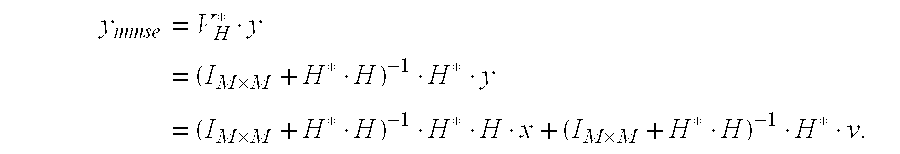Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1271results about How to "Computationally efficient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
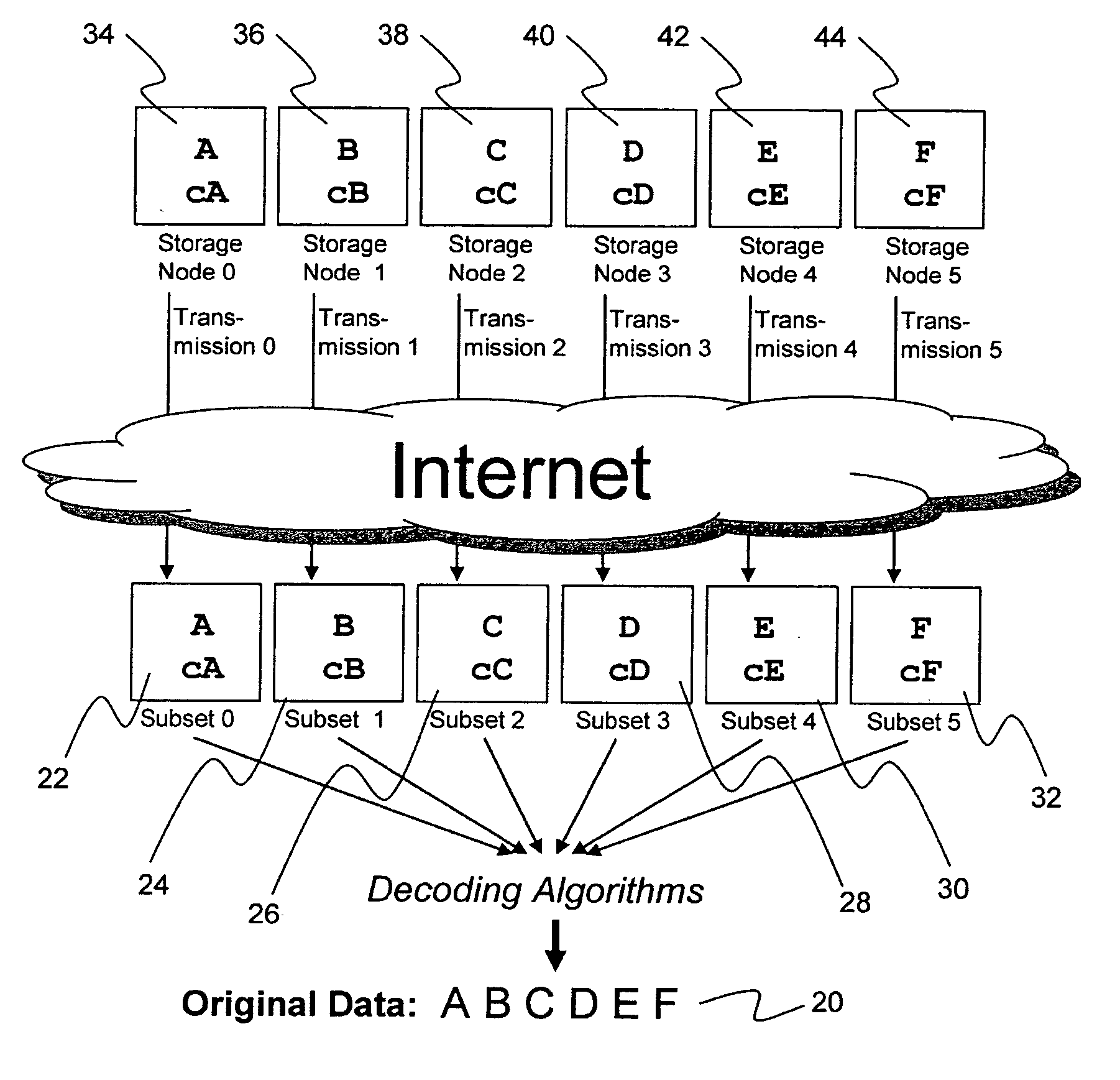
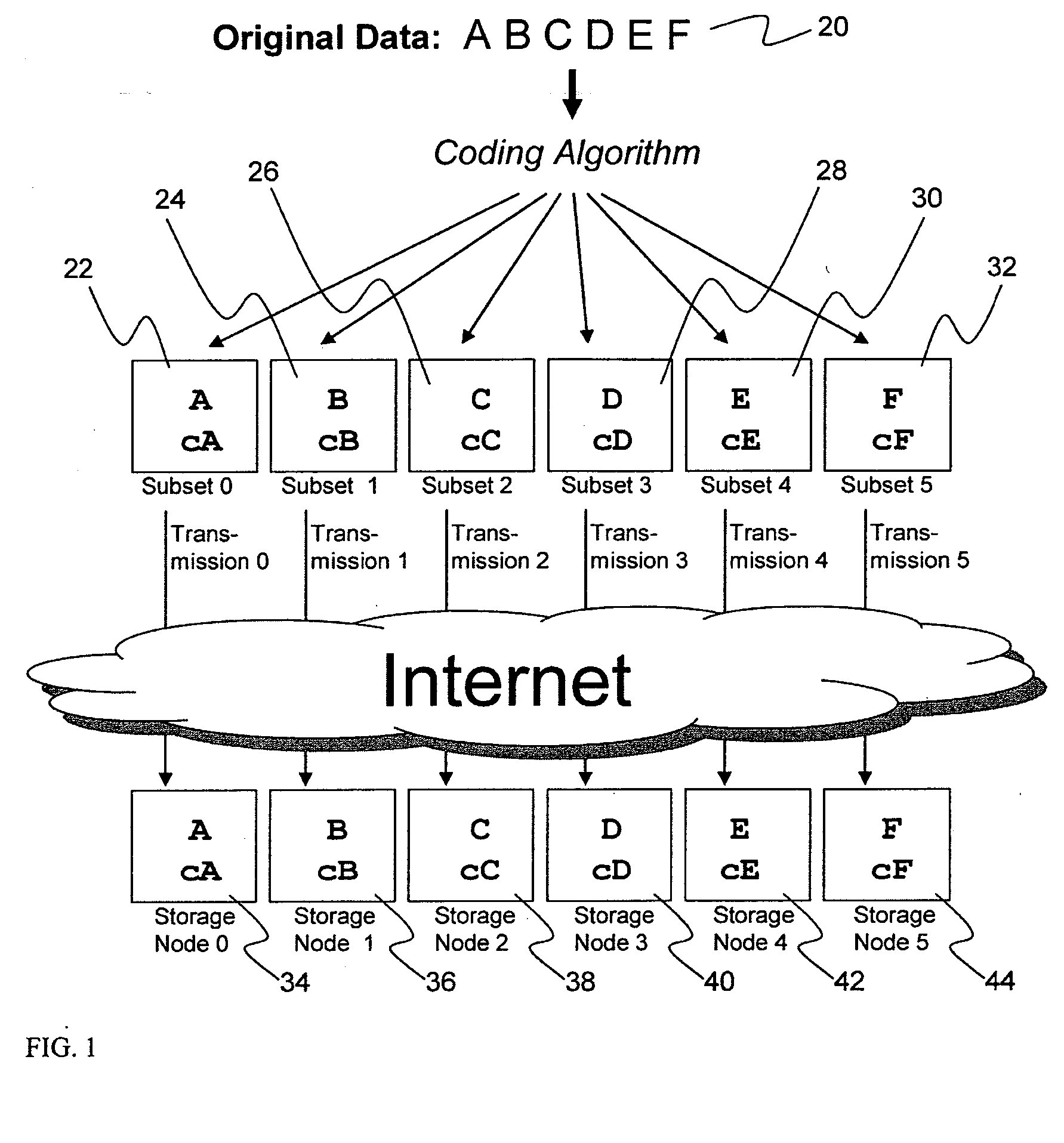
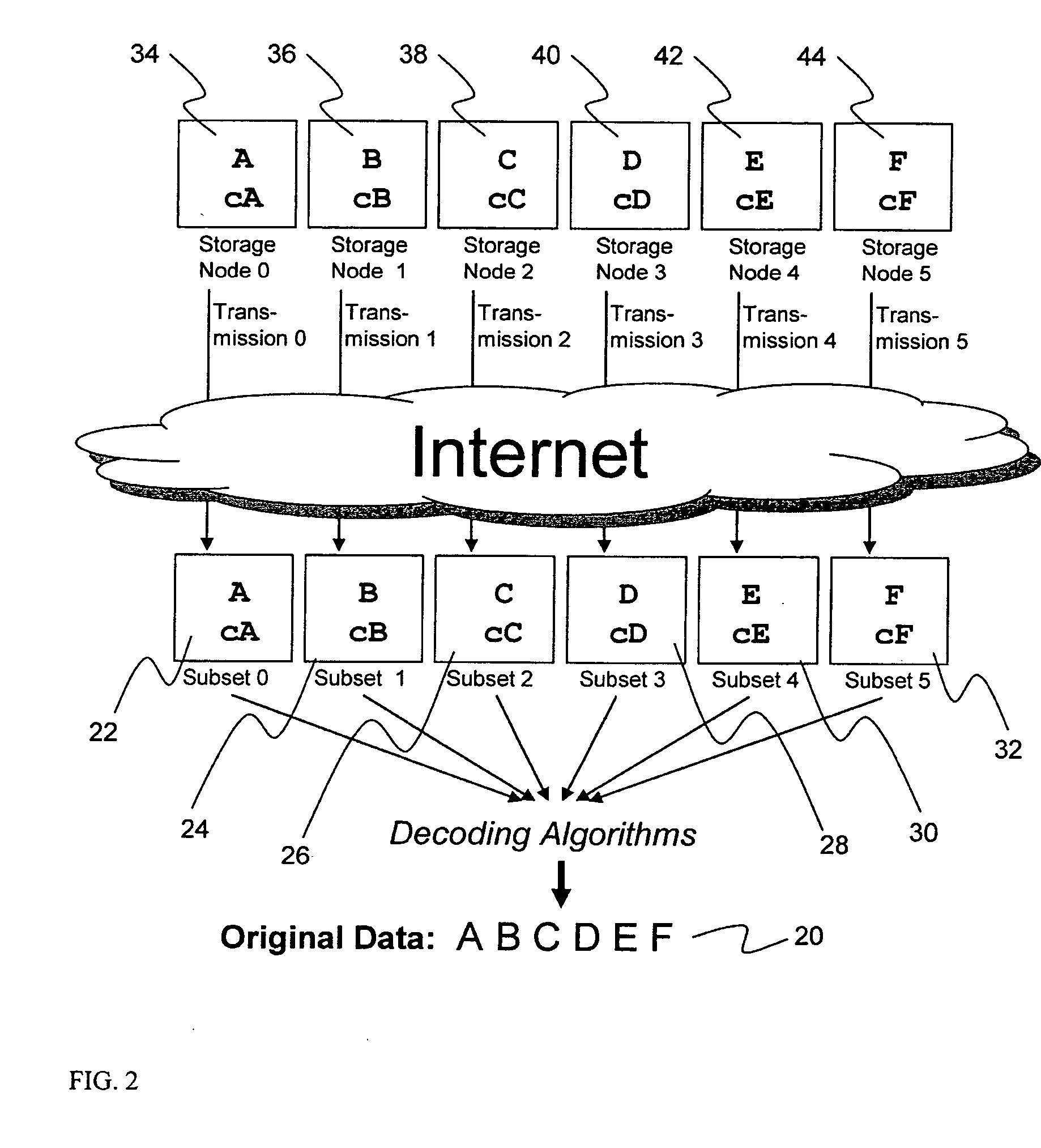
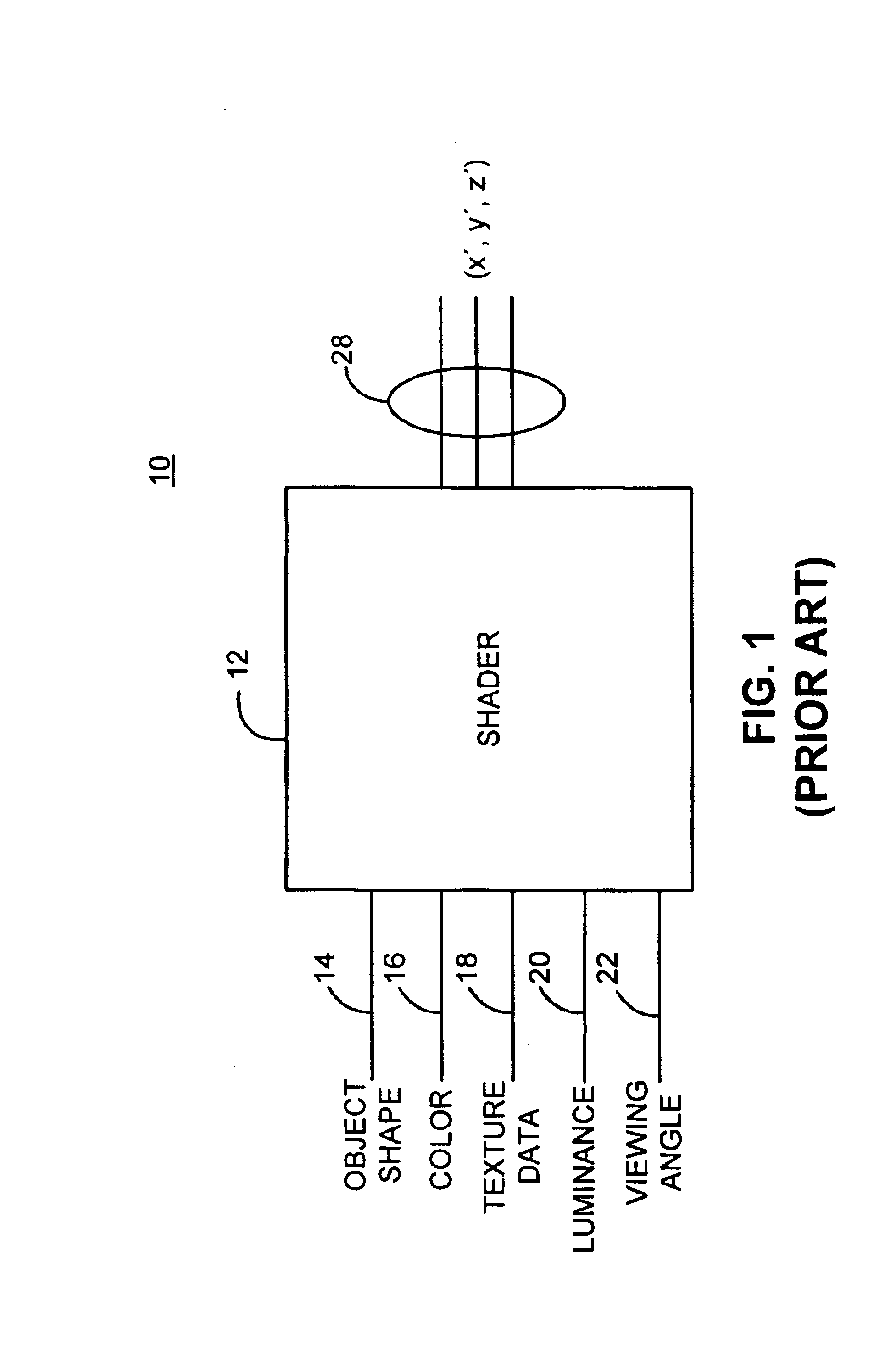
Digital data storage system
ActiveUS20070079081A1Less usableImprove privacyComputer security arrangementsMemory systemsOriginal dataSmall data
An efficient method for breaking source data into smaller data subsets and storing those subsets along with coded information about some of the other data subsets on different storage nodes such that the original data can be recreated from a portion of those data subsets in an efficient manner.
Owner:PURE STORAGE
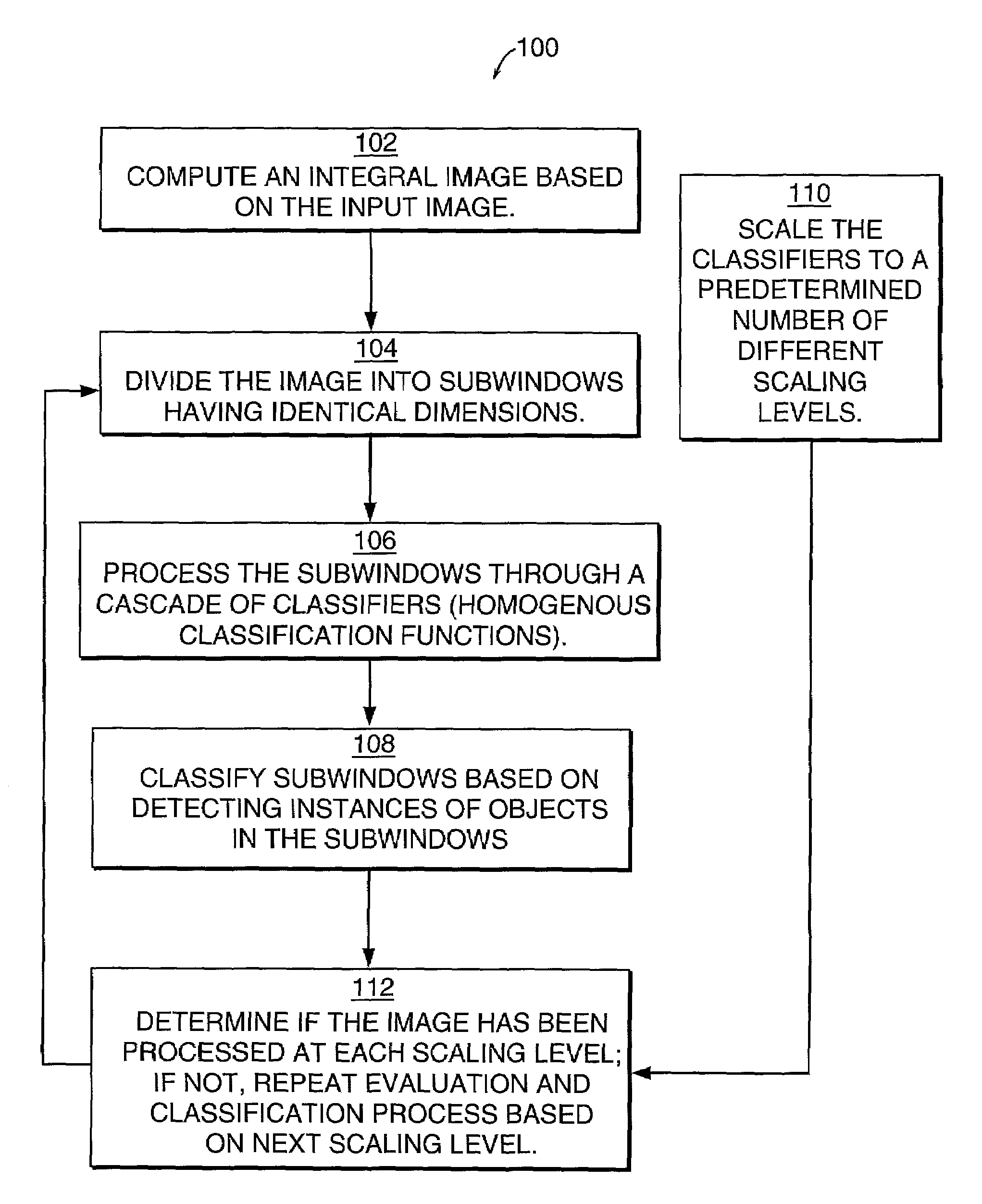
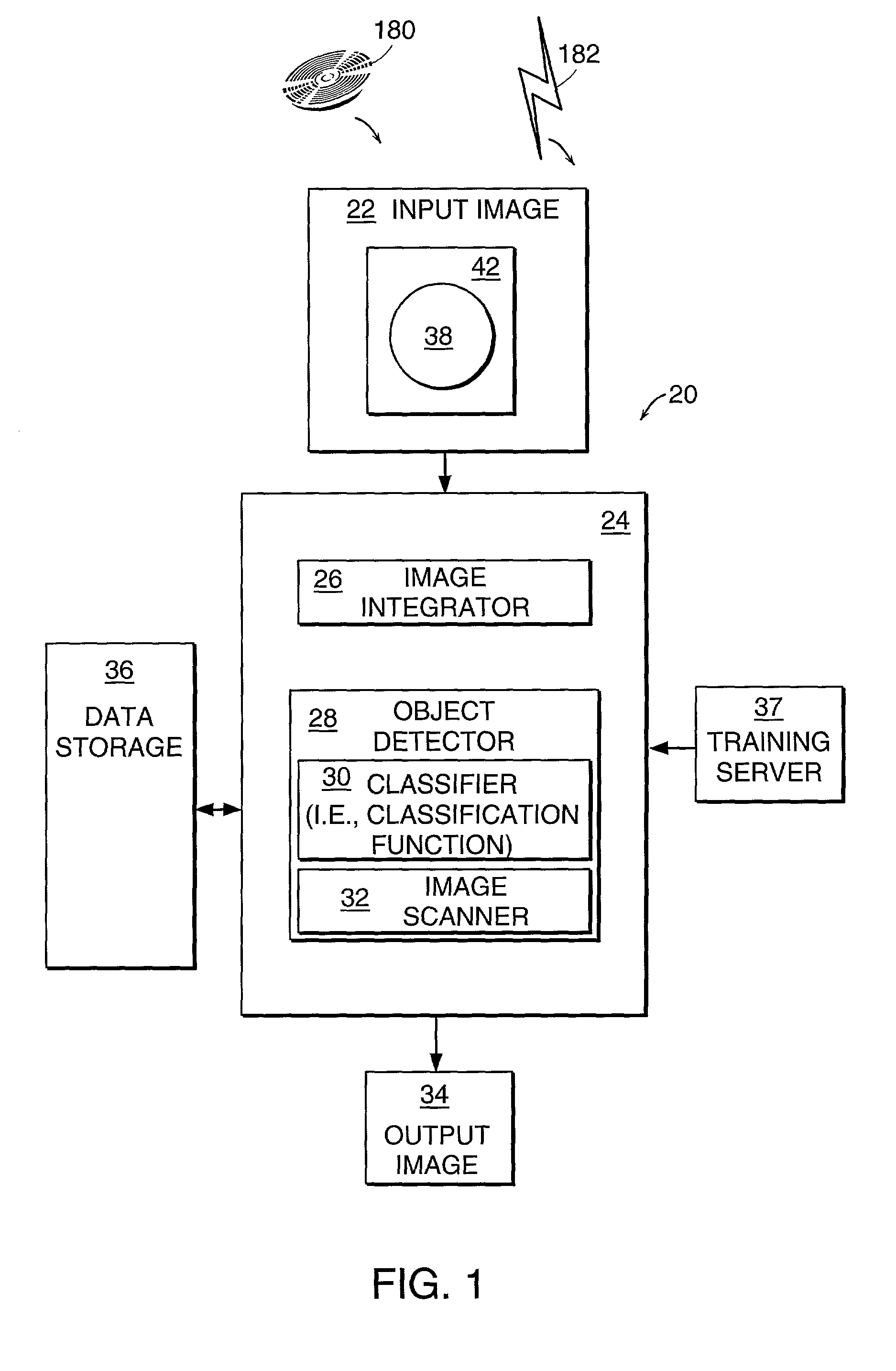
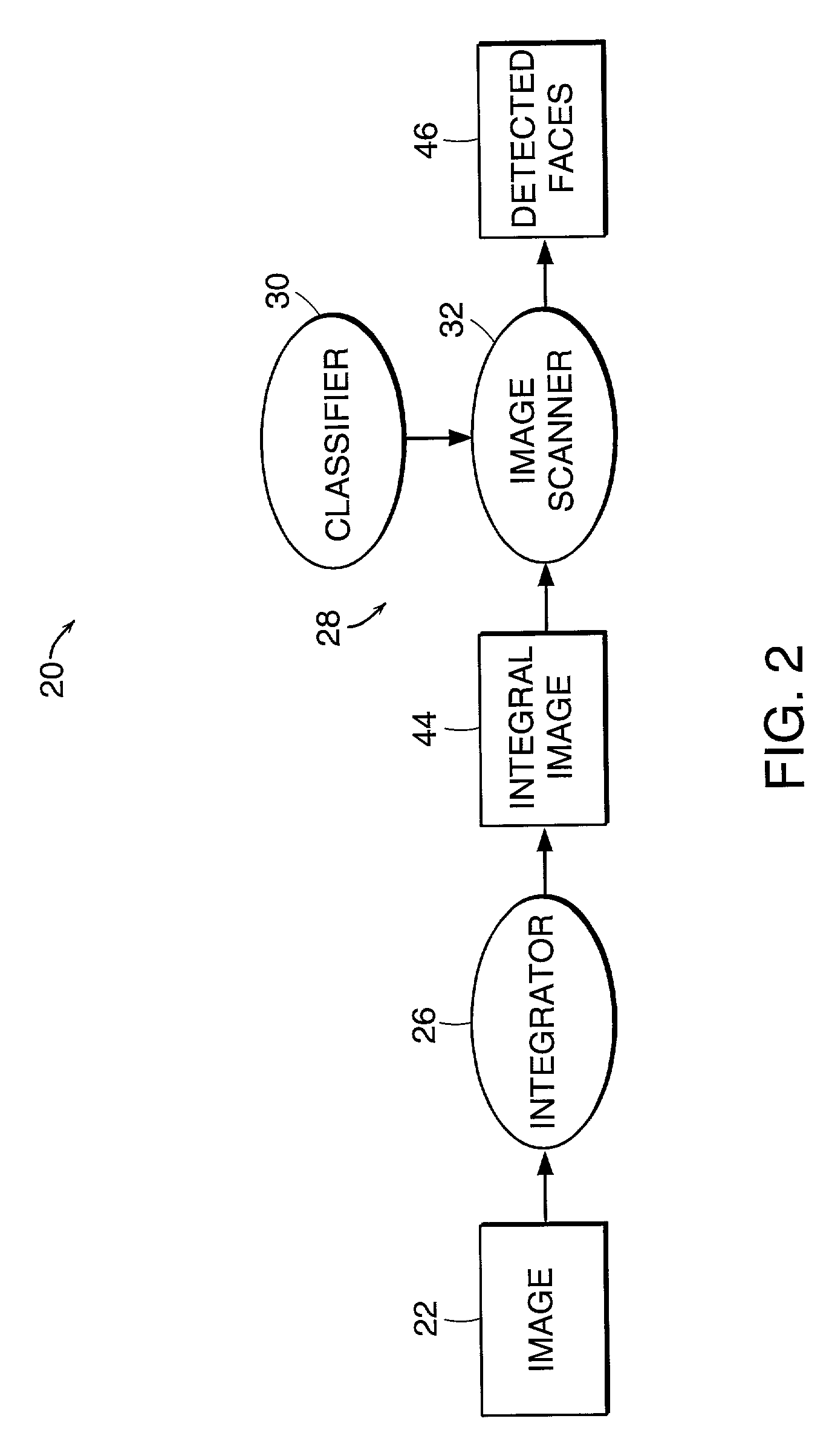
Method and system for object detection in digital images
InactiveUS7099510B2Powerful and efficientComputationally efficientCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsRadiologyDigital image
An object detection system for detecting instances of an object in a digital image includes an image integrator and an object detector, which includes a classifier (classification function) and image scanner. The image integrator receives an input image and calculates an integral image representation of the input image. The image scanner scans the image in same sized subwindows. The object detector uses a cascade of homogenous classification functions or classifiers to classify the subwindows as to whether each subwindow is likely to contain an instance of the object. Each classifier evaluates one or more features of the object to determine the presence of such features in a subwindow that would indicate the likelihood of an instance of the object in the subwindow.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Realtime object tracking system
Owner:JOLLY SEVEN SERIES 70 OF ALLIED SECURITY TRUST I
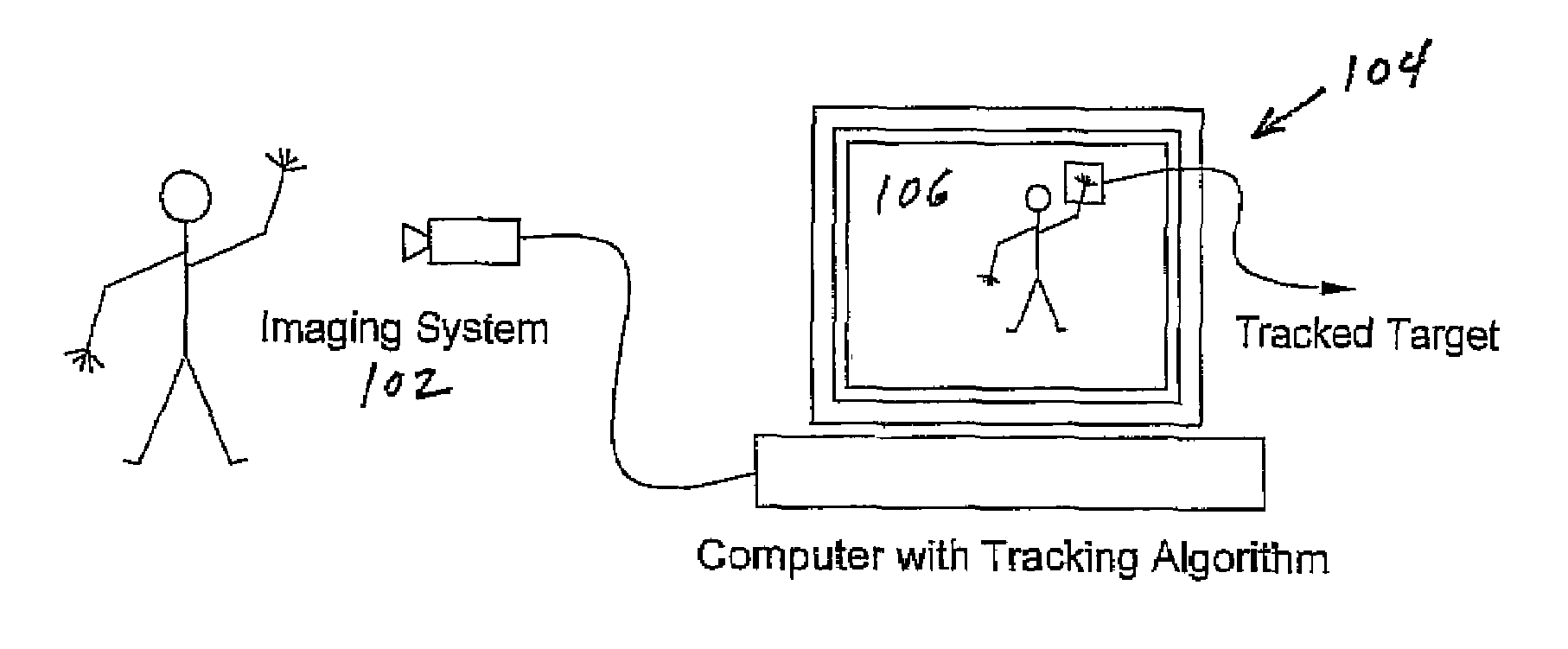
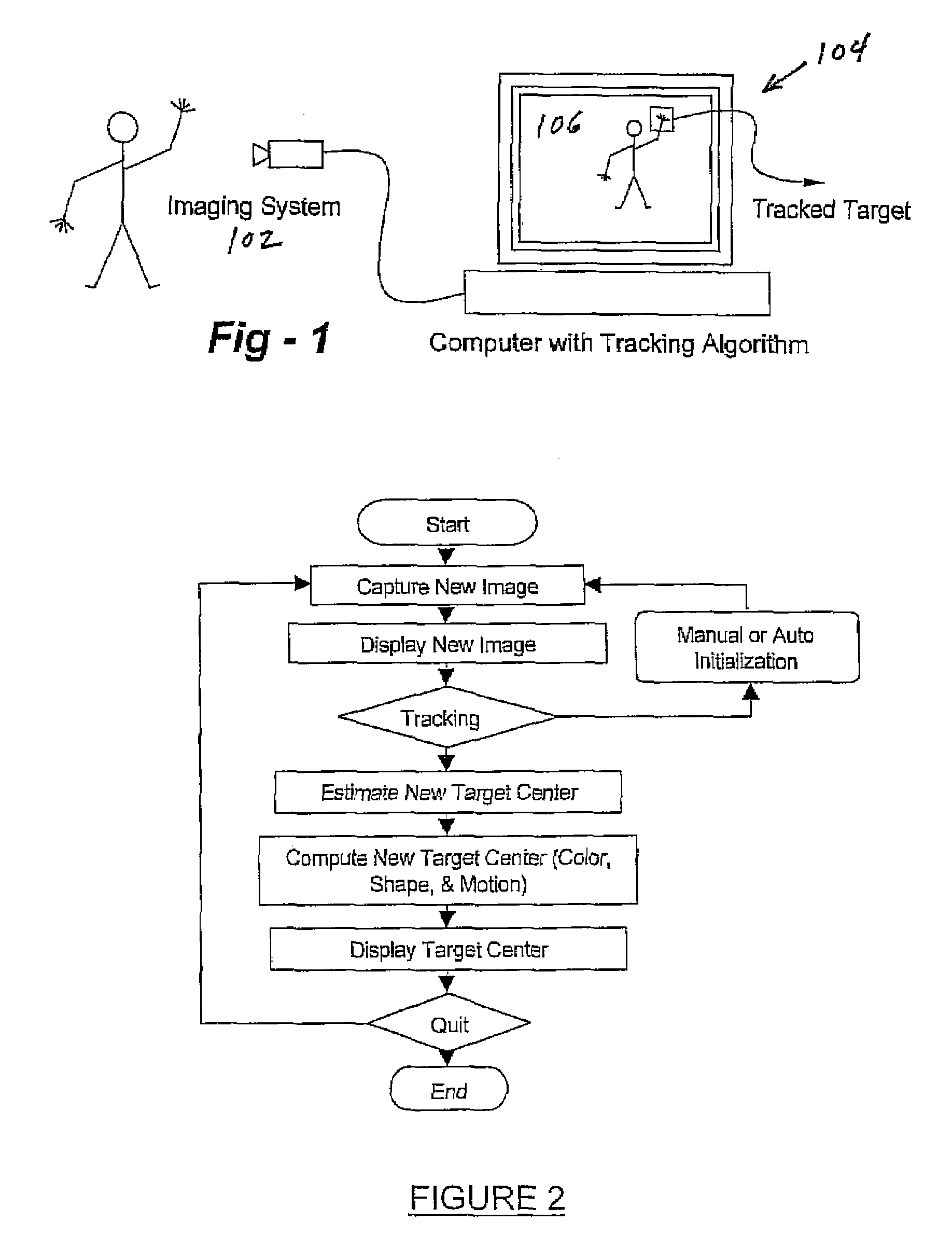
Real-time head tracking system for computer games and other applications
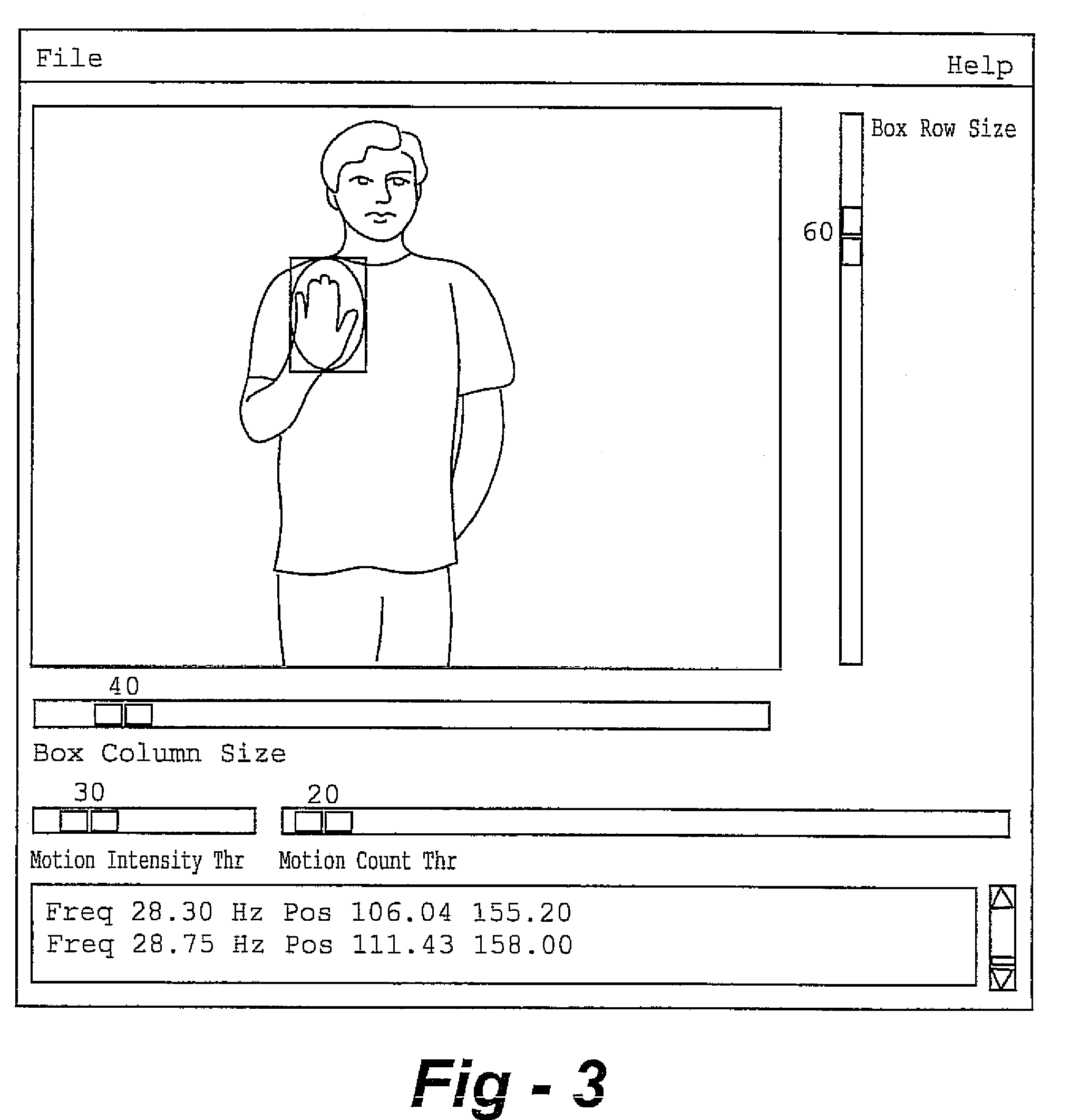
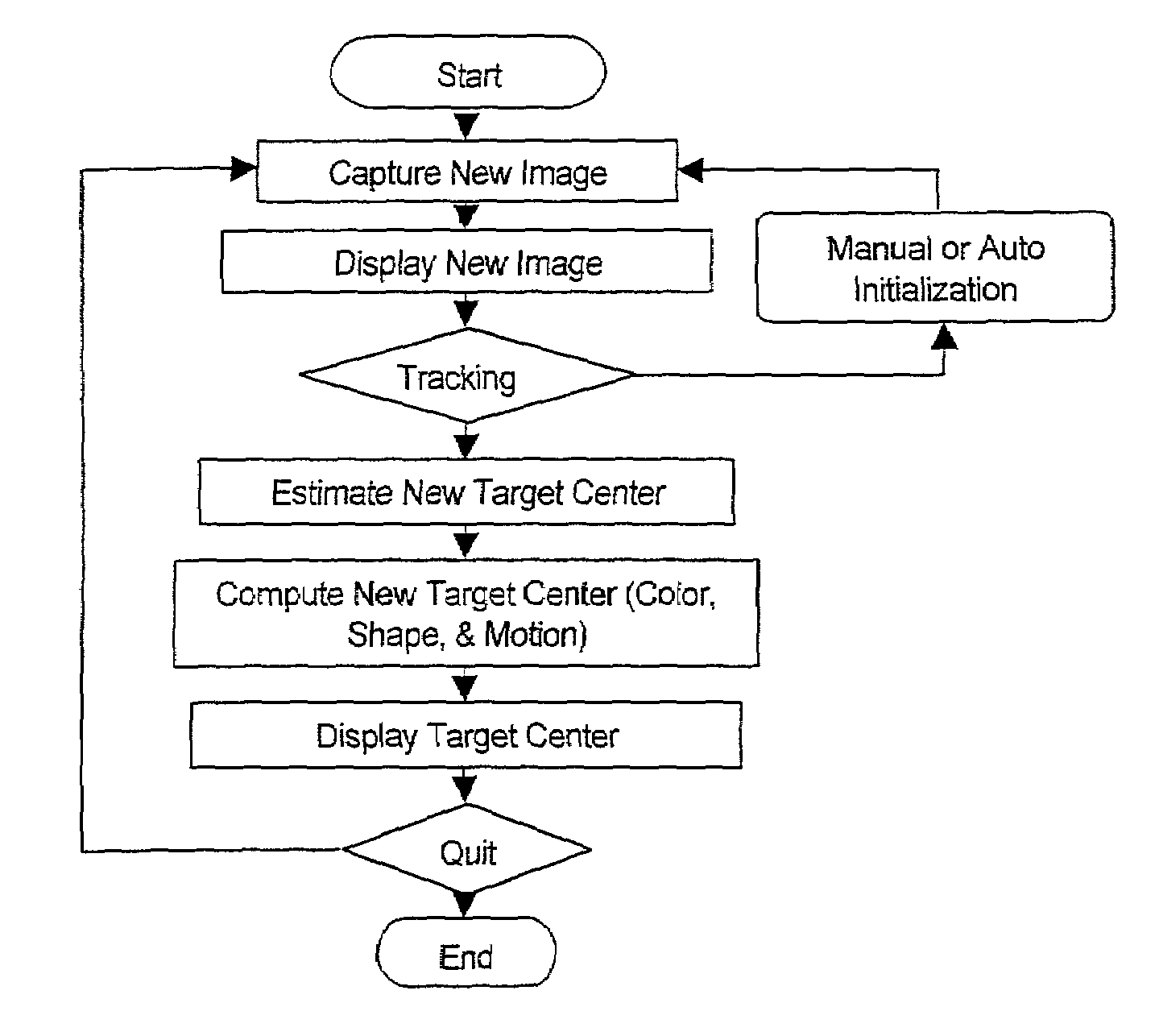
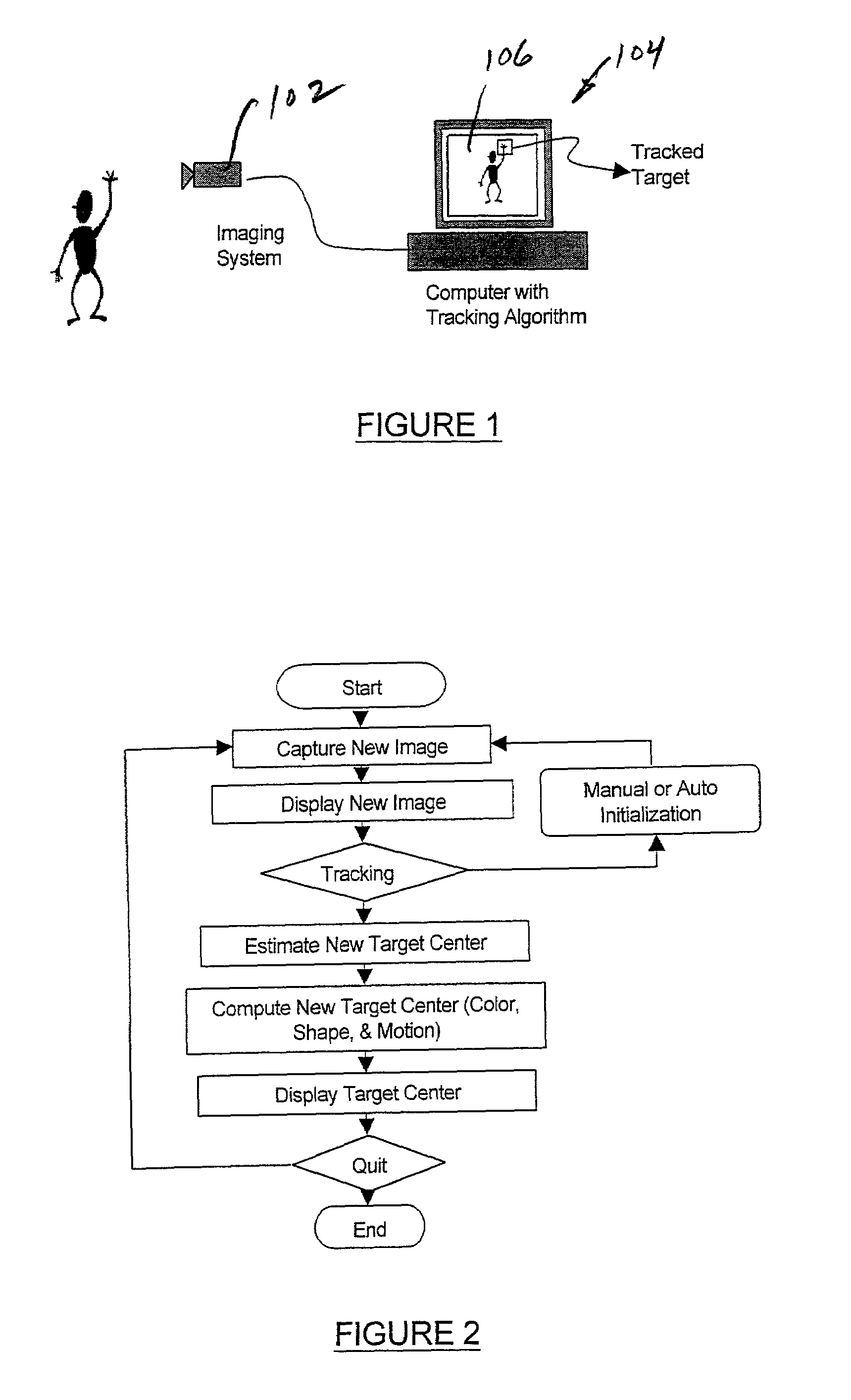
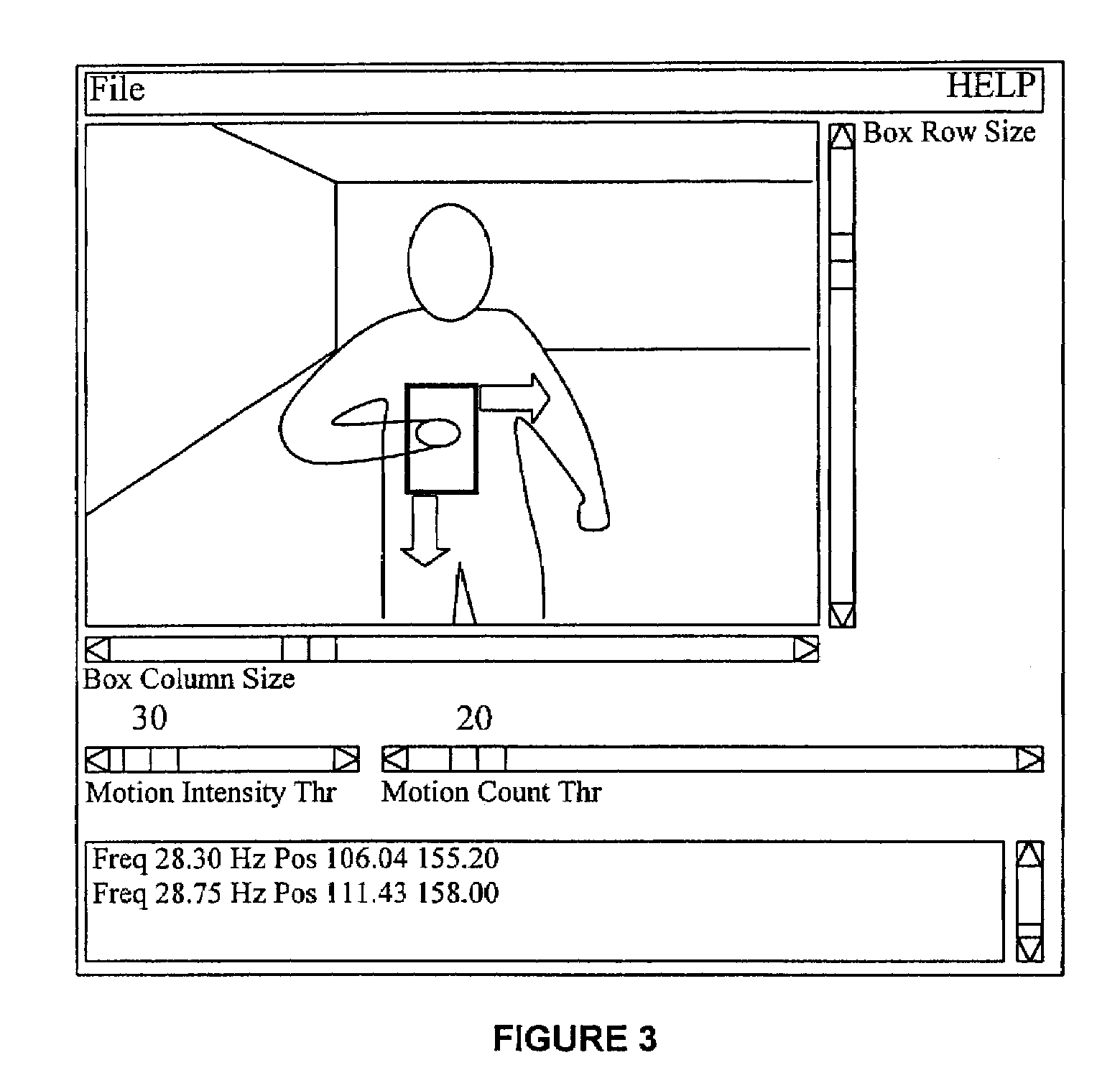
InactiveUS7121946B2Computationally efficientMinimal computationImage enhancementImage analysisA-weightingGraphical user interface
A real-time computer vision system tracks the head of a computer user to implement real-time control of games or other applications. The imaging hardware includes a color camera, frame grabber, and processor. The software consists of the low-level image grabbing software and a tracking algorithm. The system tracks objects based on the color, motion and / or shape of the object in the image. A color matching function is used to compute three measures of the target's probable location based on the target color, shape and motion. The method then computes the most probable location of the target using a weighting technique. Once the system is running, a graphical user interface displays the live image from the color camera on the computer screen. The operator can then use the mouse to select a target for tracking. The system will then keep track of the moving target in the scene in real-time.
Owner:JOLLY SEVEN SERIES 70 OF ALLIED SECURITY TRUST I
Methods for filtering data and filling in missing data using nonlinear inference
InactiveUS20100274753A1Efficient developmentComputationally efficientWeb data indexingKnowledge representationMissing dataOrthogonal basis
The present invention is directed to a method for inferring / estimating missing values in a data matrix d(q, r) having a plurality of rows and columns comprises the steps of: organizing the columns of the data matrix d(q, r) into affinity folders of columns with similar data profile, organizing the rows of the data matrix d(q, r) into affinity folders of rows with similar data profile, forming a graph Q of augmented rows and a graph R of augmented columns by similarity or correlation of common entries; and expanding the data matrix d(q, r) in terms of an orthogonal basis of a graph Q×R to infer / estimate the missing values in said data matrix d(q, r).on the diffusion geometry coordinates.
Owner:LIBERTY EDO +5
Method and system for language identification
InactiveUS7818165B2Computationally efficientNatural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsFeature setRelevant information
A method and system for language identification are provided. The system includes a feature set of a plurality of character strings of varying length with associated information. The associated information includes one or more significance scores for a character string for one or more of a plurality of languages. Means are provided for detecting character strings from the feature set within a token from an input text. The system uses a finite-state device and the associated information is provided as glosses at the final nodes of the finite-state device for each character string. The associated information can also include significance scores based on linguistic rules.
Owner:LINKEDIN
Methods for filtering data and filling in missing data using nonlinear inference
InactiveUS20070214133A1Increase in amount of trafficEfficient developmentWeb data indexingSpecial data processing applicationsMissing dataOrthogonal basis
The present invention is directed to a method for inferring / estimating missing values in a data matrix d(q, r) having a plurality of rows and columns comprises the steps of: organizing the columns of the data matrix d(q, r) into affinity folders of columns with similar data profile, organizing the rows of the data matrix d(q, r) into affinity folders of rows with similar data profile, forming a graph Q of augmented rows and a graph R of augmented columns by similarity or correlation of common entries; and expanding the data matrix d(q, r) in terms of an orthogonal basis of a graph Q×R to infer / estimate the missing values in said data matrix d(q, r) on the diffusion geometry coordinates.
Owner:LIBERTY EDO +5
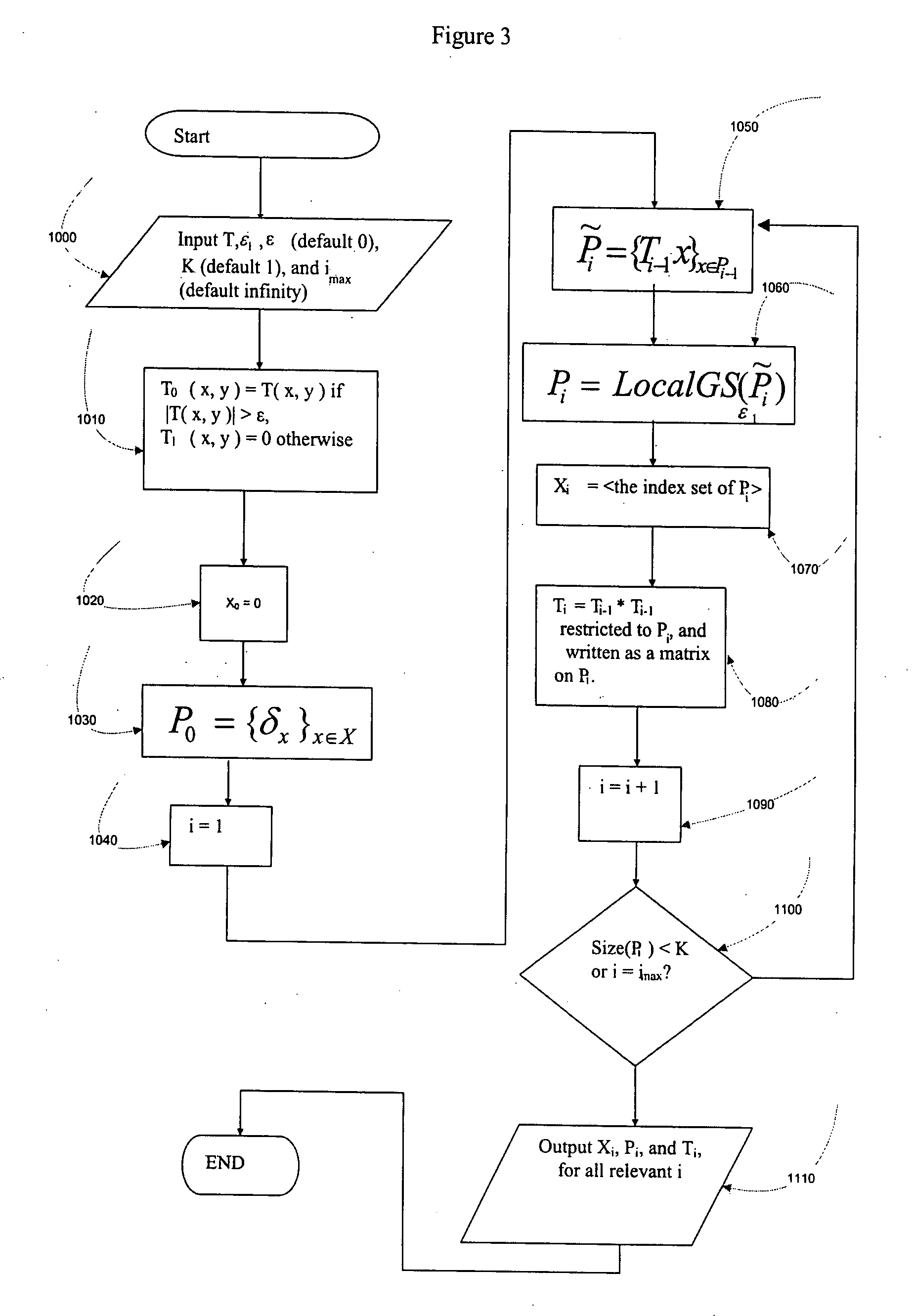
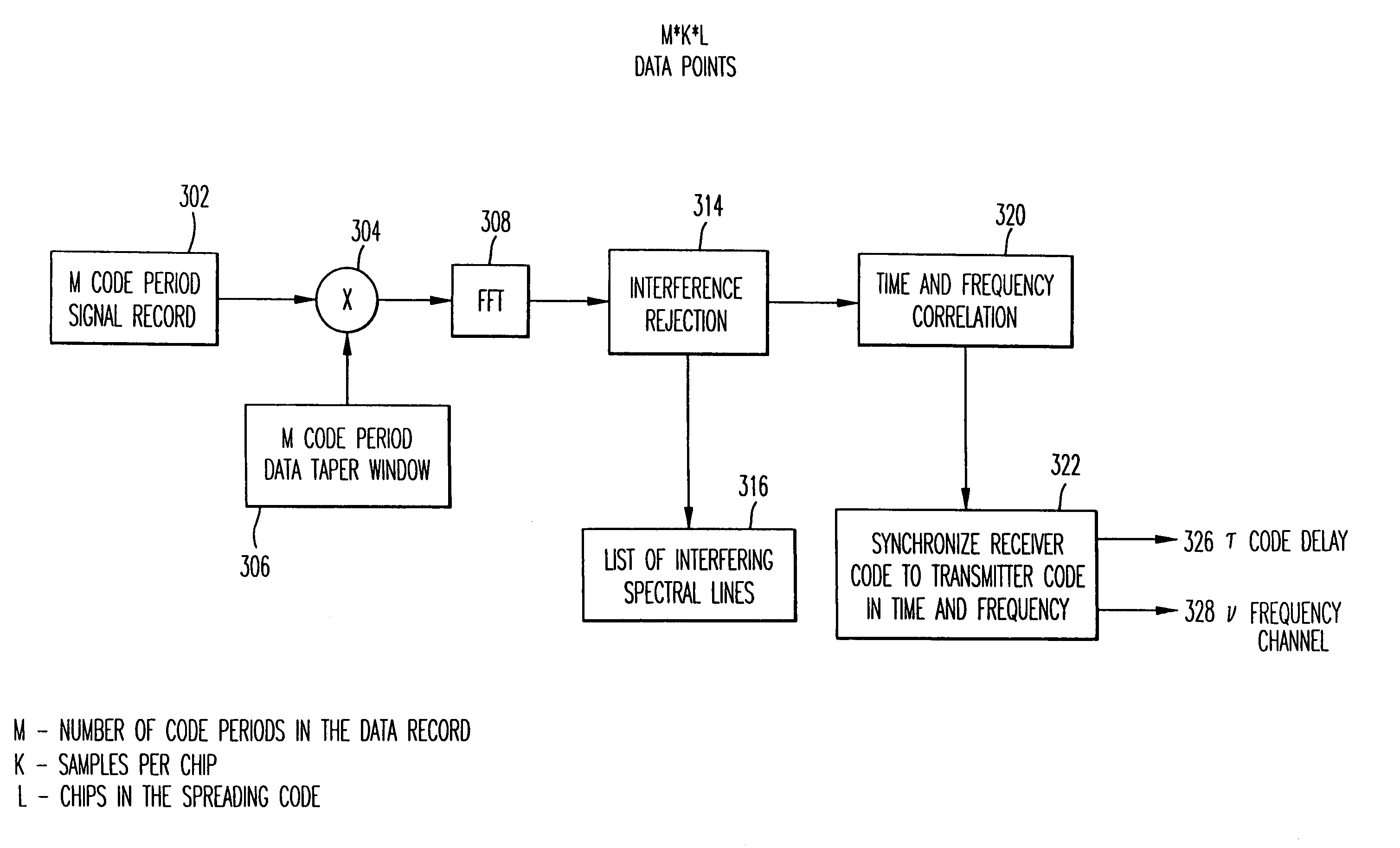
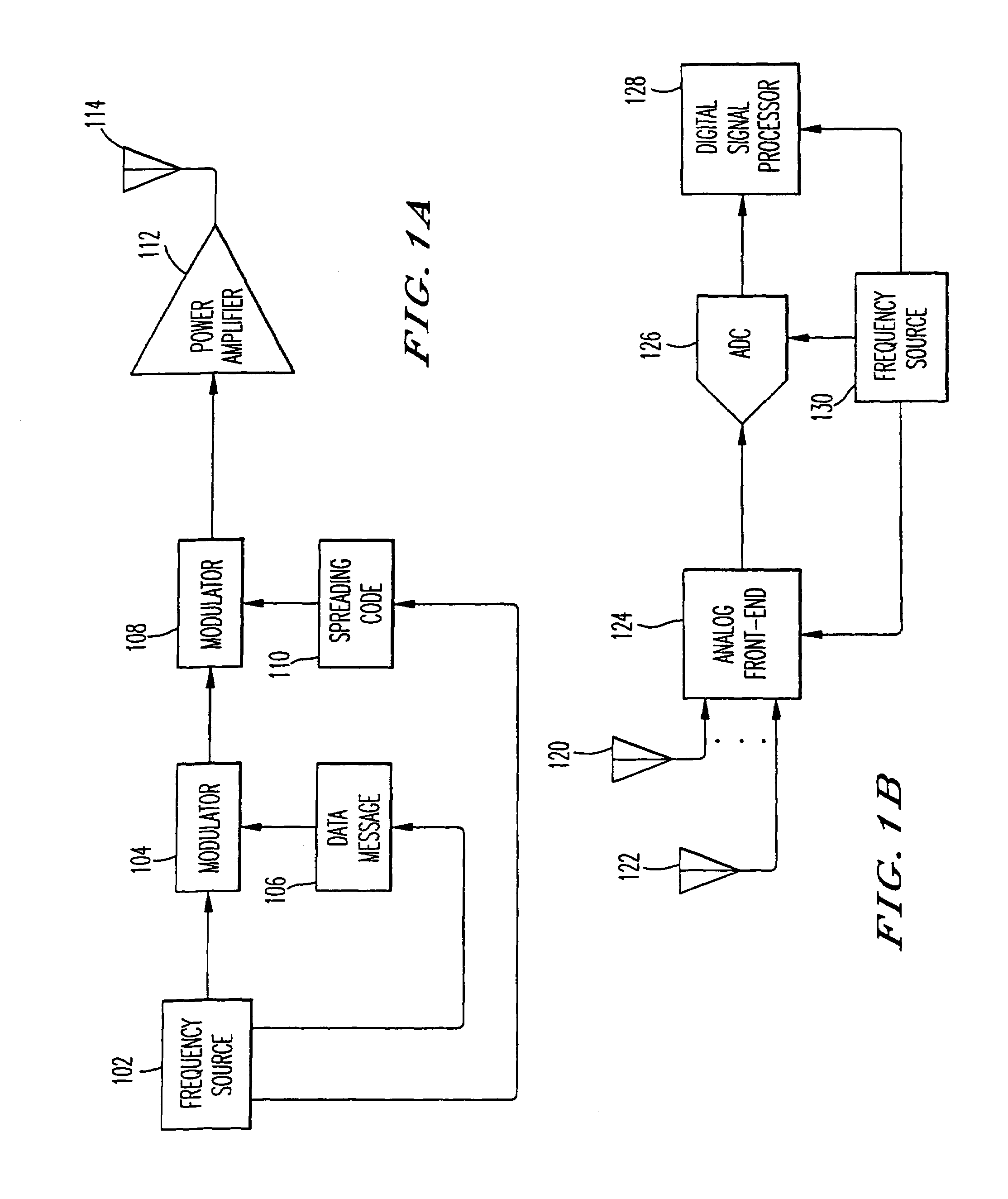
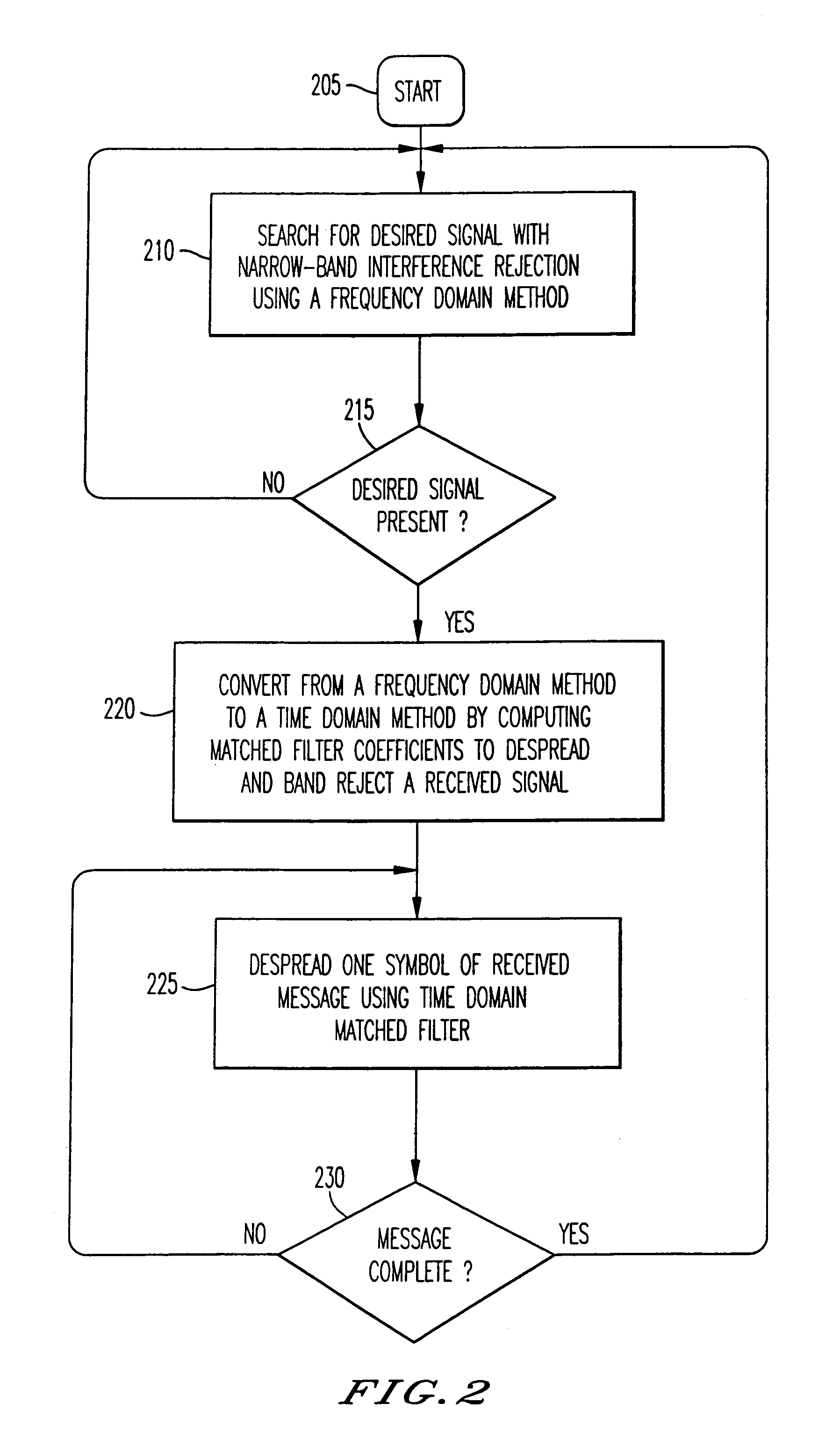
Narrow-band interference rejecting spread spectrum radio system and method
InactiveUS6975673B1Decrease requiredReduced computing resourceFrequency-modulated carrier systemsCommunication jammingTime domainDigital signal processing
A spread spectrum receiver and method having narrow-band interference rejection of narrow-band jamming signals using digital signal processing frequency domain techniques. The method performed in the receiver includes transforming the received signal to a frequency domain signal and identifying narrow-band interference components in the frequency domain signal; suppressing the identified narrow-band interference components by excising the identified narrow-band interference components from the frequency domain signal to produce an interference excised signal in the frequency domain, and storing in a memory frequencies corresponding to the identified narrow-band interference components; synchronizing a receiver code to a transmitter code in the frequency domain using the interference excised signal; generating coefficients for a time domain filter that includes notches at the frequencies corresponding to the excised narrow-band interference components and that jointly despreads and rejects narrow-band interference from the excised frequencies; applying the coefficients generated in the preceding step to the time domain filter, and despreading and filtering in real time in the time domain the received signal using the applied coefficients.
Owner:SENSUS SPECTRUM LLC
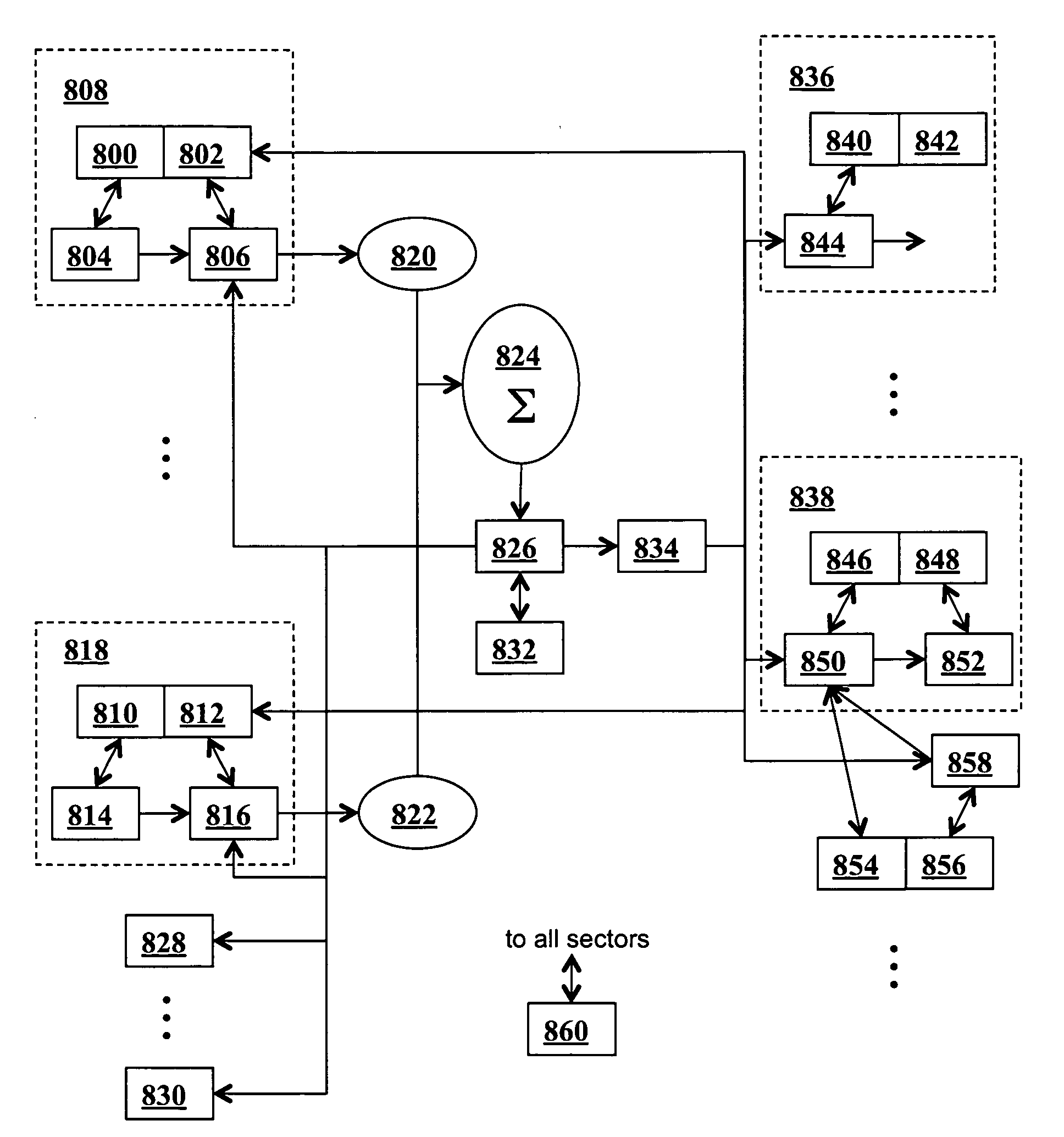
Method for efficiently simulating the information processing in cells and tissues of the nervous system with a temporal series compressed encoding neural network
ActiveUS20110016071A1Effective simulationExact reproductionDigital computer detailsDigital dataInformation processingNervous system
A neural network simulation represents components of neurons by finite state machines, called sectors, implemented using look-up tables. Each sector has an internal state represented by a compressed history of data input to the sector and is factorized into distinct historical time intervals of the data input. The compressed history of data input to the sector may be computed by compressing the data input to the sector during a time interval, storing the compressed history of data input to the sector in memory, and computing from the stored compressed history of data input to the sector the data output from the sector.
Owner:CORTICAL DATABASE
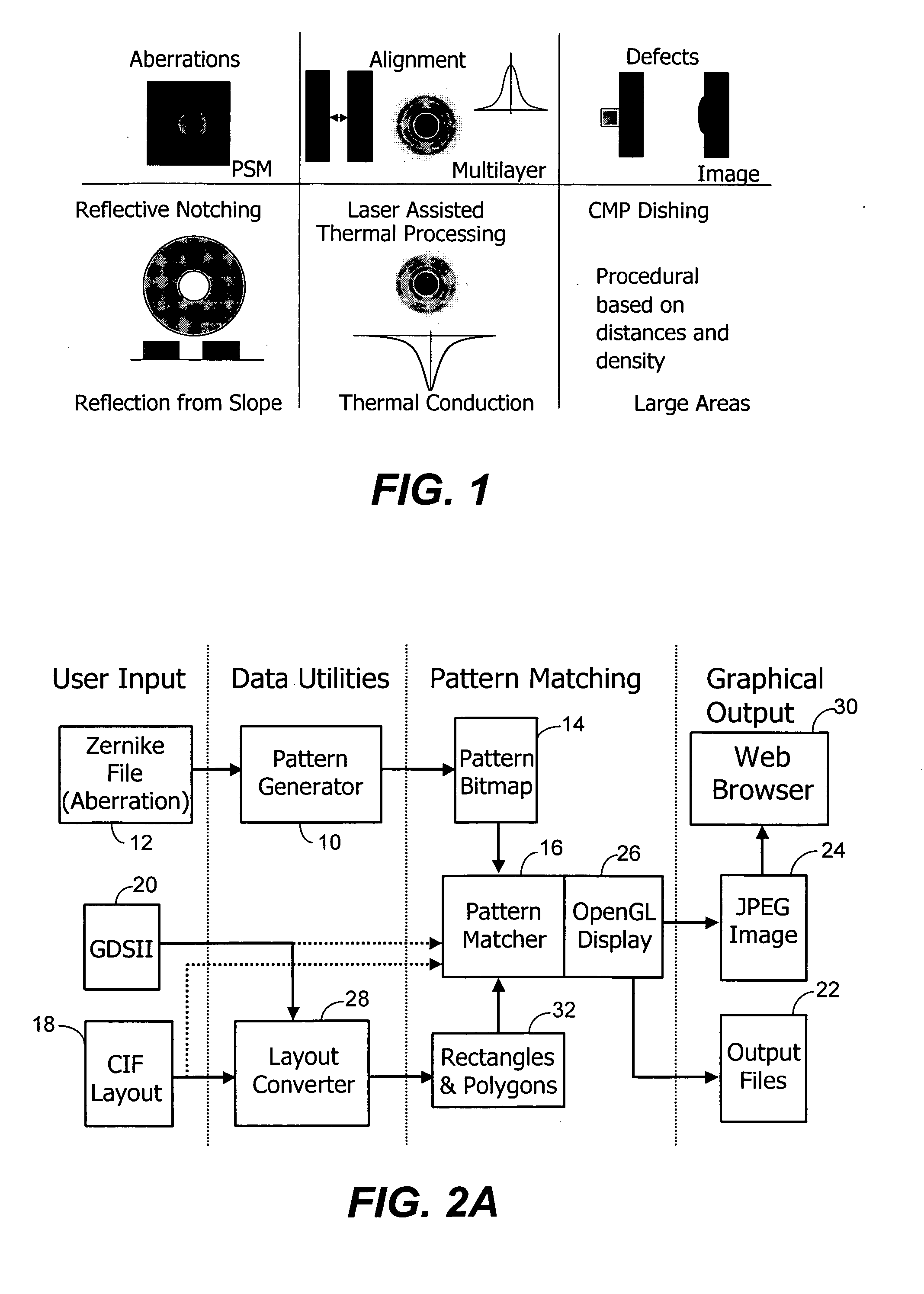
Method of locating areas in an image such as a photo mask layout that are sensitive to residual processing effects
InactiveUS20060277520A1Reduce memory usageLower matching requirementsImage enhancementImage analysisComputer graphics (images)Photomask
Images such as mask layouts, signatures, and photographs are compared to identify similarities or dissimilarities in the images. Descriptions of the images use geometric shapes including lines, rectangles, and triangles to facilitate the comparisons and decrease comparison time and decrease stored data describing the shapes. Data for pixels in the shapes are pre-integrated to reduce arithmetic operations in the comparisons.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Apparatus and method for stateless CRC calculation
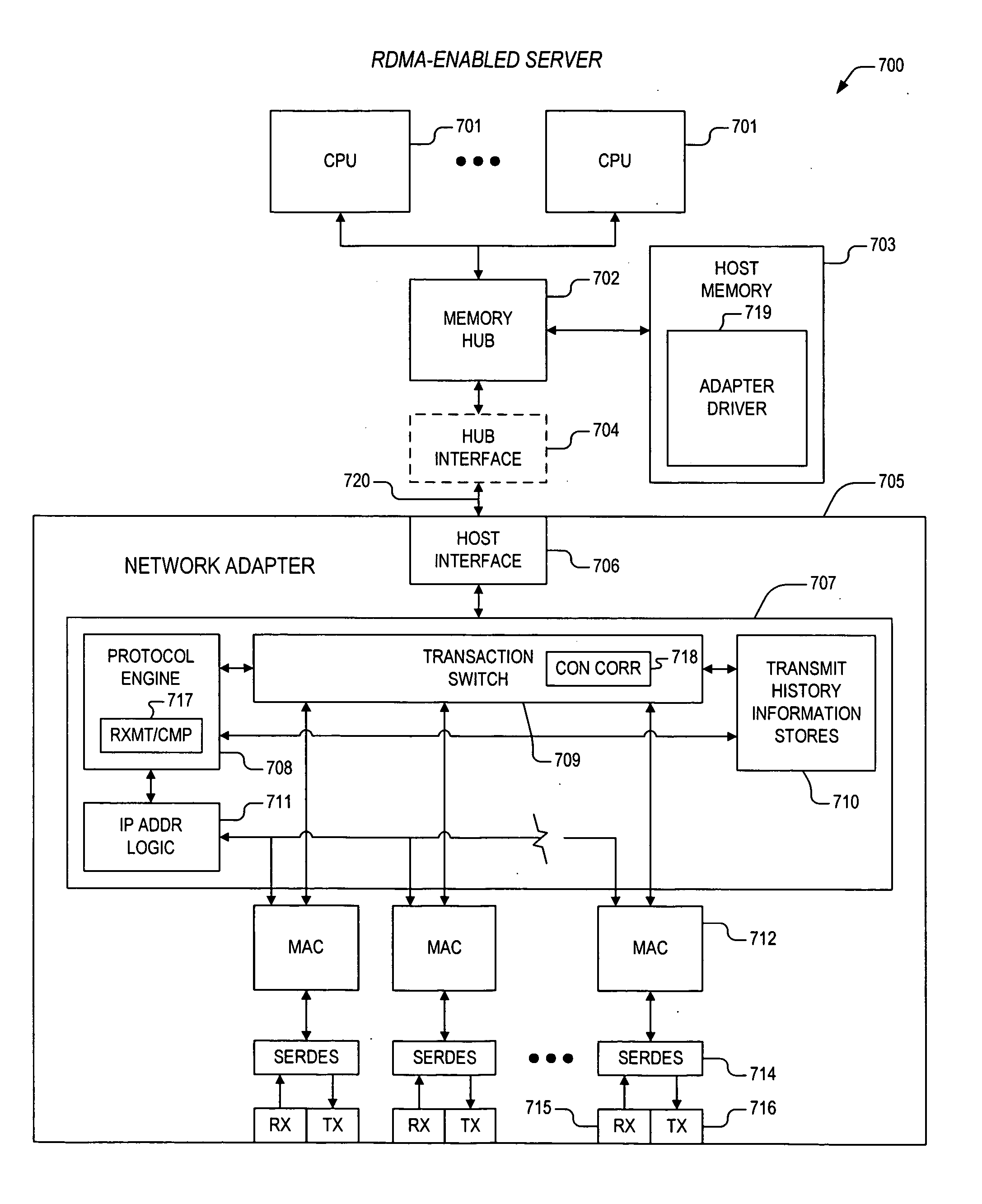
ActiveUS20070165672A1Computationally efficientCode conversionTime-division multiplexRemote direct memory accessComputer science
A mechanism for performing remote direct memory access (RDMA) operations between a first server and a second server. The apparatus includes a packet parser and a protocol engine. The packet parser processes a TCP segment within an arriving network frame, where the packet parser performs one or more speculative CRC checks according to an upper layer protocol (ULP), and where the one or more speculative CRC checks are performed concurrent with arrival of the network frame. The protocol engine is coupled to the packet parser. The protocol engine receives results of the one or more speculative CRC checks, and selectively employs the results for validation of a framed protocol data unit (FPDU) according to the ULP.
Owner:INTEL CORP
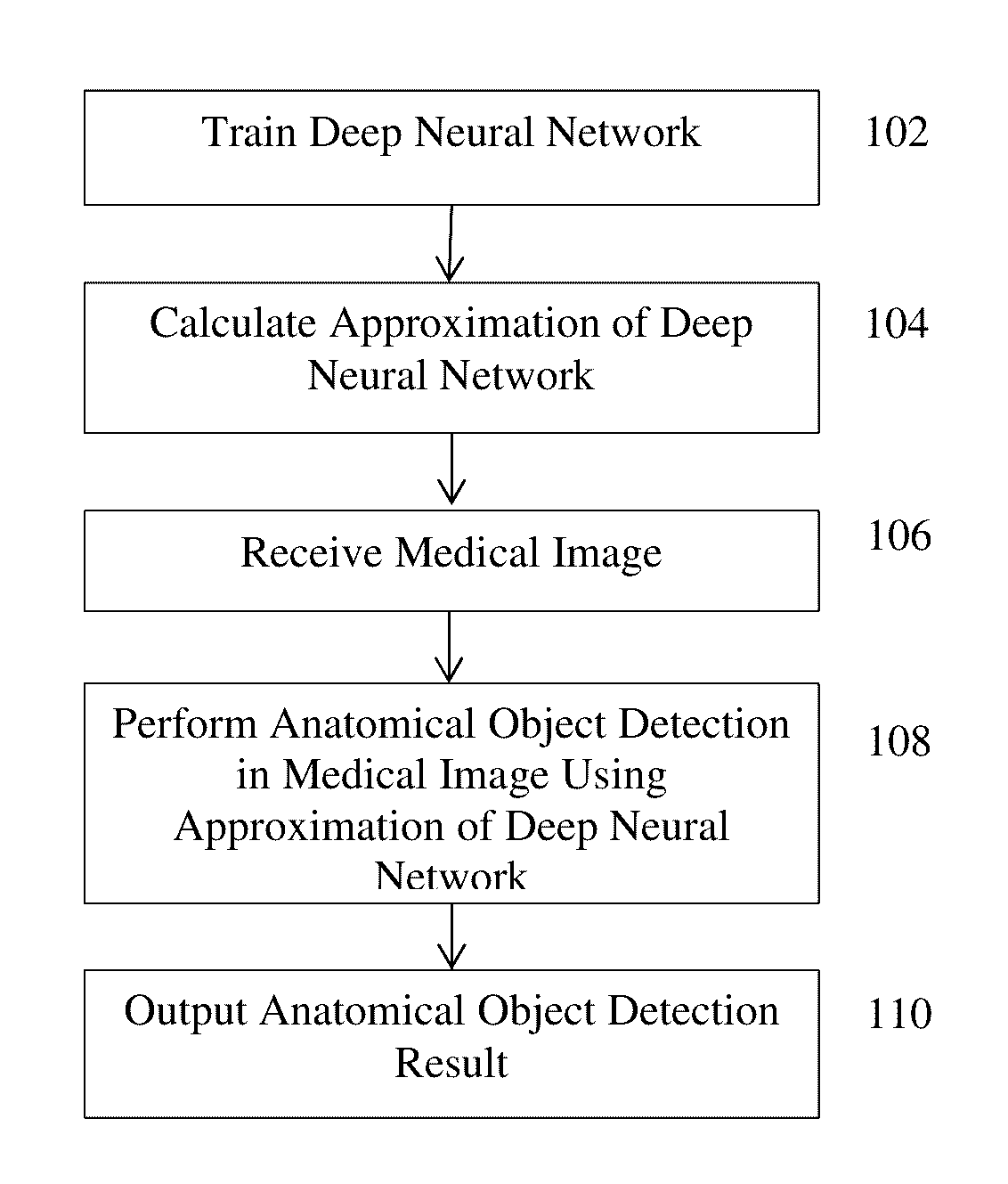
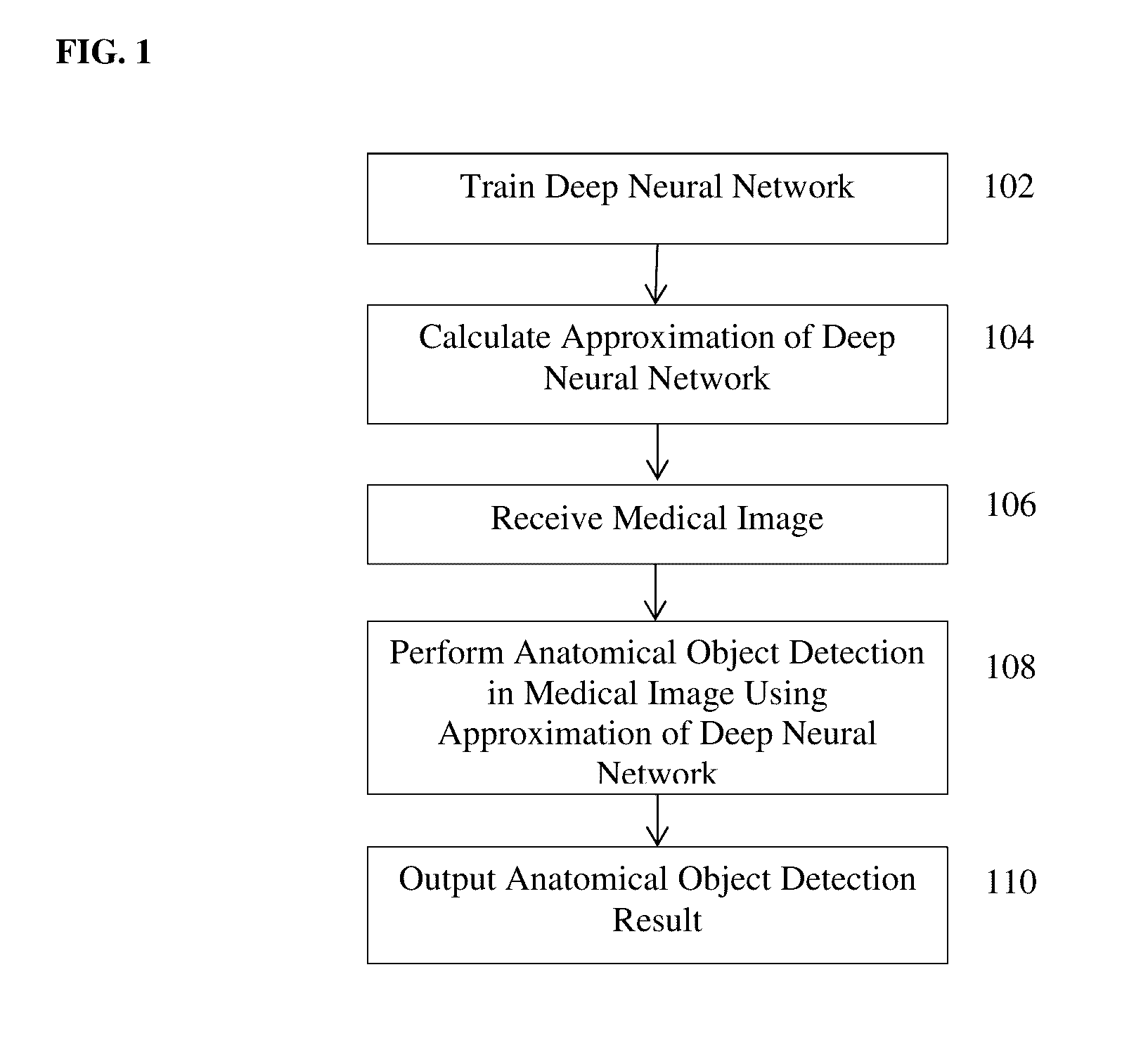
Method and System for Approximating Deep Neural Networks for Anatomical Object Detection
ActiveUS20160328643A1Reduce complexityComputationally efficientImage enhancementImage analysisComputation complexityMachine learning
A method and system for approximating a deep neural network for anatomical object detection is discloses. A deep neural network is trained to detect an anatomical object in medical images. An approximation of the trained deep neural network is calculated that reduces the computational complexity of the trained deep neural network. The anatomical object is detected in an input medical image of a patient using the approximation of the trained deep neural network.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Register retiming technique
InactiveUS7120883B1High frequencySimple designCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationTrade offsEmbedded system
An electronic automation system performs register retiming on a logic design, which may be a logic design for a programmable logic integrated circuit. Register retiming is a moving or rearranging of registers across combinatorial logic in a design in order to improve a maximum operating frequency or fmax. In one implementation, the system includes machine-readable code, which may be stored on a computer-readable medium such as a disk, executing on a computer. The system balances timing in order to trade off delays between critical and noncritical paths. Register retiming may make changes to a design at a gate level.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Kernel-based fast aerial image computation for a large scale design of integrated circuit patterns
InactiveUS6223139B1Advantageously producedComputationally efficientPump componentsBlade accessoriesFeature vectorDecomposition
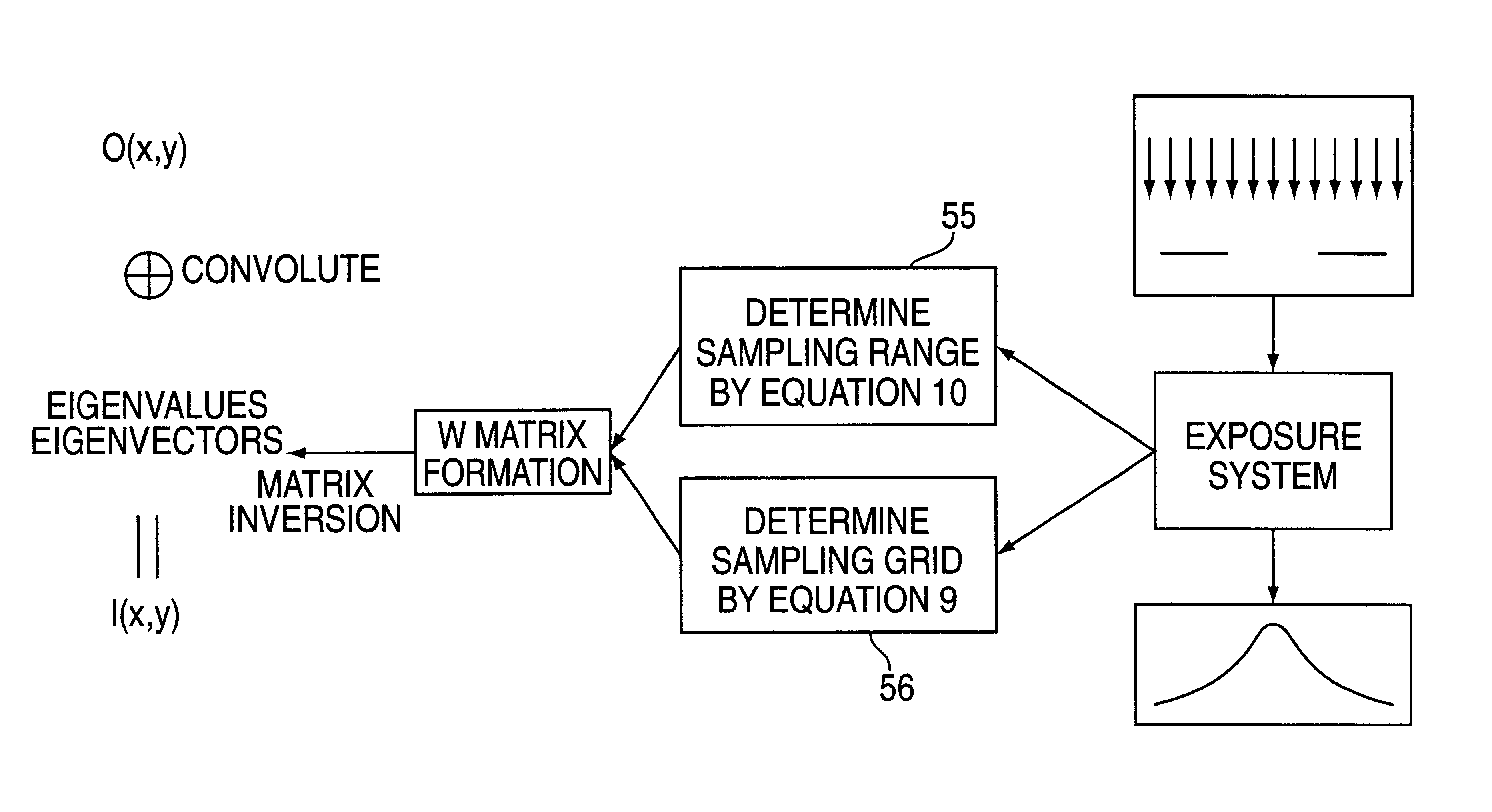
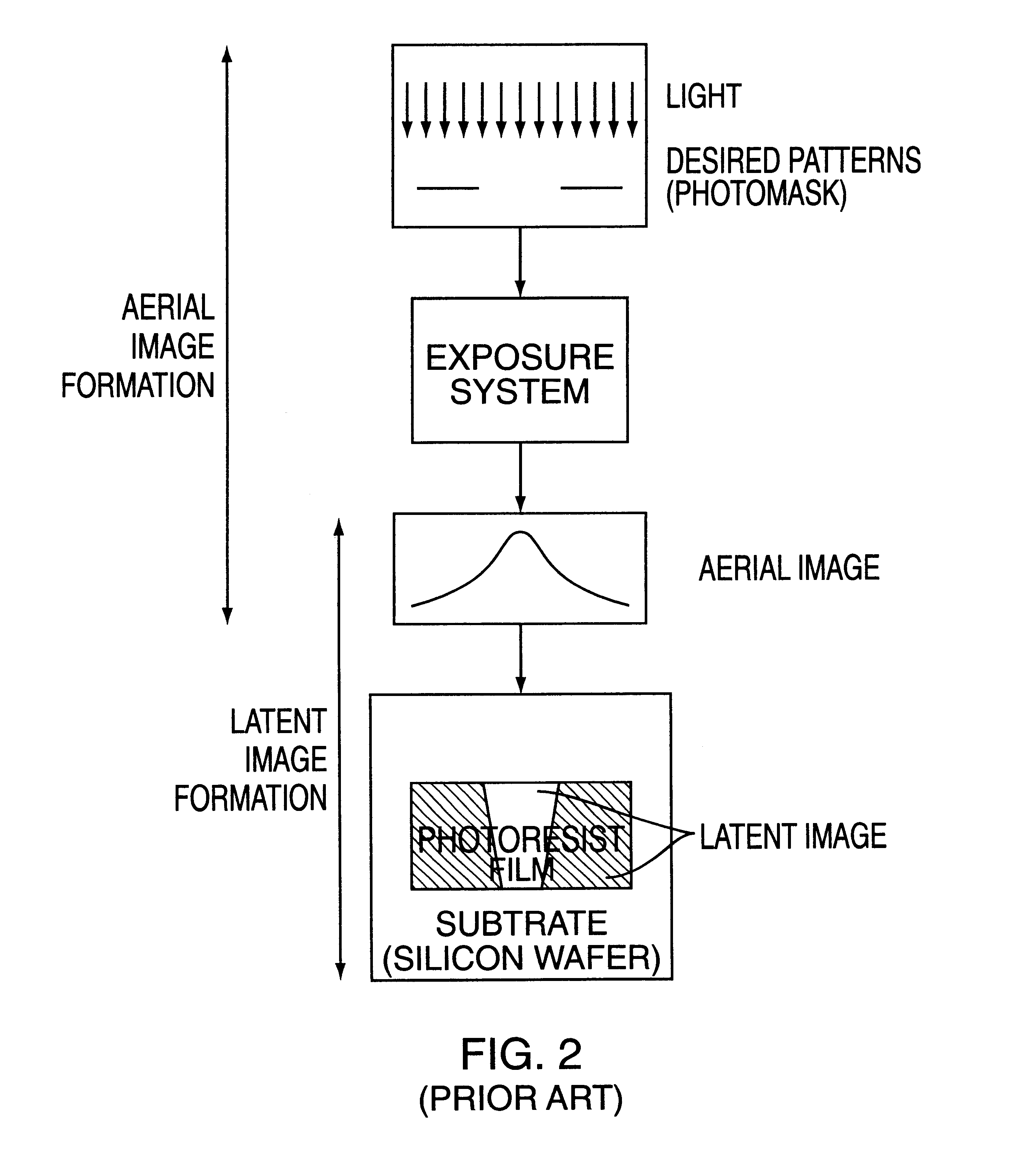
A method of simulating aerial images of large mask areas obtained during the exposure step of a photo-lithographic process when fabricating a semiconductor integrated circuit silicon wafer is described. The method includes the steps of defining mask patterns to be projected by the exposure system to create images of the mask patterns; determining an appropriate sampling range and sampling interval; generating a characteristic matrix describing the exposure system; inverting the matrix to obtain eigenvalues as well as the eigenvectors (or kernels) representing the decomposition of the exposure system; convolving the mask patterns with these eigenvectors; and weighing the resulting convolution by the eigenvalues to form the aerial images. The method is characterized in that the characteristic matrix is precisely defined by the sampling range and the sampling interval, such that the sampling range is the shortest possible and the sampling interval, the largest possible, without sacrificing accuracy. The method of generating aerial images of patterns having large mask areas provides a speed improvement of several orders of magnitude over conventional approaches.
Owner:IBM CORP
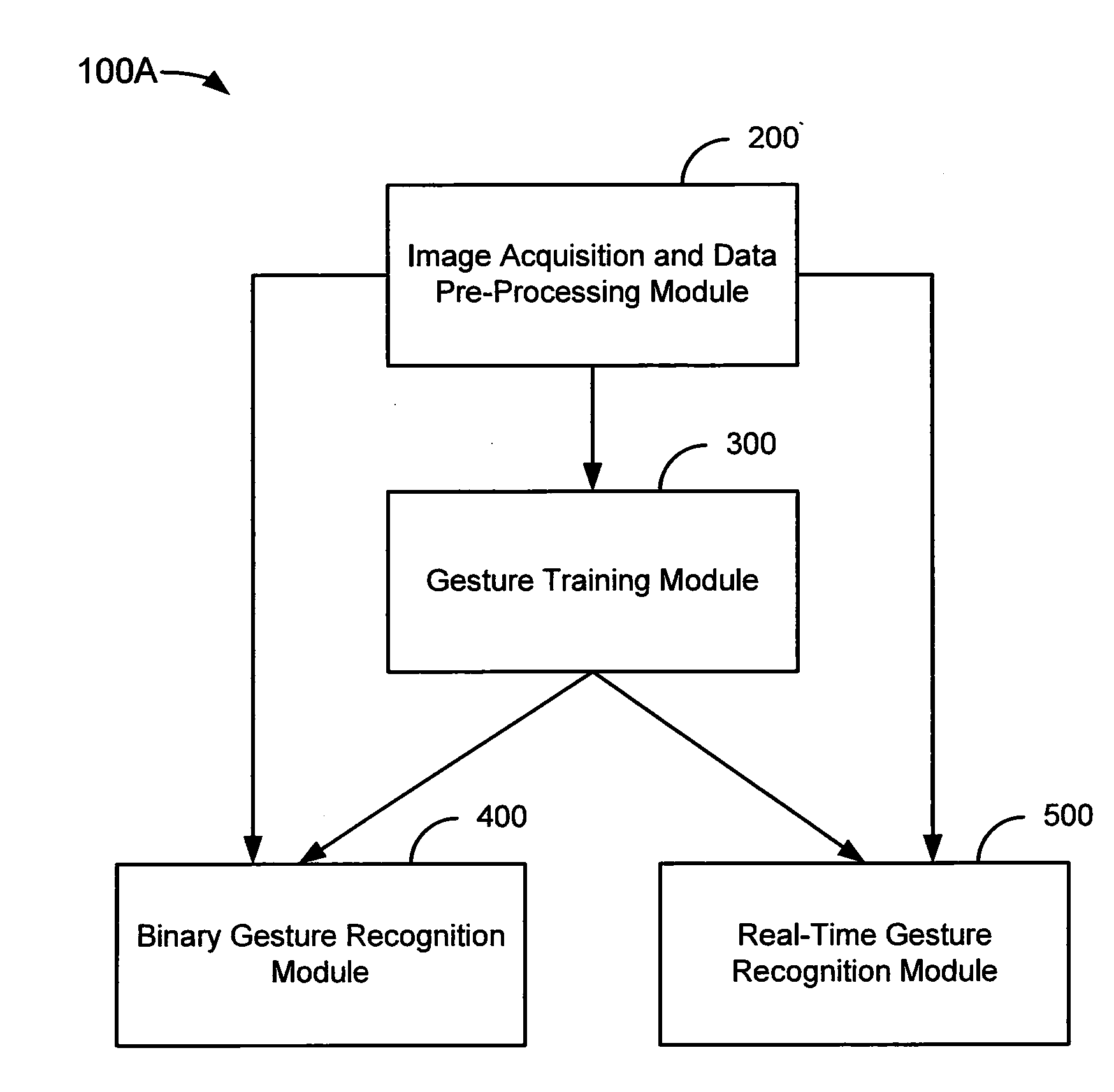
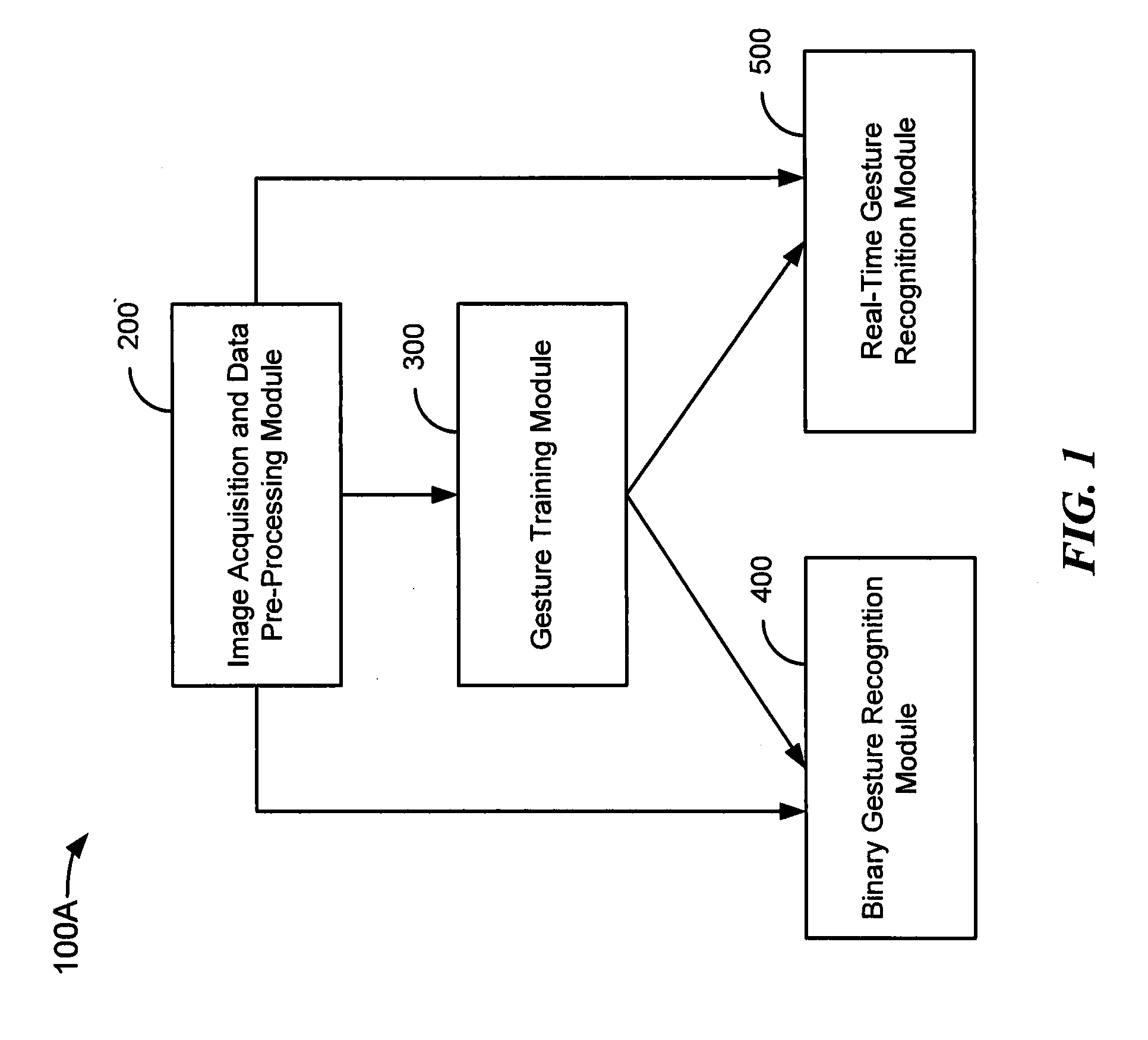
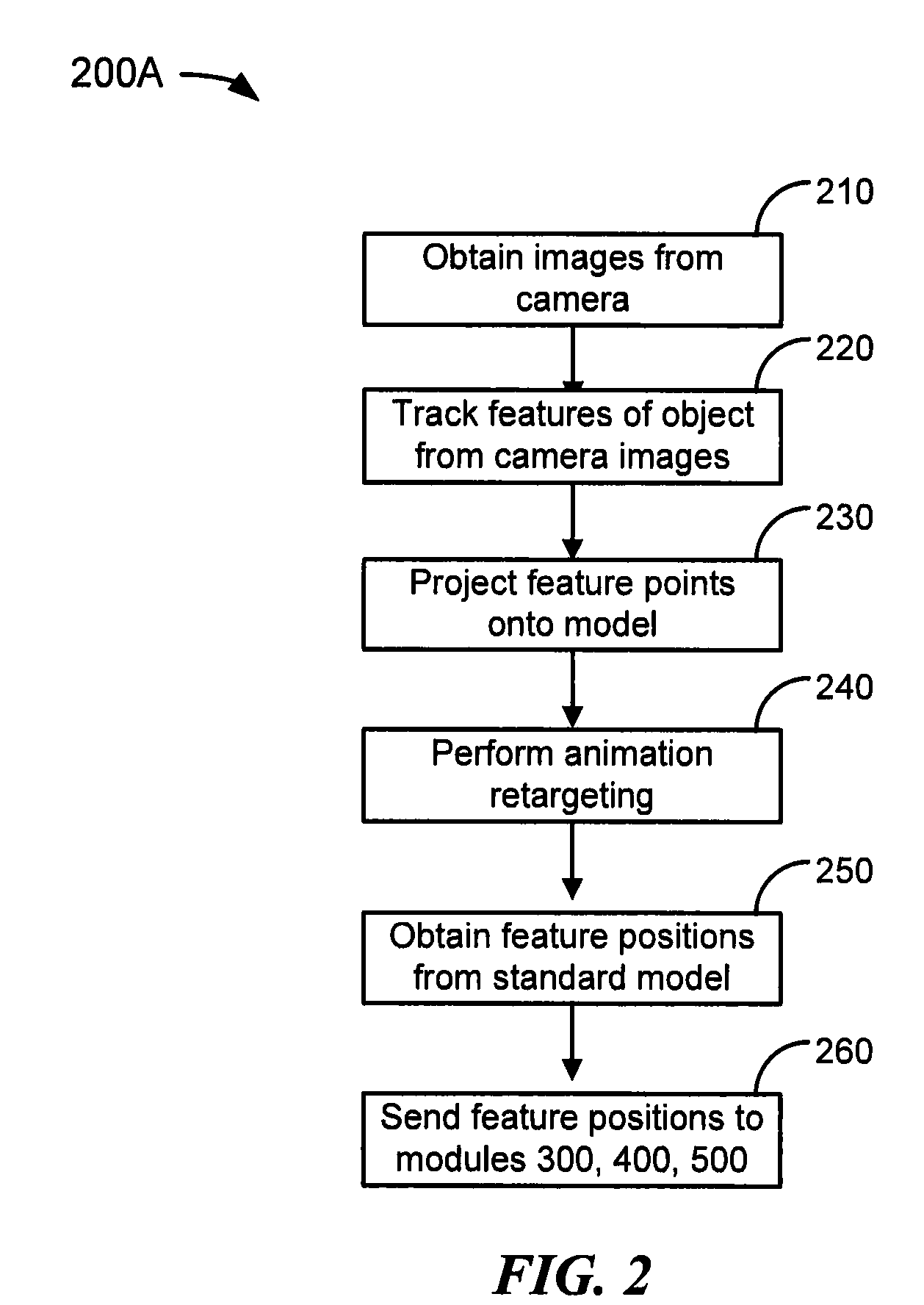
Method and system for gesture recognition
ActiveUS20100208038A1Minimize effectSmooth dataSteroscopic systemsThree-dimensional object recognitionComputer visionInverse kinematics
A method of image acquisition and data pre-processing includes obtaining from a sensor an image of a subject making a movement. The sensor may be a depth camera. The method also includes selecting a plurality of features of interest from the image, sampling a plurality of depth values corresponding to the plurality of features of interest, projecting the plurality of features of interest onto a model utilizing the plurality of depth values, and constraining the projecting of the plurality of features of interest onto the model utilizing a constraint system. The constraint system may comprise an inverse kinematics solver.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
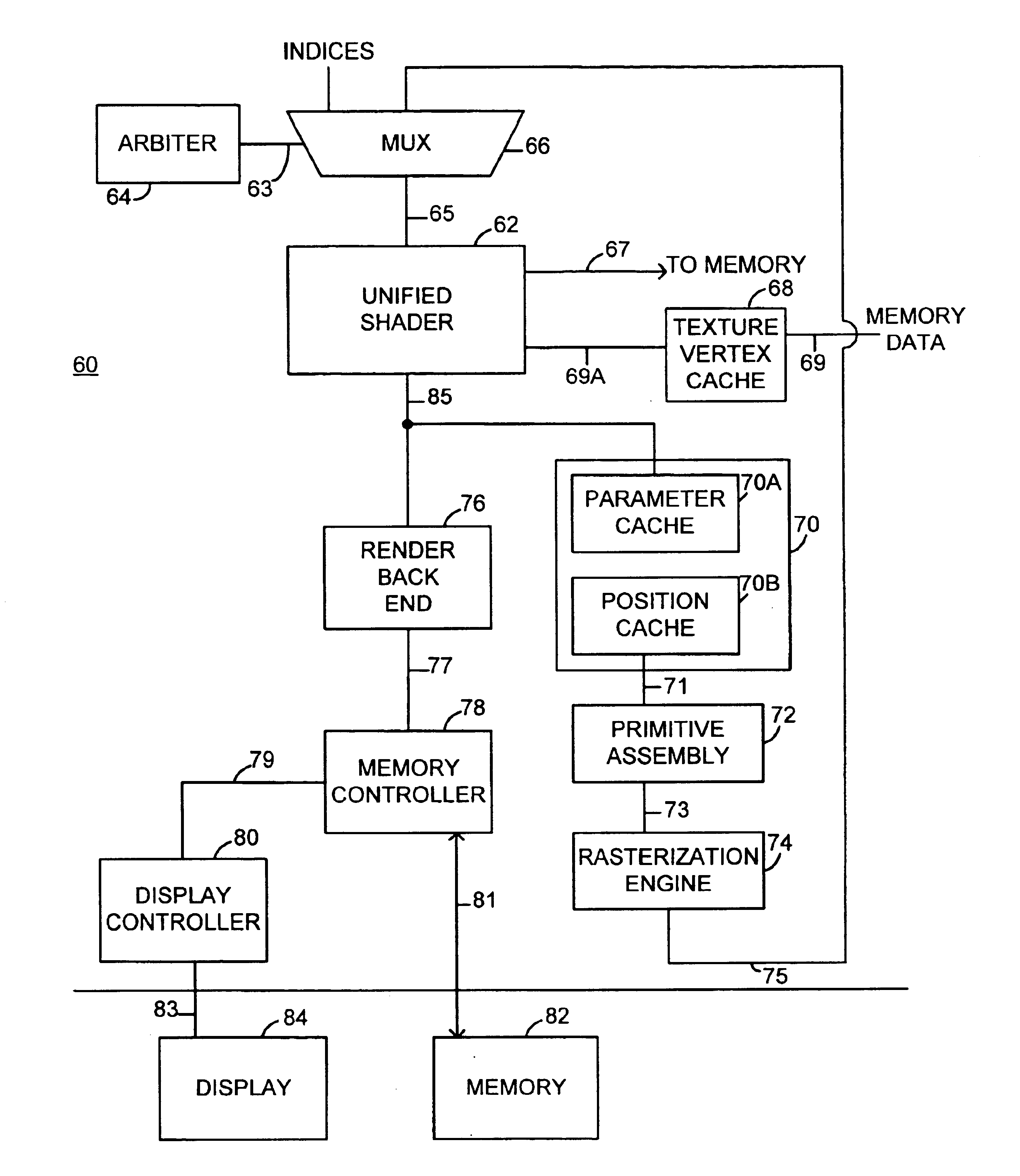
Graphics processing architecture employing a unified shader
ActiveUS6897871B1More computationally efficientFlexiblyDigital computer detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsControl signalLogical operations
A graphics processing architecture employing a single shader is disclosed. The architecture includes a circuit operative to select one of a plurality of inputs in response to a control signal; and a shader, coupled to the arbiter, operative to process the selected one of the plurality of inputs, the shader including means for performing vertex operations and pixel operations, and wherein the shader performs one of the vertex operations or pixel operations based on the selected one of the plurality of inputs. The shader includes a register block which is used to store the plurality of selected inputs, a sequencer which maintains vertex manipulation and pixel manipulations instructions and a processor capable of executing both floating point arithmetic and logical operations on the selected inputs in response to the instructions maintained in the sequencer.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
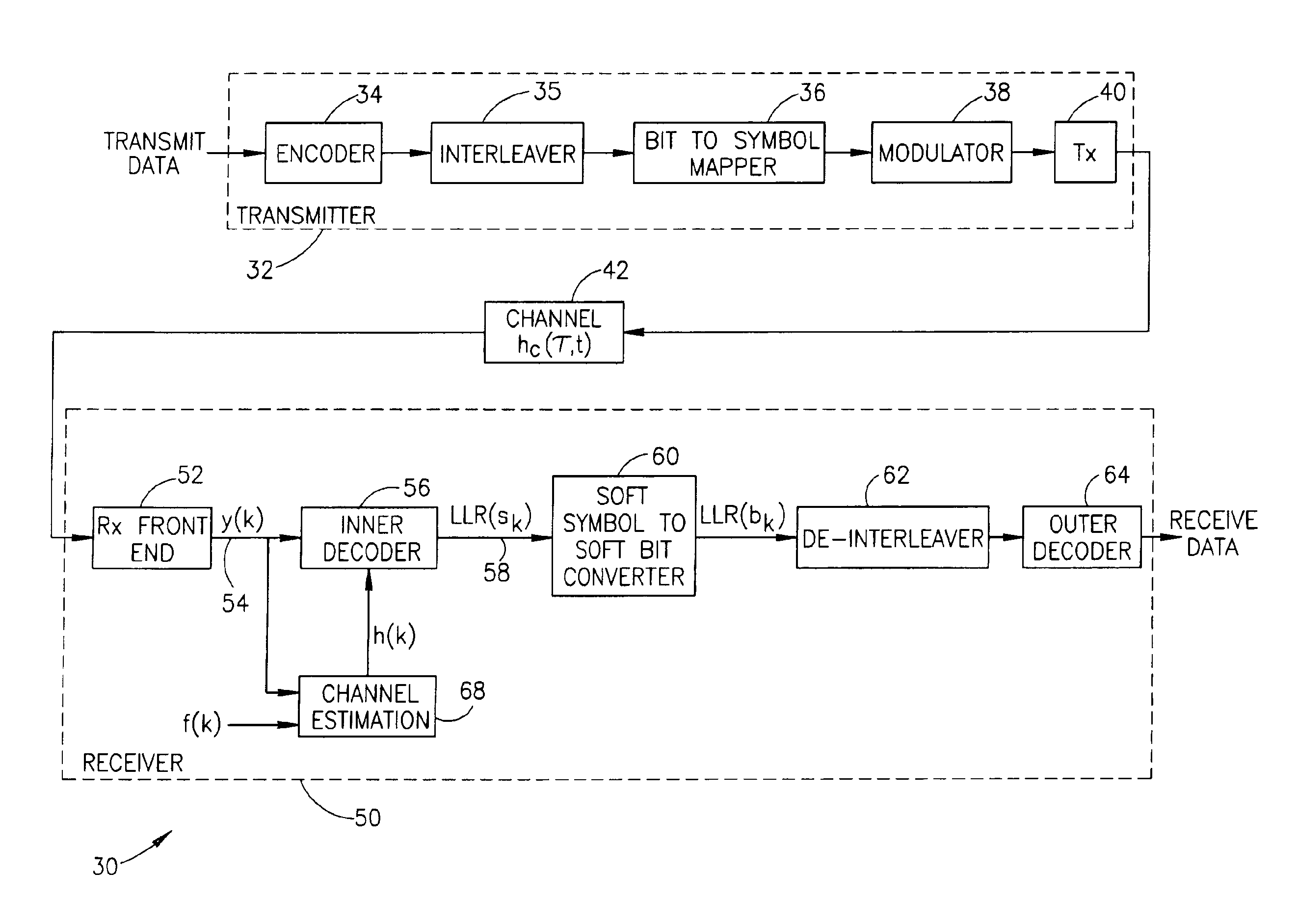
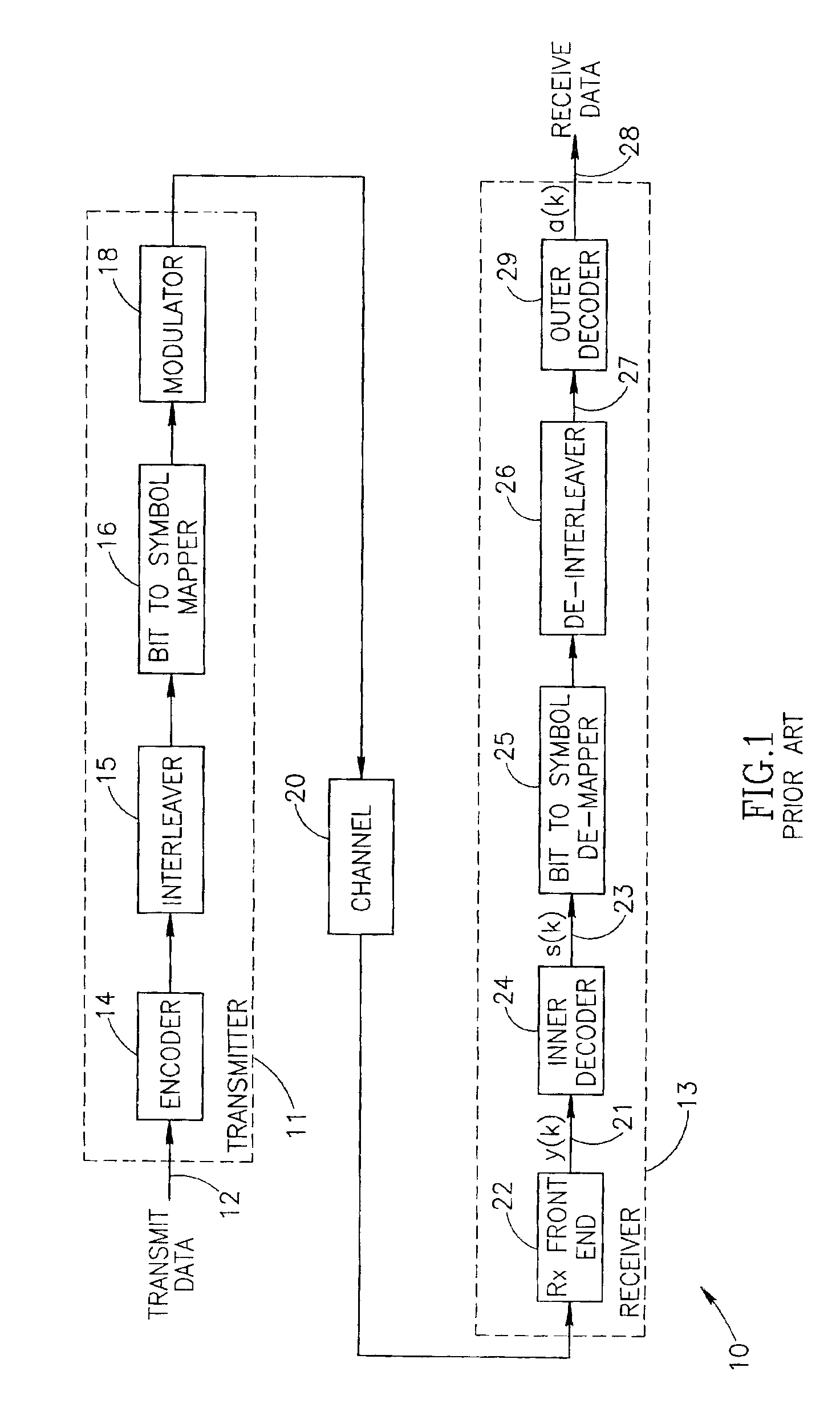
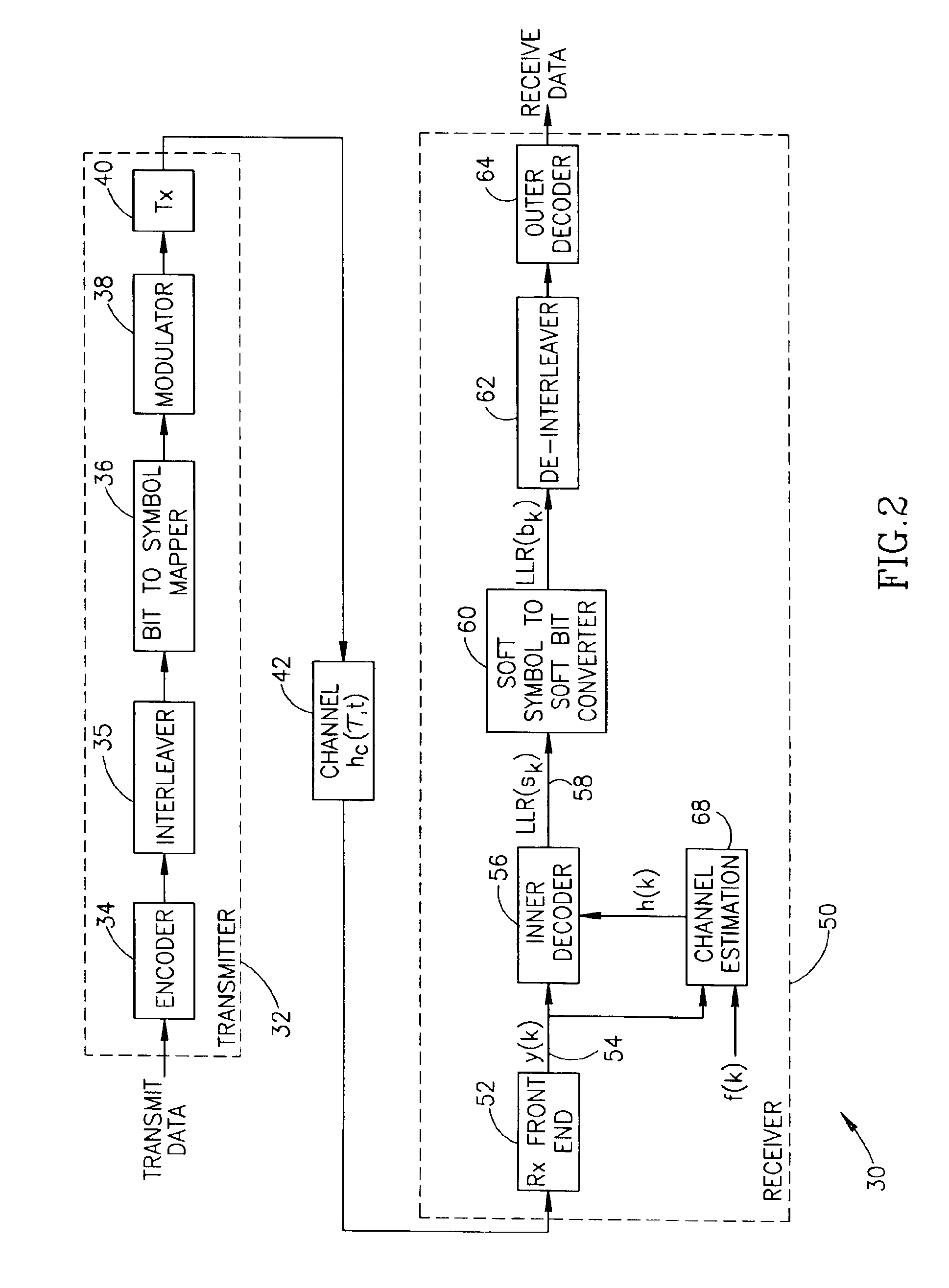
Apparatus for and method of converting soft symbol information to soft bit information
InactiveUS6944242B2Optimize performanceOvercome disadvantagesData representation error detection/correctionDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionConditional probabilitySoftware
An apparatus for and method of converting soft symbol decision information into soft bit decision information that overcomes the disadvantages of the prior art. The invention is adapted to receive M soft symbol values where each symbol represents m bits (M=2m). The output for each symbol comprises m soft values of bits representing the symbol. The invention is operative to convert the soft symbol values to soft bit values using the log likelihood ratios (LLRs) of a bit and a symbol expressed as conditional probabilities. The method of the invention is presented which can be performed in either hardware or software. A computer comprising a processor, memory, etc. is operative to execute software adapted to perform the soft symbol to bit conversion method of the present invention.
Owner:COMSYS COMM & SIGNAL PRO CESSING
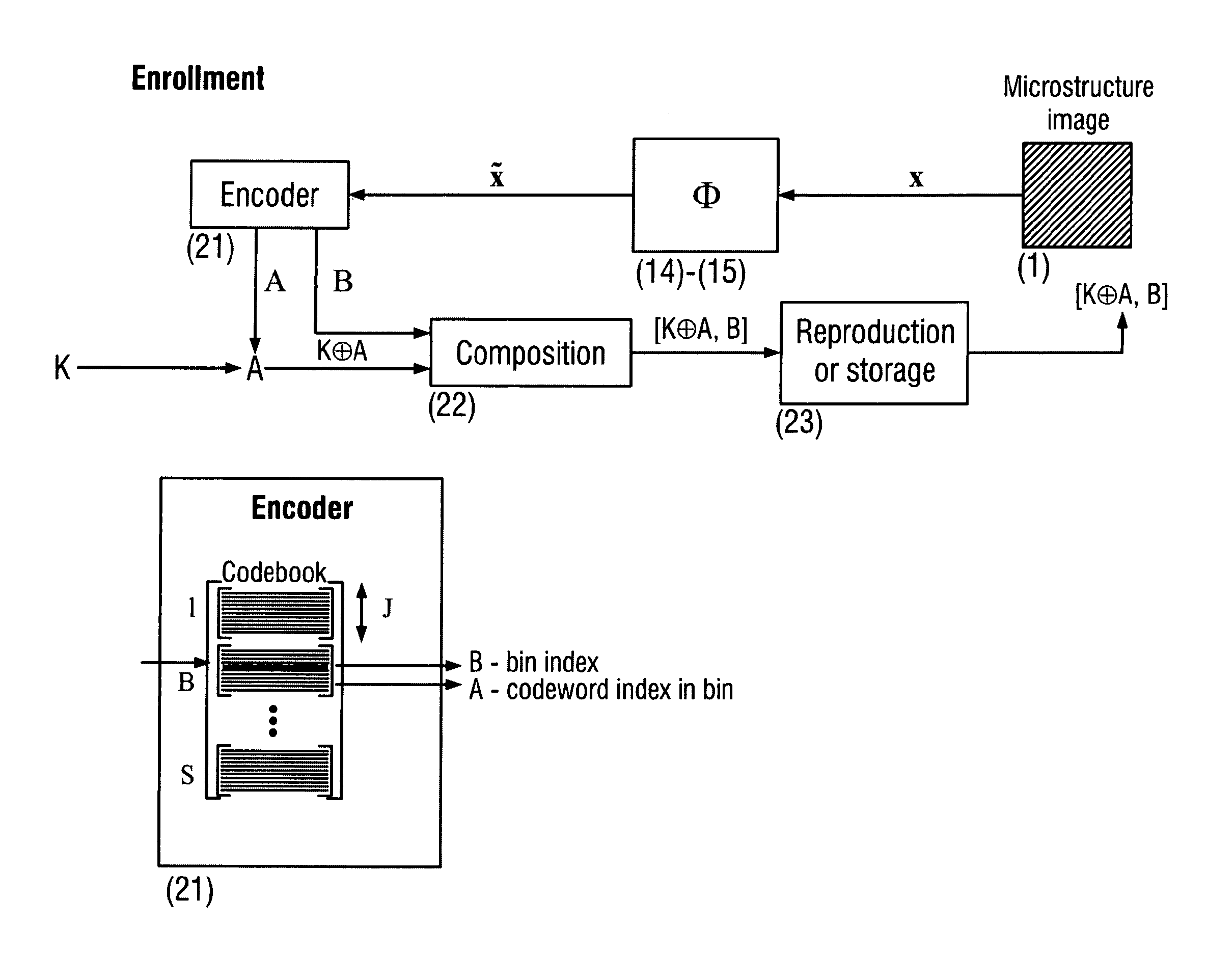
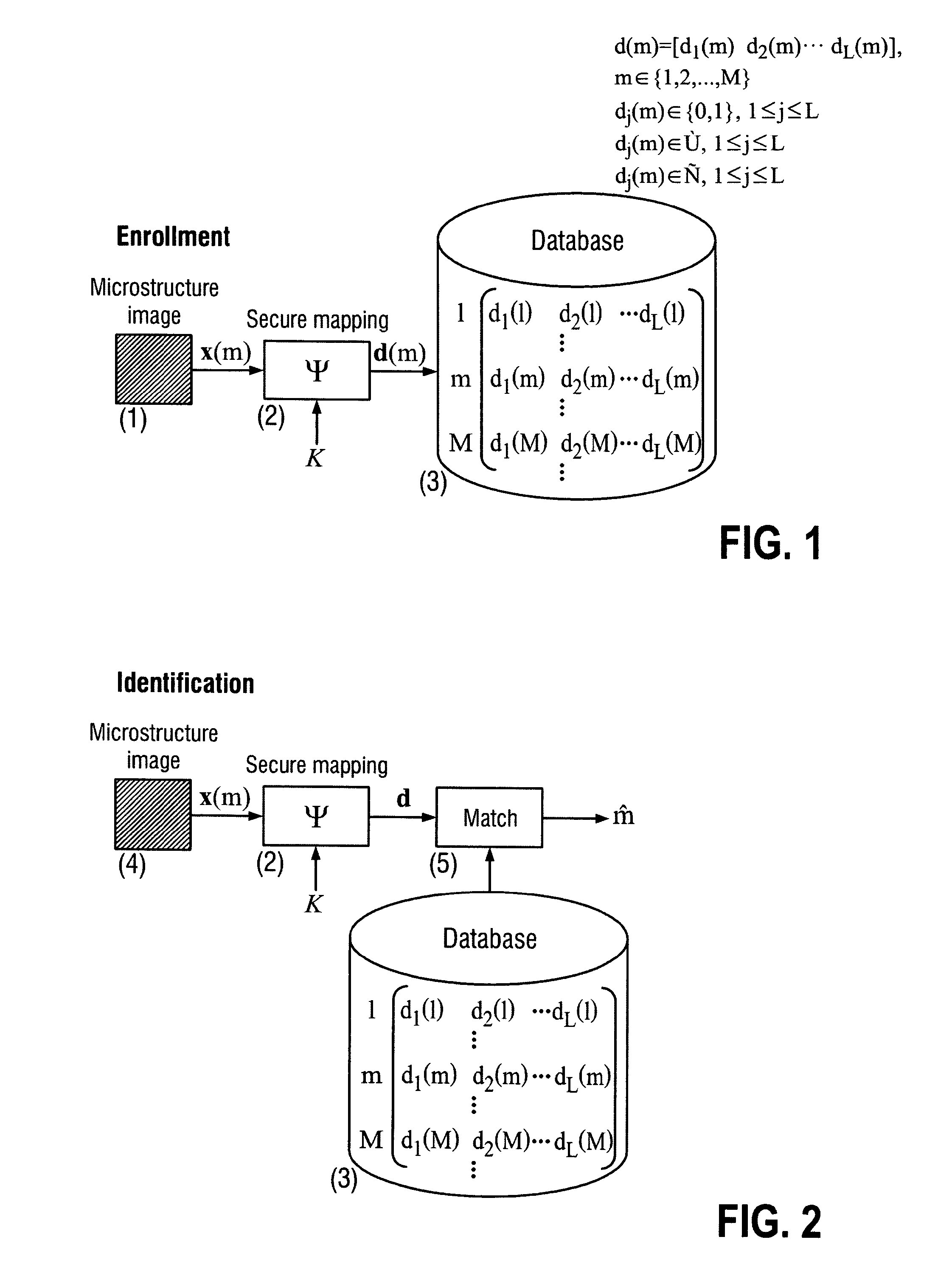
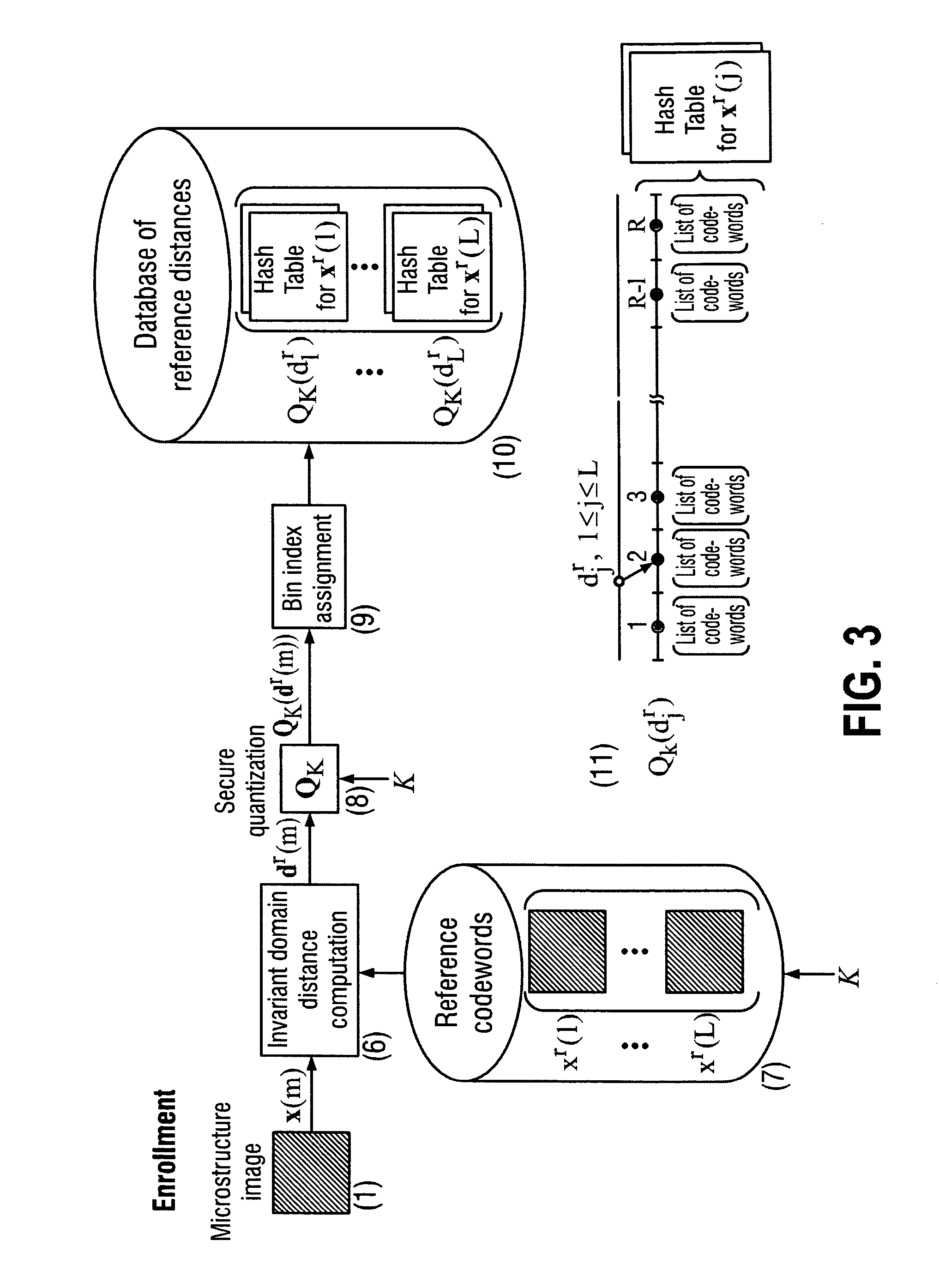
Secure item identification and authentication system and method based on unclonable features
ActiveUS20110096955A1Improve efficiencyEasy to usePaper-money testing devicesCharacter and pattern recognitionKey exchangeDistributed source
The present invention is a method and apparatus for protection of various items against counterfeiting using physical unclonable features of item microstructure images. The protection is based on the proposed identification and authentication protocols coupled with portable devices. In both cases a special transform is applied to data that provides a unique representation in the secure key-dependent domain of reduced dimensionality that also simultaneously resolves performance-security-complexity and memory storage requirement trade-offs. The enrolled database needed for the identification can be stored in the public domain without any risk to be used by the counterfeiters. Additionally, it can be easily transportable to various portable devices due to its small size. Notably, the proposed transformations are chosen in such a way to guarantee the best possible performance in terms of identification accuracy with respect to the identification in the raw data domain. The authentication protocol is based on the proposed transform jointly with the distributed source coding. Finally, the extensions of the described techniques to the protection of artworks and secure key exchange and extraction are disclosed in the invention.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GENEVA
Method and system for cache management of locale-sensitive content
ActiveUS7194506B1Computationally efficientMultiple digital computer combinationsWebsite content managementClient-sideCache management
A method and system are disclosed for cache management and regeneration of dynamically-generated locale-sensitive content (DGLSC) in one or more server computers within a client-server computer network. One embodiment of the method of this invention can comprise receiving a request for content from a user at a client computer and determining the user's locale preference with, for example, an automatic locale detection algorithm. The requested content can be dynamically generated from a template as DGLSC based on the user locale preference. If the template is a cacheable template, a locale-sensitive filename can be generated for the DGLSC based on the user locale preference. The locale-sensitive filename can be associated with the DGLSC. The DGLSC can be cached in a locale-sensitive directory, such that it can be served (and thus avoid duplicative generation of the same content) in response to subsequent requests from users having the same locale preference The DGLSC is then served to the requesting user at his or her client computer.
Owner:OPEN TEXT SA ULC
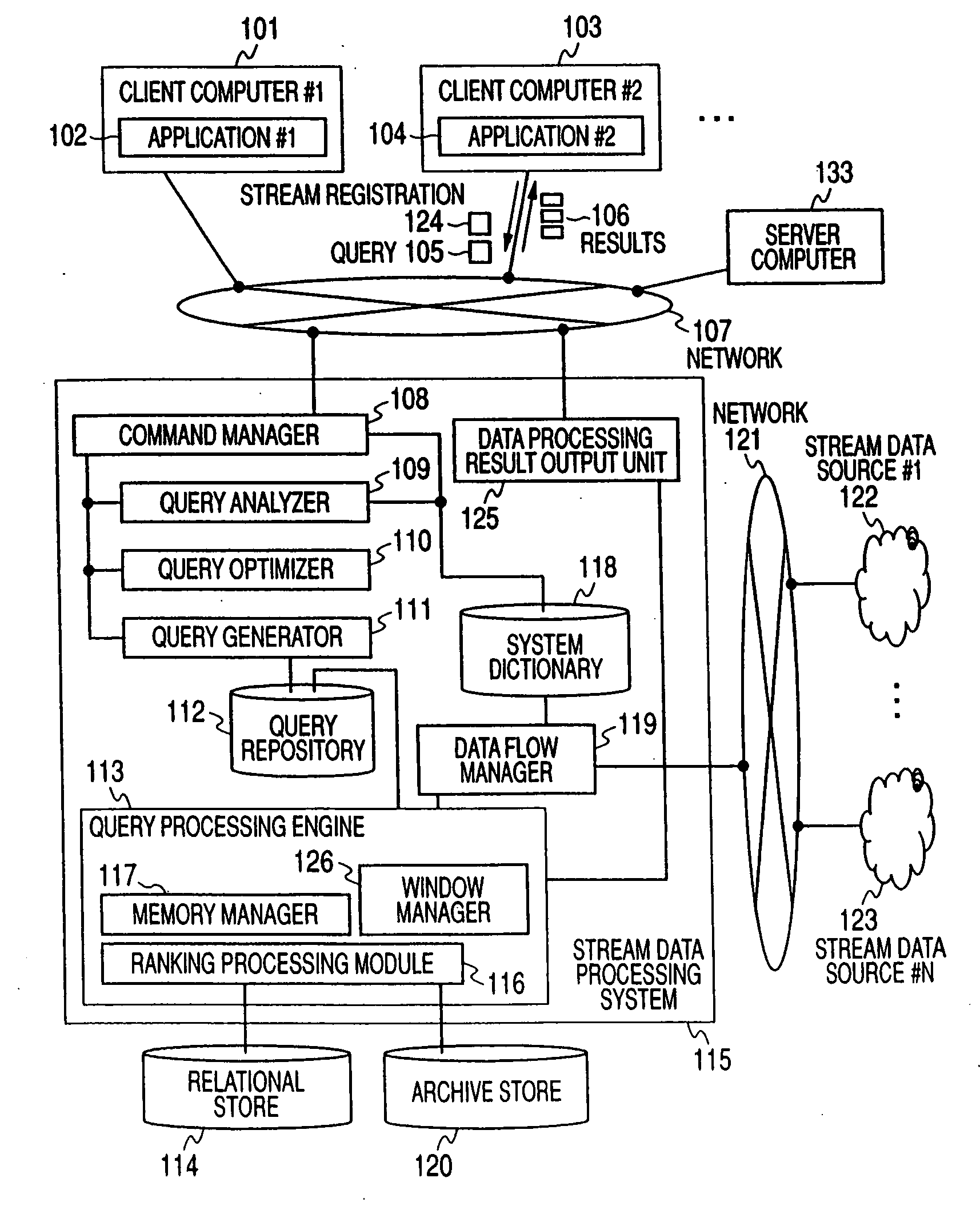
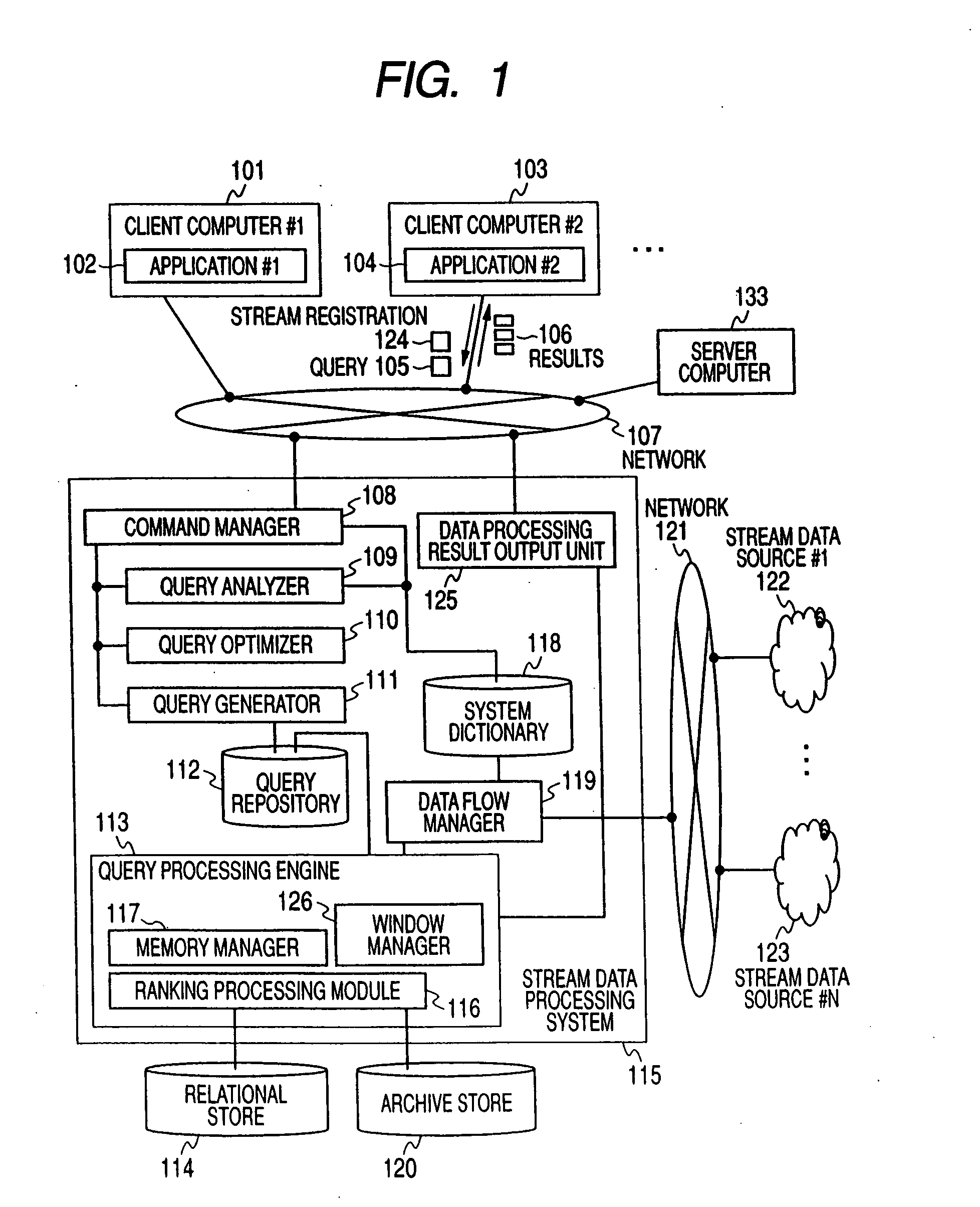
Ranking query processing method for stream data and stream data processing system having ranking query processing mechanism
InactiveUS20090112853A1High-efficiency rankingMaintain consistencyDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsStreaming dataDifferential information
A mechanism for managing ranking information using a sign of a stream tuple generated when stream data is inserted into, or deleted from, a window is provided. A mechanism for generating only the differential information of ranking calculation results, a mechanism for adding ranking information according to a request, an interface for generating and outputting all ranking information from the differential information, a mechanism for generating all ranking calculation results, and an interface for using these mechanisms are provided.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
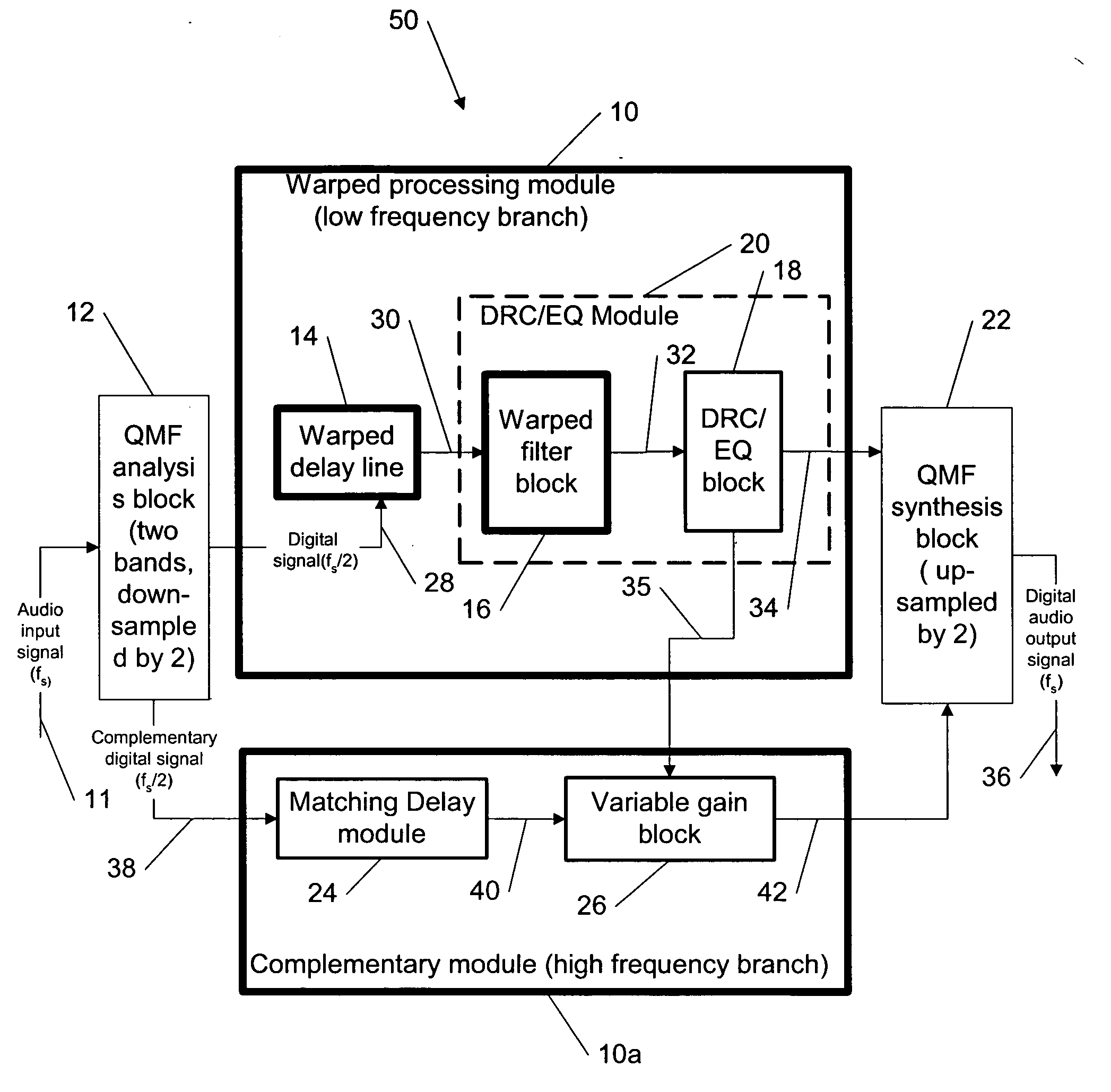
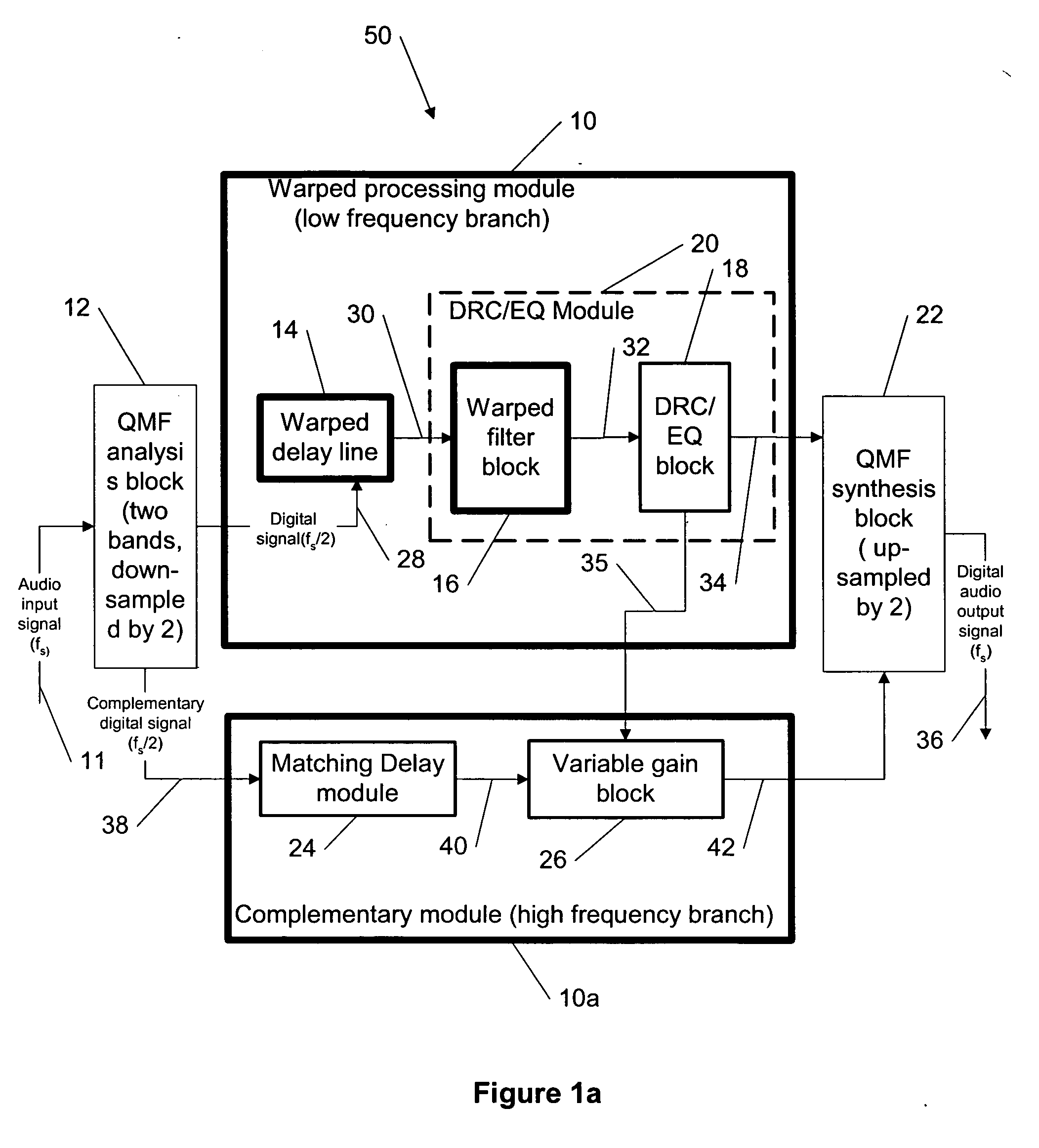
Dynamic range control and equalization of digital audio using warped processing
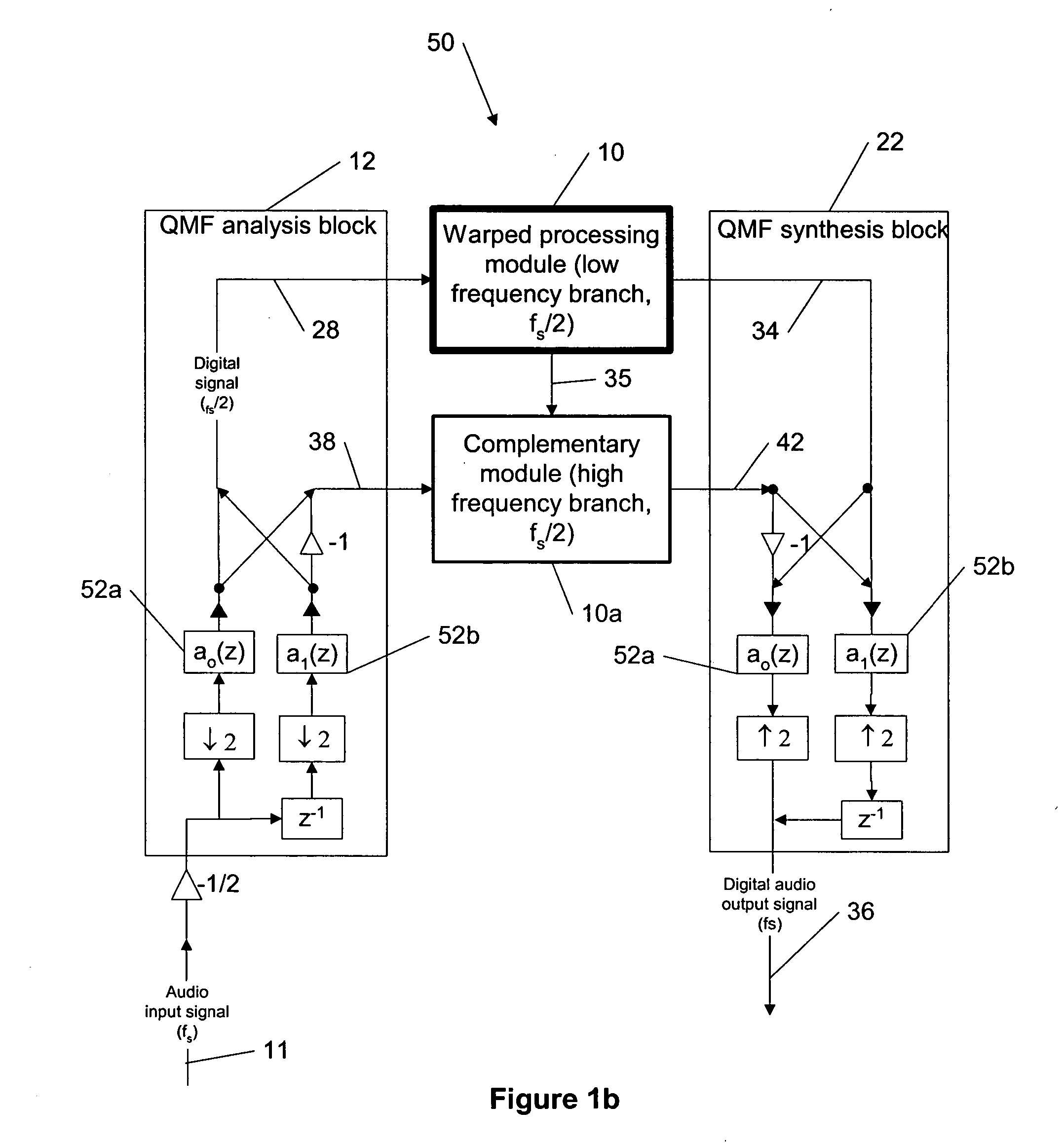
ActiveUS20050249272A1Reduce processing loadComputationally efficientMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsFrequency bandLoudness
This invention describes a method for adjusting the loudness and the spectral content of digital audio signals in a real-time using warped spectral filtering. A warped processing module modifies a spectral content of a digital audio signal with a set of gains for a plurality of non-linearly-scaled frequency bands determined by a warping factor λ of a warped delay line. Warped delay line signals, generated by the warped delay line, are processed by a warped filter block containing multiple warped finite impulse response filters, e.g., Mth band filters, using individual warped spectral filtering in said plurality of the non-linearly-scaled frequency bands, which is followed by a conventional processing by a dynamic range control / equalization block. The present invention describes another innovation, that is embedding the warped processing module in a two-channel quadrature mirror filter (QMF) bank for improving processing efficiency at high sample rates.
Owner:BEIJING XIAOMI MOBILE SOFTWARE CO LTD
Event clustering of images using foreground/background segmentation
InactiveUS6915011B2Good similarity matchingImprove performanceImage analysisStill image data indexingPattern recognitionLuminosity
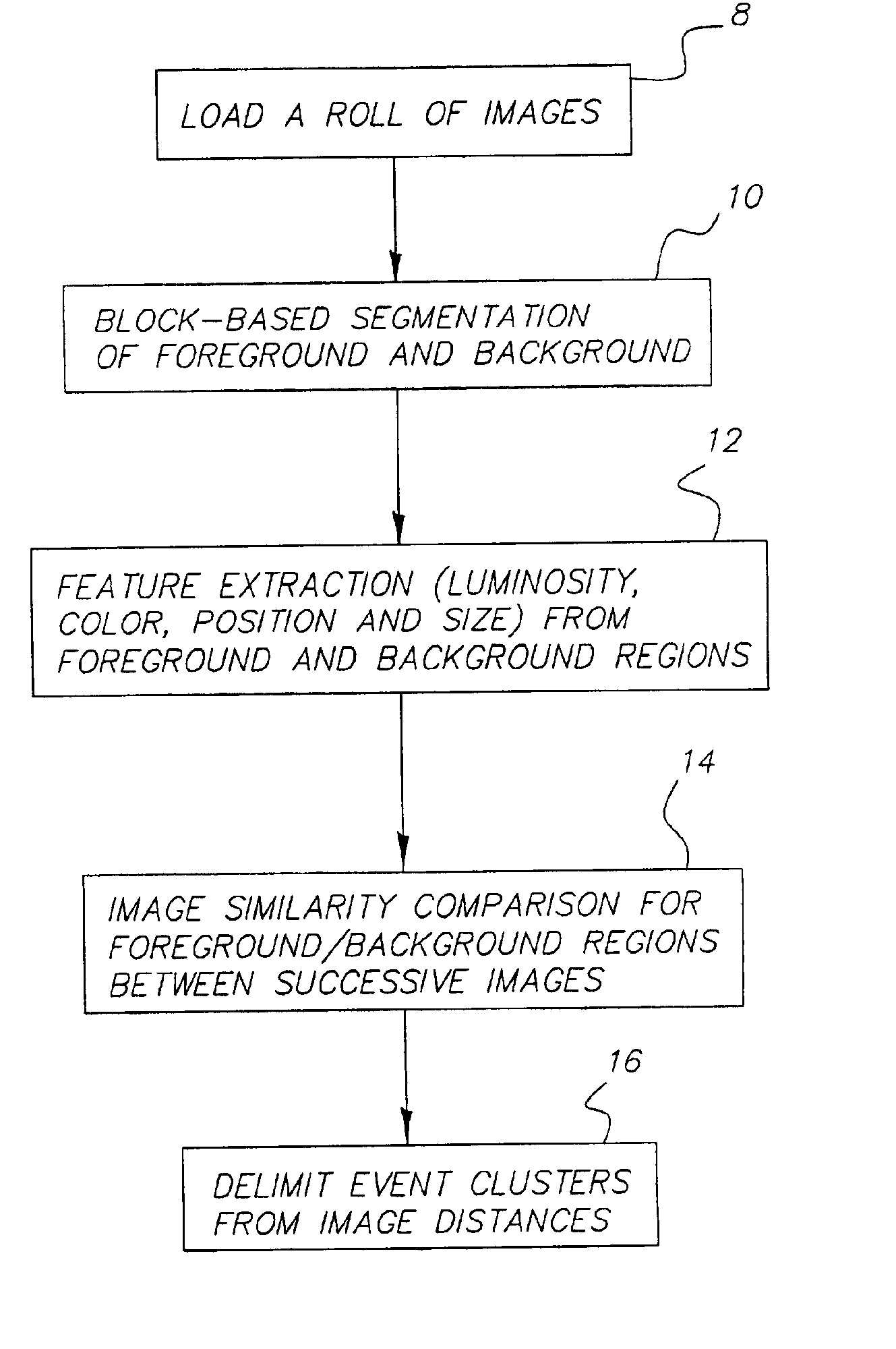
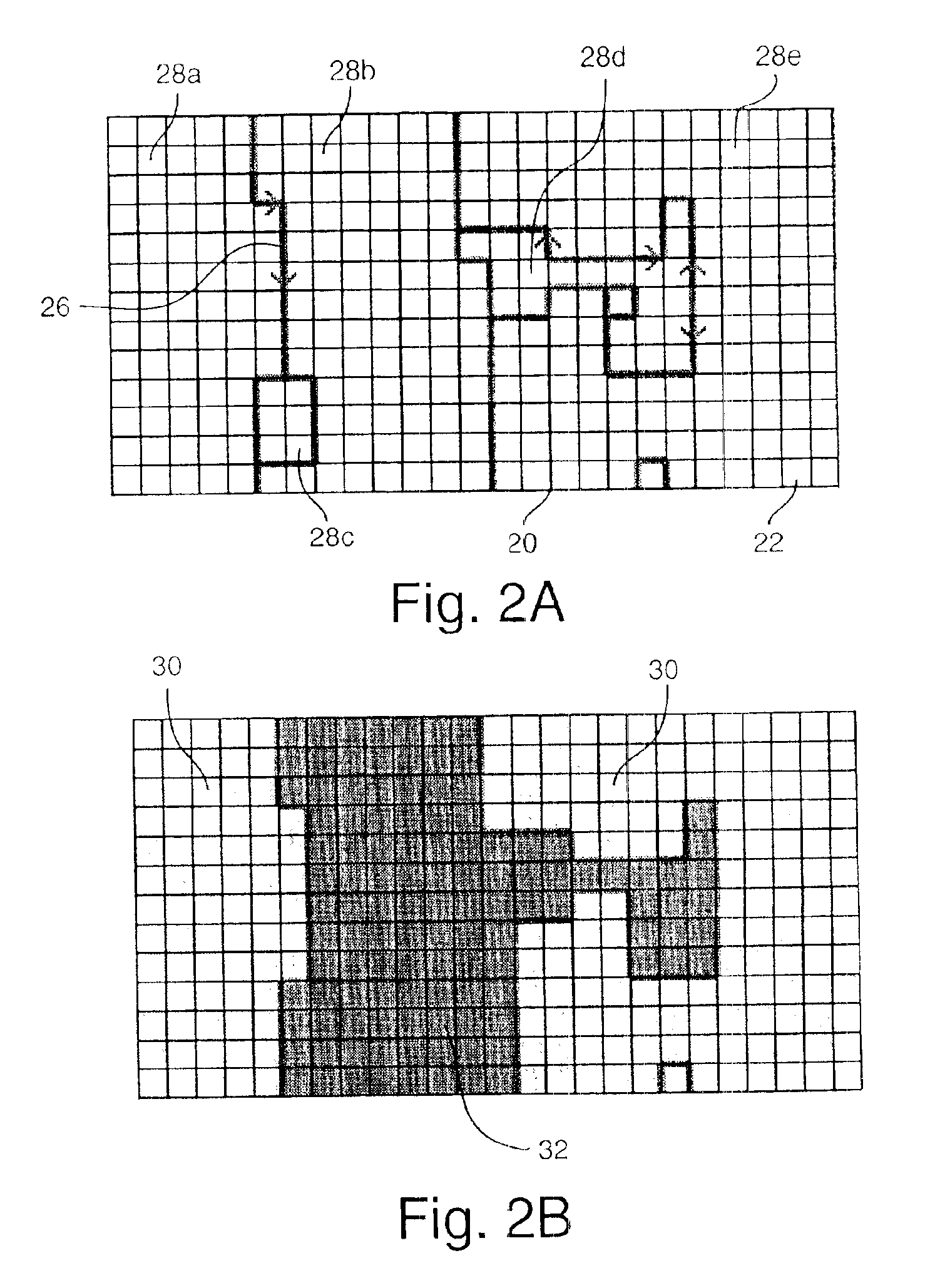
An event clustering method uses foreground and background segmentation for clustering images from a group into similar events. Initially, each image is divided into a plurality of blocks, thereby providing block-based images. Utilizing a block-by-block comparison, each block-based image is segmented into a plurality of regions comprising at least a foreground and a background. One or more luminosity, color, position or size features are extracted from the regions and the extracted features are utilized to estimate and compare the similarity of the regions comprising the foreground and background in successive images in the group. Then, a measure of the total similarity between successive images is computed, thereby providing image distance between successive images, and event clusters are delimited from the image distances.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
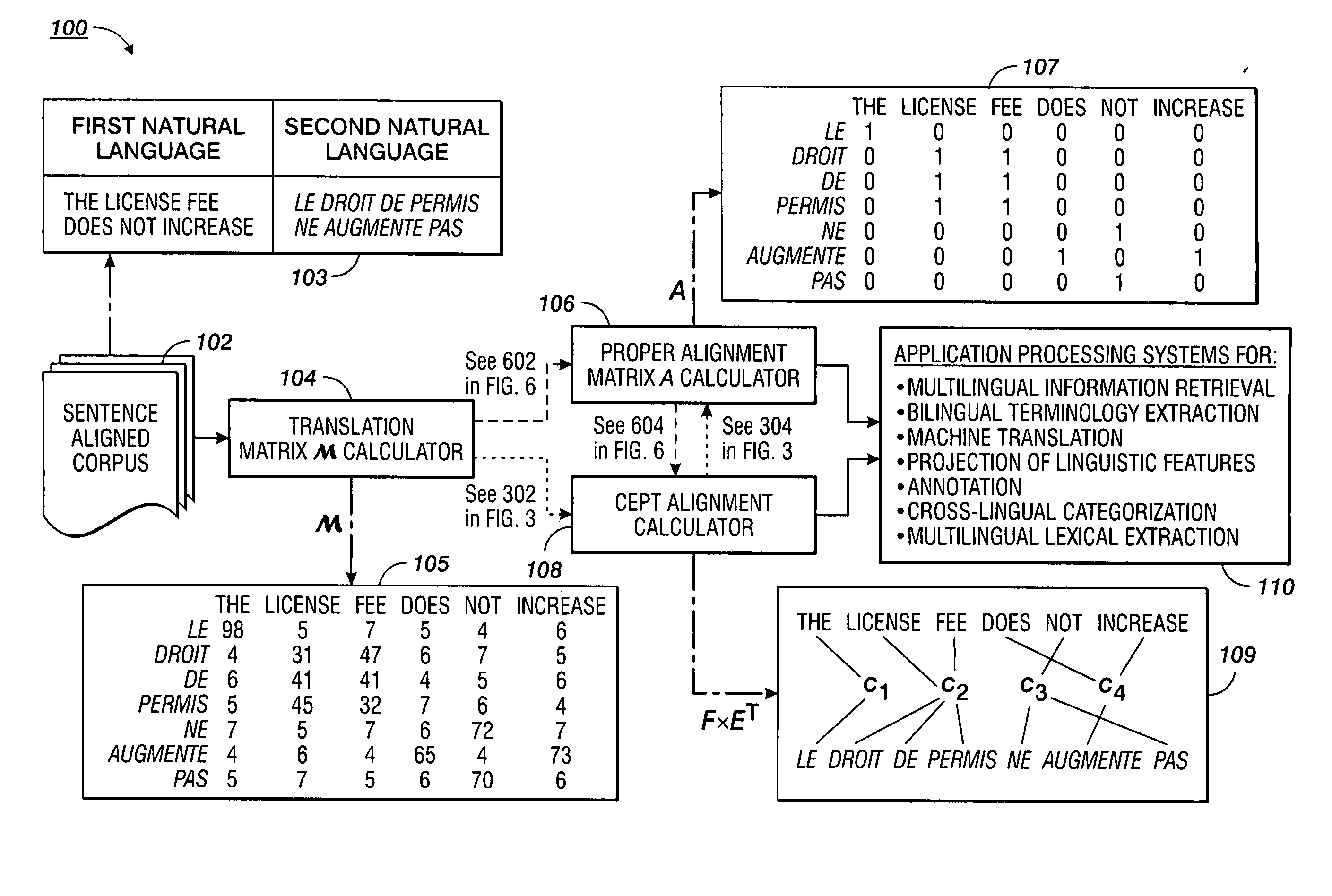
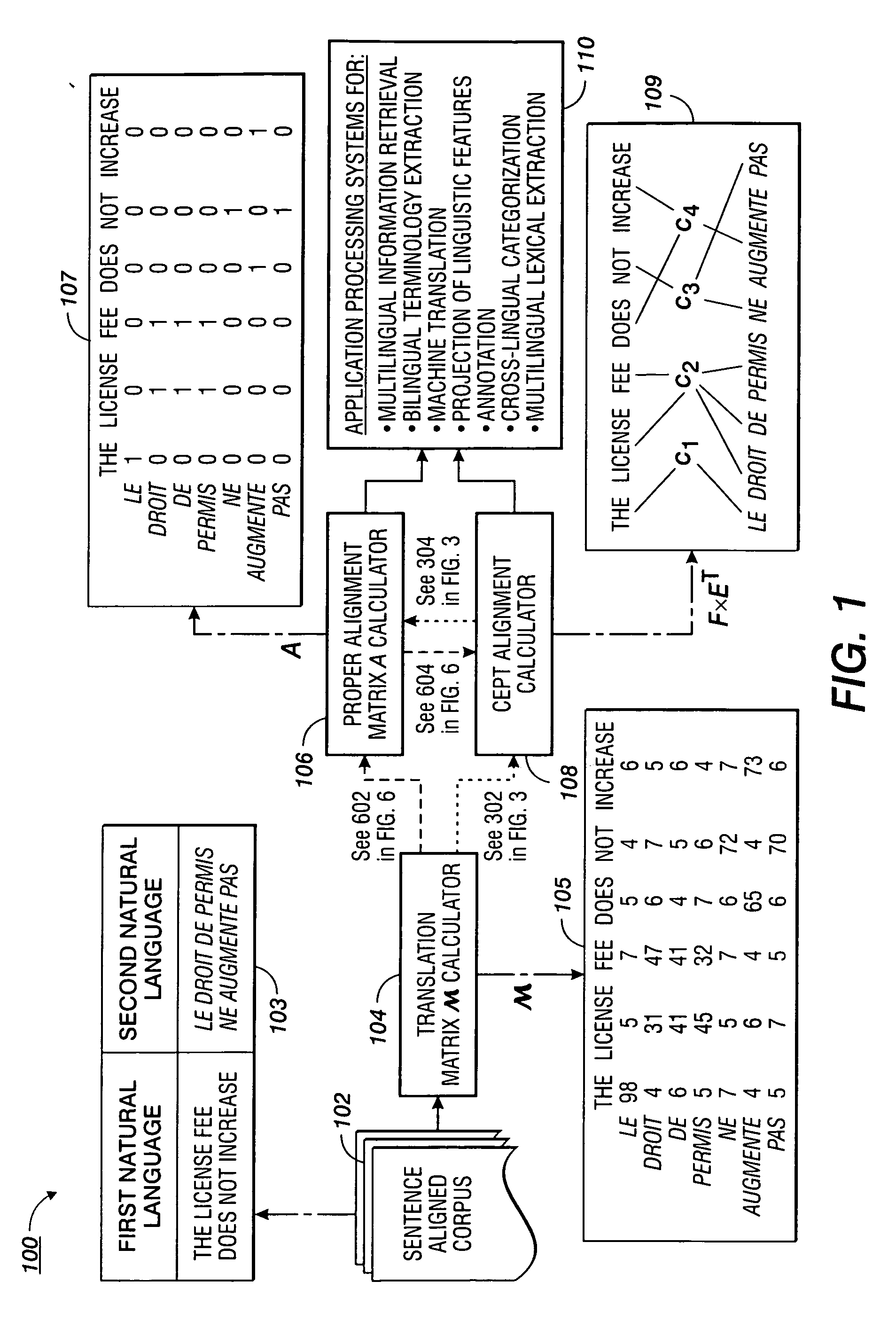
Apparatus and methods for aligning words in bilingual sentences
InactiveUS20060190241A1Improved translation modelComputationally efficientNatural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsText corpusNatural language
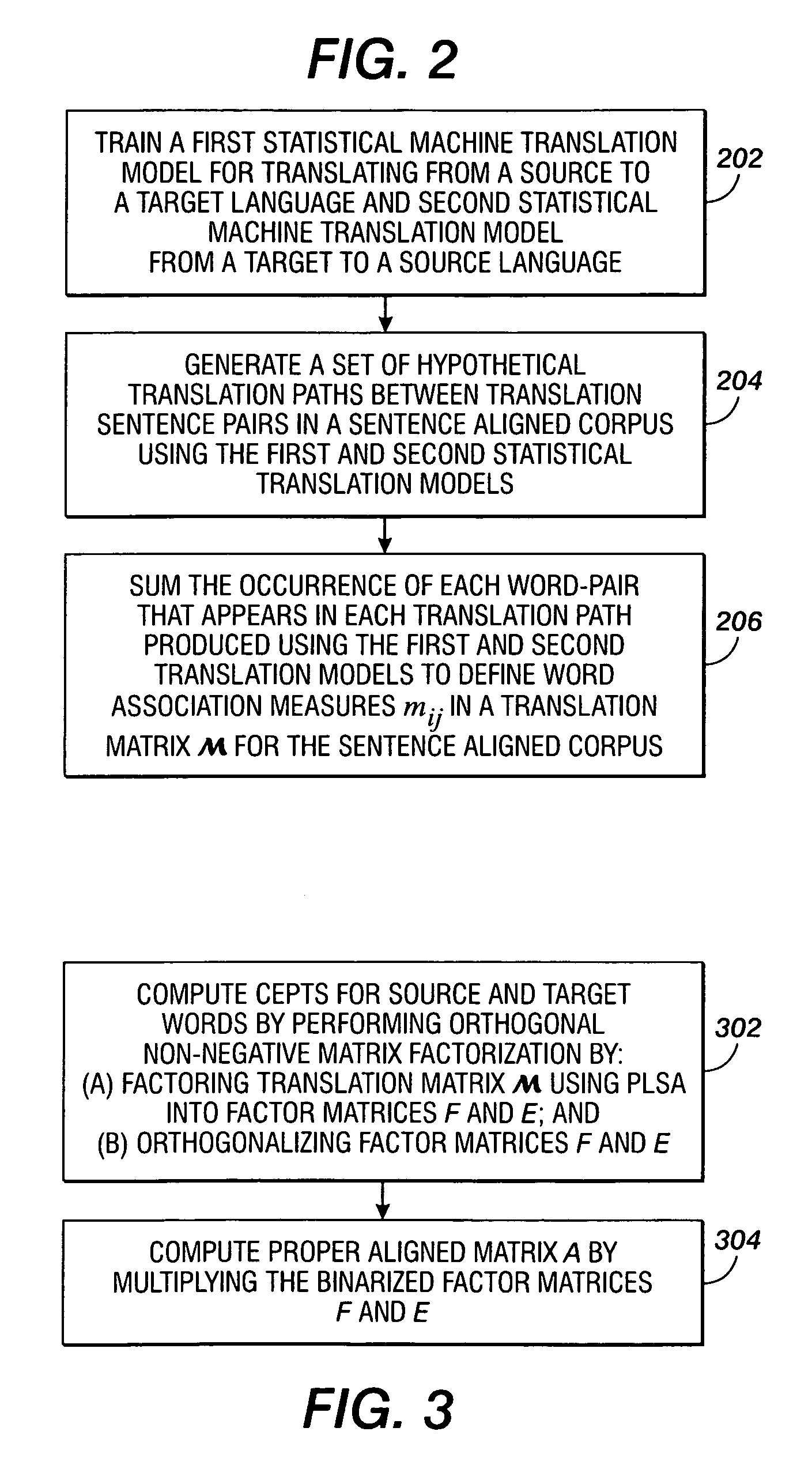
Methods are disclosed for performing proper word alignment that satisfy constraints of coverage and transitive closure. Initially, a translation matrix which defines word association measures between source and target words of a corpus of bilingual translations of source and target sentences is computed. Subsequently, in a first method, the association measures in the translation matrix are factorized and orthogonalized to produce cepts for the source and target words, which resulting matrix factors may then be, optionally, multiplied to produce an alignment matrix. In a second method, the association measures in the translation matrix are thresholded, and then closed by transitivity, to produce an alignment matrix, which may then be, optionally, factorized to produce cepts. The resulting cepts or alignment matrices may then be used by any number of natural language applications for identifying words that are properly aligned.
Owner:XEROX CORP
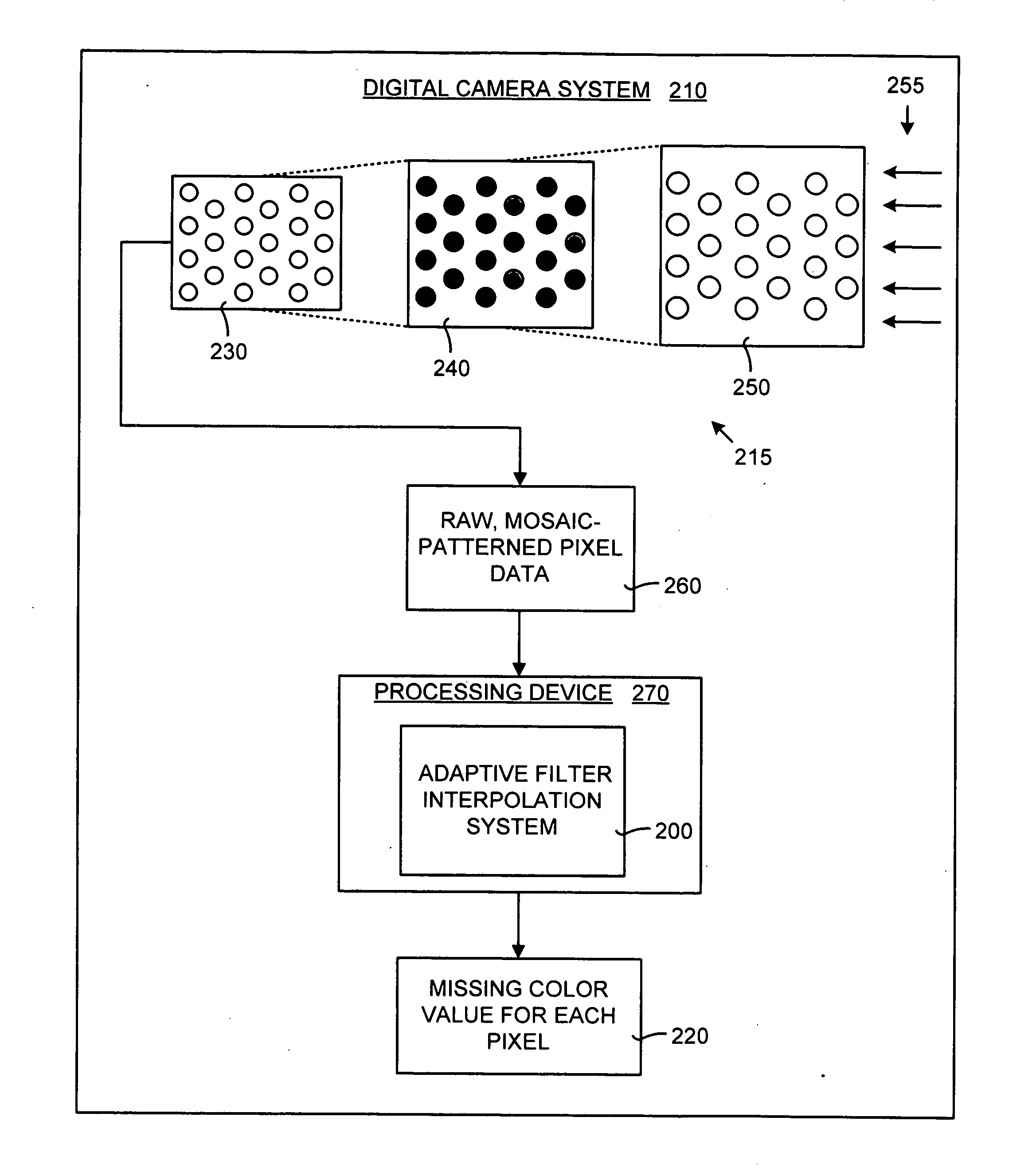
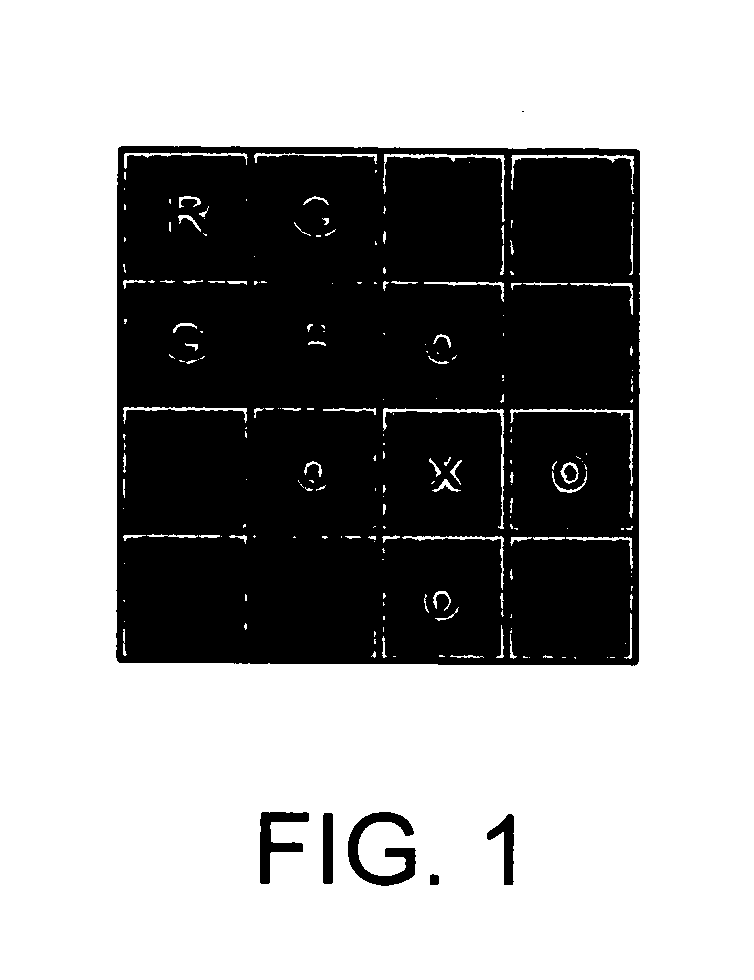
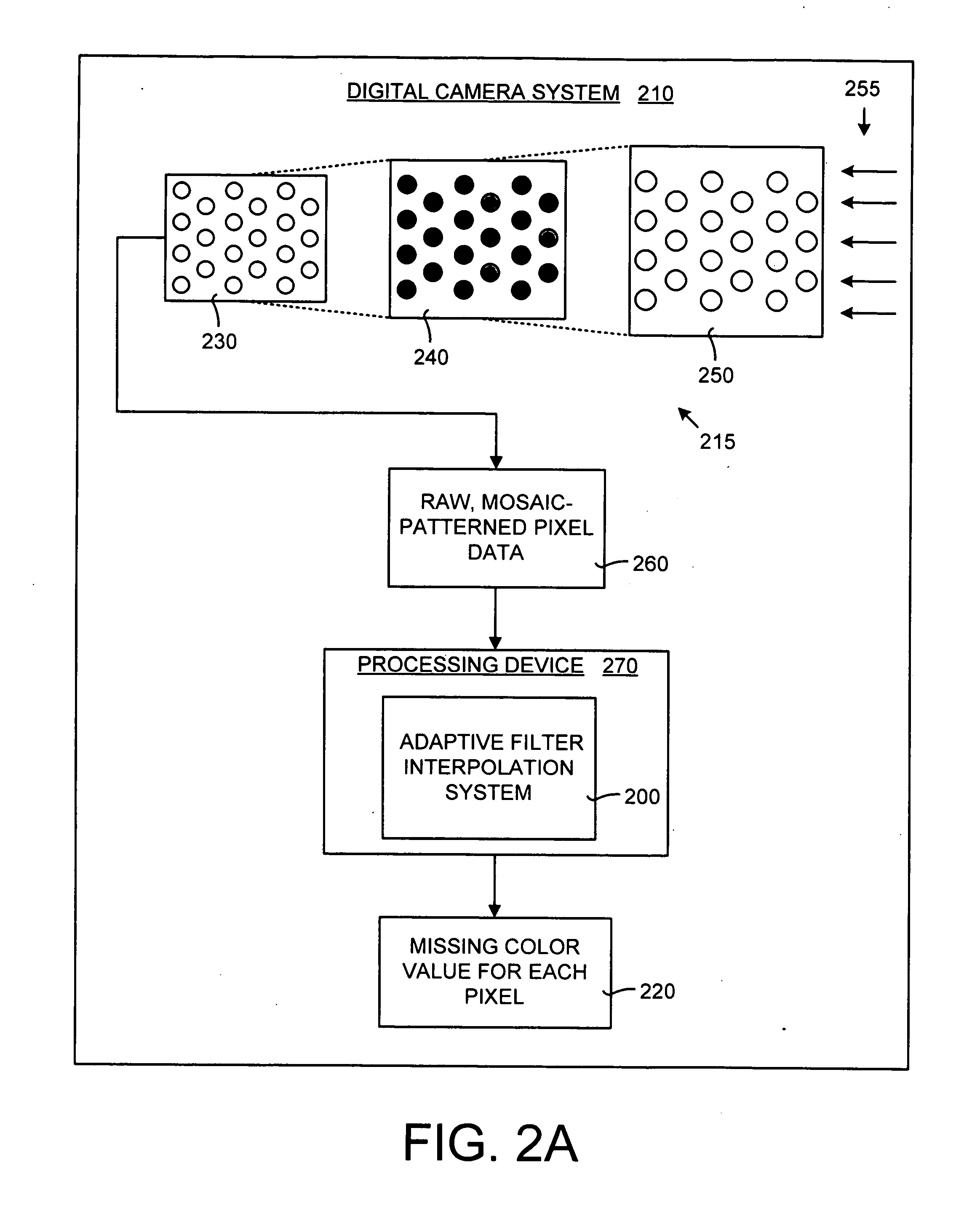
System and method for adaptive interpolation of images from patterned sensors
ActiveUS20050200733A1Computationally efficientImprove image qualityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsColor imageGrating
A adaptive filter interpolation method and system for the demosaicing of color images. In general, input pixels are input in a Bayer-mosaiced pattern (only one color per pixel), and output pixels are in full RGB mode (three color values per pixel). For each pixel location, in raster scan order, the processing steps can be summarized as follows. Following a regular raster scanning order (from left to right and top to bottom), for each pixel location horizontal and vertical gradients are first computed (whose computation depends on the available color for that pixel), and from those the appropriate interpolation filters are chosen from a small set of predetermined filters. Then, the chosen filters are applied to interpolate the missing data.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
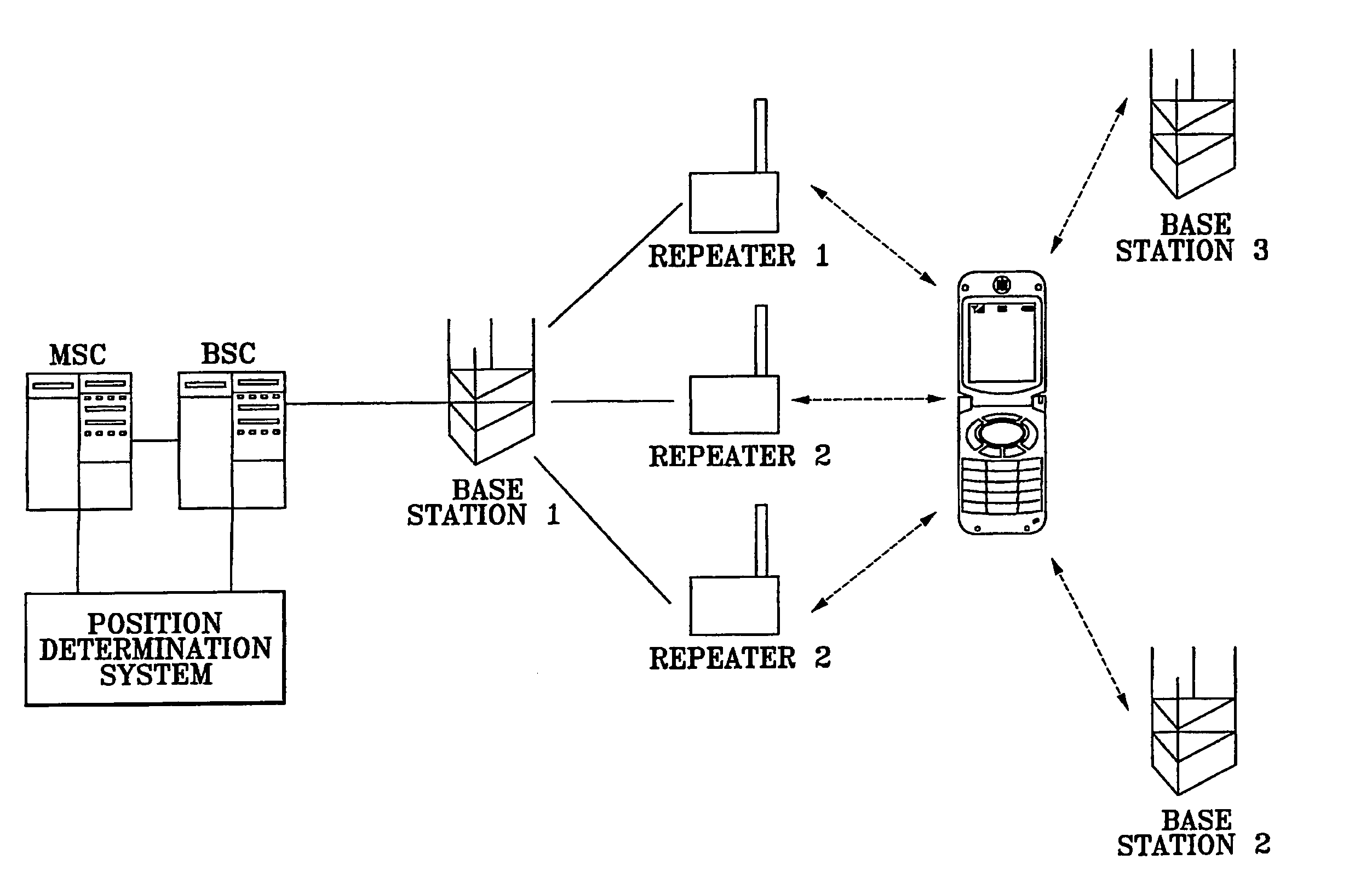
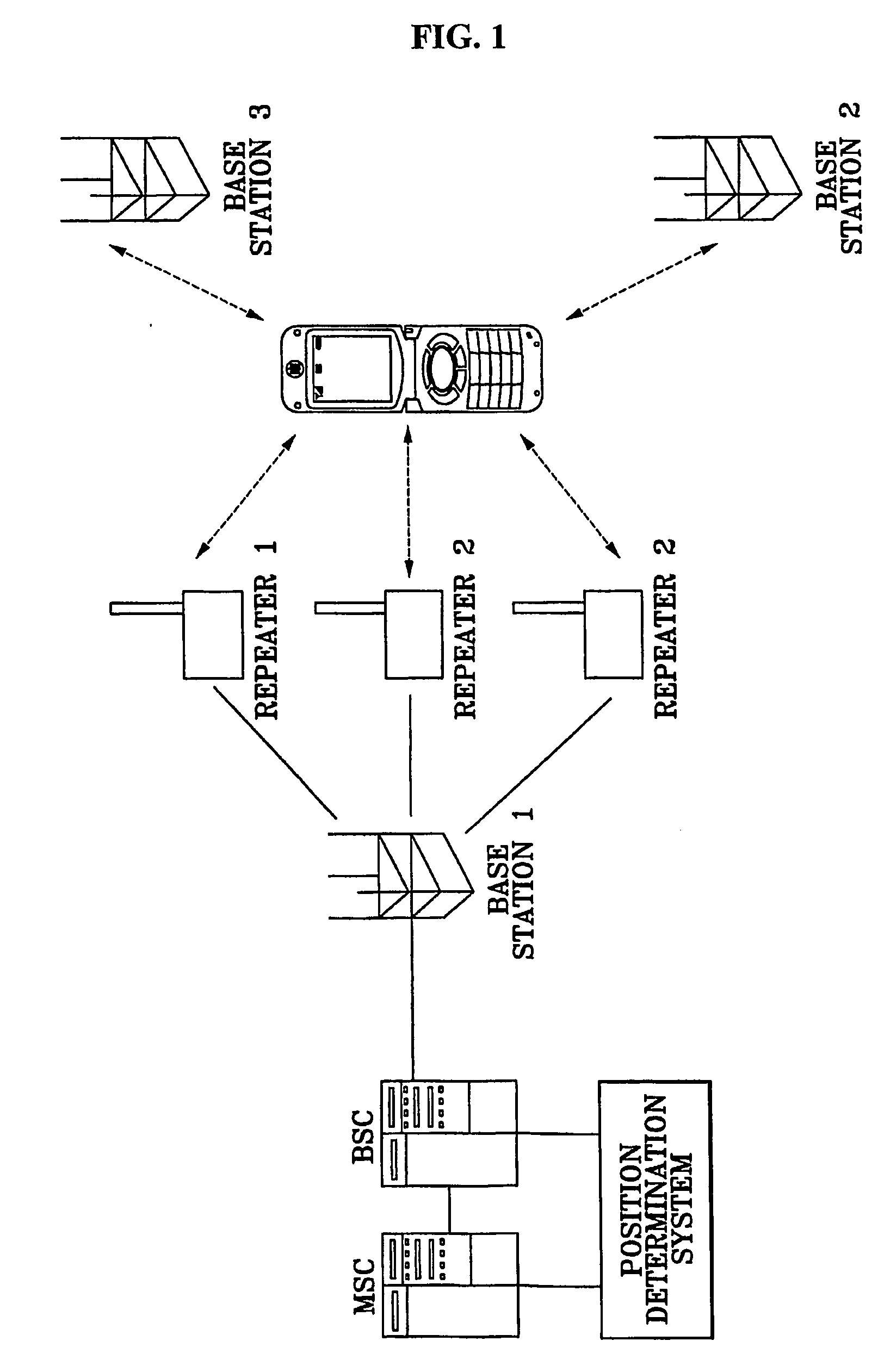
System and method for determining position of mobile communication device by grid-based pattern matching algorithm
InactiveUS20070049286A1Minimize costLow costPosition fixationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsGrid basedMobile communication network
Provided is a method and system for determining a position of a mobile communication device in a mobile communication network, the method including the steps of: dividing an area covered by the mobile communication network into a plurality of grids and collecting a first base station signal information with respect to each of the divided grids; storing and maintaining the collected first base station signal information in association with position information of the grids in a database; measuring a second base station signal information received by the mobile communication device; comparing the second base station signal information with the first base station signal information to find position information corresponding to the second base station signal information in the database; and generating final position information of the mobile communication device based on the position information found in the database.
Owner:RADIANT TECH
Effective multi-class support vector machine classification
ActiveUS7386527B2Easy to handleAccurate understandingDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsFeature vectorAlgorithm
An improved method of classifying examples into multiple categories using a binary support vector machine (SVM) algorithm. In one preferred embodiment, the method includes the following steps: storing a plurality of user-defined categories in a memory of a computer; analyzing a plurality of training examples for each category so as to identify one or more features associated with each category; calculating at least one feature vector for each of the examples; transforming each of the at least one feature vectors so as reflect information about all of the training examples; and building a SVM classifier for each one of the plurality of categories, wherein the process of building a SVM classifier further includes: assigning each of the examples in a first category to a first class and all other examples belonging to other categories to a second class, wherein if any one of the examples belongs to another category as well as the first category, such examples are assigned to the first class only; optimizing at least one tunable parameter of a SVM classifier for the first category, wherein the SVM classifier is trained using the first and second classes; and optimizing a function that converts the output of the binary SVM classifier into a probability of category membership.
Owner:KOFAX
Method and device for wireless communication using MIMO techniques
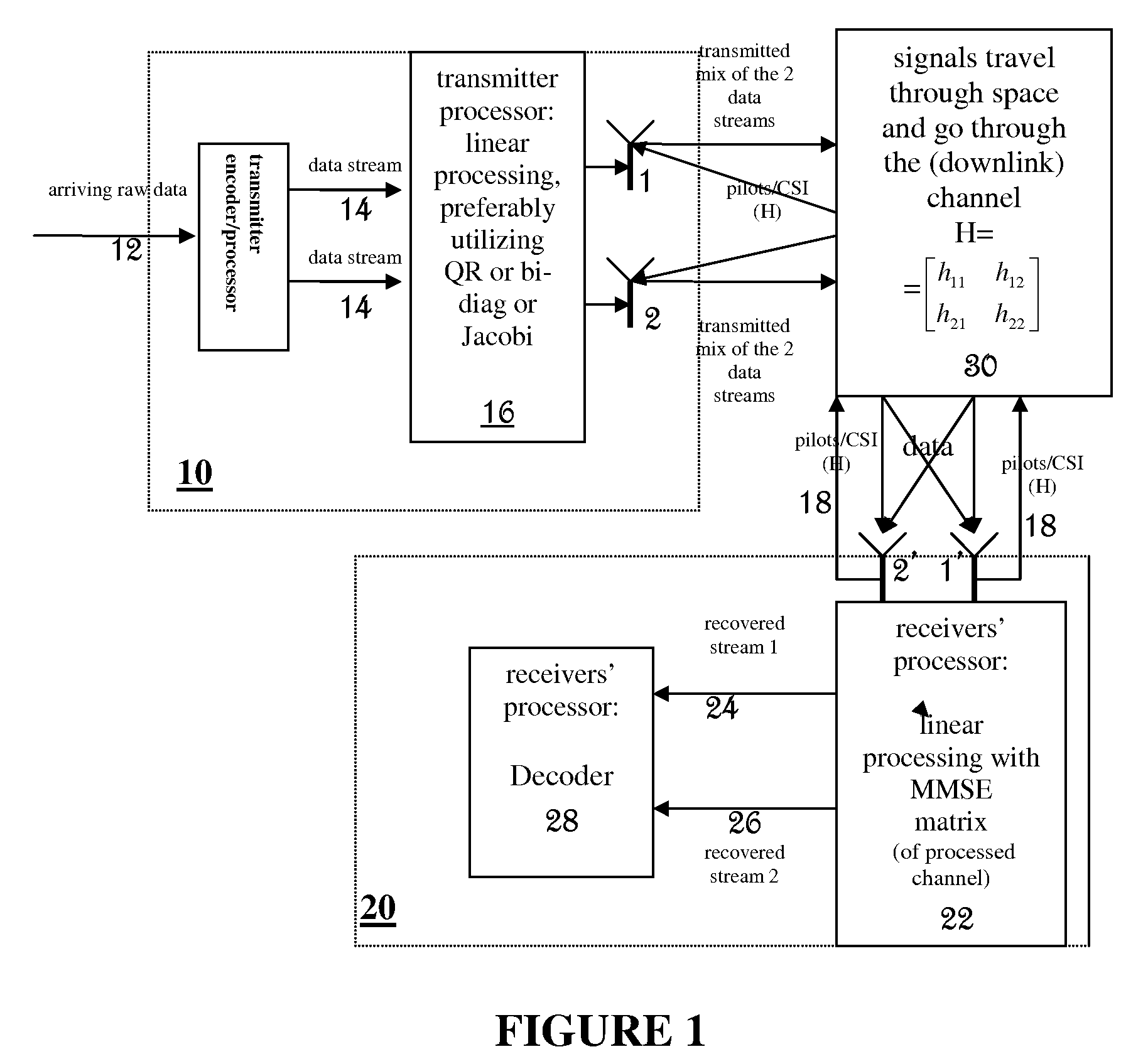
InactiveUS20090143017A1Reduce mutual interferenceExpensive circuitryResonant long antennasRadio transmissionQR decompositionChannel state information
The present invention describes a method of closed loop MIMO communication utilizing implicit or explicit channel state information (CSI) at the transmitter and the receiver. The transmitter performs linear pre-processing (for example, QR decomposition or bi-diagonal decomposition or Jacobi rotations, and / or sporadic SVDs) on a channel matrix, and the receiver mitigates the mutual interference between the streams by performing MMSE processing on the received signals. The MMSE matrix is computed with respect to the processed channel that may estimated by the receiver through preprocessed pilot signals. The transmitters preprocessing is of much lesser cost and complexity than full SVD.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
System and method for finding the direction of a wave source using an array of sensors
InactiveUS6198693B1Computationally efficientRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsPosition fixationSensor arrayClassical mechanics
A system and method for finding the direction of a wave source using an array of sensors. The system includes a sensor array for measuring waves from the wave source, an approximate-direction finder for finding the approximate direction of the wave source in terms of a sensor pair from the sensors, a precise-direction finder for finding the precise direction of the wave source based on the approximate direction found, and a measurement qualification unit for evaluating the validity of the precise direction under a measurement criterion and discarding the measurements if the criterion is not met.
Owner:ANDREA ELECTRONICS CORPORATION
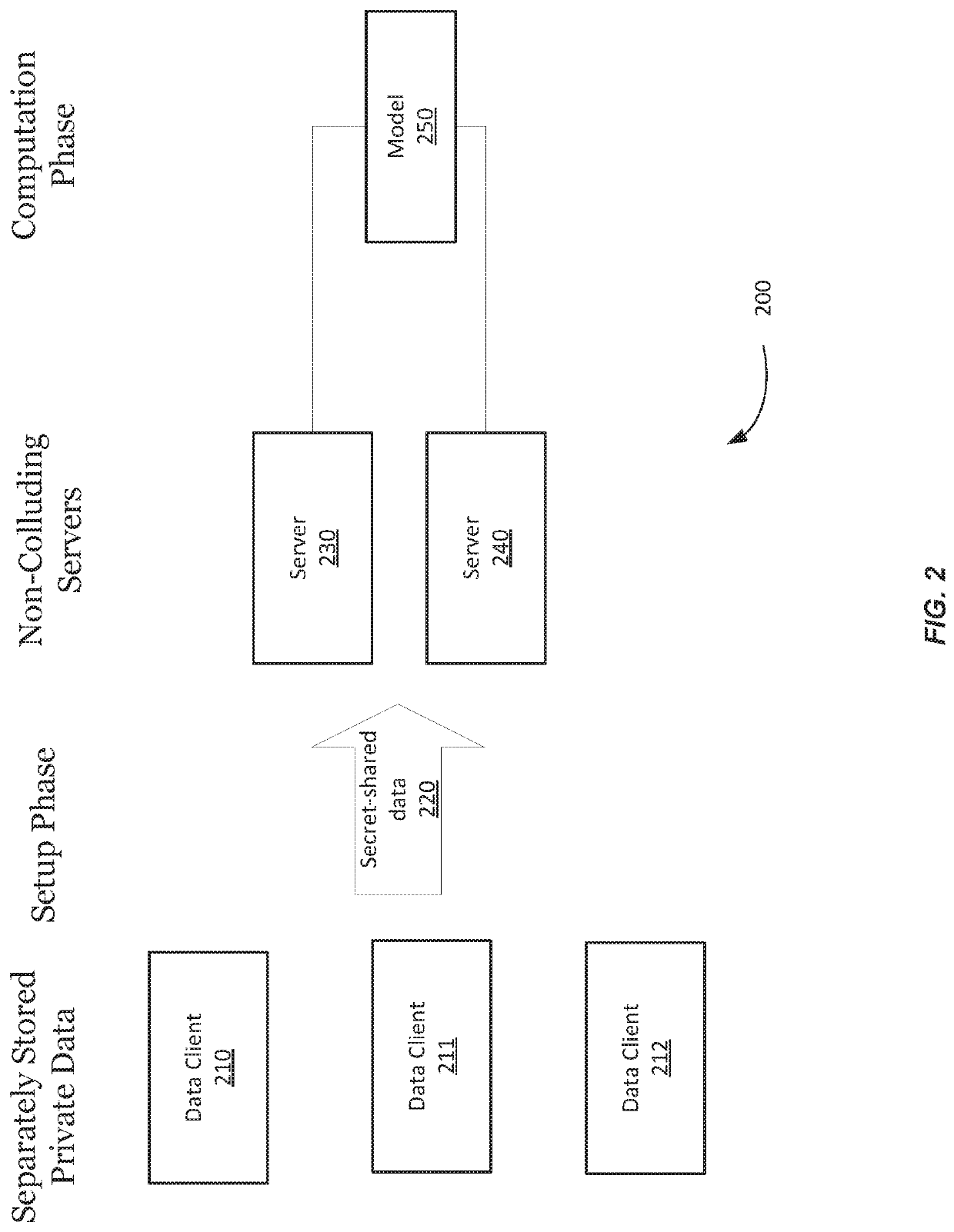
Privacy-preserving machine learning
ActiveUS20200242466A1Efficiently determinedLimited amount of memoryKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data protectionStochastic gradient descentAlgorithm
New and efficient protocols are provided for privacy-preserving machine learning training (e.g., for linear regression, logistic regression and neural network using the stochastic gradient descent method). A protocols can use the two-server model, where data owners distribute their private data among two non-colluding servers, which train various models on the joint data using secure two-party computation (2PC). New techniques support secure arithmetic operations on shared decimal numbers, and propose MPC-friendly alternatives to non-linear functions, such as sigmoid and softmax.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
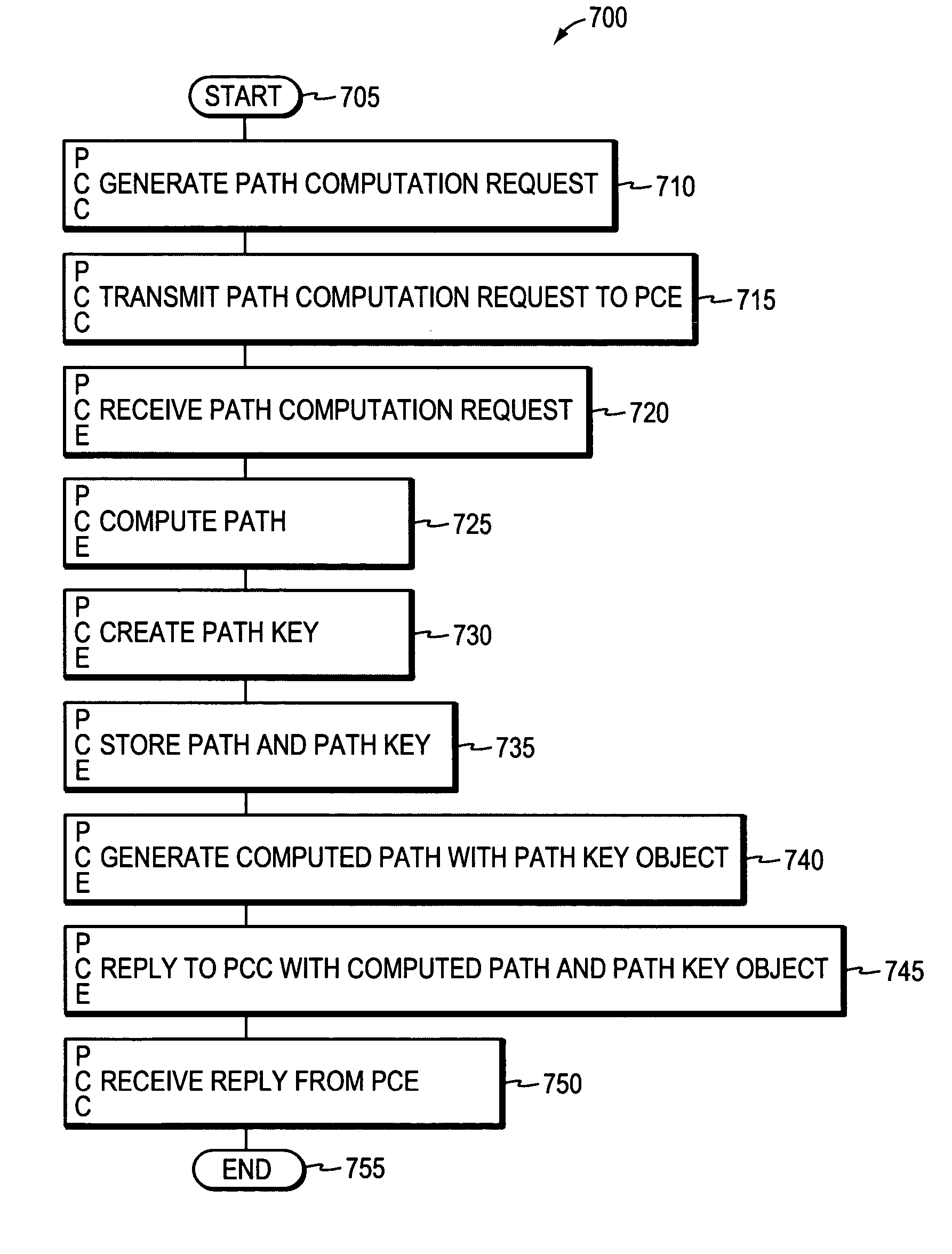
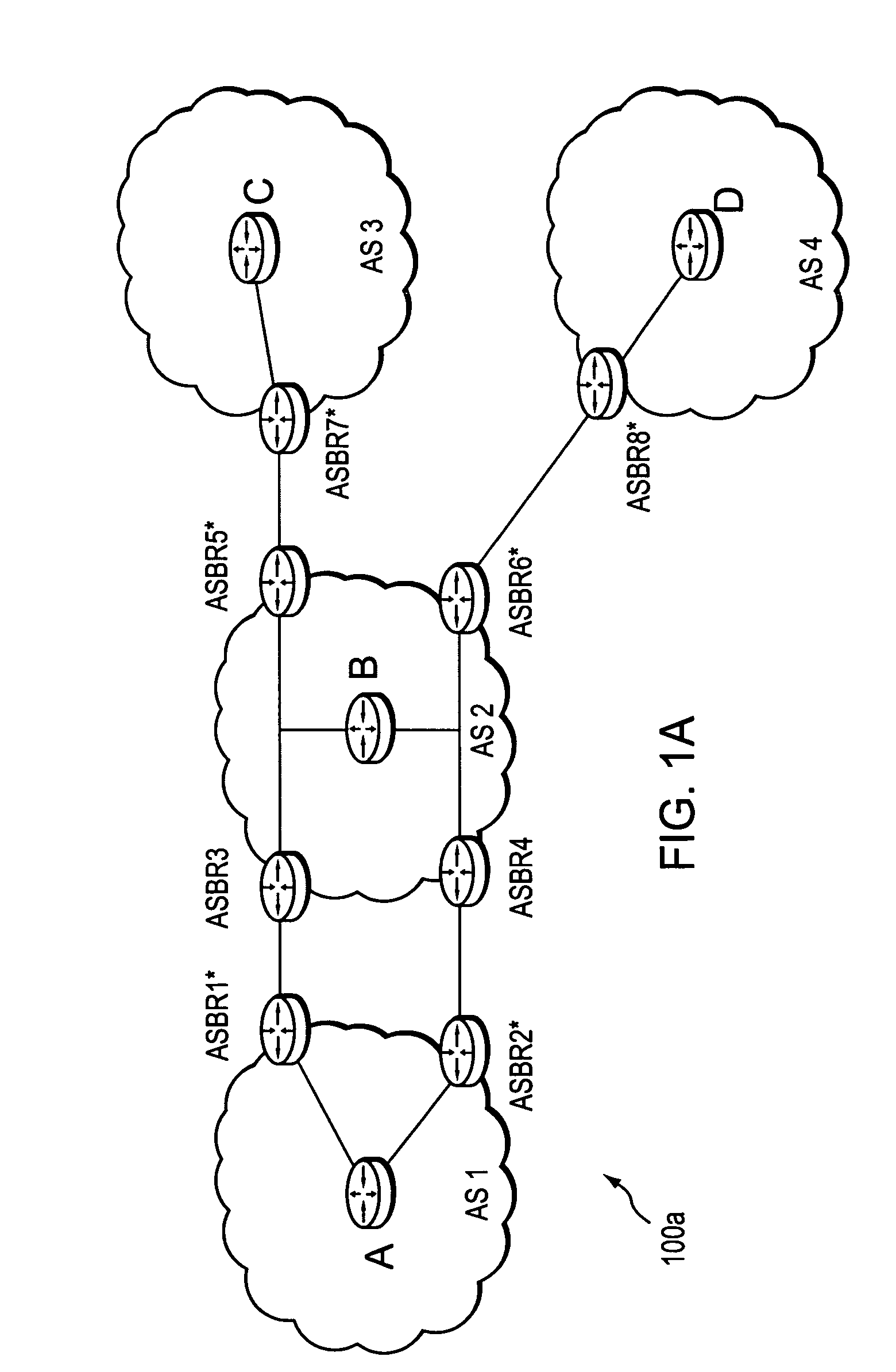
System and method for retrieving computed paths from a path computation element using a path key
ActiveUS20060098657A1Computationally efficientPreserving confidentialityError preventionTransmission systemsTime segmentPath computation element
A technique retrieves computed path segments across one or more domains of a computer network in accordance with a stateful (“semi-stateful”) path computation element (PCE) model. The stateful PCE model includes a data structure configured to store one or more path segments computed by a PCE in response to a path computation request issued by a Path Computation Client (PCC). Notably, each computed path segment stored in the data structure is identified by an associated path-key value (“path key”). The path segment and path key contents of the data structure are temporarily saved (“cached”) at a predetermined location in the network for a configurable period of time.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com