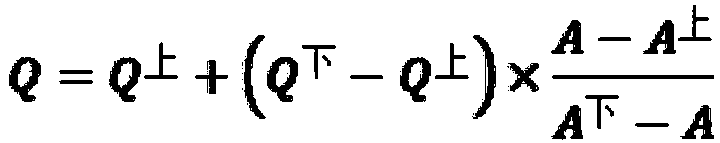Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1067 results about "Point source" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
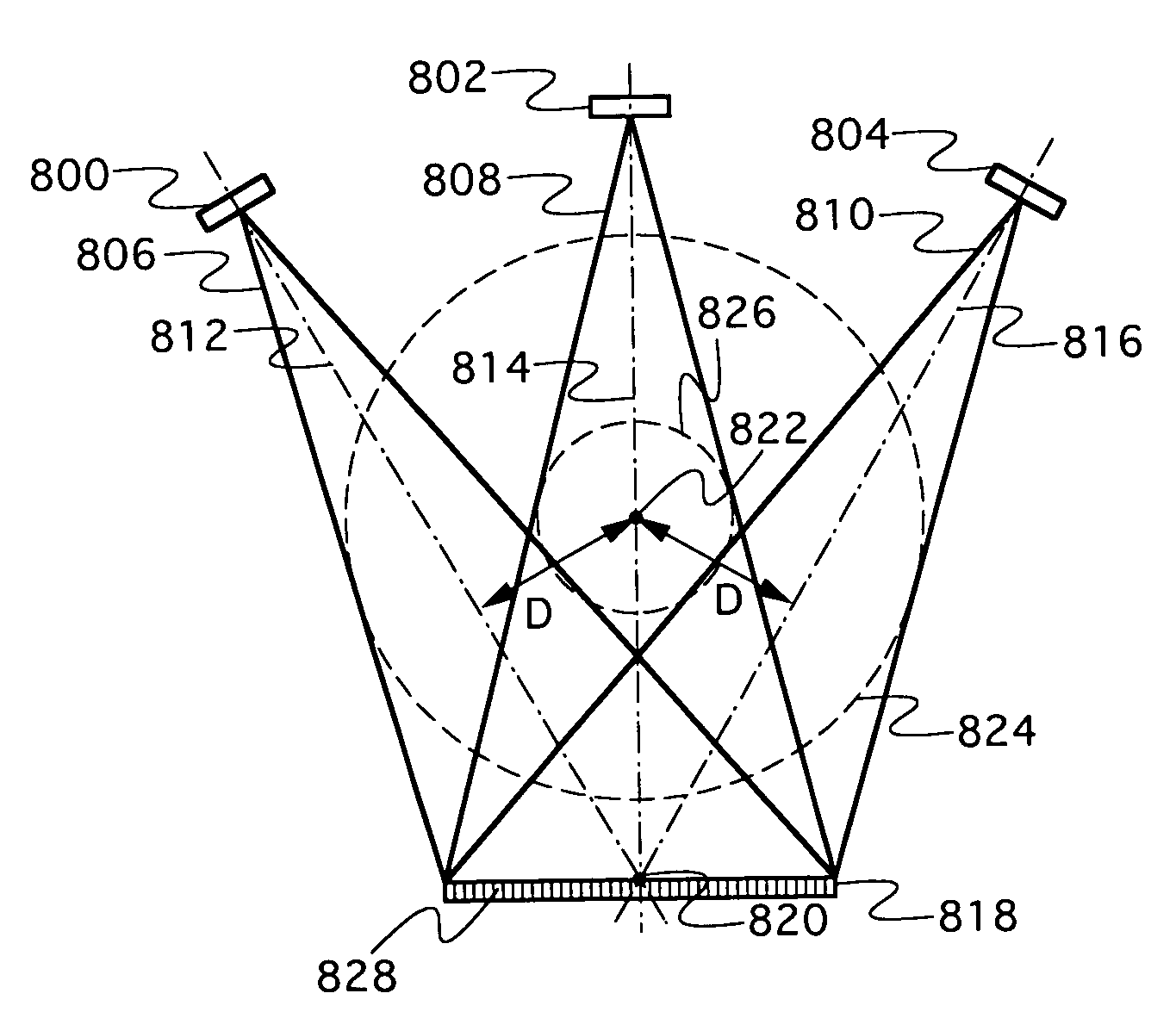
A point source is a single identifiable localised source of something. A point source has negligible extent, distinguishing it from other source geometries. Sources are called point sources because in mathematical modeling, these sources can usually be approximated as a mathematical point to simplify analysis.
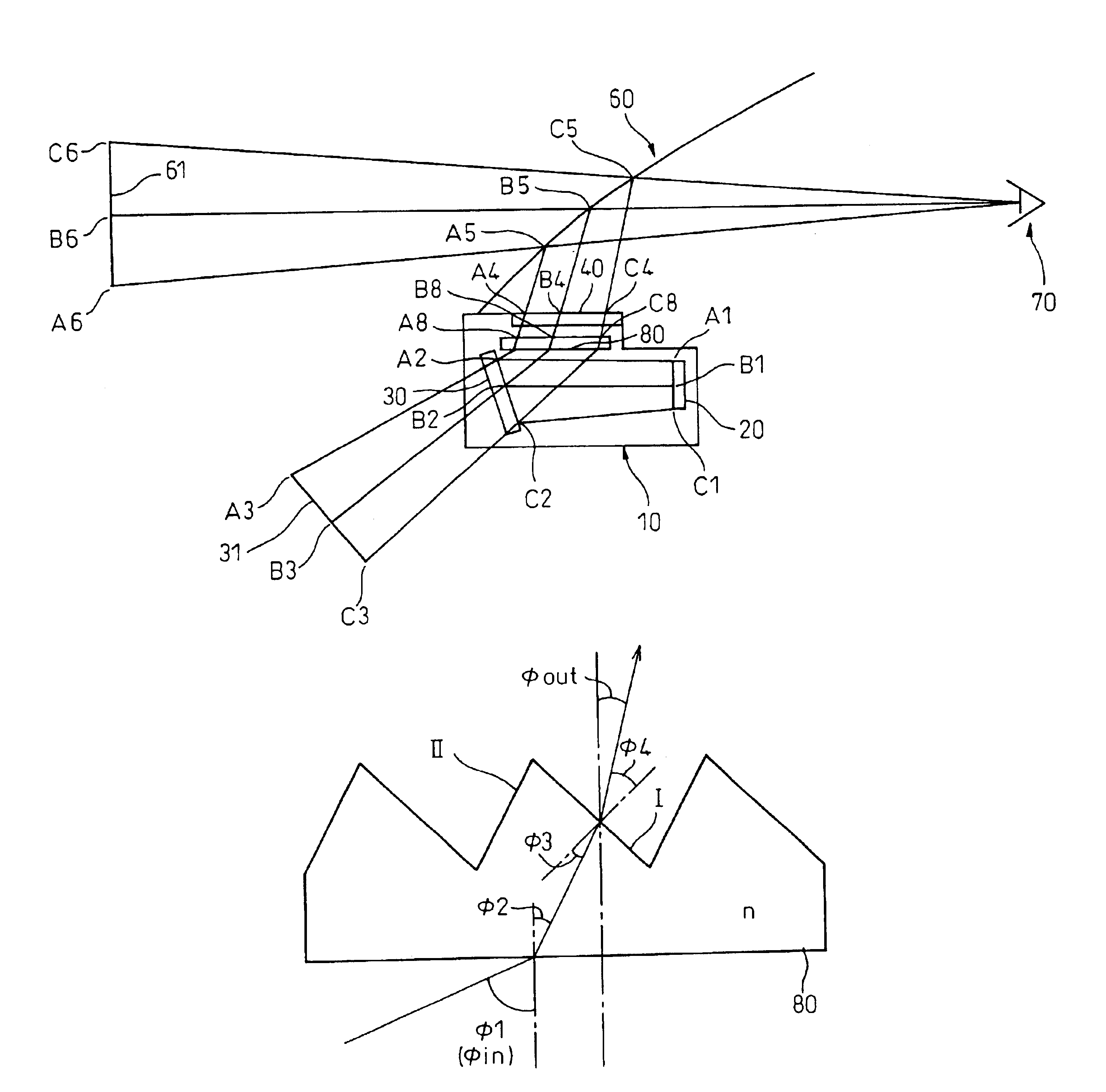
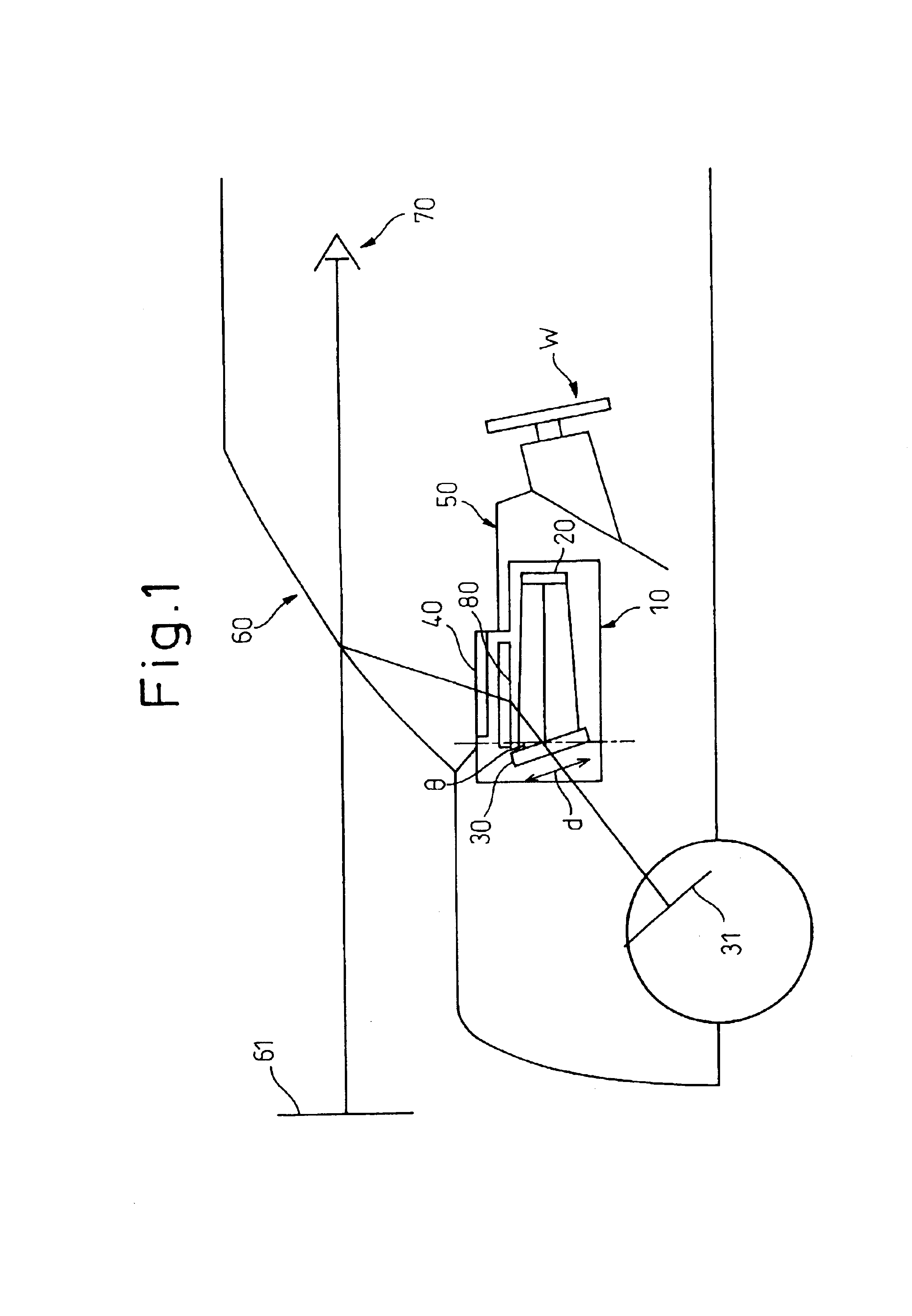
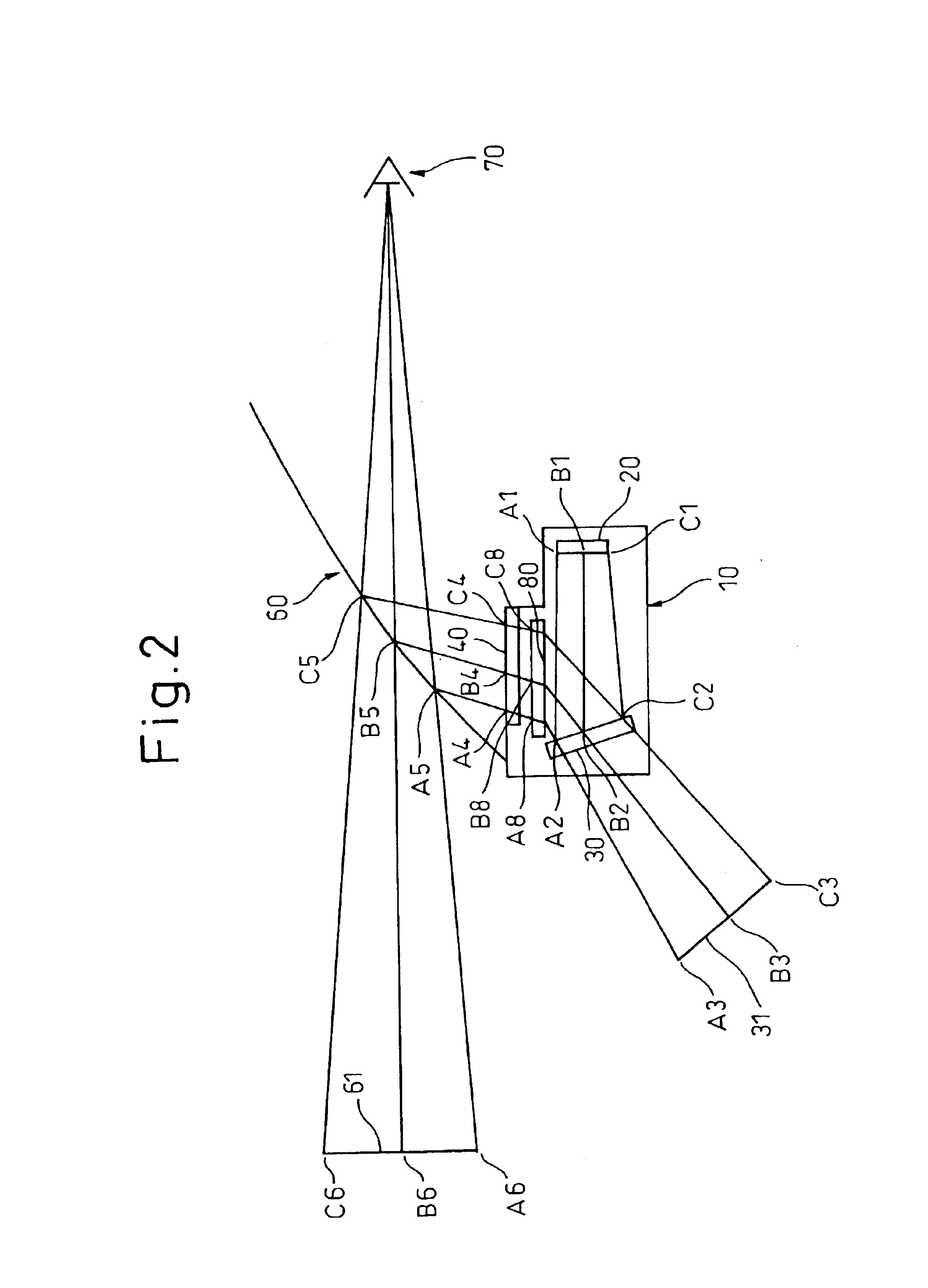
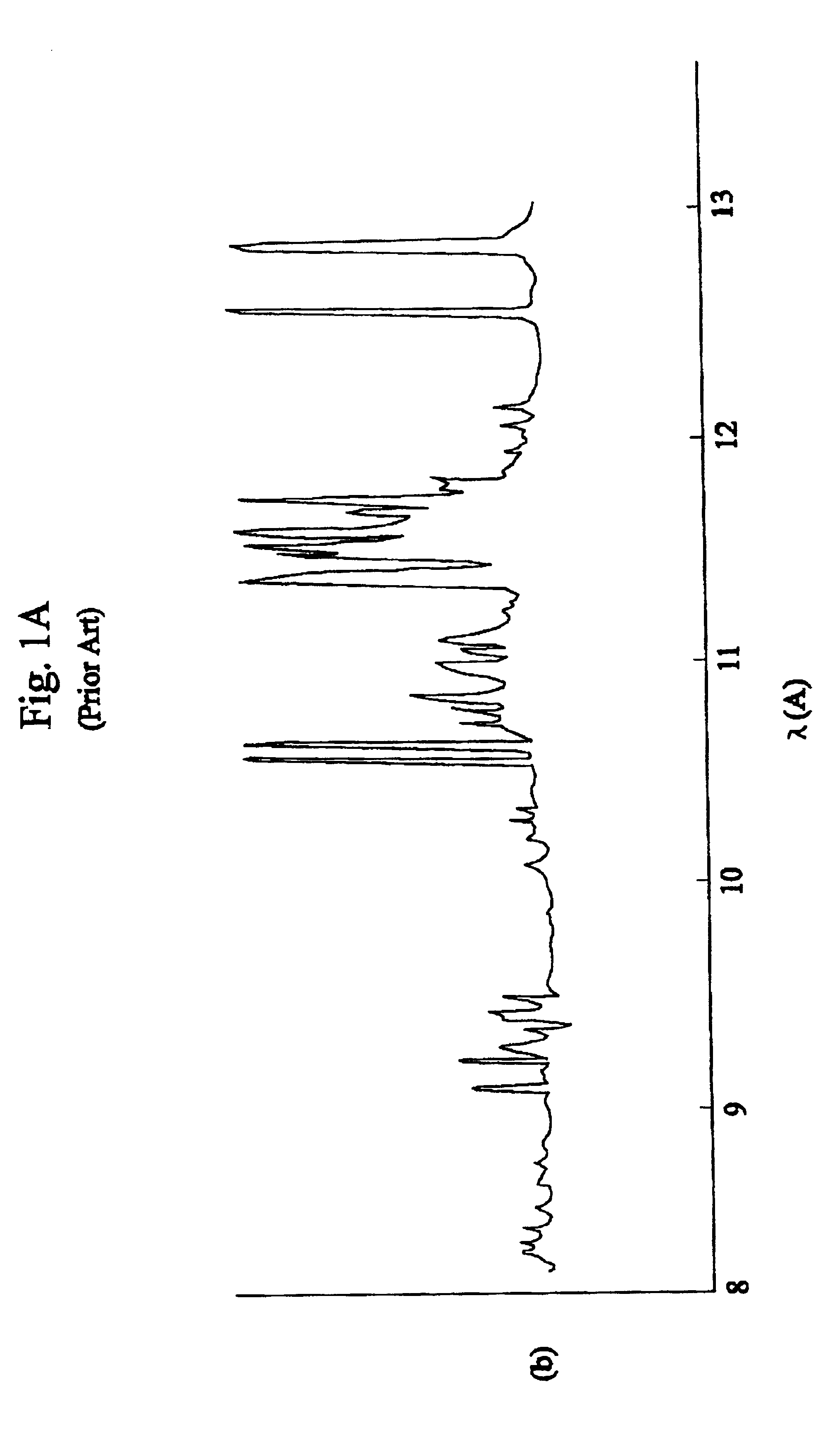
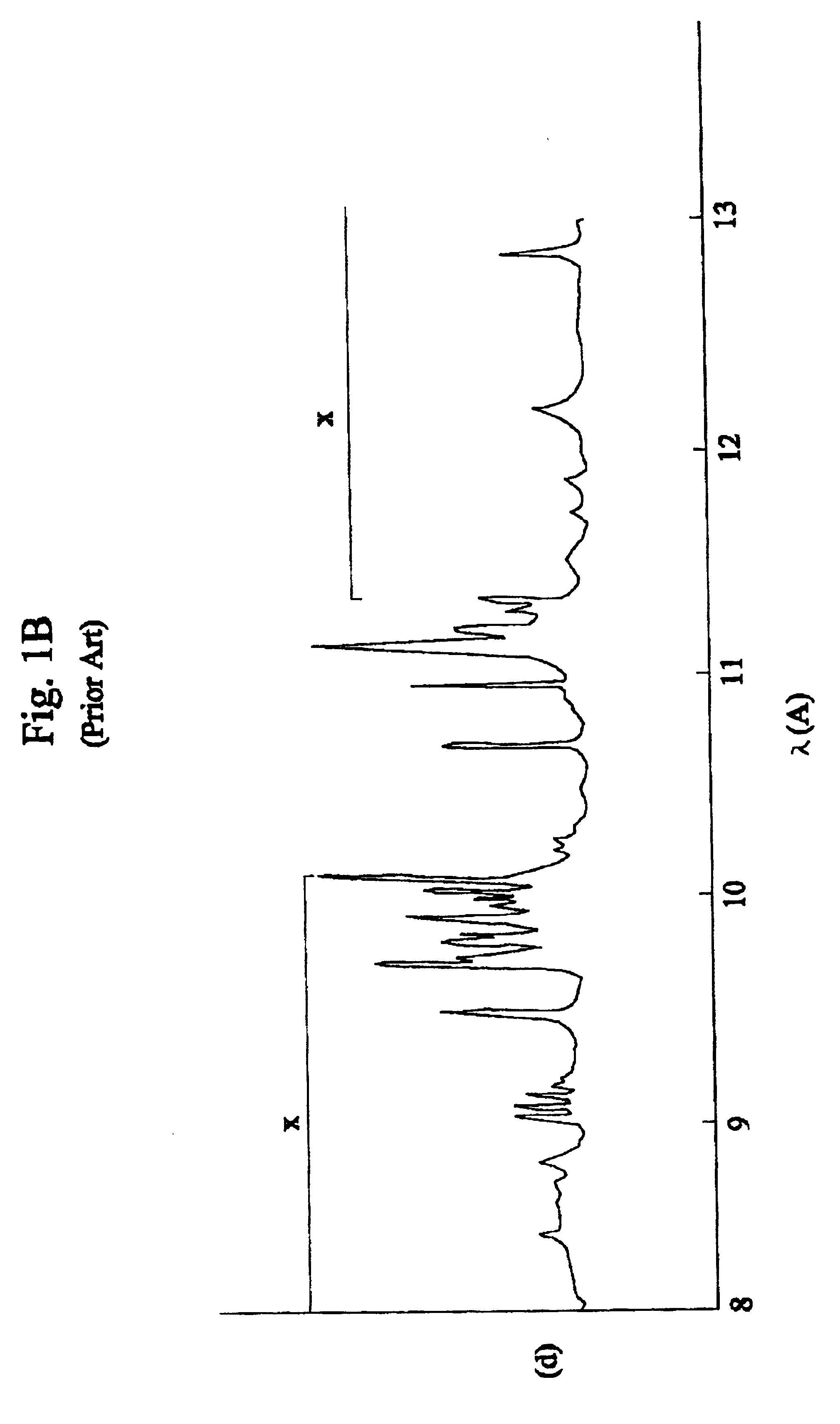
Computed tomography with increased field of view
ActiveUS7062006B1Expand field of viewLarge array sizeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingIn planeOffset distance
A volumetric computed tomography system with a large field of view has, in a forward geometry implementation, multiple x-ray point sources emitting corresponding fan beams at a single detector array. The central ray of at least one of the fan beams is radially offset from the axis of rotation of the system by an offset distance D. Consequently, the diameter of the in-plane field of view provided by the fan beams may be larger than in a conventional CT scanner. Any number of point sources may be used. Analogous systems may be implemented with an inverse geometry so that a single source array emits multiple fan beams that converge upon corresponding detectors.
Owner:AIRDRIE PARTNERS I LP +1
System for determination of a location in three dimensional space
InactiveUS6141104AReduce the impact of interferenceNarrow downInput/output for user-computer interactionPosition fixationThree-dimensional spaceMathematical correlation
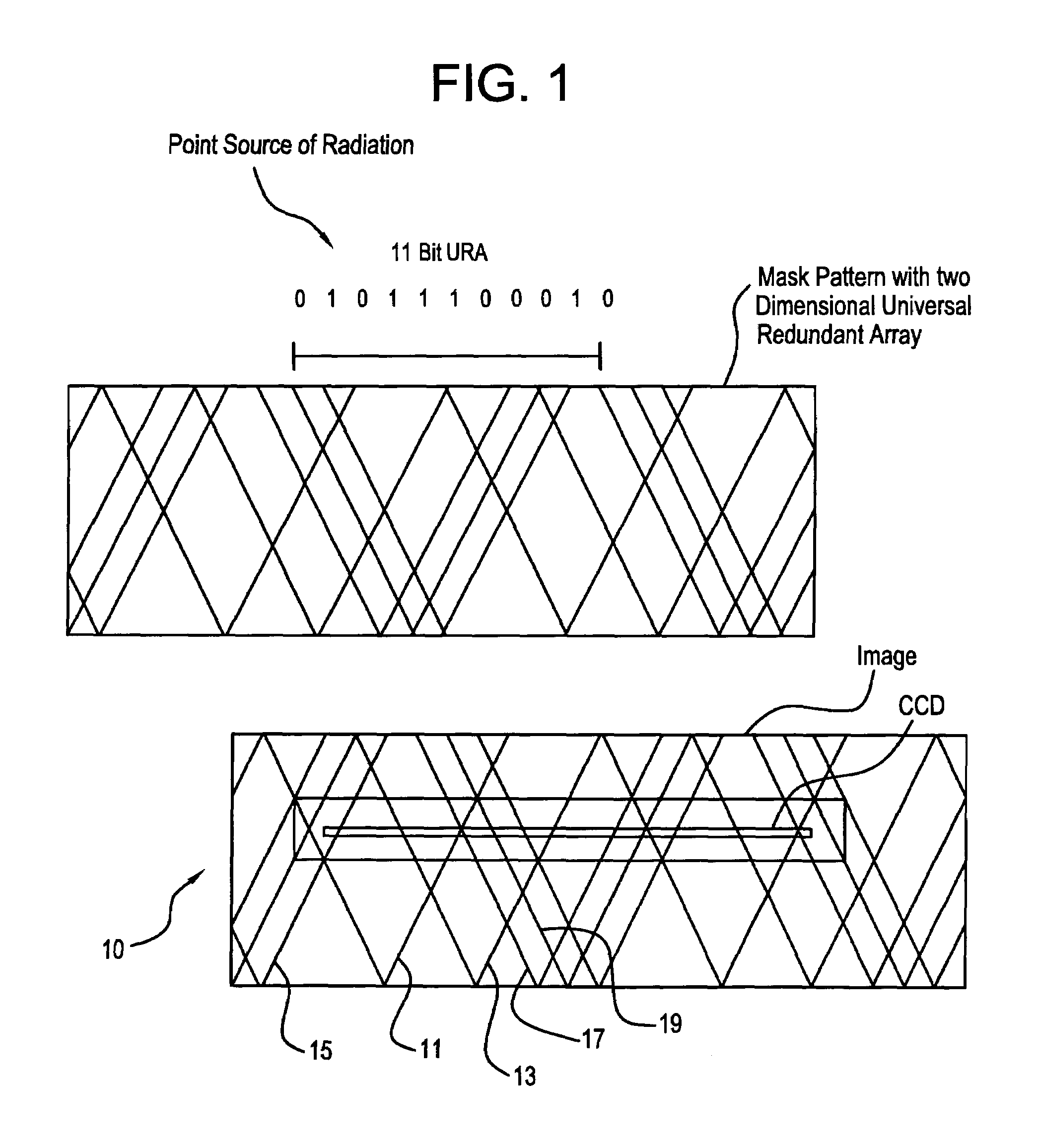
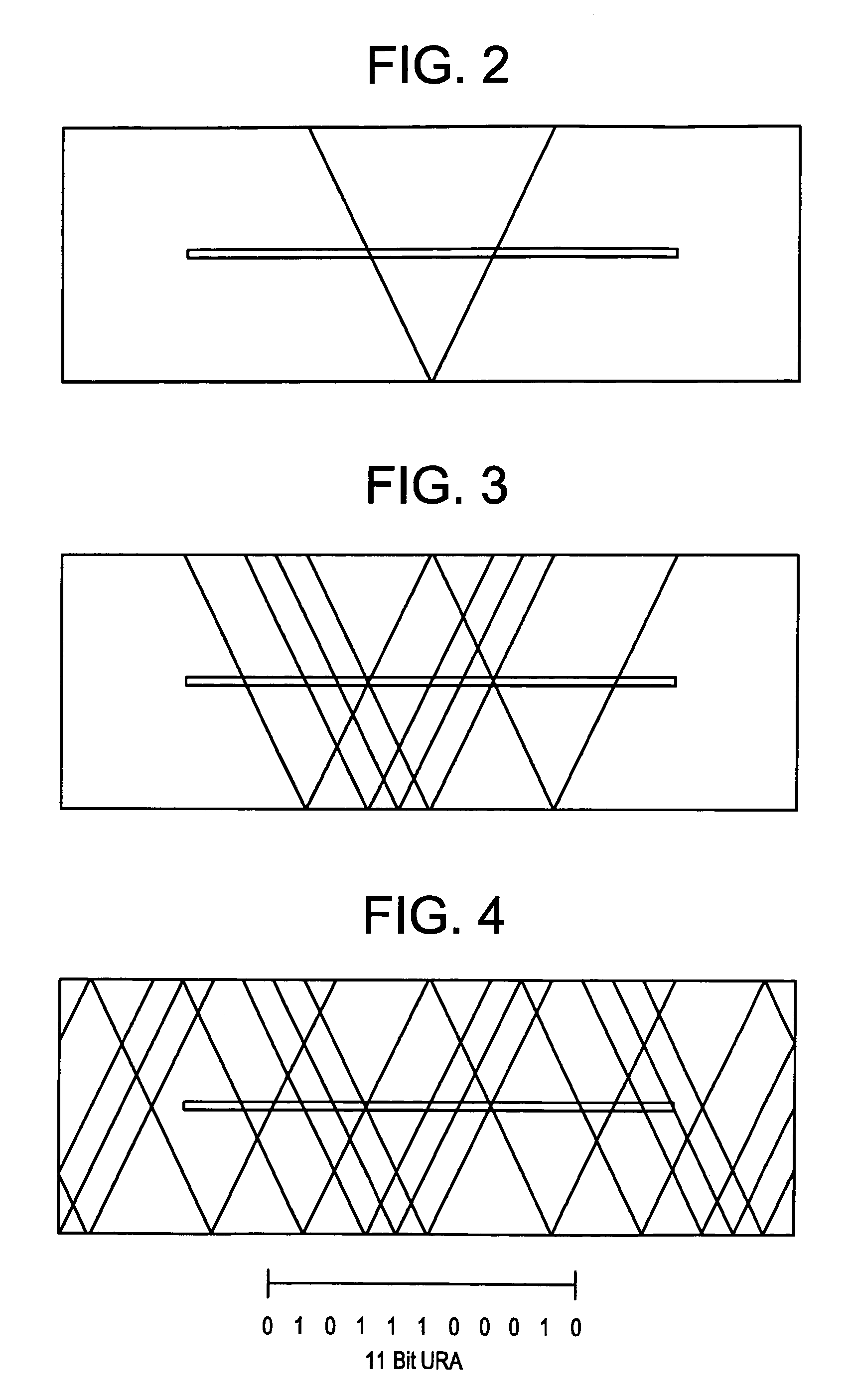
An optical improvement for angular position sensors, which may be used to determine the spatial coordinates of a small source of light (or other energy) in a 3-dimensional volume. Such sensors normally include a linear photosensitive image detector such as a photodiode array or a charge-coupled device (CCD). An irregular pattern of parallel slits is described which increases the amount of light gathered while avoiding the undesirable characteristics of lens optics for this application. One optimal type of irregular pattern is the uniformly redundant array. A mathematical correlation function together with a polynomial interpolation function can determine the displacement of the image on the detector and thereby the location of the source relative to one angular dimension. Given the locations and orientations of several sensors in a 3-dimensional coordinate system and given the angles measured by each, the location of the point source can be computed.
Owner:IMAGE GUIDED TECH
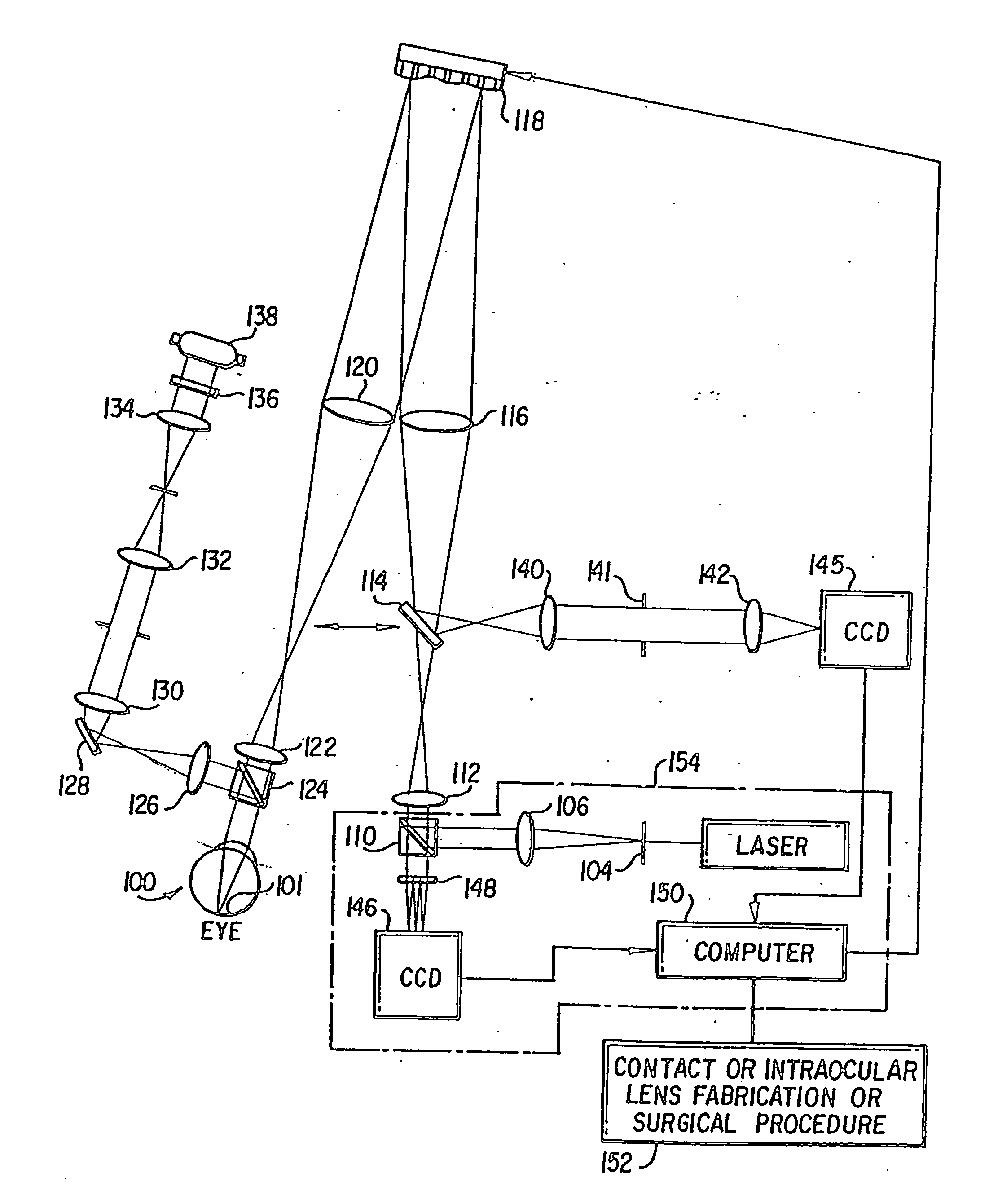
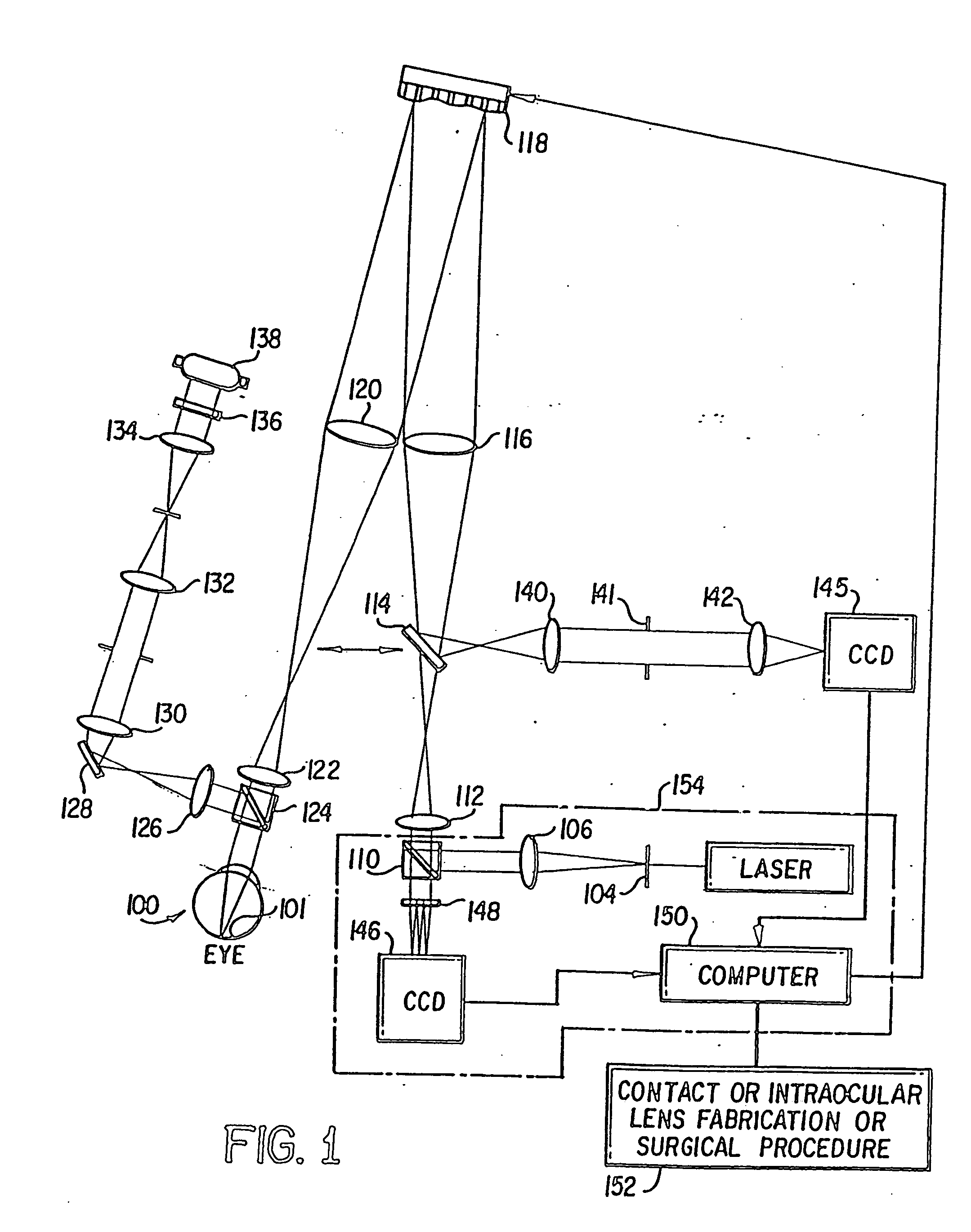
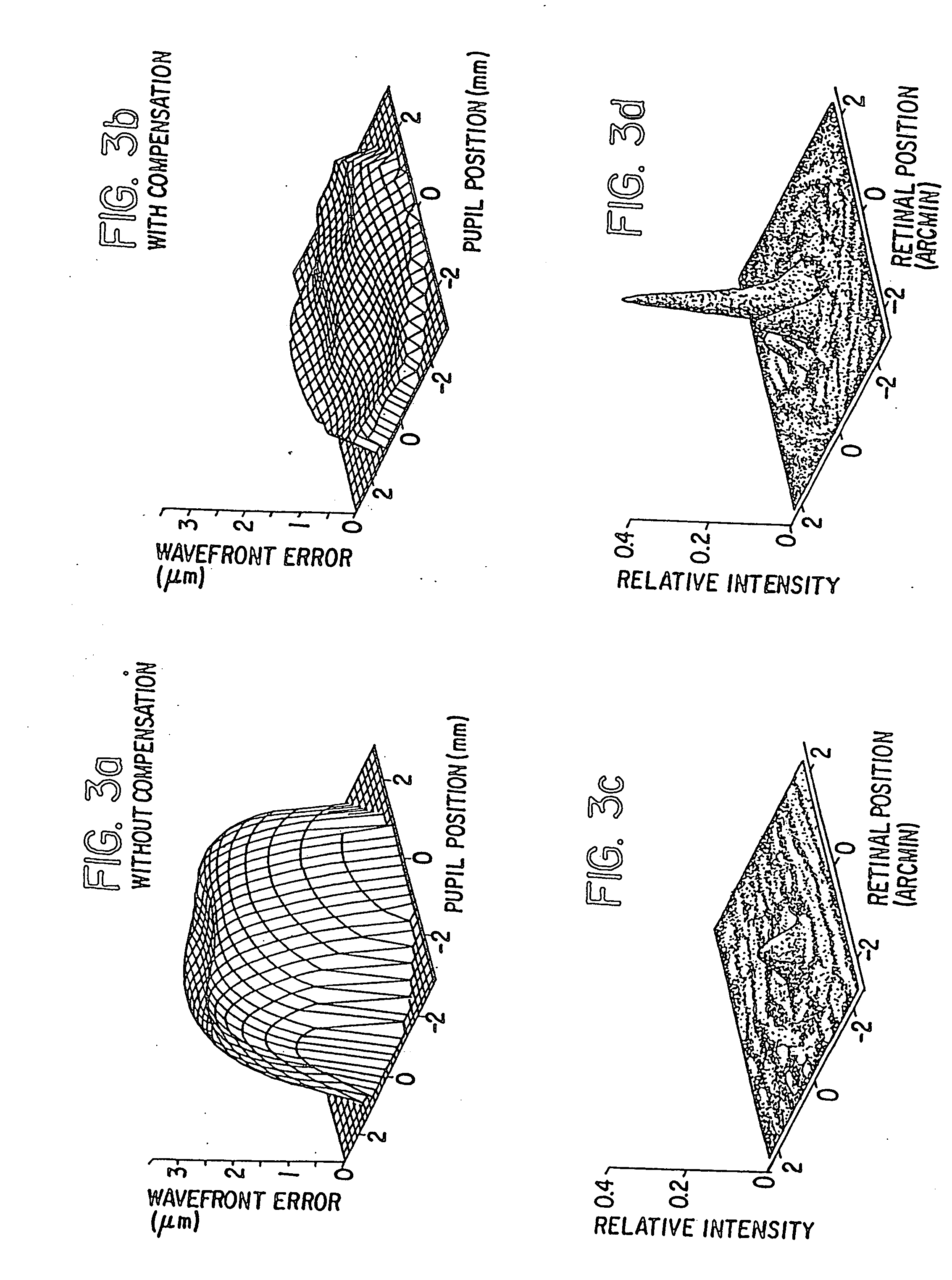
Method and apparatus for improving vision and the resolution of retinal images
InactiveUS20060044510A1Accurate measurementHigh resolutionOptical measurementsEye surgeryCcd cameraLaser beams
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Method and apparatus for pseudo-projection formation for optical tomography
ActiveUS7738945B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMultiple perspectiveOptical tomography
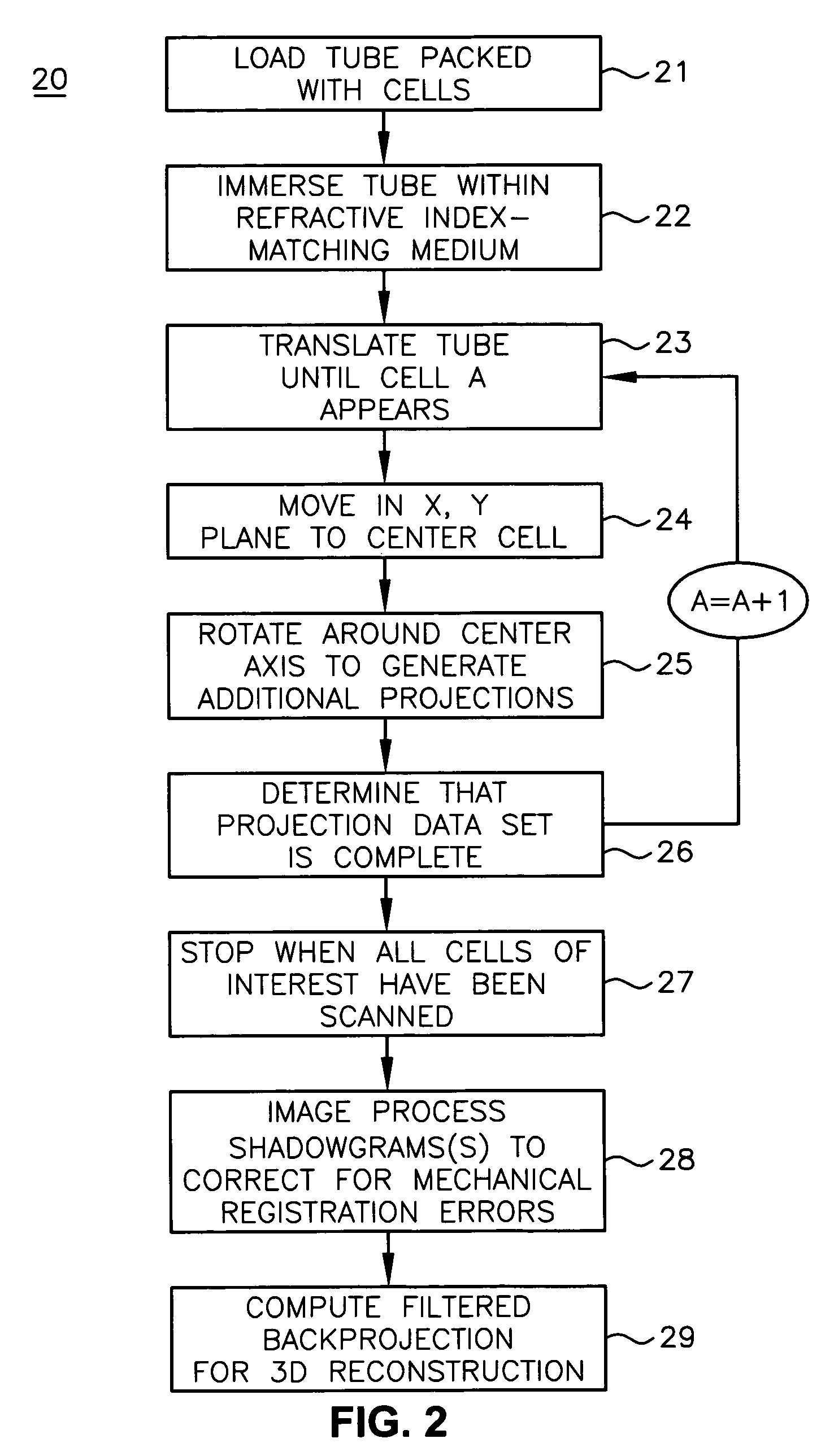
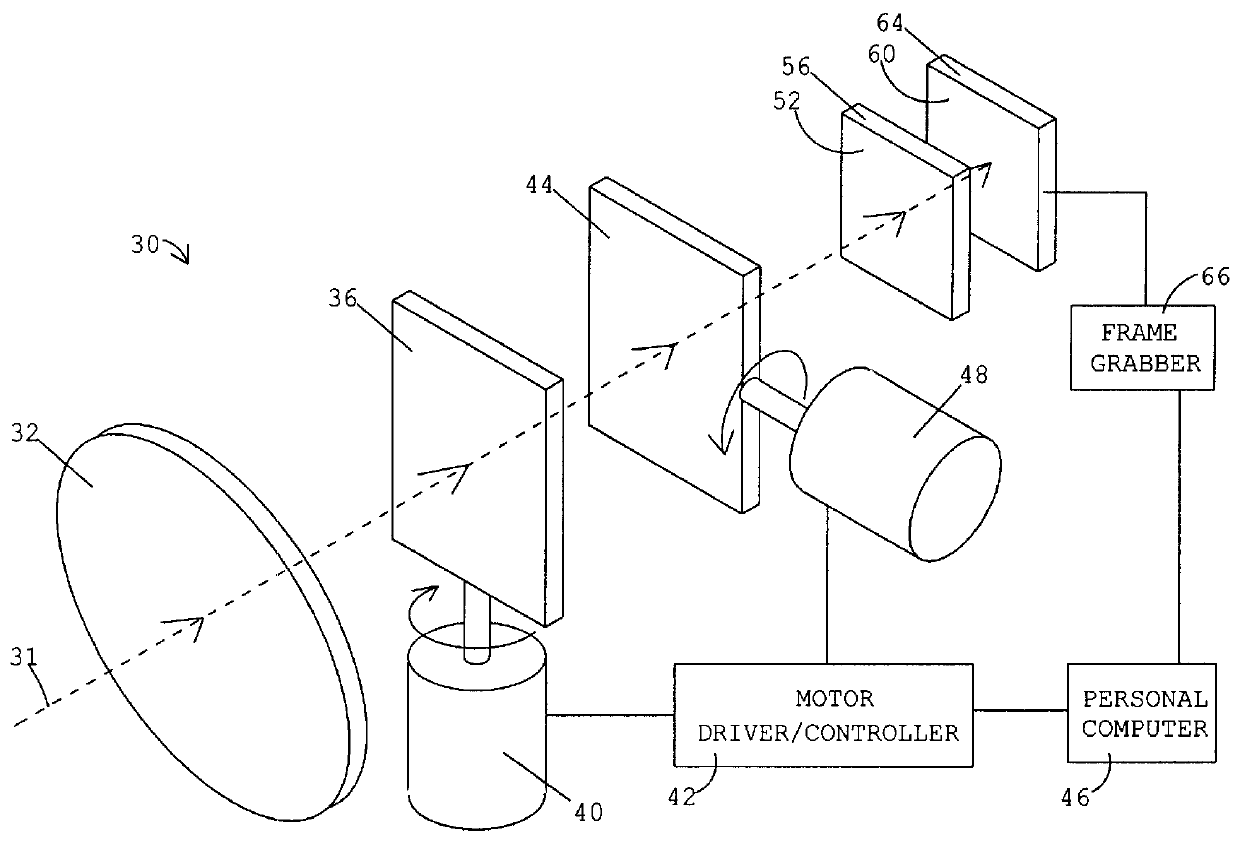
A system for optical imaging of a thick specimen that permits rapid acquisition of data necessary for tomographic reconstruction of the three-dimensional (3D) image. One method involves the scanning of the focal plane of an imaging system and integrating the range of focal planes onto a detector. The focal plane of an optical imaging system is scanned along the axis perpendicular to said plane through the thickness of a specimen during a single detector exposure. Secondly, methods for reducing light scatter when using illumination point sources are presented. Both approaches yield shadowgrams. This process is repeated from multiple perspectives, either in series using a single illumination / detection subsystem, or in parallel using several illumination / detection subsystems. A set of pseudo-projections is generated, which are input to a three dimensional tomographic image reconstruction algorithm.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
High-resolution polarization-sensitive imaging sensors
An apparatus and method to determine the surface orientation of objects in a field of view is provided by utilizing an array of polarizers and a means for microscanning an image of the objects over the polarizer array. In the preferred embodiment, a sequence of three image frames is captured using a focal plane array of photodetectors. Between frames the image is displaced by a distance equal to a polarizer array element. By combining the signals recorded in the three image frames, the intensity, percent of linear polarization, and angle of the polarization plane can be determined for radiation from each point on the object. The intensity can be used to determine the temperature at a corresponding point on the object. The percent of linear polarization and angle of the polarization plane can be used to determine the surface orientation at a corresponding point on the object. Surface orientation data from different points on the object can be combined to determine the object's shape and pose. Images of the Stokes parameters can be captured and viewed at video frequency. In an alternative embodiment, multi-spectral images can be captured for objects with point source resolution. Potential applications are in robotic vision, machine vision, computer vision, remote sensing, and infrared missile seekers. Other applications are detection and recognition of objects, automatic object recognition, and surveillance. This method of sensing is potentially useful in autonomous navigation and obstacle avoidance systems in automobiles and automated manufacturing and quality control systems.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Sensor for determining the angular position of a radiating point source in two dimensions
InactiveUS7106431B2Accurately determineAngle measurementPhotometry using reference valueAngle of incidenceDetector array
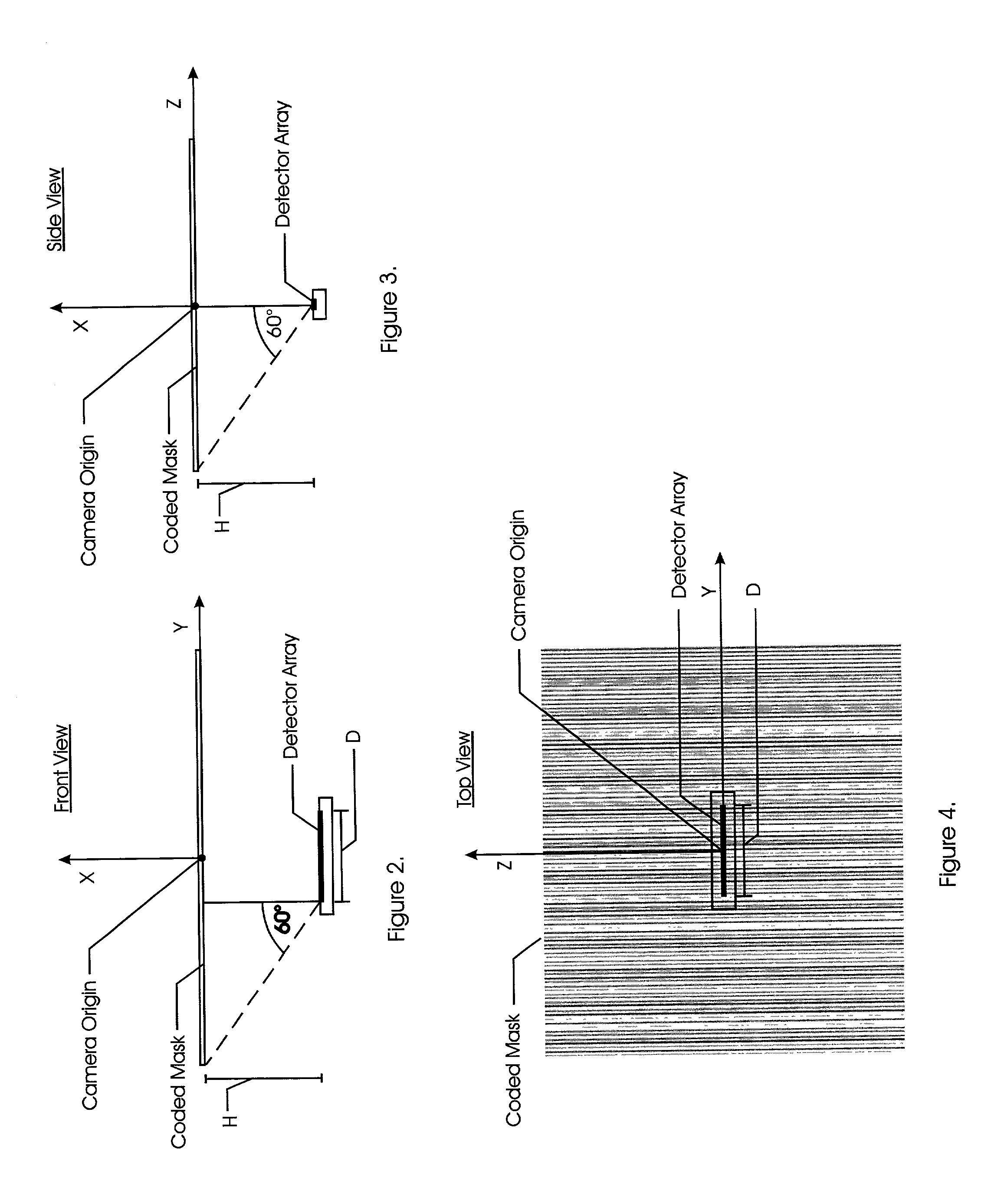
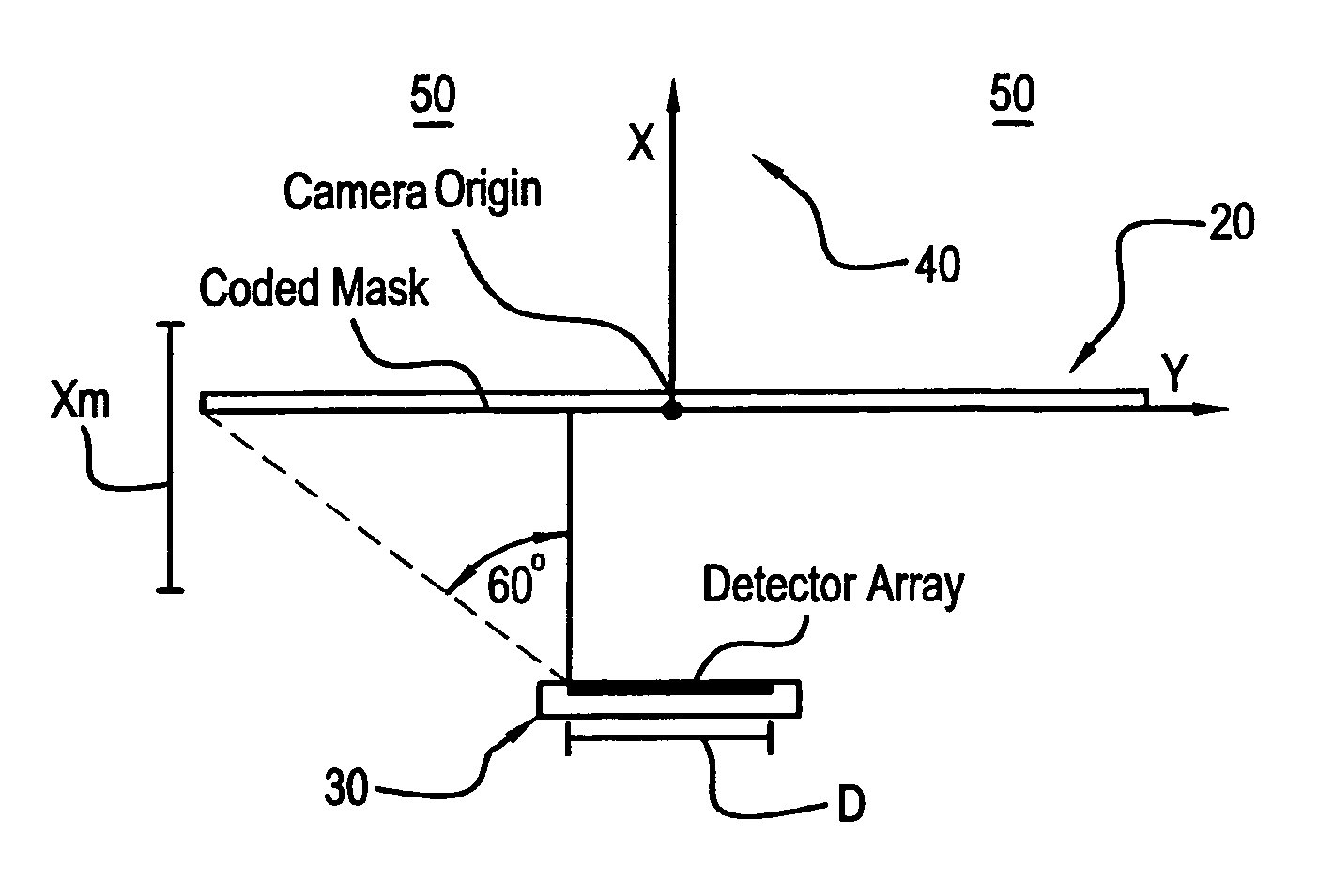
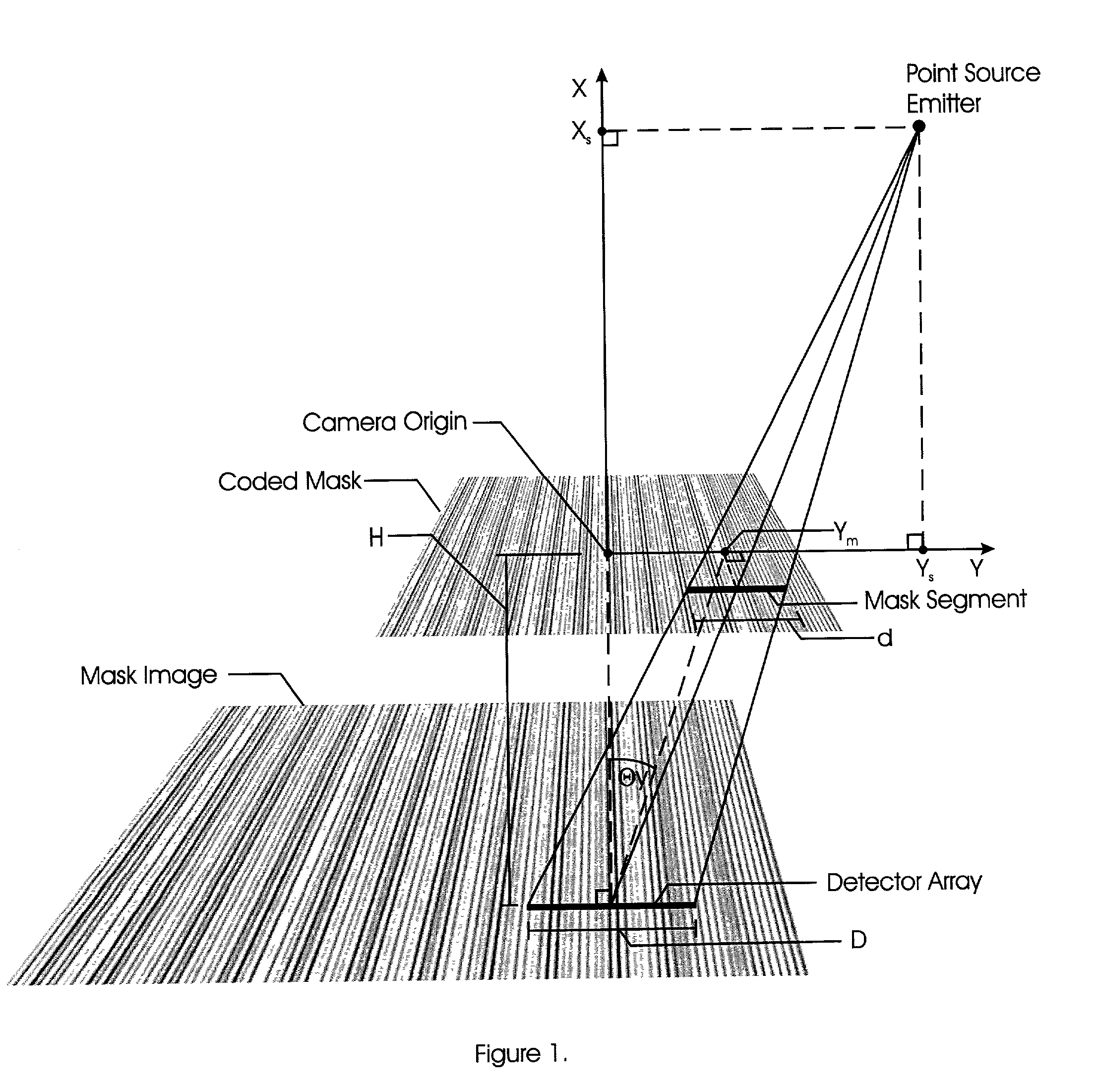
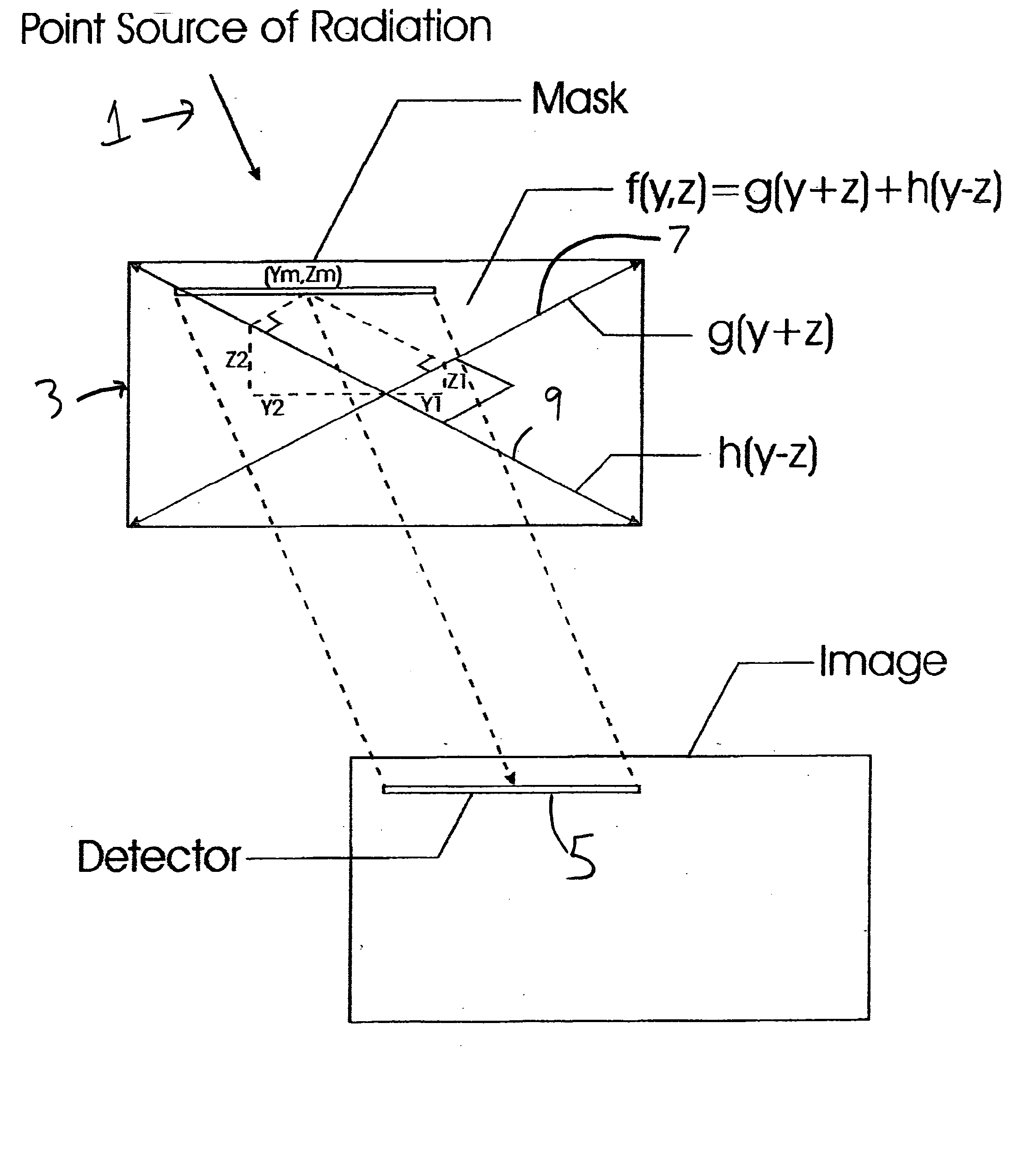
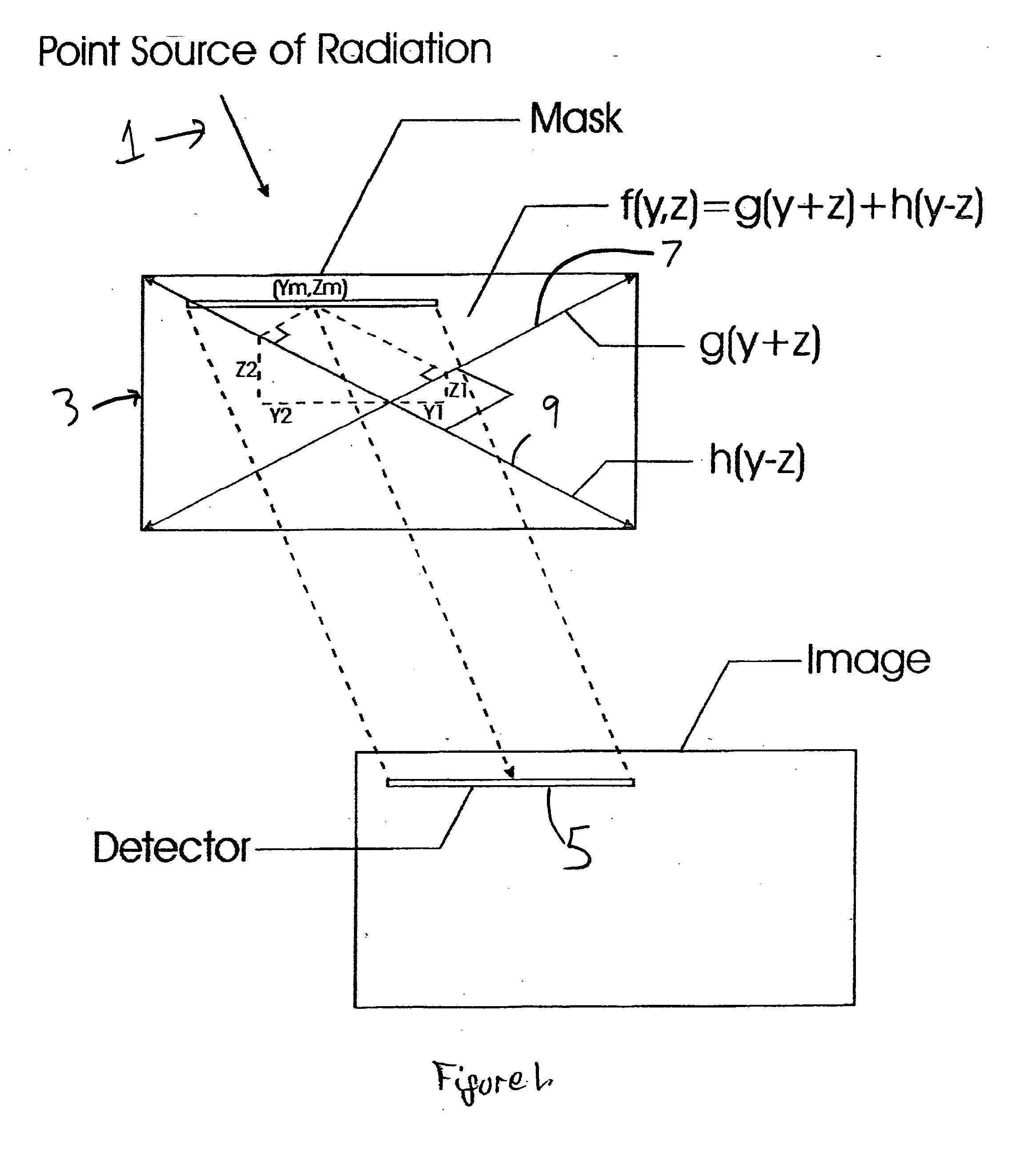
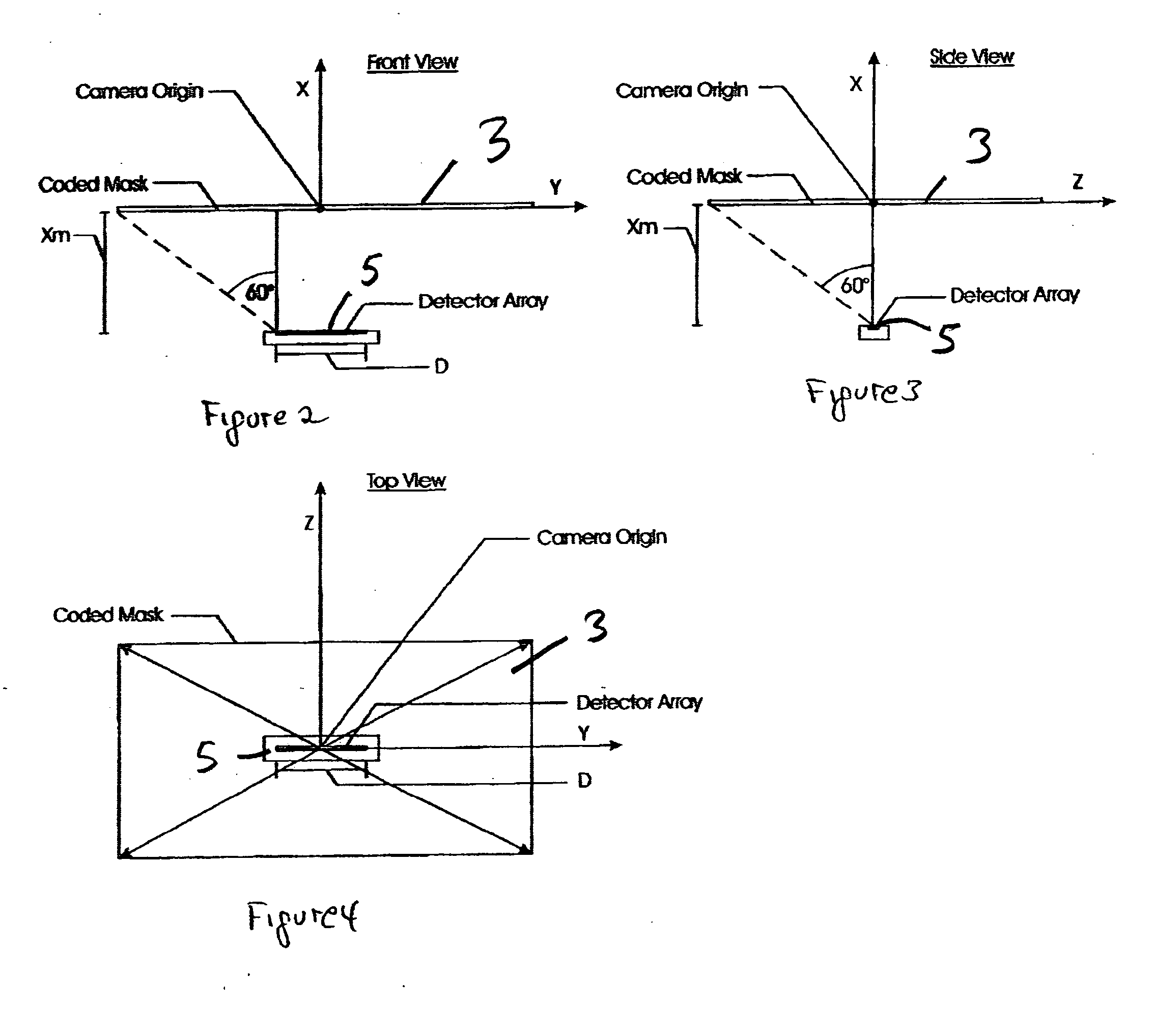
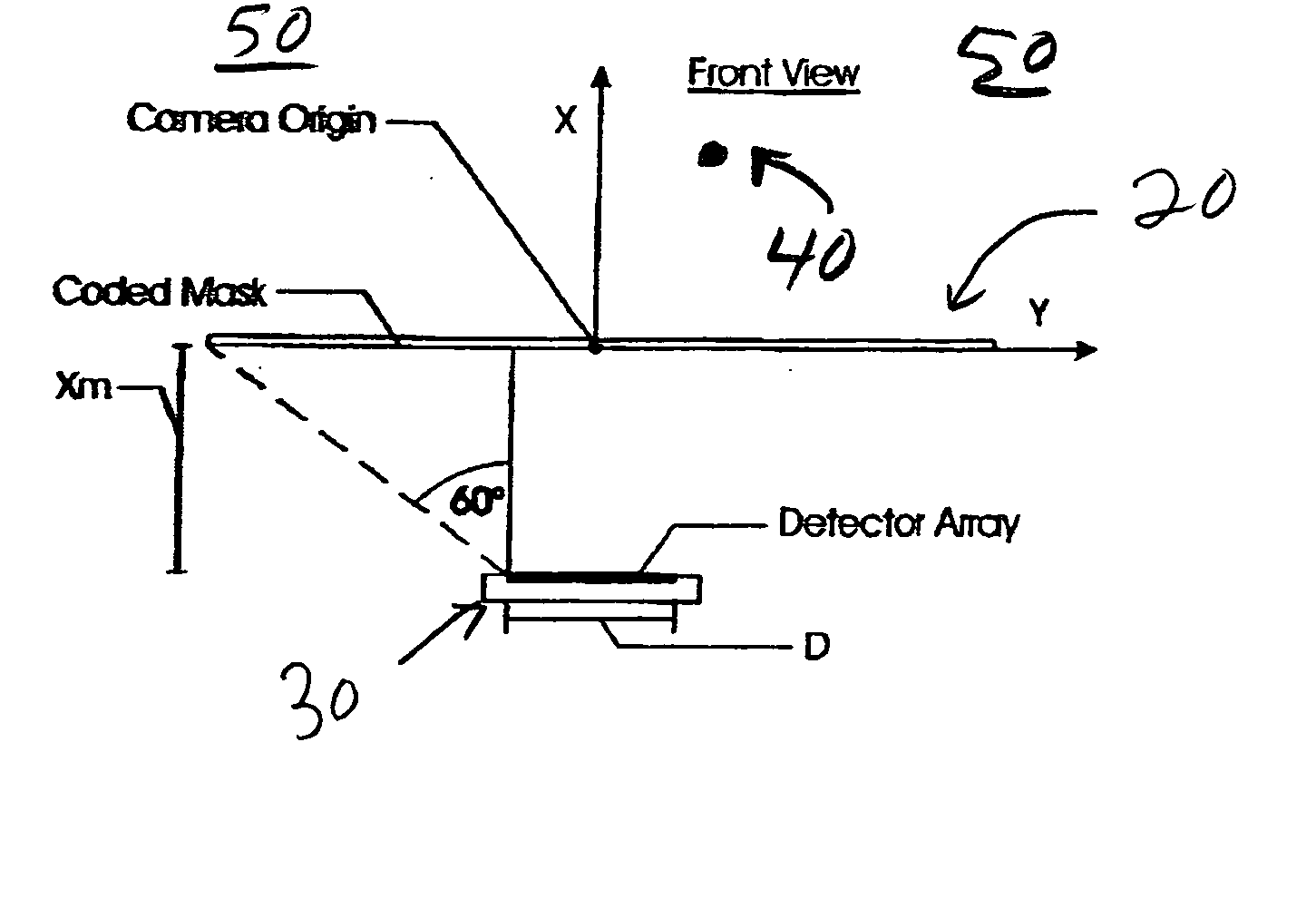
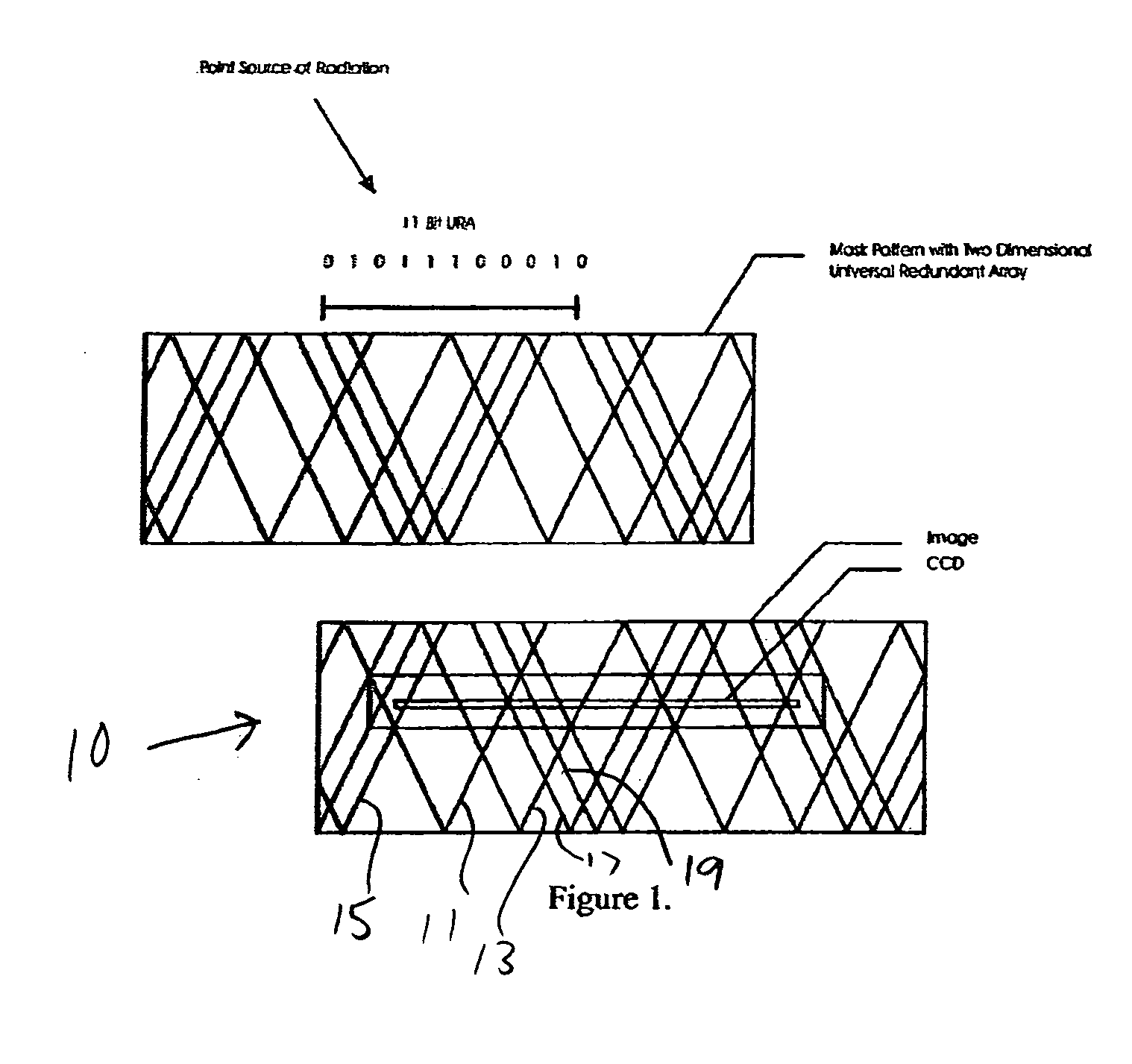
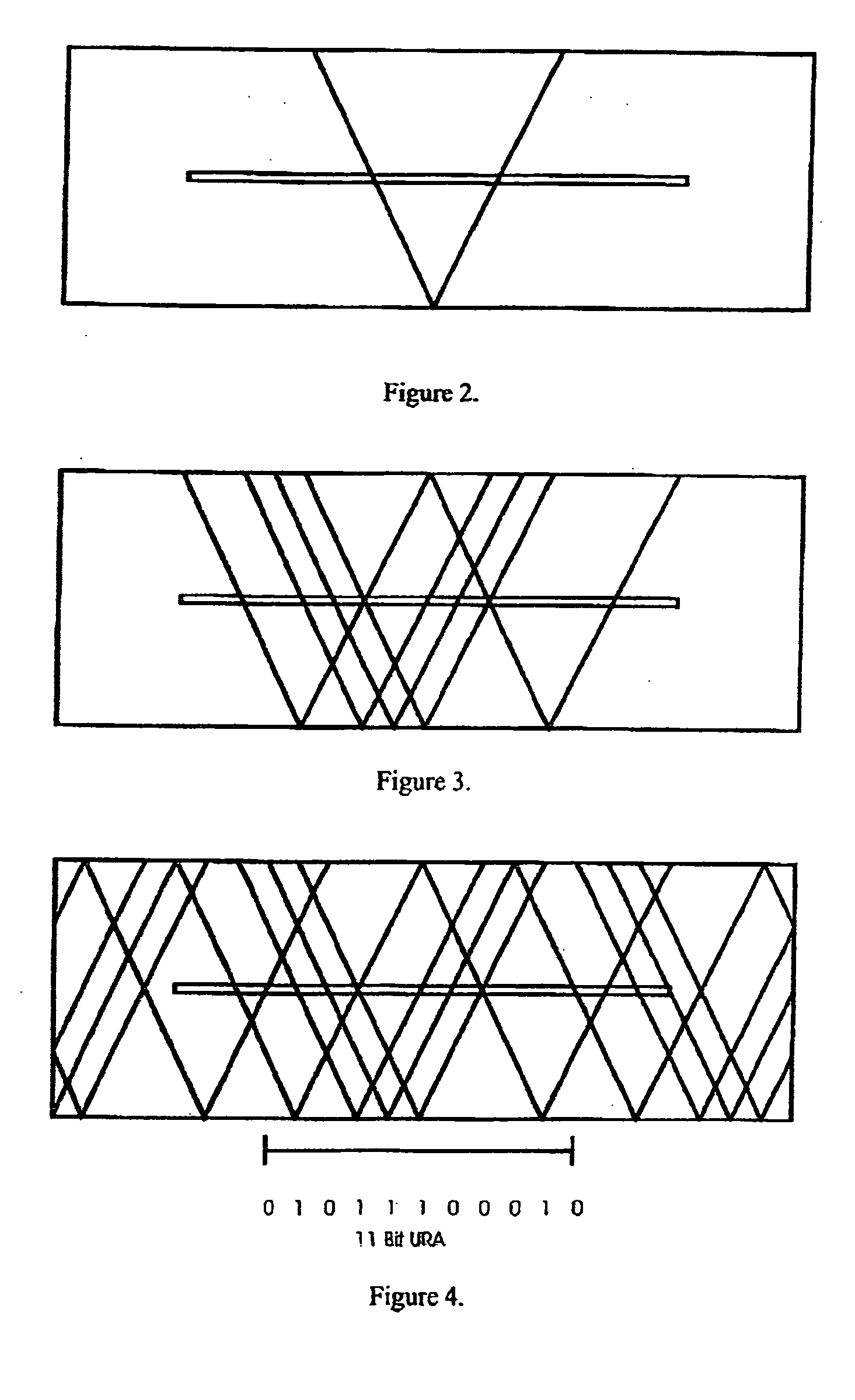
Embodiments of a device and a technique are disclosed for locating the angular position of a radiating point source with respect to a detector comprising a point source of radiation, a variable transmissivity mask with pseudo-random variations, a multi-element detector and computing means for interpreting the detected image. The mask pattern, when illuminated by a point source of radiation, casts an image on the detector array. Computing means determine the pattern shift to allow determination of point source angular location in two dimensions. The mask transmissivity pattern and corresponding image vary in two dimensions, in such a manner as to yield two correlation peaks that indicate the incident angle in two dimensions. The differential shift and common mode shift in correlation peaks indicate the respective angles of incidence, allowing determination of the angular position of the light source.
Owner:ASCENSION TECH
Range adaptable system for determining the angular position and distance of a radiating point source and method of employing
ActiveUS7027634B2Accurate measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansPosition fixationDetector arrayImage scale
A patterned mask is located at a distance from a linear detector array. A point radiating source illuminates the aperture to cast an image onto the array. A computer is employed to identify frequencies in the frequency domain to determine the image scale and shift along the detector array axis. Determination of the magnification of the aperture image is made employing frequency domain techniques, the aperture pattern being re-scaled to match that of the actual image, so that determination of pattern shift can be made. A first embodiment of the present invention has two variations, one of which employs the use of multiple single frequency components and phase methodology, the second of which uses multiple single frequency components as well as a variable frequency component. In a second embodiment, a composite image is also used except that only one single frequency component is used in addition to a non-periodic function.
Owner:NORTHERN DIGITAL
Head-up display
InactiveUS6836369B2Compact designDeterioration in display definitionOptical elementsHead-up displayDisplay device
Owner:DENSO CORP
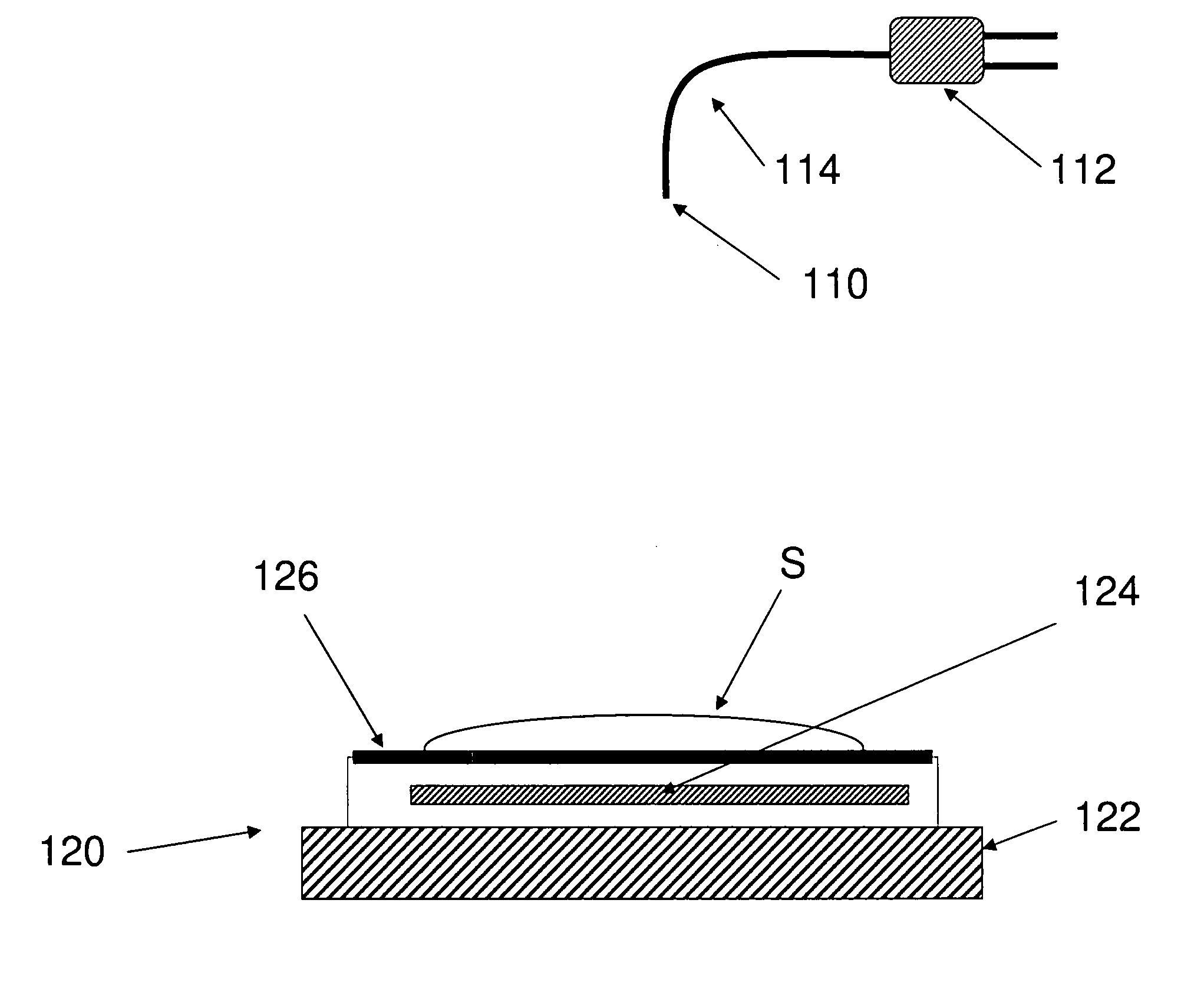
Contact microscope using point source illumination
InactiveUS7936501B2Less expensiveEasy to useTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsDigital imagingDisplay device
The embodiments of the invention include a microscope having a transparent specimen holder and a digital imaging device positioned within the transparent specimen holder. The digital imaging device can include a wireless transmitter. The transparent specimen holder can have a top surface and a bottom surface, wherein the transparent specimen holder is completely transparent between the top surface and the bottom surface. Thus, the transparent specimen holder is completely transparent above and below the digital imaging device. Furthermore, a processor is operatively connected to the digital imaging device, wherein the processor produces an image of a specimen positioned on the specimen holder. A display is operatively connected to the processor, wherein the display displays the image.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Integrated circuit-based compound eye image sensor using a light pipe bundle
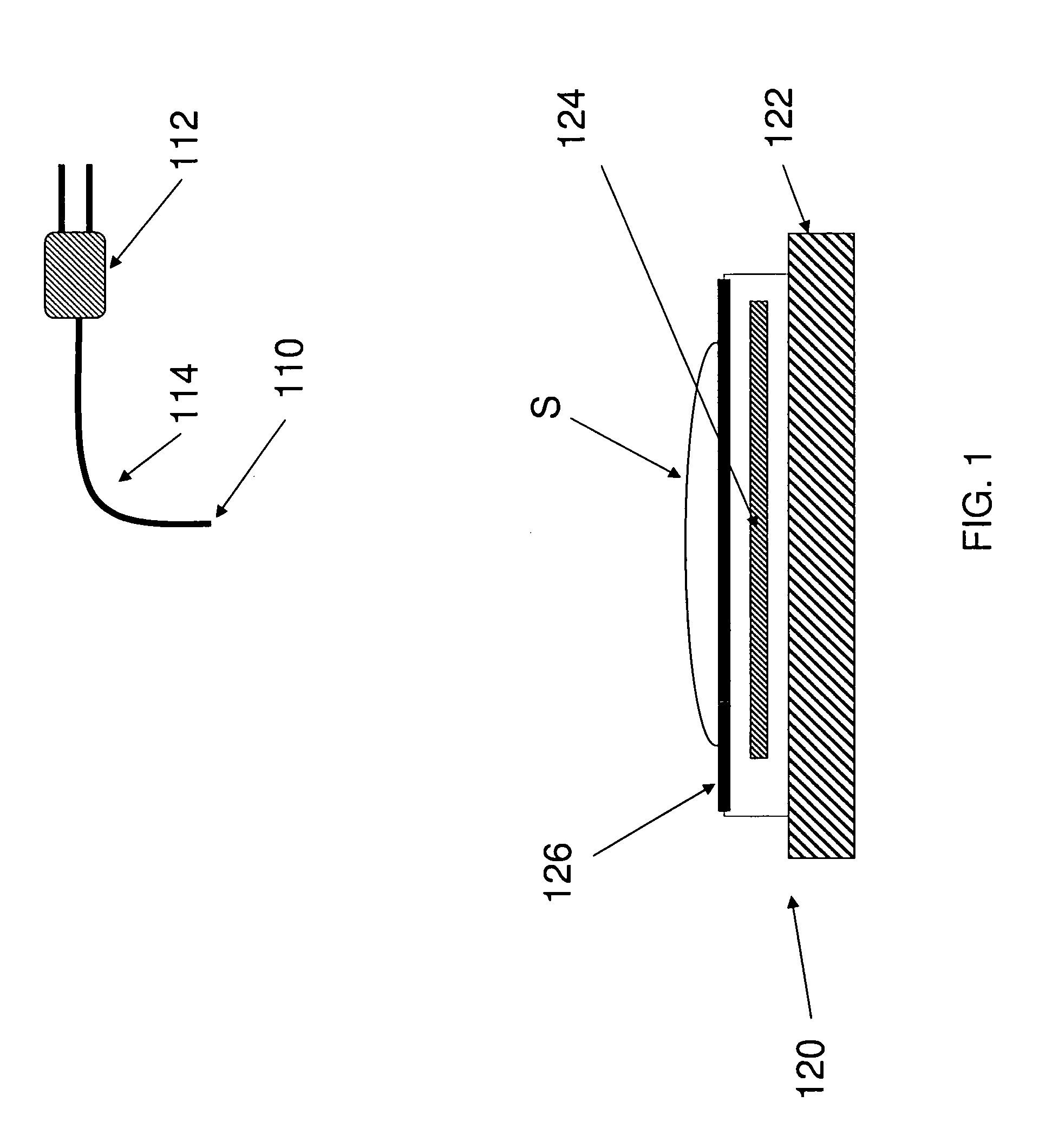
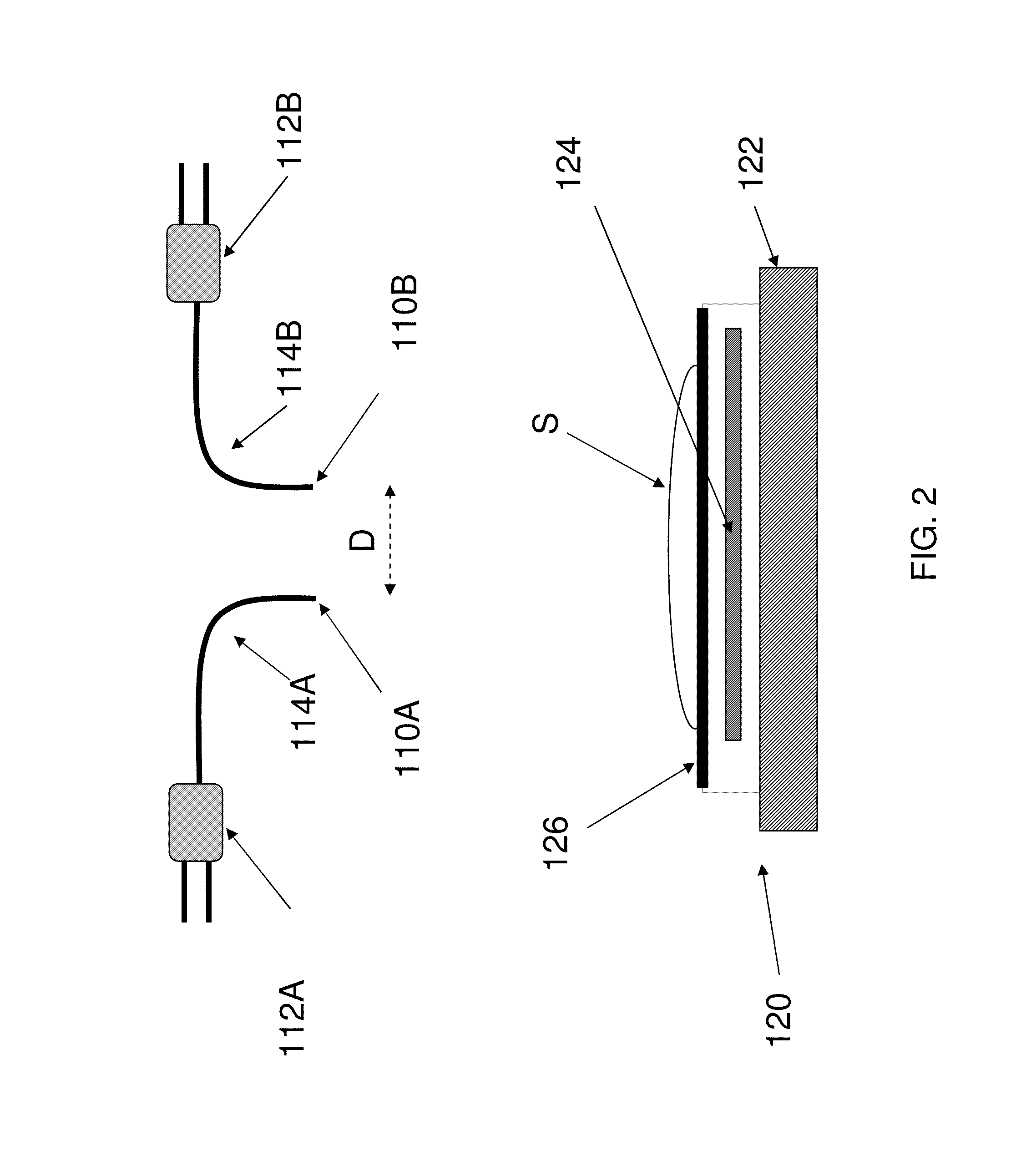
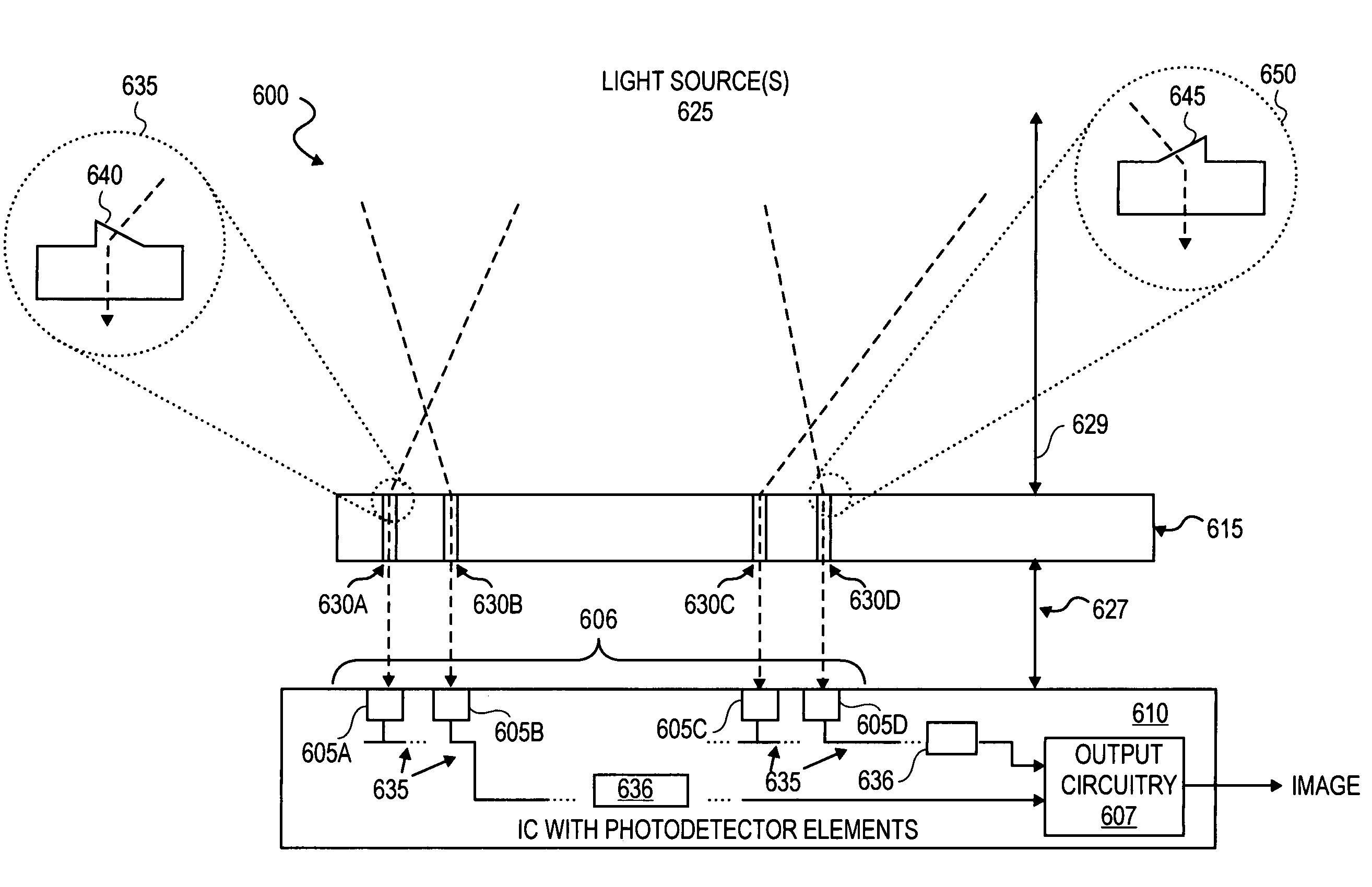
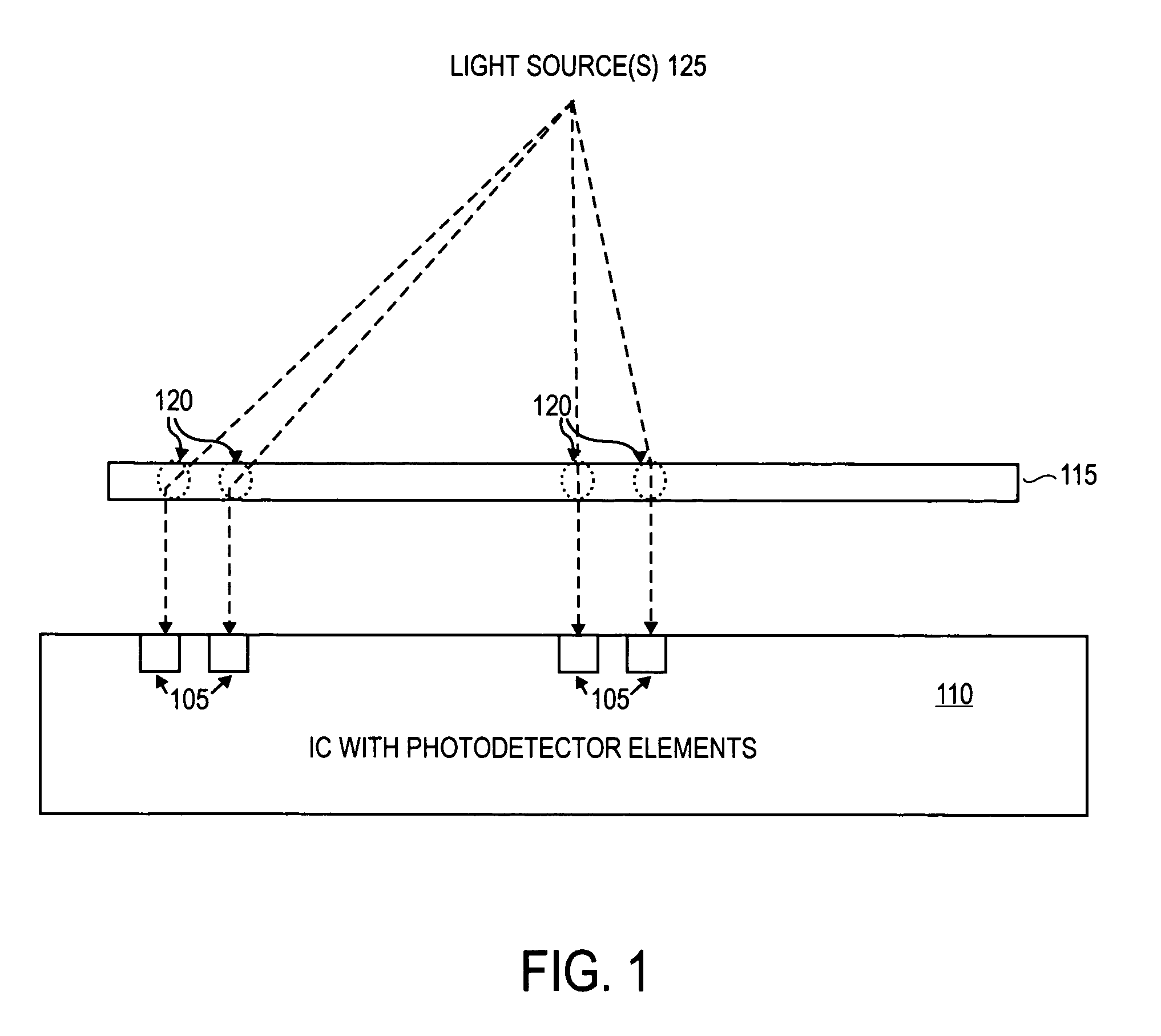
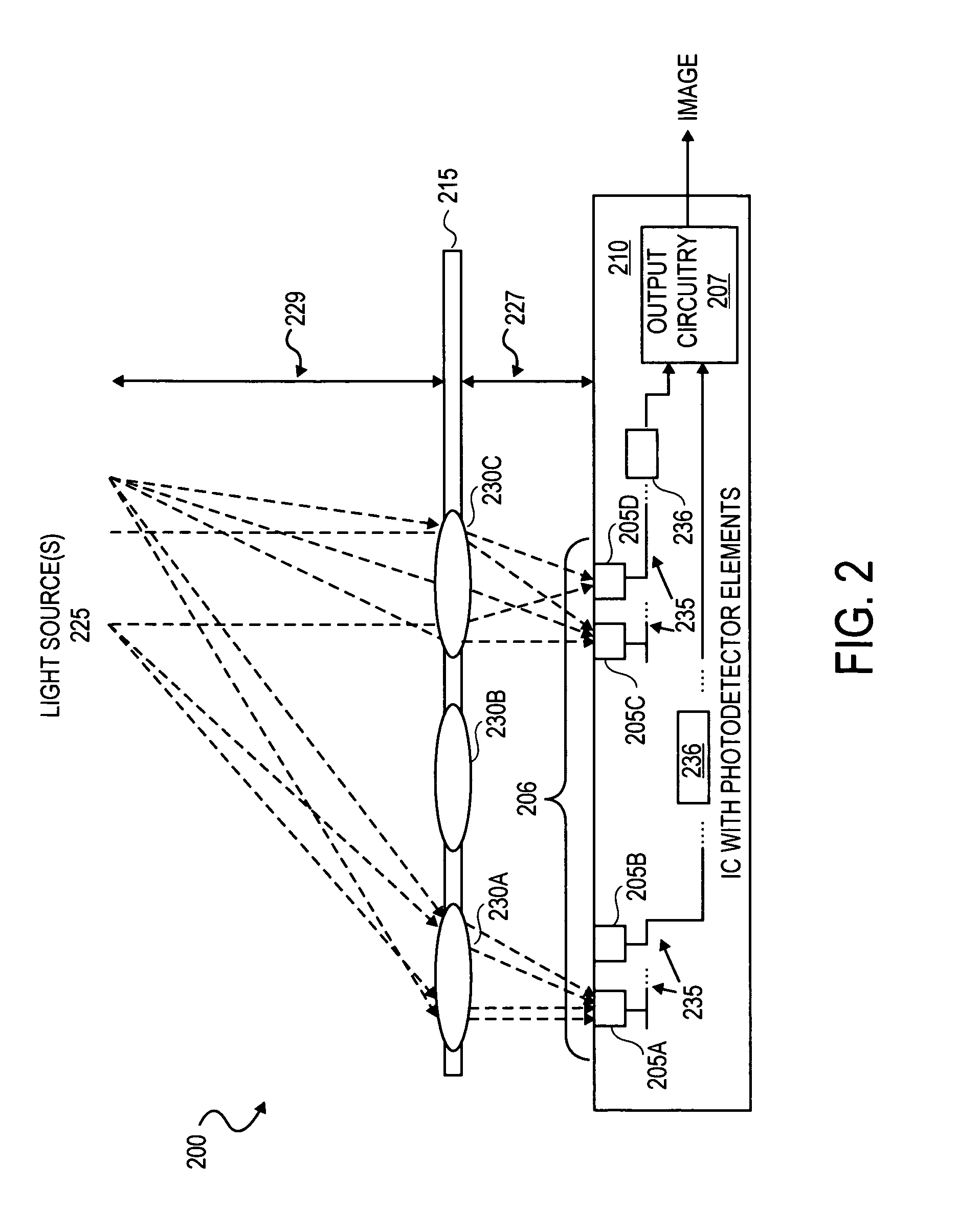
An integrated circuit-based compound eye includes a plurality of photodetector elements disposed on a semiconductor substrate. A compound light directing member includes a light pipe bundle wherein at least some of the light pipes are to individually direct light energy from one or more sources onto one or more of the photodetector elements. The compound light directing member is the primary mechanism to direct light energy onto the one or more of the photodetector elements. Outputs of the photodetector elements are electrically coupled in such a way that an image associated with the source may be synthesized at output circuitry.For another aspect, a compound exposure determining member includes a plurality of light scanning elements, each of the light scanning elements including an integrated photodetector. Each of the light scanning elements is controllable to vary an angle of the photodetector with respect to a substrate to determine from which point sources and angles light energy is received at the photodetector.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Sensor for determining the angular position of a radiating point source in two dimensions and method of operation
InactiveUS20050105101A1Image analysisInstruments for comonautical navigationFast Fourier transformFrequency spectrum
A sensor for determining the angular position of a radiating point source in two dimensions includes a mask encoded in two skewed directions with waveforms consisting of several frequencies in prescribed patterns. The frequency spectra of the received detector patterns are computed. In order to facilitate such computations, the constituent frequencies are separated so as to be distinguished in the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). Each of the frequency patterns that are coded on the variable transmissivity mask consists of a series of low frequencies followed by a series of variable frequencies, and a series of high frequencies. The variable frequencies exhibit frequency changes responsive to various image positions. The low and high frequencies are responsive in phase to variations in image position. The frequency variations in the variable frequencies are used to indicate coarse position while the phases of the fixed low and high frequencies are used to indicate medium and fine position. In a second embodiment, the mask pattern is formed by a first pattern including low variable and high frequency components, a second pattern with fixed low and high frequency components, and a third pattern with variable frequency components. The method of determining position is also disclosed.
Owner:ASCENSION TECH
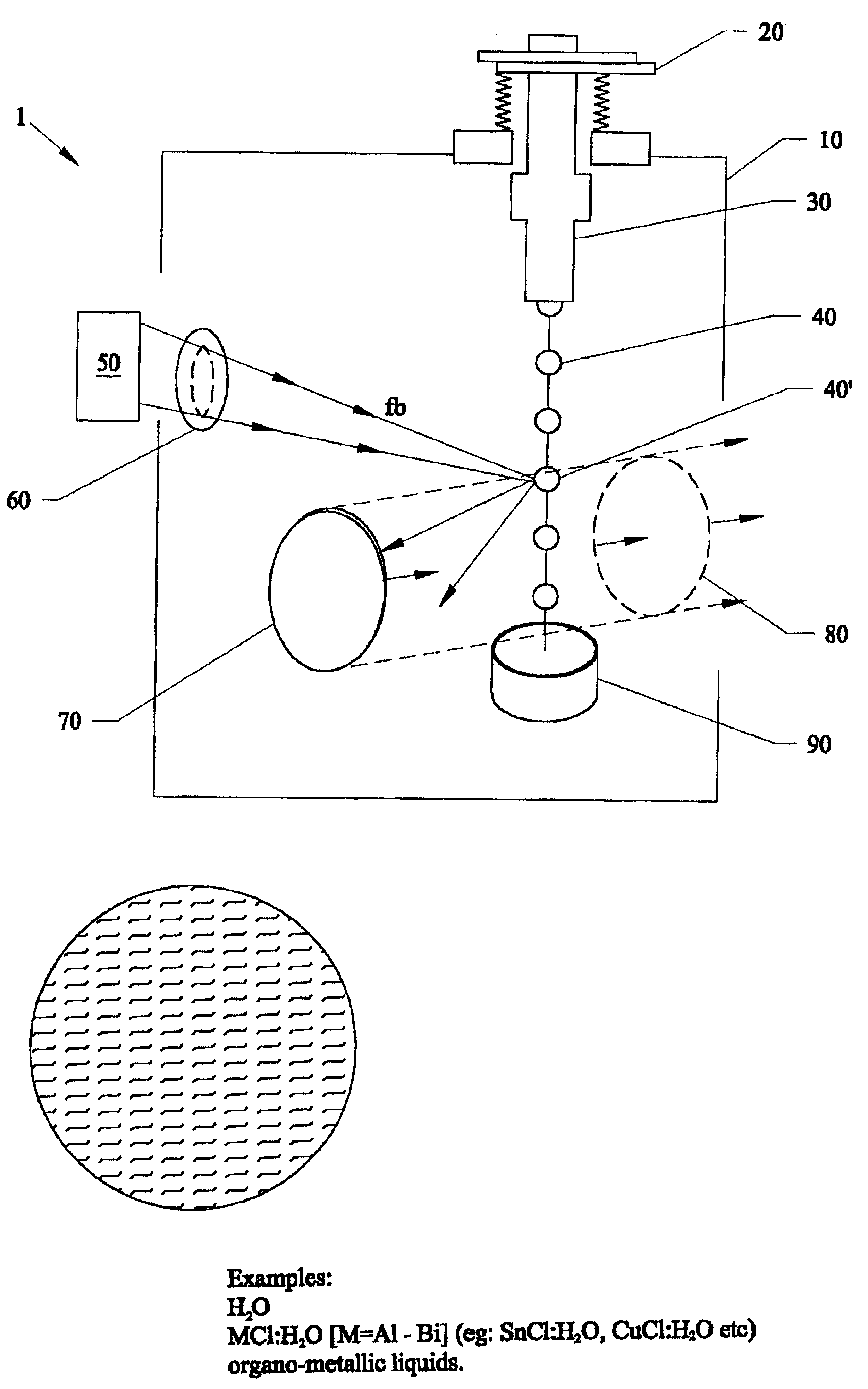
EUV, XUV, and X-ray wavelength sources created from laser plasma produced from liquid metal solutions, and nano-size particles in solutions
InactiveUS6865255B2Efficient and inexpensiveEliminate damageX-ray tube electrodesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh power lasersUltraviolet
Special liquid droplet targets that are irradiated by a high power laser and are plasmarized to form a point source EUV, XUV and x-ray source. Various types of liquid droplet targets include metallic solutions, and nano-sized particles in solutions having a melting temperature lower than the melting temperature of some or all of the constituent metals, used a laser point source target droplets. The solutions have no damaging debris and can produce plasma emissions in the X-rays, XUV, and EUV(extreme ultra violet) spectral ranges of approximately 0.1 nm to approximately 100 nm, approximately 11.7 nm and 13 nm, approximately 0.5 nm to approximately 1.5 nm, and approximately 2.3 nm to approximately 4.5 nm. The second type of target consists of various types of liquids which contain as a miscible fluid various nano-size particles of different types of metals and non-metal materials.
Owner:CENT FLORIDA UNIV OF
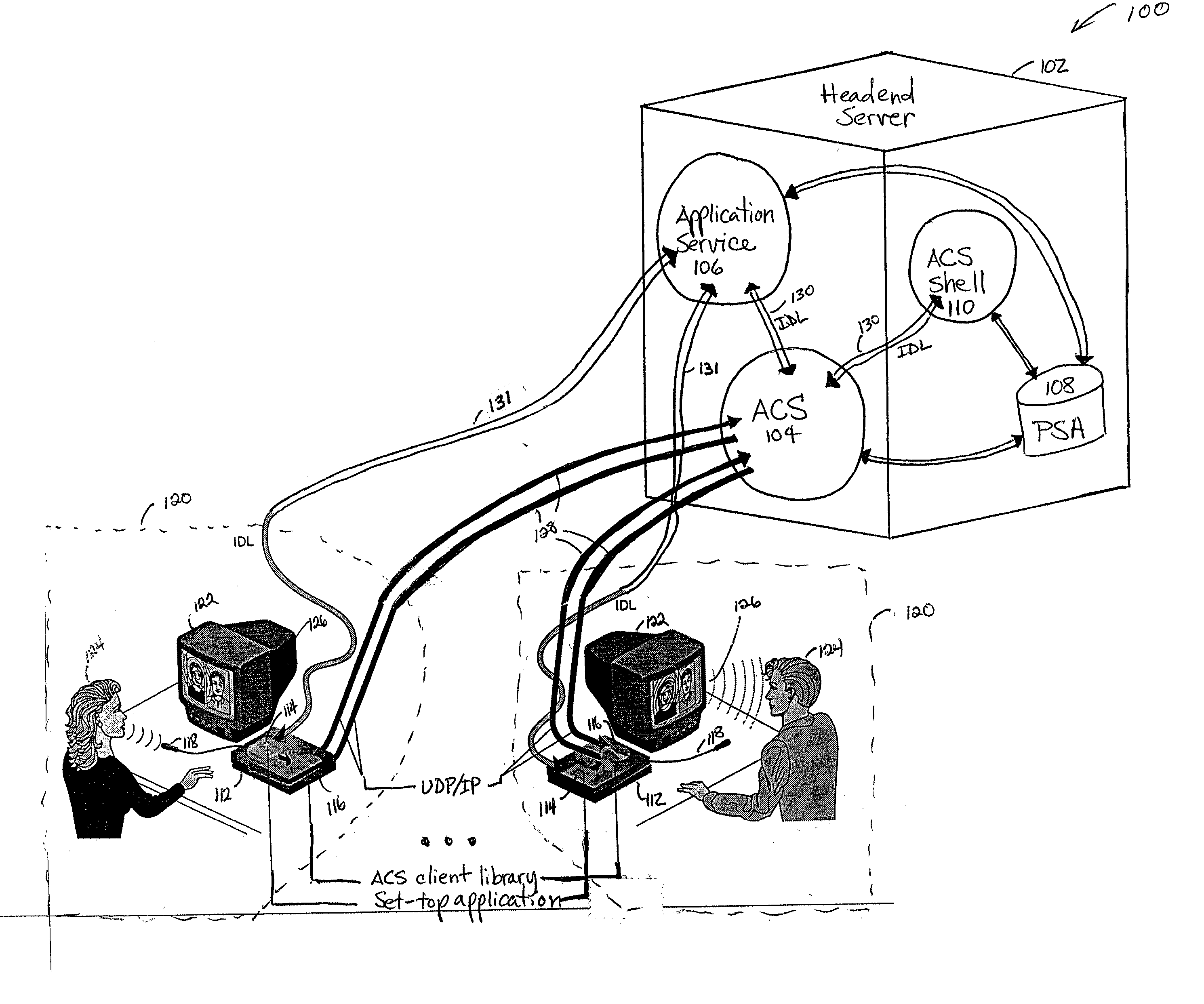
Spatialized audio in a three-dimensional computer-based scene
InactiveUS20020013813A1Special service provision for substationSpecial service for subscribersUltrasound attenuationDecay factor
A system and method for enabling an audio conference server (ACS) to provide an application program with multi-point weight controllable audio conferencing. The ACS manages a plurality of audio conferences, receives audio data from a plurality of audio clients, mixes the audio data to provide distance-based attenuation according to decay characteristics for each sound, and delivers the mixed audio data to a plurality of audio clients. Audio clients include set-top box (STB) audio clients and point source audio (PSA) audio clients. The ACS mixes the audio data by identifying a decay factor. Pre-defined decay factors include an audio big decay factor, an audio small decay factor, an audio medium decay factor, and a constant decay factor. One can also develop a customized decay factor. A weighted value for a source audio client based on the identified decay factor and the distance between the source audio client and a target audio client is determined. A mix table is generated using the weighted values for each source / target audio client pair. Then an actual mix value for each target audio client is calculated using the mix table. The present invention also includes means for refining the actual mix value.
Owner:COMP ASSOC THINK INC
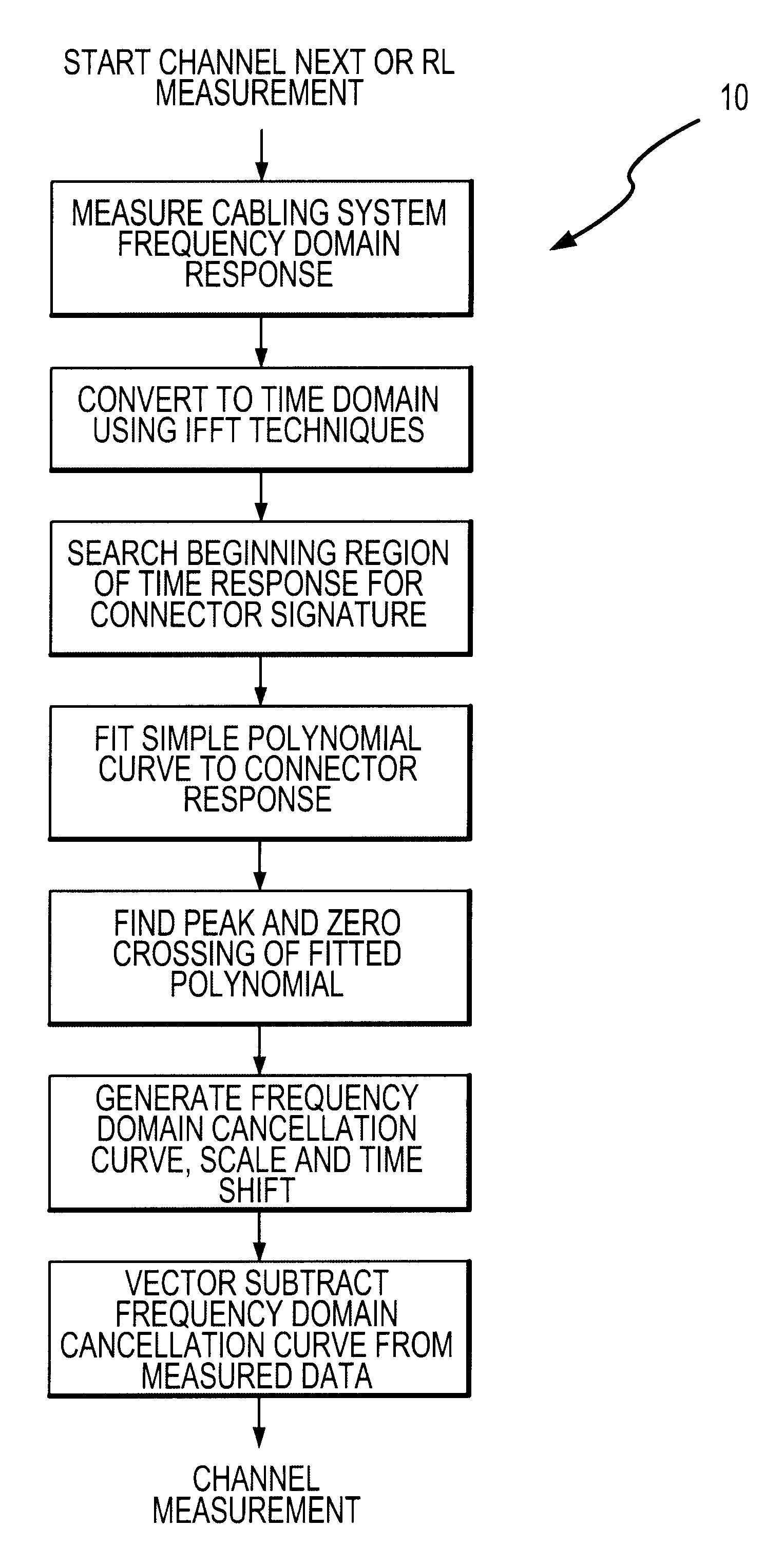
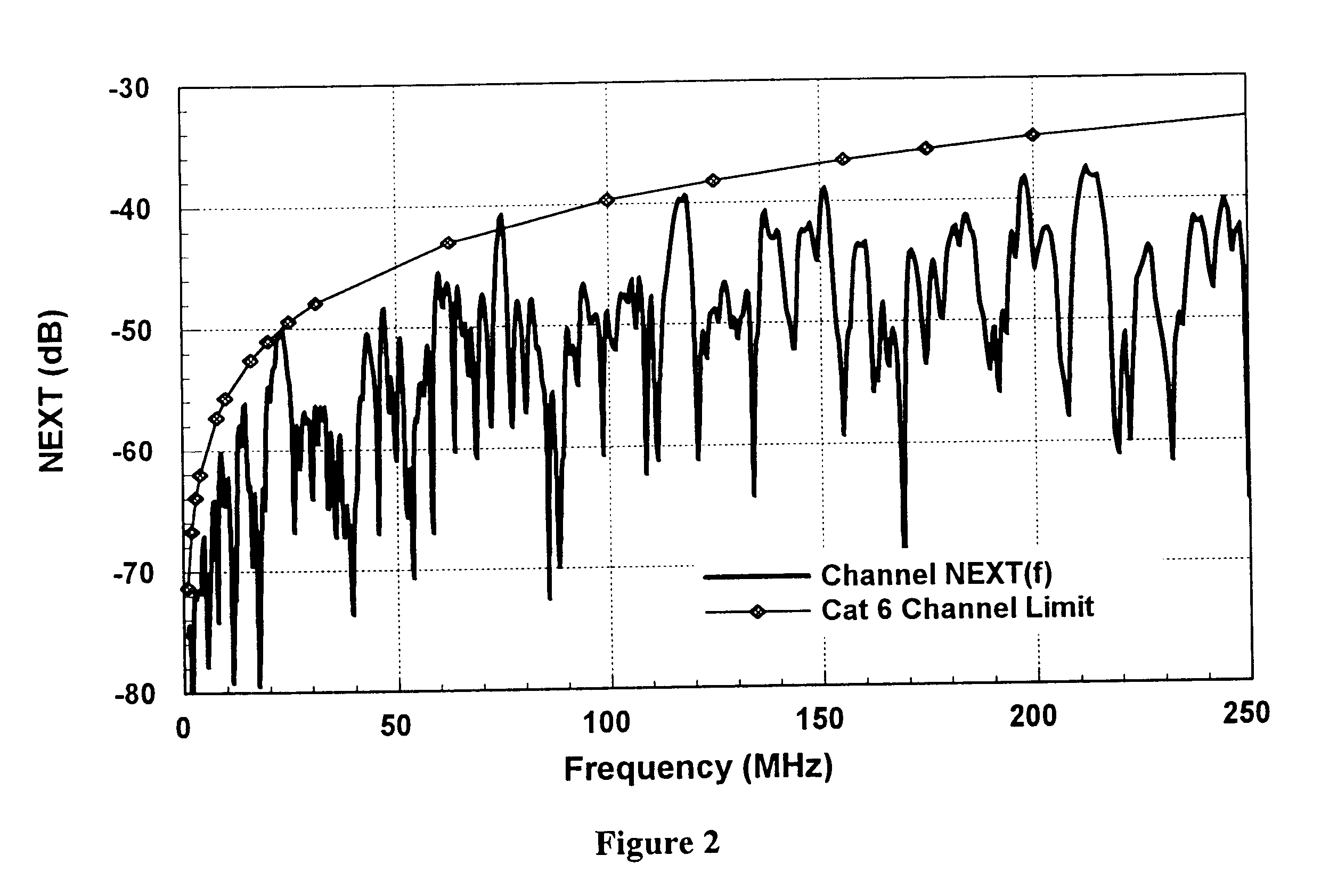
Method and apparatus for adaptive cancellation of responses in cabling
InactiveUS6522152B1Resistance/reactance/impedenceFault location by conductor typesSignal responseTime domain
An Adaptive Vector Cancellation method which uses time domain data for an instrument connection to estimate magnitude, phase, and time position of a signal response such as NEXT or Return Loss associated with the connection. Based on the estimate of the amplitude and time of the connection response, a suitable full-bandwidth frequency response that corresponds to a point source of NEXT or Return Loss is determined. This calculated connector response is then scaled to an appropriate magnitude, phase and time shifted to the estimated position of the actual connection. The scaled / shifted response is then vectorially combined with the measured sweep data to suitably cancel the connection contribution to NEXT and / or Return Loss. Thus, the amount of NEXT or return loss existing in the user's patch cord is preserved, while the NEXT or return loss due to the instrument connection is suitably suppressed. Correction is done in the frequency domain, over the full bandwidth of the measured data.
Owner:MICROTEST
Sensor for determining the angular position of a radiating point source in two dimensions
InactiveUS20050105081A1Accurately determineAngle measurementPhotometry using reference valueAngle of incidenceDetector array
Embodiments of a device and a technique are disclosed for locating the angular position of a radiating point source with respect to a detector comprising a point source of radiation, a variable transmissivity mask with pseudo-random variations, a multi-element detector and computing means for interpreting the detected image. The mask pattern, when illuminated by a point source of radiation, casts an image on the detector array. Computing means determine the pattern shift to allow determination of point source angular location in two dimensions. The mask transmissivity pattern and corresponding image vary in two dimensions, in such a manner as to yield two correlation peaks that indicate the incident angle in two dimensions. The differential shift and common mode shift in correlation peaks indicate the respective angles of incidence, allowing determination of the angular position of the light source.
Owner:ASCENSION TECH
Methods and systems for determining the orientation of natural fractures
InactiveUS6985816B2Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainHydraulic fracturing
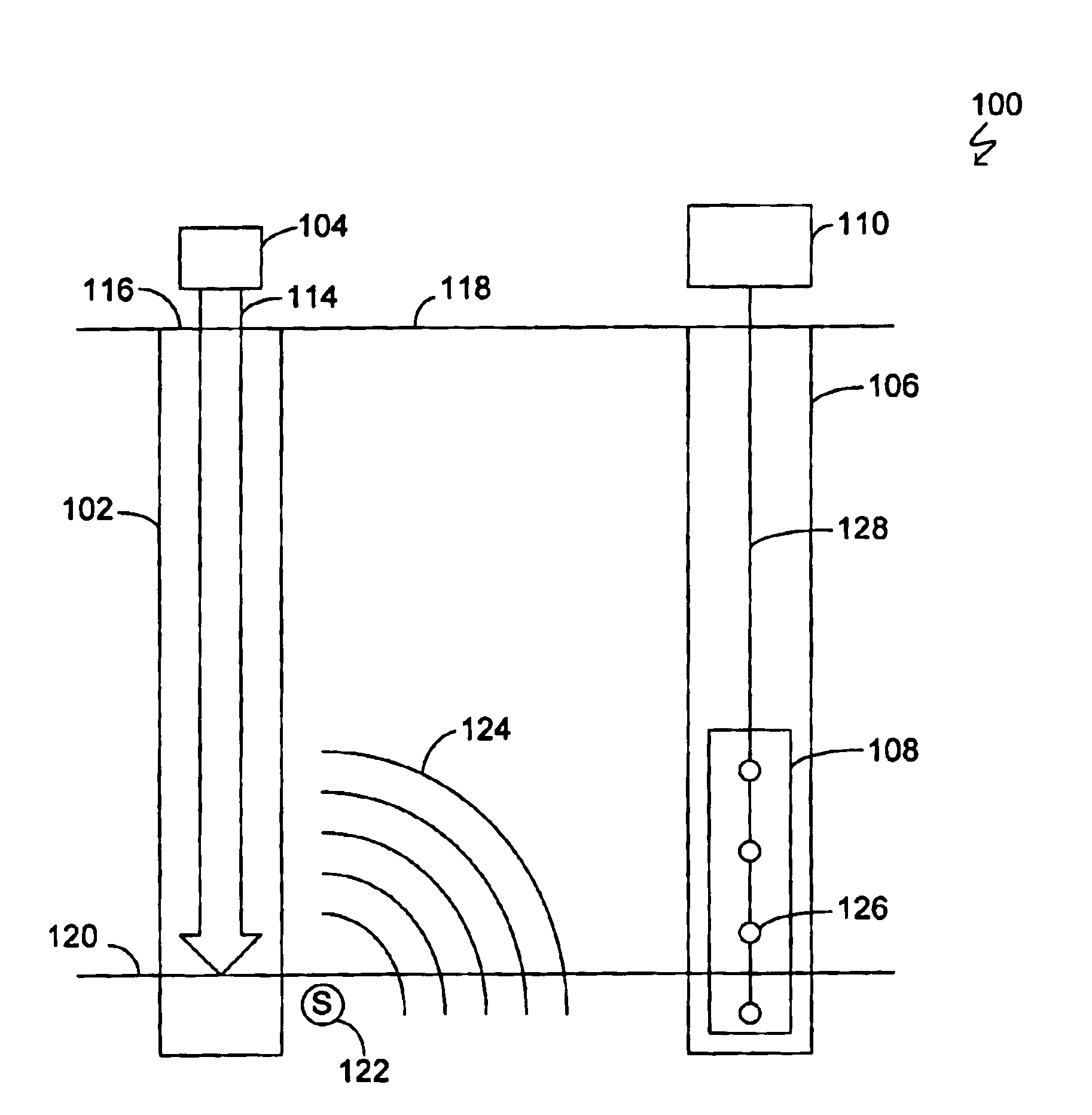
Methods, systems, and articles of manufacture consistent with the present invention provide for determining the orientation of natural fractures in the Earth resulting from hydraulic fracturing treatment. Data attribute information from a far-field point-source signal profile for a microseismic event is extracted in the time domain. An estimate of the orientation of the natural fracture is calculated in the time domain based on the extracted data attribute information.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
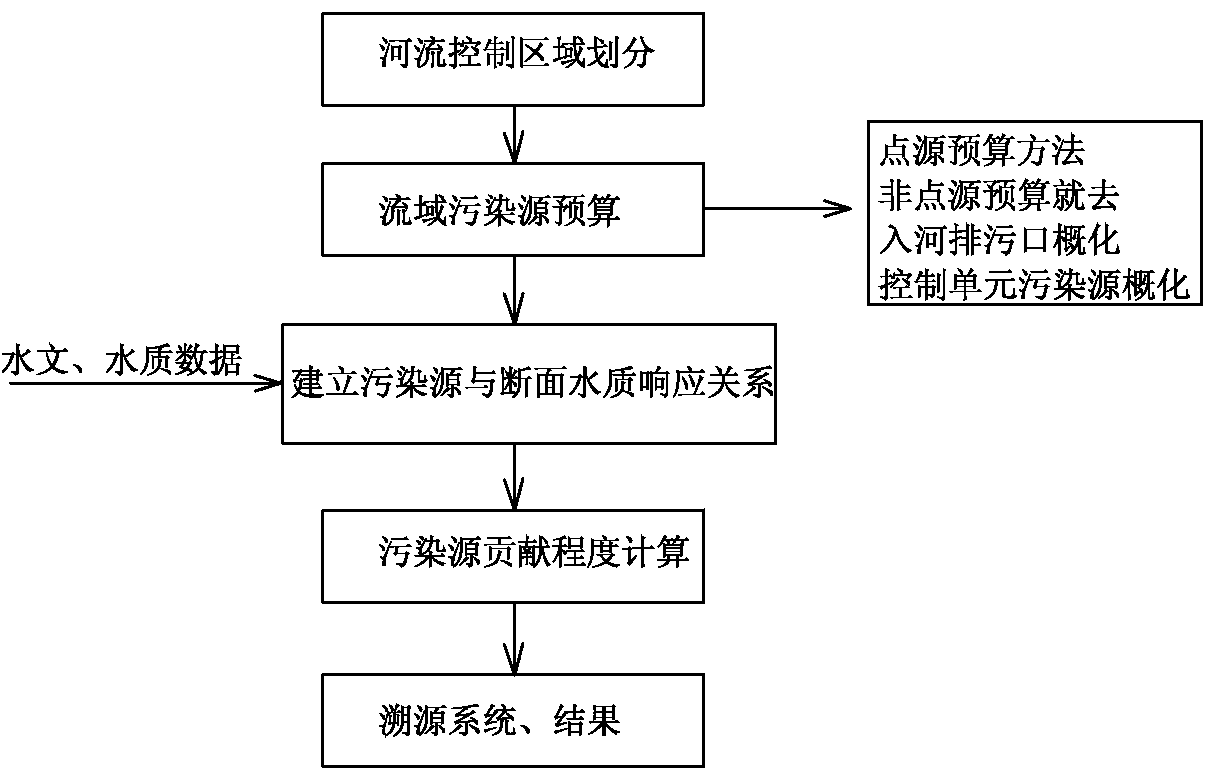
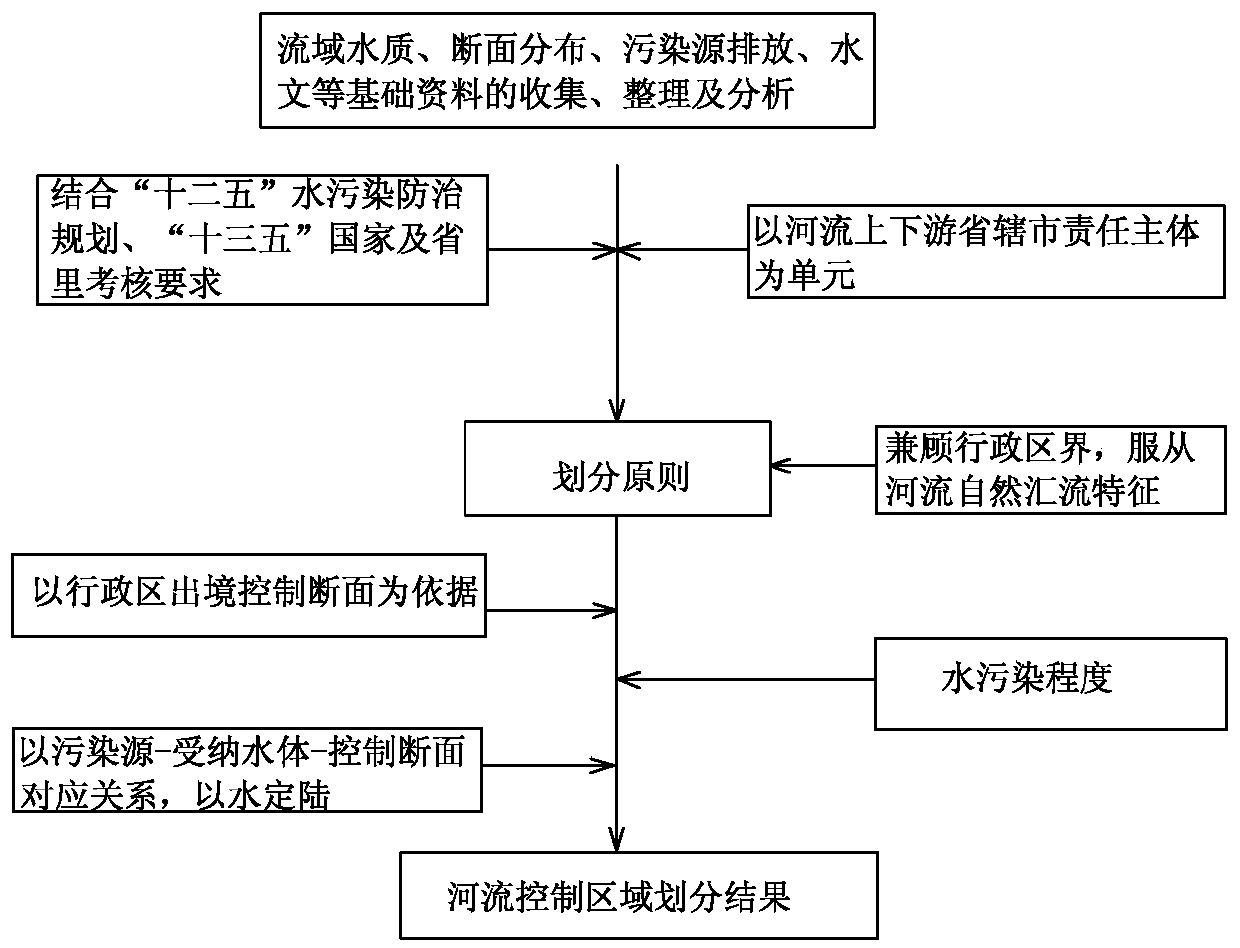
Method for calculating tracing contribution of sudden accidental water pollution source at a point source
InactiveCN107563139AEffective protectionEfficient governanceGeneral water supply conservationSpecial data processing applicationsWater qualityFluvial
The invention relates to a method for calculating the tracing contribution of a sudden accidental water pollution source at a point source, which is effective in rapid tracing of a river basin and environmental management and protection of the river basin. The method includes: according to the natural geographical features of the river basin, determining the control area corresponding to the control section of the river basin; using the monitoring data of the pollution source and the statistical data of the pollution source to budget regarding the pollution source in the river basin; using a one-dimensional unsteady water quality model to establish the relationship between pollution source and water quality of the section; using the relationship between pollution source and water quality of the section to calculate the contribution coefficient of the pollution source within the river basin and characterizing the contribution of pollution sources. The method is novel and unique, easy tooperate and use, accurate in calculation, and high in efficiency, makes full use of the basic information of the existing pollution source, quickly feeds back the state of the pollution source in theriver control section in a short time, locks the pollution source which has relatively greater contribution to the river water quality in the river basin, provides the support for the pollution tracing of the river basin, and is effectively used for the environmental protection and treatment of the river.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Practical Modeling and Acquisition of Layered Facial Reflectance
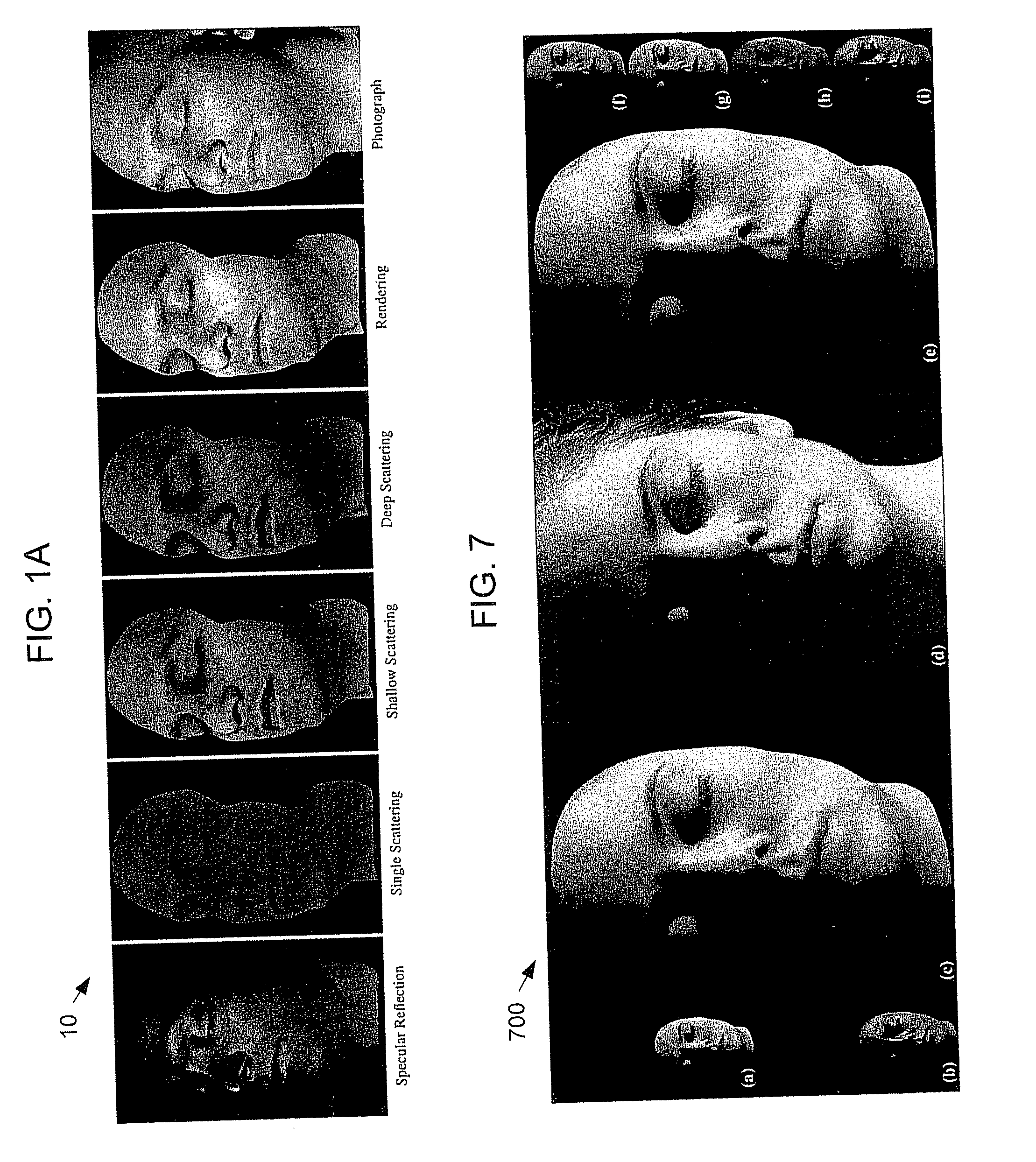
ActiveUS20090226049A1Easy to mergeConvenience to workCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsViewpointsDeep level
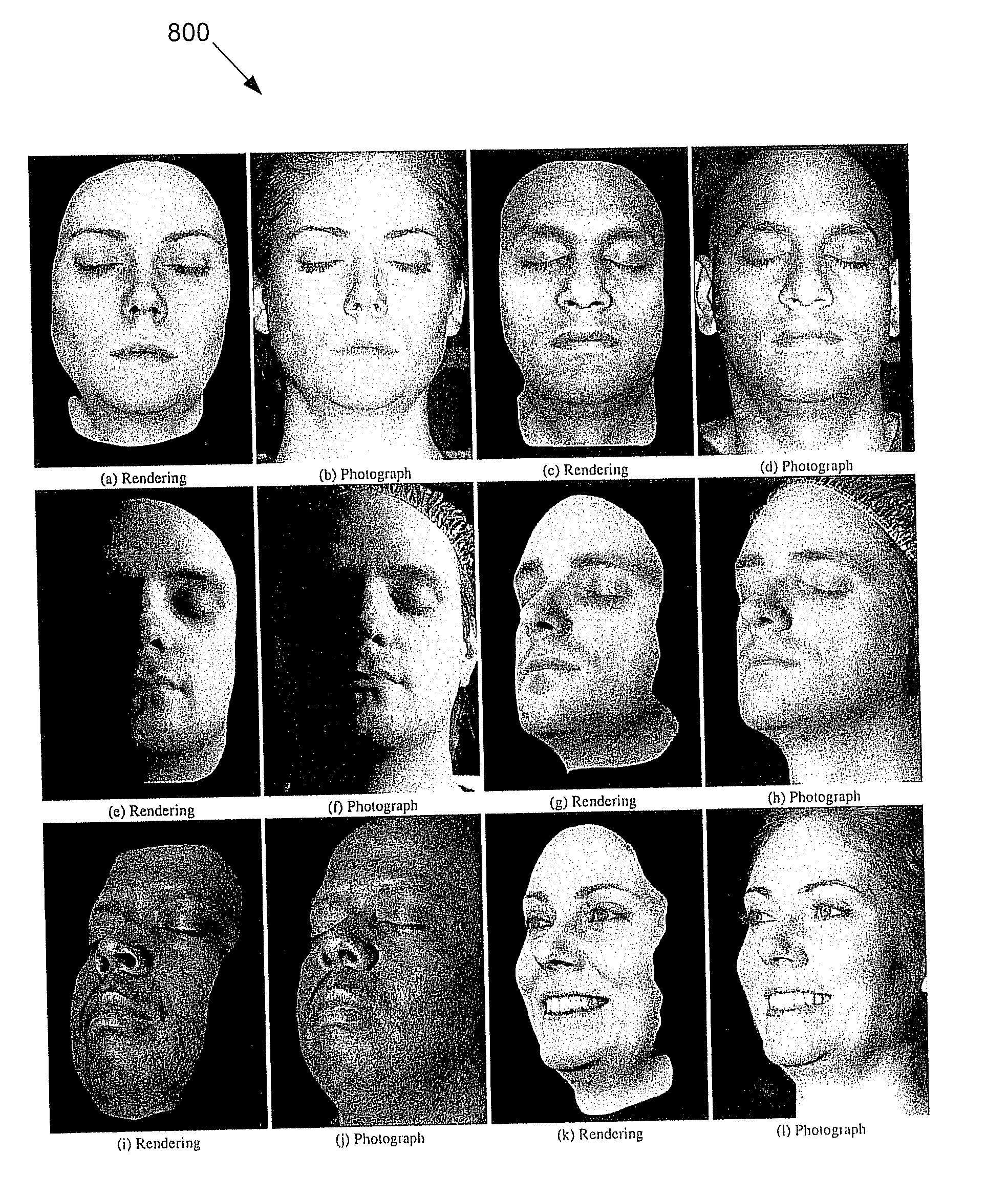
Techniques are described for modeling layered facial reflectance consisting of specular reflectance, single scattering, and shallow and deep subsurface scattering. Parameters of appropriate reflectance models can be estimated for each of these layers, e.g., from just 20 photographs recorded in a few seconds from a single view-point. Spatially-varying specular reflectance and single-scattering parameters can be extracted from polarization-difference images under spherical and point source illumination. Direct-indirect separation can be employed to decompose the remaining multiple scattering observed under cross-polarization into shallow and deep scattering components to model the light transport through multiple layers of skin. Appropriate diffusion models can be matched to the extracted shallow and deep scattering components for different regions on the face. The techniques were validated by comparing renderings of subjects to reference photographs recorded from novel viewpoints and under novel illumination conditions. Related geometry acquisition systems and software products are also described.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Methods and systems for determining the orientation of natural fractures
ActiveUS20050060099A1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainHydraulic fracturing
Methods, systems, and articles of manufacture consistent with the present invention provide for determining the orientation of natural fractures in the Earth resulting from hydraulic fracturing treatment. Data attribute information from a far-field point-source signal profile for a microseismic event is extracted in the time domain. An estimate of the orientation of the natural fracture is calculated in the time domain based on the extracted data attribute information.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
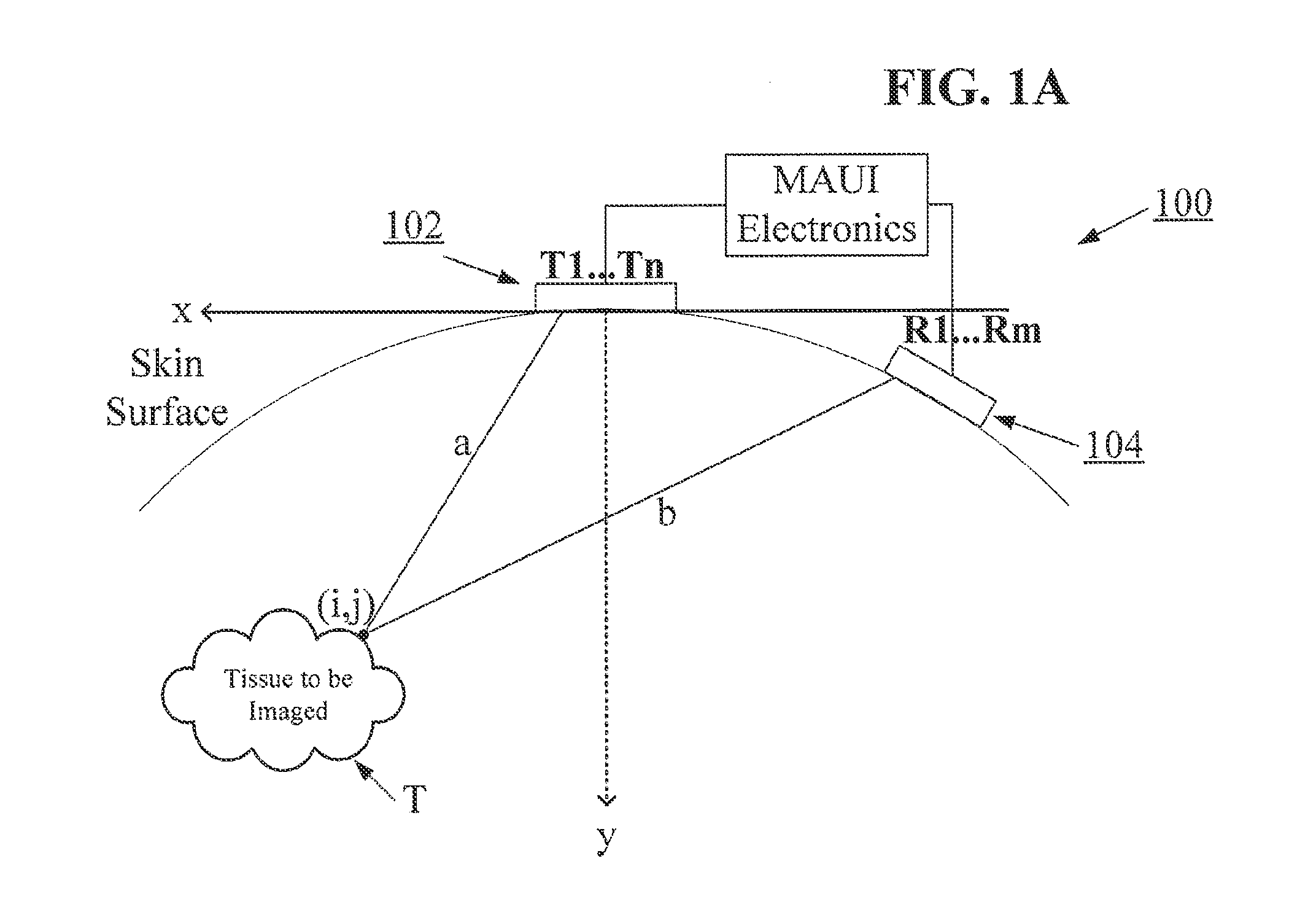
Point source transmission and speed-of-sound correction using multi-aperture ultrasound imaging
ActiveUS20110201933A1Accurate displacementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingHigh resolution ultrasound
A Multiple Aperture Ultrasound Imaging system and methods of use are provided with any number of features. In some embodiments, a multi-aperture ultrasound imaging system is configured to transmit and receive ultrasound energy to and from separate physical ultrasound apertures. In some embodiments, a transmit aperture of a multi-aperture ultrasound imaging system is configured to transmit an omni-directional unfocused ultrasound waveform approximating a first point source through a target region. In some embodiments, the ultrasound energy is received with a single receiving aperture. In other embodiments, the ultrasound energy is received with multiple receiving apertures. Algorithms are described that can combine echoes received by one or more receiving apertures to form high resolution ultrasound images. Additional algorithms can solve for variations in tissue speed of sound, thus allowing the ultrasound system to be used virtually anywhere in or on the body.
Owner:MAUI IMAGING
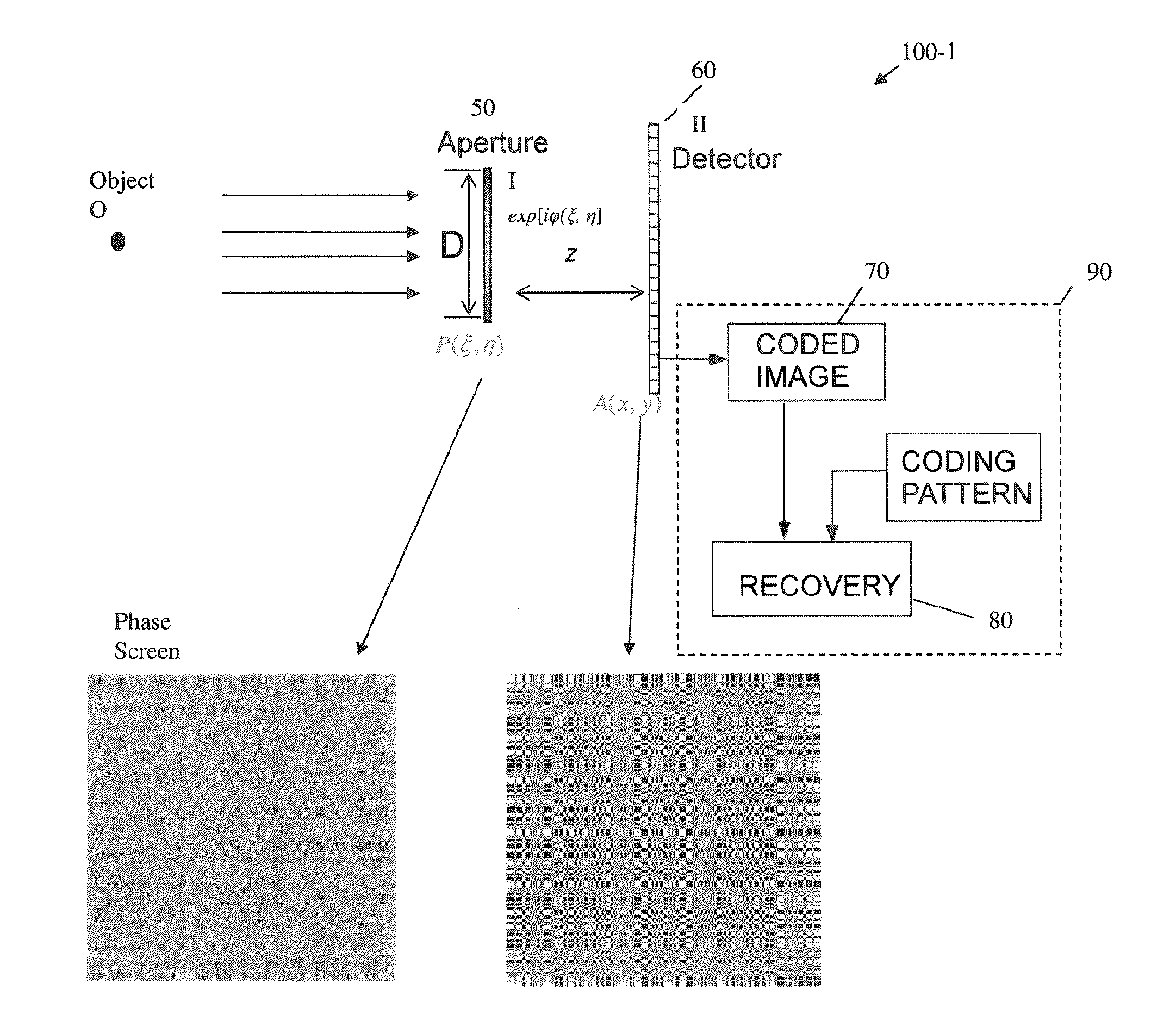
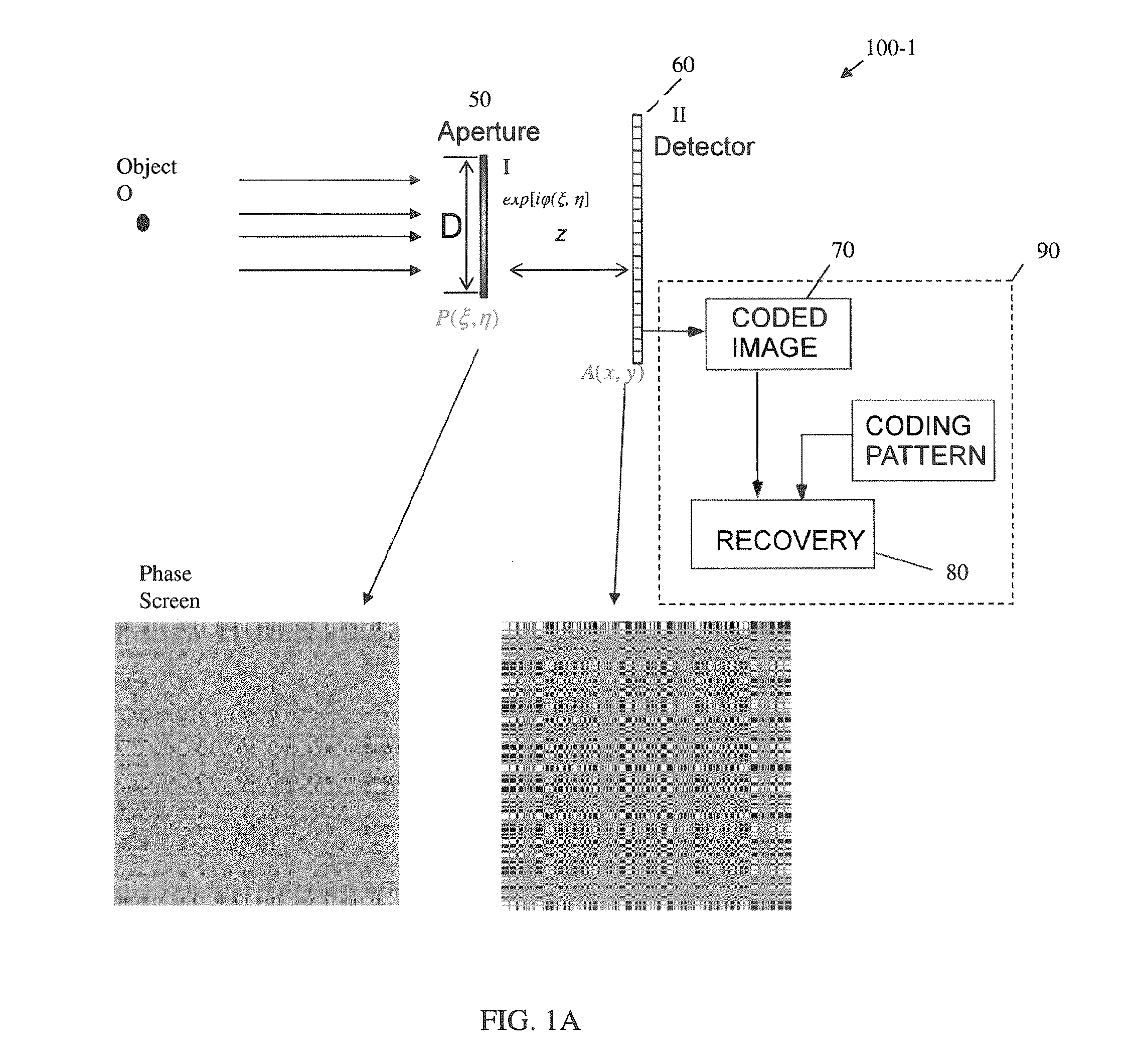
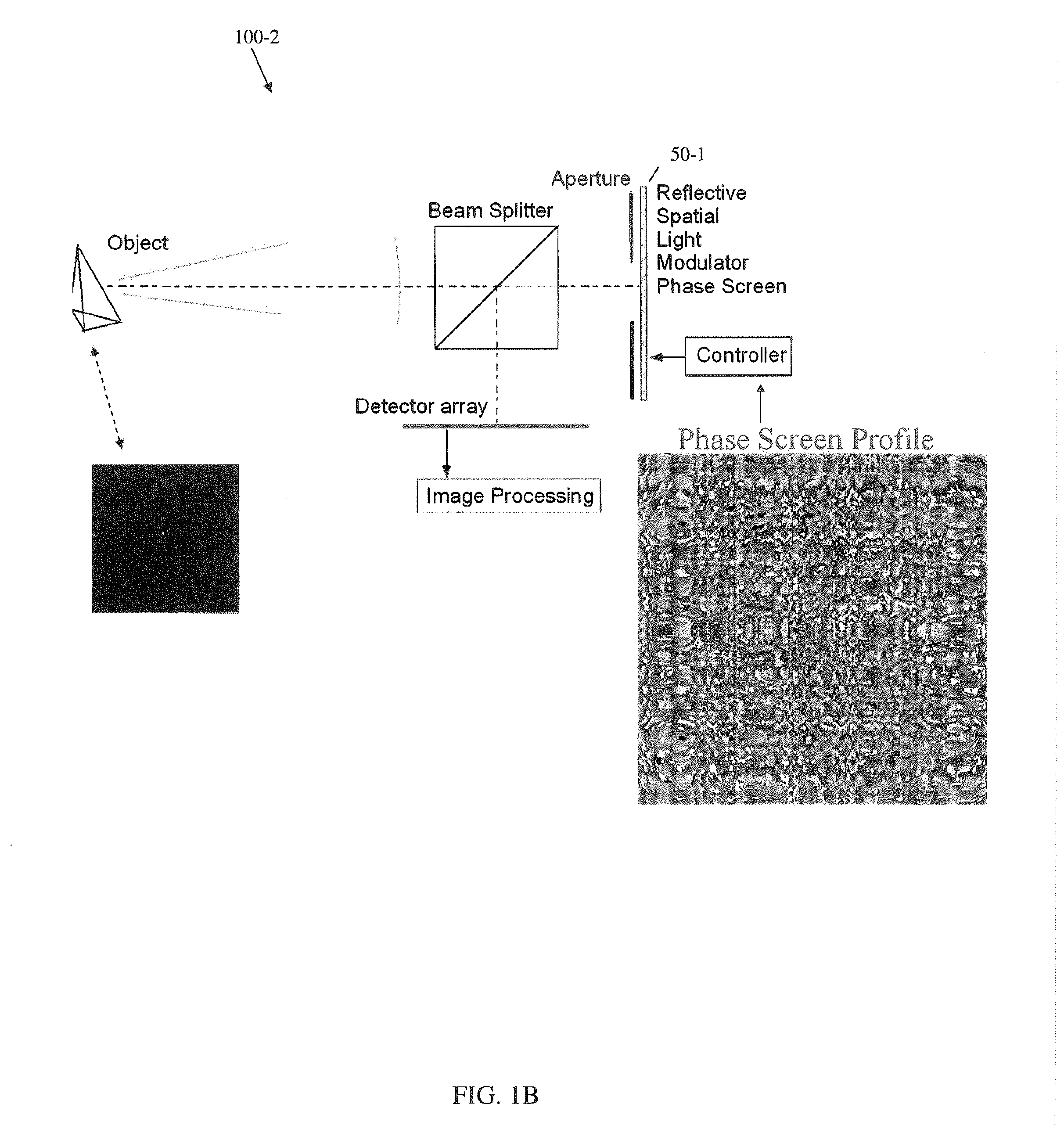
Optical element, device, method, and applications
A novel phase-coded aperture, associated imaging system, and design method is disclosed. The optical imaging system includes a coded-aperture followed optically by a detector array and includes an image processor. A diffraction pattern in the form of a band-limited uniformly redundant array is formed on the detector array when focusable radiation from a point source in object space is modulation by the transmission function of the coded-aperture. Since diffraction effects cannot be ignored in the optical regime, an iterative phase retrieval method is used to calculate the phase-coded aperture transmission function. Correlation type processing can be applied for the image recovery.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Methods and apparatus for rapid scanning continuous wave terahertz spectroscopy and imaging
Methods and apparatus are provided employing rapid scanning continuous wave terahertz spectroscopy and imaging for the non-destructive evaluation of materials such as animal hides and natural cork, and explosive detection, concealed weapon detection, and drug detection. A system employing an aperiodic detector array and implementing phase modulation at 100 kHz significantly reduces the imaging time and enables interferometric images of a THz point source to be obtained at several frequencies between 0.3 and 0.95 THz.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Landscape type multi-stage stepwise artificial wetland protection slope forming method
InactiveCN1632231AGood water permeabilityAvoid inconvenienceClimate change adaptationCoastlines protectionConstructed wetlandEutrophication
The invention relates to a slope protection forming method of a landscape-type multi-level stepped constructed wetland, which has the effect of intercepting and purifying pollutants entering river channels in the form of surface sources. Sand-free concrete piles and slabs are inserted to form pile-slab components, and a slope protection system from high to low is formed on the river bank slope from the bank slope to the river bed. Planting areas are set on the side of the pile slabs, and there are fillers inside. Geotextiles are installed on the bankside side of the slab, so that when the non-point source pollutants flow from the river bank to the river, the plants planted in the planting area absorb the eutrophication in the polluted water, and the biofilm is formed on the surface of the filler to absorb and degrade the pollutants. After this The sewage treated at the first stage continues to infiltrate or overflow, enters the second row, and goes down step by step. Finally, the sewage is purified to a greater extent and flows into the river. It solves the defects of natural, hard and ecological slope protection. The structure is simple, easy for industrial production, the construction amount is small, the land is saved, and the landscape is beautified.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
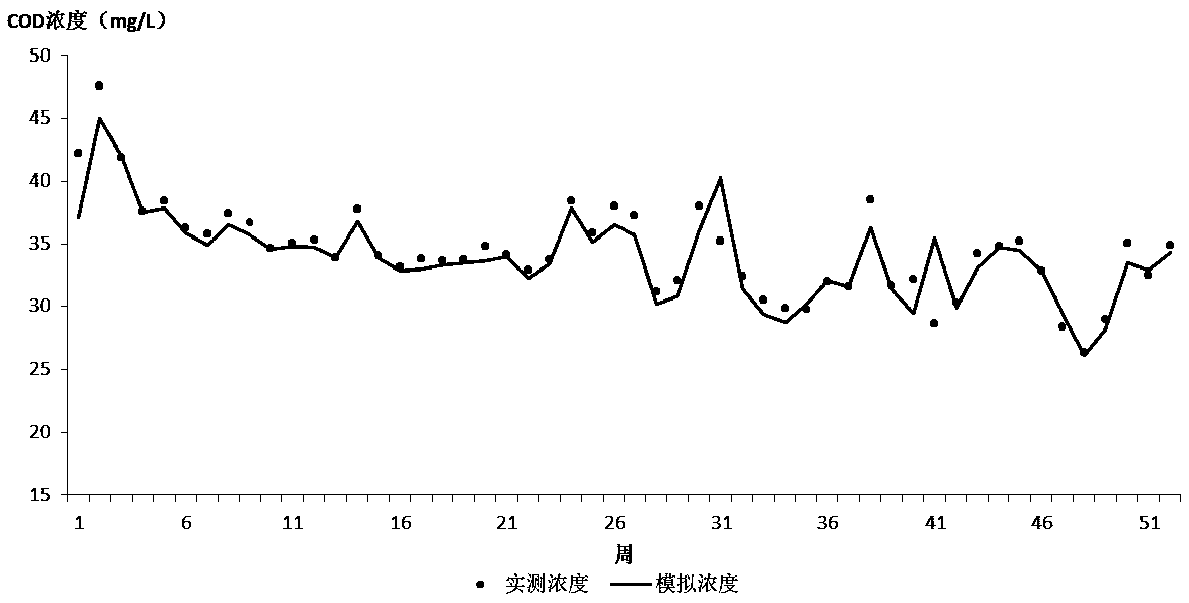
Water-quality simulation method based on control-unit water-environment-quality target management
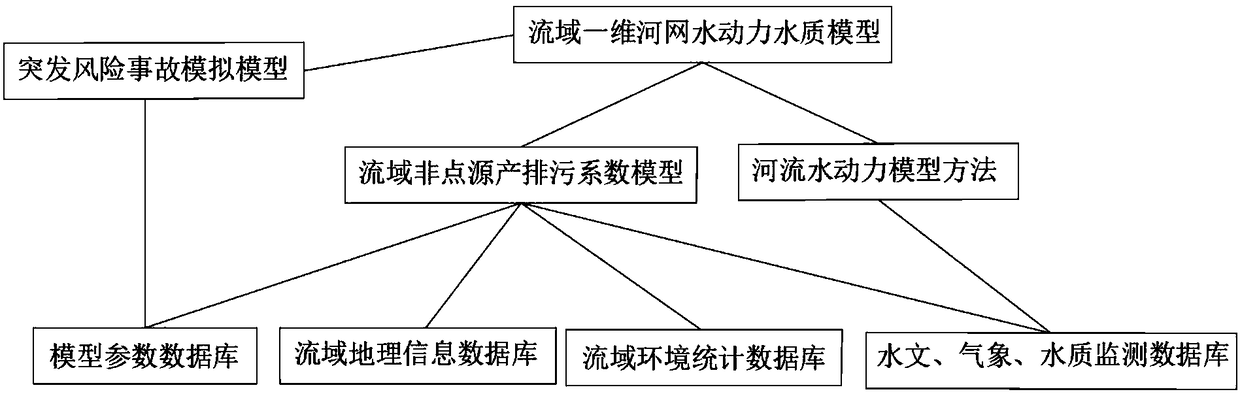
ActiveCN108287950ASolve the problem of land and water couplingData processing applicationsGeneral water supply conservationRiver networkStreamflow
The invention provides a water-quality simulation method based on control-unit water-environment-quality target management. The water-quality simulation method includes the steps that a database is built; a land-field control unit and a river-way subunit are divided; the flow, the area of the water surface and the volume of a water body of calculation unit grids are simulated through a hydraulicsmodel; the generation quantity of non-point-source pollutants in pollution sources is calculated through an output coefficient model, and the in-river sewage amount and the pollution load concentration of pollutants of a pollutant discharging opening are calculated; the water quality of the calculation unit grids is simulated through a one-dimensional water-quality model. In the water-quality simulation method, an emergent risk accident pollutant-discharging water-quality model is also used, and is used for simulating transmission of accident pollutants in a river network and the changing condition of the water quality of a downstream drainage basin after emergent-water-environment-risk-accident pollutant discharging.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL PLANNING
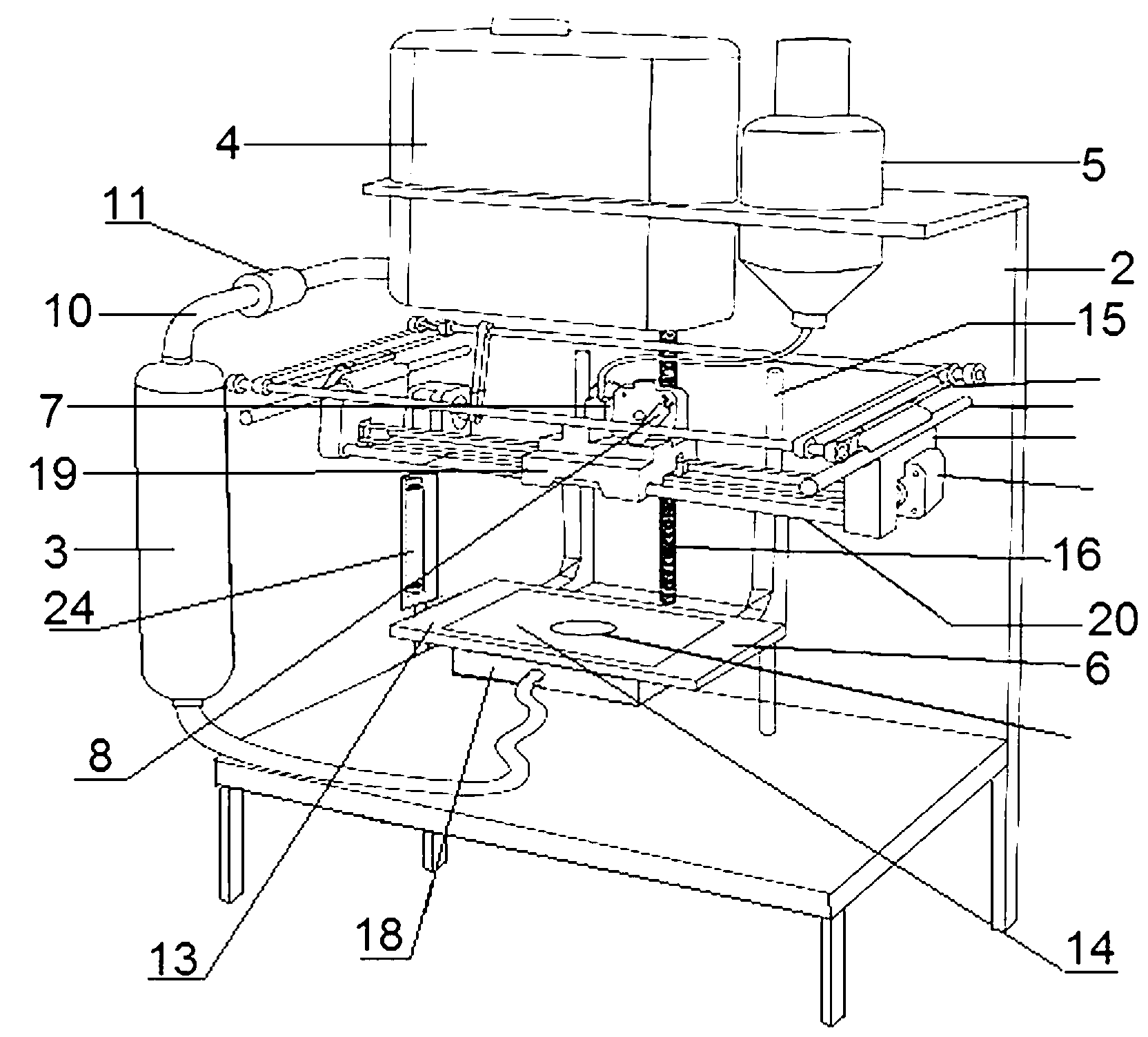
3D printer
The invention discloses a 3D (three dimensional) printer, which comprises a frame, a liquid storage pot with an upper end opening, as well as a first resin cylinder, a second resin cylinder, a lifting platform, a line extrusion device and an ultraviolet (UV) light point light source arranged on the frame. The first resin cylinder is loaded with liquid UV light cured resin, and the second resin cylinder is loaded with paste UV light cured resin. The lower part of the second resin cylinder is communicated with the line extrusion device that is provided with a nozzle, and the irradiation position of the UV light point source is located below the nozzle. The lifting platform includes a flat plate provided with a through hole in the middle part, the upper surface of the flat plate is provided with a metal net, and the flat plate is in sliding connection with two guide pillars on the frame. The lower part of the liquid storage pot is communicated with an upper end opened liquid storage box arranged on the flat plate lower surface through a duct. The 3D printer provided in the invention has high printing efficiency, and while ensuring the printing efficiency, it also can guarantee that the printed object has high density and is difficult to damage.
Owner:温州启龙电子科技有限公司
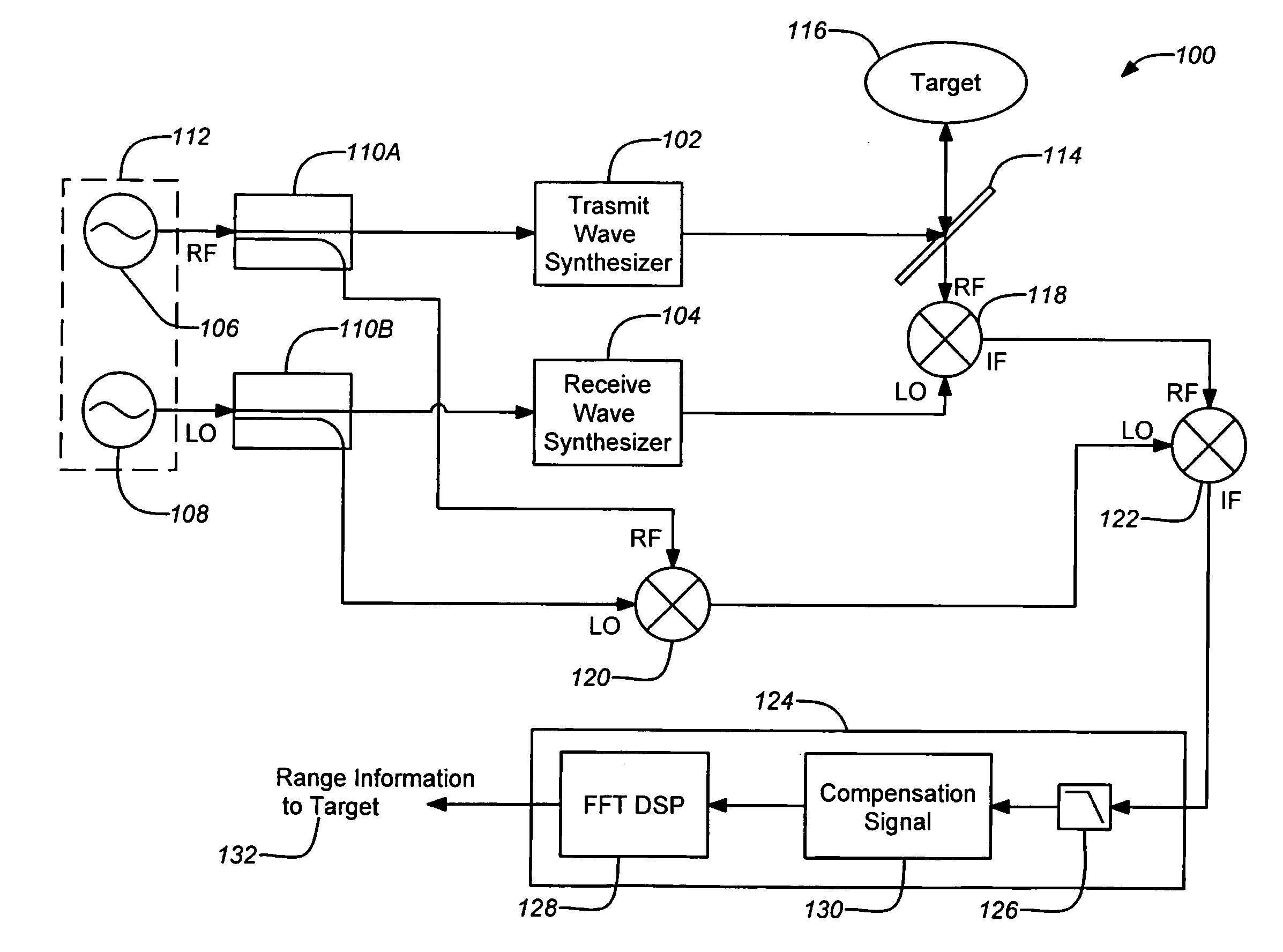
High-resolution three-dimensional imaging radar
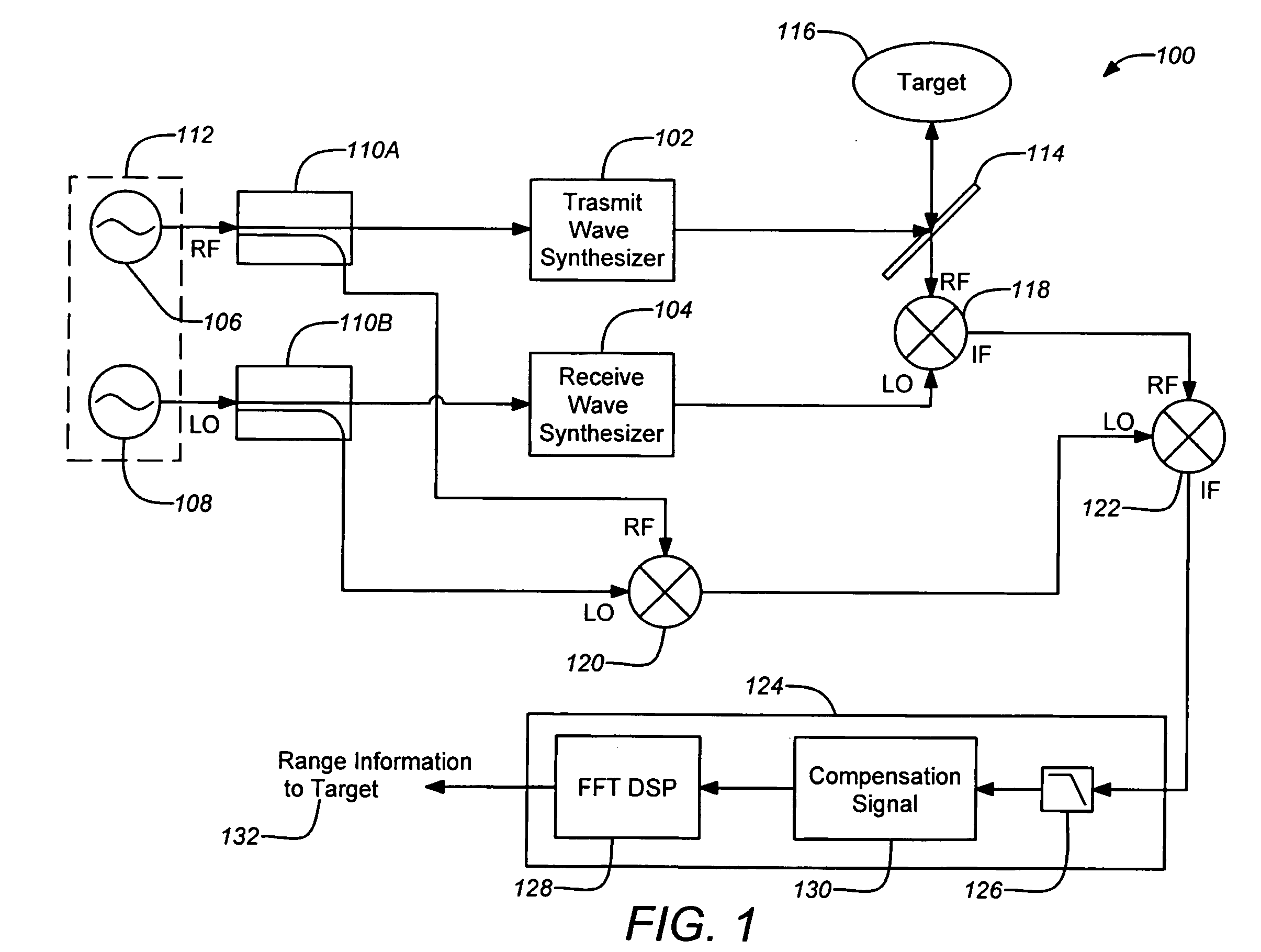
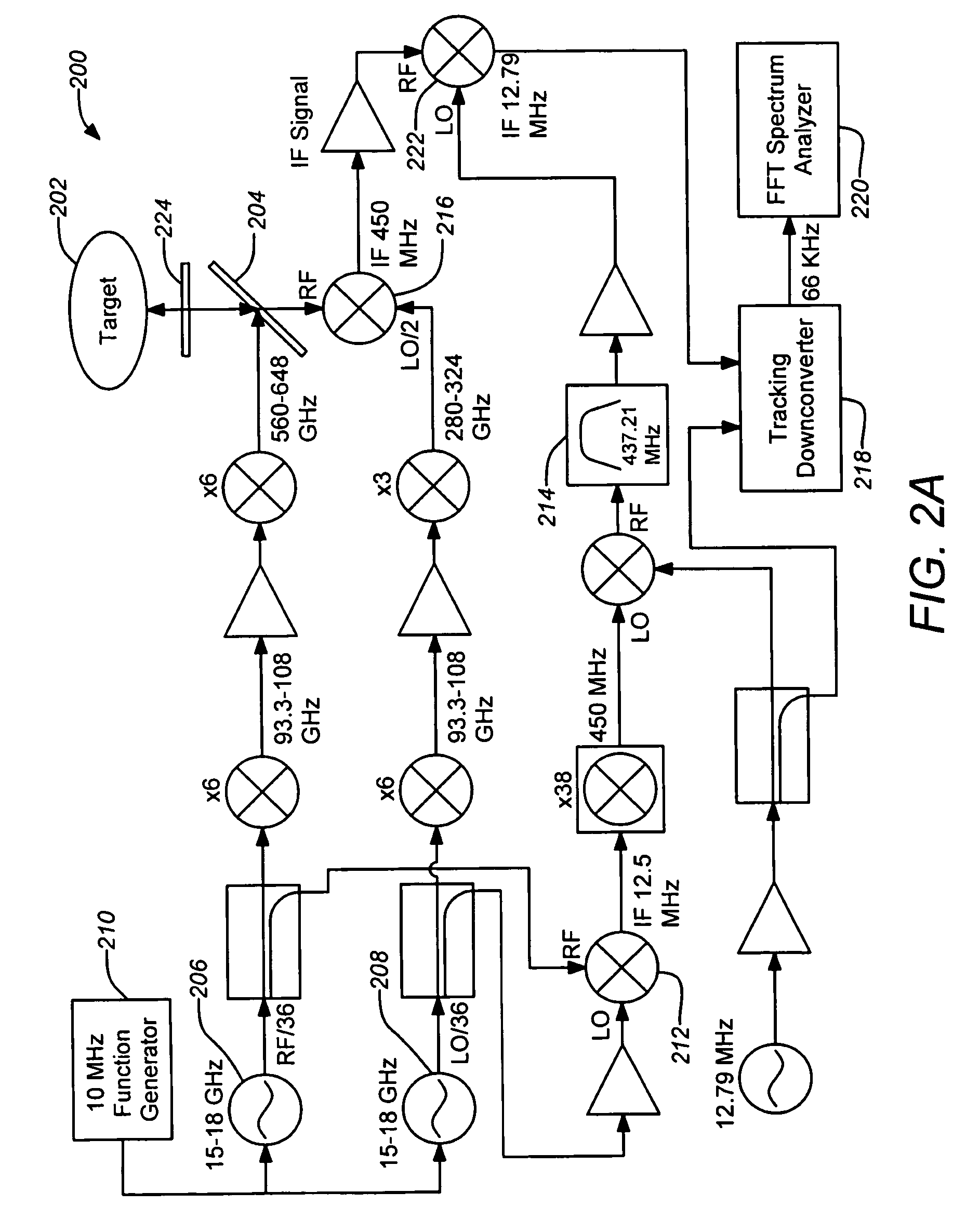
ActiveUS20080304044A1Increase signal powerHigh frequencyOptical rangefindersRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhase noisePeak value
A three-dimensional imaging radar operating at high frequency e.g., 670 GHz, is disclosed. The active target illumination inherent in radar solves the problem of low signal power and narrow-band detection by using submillimeter heterodyne mixer receivers. A submillimeter imaging radar may use low phase-noise synthesizers and a fast chirper to generate a frequency-modulated continuous-wave (FMCW) waveform. Three-dimensional images are generated through range information derived for each pixel scanned over a target. A peak finding algorithm may be used in processing for each pixel to differentiate material layers of the target. Improved focusing is achieved through a compensation signal sampled from a point source calibration target and applied to received signals from active targets prior to FFT-based range compression to extract and display high-resolution target images. Such an imaging radar has particular application in detecting concealed weapons or contraband.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
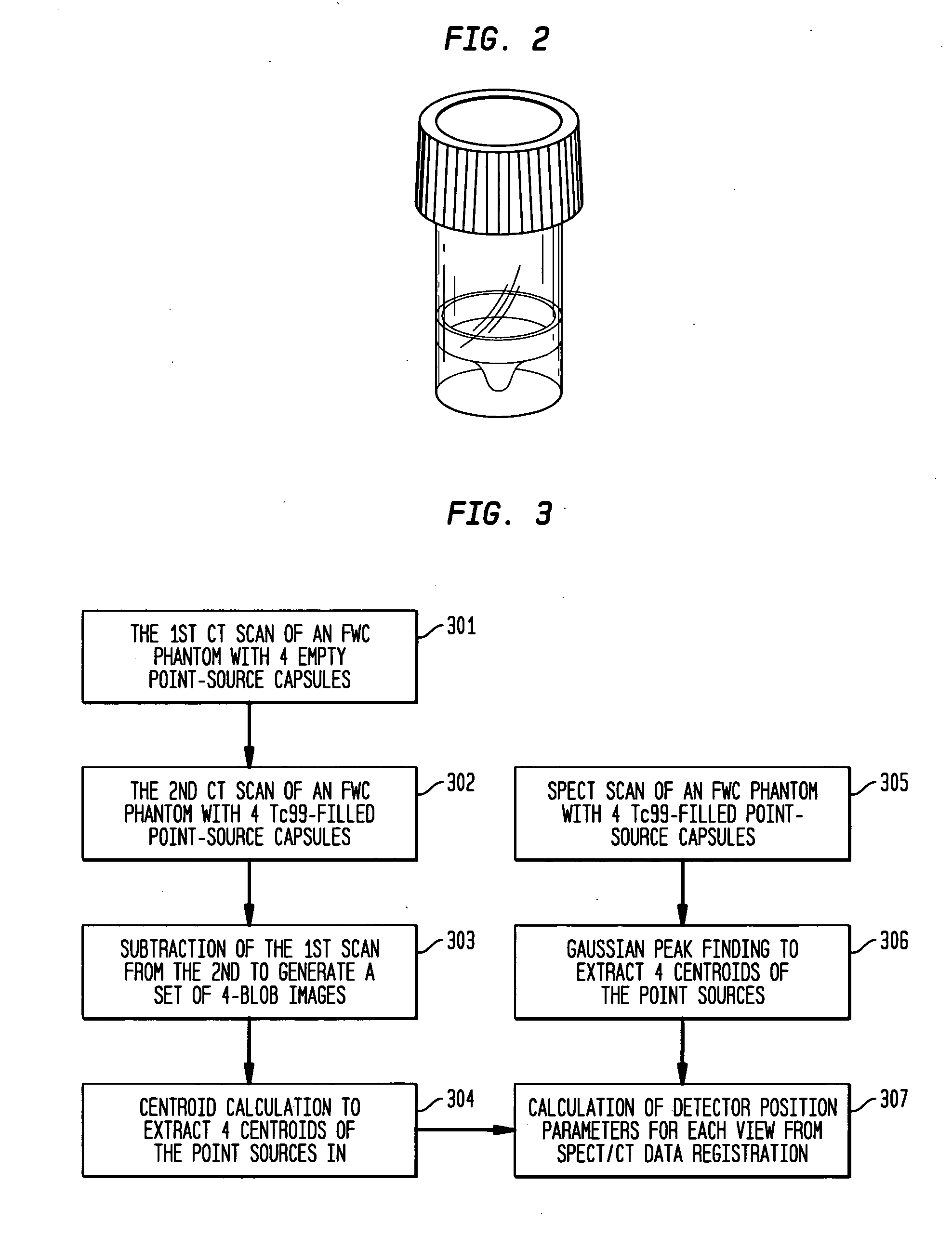
Detector head position correction for hybrid SPECT/CT imaging apparatus
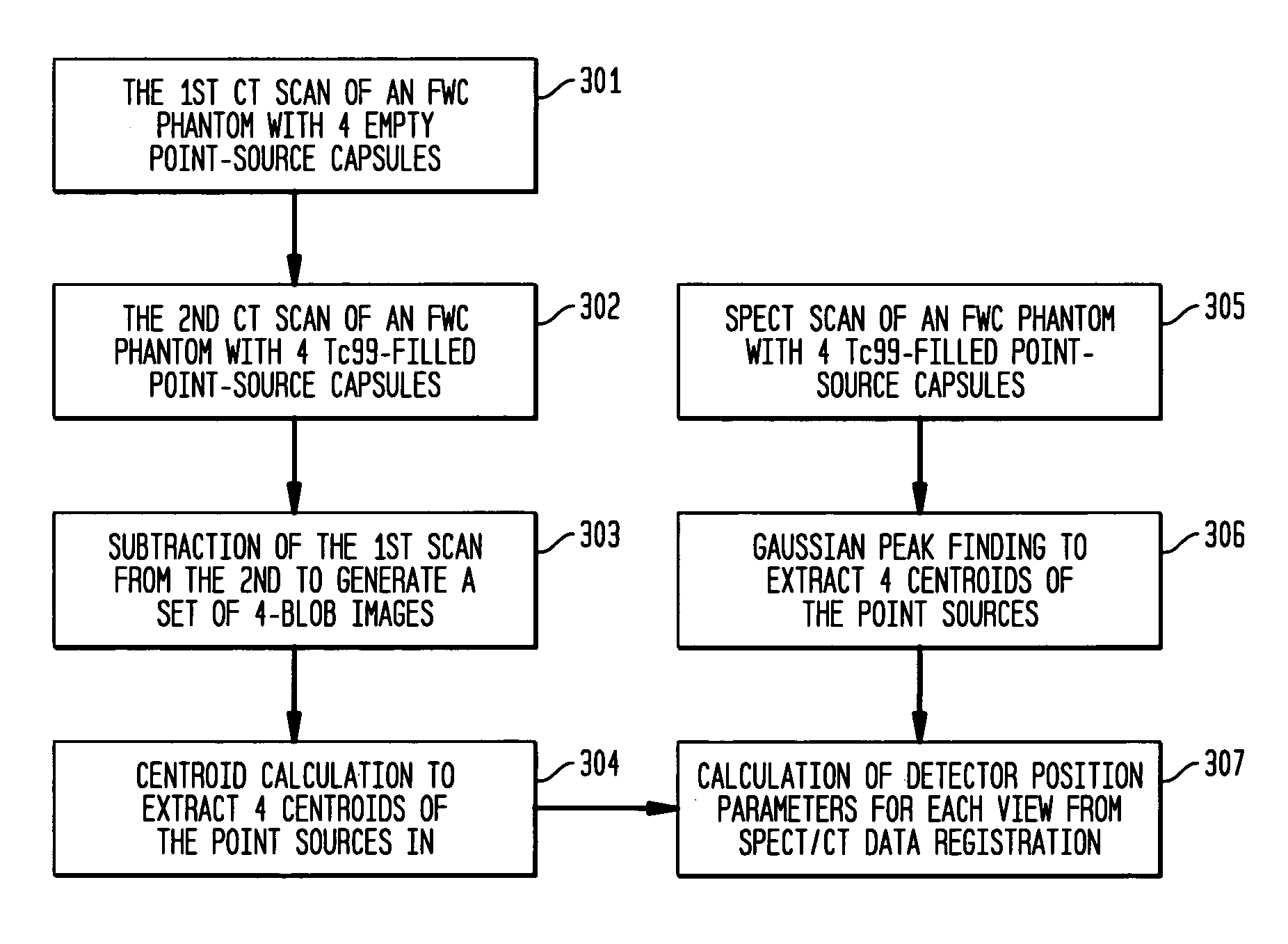
ActiveUS20060214097A1Accurate image registrationSolve the real problemMaterial analysis by optical meansCalibration apparatusThree dimensional ctProjection image
A system and method provide for more accurate SPECT / CT image registration. CT data is utilized to establish a global spatial coordinate system of a common test phantom. The common test phantom is then used to obtain a set of point source nuclear images. Three-dimensional CT point source data is mapped to a two-dimensional image plane of corresponding point source data, to obtain a pair of intersecting projection cones that are used to obtain a set of detector head position correction parameters to correct detector head positioning in the CT coordinate system when obtaining SPECT projection images of the same object.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
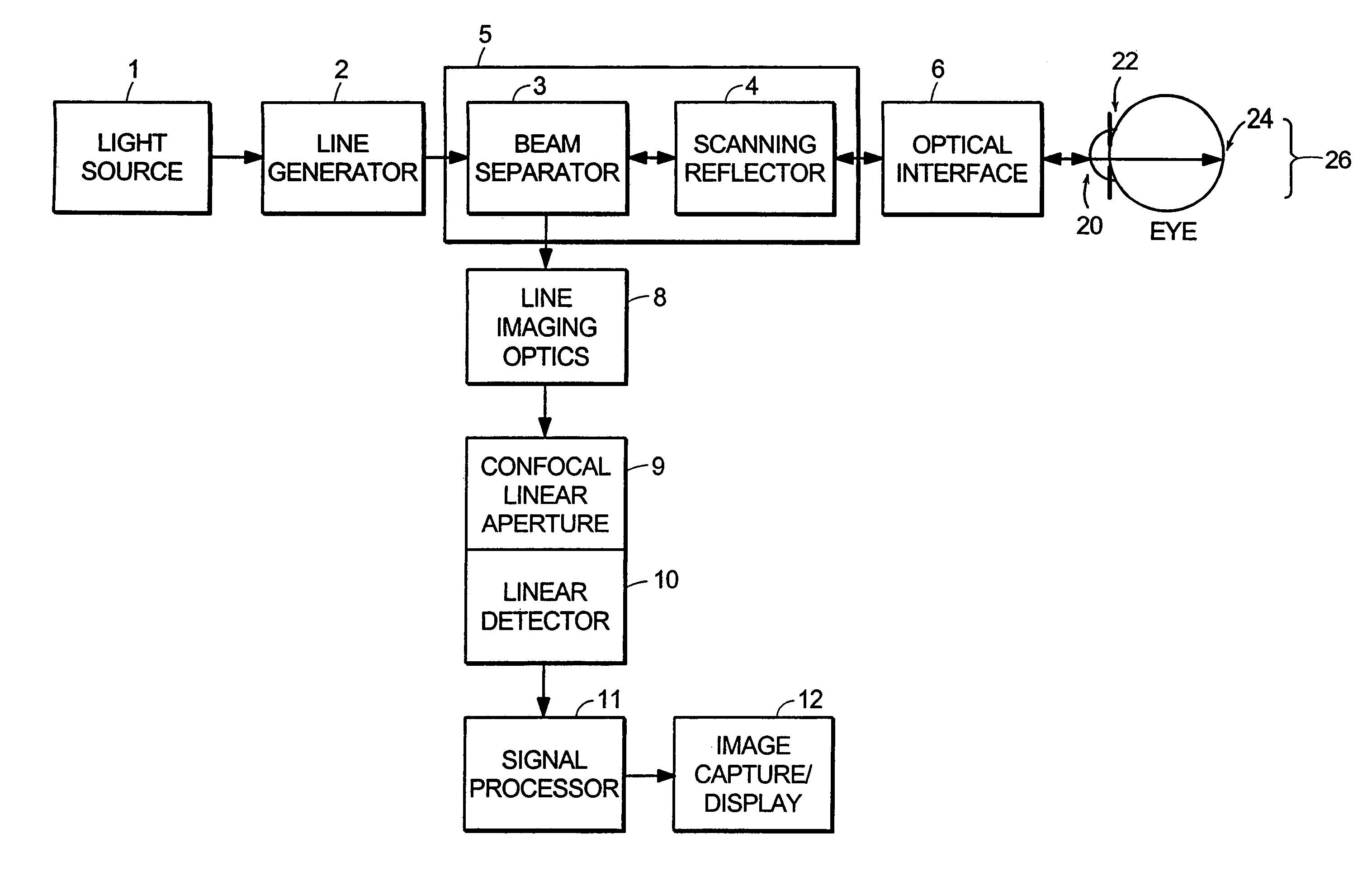
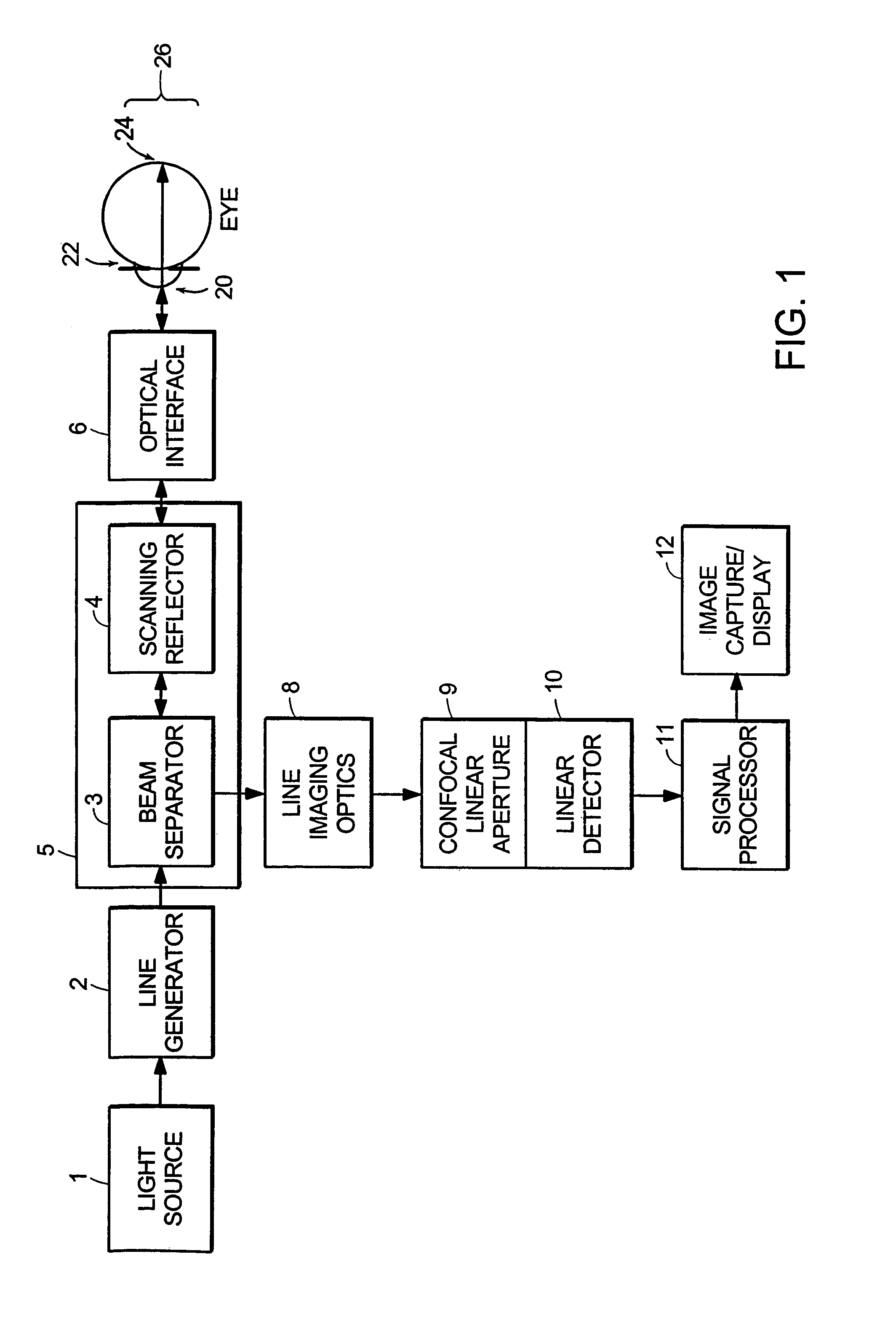
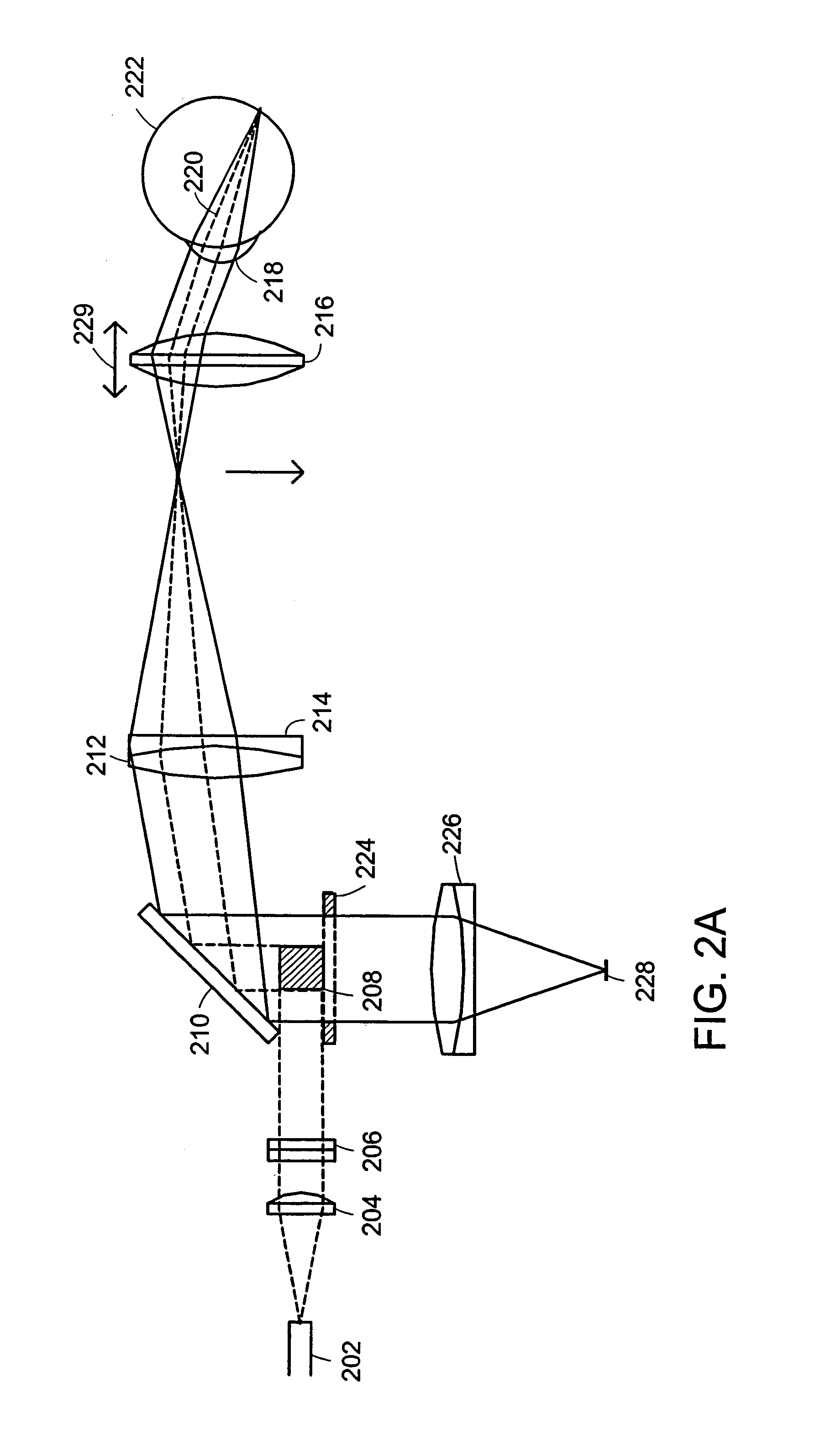
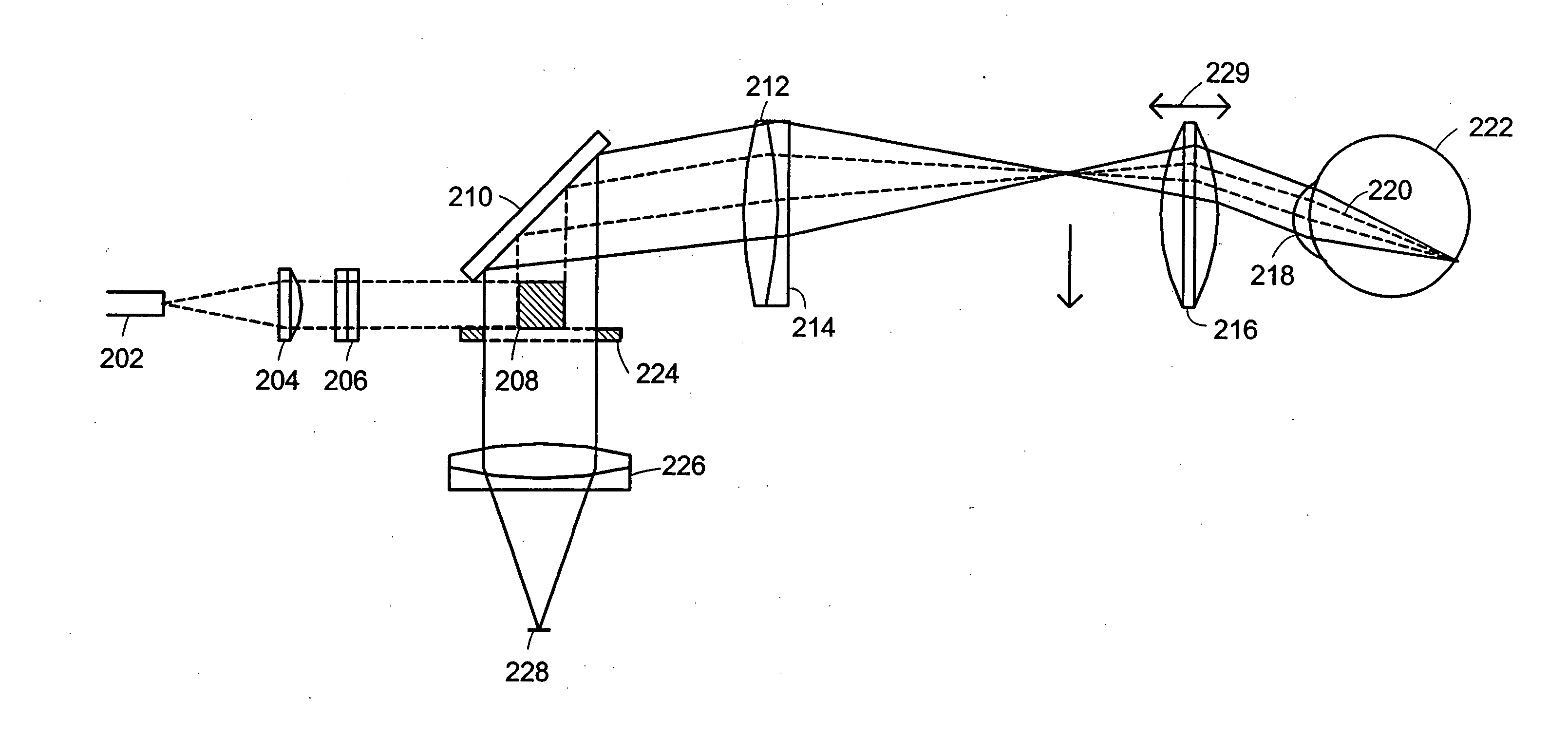
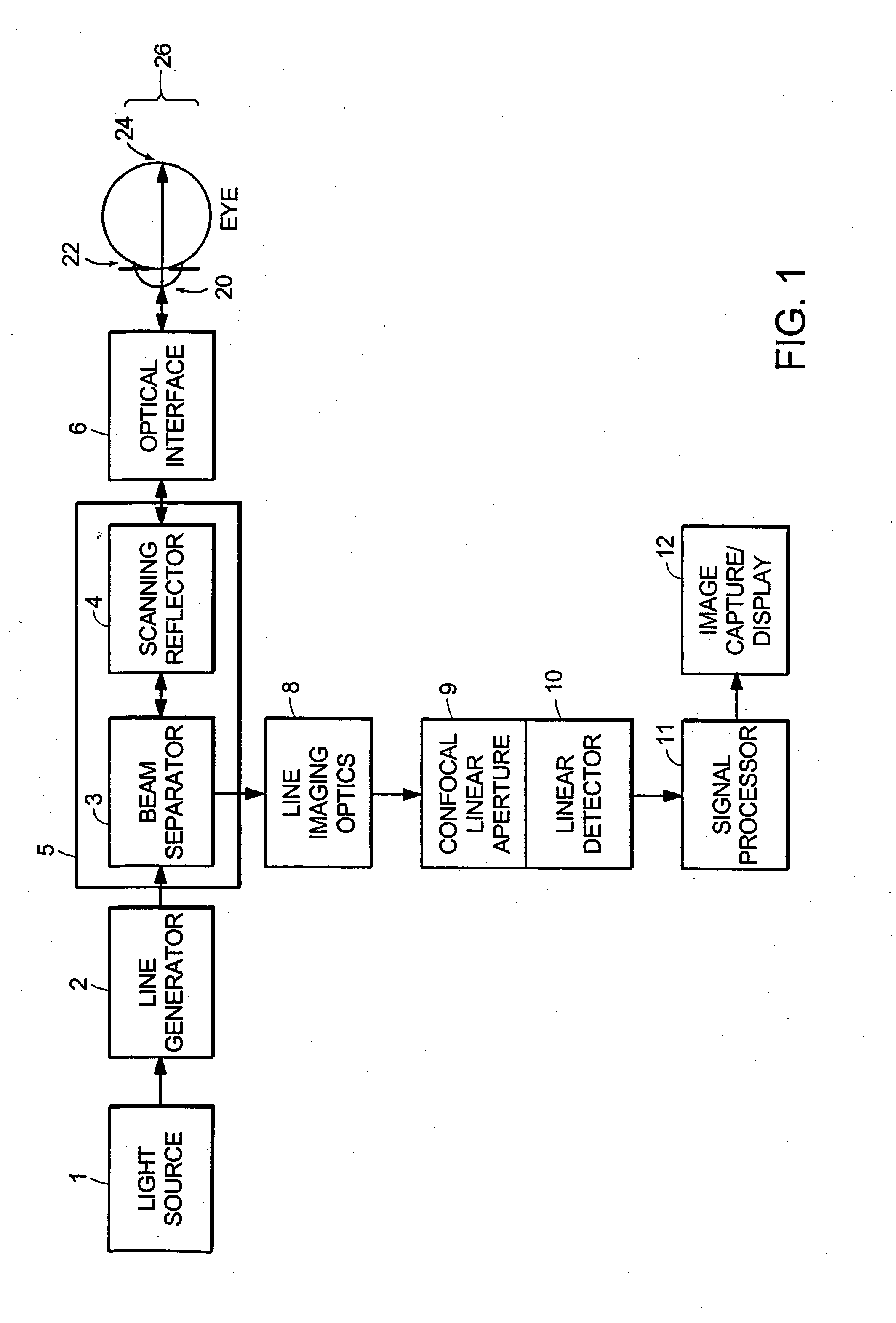
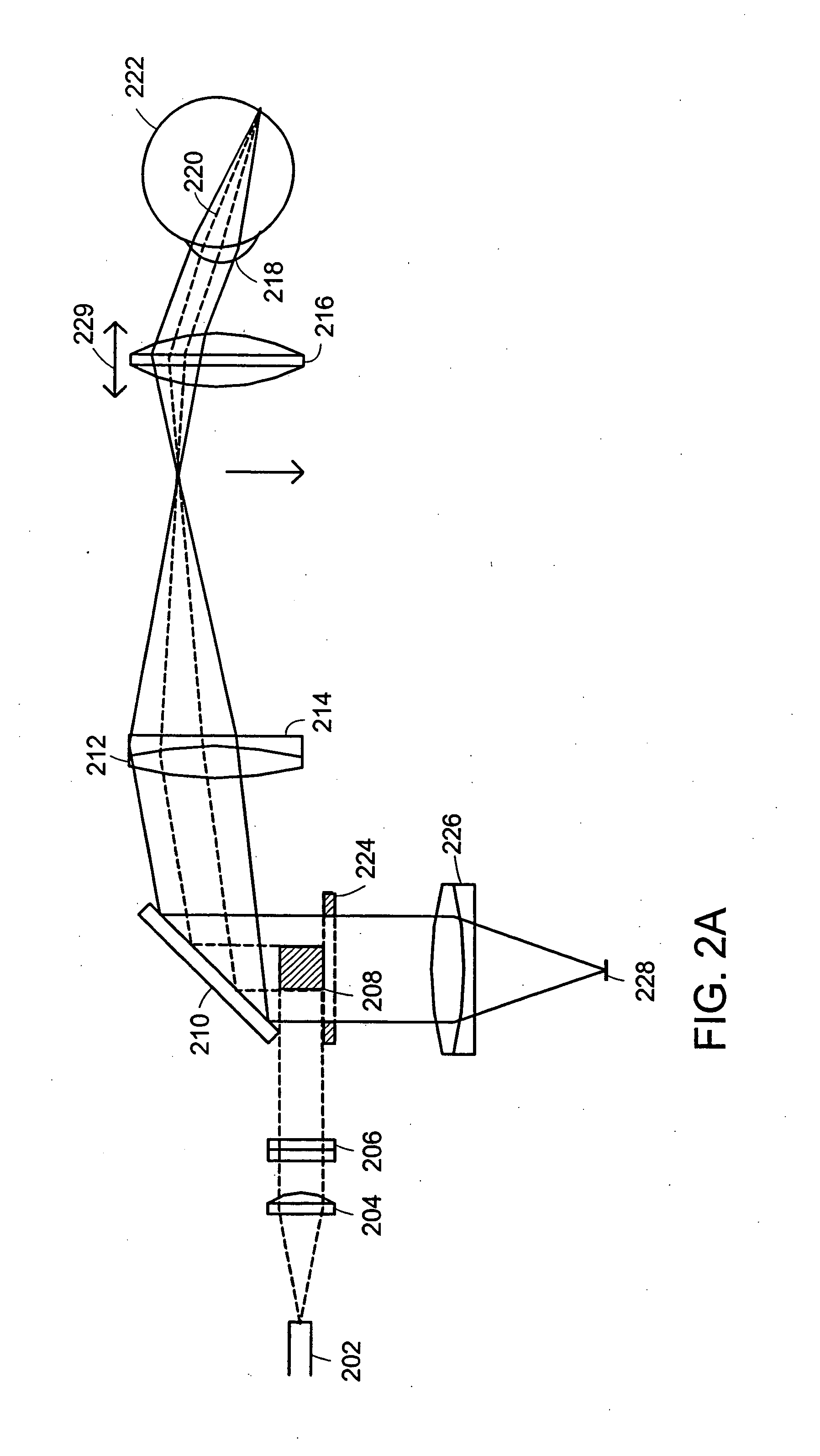
Line-scan laser ophthalmoscope
InactiveUS7284859B2Less expensiveSimple and compact designOthalmoscopesSuperluminescent diodeOphthalmoscopes
Systems and methods for providing a line-scanning laser ophthalmoscope (LSLO) are disclosed. The LSLO uses a substantially point source of light, such as an infrared laser or a super-luminescent diode. The point source is expanded to a line. The LSLO scans the line of light in a direction perpendicular to the line across a region of an eye having an undilated pupil The reflected light is received confocally, using monostatic beam geometry. A beam separator, such as a turning prism or mirror, diverts one of the incoming light and the reflected light to separate the light. An optical stop prevents non-confocally received light from reaching a one-dimensional detector, such as a linear CCD array. An electrical signal responsive to the output light at each of a plurality of locations along the line of output light is processed to provide images of the scanned portion of the eye.
Owner:PHYSICAL SCI
Line-scan laser ophthalmoscope
InactiveUS20050012899A1Significant in clarityBig contrastOthalmoscopesSuperluminescent diodeOphthalmoscopes
Systems and methods for providing a line-scanning laser ophthalmoscope (LSLO) are disclosed. The LSLO uses a substantially point source of light, such as an infrared laser or a super-luminescent diode. The point source is expanded to a line. The LSLO scans the line of light in a direction perpendicular to the line across a region of an eye having an undilated pupil The reflected light is received confocally, using monostatic beam geometry. A beam separator, such as a turning prism or mirror, diverts one of the incoming light and the reflected light to separate the light. An optical stop prevents non-confocally received light from reaching a one-dimensional detector, such as a linear CCD array. An electrical signal responsive to the output light at each of a plurality of locations along the line of output light is processed to provide images of the scanned portion of the eye.
Owner:PHYSICAL SCI
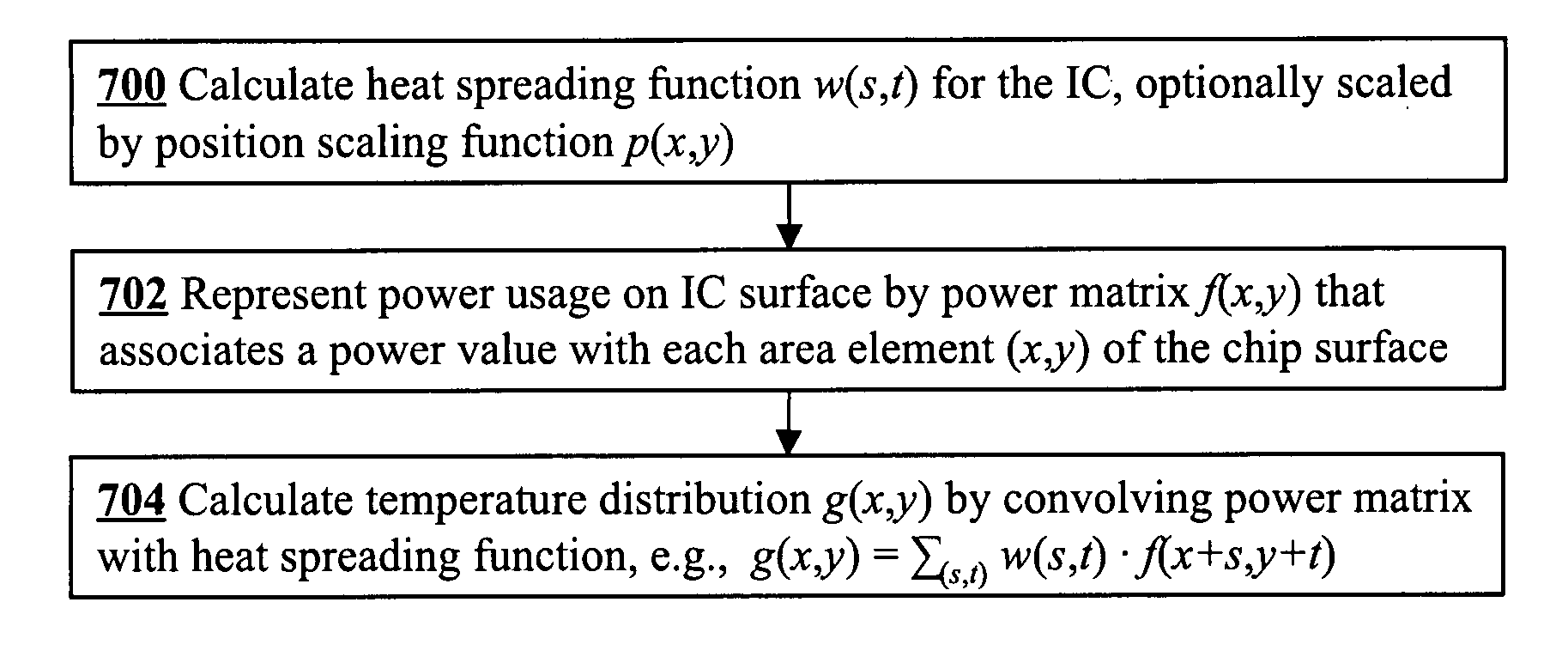
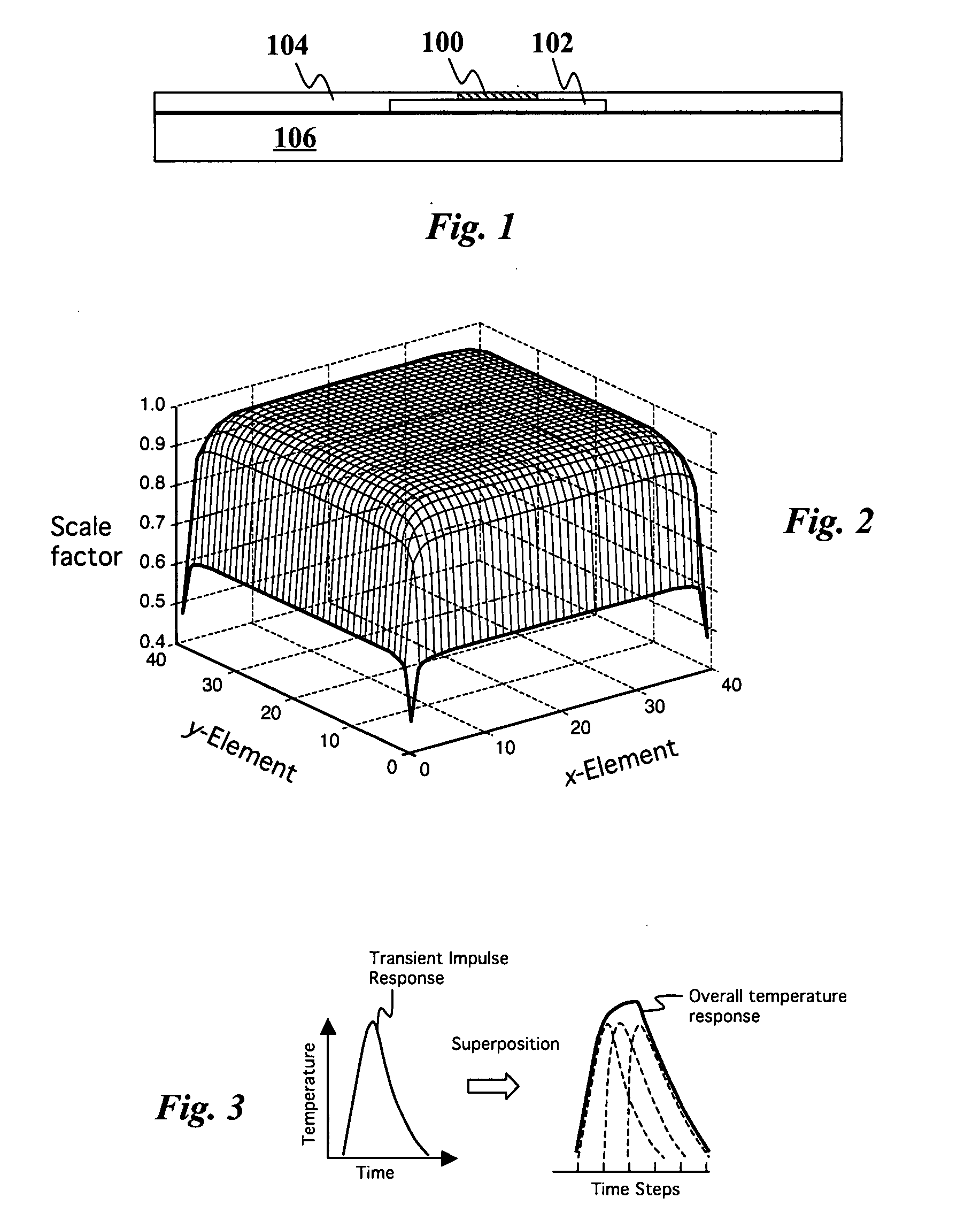
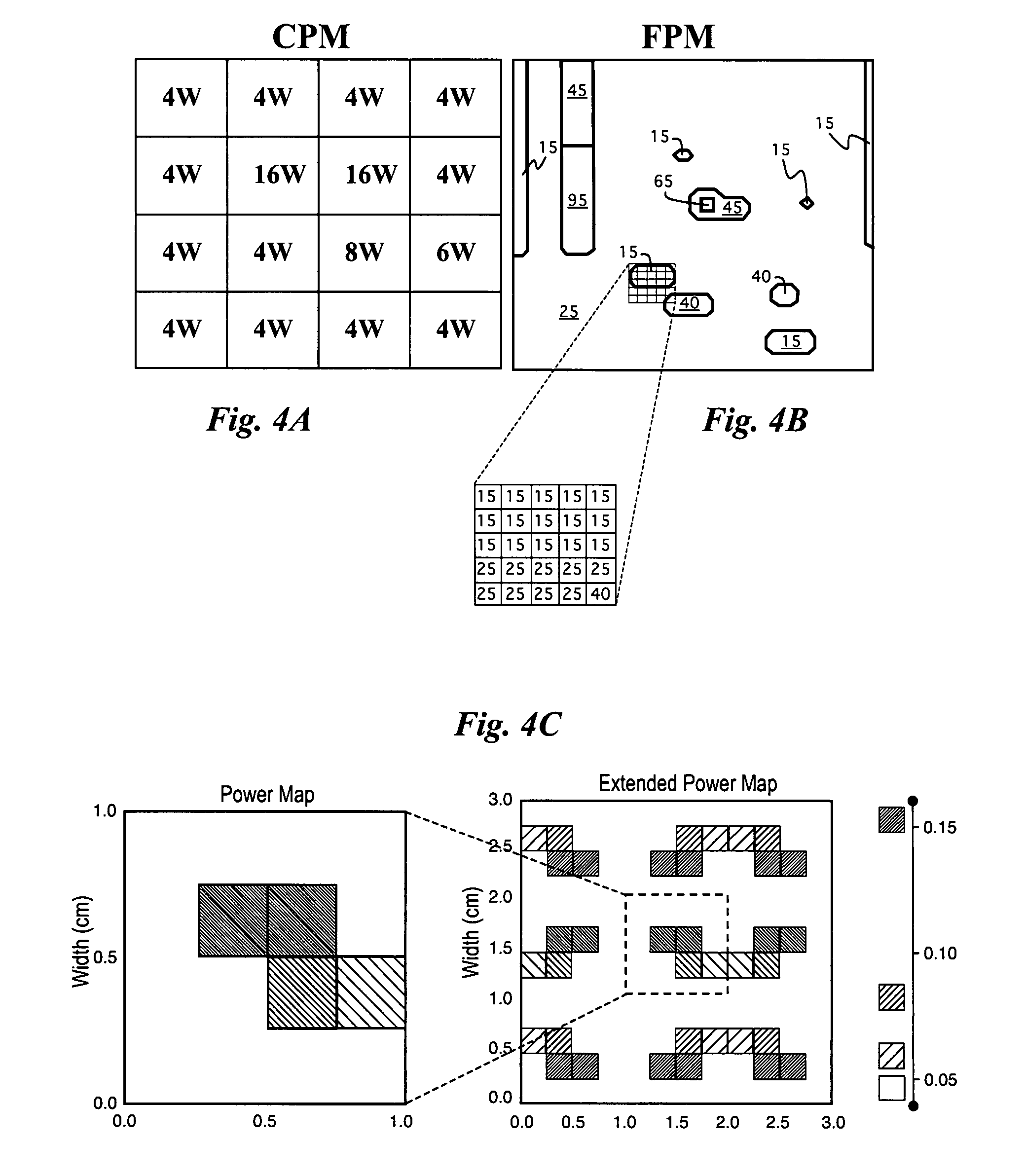
Efficient method to predict integrated circuit temperature and power maps
InactiveUS20080026493A1Fast and accurate methodMinimizes localized heatingSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDetecting faulty computer hardwareElement analysisDiffusion function
The temperature distribution associated with a design of an integrated circuit is calculated by convoluting a surface power usage represented by a power matrix with a heat spreading function. The heat spreading function may be calculated from a simulation of a point source on the integrated circuit using a finite element analysis model of the integrated circuit or other techniques. To account for spatial variations on the chip, the heat spreading function may be made dependent on position using a position scaling function. Steady-state or transient temperature distributions may be computed by using a steady-state or transient heat spreading function. A single heat spreading function may be convolved with various alternative power maps to efficiently calculate temperature distributions for different designs. In an inverse problem, one can calculate the power map from an empirically measured temperature distribution and a heat spreading function using various de-convolution techniques. While the forward problem is analogous to image blurring, the inverse problem is analogous to image restoration.
Owner:UNIV OF CALIFORNIA SANTA CRUZ
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com