Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
486 results about "Eardrum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
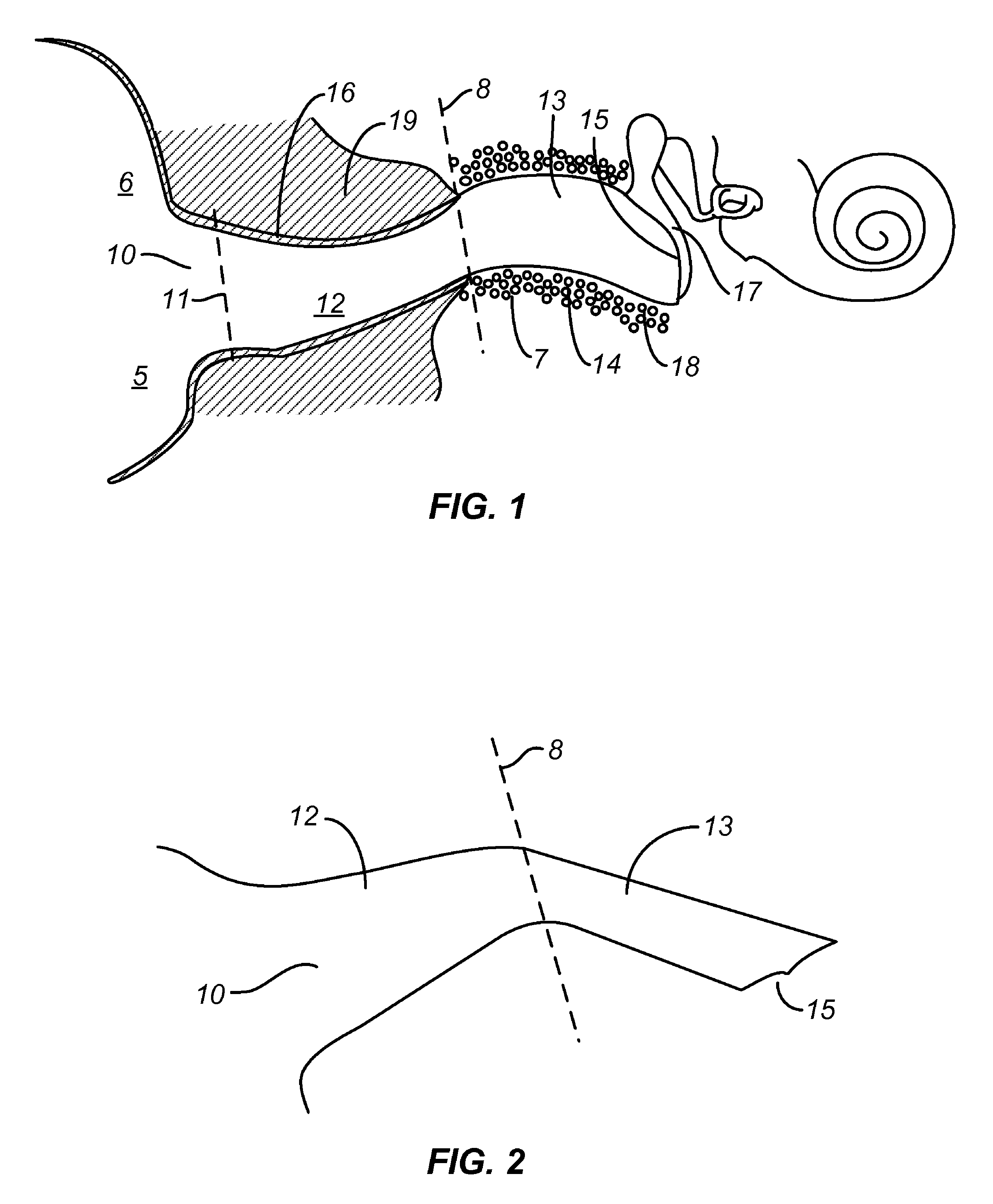
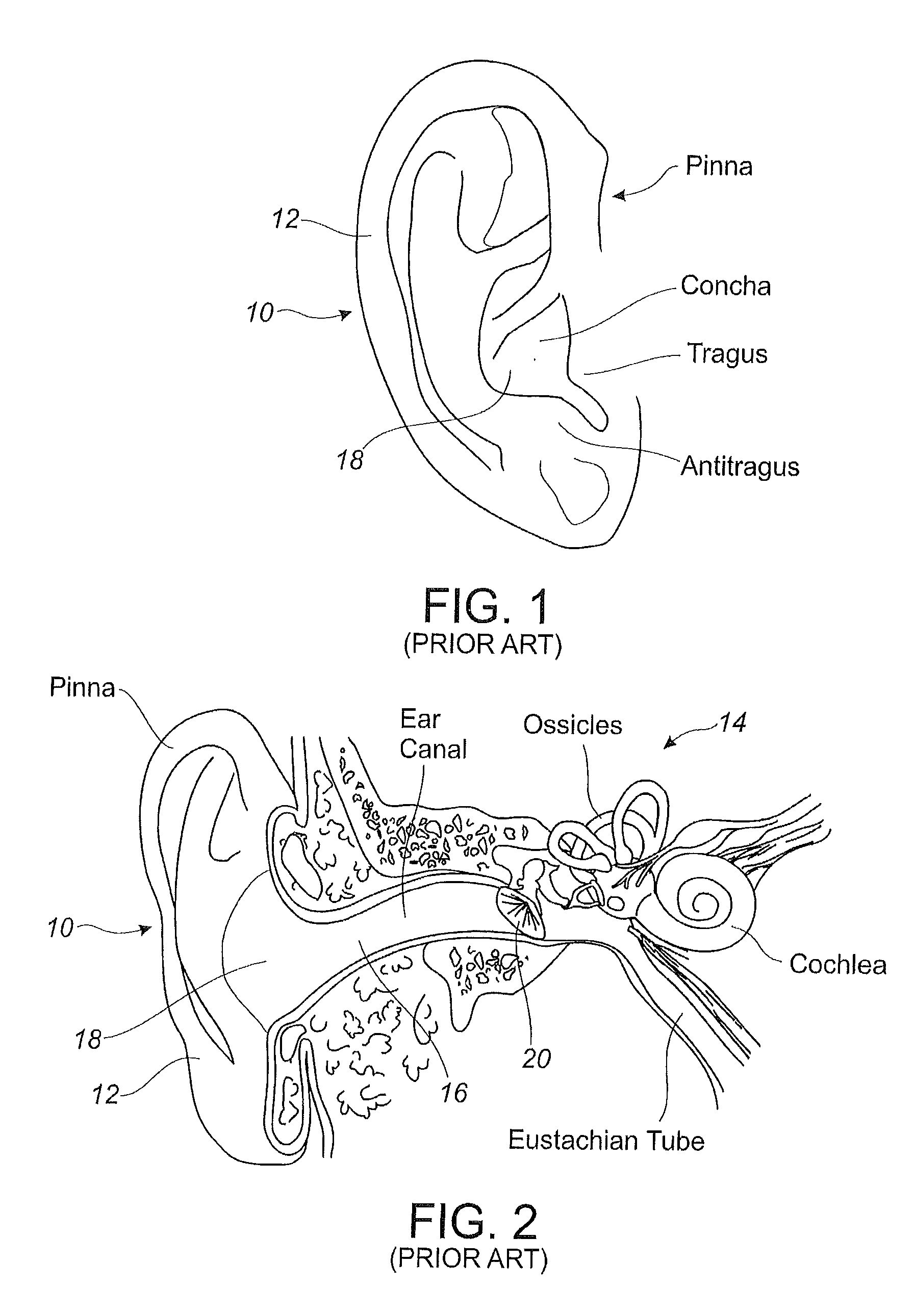
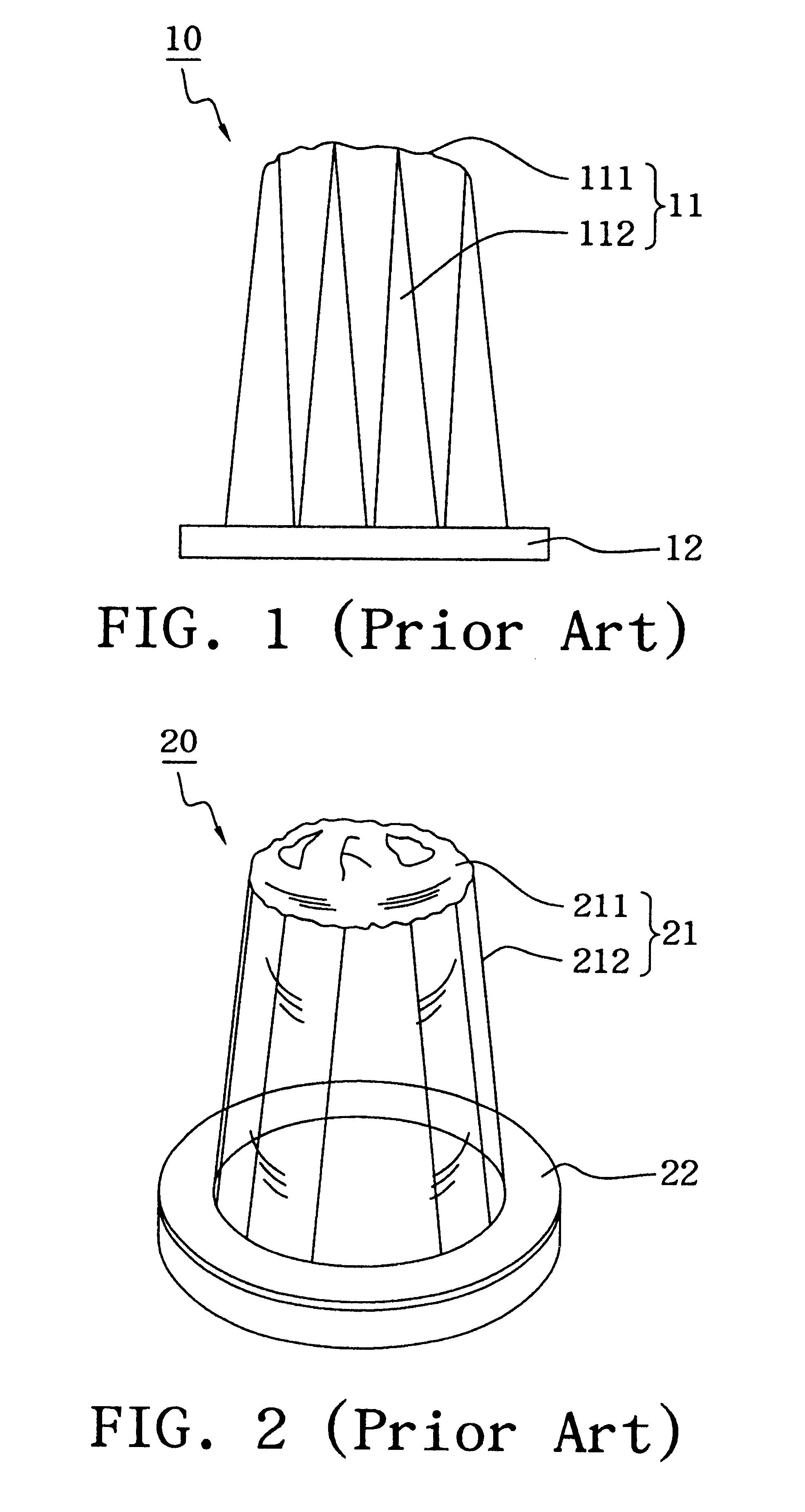
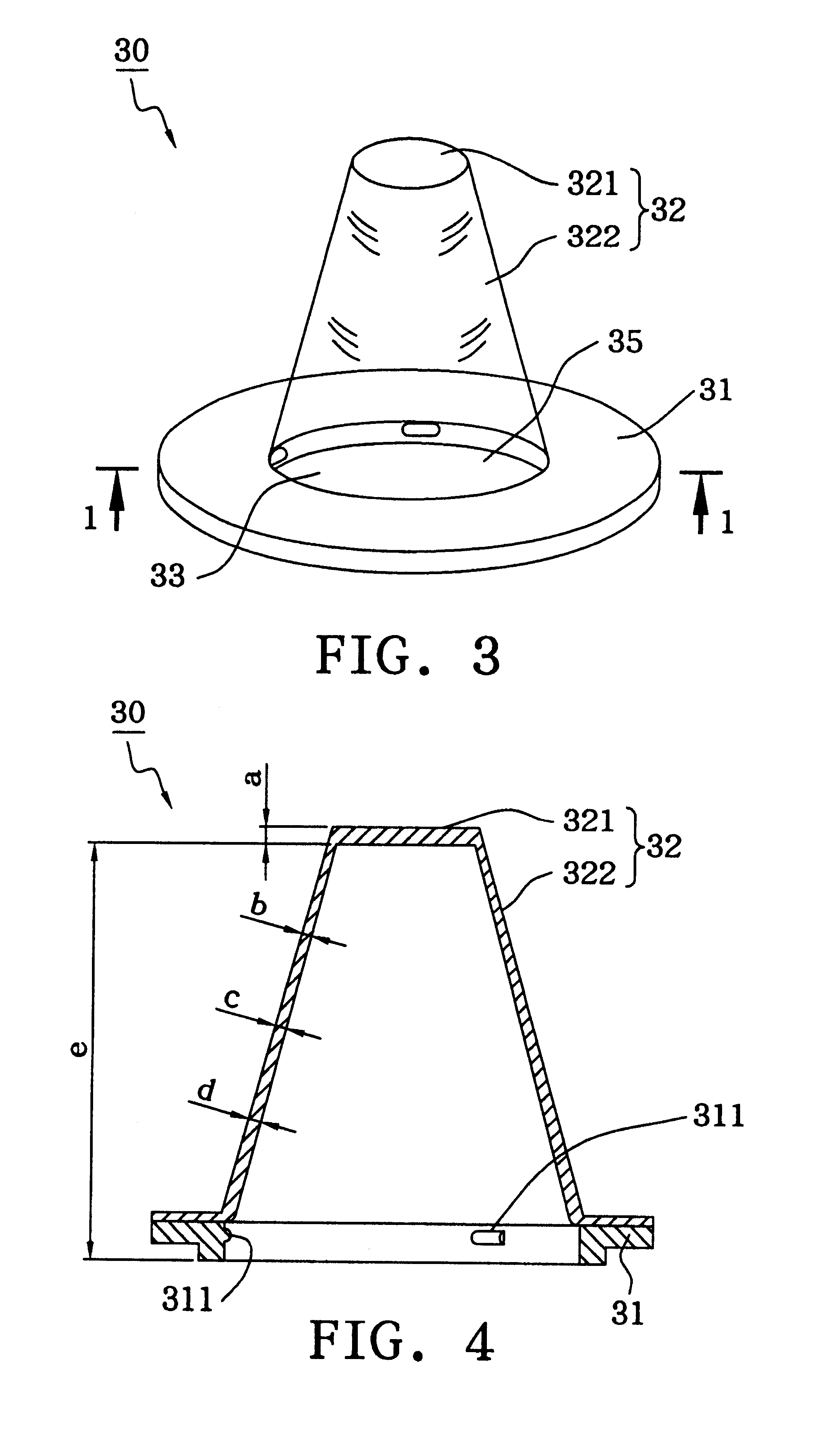
In the anatomy of humans and various other tetrapods, the eardrum, also called the tympanic membrane or myringa, is a thin, cone-shaped membrane that separates the external ear from the middle ear. Its function is to transmit sound from the air to the ossicles inside the middle ear, and then to the oval window in the fluid-filled cochlea. Hence, it ultimately converts and amplifies vibration in air to vibration in fluid. The malleus bone bridges the gap between the eardrum and the other ossicles.
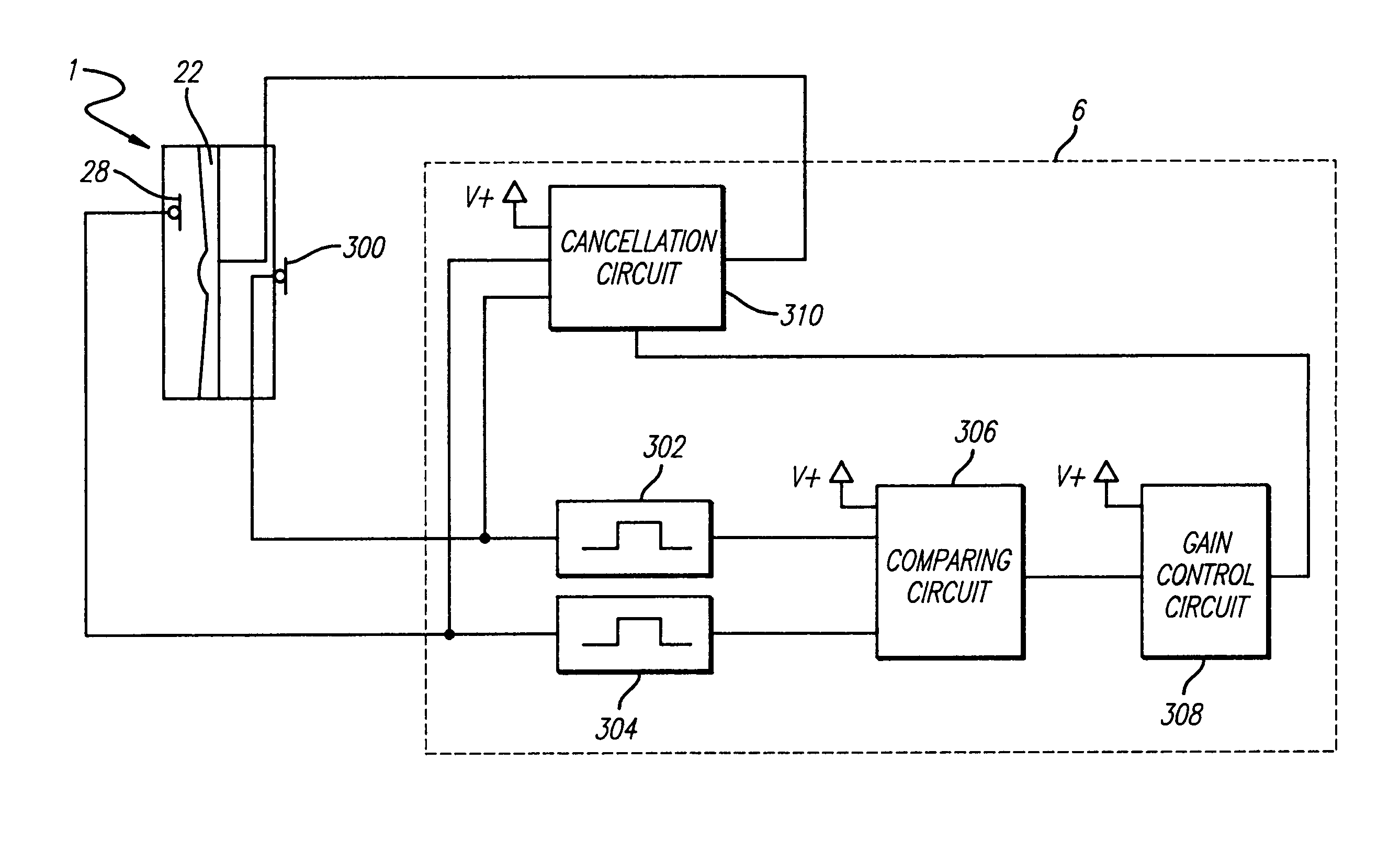
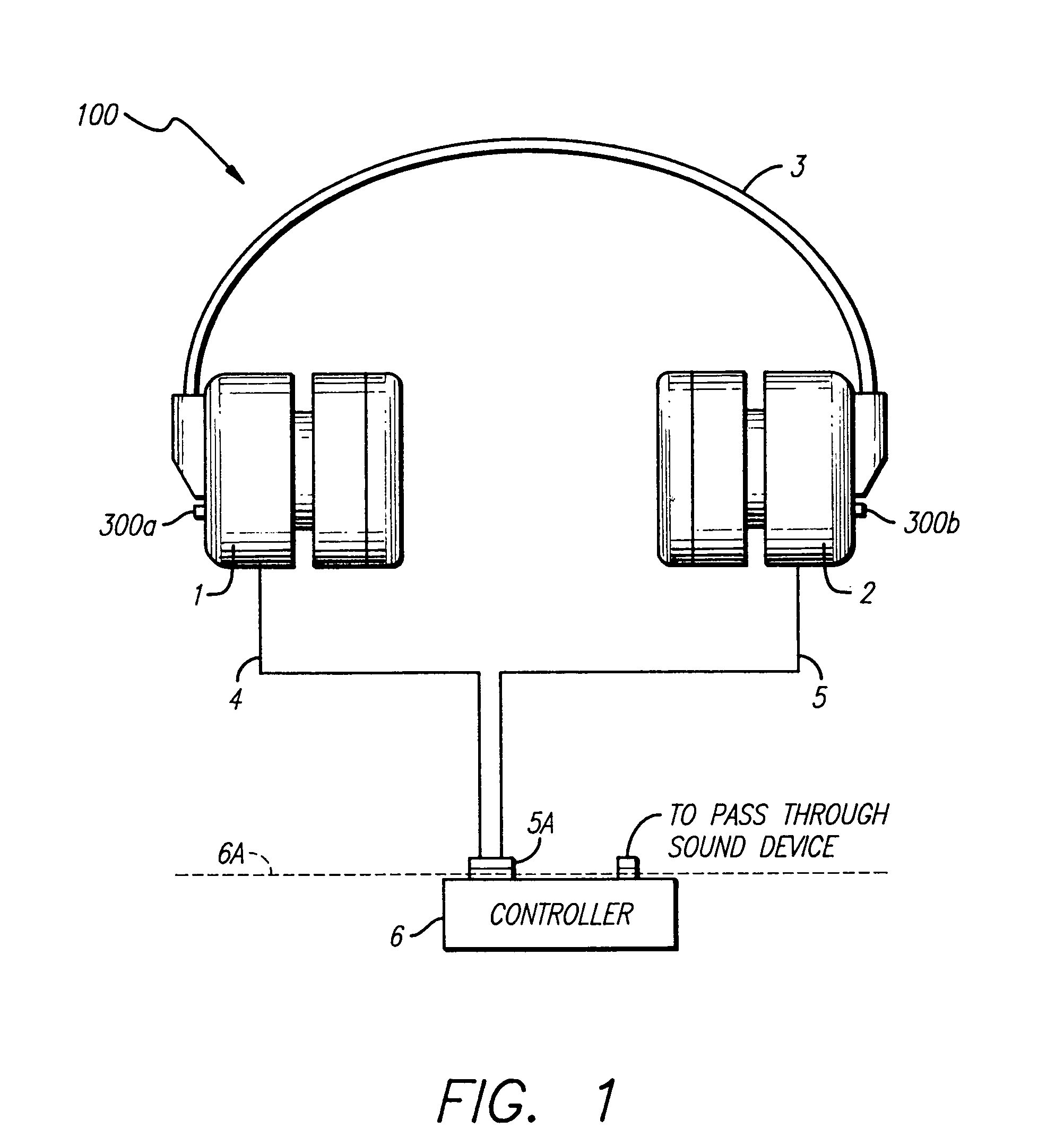
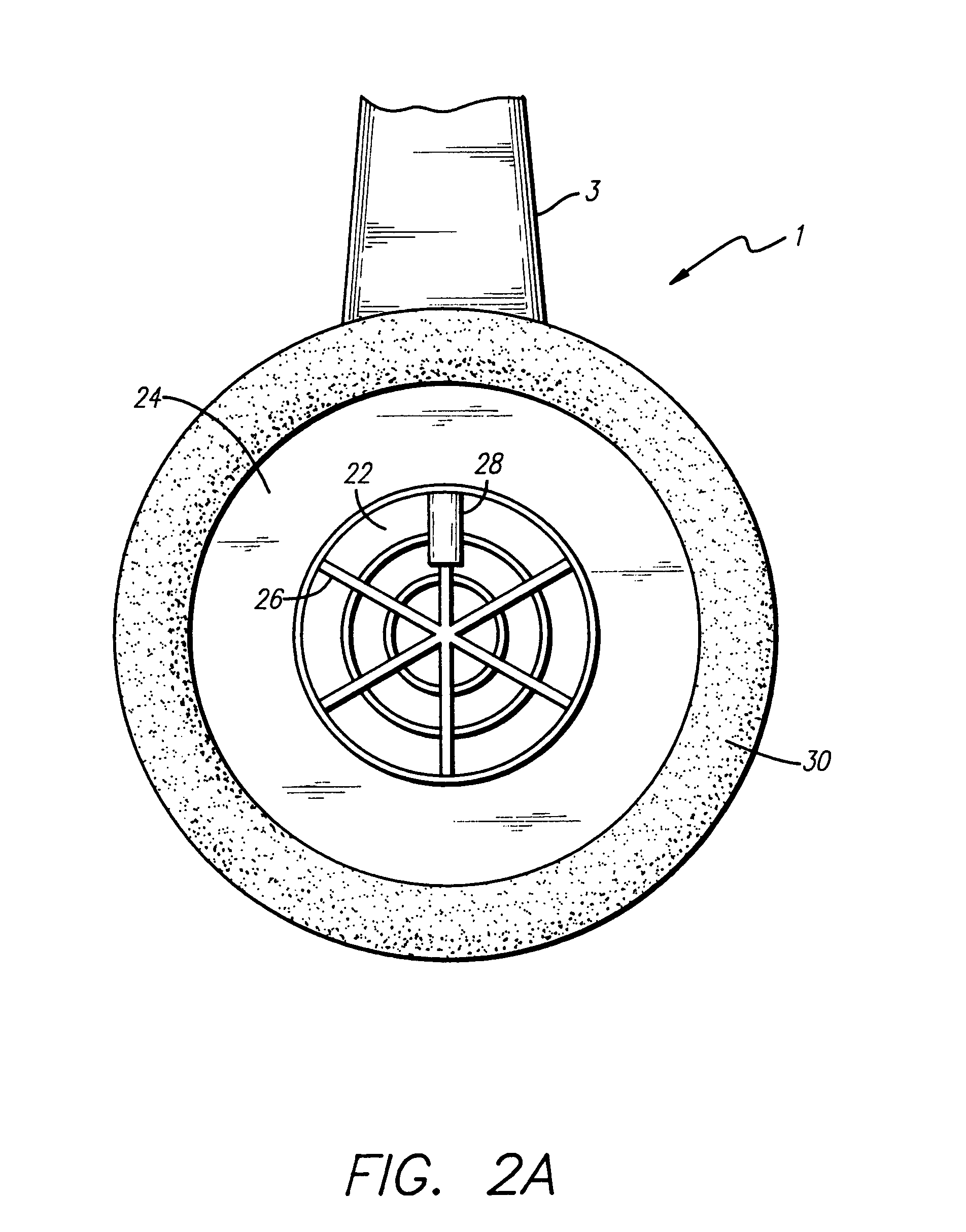
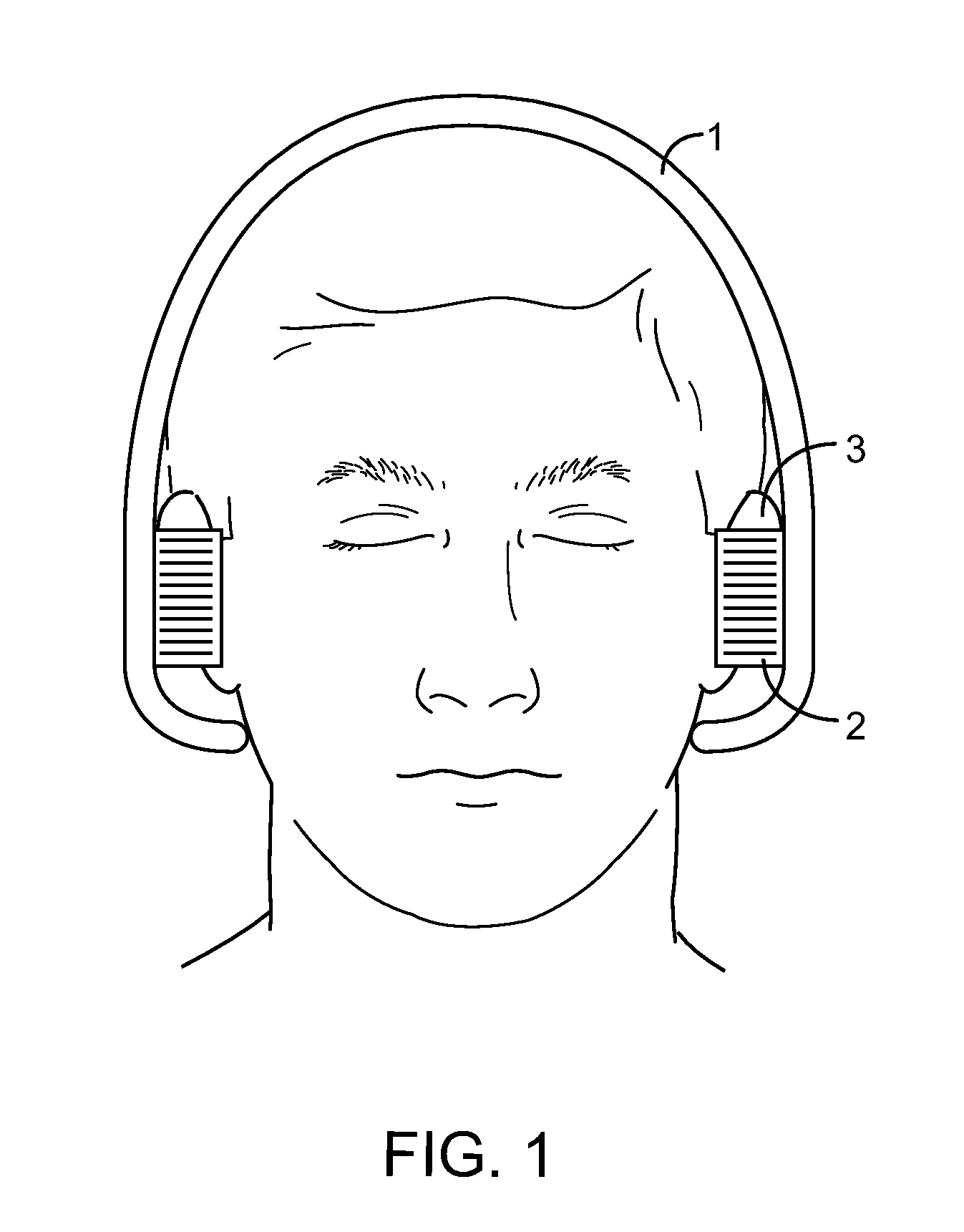
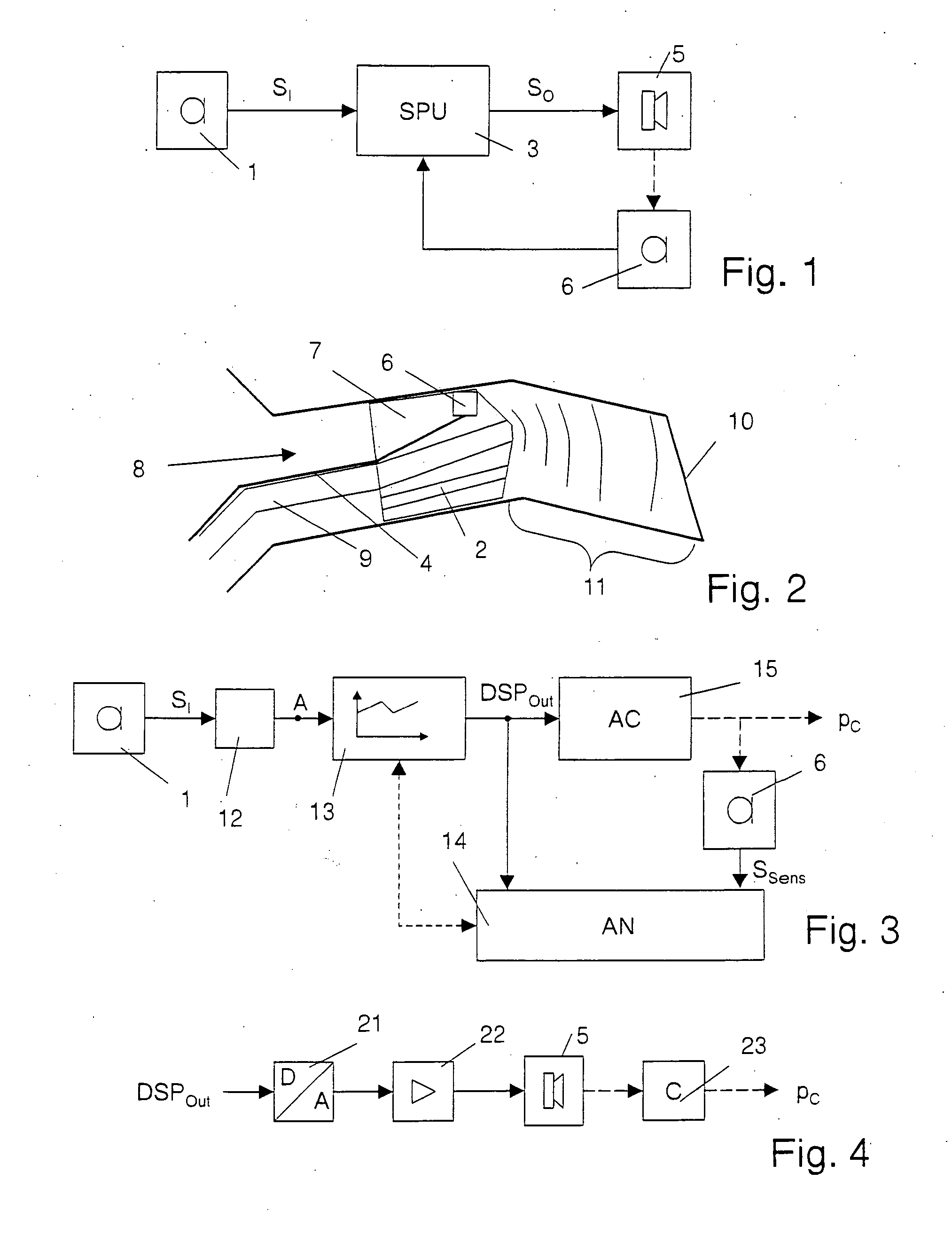
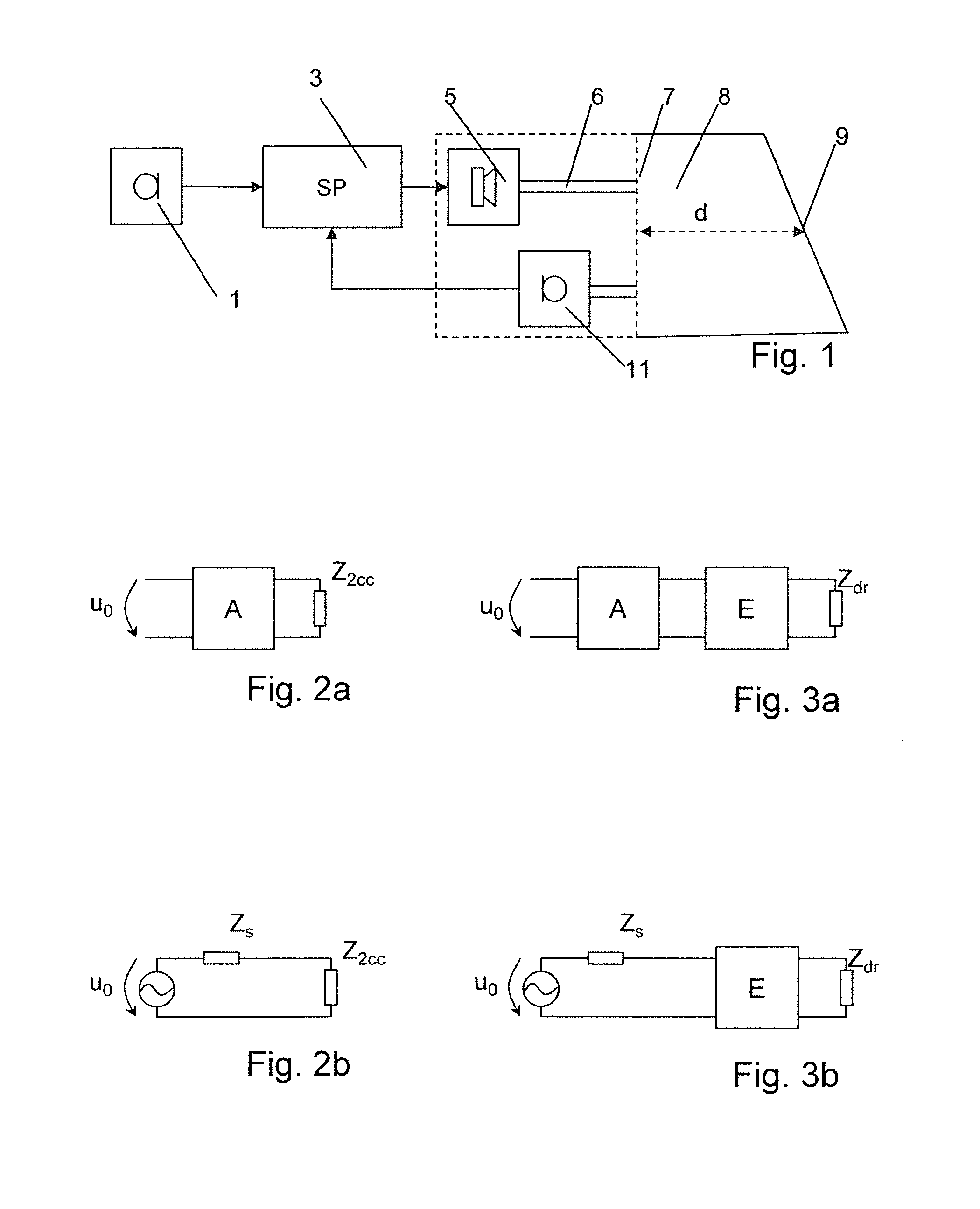
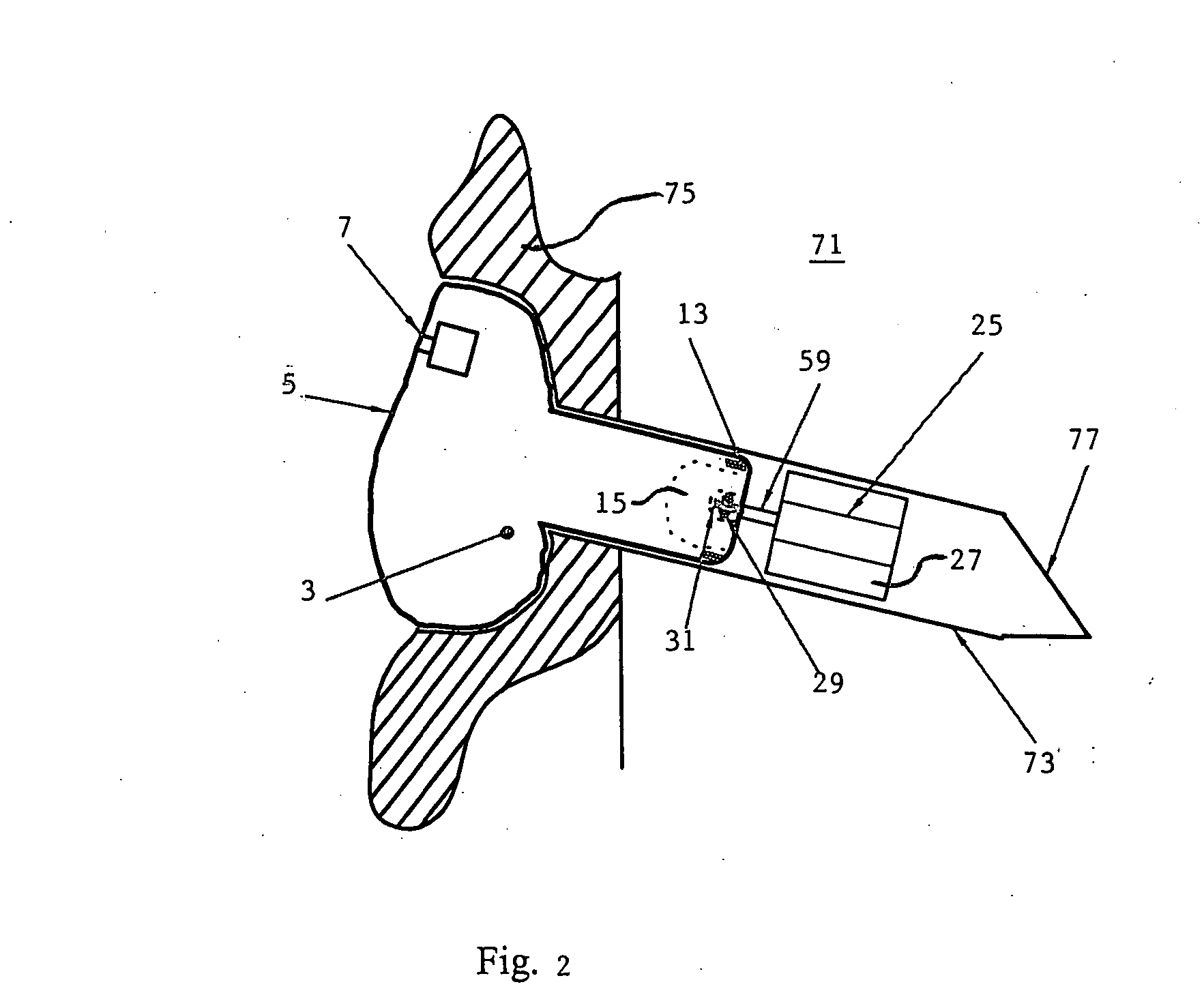
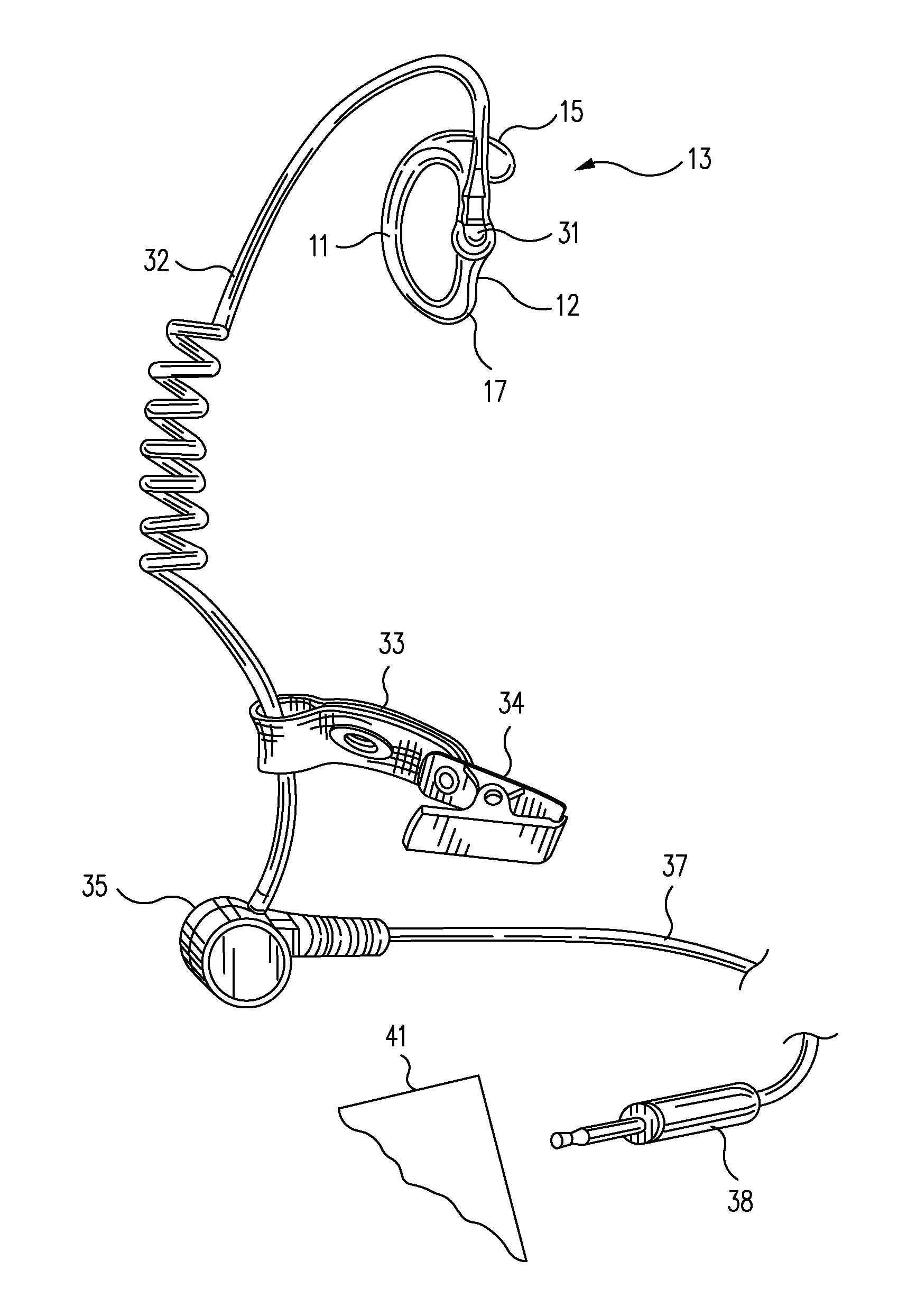
Variable gain active noise canceling system with improved residual noise sensing
InactiveUS6118878AReduce the possibilityCancellation system retains its effectiveness across its bandwidthNoise generationSound producing devicesInstabilityEngineering
An active noise cancellation system includes a series of features for more effective cancellation, greater reliability, and improved stability. A particular feature adapted for headset systems includes locating a residual microphone radially offset from the center of a sound generator to detect a signal more similar to that incident upon the eardrum of the user. In addition, an open back headset design includes perforations on the side of the headset instead of the back, so that the perforations are less susceptible to inadvertent blockage. The system also includes a mechanism for detecting changes in the acoustic characteristics of the environment that may be caused, for example, by pressure exerted upon the earpieces, and that may destabilize the cancellation system. The system automatically responds to such changes, for example, by reducing the gain or the frequency response of the system to preserve stability. The system further includes other methods for detecting imminent instability and compensating, such as detecting the onset of signals within enhancement frequencies characteristic of the onset of instability, and adjusting the gain or frequency response of the system or suppressing the enhanced signals. The system further includes a mechanism for conserving battery life by turning the system off when sound levels are low, or adjusting the power supply to the system to correspond to the current power requirements of the system.
Owner:NOISE CANCELLATION TECH
Variable gain active noise cancelling system with improved residual noise sensing
InactiveUS7103188B1Less instabilityImprove Noise CancellationEar treatmentHearing device active noise cancellationInstabilityEngineering
An active noise cancellation system includes a series of features for more effective cancellation, greater reliability, and improved stability. A particular feature adapted for headset systems includes locating a residual microphone radially offset from the center of a sound generator to detect a signal more similar to that incident upon the eardrum of the user. In addition, an open back headset design includes perforations on the side of the headset instead of the back, so that the perforations are less susceptible to inadvertent blockage. The system also includes a mechanism for detecting changes in the acoustic characteristics of the environment that may be caused, for example, by pressure exerted upon the earpieces, and that may destabilize the cancellation system. The system automatically responds to such changes, for example, by reducing the gain or the frequency response of the system to preserve stability. The system further includes other methods for detecting imminent instability and compensating, such as detecting the onset of signals within enhancement frequencies characteristic of the onset of instability, and adjusting the gain or frequency response of the system or suppressing the enhanced signals. The system further includes a mechanism for conserving battery life by turning the system off when sound levels are low, or adjusting the power supply to the system to correspond to the current power requirements of the system.
Owner:NCT GROUP
Pulse oximetry methods and apparatus for use within an auditory canal
Methods and apparatus for detecting oxygen saturation levels in blood from within an auditory canal of a living being proximal to a tympanic membrane are disclosed. The auditory canal is lined with tissue and includes a proximal bend and a distal bend located between the proximal bend and the tympanic membrane. Oxygen levels are detected by emitting one or more wavelengths of light into a first position on the tissue of the auditory canal in a first region defined by the distal bend and the tympanic membrane. The wavelengths of light are then sensed at a second position on the tissue of the auditory canal in the first region. A blood oxygen saturation level and / or pulse rate is then calculated responsive to intensity information corresponding to the wavelengths of light detected at the second position.
Owner:SARNOFF CORP
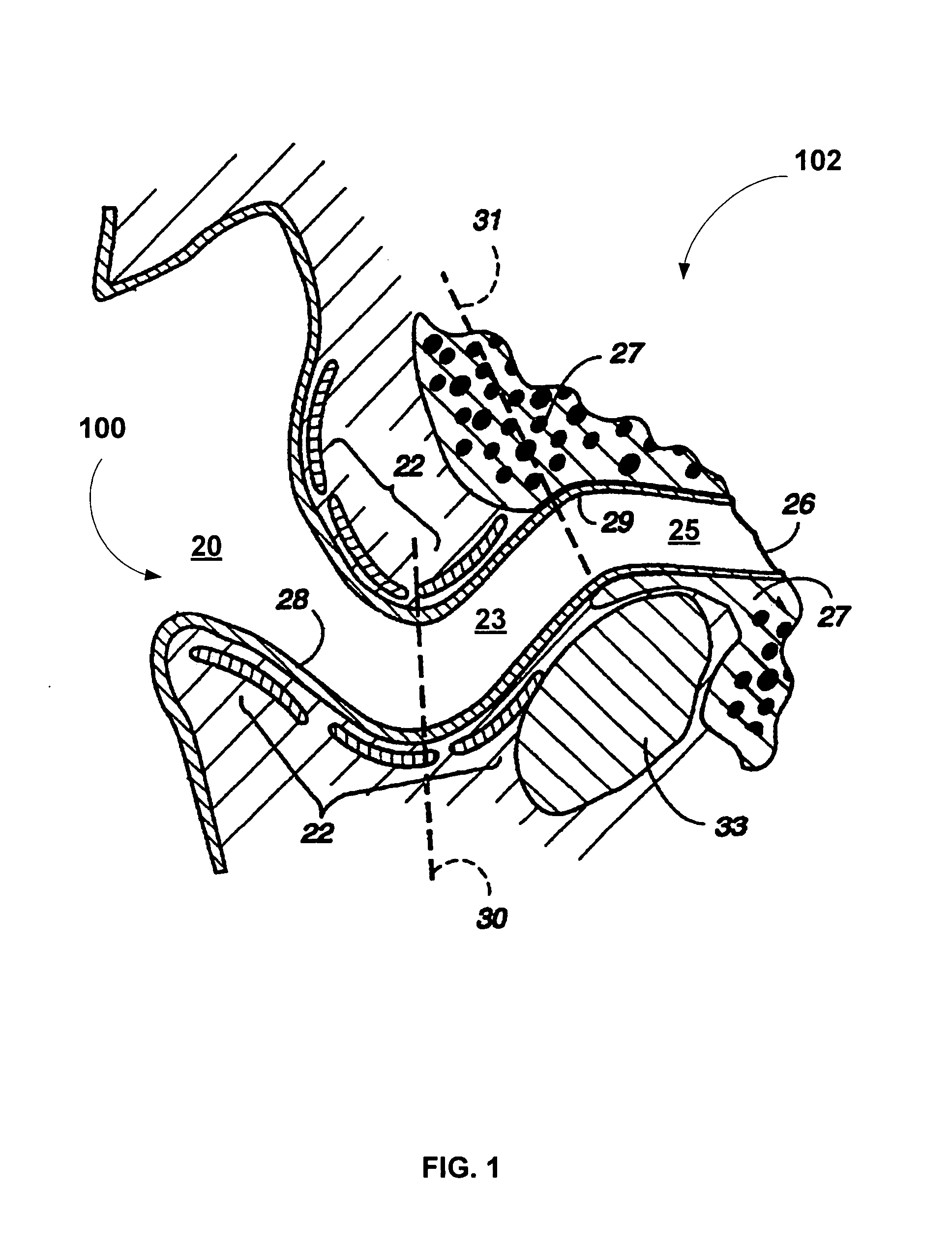
Repair of tympanic membrane using placenta derived collagen biofabric
The present invention provides a method of repairing a tympanic membrane deformity, such as a tympanic membrane perforation, commonly referred to as tympanoplasty or myringoplasty, using a collagen biofabric. The collagen biofabric is preferably laminated. The invention further provides kits comprising one or more pieces of collagen biofabric, for example laminated collagen biofabric, for the repair of a tympanic membrane.
Owner:ANTHROGENESIS CORP
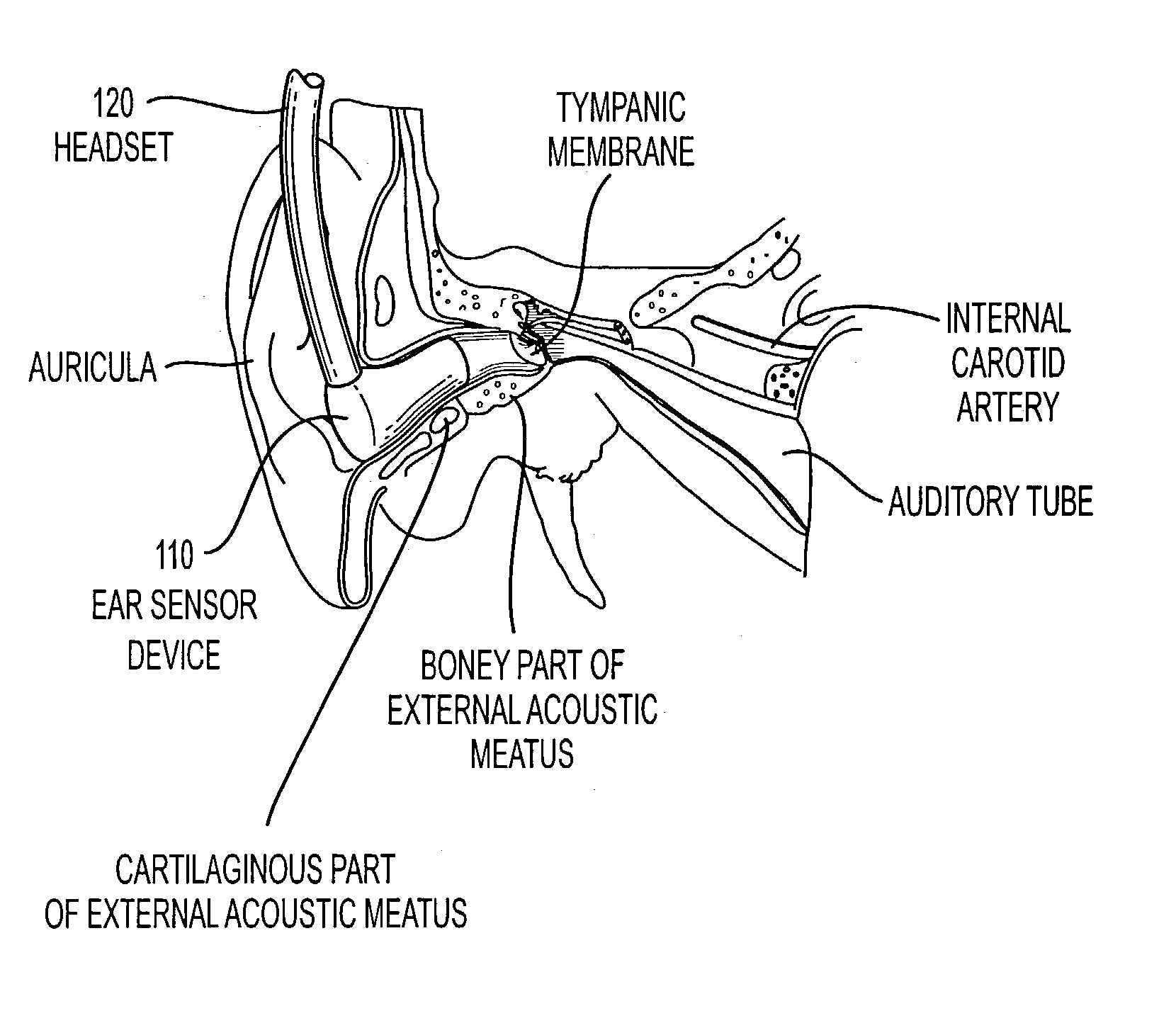
Headset for measuring physiological parameters
Methods and systems for determining physiological parameters from body sounds obtained from a person's ear. In various exemplary embodiment, the system includes an earplug housing; a sensing element disposed within a portion of the earplug housing; an acoustic shield coupled to the earplug housing, the acoustic shield reducing or eliminating extracorporeal sounds; and a preamplification circuit electrically coupled to the sensing element. In various exemplary embodiments, the system is operable to determine motion and / or vibration of the external acoustic meatus or the tympanic membrane of the ear due to internally generated body sounds.
Owner:COLIN MEDICAL TECH
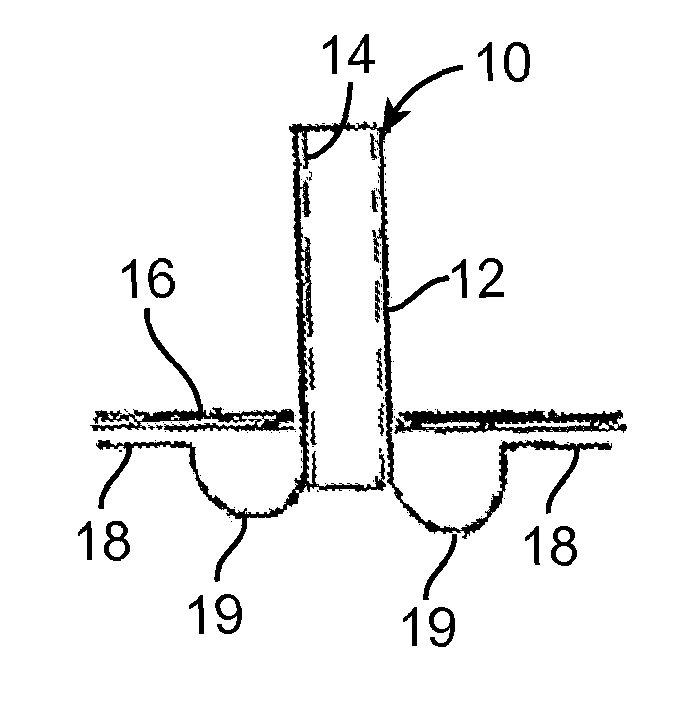
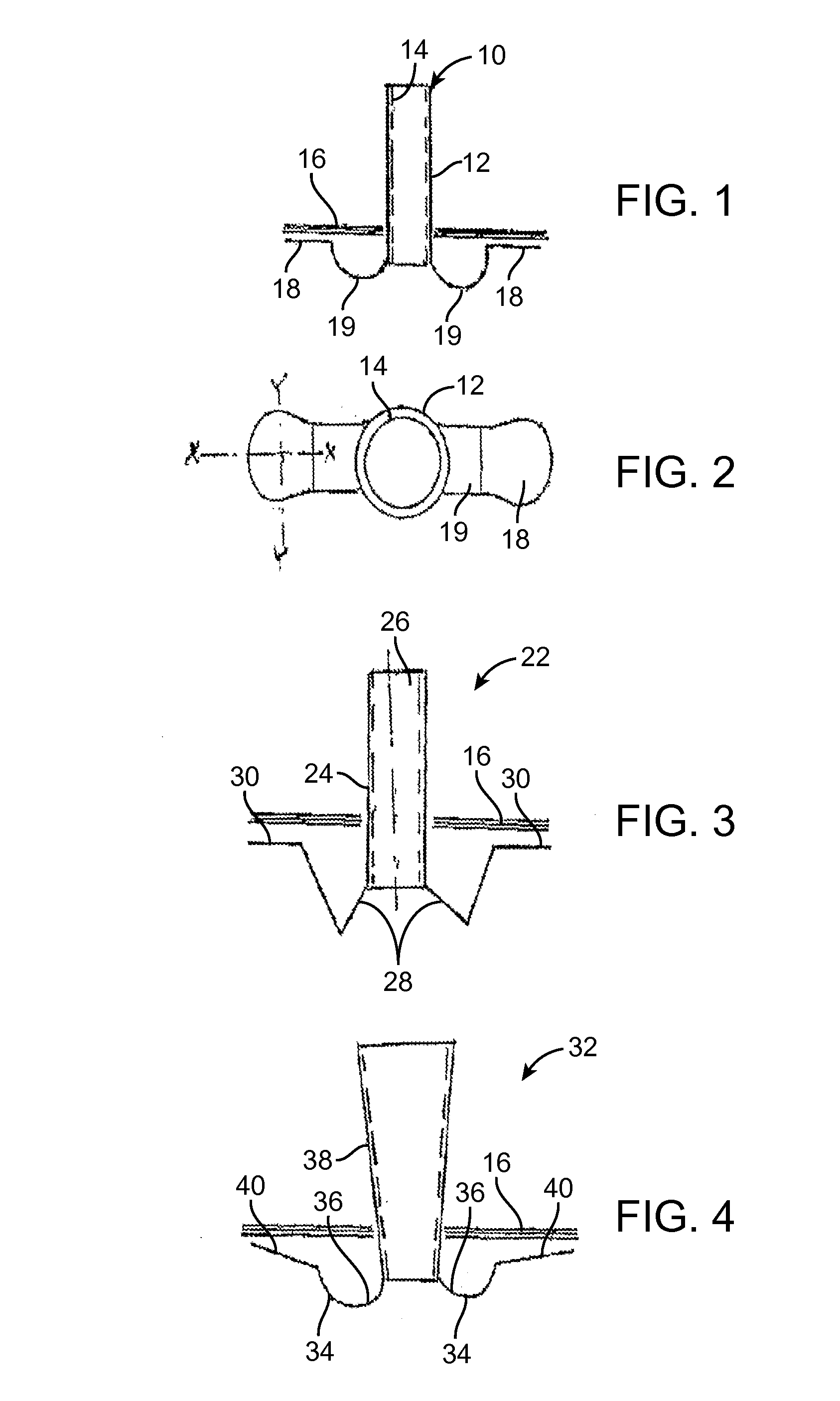
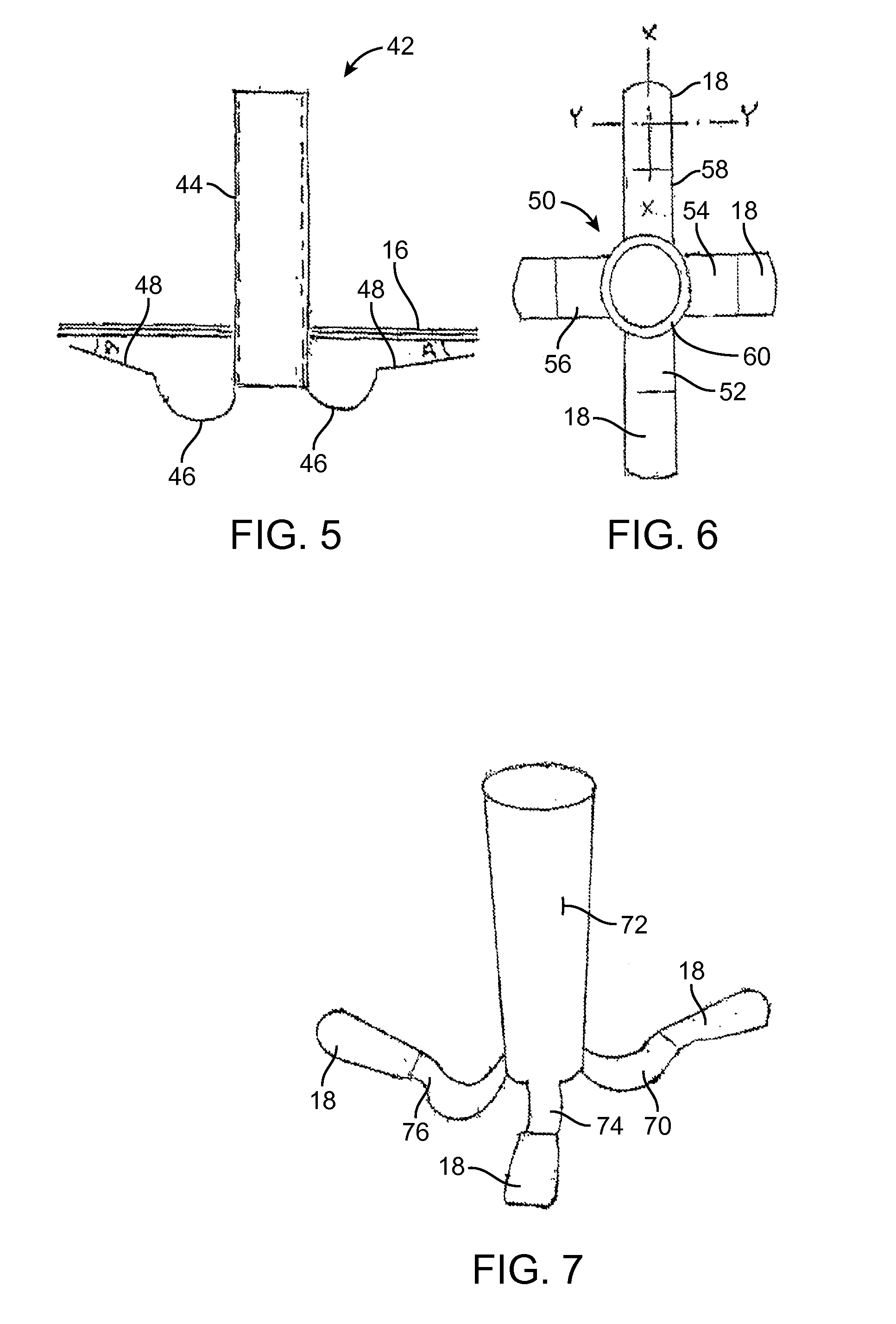
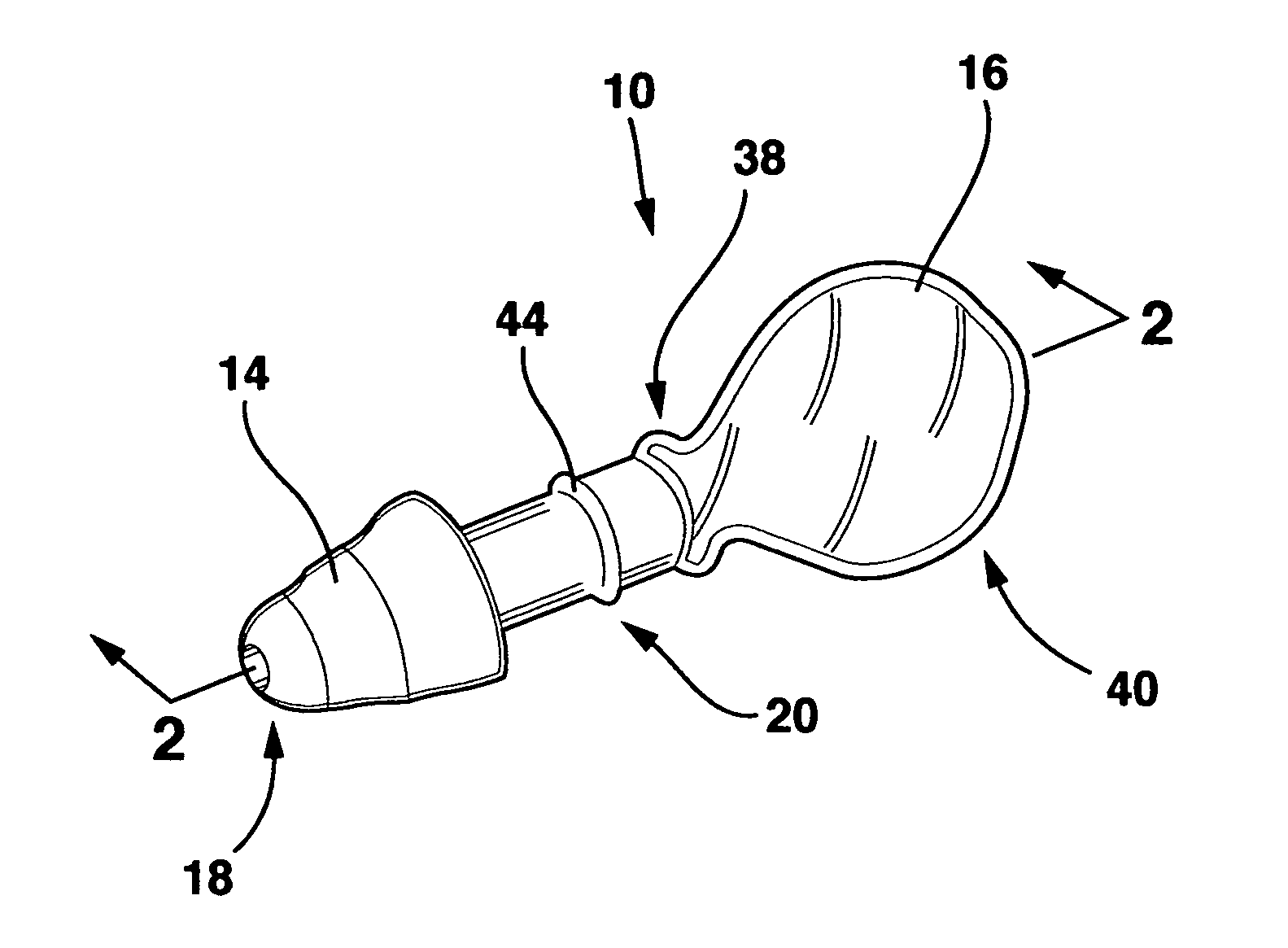
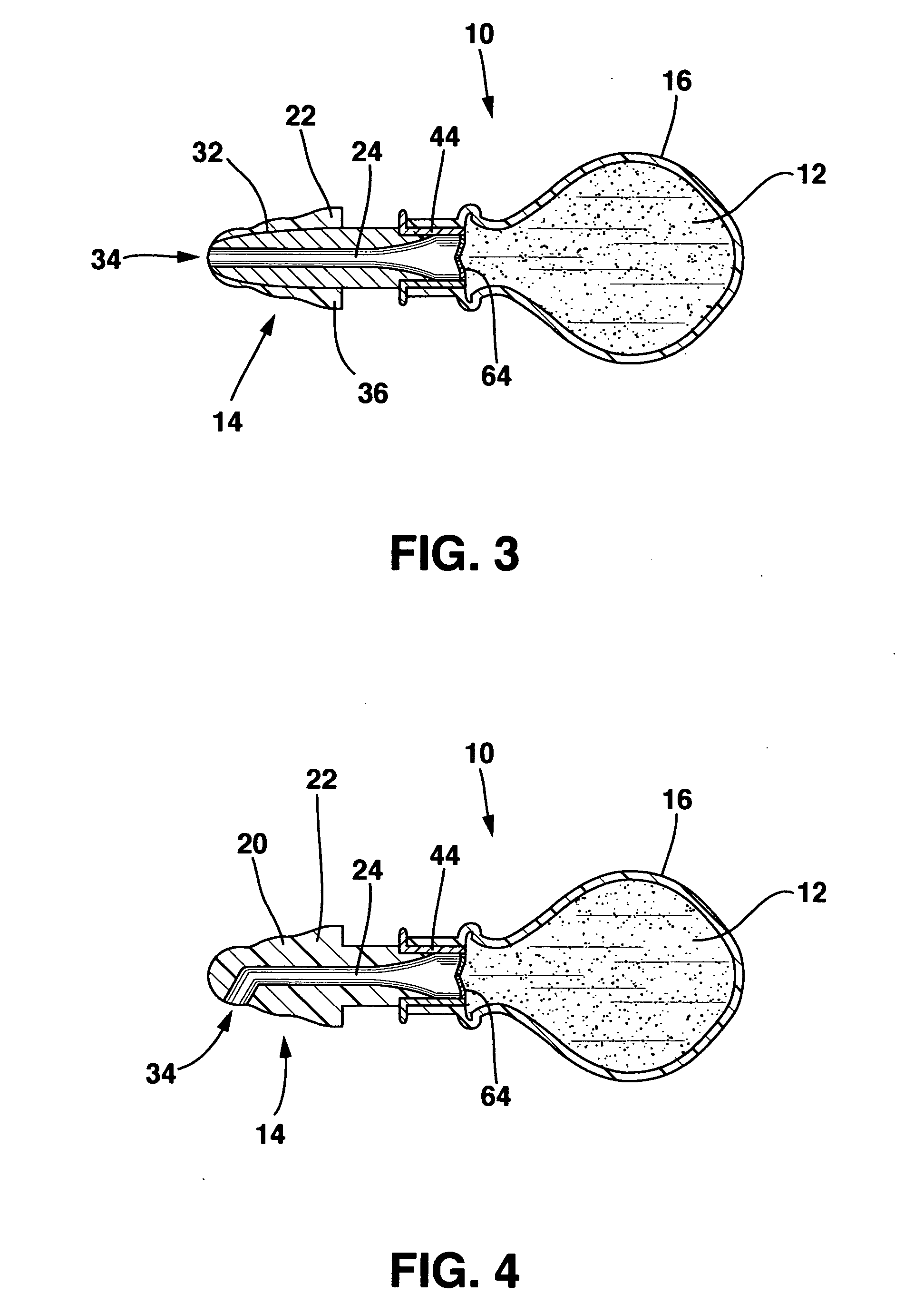
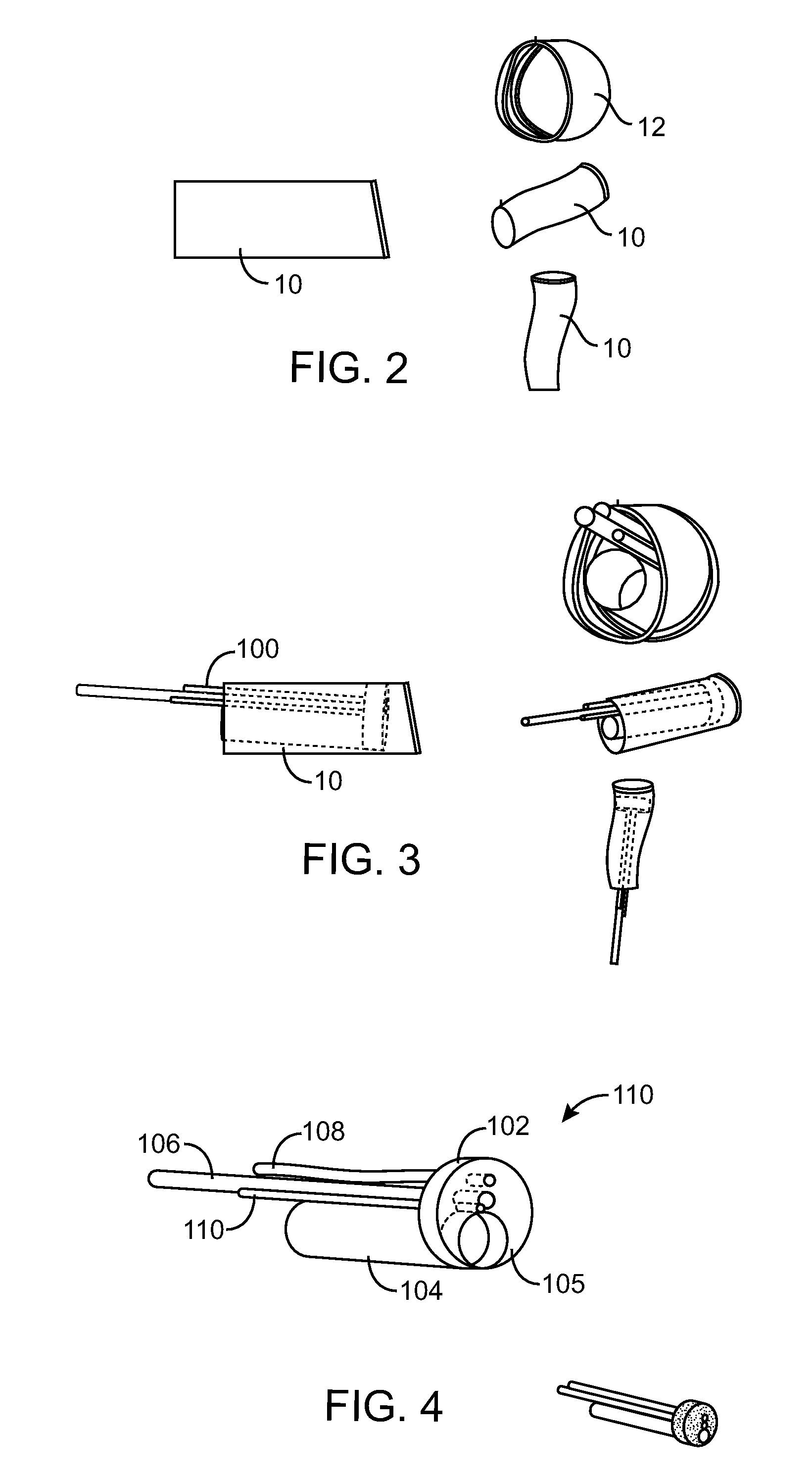
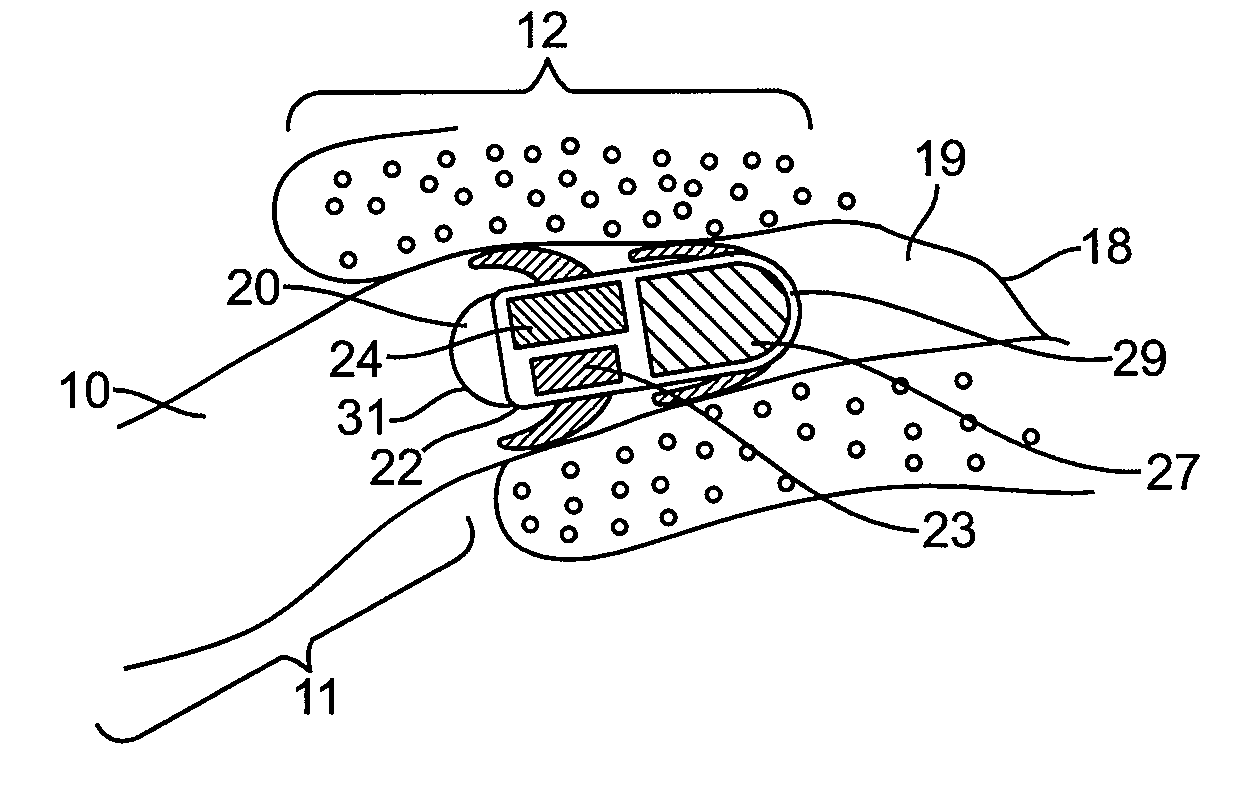
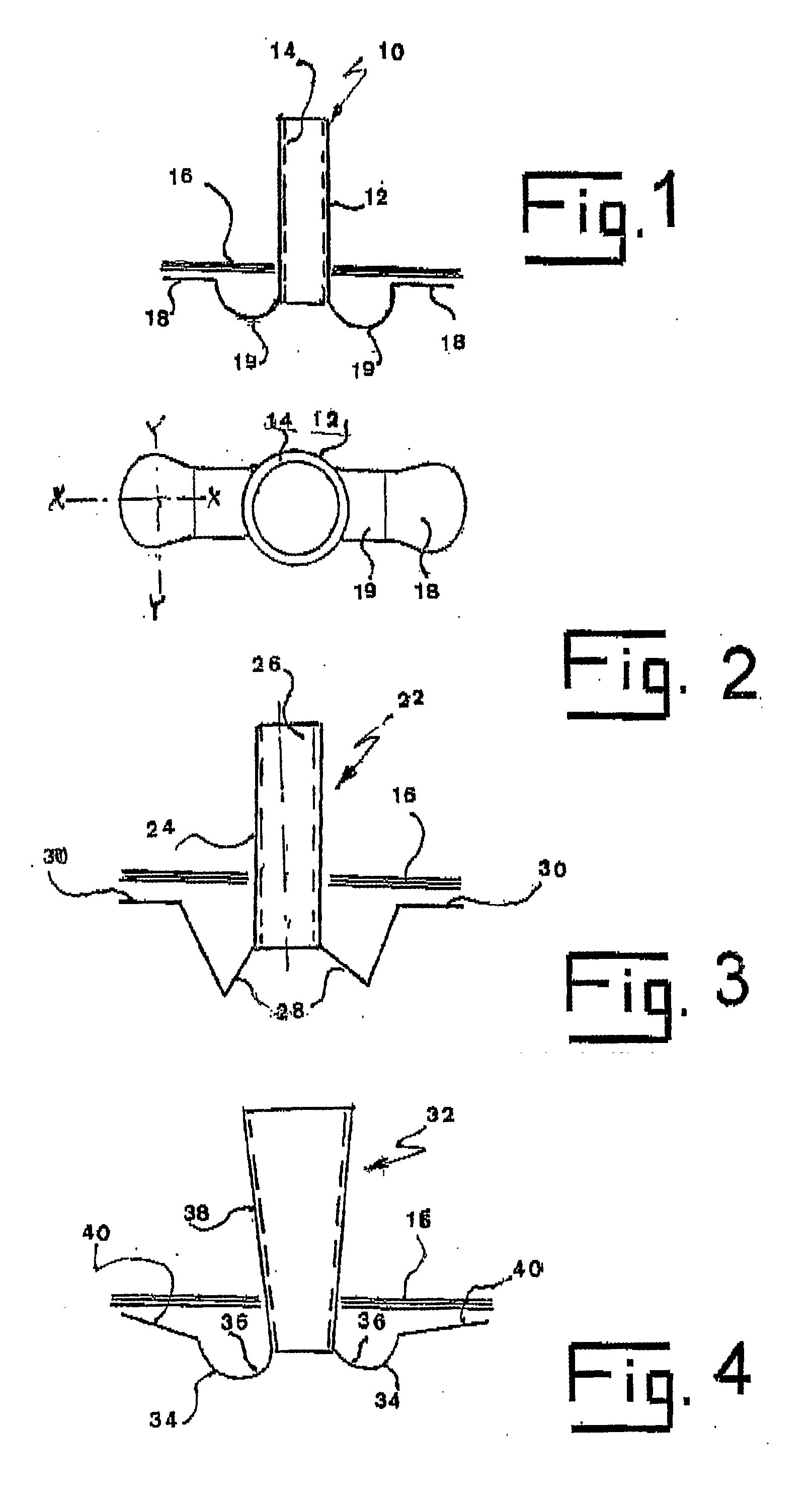
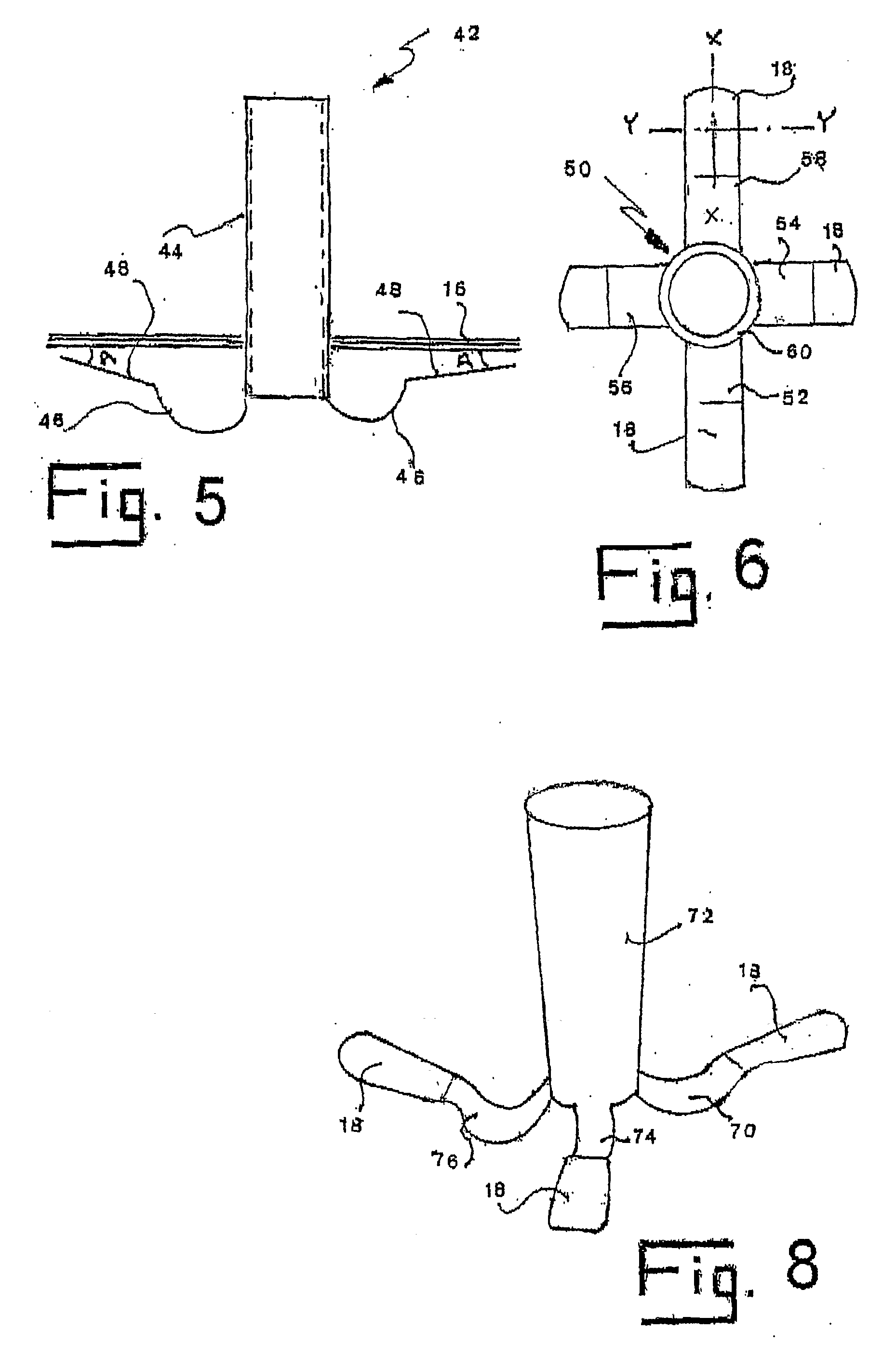
Ear tubes
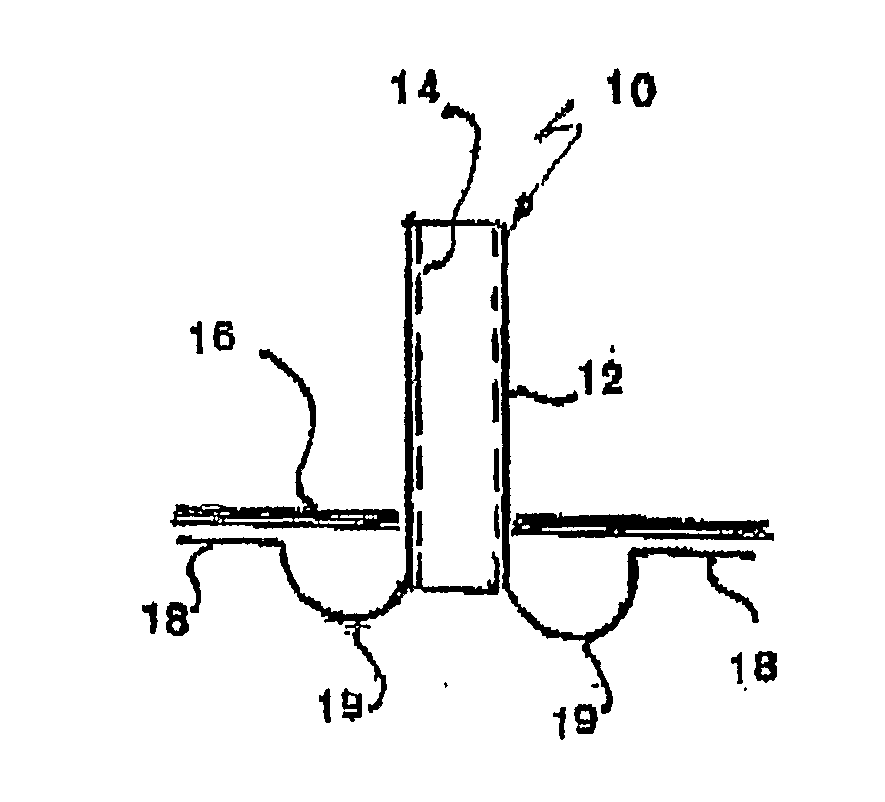
ActiveUS8197433B2Easy to insertEasy to disassembleEar treatmentIntravenous devicesMiddle earEngineering
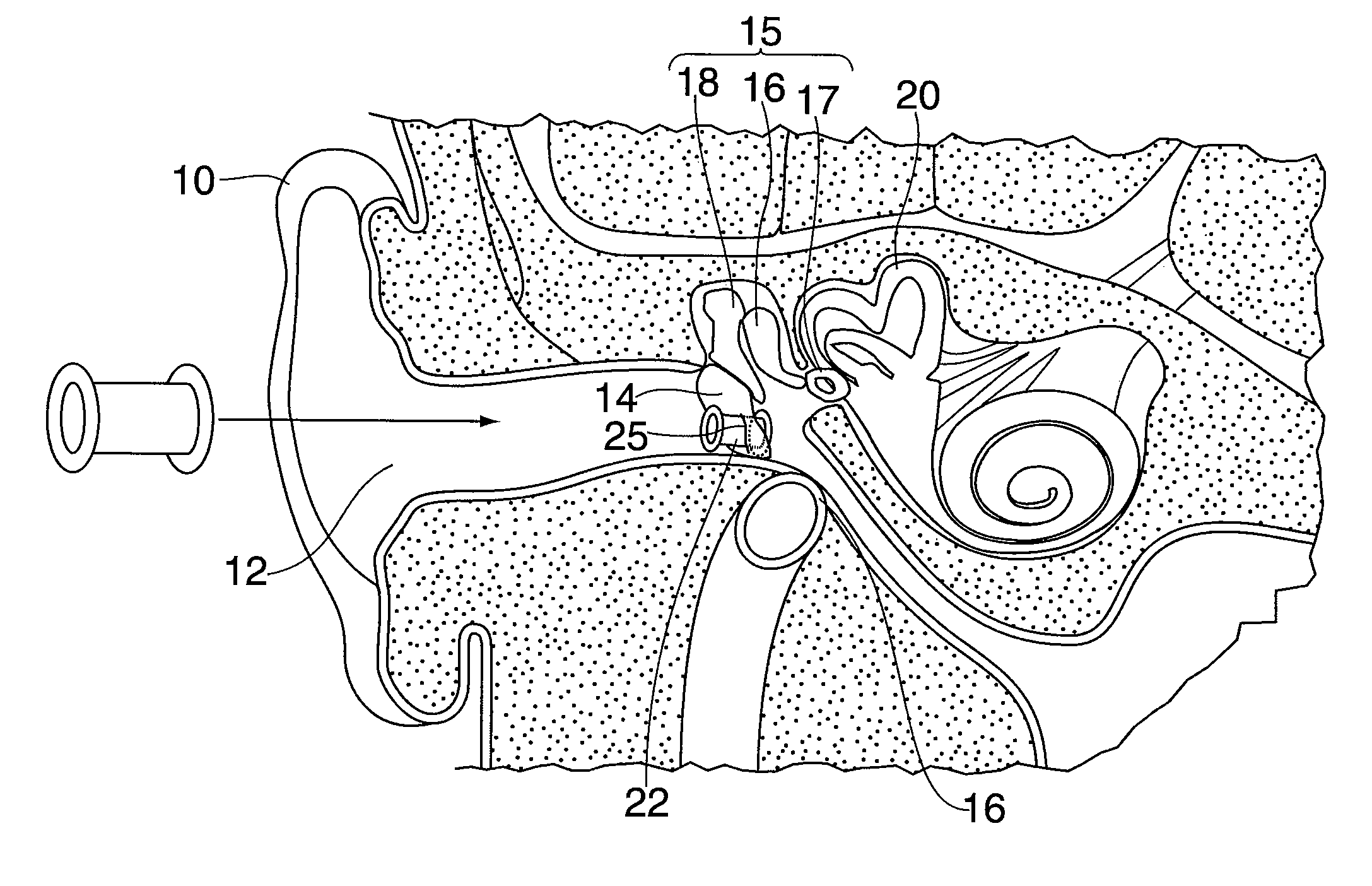
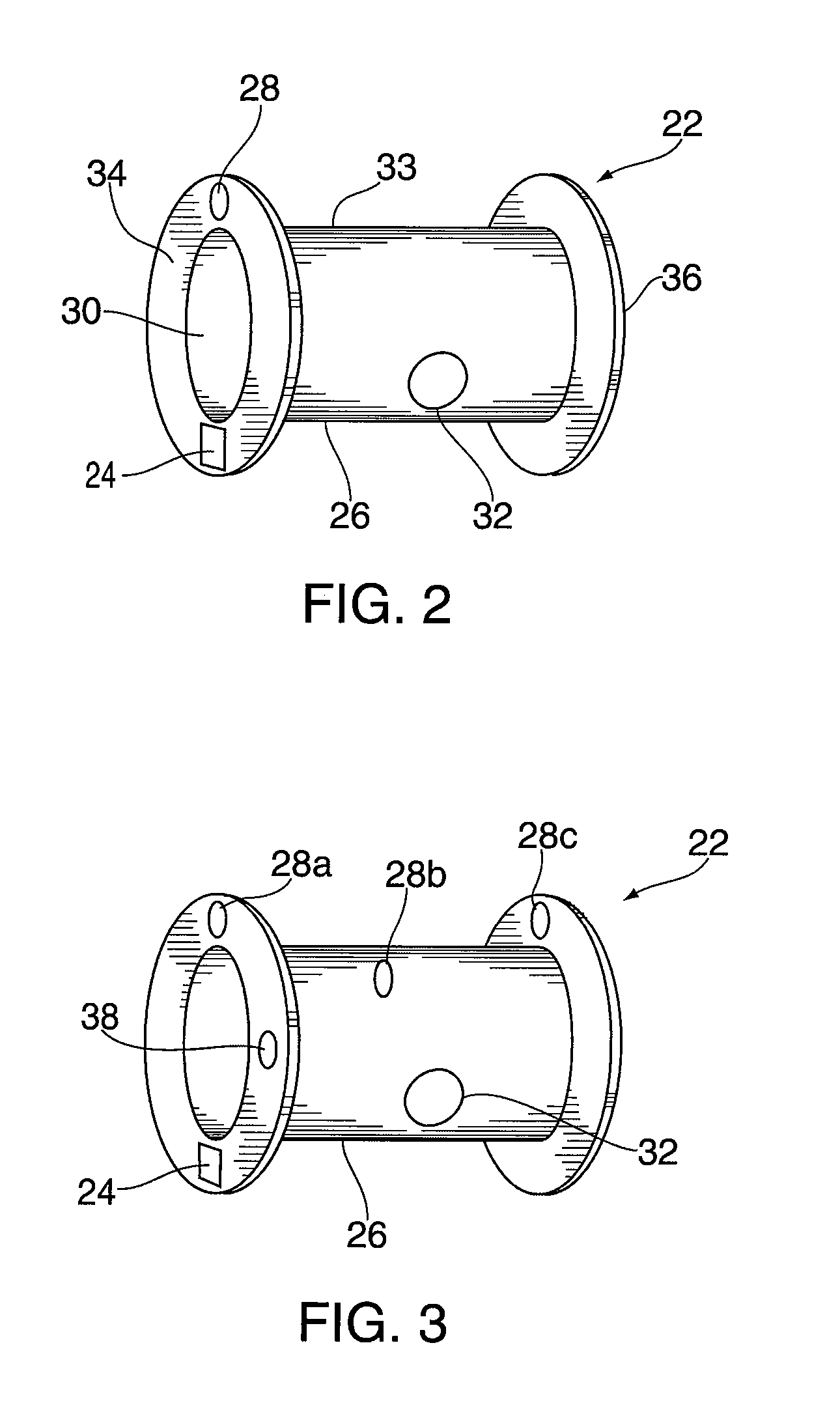
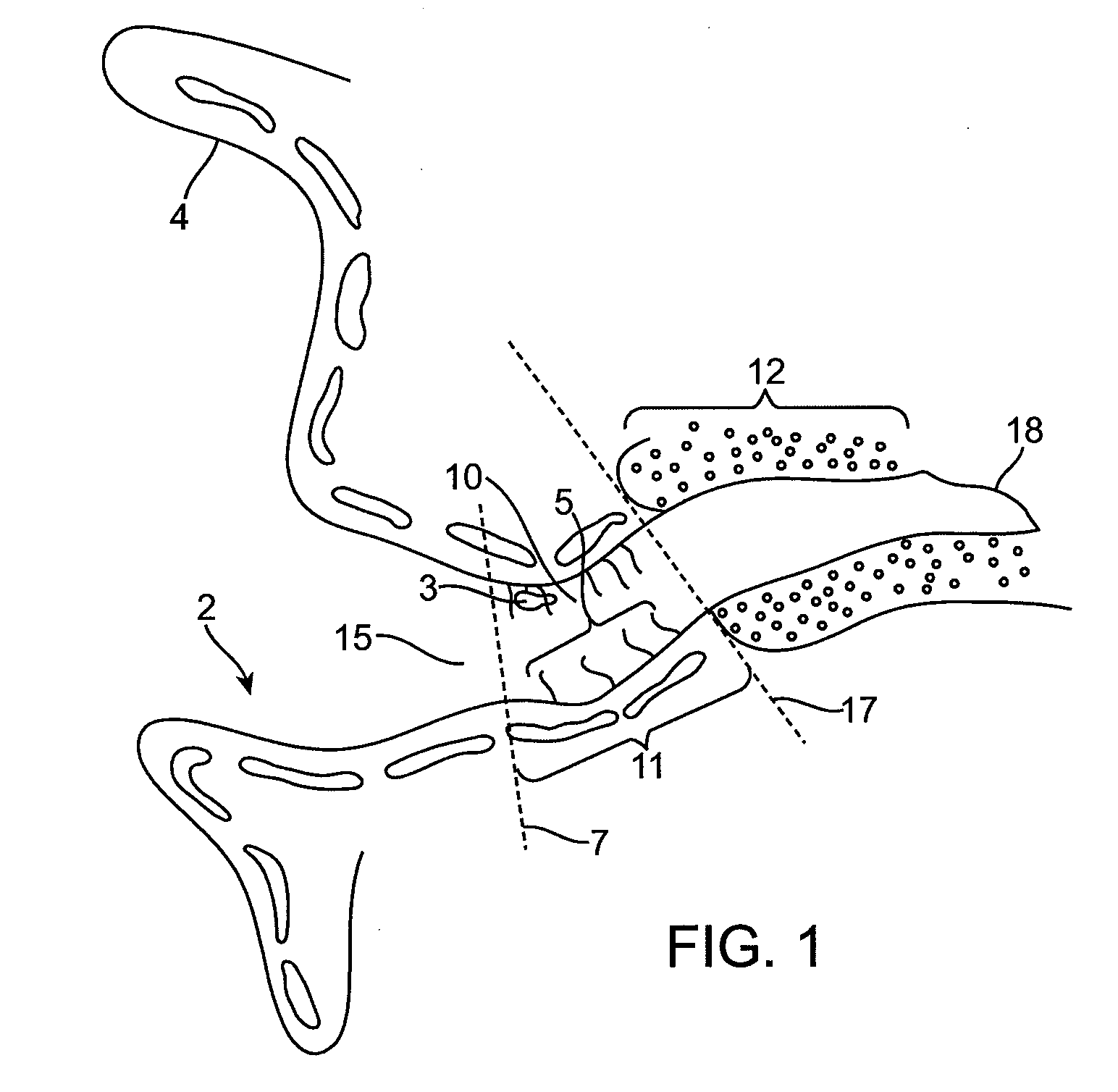
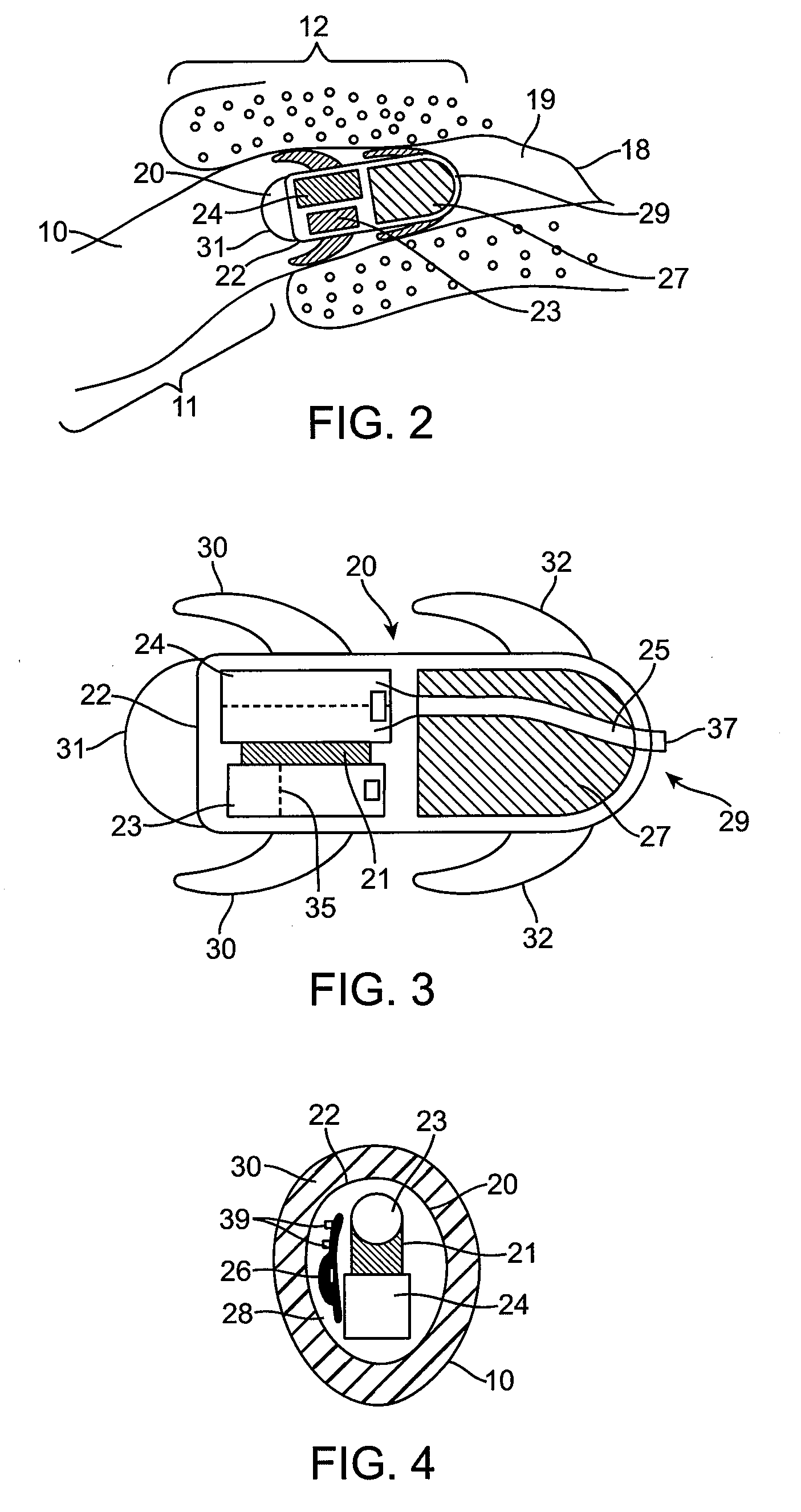
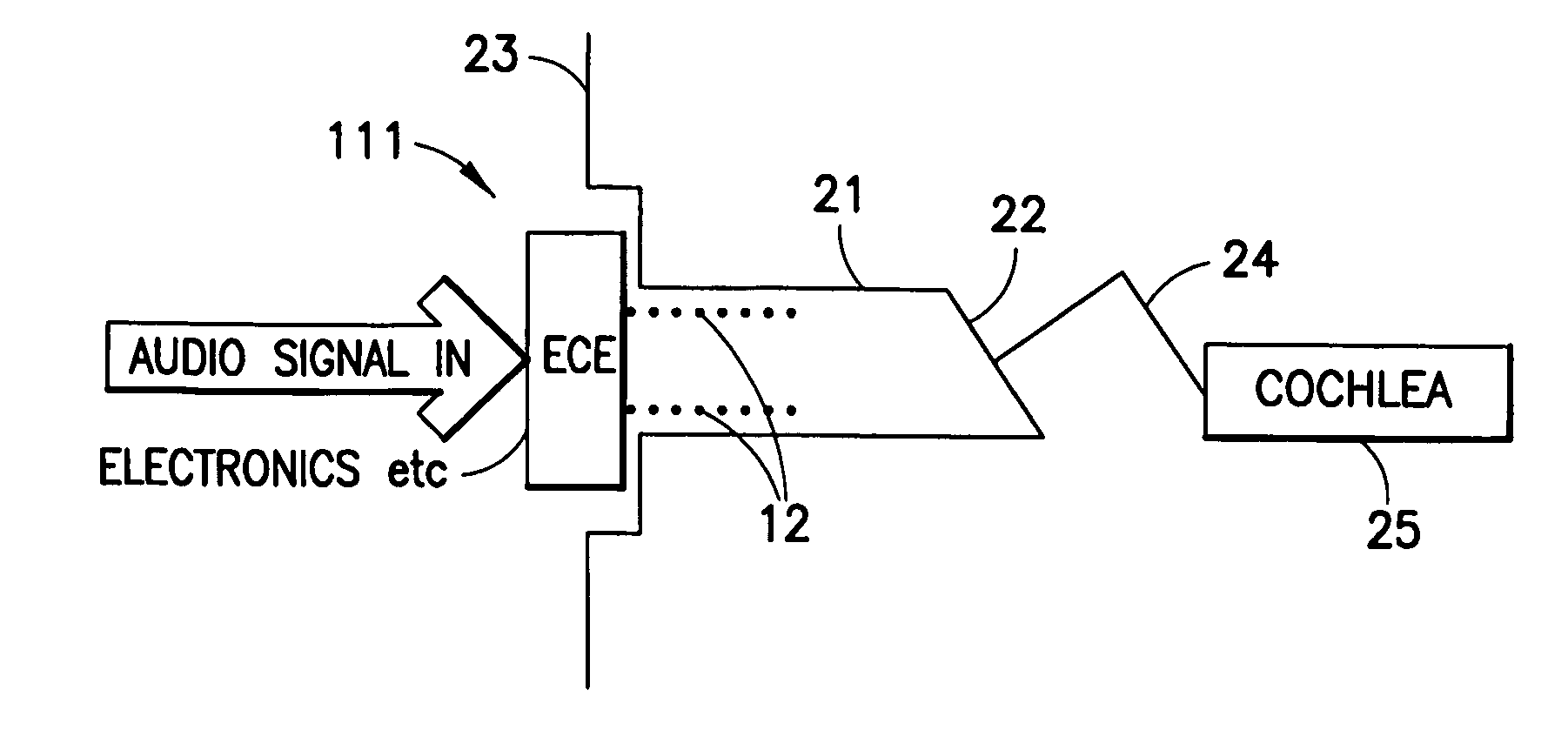
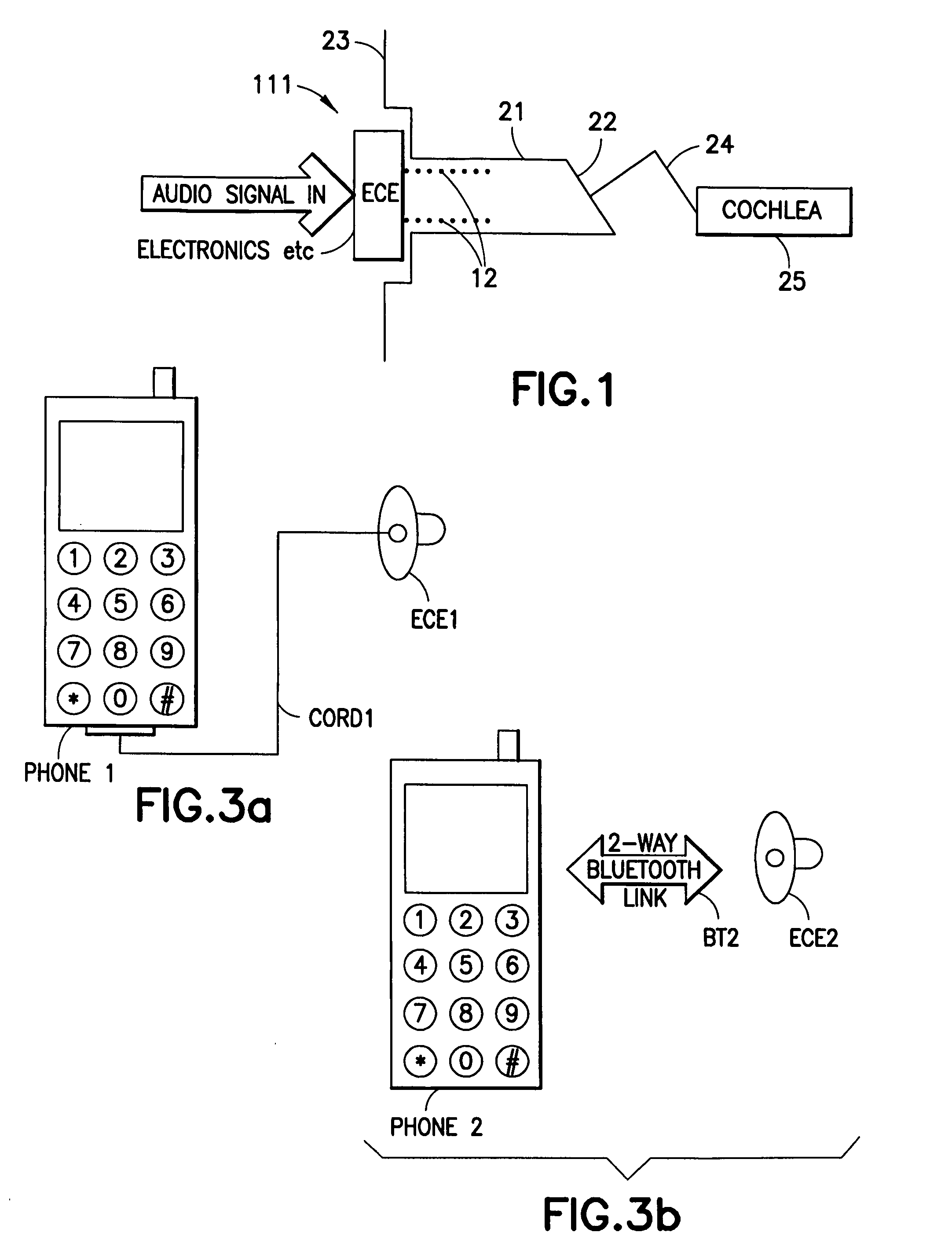
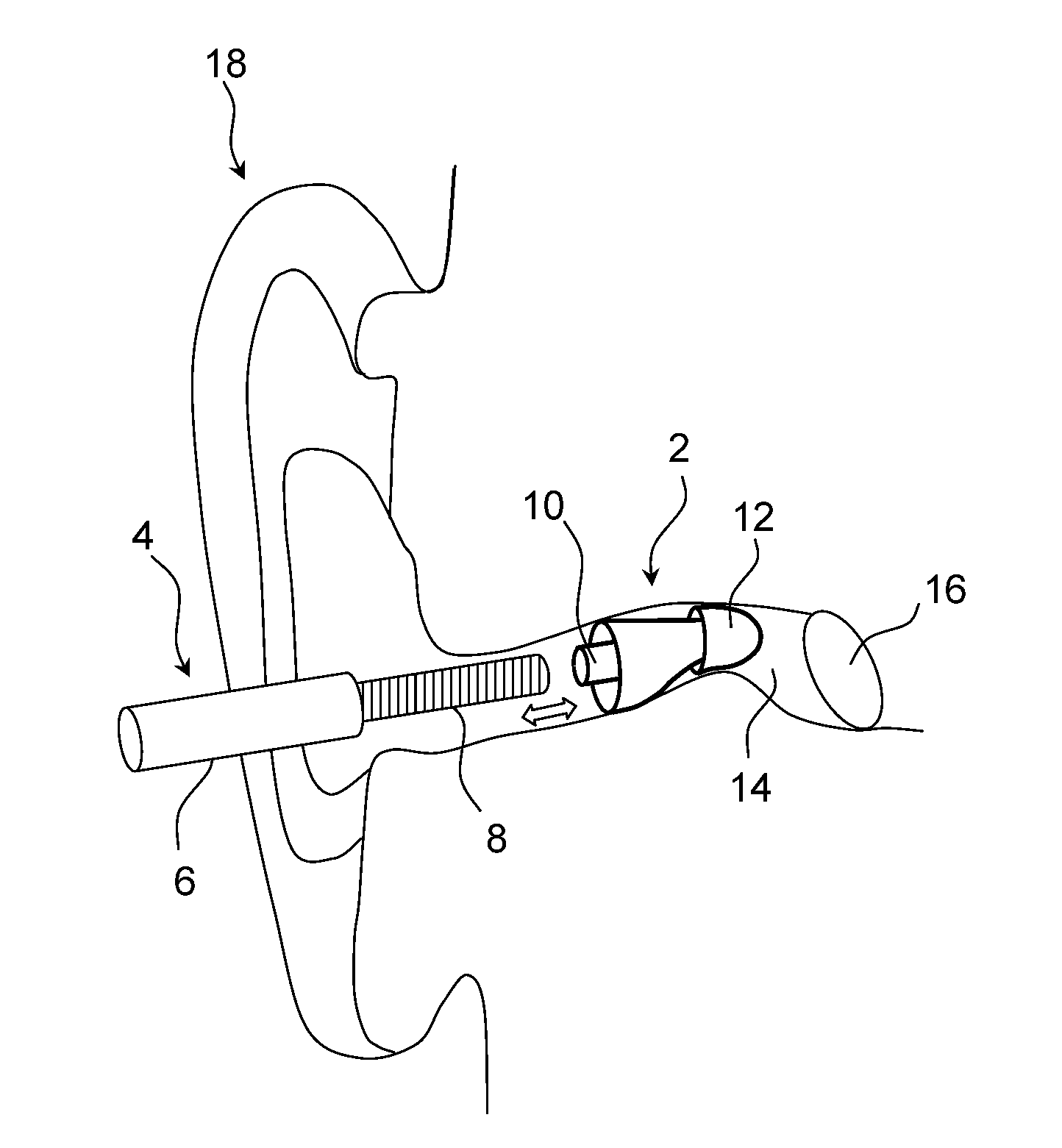
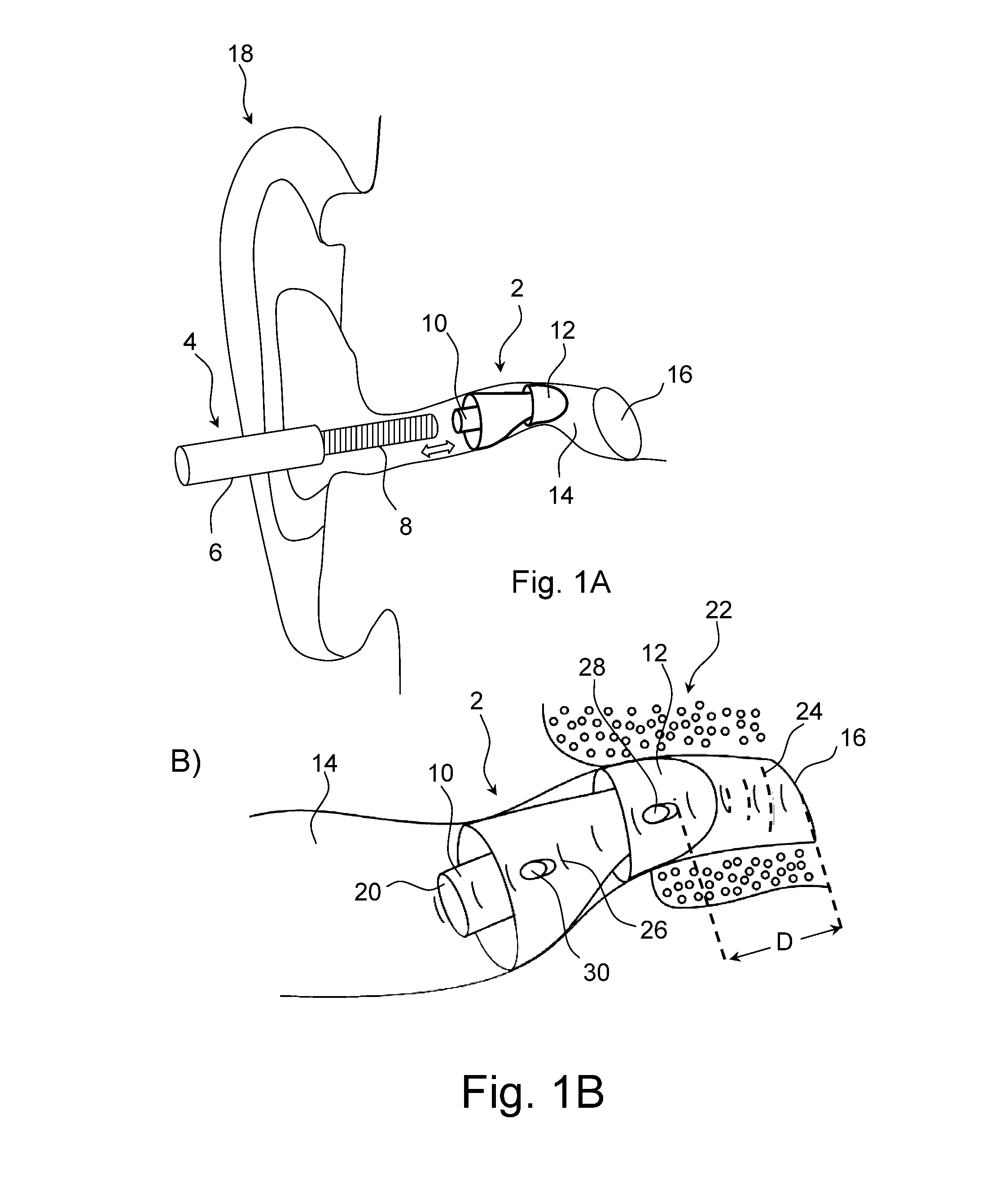
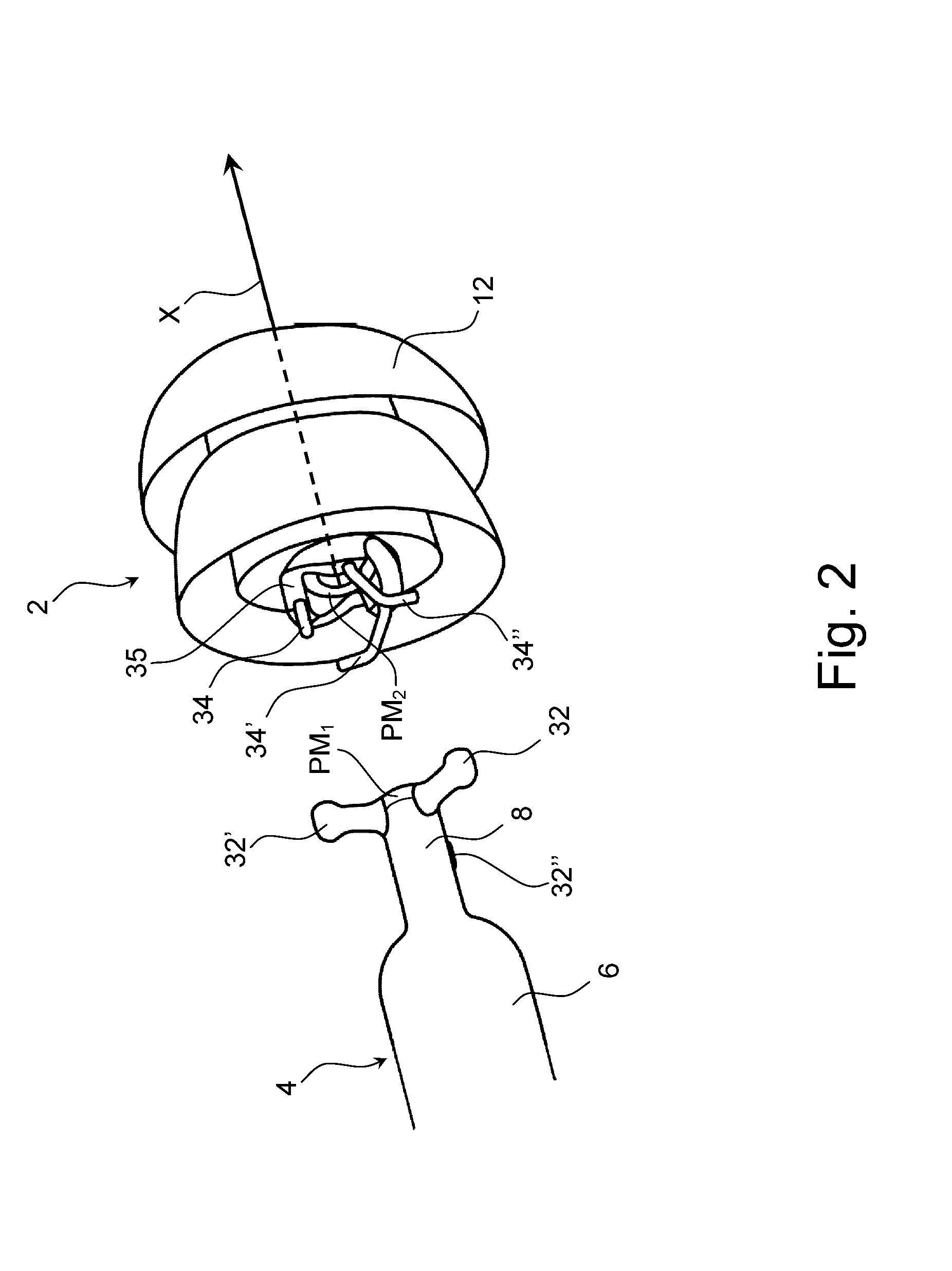
The invention provides a flexible ear tube (10) for draining and ventilating the middle ear, the tube (10) having a flexible substantially tubular stem (12) with a lumen (14), the stem (12) being sized to be inserted through an incision in the eardrum (16) and the tube having at least two separate flexible contact surfaces (18) extending from the stem (12) and adapted to engage different spaced-apart inner surfaces of the eardrum 16, each of the contact surfaces (18) having a first axis XX extending substantially perpendicularly to the central axis of the stem and a second axis YY extending substantially perpendicularly to the first axis wherein one of the axes is between 0.6 and 3 mm and the second of the axes is between 1 and 7 mm in length.
Owner:OTOMEDICS ADVANCED MEDICAL TECH
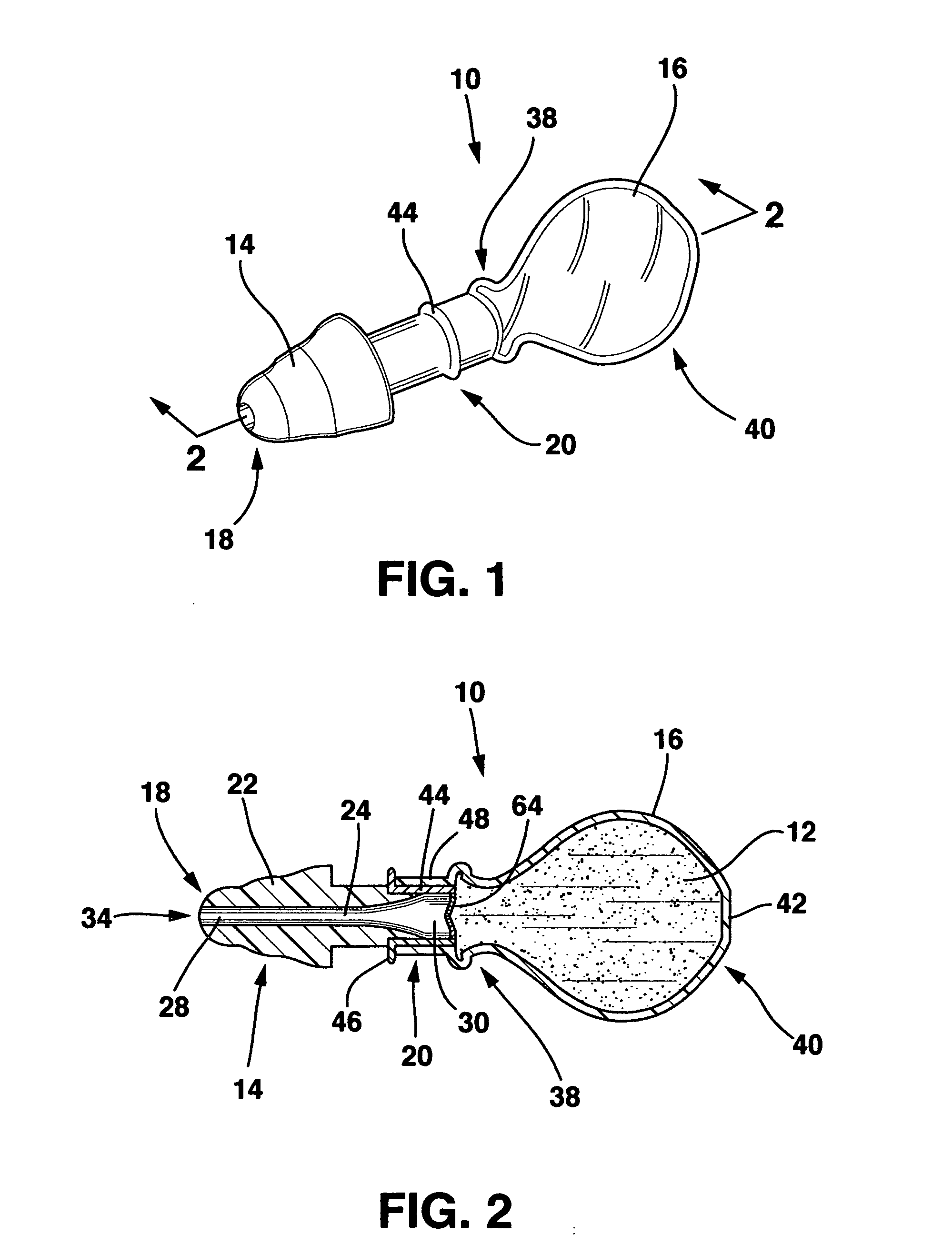
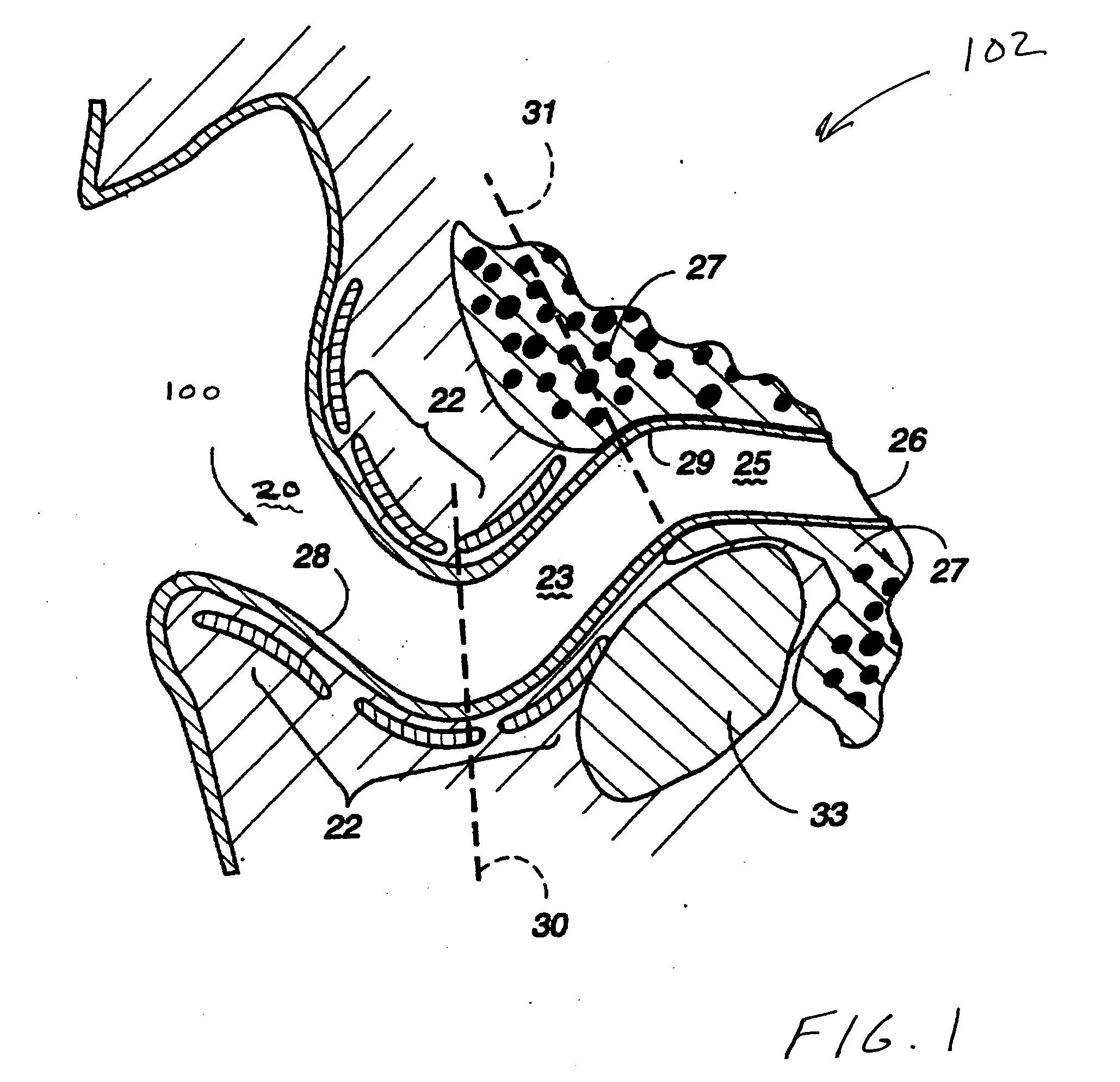
Medication delivery device
A device and method for treating maladies, particularly of the external ear canal and eardrum, is disclosed. In a preferred embodiment the device comprises an earplug or plug and a delivery bulb that holds treatment fluid. A lumen extends through the earplug and connects the delivery bulb to an orifice located at the distal end of the earplug. A one-way valve is located along the lumen to allow treatment fluid to only flow from the delivery bulb to the orifice and not vice versa. The earplug forms a seal with the patient's external ear canal and, combined with the one-way valve, retains treatment fluid in the patient's external ear canal where it can perform its therapeutic function. In one embodiment, the invention includes a collection bag connected through the earplug to an orifice near the distal end of the earplug to collected waste treatment fluid. The therapeutic method comprises using a device, as disclosed herein, to deliver treatment fluids to the patient's external ear canal for irrigation, for the therapeutic benefit of the treatment fluids for the short and long term or to deliver treatment fluid to a patient's external ear canal where it can pass into the patient's middle ear through a tympanostomy tube placed in the patient's eardrum.
Owner:VLODAVER ANER +1
Pulse oximetry methods and apparatus for use within an auditory canal
Methods and apparatus for detecting oxygen saturation levels in blood from within an auditory canal of a living being proximal to a tympanic membrane are disclosed. The auditory canal is lined with tissue and includes a proximal bend and a distal bend located between the proximal bend and the tympanic membrane. Oxygen levels are detected by emitting one or more wavelengths of light into a first position on the tissue of the auditory canal in a first region defined by the distal bend and the tympanic membrane. The wavelengths of light are then sensed at a second position on the tissue of the auditory canal in the first region. A blood oxygen saturation level and / or pulse rate is then calculated responsive to intensity information corresponding to the wavelengths of light detected at the second position.
Owner:SARNOFF CORP
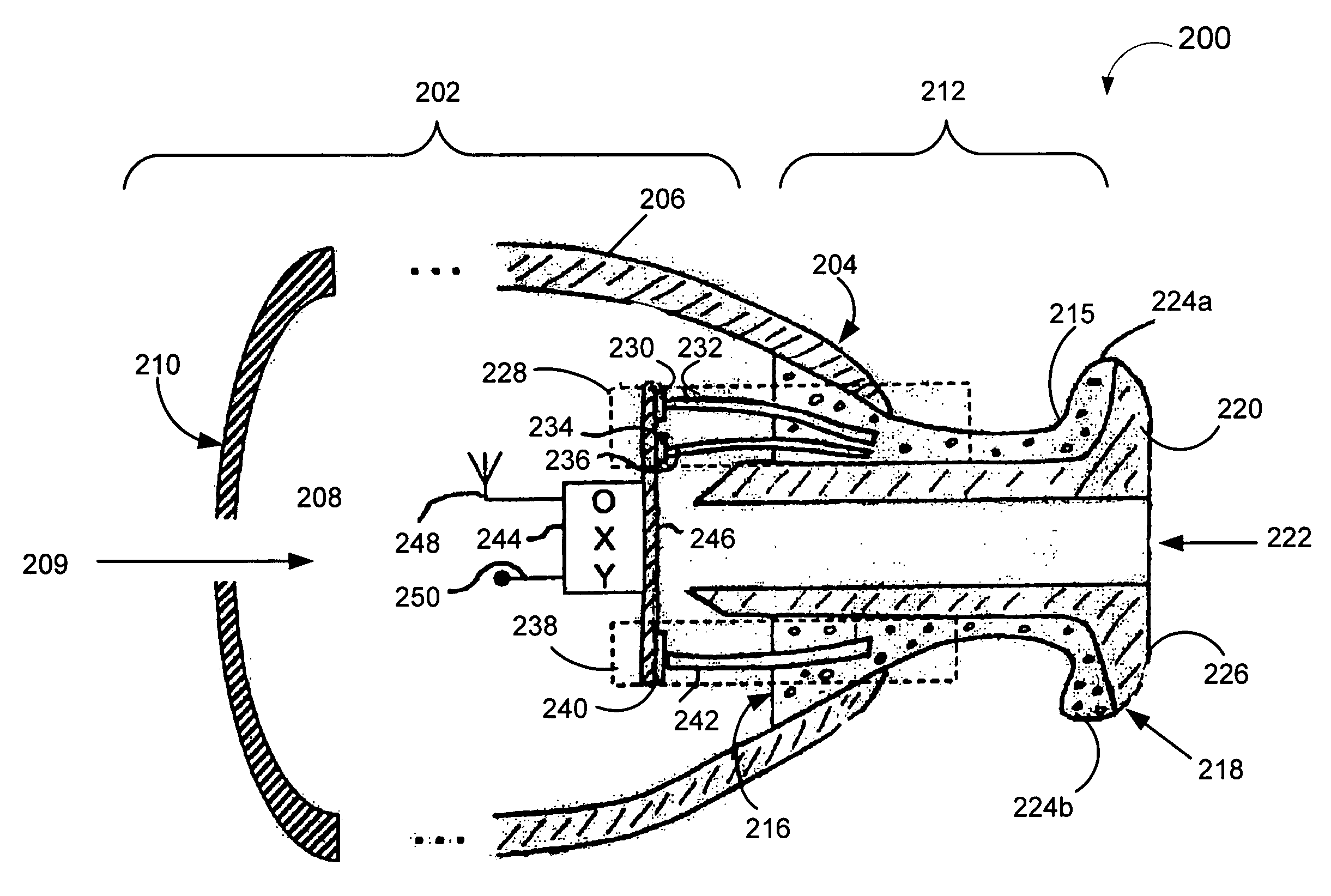
System and Method for the Simultaneous Bilateral Integrated Tympanic Drug Delivery and Guided Treatment of Target Tissues Within the Ears
ActiveUS20080262509A1Facilitate visualFacilitate optical monitoringElectrotherapyEar treatmentSupporting systemTarget tissue
Owner:TUSKER MEDICAL
Hearing device with semipermanent canal receiver module
ActiveUS8340335B1Minimizes insertion frictionImprove fitCompletely in canal hearing aidsEar supported setsEngineeringHearing perception
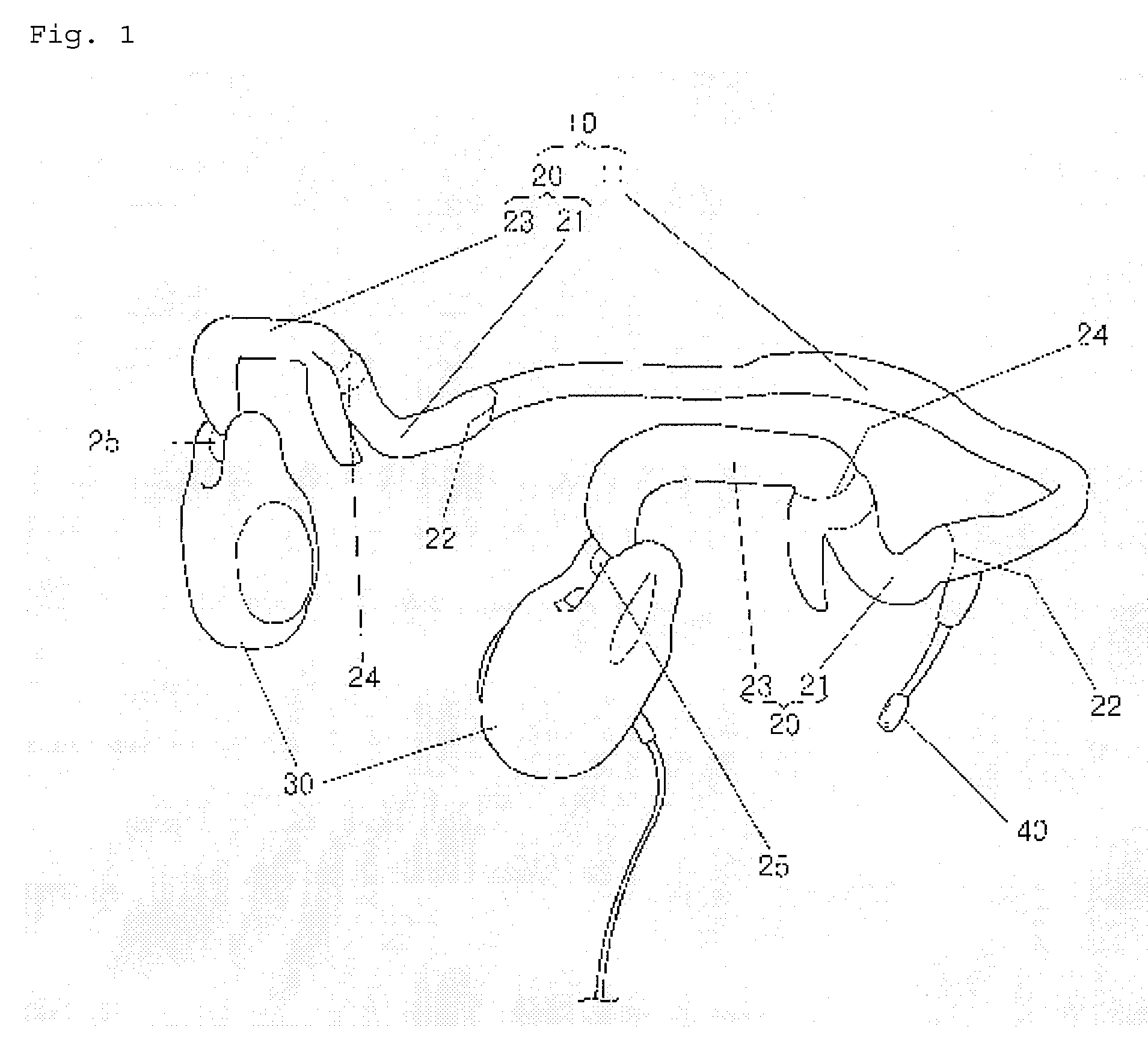
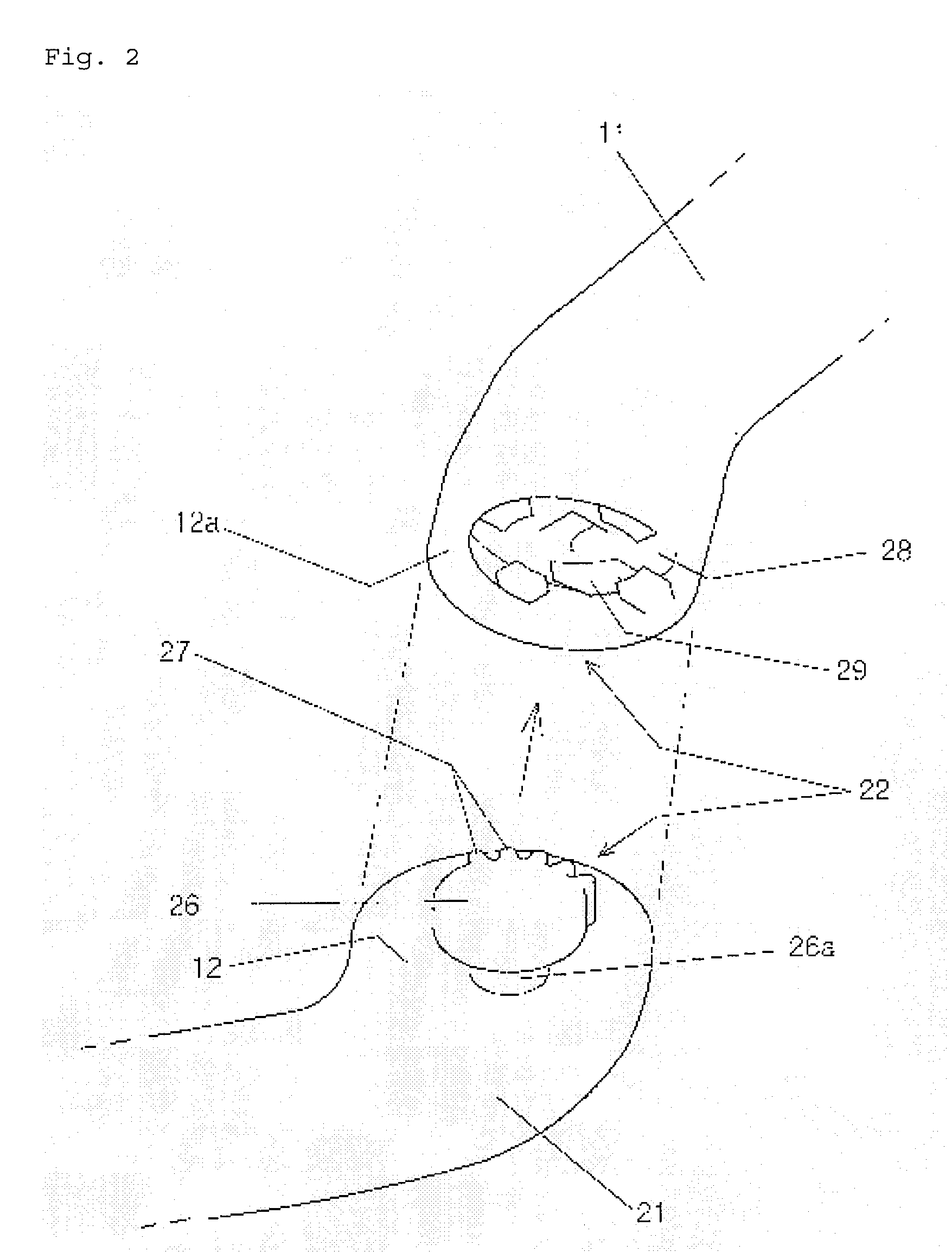
A modular canal hearing device having a speaker module placed in the bony region for extended wear while a main module is removably inserted in the cartilaginous region. The main module wirelessly activates the speaker module when placed in proximity thereto. The main module is removed daily or as needed for maintenance of the hearing device such as for battery replacement. The speaker module remains undisturbed in the bony region to avoid skin friction. The main module contains the microphone, electronics, battery and in the preferred embodiment an inductive coupling coil for inductively sending audio signals to the receiver module. The modular design allows for a highly miniaturized design that is easier to navigate in the ear canal for improved fit and sound fidelity at the eardrum while allowing easy maintenance of a removable module.
Owner:HIMPP
Implantable hearing aid
The present invention generally relates to assistive hearing devices. In one aspect, an apparatus for use in amplifying certain frequencies and canceling other frequencies is provided. The apparatus is insertable at least partially through a tympanic membrane of a user. The apparatus includes an actuator for stimulating an eardrum. The apparatus further includes an acoustic sensor for measuring a level of acoustic energy transmitted to an ear canal and / or the ear drum of the user. Additionally, the apparatus includes an electronics package for controlling the actuator and the acoustic sensor, wherein the electronics package is configured to transmit amplified selected sound waves while canceling out other sound waves having a particular frequency or frequencies. In another aspect, an apparatus for use in measuring a parameter in a body is provided. In a further aspect, a method of selectively transmitting sound waves having a predetermined frequency or frequencies is provided.
Owner:NANOEAR LLC
Method of obtaining a characteristic, and hearing instrument
InactiveUS20070036377A1Problem can be addressedOvercomes drawbackDeaf-aid setsDigital signal processingCoupling
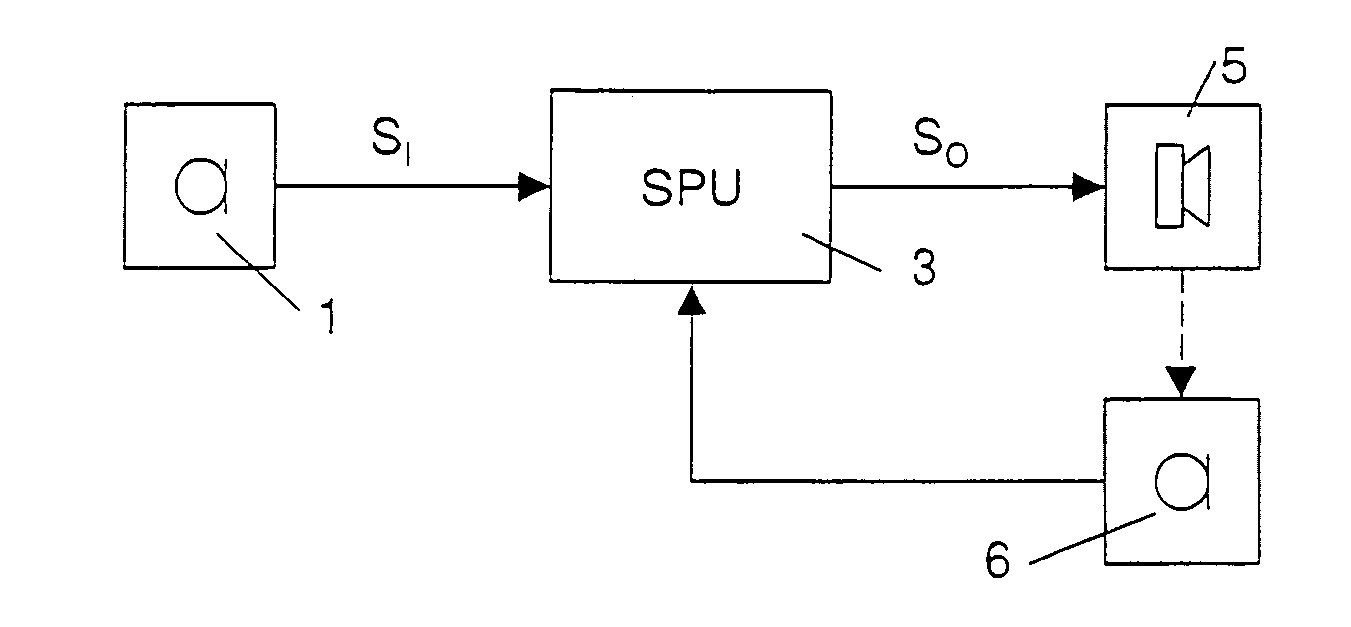
According to the invention, a hearing instrument comprising at least one inner microphone operable to determine a sensing signal representative of an acoustic signal at a position in front of the user's eardrum—which may be an acoustic signal at a position between an ITE (or ITC or CIC) hearing instrument and the eardrum or between an earpiece and the eardrum—is used. In accordance with the invention, in front of the eardrum an acoustic signal is produced. The inner microphone creates a sensing signal representative of the acoustic signal, and the signal processing unit of the hearing instrument determines a characteristic of the user's ear canal based thereon and memorizes values indicative of the characteristic. According to a preferred embodiment, the characteristic is an acoustic coupling transfer characteristic, which is determined based on a comparison of a signal representative of the output signal of the signal processing unit's digital signal processing stage and the sensing signal. In contrast to the state of the art, no control loop is necessary to adapt the gain to the ear canal characteristic, but the memorized values may be used therefor.
Owner:PHONAK
Method and apparatus for three-dimensional audio display
InactiveUS7231054B1Stereophonic systemsLoudspeaker spatial/constructional arrangementsInteraural time differenceFrequency spectrum
Owner:CREATIVE TECH CORP
Combined microphone and receiver assembly for extended wear canal hearing devices
ActiveUS20090074220A1Place safeMinimize feedbackCompletely in canal hearing aidsEar supported setsCouplingHearing apparatus
An ultra miniature hearing device for extended wear entirely in the ear canal past the cartilaginous region is provided. The hearing device comprises a microphone and a speaker, each having a respective diaphragm. The speaker and microphone are placed parallel to each other in a single lateral assembly. The microphone and speaker can be arranged such that their diaphragms are orthogonal to one another so that cross coupling of vibrations is minimized, thus reducing internal feedback. Due to the parallel co-placement of the speaker and microphone in the single lateral assembly, the length of the device is substantially shorter than that of prior hearing aid devices. The hearing device is 12 mm or less in length to fit in the bony part of the ear canal for most individuals and is placed within approximately 3 mm from the eardrum.
Owner:INSOUND MEDICAL INC
Bone conduction headset
InactiveUS20090185699A1Take advantage ofBone conduction transducer hearing devicesEarpiece/earphone mechanical/electrical switchesHeadphonesBone conduction hearing
This invention is about bone conduction headset, method of bone conduction method and eardrum, it has hearing-aid function, provide bone conduction headset which is folded compactly using first and second extension part, first and second hinge part and hinge axis, also provide bone conduction headset which is received and output the signal not only wired but also wireless method.
Owner:KIM SUNG HO
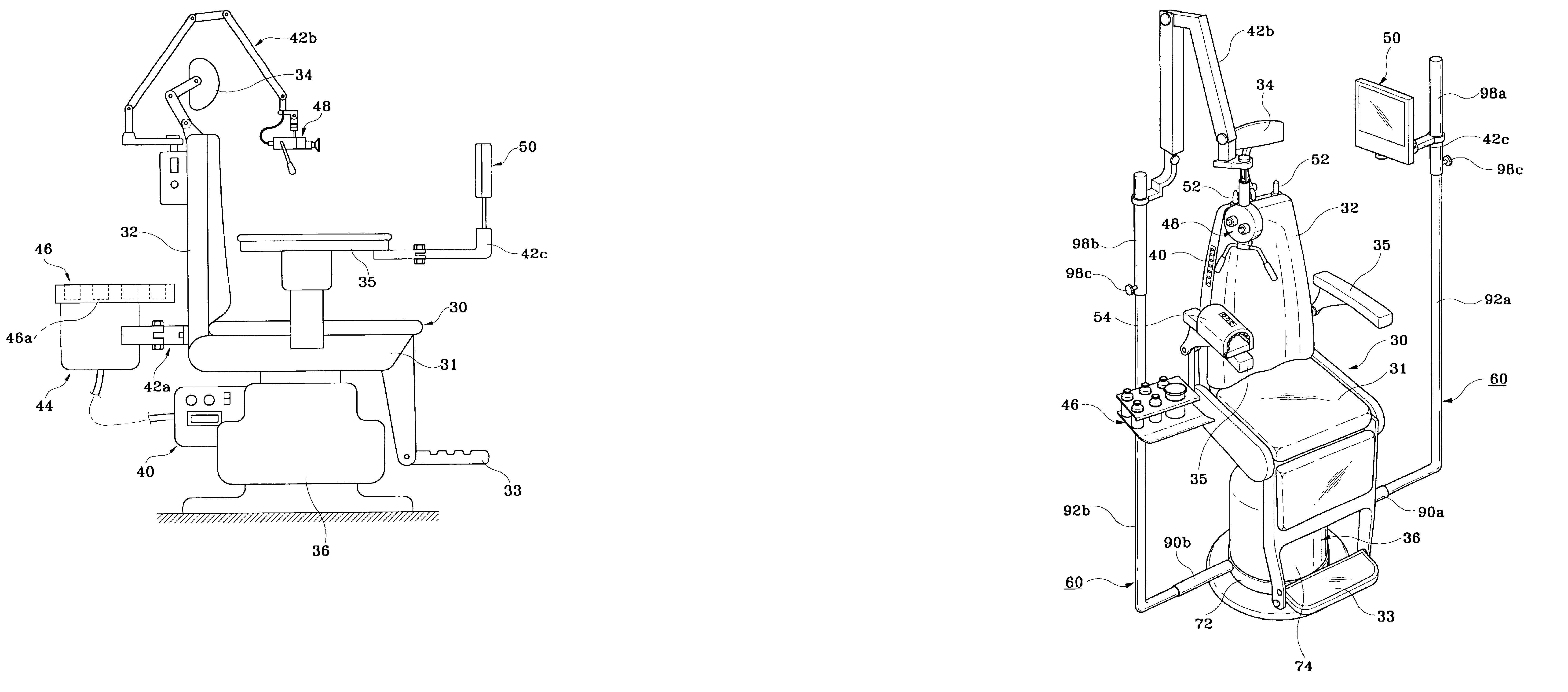
Rotating patient chair with ear diagnosis and treatment unit
InactiveUS6916065B2Shortening time of medicalMinimizing space of roomEar treatmentOperating chairsTreatment effectSwitch box
The present invention relates to a rotating patient chair mounted with an integrated ear diagnosis and treatment unit that controls the position of a microscope 48 and a monitor 50 rotating around the rotating patient chair 30 at a predetermined angle or 180 degrees, the unit including: suctioners 44, 52, a treatment board 46, a blood pressure tester 54 and a manipulating switch box 40 for controlling the diagnosis and treatment tools, and the monitor 50 and the microscope 48 positioned in correspondence with the patient's ears anatomically positioned at 180 degrees to enable the patient to observe all of the treatment processes to the ear parts including the thin, dark auditory canals and eardrums on the monitor 50 installed at an opposite side and to enable the practitioner to explain all of the treatment processes shown on the monitor to the patient and his guardians, thereby improving reliability on the practitioner and the treatment processes and maximizing the treatment effects, and performing diagnosis and treatment processes to the patient's ears by not letting the practitioner or patient move around but merely by rotating the ear diagnosis and treatment unit, minimizing discomfort and inconvenience to the practitioner or patient, shortening the medical treatment time and minimizing the space of a treatment room occupied by the diagnosis and treatment unit.
Owner:PARK & RYOUNG
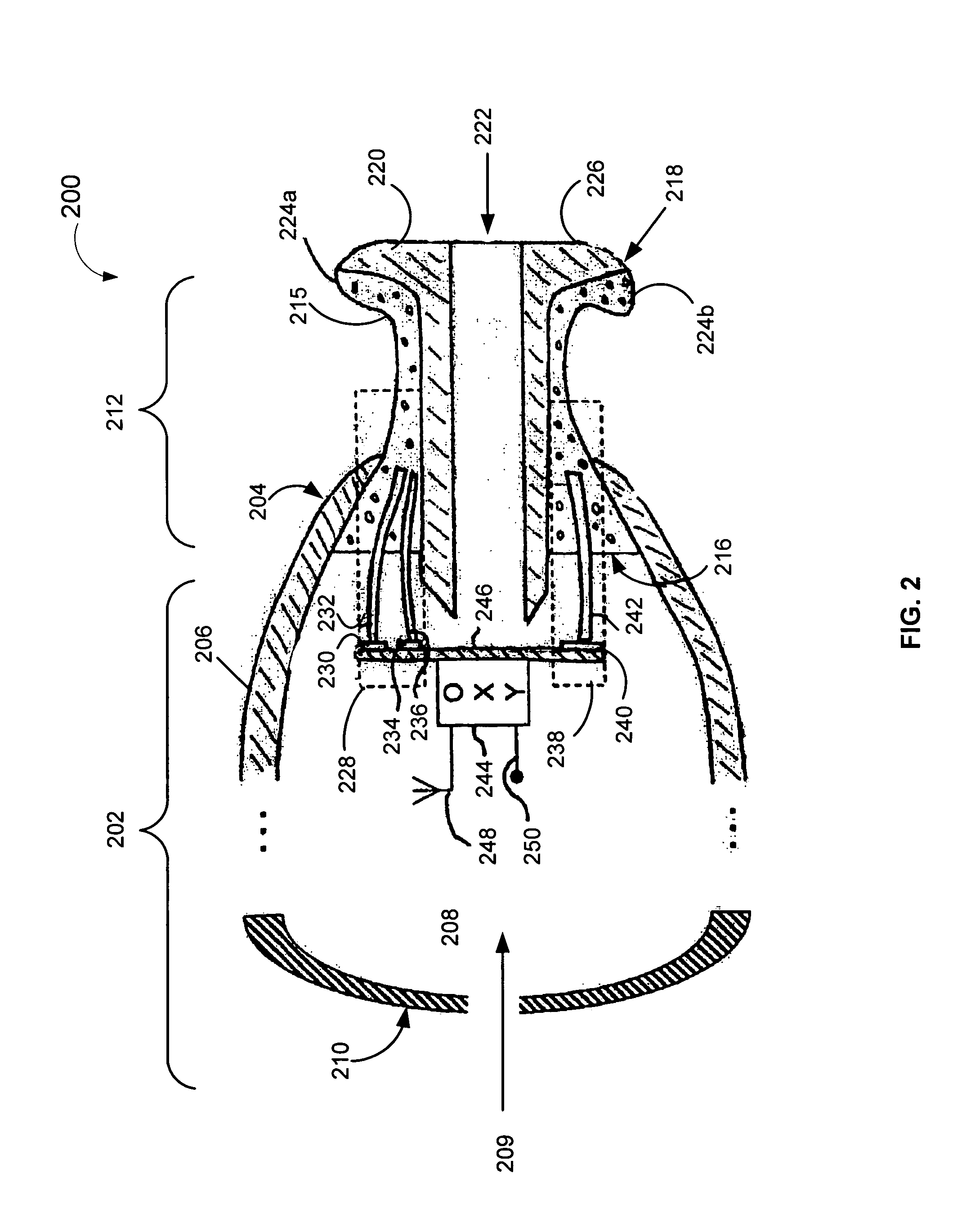
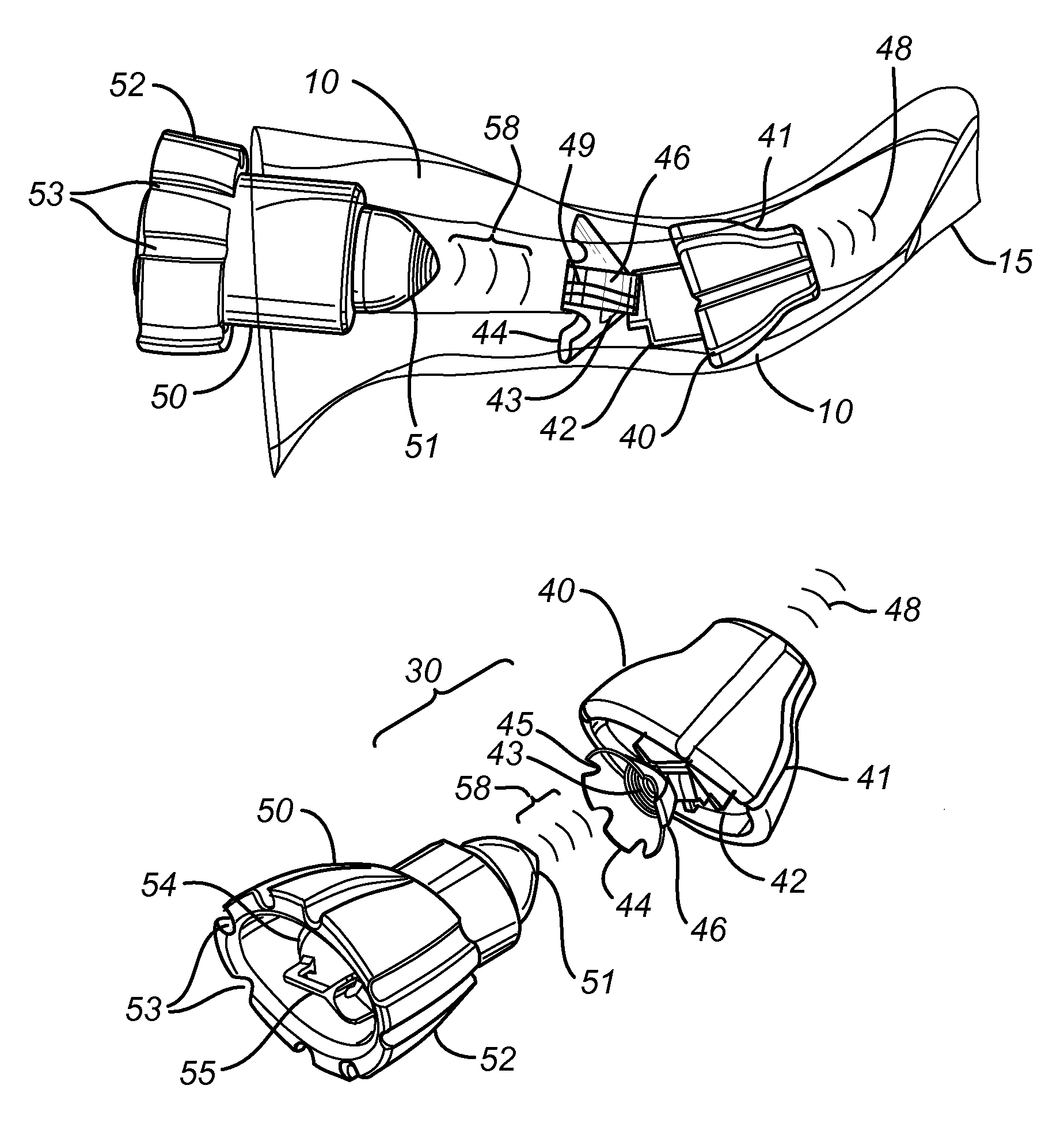
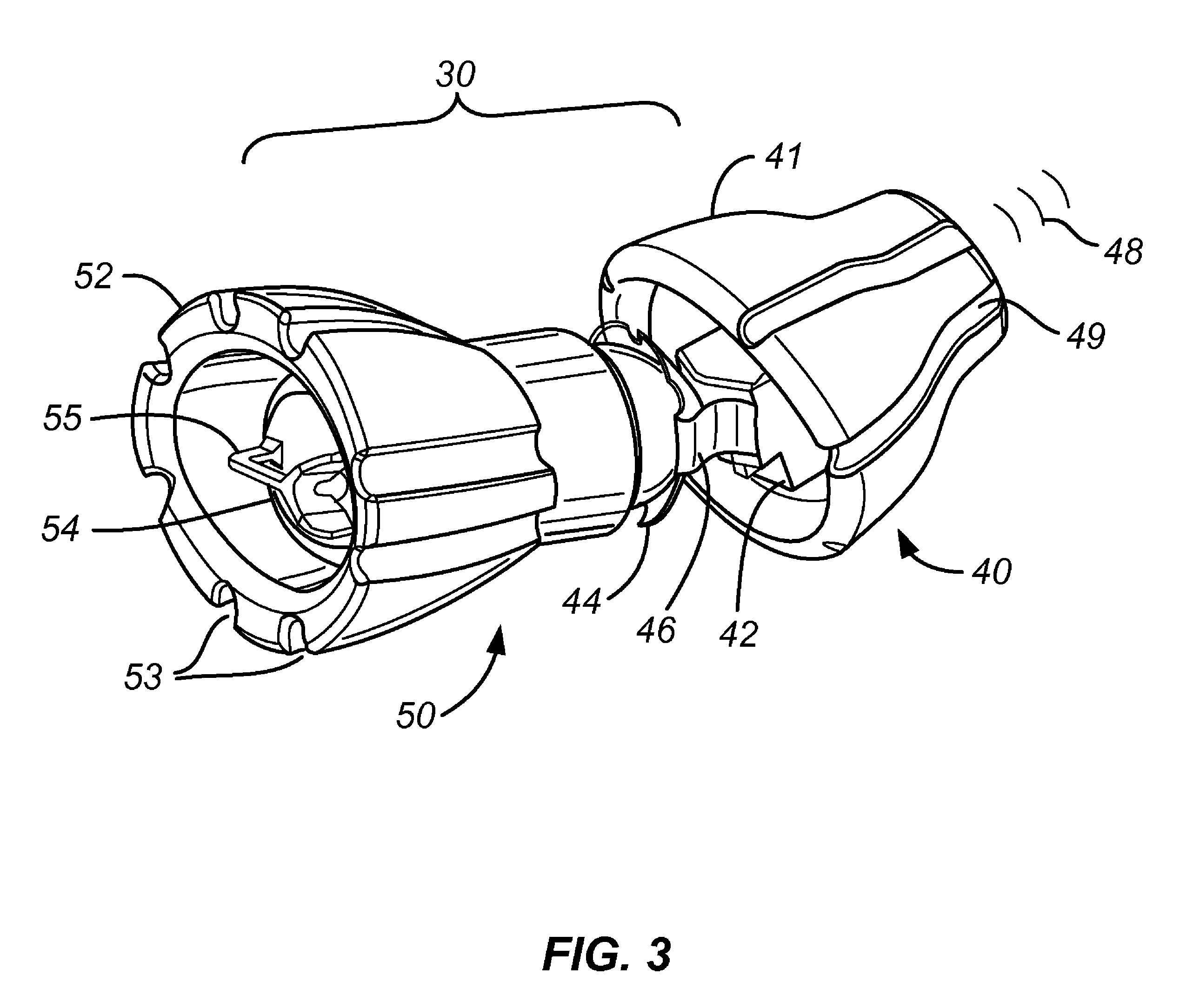
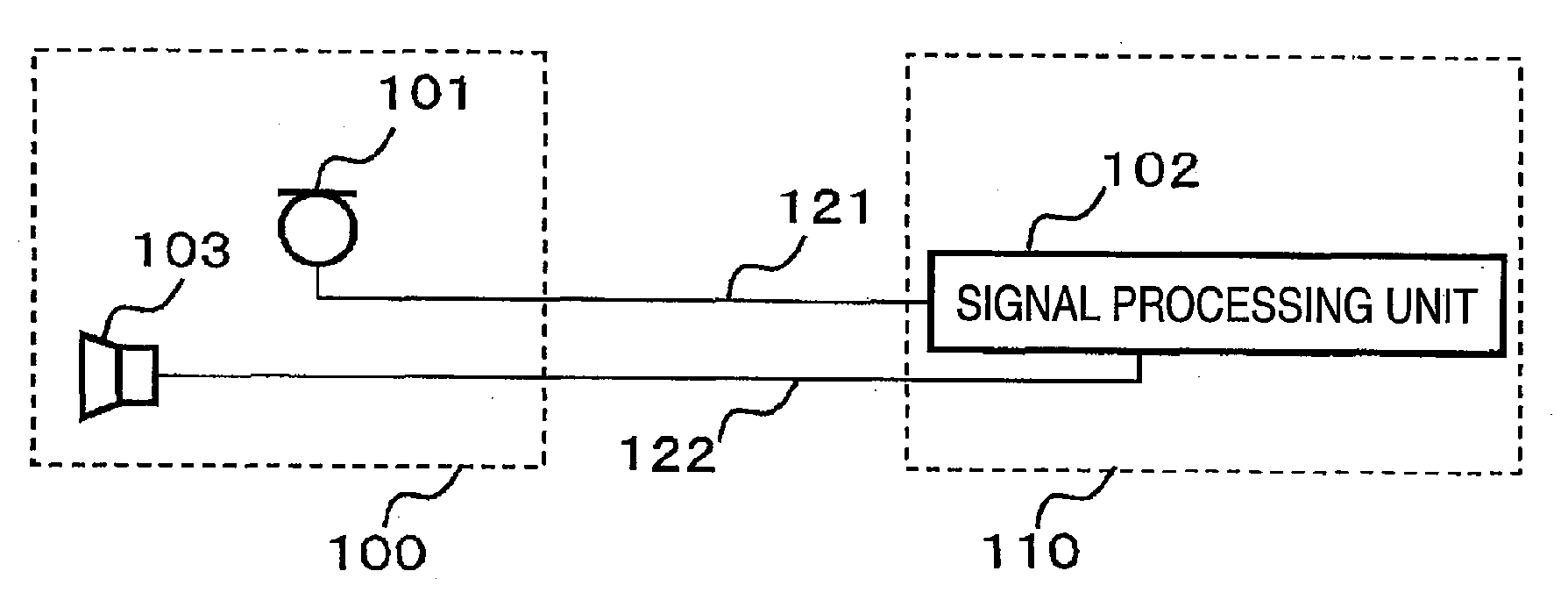
Behind-the-ear hearing aid whose microphone is set in an entrance of ear canal
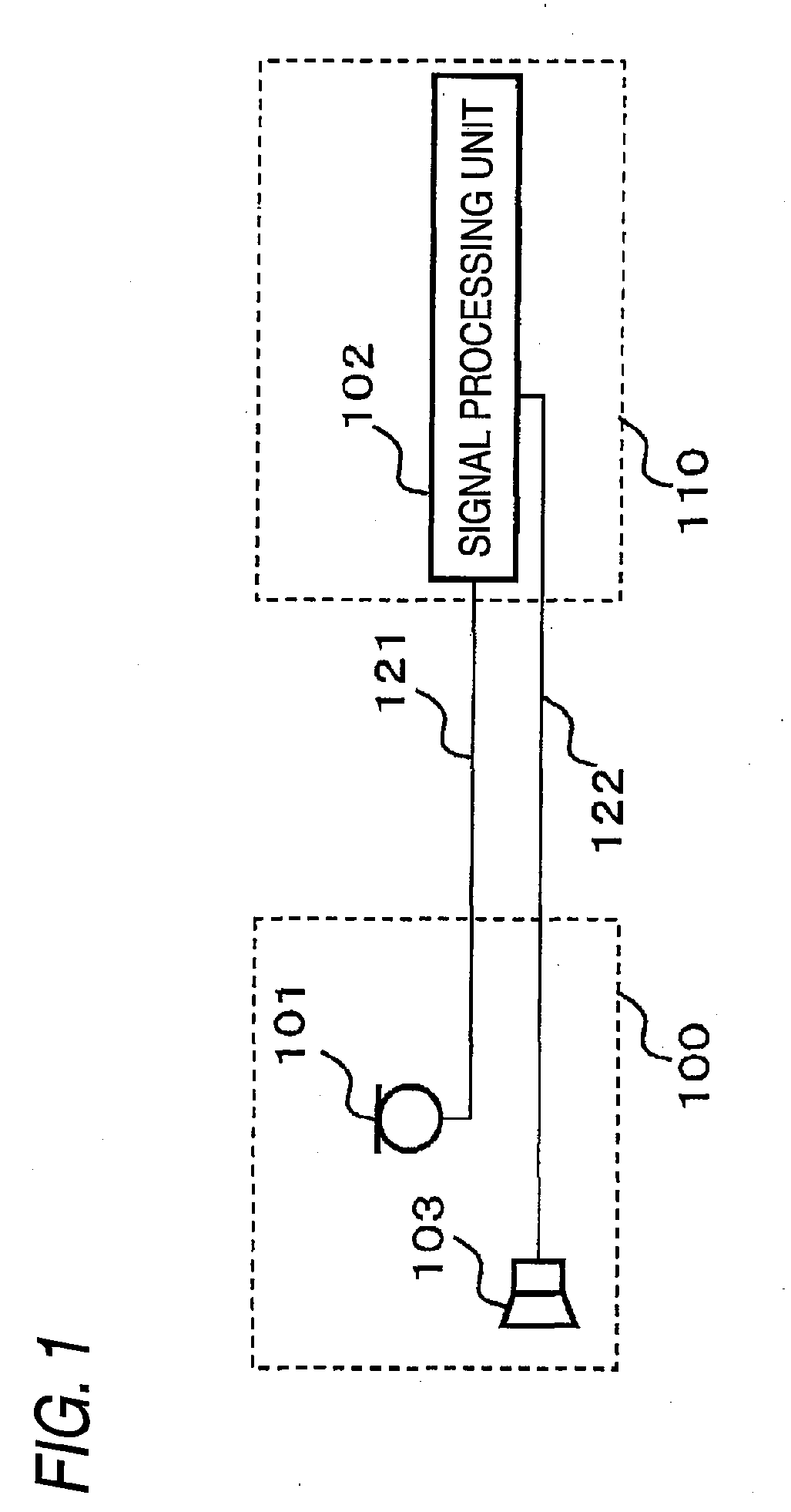
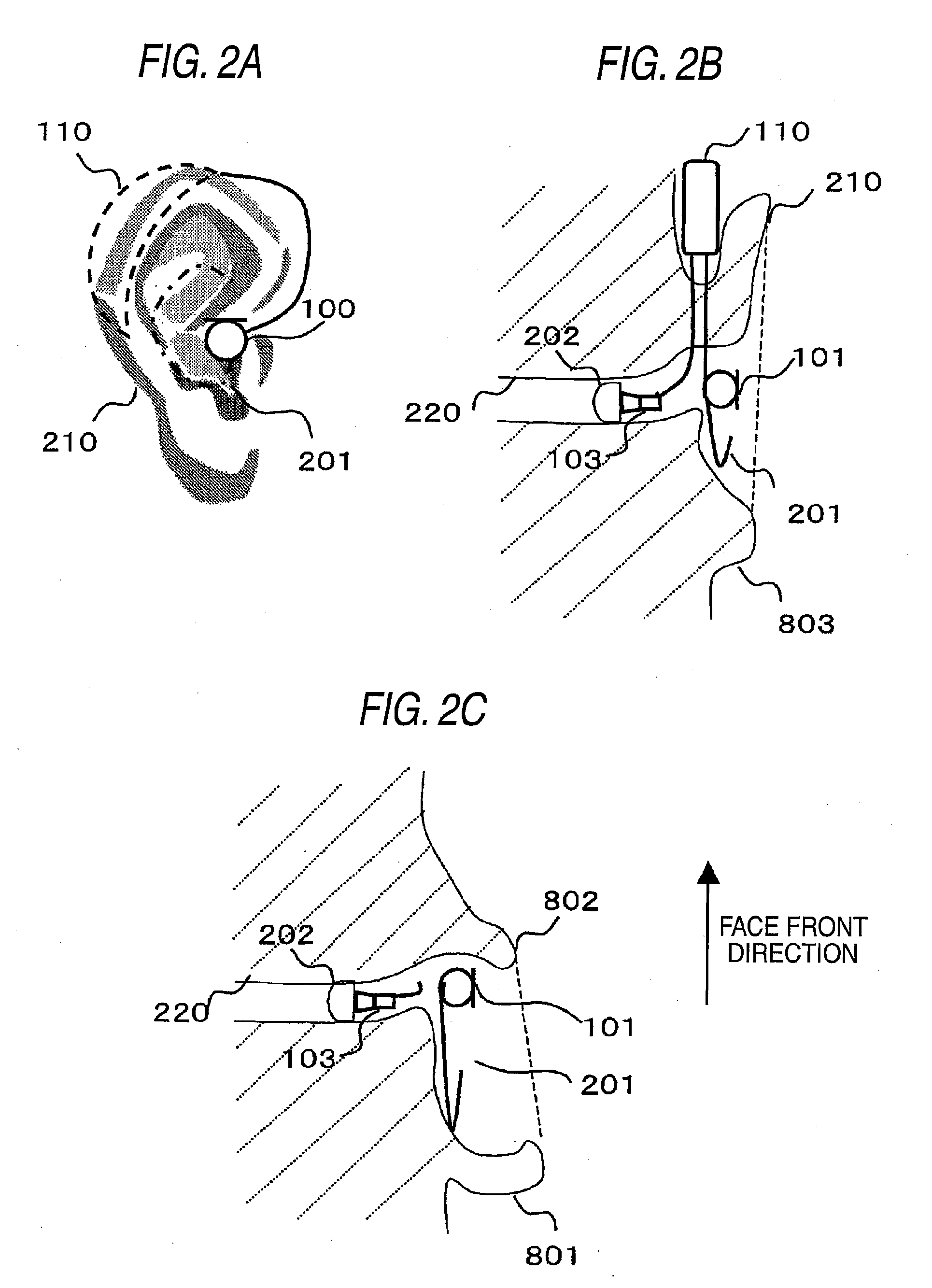
There is provided a behind-the-ear hearing aid that makes it easy for a hearing aid wearer to estimate a position of a sound source with respect to a front-back direction and that enables an increase in aesthetic property when the hearing aid is worn. A behind-the-ear hearing aid of the present invention is used while fitted to an ear of a human body, and includes at least a microphone 101 which collects ambient sound, thereby generating an input signal and signal processing unit 102 that generates an output signal from the input signal. The hearing aid also has a behind-the-ear portion 110 that can be fitted to the ear and a receiver 103 that reproduces output sound from the output signal. When the behind-the-ear portion 110 is fitted to the ear, the microphone 101 is arranged in an entrance of an ear canal that lies in the extension of an ear canal 220 and that is disposed closer to an eardrum than to a plane that is defined by a helix 901, a tragus 902, and an earlobe 903.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
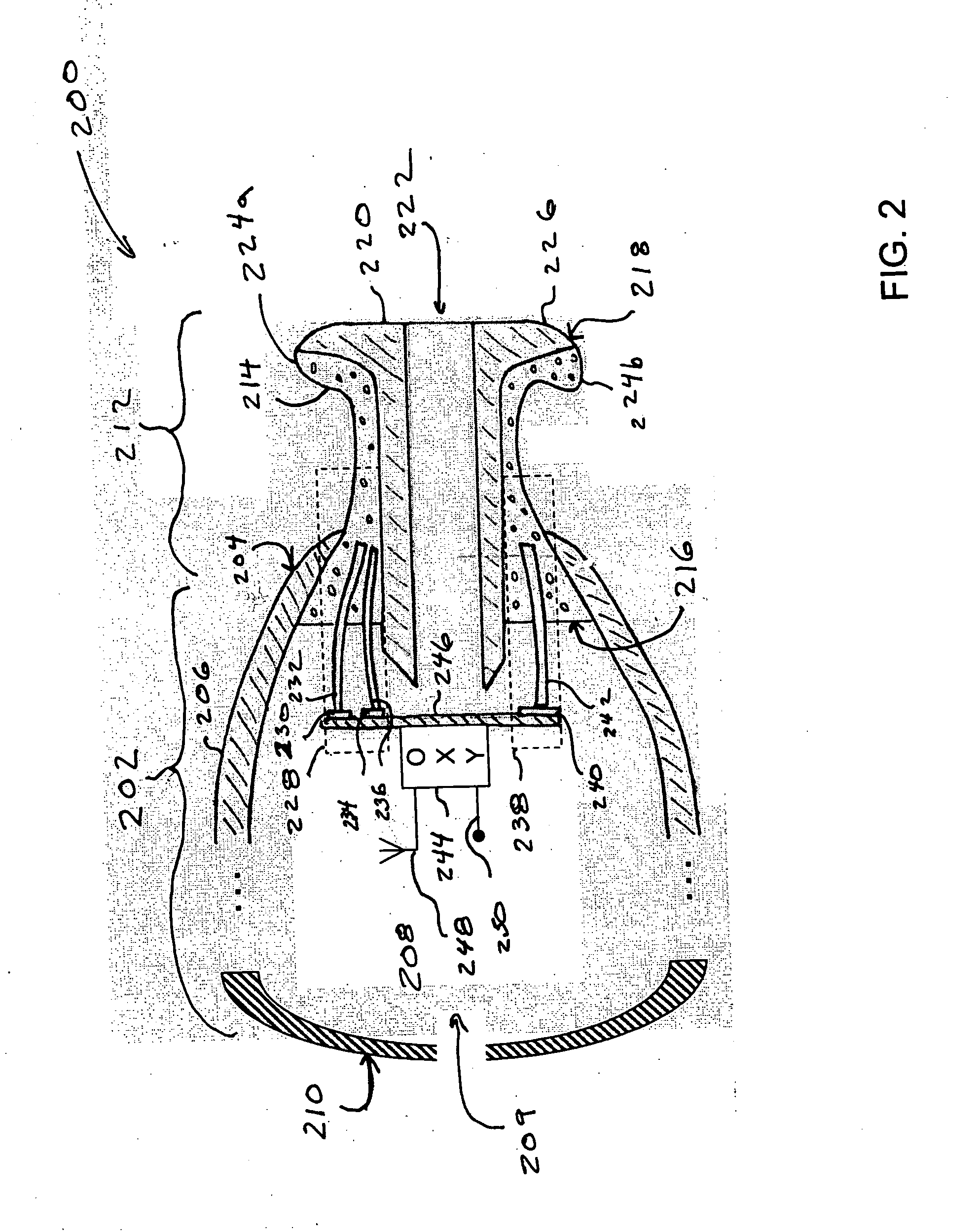
Myringotomy instrument
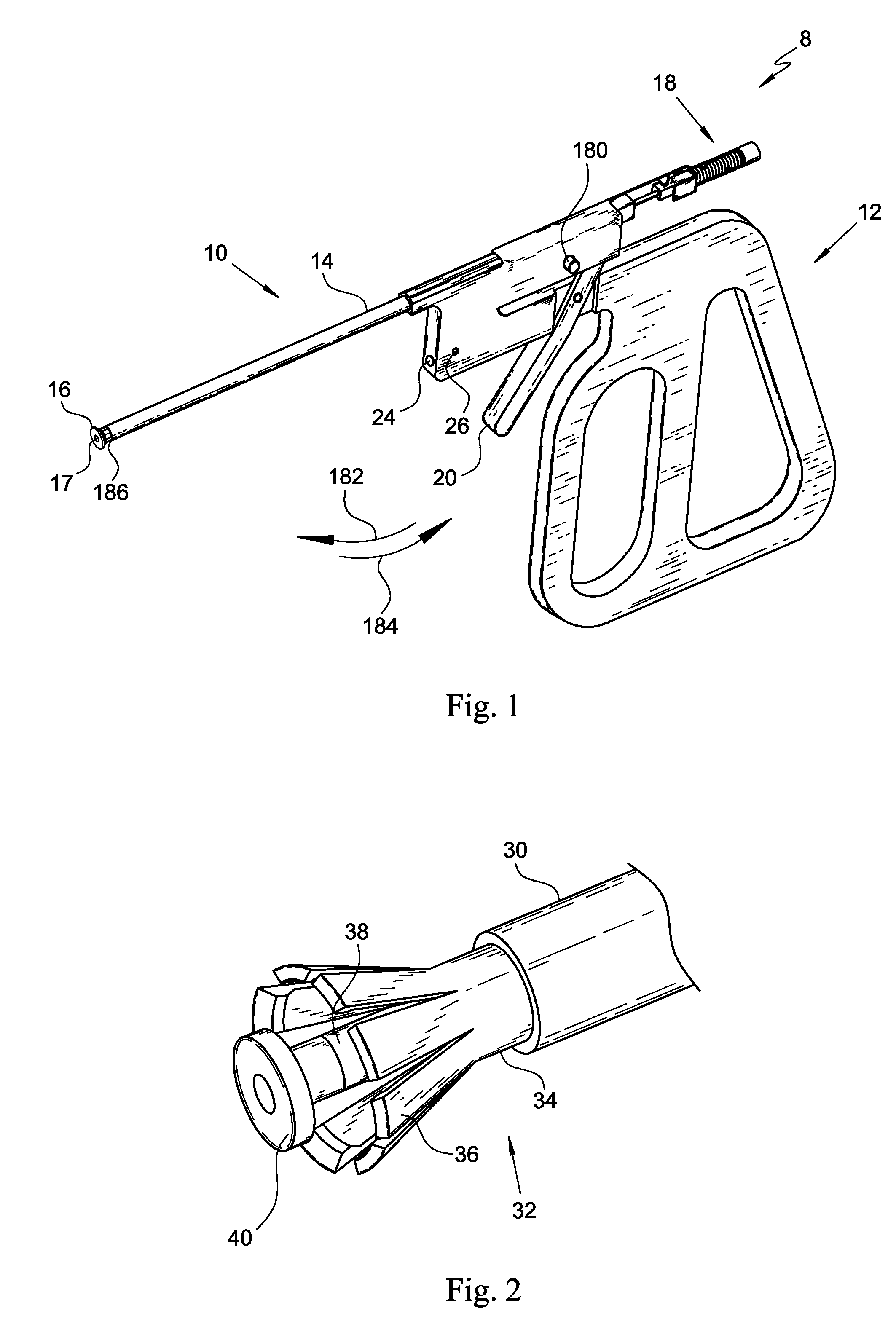
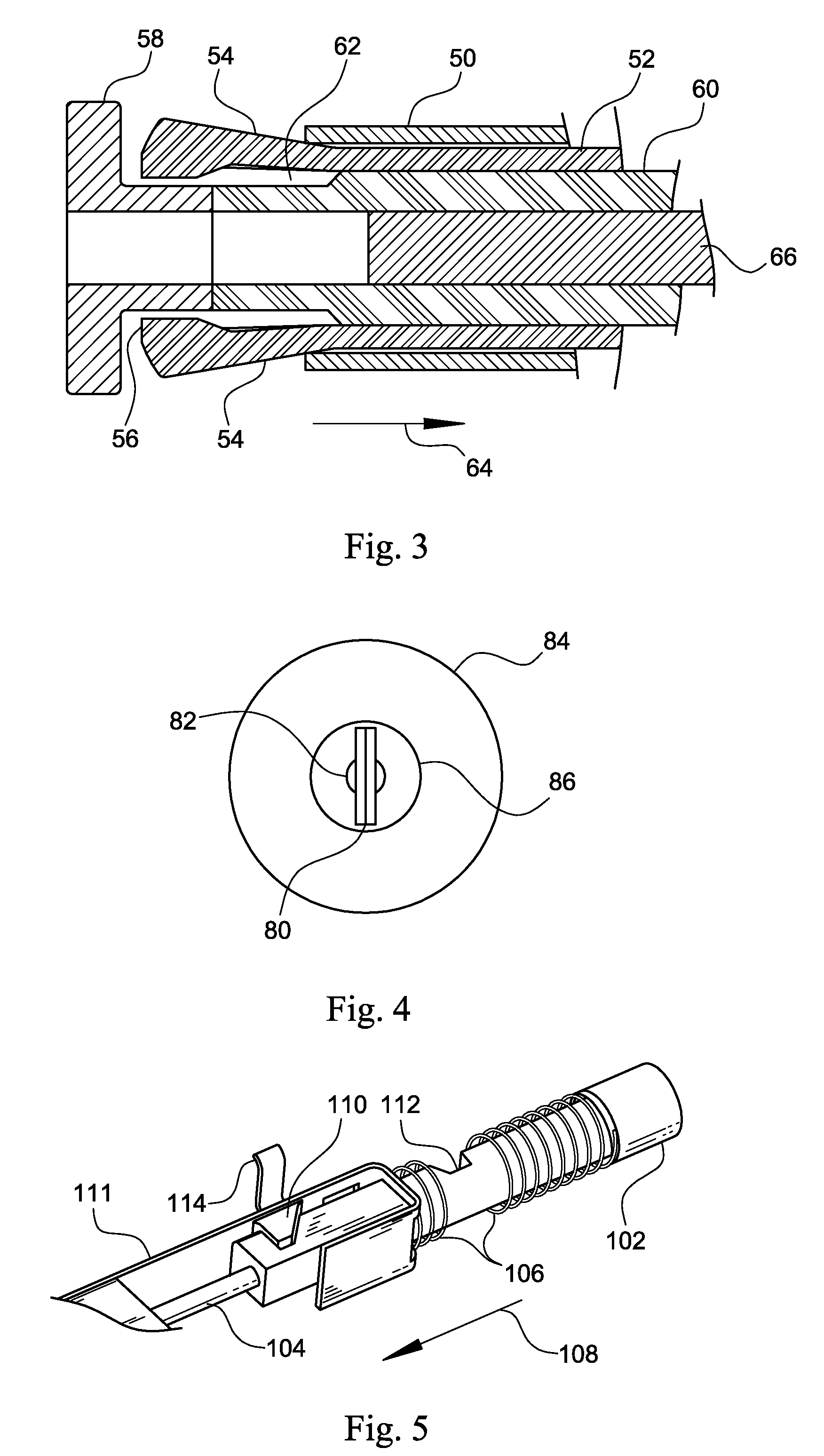
An instrument for performing myringotomy operations consists of a device for incising, suctioning and grasping a tympanostomy tube (ISGTT) attached to a gripping handle. The ISGTT consists of a gripper and a pushing and suctioning member (PS) surrounded by an external tube. Peripheral fingers of the gripper press against the surface of the tubular segment of the tympanostomy tube for grasping. An incising blade disposed within the lumen of the PS is movable coaxially with the bore of the tympanostomy tube. Blade positioning selector located at the proximal end of the ISGTT provides for drawing and withdrawing the incising blade through the bore of the gripped tympanostomy tube. A lever pivotally attached to the griping handle is used to control grasping and releasing of the tympanostomy tube when properly placed.
Owner:MYRINGO
Ear canal signal converting method, ear canal transducer and headset
ActiveUS20060159297A1Improve intelligibilityEfficient methodIntra aural earpiecesDeaf-aid setsMedicineTransducer
A method of converting electrical signals into mechanical vibration by means of a transducer in the human ear, an ear canal transducer and a headset wherein a sensation of hearing is achieved by exciting the tissue of the ear canal directly with said transducer, whereby the vibrations propagate to the tympanic membrane and into the human sound sensing organs.
Owner:RPX CORP
Method of processing a signal in a hearing instrument, and hearing instrument
ActiveUS20140321657A1Compensation effectEasy to measureCompletely in canal hearing aidsIn the ear hearing aidsMedicineHearing aid
A method of estimating an acoustic transfer quantity representative of a sound pressure transfer to the eardrum includes the steps of measuring, by an ear canal microphone of the hearing instrument, an acoustic signal in the ear canal when a sound signal is emitted into the ear canal by a receiver of the hearing instrument, the ear canal microphone being in acoustic communication with the ear canal, determining, from the acoustic signal and from a frequency dependent reference characteristics of the hearing instrument, an ear canal impedance, and, calculating, from the ear canal impedance, an estimate of the acoustic transfer quantity.
Owner:SONOVA AG
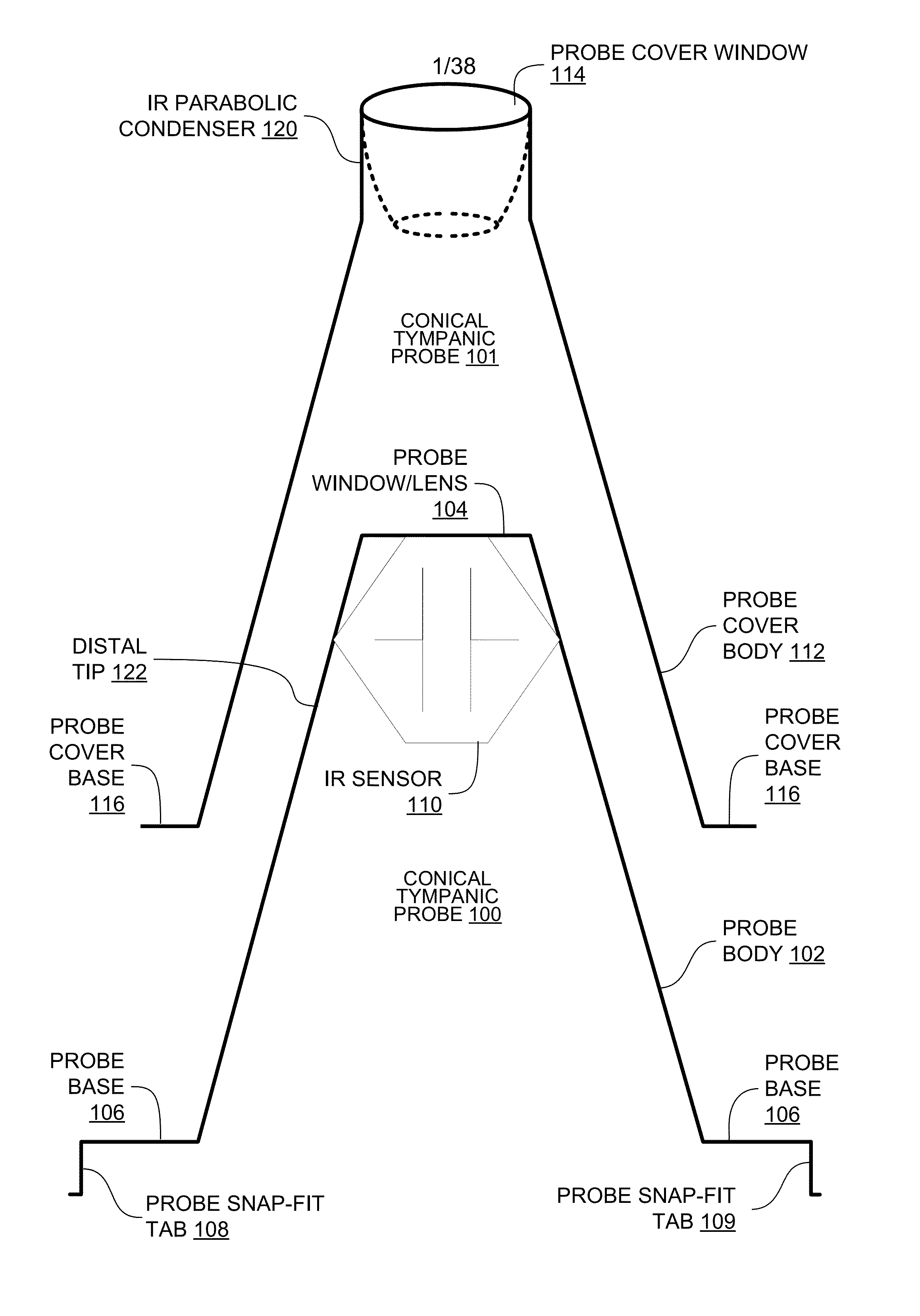
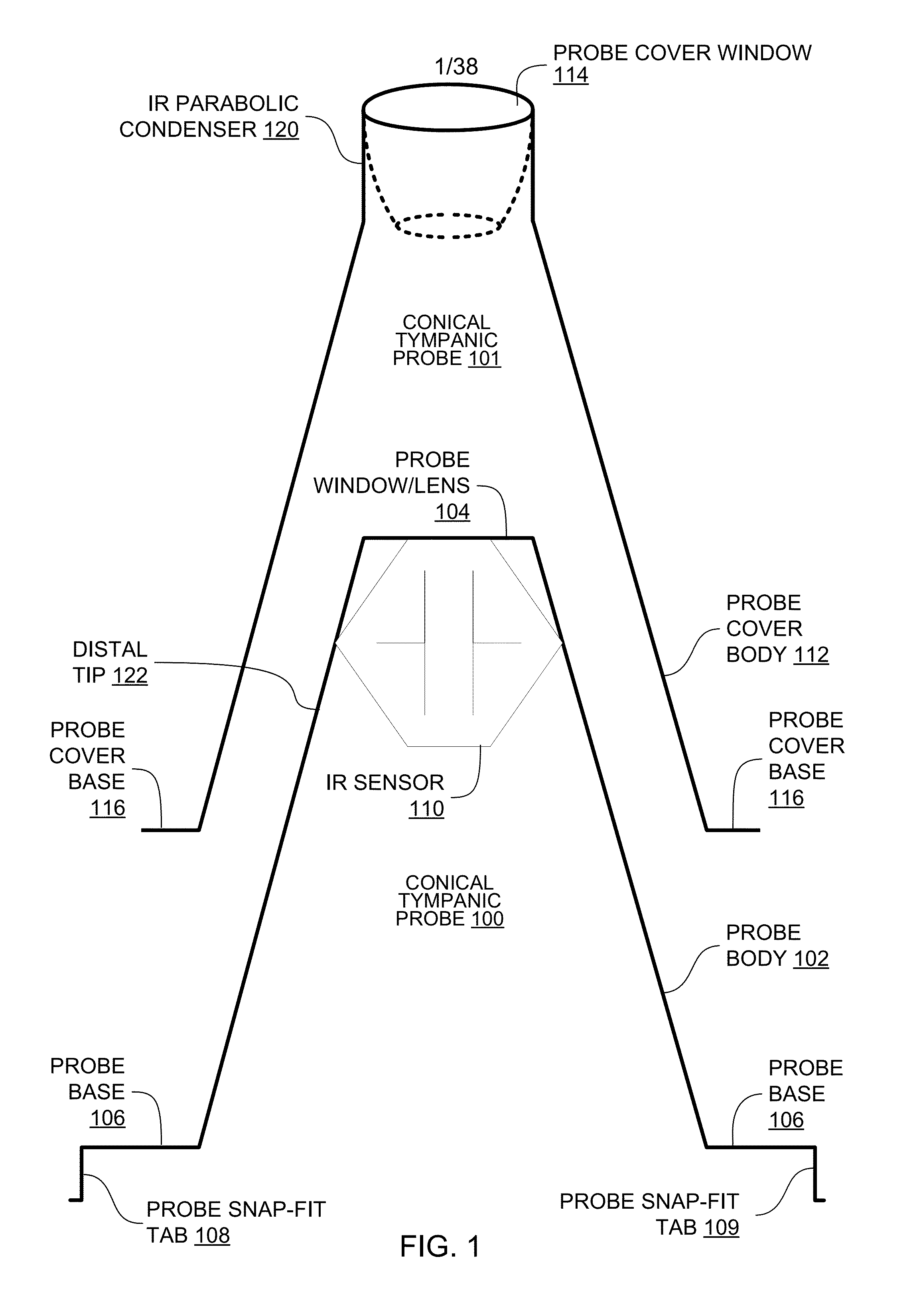
Tympanic probe cover
InactiveUS20140088434A1Diagnostics using lightDiagnostics using spectroscopyEngineeringTympanic thermometers
A digital non-contact tympanic thermometer has a tympanic probe with an IR sensor at the end of the probe in which the digital non-contact tympanic thermometer can be converted to a digital non-contact non-tympanic thermometer for non-tympanic surfaces by placement of removeable probe cover over the tympanic cover in which the probe cover includes a parabolic condenser at the tip of the probe cover that increases gathering of incoming infrared energy.
Owner:ARC DEVICES
Otoscope
An otoscope permitting examination of a patient's ear is defined by an instrument head including a proximal end and a distal insertion portion that is insertable into the ear. The otoscope includes an imaging lens train disposed within the instrument head, wherein each of the imaging lens train, an eyepiece and a distal opening of said insertion portion are aligned along an optical axis. The otoscope further includes a focusing mechanism for selectively moving at least one of the imaging lens train and the optics contained within the eyepiece relative to one another along the optical axis. The imaging lens train and the optics in the eyepiece define an optical system such that an entrance pupil is substantially located in the distal insertion portion of the instrument head, thereby enabling the entire tympanic membrane to be viewed at once by the user.
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
Hearing aid device and hearing aid device system
InactiveUS20160309266A1Precise positioningAvoid damageCompletely in canal hearing aidsIn the ear hearing aidsMedicineHearing aid
A hearing aid device configured to be partly or fully inserted into the ear canal of a user is disclosed. The hearing aid device comprises a receiver (loudspeaker) adapted to generate and send an air-borne acoustic signal towards the eardrum when the hearing aid device is partly or fully inserted into the ear canal. The hearing aid device further comprises a microphone configured to receive acoustic signals. The hearing aid device comprises a processing unit configured to determine if the hearing aid device is positioned in a correct position in the ear canal on the basis of the acoustic signals received by the microphone.
Owner:OTICON
In-Ear Utility Device Having Information Sharing
InactiveUS20170347348A1MicrophonesHearing device active noise cancellationInformation sharingMusic player
An embodiment of the invention provides a wireless in-ear utility device that rests in the user's ear canal near the user's eardrum. The in-ear utility device may be configured in a variety of ways, including, but in no way limited to a smart in-ear utility device, a flexible personal sound amplification product, a personal music player, a “walkie-talkie” and the like.
Owner:SMARTEAR INC
Canal phones with structure and method for selectively passing or blocking environmental ambient sound and switchable electrical connections
ActiveUS20120087511A1Easy to modifyMaximize and minimize acoustic isolationEarplugsIntra aural earpiecesEnvironmental noiseElectrical connection
A canal phone incorporates a transducer within an isolation sound chamber for reproducing sound from an audio source, and a sound-transmission passageway, or ambient sound port, for allowing ambient sounds to enter the isolation sound chamber. The passageway has inner and outer apertures, one oriented towards the ambient noise environment outside of the listener's ear and the other oriented toward the isolated chamber formed by the space between a loudspeaker diaphragm within the canal phone and the tympanum of the listener's ear. The canal phone has a port blocking switch mechanism that selectively opens or closes the aperture of the passageway that is open to the ambient noise. This switch mechanism may also electrically disconnect the transducer and seal either the outer or the inner end of the passageway in different embodiments of the invention.
Owner:POLK AUDIO LLC
Anti-noise earmuff device with bluetooth module and audio signal processor
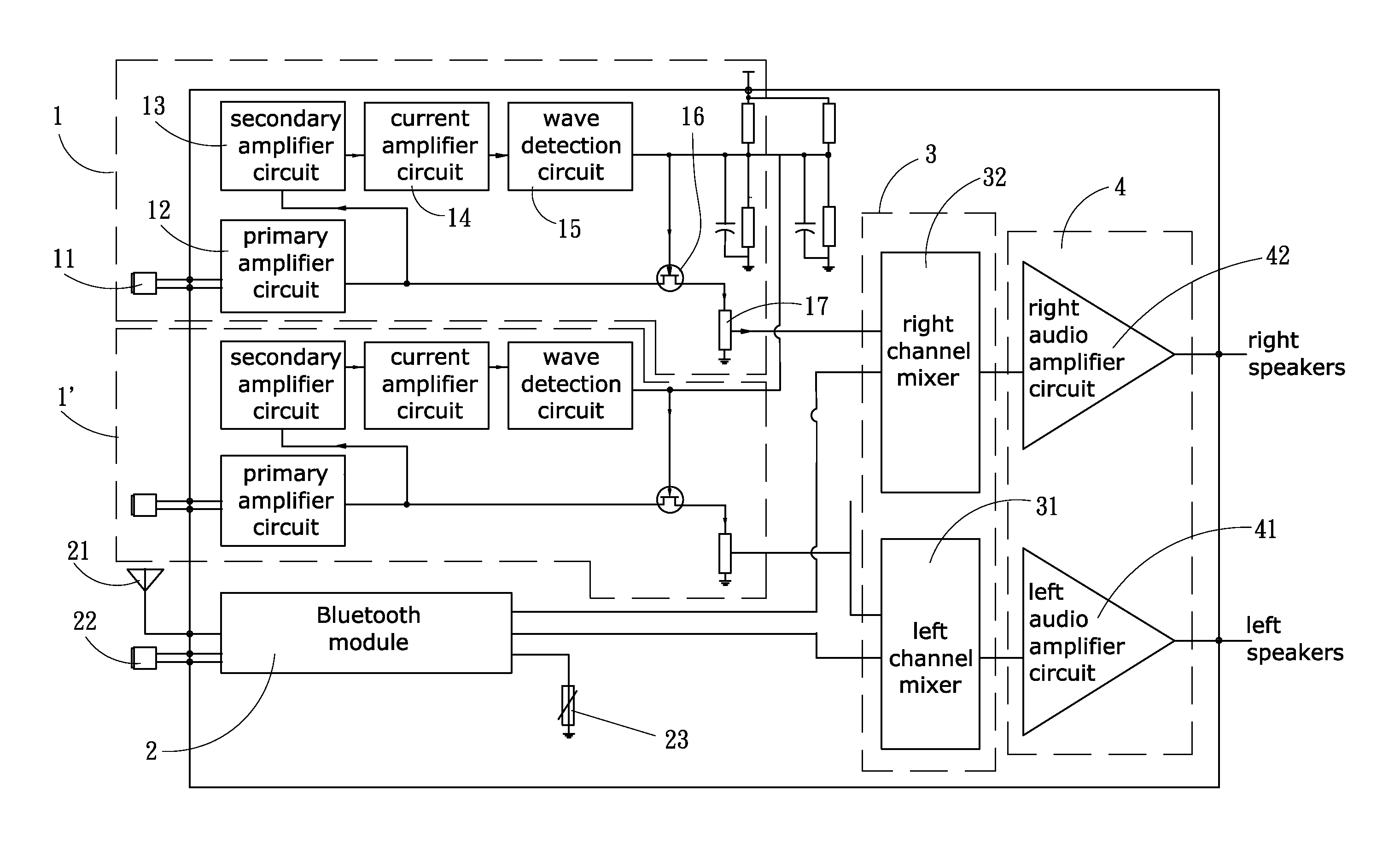
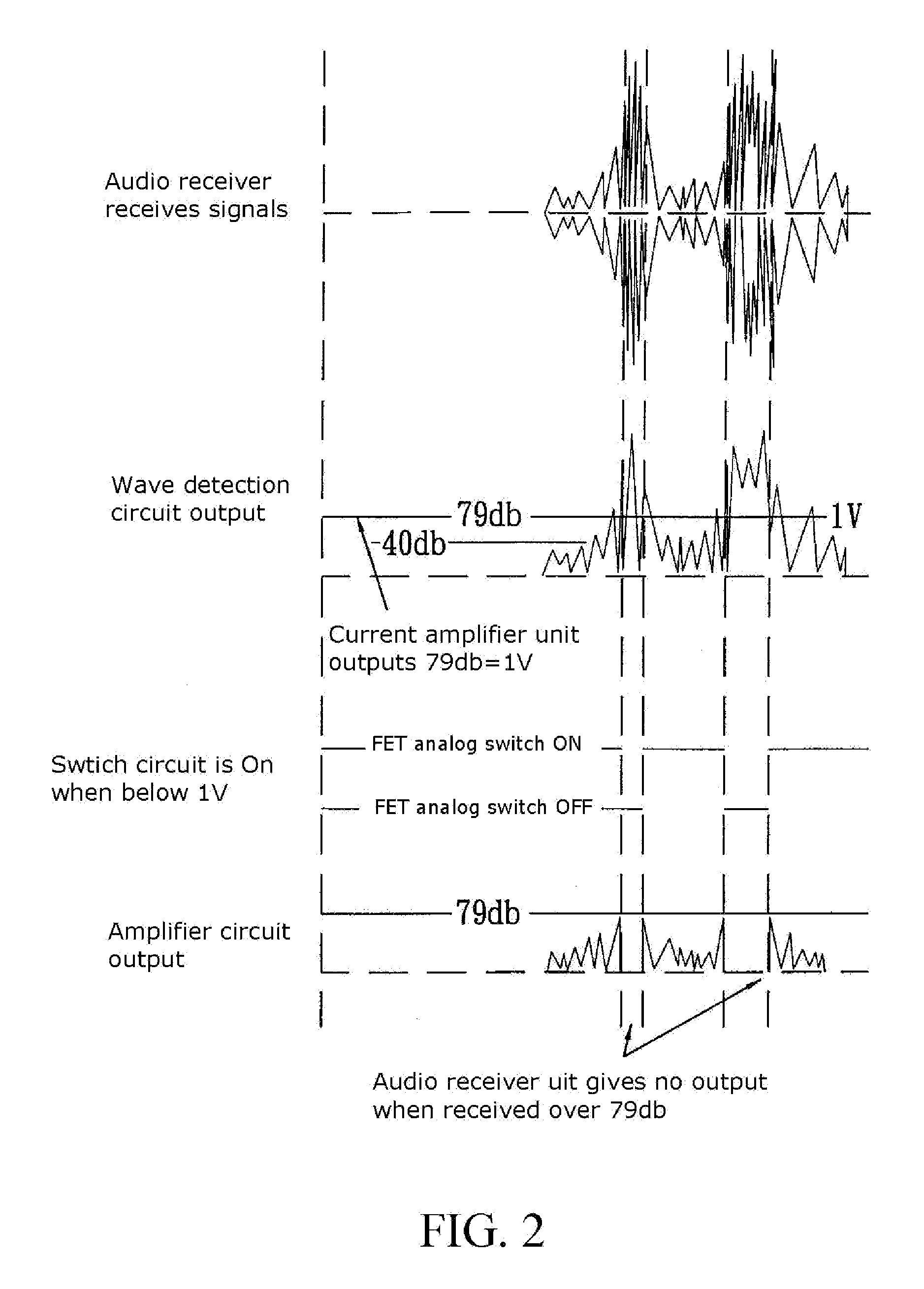
InactiveUS20130064378A1Noise protectionEar treatmentEarpiece/earphone noise reductionEarmuffsBluetooth
An anti-noise earmuff device includes an audio signal processor unit, a Bluetooth module, an audio mixer unit and an amplifier unit. The audio signal processor unit is arranged in the earmuffs for control audio signal output, protecting the user's eardrums against noise of high-decibel level. The Bluetooth module receives or communicates with a mobile communication device through an antenna, allowing the user to listen to the music and to communicate with people outside without needing taking off the earmuff device.
Owner:CHUANG CHING KUO
Ear tubes
The invention provides a flexible ear tube (10) for draining and ventilating the middle ear, the tube (10) having a flexible substantially tubular stem (12) with a lumen (14), the stem (12) being sized to be inserted through an incision in the eardrum (16) and the tube having at least two separate flexible contact surfaces (18) extending from the stem (12) and adapted to engage different spaced-apart inner surfaces of the eardrum 16, each of the contact surfaces (18) having a first axis XX extending substantially perpendicularly to the central axis of the stem and a second axis YY extending substantially perpendicularly to the first axis wherein one of the axes is between 0.6 and 3 mm and the second of the axes is between 1 and 7 mm in length.
Owner:OTOMEDICS ADVANCED MEDICAL TECH
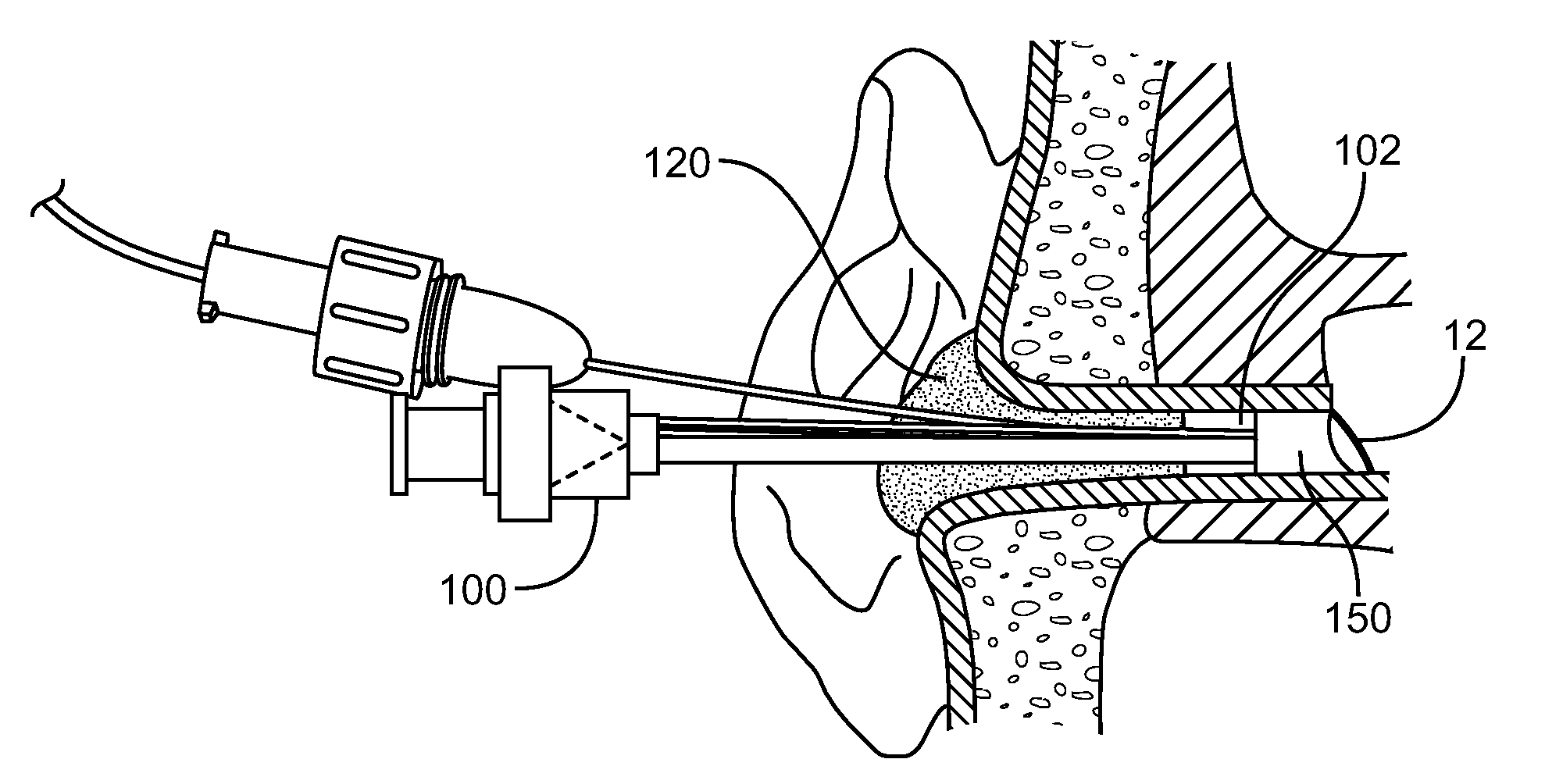
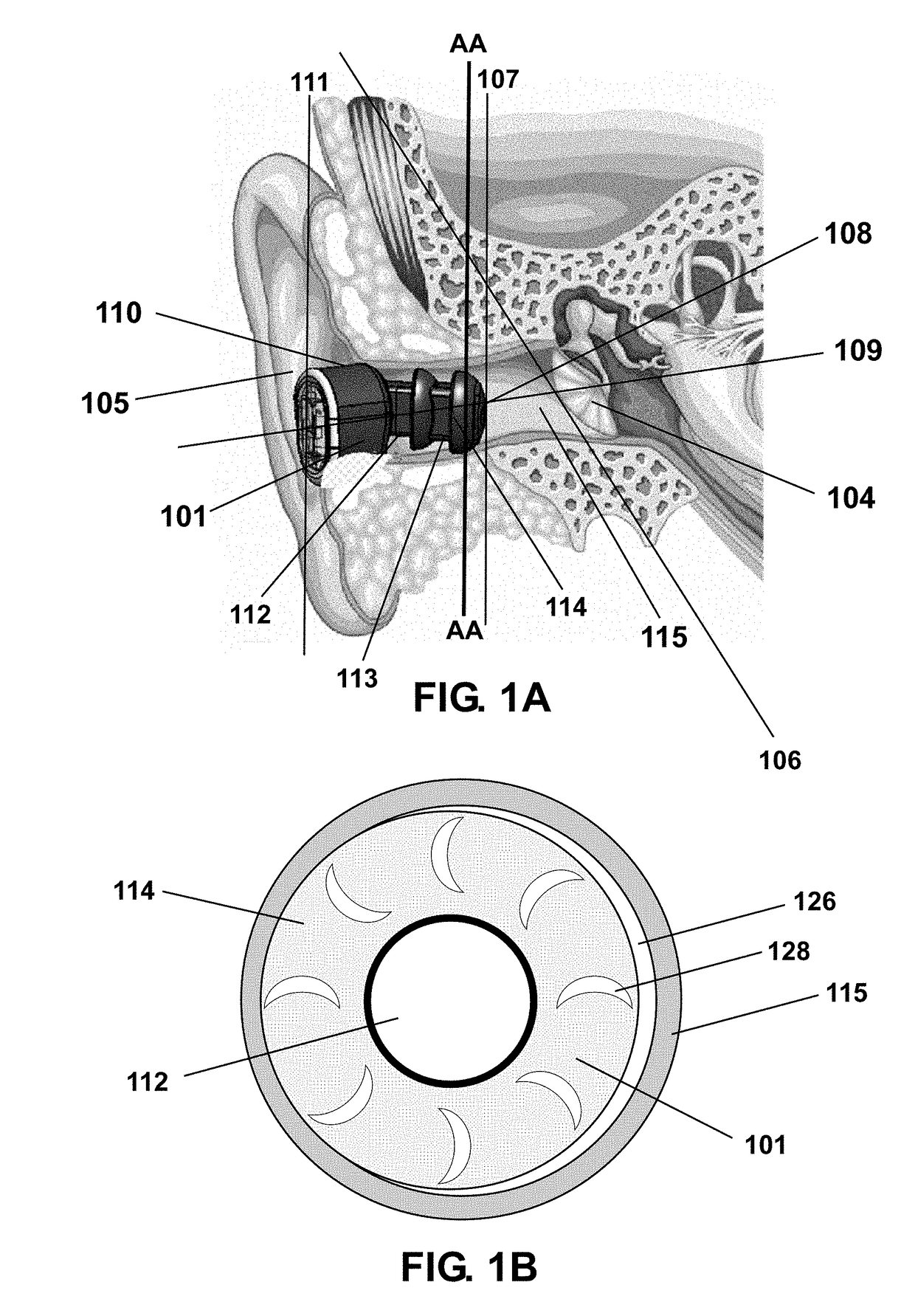
Cochlear ear implant
InactiveUS20050033384A1Not destroy residual hearingHead electrodesExternal electrodesHearing perceptionElectrode array
A simple cochlear implant is provided that can be implanted in a doctor's office under local anesthesia, which does not destroy residual hearing, and in a preferred embodiment, which is small enough to fit within a person's ear canal. The cochlear ear implant includes an exterior ear module, an interior ear module, and a cochlear electrode array. The exterior ear module includes a hollow housing within which are located the active electrical components including a microphone, power supply, and processor. The exterior ear module is easily removable from the body without surgery and is positioned in the auditory canal, the concha bowl or behind the pinna. The interior ear module is a semi-permanent assembly located immediately exterior to the tympanic membrane. It is a simple passive module for relaying signals to the electrode array. The communication of auditory signals from the exterior ear module to the interior ear module may be achieved by various techniques including by direct electrical transmission. However, the communication between the exterior and interior ear modules is preferably accomplished using a transcanal induction link. The electrode array extends from the interior ear module through the tympanic membrane to engage the cochlea. The electrode array includes an implanted active electrode, a return electrode, and a biocompatible miniature connector for connecting to the interior ear module.
Owner:SACHA MIKE K
Ergonomic earpiece and attachments
ActiveUS20120057739A1Improve comfortDisadvantages associated with the lower lobe can be mitigatedMicrophonesLoudspeakersMedicineHeadphones
An earpiece that substantially lacks a lower lobe is disclosed. In one example, the earpiece can have a generally arcuate rib having upper and lower ends. A lobe can be formed at the upper end of the arcuate rib. No lobe is formed at the lower end of the arcuate rib. An extension can extend from the earpiece and can be configured to extend into the ear canal. Eliminating the lower lobe mitigates discomfort during use and also reduces the likelihood of tissue damage and infection. The extension can enhance communication of desired sound, e.g., from a two-way radio, to an eardrum while mitigating communication of undesirable ambient noise to the eardrum. Other implementations and related methods are also disclosed.
Owner:SUREFIRE LLC
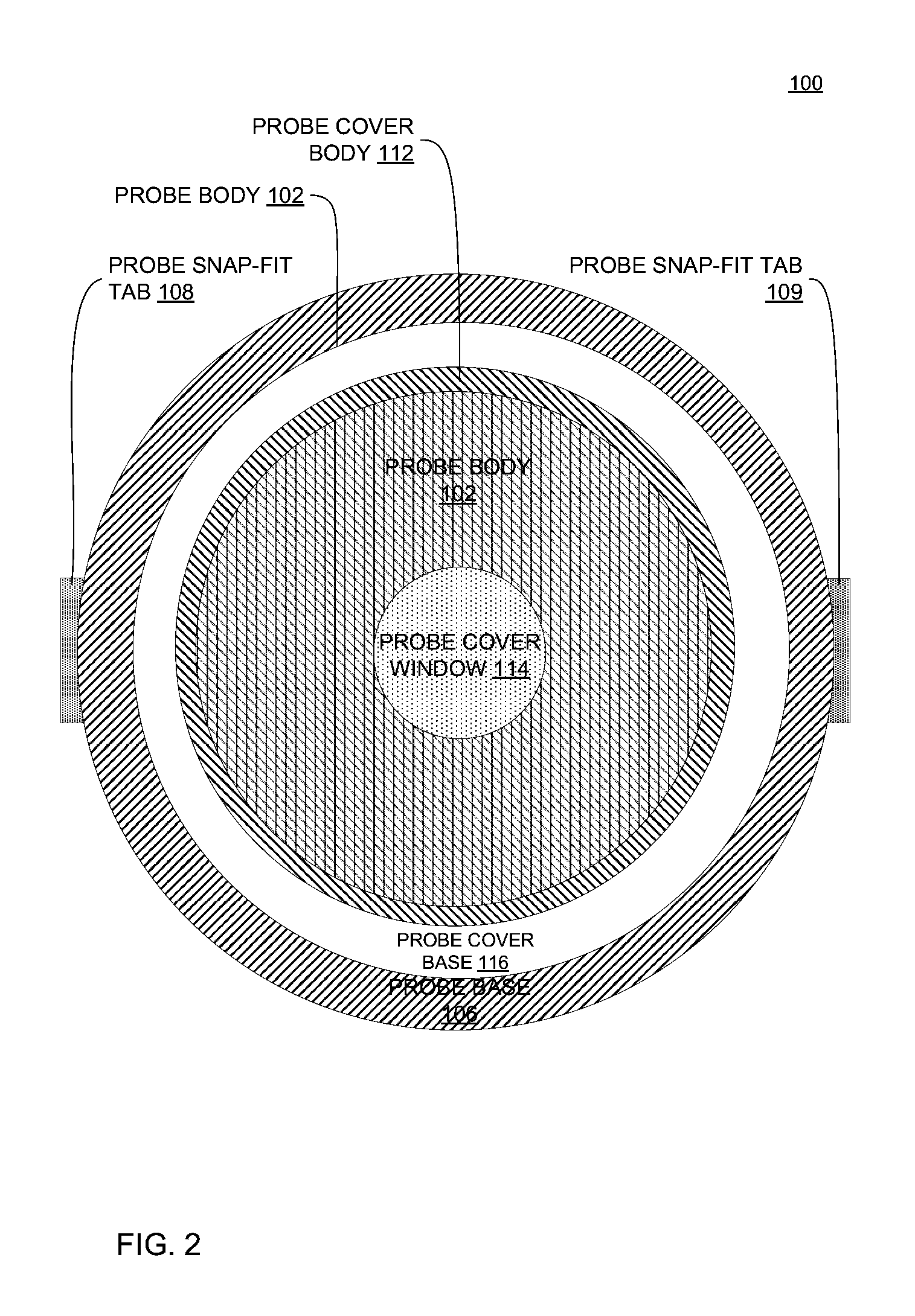
Probe cover of a tympanic thermometer and tympanic thermometer assembly
A probe cover of a tympanic thermometer and tympanic thermometer assembly includes a base and a sheath attached on the base. The base is a ring-shaped thin film object with a central opening permitting pass of the probe of a tympanic thermometer, and is engaged with flanges at the bottom of the probe. The sheath includes a circumferential wall that strains and circles around the sidewall of the probe, and an infrared window fitted on an opening at the front end of the probe. Since the thickness of the infrared window is thicker than that of the circumferential wall and the infrared window is free of pleats to keep a very uniform thickness, infrared can accurately penetrate through the infrared window to the probe of a tympanic thermometer for measuring a precise body temperature.
Owner:ORIENTAL SYST TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com