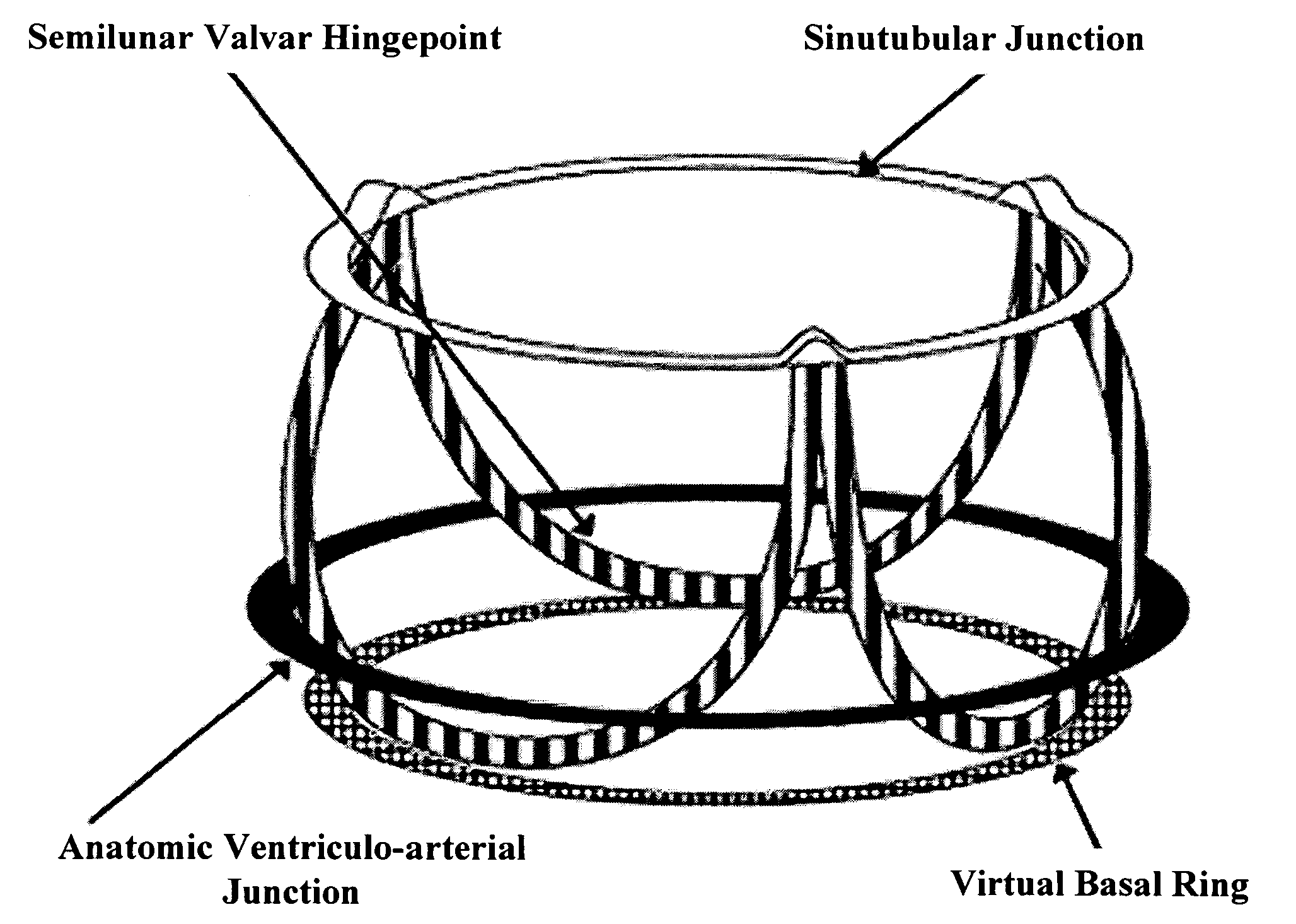
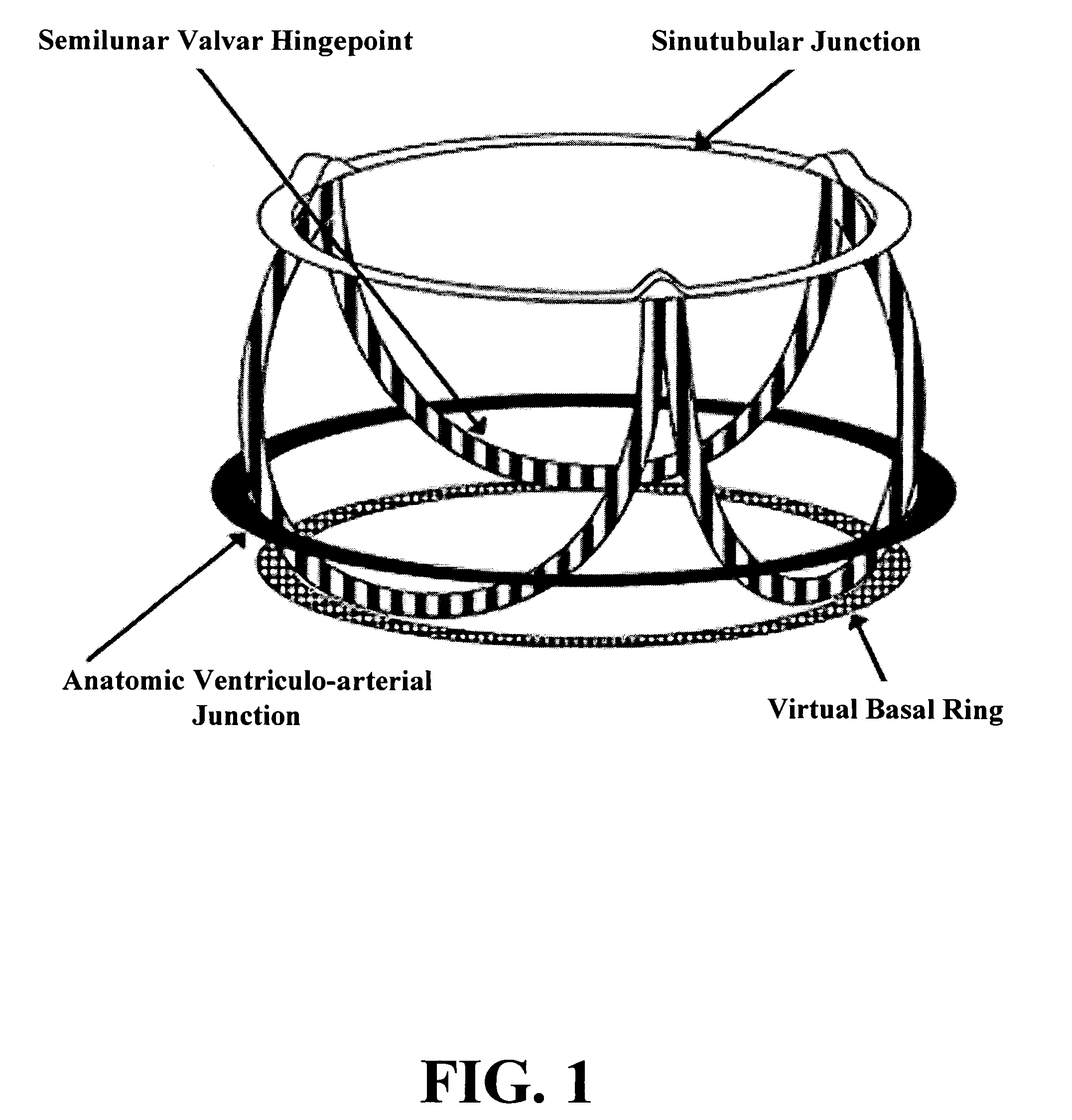
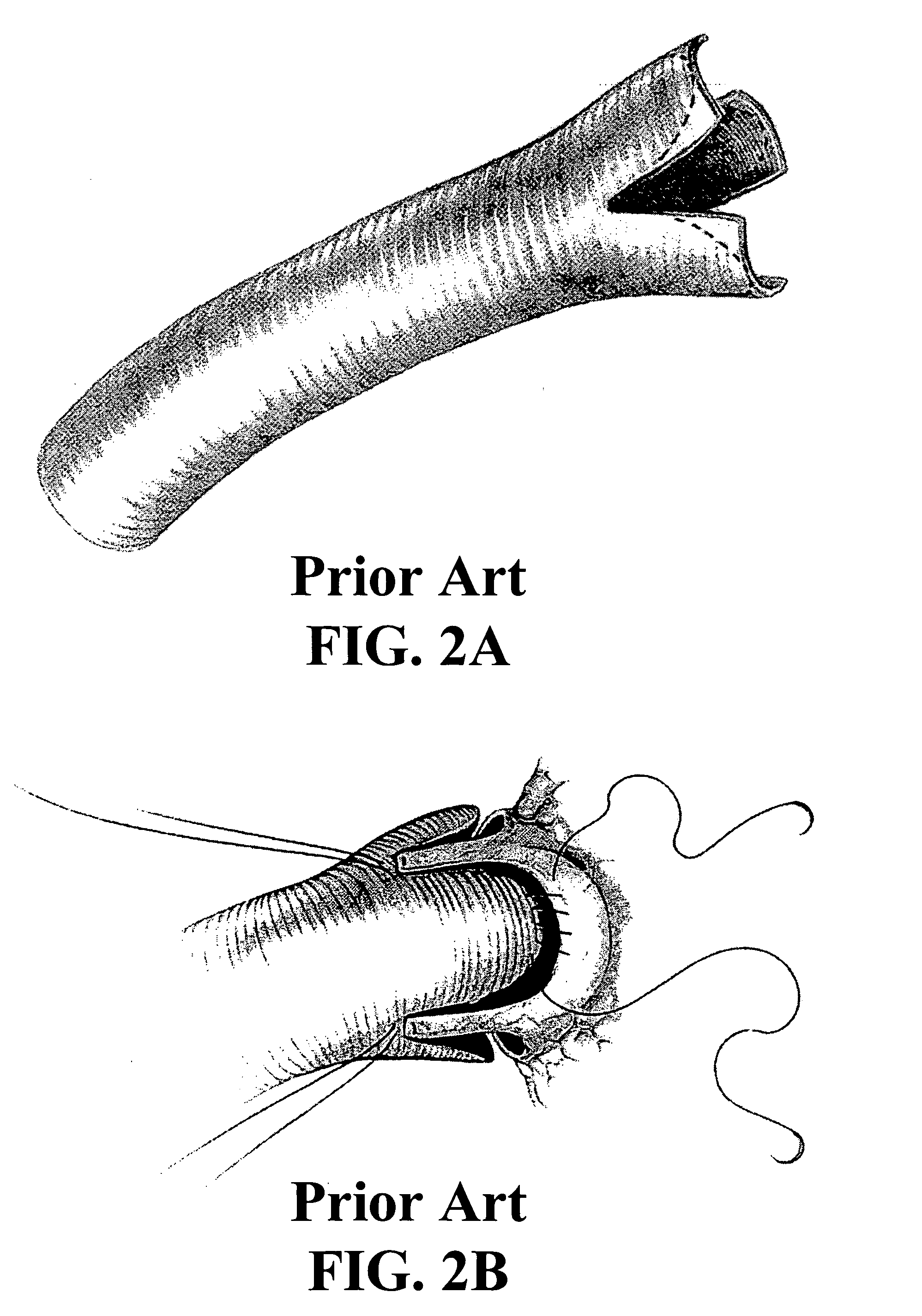
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
88 results about "Aortic root" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
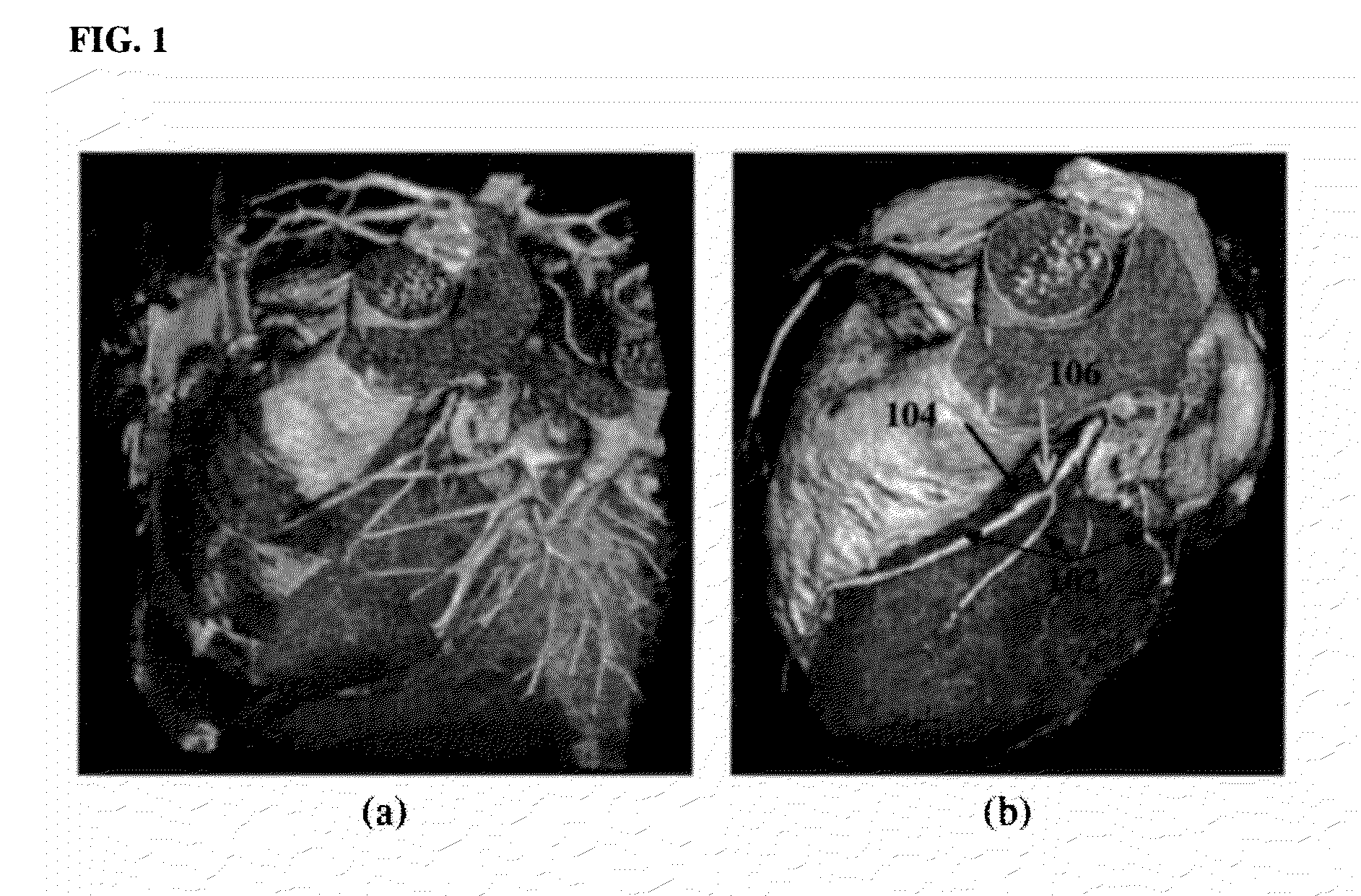
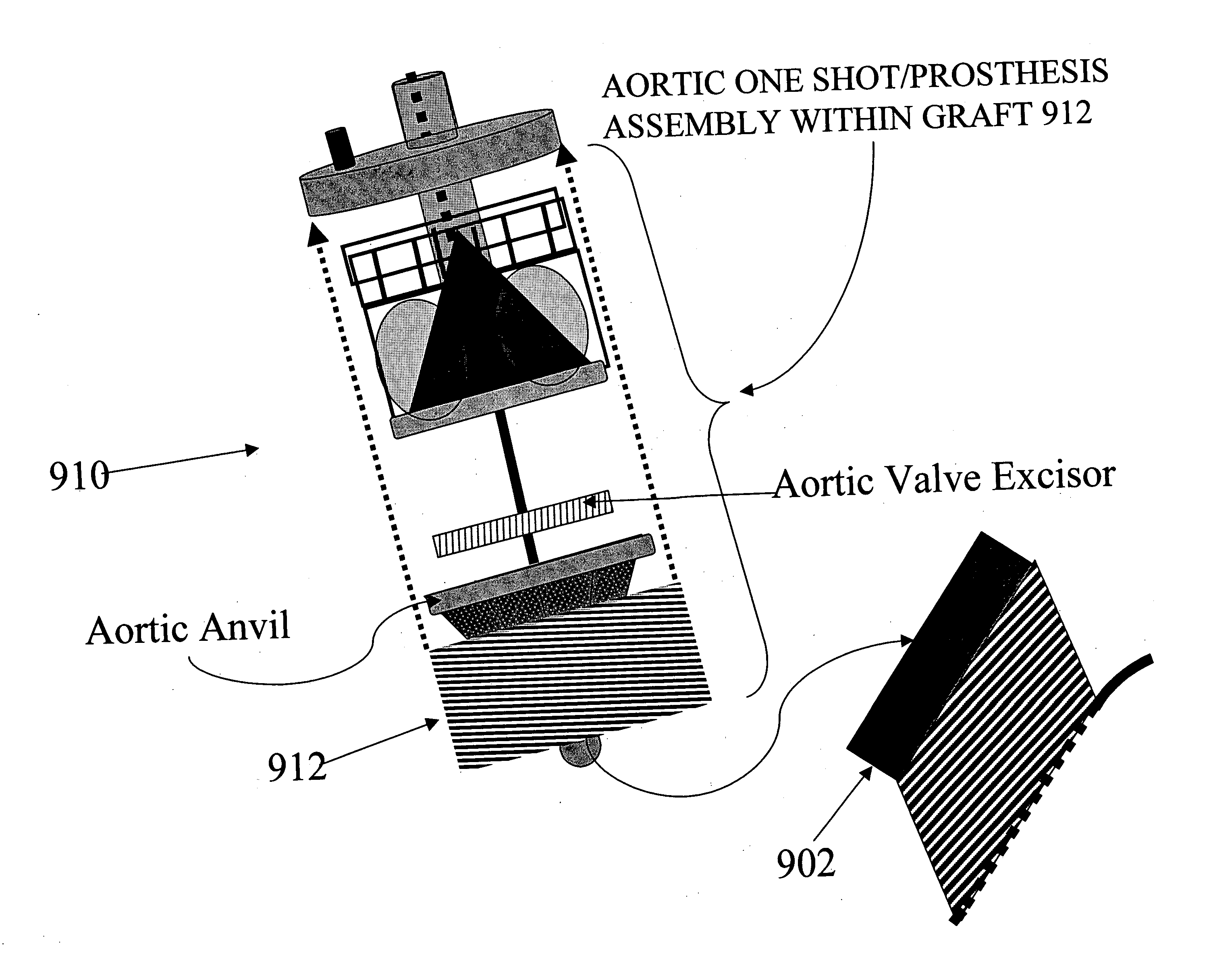
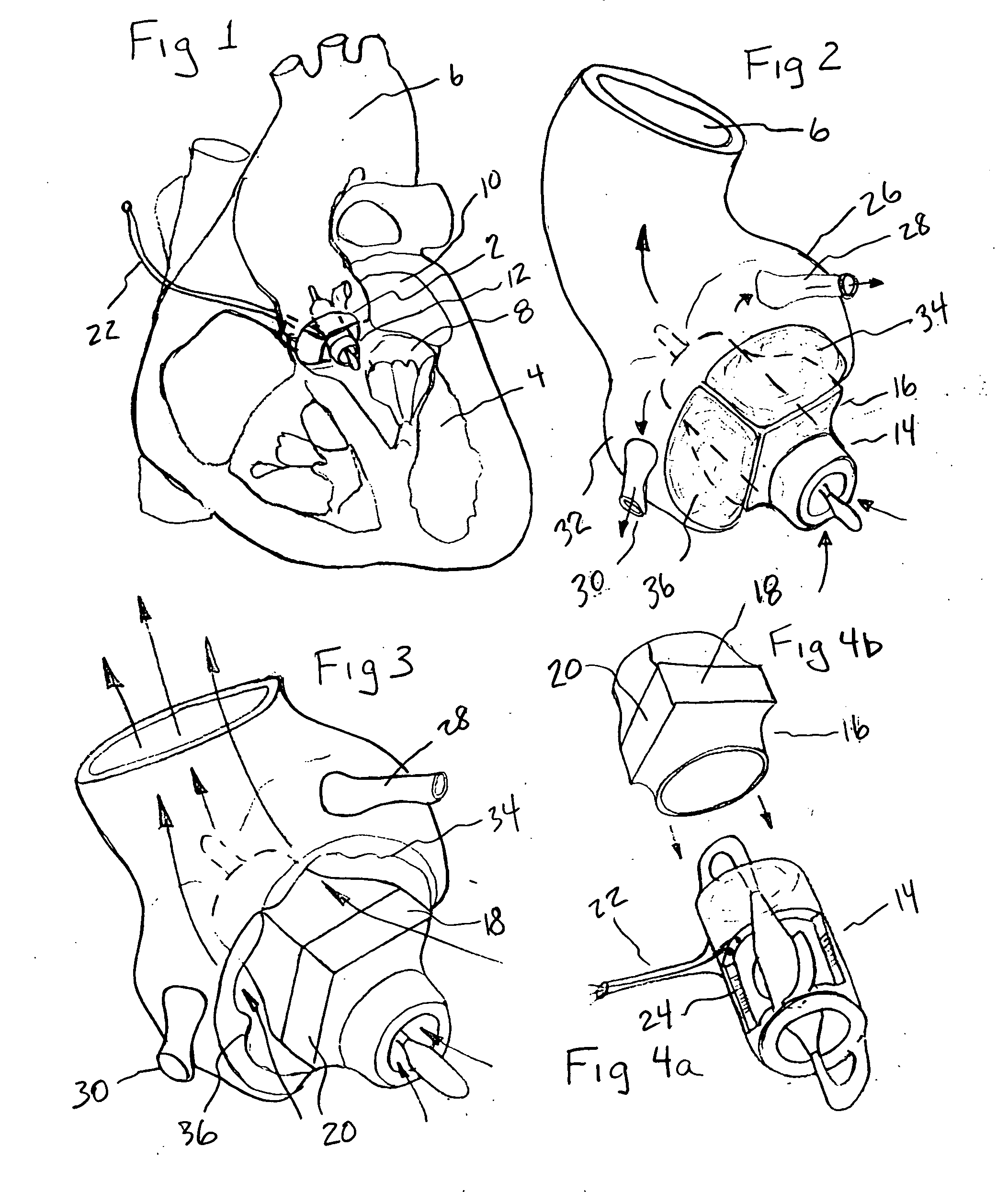
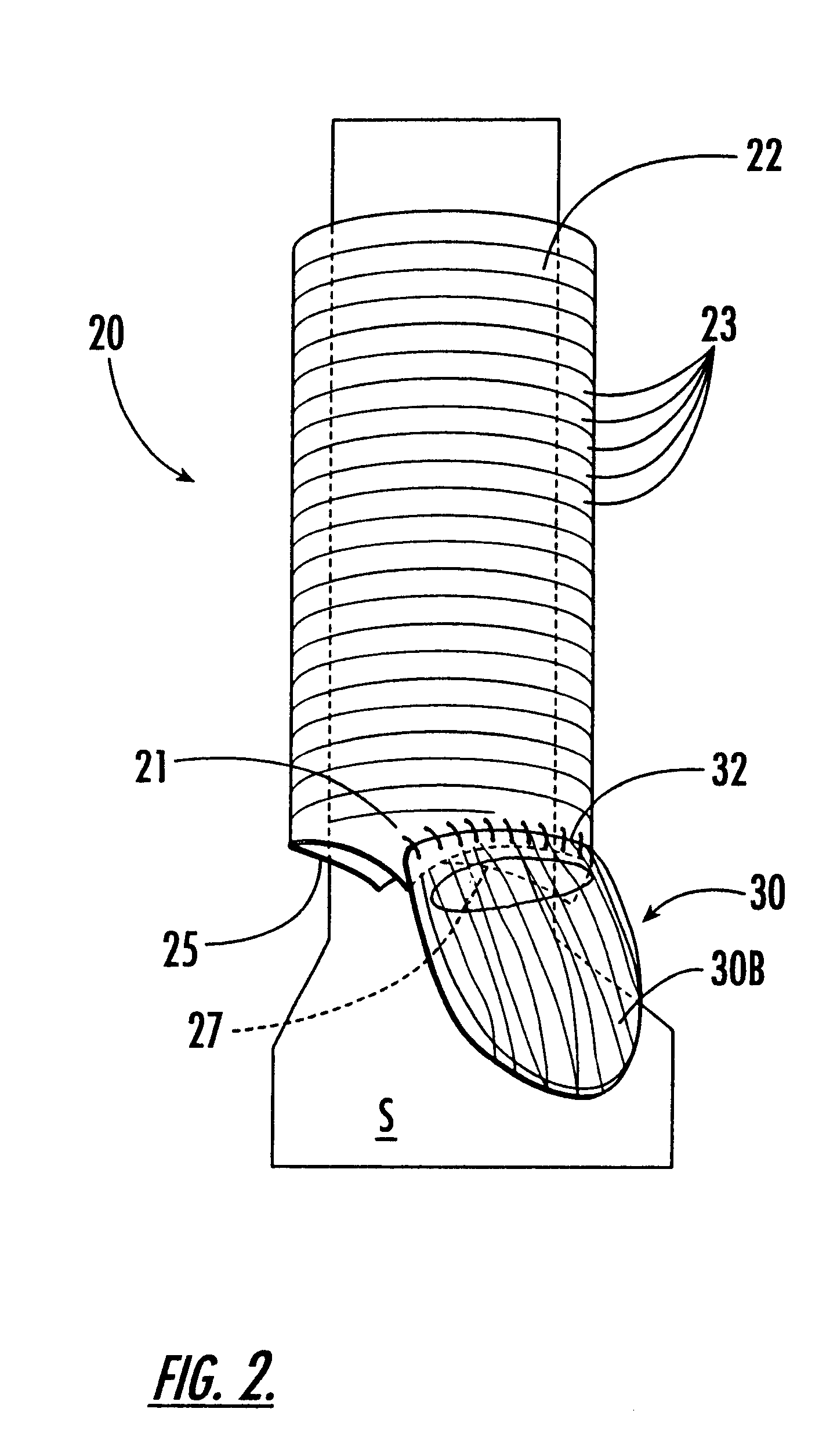
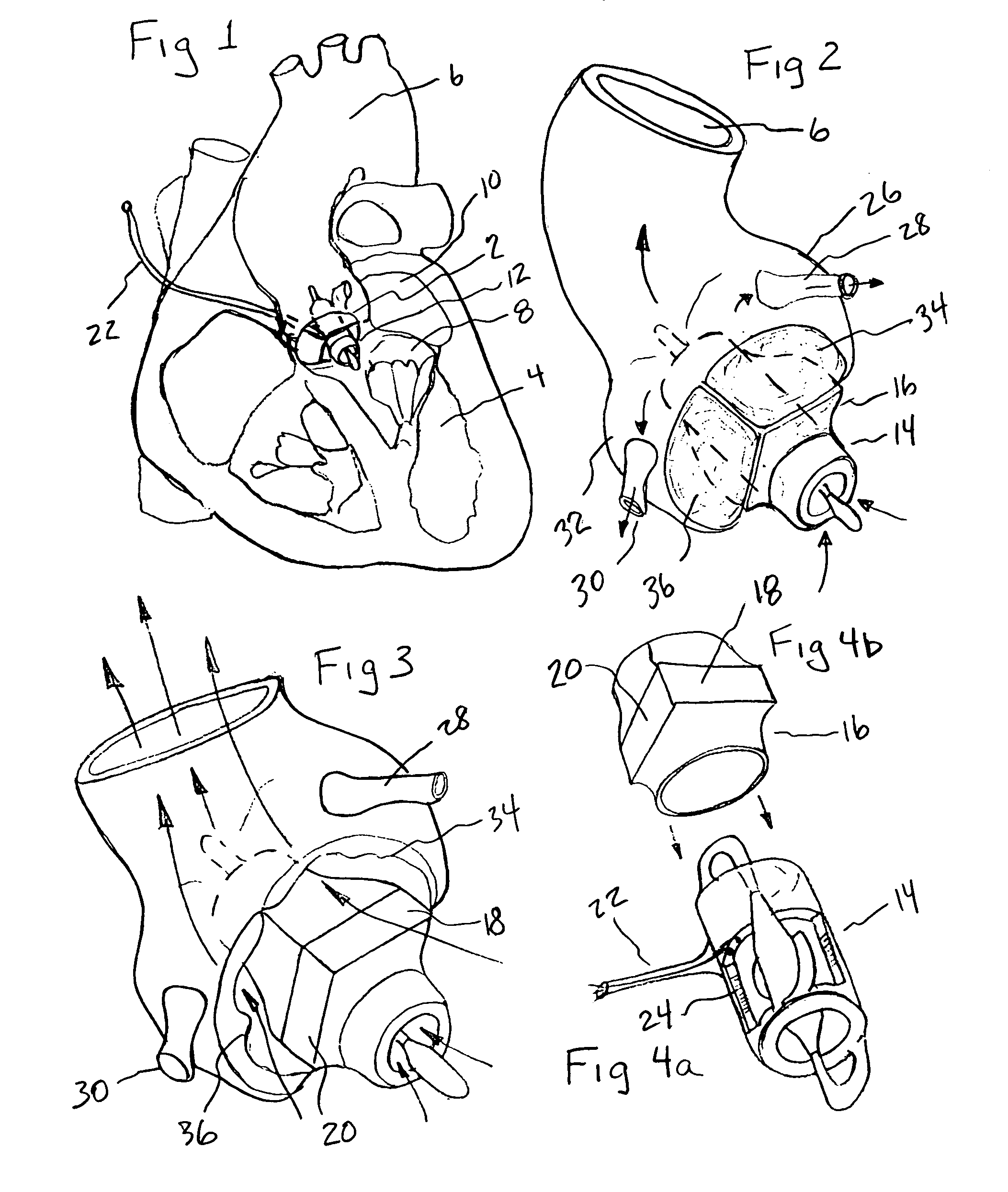
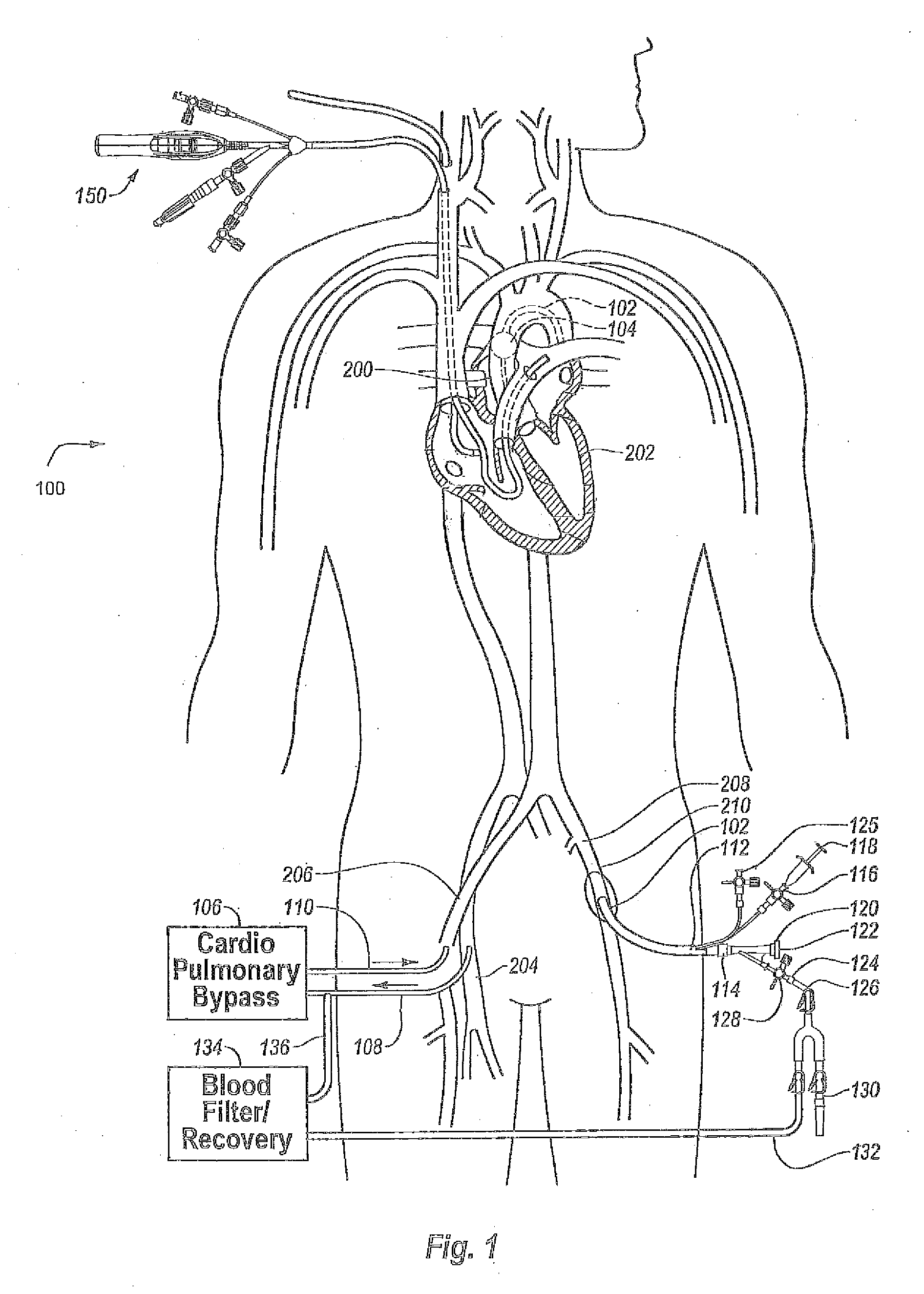
Methods and apparatus for off pump aortic valve replacement with a valve prosthesis
InactiveUS20050203549A1Promote recoveryPromote resultsHeart valvesExcision instrumentsMedicineProsthesis
Methods and apparatus are provided for valve repair or replacement. In one embodiment, the method comprises providing an apparatus having a valve prosthesis, a valve leaflet support and a valve excisor, the apparatus having a first configuration and a second configuration; accessing the aortic root without placing the patient on a heart-lung machine; advancing the apparatus in the first configuration where the valve leaflet support is advanced through a valve, wherein the support is positioned below a valve annulus; expanding the apparatus into a second configuration so that the support will engage the valve; and moving the valve leaflet support and valve excisor together to remove leaflets of the valve. Penetrating members may be advanced into the tissue wherein the penetrating members may act as fasteners to hold the prosthesis in place.
Owner:REALYVASQUEZ FIDEL
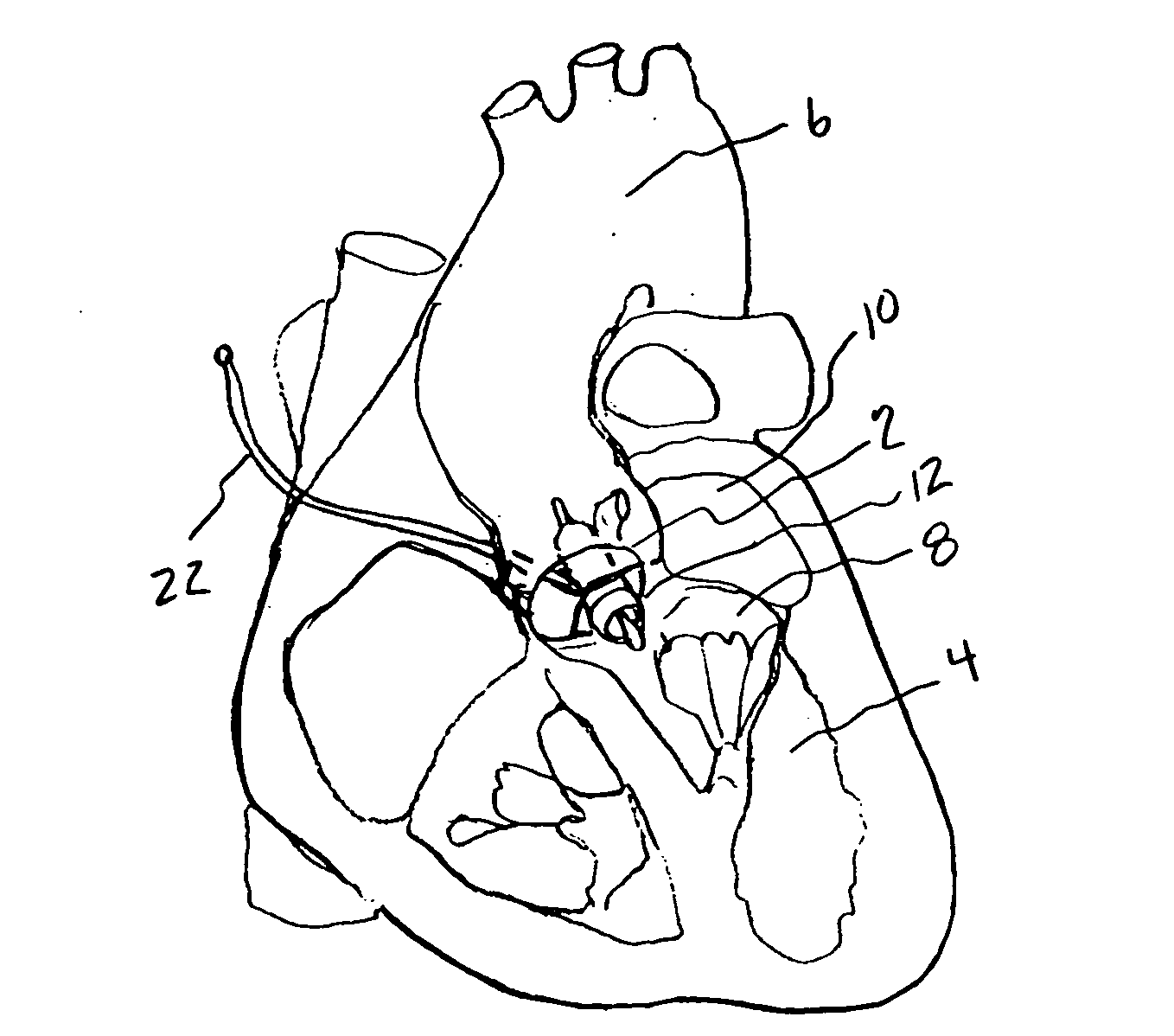
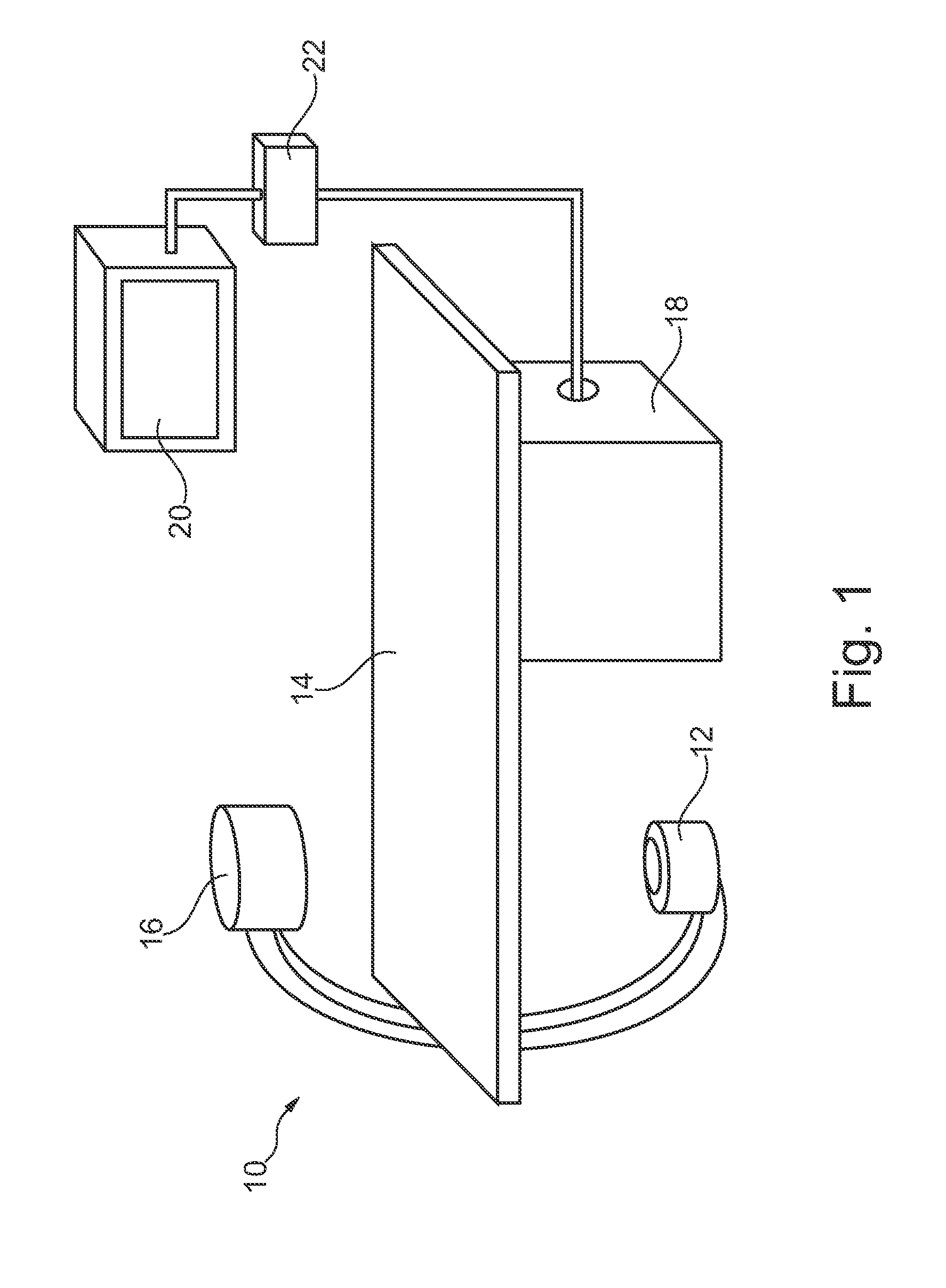
Minimally invasive transvalvular ventricular assist device
ActiveUS20060195004A1Highly effectiveHighly miniaturizedAdditive manufacturing apparatusBlood pumpsThree dimensional ctVentricular cavity
A tiny electrically powered hydrodynamic blood pump is disclosed which occupies one third of the aortic or pulmonary valve position, and pumps directly from the left ventricle to the aorta or from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery. The device is configured to exactly match or approximate the space of one leaflet and sinus of valsalva, with part of the device supported in the outflow tract of the ventricular cavity adjacent to the valve. In the configuration used, two leaflets of the natural tri-leaflet valve remain functional and the pump resides where the third leaflet had been. When implanted, the outer surface of the device includes two faces against which the two valve leaflets seal when closed. To obtain the best valve function, the shape of these faces may be custom fabricated to match the individual patient's valve geometry based on high resolution three dimensional CT or MRI images. Another embodiment of the invention discloses a combined two leaflet tissue valve with the miniature blood pump supported in the position usually occupied by the third leaflet. Either stented or un-stented tissue valves may be used. This structure preserves two thirds of the valve annulus area for ejection of blood by the natural ventricle, with excellent washing of the aortic root and interface of the blood pump to the heart. In the aortic position, the blood pump is positioned in the non-coronary cusp. A major advantage of the transvalvular VAD is the elimination of both the inflow and outflow cannulae usually required with heart assist devices.
Owner:JARVIK ROBERT
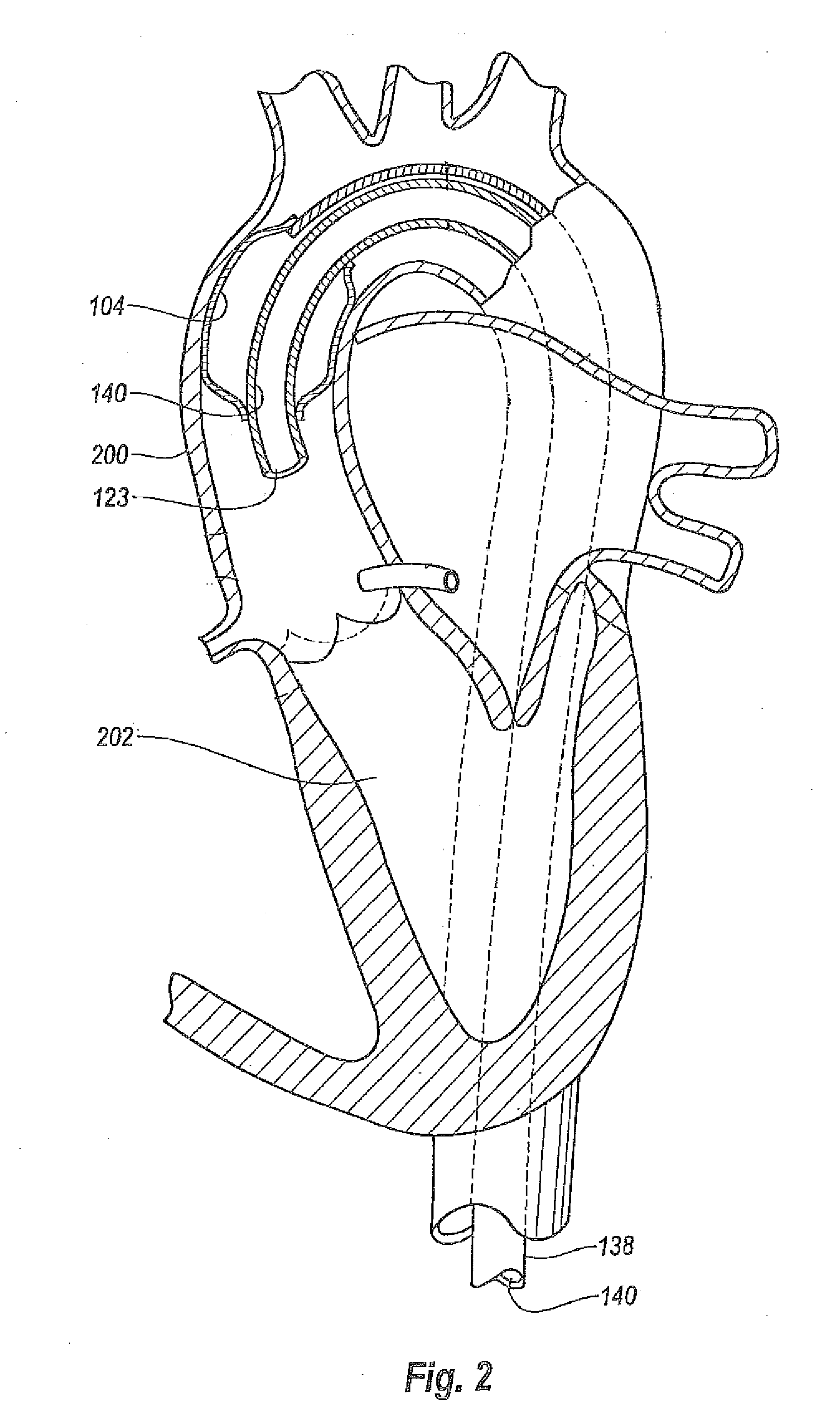
Aortic root prosthesis with compliant sinuses
An aortic root prosthesis for being implanted into a patient during a valve sparing surgery as a replacement for a biological aortic root segment of an ascending aorta is disclosed. The aortic root prosthesis includes a hollow, annular tube having proximal and distal ends, and an inner and outer wall. The distal end is for being attached to the ascending aorta. A plurality of sinuses are circumferentially connected to the proximal end of the tube. Each of the sinuses is adapted for being attached to the aortic wall. Each of the sinuses also includes contouring means for imparting a convex contour to an outer wall of the sinus to thereby create a space between the open leaflet and its respective sinus to prevent impact between the leaflet of the valve and the inner wall of the sinus.
Owner:HEINEMAN MEDICAL RES
Expandable transapical sheath and method of use
ActiveUS20110144690A1Low costShorten the timeGuide needlesBalloon catheterVentricular myocardiumAccess route
Disclosed is an expandable transluminal sheath, for introduction into the body while in a first, small cross-sectional area configuration, and subsequent expansion of at least a part of the distal end of the sheath to a second, enlarged cross-sectional configuration. The sheath is configured for use in the vascular system and has utility in the introduction and removal of implant delivery catheters. The access route is through the ventricular myocardium, more specifically at the left ventricular apex, into the aortic root. The distal end of the sheath is maintained in the first, low cross-sectional configuration during advancement to the arteries into the aorta. The distal end of the sheath is subsequently expanded using a radial dilatation device, which is removed prior to the introduction of implant delivery catheters. In an exemplary application, the sheath includes a supported proximal end, a supported distal end, and a collapsible center section. Certain configurations of the sheath are capable of being inserted in a first, small cross-sectional configuration, being expanded diametrically to a second, larger cross-sectional configuration, and then being reduced to a diametrically small size for removal.
Owner:ONSET MEDICAL CORP
Expandable transapical sheath and method of use
ActiveUS8728153B2Low costShorten the timeGuide needlesBalloon catheterVentricular myocardiumAccess route
The sheath is configured for use in the vascular system and has utility in the introduction and removal of implant delivery catheters. The access route is through the ventricular myocardium, more specifically at the left ventricular apex, into the aortic root. The distal end of the sheath is maintained in the first, low cross-sectional configuration during advancement to the arteries into the aorta. The distal end of the sheath is subsequently expanded using a radial dilatation device, which is removed prior to the introduction of implant delivery catheters. In an exemplary application, the sheath includes a supported proximal end, a supported distal end, and a collapsible center section. Certain configurations of the sheath are capable of being inserted in a first, small cross-sectional configuration, being expanded diametrically to a second, larger cross-sectional configuration, and then being reduced to a diametrically small size for removal.
Owner:ONSET MEDICAL CORP
Medical imaging device for providing an image representation supporting the accurate positioning of an invention device in vessel intervention procedures
ActiveUS20130308844A1Precise positioningConvenient registrationImage enhancementImage analysisFluorescenceX-ray
A medical imaging device and a method for providing an image representation supporting inaccurate positioning of an intervention device in a vessel intervention procedure is proposed. Therein, an anatomy representation (AR) of a vessel region of interest and at least one angiogram X-ray image (RA) and a live fluoroscopy X-ray image (LI) are acquired. The following steps are performed when a radio-opaque device is fixedly arranged within the vessel region of interest: (a) registering the anatomy representation to the at least one angiogram X-ray image in order to provide an anatomy-angiogram-registration (R1); (b) processing (DP) the at least one angiogram X-ray image and the at least one live fluoroscopy X-ray image in order to identify in each of the X-ray images the radio-opaque device; (c) registering (R2) the at least one angiogram X-ray image to the at least one live fluoroscopy X-ray image based on the identified radio-opaque device in order to provide an angiogram-fluoroscopy-registration; and (d) combining the anatomy-angiogram-registration and the angiogram-fluoroscopy-registration in order to provide an anatomy-fluoroscopy-registration (GTC; RALC). Finally, an image representation resulting from the anatomy-fluoroscopy-registration showing an overlay of live images with the anatomy representation may be output thereby helping a surgeon to accurately position for example a synthetic aortic valve within an aortic root of a heart.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Minimally invasive transvalvular ventricular assist device
ActiveUS7479102B2Highly effectiveHighly miniaturizedAdditive manufacturing apparatusBlood pumpsThree dimensional ctVentricular cavity
Owner:JARVIK ROBERT
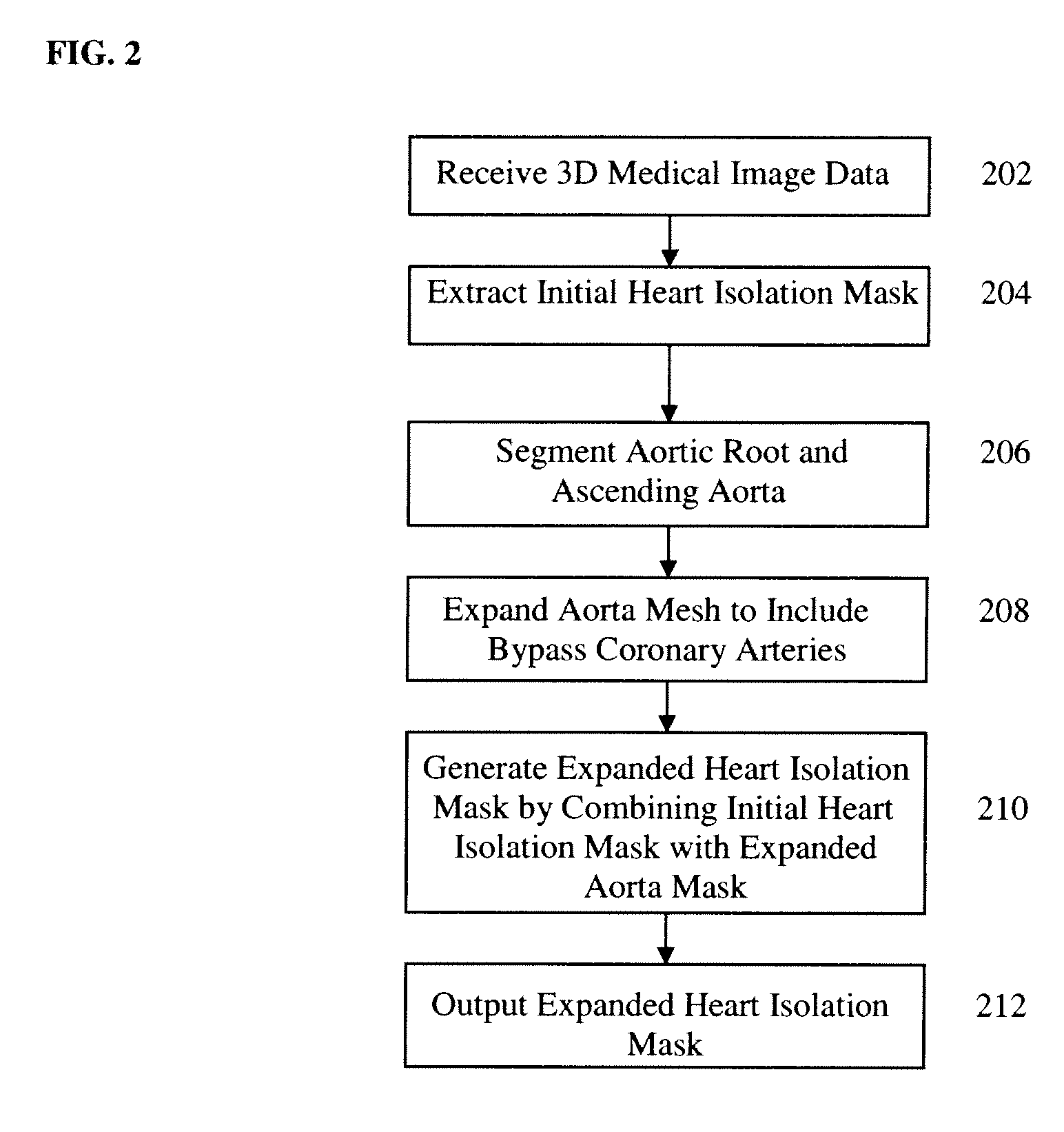
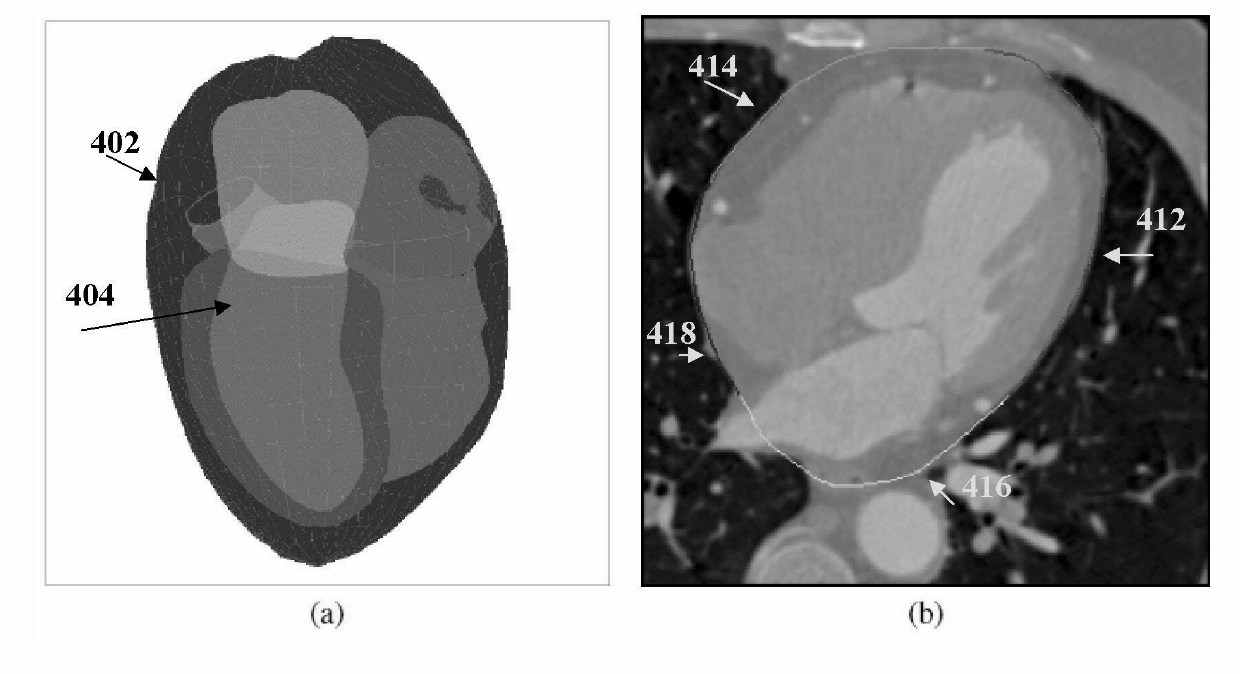
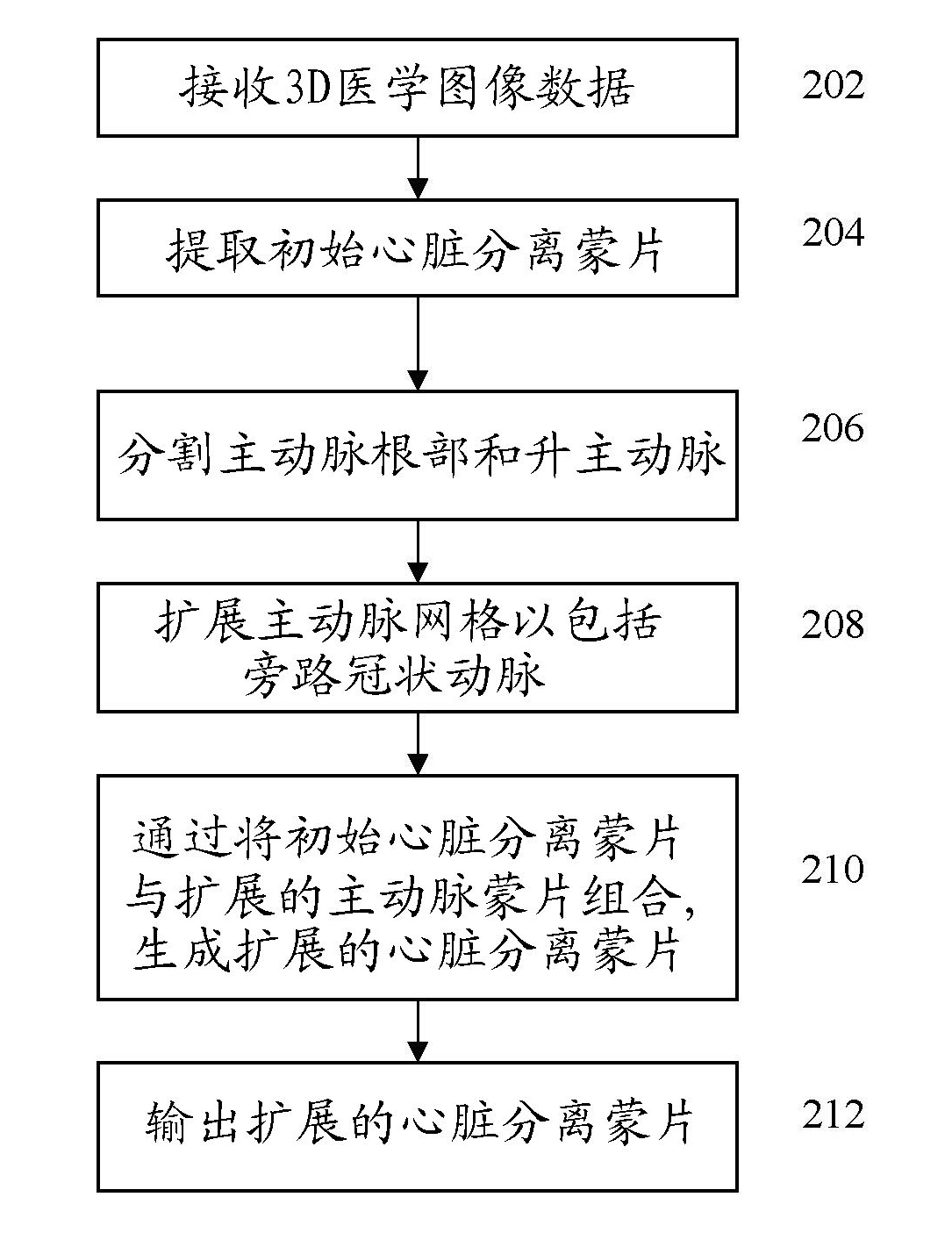
Method and System for Heart Isolation in Cardiac Computed Tomography Volumes for Patients with Coronary Artery Bypasses
ActiveUS20120134564A1Effective isolationImage enhancementImage analysisAscending aortaCoronary arteries
A method and system for isolating the heart in a 3D volume, such as a cardiac CT volume, for patients with coronary artery bypasses is disclosed. An initial heart isolation mask is extracted from a 3D volume, such as a cardiac CT volume. The aortic root and ascending aorta are segmented in the 3D volume, resulting in an aorta mesh. The aorta mesh is expanded to include bypass coronary arteries. An expanded heart isolation mask is generated by combining the initial heart isolation mask with an expanded aorta mask defined by the expanded aorta mesh.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
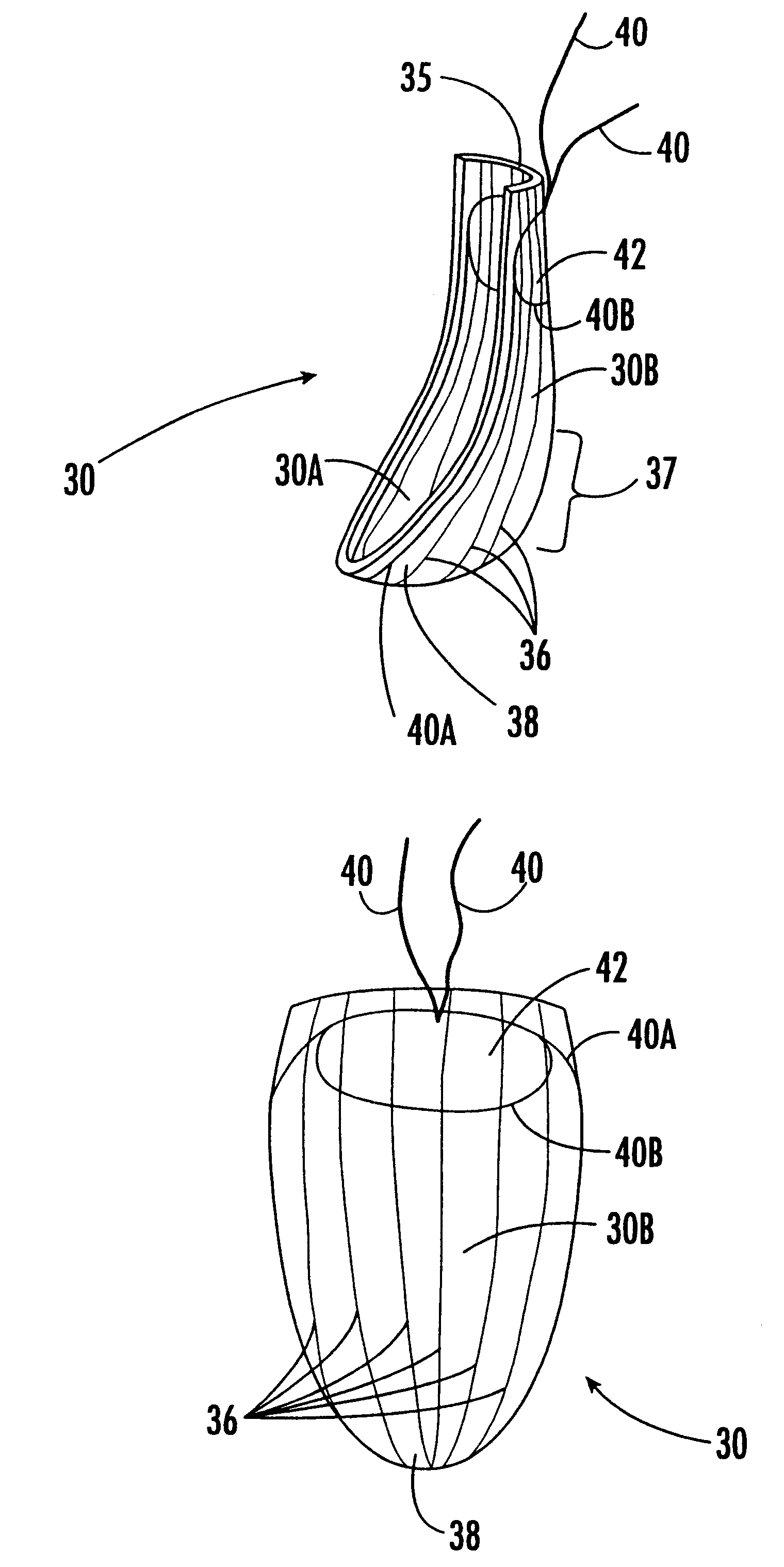
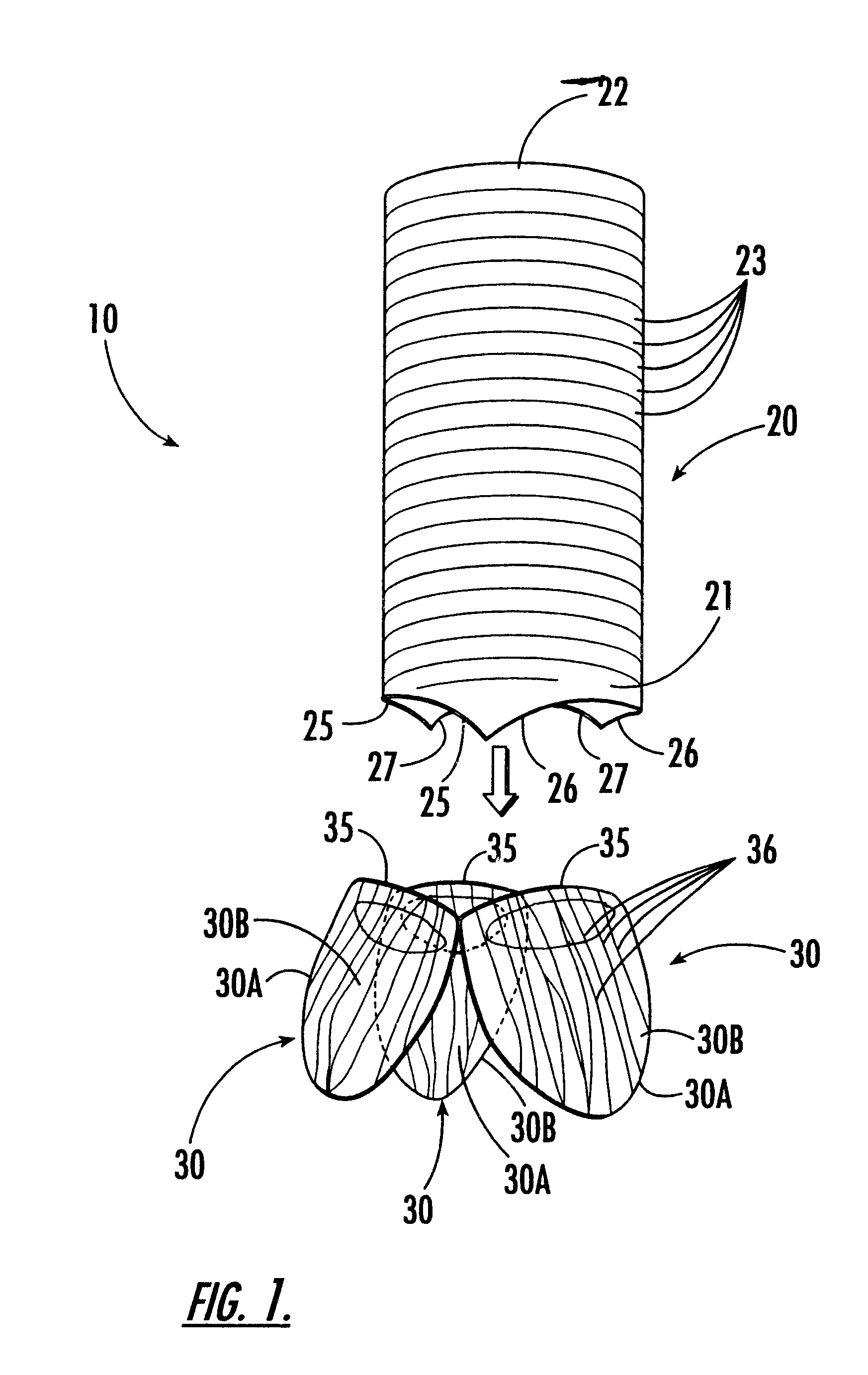
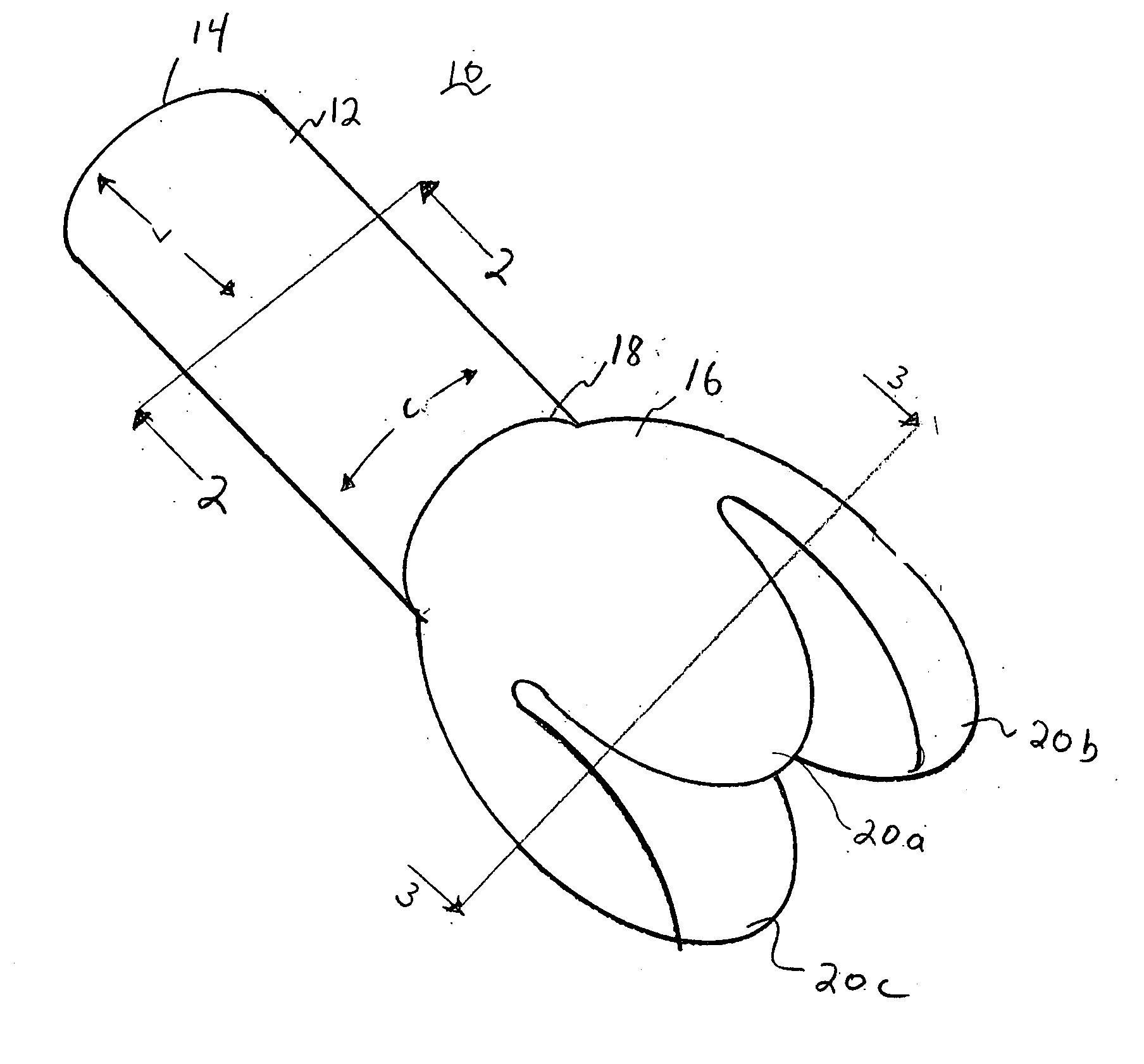
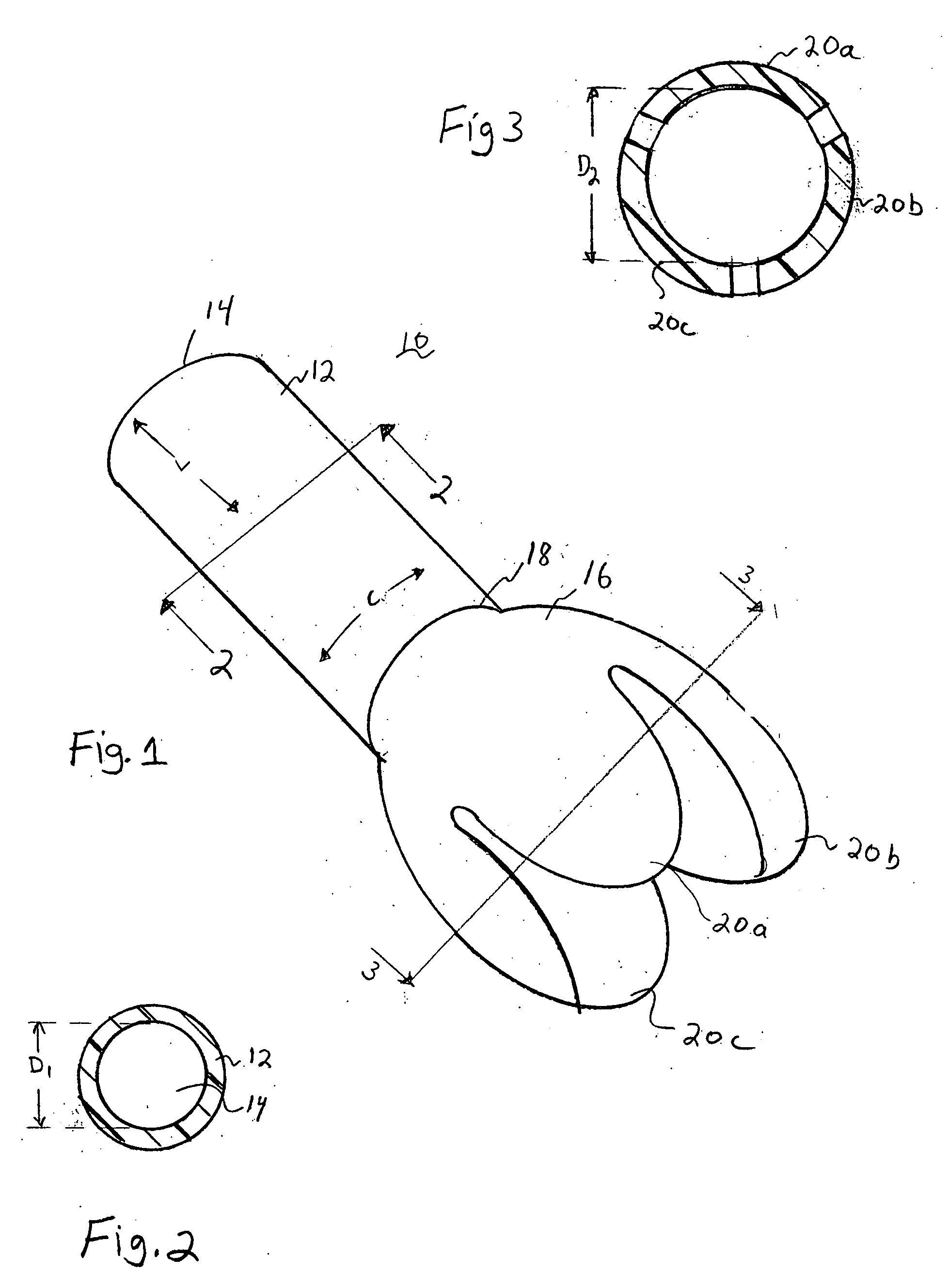
Tri-petaled aortic root vascular graft
An implantable, flat-woven multi-petaled graft includes (i) a hollow tubular woven portion having opposed first and second tubular ends, the woven portion having a number of warp yarns interlaced with a number of fill yarns in a flat-woven tubular woven pattern to define a flat-woven tubular diameter, and (ii) a bulbous woven portion having opposed first and second ends, the first bulbous end having a greater number of warp yarns interlaced with the fill yarns in a flat-woven tubular bulbous pattern contiguously woven from the second tubular end to provide a seamless woven, wherein the greater number of warp yarns are threadingly engaged with the fill yarns to define a flat-woven bulbous diameter; wherein the second end of the bulbous portion is scalloped with a plurality of petal-like projections seamlessly woven from the first bulbous end. The graft may include three petal-like projections. The bulbous woven section may be truncated, i.e., hemispherically or hemibulbously shaped
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
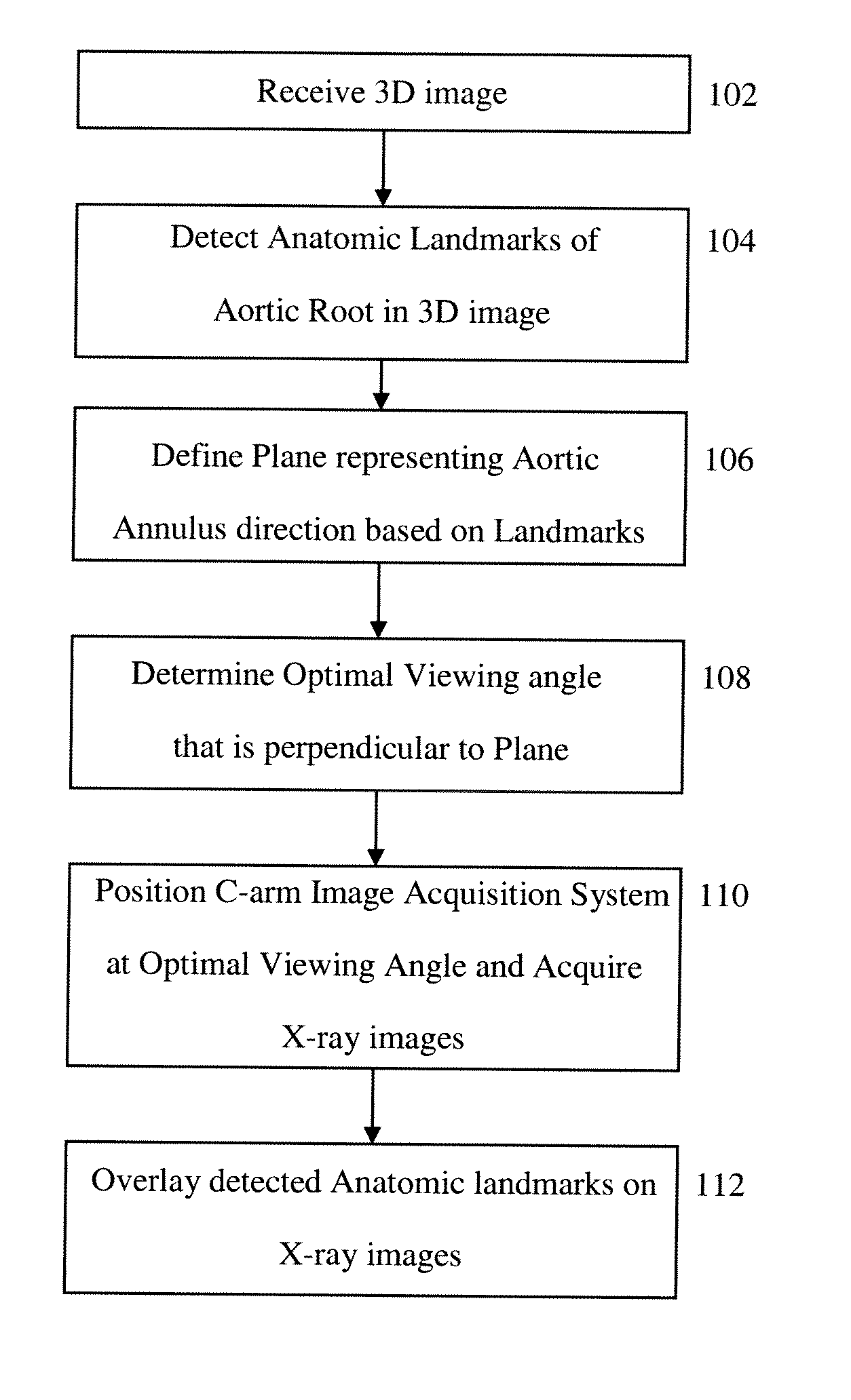
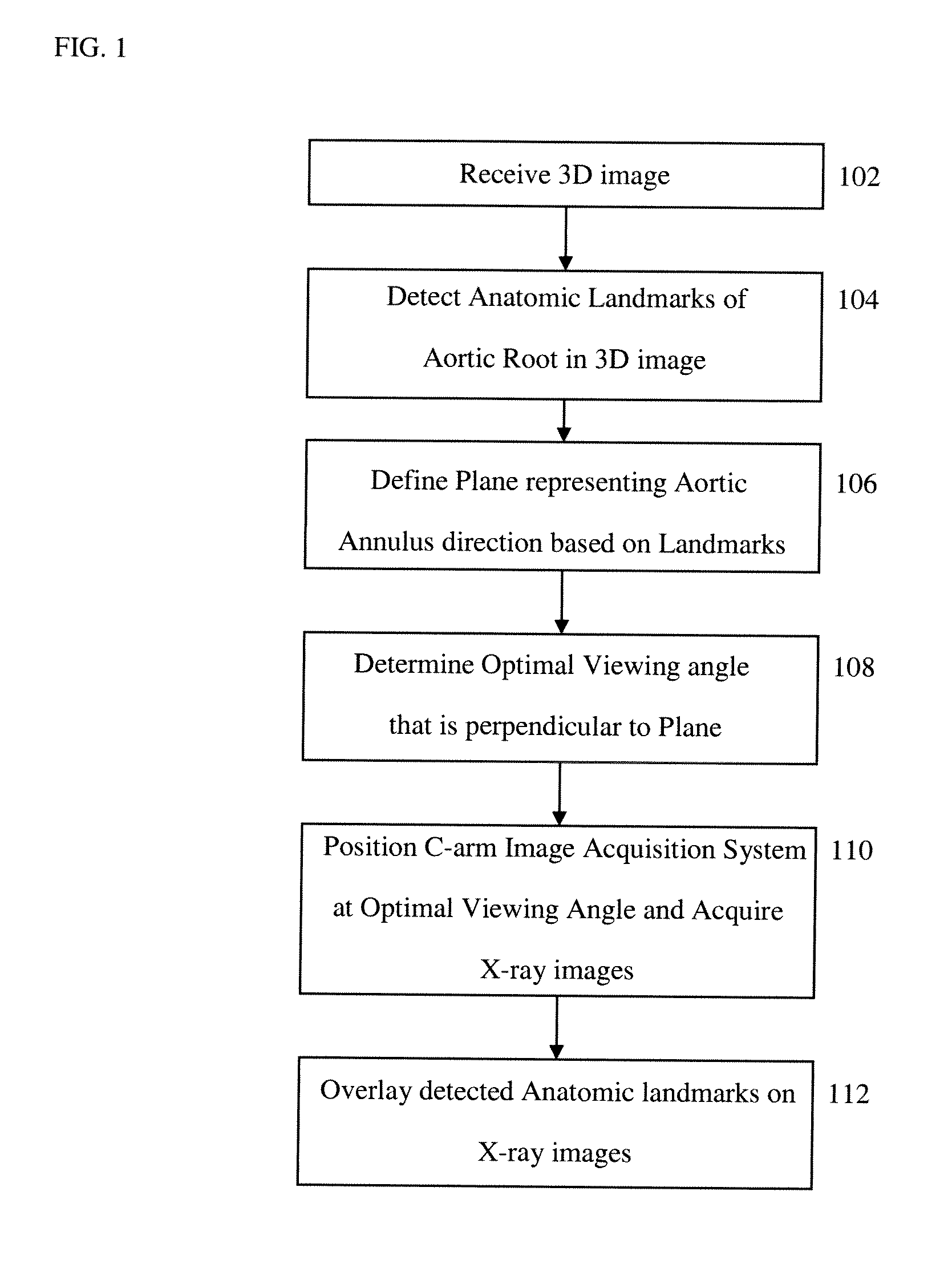
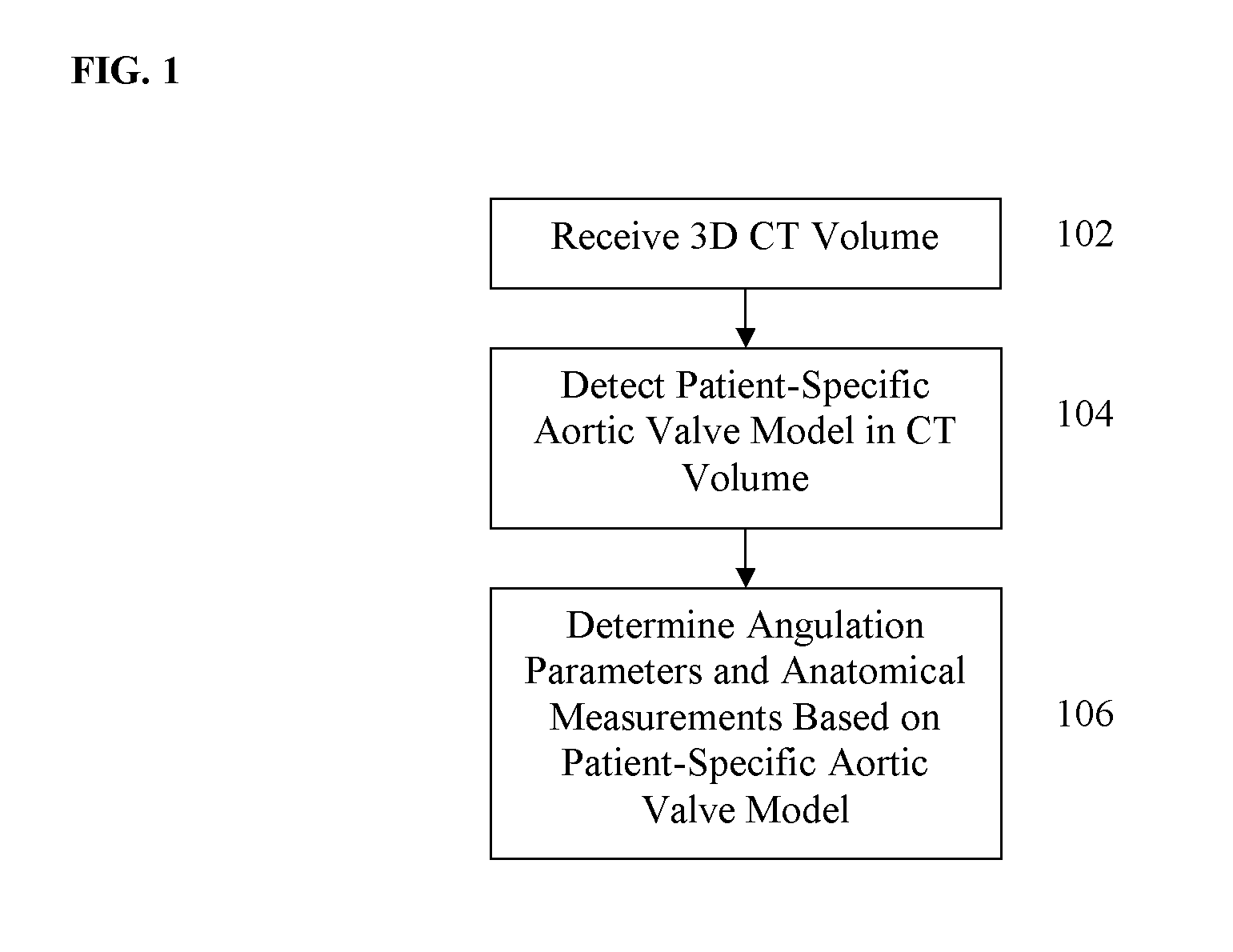
Method and Apparatus for Determining Angulation of C-Arm Image Acquisition System for Aortic Valve Implantation
A method and system for determining an angulation of a C-arm image acquisition system for aortic valve implantation is disclosed. One or more landmarks of the aortic root is detected in a 3D image. A plane representing an aortic annulus direction is defined in the 3D image based on the detected anatomic landmarks. A viewing angle is determined that is perpendicular to the defined plane.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Tri-petaled aortic root vascular graft
An implantable, flat-woven multi-petaled graft includes (i) a hollow tubular woven portion having opposed first and second tubular ends, the woven portion having a number of warp yarns interlaced with a number of fill yarns in a flat-woven tubular woven pattern to define a flat-woven tubular diameter, and (ii) a bulbous woven portion having opposed first and second ends, the first bulbous end having a greater number of warp yarns interlaced with the fill yarns in a flat-woven tubular bulbous pattern contiguously woven from the second tubular end to provide a seamless woven, wherein the greater number of warp yarns are threadingly engaged with the fill yarns to define a flat-woven bulbous diameter; wherein the second end of the bulbous portion is scalloped with a plurality of petal-like projections seamlessly woven from the first bulbous end. The graft may include three petal-like projections. The bulbous woven section may be truncated, i.e., hemispherically or hemibulbously shaped.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Image representation supporting the accurate positioning of an intervention device in vessel intervention procedures
ActiveUS9295435B2Convenient registrationPrecise positioningImage enhancementImage analysisFluorescenceX-ray
A medical imaging device and a method for providing an image representation supporting inaccurate positioning of an intervention device in a vessel intervention procedure is proposed. Therein, an anatomy representation (AR) of a vessel region of interest and at least one angiogram X-ray image (RA) and a live fluoroscopy X-ray image (LI) are acquired. The following steps are performed when a radio-opaque device is fixedly arranged within the vessel region of interest: (a) registering the anatomy representation to the at least one angiogram X-ray image in order to provide an anatomy-angiogram-registration (R1); (b) processing (DP) the at least one angiogram X-ray image and the at least one live fluoroscopy X-ray image in order to identify in each of the X-ray images the radio-opaque device; (c) registering (R2) the at least one angiogram X-ray image to the at least one live fluoroscopy X-ray image based on the identified radio-opaque device in order to provide an angiogram-fluoroscopy-registration; and (d) combining the anatomy-angiogram-registration and the angiogram-fluoroscopy-registration in order to provide an anatomy-fluoroscopy-registration (GTC; RALC). Finally, an image representation resulting from the anatomy-fluoroscopy-registration showing an overlay of live images with the anatomy representation may be output thereby helping a surgeon to accurately position for example a synthetic aortic valve within an aortic root of a heart.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Methods of implanting a heart valve at an aortic annulus
ActiveUS20160128829A1Shorten the construction periodShorten the timeBalloon catheterHeart valvesCouplingInsertion stent
An exemplary two-stage prosthetic heart valve system has a radially expandable base stent implanted within a native valve annulus. The two-stage heart valve system also has a valve component that is delivered to and mounted within the base stent in a separate or sequential operation after the base stent has been anchored within the annulus. The valve component in certain embodiments comprises a hybrid valve component that includes a conventional, non-expandable surgical valve that is modified to include an expandable coupling stent that can be expanded to engage the inner surface of the base stent, thereby anchoring the valve component to the base stent. In its expanded configuration, the outflow end portion base stent has tri-lobular shape that closely conforms to the shape of the aortic root and a support ring of the prosthetic valve that is mounted within the base stent.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Method and System for Intervention Planning for Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation from 3D Computed Tomography Data
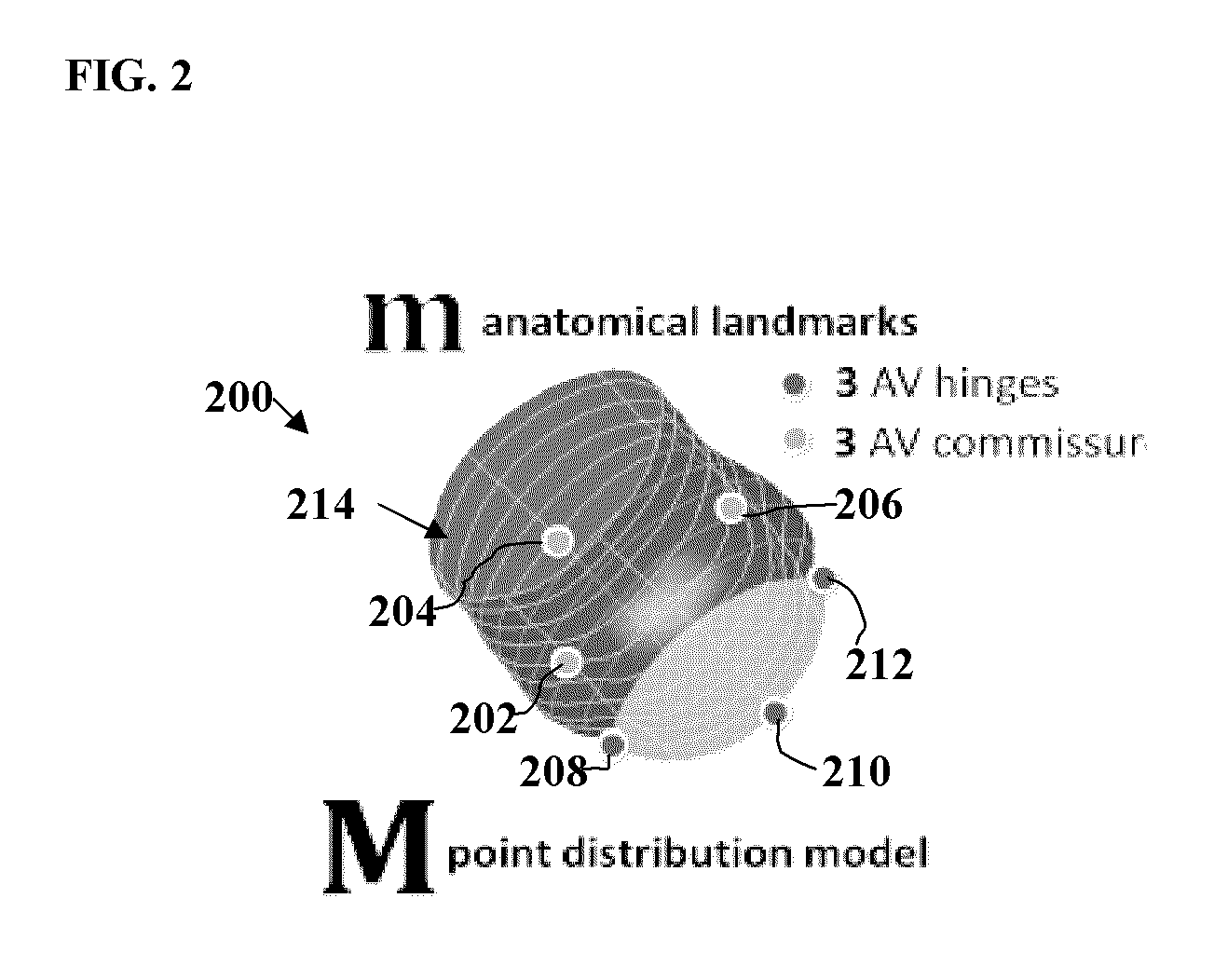
A method and system for automated intervention planning for transcatheter aortic valve implantations using computed tomography (CT) data is disclosed. A patient-specific aortic valve model is detected in a CT volume of a patient. The patient-specific aortic valve model is detected by detecting a global location of the patient-specific aortic valve model in the CT volume, detecting aortic valve landmarks based on the detected global location, and fitting an aortic root surface model. Angulation parameters of a C-arm imaging device for acquiring intra-operative fluoroscopic images and anatomical measurements of the aortic valve are automatically determined based on the patient-specific aortic valve model.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
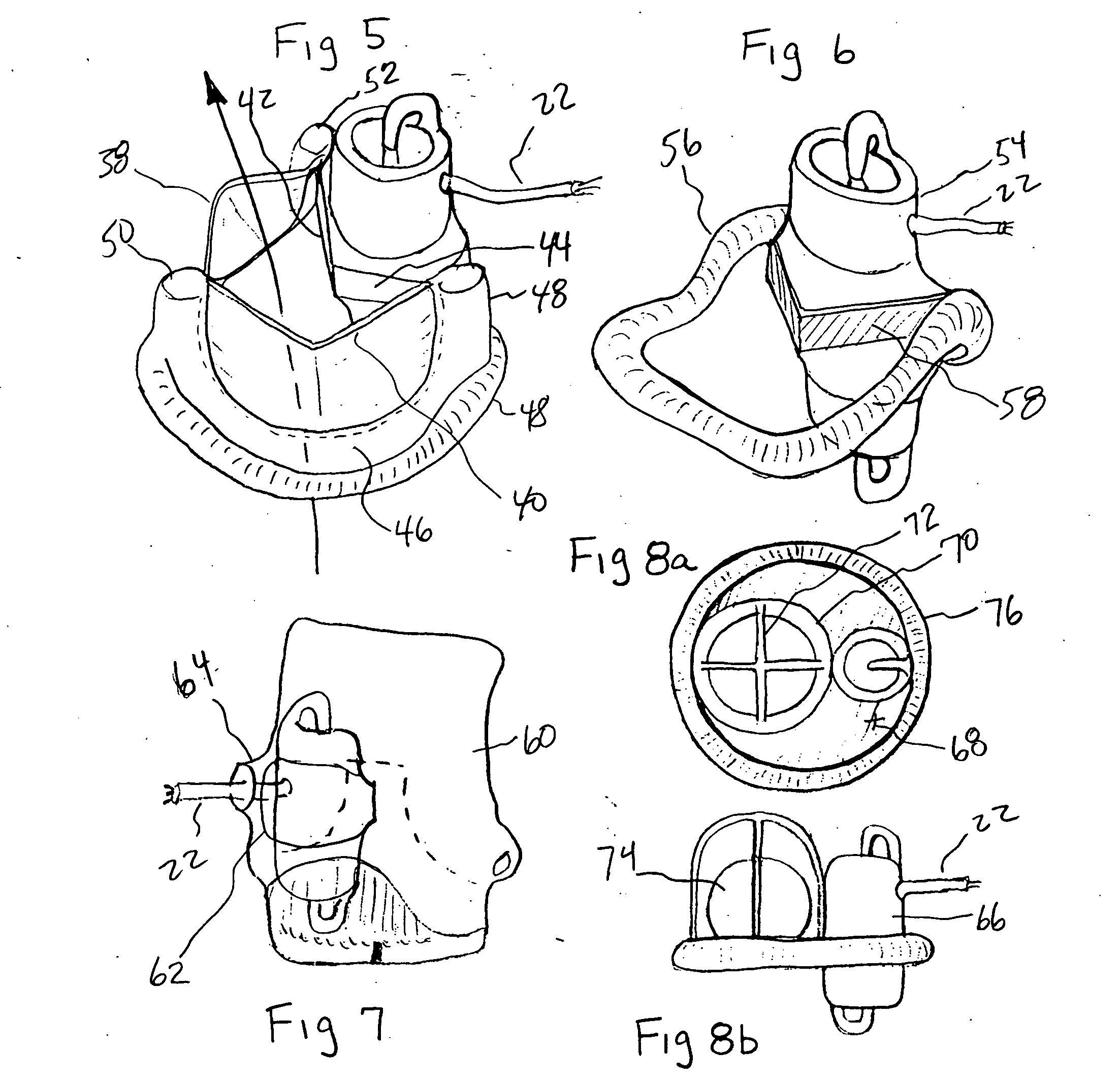
Simulated heat and valve root for training and testing
InactiveUS20070269784A1Realistic trainingMore realismEducational modelsCalcificationProsthetic heart
A simulated heart valve root used for training physicians in techniques of implantation of prosthetic heart valves as well as for more realistically testing the efficacy of prosthetic heart valves. The simulated heart valve root is made of the flexible, tubular body having an inner wall defining an annular ledge within which the prosthetic heart valve is implanted. Discrete nodes or areas of simulated calcification may be provided on the annular ledge. A simulated aortic root includes alternating cusps and commissures with calcification simulated at least at one of the commissures. A tear in the annular ledge may also be provided which simulates a tear that might occur from a valvuloplasty procedure. A reinforcing sleeve may surround the flexible tubular body to provide rigidity or hoop strength thereto. A method of testing includes mounting the simulated heart valve root in a flow conduit, implanting a prosthetic heart valve in the root, applying pulsatile flow to the assembly, and monitoring for leaks. The simulated heart valve root may also be incorporated within a larger simulated heart for use in training physicians to remotely implant prosthetic heart valves.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
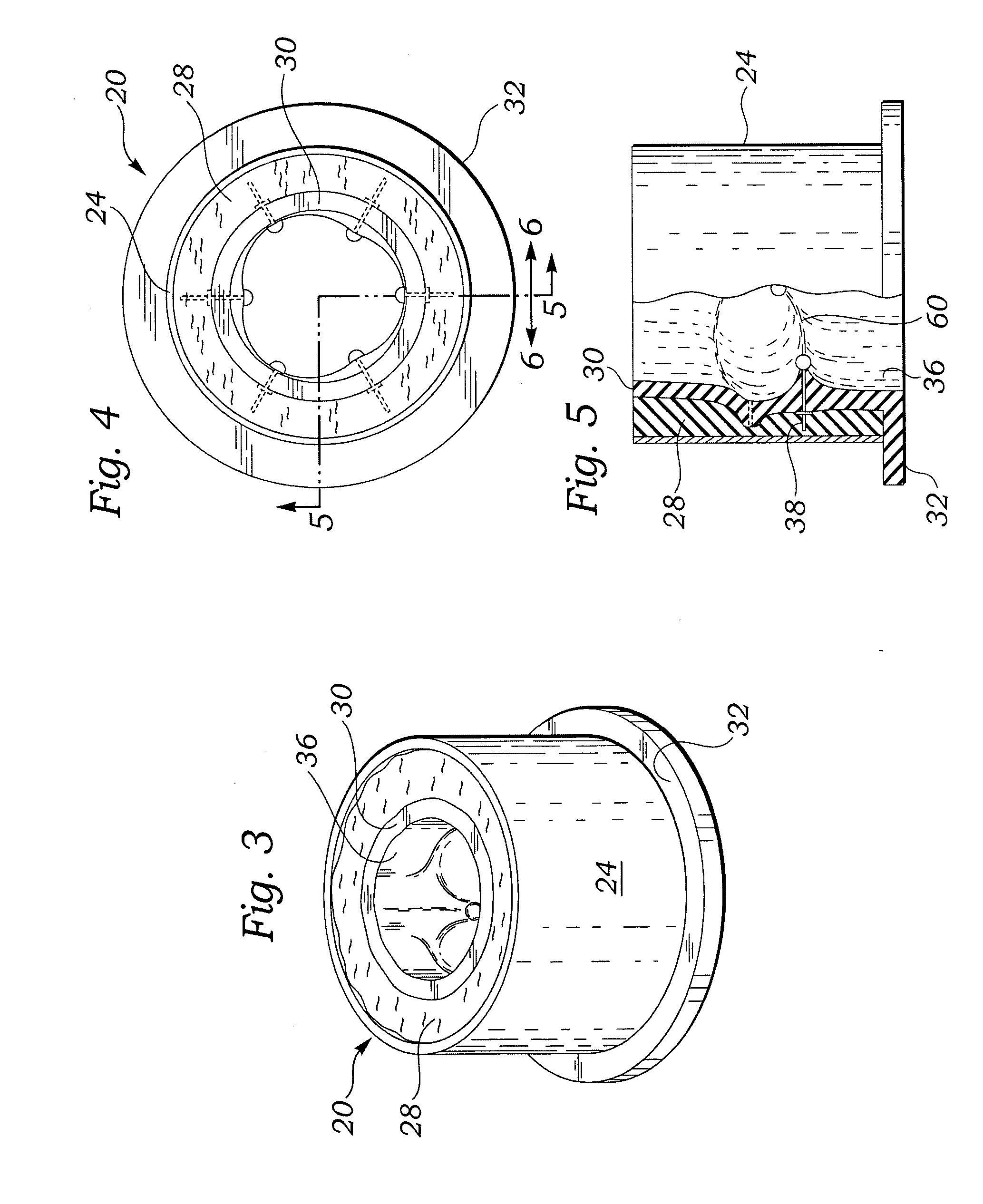
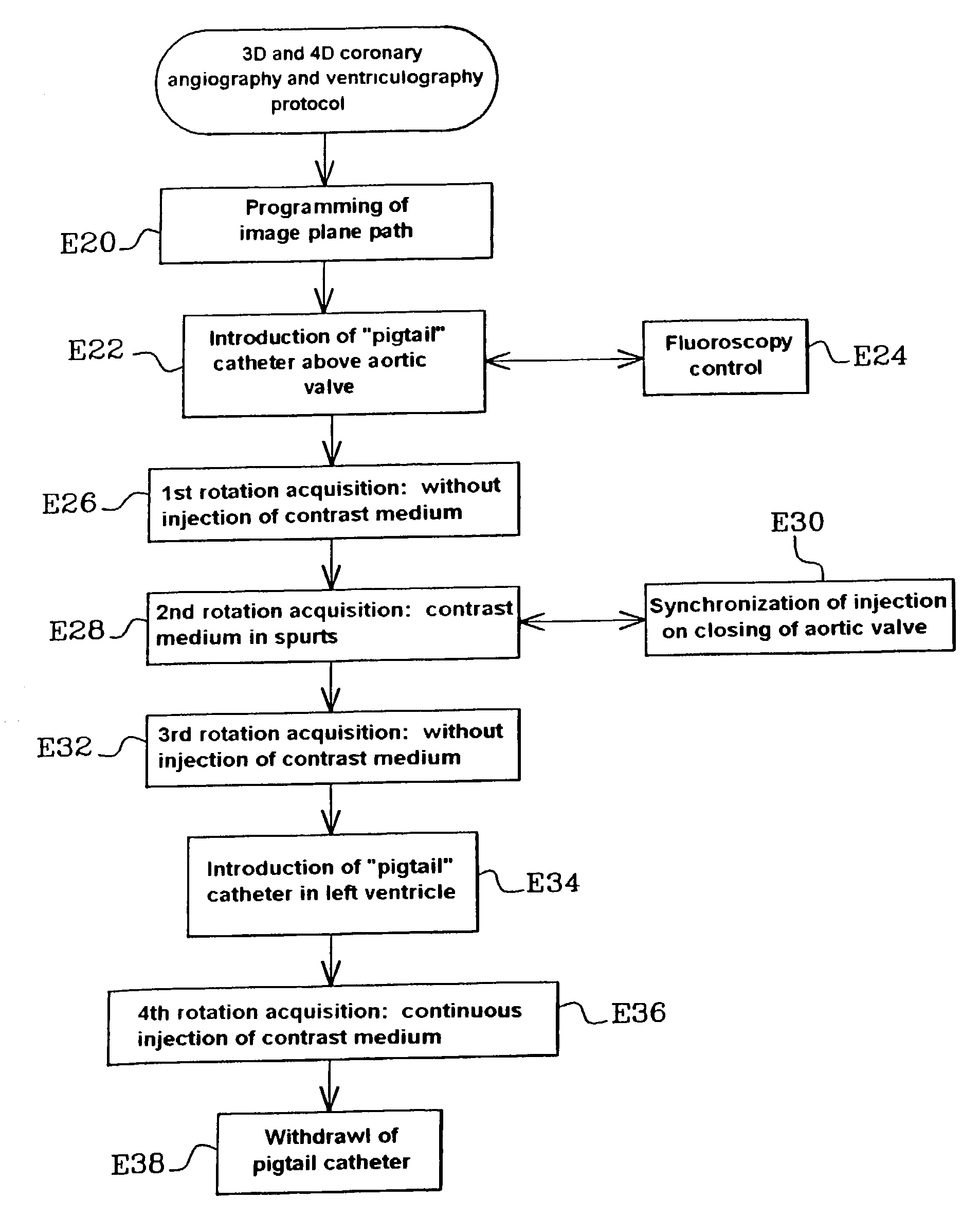
Method and apparatus for cardiac radiological examination in coronary angiography
InactiveUS7065395B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingAortic rootImage plane
A method of cardiac radiological examination for coronarography comprises the steps of:a) introducing contrast medium simultaneously in the left coronary artery and in the right coronary artery from the aortic root and, in parallel,b) acquiring a sequence of dynamic images of the propagation of the contrast medium in the left and right coronary arteries with a displacement of the image plane, during the acquisition of said images, along a determined trajectory (E28). The contrast medium can be introduced in a cyclic manner during the acquisition of dynamic images, each cycle of introduction corresponding to a phase of closure of the aortic valve in the cardiac rhythm. 3D and 4D images with optimal efficiency can be obtained in the use of contrast medium. An injection device for producing the above cycles is synchronized with the introduction of the contrast medium.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
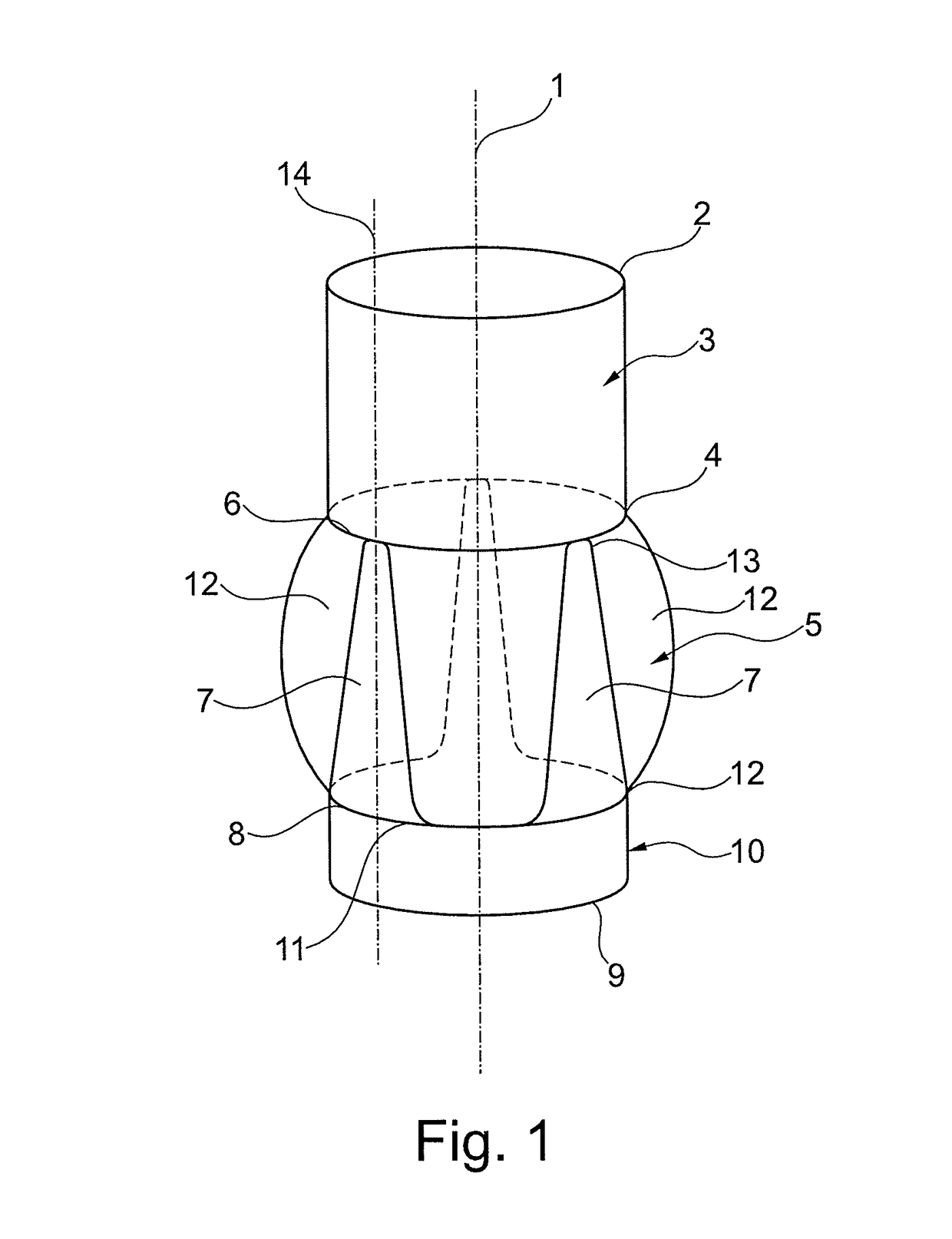
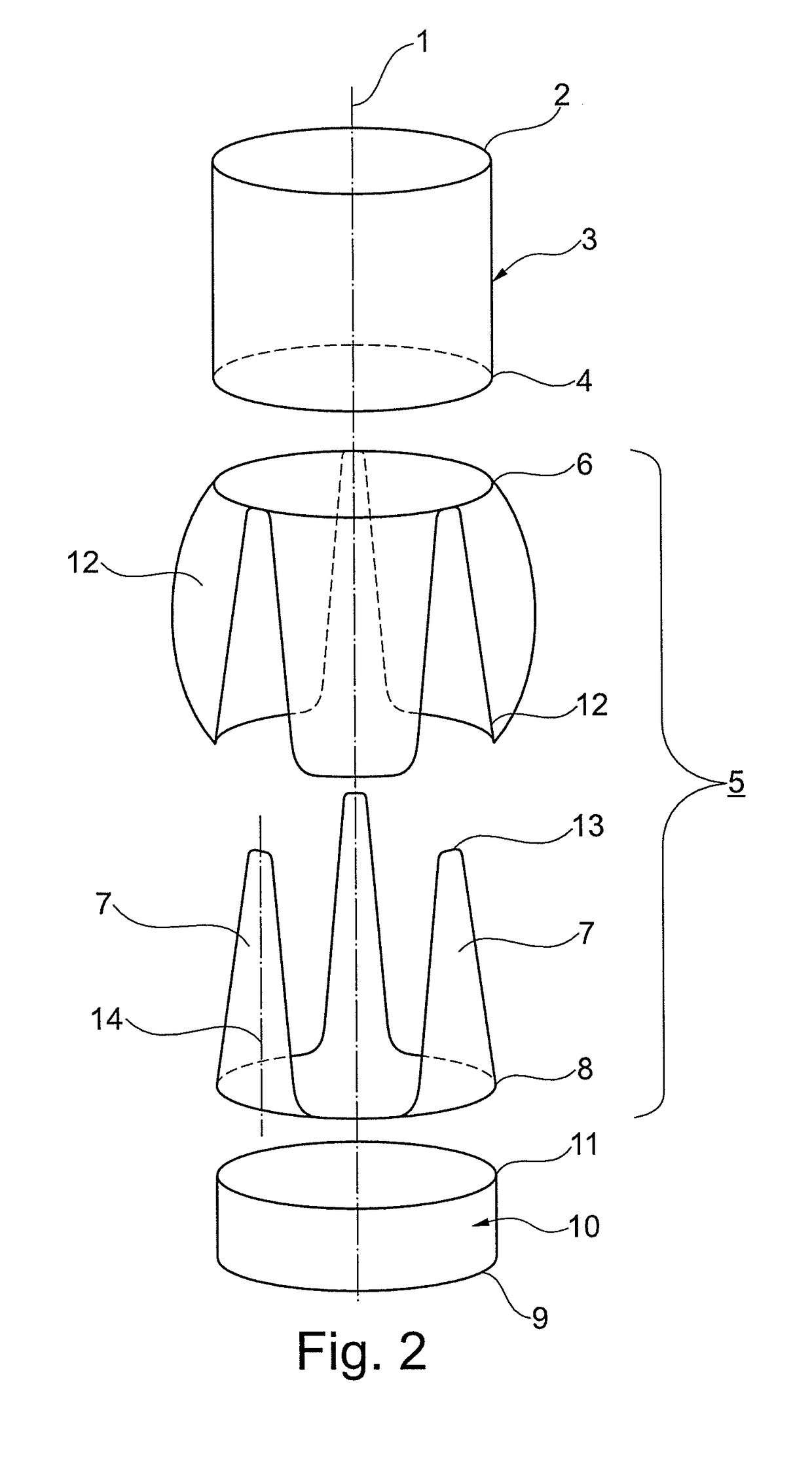
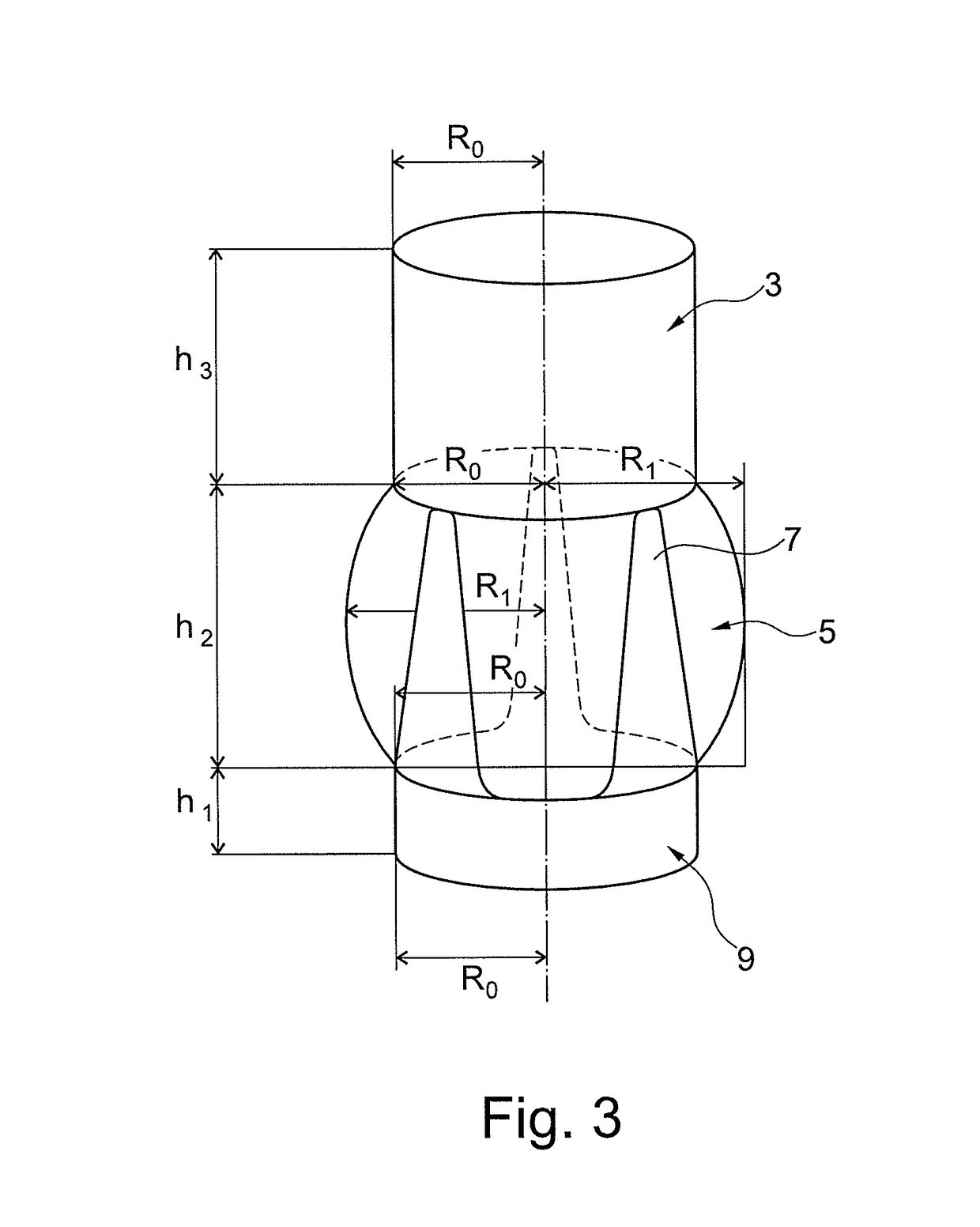
Cone-shaped aortic root replacement graft and methods for making and using same
A new aortic root replacement graft or apparatus is disclosed and method for making and using same. The graft or apparatus includes a substantially straight and uniform cylindrical conduit having an outwardly flared end section so that a diameter of the cylindrical section is less than a diameter of a distal end of the flared end section.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
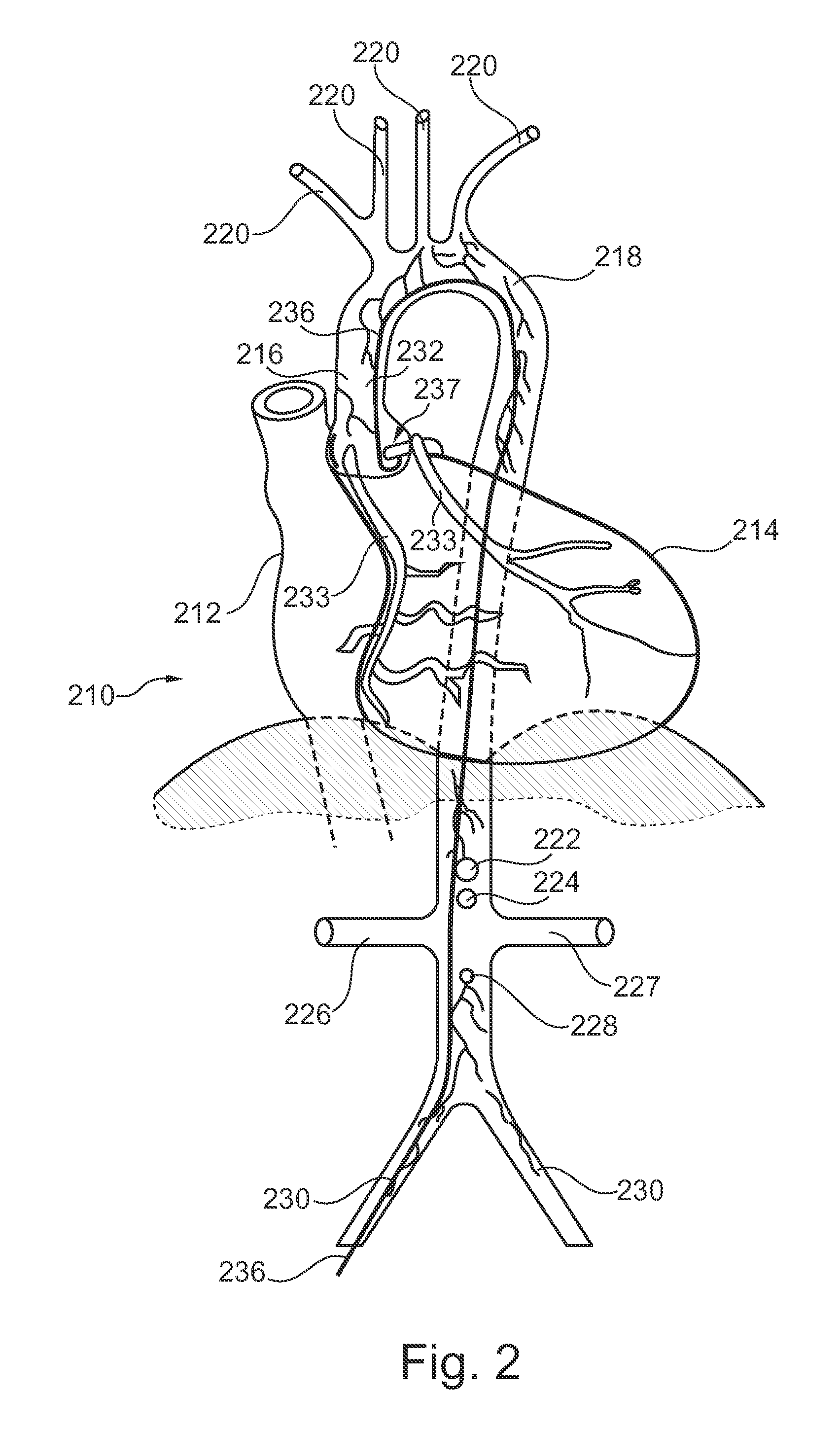
Intervention type aorta blood pump for ischemic heart diseases and installation method thereof
An intervention type aorta blood pump for ischemic heart diseases and an installation method thereof belong to the technical field of bioengineering. The intervention type aorta blood pump is composed of an aorta blood pump (2) and an aorta blood pump outer support (1), wherein the aorta blood pump (2) is in a cylinder shape and can penetrate through the aorta blood pump outer support (1). When the intervention type aorta blood pump is installed, thoracic surgery is avoided, the intervention type aorta blood pump can be pushed between an aortic root and an arcus aortae from the far end through a cathode, the intervention type aorta blood pump can be fixed in an aorta vessel though vessel outer ligation technology, and the intervention type aorta blood pump can be transplanted matched with coronary artery bypass grafting. The intervention type aorta blood pump can obviously improve coronary artery infusion amount and myocardium blood supply conditions.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Prosthetic aortic root replacement graft
InactiveUS20190015191A1More physiological solutionIncreased durabilityHeart valvesBlood vesselsProsthesisAortic arch
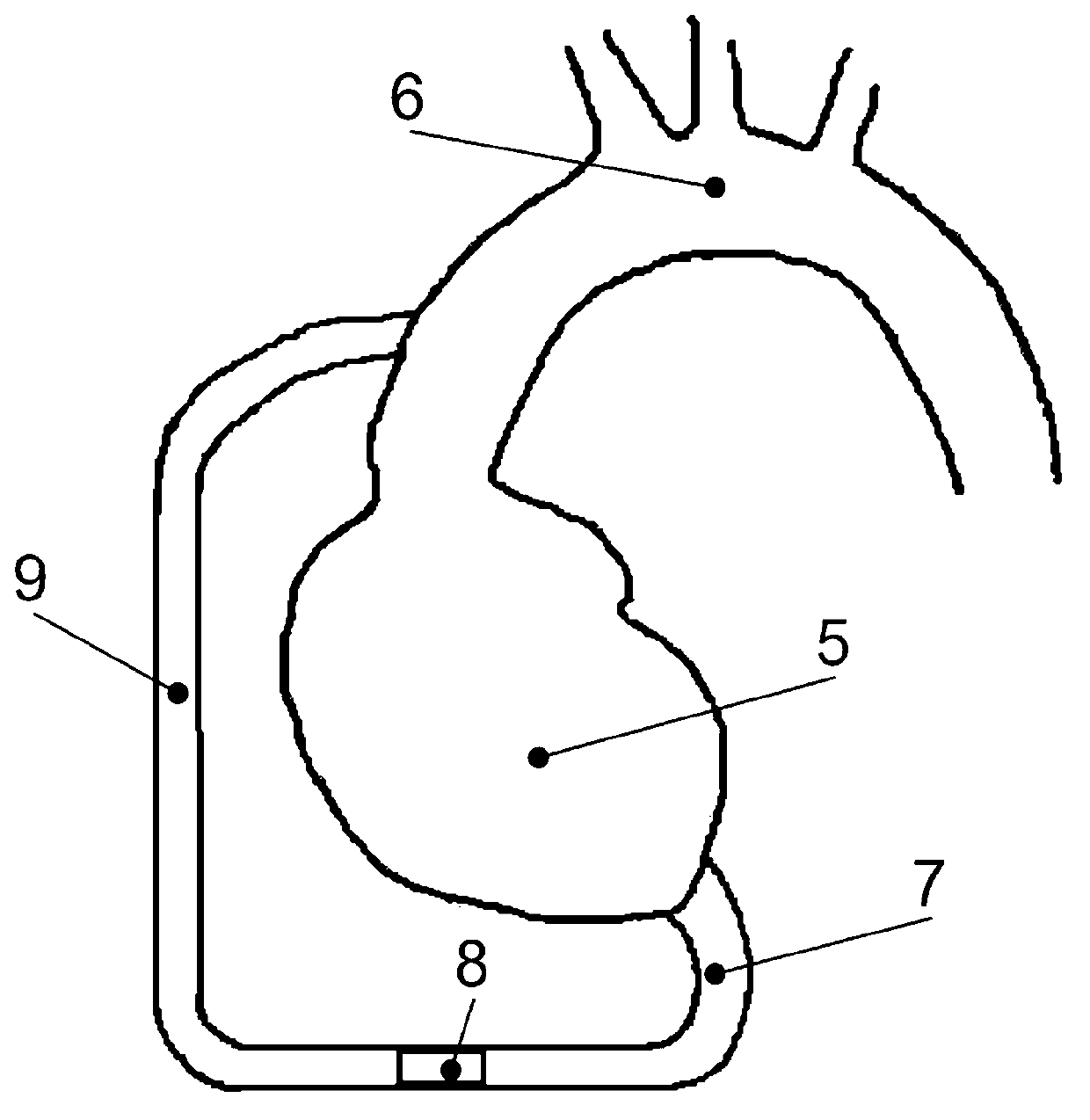
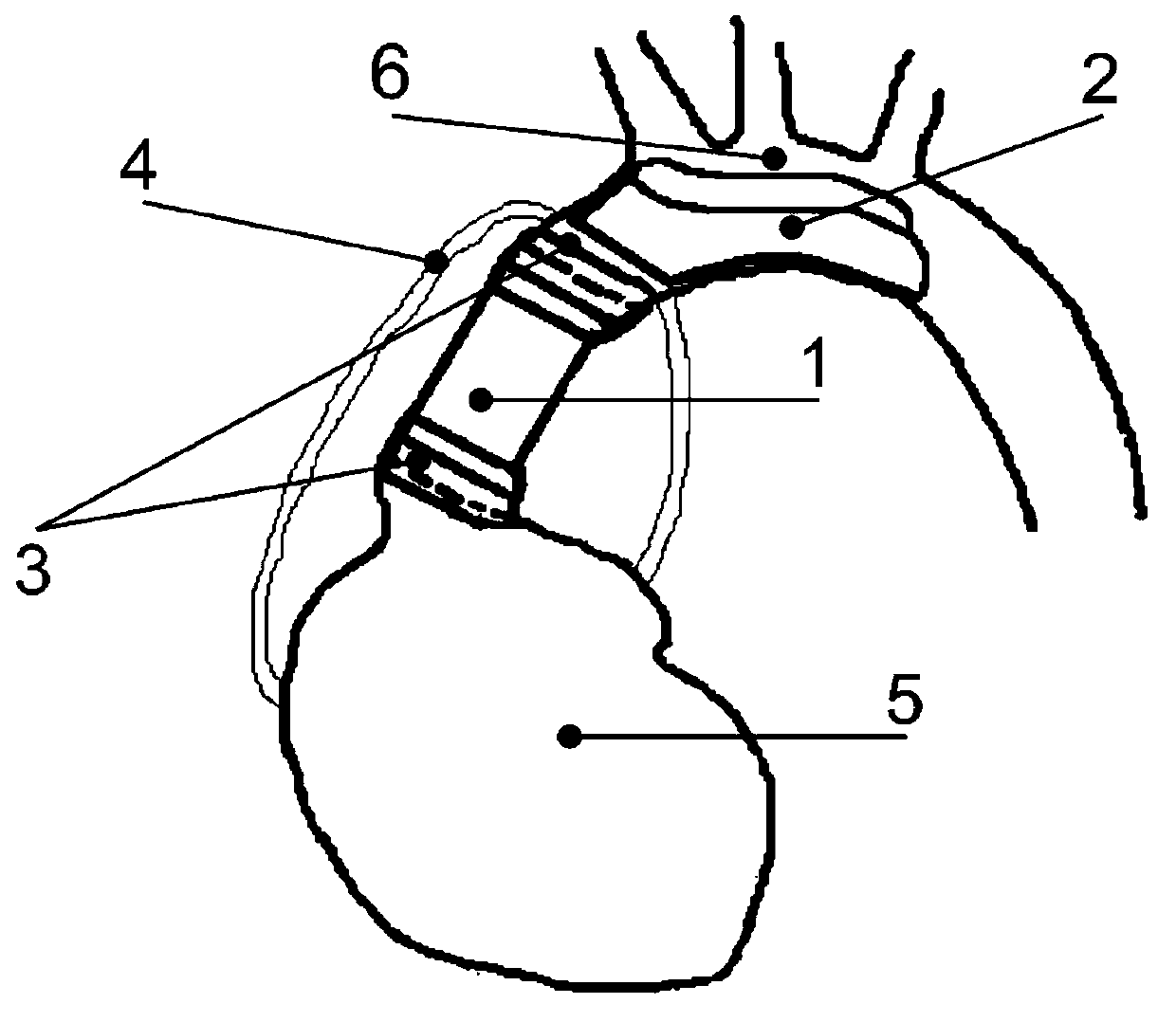
A prosthetic aortic root replacement graft for preserving the native aortic valve that includes a biocompatible flexible material havinga) a tubular superior segment (3), with an upper free edge (2) for anastomosis of the prosthesis to the aortic arch, and a lower edge (4);b) a hollow medial segment (5) with an upper edge (6) that is connected to the lower edge (4) of the superior segment (3) and a lower edge (8); andc) optionally a tubular inferior segment (10).The medial segment (5) includes three triangular-like tongues (7) tapering towards the upper edge (6) and three bulges (12). The bulges (12) and the tongues (7) are in an alternating arrangement.
Owner:BERDAJS DENIS
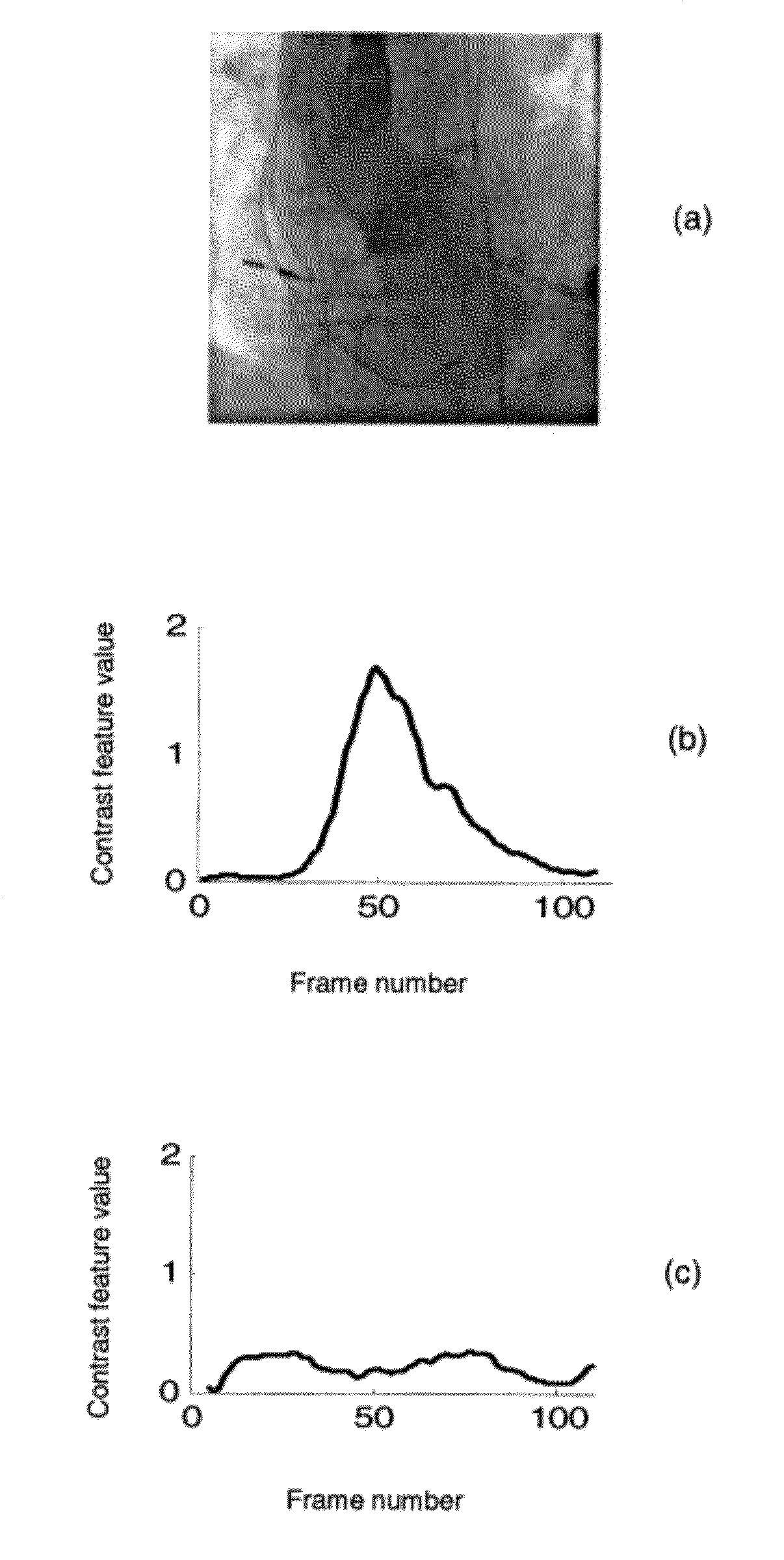
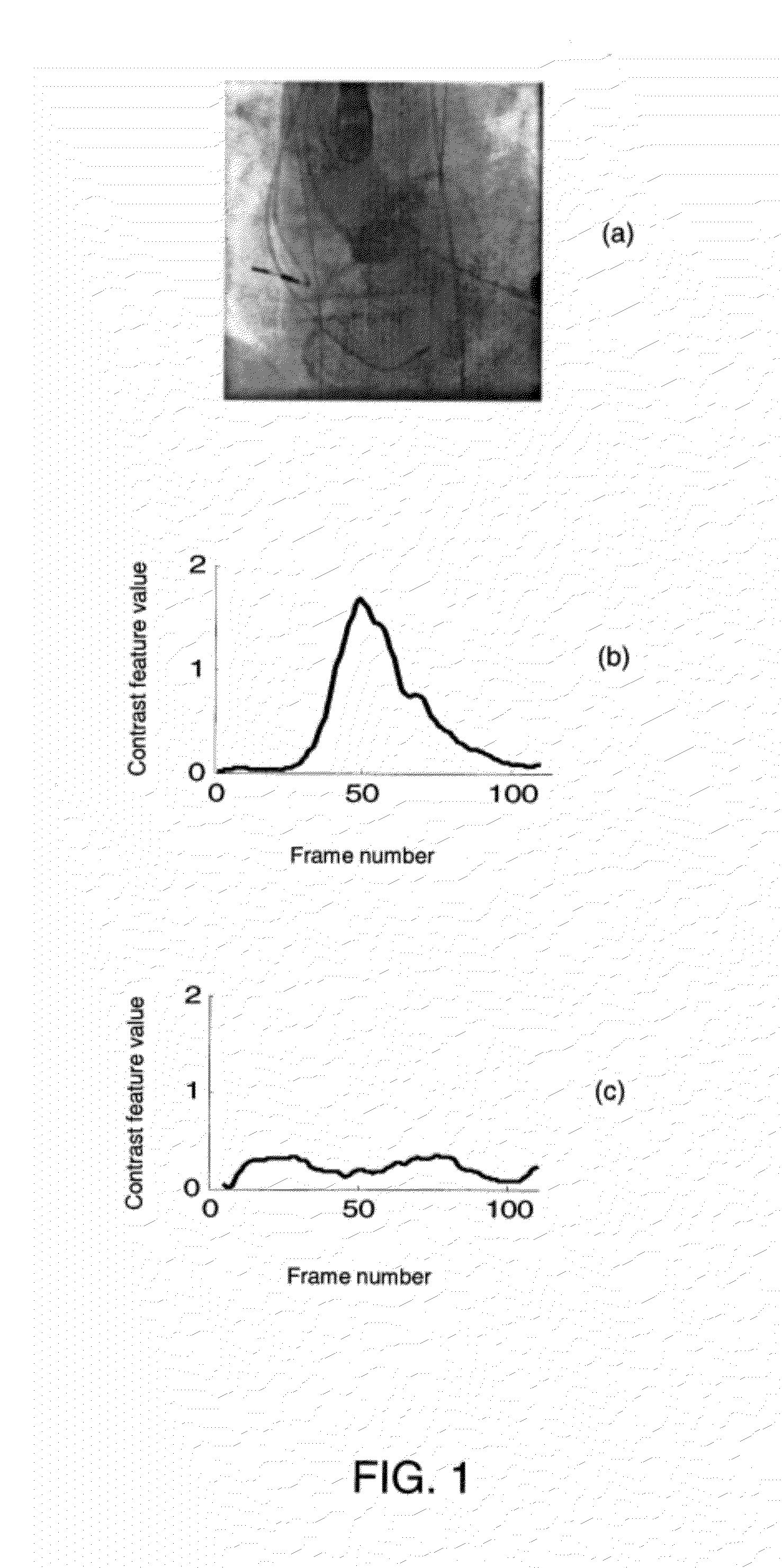
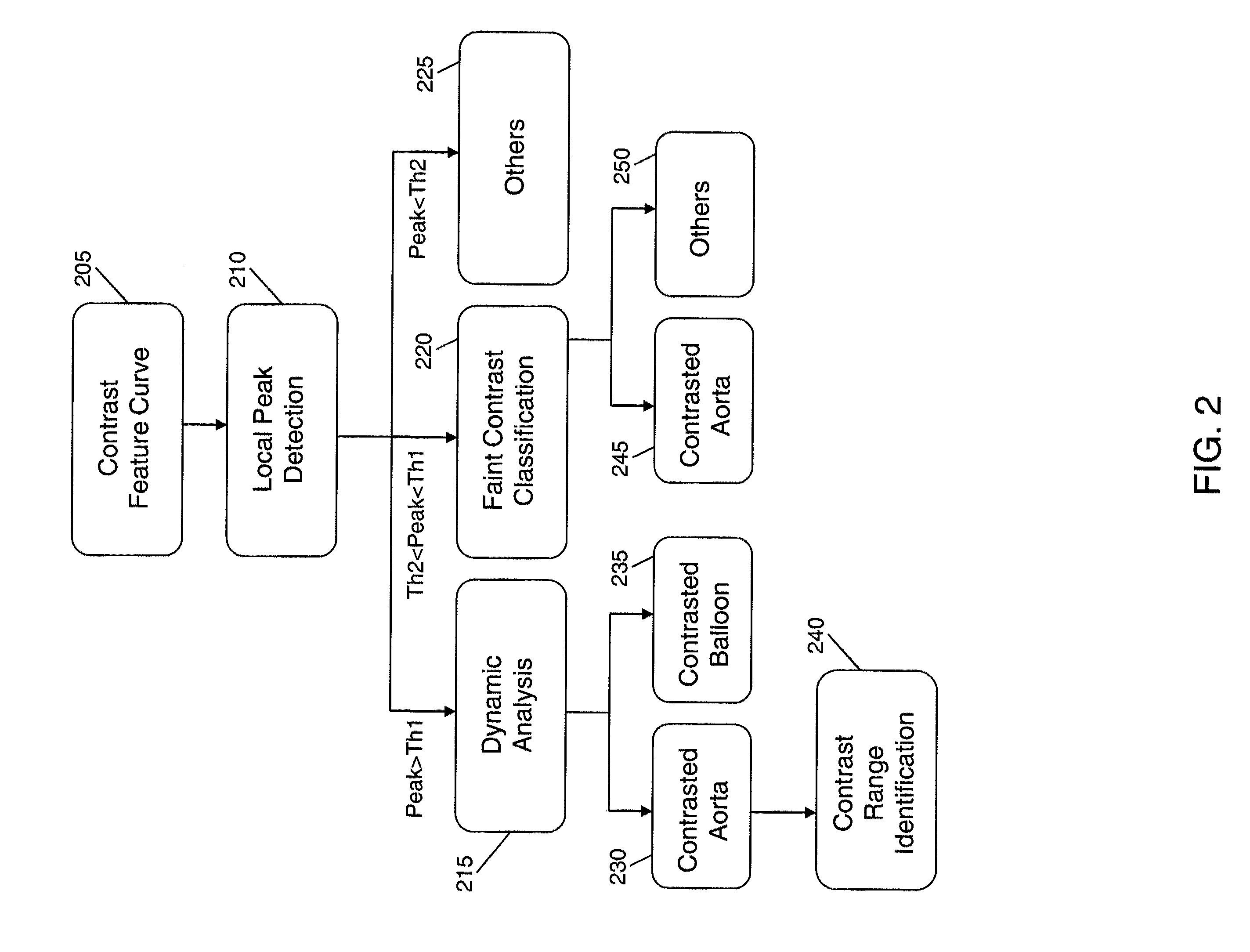
Spatio-Temporal Analysis for Automatic Contrast Injection Detection on Angiography During Trans-Catheter Aortic Valve Implantation
A method that includes generating a contrast feature curve for a medical image sequence including a plurality of frames, where the contrast feature curve represents contrast feature values of the frames. The method further includes detecting a peak in the contrast feature curve, and determining whether the peak corresponds to at least one of contrast injection in an aortic root, contrast injection in a balloon, and a non-contrast injected region.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
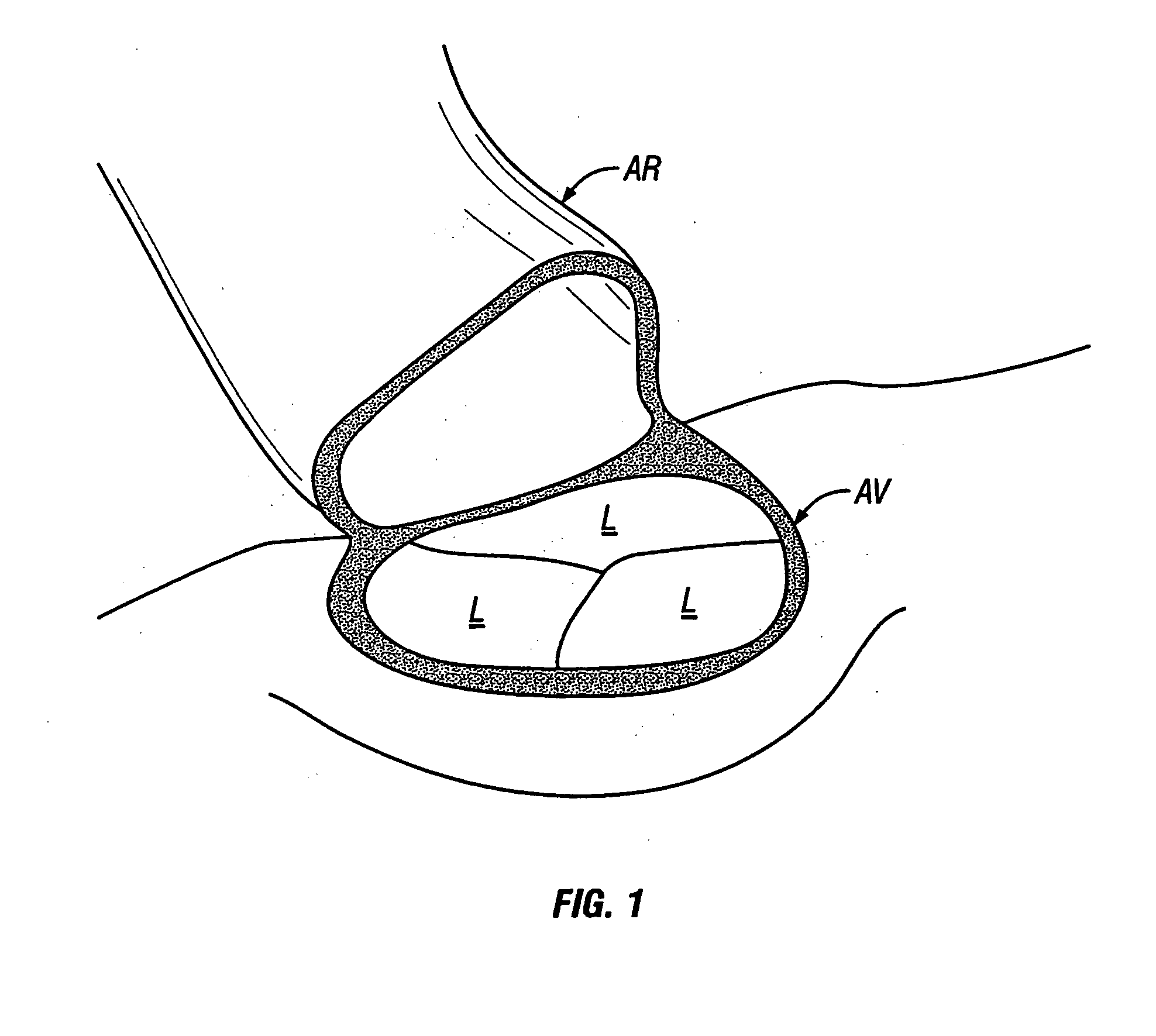
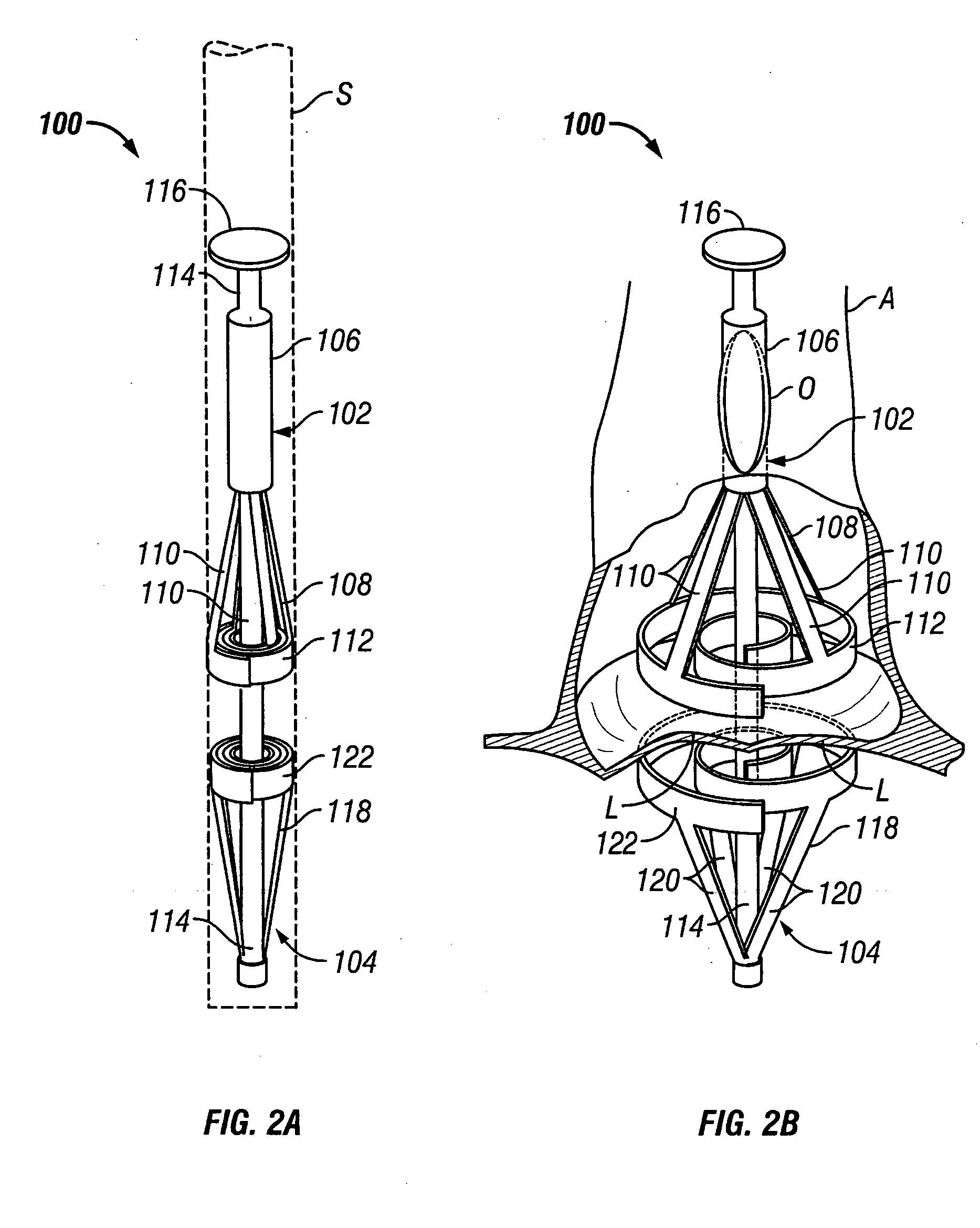
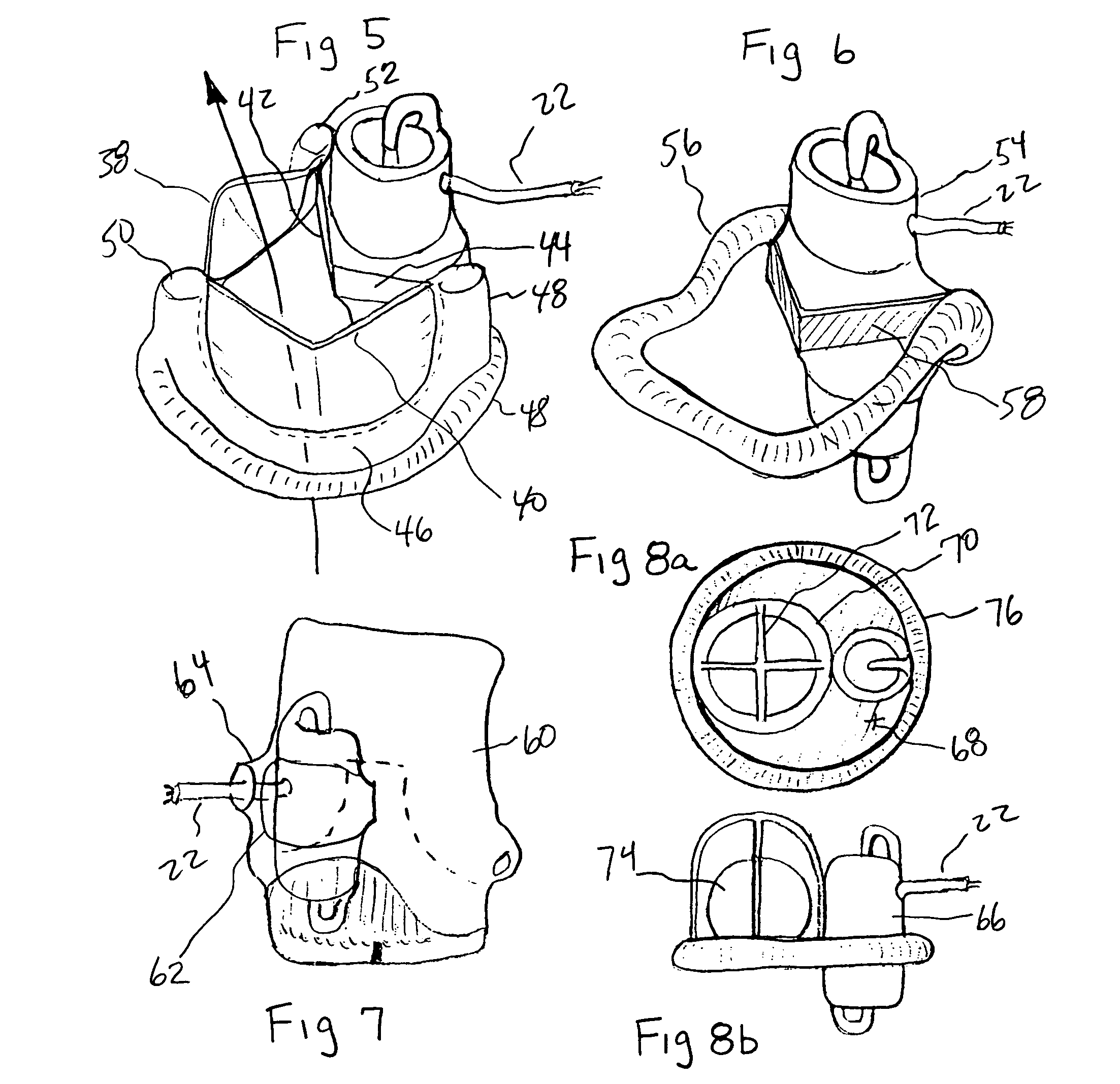
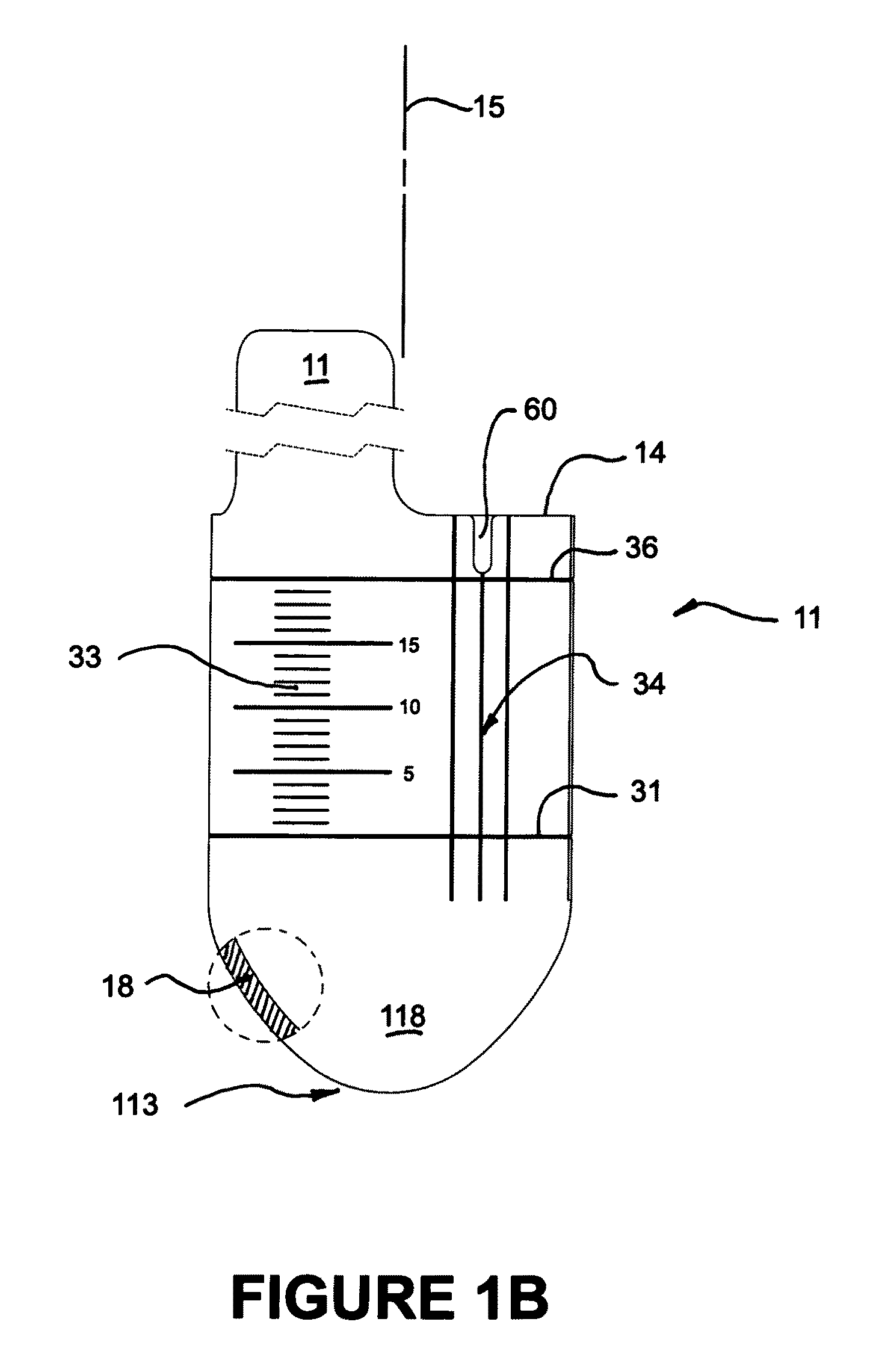
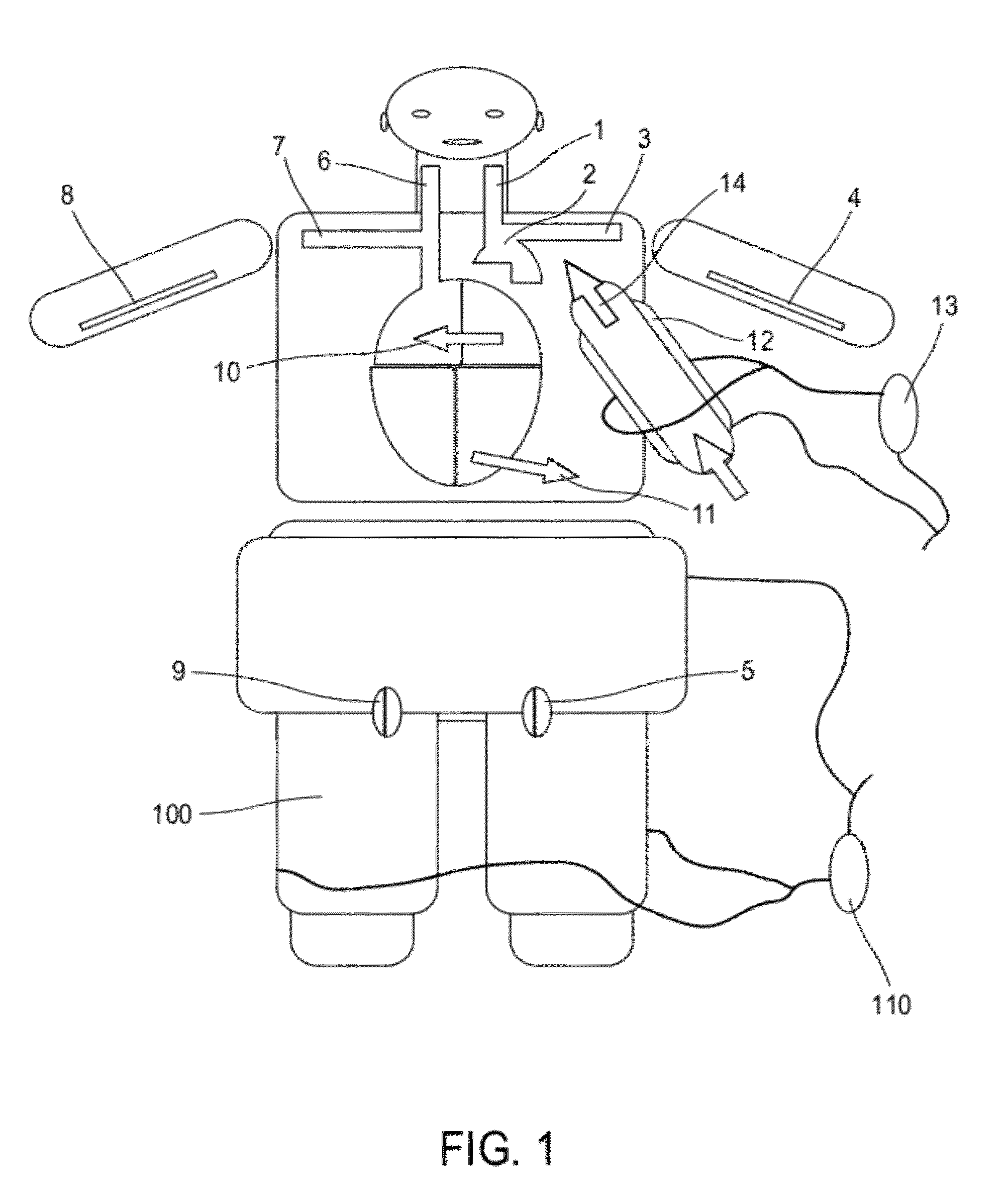
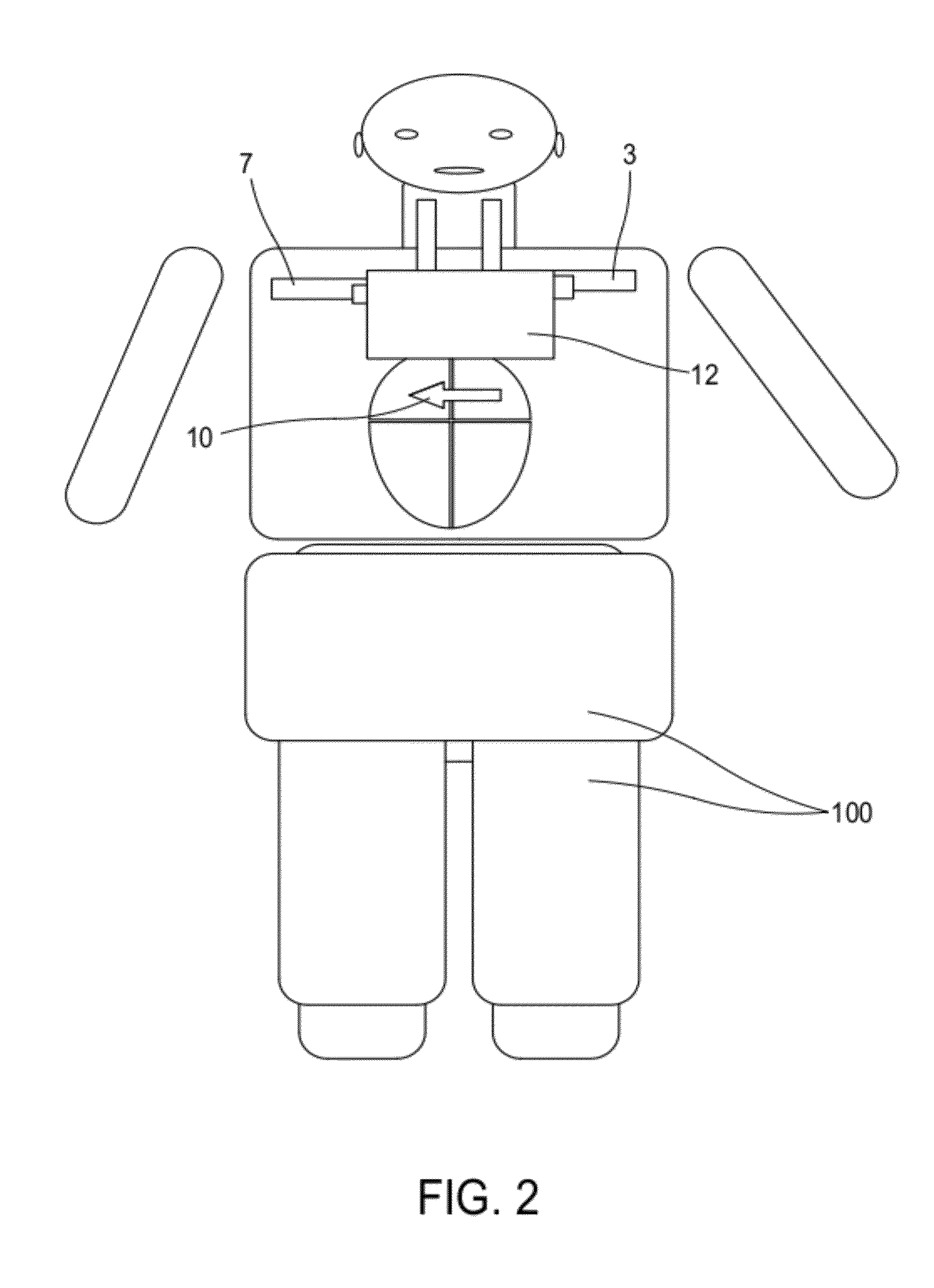
Surgical tool for measurement of valve annulus and cusp geometry
ActiveUS20100217092A1Fast constructionQuickly assess the aortic structures or anatomic parametersHeart valvesDiagnosticsMedicineAortic root
A surgical tool for visually assessing or measuring the aortic structures contained within a generally tubular aortic root. The surgical tool is appropriately configured and sized to be insertable within an aortic root during surgery. The surgical tool comprises a handle portion and a cylindrical portion connectable thereto. The cylindrical portion defines an external cylindrical surface and extends in height along a tool axis between a base portion and a top portion. The cylindrical portion being optically clear or having at least a section thereof that is sufficiently transparent whereby, in use, when the surgical tool is placed within the aortic root and the aortic structures are in contact with the external cylindrical surface, the aortic structures are visible through said optically clear or sufficiently transparent section. The cylindrical portion preferably further comprises an array of reference datum and measurement increments visible through the optically clear section such that the visualization and measurement of the aortic structures may be effected with reference to the array.
Owner:CORONEO
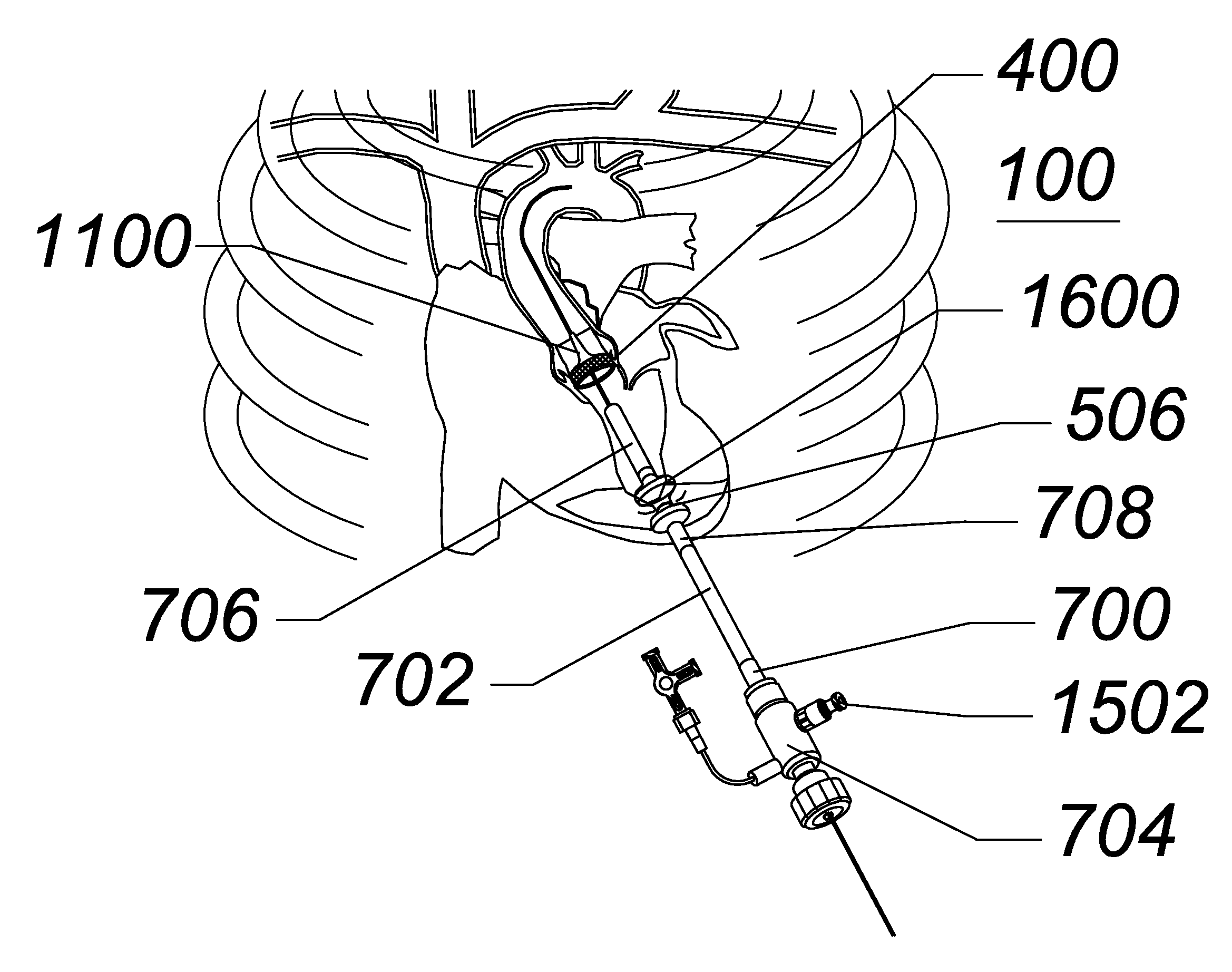
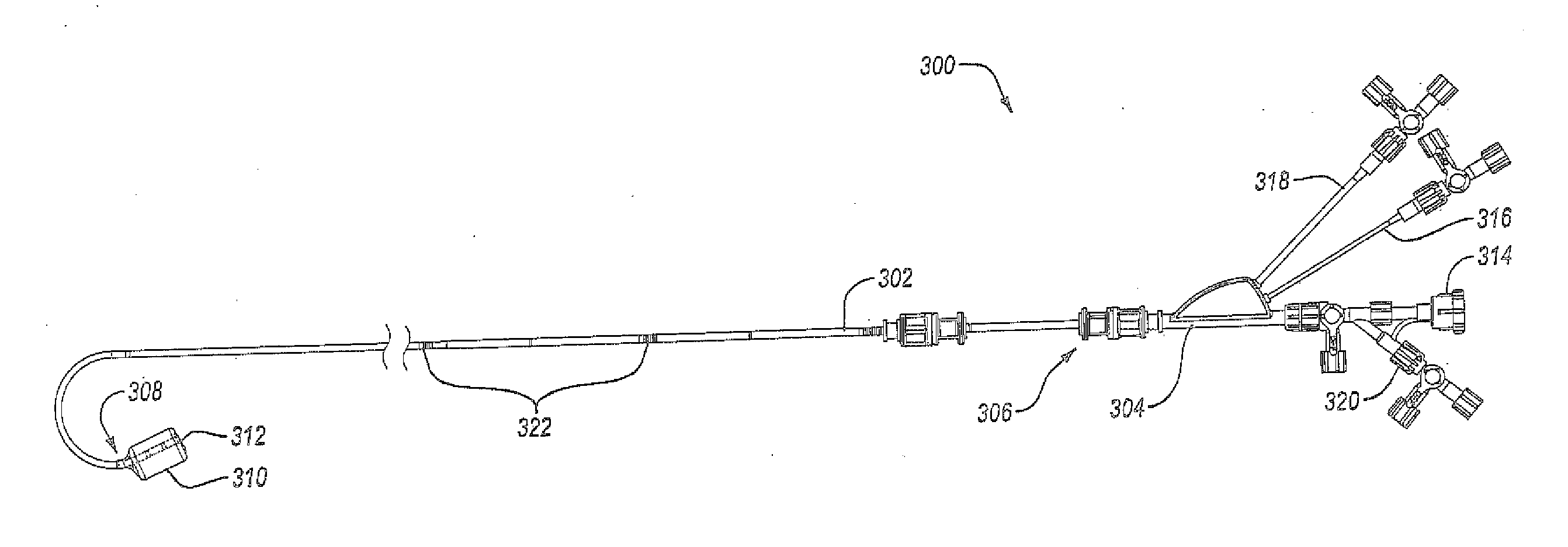
Aortic Occlusion Catheter
InactiveUS20130116654A1Avoid insufficient lengthSolve the lack of flexibilityBalloon catheterMulti-lumen catheterAscending aortaCatheter
An cardioplegic fluid delivery catheter includes an expandable member for occluding the ascending aorta of a patient. A length of the catheter allows the distal end to be within the ascending aorta while the proximal end extends from a peripheral artery. The delivery catheter has a multi-lumen construction with a primary lumen extending configured to allow a cardioplegic fluid to be delivered to the aorta. Secondary lumens provide for balloon inflation and aortic root pressure monitoring. The delivery catheter includes a shaft having a pre-determined curve profile at a distal end of the delivery catheter. The pre-determined curve profile generally corresponds to the curve of the bottom surface of the aortic arch. The shaft may be eccentric to the expandable member such that retraction of the shaft causes a distal tip to be parallel within the ascending aorta.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
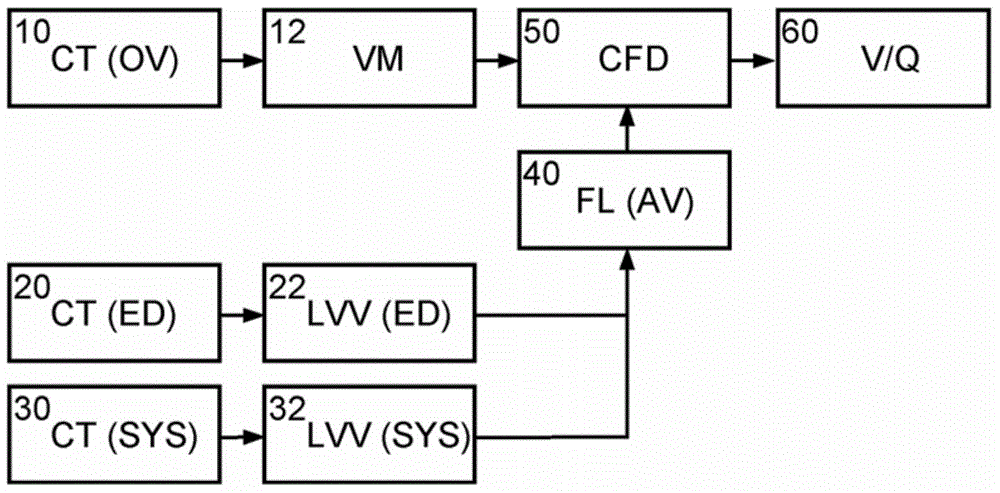
Method and apparatus for simulating blood flow under patient-specific boundary conditions derived from an estimated cardiac ejection output
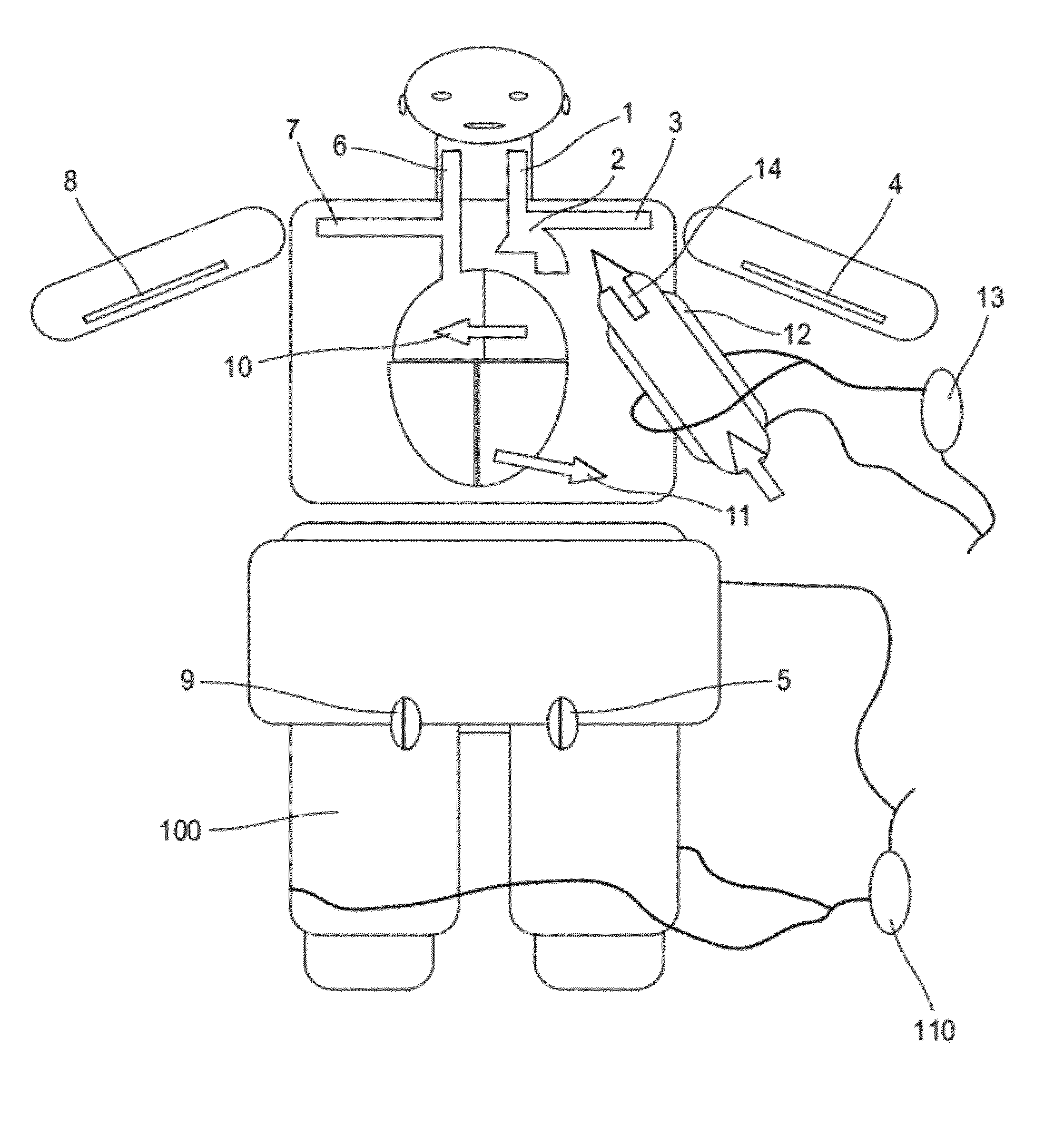
InactiveUS20150317429A1Easy to getImprove automationMedical simulationBlood flow measurement devicesSonificationBlood flow
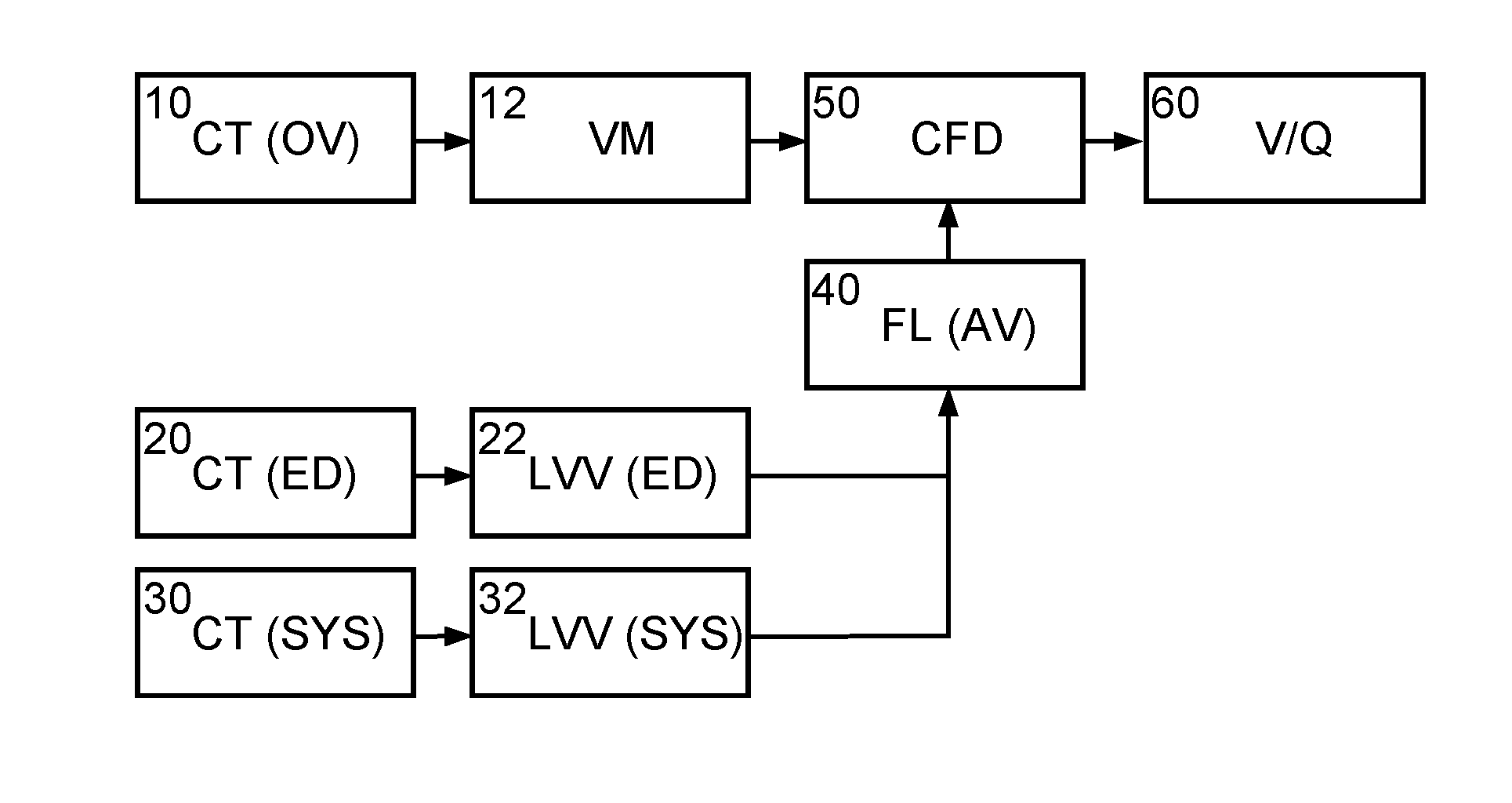
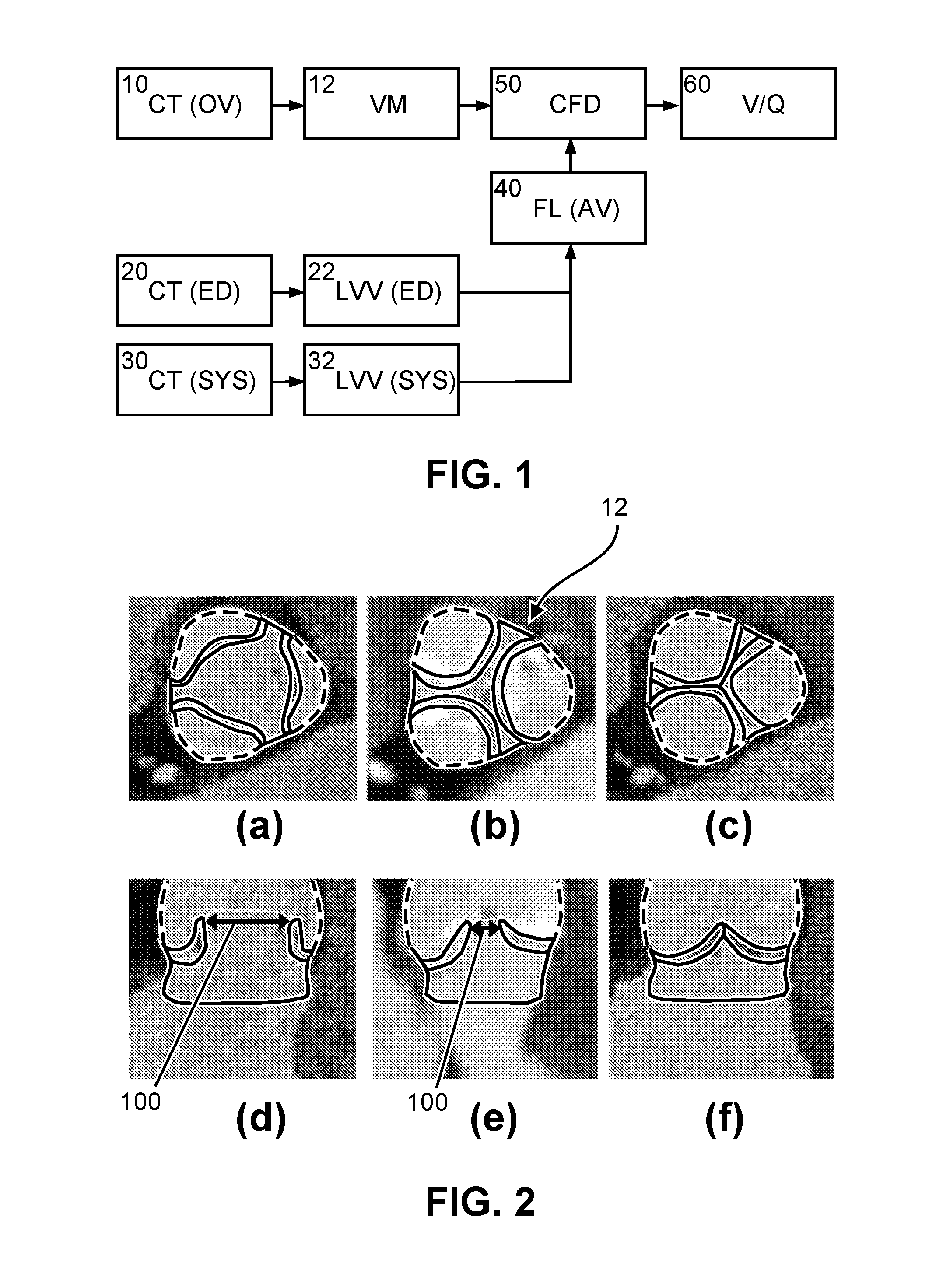
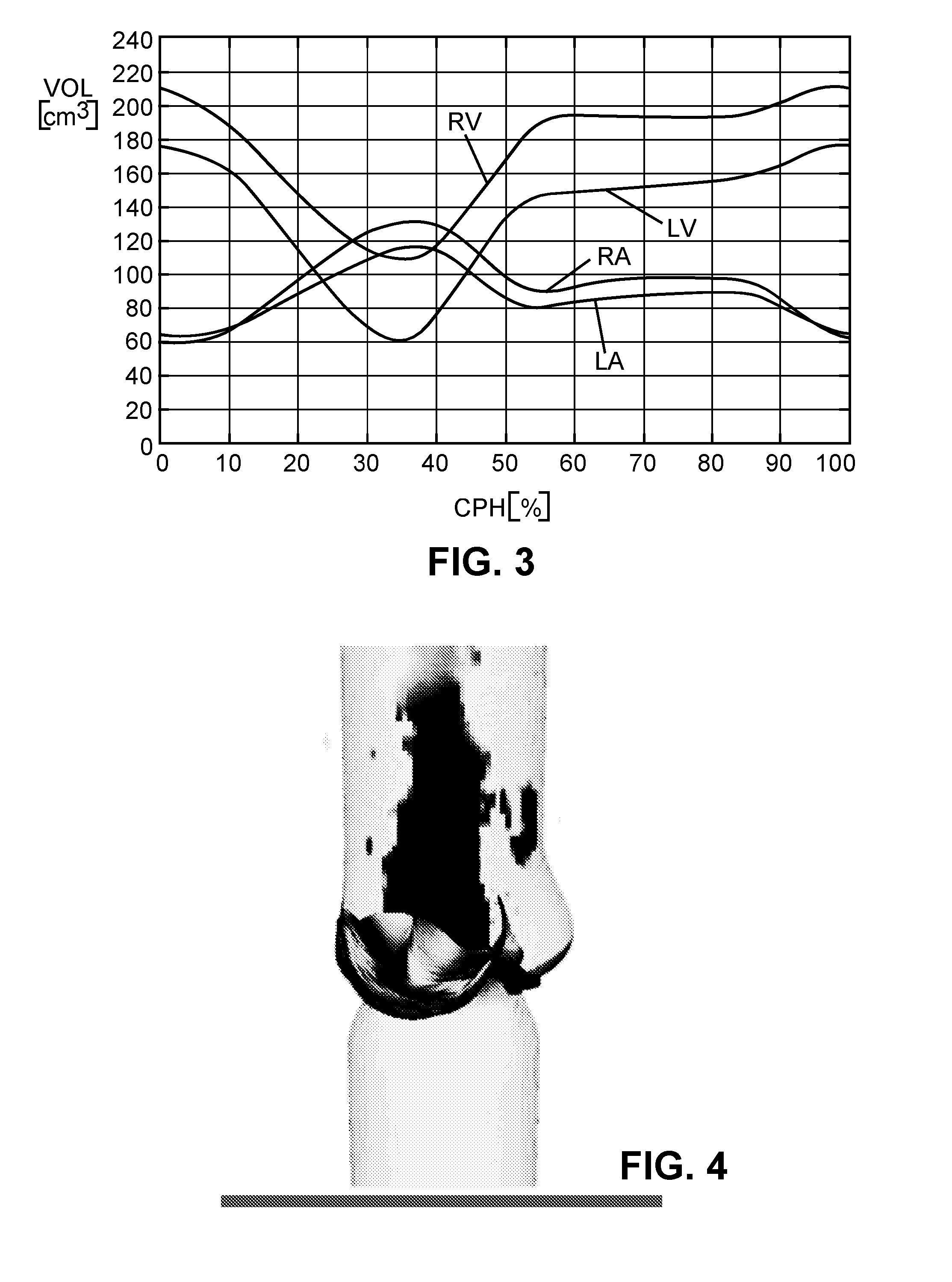
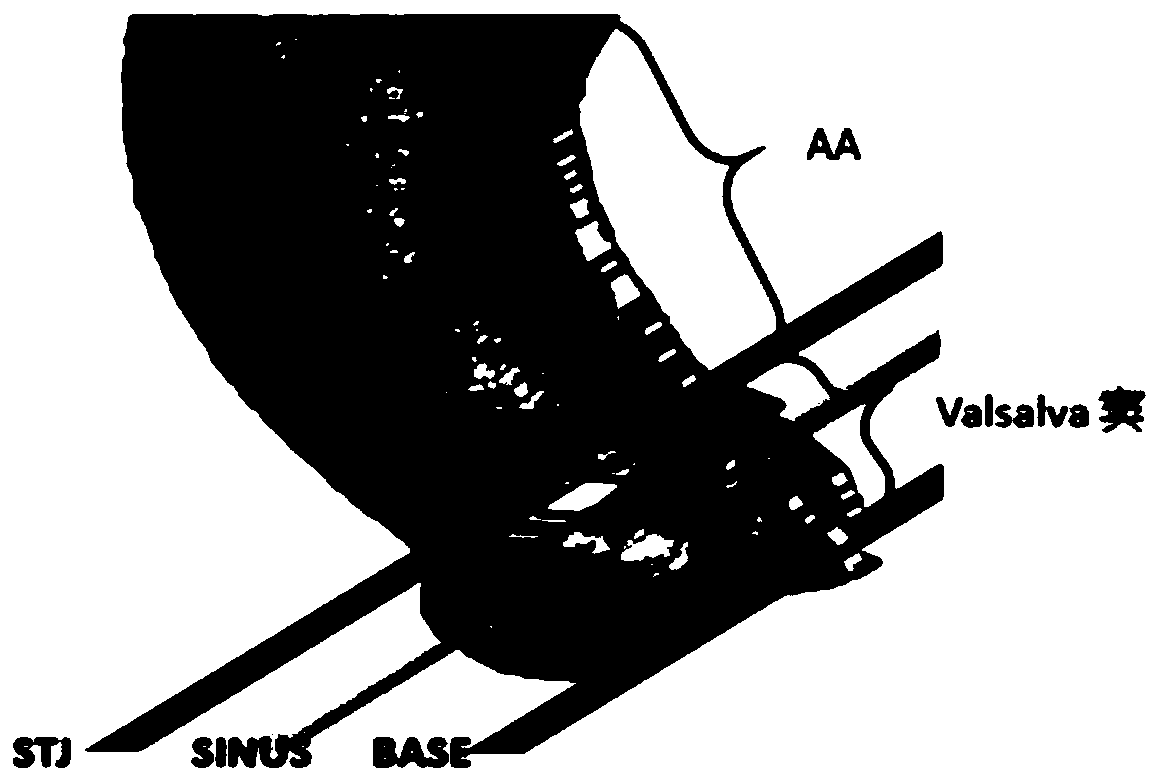
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for simulating blood flow through a cardiovascular structure, e.g. a blood cavity such as the left ventricle outflow tract, the aortic root including the AV, plus ascending aorta, a ventricle volume, the aorta or any other cavity where blood flows through, under patient-specific boundary conditions derived from the cardiac ejection output per heart stroke. The cardiac ejection output can be estimated from volumes of a heart chamber of the patient in different filling states at two or more different points in time. The results of the flow simulation can be used to derive at least one physiological parameter or can be visualized and virtual Doppler ultrasound images may be generated to allow a physician assessing the result.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Aortic valve semi-automatic segmentation method based on CTA dynamic image
ActiveCN110570424ASolving Consistency IssuesAccurately reflectImage enhancementImage analysisAutomatic segmentationFeature extraction
The invention discloses an aortic valve semi-automatic segmentation method based on a CTA dynamic image, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining CT angiography image data under electrocardio gating, carrying out the division of 20 time phases, and carrying out the following steps for an image of each time phase point: step A, segmenting Valsalva sinus according to the upper and lower boundaries of the root of an aorta; and step B, segmenting the aortic valve from the Valsalva sinus. According to the method, the feature extraction range in the CTA image is expanded, so that more completeanatomical details are presented, and the working efficiency and safety during an operation are further improved.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Auxiliary circulation blood pump adopted in serially connecting operation modes and installing method of auxiliary circulation blood pump
The invention relates to an auxiliary circulation blood pump adopted in serially connecting operation modes and an installing method of the auxiliary circulation blood pump and belongs to the field of biomedical engineering. The blood pump belongs to an implanted heart chamber auxiliary blood pump and mainly consists of an axial-flow type blood pump (1), a pump outlet support ring (2), an artificial blood vessel (3) for anastomosis and a coronary bypass tube (4). A case of the blood pump (1) is in a cylindrical shape, two ends of the pump case are designed with arc-shaped grooves, the arc-shaped groove are used for binding the artificial blood vessel (3), the artificial blood vessel (3) is used for being coincided with the artery, and the support ring (2) is arranged in an aorta arch of the pump outlet. During the installation, the artificial blood vessel is bound on the pump case in advance, the in vitro auxiliary circulation is carried out in the operation, then, the aorta is pinched off, the support ring is implanted in the aorta arch direction, the artificial blood vessel at the pump outlet is coincided with the aorta, and finally, the artificial blood vessel at the pump outlet part of the blood pump is coincided with the root part of the aorta. The blood pump is fixedly arranged inside the aorta and is then matched with the coronary artery bypass operation for transplanting. The auxiliary circulation blood pump has the advantages that the myocardial blood supply can be obviously improved, and the heart recovery is favorably realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Therapeutic and surgical treatment method for providing cardiopulmonary and circulatory assist device
The present disclosure relates to a therapeutic method for improving the hemodynamics, the overall microcirculation in organs, and the restoration and preservation of deficient endothelial function in a patient, the method includes maintaining blood circulation in the patient's veins and arteries and temporarily relieving the heart of its pumping function. Relief may be accomplished by increasing the preload of the right ventricle so as to improve oxygenation of the myocardium and its contractility, reducing and diffusing regular pulsations in the proximity of the aortic root so as to improve the hemodynamics of the left ventricle of the heart, and / or mechanically stimulating the endothelium by shear forces so as to reduce systemic and pulmonary afterload.
Owner:WU GUI FU +1
Method and system for heart isolation in cardiac computed tomography volumes
A method and a system for isolating the heart in a 3D volume, such as a cardiac CT volume, for patients with coronary artery bypasses are disclosed. An initial heart isolation mask is extracted from a 3D volume, such as a cardiac CT volume. The aortic root and ascending aorta are segmented in the 3D volume, resulting in an aorta mesh. The aorta mesh is expanded to include bypass coronary arteries. An expanded heart isolation mask is generated by combining the initial heart isolation mask with an expanded aorta mask defined by the expanded aorta mesh.
Owner:SIEMENS AG +1
Method and system for intervention planning for transcatheter aortic valve implantation from 3D computed tomography data
A method and system for automated intervention planning for transcatheter aortic valve implantations using computed tomography (CT) data is disclosed. A patient-specific aortic valve model is detected in a CT volume of a patient. The patient-specific aortic valve model is detected by detecting a global location of the patient-specific aortic valve model in the CT volume, detecting aortic valve landmarks based on the detected global location, and fitting an aortic root surface model. Angulation parameters of a C-arm imaging device for acquiring intra-operative fluoroscopic images and anatomical measurements of the aortic valve are automatically determined based on the patient-specific aortic valve model.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and apparatus for simulating blood flow under patient-specific boundary conditions derived from an estimated cardiac ejection output
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for simulating blood flow through a cardiovascular structure, e.g. a blood cavity such as the left ventricle outflow tract, the aortic root including the AV, plus ascending aorta, a ventricle volume, the aorta or any other cavity where blood flows through, under patient-specific boundary conditions derived from the cardiac ejection output per heart stroke. The cardiac ejection output can be estimated from volumes of a heart chamber of the patient in different filling states at two or more different points in time. The results of the flow simulation can be used to derive at least one physiological parameter or can be visualized and virtual Doppler ultrasound images may be generated to allow a physician assessing the result.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
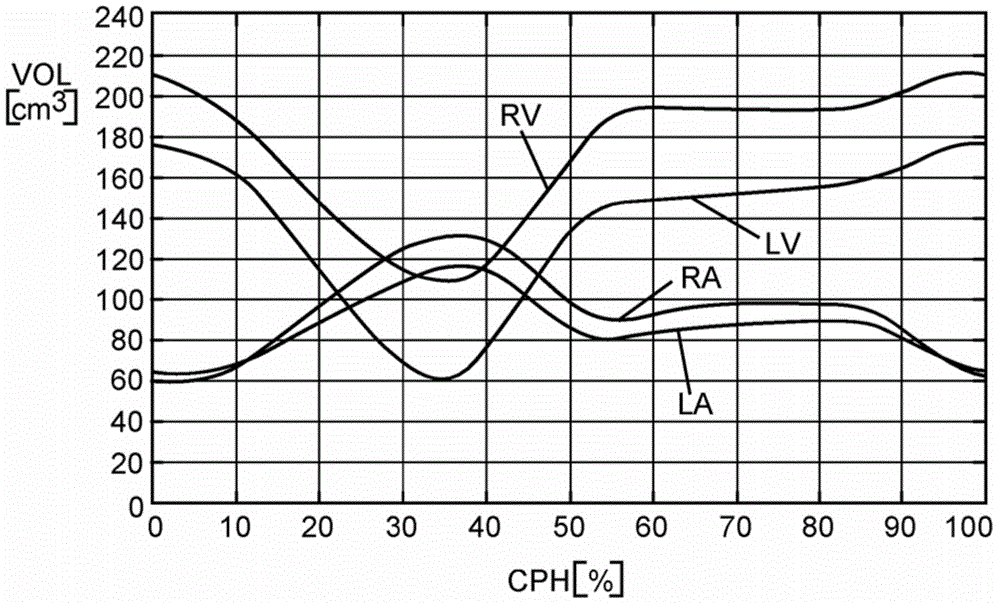
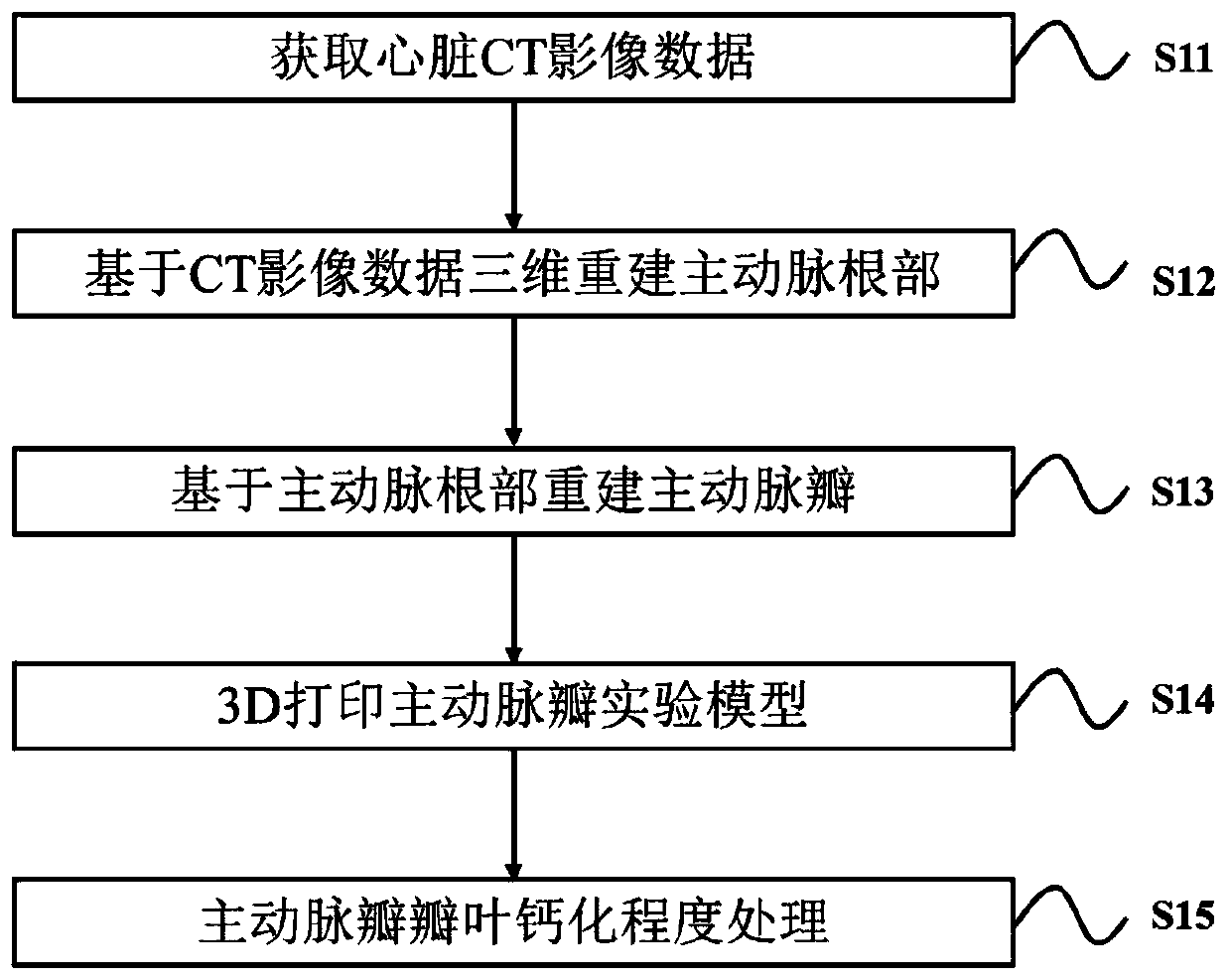
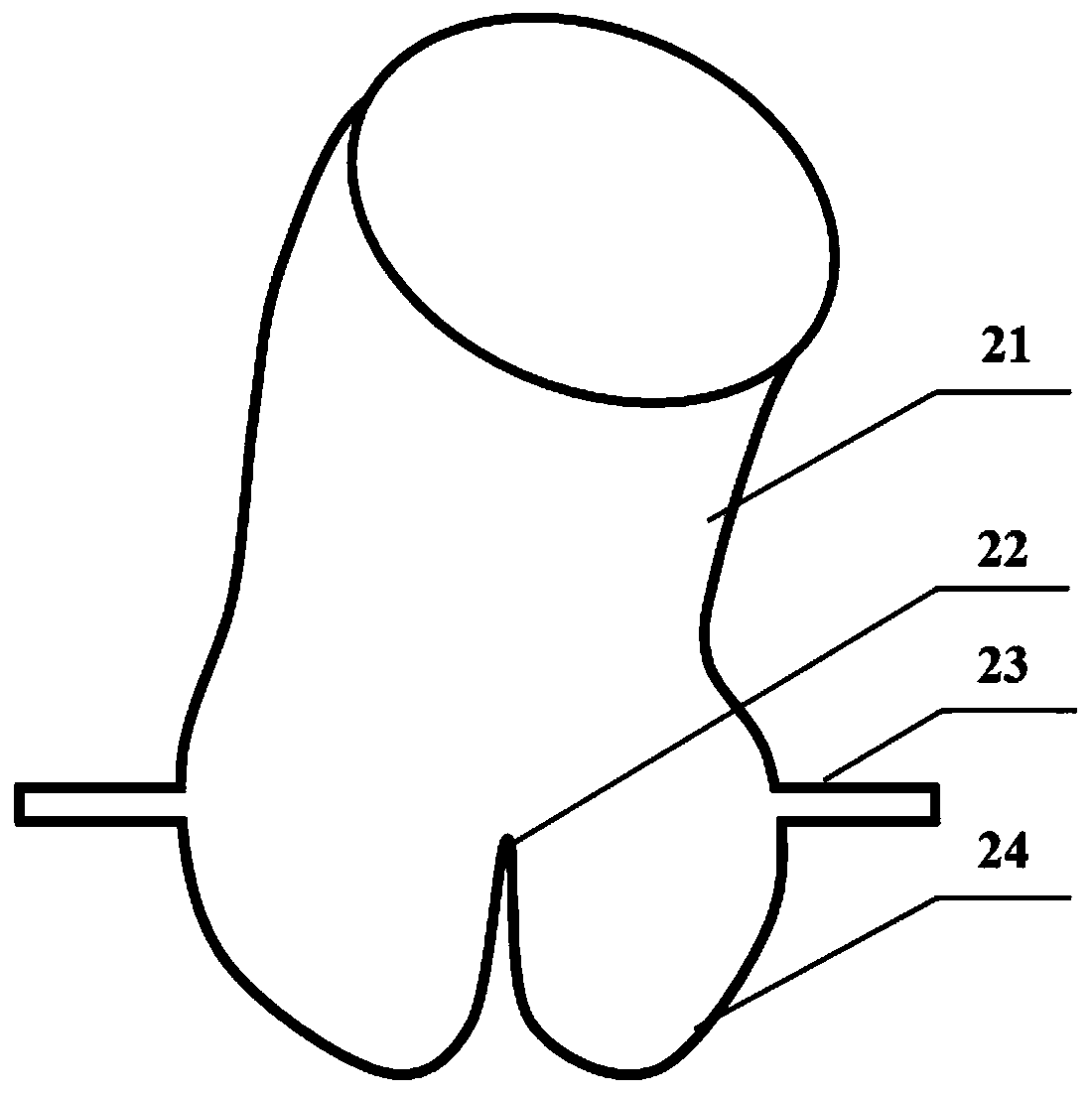
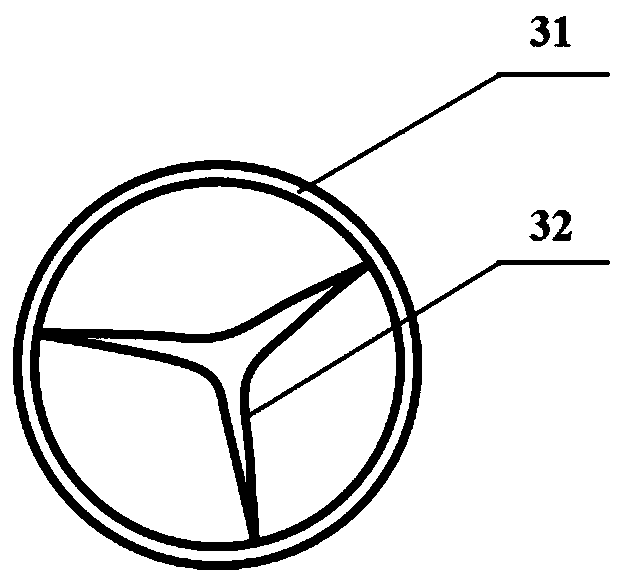
Method for preparing calcified aortic valves based on CT image data
ActiveCN109700574AAddresses the inability to accurately reconstruct the aortic valveTrue formHeart valvesProsthetic valveCalcification
The invention discloses a method for preparing calcified aortic valves based on CT image data, and belongs to the field of preparation of artificial heart valves. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring CT image data of the heart; based on the CT image data, performing 3D reconstruction of aorta roots; based on an aorta root three-dimensional model, reconstructing aortic valves; performing 3D printing of an aortic valve experiment model; and performing calcification degree treatment on the aortic valve cusps. Through intersectant geometry space of the aorta roots and left ventricle, the aortic valves are reconstructed, and the problem that the CT value of the aortic valves in the CT image data is close to the CT value of close tissue, so that the aortic valves cannot be accurately reconstructed, is solved. The aortic valves of different calcification degrees are obtained by calcification treatment on printed aortic valves. The prepared aortic valve model can be used for research on hemodynamics, and can also provide reference for design of artificial valves.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com