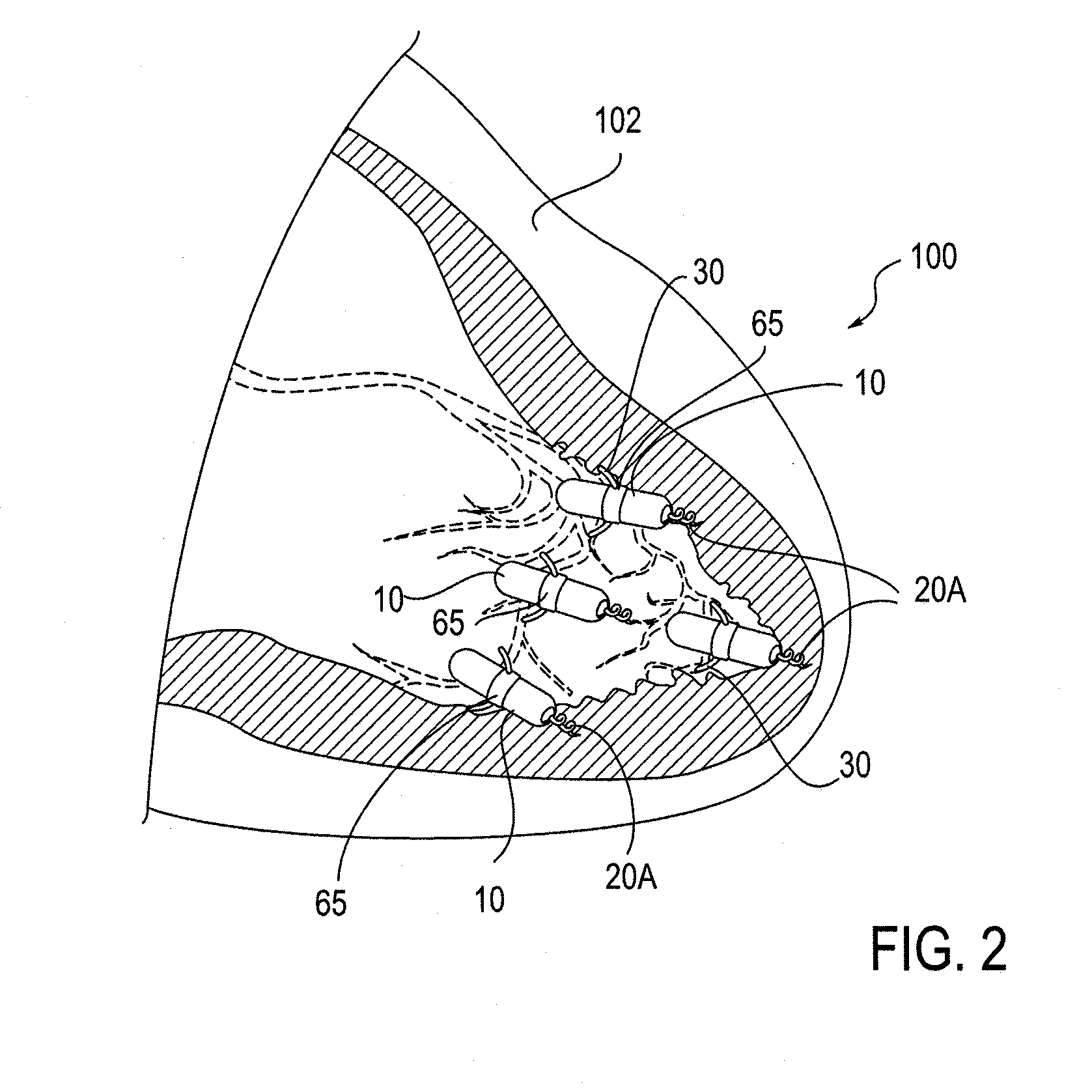
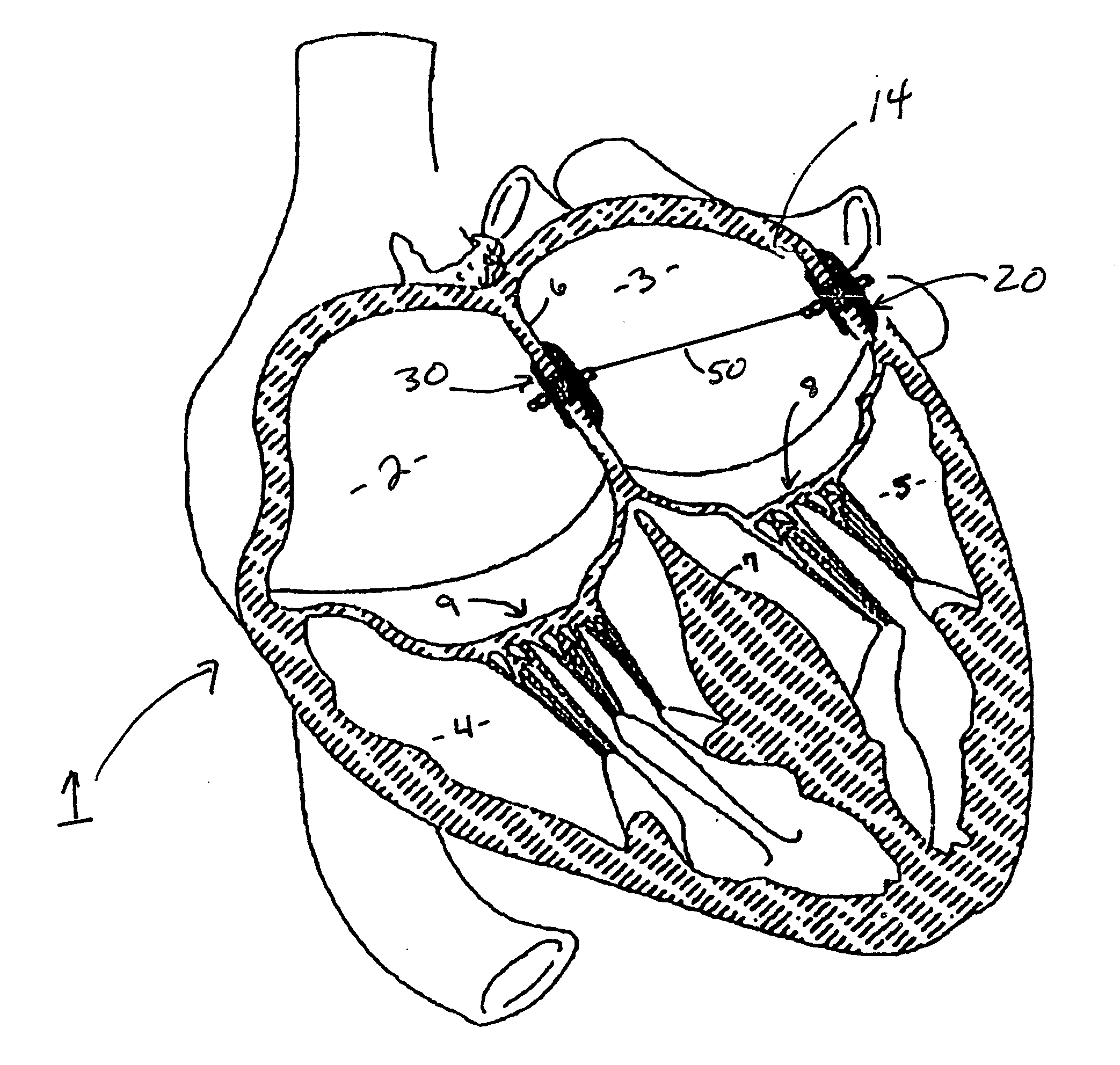
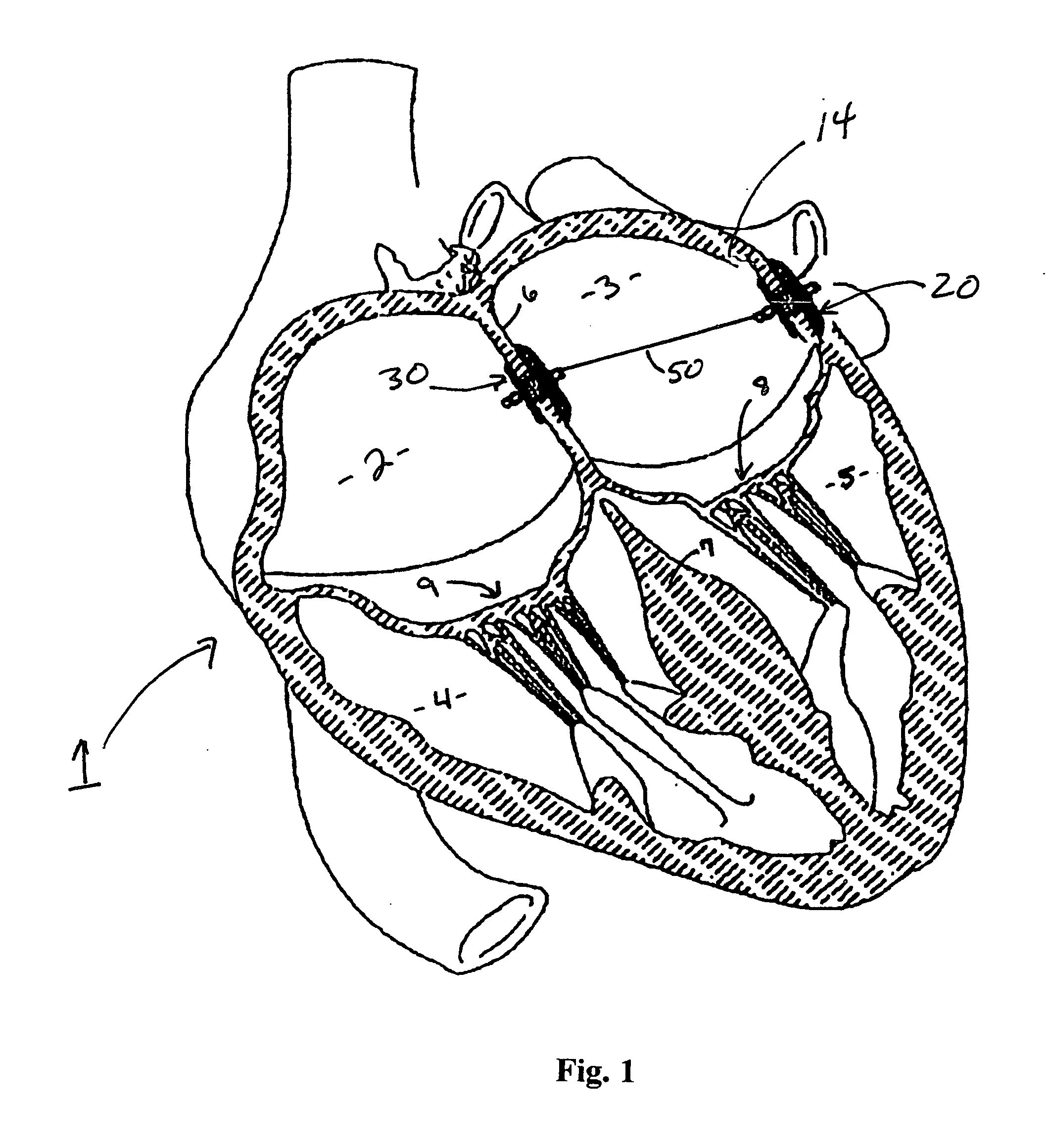
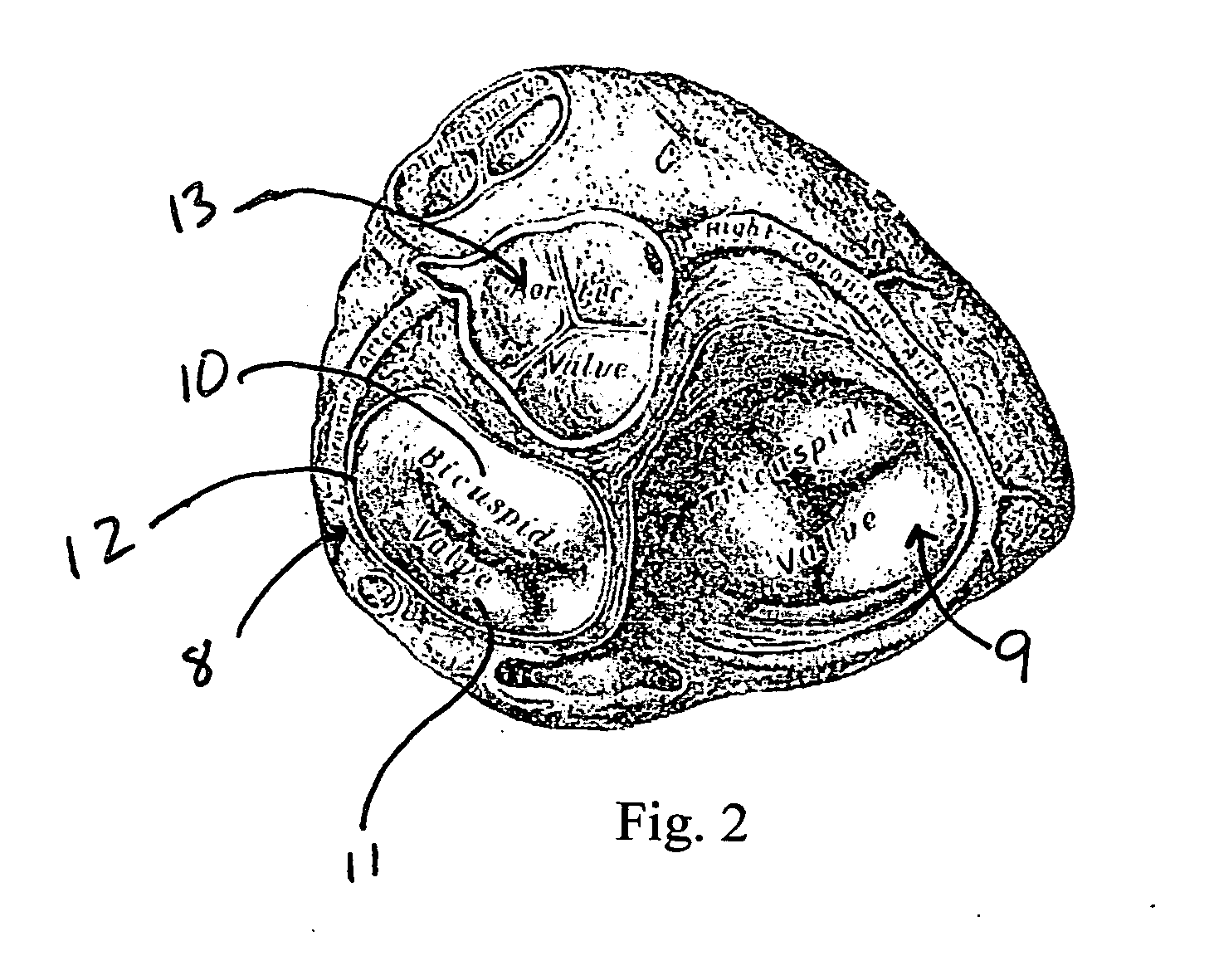
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
452 results about "Heart chamber" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
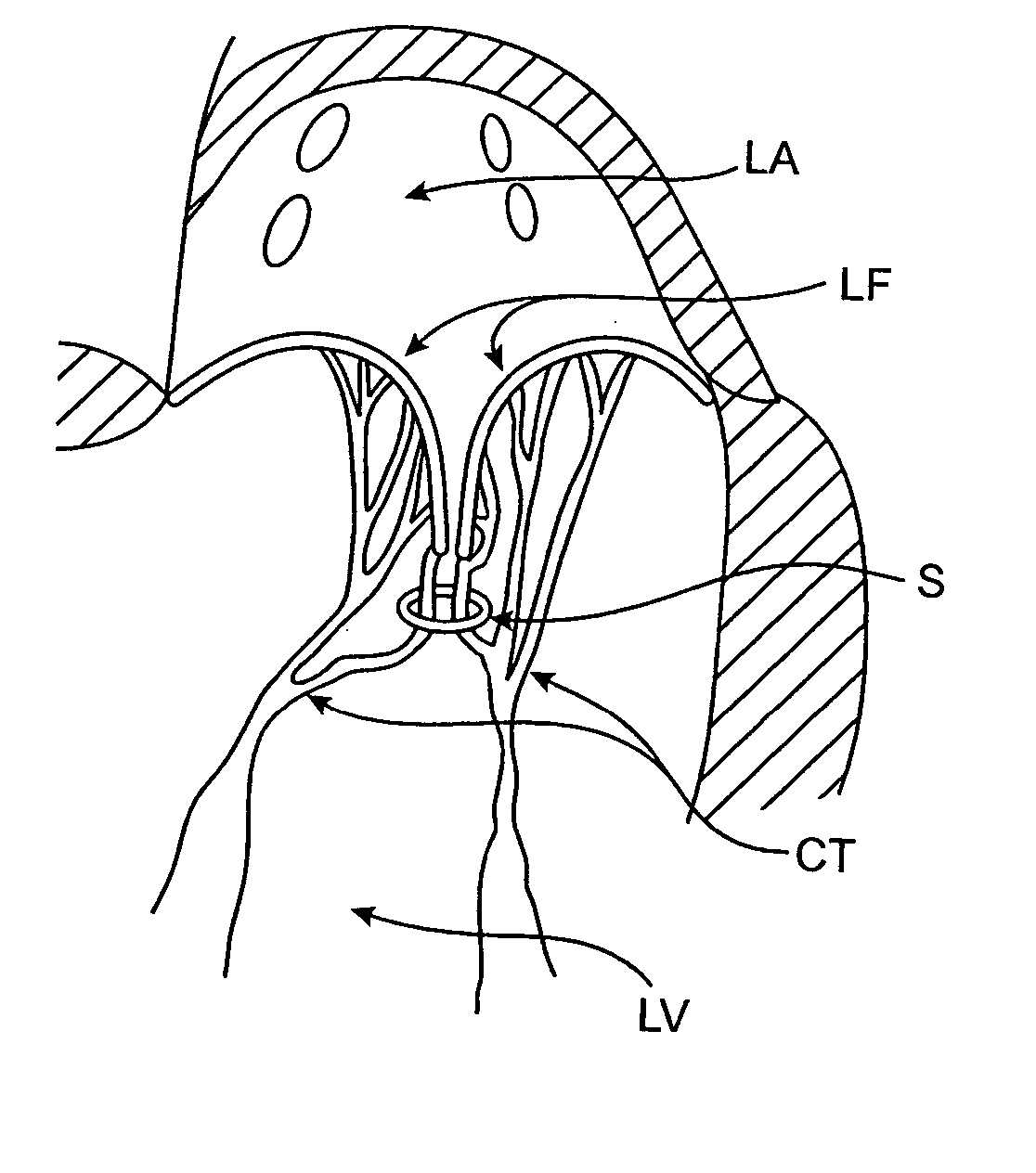
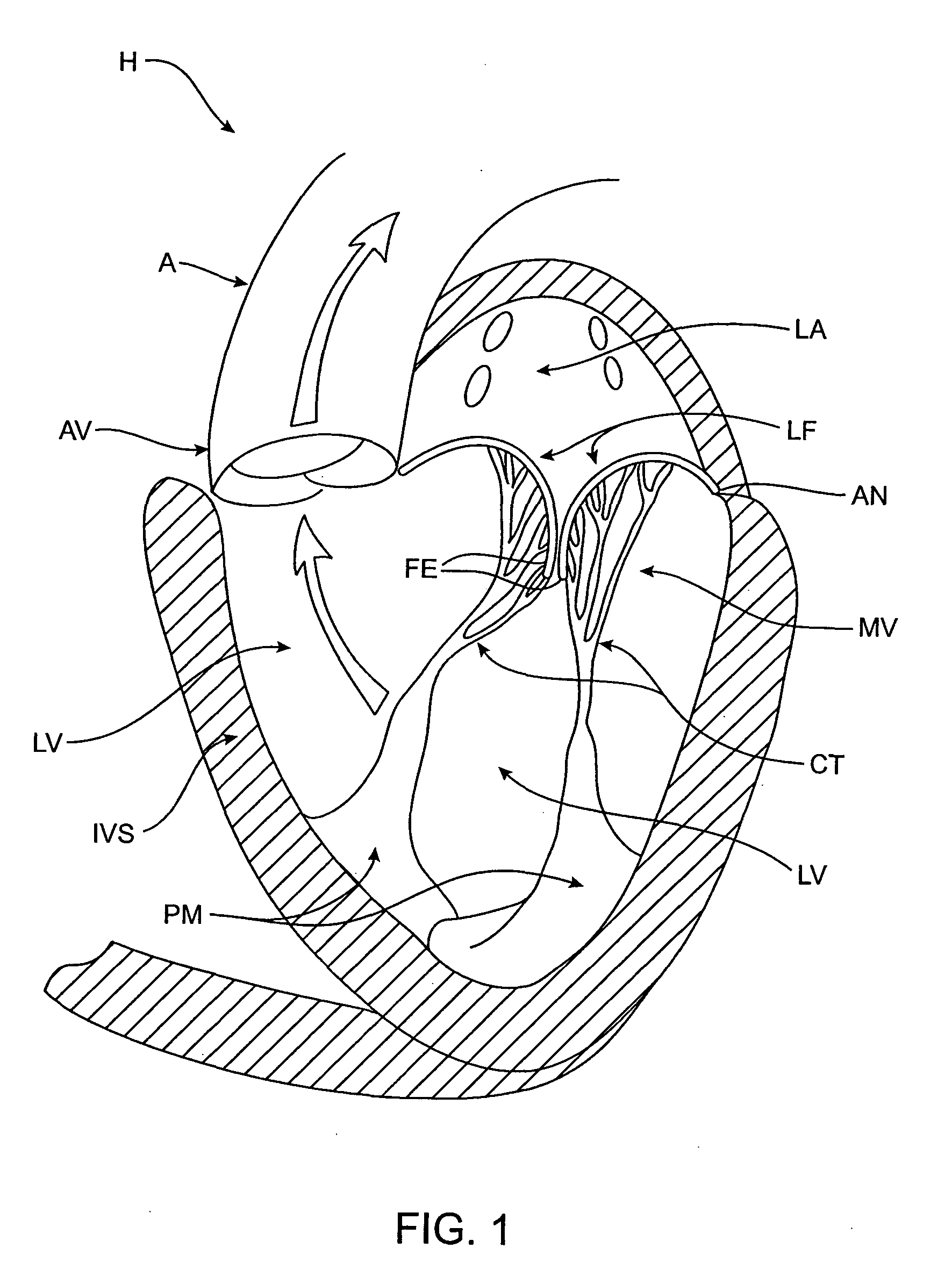
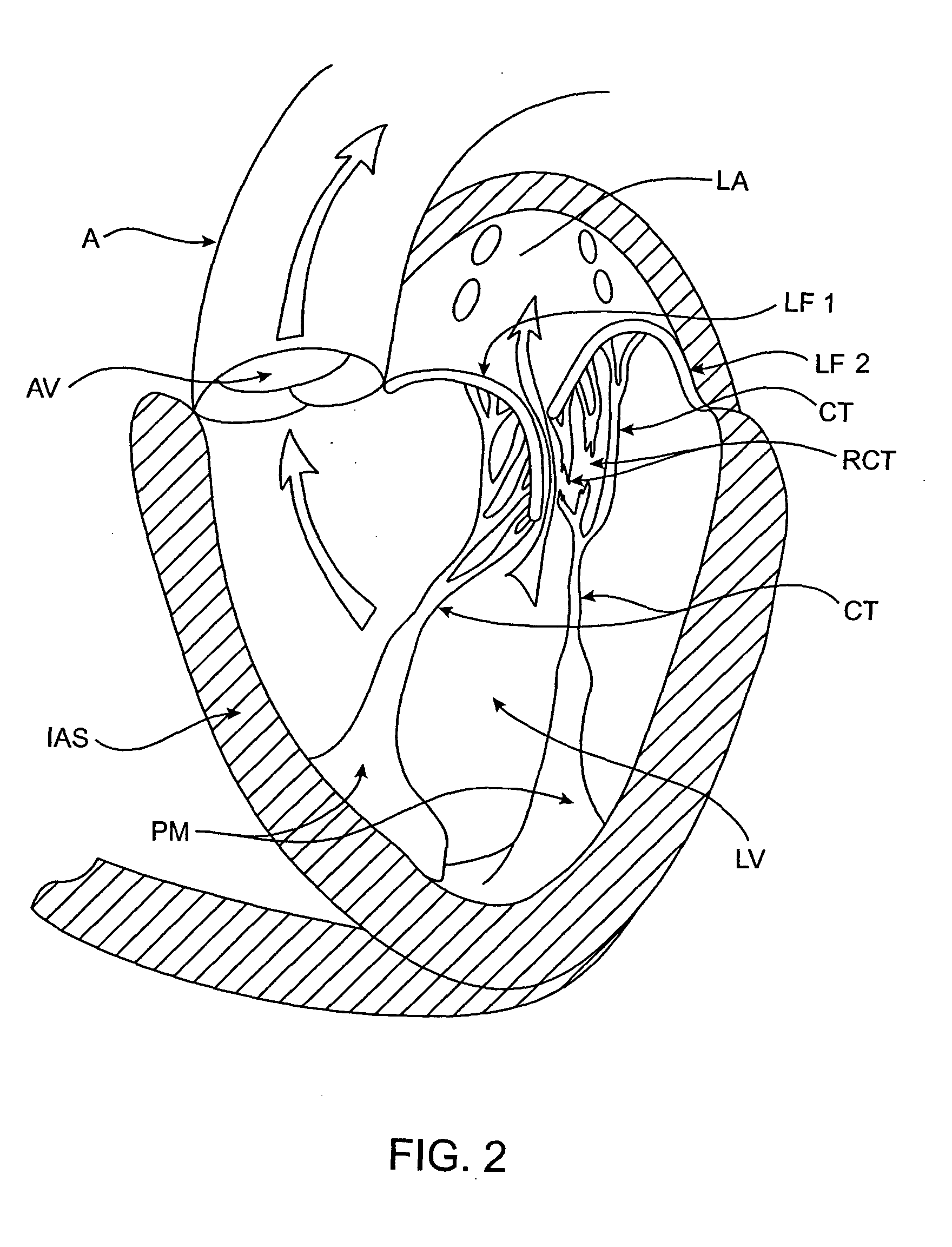
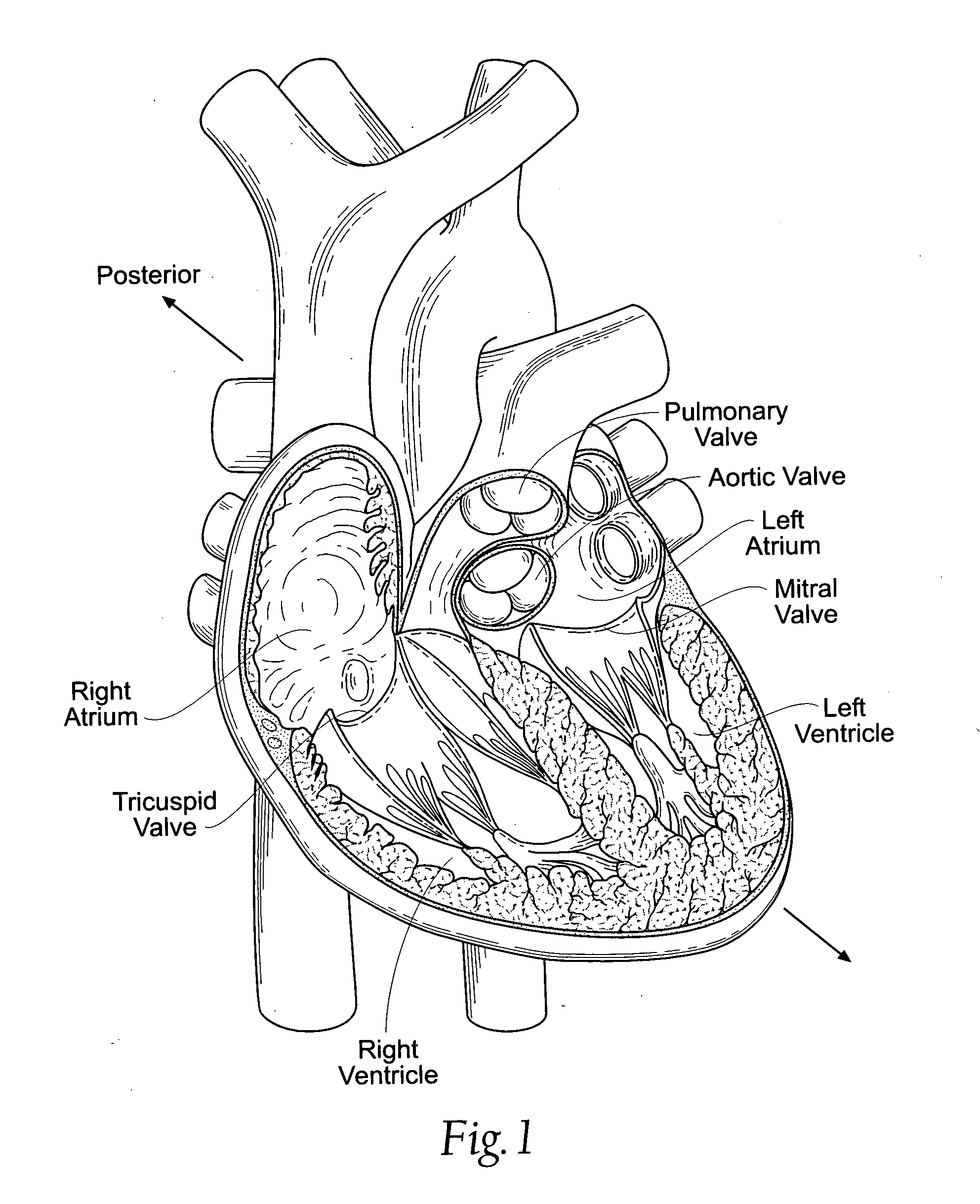
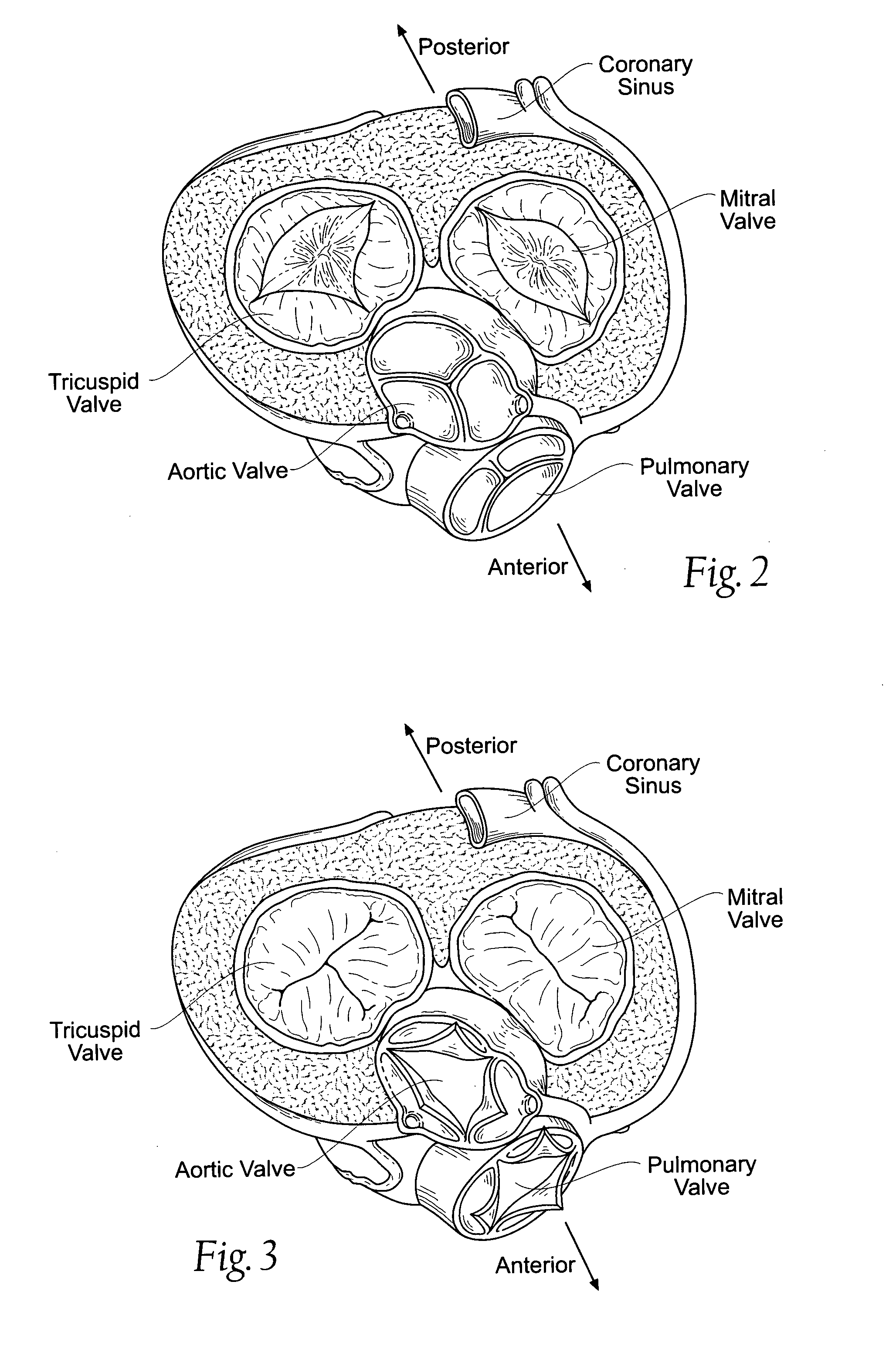
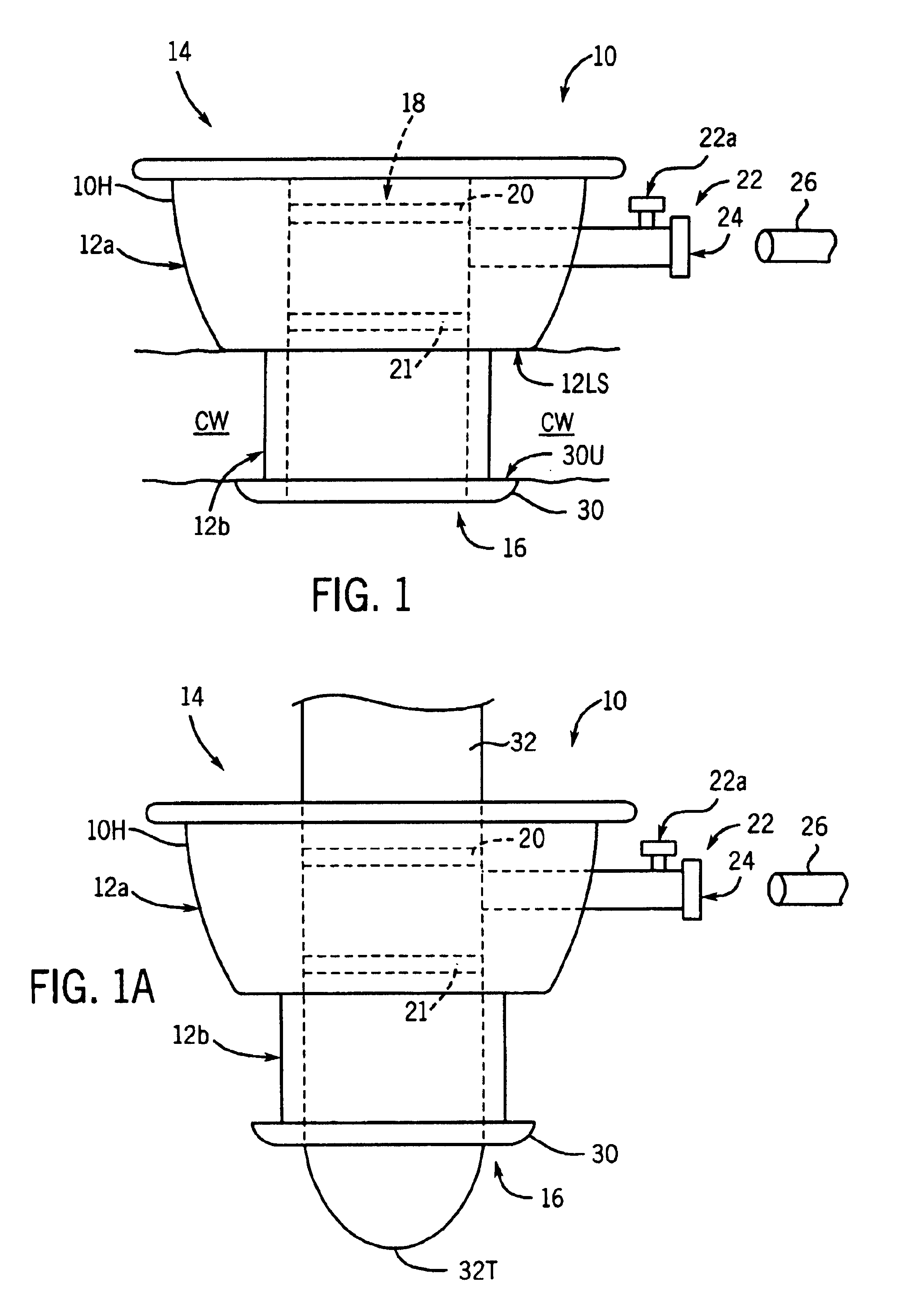
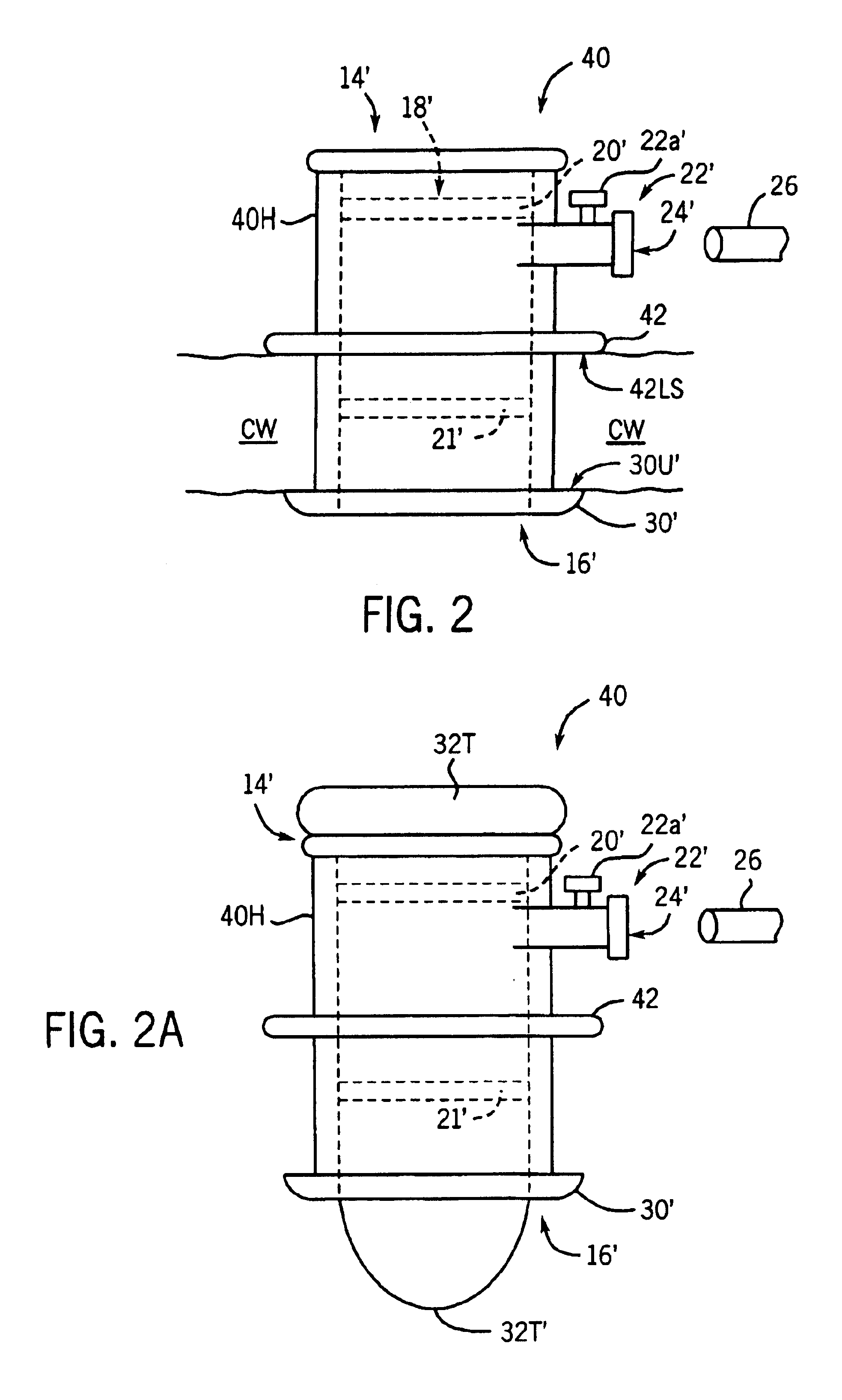
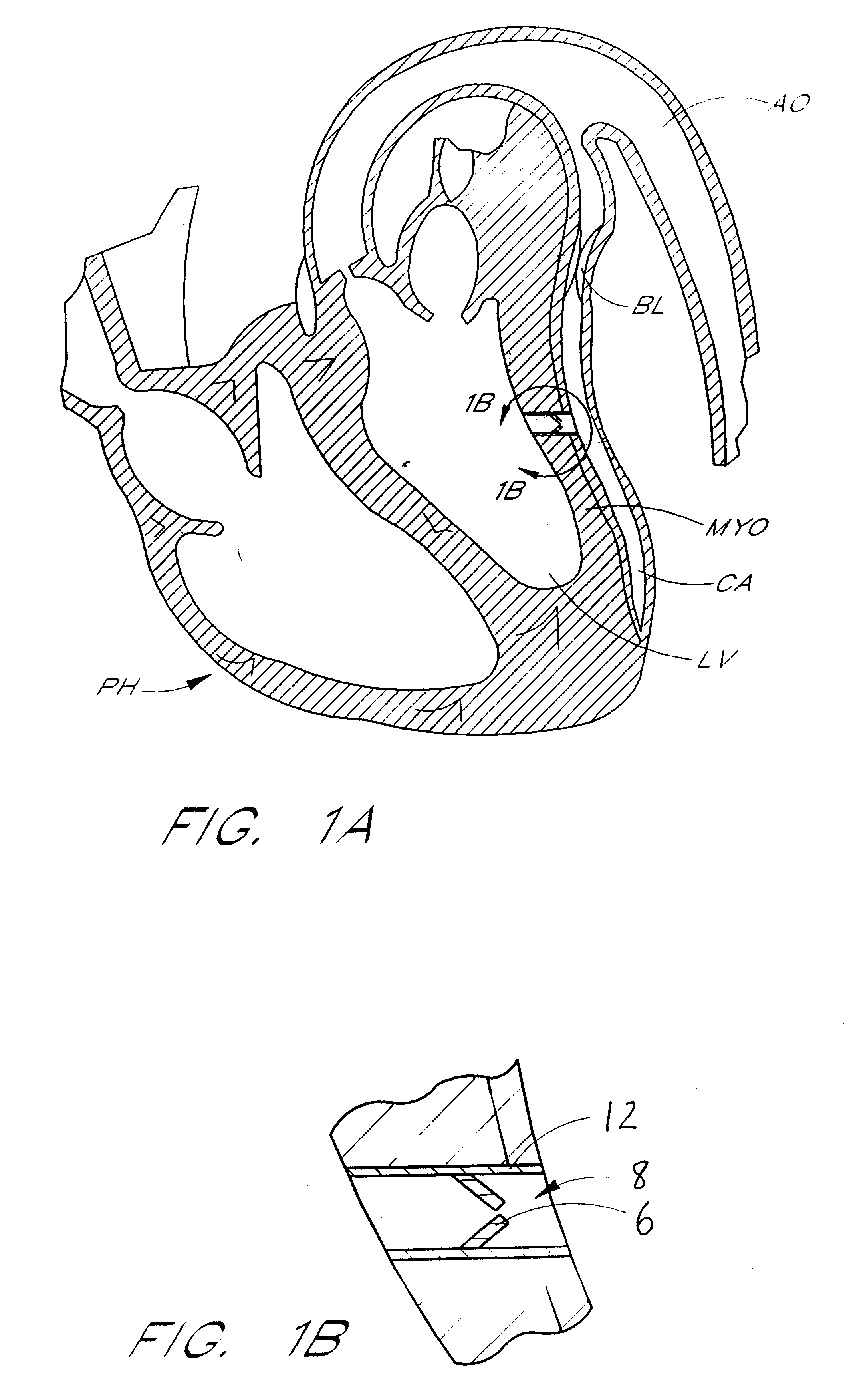
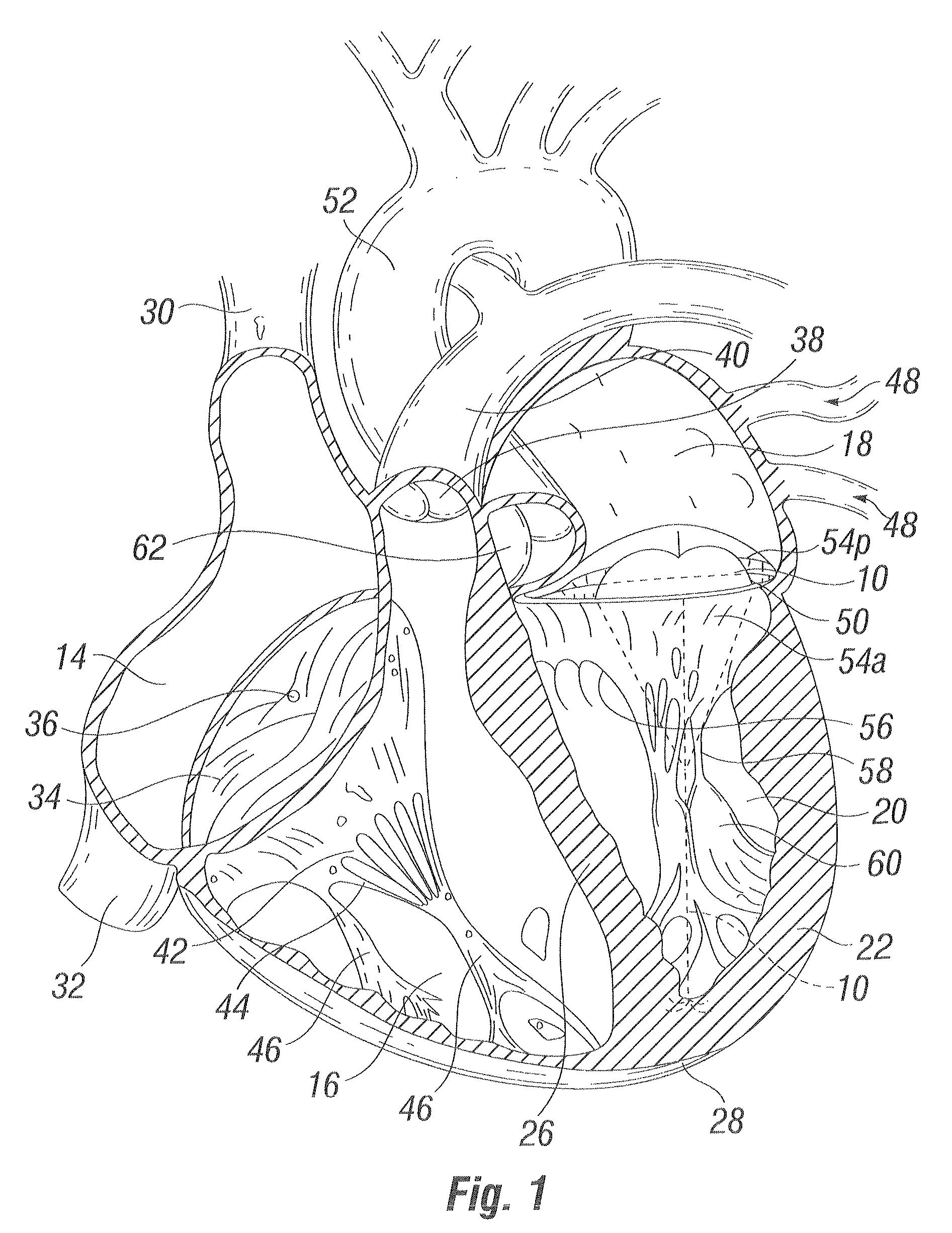
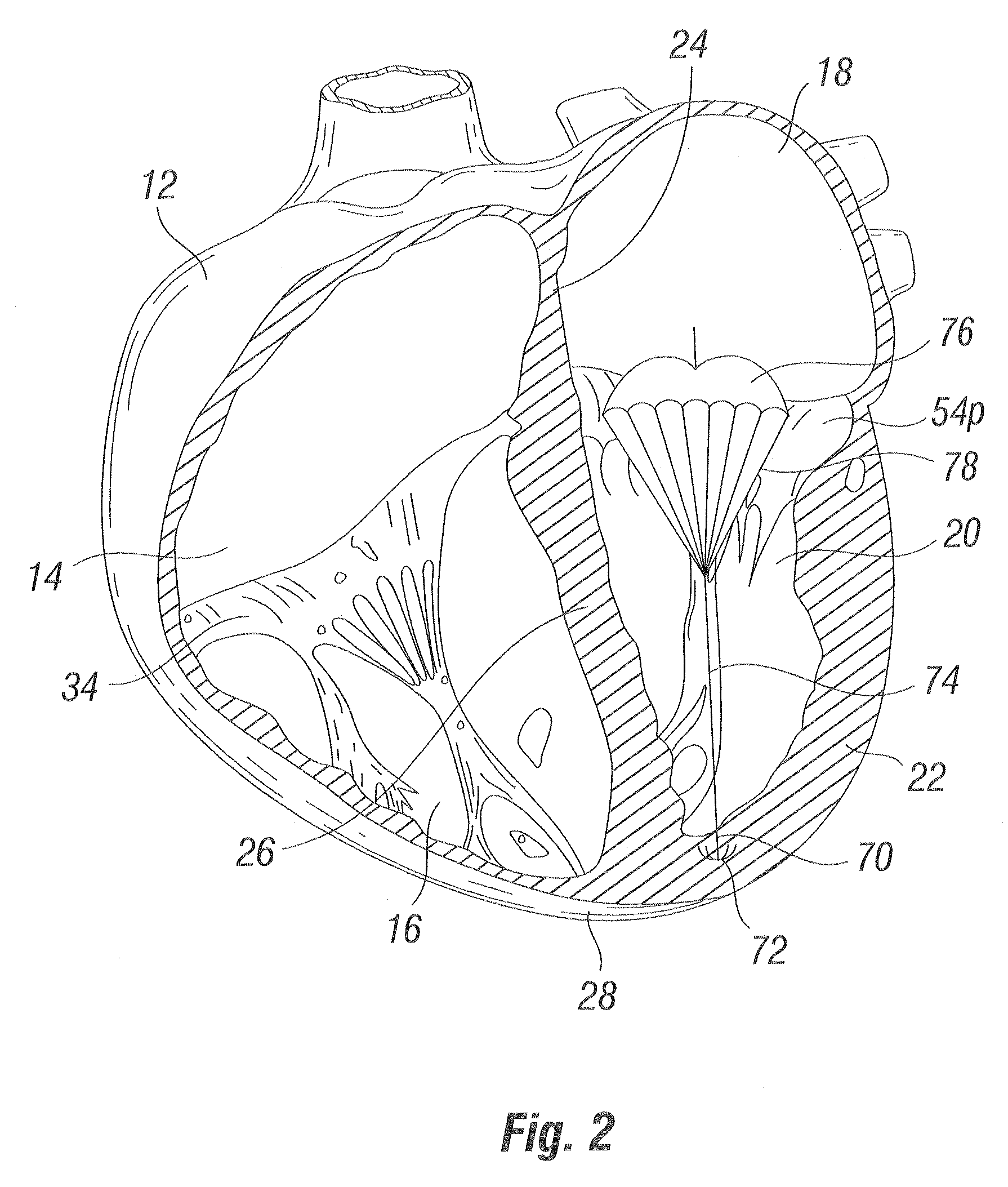
Heart chamber is a general term used to refer to any chambers of the mammalian heart. The heart consists of four chambers: the right and left atrium and the right and left ventricle. The top chambers are connected to the bottom chambers by valves and are separated by the coronary sulcus.
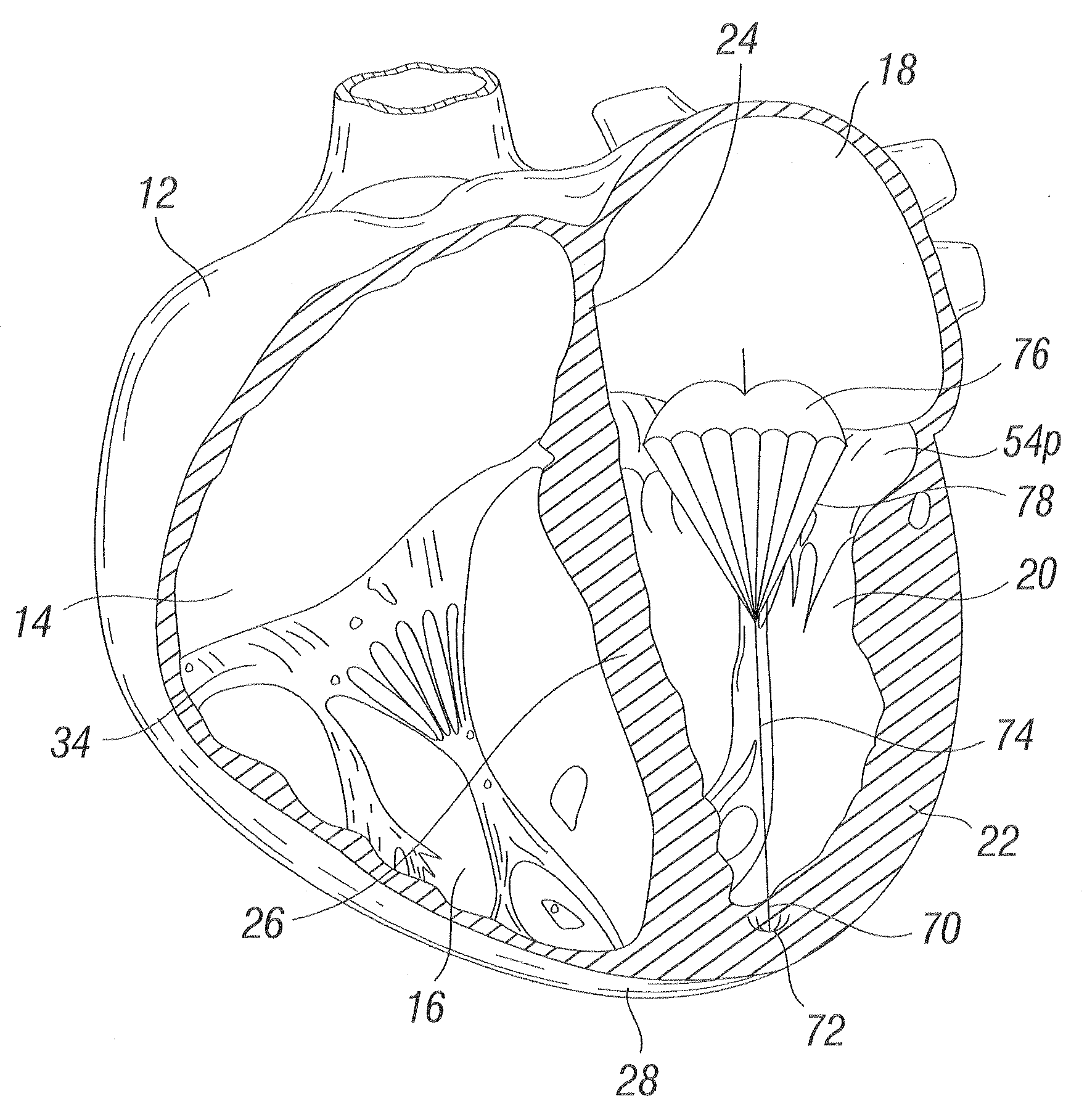
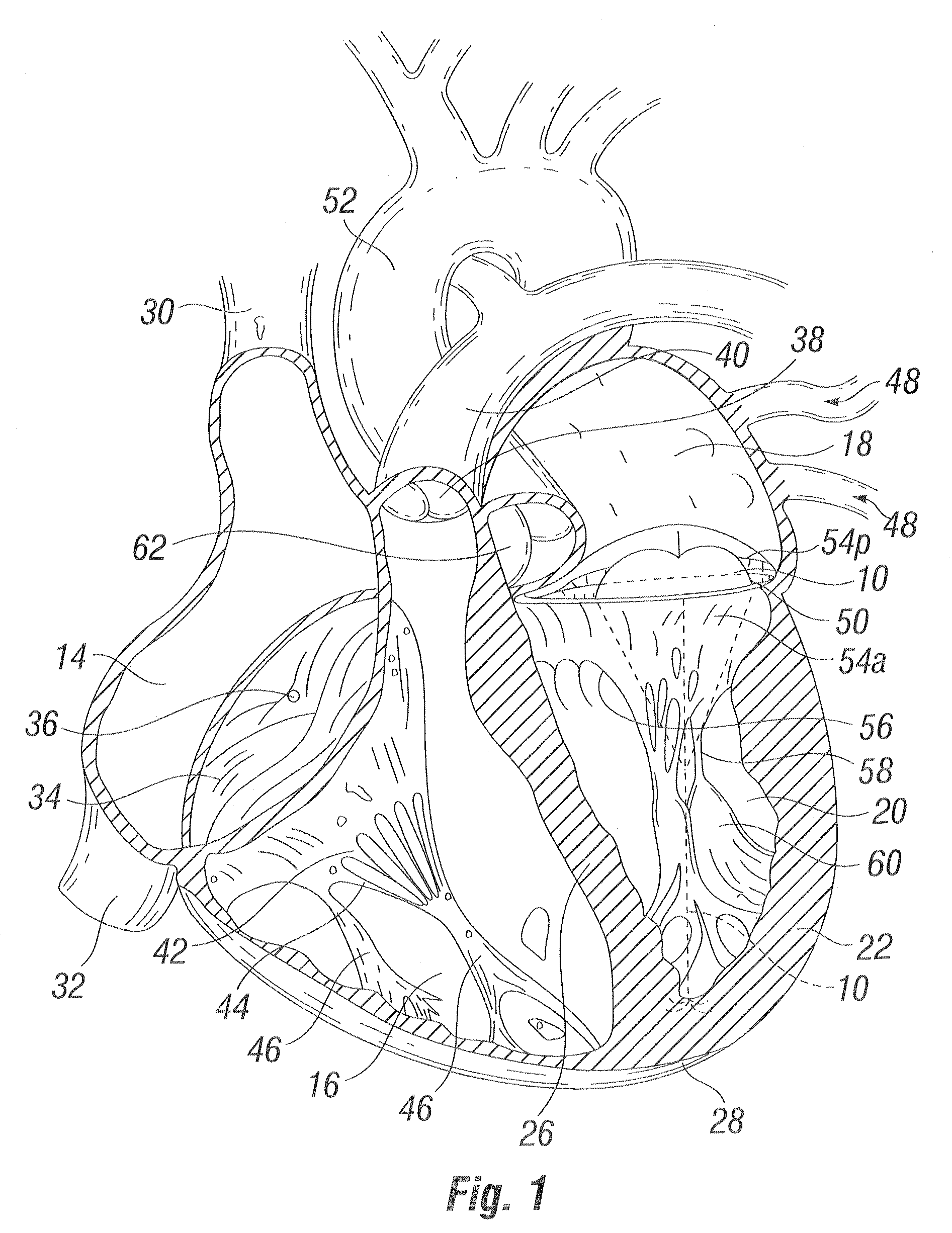
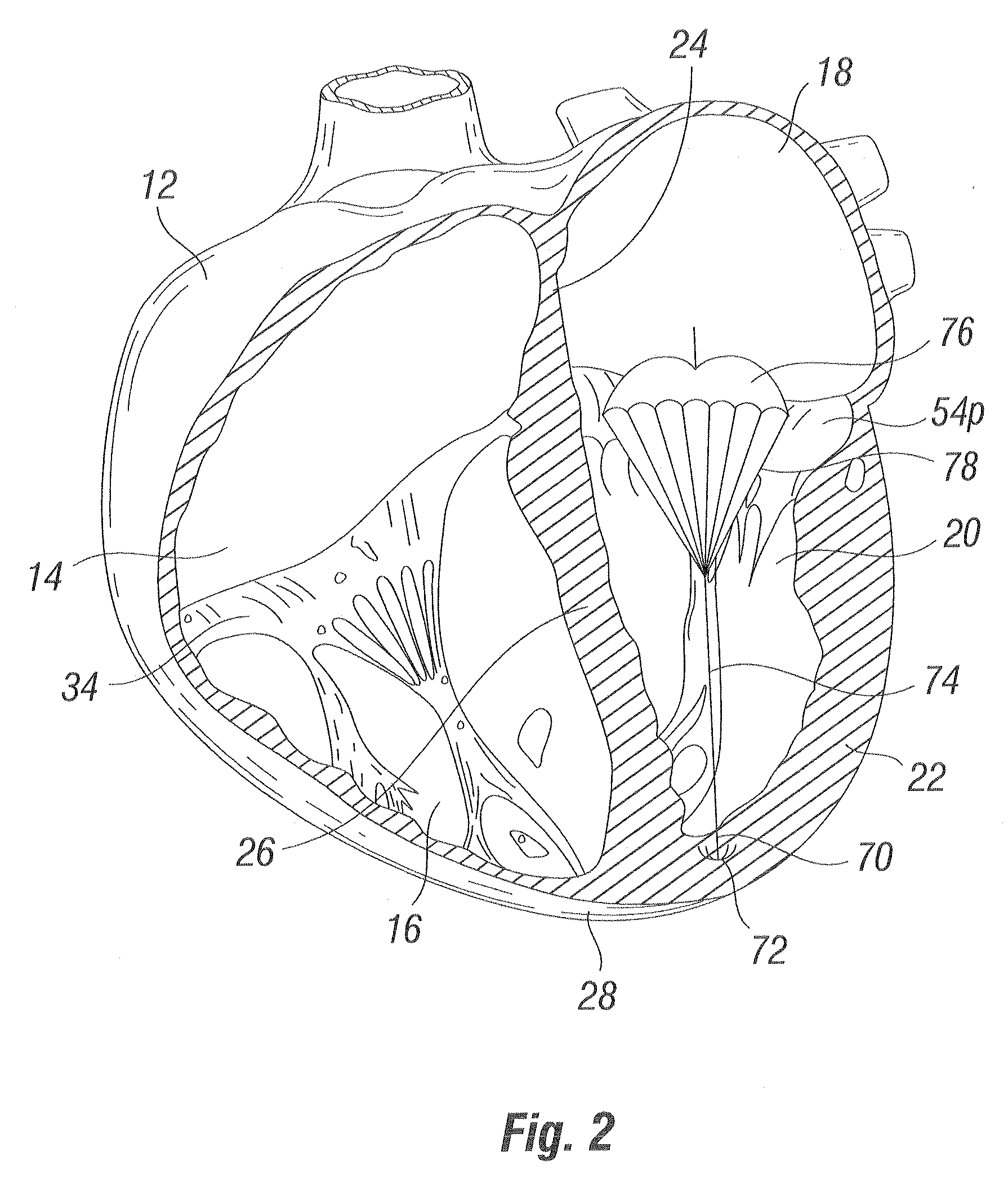
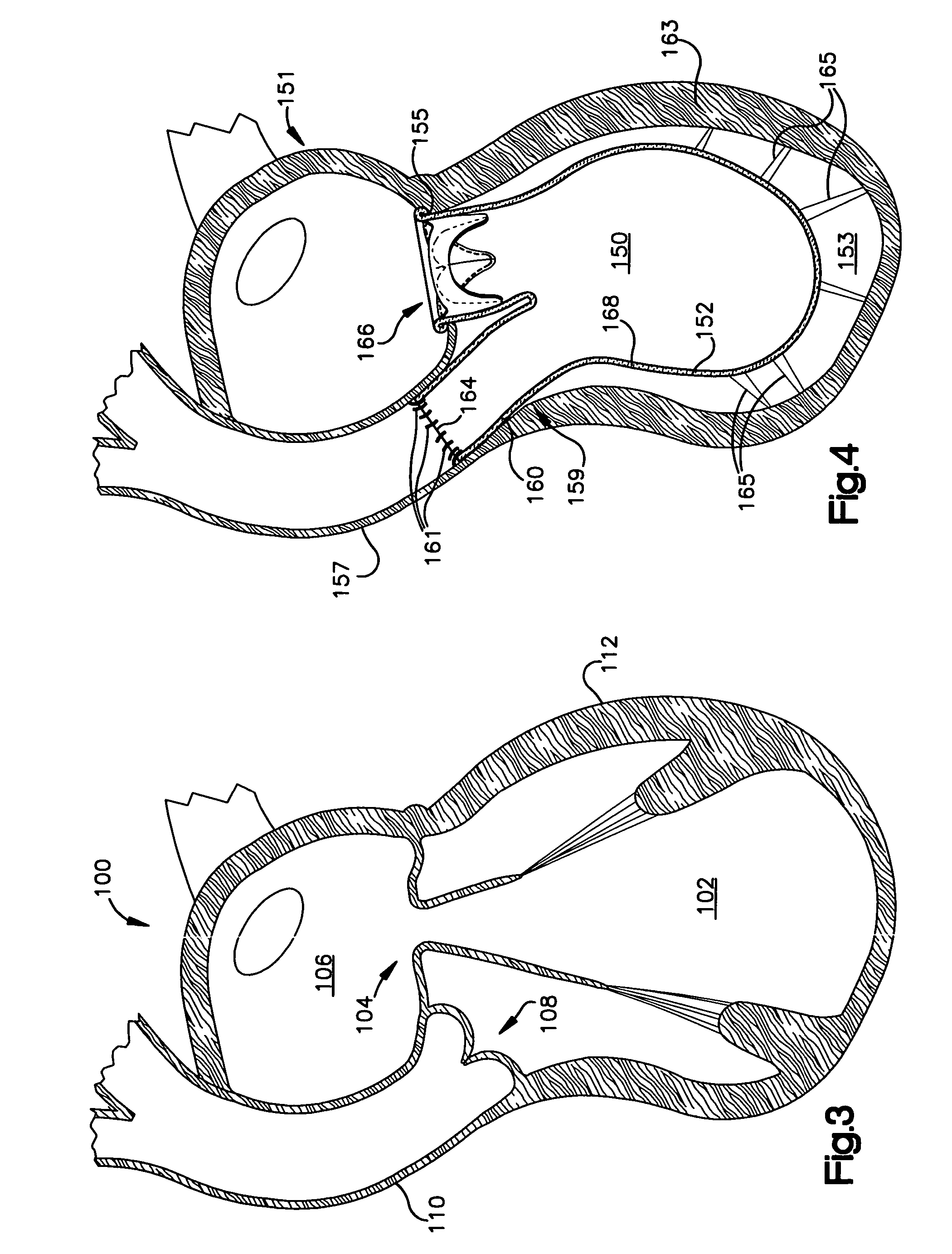
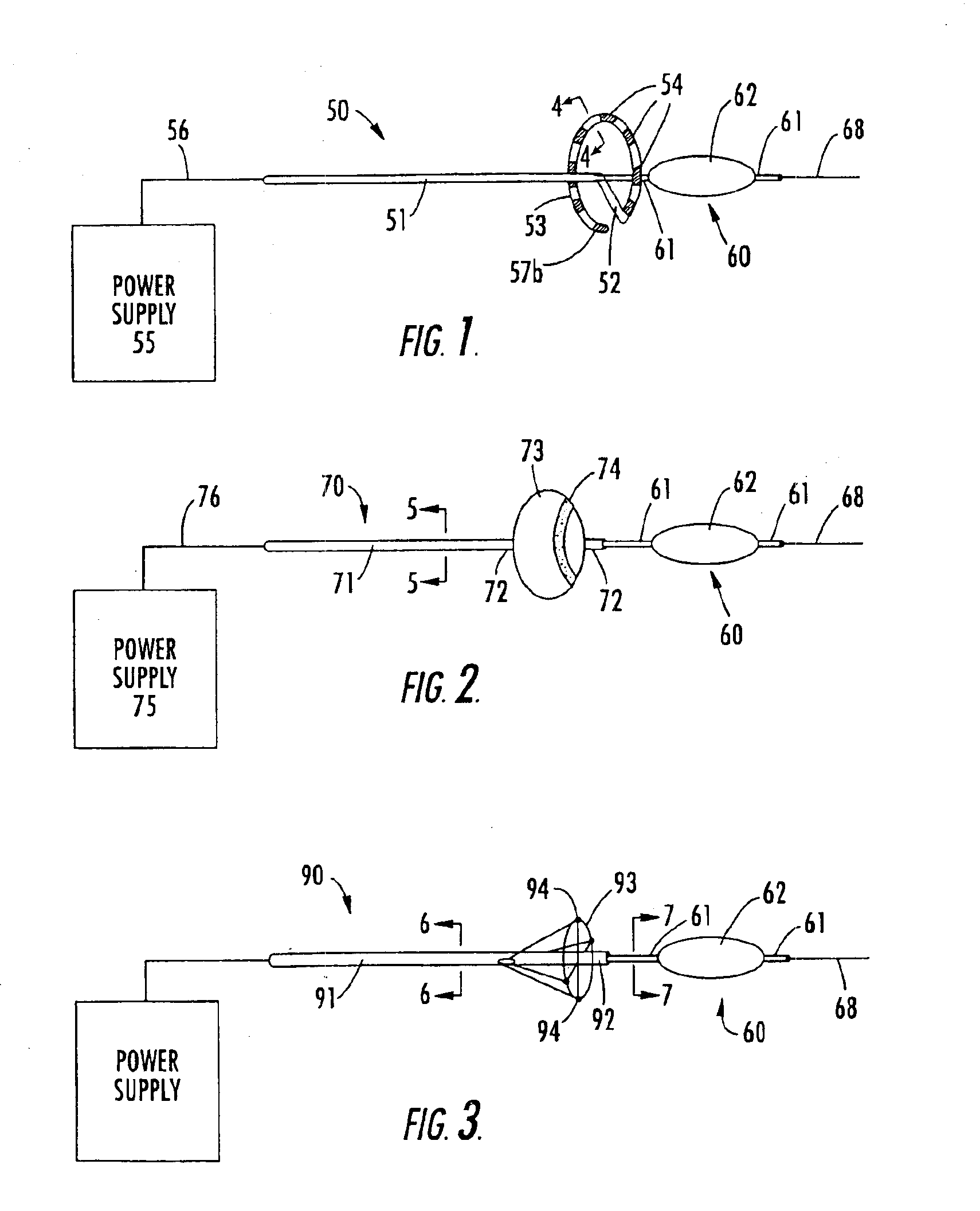
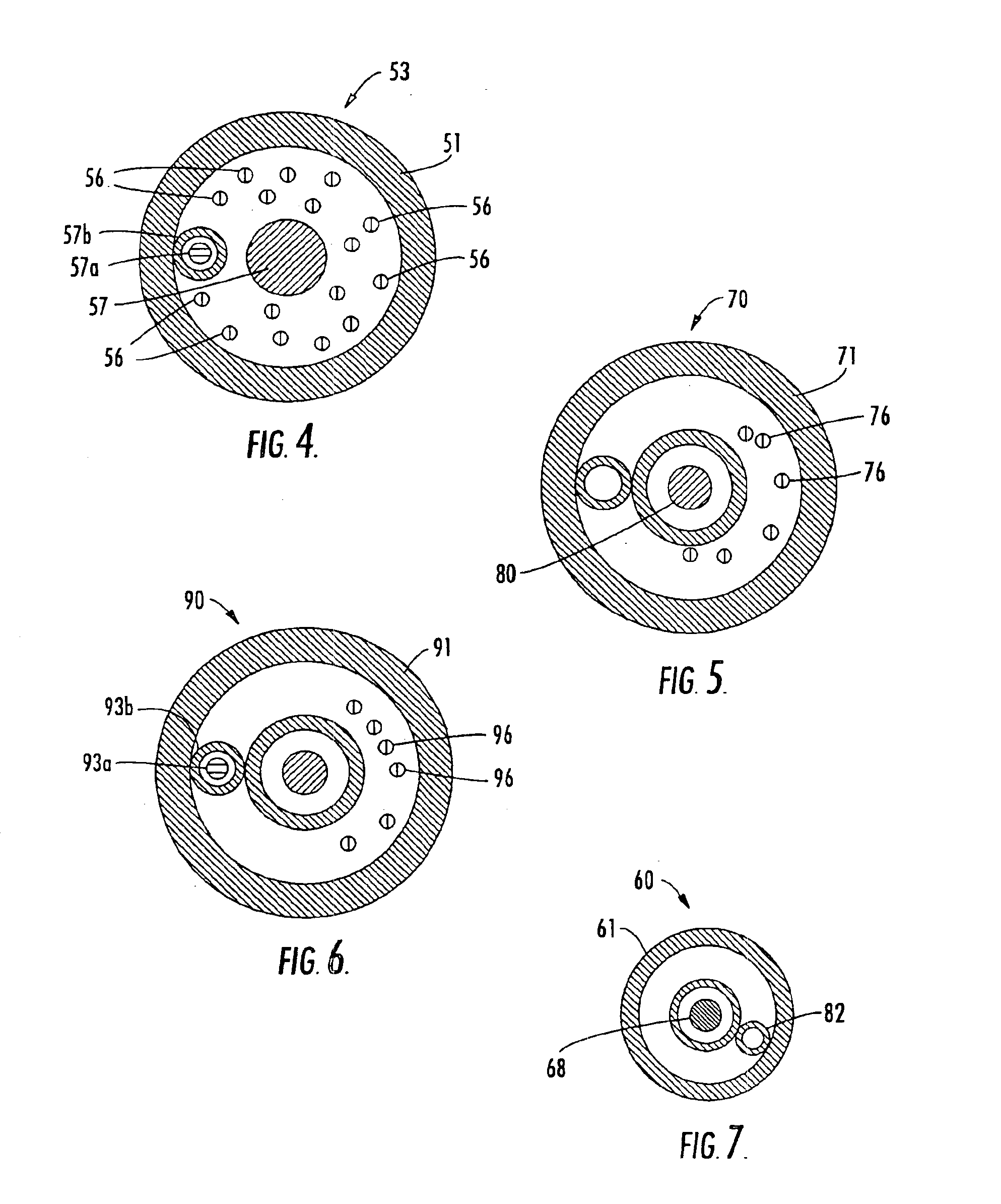
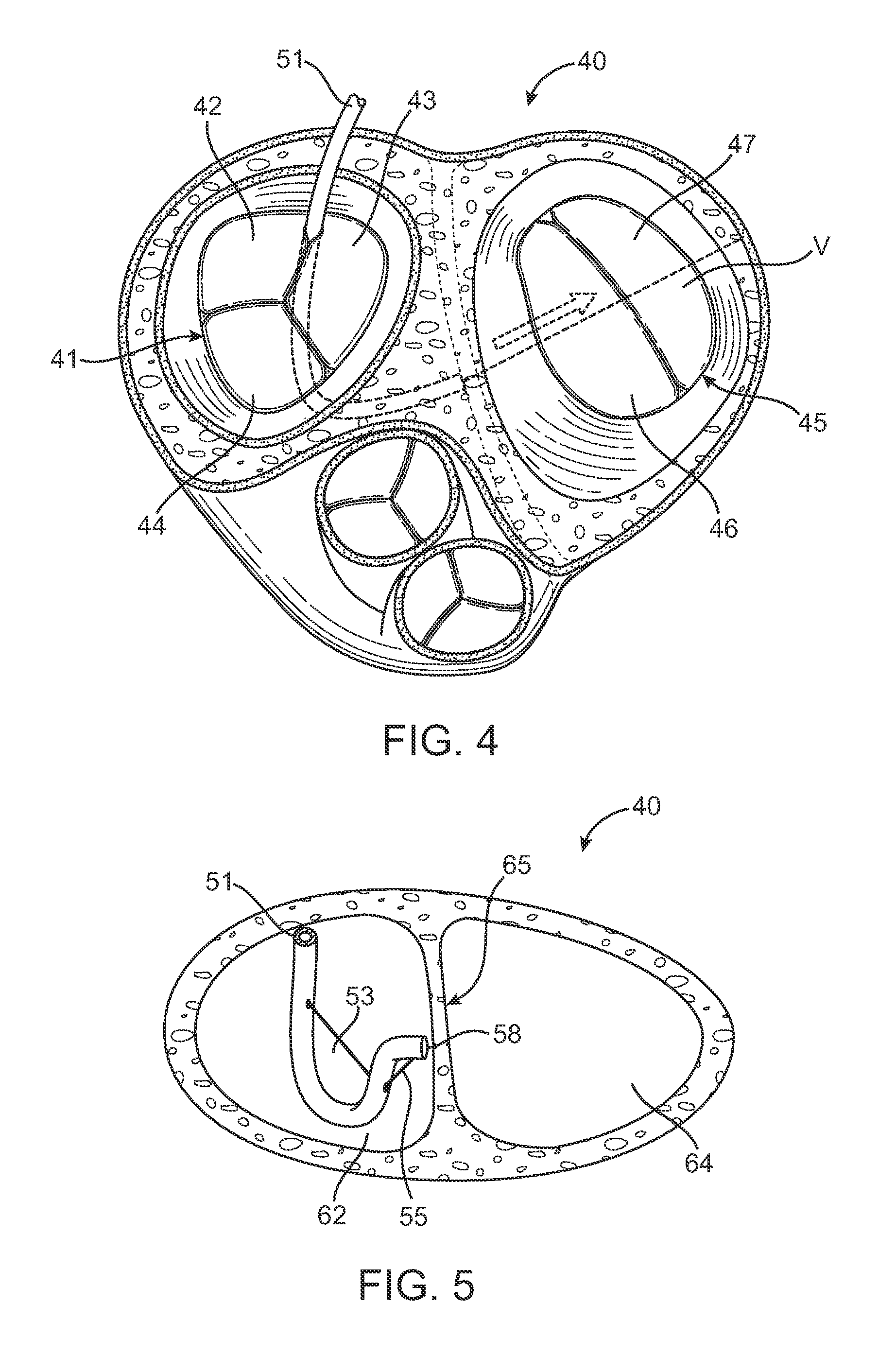
Methods and apparatus for cardiac valve repair
InactiveUS6629534B1Reduce leakageReduce regurgitationSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesHeart chamberPapillary muscle
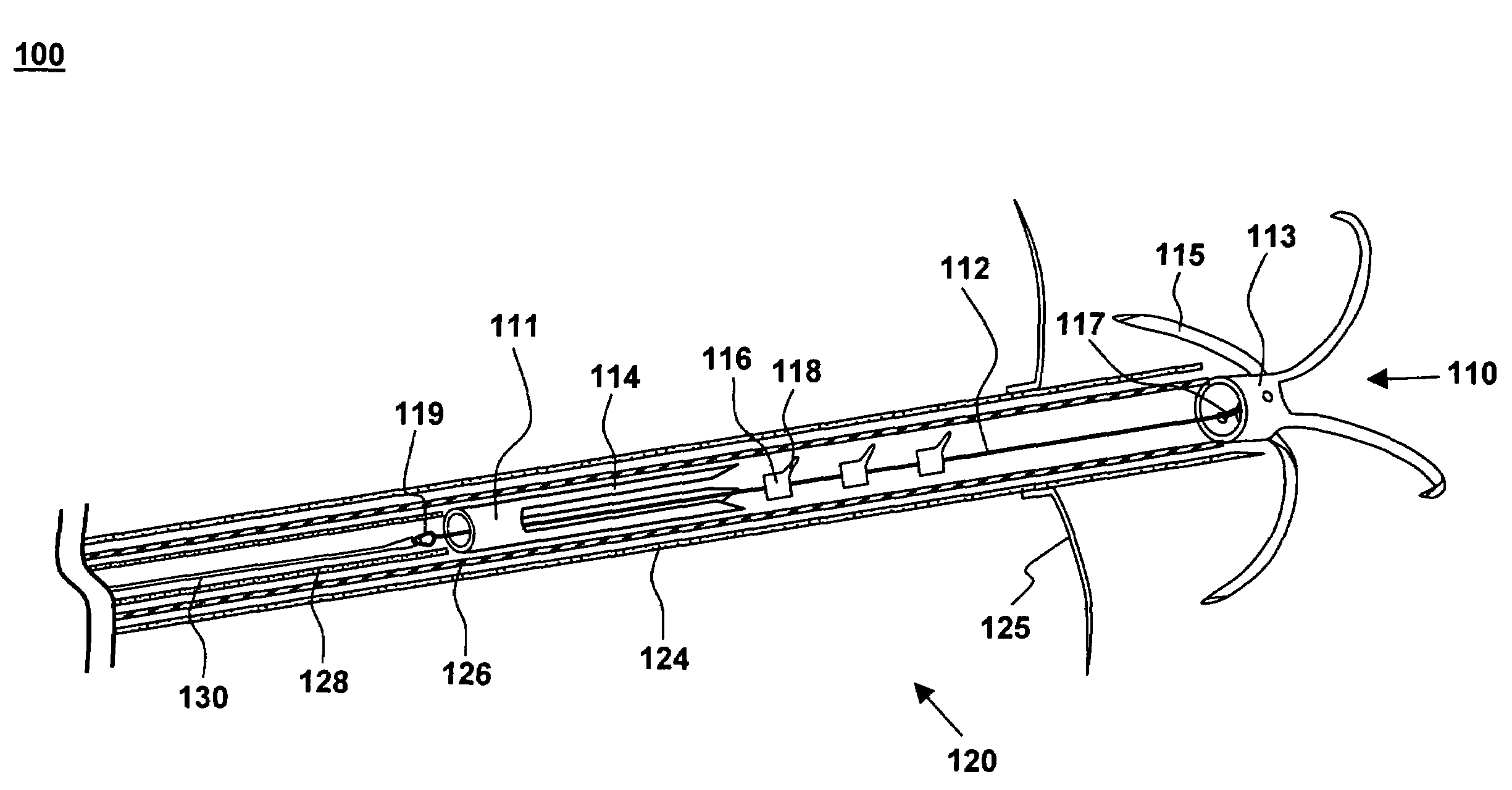
The methods, devices, and systems are provided for performing endovascular repair of atrioventricular and other cardiac valves in the heart. Regurgitation of an atrioventricular valve, particularly a mitral valve, can be repaired by modifying a tissue structure selected from the valve leaflets, the valve annulus, the valve chordae, and the papillary muscles. These structures may be modified by suturing, stapling, snaring, or shortening, using interventional tools which are introduced to a heart chamber. Preferably, the tissue structures will be temporarily modified prior to permanent modification. For example, opposed valve leaflets may be temporarily grasped and held into position prior to permanent attachment.
Owner:EVALVE
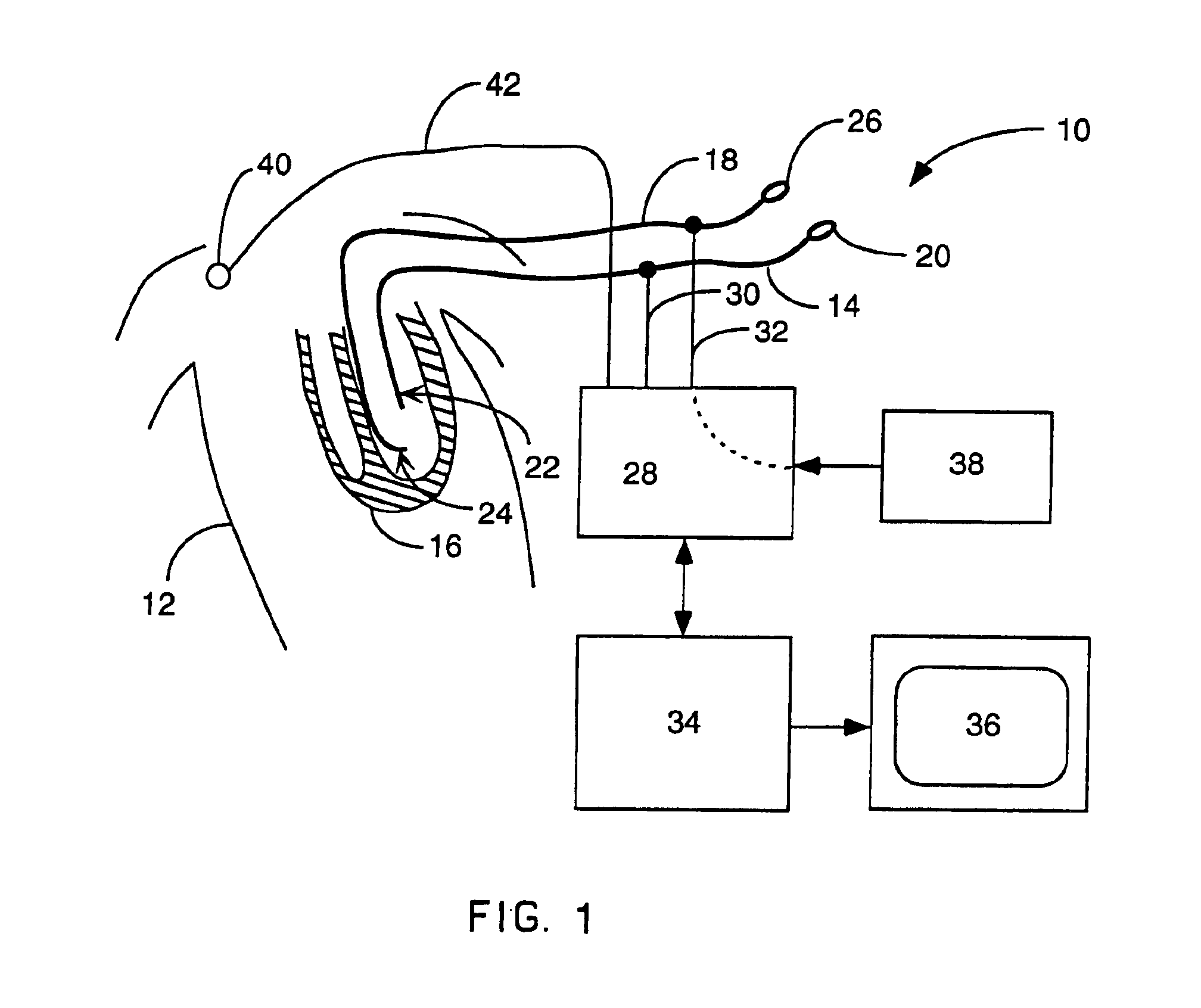
Method and apparatus for catheter navigation and location and mapping in the heart
InactiveUS7263397B2Enhance system functionsAccurate locationElectrocardiographyCatheterHeart chamberBiological activation
A medical system for finding and displaying the location of electrodes within the body. The electrodes may be used to measure the voltage on the heart wall and display this as an activation map on a geometry representing the heart chamber.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Implantable monitor
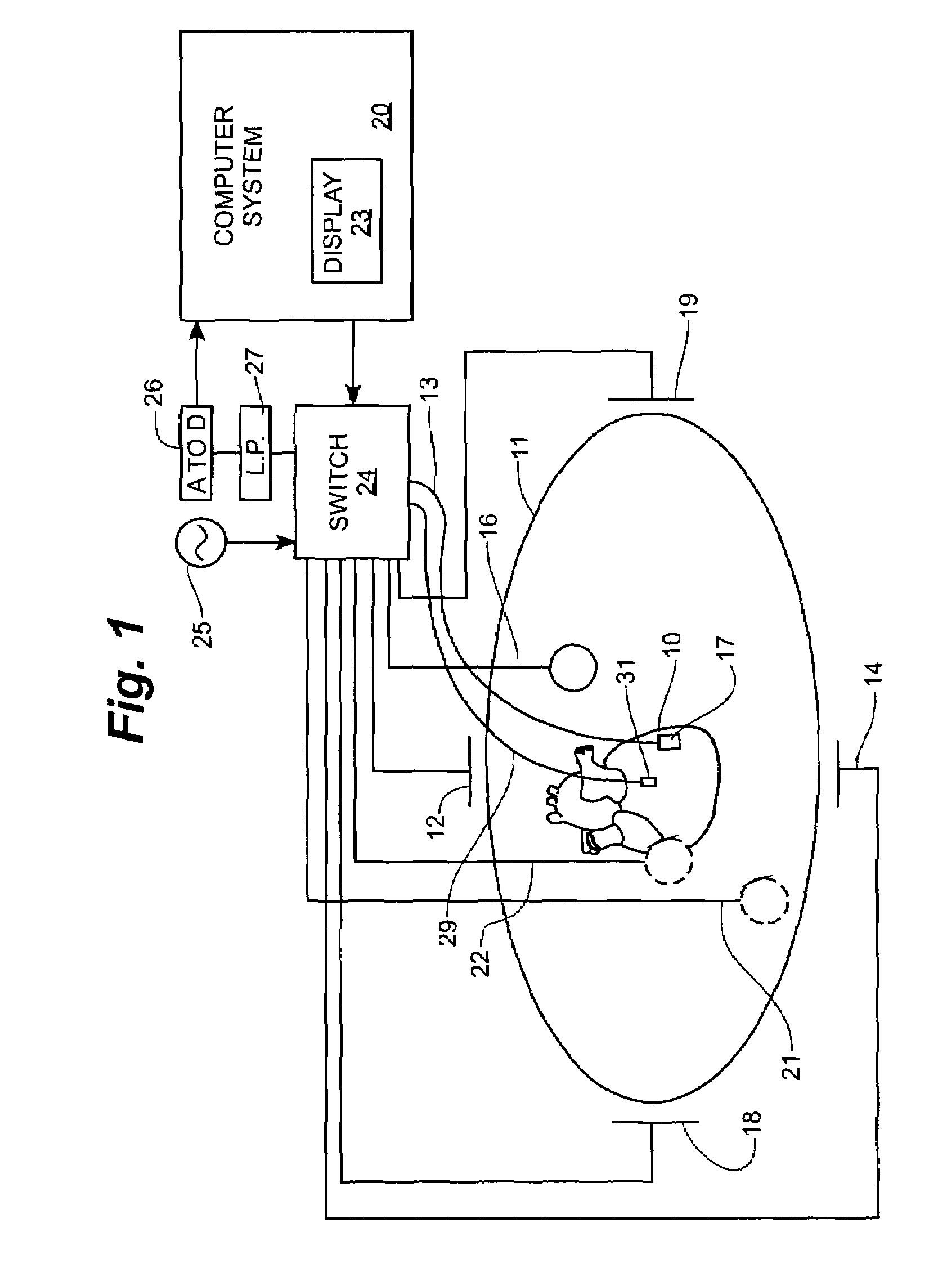
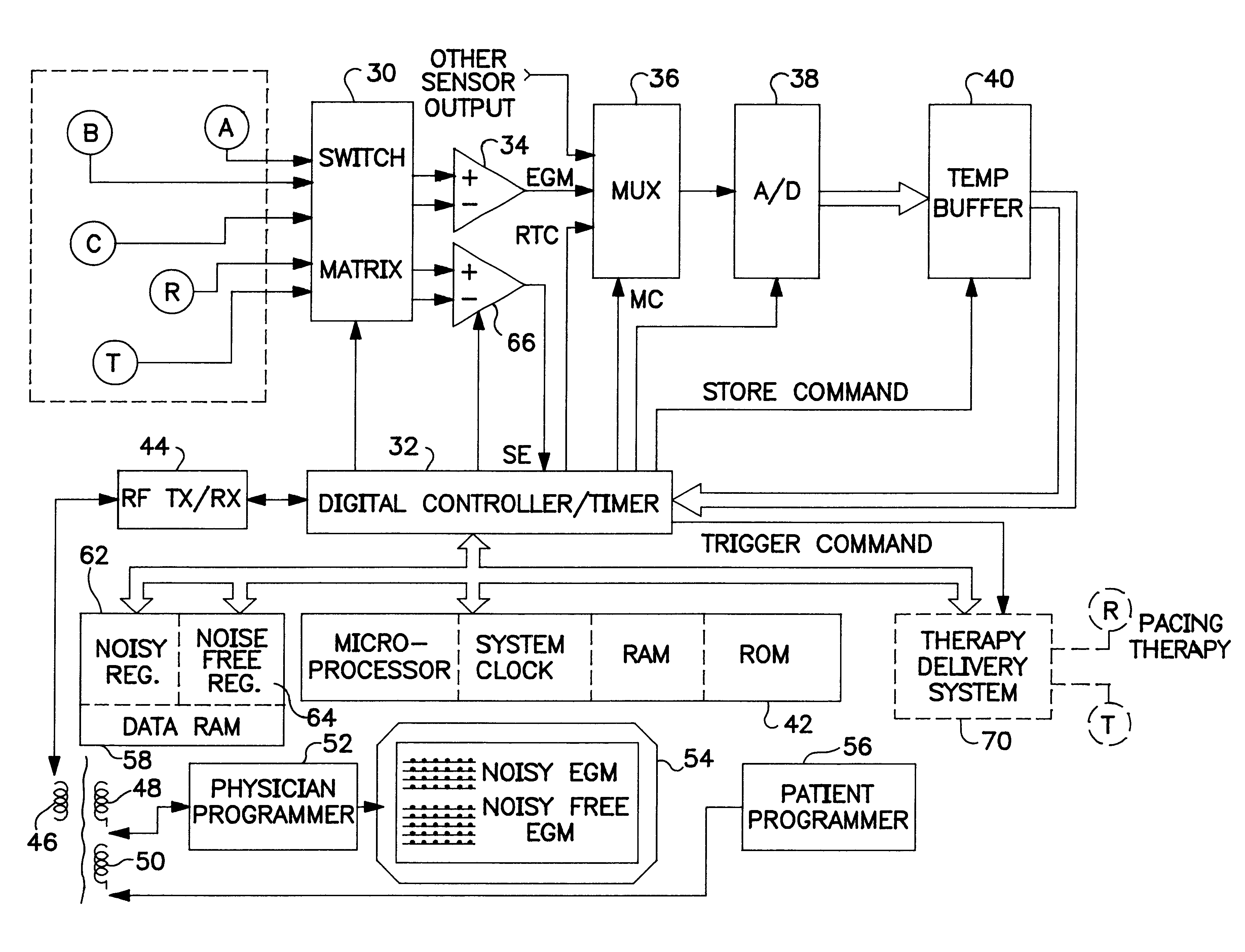
An implantable medical device (IMD) capable of monitoring physiologic data, distinguishing relatively noisy and noise free physiologic data, and recording noisy and relatively noise free segments of physiologic data in separate memory registers of a limited memory for retrieval and analysis at a later time. Preferably the physiologic data comprises the sampled EGM of the heart detected from sense electrode pairs that are implanted in the patient at sites where extraneous electrical noise, e.g., electromyographic signals, are also capable of being detected. The sense electrode pairs can constitute one or both sense electrodes located on or adjacent to the atrial and / or ventricular heart chambers and coupled to the IMD by a lead body or sense electrode pairs that are located remotely from the heart, e.g. at a subcutaneous implantation site of the IMD. A plurality of noisy EGM episode data registers store a corresponding plurality of noisy EGM episode data sets on a FIFO basis and another plurality of noise free EGM episode data registers to store a corresponding plurality of relatively noise free EGM episode data sets on a FIFO basis. Any form of discrimination of noisy data from relatively noise free data can be employed at the time of recording, but because the stored EGM episode data sets are subsequently viewed and analyzed by a physician, discrimination with absolute certainty is not required, and the physician can alter the detection criteria to fine tune it.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Implantable wireless sensor for pressure measurement within the heart
InactiveUS6855115B2Measure the pressure easily, safely, inexpensively and accuratelyElectrotherapyPerson identificationLine sensorHeart chamber
The progress of a endovascular cardiac repair can be monitored by inserting a pressure transducer sensor using a catheter into a chamber of the heart during endovascular repair and then using a small, hand-held read out device to measure pressure easily, safely, inexpensively and accurately. In one aspect a sensor is introduced into the body by the steps of folding or rolling the sensor into a cylinder, loading it into a catheter, and deploying into the heart chamber by allowing it to unroll or unfold, either by itself or facilitated by the incorporation of a super-elastic alloy component.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG II S A R L SJM LUX II
Methods and apparatus for cardiac valve repair
ActiveUS20040030382A1Reduce leakageReduce regurgitationSuture equipmentsBone implantHeart chamberPapillary muscle
The methods, devices, and systems are provided for performing endovascular repair of atrioventricular and other cardiac valves in the heart. Regurgitation of an atrioventricular valve, particularly a mitral valve, can be repaired by modifying a tissue structure selected from the valve leaflets, the valve annulus, the valve chordae, and the papillary muscles. These structures may be modified by suturing, stapling, snaring, or shortening, using interventional tools which are introduced to a heart chamber. Preferably, the tissue structures will be temporarily modified prior to permanent modification. For example, opposed valve leaflets may be temporarily grasped and held into position prior to permanent attachment.
Owner:EVALVE
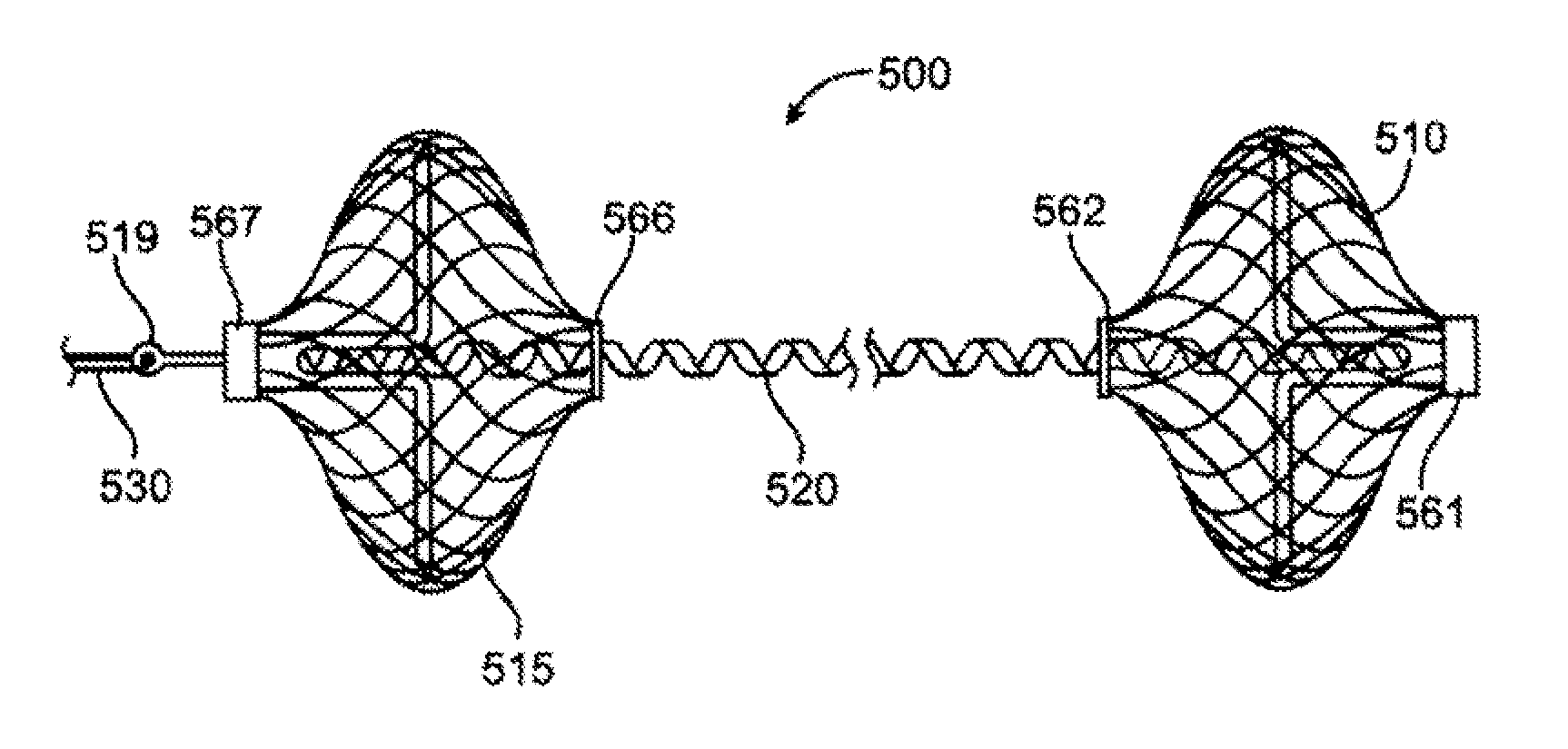
Tensioning device, system, and method for treating mitral valve regurgitation
A system for treating mitral valve regurgitation comprises a tensioning device slidably received within a delivery catheter. The tensioning device includes a tether linking proximal an anchoring member and a distal anchoring member. At least one of the anchoring members includes an elastic portion that flexes in response to a heartbeat when the tensioning device is positioned across a chamber of a heart. The tether includes at least one locking member initially positioned between the anchoring members. A method for treating mitral valve regurgitation comprises piercing a first wall of a chamber of a heart, engaging a distal anchoring member with a second wall of the heart chamber, engaging a proximal anchoring member with the first wall, and pulling a locking member affixed to a tether linking the anchoring members from an initial position between the two anchoring members to a locked position proximal the proximal anchoring member.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Suspended heart valve devices, systems, and methods for supplementing, repairing, or replacing a native heart valve
InactiveUS20050228495A1Good flexibility and compressibilityImprove foldabilityHeart valvesBlood vesselsHeart chamberBlood vessel
A valve prosthesis is sized and configured to rest within a blood path subject to antegrade and retrograde blood flow. A trestle element on the prosthesis extends across the blood path. A leaflet assembly is suspended from the trestle element and extends into the blood path in alignment with blood flow. At least one mobile leaflet member on the leaflet assembly is sized and configured to assume orientations that change according to blood flow direction. The mobile leaflet member has a first orientation that permits antegrade blood flow and a second orientation that resists retrograde blood flow. The valve prosthesis, when implanted in a heart chamber or great vessel, serves to supplement and / or repair and / or replace native one-way heart valve function.
Owner:AM DISCOVERY
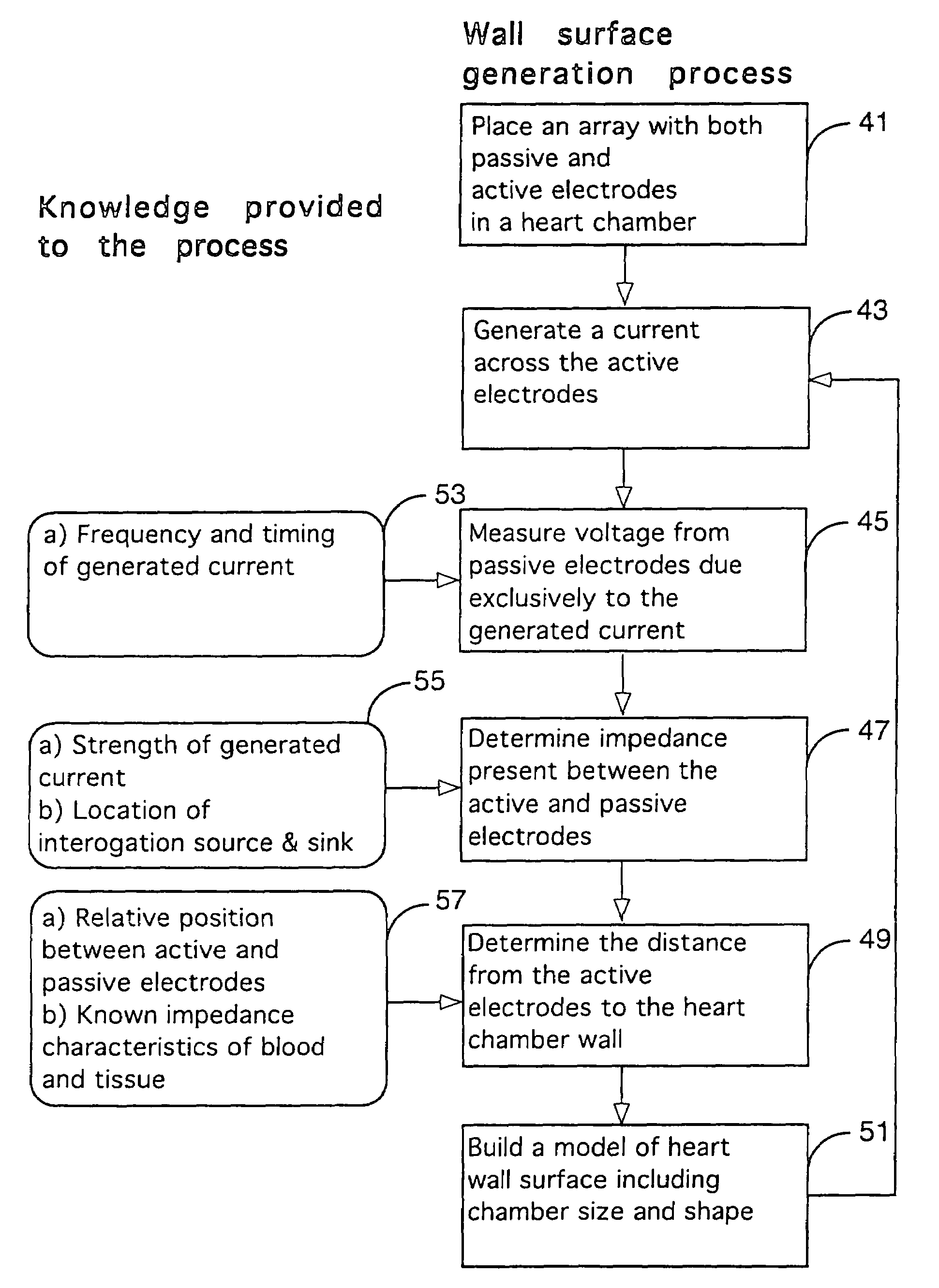
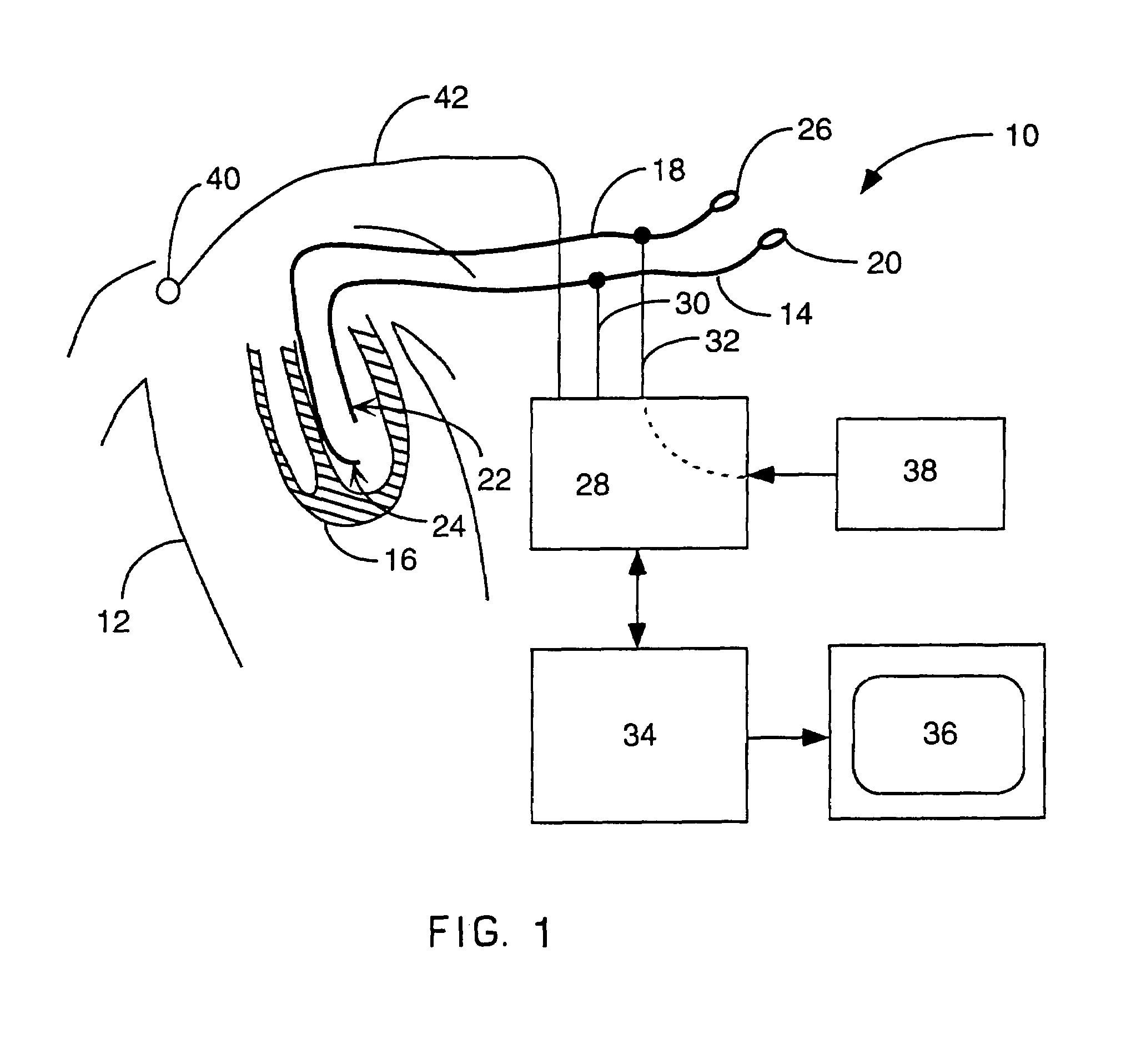
Method for mapping heart electrophysiology
A mapping catheter is positioned in a heart chamber, and active electrode sites are activated to impose an electric field within the chamber. The blood volume and wall motion modulates the electric field, which is detected by passive electrode sites on the preferred catheter. Electrophysiology measurements, as well as geometry measurements, are taken from the passive electrodes and used to display a map of intrinsic heart activity.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Device and method for improving heart valve function
ActiveUS20070270943A1Function increaseInhibit refluxSuture equipmentsHeart valvesCardiac wallHeart chamber
The invention is device and method for reducing regurgitation through a mitral valve. The device and method is directed to an anchor portion for engagement with the heart wall and an expandable valve portion configured for deployment between the mitral valve leaflets. The valve portion is expandable for preventing regurgitation through the mitral valve while allowing blood to circulate through the heart. The expandable valve portion may include apertures for reducing the stagnation of blood. In a preferred configuration, the device is configured to be delivered in two-stages wherein an anchor portion is first delivered and the valve structure is then coupled to the anchor portion. In yet another embodiment, the present invention provides a method of forming an anchor portion wherein a disposable jig is used to mold the anchor portion into a three-dimensional shape for conforming to a heart chamber.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP +1
Device for treating mitral valve regurgitation
InactiveUS20070066863A1Reduce lateral distanceReduce fatigueSuture equipmentsHeart valvesHeart chamberTonicity
A system for treating mitral valve regurgitation comprises tensioning device that can be deployed using a delivery catheter. The device includes tension member linking a proximal anchor and distal anchor. The device is constructed from a material having suitable elastic properties such that the device applies a constant tension force between the anchors, while stretching or flexing in response to a heartbeat when positioned across a chamber of a heart. The anchors may include a plurality of arms. In some embodiments, the arms may also flex in response to a heart beat. When positioned across the left ventricle of a heart, the device can reduce the lateral distance between the walls of the ventricle and thus allow better coaption of the mitral valve leaflets thereby reducing mitral regurgitation.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
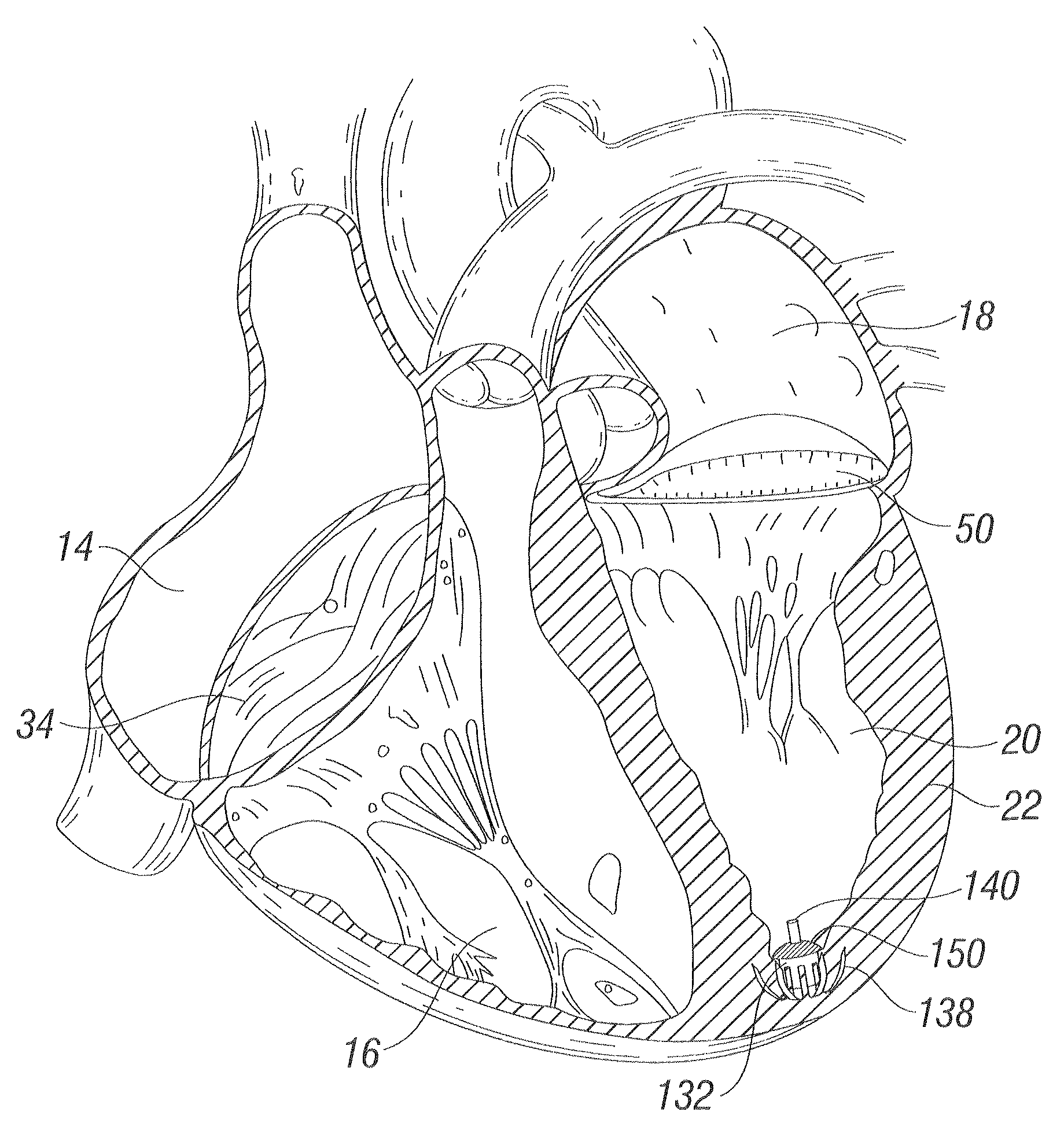
Leadless Cardiac Pacemaker with Secondary Fixation Capability
The invention relates to leadless cardiac pacemakers (LBS), and elements and methods by which they affix to the heart. The invention relates particularly to a secondary fixation of leadless pacemakers which also include a primary fixation. Secondary fixation elements for LBS's may either actively engage an attachment site, or more passively engage structures within a heart chamber. Active secondary fixation elements include a tether extending from the LBS to an anchor at another site. Such sites may be either intracardial or extracardial, as on a vein through which the LBS was conveyed to the heart, the internal or external surface thereof. Passive secondary fixation elements entangle within intraventricular structure such as trabeculae carneae, thereby contributing to fixation of the LBS at the implant site.
Owner:NANOSTIM
Anchoring and tethering system
InactiveUS20070265658A1Maximize cardiac performanceAccurate shapeSuture equipmentsHeart valvesHeart chamberEngineering
A method and apparatus for providing safe and efficient transcatheter correction of the shape of heart chambers, valves, or other body members. The apparatus generally performs this correction by securing a tether to body surfaces. The attachment device includes an anchor comprising a wire braid and at least one clamp affixed to and constraining a portion of the wire braid, the clamp having threading for temporarily coupling the anchor to a delivery member and an internal lumen through which the tether can pass. The device also includes a locking member cooperating with the lumen to lock the tether to the clamp at a preselected position along the length of the tether.
Owner:AGA MEDICAL CORP MS US
Methods and devices for improving mitral valve function
InactiveUS20050075723A1Less riskMinimally invasiveSuture equipmentsHeart valvesMitral valve functionCardiac wall
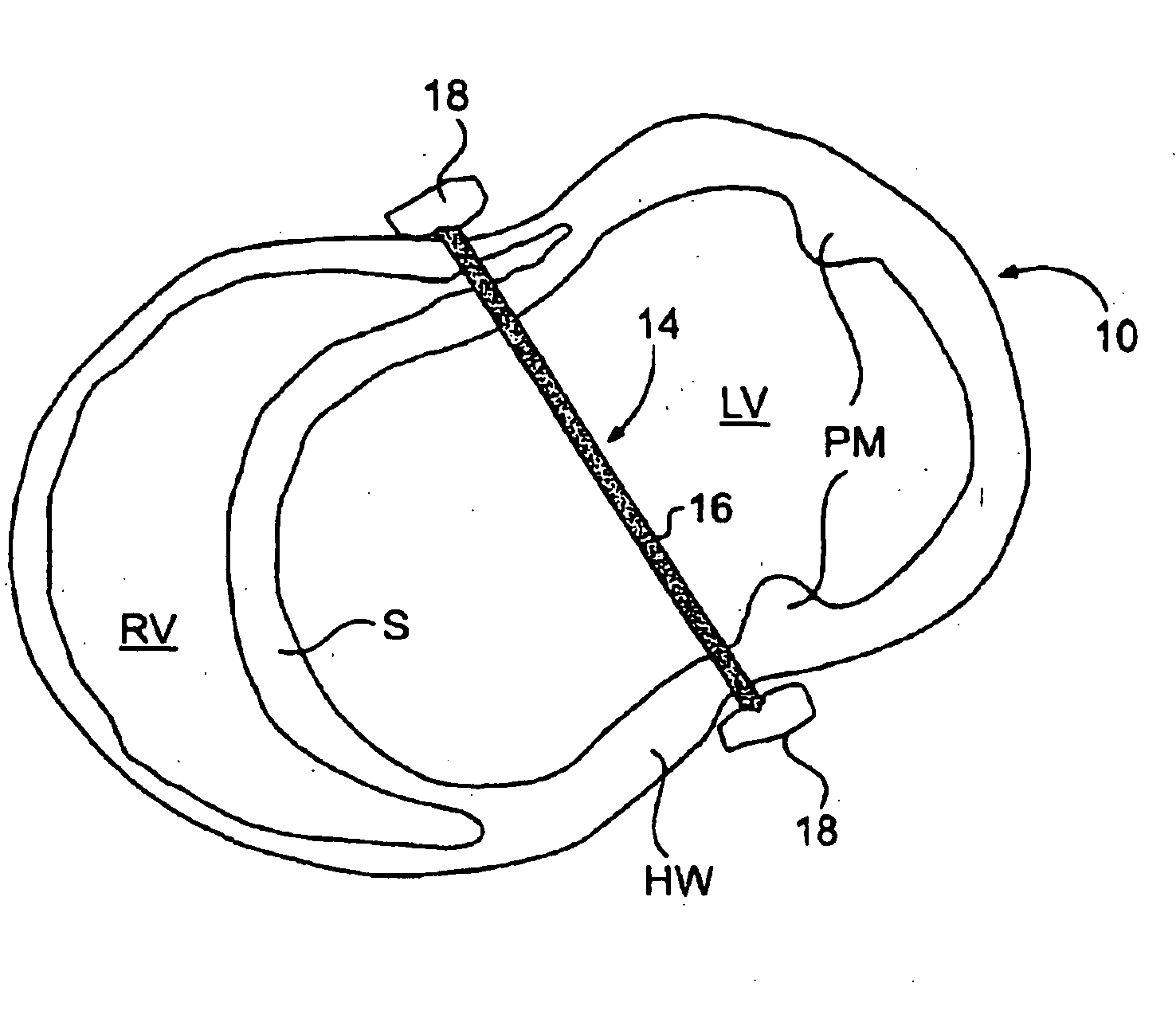
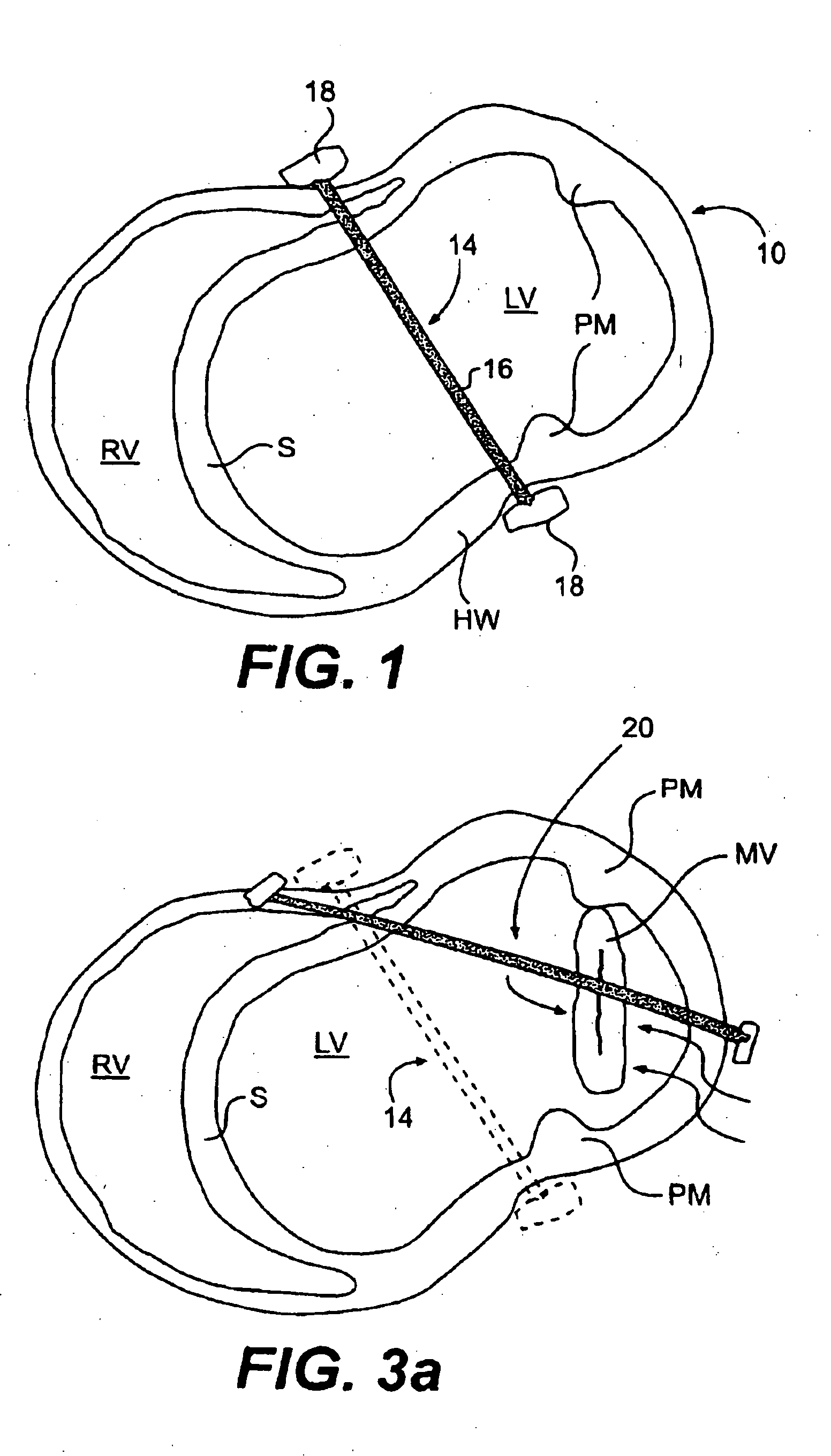
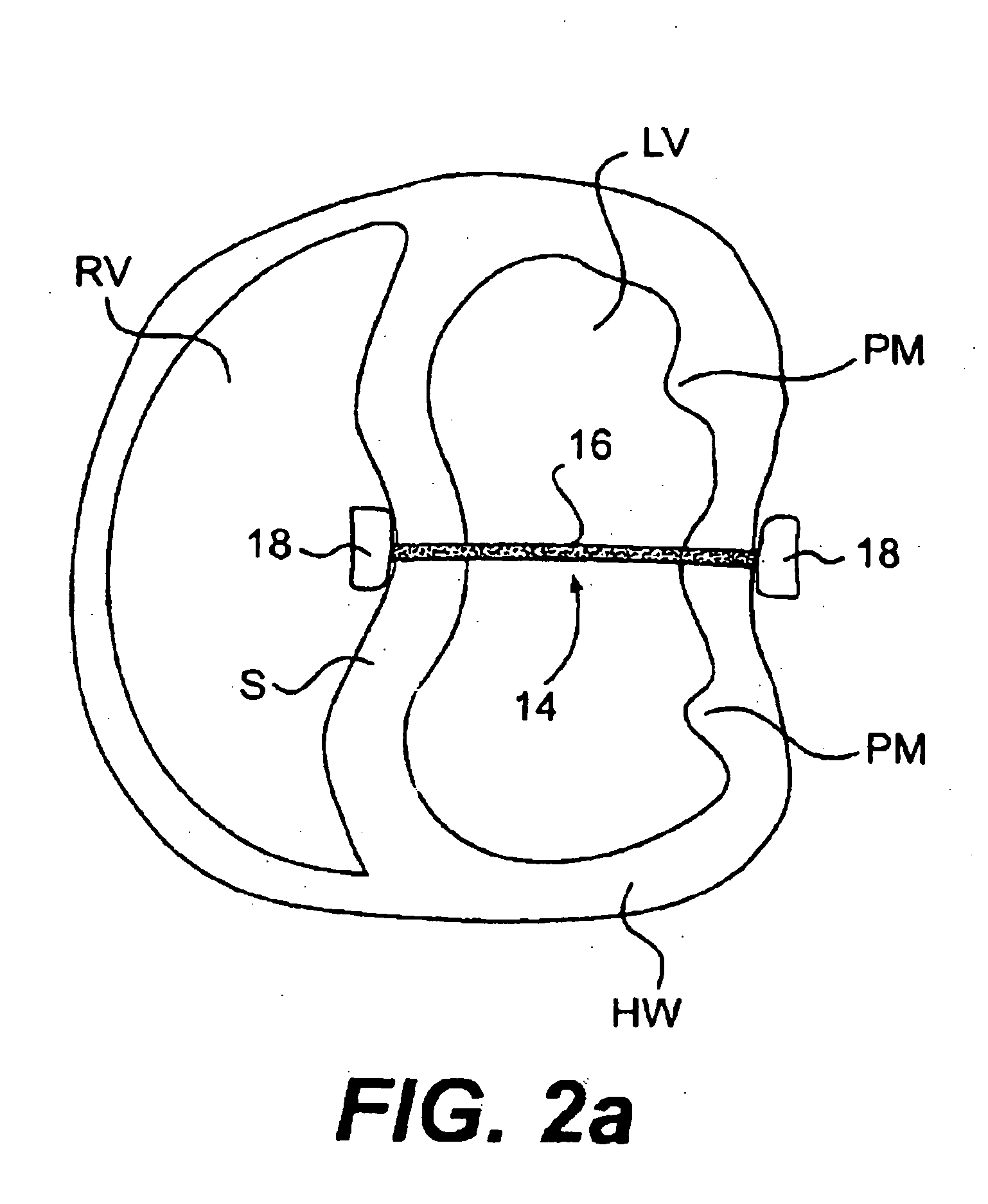
The various aspects of the invention pertain to devices and related methods for treating heart conditions, including, for example, dilatation, valve incompetencies, including mitral valve leakage, and other similar heart failure conditions. The devices and related methods of the present invention operate to assist in the apposition of heart valve leaflets to improve valve function. According to one aspect of the invention, a method improves the function of a valve of a heart by placing an elongate member transverse a heart chamber so that each end of the elongate member extends through a wall of the heart, and placing first and second anchoring members external the chamber. The first and second anchoring members are attached to first and second ends of the elongate member to fix the elongate member in a position across the chamber so as to reposition papillary muscles within the chamber. Also described herein is a method for placing a splint assembly transverse a heart chamber by advancing an elongate member through vasculature structure and into the heart chamber.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
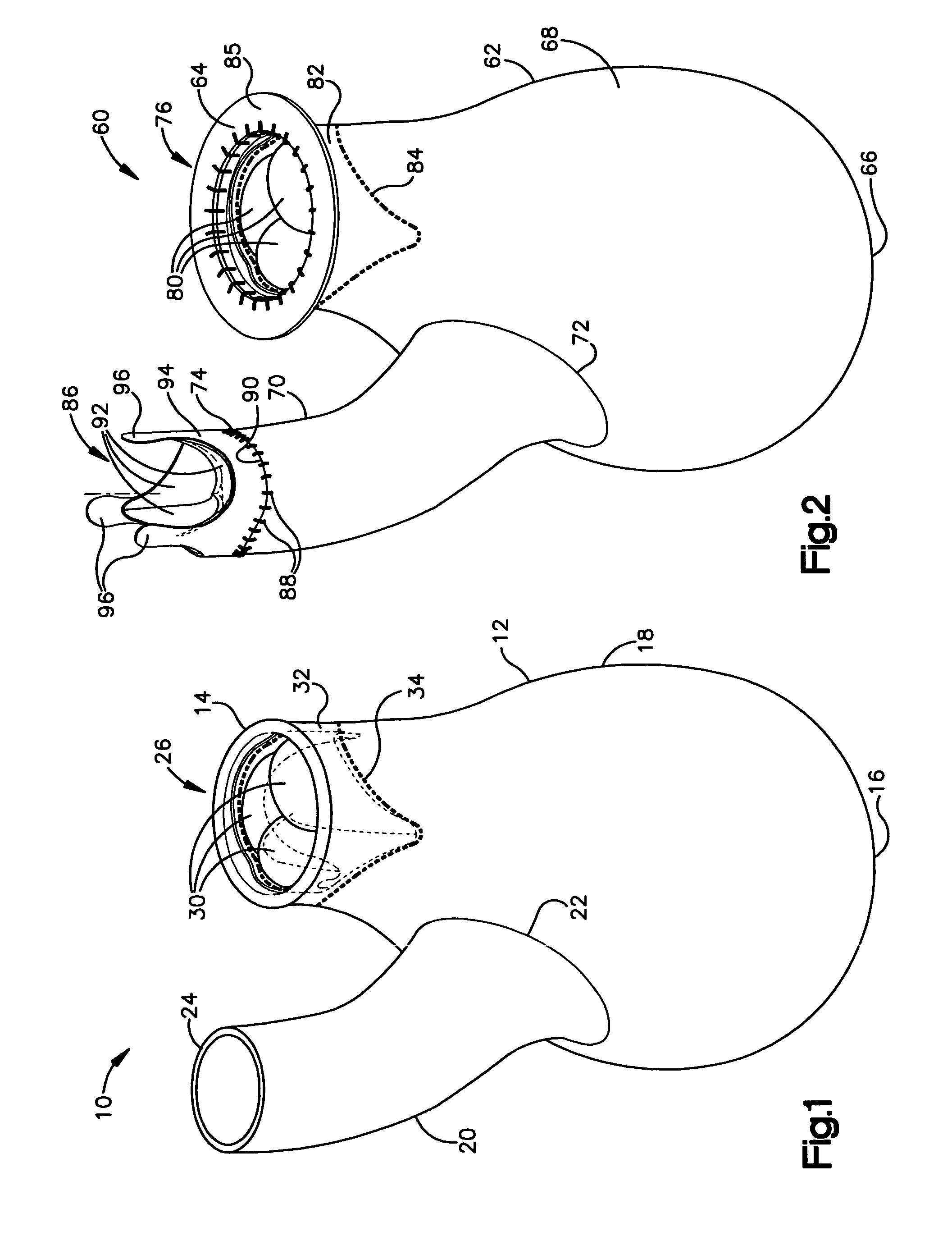
Apparatuses and methods for performing minimally invasive diagnostic and surgical procedures inside of a beating heart
InactiveUS6840246B2Reduce needRisk minimizationSuture equipmentsStapling toolsFluid transportHeart chamber
Diagnostic and surgical procedures may be performed on a beating heart using an assembly which includes a port and a fluid transport device. The port has a housing for insertion through a wall of the heart chamber and may include one valve disposed in the housing and an inlet connected to the housing. Methods for repair and diagnosis of the heart are also described. A specific method for repairing a mitral valve uses staples which may be banded together with a strip of material.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Conduit with valved blood vessel graft
Disclosed is a conduit that provides a bypass around an occlusion or stenosis in a coronary artery. The conduit is a tube adapted to be positioned in the heart wall to provide a passage for blood to flow between a heart chamber and a coronary artery, at a site distal to the occlusion or stenosis. The conduit has a section of blood vessel attached to its interior lumen which preferably includes at least one naturally occurring one-way valve positioned therein. The valve prevents the backflow of blood from the coronary artery into the heart chamber.
Owner:HORIZON TECH FUNDING CO LLC +1
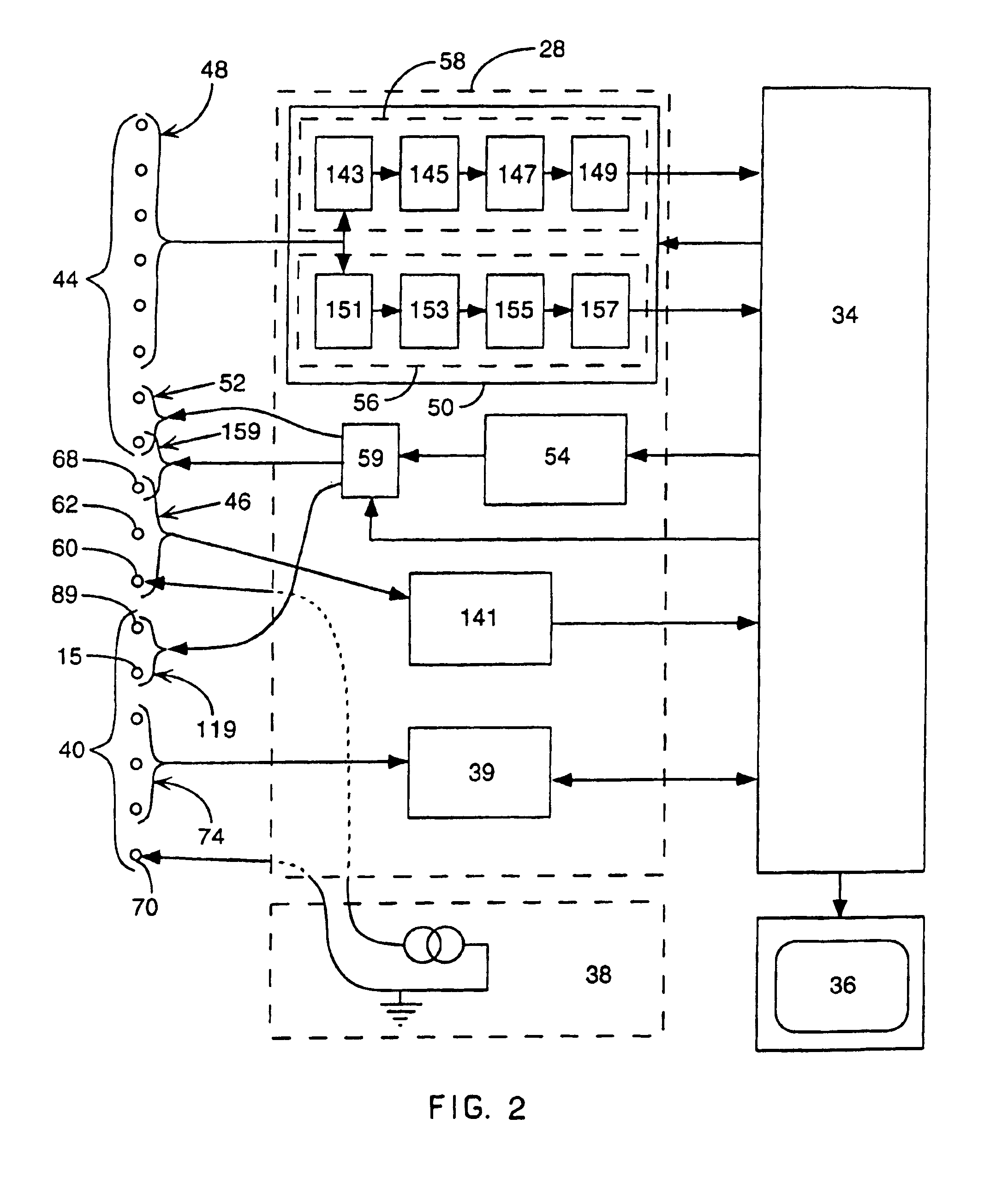
Interface system for endocardial mapping catheter
A mapping catheter is positioned in a heart chamber, and active electrode sites are activated to impose an electric field within the chamber. The blood volume and wall motion modulates the electric field, which is detected by passive electrode sites on the preferred catheter. Electrophysiology measurements, as well as geometry measurements, are taken from the passive electrodes and used to display a map of intrinsic heart activity.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Method for measuring heart electrophysiology
A mapping catheter is positioned in a heart chamber, and active electrode sites are activated to impose an electric field within the chamber. The blood volume and wall motion modulates the electric field, which is detected by passive electrode sites on the preferred catheter. Electrophysiology measurements, as well as geometry measurements, are taken from the passive electrodes and used to display a map of intrinsic heart activity.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
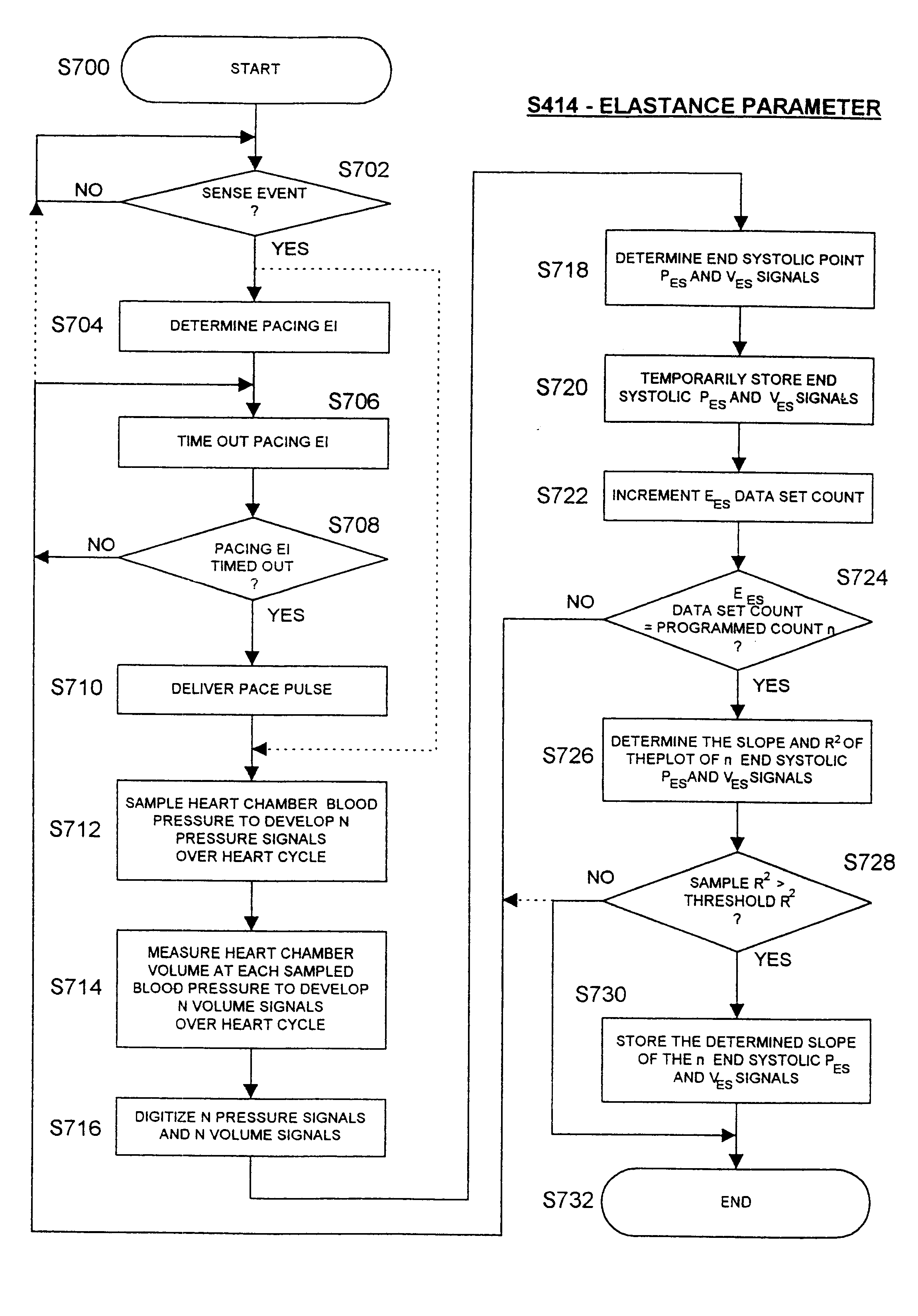
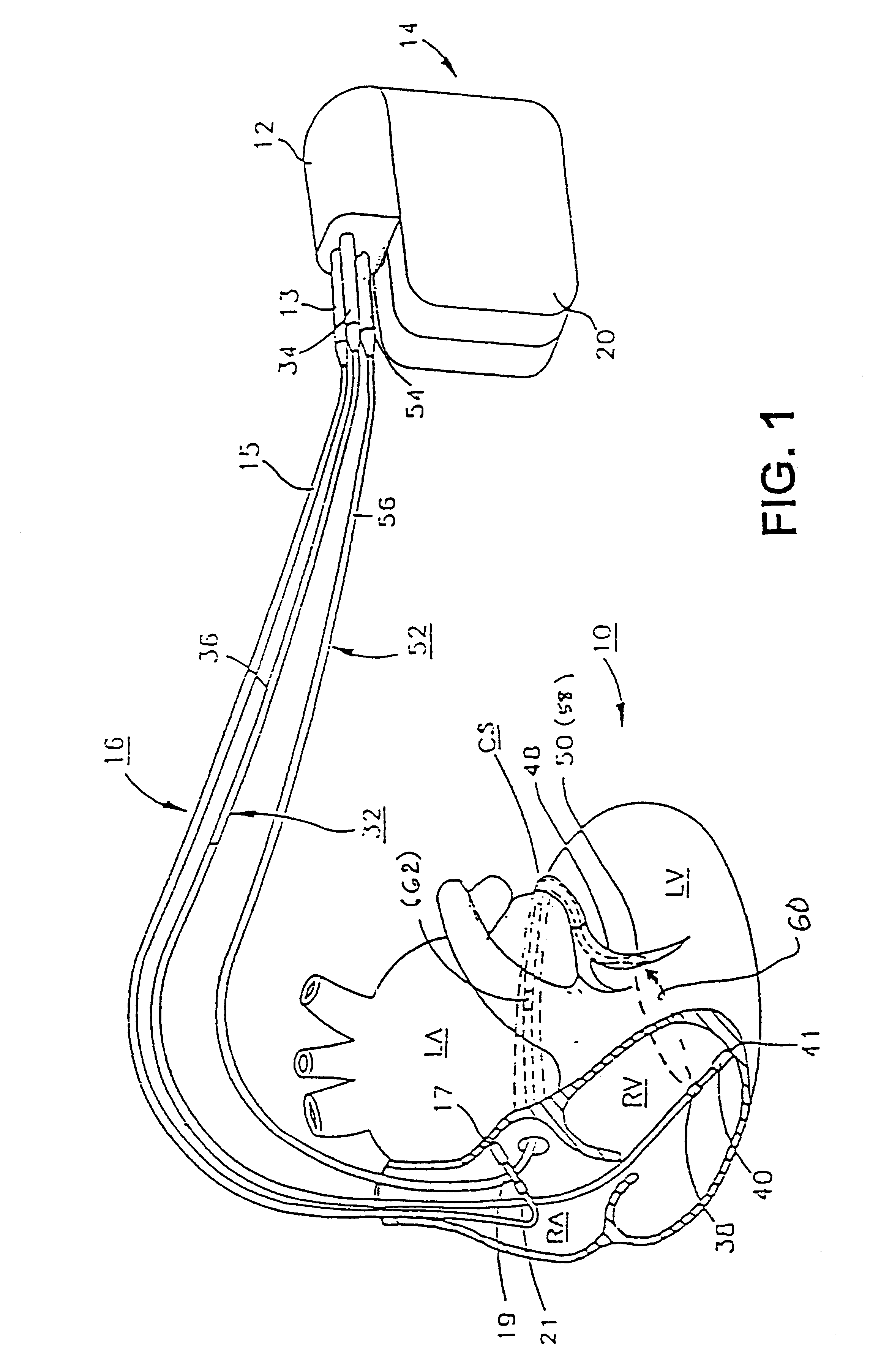
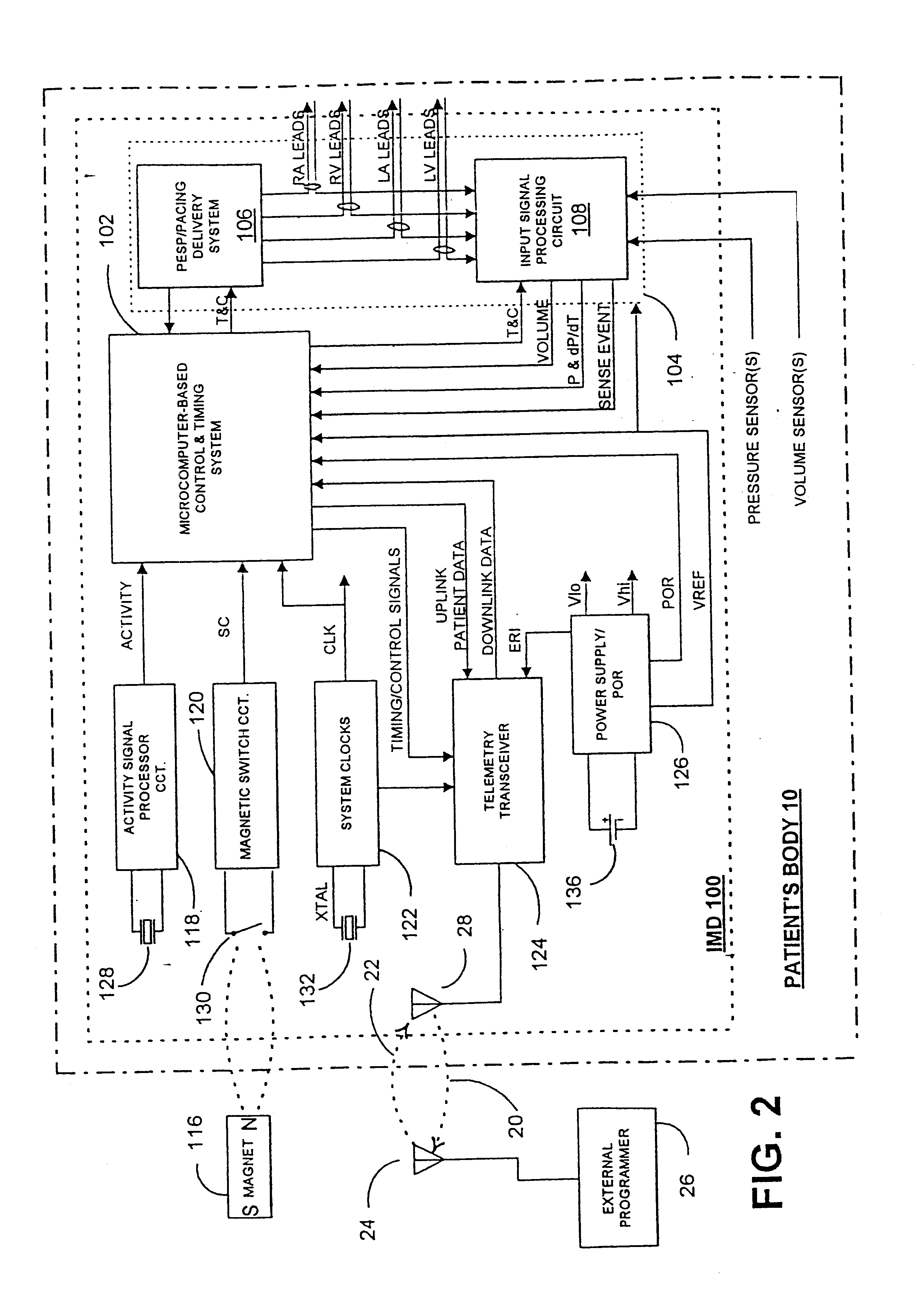
Implantable medical device for treating cardiac mechanical dysfunction by electrical stimulation
InactiveUS6738667B2Increase contractilityEasy to relaxCatheterHeart stimulatorsCardiac cycleHeart chamber
An implantable stimulator and monitor measures a group of heart failure parameters indicative of the state of heart failure employing EGM signals, measures of blood pressure including absolute pressure P, developed pressure (DP=systolic P-diastolic P), and / or dP / dt, and measures of heart chamber volume (V) over one or more cardiac cycles. These parameters include: (1) relaxation or contraction time constant tau (.tau.); (2) mechanical restitution (MR), i.e., the mechanical response of a heart chamber to premature stimuli applied to the heart chamber; (3) recirculation fraction (RF), i.e., the rate of decay of PESP effects over a series of heart cycles; and (4) end systolic elastance (E.sub.ES), i.e., the ratios of end systolic blood pressure P to volume V. These heart failure parameters are determined periodically regardless of patient posture and activity level. The physician can determine whether a particular therapy is appropriate, prescribe the therapy for a period of time while again accumulating the stored patient data for a later review and assessment to determine whether the applied therapy is beneficial or not, thereby enabling periodic changes in therapy, if appropriate. Drug therapies and electrical stimulation therapies, including PESP stimulation, and pacing therapies including single chamber, dual chamber and multi-chamber (bi-atrial and / or bi-ventricular) pacing can be delivered. In patient's prone to malignant tachyarrhythmias, the assessment of heart failure state can be taken into account in setting parameters of detection or classification of tachyarrhythmias and the therapies that are delivered.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
System and method for improving ventricular function
InactiveUS7374573B2Easy to operateControl volumeHeart valvesHeart stimulatorsHeart chamberVentricular function
An approach is disclosed for improving ventricular function of a patient's heart. According to one embodiment, the system includes a pouch that defines a chamber dimensioned and configured to simulate at least a portion of a heart chamber. The pouch has a sidewall portion extending from an inflow annulus and terminating in a closed distal end spaced apart from the inflow annulus. A generally cylindrical outflow portion extends from the sidewall portion of the pouch and terminating in an outflow annulus thereof to provide for flow of fluid from the chamber through the outflow annulus. A valve is operatively associated with the inflow annulus of the pouch to provide for substantially unidirectional flow of fluid through the inflow annulus and into the chamber.
Owner:GABBAY SHLOMO
Device and method for improving heart valve function
ActiveUS8932348B2Function increaseInhibit refluxSuture equipmentsHeart valvesHeart chamberThree dimensional shape
The invention is device and method for reducing regurgitation through a mitral valve. The device and method is directed to an anchor portion for engagement with the heart wall and an expandable valve portion configured for deployment between the mitral valve leaflets. The valve portion is expandable for preventing regurgitation through the mitral valve while allowing blood to circulate through the heart. The expandable valve portion may include apertures for reducing the stagnation of blood. In a preferred configuration, the device is configured to be delivered in two-stages wherein an anchor portion is first delivered and the valve structure is then coupled to the anchor portion. In yet another embodiment, the present invention provides a method of forming an anchor portion wherein a disposable jig is used to mold the anchor portion into a three-dimensional shape for conforming to a heart chamber.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP +1
Steerable catheter with preformed distal shape and method for use
InactiveUS6096036AReduce curvatureTransvascular endocardial electrodesSurgical instrument detailsHeart chamberCurve shape
A catheter has a stylet formed of a shape-retentive and resilient material having a preformed curved shape at its distal end resulting in the catheter sheath having the preformed curved shape. The catheter sheath has a plurality of electrodes at its distal end for contacting selected biological tissue for imparting ablation energy thereto. The catheter sheath also has an axially mounted tendon for causing deflection of the distal end. The stylet material permits straightening the catheter sheath during insertion into the patient and advancing the electrodes to the target tissue. Upon removal of the straightening forces, such as by entry into a chamber of the heart, the stylet material resumes its preformed curved distal shape thereby forcing the catheter distal end with the electrodes into the same preformed curved shape. The operator may place the curved distal end into contact with the target tissue and axially move the tendon as desired to gain greater control over the bend in the distal end of the catheter sheath to adjust the radius of curvature of the distal end to obtain greater contact of the electrodes with the heart tissue. Preferably, the stylet is formed of nitinol.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
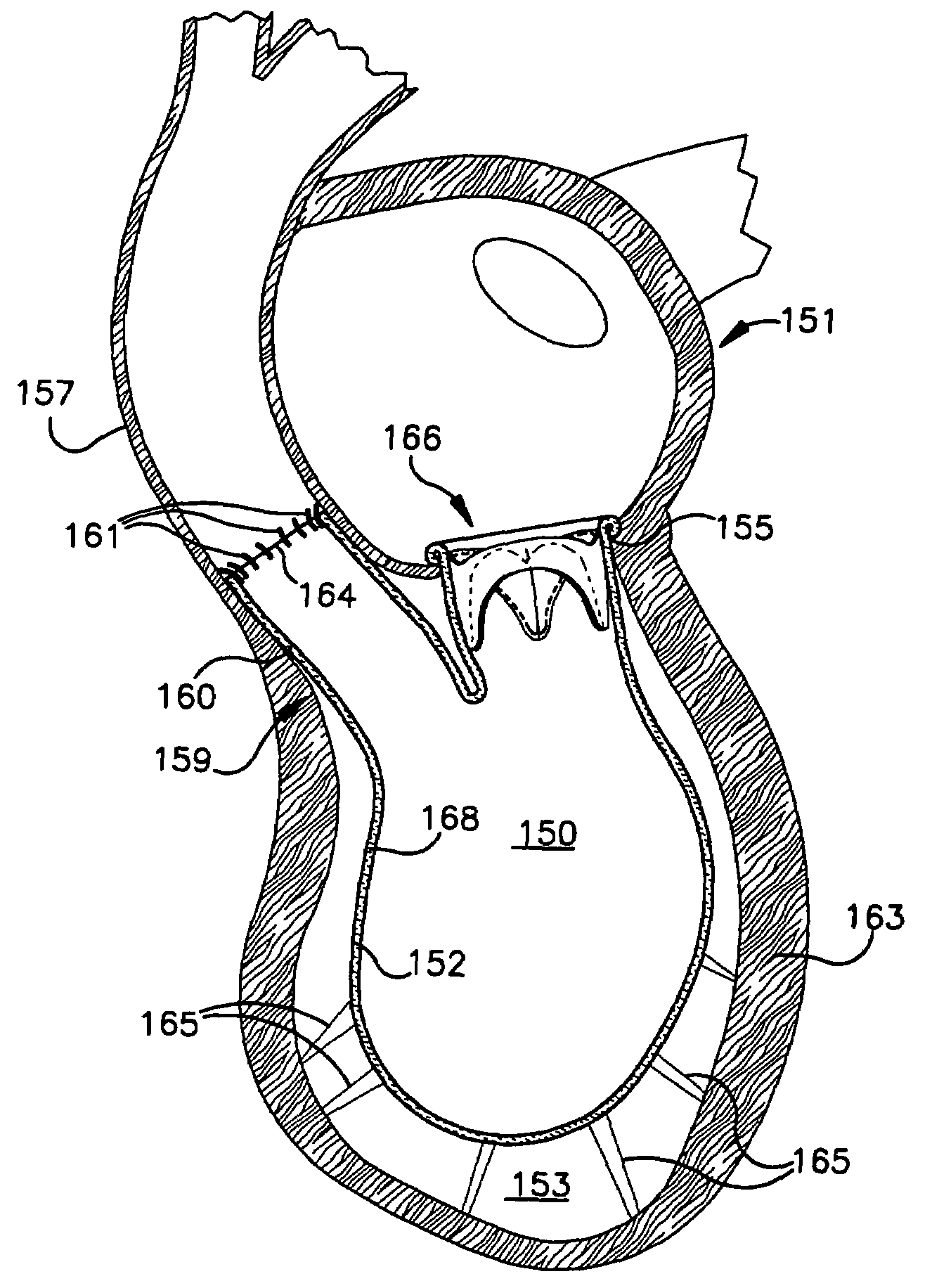
Ventricular partitioning device
ActiveUS20050154252A1Lower the volumeImprove ejection fractionHeart valvesHeart stimulatorsHeart chamberNon traumatic
This invention is directed to a partitioning device for separating a patient's heart chamber into a productive portion and a non-productive portion. The device is particularly suitable for treating patients with congestive heart failure. The partitioning device has a reinforced, expandable membrane which separates the productive and non-productive portions of the heart chamber and a support or spacing member extending between the reinforced membrane and the wall of the patient's heart chamber. The support or spacing member has a non-traumatic distal end to engage the ventricular wall.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Implantable pressure sensor and method of fabrication
A body implantable pressure sensor attached to an endocardial lead for implantation in a heart chamber or cardiac blood vessel for sensing blood pressure and providing blood pressure signals to an implanted or external hemodynamic monitor and / or therapy delivery device and method of fabrication thereof. A pressure sensor module is formed of an elongated receptacle having an elongated receptacle cavity for receiving a calibrated, micro-machined pressure transducer having a pressure responsive element. The receptacle cavity is covered by a diaphragm disposed alongside the lead body and in parallel with the lead axis. The receptacle cavity is filled with a incompressible oil for transferring pressure forces that are applied to the diaphragm to the pressure transducer. The oil is introduced through a fill port, and the fill port is sealed after the oil is introduced to prevent leakage of the oil from the receptacle cavity and to complete the hermetic sealing of the receptacle cavity. The fill port further comprises a fill tube having a fill tube lumen extending outward of an end wall of the receptacle cavity to a fill tube end, and said sealing step further comprises the steps of crimping or otherwise obstructing the fill tube end to close the fill tube lumen, fitting a fill port cover having an abutting edge over the crimped fill tube end and against the end wall of the receptacle to enclose the sealed fill tube end within a fill port cover cavity, and sealing the abutting edge against the receptacle end wall to hermetically enclose the sealed fill tube end within the fill port cover cavity.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Ventricular partitioning device
InactiveUS20060030881A1Lower the volumeImprove ejection fractionOcculdersSurgical veterinaryHeart chamberNon traumatic
This invention is directed to a partitioning device for separating a patient's heart chamber into a productive portion and a non-productive portion. The device is particularly suitable for treating patients with congestive heart failure. The partitioning device has a frame-reinforced, expandable membrane which separates the productive and non-productive portions of the heart chamber. The proximal ends of the ribs of the frame have tissue penetrating elements about the periphery thereof which are configured to penetrate tissue lining the heart wall at an angle approximately perpendicular to a longitudinal axis of the partitioning device. The partitioning device has a hub with a non-traumatic distal end to engage the ventricular wall.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Implantable medical device for monitoring cardiac blood pressure and chamber dimension
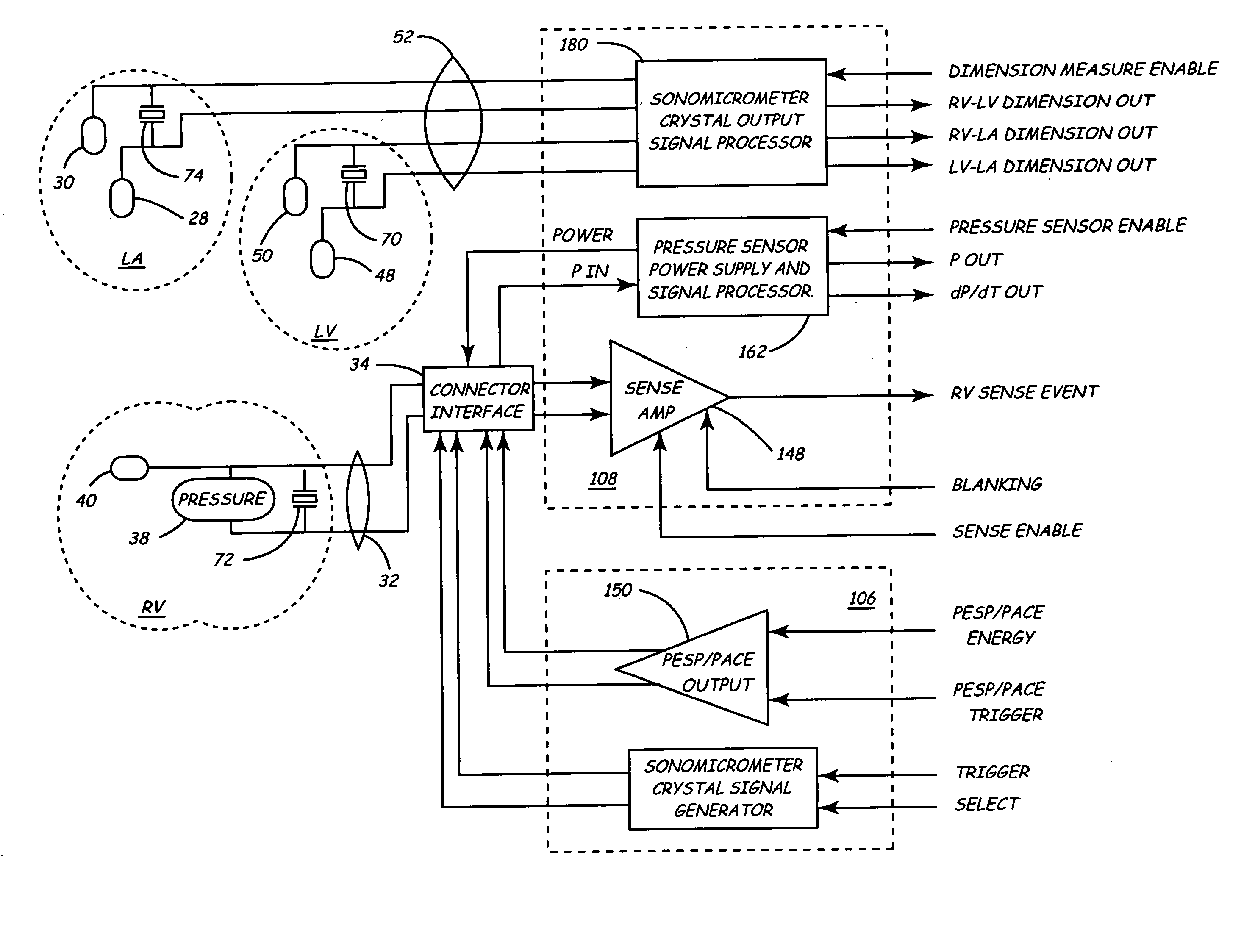
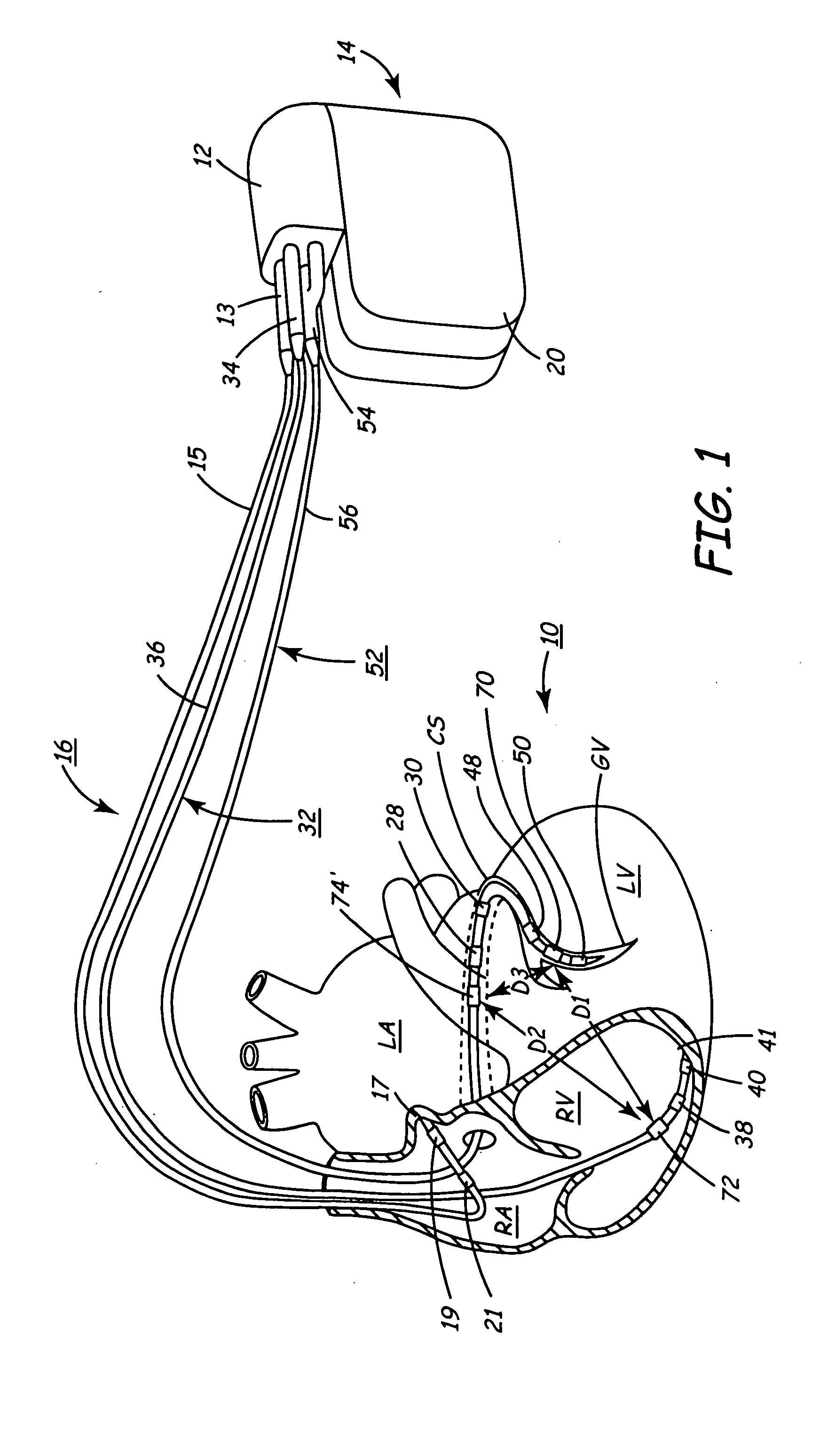
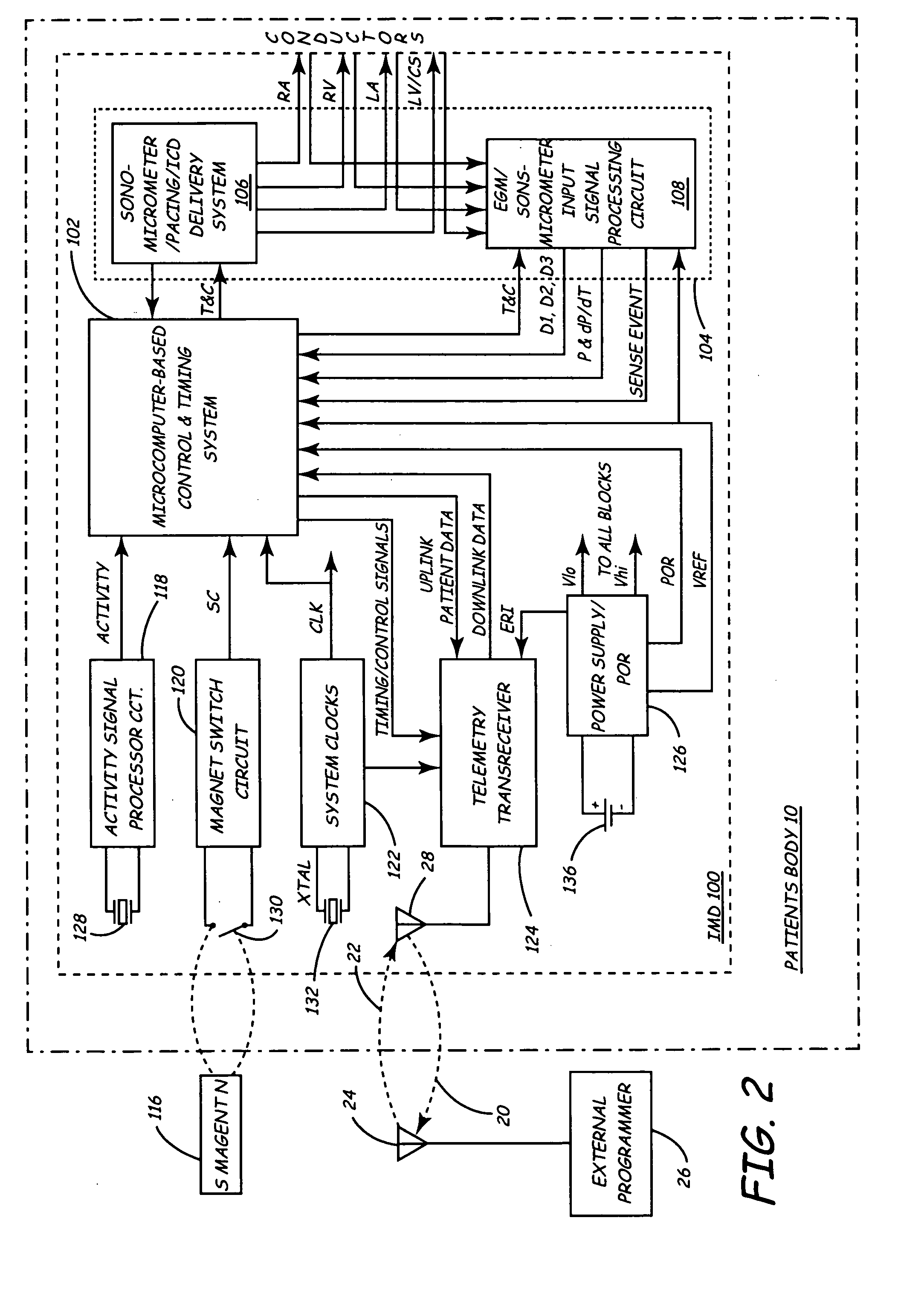
InactiveUS20050027323A1Maximize cardiac outputConvenient timeCatheterHeart stimulatorsSonificationHeart chamber
Implantable medical devices (IMDs) for monitoring signs of acute or chronic cardiac heart failure by measuring cardiac blood pressure and mechanical dimensions of the heart and providing multi-chamber pacing optimized as a function of measured blood pressure and dimensions are disclosed. The dimension sensor or sensors comprise at least a first sonomicrometer piezoelectric crystal mounted to a first lead body implanted into or in relation to one heart chamber that operates as an ultrasound transmitter when a drive signal is applied to it and at least one second sonomicrometer crystal mounted to a second lead body implanted into or in relation to a second heart chamber that operates as an ultrasound receiver. The ultrasound receiver converts impinging ultrasound energy transmitted from the ultrasound transmitter through blood and heart tissue into an electrical signal. The time delay between the generation of the transmitted ultrasound signal and the reception of the ultrasound wave varies as a function of distance between the ultrasound transmitter and receiver which in turn varies with contraction and expansion of a heart chamber between the first and second sonomicrometer crystals. One or more additional sonomicrometer piezoelectric crystal can be mounted to additional lead bodies such that the distances between the three or more sonomicrometer crystals can be determined. In each case, the sonomicrometer crystals are distributed about a heart chamber such that the distance between the separated ultrasound transmitter and receiver crystal pairs changes with contraction and relaxation of the heart chamber walls.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Ablation catheter, system, and method of use thereof
InactiveUS6893438B2Simple formatMechanically simpleElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingHeart chamberCardiac Ablation
A cardiac ablation apparatus for producing a circumferential ablation that electrically isolates a heart chamber wall portion from vessel such as a pulmonary vein extending into said wall portion comprises (a) an elongate centering catheter having a distal end portion; (b) an expandable centering element connected to said centering catheter distal end portion and configured for positioning within said vessel when in a retracted configuration, and for securing said elongate centering catheter in a substantially axially aligned position with respect to said vessel when said centering element is in an expanded configuration; (c) an ablation catheter slidably connected to said centering catheter said ablation element having a distal end portion, and (d) an expandable ablation element connected to said ablation catheter distal end portion. The ablation element is configured to form a circumferential ablation on the wall around the elongate centering catheter when the centering catheter is axially aligned with respect to the vessel. In a further embodiment, a non-expandable, compliant centering element is employed, such as an elastic finger. Systems incorporating such an apparatus and methods of use thereof are also disclosed.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
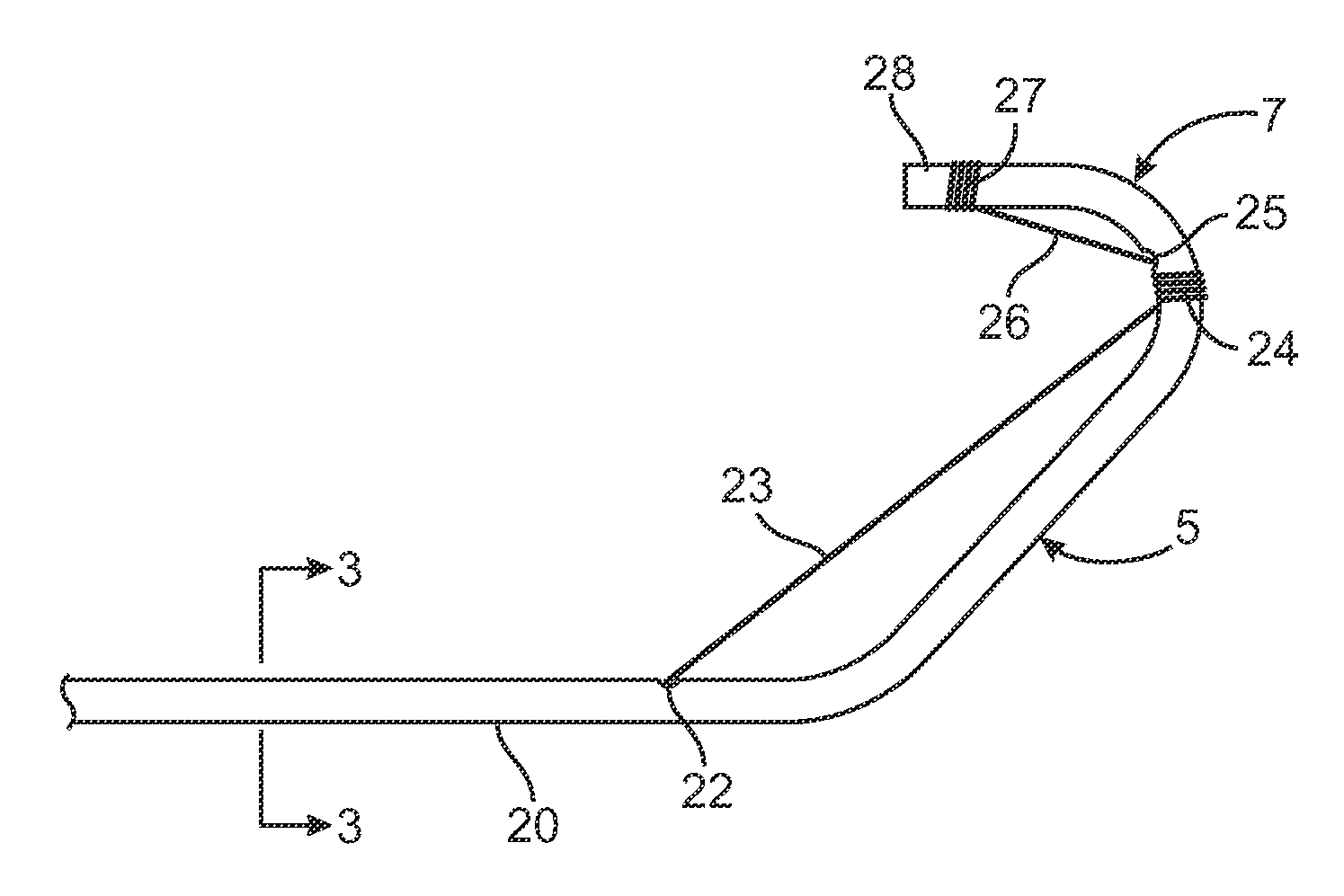
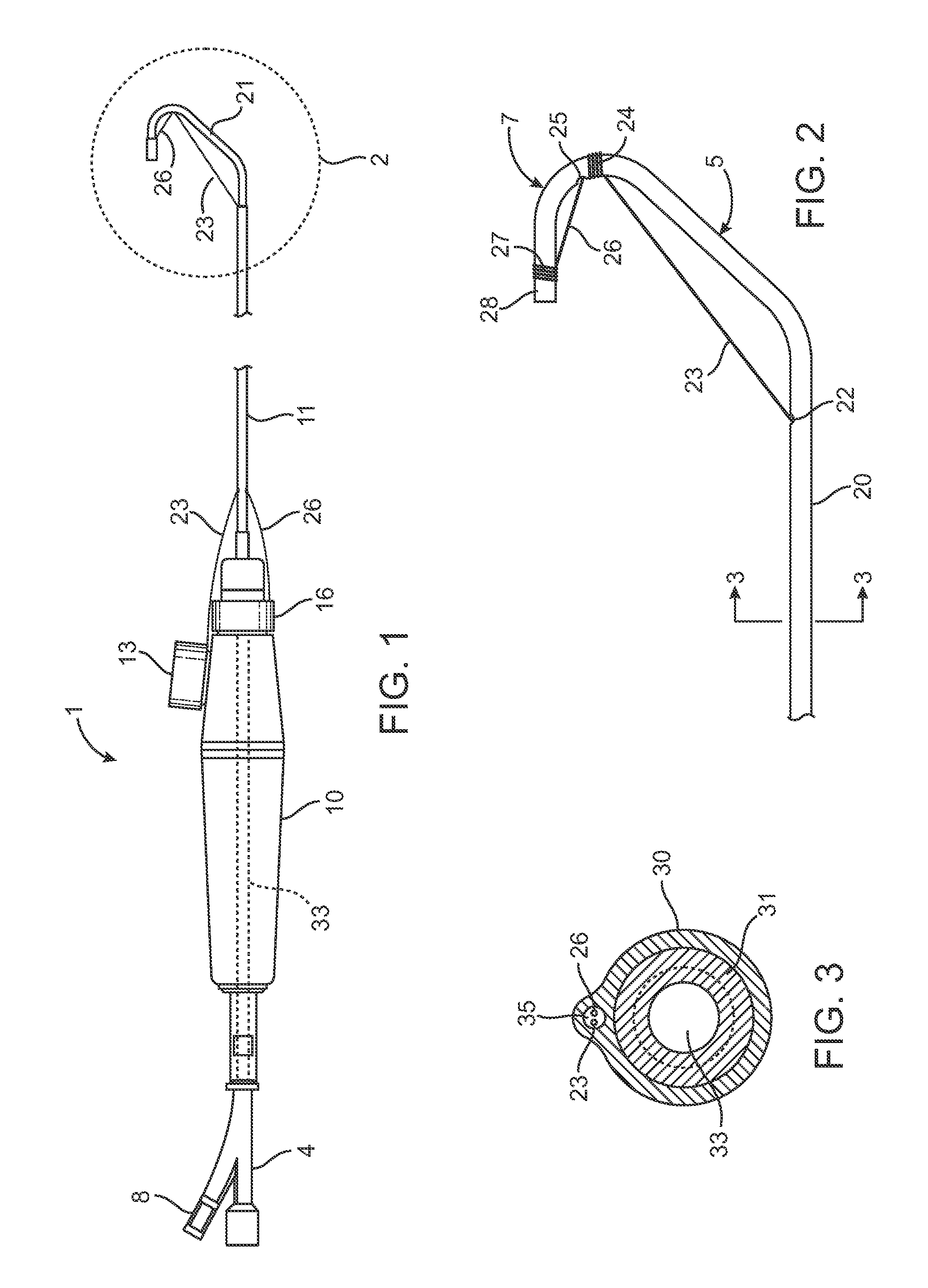
Catheter Having a Selectively Formable Distal Section
The current invention discloses a delivery catheter with a selectively formable distal section. The catheter comprises a central lumen that is configured to receive a puncture catheter that is used for puncturing the septum of a heart and to emplace devices used for treating mitral regurgitation. The delivery catheter includes control members disposed in a control lumen, and a plurality curved areas can be selectively formed in the distal section of the delivery catheter by applying tension to the control members. A first curve is shaped to conform to the interior of a heart chamber and a combination of the first curve and a second curve allows a clinician to manipulate the distal end of the catheter for selection of the proper vector for deploying a treatment device, or for guiding a treatment device around obstacles in a heart chamber.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Expandable myocardial implant
InactiveUS6350248B1Improve visualizationReduce oxygen requirementStentsDiagnosticsCoronary arteriesHeart chamber
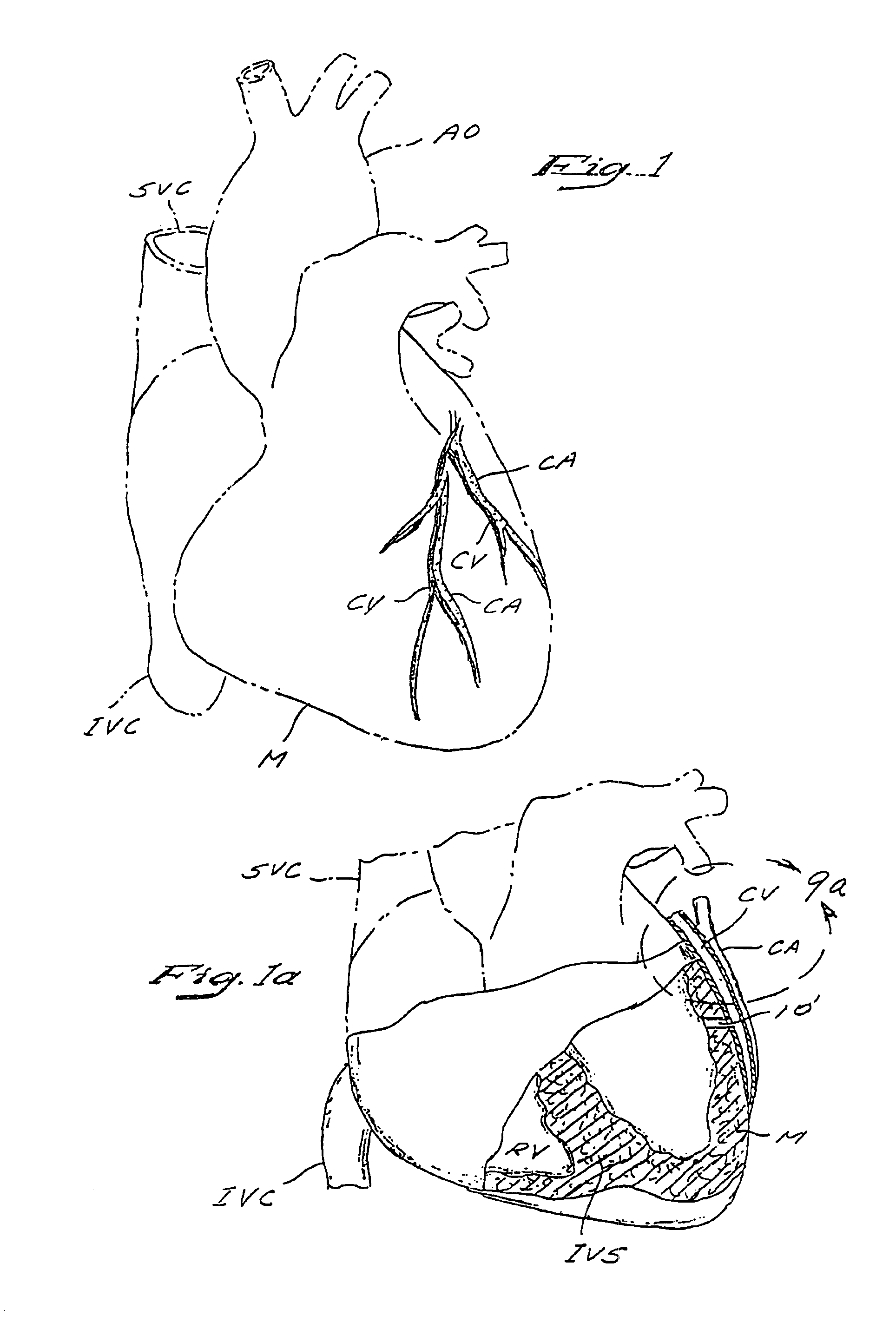
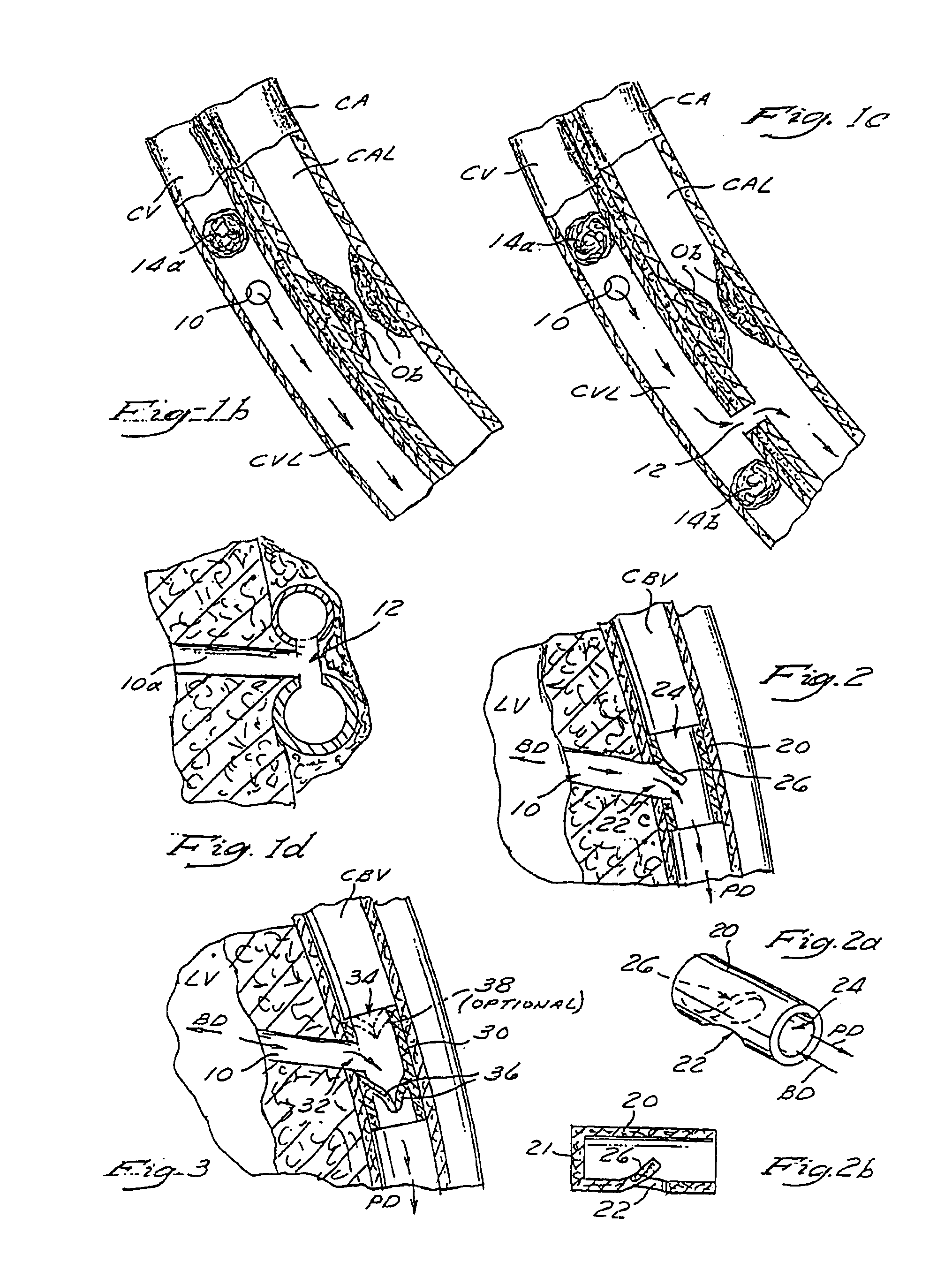
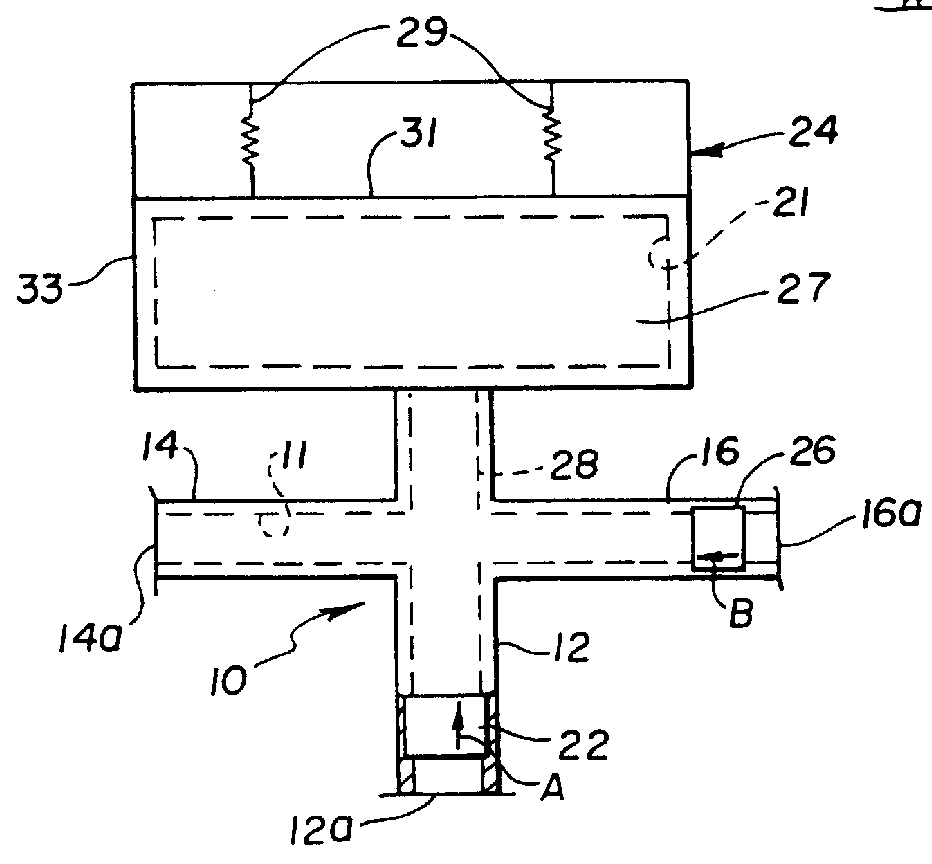
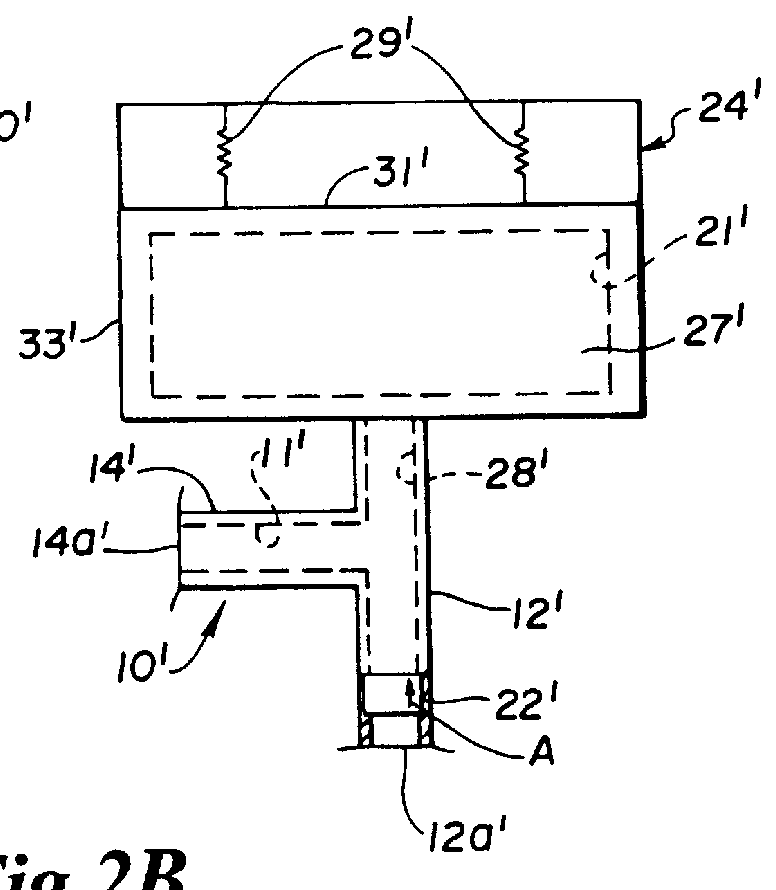
A method and apparatus for performing coronary artery bypass surgery establishes a channel leading directly from a chamber of a heart into a coronary artery. The coronary artery bypass procedure may be performed with or without cardiopulmonary bypass.
Owner:HORIZON TECH FUNDING CO LLC
Method and apparatus for transmyocardial direct coronary revascularization
InactiveUS6929009B2Facilitate valvingShortening and thickeningEar treatmentCannulasVeinHeart chamber
Methods and apparatus for direct coronary revascularization wherein a transmyocardial passageway is formed between a chamber of the heart and a coronary blood vessel to permit blood to flow therebetween. In some embodiments, the transmyocardial passageway is formed between a chamber of the heart and a coronary vein. The invention includes unstented transmyocardial passageways, as well as transmyocardial passageways wherein protrusive stent devices extend from the transmyocardial passageway into an adjacent coronary vessel or chamber of the heart. The apparatus of the present invention include protrusive stent devices for stenting of transmyocardial passageways, intraluminal valving devices for valving of transmyocardial passageways, intracardiac valving devices for valving of transmyocardial passageways, endogenous tissue valves for valving of transmyocardial passageways, and ancillary apparatus for use in conjunction therewith.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Closed chest coronary bypass
InactiveUS6123682AImprove visualizationReduce oxygen requirementStentsDiagnosticsCoronary arteriesHeart chamber
A method and apparatus for performing coronary artery bypass surgery establishes a channel leading directly from a chamber of a heart into a coronary artery. The coronary artery bypass procedure may be performed with or without cardiopulmonary bypass.
Owner:HORIZON TECH FUNDING CO LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com