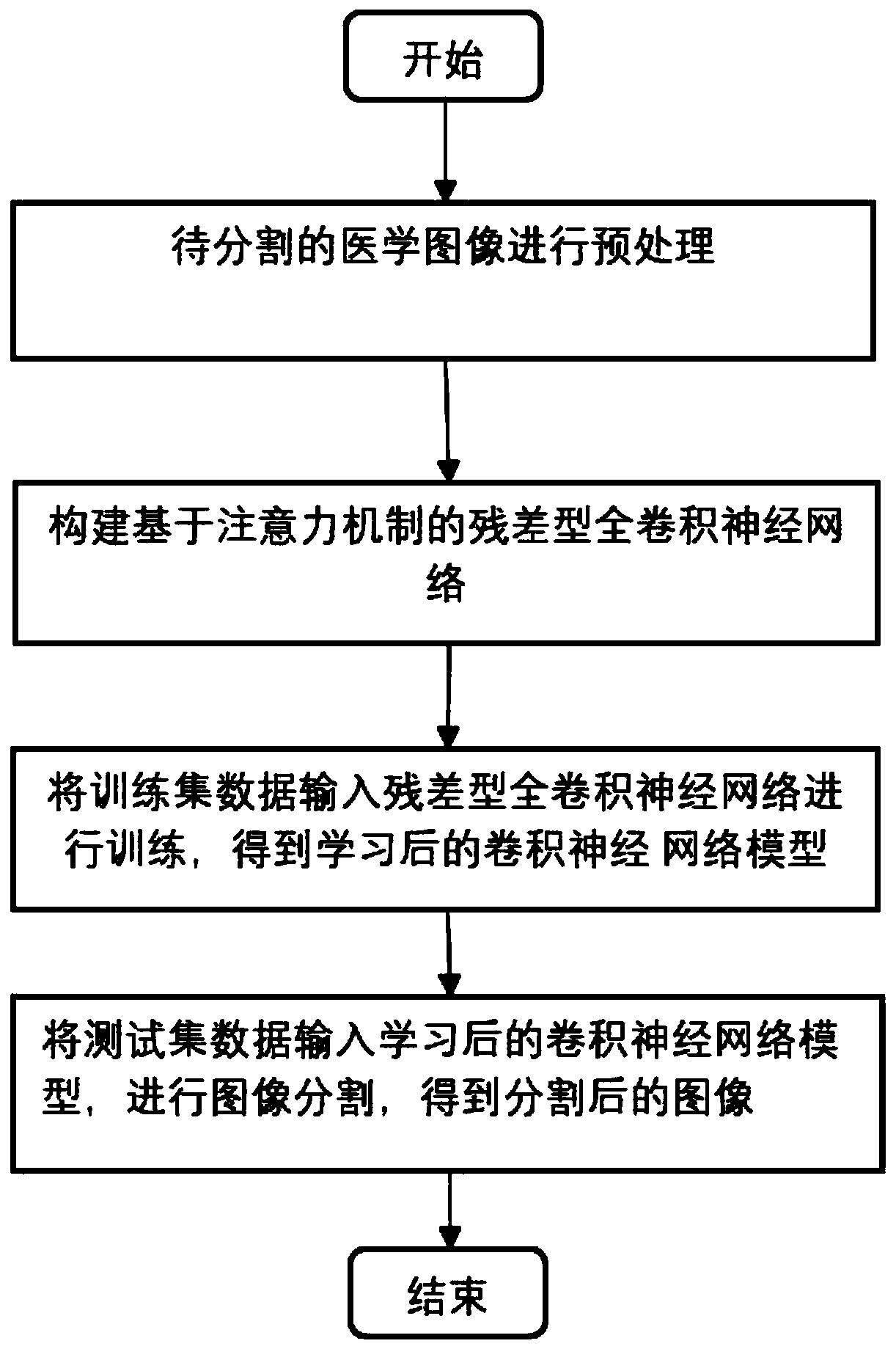
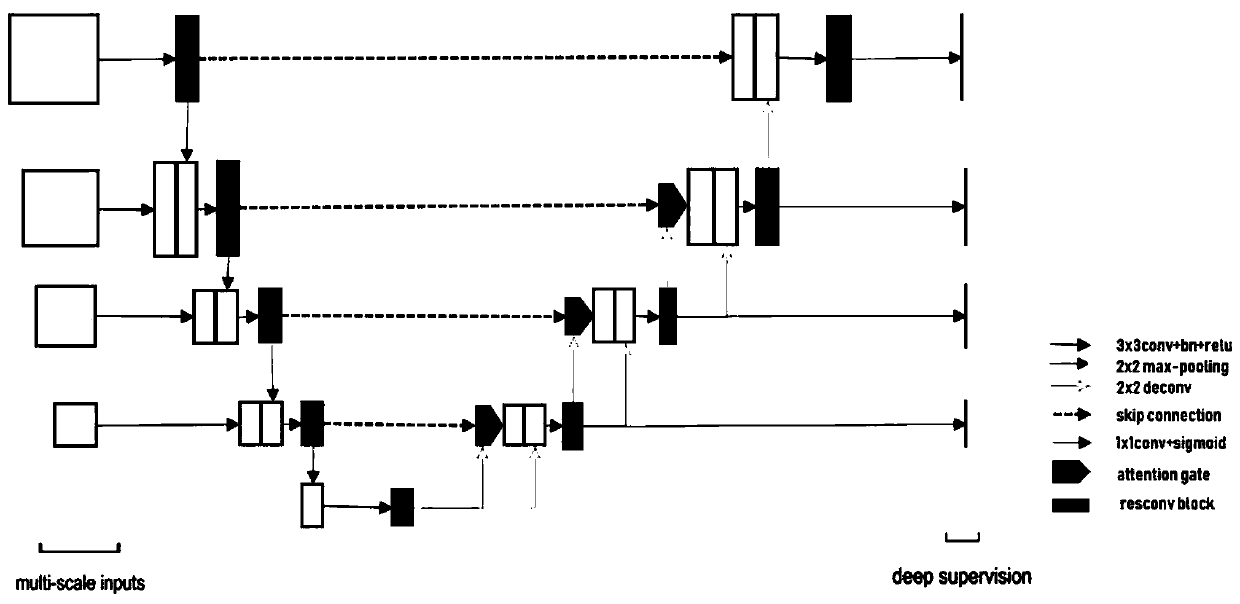
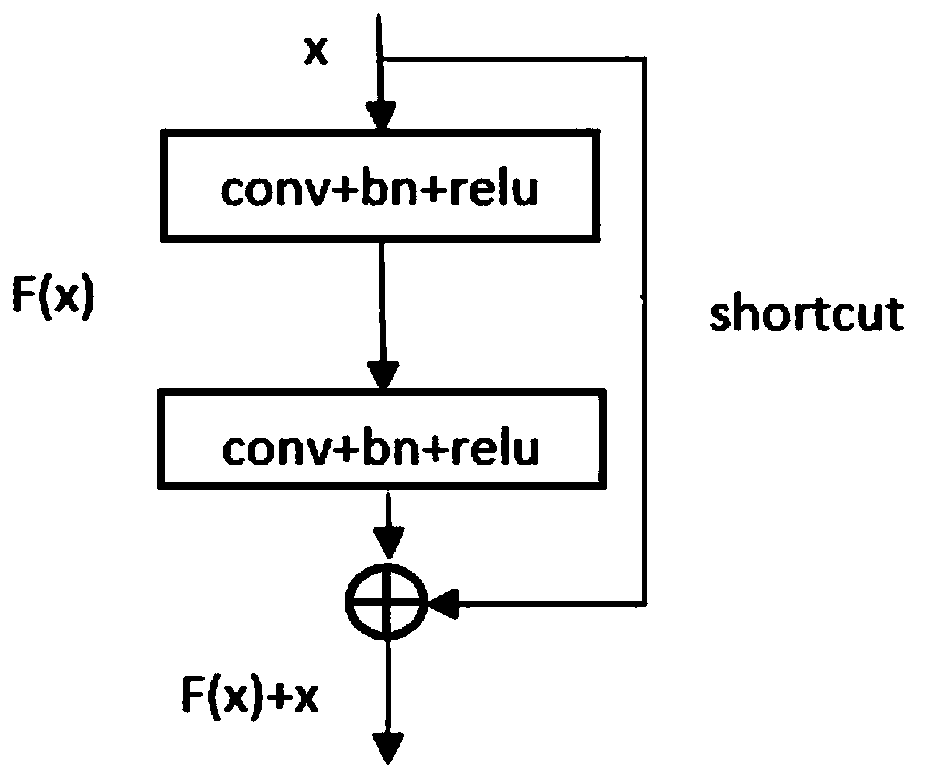
Medical image segmentation method of residual full convolutional neural network based on attention mechanism
ActiveCN110189334ASolve the problem of lack of spatial features of imagesReduce redundancyImage enhancementImage analysisImage segmentationImaging Feature
The invention provides a medical image segmentation method of a residual full convolutional neural network based on an attention mechanism. The medical image segmentation method comprises the steps: preprocessing a to-be-segmented medical image; constructing a residual full convolutional neural network based on the attention mechanism, wherein the residual full convolutional neural network comprises a feature map contraction network, an attention network and a feature map expansion network group; inputting the training set data into a residual error type full convolutional neural network for training to obtain a learned convolutional neural network model; and inputting the test set data into the learned convolutional neural network model, and performing image segmentation to obtain segmented images. According to the medical image segmentation method, an attention network is utilized to effectively transmit image features extracted from a feature map contraction network to a feature mapexpansion network; and the problem of lack of image spatial features in an image deconvolution process is solved while the attention network can also inhibit image regions irrelevant to a segmentation target in a low-layer feature image, so that the redundancy of the image is reduced, and meanwhile, the accuracy of image segmentation is also improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method And System For Optical Imaging And Ranging
ActiveUS20080137059A1Maximises informationOptimize depth estimationOptical rangefindersSensor arrayCMOS
The distance of objects to an optical system is estimated. An optical mask such as a diffractive optical element, continuous phase mask, hologram, amplitude mask, or combination thereof is placed within the optics in front of a sensor array such as a CCD, CID or CMOS device. The optical mask encodes the three-dimensional response of the system. The mask is designed to optimize depth estimation, for example, by maximizing Fisher information. A particular implementation creates a point spread function (“PSF”) that rotates as a function of the object position. The image or images obtained with different PSFs may be digitally processed to recover both a depth map of the scene and other parameters such as image brightness. The digital processing used to recover the depth map of the object may include deconvolution of a PSF from detected images.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD +1
Method and apparatus for motion invariant imaging
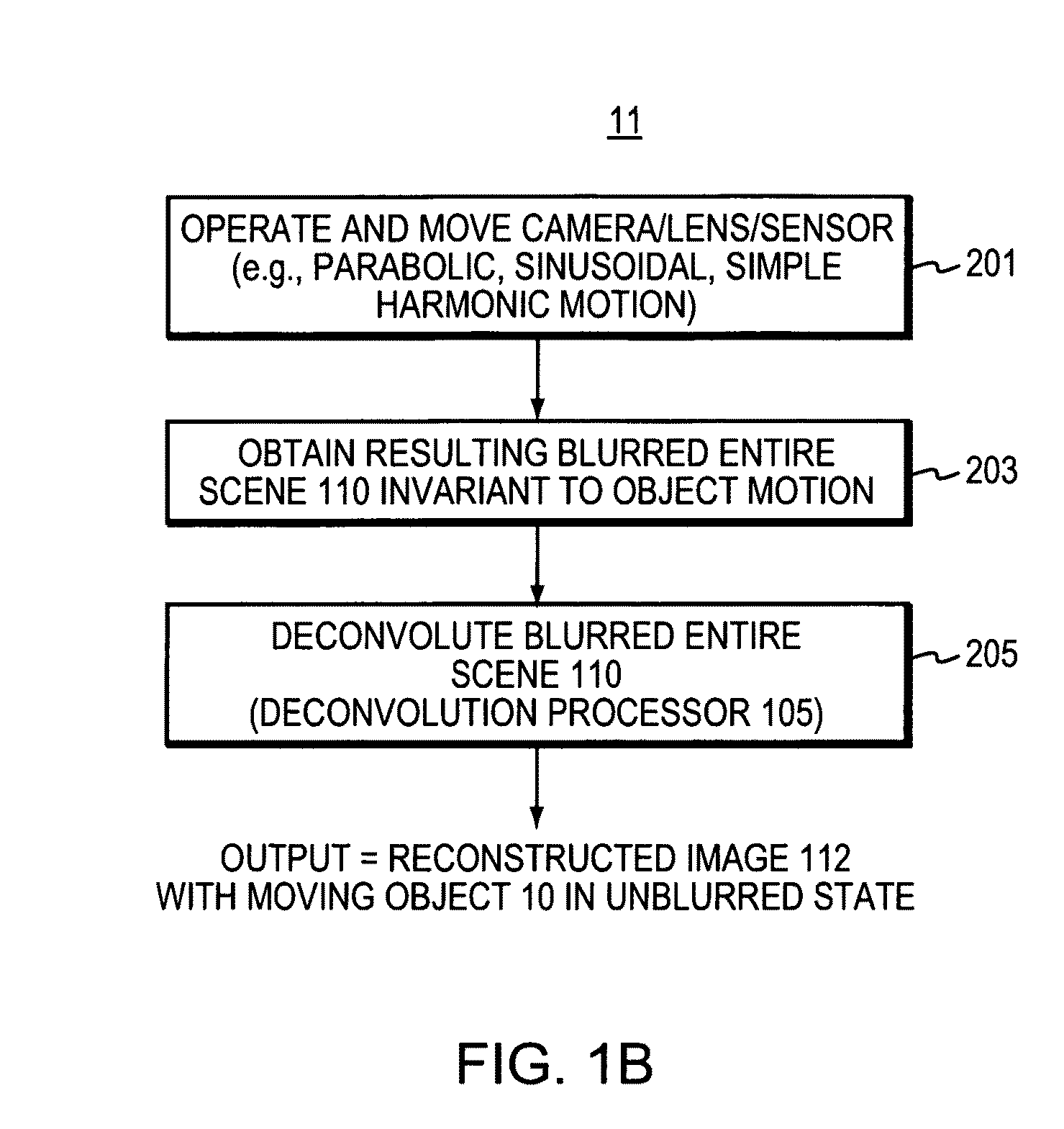
ActiveUS20090244300A1Easily invertedImage enhancementTelevision system detailsObject motionRange of motion
Object motion during camera exposure often leads to noticeable blurring artifacts. Proper elimination of this blur is challenging because the blur kernel is unknown, varies over the image as a function of object velocity, and destroys high frequencies. In the case of motions along a 1D direction (e.g. horizontal), applicants show that these challenges can be addressed using a camera that moves during the exposure. Through the analysis of motion blur as space-time integration, applicants show that a parabolic integration (corresponding to constant sensor acceleration) leads to motion blur that is not only invariant to object velocity, but preserves image frequency content nearly optimally. That is, static objects are degraded relative to their image from a static camera, but all moving objects within a given range of motions reconstruct well. A single deconvolution kernel can be used to remove blur and create sharp images of scenes with objects moving at different speeds, without requiring any segmentation and without knowledge of the object speeds.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com