Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
13070results about "Transmission noise suppression" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
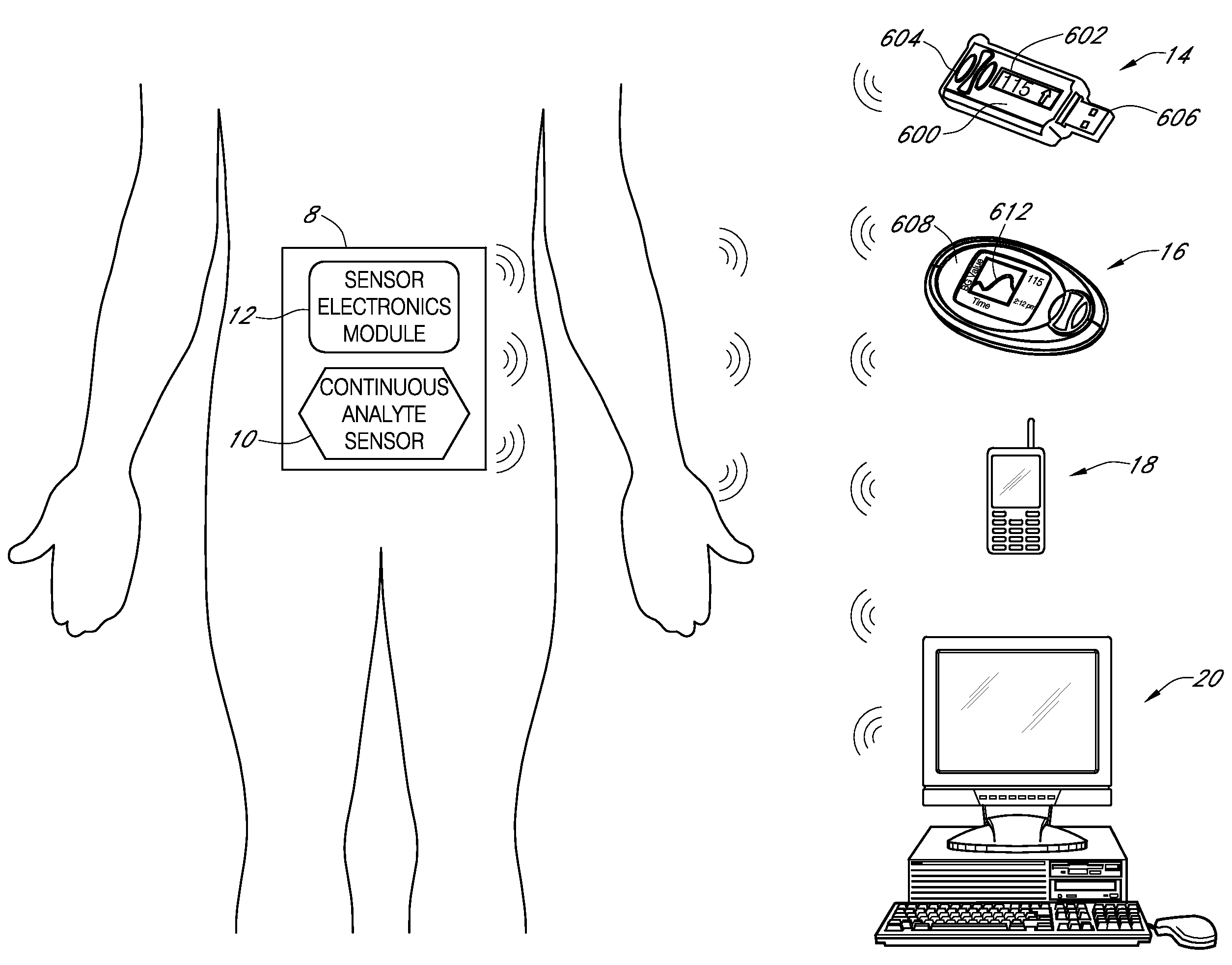
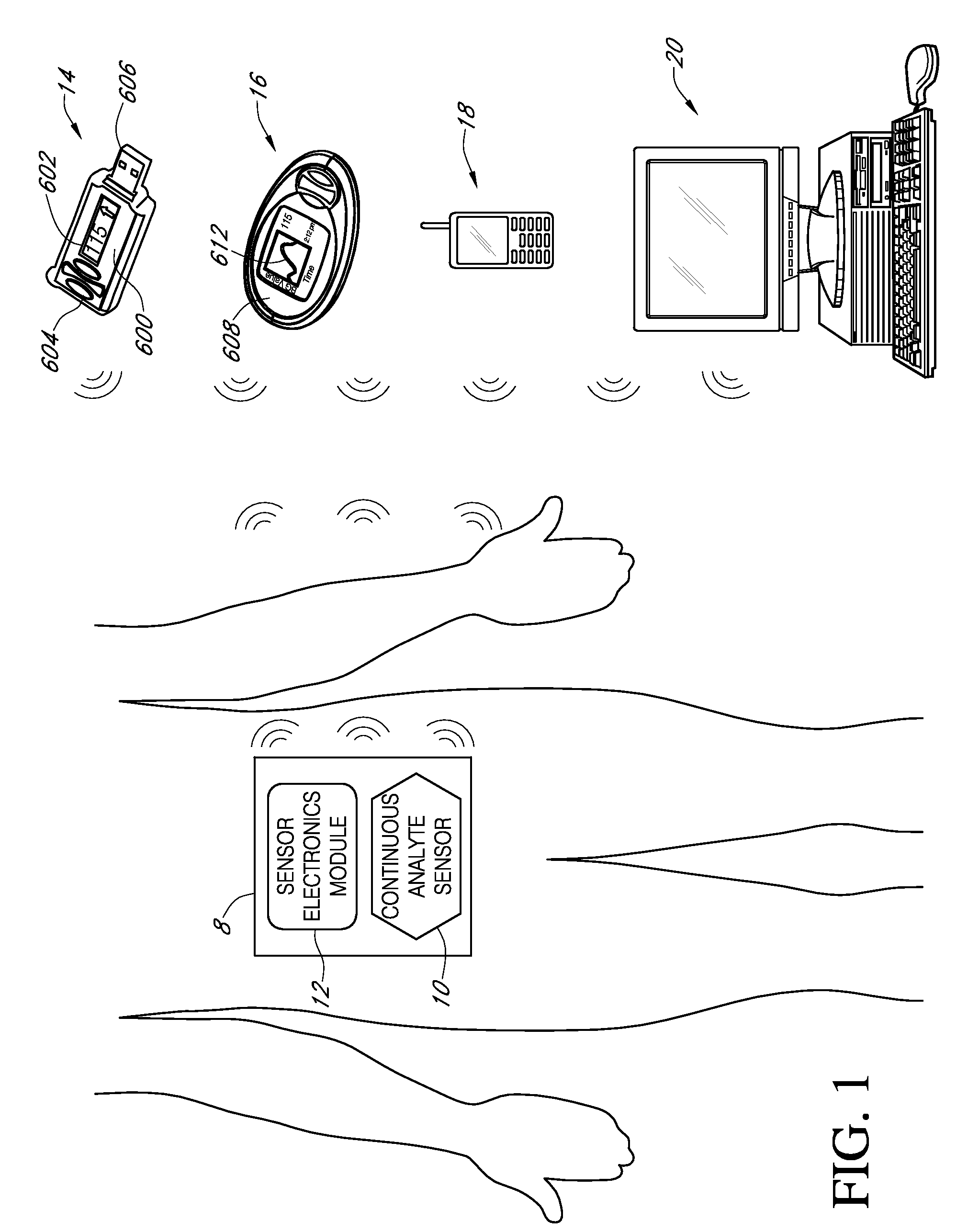
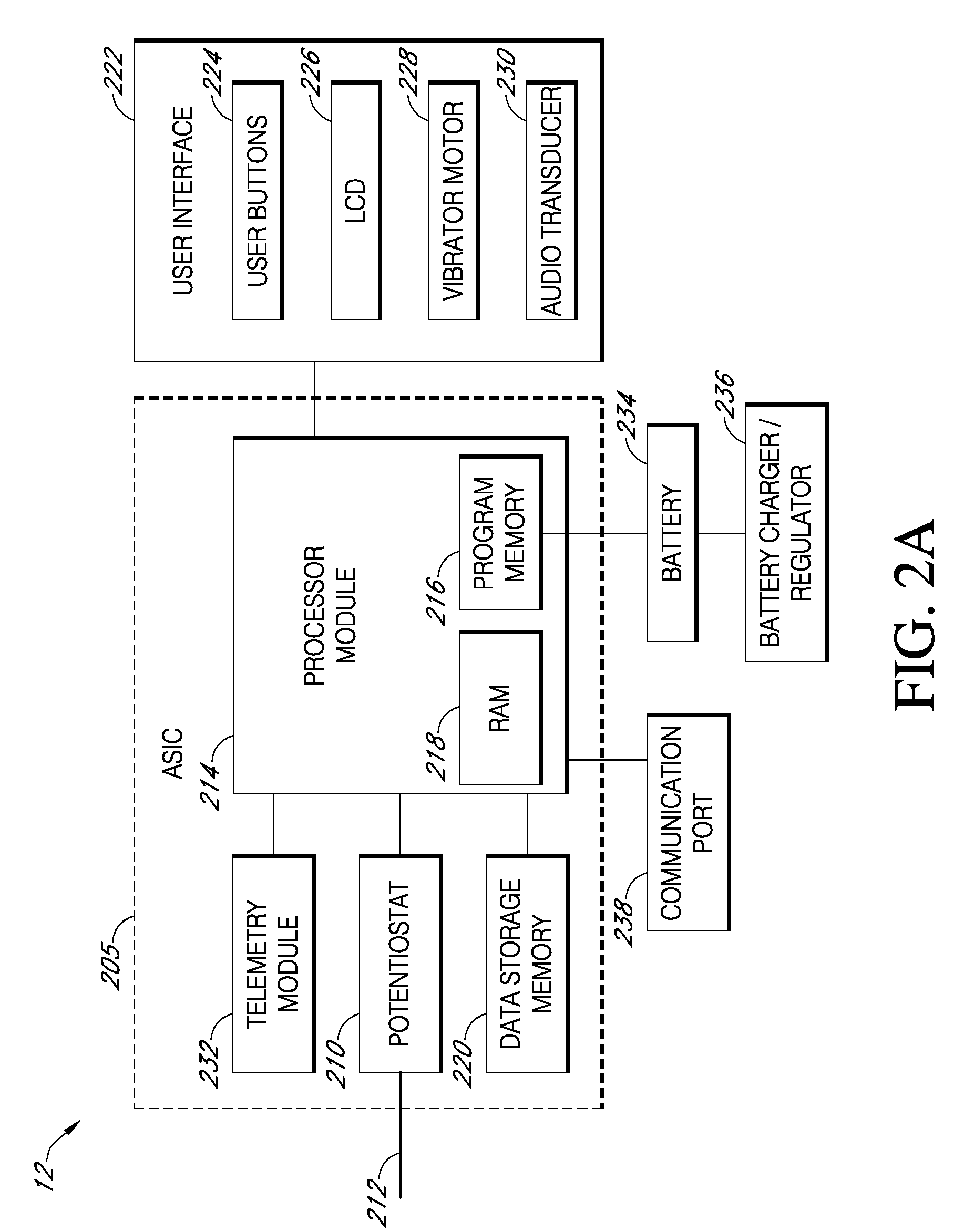
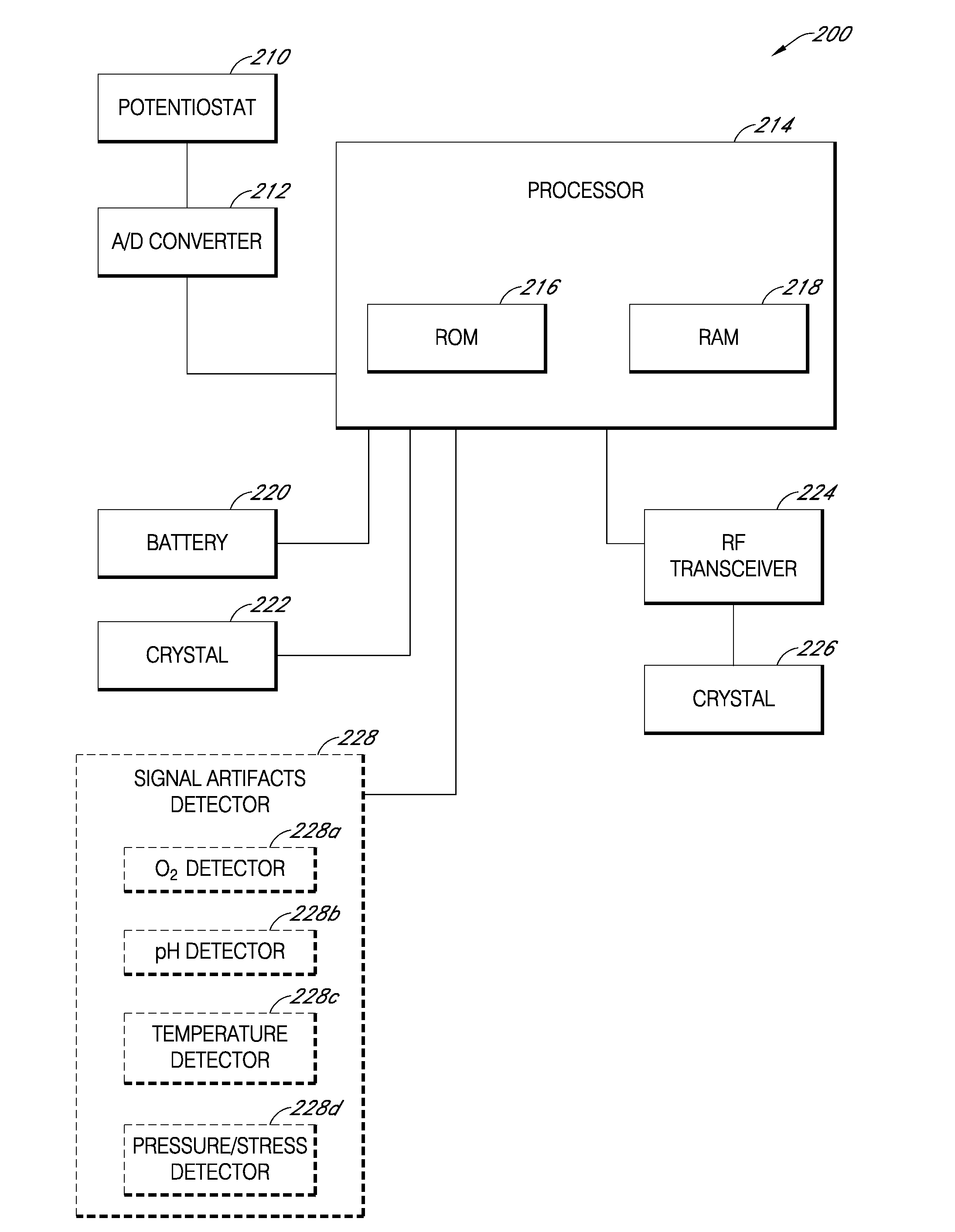
Systems and methods for customizing delivery of sensor data
ActiveUS20090240193A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceLocal control/monitoringContinuous measurementAnalyte
Systems and methods for continuous measurement of an analyte in a host are provided. The system generally includes a continuous analyte sensor configured to continuously measure a concentration of analyte in a host and a sensor electronics module physically connected to the continuous analyte sensor during sensor use, wherein the sensor electronics module is further configured to directly wirelessly communicate displayable sensor information to a plurality of different types of display devices.
Owner:DEXCOM
Systems and methods for processing sensor data
Systems and methods for processing sensor data are provided. In some embodiments, systems and methods are provided for calibration of a continuous analyte sensor. In some embodiments, systems and methods are provided for classification of a level of noise on a sensor signal. In some embodiments, systems and methods are provided for determining a rate of change for analyte concentration based on a continuous sensor signal. In some embodiments, systems and methods for alerting or alarming a patient based on prediction of glucose concentration are provided.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
Systems and methods for processing sensor data
Systems and methods for processing sensor data are provided. In some embodiments, systems and methods are provided for calibration of a continuous analyte sensor. In some embodiments, systems and methods are provided for classification of a level of noise on a sensor signal. In some embodiments, systems and methods are provided for determining a rate of change for analyte concentration based on a continuous sensor signal. In some embodiments, systems and methods for alerting or alarming a patient based on prediction of glucose concentration are provided.
Owner:DEXCOM
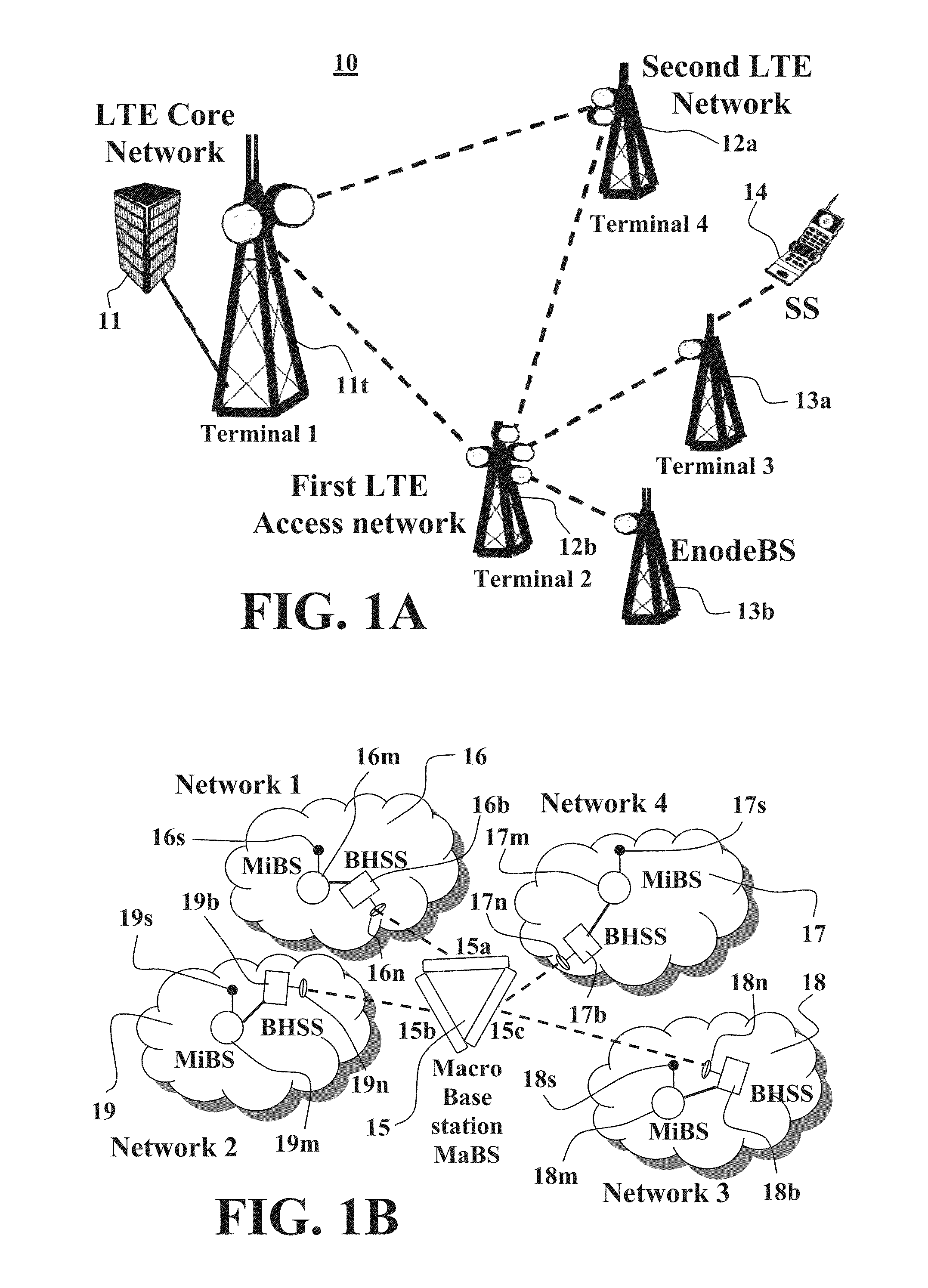
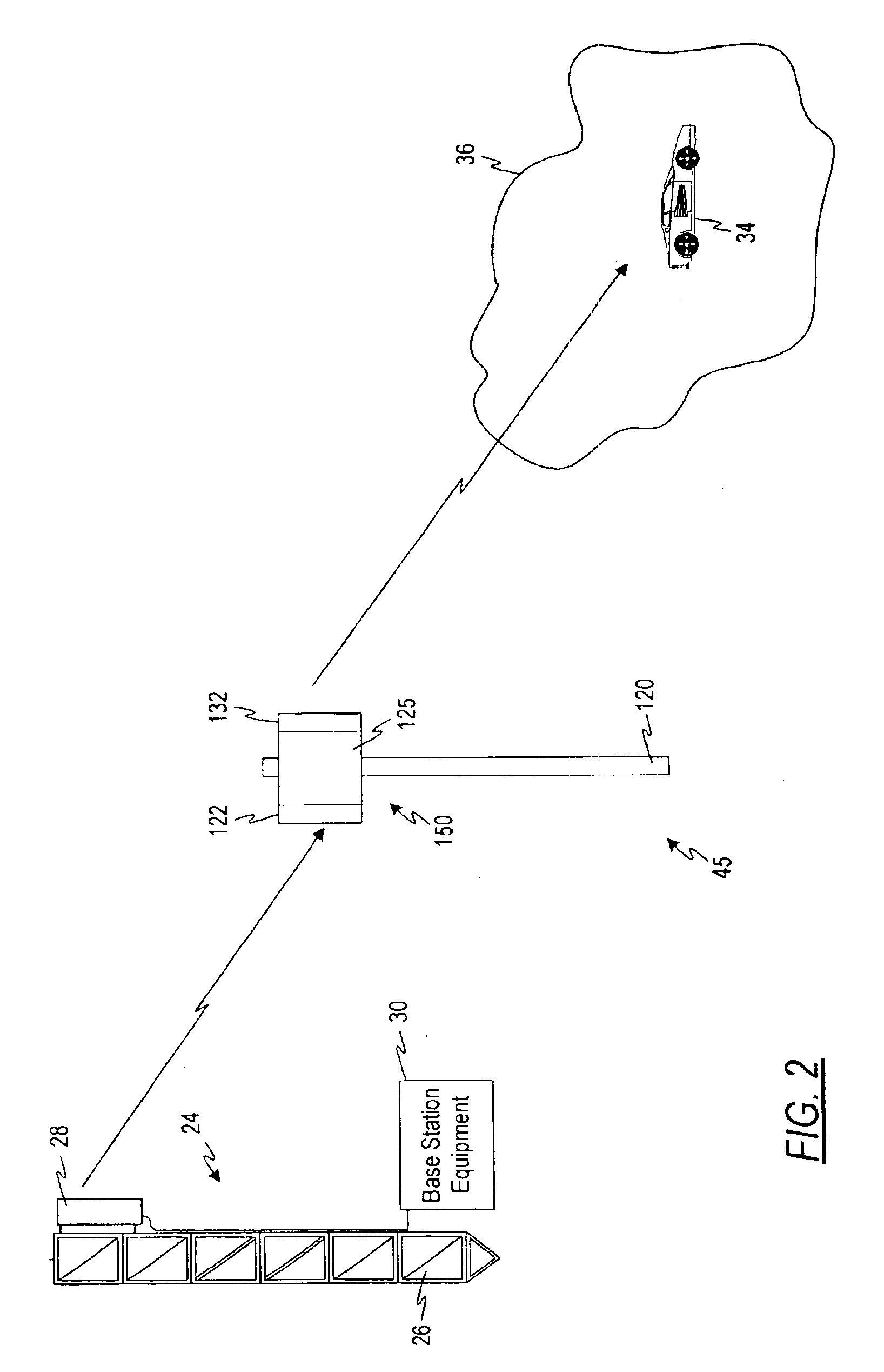
Cellular systems with distributed antennas
InactiveUS20090258652A1Efficient use ofIncrease data rateNetwork topologiesInformation formatWireless transceiverTransceiver
A communication system providing wireless communication among wireless users through a number of cellular base stations, each including at least transport management equipment and broadband equipment, at least one of which supports at least remote cellular station including RF equipment for communication with users of cellular devices. The system includes at lease one wireless narrow beam communication link operating at millimeter wave frequencies in excess of 60 GHz connecting a remote cellular station with a cellular base station equipped with broad band conversion electronic equipment and transport management equipment. In preferred embodiment the communication system includes a large number of remote cellular stations with each remote cellular station serving a separate communication cell. Each remote cellular station is equipped with a low frequency wireless transceiver for communicating with the wireless users within the cell at a radio frequency lower than 6 GHz and a narrow beam millimeter wave wireless transceiver operating at a millimeter wave frequency higher than 60 GHz for communicating with another millimeter wave transceiver at another remote cellular station or a millimeter wave transceiver at a base station.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
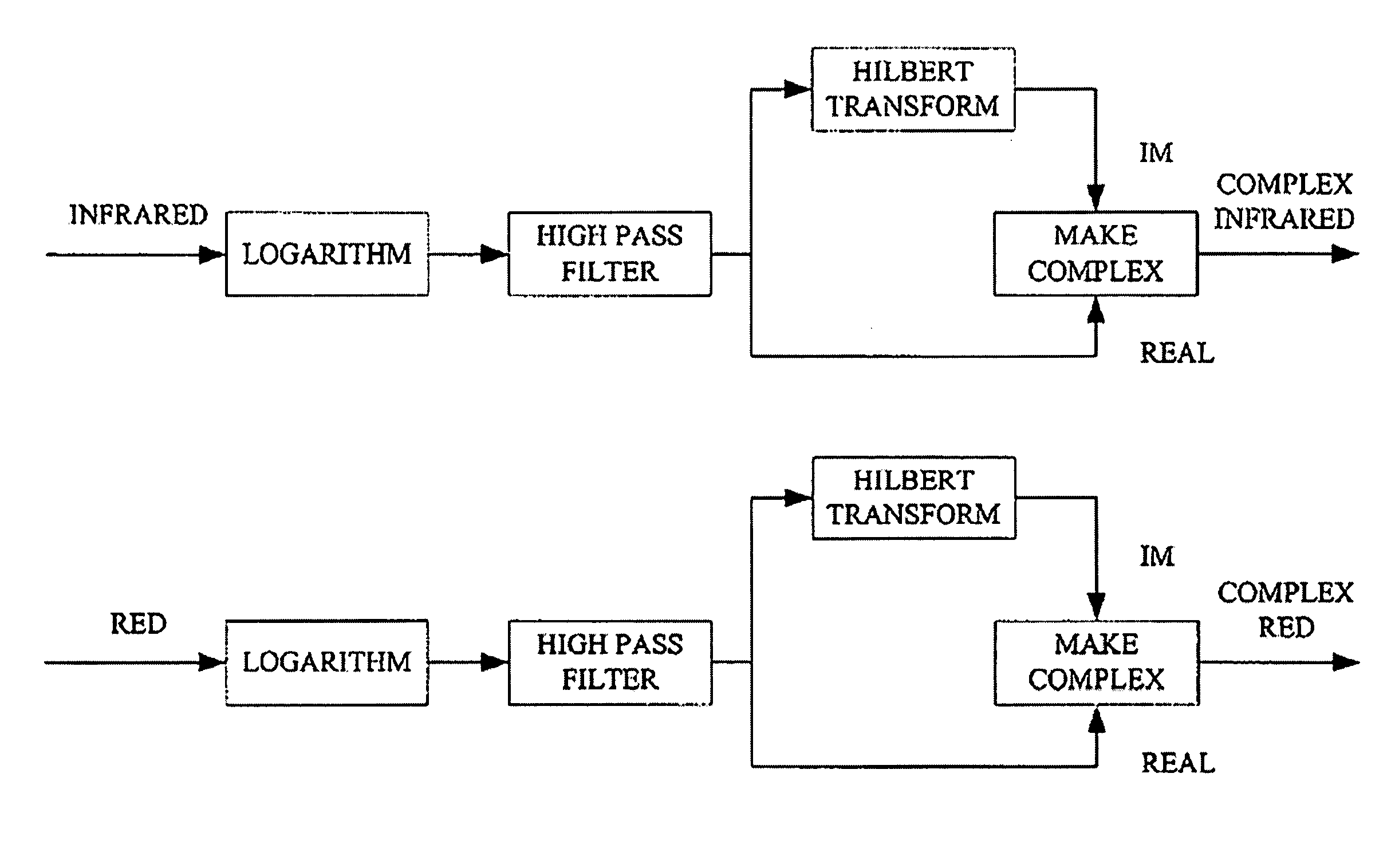
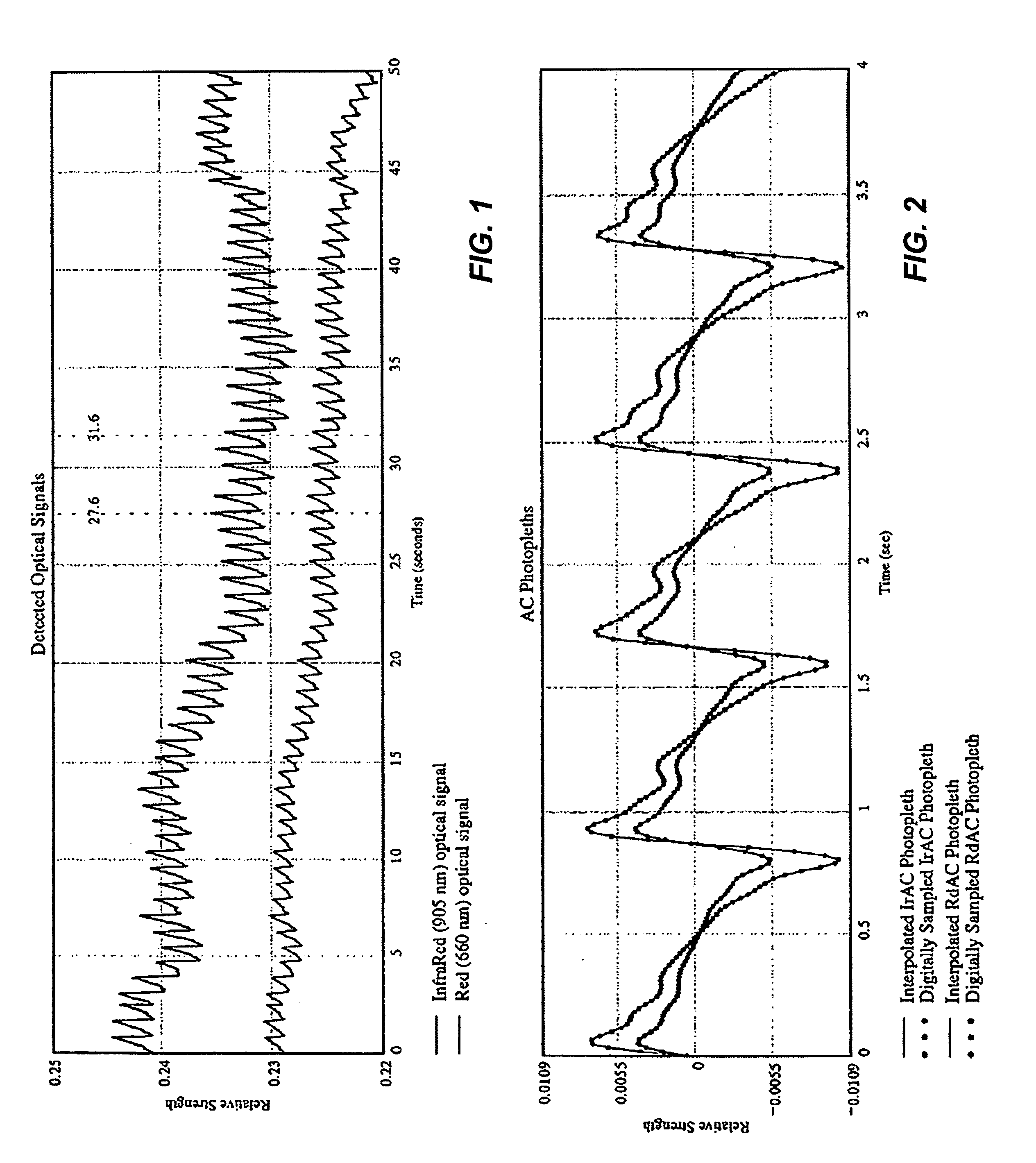
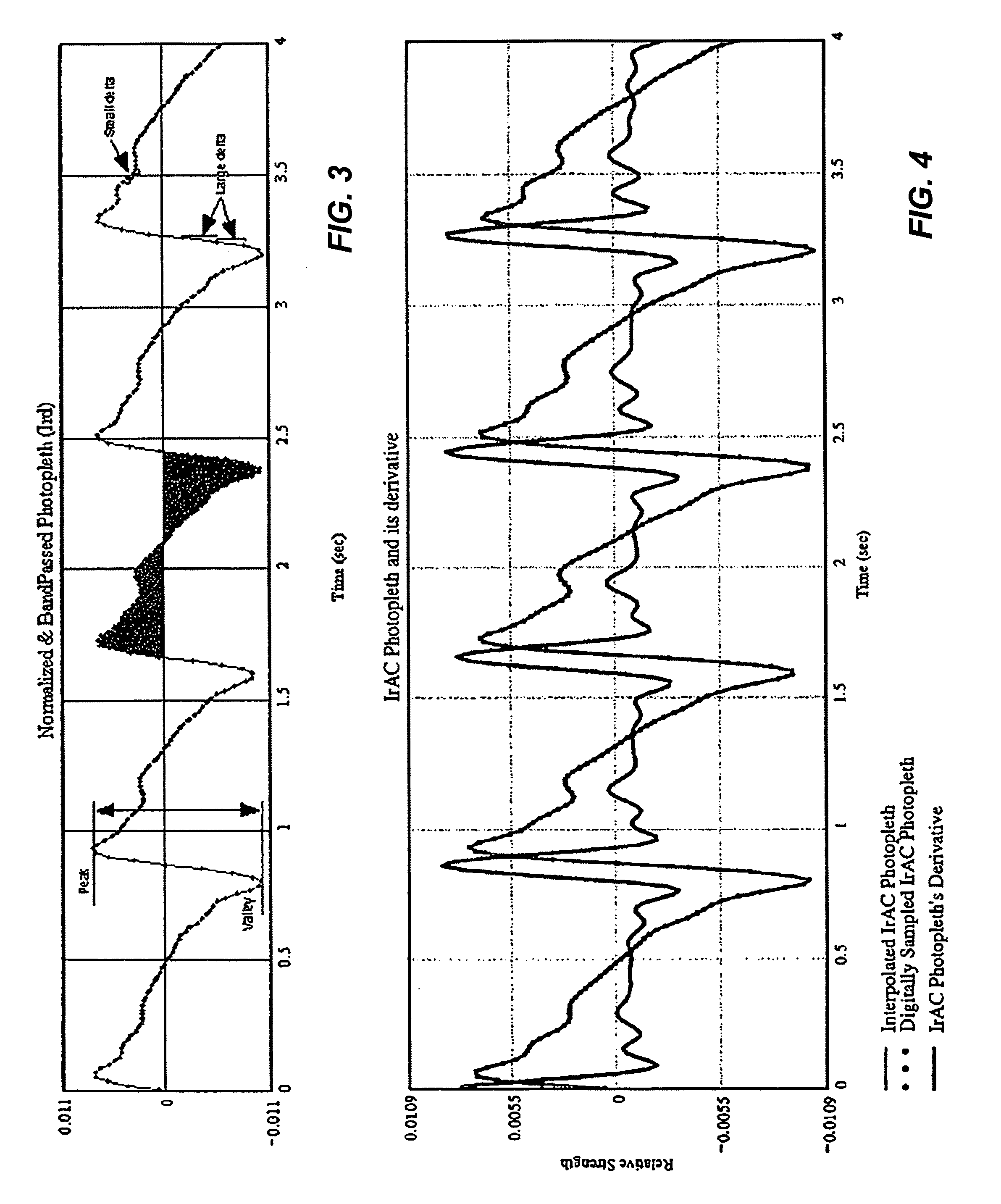
Systems and methods for determining blood oxygen saturation values using complex number encoding
ActiveUS6970792B1Sheer diagnostic valueFavorable for determinationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsStatistical analysisPulse oximetry
The disclosure includes pulse oximetry systems and methods for determining point-by-point saturation values by encoding photoplethysmographs in the complex domain and processing the complex signals. The systems filter motion artifacts and other noise using a variety of techniques, including statistical analysis such as correlation, or phase filtering.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Method of interference management for interference/collision avoidance and spatial reuse enhancement
InactiveUS20050058151A1Improve rendering capabilitiesImprove channel utilizationEnergy efficient ICTPower managementDifferentiated servicesDifferentiated service
A method called the evolvable interference management (EIM) method is disclosed in this patent for avoiding interference and collision and increasing network throughput and energy efficiency in wireless networks. EIM employs sensitive CSMA / CA, patching approaches, interference engineering, differentiated multichannel, detached dialogues, and / or spread spectrum techniques to solve the interference and QoS problems. EIM-based protocols can considerably increase network throughput and QoS differentiation capability as compared to IEEE 802.11e in multihop networking environments. Due to the improvements achievable by EIM, the techniques and mechanisms presented in this application may be applied to obtain an extension to IEEE 802.11 to better support differentiated service and power control in ad hoc networks and multihop wireless LANs. New protocols may also be designed based on EIM.
Owner:YEH CHIHSIANG
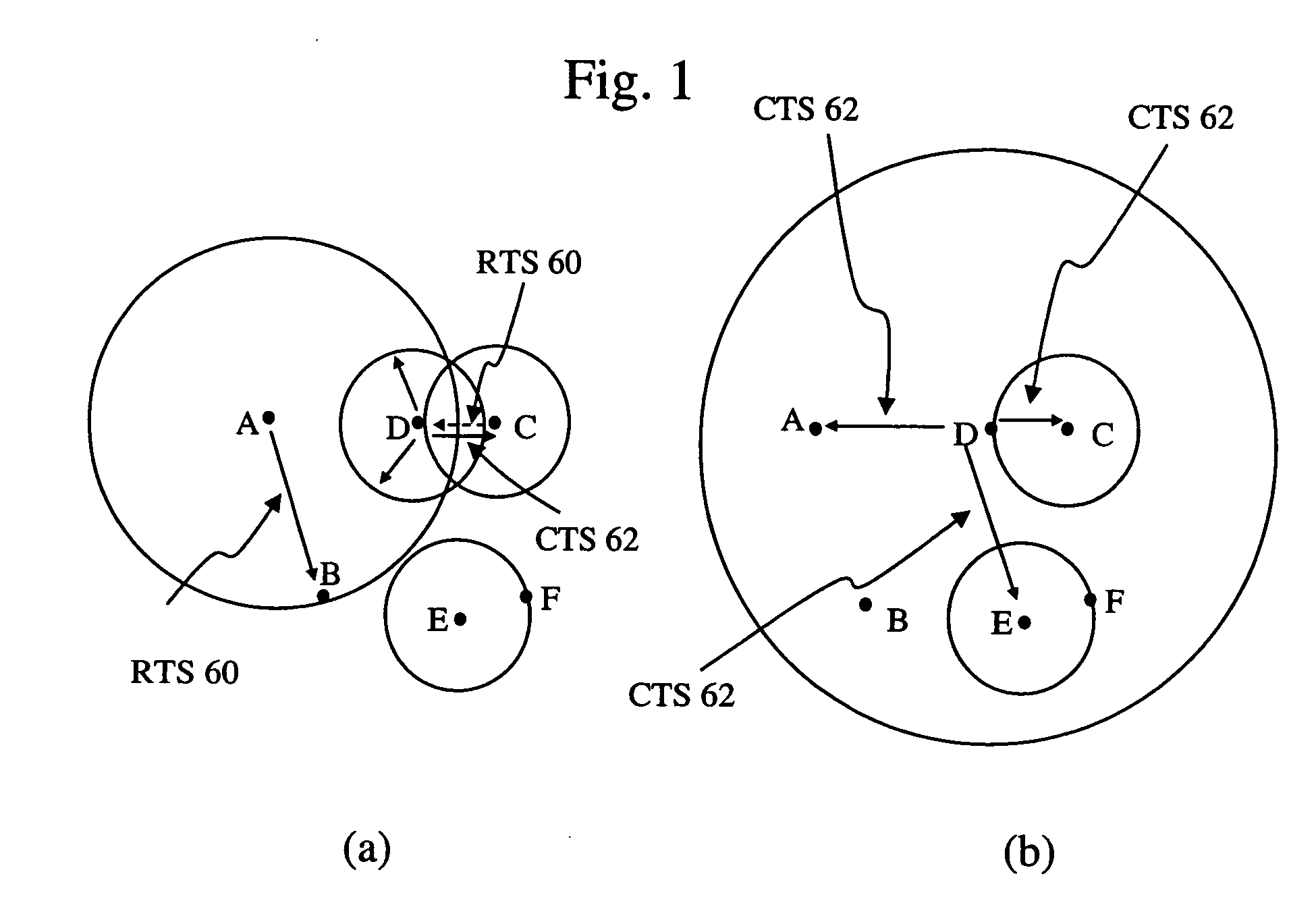
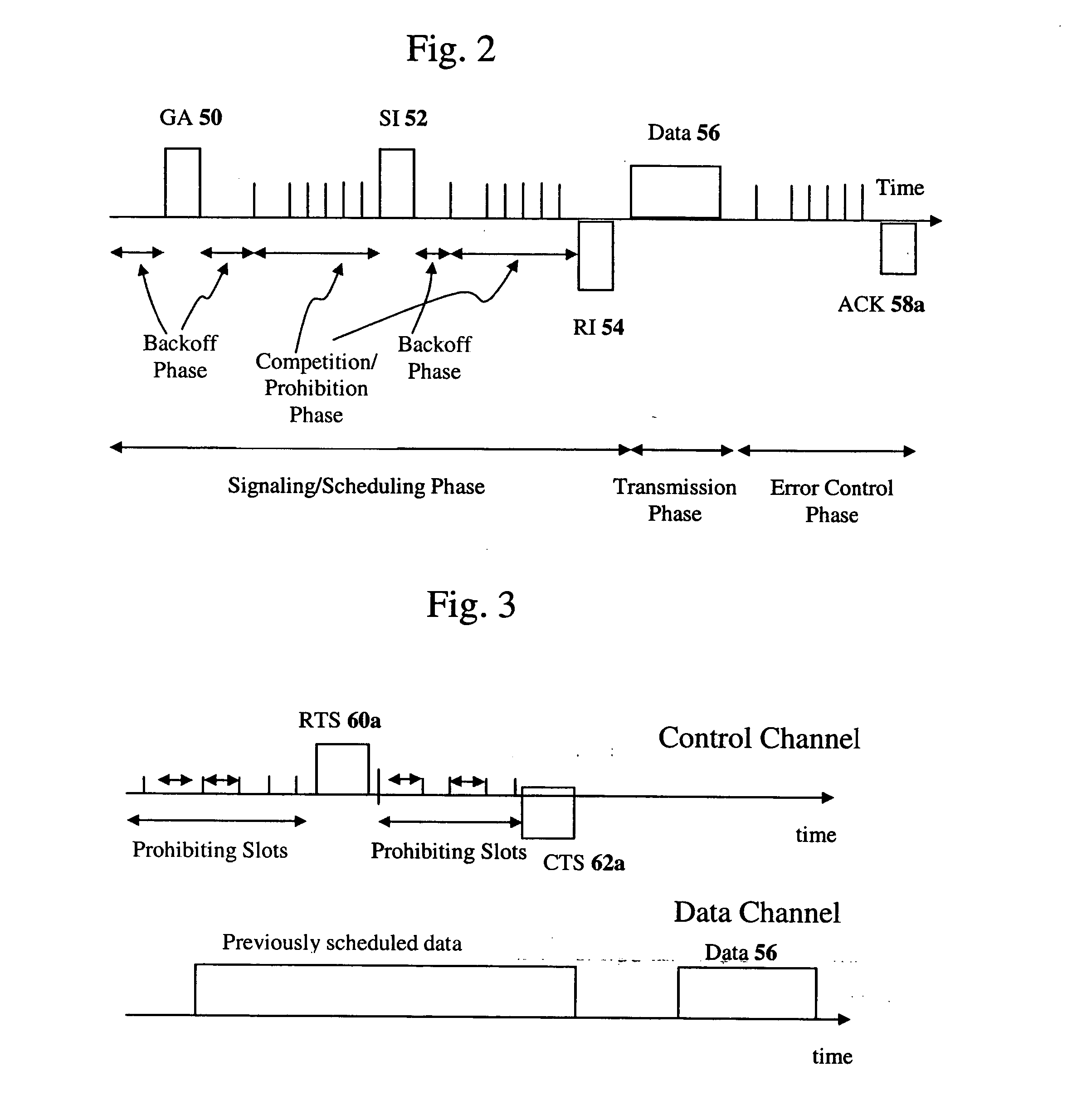
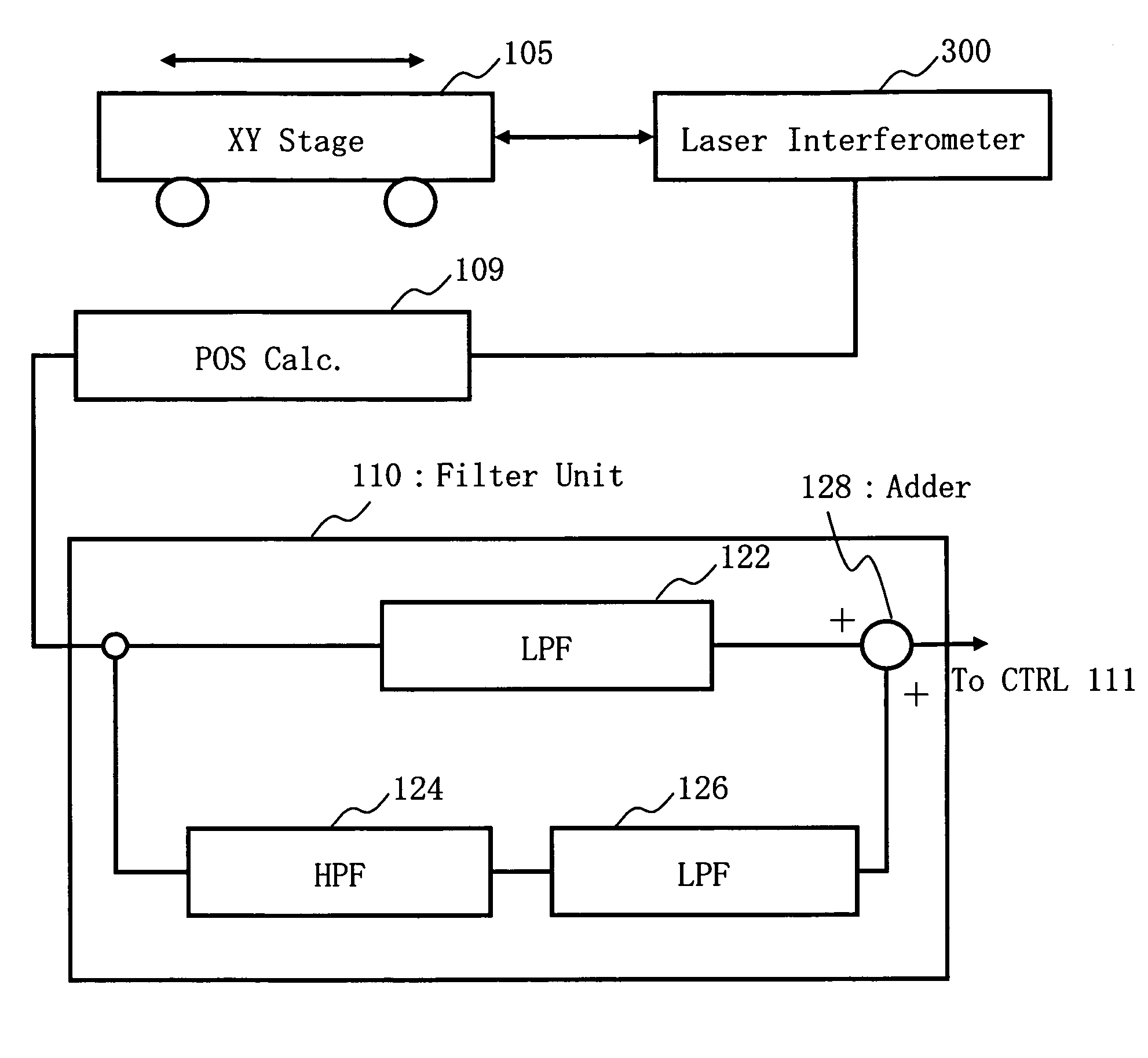
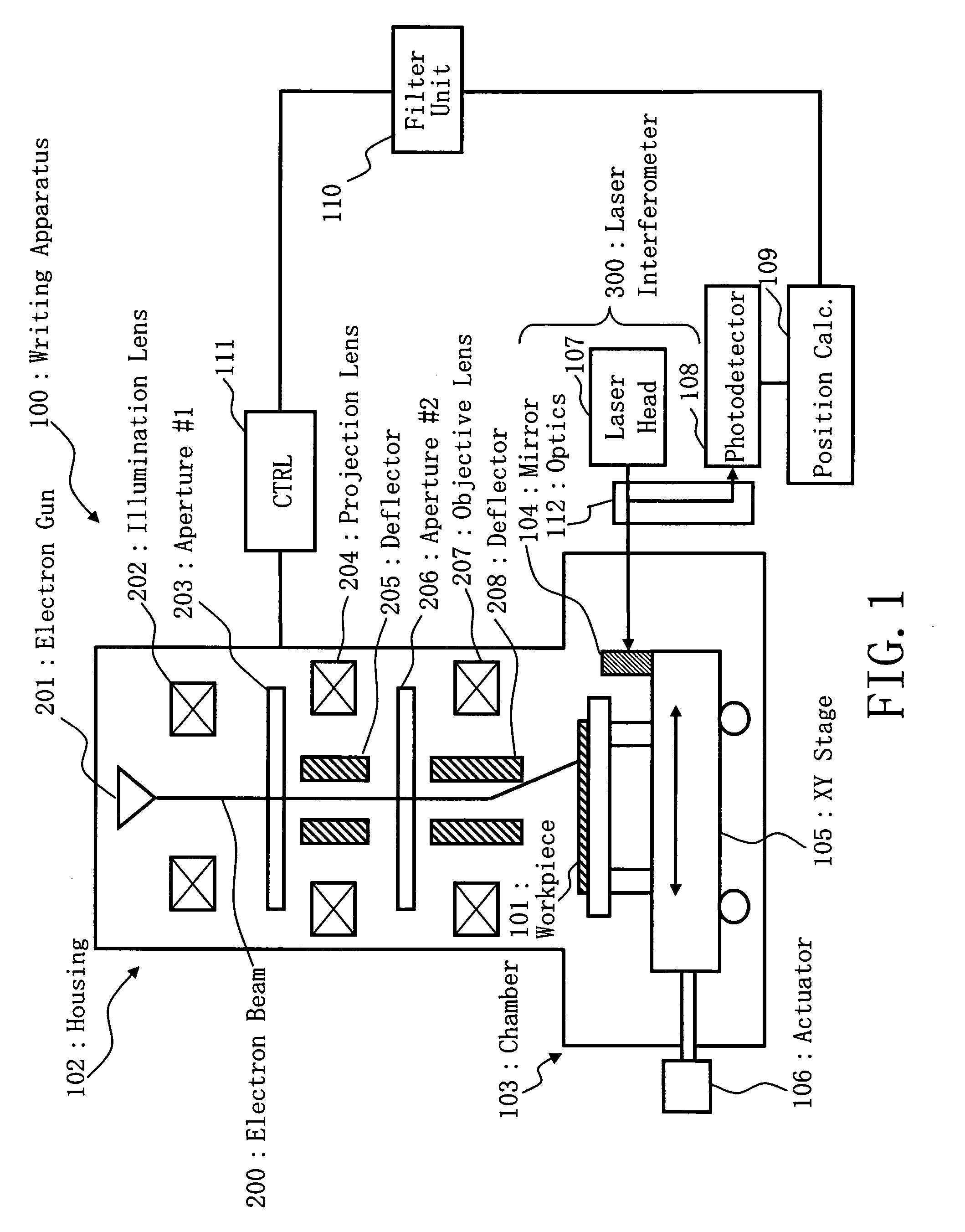
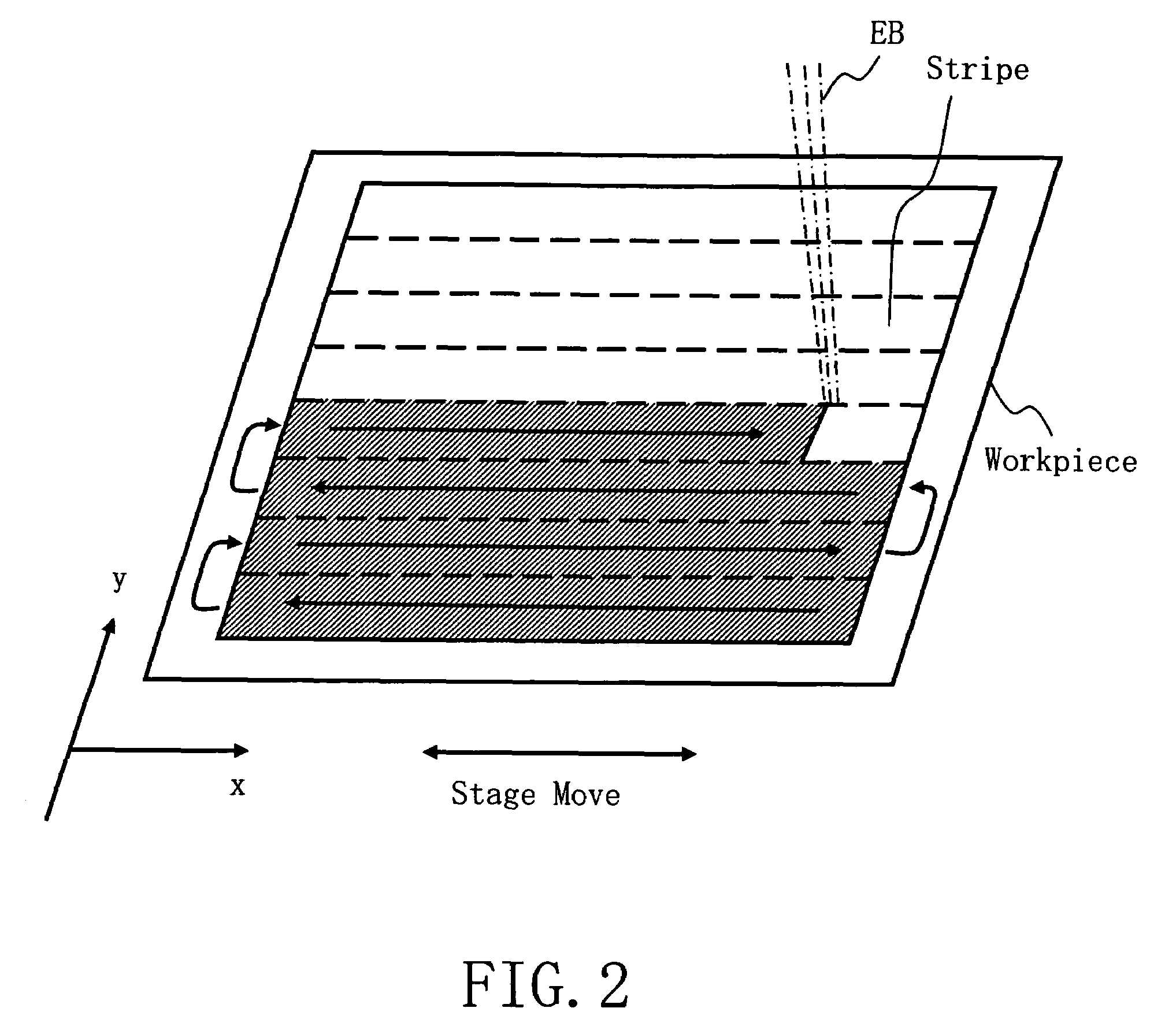
Position measurement apparatus and method and pattern forming apparatus and writing method
ActiveUS7640142B2Accurate measurementAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceElectric discharge tubesLaserElectrical and Electronics engineering
A position measurement apparatus includes a movable stage structure, a measurement unit using a laser to measure a moved position of the stage and to output a corresponding measured value, a first filter configured to attenuate a first component of a certain frequency region of the measured value outputted by the measurement unit, a second filter connected in parallel with the first filter configured to attenuate a second component other than the certain frequency region of the measured value outputted by the measurement unit, a third filter connected in series to the second filter with the series connection of the second and third filters connected in parallel with the first filter, configured to attenuate the first component of the certain frequency region of the measured value outputted by the measurement unit, and a processing unit configured to combine an output of the first filter and an output of the series connection of the second and third filters and to thereby output a first combined value.
Owner:NUFLARE TECH INC
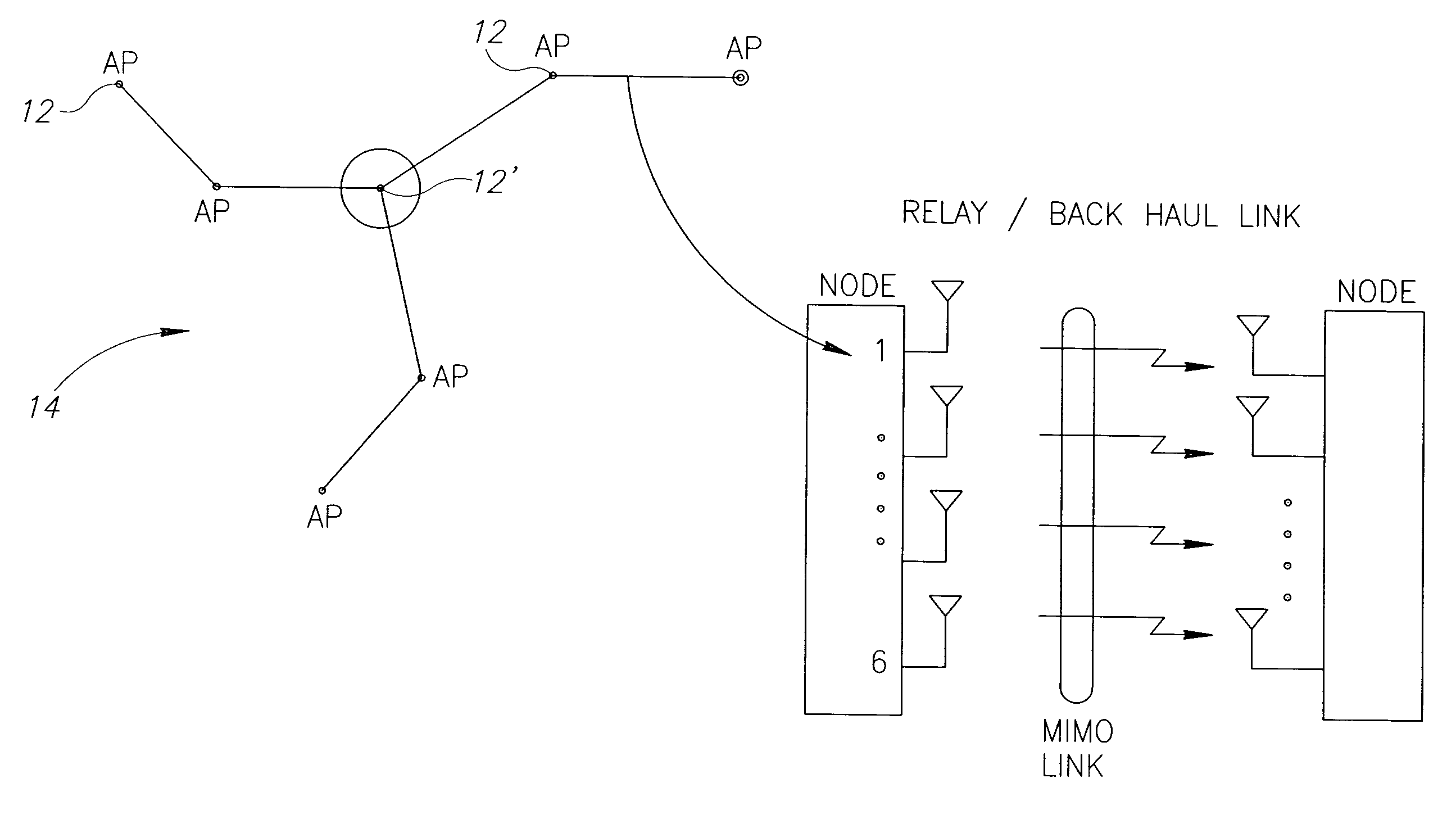
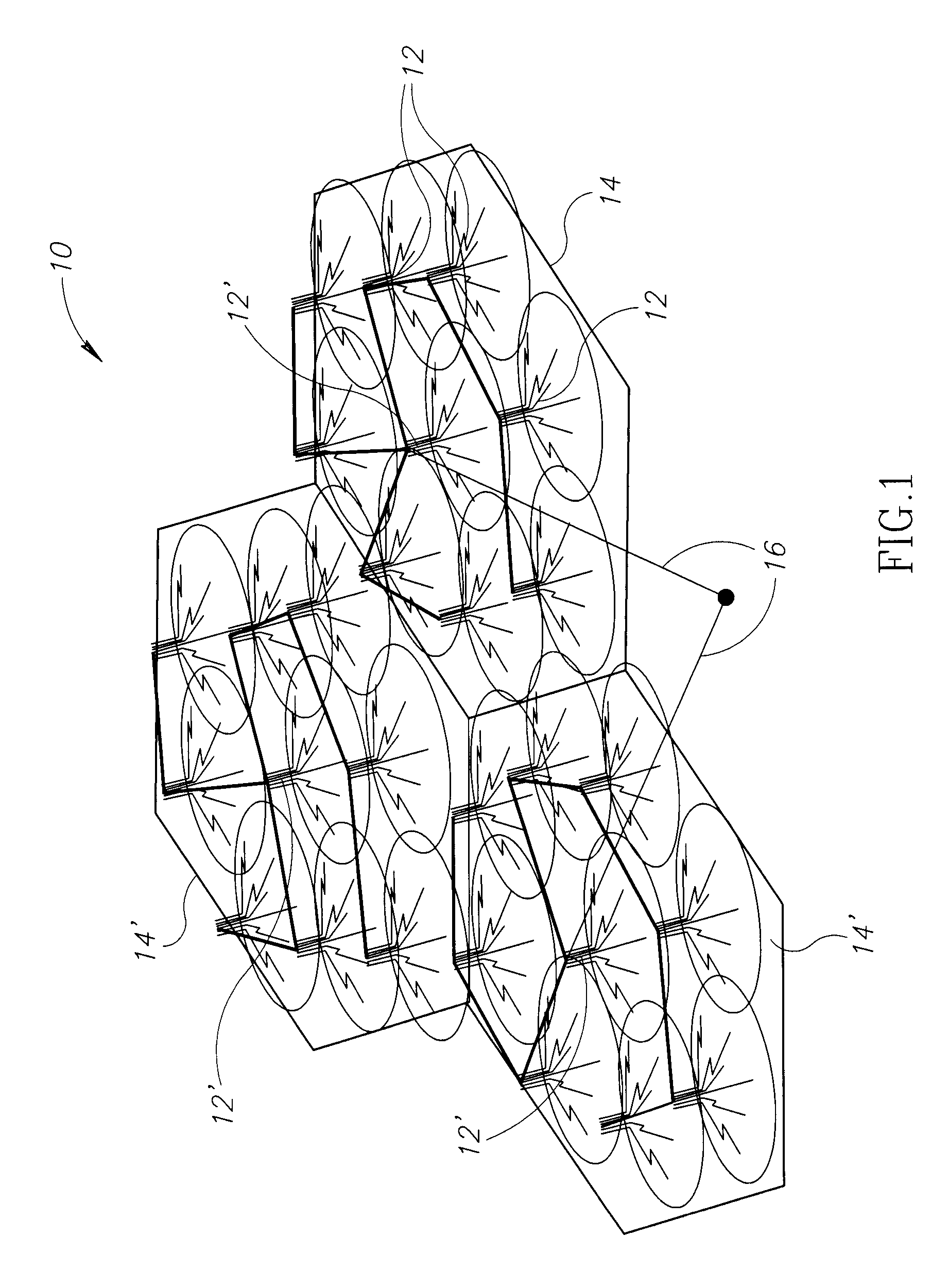
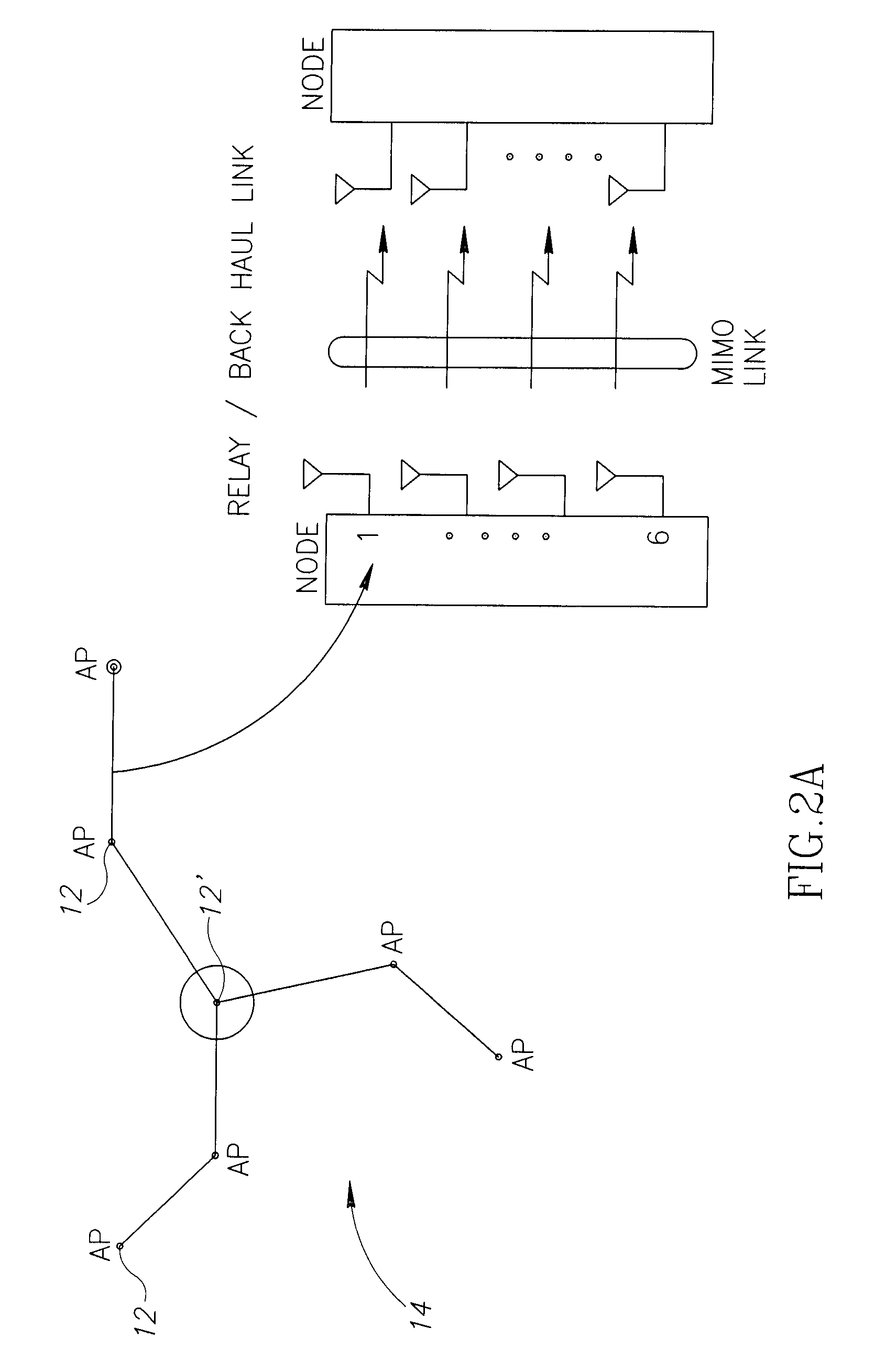
Mobile broadband wireless access point network with wireless backhaul
ActiveUS7620370B2Low costLarge capacityPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementTransceiverModem device
A WiMAX network and communication method, the network including a plurality of WiMAX nodes deployed in micro or pico cells for providing access service to a plurality of mobile subscribers, a plurality of these nodes being arranged in a cluster, one of the nodes in each cluster being a feeder node coupled to a core network, the nodes in each cluster being coupled for multi-hop transmission to the feeder node. According to a preferred embodiment, each node includes a transceiver with associated modem, an antenna arrangement coupled to the modem and arranged for multiple concurrent transmissions, and a MAC controller for controlling the transceiver, modem and antenna arrangement for providing both access and backhaul communication.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Variable gain active noise canceling system with improved residual noise sensing
InactiveUS6118878AReduce the possibilityCancellation system retains its effectiveness across its bandwidthNoise generationSound producing devicesInstabilityEngineering
An active noise cancellation system includes a series of features for more effective cancellation, greater reliability, and improved stability. A particular feature adapted for headset systems includes locating a residual microphone radially offset from the center of a sound generator to detect a signal more similar to that incident upon the eardrum of the user. In addition, an open back headset design includes perforations on the side of the headset instead of the back, so that the perforations are less susceptible to inadvertent blockage. The system also includes a mechanism for detecting changes in the acoustic characteristics of the environment that may be caused, for example, by pressure exerted upon the earpieces, and that may destabilize the cancellation system. The system automatically responds to such changes, for example, by reducing the gain or the frequency response of the system to preserve stability. The system further includes other methods for detecting imminent instability and compensating, such as detecting the onset of signals within enhancement frequencies characteristic of the onset of instability, and adjusting the gain or frequency response of the system or suppressing the enhanced signals. The system further includes a mechanism for conserving battery life by turning the system off when sound levels are low, or adjusting the power supply to the system to correspond to the current power requirements of the system.
Owner:NOISE CANCELLATION TECH
Non-optical signal isolator
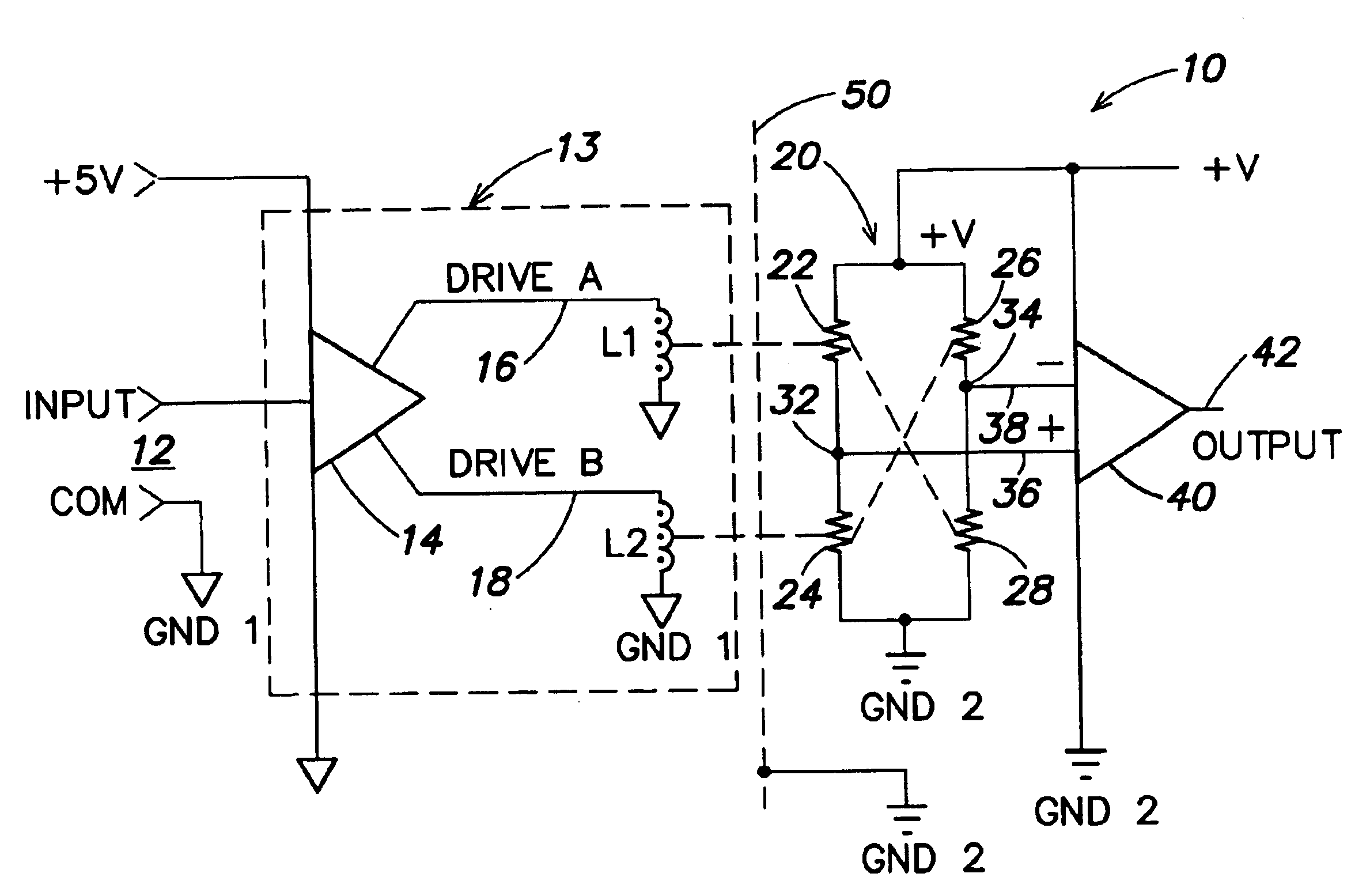
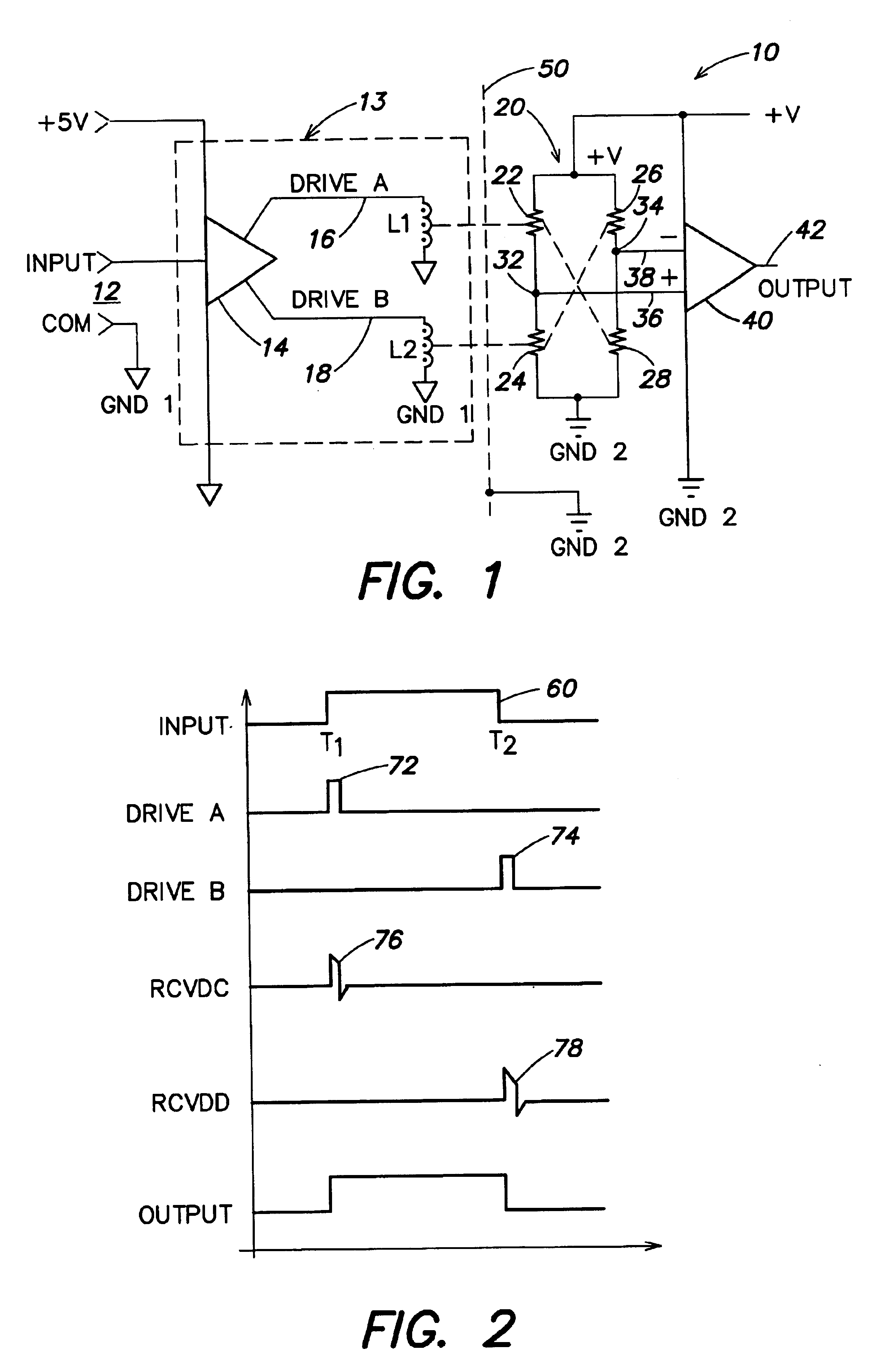
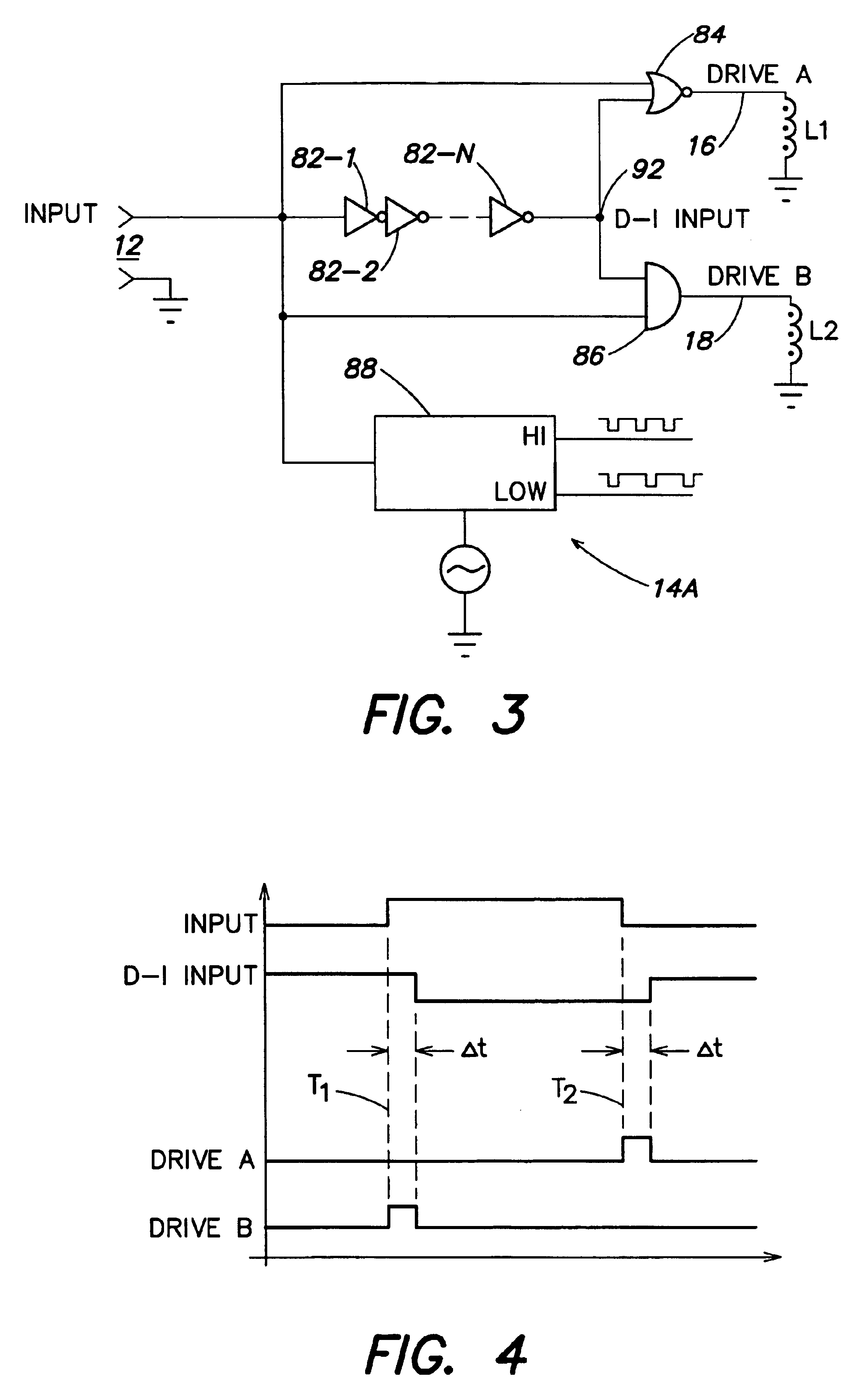
InactiveUS6873065B2Magnetic/electric field screeningSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDriver circuitOptical isolator
A non-optical isolator having a driver circuit for providing an input signal to one or more first passive components which are coupled across a galvanic isolation barrier to one or more corresponding second passive components, and an output circuit that converts the signal from the second passive components to an output signal corresponding to the input signal. The entire structure may be formed monolithically as an integrated circuit on one or two die substrates, for low cost, small size, and low power consumption. The passive components may be coils or capacitor plates, for example. When the first and second passive components are capacitor plates, a Faraday shield may be provided between them, with the first and second passive components being referenced to separate grounds and the Faraday shield referenced to the same ground as the second passive components.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Method and apparatus for adaptive carrier allocation and power control in multi-carrier communication systems
InactiveUS6751444B1Power managementFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemCarrier signal
An apparatus and process for allocating carriers in a multi-carrier system is described. In one embodiment, the process comprises determining a location of a subscriber with respect to a base station, selecting carriers from a band of carriers to allocate to the subscriber according to the location of the subscriber with respect to the base station, and allocating selected carriers to the subscriber.
Owner:KAON SYST +1
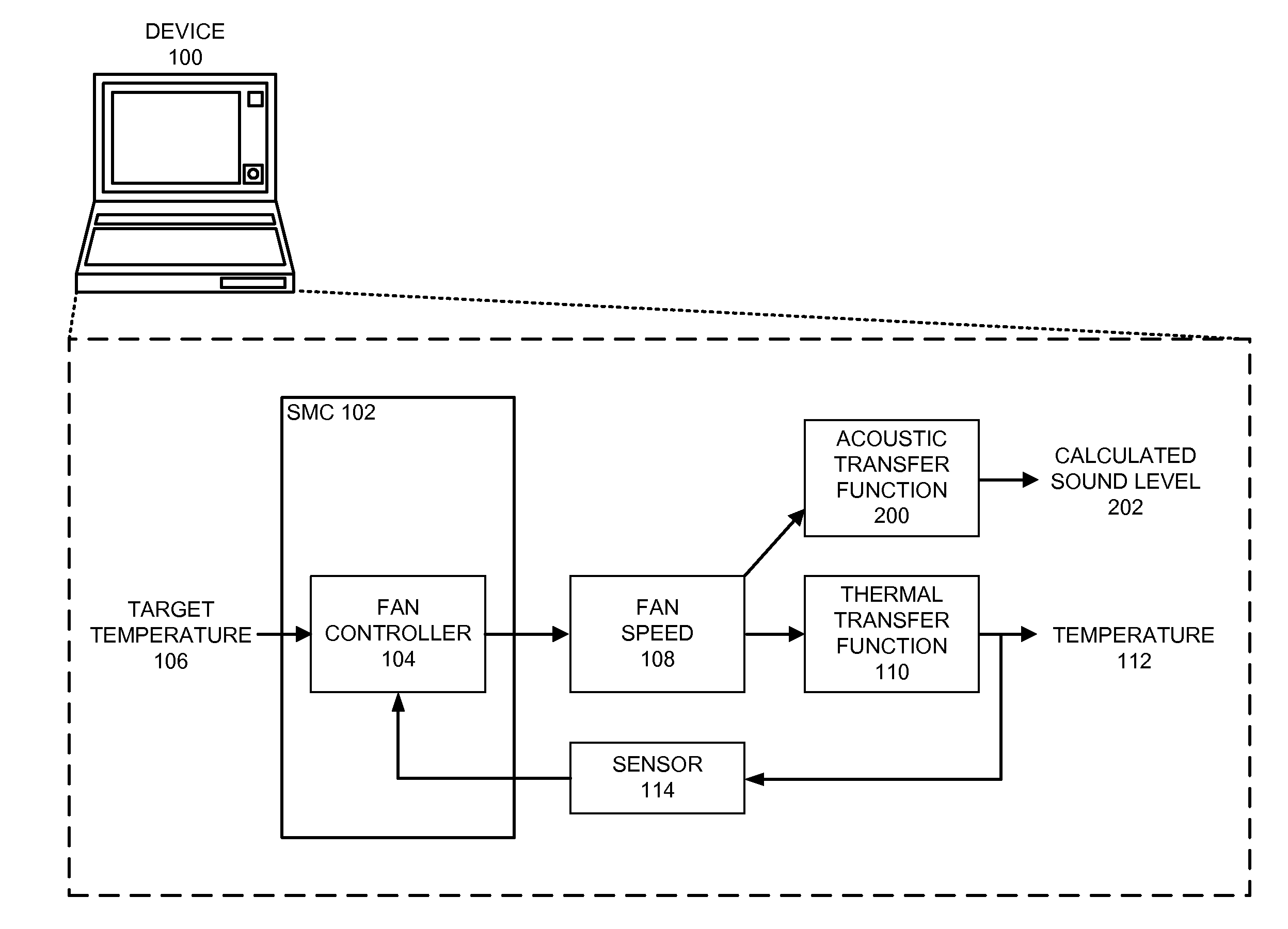
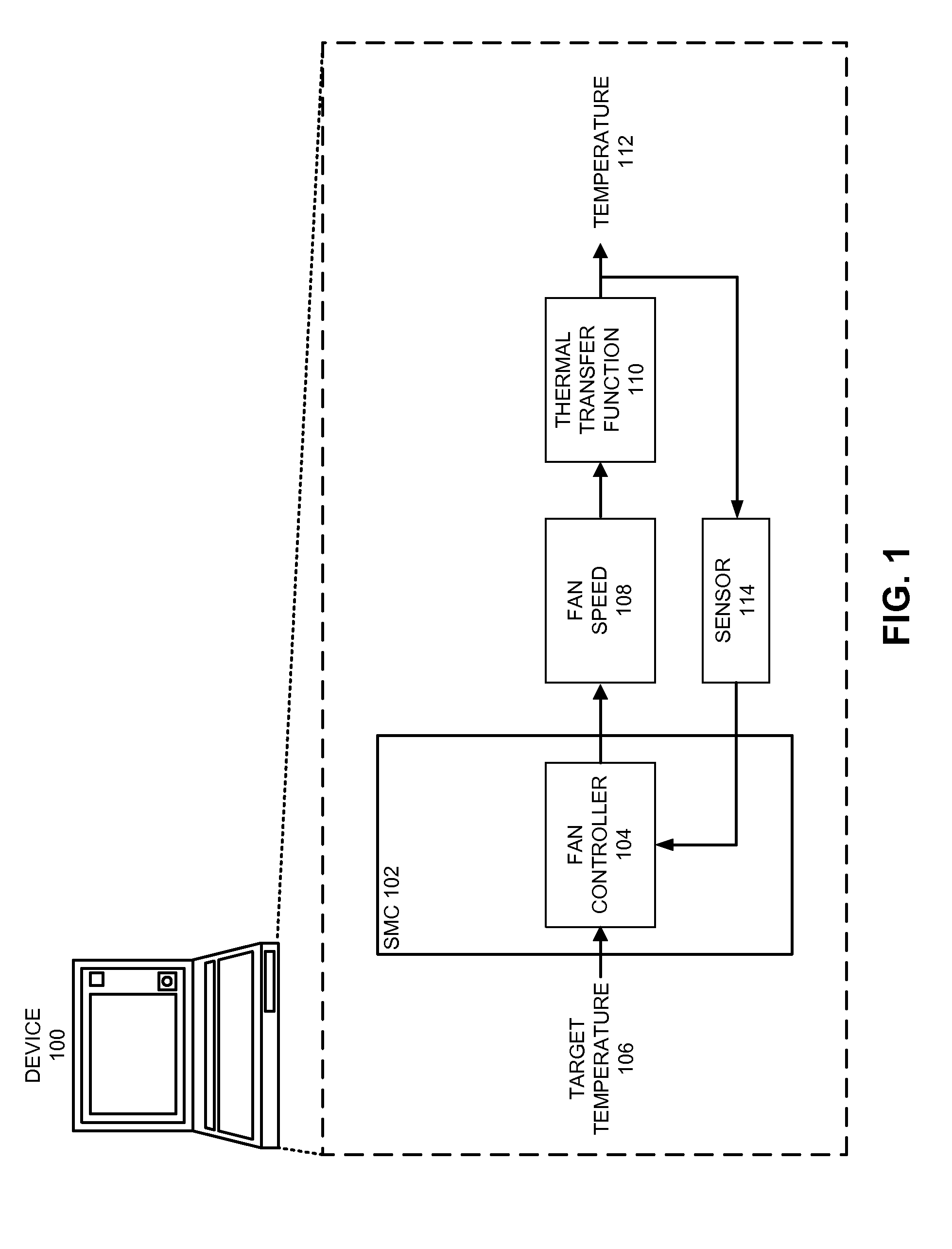
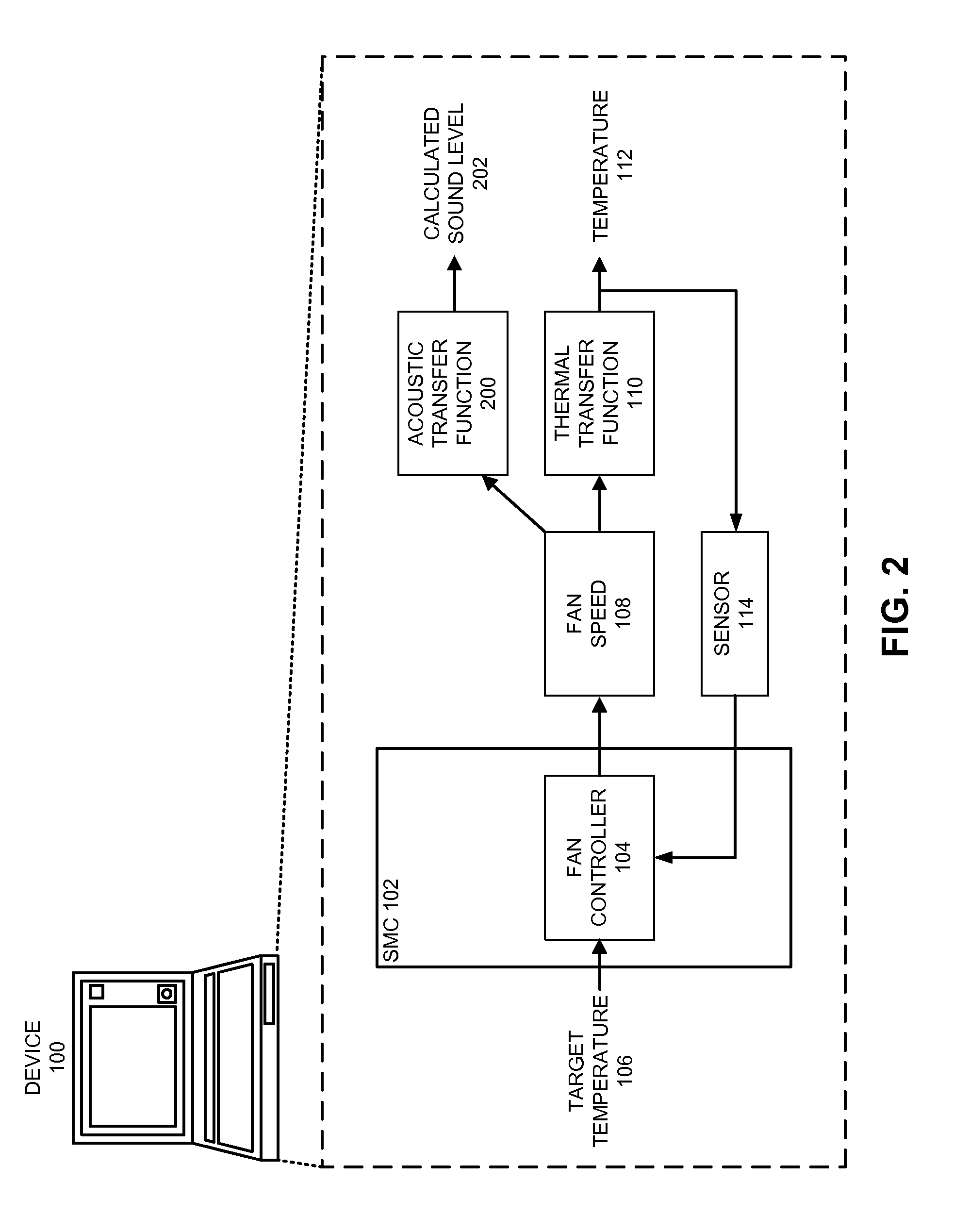
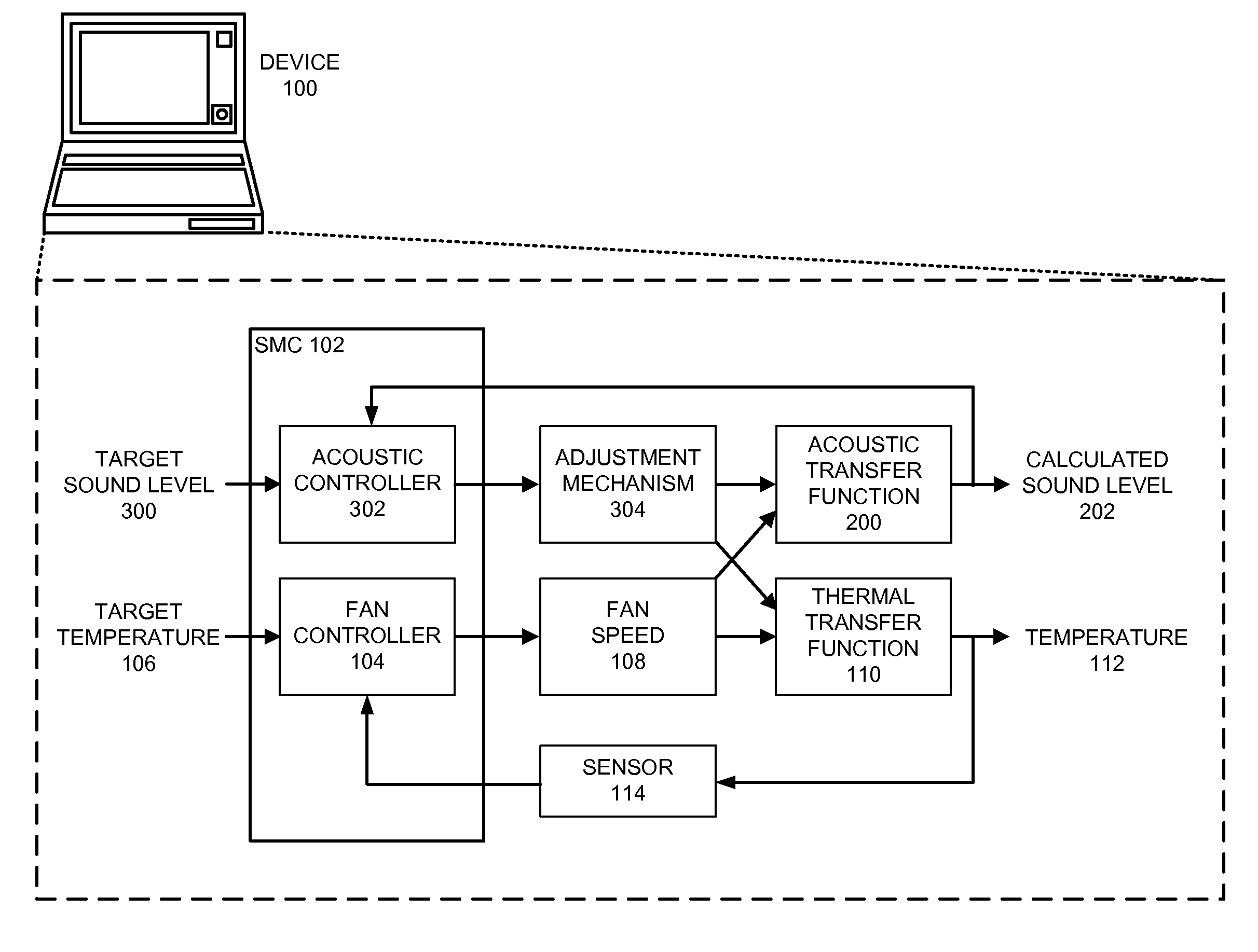
Reducing annoyance by managing the acoustic noise produced by a device
ActiveUS20090092261A1Less worryReduce user annoyanceEnergy efficient ICTEar treatmentAcousticsNoise estimation
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that reduces annoyance by managing the acoustic noise produced by a device. During operation, the system receives a set of acoustic characteristics for noise-producing components within the device. The system then uses these acoustic characteristics to estimate the acoustic noise being generated by each of these noise-producing components. Next, the system aggregates this set of acoustic noise estimates to produce an aggregate estimate for the acoustic noise produced by the device. The system then analyzes this aggregate estimate using an acoustic annoyance model to determine the acoustic annoyance level. The system then adjusts a setting in the device to manage the acoustic annoyance level produced by the device.
Owner:APPLE INC
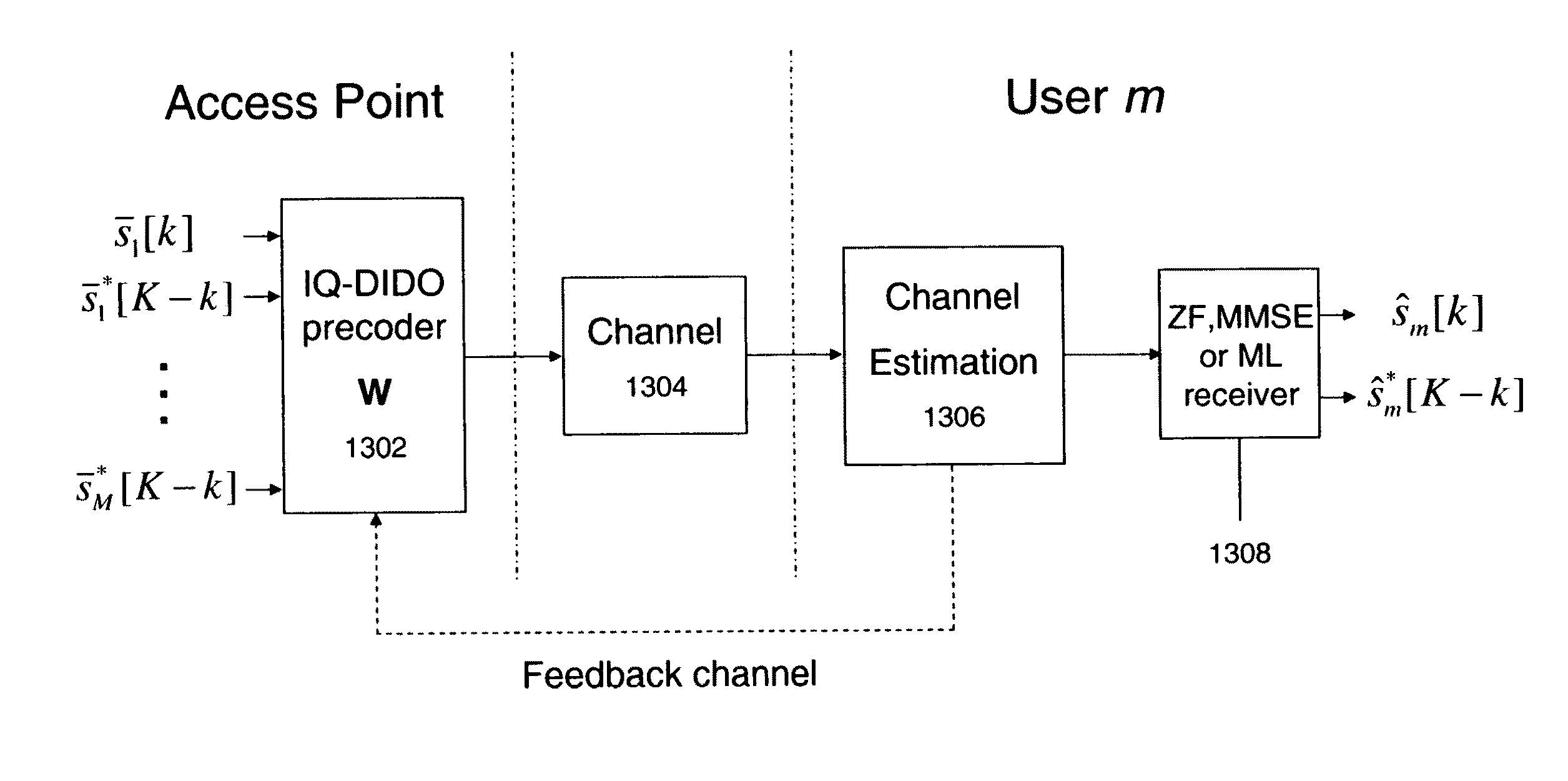
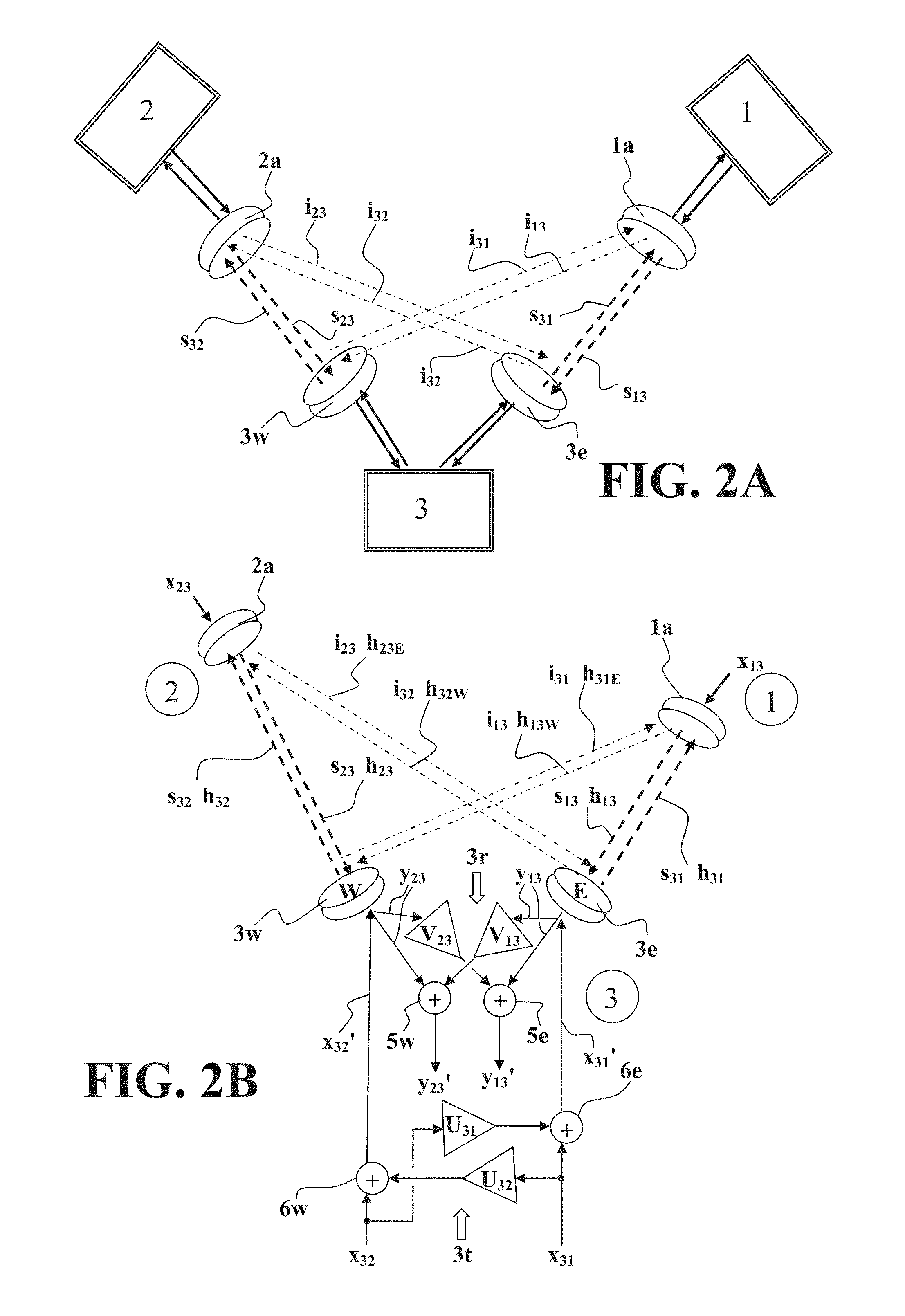
System and method for distributed input distributed output wireless communications
A system and method are described for compensating for frequency and phase offsets in a multiple antenna system (MAS) with multi-user (MU) transmissions (“MU-MAS”). For example, a method according to one embodiment of the invention comprises: transmitting a training signal from each antenna of a base station to one or each of a plurality of wireless client devices, one or each of the client devices analyzing each training signal to generate frequency offset compensation data, and receiving the frequency offset compensation data at the base station; computing MU-MAS precoder weights based on the frequency offset compensation data to pre-cancel the frequency offset at the transmitter; precoding training signal using the MU-MAS precoder weights to generate precoded training signals for each antenna of the base station; transmitting the precoded training signal from each antenna of a base station to each of a plurality of wireless client devices, each of the client devices analyzing each training signal to generate channel characterization data, and receiving the channel characterization data at the base station; computing a plurality of MU-MAS precoder weights based on the channel characterization data, the MU-MAS precoder weights calculated to pre-cancel frequency and phase offset and / or inter-user interference; precoding data using the MU-MAS precoder weights to generate precoded data signals for each antenna of the base station; and transmitting the precoded data signals through each antenna of the base station to each respective client device.
Owner:REARDEN LLC
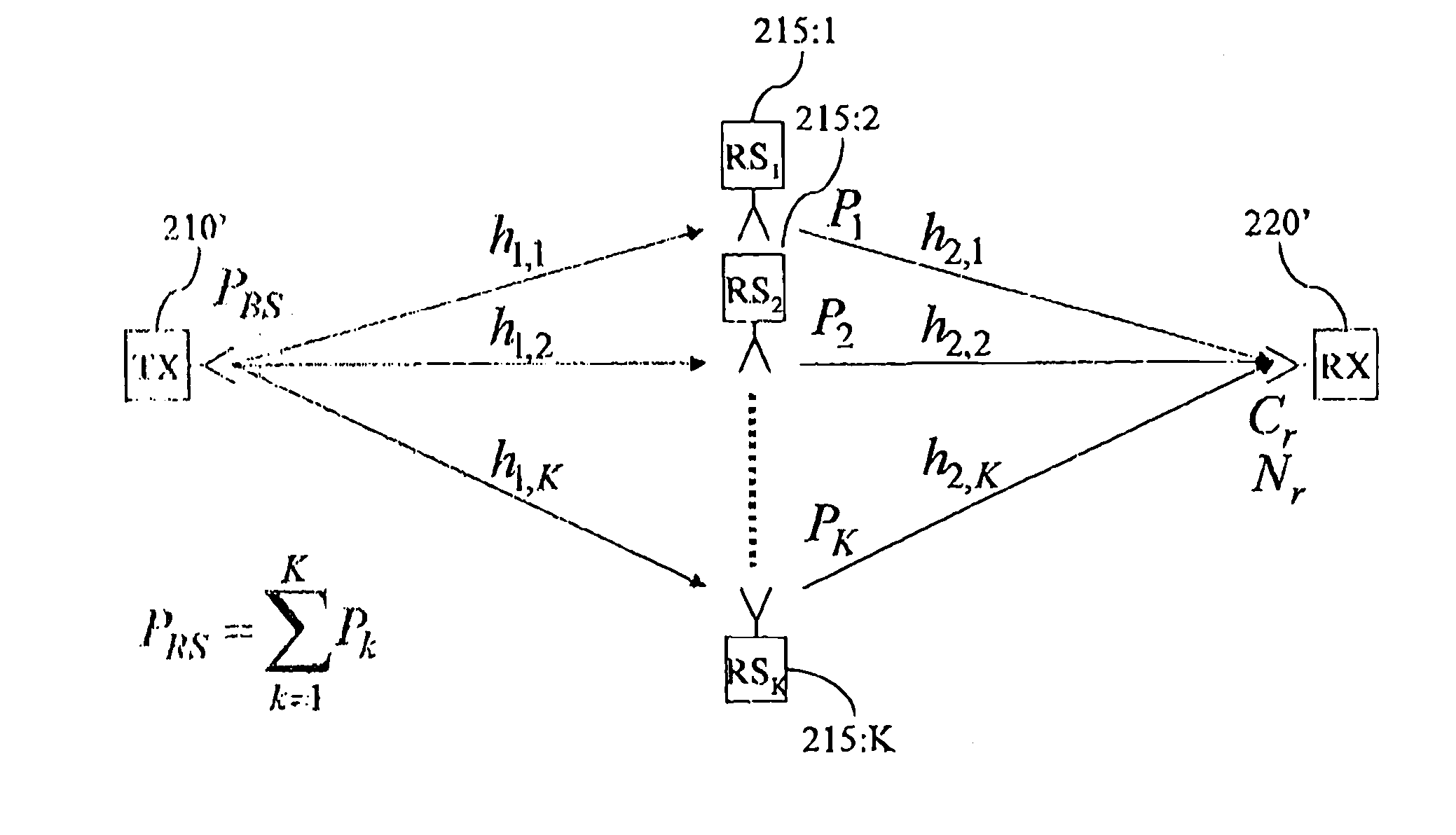
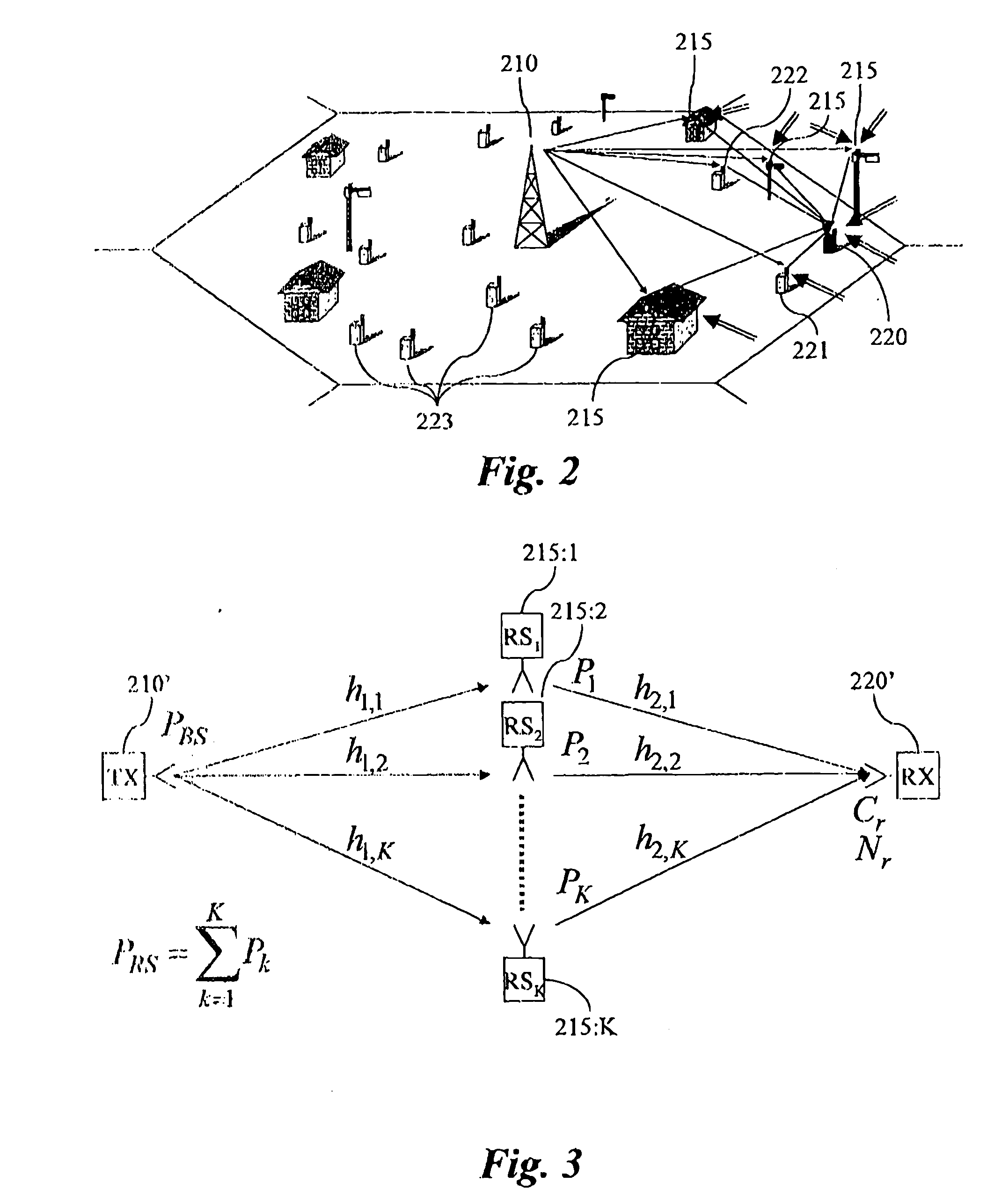
Method and system for wireless communication networks using relaying
InactiveUS20050014464A1Easy to adjustCharacterization is accurate and reliableSite diversityTransmission path divisionRadio channelTransmitter
The present invention relates to wireless networks using relaying. In the method according to the present invention of performing communication in a two-hop wireless communication network, a transmitter 210, a receiver 220 and at least one relay station 215 are engaged in a communication session. The relay station 215 forwards signals from a first link between the transmitter 210 and the relay station 215 to a second link between the relay stations 215 and the receiver 220. The forwarding performed by the at least one relay station 215 is adapted as a response to estimated radio channel characteristics of at least the first link. Preferably the forwarding is adapted as a response to estimated radio channel characteristics of both the first and second link.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
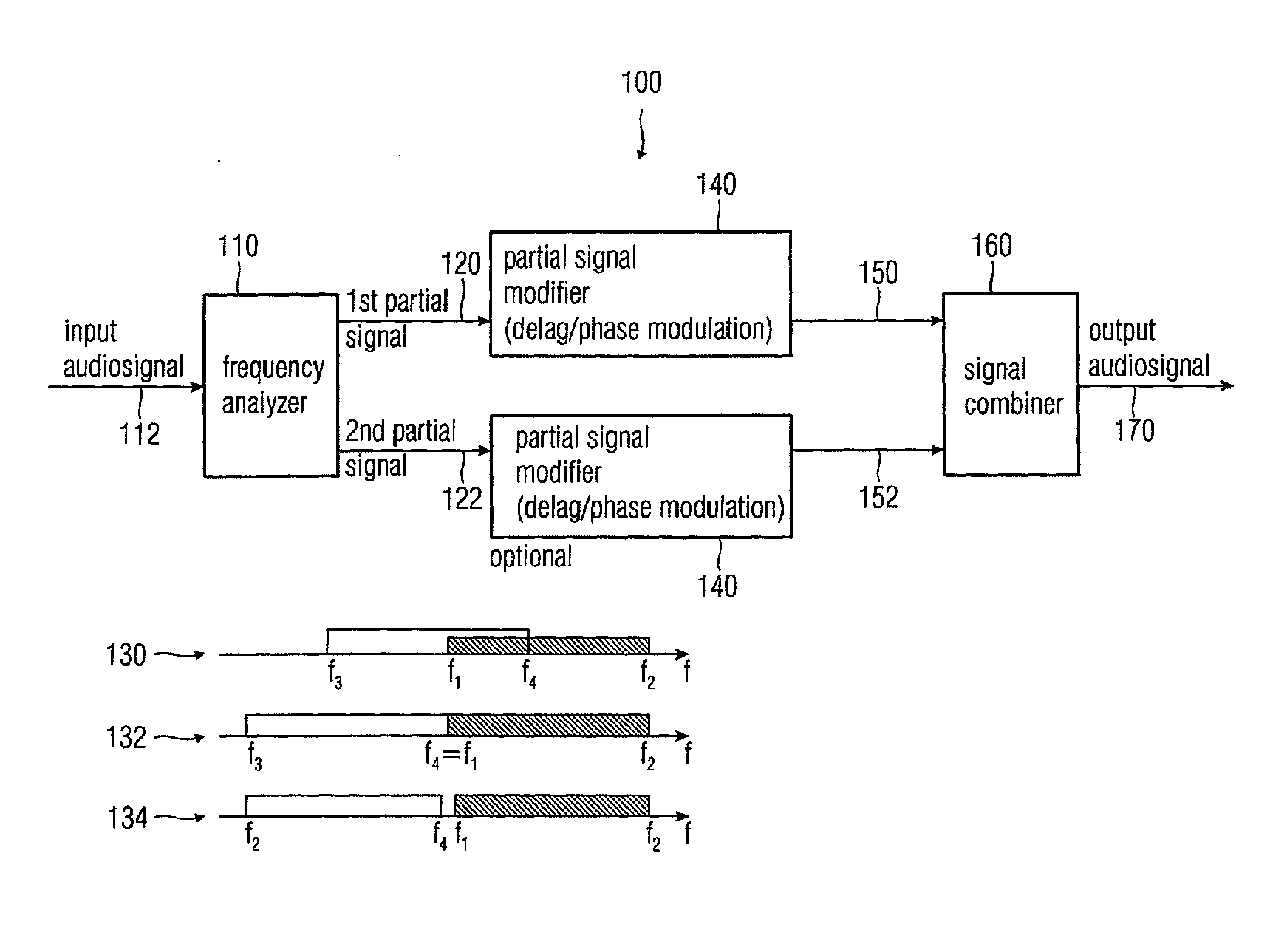
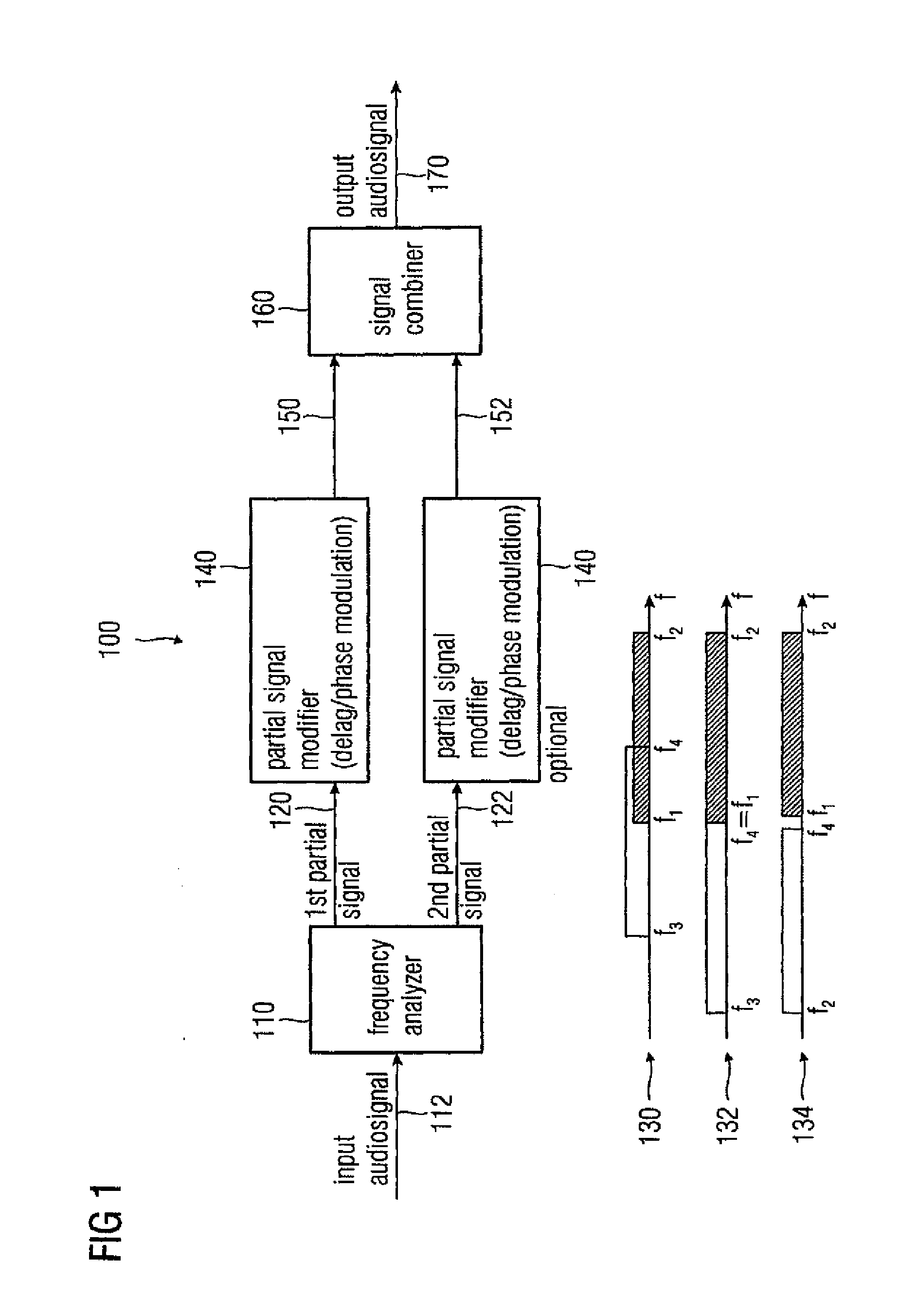
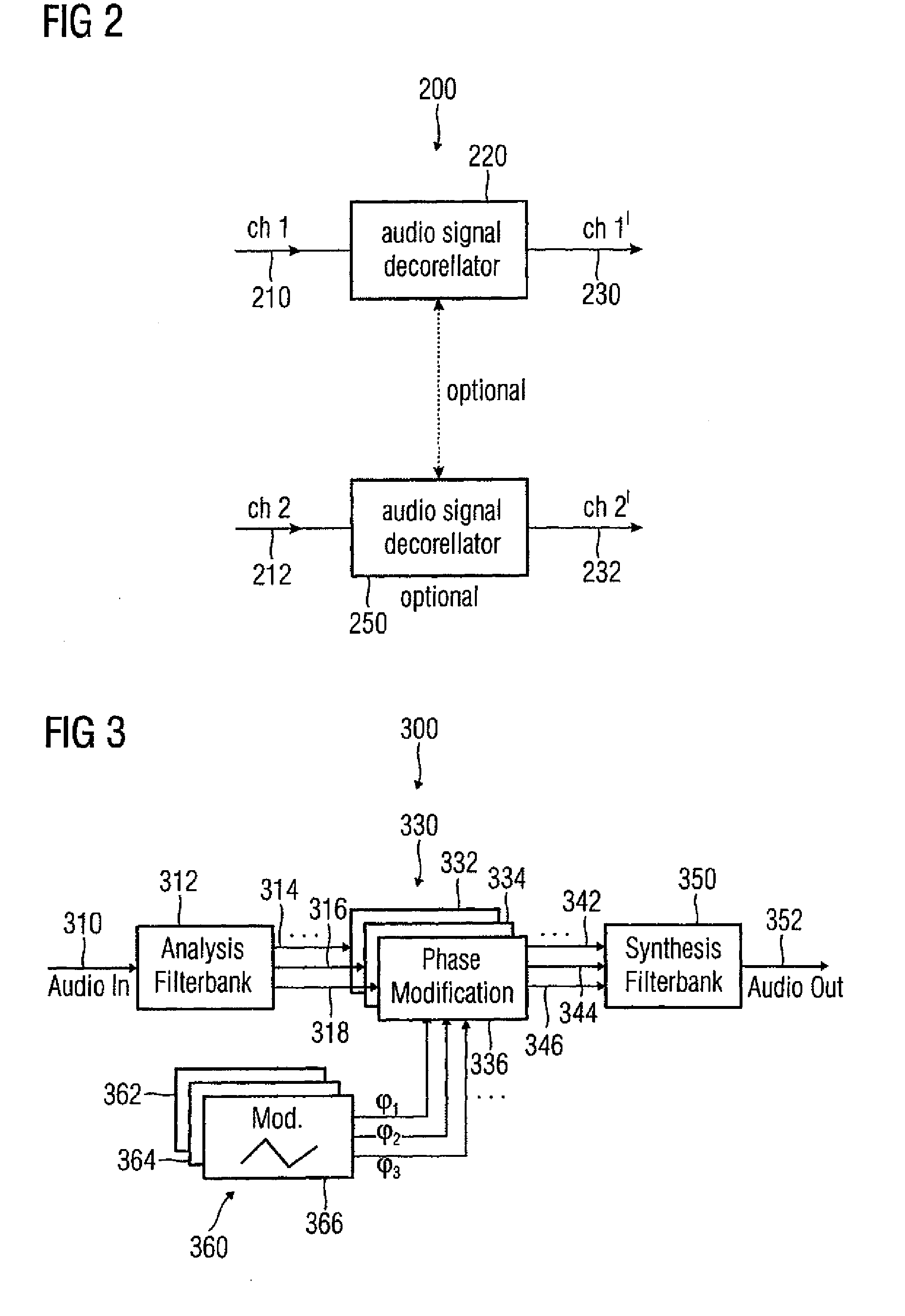
Audio signal decorrelator, multi channel audio signal processor, audio signal processor, method for deriving an output audio signal from an input audio signal and computer program
ActiveUS20090304198A1Simple designReducing and removing audio contentTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSpeech analysisVIT signalsAudio signal
An audio signal decorrelator for deriving an output audio signal from an input audio signal has a frequency analyzer for extracting from the input audio signal a first partial signal descriptive of an audio content in a first audio frequency range and a second partial signal descriptive of an audio content in a second audio frequency range having higher frequencies compared to the second audio frequency range. A partial signal modifier for modifies the first and second partial signals, to obtain first and second processed partial signals, so that a modulation amplitude of a time variant phase shift or time variant delay applied to the first partial signal is higher than that applied to the second partial signal, or for modifying only the first partial signal. A signal combiner combines the first and second processed partial signals, or combines the first processed partial signal and the second partial signal, to obtain an output audio signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
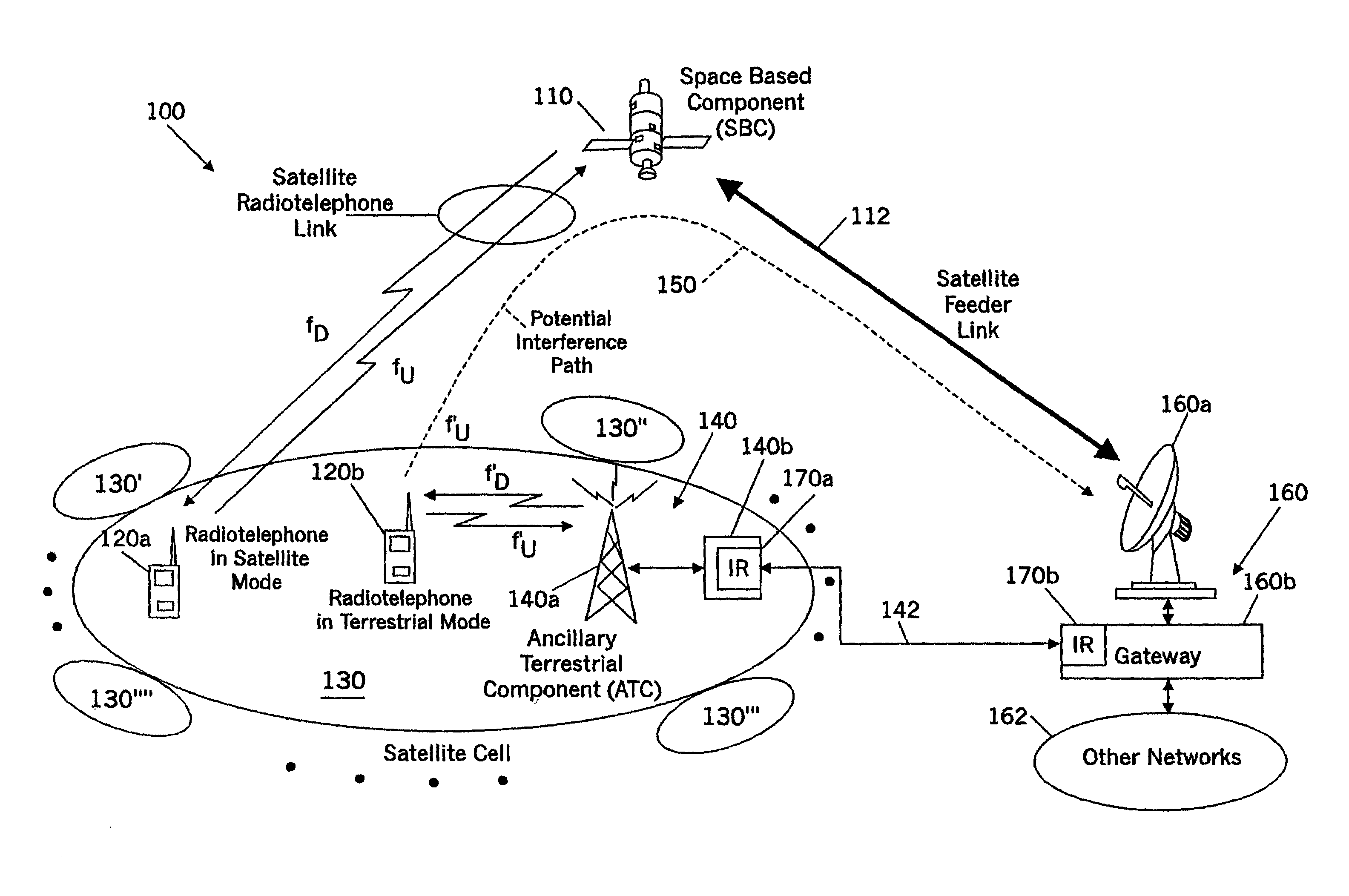
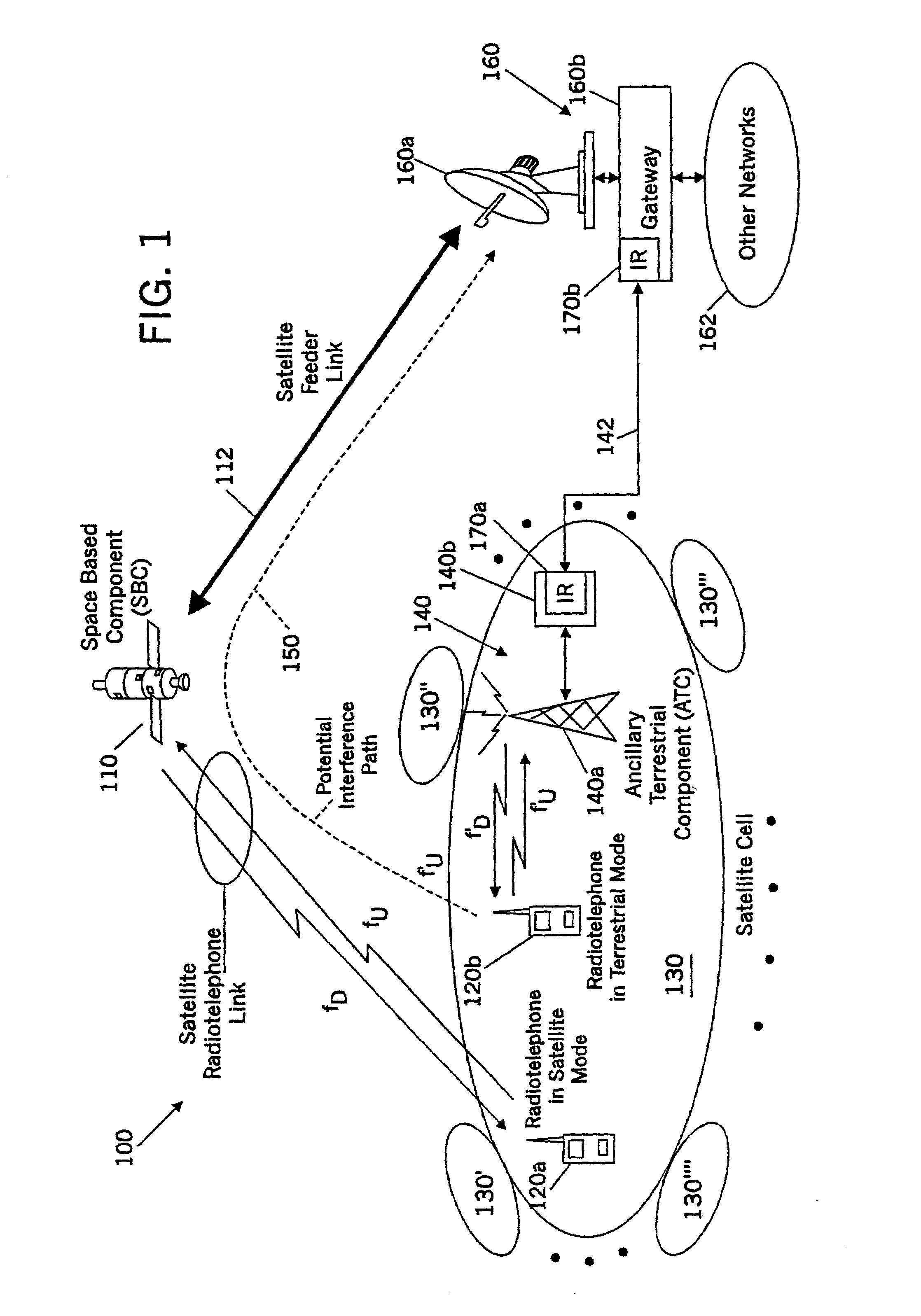
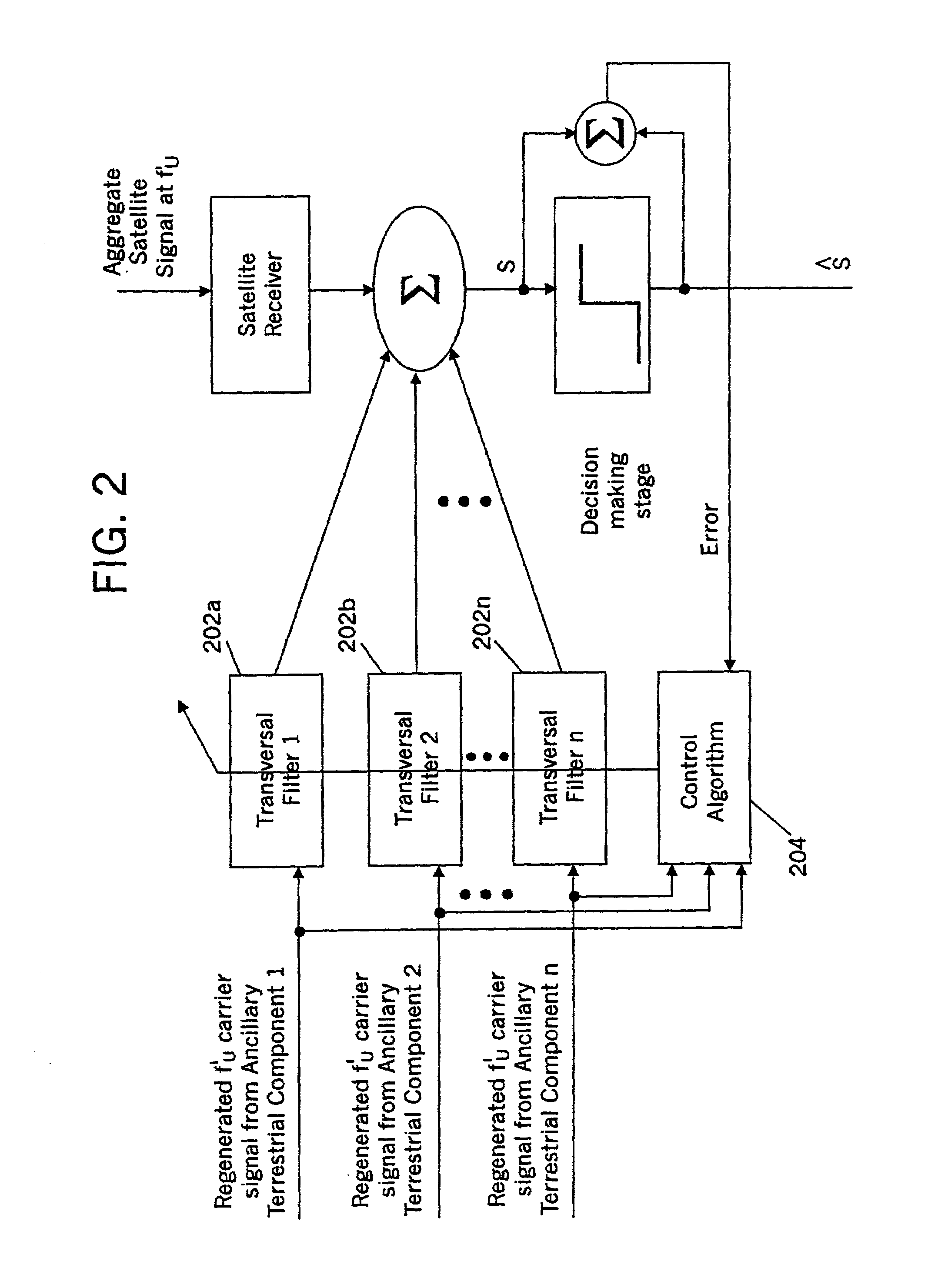
Spatial guardbands for terrestrial reuse of satellite frequencies
InactiveUS6999720B2Reduce distractionsAvoid interferenceTransmission monitoringRadio transmissionEngineeringSatellite
Satellite radiotelephone systems include a space-based component that is configured to provide wireless radiotelephone communications in a satellite footprint over a satellite radiotelephone frequency band. The satellite footprint is divided into a plurality of satellite cells, in which satellite radiotelephone frequencies of the satellite radiotelephone frequency band are spatially reused. An ancillary terrestrial network is configured to terrestrially reuse at least one of the ancillary radiotelephone frequencies that is used in a satellite cell in the satellite footprint, outside the cell and in some embodiments separated therefrom by a spatial guardband.
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
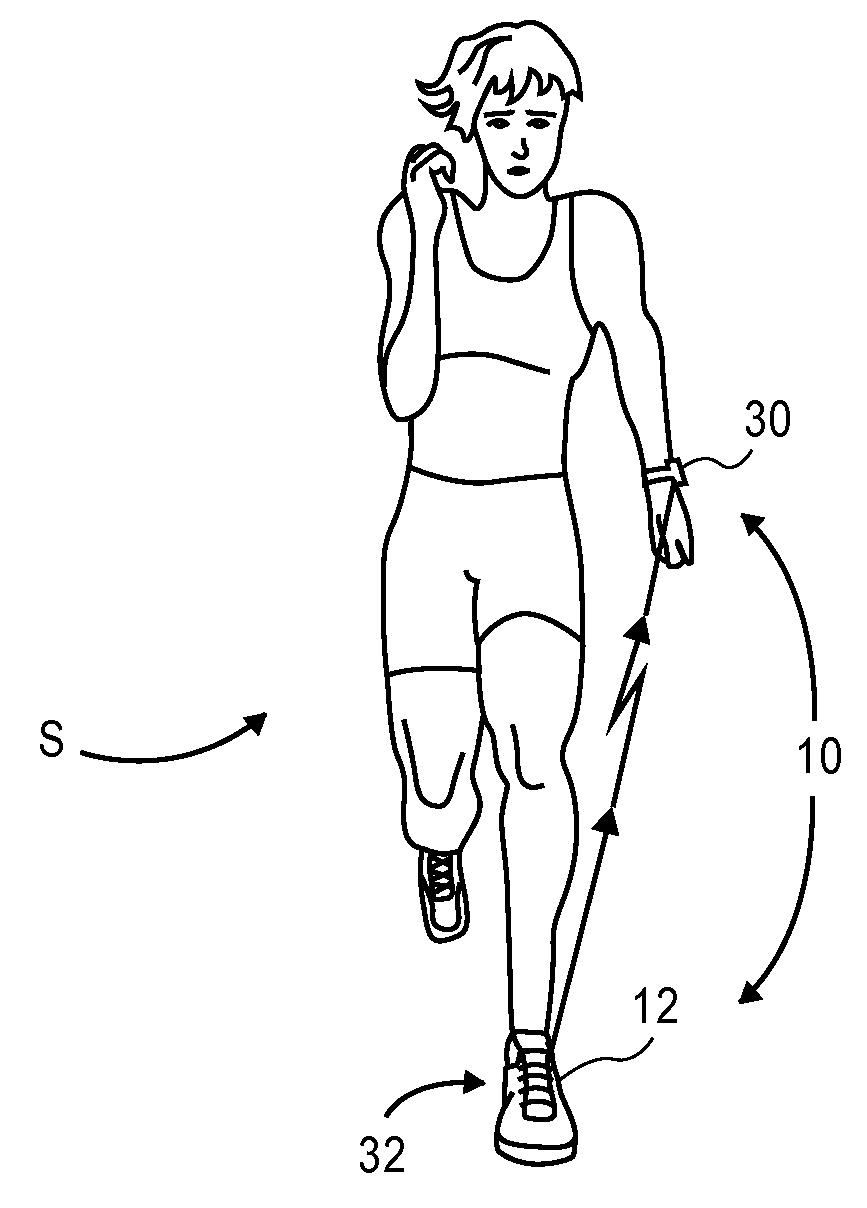
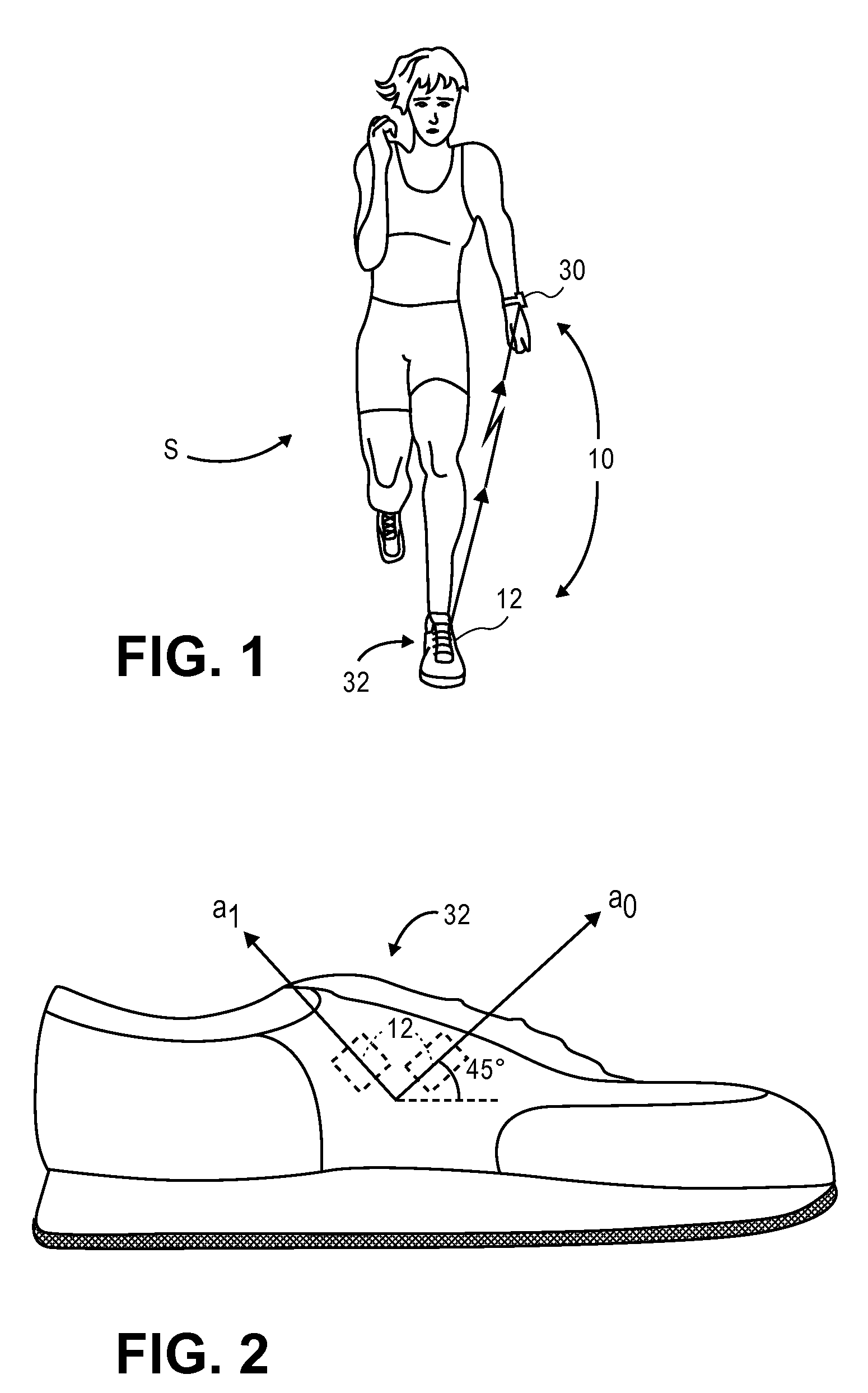
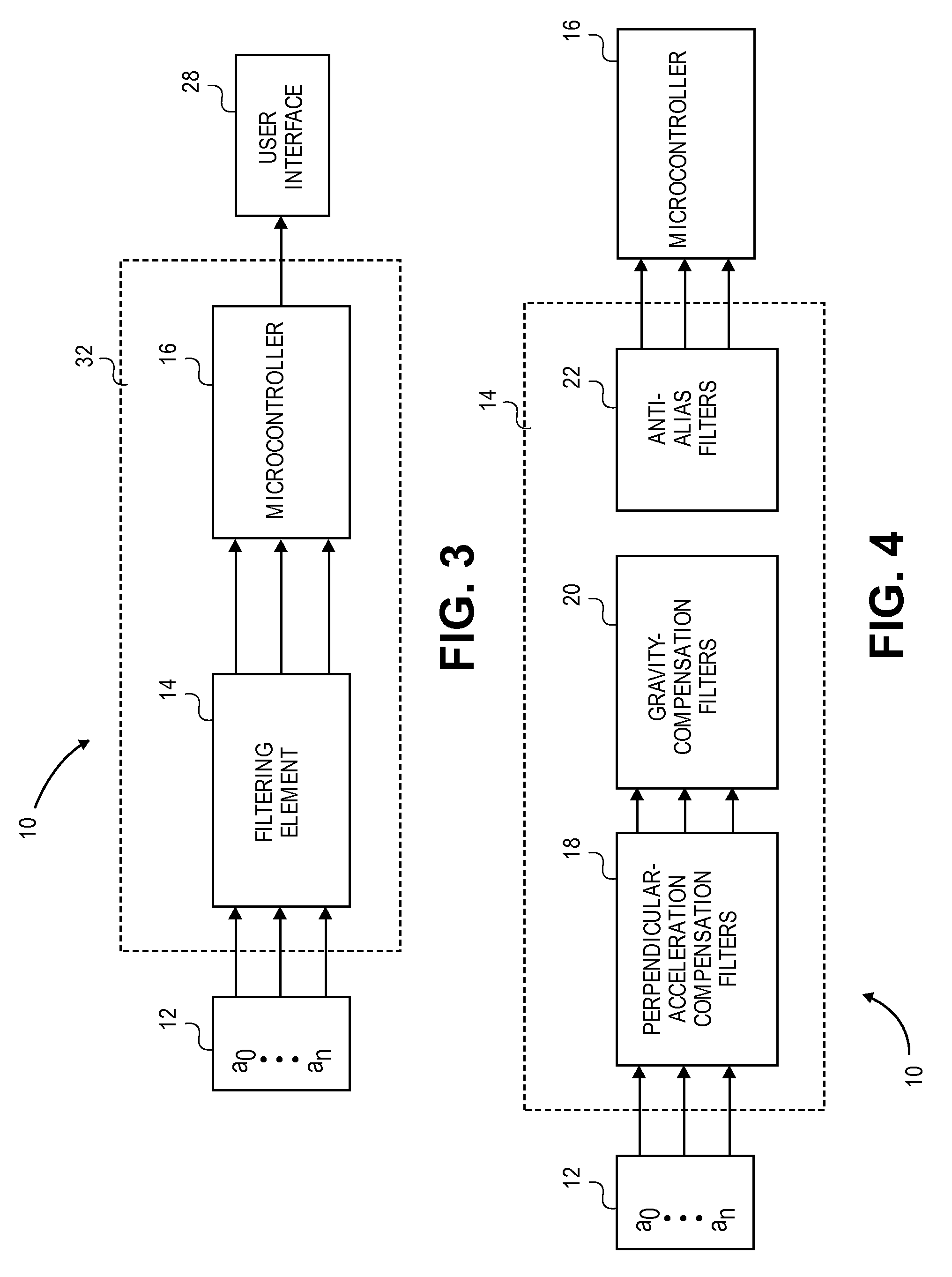
Method and apparatus for estimating a motion parameter
ActiveUS20070208544A1Accurately user performanceAccurate performancePhysical therapies and activitiesInertial sensorsAccelerometerMotion parameter
A method and apparatus for estimating a motion parameter corresponding to a subject element employs one or more accelerometers operable to measure accelerations and a processing system operable to generate a motion parameter metric utilizing the acceleration measurements and estimate the motion parameter using the motion parameter metric.
Owner:GARMIN
System and method for beamforming using a microphone array
InactiveUS20050195988A1Maximal noise suppressionIncrease widthPosition fixationMicrophones signal combinationEnvironmental noiseSound sources
The ability to combine multiple audio signals captured from the microphones in a microphone array is frequently used in beamforming systems. Typically, beamforming involves processing the output audio signals of the microphone array in such a way as to make the microphone array act as a highly directional microphone. In other words, beamforming provides a “listening beam” which points to a particular sound source while often filtering out other sounds. A “generic beamformer,” as described herein automatically designs a set of beams (i.e., beamforming) that cover a desired angular space range within a prescribed search area. Beam design is a function of microphone geometry and operational characteristics, and also of noise models of the environment around the microphone array. One advantage of the generic beamformer is that it is applicable to any microphone array geometry and microphone type.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and system of interference cancelation in collocated transceivers configurations
ActiveUS20130102254A1Reduce distractionsDegree of freedom is loweredTransmission noise suppressionVIT signalsTransceiver
The present invention, in some embodiments thereof, relates to a method of cancelling interference in a wireless system, wherein the interference introduced by an interfering signal causing reception of an interfered signal responsive to transmission of a desired signal, the method comprising acquiring the interfering signal from a transmitter during or before transmission thereof, generating an analog cancellation signal based on the acquired interfering signal, and injecting said analog cancellation signal into an interfered receiver receiving said interfered signal to reduce said interference therefrom.
Owner:UBIQAM
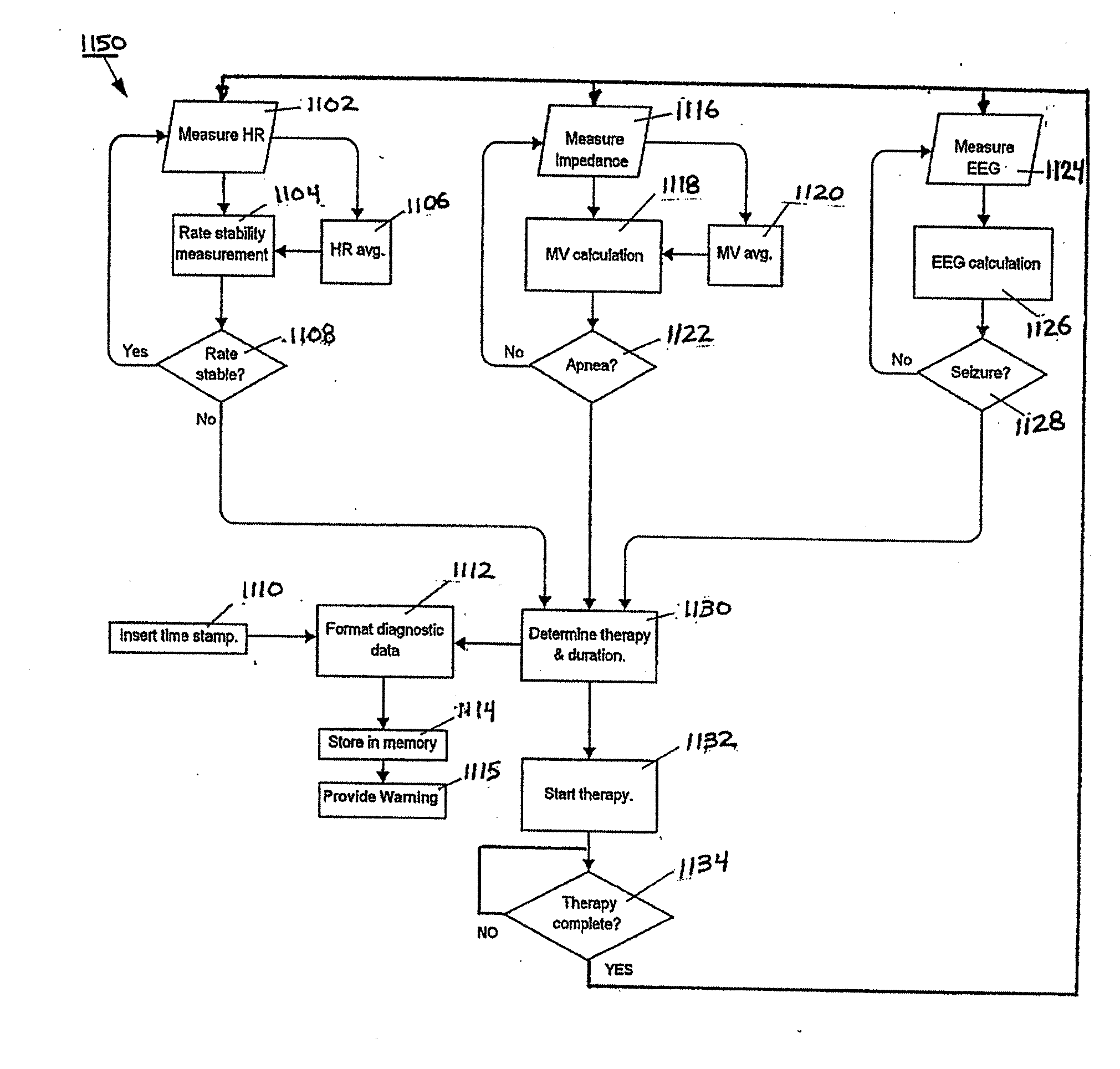
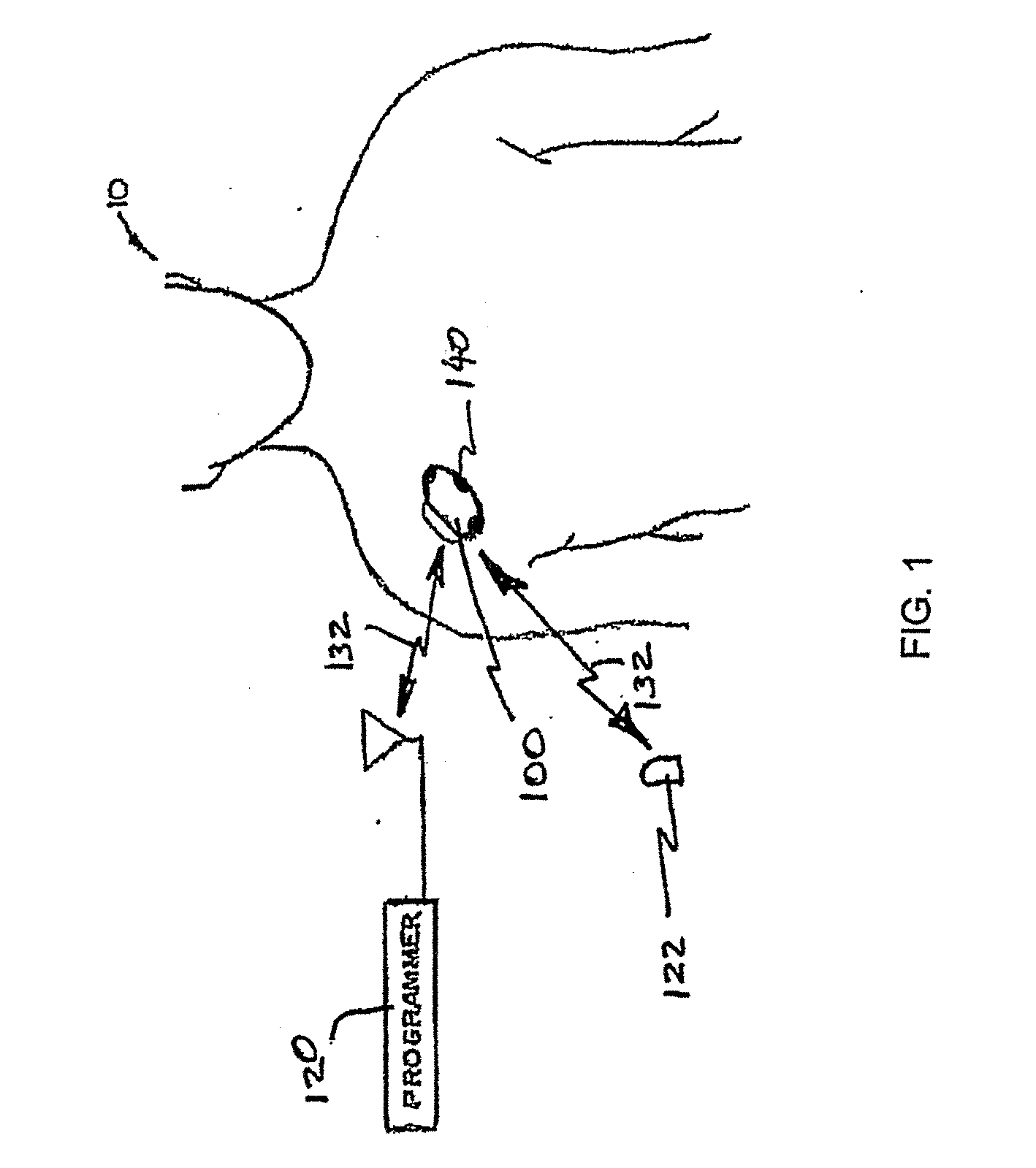
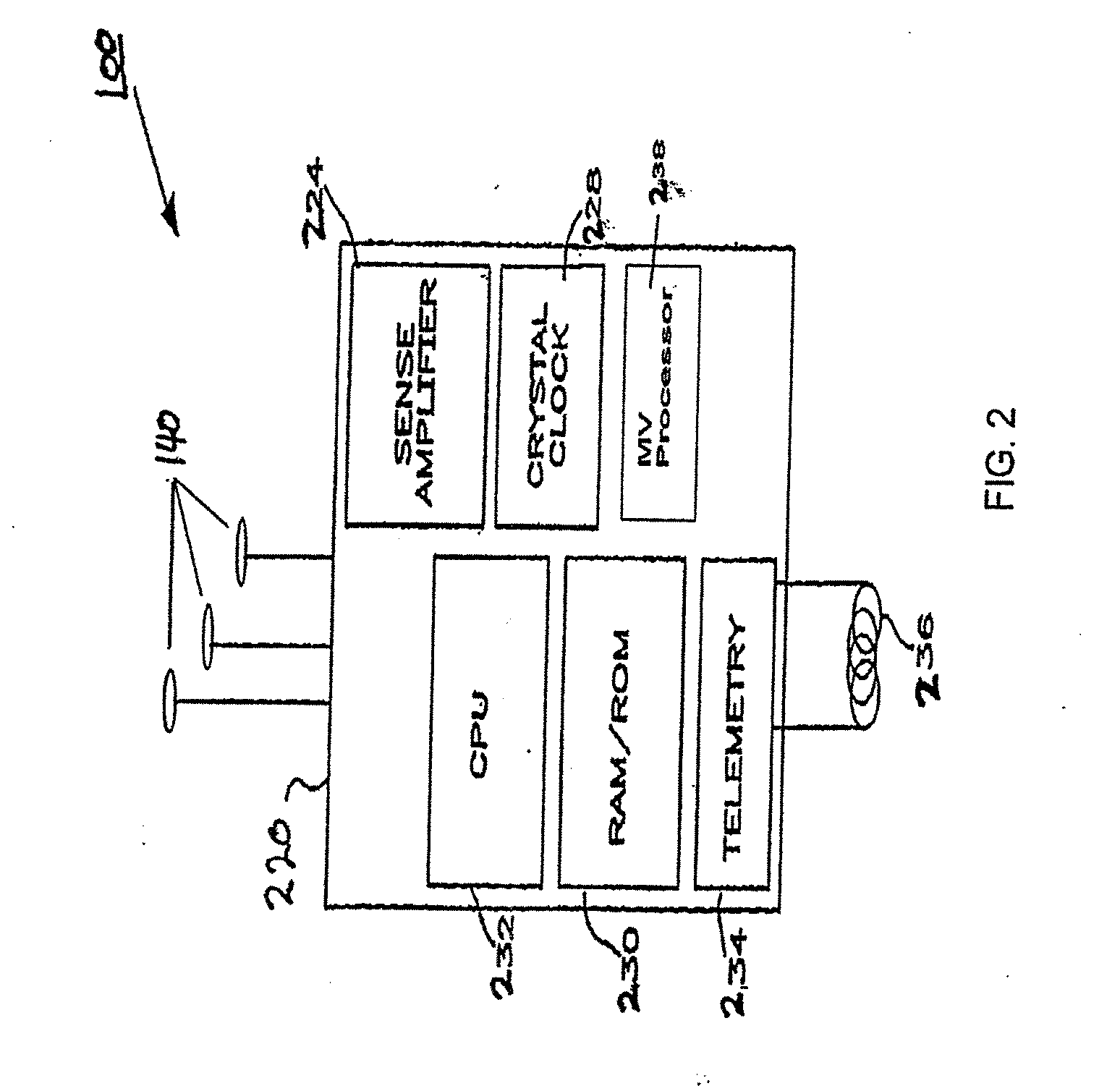
Peak data retention of signal data in an implantable medical device
InactiveUS20070255531A1ElectrotherapyAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influencePeak valueData recording
Methods and apparatus for storing data records associated with an extreme value are disclosed. Signal data is stored in a first buffer of a set of buffers. If a local extreme value for the first buffer exceeds a global extreme value, signal data is stored in a second buffer of the set of buffers. This process is repeated, wrapping around and overwriting buffers until the signal data in a current buffer does not have a local extreme value that exceeds the global extreme value. When this happens, signal data may be stored in a subsequent buffer and if a local extreme value of the subsequent buffer does not exceed the global extreme value, further signal data may be stored in the subsequent buffer in a circular manner until either an instantaneous extreme value exceeds the global extreme value or the recording period ends. In an embodiment, the extreme value may be a peak value.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
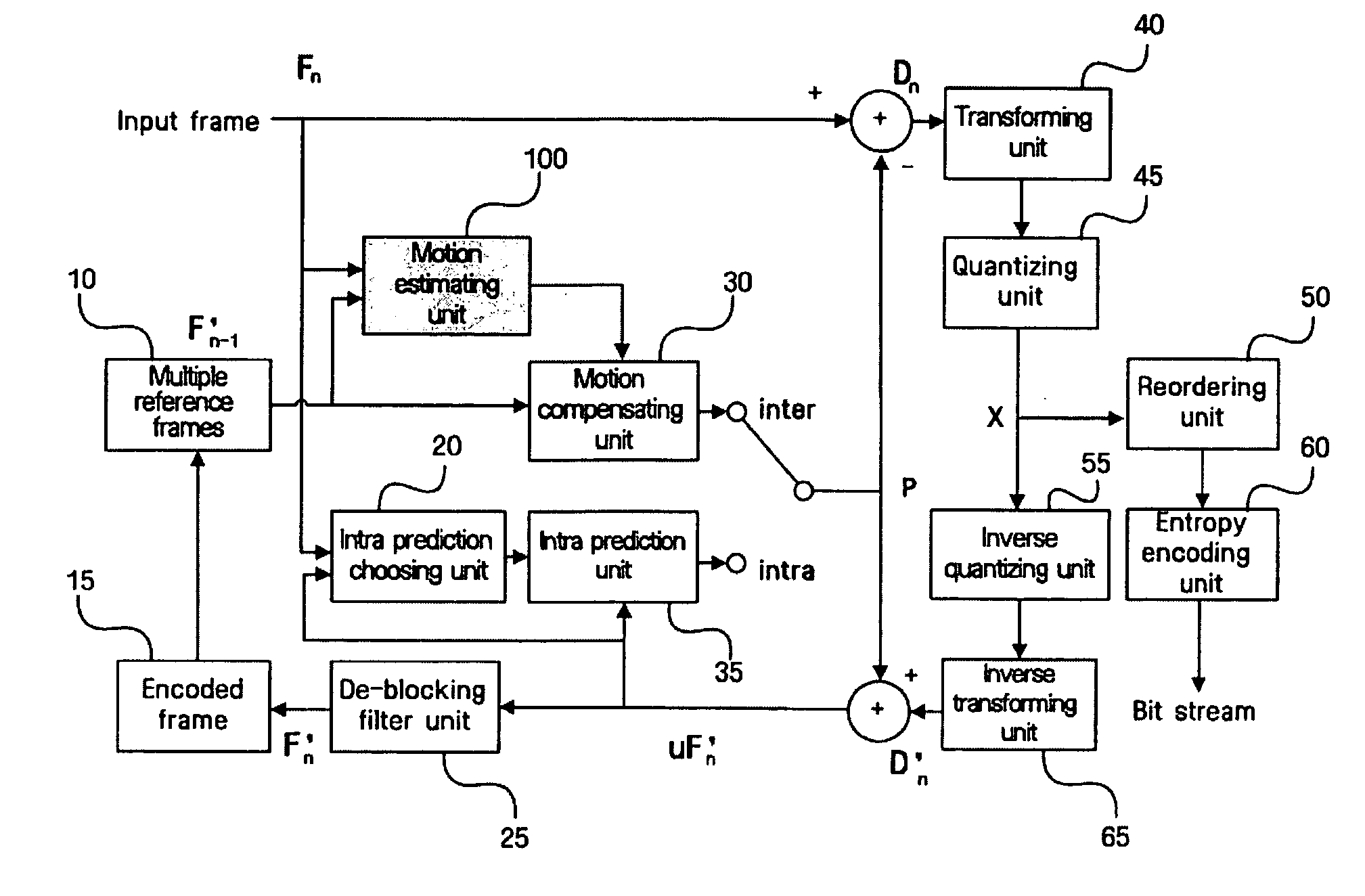
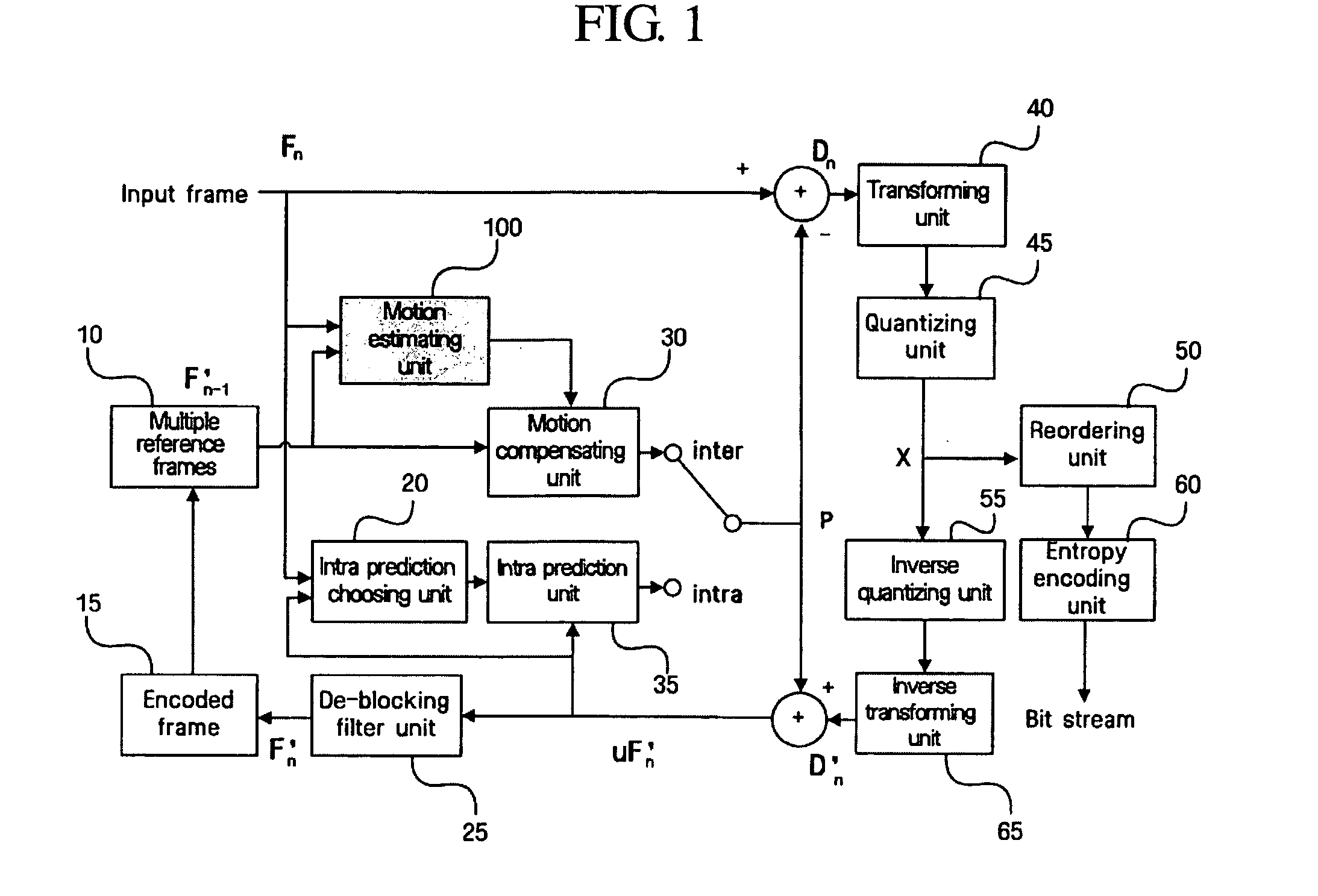
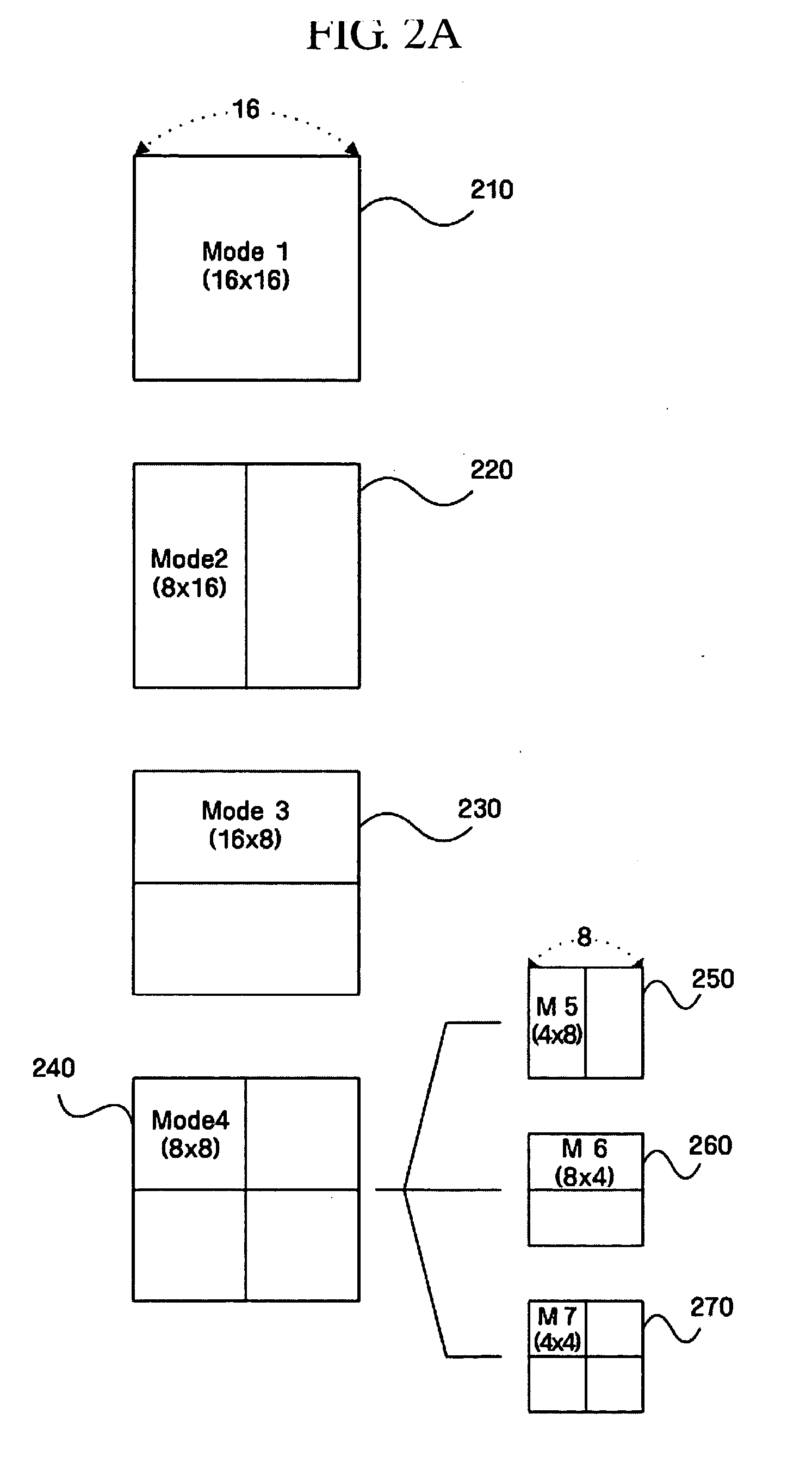
Method and apparatus for motion estimation using variable block size of hierarchy structure
InactiveUS20050114093A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsMotion vectorComputer science
Disclosed is a method and apparatus for a motion estimation using a variable block size of a hierarchy structure. The method includes: calculating each of a motion vector of a desired minimum unit variable block; determining a similarity of the calculated motion vectors between the minimum unit variable blocks in a higher hierarchy including the minimum unit variable block; establishing a mode of the variable block according to the determined similarity; and deciding a motion vector with respect to the mode established variable block. The complexity of the method of compressing a motion picture of a hierarchy structure having a plurality of block sizes can be reduced by selecting a mode of the optimal block size on the basis of a motion vector with respect to the minimum unit and the cost occurred at that time without performing the motion estimation with respect to each mode each time.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Instrumented sports apparatus and feedback method
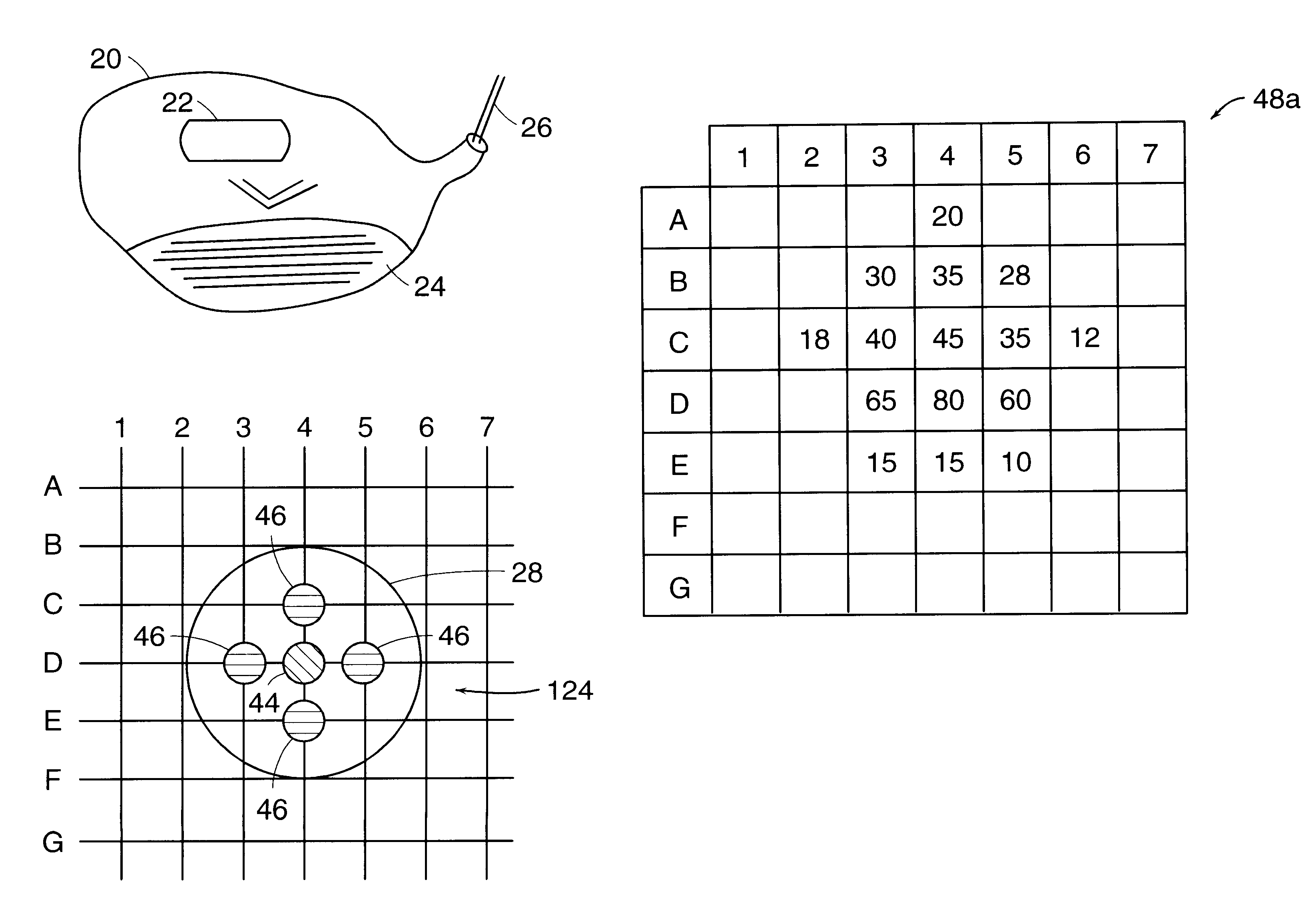
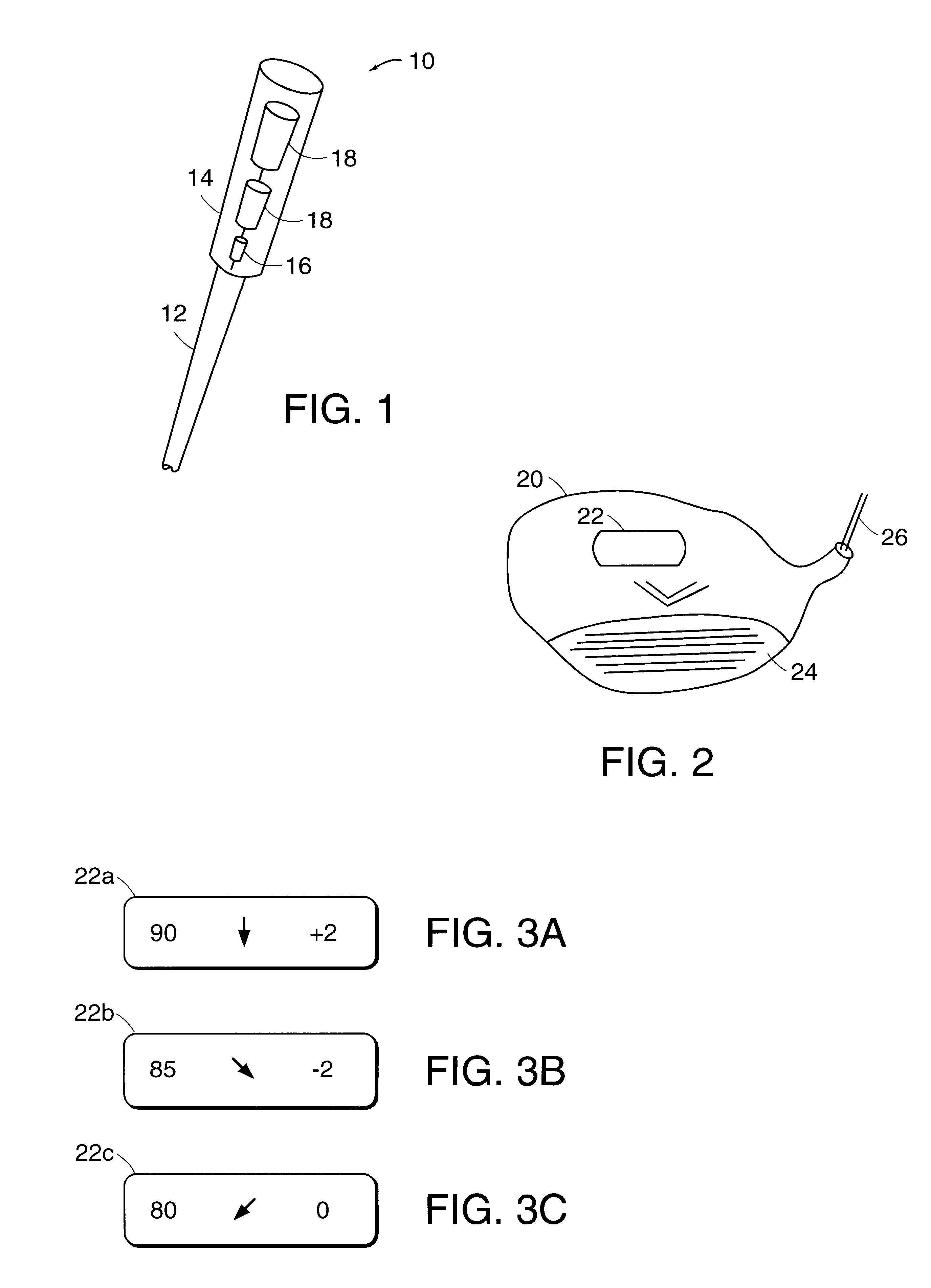
InactiveUS6196932B1Inflated body pressure measurementPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesGolf course turfSports equipment
An instrumented sports apparatus includes a closely spaced array of discrete sensor elements coupled to a contact surface thereof for converting a contact force between the contact surface and an object into a plurality of discrete output signals. The signals are processed and information based thereon generated, which is representative of one or more parameters of interest. In an exemplary embodiment, as instrumented golf club displays information such as club head speed, club head angle, and club head elevation upon impact with a golf ball, permitting the golfer to adjust his swing on the next stroke. Since the instrumentation and display are entirely self-contained in the club, a golfer is not constrained in the use of the club and may enjoy the benefits thereof during play on a golf course.
Owner:MARSH DONALD JAMES +1
Managing acoustic noise produced by a device
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that manages the acoustic noise produced by a device. During operation, the system receives a set of acoustic characteristics for the device. The system then uses these acoustic characteristics to estimate the acoustic noise being generated by the device. Next, the system uses the estimated acoustic noise to adjust a setting in the device to manage the acoustic noise produced by the device.
Owner:APPLE INC
Integrated repeater
An integrated repeater includes a housing having opposing sides, a donor antenna mounted on one of the opposing sides, a null antenna mounted on the other of the opposing sides, and repeater electronics mounted in the housing and operatively interconnecting the donor antenna and the null antenna. The repeater electronics include a beamforming arrangement for creating a desired antenna pattern of the donor antenna relative to a base station and a desired antenna pattern of the null antenna relative to subscriber equipment, and interference cancellation electronics for cancelling interference feedback signals between the donor antenna and the null antenna in both an uplink path and a downlink path.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
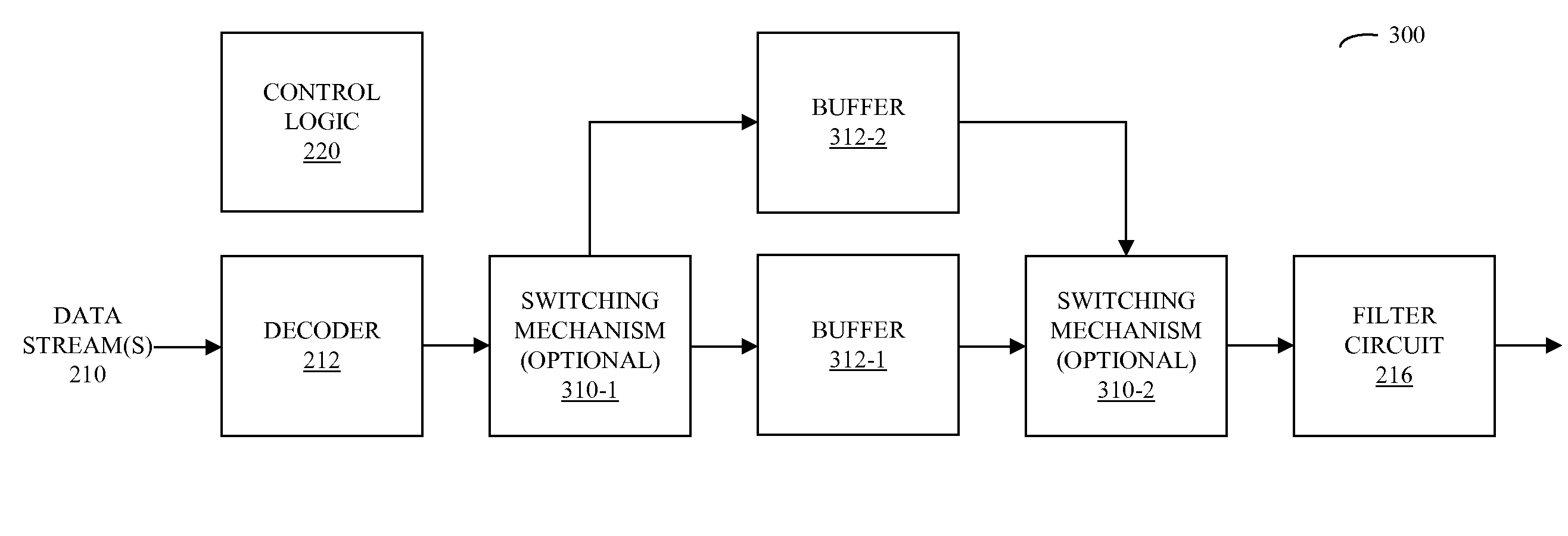
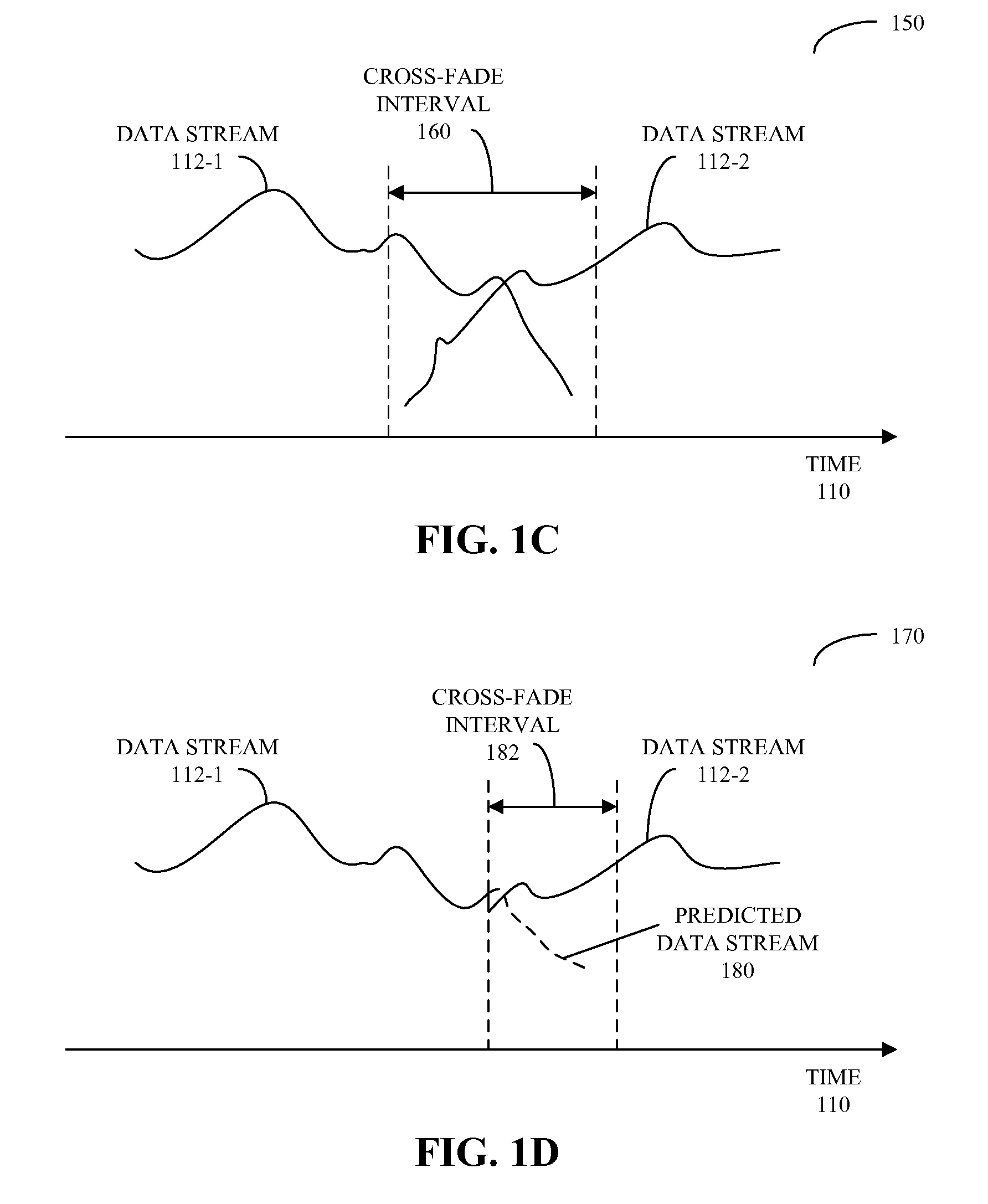
Zero-gap playback using predictive mixing
ActiveUS20090083047A1Reducing and eliminating gapReduce discontinuityElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsSpeech analysisElectricityData stream
Circuits and methods for providing zero-gap playback of consecutive data streams in portable electronic devices, such as media players, are described. In some embodiments, a circuit includes a decoder circuit configured to receive encoded audio data and to output decoded audio data including data streams associated with a data file and a subsequent data file. Moreover, a predictive circuit, which is electrically coupled to the decoder circuit, is configured to selectively generate additional samples based on samples in the data file, where the additional samples correspond to times after the end of a data stream associated with the data file. Additionally, a filter circuit, which is electrically coupled to the decoder circuit and selectively electrically coupled to the predictive circuit, is configured to selectively combine or blend samples at a beginning of the subsequent data file with the additional samples. Note that the circuit may be included in an integrated circuit.
Owner:APPLE INC
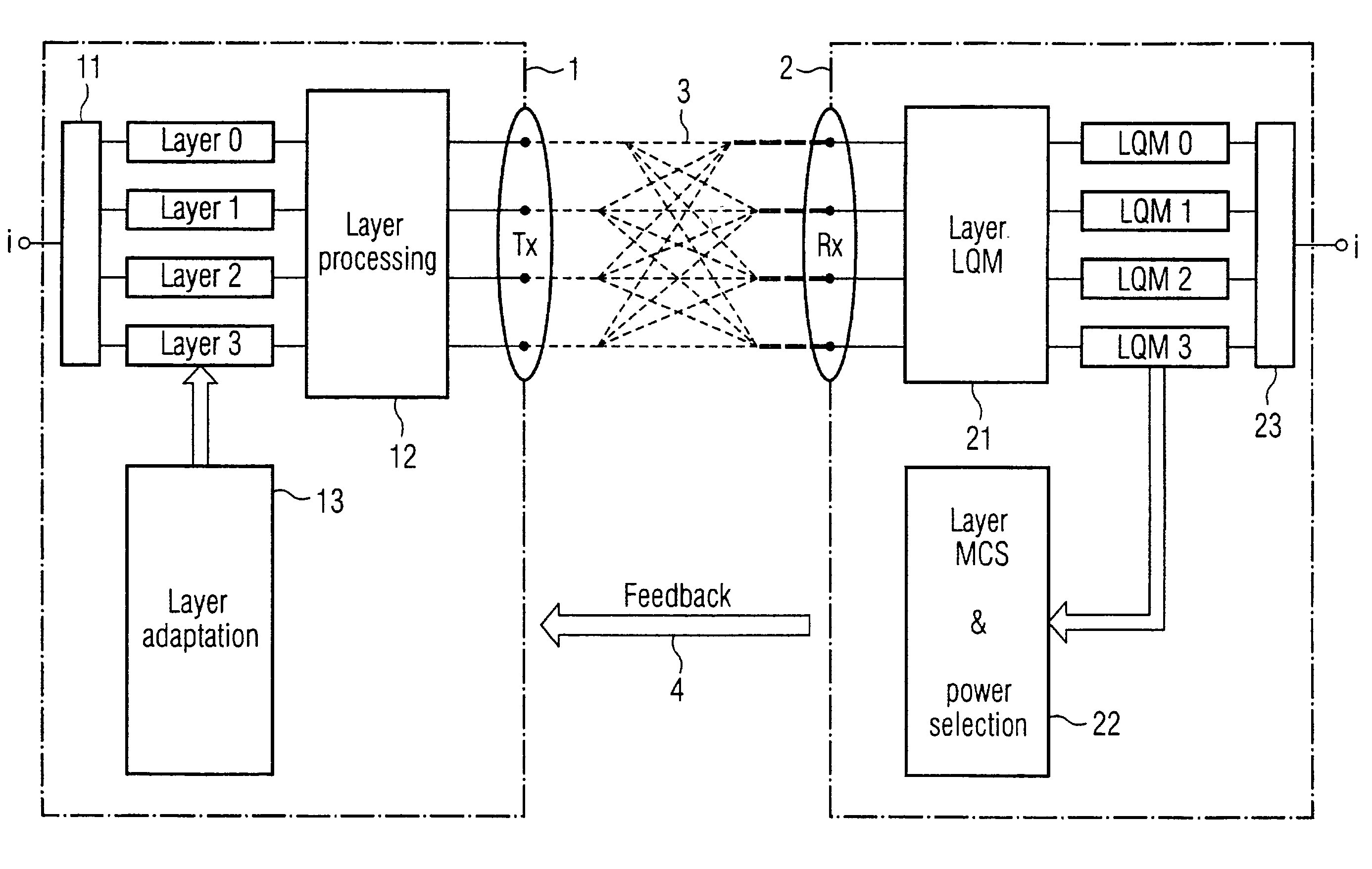
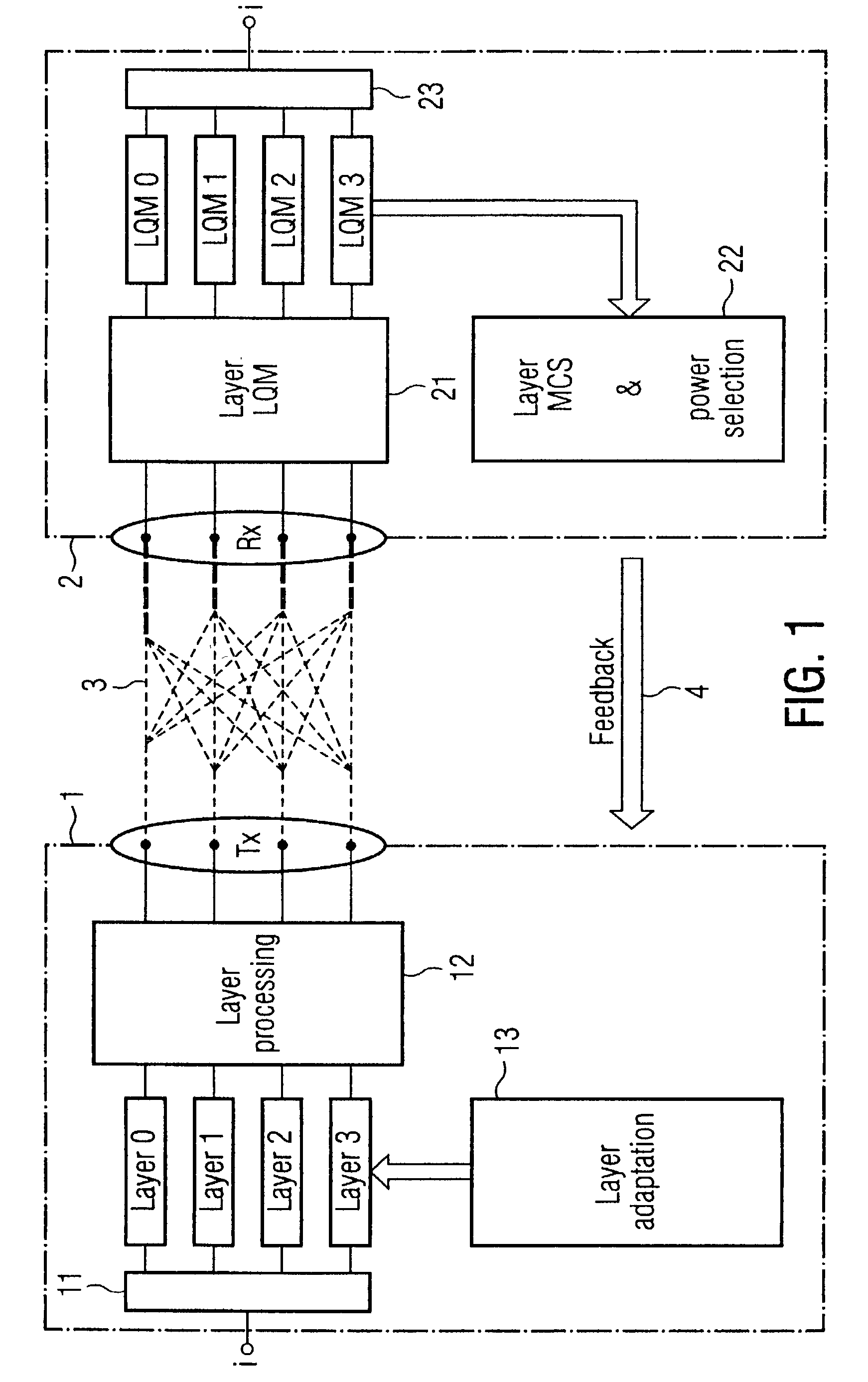
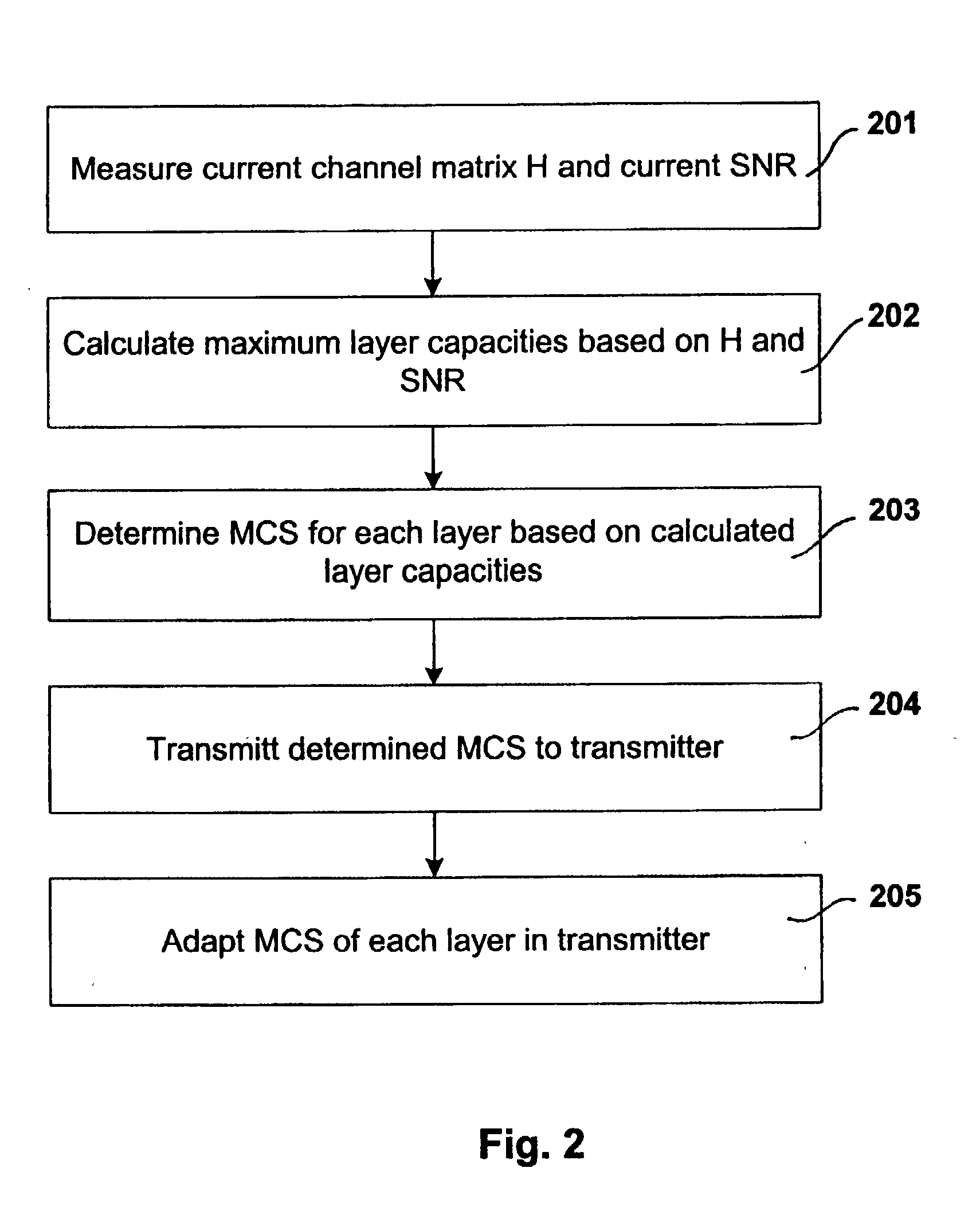
Link adaptation for MIMO transmission schemes
ActiveUS20030003863A1Reduce in quantitySmall rateError prevention/detection by using return channelSpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemMimo transmission
MIMO transmission methods are applied to communicaiton systems in which a transmitter has more than one transmit antenna and a receiver has more than one receive antenna. Information to be transmitted is divided into a plurality of subsignals according to the number of used transmit antennas and each subsignal is processed separately before it is emitted by the respective transmit antenna. In the receiver the different receive signals are processed thus that subsignals are detected and decoded and the contribution of each detected and decoded subsignal is subtracted from the receive signals and whereby a feedback channel from receiver to transmitter is used to send control information to the transmitter depending on the receive situation. In order to optimize the usage of the MIMO channel the invention proposes the in the receiver the link quality of each subsignal is determined and information of each subsignal is transmitted to the receiver via the feedback channel and that in the transmitter properties of the subsignals are controlled by the link quality information.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
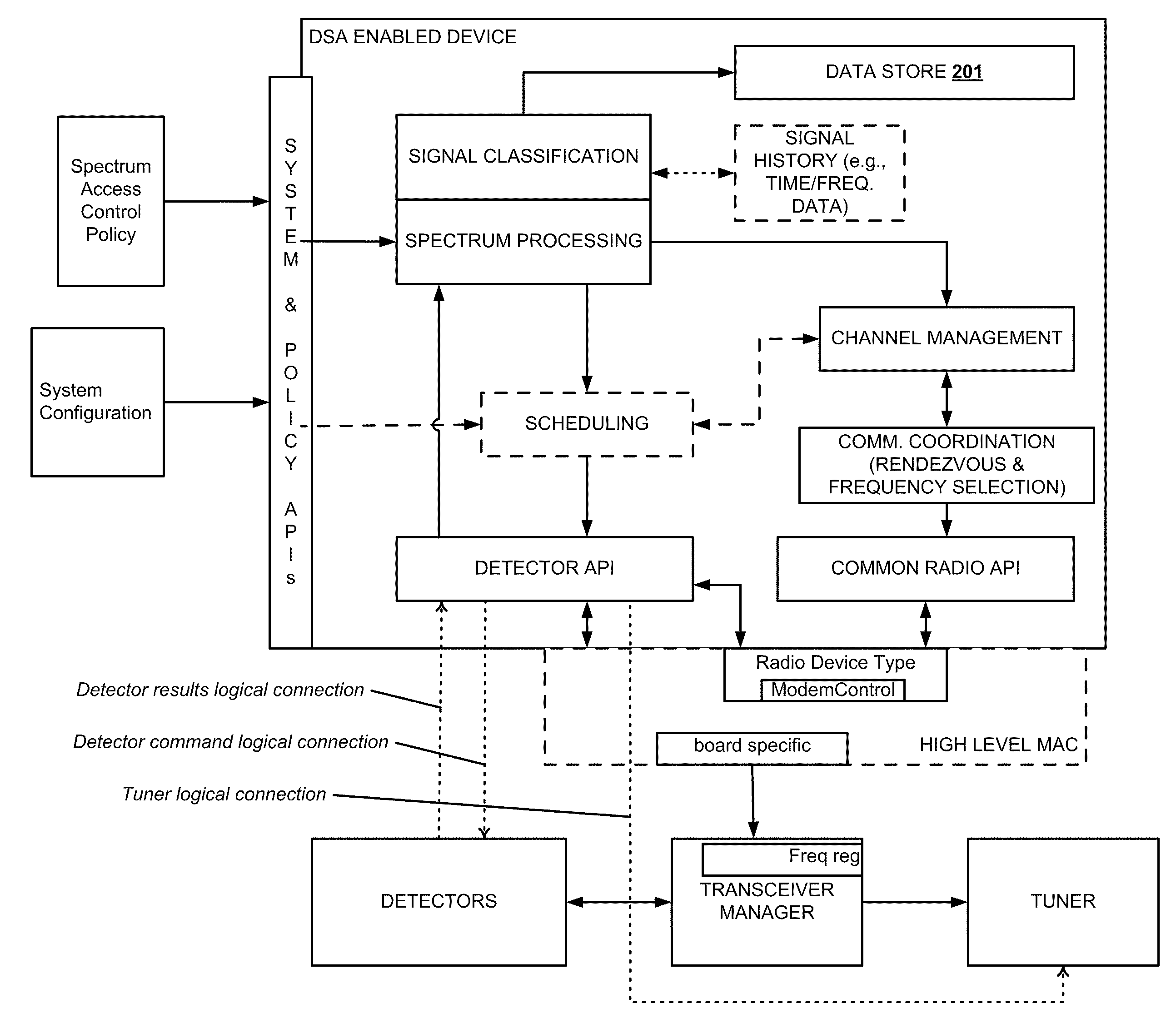
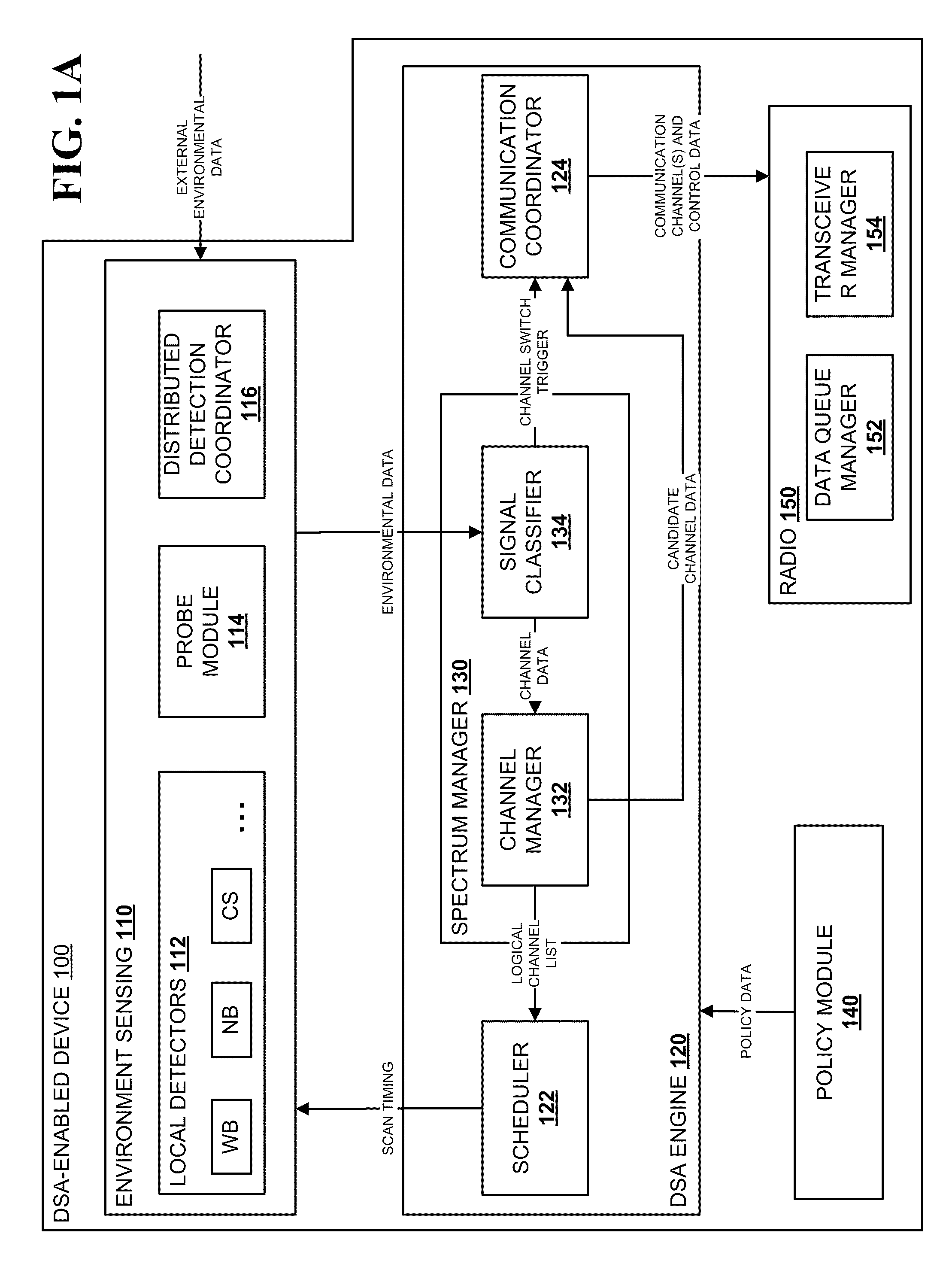
Method and System for Dynamic Spectrum Access
InactiveUS20100173586A1Reduce the valueReduce valueSpectral gaps assessmentTransmission monitoringAccess methodTelecommunications
Methods and systems for dynamic spectrum access (DSA) in a wireless network are provided. A DSA-enabled device may sense spectrum use in a region and, based on the detected spectrum use, select one or more communication channels for use. The devices also may detect one or more other DSA-enabled devices with which they can form DSA networks. A DSA network may monitor spectrum use by cooperative and non-cooperative devices, to dynamically select one or more channels to use for communication while avoiding or reducing interference with other devices.
Owner:SHARED SPECTRUM
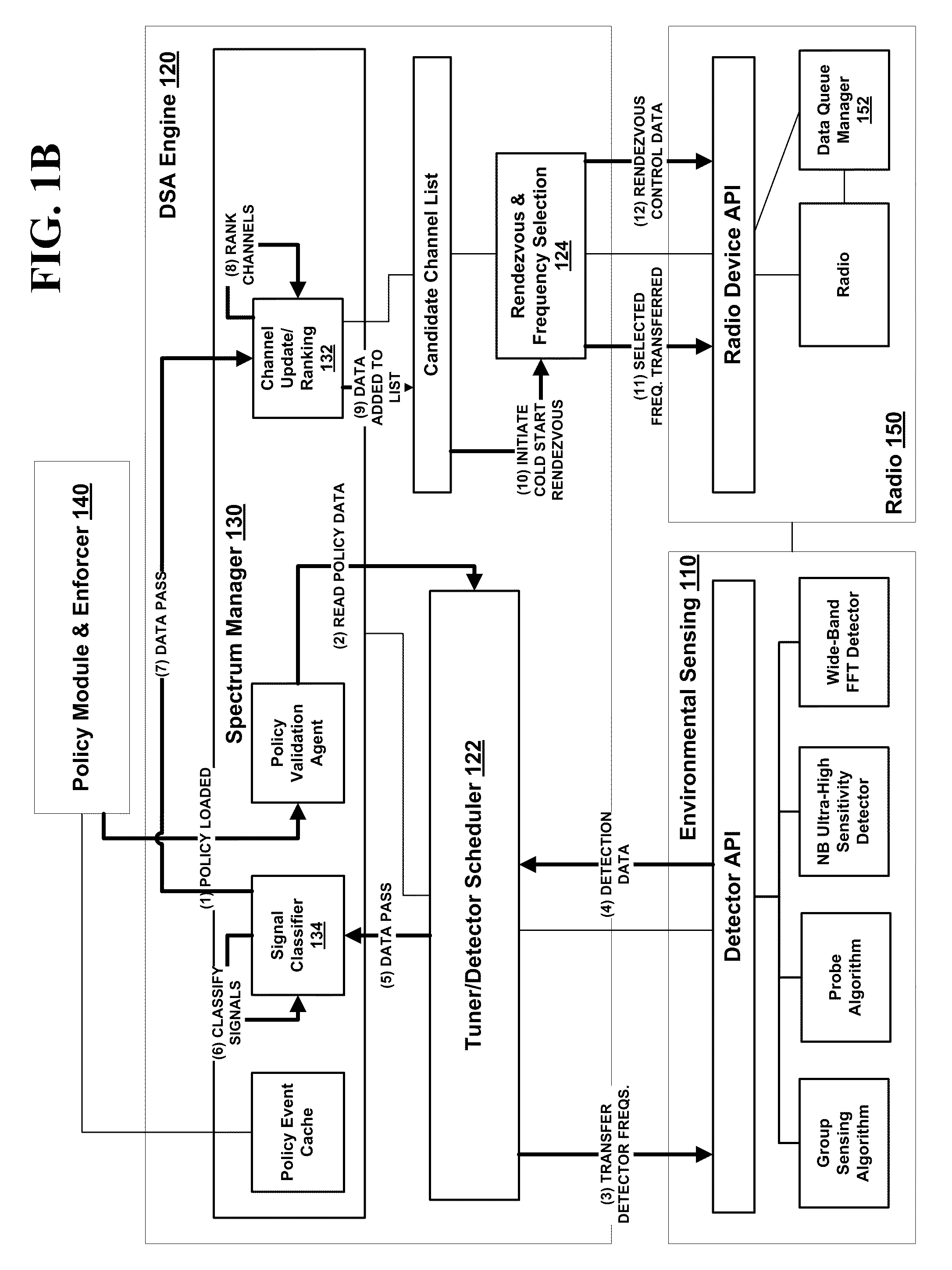
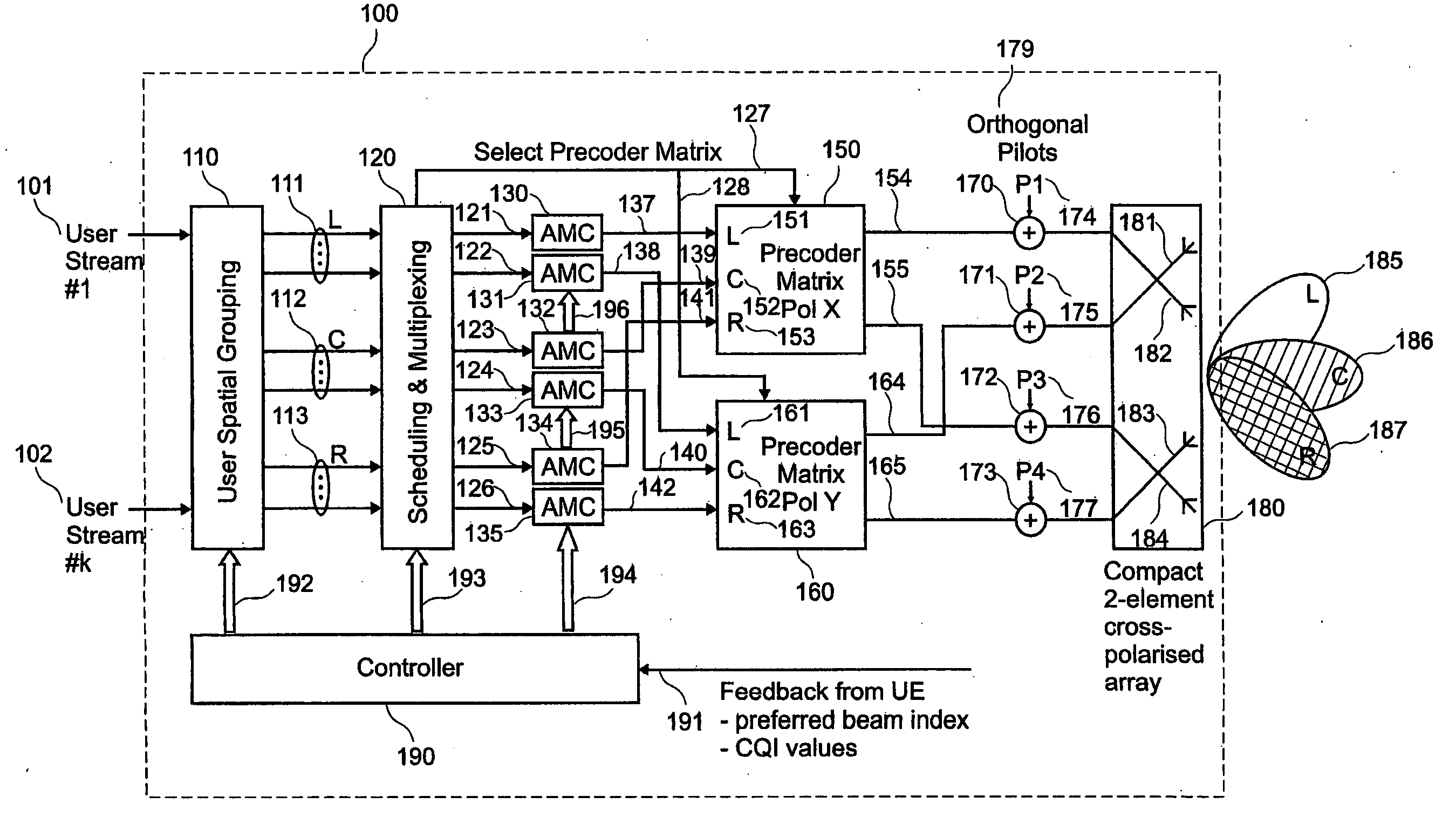
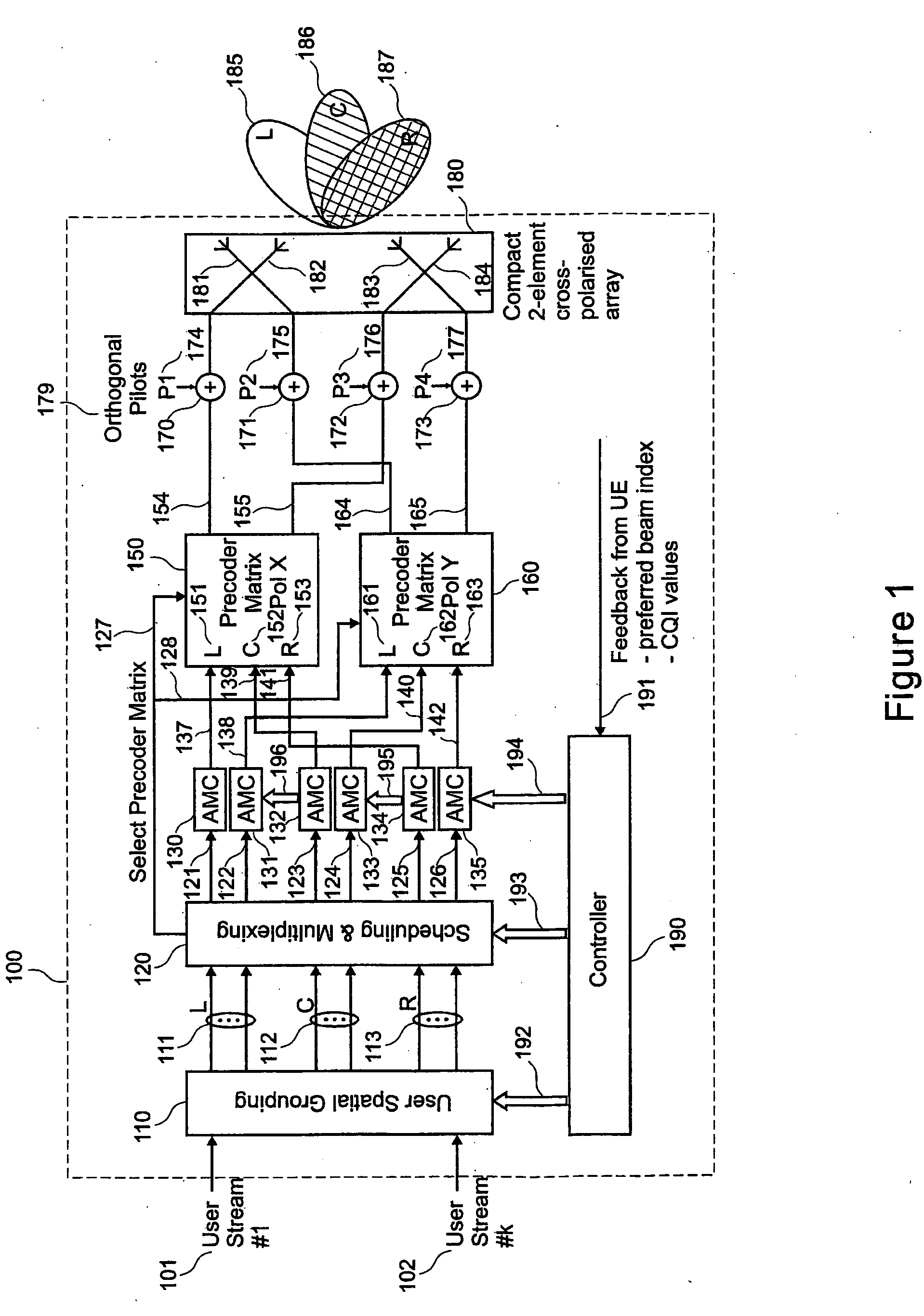
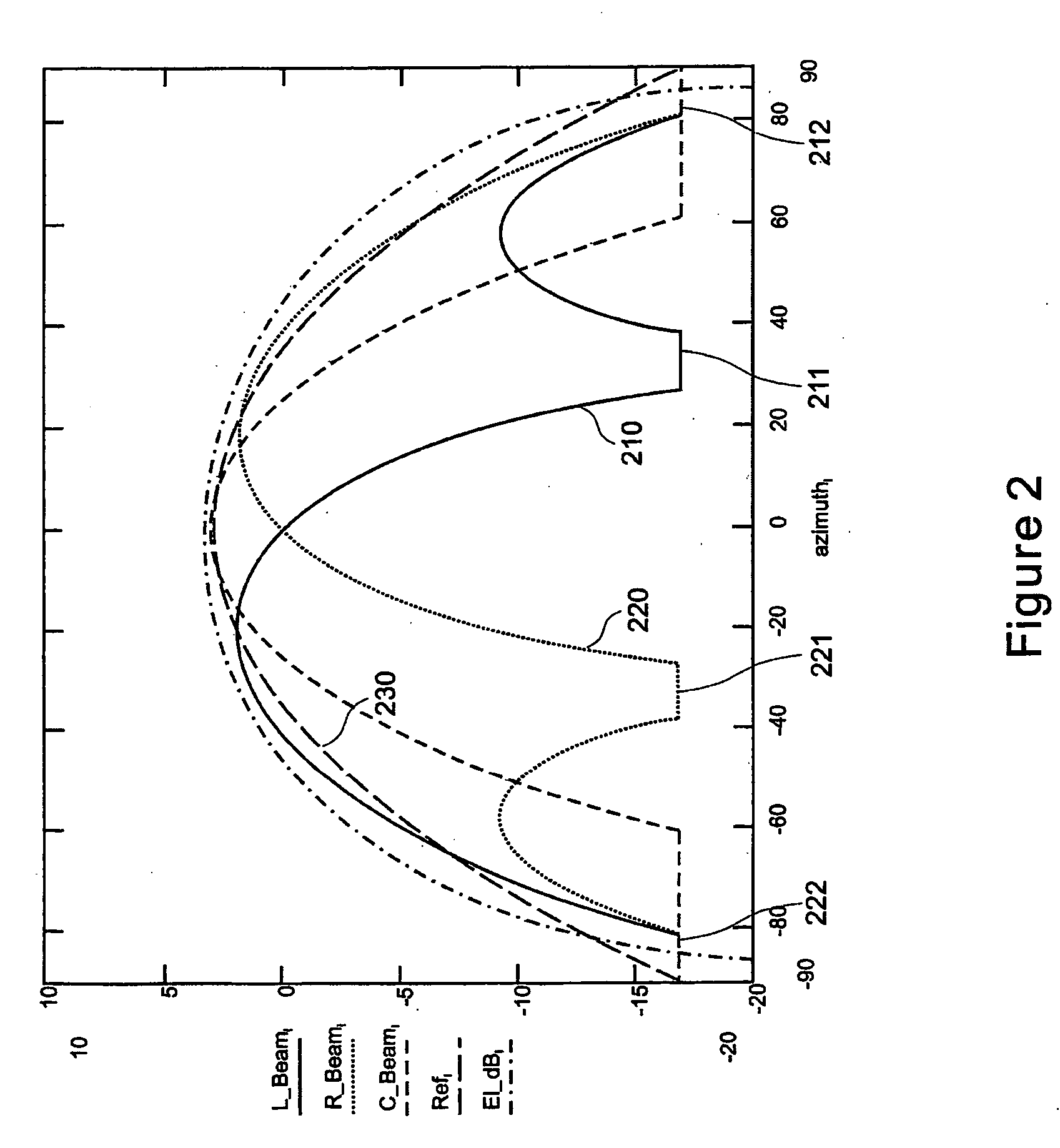
Pre-coded diversity forward channel transmission system for wireless communications systems supporting multiple MIMO transmission modes
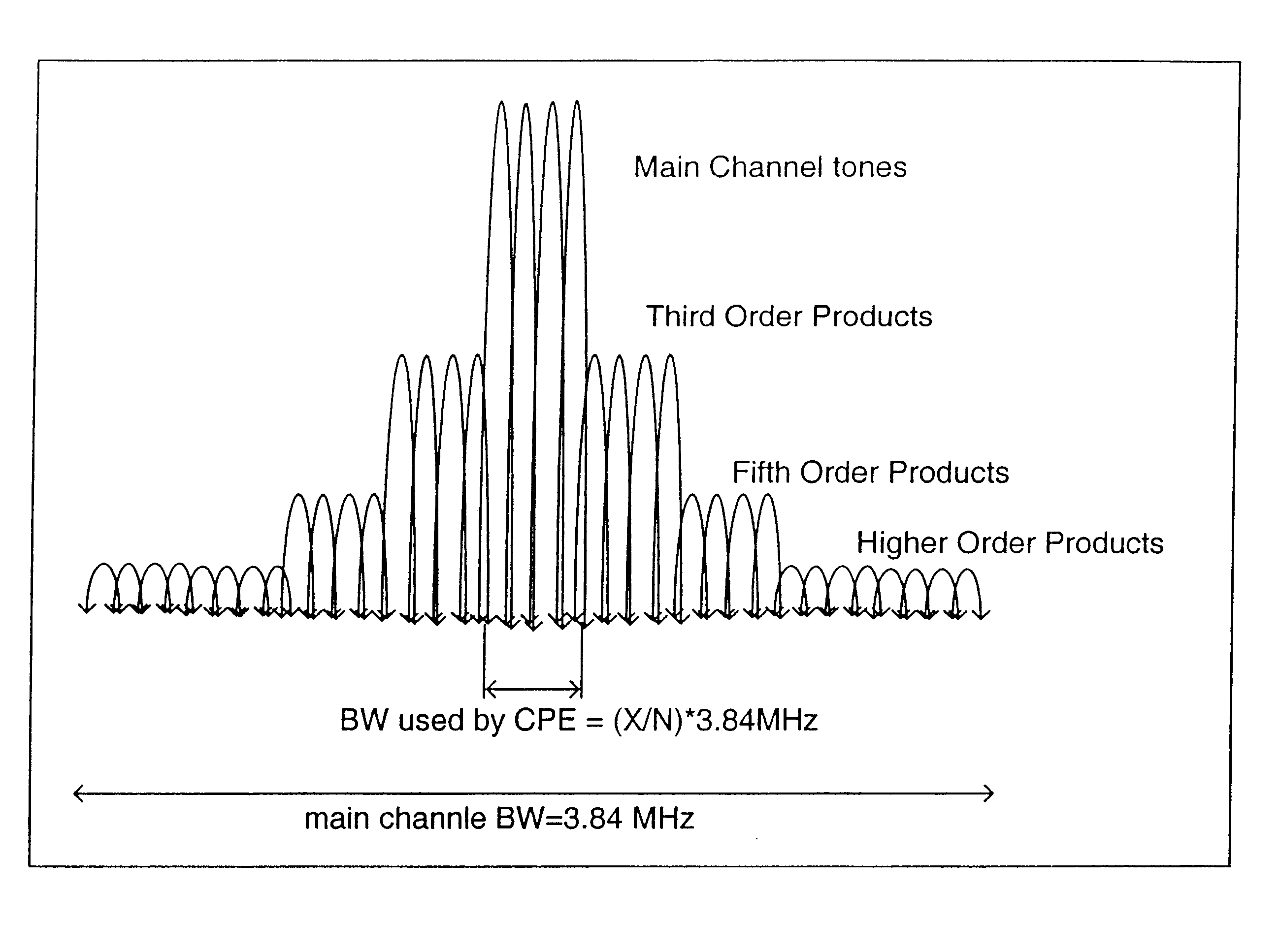
InactiveUS20070099578A1Polarisation/directional diversityTransmission noise suppressionPolarization diversityMimo transmission
A wireless communications system supporting multiple MIMO transmission modes supporting both diversity and directional transmissions under a plurality of different transmission modes comprises a plurality of transmit and receive antenna elements where the transmit antenna elements are arranged to provide polarization diversity. The transmitting station derives actual knowledge of the forward channel by feeding back certain information such as a preferred beam index and a channel quality indicator figure of merit for that beam from the receiving station to the transmitting station along a reverse channel. The receiving station knows the beam weights used by the transmitting station. The transmitting station applies the fed back information to transmit user data intended for the receiving station in the optimal fashion, such as along the preferred beam and at a time when forward channel conditions are satisfactory. The system provides robust single or multiple stream diversity transmission, together with the option of single user or multi-user beamforming to allow on-the-fly trade-offs between coverage gain and capacity in a wireless telecommunications system.
Owner:TENXC WIRELESS
Method and apparatus for reducing interference associated with wireless communication
ActiveUS7359730B2Reduce distractionsPower managementRadio transmissionTelecommunicationsCommunication device
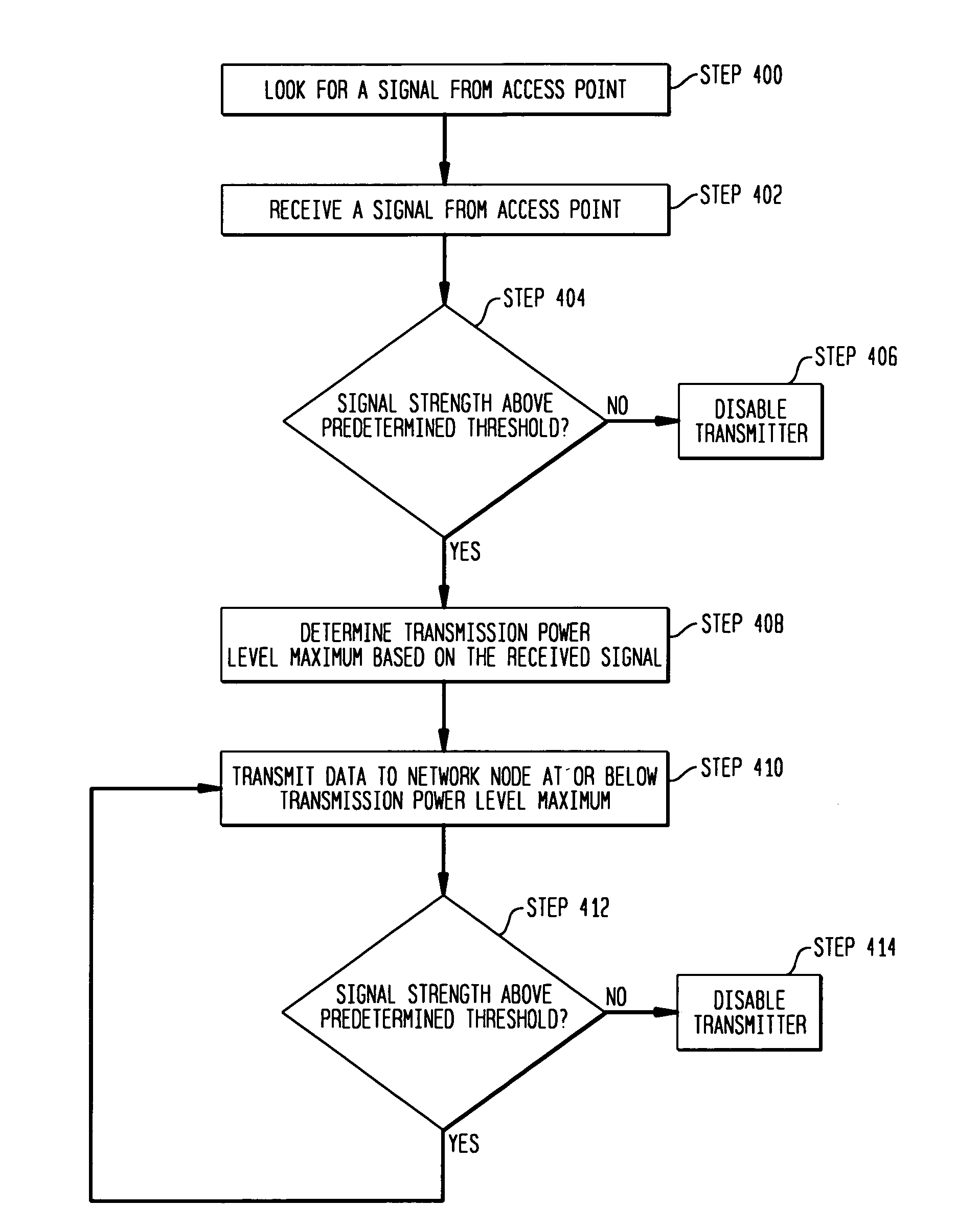
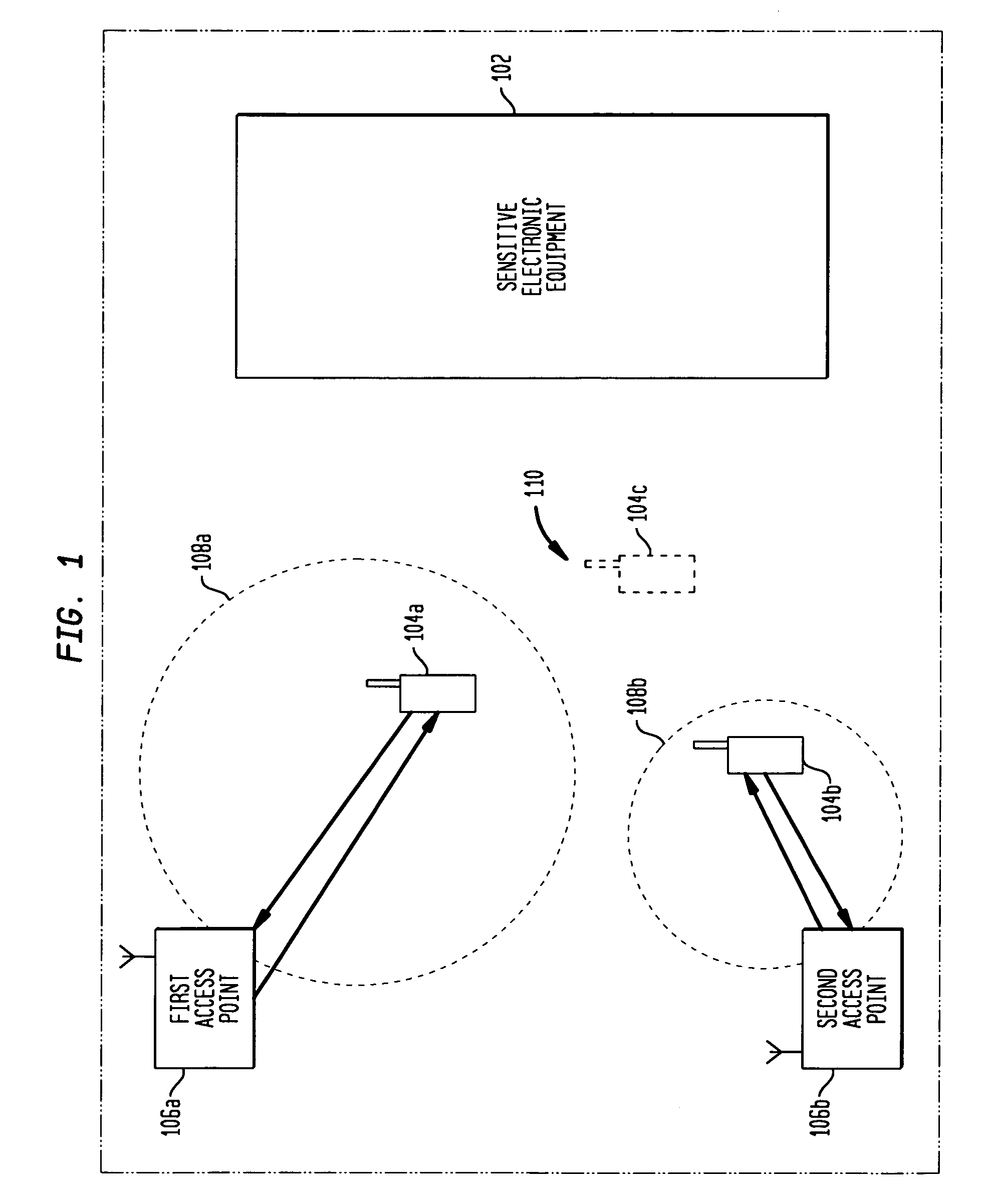
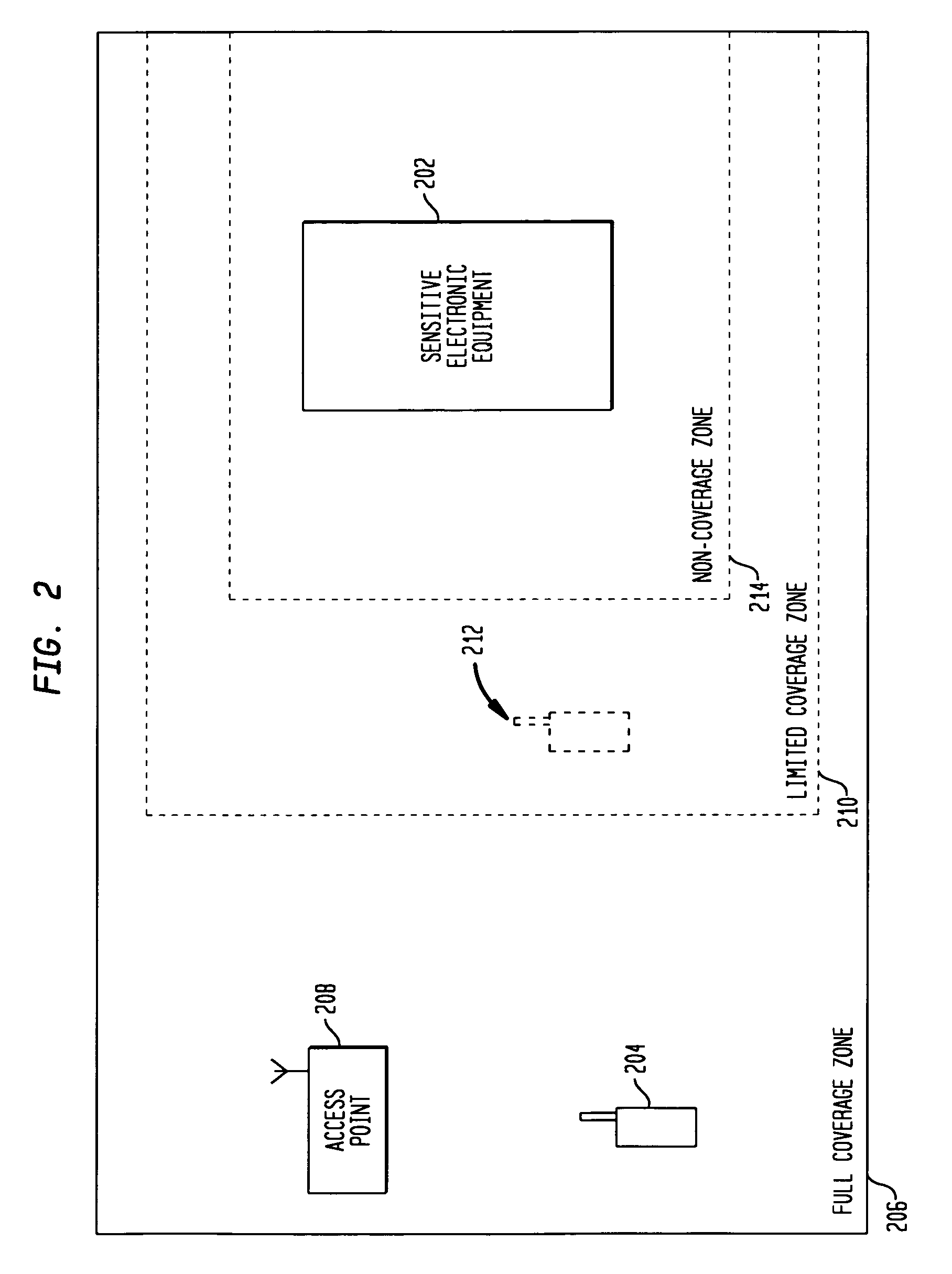
The present invention provides for a method and apparatus for reducing interference associated with wireless communication in an area having sensitive electronic equipment. A wireless communications device receives, from an access point, a signal having a signal strength above a predetermined threshold. The wireless communications device determines a transmission power level maximum based on the received signal and then transmits a signal to the access point at a transmission power level at or below the transmission power level maximum. The wireless communications device disables the transmission when the signal strength falls below the predetermined threshold.
Owner:NYTELL SOFTWARE LLC
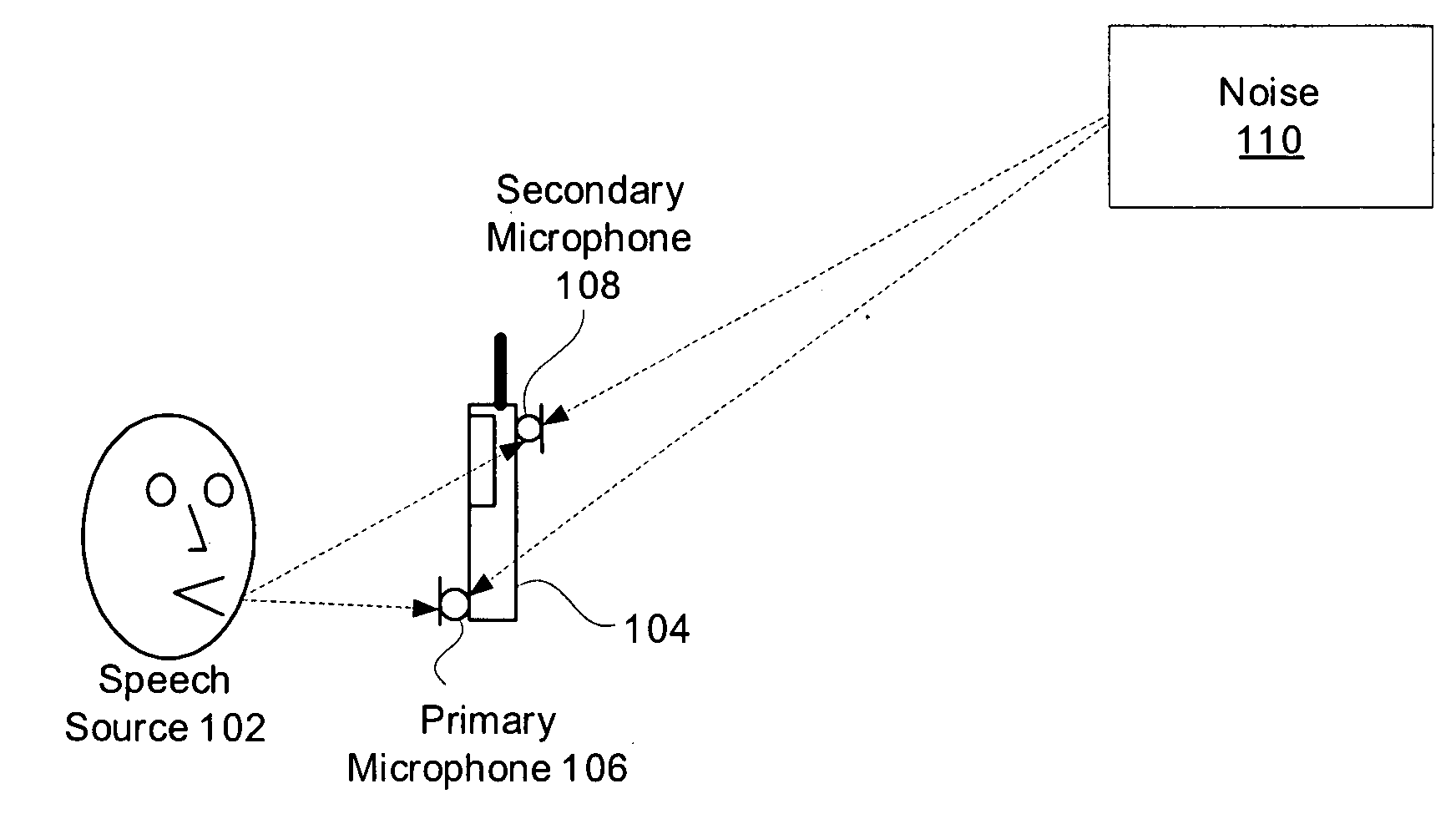
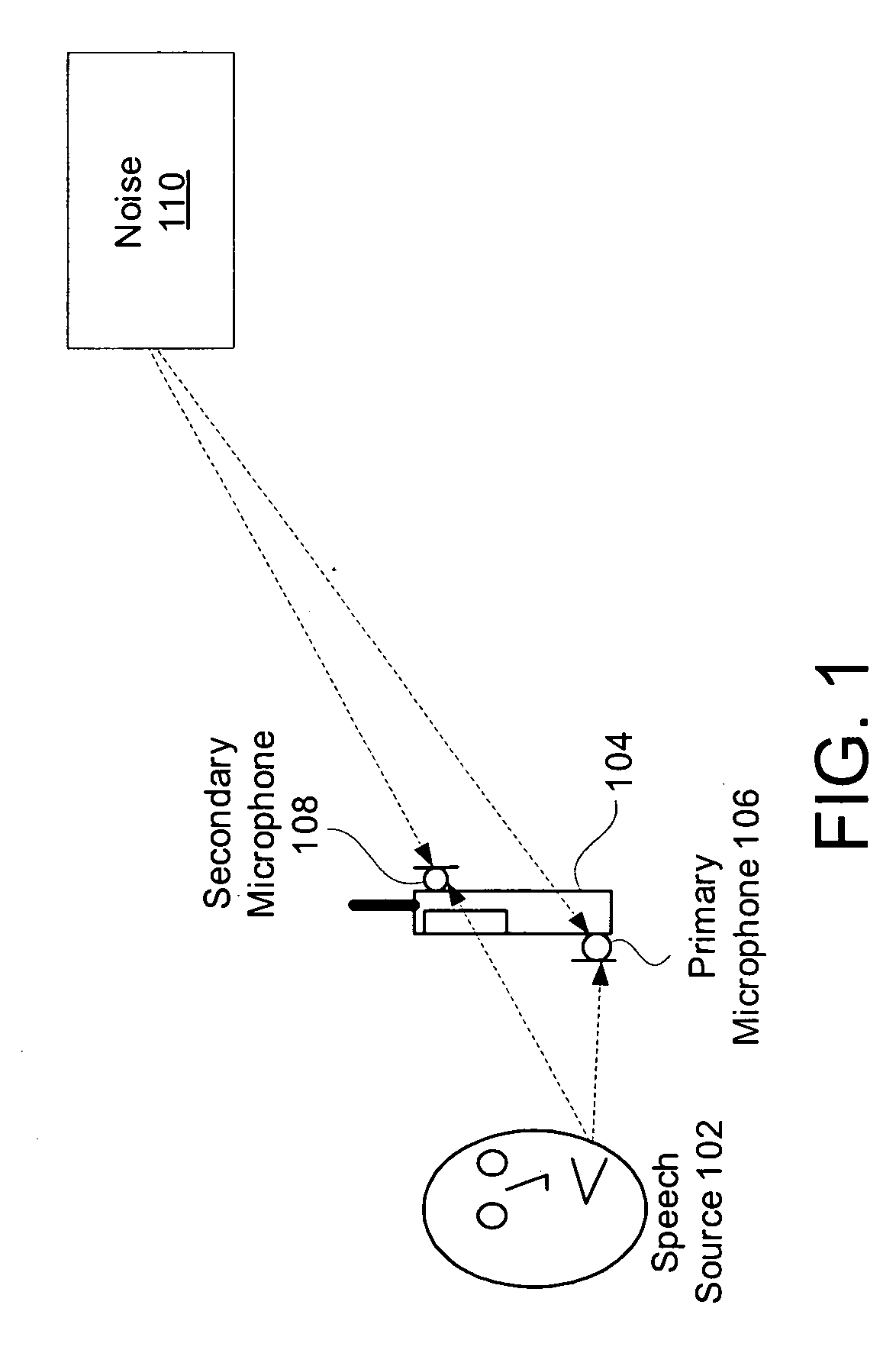
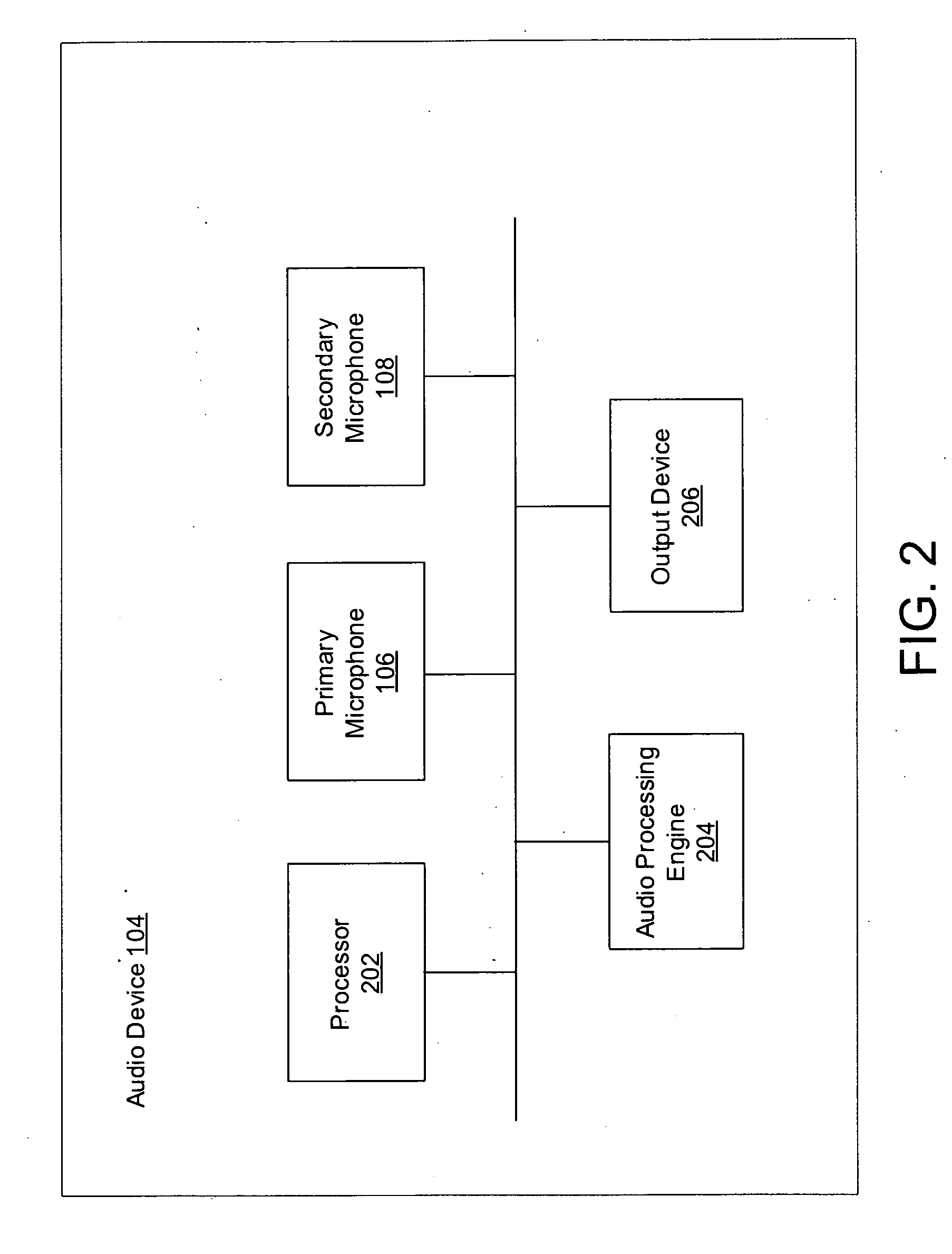
System and method for providing single microphone noise suppression fallback
Systems and methods for providing single microphone noise suppression fallback are provided. In exemplary embodiments, primary and secondary acoustic signals are received. A single microphone noise estimate may be generated based on the primary acoustic signal, while a dual microphone noise estimate may be generated based on the primary and secondary acoustic signals. A combined noise estimate based on the single and dual microphone noise estimates is then determined. Using the combined noise estimate, a gain mask may be generated and applied to the primary acoustic signal to generate a noise suppressed signal. Subsequently, the noise suppressed signal may be output.
Owner:KNOWLES ELECTRONICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com