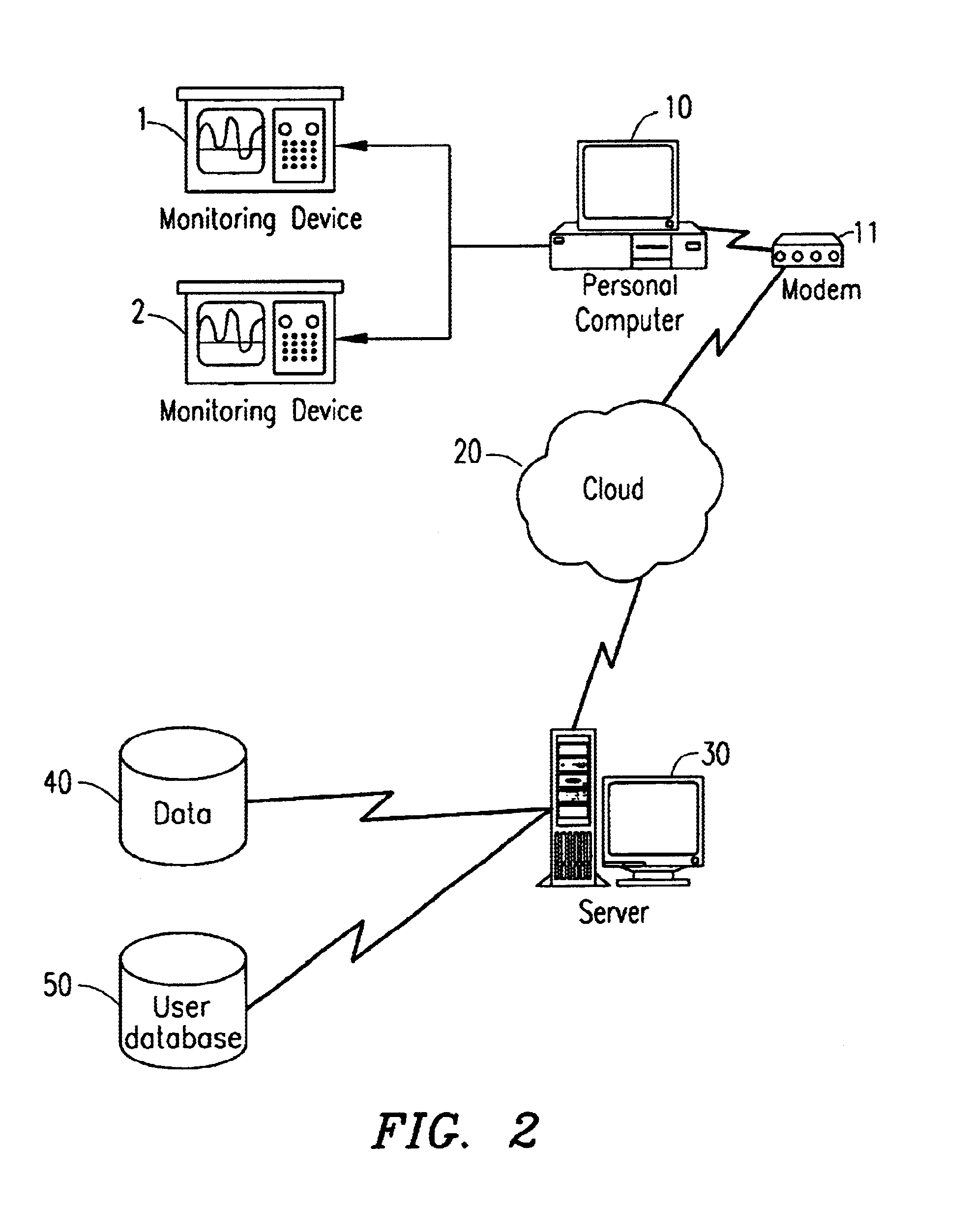
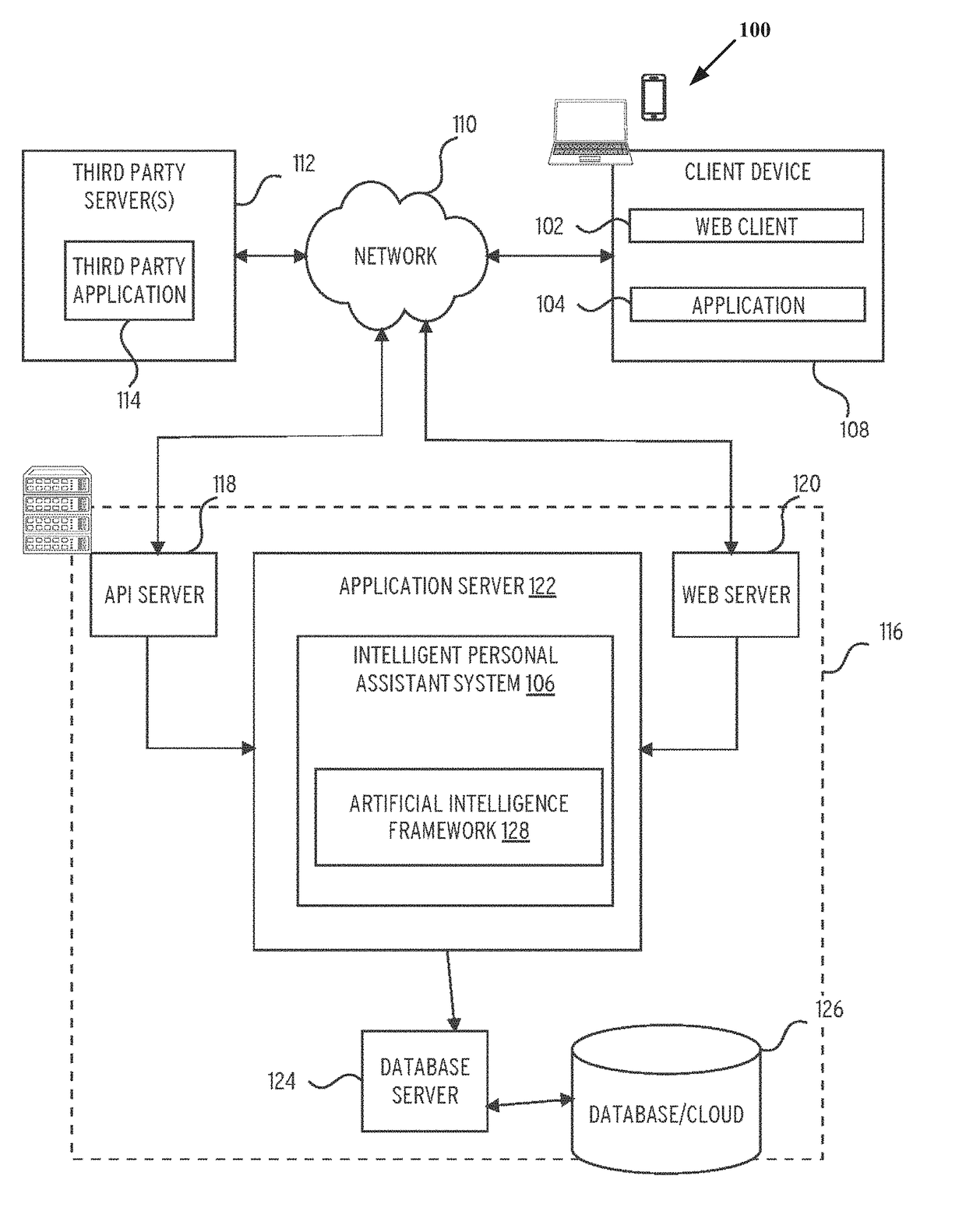
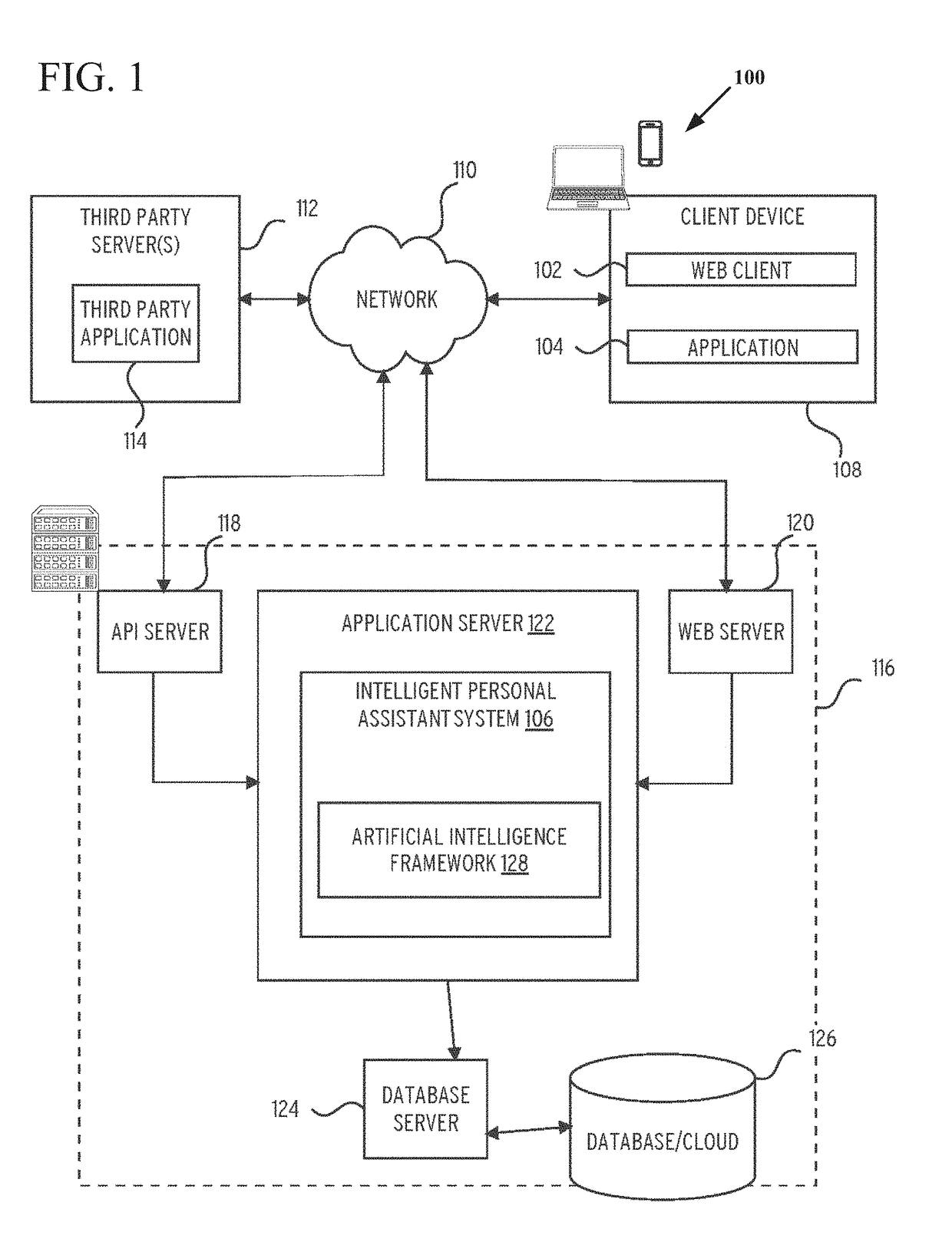
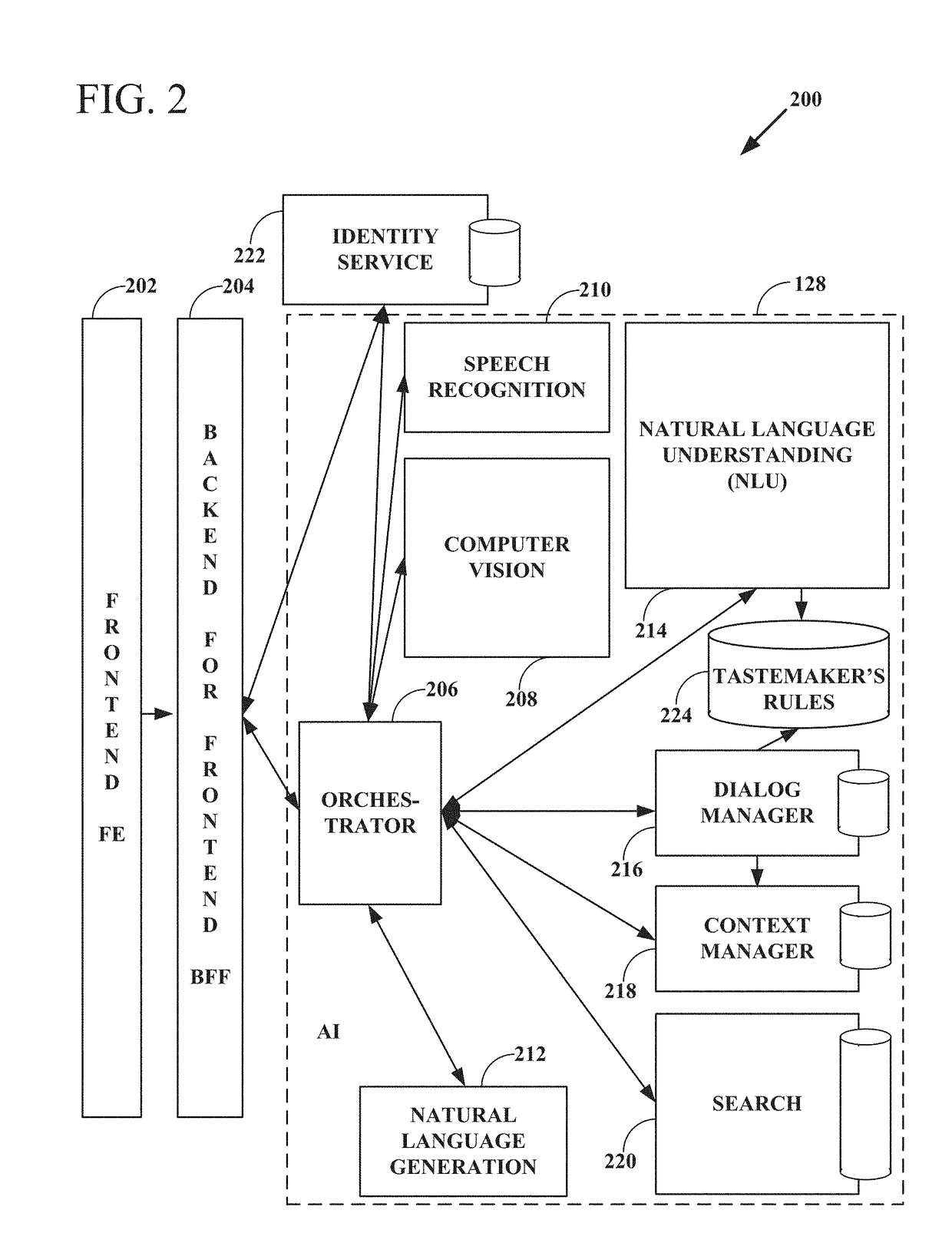
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
649 results about "Conditional probability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In probability theory, conditional probability is a measure of the probability of an event occurring given that another event has (by assumption, presumption, assertion or evidence) occurred. If the event of interest is A and the event B is known or assumed to have occurred, "the conditional probability of A given B", or "the probability of A under the condition B", is usually written as P(A | B), or sometimes PB(A) or P(A / B). For example, the probability that any given person has a cough on any given day may be only 5%. But if we know or assume that the person has a cold, then they are much more likely to be coughing. The conditional probability of coughing by the unwell might be 75%, then: P(Cough) = 5%; P(Cough | Sick) = 75%
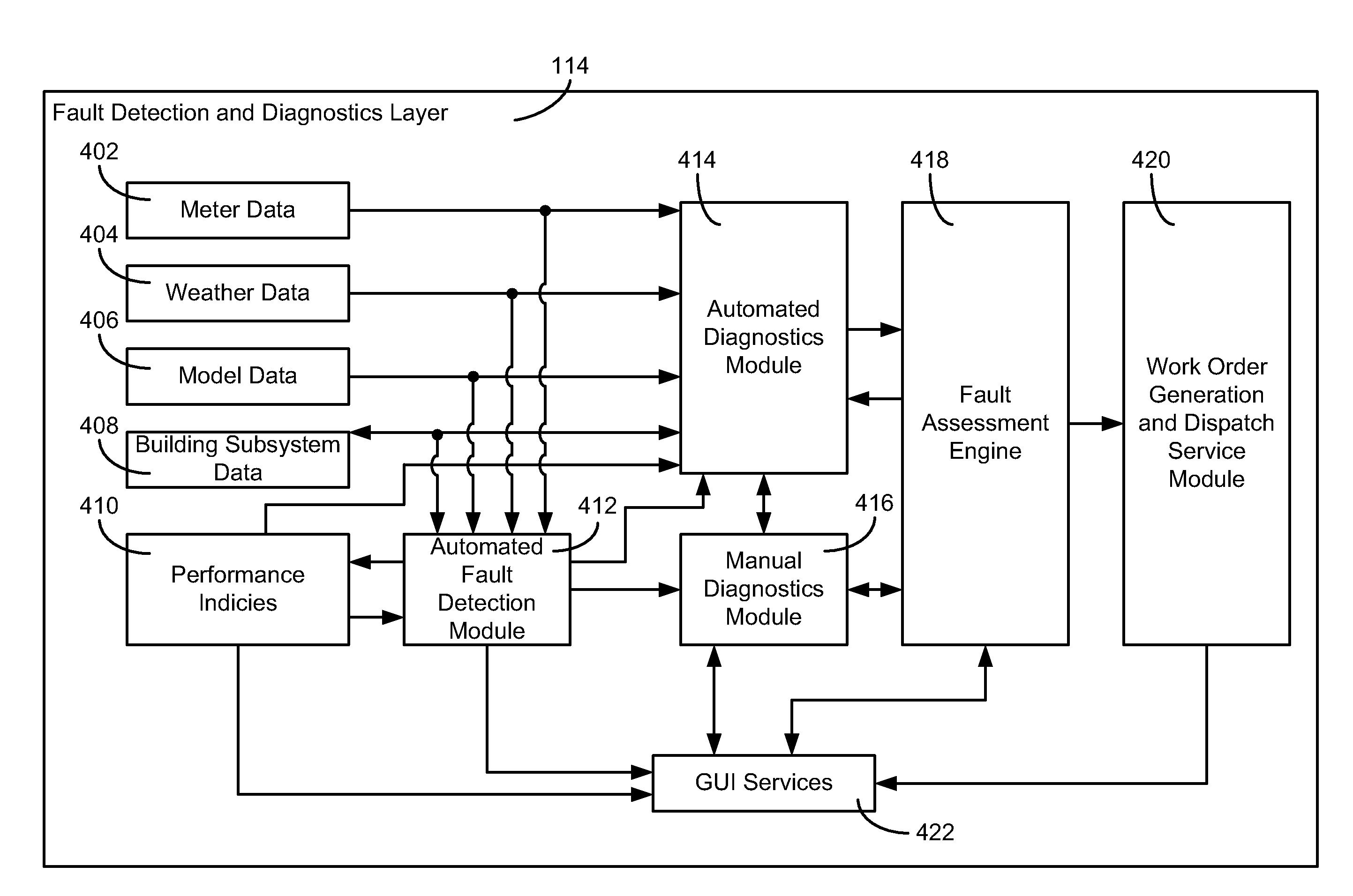
Building management system with fault analysis
ActiveUS20110178977A1Enhance data loggingTechnology managementFuzzy logic based systemsEngineeringFault analysis
Owner:JOHNSON CONTROLS TECH CO
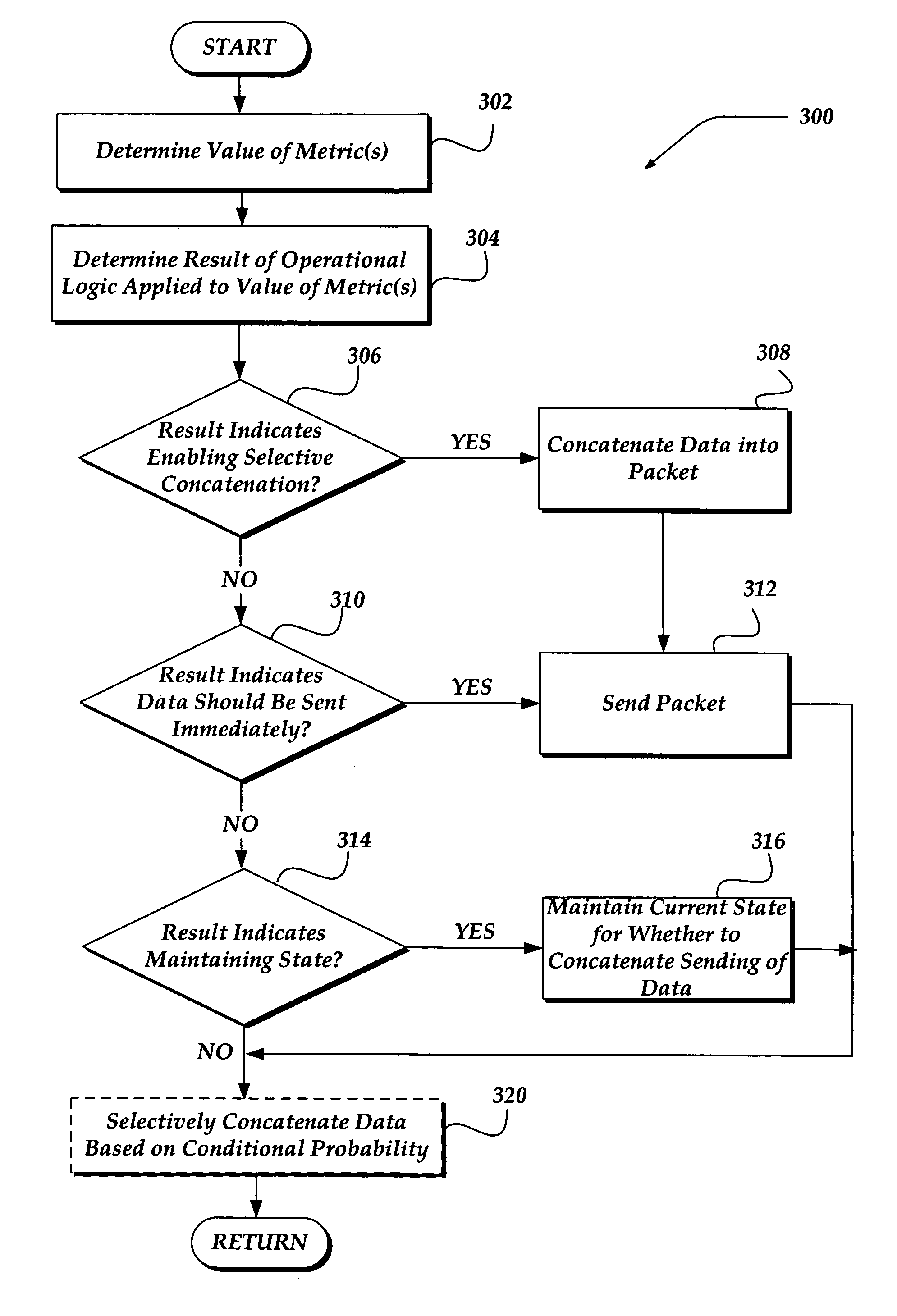
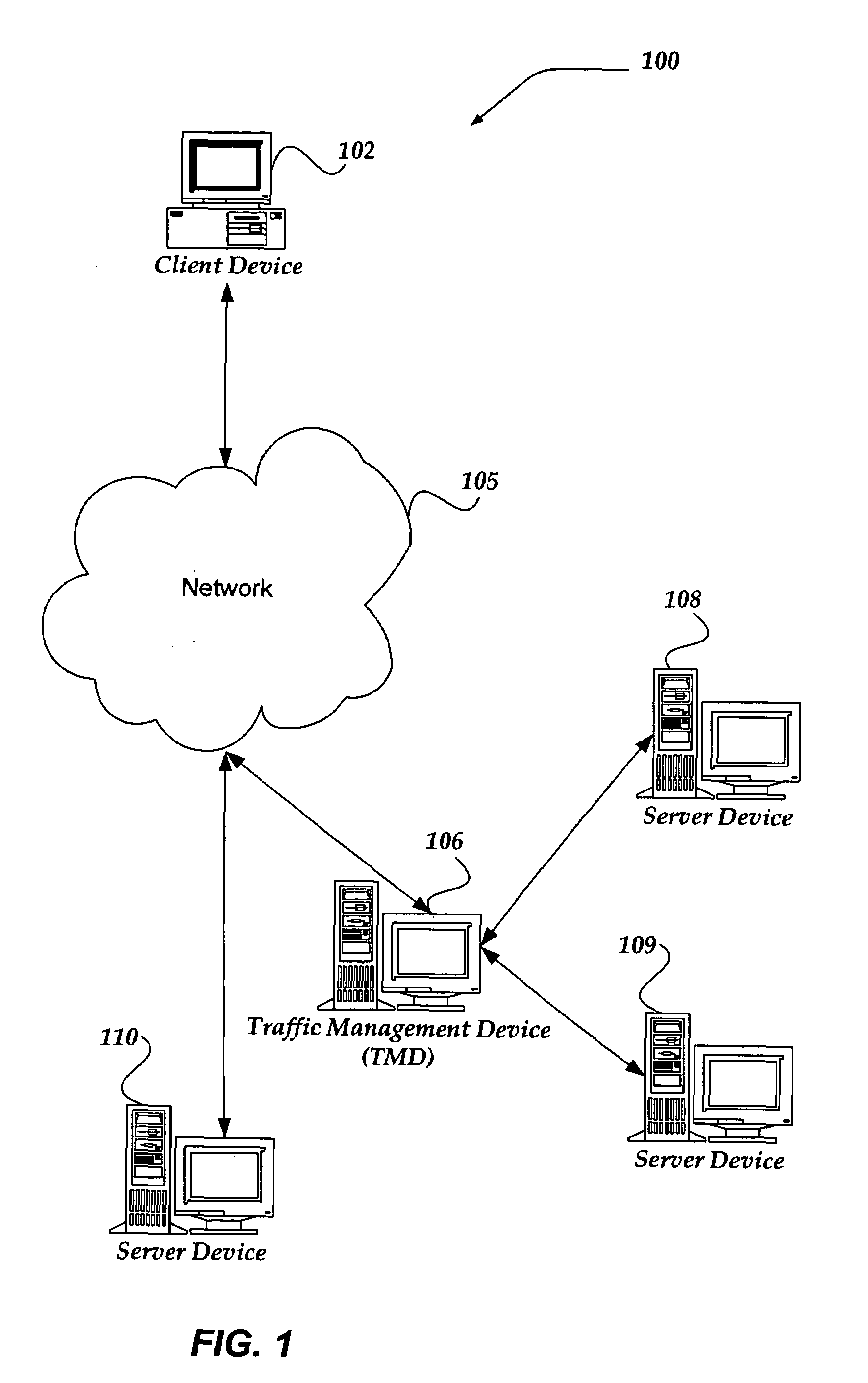
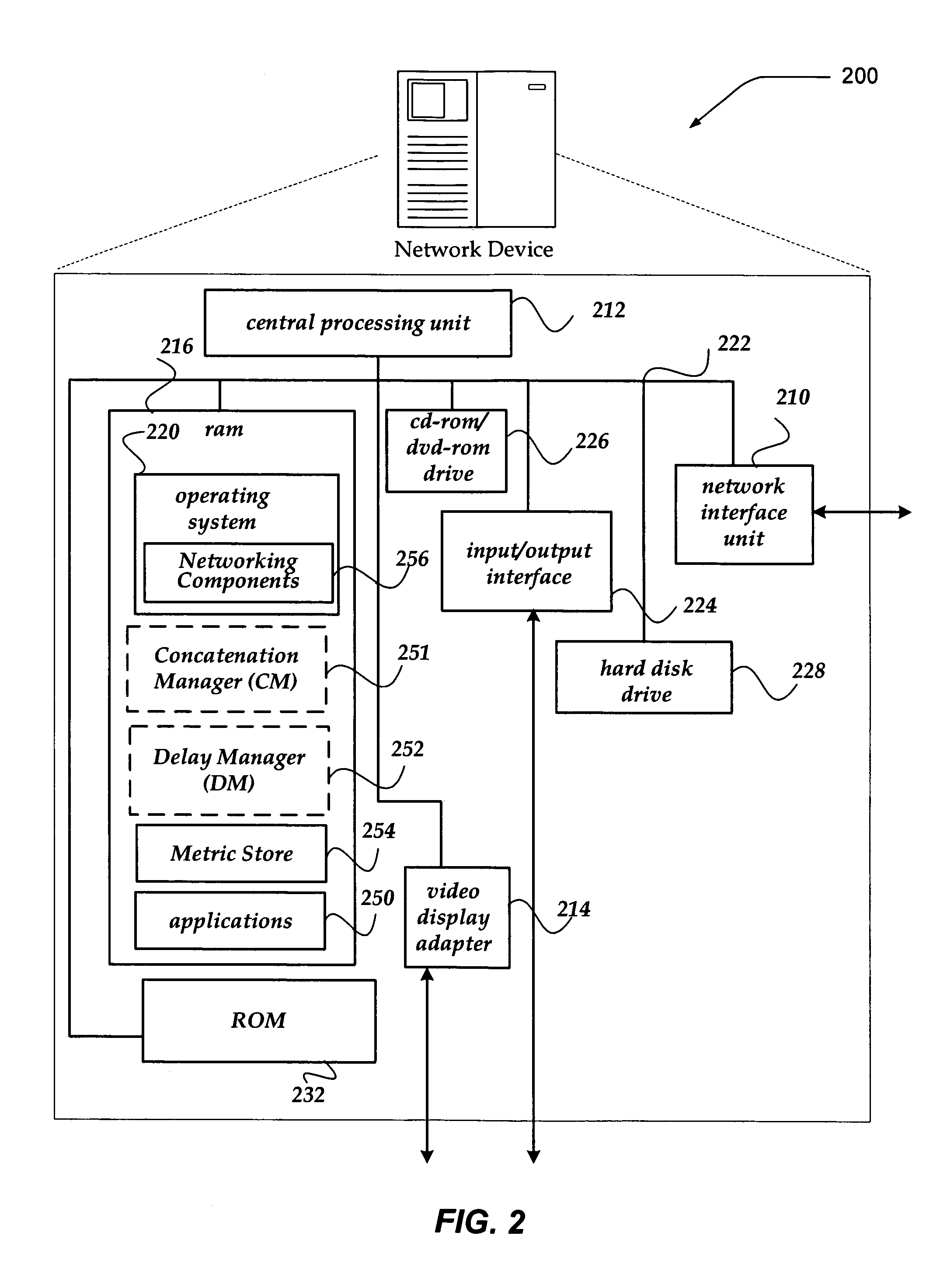
Selectively enabling network packet concatenation based on metrics
InactiveUS7873065B1Data switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsData connectionNetwork packet
A method, system, and apparatus are directed towards selectively concatenating data into a packet to modify a number of packets transmitted over a network based on a combination of network and / or send-queue metrics. In one embodiment, Nagle's algorithm is used for concatenating data into a packet. The concatenation may be selectively enabled based on heuristics applied to the combination of metrics. In one embodiment, the result may indicate that there should be a concatenation, or that data should be sent immediately, or that a current state for whether to concatenate or not should be maintained. The heuristics may include an expert system, decision tree, truth table, function, or the like. The heuristics may be provided by a user, or another computing device. In another embodiment, the concatenation may be enabled based on a conditional probability determined from the combination of metrics.
Owner:F5 NETWORKS INC
Automated medical decision making utilizing bayesian network knowledge domain modeling
InactiveUS6687685B1Reliable and statistically sound and convenient methodEasy to manageBiological neural network modelsComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionTriageMedical knowledge
The present invention relates to a system and method of medical knowledge domain modeling and automated medical decision-making, such as for online, questionnaire-based medical triage. In the present invention, information such as conditions and characteristics related to a diagnosis or disposition level is modeled in a Bayesian Network. The Bayesian Network may comprise instantiable nodes, fault nodes, intermediary nodes, a utility node and a decision node. Using Bayesian inference, the conditional probability of any pair in the network may be determined in real-time. These conditional probabilities are modified upon the input of evidence, which is typically in the form of answers to a dynamic set of questions designed to identify a diagnosis or disposition level for the patient under evaluation.
Owner:DR RED DUKE
Knowledge Discovery Agent System and Method
ActiveUS20070203693A1Maximizes rangeFacilitate communicationWeb data indexingNatural language data processingUnstructured dataConditional probability
A system and method for processing information in unstructured or structured form, comprising a computer running in a distributed network with one or more data agents. Associations of natural language artifacts may be learned from natural language artifacts in unstructured data sources, and semantic and syntactic relationships may be learned in structured data sources, using grouping based on a criteria of shared features that are dynamically determined without the use of a priori classifications, by employing conditional probability constraints.
Owner:DIGITAL REASONING SYST
Knowledge discovery agent system and method
ActiveUS7249117B2Facilitate communicationMaximizes rangeChaos modelsNon-linear system modelsUnstructured dataConditional probability
A system and method for processing information in unstructured or structured form, comprising a computer running in a distributed network with one or more data agents. Associations of natural language artifacts may be learned from natural language artifacts in unstructured data sources, and semantic and syntactic relationships may be learned in structured data sources, using grouping based on a criteria of shared features that are dynamically determined without the use of a priori classifications, by employing conditional probability constraints.
Owner:DIGITAL REASONING SYST
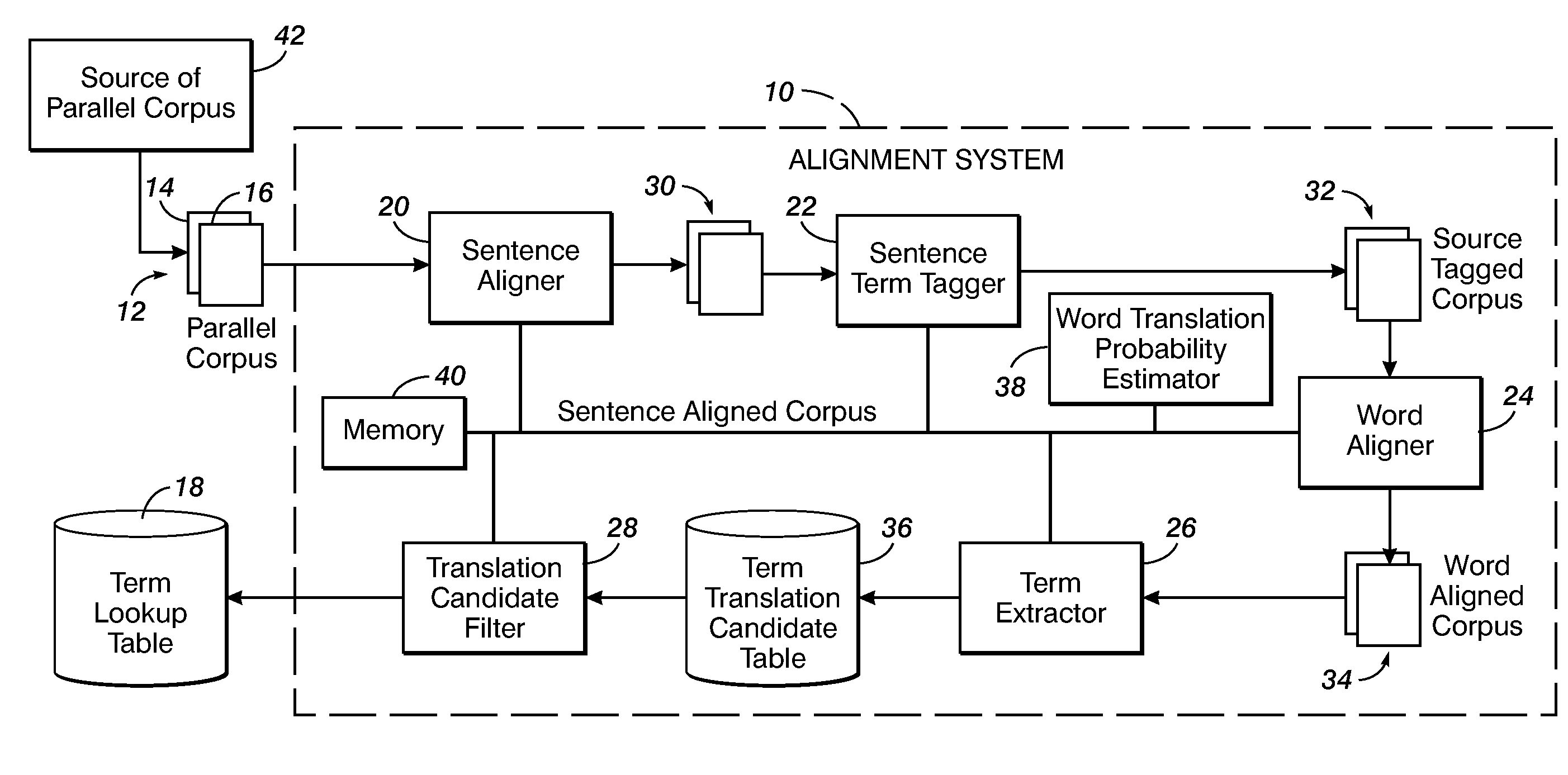
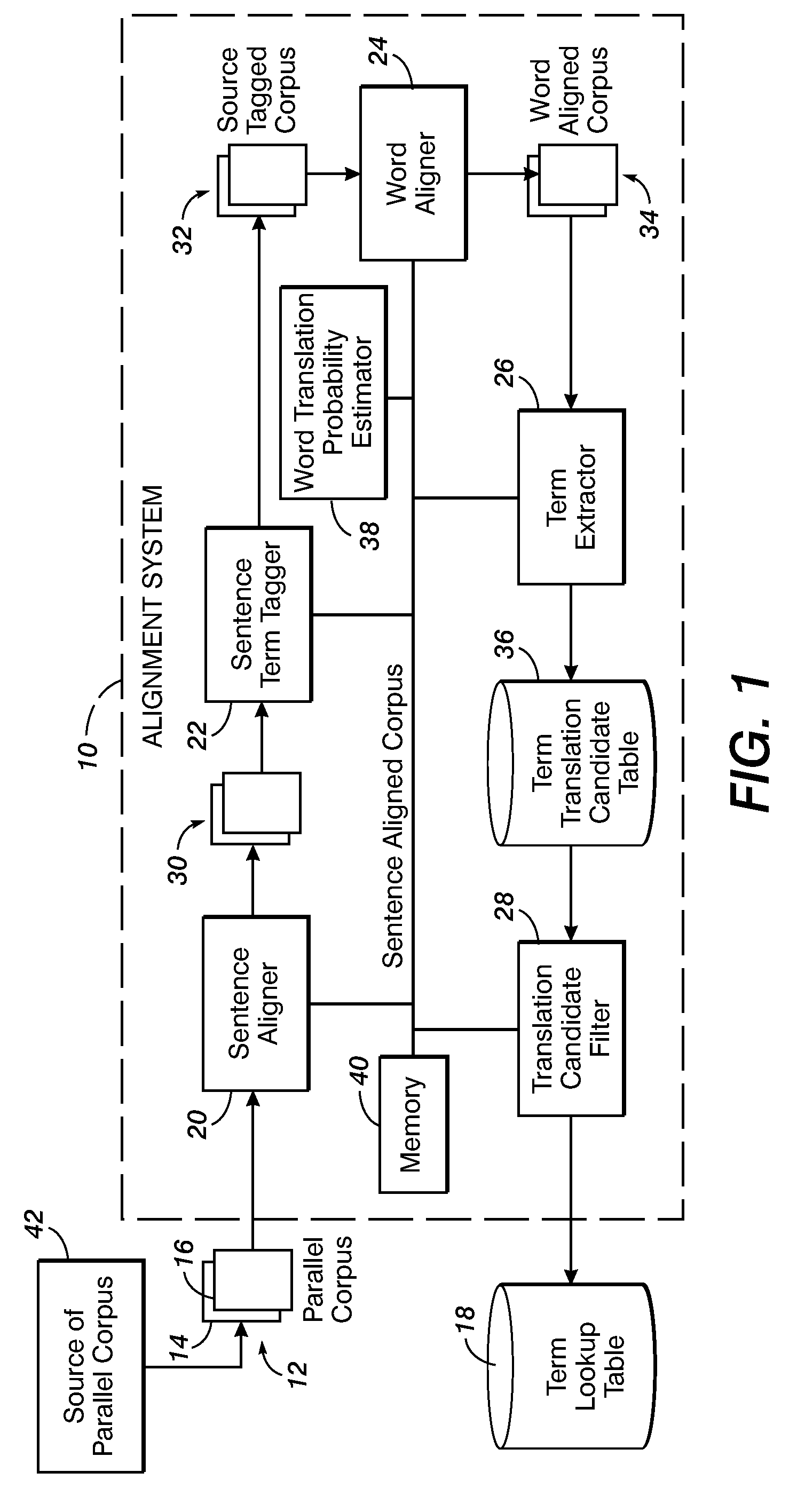
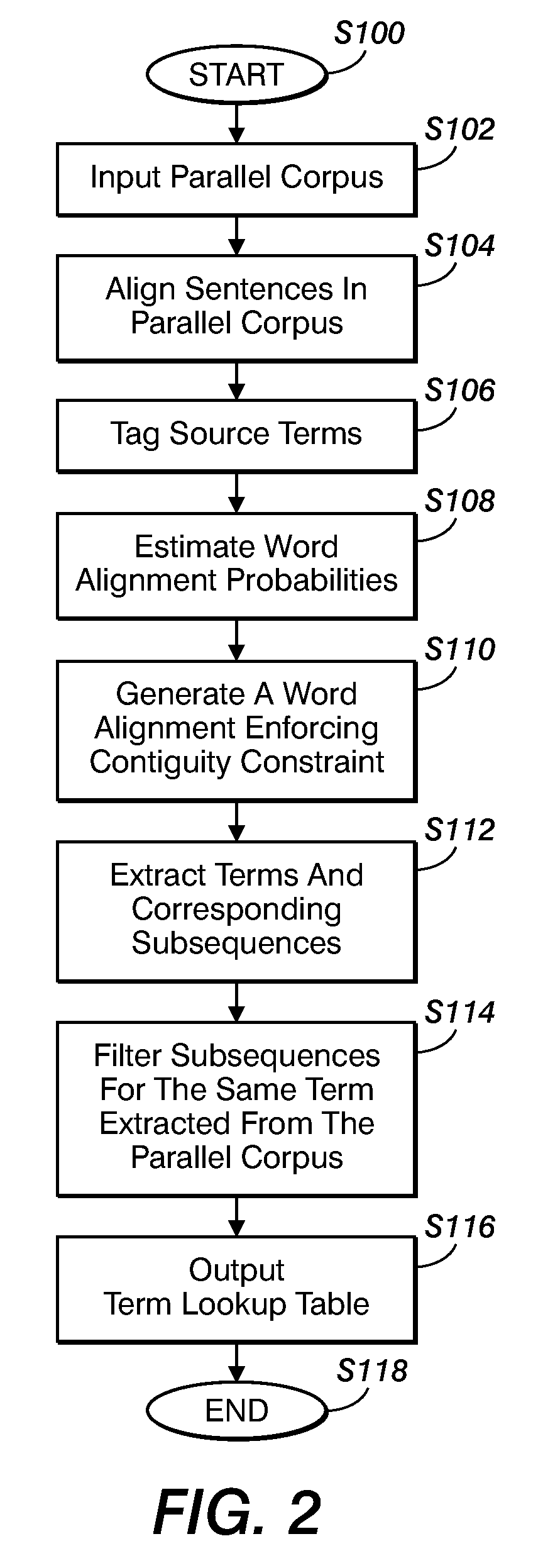
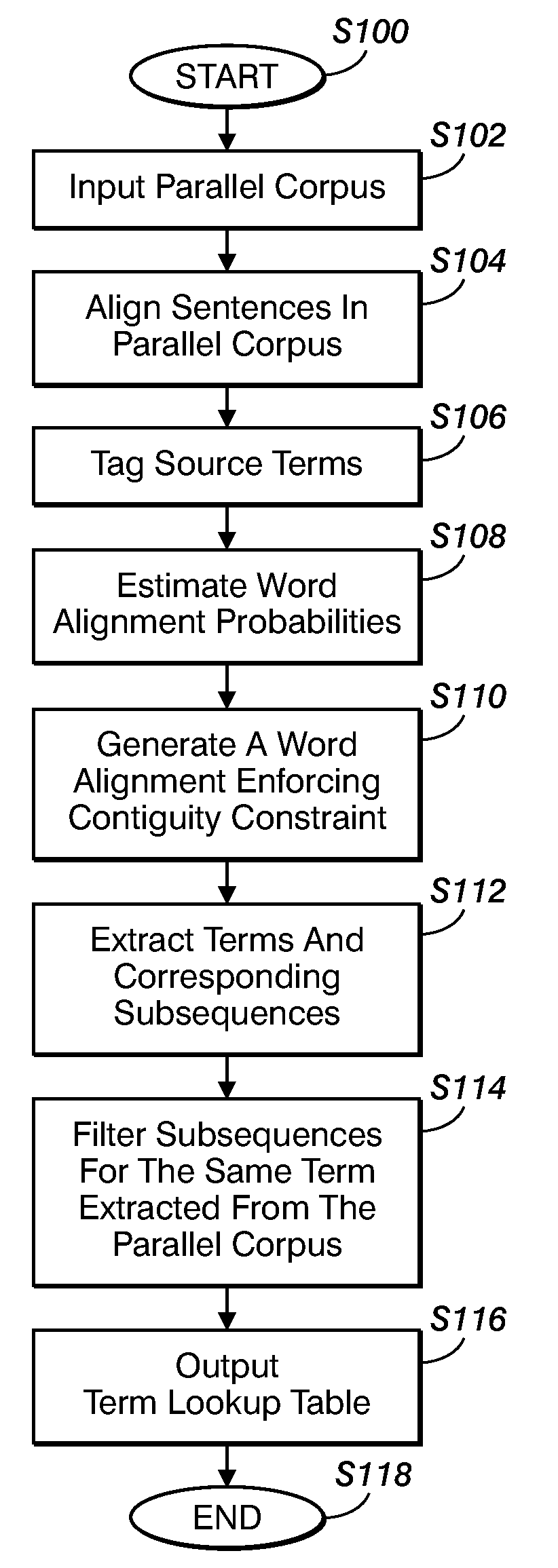
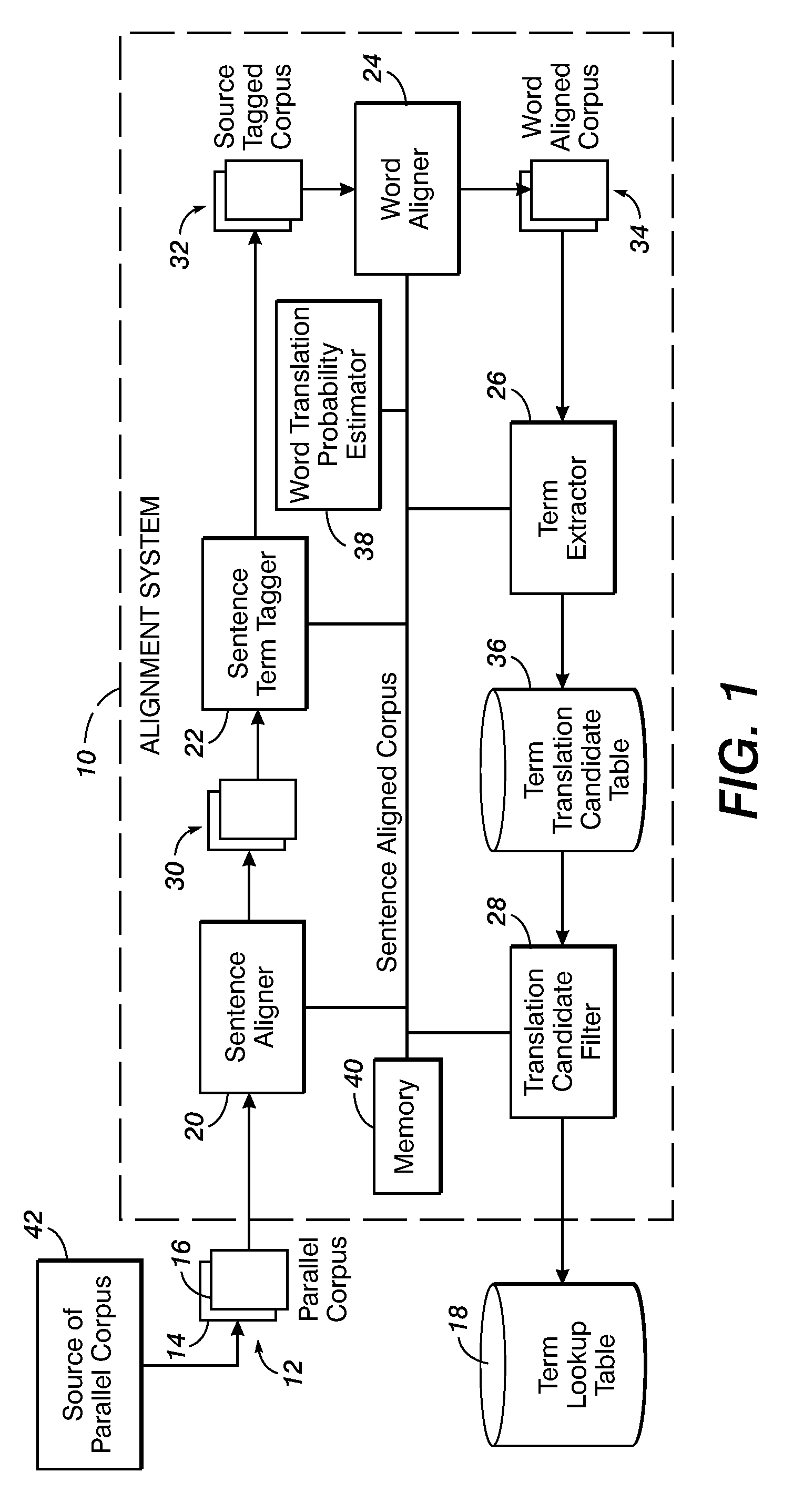
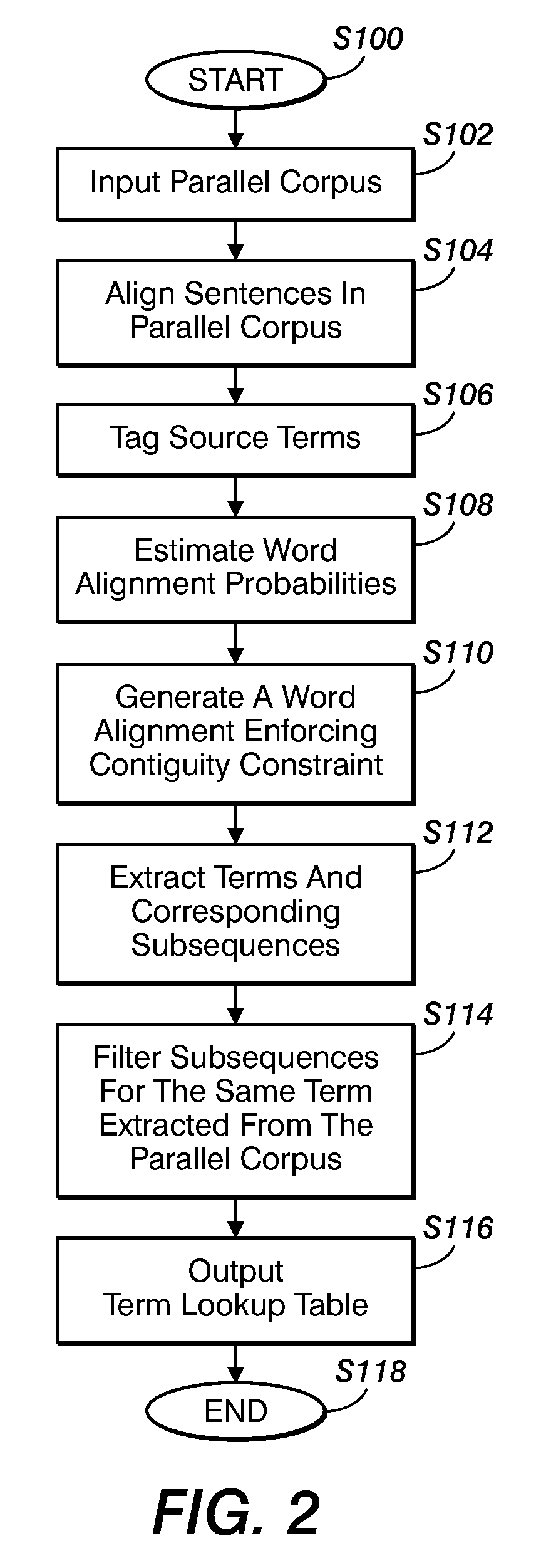
Method for aligning sentences at the word level enforcing selective contiguity constraints
InactiveUS9020804B2Natural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsProbit modelConditional probability
An alignment method includes, for a source sentence in a source language, identifying whether the sentence includes at least one candidate term comprising a contiguous subsequence of words of the source sentence. A target sentence in a target language is aligned with the source sentence. This includes developing a probabilistic model which models conditional probability distributions for alignments between words of the source sentence and words of the target sentence and generating an optimal alignment based on the probabilistic model, including, where the source sentence includes the at least one candidate term, enforcing a contiguity constraint which requires that all the words of the target sentence which are aligned with an identified candidate term form a contiguous subsequence of the target sentence.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Proactive on-line diagnostics in a manageable network
InactiveUS7113988B2Small sizeWithout costsDigital computer detailsData switching networksConditional probabilityReliability engineering
A method for diagnosis of a system made up of a plurality of interlinked modules includes receiving an alarm from the system indicative of a fault in one of the modules. Responsive to the alarm, a causal network is constructed associating the fault with malfunctions in one or more of the modules that may have led to the fault and relating a conditional probability of the fault to respective probabilities of the malfunctions. Based on the alarm and the causal network, at least one of the probabilities of the malfunctions is updated. A diagnosis of the alarm is proposed responsive to the updated probabilities.
Owner:LINKEDIN
Stacked generalization learning for document annotation
A document annotation method includes modeling data elements of an input document and dependencies between the data elements as a dependency network. Static features of at least some of the data elements are defined, each expressing a relationship between a characteristic of the data element and its label. Dynamic features are defined which define links between an element and labels of the element and of a second element. Parameters of a collective probabilistic model for the document are learned, each expressing a conditional probability that a first data element should be labeled with information derived from a label of a neighbor data element linked to the first data element by a dynamic feature. The learning includes decomposing a globally trained model into a set of local learning models. The local learning models each employ static features to generate estimations of the neighbor element labels for at least one of the data elements.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method for aligning sentences at the word level enforcing selective contiguity constraints
InactiveUS20080300857A1Natural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsProbit modelConditional probability
An alignment method includes, for a source sentence in a source language, identifying whether the sentence includes at least one candidate term comprising a contiguous subsequence of words of the source sentence. A target sentence in a target language is aligned with the source sentence. This includes developing a probabilistic model which models conditional probability distributions for alignments between words of the source sentence and words of the target sentence and generating an optimal alignment based on the probabilistic model, including, where the source sentence includes the at least one candidate term, enforcing a contiguity constraint which requires that all the words of the target sentence which are aligned with an identified candidate term form a contiguous subsequence of the target sentence.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Provision of data for analysis
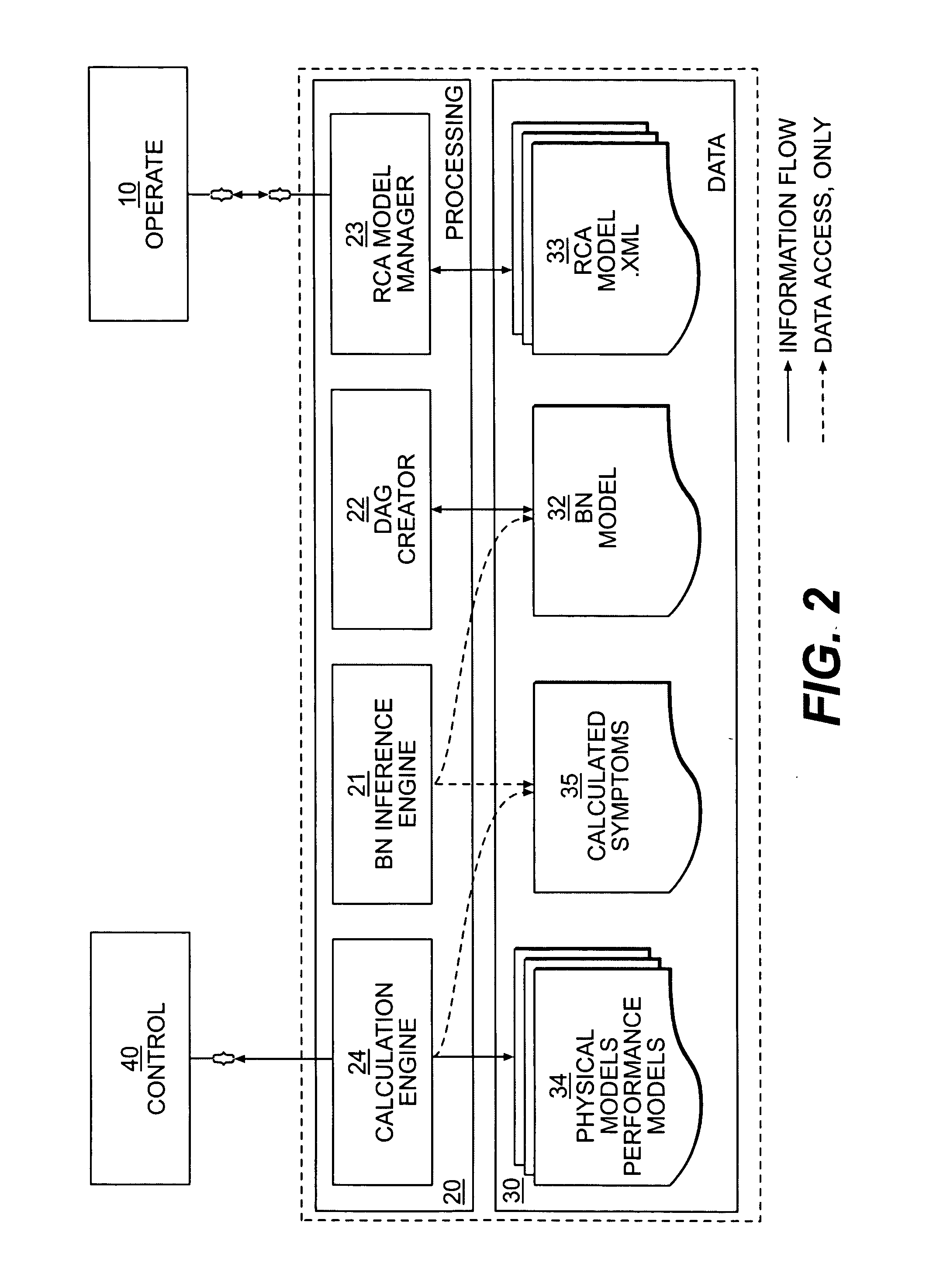
InactiveUS20050049988A1Fast operator guidanceQuick and flexible supportElectric testing/monitoringGeneral purpose stored program computerAnalysis dataRoot cause analysis
A method of providing data for root cause analysis. Data is transferred from a structured data model into a causally oriented data model. The causally oriented data model is complemented with information associated with conditional probabilities between at least two objects of the causally oriented data model.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Method and system for determining user location in a wireless communication network
InactiveUS20050243936A1Maximize probabilityAccurate measurementData switching by path configurationSatellite radio beaconingProbit modelRadio map
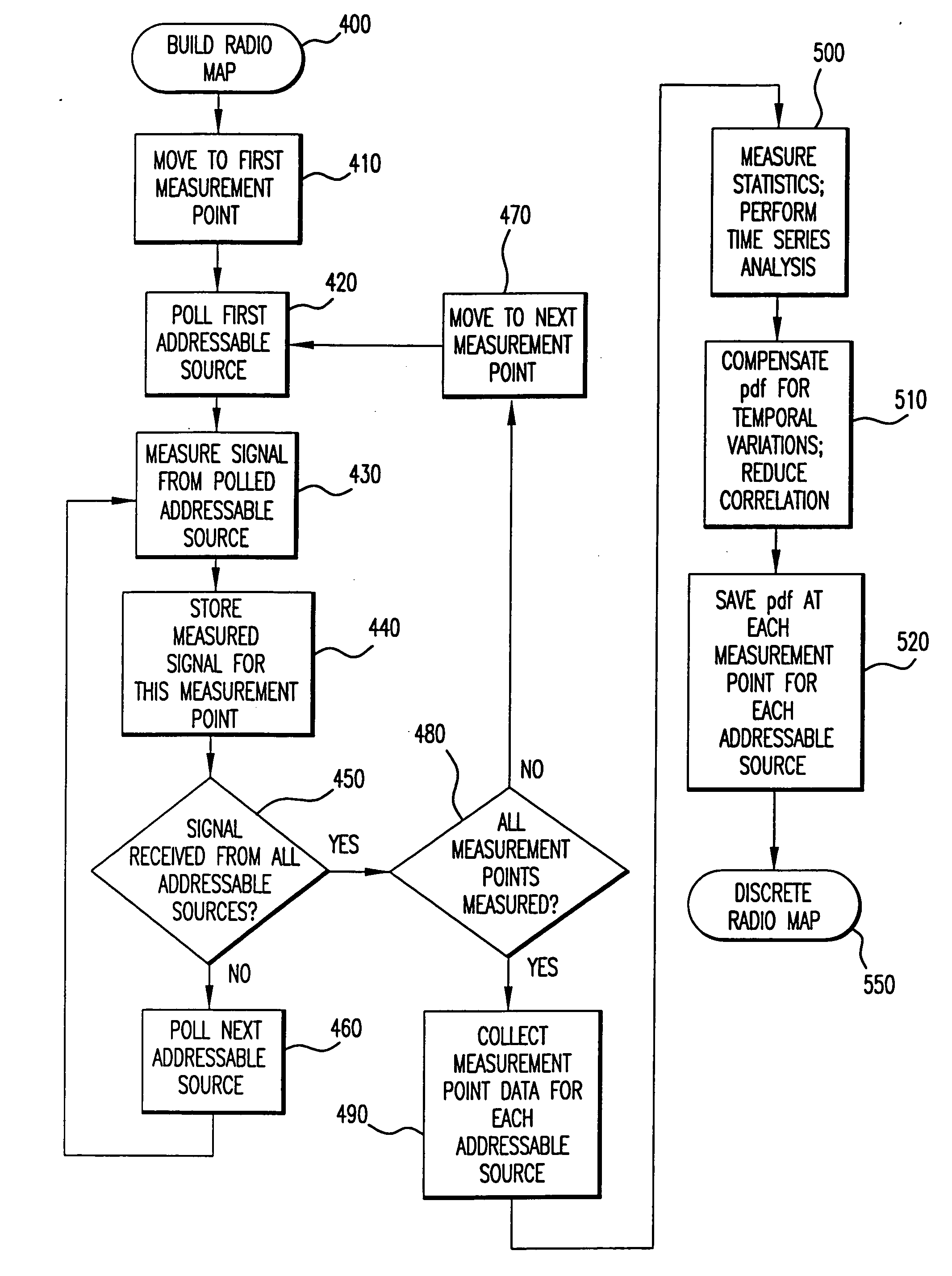
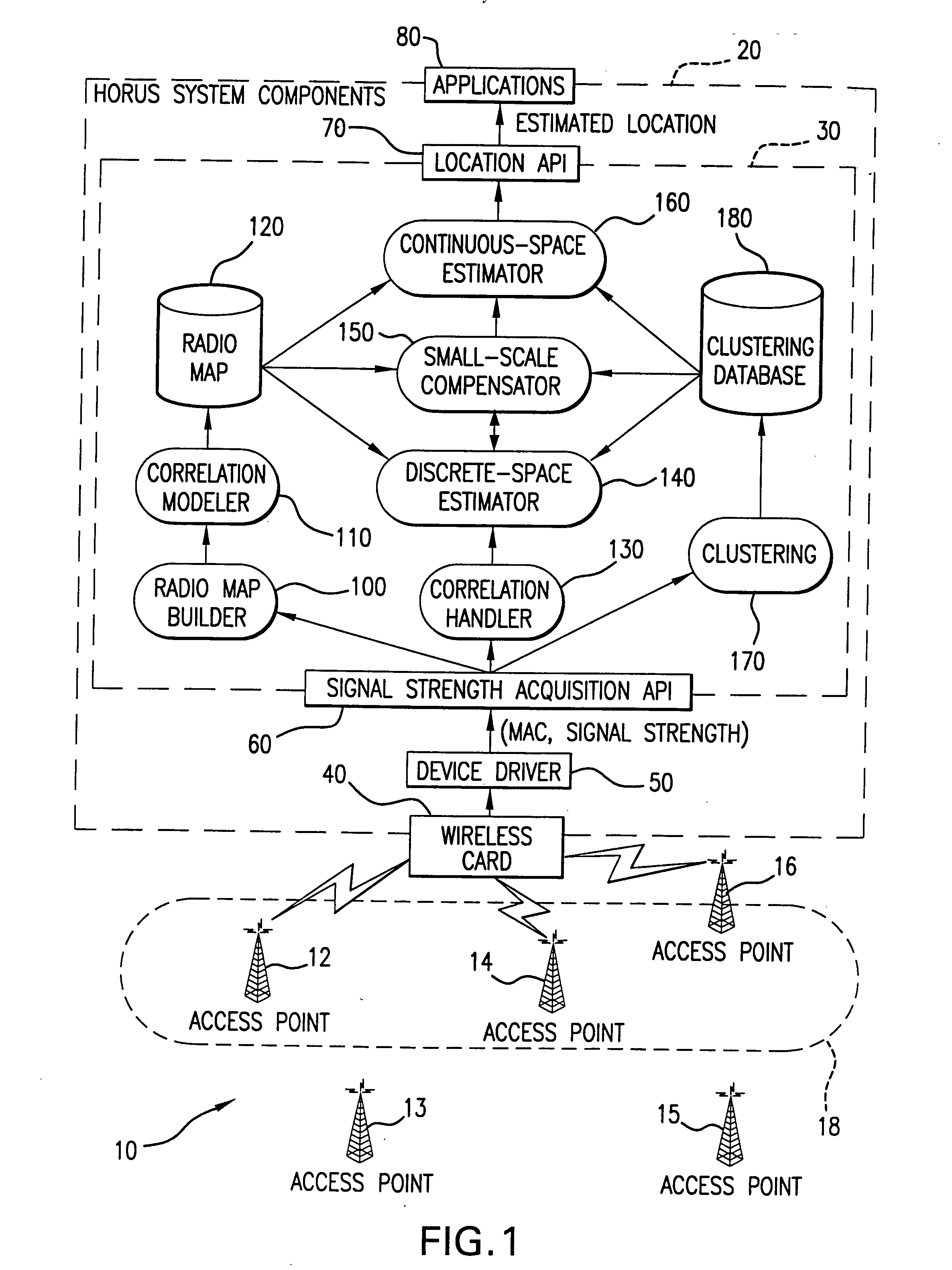
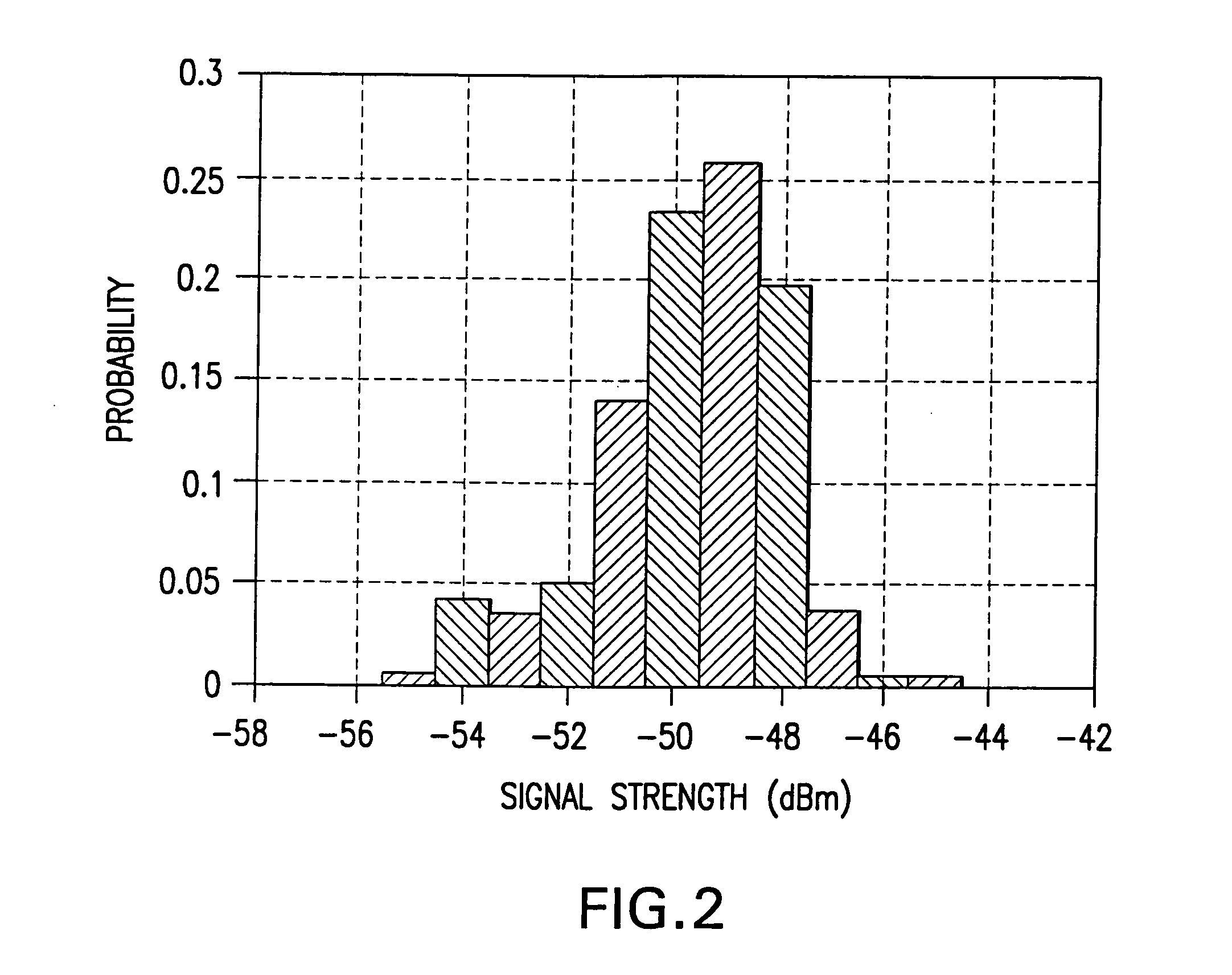
In a wireless communication network, the location of an addressable receiver relative to the locations of a plurality of addressable sources of electromagnetic radiation is found using probabilistic models of the signal strength measured at the addressable receiver. The inventive method provides location determination on a finer spatial scale than was heretofore available. A region of interest is calibrated via a discrete-space radio map storing probability distributions of received signal strength at the measurement locations. The stored probability distributions are compensated for temporal variability and biases, such as through temporal correlations of the sampled received signal strength. A measurement of the signal strength at the addressable receiver from each of the plurality of addressable sources is used in conjunction with the discrete-space radio map to identify one of the coordinates thereof that maximizes the conditional probability P(x|s), where x is the radio map location and s is a vector of measured signal strengths. Small spatial scale variability can be compensated for using a perturbation technique. The method further implements a continuous-space estimator to return an estimated user location that falls between discrete-space radio map locations.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
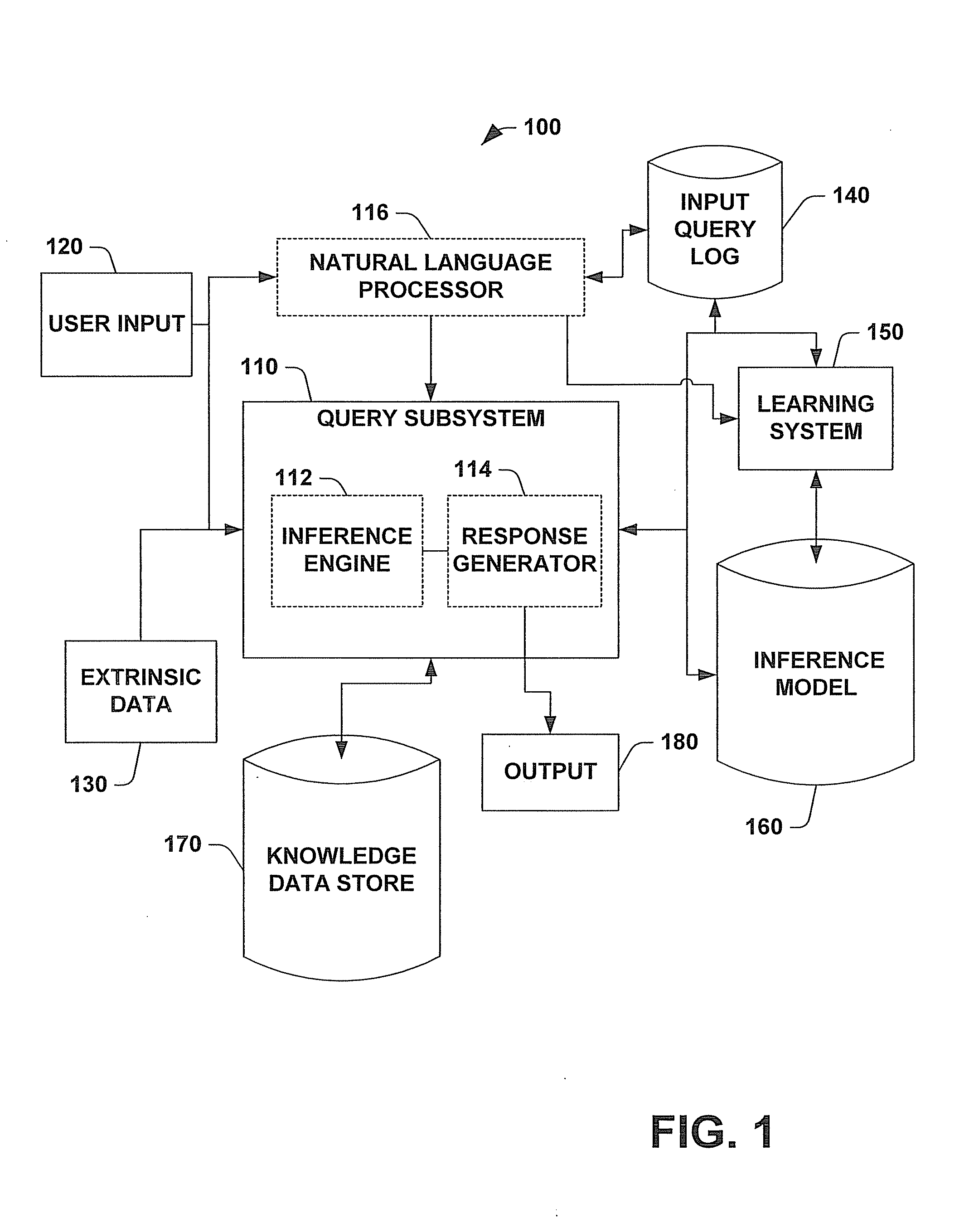
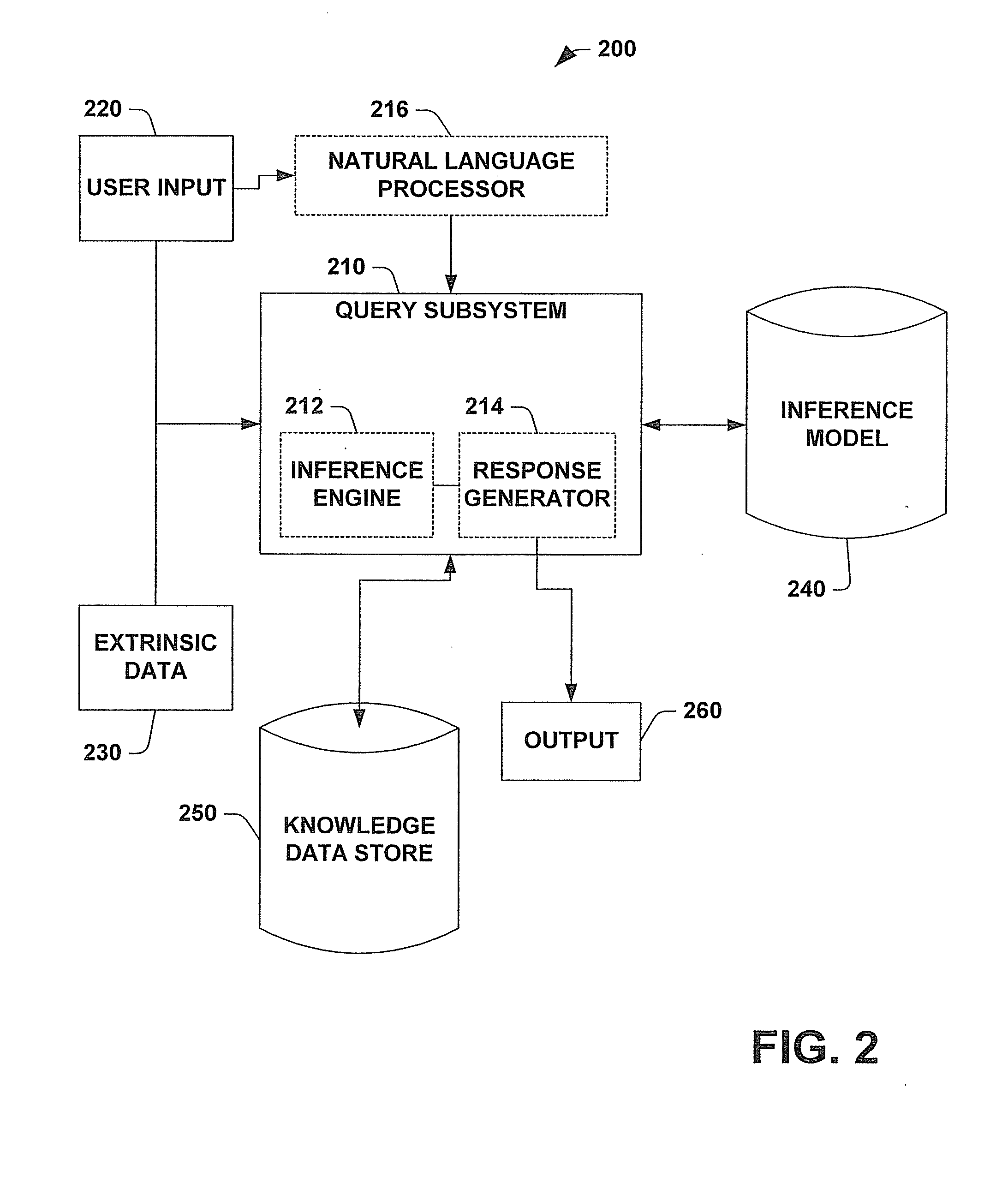
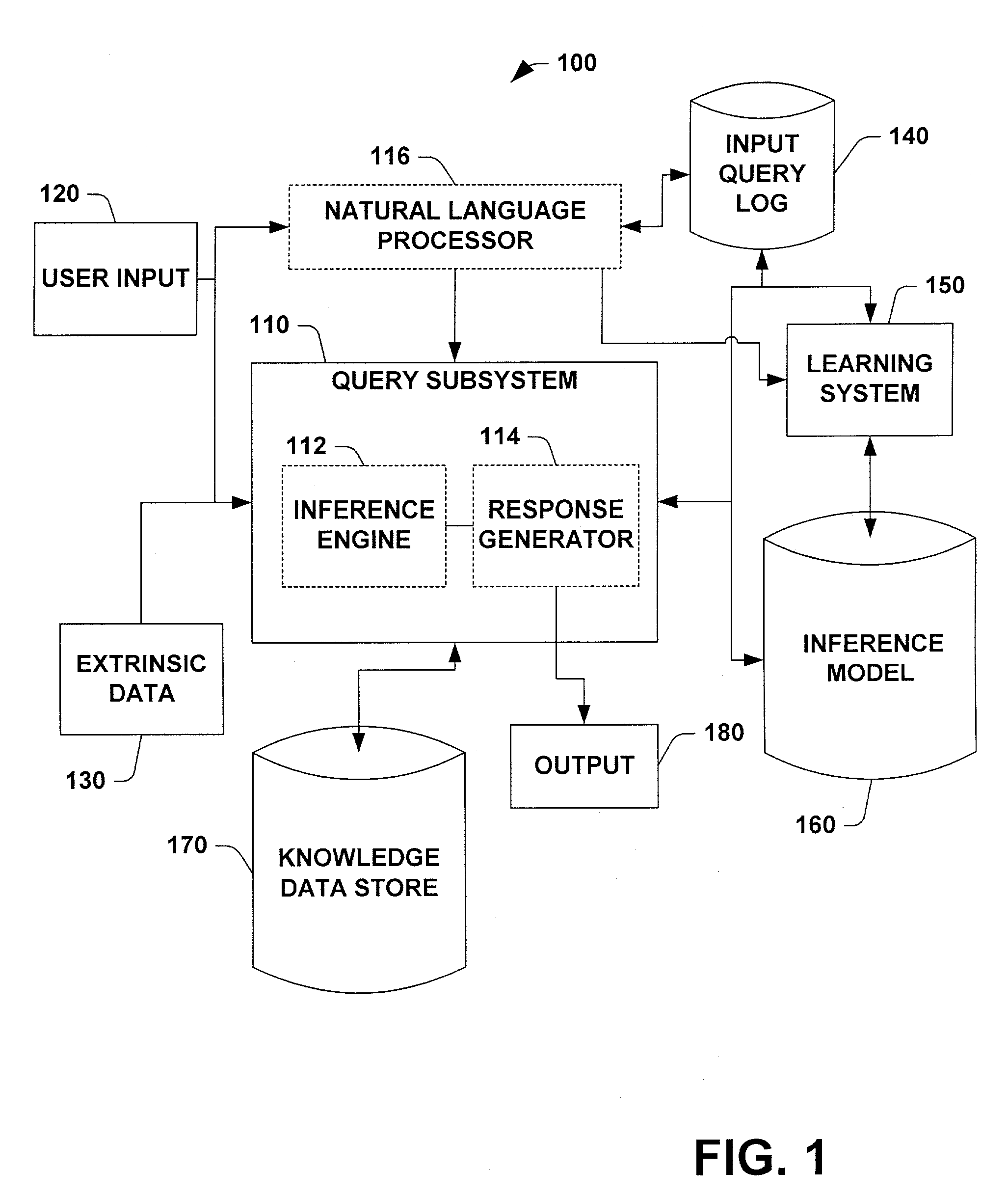
System and methods for inferring informational goals and preferred level of detail of answers
InactiveUS20090037398A1Improve responseEnhanced informationData processing applicationsNatural language data processingLevel of detailStatistical analysis
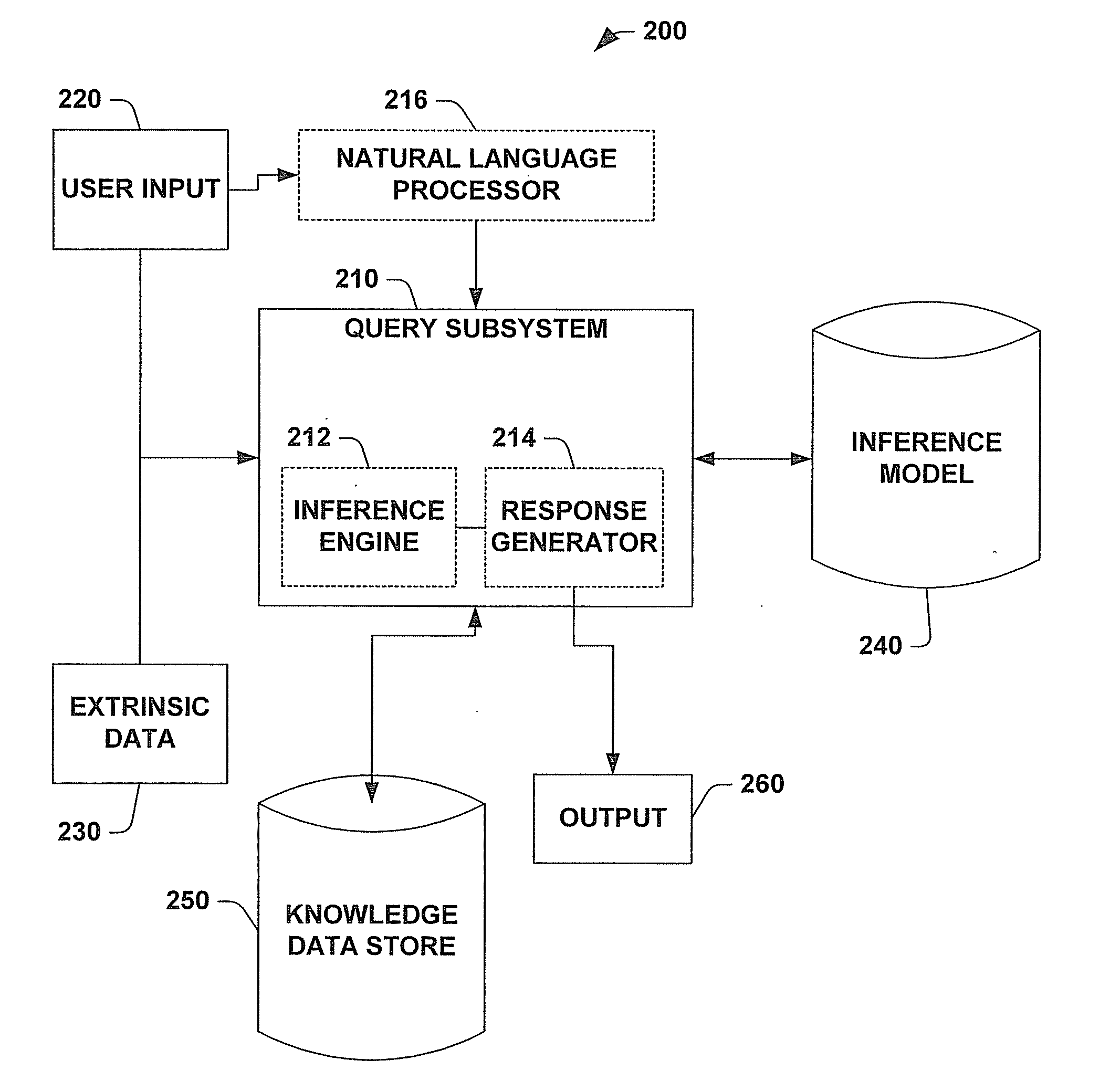
A system and method for inferring informational goals and preferred level of details in answers in response to questions posed to computer-based information retrieval or question-answering systems is provided. The system includes a query subsystem that can receive an input query and extrinsic data associated with the query and which can output an answer to the query, and / or rephrased queries or sample queries. The query subsystem accesses an inference model to retrieve conditional probabilities that certain informational goals are present. One application of the system includes determining a user's likely informational goals and then accessing a knowledge data store to retrieve responsive information. The system includes a natural language processor that parses queries into observable linguistic features and embedded semantic components that can be employed to retrieve the conditional probabilities from the inference model. The inference model is built by employing supervised learning and statistical analysis on a set of queries suitable to be presented to a question-answering system. Such a set of queries can be manipulated to produce different inference models based on demographic and / or localized linguistic data.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
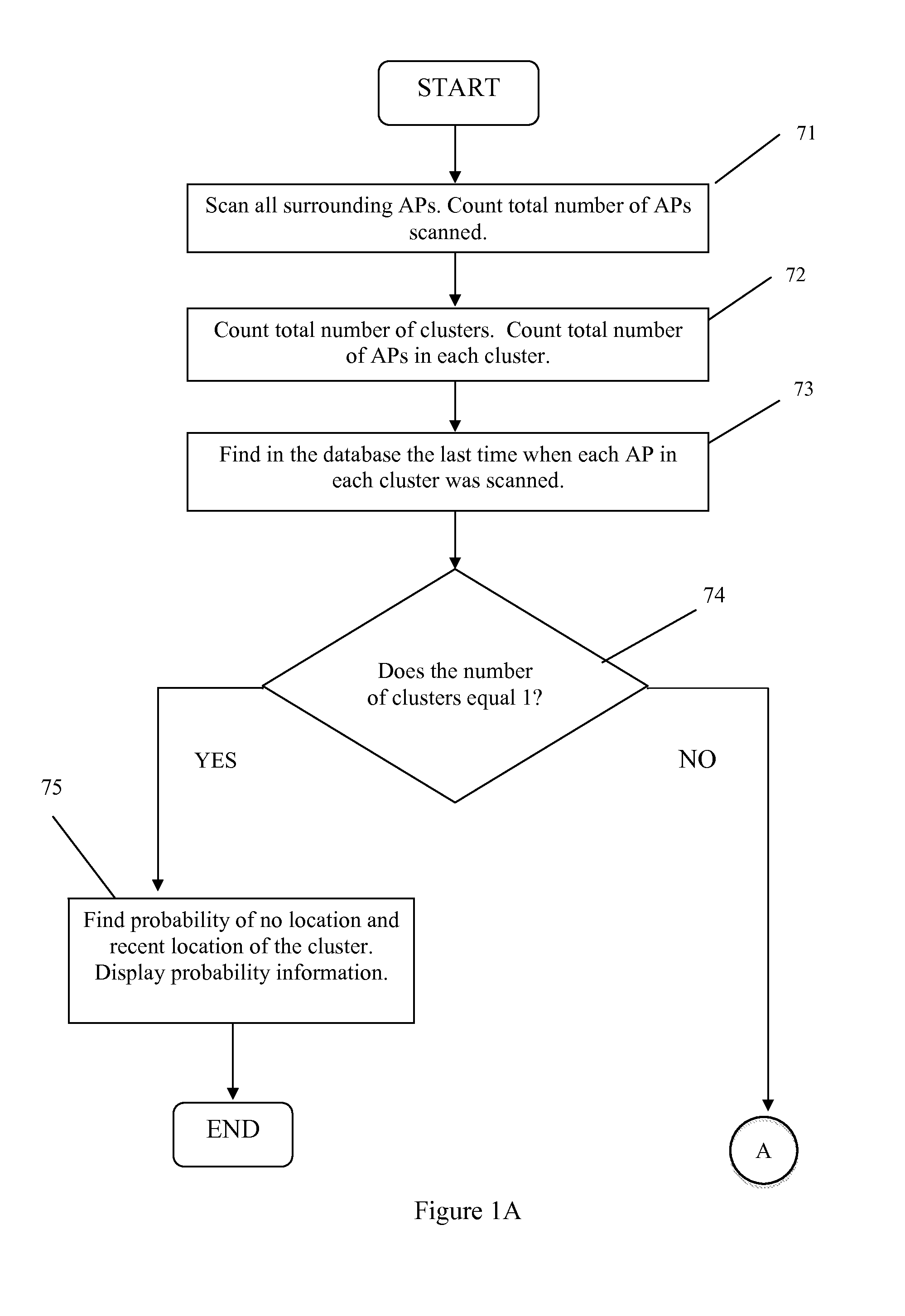
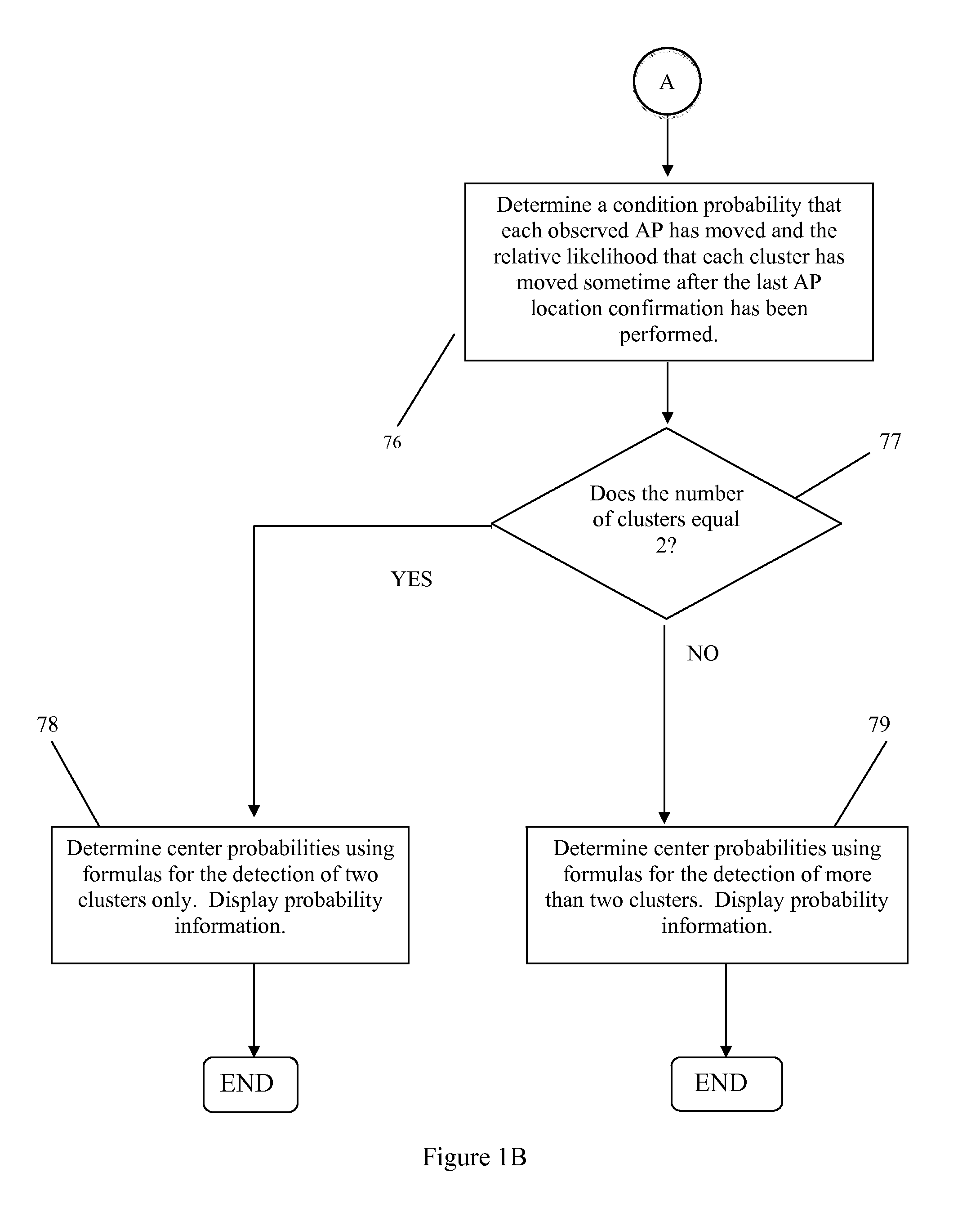
System and Method for Resolving Multiple Location Estimate Conflicts in a WLAN-Positioning System
ActiveUS20110235532A1Improve position estimate performanceError preventionTransmission systemsWi-FiPoint cluster
Methods of and systems for resolving multiple location estimate conflicts in a WLAN-positioning system are provided. Disclosed are methods to quantify the probability that a particular location estimate of a mobile device made by a Wi-Fi based positioning system is correct to within an arbitrary accuracy. Implementations use observed access point cluster size, age information for access point location determination, and / or cumulative distribution functions that characterize the conditional probability that one or more access points detected by the mobile device have relocated within a specified time interval to make the probability determinations.
Owner:SKYHOOK WIRELESS
Knowledge graph construction for intelligent online personal assistant
InactiveUS20180052884A1Improve identityDigital data information retrievalNatural language analysisMarket basedMetadata
Processing natural language user inputs into a more formal, machine-readable, structured query representation used for making an item recommendation. Analyses of user inputs are coordinated via a knowledge graph constructed from categories, attributes, and attribute values describing relatively frequently occurring prior interactions of various users with an electronic marketplace. The knowledge graph has directed edges each with a score value based on: the conditional probabilities of category / attribute / attribute value interactions calculated from user behavioral patterns, associations between user queries and structured data based on historical buyer behavioral patterns in the marketplace, metadata from items made available for purchase by sellers used to better define buyers' requirements, and / or world knowledge of weather, locations / places, occasions, and item recipients that map to inventory-related data, for generating relevant prompts for further user input. The knowledge graph may be dynamically updated during a multi-turn interactive dialog.
Owner:EBAY INC
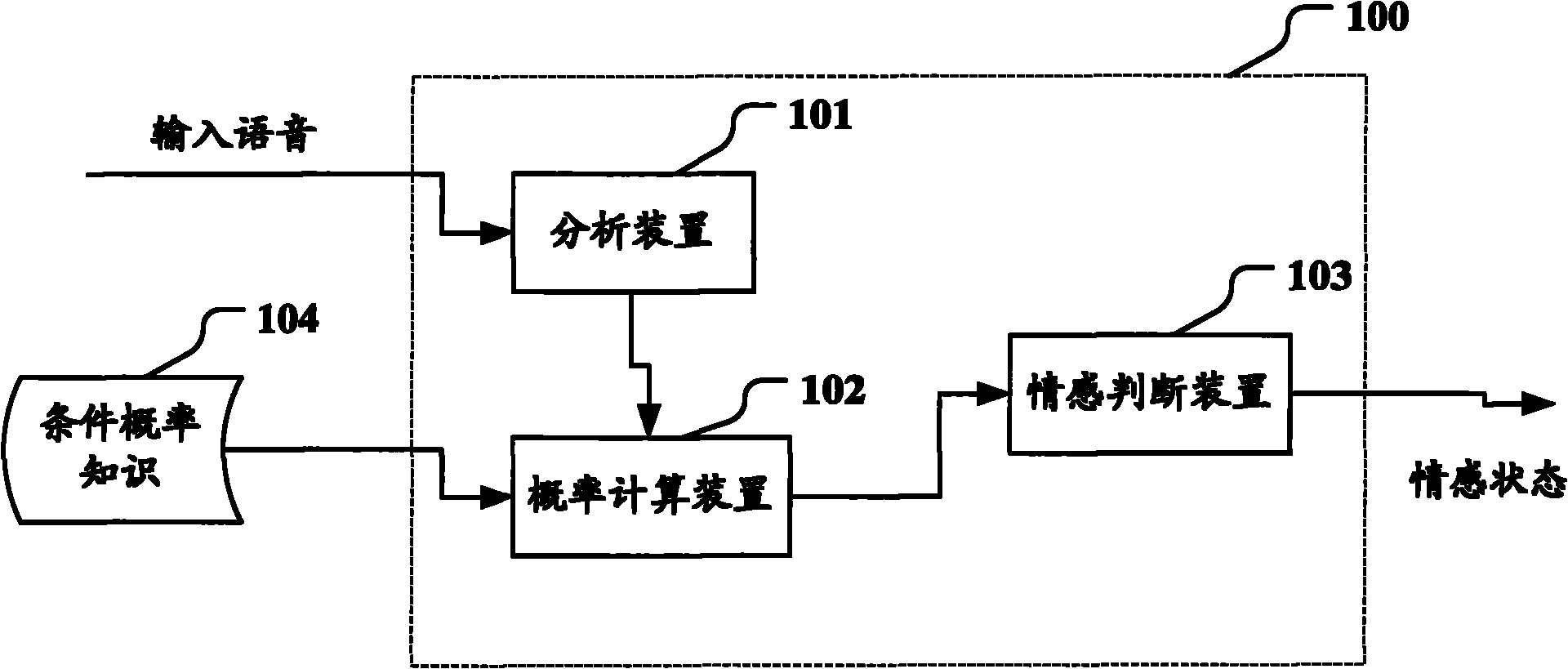
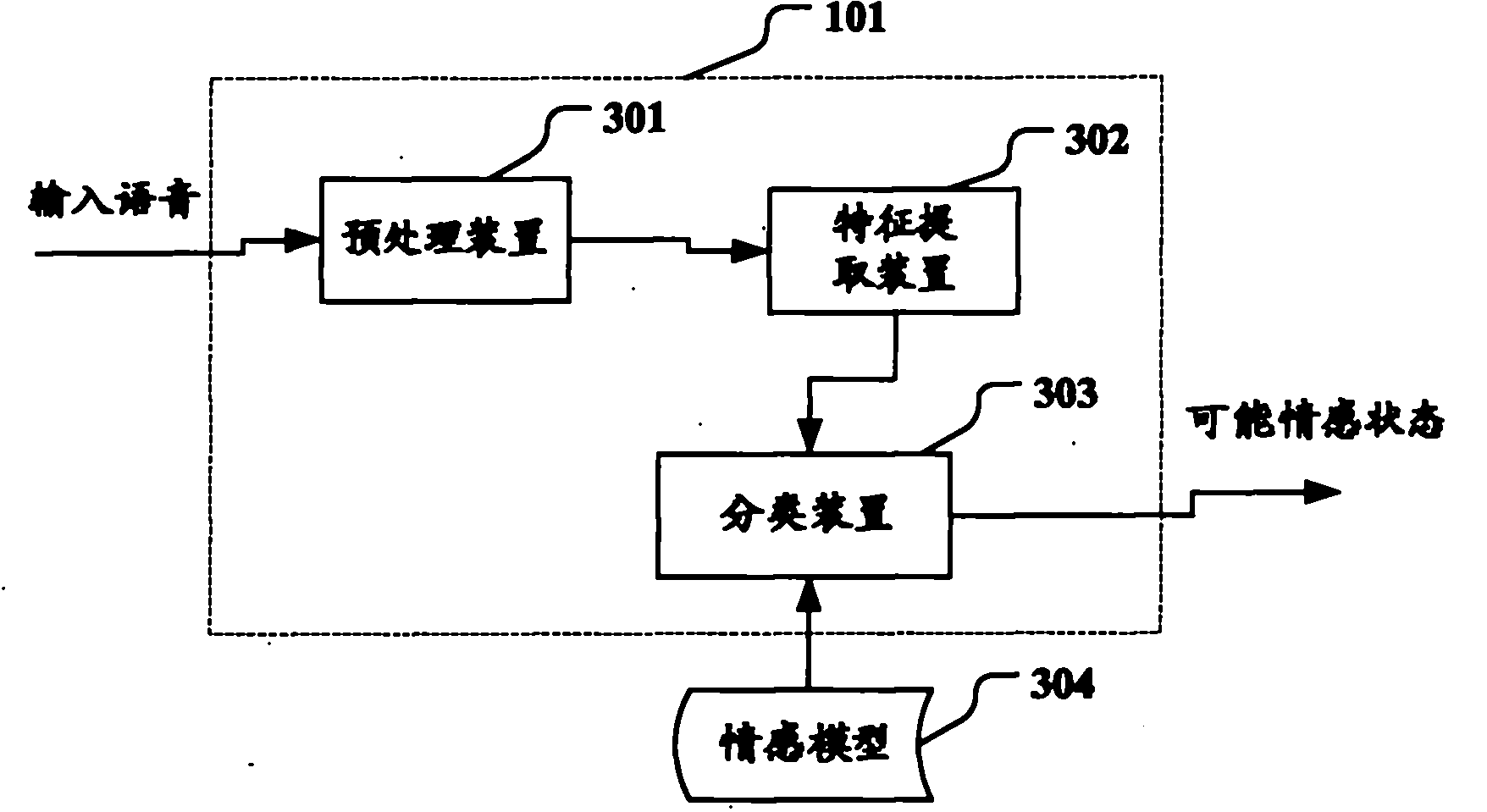
Speech emotion recognition equipment and speech emotion recognition method
The invention relates to speech emotion recognition equipment and a speech emotion recognition method. The speech emotion recognition equipment comprises an analysis device, a probability calculating device and an emotion judging device, wherein the analysis device matches emotional characteristics of input speech with a plurality of emotion models so as to ensure a plurality of possible emotional states; the probability calculating device calculates the final probability of the possible emotional states in the previous emotional states of a speaker according to the knowledge of conditional probability converted among the emotional states in the speaking process of the speaker; and the emotion judging device selects a possible emotional state with the maximum final probability from the possible emotional states as the emotional state of the input speech.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
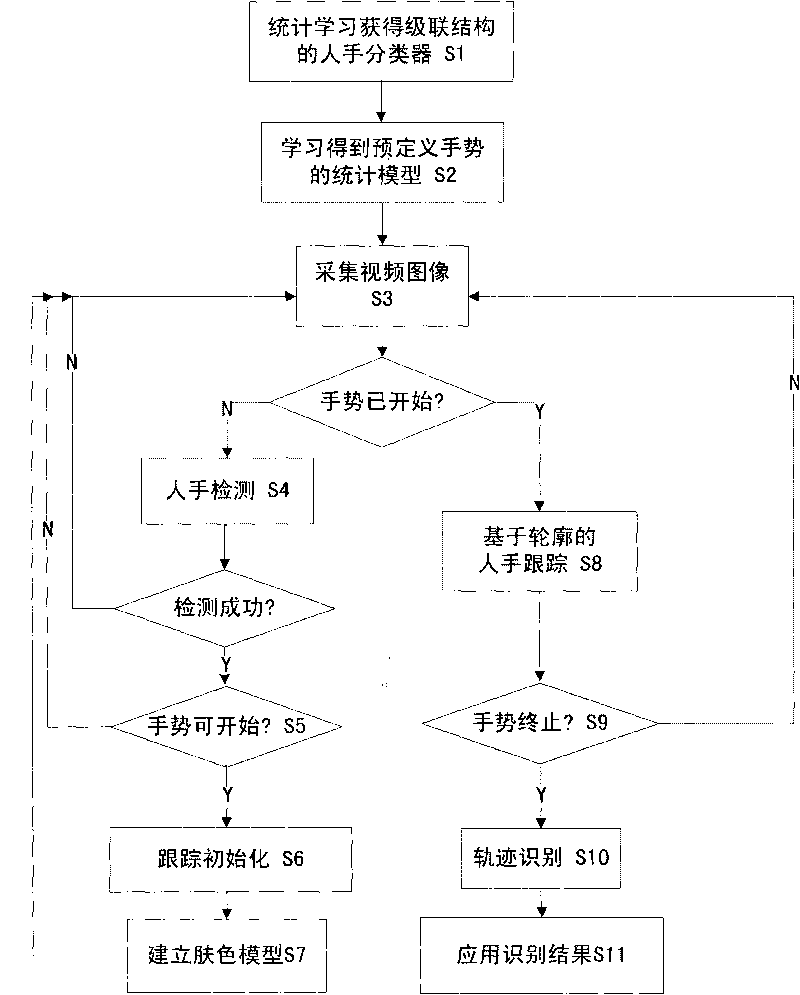
Real-time gesture interaction method based on computer vision
InactiveCN101763515AVisual technology is matureComprehensive effectCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer usersCombined method
The invention discloses a real-time gesture interaction method based on computer vision, which comprises the following steps: acquiring a digital image from an image input device; detecting hands by a statistical learning method; initializing a hand contour tracker according to the detecting result, and calculating a skin color model of a specific hand; tracking the hand contour by a combined method of a conditional probability density transmission algorithm and a heuristic search technology; analyzing the moving track of the hands by a Hidden Markov Model to obtain the gesture identifying result; and applying the gesture analyzing result to the interaction of various application programs. The real-time gesture interaction method of the invention expands the interactive mode of the traditional mouse and keyboard, realizes automatic hand detection, tracking and gesture identification by the computer vision and image processing techniques, has real-time performance, robustness and easy realization and operation, and can enable computer users to interact with the computer more naturally, visually and intelligently by hand gestures.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
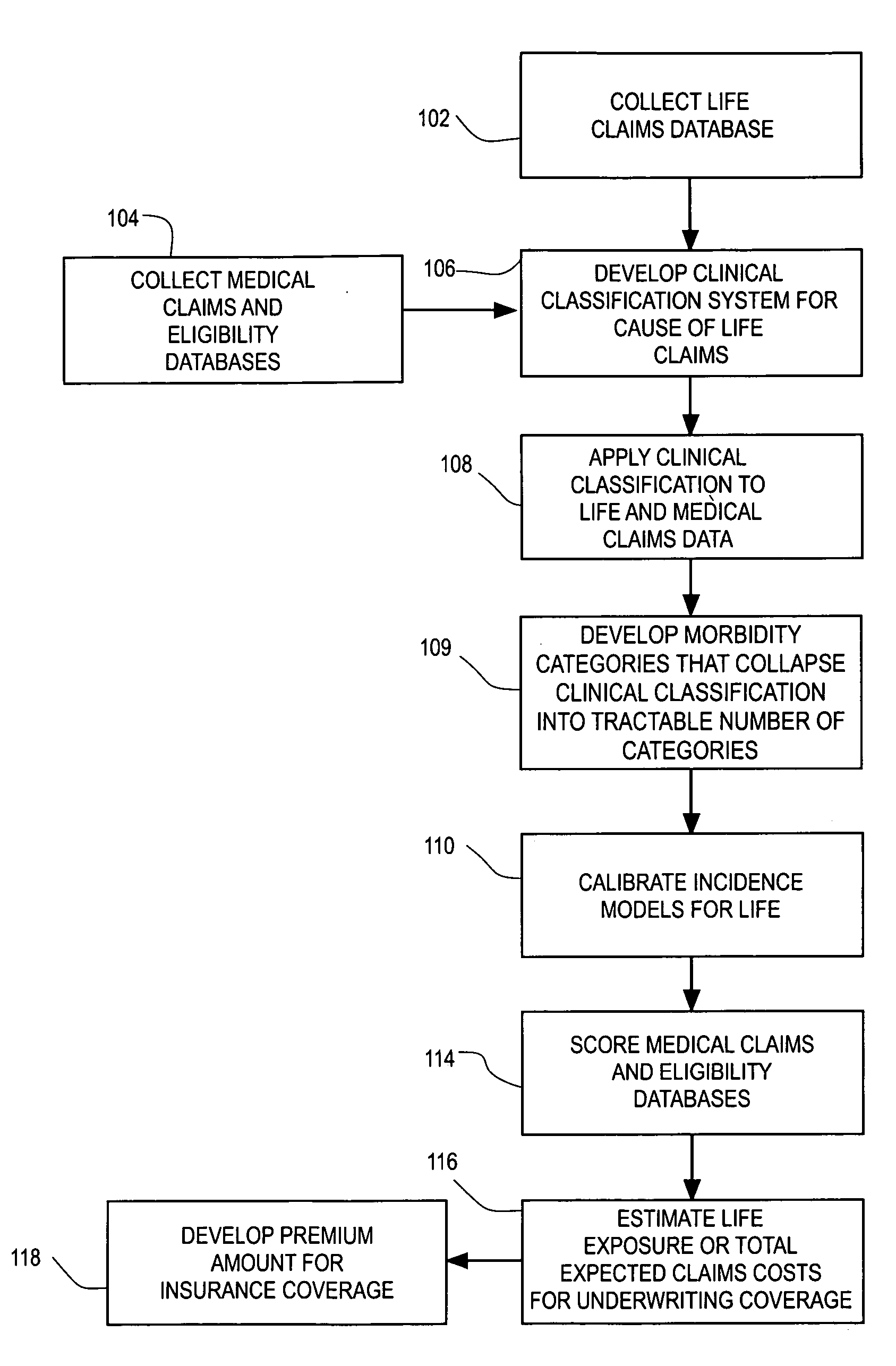
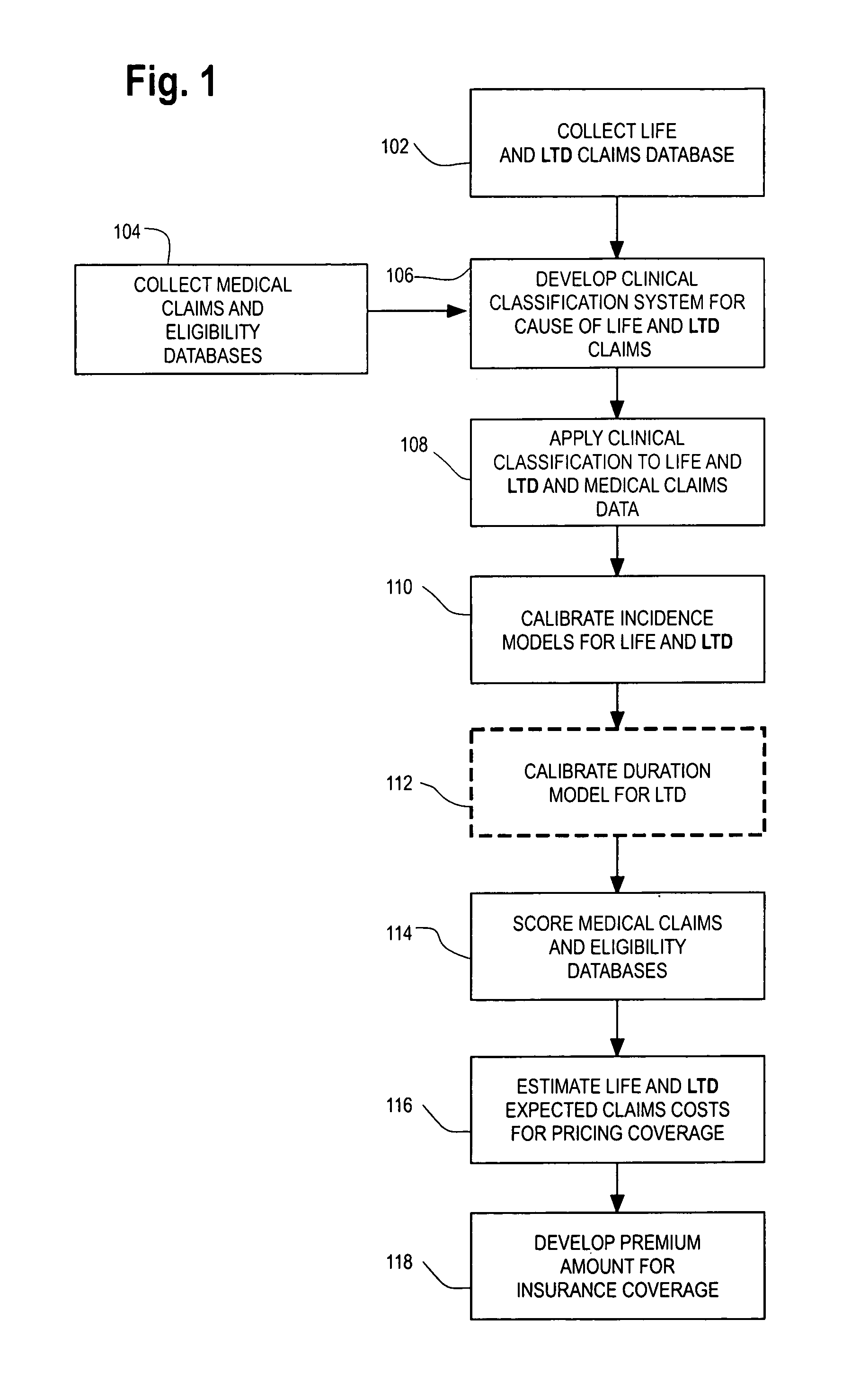
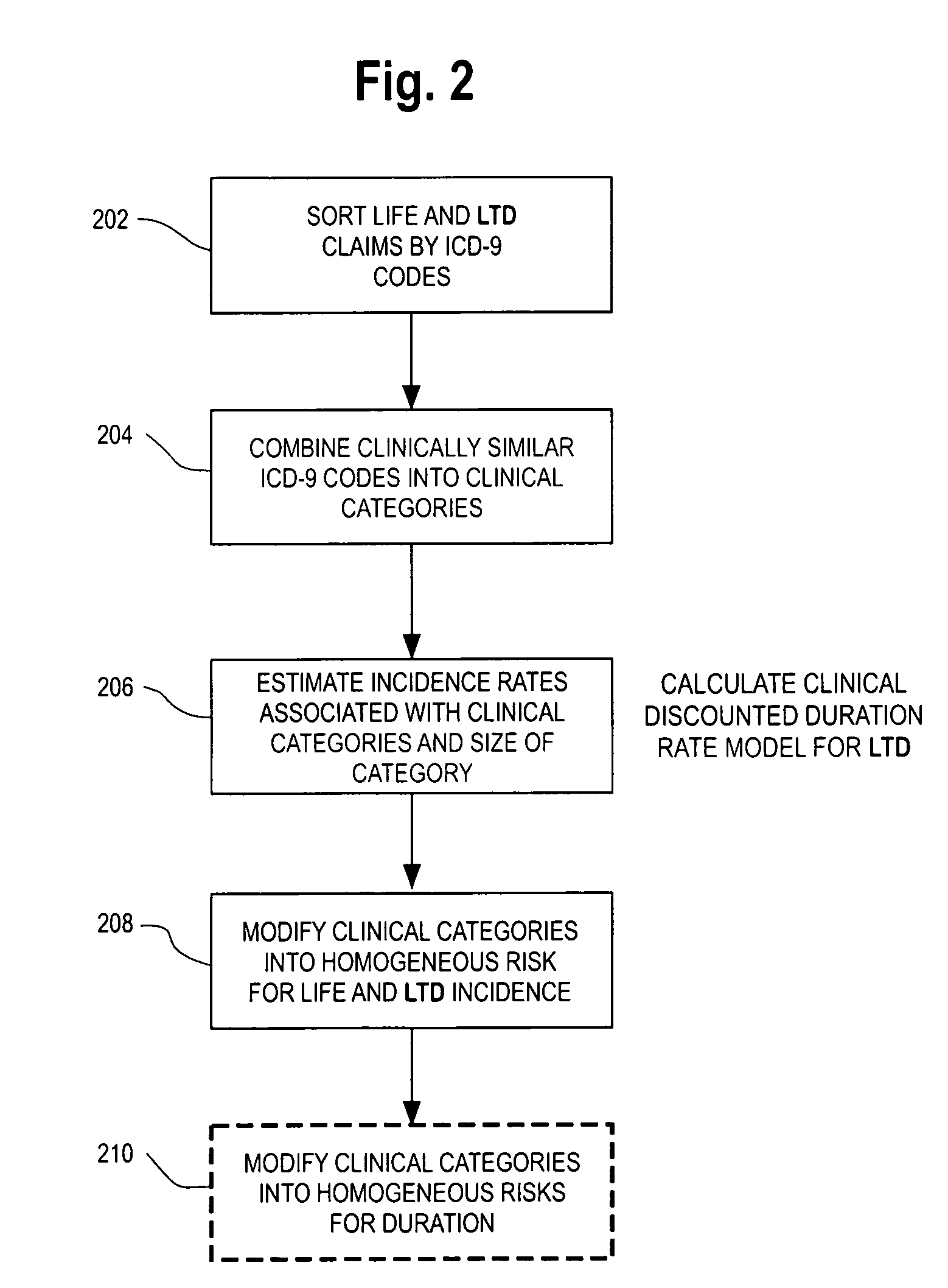
Computerized medical modeling of group life insurance using medical claims data
ActiveUS20070021987A1Improve measuring risk of deathFinanceCash registersConditional probabilityProbit model
A method of model development for use in underwriting group life insurance for a policy period includes collecting medical claims data for the group to be underwritten, where each medical claim being related to a particular employee of the group. Morbidity categories are provided that categorize the medical claims in the medical claims data. A conditional probability model is developed and applied to the morbidity categories for each employee in the group using his medical claims, thereby calculating the expected conditional probability for each employee dying during the policy period. For each employee, an estimate of the expected life claim cost is estimated using an index of the life coverage to salary. Combining the expected conditional probability for each employee dying during the policy period with the estimate of the expected claim cost of death gives an estimate of the group's total life exposure.
Owner:TRURISK
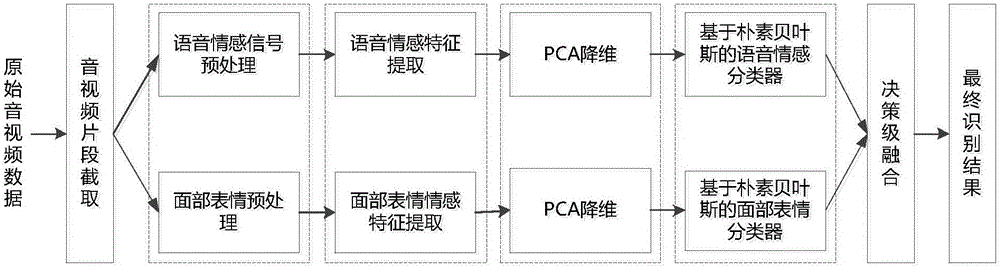
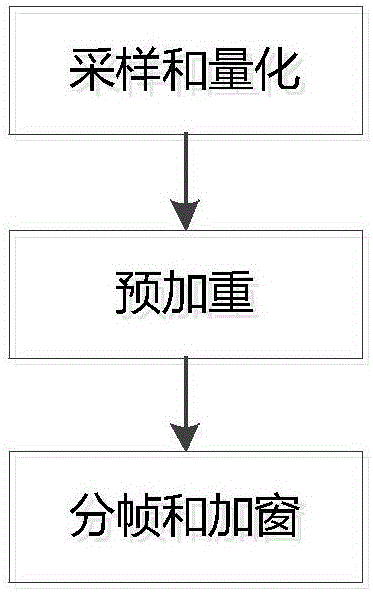
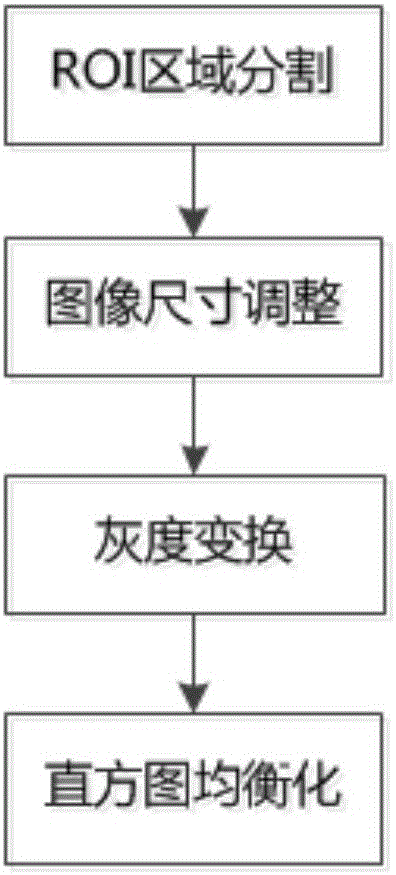
Voice-and-facial-expression-based identification method and system for dual-modal emotion fusion
ActiveCN105976809AImprove accuracyImprove reliabilitySpeech recognitionCorresponding conditionalDimensionality reduction
The invention relates to a voice-and-facial-expression-based identification method for dual-modal emotion fusion. The method comprises: S1, audio data and video data of a to-be-identified object are obtained; S2, a face expression image is extracted from the video data and segmentation of an eye region, a nose region, and a mouth region is carried out; S3, a facial expression feature in each regional image is extracted from images of the three regions; S4, PCA analysis and dimensionality reduction is carried out on voice emotion features and the facial expression features; and S5, naive Bayesian emotion voice classification is carried out on samples of two kinds of modes and decision fusion is carried out on a conditional probability to obtain a final emotion identification result. According to the invention, fusion of the voice emotion features and the facial expression features is carried out by using a decision fusion method, so that accurate data can be provided for corresponding conditional probability calculation carried out at the next step; and an emotion state of a detected object can be obtained precisely by using the method, so that accuracy and reliability of emotion identification can be improved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Method and system for generating natural languages for describing image contents
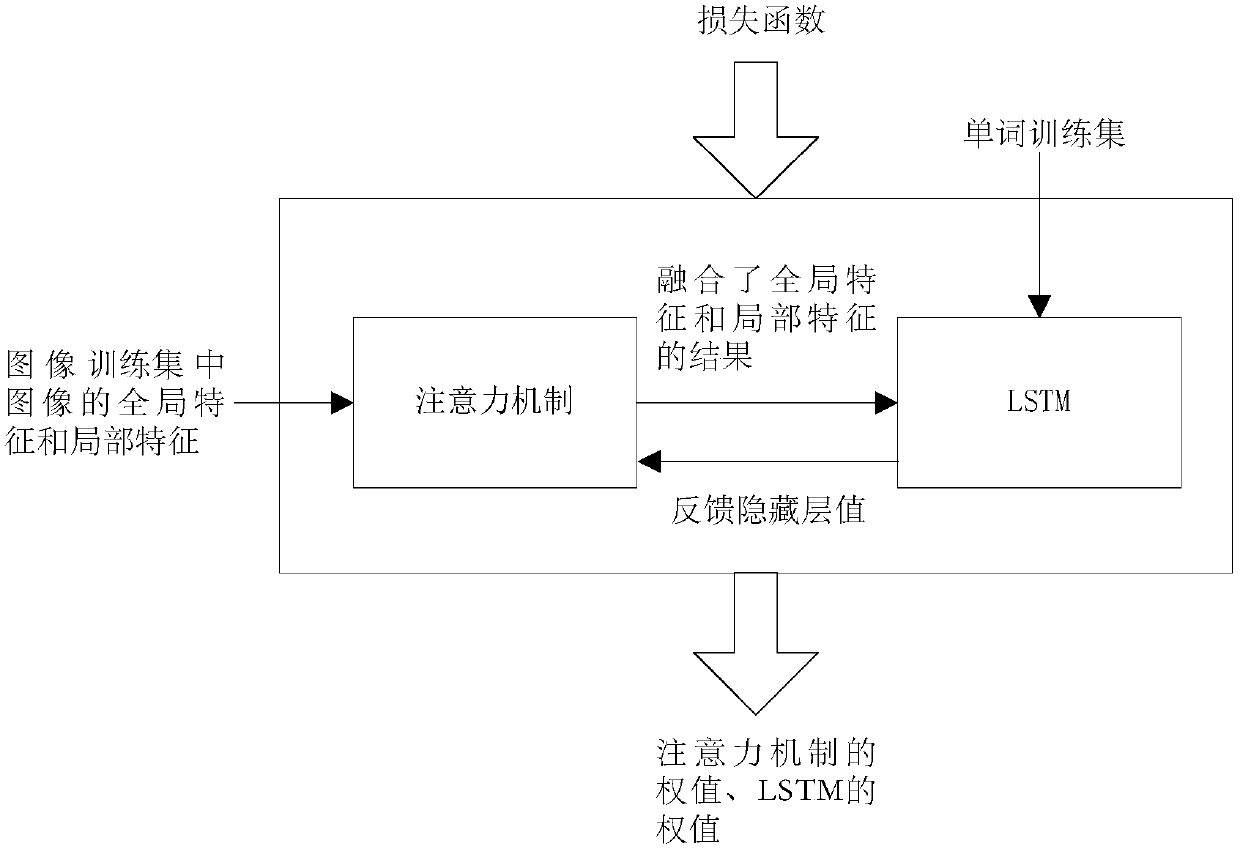
ActiveCN107918782ACharacter and pattern recognitionNatural language data processingConditional probabilityMachine learning
The invention provides a method for training a model for generating natural languages for describing image contents, and a method for generating natural languages for describing image contents by adoption of the model. The training method comprises the following steps of: A1) taking global features and local features of images in an image training set as inputs of an attention mechanism, so as toobtain a fusion result comprising the global features and the local features at the same time; and A2) taking the fusion result and a word training set as inputs of a long short-term memory network, and training the attention mechanism and the long short-term memory network by utilizing a loss function so as to obtain a weight of the attention mechanism and a weight of the long short-term memory network, wherein the loss function is a function of a condition probability of the previous word or the ith word of a plurality of words in the content of a known image and a natural sentence for describing the image content, and i is equal to 1,to imax.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Apparatus and method for monitoring of infrastructure condition
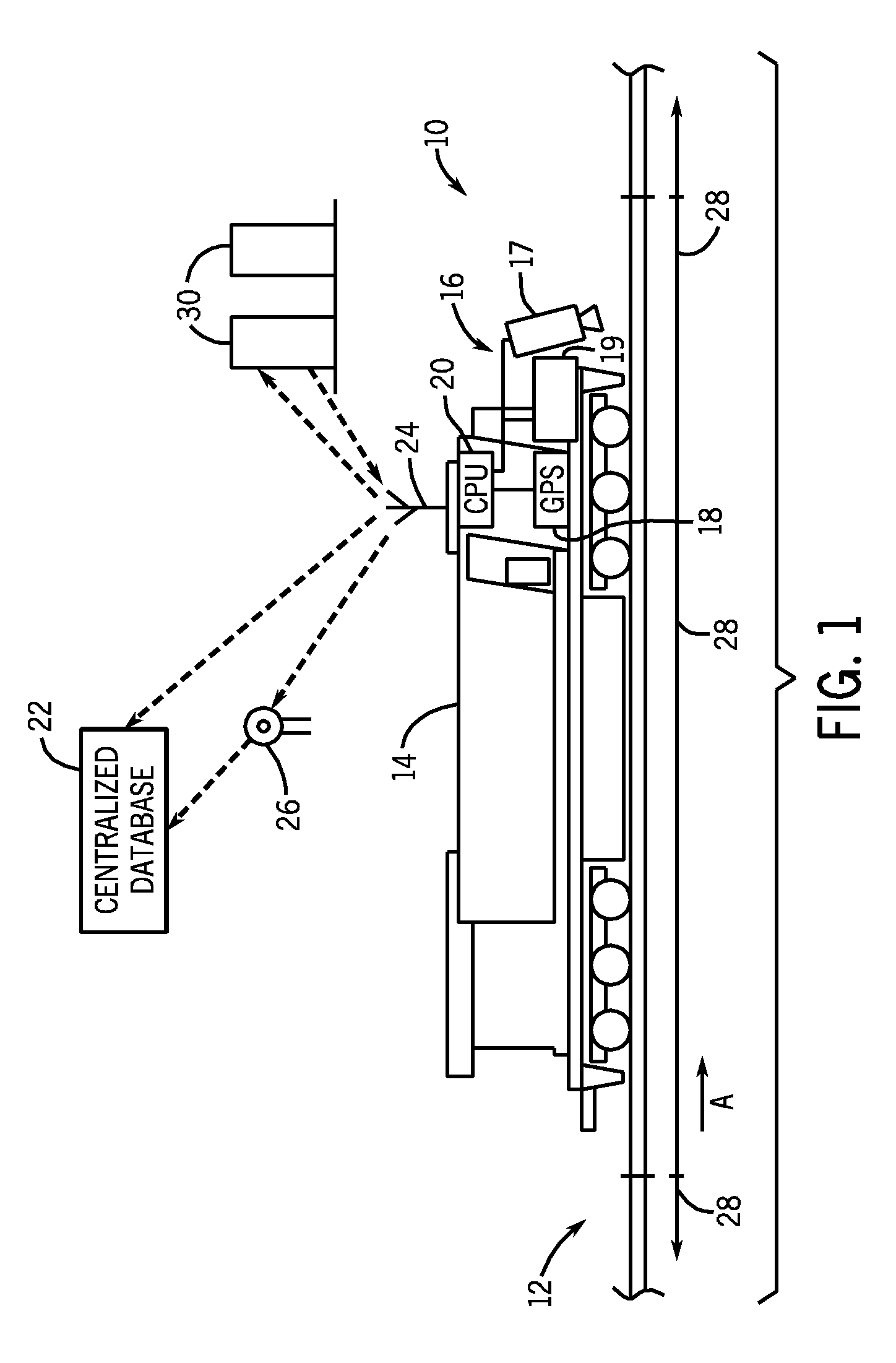
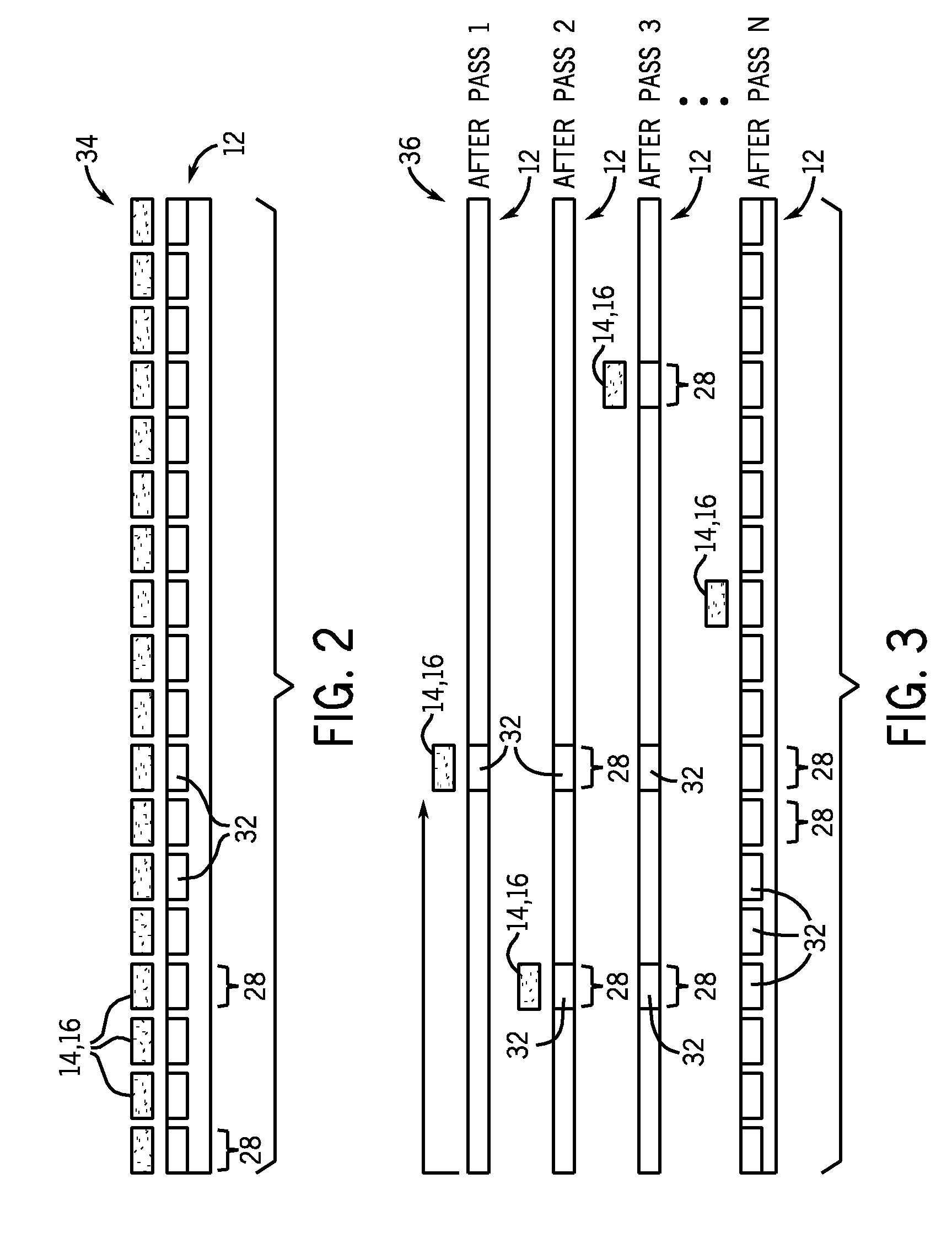
InactiveUS20100004804A1Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesCentralized computingMonitoring system
A system and method for vehicle-centric infrastructure monitoring system includes an inspection system mountable on a vehicle configured to travel over an expanse of rail track having a plurality of track blocks. The inspection system acquires track data for at least some track blocks along the expanse of rail track. The monitoring system also includes a positioning system to determine a location of the vehicle and generate location data indicative of an associated track block location, a communications device to transmit the track / location data to a remote location, and a centralized computing system positioned at the remote location to receive the transmitted track / location data. The centralized computing system is programmed to determine a current probability of a track condition for a track block and combine the current track condition probability with a previously determined cumulative track condition probability to provide an updated track condition probability for the track block.
Owner:GE GLOBAL SOURCING LLC
System and process for bootstrap initialization of nonparametric color models
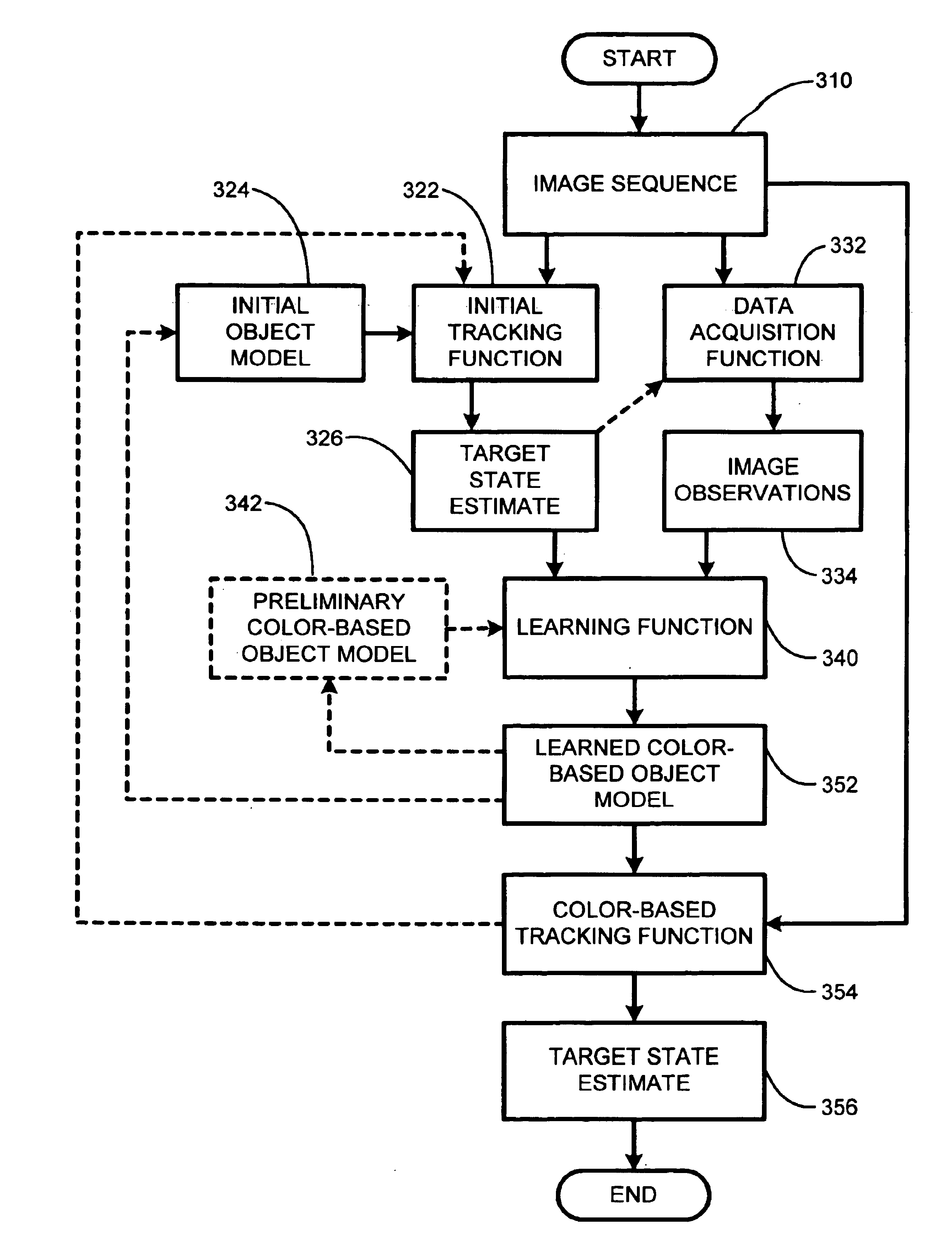
InactiveUS6937744B1Improve accuracyGreat likelihoodTelevision system detailsImage analysisProbabilistic methodData acquisition
The present invention is embodied in a system and process for automatically learning a reliable color-based tracking system. The tracking system is learned by using information produced by an initial object model in combination with an initial tracking function to probabilistically determine the configuration of one or more target objects in a temporal sequence of images, and a data acquisition function for gathering observations relating to color in each image. The observations gathered by the data acquisition function include information that is relevant to parameters desired for a final color-based object model. A learning function then uses probabilistic methods to determine conditional probabilistic relationships between the observations and probabilistic target configuration information to learn a color-based object model automatically tailored to specific target objects. The learned object model is then used in combination with the final tracking function to probabilistically locate and track specific target objects in one or more sequential images.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and System for Determining Relation Between Search Terms in the Internet Search System
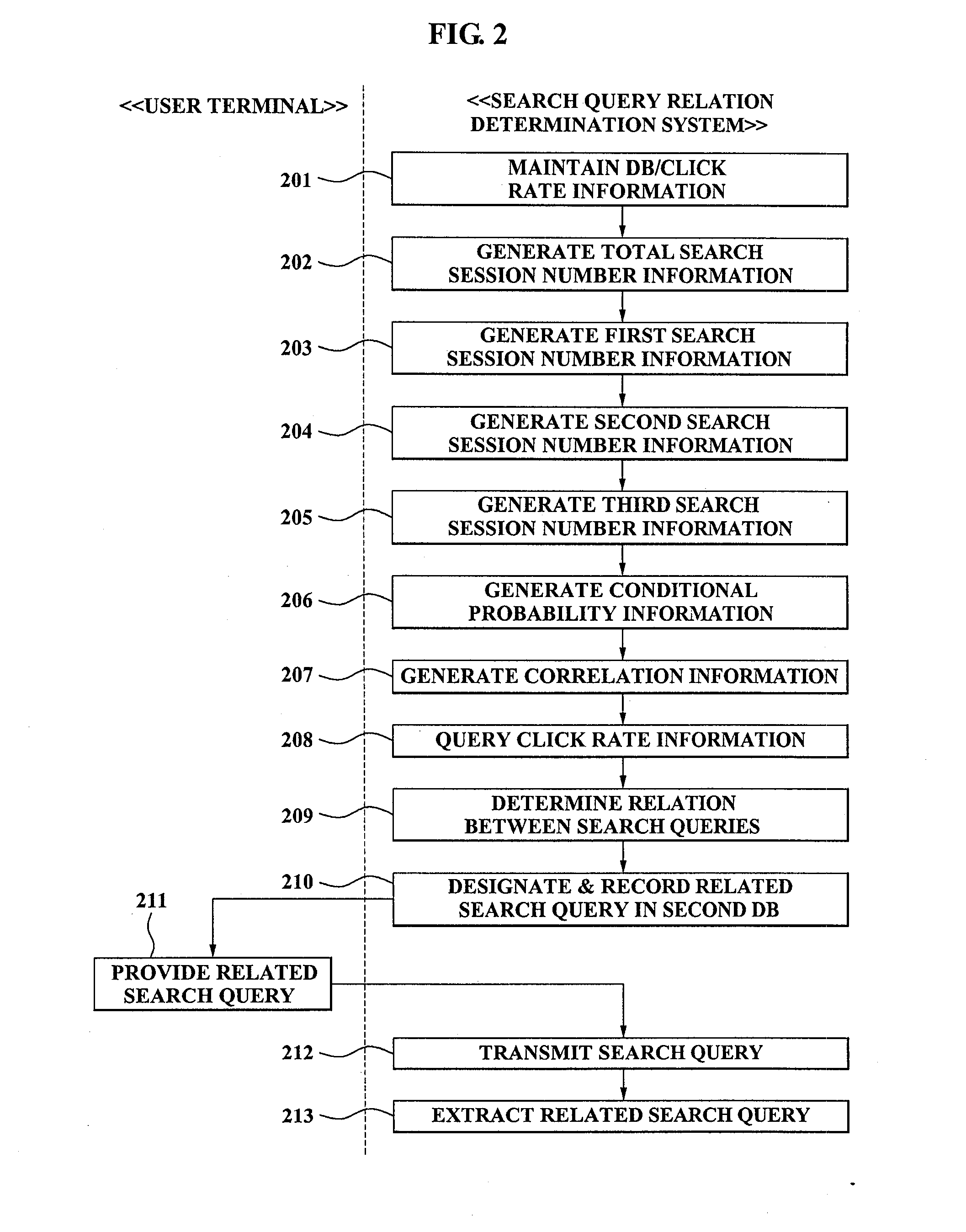
ActiveUS20080201297A1Reduce temporal loss lossReduce economic lossWeb data indexingDigital data processing detailsReference databaseRelevant information
A method of determining a relation between search queries, includes: maintaining a database comprising a search session and a record about a search query which is received from a user terminal during the search session; recording and maintaining click rate information for each of the search queries in a predetermined storage unit; generating total search session number information by counting a total number of search sessions which is set during the time interval generating first search session number information by counting a number of search sessions where a first search query is received during the time interval, and generating second search session number information by counting a number of search sessions where a second search query is received during the time interval, by referring to the database; generating third search session number information by counting a number of search sessions where the first search query and the second search query are received during the time interval, by referring to the database; generating conditional probability information by using the first search session number information and the third search session number information; generating correlation information by using the total search session number information, the first search session number information, the second search session number information, and the third search session number information; querying click rate information of the second search query by referring to the storage unit; and determining a relation between the first search query and the second search query, based on the conditional probability information, the correlation information, and the click rate information.
Owner:NHN CORP
Adaptive information extraction method for webpage characteristics
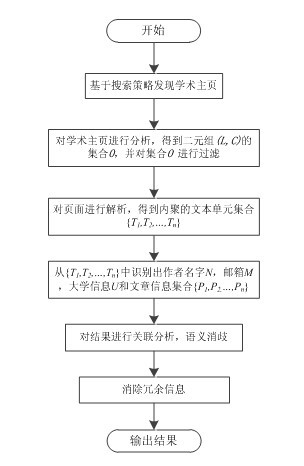
InactiveCN102254014ASolve the problem of inconsistent formatAdapt to changing situationsSpecial data processing applicationsInformation typeHome page
The invention discloses a method for extracting information from an academic home page. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) finding an academic home page from Internet; (2) crawling and analyzing the academic home page, wherein the crawling of an irrelevant page is reduced by using a heuristic strategy so as to accelerate analysis speed; (3) analyzing the page into a form of documentobject module (DOM), and dividing according to attributes and contents of elements so as to acquire a cohesive text unit list; (4) identifying the text unit by using an information recognizer, wherein each information recognizer only identifies one information type, and performing subfield extraction on the text information; (5) performing association analysis on the extraction result, eliminating different meanings by using the association of the information, and complementing the missing field; and (6) matching the extraction result and a database, and eliminating the redundant data, wherein the extraction result is stored in a semantic database in a form of semantic data. In the method, by combination of heuristic rules, a machine learning method and a conditional probability model, academic information can be extracted efficiently and accurately from the academic home page.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
System and method for image annotation and multi-modal image retrieval using probabilistic semantic models
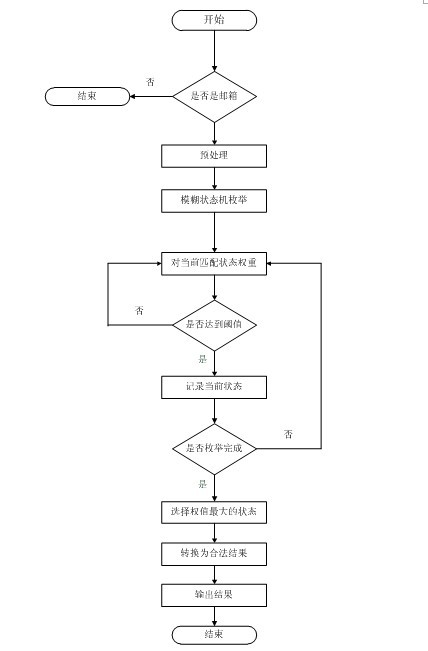
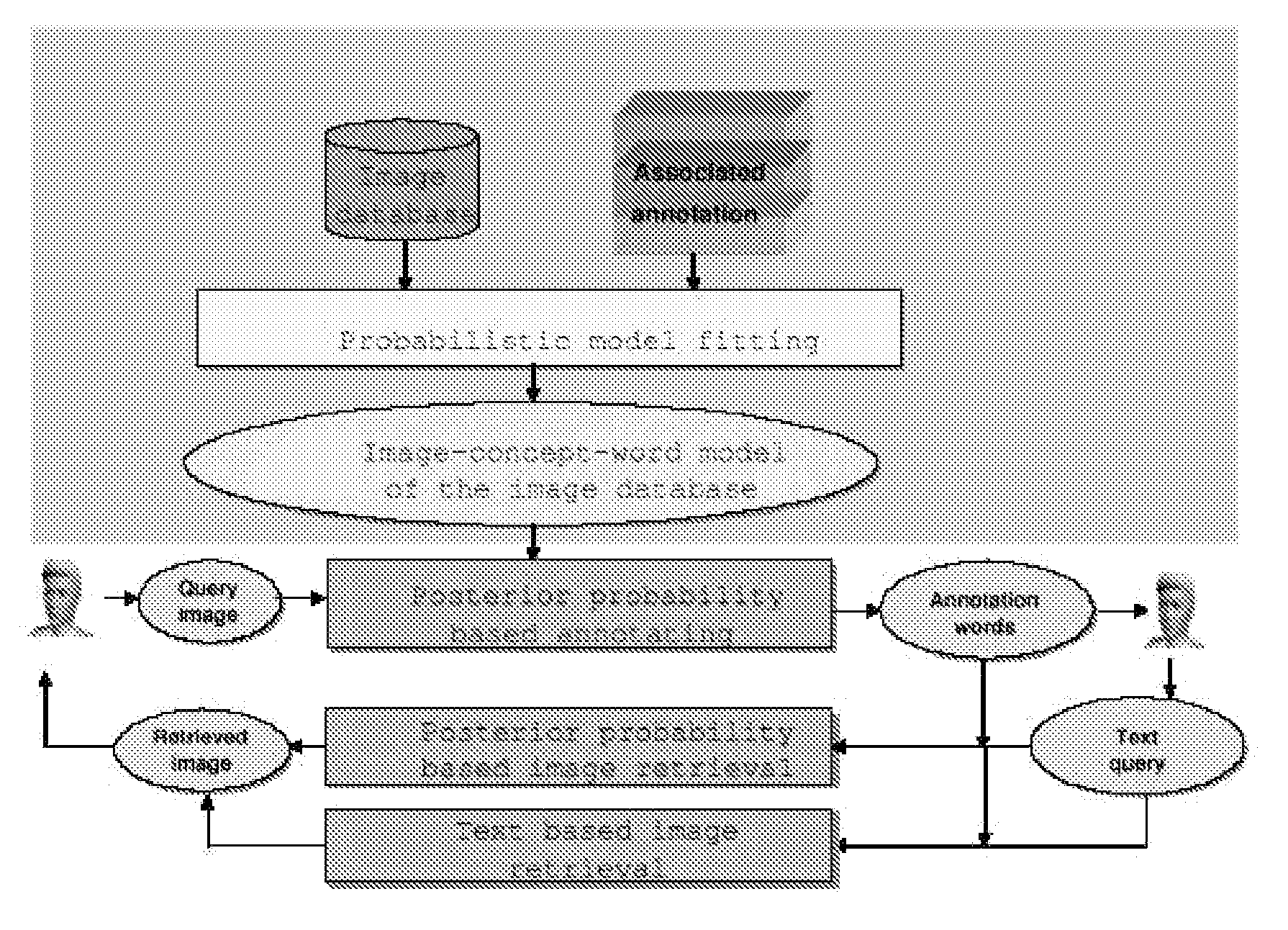
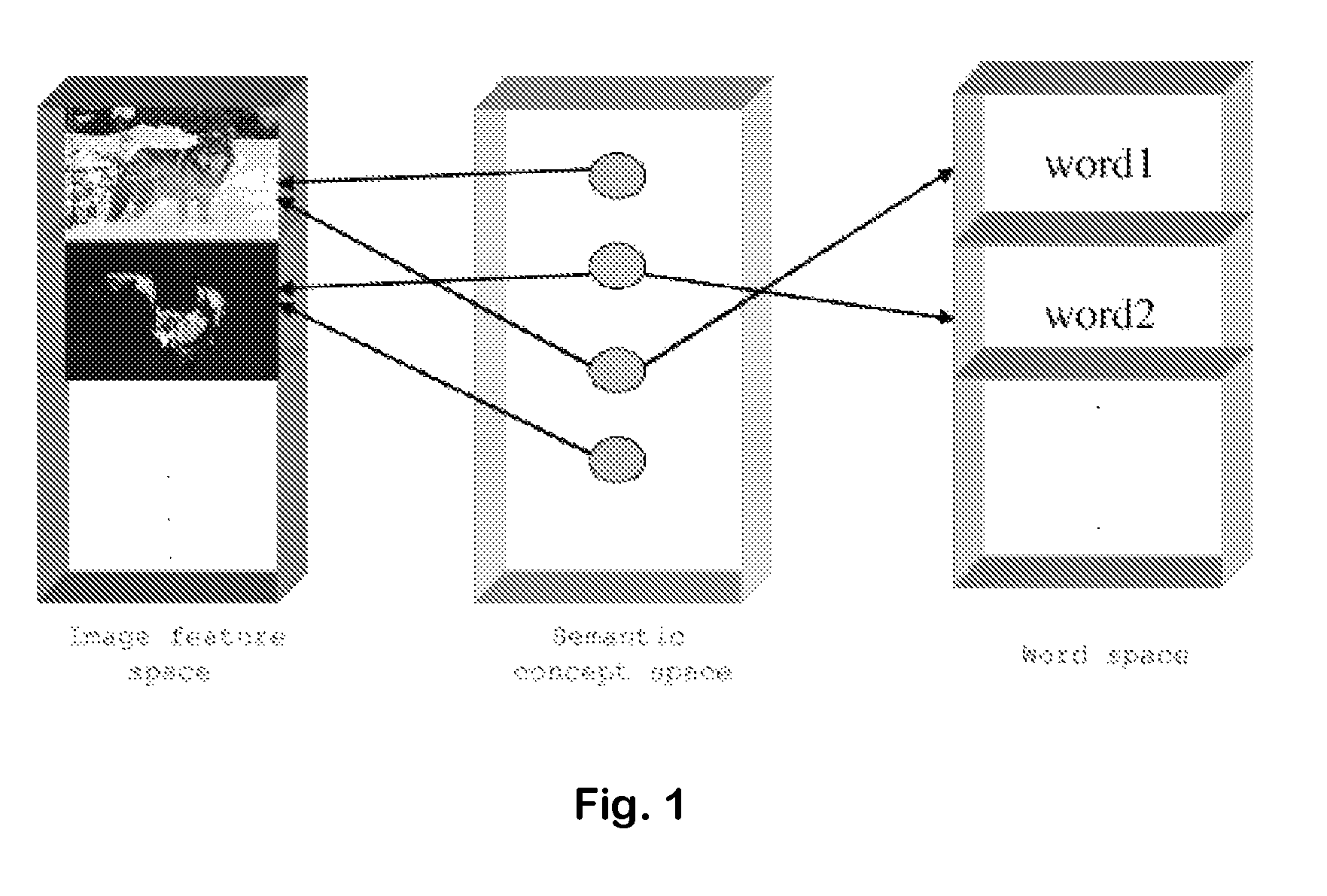
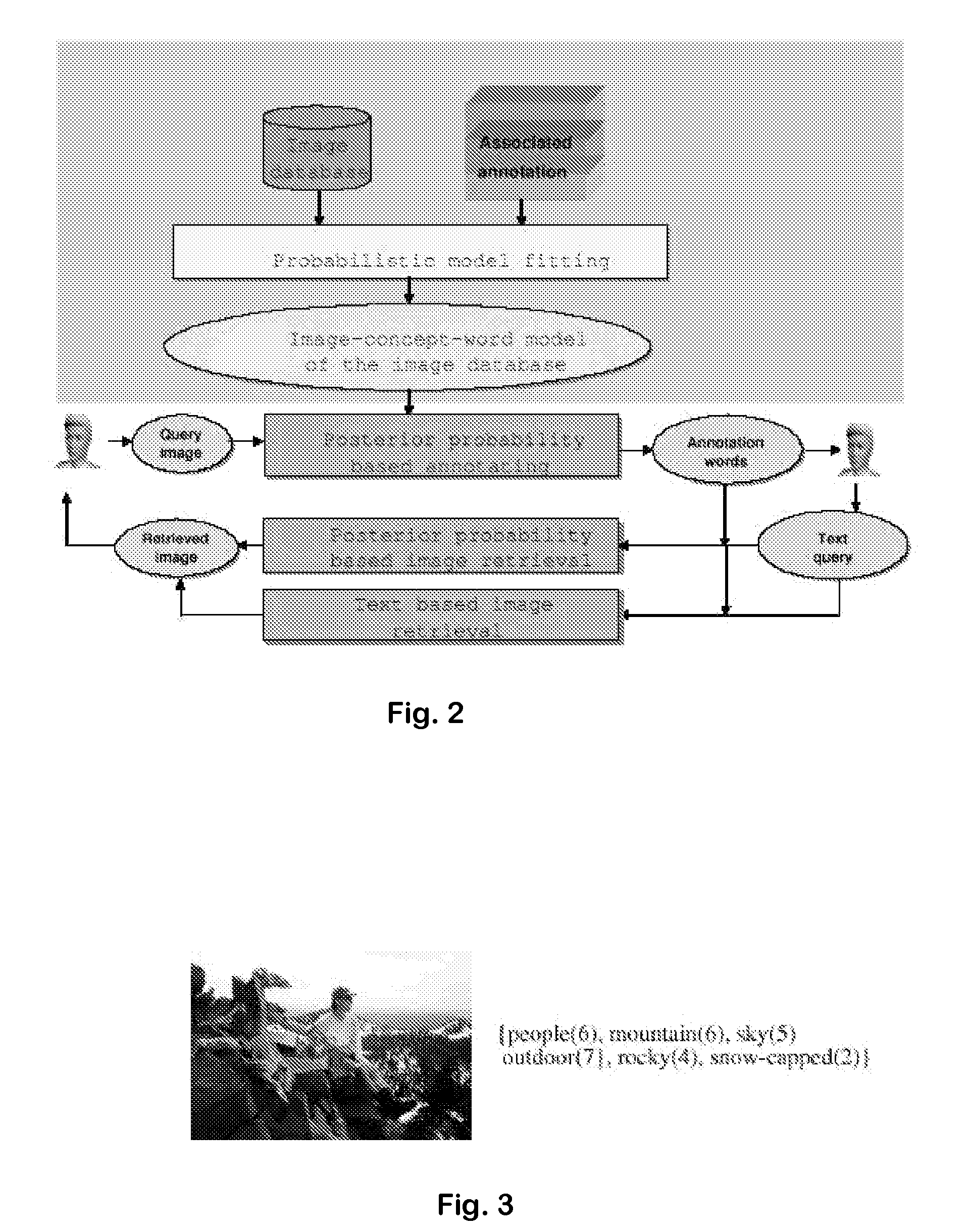
ActiveUS7814040B1Easy to annotate and retrieveEvaluation lessMathematical modelsDigital data information retrievalAlgorithmCorresponding conditional
Systems and Methods for multi-modal or multimedia image retrieval are provided. Automatic image annotation is achieved based on a probabilistic semantic model in which visual features and textual words are connected via a hidden layer comprising the semantic concepts to be discovered, to explicitly exploit the synergy between the two modalities. The association of visual features and textual words is determined in a Bayesian framework to provide confidence of the association. A hidden concept layer which connects the visual feature(s) and the words is discovered by fitting a generative model to the training image and annotation words. An Expectation-Maximization (EM) based iterative learning procedure determines the conditional probabilities of the visual features and the textual words given a hidden concept class. Based on the discovered hidden concept layer and the corresponding conditional probabilities, the image annotation and the text-to-image retrieval are performed using the Bayesian framework.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
System and method for vascular segmentation by Monte-Carlo sampling
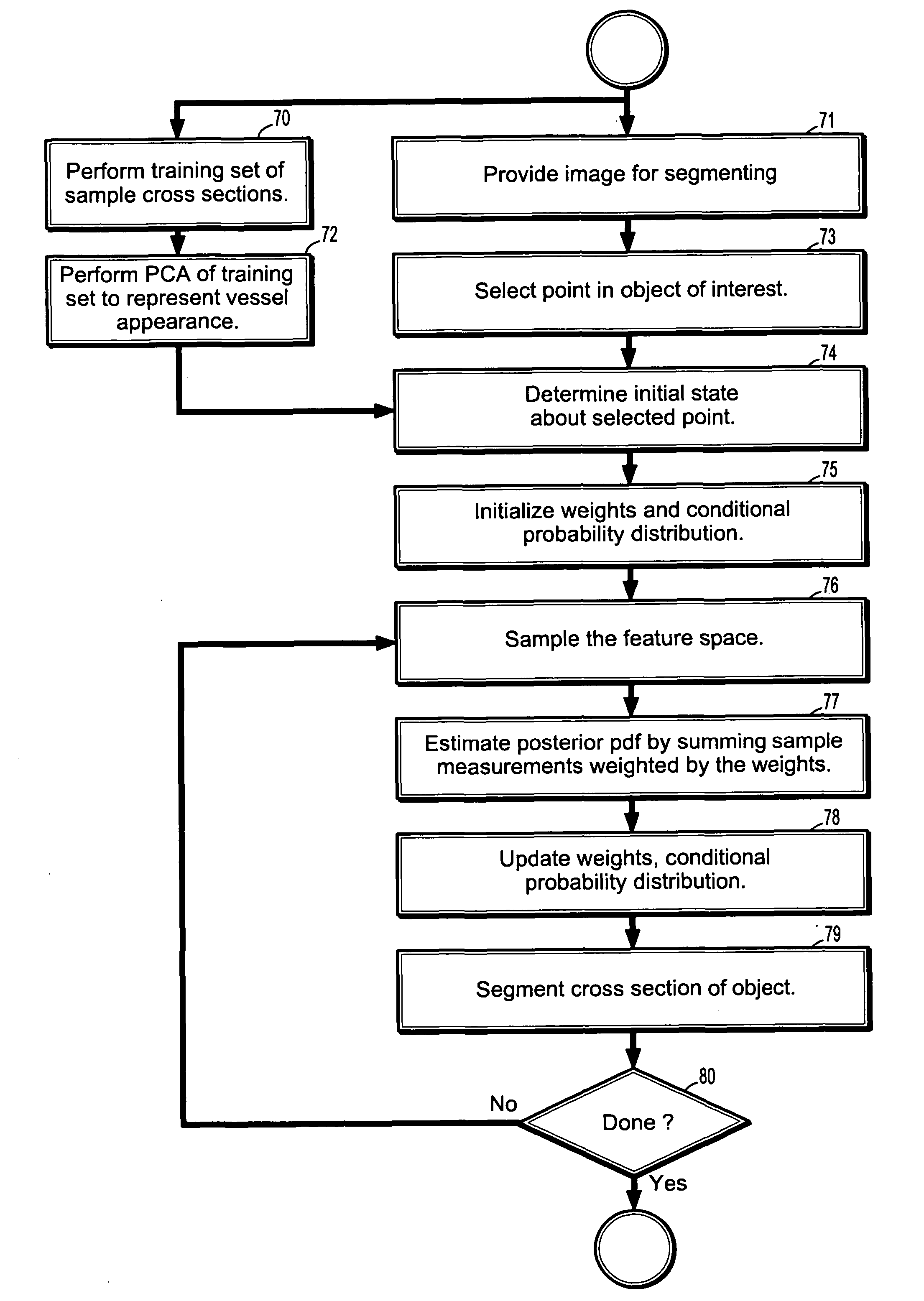
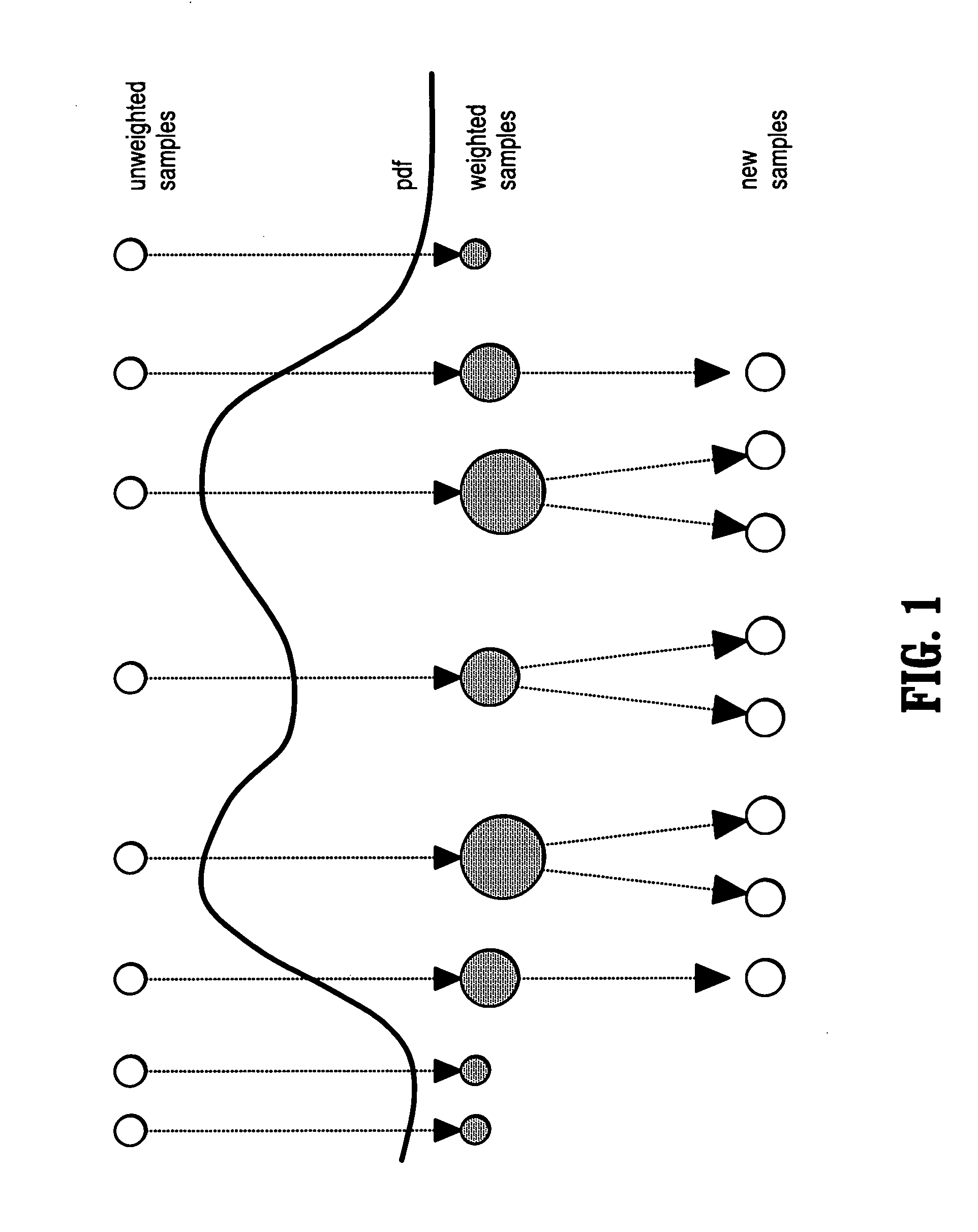
InactiveUS7715626B2Reduce in quantityIssue to overcomeImage enhancementImage analysisCharacteristic spaceDigital image
A method of segmenting tubular structures in digital images includes selecting a point in an image of a tubular object to be segmented, defining an initial state of the selected point, initializing measurement weights, a conditional probability distribution and a prior probability distribution of a feature space of the initial state, sampling the feature space from the prior probability distribution, estimating a posterior probability distribution by summing sample measurements weighted by the measurement weights, and segmenting a cross section of the tubular object from the posterior probability distribution.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Computerized medical underwriting of group life and disability insurance using medical claims data
ActiveUS7249040B1Improve measuring risk of disabilityAccurate estimateFinanceOffice automationProbit modelConditional probability
A method of underwriting group disability insurance for a policy period includes collecting medical claims data for the group to be underwritten, where each medical claim being related to a particular employee of the group. Morbidity categories are provided that categorize the medical claims in the medical claims data. A conditional probability model is developed and applied to the morbidity categories for each employee in the group using his medical claims, thereby calculating the expected conditional probability for each employee of incurring a disability during the policy period. A further statistical model of the estimated cost of the disability is developed and applied based on the employees' morbidity categories from the medical claims data. For each employee, an estimate of the expected cost of incurring a disability given their morbidity categories is derived from his medical claims data. Combining the expected conditional probability for each employee incurring a disability during the policy period with the estimate of the expected cost of that disability gives an estimate of the group's total disability exposure. Thereby, the expected disability exposure is used to determine a premium amount for disability insurance coverage during the policy period for the group.
Owner:TRURISK
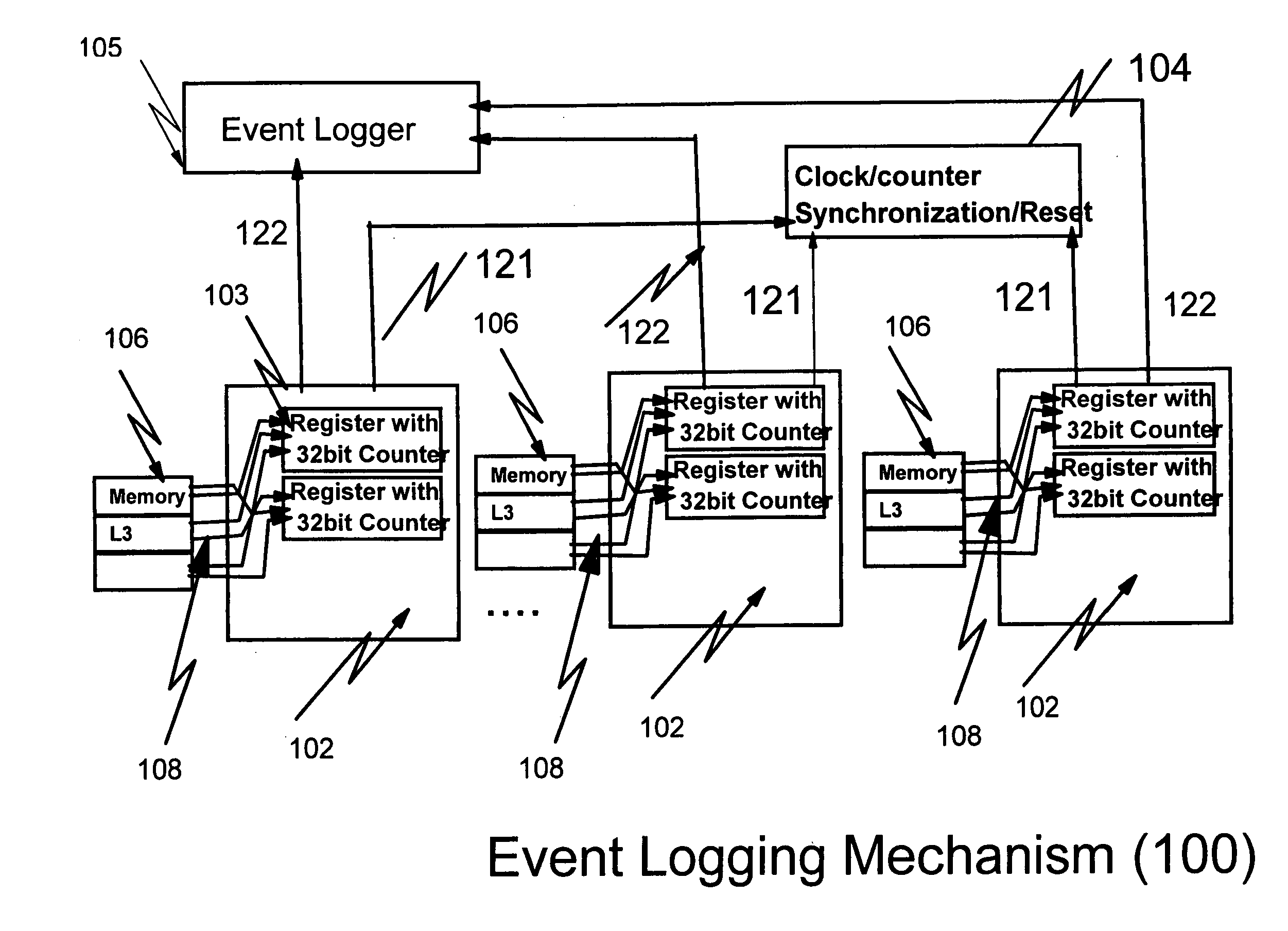
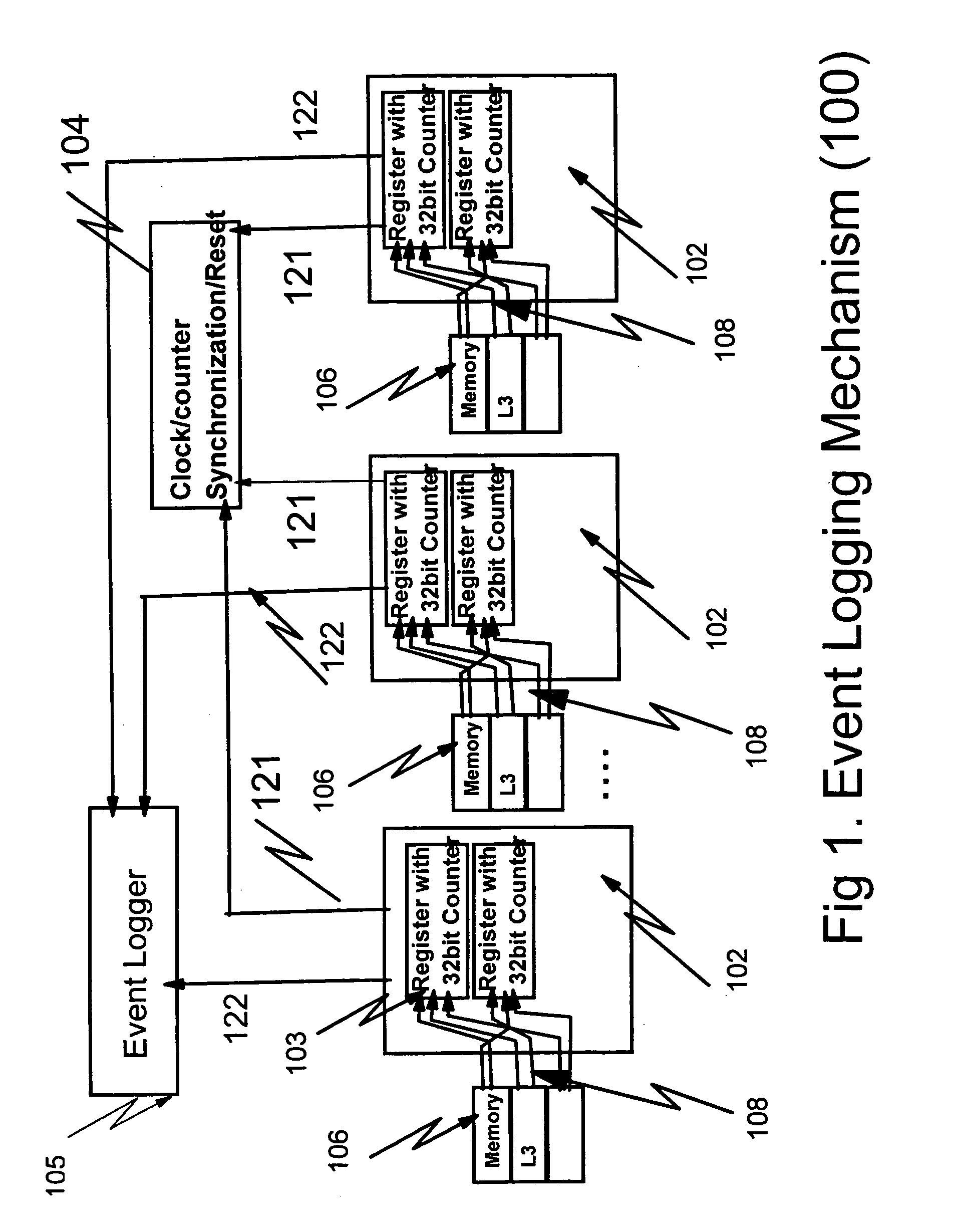
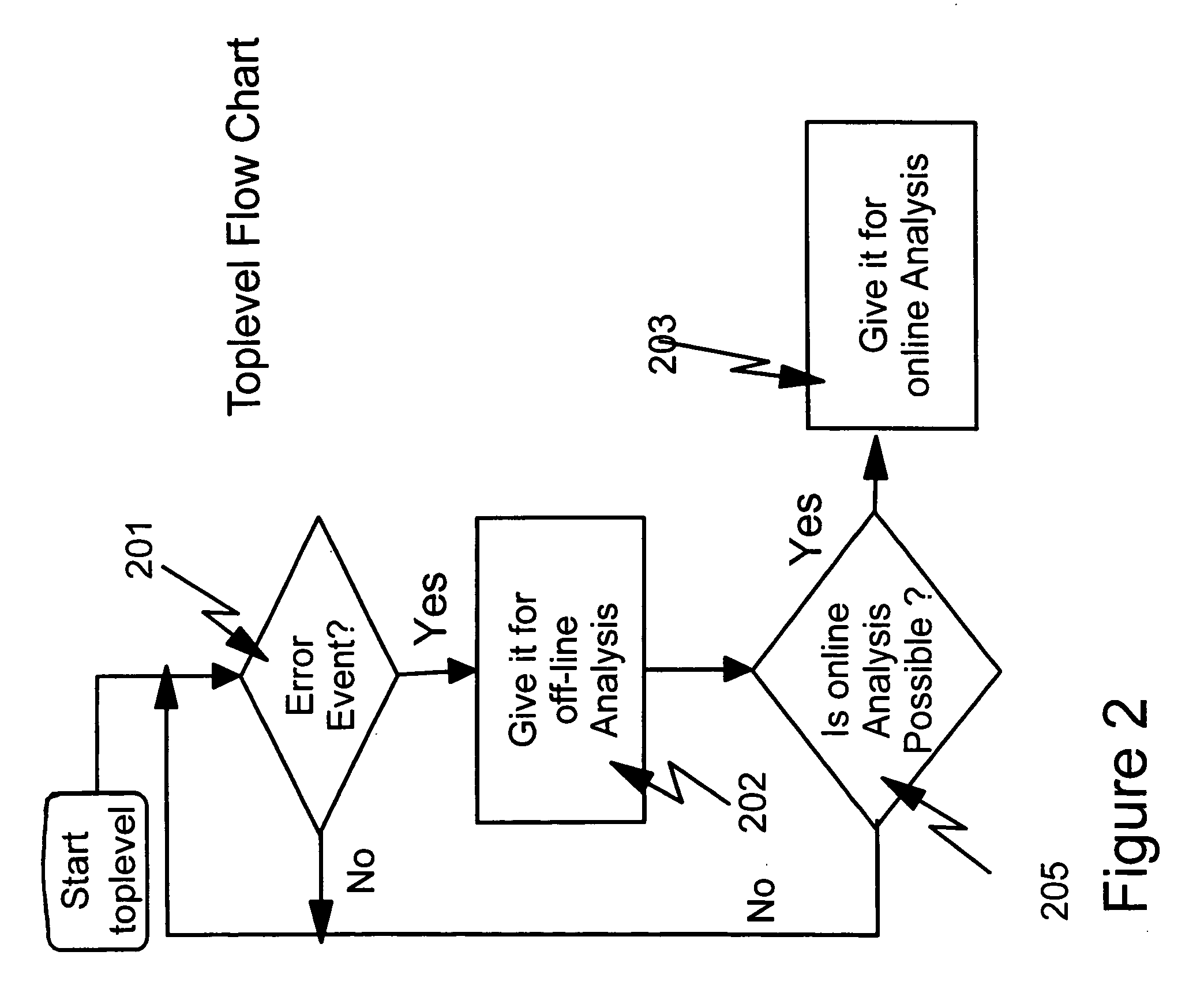
Hardware/software based indirect time stamping methodology for proactive hardware/software event detection and control
InactiveUS20050144532A1Error detection/correctionDigital computer detailsEvent triggerRemedial action
An improved method and apparatus for time stamping events occurring on a large scale distributed network uses a local counter associated with each processor of the distributed network. Each counter resets at the same time globally so that all events are recorded with respect to a particular time. The counter is stopped when a critical event is detected. The events are masked or filtered in an online or offline fashion to eliminate non-critical events from triggering a collection by the system monitor or service / host processor. The masking can be done dynamically through the use of an event history logger. The central system may poll the remote processor periodically to receive the accurate counter value from the local counter and device control register. Remedial action can be taken when conditional probability calculations performed on the historical information indicate that a critical event is about to occur.
Owner:IBM CORP
Inferring informational goals and preferred level of detail of answers based on application being employed by the user
InactiveUS7409335B1Improve accuracyImprove efficiencyData processing applicationsNatural language data processingStatistical analysisLevel of detail
A system and method for inferring informational goals and preferred level of details in answers in response to questions posed to computer-based information retrieval or question-answering systems is provided. The system includes a query subsystem that can receive an input query and extrinsic data associated with the query and which can output an answer to the query. The query subsystem accesses an inference model to retrieve conditional probabilities that certain informational goals are present. One application of the system includes determining a user's likely informational goals and then accessing a knowledge data store to retrieve responsive information. Determining a user's likely informational goals can include inferring a desired level of detail of answers to the query based on the application being employed by the user at the time the query is submitted. The system includes a natural language processor that parses queries into observable linguistic features and embedded semantic components that can be employed to retrieve the conditional probabilities from the inference model. The inference model is built by employing supervised learning and statistical analysis on a set of queries suitable to be presented to a question-answering system. Such a set of queries can be manipulated to produce different inference models based on demographic and / or localized linguistic data.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Apparatus and method for monitoring of infrastructure condition
InactiveUS8412393B2Registering/indicating working of vehiclesRoad vehicles traffic controlCentralized computingMonitoring system
A system and method for vehicle-centric infrastructure monitoring system includes an inspection system mountable on a vehicle configured to travel over an expanse of rail track having a plurality of track blocks. The inspection system acquires track data for at least some track blocks along the expanse of rail track. The monitoring system also includes a positioning system to determine a location of the vehicle and generate location data indicative of an associated track block location, a communications device to transmit the track / location data to a remote location, and a centralized computing system positioned at the remote location to receive the transmitted track / location data. The centralized computing system is programmed to determine a current probability of a track condition for a track block and combine the current track condition probability with a previously determined cumulative track condition probability to provide an updated track condition probability for the track block.
Owner:GE GLOBAL SOURCING LLC
Processing associations in knowledge graphs
InactiveUS20160224637A1Web data indexingSpecial data processing applicationsRegular conditional probabilitySemantic Web
A data infrastructure for graph-based computing that combines the natural language expressiveness of the Semantic Web and the mathematical rigor of graph theory to discover meaningful associations across multiple sources towards computer-assisted serendipitous insight discovery. The process automatically integrates massive size datasets accessed using Semantic Web standards and technologies and normalizes data in graphs. The process generates a plurality of conditional probability distributions based on type-triple meta-data and triple statistics to model saliency and automatically construct and evaluate a plurality of sub-graphs based on the plurality of conditional probabilities for contextual-saliency. The process then renders a plurality of paths (i.e. sequence of associations) that model meaningful pairwise relations between objects of the normalized integrated data. The pluralities of conditional probabilities reveal and rank previously unknown associations between entities of user-interest in the knowledge graph.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com