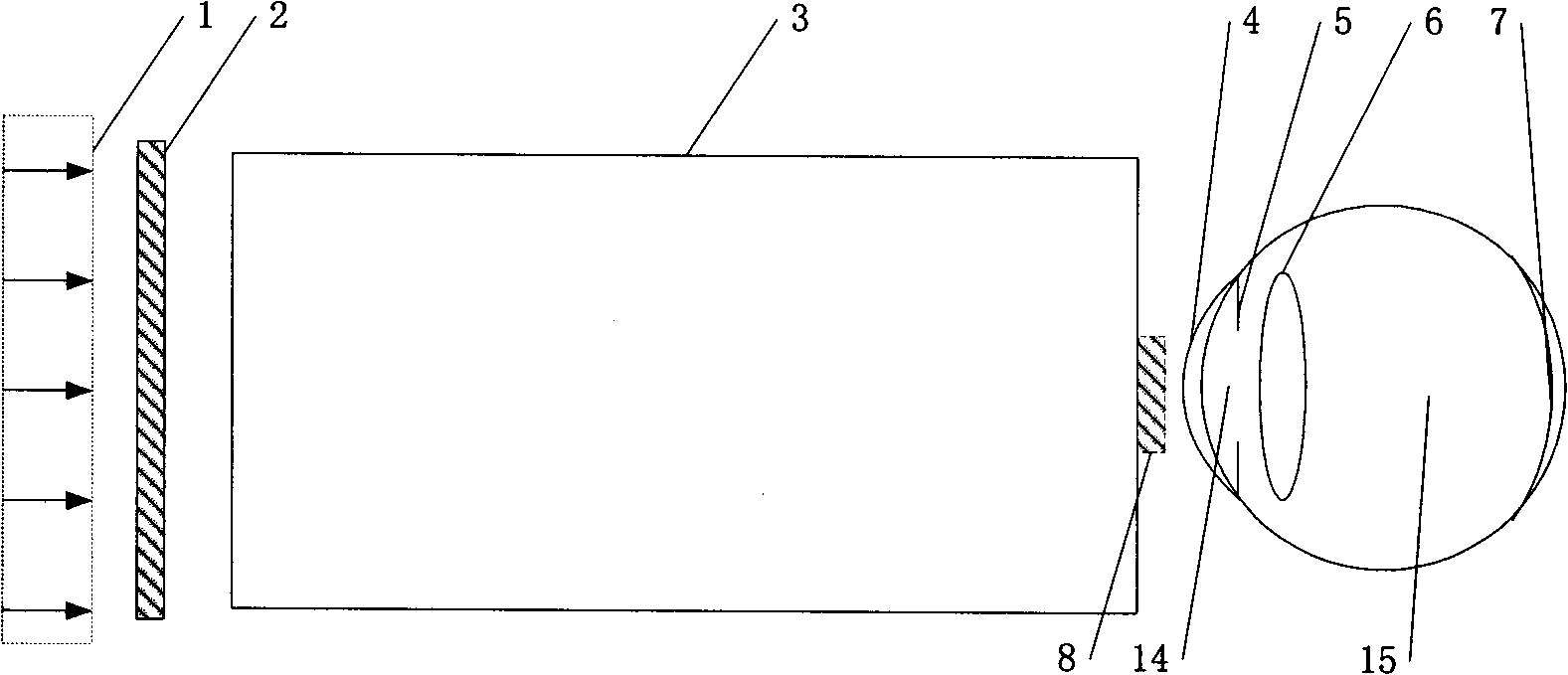Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
393 results about "Amplitude distribution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
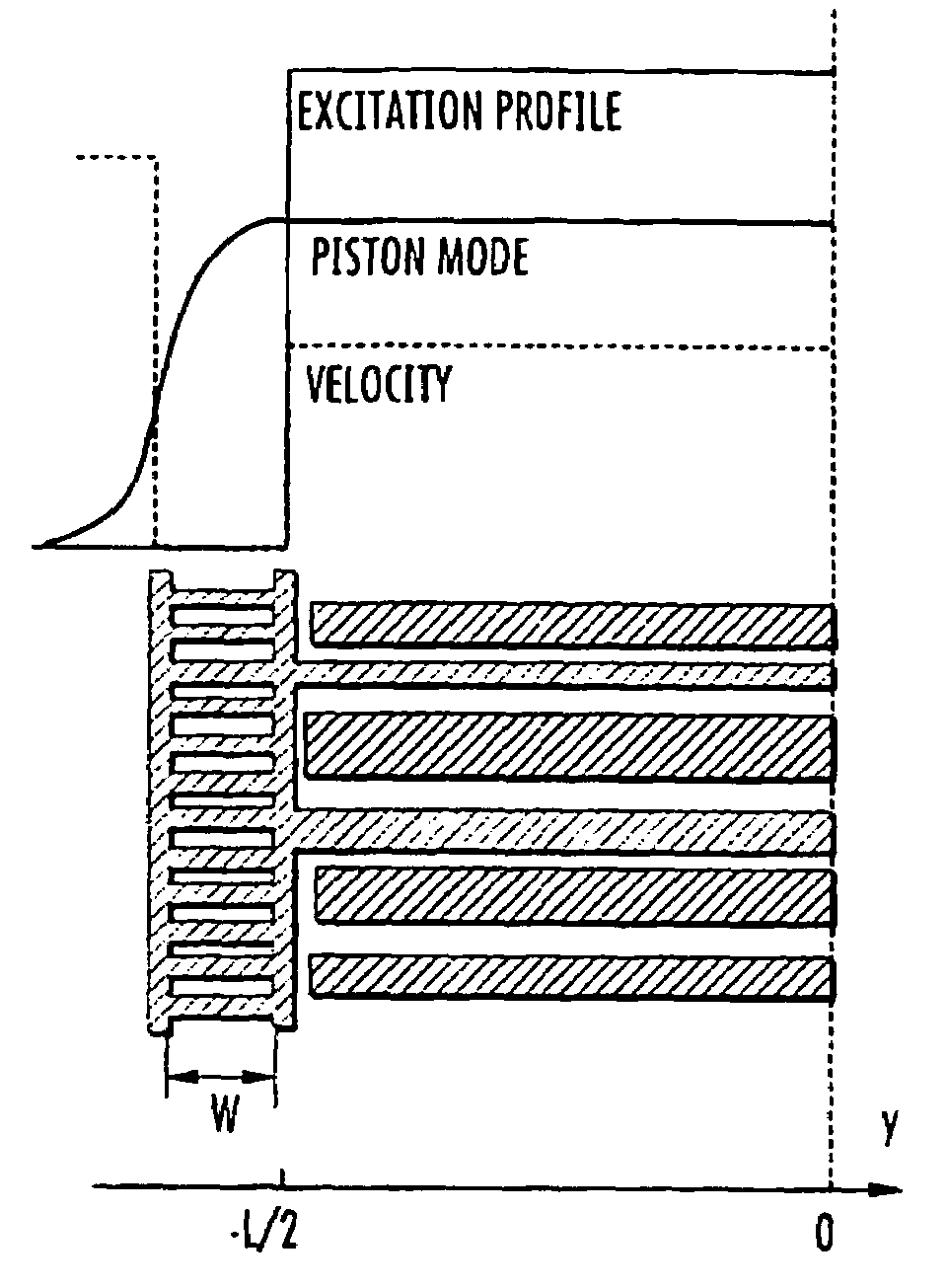
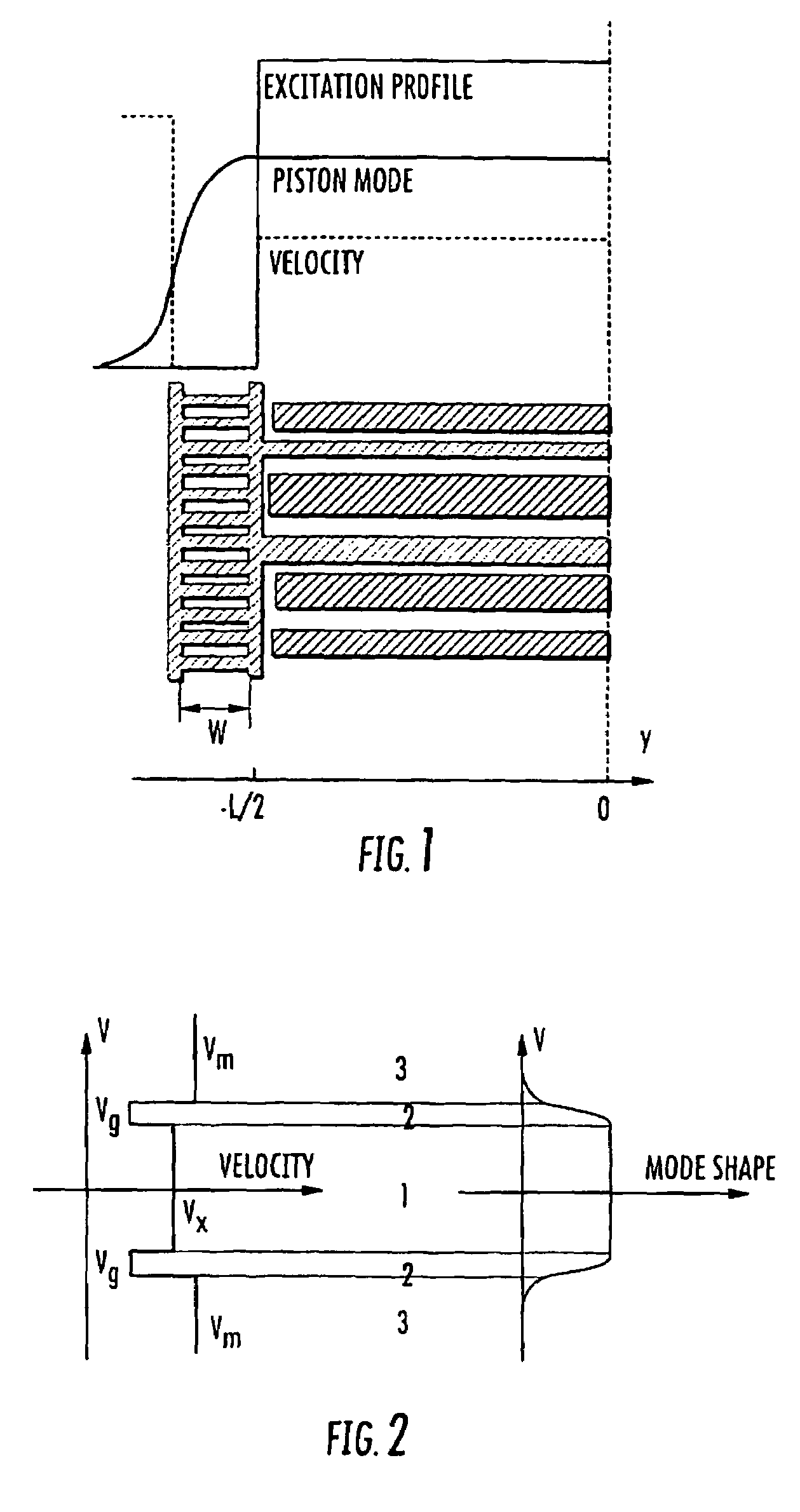
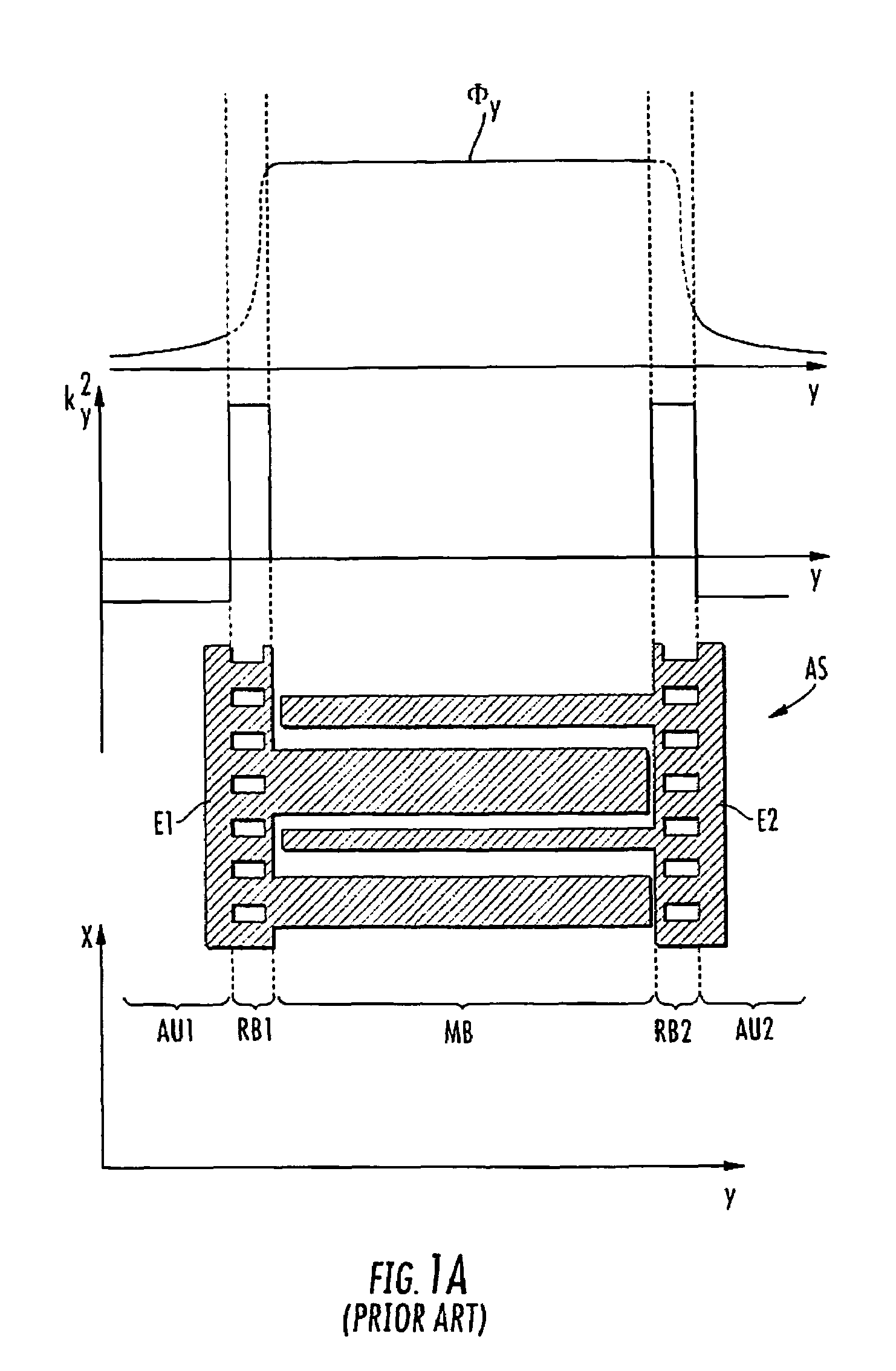
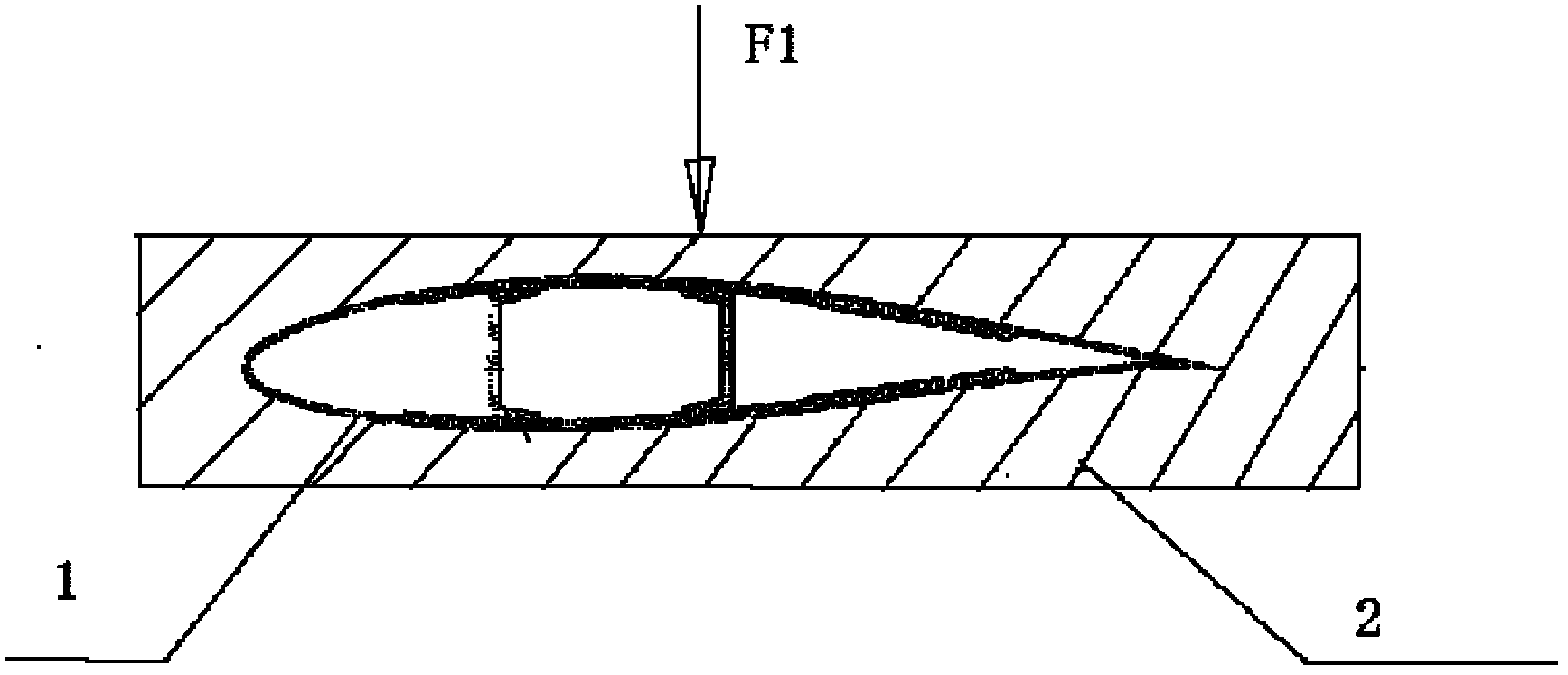
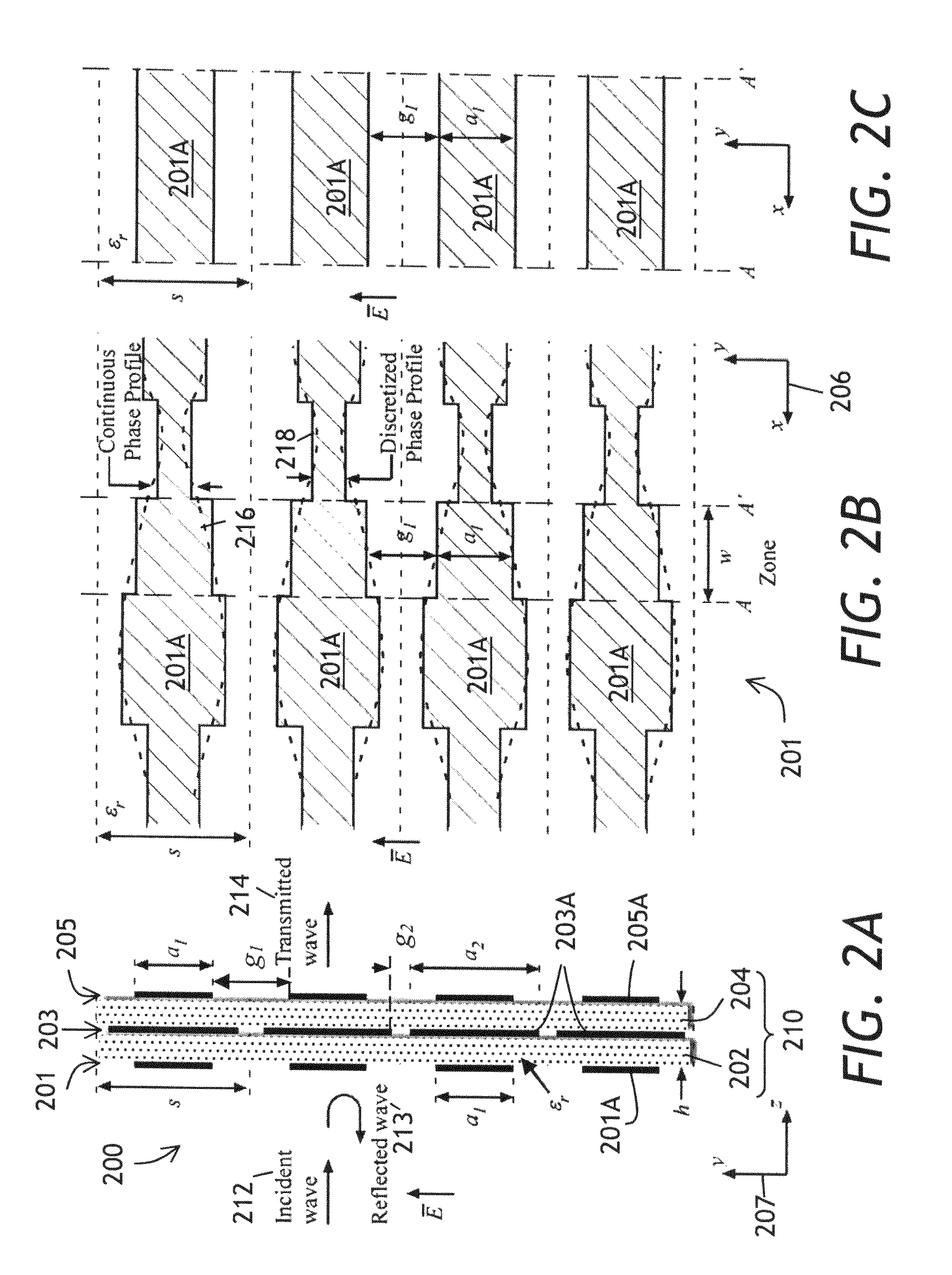
SAW filter operable in a piston mode
ActiveUS7576471B1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksTransducerWave velocity
A SAW transducer includes a pair of opposing bus bars formed on a surface of a piezoelectric substrate with a plurality of interdigital electrodes extending from each of the opposing bus bars. A center region and opposing edge regions are formed, wherein each edge region is proximate each bus bar and includes free end portions of the electrodes such that a wave velocity in each edge region is substantially lower than a wave velocity in the bus bars and in the center region, and wherein electro-acoustic sources extend into the edge regions for providing a SAW transducer having the piezoelectrically excited strongest mode is a piston mode with an amplitude distribution generally flat across most of the resonator area.
Owner:QORVO US INC
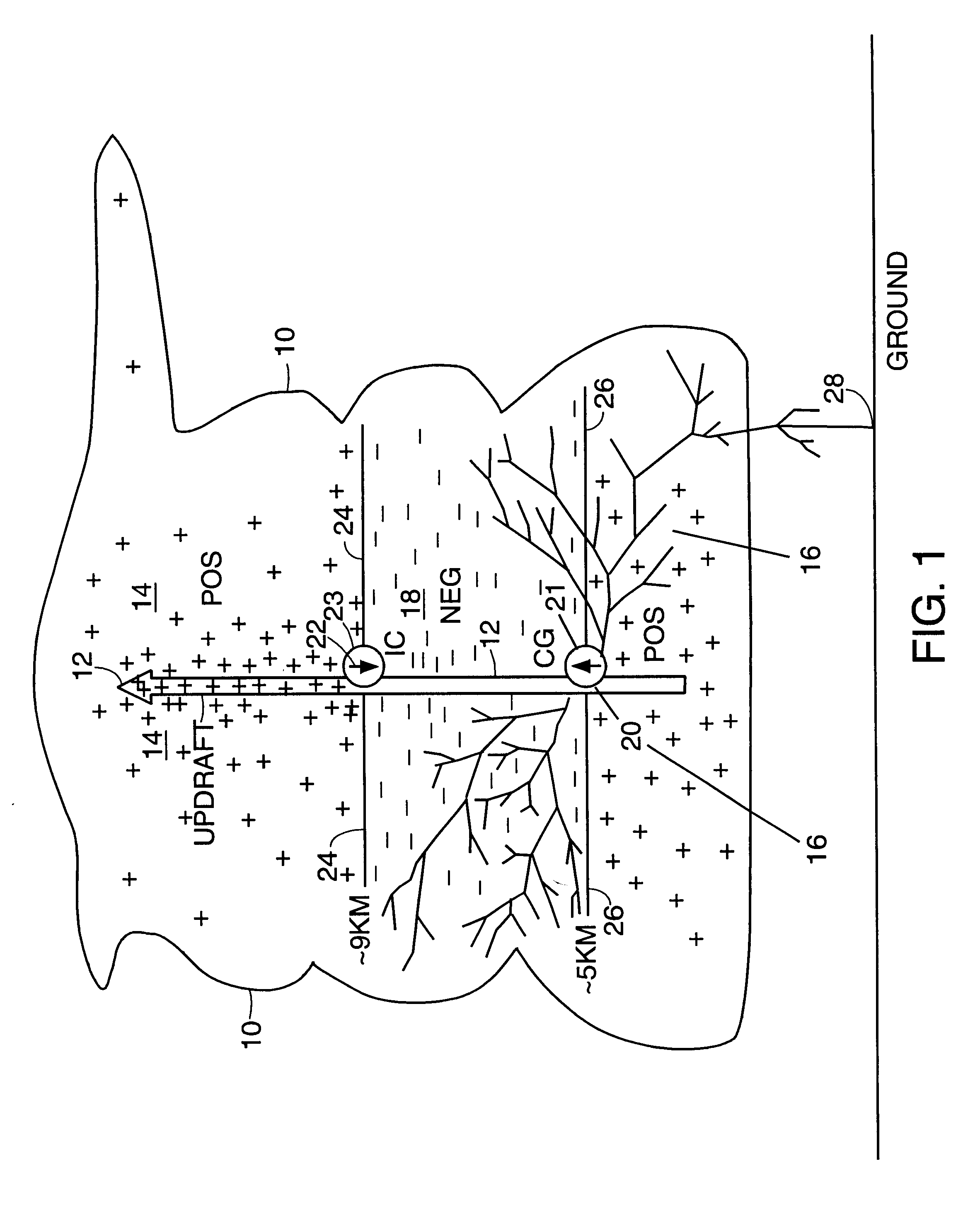
Lightning locating system
InactiveUS6246367B1Accurately determineRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsElectrical testingWeather radarAtmospheric sciences
A lightning detection system for detecting and locating an initial discharge of an initial leader stroke of a lightning flash. An initial lightning discharge produces a pulse that can be used to accurately detect lightning, and more particularly, the location of the initial lightning discharge. In one embodiment, at least three sensors detect and determine the location of the first pulses from initial lightning discharges using time difference of arrival information of the pulses at each of the three sensors. In another embodiment, a single sensor is used to determine the range of an initial lightning discharge from the amplitude of a corresponding initial detected pulse, and to determine the direction from a crossed loop antenna An alternative embodiment of a single sensor system determines a distance of a lightning event from a peak amplitude value derived from a pulse amplitude distribution. In a further embodiment, a lightning detection system provides enhanced lightning location by incorporating weather data from a weather radar with detected lightning information.
Owner:STRATEGIC DESIGN FEDERATION W LLC
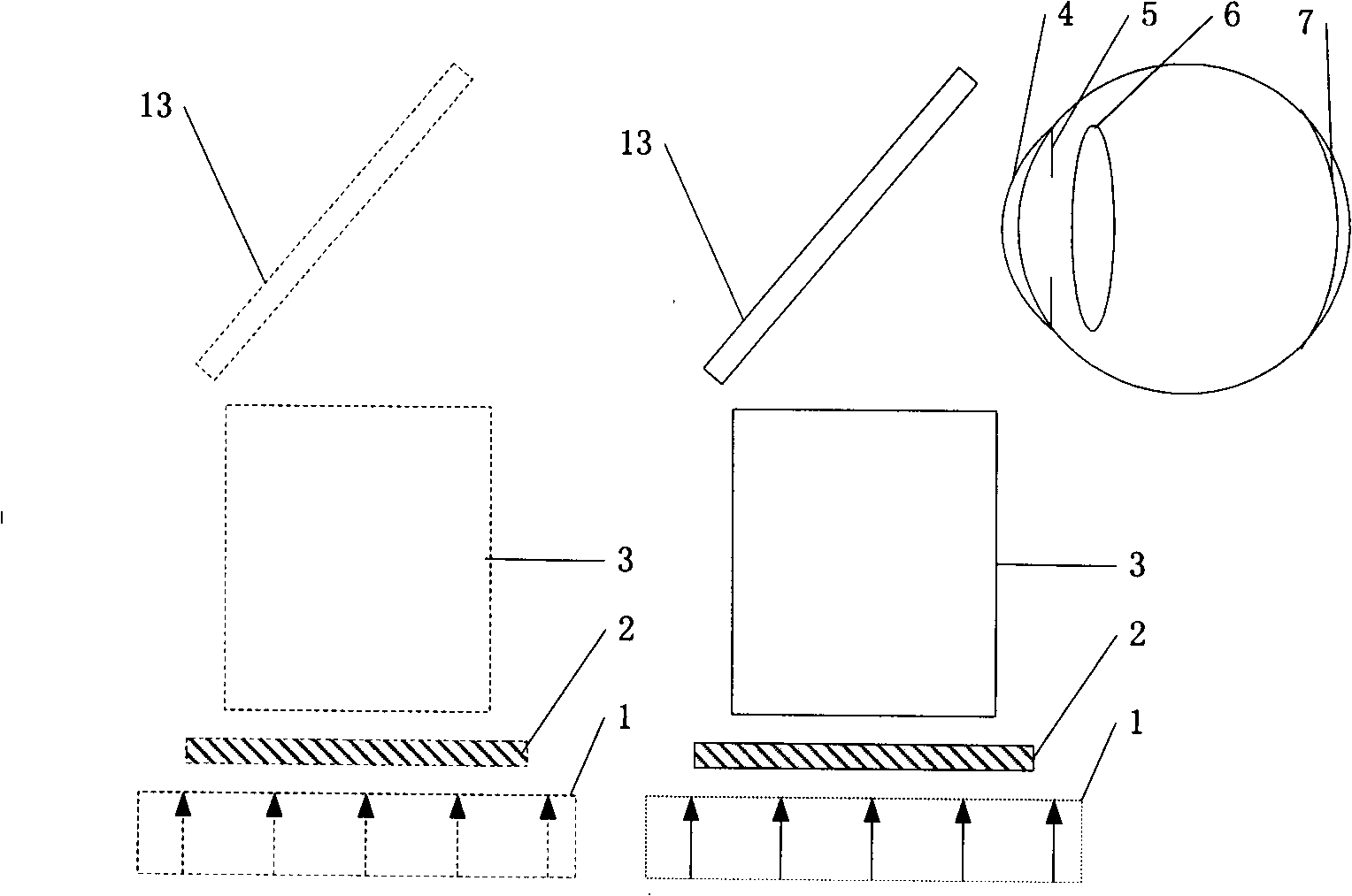
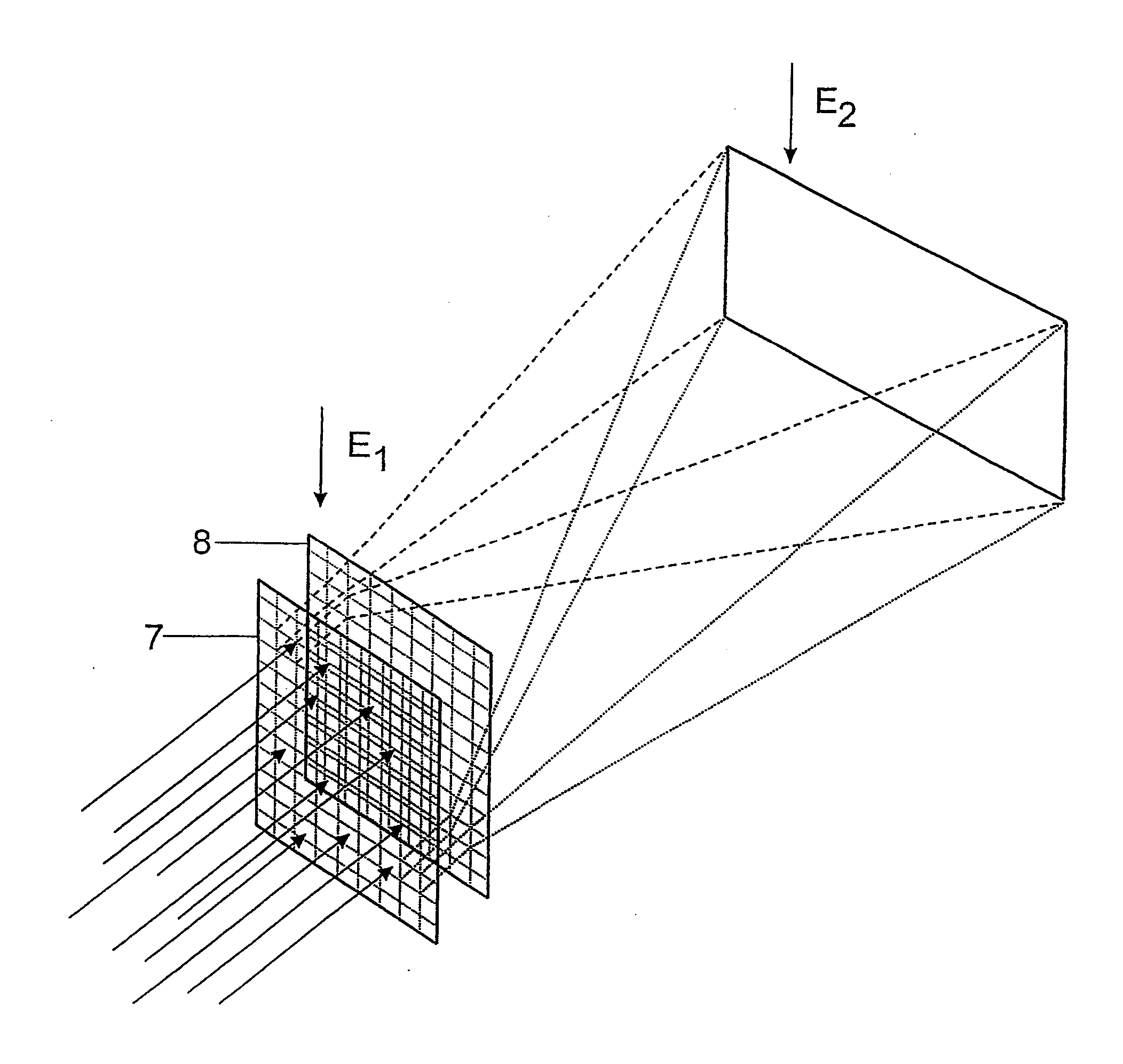
Imaging device of coherent light
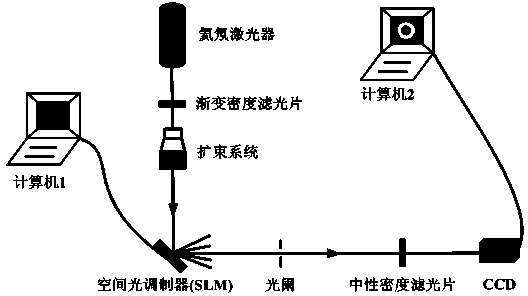
ActiveCN101359098AEnhanced medical diagnosisSimple structureEye diagnosticsOptical elementsSpatial light modulatorPupil
A coherent light imaging device adopts a coherent light source 1 to irradiate an all-phase spatial light modulator 2; the coherent light transmitted by the all-phase spatial light modulator 2 is propagated through an optical system 3; the optical system transmits an optical pupil 8 in front of a cornea 4; the coherent light goes through the cornea 4, an iris 5, a lens 6, and finally reaches a retina 7; the amplitude distribution pf the coherent optical fields on a plurality of imaging planes before and behind the retina 7 is modulated by the all-phase spatial light modulator 2. The coherent light imaging device enables two-dimensional or three-dimensional images to be directly imaged the retina and has a simple structure, which can be applied to virtual reality display, augmented reality display and fundus medical diagnosis.
Owner:东莞市芯萌慧显电子科技有限公司
Vector averaging calibration method for phased-array antenna
InactiveCN102412441AHigh precisionReducing the Effect of Phase Shift Errors in CalibrationAntenna arraysPhase shiftedDesign phase
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Method for optimising the focussing of waves through an aberration-inducing element
ActiveUS20090093724A1Accurate focusAvoid disadvantagesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyPhase shiftedClassical mechanics
The invention concerns a method for optimizing the focusing of waves in a zone of interest of a medium, with the waves being emitted by a network of sources to the medium through an aberration-inducing element that introduces an initially indeterminate phase shift. The method according to the invention proposes to use M−1 successive modifications of the emitted wave, each giving rise to a perturbation. According to the invention, the M perturbations are measured in the zone of interest at each modification of the phase and / or amplitude distributions, and these measurements are used to deduce optimal focusing characteristics to maximize the perturbation induced in the zone of interest.
Owner:SUPER SONIC IMAGINE +1
Method for determining the image quality of an optical imaging system
InactiveUS20060072104A1Avoid loweringImprove image qualityPhotometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansSpatially resolvedImaging processing
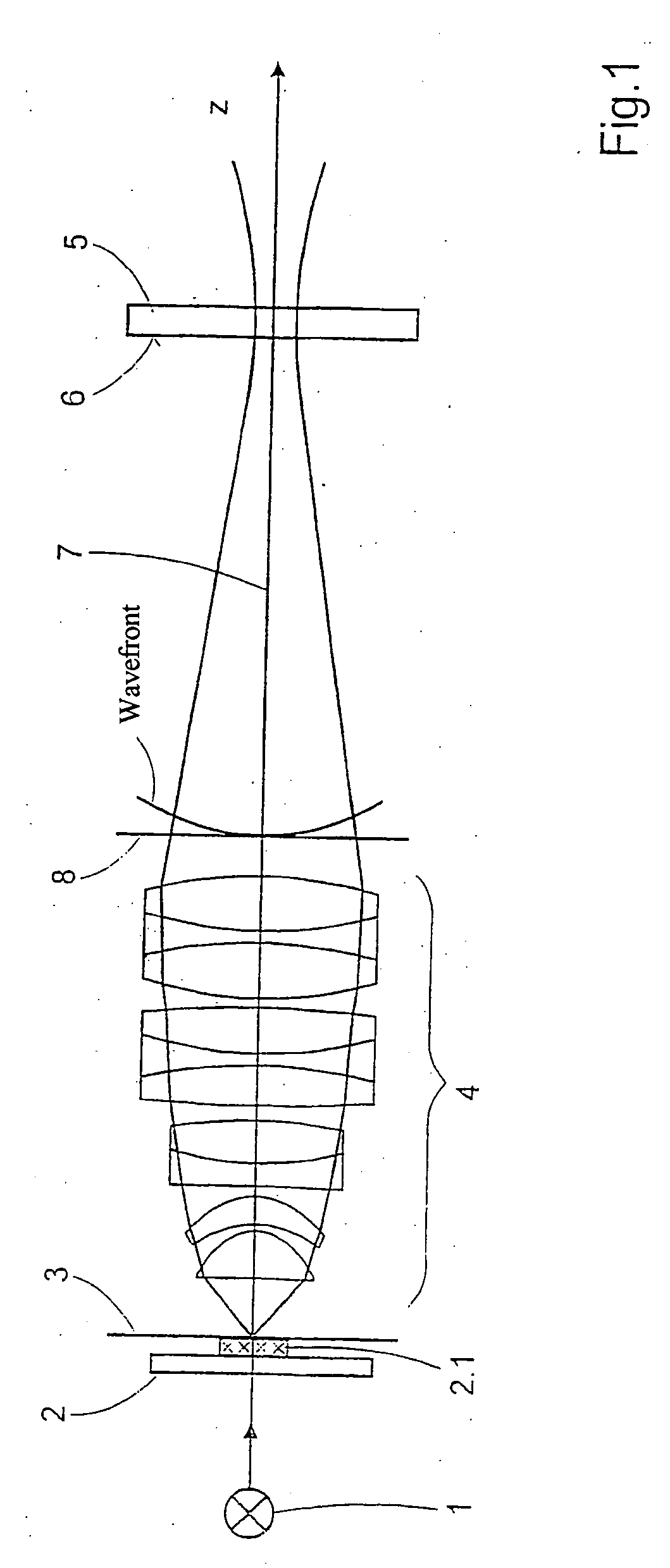
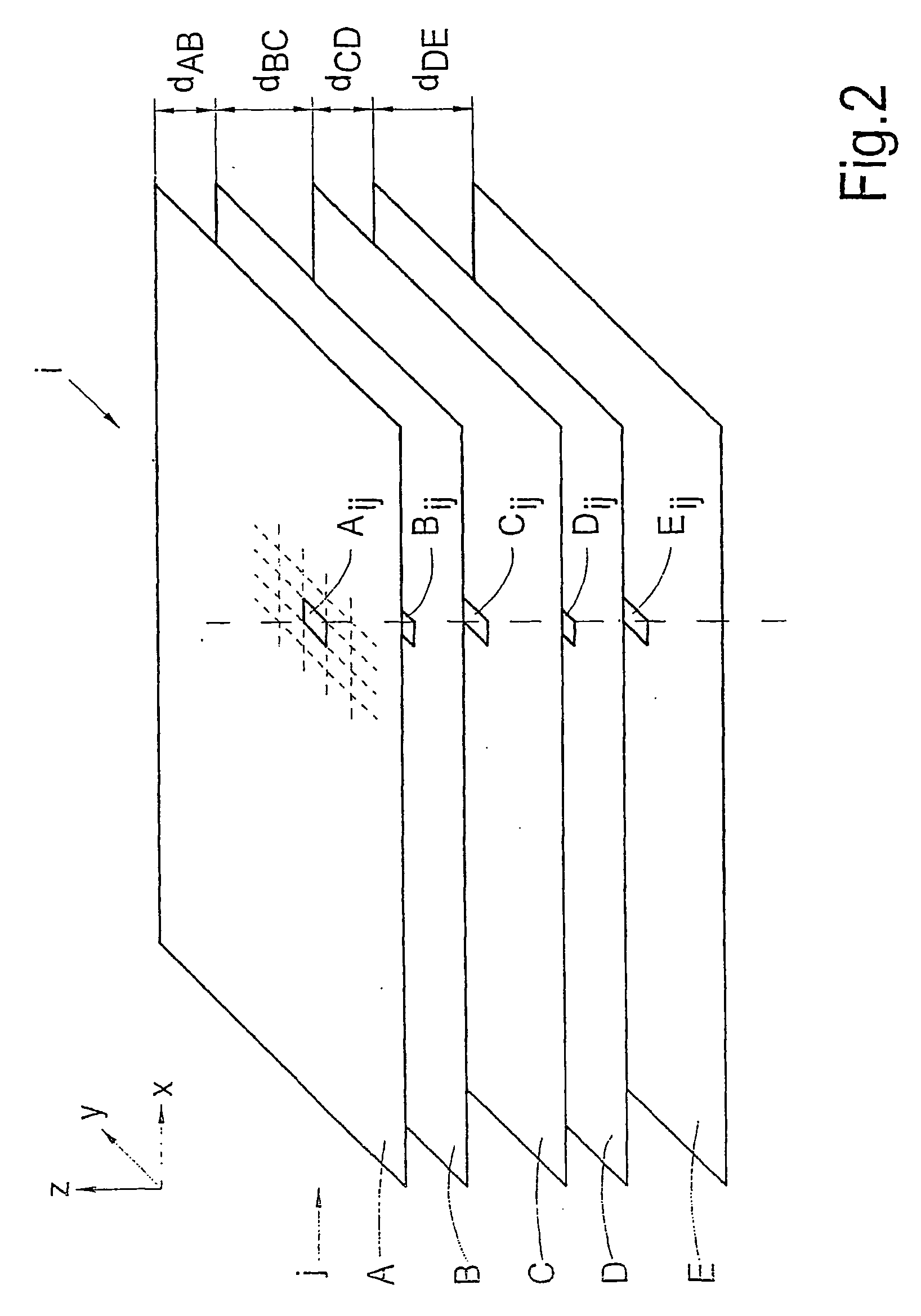
The invention is directed to a method for determining the image quality of an optical imaging system and to the use of the method according to the invention for determining the influence of samples on the amplitude distribution and phase front distribution of the illumination light, of which the amplitude distribution is known in particular. The invention comprises the following steps: adjusting the subassemblies relative to one another in such a way that it is possible to project images of a sample on the detection device; recording a plurality of images of the sample from different reference planes near the focus plane; improving the image quality by image processing, particularly to reduce noise, to compensate for local variations in sensitivity of the detection device, and to center the intensity centroids respectively on a predetermined location in the images; computational linking of the spatially resolved image information, of adjustment values and system variables relating to the optical imaging system, and of information concerning the sample with the aim of determining characteristic numbers that are characteristic of the wavefront deformation caused by the imaging system; and outputting the characteristic numbers and associating them with the imaging system for describing the image quality.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
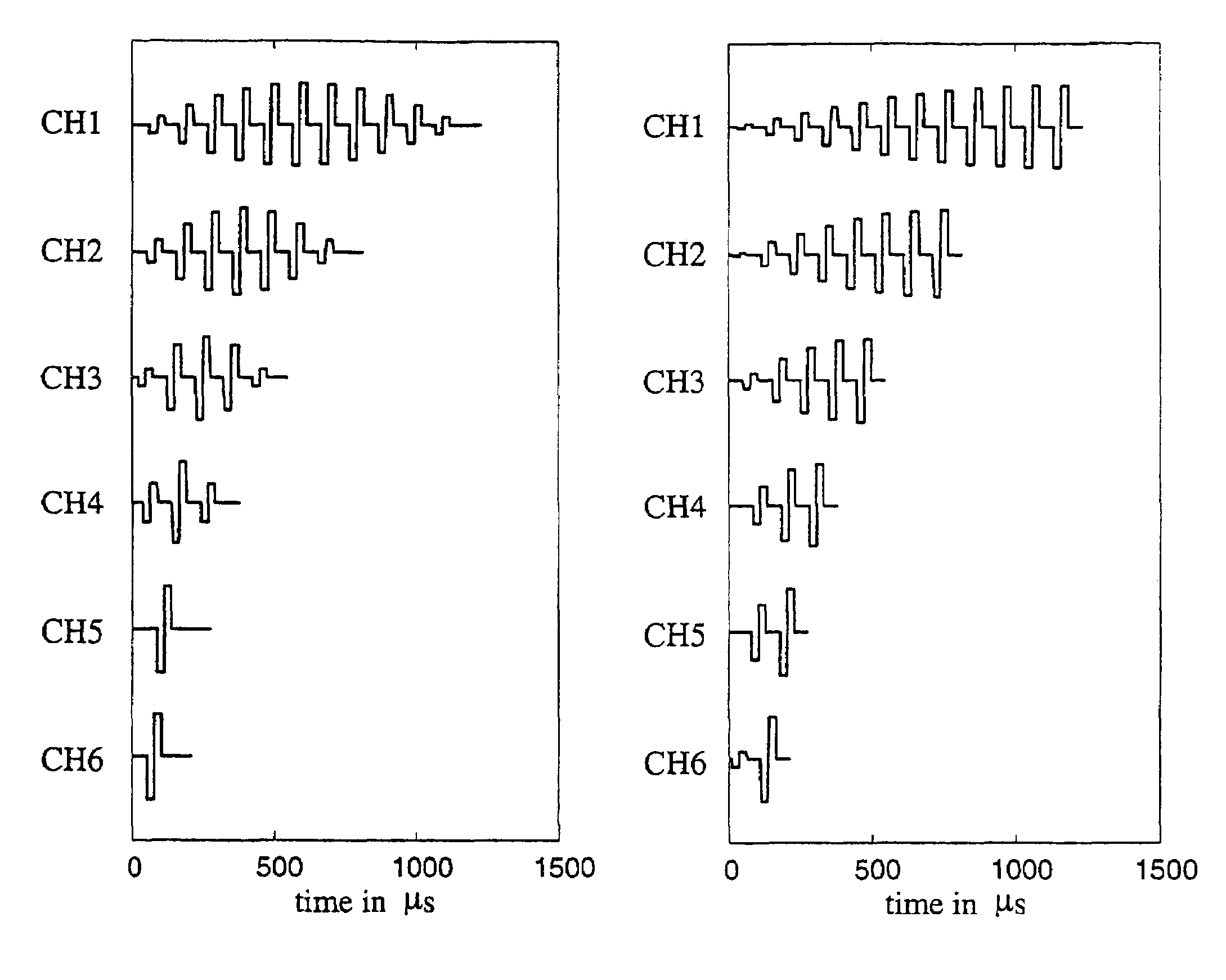
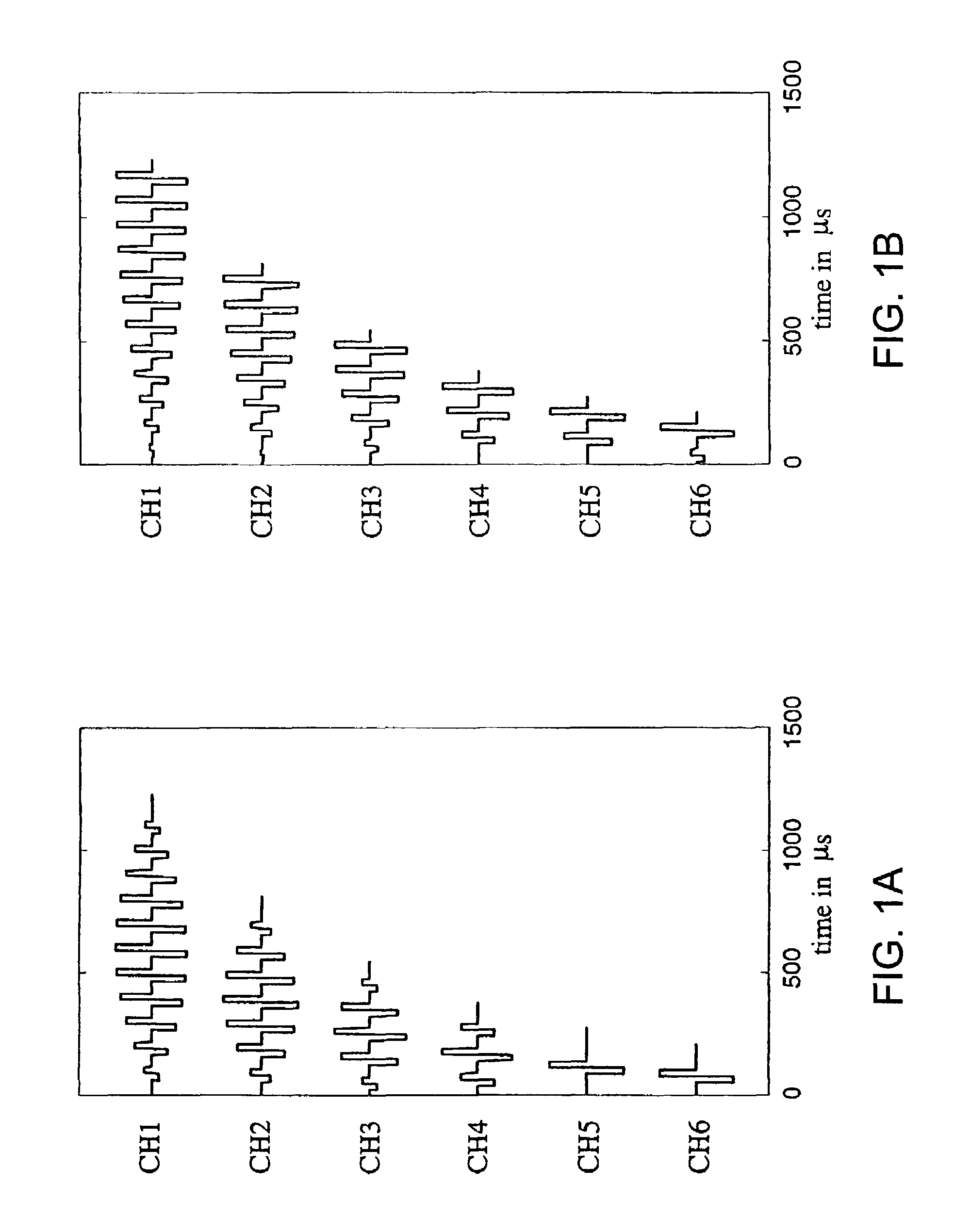
Electrical Nerve Stimulation Based on Channel Specific Sequences
A method of activating at least two electrodes in a multichannel electrode array using channel specific sampling sequences is presented. A channel specific sampling sequence is defined for each electrode, the sequence having a particular duration, pulse amplitude distribution, and number of pulses. A weighting factor is applied to the channel specific sampling sequence. Each electrode in the multichannel electrode array is then simultaneously activated using sign-correlated pulses, the sign-correlated pulses based on parameters of spatial channel interaction reflecting geometric overlapping of electrical fields from each electrode, non-linear compression, and each electrode's weighted channel specific sampling sequence.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
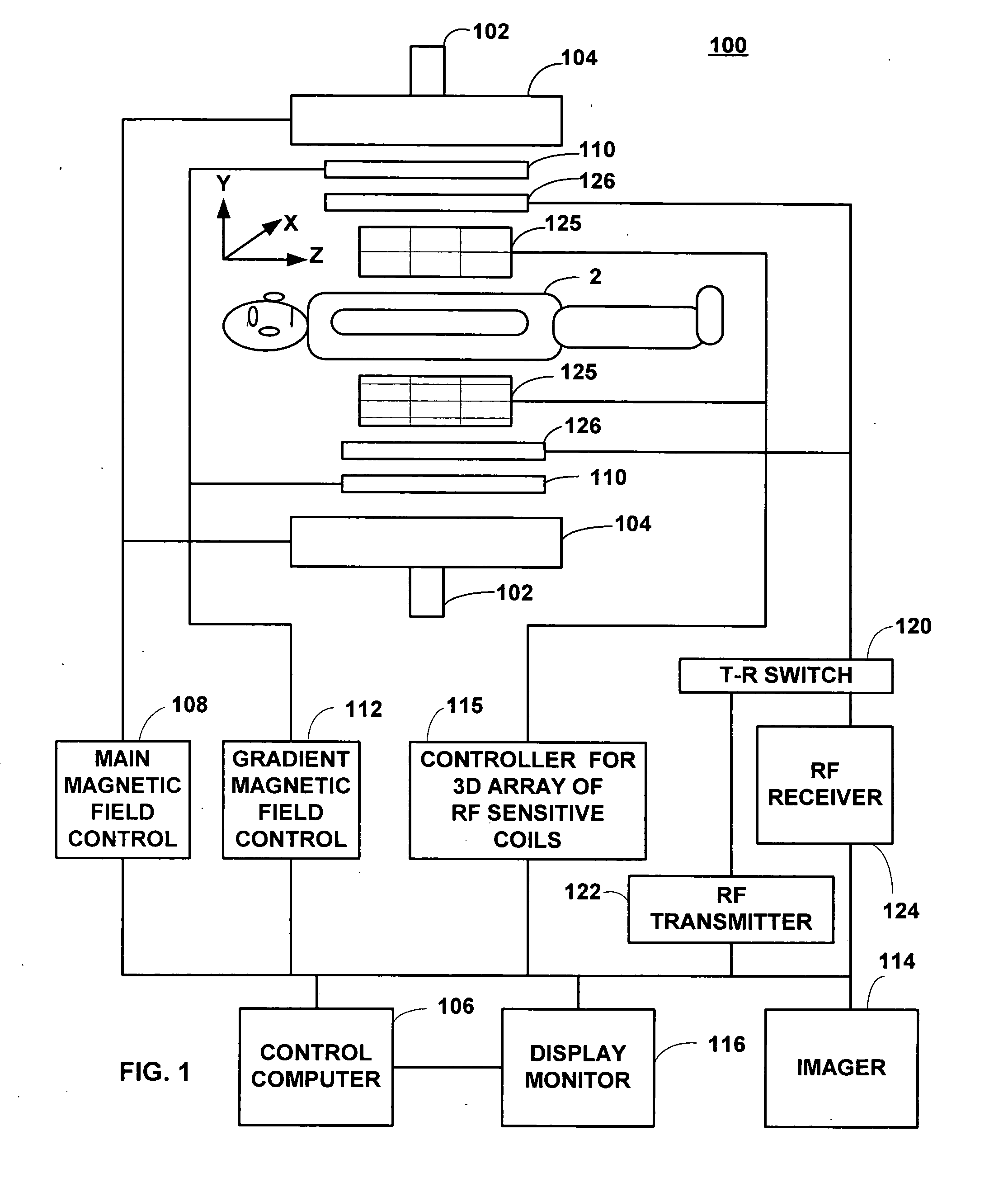
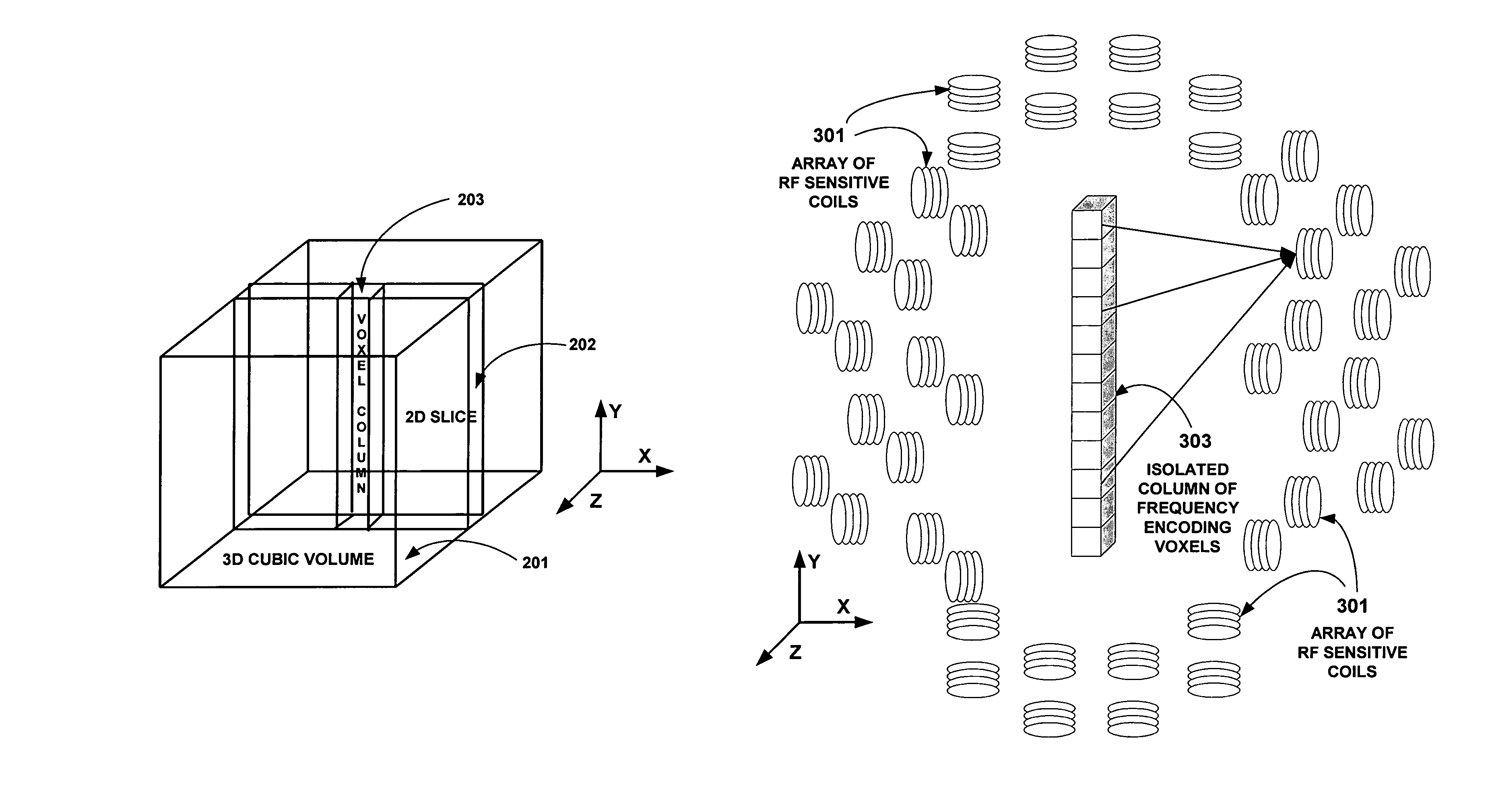
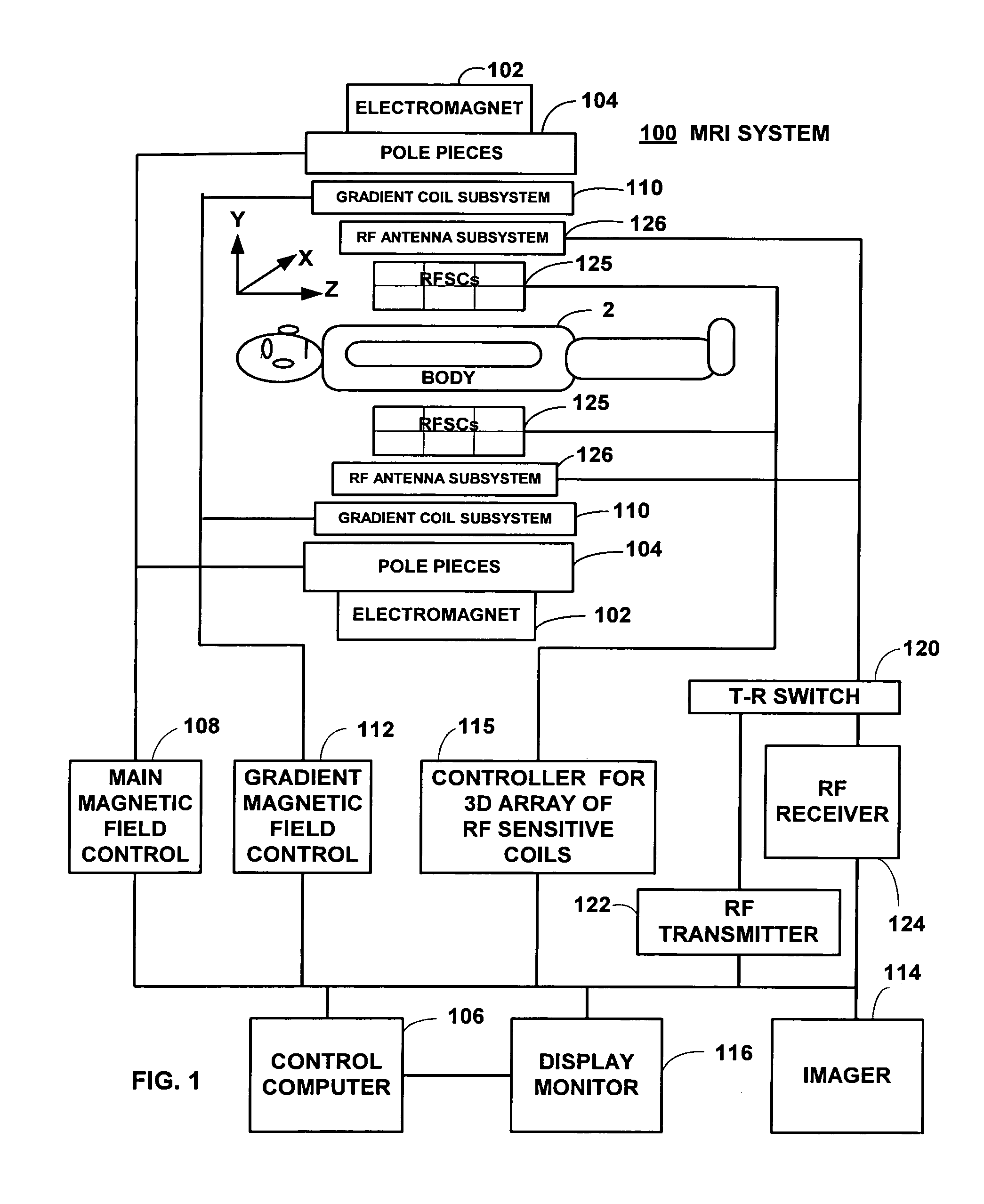
Field image tomography for magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20110115485A1Shorten the length of timeReduce usageMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionObject basedSystem matrix
Field Image Tomography (FIT) is a fundamental new theory for determining the three-dimensional (3D) spatial density distribution of field emitting sources. The field can be the intensity of any type of field including (i) Radio Frequency (RF) waves in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), (ii) Gamma radiation in SPECT / PET, and (iii) gravitational field of earth, moon, etc. FIT exploits the property that field intensity decreases with increasing radial distance from the field source and the field intensity distribution measured in an extended 3D volume space can be used to determine the 3D spatial density distribution of the emitting source elements. A method and apparatus are disclosed for MRI of target objects based on FIT. Spinning atomic nuclei of a target object in a magnetic field are excited by beaming a suitable Radio Frequency (RF) pulse. These excited nuclei emit RF radiation while returning to their normal state. The intensity or amplitude distribution of the RF emission field g is measured in a 3D volume space that may extend substantially along the radial direction around the emission source. g is related to the 3D tomography f through a system matrix H that depends on the MRI apparatus, and noise n through the vector equation g=Hf+n. This equation is solved to obtain the tomographic image f of the target object by a method that reduces the effect of noise.
Owner:SUBBARAO MURALIDHARA
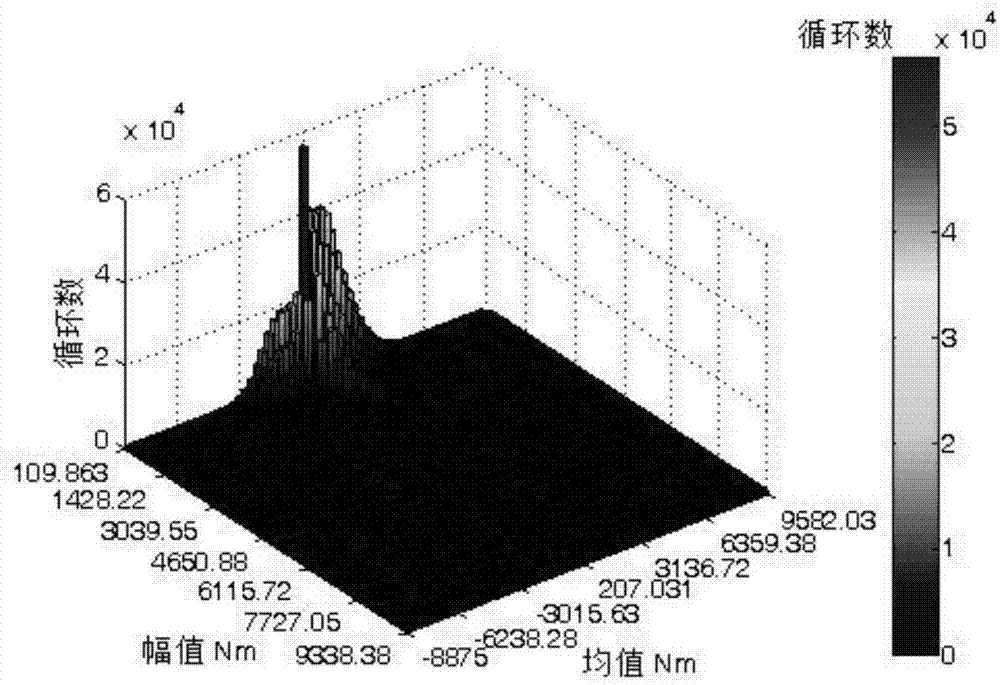
Kernel density estimation-based load spectrum compilation method for transmission shaft of tracked vehicle
ActiveCN106886638ARaise the confidence levelRealize reasonable extrapolationGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsSpectral density estimationDrive shaft
The invention relates to a kernel density estimation-based load spectrum compilation method for a transmission shaft of a tracked vehicle. The method comprises the following steps of S1, collecting and preprocessing torque load sample data of the tracked vehicle; and S2, generating a two-dimensional load spectrum through first two-time rain flow counting, mean amplitude extremum inference, second rain flow counting, two-dimensional kernel density estimation, multi-condition synthesis and extrapolation in sequence. According to the method, the two-time rain flow counting is adopted; a first rain flow counting result is used for the mean amplitude extremum inference; a second rain flow counting result is used for the kernel density estimation; mean amplitude distribution can be well fitted; and an actually measured rain flow matrix can be reasonably extrapolated. The load spectrum compiled by adopting the method and the actually measured rain flow matrix have highly similar probability density distribution, reasonable extrapolation of the actually measured rain flow matrix is realized, and an expected effect is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
Evaluation method for fatigue damage and service life of horizontal axis wind turbine blade
ActiveCN102607831AGet actual lifespanShort cycleMachine part testingStrength propertiesFatigue damageImpeller
The invention discloses a test method for the fatigue damage and the service life of a horizontal axis wind turbine blade, aiming to obtain a more exact blade fatigue performance parameter by adopting a test detection and computational analysis means having low cost and high efficiency so as to meet the requirements of blade design, research and development and detection. The method is characterized in that on the basis of the characteristic that the impeller speed of a horizontal axis wind turbine is lower, and the period change frequency of various fatigue loads is also lower, a series of steps of carrying out static loading testing on the wind turbine blade to obtain a stress / strain amplitude distribution condition under the effect of various fatigue loads and analyzing by combining a material property curve and a cumulative damage theory are adopted to realize the evaluation to the blade fatigue performance. Compared with the traditional horizontal axis wind turbine blade fatigue testing technology, the method has the advantages of short period, low cost, capability of obtaining a final service life parameter of the blade, and the like.
Owner:INST OF ENGINEERING THERMOPHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
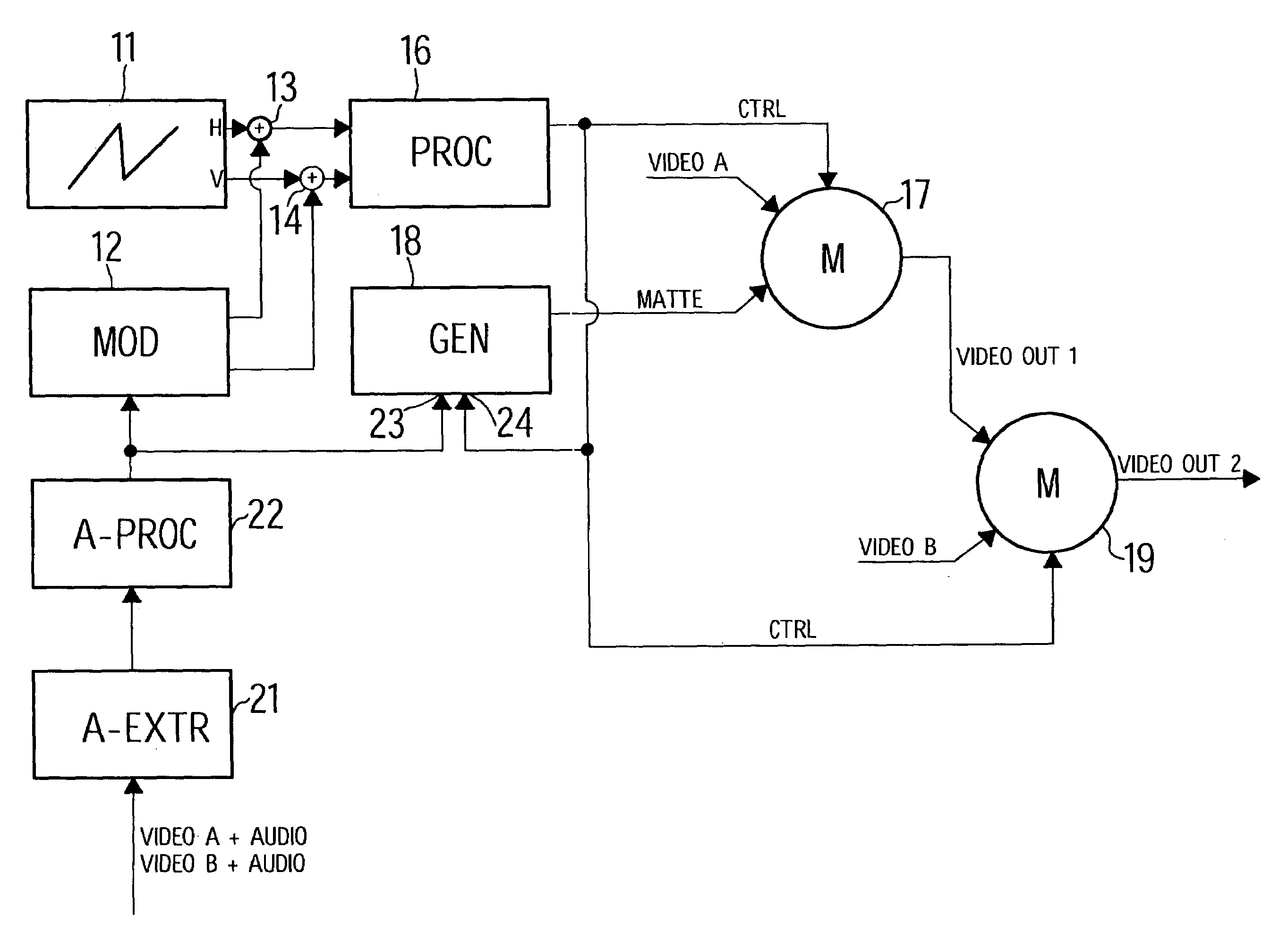
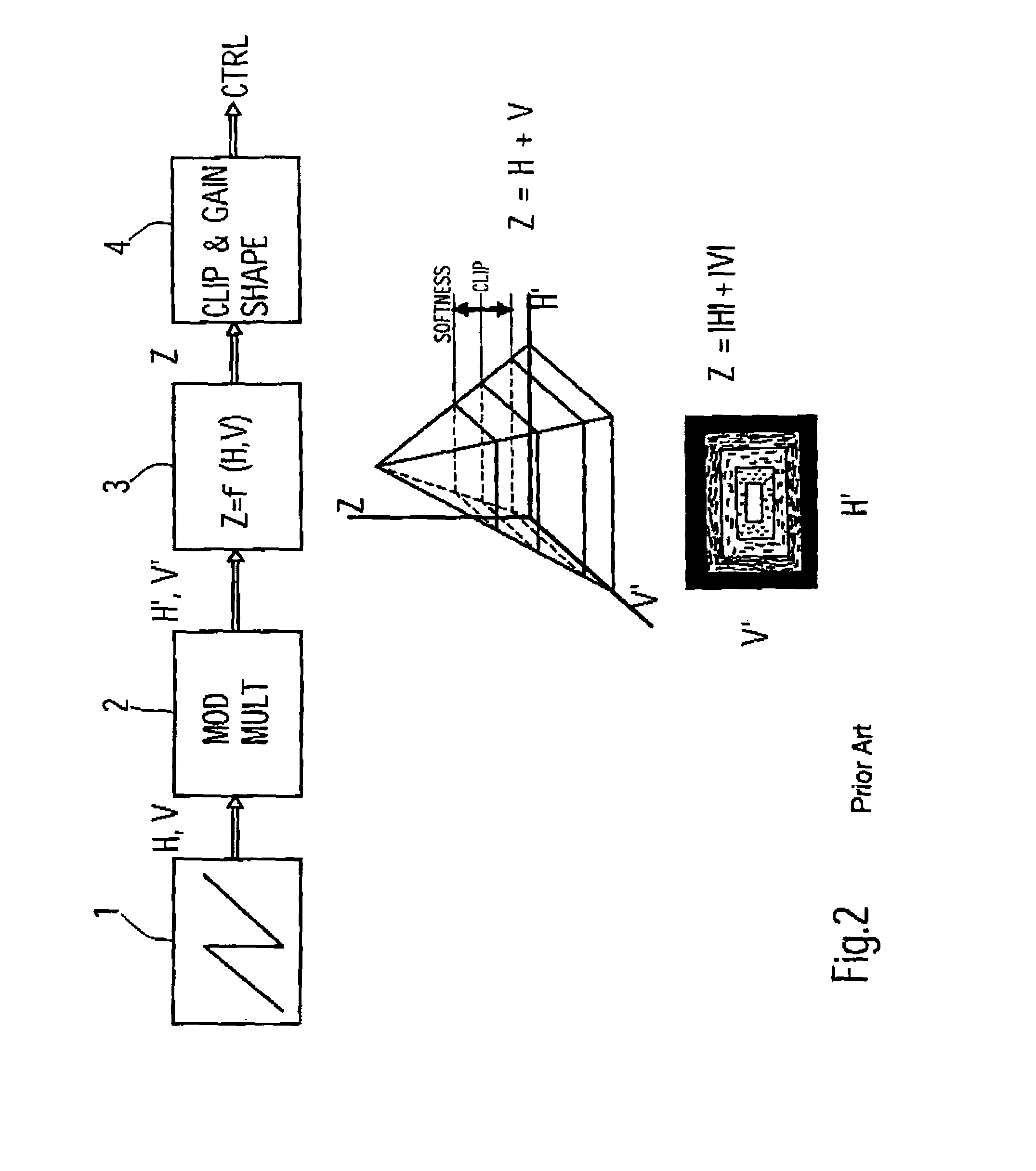
Method and device for generating a video effect
InactiveUS7400361B2Promote productionImprove configuration effectTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsControl signalHorizontal and vertical
A method for generating a video effect using a video signal processing device. The method comprises generating horizontal and vertical gating base signals. The horizontal gating base signal is combined with a first modulation signal and the vertical gating base signal is combined with a second modulation signal. An amplitude distribution is generated from the modulated horizontal and vertical gating base signals. A control signal is generated from the amplitude distribution for controlling a mixing stage. A third modulation signal is derived from a sound signal for modulating the control signal.
Owner:GVBB HLDG R L
Electrical nerve stimulation based on channel specific sampling sequences
A method of activating at least two electrodes in a multichannel electrode array uses channel specific sampling sequences. More particularly, a channel specific sampling sequence is defined for each electrode, the sequence having a particular duration, pulse amplitude distribution, and number of pulses. A weighting factor is applied to the channel specific sampling sequence. Each electrode in the multichannel electrode array is then simultaneously activated using sign-correlated pulses. The sign-correlated pulses are based on parameters of spatial channel interaction reflecting geometric overlapping of electrical fields from each electrode, wherein calculating the amplitudes of the sign-correlated pulses includes compensating for geometric overlapping of electrical fields from each electrode. Furthermore, the sign-correlated pulses are based on each electrode's weighted channel specific sampling sequence.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
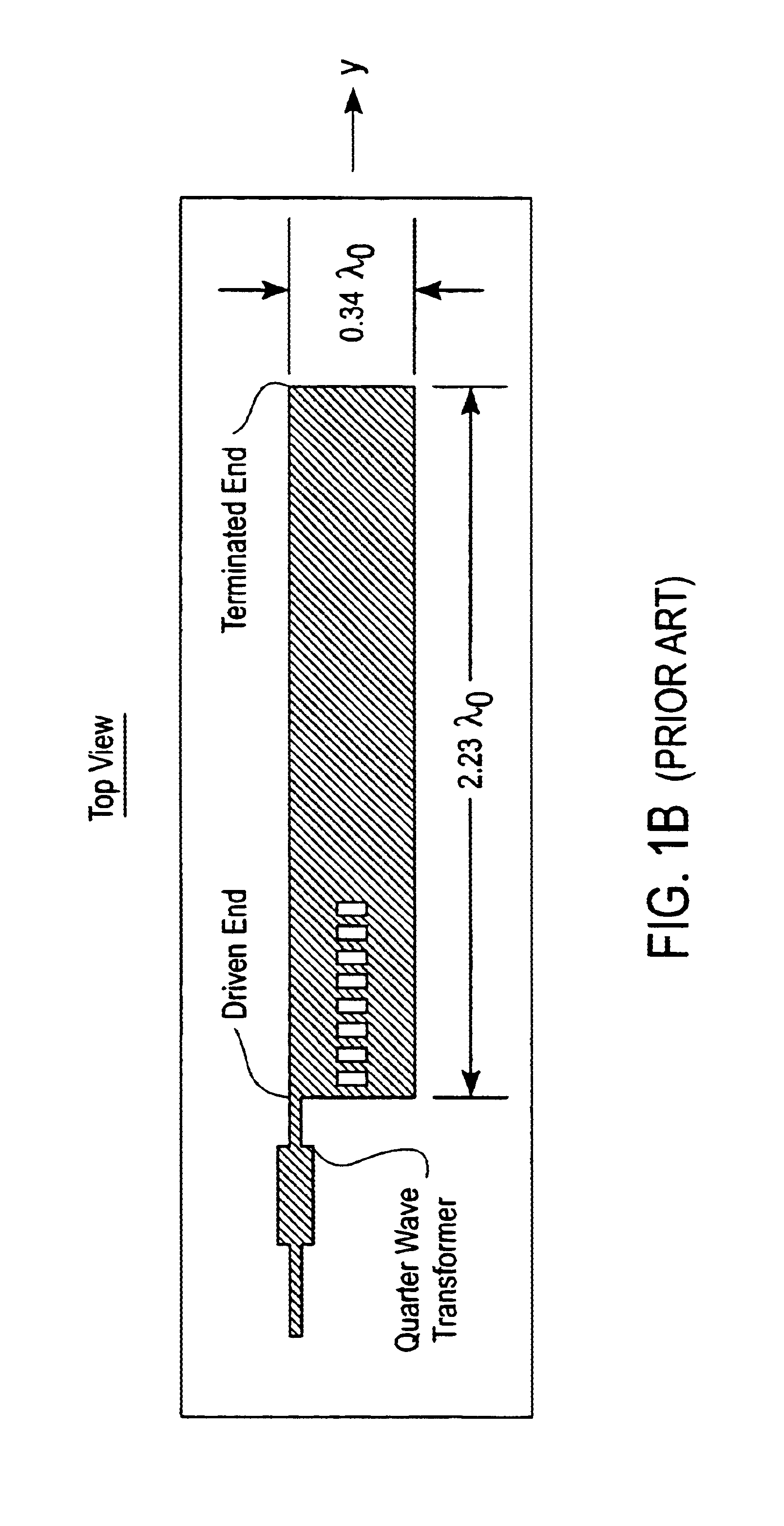
Leaky wave microstrip antenna with a prescribable pattern
InactiveUS6839030B2Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDielectricElectricity
A system and method for prescribing an amplitude distribution to a leaky-wave microstrip antenna having an array of radiating cells. The leaky-wave microstrip antenna includes a grounded element, a dielectric member coupled to the grounded element and a top conducting strip coupled to the dielectric member, the conducting strip including a first and second non-radiating conducting strip and a plurality of radiating cells. This distribution requires that the microstrip antenna possess a variable leakage-constant profile along its length, and is chosen so as to yield an H-plane power-gain pattern having low sidelobes. The leakage-constant profile is achieved by configuring the width and inter-cell spacing of the antenna radiating cells and keeping the phase constant fixed. The length or loading of the radiating cells may also be manipulated to achieve the desired leakage constant profile. This results in the desired distribution along the antenna's aperture and yields a power-gain pattern with low sidelobes. The antenna is excited by two equal-amplitude and 180° out-of-phase signals. These signals are applied to the feed end of the microstrip at two feeding ports. The microstrip antenna length is chosen such that more than 97% of the input power is radiated by the traveling electromagnetic, wave, while the remaining power is absorbed by the resistively terminated antenna end.
Owner:ANRITSU CORP
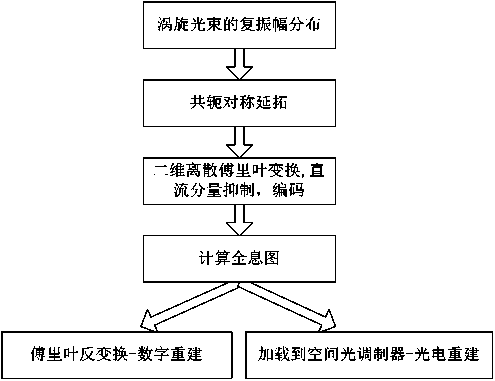
Method for generating vortex light beam by use of calculation hologram
InactiveCN103984103AGenerate flexibleThe production is controllableComplex mathematical operationsOptical elementsSource planeComplex amplitude
The invention discloses a method for generating a vortex light beam by use of a calculation hologram. The steps comprise: (1), utilizing a monocyclic Laguerre-Gaussian (LG) vortex light beam in a source plane (z=0m) coordinate system; (2), performing conjugate symmetrical extension on the complex amplitude of the vortex light beam, and obtaining symmetrical vortex light beam complex amplitude distribution; (3), performing Fourier transformation on the conjugate symmetrical vortex light beam complex amplitude distribution to obtain two-dimensional discrete real function distribution, performing DC component inhibition on real functions, and coding to form the vortex light beam calculation hologram; (4), performing Fourier inverse transformation on the calculation hologram, obtaining the light intensity distribution and the phase distribution of the vortex light beam, and taking the left half portions of the light intensity distribution and the phase distribution as the vortex light beam for digital reconstruction; and (5), loading the vortex light beam calculation hologram on a spatial light modulator, modulating incident laser and reconstructing the vortex light beam in a photoelectric mode. The method employs a conjugate symmetrical extension Fourier calculation holographic algorithm, the algorithm is rapid and simple, the calculation efficiency is high, and sidelobe-free high-quality vortex light beams can be generated.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
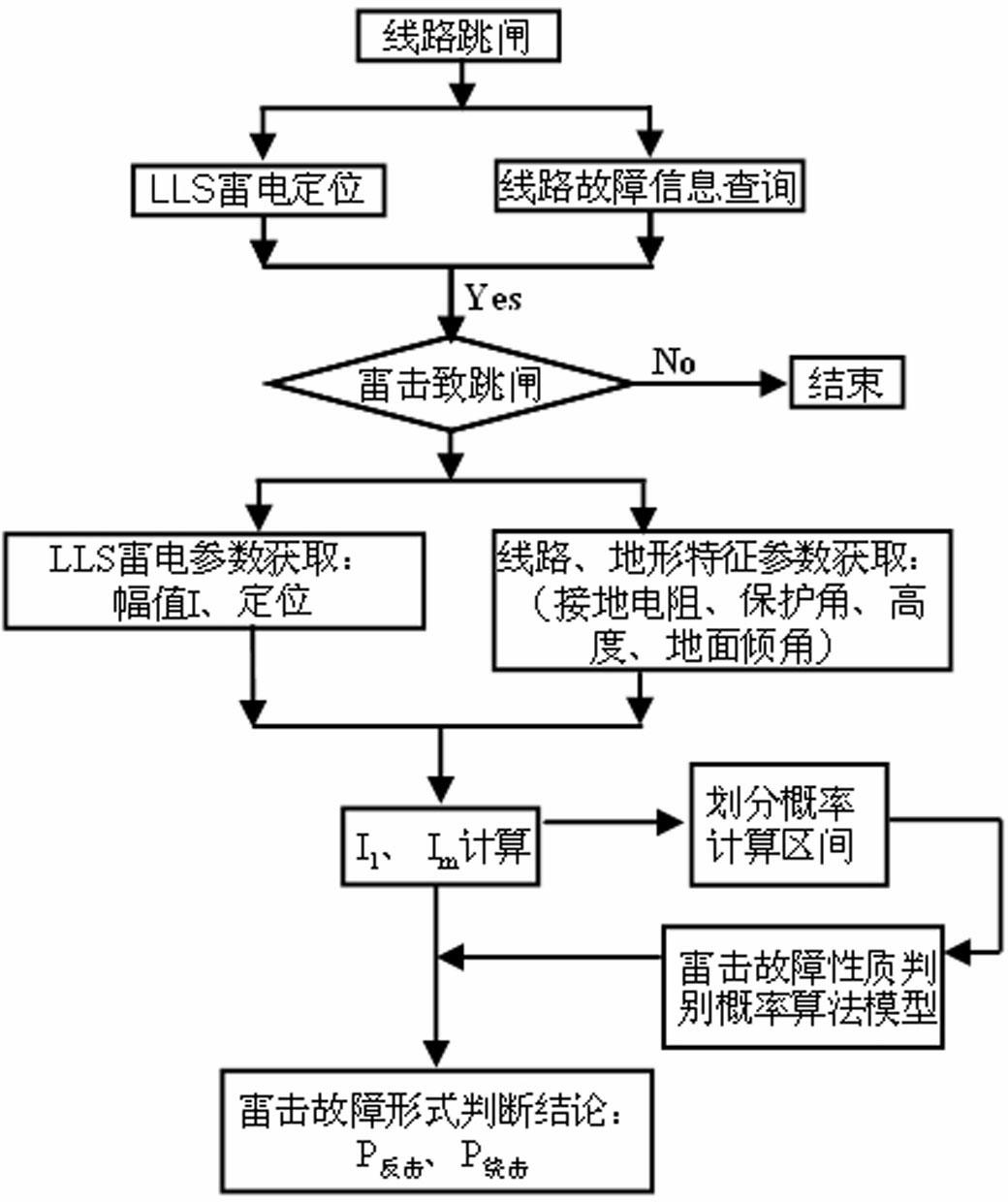
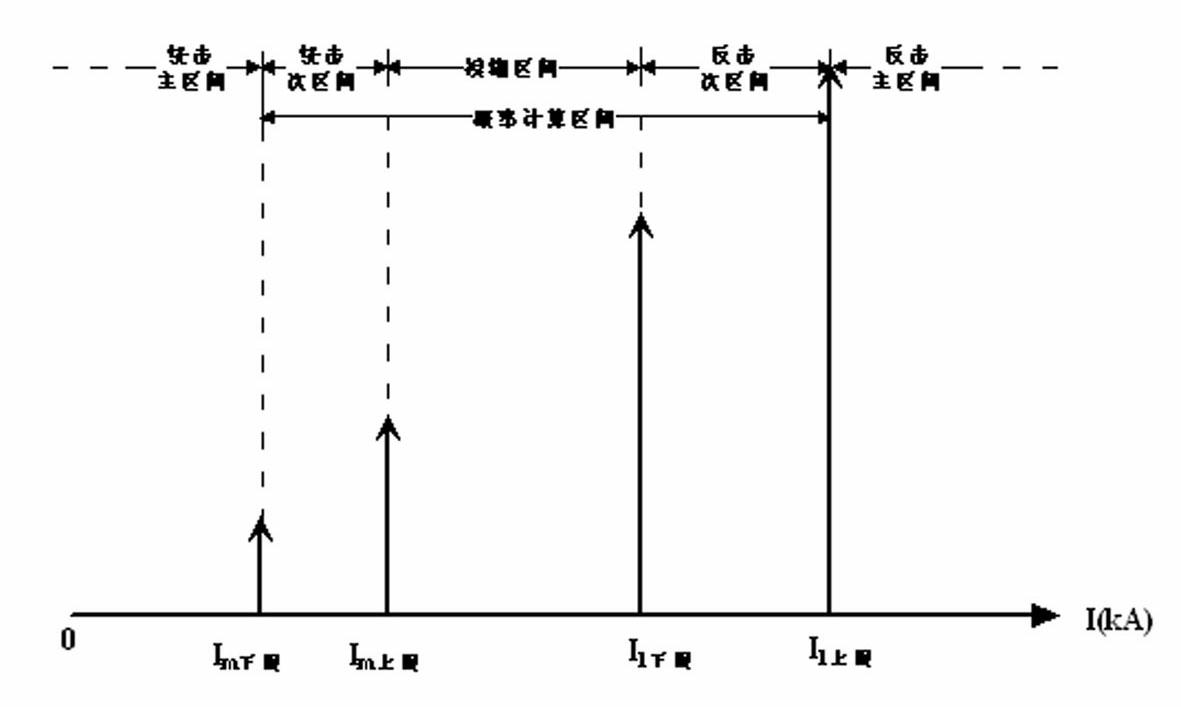
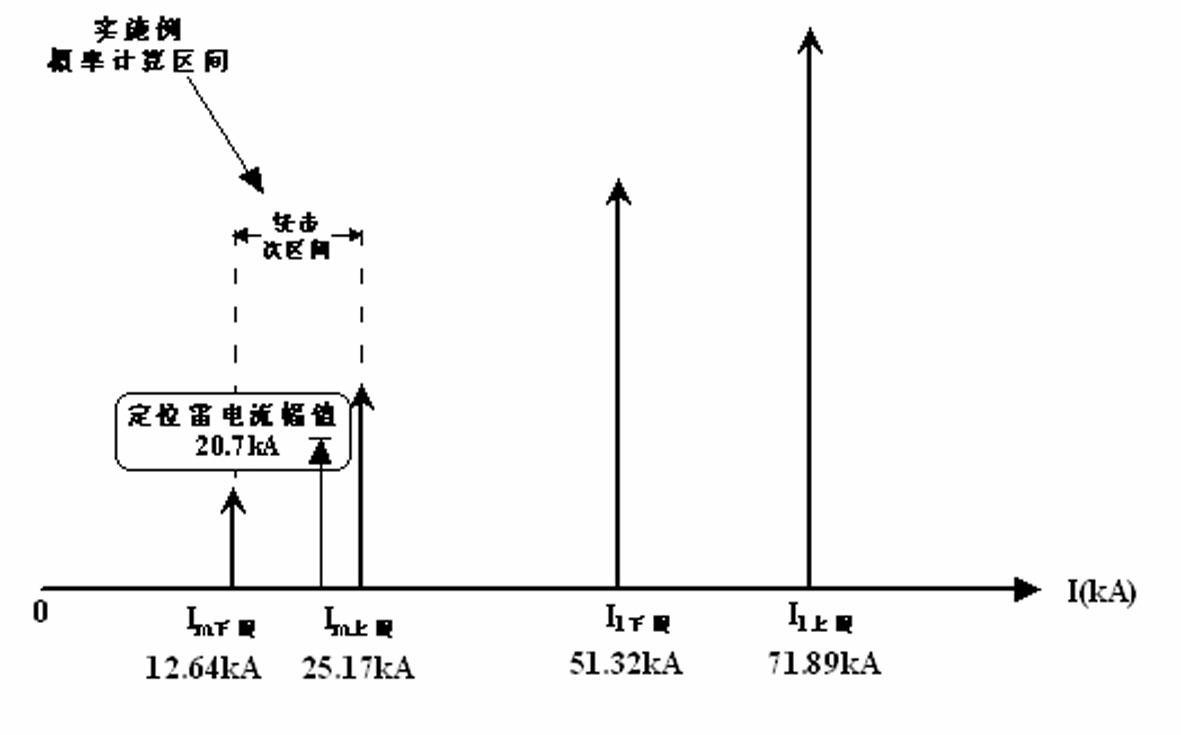
Method for identifying properties of lightning faults of overhead line on basis of amplitude interval distribution of lightning current
ActiveCN102565628AEasy accessLess fault informationFault locationGrounding resistanceCurrent amplitude
The invention relates to a method for identifying properties of lightning faults of an overhead line on the basis of the interval distribution of lightning current amplitude and belongs to the technical field of a high voltage. After the overhead line has a lightning tripping fault, fault information such as a grounding resistance of a fault tower, characteristic parameters of a tower rod, positioning information of a lightning monitoring system, topographic parameters and the like are collected; according to a circuit lightning protection performance algorithm and a shielding failure electrical geometric model principle, the counterattack lightning withstand level of the circuit suffering from lightning stroke and the amplitude distribution interval of the shielding failure critical lightning current are calculated by integrating a statistics rule of structural parameters of the tower and the line; and finally, the occurrence probabilities corresponding different lightning fault types of the line are obtained by utilizing a line lightning fault property judgment probabilistic algorithm model. According to the invention, the objective and reliable lightning fault type occurrence probabilities are obtained by utilizing the lightning fault property judgment probabilistic algorithm model; a judging result contains a certain fault-tolerant margin; the aims that information amount required by the lightning fault property judgment is small and the fault information is easy to acquire by operation and maintenance personnel of the line are fulfilled; and the judgment method is simple and rapid and has strong practicality.
Owner:云南电力试验研究院(集团)有限公司
Field image tomography for magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS8378682B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionObject basedSystem matrix
Field Image Tomography (FIT) is a fundamental new theory for determining the three-dimensional (3D) spatial density distribution of field emitting sources. The field can be the intensity of any type of field including (i) Radio Frequency (RF) waves in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), (ii) Gamma radiation in SPECT / PET, and (iii) gravitational field of earth, moon, etc. FIT exploits the property that field intensity decreases with increasing radial distance from the field source and the field intensity distribution measured in an extended 3D volume space can be used to determine the 3D spatial density distribution of the emitting source elements. A method and apparatus are disclosed for MRI of target objects based on FIT. Spinning atomic nuclei of a target object in a magnetic field are excited by beaming a suitable Radio Frequency (RF) pulse. These excited nuclei emit RF radiation while returning to their normal state. The intensity or amplitude distribution of the RF emission field g is measured in a 3D volume space that may extend substantially along the radial direction around the emission source. g is related to the 3D tomography f through a system matrix H that depends on the MRI apparatus, and noise n through the vector equation g=Hf+n. This equation is solved to obtain the tomographic image f of the target object by a method that reduces the effect of noise.
Owner:SUBBARAO MURALIDHARA
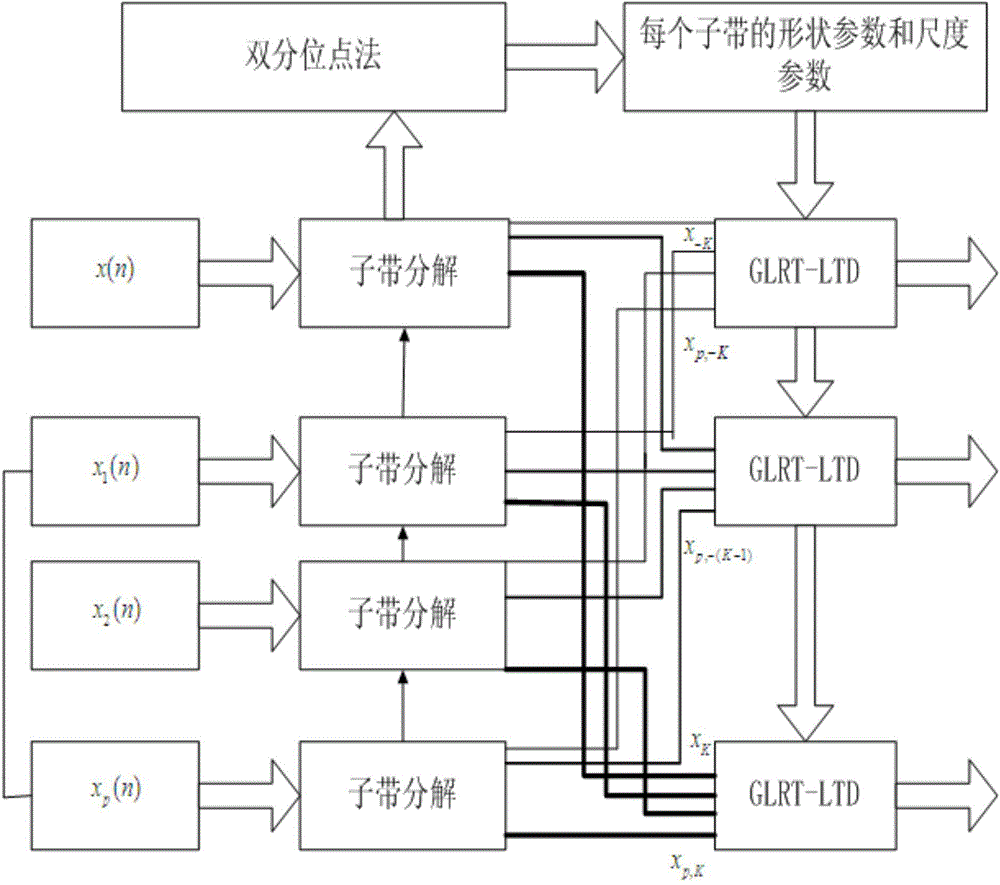
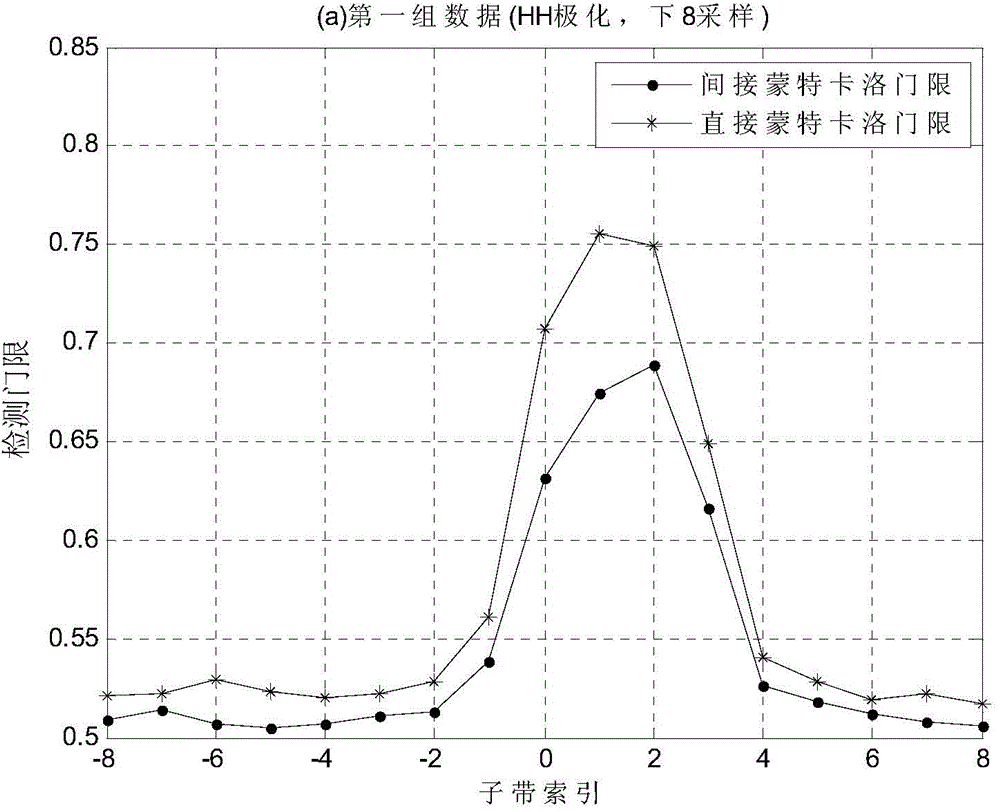
Sub-band self-adaptive GLRT-LTD detection method under sea clutter background
ActiveCN104569948AAccurate detection verdictEasy to detectWave based measurement systemsDecompositionRadar
The invention belongs to the field of radar target detection, and particularly relates to a sub-band self-adaptive GLRT-LTD detection method under a sea clutter background. The sub-band self-adaptive GLRT-LTD detection method under the sea clutter background comprises the steps that a DFT modulation filter set is utilized to carry out sub-band decomposition on a sea return time sequence received by a radar, a sub-band decomposition signal of each sub-band filter in the DFT modulation filter set is obtained, and the sub-band decomposition signal of the Kth sub-band filter is expressed as Xk; K1 down-sampling is carried out on the sub-band decomposition signal Xk of the Kth sub-band filter to obtain a corresponding K1 down-sampling post signal; a scale parameter lambda k and a shape parameter eta k of a sea clutter Pareto amplitude distribution model corresponding to the Kth sub-band filter are determined; a sub-band self-adaptive GLRT-LTD detection statistical magnitude tk,k1 of a kth sub-band subjected to the K1 down-sampling is obtained, a constant false-alarm threshold is set, the detection statistical magnitude of each sub-band is compared with the constant false-alarm threshold of the sub-band, and whether a target exists or not is judged.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
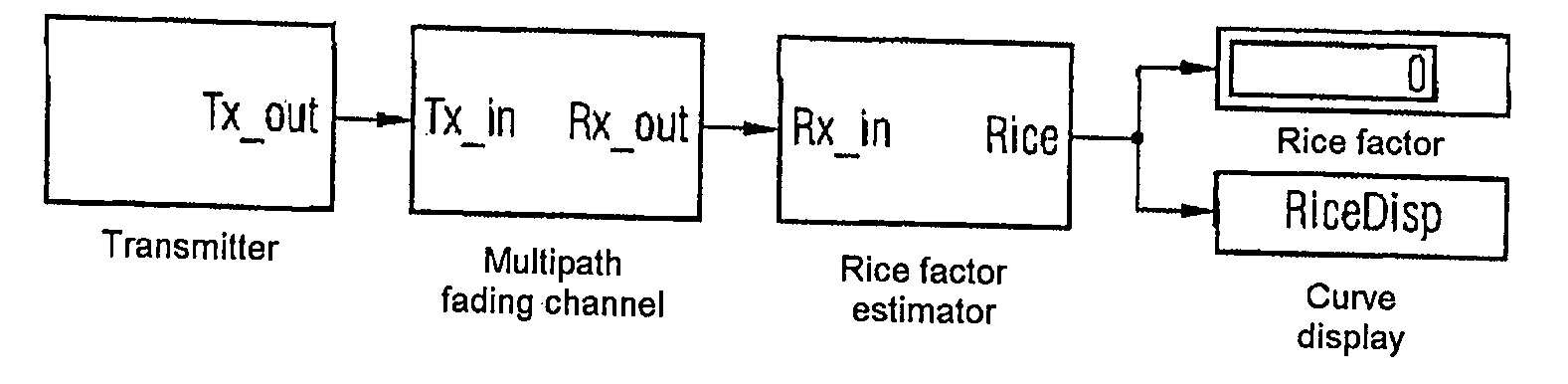
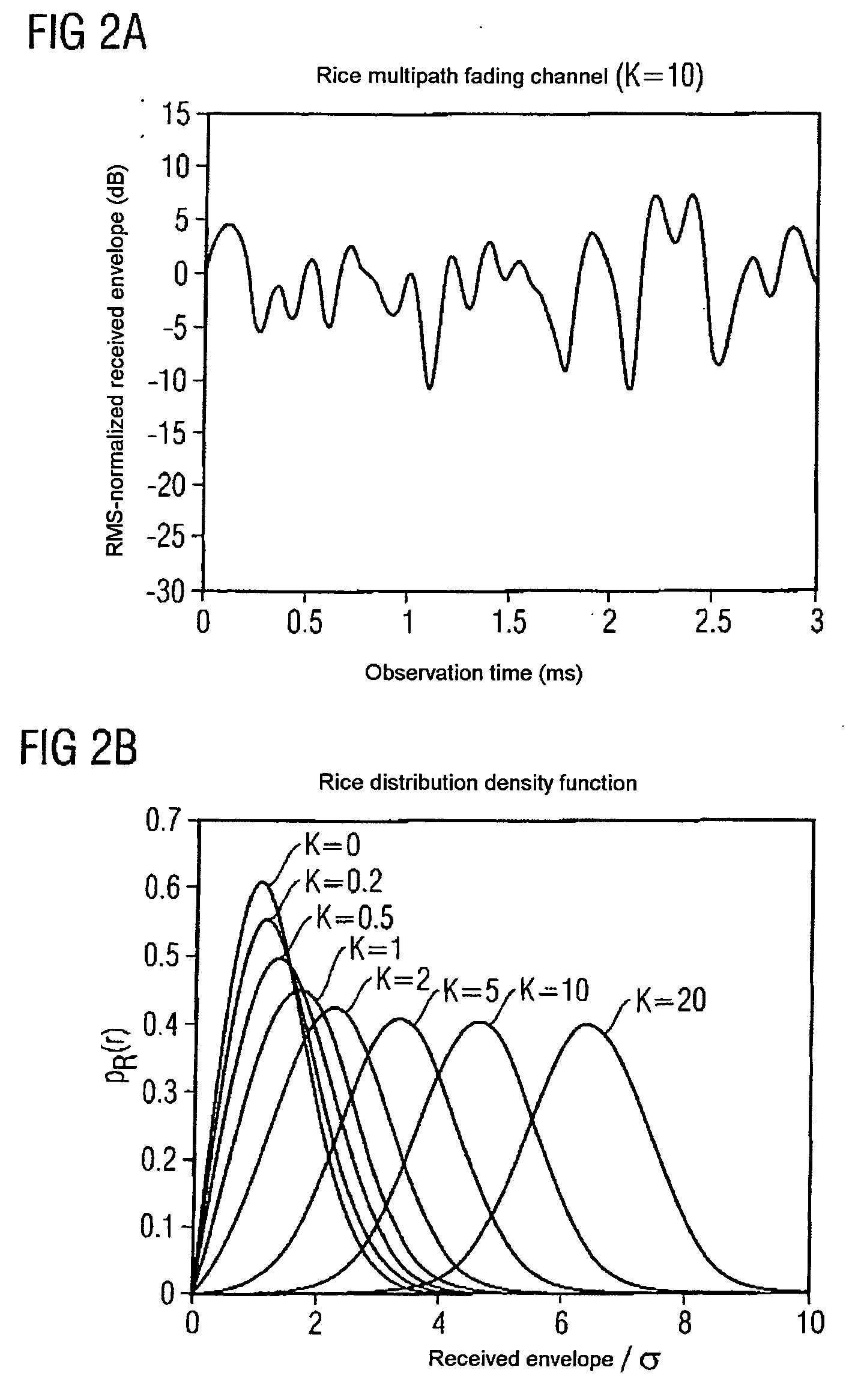
Reliability and the accuracy of position-finding methods by estimation of the rice factor of a radio link
InactiveUS20060012523A1Improve reliabilityExtra componentRadio wave finder detailsBeacon systemsEngineeringSignal strength
In order to improve the reliability and the accuracy of a position-finding method such as the GPS method, the quality of a radio link which is used for the position-finding method is determined by estimating a parameter, in particular the Rice factor of the amplitude distribution density, which is characteristic of the ratio of the strength of a signal transmitted via a line-of-sight path, with respect to the strength of the signals transmitted via non-line-of-sight paths.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Optical System For Converting A Primary Intensity Distribution Into A Predefined Intensity Distribution That Is Dependent On A Solid Angle
InactiveUS20080074746A1Reduce destructive effectsHigh apertureOptical elementsDiffraction orderUltimate tensile strength
It is the object of an optical system and a method for converting a primary intensity distribution into a predetermined intensity distribution dependent on a solid angle to reduce the disruptive influence of the zeroth diffraction order beyond the limits imposed by the manufacturing accuracy in the manufacture of the diffractive structures, also with increasingly higher apertures, while making use of the advantages of diffractive structures in providing variously shaped intensity distributions. In a first plane, in which first micro-optic homogenization structures generate a finely structured amplitude distribution and phase distribution from the primary intensity distribution, there are arranged second diffractive micro-optic homogenization structures which are adapted to the finely structured amplitude distribution and phase distribution and which generate the predetermined solid angle-dependent intensity distribution in a second plane from the finely structured amplitude distribution and phase distribution.
Owner:JENOPTIK LASER OPTIK SYST
CU division and PC prediction mode selection method and system in HEVC frame
ActiveCN108184115AQuick selectionReduce in quantityDigital video signal modificationComputation complexityRate distortion
The invention discloses a CU division and PC prediction mode selection method and system in an HEVC frame. The method comprises steps that coding mode to-be-selected CTU are successively extracted; aprediction angle in a 180-DEG frame is divided into 8 texture direction ranges, the histogram statistics method is utilized in combination with the superimposable characteristic of a histogram to acquire texture direction range-amplitude distribution histograms under different CU sizes, and the corresponding optimal texture direction range, texture intensity and texture complexity; whether a CU block is divided is determined according to texture complexity of the CU block; a candidate mode list is determined according to texture intensity of a PU block, the optimal texture direction range of the PU block and a prediction mode of a neighboring PU block; the rate distortion cost of candidate modes is calculated, and the mode with the lowest rate distortion cost is selected as the optimal prediction mode for the PU blocks. The method is advantaged in that computational complexity is significantly reduced, the PU optimal prediction mode is rapidly selected, and the method can be widely applied to the video coding field.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Phase element for introducing a phase shift pattern into an electromagnetic wave
InactiveUS20110025432A1Increased transmission lossLow amplitude shiftOptical articlesDelay linesPhase shiftedMicrowave
A thin electromagnetic phase shifting element, named phase and amplitude shifting surface (PASS), is disclosed. The PASS is capable of independently altering both the phase and the amplitude distribution of the electromagnetic fields propagating through the structure. The element comprises a few patterned metallic layers separated by dielectric layers. The patterns of the metallic layers are tuned to locally alter the phase and / or the amplitude of an incoming electromagnetic wave to a prescribed set of desired values for the outgoing electromagnetic wave. The PASS can be applied to design components such as gratings, lenses, holograms, and various types of antennas in the microwave, millimetre wave and sub-millimetre wave.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
Quantitative assessment method for feathering drifting of maritime three-dimensional seismological observation system
The invention relates to a quantitative assessment method for the feathering drifting a maritime three-dimensional seismological observation system, which comprises the following steps of: 1) importing maritime seismological observation system data; 2) classifying information of source points and demodulator probes at binning positions in the observation system data; 3) calculating weight coefficients of each group of offset pairs according the transmission-reflection-transmission characteristic of seismic waves; 4) summarizing weight coefficients of all binning positions to obtain seismic wave amplitude values at all binning positions of a target horizon, and drawing a binning amplitude distribution map; and 5) performing statistic analysis on the binning amplitude distribution map, calculating the mean-square deviation of the binning amplitude distribution map to realize the quantitative assessment of feathering drifting, wherein when a mean-square deviation value is smaller, the degree of the feathering drifting is smaller. In the method, three-dimensional seismic wave does not need to be simulated, the influences of different kinds of feathering drifting on the distribution ofoffset points can be calculating directly in an analytical mode, and the influence degree of the feathering drifting on seismic wave amplitude energy can be analyzed, so that the quantitative assessment on the feathering drifting degree of the integral maritime seismological observation system is realized.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +2
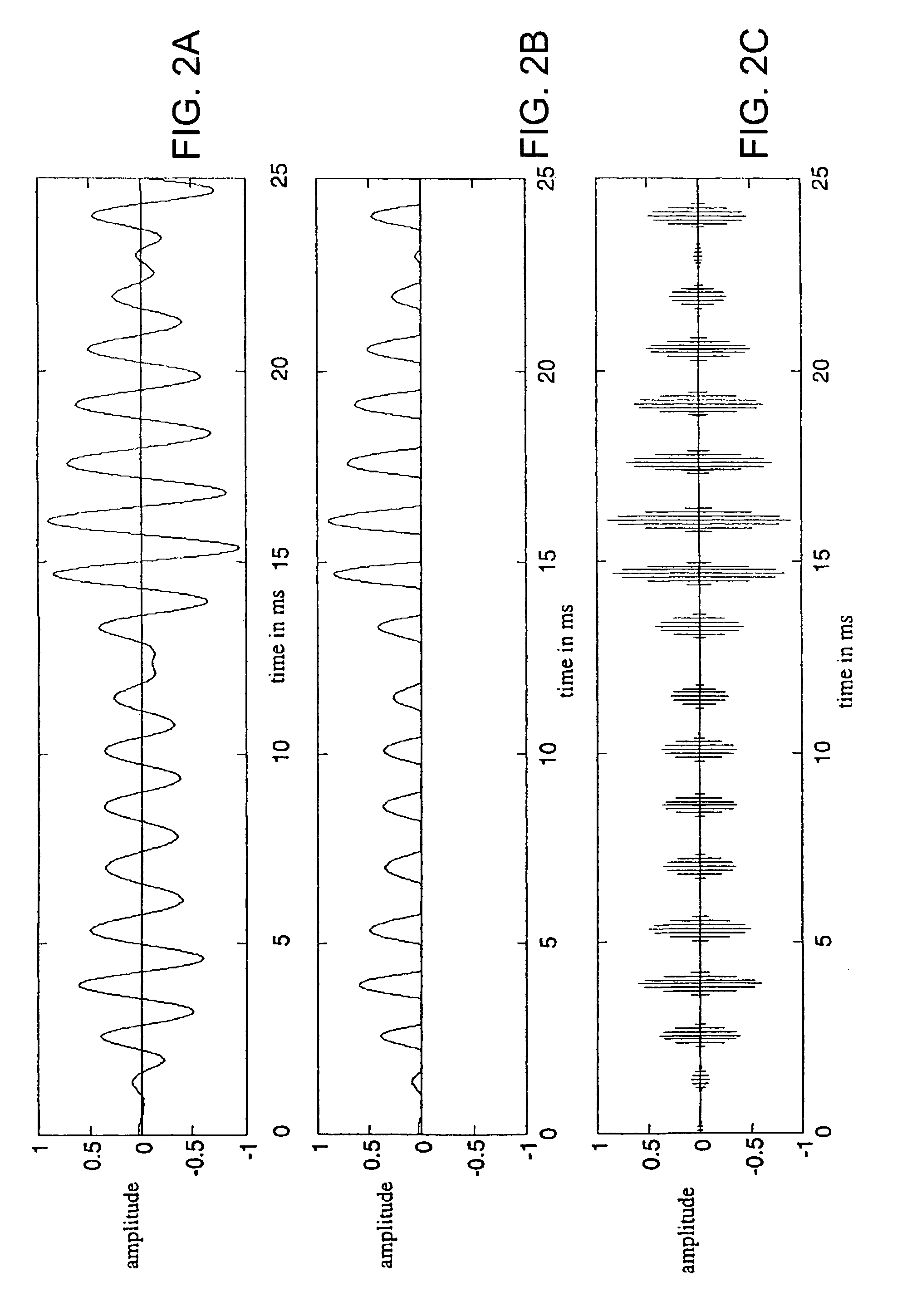
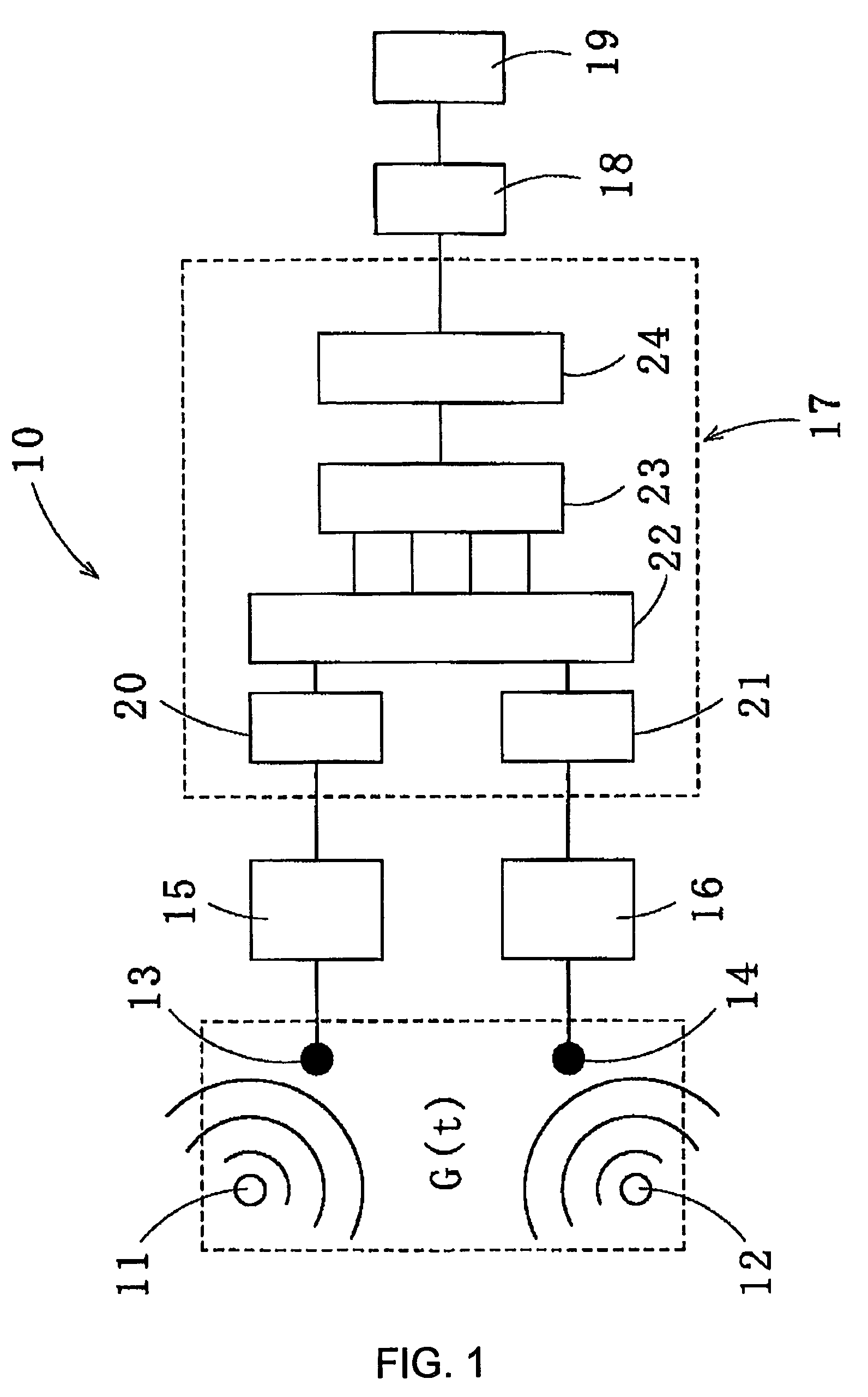
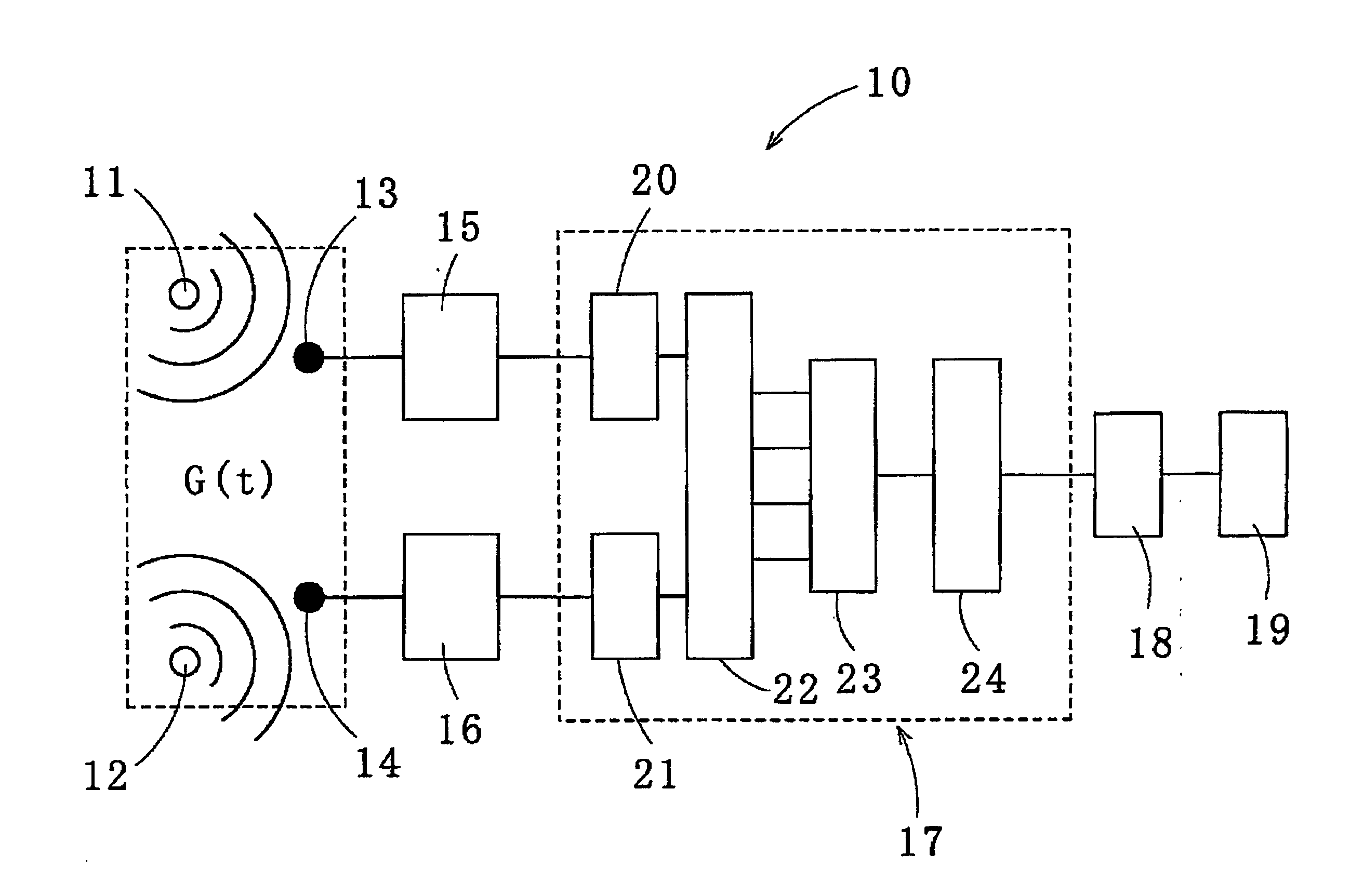
Method for recovering target speech based on amplitude distributions of separated signals
InactiveUS7562013B2Reduce computing loadAccurate assessmentSpeech recognitionTransmission noise suppressionTime domainFrequency spectrum
Owner:KITAKYUSHU FOUND FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF IND
Cycloid bevel gear fault diagnosis method based on empirical mode decomposition and cepstrum
InactiveCN104006961AExtract fault characteristic frequencyExtract fault featuresMachine gearing/transmission testingDecompositionEngineering
The invention relates to a cycloid bevel gear fault diagnosis method based on empirical mode decomposition and cepstrum, and belongs to the technical field of fault diagnosis. The method includes the steps that (1), a cycloid bevel gear pair is measured through an acceleration sensor, and accelerated speed vibration signals are collected and used as signals to be analyzed; (2), the collected signals are guided into Matlab software to obtain original signals, and the original signals are decomposed into a series of intrinsic mode function (IMF) components through an empirical mode decomposition (EMD) method; (3), the IMF components of the previous orders are analyzed in a cepstrum mode to obtain amplitude cepstrum of the IMF components; (4), the amplitude cepstrum is drawn by adopting a drawing tool of the Matlab software, and fault feature information is extracted according to amplitude distribution in the cepstrum. The method can be applied to cycloid bevel gear fault diagnosis and can accurately extract fault feature frequency. A new method is provided for cycloid bevel gear fault diagnosis, and effective reference is provided for other rotating machine fault diagnosis technologies.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
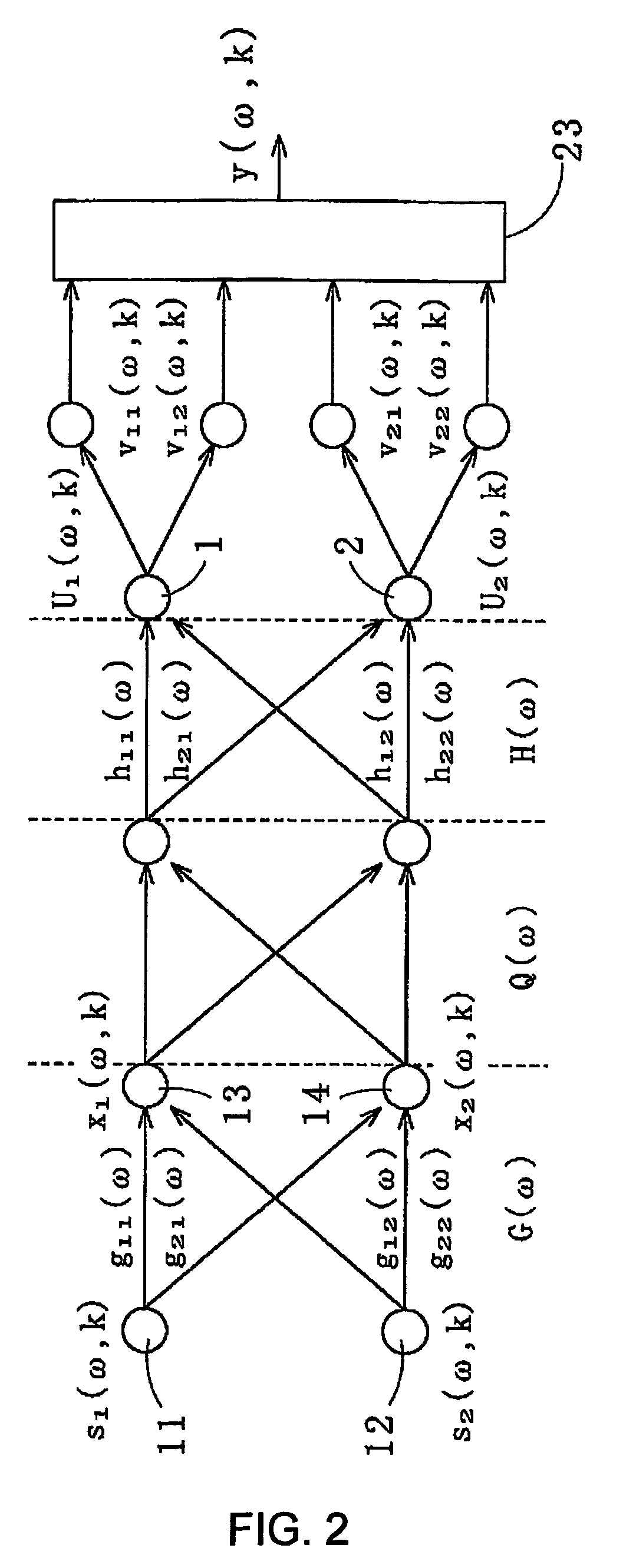
Method for recovering target speech based on amplitude distributions of separated signals
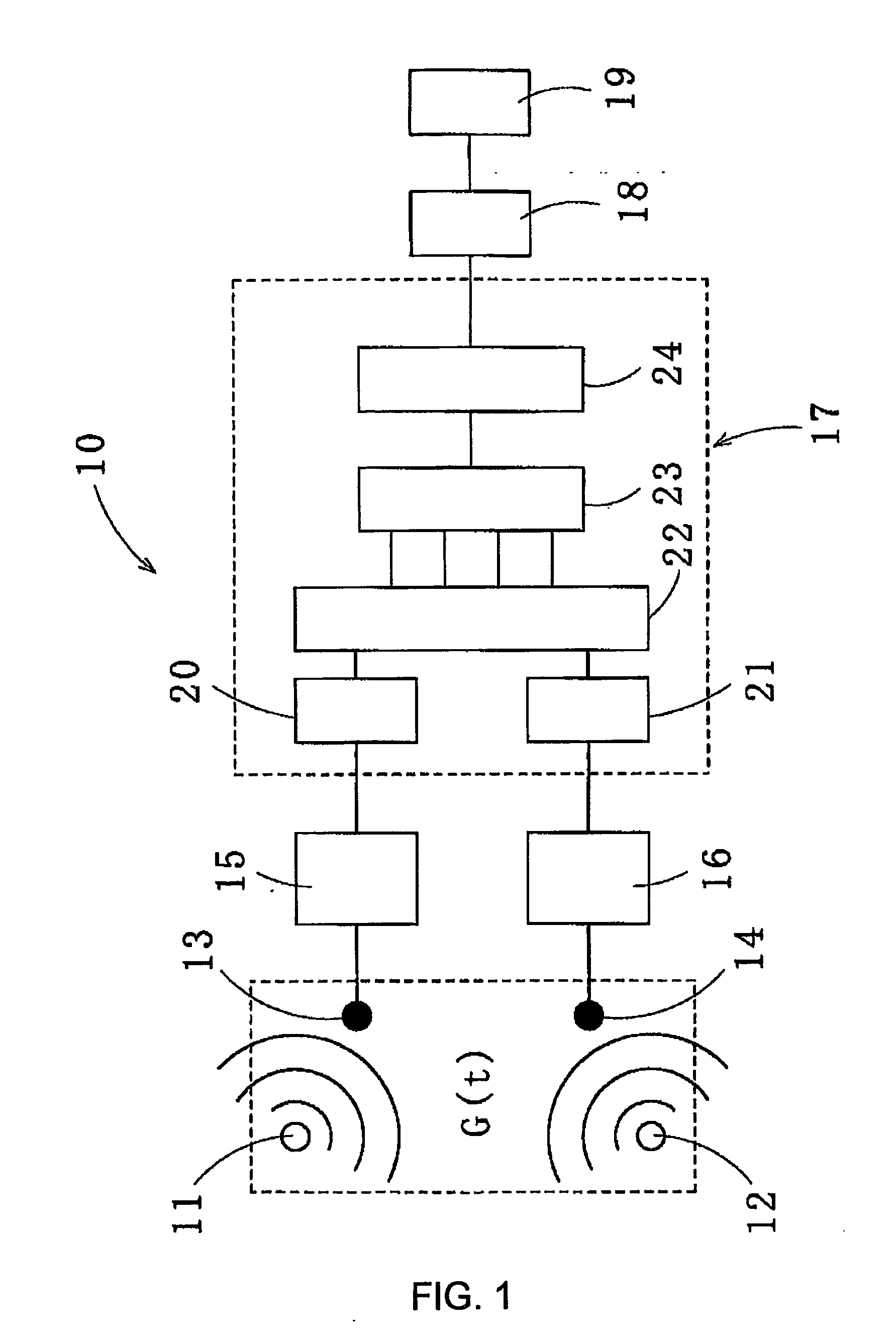
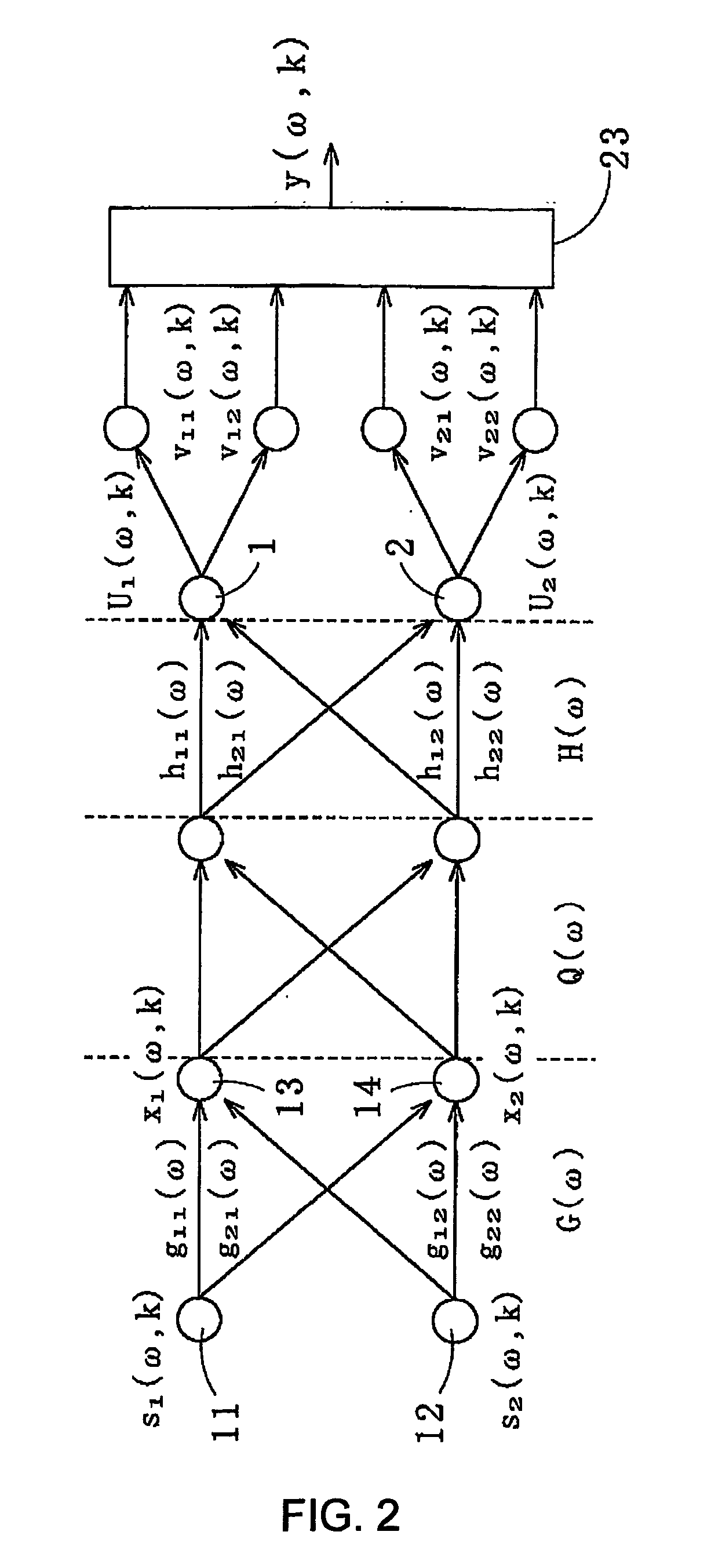
The present invention provides a method for recovering target speech based on shapes of amplitude distributions of split spectra obtained by use of blind signal separation. This method includes: a first step of receiving target speech emitted from a sound source and a noise emitted from another sound source and forming mixed signals of the target speech and the noise at a first microphone and at a second microphone; a second step of performing the Fourier transform of the mixed signals from the time domain to the frequency domain, decomposing the mixed signals into two separated signals U1 and U2 by use of the Independent Component Analysis, and, based on transmission path characteristics of the four different paths from the two sound sources to the first and second microphones, generating the split spectra v11, v12, v21 and v22 from the separated signals U1 and U2; and a third step of extracting estimated spectra Z* corresponding to the target speech to generate a recovered spectrum group of the target speech, wherein the split spectra v11, v12, v21, and v22 are analyzed by applying criteria based on the shape of the amplitude distribution of each of the split spectra v11, v12, v21, and v22, and performing the inverse Fourier transform of the recovered spectrum group from the frequency domain to the time domain to recover the target speech.
Owner:KITAKYUSHU FOUND FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF IND SCI & TECH
Frequency scanning antenna array capable of realizing wide-angle scanning in limited bandwidth
InactiveCN101888019AEasy to achieve amplitude distributionSimple structureAntenna arraysWave structureCoaxial line
The invention discloses a frequency scanning antenna array capable of realizing wide-angle scanning in a limited bandwidth, which comprises microstrip patch units [1], absorbing loads [2] and slow wave structures [3]. The frequency scanning antenna array is divided into a plurality of sub-arrays [6], wherein the sub-array is provided with a feed coaxial line [4]; one end of the coaxial line is connected with the slow wave structures [3], while the other end is connected with a power divider [5]; the slow wave structure comprises a three-path power divider [8] and a coupling linear power divider [9] which are in mixed-use; and the microstrip path unit [1] is a caliber-coupled microstrip antenna unit. The frequency scanning antenna array adopts microstrip antennae so as to realize the advantages of simple structure and light weight, adopts the slow wave structures mixing the coaxial lines and microstrip lines so as to reduce loss by over 30 percent than that of the conventional frequency scanning microstrip antenna at the same time of realizing the wide-angle scanning in the limited bandwidth, and adopts the three-path power divider and the coupling linear power divider which are in mixed-use so as to realize the advantage of the amplitude distribution of the antenna array.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for recovering target speech based on speech segment detection under a stationary noise
InactiveUS20070055511A1Minimizing residual noiseNoise minimizationSpeech recognitionFrequency spectrumPresent method
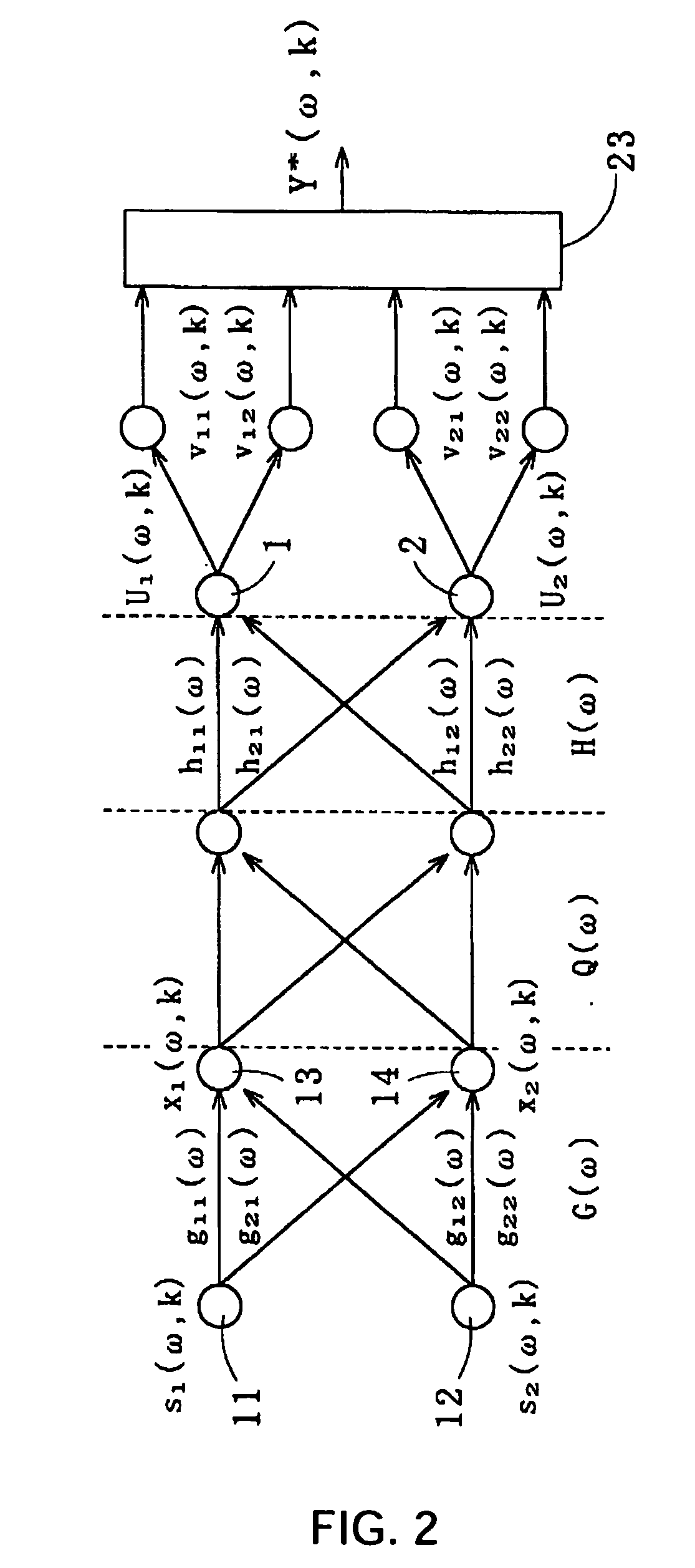
Method for recovering target speech by extracting signal components falling in a speech segment, which is determined based on separated signals obtained through the Independent Component Analysis, thereby minimizing the residual noise in the recovered target speech. The present method comprises: the first step of receiving target speech emitted from a sound source and a noise emitted from another sound source and extracting estimated spectra Y* corresponding to the target speech by use of the Independent Component Analysis; the second step of separating from the estimated spectra Y* an estimated spectrum series group y* in which the noise is removed by applying separation judgment criteria based on the kurtosis of the amplitude distribution of each of estimated spectrum series in Y*; the third step of detecting a speech segment and a noise segment of the total sum F of all the estimated spectrum series in y* by applying detection judgment criteria based on a predetermined threshold value T that is determined by the maximum value of F; and the fourth step of extracting components falling in the speech segment from the estimated spectra Y* to generate a recovered spectrum group of the target speech for recovering the target speech.
Owner:KITAKYUSHU FOUND FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF IND SCI & TECH +1
Method and system for estimating sea clutter amplitude distribution parameter
ActiveCN110275148AImprove estimation accuracyImprove real-time performanceWave based measurement systemsModel parametersNetwork model
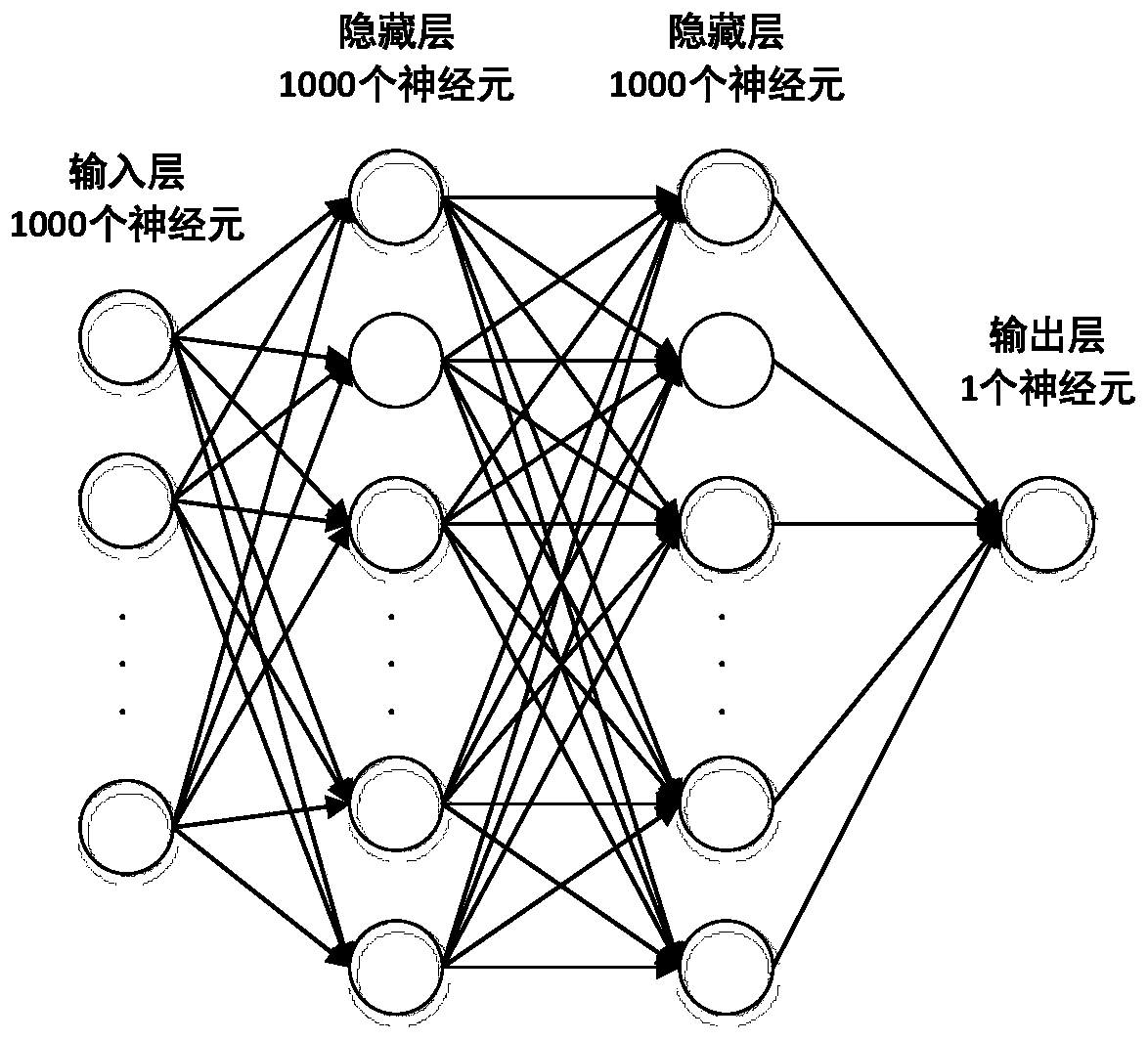
The embodiment of the present invention provides a method and system for estimating a sea clutter amplitude distribution parameter. The method comprises the steps of: obtaining the actually measured data of sea clutter amplitude distribution; performing an amplitude statistic process on the actually measured data to obtain actually measured probability data; and inputting the actually measured probability data into a statistical distribution model to obtain an actually measured statistical model parameter of the statistical distribution model output, wherein the statistical distribution model is obtained by training the simulation training data based on the sea clutter amplitude distribution and a simulation statistical model parameter corresponding to the simulation training data. The embodiment of the invention provides a deep learning method to estimate the sea clutter parameter, which obtains the actually measured probability data by processing the actually measured data, trains a neural network model based on the simulation data, and then inputs the actually measured probability data into the trained statistical distribution model to obtain the actually measured statistical model parameter. The model training can be performed offline by using the simulation data. The trained model has good real-time performance and high parameter estimation accuracy when processing the actually measured data.
Owner:NAVAL AVIATION UNIV
Adaptive processing method of clutter rejection in a phased array beam pattern
ActiveUS7728769B2Effective clutter rejectionIndividually energised antenna arraysRadio wave reradiation/reflectionBeam patternLight beam
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
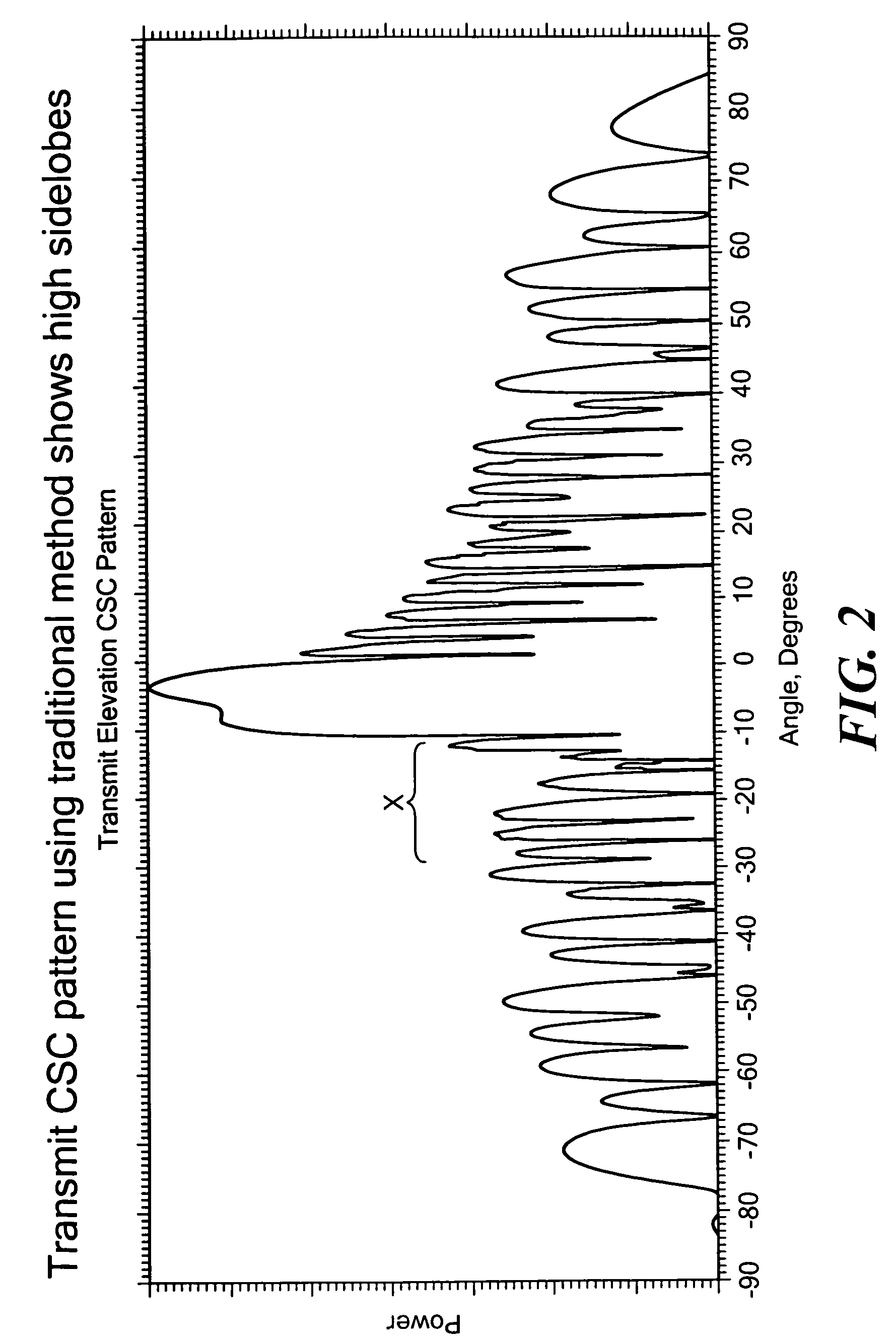
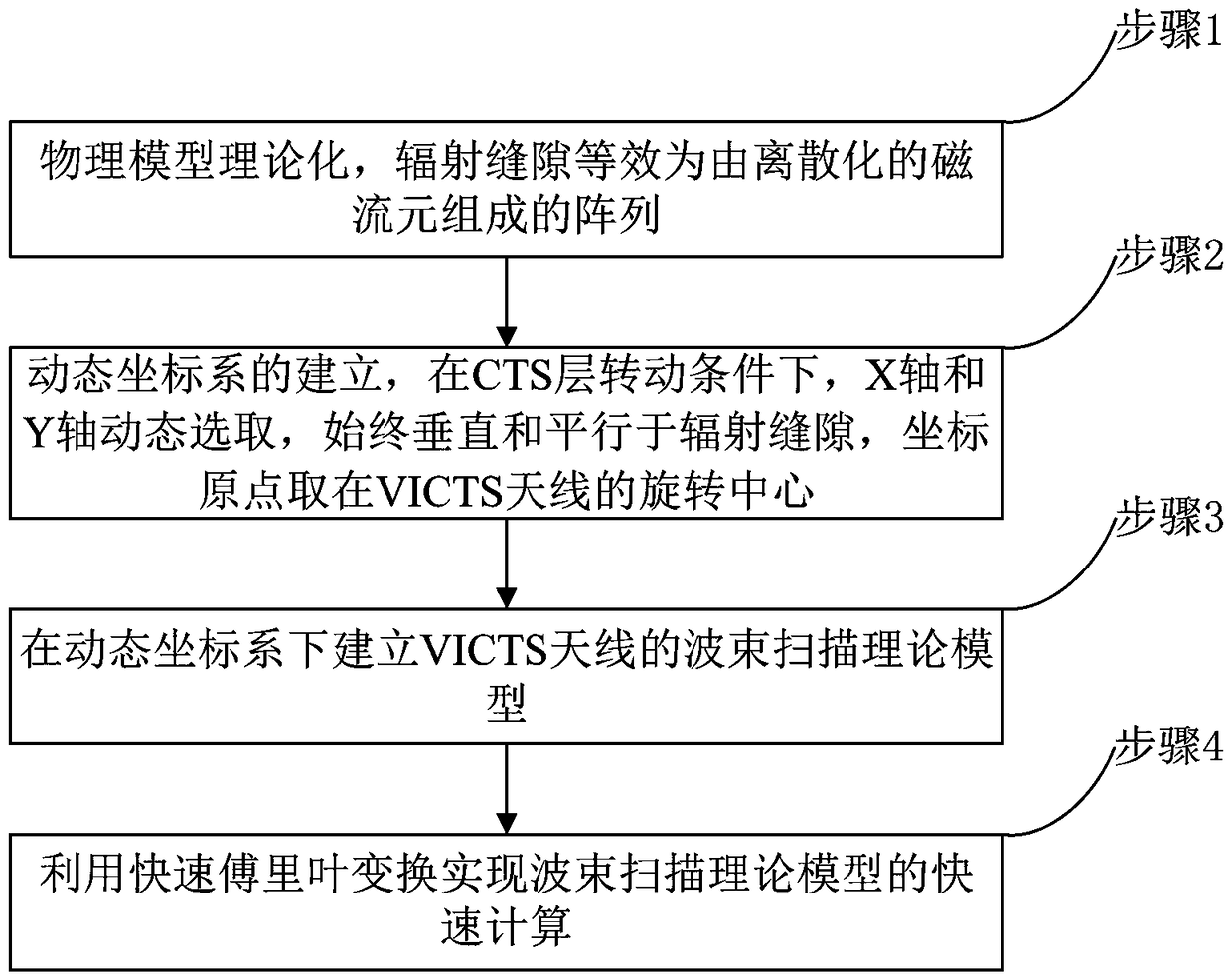
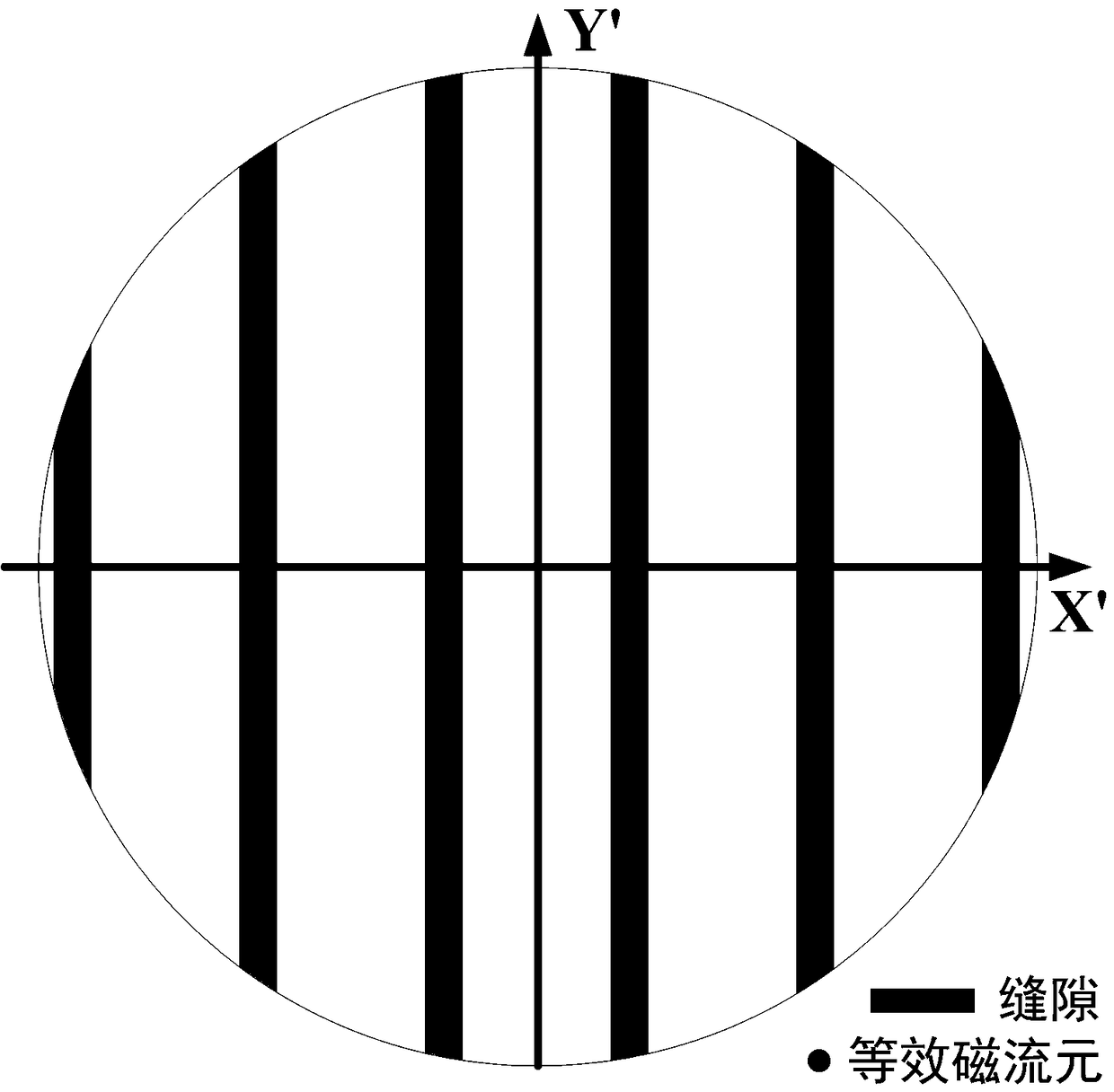
Quick calculation method for direction pattern and beam pointing direction of VICTS antenna
ActiveCN108197362AEasy to set upEliminate Inherently Large ErrorsAntenna arraysDesign optimisation/simulationMagnetic currentFast Fourier transform
The invention belongs to the technical field of satellite communication antennae and particularly relates to a quick calculation method for a direction pattern and a beam pointing direction of a VICTSantenna. The method comprises the steps of firstly, theorizing a physical model, and making a radiation slot equivalent to an array consisting of discretized magnetic current elements; secondly, establishing a dynamic coordinate system, under a CTS layer rotation condition, dynamically selecting an X axis and a Y axis to be always vertical and parallel to the radiation slot, taking a rotary center of the VICTS antenna as a coordinate origin, and building a beam scanning theoretical model of the VICTS antenna in the dynamic coordinate system; and realizing quick calculation of the beam scanning theoretical model by utilizing fast Fourier transform. Based on the dynamic coordinate system, the beam scanning theoretical model of the VICTS antenna is built; and the method can be used for quickly calculating the beam pointing direction of the antenna and the direction pattern of the VICTS antenna with any aperture shape and any amplitude distribution.
Owner:PLA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE INFORMATION ENG UNIV PLA SSF IEU +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com