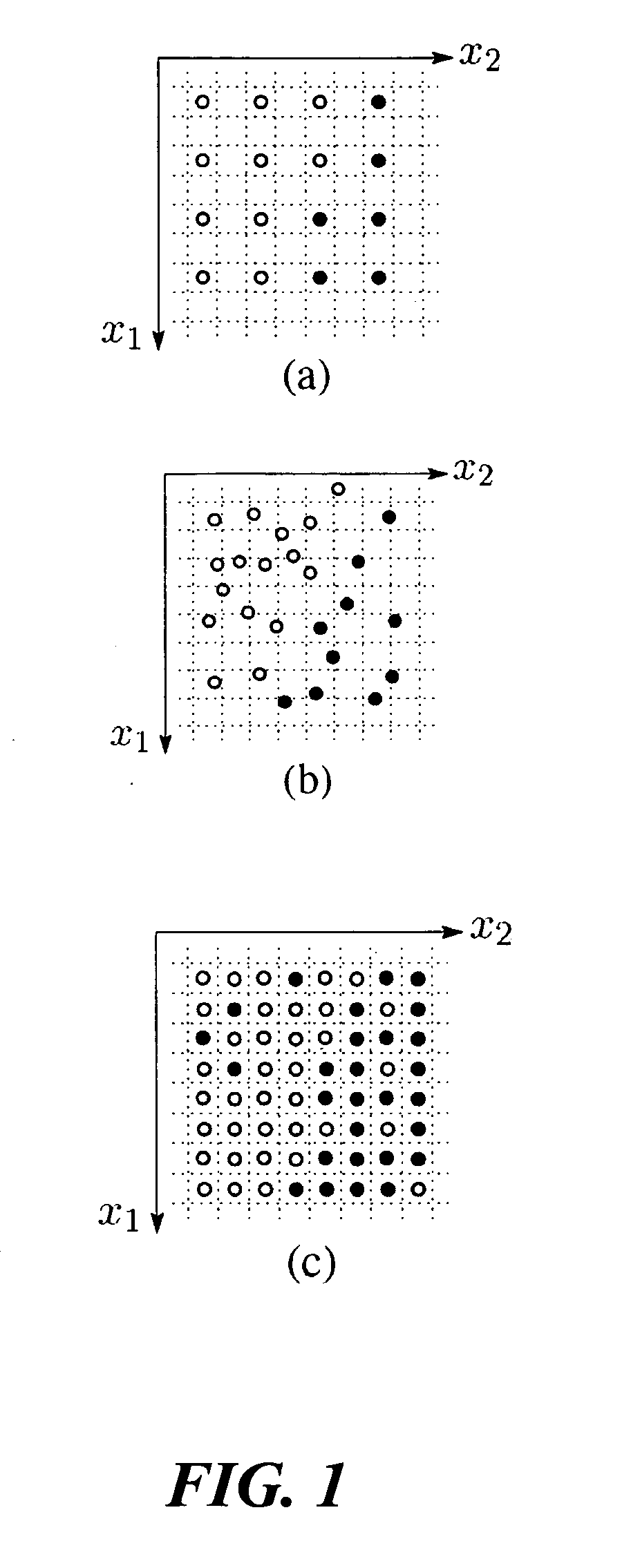
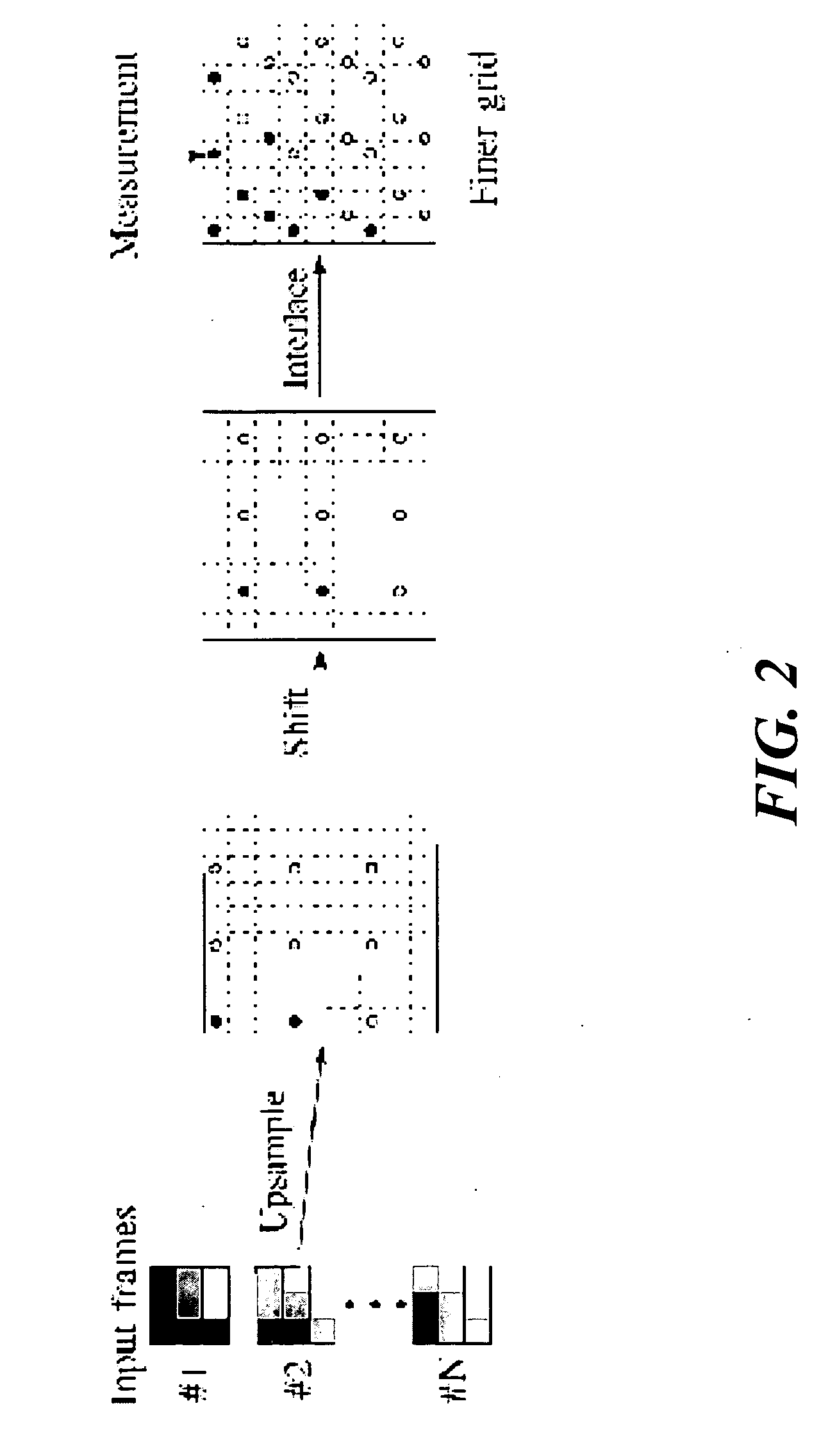
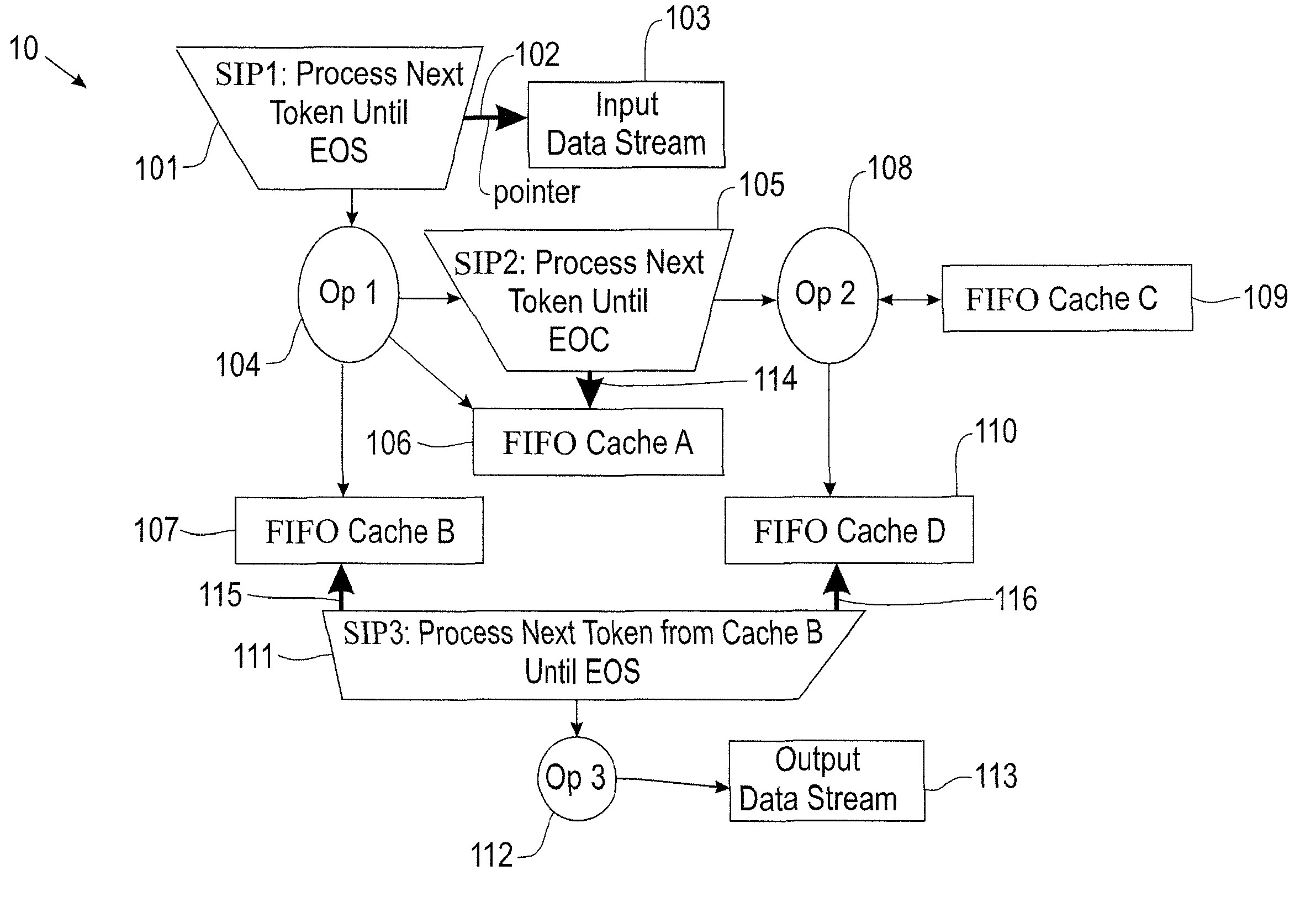
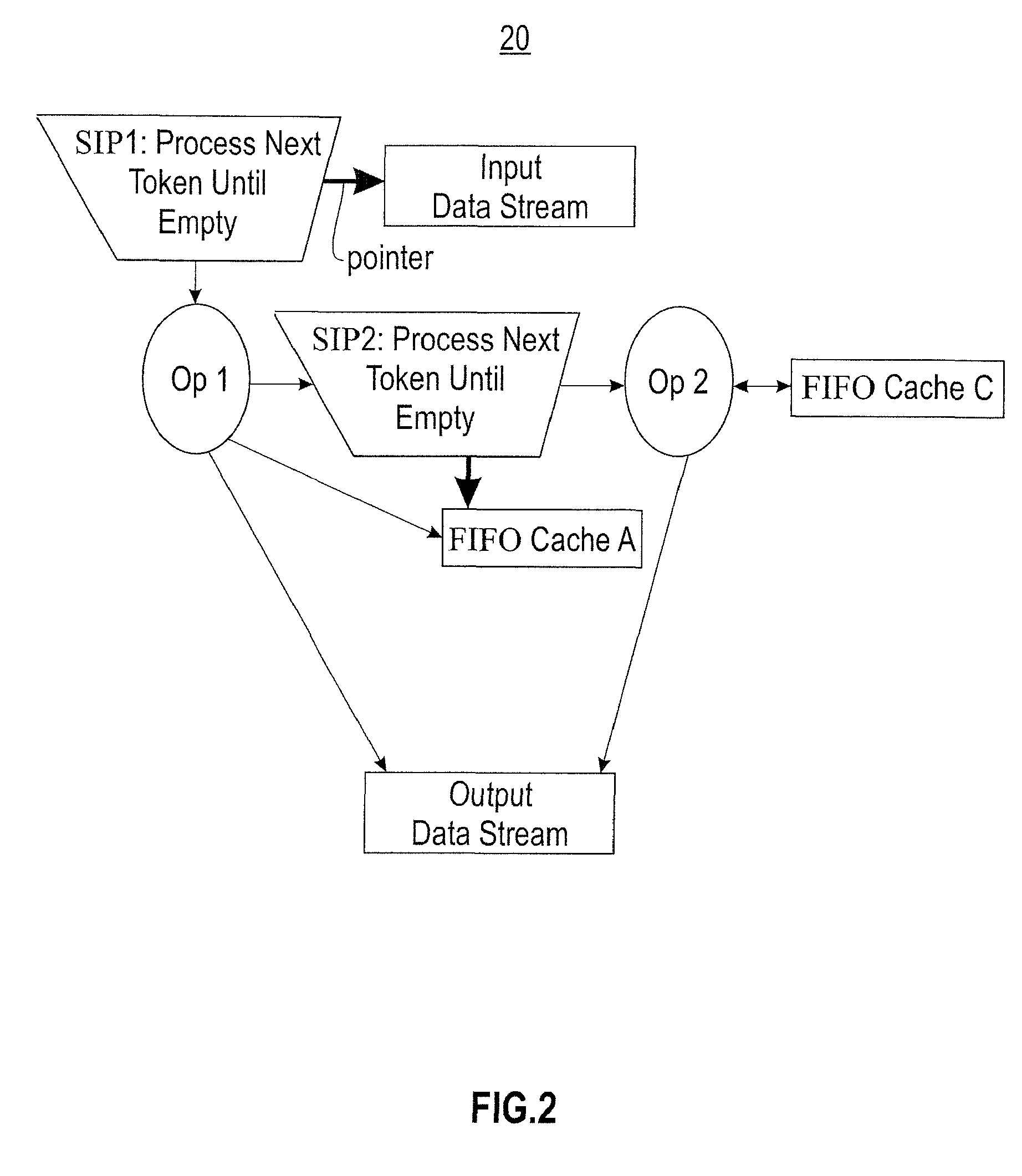
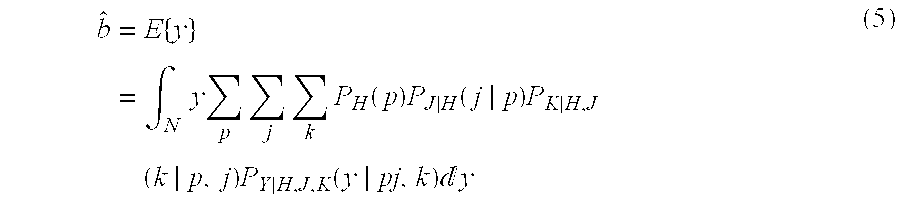Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
154 results about "Noisy data" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Noisy data is data that is corrupted, or distorted, or has a low Signal-to-Noise Ratio. Improper procedures (or improperly-documented procedures) to subtract out the noise in data can lead to a false sense of accuracy or false conclusions.
Implantable monitor
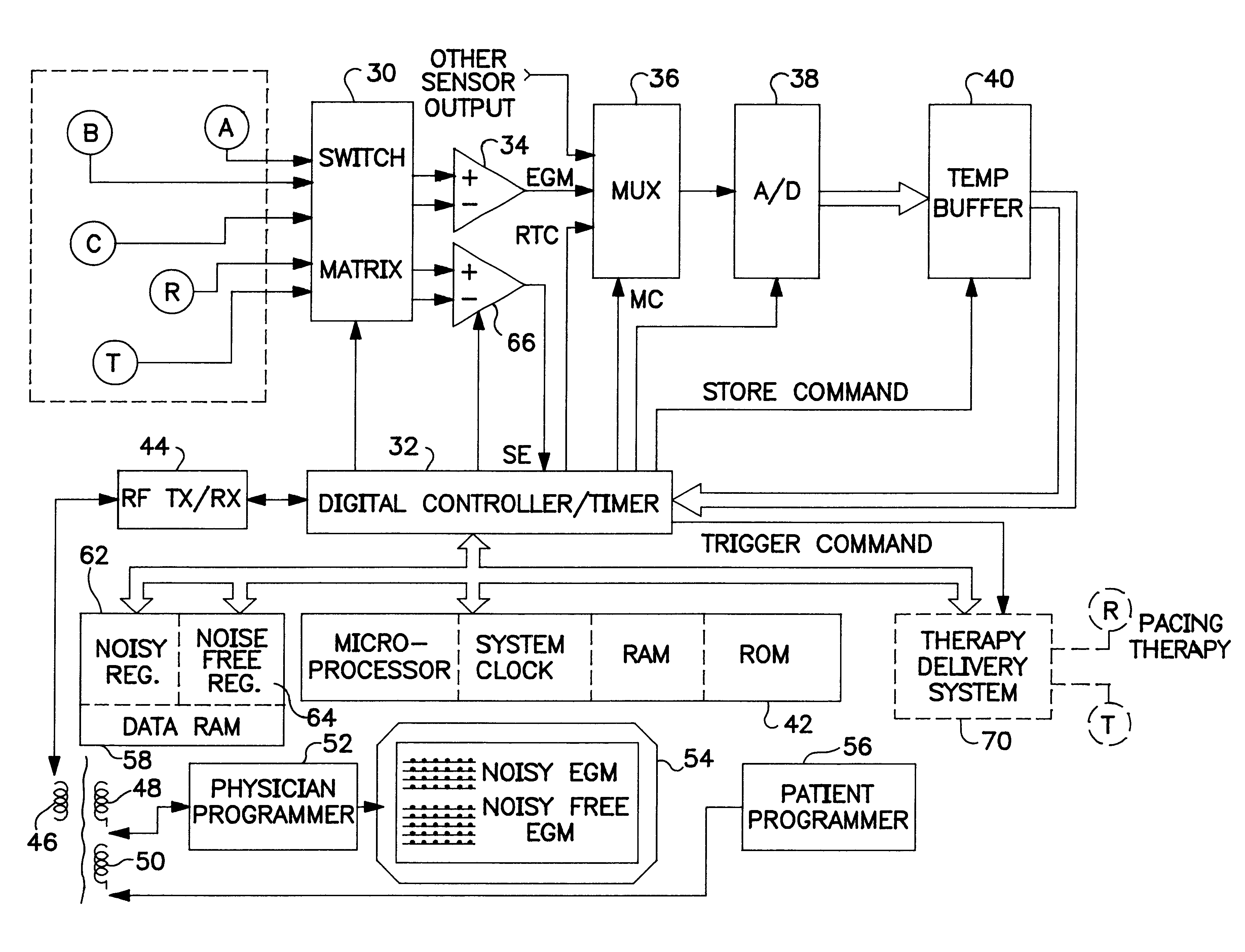
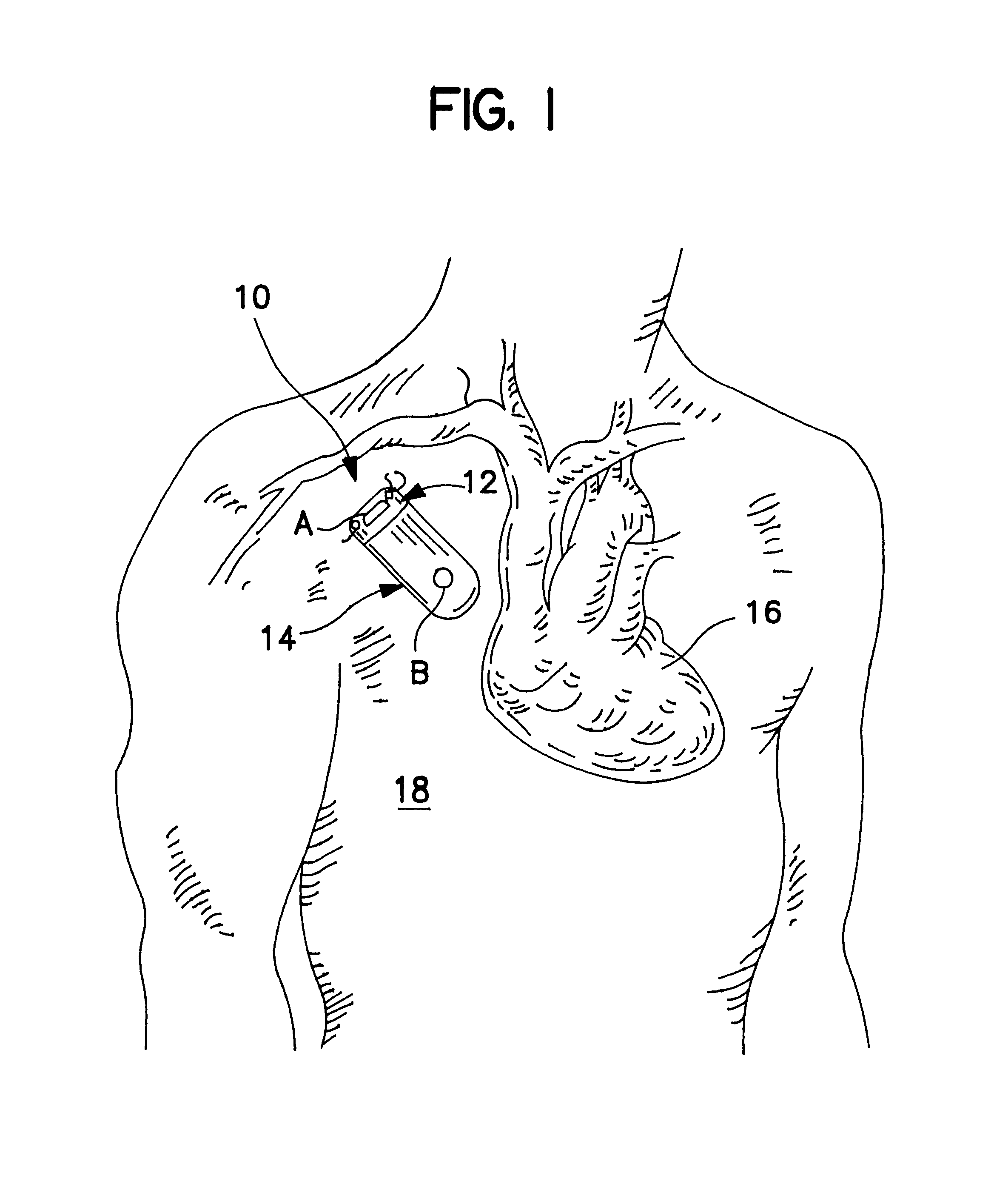
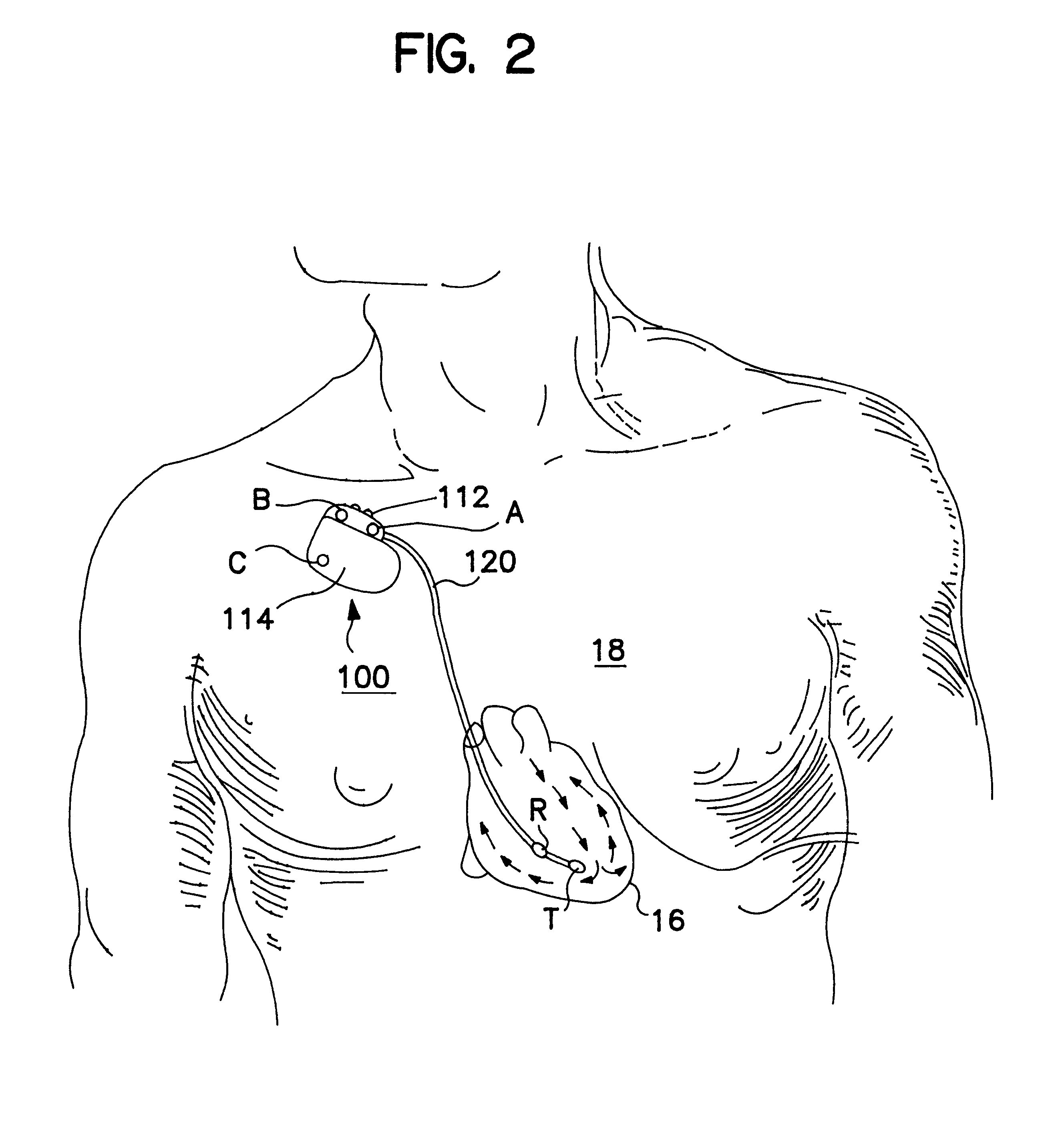
An implantable medical device (IMD) capable of monitoring physiologic data, distinguishing relatively noisy and noise free physiologic data, and recording noisy and relatively noise free segments of physiologic data in separate memory registers of a limited memory for retrieval and analysis at a later time. Preferably the physiologic data comprises the sampled EGM of the heart detected from sense electrode pairs that are implanted in the patient at sites where extraneous electrical noise, e.g., electromyographic signals, are also capable of being detected. The sense electrode pairs can constitute one or both sense electrodes located on or adjacent to the atrial and / or ventricular heart chambers and coupled to the IMD by a lead body or sense electrode pairs that are located remotely from the heart, e.g. at a subcutaneous implantation site of the IMD. A plurality of noisy EGM episode data registers store a corresponding plurality of noisy EGM episode data sets on a FIFO basis and another plurality of noise free EGM episode data registers to store a corresponding plurality of relatively noise free EGM episode data sets on a FIFO basis. Any form of discrimination of noisy data from relatively noise free data can be employed at the time of recording, but because the stored EGM episode data sets are subsequently viewed and analyzed by a physician, discrimination with absolute certainty is not required, and the physician can alter the detection criteria to fine tune it.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Noise Reduction in Capacitive Touch Sensors
ActiveUS20100139991A1Compromise integrityOptimize dataTransmission systemsElectronic switchingSensor arrayNoisy data
Noise reduction in a one- or two-dimensional capacitive sensor array is achieved by rejecting and re-acquiring noisy signals. The sensor array is formed of crossed X and Y lines for drive and sense functions respectively, each of the X lines being driven in turn to acquire a full frame of data from the sensor array. A controller actuates the X lines in turn and, for each X line, charge is transferred to charge measurement capacitors connected to respective ones of the Y lines. The controller measures a signal value from a first one of the measurement capacitors, and then tests if that Y signal value has a magnitude lying within an acceptable range. If not, the measurement capacitors are all reset without their signal values being measured, and the controller re-drives the same X line to initiate another charge transfer into the measurement capacitors for that X line. It is then attempted once again to acquire Y signal values for that X line. Noisy signal values are thus rejected, and the sensor re-acquires substitute signal values. This is distinct from the approach of acquiring data and then reprocessing it to remove or suppress noisy data as in the prior art.
Owner:NEODRON LTD
Kernel regression for image processing and reconstruction
ActiveUS20070047838A1Improve local image structure informationImproves gradient and pixel valueImage enhancementImage analysisSingular value decompositionKernel regression
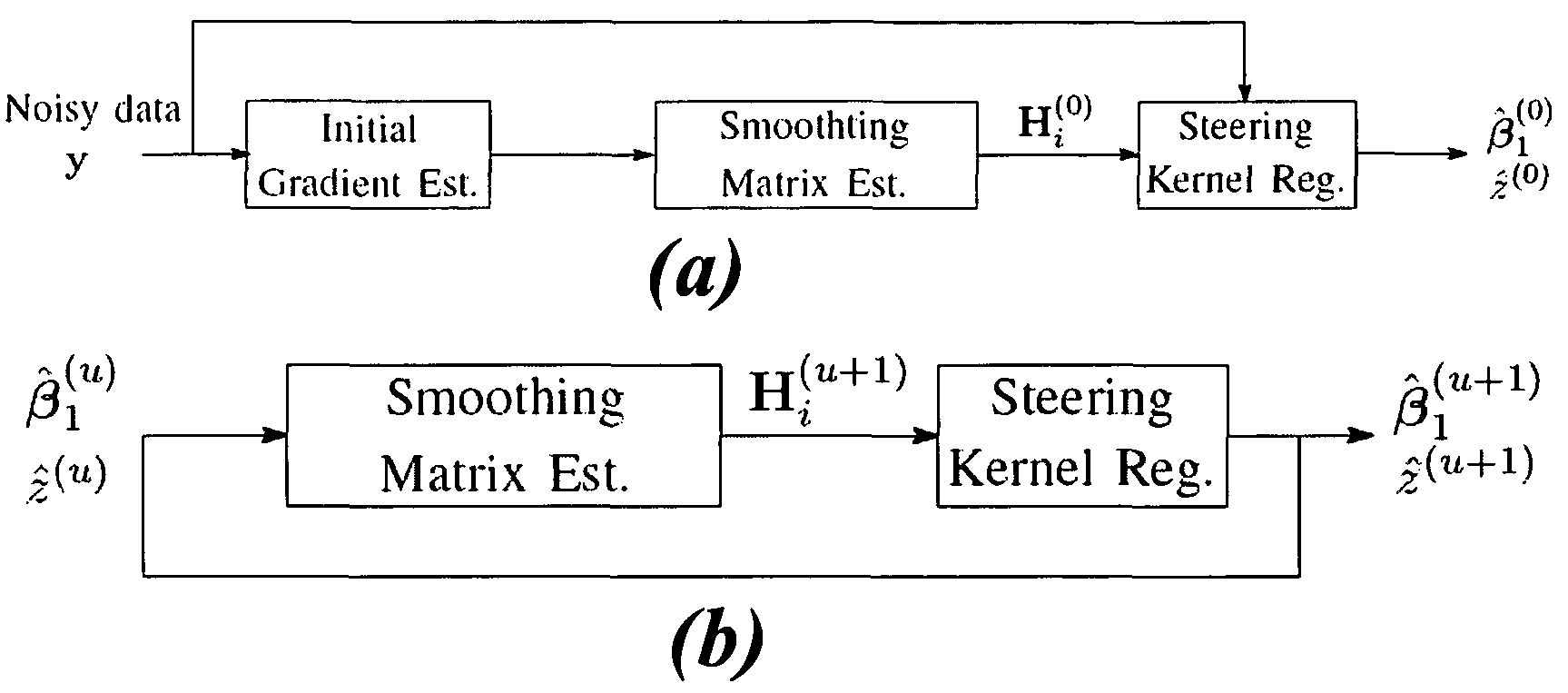
A method of image processing using kernel regression is provided. An image gradient is estimated from original data that is analyzed for local structures by computing a scaling parameter, a rotation parameter and an elongation parameter using singular value decomposition on local gradients of the estimated gradients locally to provide steering matrices. A steering kernel regression having steering matrices is applied to the original data to provide a reconstructed image and new image gradients. The new gradients are analyzed using singular value decomposition to provide new steering matrices. The steering kernel regression with the new steering matrices is applied to the noisy data to provide a new reconstructed image and further new gradients. The last two steps are repeated up to ten iterations to denoise the original noisy data and improve the local image structure.
Owner:UNIV OF CALIFORNIA SANTA CRUZ
Simplifying complex data stream problems involving feature extraction from noisy data
InactiveUS7805445B2Digital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsFeature extractionData stream
Methods, systems and computer program products for simplifying complex data stream problems involving feature extraction from noisy data. Exemplary embodiments include a method for processing a data stream, including applying multiple operators to the data stream, wherein an operation by each of the multiple operators includes retrieving the next chunk for each of set of input parameters, performing digital processing operations on a respective next chunk, producing sets of output parameters and adding data to one or more internal data stores, each internal data store acting as a data stream source.
Owner:IBM CORP
Peak selection in multidimensional data
InactiveUS6873915B2Improve automationValid choiceParticle separator tubesComponent separationPattern recognitionData set
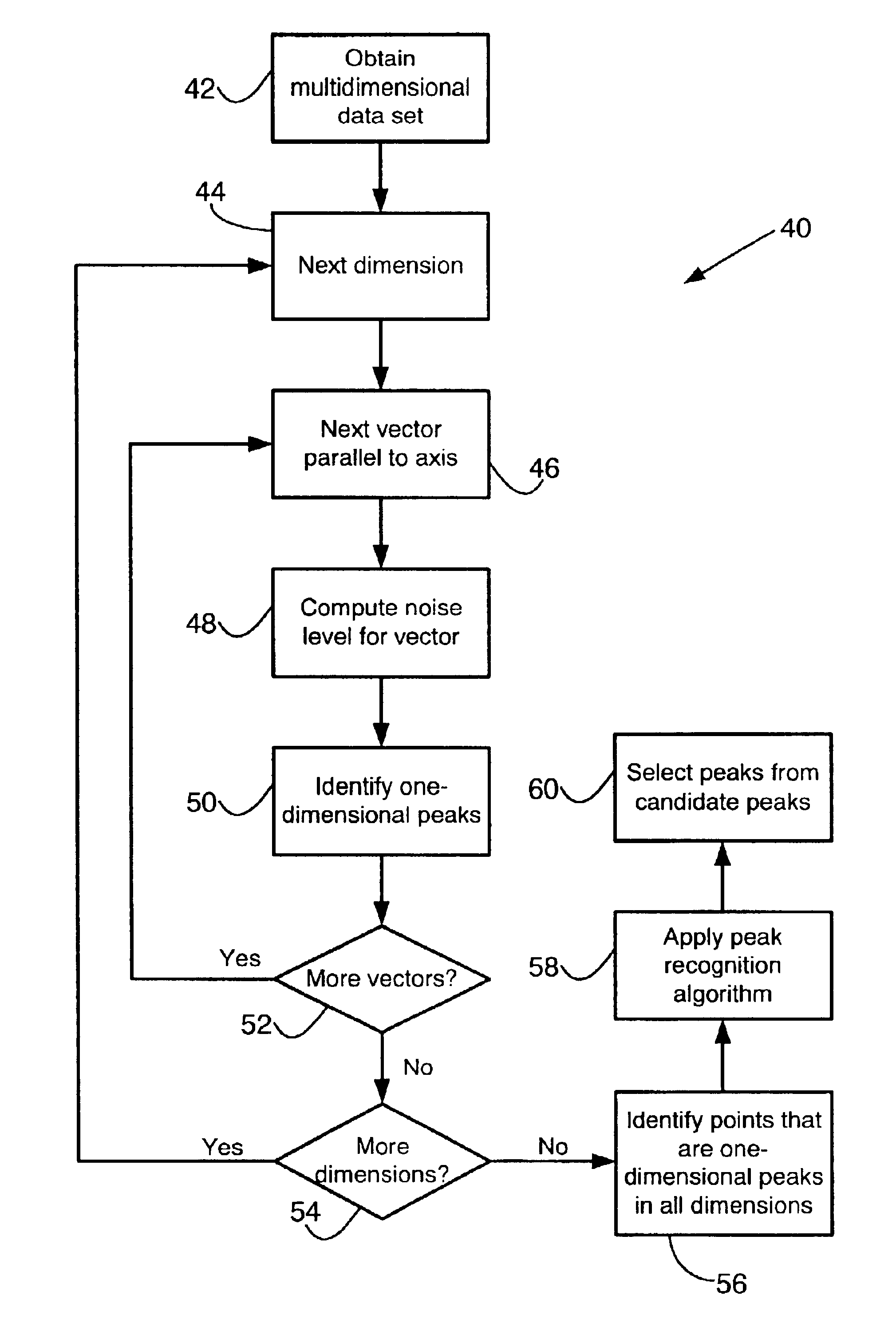
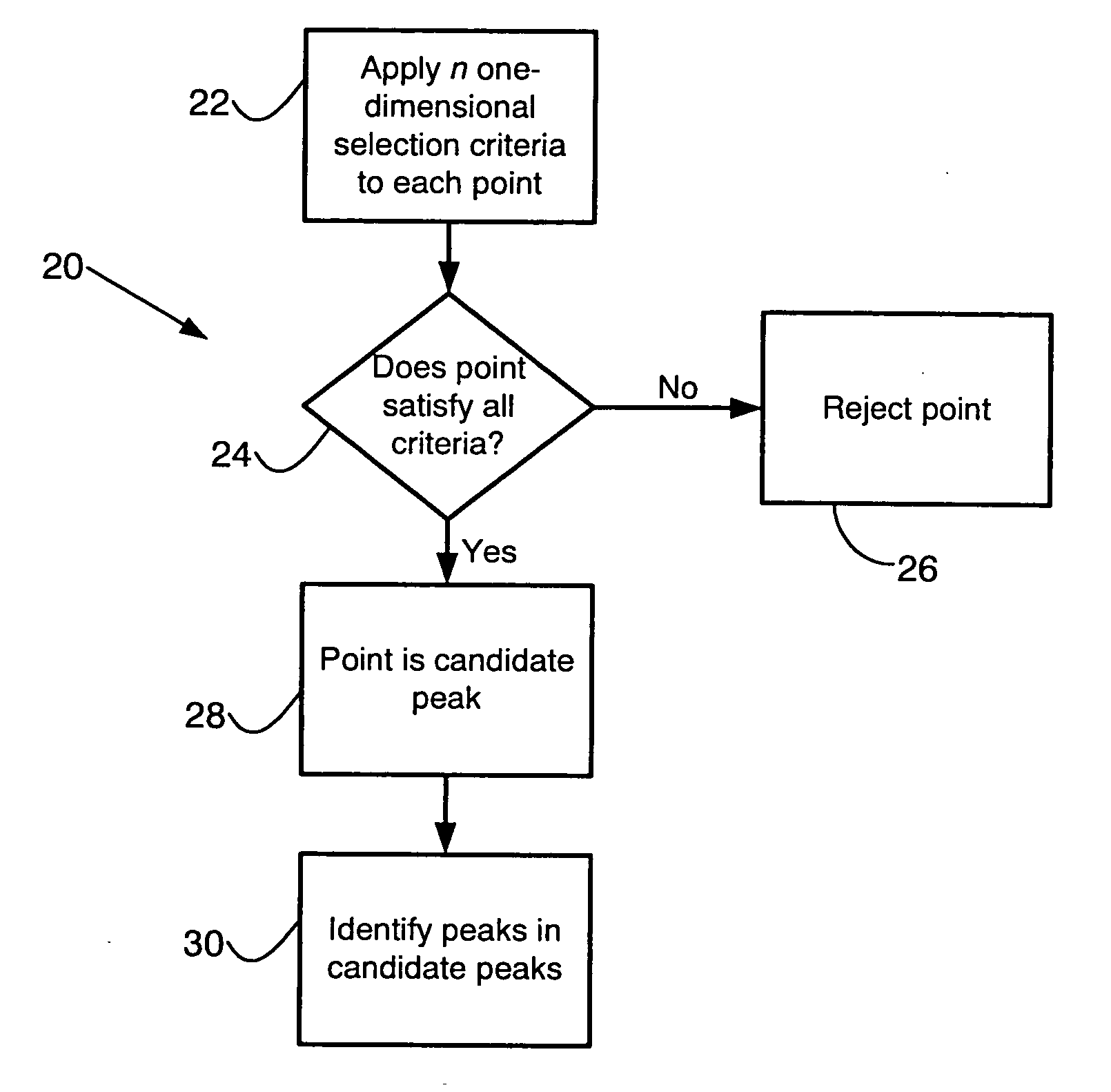
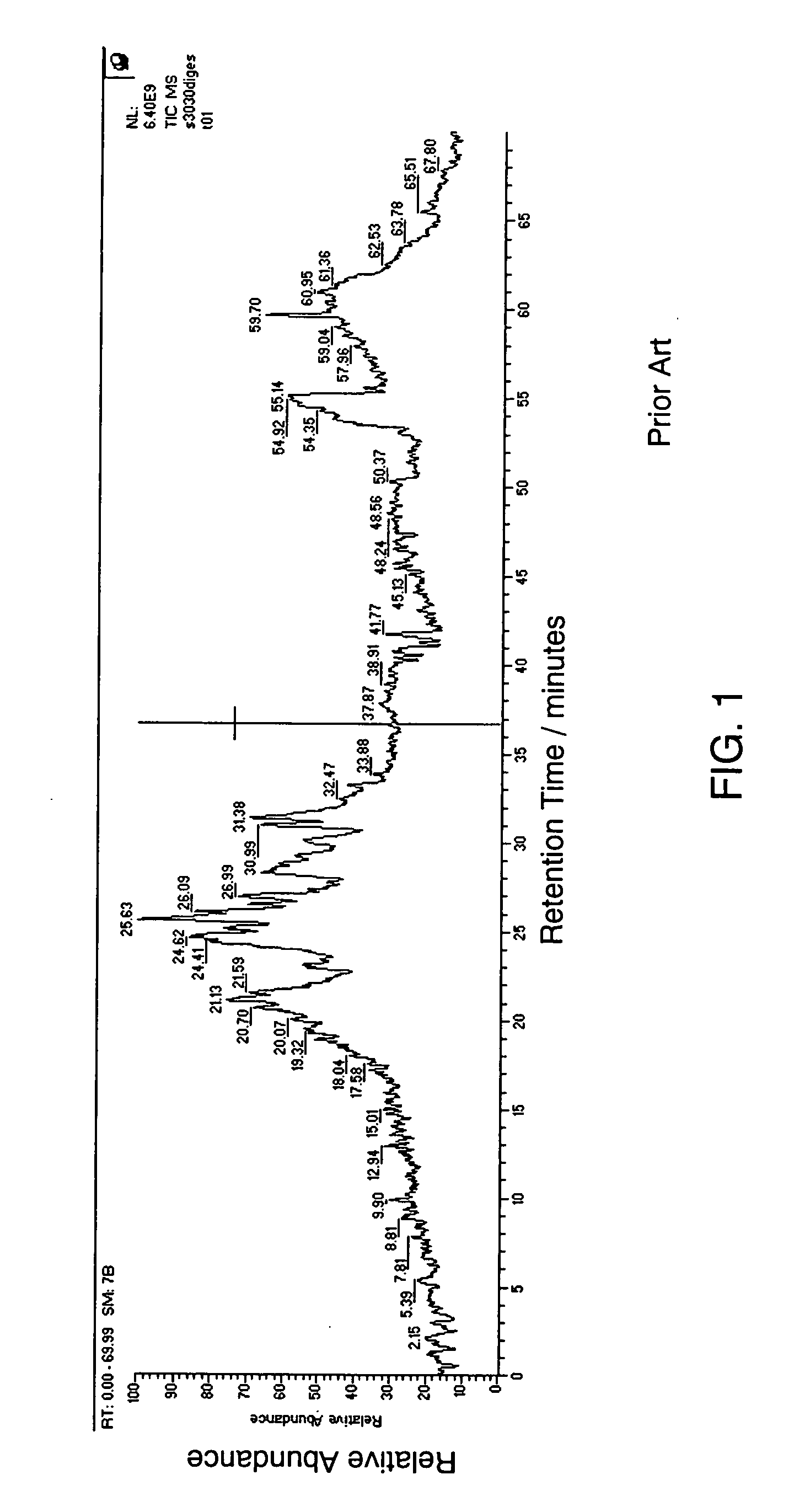
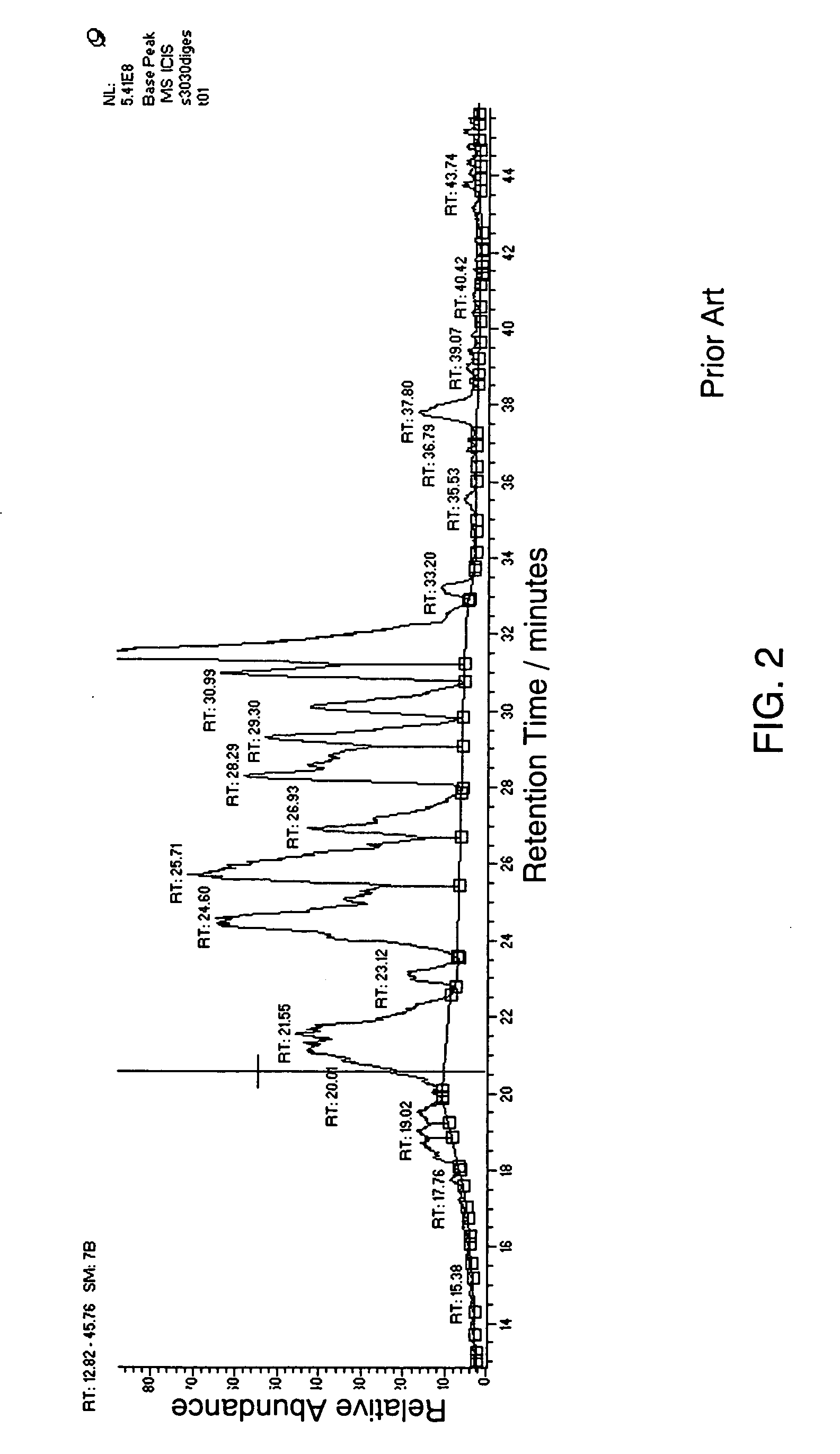
An automatic peak selection method for multidimensional data that selects peaks from very noisy data such as two-dimensional liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) data is described. Such data are characterized by non-normally distributed noise that varies in different dimensions. The method computes local noise thresholds for each one-dimensional component of the data. Each point has a local noise threshold applied to it for each dimension of the data set, and a point is selected as a candidate peak only if its value exceeds all of the applied local noise thresholds. Contiguous candidate peaks are clustered into actual peaks. The method is preferably implemented as part of a high-throughput platform for analyzing complex biological mixtures.
Robust OFDM carrier recovery methods and apparatus
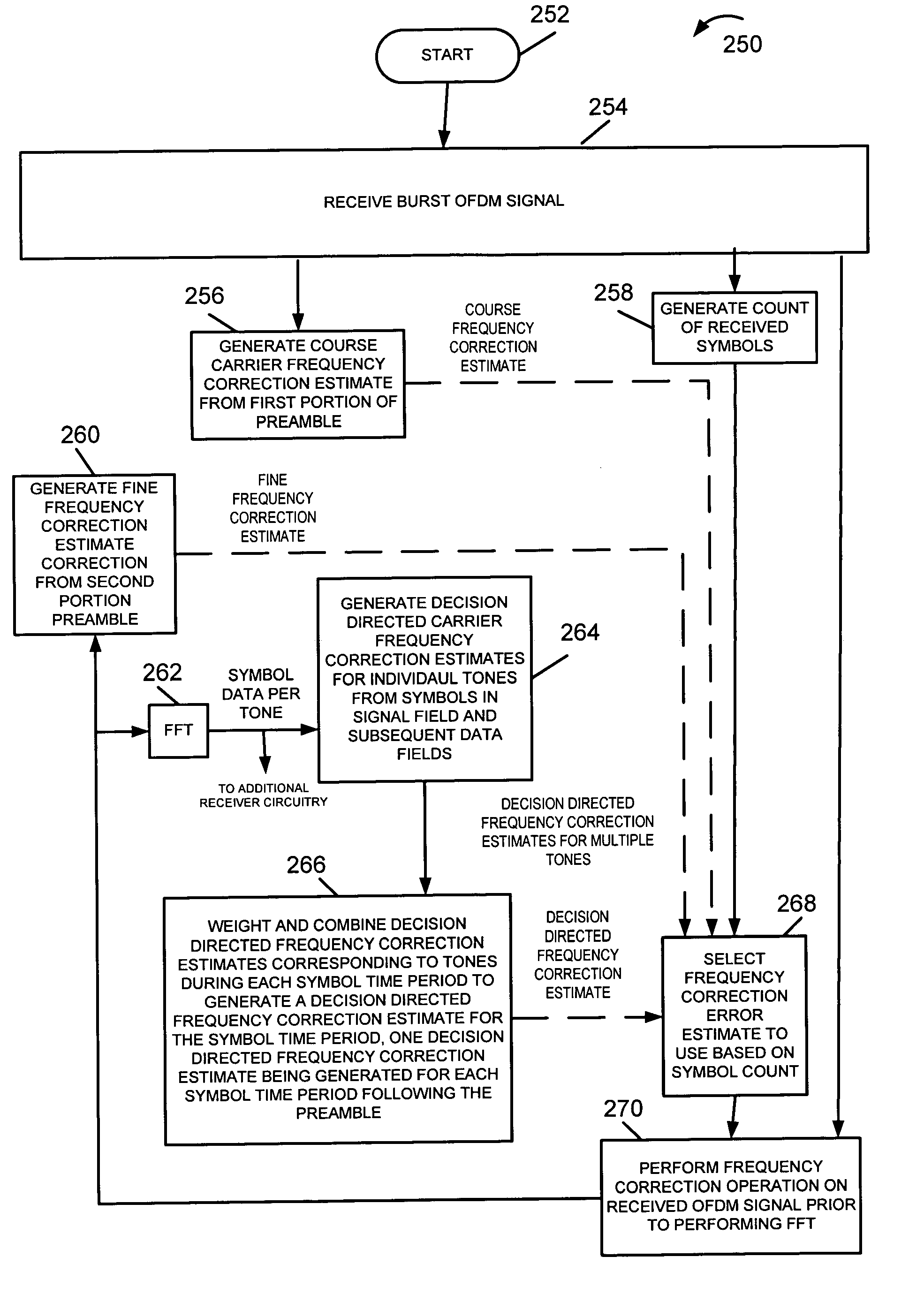
InactiveUS7139340B2Carrier frequency errorEasy and inexpensive mannerAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsMulti-frequency code systemsData fieldCarrier frequency offset
Methods and apparatus for estimating and correcting carrier frequency offsets in a bust multi-tone receiver are described. Course and fine carrier frequency estimates are generated from the signal's preamble. Decision directed carrier frequency offset estimates are then generated from the signal field and data fields of the multi-tone signal. Frequency error estimates are generated for each tone of the signal and combined using a weighted average to generate the frequency error estimate used to perform the correction operation. Error estimates corresponding to noisy data tones are weighted less then estimates corresponding to less noisy data tones. In cases of low SNR frequency error estimates corresponding to pilots are weighted by an extra amount as compared to error estimates corresponding to tones used to transmit data symbols. During times of high SNR error estimates corresponding to pilot tones are weighted in the same manner as error estimates corresponding to data tones.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method and apparatus for nearly optimal private convolution
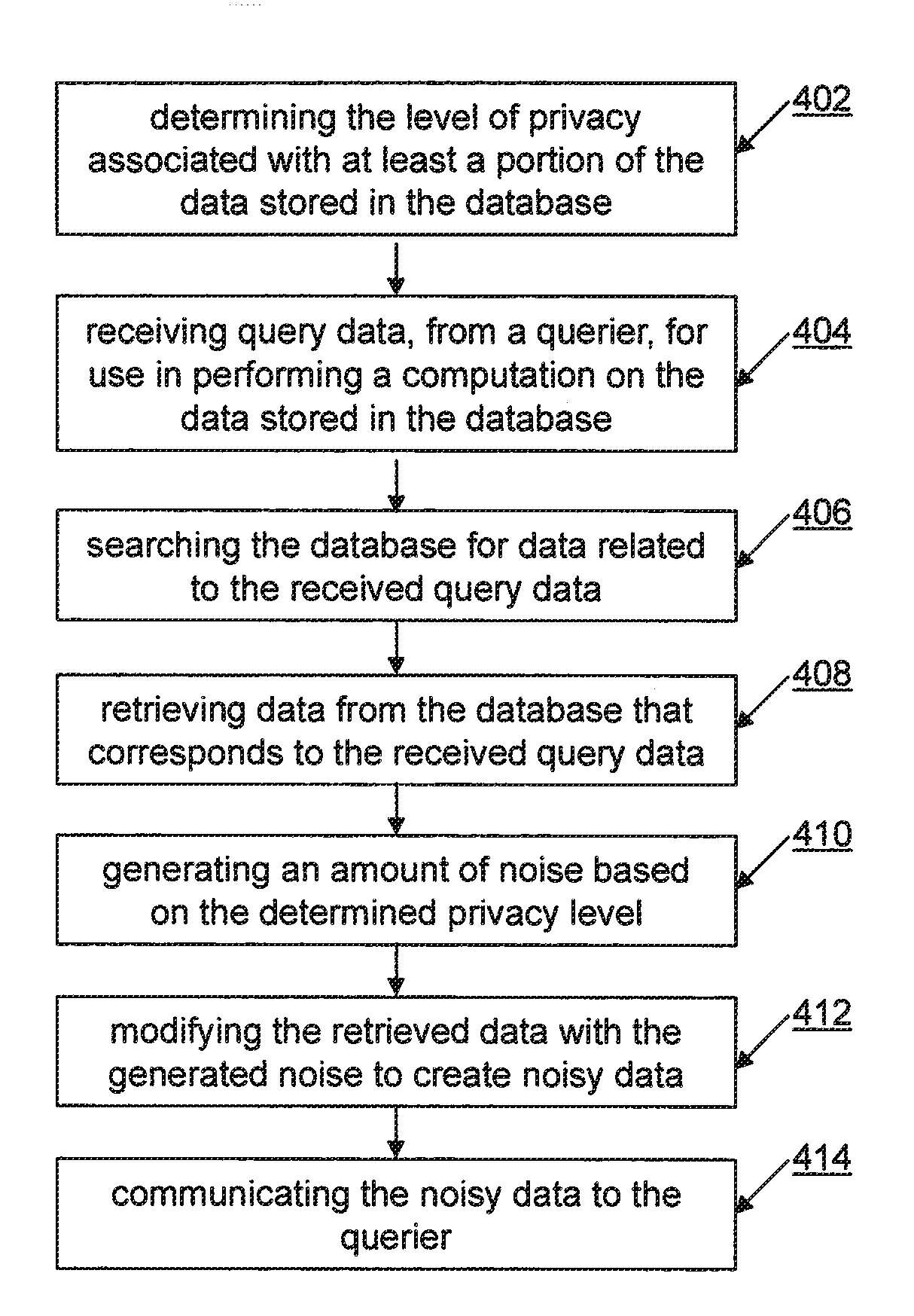
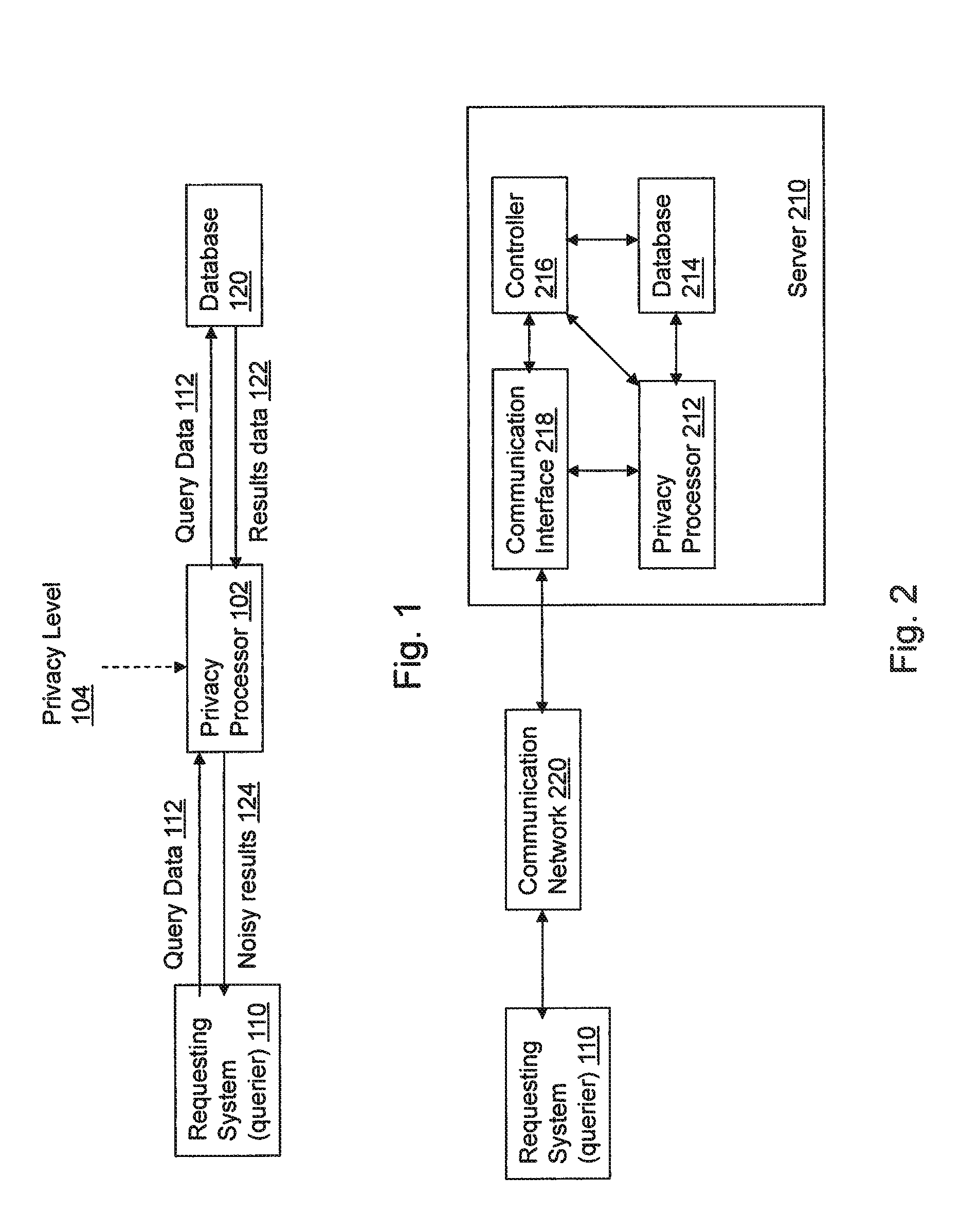
InactiveUS20150286827A1Ensuring level of privacyPrivacy protectionDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsNoisy dataData mining
A method and apparatus for ensuring a level of privacy for answering a convolution query on data stored in a database is provided. The method and apparatus includes the activities of determining (402) the level of privacy associated with at least a portion of the data stored in the database and receiving (404) query data, from a querier, for use in performing a convolution over the data stored in the database. The database is searched (406) for data related to the received query data and the data that corresponds to the received query data is retrieved (408) from the database. An amount of noise based on the determined privacy level is generated (410) and added (412) to the retrieved data to create noisy data which is then communicated (414) to the querier.
Owner:FAWAZ NADIA +2
Systems and methods for network pattern matching
ActiveUS20150049634A1Data processing applicationsData switching by path configurationPattern matchingGraph match
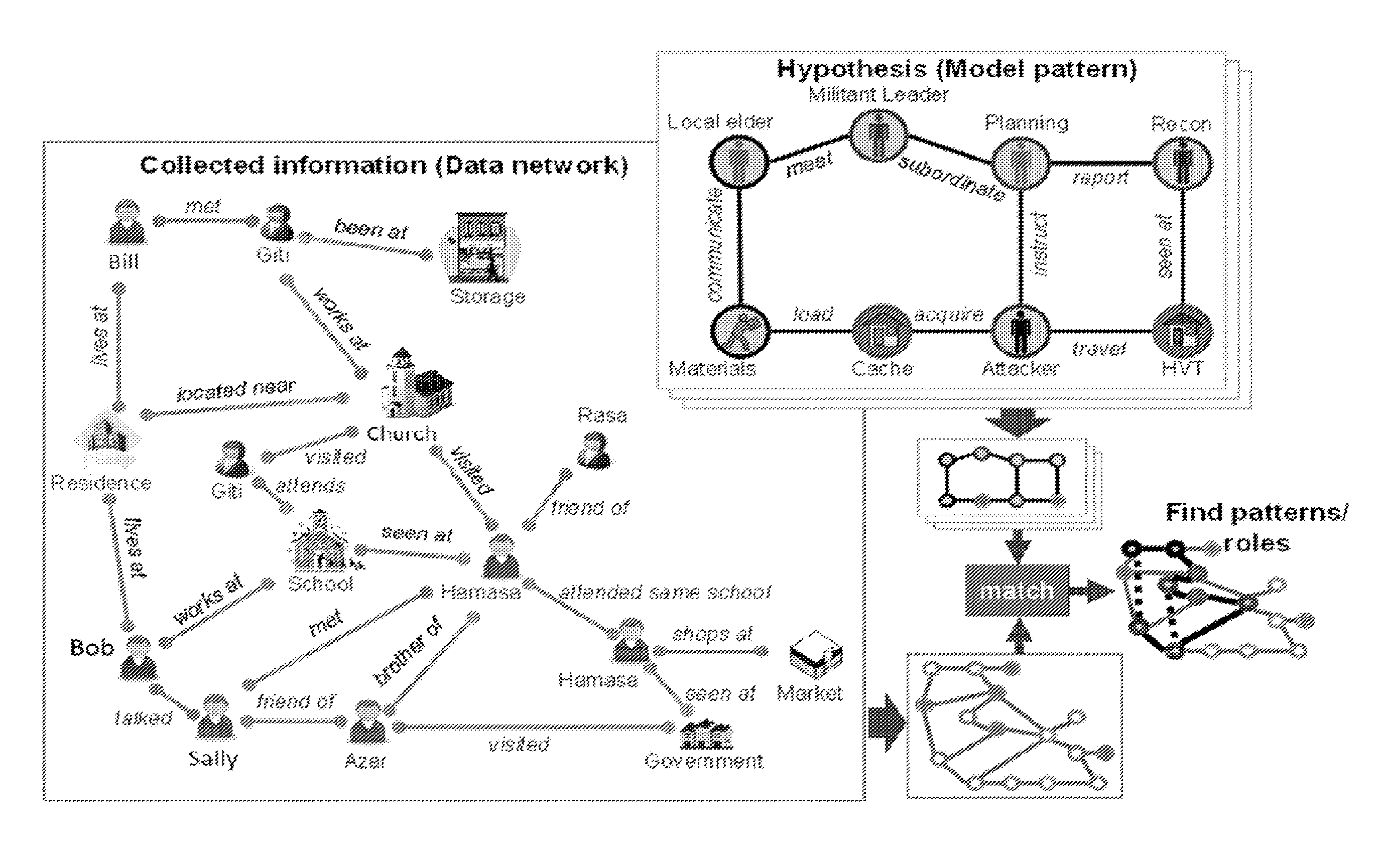
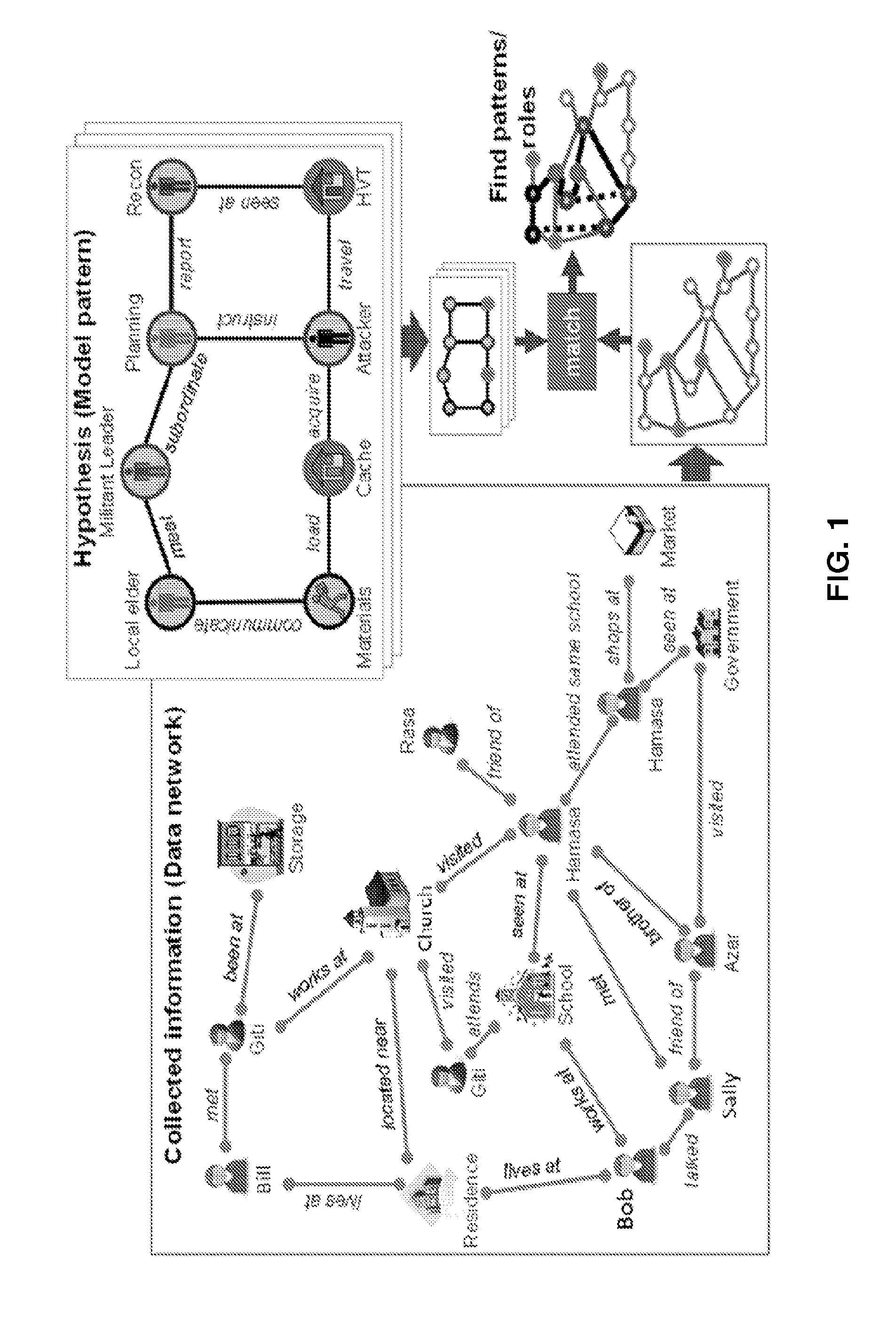
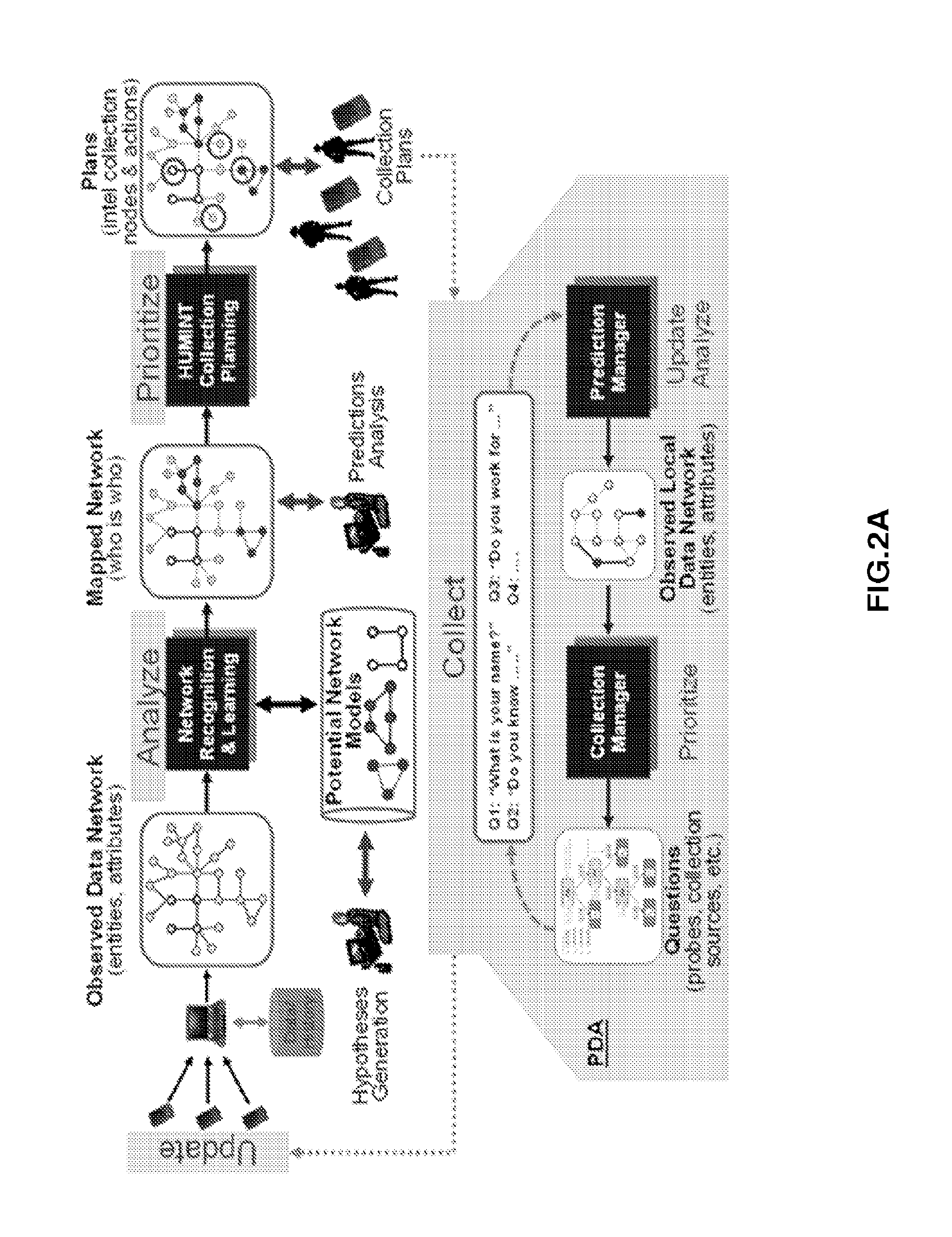
Example embodiments of systems and methods for network pattern matching provide the ability to match hidden networks from noisy data sources using probabilistic multi-attribute graph matching analysis. The algorithms may map roles and patterns to observed entities. The outcome is a set of plausible network models. The pattern-matching methodology of these systems and methods may enable the solution of three challenges associated with social network analysis, namely network size and complexity, uncertain and incomplete data, and dynamic network structure.
Owner:APTIMA
Abnormal data filtration method for interference elimination of automatic data acquisition system
ActiveCN102184267AAutomated filteringImprove responsivenessData acquisition and loggingInterference eliminationProgram planning
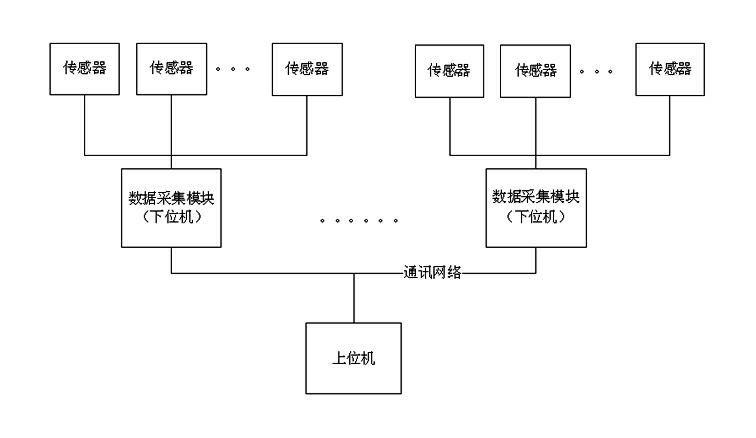
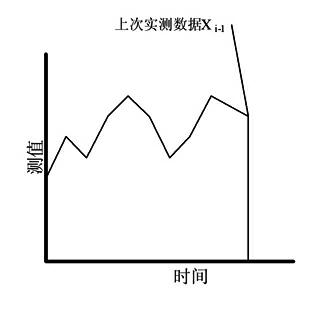
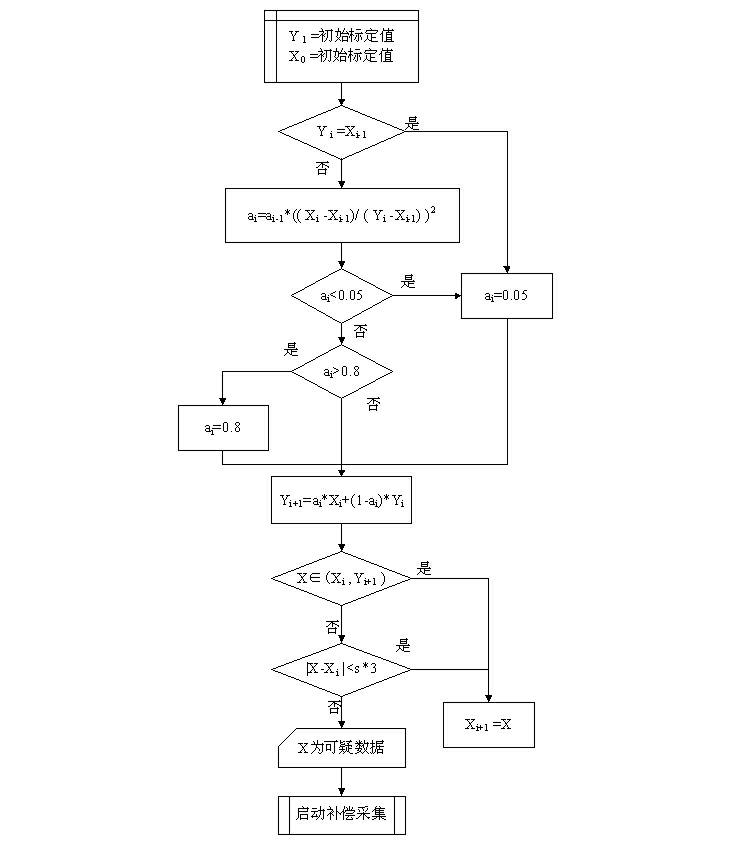
The invention discloses an abnormal data filtration method for interference elimination of an automatic data acquisition system. The method is characterized in that: the automatic data acquisition system comprises four basic parts, namely a sensor network, a lower computer, an upper computer and a communication network; abnormal data is judged and rejected on the basis of the upper computer; a data acquisition plan is set and initiated by the upper computer; data acquired by a data acquisition module is transmitted to the upper computer in real time, and the upper computer filters the abnormal data; the abnormal data is filtered by a method of comparing a predicted value with an actually-measured value obtained by trend analysis; and factors in varied aspects of the actually-measured value of acquired data, the predicted value, variable quantity and variable direction are taken into comprehensive consideration. By adoption of the method, the automatic data acquisition system can effectively and automatically realize the filtration of interfered data and greatly reduce influence of noisy data on analysis.
Owner:SHANGHAI TONGYAN CIVIL ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY CORP LTD
Systems and methods for using statistical techniques to reason with noisy data
Systems and methods are presented that enable logical reasoning even in the presence of noisy (inconsistent) data. The knowledge base is processed in order to make it consistent and is also compiled. This processing includes checking and correcting spelling, removing stopwords, performing, grouping words of similar and related meaning, and compacting the knowledge base. A robot can use the processed knowledge base to perform many different types of tasks, such as answering a query, determining a course of action that is designed to achieve a particular goal, and determining its own location.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
System and method for estimating turbine engine deterioration rate with noisy data
A method for monitoring engine performance includes sampling exhaust gas temperature associated with a turbine engine over an interval of operational time of the turbine engine. The method further includes applying a first test to identify statistical outliers on the sampled exhaust gas temperature data and removing identified statistical outliers from the sampled exhaust gas temperature data. Subsequently, the method includes applying a second test to identify step changes in slope of the exhaust gas temperature data and dividing the interval of operational time into one or more segments based upon the identified step changes. Finally, the method includes determining a slope for each segment and combining the segments to obtain a rate of performance deterioration of the turbine engine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
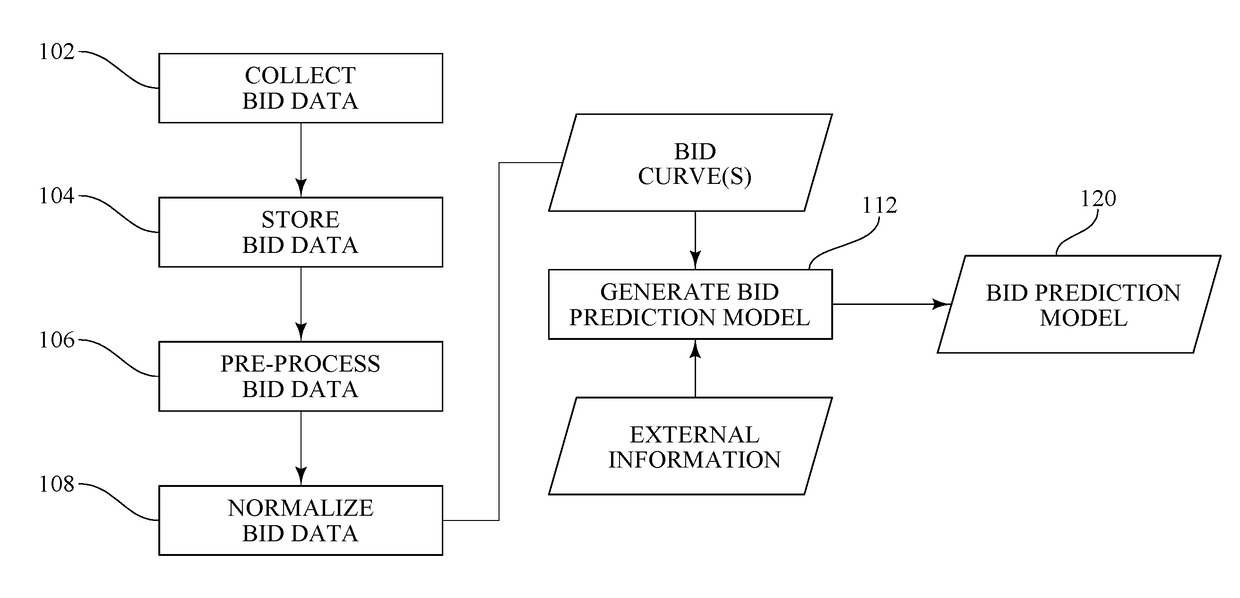
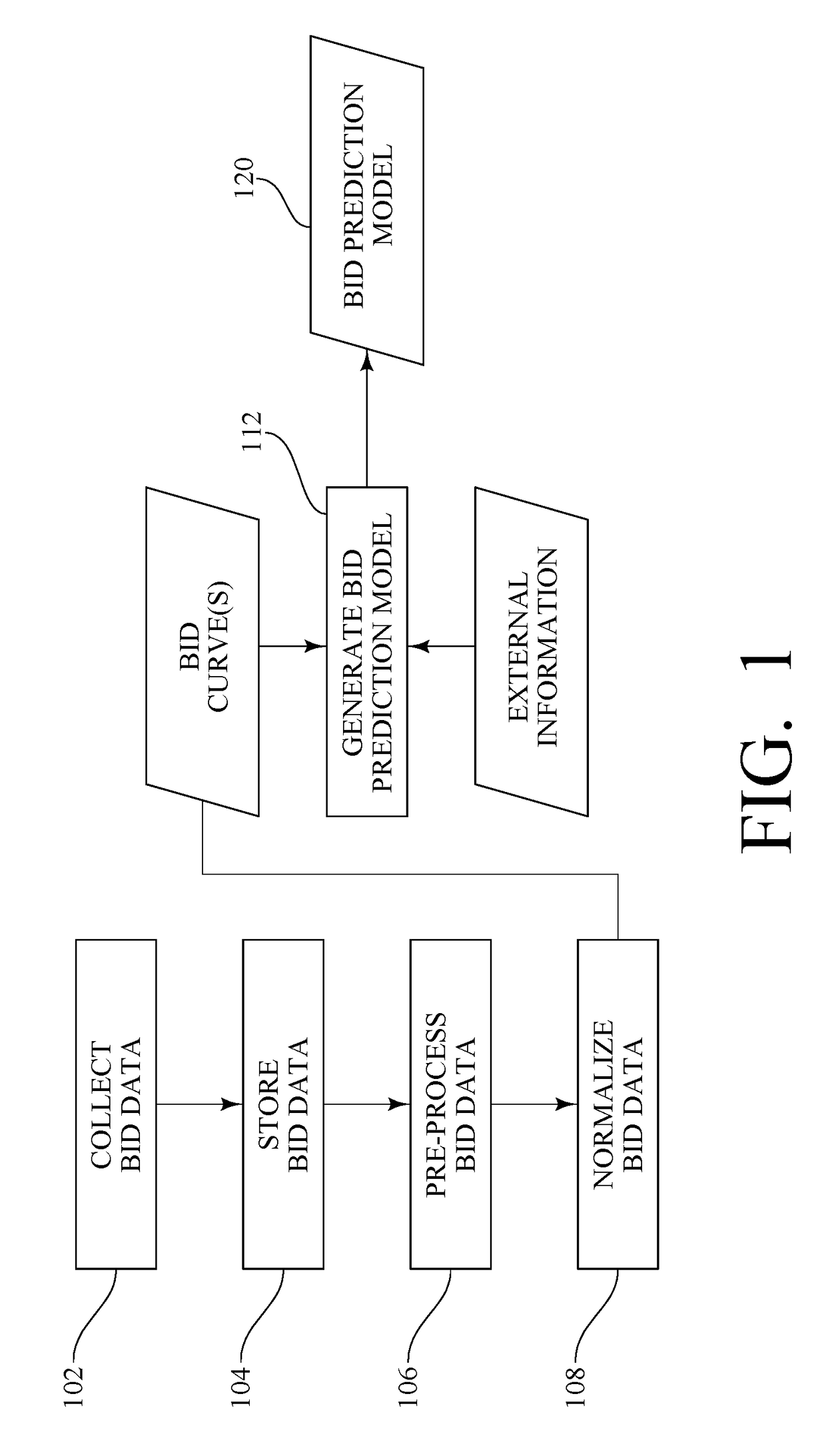
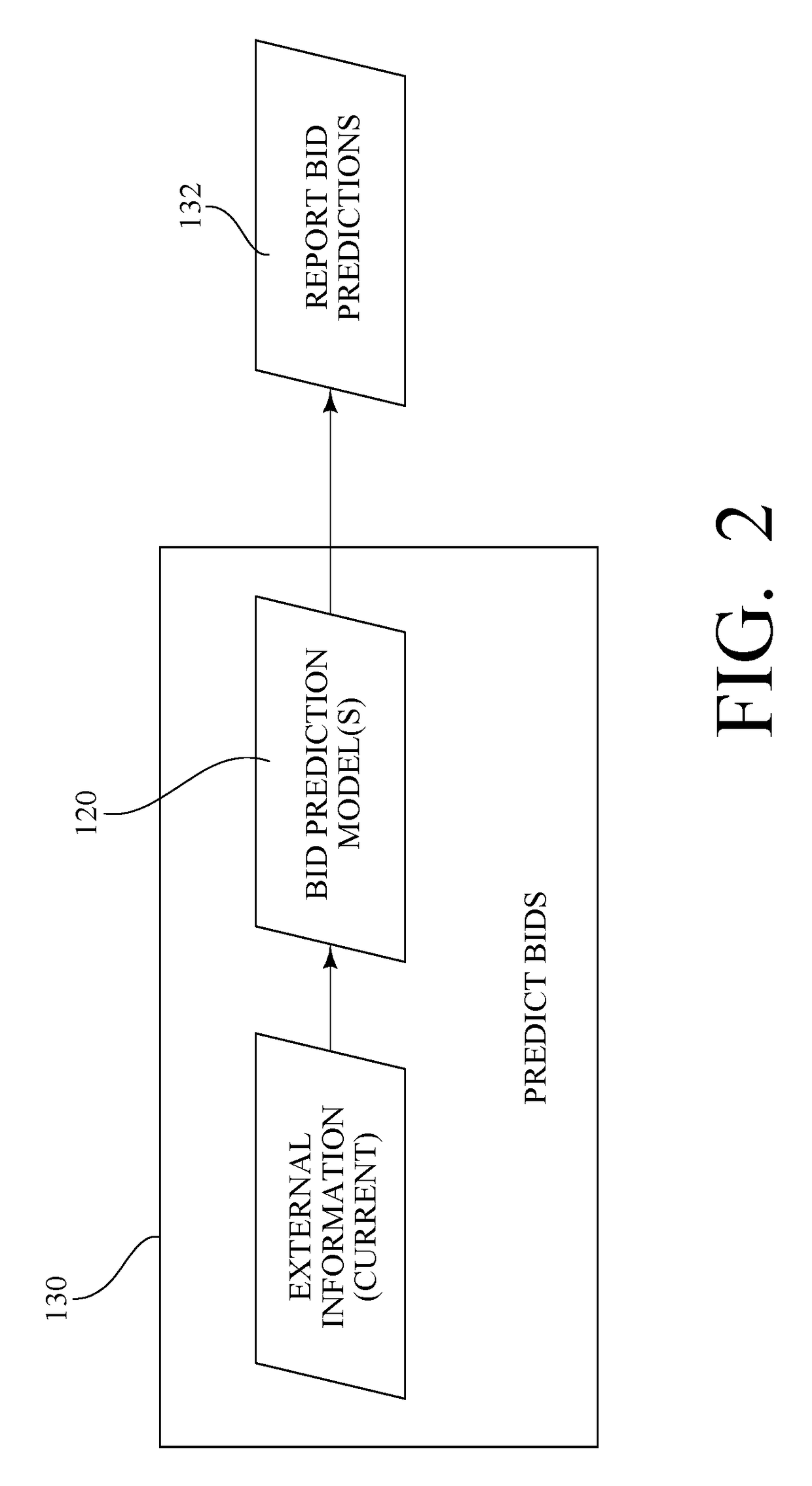
Method and system for analyzing and predicting bidding of electric power generation
InactiveUS20170200229A1Increase supplyFinanceInformation technology support systemNoisy dataData mining
In a method and system for analyzing and predicting bidding of electric power generation, bid data is collected for a selected region. The bid data is preprocessed to decode the identity of the bidding entities and / or to remove erroneous or noisy data. External information, such as fuel prices, weather data, and / or generator outage data, is also collected. A bid prediction model is generated for one or more of the bidding entities from the bid data and the external information. External information is subsequently received, and the bid prediction model is applied to that current external information to predict future bids for one or more of the bidding entities. The predicted future bids are then reported.
Owner:GENSCAPE INTANGIBLE HOLDING INC
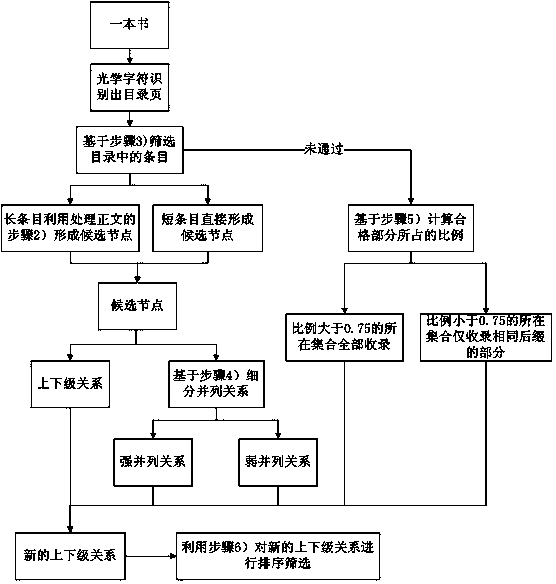
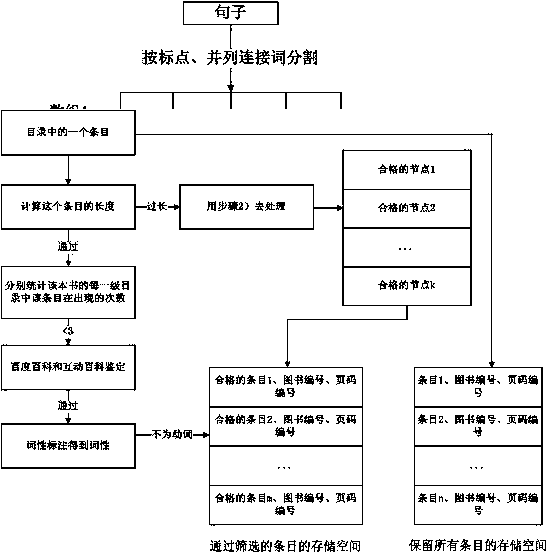
Method for establishing mapping knowledge domain based on book catalogue
ActiveCN103729402AImprove scalabilityRelationship richSpecial data processing applicationsNODALArray data structure
The invention discloses a method for establishing a mapping knowledge domain based on a book catalogue. The method comprises the steps that a catalogue page in a digitized book is extracted, the lengths of items in the catalogue are differentiated, and part-of-speech tagging is conducted on the long items through a natural language processing tool, so that part-of-speech arrays are obtained, and candidate nodes are extracted according to rules of conjunctions, punctuations and parts of speech; the long items and the short items are authenticated in the Baidu encyclopedia and the Hudong encyclopedia, a leader-member relation and parallel relations are formed through a catalogue structure and serve as a framework of the mapping knowledge domain, the strong and weak parallel relations are differentiated and serve as increments respectively, and the leader-member relation is supplemented with the strong and weak parallel relations; according to a noisy data excavating algorithm with suffixes serving as a base, nodes are selected from the items which do not pass the authentication of the encyclopedias and the mapping knowledge domain is supplemented with the selected nodes; finally, the weights of relations in the supplemented mapping knowledge domain are calculated and ranked, so that noise is removed through screening. Compared with an existing mapping knowledge domain, the mapping knowledge domain established through the method is richer in node, better in expandability and higher in accuracy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for recognizing and interpreting patterns in noisy data sequences
Owner:POTTER JERRY LEE
Method for data compression and inference
InactiveUS20140132429A1Competitive compression performanceSmooth transitOther decoding techniquesCode conversionData compressionLossless coding
Lossless and lossy codes are combined for data compression. In one embodiment, the most significant bits of each value are losslessly coded along with a lossy version of the original data. Upon decompression, the lossless reduced-precision values establish absolute bounds for the lossy code. Another embodiment losslessly codes the leading bits while trailing bits undergo lossy coding. Upon decompression, the two codes are summed. The method preserves edges and other sharp transitions for superior lossy compression. Additionally, the method enables description-length inference using noisy data.
Owner:SCOVILLE JOHN CONANT
Method of speech recognition with compensation for both channel distortion and background noise
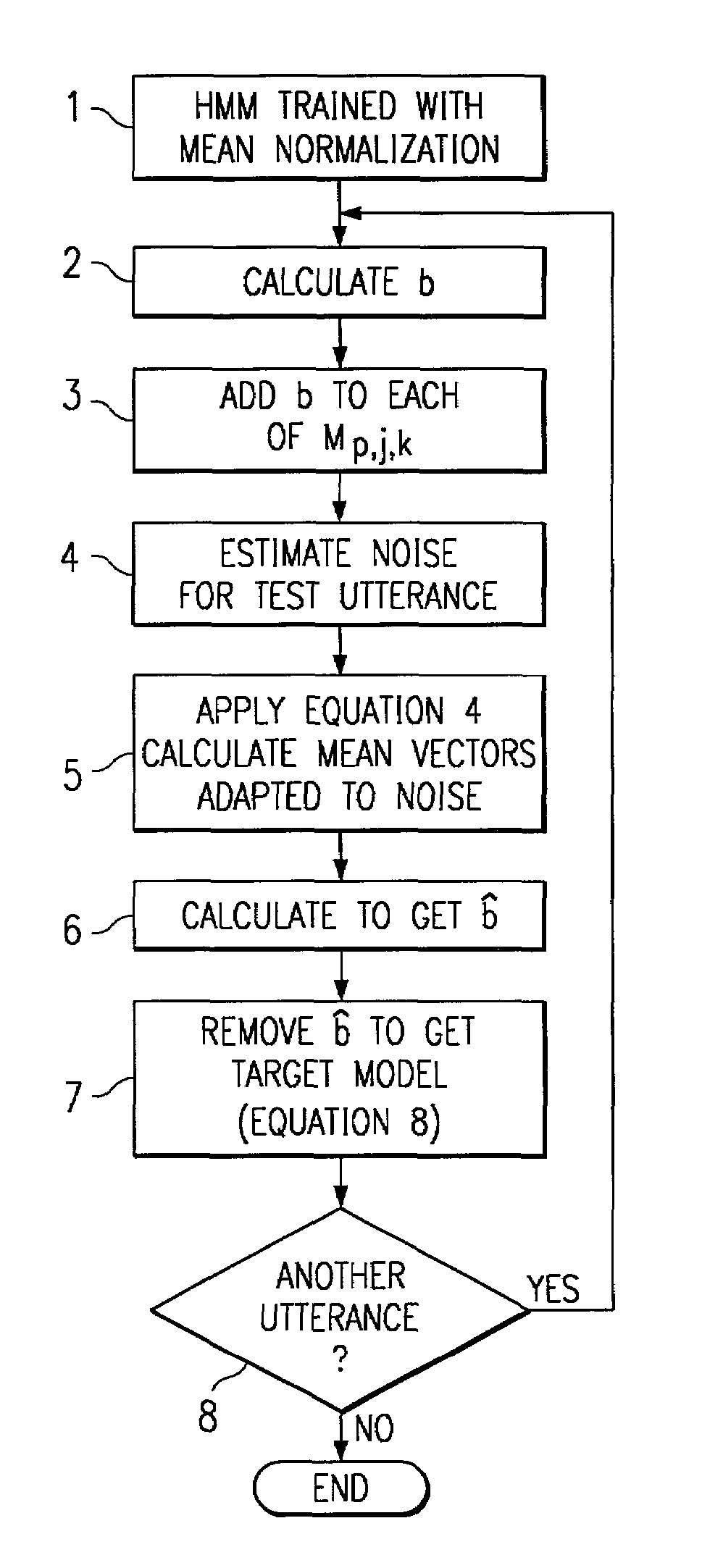
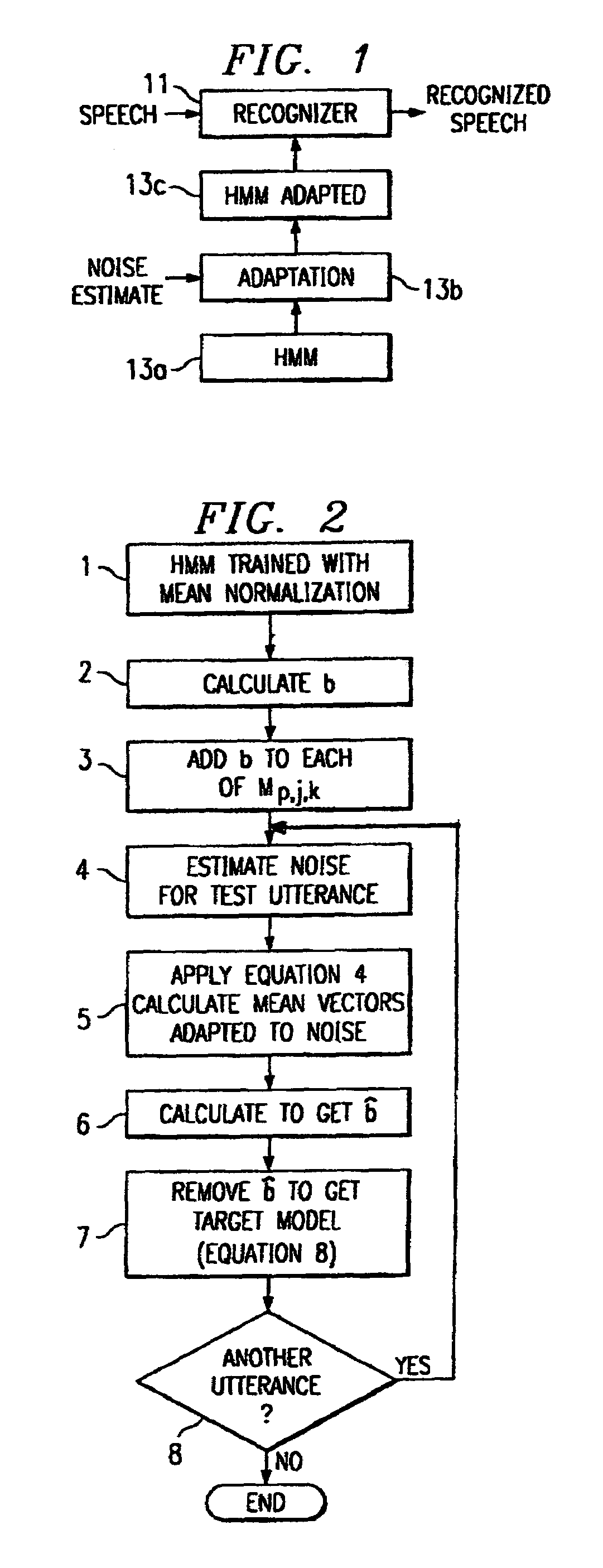
A method of speech recognition with compensation is provided by modifying HMM models trained on clean speech with cepstral mean normalization. For all speech utterances the MFCC vector is calculated for the clean database. This mean MFCC vector is added to the original models. An estimate of the background noise is determined for a given speech utterance. The model mean vectors adapted to the noise are determined. The mean vector of the noisy data over the noisy speech space is determined and this is removed from model mean vectors adapted to noise to get the target model.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method for swell noise detection and attenuation in marine seismic surveys
Spatial data sequences are extracted in a frequency-space domain at selected frequencies in selected data windows in seismic data. A signal model and residuals are iteratively constructed for each extracted spatial data sequence. Each data sample in each extracted spatial data sequence is assessed to determine if the data sample is noisy. Each noisy data sample in each data sequence is replaced by a corresponding signal model value. The earth's subsurface is imaged using the noise-attenuated seismic data.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
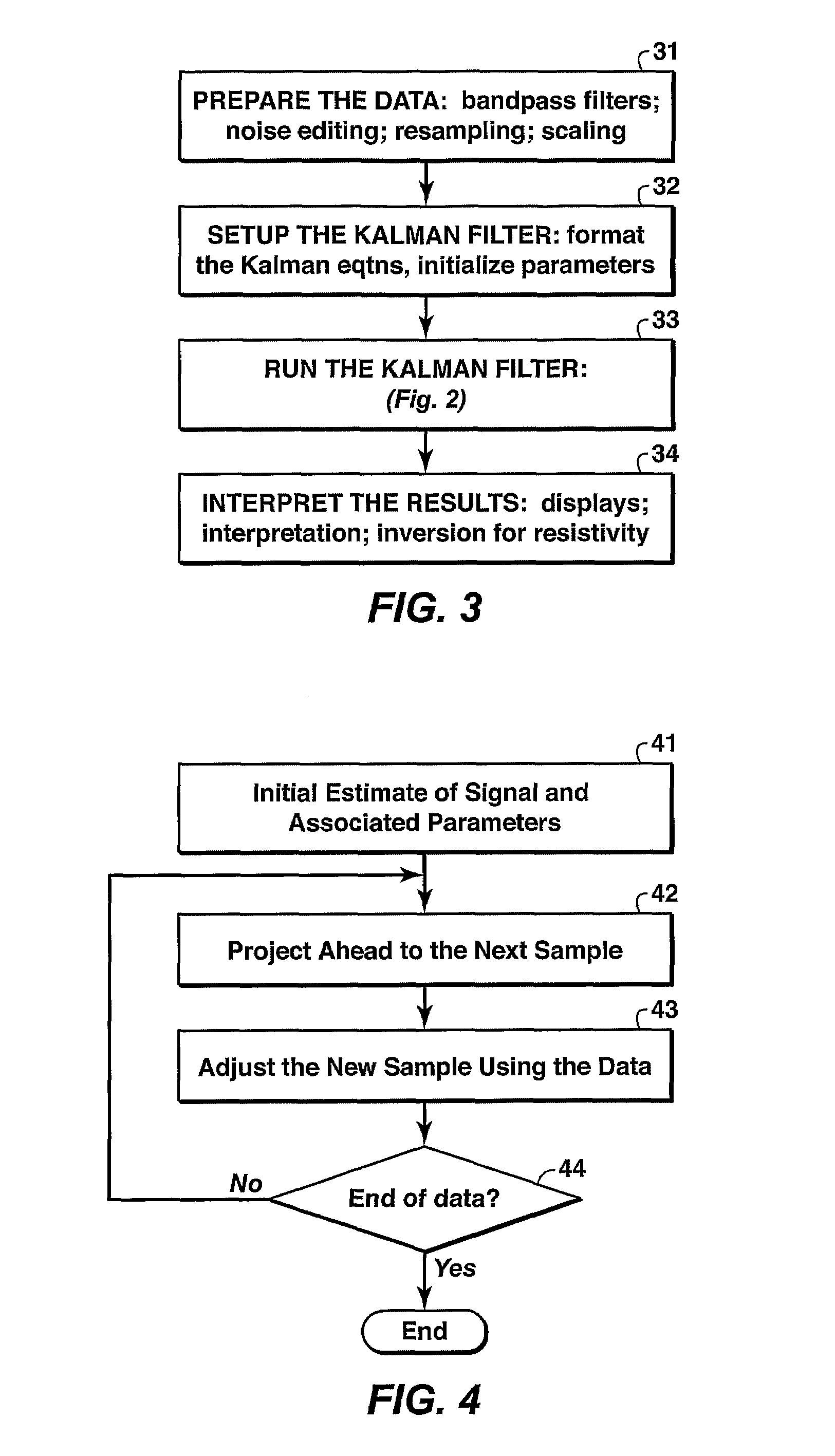
Kalman filter approach to processing electromagnetic data
InactiveUS7536262B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurement arrangements for variableKaiman filterControlled source electro-magnetic
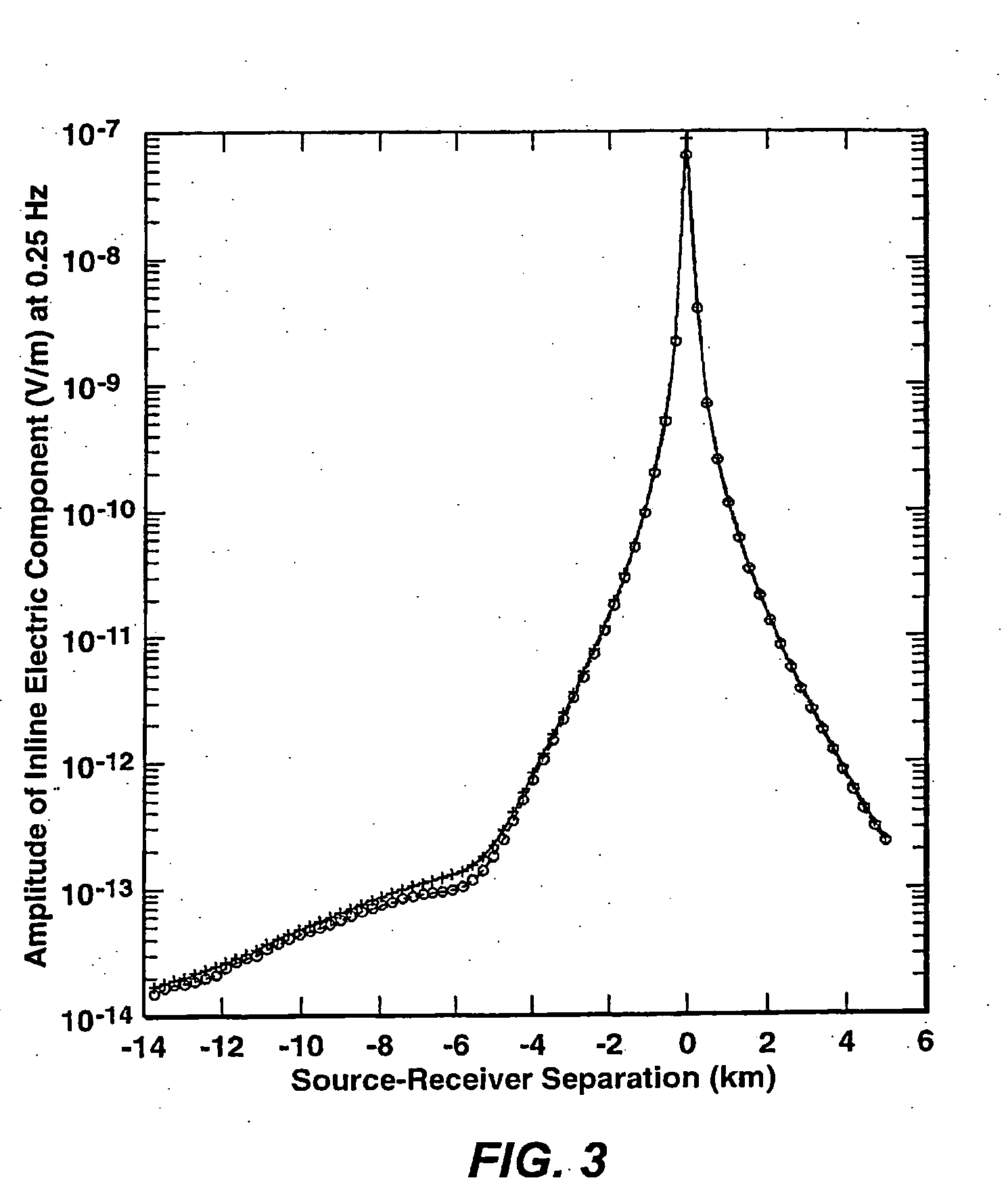
A method for tracking a sinusoidal electromagnetic signal in noisy data using a Kalman filter or other tracking algorithm. The method is useful for controlled source electromagnetic surveying where longer source-receiver offsets can cause the source signal to decay significantly and be difficult to retrieve from magnetotelluric or other electromagnetic background.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Microblog topic detection and hotspot evaluation method based on semantic expansion
The invention discloses a microblog topic detection and hotspot evaluation method based on semantic expansion, belongs to the field of text information processing, and particularly relates to microblog noisy data filtering and a microblog topic detection and topic hotspot evaluation method and system based on semantic expansion. The method comprises the steps of firstly giving out a microblog noisy data filtering method for filtering microblogs with low information content, then supplementing effective semantic information in microblog comments into microblog semanteme so as to improve the detection effect of microblog topics, finally carrying out microblog topic hotspot evaluation, and thus obtaining hot topics.
Owner:GOONIE INT SOFTWARE BEIJING
Automated anomaly detection
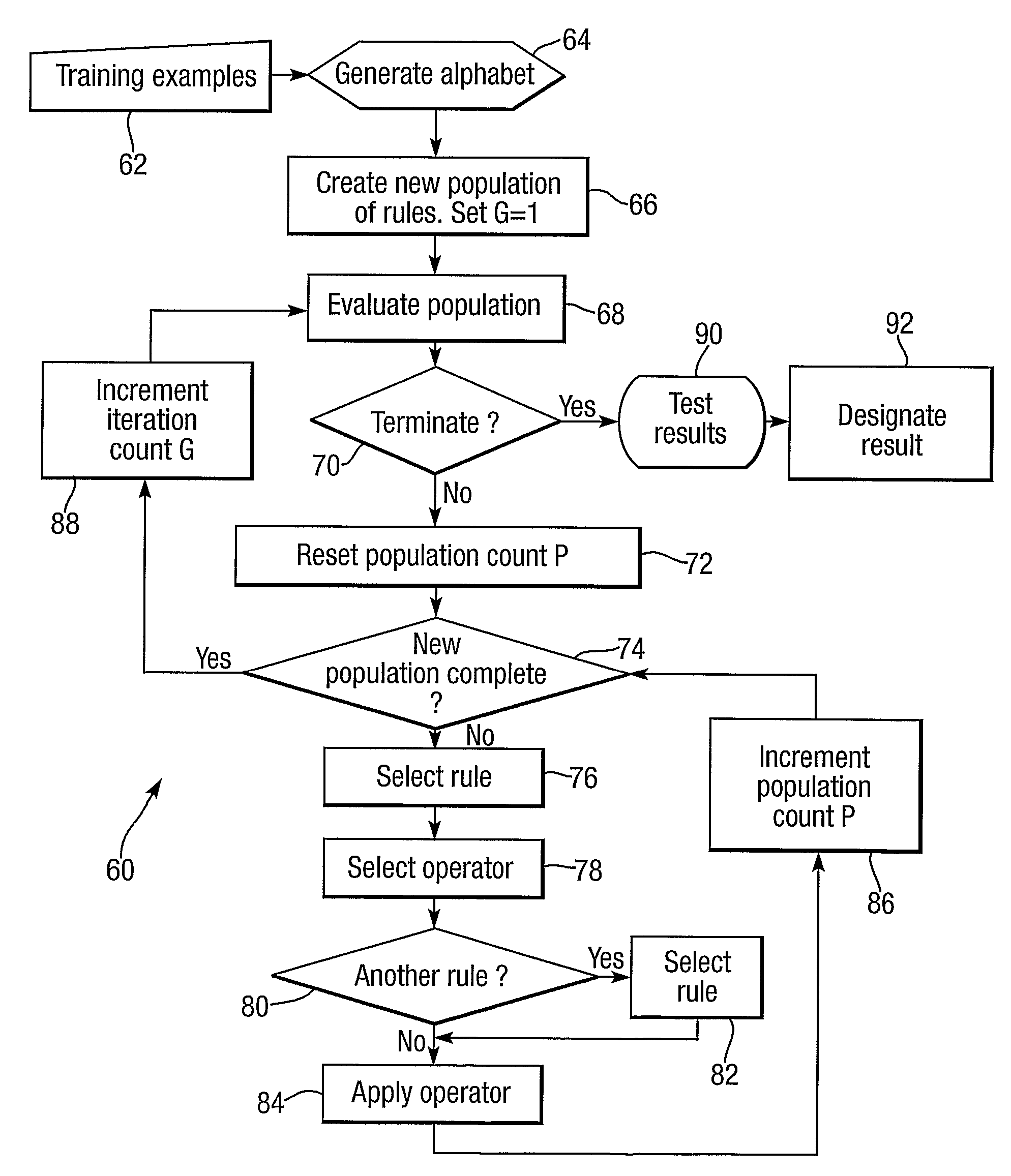
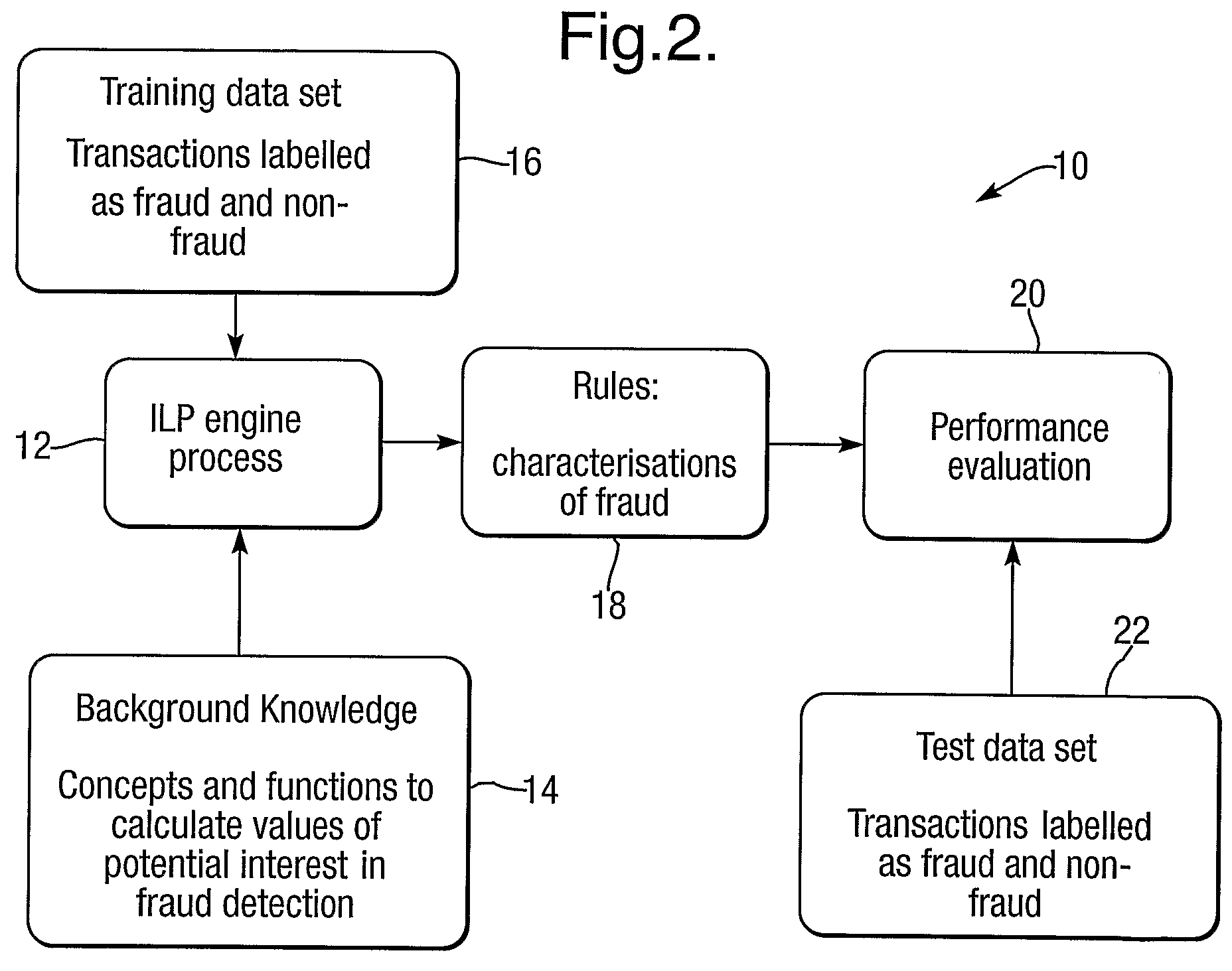
ActiveUS7627543B2Avoid overfitting noisy dataError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsData setNoisy data
A method of anomaly detection applicable to telecommunications or retail fraud or software vulnerabilities uses inductive logic programming to develop anomaly characterization rules from relevant background knowledge and a training data set, which includes positive anomaly samples of data covered by rules. Data samples include 1 or 0 indicating association or otherwise with anomalies. An anomaly is detected by a rule having condition set which the anomaly fu,lfils. Rules are developed by addition of conditions and unification of variables, and are filtered to remove duplicates, equivalents, symmetric rules and unnecessary conditions. Overfitting of noisy data is avoided by an encoding cost criterion. Termination of rule construction involves criteria of rule length, absence of negative examples, rule significance and accuracy, and absence of recent refinement. Iteration of rule construction involves selecting rules with unterminated construction, selecting rule refinements associated with high accuracies, and iterating a rule refinement, filtering and evaluation procedure to identify any refined rule usable to test data. Rule development may use first order logic or Higher Order logic.
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
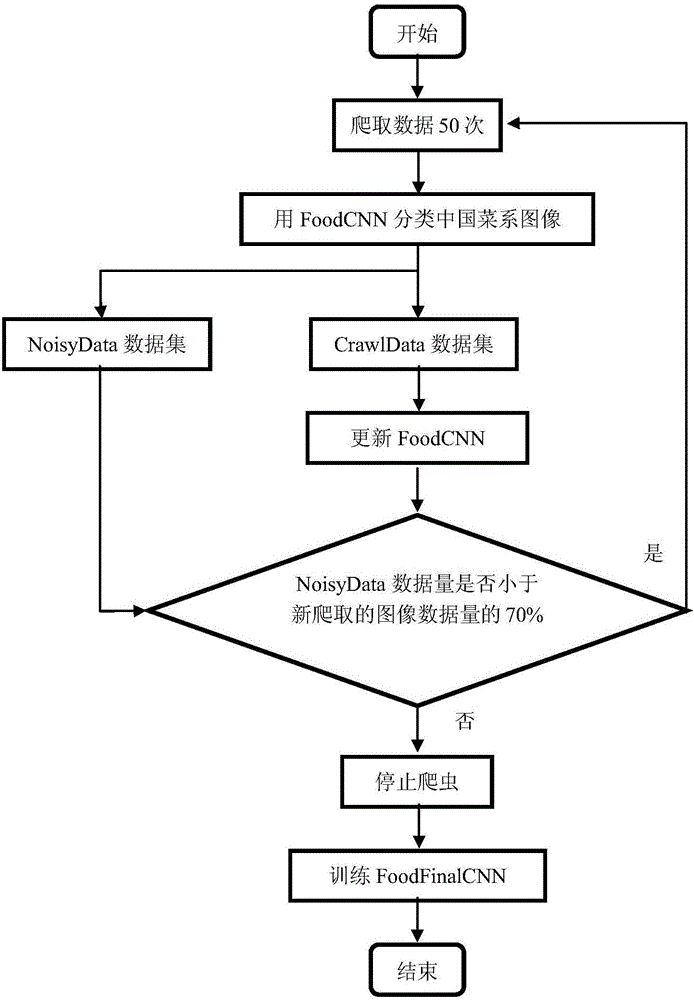
Food image automatic classification method based on convolutional neural networks
ActiveCN106529564AImprove work efficiencyShorten the timeWeb data indexingBiological neural network modelsData setThe Internet
The invention discloses a food image automatic classification method based on convolutional neural networks. The food image automatic classification method comprises steps that 1) food image data is crawled by a network crawler from Internet, and food images having correct labels are artificially screened out and filed in an Initial Data data set; 2) the network crawler is used to search a lot of food image data of the target classification in a mainstream search engine and an image sharing website, and at the same time, a step 4) is executed regularly; 4) a Food CNN network is used for data screening, and the data is divided into a Crawl Data and a Noisy Data; 5) the expanded data Crawl Data is used to update the Food CNN network; 6) whether the Noisy Data data size is reasonable is determined, and whether the crawling is continued is determined; 7) the crawling is stopped, and a Food Final CNN is trained. A correction rate is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Systems and methods for using statistical techniques to reason with noisy data
Systems and methods are presented that enable logical reasoning even in the Presence of noisy (inconsistent) data. The knowledge base is processed in order to make it consistent and is also compiled. This processing includes checking and correcting spelling, removing stopwords, performing, grouping words of similar and related meaning, and compacting the knowledge base. A robot can use the processed knowledge base to perform many different types of tasks, such as answering a query, determining a course of action that is designed to achieve a particular goal, and determining its own location.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Automated data alignment based upon indirect device relationships
A noisy data alignment algorithm for determining cycle count offsets for noisy pairs of n monitoring devices. A direct cycle count offset matrix is determined based upon the highest correlation coefficients produced by correlating frequency variation data from each device pair Dij. For each direct cycle count offset Mij, indirect cycle count offsets are calculated as a function of at least Mk, where k≠i≠j, to produce indirect cycle count offsets. The statistical mode of these indirect offsets is compared with the corresponding Mij in the matrix. When they differ, Mij in the direct matrix is adjusted to be equal to the statistical mode. All indirect cycle count offsets for all other unique device pairs, Mij, are calculated to iterate to a single solution in which all indirect cycle count offsets are equal to the corresponding direct cycle count offset. An optional verification algorithm is also provided.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC USA INC
Training and identification method and system of bidirectional neural network model
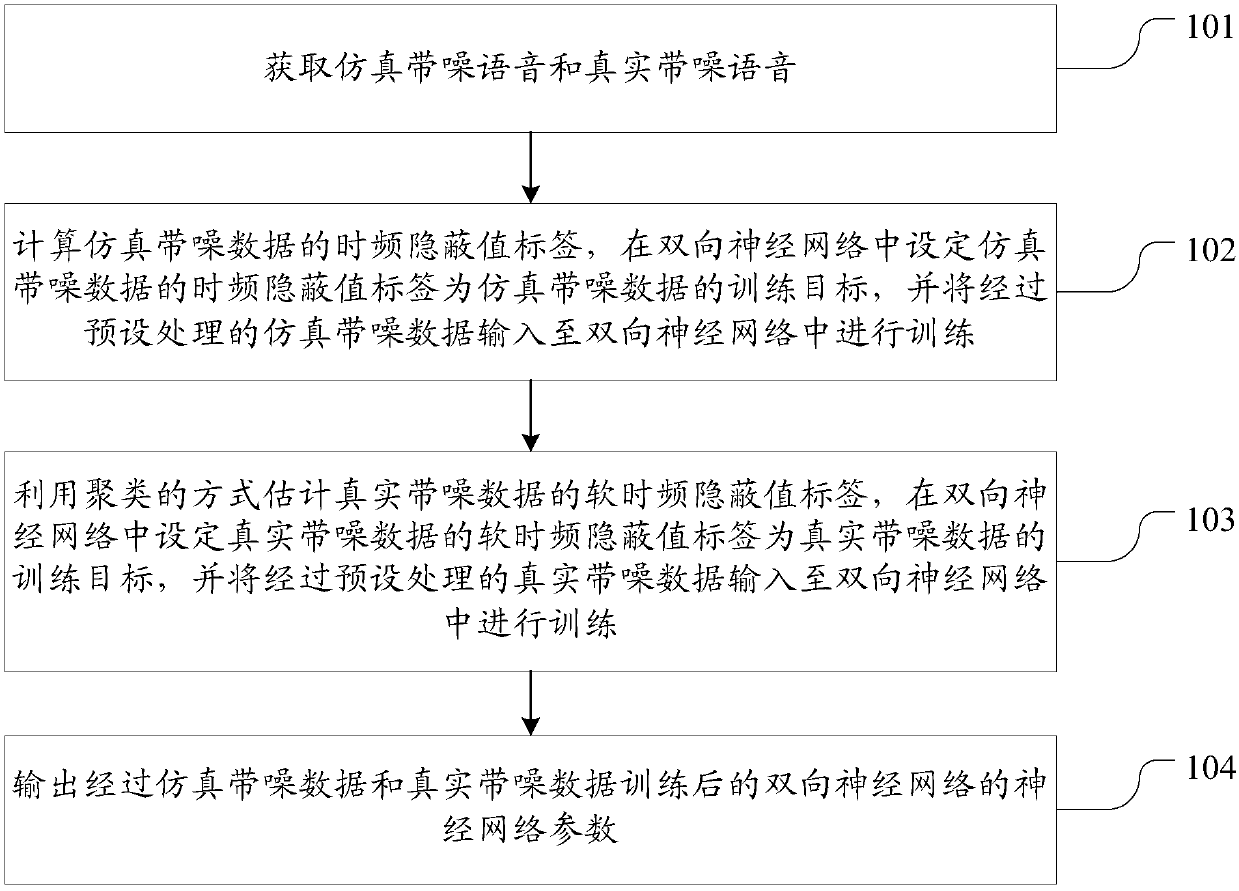
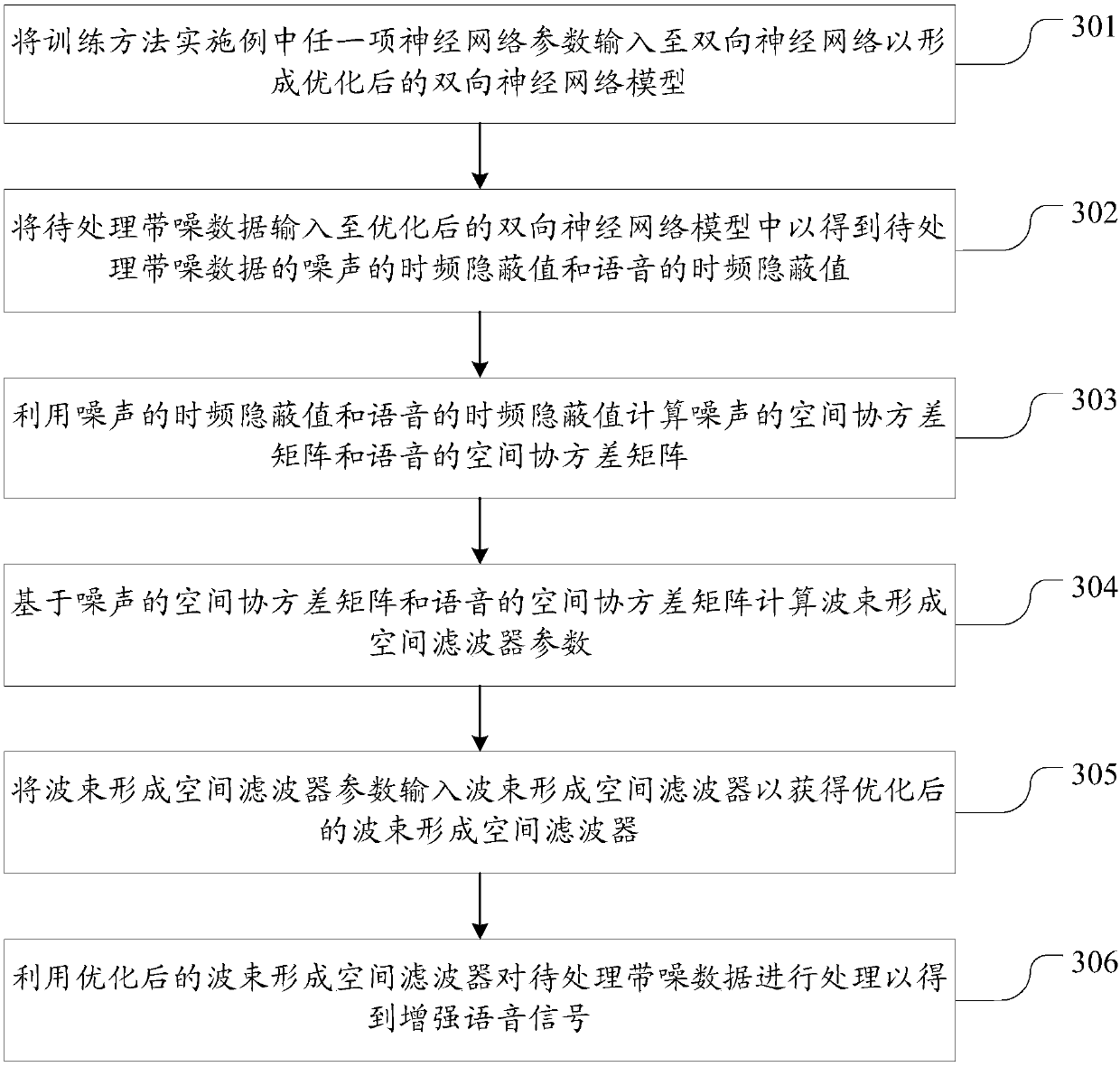
ActiveCN108417224AReduce mismatchIncrease the amount of training dataSpeech analysisNeural architecturesNerve networkNoisy data
The invention discloses the training and identification method and system of a bidirectional neural network model used for processing a noisy voice. The method comprises the followings steps of acquiring simulation noisy data and real noisy data; calculating the time-frequency hidden value label of the simulation noisy data, setting the label of the simulation noisy data to be a training target ina bidirectional neural network, and inputting the simulation noisy data after preset processing into the bidirectional neural network so as to carry out training; using a clustering mode to estimatethe soft time-frequency hidden value label of the real noisy data, setting the soft label of the real noisy data in the bidirectional neural network to be the training target, and inputting the real noisy data after preset processing into the bidirectional neural network so as to carry out training; and outputting the neural network parameters of the trained bidirectional neural network. In the invention, through introducing the real and non-simulated training data, the neural network model is trained. On one hand, a training data size is increased; on the other hand, the mismatching of the simulation data and the real data is reduced.
Owner:AISPEECH CO LTD
System and method for quality control of noisy data
Disclosed is a method for evaluating seismic data, the method including identifying seismic data sets which are homogeneous; and identifying noise in the data sets by at least one of performing a macro analysis of the data sets to identify noise components; performing a correlation analysis of the data sets to identify correlating noise data; performing a polarization analysis to identify a direction of noise; and performing a spectral analysis to identify frequencies associated with noise. An associated system and computer program product are provided.
Owner:MAGNITUDE SPAS
Kernel regression for image processing and reconstruction
ActiveUS7889950B2Improves gradient and pixel valueEnhanced informationImage enhancementTelevision system detailsSingular value decompositionKernel regression
Owner:UNIV OF CALIFORNIA SANTA CRUZ
Peak selection in multidimensional data
InactiveUS20050209789A1Improve automationValid choiceParticle separator tubesComponent separationPattern recognitionData set
An automatic peak selection method for multidimensional data can efficiently select peaks from very noisy data such as two-dimensional liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) data. Such data are characterized by non-normally distributed noise that varies in different dimensions. The method computes local noise thresholds for each one-dimensional component of the data. Each point has a local noise threshold applied to it for each dimension of the data set, and a point is selected as a candidate peak only if its value exceeds all of the applied local noise thresholds. Contiguous candidate peaks are clustered into actual peaks. The method is preferably implemented as part of a high-throughput platform for analyzing complex biological mixtures.
Owner:CAPRION PROTEOMICS INC
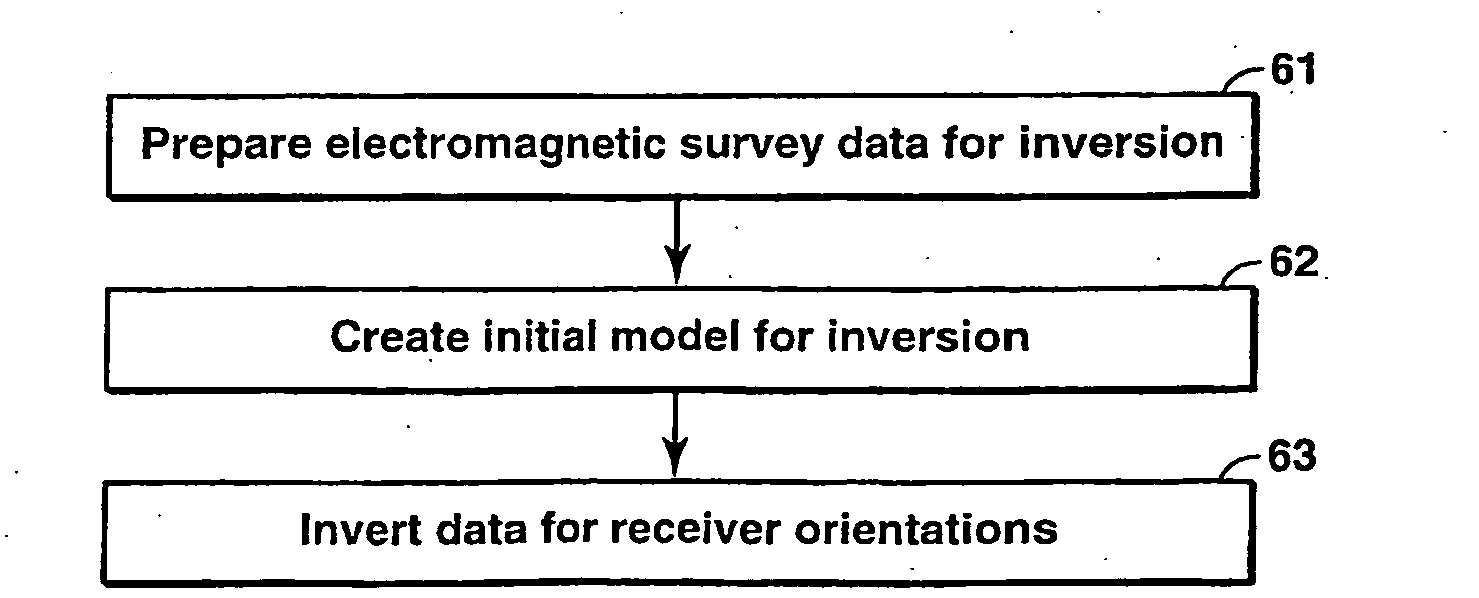
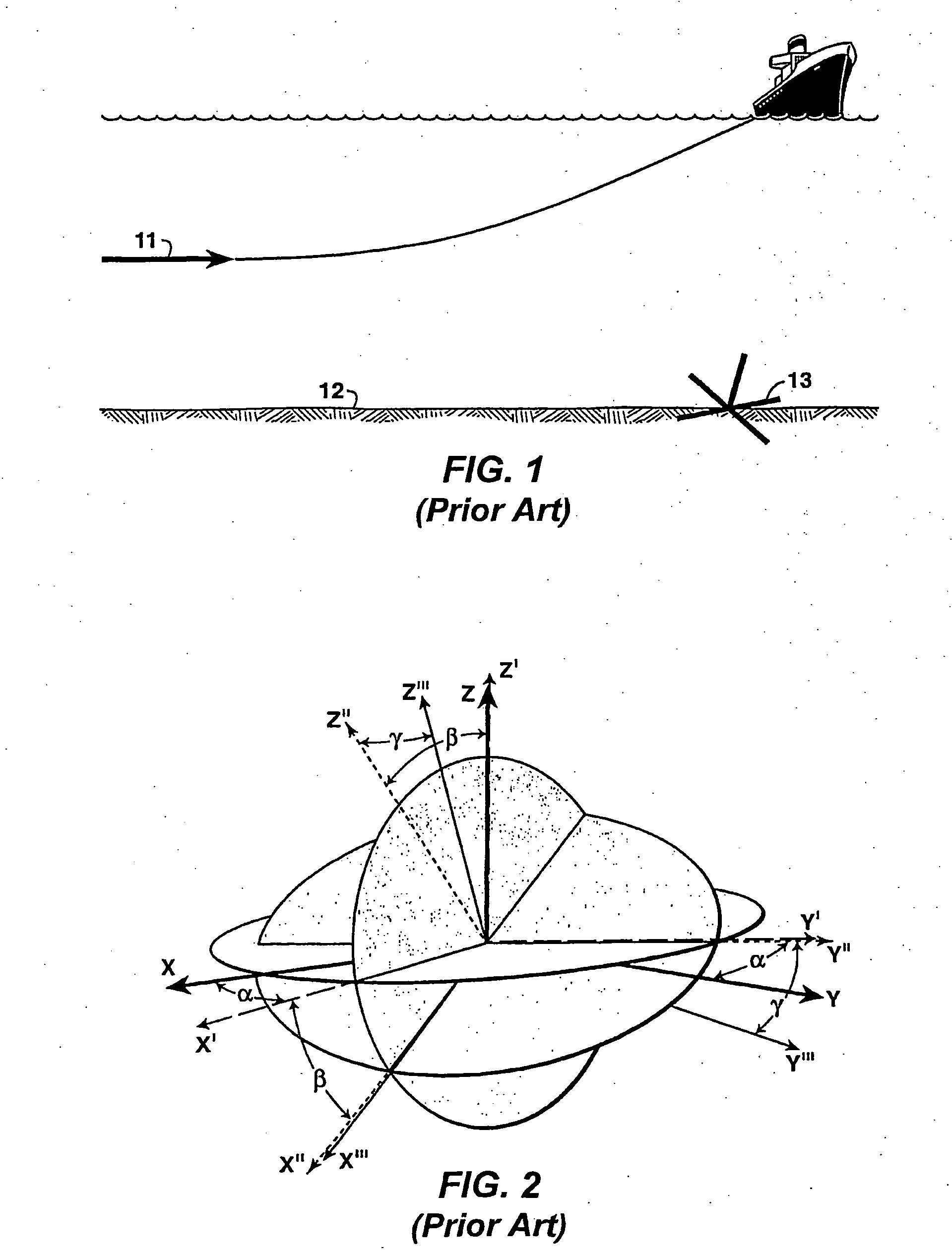
Method for Determining Receiver Orientations
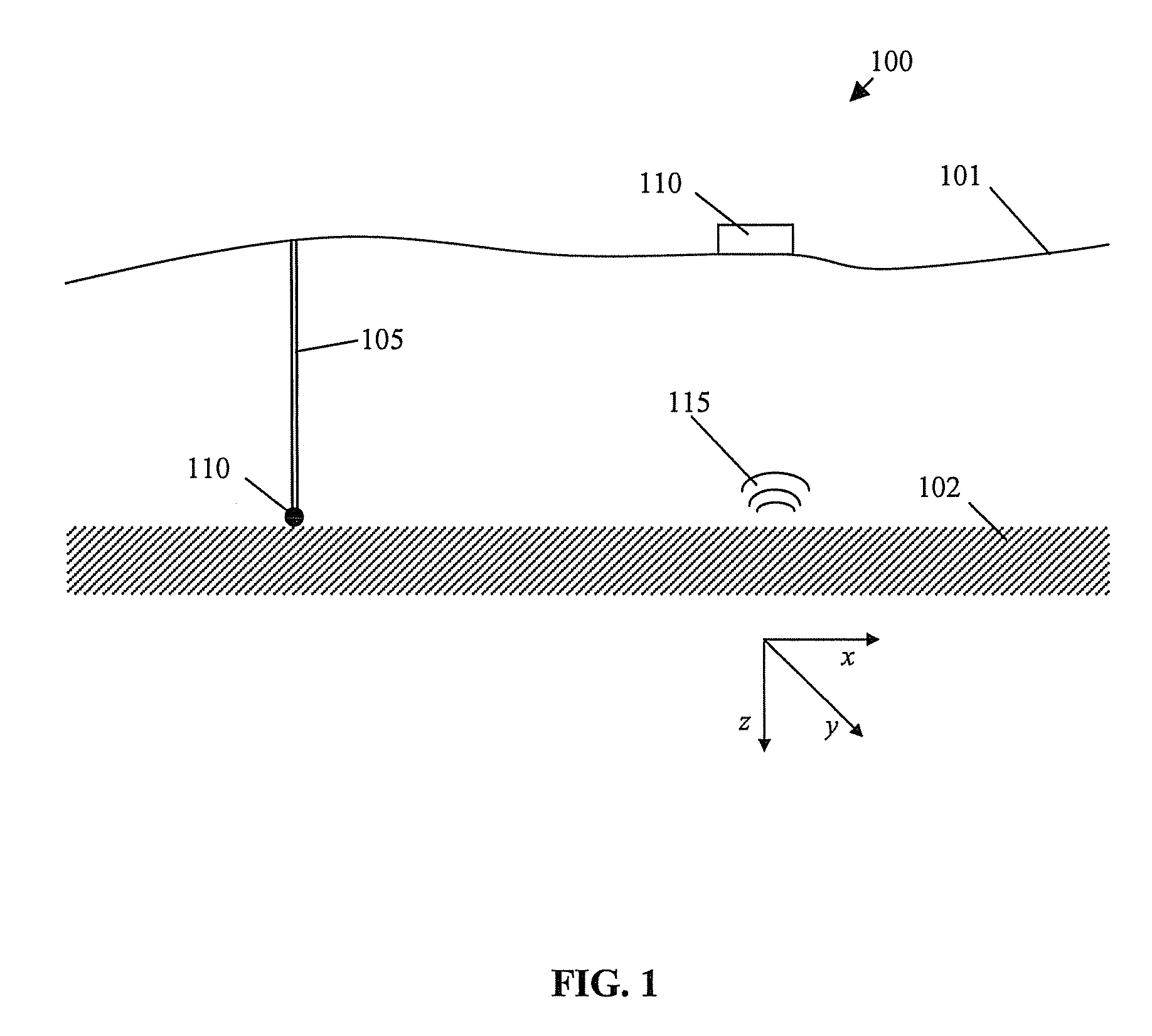
InactiveUS20090171587A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementOcean bottomNoisy data
Method for completely specifying orientation of electromagnetic receivers dropped to the ocean bottom in an electromagnetic survey. Survey data are selected, rejecting noisy data with long offsets and data where the receiver has saturated with short offsets (61). A model is developed comprising three independent receiver orientation angles completely specifying the receiver orientation in three dimensions, and an earth resistivity model including a water layer and possibly an air layer (62). Maxwell's equations, applied to the model and the selected data, are then inverted to determine the receiver orientations (63).
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
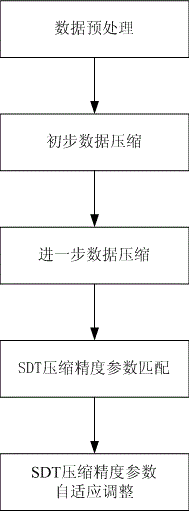
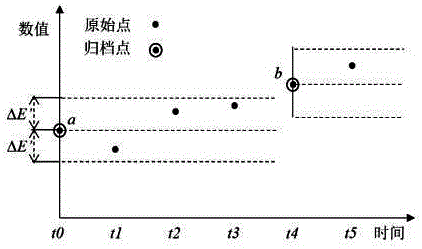
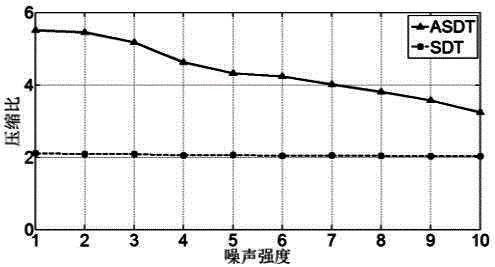
Monitoring data compression method applicable to operation and maintenance automation system
InactiveCN106649026AIdentify key trendsReduced impact on compression performanceHardware monitoringData compressionComplete data
The invention discloses a monitoring data compression method applicable to an operation and maintenance automation system. The method includes the following steps that 1, data preprocessing is conducted, wherein smoothing is conducted on original data to reduce interference with an SDT algorithm from noisy data; 2, preliminary data compression is conducted, wherein a control algorithm is adopted to compress data preliminarily; 3, further data compression is conducted, wherein the SDT algorithm is adopted for further compression; 4, SDT compression precision parameter matching is conducted, wherein after each time of data compression, compression precision parameters are matched with the characteristics of data fluctuation changes according to the data fluctuation changes, and compression precision parameters generated after matching are obtained; 5, adaptive adjustment of the SDT compression precision parameters is conducted, wherein the step 2, the step 3 and the step 4 are repeated according to the compression precision parameters generated after matching, and then the compression precision parameters are adaptively adjusted; 6, the step 2, the step 3 and the step 5 are repeated until the compression precision parameters are completely matched with the characteristics of the data fluctuation changes, the optimal compression precision parameters are obtained, and then the step 2 and the step 3 are repeated to complete data compression.
Owner:国家电网公司北京电力医院 +1
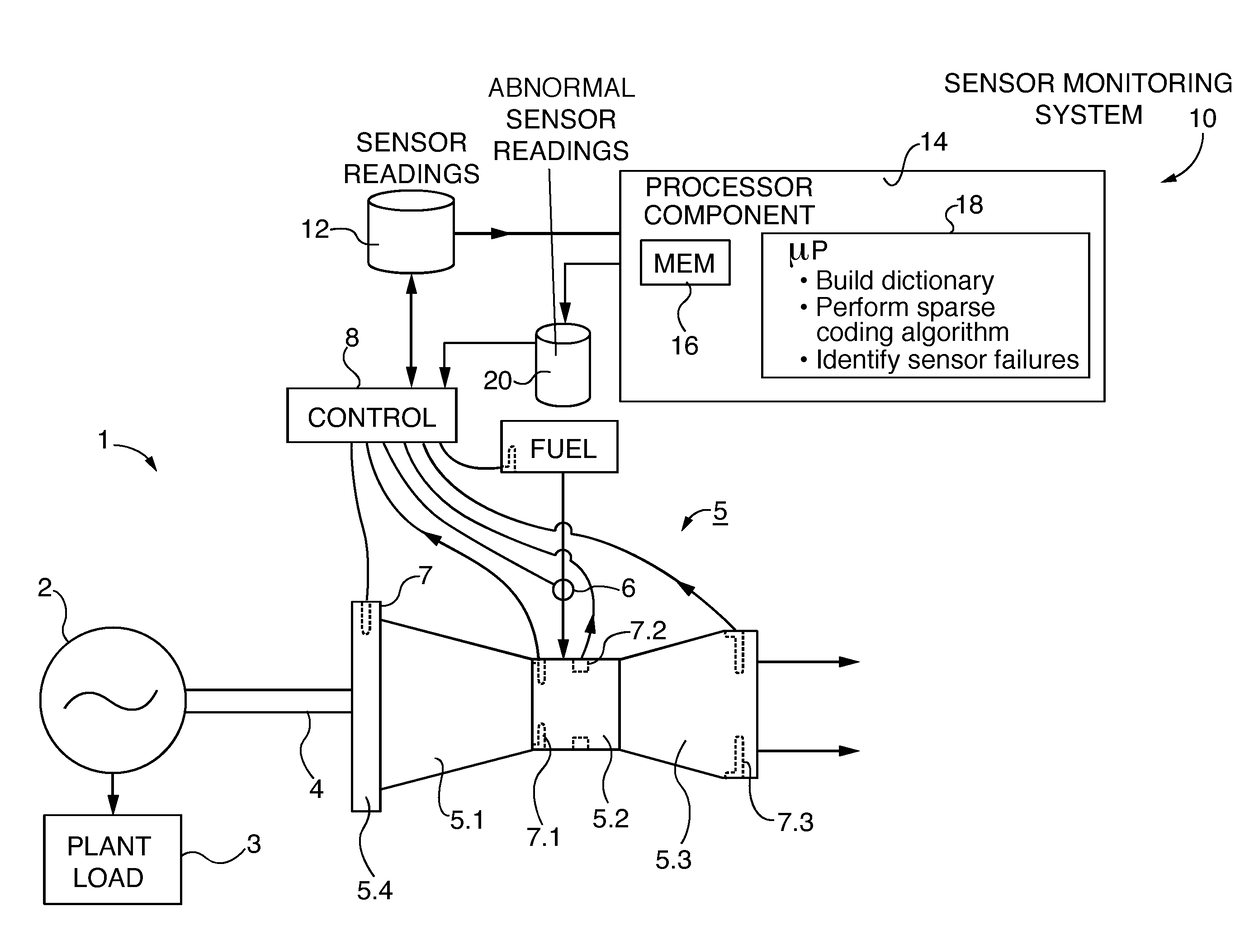
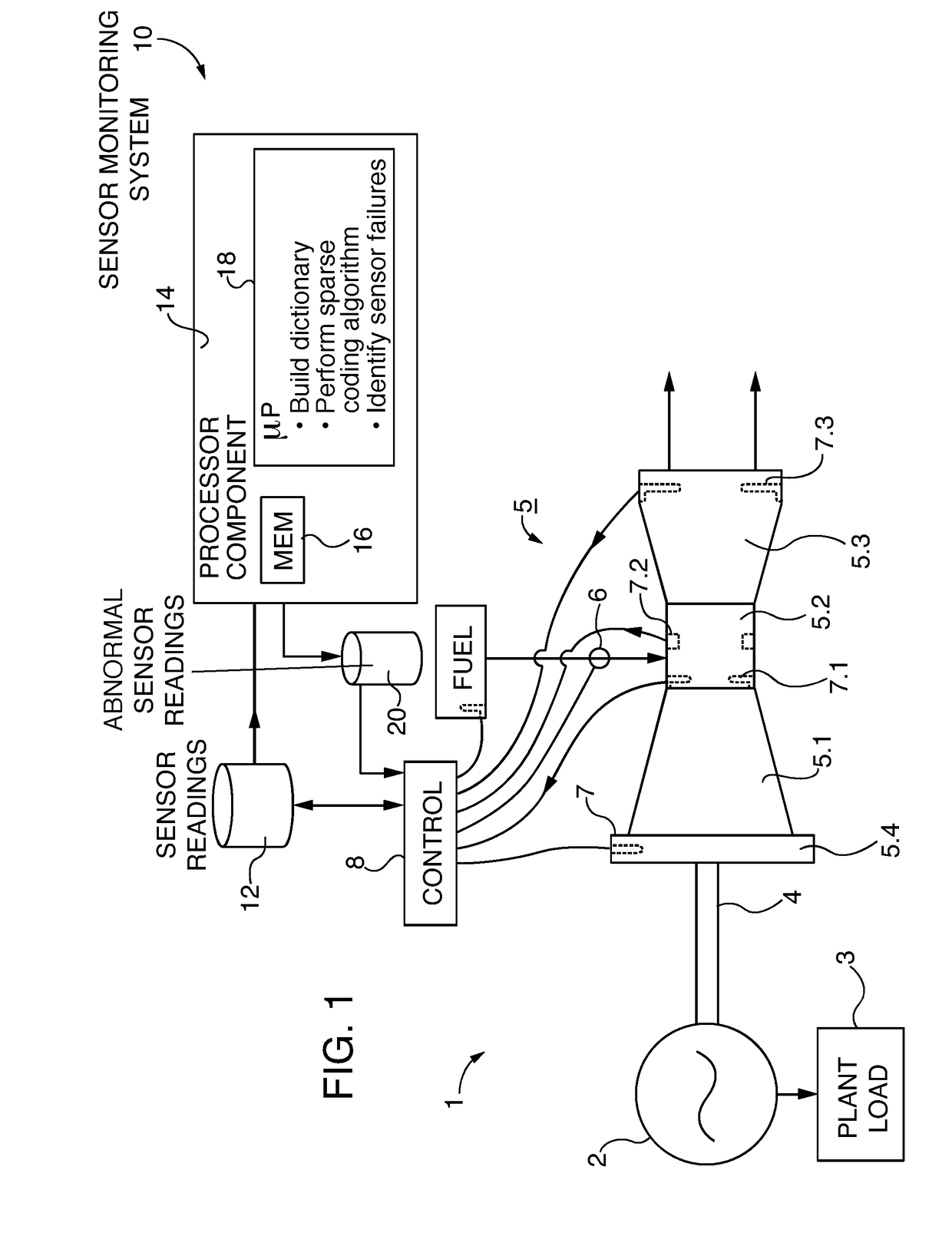
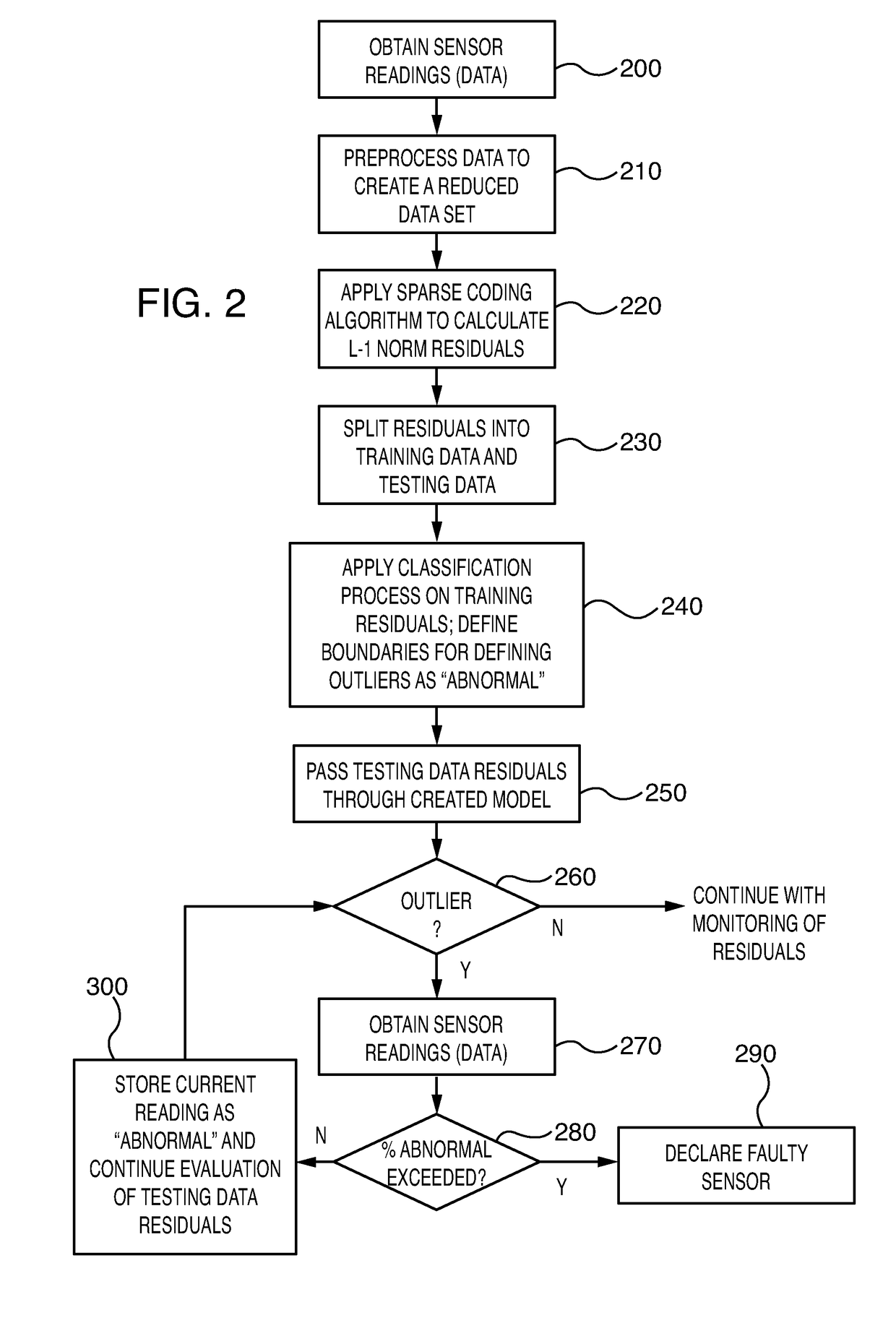
Gas turbine sensor failure detection utilizing a sparse coding methodology
ActiveUS20180231394A1Improve abilitiesGas-turbine engine testingElectric testing/monitoringArray data structureOutlier
A method and system for recognizing (and / or predicting) failures of sensors used in monitoring gas turbines applies a sparse coding process to collected sensor readings and defines the L-1 norm residuals from the sparse coding process as indicative of a potential sensor problem. Further evaluation of the group of residual sensor readings is perform to categorize the group and determine if there are significant outliers (“abnormal data”), which would be considered as more likely associated with a faulty sensor than noisy data. A time component is introduced into the evaluation that compares a current abnormal result with a set of prior results and making the faulty sensor determination if a significant number of prior readings also have an abnormal value. By taking the time component into consideration, the number of false positives is reduced.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com