Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
139 results about "Extracorporeal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
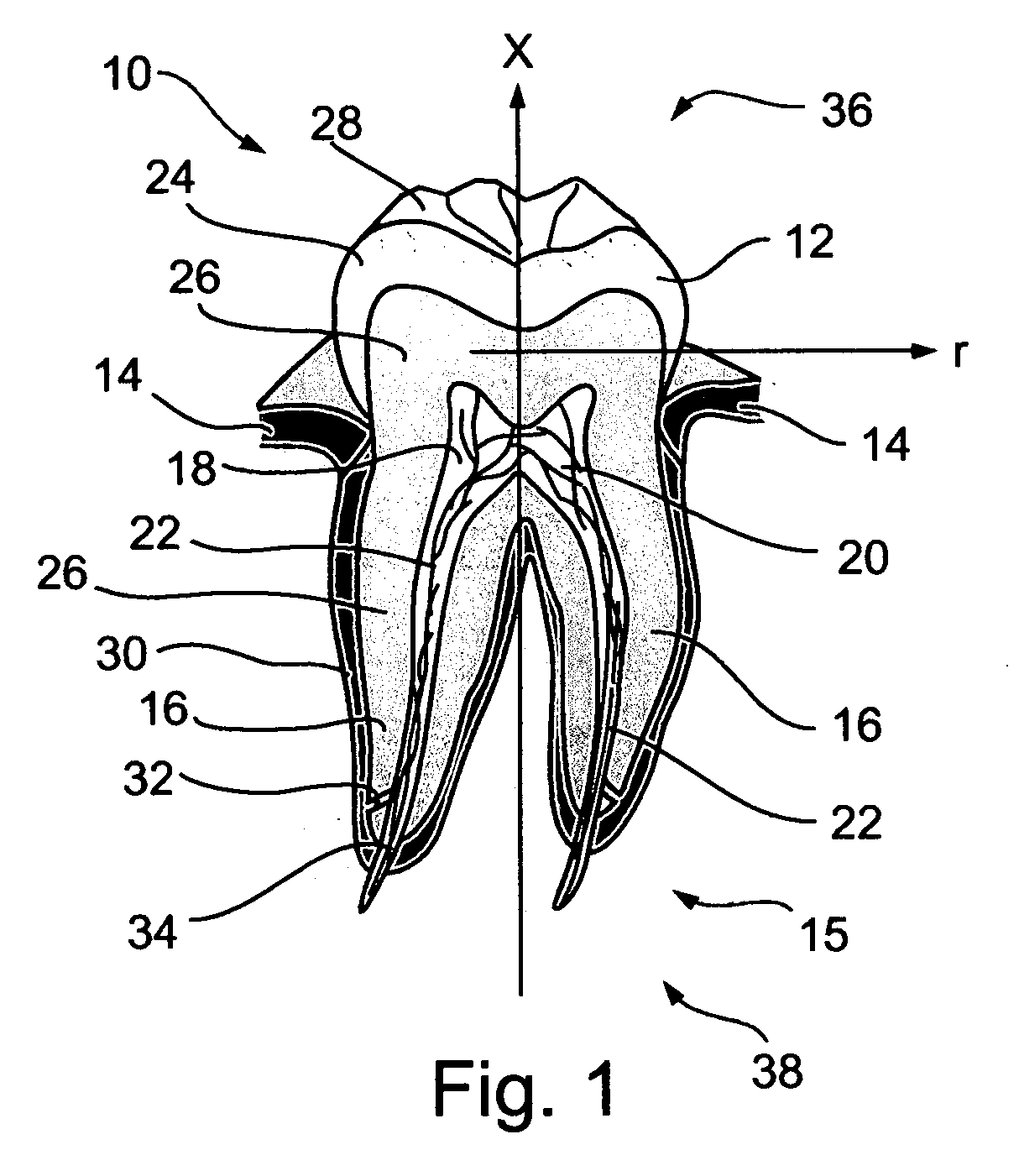
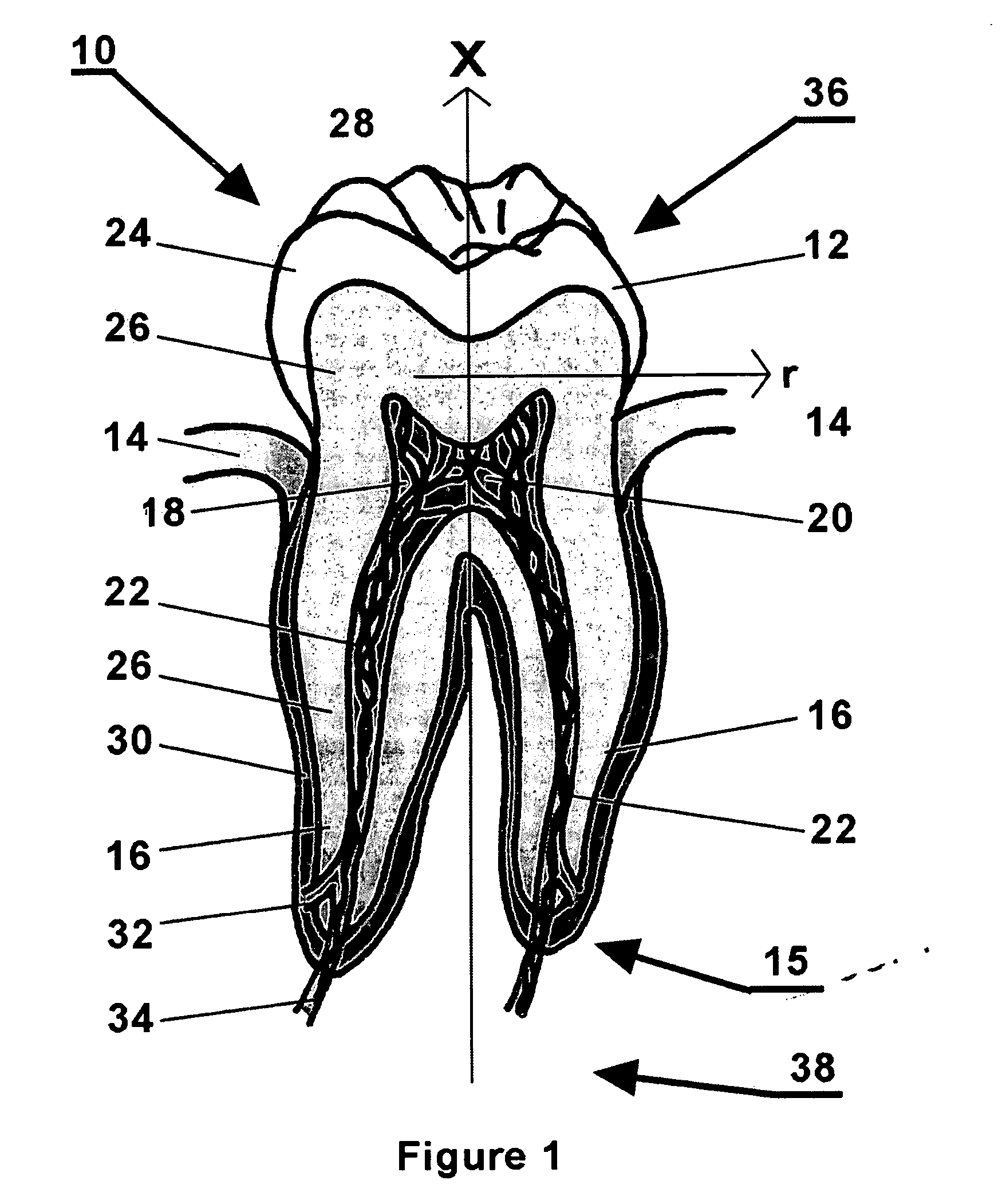
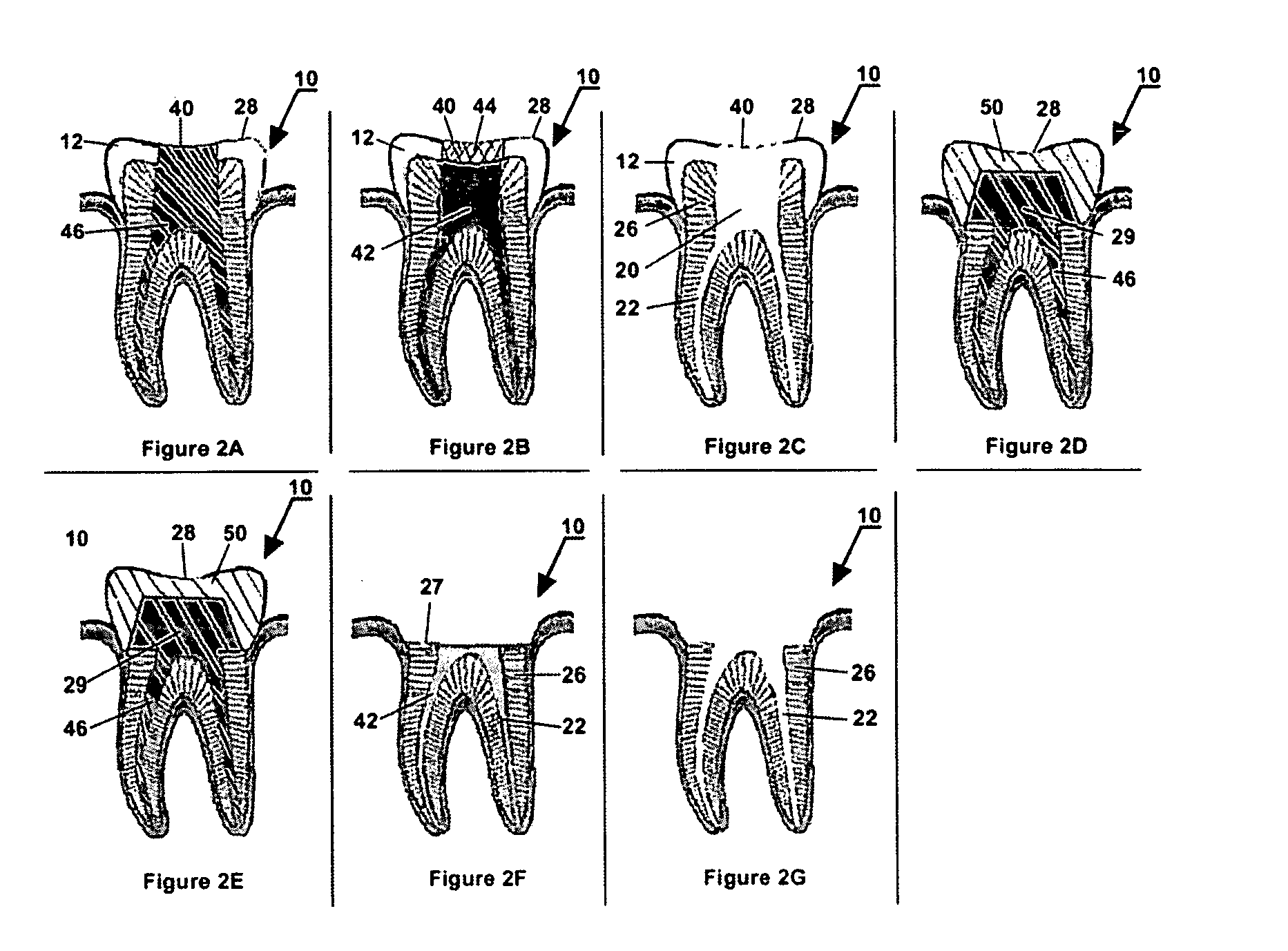
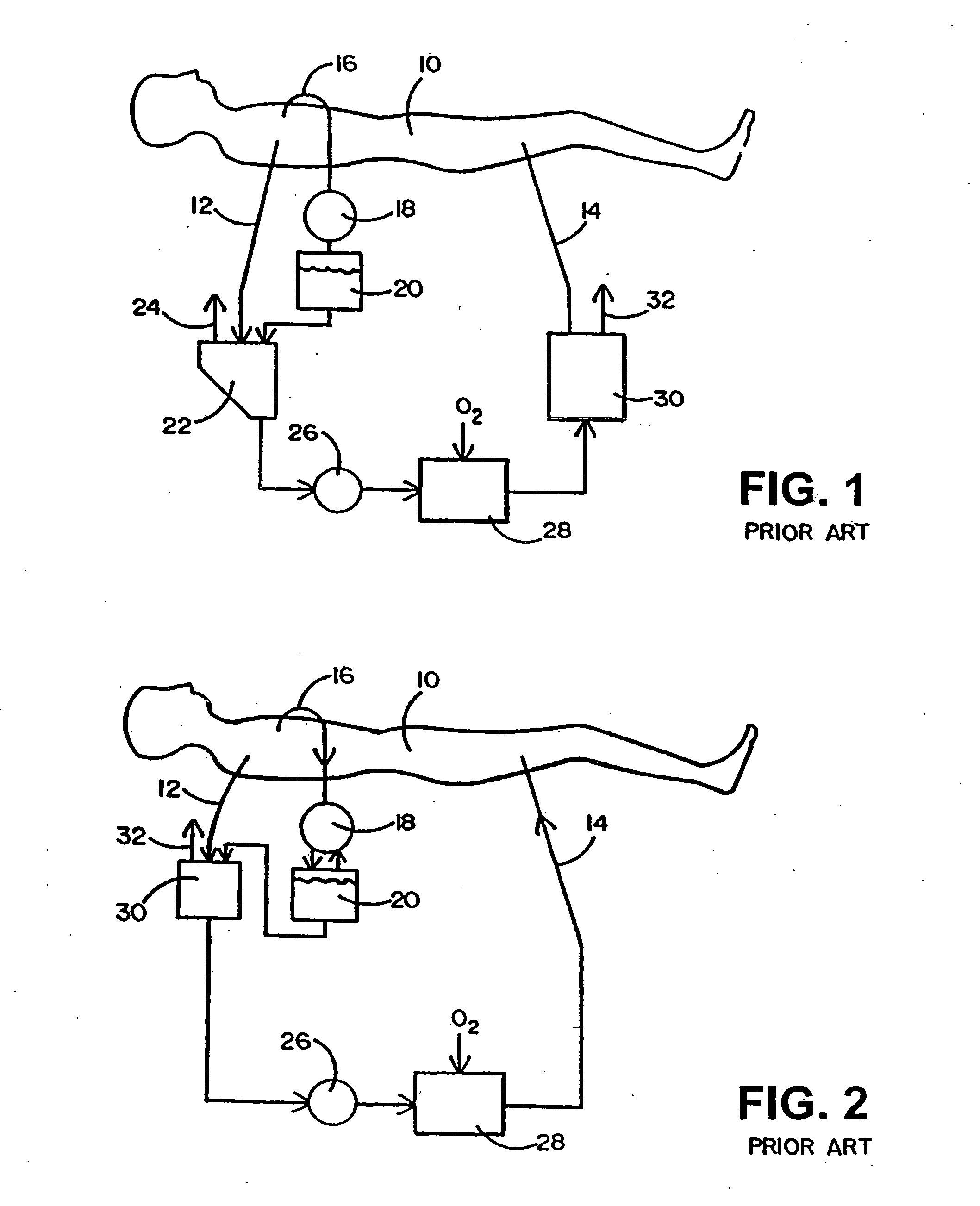
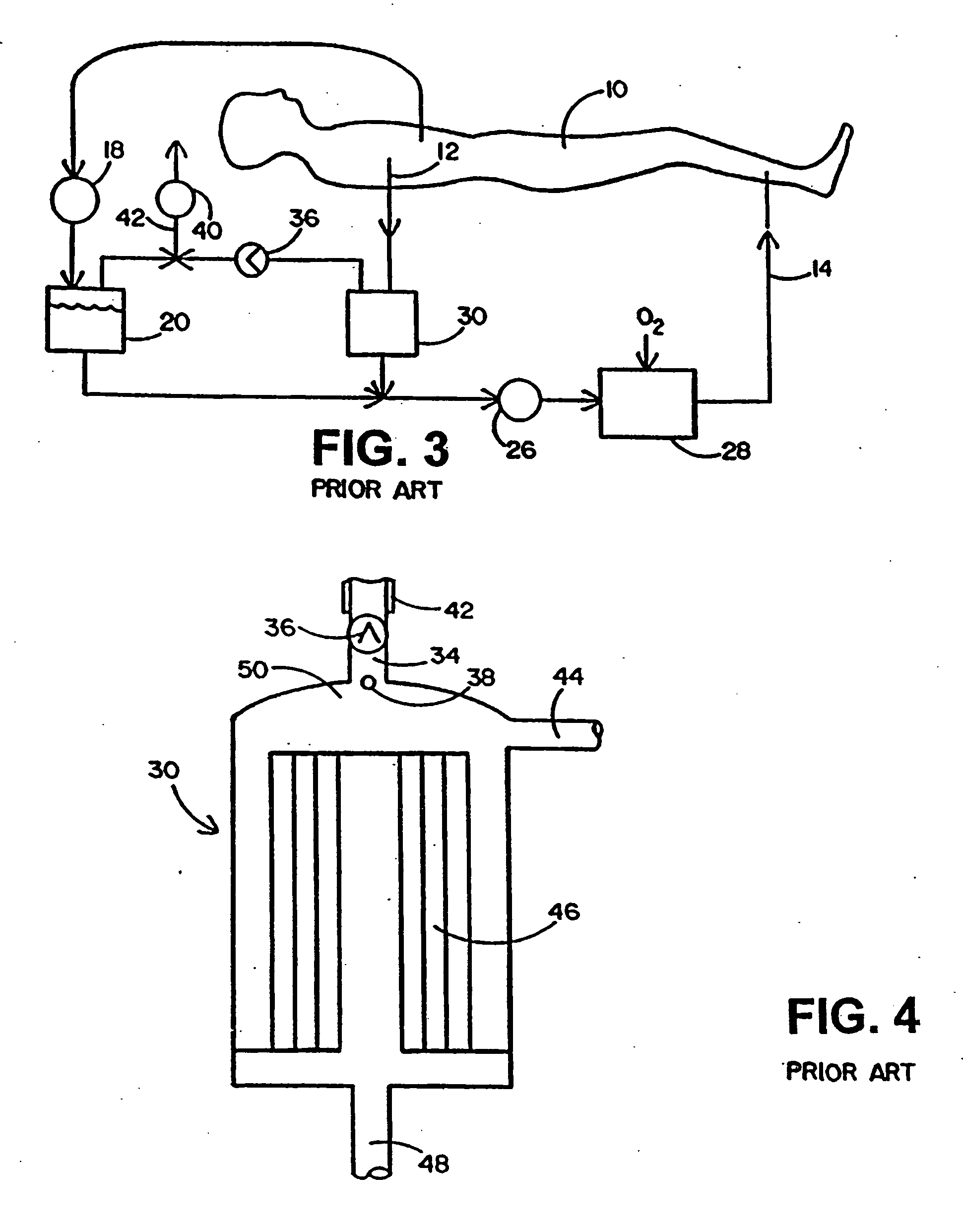
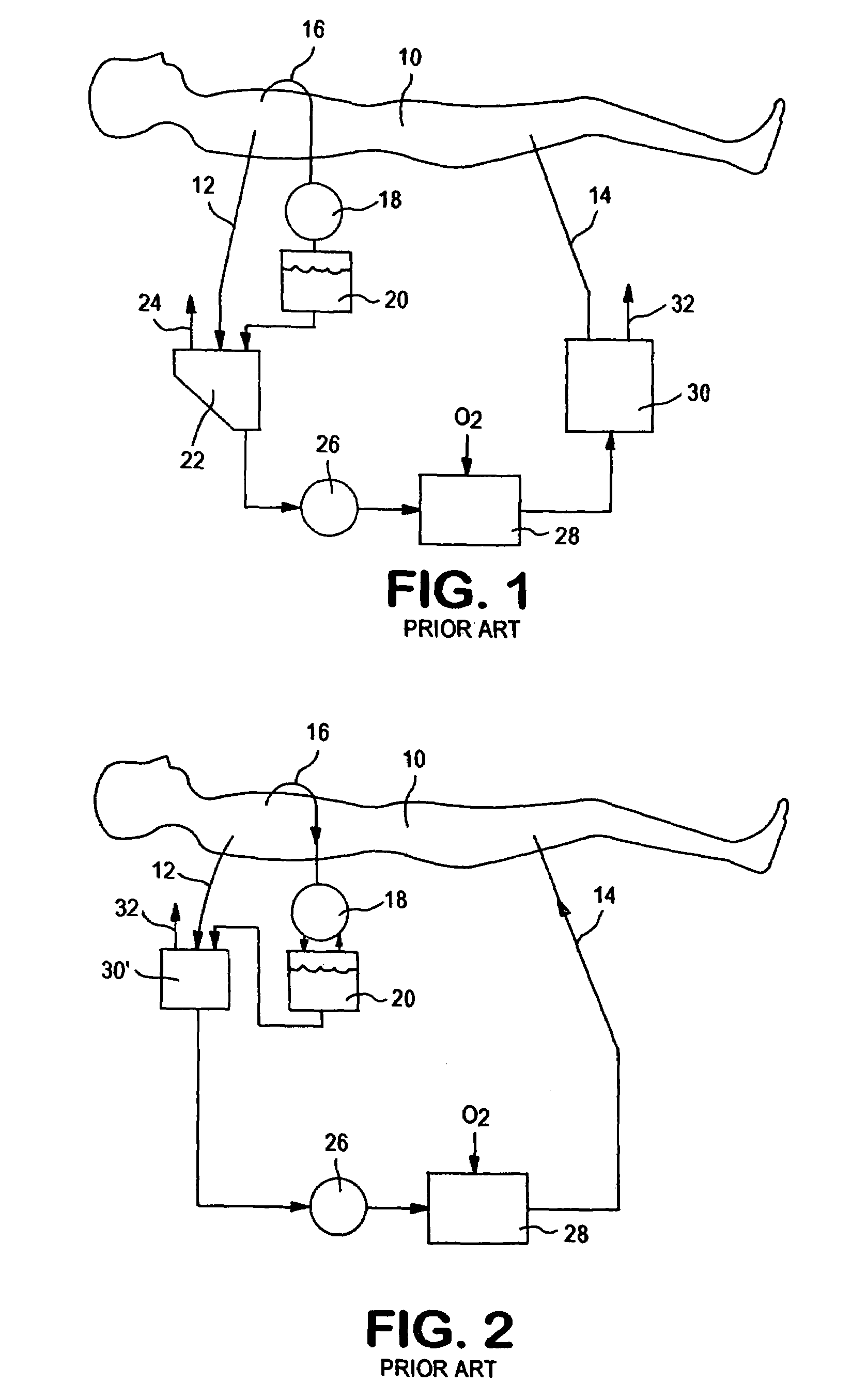
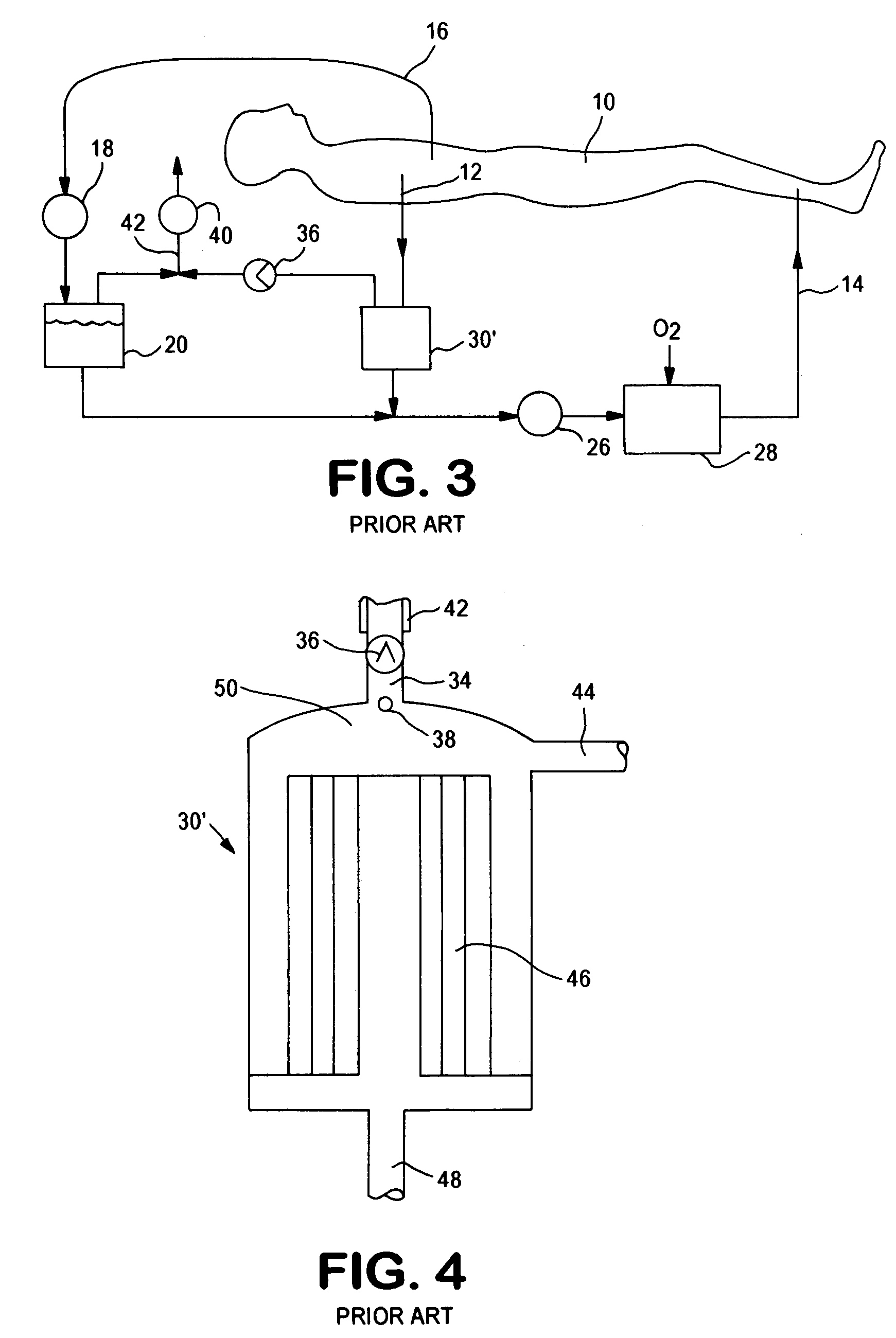
An extracorporeal is a medical procedure which is performed outside the body.
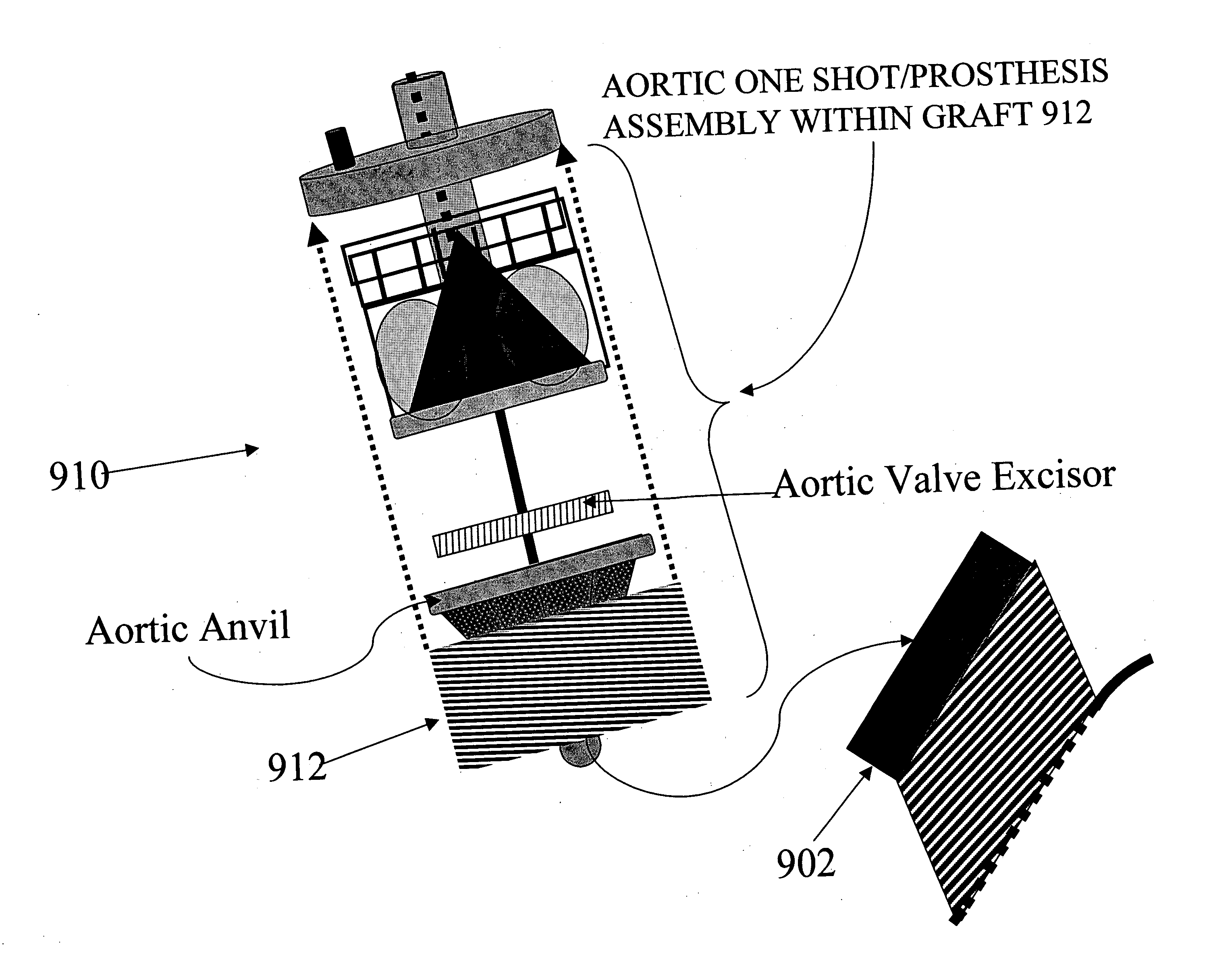
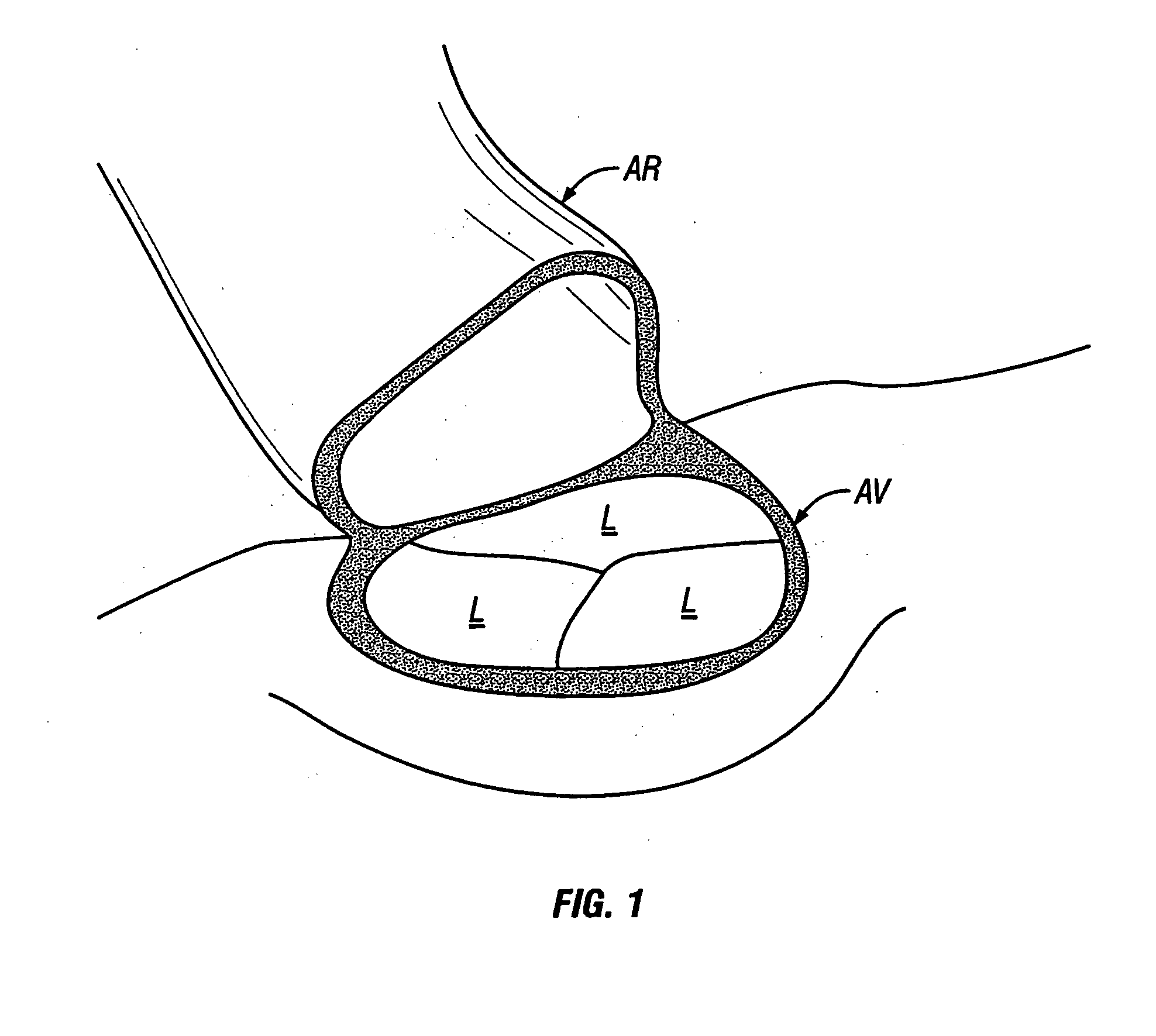
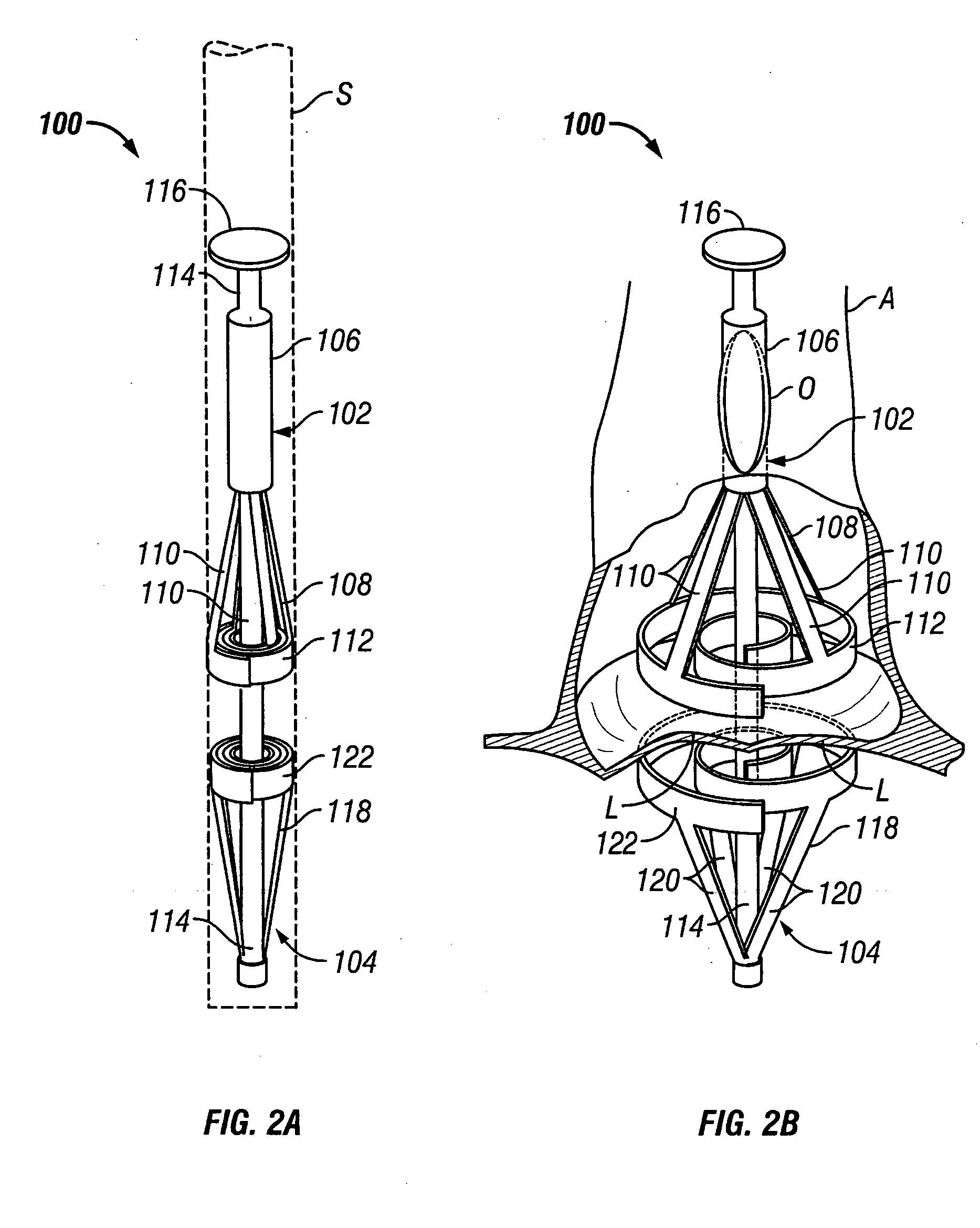
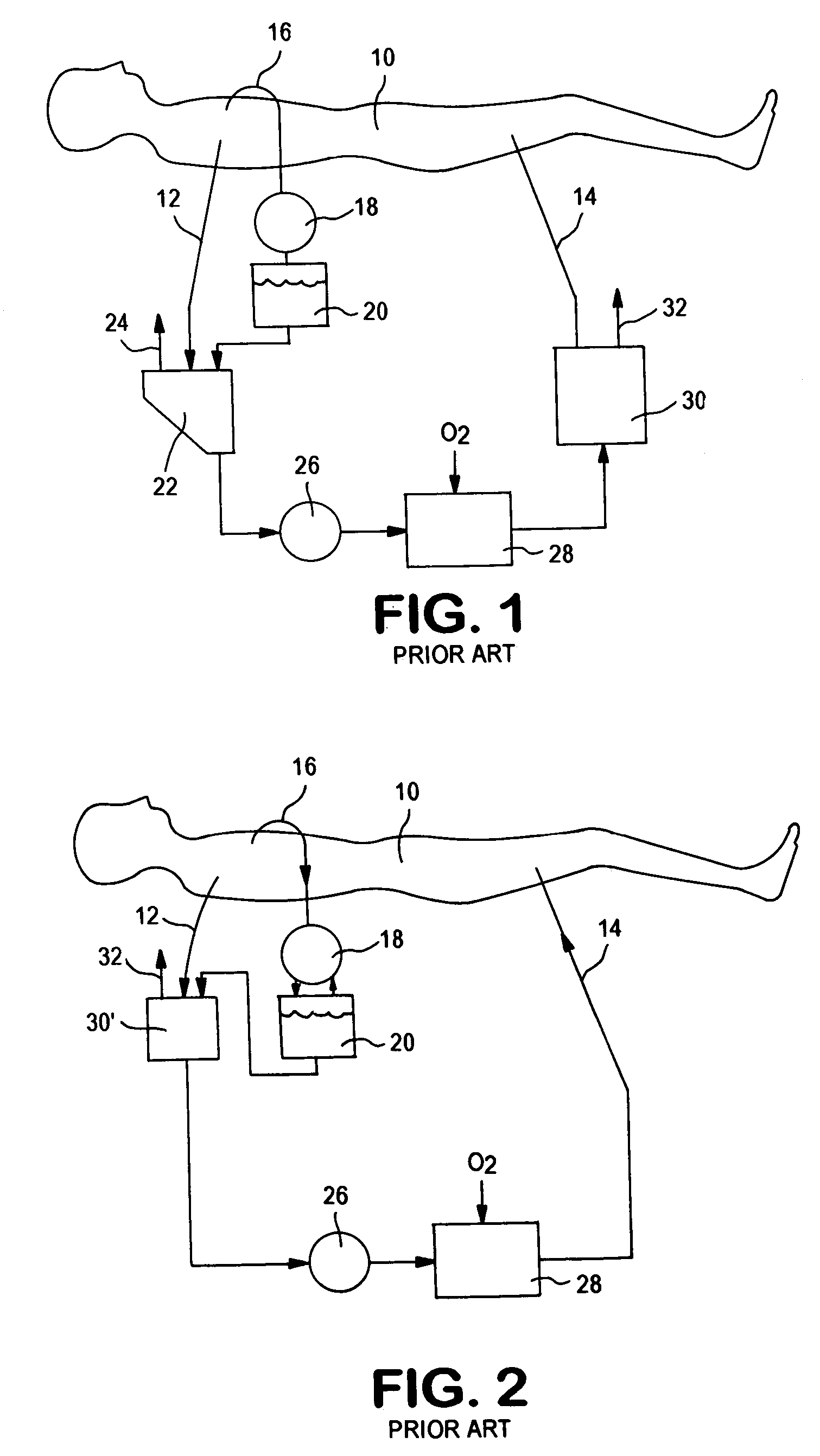
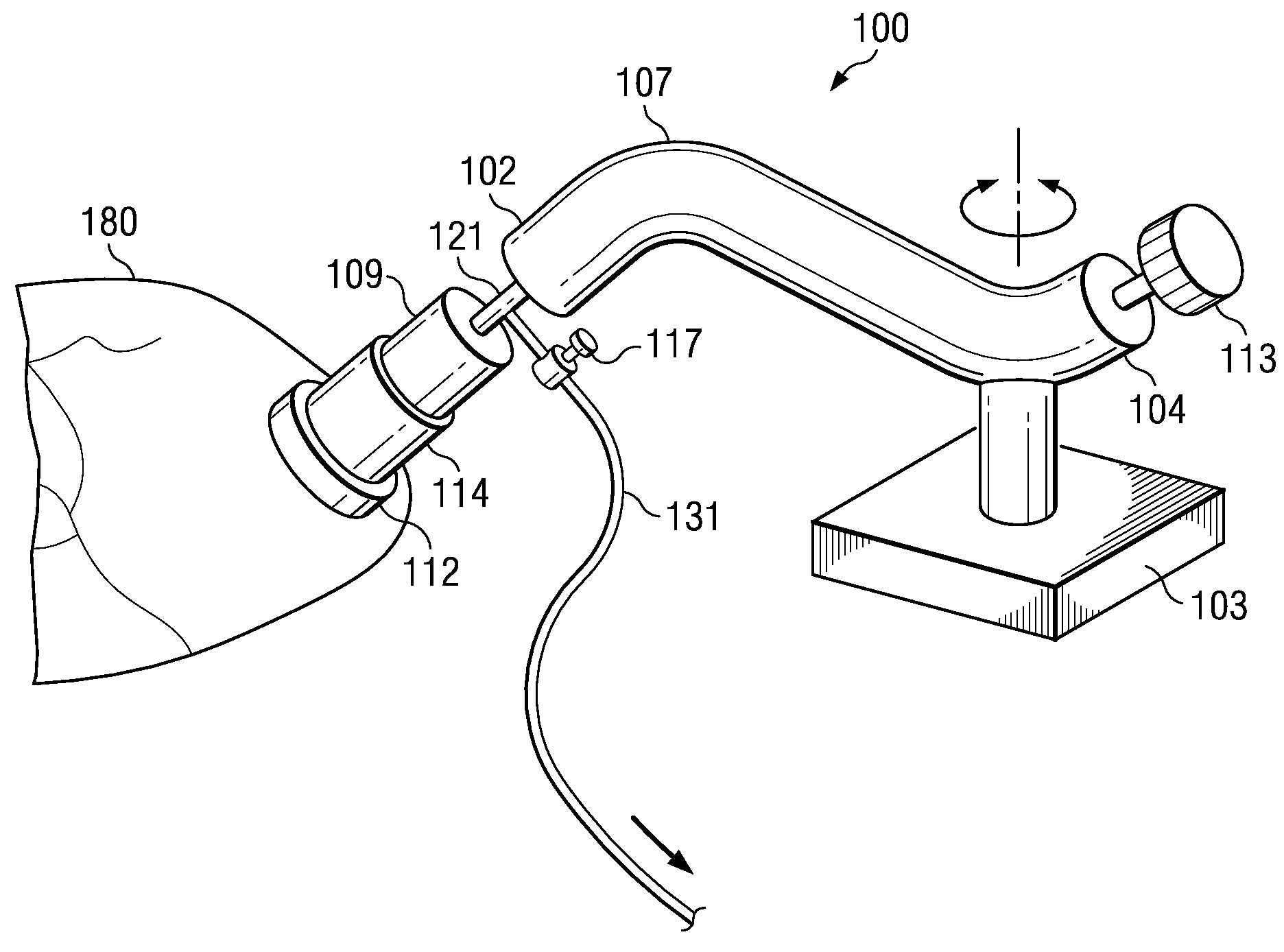
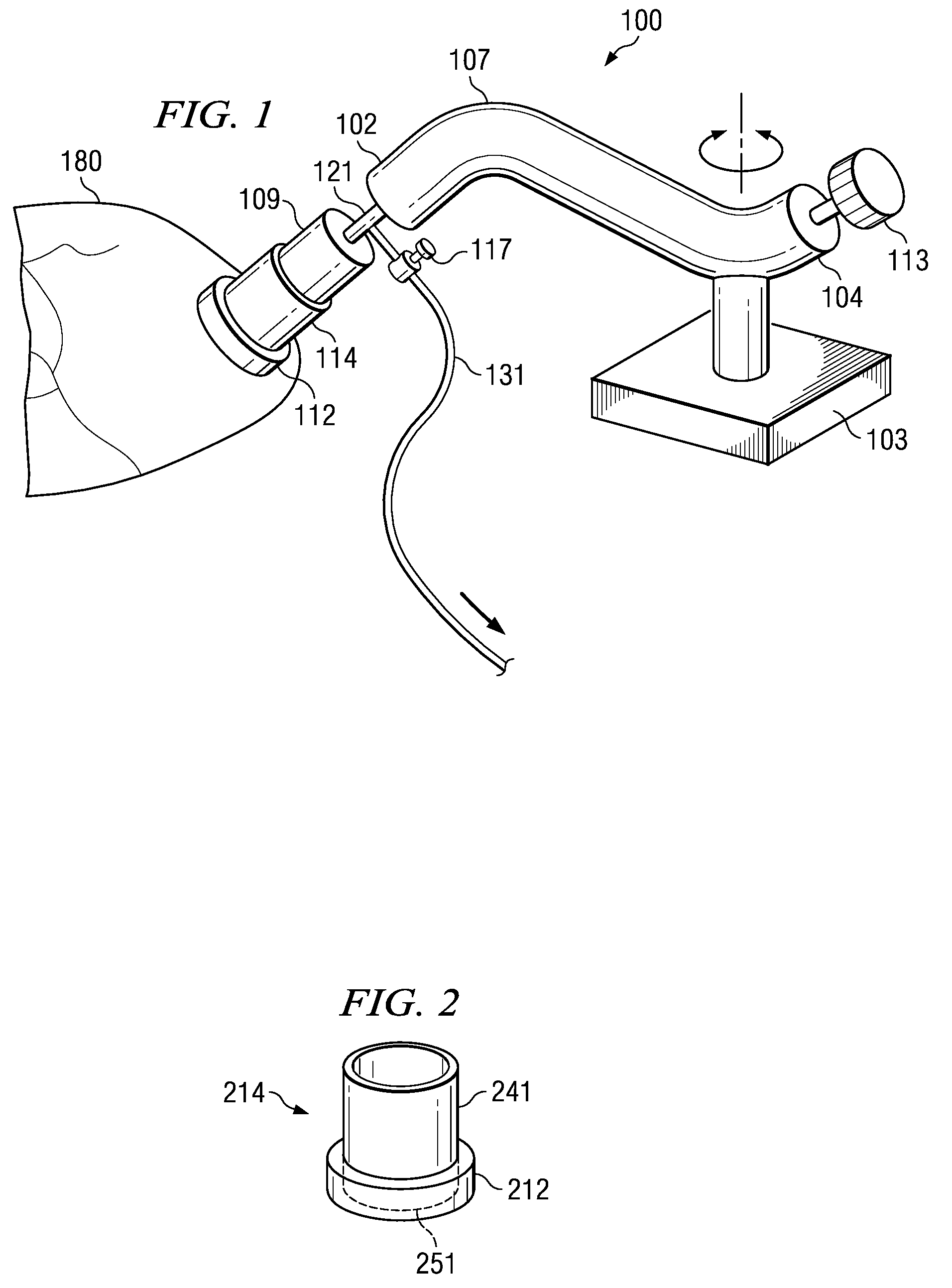
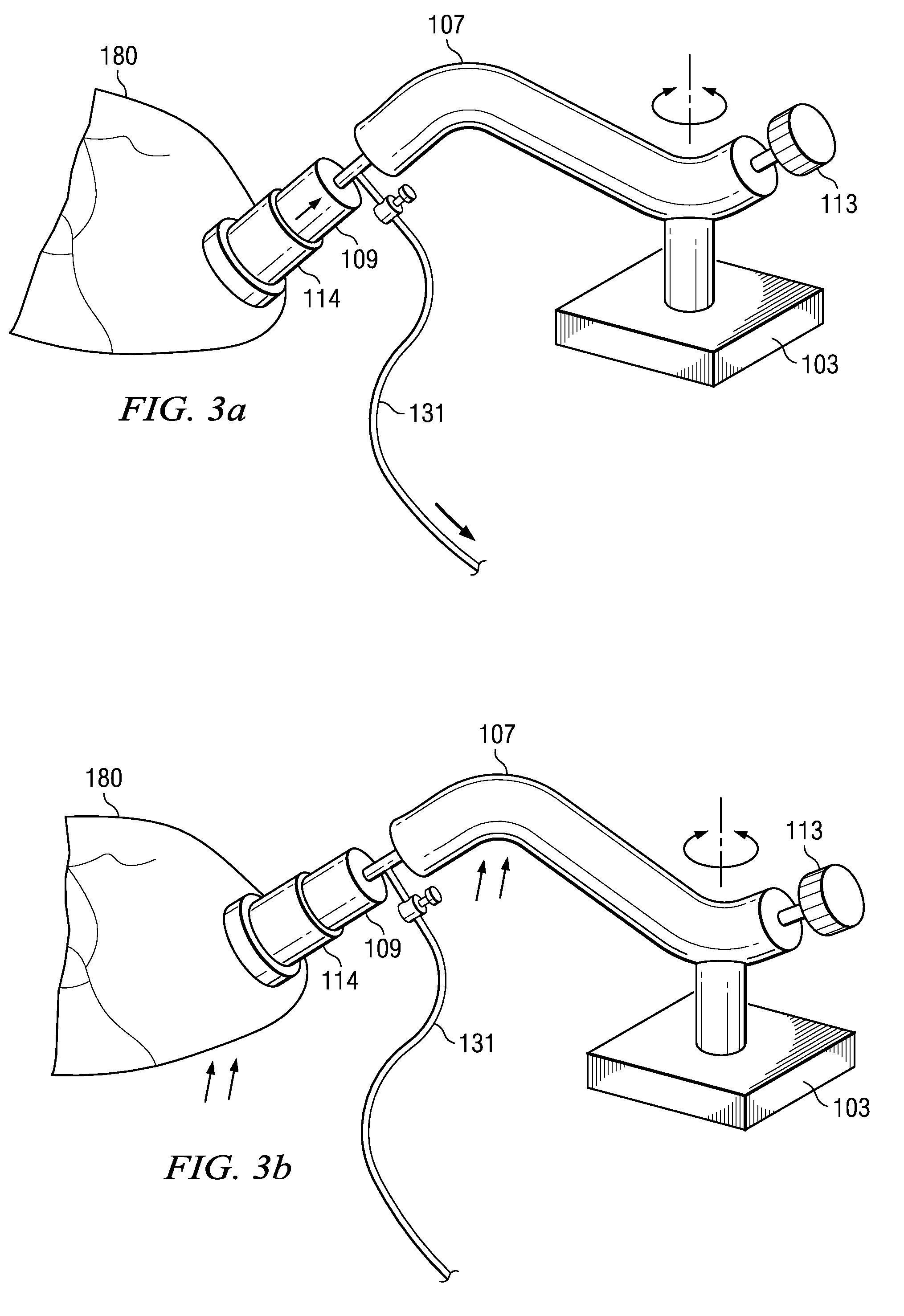
Methods and apparatus for off pump aortic valve replacement with a valve prosthesis
InactiveUS20050203549A1Promote recoveryPromote resultsHeart valvesExcision instrumentsMedicineProsthesis
Methods and apparatus are provided for valve repair or replacement. In one embodiment, the method comprises providing an apparatus having a valve prosthesis, a valve leaflet support and a valve excisor, the apparatus having a first configuration and a second configuration; accessing the aortic root without placing the patient on a heart-lung machine; advancing the apparatus in the first configuration where the valve leaflet support is advanced through a valve, wherein the support is positioned below a valve annulus; expanding the apparatus into a second configuration so that the support will engage the valve; and moving the valve leaflet support and valve excisor together to remove leaflets of the valve. Penetrating members may be advanced into the tissue wherein the penetrating members may act as fasteners to hold the prosthesis in place.
Owner:REALYVASQUEZ FIDEL
Oral devices and methods for controlled drug release
Drug dosage forms, which are housed in oral devices, and methods for controlled drug release are provided. The oral devices are permanently or removably inserted in the oral cavity and refilled or replaced as needed. The controlled drug release may be passive, based on the dosage form, or electronically controlled, for a high-precision, intelligent, drug delivery. Additionally, the controlled release may be any one of the following: release in accordance with a preprogrammed schedule, release at a controlled rate, delayed release, pulsatile release, chronotherapeutic release, closed-loop release, responsive to a sensor's input, release on demand from a personal extracorporeal system, release in accordance with a schedule specified by a personal extracorporeal system, release on demand from a monitoring center, via a personal extracorporeal system, and release in accordance with a schedule specified by a monitoring center, via a personal extracorporeal system. Drug absorption in the oral cavity may be assisted by an electrotransport mechanism. The oral devices require refilling or replacement at relatively long intervals of weeks or months, maintain a desired dosage level in the oral cavity, hence in the gastrointestinal tract, for extended periods, address situations of narrow drug therapeutic indices, and by being automatic, ensure adherence to a prescribed medication regimen.
Owner:WOLFAF ANDY +1
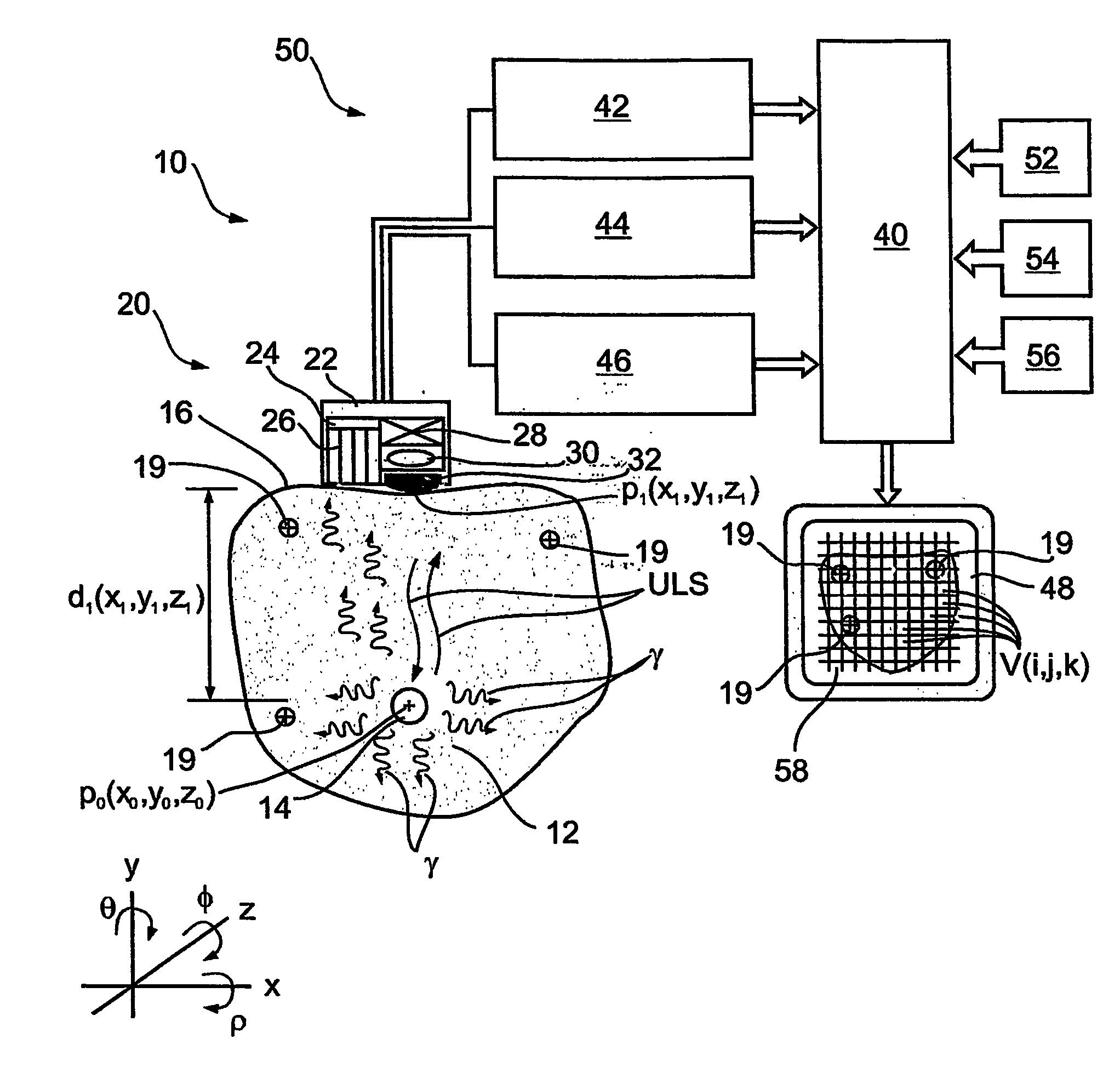
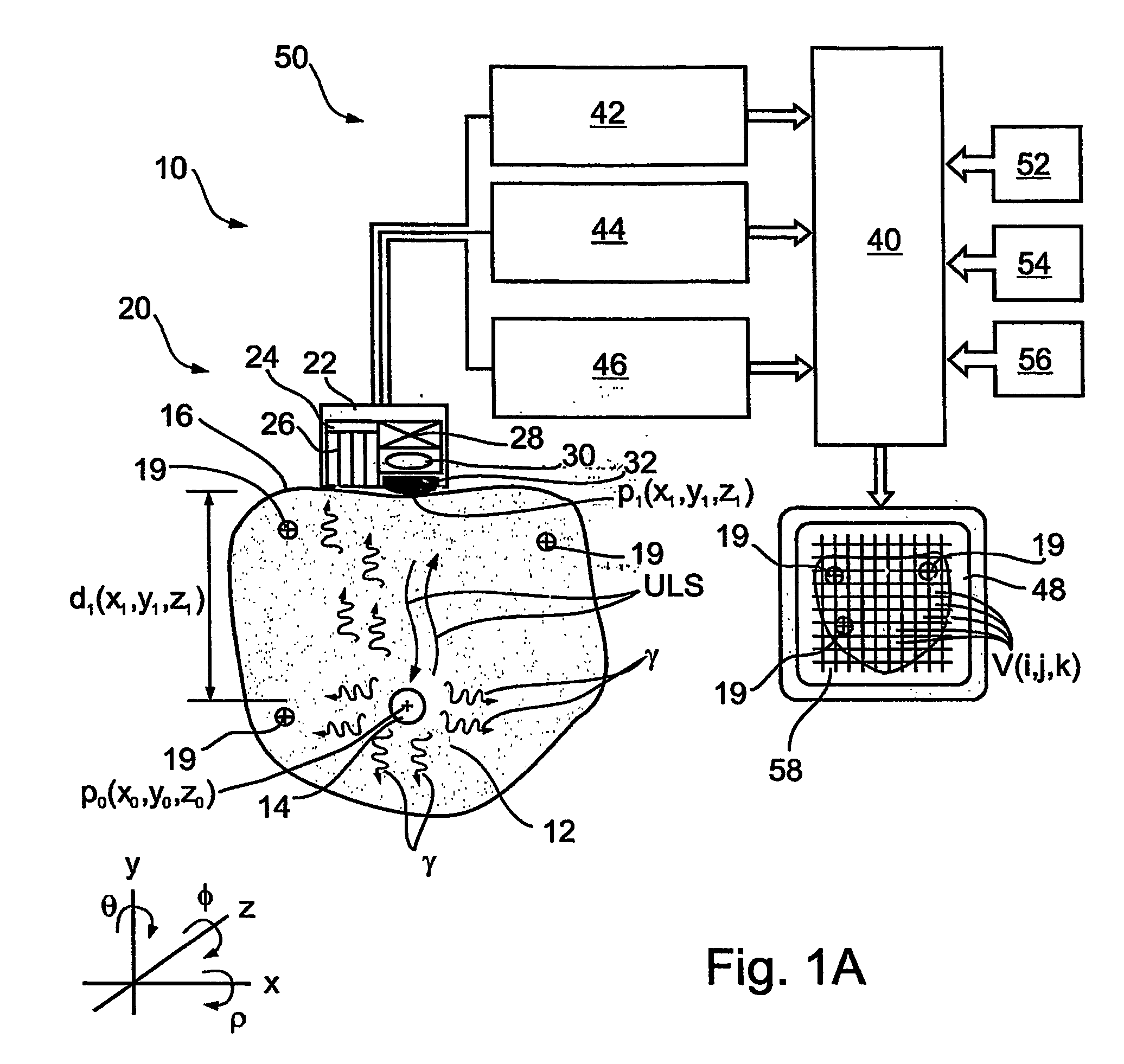
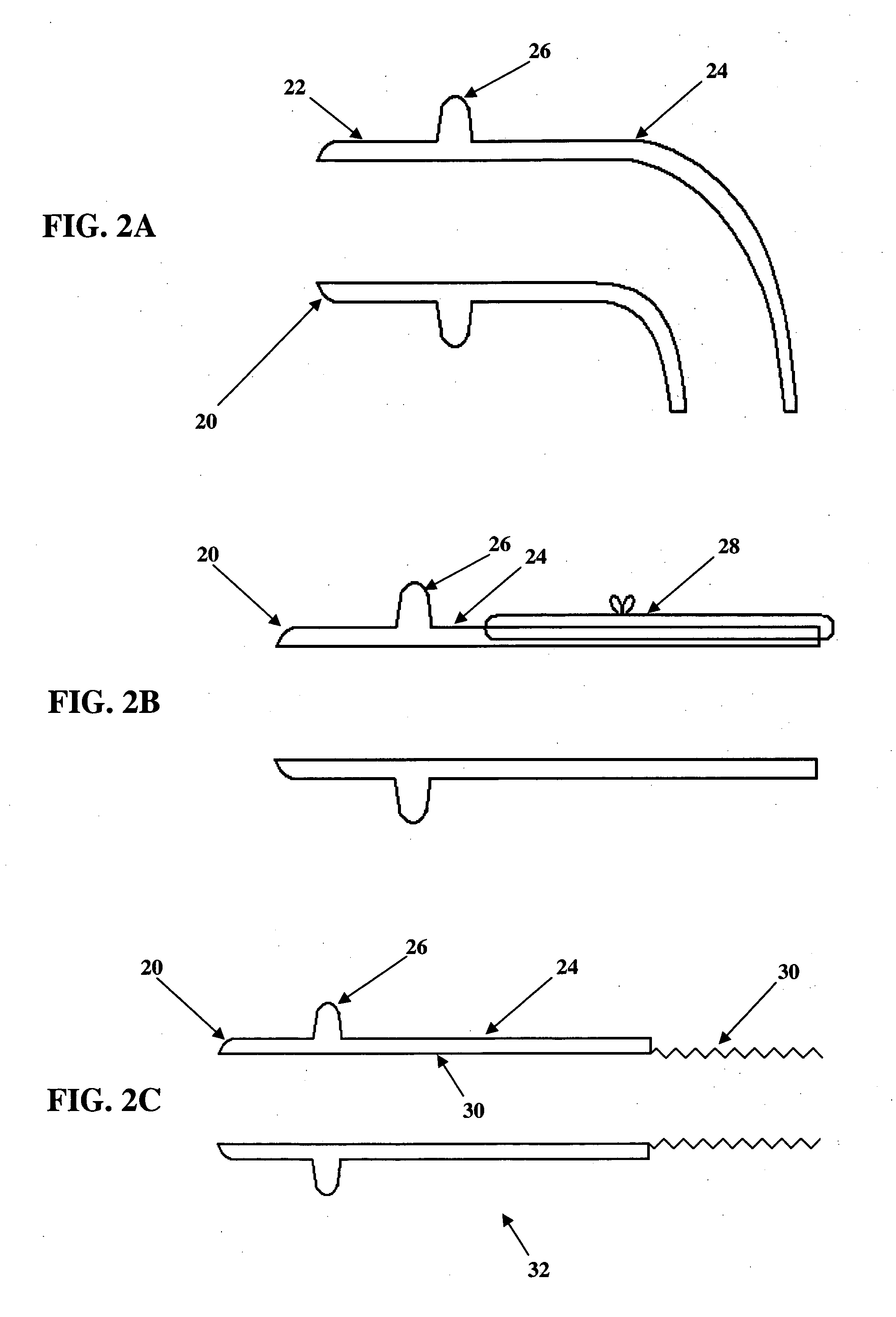
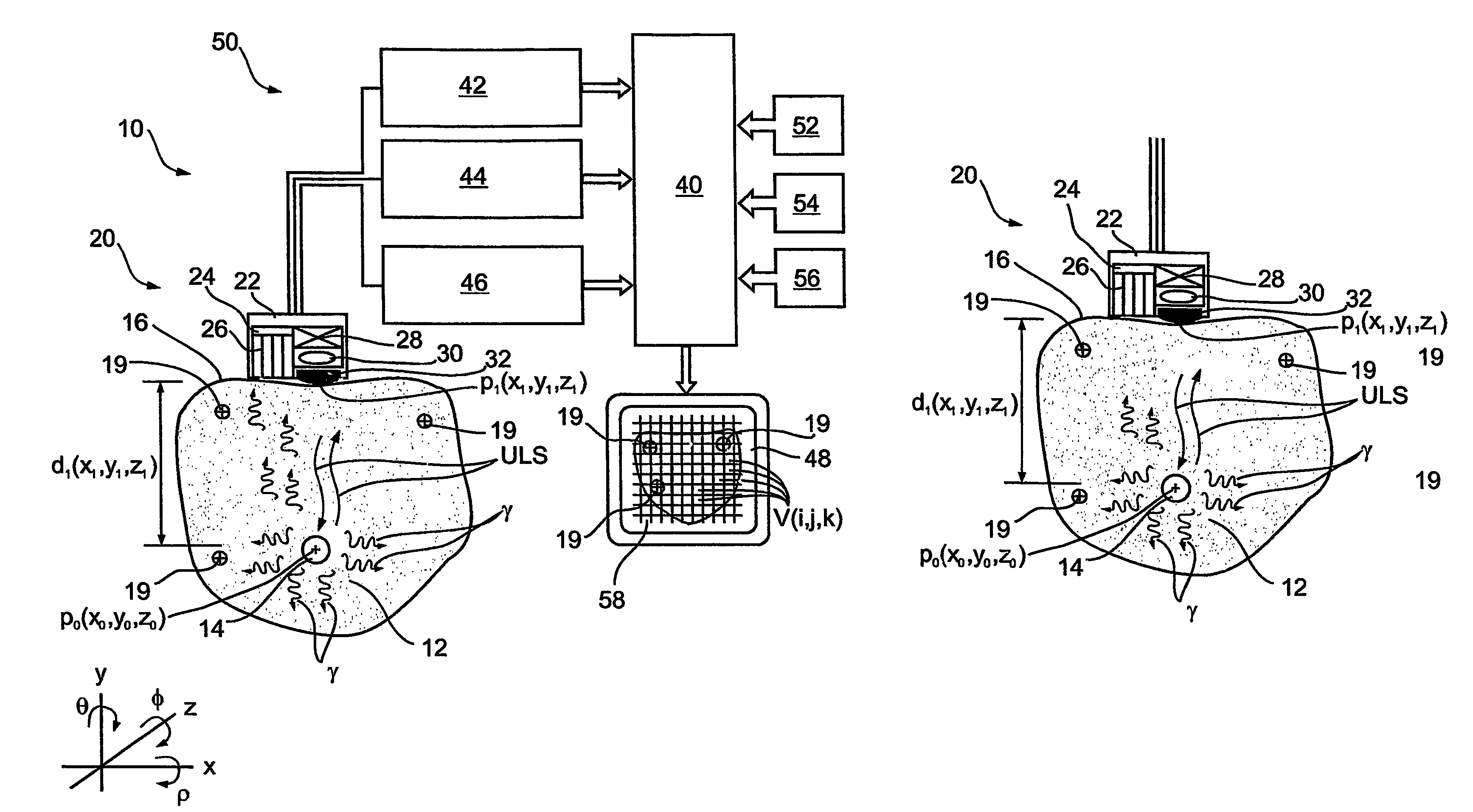
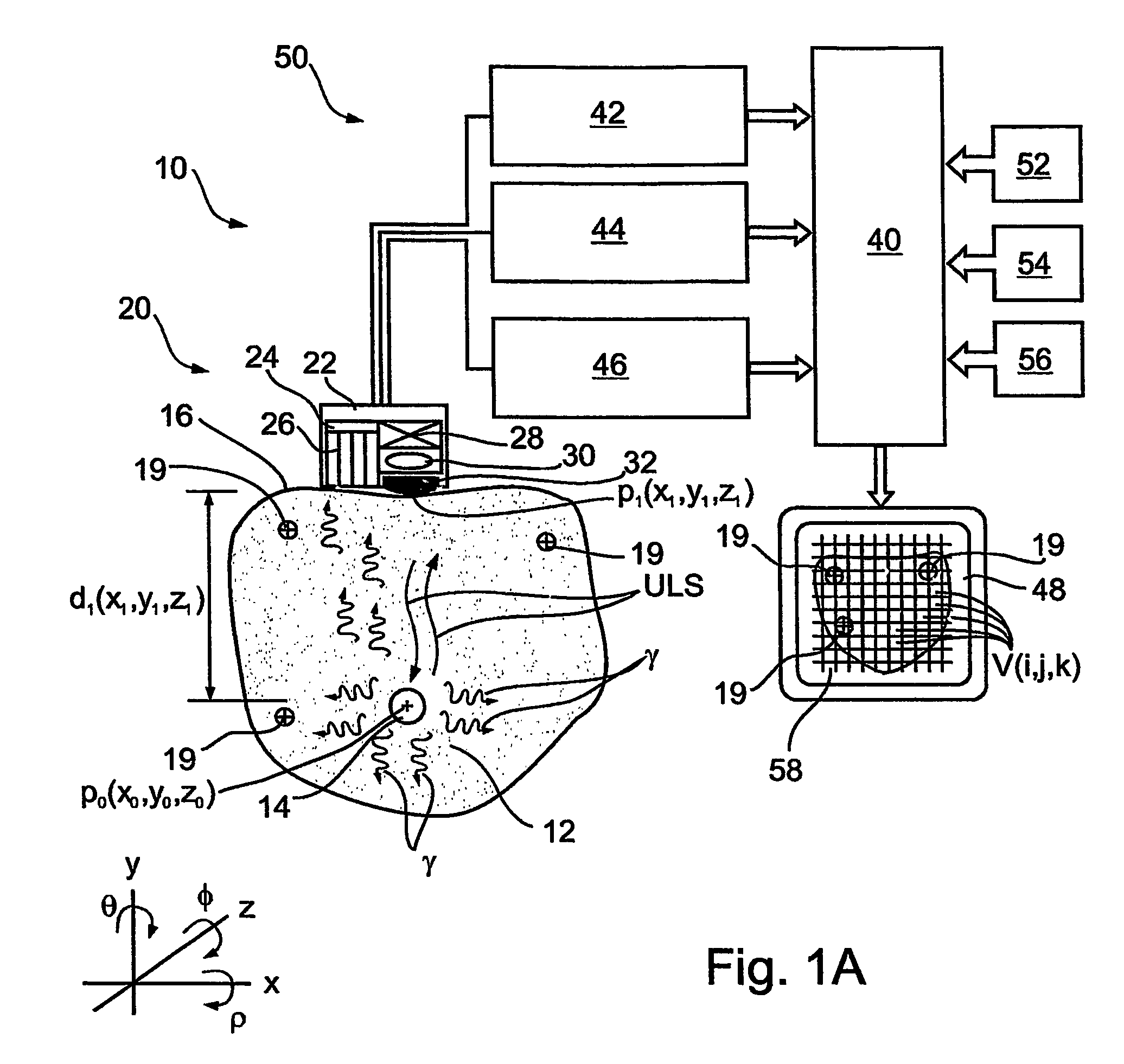
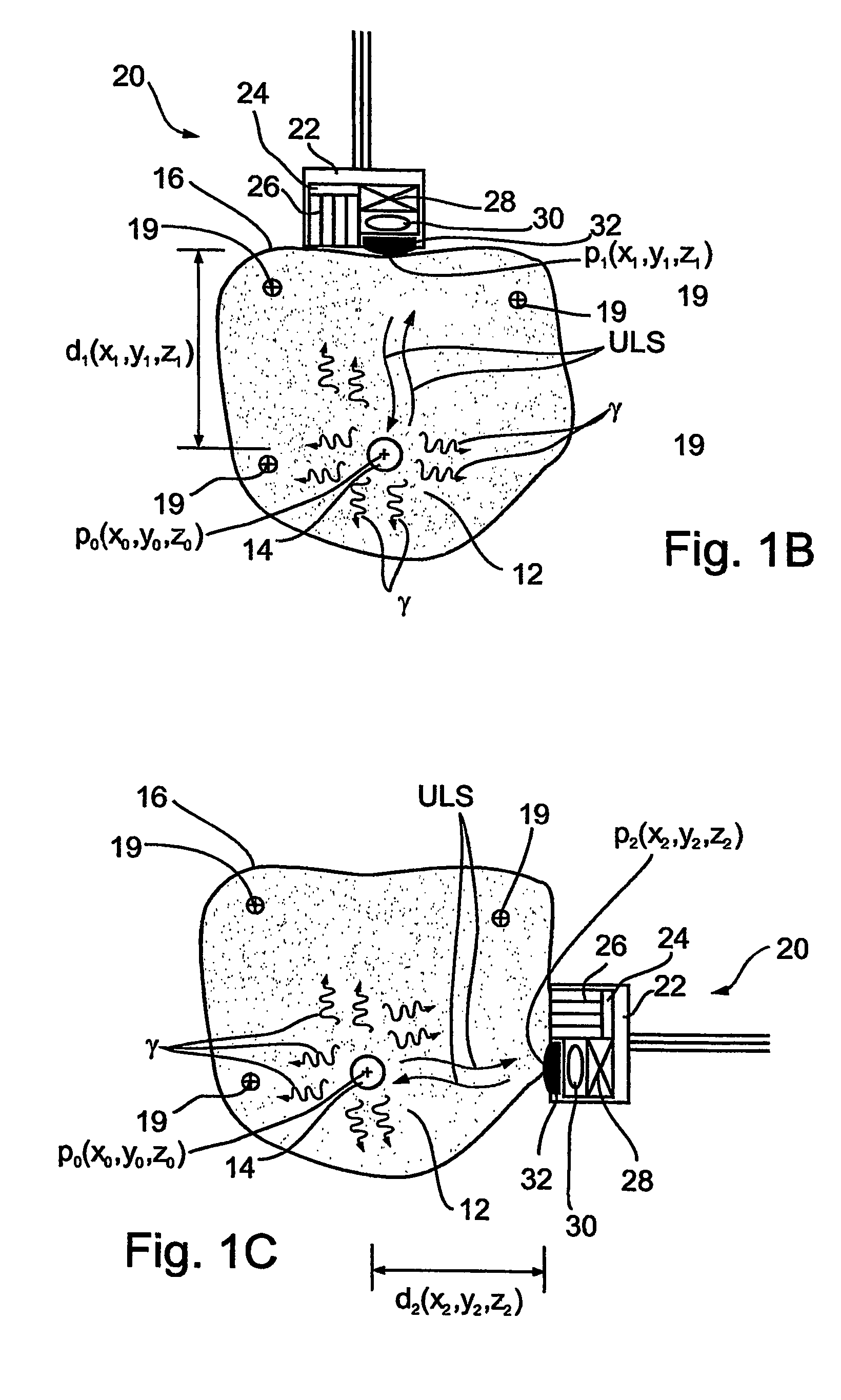
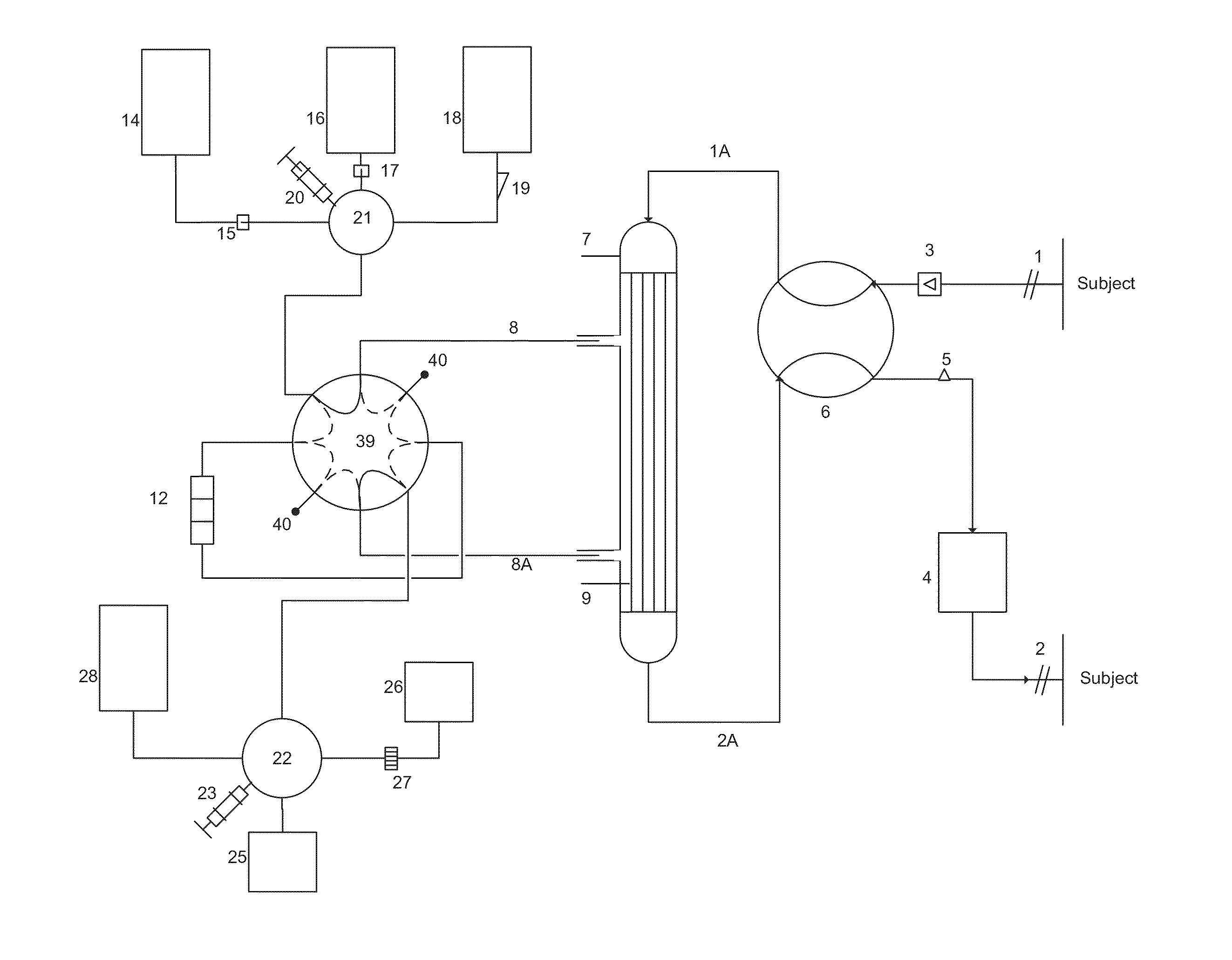
Apparatus and methods for imaging and attenuation correction
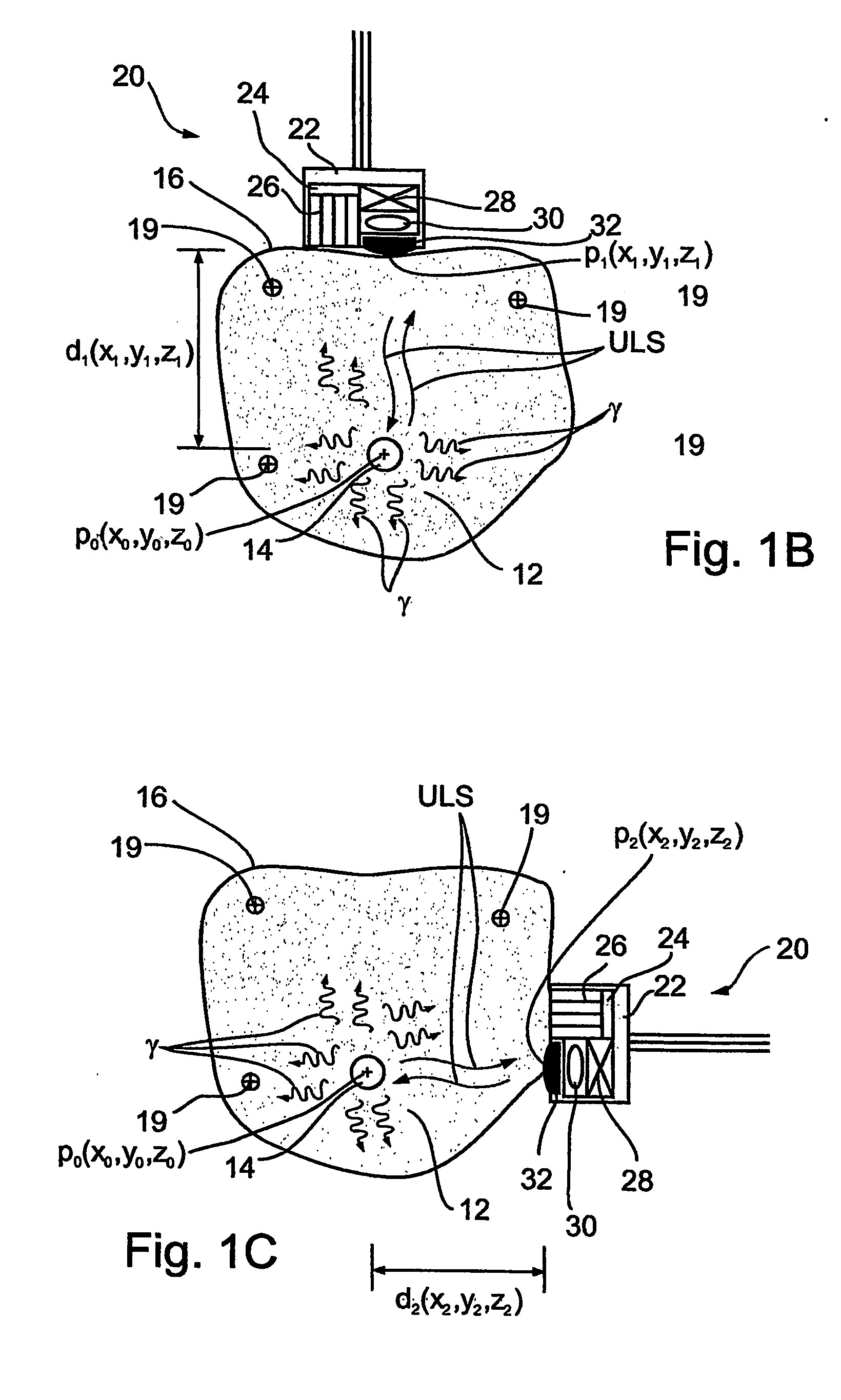
Imaging apparatus, is provided, comprising a first device, for obtaining a first image, by a first modality, selected from the group consisting of SPECT, PET, CT, an extracorporeal gamma scan, an extracorporeal beta scan, x-rays, an intracorporeal gamma scan, an intracorporeal beta scan, an intravascular gamma scan, an intravascular beta scan, and a combination thereof, and a second device, for obtaining a second, structural image, by a second modality, selected from the group consisting of a three-dimensional ultrasound, an MRI operative by an internal magnetic field, an extracorporeal ultrasound, an extracorporeal MRI operative by an external magnetic field, an intracorporeal ultrasound, an intracorporeal MRI operative by an external magnetic field, an intravascular ultrasound, and a combination thereof, and wherein the apparatus further includes a computerized system, configured to construct an attenuation map, for the first image, based on the second, structural image. Additionally, the computerized system is configured to display an attenuation-corrected first image as well as a superposition of the attenuation-corrected first image and the second, structural image. Furthermore, the apparatus is operative to guide an in-vivo instrument based on the superposition.
Owner:SPECTRUM DYNAMICS MEDICAL LTD
Usage of Extracorporeal and Intracorporeal Pressure Shock Waves in Medicine
ActiveUS20110034832A1Reduce inflammationPromote nerve regenerationUltrasound therapyPneumatic massageMedicineFocal volume
A shock wave applicator includes a shock wave generator and an asymmetrical reflector portion in a housing. Asymmetry of the reflector portion is combined with one or more wave generators to produce a variety of focal volumes and wave fronts for medical treatment.
Owner:SANUWAVE INC
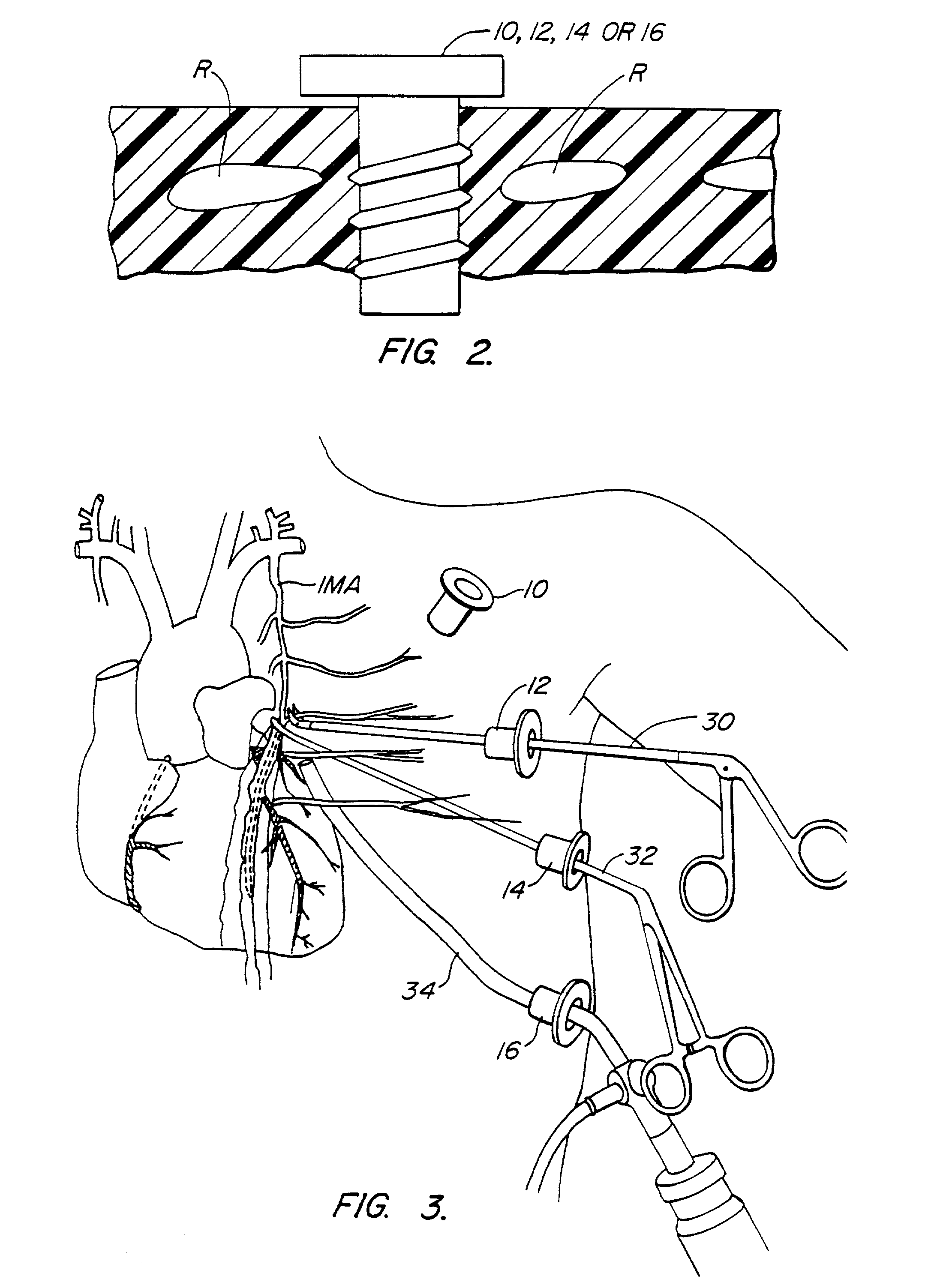
Methods and systems for performing thoracoscopic coronary bypass and other procedures
InactiveUS6027476AImprove isolationReduce complicationsSuture equipmentsCannulasThoracoscopeHeart operations
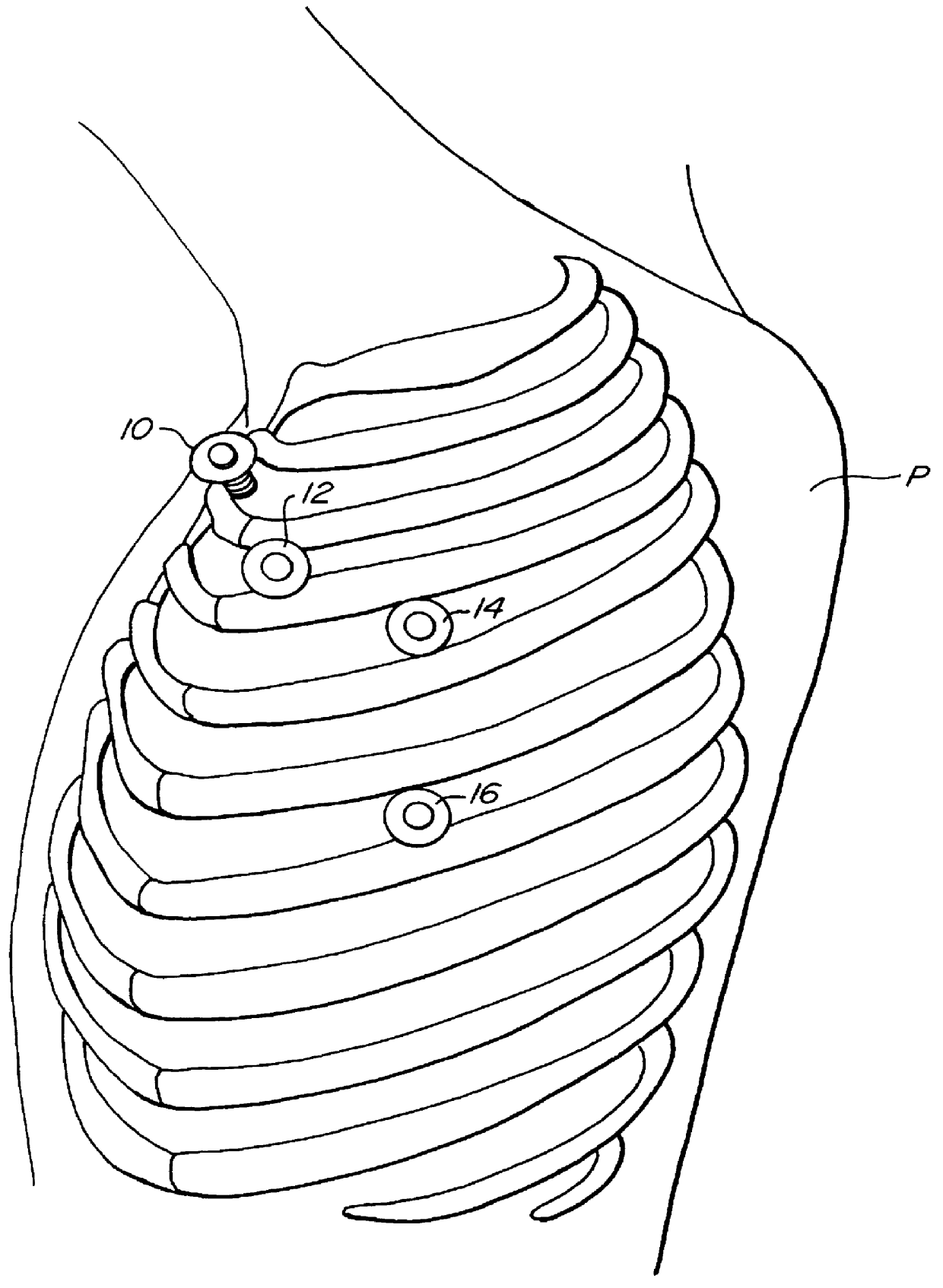
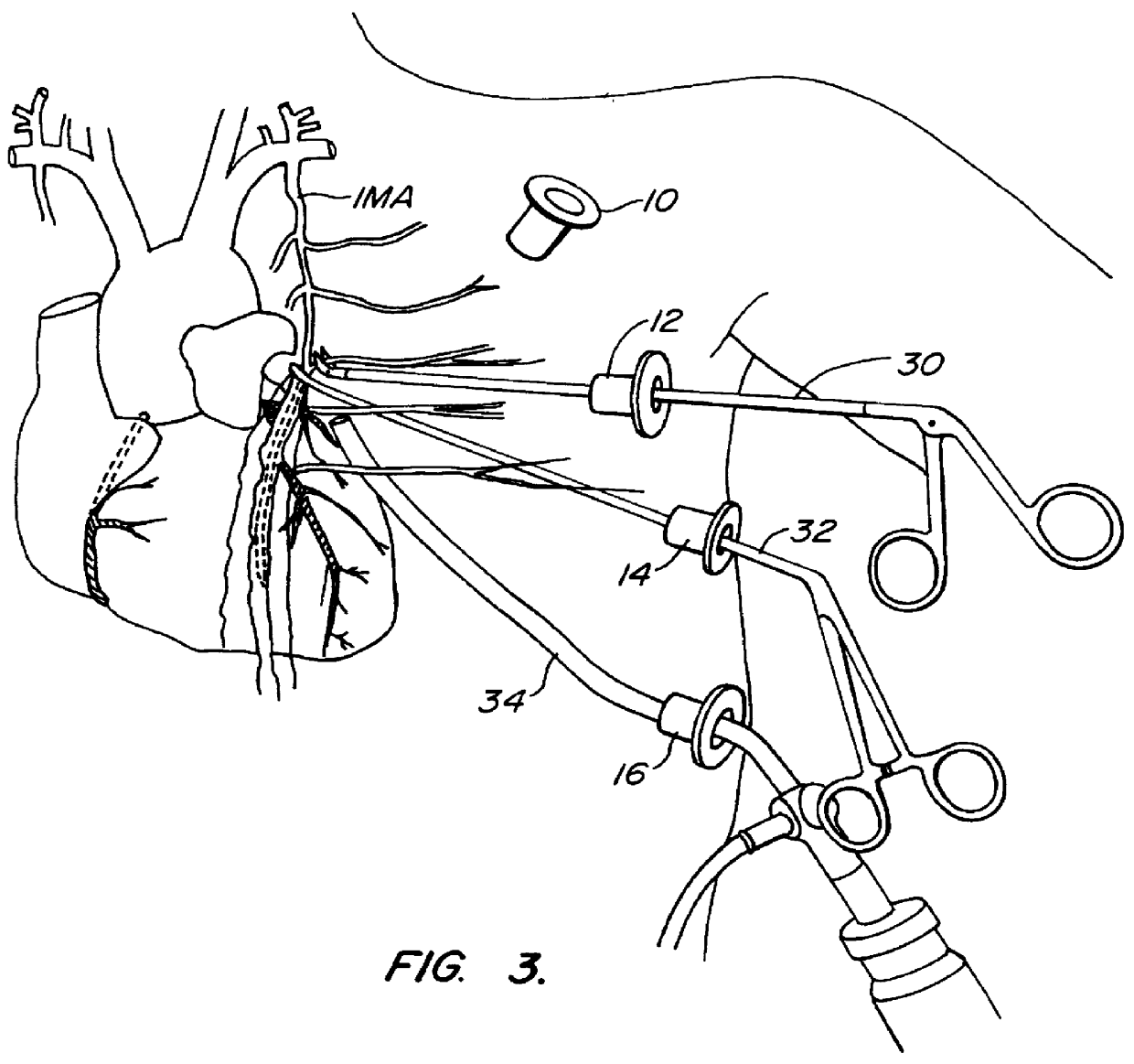
A method for closed-chest cardiac surgical intervention relies on viewing the cardiac region through a thoracoscope or other viewing scope and endovascularly partitioning the patient's arterial system at a location within the ascending aorta. The cardiopulmonary bypass and cardioplegia can be induced, and a variety of surgical procedures performed on the stopped heart using percutaneously introduced tools. The method of the present invention will be particularly suitable for forming coronary artery bypass grafts, where an arterial blood source is created using least invasive surgical techniques, and the arterial source is connected to a target location within a coronary artery while the patient is under cardiopulmonary bypass and cardioplegia.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Intraoral apparatus for non-invasive blood and saliva monitoring & sensing
Controlled-specimen-sampling oral devices are described, implanted or inserted into an oral cavity, built onto a prosthetic tooth crown, a denture plate, braces, a dental implant, or the like. The devices are replaced as needed. The controlled specimen sampling may be passive, based on a dosage form, or electro-mechanically controlled, for a high-precision, intelligent, specimen sampling. Additionally, the controlled sampling may be any one of the following: sampling in accordance with a preprogrammed regimen, sampling at a controlled rate, delayed sampling, pulsatile sampling, chronotherapeutic sampling, closed-loop sampling, responsive to a sensor's input, sampling on demand from a personal extracorporeal system, sampling regimen specified by a personal extracorporeal system, sampling on demand from a monitoring center, via a personal extracorporeal system, and sampling regimen specified by a monitoring center, via a personal extracorporeal system. Specimen collection in the oral cavity may be assisted or induced by a transport mechanism, such as any one of, or a combination of iontophoresis, electroosmosis, electrophoresis, electroporation, sonophoresis, and ablation. The oral devices require replacement at relatively long intervals of weeks or months. The oral devices and methods for controlled specimen sampling apply to humans and animals.
Owner:BEISKI BEN ZION +1
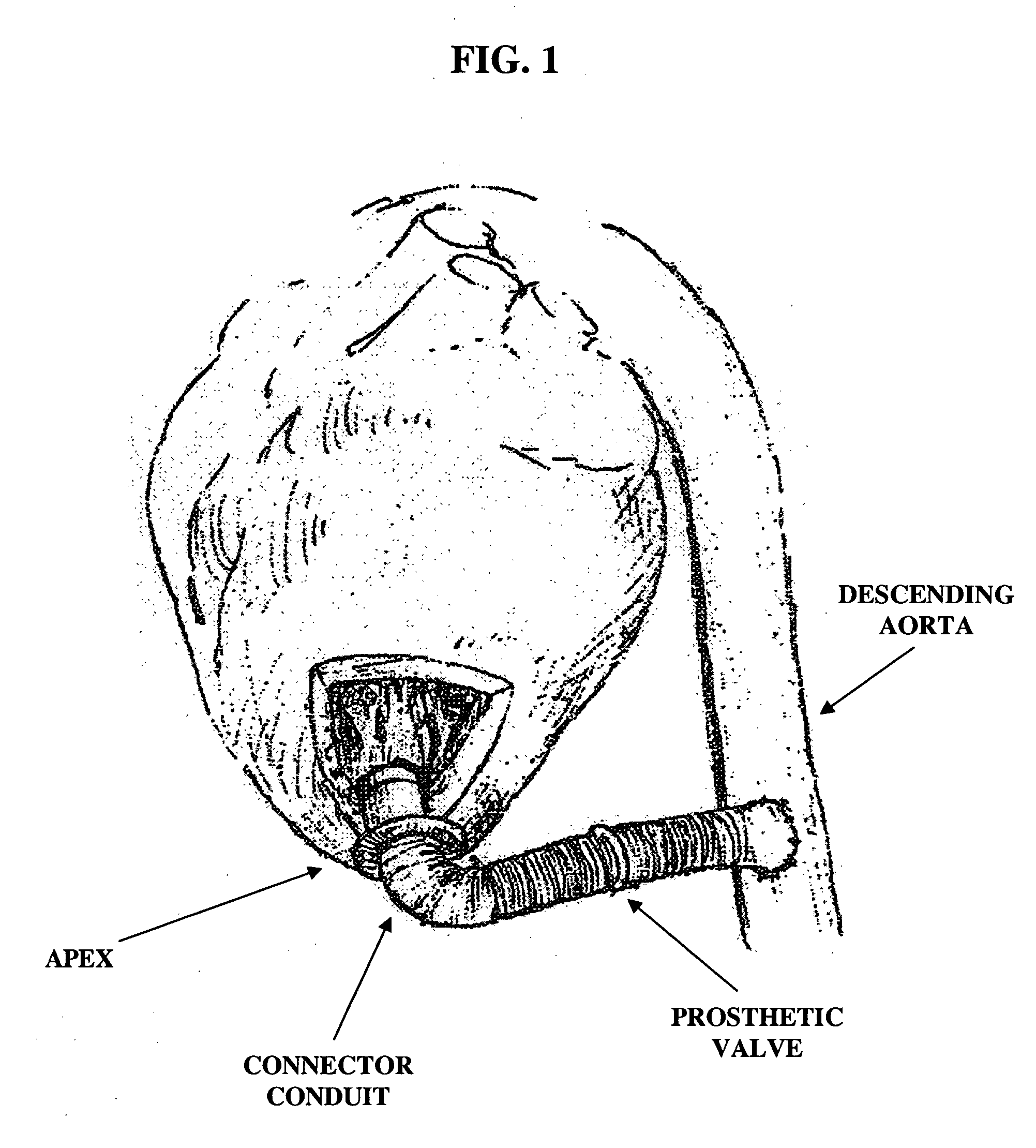
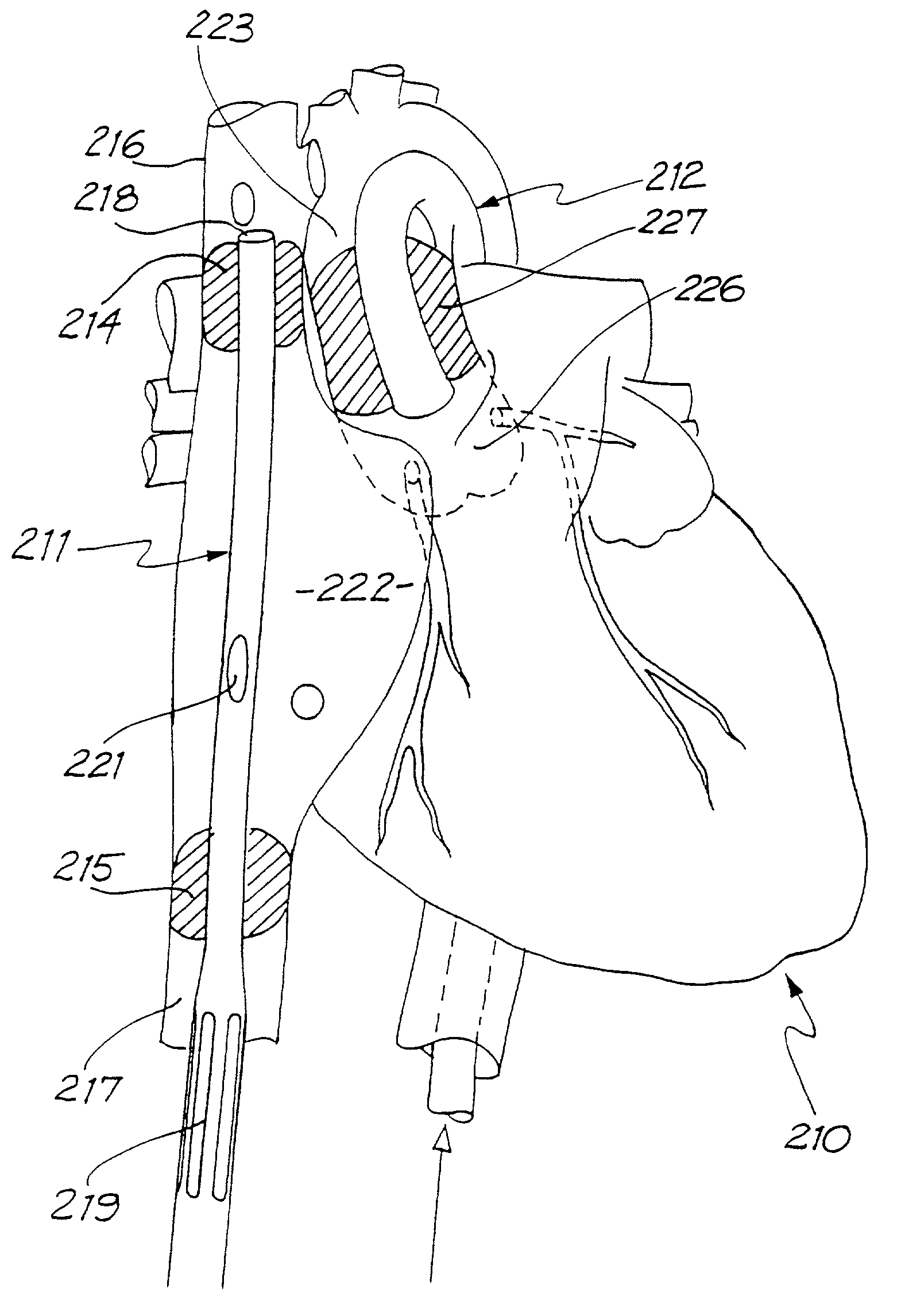
Apparatus and method for connecting a conduit to a hollow organ
InactiveUS20050251187A1Easy to optimizeReduce the possibilitySurgical instrument detailsExcision instrumentsExtracorporeal circulationProsthetic valve
An apparatus and method for connecting a first conduit to the heart without the need for cardiopulmonary bypass. The first conduit may then be attached to a second conduit that has a prosthetic device interposed. The second conduit may be connected to the aorta prior to the first conduit being attached to the heart. The prosthetic device may be a prosthetic valve or a pump, for example. The apparatus of the present invention includes an implantable connector with first conduit component, a retractor expansion component, a coring component, and a pushing component. The retractor expansion component is slide-ably coupled to the coring component. The retractor expansion component serves to seat against and separate the inside apical wall of the left ventricle so that the coring component may cut cleanly through the myocardium to form a tissue plug without leaving any hanging attachments to the inside walls. By remaining seated against the inside wall, the retractor expansion component follows the tissue plug into the coring component. The surgeon applies force and rotary motion to the pushing component sufficient to cut the tissue plug and implant the prosthetic component.
Owner:CORREX
Apparatus and methods for imaging and attenuation correction
InactiveUS7652259B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementDiagnostic Radiology ModalitySonification
Owner:SPECTRUM DYNAMICS MEDICAL LTD
Methods and systems for performing thoracoscopic coronary bypass and other procedures
InactiveUS20020013569A1Reduce complicationsEvenly distributedSuture equipmentsCannulasSurgical operationCoronary artery graft bypass
A method for closed-chest cardiac surgical intervention relies on viewing the cardiac region through a thoracoscope or other viewing scope and endovascularly partitioning the patient's arterial system at a location within the ascending aorta. The cardiopulmonary bypass and cardioplegia can be induced, and a variety of surgical procedures performed on the stopped heart using percutaneously introduced tools. The method of the present invention will be particularly suitable for forming coronary artery bypass grafts, where an arterial blood source is created using least invasive surgical techniques, and the arterial source is connected to a target location within a coronary artery while the patient is under cardiopulmonary bypass and cardioplegia
Owner:HEARTPORT
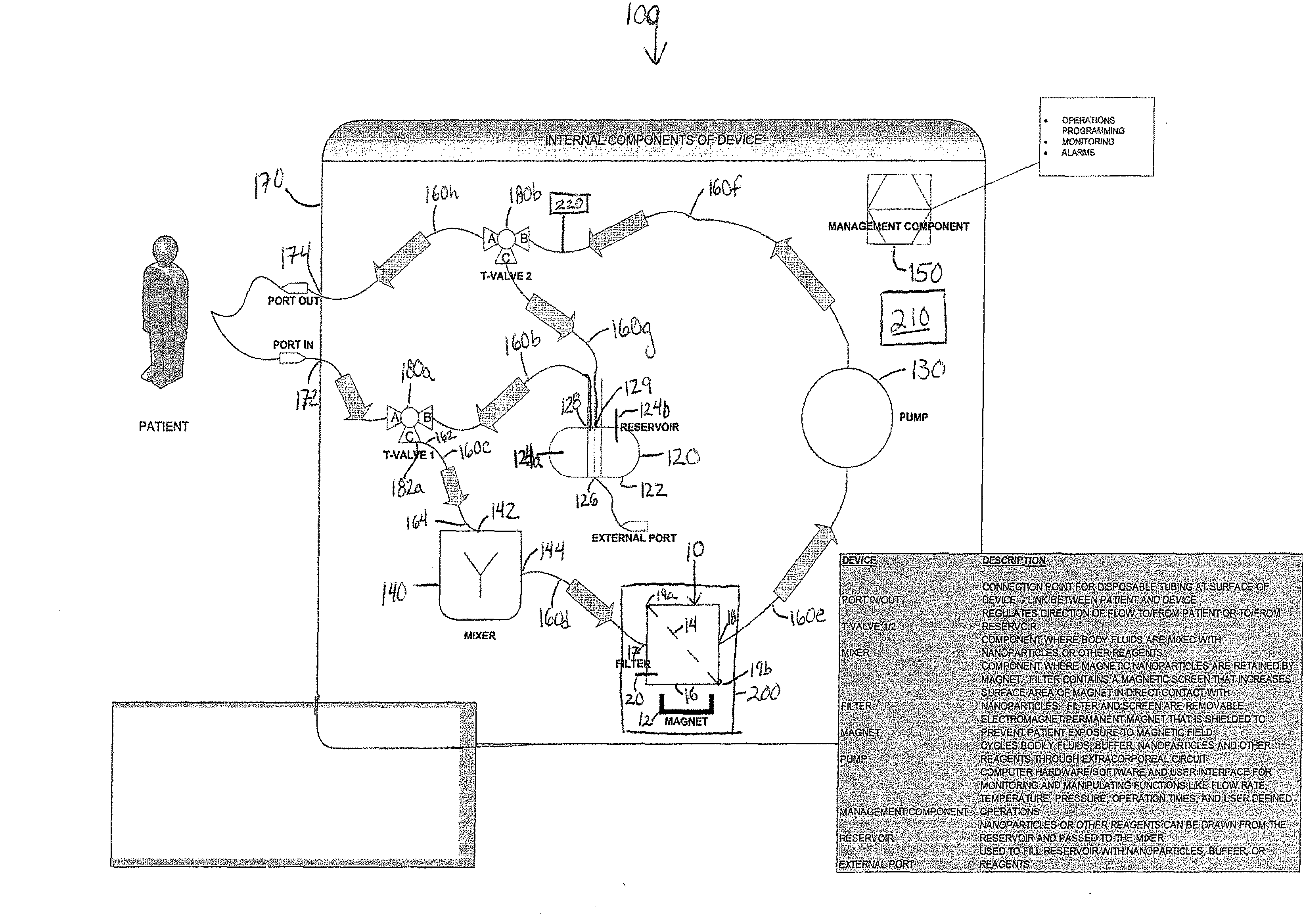
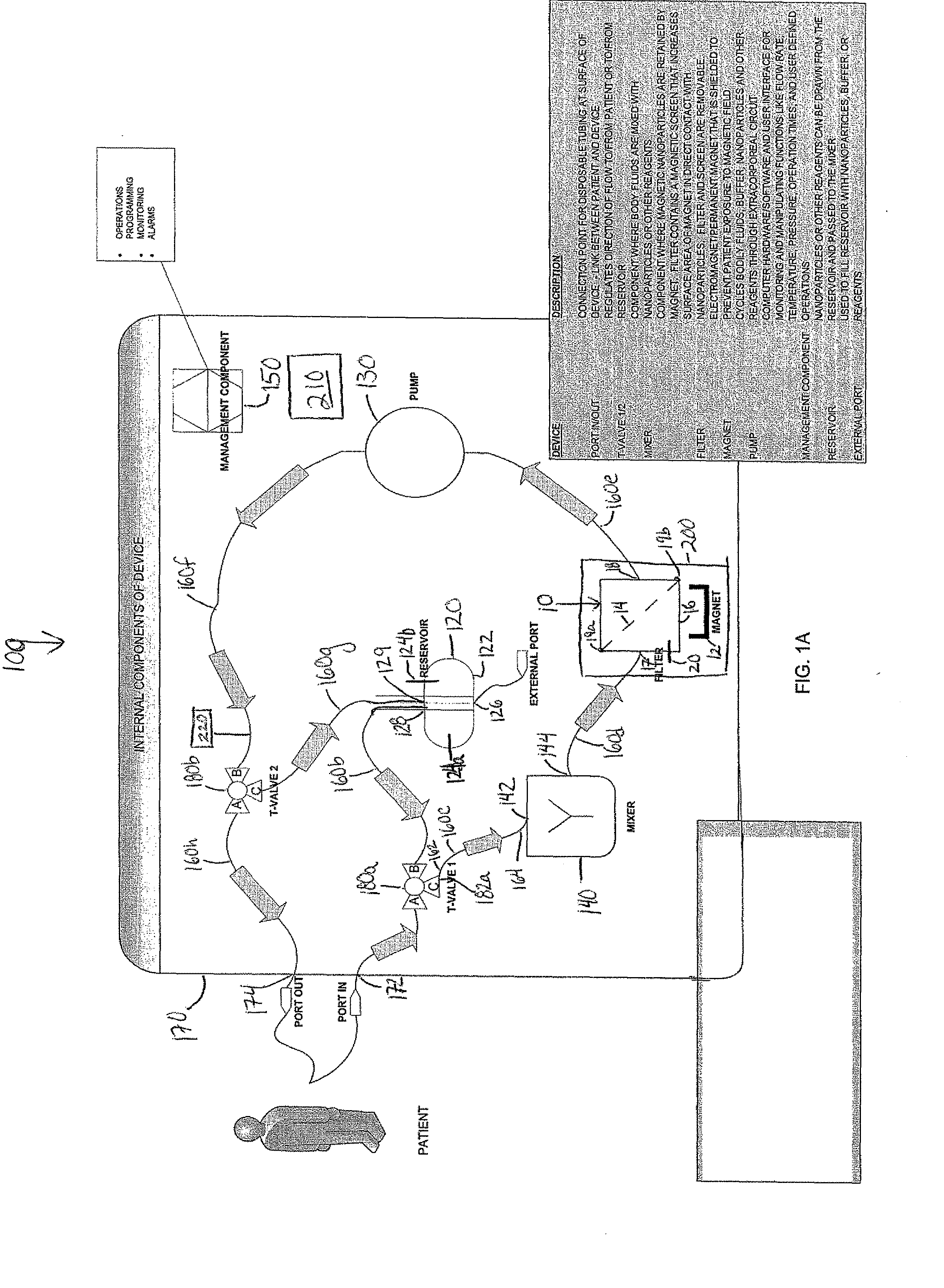
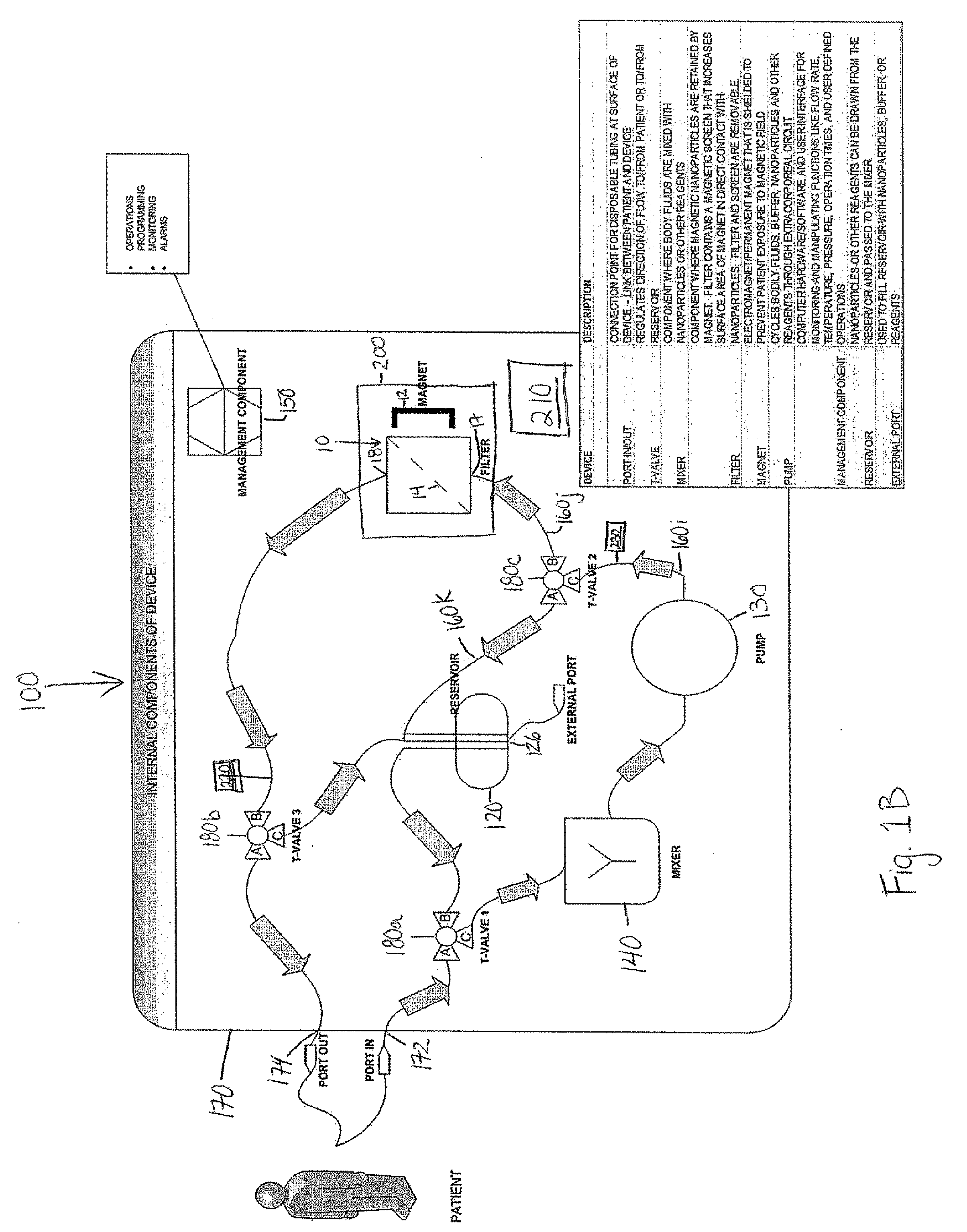
Device and method of using superparamagnetic nanoparticles in treatment and removal of cells
InactiveUS20110098623A1Simple methodAntibacterial agentsOther blood circulation devicesCancer cellFunctionalized nanoparticles
Methods and devices for selectively removing from a subject a target cell, pathogen, or virus expressing a binding partner on its surface are presented. In one embodiment, the device contains an excorporeal circuit, which includes, at least, a magnetic filter comprising a magnet and a removable, magnetizable substrate capable of capturing magnetic nanomaterials; and a pump in fluid communication with the magnetic filter, wherein the pump moves fluid through the excorporeal circuit. The magnet is capable of generating a magnetic field sufficient to capture magnetic nanomaterials in the magnetic field. In a preferred embodiment, the target cells are cancer cells and / or cells infected with pathogenic agents. The devices may be designed for extracorporeal or in vivo uses. Functionalized superparamagnetic nanoparticles are either mixed ex vivo with a biological fluid from the patient or injected into the patient. Then the biological fluid, which includes the nanoparticles is transported to the magnetic filter to remove any nanoparticles that are complexed to the target cells, pathogens, or virus, and any free nanoparticles. Optionally, the functionalized nanoparticles contain and deliver a therapeutic agent. In one embodiment, the therapeutic agent is released when the nanoparticle binds to the target cells, pathogens, or virus.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
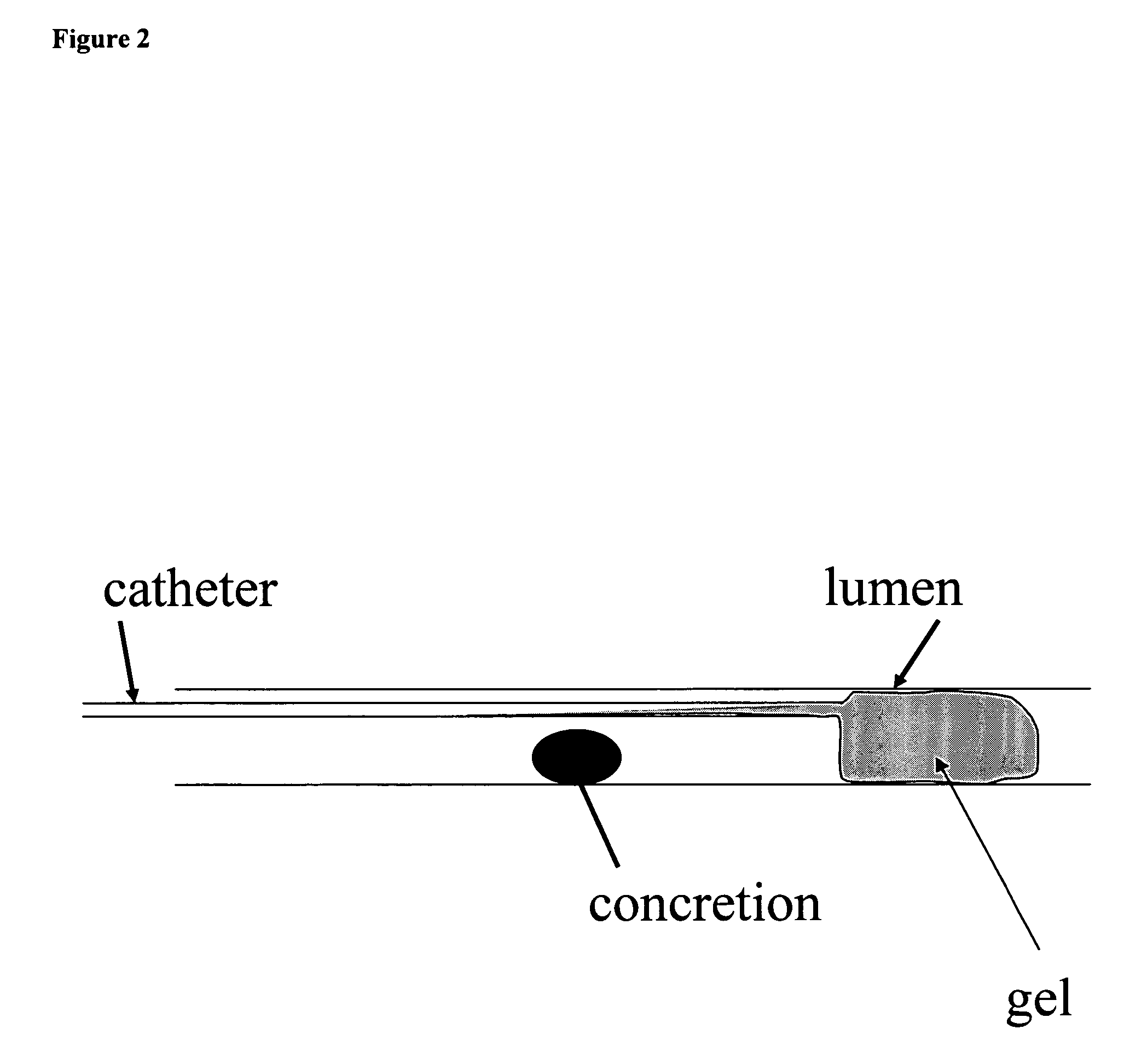
Confinement of kidney-stone fragments during lithotripsy
InactiveUS20050143678A1Surgical drugsChiropractic devicesIntracorporeal lithotripsyThermosensitive polymer
The present invention improves significantly the success rate of lithotripsy and reduces the risk of tissue damage, by injecting temporary plugs in front and behind a concretion (for extracorporeal lithotripsy) or behind a concretion (for intracorporeal lithotripsy). One aspect of the present invention relates to injecting an inverse thermosensitive polymer solution into a lumen, thereby preventing the migration of a concretion, or its fragments, upon extracorporeal or intracorporeal lithotripsy.
Owner:GENZYME CORP +1
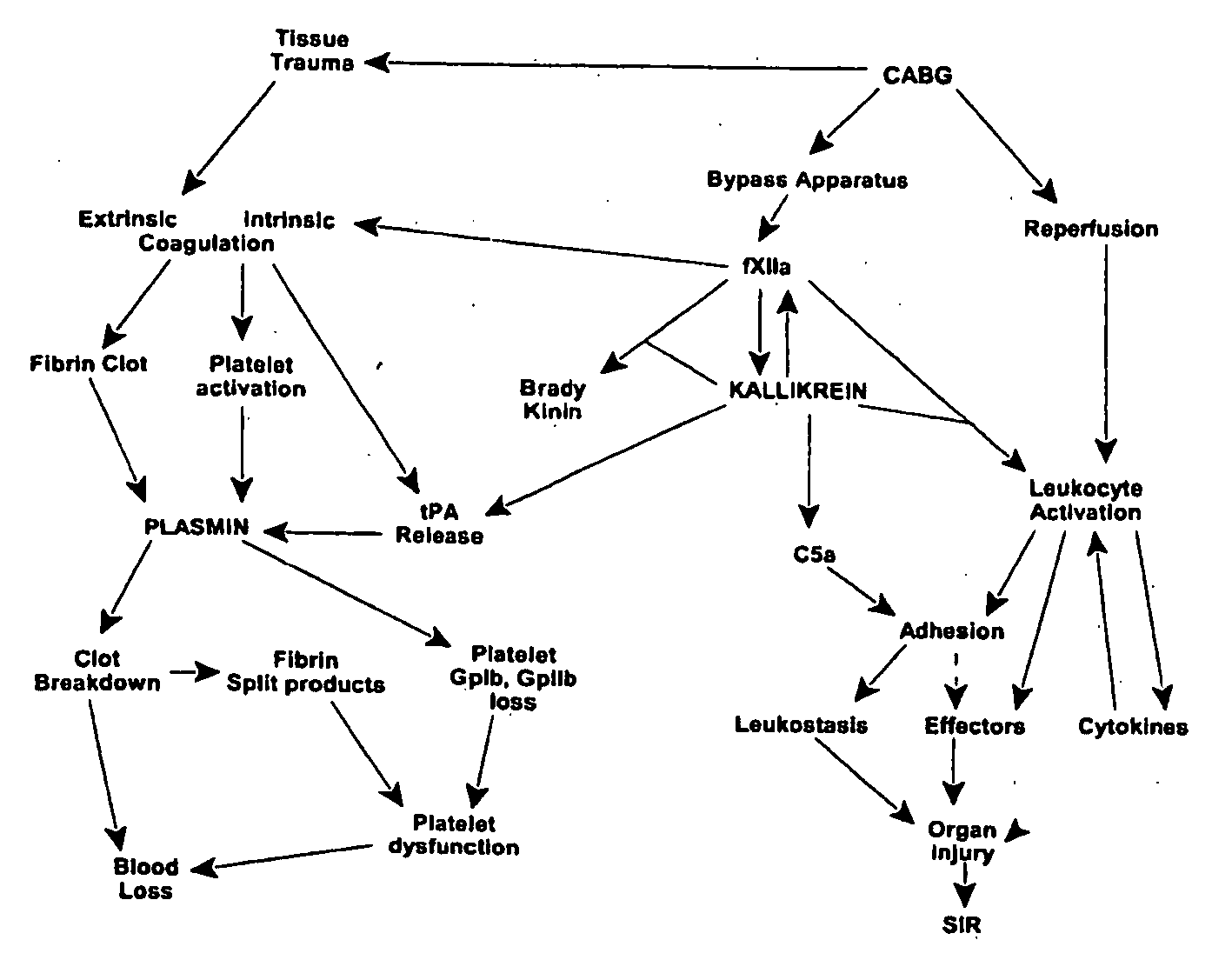
Prevention and reduction of blood loss
InactiveUS20080064637A1Nervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsWhole bodyCardiopulmonary bypass time
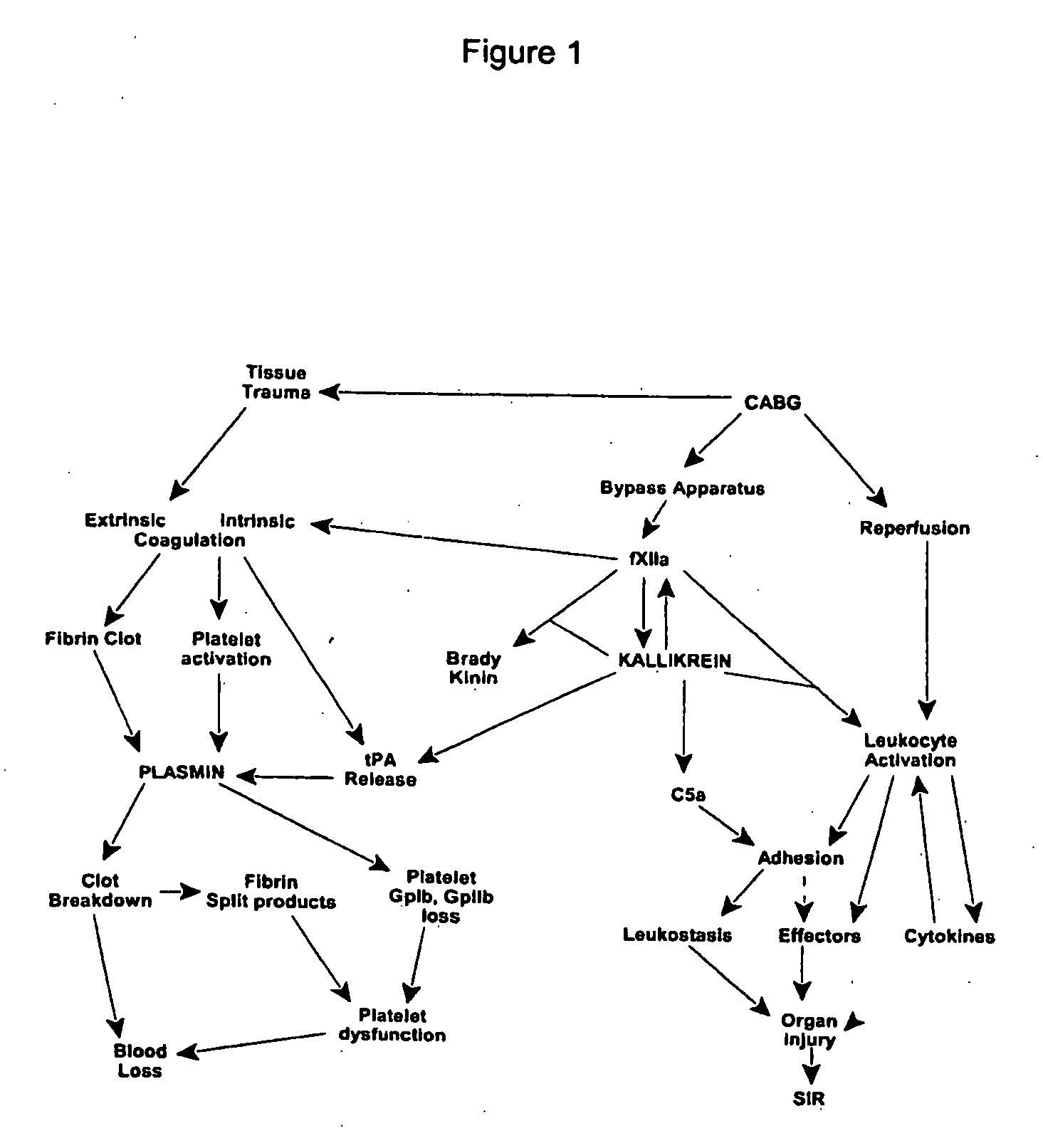
Methods are described for preventing or reducing ischemia and / or systemic inflammatory response in a patient such as perioperative blood loss and / or systemic inflammatory response in a patient subjected to cardiothoracic surgery, e.g. coronary artery bypass grafting and other surgical procedures, especially when such procedures involve extra-corporeal circulation, such as cardiopulmonary bypass.
Owner:DYAX CORP
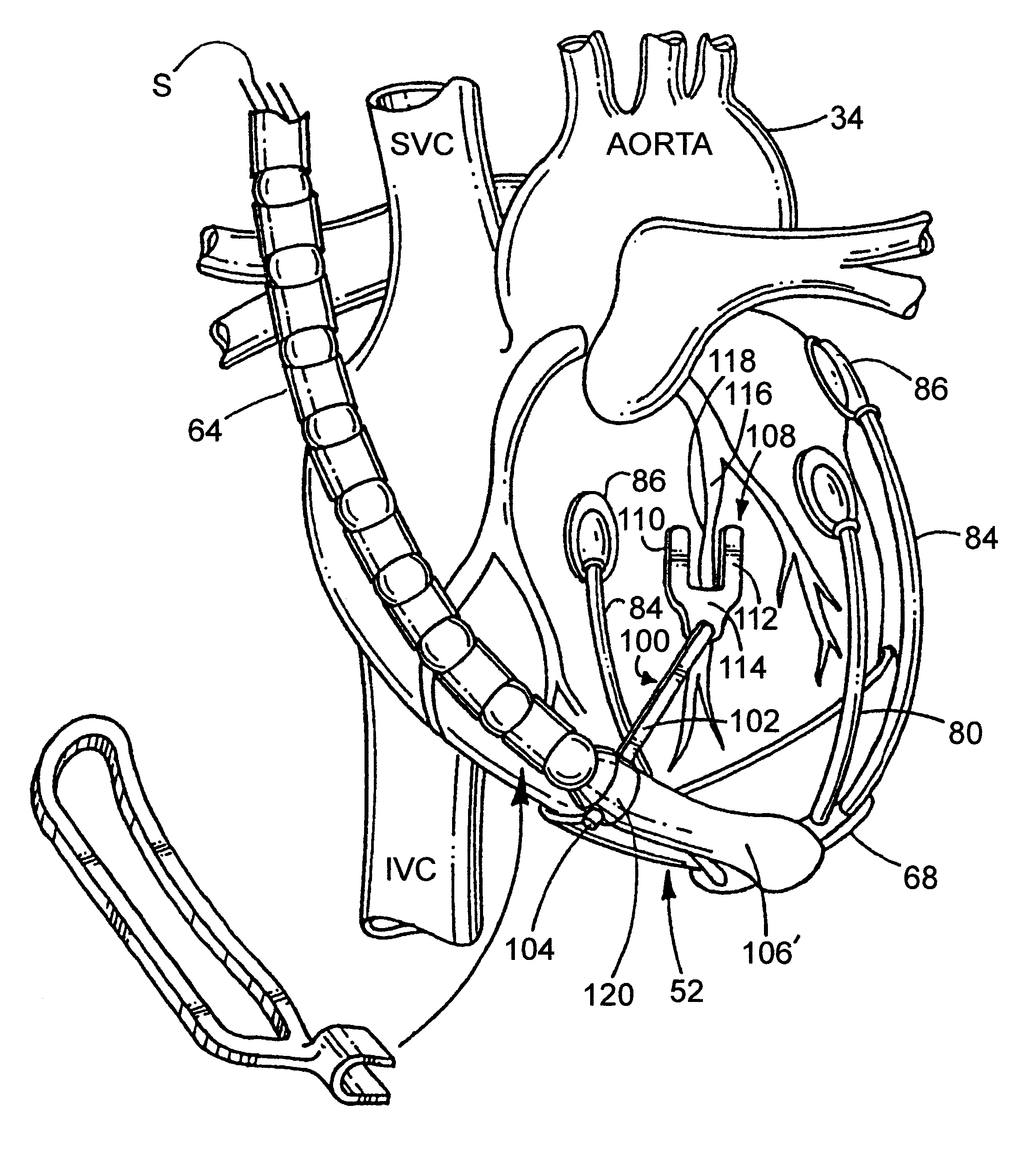
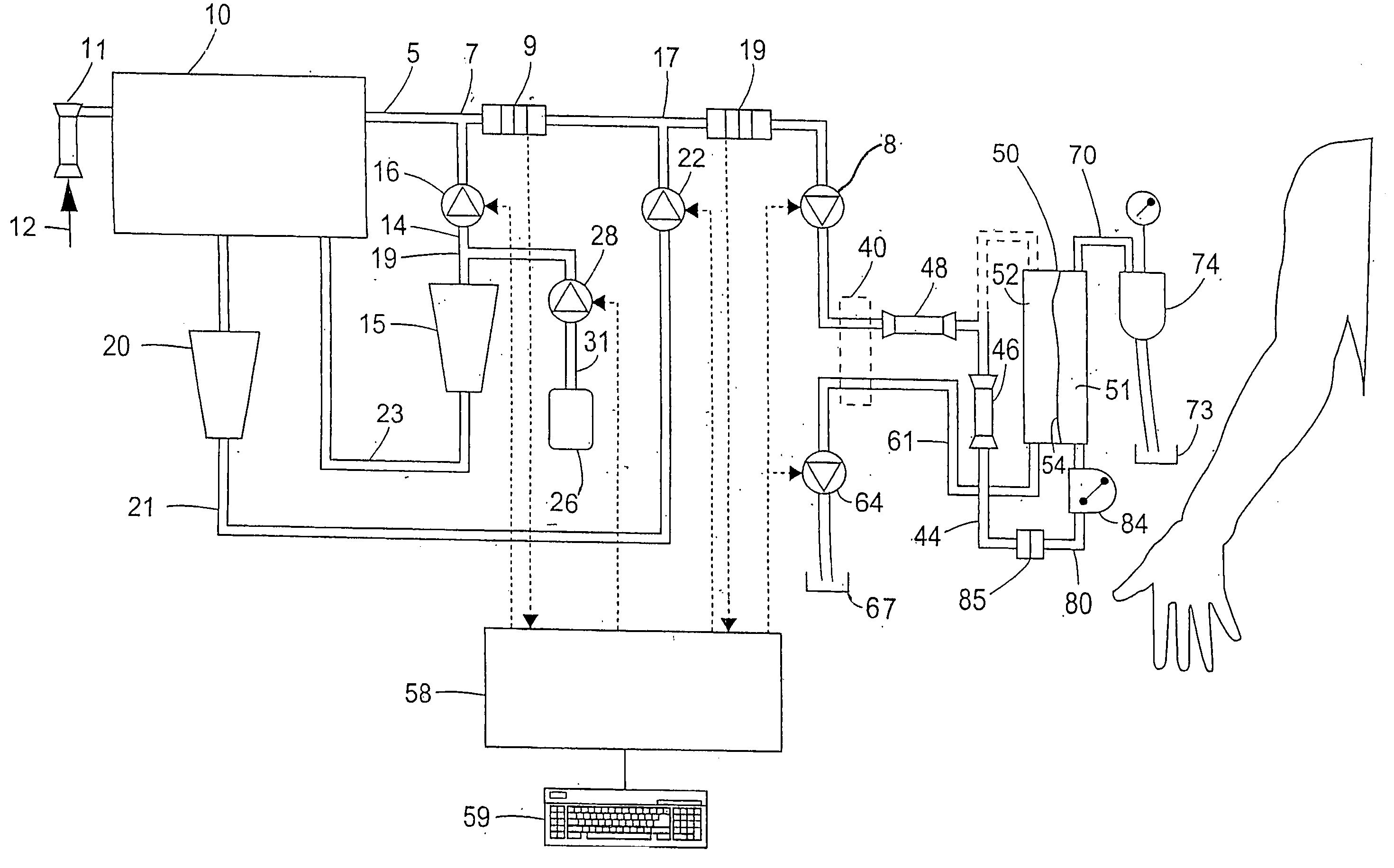
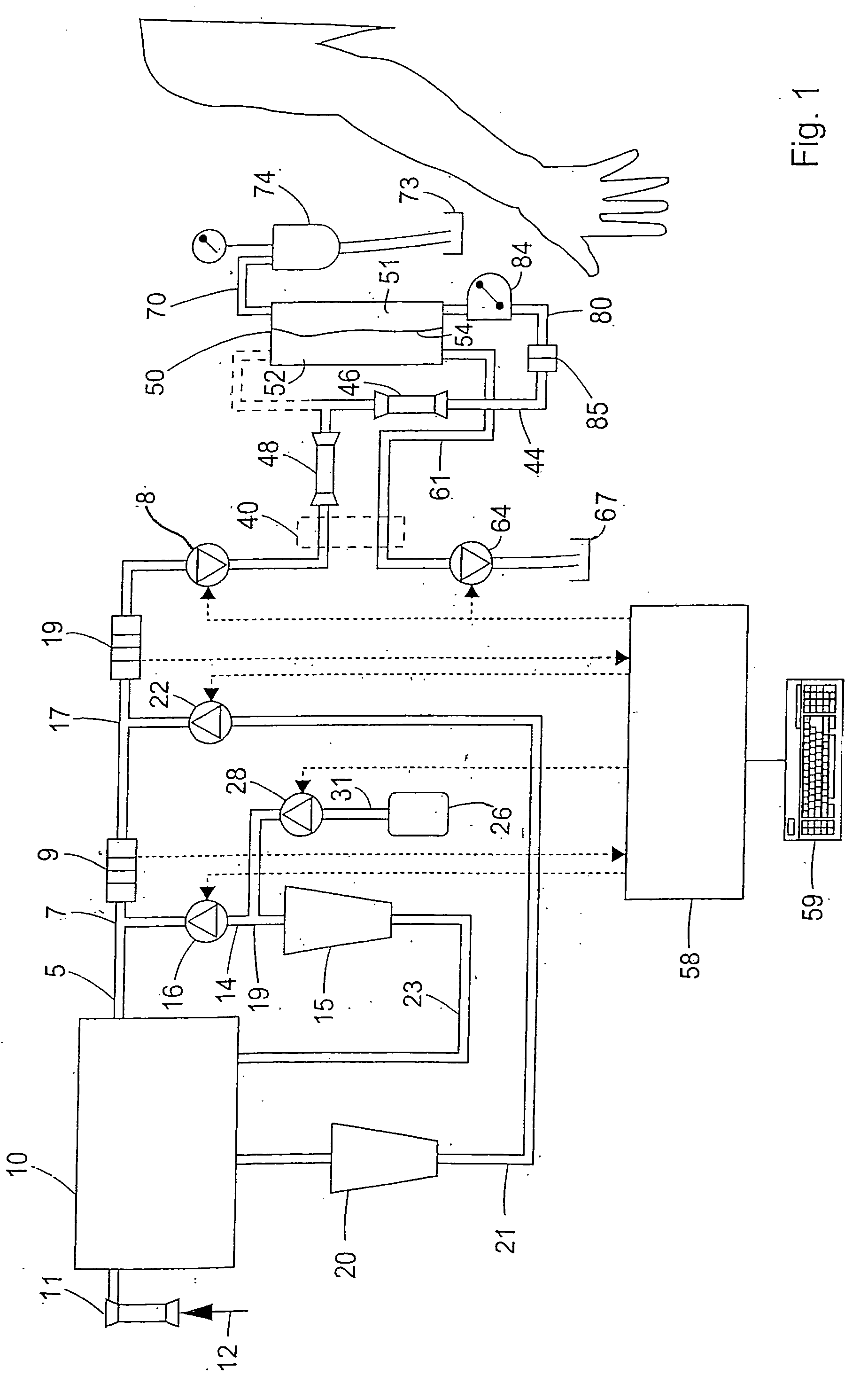
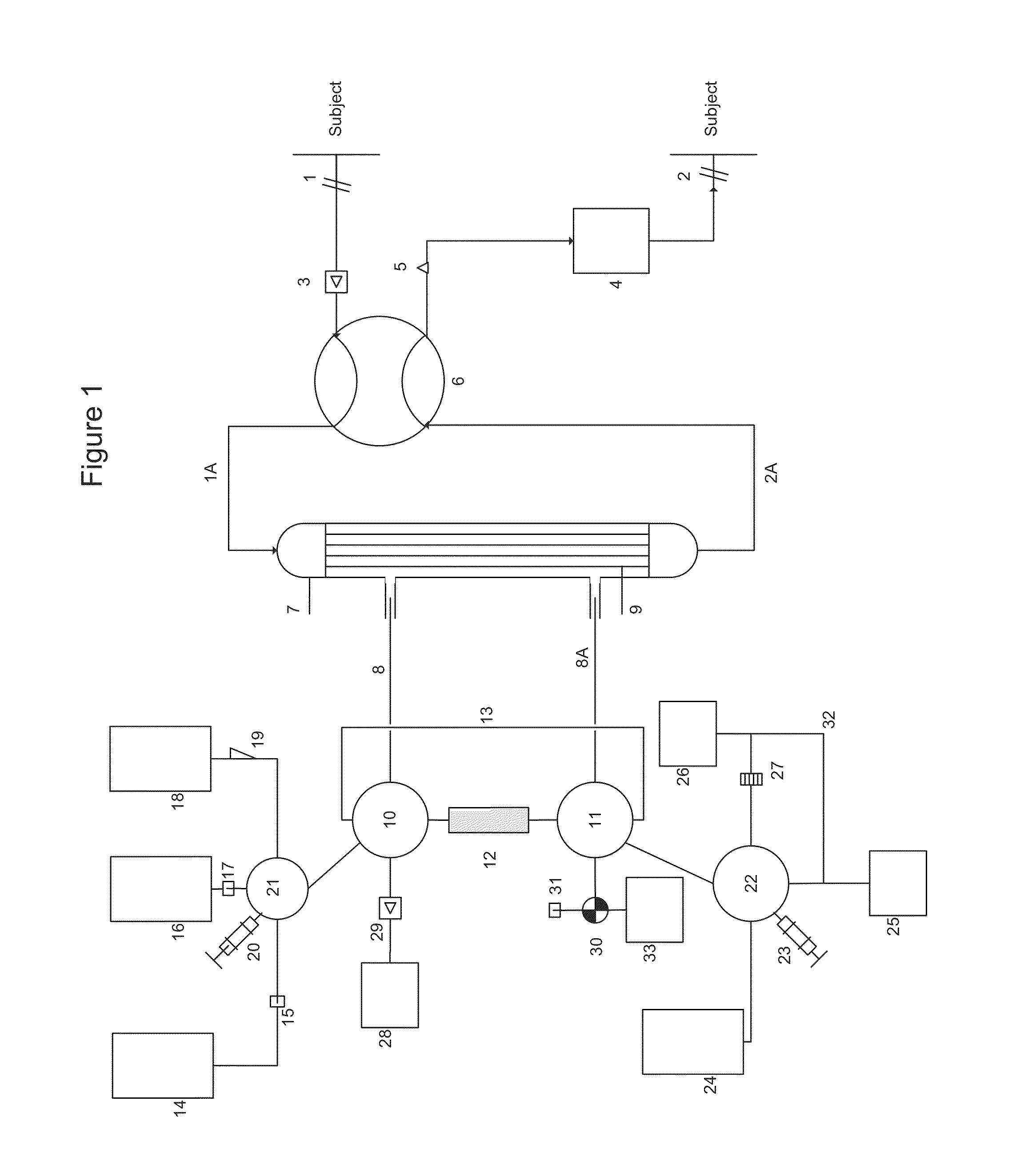
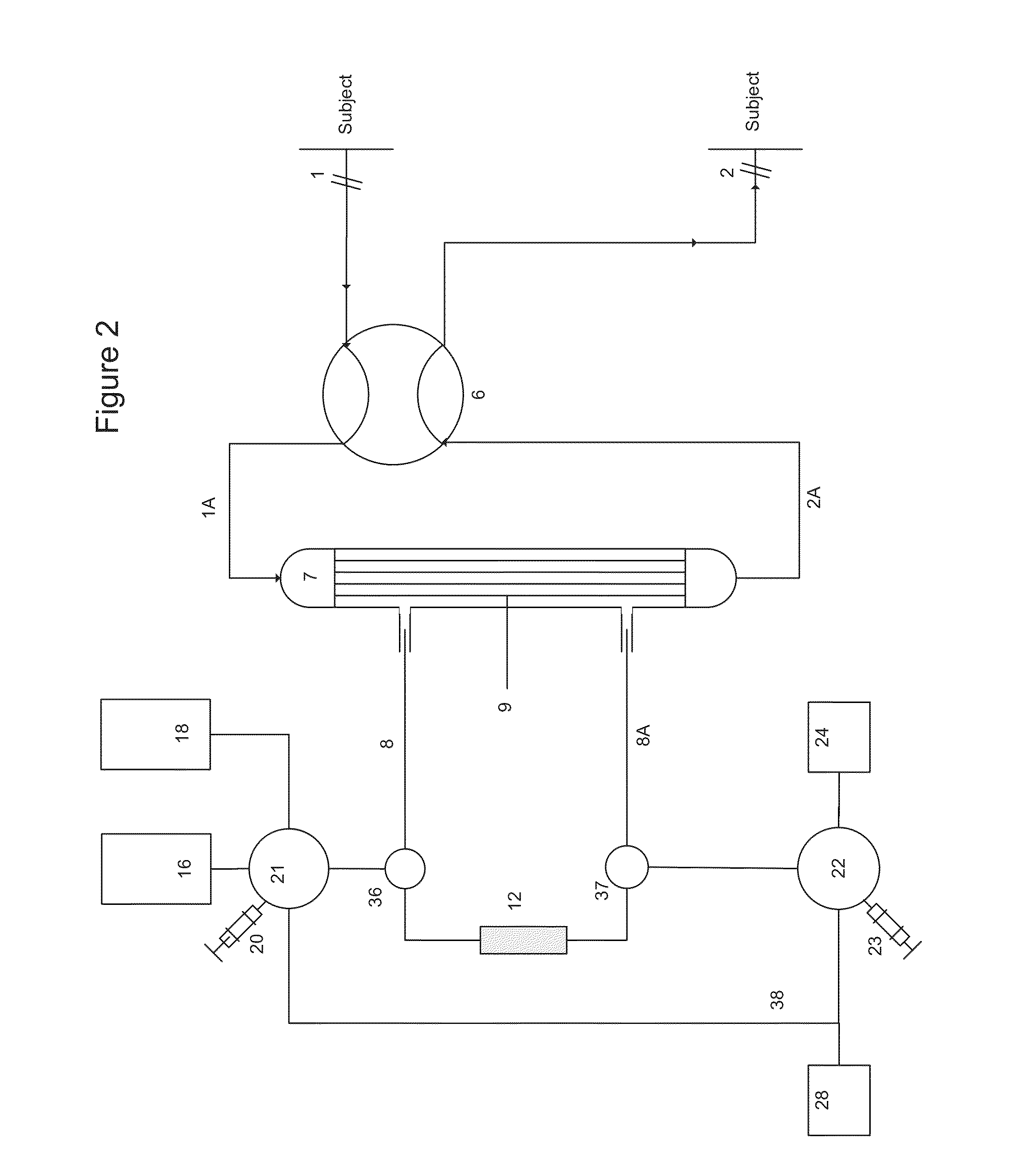
Apparatus for controlling blood flow in an extracorporeal circuit
ActiveUS7794419B2Semi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionExtracorporeal circulationAngular velocity
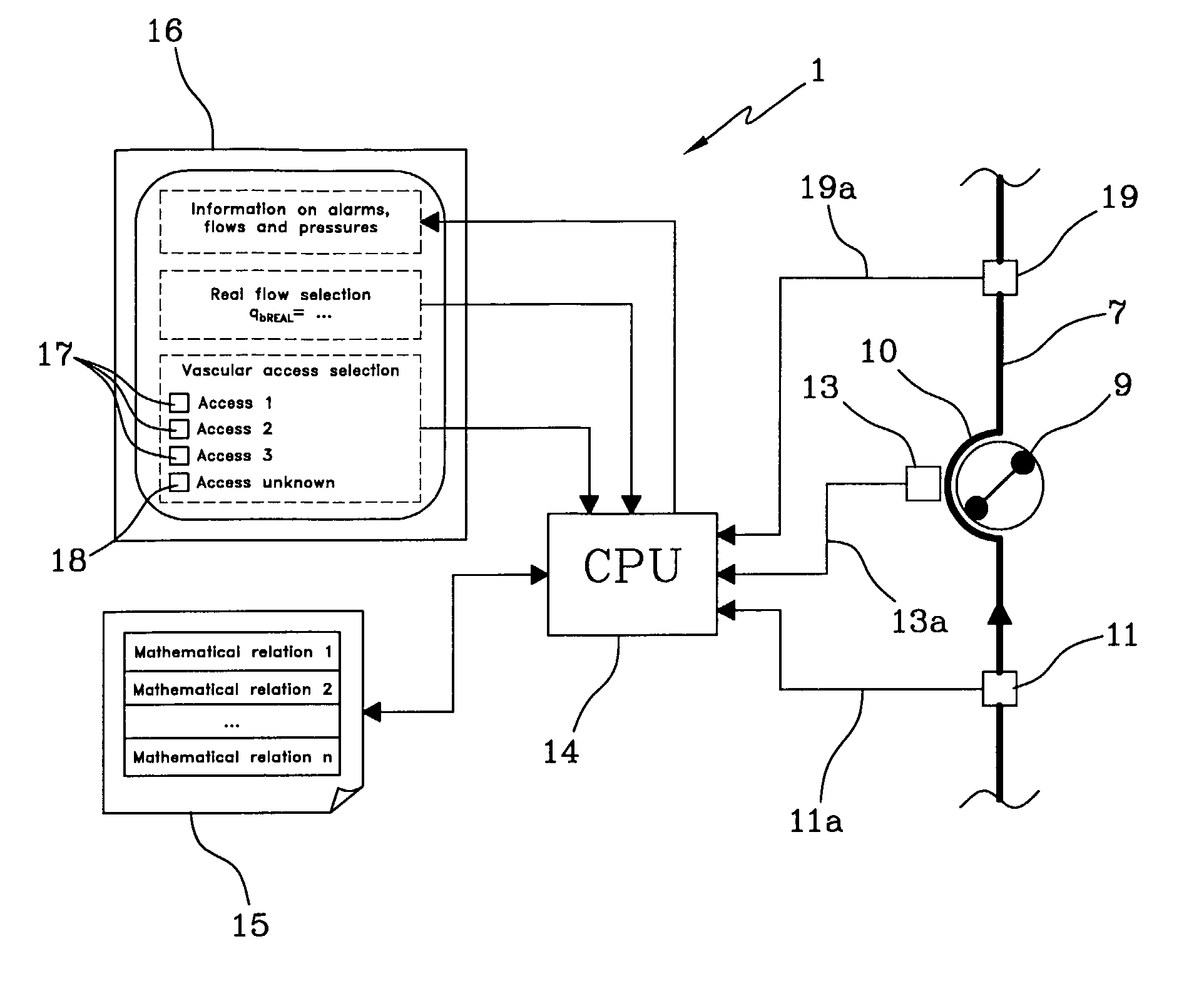
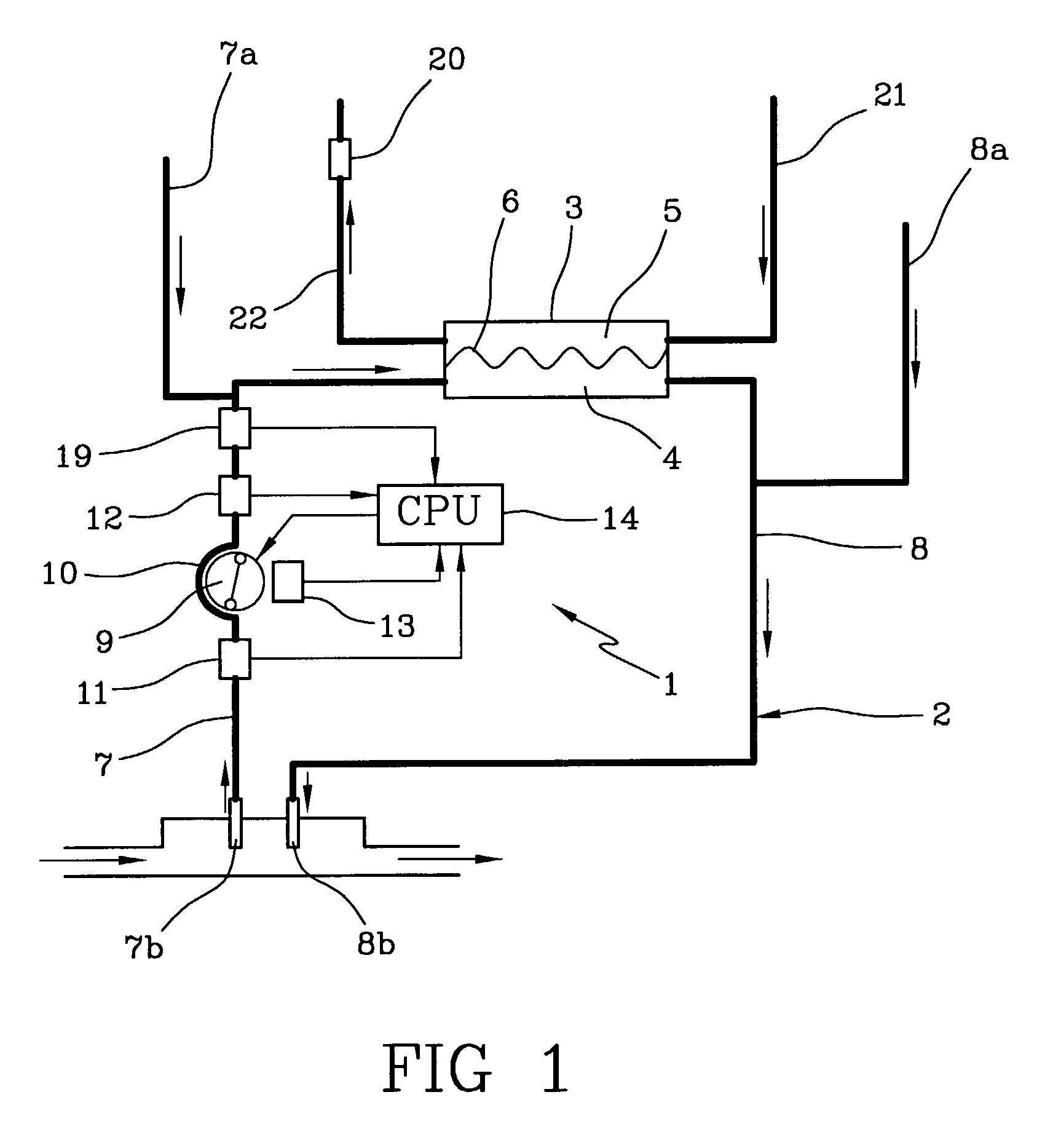
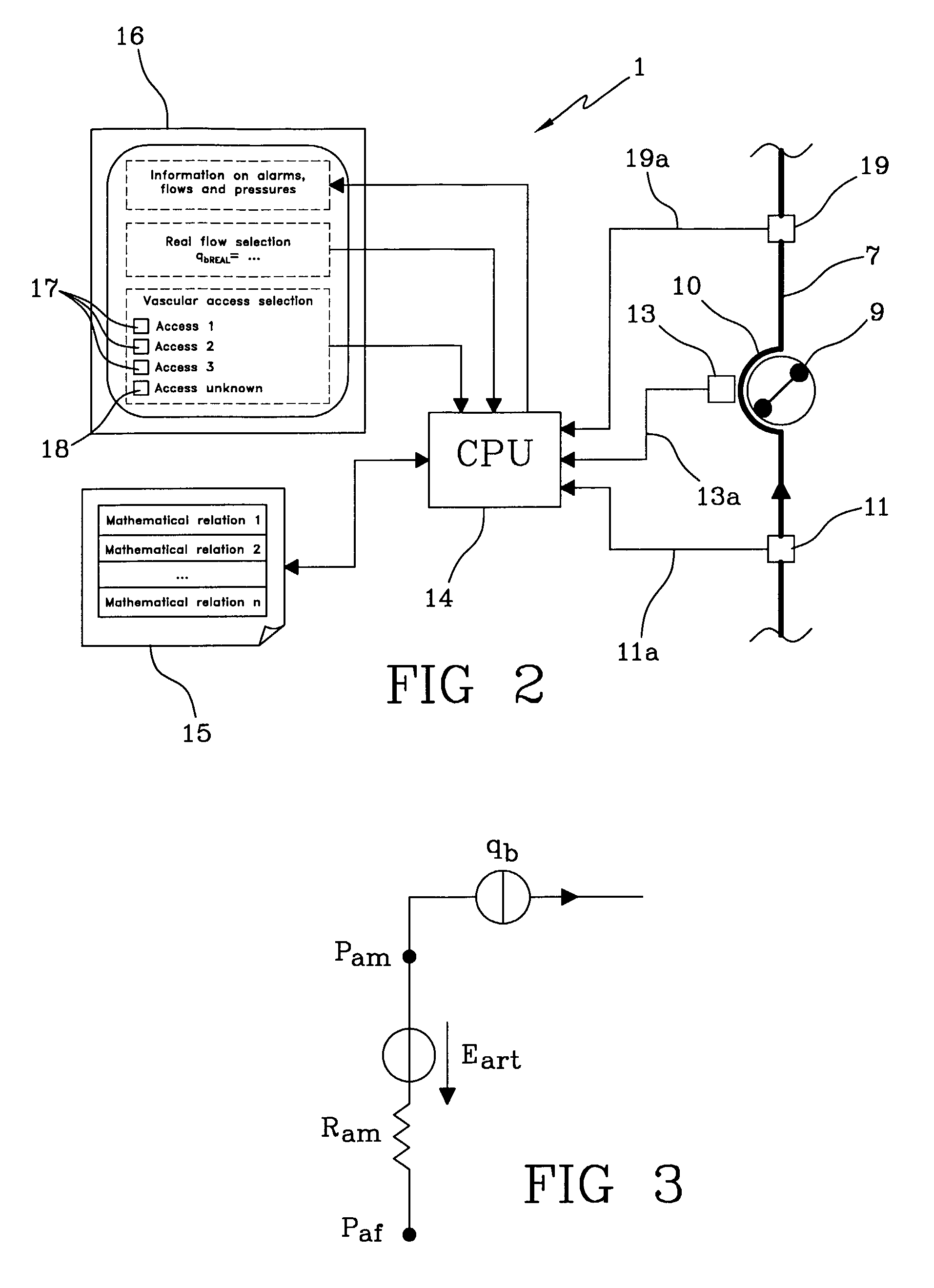
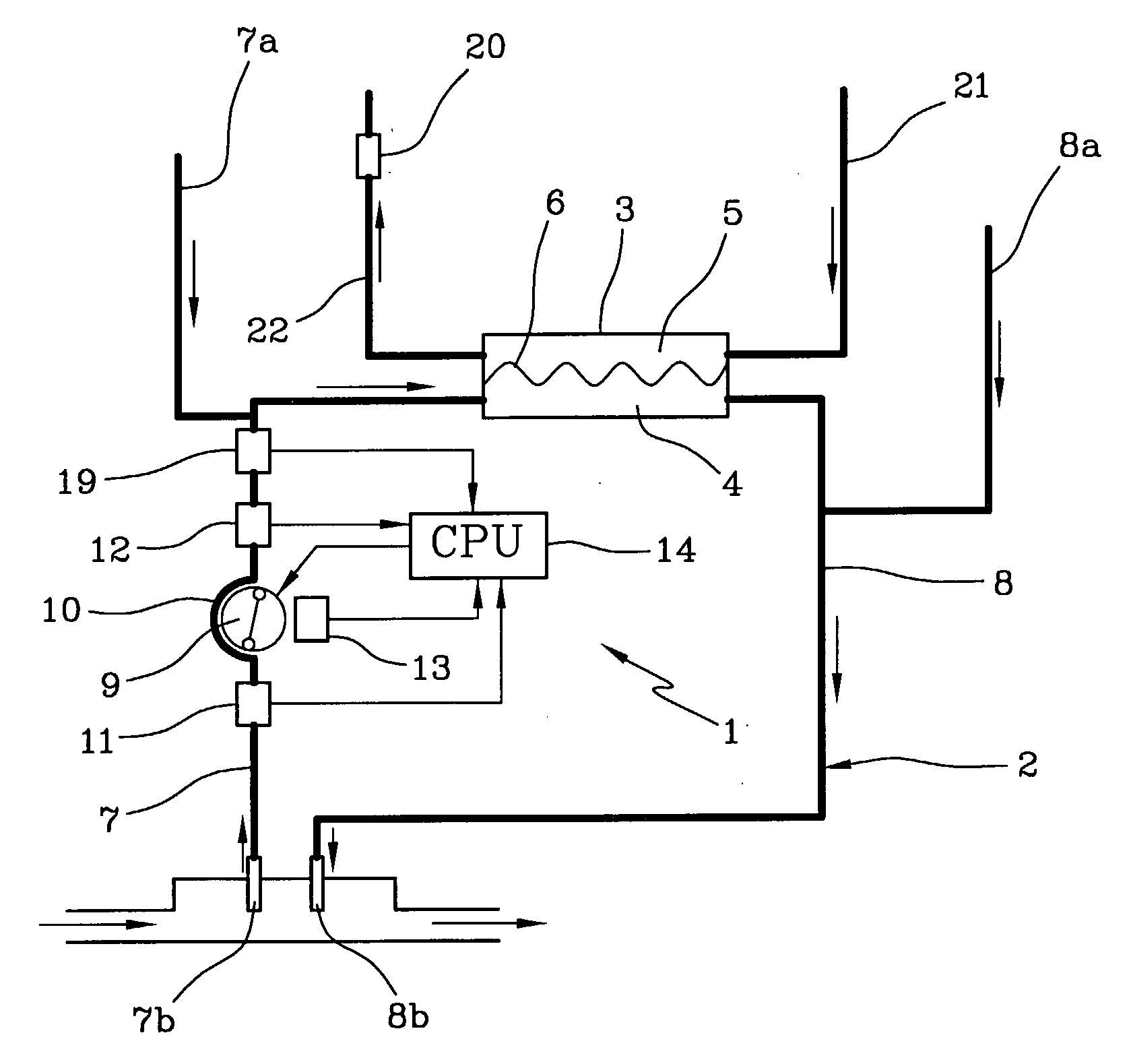
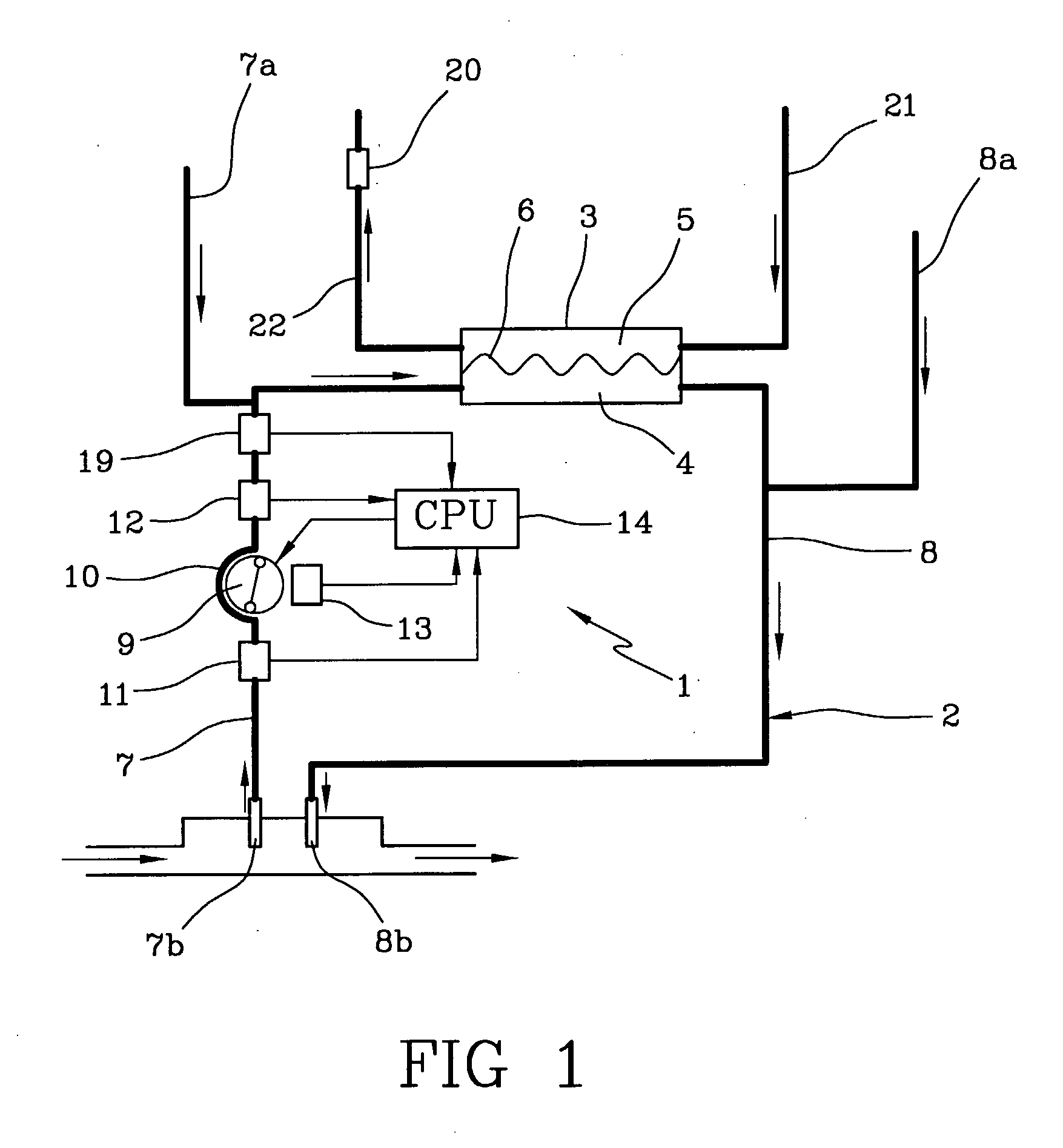
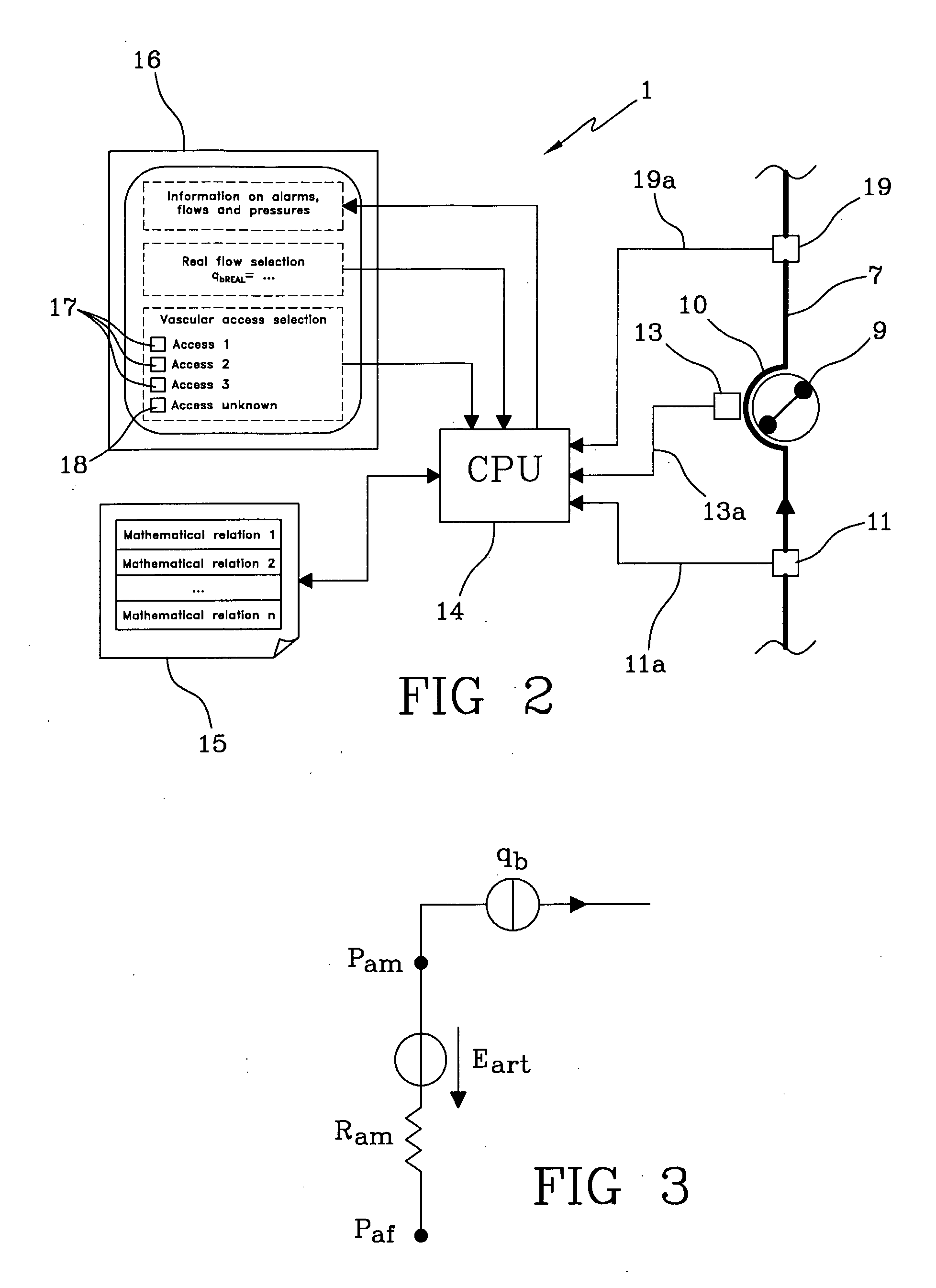
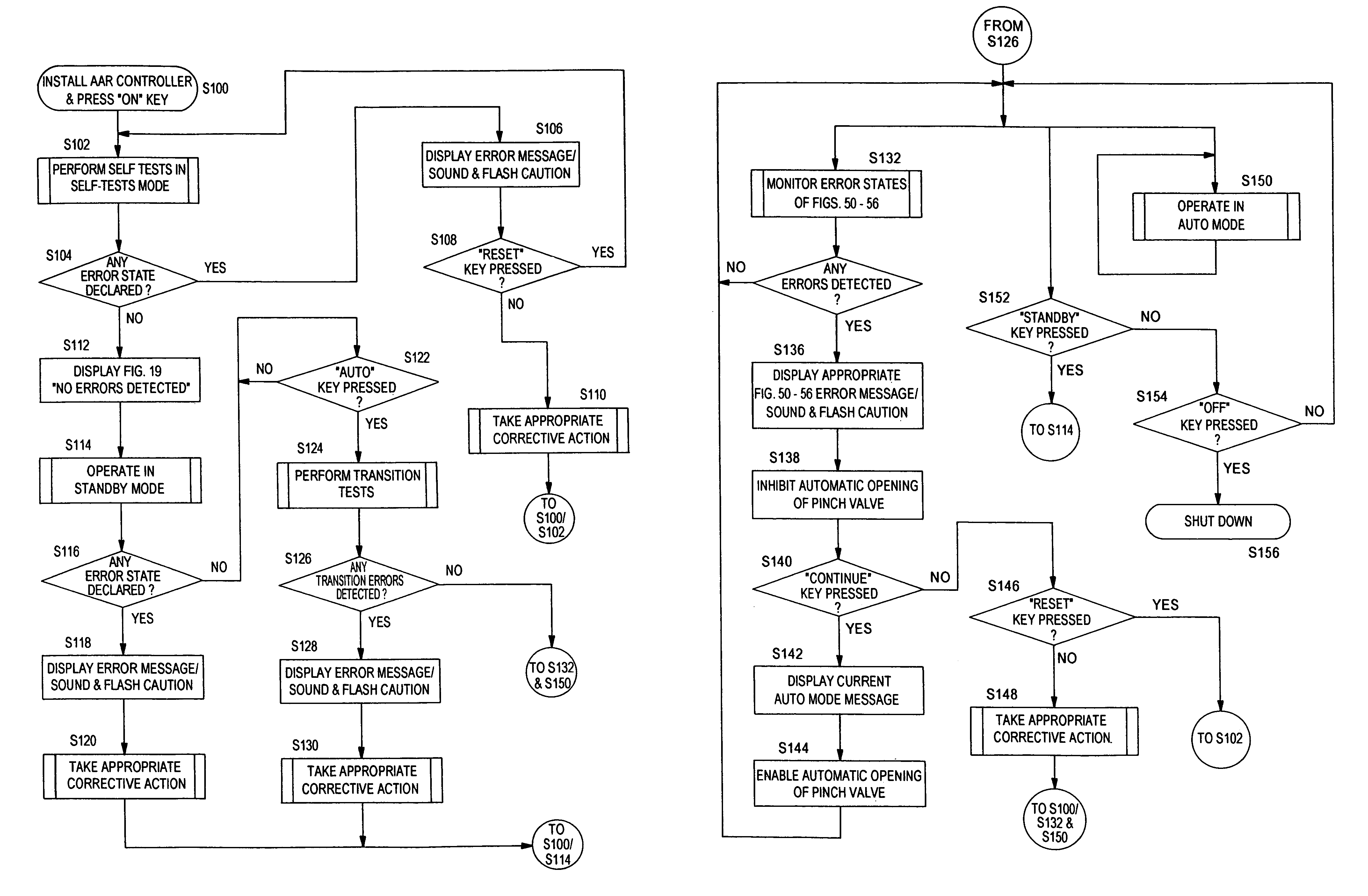
The apparatus for blood flow control in an extracorporeal circuit comprises: a user interface for setting a desired blood flow value (qbREAL) and a datum relating to the vascular access, a memory for recording a plurality of mathematical relations having mathematical expressions relating to the vascular access organ to be used, and a control unit. The control unit identifies the vascular access, selects, from among the plurality of mathematical relations present in the memory, a relation which corresponds to the vascular access identified, and calculates, as a mathematical function of the set value for the desired flow (qbREAL), a value at which to set the angular velocity of the pump associated to the extracorporeal circuit and / or a theoretical value of the arterial pressure upstream of the pump.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Device to permit offpump beating heart coronary bypass surgery
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC +1
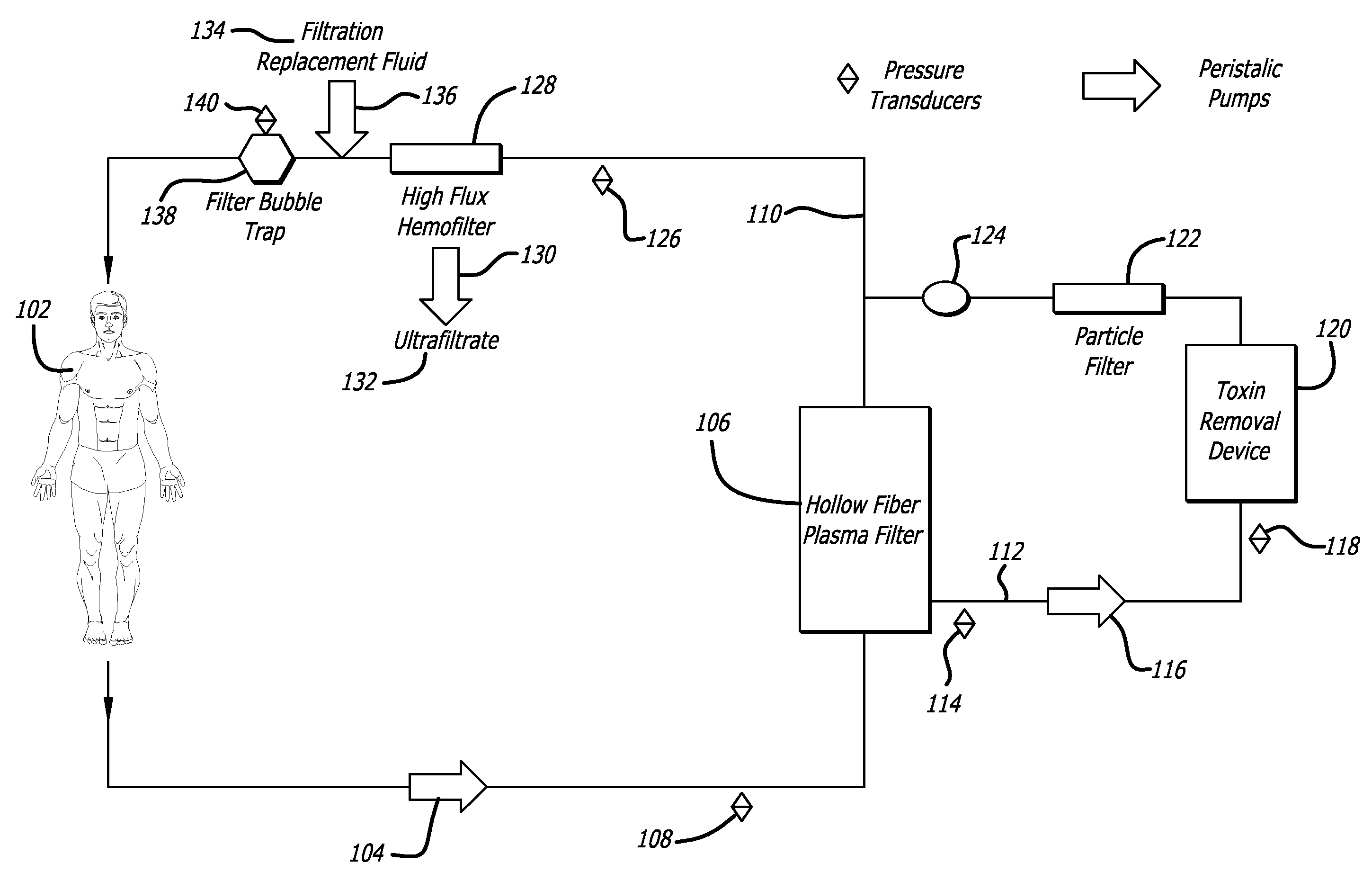
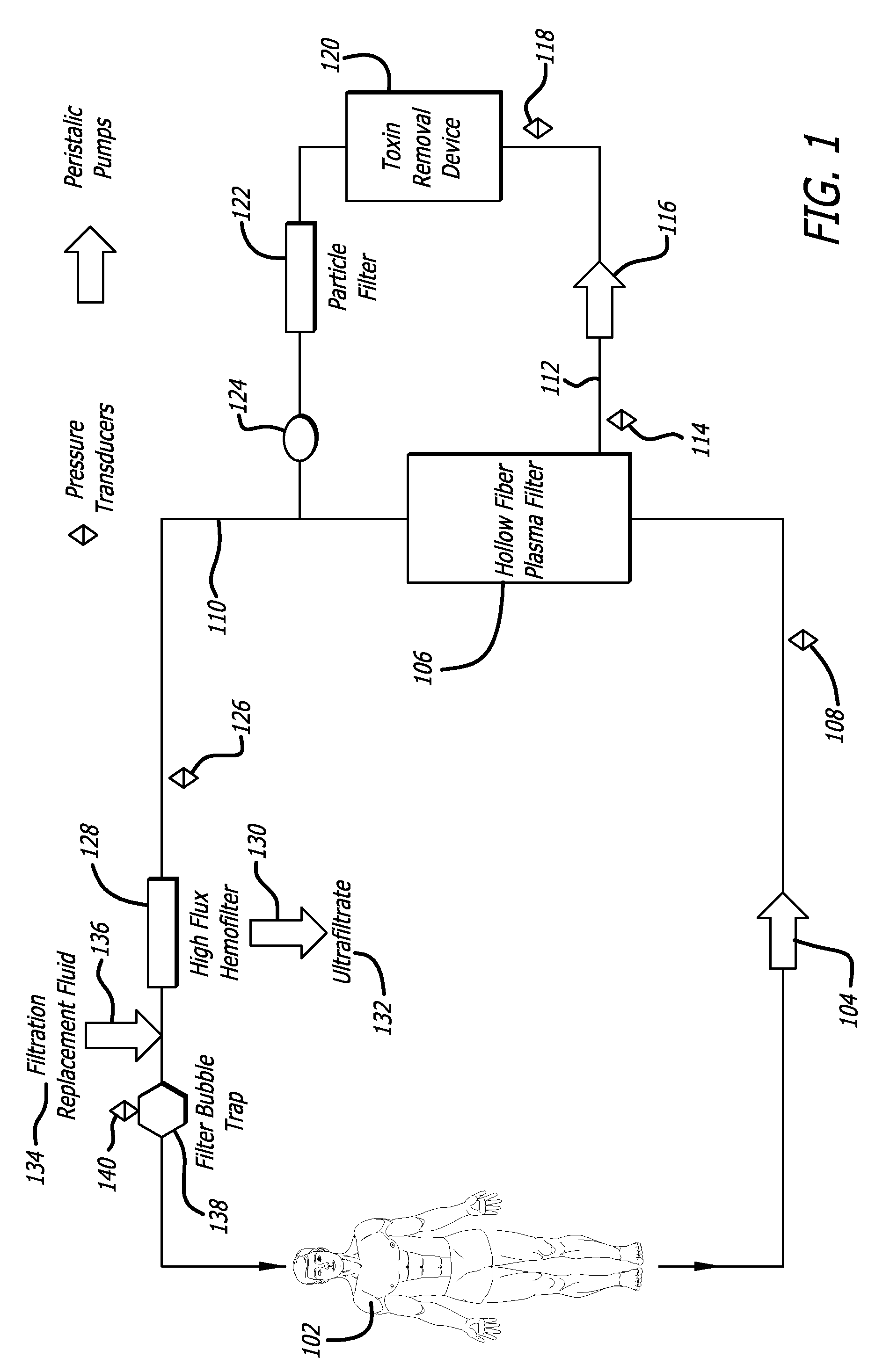
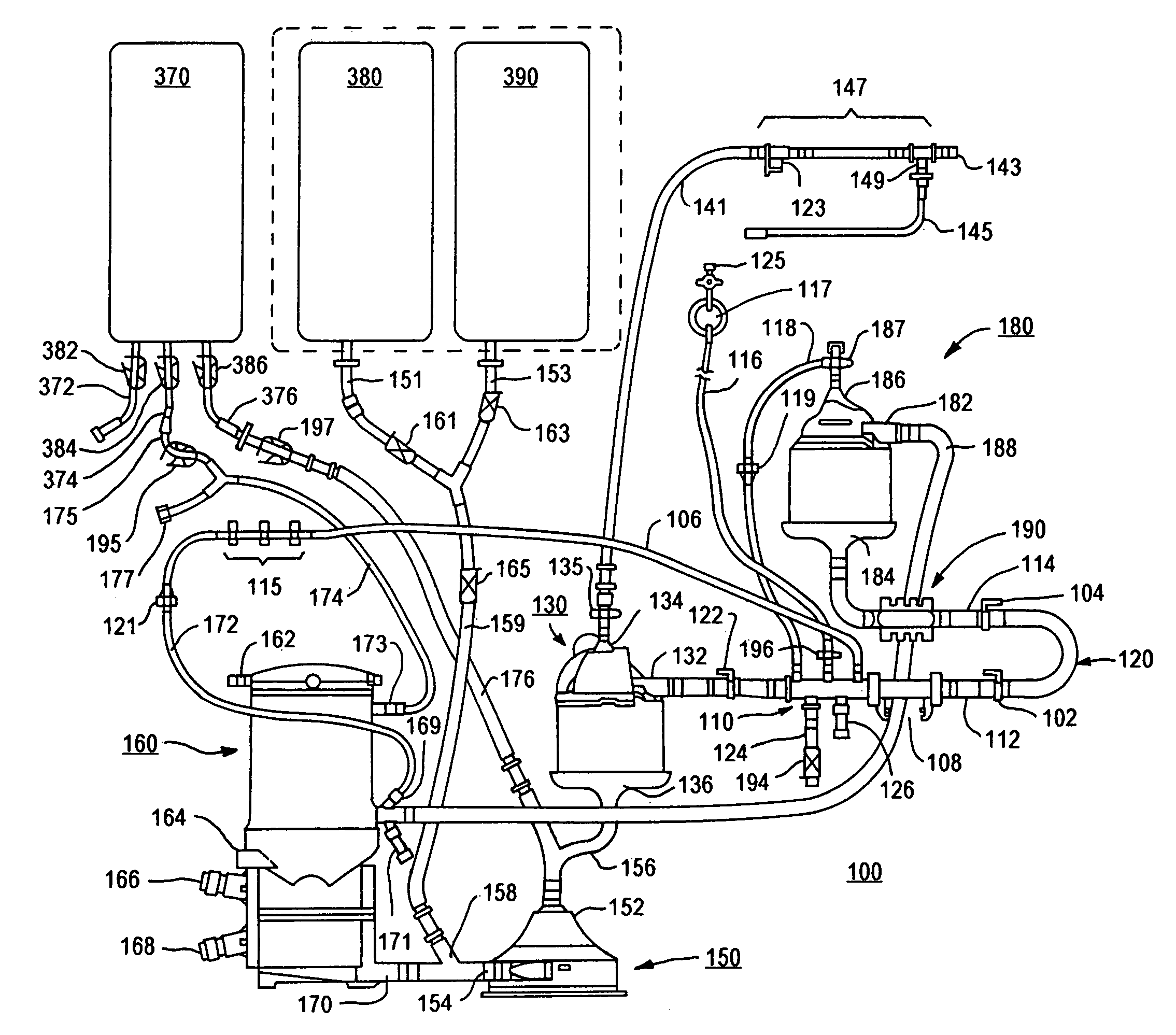
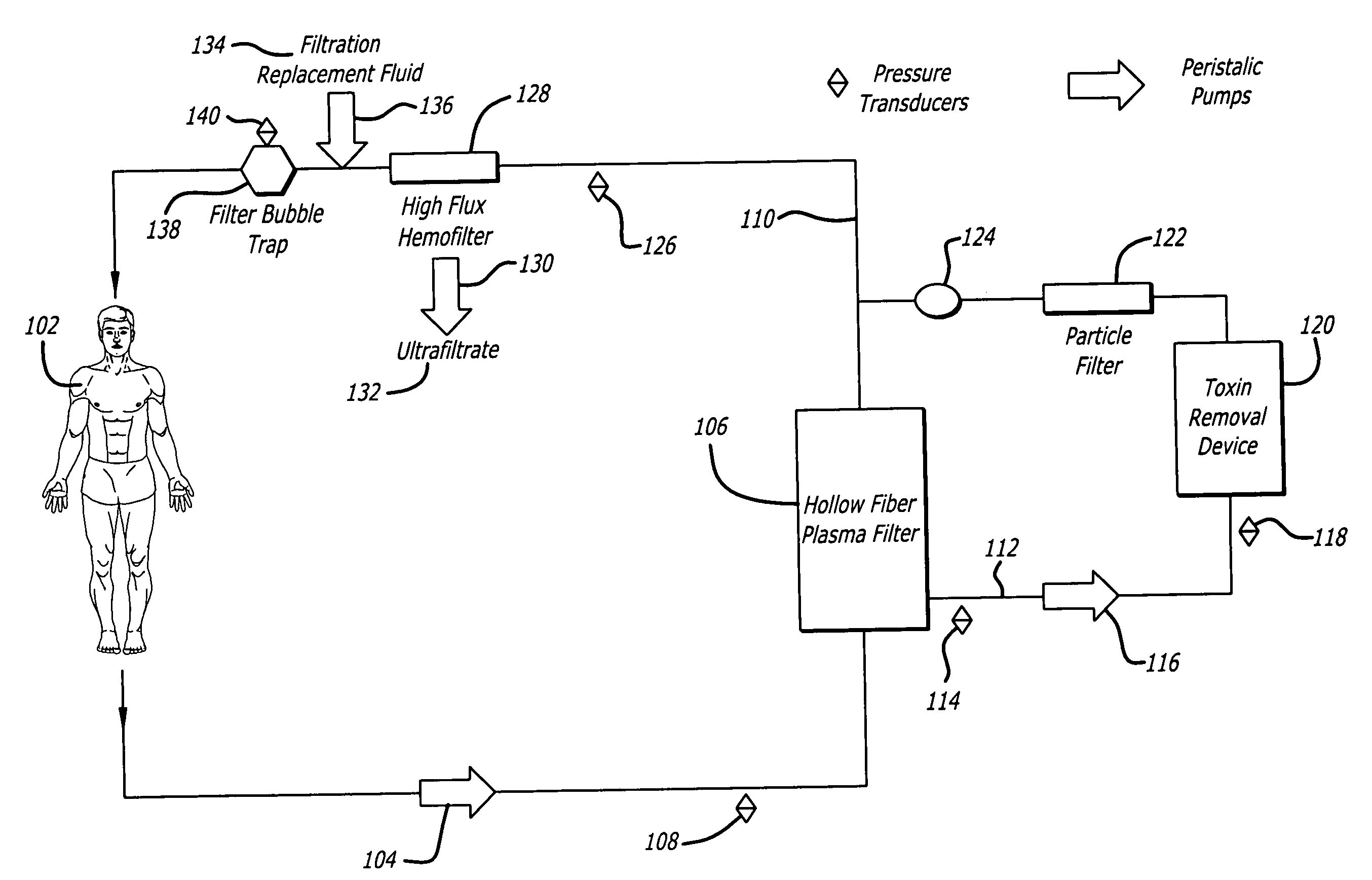
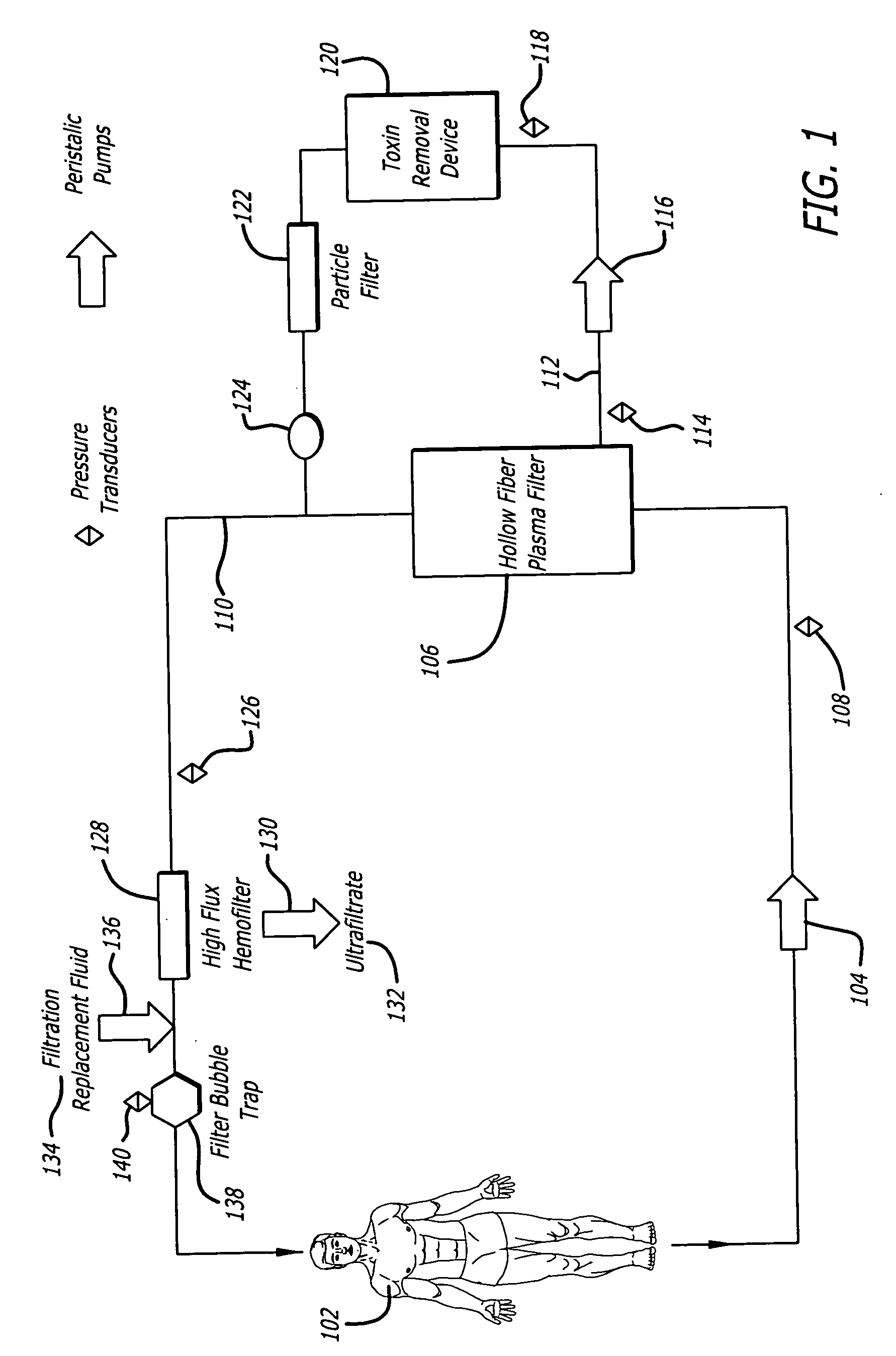
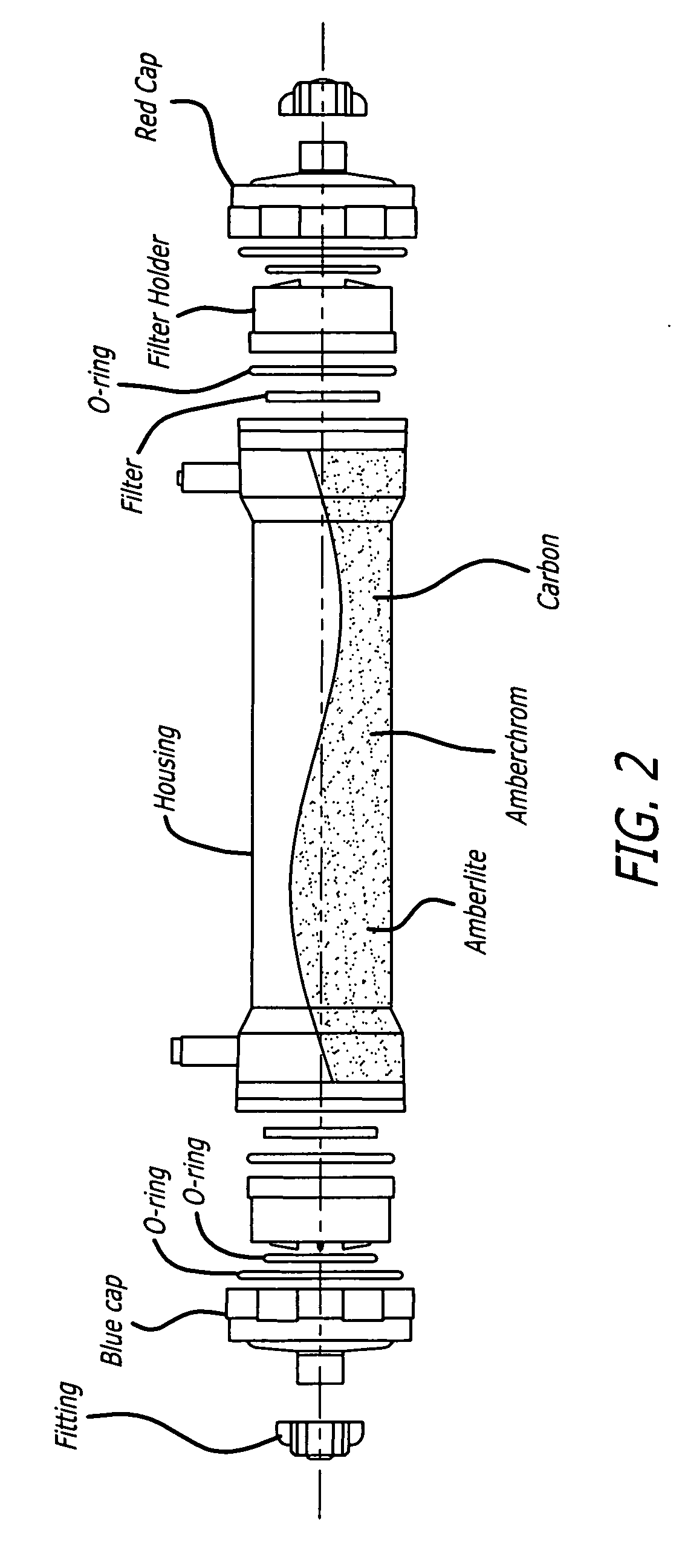
Plasma detoxification and volume control system and methods of use
ActiveUS20070181499A1Effectively detoxify human plasma and balance blood volumeSolvent extractionSolid sorbent liquid separationIon exchangeBlood plasma
An extracorporeal circuit for removing toxins from the blood and plasma volume control in patients suffering from sepsis and renal failure. The extracorporeal circuit disclosed herein comprises a plasma filter, a toxin removal device and optionally a hemofilter that minimizes electrolyte and protein depletion from the treated plasma while effectively removing both free and protein-bound toxins. The toxin removal device comprises adsorbent materials selected from the group consisting of activated carbon, ion exchange resins and non-ionic exchange resins and the adsorbent materials are coated with albumin. Also provided are associated methods for treating patients suffering from sepsis and renal failure using the disclosed extracorporeal circuit and toxin removal device.
Owner:MARKER HLDG AG
Valve mechanism for infusion fluid systems
InactiveUS7306736B2Prevent backflowLow costLiquid separation auxillary apparatusSolvent extractionWhole blood productPinch valve
A method and an apparatus are provided for preventing retrograde flow of fluid, e.g., blood products, into a source of sterile substitution fluid (50). The apparatus of the present invention includes a controllable pinch valve member (110) that is placed on a section of a conduit (90) which carries sterile substitution fluid to an extracorporeal circuit (30). In one embodiment, control over the valve member (110) is based on a control unit (120) using fluid pressures that are sensed upstream and downstream of the valve member (110) by upstream sensor (121) and downstream pressure (122) respectively. The valve member (110) is preferably opened only when the upstream pressure is greater than the downstream pressure. This assures that the substitution fluid flows only in a single direction when the pinch valve member (110) completely occludes the conduit (90) when in a closed position. Therefor, blood will not contaminate the sterile fluid by being drawn into the conduit (90) due to pressure differences.
Owner:LAMBDA INVESTORS
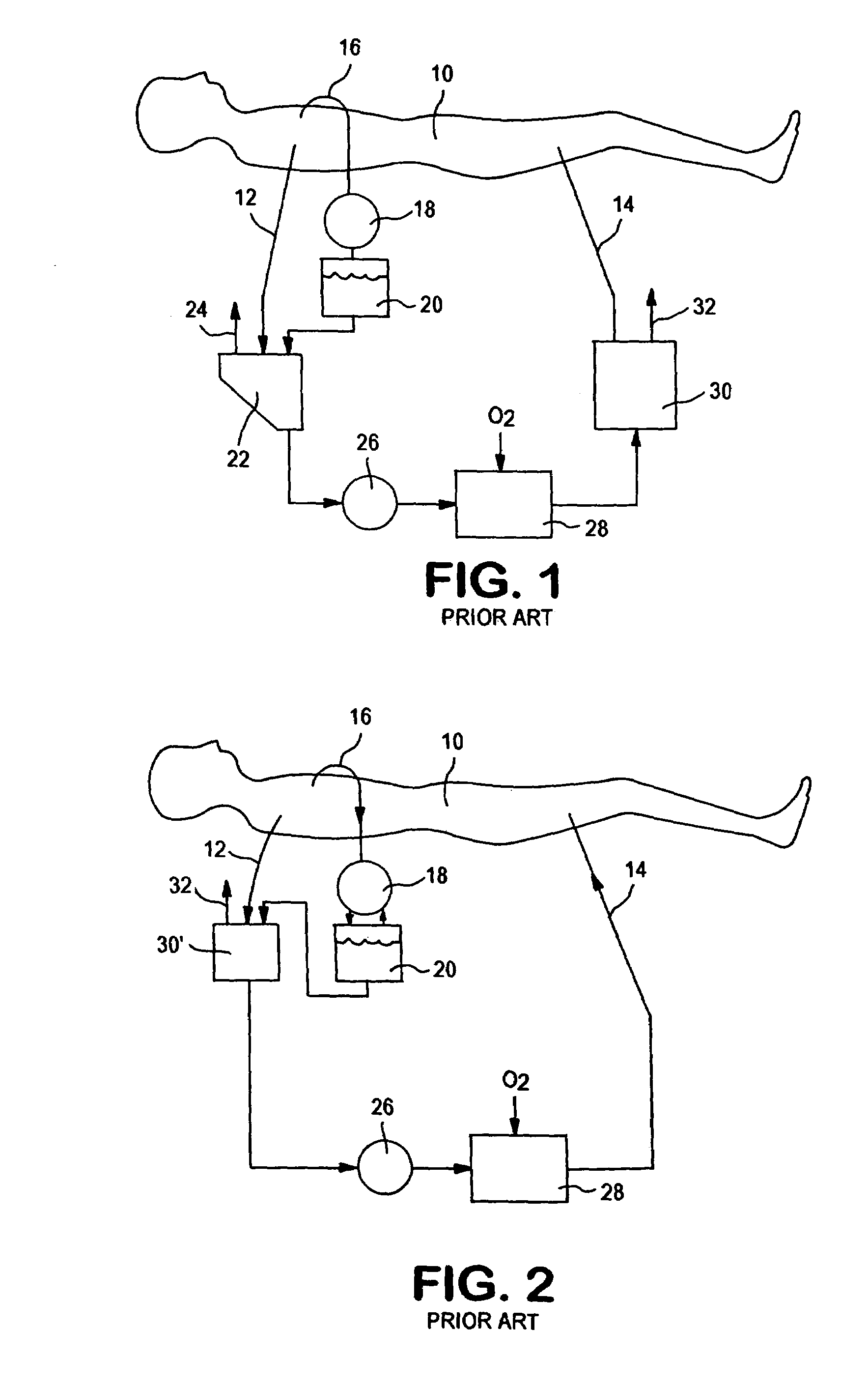
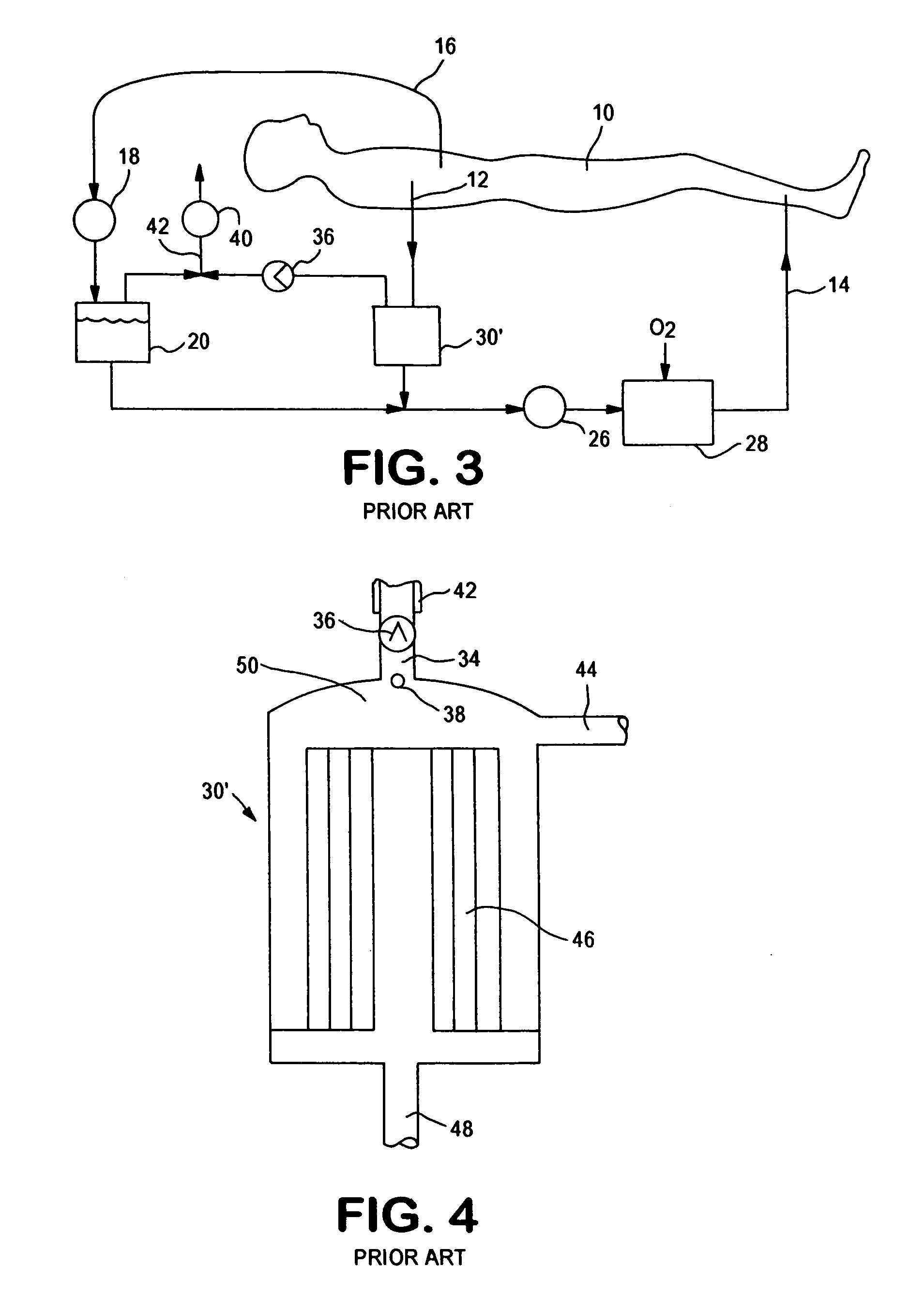
Cardiopulmonary bypass extracorporeal blood circuit apparatus and method
InactiveUS20050118059A1Implement extensionsSignificant improvementOther blood circulation devicesHaemofiltrationBlood levelVein
An extracorporeal blood circuit for use with a venous return line and an arterial line coupled to a patient. The extracorporeal blood circuit can include a venous air removal device coupled to the venous return line. The venous air removal device can perform an active air removal function. The extracorporeal blood circuit can include a sensor that determines a blood level in the venous air removal device, a purge line coupled to the venous air removal device, and a controller connected to the sensor. The controller can cause the venous air removal device to perform the active air removal function through the purge line when the blood level is less than a threshold. The extracorporeal blood circuit can further include a pump coupled to the venous air removal device, an oxygenator coupled to the pump, and a blood filter coupled to the oxygenator and the arterial line.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
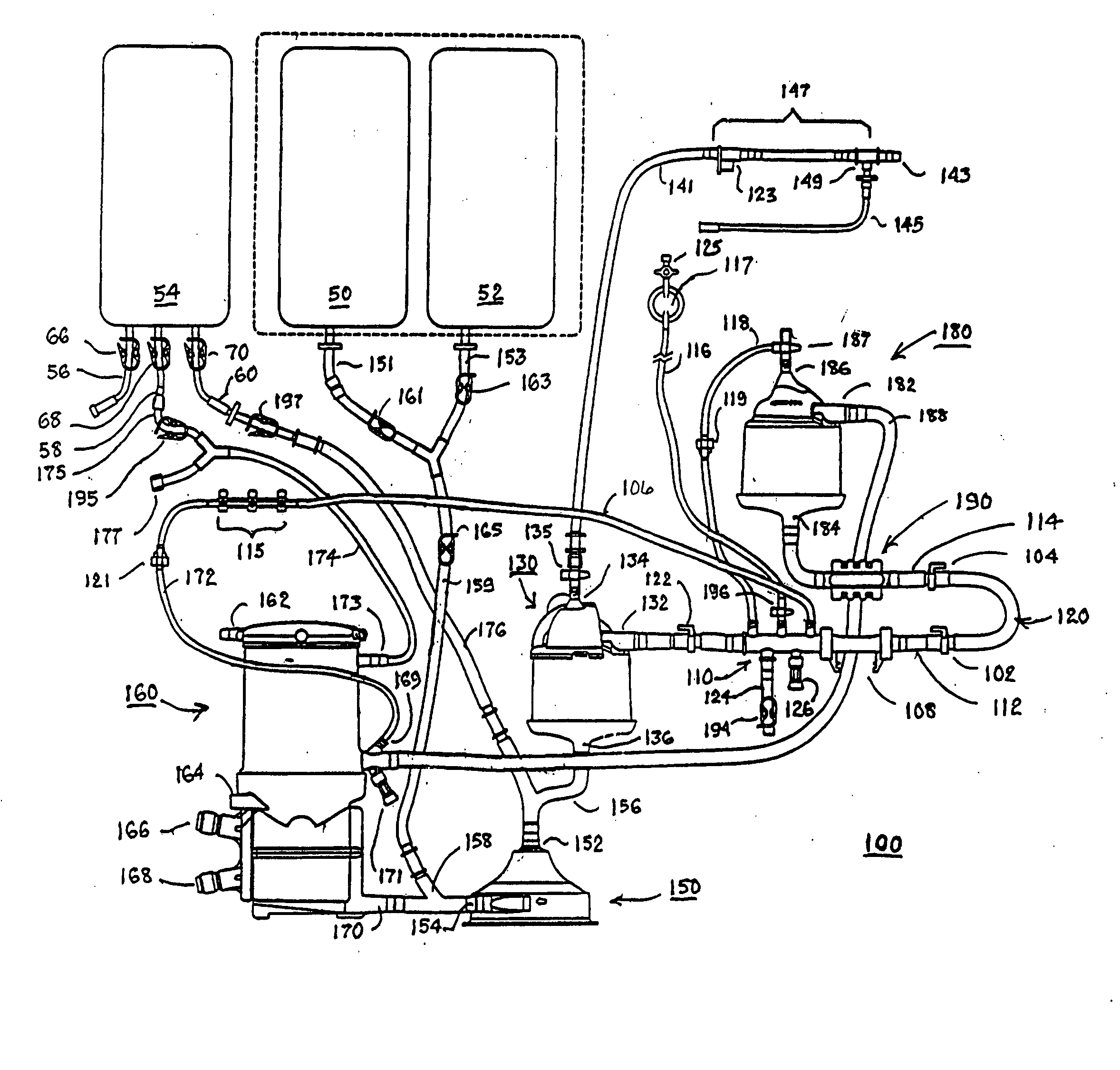
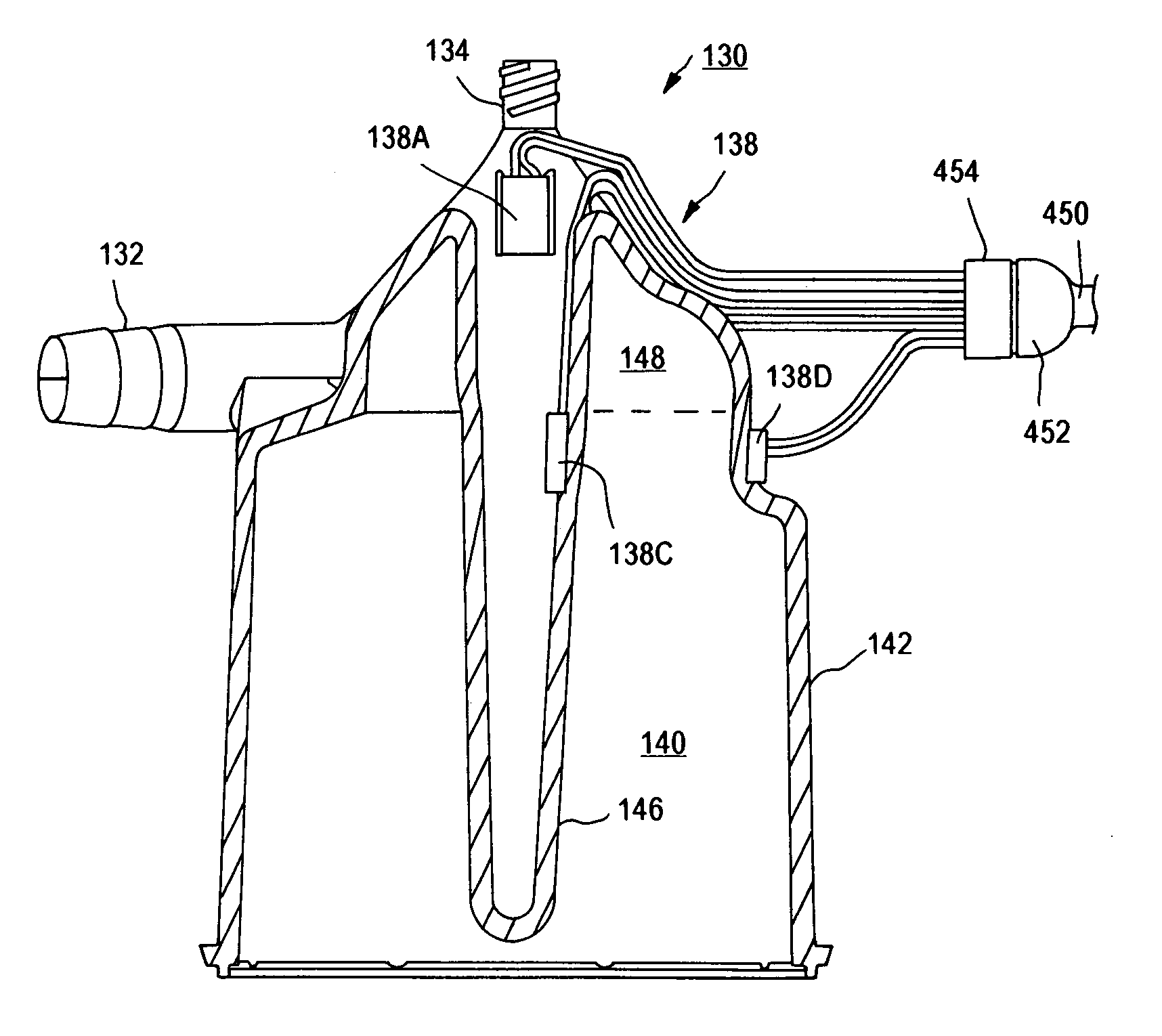
Disposable, integrated, extracorporeal blood circuit
ActiveUS7198751B2Save spaceIncrease contactSemi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionExtracorporeal circulationVenous blood
A disposable, integrated extracorporeal blood circuit employed during cardiopulmonary bypass surgery performs gas exchange, heat transfer, and microemboli filtering functions in a way as to conserve volume, to reduce setup and change out times, to eliminate a venous blood reservoir, and to substantially reduce blood-air interface. Blood from the patient or prime solution is routed through an air removal device that is equipped with air sensors for detection of air. An active air removal controller removes detected air from blood in the air removal device. A disposable circuit support module is used to mount the components of the disposable, integrated extracorporeal blood circuit in close proximity and in a desirable spatial relationship to optimize priming and use of the disposable, integrated extracorporeal blood circuit. A reusable circuit holder supports the disposable circuit support module in relation to a prime solution source, the active air removal controller and other components.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Plasma detoxification and volume control system and methods of use
InactiveUS20050281809A1Effectively detoxify human plasma and balance blood volumeSemi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionBlood plasmaPlasma volume
An extracorporeal circuit for removing toxins from the blood and plasma volume control in patients suffering from sepsis and renal failure. The extracorporeal circuit disclosed herein comprises a plasma filter, a toxin removal device and optionally a hemofilter that minimizes electrolyte and protein depletion from the treated plasma while effectively removing both free and protein-bound toxins. Also provided are associated methods for treating patients suffering from sepsis and renal failure using the disclosed extracorporeal circuit and toxin removal device.
Owner:HEMOLIFE MEDICAL
Extracorporeal blood circuit air removal system and method
A disposable, integrated extracorporeal blood circuit employed during cardiopulmonary bypass surgery performs gas exchange, heat transfer, and microemboli filtering functions in a way as to conserve volume, to reduce setup and change out times, to eliminate a blood reservoir, and to substantially reduce blood-air interface. Blood from the patient or prime solution is routed through an air removal device that is equipped with air sensors for detection of air. An active air removal controller removes detected air from blood in the air removal device. A disposable circuit support module is used to mount the components of the disposable, integrated extracorporeal blood circuit in close proximity and in a desirable spatial relationship to optimize priming and use of the disposable, integrated extracorporeal blood circuit. A reusable circuit holder supports the disposable circuit support module in relation to a prime solution source, the active air removal controller and other components.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
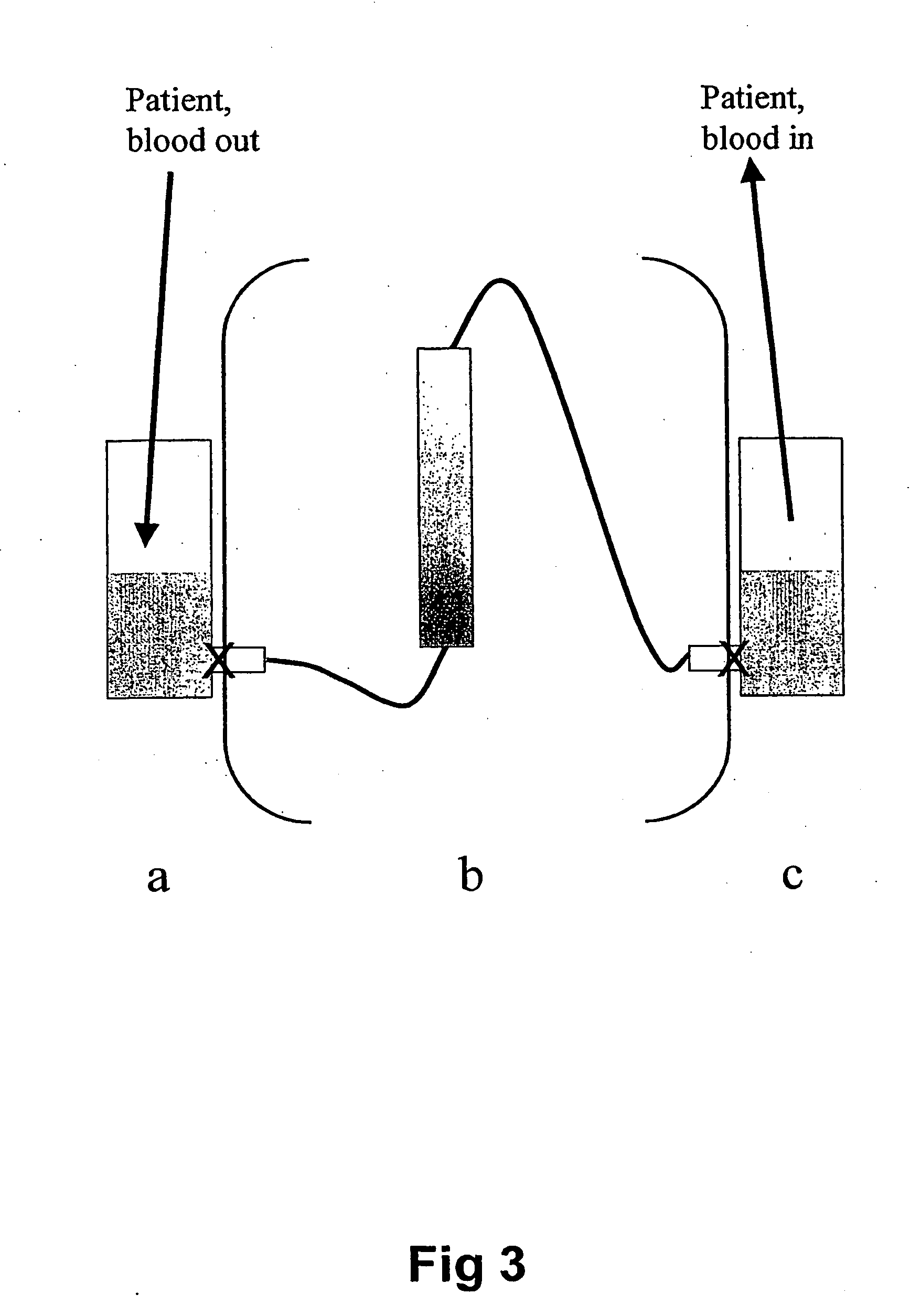
Method of operating a dialysis machine
A method and apparatus of priming or rinse back of an extracorporeal circuit using a dialysis machine comprising a dialysis liquid preparation system. The dialysis machine is used to prepare a saline solution on-line. The extracorporeal circuit is connected to the dialysis machine and primed with the saline solution.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
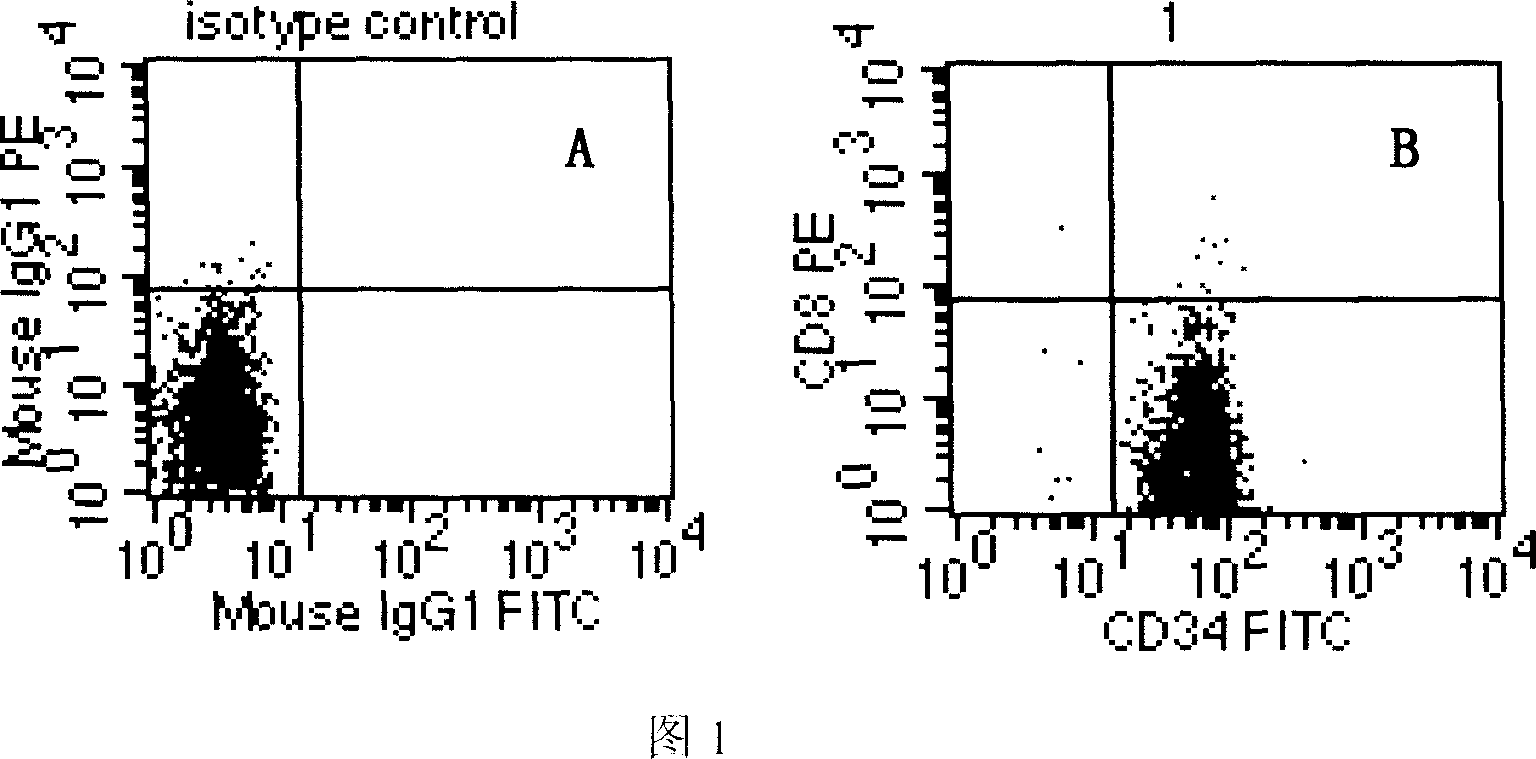
Extracorporeal induction process for differentiating hemopoietic stem/ancestral cell into mature red blood cell and its application
The present invention relates to biomedicine technology, and is especially technological process of inducing and differentiating hemopoietic stem / ancestral cell of different sources into mature red blood cell by means of the support of stroma cell in a serum-free culture system. By means of the common culturing of stroma cell originated from embryo liver or mesenchyme stem cell originated from embryo marrow and erythron ancestral cell in different extracorporeal induction stages, the present invention realizes complete denucleation of erythrocyte to create erythrocyte with complete function. The present invention makes it possible to provide great amount of general or rare hematypic erythrocyte products for medical application.
Owner:FIELD OPERATION BLOOD TRANSFUSION INST OF PLA SCI ACAD OF MILITARY
Oral devices and methods for controlled drug delivery
Controlled-drug-delivery oral devices are implanted or inserted into an oral cavity, built onto a prosthetic tooth crown, a denture plate, braces, a dental implant, or the like. The devices are refilled or replaced as needed. The controlled drug delivery may be passive, based on a dosage form, or electro-mechanically controlled, for a high-precision, intelligent, drug delivery. Additionally, the controlled delivery may be any one of the following: delivery in accordance with a preprogrammed regimen, delivery at a controlled rate, delayed delivery, pulsatile delivery, chronotherapeutic delivery, closed-loop delivery, responsive to a sensor's input, delivery on demand from a personal extracorporeal system, delivery regimen specified by a personal extracorporeal system, delivery on demand from a monitoring center, via a personal extracorporeal system, and delivery regimen specified by a monitoring center, via a personal extracorporeal system. Drug absorption in the oral cavity may be assisted or induced by a transport mechanism, such as any one of, or a combination of iontophoresis, electroosmosis, electrophoresis, electroporation, sonophoresis, and ablation. The oral devices require refilling or replacement at relatively long intervals of weeks or months, maintain a desired dosage level in the oral cavity, hence in the gastrointestinal tract, for extended periods, address situations of narrow drug therapeutic indices, and by being automatic, ensure adherence to a prescribed medication regimen. The oral devices and methods for controlled drug delivery apply to humans and animals.
Owner:安迪·沃尔夫 +1
Extracorporeal blood circuit priming system and method
ActiveUS7189352B2Overcome difficultiesSemi-permeable membranesOther blood circulation devicesExtracorporeal circulationAir interface
A disposable, integrated extracorporeal blood circuit employed during cardiopulmonary bypass surgery performs gas exchange, heat transfer, and microemboli filtering functions in a way as to conserve volume, to reduce setup and change out times, to eliminate a venous blood reservoir, and to substantially reduce blood-air interface. Blood from the patient or prime solution is routed through an air removal device that is equipped with air sensors for detection of air. An active air removal controller removes detected air from blood in the air removal device. A disposable circuit support module is used to mount the components of the disposable, integrated extracorporeal blood circuit in close proximity and in a desirable spatial relationship to optimize priming and use of the disposable, integrated extracorporeal blood circuit. A reusable circuit holder supports the disposable circuit support module in relation to a prime solution source, the active air removal controller and other components.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and apparatus for stabilization and positioning during surgery
Owner:TEXAS HEART INST
Closed-circuit device and methods for isolation, modification, and re-administration of specific constituents from a biological fluid source
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for the isolation, modification and re-administration of a molecule or biomolecule, or a class of biomolecules, from the body fluid of a mammal via an extracorporeal closed circuit device. The device is able to capture and modify the biomolecule by the covalent or non-covalent attachment of a secondary molecule or protein, by cross-linking the captured molecule, or by altering the structure of the molecule (for example, by deglycosylation, peptide cleavage, or aggregation). The apparatus can be used to return the modified molecule or biomolecule to the mammalian subject. The device and methods may be utilized for the patient-specific diagnosis and / or treatment of a disease state which presents an associated molecule or protein in plasma or any other fluidized physiological system.The methods and apparatus may also be employed as a closed system allowing the on-line purification and / or modification of a target molecule or biomolecule from a fluid source such as a bioreactor or perfusion bioreactor.
Owner:MCNEIL GARY L
Extracorporeal stablised expanded bed adsorption method for the treatment of sepsis
InactiveUS20050249724A1Increase flow rateSpecific componentIon-exchange process apparatusOther chemical processesExpanded bed adsorptionHematological test
The present invention provides an extracorporeal adsorption method for removing harmful substances from blood in a way that is practicable in everyday clinical practice and applicable for the timely intervention to present the development of sepsis. Said extracorporeal adsorption method being effected by an adsorption column assembly where the adsorption column assembly comprising a column and an adsorption medium in the form of particles. The sedimented volume of said particles being at the most 80% of the volume of the column.
Owner:UPFRONT CHROMATOGRAPHY
Apparatus for Controlling Blood Flow in an Extracorporeal Circuit
The apparatus for blood flow control in an extracorporeal circuit comprises: a user interface for setting a desired blood flow value (qbREAL) and a datum relating to the vascular access, a memory for recording a plurality of mathematical relations having mathematical expressions relating to the vascular access organ to be used, and a control unit. The control unit identifies the vascular access, selects, from among the plurality of mathematical relations present in the memory, a relation which corresponds to the vascular access identified, and calculates, as a mathematical function of the set value for the desired flow (qbREAL), a value at which to set the angular velocity of the pump associated to the extracorporeal circuit and / or a theoretical value of the arterial pressure upstream of the pump.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Active air removal system operating modes of an extracorporeal blood circuit
ActiveUS7201870B2Overcome difficultiesSemi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionExtracorporeal circulationAir interface
A disposable, integrated extracorporeal blood circuit employed during cardiopulmonary bypass surgery performs gas exchange, heat transfer, and microemboli filtering functions in a way as to conserve volume, to reduce setup and change out times, to eliminate a venous blood reservoir, and to substantially reduce blood-air interface. Blood from the patient or prime solution is routed through an air removal device that is equipped with air sensors for detection of air. An active air removal controller removes detected air from blood in the air removal device. A disposable circuit support module is used to mount the components of the disposable, integrated extracorporeal blood circuit in close proximity and in a desirable spatial relationship to optimize priming and use of the disposable, integrated extracorporeal blood circuit. A reusable circuit holder supports the disposable circuit support module in relation to a prime solution source, the active air removal controller and other components.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com