Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
72 results about "Heart-Assist Devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
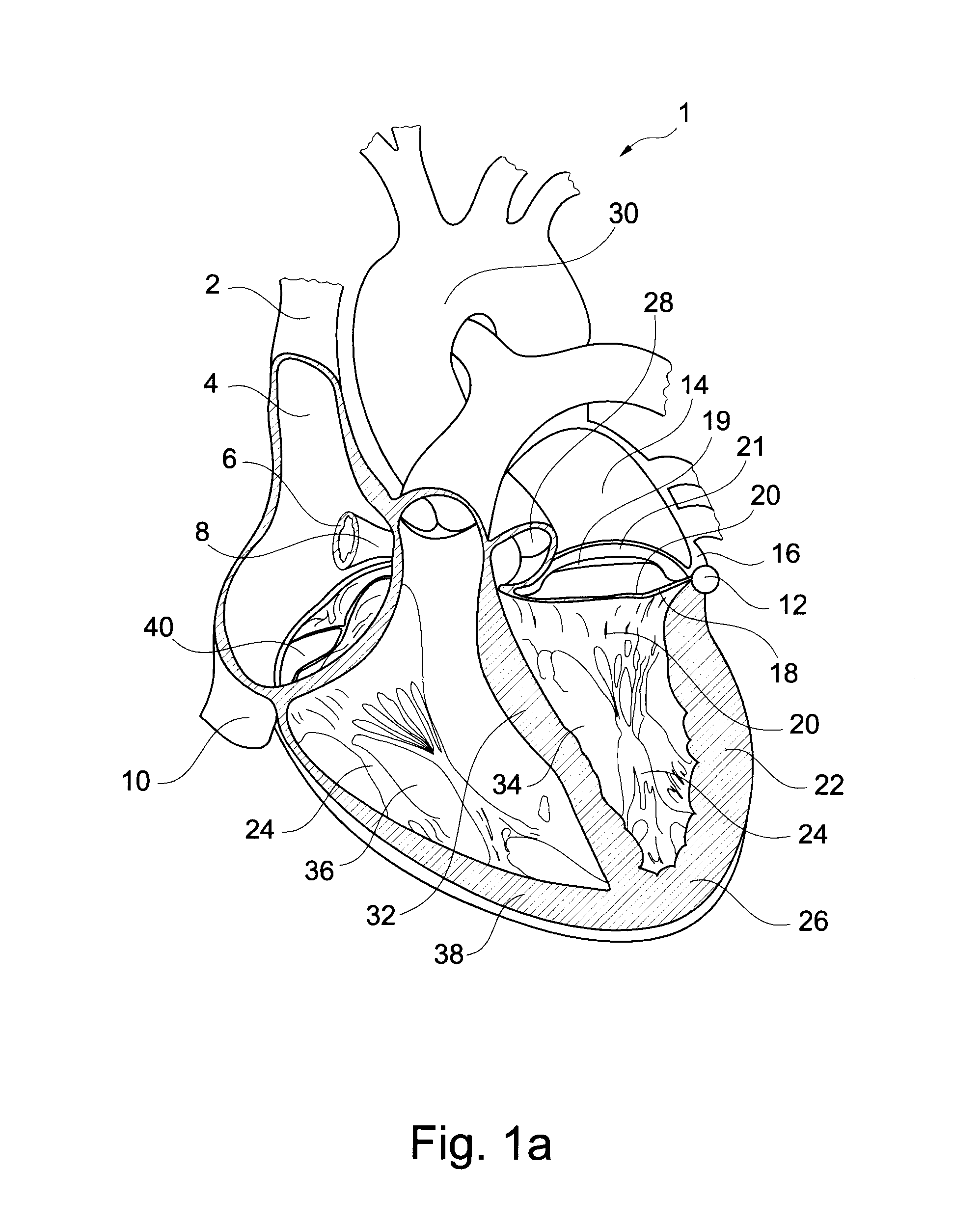
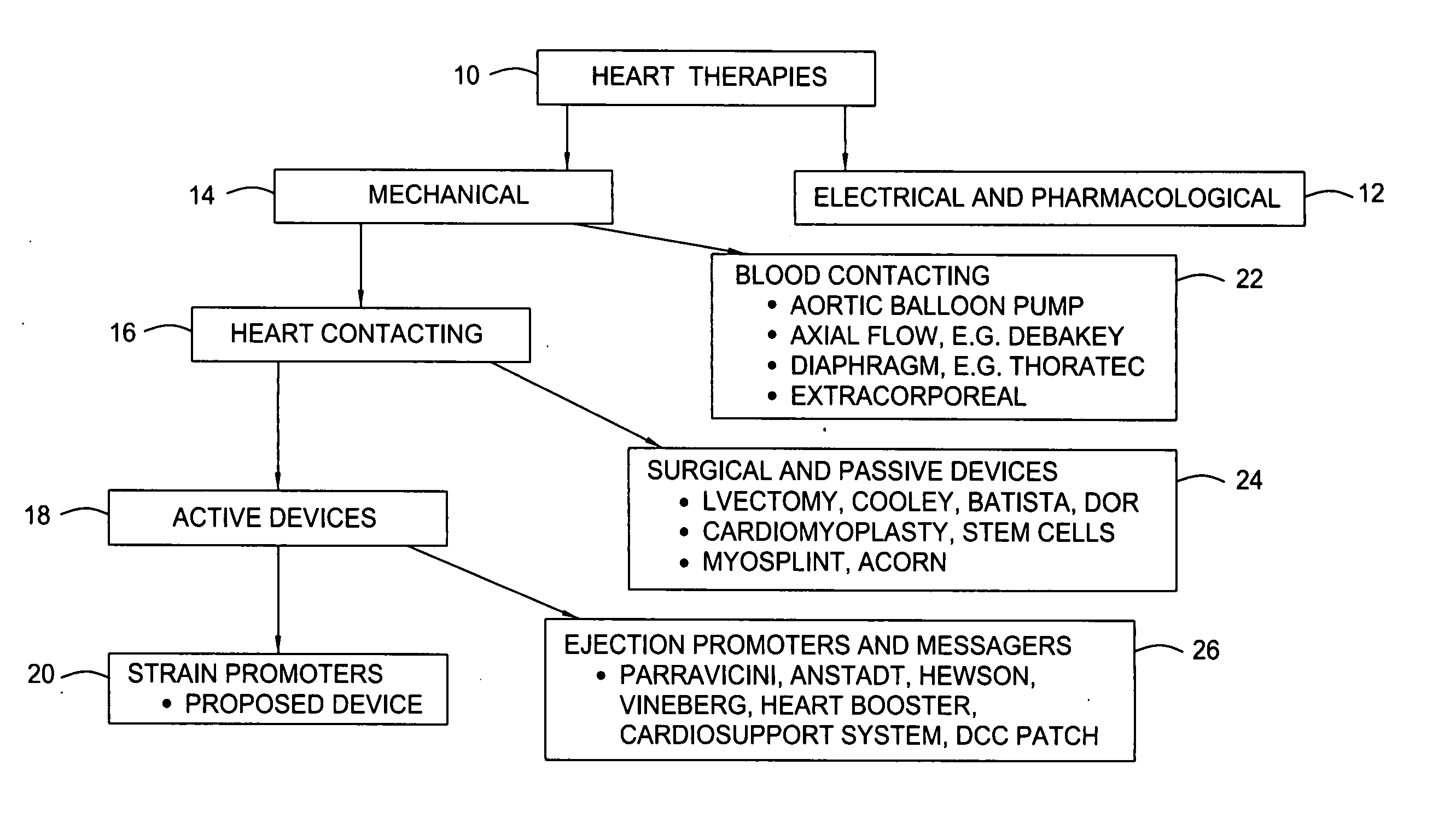
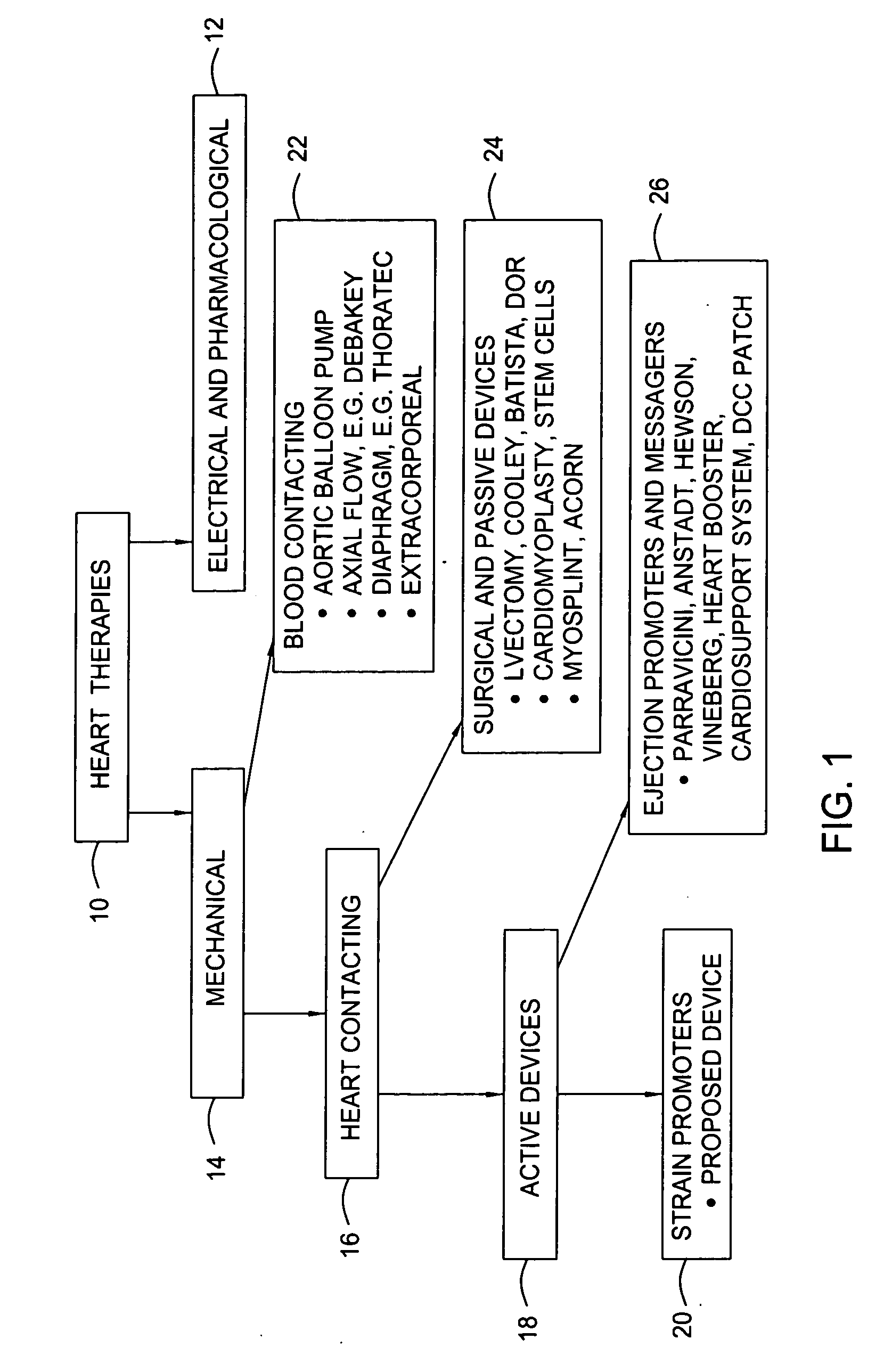
Small pumps, often implantable, designed for temporarily assisting the heart, usually the LEFT VENTRICLE, to pump blood. They consist of a pumping chamber and a power source, which may be partially or totally external to the body and activated by electromagnetic motors.
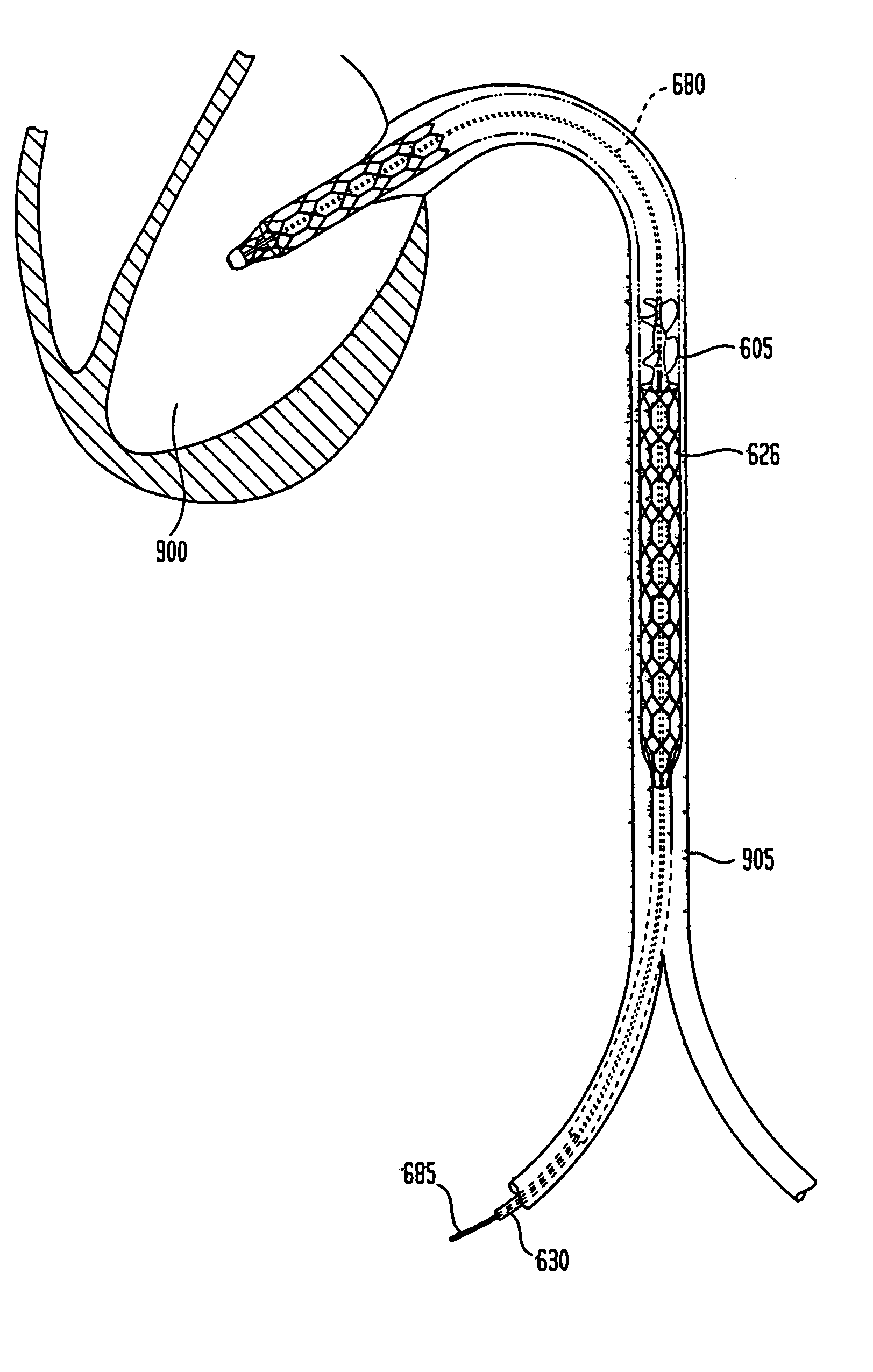
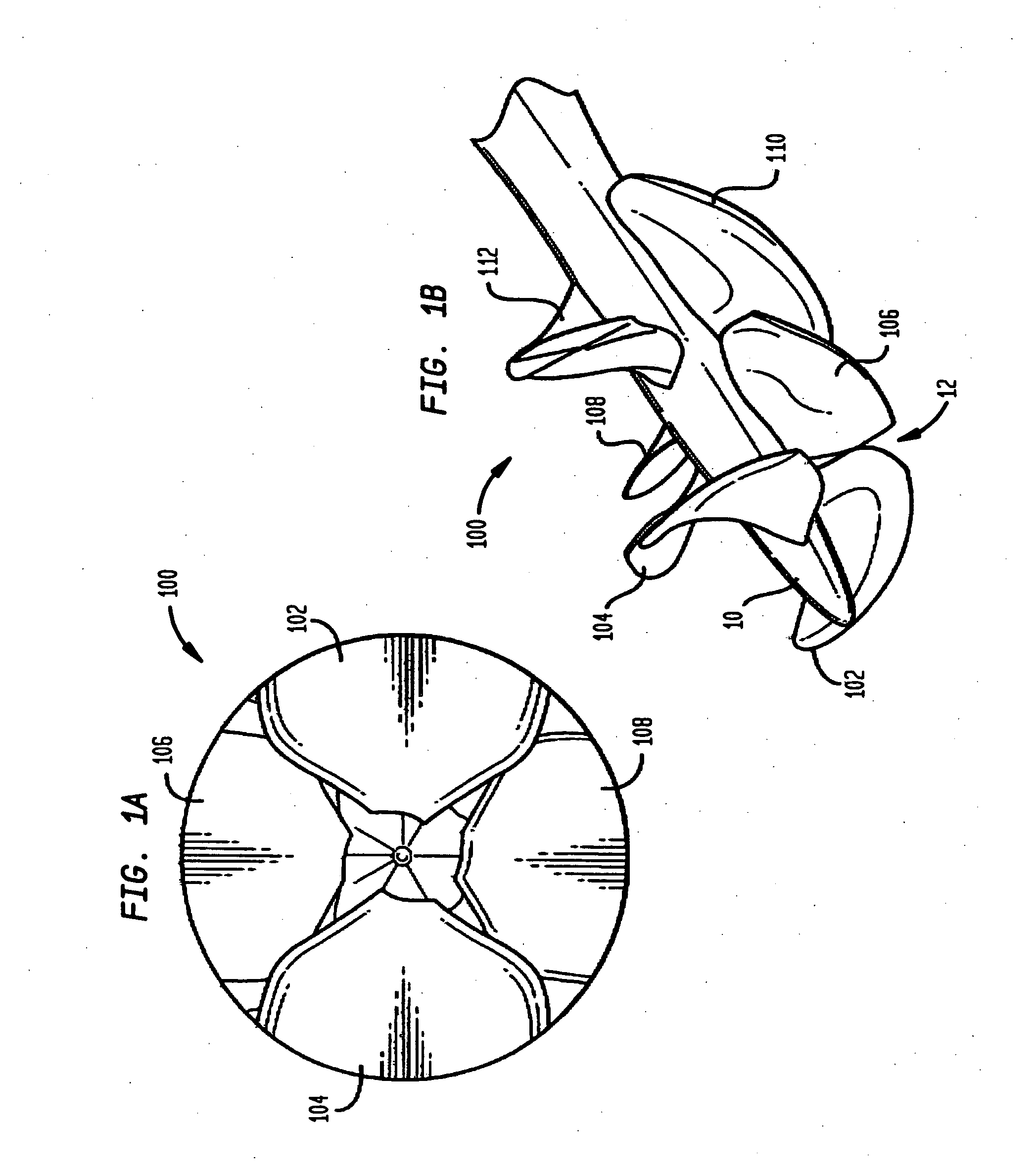
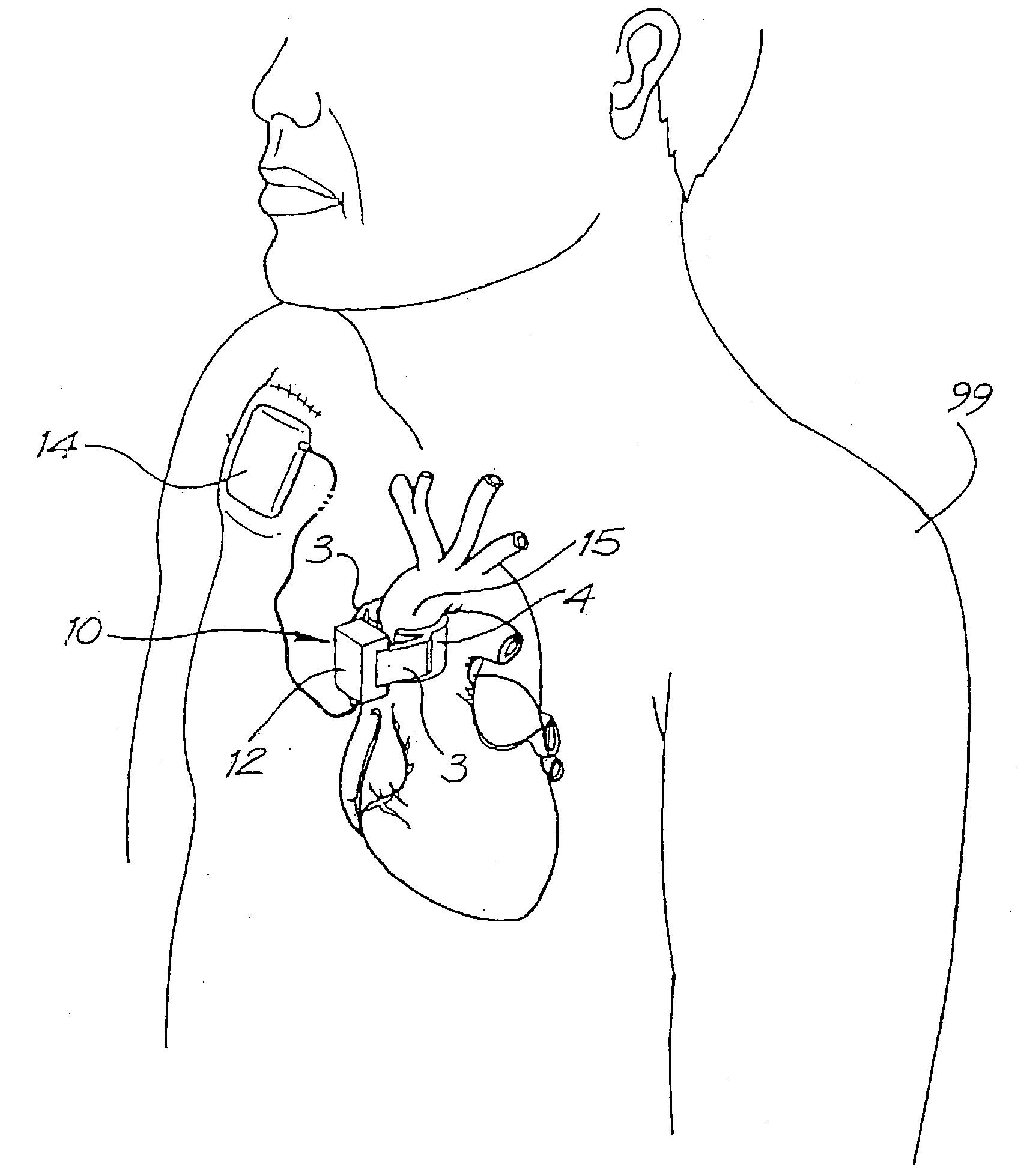
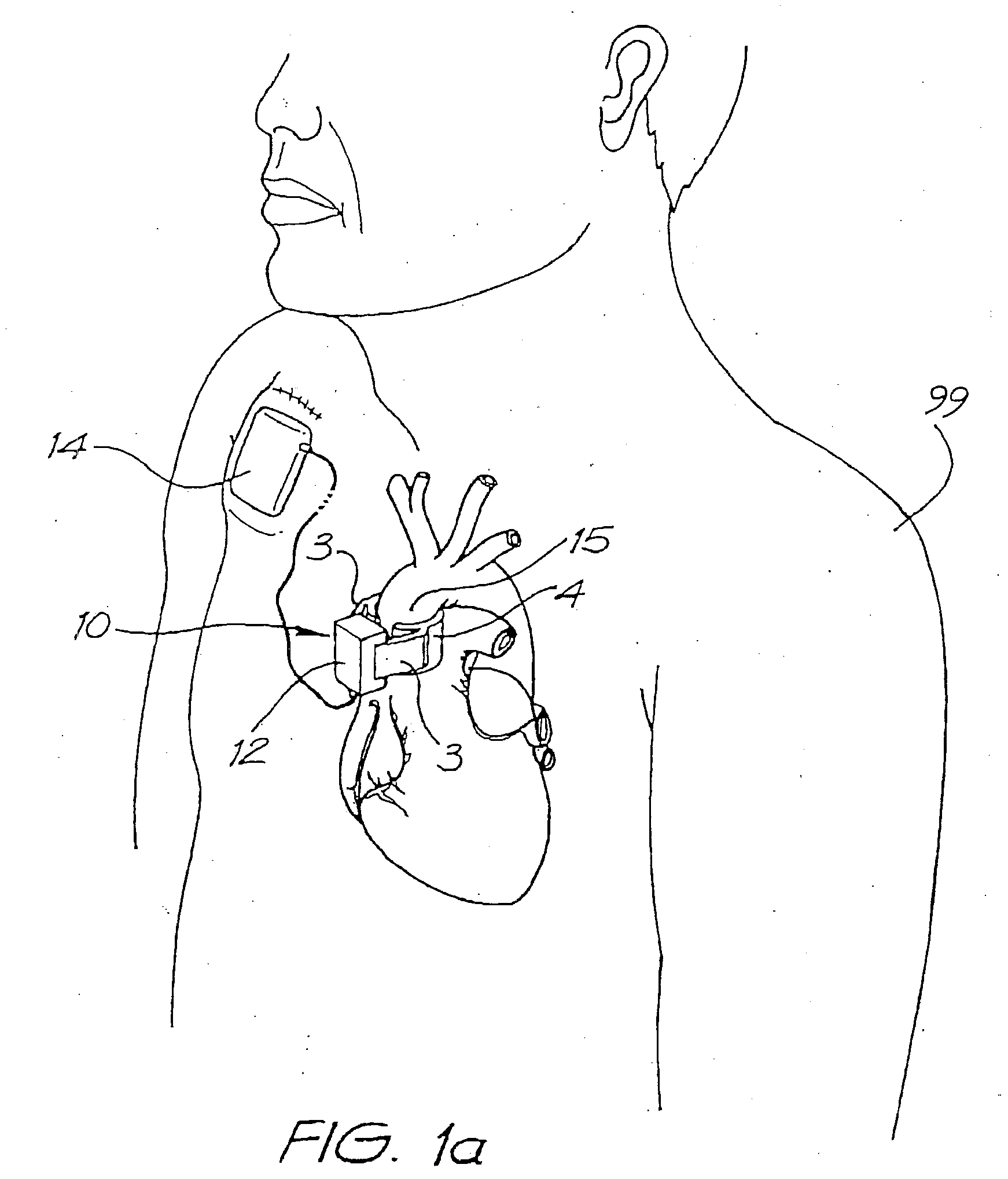
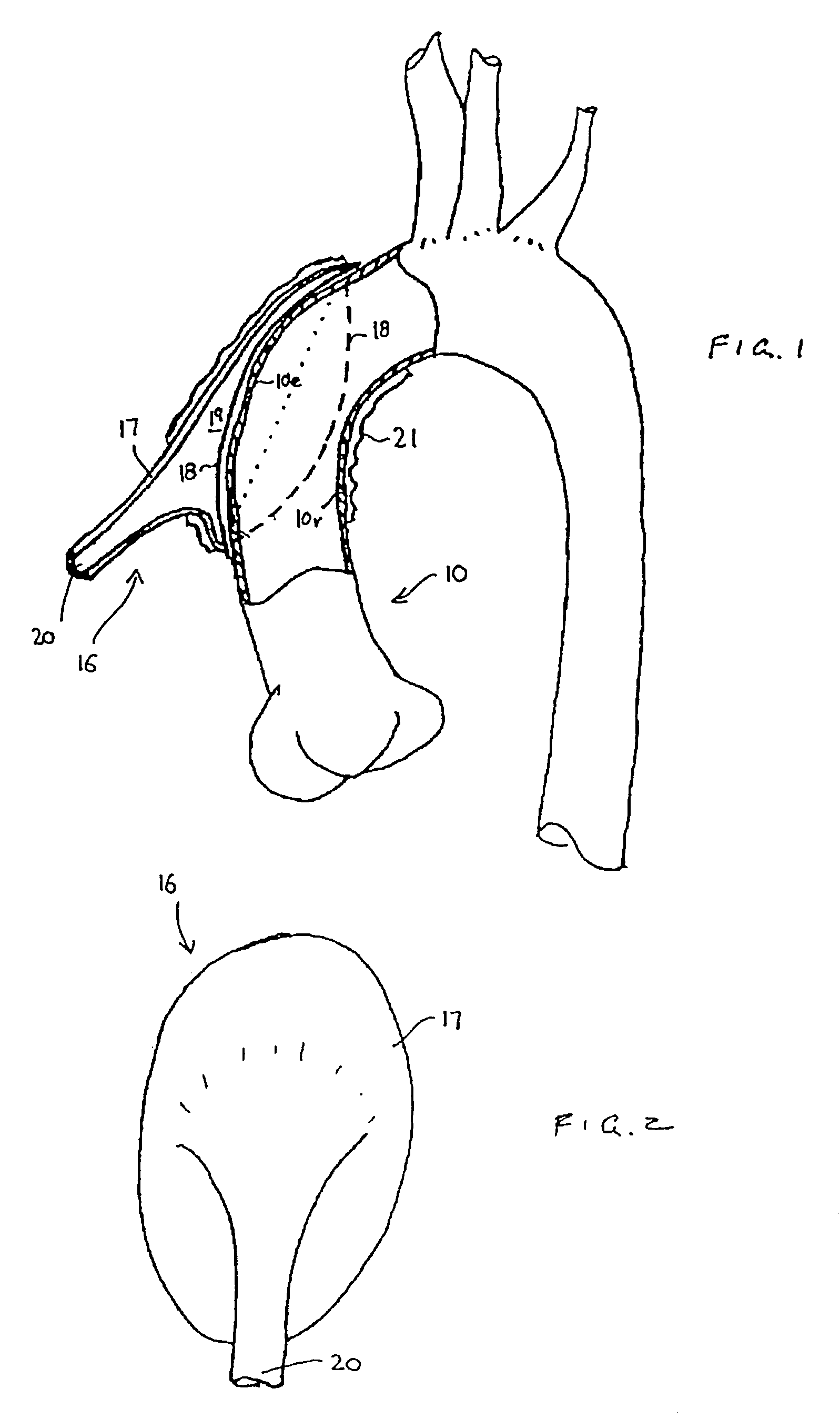
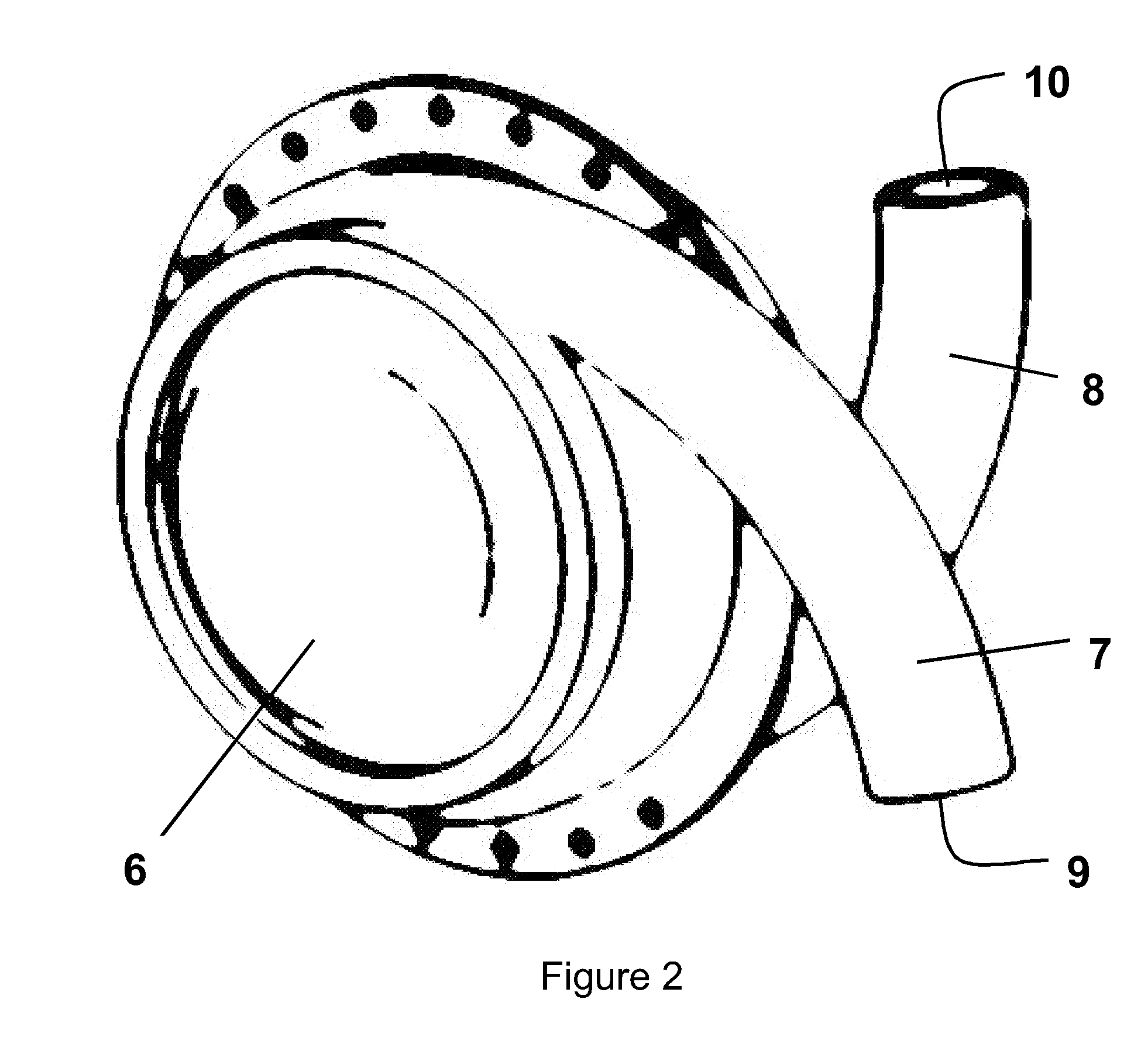
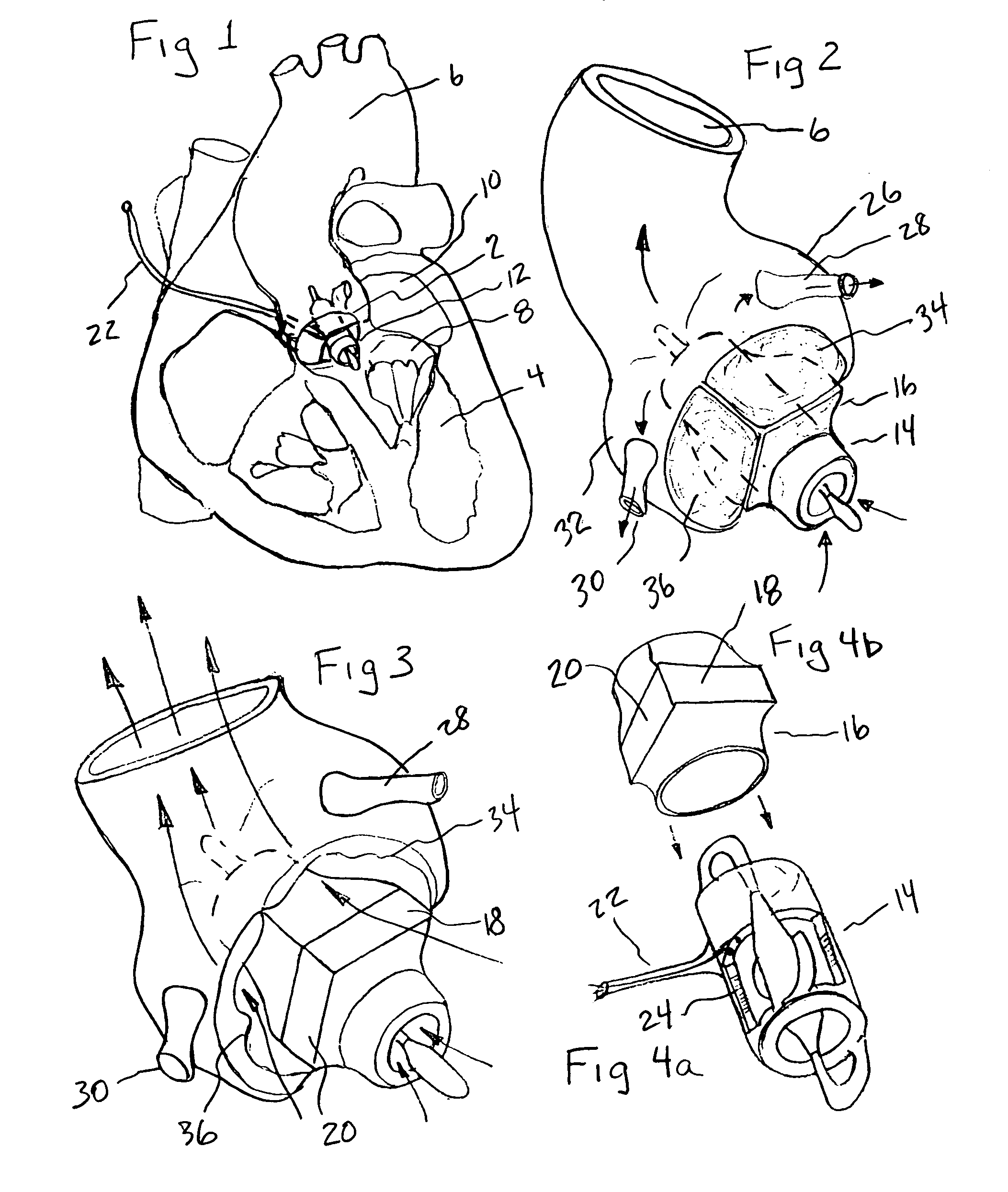
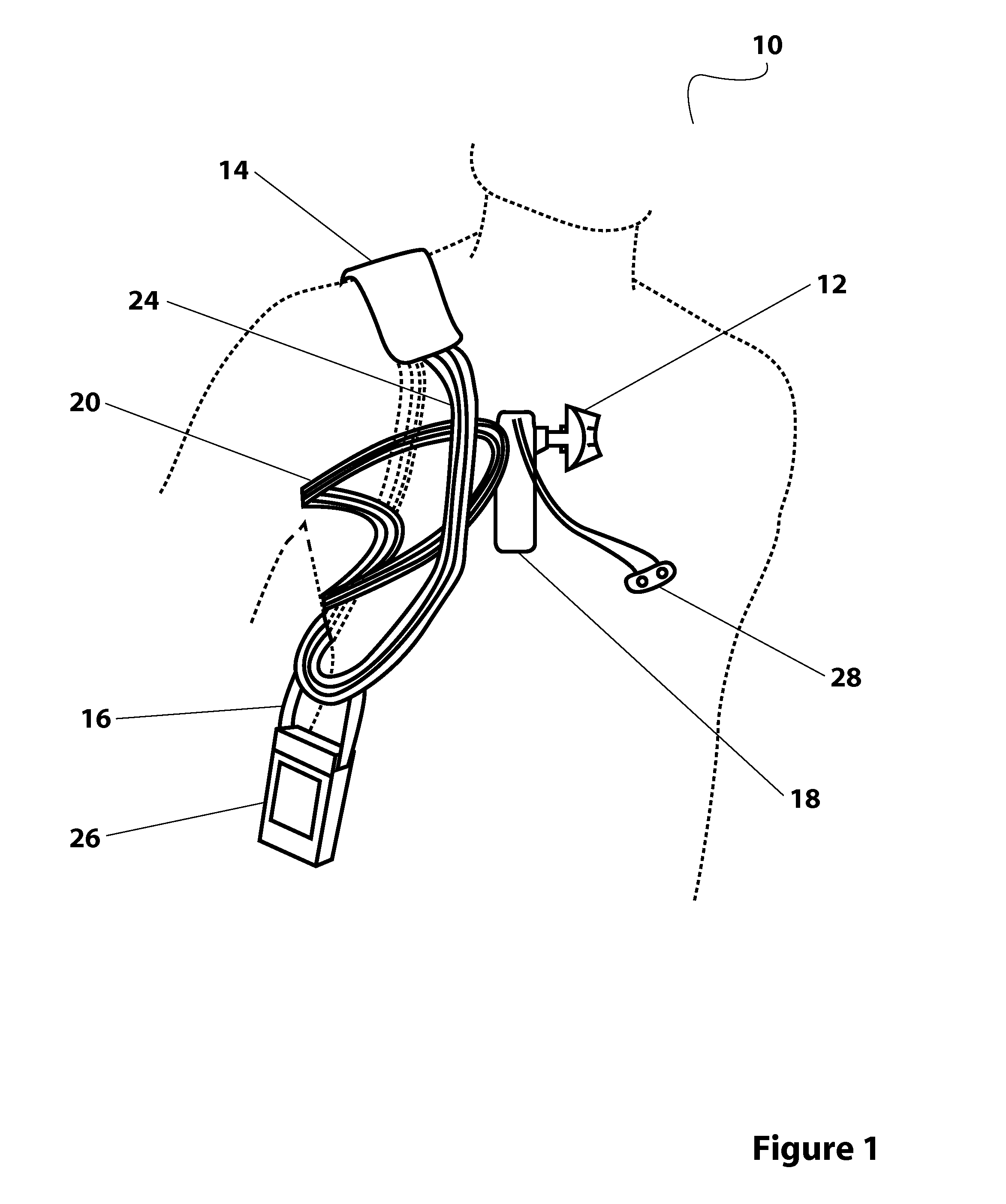
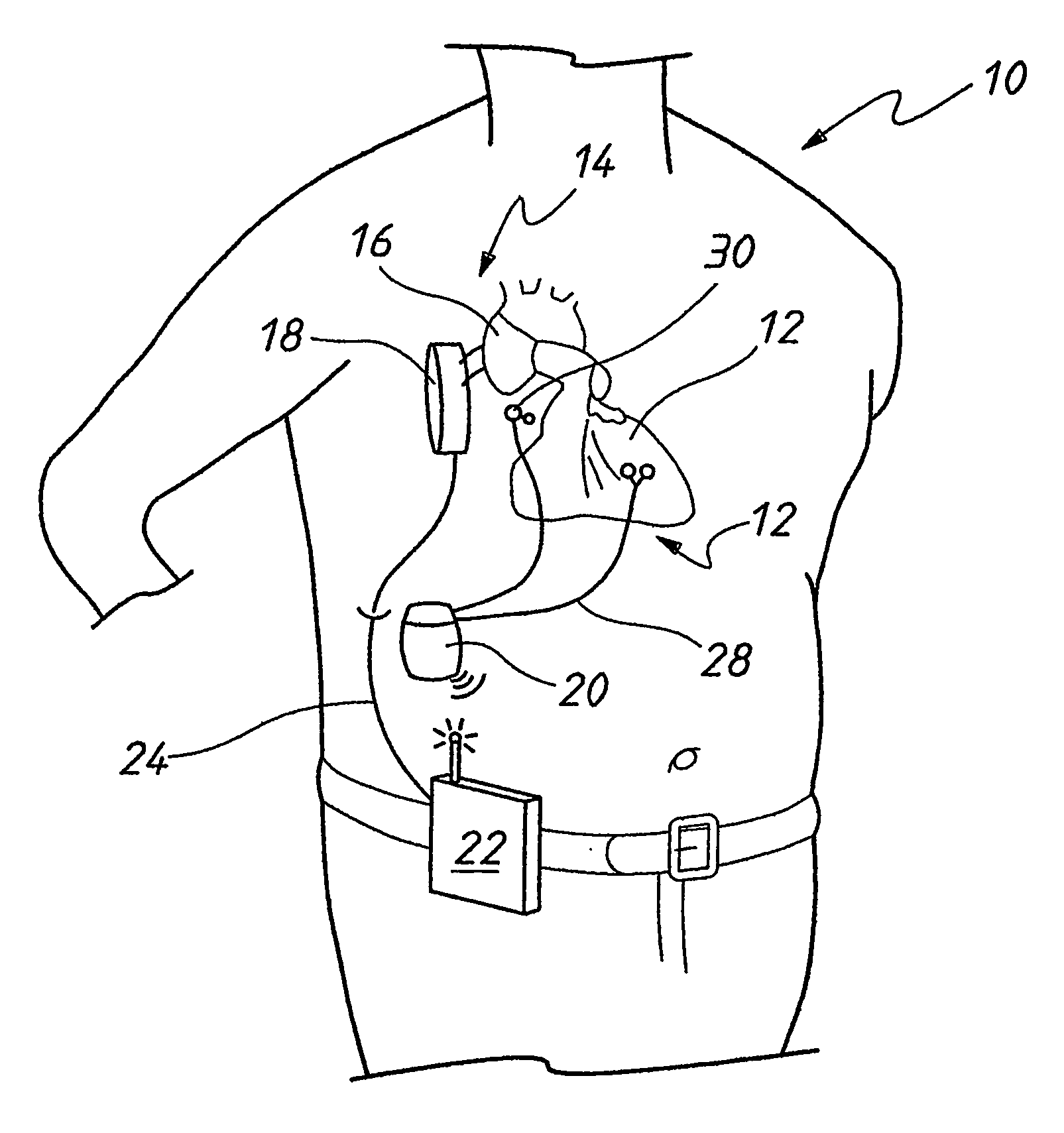
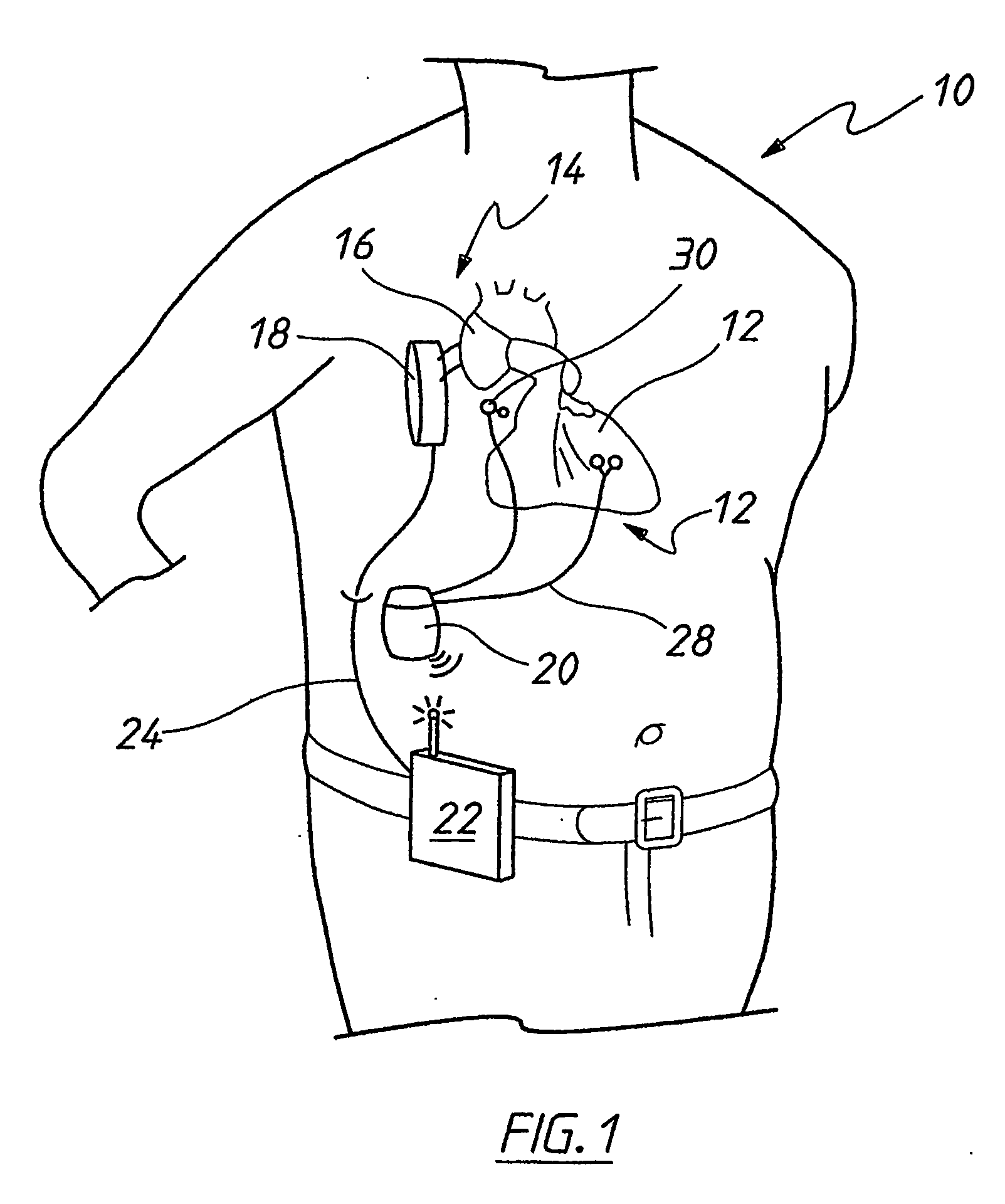
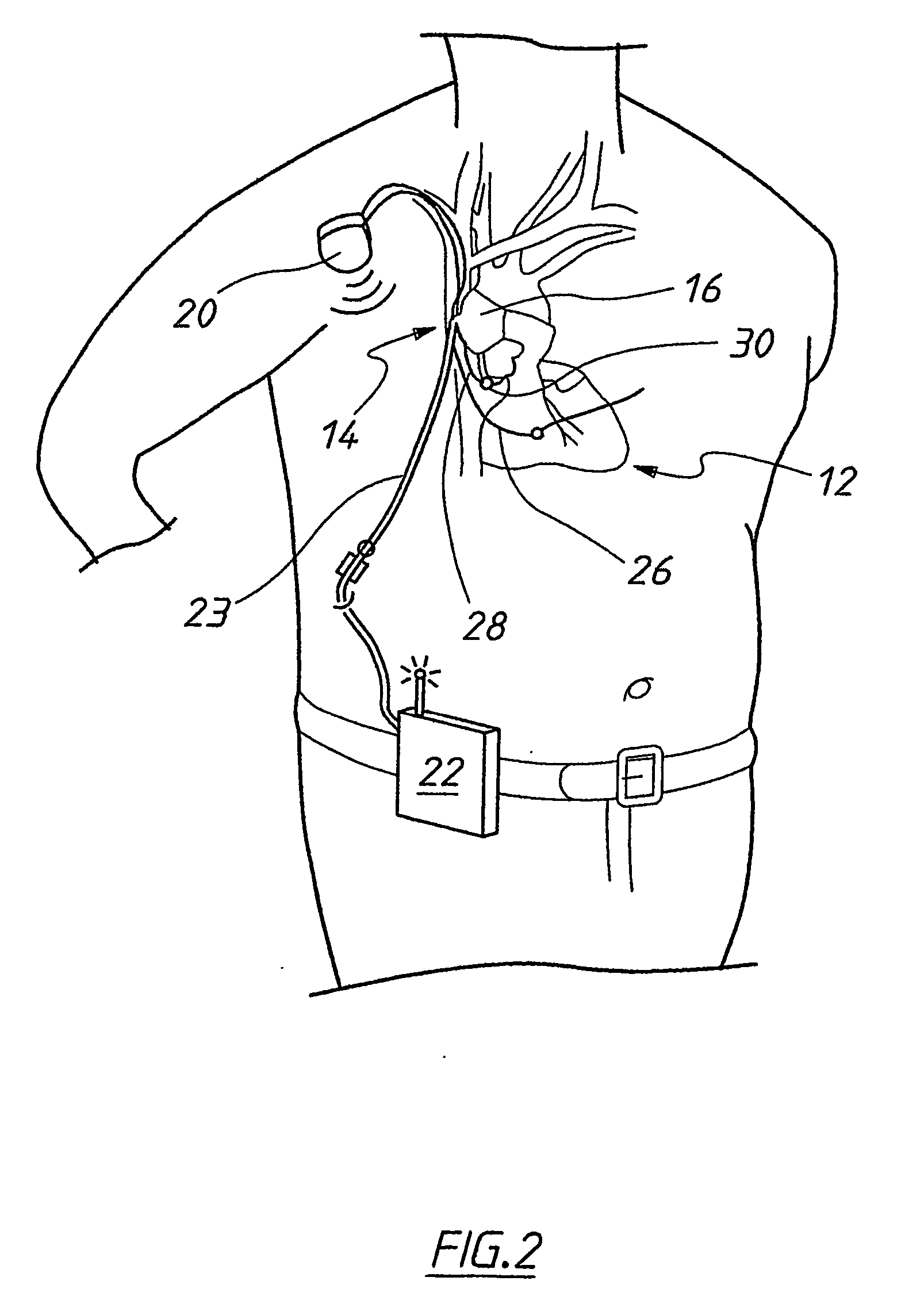
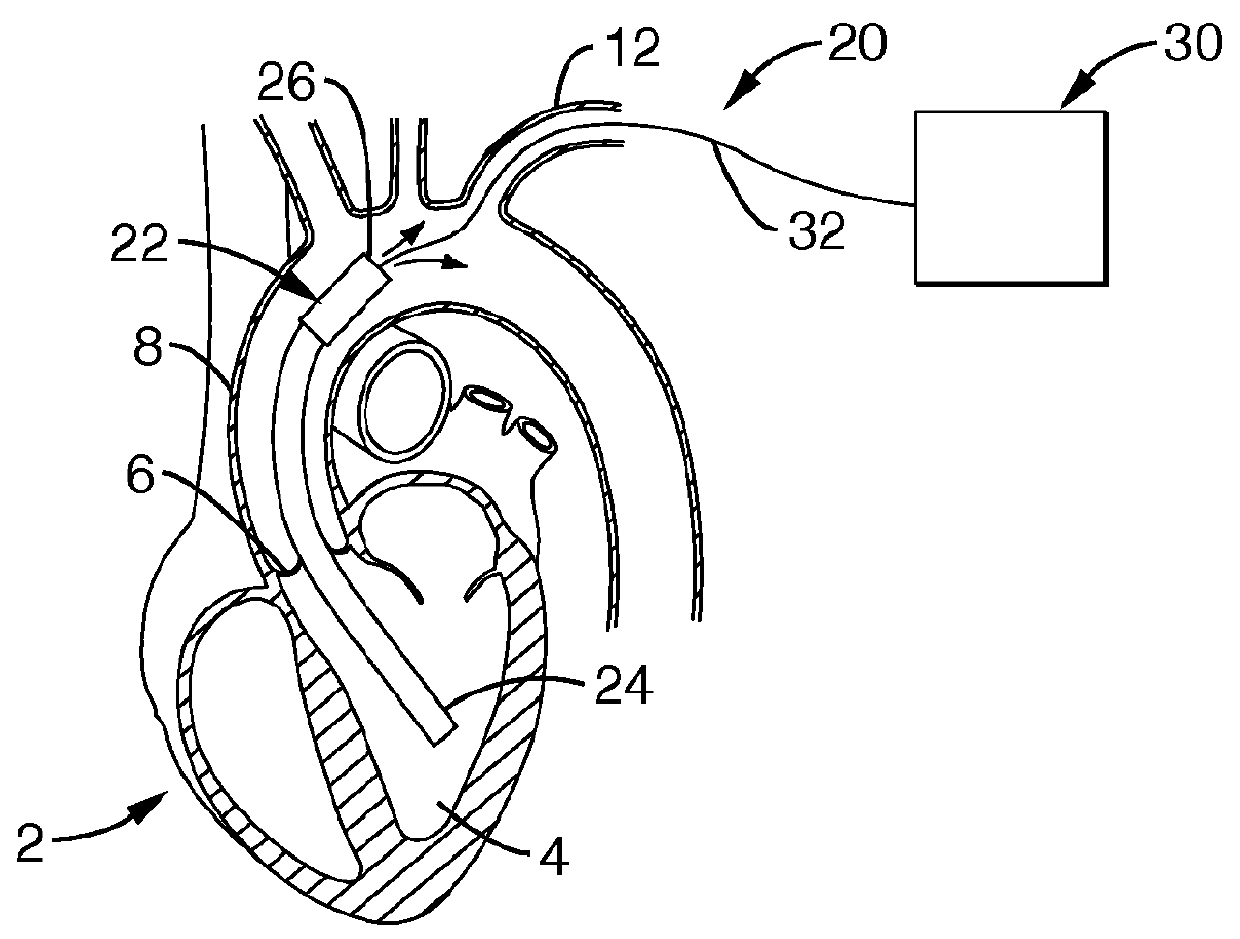
Heart assist device with expandable impeller pump
An impeller includes a hub and at least one blade supported by the hub. The impeller has a stored configuration in which the blade is compressed so that its distal end moves towards the hub, and a deployed configuration in which the blade extends away from the hub. The impeller may be part of a pump for pumping fluids, such as pumping blood within a patient. A blood pump may include a cannula having a proximal portion with a fixed diameter, and a distal portion with an expandable diameter. The impeller may reside in the expandable portion of the cannula. The cannula may have a compressed diameter which allows it to be inserted percutaneously into a patient. Once at a desired location, the expandable portion of the cannula may be expanded and the impeller expanded to the deployed configuration. A flexible drive shaft may extend through the cannula for rotationally driving the impeller within the patient's body.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +2
Heart assist device with expandable impeller pump
An impeller includes a hub and at least one blade supported by the hub. The impeller has a stored configuration in which the blade is compressed so that its distal end moves towards the hub, and a deployed configuration in which the blade extends away from the hub. The impeller may be part of a pump for pumping fluids, such as pumping blood within a patient. A blood pump may include a cannula having a proximal portion with a fixed diameter, and a distal portion with an expandable diameter. The impeller may reside in the expandable portion of the cannula. The cannula may have a compressed diameter which allows it to be inserted percutaneously into a patient. Once at a desired location, the expandable portion of the cannula may be expanded and the impeller expanded to the deployed configuration. A flexible drive shaft may extend through the cannula for rotationally driving the impeller within the patient's body.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +2
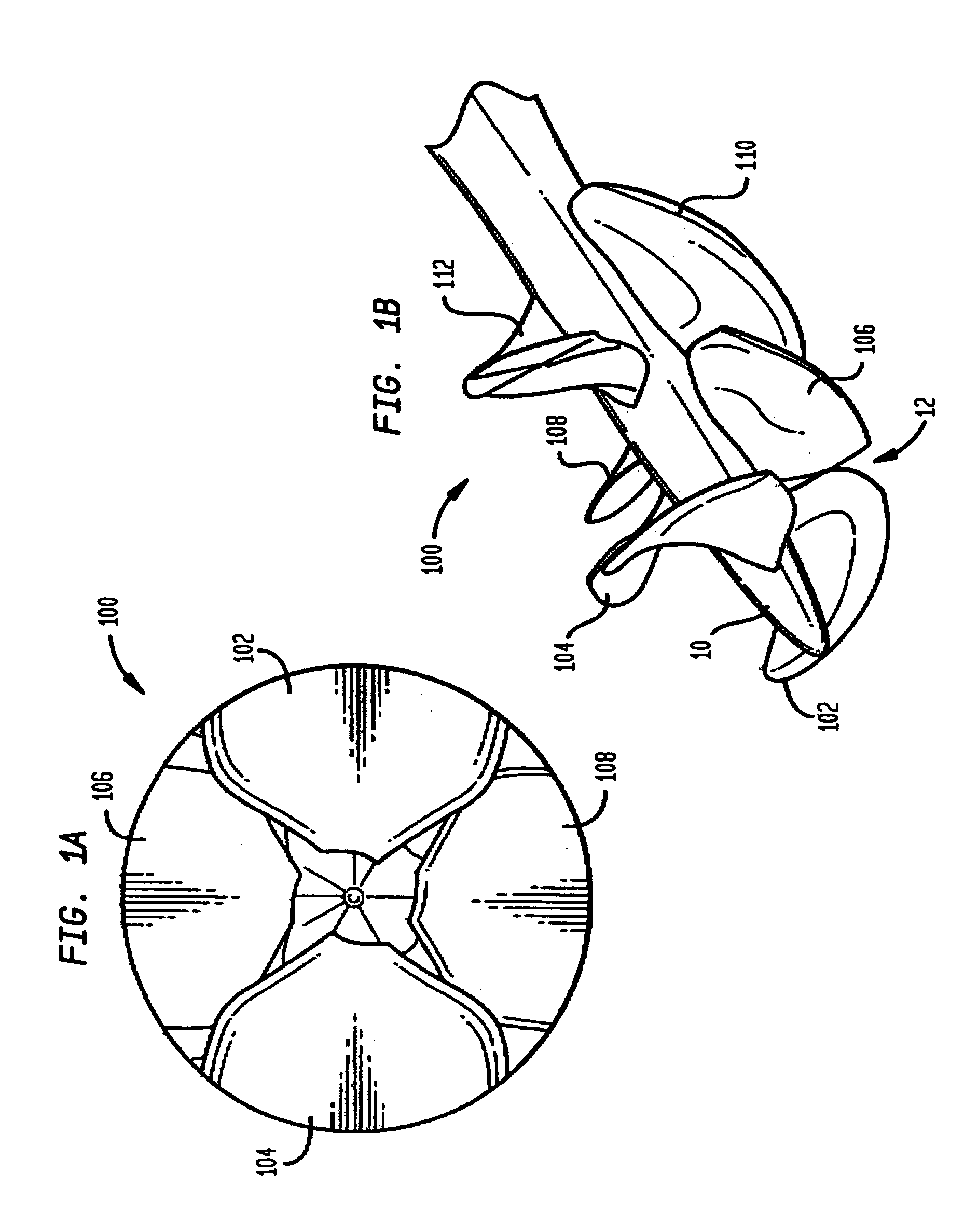
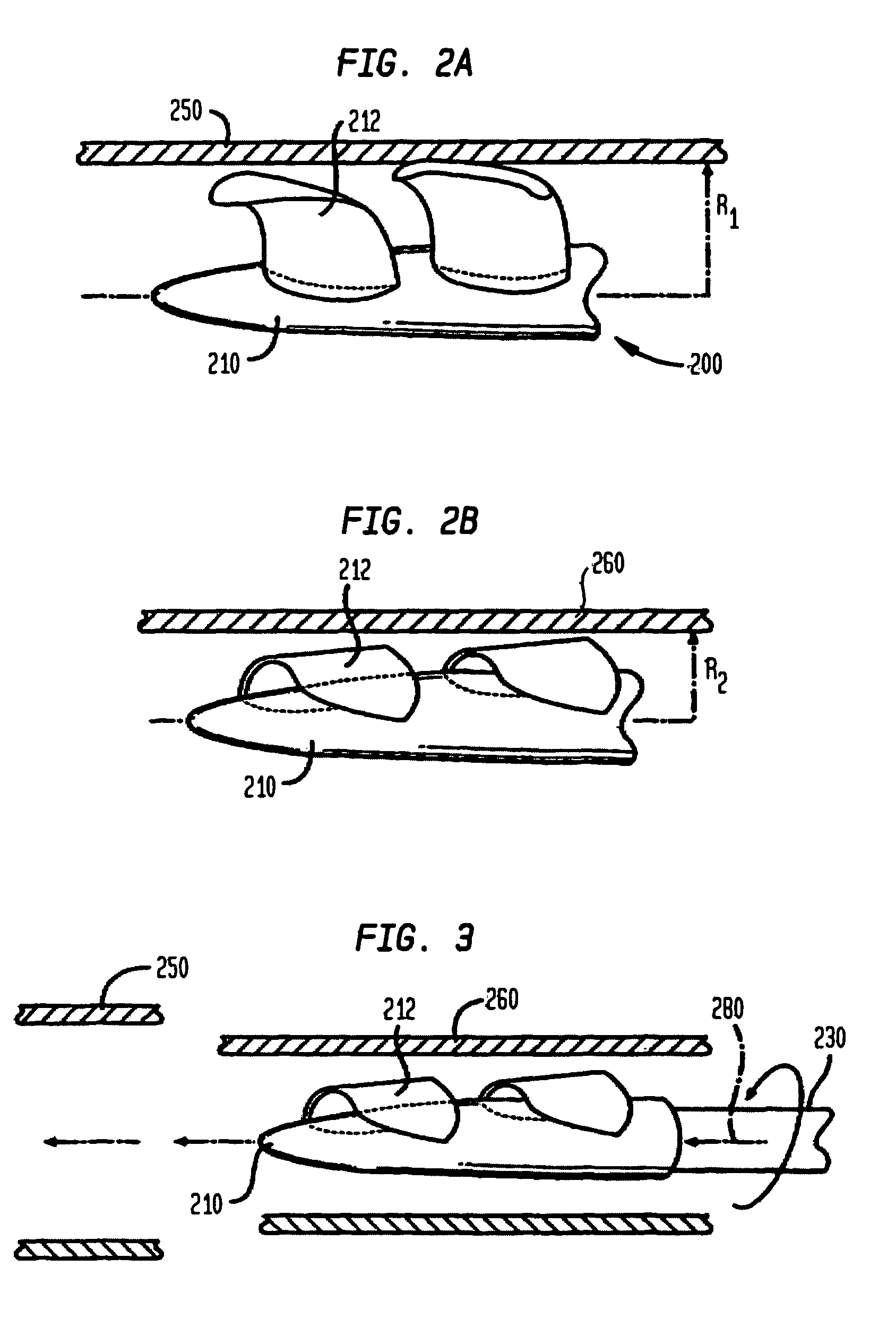
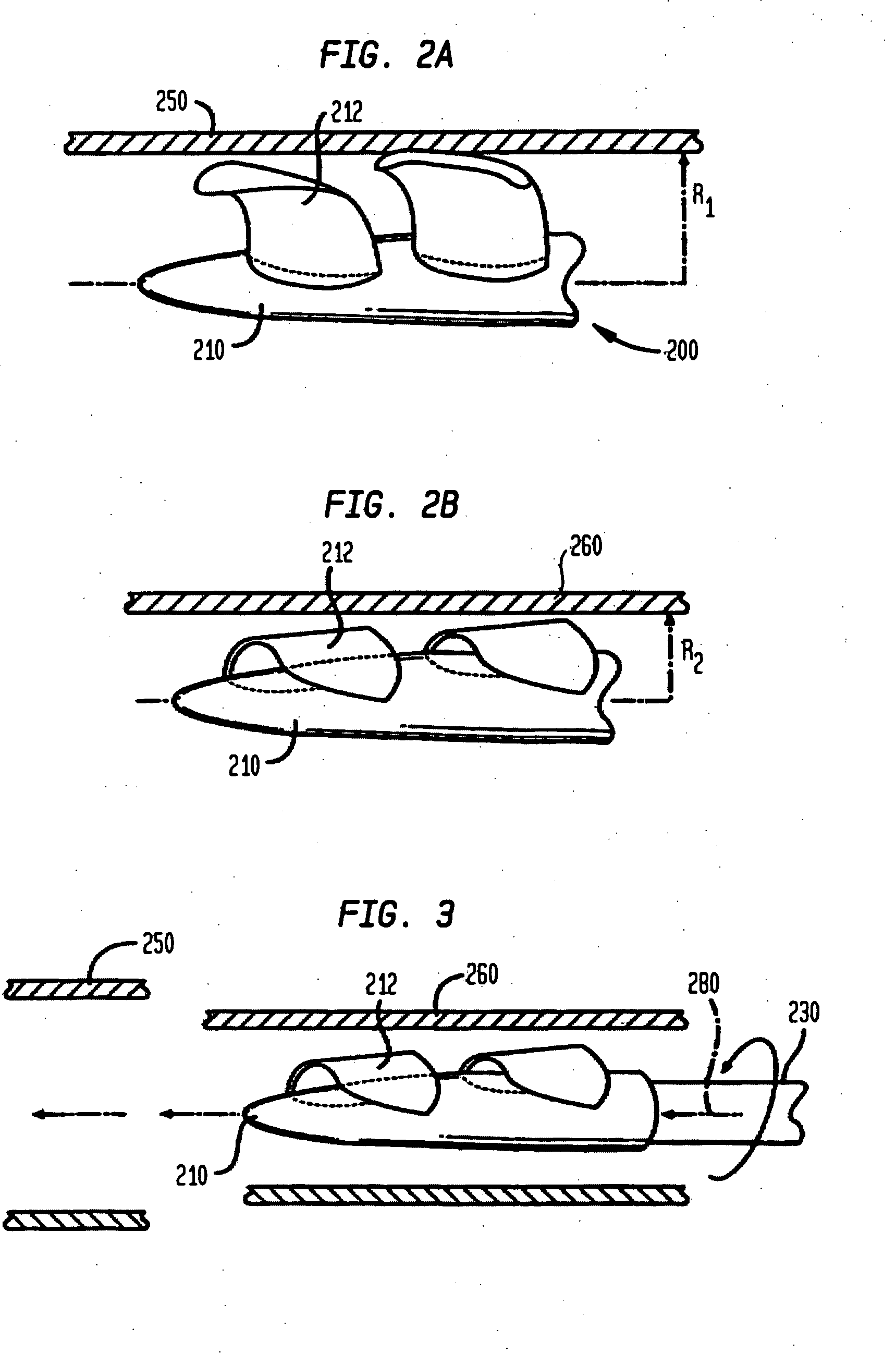
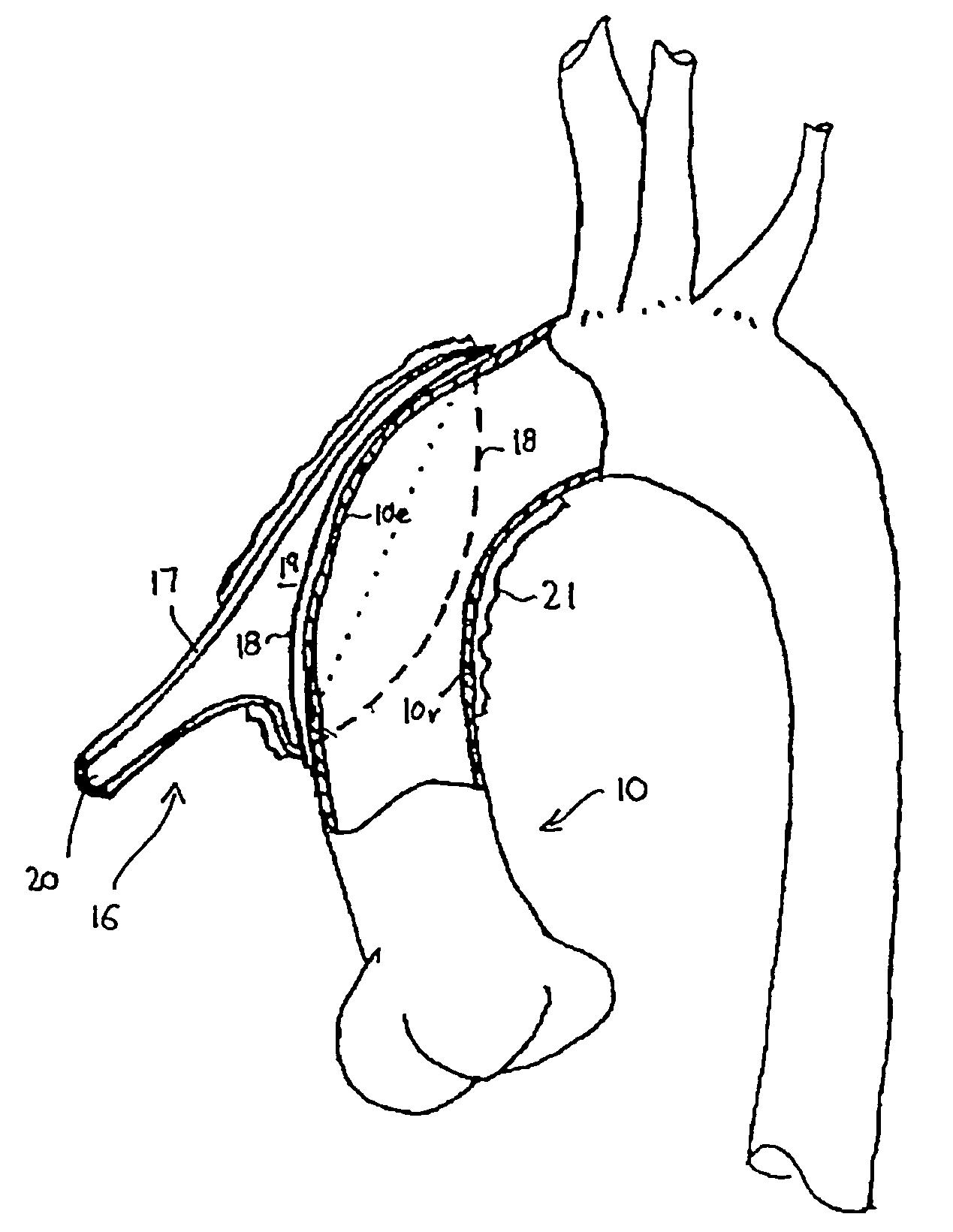
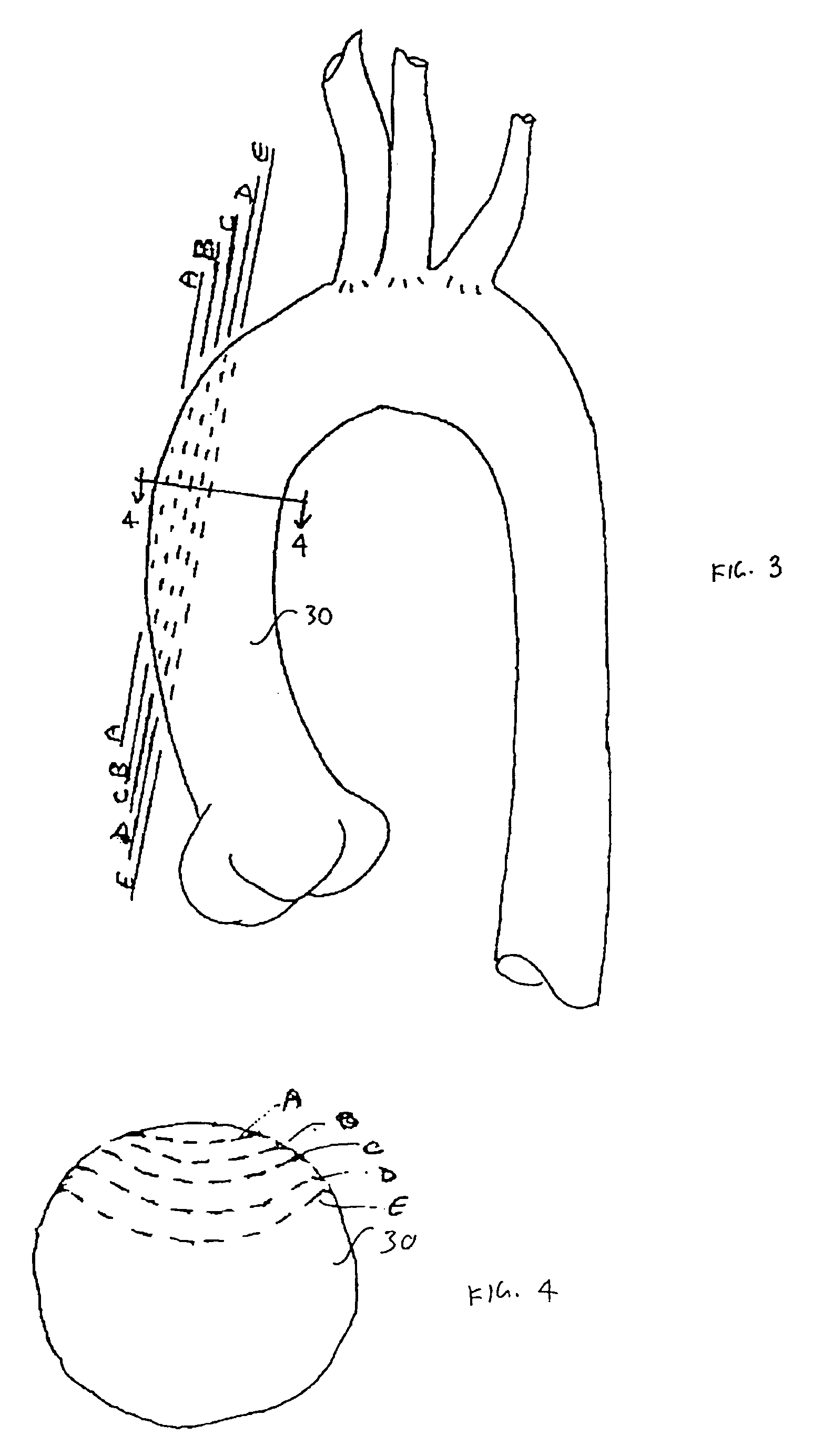
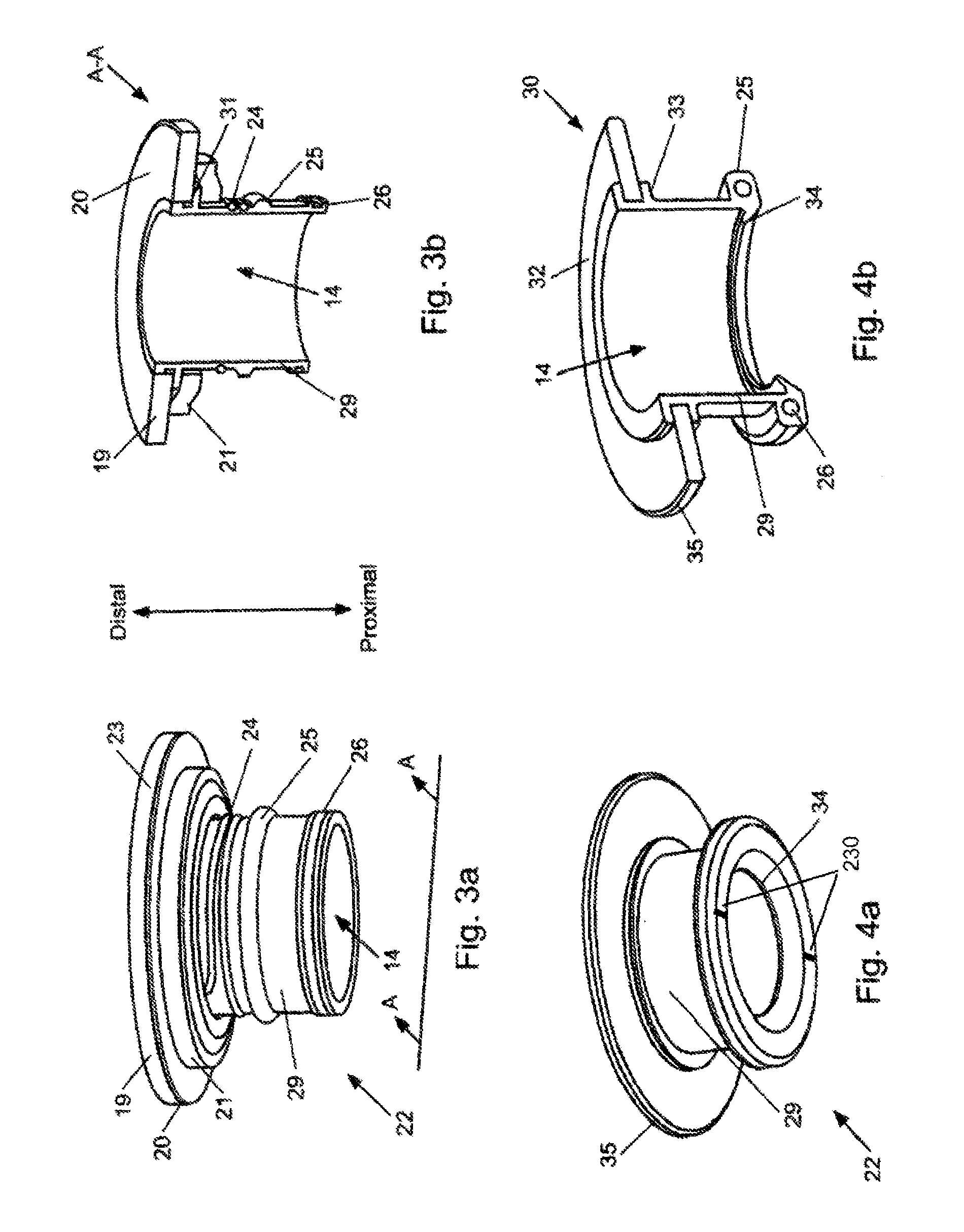
Minimally invasive transvalvular ventricular assist device
ActiveUS20060195004A1Highly effectiveHighly miniaturizedAdditive manufacturing apparatusBlood pumpsThree dimensional ctVentricular cavity
A tiny electrically powered hydrodynamic blood pump is disclosed which occupies one third of the aortic or pulmonary valve position, and pumps directly from the left ventricle to the aorta or from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery. The device is configured to exactly match or approximate the space of one leaflet and sinus of valsalva, with part of the device supported in the outflow tract of the ventricular cavity adjacent to the valve. In the configuration used, two leaflets of the natural tri-leaflet valve remain functional and the pump resides where the third leaflet had been. When implanted, the outer surface of the device includes two faces against which the two valve leaflets seal when closed. To obtain the best valve function, the shape of these faces may be custom fabricated to match the individual patient's valve geometry based on high resolution three dimensional CT or MRI images. Another embodiment of the invention discloses a combined two leaflet tissue valve with the miniature blood pump supported in the position usually occupied by the third leaflet. Either stented or un-stented tissue valves may be used. This structure preserves two thirds of the valve annulus area for ejection of blood by the natural ventricle, with excellent washing of the aortic root and interface of the blood pump to the heart. In the aortic position, the blood pump is positioned in the non-coronary cusp. A major advantage of the transvalvular VAD is the elimination of both the inflow and outflow cannulae usually required with heart assist devices.
Owner:JARVIK ROBERT
Methods and apparatus for controlling heart assist devices
InactiveUS7169109B2Improve accuracyElectrocardiographyOther blood circulation devicesDecreased mean arterial pressurePulse pressure
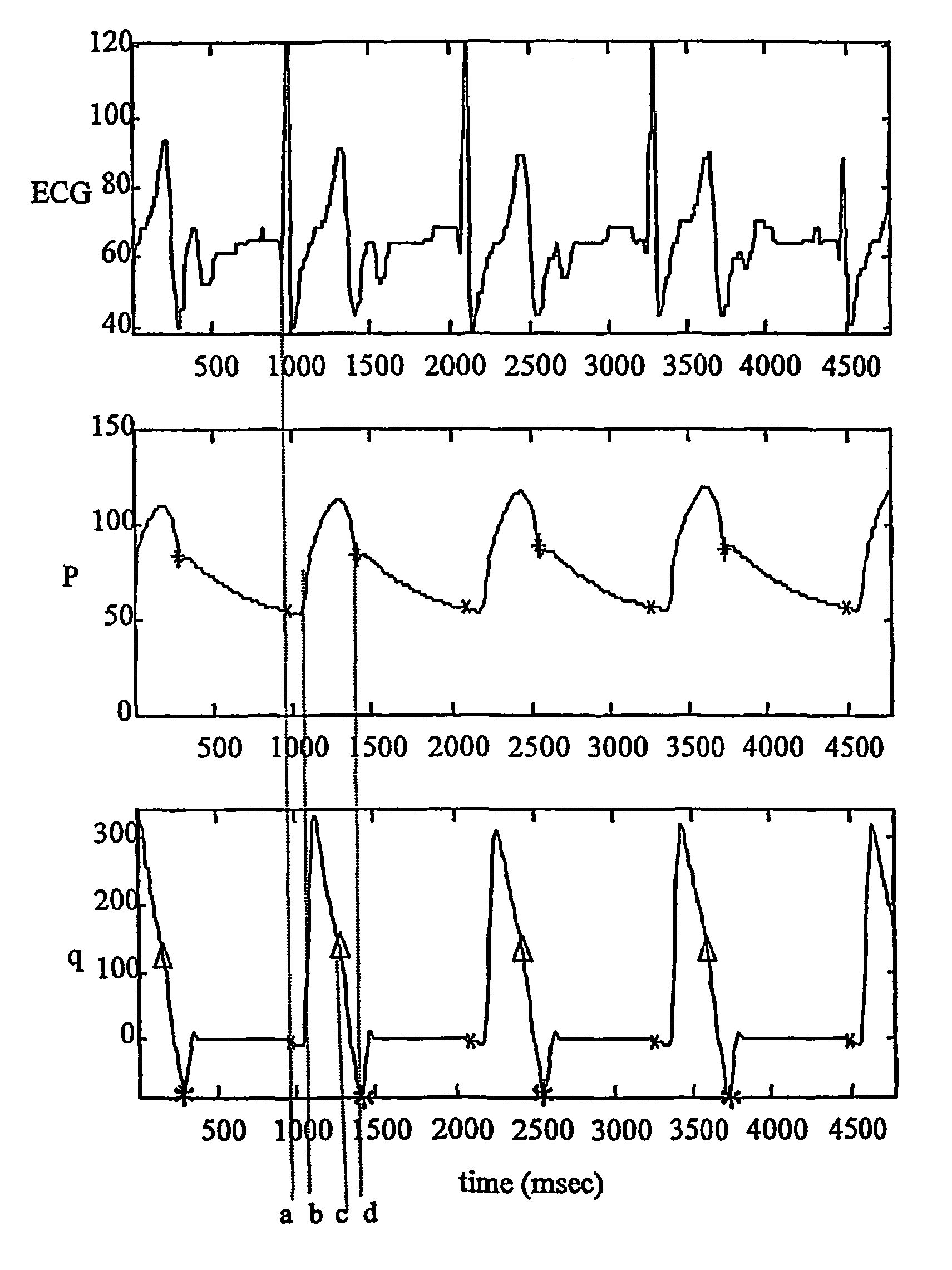
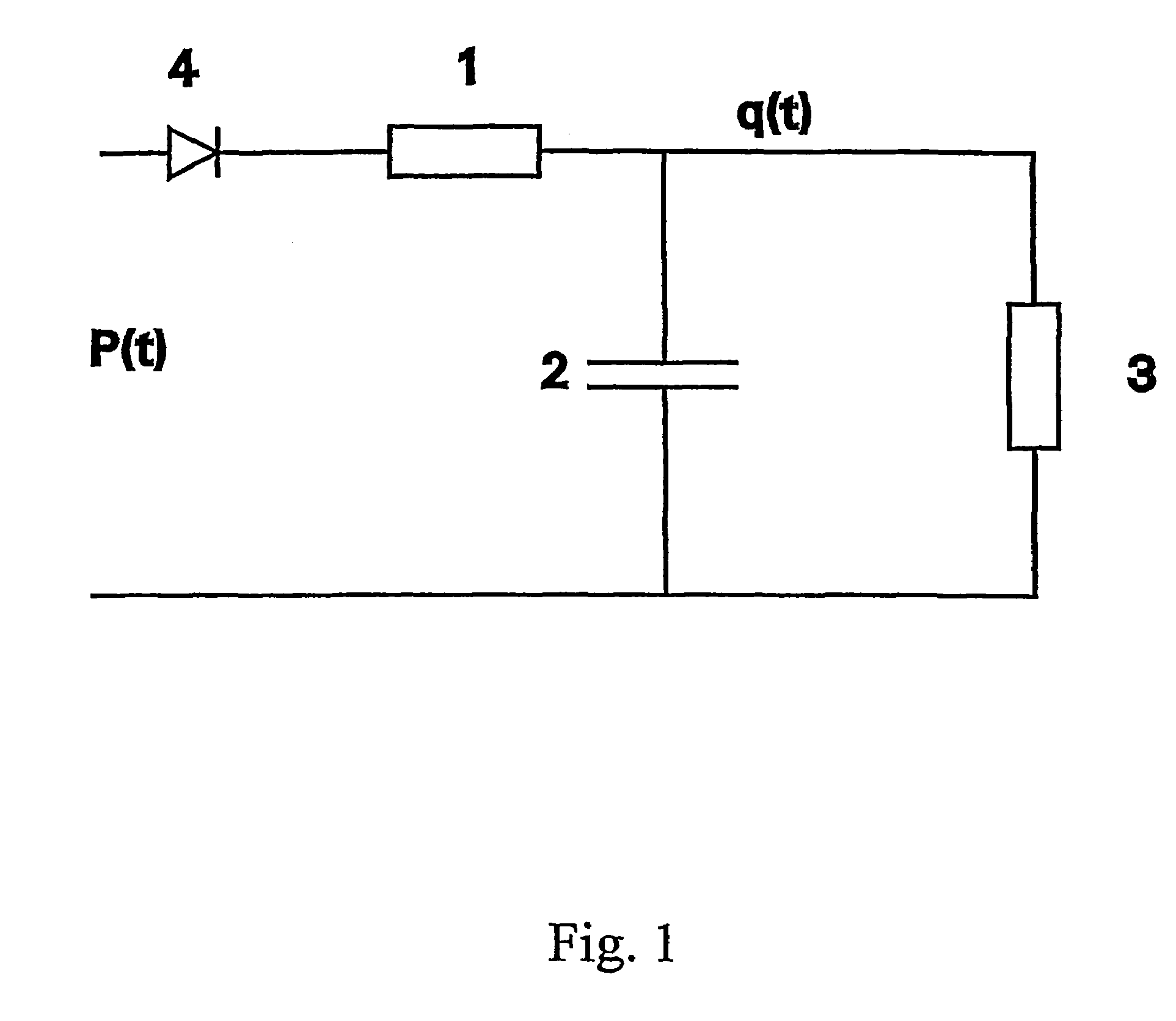
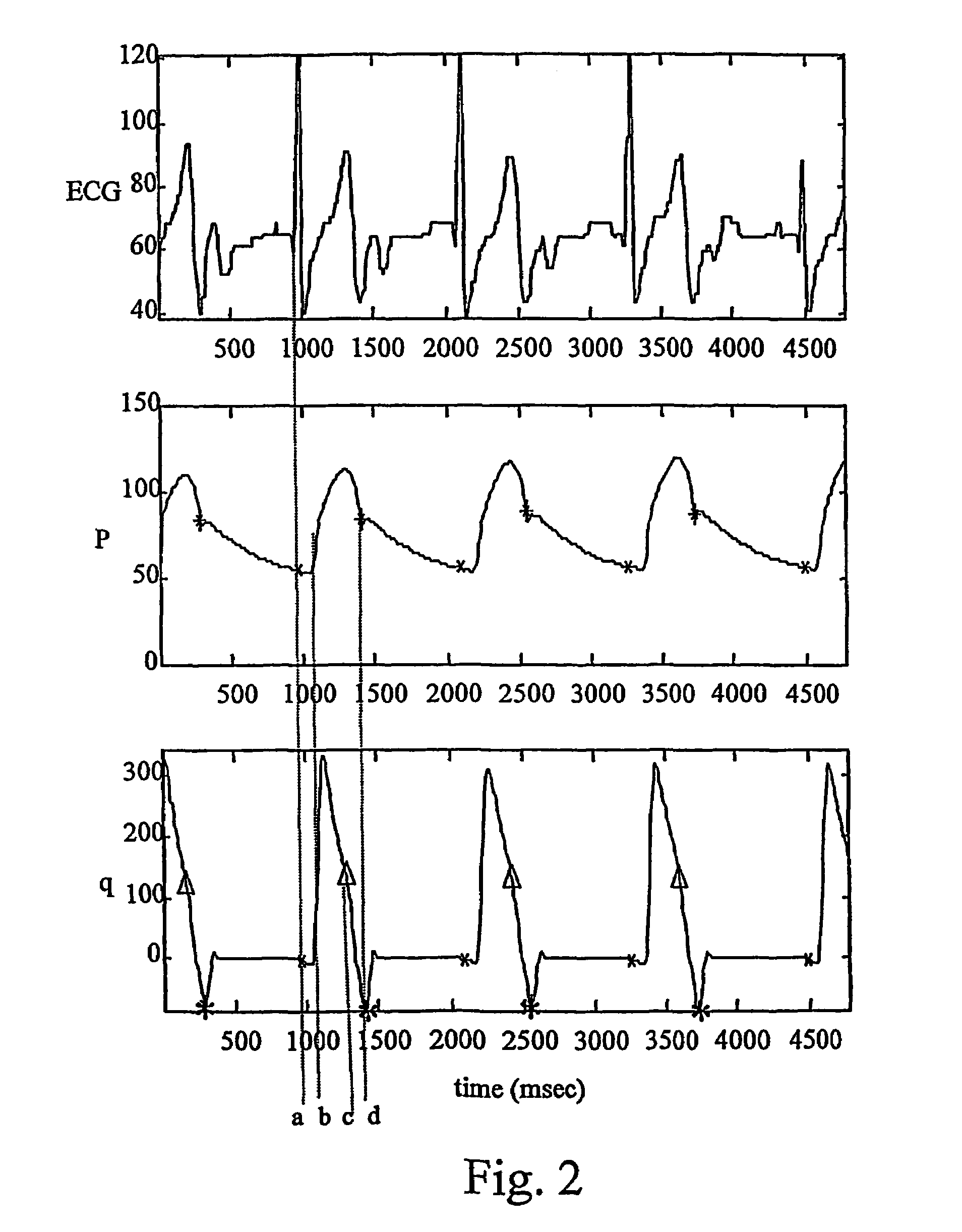
An apparatus for a heart assist device, comprising a processing unit for computing the blood flow rate from the arterial pressure curve and for predicting at every heartbeat the closing time of the heart valve from the curve of the blood flow rate. The processing unit is adapted to deliver a signal for controlling a heart assist device at a point in time, a period ahead in time of the closing time of the heart valve, wherein the mechanical properties of the said heart assist device are taken into account in determining the period. The apparatus adapts itself to changes in a patient's heart frequency and aortic pressure.
Owner:ARROW INT INC
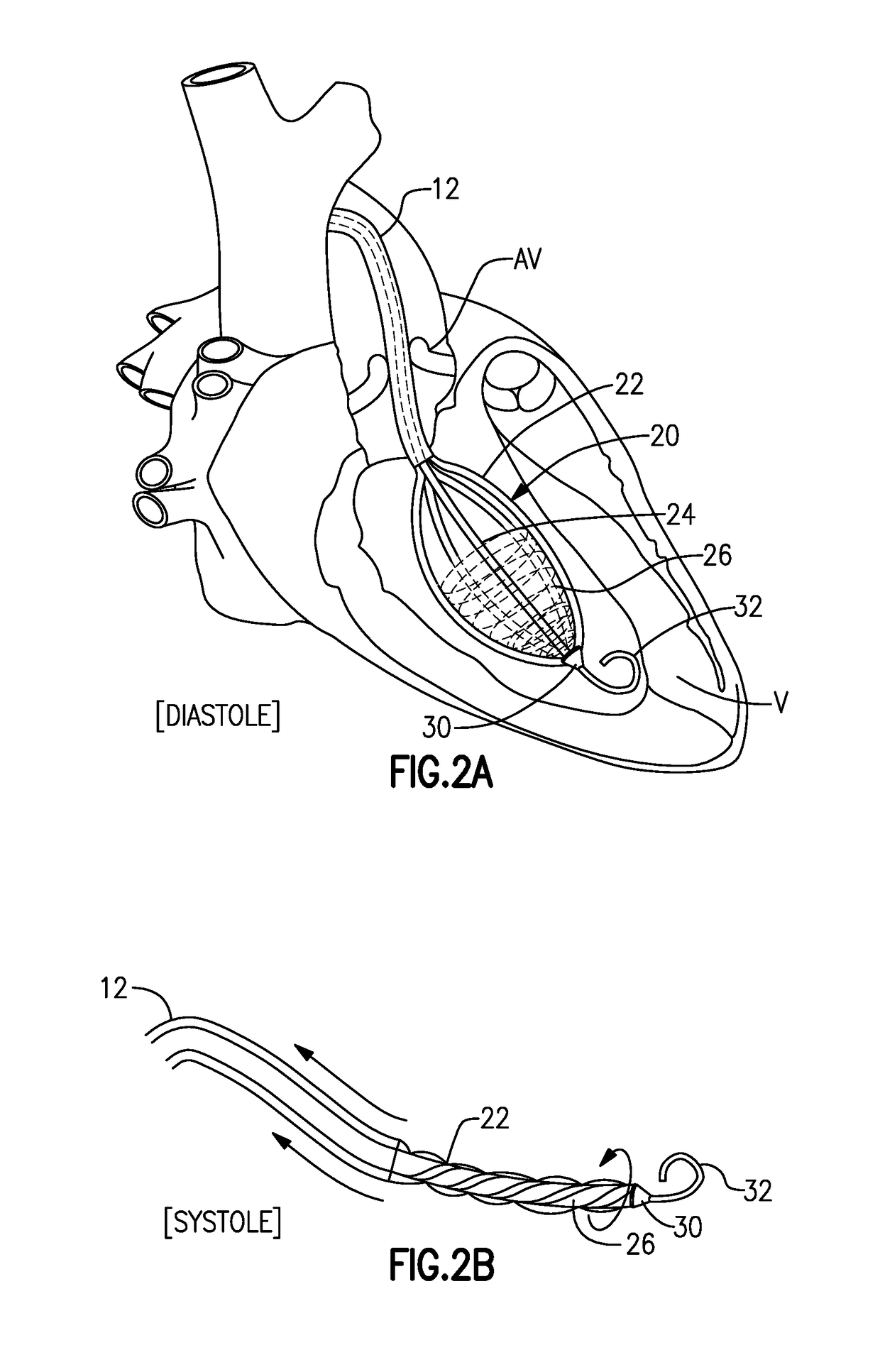
Left Heart Assist Device and Method
ActiveUS20130304198A1Improve understandingAugment, improve, enhance or support the remaining natural pump functionAnnuloplasty ringsControl devicesLeft ventricular sizeLong axis
A device, a kit and a method is presented for permanently augmenting the pump function of the left heart. The mitral valve plane is assisted in a movement along the left ventricular long axis during each heart cycle. The very close relationship between the coronary sinus and the mitral valve is used by various embodiments of a medical device providing this assisted movement. By means of catheter technique an implant is inserted into the coronary sinus, the device is augmenting the up and down movement of the mitral valve and thereby increasing the left ventricular diastolic filling when moving upwards and the piston effect of the closed mitral valve when moving downwards.
Owner:SYNTACH AG
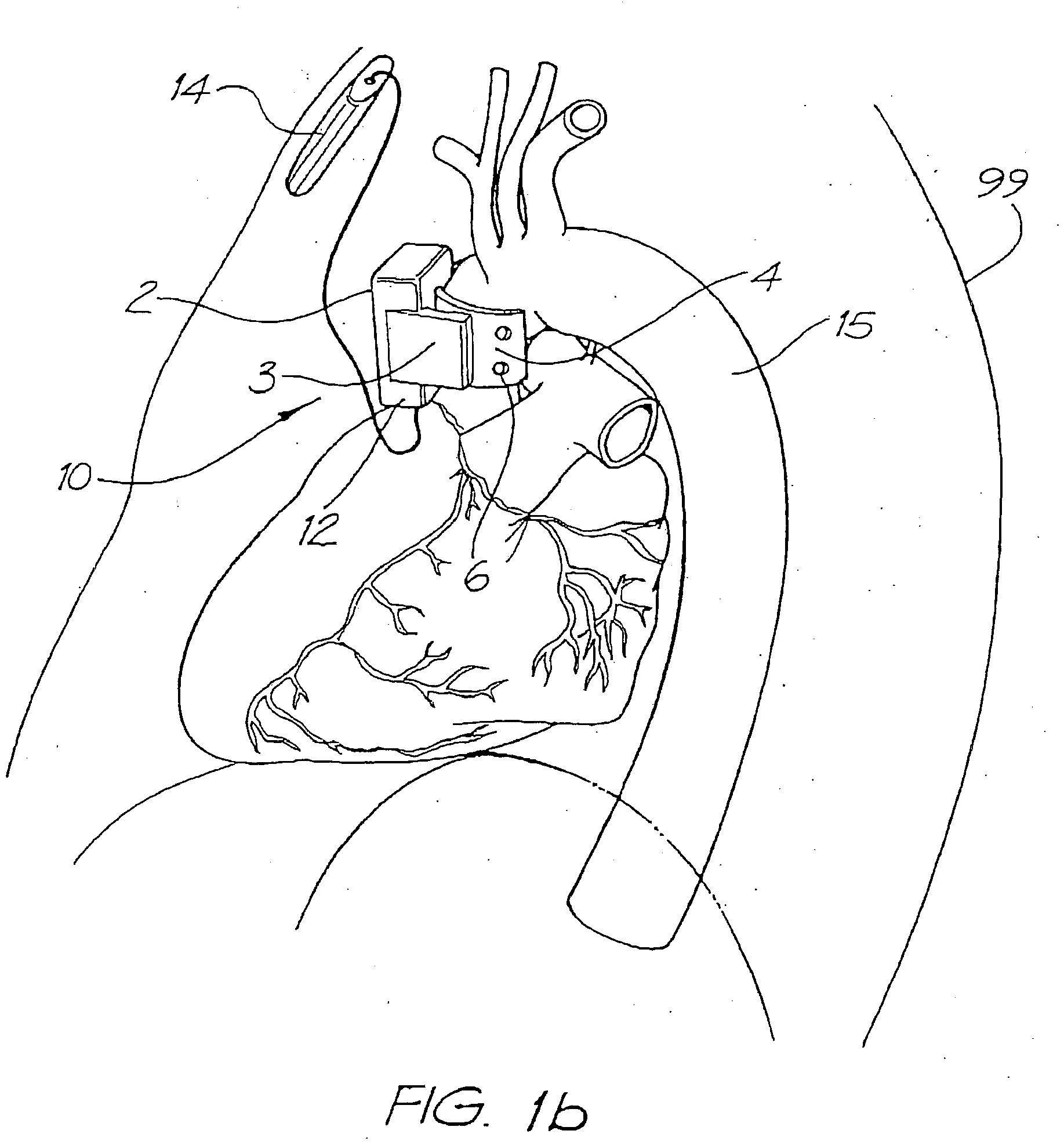
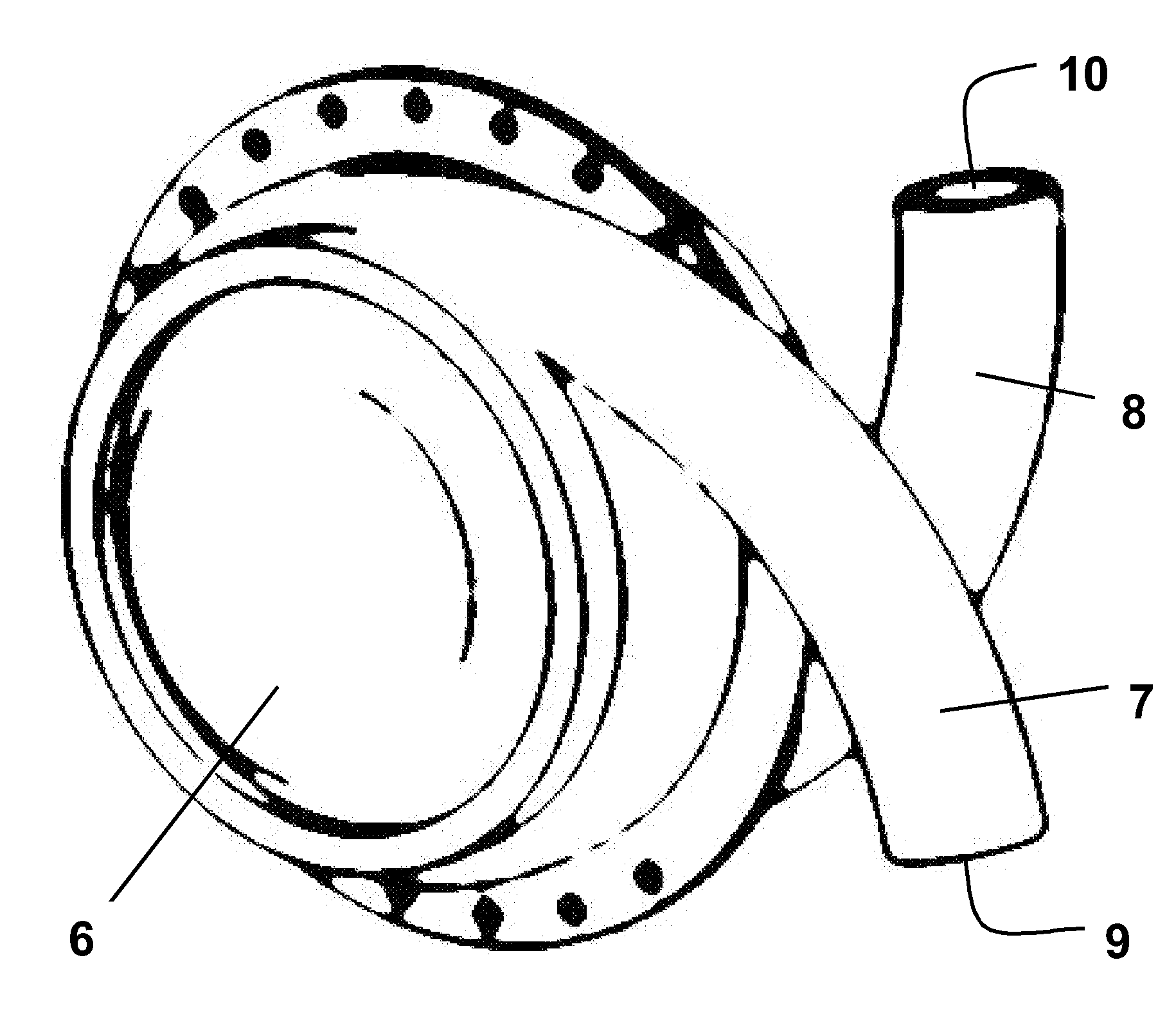
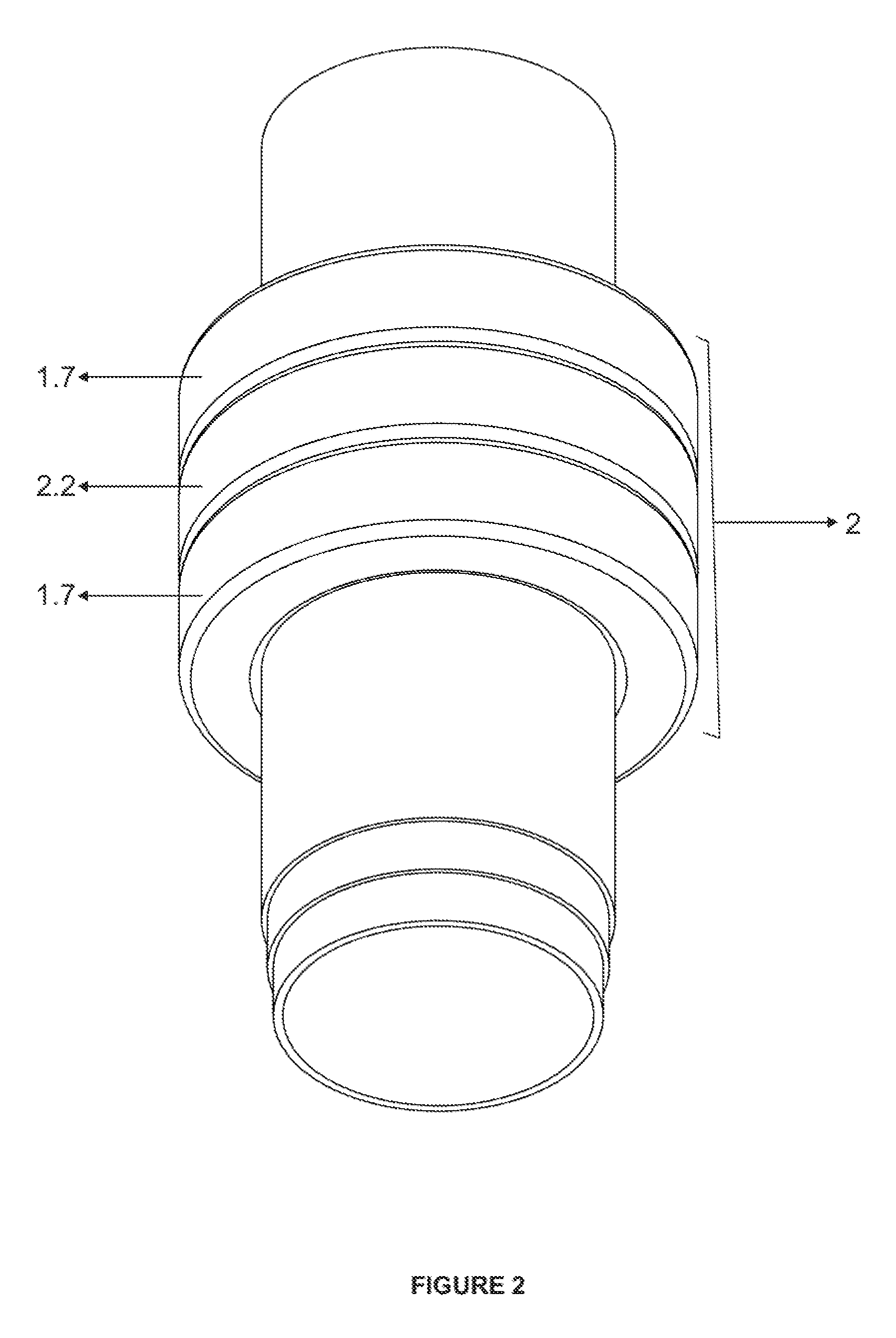
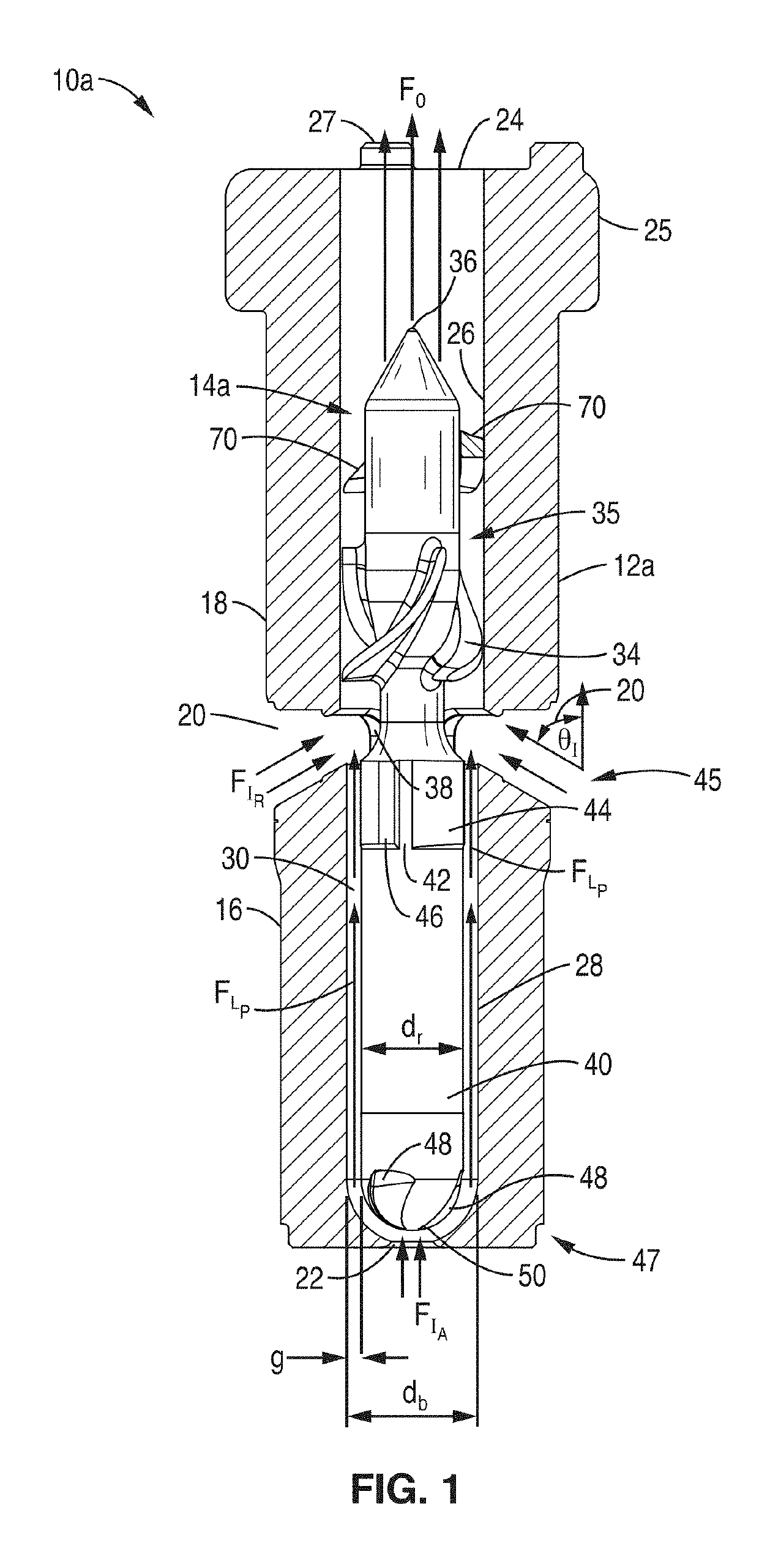
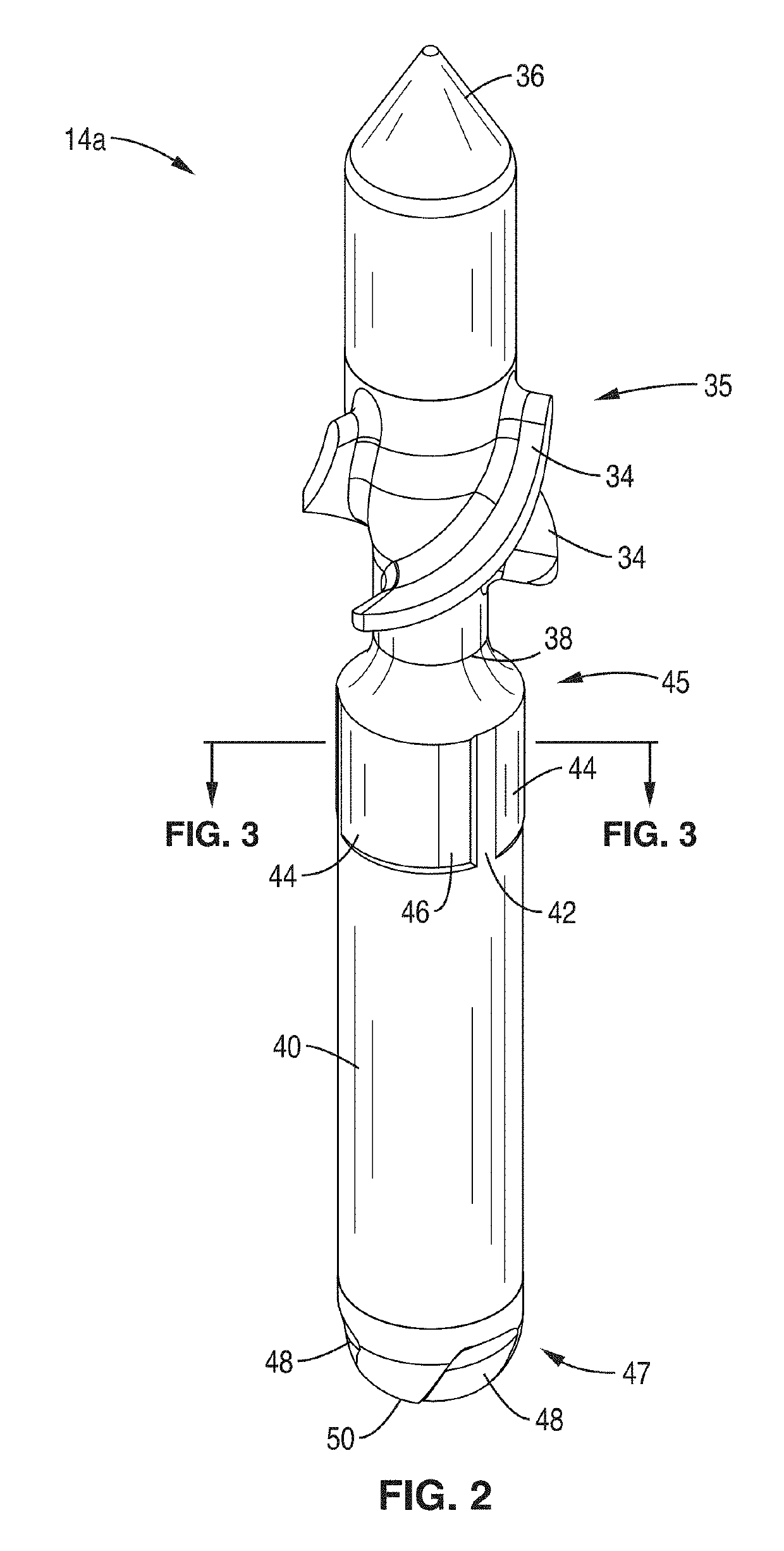
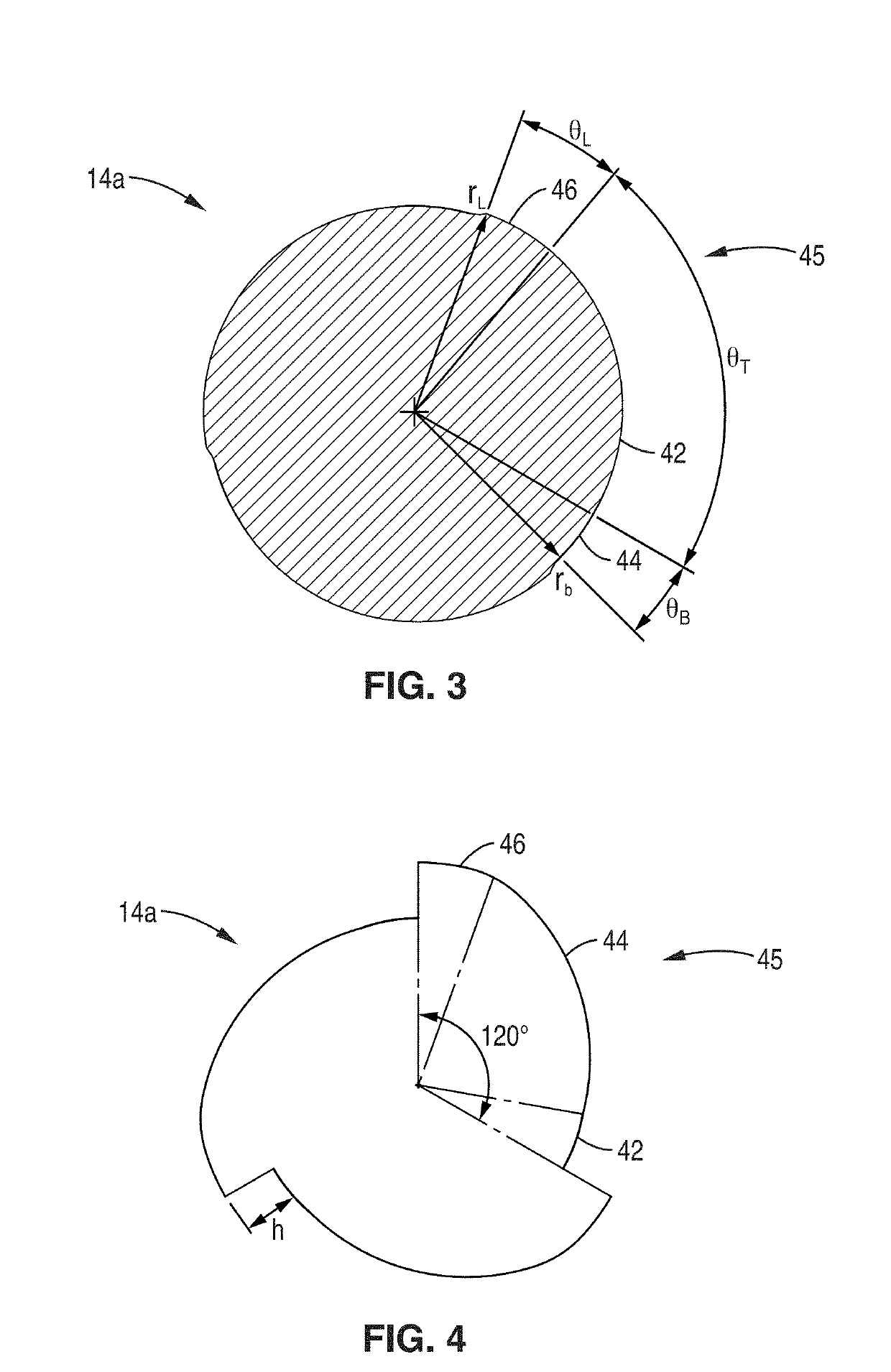
Heart assist device
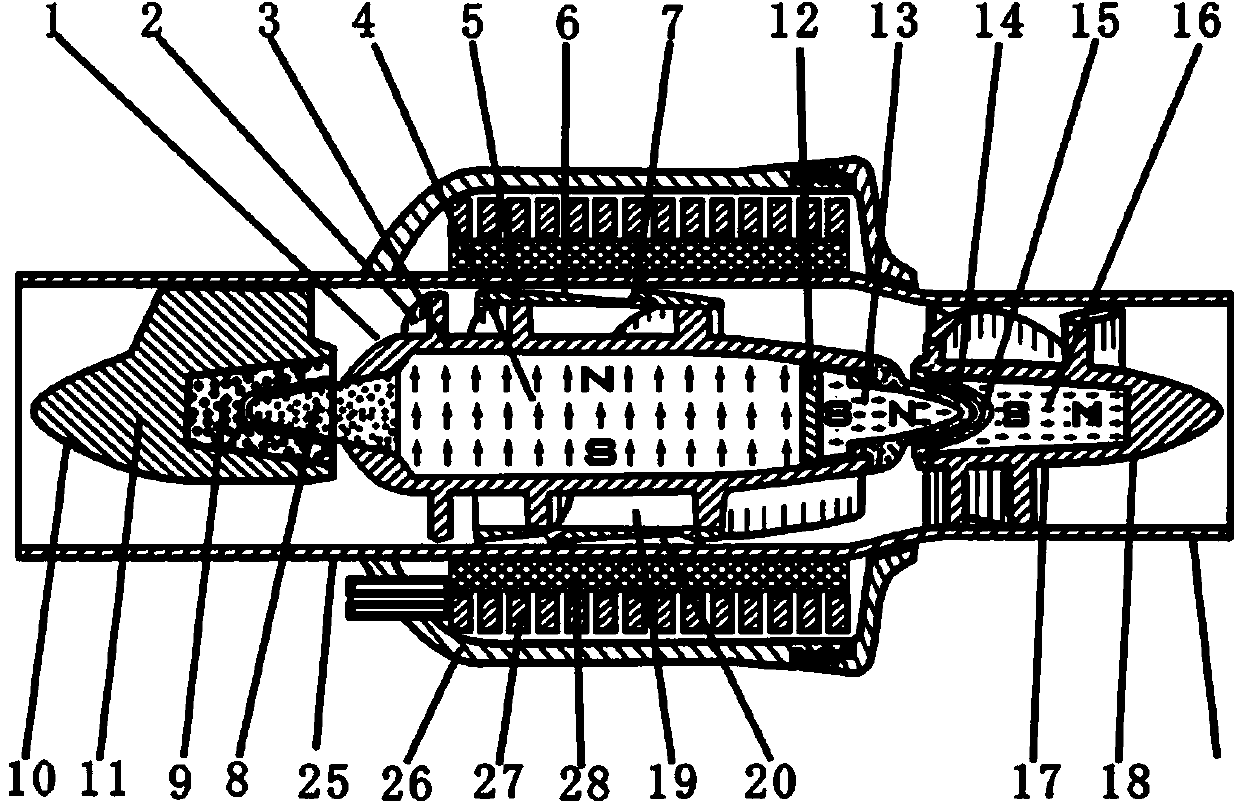
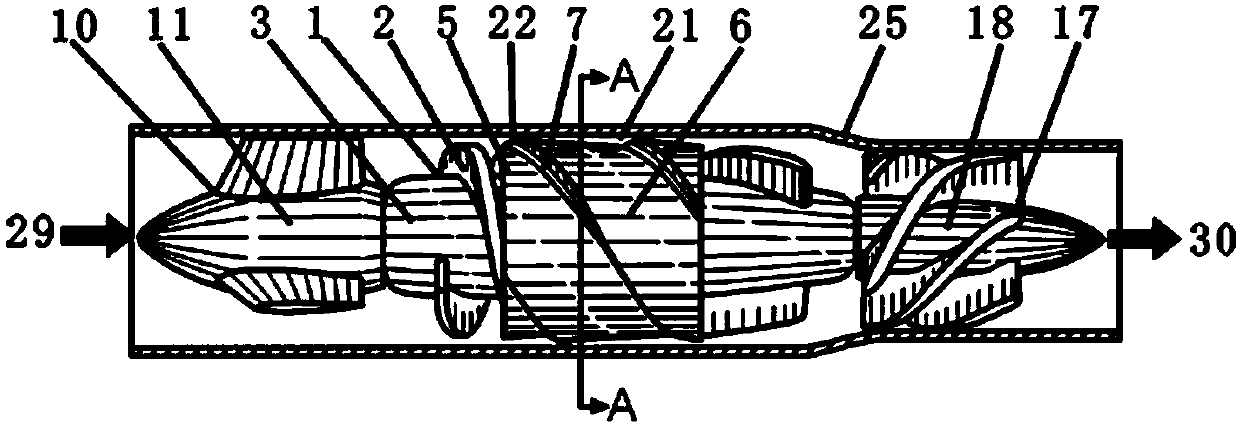
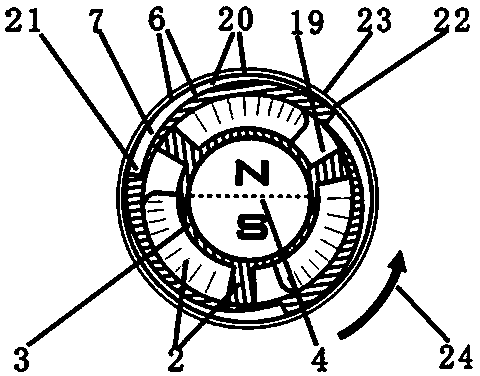
A heart assist device comprising a rotary pump housing having a cylindrical bore, a pumping chamber and a motor stator including an electrically conductive coil located within the housing and surrounding a portion of the cylindrical bore. A rotor has a cylindrical shaft, at least one impeller appended to one end of the shaft, and a plurality of magnets located within the shaft. The rotor shaft is positioned within the housing bore with the magnets opposite the motor stator, and the impeller is positioned within the pumping chamber. The housing bore is closely fitted to the outer surface of the shaft forming a hydrodynamic journal bearing, with the pumping chamber and journal bearing connected by a leak path of blood flow between the pumping chamber and the journal bearing. A backiron of the motor stator attracts the rotor magnets to resist longitudinal displacement of the rotor within the housing during operation. The relative orientation of positions of the inflow, outflow, and leakage flow paths may be varied within the pump, such as to accommodate different intended methods for implantation and / or use.
Owner:VADOVATIONS INC
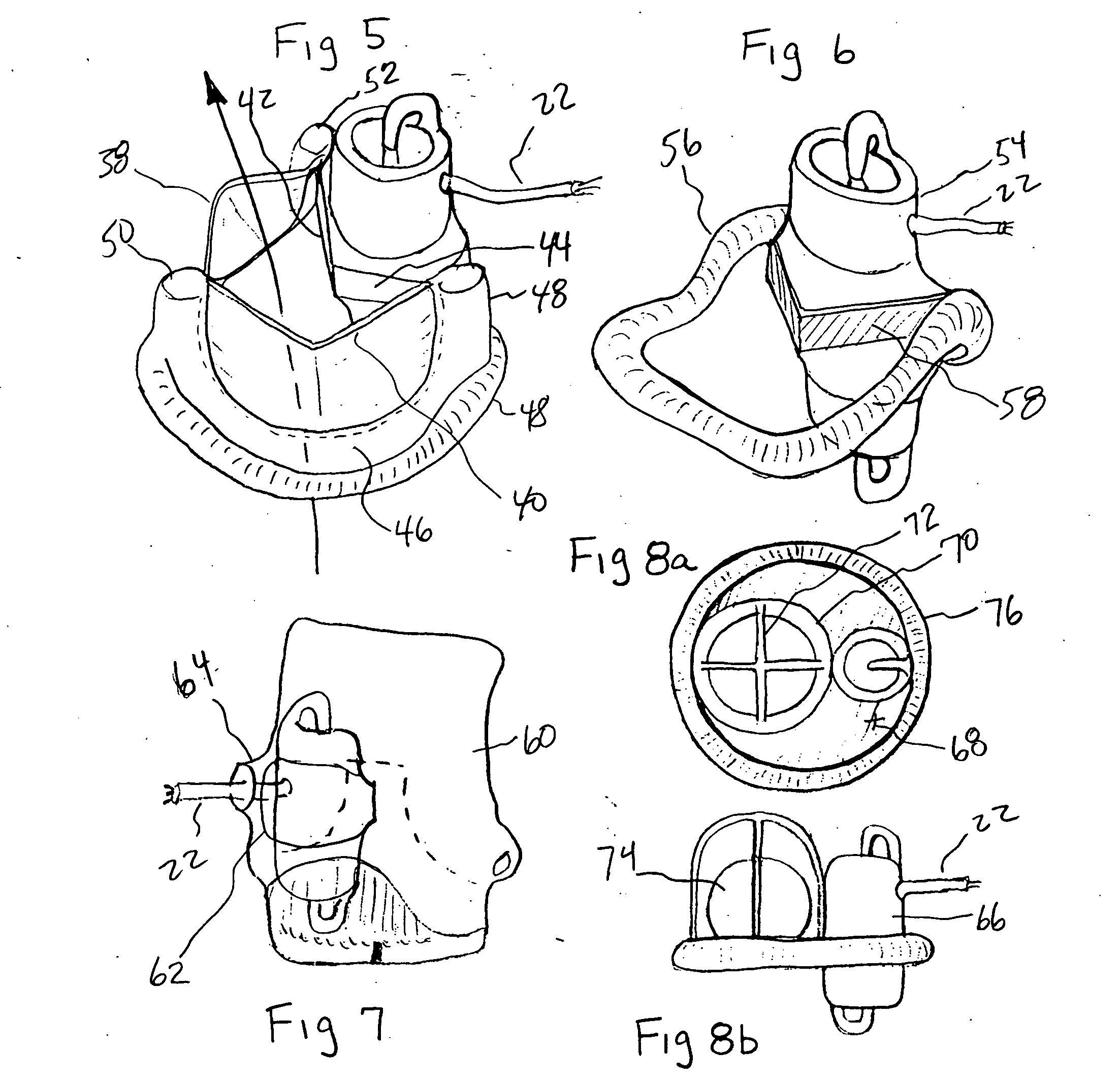
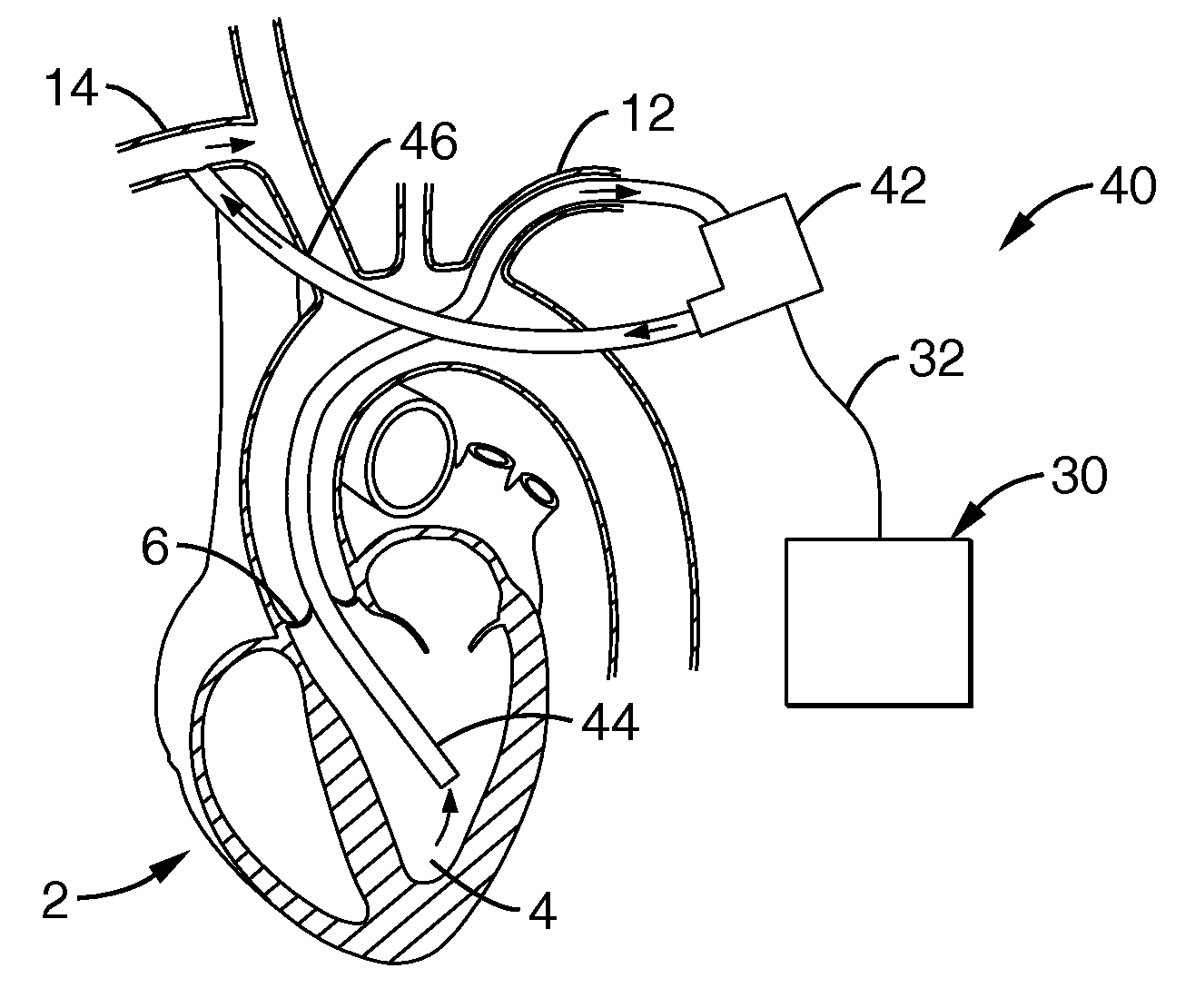
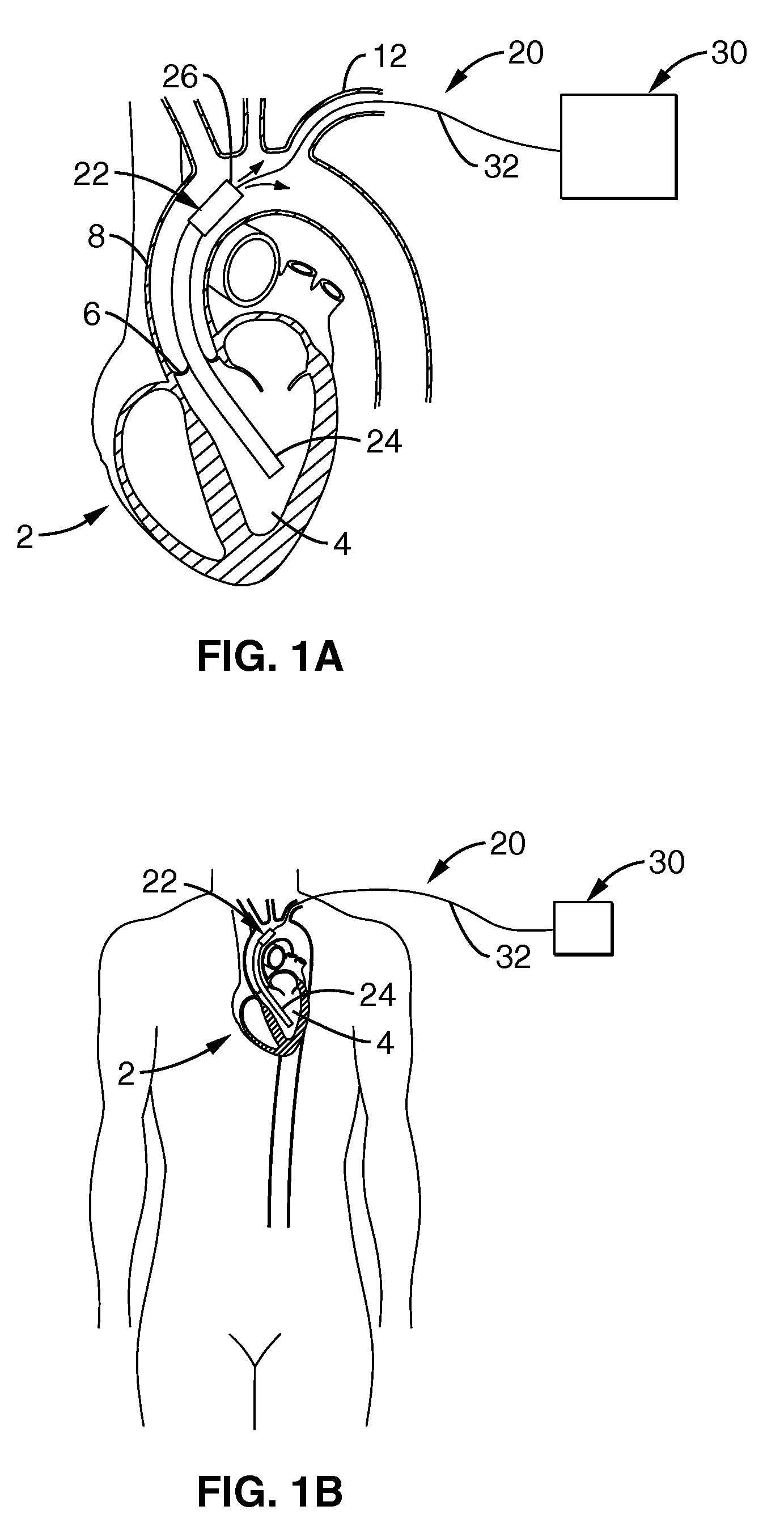
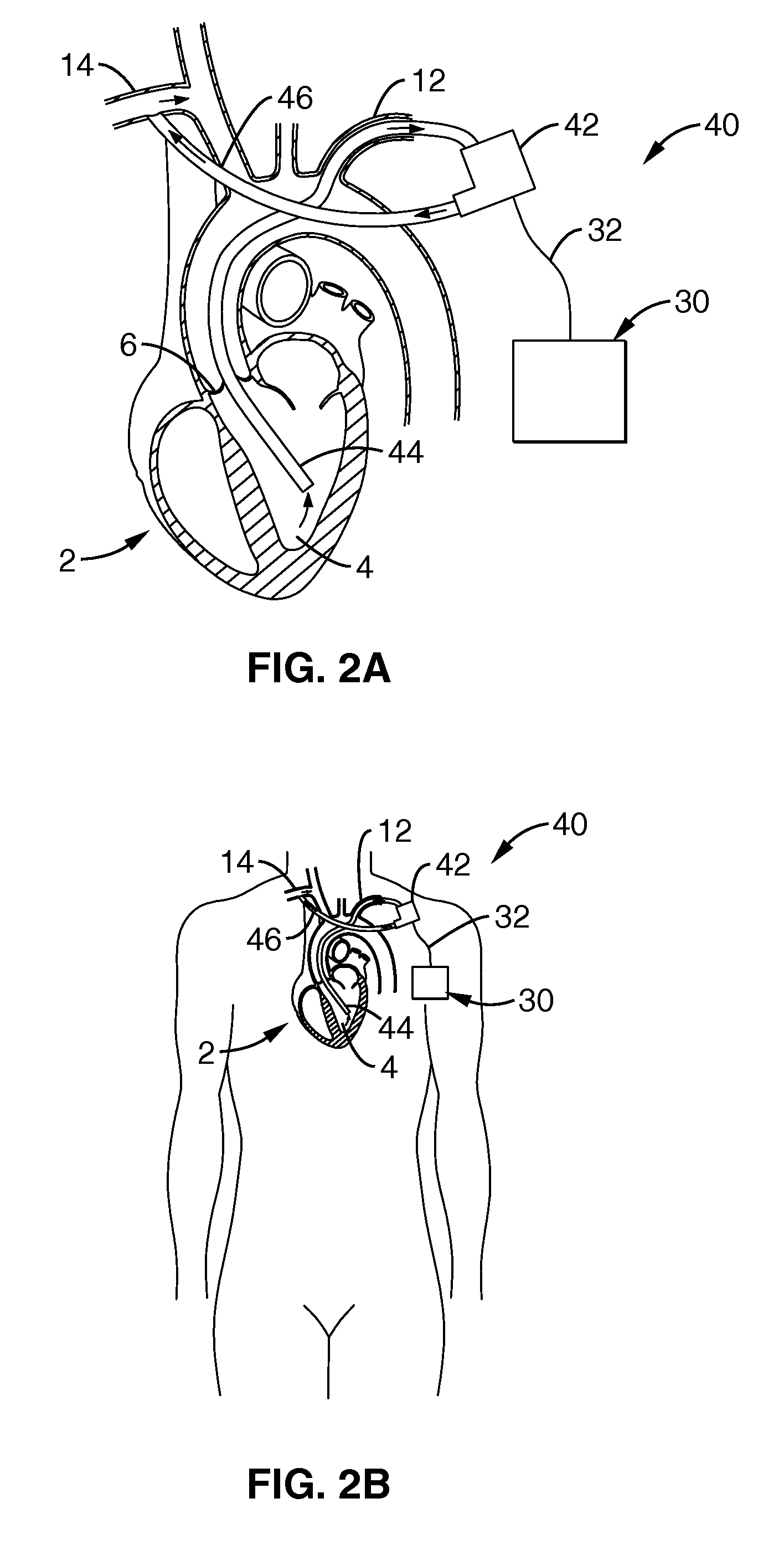
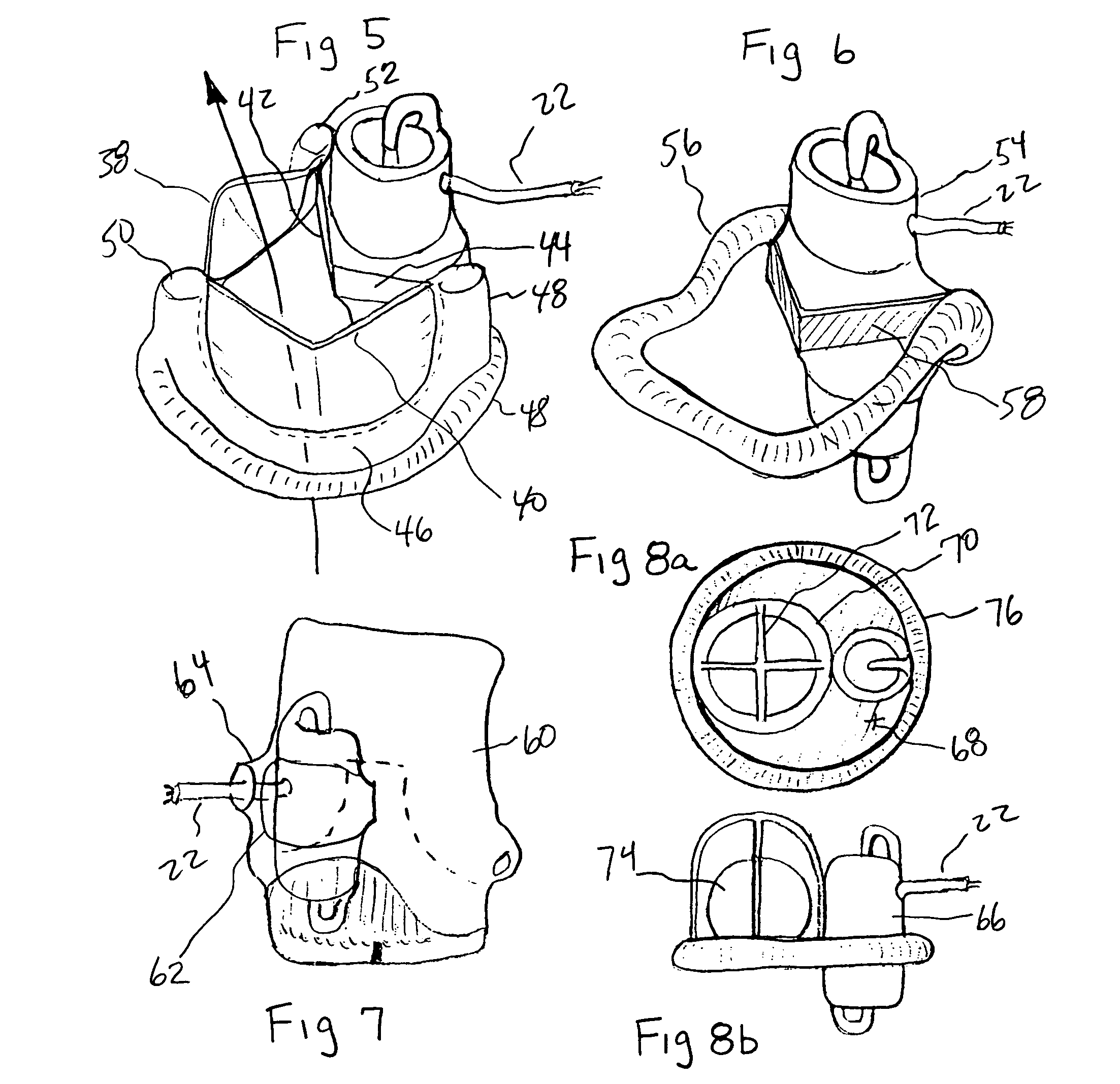
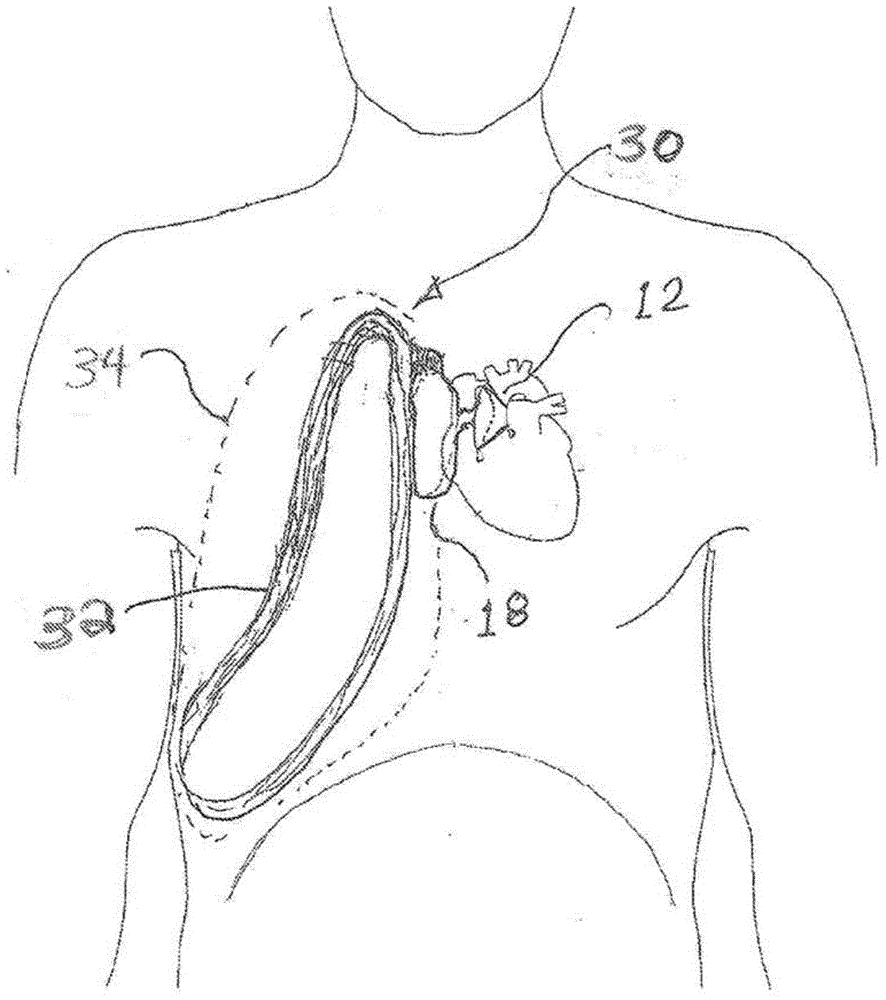
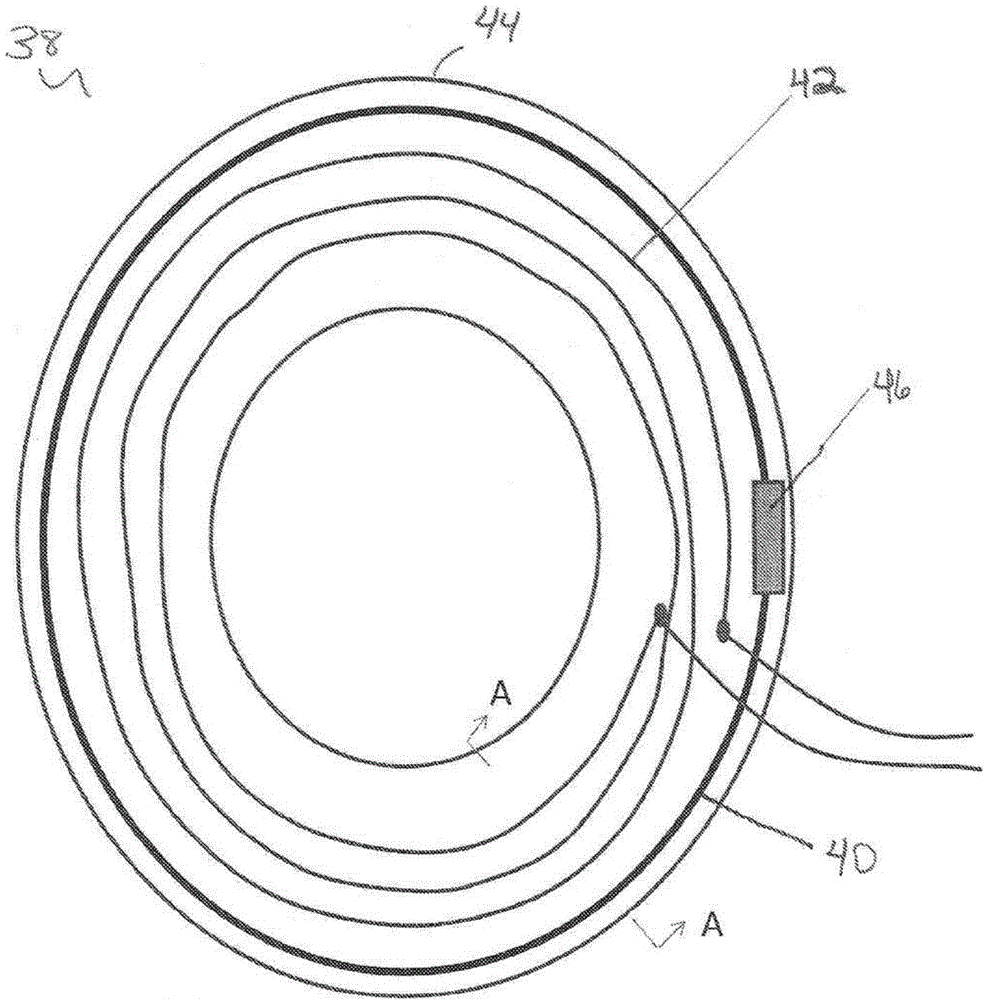
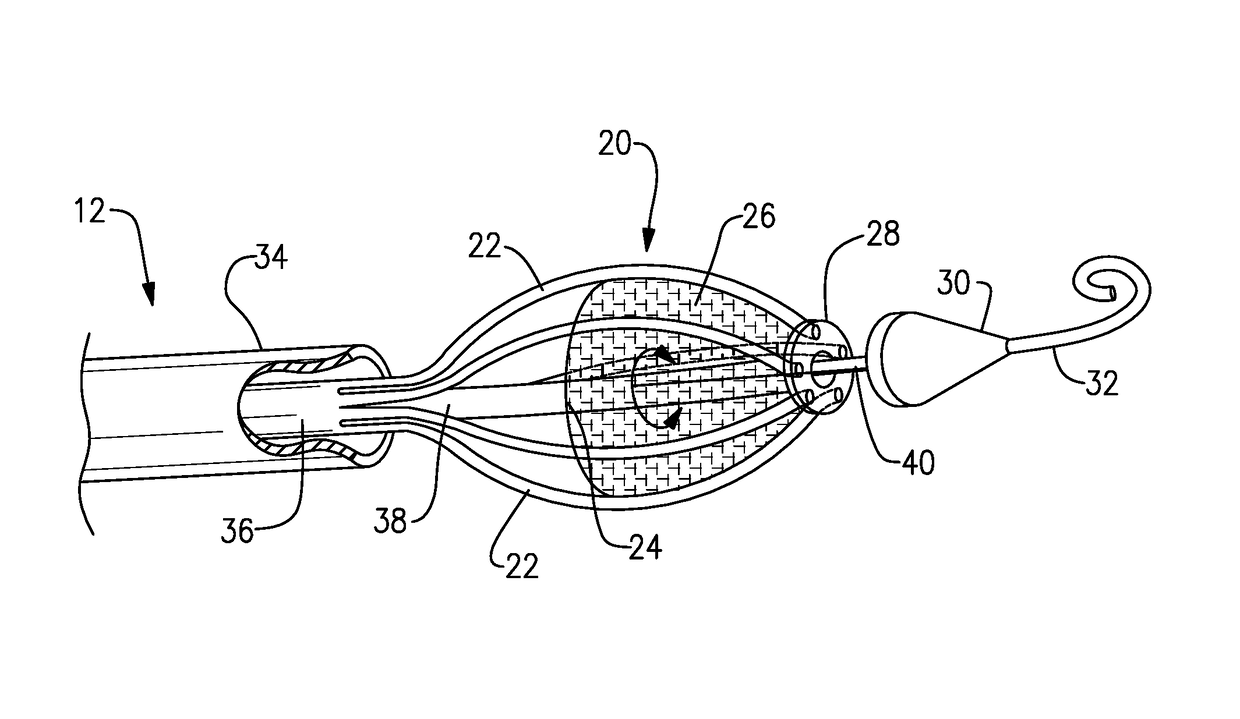
Heart Assist Devices, Systems and Methods
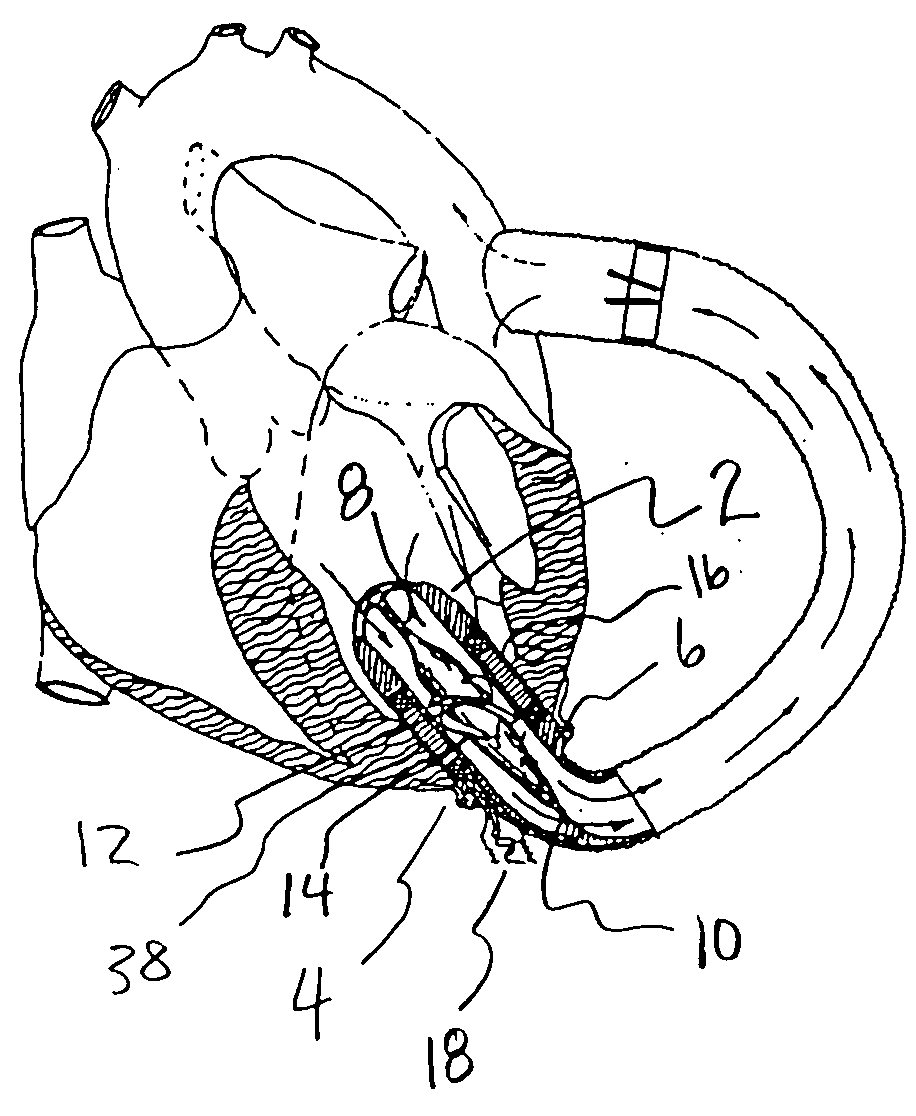
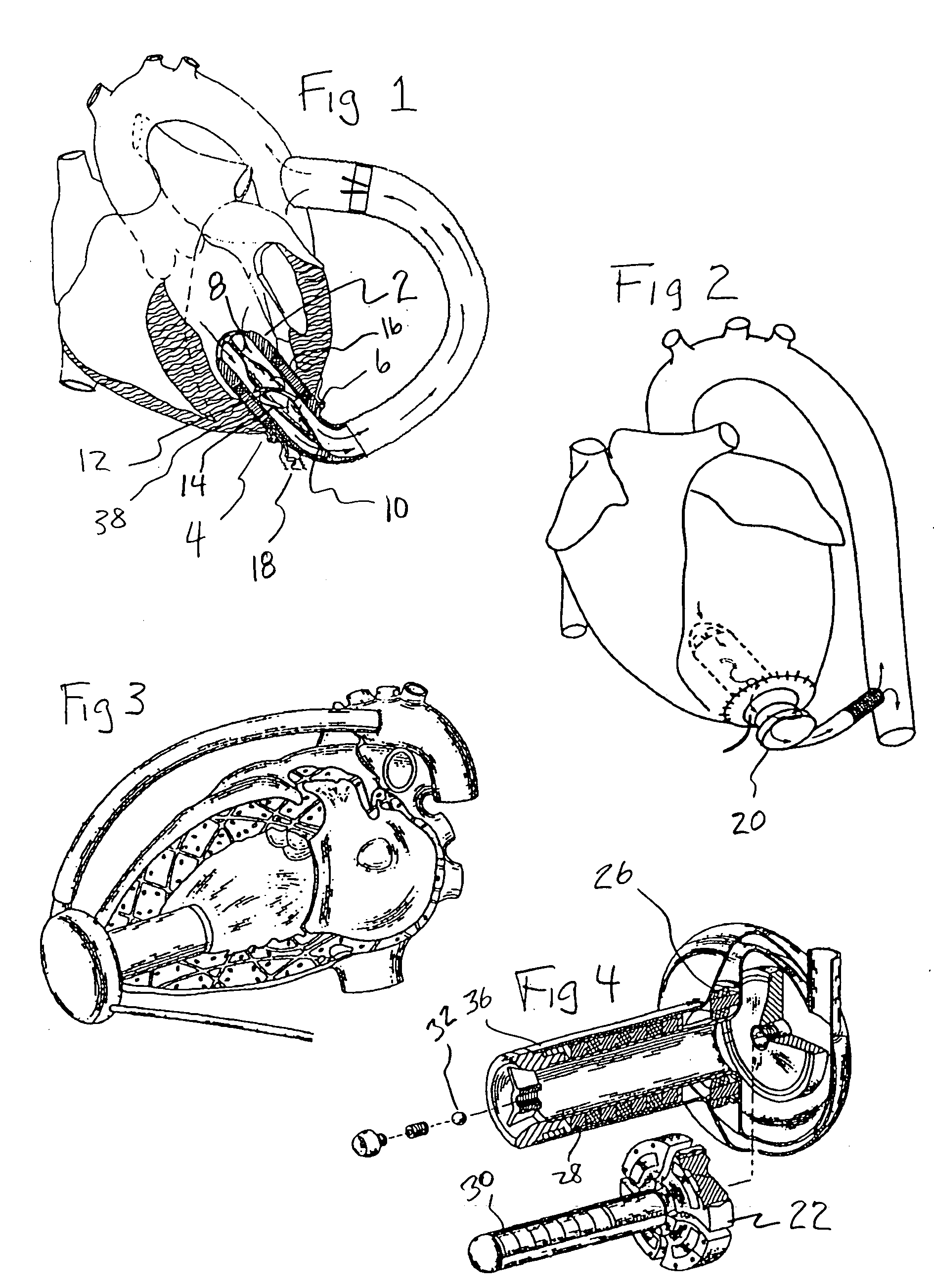
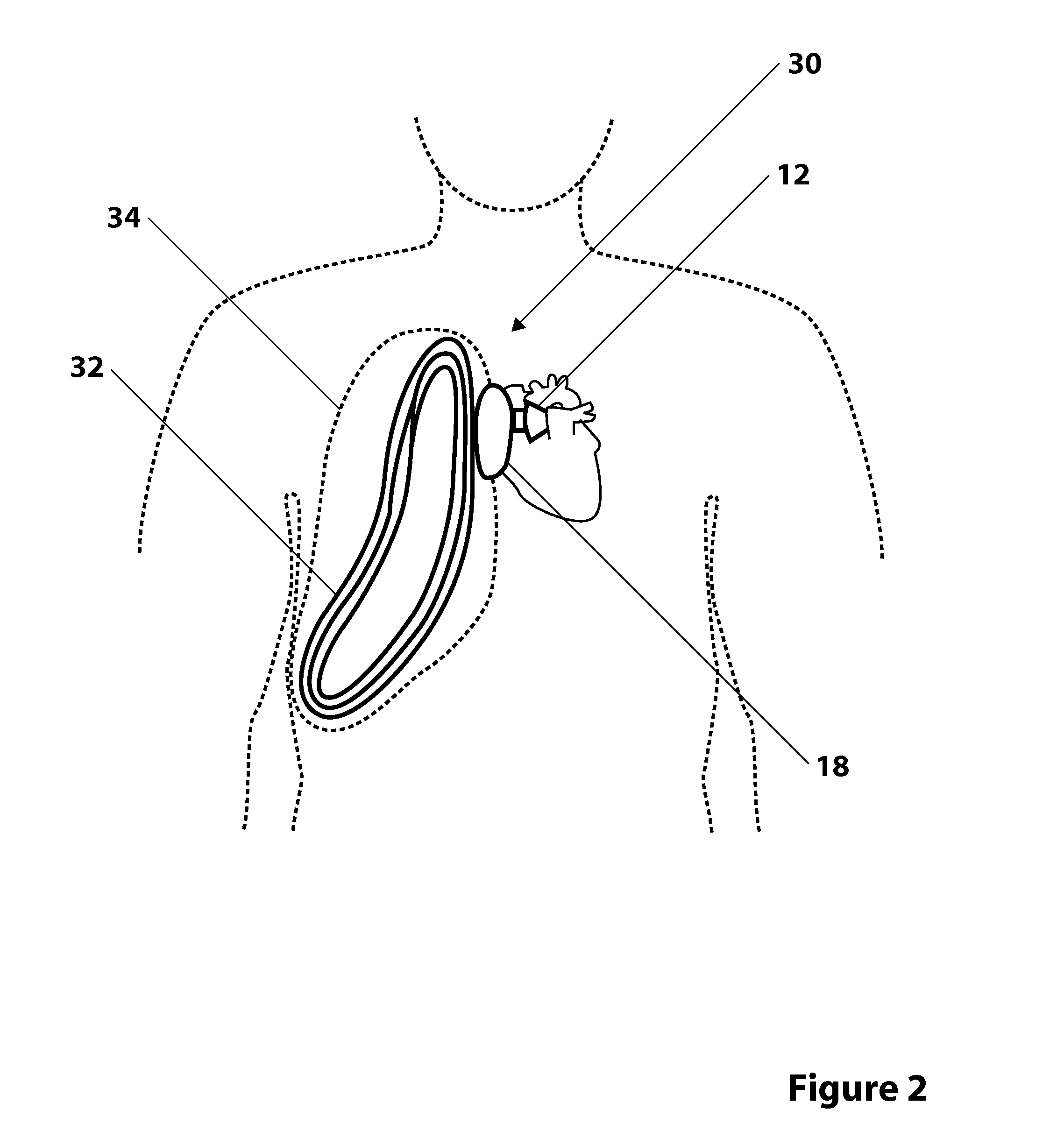
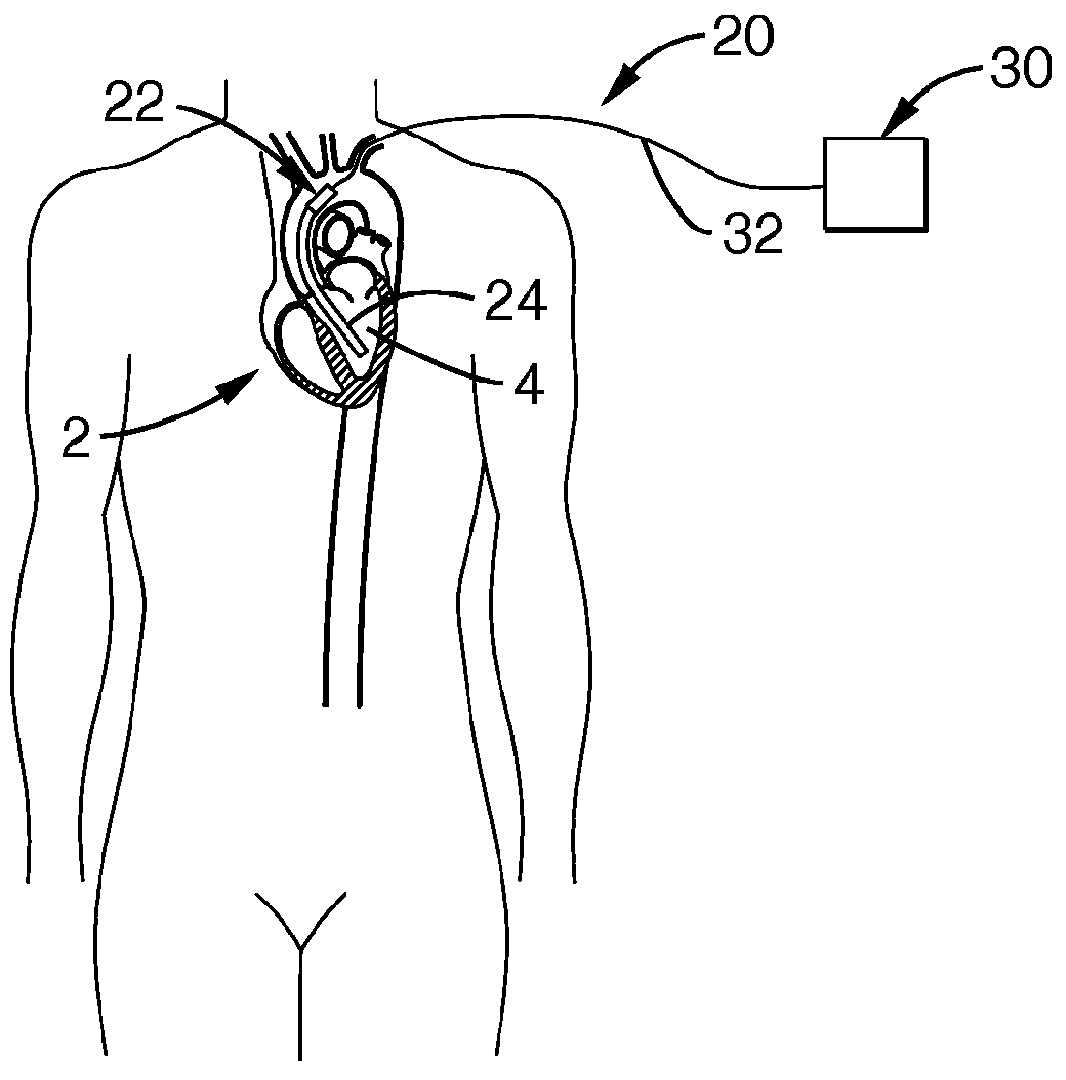
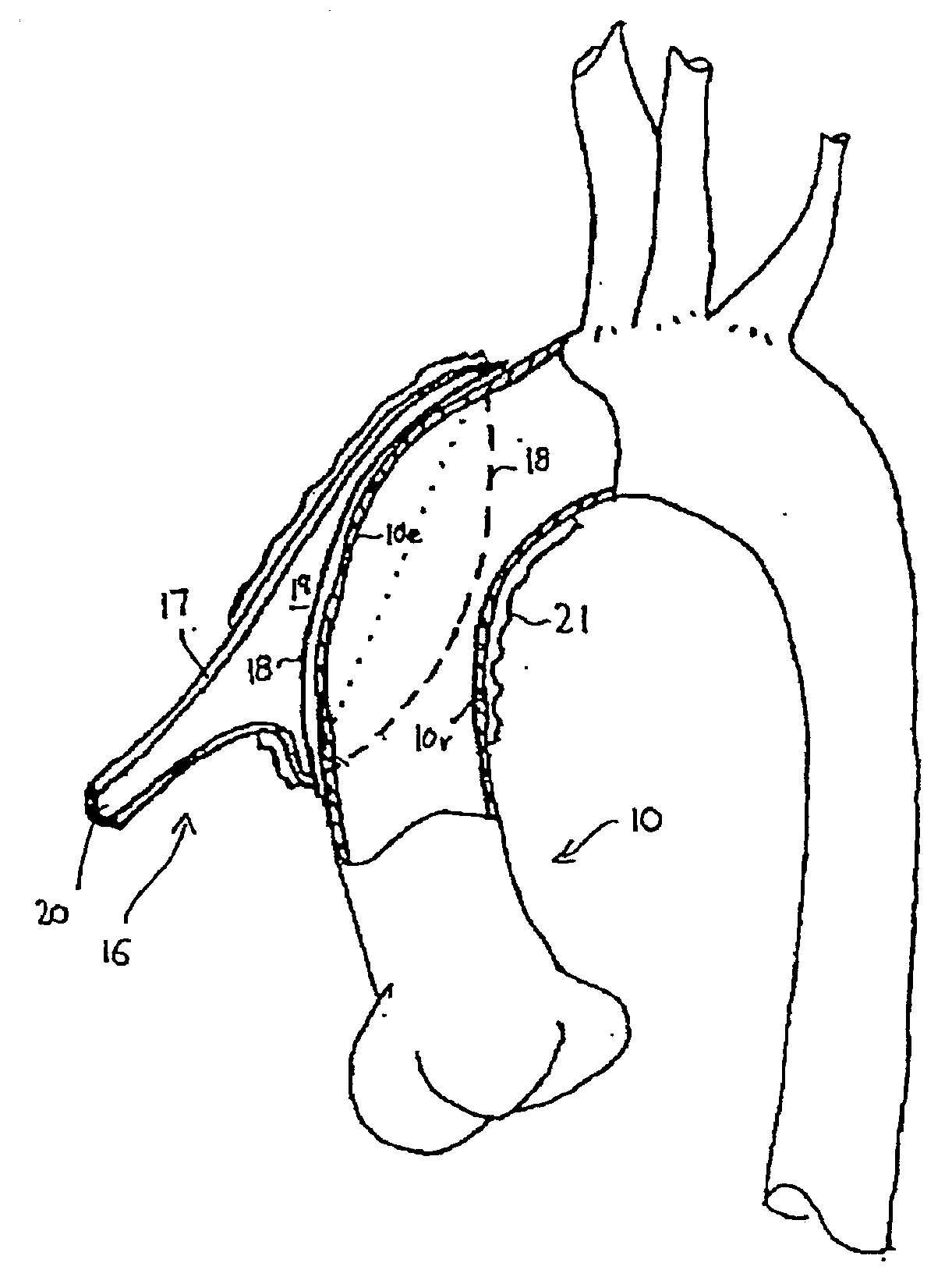
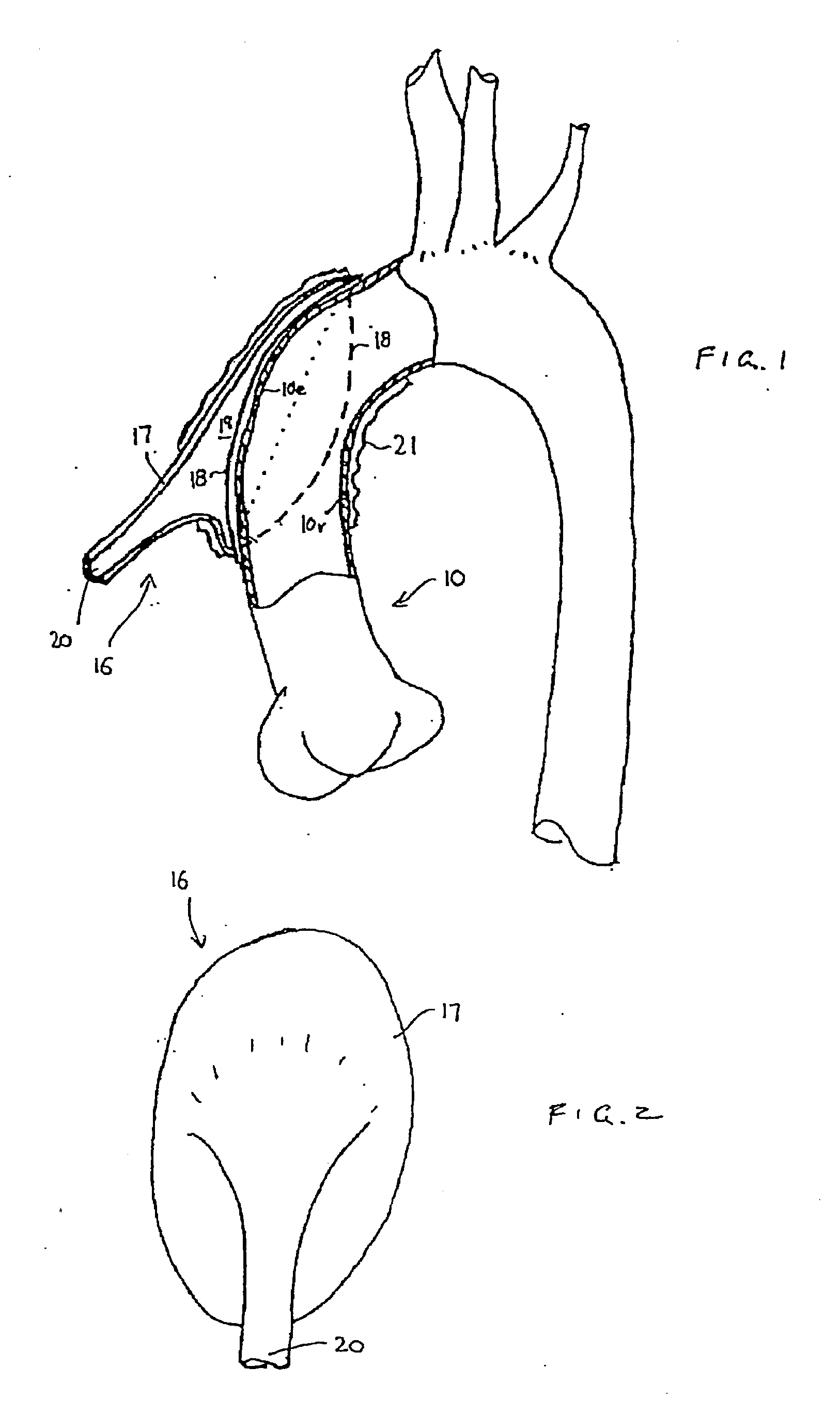
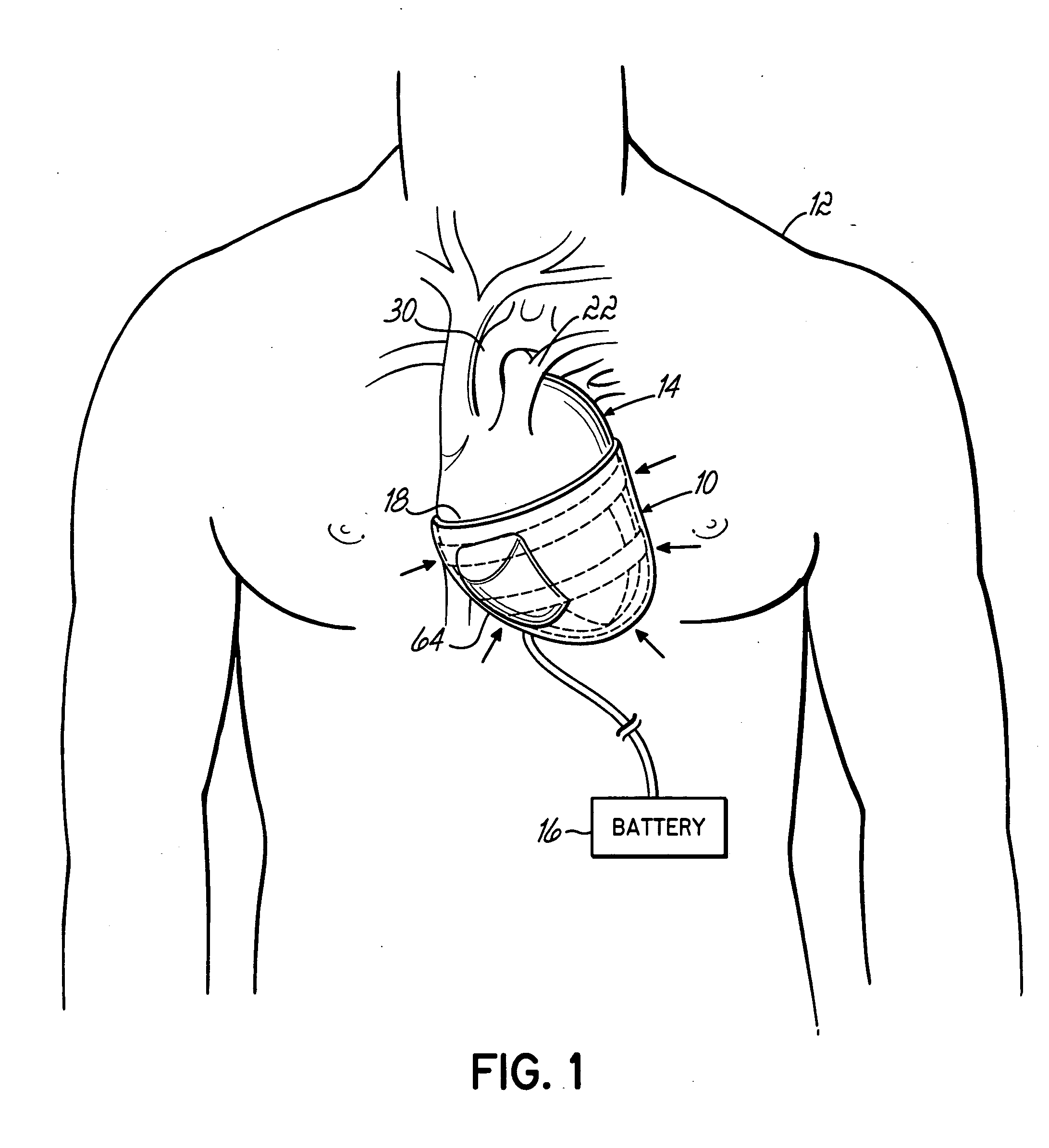
An apparatus and method for use in assisting a human heart are disclosed. The apparatus comprises an aortic compression means which may be fully implanatable, a fluid reservoir and a pump means adapted to pump a fluid from the reservoir to the aortic compression means so as to actuate the aortic compression means at least partly in counterpulsation with the patient's heart. In addition, the device is adapted to be wholly positioned within the right chest cavity of the patient. The aortic compression means of the device may be curved along its length so as to substantially replicate the curve of the ascending aorta.
Owner:NUWELLIS INC
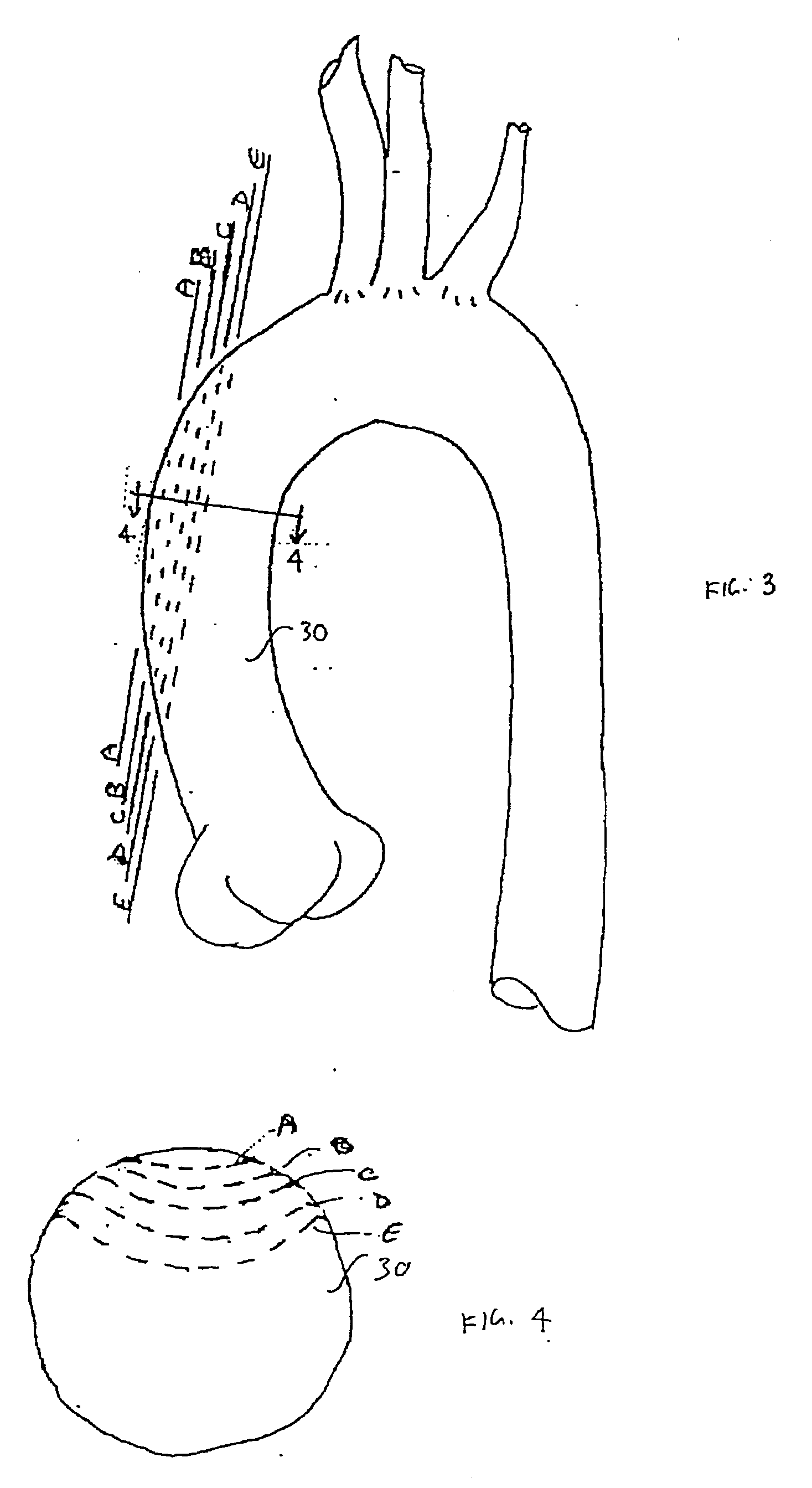
Heart assist device utilising aortic deformation
The present invention relates to providing counter-pulsation heart assist by deforming the aorta. In a preferred embodiment, the deformation pressure is applied by cyclically, preferably in synchrony with the diastolic period of the heart. The deformation pressure may be applied to the outer wall of the aorta or to a patch covering a resected opening in the wall of the aorta.
Owner:NUWELLIS INC
Heart assist device
InactiveUS20110071337A1Prevent backflowEnhancing natural flow of bloodControl devicesBlood pumpsInterior spaceVentricular assistance
A ventricular assist device comprising a housing defining an interior space, at least two ports opening into said interior space, and at least one pump for pumping blood between the ports through said interior space, the ports and interior space providing a continuous blood flow path that is not interrupted by valves.
Owner:CARDIO ASSIST
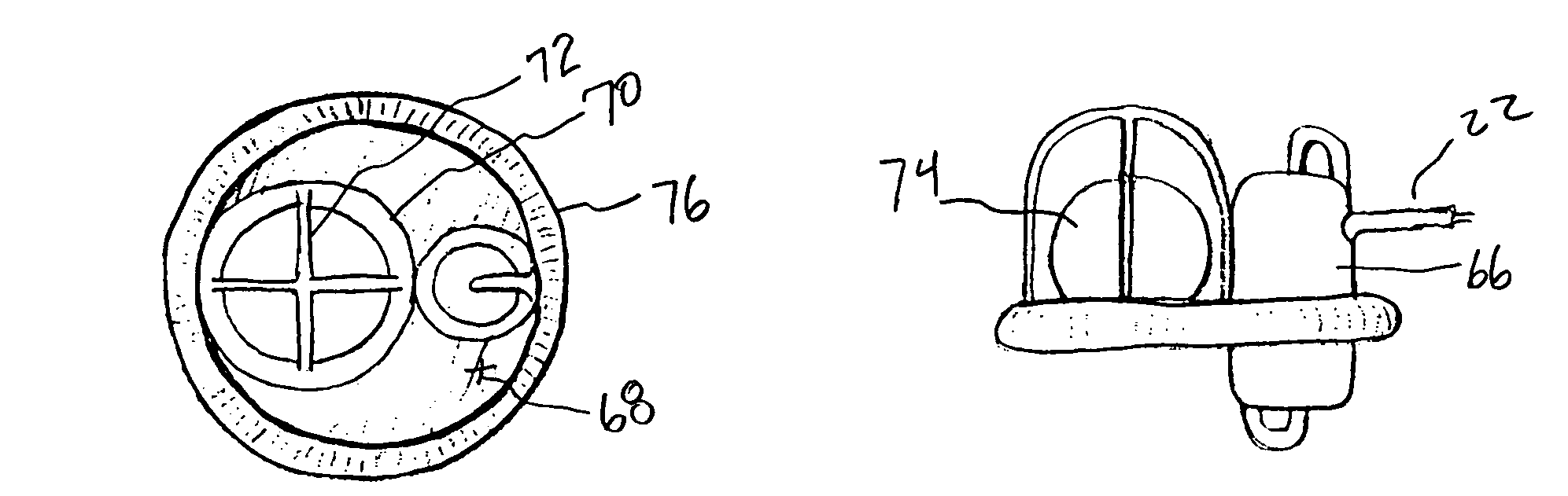
Textured conforming shell for stabilization of the interface of precision heart assist device components to tissues
InactiveUS20070299297A1Quantity minimizationPrevent thrombosisBlood pumpsMedical devicesMicrospherePolymer insulation
The blood contacting surfaces of heart assist devices must avoid excessive thrombus formation, which can break off and cause thromboembolism, become infected and cause other problems. Certain textured surface coatings, such as sintered titanium microsphere coatings, form a thin layer of living cells on the surface that becomes endothelized and is highly resistant to thrombus generation. Some of these coatings require high processing temperatures. Simple thick wall conduit tubes, which do not require high precision, coated with sintered microspheres, have been used successfully as inlet cannulae. Thick wall titanium pump components have also been successfully coated with sintered microspheres, using methods to retain their shape in the furnace and avoid excessive deformation. Blood pumps or portions of blood pumps that utilize high precision components subject to damage or warping if exposed to high temperatures cannot be directly coated. This applies to intraventricular and other blood pumps with precision heat sensitive components, such as polymer insulated wires, placed at least partly within an organ of the cardiovascular vascular system. The present invention provides a thin wall textured surface shell that is coated at high temperature and then, after finish machining, is affixed over the heat sensitive precision blood pump to serve as the interface with biological tissues.
Owner:JARVIK ROBERT
Minimally invasive transvalvular ventricular assist device
ActiveUS7479102B2Highly effectiveHighly miniaturizedAdditive manufacturing apparatusBlood pumpsThree dimensional ctVentricular cavity
Owner:JARVIK ROBERT
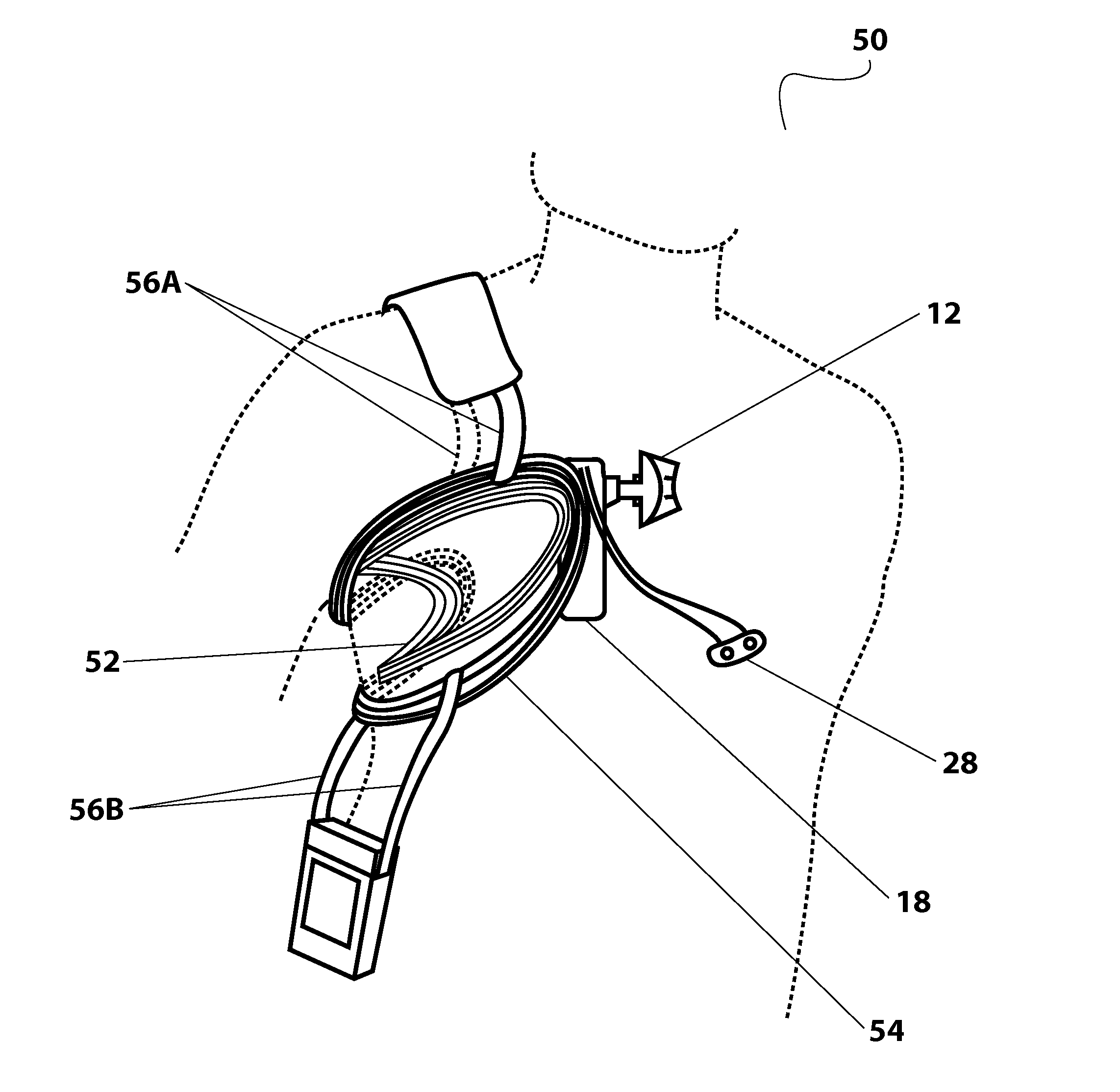
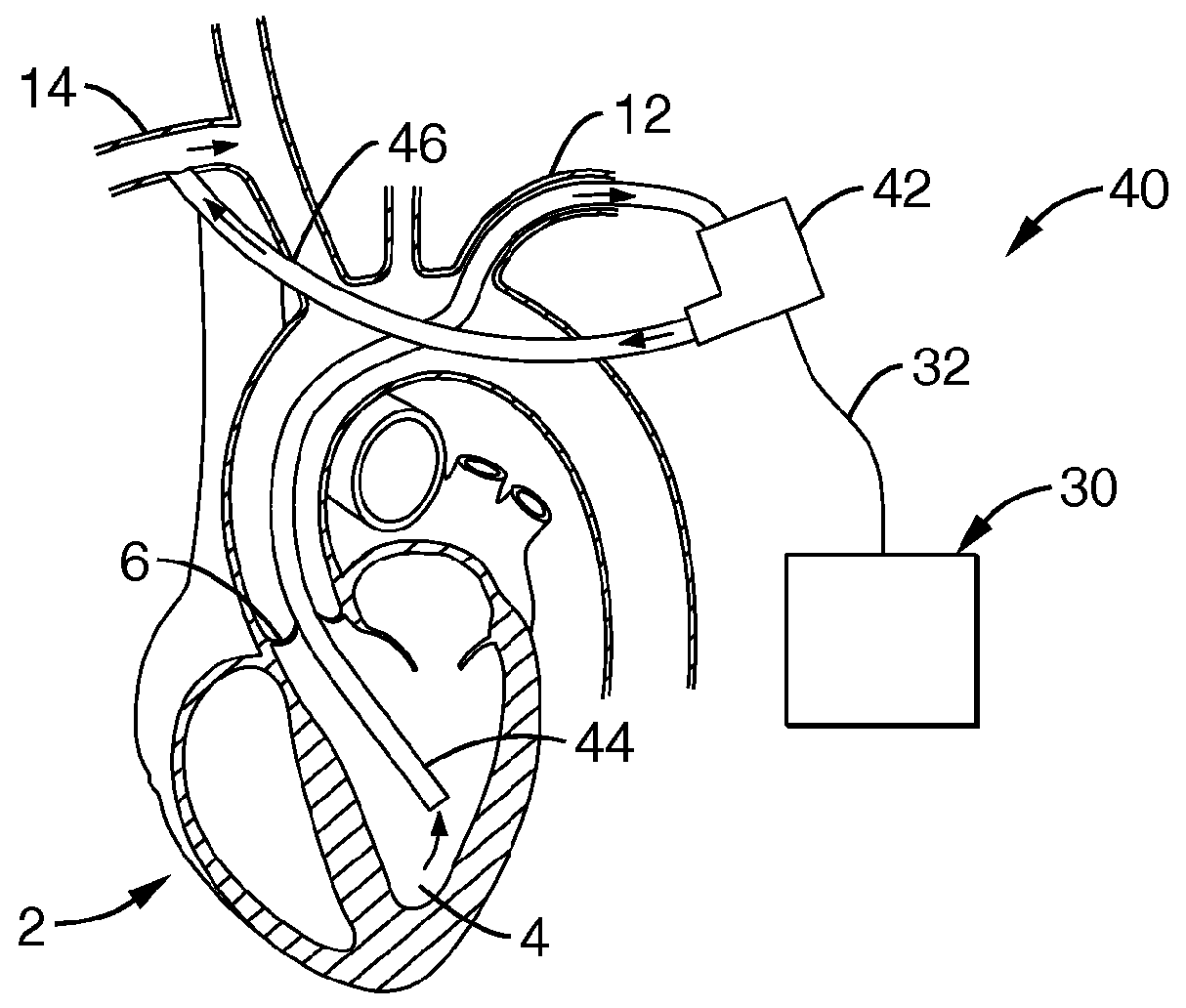
Methods, Systems, and Devices Relating to Wireless Power Transfer
InactiveUS20130310629A1Inhibition formationBatteries circuit arrangementsDiagnosticsEnergy transferEngineering
The various embodiments disclosed herein relate to transcutaneous energy transfer systems comprising an internal coil positioned within a cavity of a patient and an external coil inductively coupled to the internal coil. The systems can be coupled to any implantable medical devices, such as, for example, a heart assist device.
Owner:SUNSHINE HEART PTY LTD
Heart assist devices, systems and methods
InactiveUS7357771B2Promote blood circulationChronic heart failureElectrocardiographyBlood pumpsAscending aortaThoracic cavity
An apparatus and method for use in assisting a human heart are disclosed. The apparatus comprises an aortic compression means which may be fully implanatable, a fluid reservoir and a pump means adapted to pump a fluid from the reservoir to the aortic compression means so as to actuate the aortic compression means at least partly in counterpulsation with the patient's heart. In addition, the device is adapted to be wholly positioned within the right chest cavity of the patient. The aortic compression means of the device may be curved along its length so as to substantially replicate the curve of the ascending aorta.
Owner:NUWELLIS INC
Synchronization control system
InactiveUS7765003B2Rapid isolationRapidly correcting the condition causing the malfunctionElectrocardiographyControl devicesControl systemSynchronous control
Owner:SUNSHINE HEART PTY LTD
Synchronization control system
InactiveUS20070060787A1Quick correctionGuaranteed uptimeElectrocardiographyStethoscopeSynchronous controlControl system
Owner:SUNSHINE HEART PTY LTD
Heart assist device
Owner:STAR BP INC
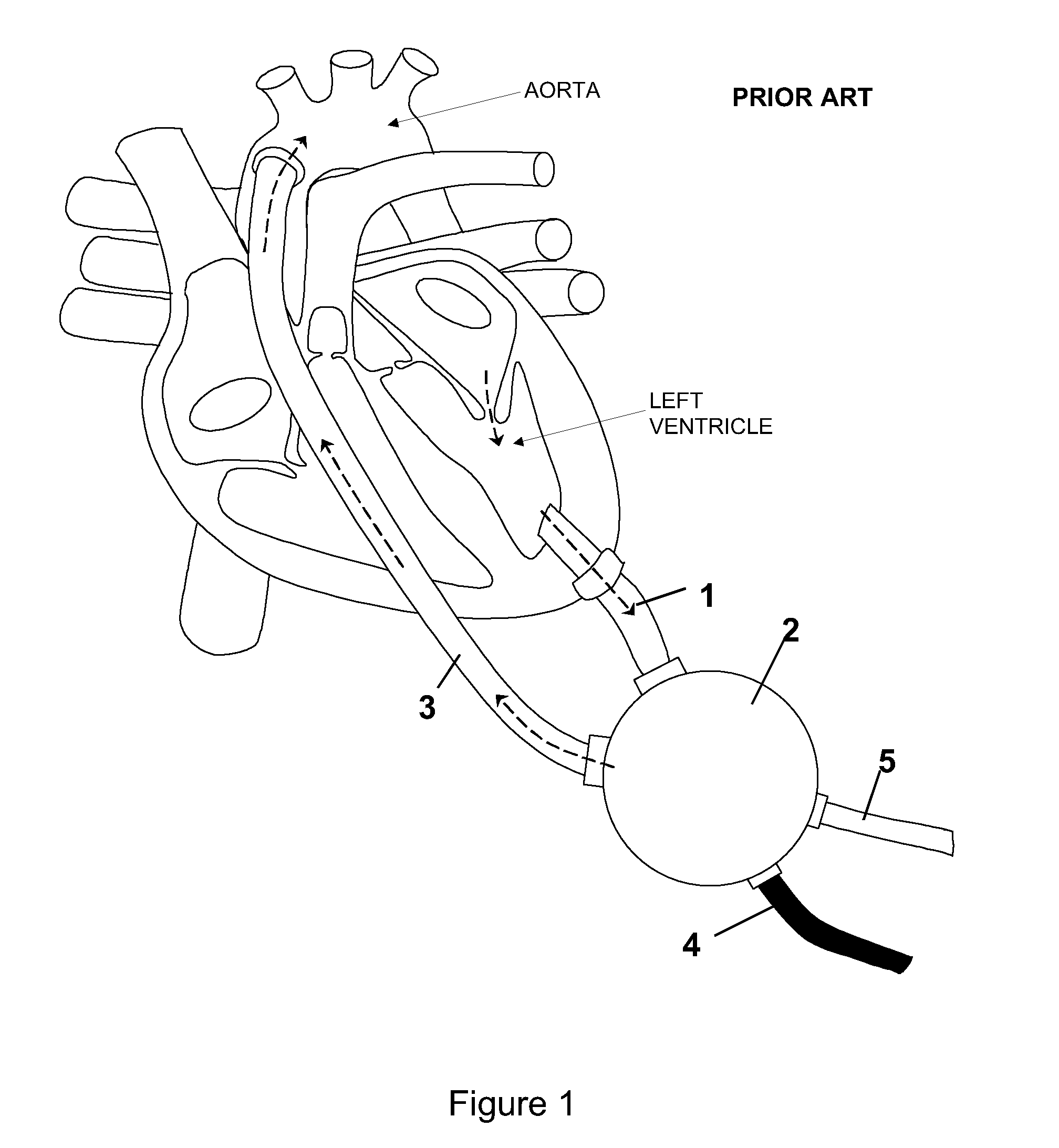
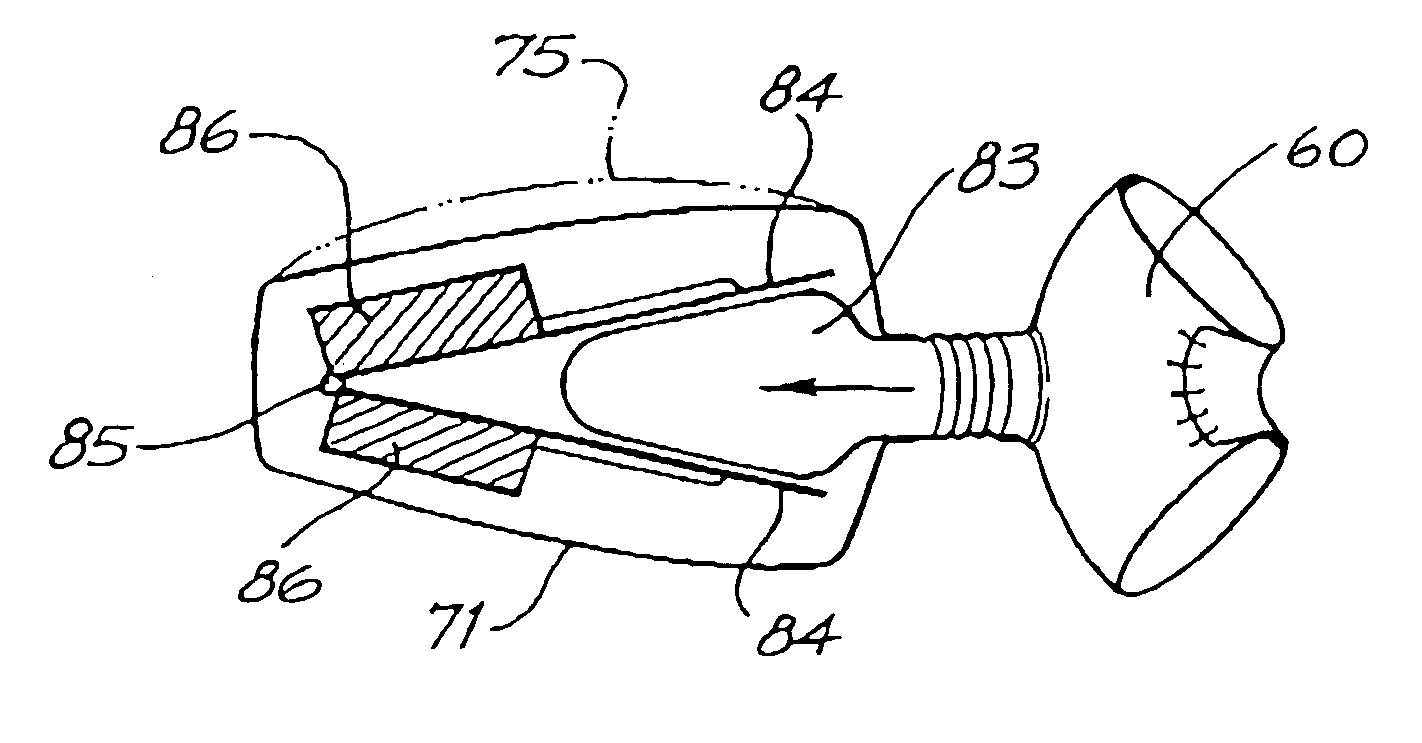
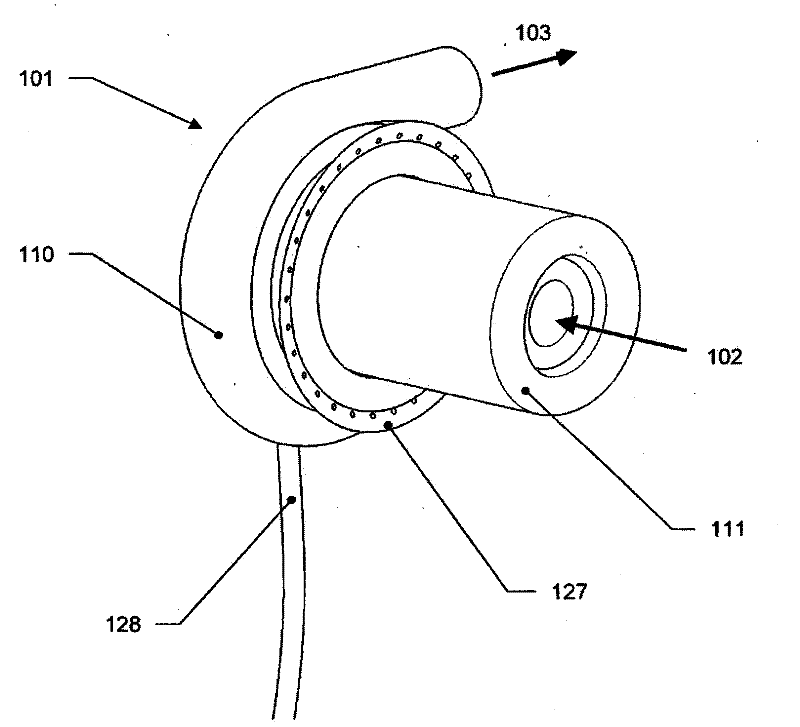
Assembly and method of implanting a heart assist system
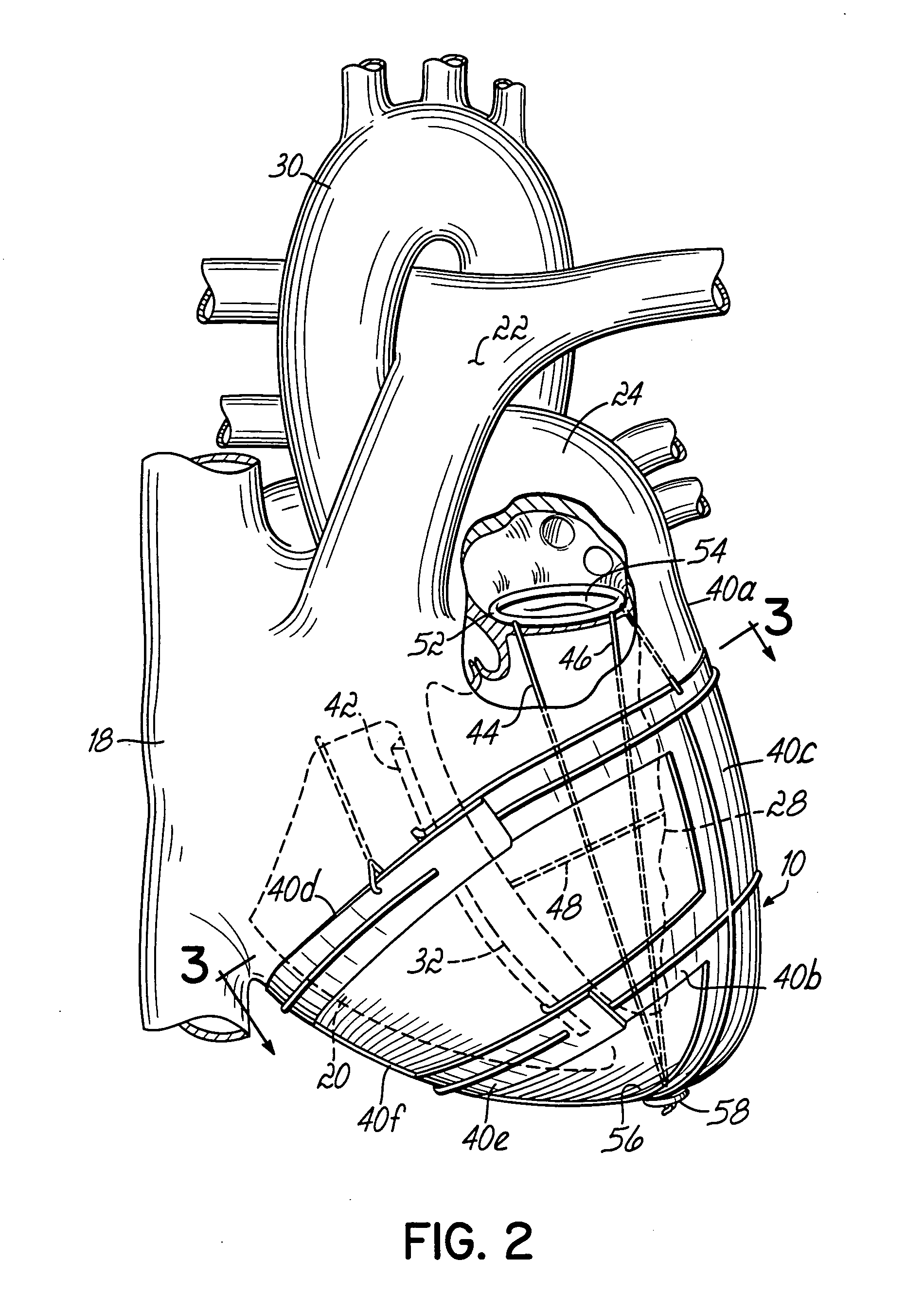
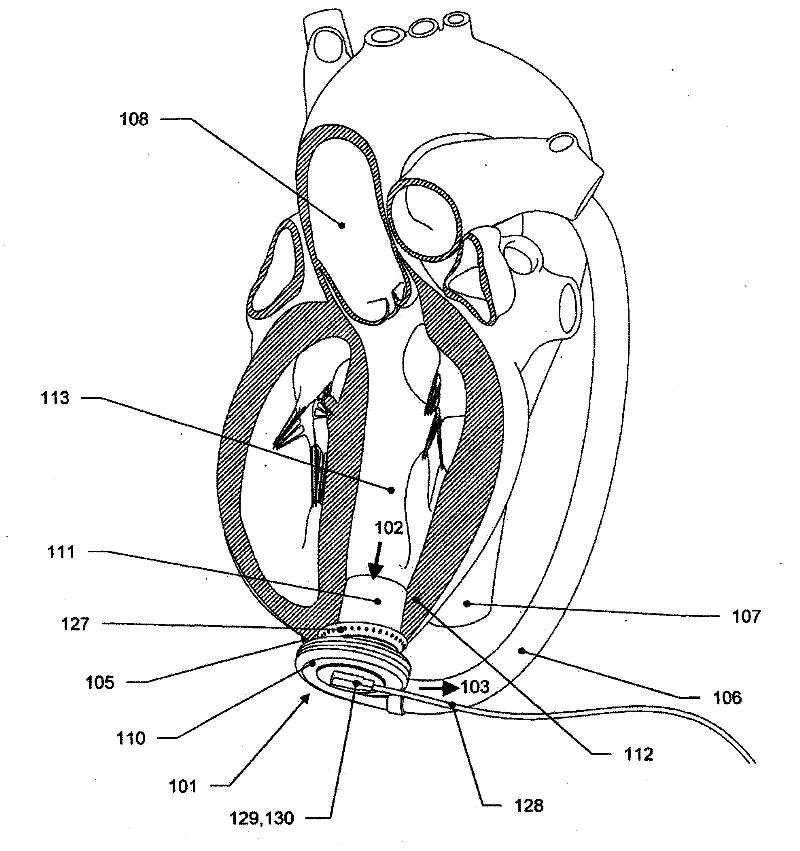
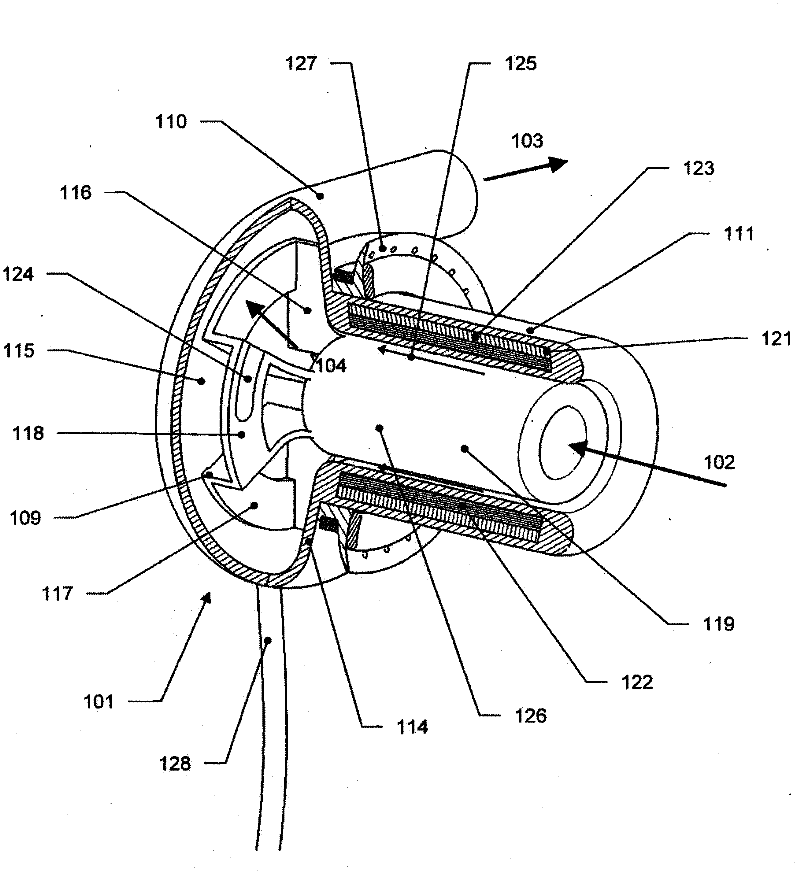
A needle guard is used when suturing the cuff of an attachment ring to the heart. The needle guard is disposed in the attachment ring to prevent other parts of the attachment ring from being punctured by a suturing needle. The needle guard can include one or more grooves to inhibit relative movement between the needle guard and the attachment ring during suturing. The needle guard is removed upon completion of suturing and to allow insertion into attachment ring of an inflow conduit of a heart assist device. An articulated clamp is used to compress the attachment ring into engagement with the inflow conduit. The attachment include an annular rib that grabs the inflow conduit.
Owner:TC1 LLC
Heart Assist Device Utilising Aortic Deformation
The present invention relates to providing counter-pulsation heart assist by deforming the aorta. In a preferred embodiment, the deformation pressure is applied by cyclically, preferably in synchrony with the diastolic period of the heart. The deformation pressure may be applied to the outer wall of the aorta or to a patch covering a resected opening in the wall of the aorta.
Owner:NUWELLIS INC
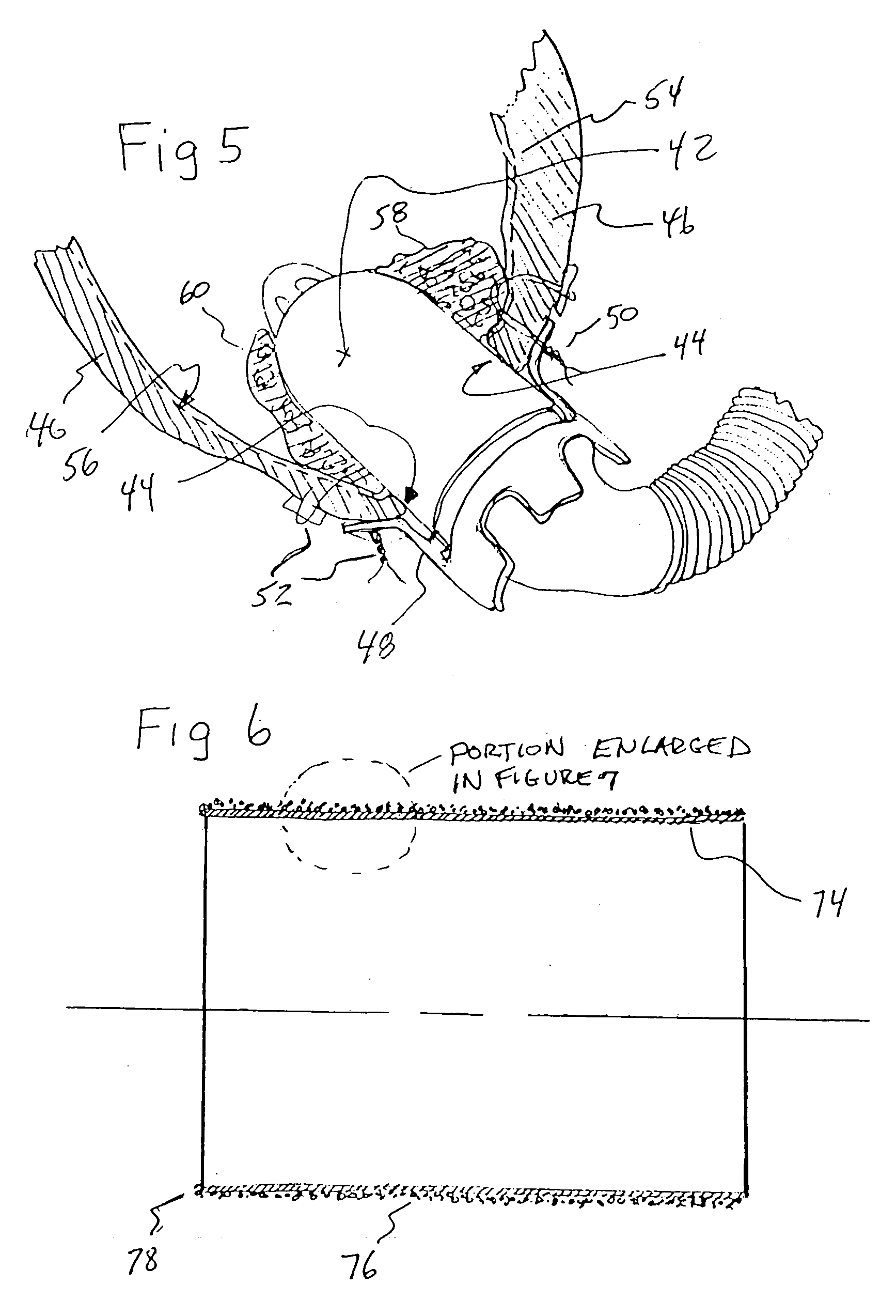
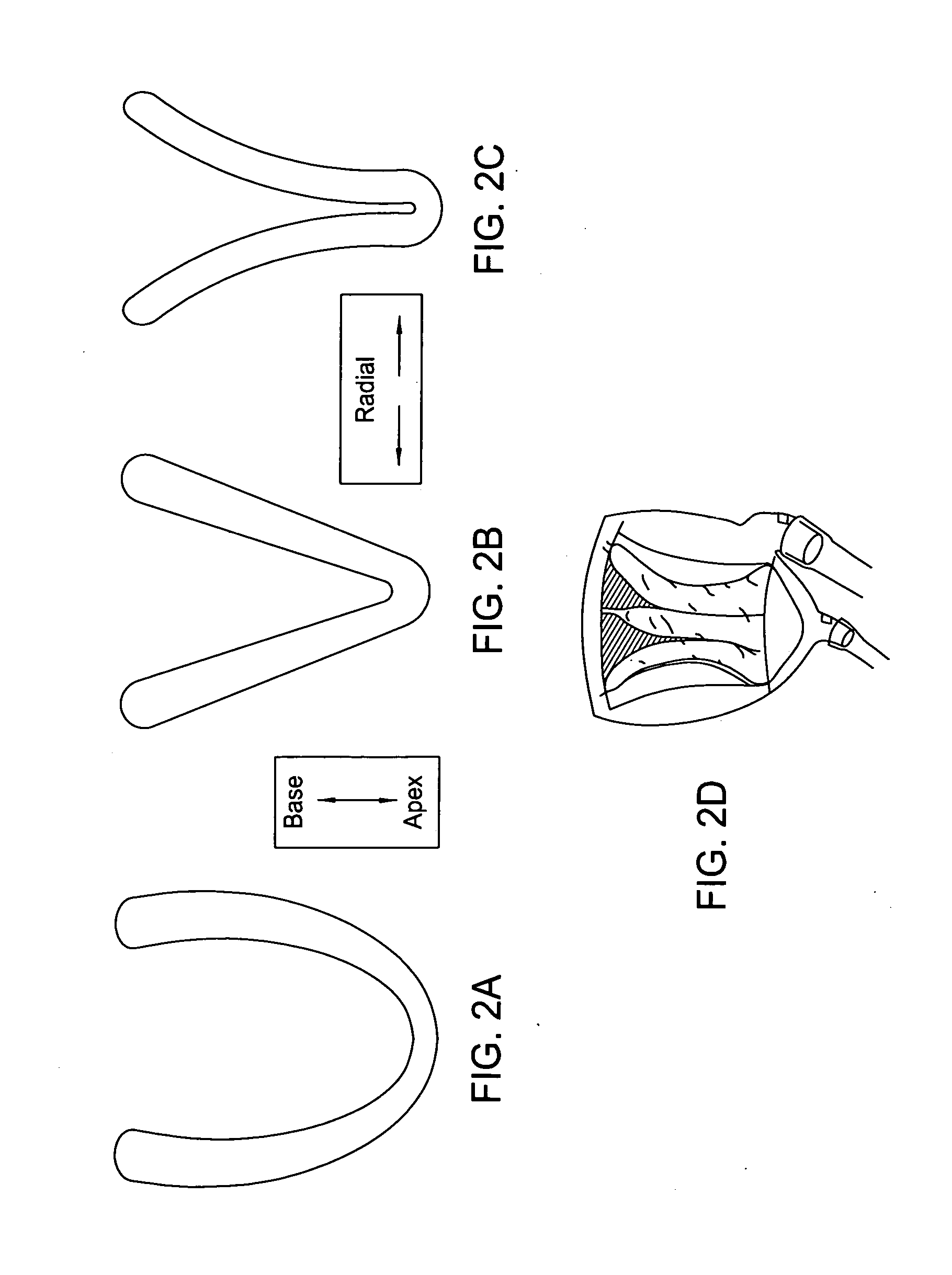
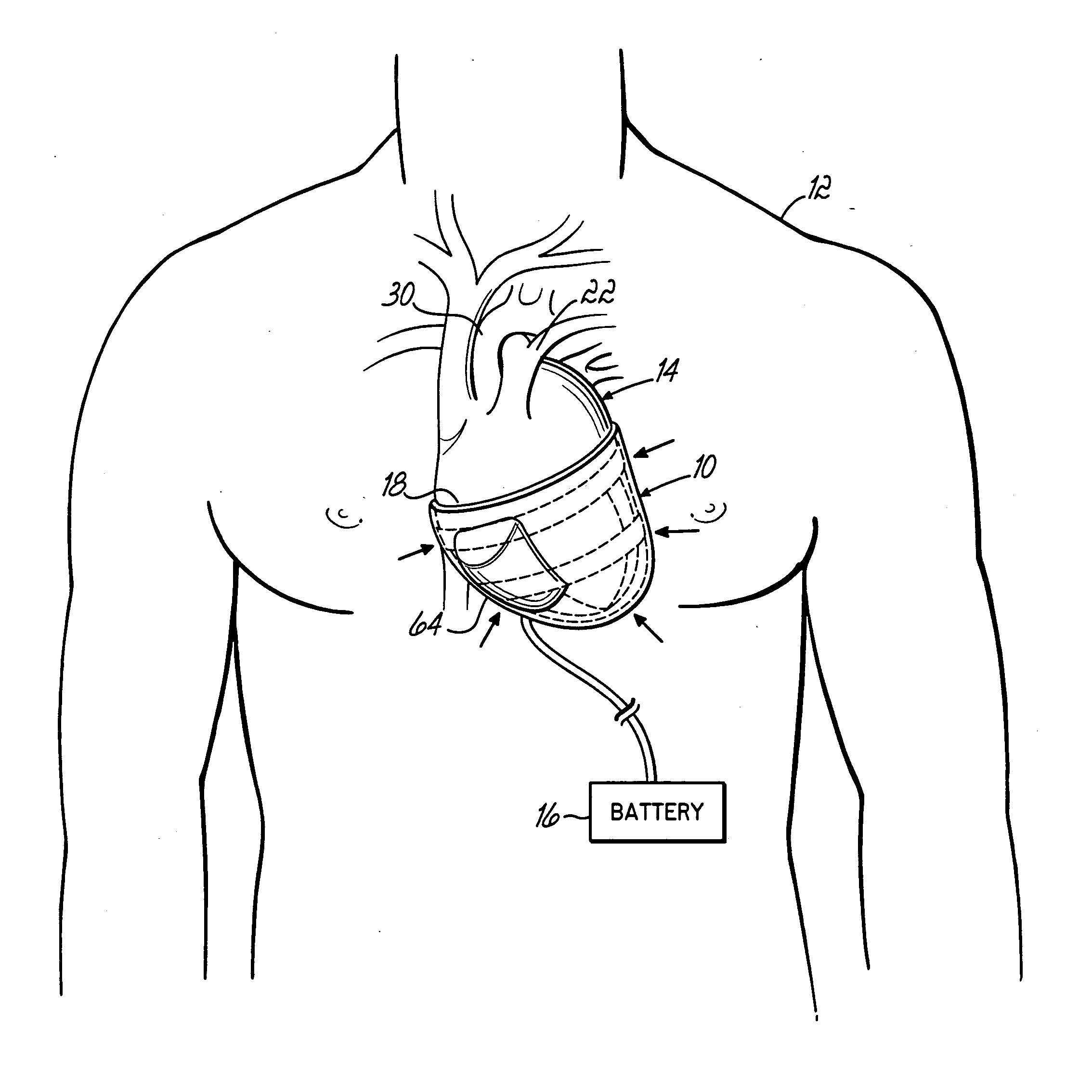
Device for proactive modulation of cardiac strain patterns
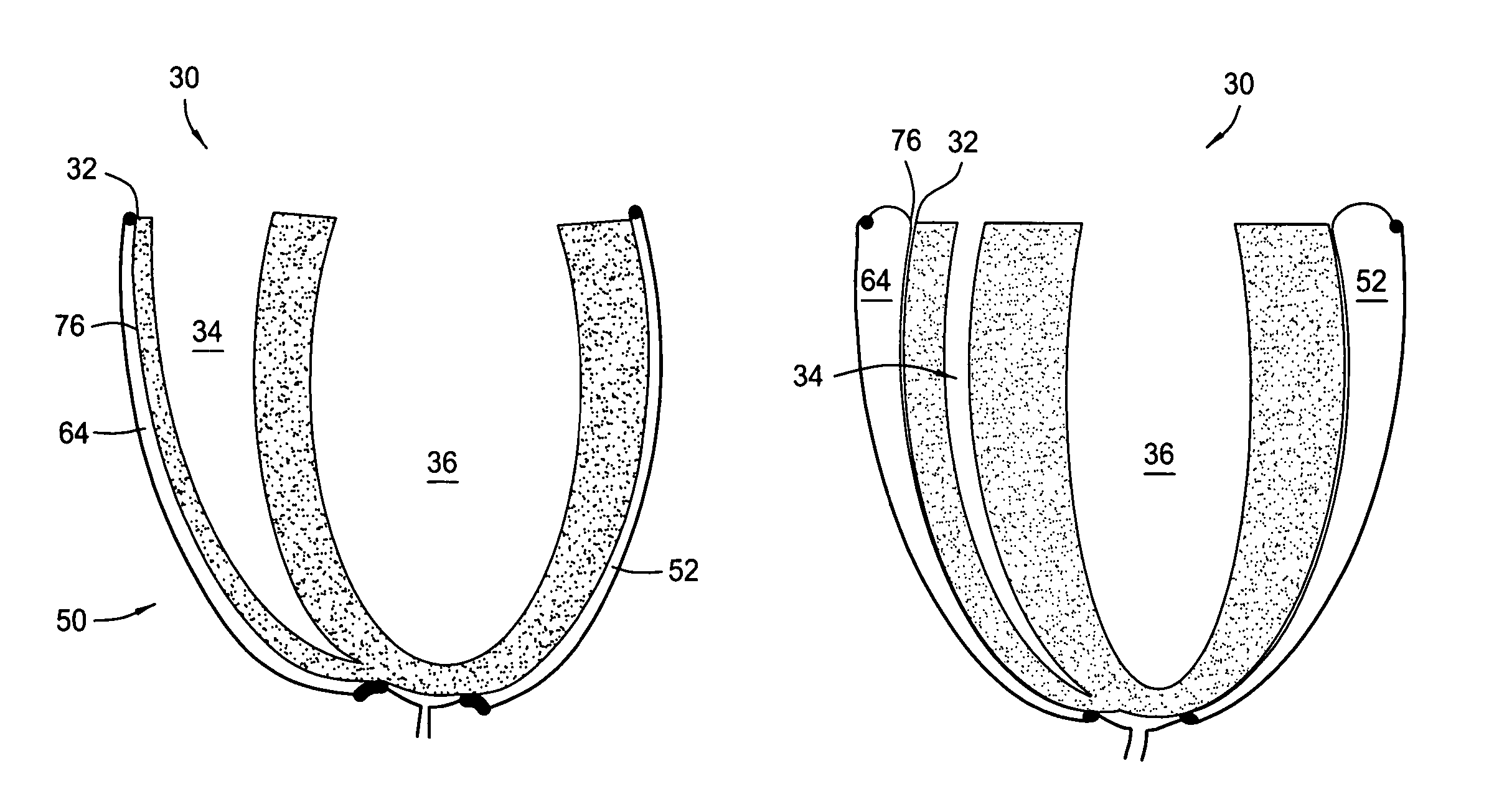
ActiveUS20070260108A1Reduce structural stiffnessMinimally invasiveIntravenous devicesHeart stimulatorsHeart-Assist DevicesUrinary bladder
The present invention provides methods, systems and devices that reduce dyskinesis and hypokinesis. The contoured heart assist device of the present invention includes a selectively inflatable end-systolic heart shaped bladder with one or more contoured supports configured to surround at least a portion of the heart and provide curvatures similar to the proper shape of the heart when the device is pressurized and one or more fluid connections in communication with the selectively inflatable end-systolic heart shaped bladder for pressurization and depressurization.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY +1
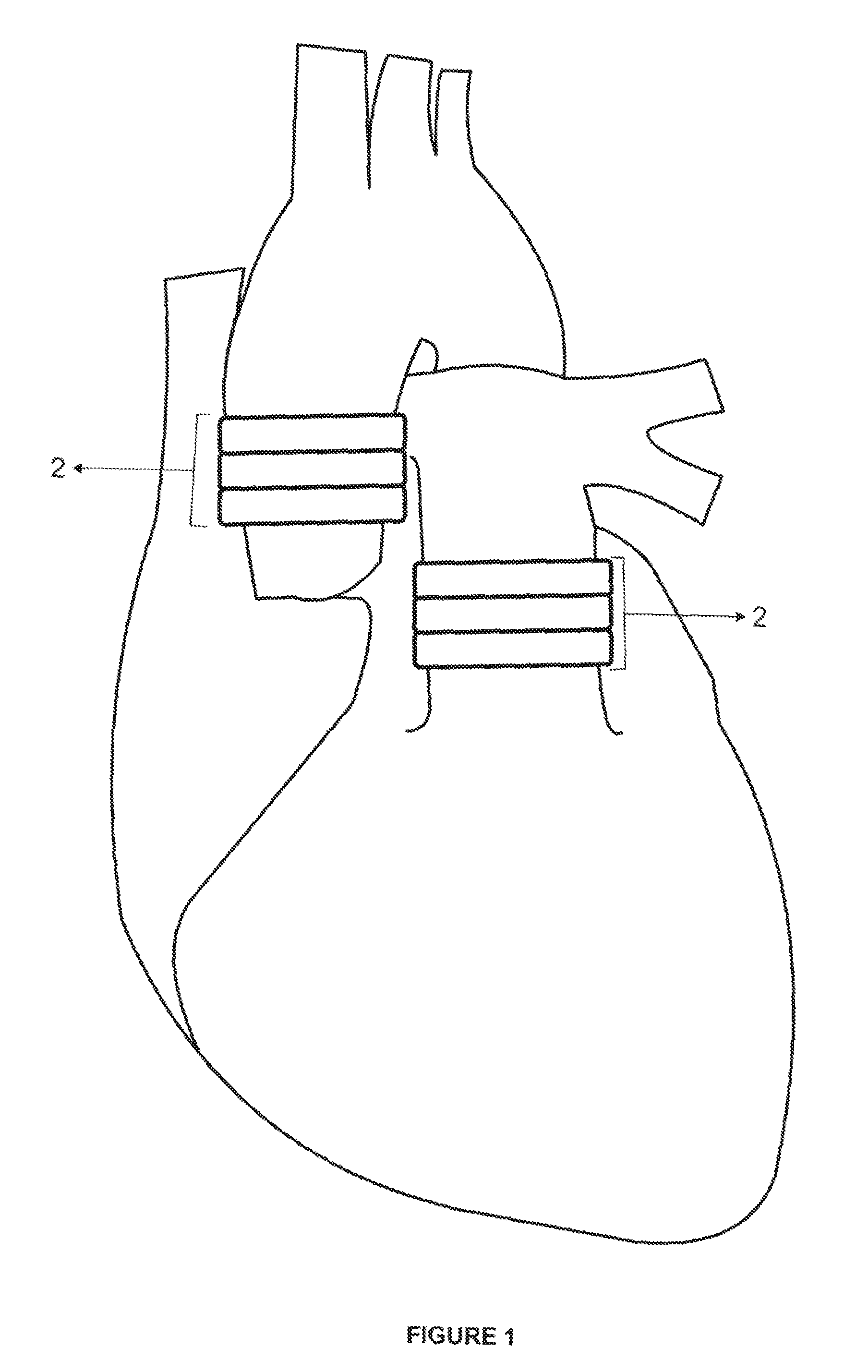
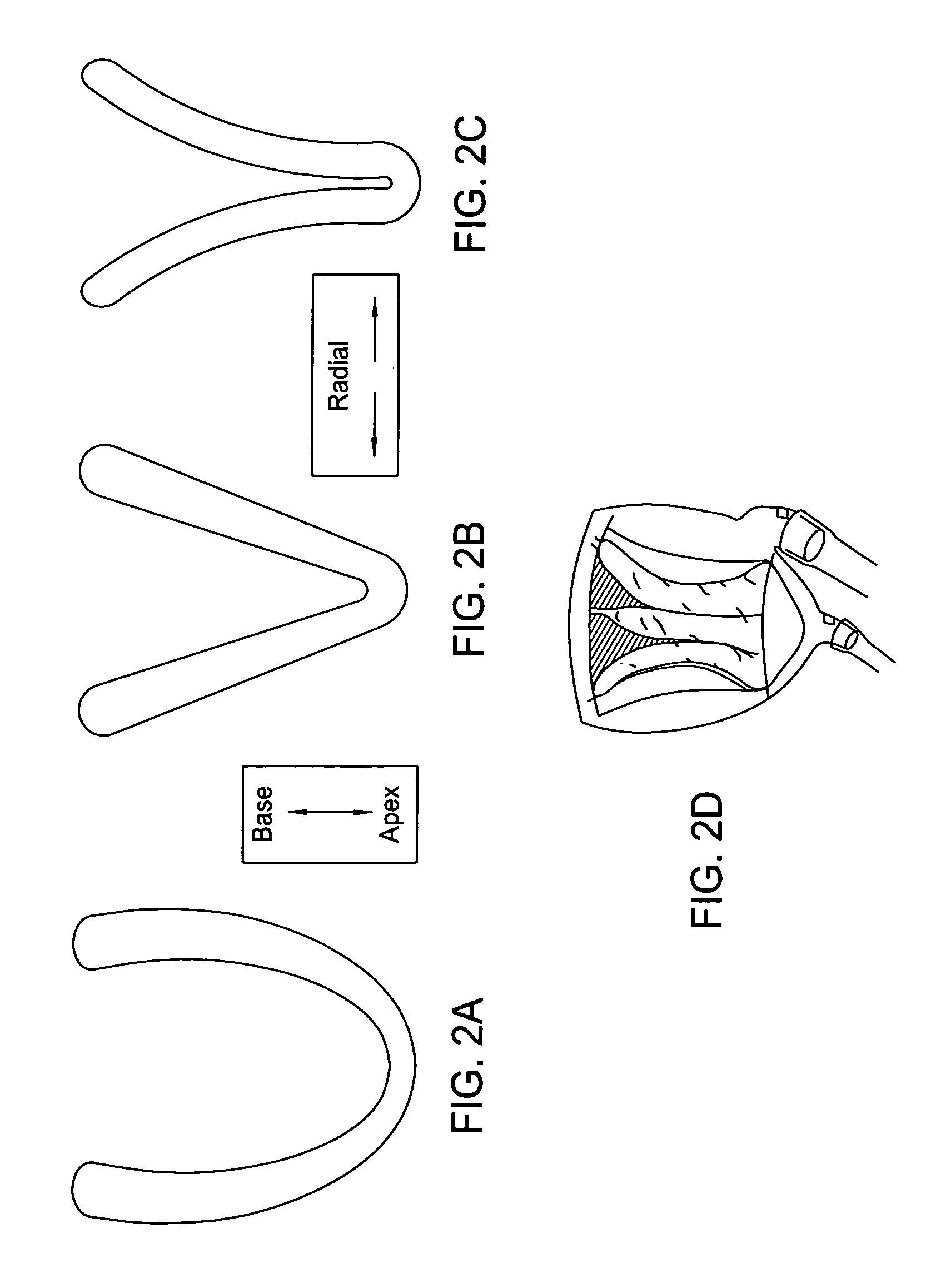
Implantable heart assist devices and methods
InactiveUS20050113632A1Minimize traumaLong axis and short axis shortening of the heart muscleHeart valvesSurgeryHeart-Assist DevicesCatheter device
Heart support and assist devices for supporting and assisting the pumping action of the heart. Various embodiments include mesh support devices, devices using straps, spiral-shaped devices, catheter-based devices and related methods.
Owner:PAUL A SPENCE
Endovascular heart assist device
ActiveUS9555175B2Maintain blood circulationConsumes less energyElectrocardiographyControl devicesCellular componentThrombus
The invention is a next generation miniature heart assist device developed in order to maintain the blood circulation in patients with severe heart failure, and is applied endovascularly to the large arteries. This device is technically a kind of synchronous servo electric motor using “direct drive technology”. It provides longer battery life and high blood flow. Small volume and very low energy consumption provide a much longer battery life and a high blood flow. As the outer surface of the parts placed into the blood vessel will be completely covered with the endothelial cells and the intima layer of the arteries in time, there will be no foreign surface contacting directly with blood. As a result, no thromboembolic event or any negative effect on the cellular components of blood is expected.
Owner:BULENT ORAN +2
Heart assist device
ActiveUS20190125948A1Less invasive cannulationIncrease the number ofControl devicesBlood pumpsRotational stabilityRotary pump
A heart assist device comprising a rotary pump housing having a cylindrical bore, a pumping chamber and a motor stator including an electrically conductive coil located within the housing and surrounding a portion of the cylindrical bore. A rotor has a cylindrical shaft with an impeller and one or of magnets located within the shaft that are responsive to the motor stator to drive actuation of the rotor. The housing bore is closely fitted to the outer surface of the shaft forming a hydrodynamic journal bearing with an annular clearance defining a leakage flow path. One or more of radial or axial thrust bearings may be provided to provide rotation stability to the rotor and flow within the leakage flow path. The relative orientation of positions of the inflow, outflow, and leakage flow paths may be varied within the pump, such as to accommodate different intended methods for implantation and / or use.
Owner:VADOVATIONS INC
Device for proactive modulation of cardiac strain patterns
ActiveUS7935045B2Decrease end-diastolic volumeRelieve pressureIntravenous devicesHeart stimulatorsHeart-Assist DevicesUrinary bladder
The present invention provides methods, systems and devices that reduce dyskinesis and hypokinesis. The contoured heart assist device of the present invention includes a selectively inflatable end-systolic heart shaped bladder with one or more contoured supports configured to surround at least a portion of the heart and provide curvatures similar to the proper shape of the heart when the device is pressurized and one or more fluid connections in communication with the selectively inflatable end-systolic heart shaped bladder for pressurization and depressurization.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY +1
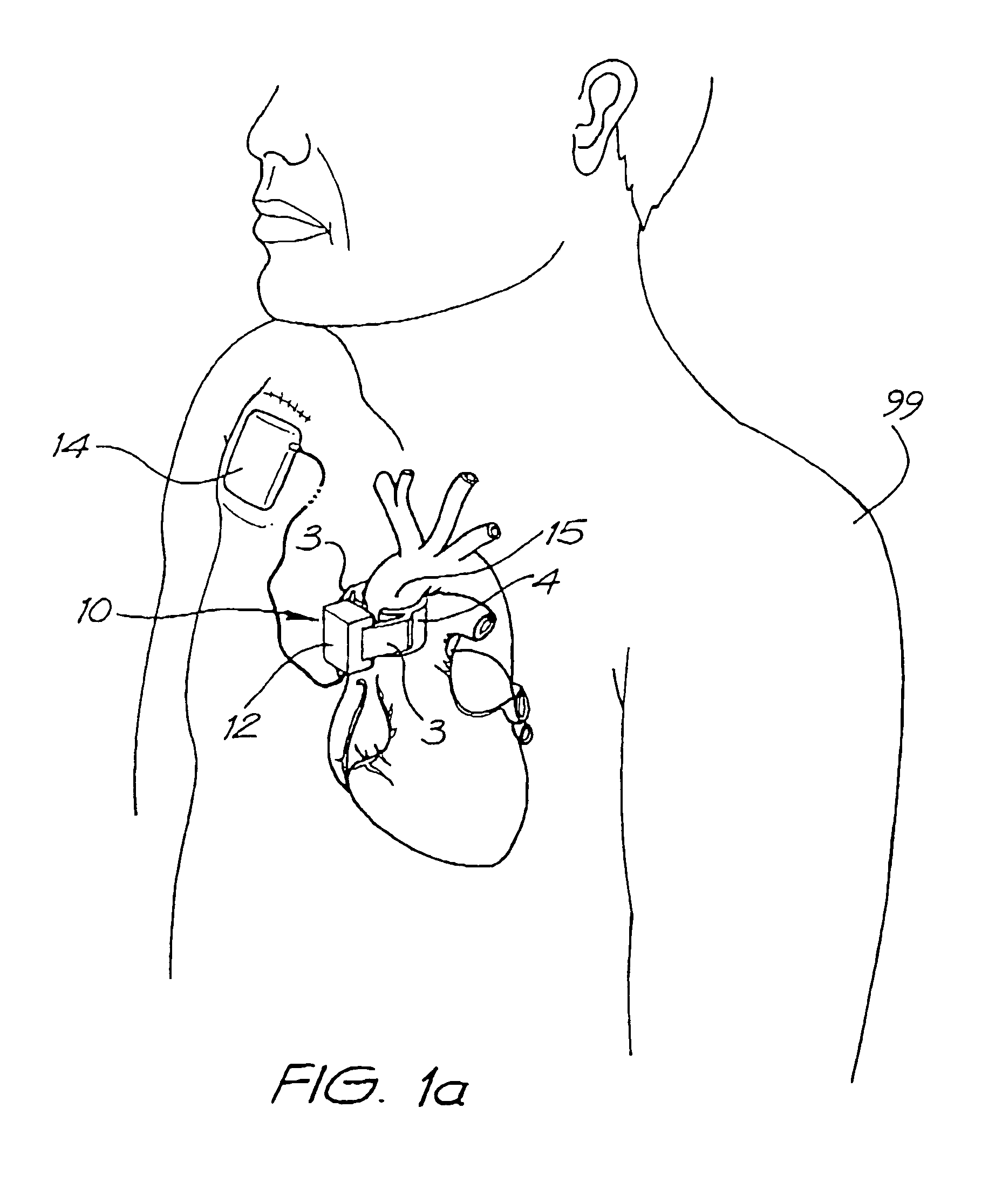
Heart assist apparatus
The apparatus is a ventricular assist device comprising: a pump with a housing having therein radial a impeller, and a rotor for driving the impeller, both the rotor and the impeller being hydrodynamically suspended within the housing in us, the pump further including a stator for driving the rotor; an inlet cannula section arranged to extend from an internal part of the ventricle to straddle the wall of the ventricle, the stator being within the inlet cannula section to be located in the internal part of the ventricle; and an outlet for blood driven by the impeller such that the pump is a radial pump. Both the outlet and the impeller are arranged to reside outside of the heart.
Owner:CALON CARDIO TECH
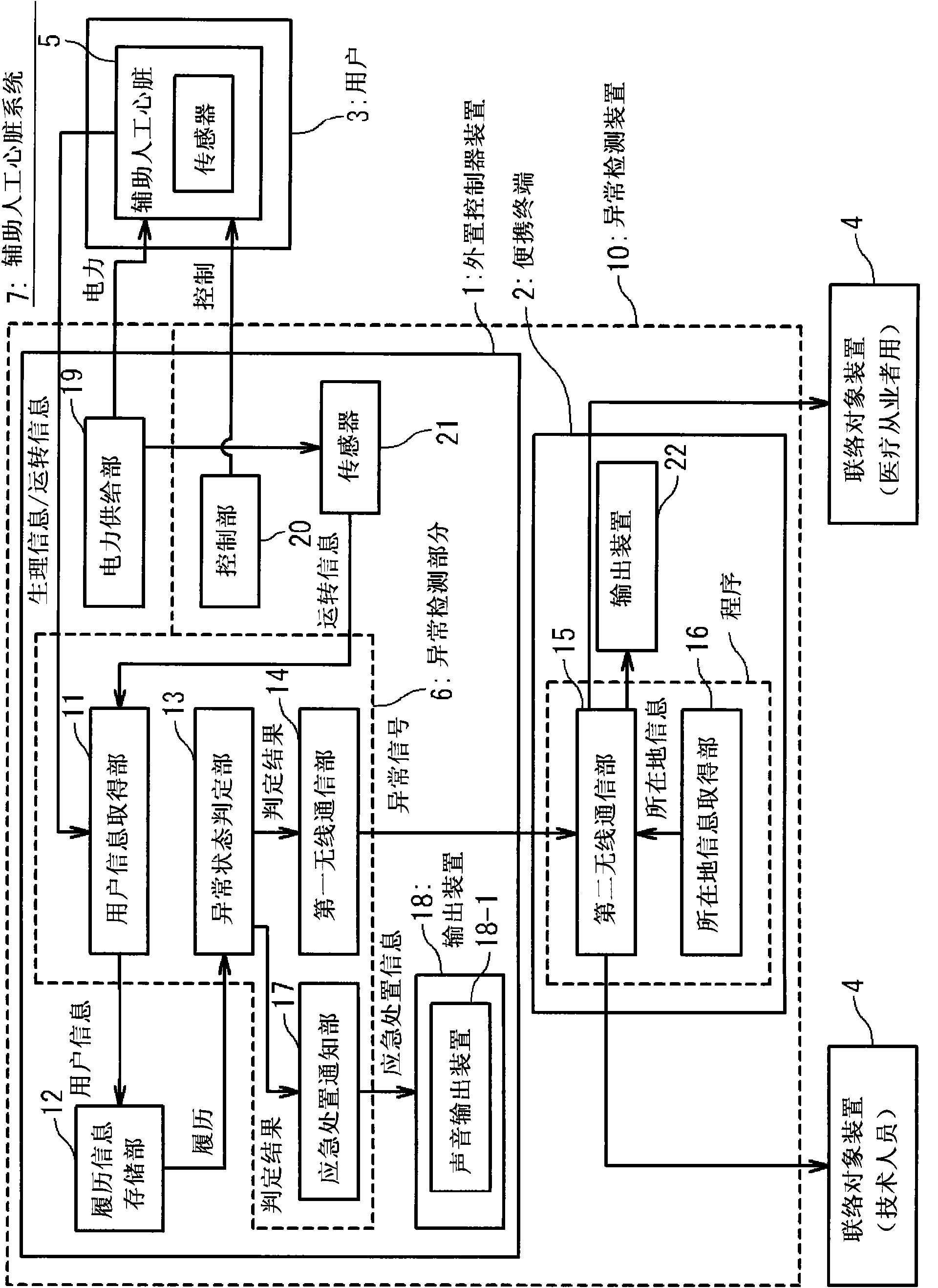
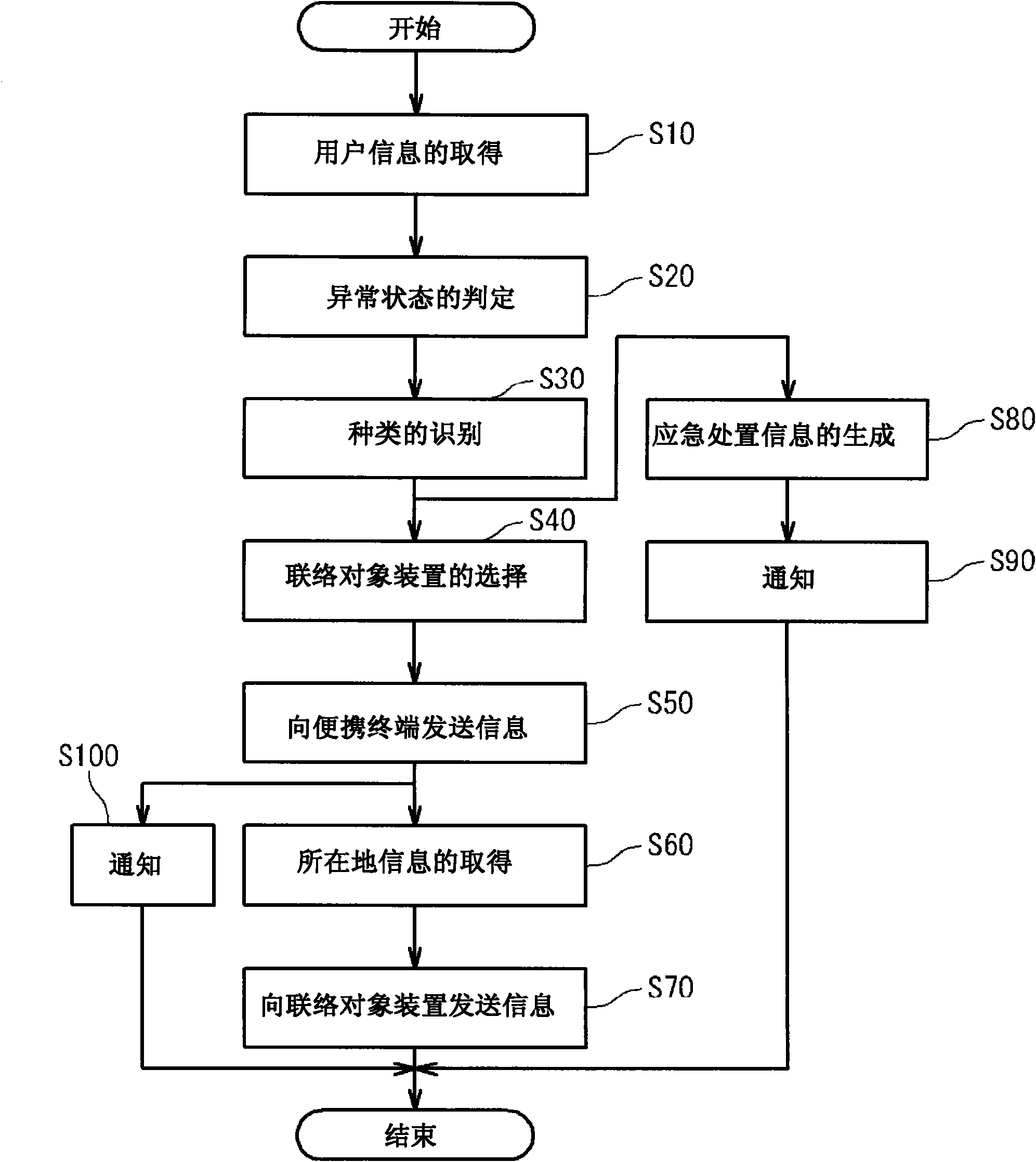
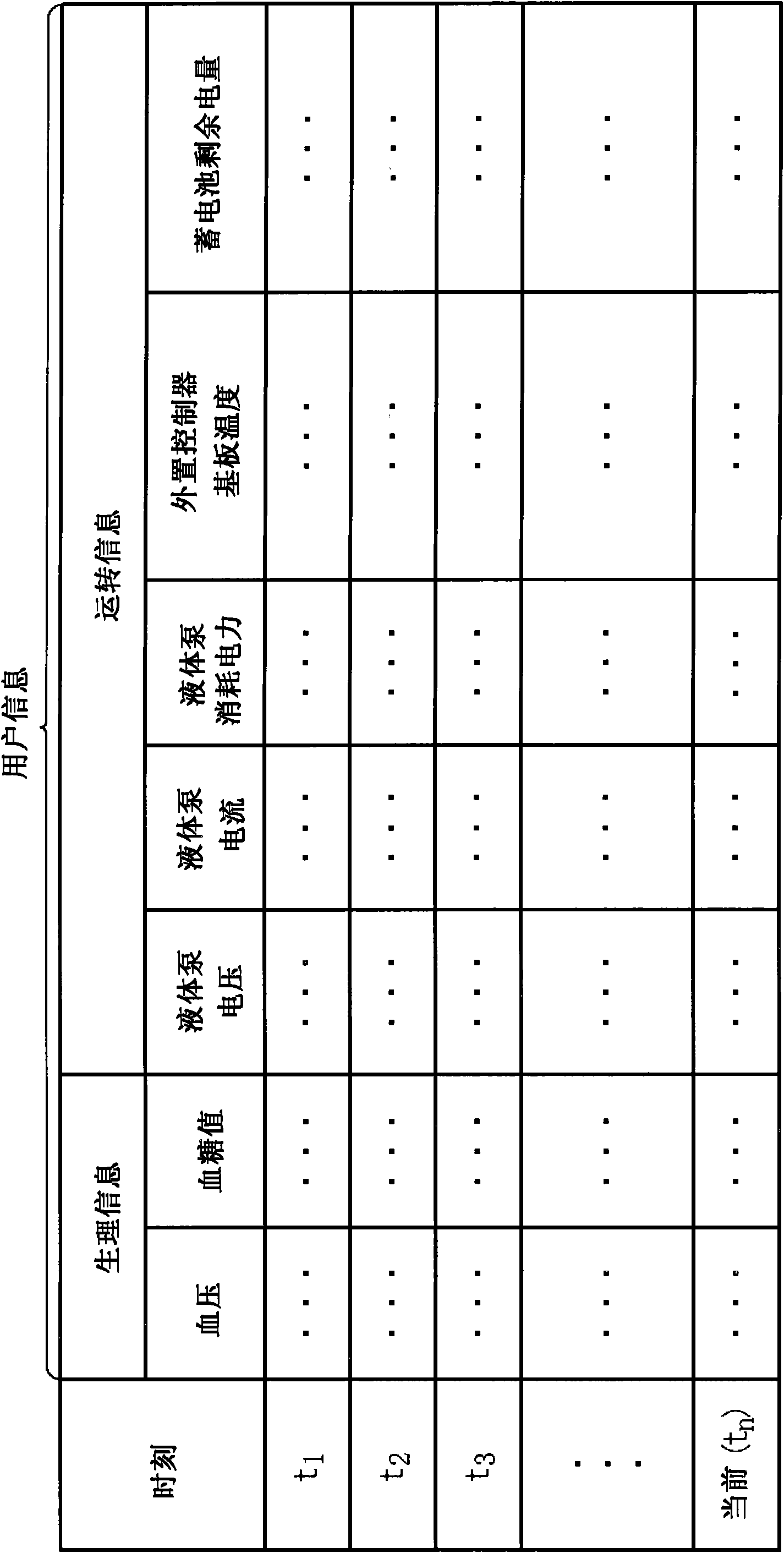
Device, method and program for detecting abnormal state of auxiliary artificial heart
In order to provide an abnormality detecting device for a heart assist device, a method for detecting an abnormality of a heart assist device and an abnormal state of a heart assist device detecting program which can early detect an abnormal state, the abnormality detecting device for a heart assist device according to the present invention includes a user information acquiring means for obtaining user information that indicates an operation state of the heart assist device implanted in a body of a user or a biological state of the user measured by the heart assist device and associating said user information with time to store in a history information storing means, and an abnormal state judging means for referring said history information storing means and judging whether or not an abnormal state is present based on a history of said user information.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Heart assist apparatus and method of use thereof
The invention comprises a heart assist device. In one embodiment, the heart assist device comprises a compressible sleeve about a body part, where one or more portions of the sleeve compress to provide a force on blood generating a flow or pulse of blood in the human circulatory system. In one case, the sleeve is external to the body, such as circumferentially about a limb or about a body extremity. In another case, the sleeve is internal to the body, such as circumferentially about an artery or vein. In still another case, two or more sleeves cooperatively function in parallel and / or in series. The heart assist device is optionally configured to auto-start in an emergency system, is in on-demand or in continuous contact with an emergency response system, and / or is linked to a medical professional's system.
Owner:ROTH MICHAEL D
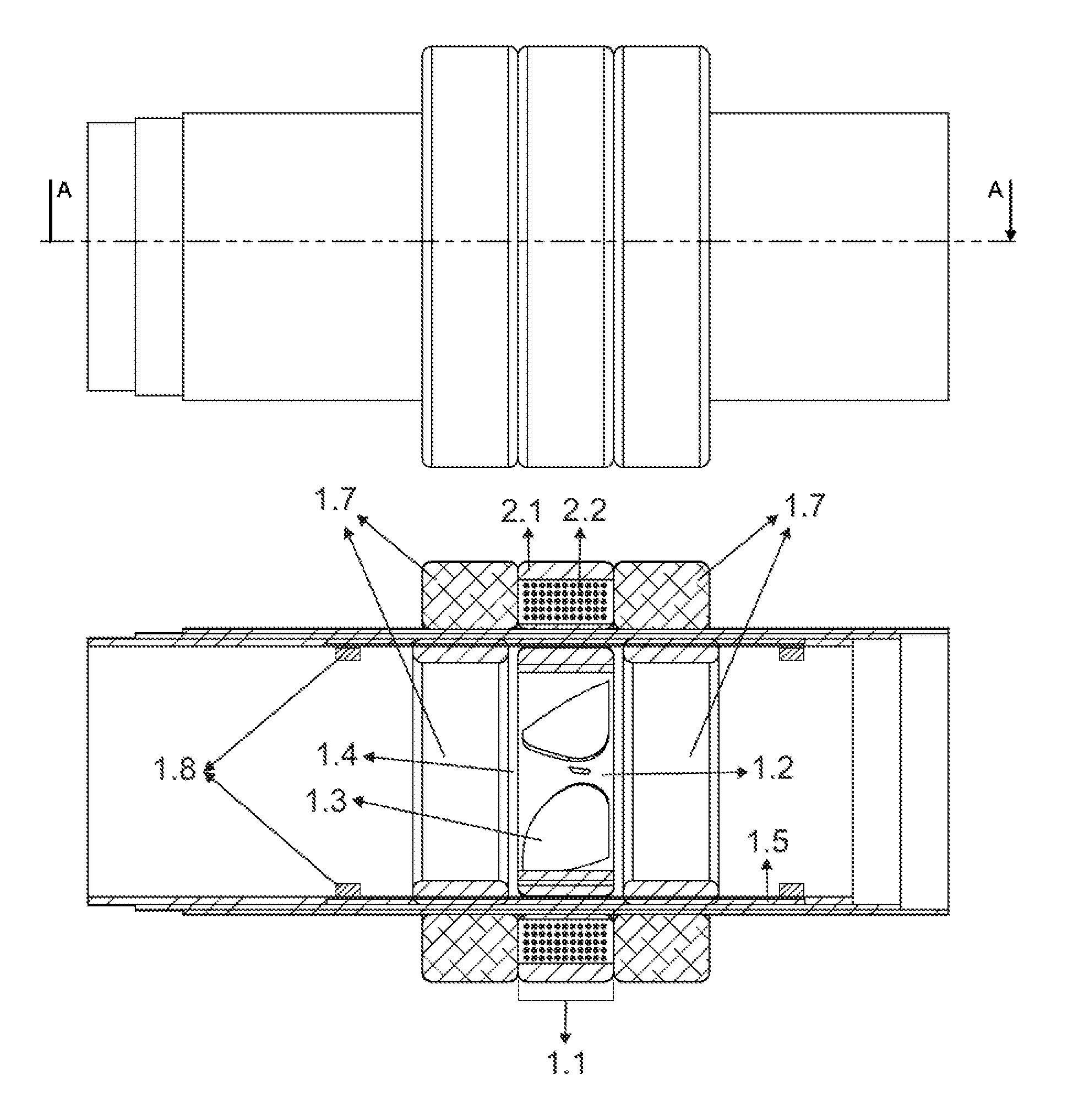
Magnetic fluid suspension type axial pump heart assisting device
ActiveCN104208764AImprove reliabilityImprove stabilityIntravenous devicesSuction devicesImpellerAxial-flow pump
The invention relates to a heart assisting device, in particular to a magnetic fluid suspension type axial pump heart assisting device implanted into the human body in the field of biomedical engineering. The magnetic fluid suspension type axial pump heart assisting device is characterized in that a section of flow channel is divided into an inner flow channel and an outer flow channel by an outer ring wrapping the middle section of an impeller blade, and spiral tooth ripples are engraved on the outer wall of the ring; the top wall of the tooth ripples is in an oblique shape, so that an inflowing opening of the outer flow channel is large, and an outflowing opening is small, and an impeller is subjected to hydraulic pressure when rotating to be radially suspended; an opening is formed in the side wall of the tooth ripples; a pair of convex-concave magnetic cones are embedded in the back end of an impeller hub and a back guide blade hub, and are in the axial magnetic direction, and unlike poles attract each other; a backward pull force generated on the impeller resists the blood forward push force borne by rotating the impeller, and a stator iron core has a binding force, so that the impeller is axially suspended, and thus the impeller is fully suspended; the impeller and front and back guide blade hubs are respectively embedded with two pairs of sliding bearings, which protect the magnetic cones, blades, and the inner wall of a pump pipe, and position and help the impeller suspension.
Owner:CHANGZHI JIUAN ARTIFICIAL HEART TECH DEV
Methods, systems, and devices relating to wireless power transfer
InactiveCN104487131ABatteries circuit arrangementsDiagnosticsElectric power transmissionEnergy transfer
The various embodiments disclosed herein relate to transcutaneous energy transfer systems comprising an internal coil positioned within a cavity of a patient and an external coil inductively coupled to the internal coil. The systems can be coupled to any implantable medical devices, such as, for example, a heart assist device.
Owner:SUNSHINE HEART PTY LTD
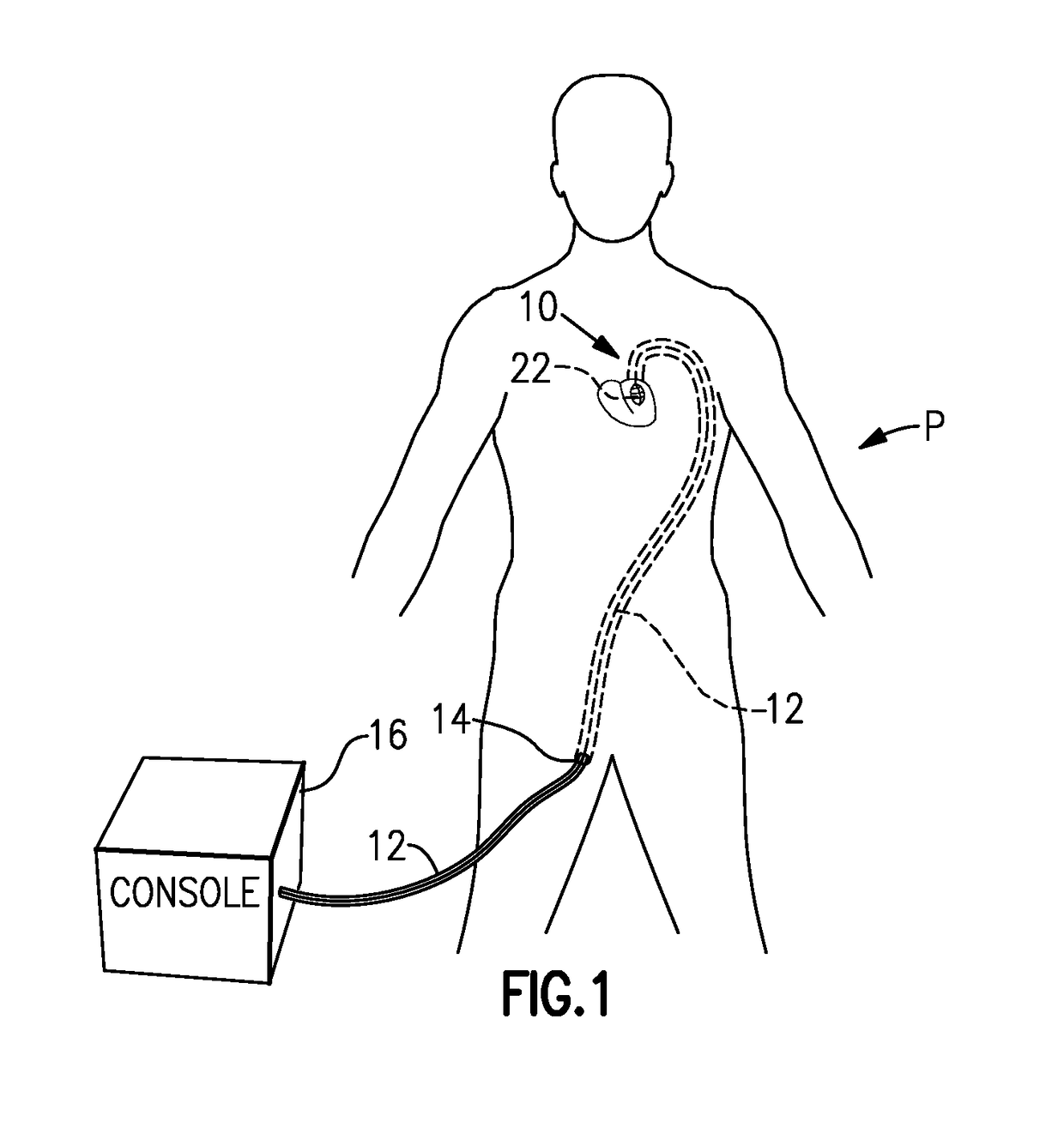
Left ventricle heart-assist device
InactiveUS9623163B1Increase cardiac outputGreat suctionElectrocardiographyControl devicesSystoleLeft ventricular size
A left-ventricular assist device (LVAD) has a generally ellipsoidal capsule fitted into a patient's ventricle, formed of a cage or frame of shape-memory wire which can be twisted open and shut to expand and collapse a thin membrane, to inflate with the incoming blood during diastole and to contract and squeeze out the blood during systole. A catheter extends from outside the patient's body through a major blood vessel and the patient's aortal valve into the left ventricle. The catheter has an external sheath, an outer tubular shaft onto which proximal ends of the shape-retaining wires are affixed, and a middle shaft extending through the hollow core of the outer shaft and which is affixed to a central shaft of the capsule. A control console has mechanical geared drives coupled to the outer and middle catheter shafts within the catheter. A sensor arrangement synchs action of the LVAD with systole and diastole of the patient's heart.
Owner:FISCHI MICHAEL
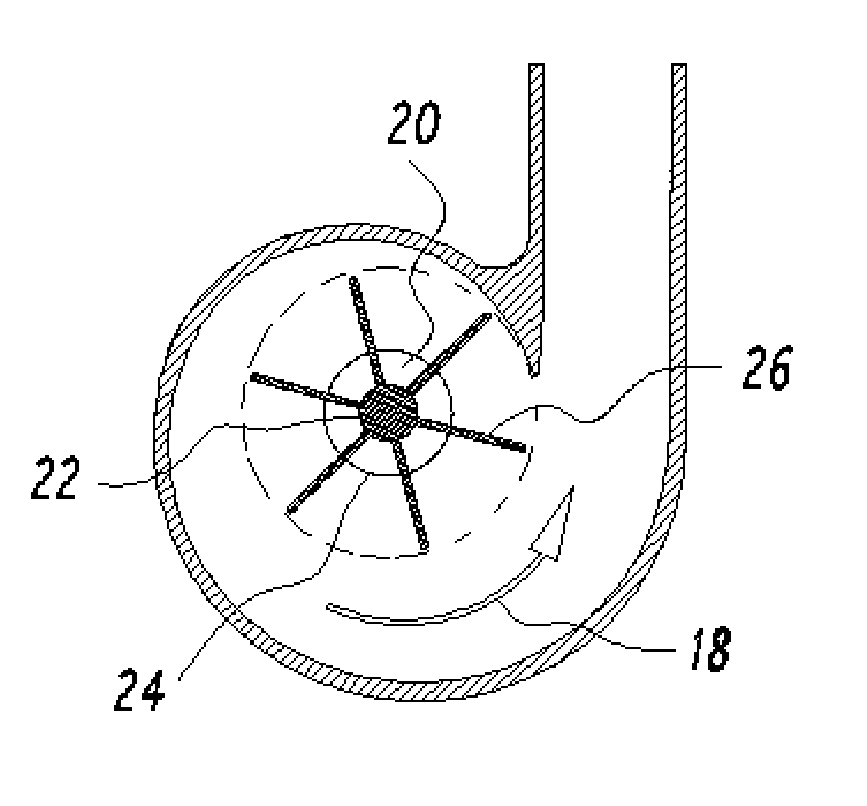
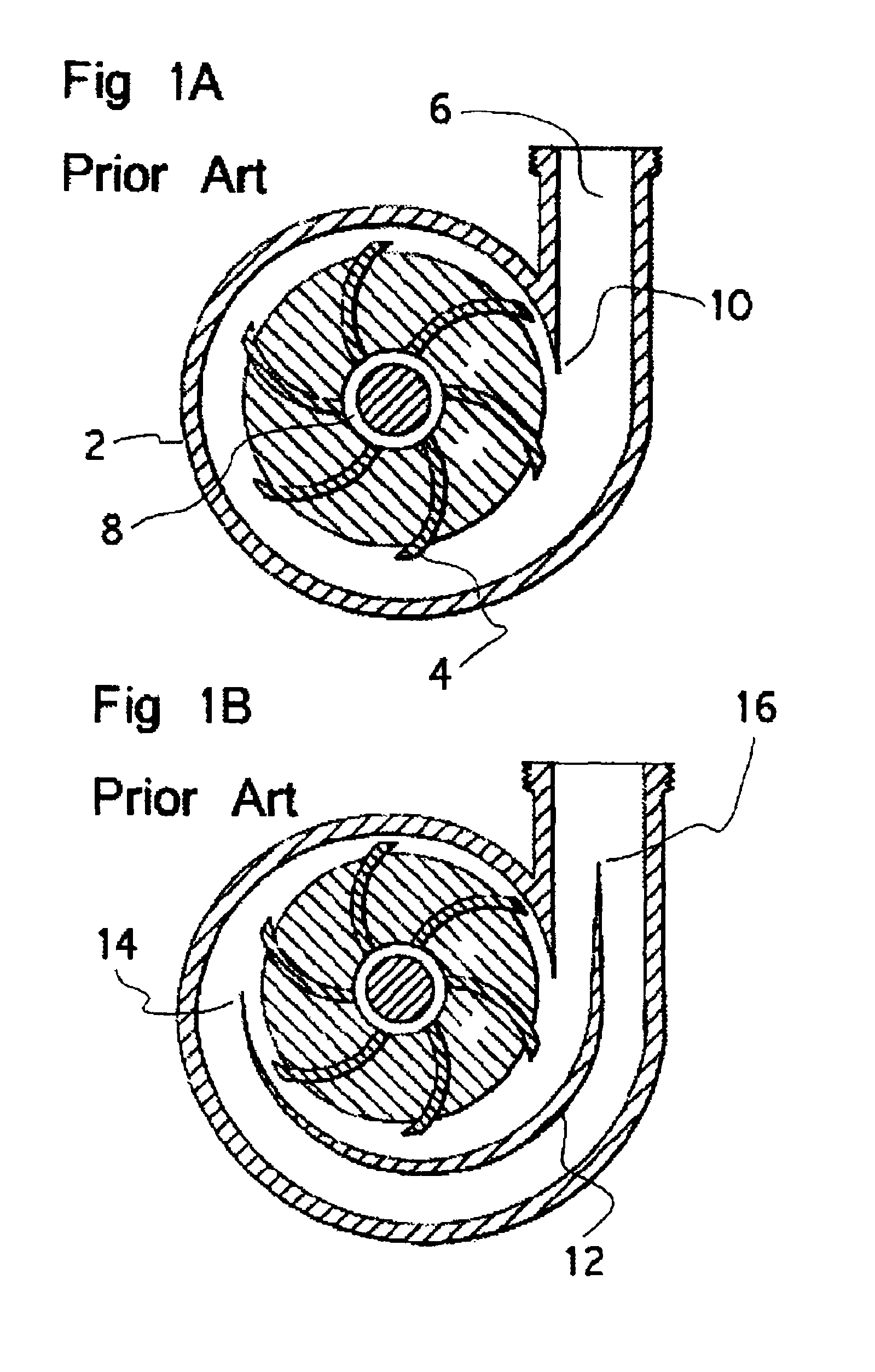
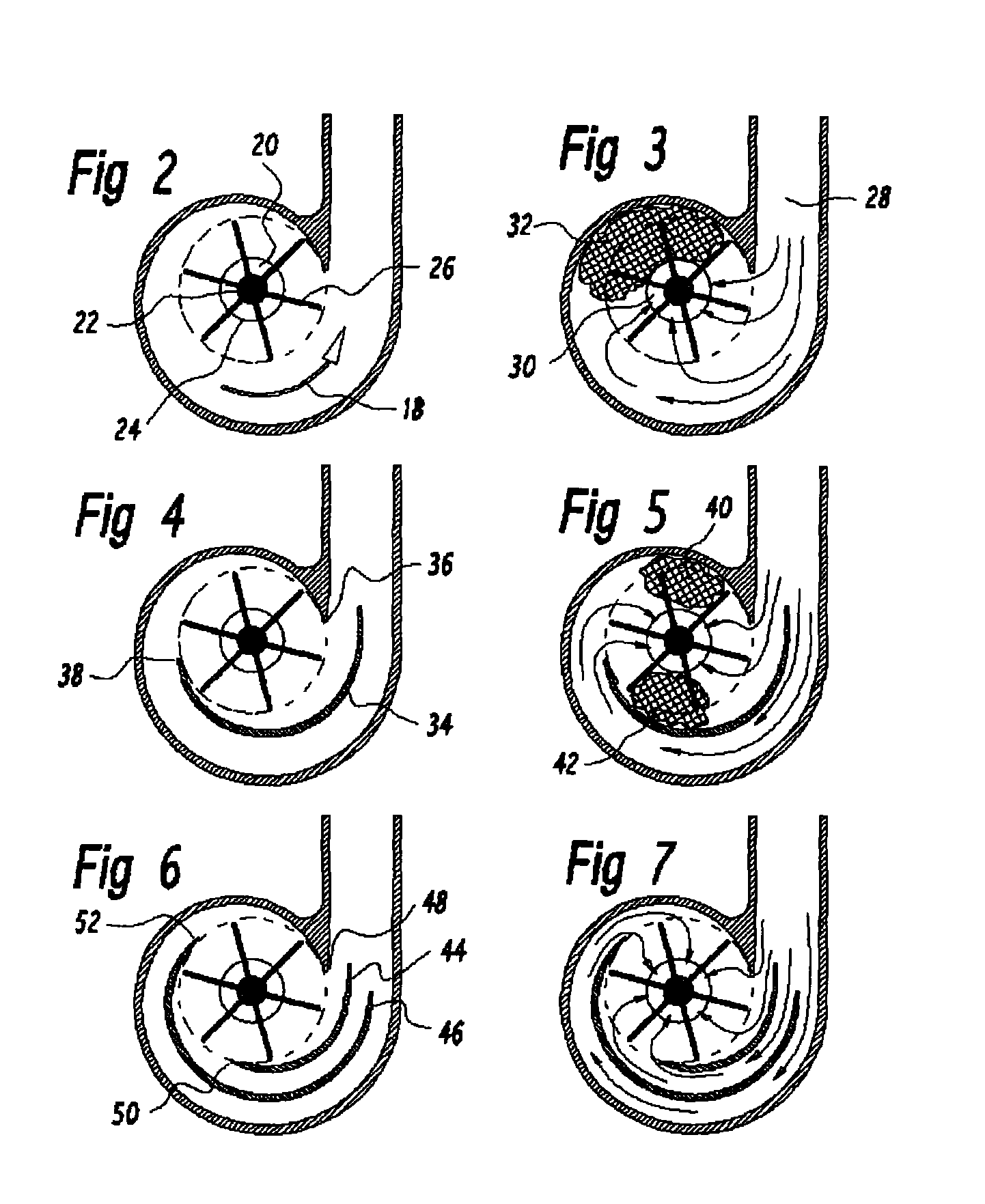
Centrifugal blood pumps with reverse flow washout
Blood pumps used as heart assist devices are commonly powered by an external battery and control system. If the external power is interrupted, such as by damaging an external cable, patients will have backflow across the pump. If the flow is too high, they may decompensate and die. If the backflow is relatively low, patients can survive until power is restored, but their blood pump must be sufficiently washed to prevent thrombus. Centrifugal blood pumps have been designed for good pumping performance, low blood damage, and avoidance of thrombus when they are running. The present invention recognizes the need to also provide enough washing to prevent thrombus when the pump power is turned off. The invention provides centrifugal pumps with triple or quadruple volute designs, or with axial flow impellers on the same shaft as the centrifugal pump impeller to help drive the rotor in reverse and enhance washing even with relatively low backflow. Also, in the preferred embodiment the centrifugal rotor is supported by low friction mechanical blood immersed bearings, to avoid contact of the rotor with the housing that creates small poorly washed crevices where thrombus can form.
Owner:JARVIK ROBERT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com