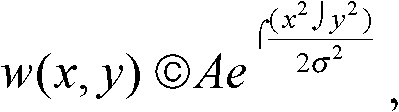Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
558 results about "Diffusion function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
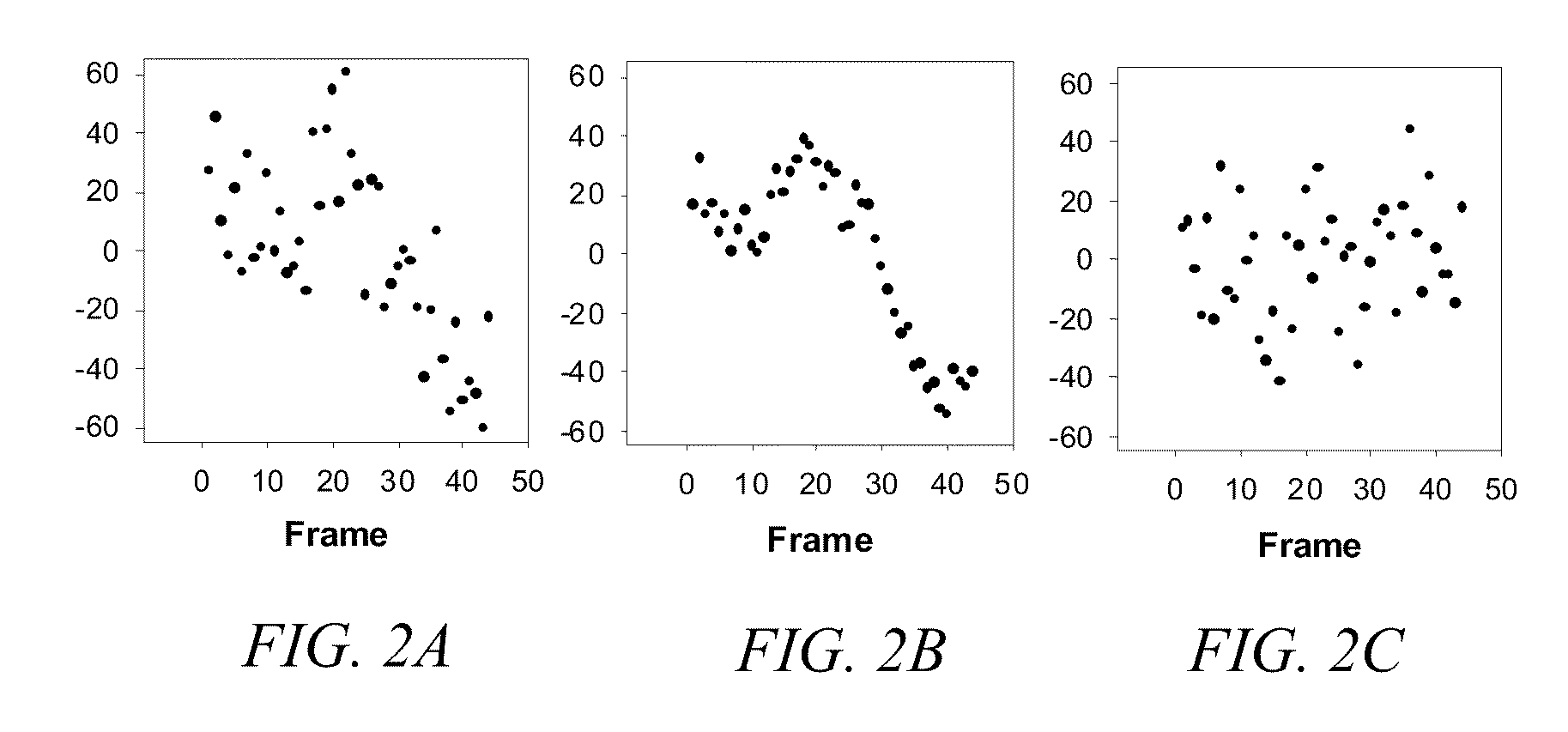
Diffusion is an essential function in living organisms. Diffusion is the random but directional movement of molecules from a place of high concentration to a place of low concentration. ... An electrical signal is generated when the membrane lets ions from outside flow into the cell. This inflow changes the charge on the inside of the membrane from negative to positive.
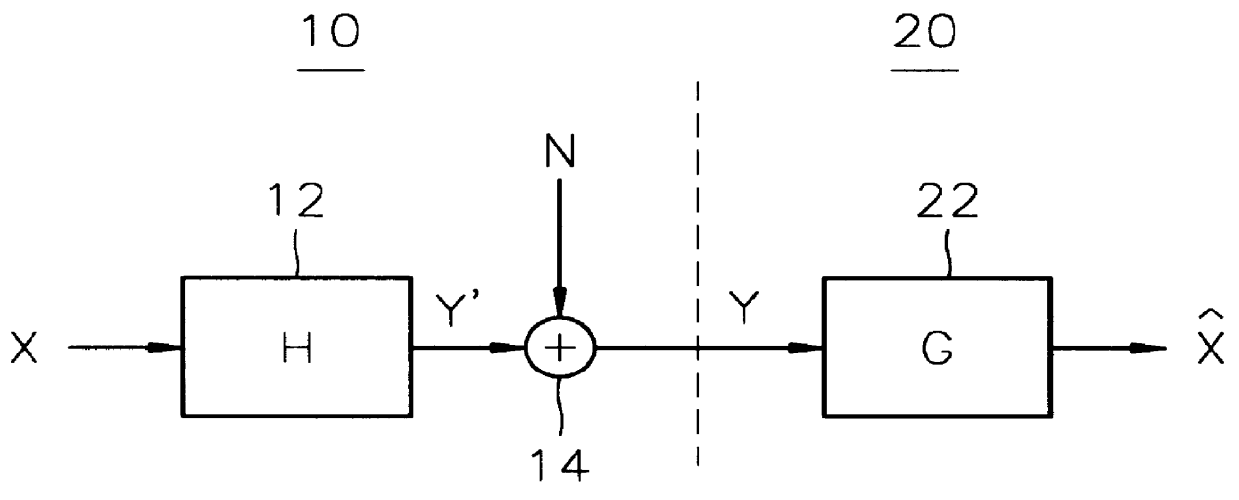
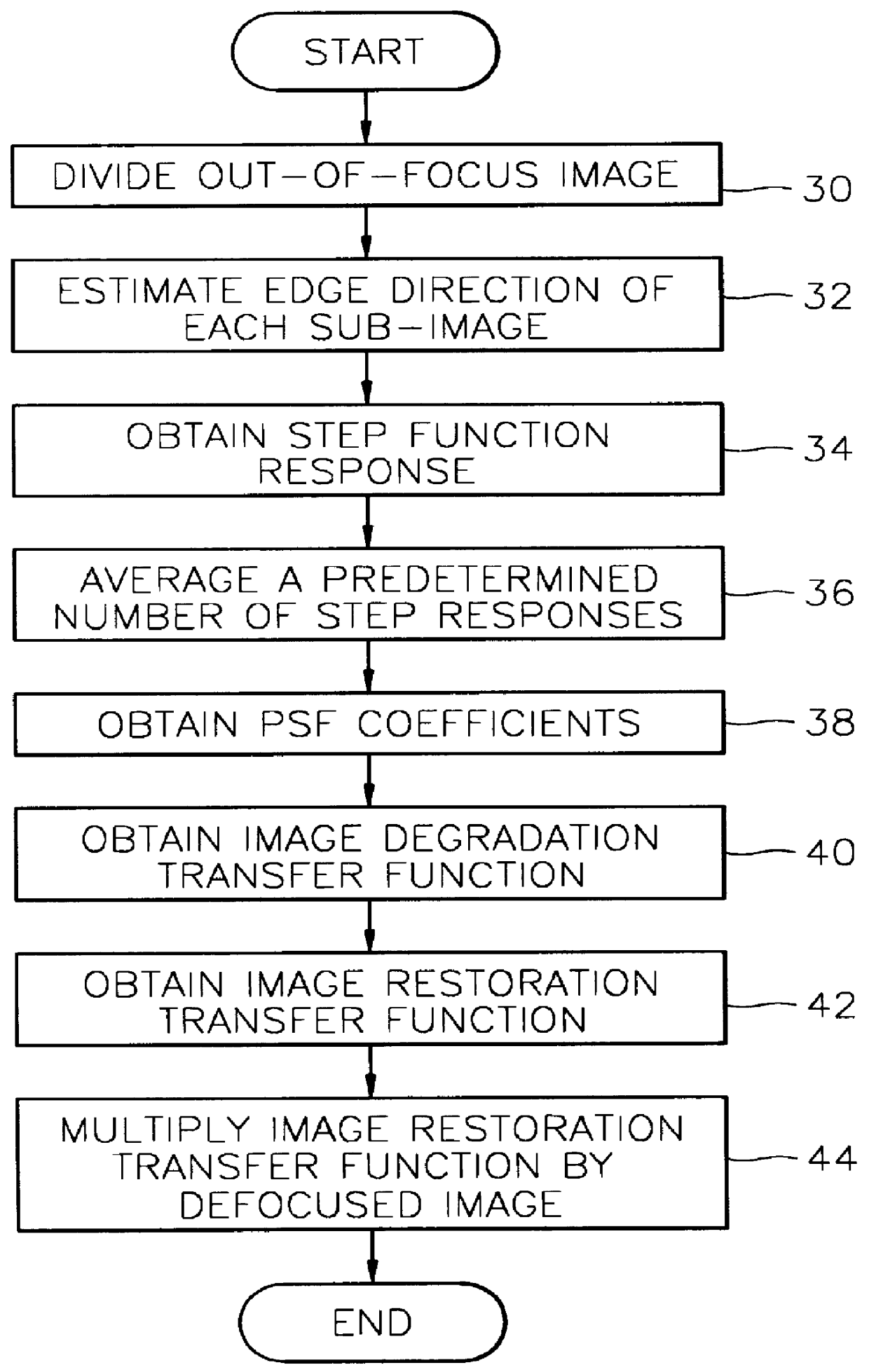
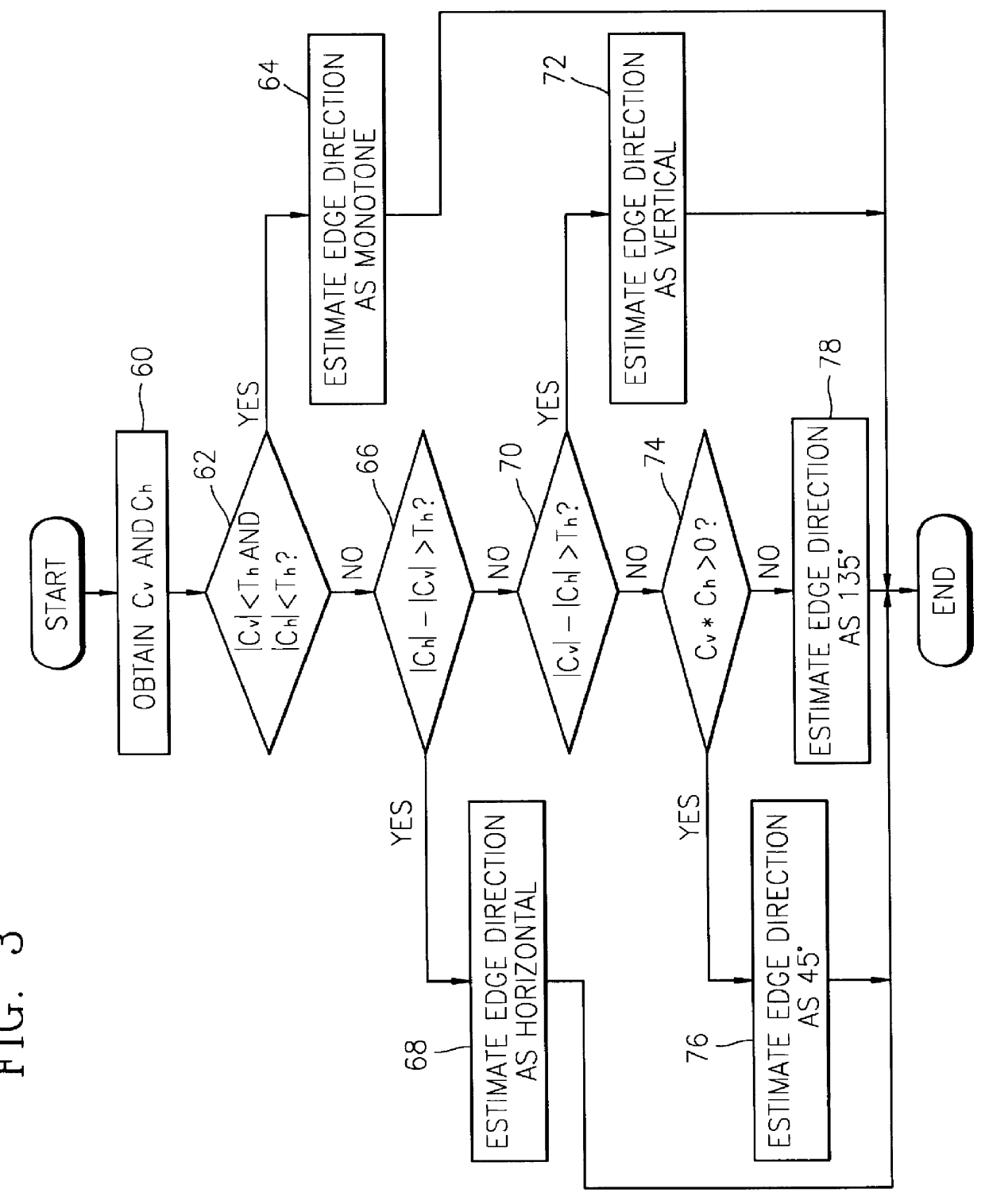
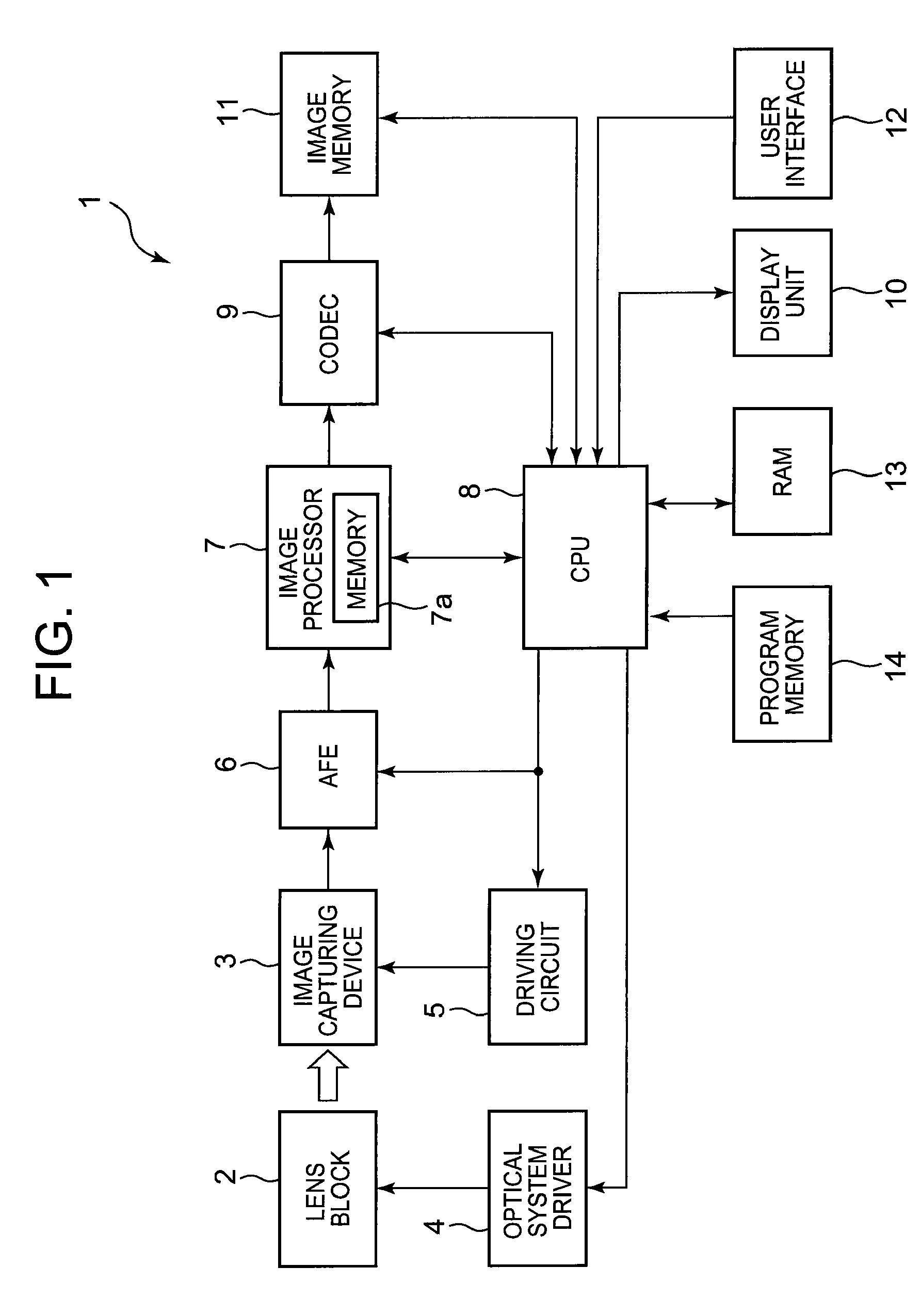
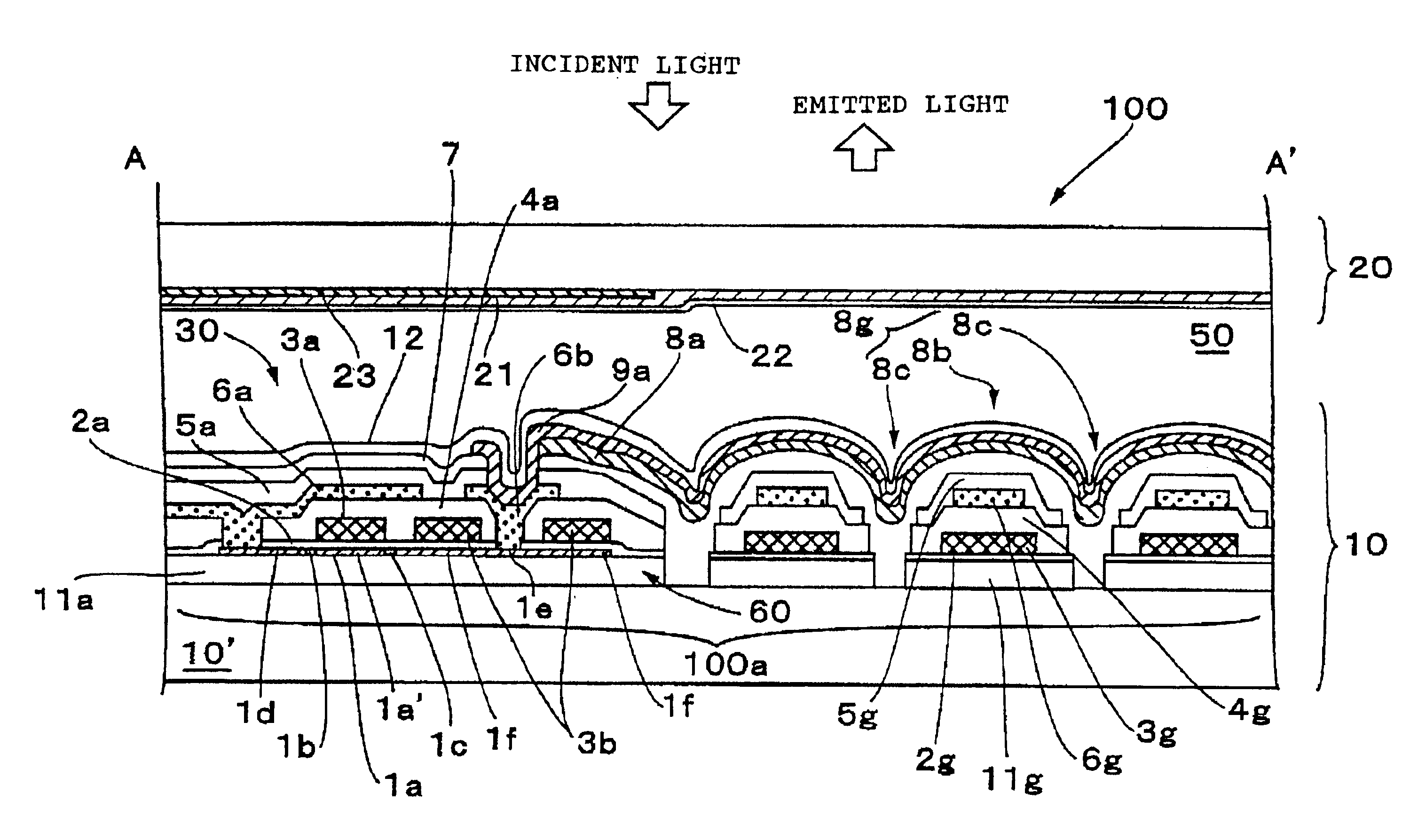
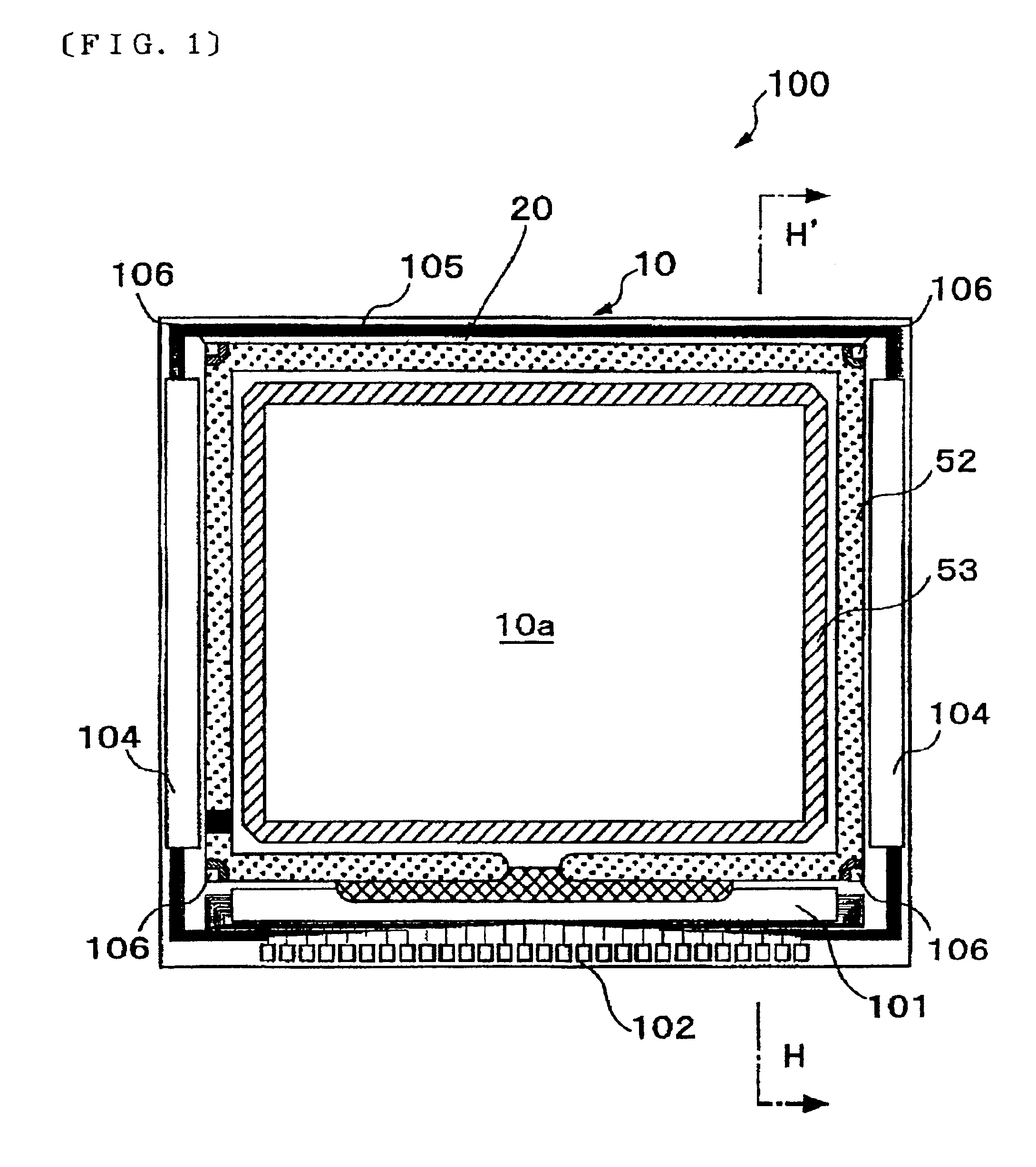
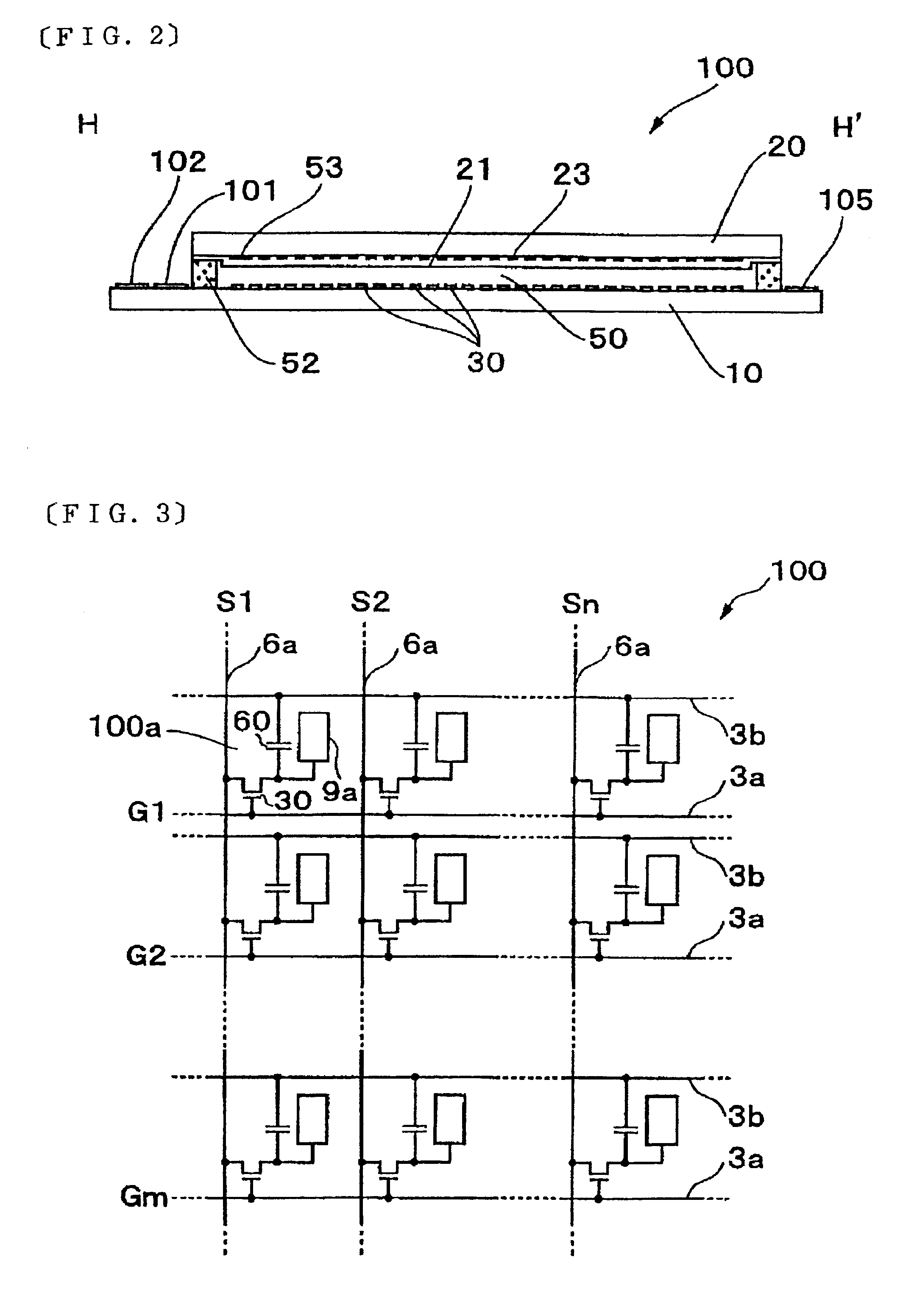
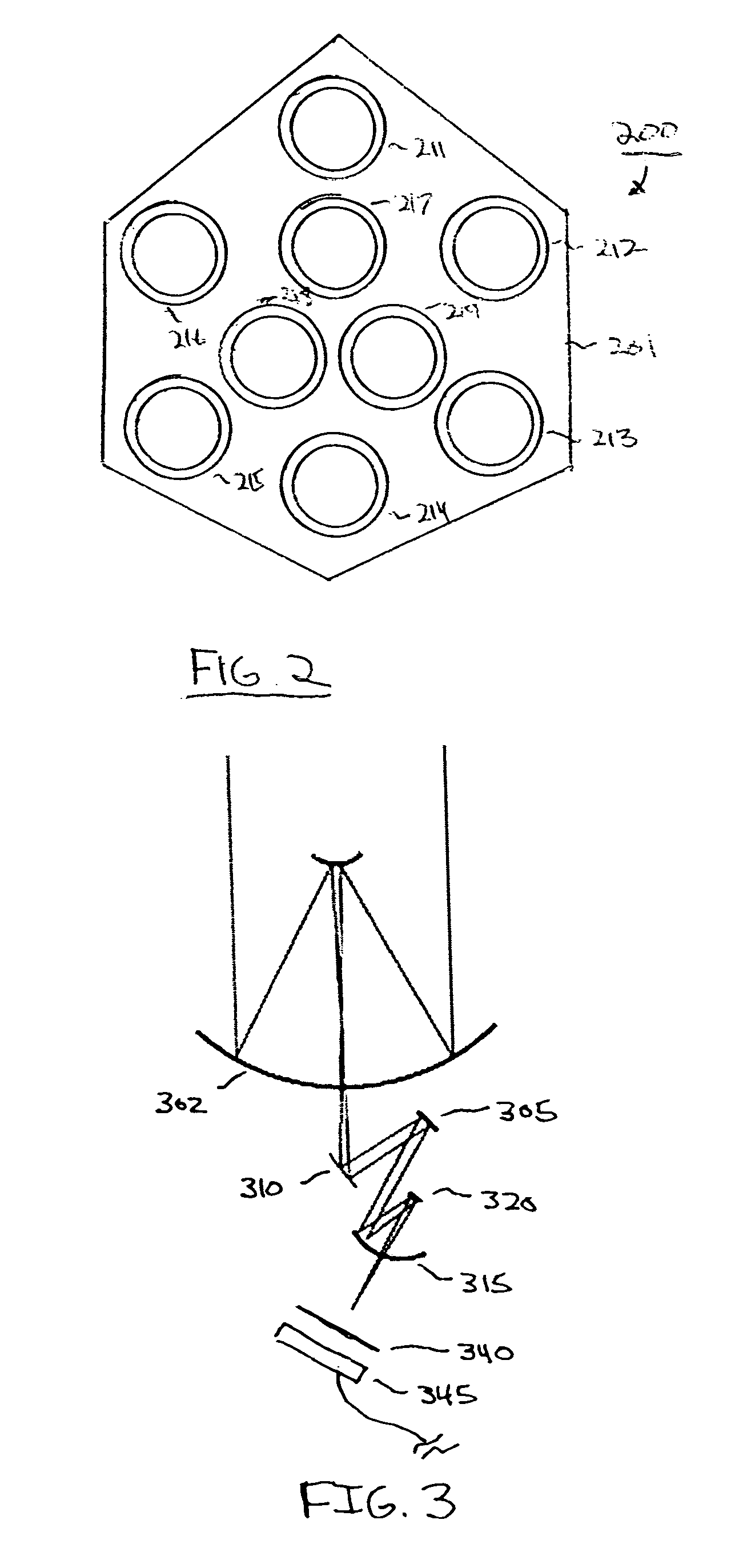
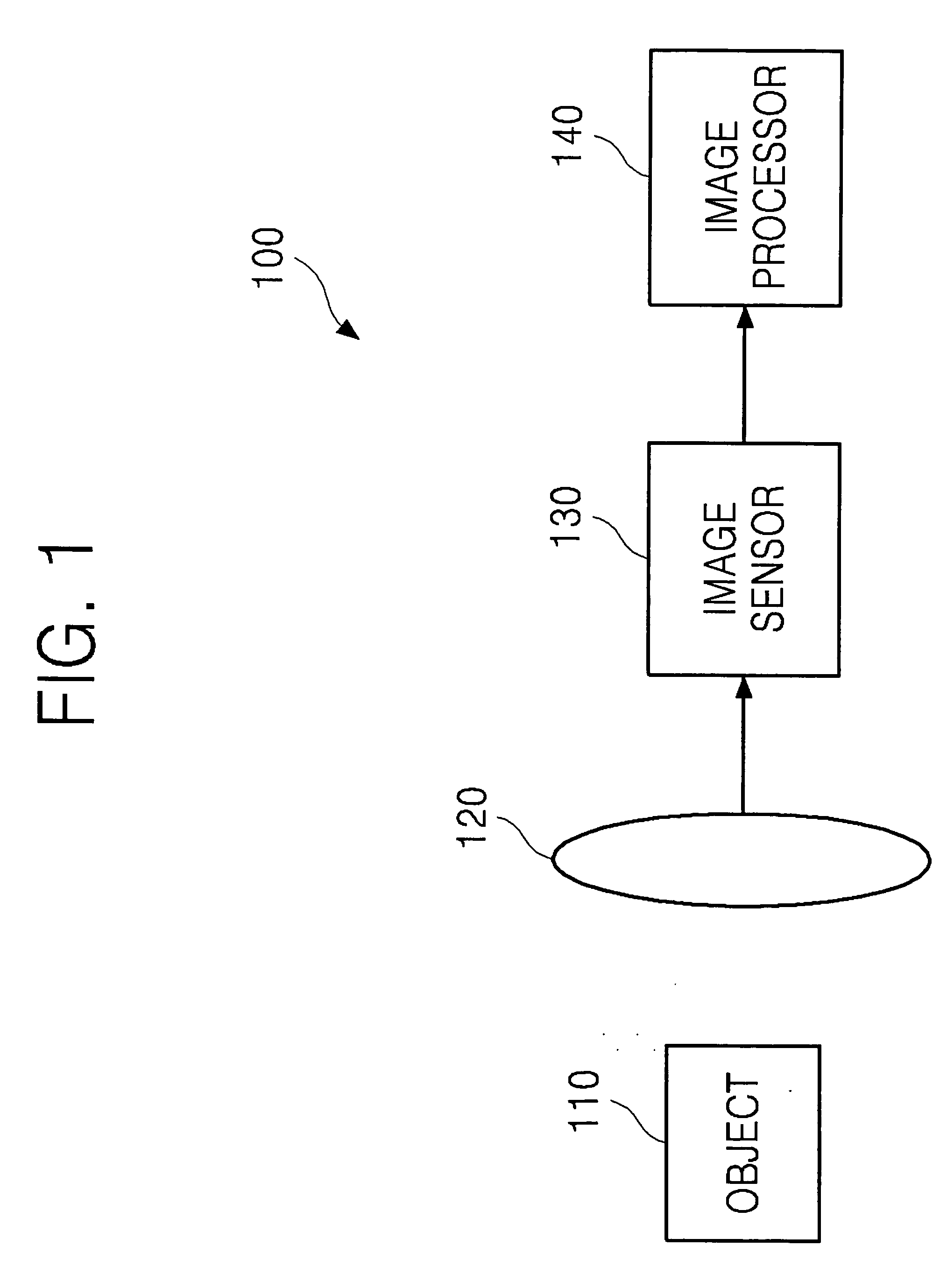
Digital focusing method and apparatus in image processing system
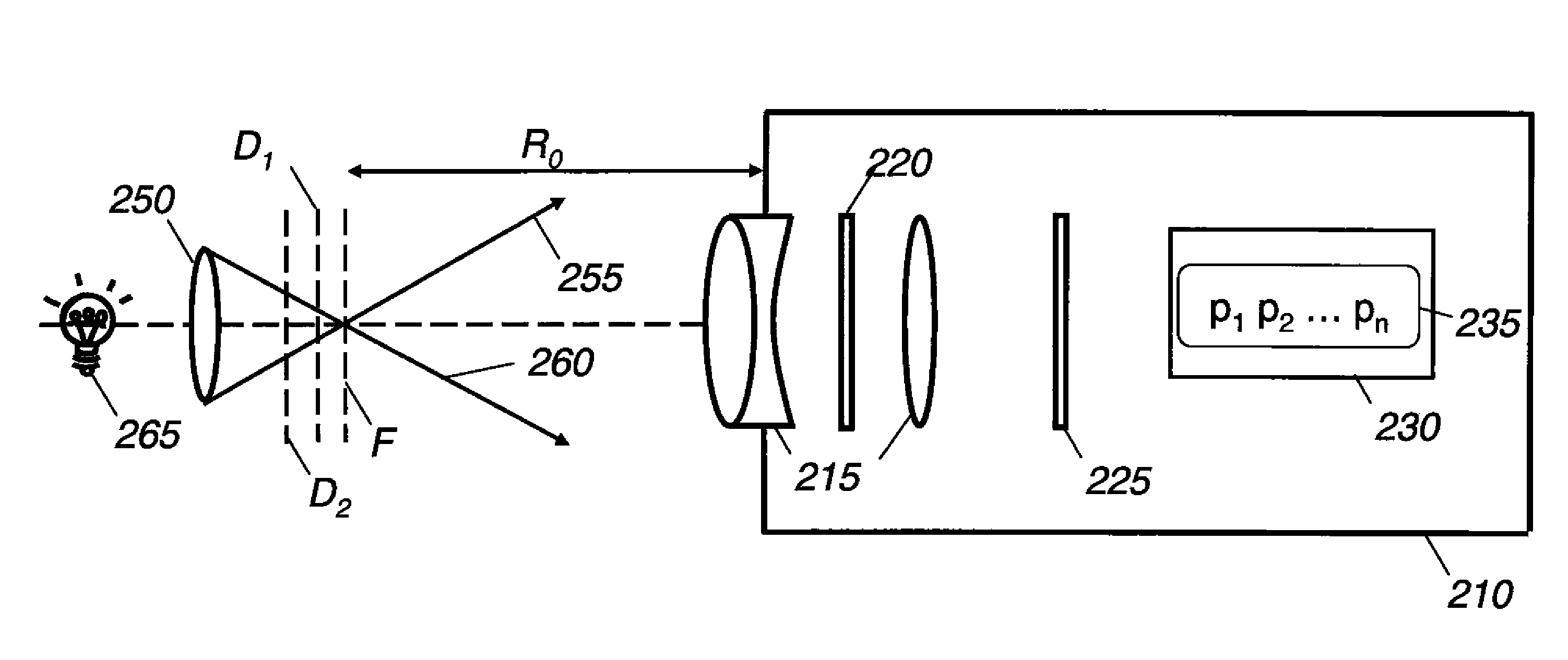
Digital focusing method and apparatus in an image processing system, for digitally focusing an out-of-focus image, are provided. A defocused image is divided into sub-images of a predetermined size. An edge direction of each of the divided sub-images is estimated. Step responses with respect to the respective edge directions are calculated. A mean step response is obtained by averaging a predetermined number of the step responses. Point Spread Function (PSF) coefficients are obtained using the mean step response. An image blur transfer function is obtained using the PSF coefficients. An image restoration transfer function is obtained using the image blur transfer function. An original in-focused image is obtained by multiplying the image restoration transfer function by the defocused image in a frequency domain. Thus, an image can be restored in real time, and the size and weight of the image processing system can be reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method to control point spread function of an image
ActiveUS20060103951A1Guaranteed preservation qualityMore interferenceTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging qualityPoint spread function
A method of controlling the point spread function of an image projected with said image being diffused by a filter; said point spread function is a result of the application of spatial filter(s) on said image; with said control of the point spread function effected by varying the distance between such image and said spatial filter(s) and varying the bidirectional scattering transmission function of the spatial filter(s). Said spatial filter may be a holographic diffuser, which by method of manufacture has a ell defined bi-directional scattering transmission spread function. Control of said spread function is particularly useful to maintain image quality while abating moiré interference in situations where two periodic patterns are layered causing moiré interference.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Method and apparatus for scanning with controlled spherical aberration
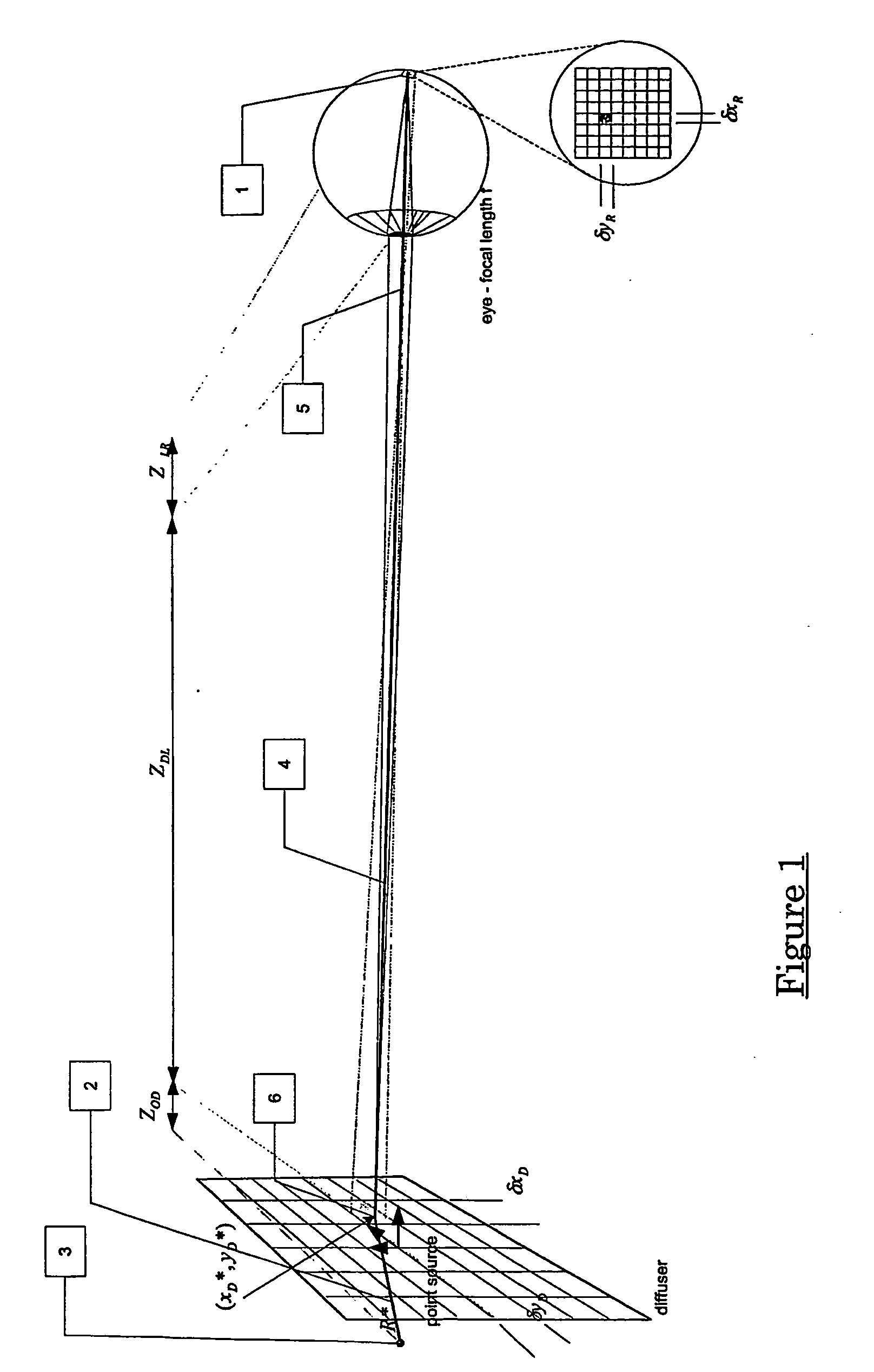
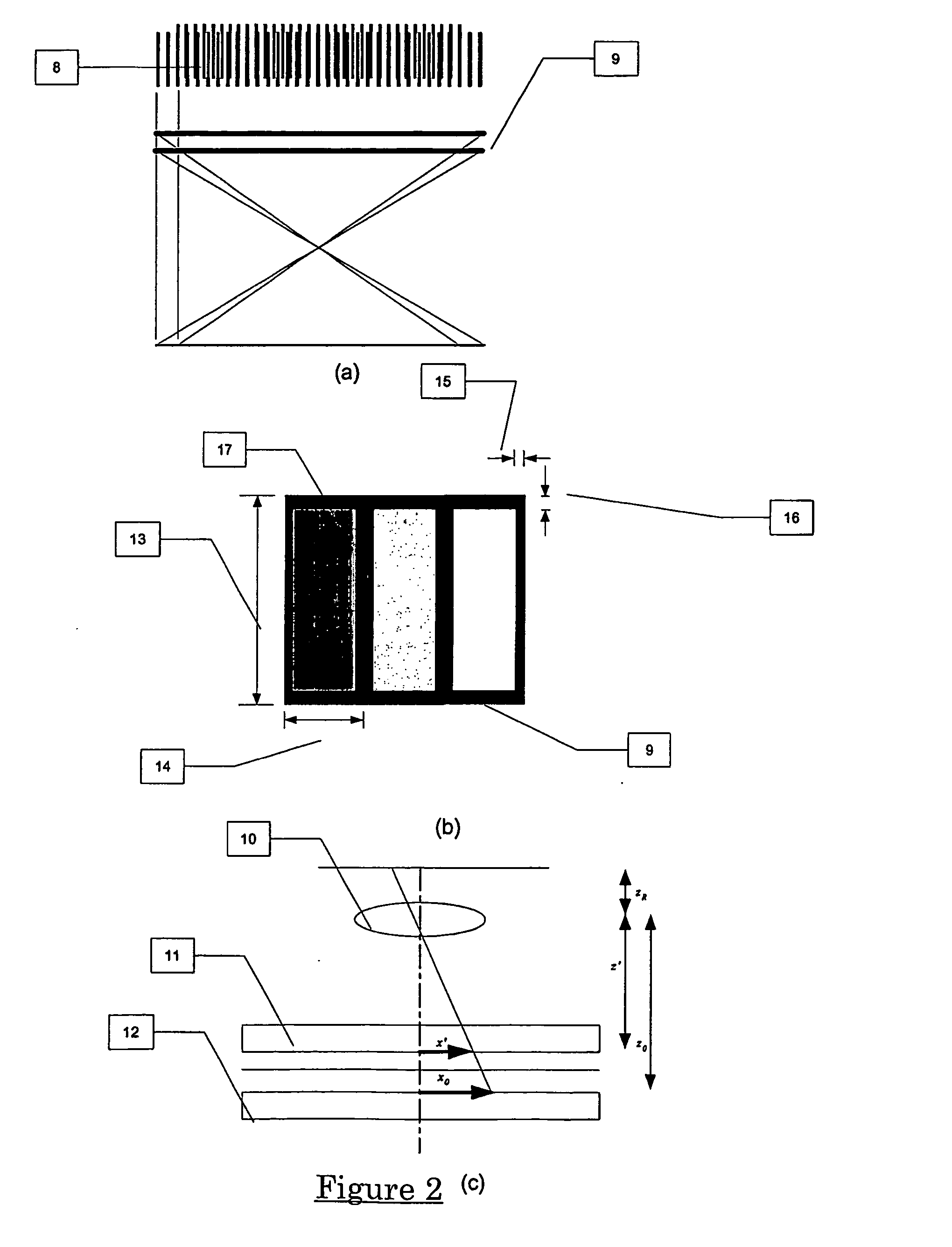
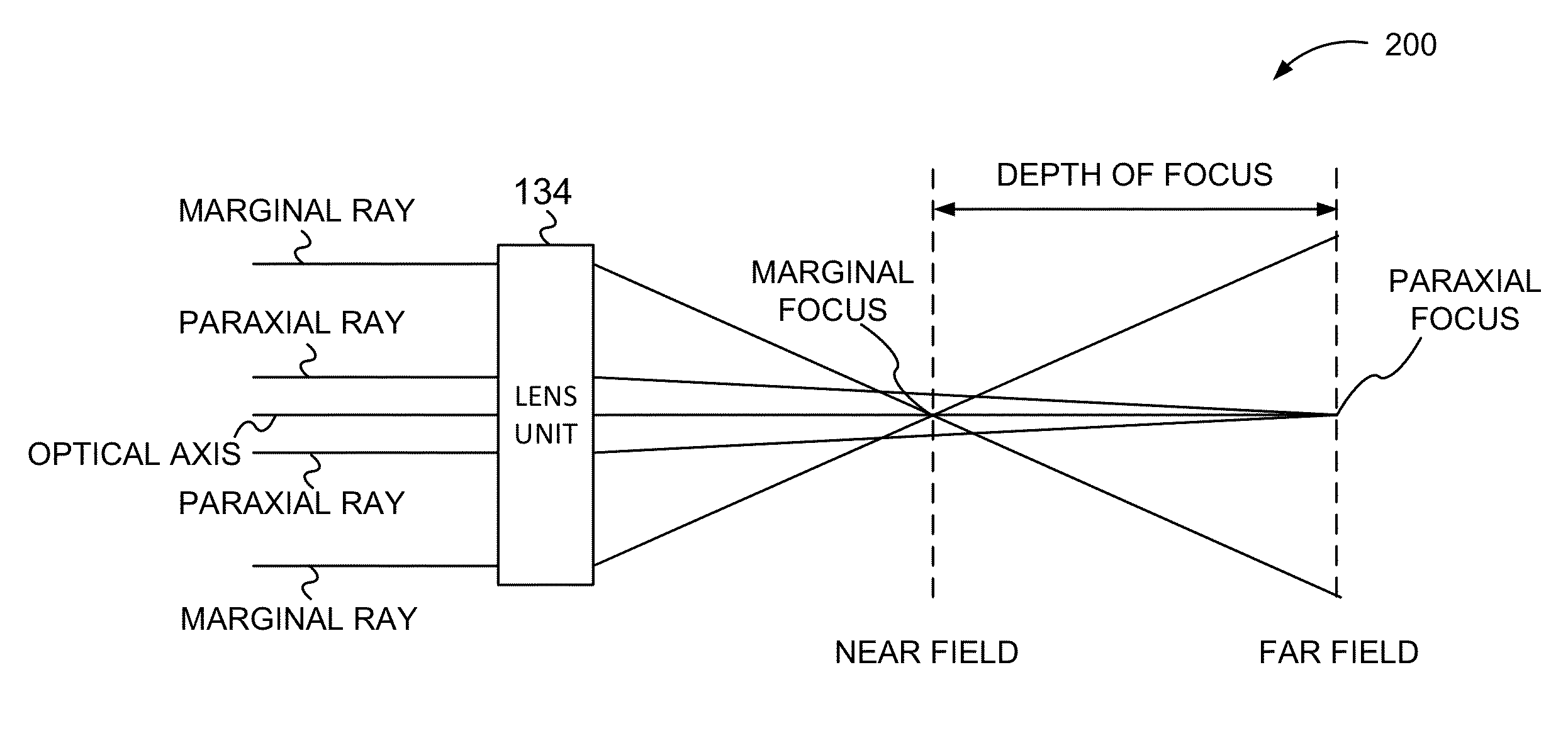
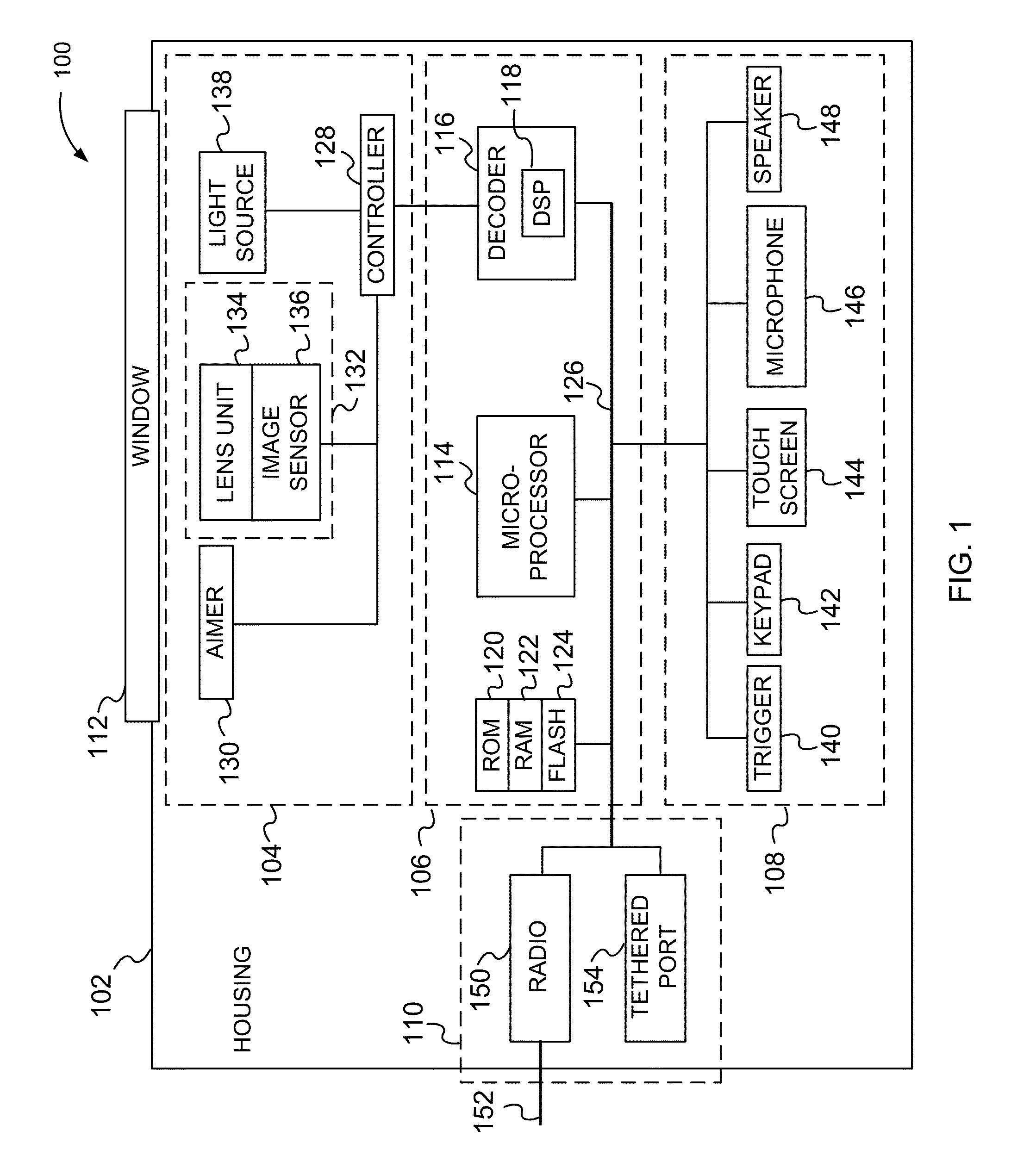
A reader obtains image data corresponding to an image of optically encoded information that is received via a lens unit that causes controlled spherical aberration blurring that is precisely known. The reader may perform deconvolution processing on the image data to render it decodable. The deconvolution processing may implement a Weiner filter that uses data corresponding to a near-field point spread function of the lens unit. The depth of field of the reader is greater than that of conventional reader in all lighting conditions.
Owner:INTERMEC TECH
Method and system for obtaining a point spread function using motion information
InactiveUS8648918B2Function increaseLess complexImage enhancementTelevision system detailsDiffusion functionPoint spread function
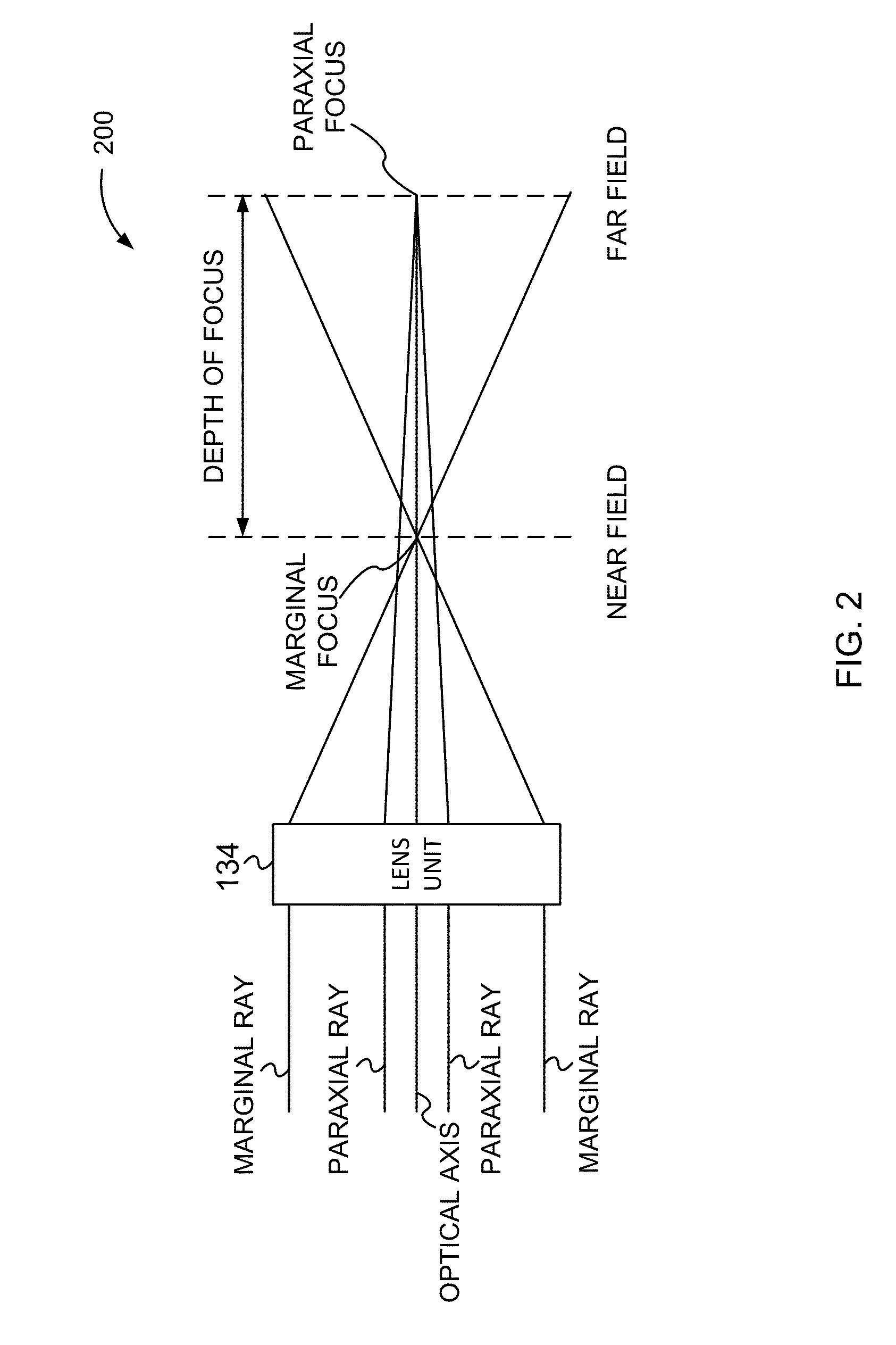
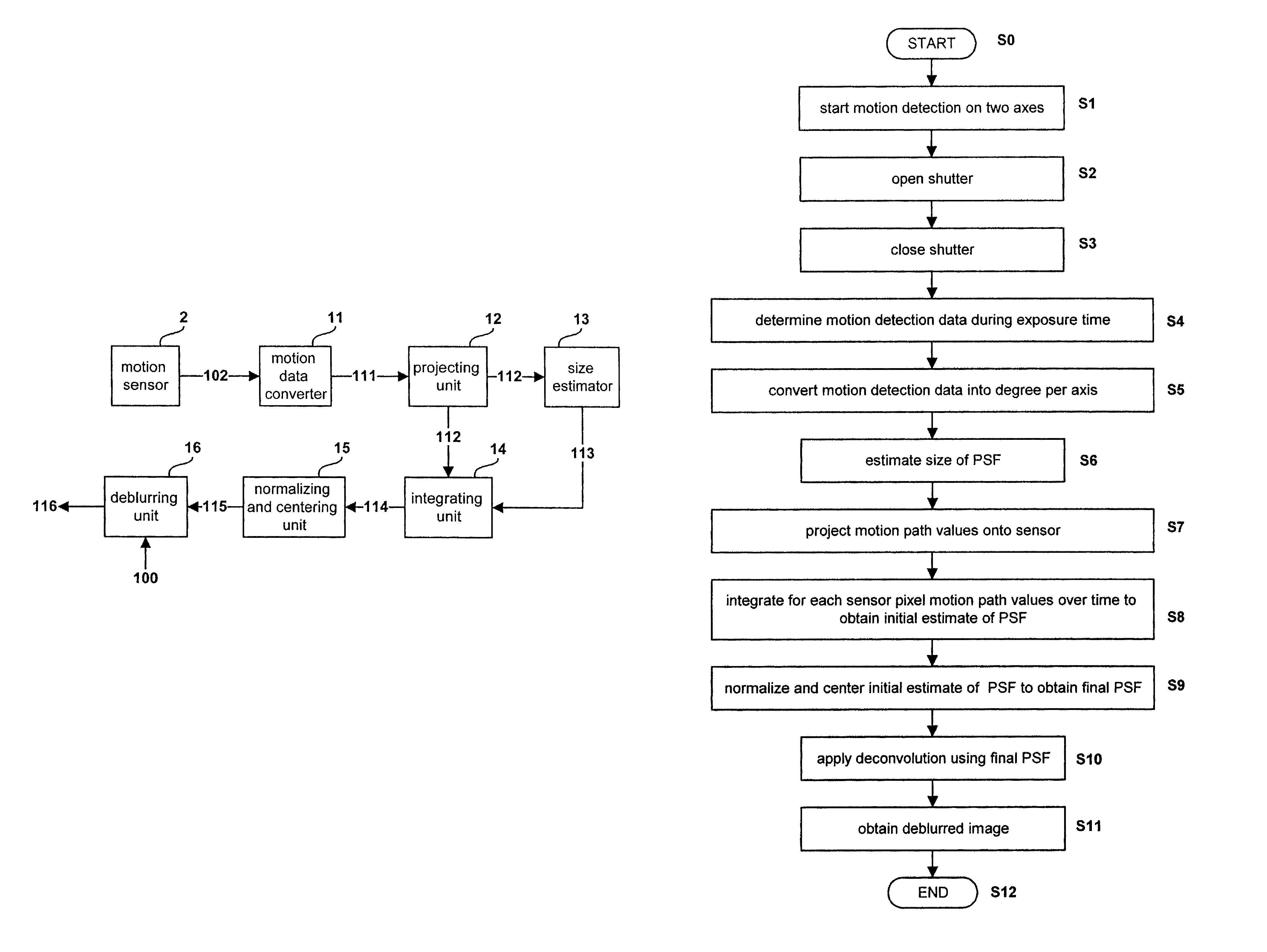
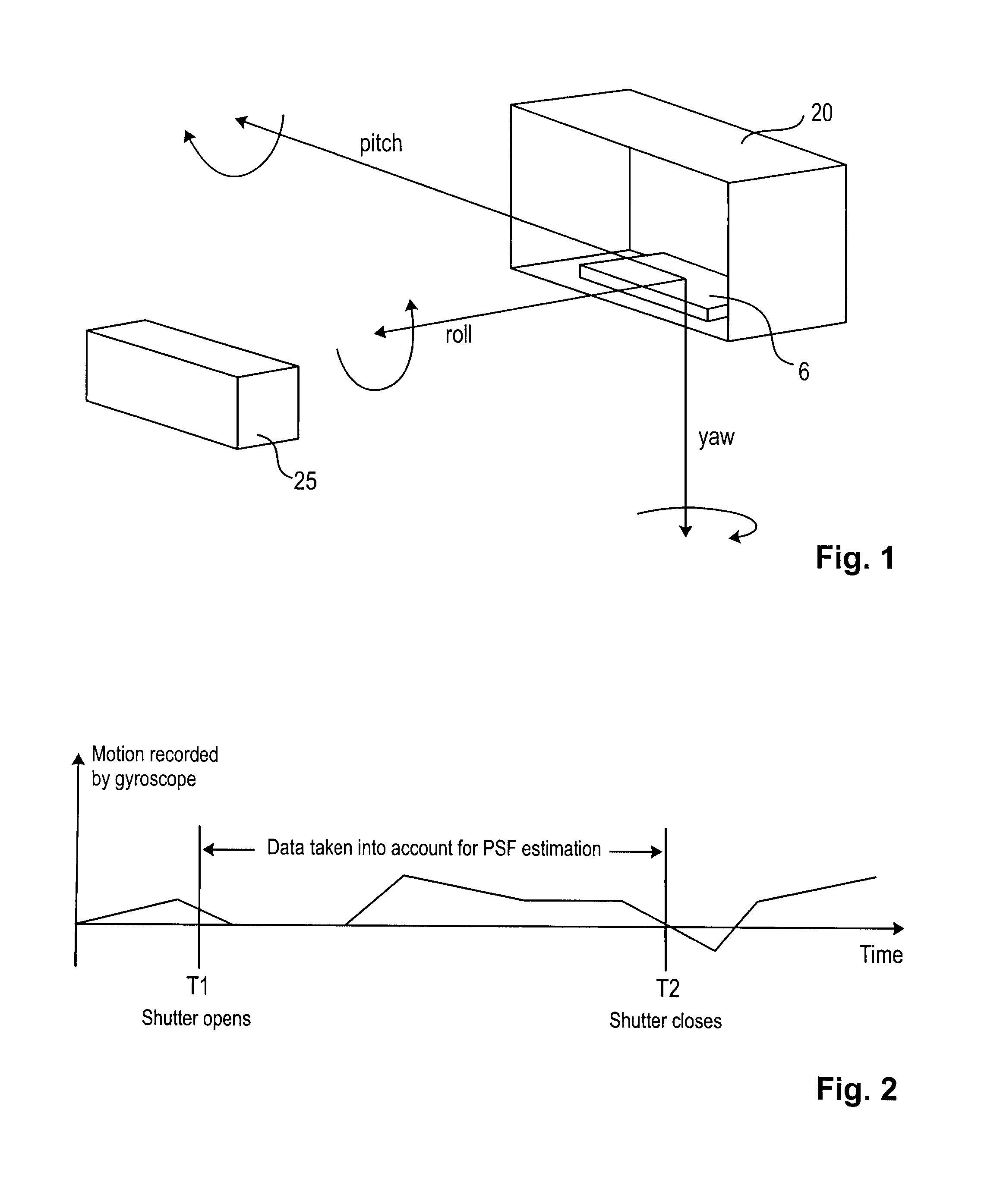
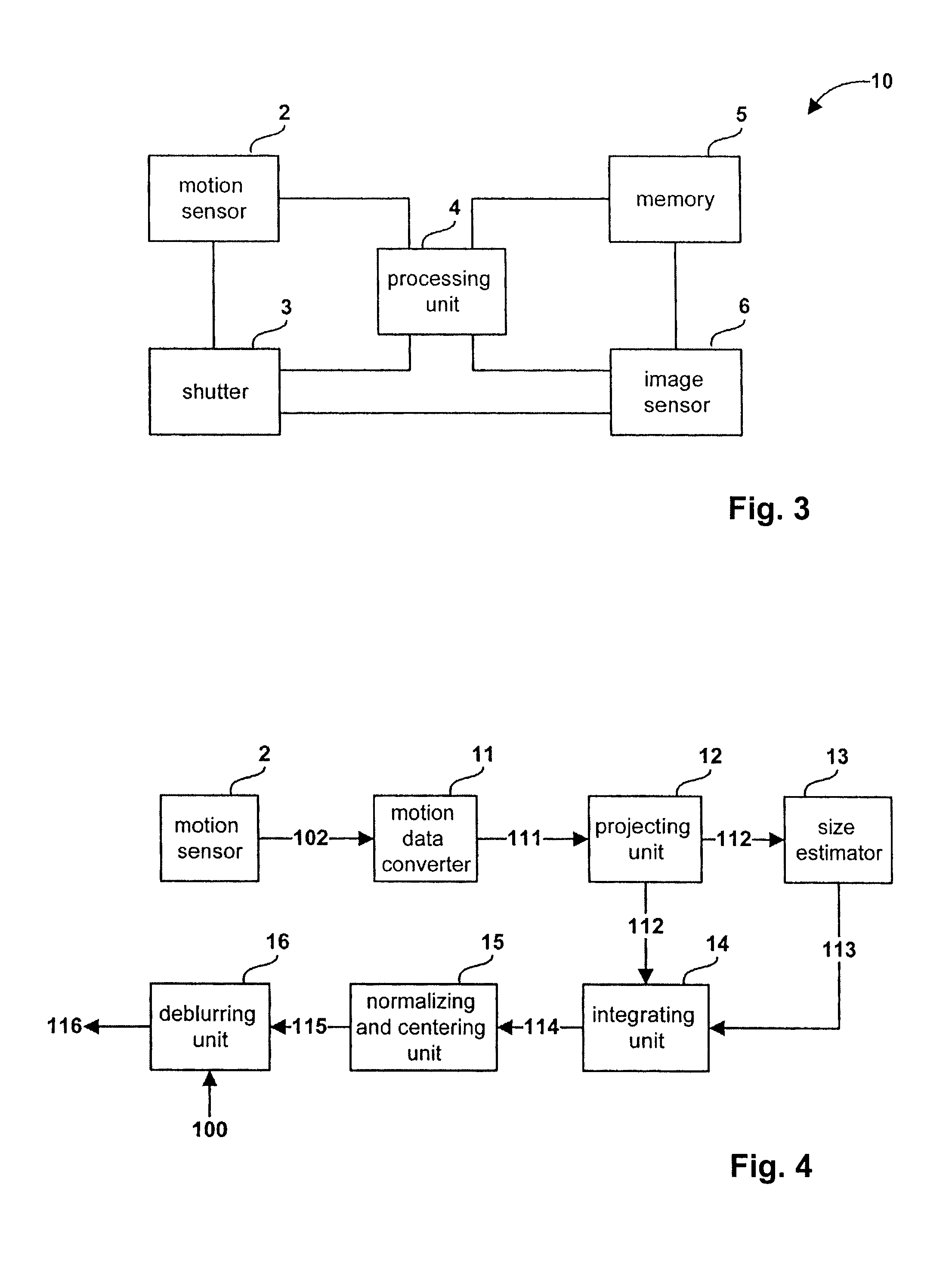
The present invention relates to a method and system for obtaining a point spread function for deblurring image data captured by an imaging device comprising a motion sensor. First, motion path values indicating the motion of the imaging device during the exposure time are acquired. The motion path values of the imaging device are then projected onto the sensor plane and for each sensor pixel the projected motion path values are integrated over time. Said integrated value represents for each sensor pixel an initial estimate of the point spread function. Optionally, the size of the point spread function can also be estimated based on the distance of the focused object and taken into account during the projecting step.
Owner:SONY CORP
Post processing of iris images to increase image quality
ActiveUS7869627B2Quality improvementLow resolution imageTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersDiffusion functionImage resolution
A rapid iris acquisition, tracking, and imaging system can be used at longer standoff distances and over larger capture volumes, without the active cooperation of subjects. Light illuminates the subjects' eyes and a high resolution camera captures images of the irises. The images of the irises are processed by a post processing module to improve their quality. In one approach, the point spread function of the image capture subsystem is estimated using glint reflections from the eye, and the estimated point spread function is used in deconvolution to increase the resolution of the iris images. The post processed iris images have sufficient resolution to be used for biometric identification.
Owner:TASCENT INC
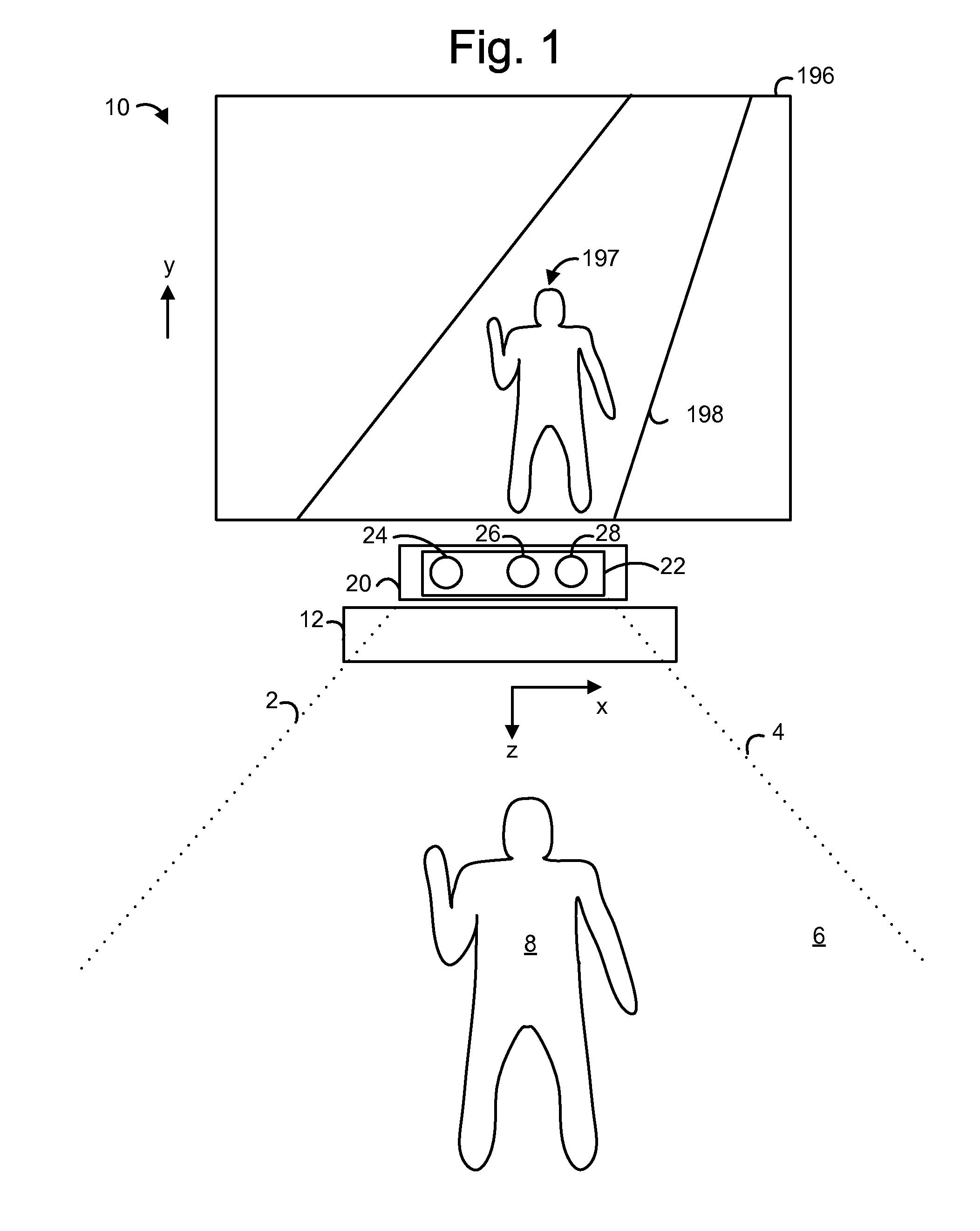
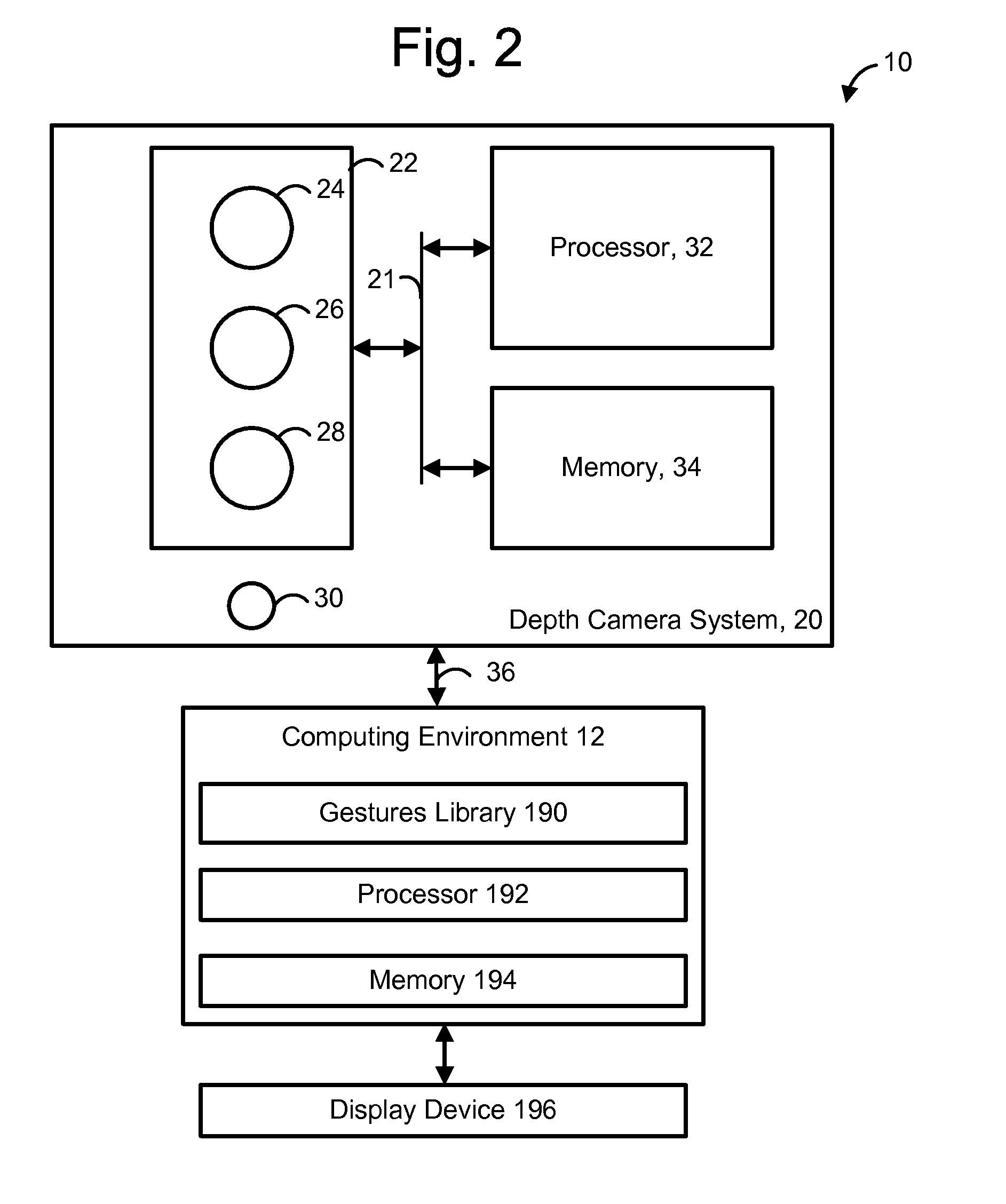
Use of wavefront coding to create a depth image
ActiveUS20110310226A1Well formedCharacter and pattern recognitionUsing optical meansDiffusion functionMotion capture
A 3-D depth camera system, such as in a motion capture system, tracks an object such as a human in a field of view using an illuminator, where the field of view is illuminated using multiple diffracted beams. An image sensing component obtains an image of the object using a phase mask according to a double-helix point spread function, and determines a depth of each portion of the image based on a relative rotation of dots of light of the double-helix point spread function. In another aspect, dual image sensors are used to obtain a reference image and a phase-encoded image. A relative rotation of features in the images can be correlated with a depth. Depth information can be obtained using an optical transfer function of a point spread function of the reference image.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
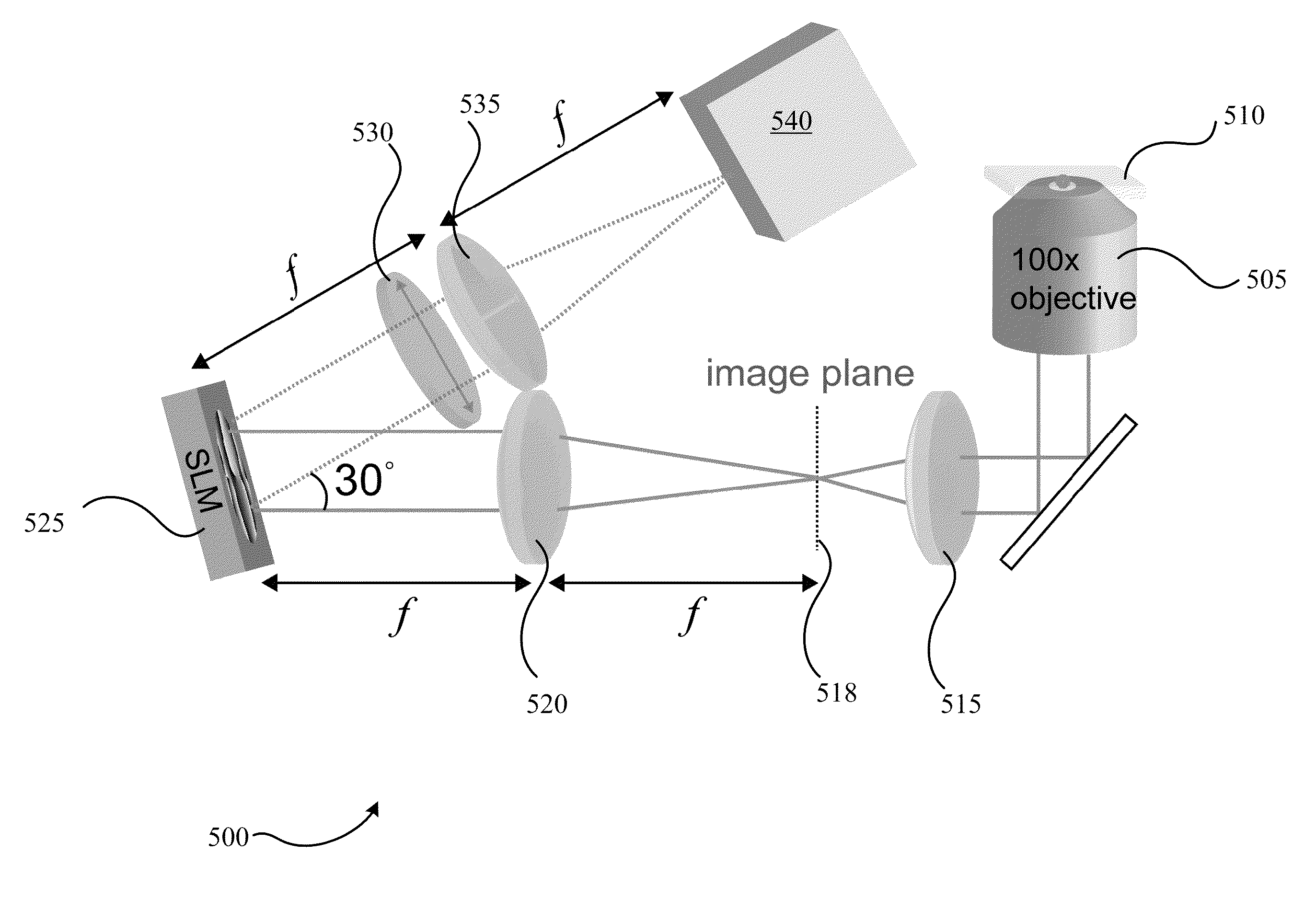
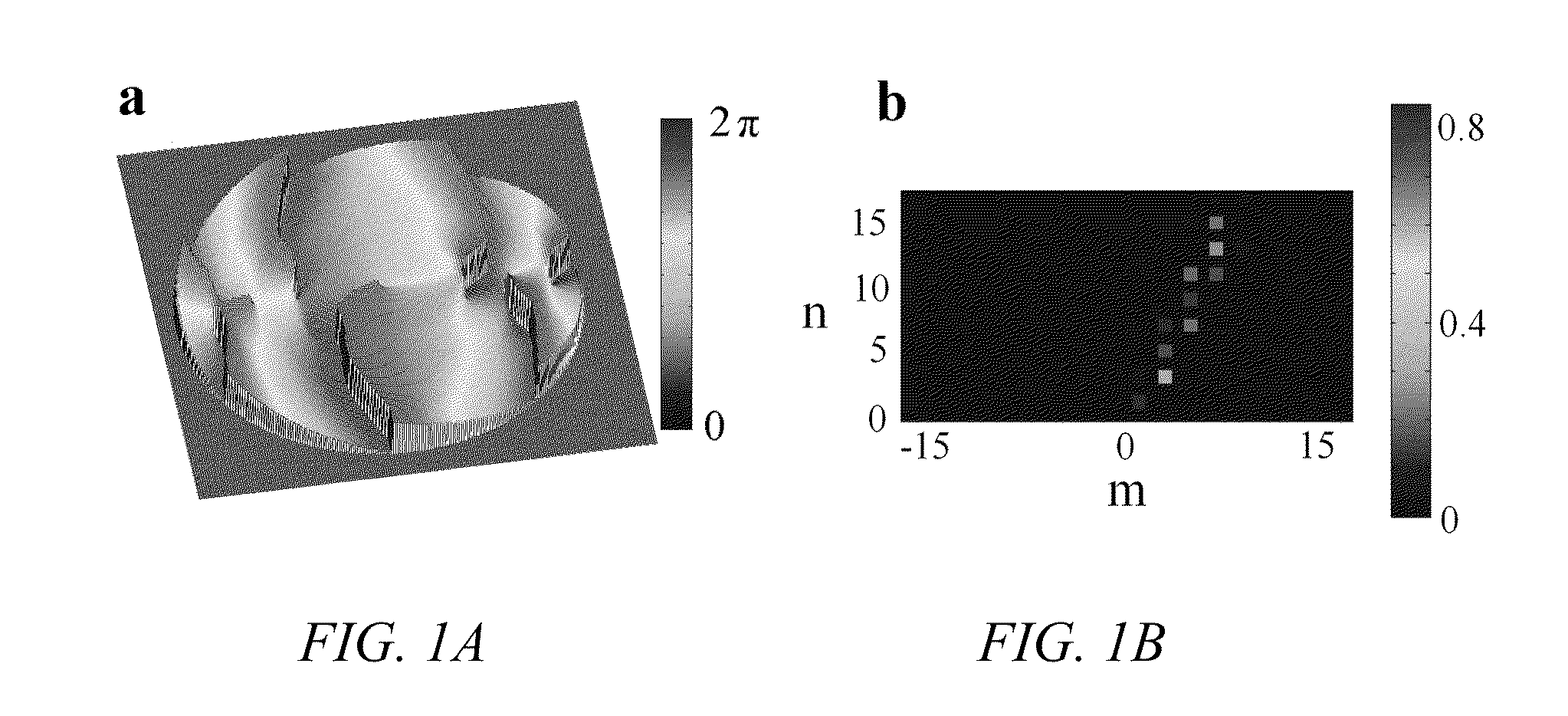
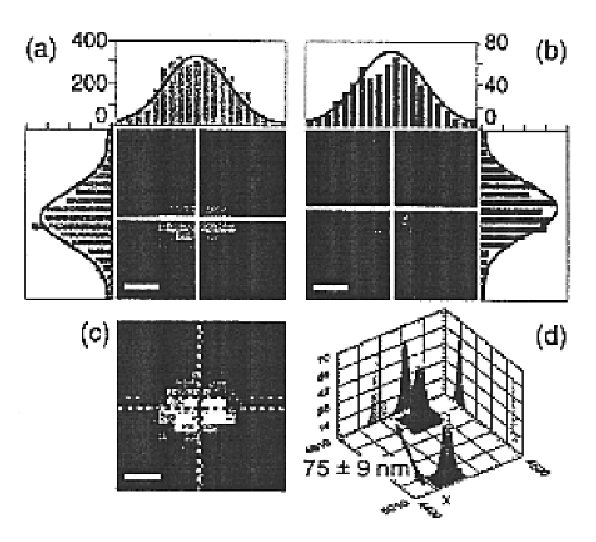
Three-dimensional single-molecule fluorescence imaging beyond the diffraction limit using a double-helix point spread function
Embodiments of the present invention can resolve molecules beyond the optical diffraction limit in three dimensions. A double-helix point spread function can be used to in conjunction with a microscope to provide dual-lobed images of a molecule. Based on the rotation of the dual-lobed image, the axial position of the molecule can be estimated or determined. In some embodiments, the angular rotation of the dual-lobed imaged can be determined using a centroid fit calculation or by finding the midpoints of the centers of the two lobes. Regardless of the technique, the correspondence between the rotation and axial position can be utilized. A double-helix point spread function can also be used to determine the lateral positions of molecules and hence their three-dimensional location.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
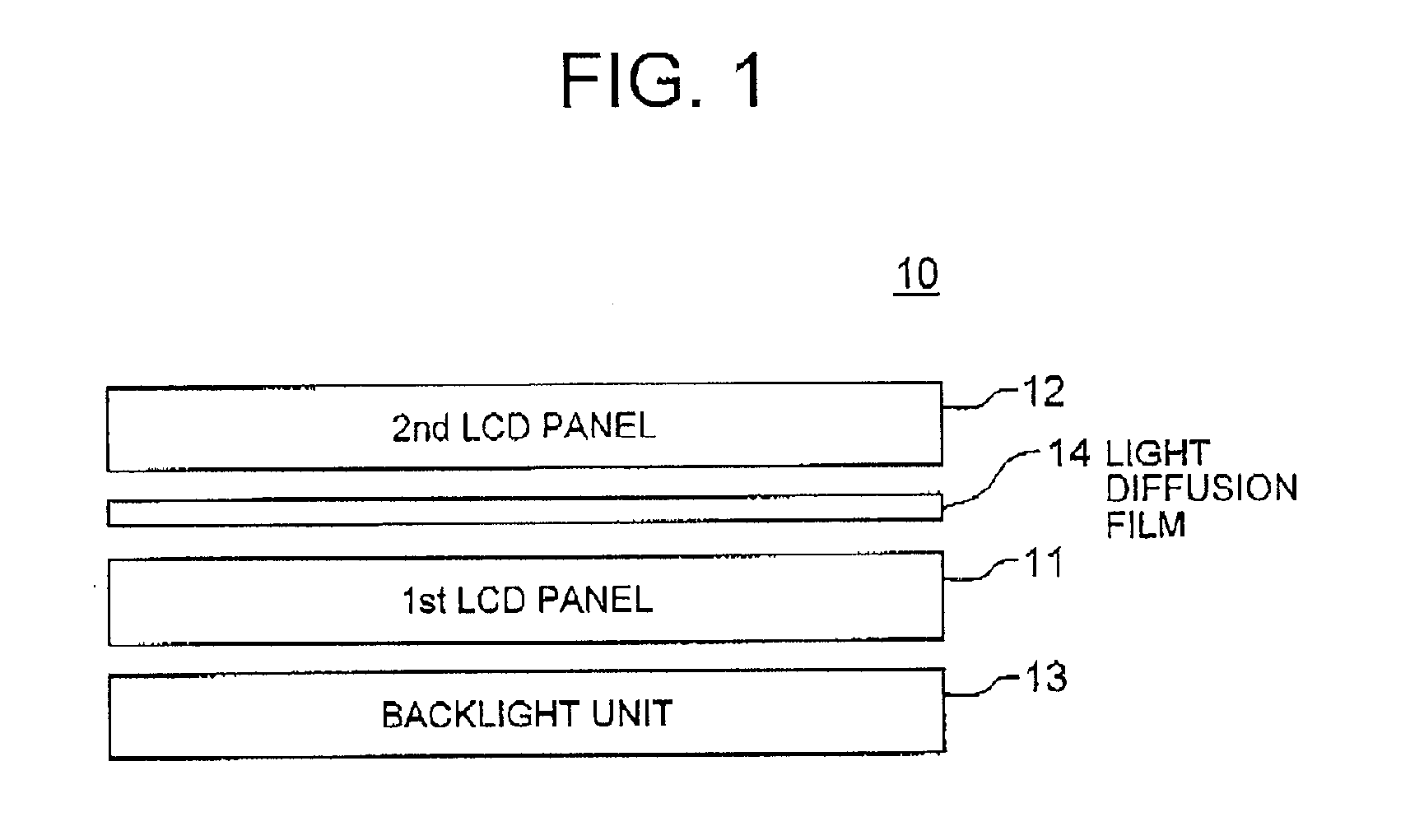
Liquid crystal display device
ActiveUS20070242028A1Suppressing degradation in image qualitySuppresses degradation of image qualityStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayDiffusion function
A LCD device includes first and second LCD panels stacked one on another. Each of the first and second LCD panels includes a pair of transparent substrates, a liquid crystal layer sandwiched therebetween, and a pair of polarizing films sandwiching therebetween the pair of transparent substrates. A light diffusion layer having light diffusion function is interposed between the first LCD panel and the second LCD panel. The light diffusion layer reduces the intensity of the light passed by the first LCD panel, thereby alleviating the periodicity of the arrangement of dark areas and bright areas to alleviate the moire caused by light interference.
Owner:NEC LCD TECH CORP
Ultrahigh resolution multicolor colocalization of single fluorescent probes
InactiveUS6844150B2Improve spatial resolutionLimited ability to compensate for aberrationSamplingMicrobiological testing/measurementDiffusion functionLasing wavelength
A novel optical ruler based on ultrahigh-resolution colocalization of single fluorescent probes is described. Two unique families of fluorophores are used, namely energy-transfer fluorescent beads and semiconductor nanocrystal (NC) quantum dots, that can be excited by a single laser wavelength but emit at different wavelengths. A novel multicolor sample-scanning confocal microscope was constructed which allows one to image each fluorescent light emitter, free of chromatic aberrations, by scanning the sample with nanometer scale steps using a piezo-scanner. The resulting spots are accurately localized by fitting them to the known shape of the excitation point-spread-function of the microscope.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Image processing for pattern detection
InactiveUS7237721B2Improve captured image qualityReliable detectionImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging processing
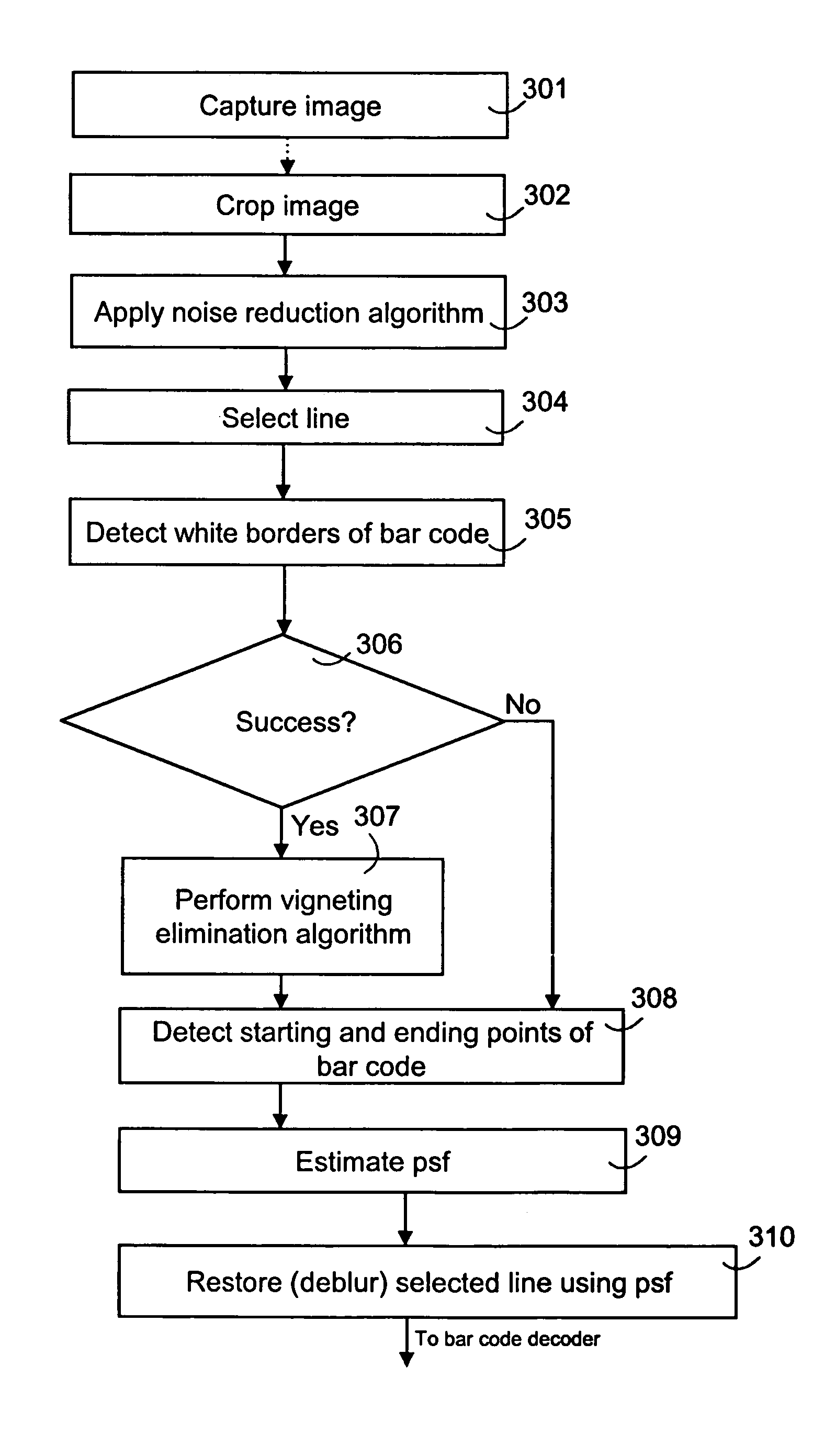
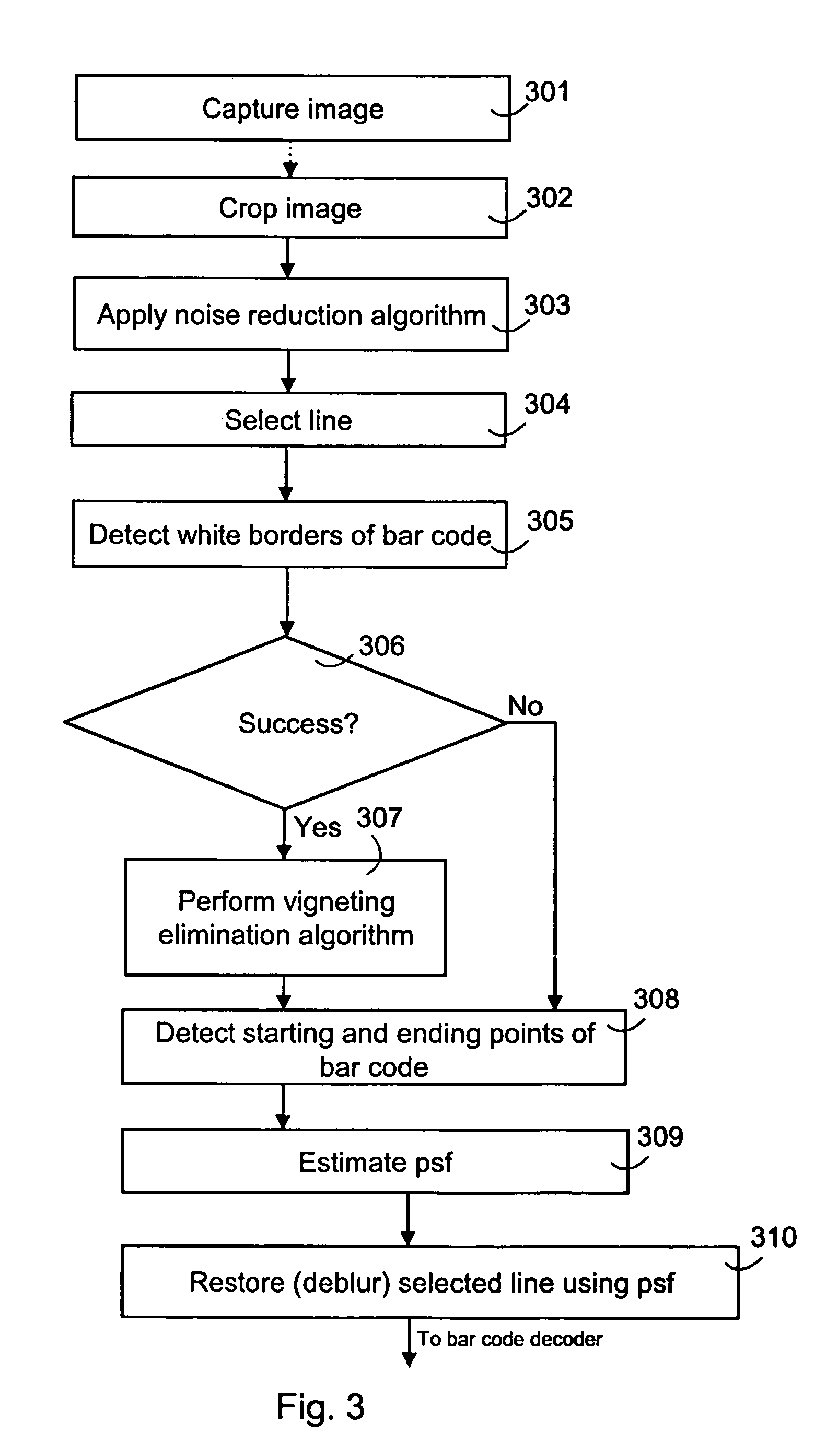
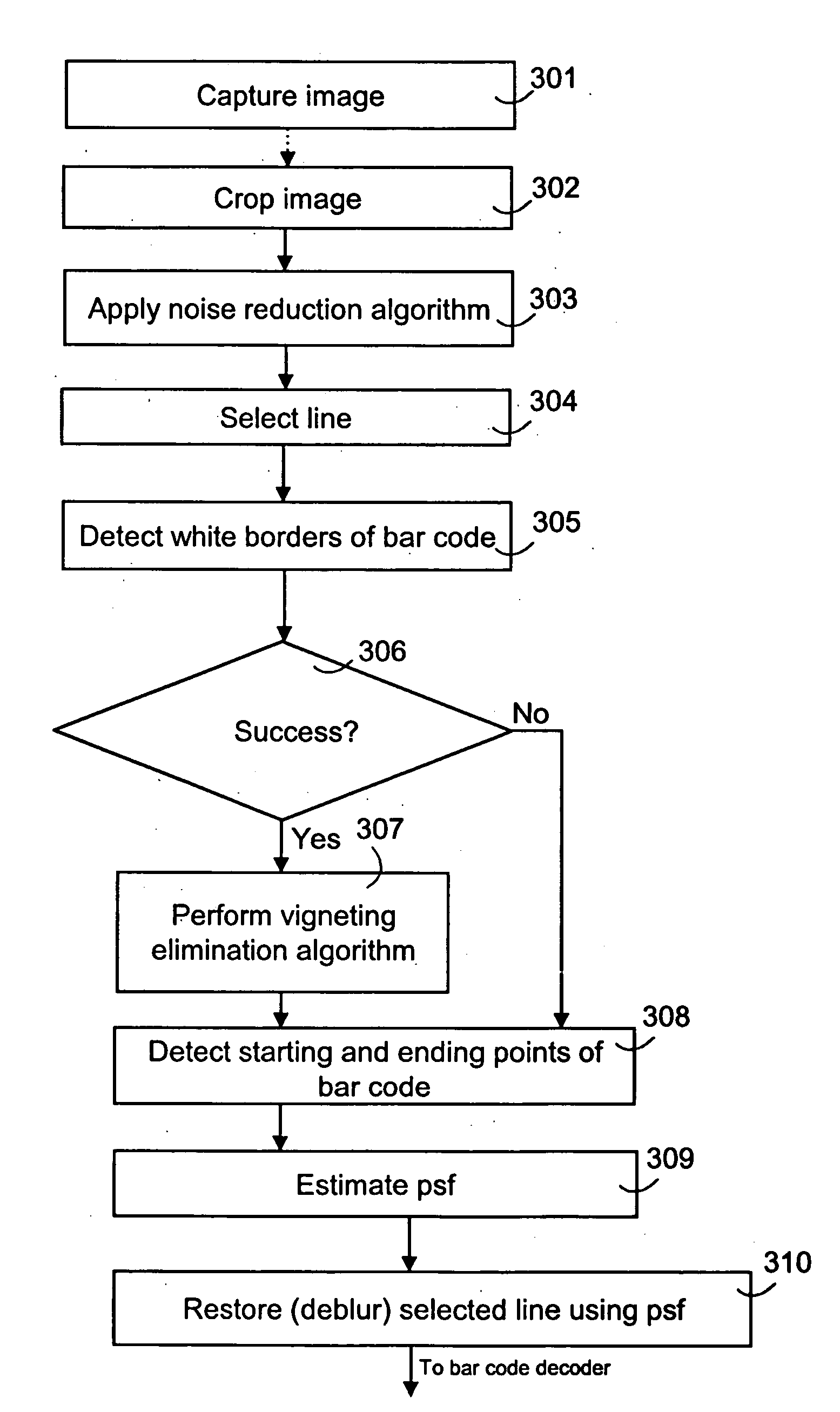
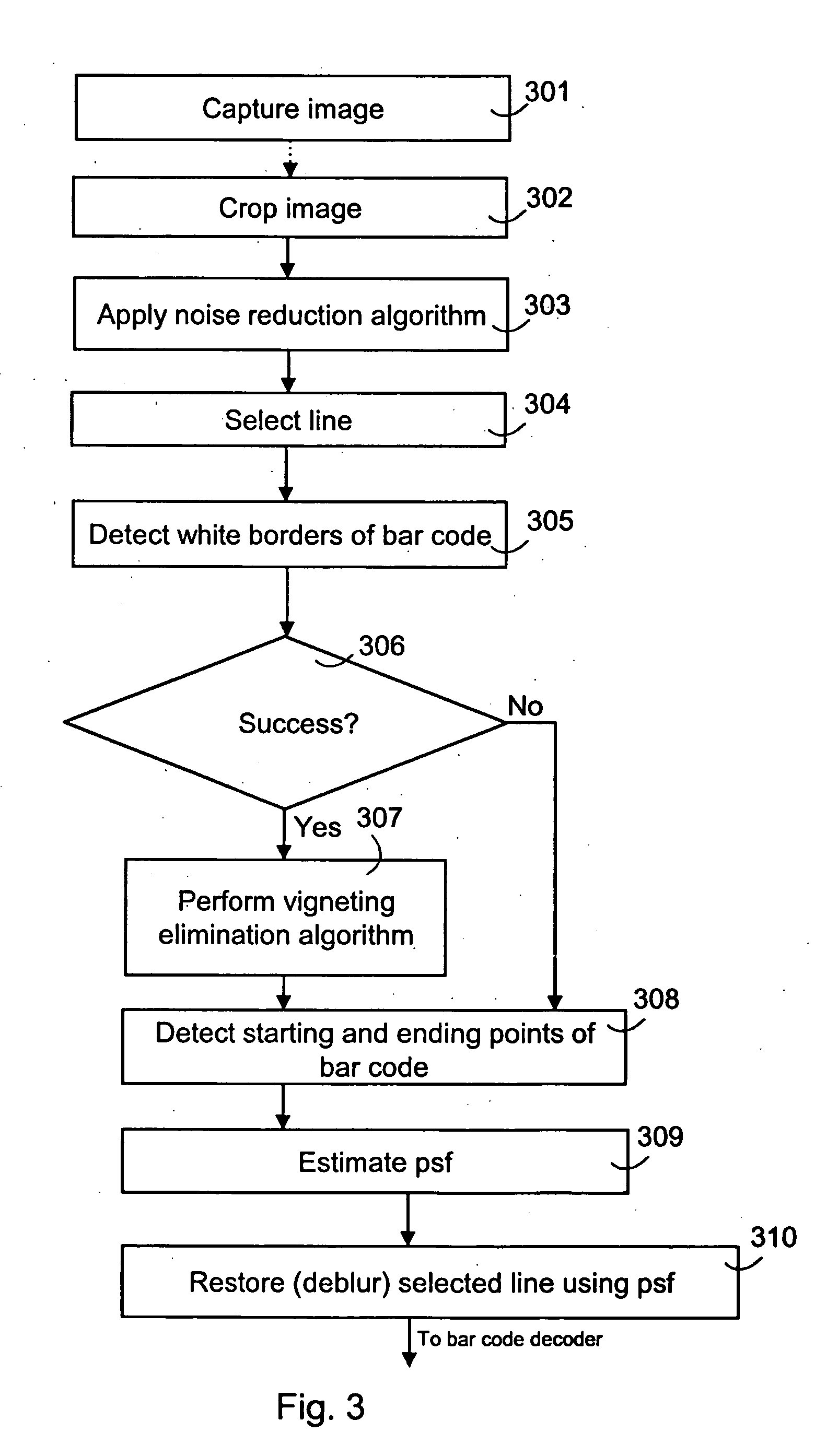
The present invention relates to an image pre-processing method for a pattern detection system, such as a bar code detection system. The method comprises the steps of: detecting a start point and an end point of a pattern on the basis of image data of at least a portion of a captured image, estimating a point spread function from the image data or a modified image data on the basis of the detected start point and the end point, and restoring the image data or the modified image data using the estimated point spread function.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Blur correction camera system
InactiveUS20060110147A1Lower the volumeIncrease in sizeTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementImaging processingPoint spread function
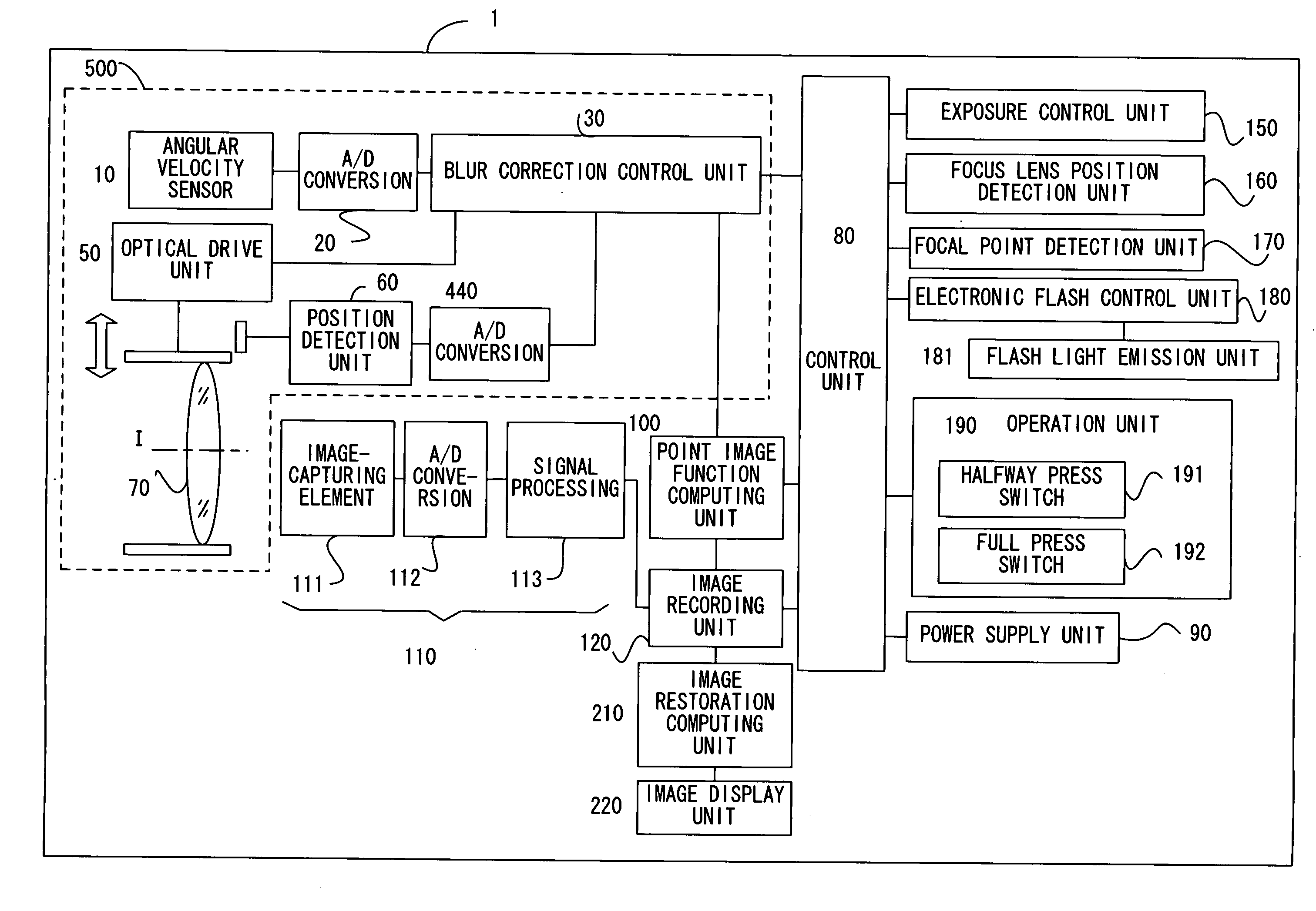
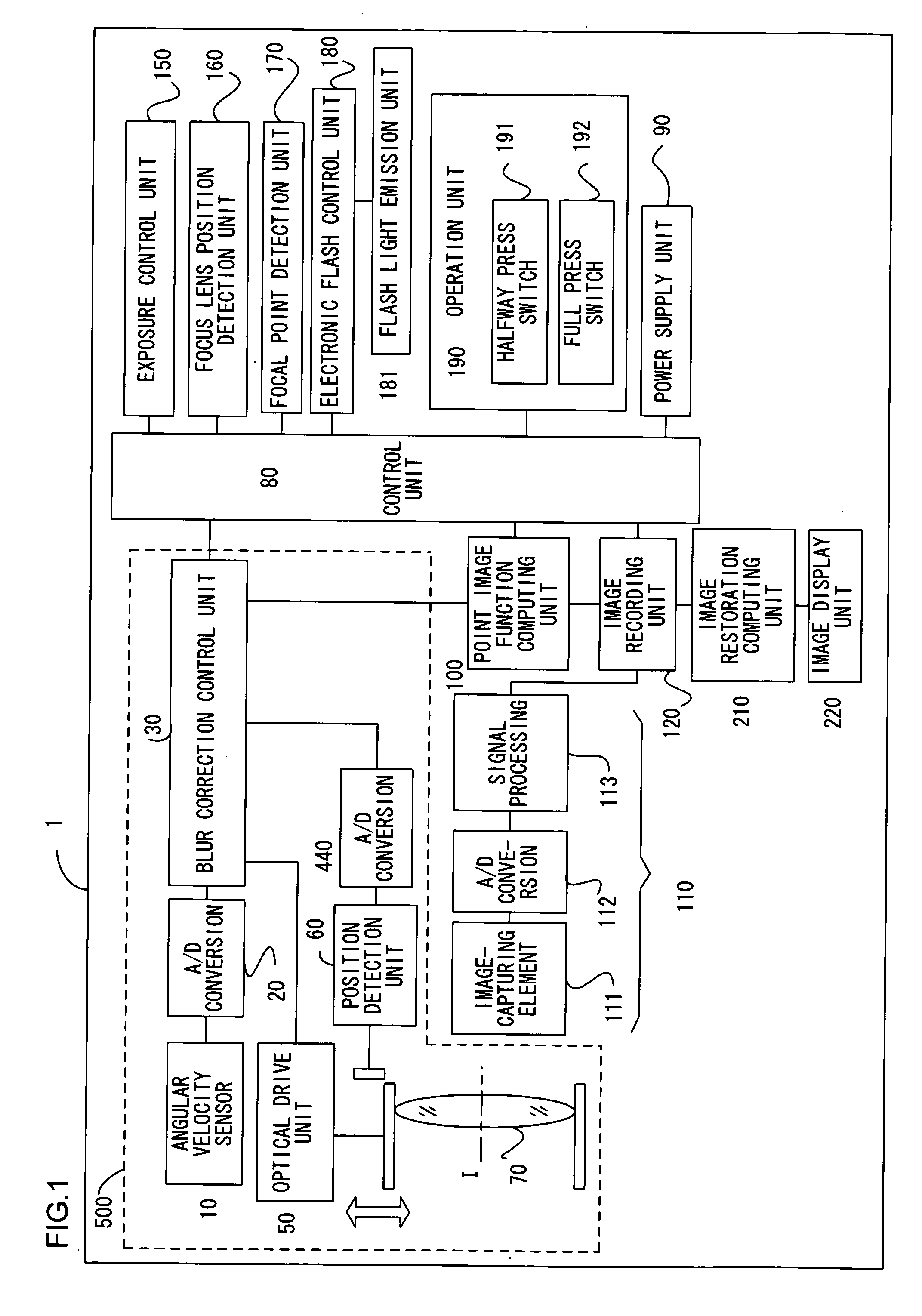
A blur correction camera system includes a blur correction lens driven based upon the vibration detection signal detected by an angular velocity sensor, that corrects an image blur, a point-image function computing unit that computes a point spread function, and an image restoration computing unit that corrects an image blur by executing image restoration through image processing on a captured image by using the point spread function. The image blur that cannot be completely corrected by the blur correction lens is further corrected through image restoration so as to obtain a high quality image.
Owner:NIKON CORP
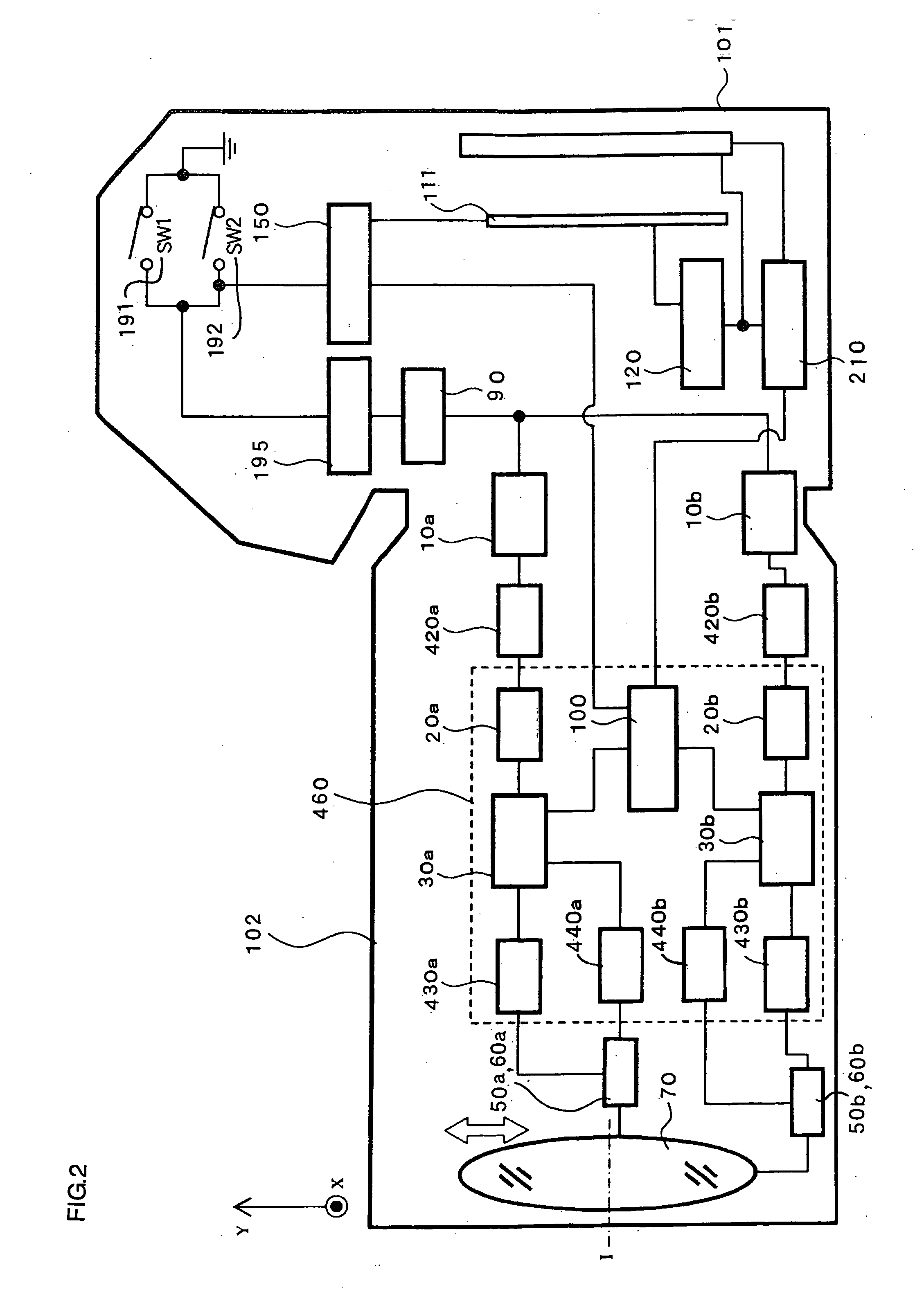
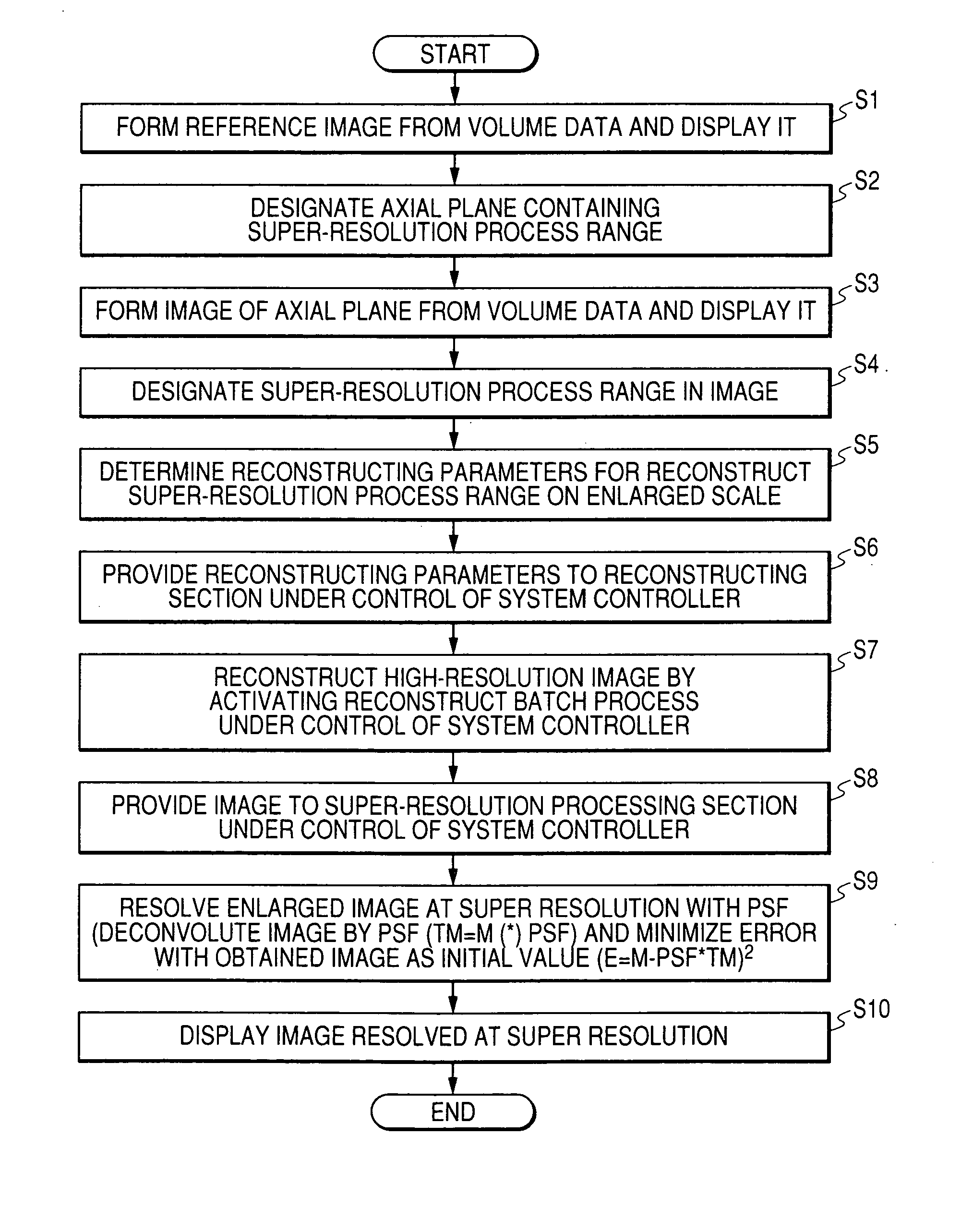
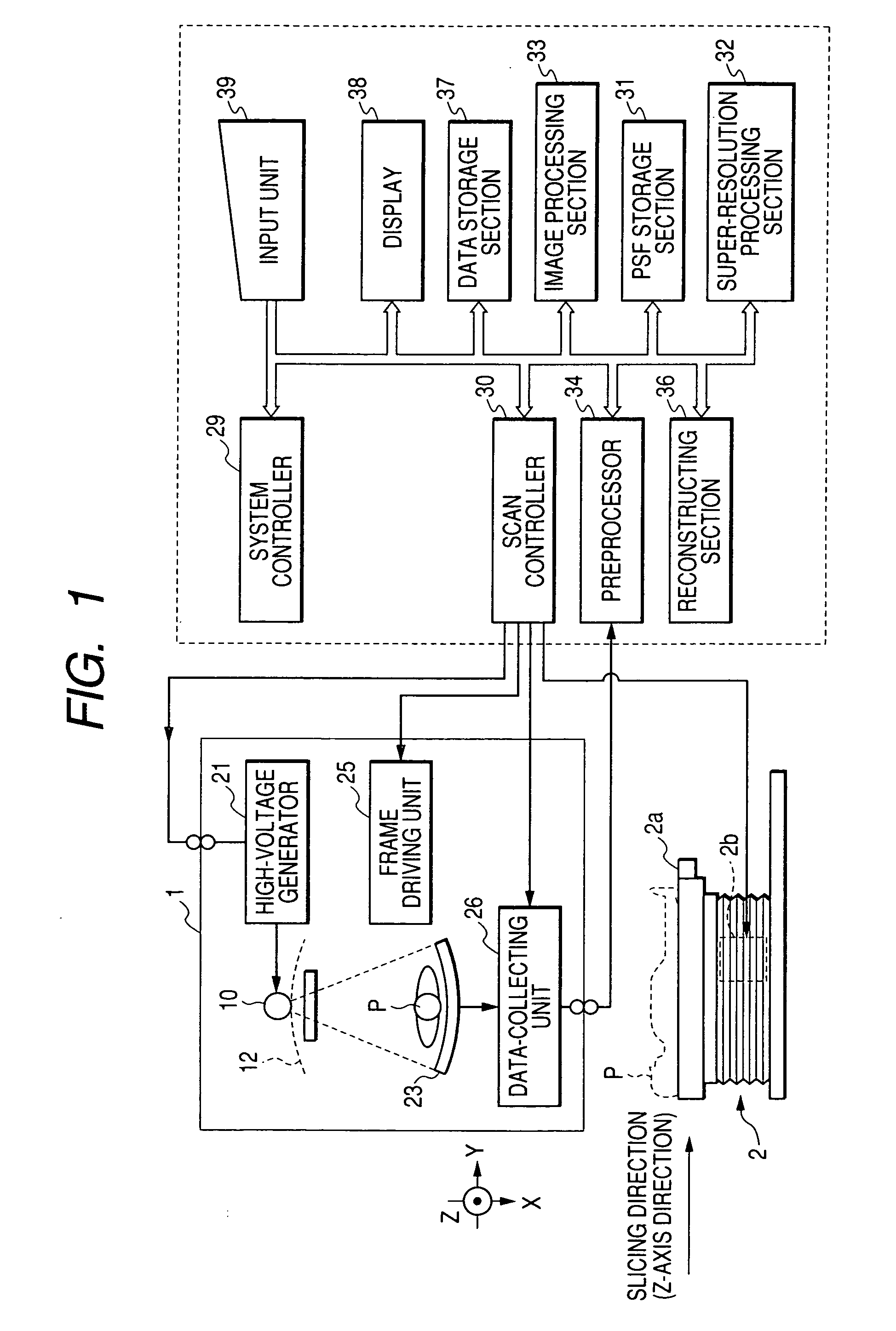
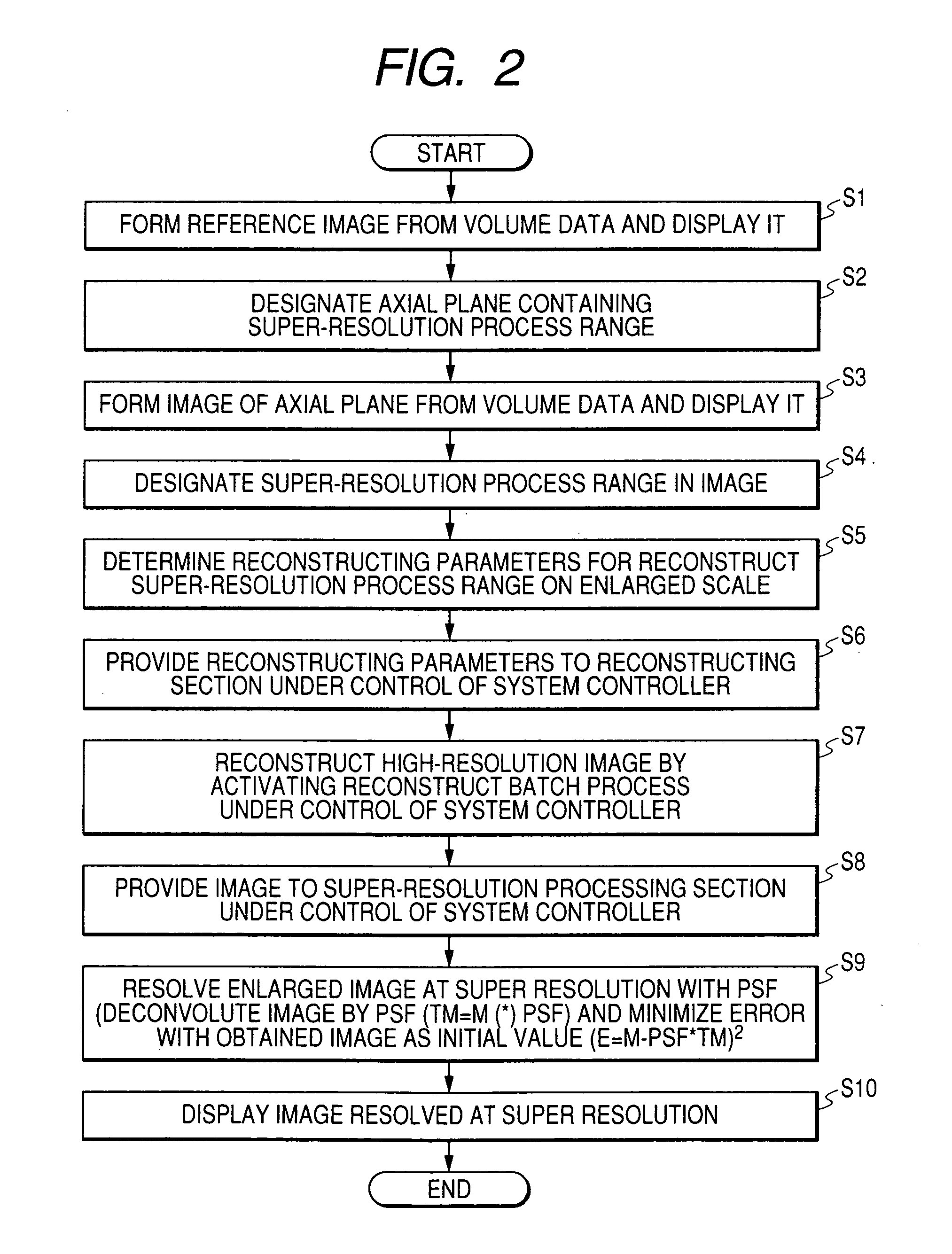
Super-resolution processor and medical diagnostic imaging apparatus
A super-resolution processor includes a storage section for storing data of point spread functions of an X-ray CT scanner which are acquired using a phantom and a super-resolution processing section performing super-resolution of image data of a sample generated by the X-ray CT scanner using the stored point spread functions.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
Image processing for pattern detection
InactiveUS20060266836A1Reliable detectionReduce different distortionImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging processing
The present invention relates to an image pre-processing method for a pattern detection system, such as a bar code detection system. The method comprises the steps of: detecting a start point and an end point of a pattern on the basis of image data of at least a portion of a captured image, estimating a point spread function from the image data or a modified image data on the basis of the detected start point and the end point, and restoring the image data or the modified image data using the estimated point spread function.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Efficient method to predict integrated circuit temperature and power maps
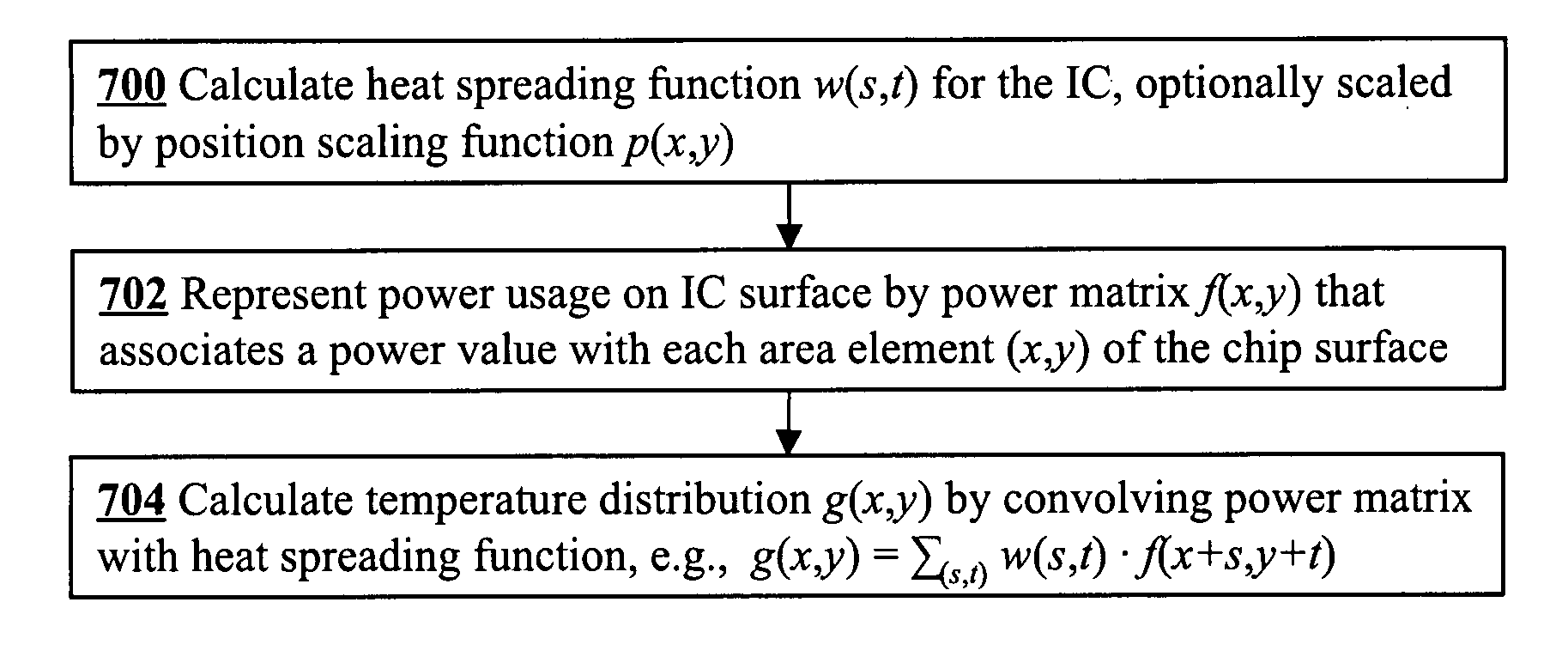
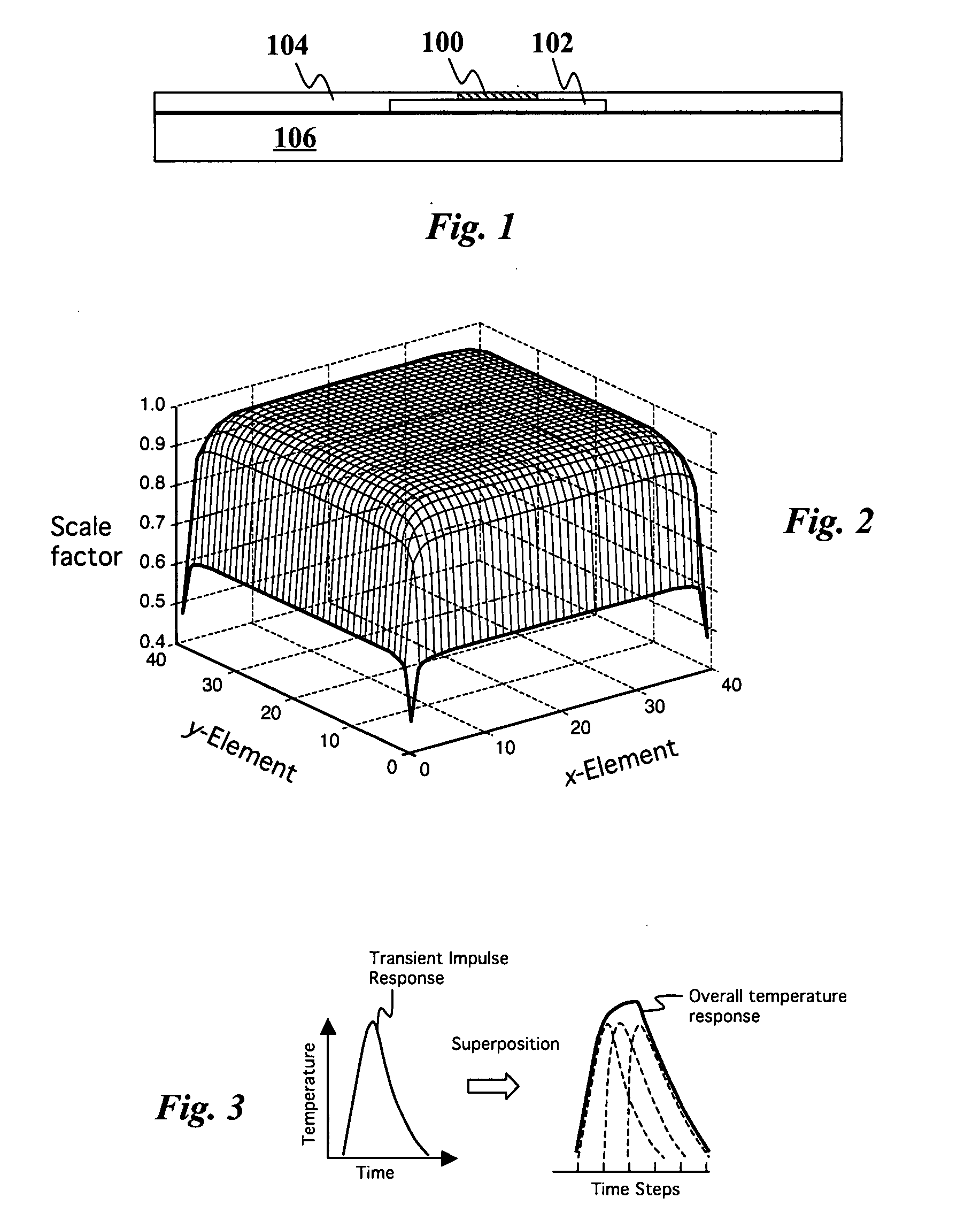
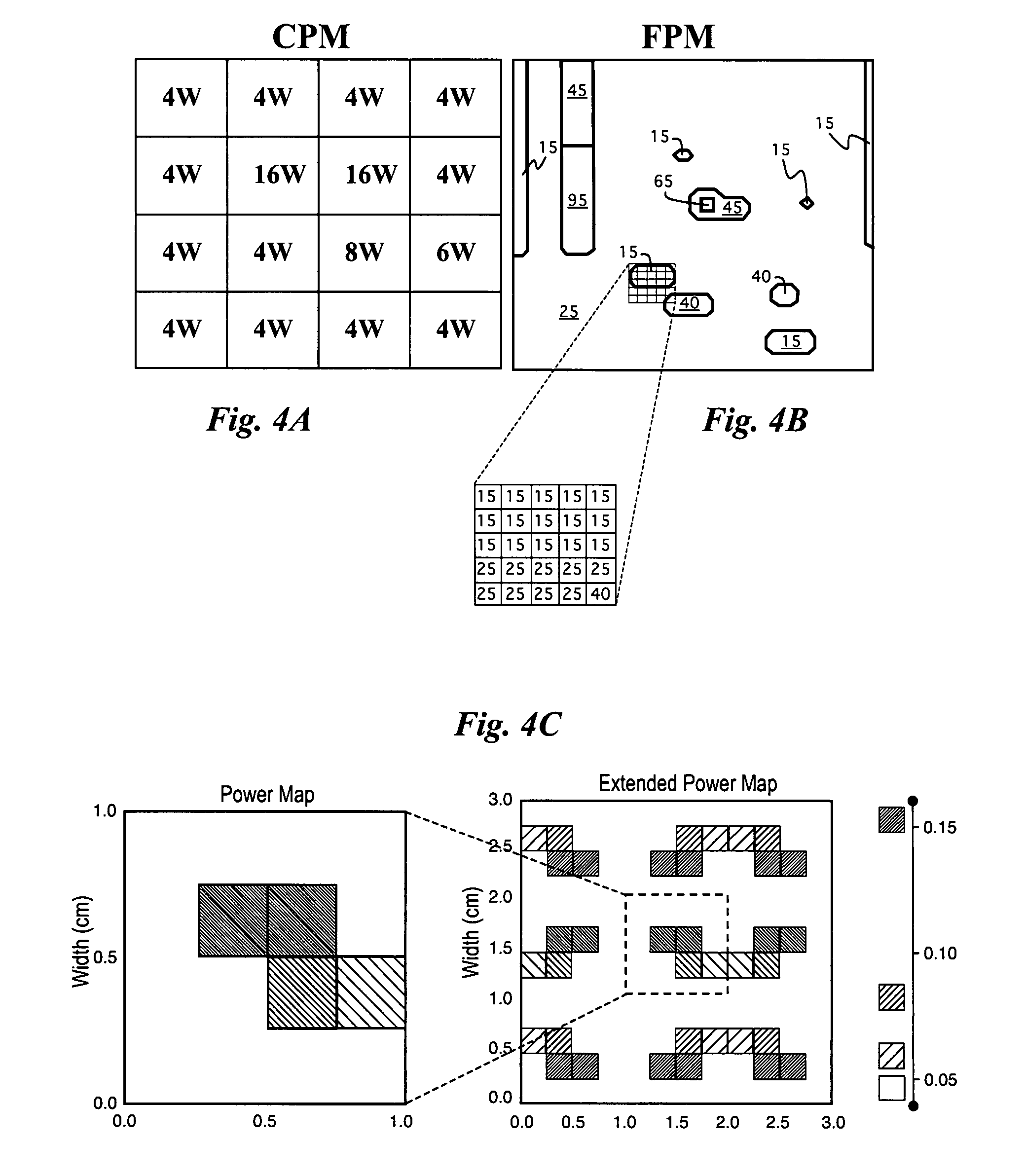
InactiveUS20080026493A1Fast and accurate methodMinimizes localized heatingSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDetecting faulty computer hardwareElement analysisDiffusion function
The temperature distribution associated with a design of an integrated circuit is calculated by convoluting a surface power usage represented by a power matrix with a heat spreading function. The heat spreading function may be calculated from a simulation of a point source on the integrated circuit using a finite element analysis model of the integrated circuit or other techniques. To account for spatial variations on the chip, the heat spreading function may be made dependent on position using a position scaling function. Steady-state or transient temperature distributions may be computed by using a steady-state or transient heat spreading function. A single heat spreading function may be convolved with various alternative power maps to efficiently calculate temperature distributions for different designs. In an inverse problem, one can calculate the power map from an empirically measured temperature distribution and a heat spreading function using various de-convolution techniques. While the forward problem is analogous to image blurring, the inverse problem is analogous to image restoration.
Owner:UNIV OF CALIFORNIA SANTA CRUZ
Coded aperture camera with adaptive image processing
ActiveUS20120076362A1Increase valueReduce complexityImage enhancementImage analysisCamera lensImaging processing
An image capture device is used to identify object range information, and includes: providing an image capture device, an image sensor, a coded aperture, and a lens; and using the image capture device to capture a digital image of the scene from light passing through the lens and the coded aperture, the scene having a plurality of objects. The method further includes: dividing the digital image into a set of blocks; assigning a point spread function (psf) value to each of the blocks; combining contiguous blocks in accordance with their psf values; producing a set of blur parameters based upon the psf values of the combined blocks and the psf values of the remaining blocks; producing a set of deblurred images based upon the captured image and each of the blur parameters; and using the set of deblurred images to determine the range information for the objects in the scene.
Owner:APPLE INC
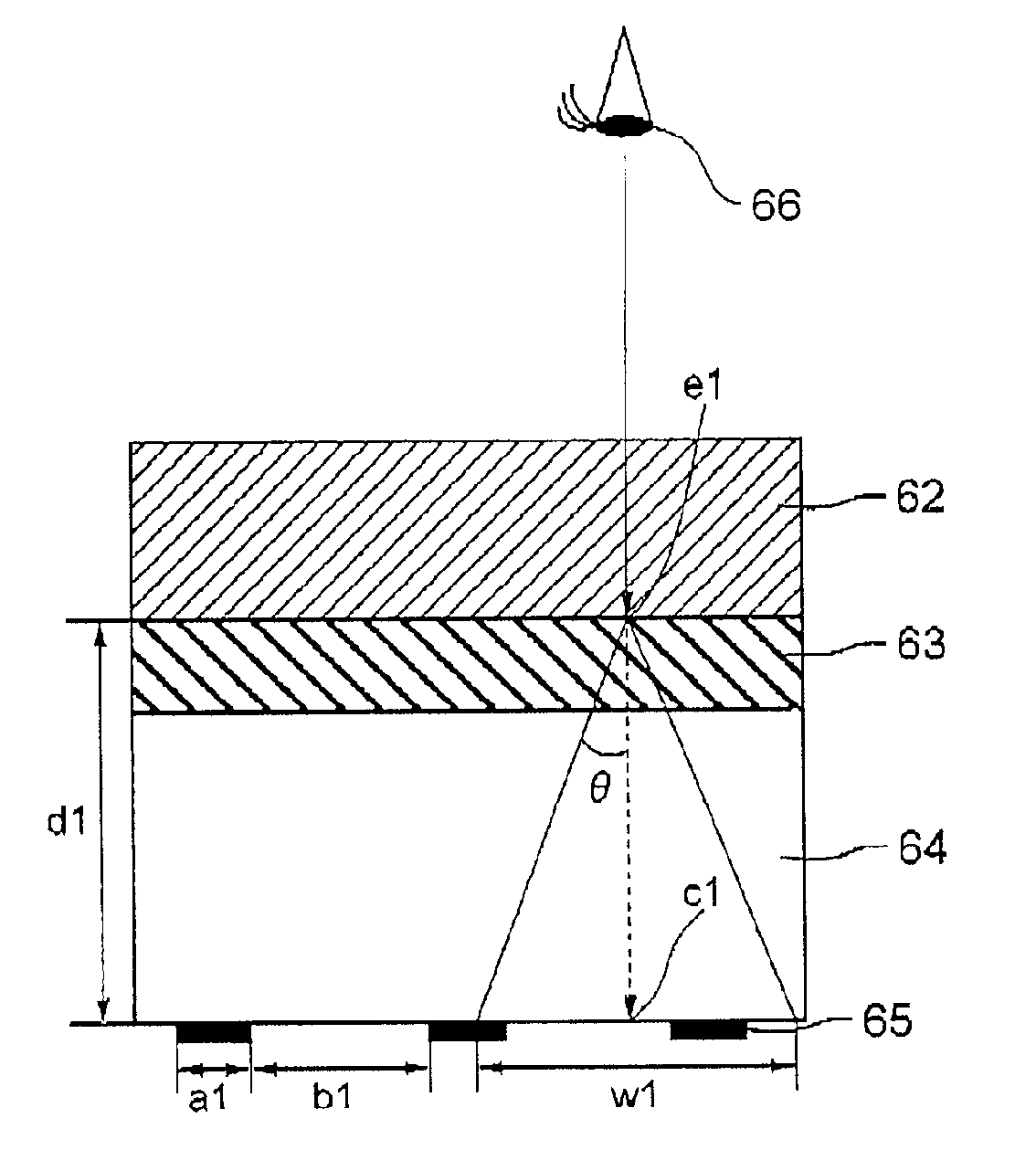
Optical adjusting member, and illumination device and liquid crystal display device including the same
InactiveUS20080303777A1Suppressing damages at the top edgeConvenient lightingStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsOptical transparencyLiquid-crystal display
An optical adjusting member according to the invention includes a base member, a plurality of lenses, and a light diffusion layer. The base member has optical transparency. The plurality of lenses are formed on the base member. The light diffusion layer is formed on the plurality of lenses, and at least top edge parts of the lenses are buried in the light diffusion layer. In the optical adjusting member according to the invention, at least the top edge parts of the plurality of lenses are buried in the light diffusion layer and therefore the lenses are less susceptible to damages. The optical adjusting member according to the invention has a light collecting function by the lenses and a diffusion function by the light diffusion layer.
Owner:HITACHT MAXELL LTD
Method and device for recovering a digital image from a sequence of observed digital images
ActiveUS20130242129A1Efficient implementationComputationally efficientTelevision system detailsImage enhancementDiffusion functionPoint spread function
A computer-implemented method for recovering a digital image (x) from a sequence of observed digital images (y1, . . . , yT), includes: obtaining an observed digital image (yt); estimating a point spread function (ft) based on the observed image (yt); estimating the recovered digital image (x), based on the estimated point spread function (ft) and the observed image (yt); and repeating the above steps. In order to correct optical aberrations of a lens, a point spread function of the lens may be used.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
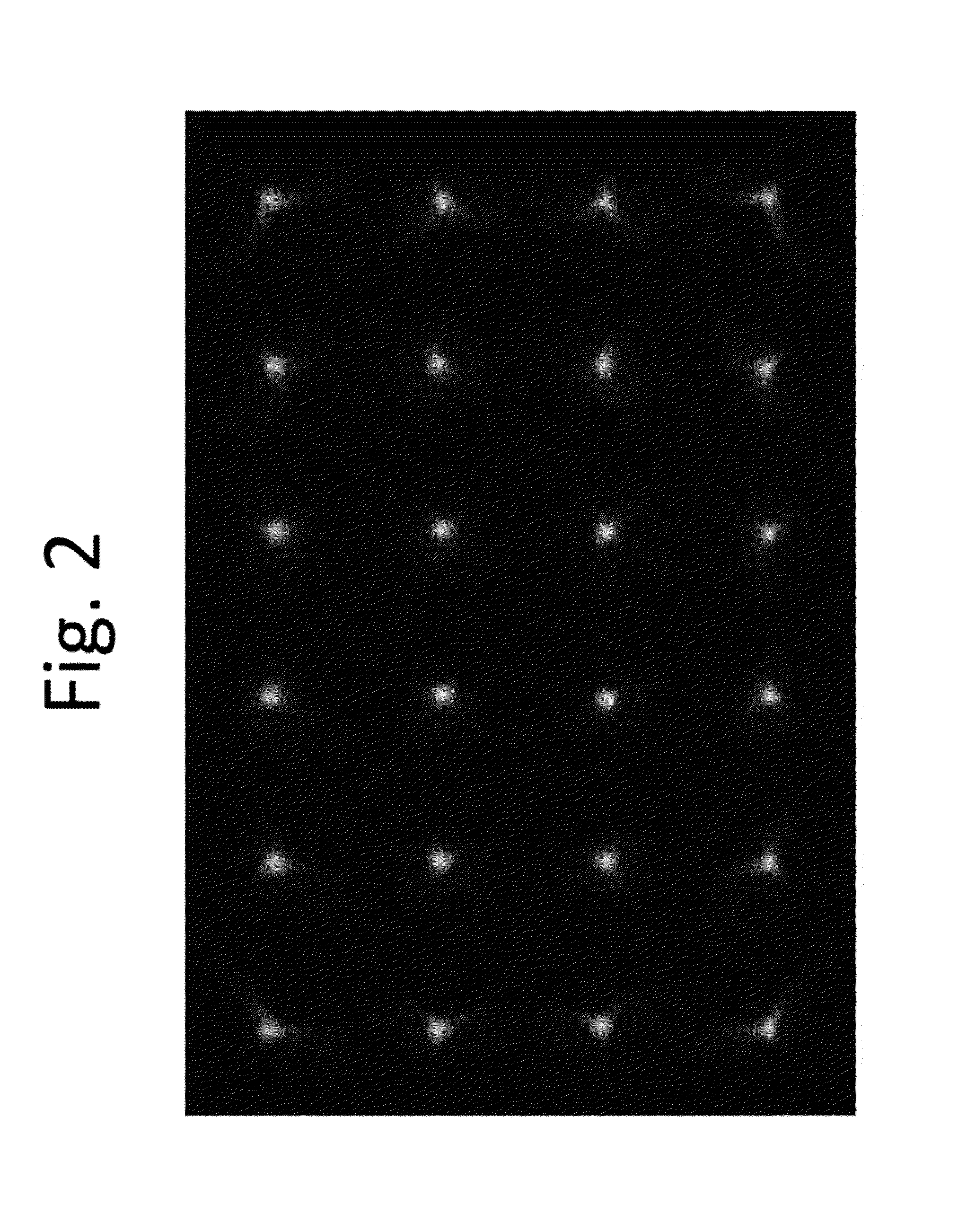
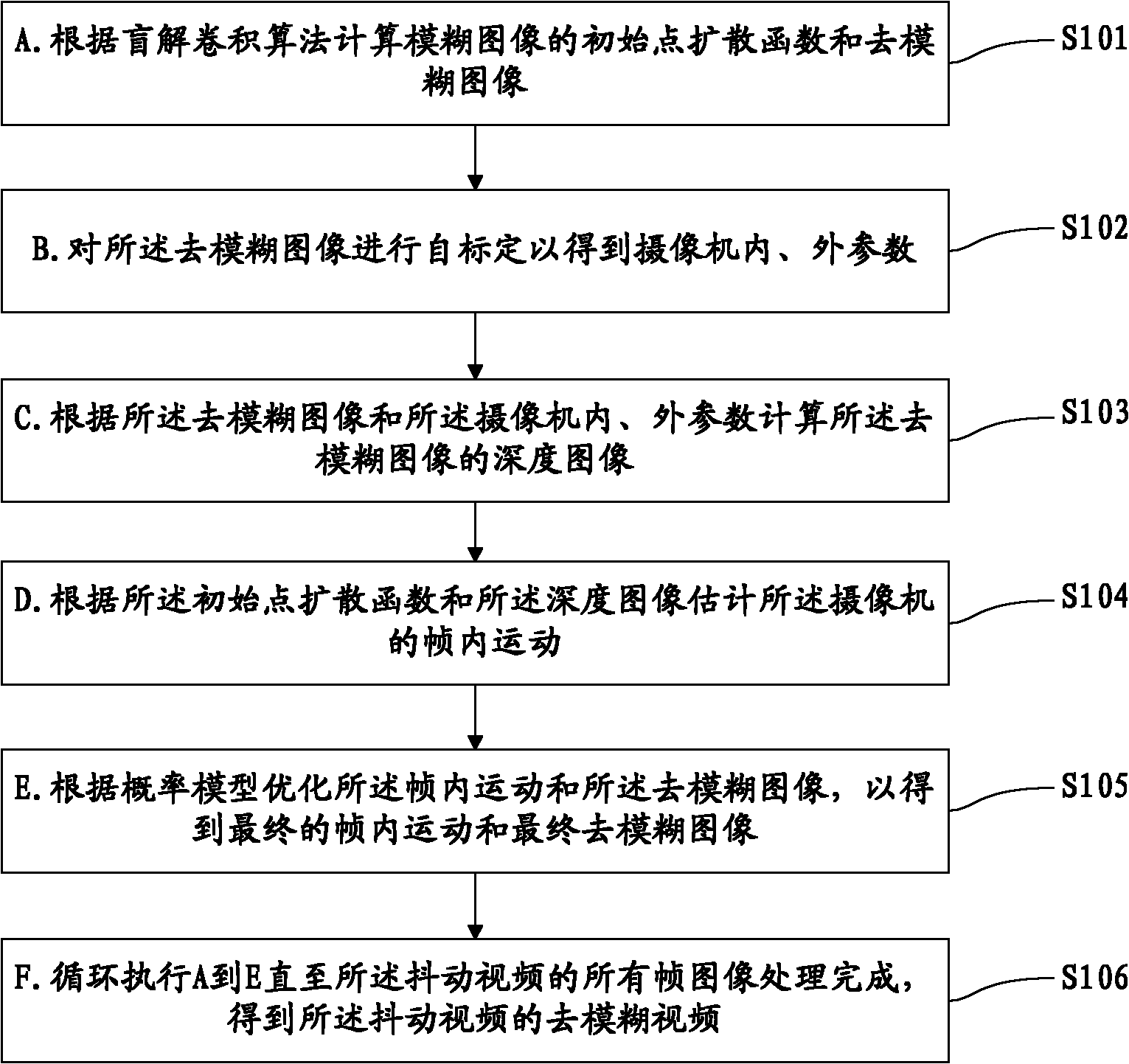
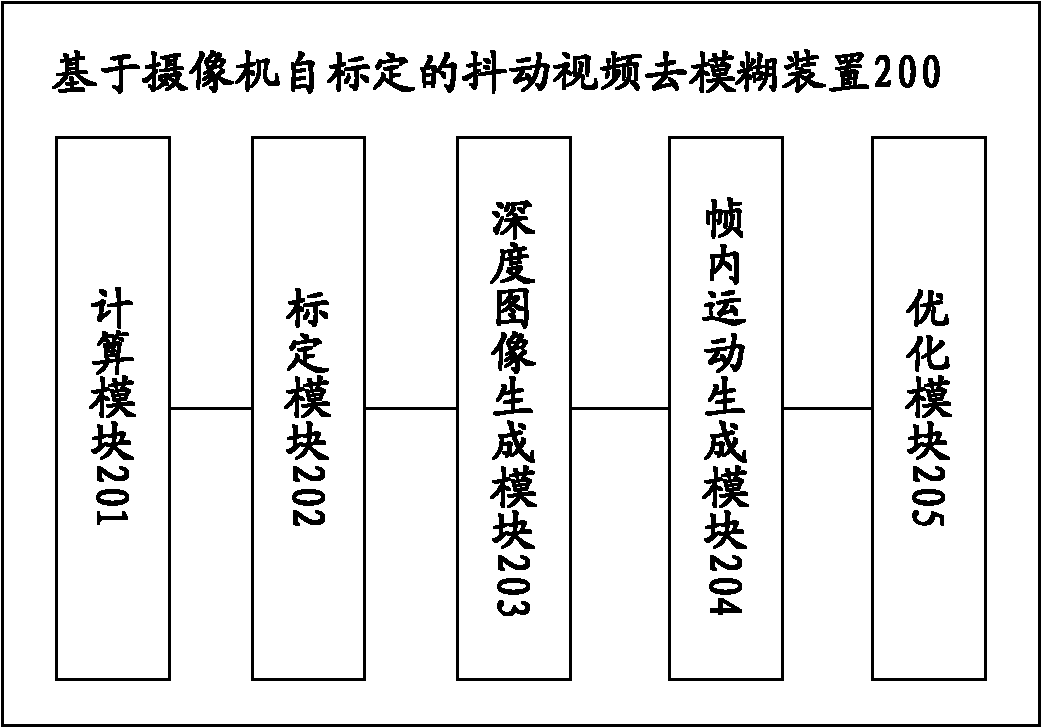
Camera self-calibration-based jittering video deblurring method and device
The invention provides a camera self-calibration-based jittering video deblurring method and a camera self-calibration-based jittering video deblurring device. The method comprises the following steps: A, calculating the initial point diffuse function and deblurred image of a blurred image; B, performing self-calibration on the deblurred image to obtain the internal and external parameters of a camera; C, calculating a depth map according to the deblurred image and the internal and external parameters; D, estimating the intra-frame motion of the camera according to the initial point diffuse function and the depth map; E, optimizing intra-frame motion and the deblurred image according to a probability model to obtain the final intra-frame motion and the final deblurred image; and F, executing the steps from A to E circularly to obtain the deblurred video of a jittering video. In the method, depth-associated video image sequence deblurring is realized by a camera self-calibration technique, so the video image sequence has a better deblurring effect and the image deblurring efficiency is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
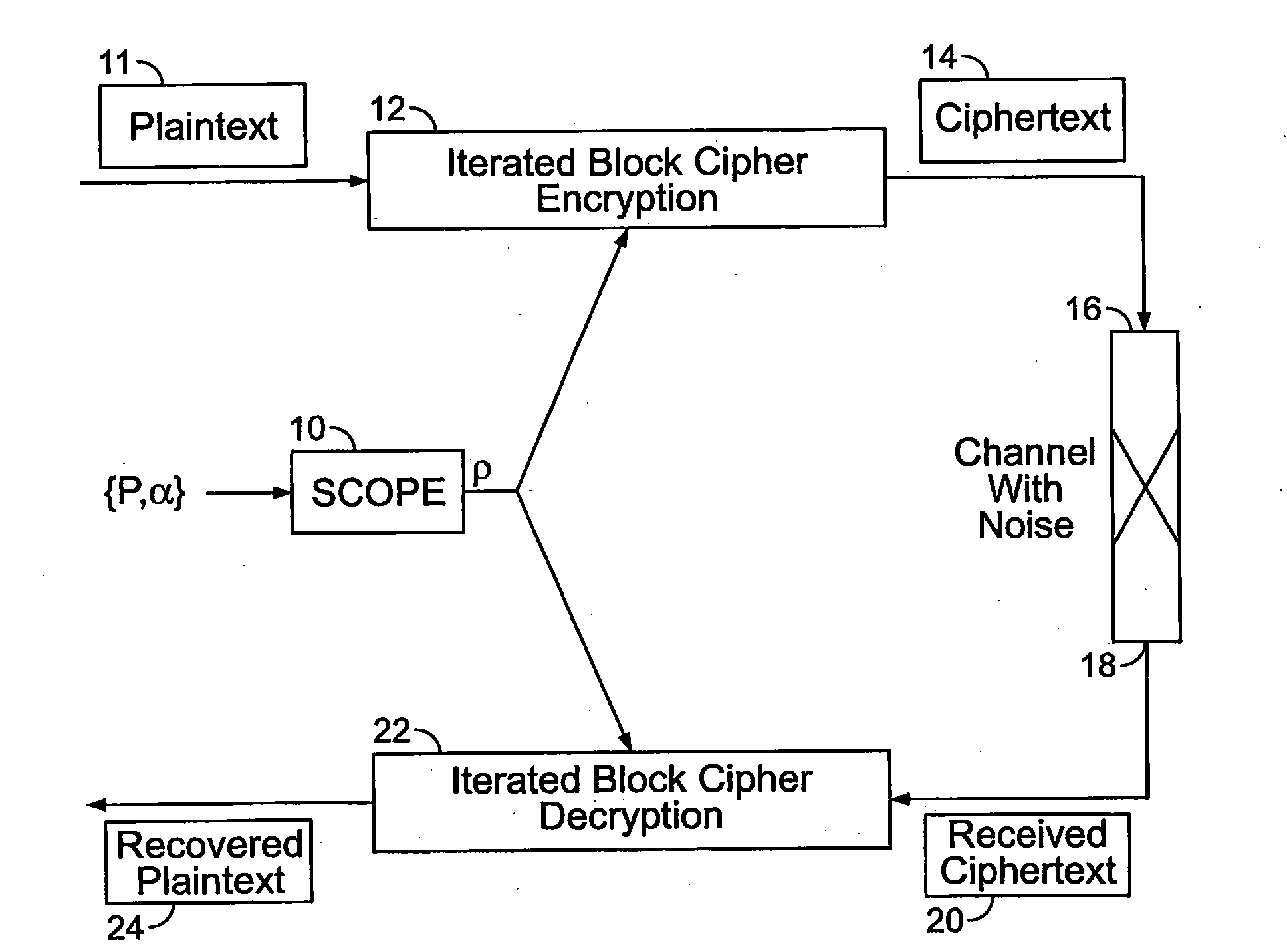
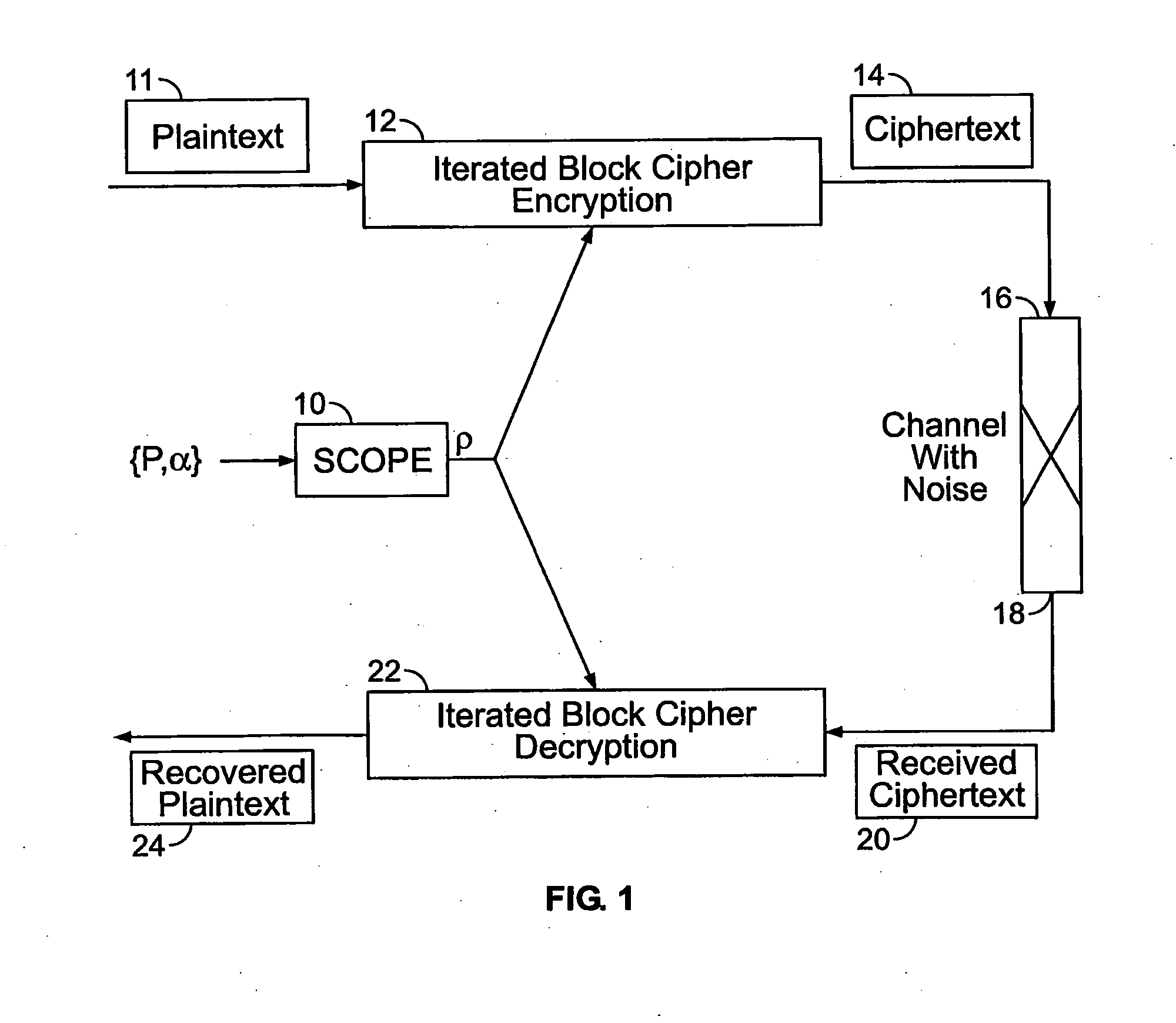
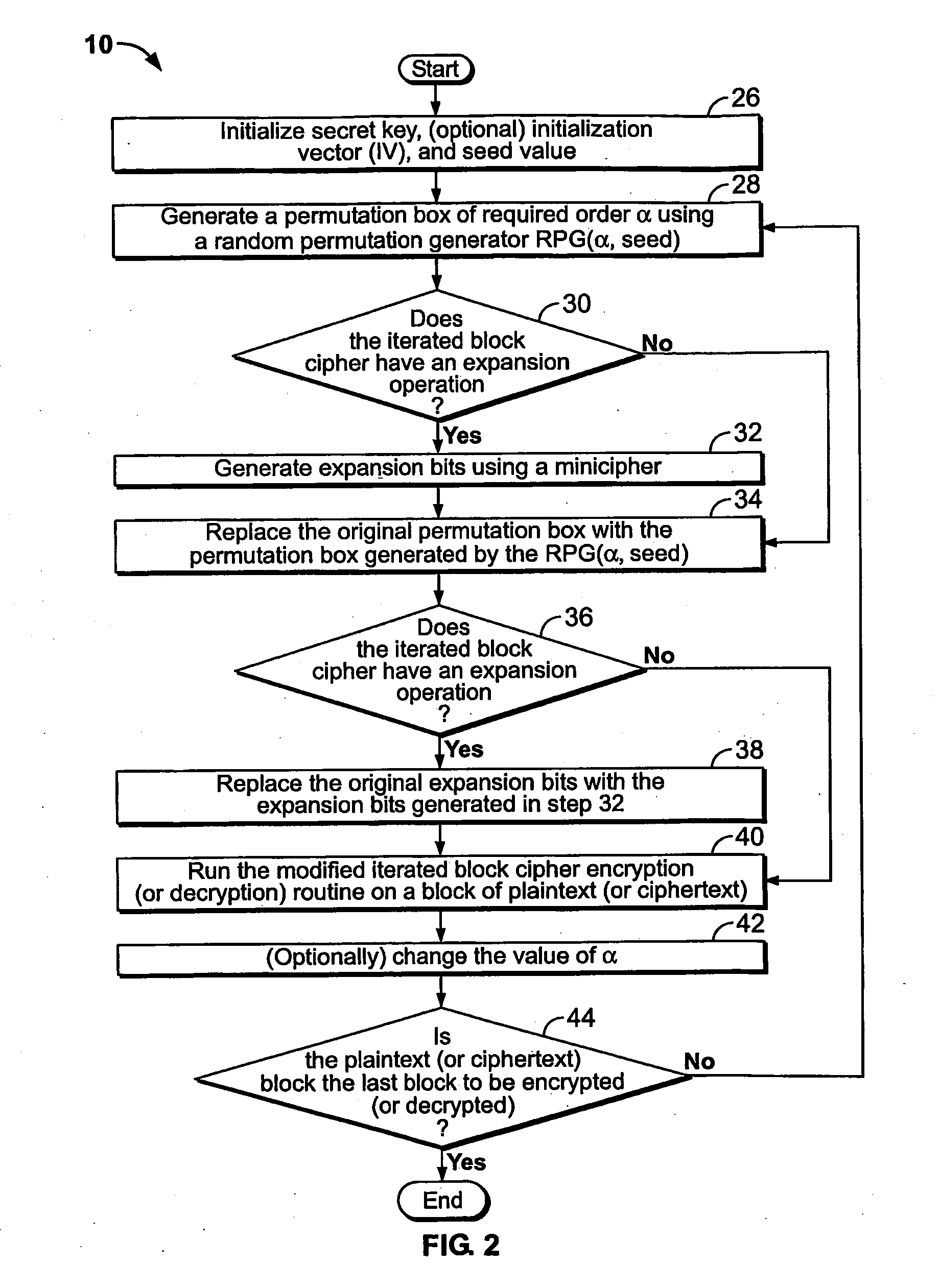
Method and apparatus for maintaining data integrity for block-encryption algorithms
InactiveUS20100067687A1Telegraphic message interchanged in timeSecret communicationPlaintextComputer hardware
A method is disclosed for modifying an iterated block cipher by controlling the operations and transformations that cause diffusion. In one embodiment which is applicable to any iterated block cipher (12), a diffusion function (10), during encryption, is selected based on a parameter which measures the order of permutation of the diffusion function (10) and applies the diffusion function (10) to the encryption routine (12). The user chooses the required amount of diffusion for a given block of plaintext (11). The plaintext (11) is then encrypted using the modified diffusion function (10) to produce a ciphertext (14) which is then sent over a communications channel (16) which may be noisy. At the receiving end (18) of the communications channel (16), the received ciphertext (20), which now may be corrupted by bit errors, is passed through an iterated block cipher decryption routine (22) using the same diffusion function (10) selected earlier during encryption. In a second embodiment, the SCOPE method is applied to the DES encryption and decryption standard. The expansion bits (82) of DES are replaced with a minicipher (98a-98n), and the DES standard permutation box (88) is replaced with a permutation box (104a-104n) modified according to a user-specified order of permutation. In a third embodiment, the SCOPE method is applied to the AES encryption and decryption standard. In the SCOPE-enhanced version of AES, diffusion is controlled by altering the diffusion of the “MixColumn” or “InvMixColumn” transformation based on its branch number and by changing the number of shifts in the “ShiftRow” or “InvShfitRow” transformations.
Owner:STEVENS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
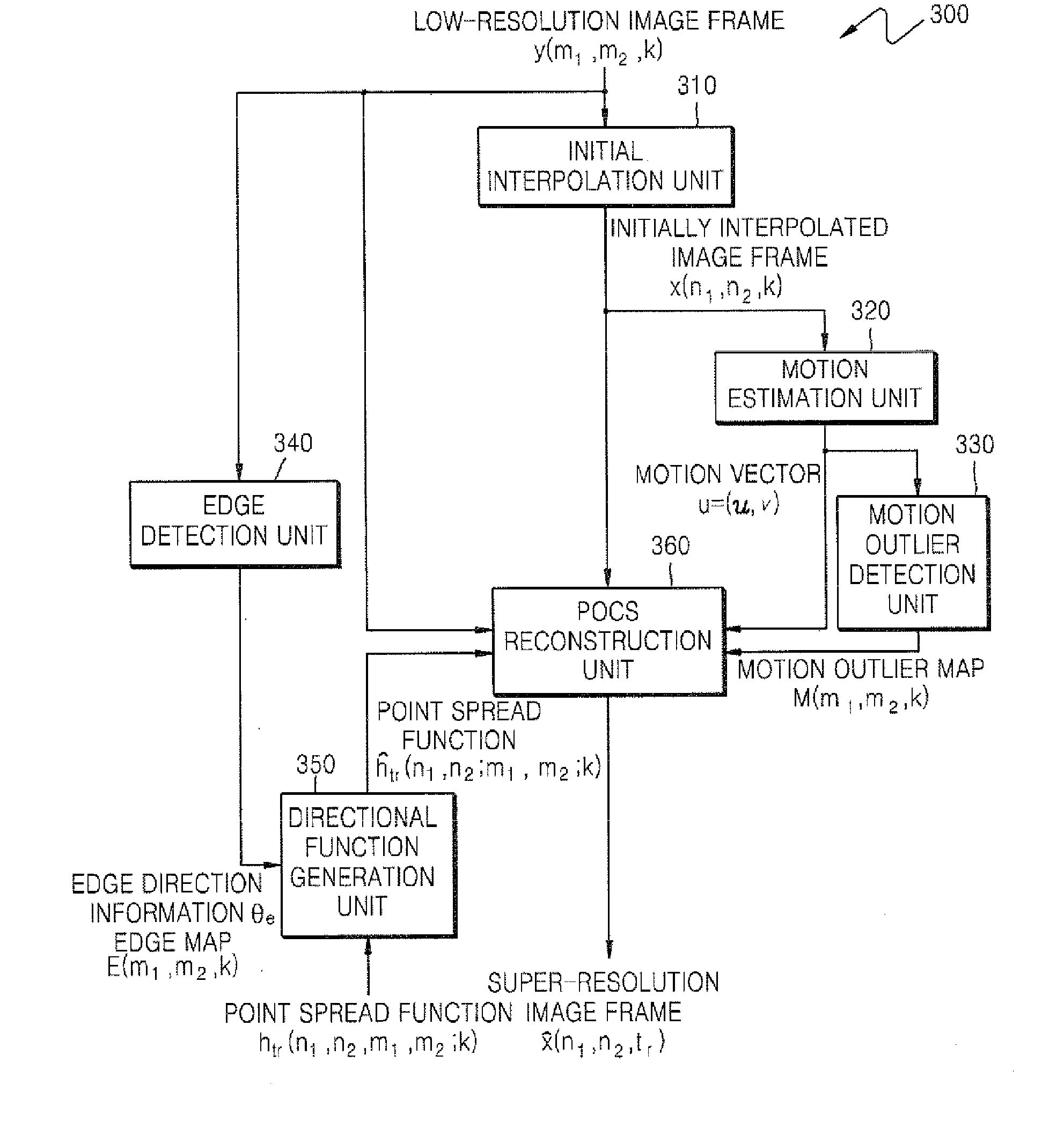
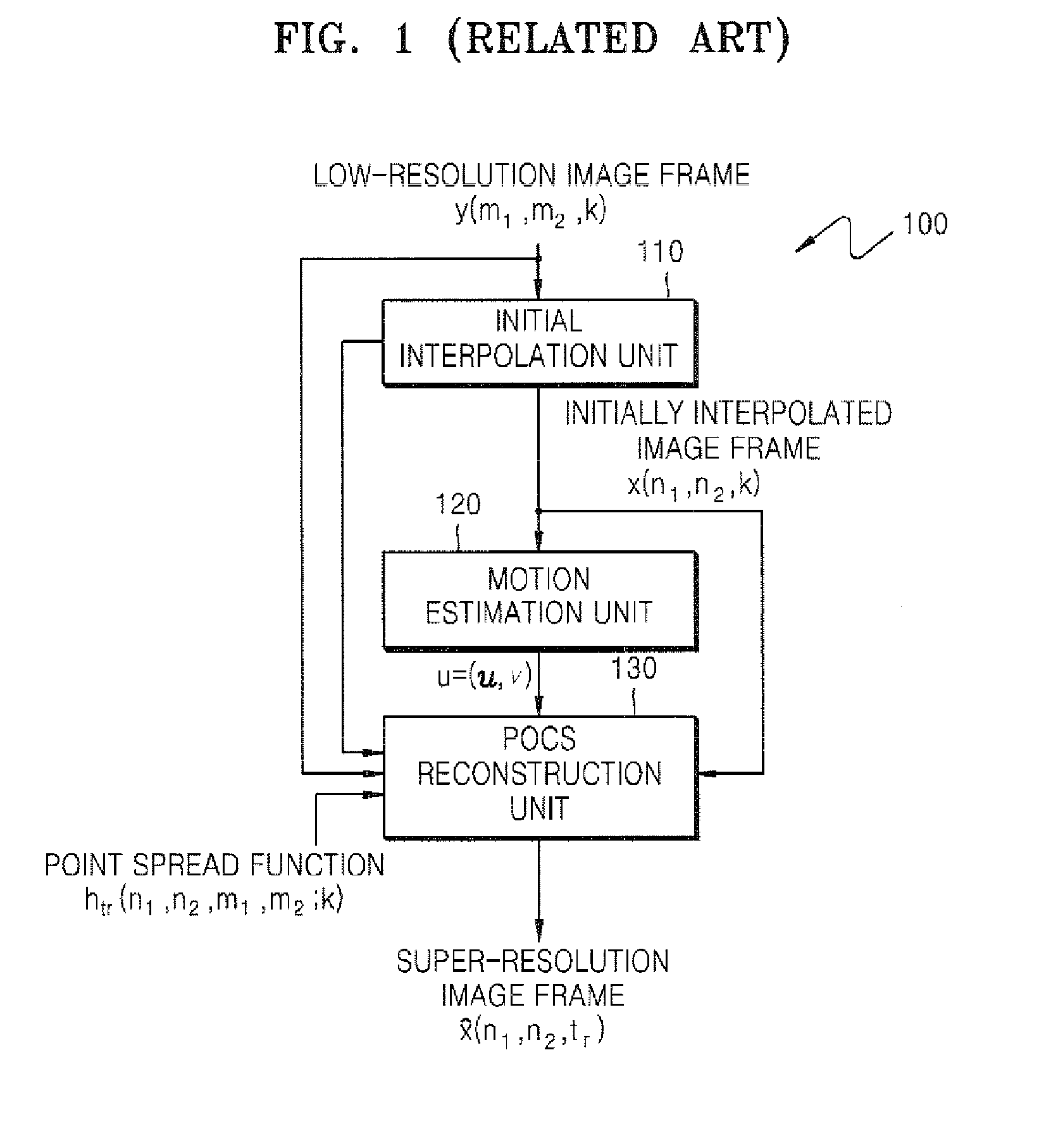
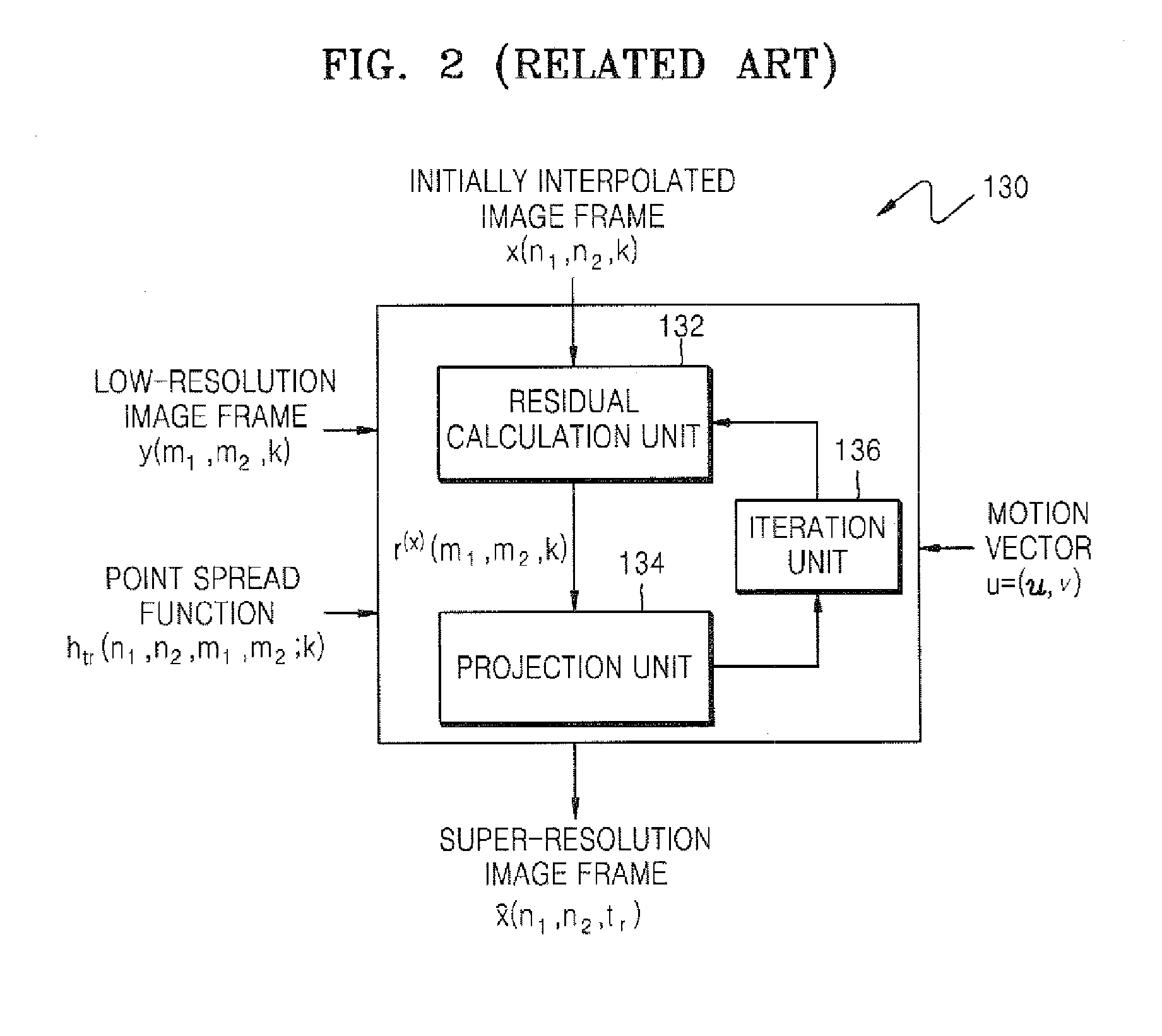
Image resolution conversion method and apparatus
InactiveUS20070291170A1High resolutionImage analysisGeometric image transformationEdge mapsDiffusion function
An image resolution conversion method and apparatus based on a projection onto convex sets (POCS) method are provided. The image resolution conversion method comprises detecting an edge region and a direction of the edge region in an input low-resolution image frame in order to generate an edge map and edge direction information, generating a directional point spread function based on the edge map and the edge direction information, interpolating the input low-resolution image frame into a high-resolution image frame, generating a residual term based on the input low-resolution image frame, the high-resolution image frame, and the directional point spread function, and renewing the high-resolution image frame according to a result of comparing the residual term with a threshold.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Wave field microscope with detection point spread function
InactiveUS7342717B1Easy to analyzeEliminate needBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsObject structureFluorescence
The present invention relates to two new wave field microscopes, type I and type II, which are distinguished by the fact that they each have an illumination and excitation system, which include at least one real and one virtual illumination source, and at least one objective lens (in the case of type II), i.e., two objective lenses (in the case of type I), with the illumination sources and objective lenses being so positioned with respect to one another that they are suited for generating one-, two-, and three-dimensional standing wave fields in the object space. The calibration method in accordance with the present invention is adapted to this wave field microscopy and permits geometric distance measurements between fluorochrome-labeled object structures, whose distance can be less than the width at half maximum intensity of the effective point spread function. The invention relates moreover to a method of wave-field microscopic DNA sequencing.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF HEIDELBERG
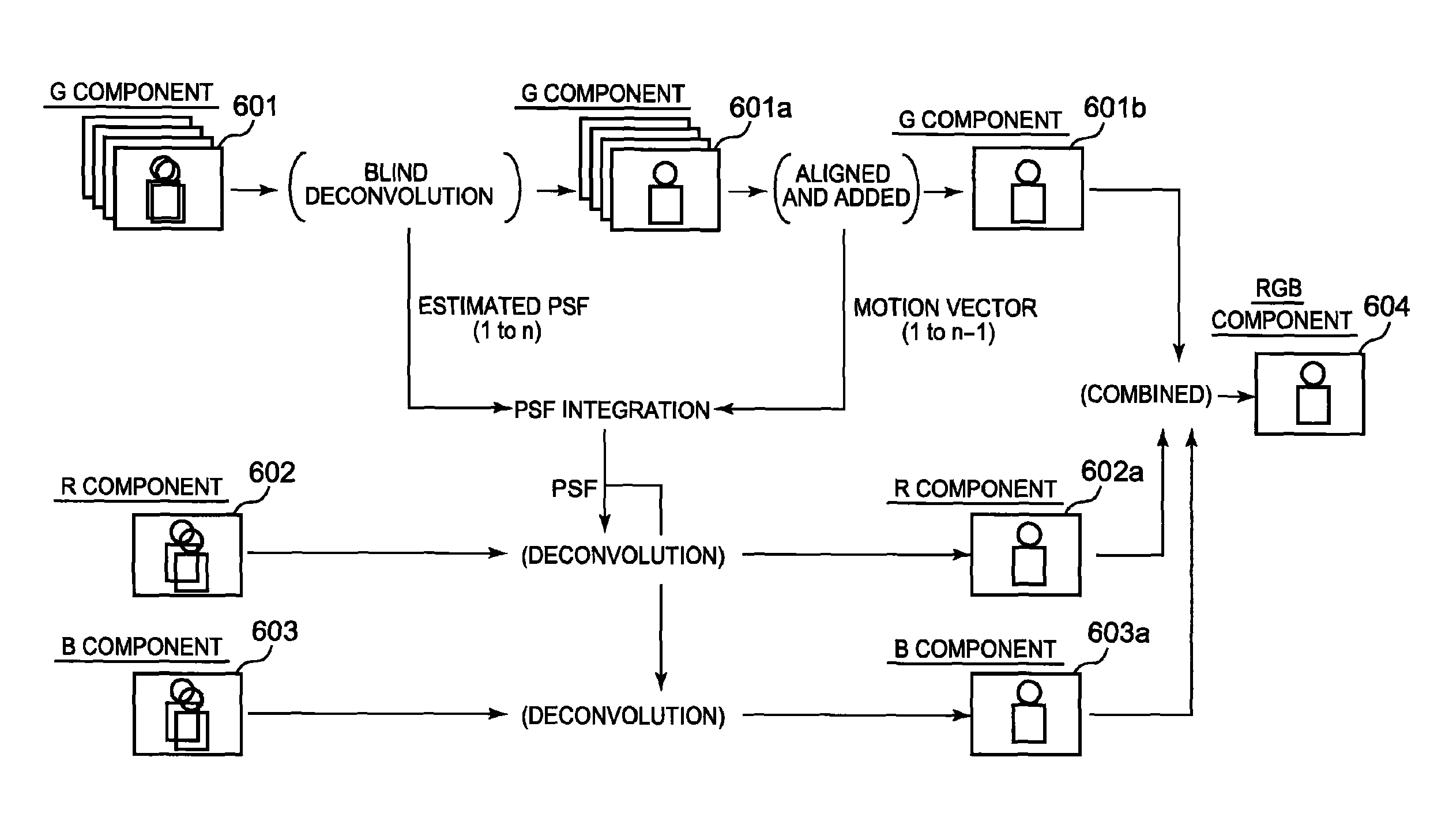
Image capturing apparatus and camera shake correction method, and computer-readable medium
InactiveUS8581992B2Improve image qualityImprove accuracyTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsDiffusion functionPoint spread function
An image capturing apparatus includes: an image capturing unit capturing an image of an object; an image capture controller that causes the image capturing unit to capture first color component images having a first color component by multi-shot exposure, and causes the image capturing unit to capture second and third color component images, a displacement information acquiring unit that acquires displacement information; an image adding unit that aligns and adds the first color component images based on the displacement information to generate an added image; a calculator that calculates a first point spread function based on the displacement information; a first correcting unit that corrects the second and third color component images using the first point spread function; and a combining unit that combines the added image with the corrected second and third color component images.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
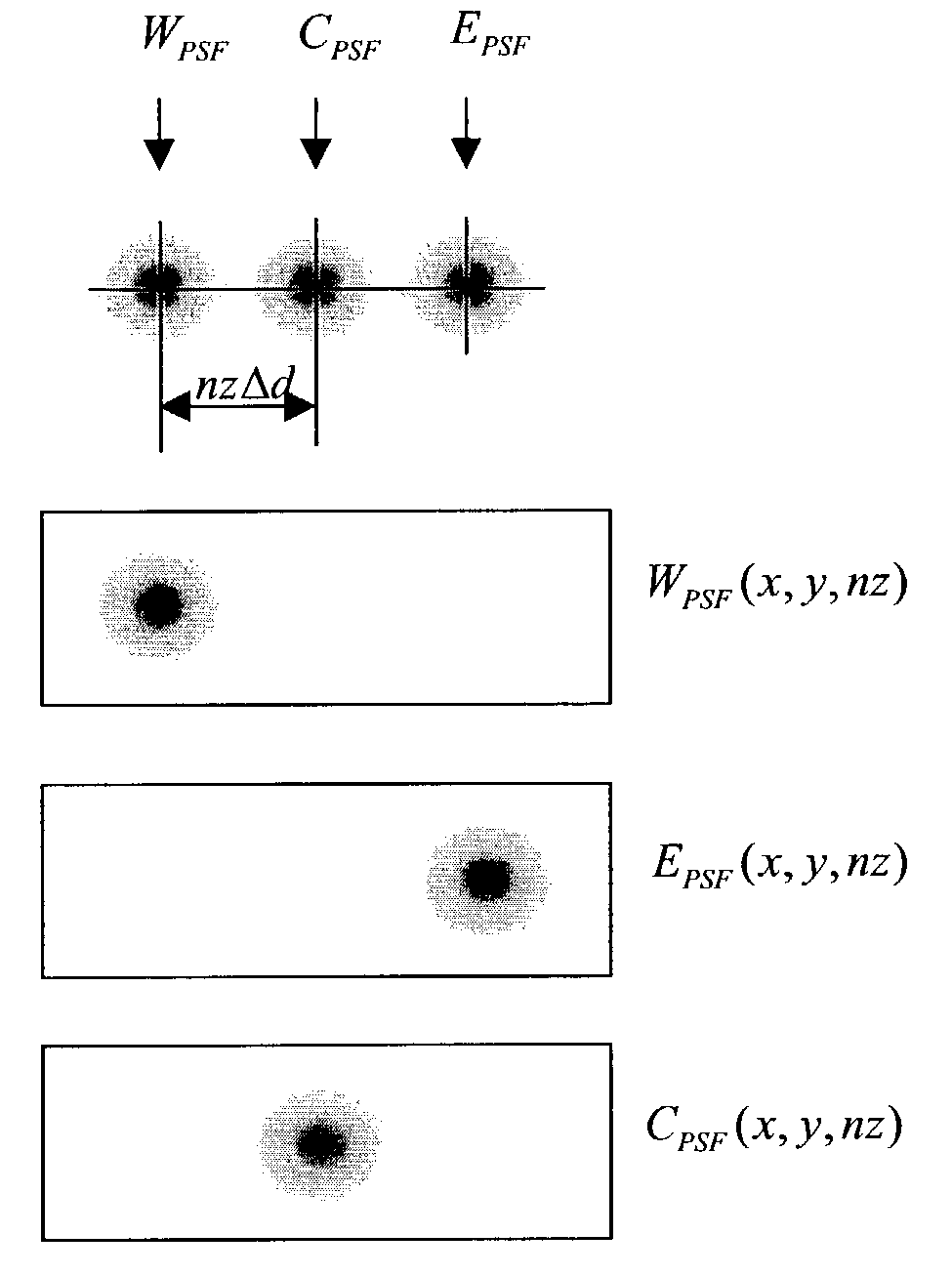
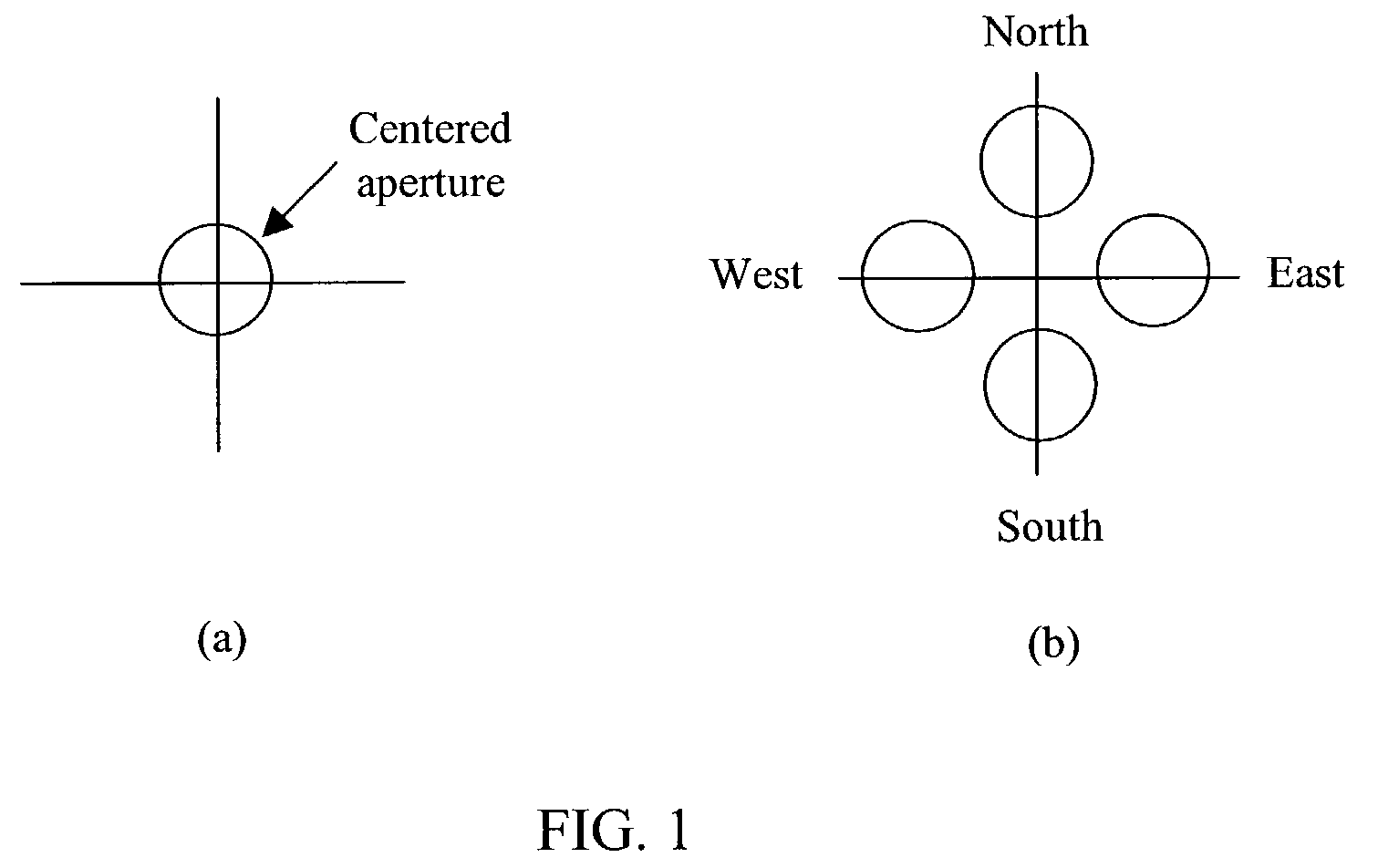
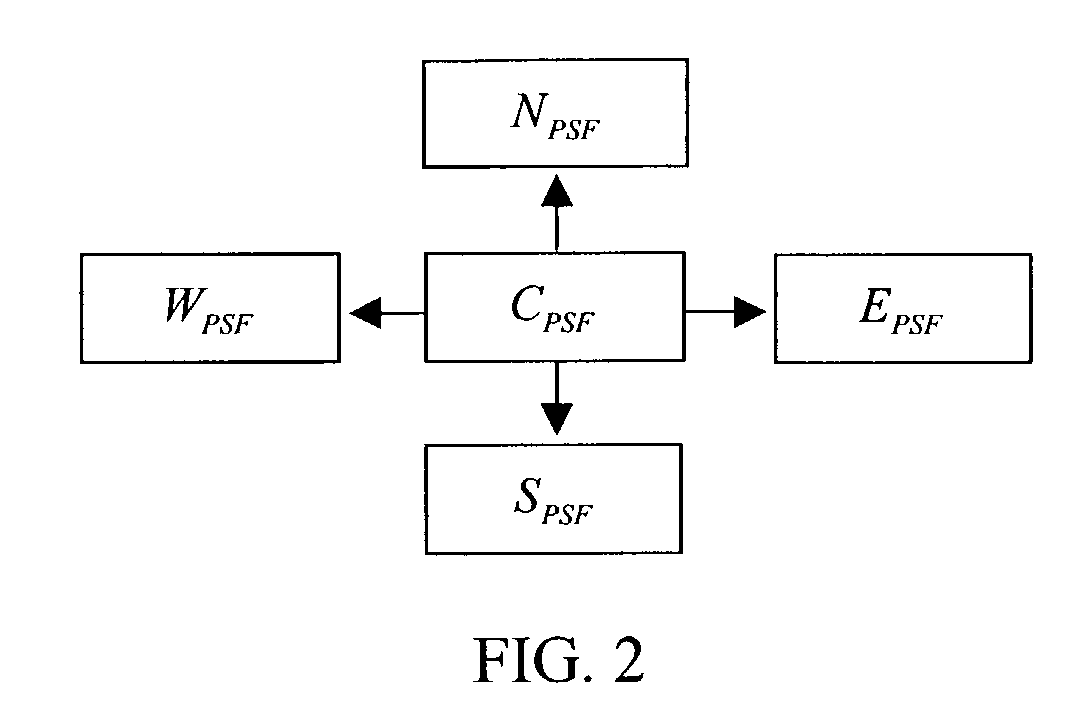
Apparatus and method for three dimensional image reconstruction
InactiveUS7197193B2Improve image acquisition efficiencyEliminate effect caused by motionImage enhancementImage analysisPoint spread functionDiffusion function
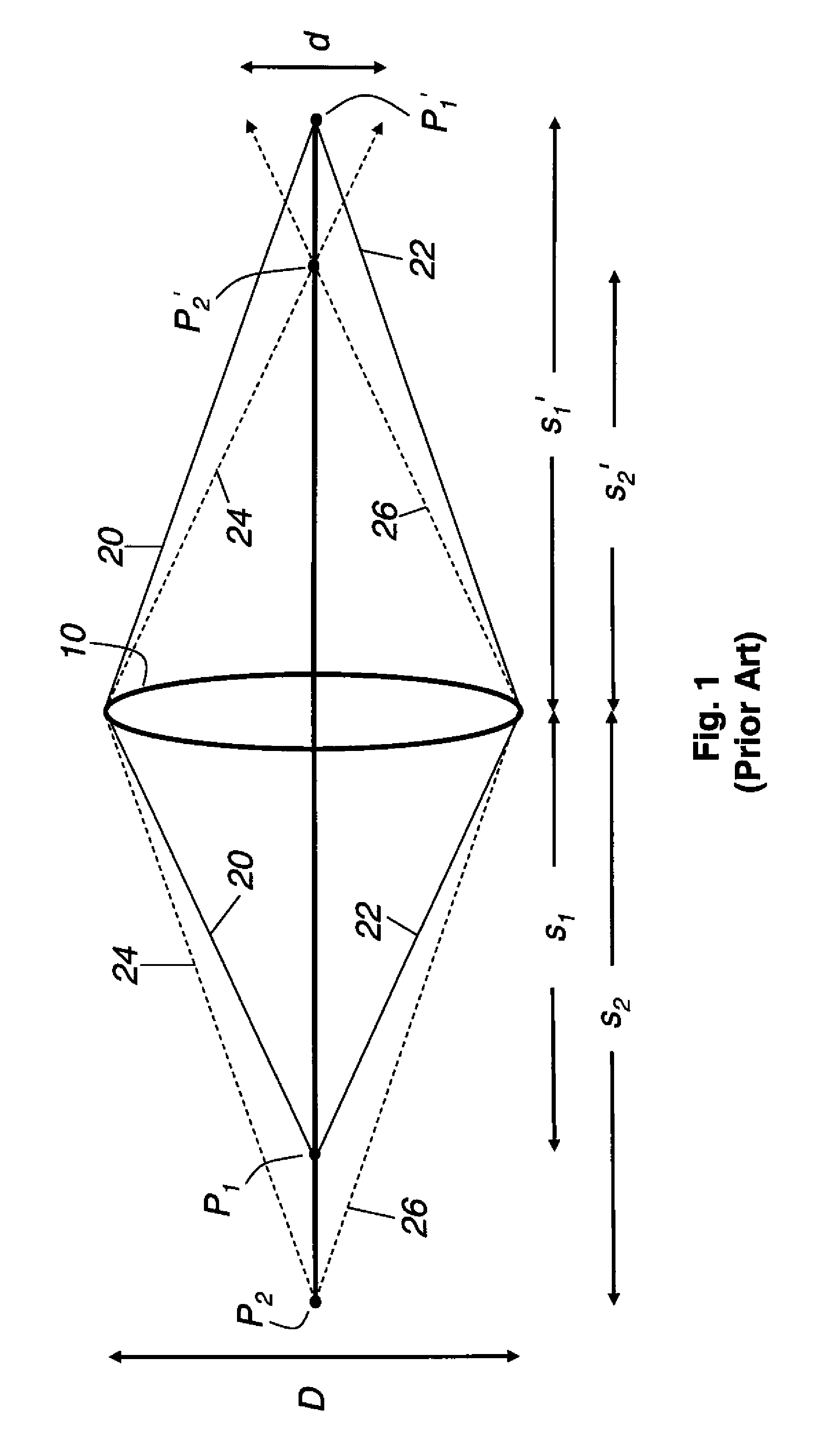
An instrument to acquire and methods to obtain three-dimensional (3D) images from a series of two-dimensional (2D) images which are obtained without moving the relative positions of the target, the detector, or the focusing lens is disclosed. The 2D images consist of one centered image obtained with the aperture at the center of optical system, and at least two directional images obtained with apertures at off-axis locations. The images can be obtained simultaneously or sequentially. The blurred 2D images are sectioned by computational method using point spread function of the optical system resulting in a set of decoupled 2D layers of the 3D object. The layered images are then sharpened by deconvolution using point spread function. The 3D reconstructed image is displayed. This technique provides fast data acquisition and fast image reconstruction and eliminates problems associated with motion, phototoxicity and photobleaching.
Owner:CREATV MICROTECH
Electro-optical device having irregularity-forming thin film and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS6839107B2Improve image qualityIncrease brightnessTransistorTelevision system detailsDiffusion functionActive matrix
The invention provides an electro-optical device provided including a light reflector having a light diffusion function in a preferable condition while an increase in manufacturing cost thereof is minimized, and also provides an electronic apparatus using the same. The present invention can include an active matrix type reflective or transflective electro-optical device wherein, on a surface of a light reflector of an array substrate, irregularity-forming thin-films can be formed by patterning thin-films composed of the same layers as those forming a underlying protection film, a gate insulation film, a scanning line, a first interlayer insulation film, a data line, and a second interlayer insulation film so as to have predetermined patterns. Since an irregular pattern is formed by steps and irregularity of the irregularity-forming thin-films mentioned above, incident light on an counter substrate can be reflected thereto while being diffused.
Owner:138 EAST LCD ADVANCEMENTS LTD
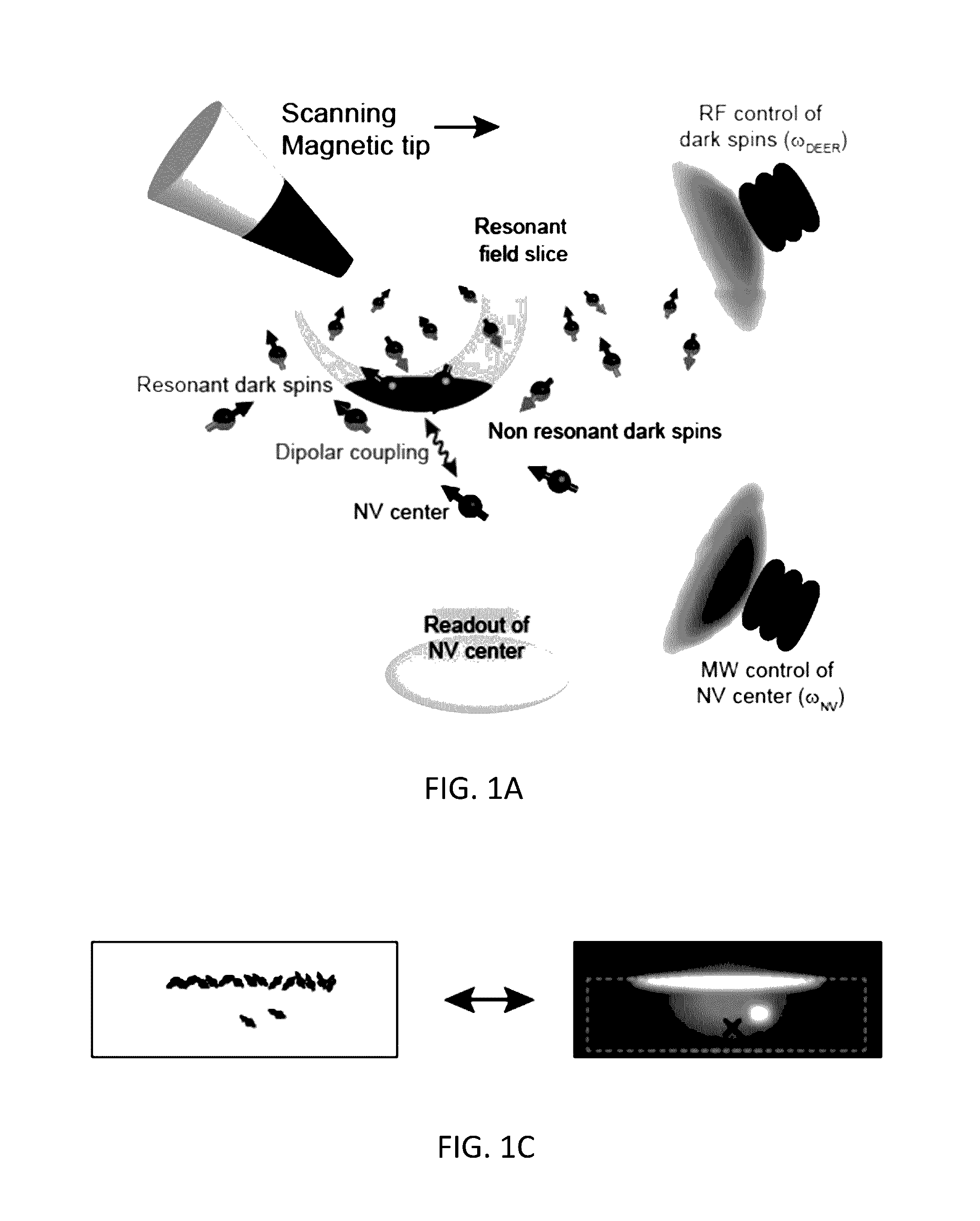
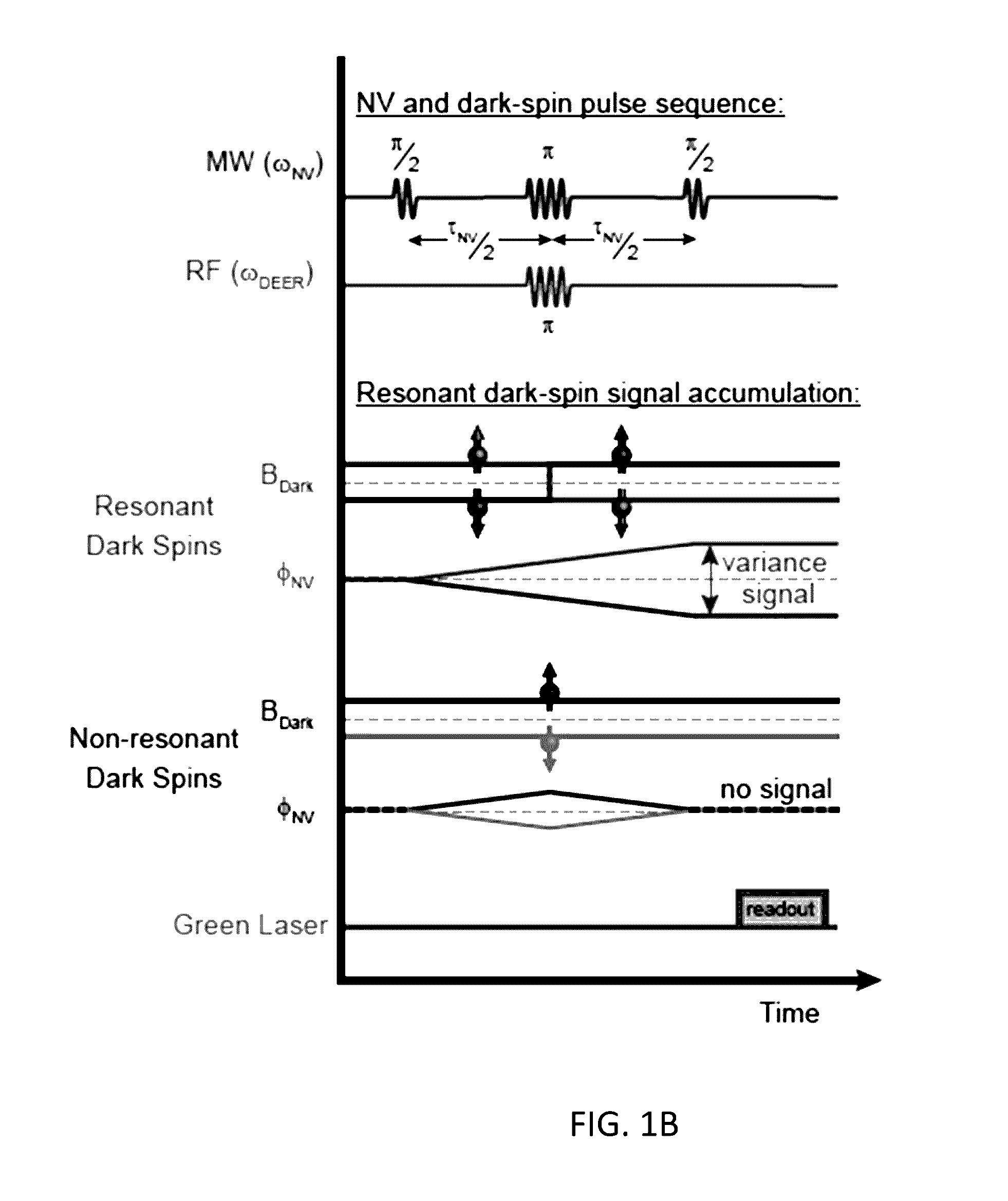
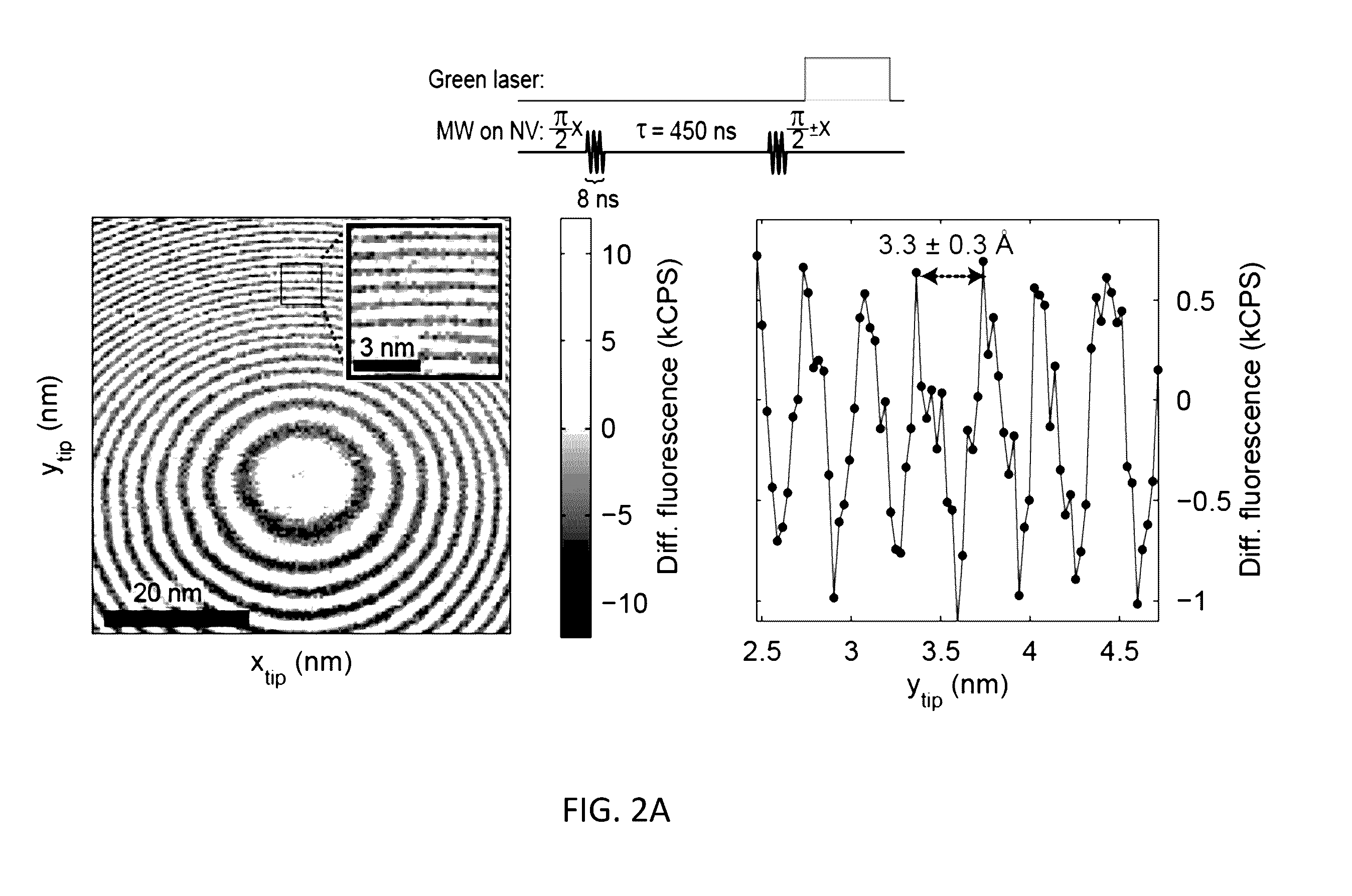
Method And System For Magnetic Resonance Imaging Using Nitrogen-Vacancy Centers
InactiveUS20170038411A1Measurements using double resonanceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic field gradientElectronic spin
A method for performing sub-nanometer three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging of a sample under ambient conditions using a diamond having at least one shallowly planted nitrogen-vacancy (NV) center. A driving radio-frequency (RF) signal and a microwave signal are applied to provide independent control of the NV spin and the target dark spins. A magnetic-field gradient is applied to the sample with a scanning magnetic tip to provide a narrow spatial volume in which the target dark electronic spins are on resonance with the driving RF field. The sample is controllably scanned by moving the magnetic tip to systematically bring non-resonant target dark spins into resonance with RF signal. The dark spins are measured and mapped by detecting magnetic resonance of said nitrogen-vacancy center at each of said different magnetic tip positions. The dark-spin point-spread-function for imaging the dark spins is directly measured by the NV center.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Imaging spectroscopy based on multiple pan-chromatic images obtained from an imaging system with an adjustable point spread function
ActiveUS7385705B1Avoid introduction of noiseHigh resolutionRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryData setDiffusion function
Generating a multispectral or hyperspectral image of an image source with an optical system having an adjustable, wavenumber-dependent point spread function, by collecting panchromatic images of the image source, each of which corresponds to a selected point spread function and includes a measured intensity data set corresponding to a range of wavelengths, transforming the panchromatic images into the spatial frequency domain by using a Fourier transform, solving a matrix equation at each spatial frequency, in which a vector of the transformed panchromatic images is equal to the product of a predetermined matrix of discrete weighting coefficients and a vector representing a wavenumber content of the image source at each spatial frequency, resulting in a determined wavenumber content of the image source in the spatial frequency domain, and inverse transforming the determined wavenumber content of the image source from the spatial frequency domain into the image domain, resulting in the multispectral or hyperspectral image.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
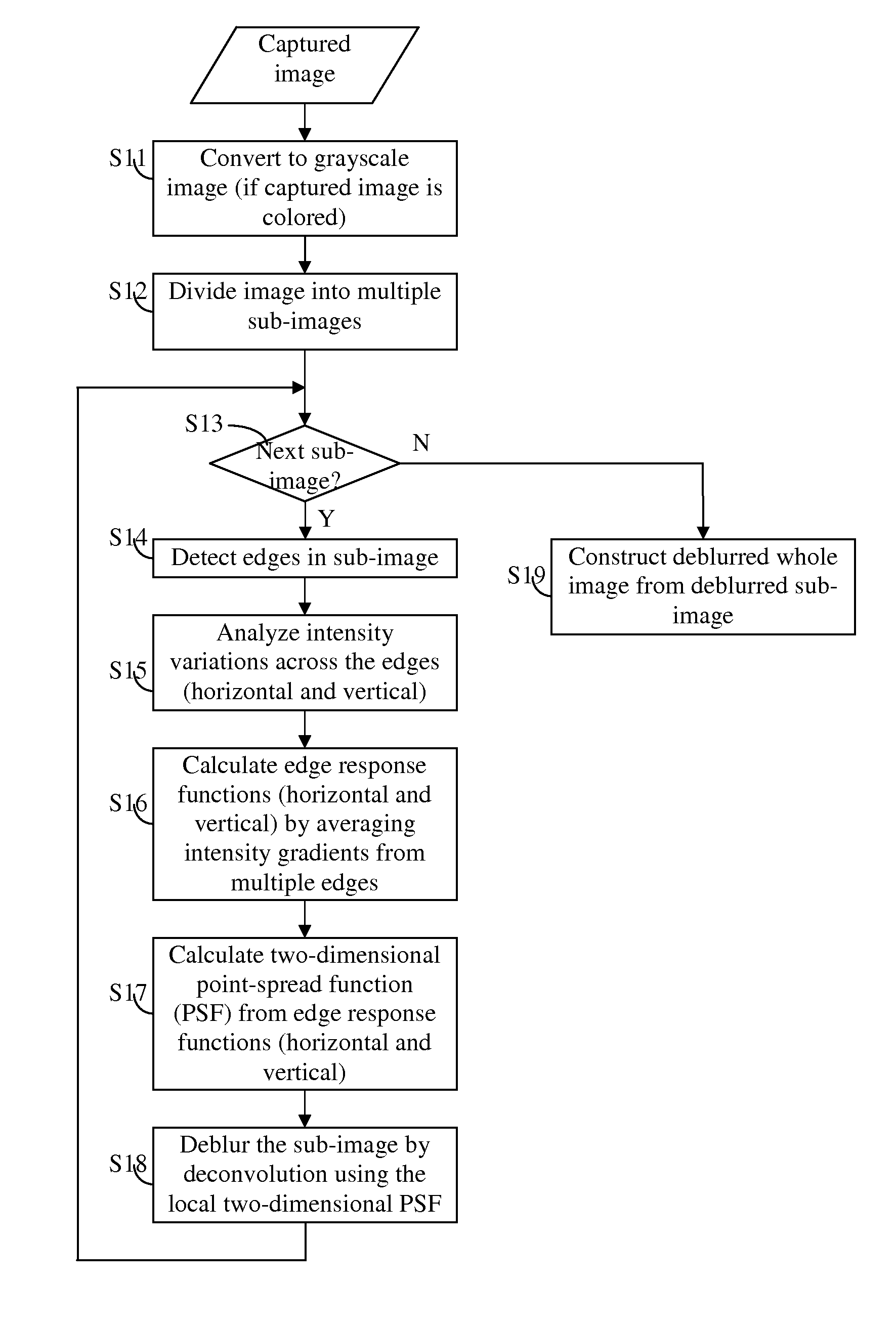
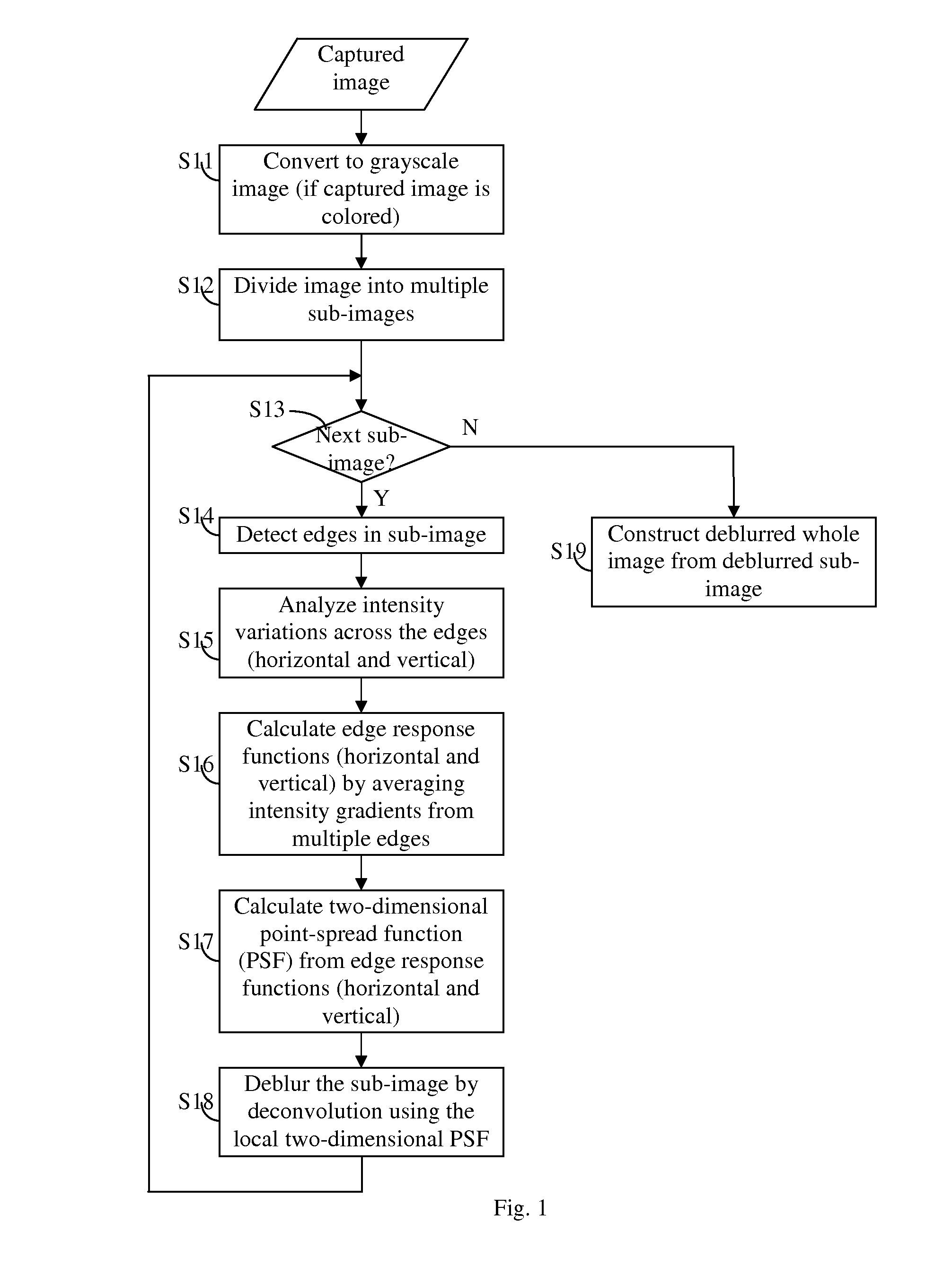
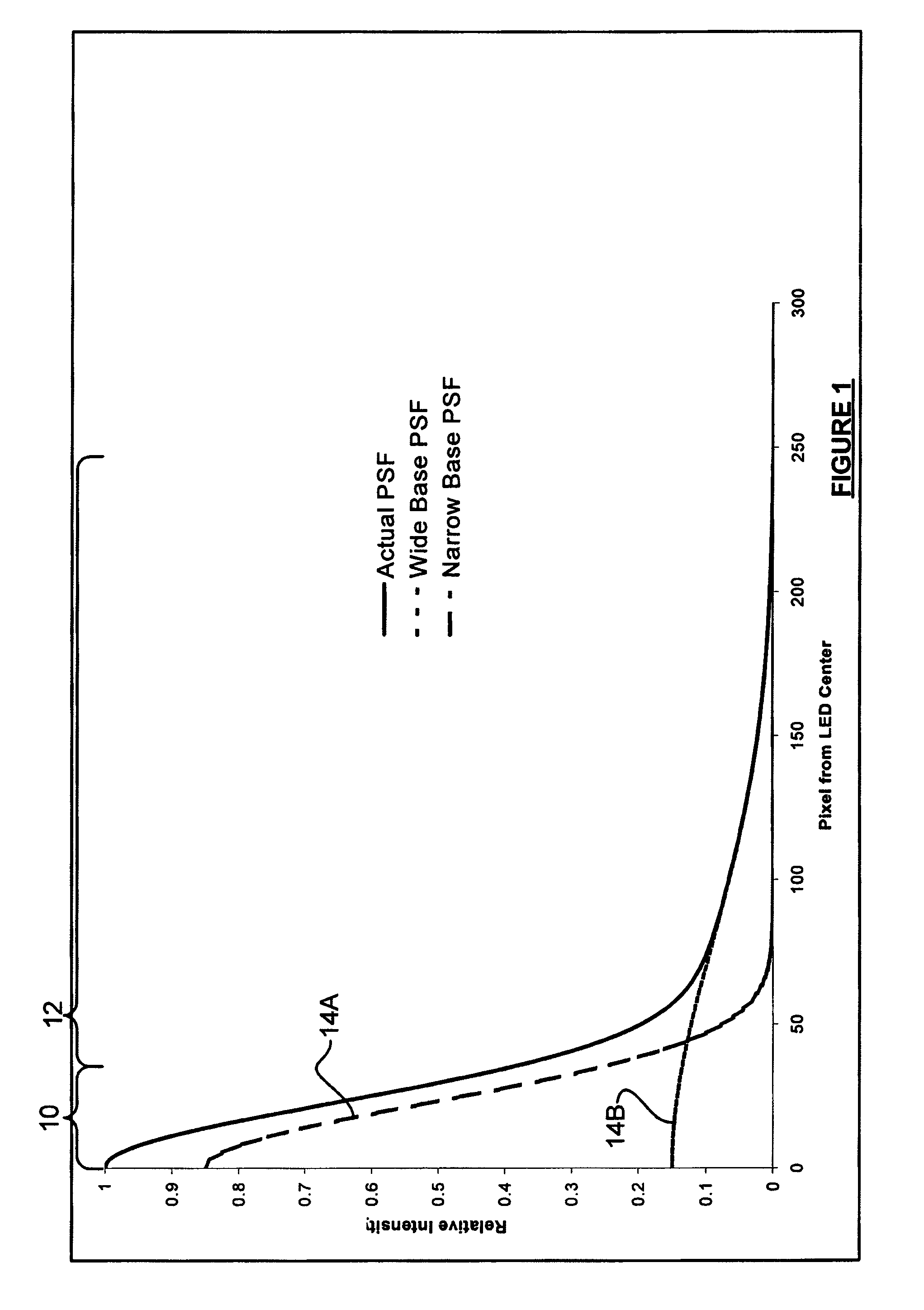
Adaptive deblurring for camera-based document image processing
InactiveUS20110044554A1Improve image qualityReduce adverse effectsImage enhancementImage analysisDiffusion functionPoint spread function
An image deblurring method for camera-based document image processing is described. A document image captured by a digital camera is divided into multiple overlapping or non-overlapping sub-images. A point spread function is derived for each sub-image by analyzing the gradient information along edges contained in the sub-image. Each sub-image is deblurred by using its local point-spread function. The whole deblurred image is constructed from deblurred sub-images. In cases where information of interest is located in localized parts of the document image, dividing the image into sub-images may be done by extracting the area of interest from the captured image. This deblurring method improves the quality of the deblurred image when the camera-captured image is blurred by variable amount of location-dependent defocus.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA LAB U S A INC
Plane light source apparatus and prism sheet and liquid crystal display apparatus
InactiveUS20070279352A1Reduce power consumptionReduce thicknessStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayDiffusion function
The present invention provides a LCD panel with an isosceles triangular cross-section having a base angle of 50 to 55 degrees, and an incident angle equal to 10 to 24 degrees. Several triangular prisms are installed downwardly on a prism sheet by using the base angle as a vertex angle for controlling the light to be travel in a parallel direction, and incident in a direction perpendicular to an oblique surface of a smaller surface of the prism. The oblique surface of a larger surface of the prism reflects the incident light completely and projects the light perpendicular to the bottom of the prism. An optical system provides a backlight for a liquid crystal display apparatus and an anisotropic diffuser installed at an orthogonal direction of a prism has a diffusion function such that the light can be diffused by the LCD panel and the two orthogonally installed polarizers.
Owner:MIKUNI ELECTORON CO LTD
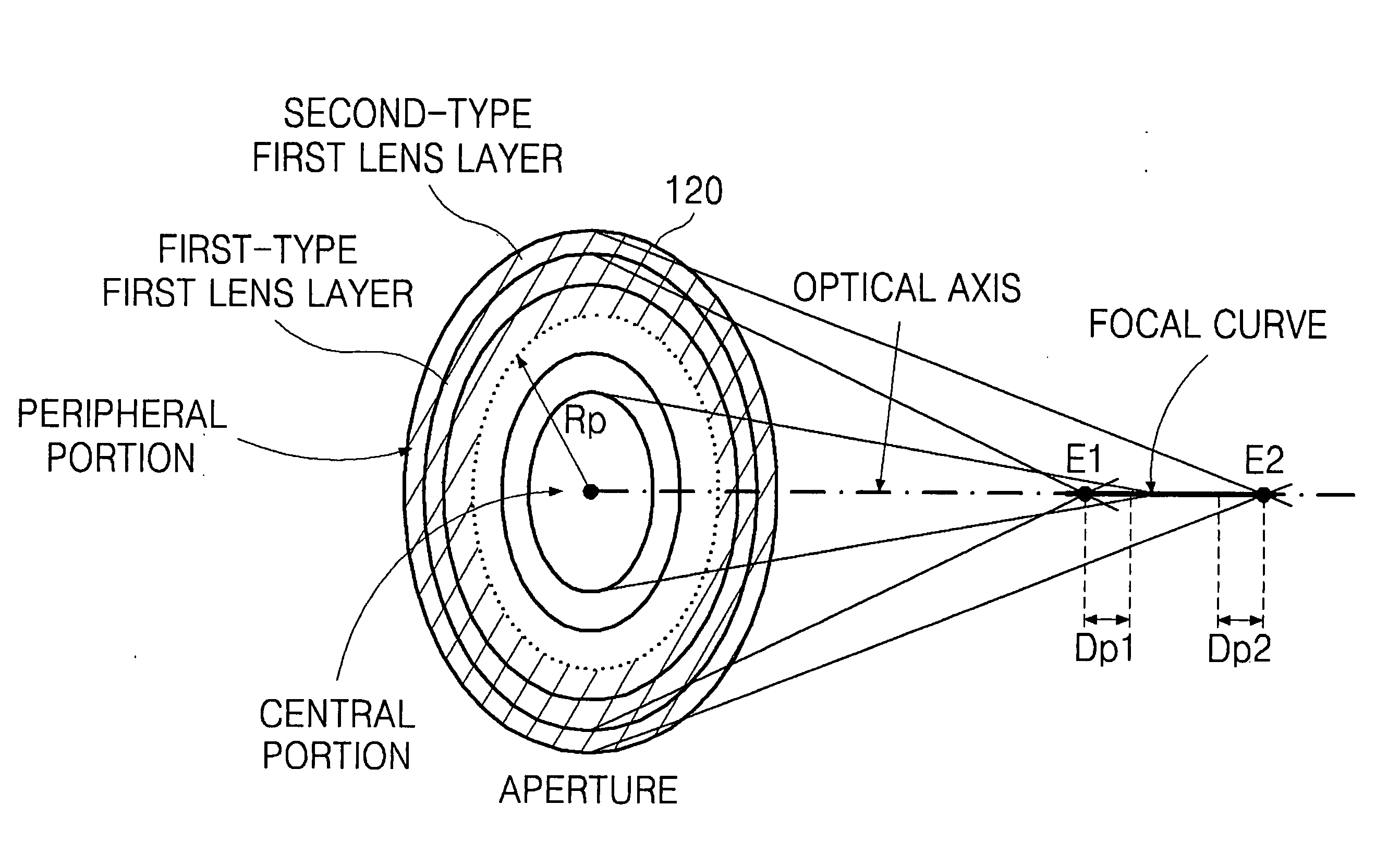
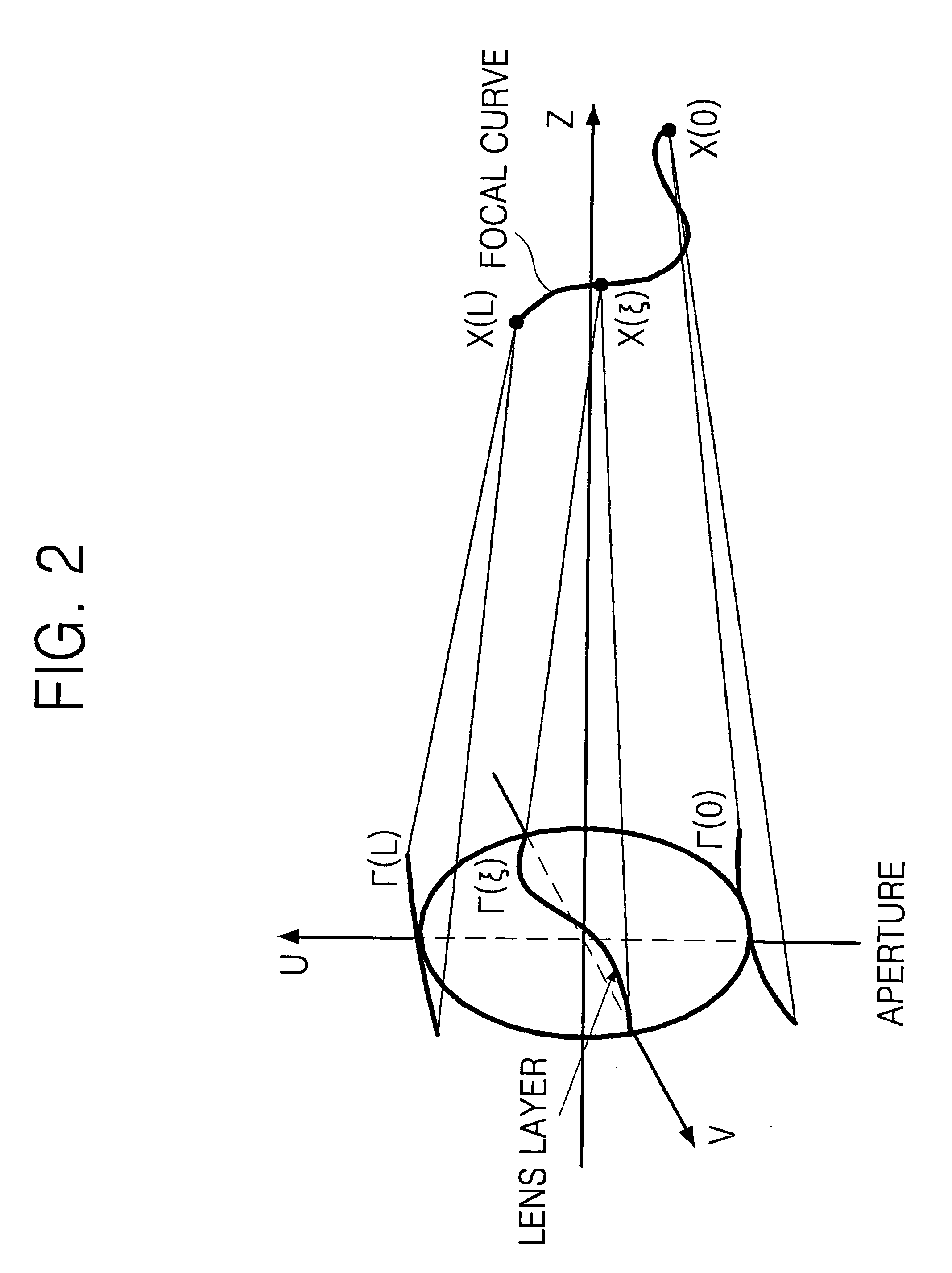
Lens having extended depth of focus, method for designing the same, and optical system having the same
ActiveUS20090279189A1Simplify point spread functionSimple designMountingsExposure controlOptical axisPoint spread function
The lens includes a plurality of lens layers, each lens layer being axi-symmetric and having an extended depth of focus to focus light in a corresponding section of a focal curve in the form of a straight line located on an optical axis. In the optical system, light is focused on an optical axis to obtain a clear image in a wide distance range between a camera and an object. The optical system has a point spread function that is simpler and more symmetric. That is, the optical system provides improved continuity of a lens surface and easiness and flexibility in optical designing.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
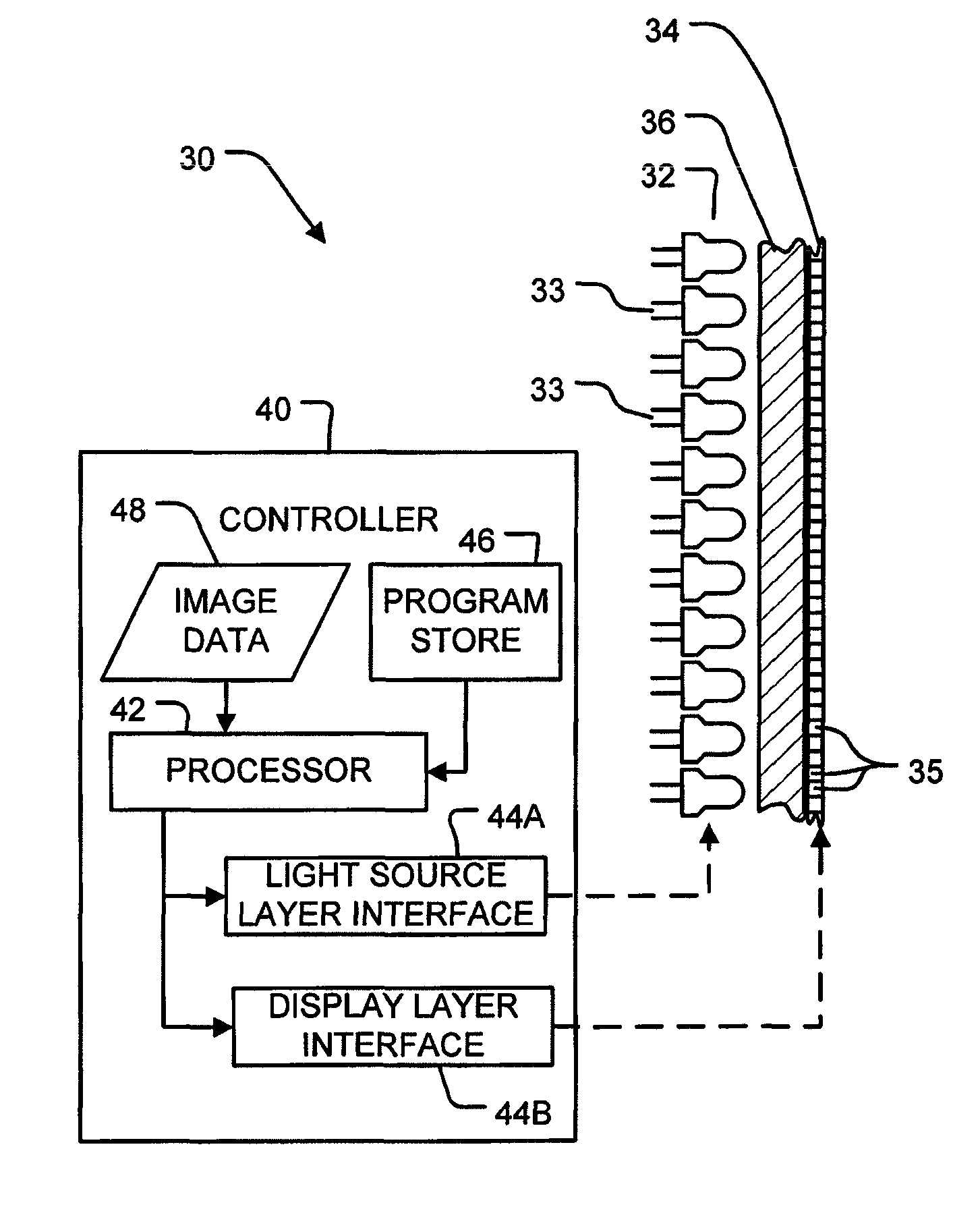
Rapid image rendering on dual-modulator displays
ActiveUS8217970B2Geometric image transformationCathode-ray tube indicatorsDiffusion functionImage resolution
Apparatus and methods are provided that employ one or more of a variety of techniques for reducing the time required to display high resolution images on a high dynamic range display having a light source layer and a display layer. In one technique, the image resolution is reduced, an effective luminance pattern is determined for the reduced resolution image, and the resolution of the effective luminance pattern is then increased to the resolution of the display layer. In another technique, the light source layer's point spread function is decomposed into a plurality of components, and an effective luminance pattern is determined for each component. The effective luminance patterns are then combined to produce a total effective luminance pattern. Additional image display time reduction techniques are provided.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com