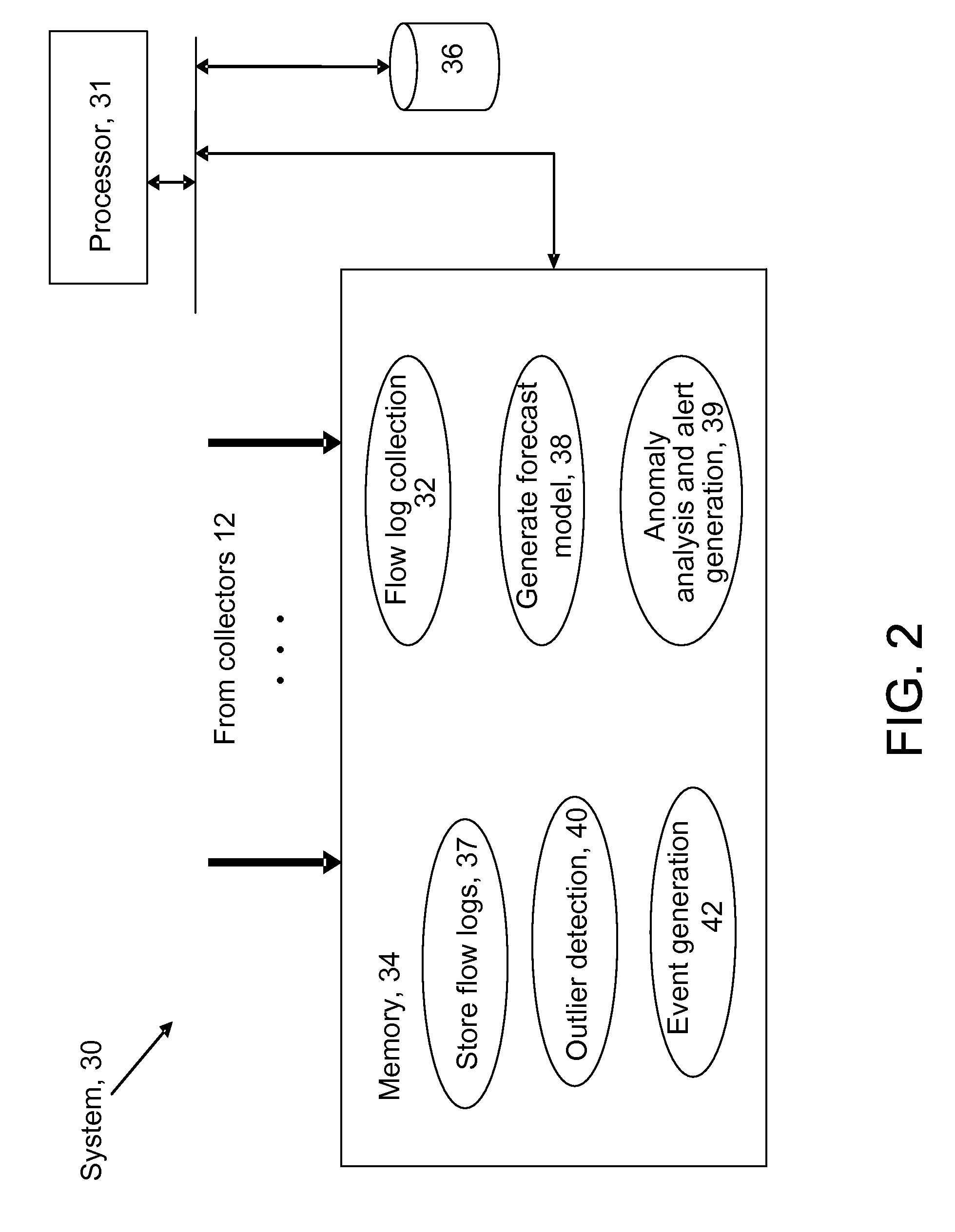
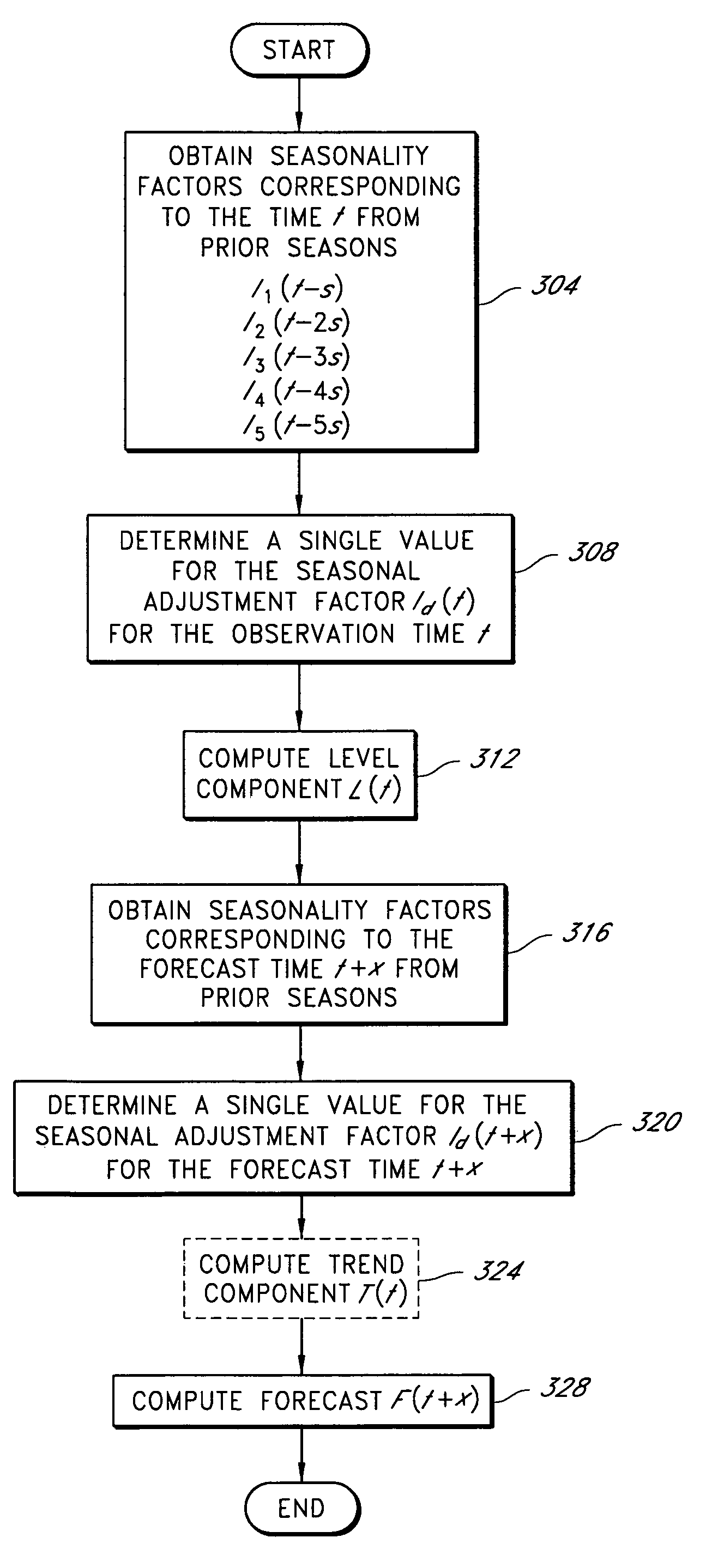
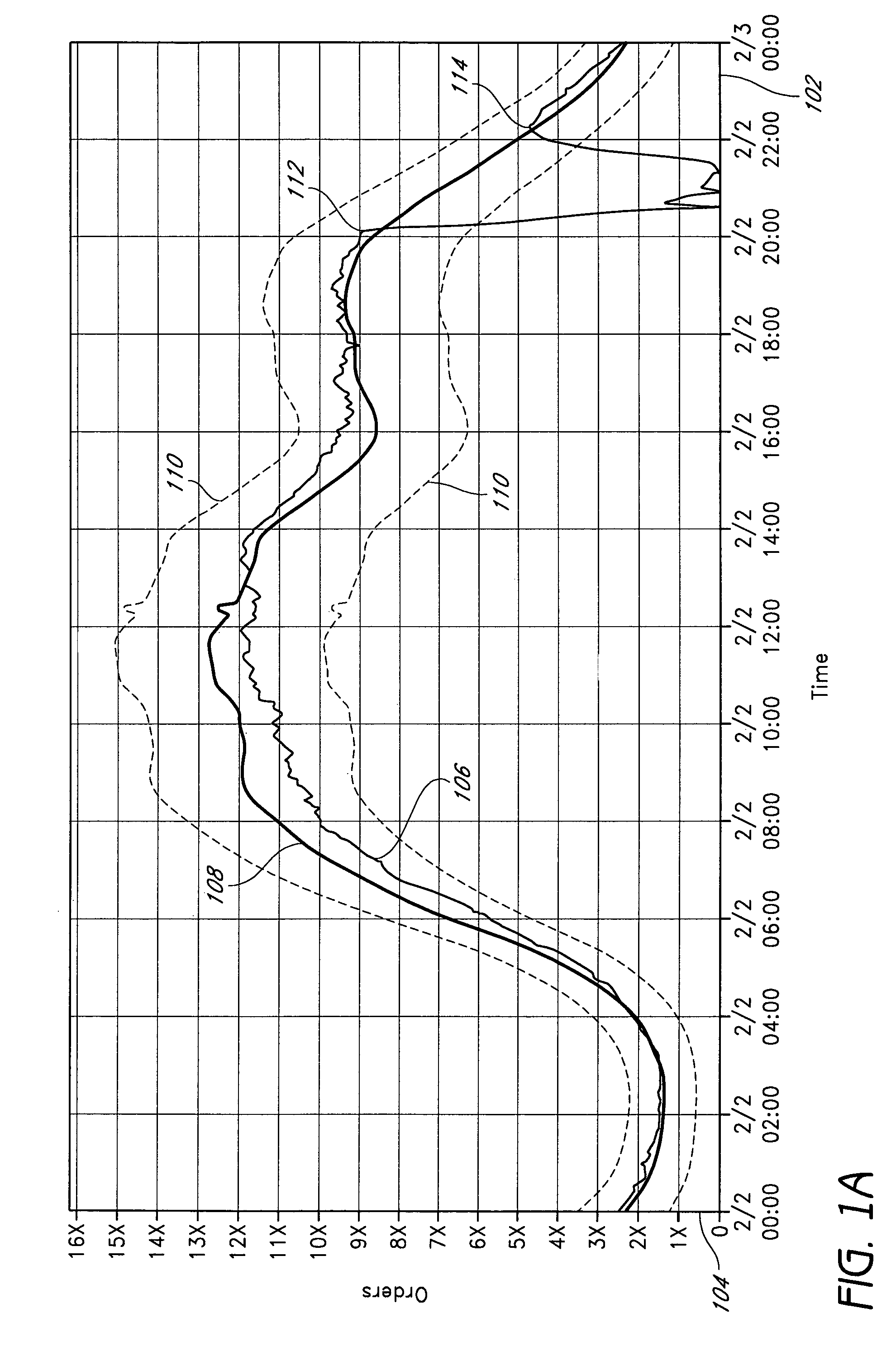
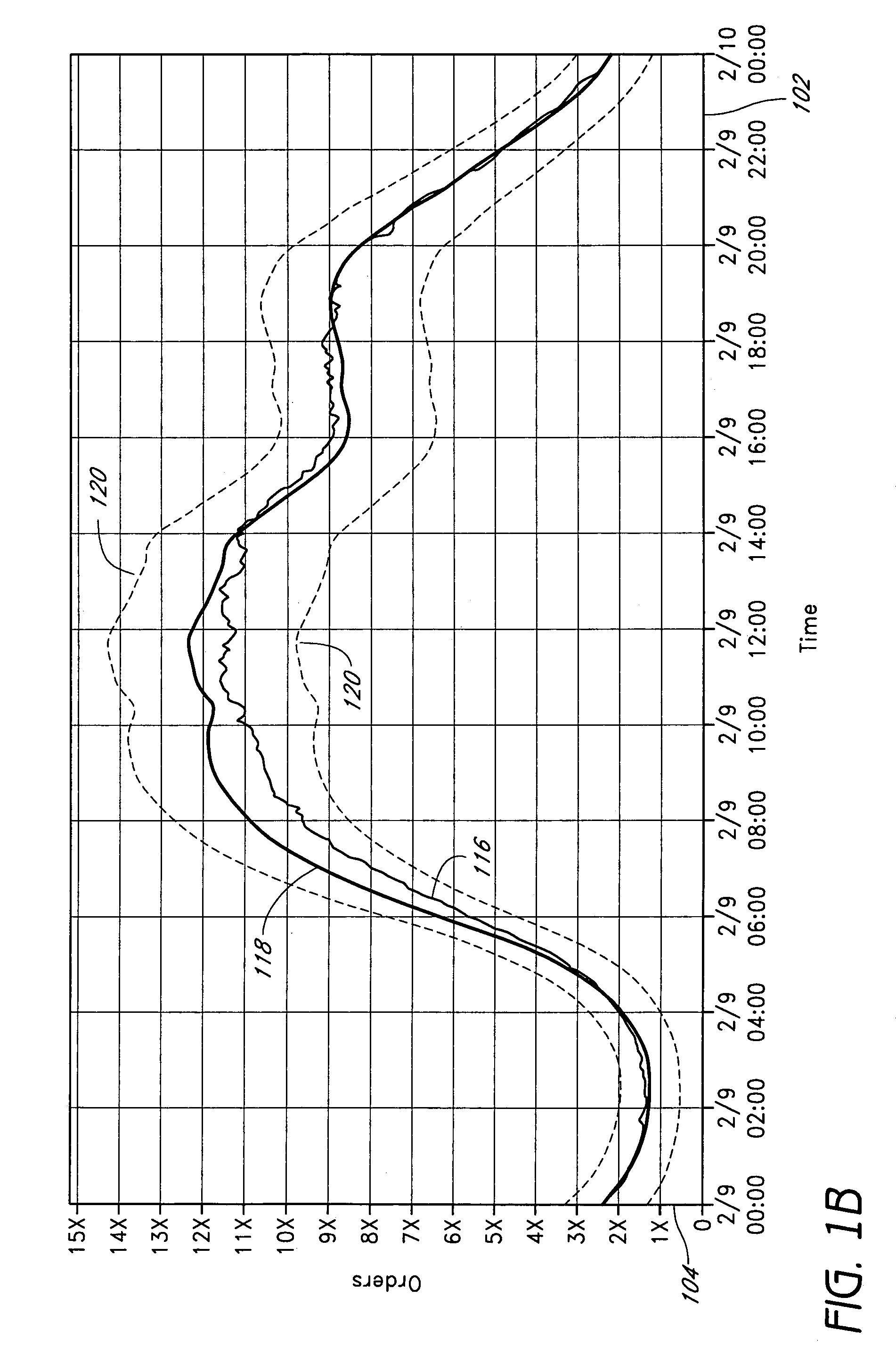
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1451 results about "Outlier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
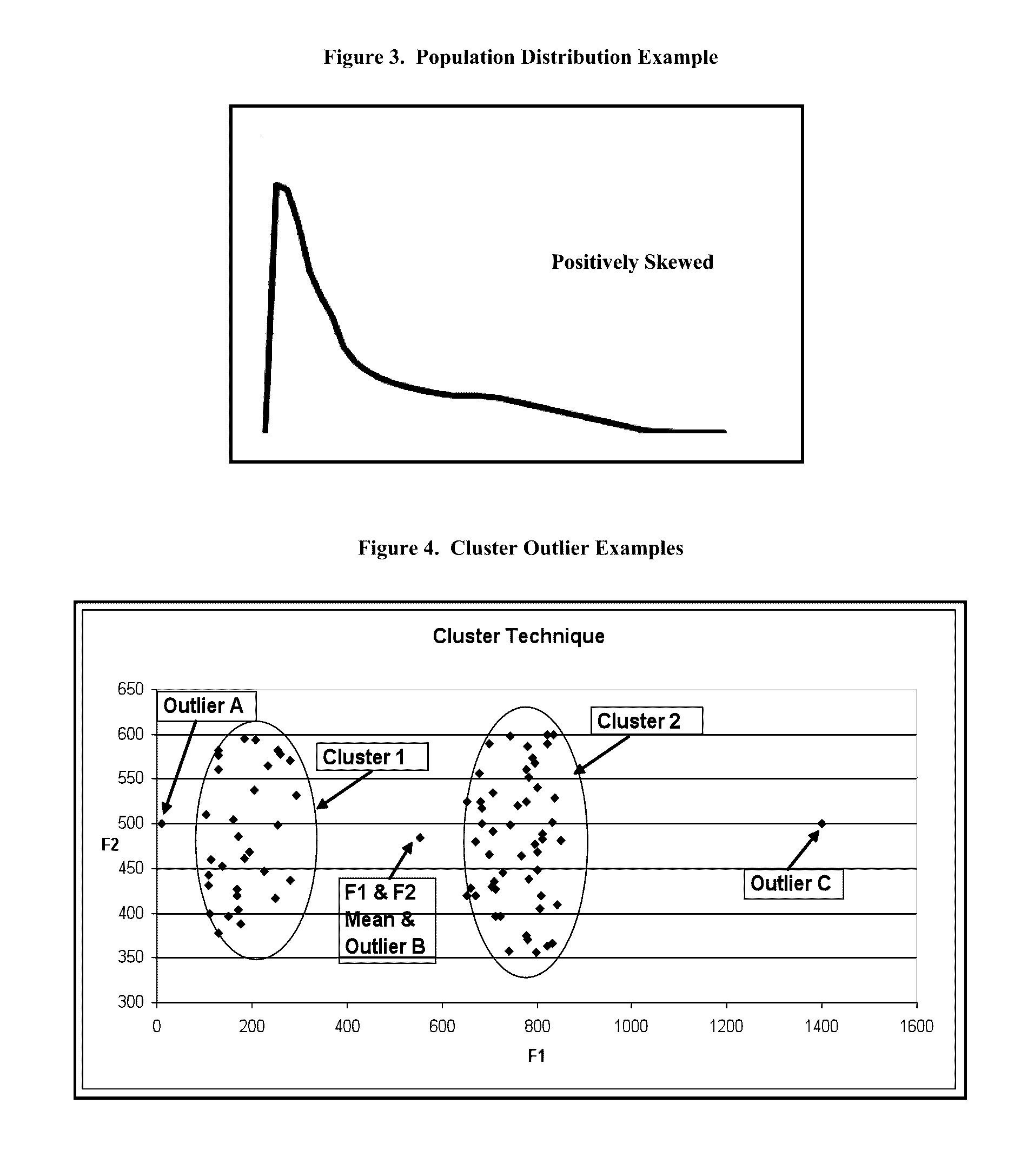
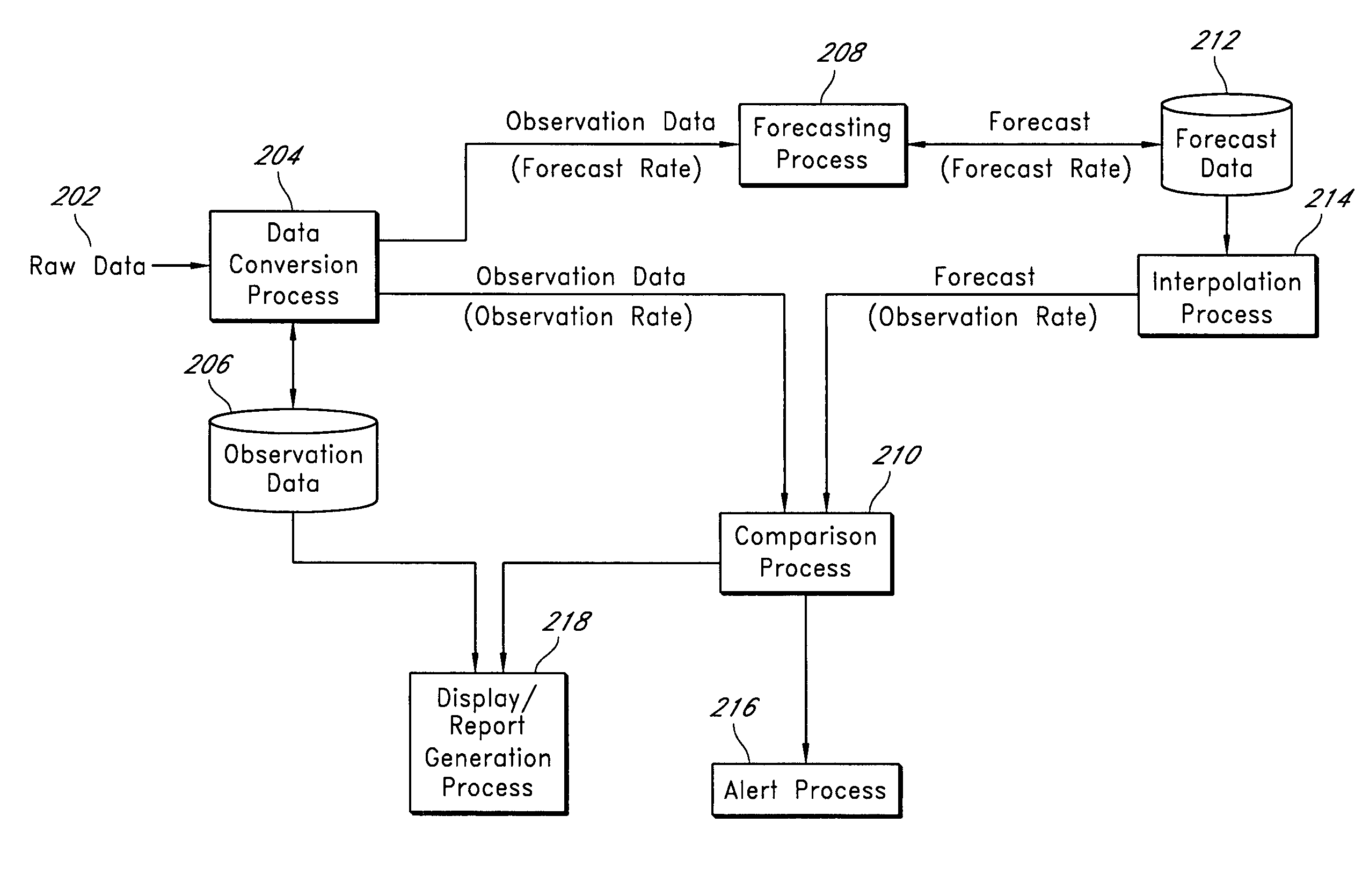
In statistics, an outlier is a data point that differs significantly from other observations. An outlier may be due to variability in the measurement or it may indicate experimental error; the latter are sometimes excluded from the data set. An outlier can cause serious problems in statistical analyses.
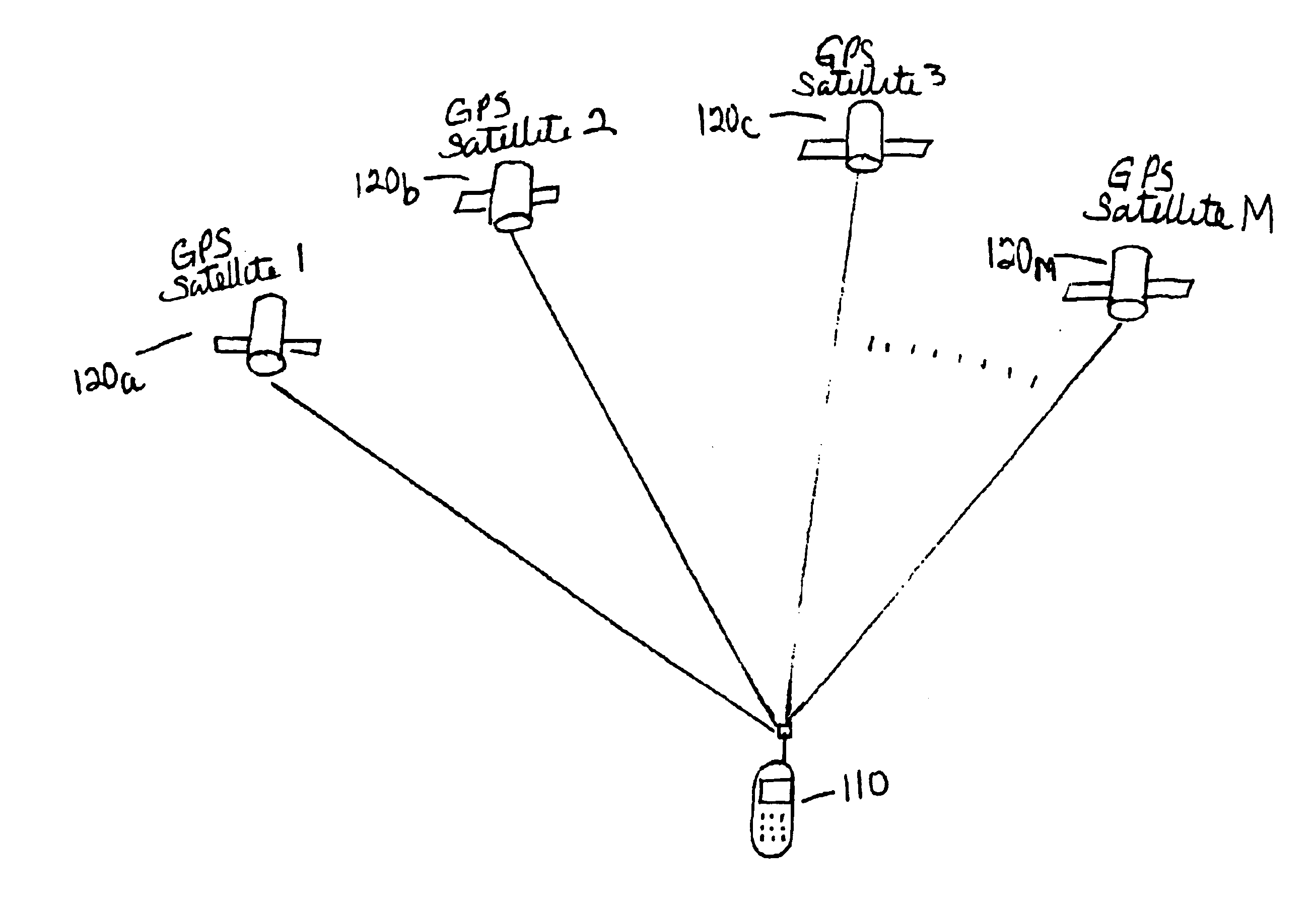
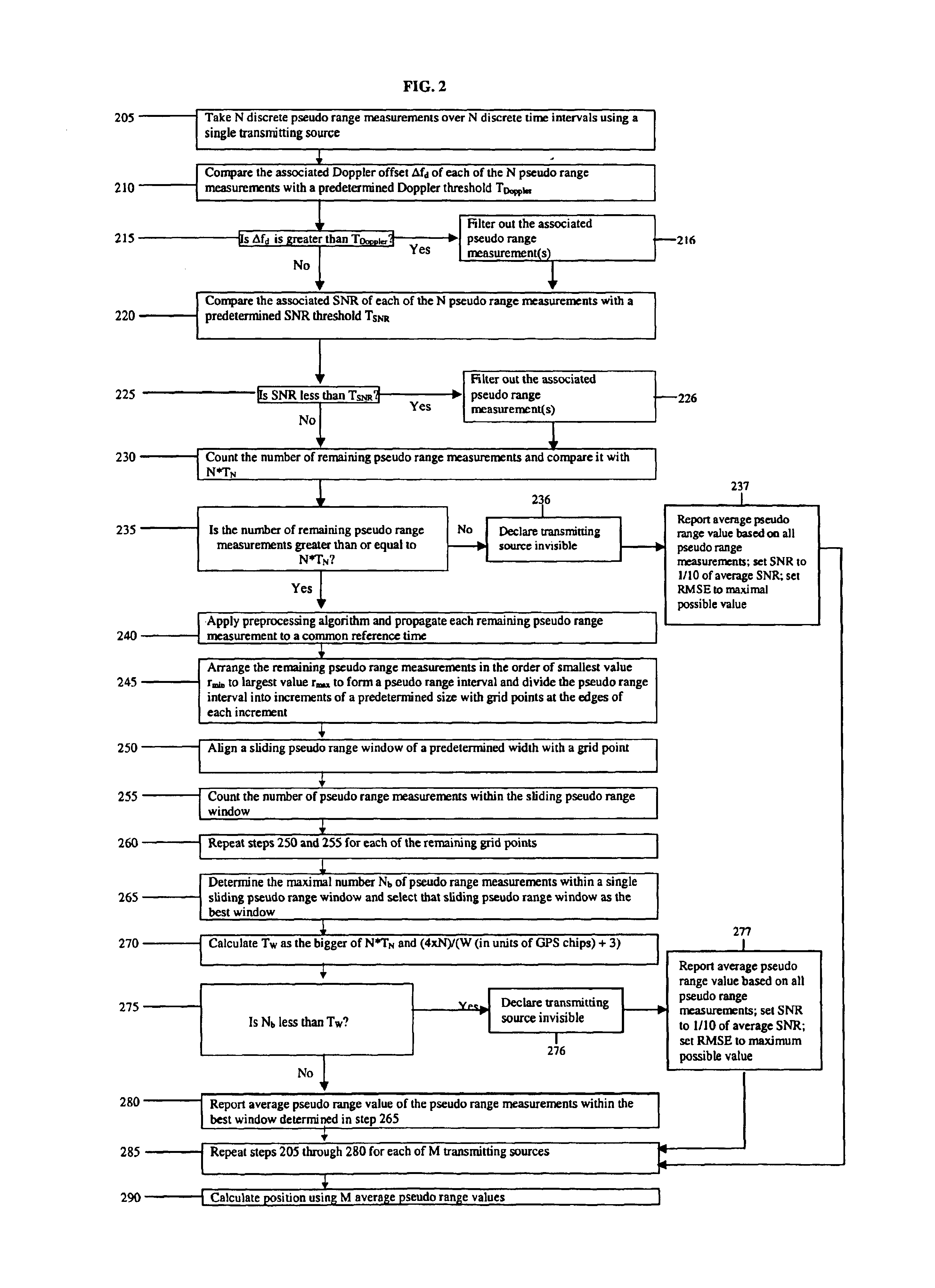
Multiple measurements per position fix improvements
InactiveUS6842715B1More accurate)Good estimateDigital computer detailsPosition fixationCombined useOutlier
Methods and apparatuses for improved position determination of a device using multiple pseudo range measurements from transmitting sources at known locations, such as GPS satellites. A plurality of pseudo range measurements for each transmitting source are processed together to obtain a simplified maximum likelihood estimate for the pseudo range for that transmitting source at a common reference time. The processed pseudo range estimates for all transmitting sources are then combined using conventional position determination algorithms. This technique facilitates removal of raw measurement outliers prior to position determination, which results in improved (i.e., more accurate) position fixes of the device. In addition, improved measurement integrity monitoring of the pseudo range measurements is a feature of this invention.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
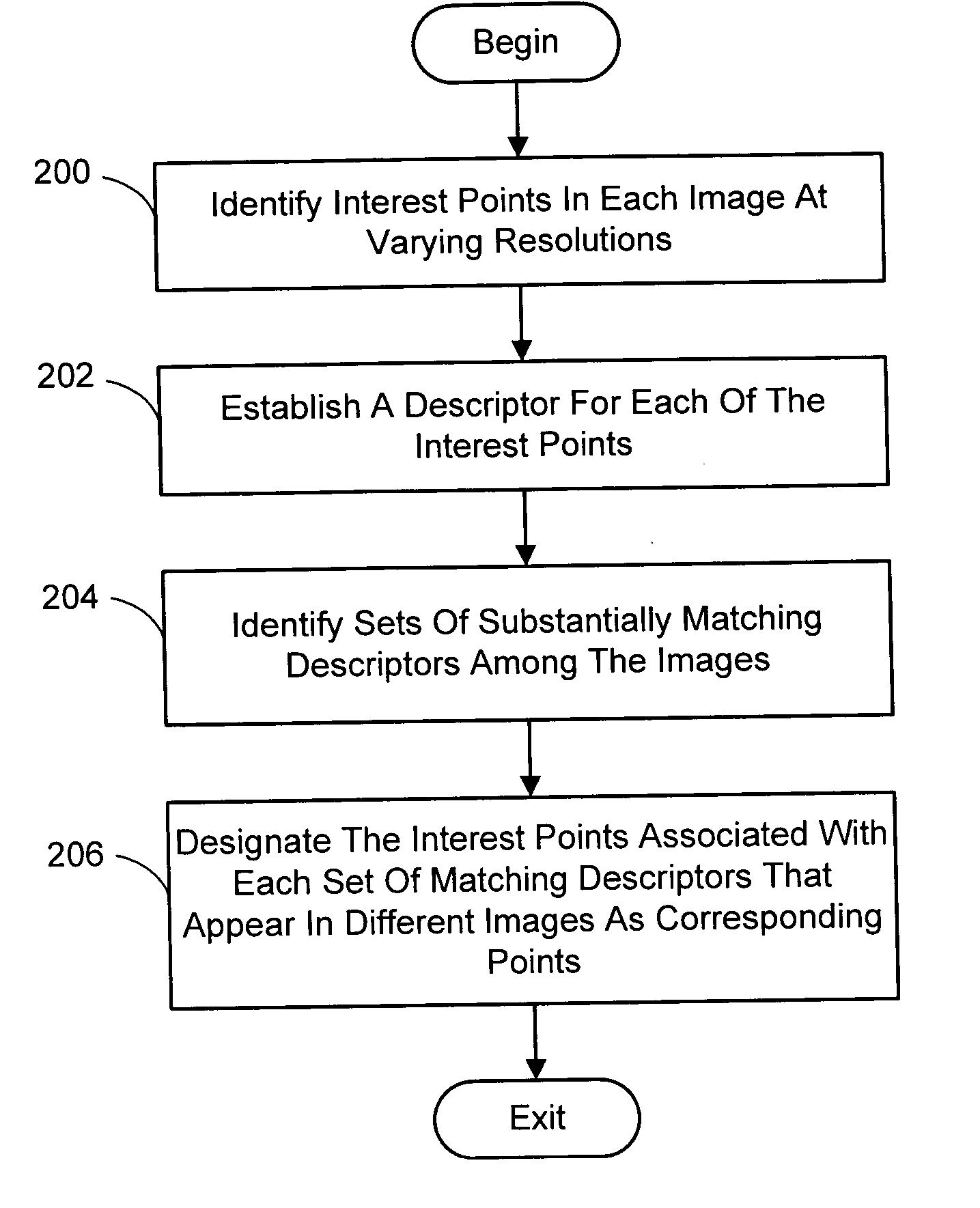
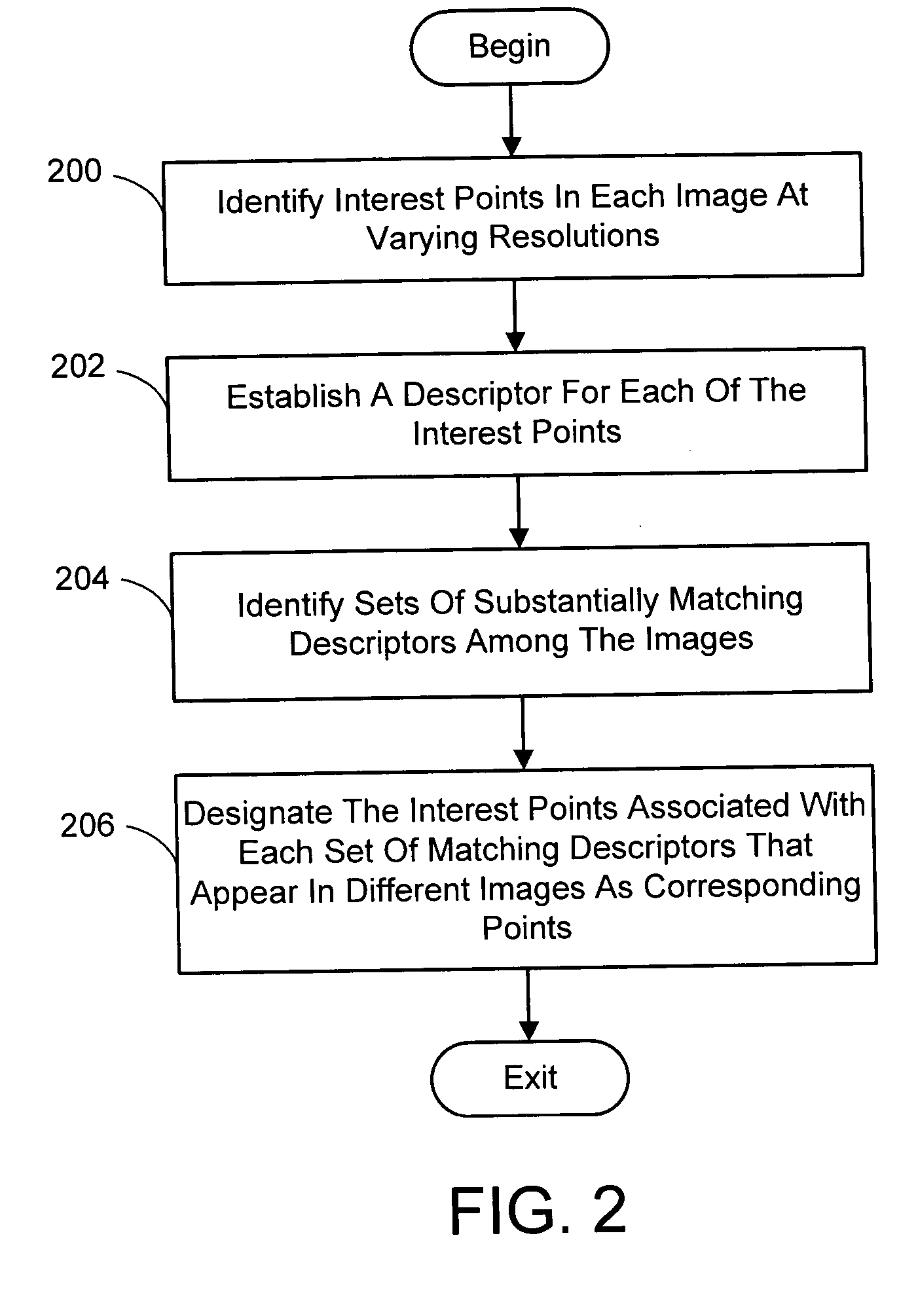
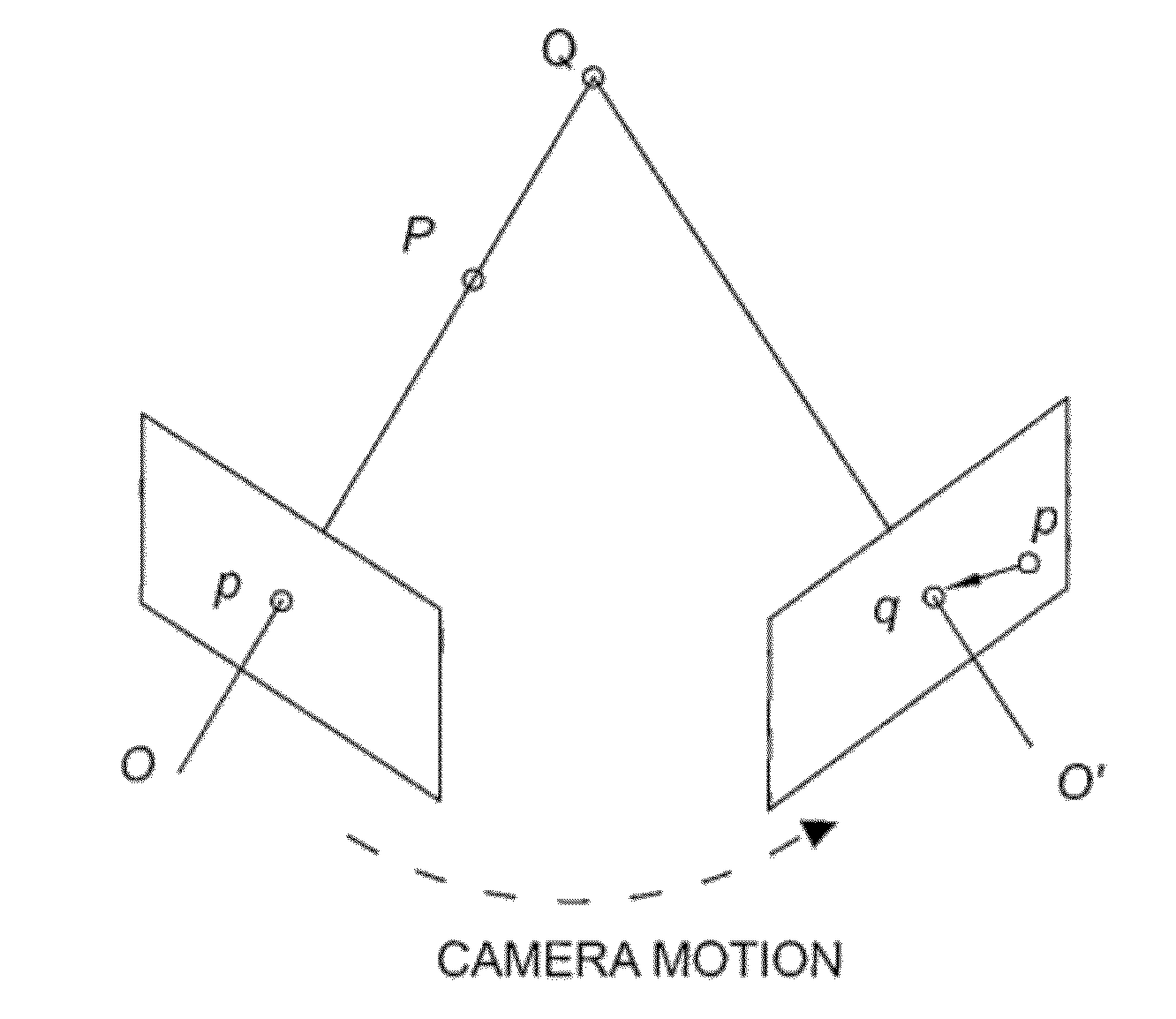
Multi-image feature matching using multi-scale oriented patches
InactiveUS20050238198A1Quick extractionEasy to liftConveyorsImage analysisPattern recognitionNear neighbor
A system and process for identifying corresponding points among multiple images of a scene is presented. This involves a multi-view matching framework based on a new class of invariant features. Features are located at Harris corners in scale-space and oriented using a blurred local gradient. This defines a similarity invariant frame in which to sample a feature descriptor. The descriptor actually formed is a bias / gain normalized patch of intensity values. Matching is achieved using a fast nearest neighbor procedure that uses indexing on low frequency Haar wavelet coefficients. A simple 6 parameter model for patch matching is employed, and the noise statistics are analyzed for correct and incorrect matches. This leads to a simple match verification procedure based on a per feature outlier distance.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Linear system based, qualitative independent motion detection from compressed mpeg surveillance video
InactiveUS8164629B1Shorten the timeExtra computationImage enhancementImage analysisIndependent motionMotion vector
The present invention features a qualitative method to detect independent motion revealed in successive frames of a compressed surveillance MPEG video stream using linear system consistency analysis without decompression of the stream, identifying the segments containing independent motion in a real-time or faster manner, for the retrieval of these segments. The linear system is constructed using the macroblocks of MPEG compressed video frames. The normal flow value of the macroblock is obtained by taking the dot product between the macroblock gradient vector, computed by averaging the four block gradient vectors, and the motion vector of this macroblock. The normal flow value is filtered for inclusion in the linear system, and the statistic of the matrices of the resulting linear system is determined, filtered to screen out false negatives and outliers, and used to determine the presence or absence of independent motion.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
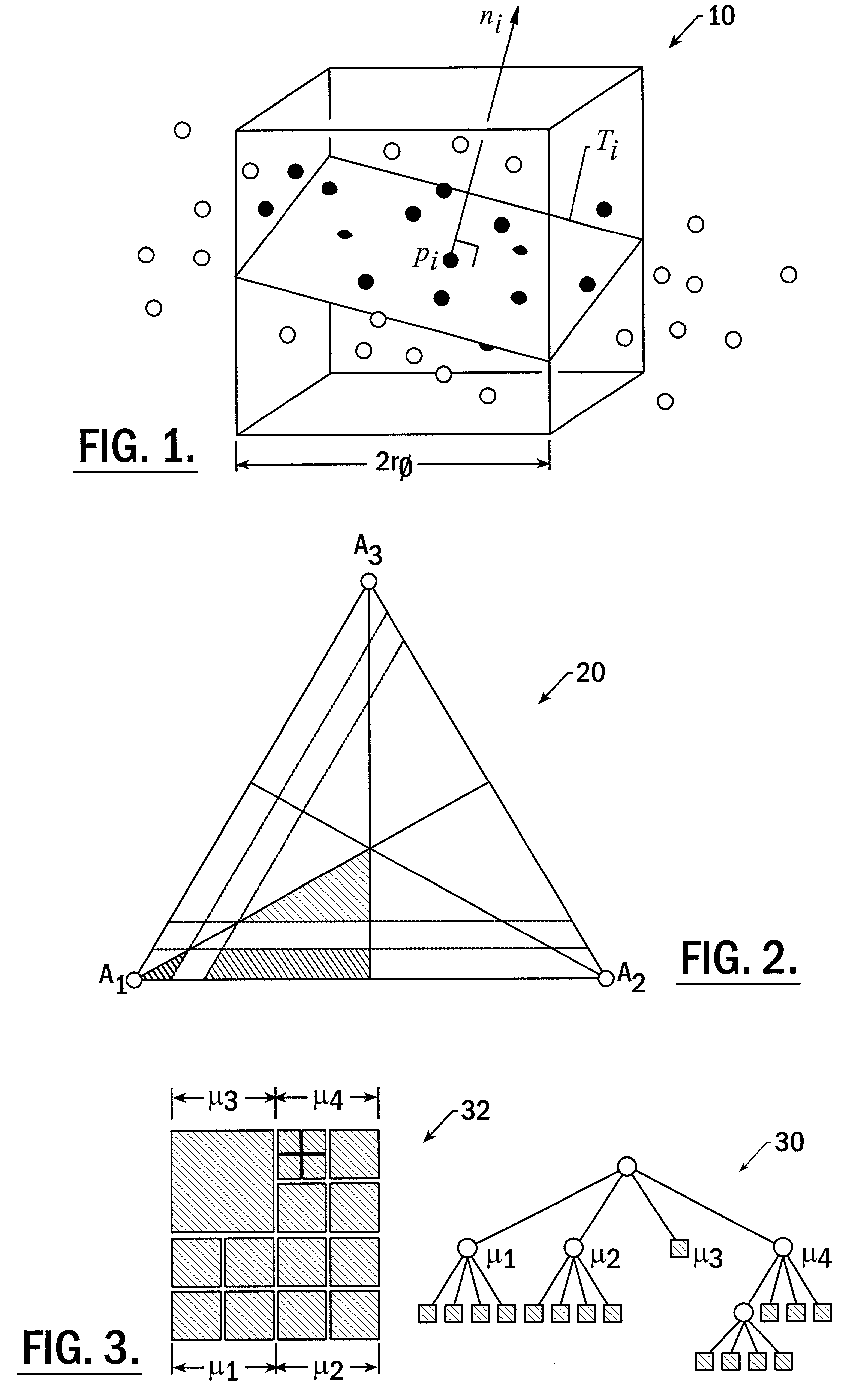
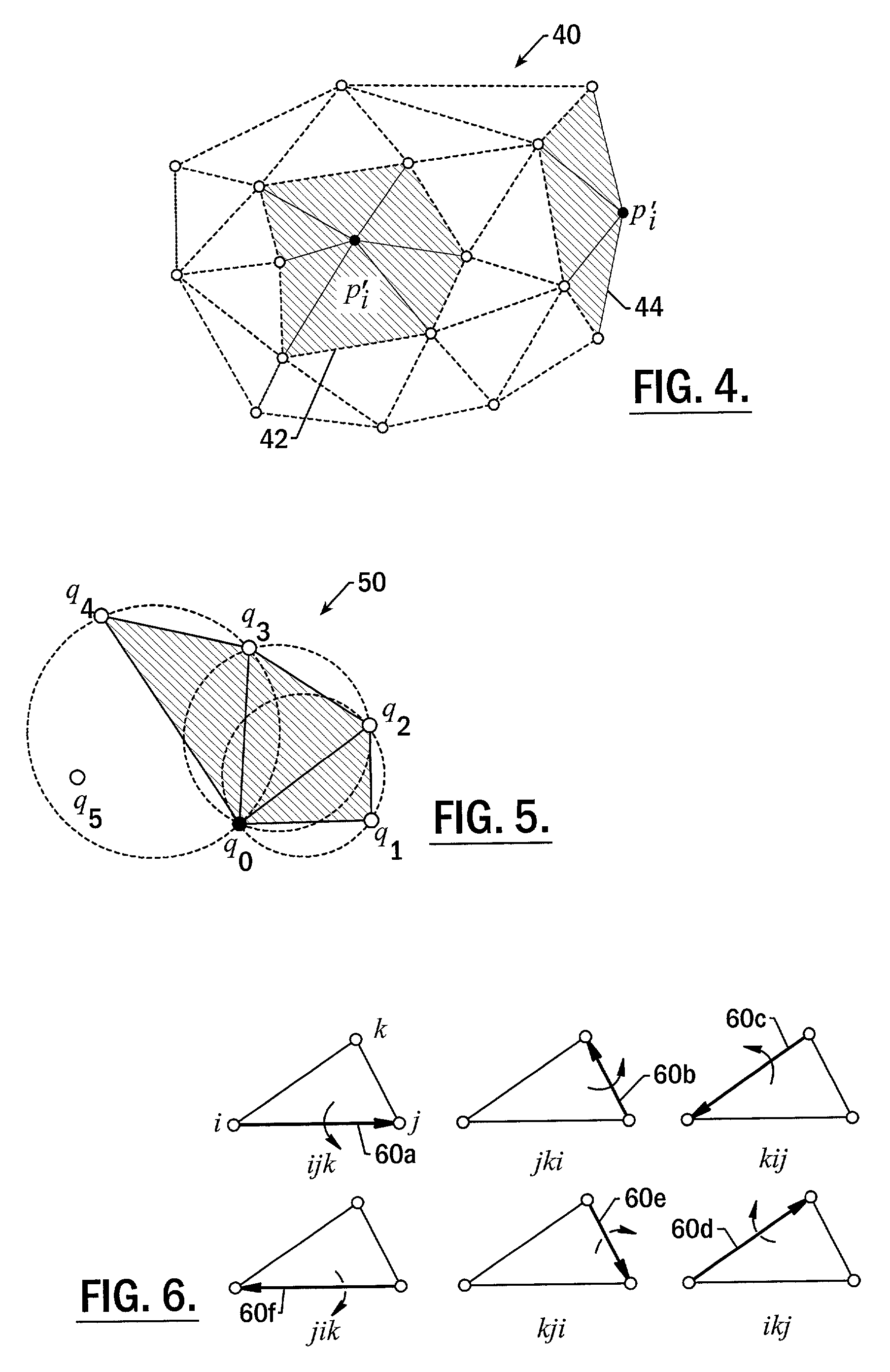
Methods, apparatus and computer program products that reconstruct surfaces from data point sets
ActiveUS7023432B2Quality improvementReduce noiseAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D-image renderingPoint cloudDigital mockup
Methods, apparatus and computer program products provide efficient techniques for reconstructing surfaces from data point sets. These techniques include reconstructing surfaces from sets of scanned data points that have preferably undergone preprocessing operations to improve their quality by, for example, reducing noise and removing outliers. These techniques include reconstructing a dense and locally two-dimensionally distributed 3D point set (e.g., point cloud) by merging stars in two-dimensional weighted Delaunay triangulations within estimated tangent planes. The techniques include determining a plurality of stars from a plurality of points pi in a 3D point set S that at least partially describes the 3D surface, by projecting the plurality of points pi onto planes Ti that are each estimated to be tangent about a respective one of the plurality of points pi. The plurality of stars are then merged into a digital model of the 3D surface.
Owner:3D SYST INC
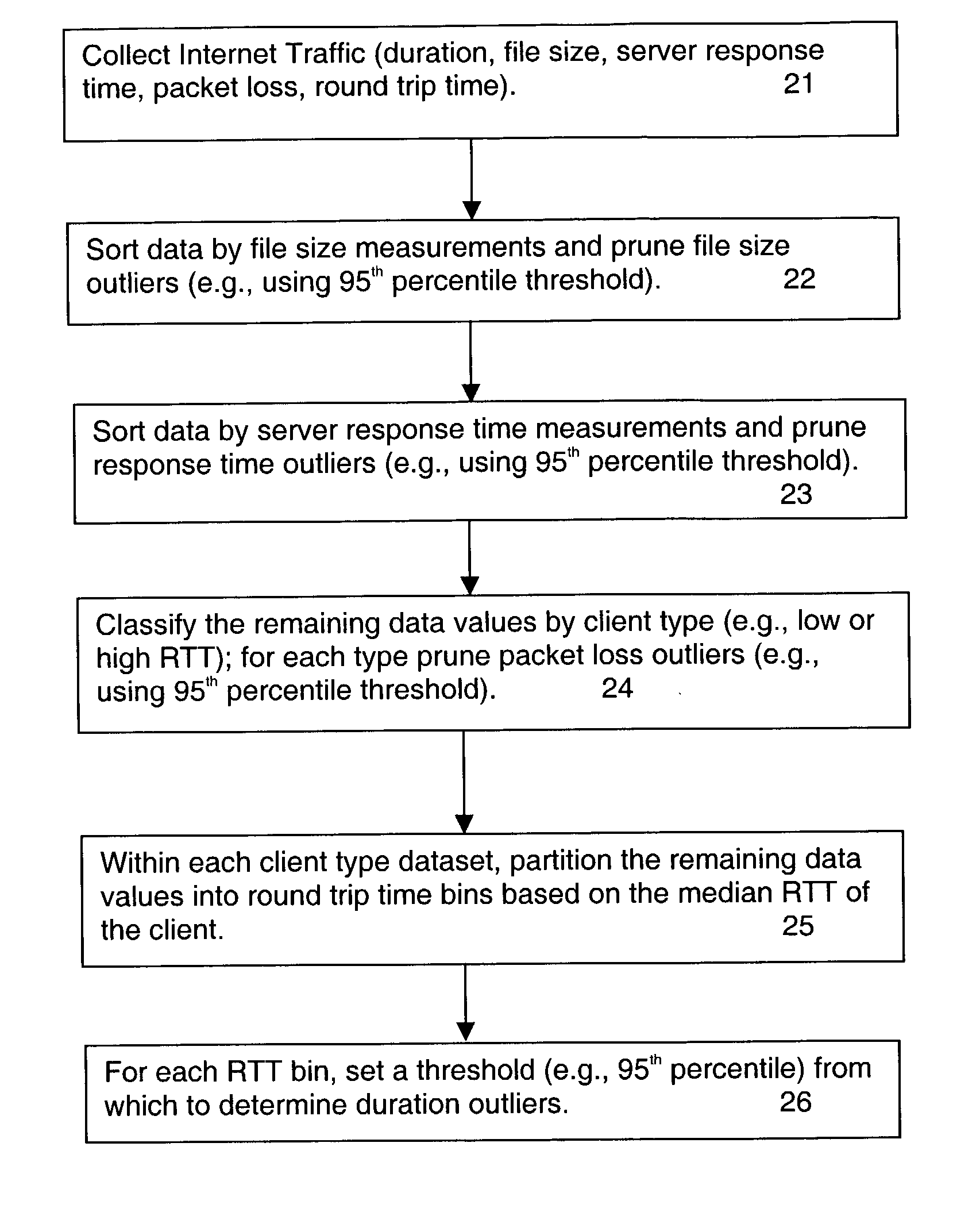
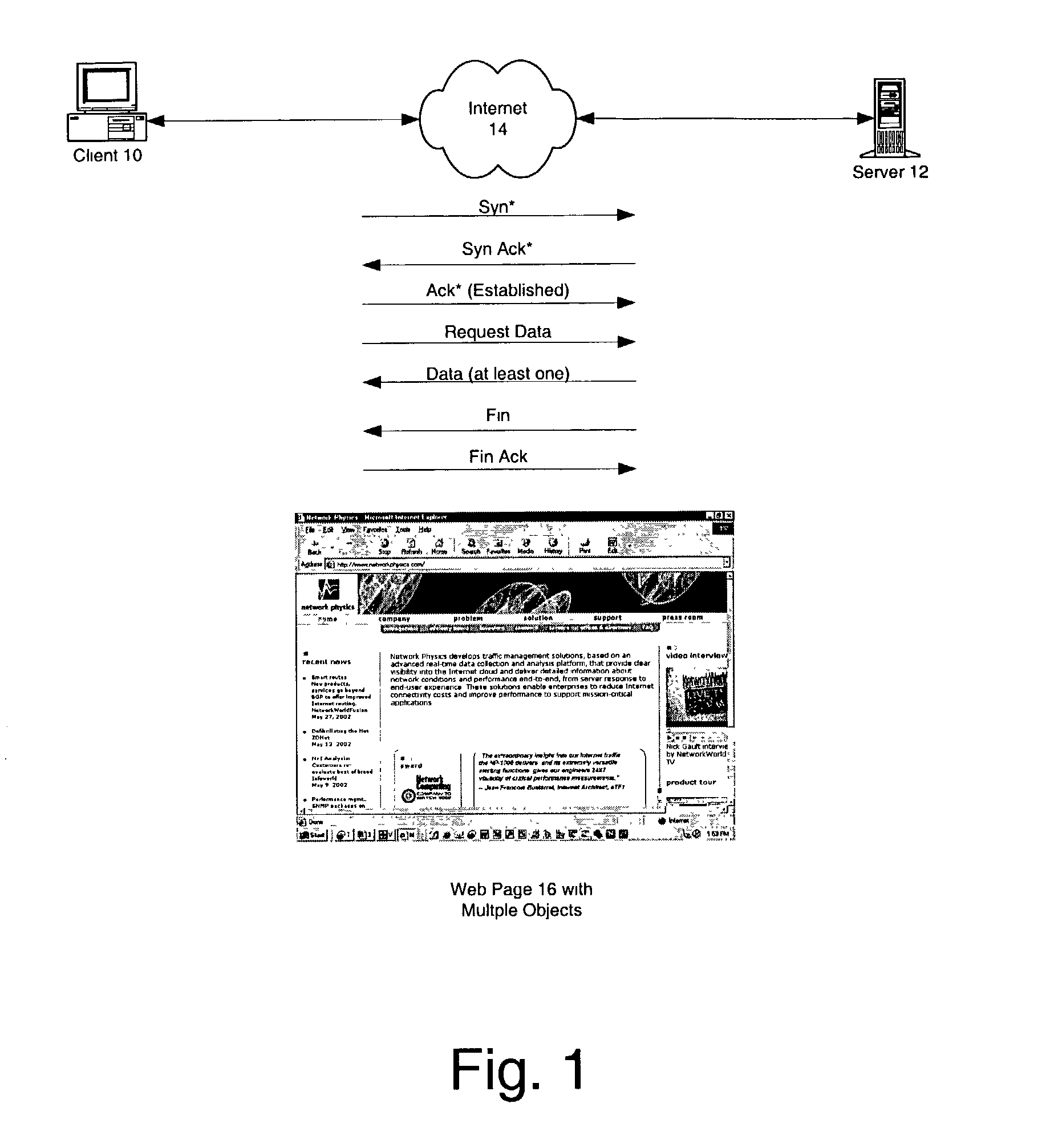
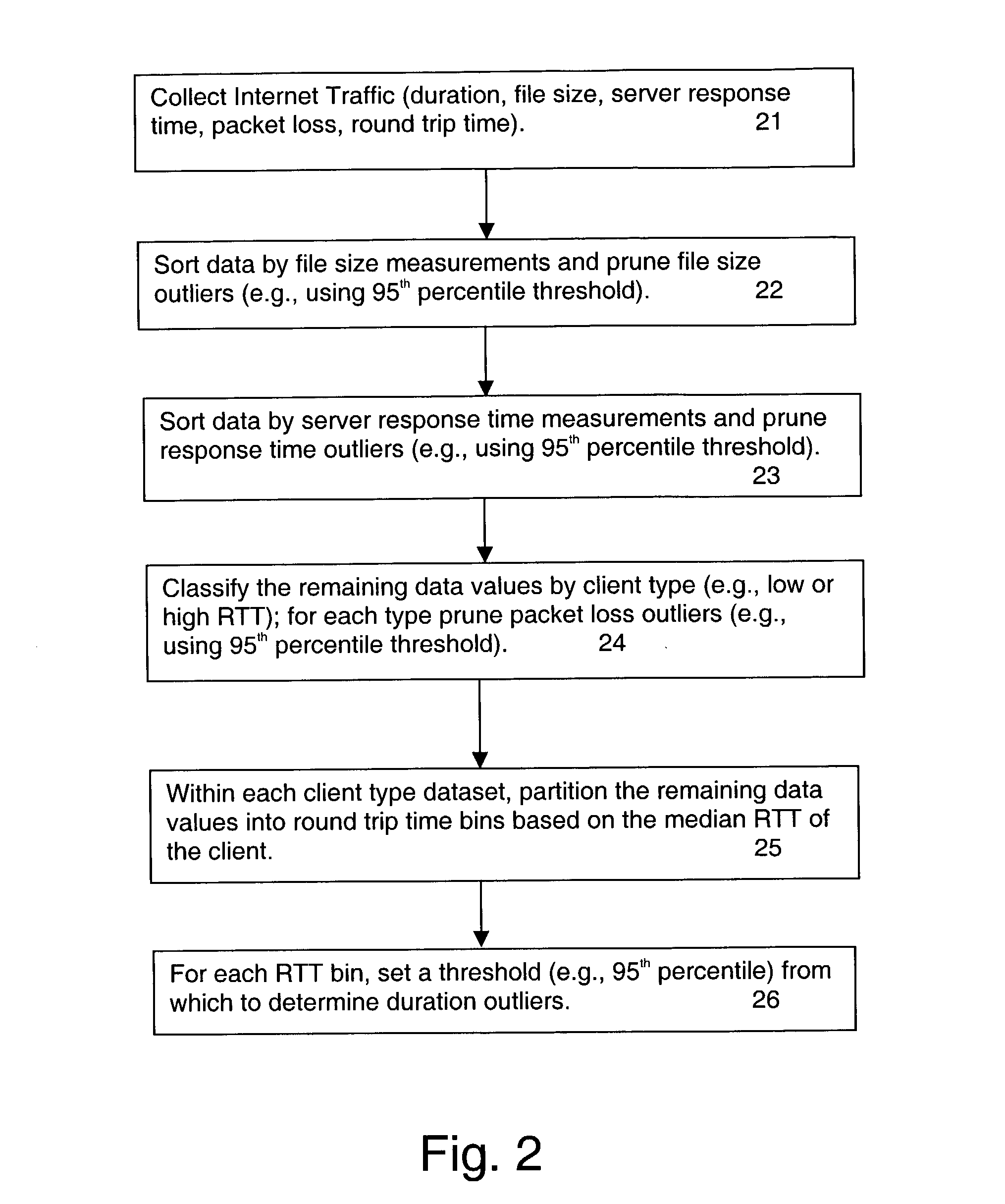
Method for detecting congestion in internet traffic
A baseline for internet traffic duration is established by (i) collecting internet traffic data regarding file size, server response time, packet loss and round trip time, (ii) removing from this data outliers associated with file size, server response time and packet loss per client type, and (iii) organizing any remaining data into round trip time bins according to median values of round trip time per client type. Thereafter, historical or newly collected Internet traffic data is compared against threshold values for each round trip time bin to locate duration outliers. These duration outliers are indicators of congestion and congestion episodes may be identified by the continued presence of such outliers over successive time intervals.
Owner:RIVERBED TECH LLC
Content evaluation
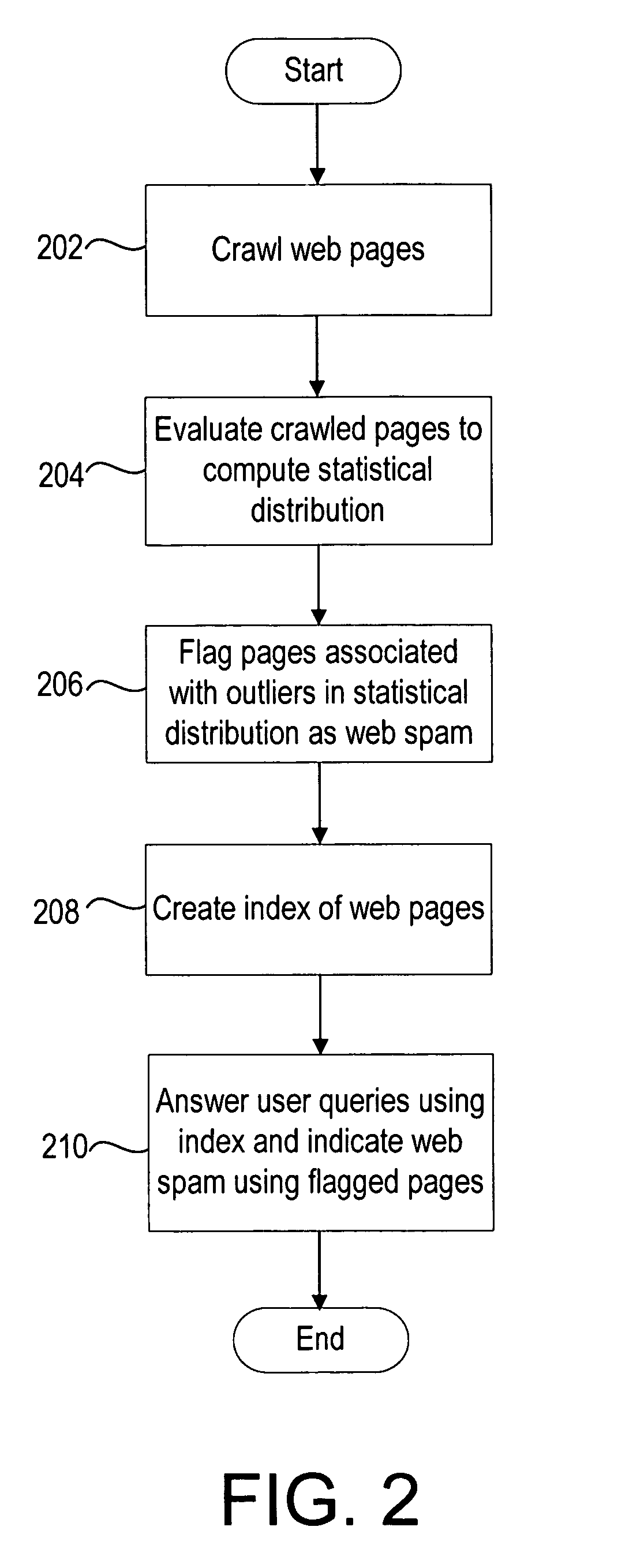
Evaluating content is described, including generating a data set using an attribute associated with the content, evaluating the data set using a statistical distribution to identify a class of statistical outliers, and analyzing a web page to determine whether it is part of the class of statistical outliers. A system includes a memory configured to store data, and a processor configured to generate a data set using an attribute associated with the content, evaluate the data set using a statistical distribution to identify a class of statistical outliers, and analyze a web page to determine whether it is part of the class of statistical outliers. Another technique includes crawling a set of web pages, evaluating the set of web pages to compute a statistical distribution, flagging an outlier page in the statistical distribution as web spam, and creating an index of the web pages and the outlier page for answering a query.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Coupling time evolution model with empirical regression model to estimate mechanical wear
ActiveUS8600917B1Low variabilityEasy to operateDigital computer detailsMachine learningMechanical wearStatistical learning
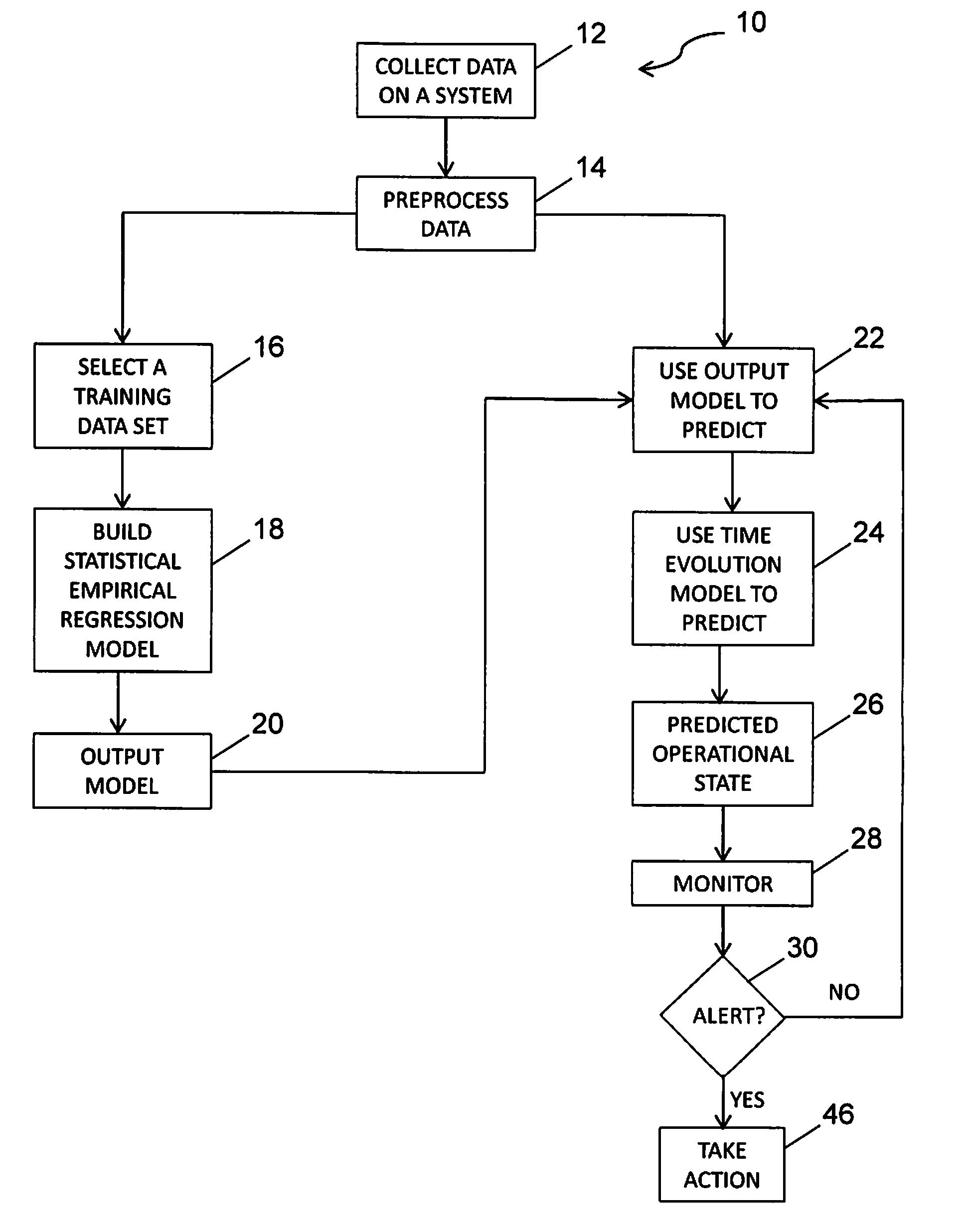
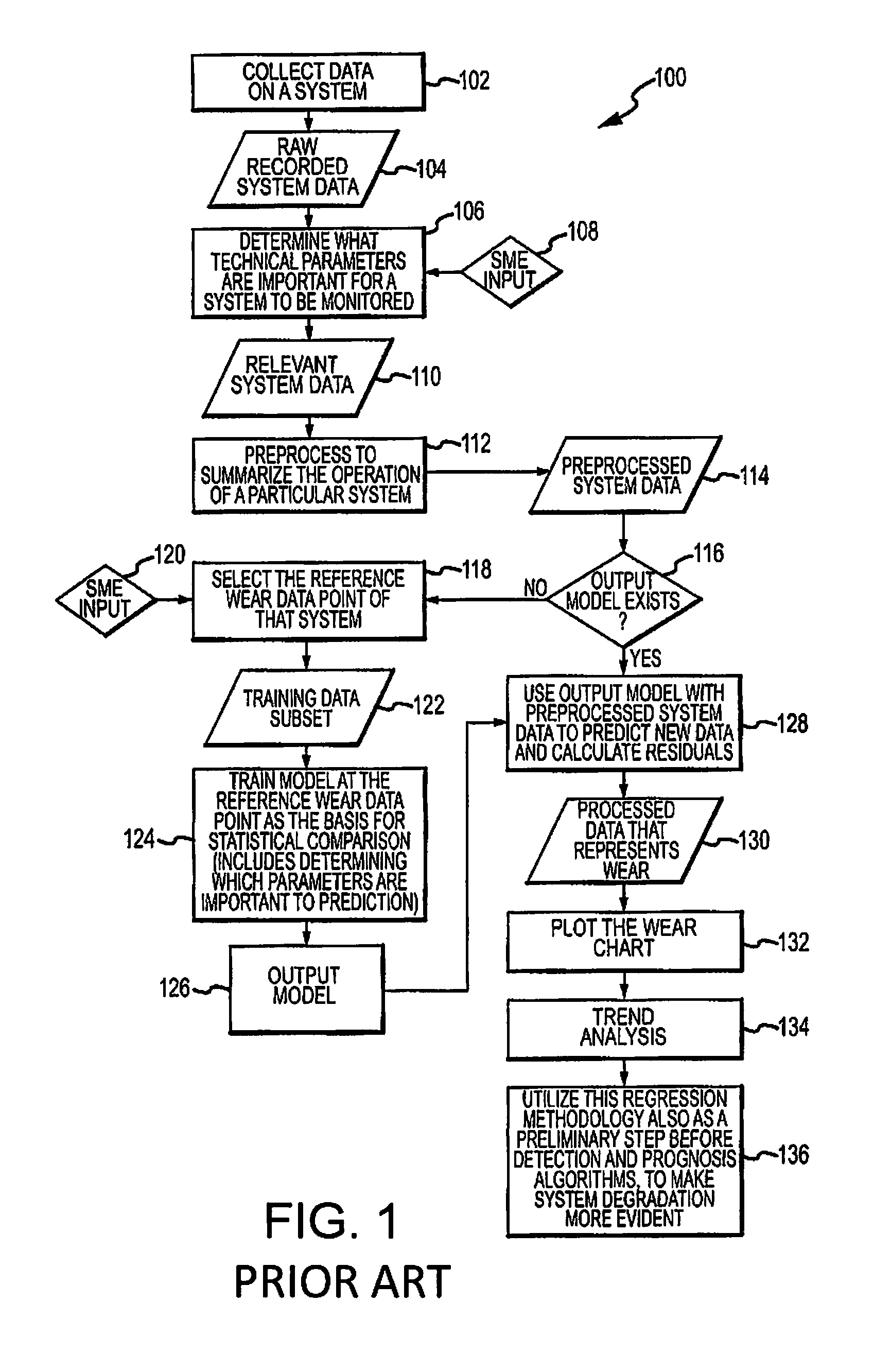
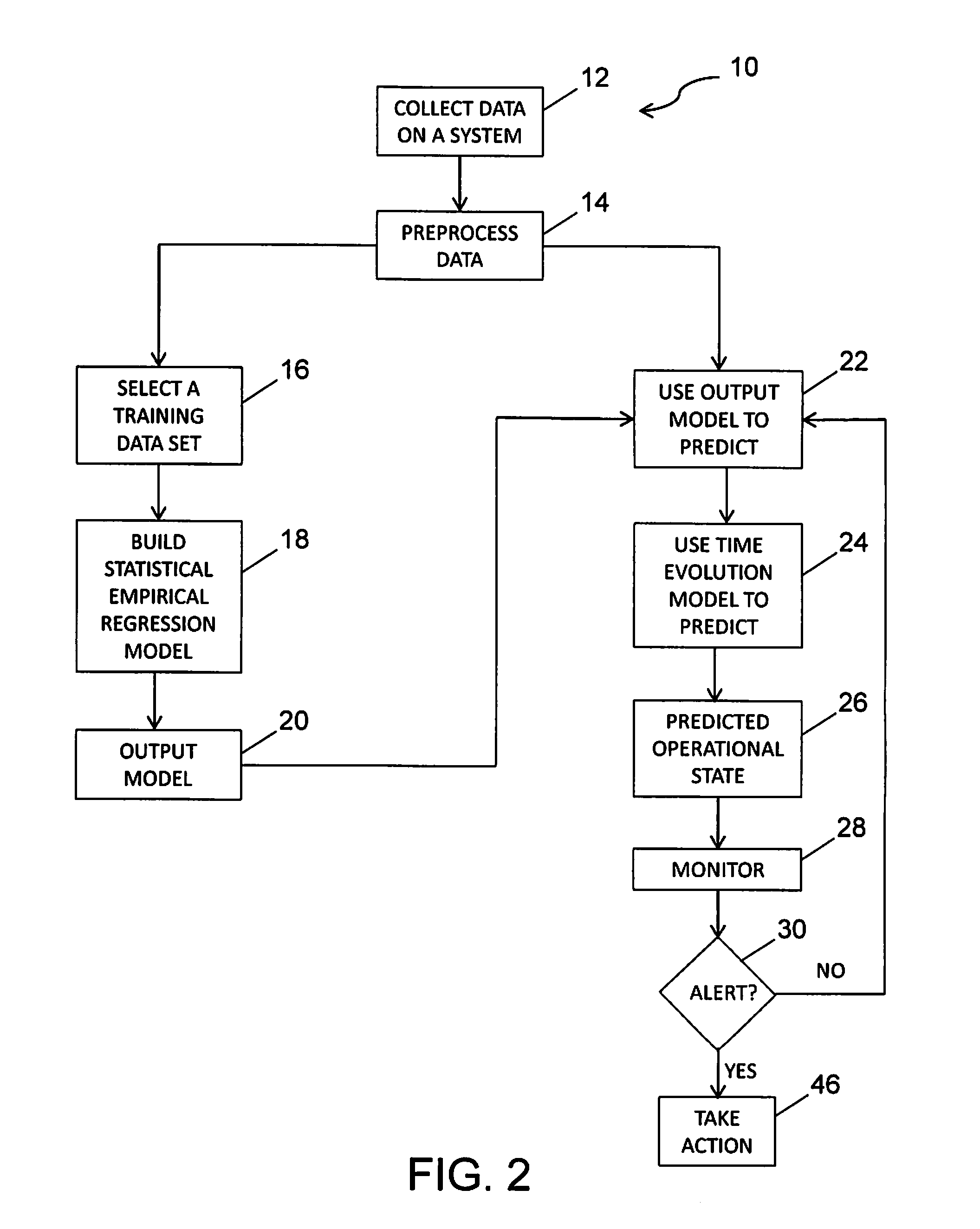
Mechanical systems wear or change over time. Data collected over a system's life can be input to statistical learning models to predict this wear / change. Previous work by the inventors trained a flexible empirical regression model at a fixed point of wear, and then applied it independently at time points over the life of an engine to predict wear. The embodiment disclosed herein relates those wear predictions over time using a time evolution model. The time evolution model is sequentially updated with new data, and effectively tunes the empirical model for each engine. The combined model predicts wear with dramatically reduced variability. The benefit of reduced variability is that engine wear is more evident, and it is possible to detect operational anomalies more quickly. In addition to tracking wear, the model is also used as the basis for a Bayesian approach to monitor for sudden changes and reject outliers, and adapt the model after these events.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
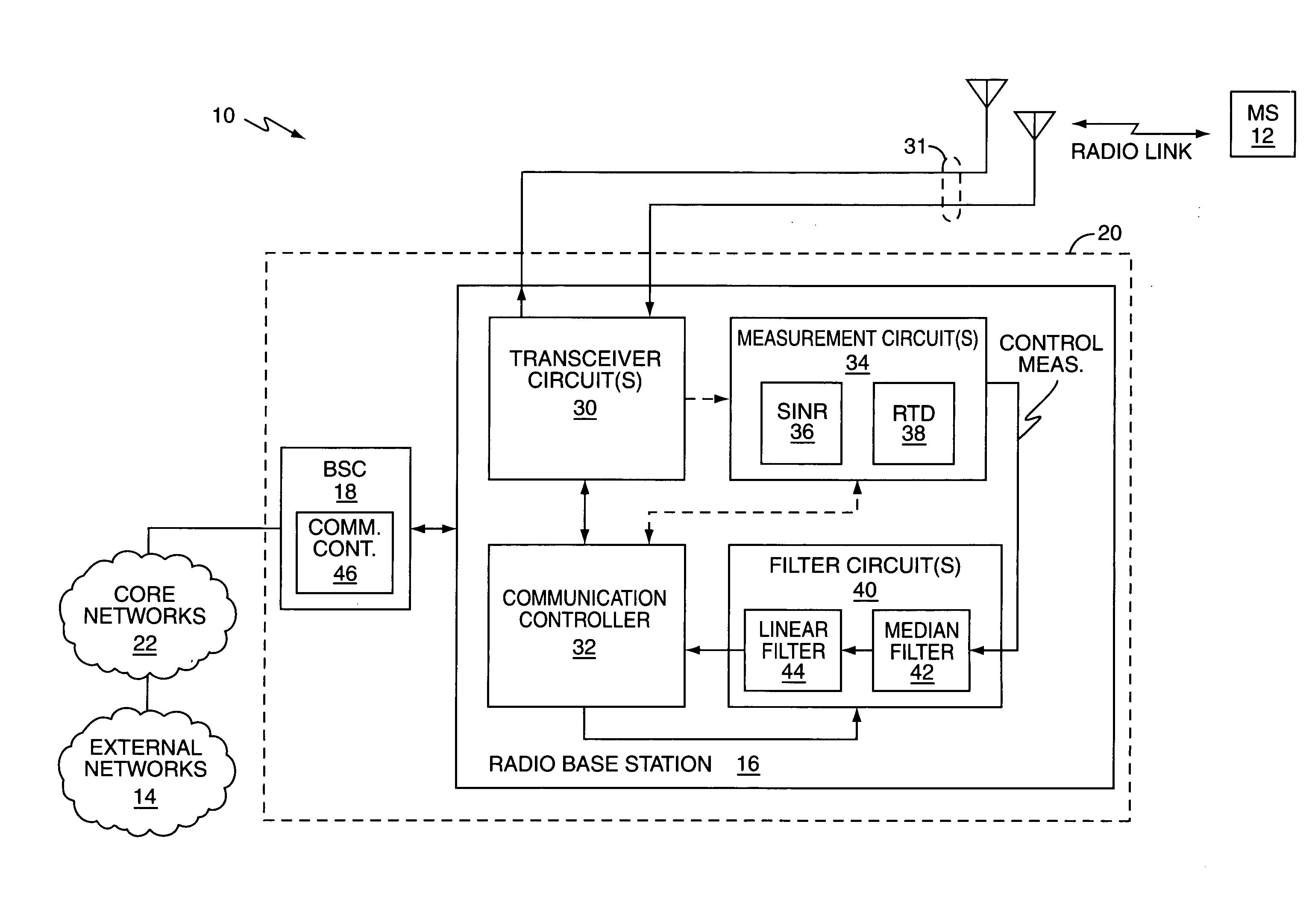
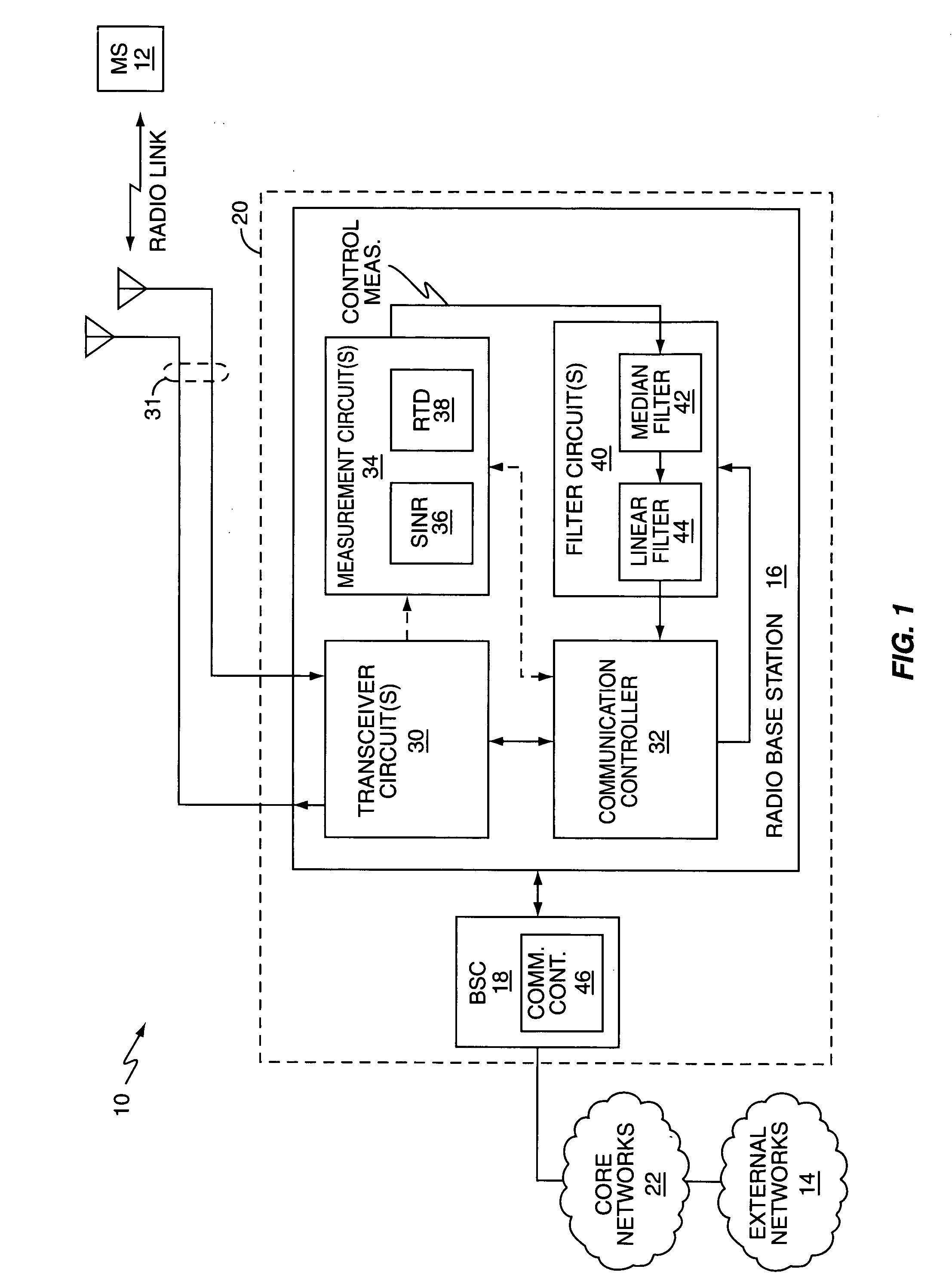
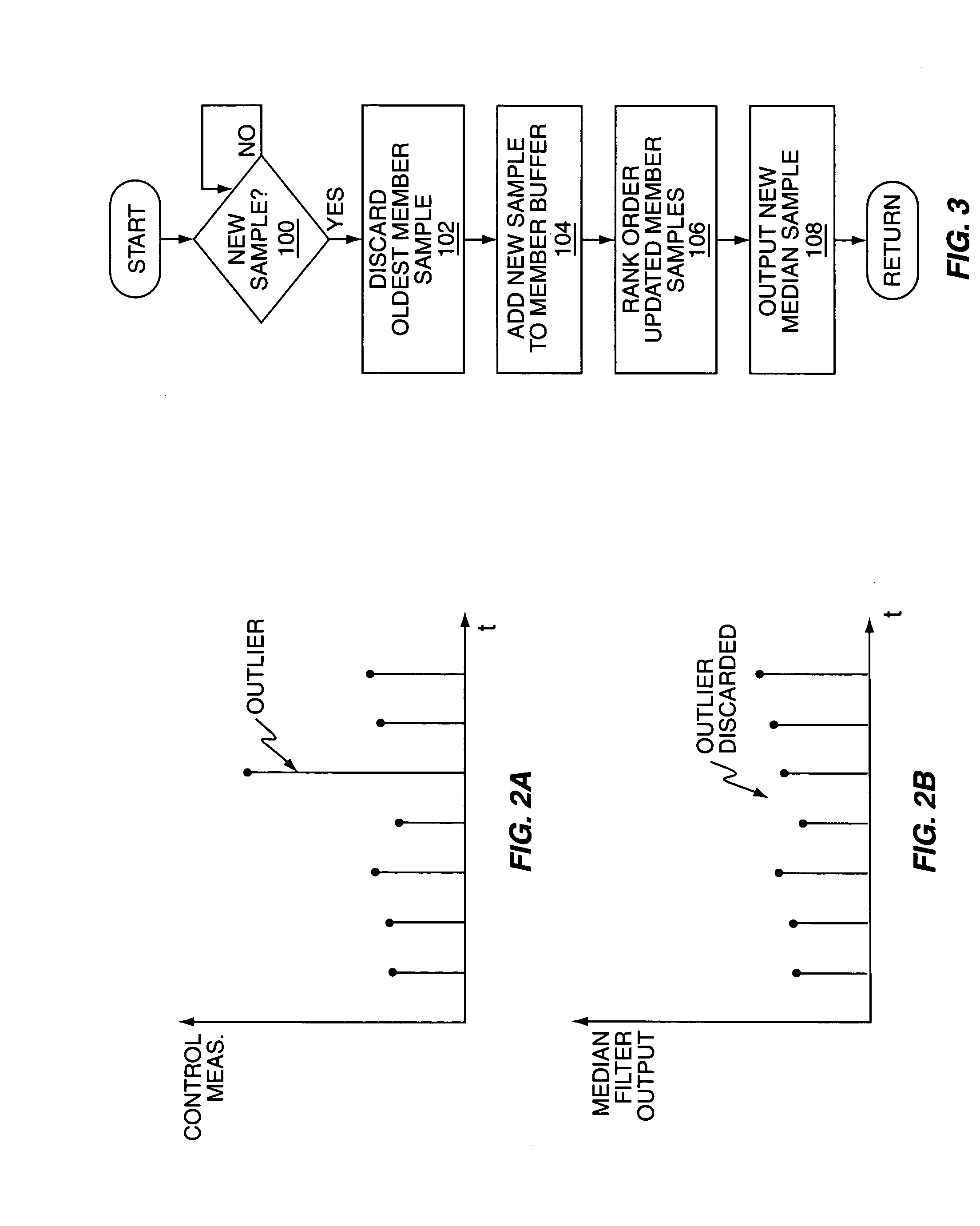
Method and apparatus to reduce multipath effects on radio link control measurements
InactiveUS20050239410A1Reduce multipath effectsEffectively ignoreReceivers monitoringElectric devicesSignal qualityLinear filter
One or more median filter circuits are used to filter radio link control measurements corresponding to one or more radio link parameters of interest, such as received signal quality or round trip delay measurements, such as might be used by a base station to trigger mobile station handoff. As such measurements are particularly susceptible to measurement outliers arising from rapid but short-lived changes in radio link propagation paths, for example, the application of median filtering to such measurements is particularly advantageous. That is, by operation of median filtering, which is a non-linear filtering process, outliers in a stream of control measurements, such as are caused by instantaneous changes in channel fading or other propagation phenomena, are discarded rather than averaged in with the other measurements. Non-linear filtering as implemented by exemplary median filtering does not impair or otherwise limit the bandwidth of the underlying control measurements.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
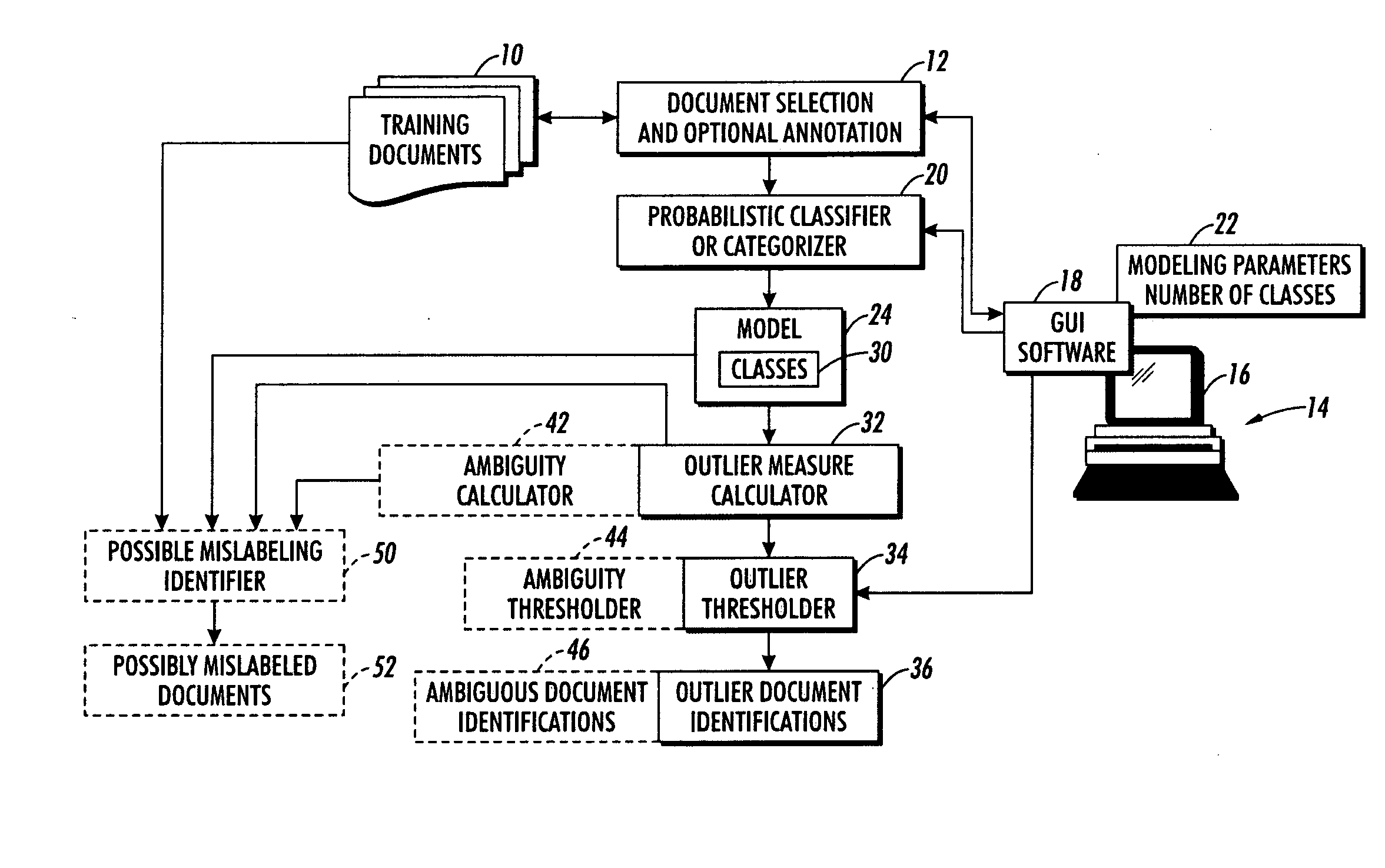
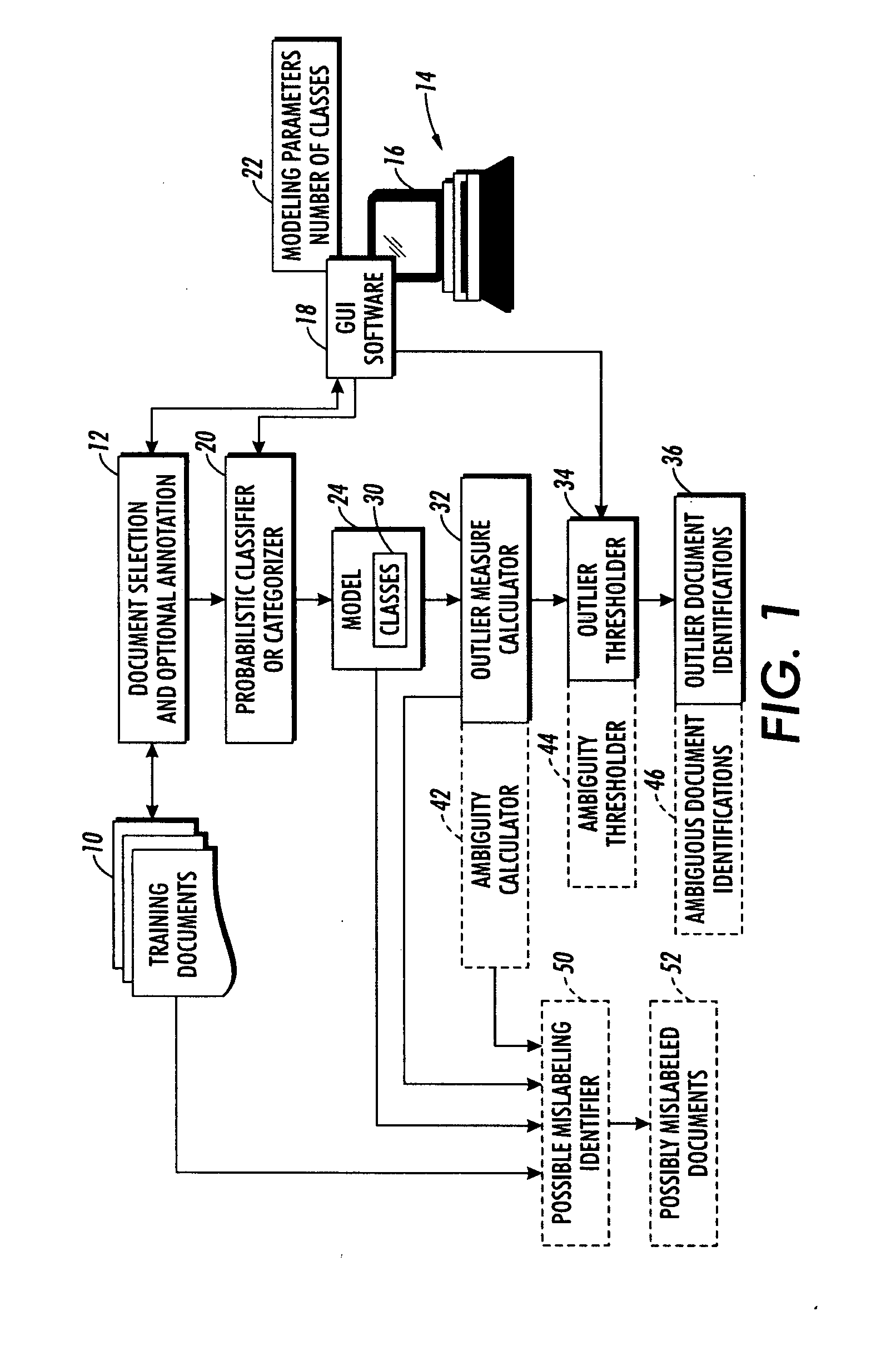
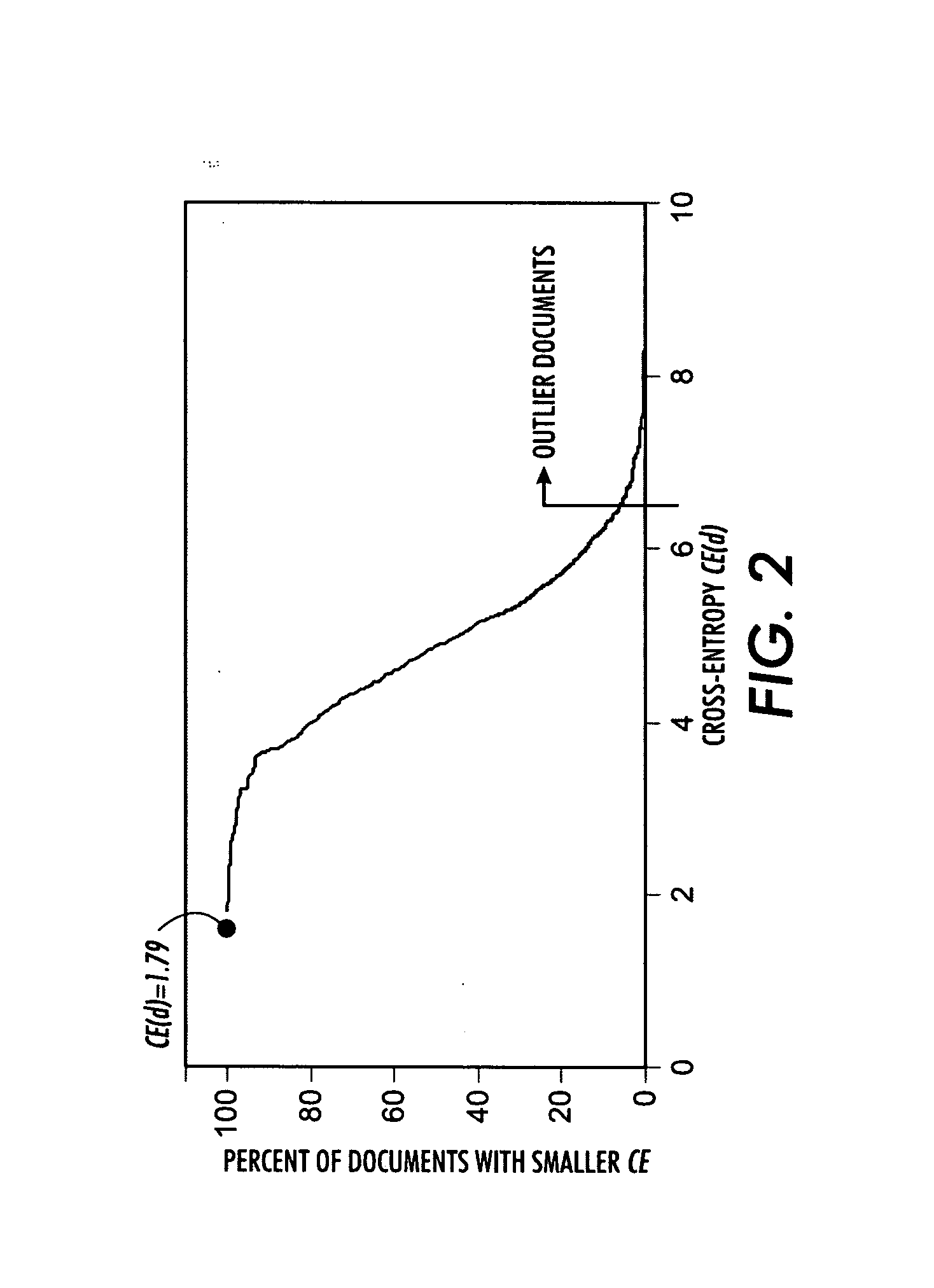
Interactive cleaning for automatic document clustering and categorization
ActiveUS20080249999A1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalUser inputAmbiguity
Documents are clustered or categorized to generate a model associating documents with classes. Outlier measures are computed for the documents indicative of how well each document fits into the model. Outlier documents are identified to a user based on the outlier measures and a user selected outlier criterion. Ambiguity measures are computed for the documents indicative of a number of classes with which each document has similarity under the model. If a document is annotated with a label class, a possible corrective label class is identified if the annotated document has higher similarity with the possible corrective label class under the model than with the annotated label class. The clustering or categorizing is repeated adjusted based on received user input to generate an updated model associating documents with classes. Outlier and. ambiguity measures are also calculated at runtime for new documents classified using the model.
Owner:XEROX CORP
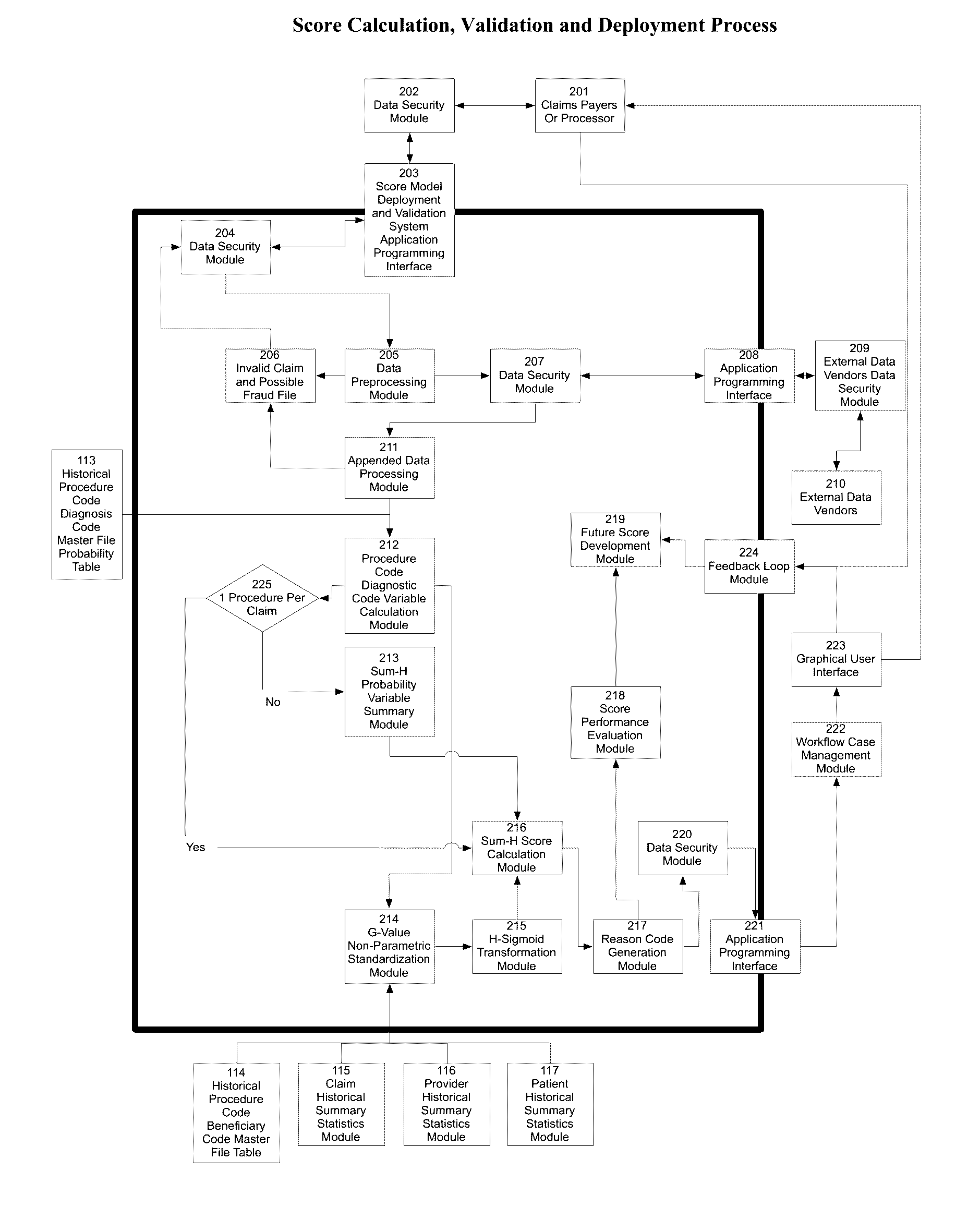
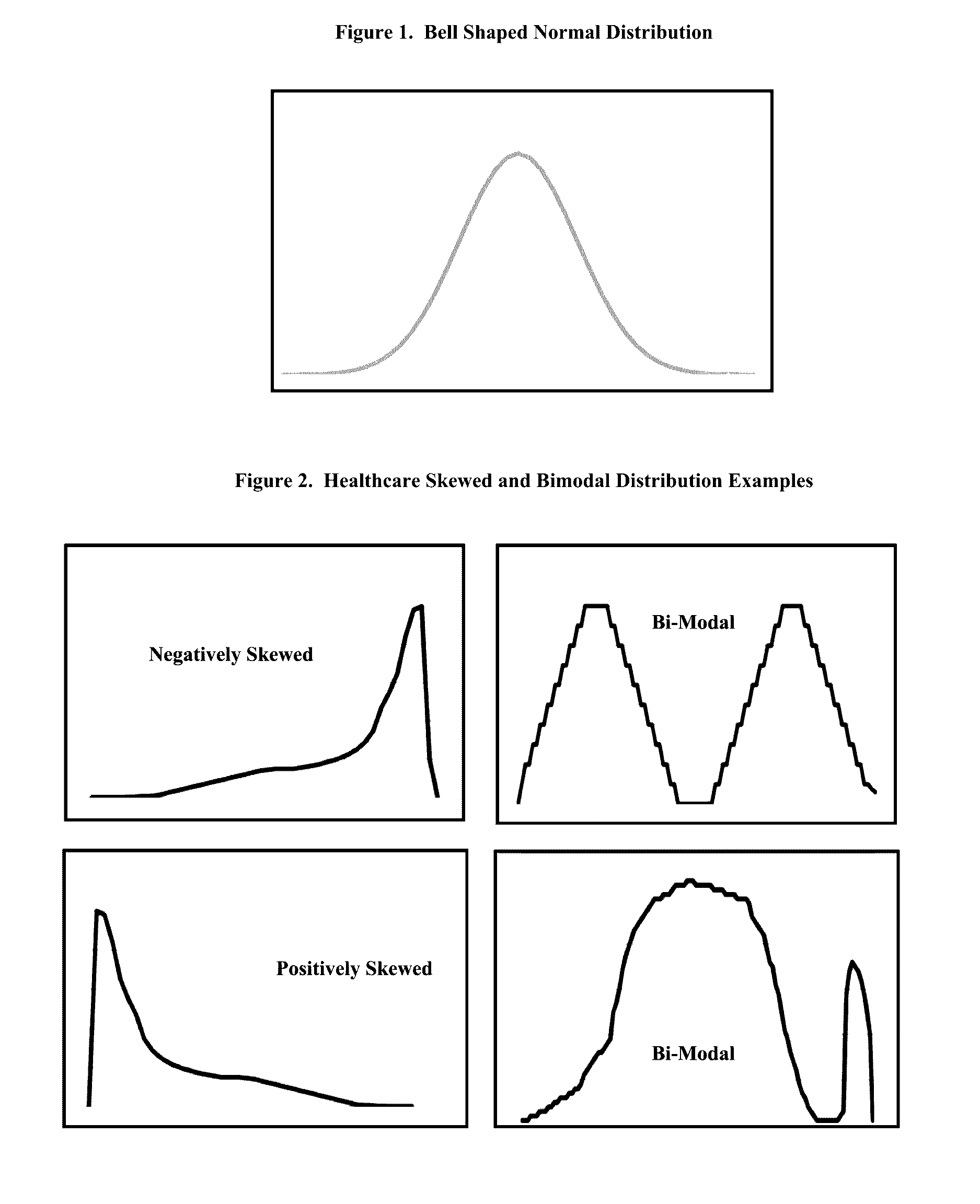
Healthcare claims fraud, waste and abuse detection system using non-parametric statistics and probability based scores
The present invention is in the field of Healthcare Claims Fraud Detection. Fraud is perpetrated across multiple healthcare payers. There are few labeled or “tagged” historical fraud examples needed to build “supervised”, traditional fraud models using multiple regression, logistic regression or neural networks. Current technology is to build “Unsupervised Fraud Outlier Detection Models”.Current techniques rely on parametric statistics that are based on assumptions such as outlier free and “normally distributed” data. Even some non-parametric statistics are adversely influenced by non-normality and the presence of outliers.Current technology cannot represent the combined variable values into one meaningful value that reflects the overall risk that this observation is an outlier. The single value, the “score”, must be capable of being measured on the same scale across different segments, such as geographies and specialty groups. Lastly, the score must substantially, monotonically rank the fraud risk and give reasons to substantiate the score.
Owner:FORTEL ANALYTICS LLC
Robust forecasting techniques with reduced sensitivity to anomalous data
ActiveUS7610214B1Improve accuracySufficiently computationally efficientReliability/availability analysisCommerceOutlierData mining
Robust forecasting techniques are relatively immune from anomalies or outliers in observed data, such as a stream of data values reflective of the operation or use of a computer system. One robust technique provides a relatively accurate forecast of seasonal behavior even in the presence of an anomaly in corresponding historical data. Another robust forecasting technique provides a relatively accurate forecast even in the presence of an anomaly that spans multiple recent observations. In one embodiment, both techniques are used in combination to automatically detect anomalies in the operation and / or use of a multi-user computer system.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
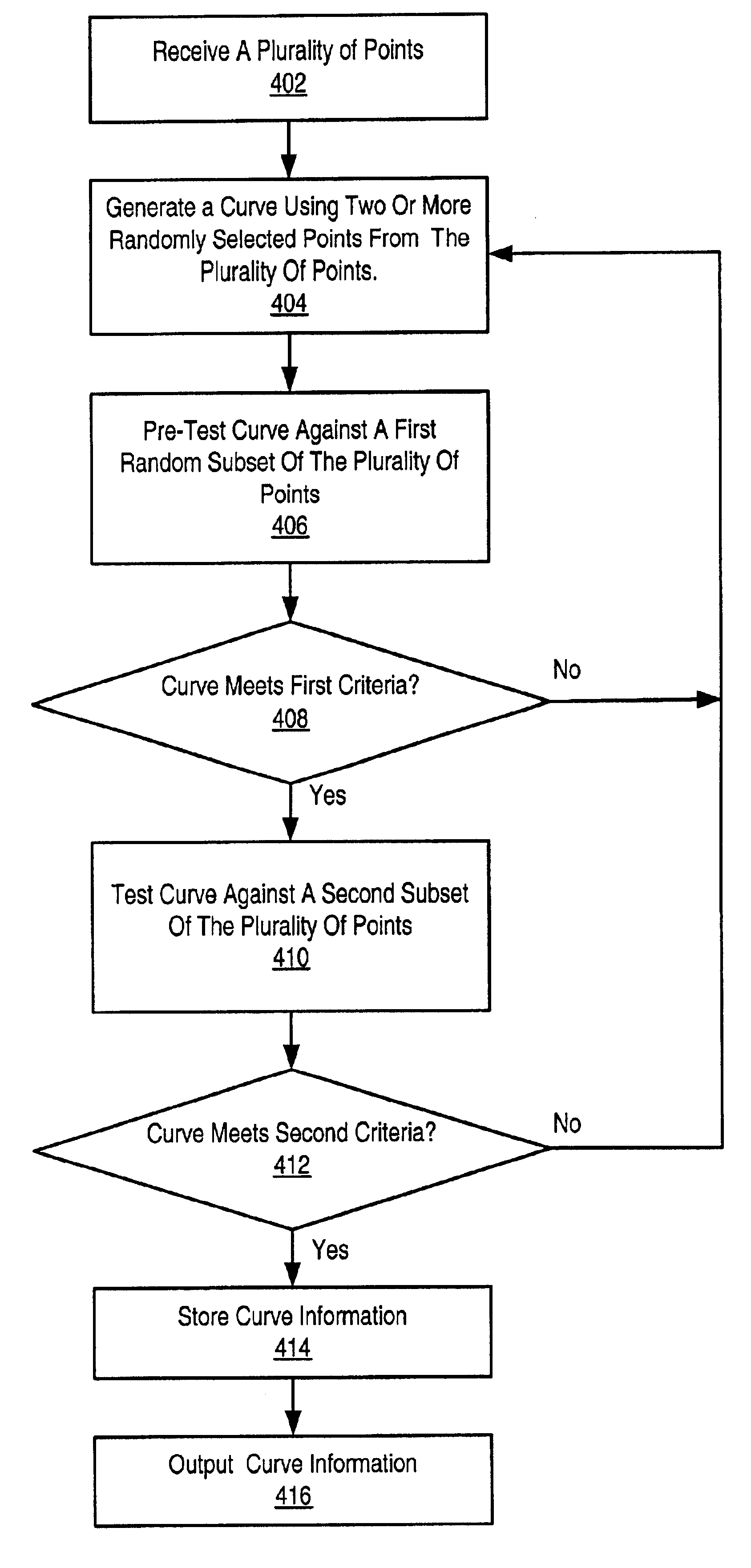
System and method for curve fitting using randomized techniques
InactiveUS6882958B2Improve method performanceAvoid calculationMeasurement devicesDigital computer detailsTheoretical computer scienceCurve fitting
A system and method for performing a curve fit on a plurality of data points. In an initial phase, a subset Pmax of the plurality of points which represents an optimal curve is determined. This phase is based on a statistical model which dictates that after trying at most Nmin random curves, each connecting a randomly selected two or more points from the input set, one of the curves will pass within a specified radius of the subset Pmax of the input points. The subset Pmax may then be used in the second phase of the method, where a refined curve fit is made by iteratively culling outliers from the subset Pmax with respect to a succession of optimal curves fit to the modified subset Pmax at each iteration. The refined curve fit generates a refined curve, which may be output along with a final culled subset Kfinal of Pmax.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
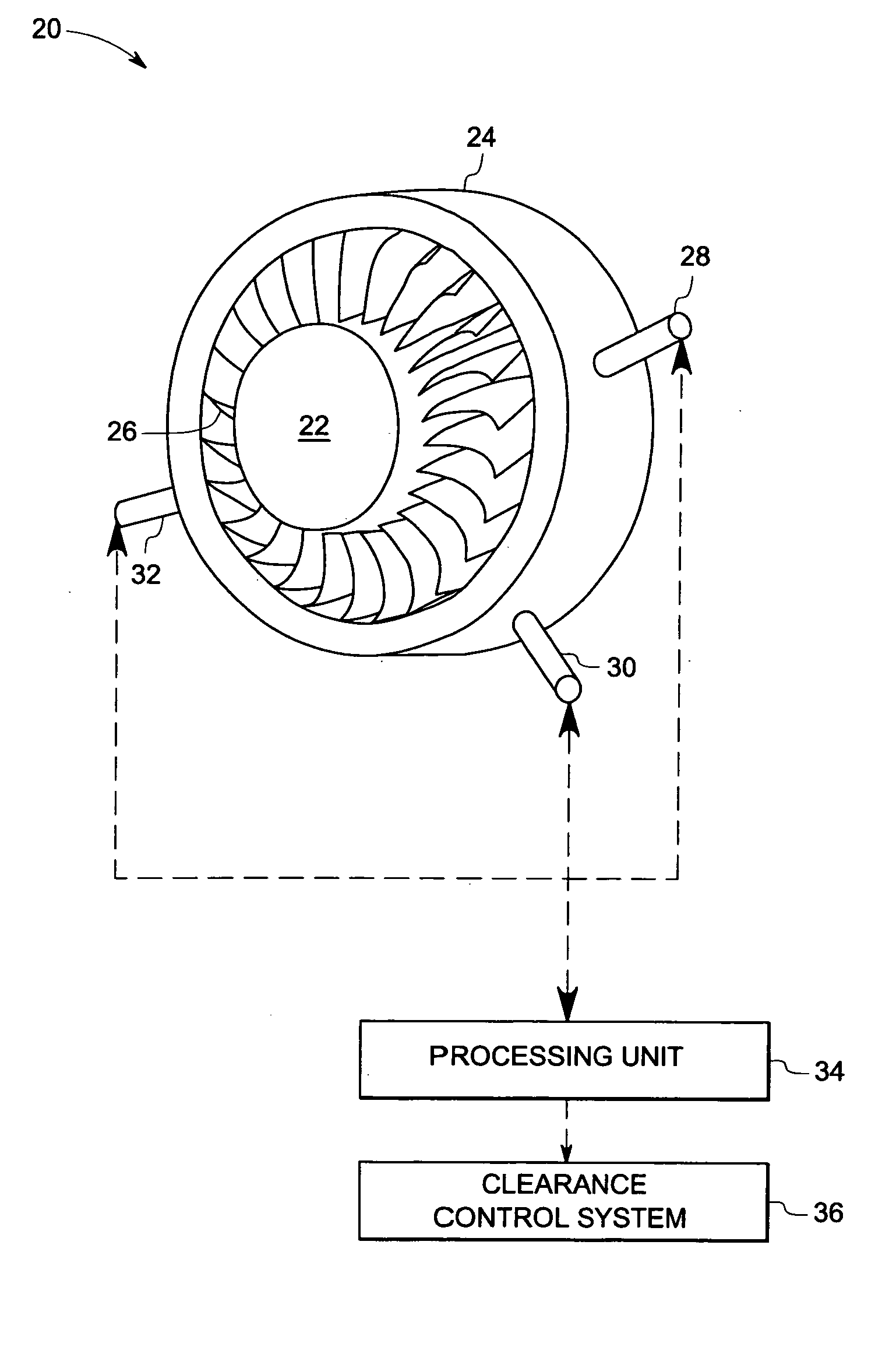
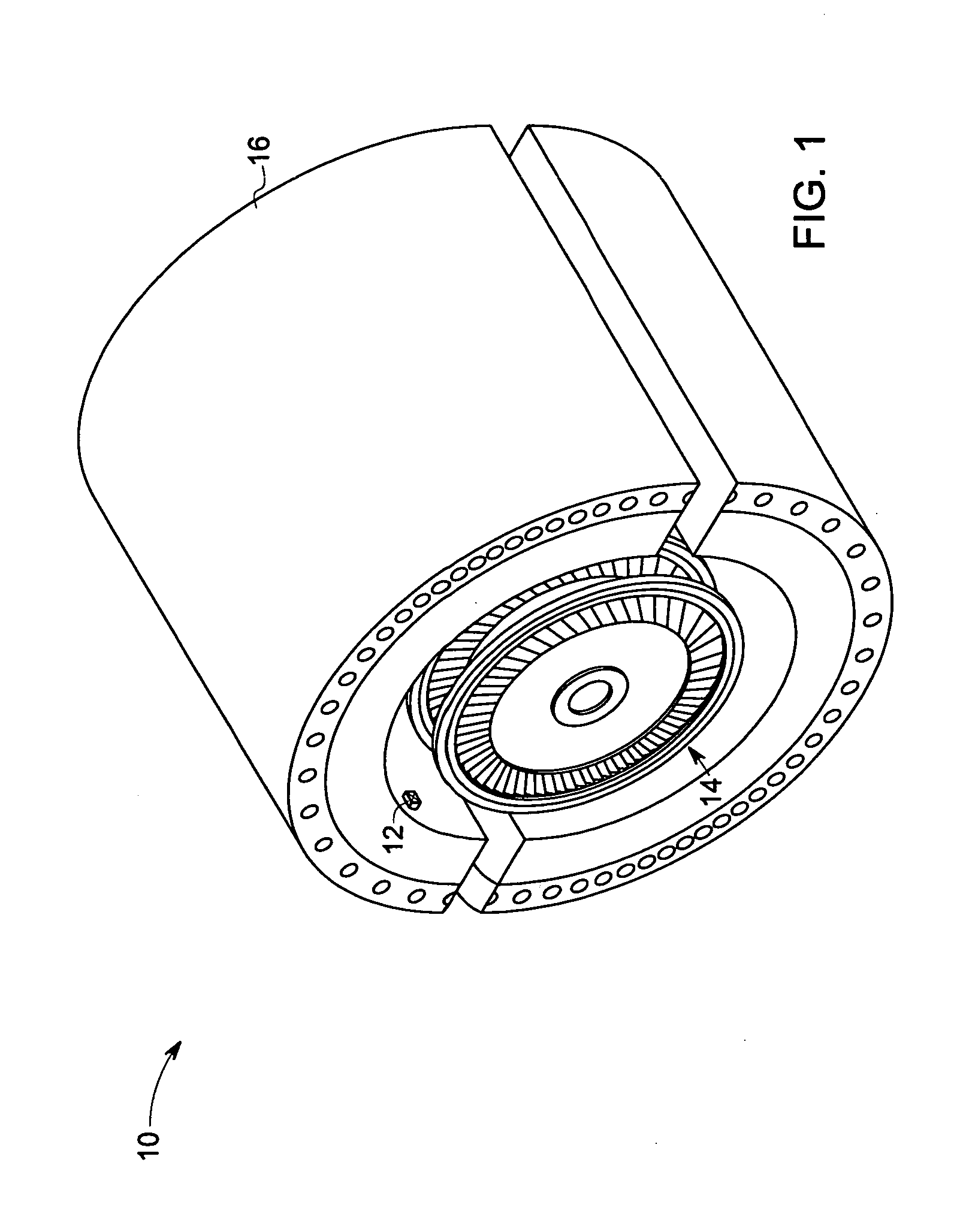
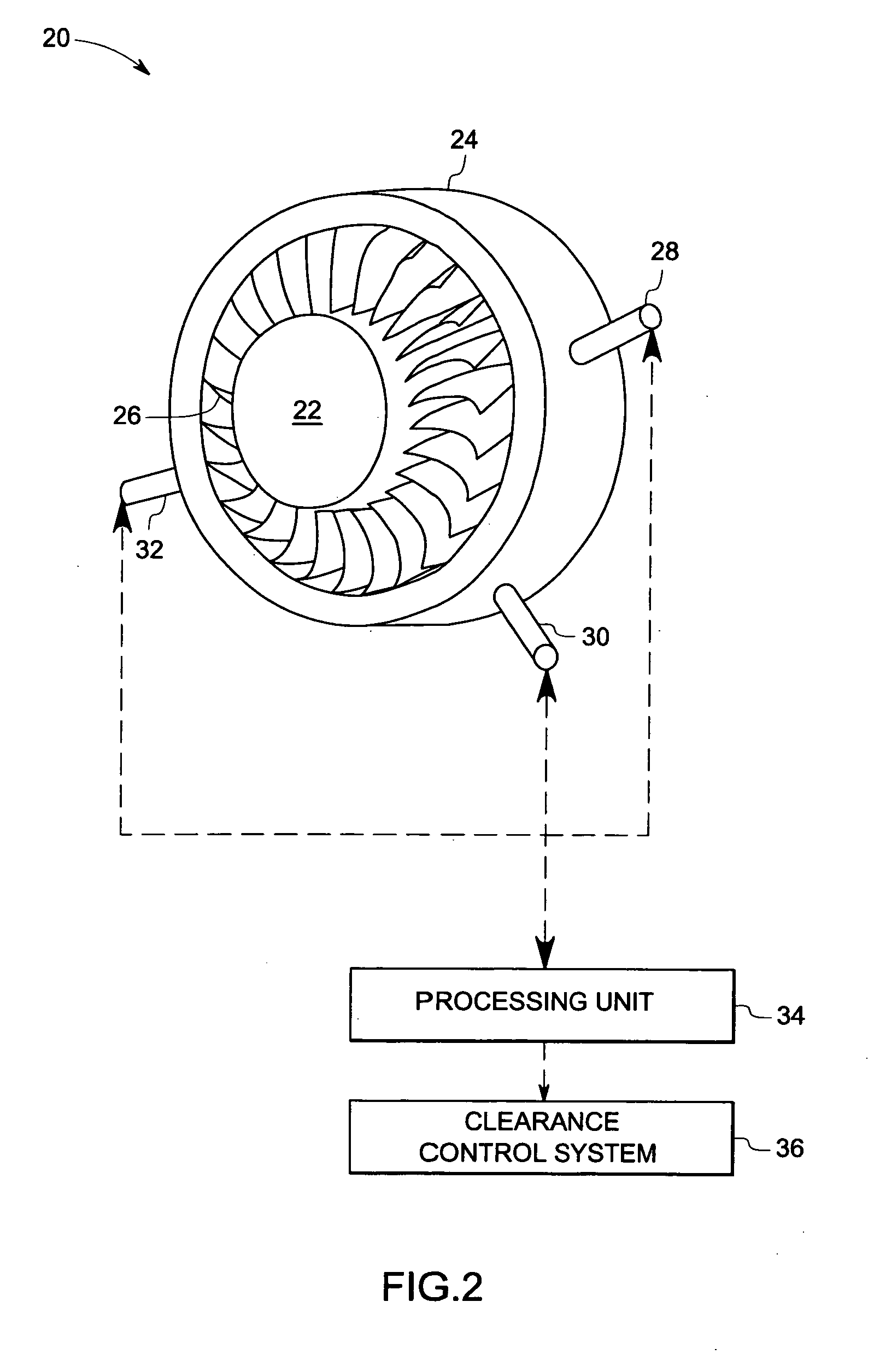
Multi tip clearance measurement system and method of operation
A multi tip clearance measurement system is provided. The clearance measurement system includes a sensor disposed on a first object, wherein the sensor comprises a plurality of probe tips configured to generate signals representative of a sensed parameter corresponding to a second object and a processing unit configured to evaluate the signals from subsets of the sensed parameters from the probe tips to detect an outlier probe tip and to adjust a gain, or an offset of the respective outlier probe tip for estimating the clearance between the first and second objects based upon the signals.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Detecting Outliers in Network Traffic Time Series
ActiveUS20100030544A1Reduce false alarm rateComputationally efficientAnalogue computers for electric apparatusTransmissionTraffic capacityOutlier
According to an aspect of the invention, a system and method is configured to detect time series outliers in network traffic.
Owner:RIVERBED TECH LLC
Robust forecasting techniques with reduced sensitivity to anomalous data
ActiveUS7739143B1Prevent wrong actionImprove accuracyForecastingCommerceObservation dataComputerized system
Robust forecasting techniques are relatively immune from anomalies or outliers in observed data, such as a stream of data values reflective of the operation or use of a computer system. One robust technique provides a relatively accurate forecast of seasonal behavior even in the presence of an anomaly in corresponding historical data. Another robust forecasting technique provides a relatively accurate forecast even in the presence of an anomaly that spans multiple recent observations. In one embodiment, both techniques are used in combination to automatically detect anomalies in the operation and / or use of a multi-user computer system.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
Computer storage capacity forecasting system using cluster-based seasonality analysis
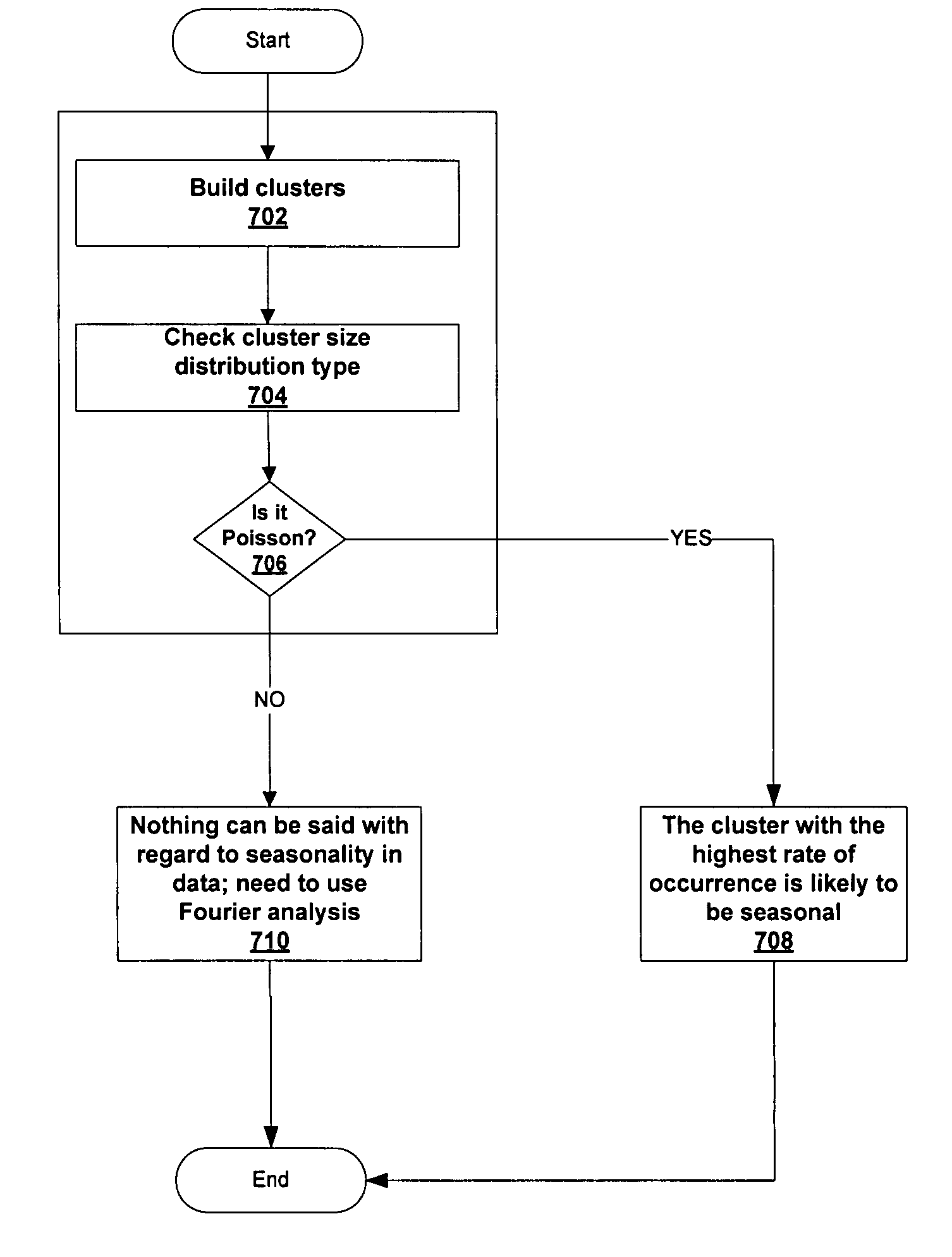
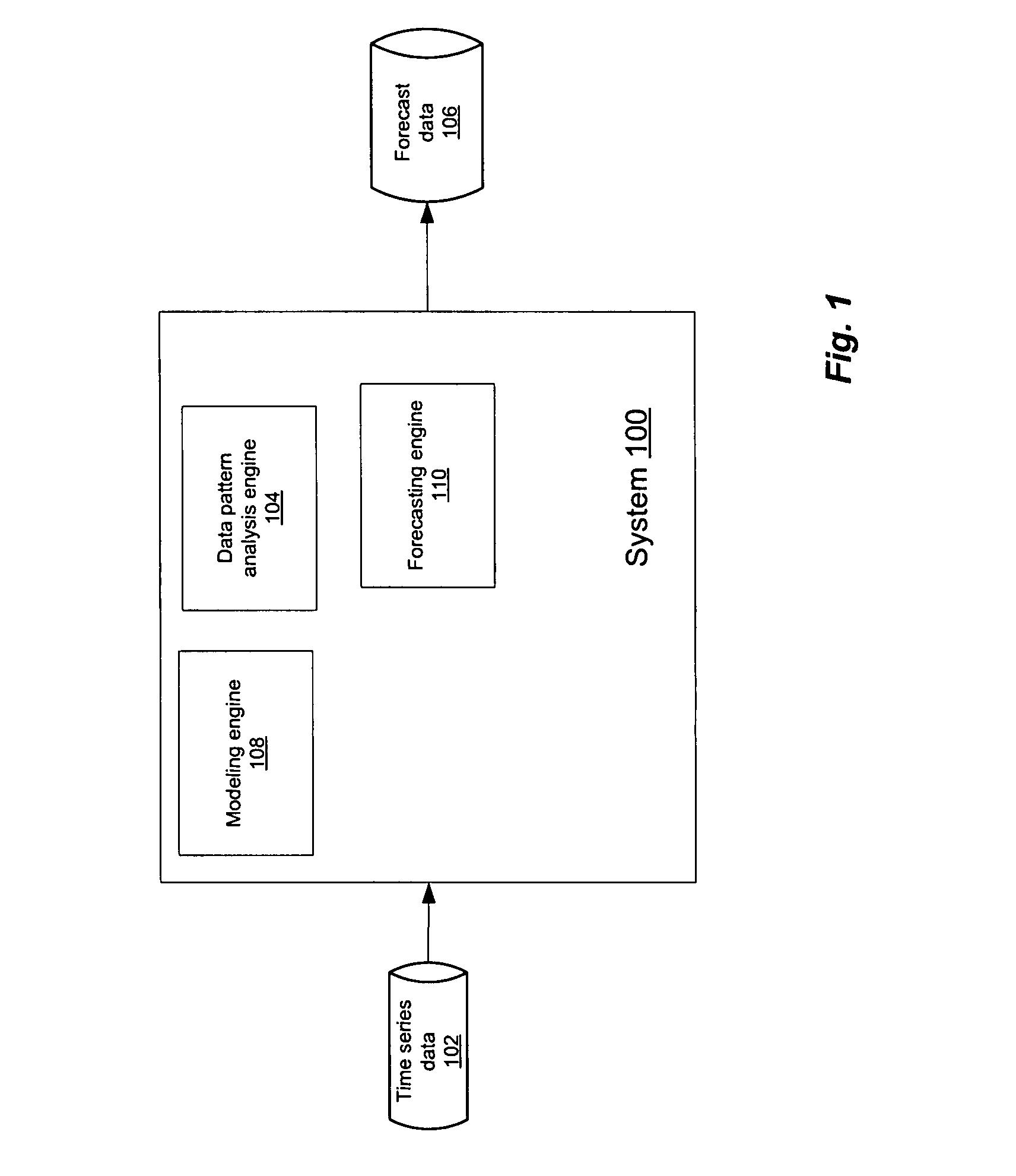
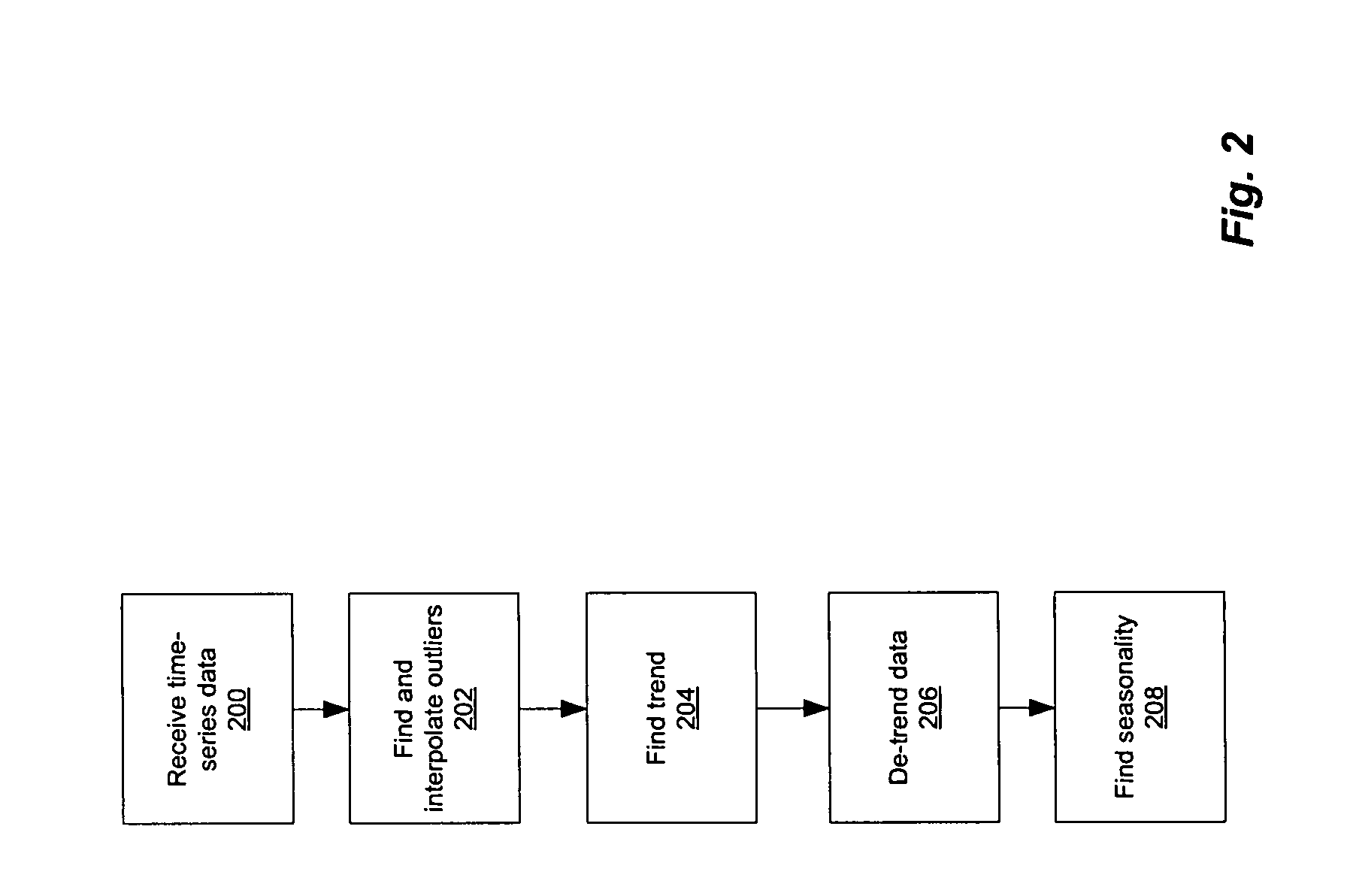
ActiveUS7783510B1Easy to shapeAccurate predictionCommerceSpecial data processing applicationsData setDecomposition
A methodology for automatic a priori data pattern analysis is provided. Described methods allow consistent and objective determination of outliers; trend; seasonality; and level shifts; and the production of better models and more accurate forecasts. In addition, a two-step way to automatically determine seasonality and locate possible events in the data set is described. Decomposition of data into seasonal, trend and level components; detection of outliers and level-shift events in the time series based on statistical analysis of the time series; detection of seasonality based on statistical analysis of clusters of data, known as cluster-based seasonality analysis, or CBSA; evaluation of the goodness of fit of a model to data, using the existing goodness of fit indicator, R2; and seasonality analysis, using a sequence of cluster-based seasonality analysis (CBSA) and Fourier analysis are described.
Owner:MONOSPHERE
Method and system for training a big data machine to defend
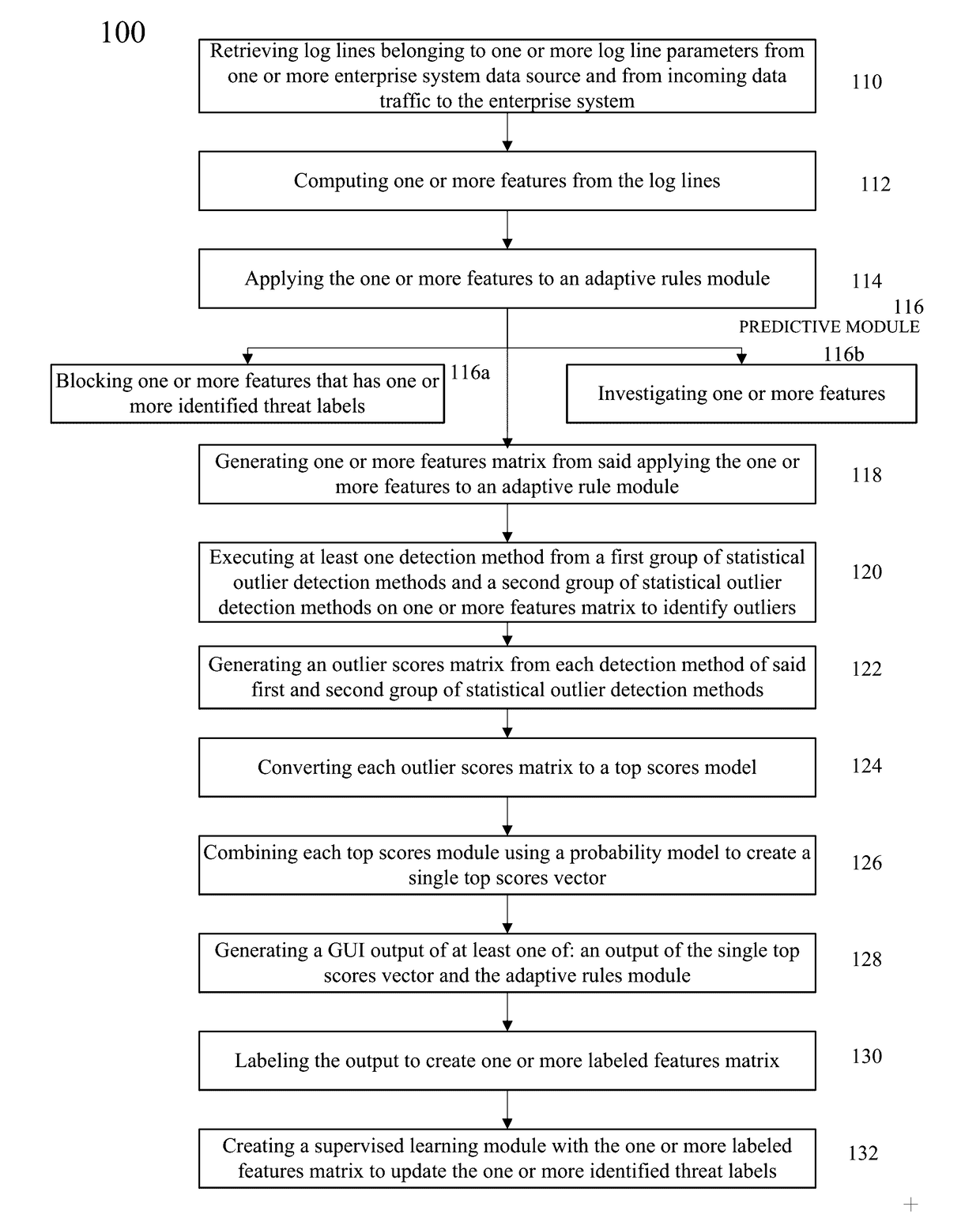
ActiveUS20170169360A1Reduce time elapsingAvoid accessMathematical modelsBiological modelsProbit modelData source
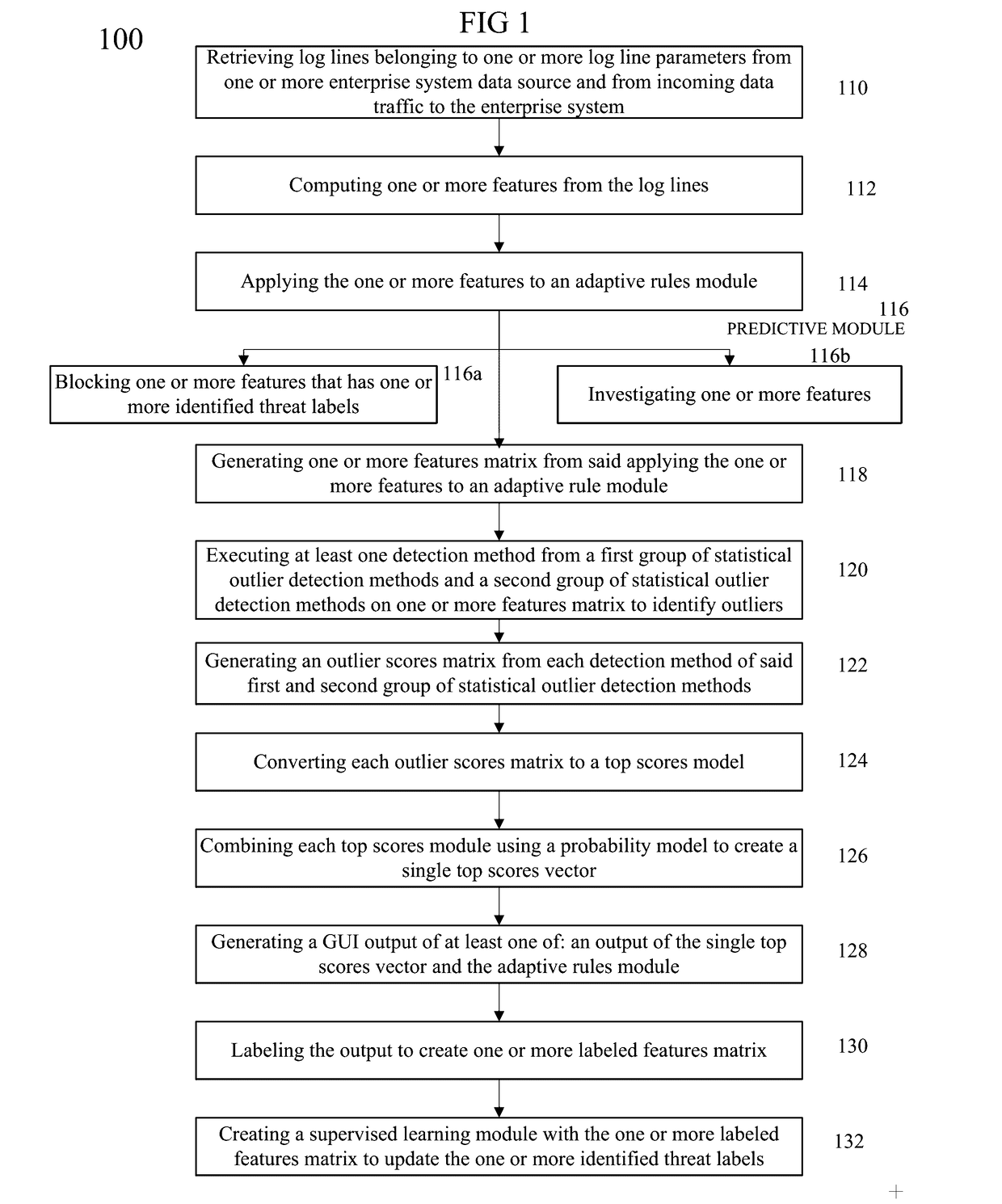
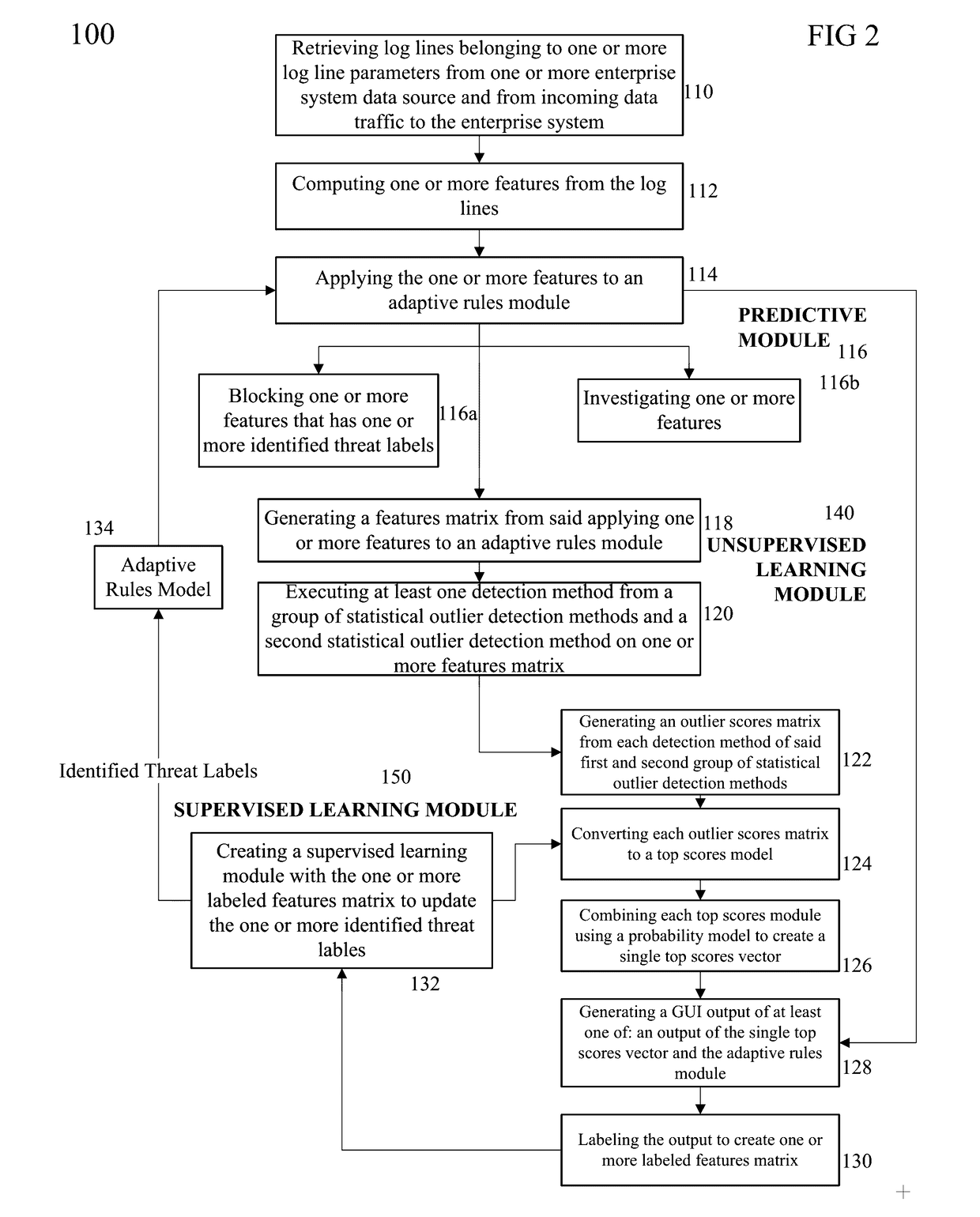
Disclosed herein are a method and system for training a big data machine to defend, retrieve log lines belonging to log line parameters of a system's data source and from incoming data traffic, compute features from the log lines, apply an adaptive rules model with identified threat labels produce a features matrix, identify statistical outliers from execution of statistical outlier detection methods, and may generate an outlier scores matrix. Embodiments may combine a top scores model and a probability model to create a single top scores vector. The single top scores vector and the adaptive rules model may be displayed on a GUI for labeling of malicious or non-malicious scores. Labeled output may be transformed into a labeled features matrix to create a supervised learning module for detecting new threats in real time and reducing the time elapsed between threat detection of the enterprise or e-commerce system.
Owner:CORELIGHT INC
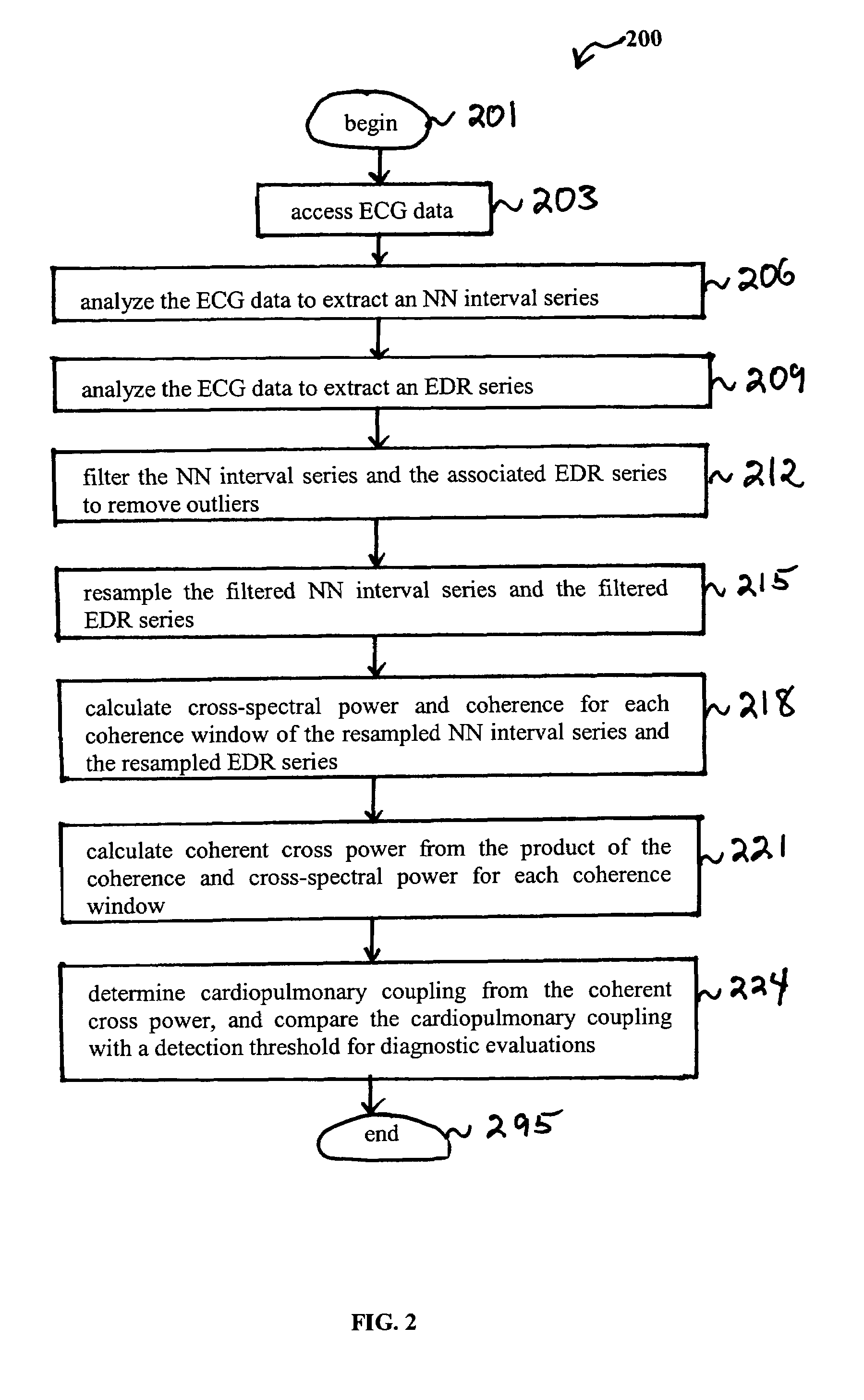
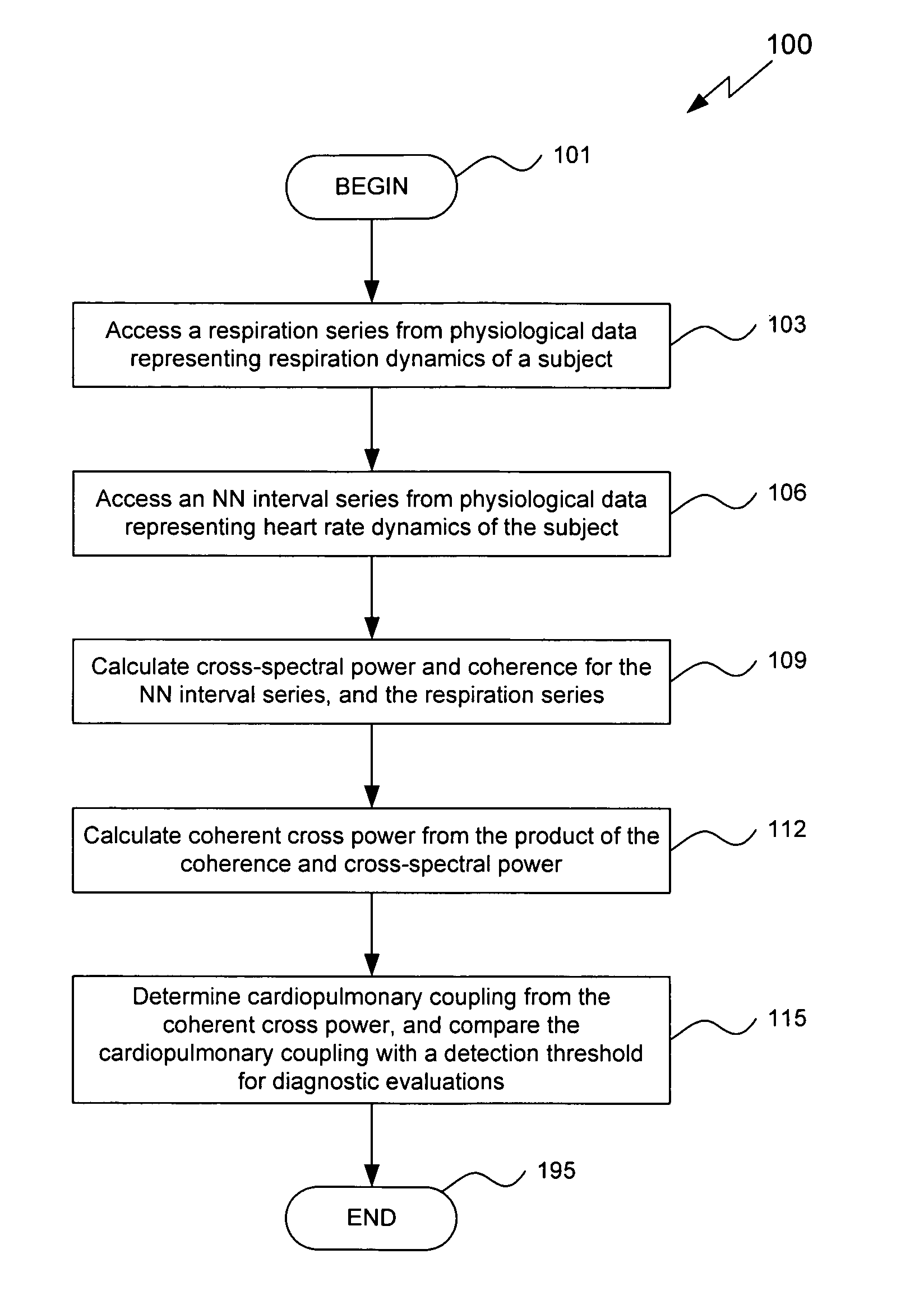
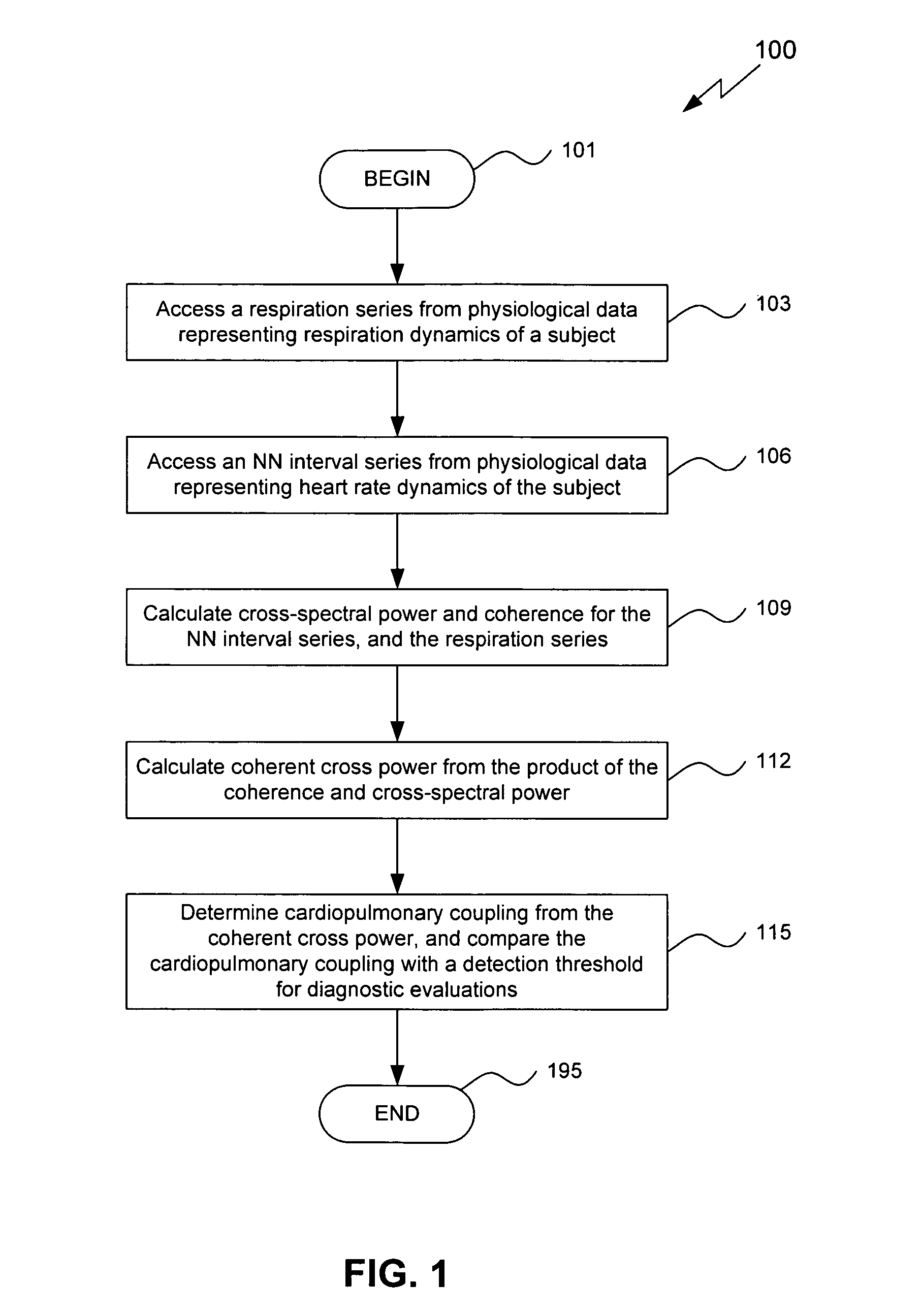
Assessment of sleep quality and sleep disordered breathing based on cardiopulmonary coupling
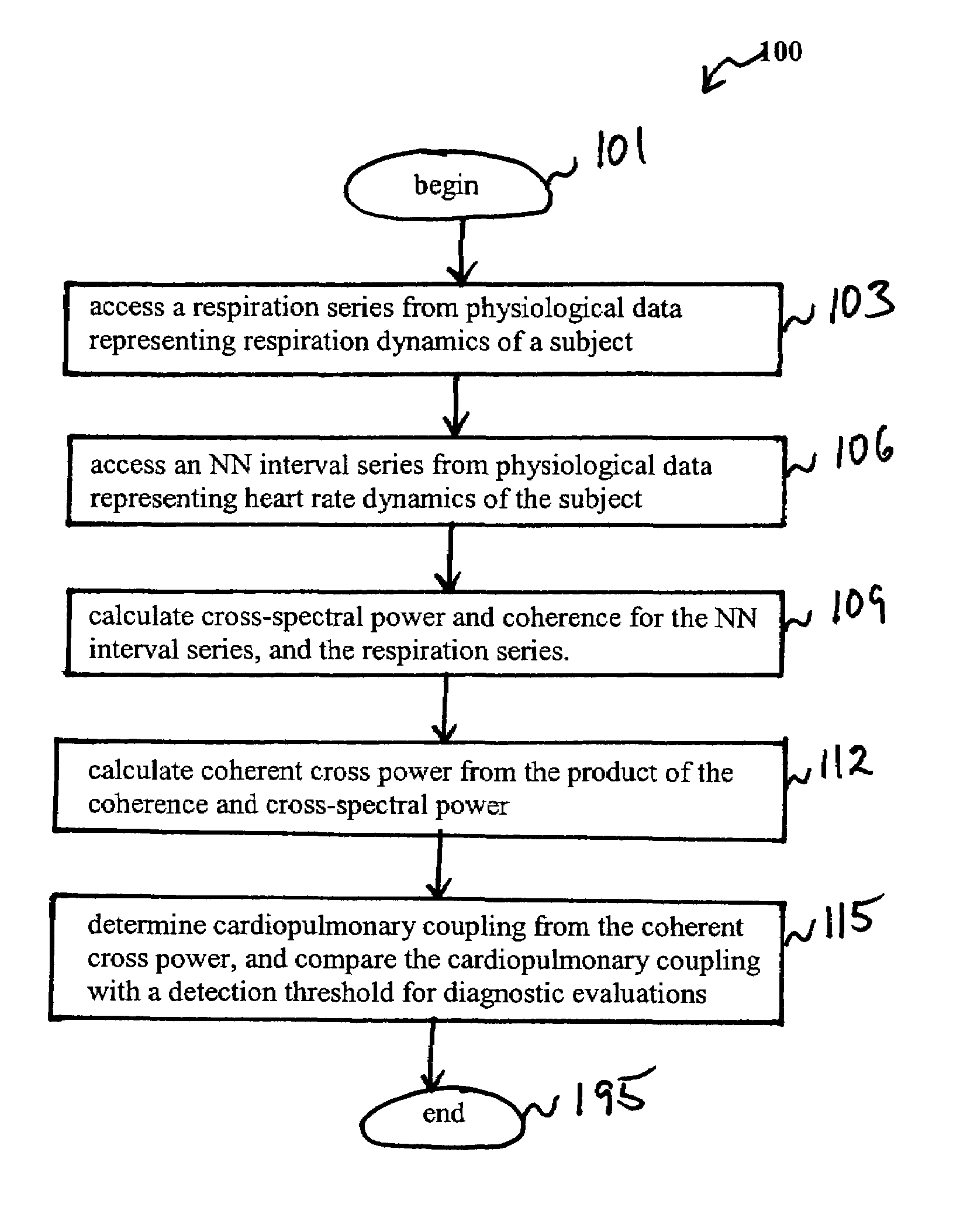
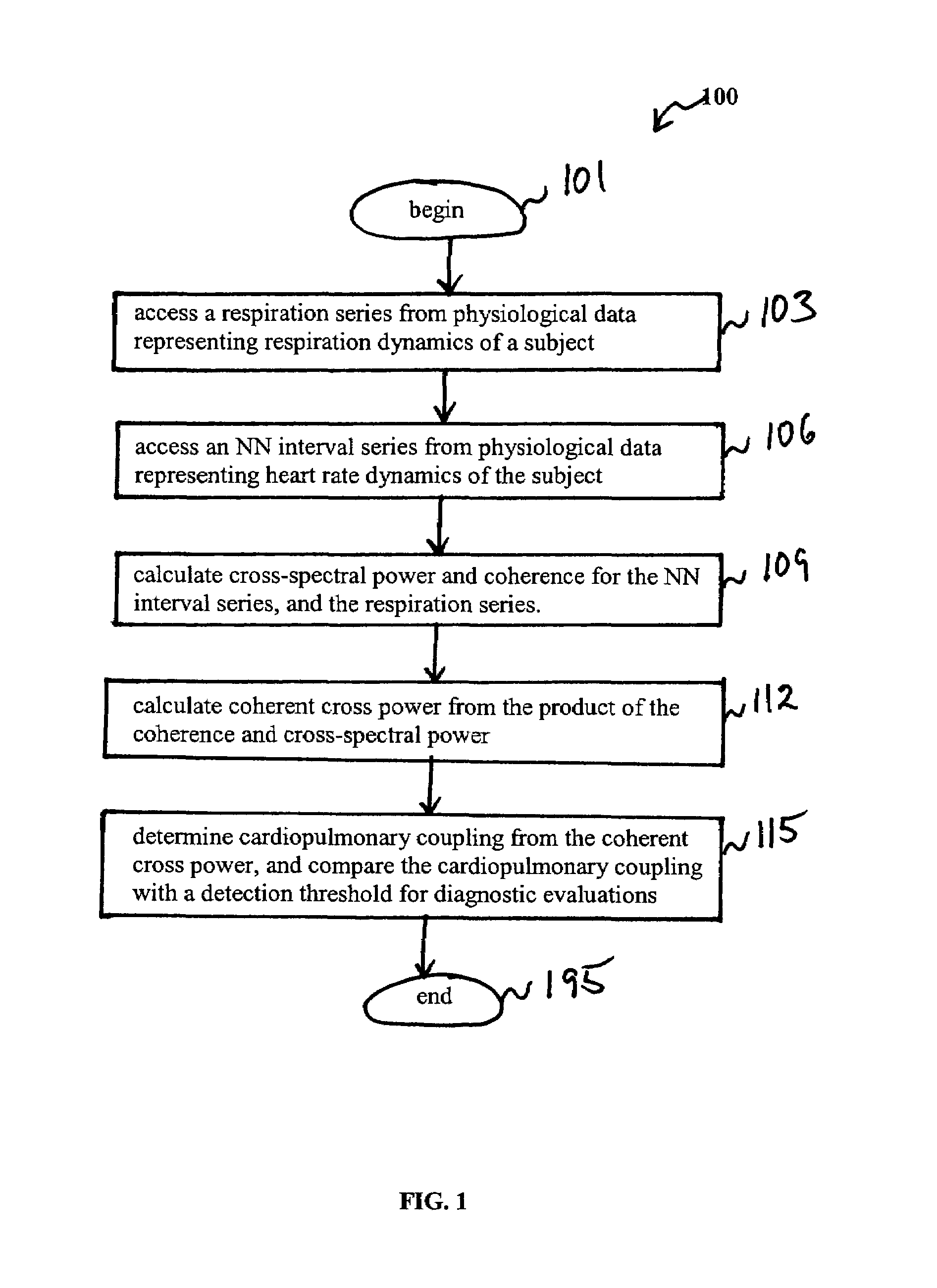
An assessment of sleep quality and sleep disordered breathing is determined from the cardiopulmonary coupling between two physiological data series. In an embodiment, an R-R interval series is derived from an electrocardiogram (ECG) signal. The normal beats from the R-R interval series are extracted to produce a normal-to-normal (NN) interval series. The amplitude variations in the QRS complex are used to extract to a surrogate respiration signal (i.e., ECG-derived respiration (EDR)) that is associated with the NN interval series. The two series are corrected to remove outliers, and resampled. The cross-spectral power and coherence of the two resampled signals are calculated over a plurality of coherence windows. For each coherence window, the product of the coherence and cross-spectral power is used to calculate coherent cross power. Using the appropriate thresholds for the coherent cross power, the proportion of sleep spent in CAP, non-CAP, and wake and / or REM are determined.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
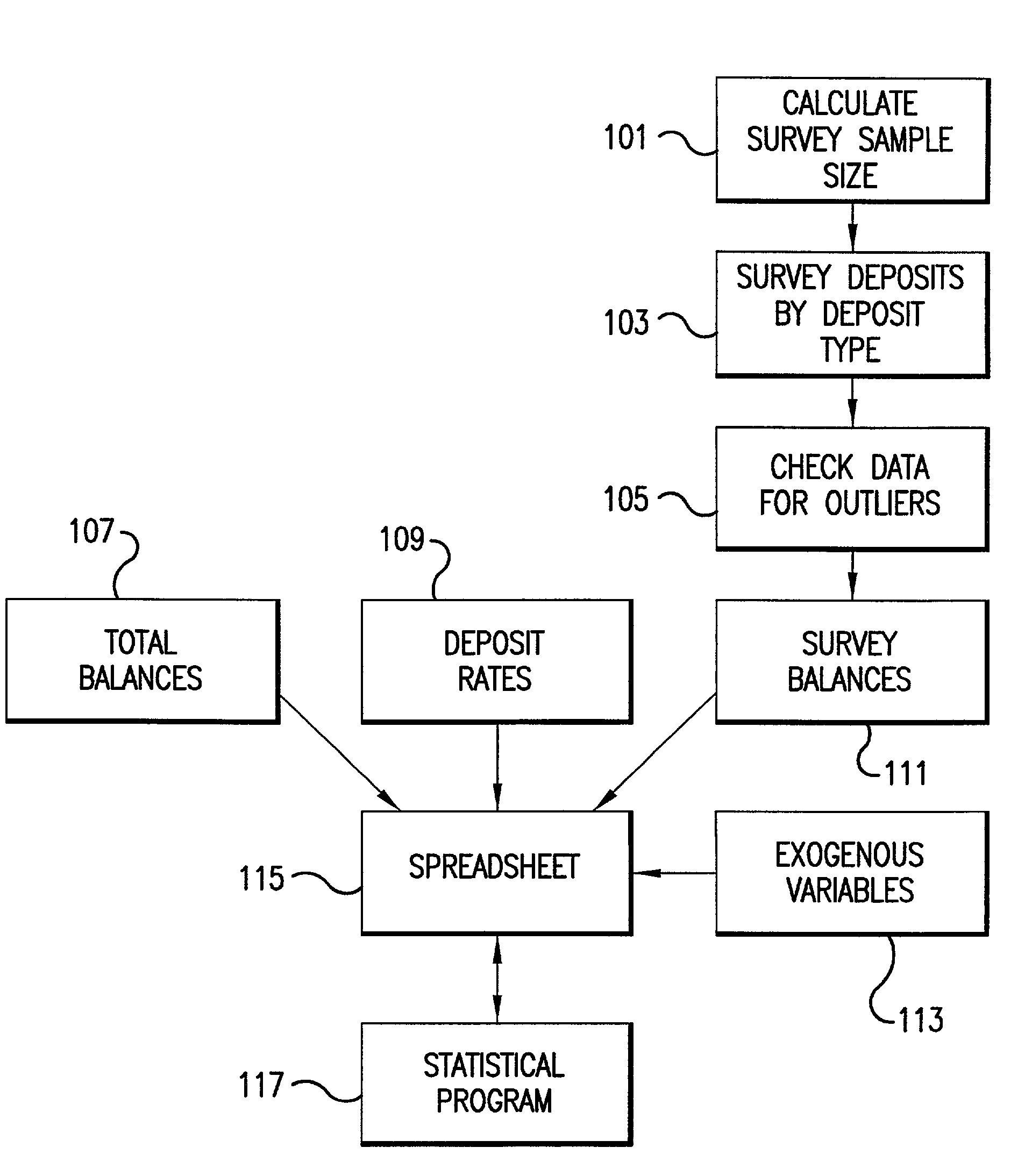
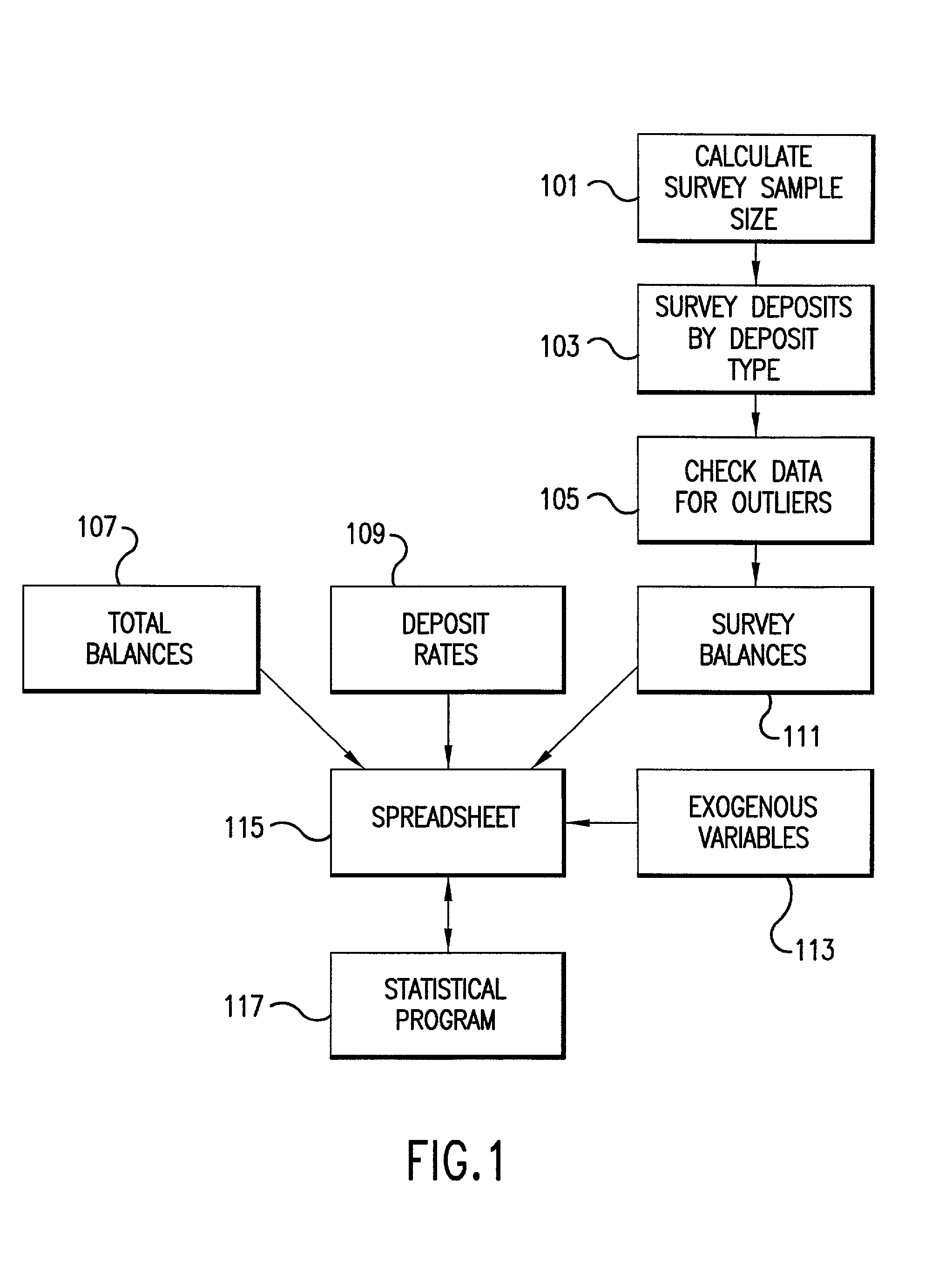
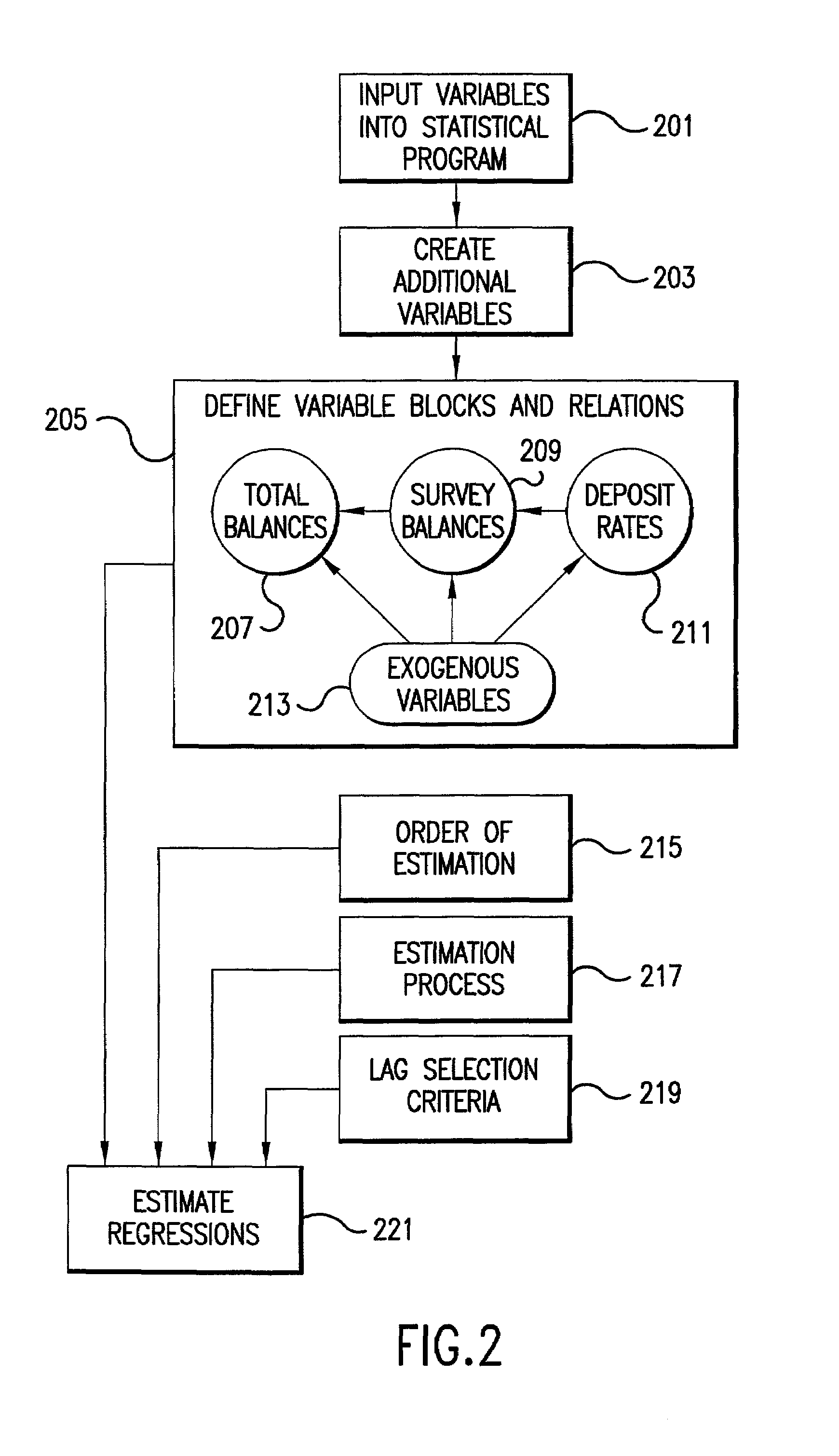
System for determining a useful life of core deposits and interest rate sensitivity thereof
A method and system for determining a useful life of financial instruments, such as financial assets and liabilities. A dynamic calculation of a first retention rate is performed for each of several financial assets; a steady-state calculation of a second retention rate is performed for the financial assets; and the first and second retention rates are combined to determine a predicted useful life of the combined financial assets.Optionally, one of several variables affecting at least one of the retention rates is selected. A sensitivity of financial asset variables to other financial asset variables is determined. Scenarios are forecast, extrapolated from the retention rate. The financial assets may include deposits and / or financial instruments. Outliers in the financial assets may be checked, in one variation of the invention. Exogenous variables may be included in at least one of the calculations. The exogenous variables are selected from the set including seasonal variables, day-of-the-month variables, treasury interest rates, deposit rates, local unemployment rate, local personal income, and local retail sales, and the like. Interest rate spread may be included in at least one of the calculations. Forecast scenarios may include future values for use in at least one of the calculations. The future values may be selected from the set including forecast treasure rates, forecast horizon, forecast deposits, forecast retention rates, and forecast interest rates, and the like.
Owner:MCGUIRE PERFORMANCE SOLUTIONS
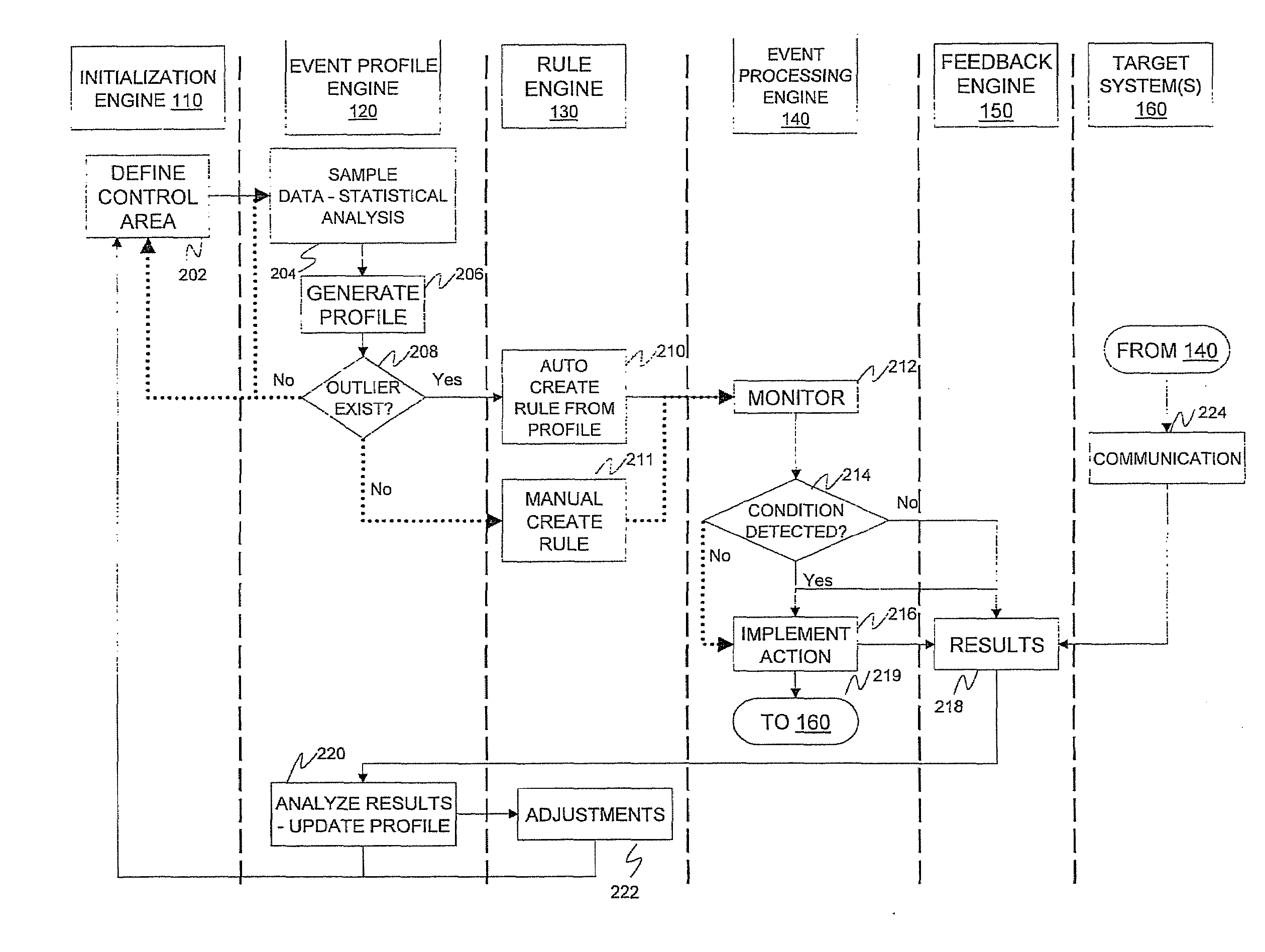
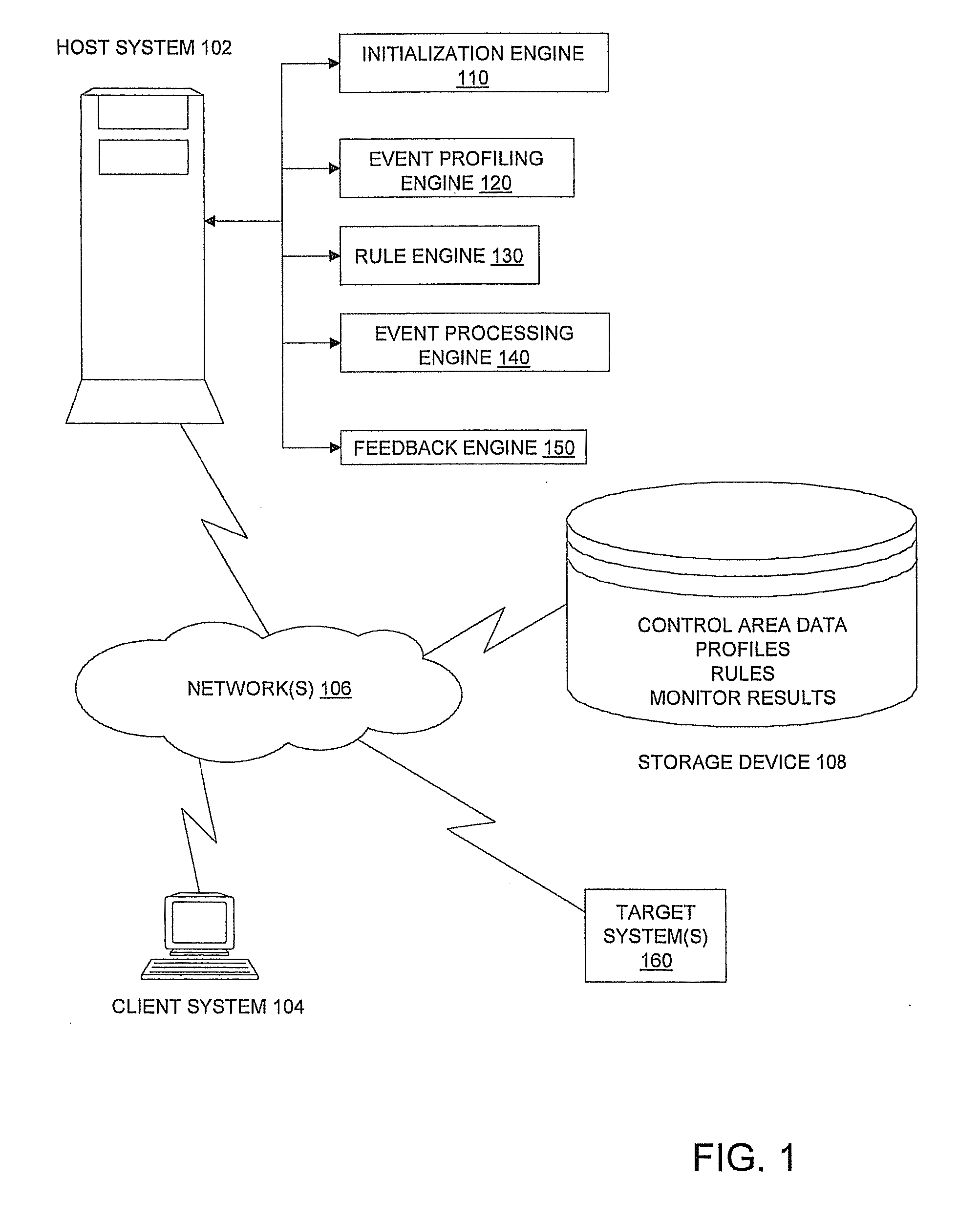
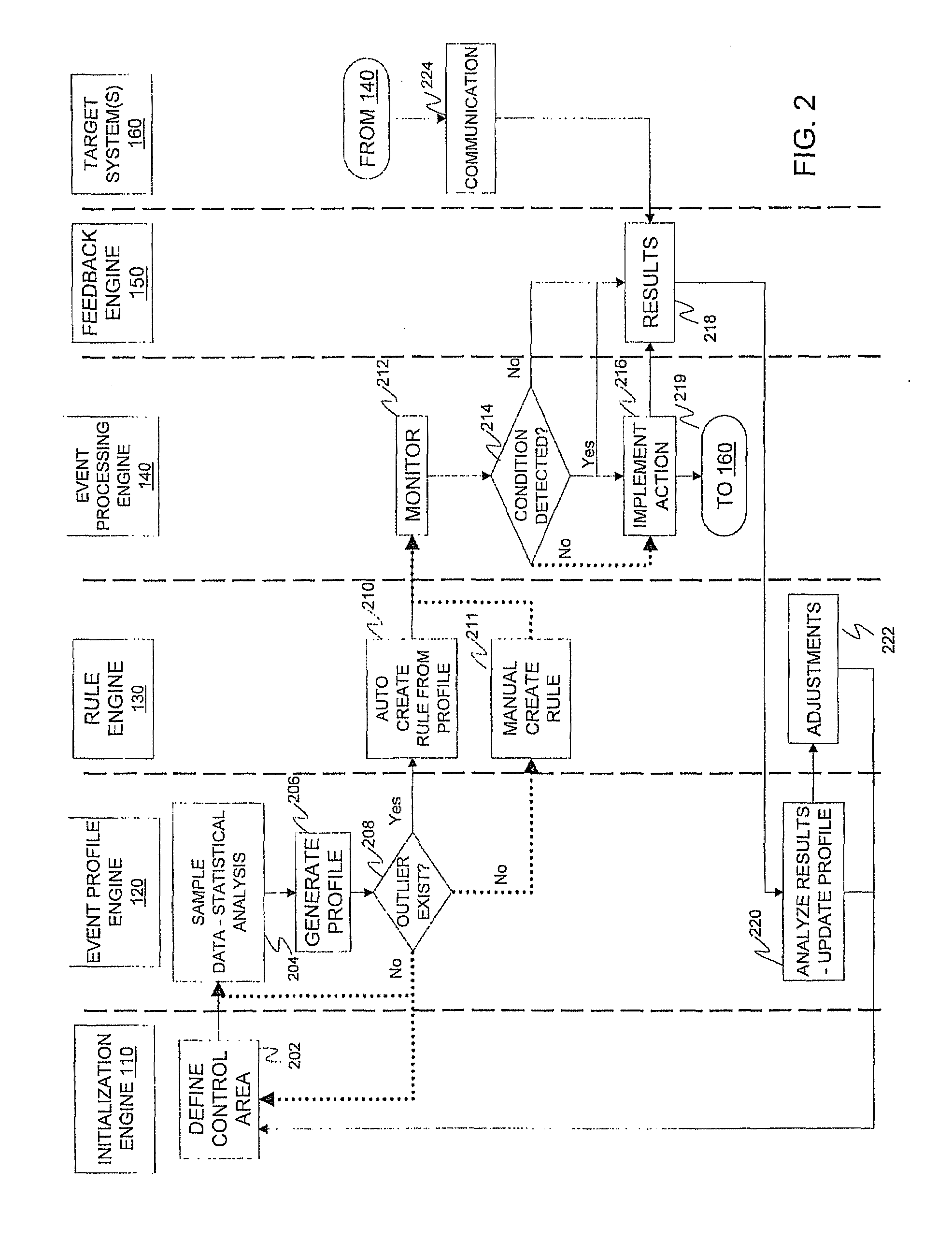
Statistical condition detection and resolution management
InactiveUS20110010209A1Digital computer detailsKnowledge representationImage resolutionStatistical analysis
A statistical condition detection and resolution management method includes sampling data and performing statistical analysis on the sampled data, the sampled data representing events detected by an event profiling engine. The method also includes generating, a profile from results of the statistical analysis, the profile indicating a normative value of an attribute identified in the sampled data, and any outliers identified in the sampled data. Upon discovering an outlier, the method includes creating, via a rule engine in communication with the event profiling engine, a rule that defines an action to be taken for a condition identified as a result of the statistical analysis, and monitoring, via an event processing engine in communication with the rule engine, real-time operational data corresponding to attributes of the profile. When in response to the monitoring the condition is met, the method includes implementing the action identified in the rule.
Owner:IBM CORP
Detecting and error-correcting method capable of rapidly and accurately obtaining element center and deflection angle
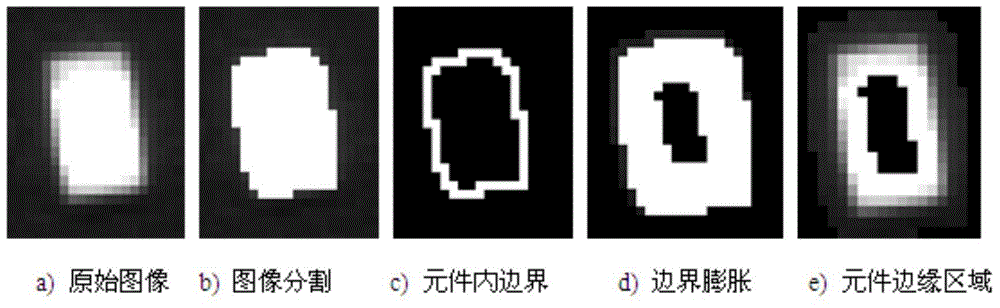
ActiveCN104981105AFind out exactlyOvercoming complex shortcomingsPrinted circuit assemblingCircuit board tools positioningCurve fittingEdge extraction
A detecting and error-correcting method capable of rapidly and accurately obtaining an element center and a deflection angle is disclosed. Interested edge area can be rapidly and accurately found out through an automatic edge area extraction method based on combination of binary morphology and image reduction, and subsequent edge extraction image scope is minimized as possible. Pixel level edge is roughly positioned at first, and accordingly a sub-pixel edge is rapidly extracted by one-dimensional curve fitting method. The method overcomes the defect of complex algorithm of a conventional sub-pixel edge extraction algorithm based on two-dimensional images, and the time of extracting accurate sub-pixel edge can be shortened. Weighted least square rectangular edge fitting algorithm based on linear hazen paradigm can detect straight lines on any positions of an image, and effectively minimizes influence of outlier on fitting precision due to uneven edges. The central positions of a plurality of elements and deflect angles can be rapidly and accurately detected at once, and the efficiency of visual detection is improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Multi-image feature matching using multi-scale oriented patches
InactiveUS7382897B2Quick extractionEasy to liftConveyorsImage analysisPattern recognitionNear neighbor
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Electric arc welder and method of designing waveforms therefor
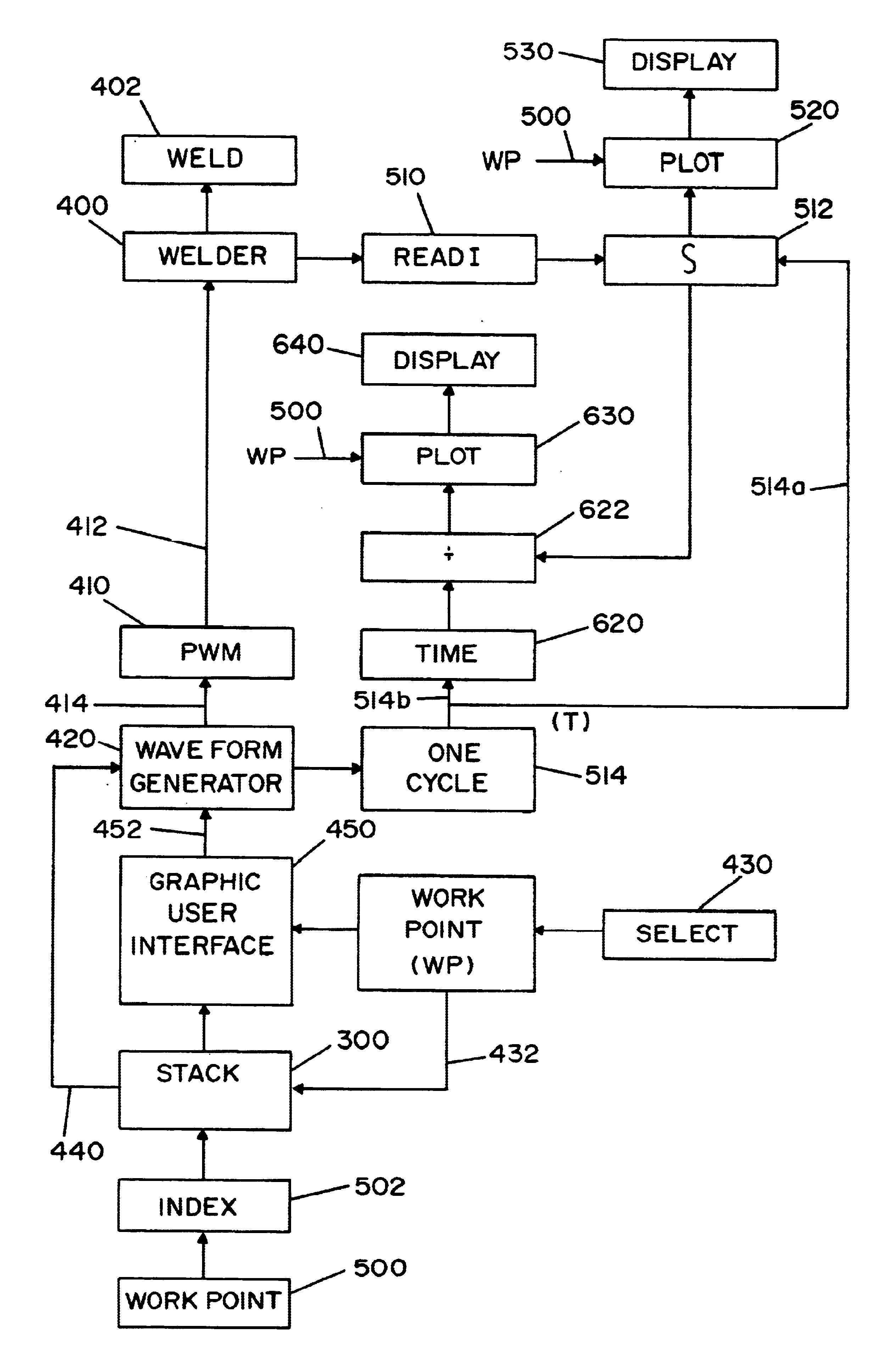
A method of designing a series of waveforms for current cycles generated by a waveform generator to control the waveforms of a welding process performed by an electric arc welder, where the waveforms are stored in a memory stack by work points. The method comprises: integrating the arc current of the waveform designed for each of the many work points to obtain an integrated amount; plotting the integrated amounts for each of the work points; creating a regression curve statistically matching the plotted amounts to reveal outlier amounts; selecting an outlier amount; and, changing the waveform corresponding to the selected outlier amount to decrease the deviation of the integrated amount of the changed waveform from the regression curve.
Owner:LINCOLN GLOBAL INC
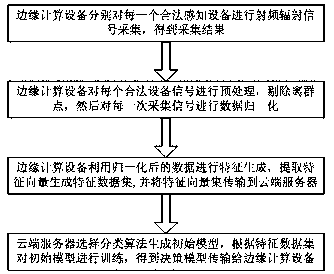
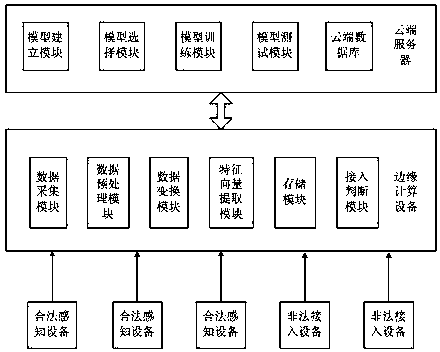
Internet of things terminal secure access method and system based on edge computing
ActiveCN107770263AReduce computational complexityReduce latencyTransmission monitoringSecurity arrangementComputation complexityData set
The invention discloses an Internet of things terminal secure access method and system based on edge computing. The method comprises the steps that an edge computing device carries out radio frequencyradiation signal collection on each legal sensing device, thereby obtaining collection results; the edge computing device preprocesses each legal device signal, removes outliers and carries out datanormalization on collected signals of each time; the edge computing device generates features through utilization of the normalized data, extracts feature vectors to generate feature data sets and transmits the feature vector sets to a cloud server; and the cloud server selects a classification algorithm to generate a data model, trains the data model according to the feature data sets and transmits an obtained decision-making model to the edge computing device. According to the method and the system, the data processing and access judgment are carried out at the edge computing side, and the method and the system are applicable to an Internet of things device interconnection scheme with limited resources and have the advantages of low computing complexity and high authentication accuracy.
Owner:CERTUS NETWORK TECHNANJING
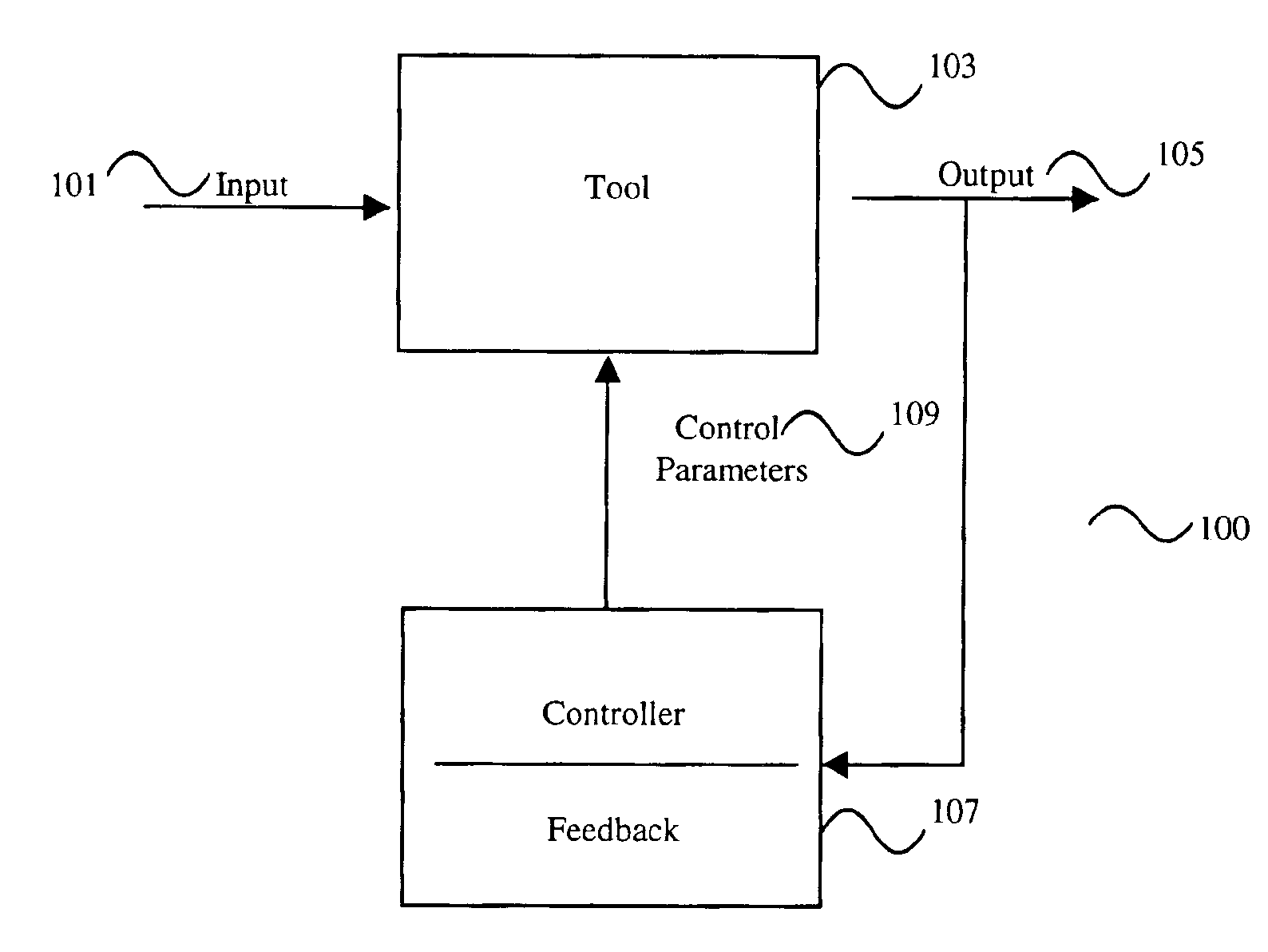
Method, system, and medium for handling misrepresentative metrology data within an advanced process control system
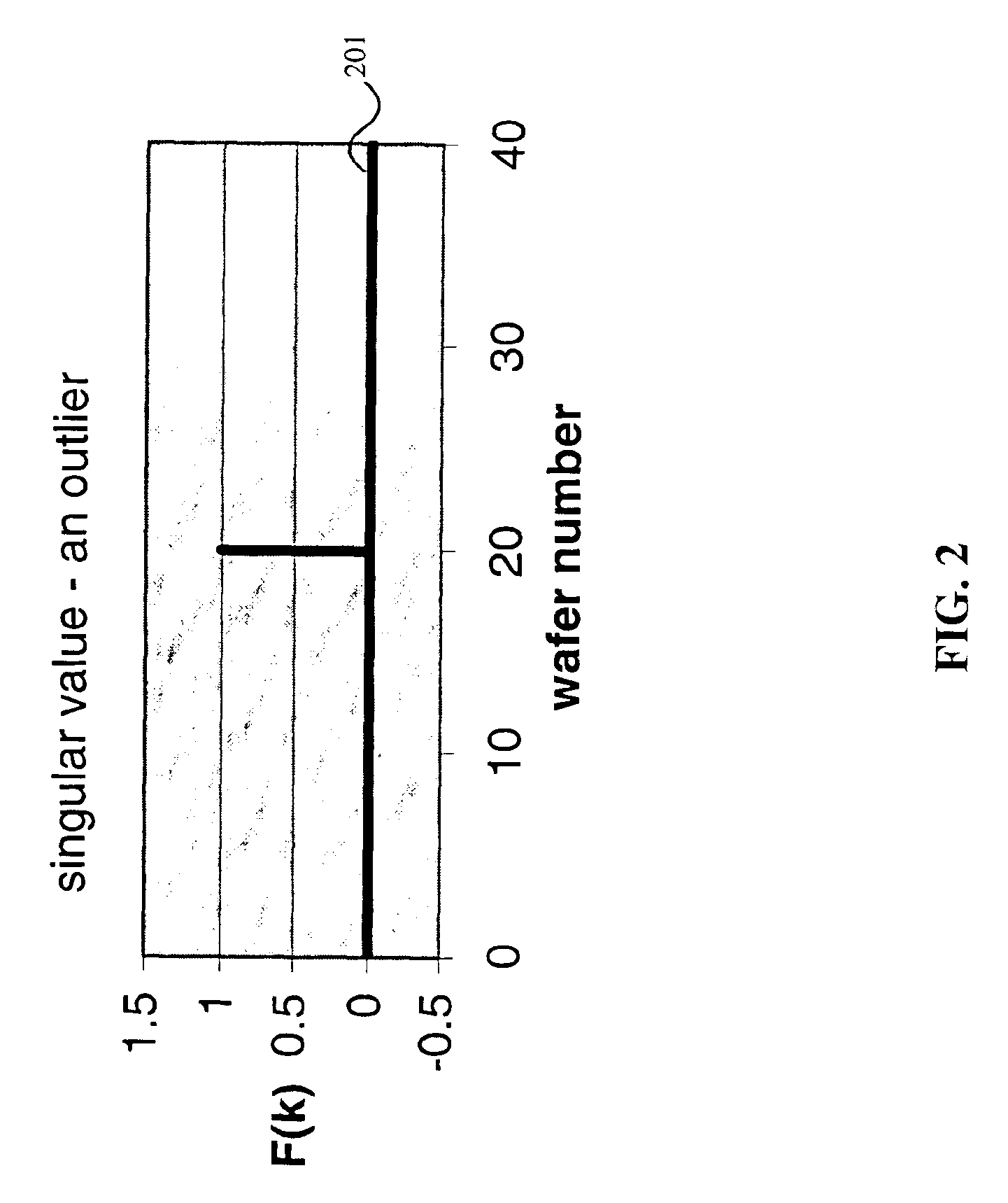
InactiveUS6999836B2Accurate measurementSampled-variable control systemsComputer controlMetrologyOutlier
A system, method and medium of controlling a semiconductor manufacturing tool using a feedback control mechanism. The feedback control mechanism includes features for receiving data points relating to an output of the tool. The data points include a current data point and at least one previous data point. The feedback control mechanism also includes features for determining whether the current data point is an erroneous outlier by comparing the current data point to a statistical representation of the at least one previous data point, and based on whether the at least one previous data point is an outlier. The feedback control mechanism further includes features for disregarding the current data point in calculating a feedback value of the feedback control mechanism if the current data point is determined as an erroneous outlier.
Owner:APPL MATERIALS ISRAEL LTD
Levenberg-Marquardt outlier spike removal method
ActiveUS20070148632A1Robust estimationMicrobiological testing/measurementRecognisation of pattern in signalsData setAlgorithm
Systems and methods for identifying and removing spikes in data sets representing PCR growth curves or other sigmoid type curves or growth curves. A double sigmoid function with parameters determined using a Levenberg-Marquardt regression algorithm is used to find an approximation to the curve, and a statistical test such as a z-test is then used to identify spikes by identifying data points in the data set that do not fit well with the approximation. The identified spike(s) are removed from the data set and / or replaced with interpolated data points determined by using data points surrounding the identified spike(s). In one aspect, a spline interpolation process such as a cubic spline interpolation process is used to find an approximation to the data set with the identified spike points removed. Interpolated values to replace the spike points are then calculated using the cubic spline interpolation approximation curve.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Space carving in 3D data acquisition
ActiveUS20130335417A1Improve accuracyIncrease speedDentistryDiagnostic recording/measuringData acquisitionOutlier
Three-dimensional scanning is improved with the use of space carving to exclude certain scan results from processing and display. Using space carving techniques, a spatial matrix is maintained to store data on volumetric regions (or voxels) known to be empty. By excluding or modifying processing of outlier data from within these unoccupied voxels, a three-dimensional reconstruction process can achieve concurrent improvements in accuracy and speed. In addition, a real time display of scan results can be improved by modifying how such outliers are rendered.
Owner:MEDIT CORP
Generating complex event processing rules utilizing machine learning from multiple events
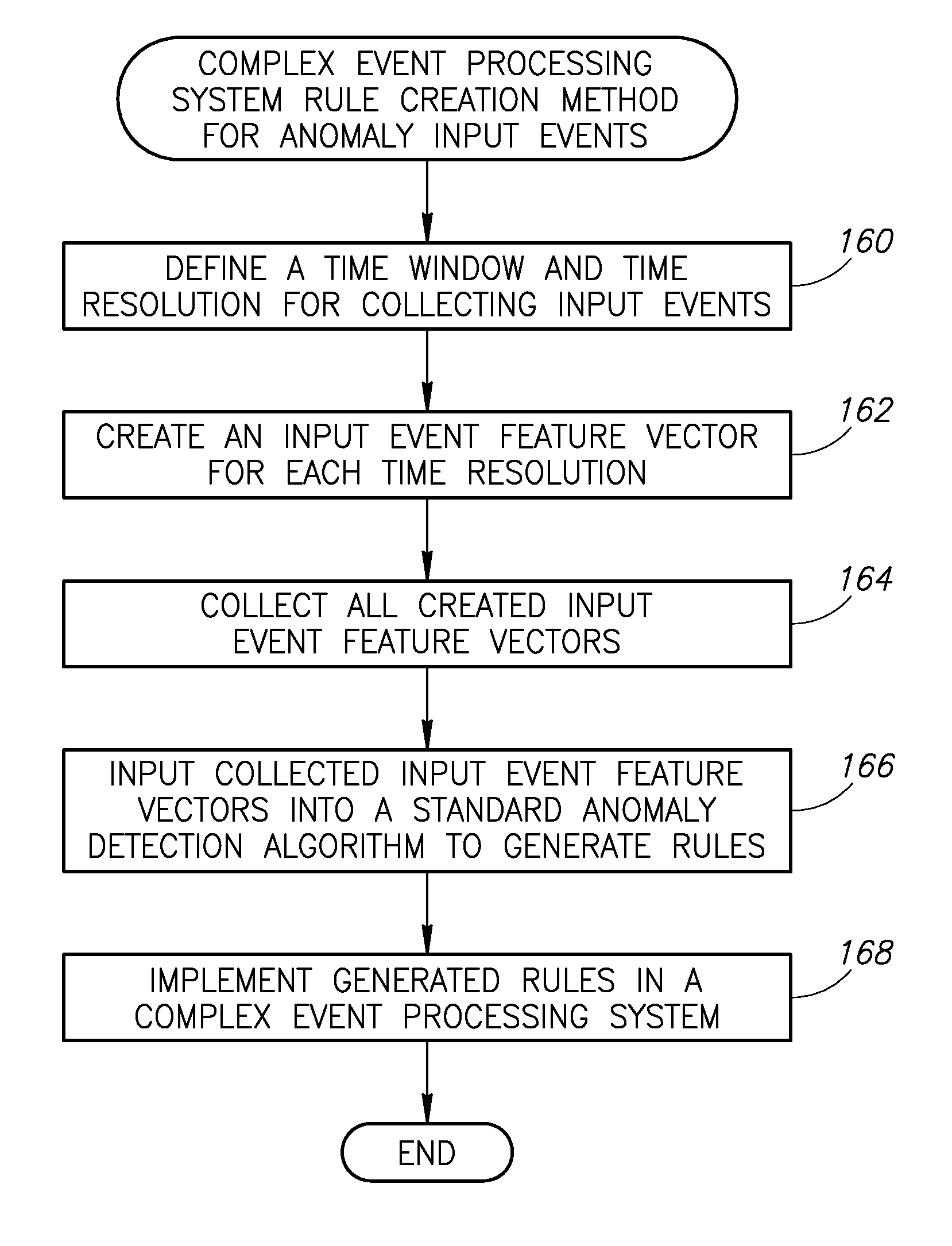
ActiveUS8078556B2Improve system performanceSystem support costs and system downtime can be reducedDigital computer detailsChaos modelsFeature vectorComplex event processing
A novel and useful mechanism enabling a standard learning algorithm to generate rules for complex event processing (CEP) systems. The method creates rules that infer previously defined output events by creating input event feature vectors for each targeted output event. In addition, a method for automatically generating CEP system rules to infer output events which are anomalies (i.e. statistical outliers) of input event sequences is disclosed. Input feature vectors consisting of multiple input events and parameters for each targeted output event are then input into a standard learning algorithm to generate CEP system rules.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Behavioral clustering for removing outlying healthcare providers
InactiveUS20130197925A1Resulting strongData processing applicationsHospital data managementClinical informationOutlier
Behavioral clustering of providers may be used to identify outliers of a group of providers. Groups of healthcare providers may be built based on analysis of clinical information related to medical treatments. A plurality of subgroups of healthcare providers may be constructed in the groups, based on analysis of non-clinical information related to demographical information. First-level outlier healthcare providers may be removed from a particular group of healthcare providers, and second-level outlier healthcare providers may be removed from a particular subgroup of healthcare providers. The second-level outlier healthcare providers removed from the particular subgroup may remain in a group that contains the particular subgroup.
Owner:OPTUMINSIGHT
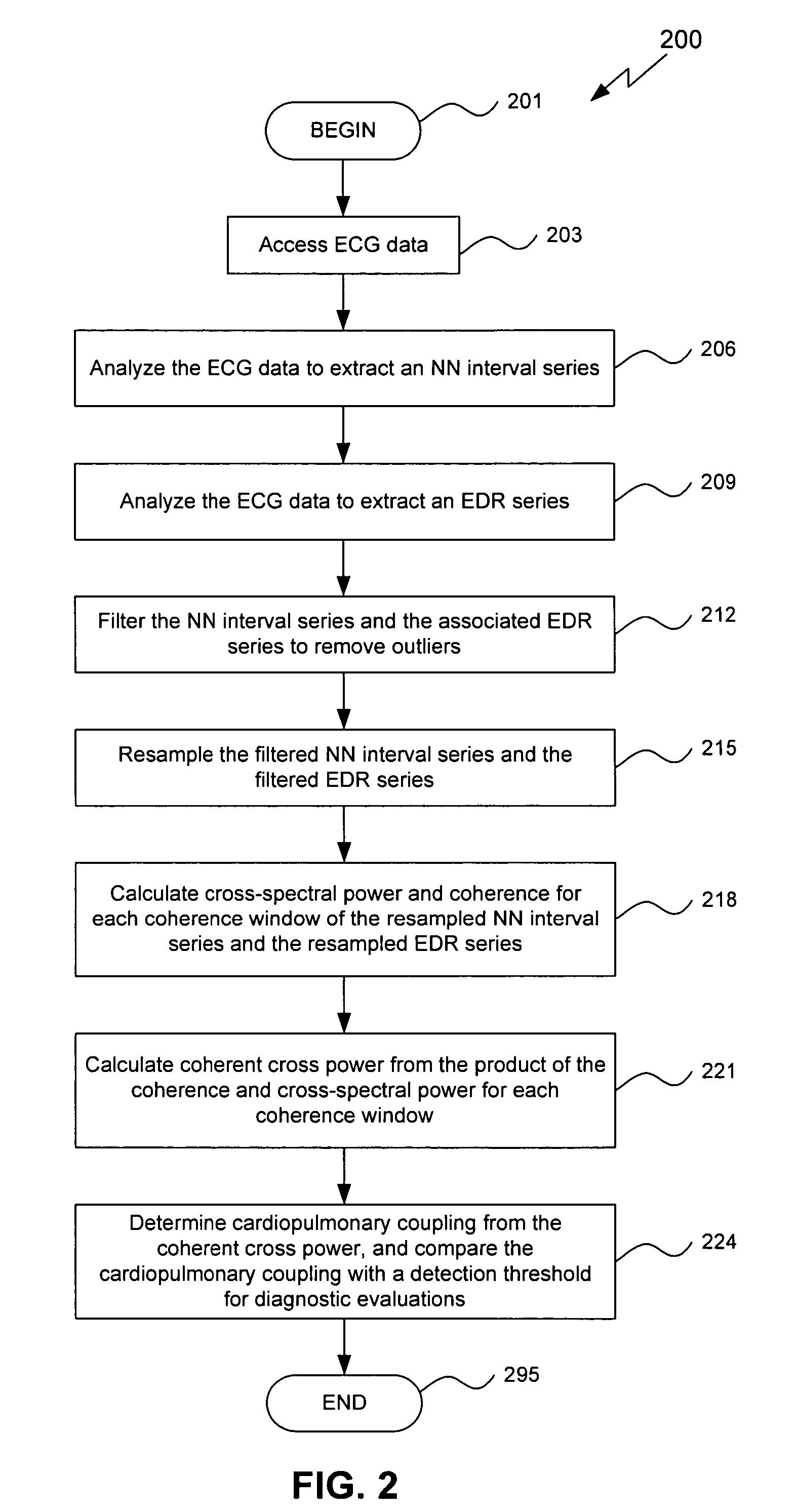
Assessment of sleep quality and sleep disordered breathing based on cardiopulmonary coupling
An assessment of sleep quality and sleep disordered breathing is determined from cardiopulmonary coupling between two physiological data series. An R-R interval series is derived from an electrocardiogram (ECG) signal. The normal beats from the R-R interval series are extracted to produce a normal-to-normal interval series. The amplitude variations in the QRS complex are used to extract a surrogate respiration signal (i.e., ECG-derived respiration) associated with the NN interval series. The two series are corrected to remove outliers, and resampled. The cross-spectral power and coherence of the two resampled signals are calculated over a plurality of coherence windows. For each coherence window, the product of the coherence and cross-spectral power is used to calculate coherent cross-power. Using the appropriate thresholds for the coherent cross-power, the proportion of sleep spent in CAP, non-CAP, and wake and / or REM are determined. Coherent cross-power can be applied to differentiate obstructive from non-obstructive disease, and admixtures of the same.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com