Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
161 results about "Rf radiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
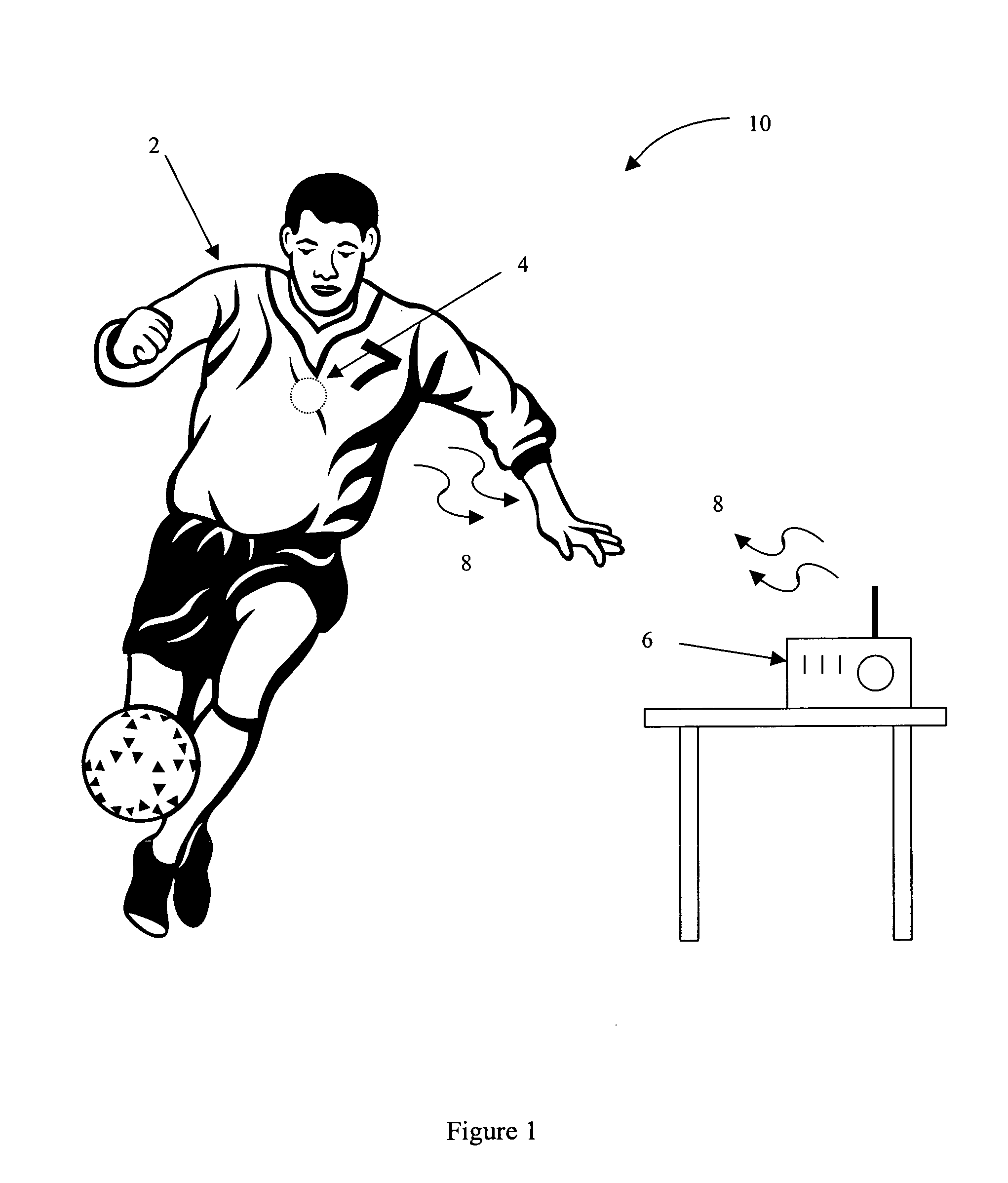
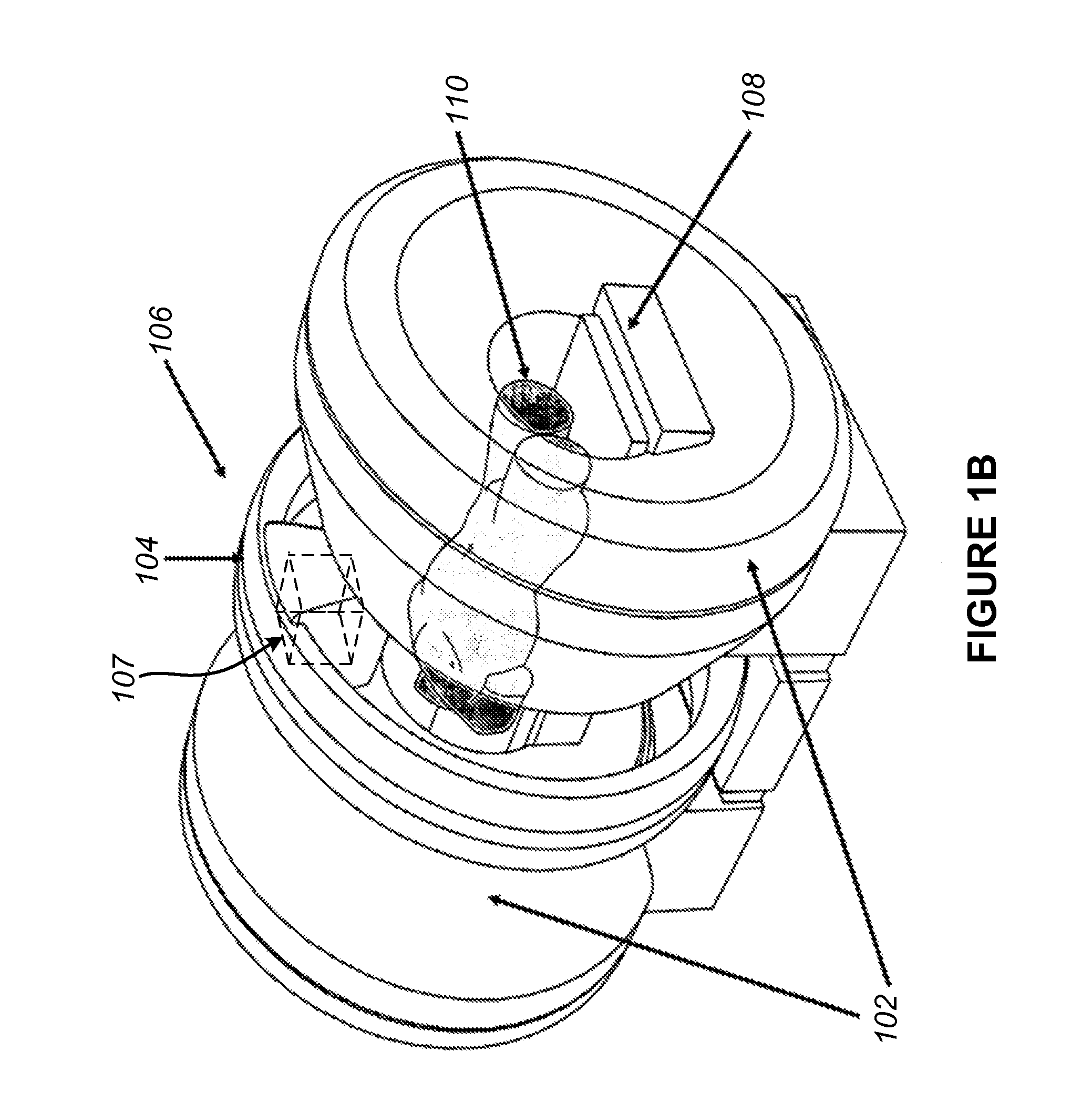
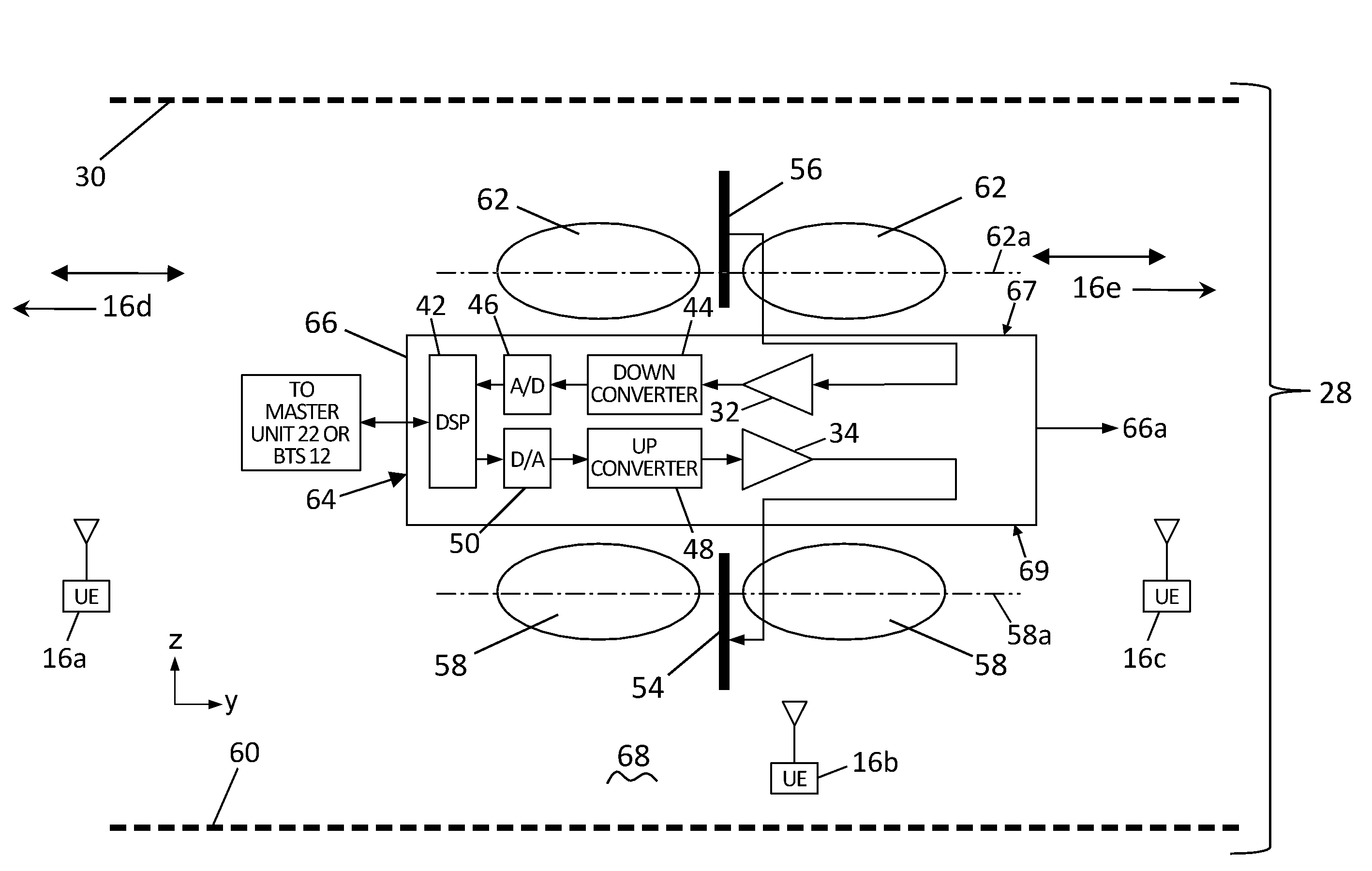
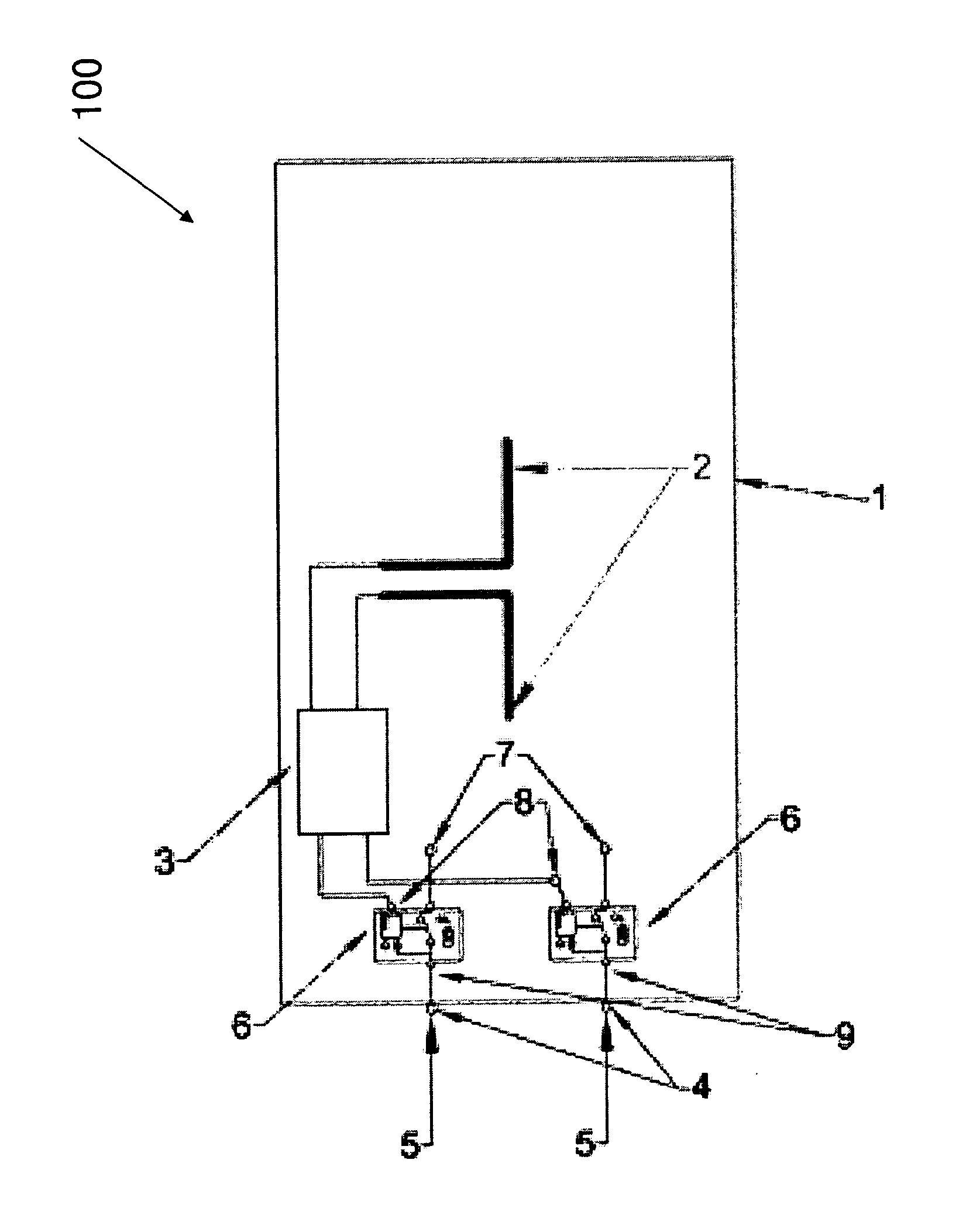
Wireless energy transfer system
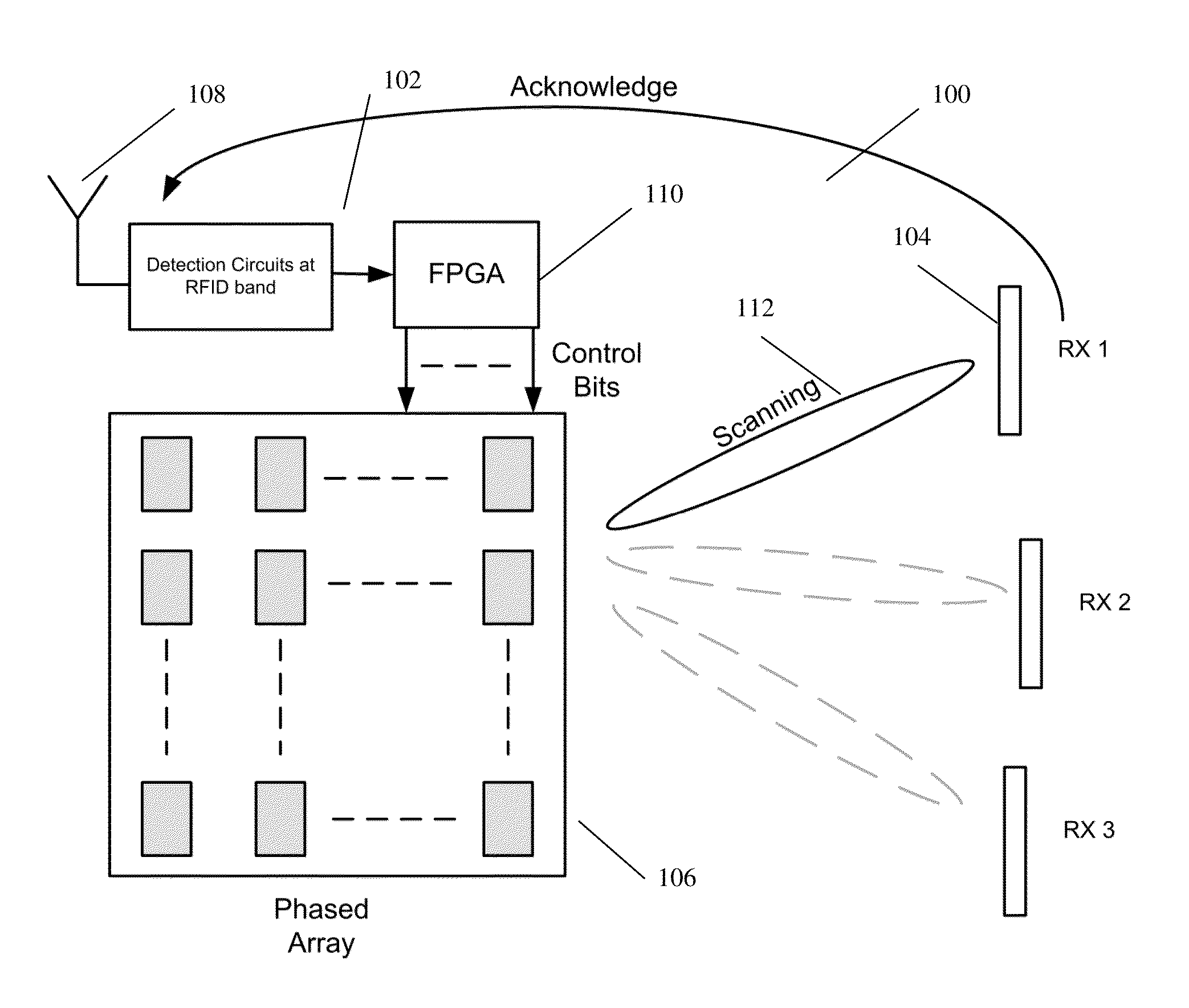
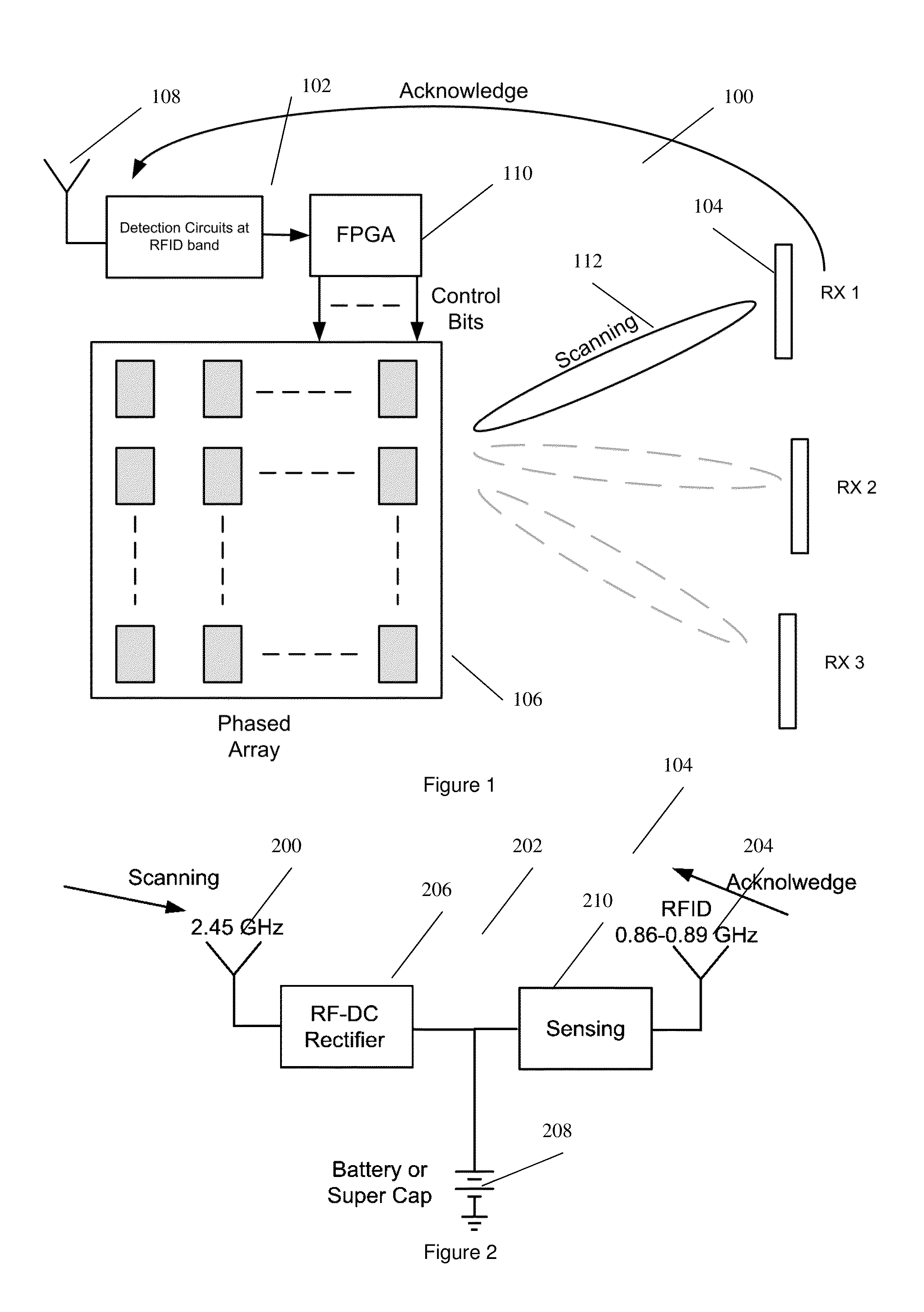
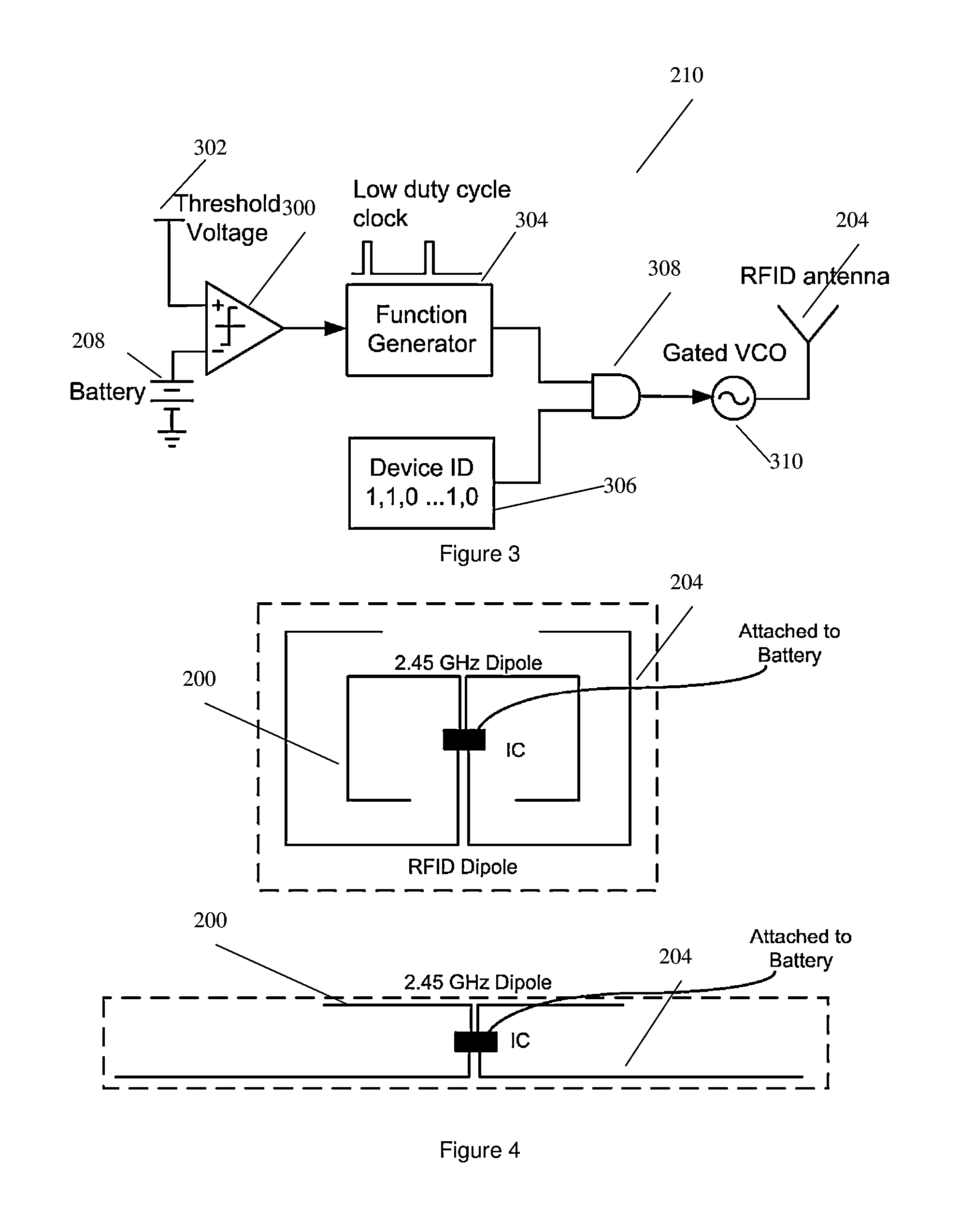
InactiveUS20130137455A1Prevent unnecessary radiationAccurate locationElectromagnetic wave systemTransformersEnergy transferEngineering
A wireless energy transfer system comprising: a transmitter configured to beam scan RF radiation across a plurality of sectors at a first frequency, a receiver storing energy from the RF radiation, and sending acknowledgements at a second frequency, the first frequency being significantly different from the second frequency, and a controller configured to direct wireless energy transfer from the transmitter substantially at the receiver based on the acknowledgements.
Owner:SONY CORP
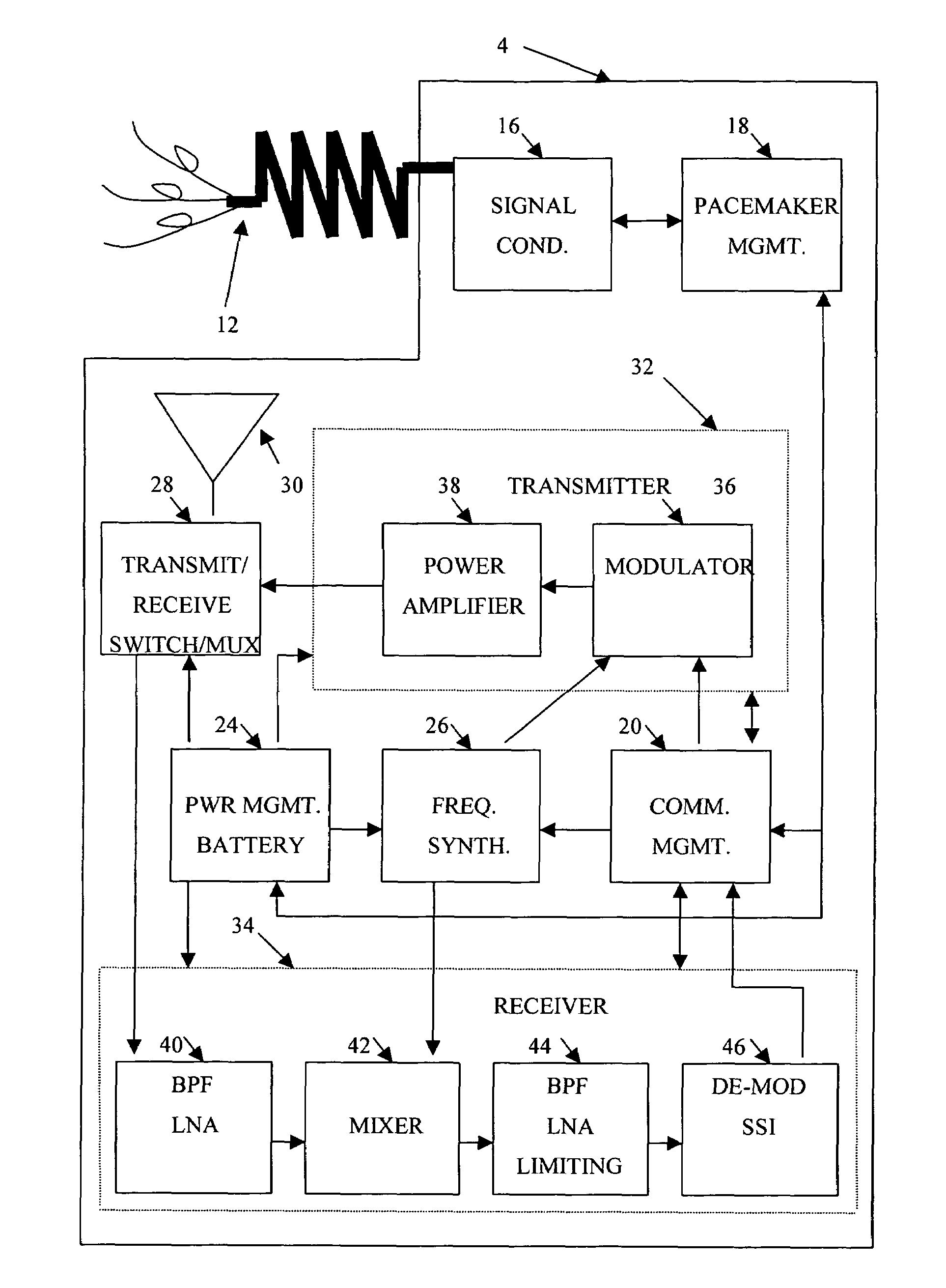
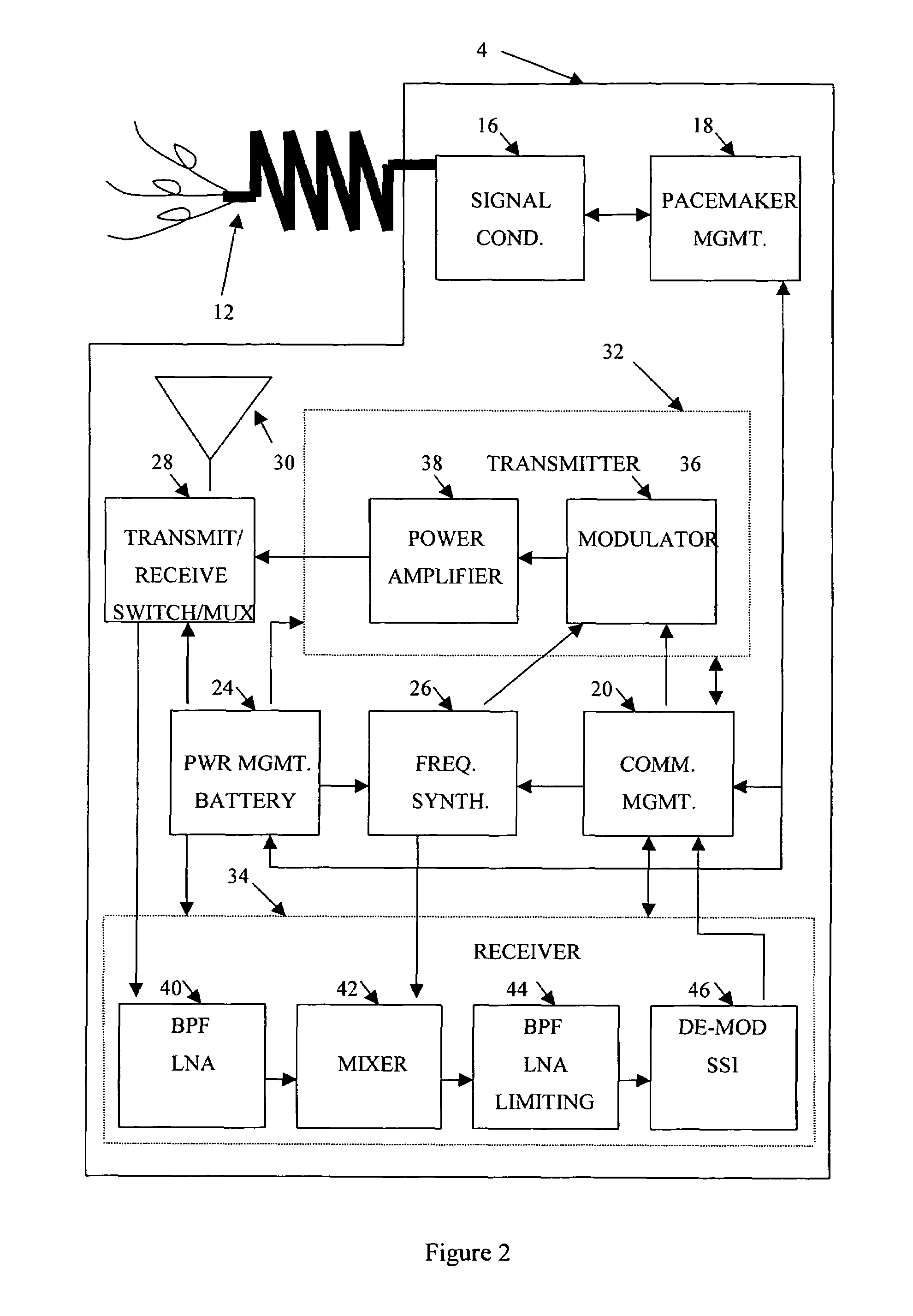
High frequency wireless pacemaker
InactiveUS7289853B1High-frequency operationLow pacemaker power consumptionHeart stimulatorsCommunications systemCardiac pacemaker electrode
A wireless communications system optimizes performance by dividing communications functionality between a wireless pacemaker and a wireless monitoring base station according to the design constraints imposed by the system elements. Typical design constraints include high frequency operation, low pacemaker power consumption, reasonable range, high data rate, minimal RF radiation of internal circuitry, small pacemaker antenna system, simple pacemaker RF circuit design, high reliability, low pacemaker cost, and use of existing pacemaker construction methodologies.
Owner:CAMPBELL DAVID +1
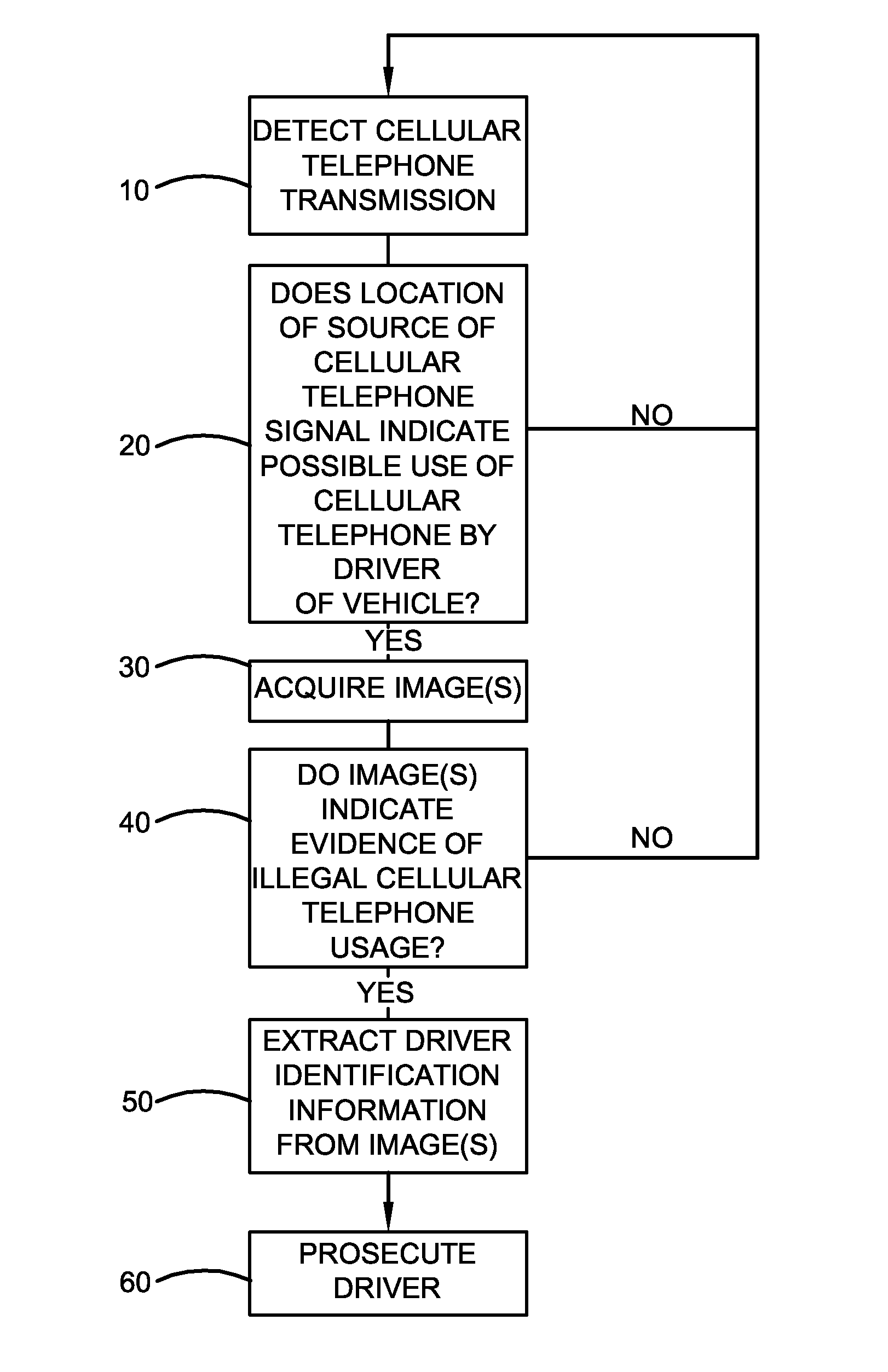
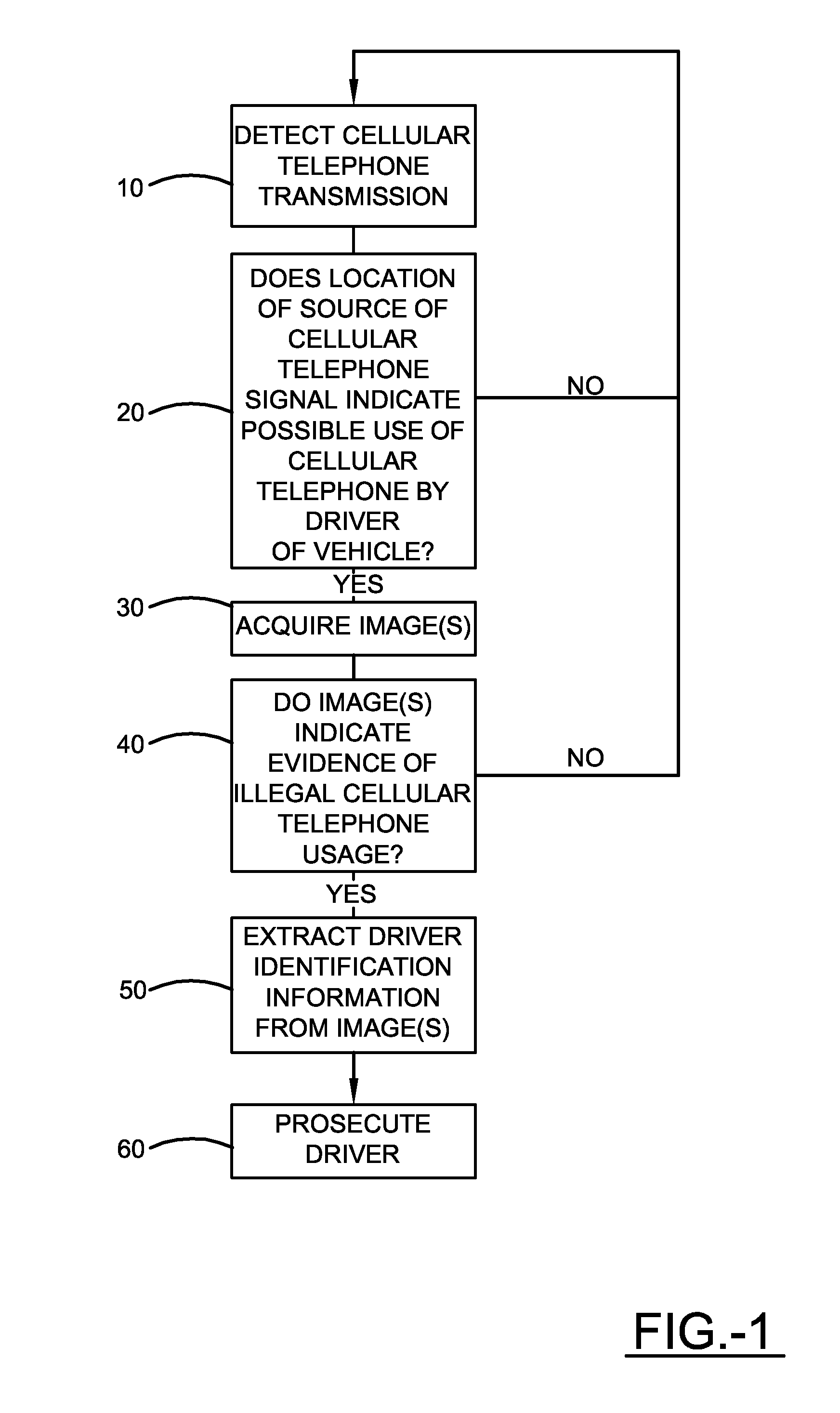
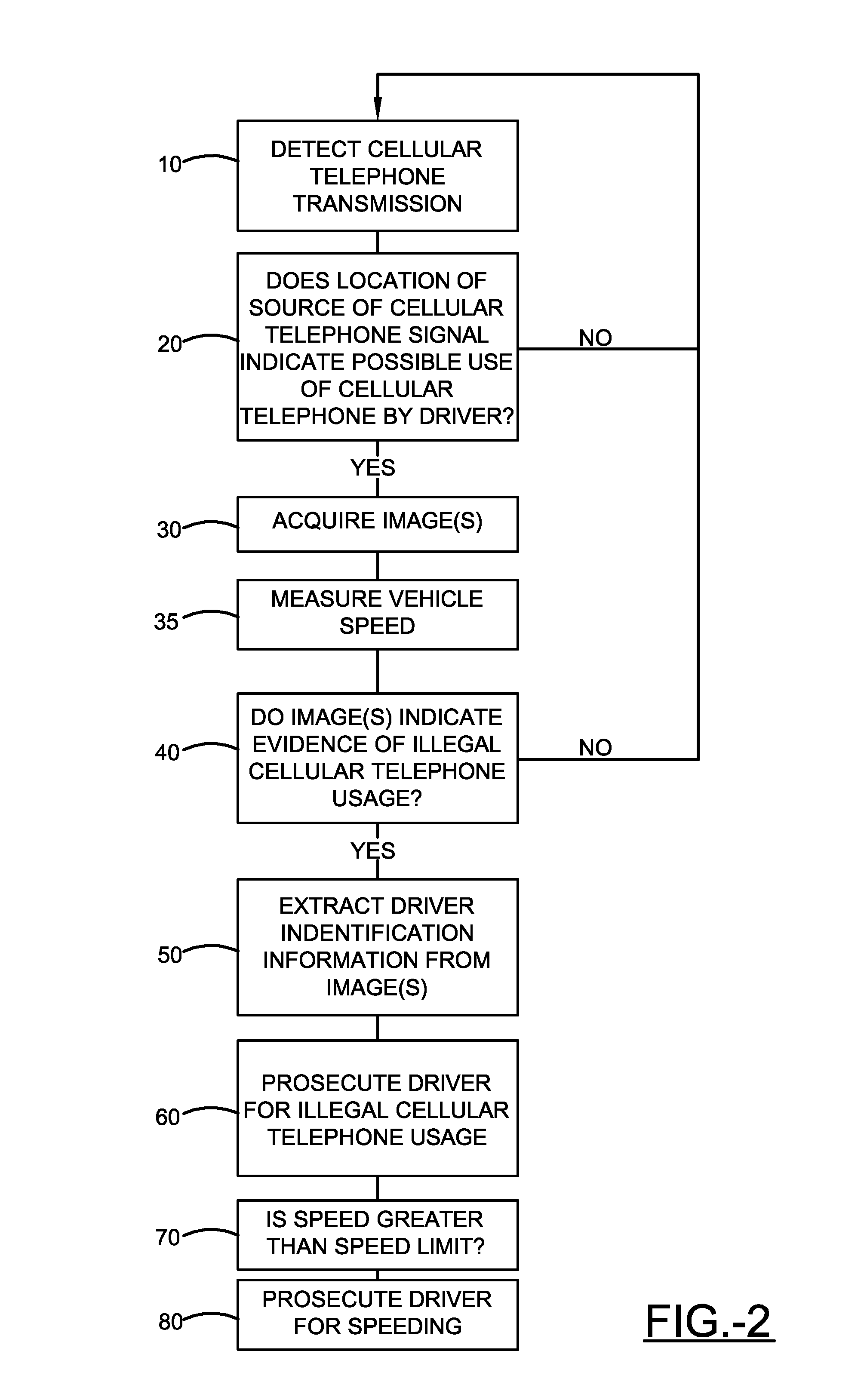
Method and apparatus for detecting mobile phone usage
InactiveUS20150054639A1Reduce violationsRoad vehicles traffic controlParticular environment based servicesComputer scienceMobile phone
An apparatus that includes a mobile phone detection system is provided. The apparatus comprises a wearable device having a pulse detection sensor, an RF detection sensor, and at least one processor. The pulse detection sensor is configured to detect a heart beat pulse of a body of a user wearing the wearable device. The RF detection sensor is configured to detect RF radiation signals from the body of the user wearing the wearable device. The processor may be operative responsive: to the pulse detection device detecting the pulse of the user; and the RF detection sensor detecting an RF radiation signal indicative of the user using a mobile phone; to output at least one notification signal indicative of the user using the mobile phone.
Owner:ROSEN MICHAEL
Lighting device with built-in RF antenna
ActiveUS20120274208A1Remove unavoidable heat dissipationSmall sizeLight source combinationsPoint-like light sourceRemote controlOptical axis
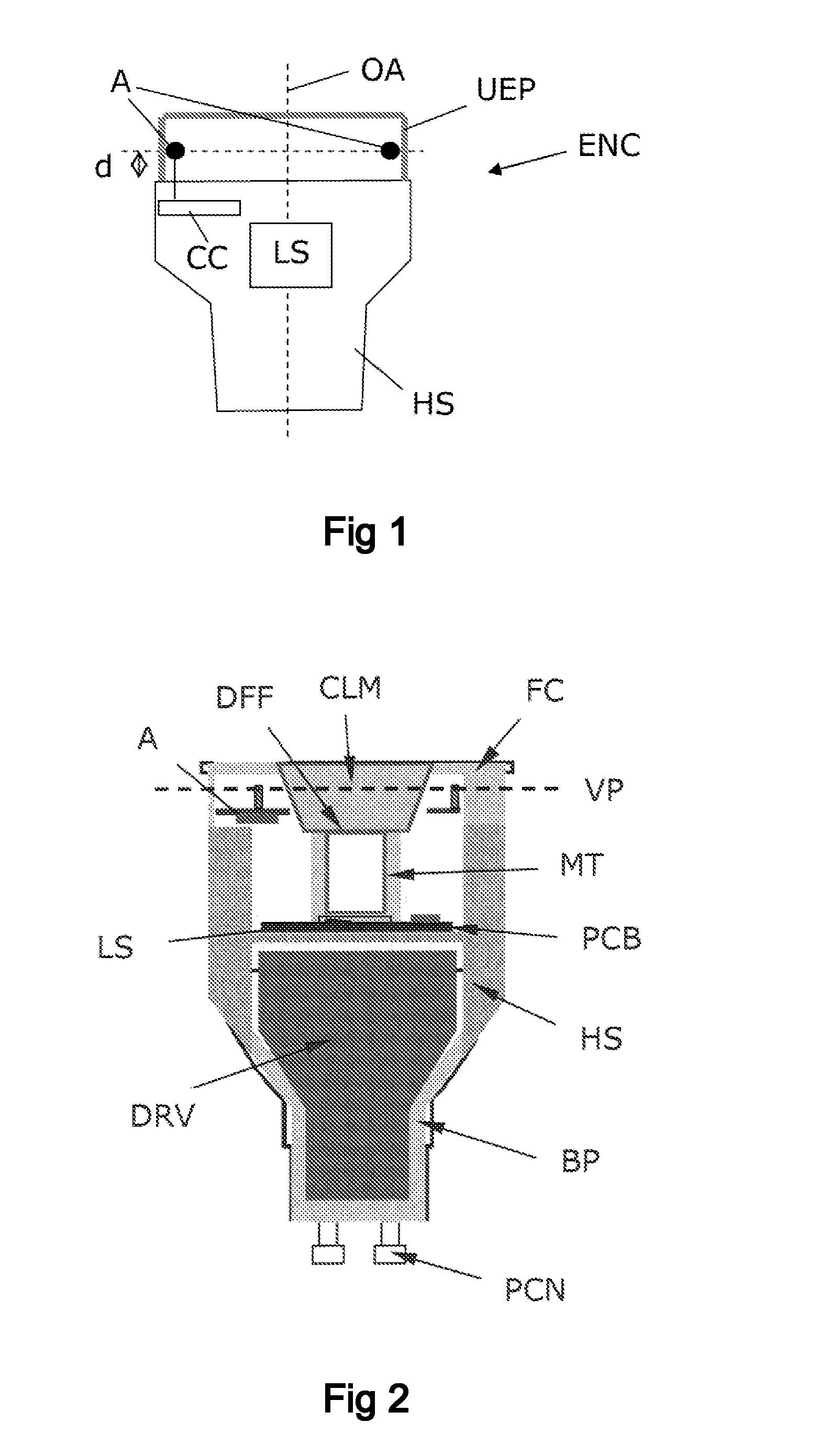
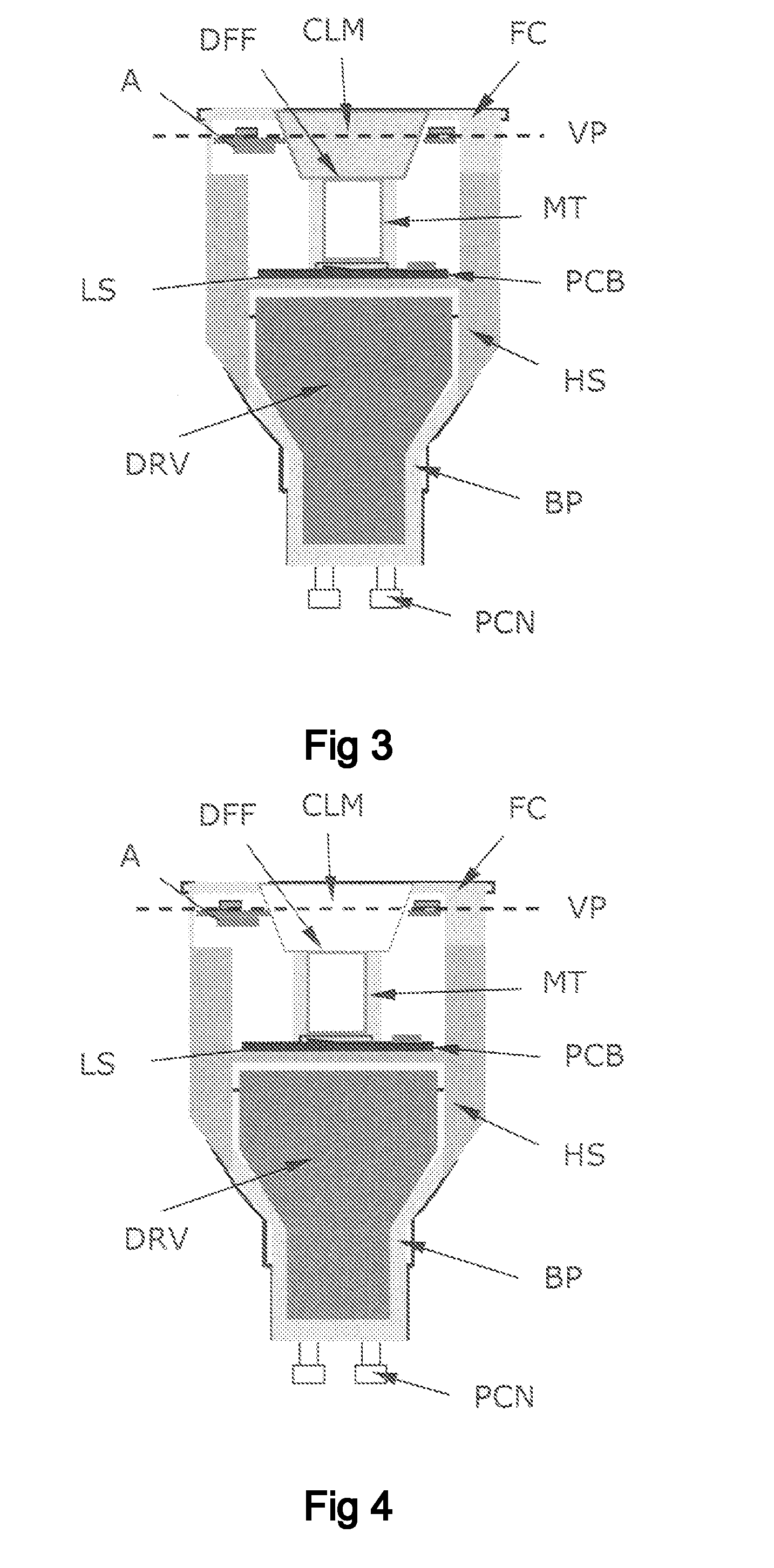
A lighting device, such as a replacement lighting device, comprising a light source (LS), e.g. LEDs, for producing light along an optical axis (OA). A heat sink (HS) made of a material with an electrical resistivity being less than 0.01 Ωm, e.g. a metallic heat sink being a part of the housing, transports heat away from the light source (LS). A Radio Frequency (RF) communication circuit (CC) connected to an an antenna (A) serves to enable RF signal communication, e.g. to control the device via a remote control. Metallic components, including the heat sink (HS), having an extension larger than 1 / 10 of a wavelength of the RF signal are arranged below a virtual plane (VP) drawn orthogonal to the optical axis (OA) and going through the antenna (A). Hereby a compact device can be obtained, and still a satisfying RF radiation pattern can be obtained. The antenna can be a wire antenna or a PCB antenna, e.g. a PIFA or a IFA type antenna. In a special embodiment the antenna is formed on a ring-shaped PCB with a central hole allowing passage of light from the light source. Preferably, the antenna is positioned at least 2 mm in front of the heat sink (HS).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
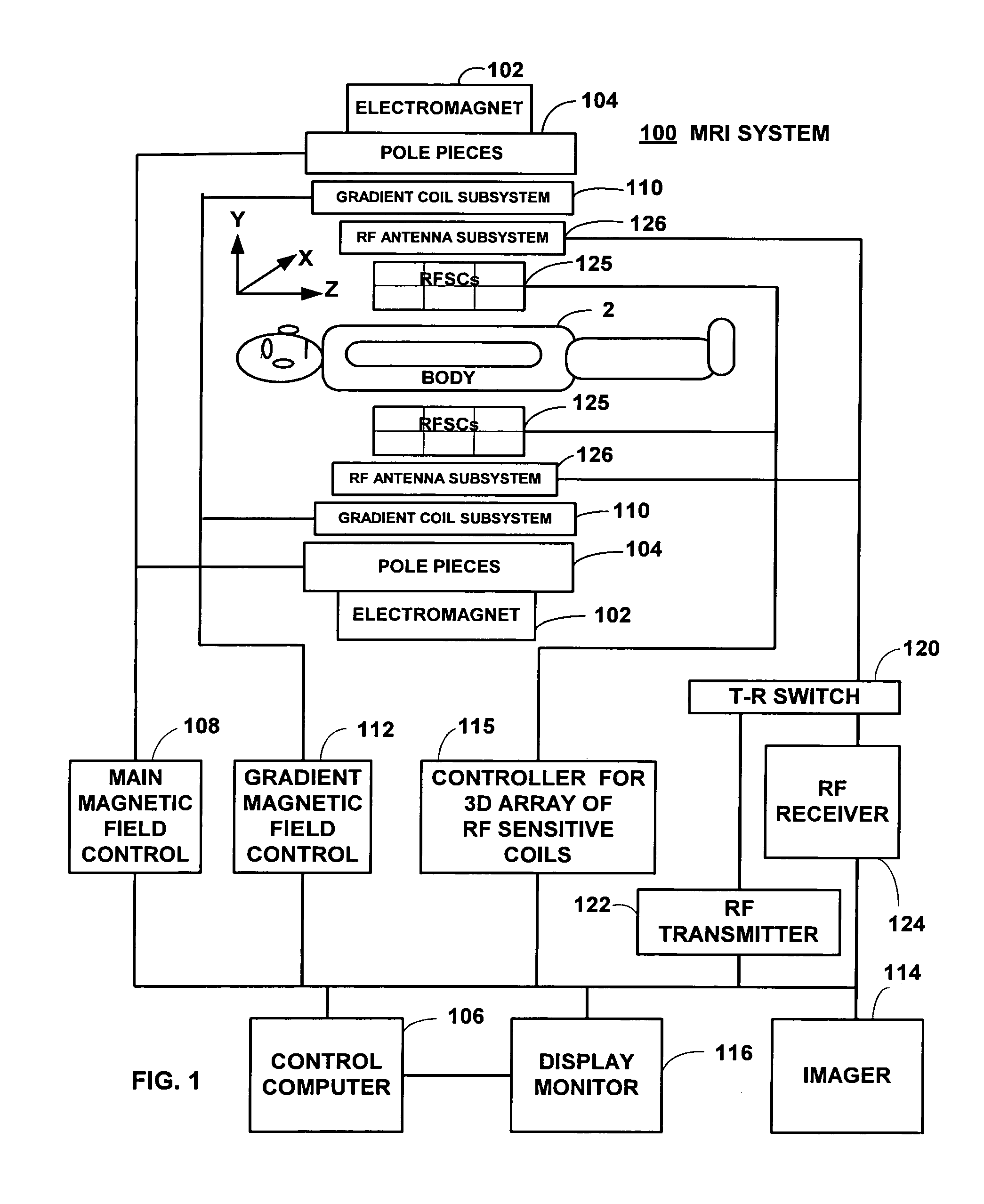
Method and apparatus for shielding a linear accelerator and a magnetic resonance imaging device from each other
InactiveUS20110012593A1Improve permeabilityReduce flux densityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSplit magnetResonance
A radiation therapy system comprises a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system combined with an irradiation system, which can include one or more linear accelerators (linacs) that can emit respective radiation beams suitable for radiation therapy. The MRI system includes a split magnet system, comprising first and second main magnets separated by gap. A gantry is positioned in the gap between the main MRI magnets and supports the linac(s) of the irradiation system. The gantry is rotatable independently of the MRI system and can angularly reposition the linac(s). Shielding can also be provided in the form of magnetic and / or RF shielding. Magnetic shielding can be provided for shielding the linac(s) from the magnetic field generated by the MRI magnets. RF shielding can be provided for shielding the MRI system from RF radiation from the linac.
Owner:VIEWRAY TECH
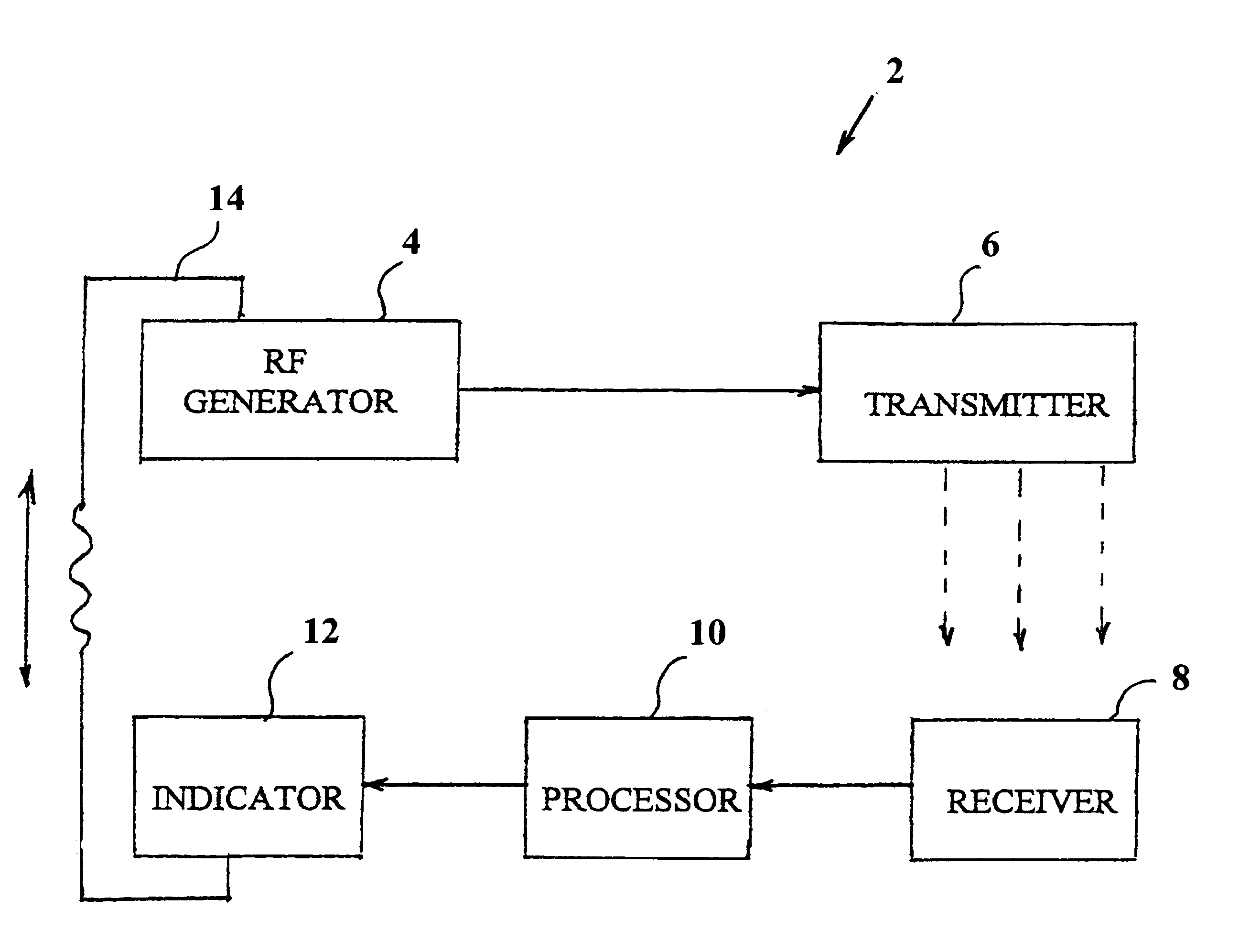
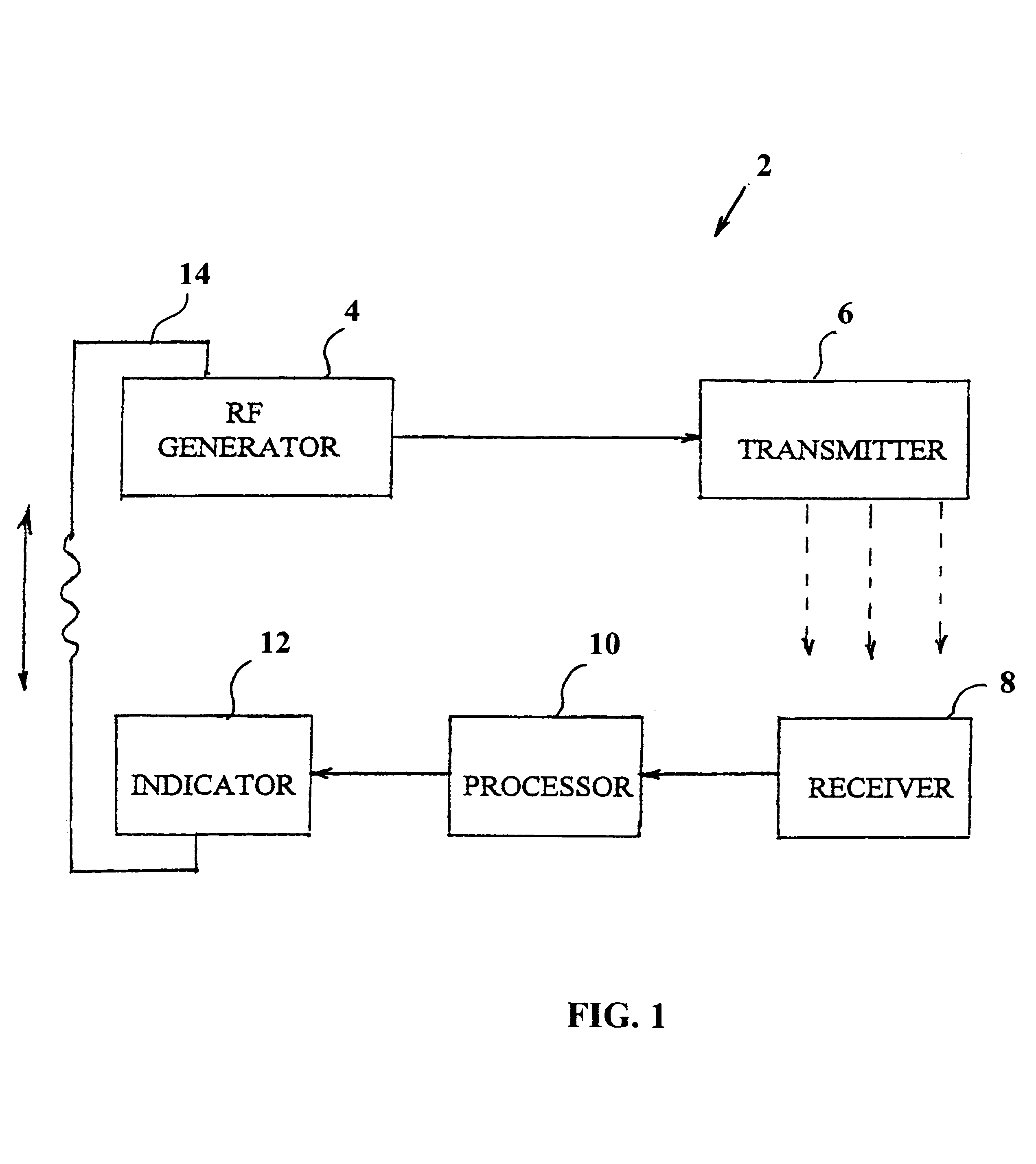
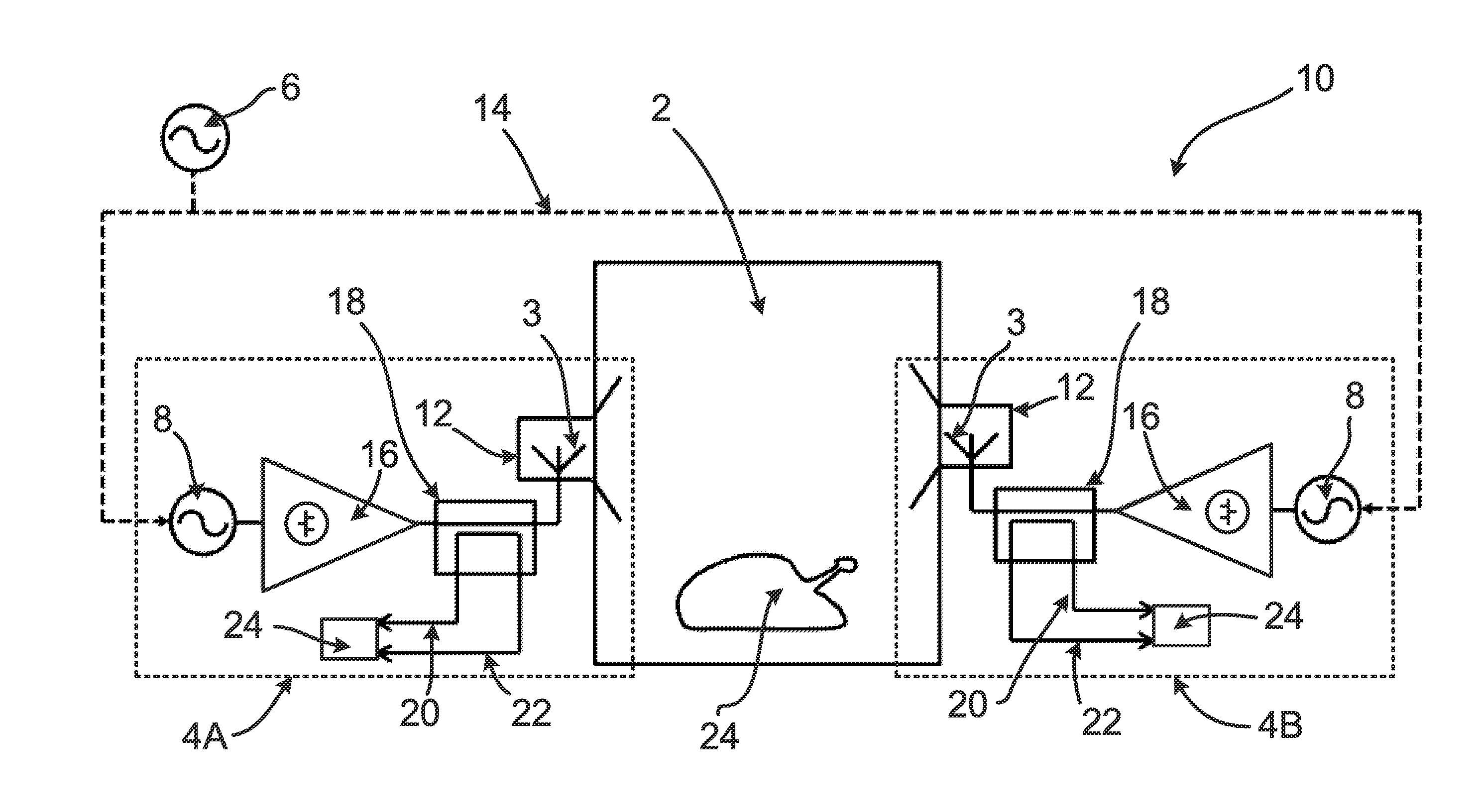
System and method for detecting the state of hydration of a living specimen
The invention provides a system (2) for non-invasive detection of the state of hydration in a living specimen, the system including an RF generator / transmitter (416) for emitting RF radiation signals and for transmitting the radiation signals through a tissue of a living specimen; an RF receiver (8) for receiving RF signals transmitted through the tissue, and for feeding the signals to a processor (10) for comparison of relative attenuation of RF frequencies passing through the tissue with a reference attenuation ratio signal, and an indicator unit (12) for providing an output signal representative of the water content level of the tissue. A method for non-invasive detection of the state of hydration in a living specimen is also described and claimed.
Owner:EYAL BICKELS ELAZAR +1
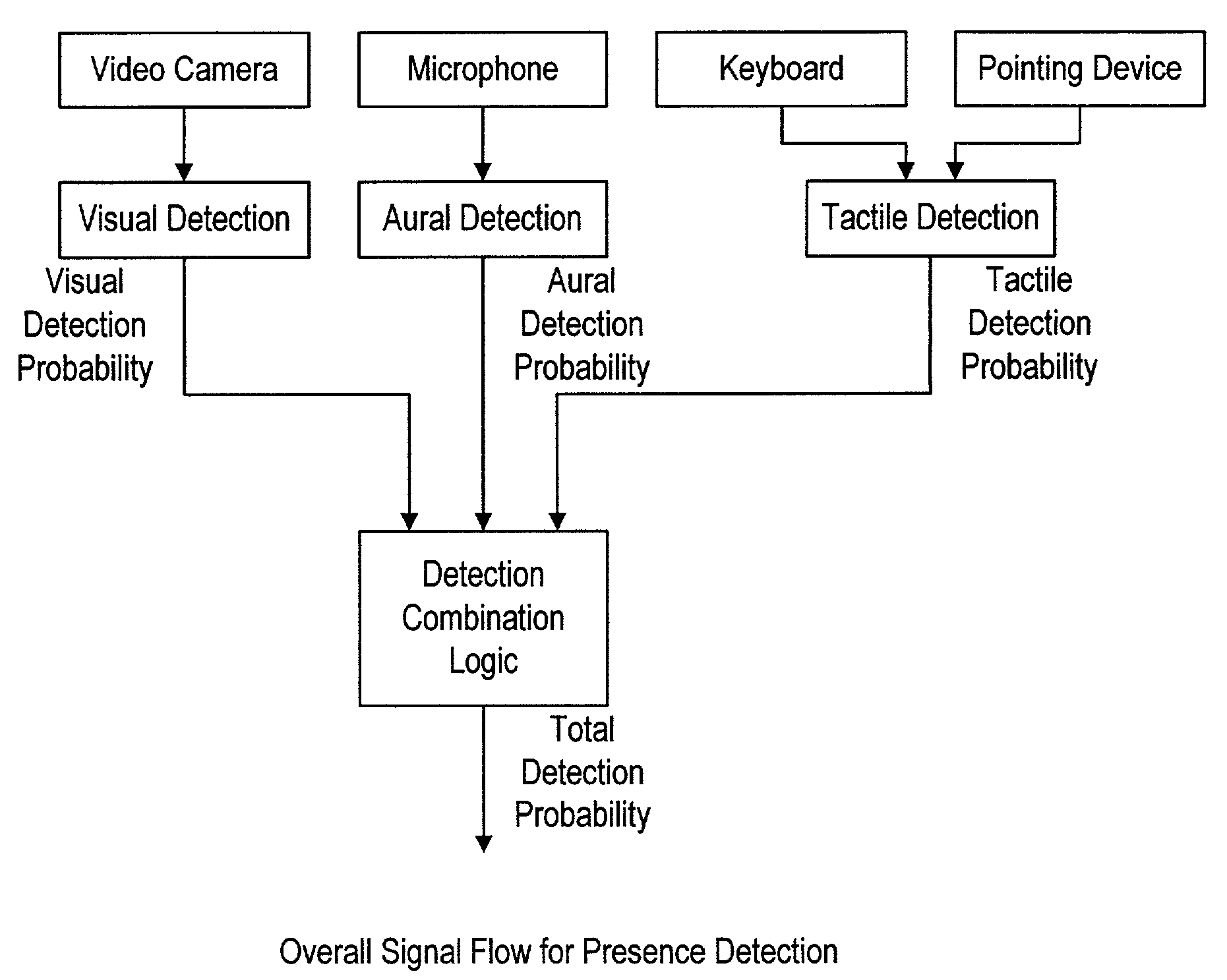
Methods of establishing a communications link using perceptual sensing of a user's presence
InactiveUS7242421B2Telephonic communicationTwo-way working systemsTelecommunications linkImaging processing
Owner:PERCEPTIVE NETWORK TECH
Broadband transceiver and distributed antenna system utilizing same
ActiveUS20110243201A1Indoor communication adaptationAntenna couplingsTransceiverDistributed antenna system
A broadband transceiver includes at least one layer structure that is substantially impermeable to RF radiation. The layer structure includes a first face surface substantially opposite a second face surface. A receive antenna is located proximate the first face surface and configured to receive RF transmissions. A transmit antenna is located proximate the second surface and configured to transmit RF transmissions. At least one of the receive and transmit antennas generates a generally toroidal radiation pattern that is stronger in a direction substantially parallel to the respective layer structure face surface compared to a direction substantially perpendicular to the face surface.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
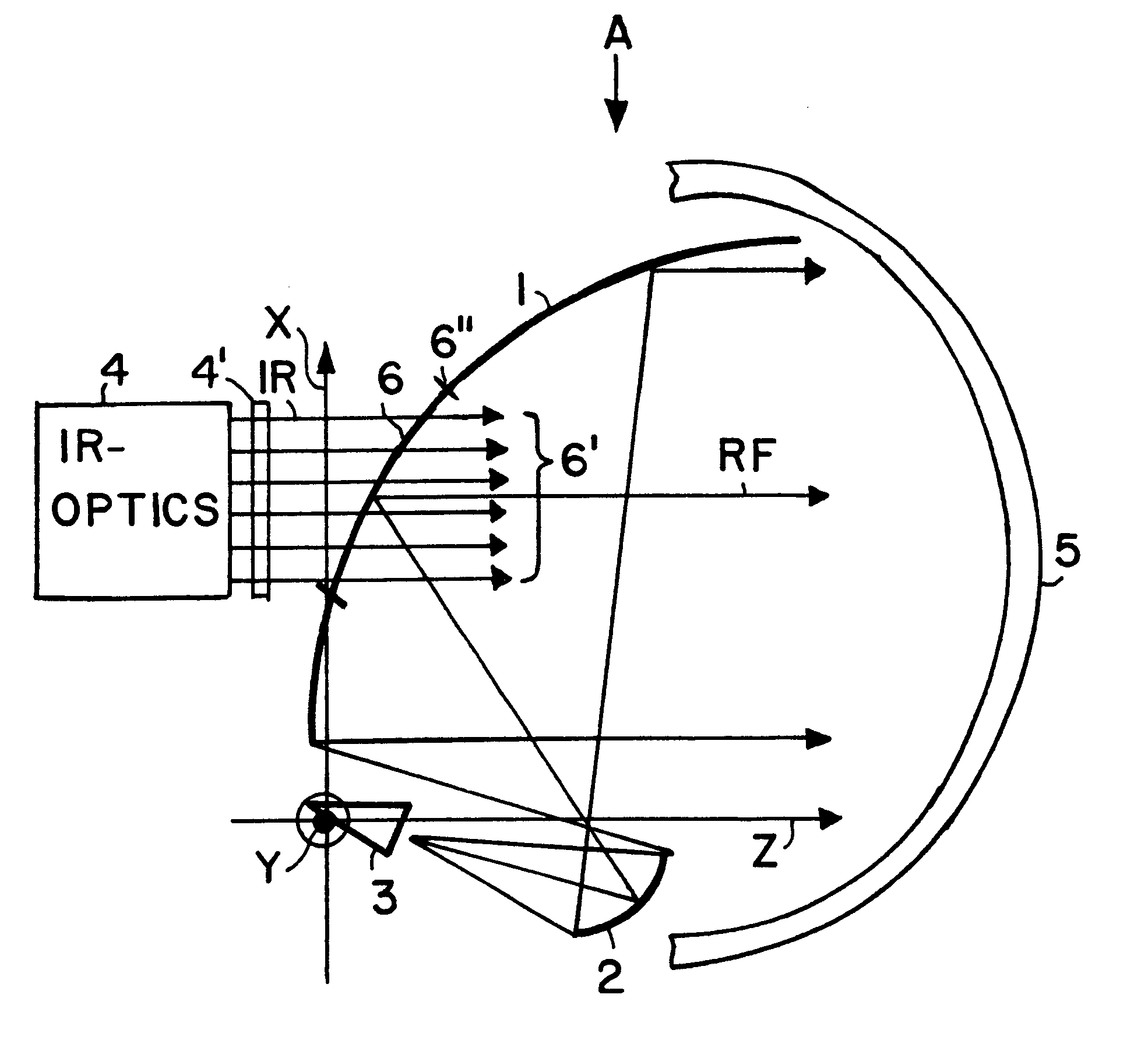
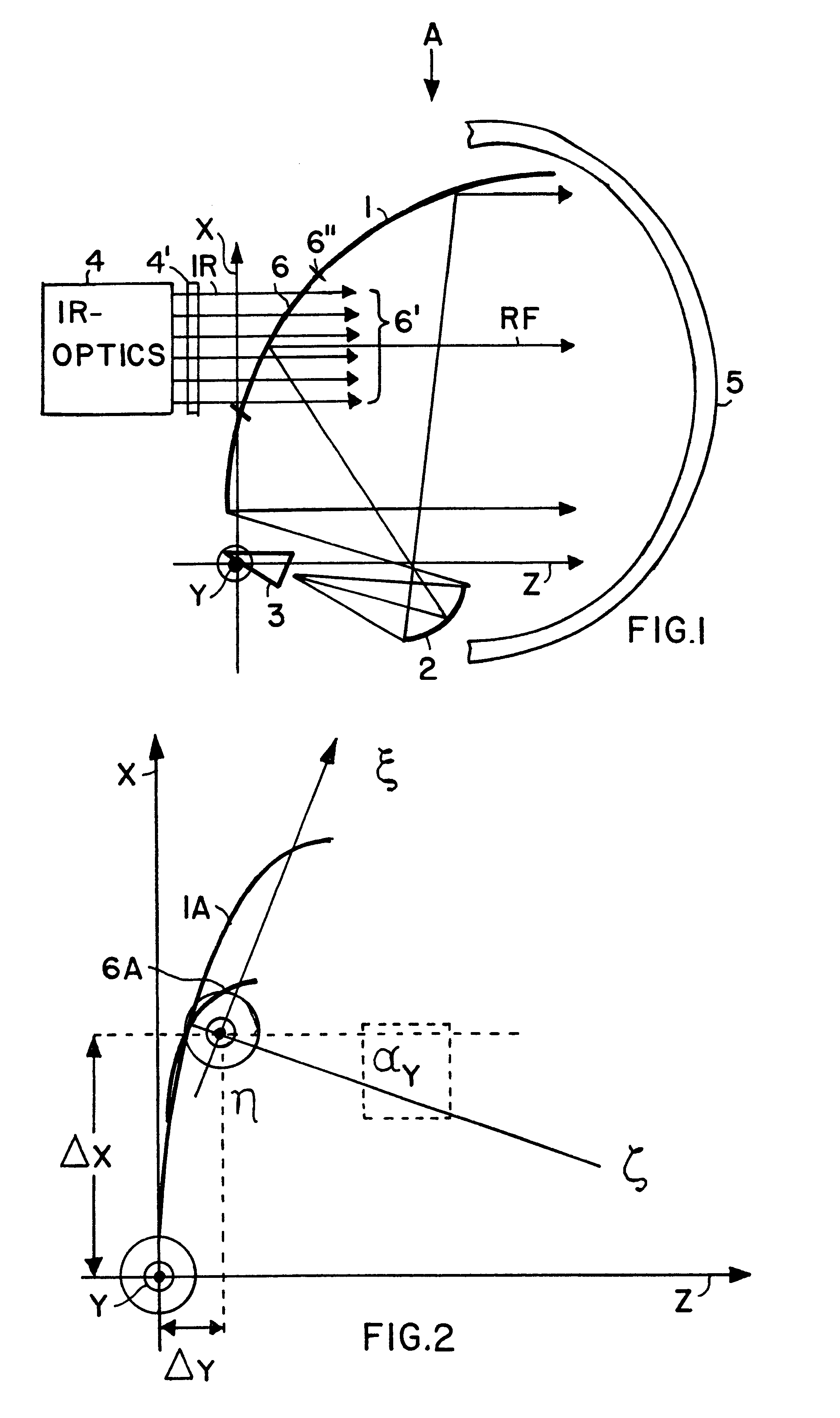
RF and IR bispectral window and reflector antenna arrangement including the same
InactiveUS6307521B1Undesirable side effect can be preventedCompact and space-saving arrangementSimultaneous aerial operationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionLight beamSignal beam
A reflector antenna arrangement can transmit and receive both infrared (IR) and millimeter wave (RF) radiation. The arrangement includes a main reflector (1), a subreflector (2), an IR feed system (4), an RF feed system (3), a radome (5), and a bispectral window (6) arranged in an opening provided in a central area of the main reflector (1). The RF feed system is oriented so that the RF radiation path includes a double reflection from the subreflector and from the main reflector, while the IR feed system is arranged directly behind the bispectral window so that the IR beam path extends directly through the bispectral window without reflecting from the main reflector or the subreflector. The bispectral window has a high reflectance for the RF radiation and a high transmittance of the IR radiation. The bispectral window is made of a dielectric material and has rotationally symmetrical front and back surfaces, whereby the front surface contour is optimally matched to the front surface of the main reflector and the back surface contour achieves an optimal reflectivity of the RF radiation and an optimal transmissivity of the IR radiation. Undesired influences between the IR radiation and the RF radiation are avoided by the separation of the signal beam paths.
Owner:MBDA DEUTSCHLAND GMBH
Method and apparatus for improving the interrogation range of an RF-Tag
InactiveUS6590498B2Near-field transmissionRoad vehicles traffic controlCommunications systemAntenna element
A method for increasing the interrogation range of an RF Tag in a radio communication system using RF Tags with multiple reflecting antenna elements. The reflecting antenna elements are predeterminately positioned, and preferably aligned, with respect to each other in the direction of expected incident RF radiation. The reflecting antenna elements are sequentially pulsed on and off such that while the first reflecting antenna element is in a signal reflecting operating state, the remaining reflecting antenna elements are in a substantially non-reflecting state, and when the second reflecting element is in a reflecting operating state, the remaining reflecting elements are in a non-reflecting state, etc. The sequential pulsing and predetermined fixed spacing between the reflector elements generates constructive interference between the reflected signals of the reflecting antenna elements which increases the power of the resulting reflected signal.
Owner:LGS INNOVATIONS +1
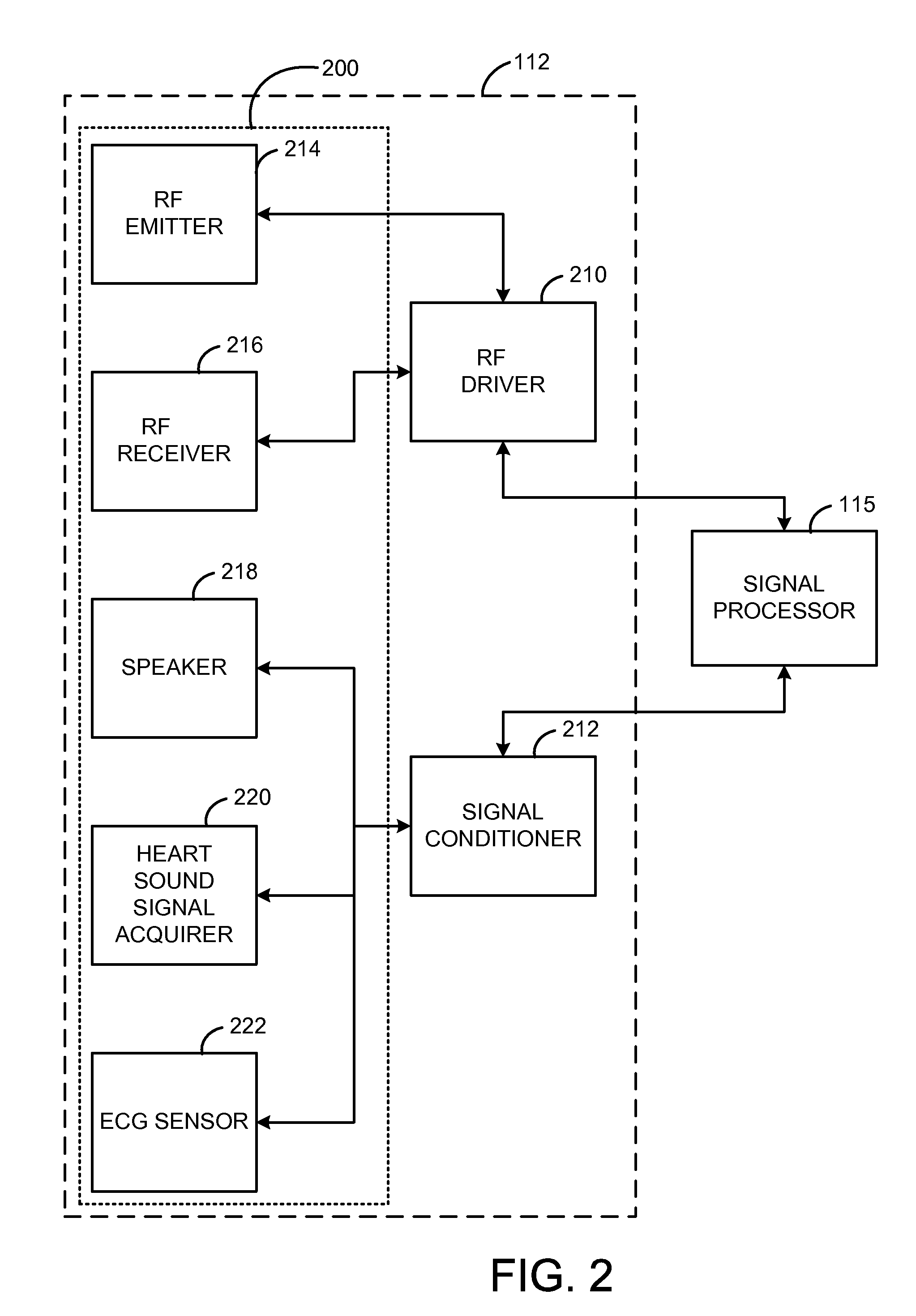
Systems and methods for determining systolic time intervals
InactiveUS20080167566A1Efficiently and accurately diagnoseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrocardiographyCardiac cycleData profiling
A method and system for determining systolic time intervals, by analysis of radio frequency (RF) scatter patterns in conjunction with Electrocardiogram (ECG) data, is provided. An RF emitter is placed on the cardiac patient. The emitter includes two or more transmitting antennas which emit RF radiation into the cardiac patient, resulting in an RF scatter pattern. An RF sensor receives the scattered RF signals. The RF emitted from the antennas will differ spatially with regard to the RF sensor, causing the RF scatter patterns to differ from one another. A signal processor analyzes these differences to identify inhomogeneous structures, and to identify aortic valve motion, including aortic valve opening and closure. An electrocardiogram identifies the onset of the cardiac cycle. Systolic intervals are determined using the onset of the cardiac cycle and the aortic valve motion. Cardiac contractility also is determined by correlation to systolic intervals. An acoustic sensor is used to verify the aortic valve closure.
Owner:UNVER KAMIL +3
Method and apparatus for shielding a linear accelerator and a magnetic resonance imaging device from each other
InactiveUS8836332B2Improve permeabilityReduce flux densityDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSplit magnetResonance
A radiation therapy system comprises a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system combined with an irradiation system, which can include one or more linear accelerators (linacs) that can emit respective radiation beams suitable for radiation therapy. The MRI system includes a split magnet system, comprising first and second main magnets separated by gap. A gantry is positioned in the gap between the main MRI magnets and supports the linac(s) of the irradiation system. The gantry is rotatable independently of the MRI system and can angularly reposition the linac(s). Shielding can also be provided in the form of magnetic and / or RF shielding. Magnetic shielding can be provided for shielding the linac(s) from the magnetic field generated by the MRI magnets. RF shielding can be provided for shielding the MRI system from RF radiation from the linac.
Owner:VIEWRAY TECH
Apparatus and method for concentrating electromagnetic energy on a remotely-located object
InactiveUS7994962B1Reduce undesired reflectionWave based measurement systemsCommunication jammingResonanceElectromagnetic shielding
A method for concentrating radio frequency (RF) radiation on an object located in proximity to a reflector includes the steps of: selecting a target reflector and a level of power for conveying to the target reflector by reradiation from the target reflector, determining a resonance profile of the target reflector, the resonance profile including at least one resonant frequency of the target reflector, selecting a transmission profile matching the resonance profile, the transmission profile comprising the at least one resonant frequency, and transmitting RF radiation in accordance with the transmission profile towards the target reflector.
Owner:DROSERA
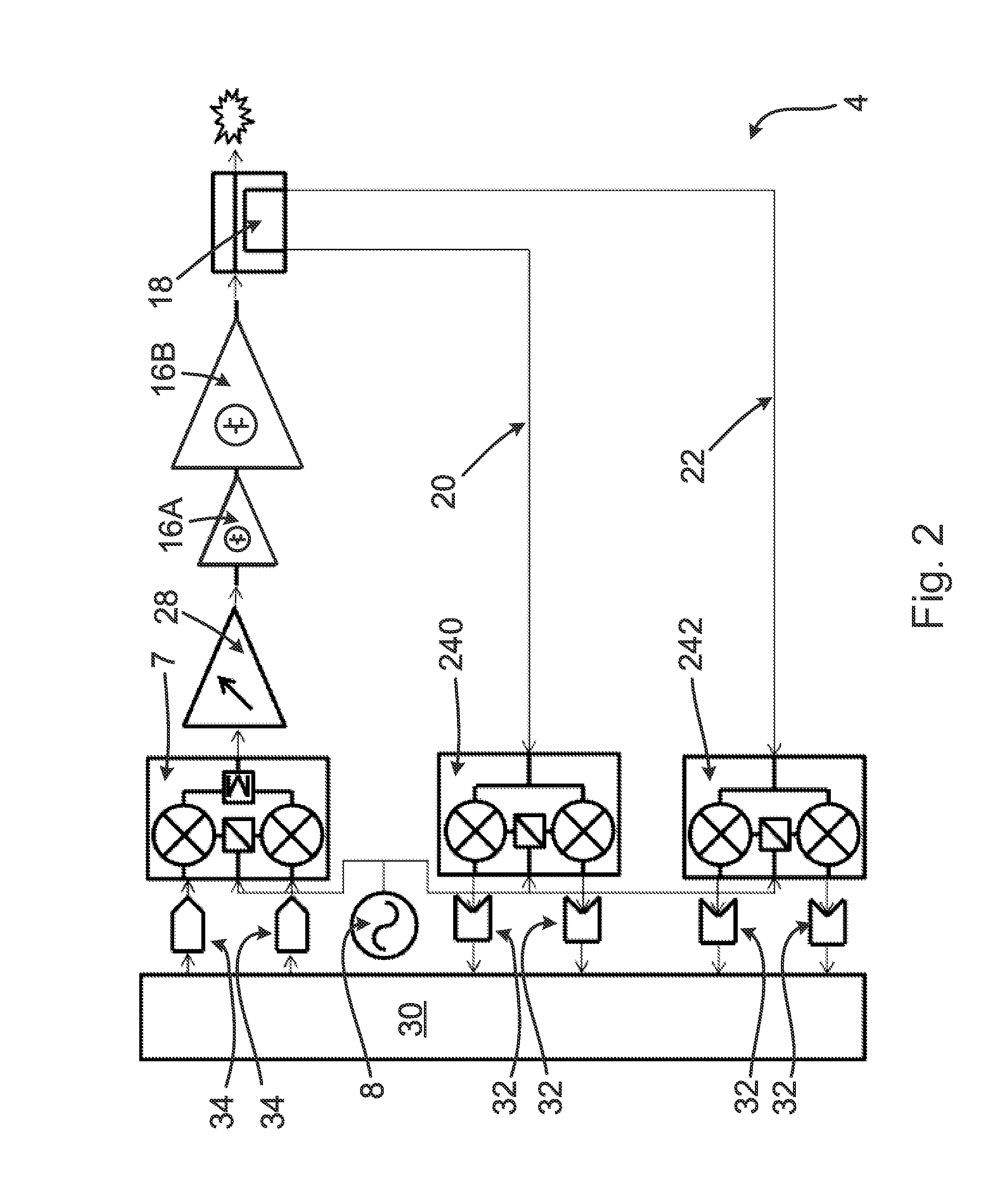
Radio frequency heating apparatus
ActiveUS20150351164A1Easy to controlIncrease flexibilityMicrowave heatingHome appliance efficiency improvementAudio power amplifierFrequency spectrum
A radio frequency (RF) heating apparatus and a microwave oven comprising an RF heating apparatus. The apparatus includes a cavity for receiving an object to be heated. The apparatus also includes a plurality of channels for generating RF radiation to be introduced into the cavity. Each channel includes a frequency synthesiser, a power amplifier and an antenna. Each channel is operable to use a common phase reference signal for generating the RF radiation. Each channel may be controllably operable to generate RF radiation having different, respective frequency spectra. Forward and reverse signal detection circuitry may be provided that is operable to determine amplitude, frequency and / or phase information relating to RF radiation in the cavity. This information may be used for adaptively controlling the RF radiation generated by each channel.
Owner:AMPLEON NETHERLANDS
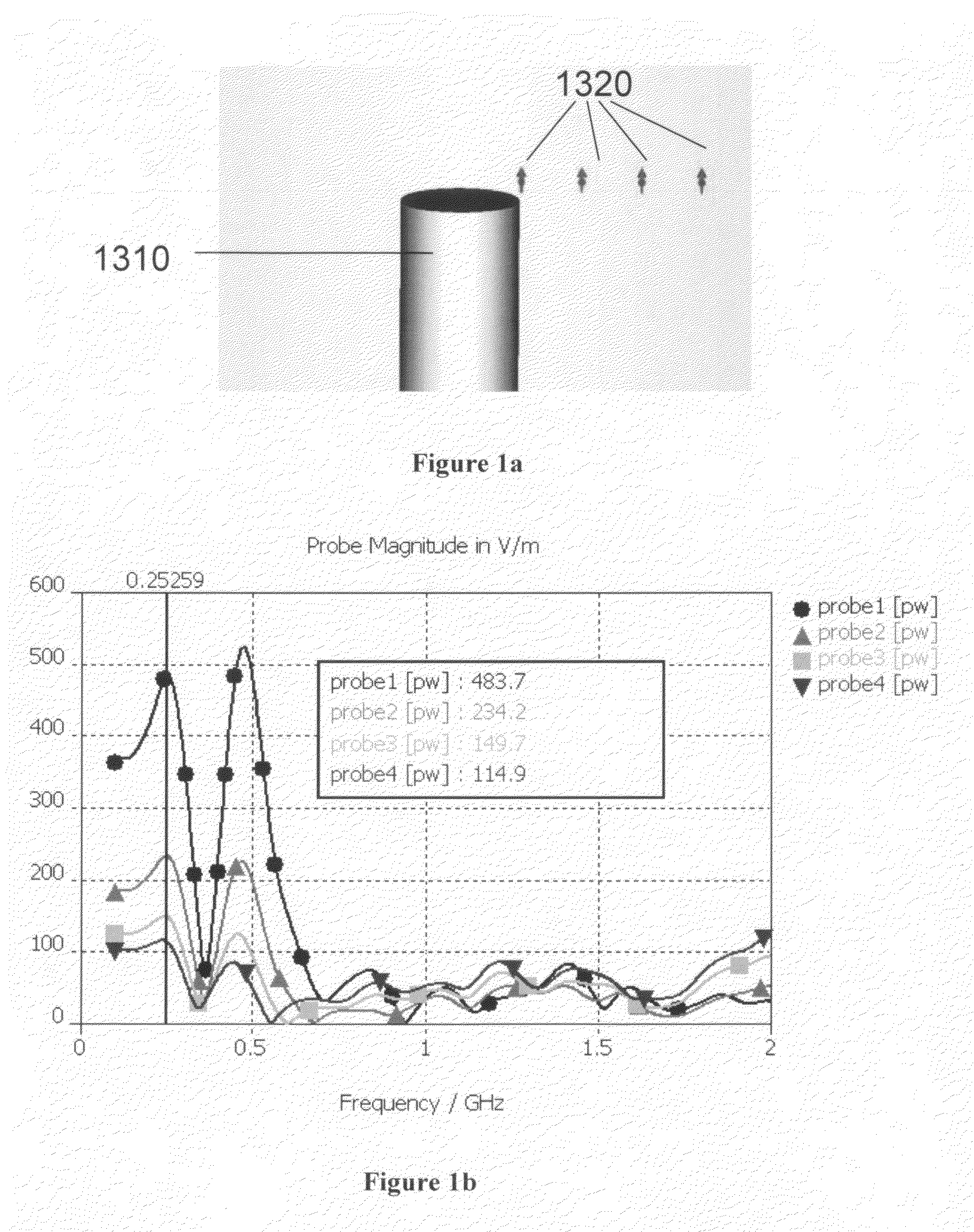
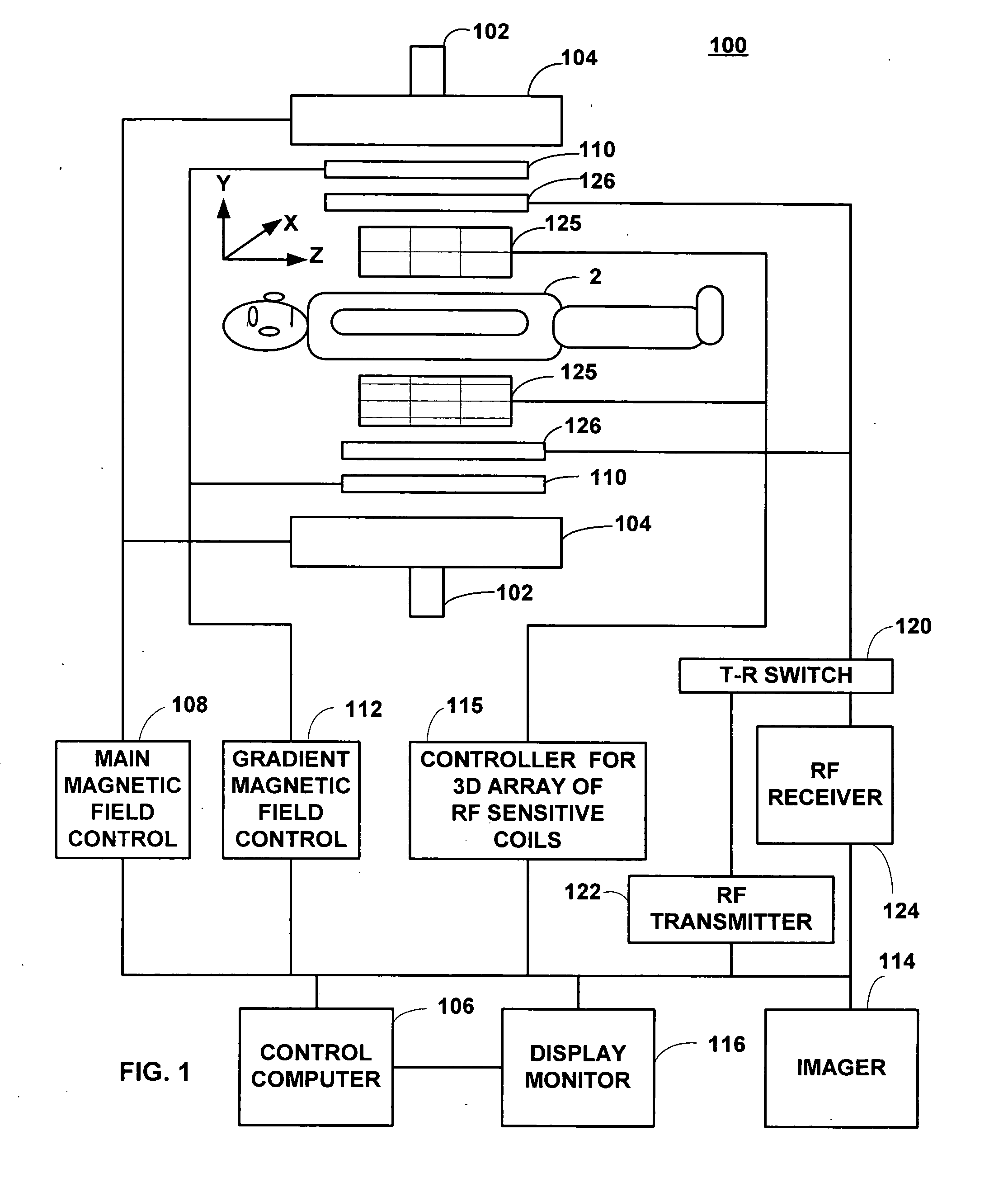
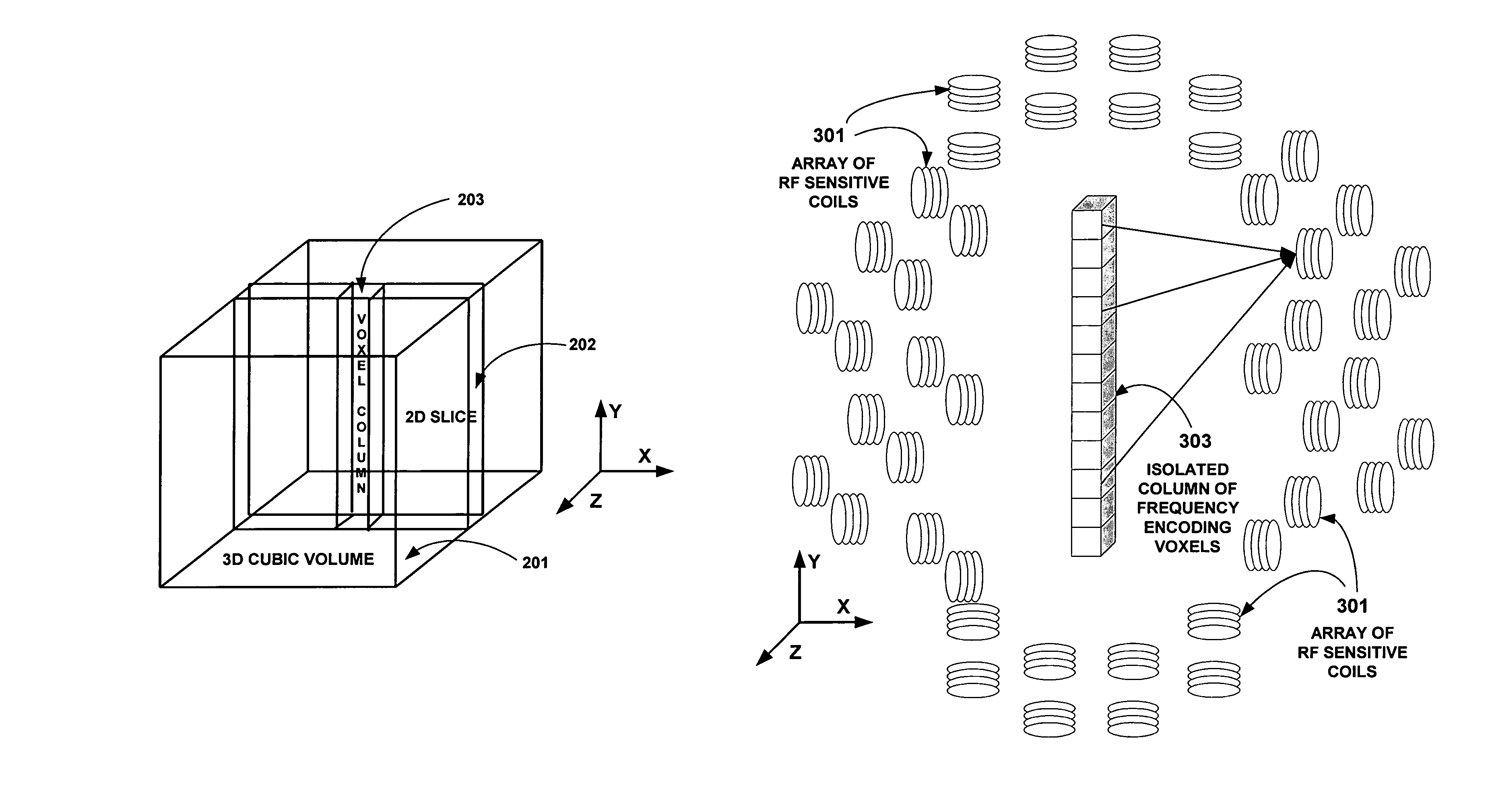
Field image tomography for magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20110115485A1Shorten the length of timeReduce usageMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionObject basedSystem matrix
Field Image Tomography (FIT) is a fundamental new theory for determining the three-dimensional (3D) spatial density distribution of field emitting sources. The field can be the intensity of any type of field including (i) Radio Frequency (RF) waves in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), (ii) Gamma radiation in SPECT / PET, and (iii) gravitational field of earth, moon, etc. FIT exploits the property that field intensity decreases with increasing radial distance from the field source and the field intensity distribution measured in an extended 3D volume space can be used to determine the 3D spatial density distribution of the emitting source elements. A method and apparatus are disclosed for MRI of target objects based on FIT. Spinning atomic nuclei of a target object in a magnetic field are excited by beaming a suitable Radio Frequency (RF) pulse. These excited nuclei emit RF radiation while returning to their normal state. The intensity or amplitude distribution of the RF emission field g is measured in a 3D volume space that may extend substantially along the radial direction around the emission source. g is related to the 3D tomography f through a system matrix H that depends on the MRI apparatus, and noise n through the vector equation g=Hf+n. This equation is solved to obtain the tomographic image f of the target object by a method that reduces the effect of noise.
Owner:SUBBARAO MURALIDHARA
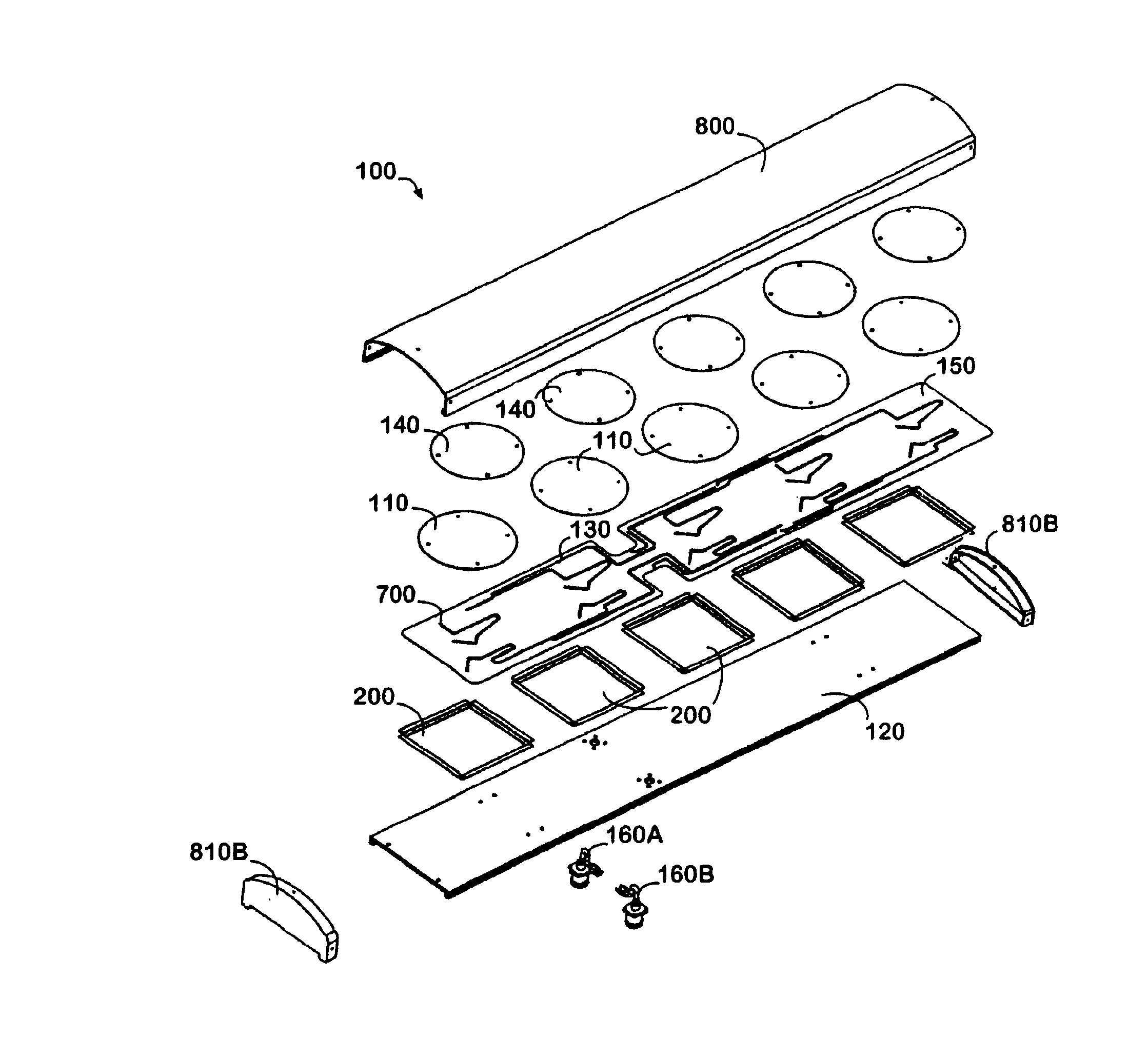
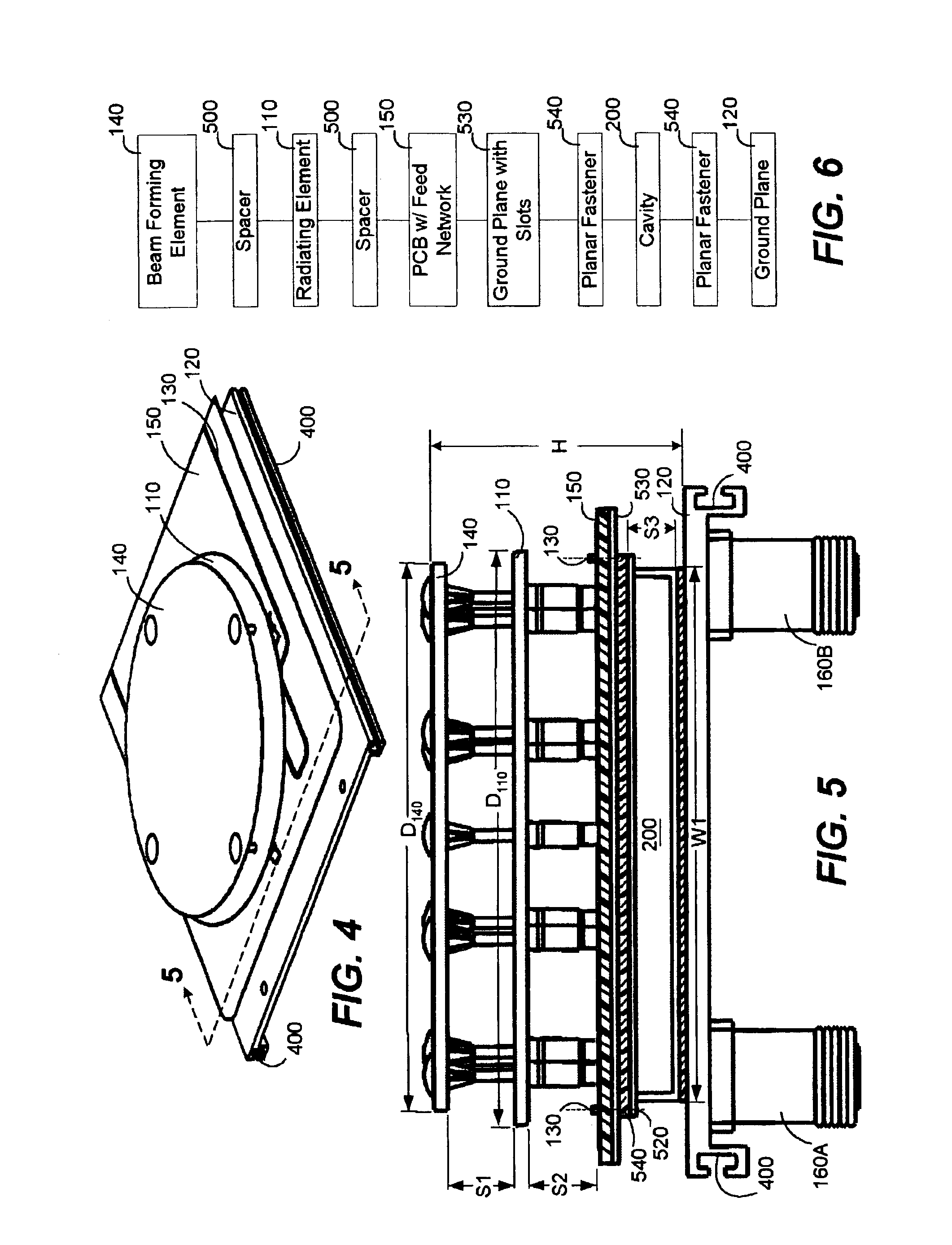
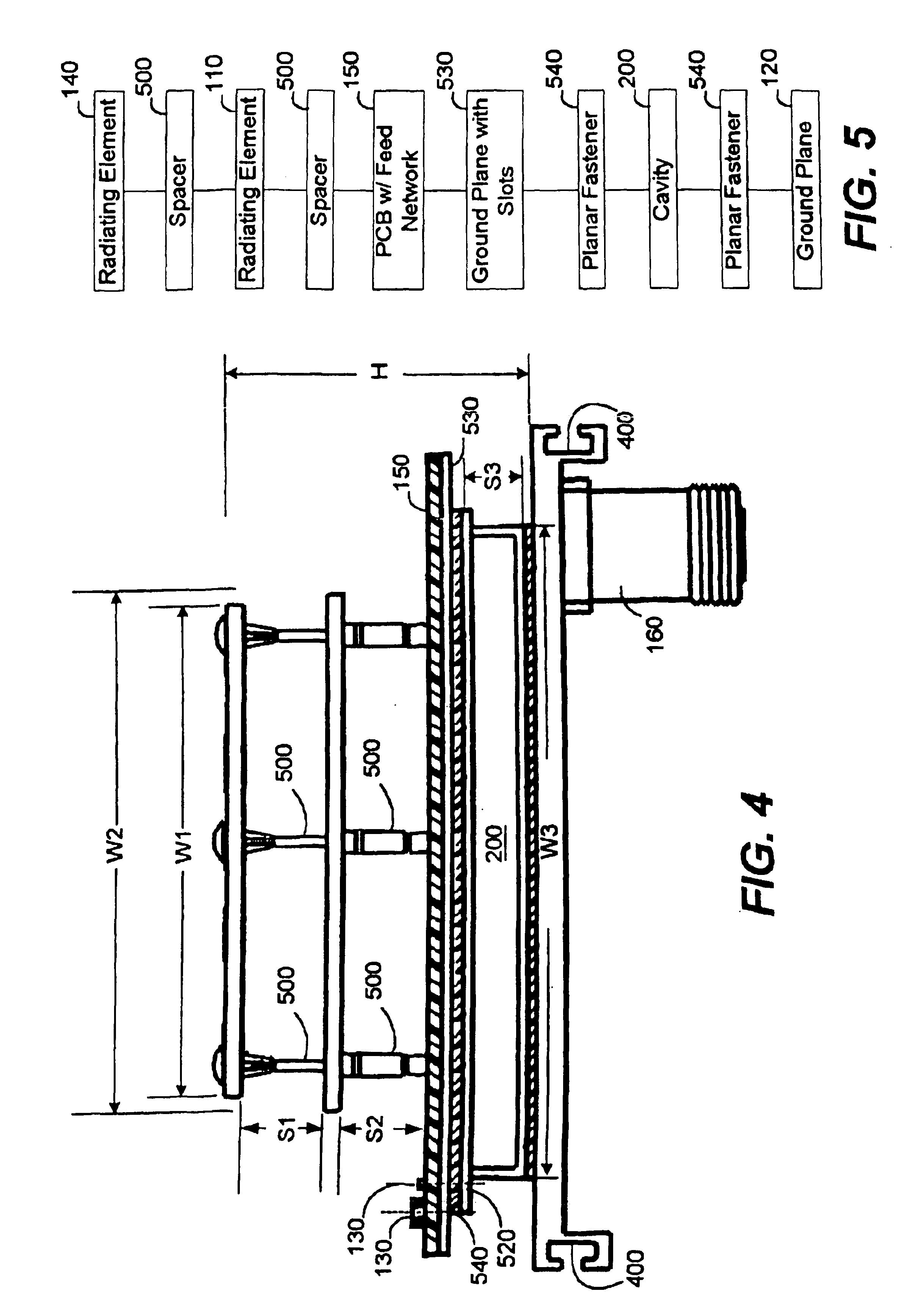
Patch and cavity for producing dual polarization states with controlled RF beamwidths
InactiveUS6911939B2Function increaseImprove discriminationSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsRf fieldDielectric
An antenna system can generate RF radiation fields having dual simultaneous polarization states and having substantially rotationally symmetric radiation patterns. The antenna system generates RF radiation patterns where the beamwidths of respective RF fields for respective radiating elements are substantially equal and are relatively large despite the compact, physical size of the antenna system. The antenna system can include one or more patch radiators and a non-resonant patch separated from each other by an air dielectric and by relatively small spacer elements. The patch radiators and non-resonant patch can have predefined shapes for increasing polarization discrimination. The lower patch radiators can be mounted to a printed circuit board that can include an RF feed network and a ground plane which defines a plurality of symmetrically, shaped slots. The slots within the ground plane of the printed circuit board can be excited by stubs that are part of the feed network of the printed circuit board. The slots, in turn, can establish a transverse magnetic mode of RF radiation in a cavity which is disposed adjacent to the ground plane of the printed circuit board and a ground plane of the antenna system. The feed network of the printed circuit board can be aligned with portions of the cavity such that the portions of the cavity function as a heat sink for absorbing or receiving thermal energy produced by the feed network.
Owner:ANDREW CORP
Device, method and system for activating an in-vivo imaging device
A device, system, and method for activating an ingestible imaging device with an RF radiation signal such that an imaging device that may be initially in a dormant state may be activated prior to ingestion by exposure to RF radiation The device may include an RF switch that may facilitate powering of one or more electrical components of the device when toggled. RF switch may also serve deactivate the ingestible imaging device.
Owner:GIVEN IMAGING LTD
Method And Apparatus For Shielding A Linear Accelerator And A Magnetic Resonance Imaging Device From Each Other
ActiveUS20150065860A1Improve permeabilityReduce flux densityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSplit magnetResonance
A radiation therapy system comprises a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system combined with an irradiation system, which can include one or more linear accelerators (linacs) that can emit respective radiation beams suitable for radiation therapy. The MRI system includes a split magnet system, comprising first and second main magnets separated by gap. A gantry is positioned in the gap between the main MRI magnets and supports the linac(s) of the irradiation system. The gantry is rotatable independently of the MRI system and can angularly reposition the linac(s). Shielding can also be provided in the form of magnetic and / or RF shielding. Magnetic shielding can be provided for shielding the linac(s) from the magnetic field generated by the MRI magnets. RF shielding can be provided for shielding the MRI system from RF radiation from the linac.
Owner:VIEWRAY TECH
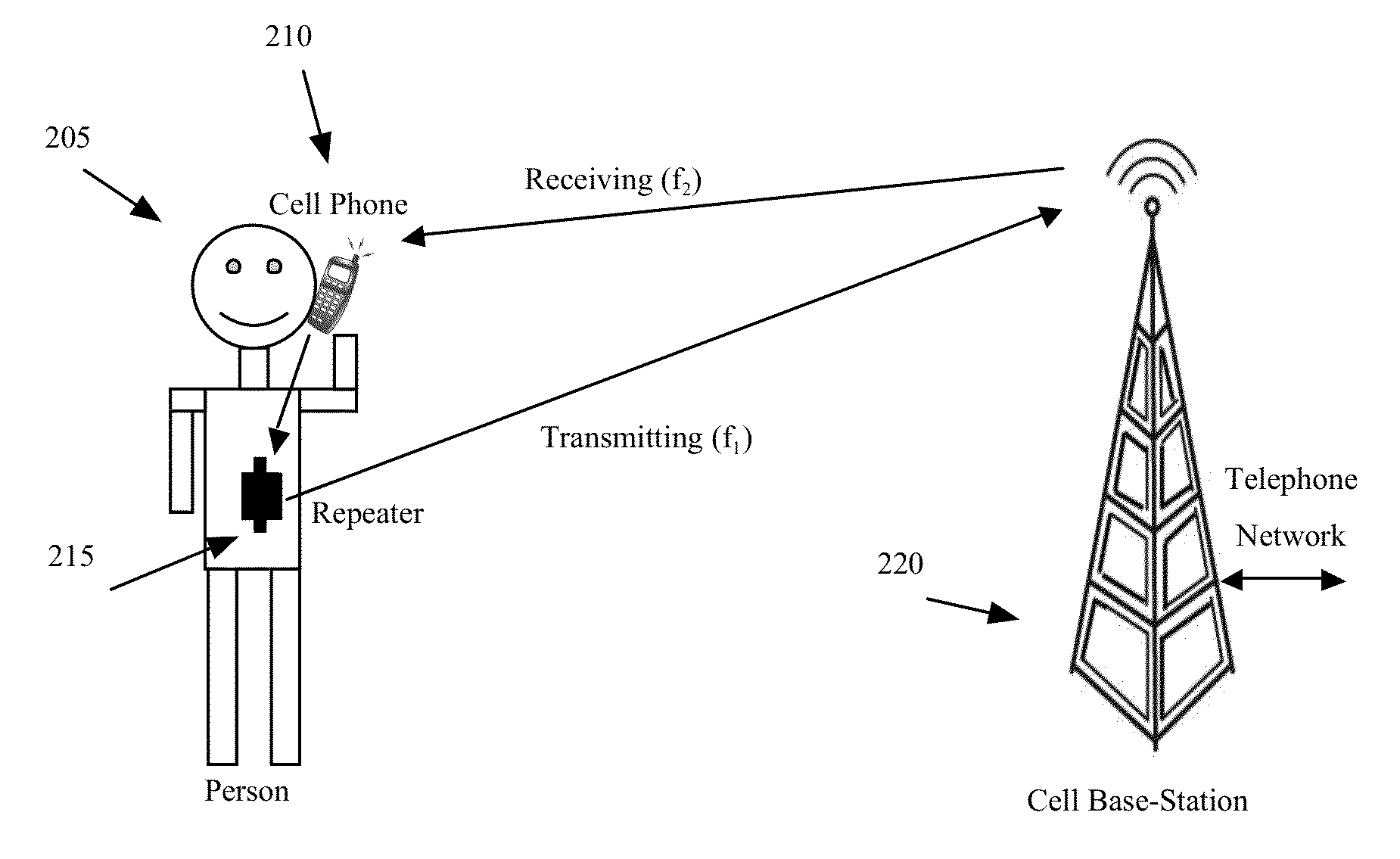
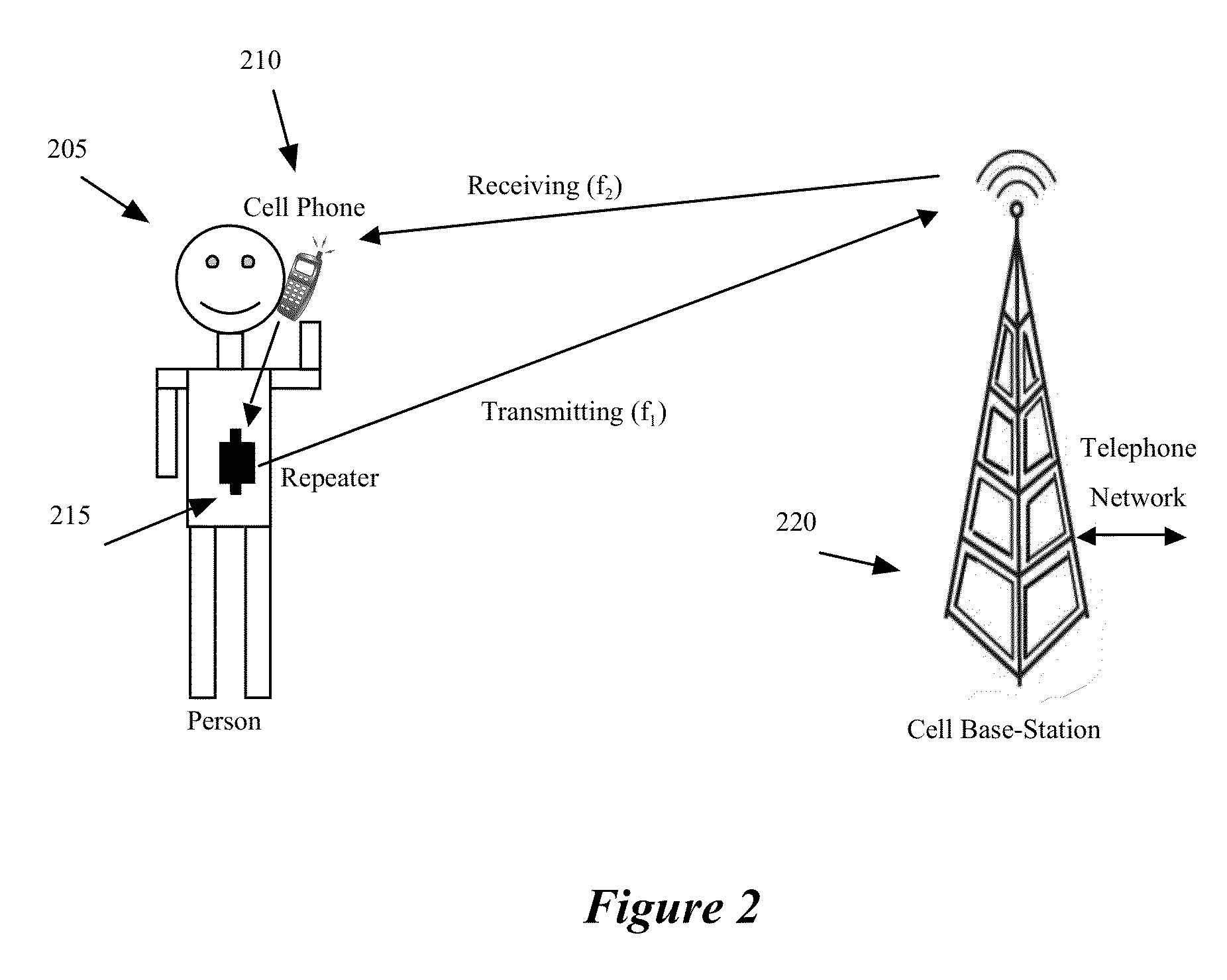
Repeater device for reducing the electromagnetic radiation transmitted from cellular phone antennas and extending phone battery life
InactiveUS20130035090A1Reduce transmit powerIncrease rangeEnergy efficient ICTPower managementTransmitted powerCarrier signal
A cellular communication system and method is described where a low-cost repeater is used to reduce the transmit power of a cell phone. The cell phone transmits a low-power modulated carrier signal to a nearby repeater. The repeater amplifies the signal and transmits it to a cellular base-station. The reduction of cell phone transmit power lowers the exposure of humans to RF radiation and increases the battery life of the cell phone.
Owner:GOLBA LLC
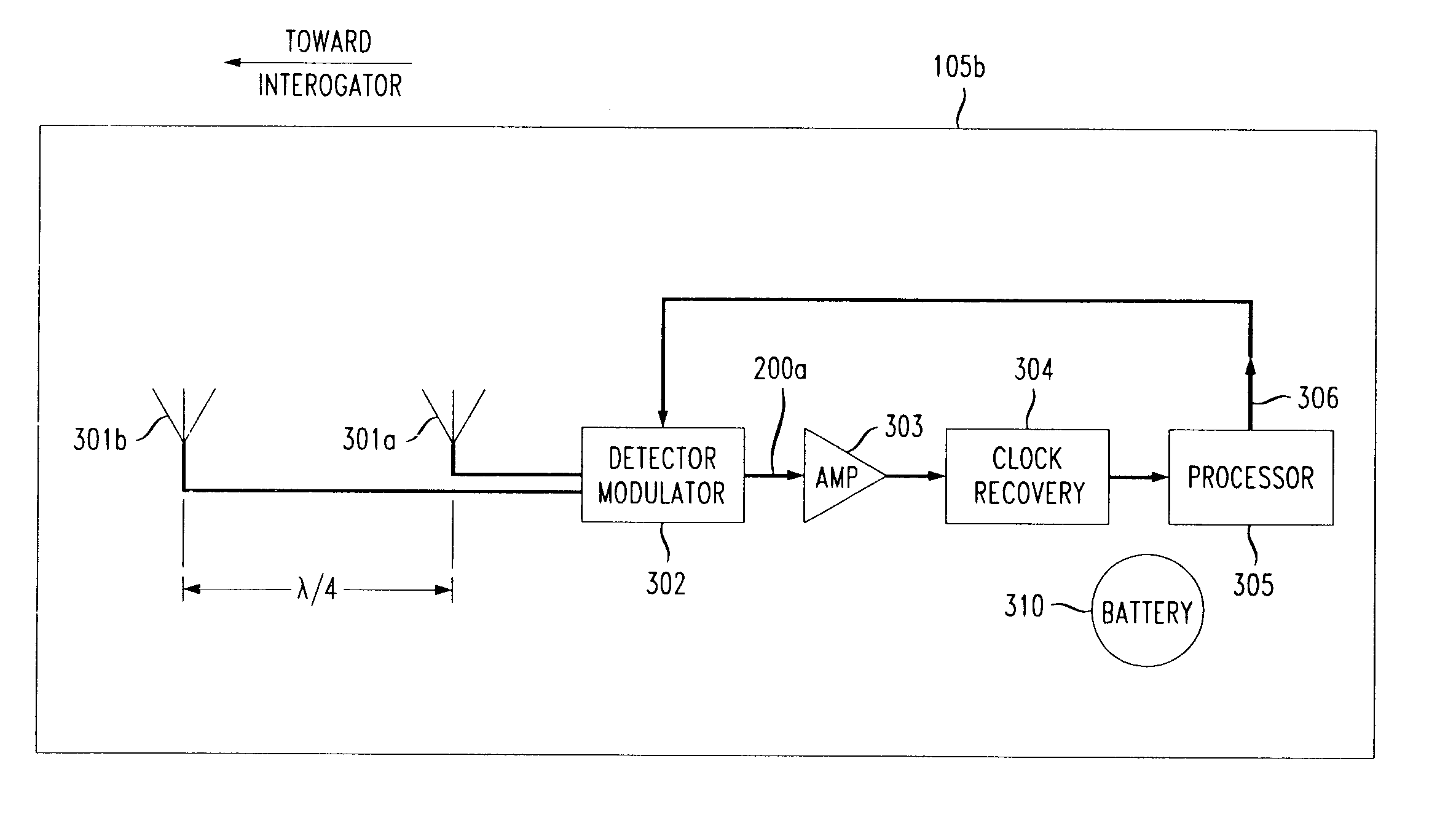
Radio Frequency Identification System and Data Reading Method
InactiveUS20090014520A1Correction errorHigh densitySensing record carriersRecord carriers used with machinesEngineeringMachine-readable data
A system and method for reading an RFID data tag comprising a plurality of diffractive elements being indicative of machine-readable data carried by the tag are provided. The diffractive elements have such shape that the dimension of the diffractive elements along one axis is substantially different than the dimension of the elements along the perpendicular axis. Each diffractive element is oriented in a direction other than the direction of its neighboring elements. The system comprises a transmitting antenna configured for emitting an RF radiation signal at a predetermined polarization towards the tag; and a receiving antenna configured for collecting re-radiated RF radiation produced by the tag in response to the RF radiation signal at a polarization orthogonal to the polarization of the transmitting antenna and generating electromagnetic signals indicative of the data carried by the tag. The system also includes an interrogator unit configured for generating the transmitted RF radiation signal and processing the electromagnetic signals produced by the receiving antenna for determining the data carried by the tag.
Owner:INKSURE RF
Aperture Coupled Cavity Backed Patch Antenna
InactiveUS6897809B2Facilitate easeLow intermodulationSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsGround planePrinted circuit board
A compact antenna system can generate RF radiation fields having increased beamwidths and bandwidths. The antenna system can include one or more patch radiators. The lower patch radiators can be mounted to a printed circuit board that can include a ground plane which defines a plurality of slots. The slots within the ground plane of the printed circuit board can be excited by stubs that are part of the feed network of the printed circuit board. The slots, in turn, can establish RF radiation in a cavity which is disposed adjacent to the ground plane of the printed circuit board and a ground plane of the antenna system.
Owner:ANDREW CORP
Antenna system to control RF radiation exposure
ActiveUS20130281036A1Antenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsControl systemEngineering
An antenna measurement and control system for use with a transmitting antenna, the system comprising a sensor configured to determine an indication of the radiation emitted by the antenna; control circuitry connectable to the antenna and configured to selectively vary, or disengage, the power supplied to the antenna, and a processor connectable to the sensor and control circuitry, wherein the processor is configured to control the control circuitry in response to the determined indication of the emitted radiation.
Owner:FASMETRICS LTD
Wireless energy transfer system
The invention relates to a wireless energy transfer system, comprising: a transmitter configured to beam scan RF radiation across a plurality of sectors at a first frequency, a receiver storing energy from the RF radiation, and sending acknowledgements at a second frequency, the first frequency being significantly different from the second frequency, and a controller configured to direct wireless energy transfer from the transmitter substantially at the receiver based on the acknowledgements.
Owner:SONY CORP
Hat cell phone or wireless device for hands-free user-safe operation
InactiveUS20070072655A1Special service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsDisplay deviceEngineering
A cellphone or wireless phone device has separate components which are carried or mounted in corresponding parts of a hat, cap, or other headgear worn by the user. The cellphone microphone or voice pickup component, preferably as a unidirectional device, may be carried in the forward brim of a hat or visor of a cap, the antenna may be lined in the rear part of the hat or cap, the speaker earpiece may be attached to one or both sides of the hat, the keypad may be mounted between the fabric layers of the visor of a cap or the inner liner of a hat or headgear, and the electronic circuitry, including parts such as amplifier, signal processor and switcher, and battery may be mounted in an internal part or inner liner of the hat. Preferably, the sound receiving and reproducing is achieved using transducer membranes. The hat may have battery recharge pins or points exposed for attachment to an external recharging unit. A metallized RF-blocking layer may be provided on an inner layer of the hat to block RF radiation from the antenna from the user's head. A global position system (GPS) unit is preferably provided on the hat. A first liquid crystal display (LCD) is provided, preferably on the brim or visor, to show the time, channel, cell phone displays, text messaging and GPS latitude and longitude coordinates. A second LCD is provided and hinged on the underside of the brim or visor. The second LCD can be folded up flat when it is not in use or folded down directly in front of either or both the wearer's eyes when it is in use. The second LCD is provided to display video images and text information received and / or controlled with the keypad.
Owner:CASCONE PETER
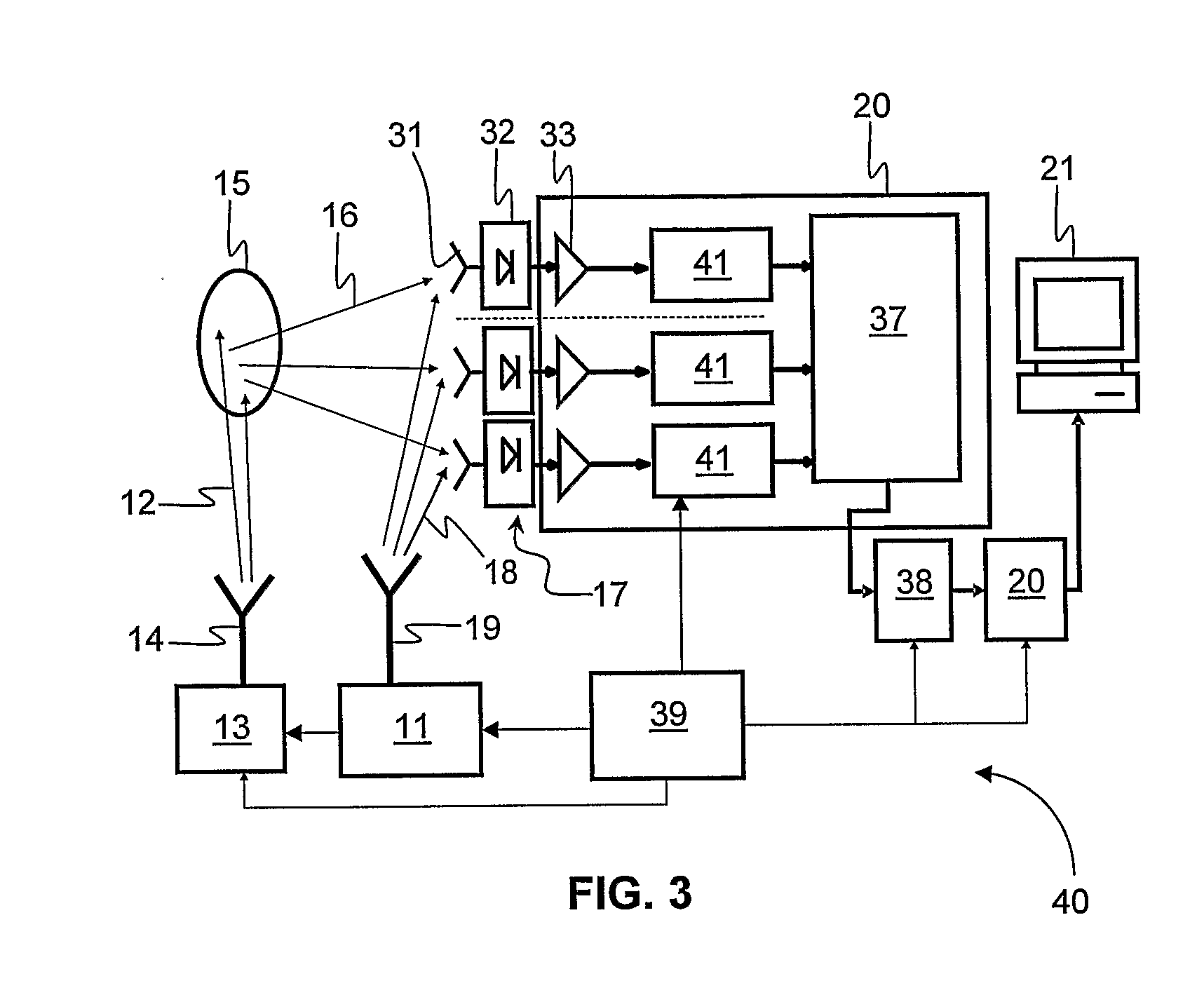
Video-Rate Holographic Surveillance System
In a holographic surveillance system (10) for near real-time imaging of a target (15), a source of RF radiation directs a non-amplified reference beam of pulsed coherent RF electromagnetic radiation toward a target. An array of antennas (31) receives a reflected beam from the target together with a component of the reference beam so as to produce a signal representative of phase and amplitude data of received energy, and a processor (20) processes the signals so as to produce a holographic image for display on a display device coupled to the processor.
Owner:CMR NAVISCAN CORP +1
Field image tomography for magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS8378682B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionObject basedSystem matrix
Field Image Tomography (FIT) is a fundamental new theory for determining the three-dimensional (3D) spatial density distribution of field emitting sources. The field can be the intensity of any type of field including (i) Radio Frequency (RF) waves in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), (ii) Gamma radiation in SPECT / PET, and (iii) gravitational field of earth, moon, etc. FIT exploits the property that field intensity decreases with increasing radial distance from the field source and the field intensity distribution measured in an extended 3D volume space can be used to determine the 3D spatial density distribution of the emitting source elements. A method and apparatus are disclosed for MRI of target objects based on FIT. Spinning atomic nuclei of a target object in a magnetic field are excited by beaming a suitable Radio Frequency (RF) pulse. These excited nuclei emit RF radiation while returning to their normal state. The intensity or amplitude distribution of the RF emission field g is measured in a 3D volume space that may extend substantially along the radial direction around the emission source. g is related to the 3D tomography f through a system matrix H that depends on the MRI apparatus, and noise n through the vector equation g=Hf+n. This equation is solved to obtain the tomographic image f of the target object by a method that reduces the effect of noise.
Owner:SUBBARAO MURALIDHARA
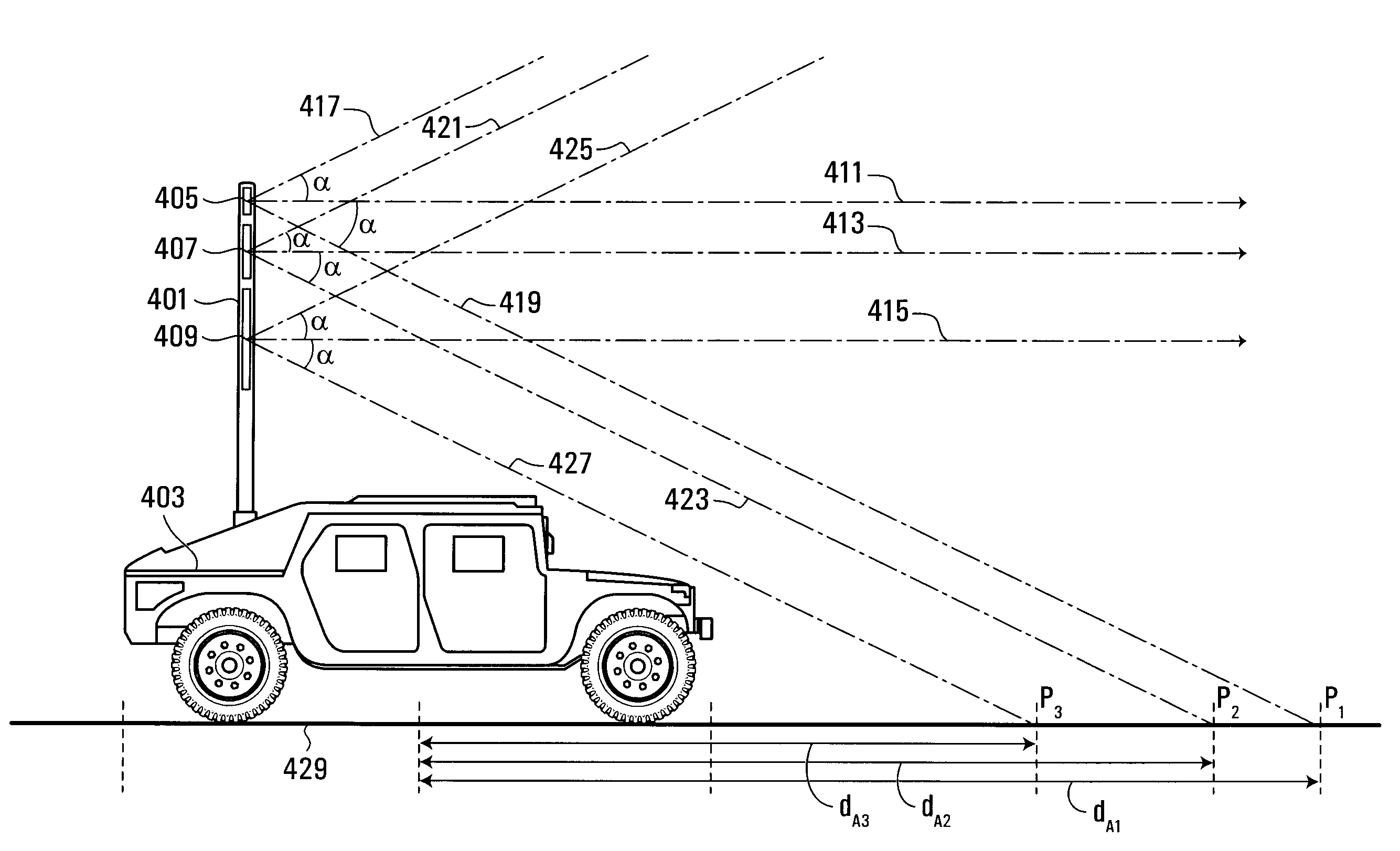
Radio Antenna Assembly and Apparatus for Controlling Transmission and Reception of RF Signals
InactiveUS20090140921A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioDetect presenceIndividually energised antenna arraysAntenna feed intermediatesVertical planeElectrical and Electronics engineering
An apparatus includes an antenna for transmitting RF radiation and being structured to enable the distribution of RF energy emitted therefrom to be varied in the vertical plane. The apparatus comprises a generator for generating an RF signal and to pass the signal to the antenna, and a controller arranged to control the distribution of RF energy emitted from the antenna in the vertical plane in response to positional information about an object.
Owner:ALLEN VANGUARD
Biosensor with rf signal transmission
InactiveUS20060019373A1High sensitivityReduce complexityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesBinding siteCoupling
A device (1) and method for measuring and or detecting the presence of biomolecules. The device comprises a resonance circuit arranged to operate and emit a resonance frequency (f). The resonance circuit comprises or is coupled to a sensor element (5) for detecting the binding of biomolecules (6a) to binding sites (5a). The binding of the biomolecules changes a physical property (R, L, C. mass) of the sensor element (5), which in it's turn, either directly when the sensor element forms part of the resonance circuit, or via a coupling of the sensor element to the resonance circuit, the resonance frequency. The change in the resonance frequency is detected. The device comprises a remote power transmission element, such as a photodiode or coil, for providing power to the resonance circuit using light or RF radiation respectively.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Radio frequency data carrier and method and system for reading data stored in the data carrier
InactiveUS6997388B2Increase information densityLarge componentRecord carriers used with machinesBurglar alarm electric actuationLength waveData storing
A radio frequency (RF) data carrier is presented. The RF data carrier comprises at least one diffraction element that has a dimension of the order of a wavelength of RF radiation and is responsive to RF irradiation, the response produced by the diffraction elements in the data carrier being indicative of machine-readable data carried by data carrier.
Owner:INKSURE RF
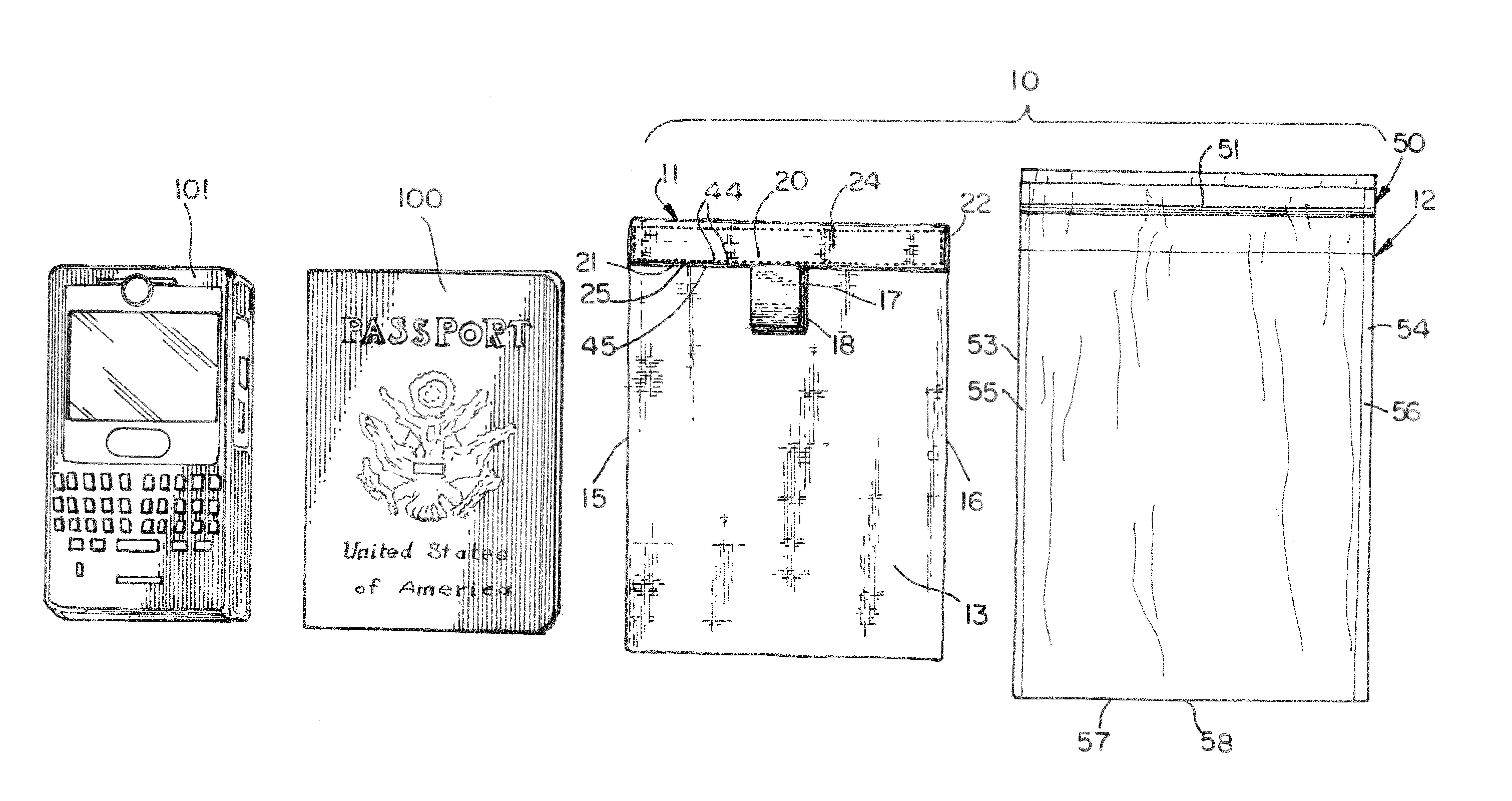
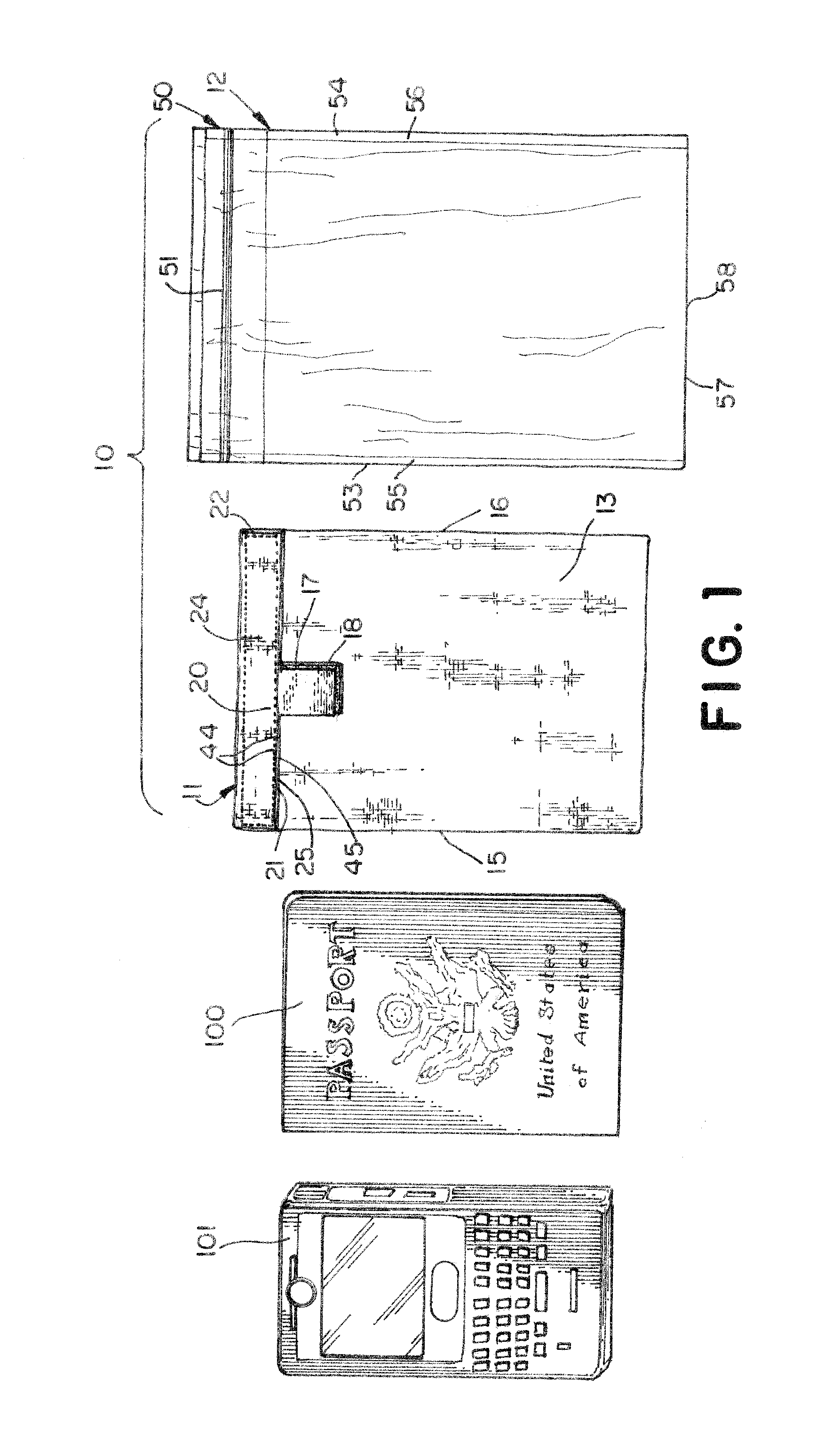
Shieldable bag system and devices
InactiveUS20120061134A1Avoid accessSecure closureMagnetic/electric field screeningSubstation equipmentEngineeringElectromagnetic radiation
A storage system and devices are provided for containing items and shielding the items from electromagnetic radiation, in particular, RF radiation, and holding the items in a waterproof environment. The storage system includes a first storage component which is constructed from a fabric having shieldable properties and is configured to envelope contents held therein in a shielded environment, and a second storage component which is constructed to receive the first storage component therein and provide waterproof storage for the contents. The storage system protects contents from unauthorized or surreptitious reads of stored data that may be carried on the content items by readers. The storage components of the storage system may be used independently of each other or together, as needed or desired.
Owner:KENNEDY LINDA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com