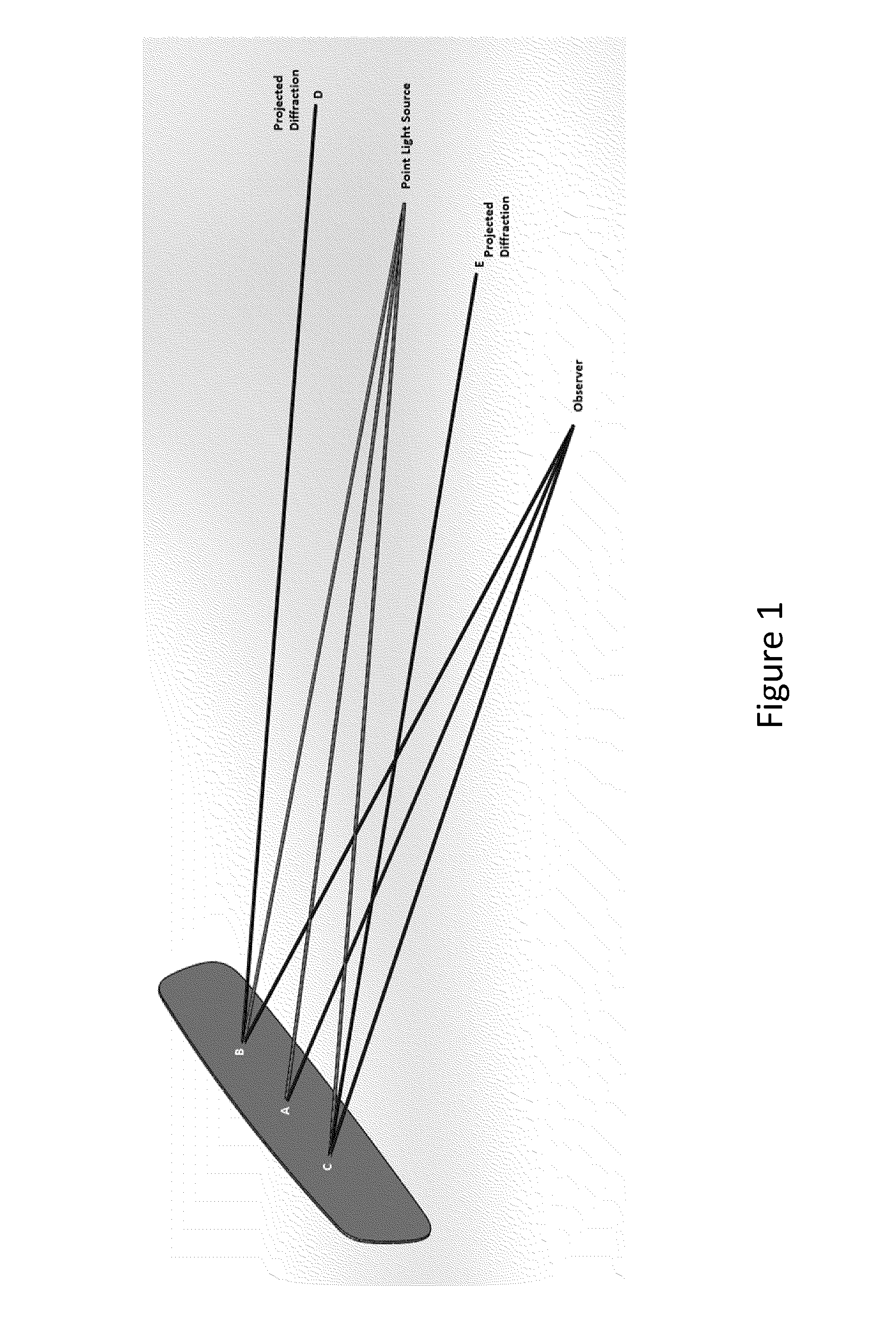
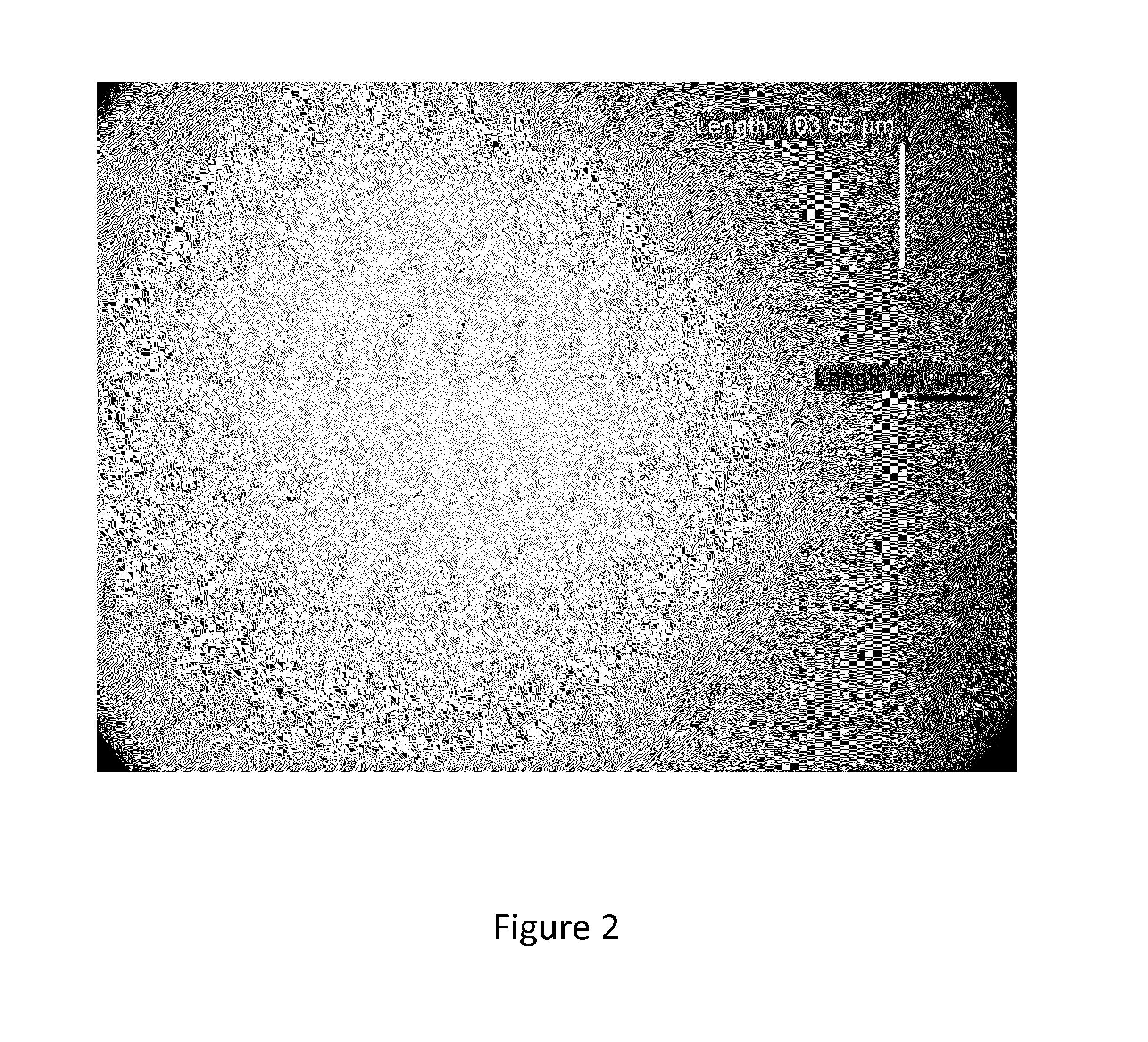
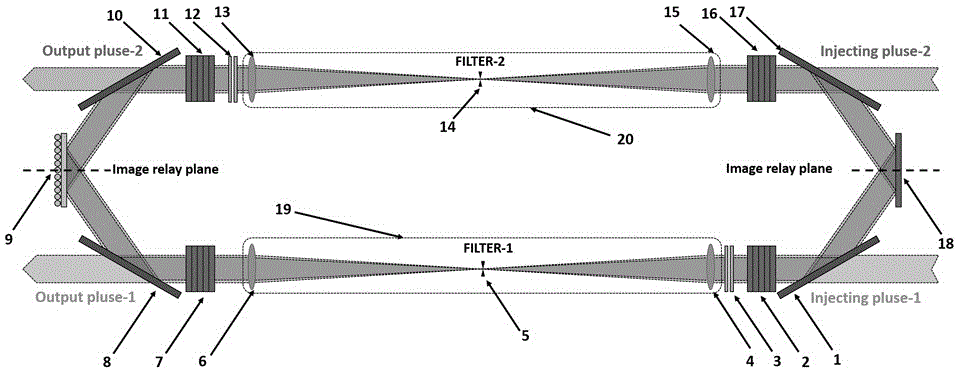
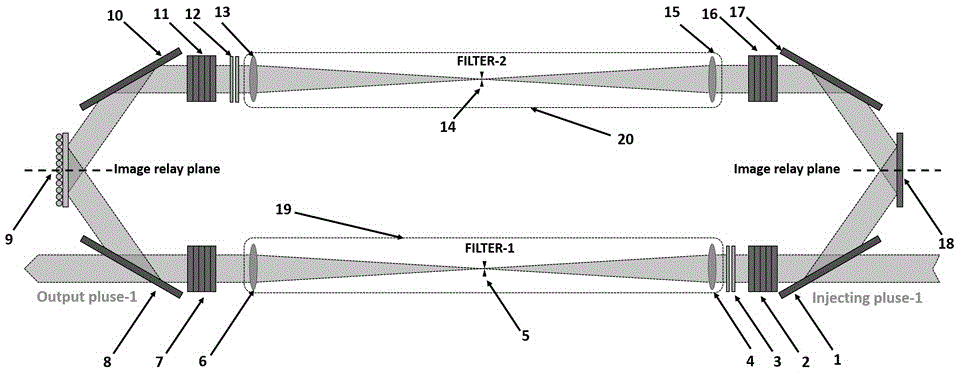
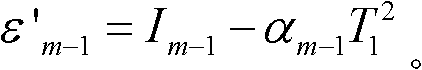Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
326 results about "Diffraction effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
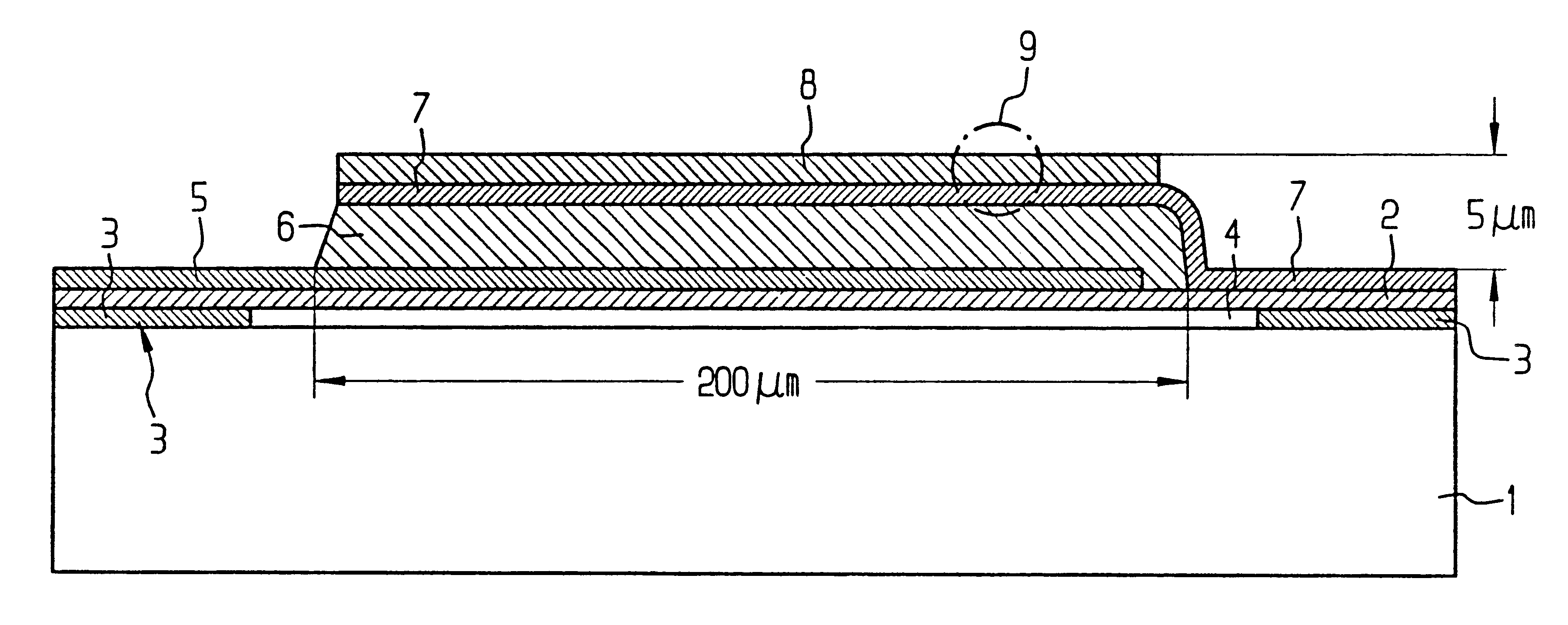
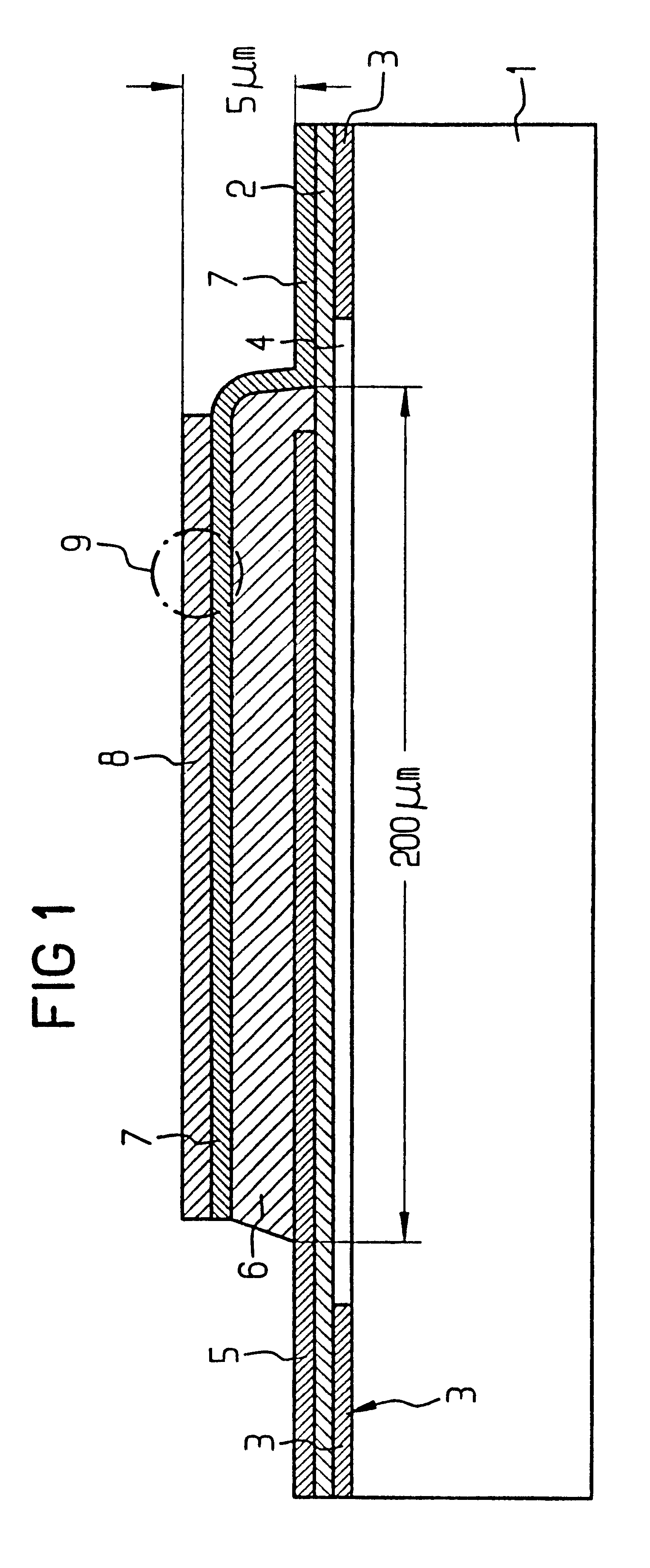
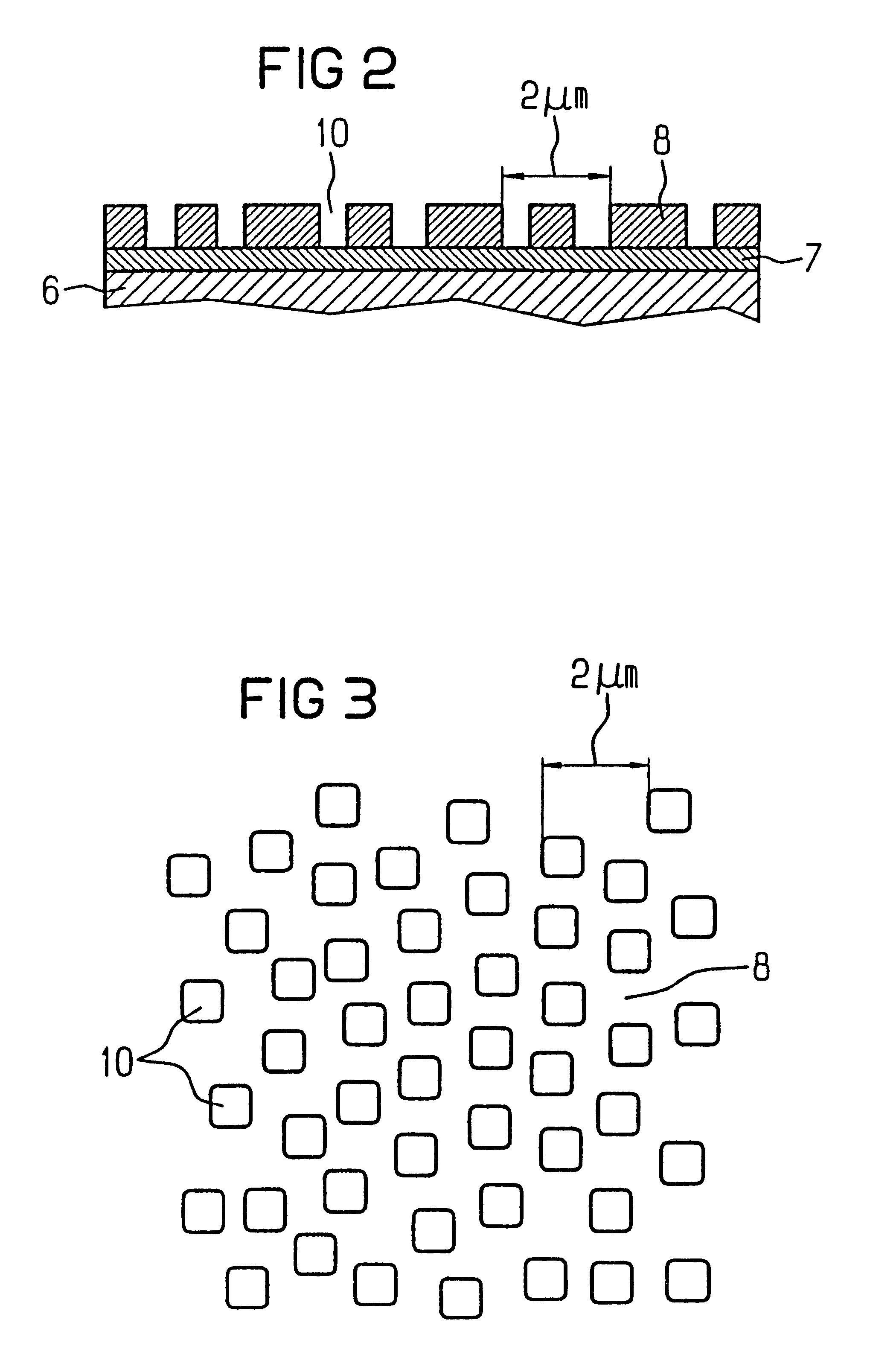
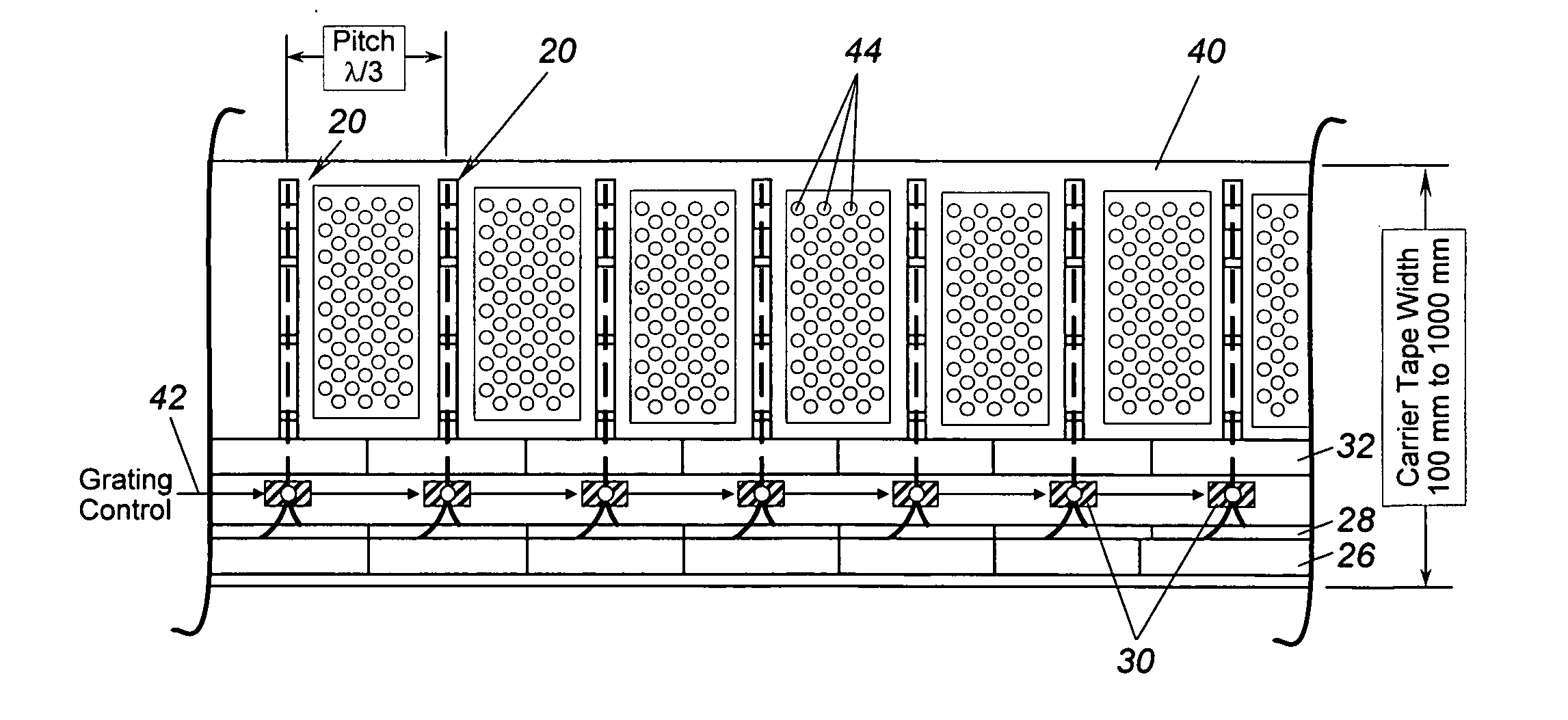
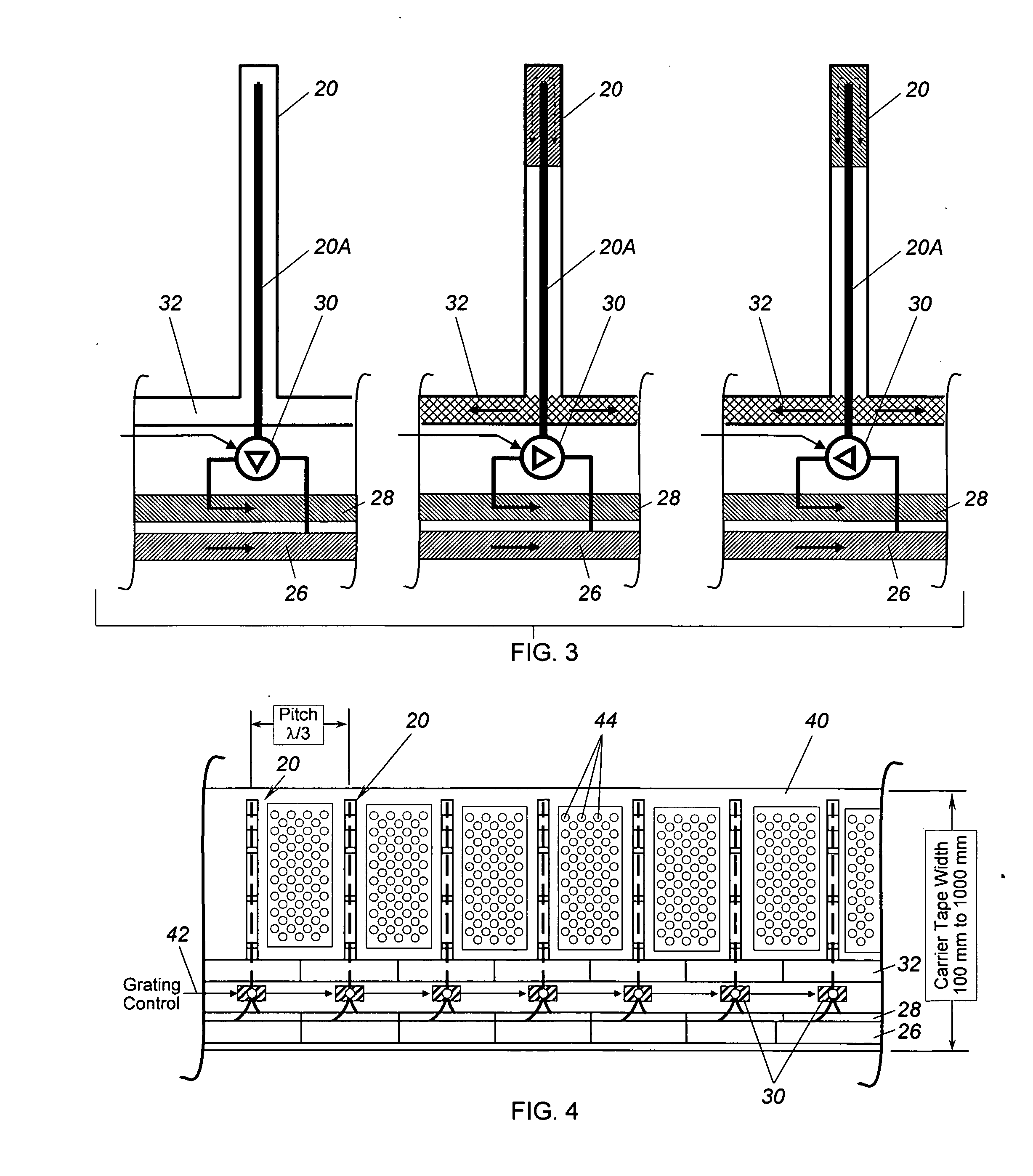
Thin film piezoelectric resonator
InactiveUS6657363B1Improve accuracySimple meansImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesDiffraction effectLength wave
The layer of the cover electrode, or an additional layer on the cover electrode is formed with holes, preferably produced lithographically, or similar structures. The structures have a mean spacing from one another which is smaller than the wavelength for operating the component. The structures are preferably distributed with a uniformity sufficient to effect a uniform change in the mass of the layer per area, thus producing a specific setting of the resonant frequency / frequencies, and are preferably, on the other hand, distributed so irregularly that diffraction effects are avoided.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
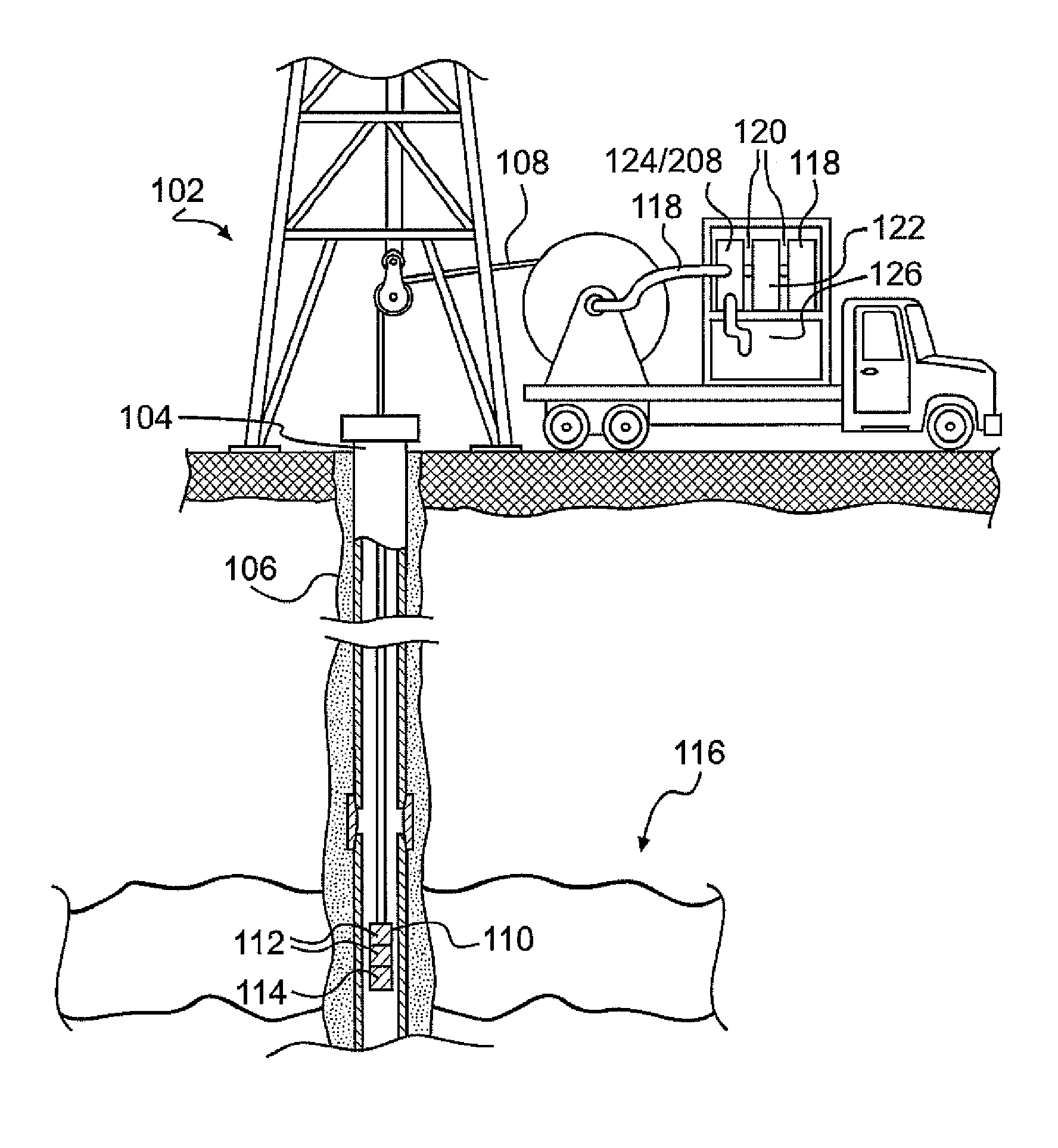
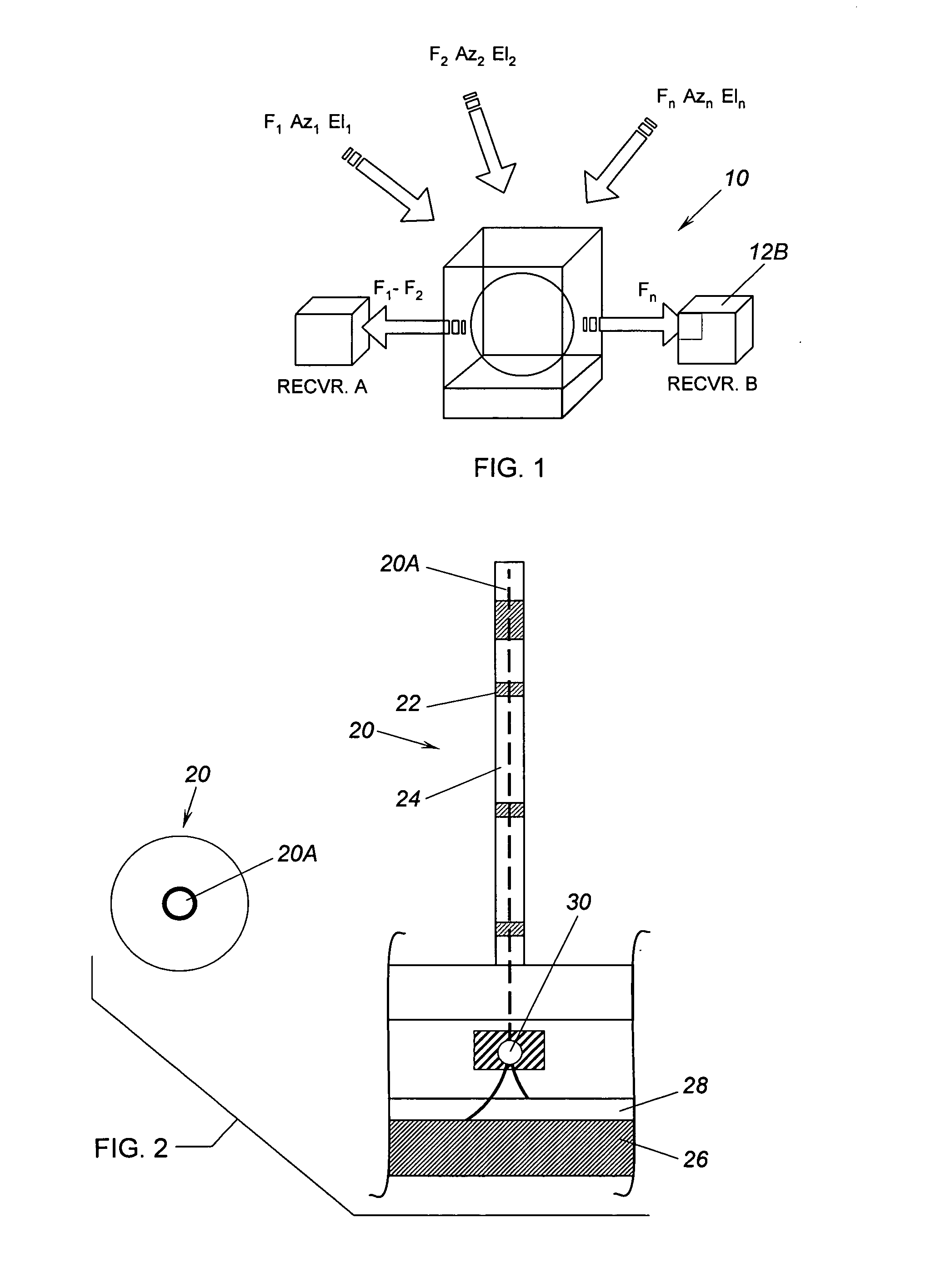
Optical fiber system and method for wellhole sensing of magnetic permeability using diffraction effect of faraday rotator
Systems and methods for optically determining casing collar and / or corrosion locations within boreholes, using the diffraction effect of Faraday crystals through which depolarized continuous light is transmitted within optical fibers.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Diffractive device
InactiveUS20100085642A1Good for observationDiffusing elementsLighting elementsDiffraction effectNon symmetric
The invention provides in particular for an achromatic diffractive diffuser comprising a surface relief diffractive device arranged such that, under illumination by ambient light, the diffractive effect serves to provide a uniform achromatic diffuser reflection into a defined viewing zone for observation by an observer, and also such that the achromatic diffractive replay of the device has a non-symmetric distribution of diffractive light intensity between positive and negative diffractive order such that the diffractive efficiency in the desired diffractive order is enhanced over that of the undesired order to provide an enhanced brightness achromatic device.
Owner:OPTAGLIO
Optical element, device, method, and applications
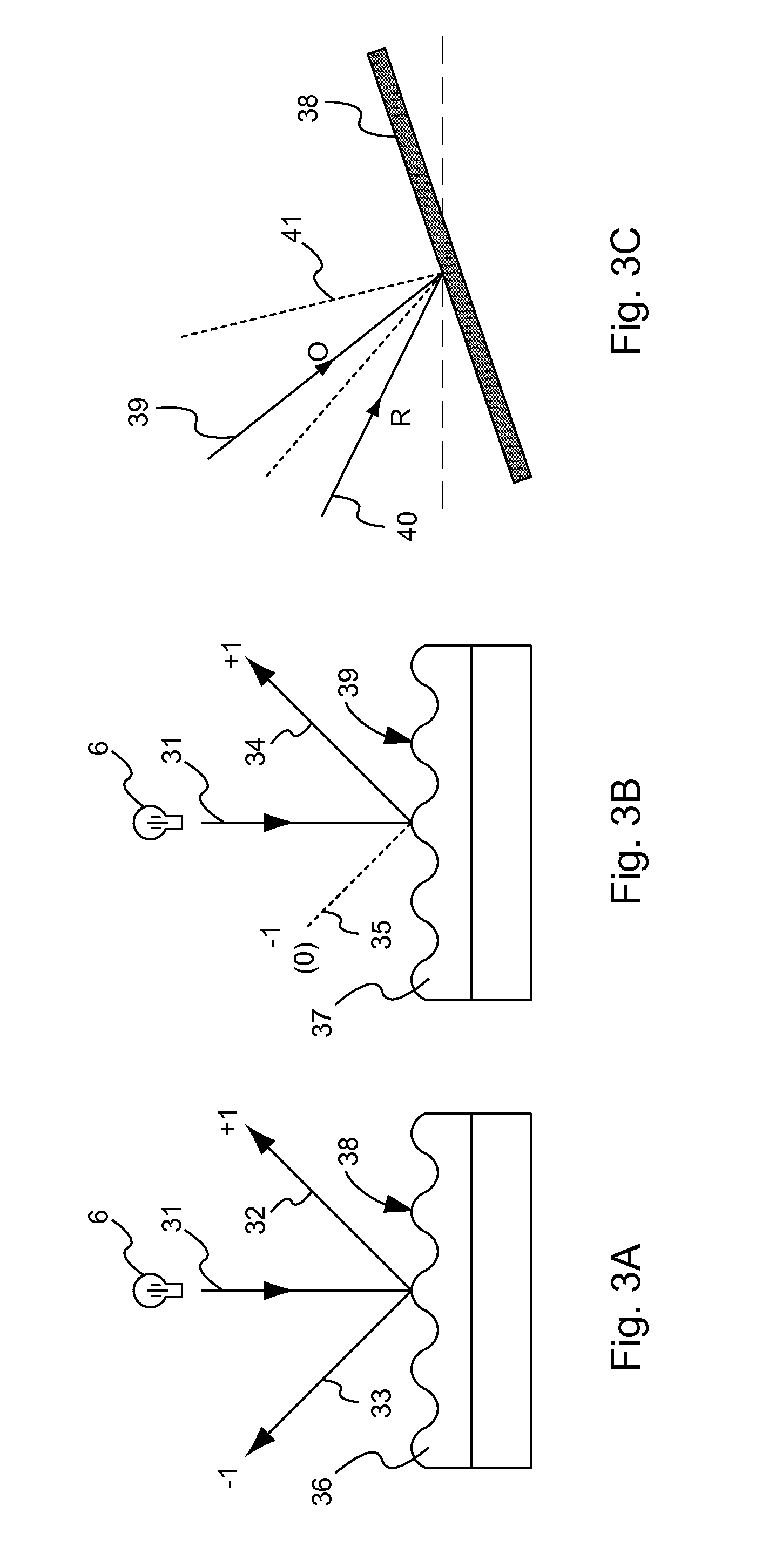
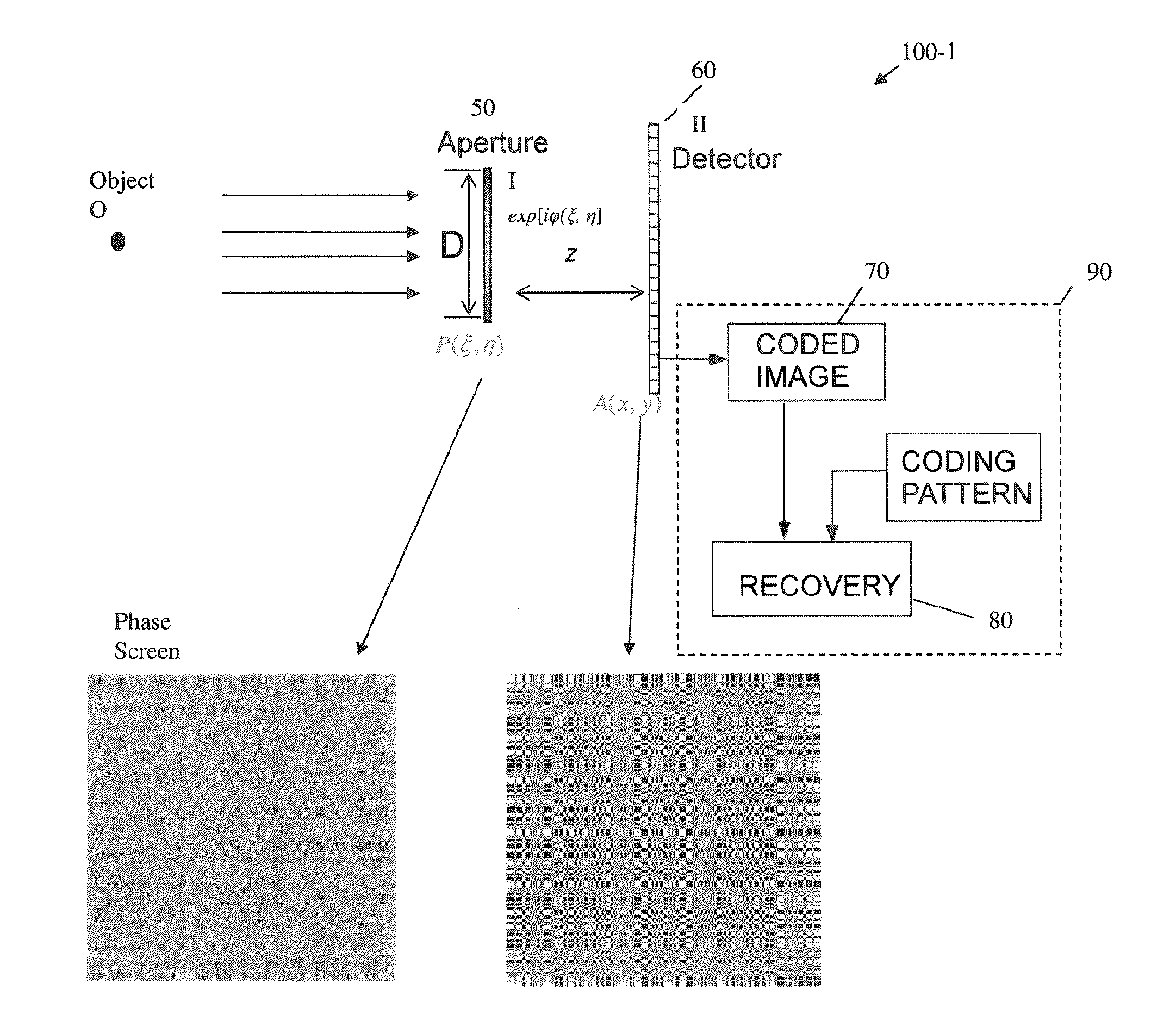
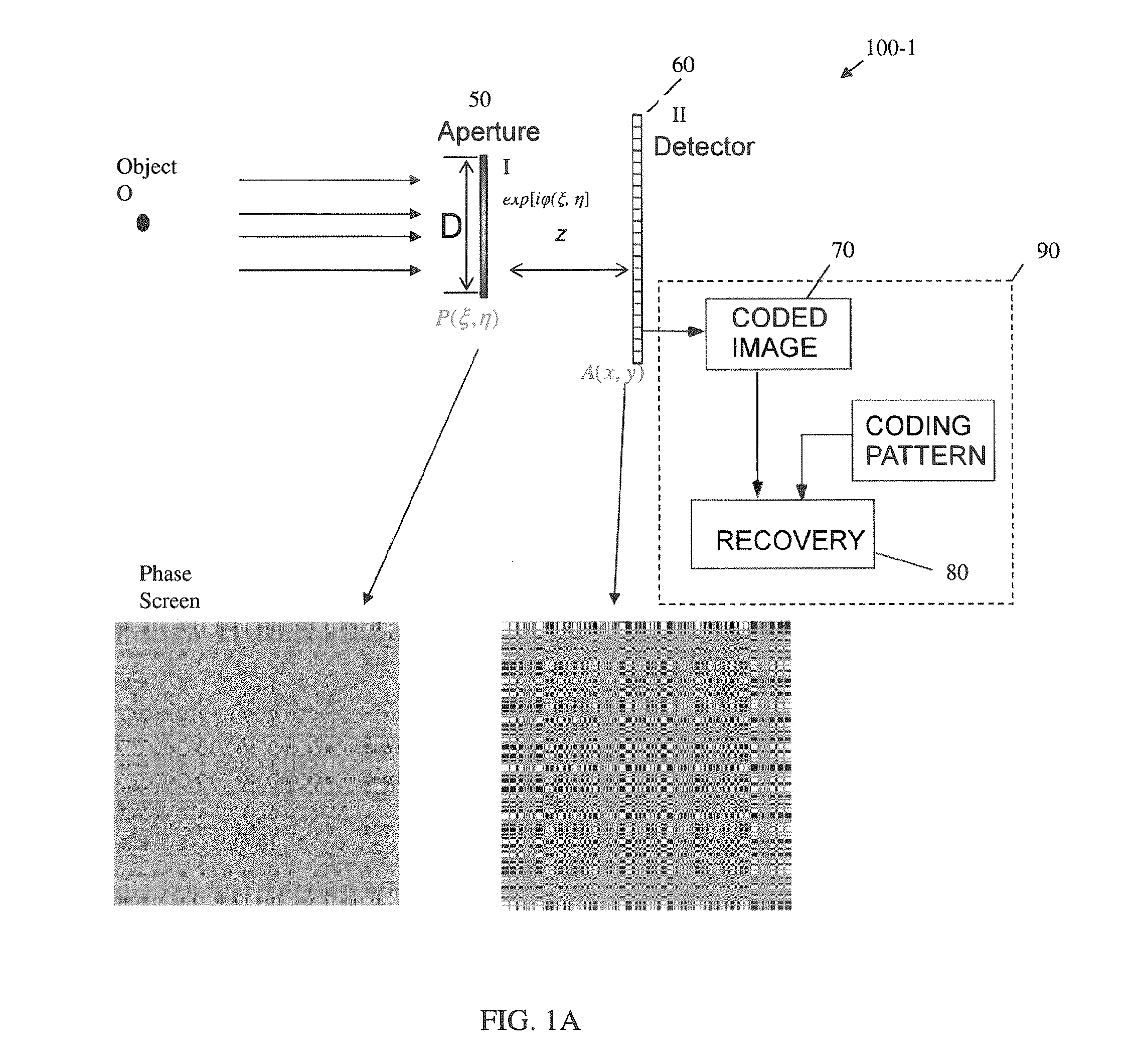
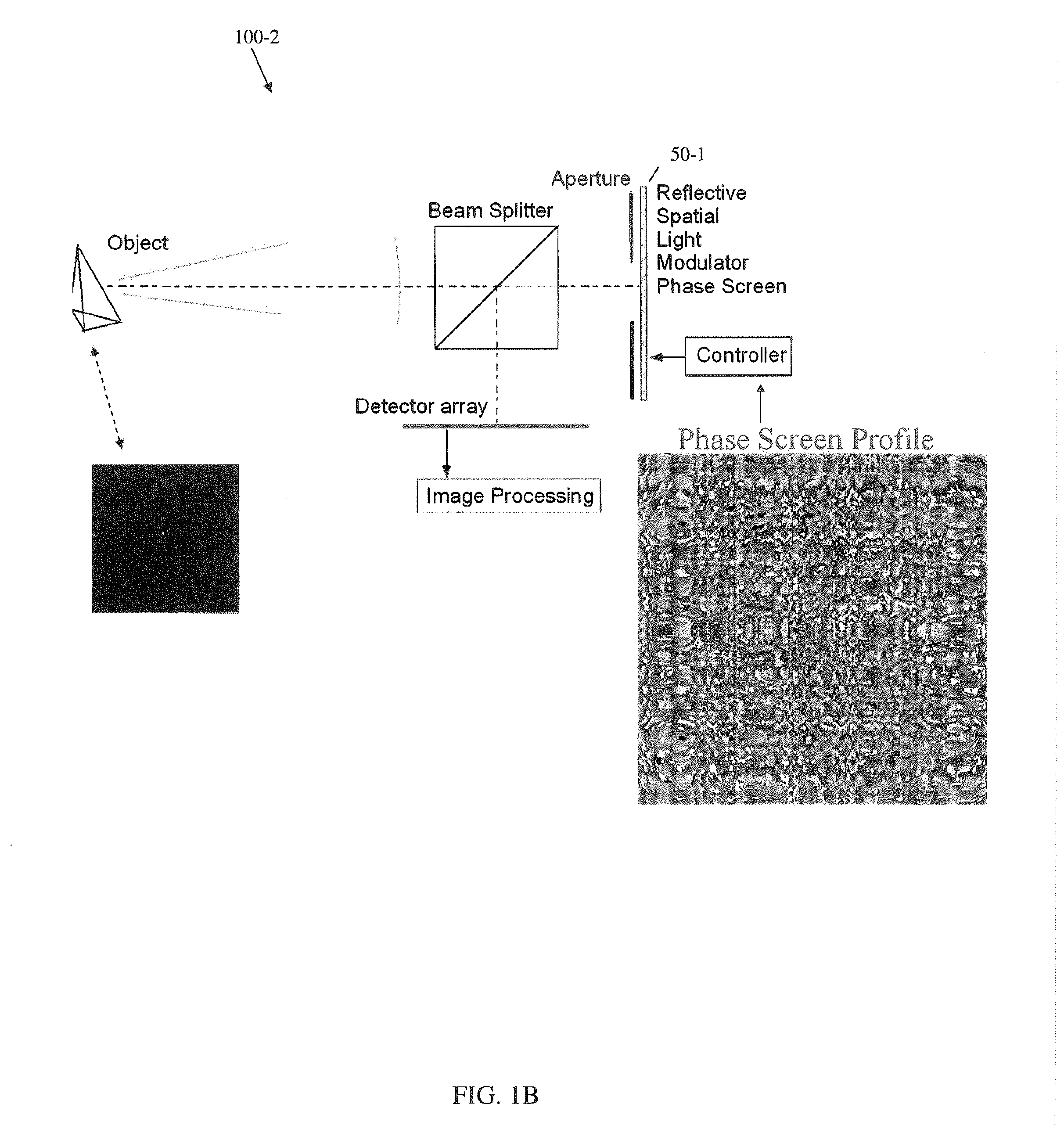
A novel phase-coded aperture, associated imaging system, and design method is disclosed. The optical imaging system includes a coded-aperture followed optically by a detector array and includes an image processor. A diffraction pattern in the form of a band-limited uniformly redundant array is formed on the detector array when focusable radiation from a point source in object space is modulation by the transmission function of the coded-aperture. Since diffraction effects cannot be ignored in the optical regime, an iterative phase retrieval method is used to calculate the phase-coded aperture transmission function. Correlation type processing can be applied for the image recovery.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Security element and security document with one such security element
InactiveUS20050127663A1Improve anti-counterfeiting performanceImprove reflective effectOther printing matterHolographic optical componentsColor shiftComputer science
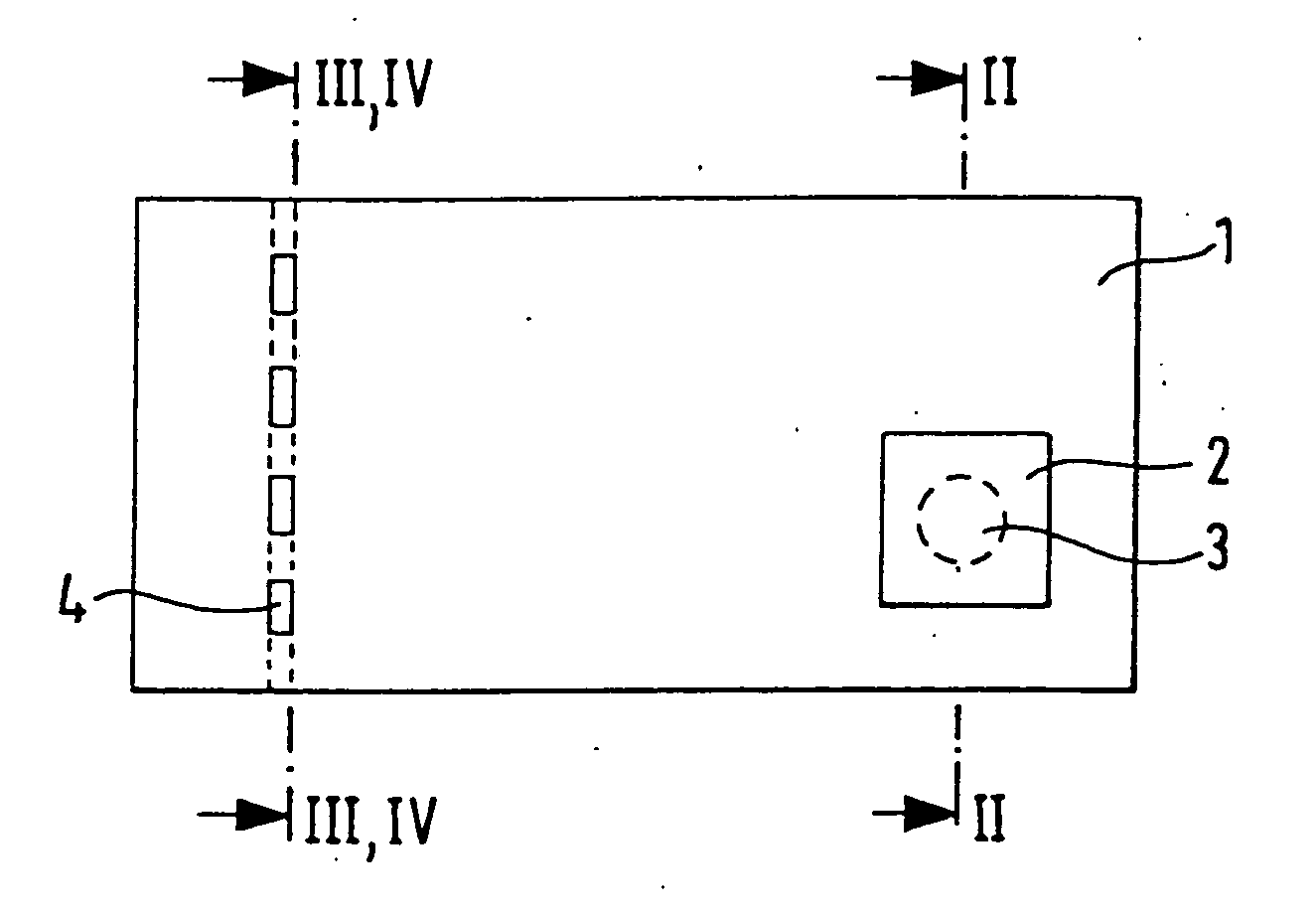
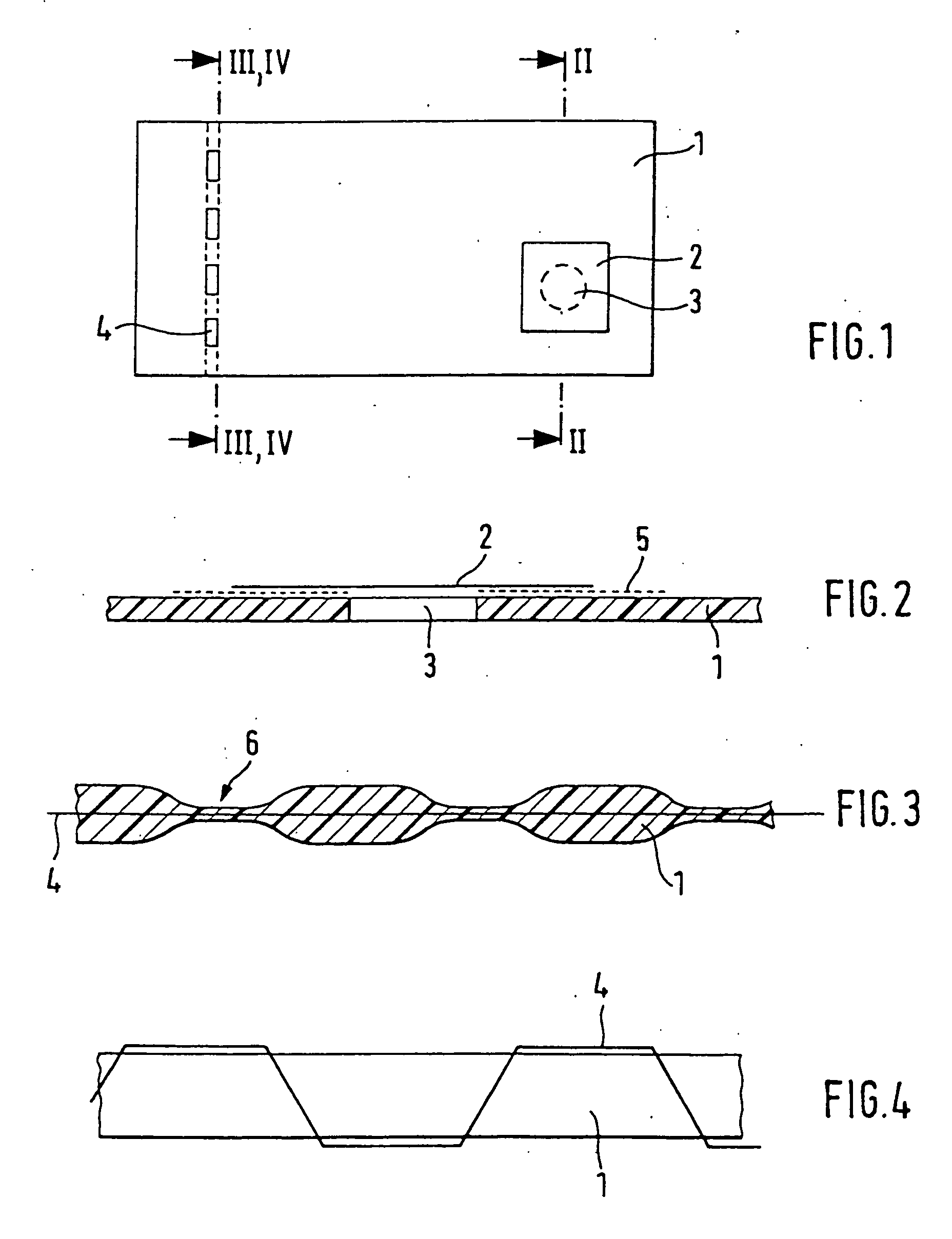
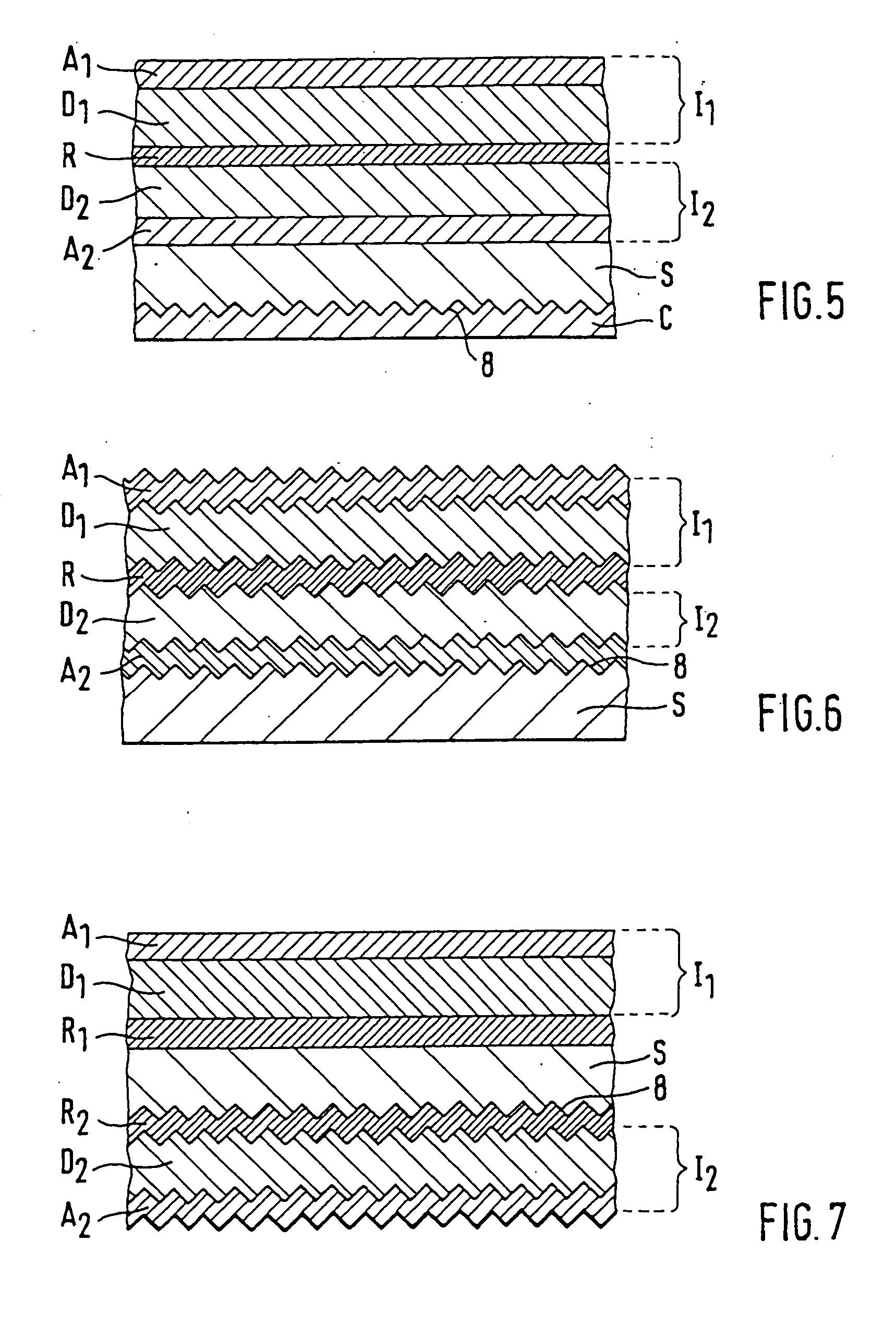
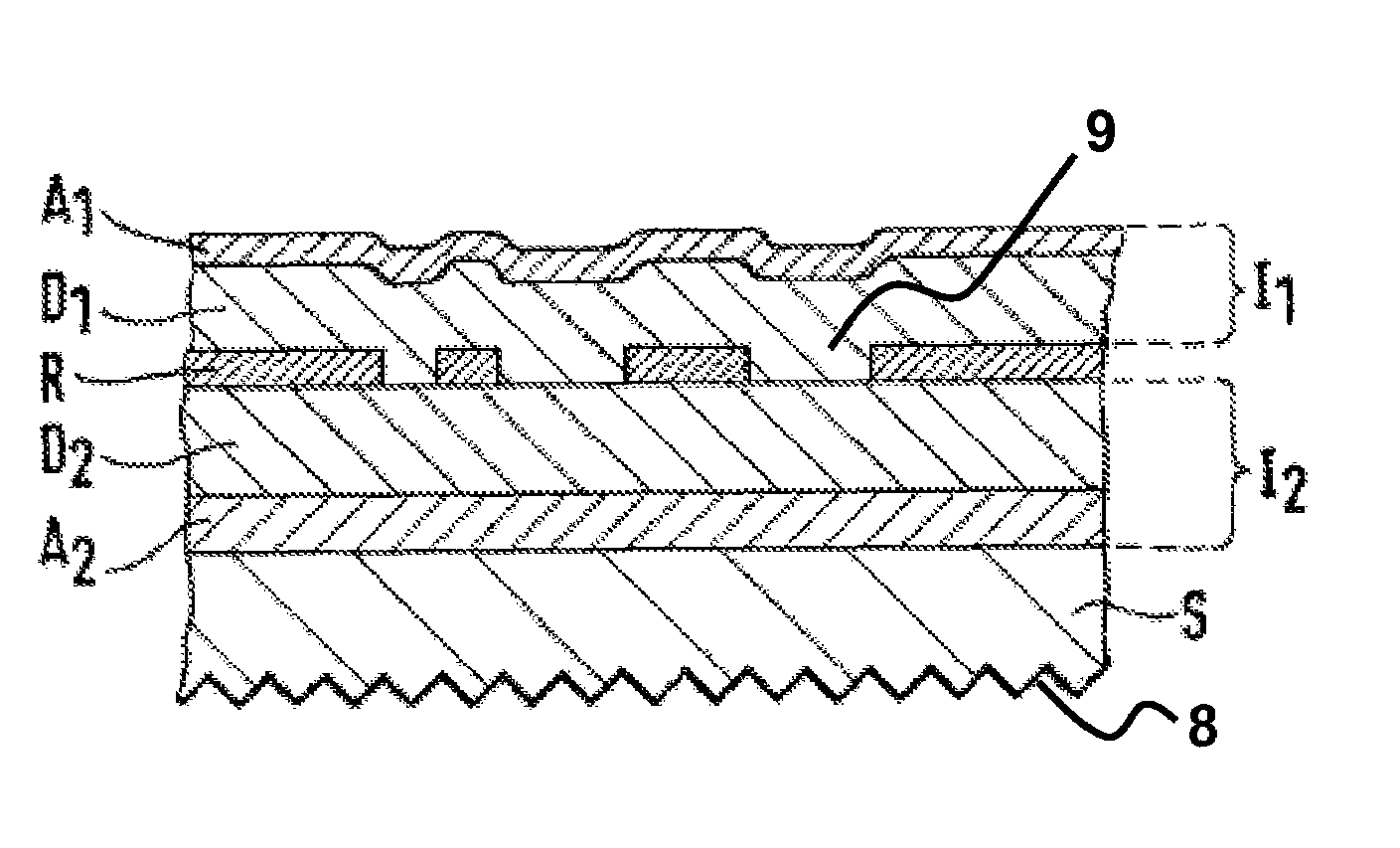
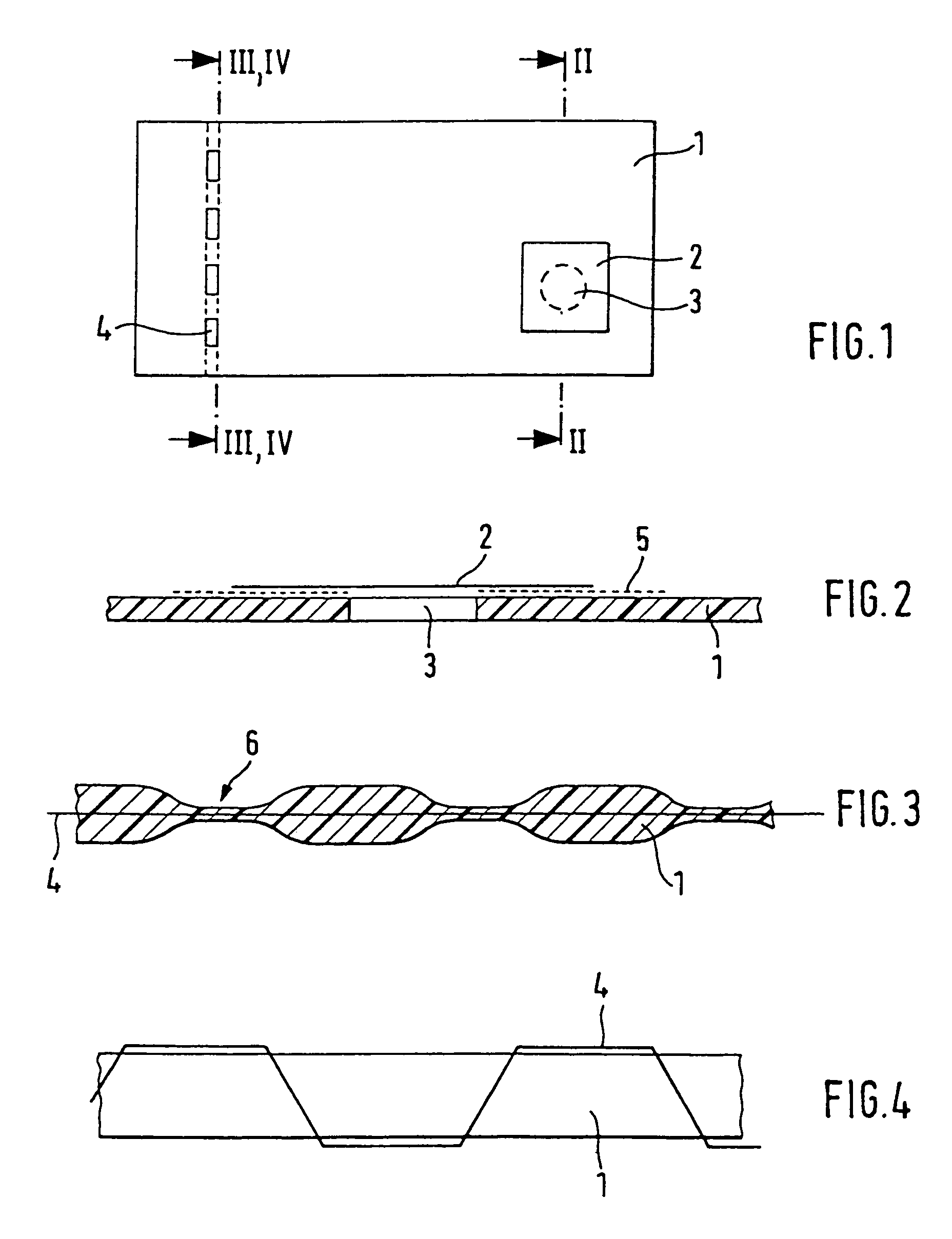
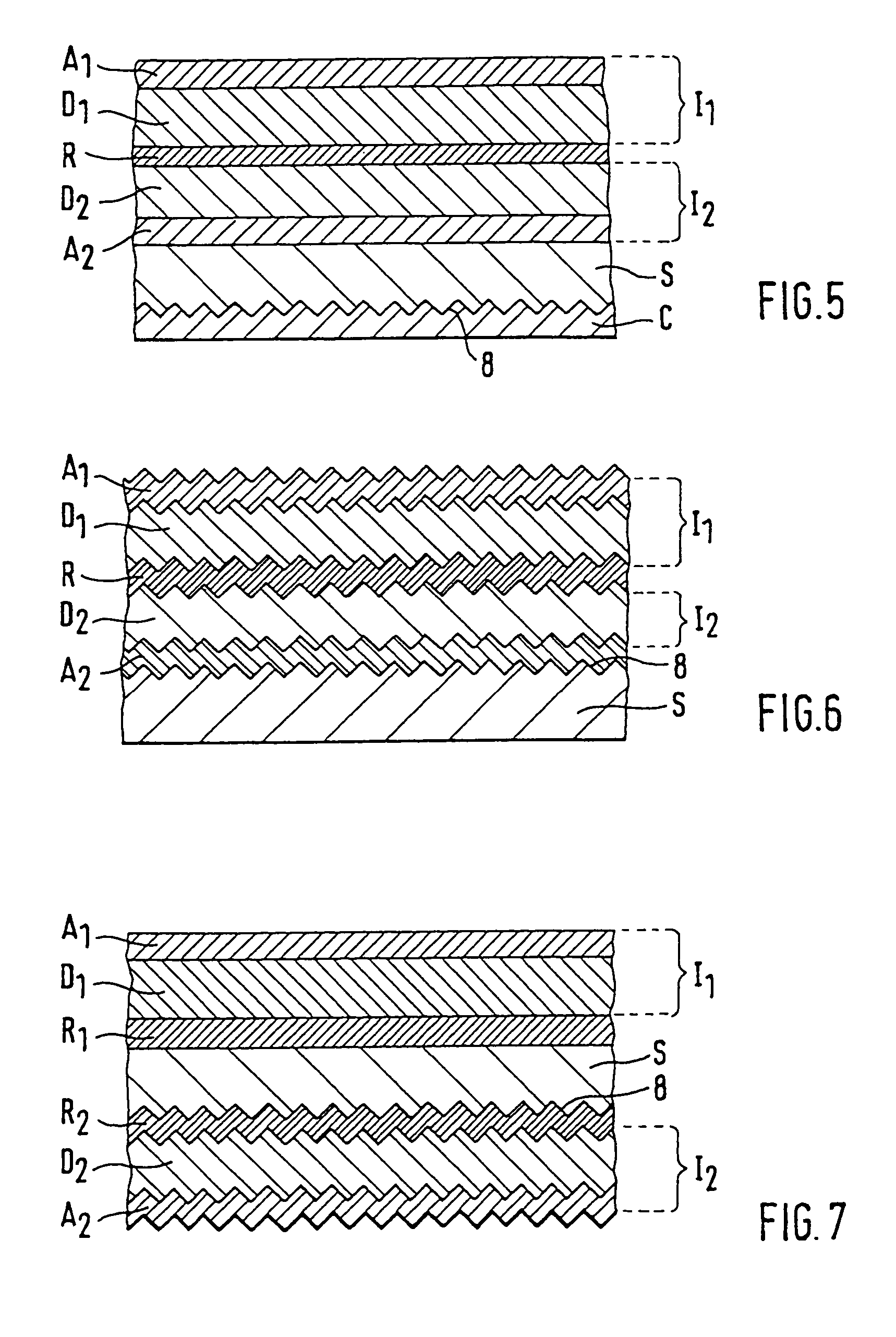
A security element 2, 4 for embedding in or application to a security document in such a way that it is visually recognizable from both sides of the security document 1, is structured in a multilayer fashion and includes two interference elements I1, I2 with color shift effect, a metallic reflection layer R located in between as well as, optionally, diffraction structures 8. Depending on the disposition of the layers I1, R, I2 and the optionally present diffraction structures. 8 on a transparent substrate S the color shift effect and / or the diffractive effects are perceptible-from-one or from both sides of the security element 2, 4. The security element is particularly suitable as a two-sided window thread 4 and as a label or transfer element 2 above a hole 3 in the security document 1.
Owner:GIESECKE & DEVRIENT CURRENCY TECHNOLOGY GMBH
Method and device for producing a coupling grating for a waveguide
InactiveUS20040042724A1Reduce contrastAdequate averagingCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideDiffraction effectEffective solution
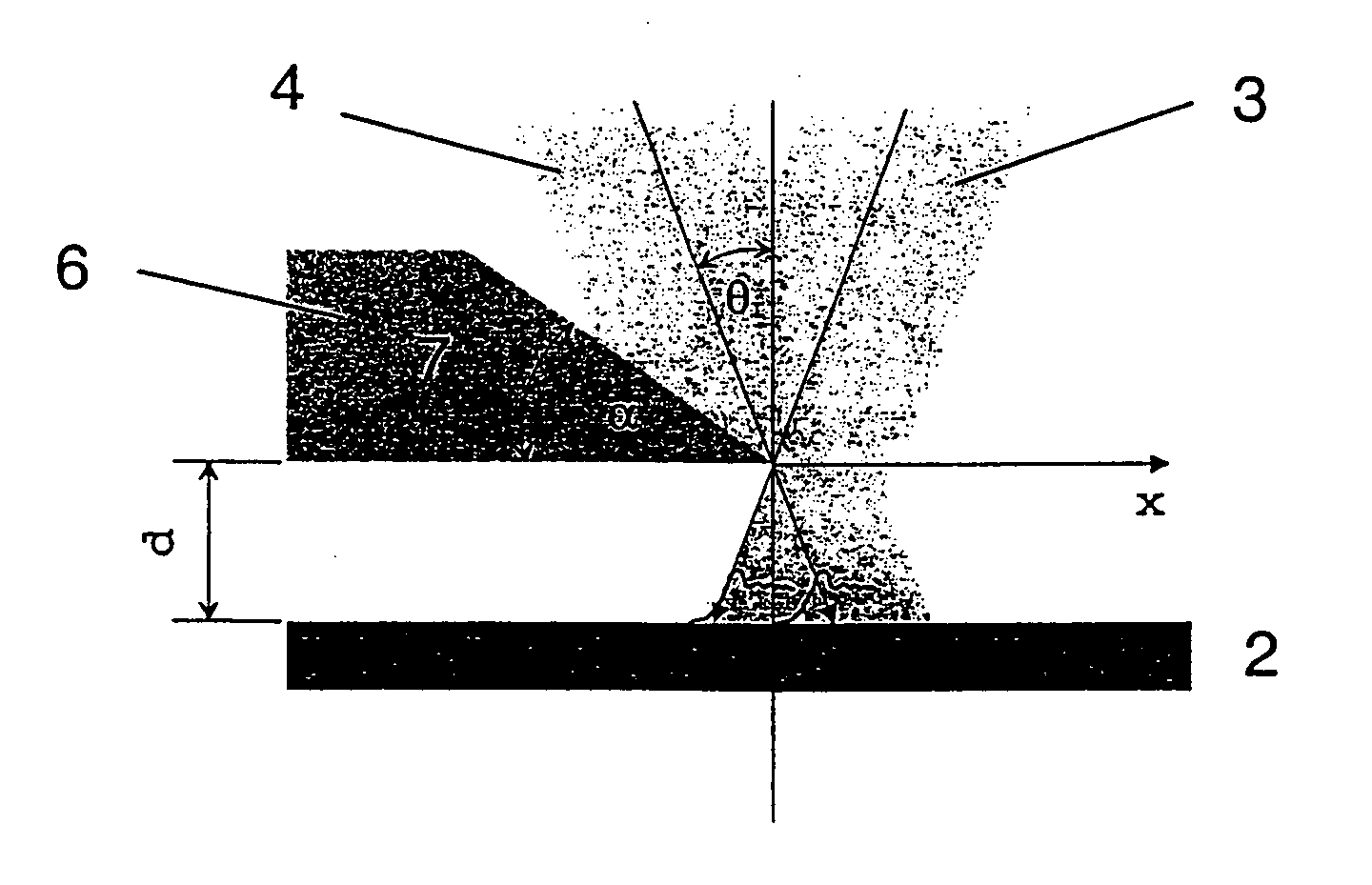
The invention relates to a method and a device for producing a coupling grating (5) for a waveguide. The method relies on the technique of interference lithography, whereby an interference pattern on a light-sensitive layer (2) is exposed by superimposing two coherent light beams (3, 4) on said light-sensitive layer (2). Said pattern is then transferred onto the surface of the substrate (1) that lies underneath by subsequent developing and an etching process. The method is characterized in that it uses a shadow mask (6) that is mounted at minimum clearance relative to the surface of the light-sensitive layer (2). By observing said minimum clearance, the Fresnel diffraction images of both light beams (3, 4) are separated on the edge(7). The thickness of the light-sensitive layer (2) is selected in such a way that the superimposition of the Fresnel diffraction pattern of one light beam with the other undisturbed light beam suffices to uncover areas of the substrate (1) during subsequent developing of the layer (2). The method makes it possible to avoid transfer of unwanted diffraction effects on the edge of the shadow mask to the substrate. The method provides a cost-effective solution for the production of large-surface coupling grating matrices.
Owner:GOMBERT ANDREAS +2
Polarization-sensitive infrared image sensor including a plurality of optical fibers
A polarization-sensitive infrared image sensor (also termed a snapshot polarimeter) utilizing a 2-D array of polarizers to filter infrared light from a scene according to polarization, and a 2-D array of photodetectors (i.e. a focal plane array) to detect the filtered infrared light and generate polarization information which can be used to form a polarization-sensitive image of the scene. By forming each polarizer on an optical fiber in a fiber optic faceplate, the polarizers can be located facing a 2-D array of retarders to minimize diffraction effects of the infrared light. The optical fibers also guide the filtered infrared light to the photodetectors to reduce cross-talk in the polarization information. The polarizers can be formed as wire grid polarizers; and the retarders can be formed as subwavelength surface-relief gratings.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
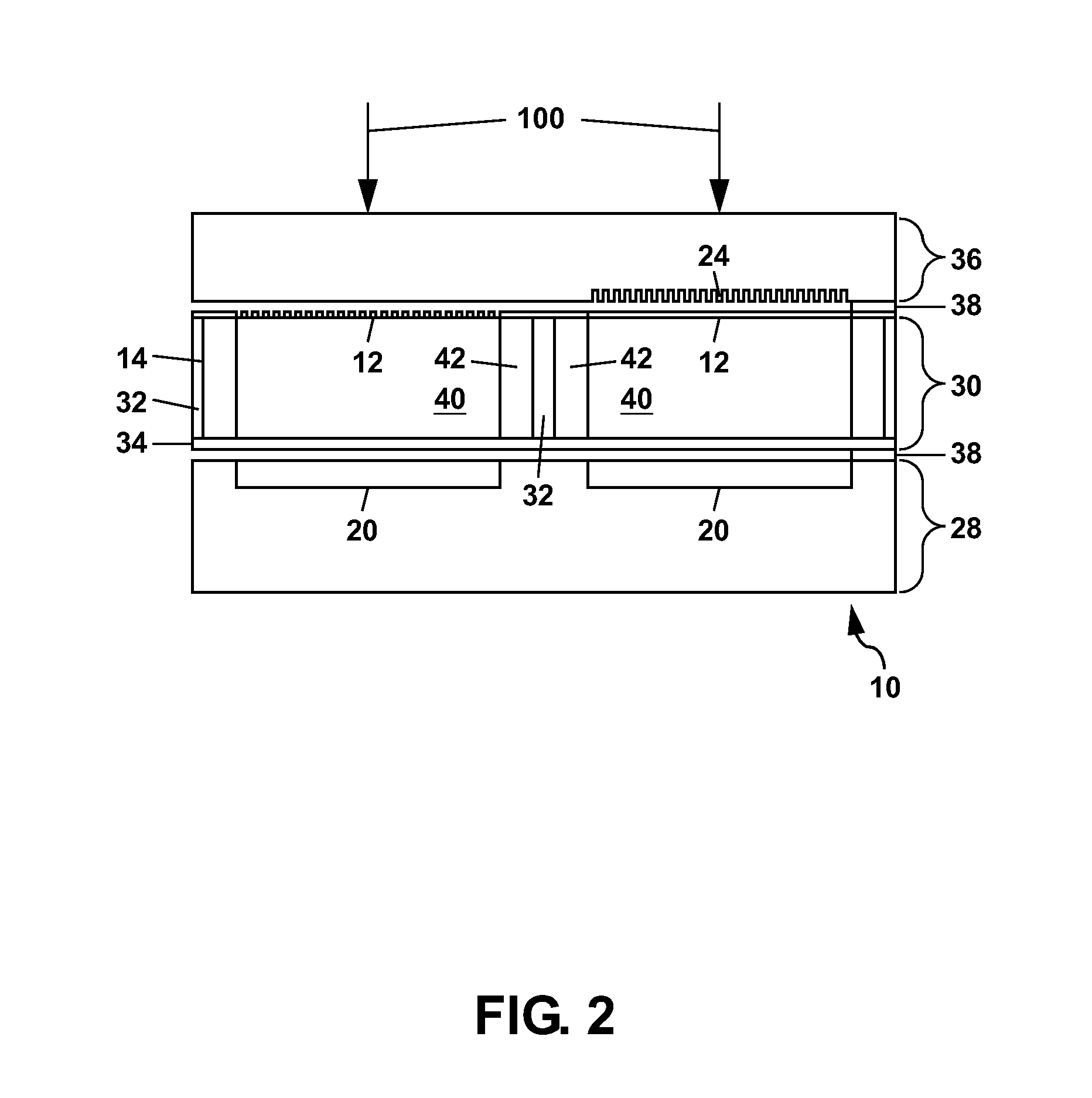
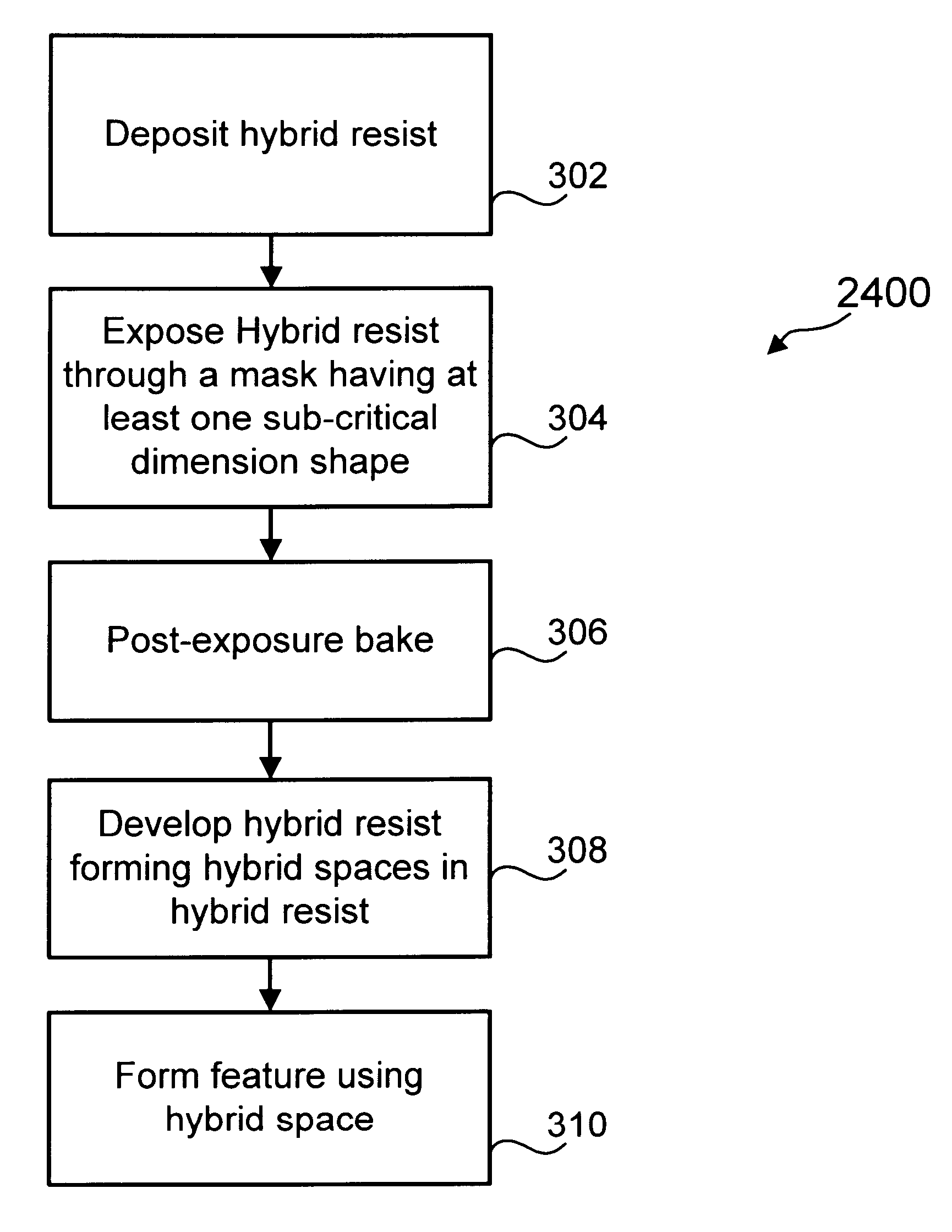
Fused hybrid resist shapes as a means of modulating hybrid resist space width
InactiveUS6184041B1Positive toneNegative responsePhoto-taking processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiffraction effectResist
The preferred embodiment of the present invention overcomes the limitations of the prior art and provides a method to form spaces in hybrid resist with varying widths. In particular, the preferred method facilitates the formation of spaces with different widths by using mask shapes (either openings or lines) that are smaller than the diffraction limit of the photolithography tool. Diffraction effects at these dimensions reduce the light intensity reaching the resist surface such that the hybrid resist receives an intermediate exposure. These portions of hybrid resist that receive an intermediate exposure are soluble in developer and thus develop away to form spaces in the hybrid resist. Thus, spaces in the hybrid resist of varying widths can be formed.
Owner:IBM CORP
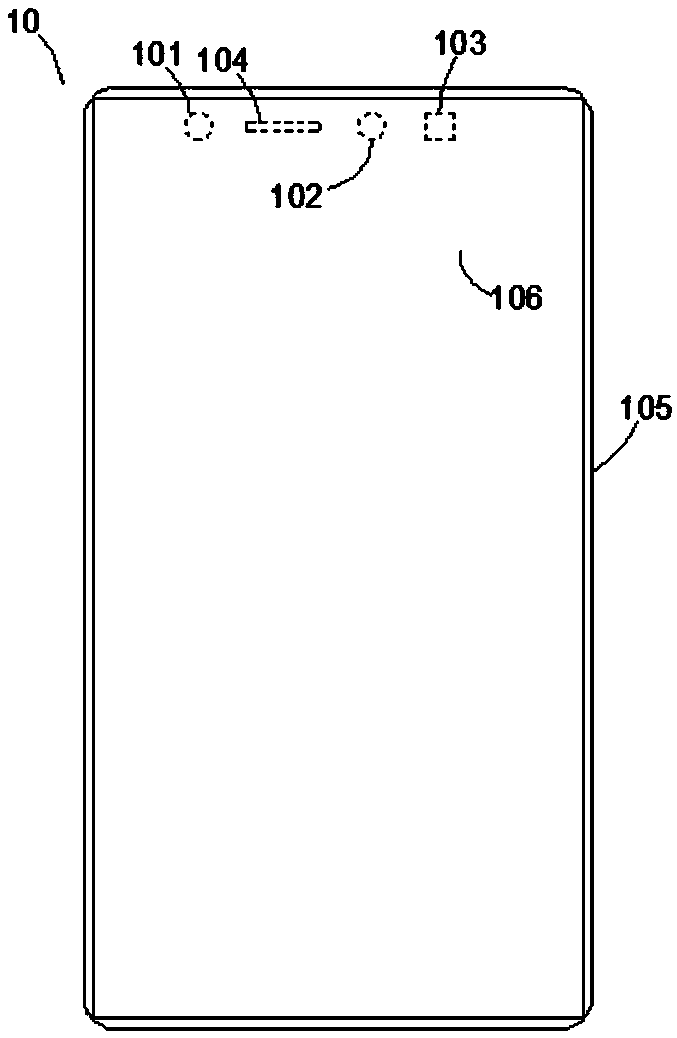
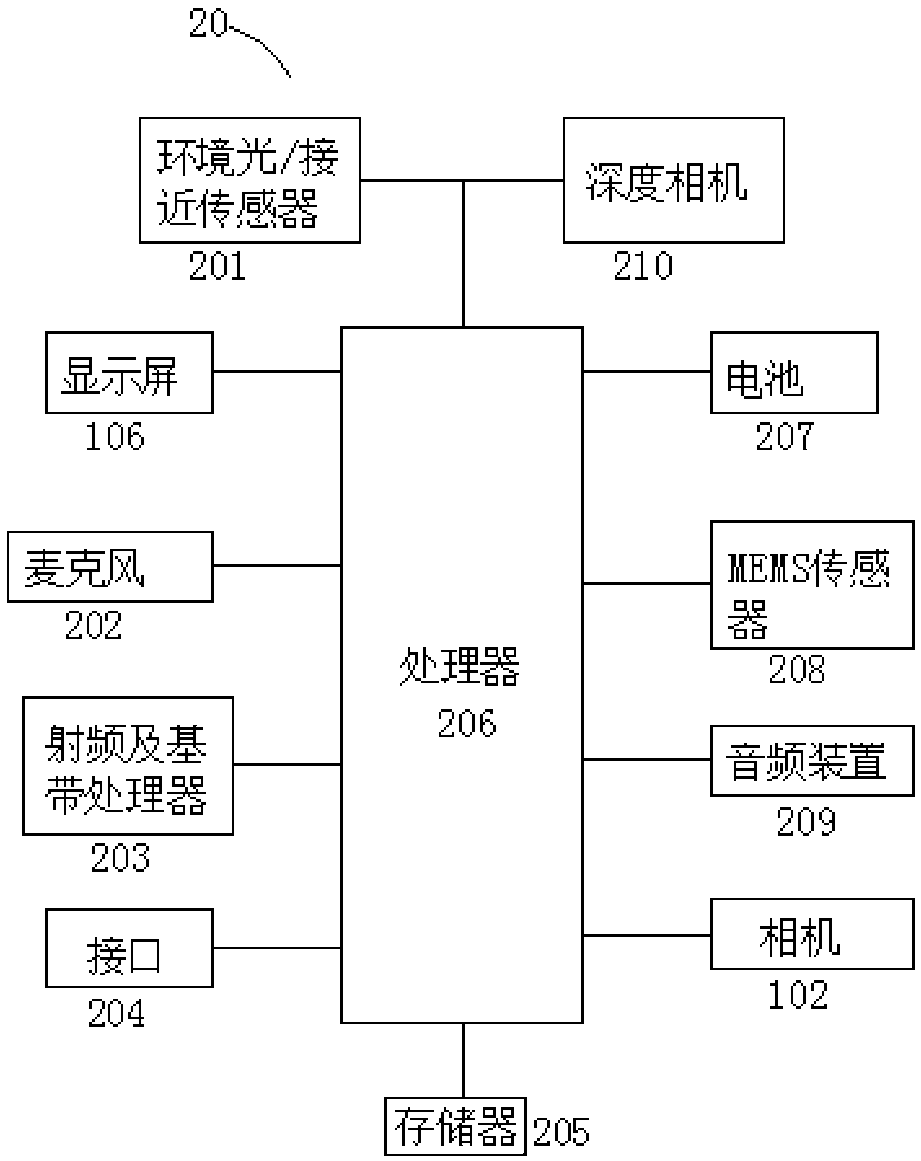
Compensation display screen, in-screen optical system and electronic device
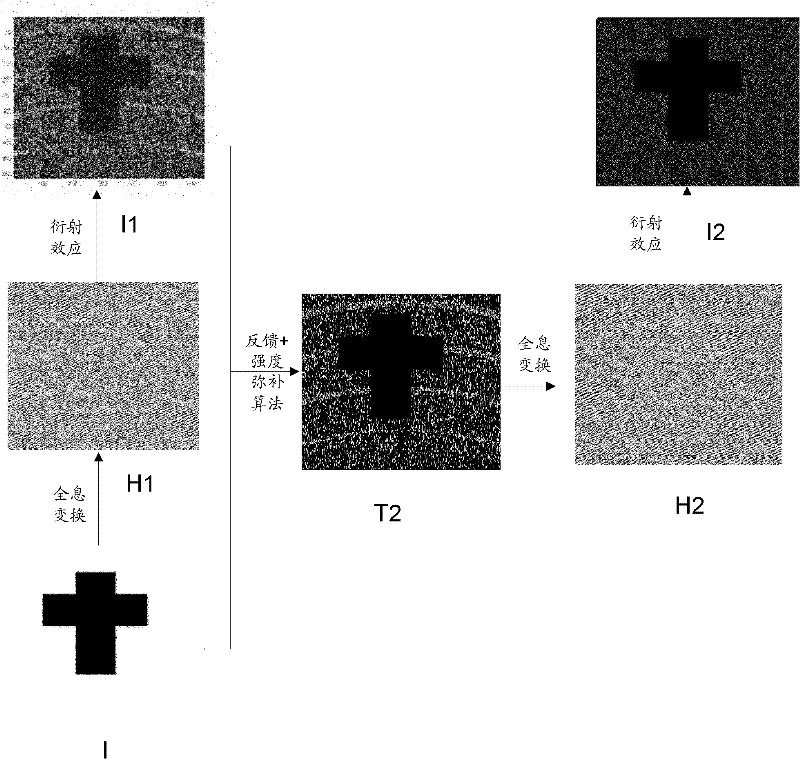
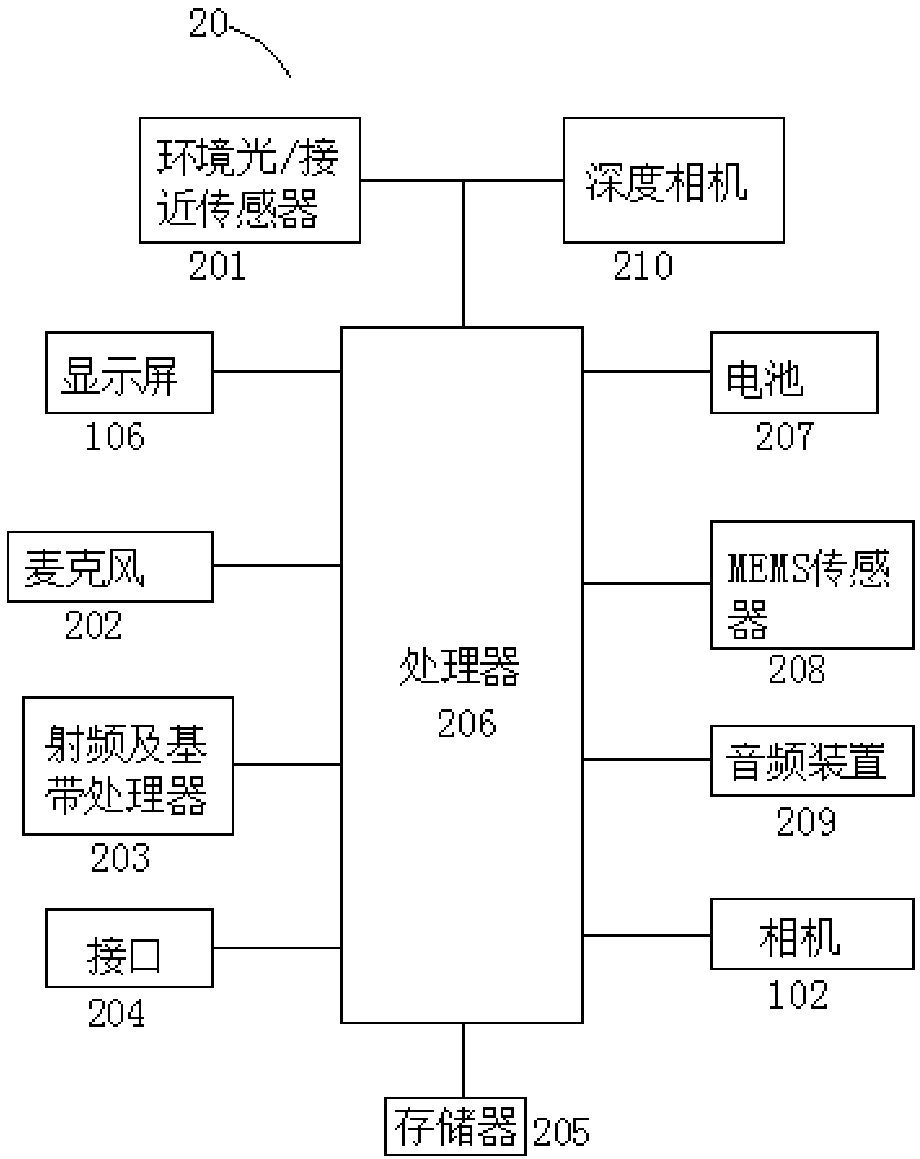
ActiveCN109143607AAvoid Diffraction EffectsQuality improvementNon-linear opticsOptical elementsDiffraction effectLight beam
The invention is applicable to the technical field of electronics, and provides a compensation display screen, an in-screen optical system and an electronic device. The compensation display screen comprises a transparent display screen consisting of a plurality of periodically arranged pixel units used for displaying, and a compensation component, wherein the transparent display screen includes aplurality of periodically arranged pixel units used for displaying, and the compensation component is configured to be complementary to the diffraction effect of the transparent display screen, so that the same preset light beam is emitted after the preset light beam enters the compensation display screen. The compensation component which is complementary to the diffraction effect of the transparent display screen is arranged, and the diffraction effect caused by the periodic pixel diffraction structure of the light beam passing through the transparent display screen is counteracted, so that when the preset light beam enters the compensation display screen to be emitted out as the same preset light beam, the diffraction effect of the transparent display screen on incident light beams is avoided, and the quality and effect of imaging or projection are improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN ORBBEC CO LTD
Optical Device Exhibiting Color Shift Upon Rotation
An optical device exhibiting a color shift upon rotation is disclosed. The optical device has a textured surface having a relief structure finer than a human eye resolution but large enough not to exhibit diffraction effects. The textured surface is coated with an interference thin film that exhibits a color shift with tilt. A uniform color seen at one angle of rotation changes to another uniform color when the optical device is rotated in its own plane. A method of manufacturing of such an optical device, as well as the use of the optical device as an optical security and authentication element, is also disclosed.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Optical add-drop multiplexer architecture with reduced effect of mirror edge diffraction
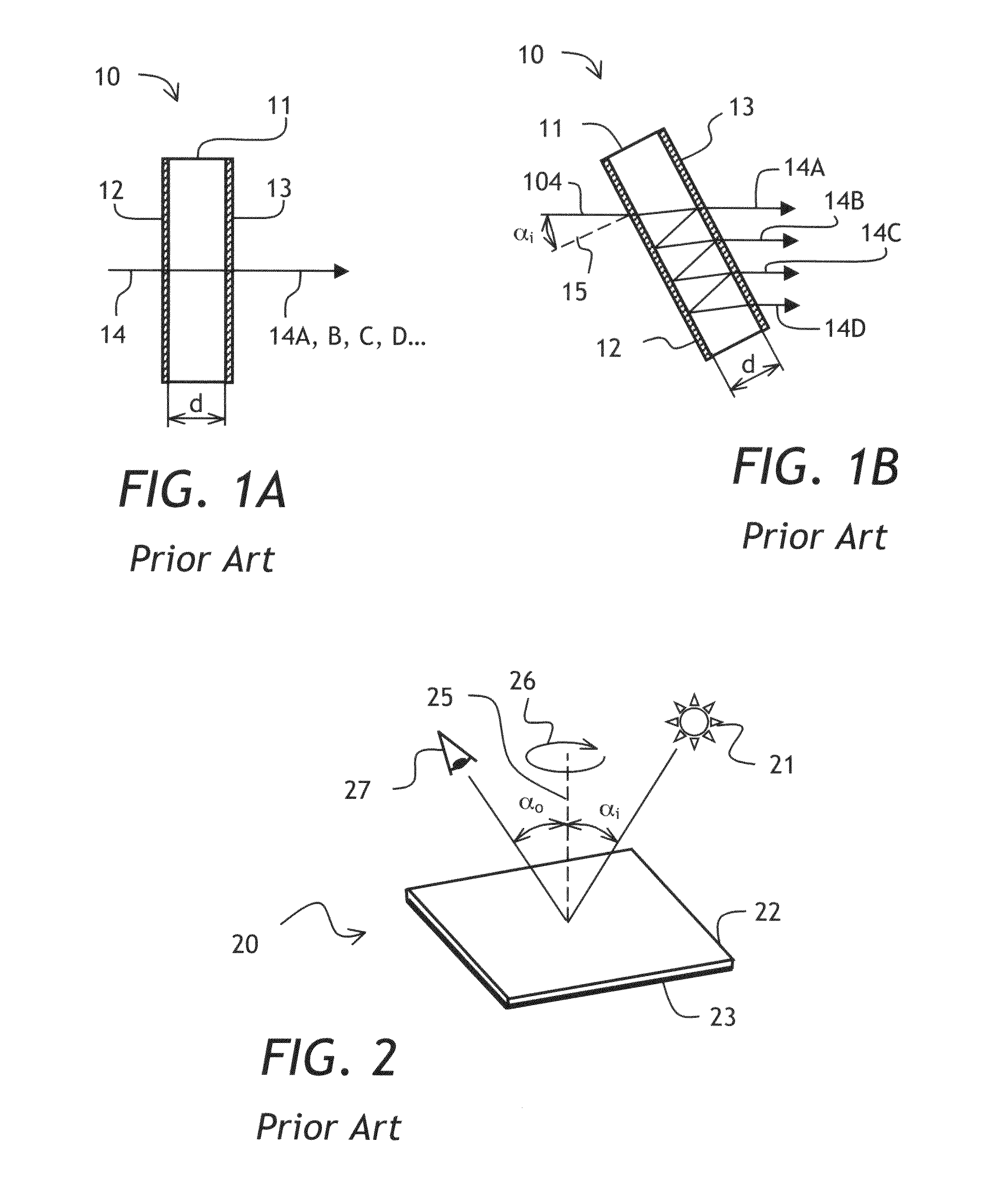
ActiveUS20060228070A1Optimize passbandReduce power levelCoupling light guidesDiffraction effectAngular frequency
Effects of diffraction of a spectral beam from an edge of the micromirrors are reduced in order to optimize the passband in a wavelength selective switch. The effects of diffraction on the pass band may be reduced by appropriate modification of the edges of the micromirrors, by modification of the input and / or output ports to allow for attenuation by rotation of the micromirror about the switching axis, by using rotation of the micromirror about both the attenuation axis and the switching axis to achieve the desired level of attenuation, by inserting an aperture at a focal plane or external to the device to reduce the magnitude of the micromirror edge diffraction transmitted to any or all output ports, or by appropriate filtering of angular frequencies with a diffraction grating used to separate a multi-channel optical signal into constituent spectral beams.
Owner:CAPELLA PHOTONICS INC
Optical Measuring Device and Process
ActiveUS20170336326A1Quick scanReduced functionalityMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceDiffraction effectOptical measurements
An achromatic 3D STED measuring optical process and optical method, based on a conical diffraction effect or an effect of propagation of light in uniaxial crystals, including a cascade of at least two uniaxial or conical diffraction crystals creating, from a laser source, all of the light propagating along substantially the same optical path, from the output of an optical bank to the objective of a microscope. A spatial position of at least one luminous nano-emitter, structured object or a continuous distribution in a sample is determined.Reconstruction of the sample and its spatial and / or temporal and / or spectral properties is treated as an inverse Bayesian problem leading to the definition of an a posteriori distribution, and a posteriori relationship combining, by virtue of the Bayes law, the probabilistic formulation of a noise model, and possible priors on a distribution of light created in the sample by projection.
Owner:BIOAXIAL
Optical waveguide circuit, and method for compensating the light transmission wavelength
InactiveUS6377723B1Low costLow temperature dependenceCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideDiffraction effectLength wave
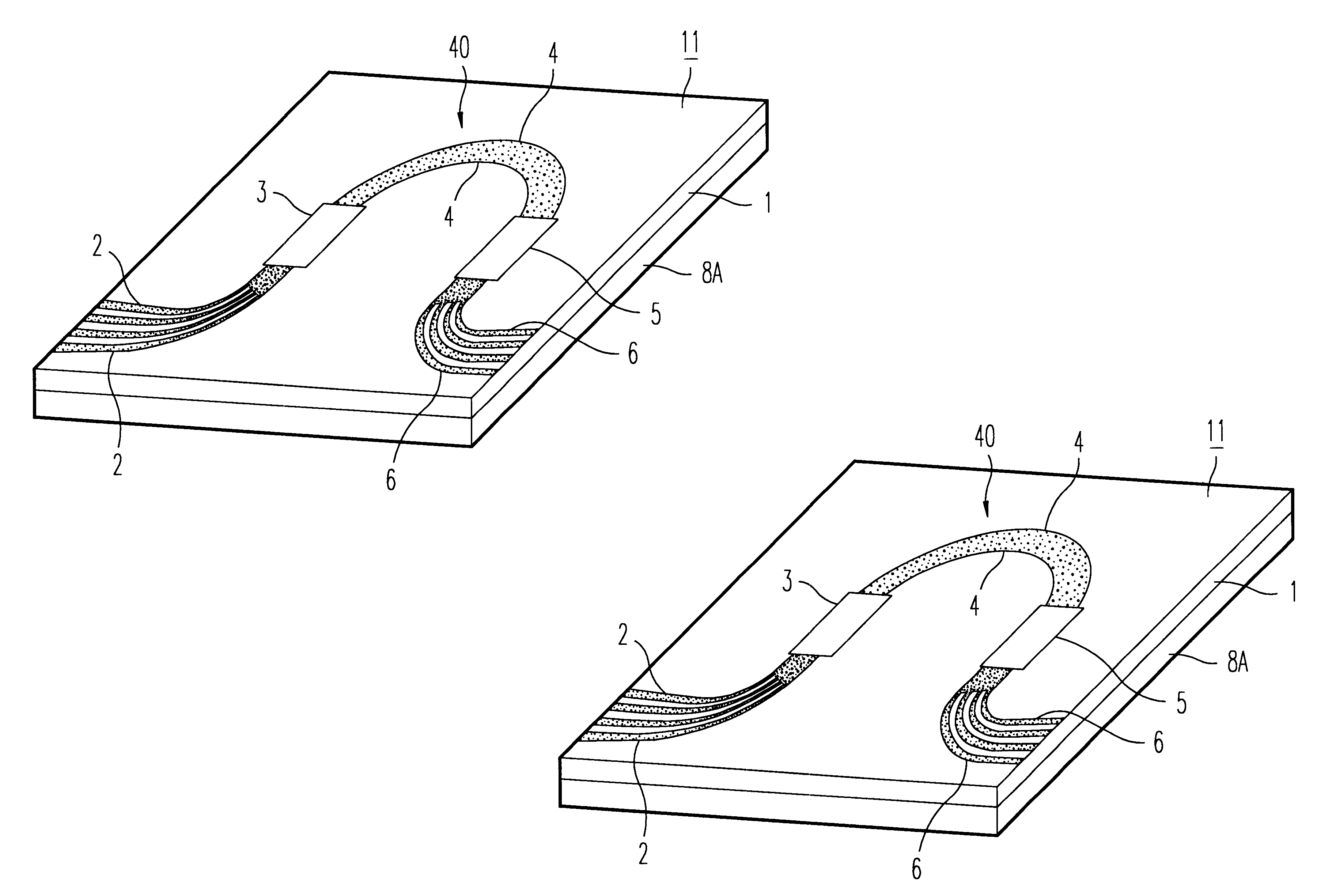
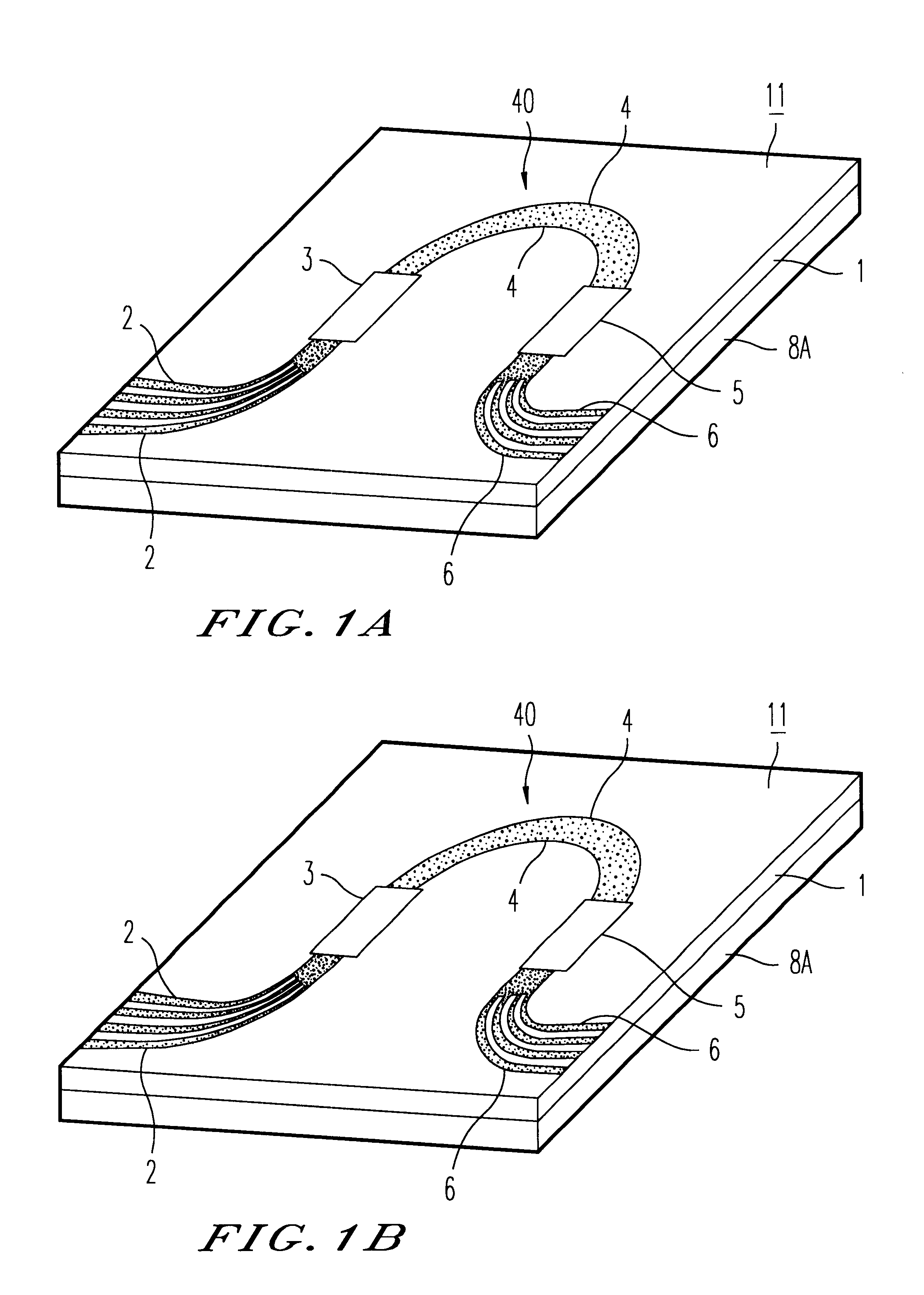
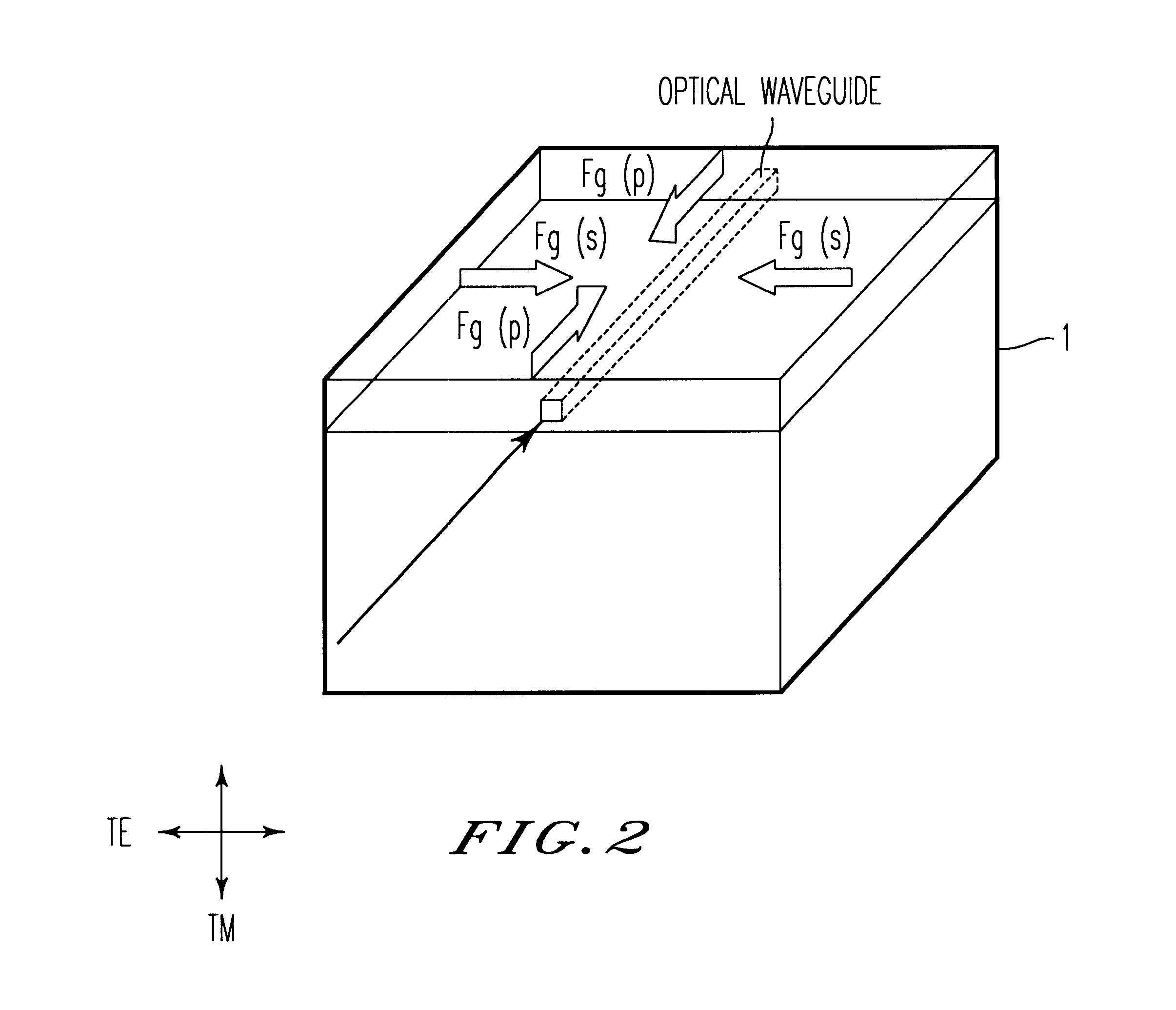
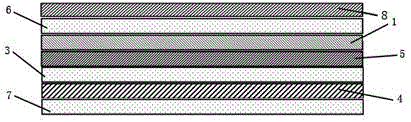
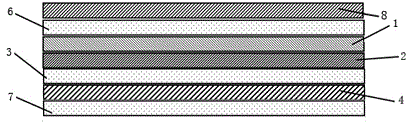
A plate-shaped member (8a) whose linear expansion coefficient is larger than that of a substrate (1) is provided on the rear side of the substrate (1) of an arrayed waveguide diffraction grating (11) which divides, by a diffraction effect of an array waveguide (40), lights of a plurality of wavelengths from those having a plurality of wavelengths different from each other, which are inputted from an optical input waveguide (2), and outputs these lights from the respective optical output waveguides (6). A light transmission feature of the respective output lights includes a light transmission feature for causing lights to be transmitted, centering around the center wavelengths of light transmission, which are different from each other, wherein the center wavelengths of light transmission shifts to the long wavelength side by a temperature rise.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Pearlescent laser paper and preparation process thereof
ActiveCN104960353AStrong laser effectWith flickering illusion effectLamination ancillary operationsDuplicating/marking methodsDiffraction effectBiochemical engineering
The invention relates to pearlescentlaser paper and a preparation process thereof. The pearlescent laser paper comprises a finishing coat, a laser layer, a pearlescent transfer layer, an aluminizing or dielectric coating layer, a transfer glue layer, base paper and a back coating. The preparation process comprises the following steps of firstly, coating pearlescent pigment on a Bopp basement membrane with the laser layer to form the pearlescent transfer layer; secondly, performing surface tension enhancing treatment on the pearlescent transfer layer; thirdly, performing aluminizing or dielectric coating on the pearlescent transfer layer to form the aluminizing or dielectric coating layer; fourthly, coating transfer glue on the aluminizing or dielectric coating layer to form the transfer glue layer; fifthly, performing back coating on the back side of the base paper to form the back coating layer, and compounding the front side of the base paper with the transfer glue layer; sixthly, stripping off the Bopp basement membrane; seventhly, performing finishing coating on the laser layer to form the finishing coating layer. The paper disclosed by the invention has a stronger laser diffraction effect and a colorful twinkling effect of the pearlescent pigment, so that the application grade is improved; the Bopp basement membrane in the preparation process can be repeatedly used, so that the production cost of products is greatly reduced.
Owner:GUANGDONG XINRUI NEW MATERIAL TECH
Three-dimensional image communication terminal and projection-type three-dimensional image display apparatus
ActiveUS20060209066A1Simple configurationGood lookingSteroscopic systems3D modellingCamera lensParallax
It is possible to provide a three-dimensional image display apparatus which can reproduce a three-dimensional image having an appearance of solidity with a simple configuration. The three-dimensional image reproduction apparatus includes: a display device 2 for displaying two-dimensional element images having a plurality of horizontal and vertical parallax images 1 containing information on a parallax and an image at the time of reproducing a three-dimensional solid image 7; and a lens 3 for forming the three-dimensional solid image 7 at a predetermined spatial intersection from the element images displayed by the display device 2. Here, the lens 3 diffracts the element images and forms the three-dimensional image by the use of a diffraction effect when the element images are emitted from the display device 2.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Security element and security document with one such security element
InactiveUS7699350B2Improve anti-counterfeiting performanceImprove reflective effectOther printing matterHolographic optical componentsColor shiftComputer science
A security element 2, 4 for embedding in or application to a security document in such a way that it is visually recognizable from both sides of the security document 1, is structured in a multilayer fashion and includes two interference elements I1, I2 with color shift effect, a metallic reflection layer R located in between as well as, optionally, diffraction structures 8. Depending on the disposition of the layers I1, R, I2 and the optionally present diffraction structures 8 on a transparent substrate S the color shift effect and / or the diffractive effects are perceptible from one or from both sides of the security element 2, 4. The security element is particularly suitable as a two-sided window thread 4 and as a label or transfer element 2 above a hole 3 in the security document 1.
Owner:GIESECKE & DEVRIENT CURRENCY TECHNOLOGY GMBH
Process for processing surface plasmon polariton coupled nano array based on scallop effect
ActiveCN104495742AOptimized Design Coupling StructureConvenient researchDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingDiffraction effectNano structuring
The invention discloses a method for preparing a surface plasmon polariton coupled nano array. The method comprises the following steps: performing deep reactive ion etching on a substrate by adopting a nano-scale etching mask which is manufactured by electron beam exposure, and then performing metallic membrane plating to obtain a three-dimensional 'metal nano structure array-nano space layer-metallic film' structure. The metallic nano structure generates local electromagnetic field resonance of photon and free electron to generate a very strong local surface plasmon polariton, and a diffraction effect provides wave vector compensation to excite a propagating type surface plasmon polariton of the metallic film so as to form local surface plasmon polariton-propagating type surface plasmon polariton coupling, so that light is restrained in a nano scale to initiate very strong surface local near field enhancement between a metal and a medium interface. The structure manufactured by the process disclosed by the invention can promote new mechanism exploration of the surface plasmon polariton, and has important application prospects in the fields of metamaterials, ultrahigh-sensitivity optical biosensing and the like.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Intraocular Lens with Fresnel Prism
InactiveUS20120277857A1Reduce impactReduce dispersionIntraocular lensDiffraction effectIntraocular lens
An intraocular lens is described which comprises, as one face thereof, a linear Fresnel prism array with facets angled relative to the optical axis of the lens so as to deviate light incident thereon to an off-axis position. The facets are modified so as to reduce at least one of diffraction effects and astigmatism associated with the Fresnel prism. In particular, by varying the pitch of the prism elements across the array, which may comprise varying their size, a diffraction grating effect can be reduced or negated, such that light is not diffracted into undesirable orders and multiple images can be avoided. Furthermore, chromatic angular dispersion associated with the diffraction grating effect may be reduced. The pitch variation can be random. By varying the angle of the facets across the array, astigmatism that would otherwise result from the presence of the Fresnel prism can also be compensated.
Owner:RAYNER INTRAOCULAR LENSES
Broadband wire source for planar waveguide CTS antenna feed device
The invention discloses a broadband wire source for a planar waveguide CTS antenna feed device. The broadband wire source comprises an H-plane sectorial horn antenna, a bias parabolic reflection plane and a flat waveguide. The H-plane sectorial horn antenna and the bias parabolic reflection plane are arranged inside the flat waveguide, and the phase center of the H-plane sectorial horn antenna is arranged at the focus of the bias parabolic reflection plane. According to the invention, cylindrical waves are converted into plane waves, the plane waves are generated by using a reflector antenna principle, and the horn antenna is arranged at the focus of a paraboloid reflector so that a horn antenna radiation field passes through the reflector and generates the plane wave with equal amplitude and the same phase at the caliber surface of the reflector. The working frequency band is wide; the feed source shielding is eliminated and the caliber efficiency is enhanced through a bias; the structure is enclosed so that the edge diffraction effects of a conventional bias paraboloid are removed; and the structure is simple so that adjusting and assembling are easy, late use and maintenance are convenient, and the problem can be solved that the ideal wire source with equal amplitude and the same phase, generated by a conventional waveguide CTS antenna, cannot be realized in an actual project.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Microlens arrays for enhanced light concentration
ActiveUS20110284725A1Beam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsSolid-state devicesMicron scaleDiffraction effect
A novel micron-scale lens, a microlens, is engineered to concentrate light efficiently onto an area of interest, such as a small, light-sensitive detector element in an integrated electronic device. Existing microlens designs imitate the form of large-scale lenses and are less effective at small sizes. The microlenses described herein have been designed to accommodate diffraction effects, which dominate the behavior of light at small length scales. Thus a new class of light-concentrating optical elements with much higher relative performance has been created. Furthermore, the new designs are much easier to fabricate than previous designs.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
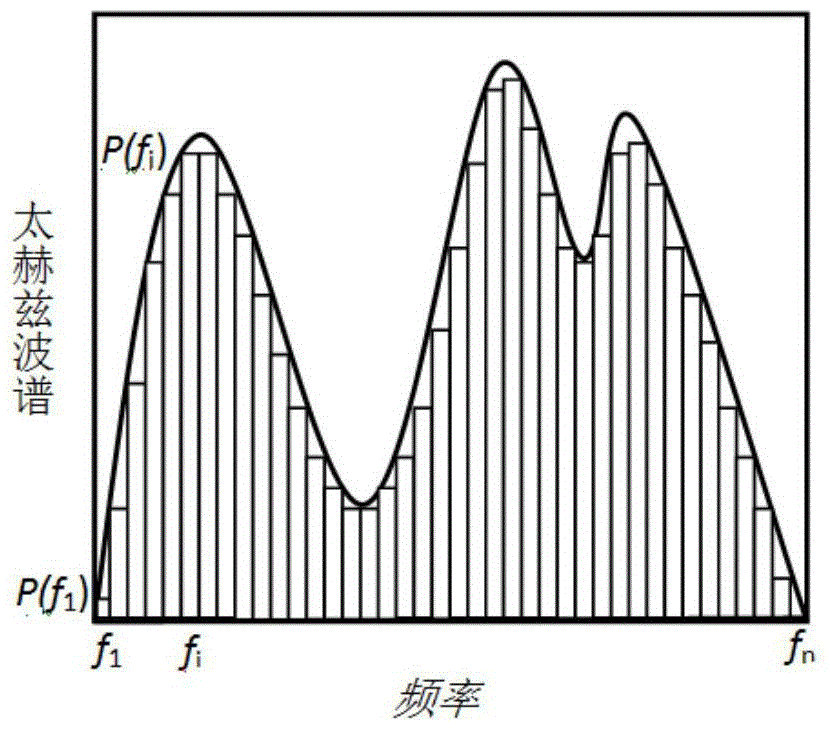
Terahertz wave spectrum measurement device and measurement method thereof based on diffraction effect
ActiveCN105675131AAchieving Spectral RestorationLow costRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationDiffraction effectTime domain
The invention discloses a terahertz wave spectrum measurement device and measurement method thereof based on diffraction effect. A to-be-measured terahertz wave forms a terahertz diffracted wave after going through a diffraction device, and the diffracted wave is received by a detector under the force of different control conditions of a diffraction controller. The diffraction device can drive incident terahertz waves of different frequencies to form different diffracted wave intensity angular distributions. The diffraction controller is used to change the diffraction field distribution of the terahertz diffracted wave, passing through the diffraction device, at the position of the detector, so that the detector detects different diffracted wave intensities of the constant frequency incident terahertz wave under the force of the different control conditions of the diffraction controller. A calculation processing unit is used to receive measurement results of the detector and conducts data analysis and processing. Compared with terahertz time-domain wave spectrum measurement devices in the prior art, the device is smaller in size, easier to produce, and lower in cost. The device is high in frequency resolution and wide in spectrum measurement range.
Owner:南京华睿智光信息科技研究院有限公司
Quantum dot implant reflection type active grating and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102096134AAchieve mass productionSolve the problem of batch manufacturingPhotomechanical apparatusDiffraction gratingsDiffraction effectGroove width
The invention discloses a quantum dot implant reflection type active grating and a manufacturing method thereof, wherein the quantum dot is firstly embedded in a grating structure by means of impressing process based on the excellent photoluminescence capability of the quantum dot and the wide chromaticity selection range, the light emitted by the quantum dot and the light reflected by the grating are jointly diffracted by means of structural design and selection for the type of the quantum dot, and the diffraction effect is increased. The manufacturing process provided by the invention is as follows: the quantum dot and the grating mould are manufactured by means of electron beam lithography and vacuum casting method, microstructure patterns of the quantum dot and the grating are manufactured by means of impressing process, and the grating structure is formed finally. The period of the grating is 20 nm to 20 microns, the groove width is 20 nm to 20 microns, and the height is 20 nm to 20 microns; the microstructure of the grating is cylindrical, square, rectangular, rhombic or hexagonal and trapezoidal and the like; the included angle between the edge of the microstructure and the vertical direction is controllable, and the range of the included angle is 0 to 90 DEG.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Headphone device
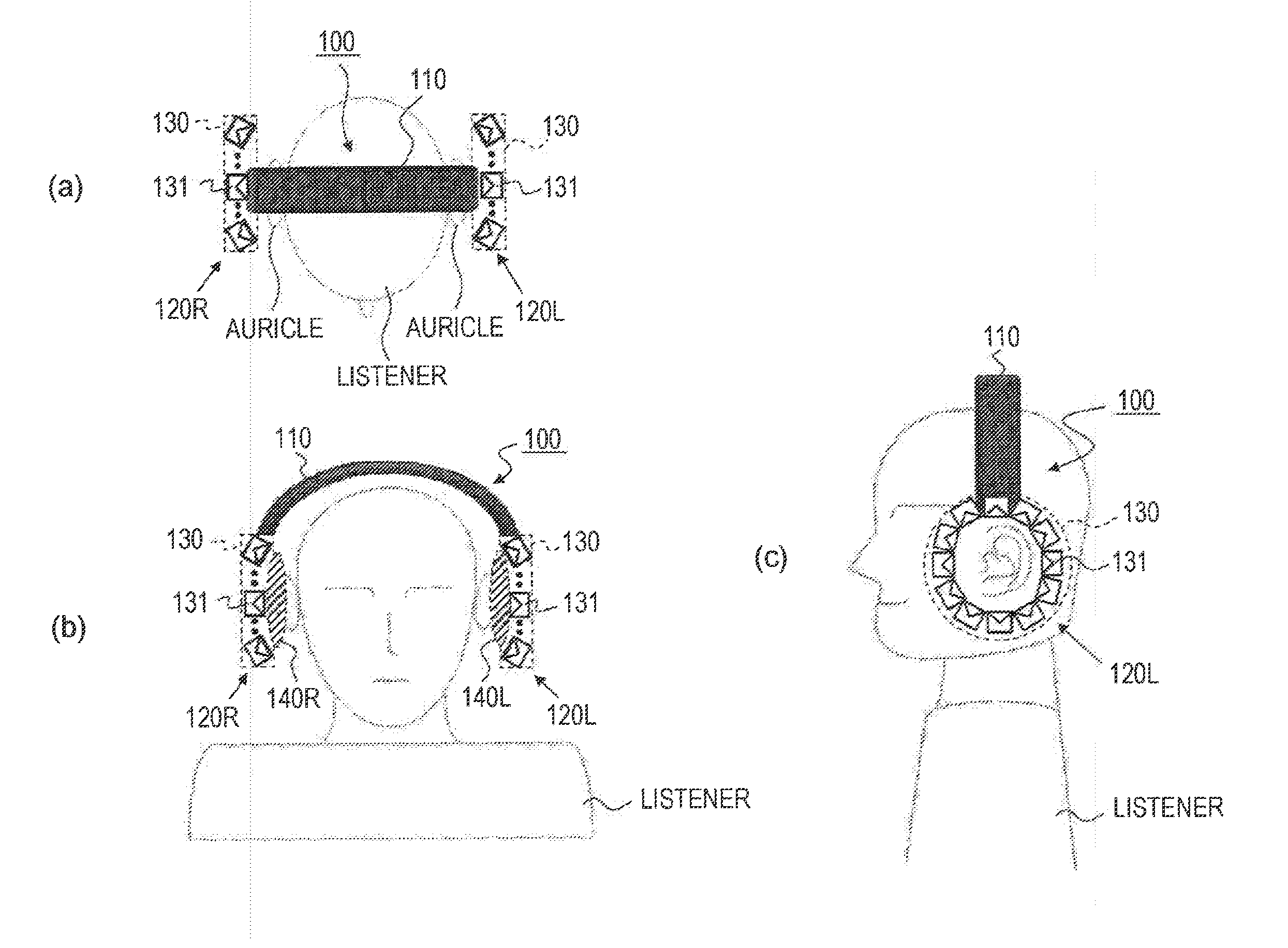
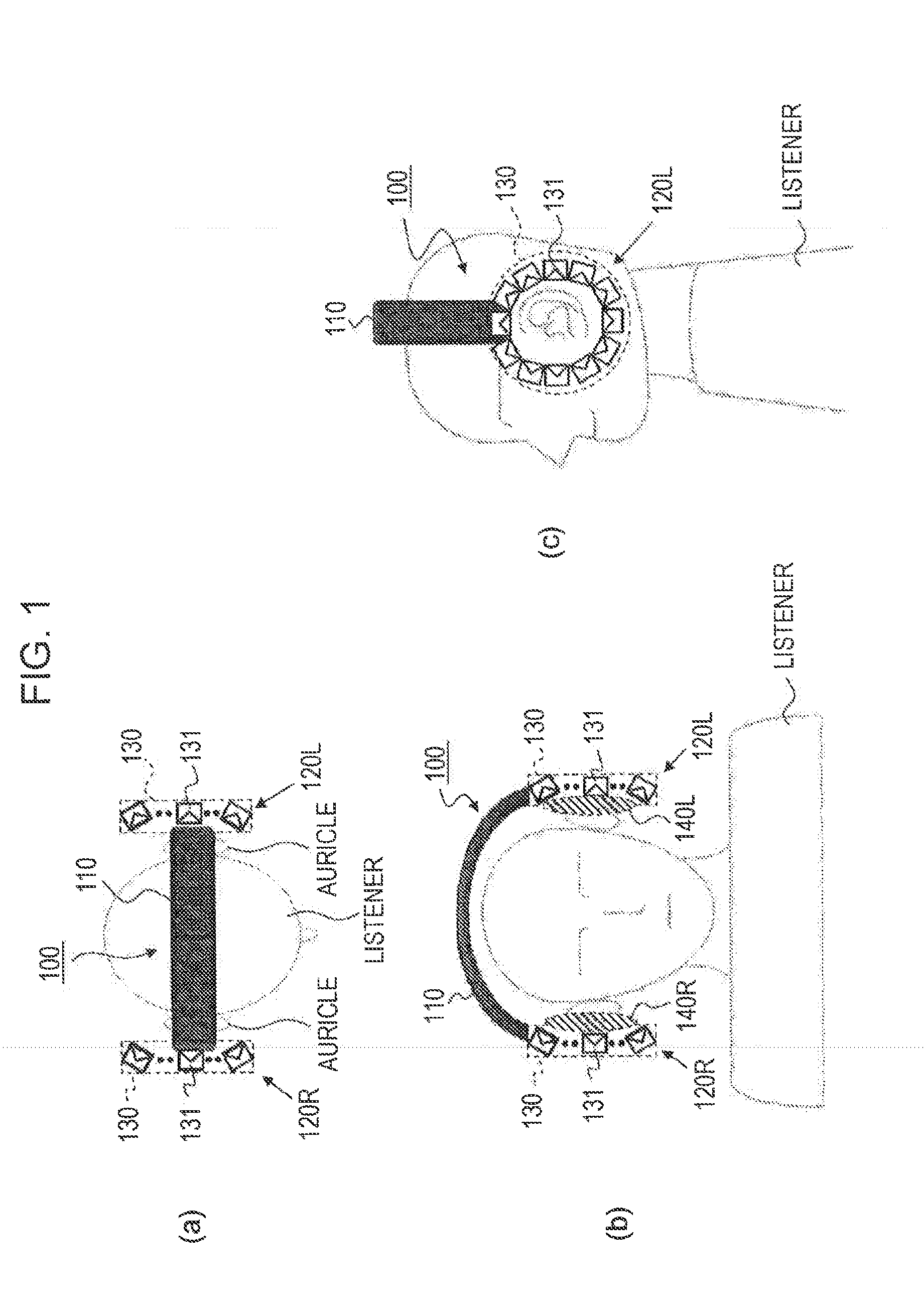
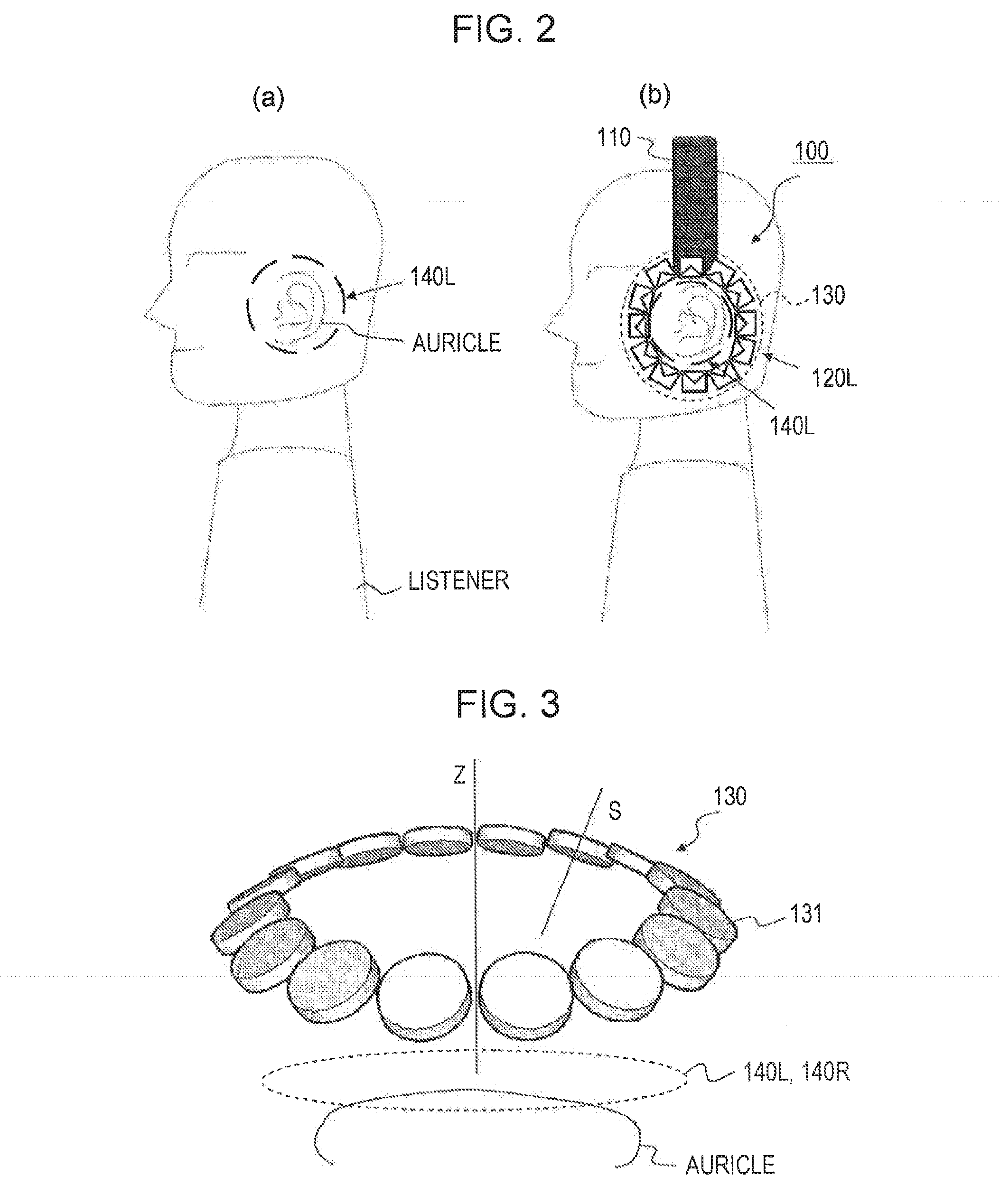
ActiveUS20130216074A1Headphones for stereophonic communicationSupra/circum aural earpiecesDiffraction effectEar Auricle
[Object] To provide a headphone device in which the influence of individual differences in virtual sound field reproduction is less likely to occur and which may listen external sounds naturally,[Solution] A left-side headphone body and a right-side headphone body include speaker arrays which are formed of a plurality of speaker units which are arranged to surround auricles, respectively. The speaker array of the headphone body reproduces a sound field inside a closed curved surface in the vicinity of the auricle using wave field synthesis, and since reverberation or a diffraction effect occurs in the ear of each individual, the influence caused by individual differences is less likely to occur. In addition, the speaker array has the plurality of the speaker units arranged to surround the auricle and is not of a shape that blocks the ear of the listener, and then the external sound can be heard naturally.
Owner:SONY CORP
Radio frequency holographic transformer
ActiveUS20070103381A1Rapidly and conveniently programmedDifferent frequency bandwidthAntennasDiffraction effectTransformer
A three-dimensional holographic array of radio-frequency (RF) diffraction gratings, each of which has lengths of conductive and insulating fluid that are selected and adjusted to provide a desired diffraction effect on incident RF radiation. The three-dimensional array functions analogously to an optical hologram, and is programmable to provide desired refraction and focusing effects on multiple RF incident beams, which may be selectively directed to receivers or, if interferers, ignored. Because the gratings employ conductive and insulating fluids, the array can be reprogrammed in near real time to adapt to changes in the incident RF radiation.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
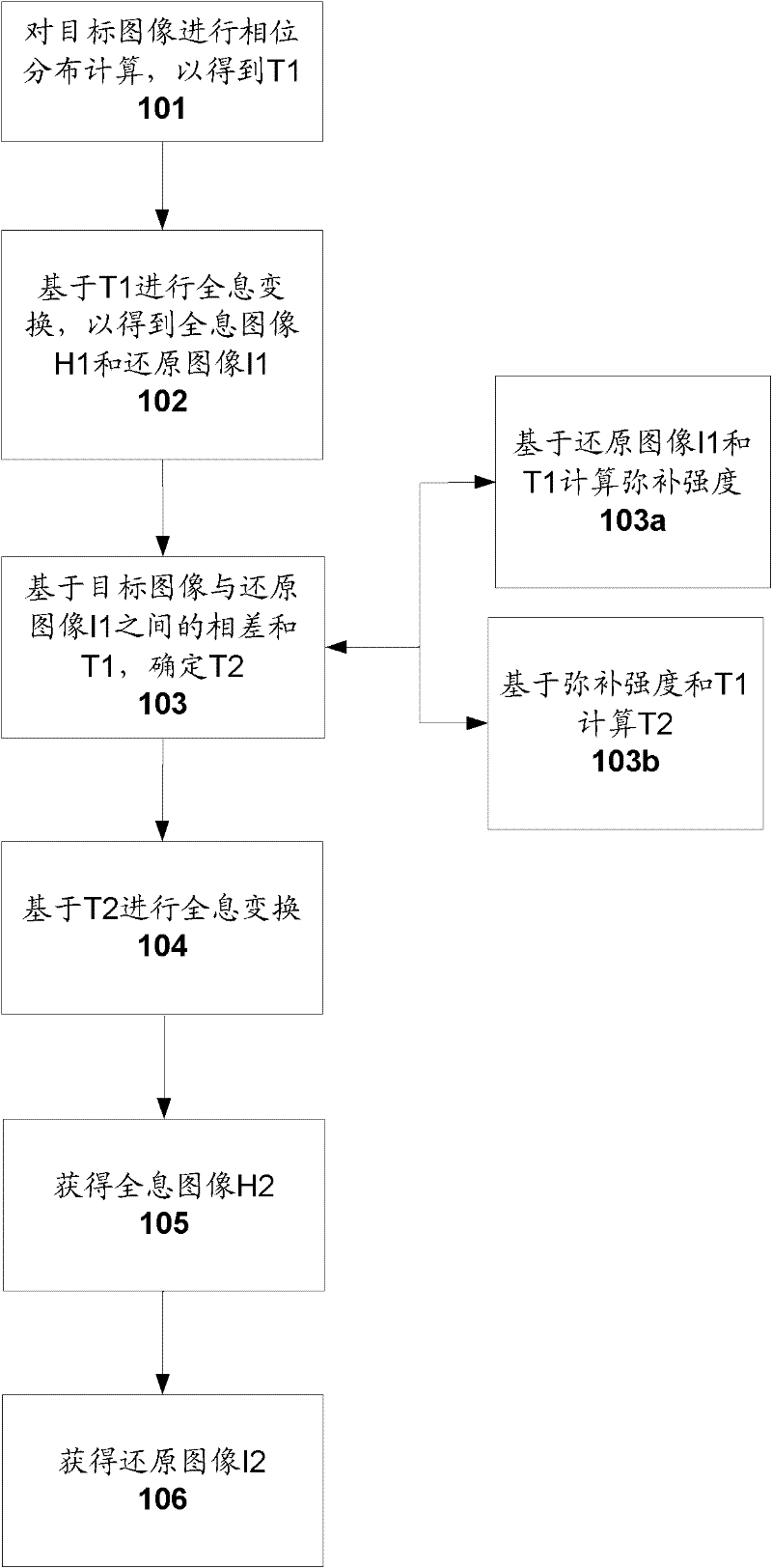
Method for generating holograms
ActiveCN102542581AReduce noiseImprove image qualityImage enhancement2D-image generationDiffraction effectComputer science
Owner:JIANGSU INTELIGHT ELECTRONICS TECH
Electronic device
ActiveCN109274789ACounteract the effects of diffractionQuality improvementTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDiffraction effectOptical Module
The invention is applicable to the field of electronic technology, An electronic device is provided, and includes a transparent display screen, an optical module, a light filter and a compensation element; the transparent display screen includes a plurality of periodically arranged pixel units for display, the optical module is used for receiving the light beam from the transparent display screenor emitting the light beam outwardly through the transparent display screen, A light filt is disposed between that transparent display screen and the optical module, The compensation element is disposed between the transparent display screen and the optical module, and is configured to be complementary to the diffraction effect of the transparent display screen so as to exit with the same preset beam when the preset beam passes through the transparent display screen and the compensation element. By arranging an optical filter and a compensation element between the back surface of the transparent display screen and the optical module, the invention realizes the overall screen, improves the display effect, cancels the diffraction effect of the transparent display screen, and improves the quality and effect of imaging or projection.
Owner:SHENZHEN ORBBEC CO LTD
Reflecting pyramid wave-front sensor
InactiveCN101614593ASimple structureReduce volumeOptical measurementsDiffraction effectWavefront sensor
The invention relates to a reflecting pyramid wave-front sensor. Four reflecting mirrors and reflecting pyramids are matched for carrying out splitting reflecting on incident light; 2*2 micro-lenses arrays carry out relay imaging on reflecting sub light beam; four sub pupil images are formed on the four quadrants of a photo detector; wave-front slop information is calculated according to the light intensity distribution difference of the four sub pupil images; and wave front distortion phase distribution is further reconstructed. The reflecting pyramid wave-front sensor has the advantages that the light utilization rate is high, the measurement dynamic range is large, dispersion effect and diffraction effect do not occur, the volume is small, the structure is compact and the adjustment is easy, and the reflecting pyramid wave-front sensor can be applied to the measurement on wave front by an adaptive optical system.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical pickup apparatus, condensing optical system, and optical element
InactiveUS6952390B2Improve aberrationExcellent characteristicsOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageOptical pickupDiffraction effect
This invention is directed to an optical pickup apparatus, condensing optical system, and optical element which can at least reproduce and / or record information from / on a first optical information recording medium having a protective substrate thickness t1 by using a light beam of a first wavelength λ1 emitted from a first light source, and reproduce and / or record information from / on a second optical information recording medium having a protective substrate thickness t2 (t2≧t1) by using a light beam of a second wavelength λ2 (λ2>λ1) emitted from a second light source. The optical pickup apparatus of the invention includes a first phase modulator which gives a diffraction effect to only the light beam of the wavelength λ1 on at least one optical surface, of a plurality of optical surfaces of a plurality of optical elements arranged on a common optical path through which the light beam of the first wavelength λ1 and the light beam of the second wavelength λ2 pass, and a second phase modulator which gives a diffraction effect to only the light beam of the wavelength λ2 on at least one of the remaining optical surfaces. Each of the first phase modulator and second phase modulator has staircase-like discontinuous parts, each formed from a predetermined number of stepped portions, formed concentrically around an optical axis at the pitch defined by an optical path difference function.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Reducing diffraction effects on an ablated surface
ActiveUS20160114523A1Non-linear opticsLaser beam welding apparatusDiffraction effectClassical mechanics
A method is provided for laser ablation that reduces or eliminates a diffraction effect produced by damage to a surface from which an ablated material is removed. The method includes at least one of reducing the amount of surface damage produced and altering the damage structure produced such that it is irregular.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com