Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
93results about How to "Issue to overcome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
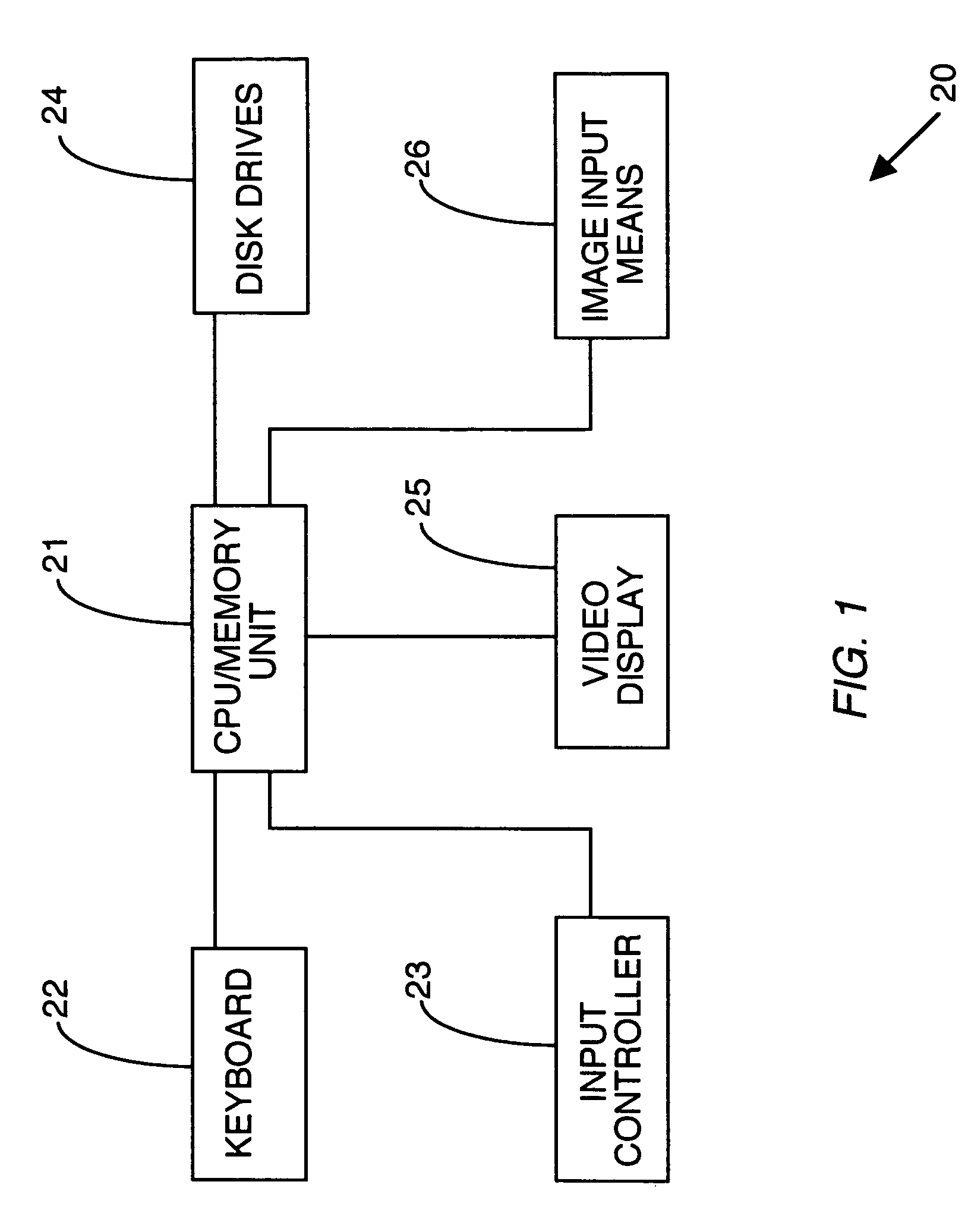
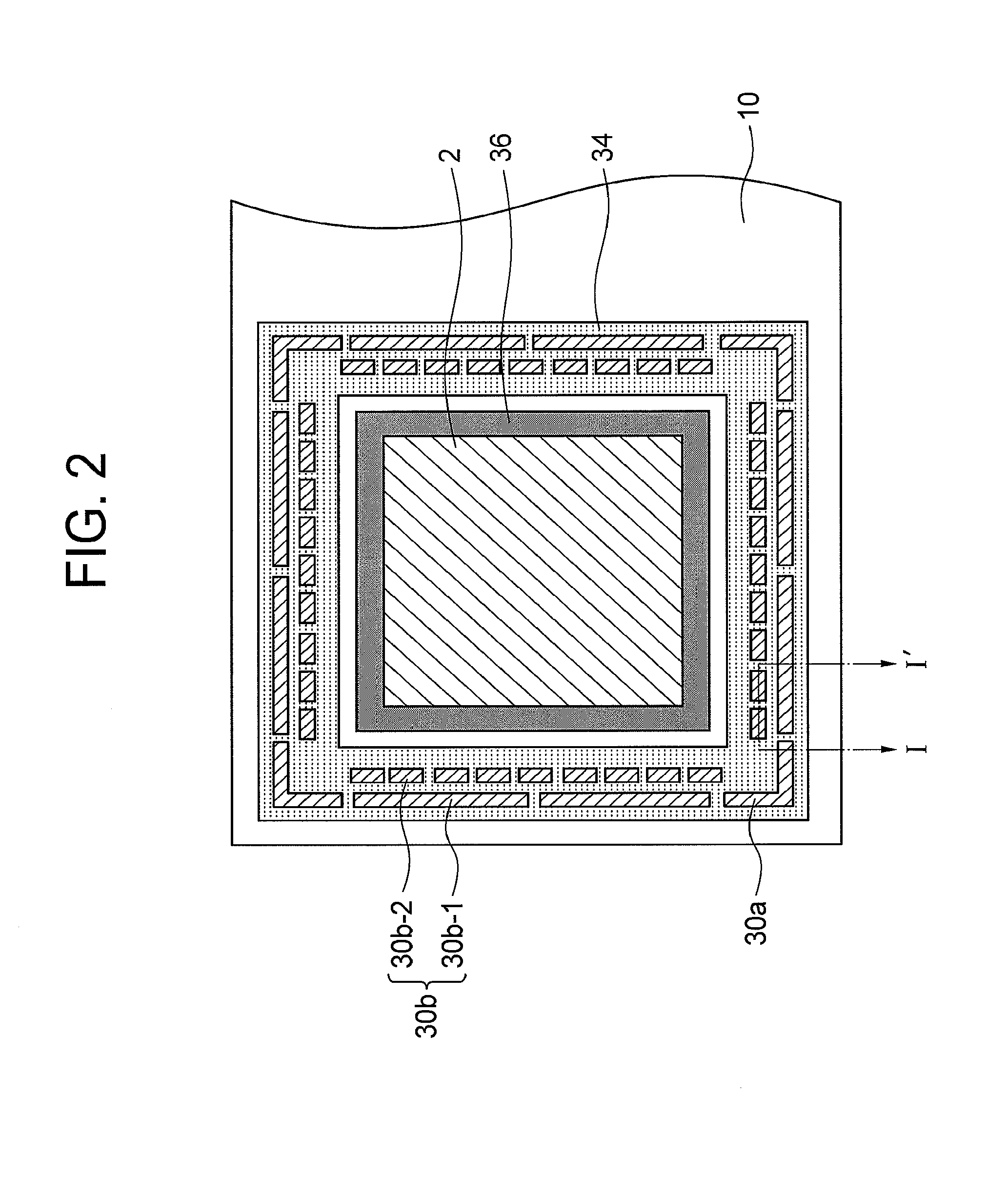
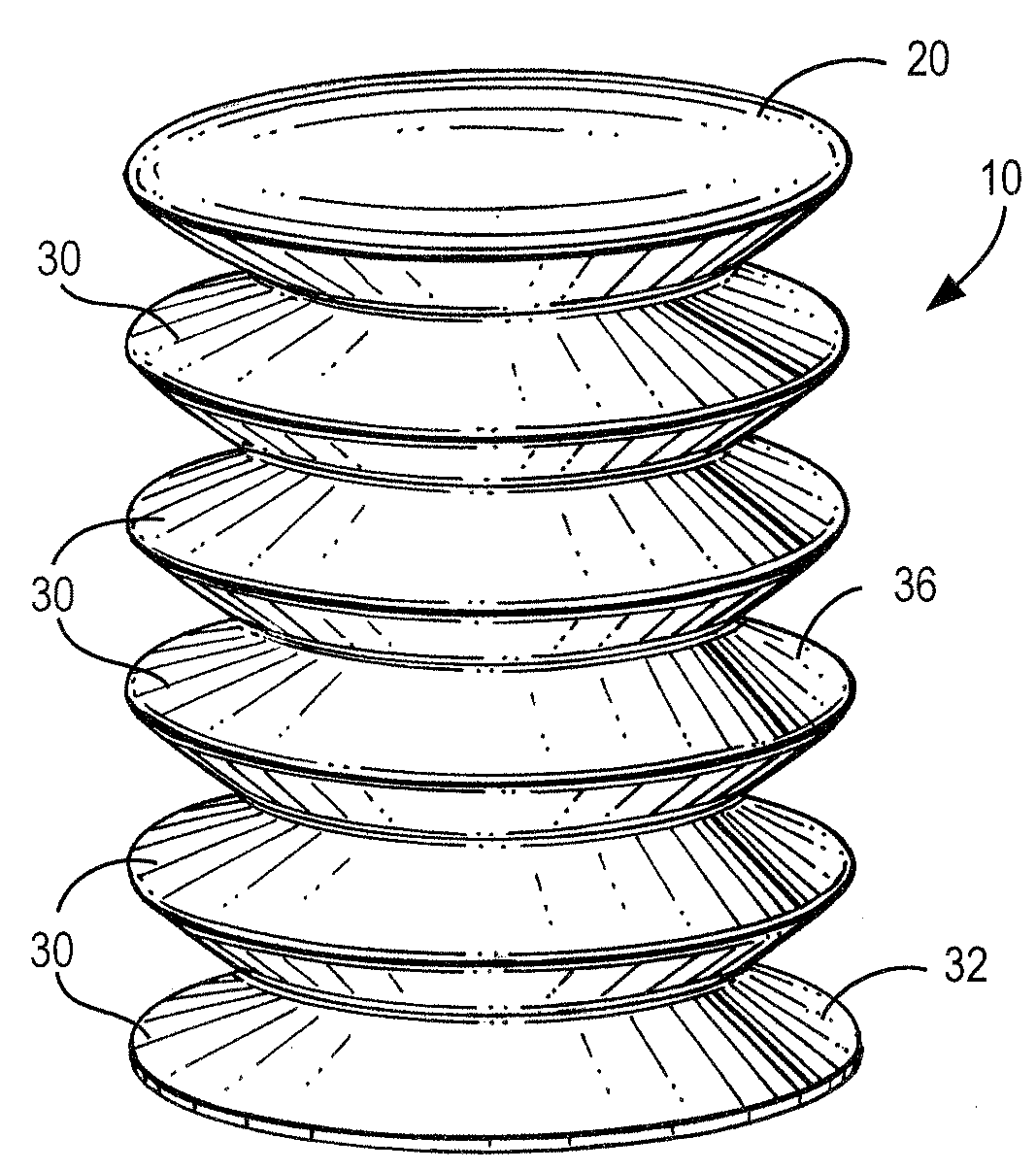
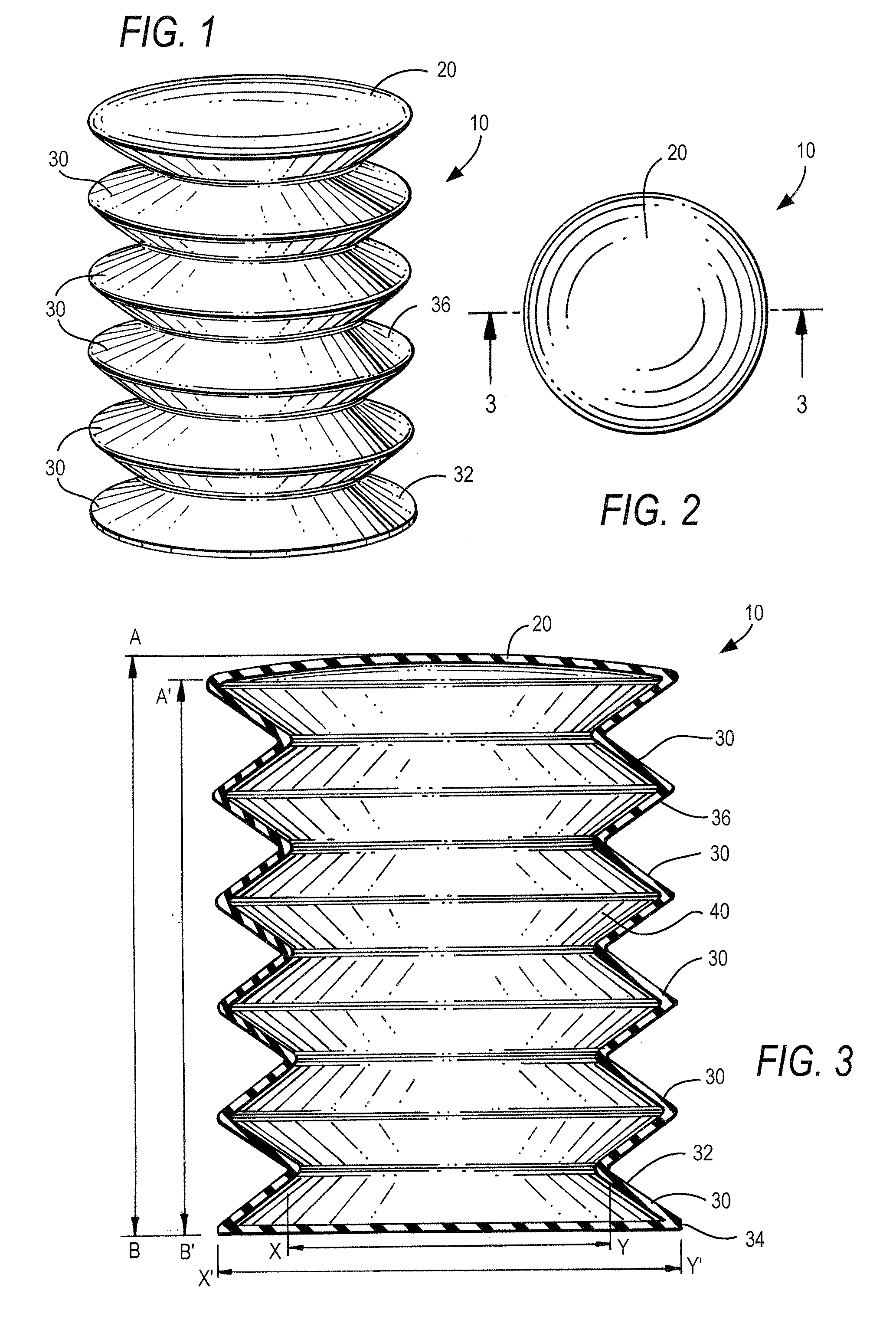
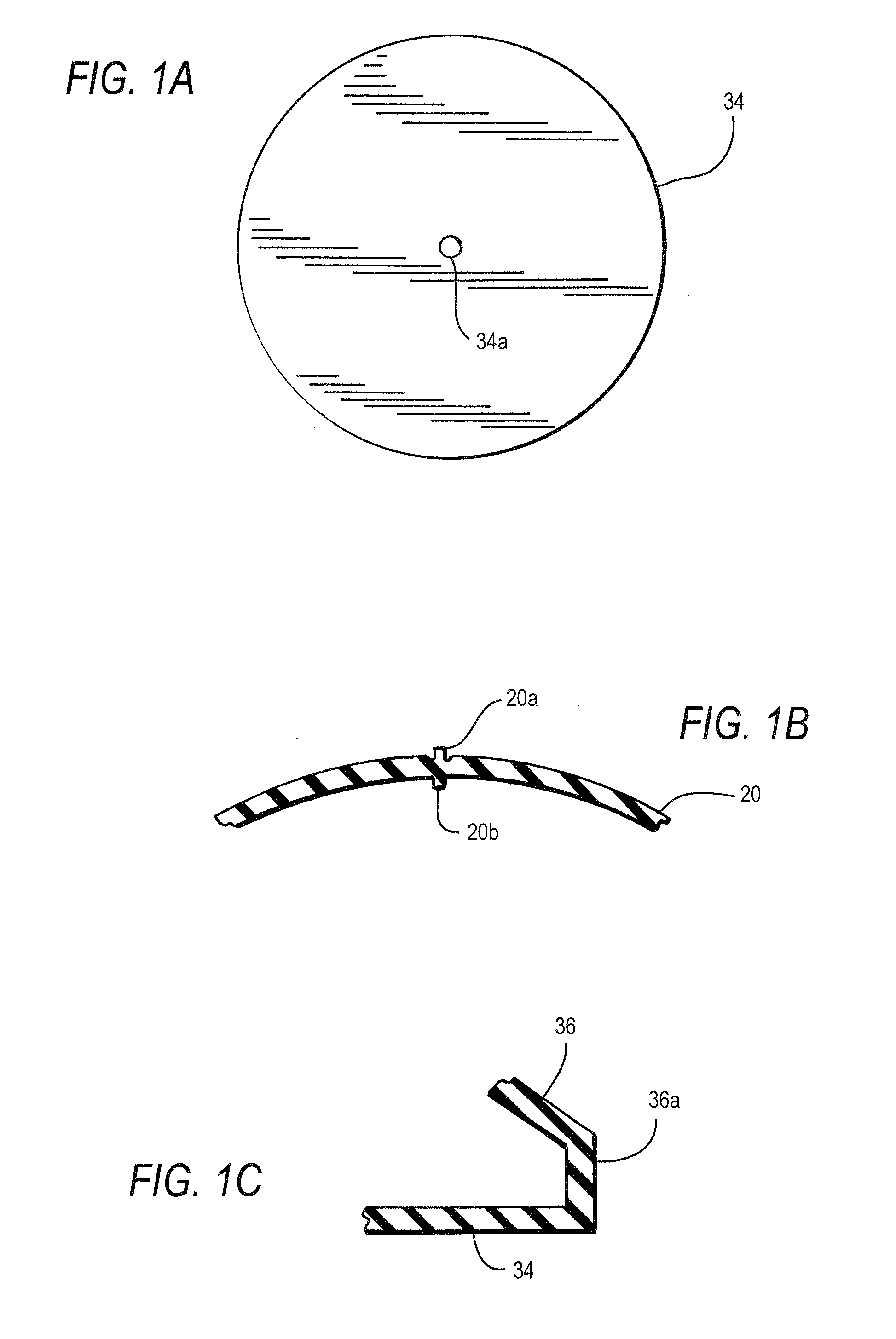
Speed cooking oven with sloped oven floor and reversing gas flow
ActiveUS8011293B2Single rack cooking speedsHigh heat transfer rateAir-treating devicesDomestic stoves or rangesProcess engineering
Owner:TURBOCHEF TECH INC
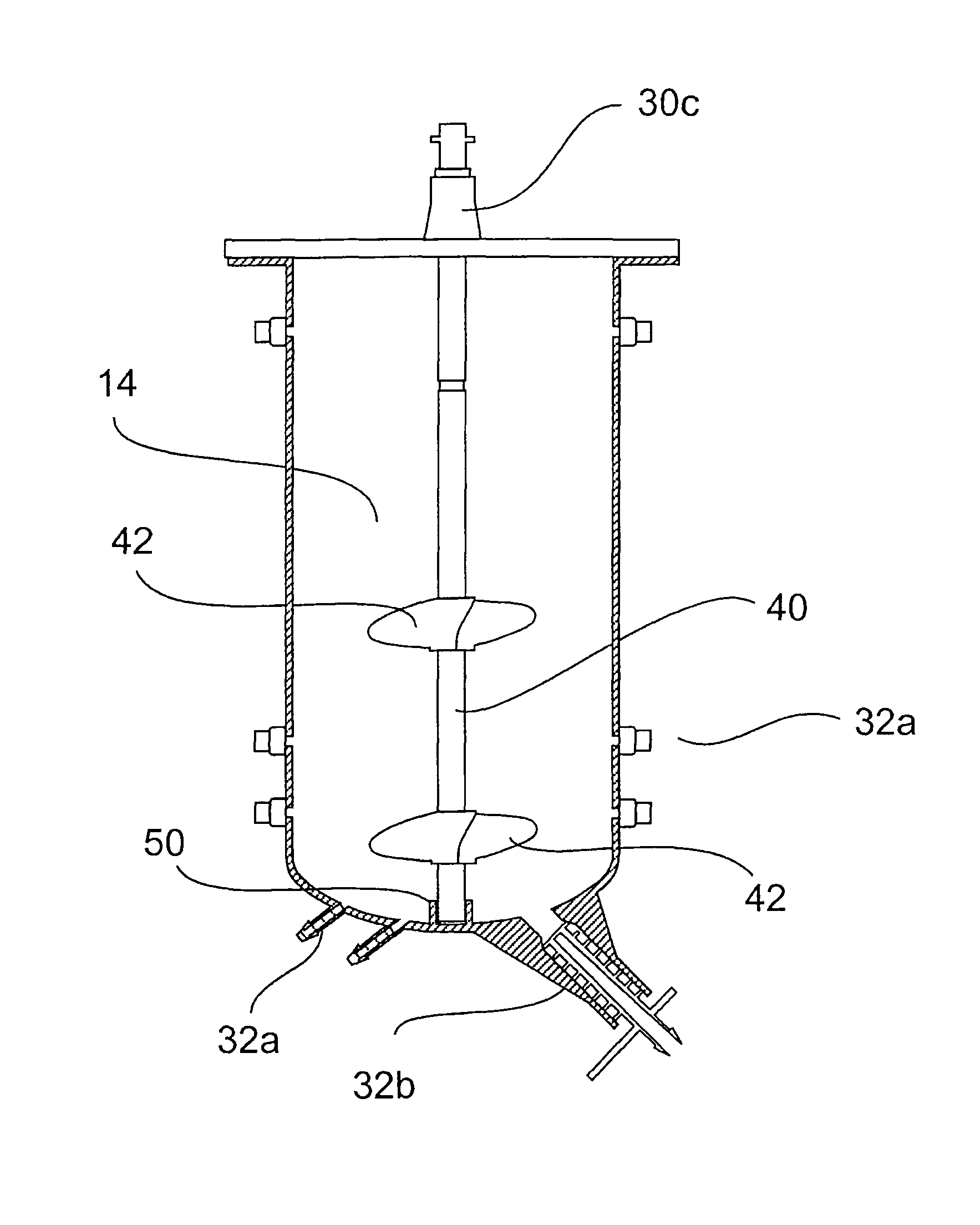
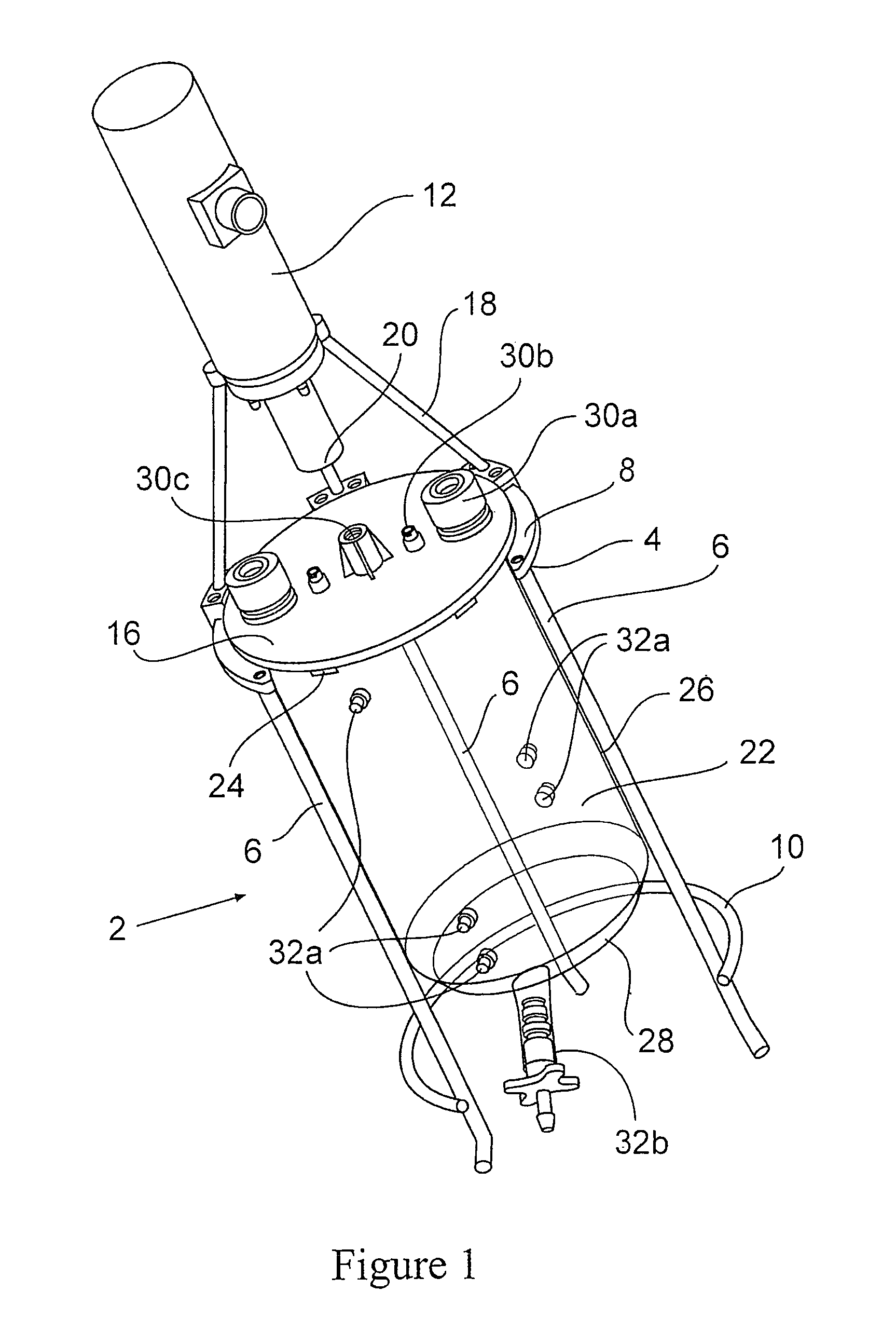
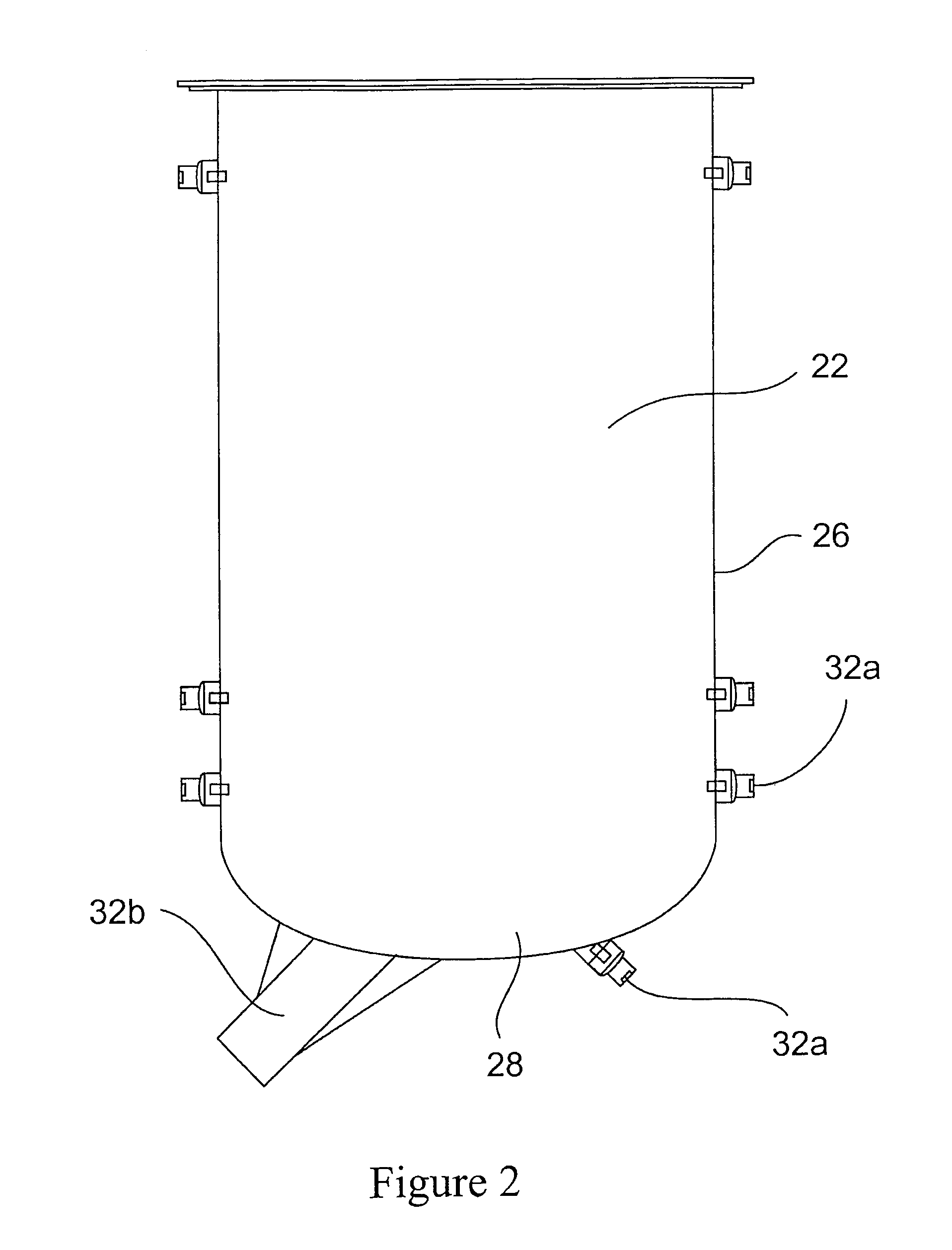
Stirred tank bioreactor
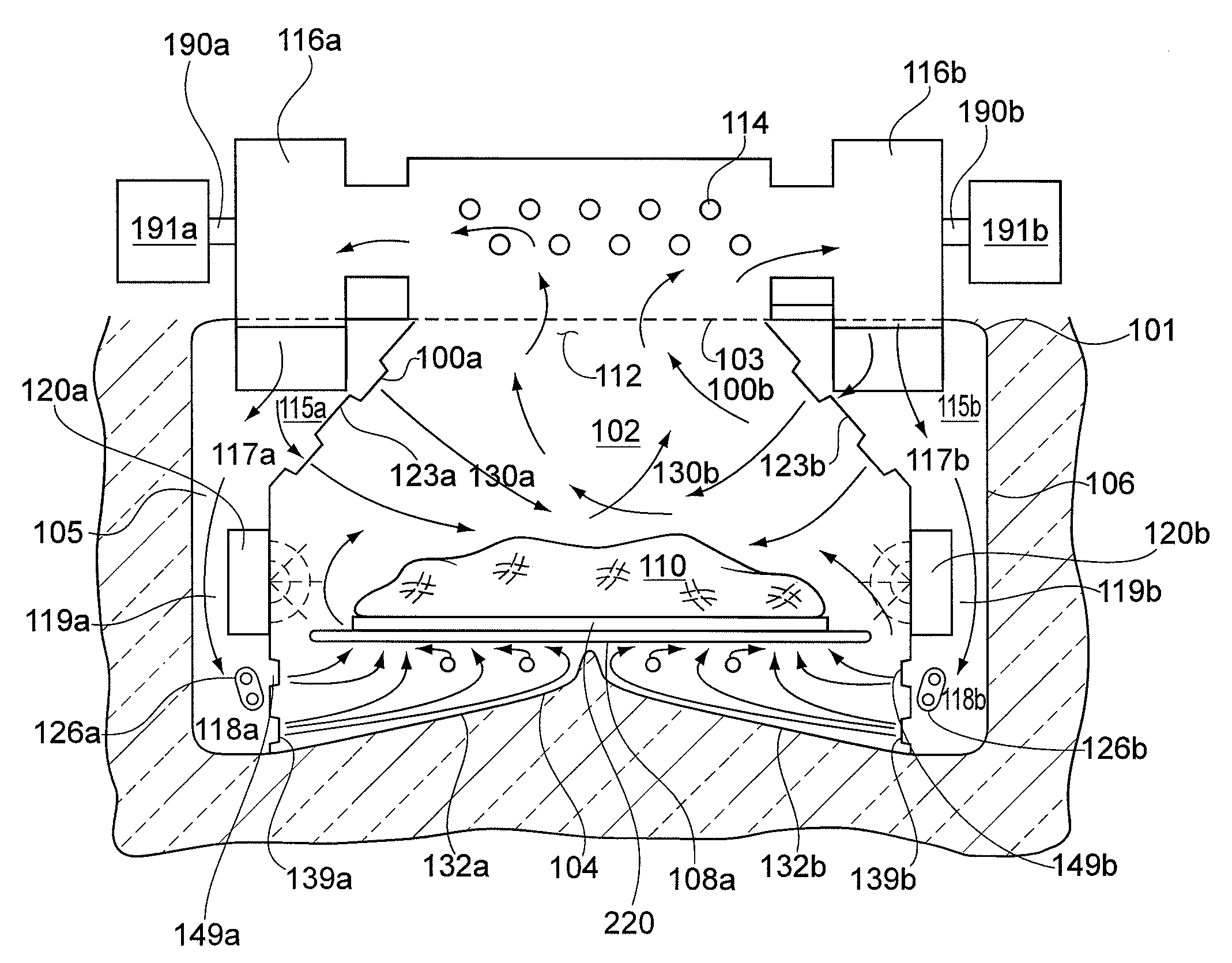
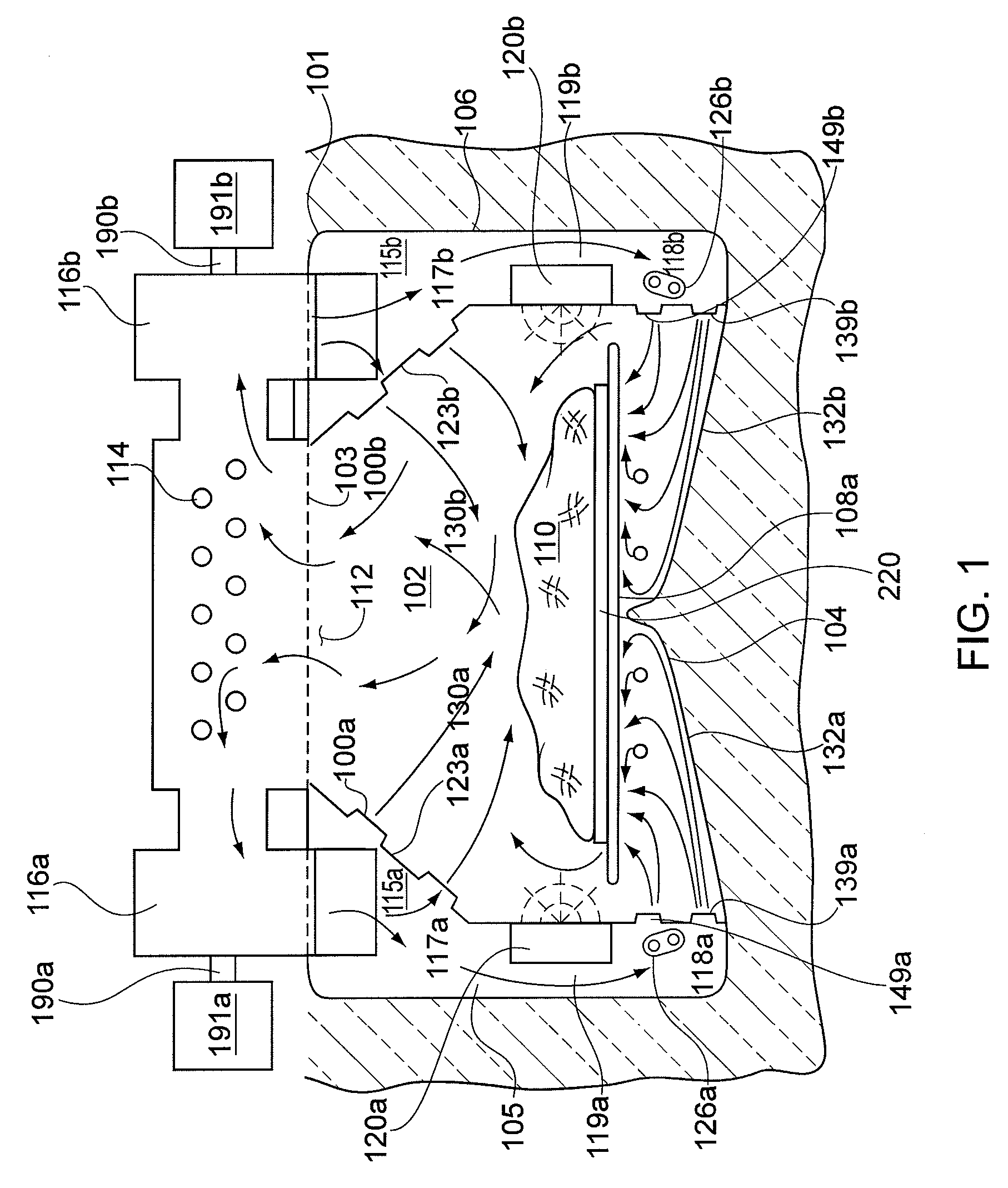
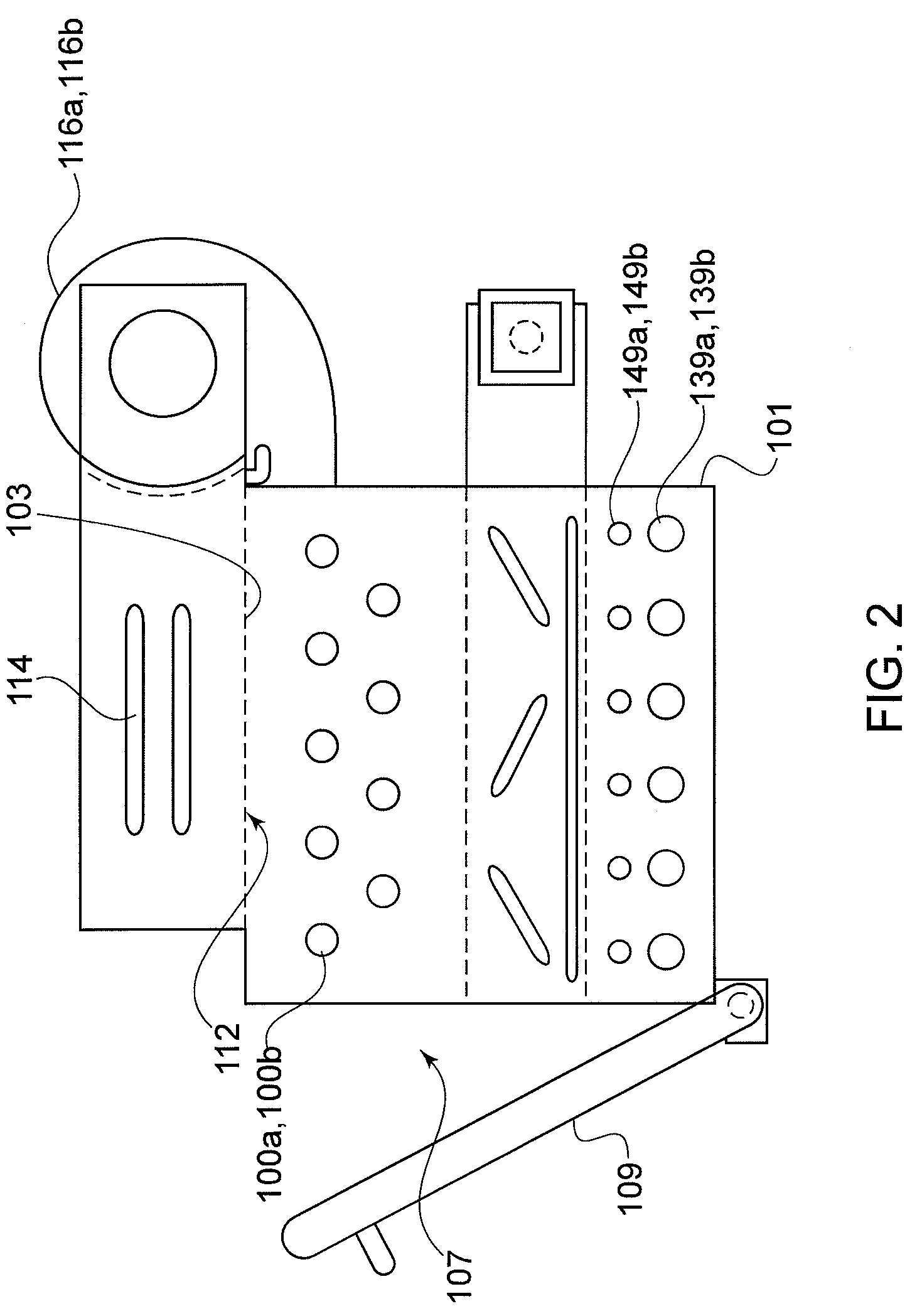
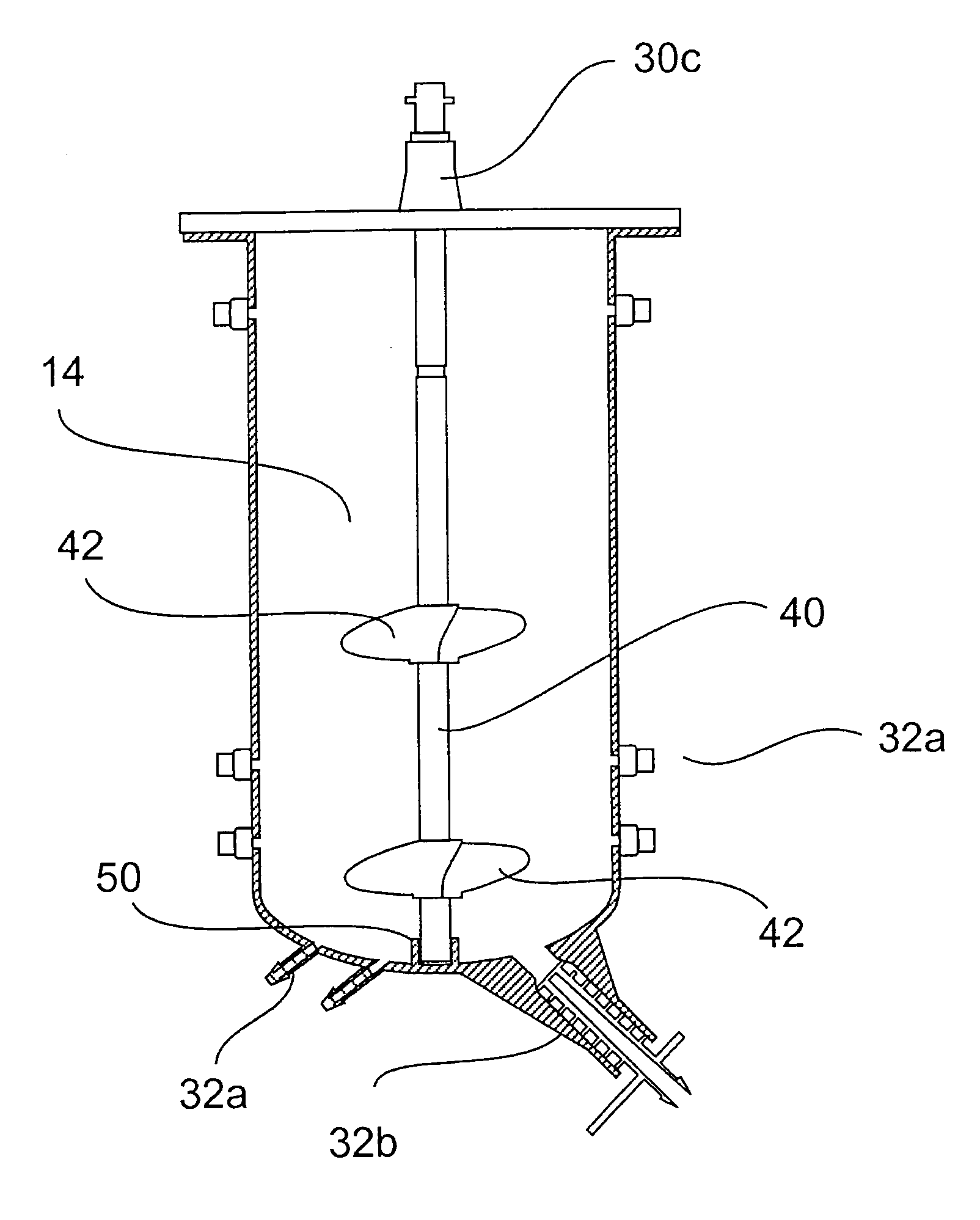
ActiveUS20090311776A1Eliminate riskIssue to overcomeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAir interfaceCholesterol binding
The present invention is a disposable bioreactor formed of molded plastic. The bioreactor is presterilized and has a top and body sealed to each other. One or more ports are formed in the top and side of the housing. Preferably at least one port is below the liquid / air level for the housing. The one or more ports that are below the liquid / air interface level may be used as sampling ports or access ports for probes or drains or supply ports for liquids or gases. The bioreactor provides a direct retrofit for the existing glass or steel assembly that utilizes the existing support structures and controls. The molded design overcomes issues of discontinuity, dead spots and the like due to its fixed dimensions that are built in by the molding process. Reproducible probe and other equipment location is also guaranteed through the use of the molded port features. The molded plastic allows for greater flexibility in material selection to reduce or eliminate lipid or cholesterol binding.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
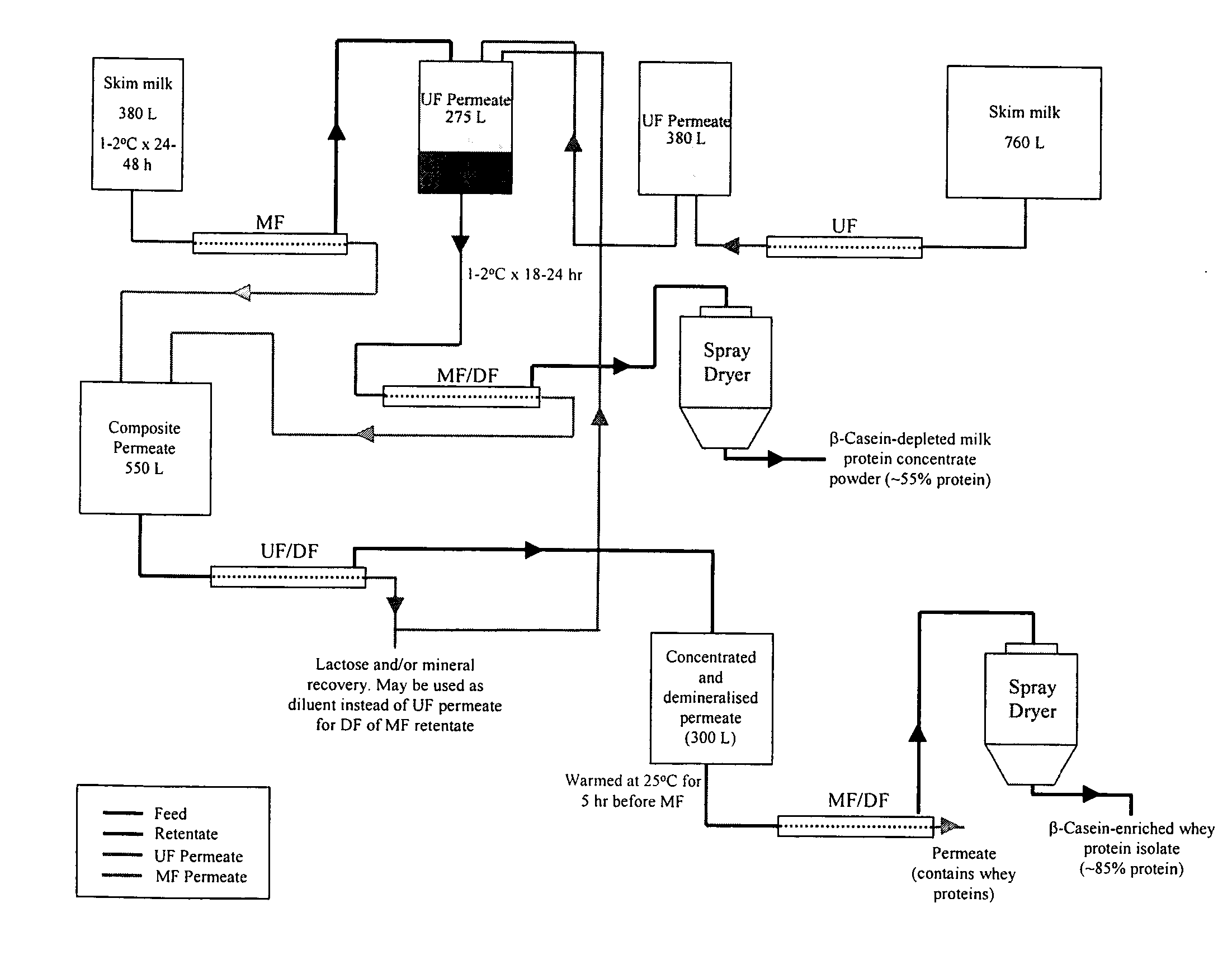
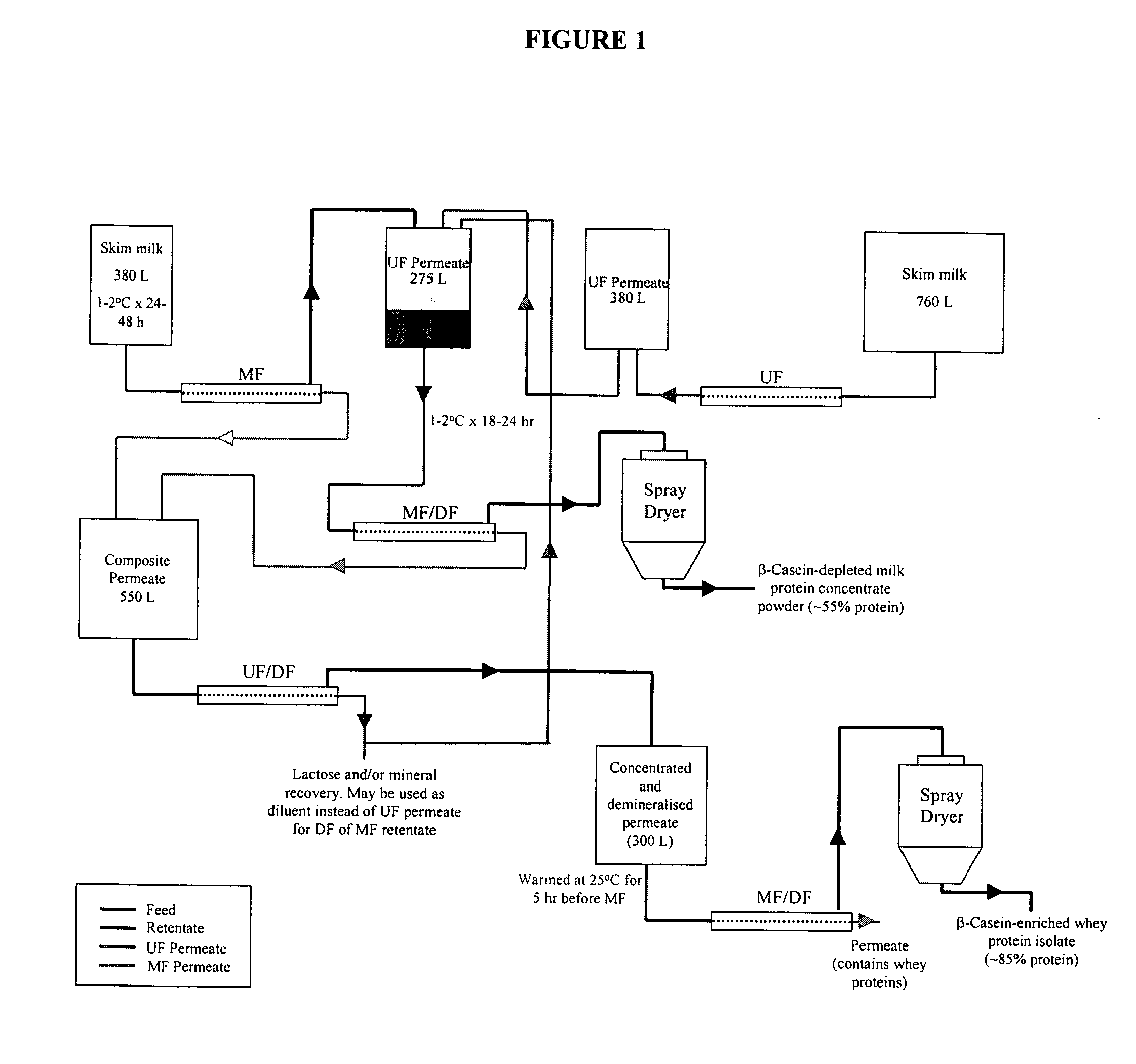
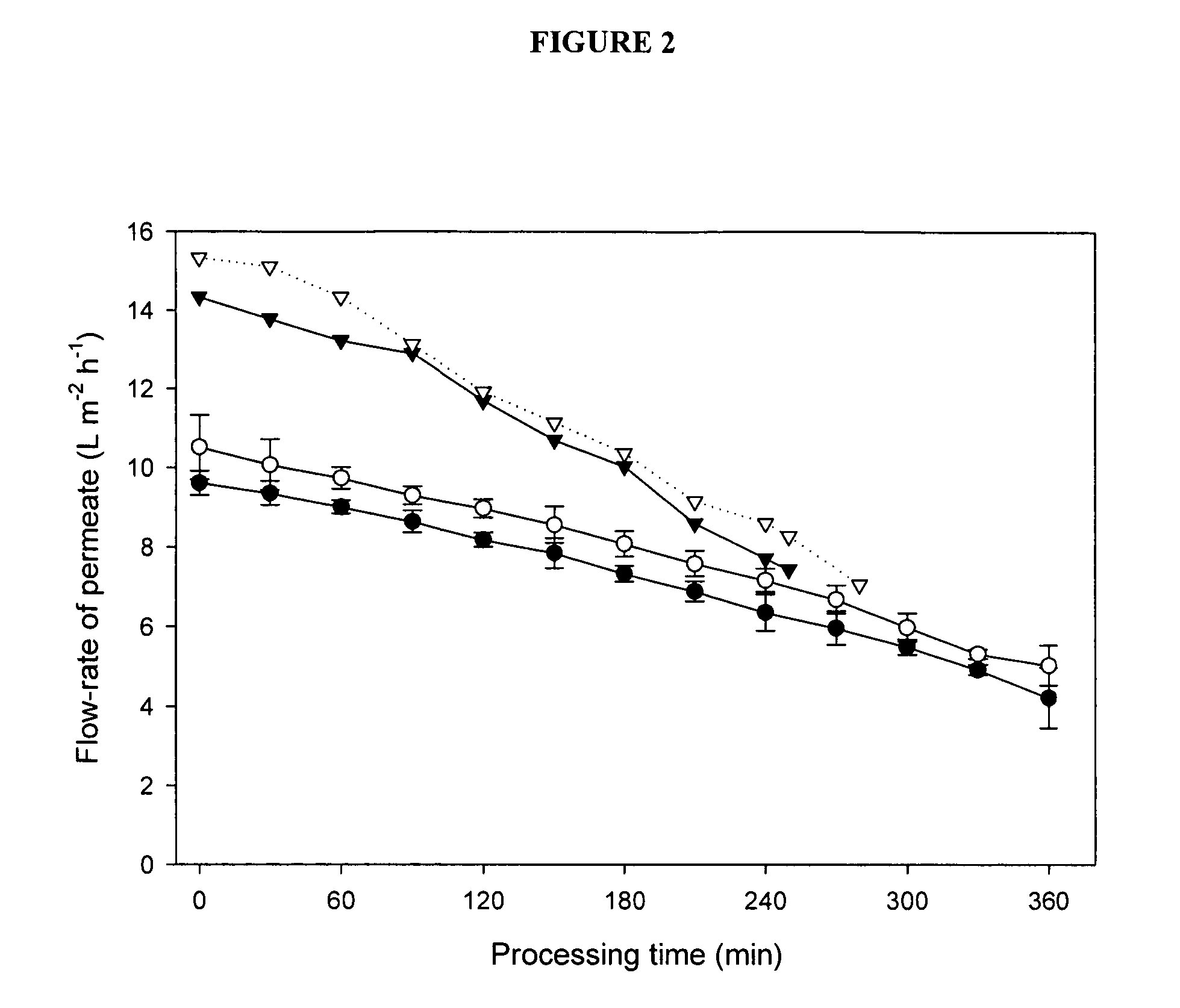
Purification of beta casein from milk
ActiveUS20070104847A1Without negatively impactingFunctionalMilk preparationFood membrane processMilk SerumMicrofiltration membrane
A method is provided for obtaining β-casein from skim milk. Purification of β-casein from milk is achieved through a process of microfiltration using cross-flow polymeric microfiltration membranes. Cooling of the milk prior to microfiltration results in improved separation of β-casein from the other milk serum proteins. Further filtration and demineralization of the microfiltered permeate results in enrichment of the fraction containing soluble β-casein. An integrated scheme that allows a dairy plant to continuously separate and purify β-casein is provided. Also provided is a method for obtaining cheese with improved meltability and reduced bitterness.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
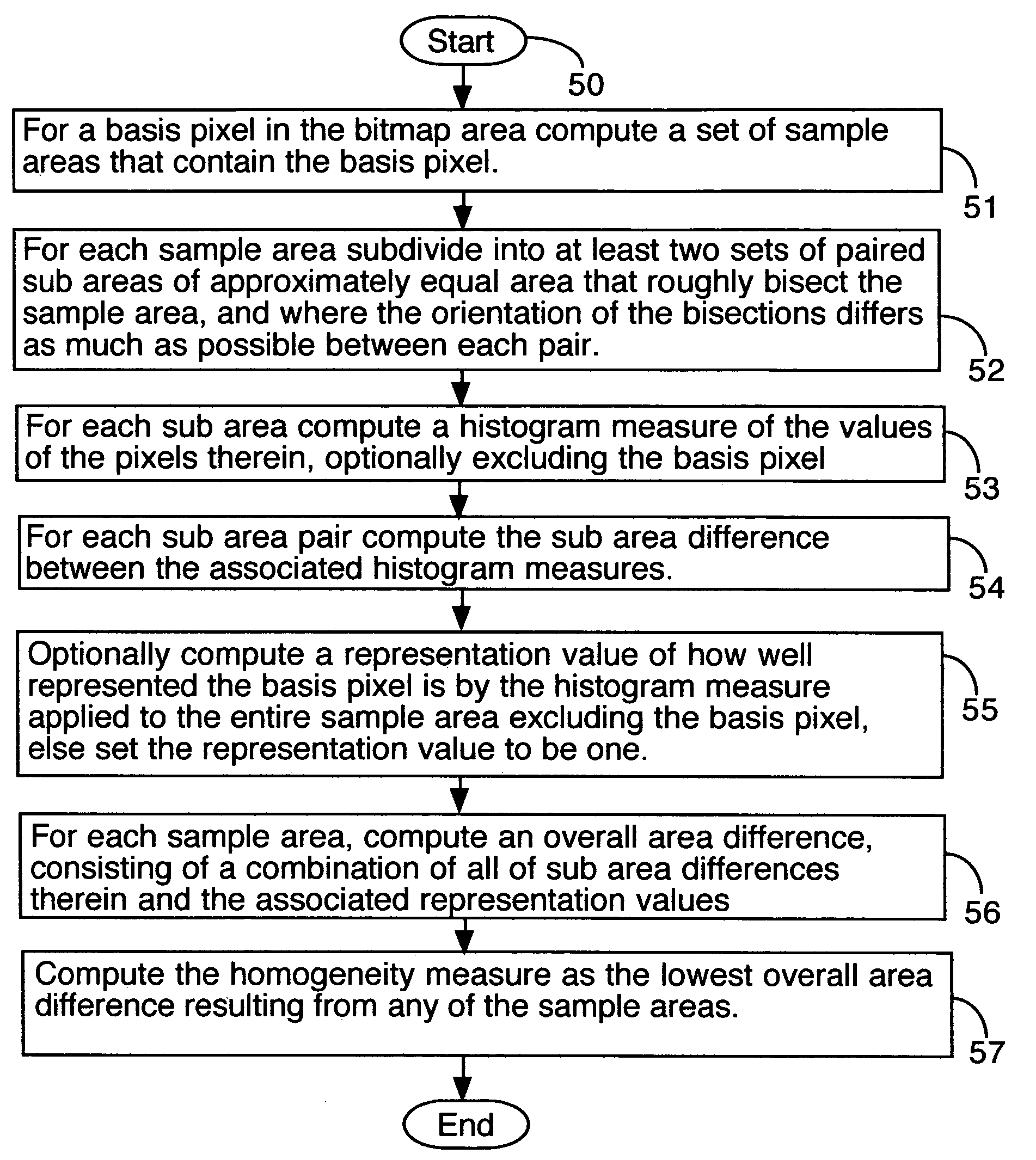
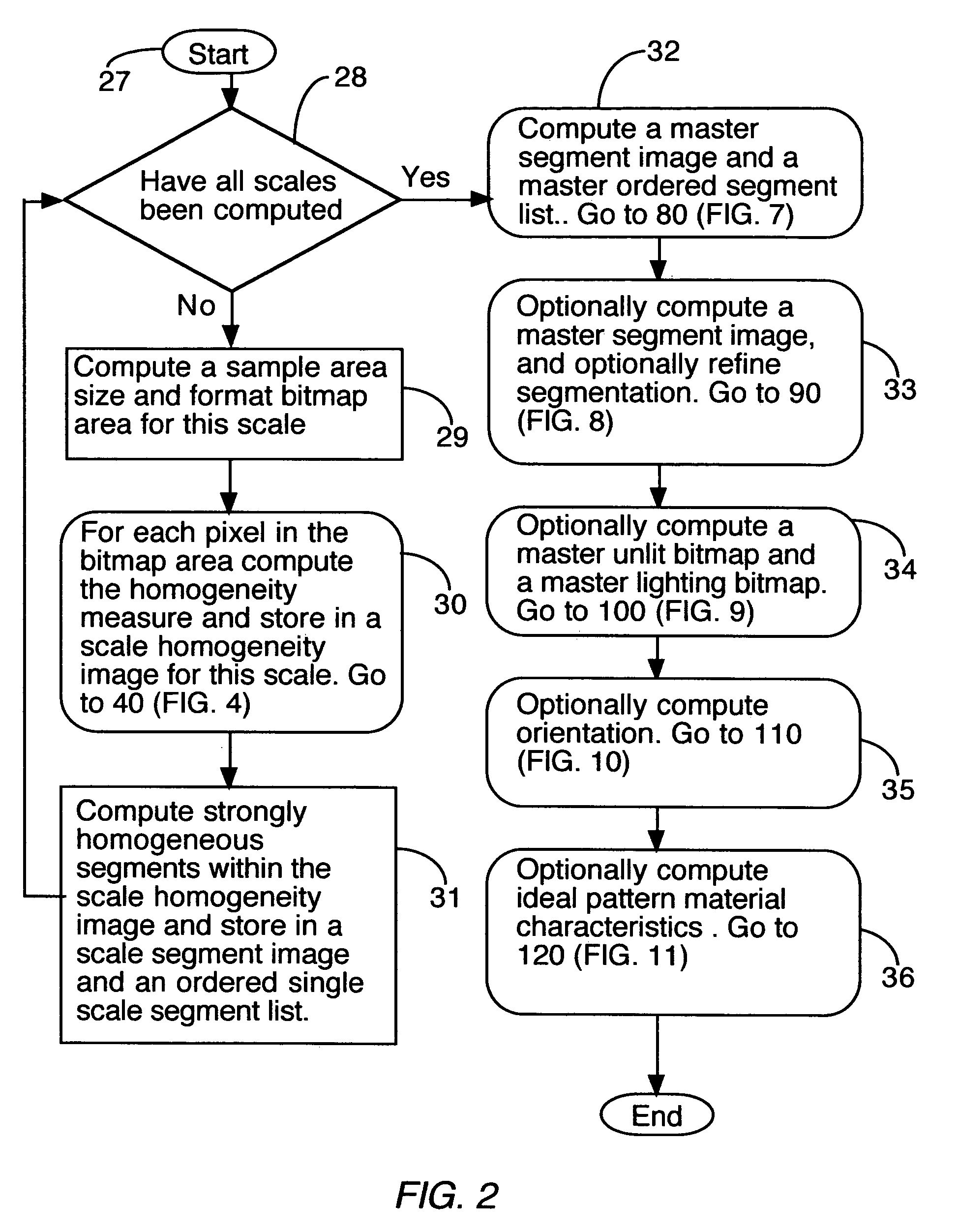
Image analysis, editing and search techniques
InactiveUS7421125B1Issue to overcomeEasy to detectCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionImaging analysis
Disclosed is a method for characterizing the content of a digital image. A component of the method is the homogeneity measure, which calculates a value or values based on the local similarity of portions of a sample area. A further component is a means of optimally adjusting the shape and offset of the local sample area to improve the resulting measure. The homogeneity measure may be applied at a higher level to segment an image, by grouping together larger portions of an image whose sub-components are locally similar. A strongly homogeneous region is a contiguous region composed of elements exhibiting local homogeneity better than that of surrounding elements, and may be applied to identify the scale and other characteristics of a portion of an image. This may be used to facilitate algorithms that separate lighting and texturing information, and in identifying the composition of an image.
Owner:ALTOR SYST
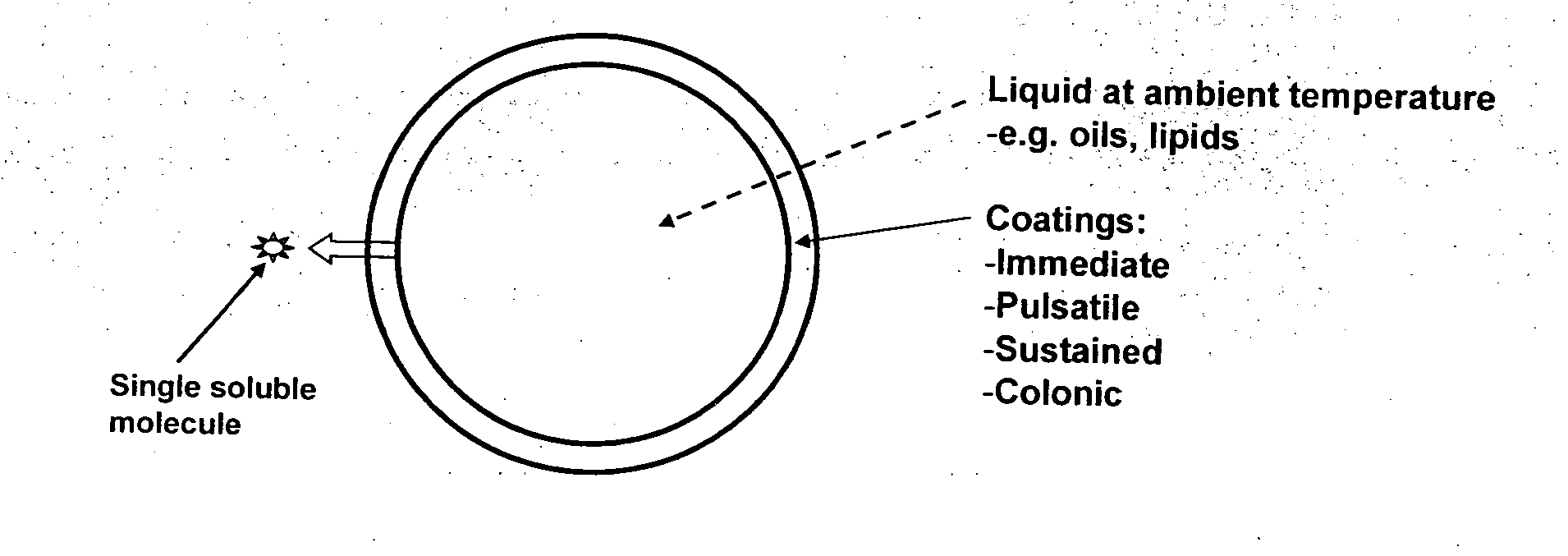
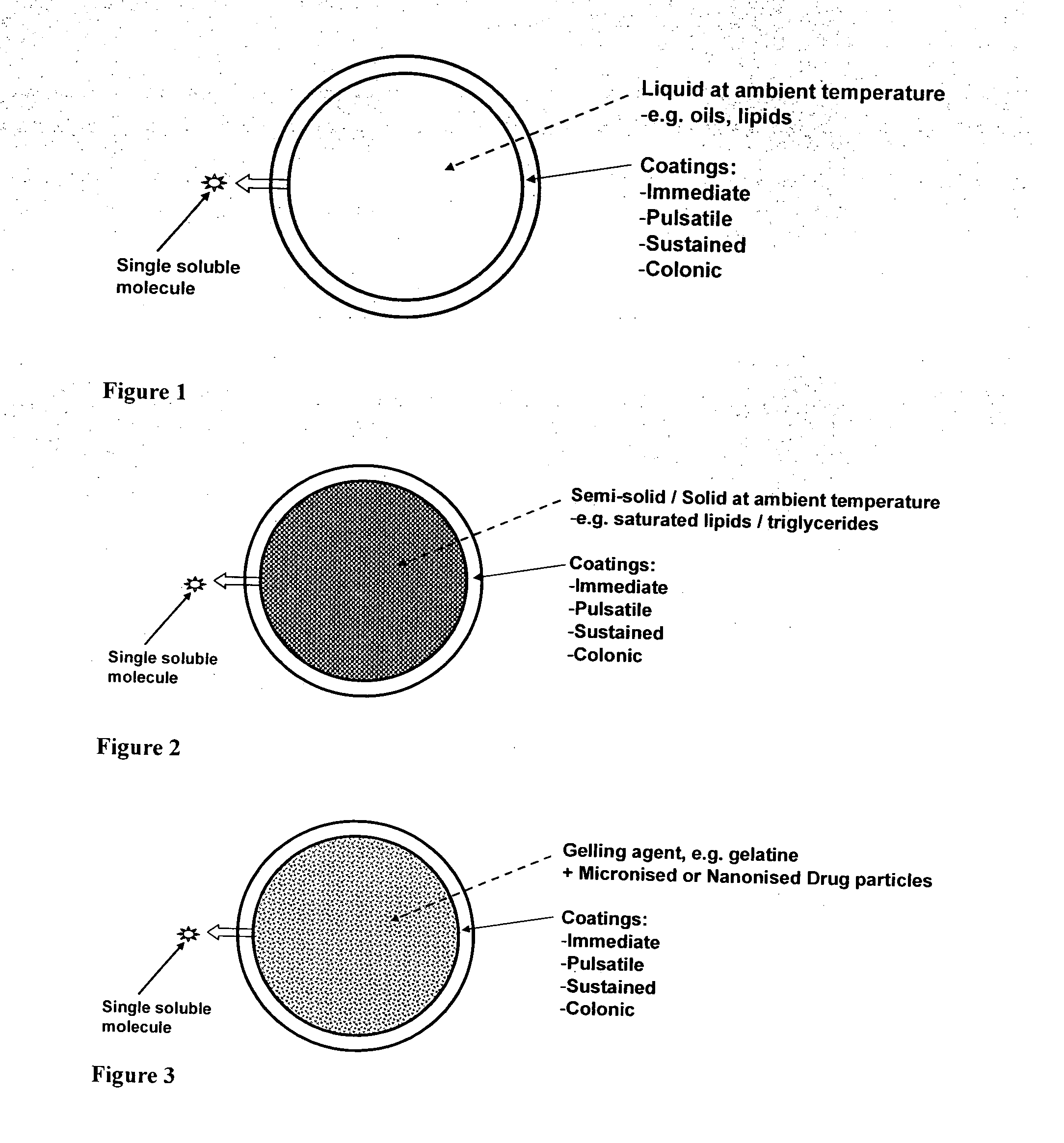
Oral pharmaceutical composition
ActiveUS20100255087A1Improve solubilityImprove breathabilityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderSolid coreGastrointestinal tract
Owner:SUBLIMITY THERAPEUTICS LTD
Speed cooking oven with sloped oven floor and reversing gas flow
ActiveUS20080105135A1Single rack cooking speedsHigh heat transfer rateAir-treating devicesDomestic stoves or rangesProcess engineeringAirflow
A speed cooking oven with sloped oven floor and reversing gas flow is disclosed comprising a cooking cavity, a controller, thermal heating source, blower assembly, air directing means, and a sloped oven floor that directs air flow from the oven side walls to oven center thereby producing a highly turbulent reversed air flow.
Owner:TURBOCHEF TECH INC
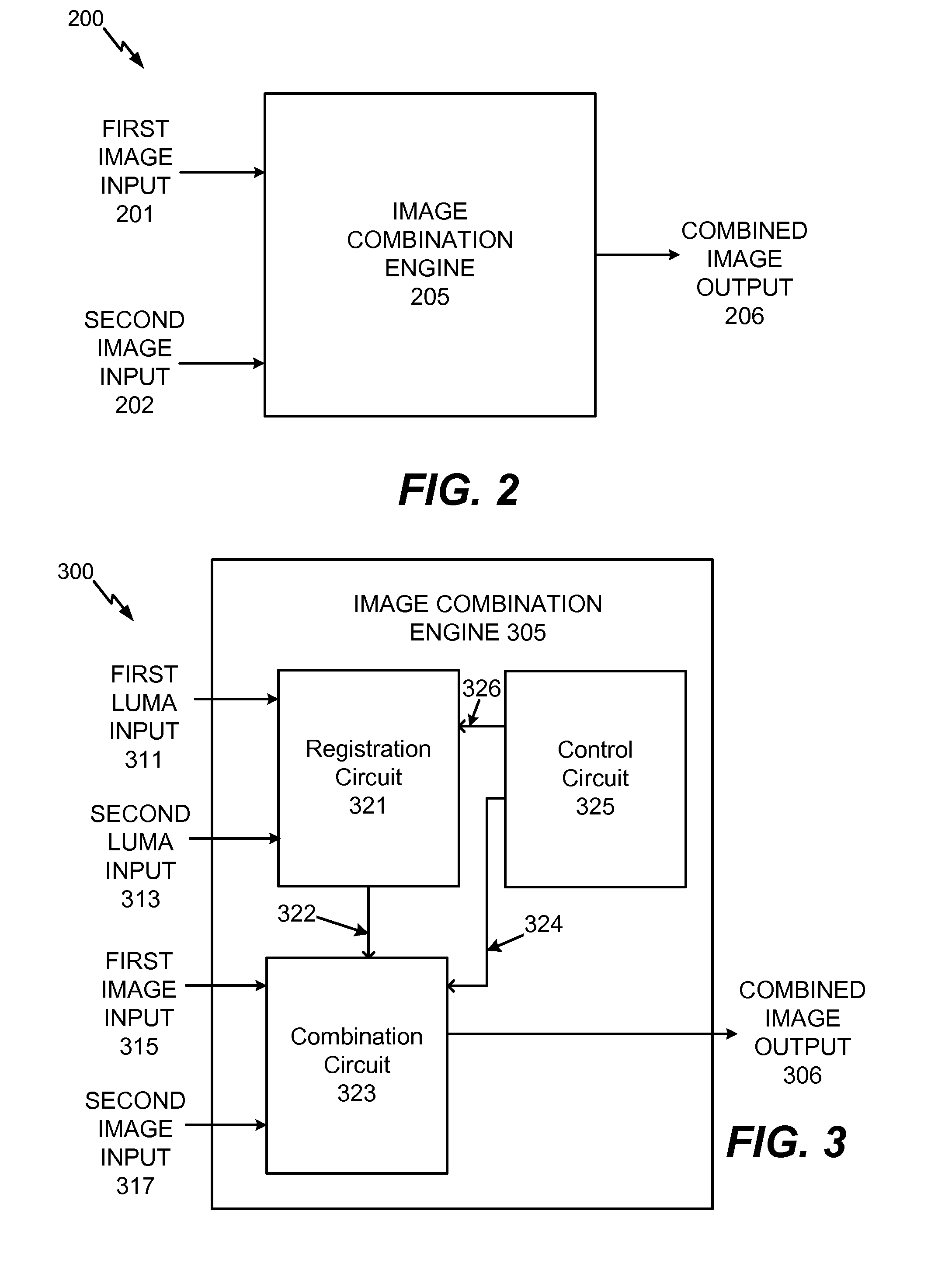
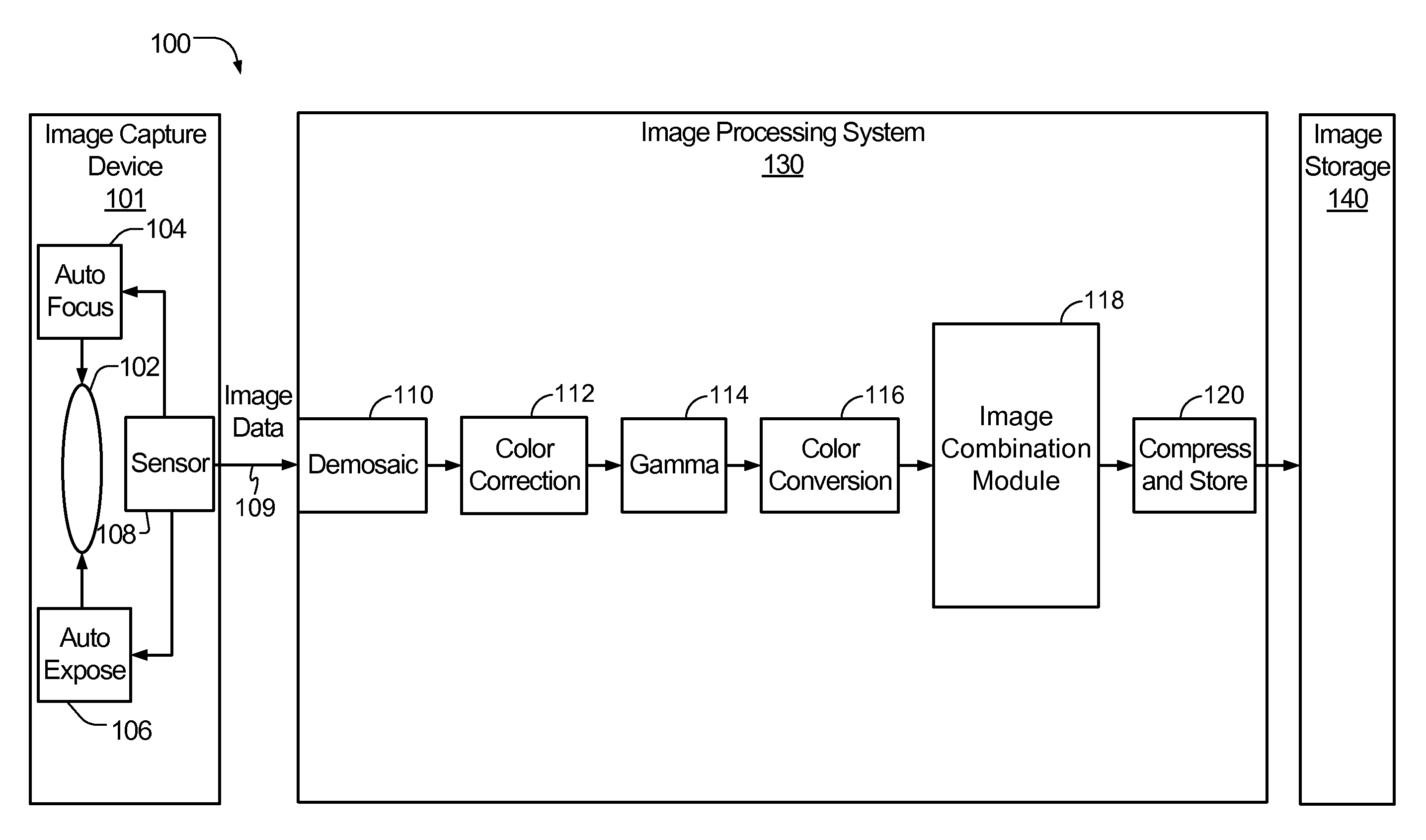
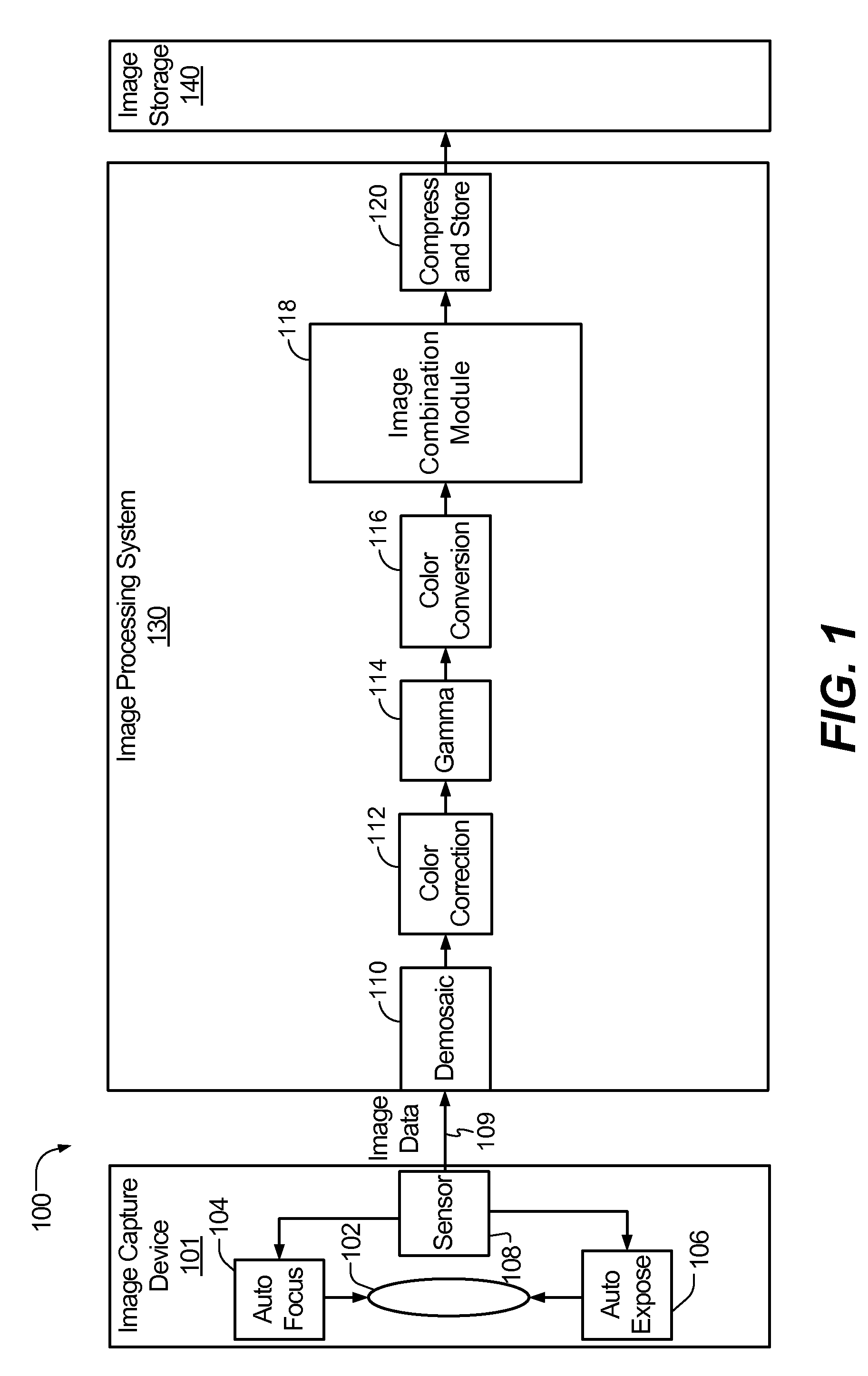
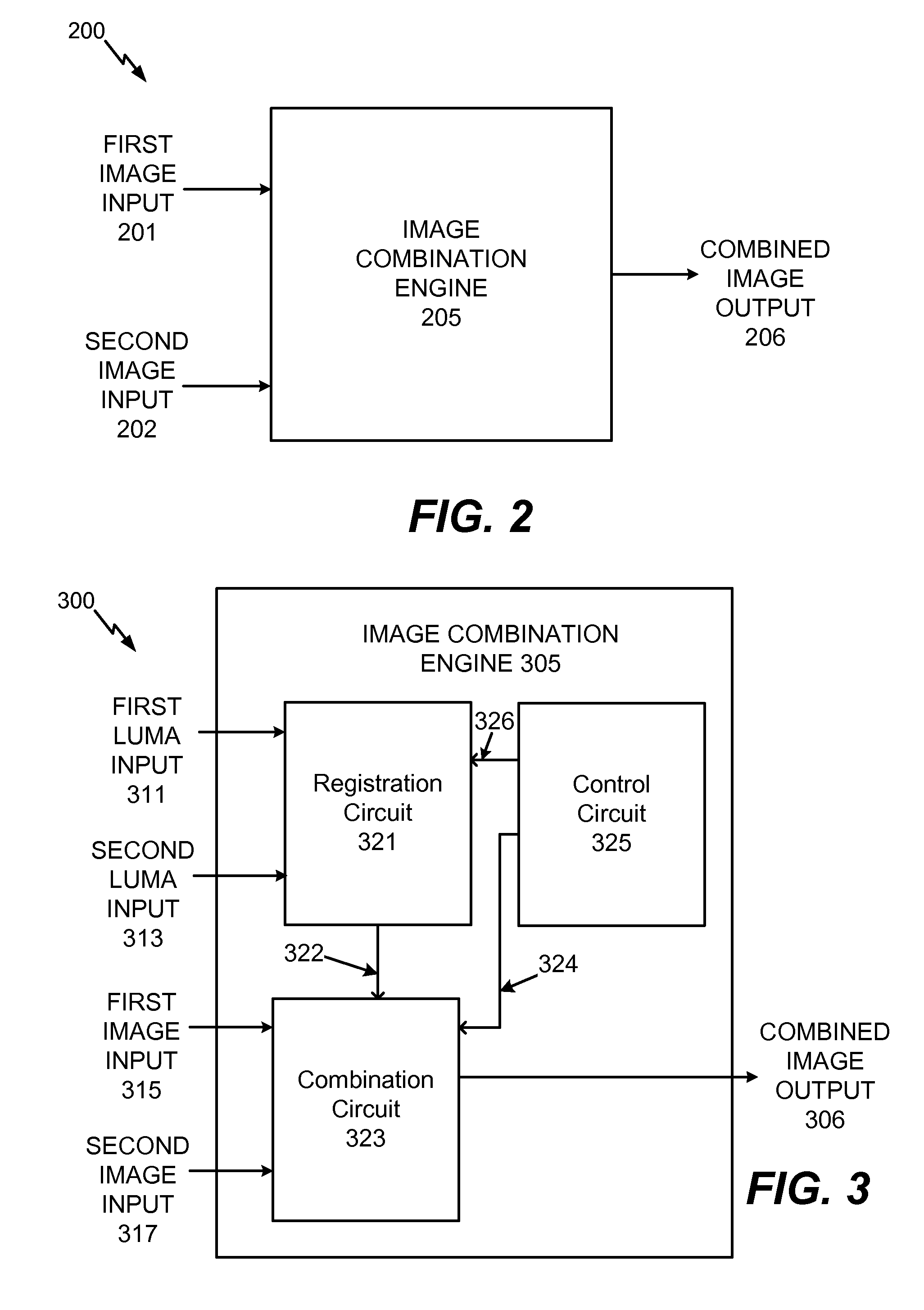
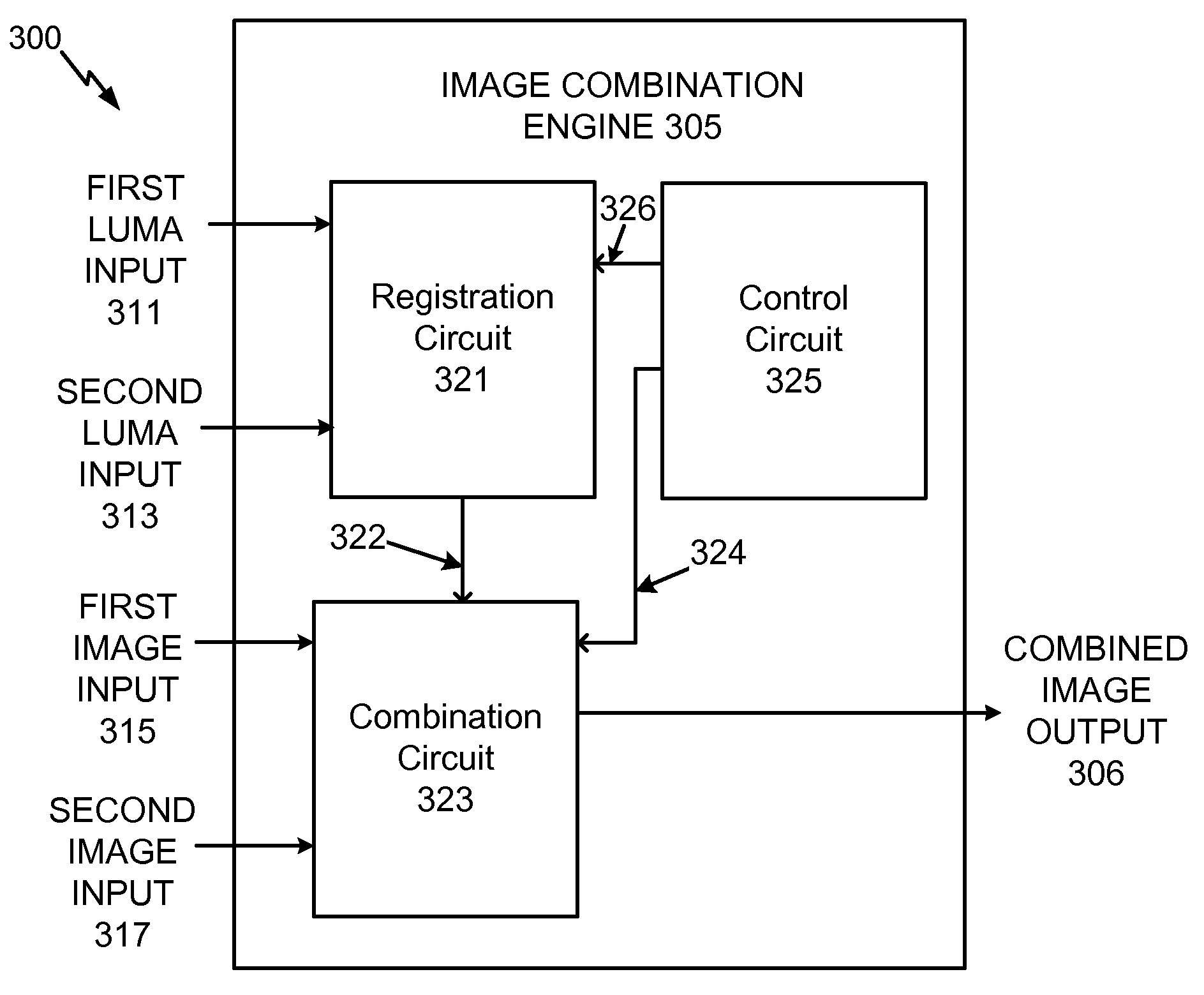
System and method to selectively combine images
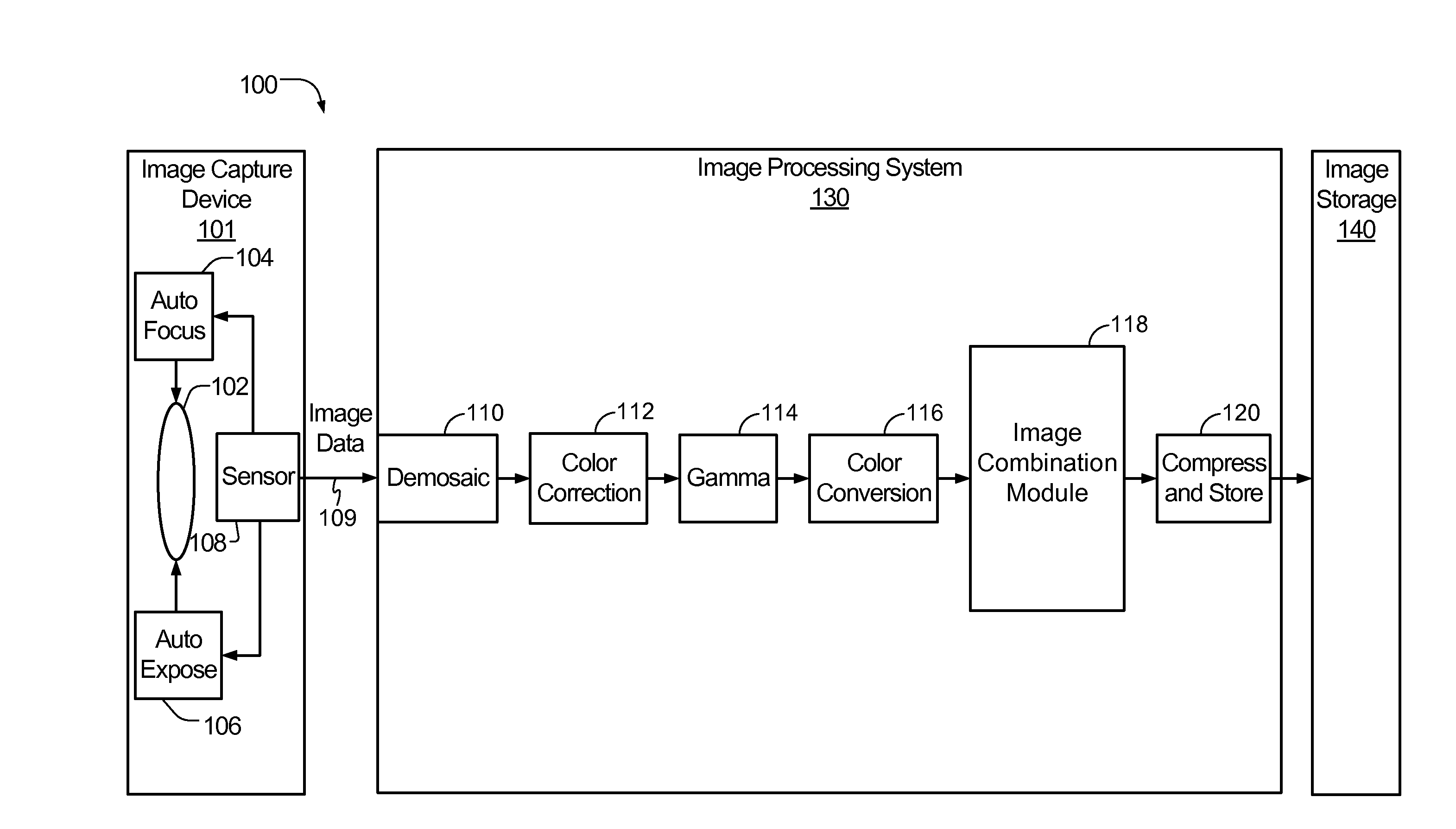
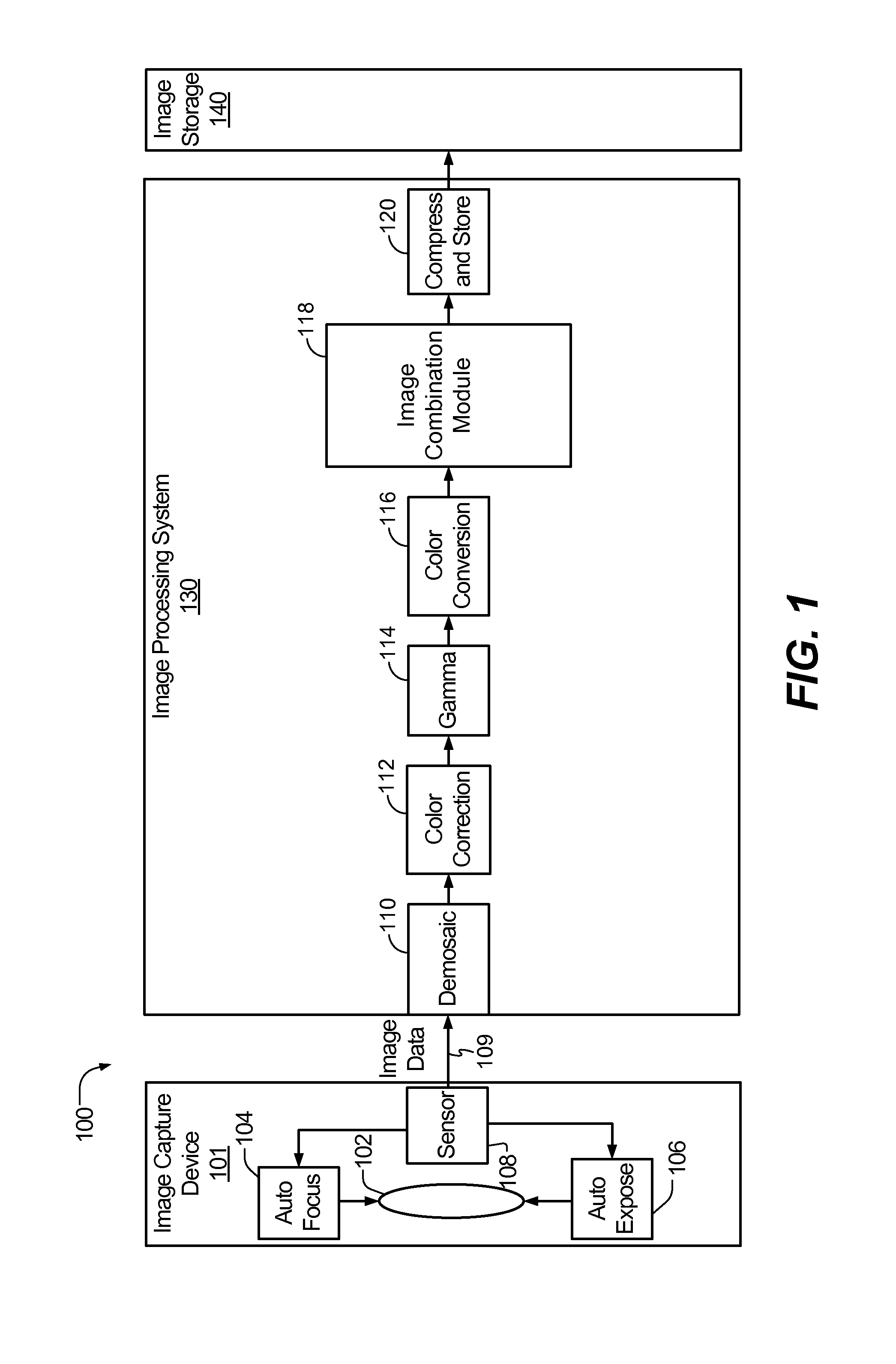
InactiveUS20100157079A1Issue of imageReduce ghostingImage enhancementTelevision system detailsMotion vectorControl circuit
Systems and methods to selectively combine images are disclosed. In a particular embodiment, an apparatus includes a registration circuit configured to generate a set of motion vector data based on first image data corresponding to a first image and second image data corresponding to a second image. The apparatus includes a combination circuit to selectively combine the first image data and adjusted second image data that corresponds to the second image data adjusted according to the motion vector data. The apparatus further includes a control circuit to control the combination circuit to generate third image data.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
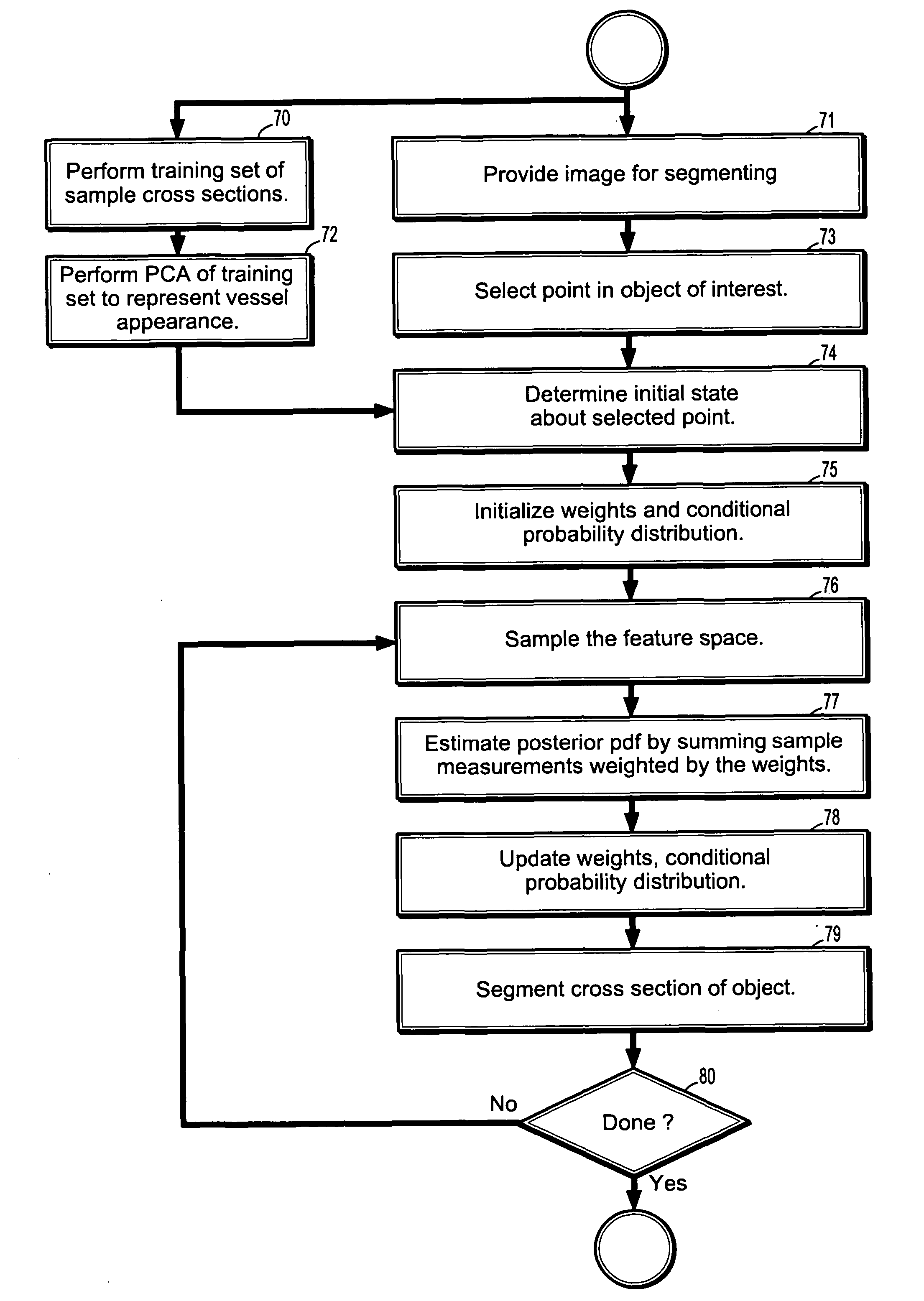
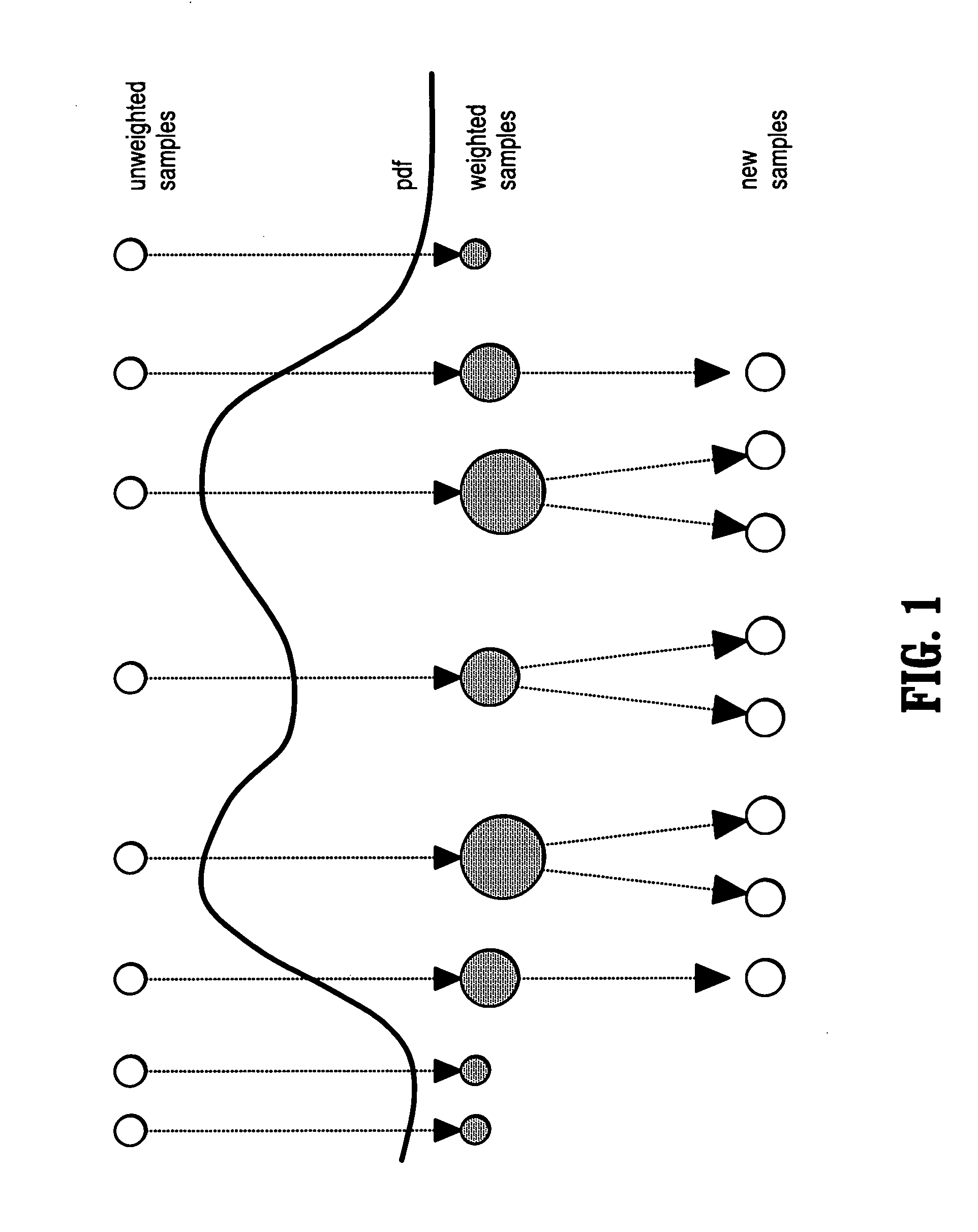
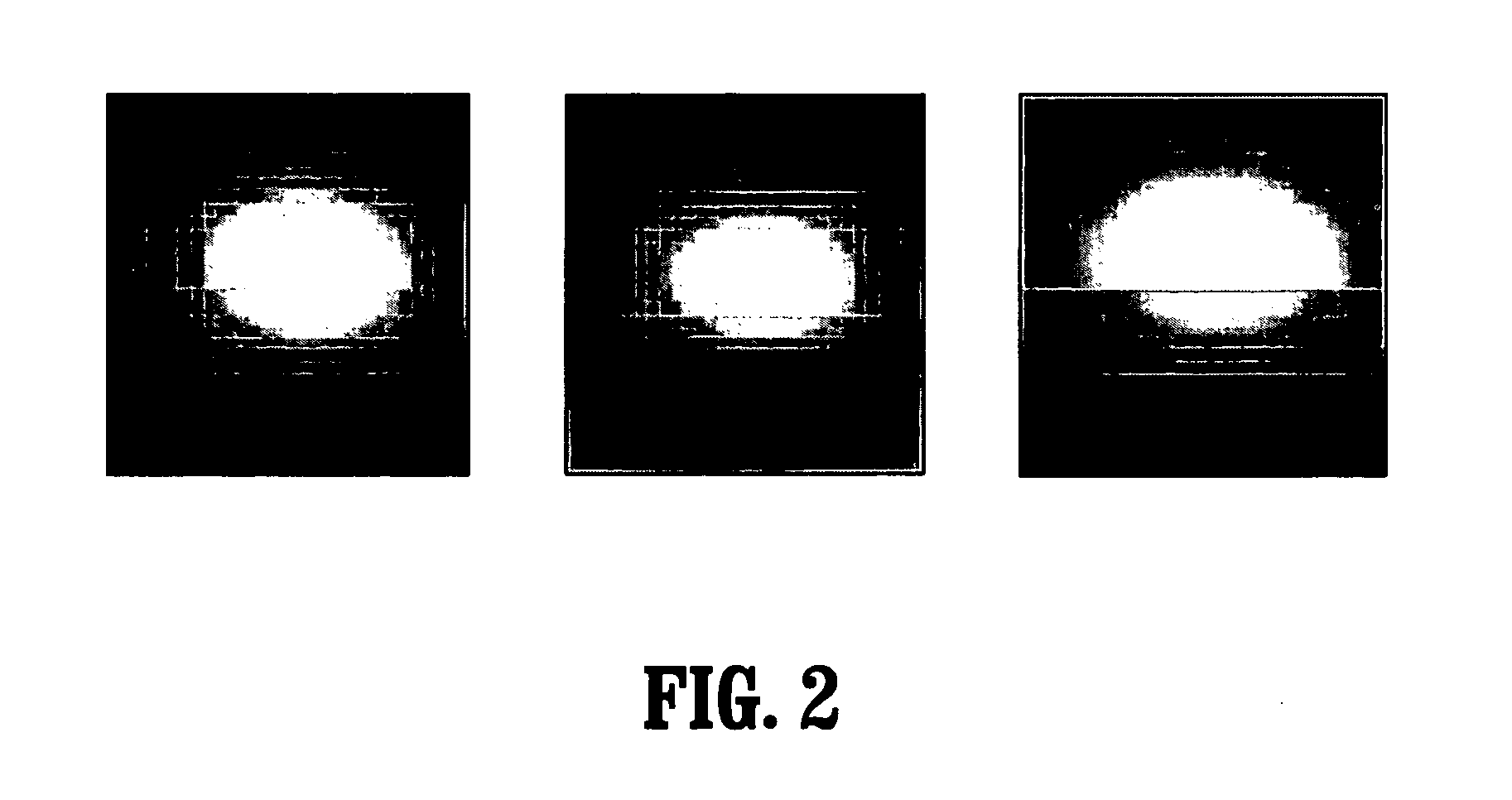
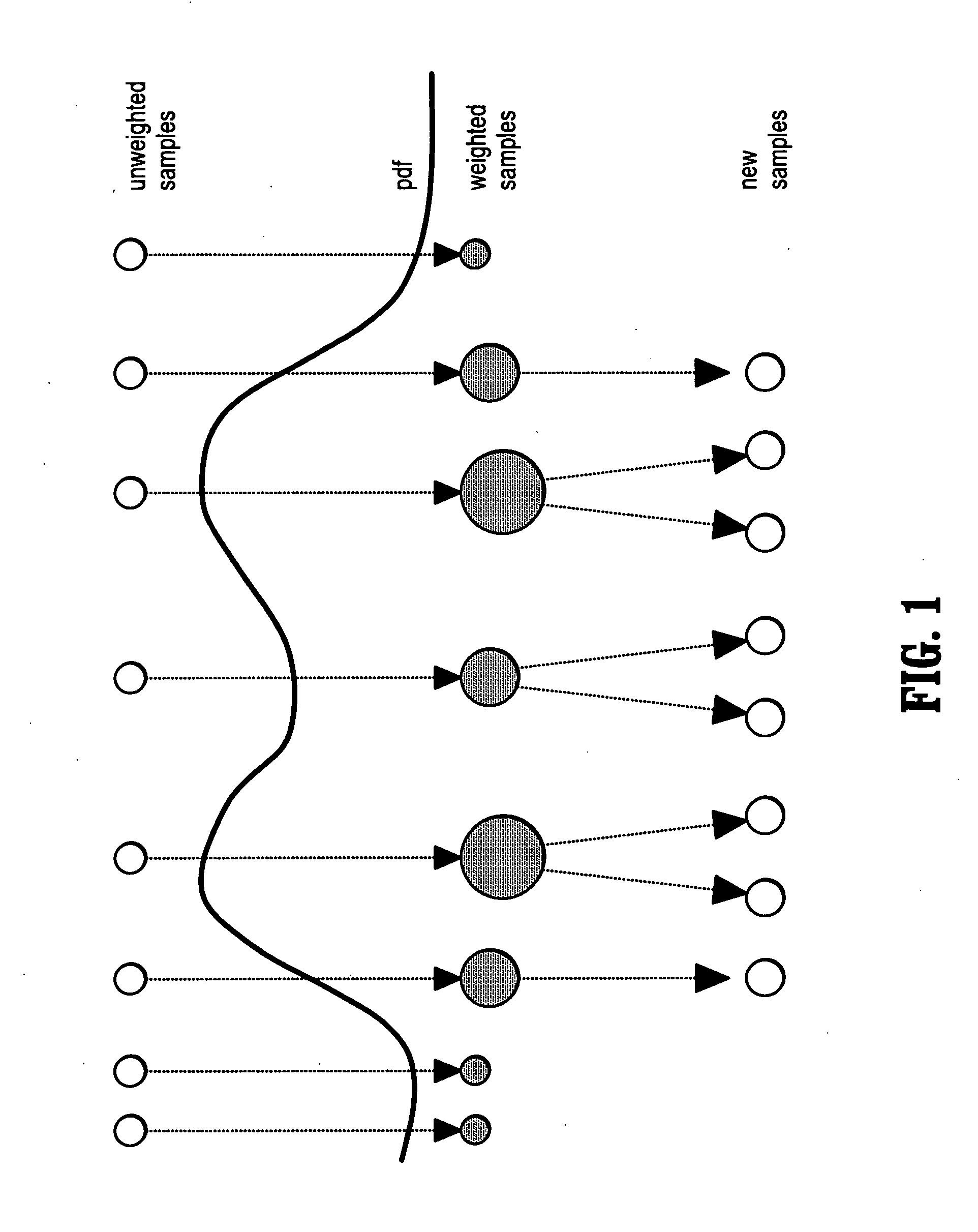
System and method for vascular segmentation by Monte-Carlo sampling
InactiveUS7715626B2Reduce in quantityIssue to overcomeImage enhancementImage analysisCharacteristic spaceDigital image
A method of segmenting tubular structures in digital images includes selecting a point in an image of a tubular object to be segmented, defining an initial state of the selected point, initializing measurement weights, a conditional probability distribution and a prior probability distribution of a feature space of the initial state, sampling the feature space from the prior probability distribution, estimating a posterior probability distribution by summing sample measurements weighted by the measurement weights, and segmenting a cross section of the tubular object from the posterior probability distribution.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
System and method to selectively combine video frame image data
ActiveUS20100271498A1Issue of imageReduce hand jitterImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImaging dataImage sensor
Systems and methods to selectively combine video frame image data are disclosed. First image data corresponding to a first video frame and second image data corresponding to a second video frame are received from an image sensor. The second image data is adjusted by at least partially compensating for offsets between portions of the first image data with respect to corresponding portions of the second image data to produce adjusted second image data. Combined image data corresponding to a combined video frame is generated by performing a hierarchical combining operation on the first image data and the adjusted second image data.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
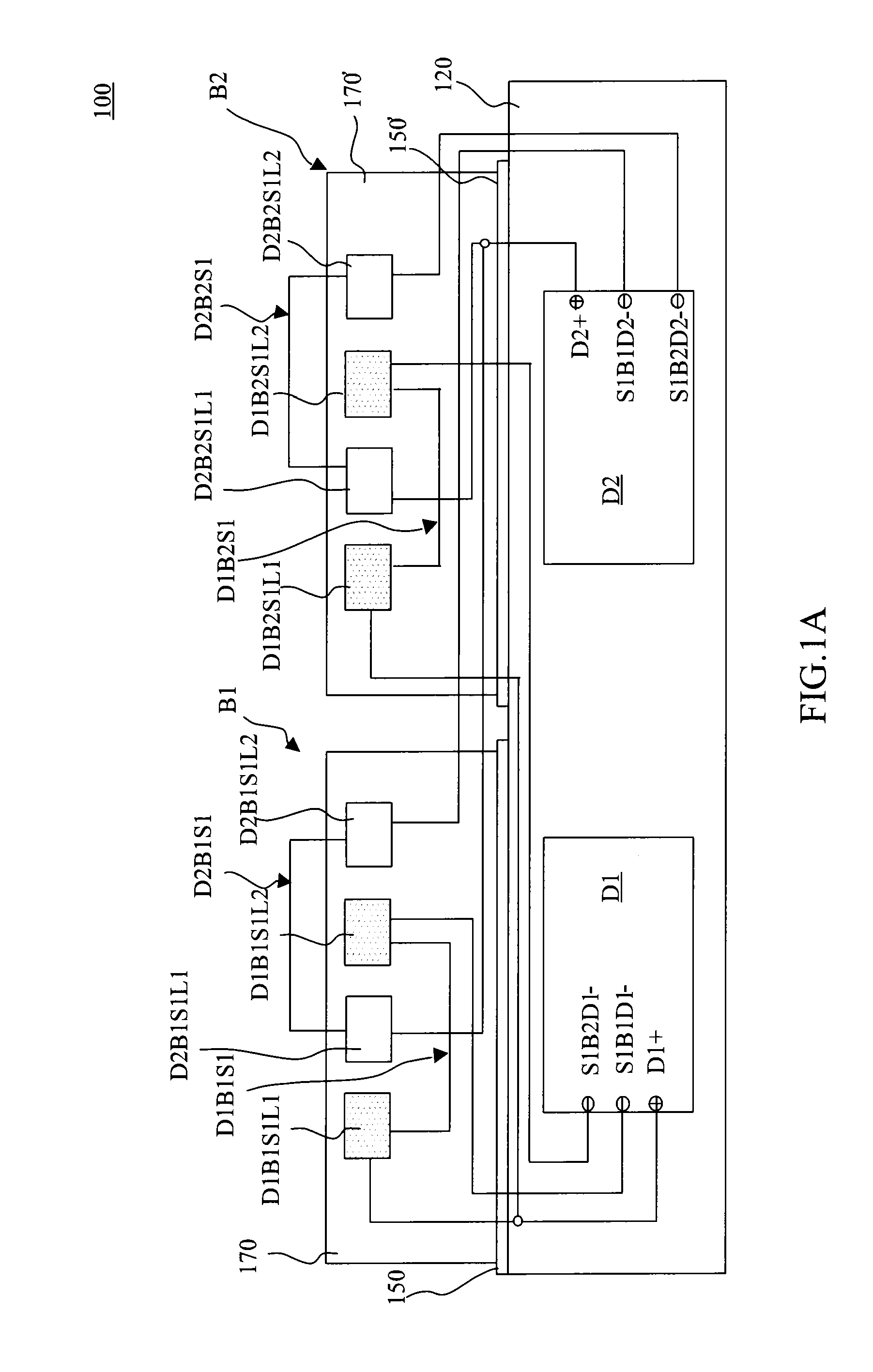
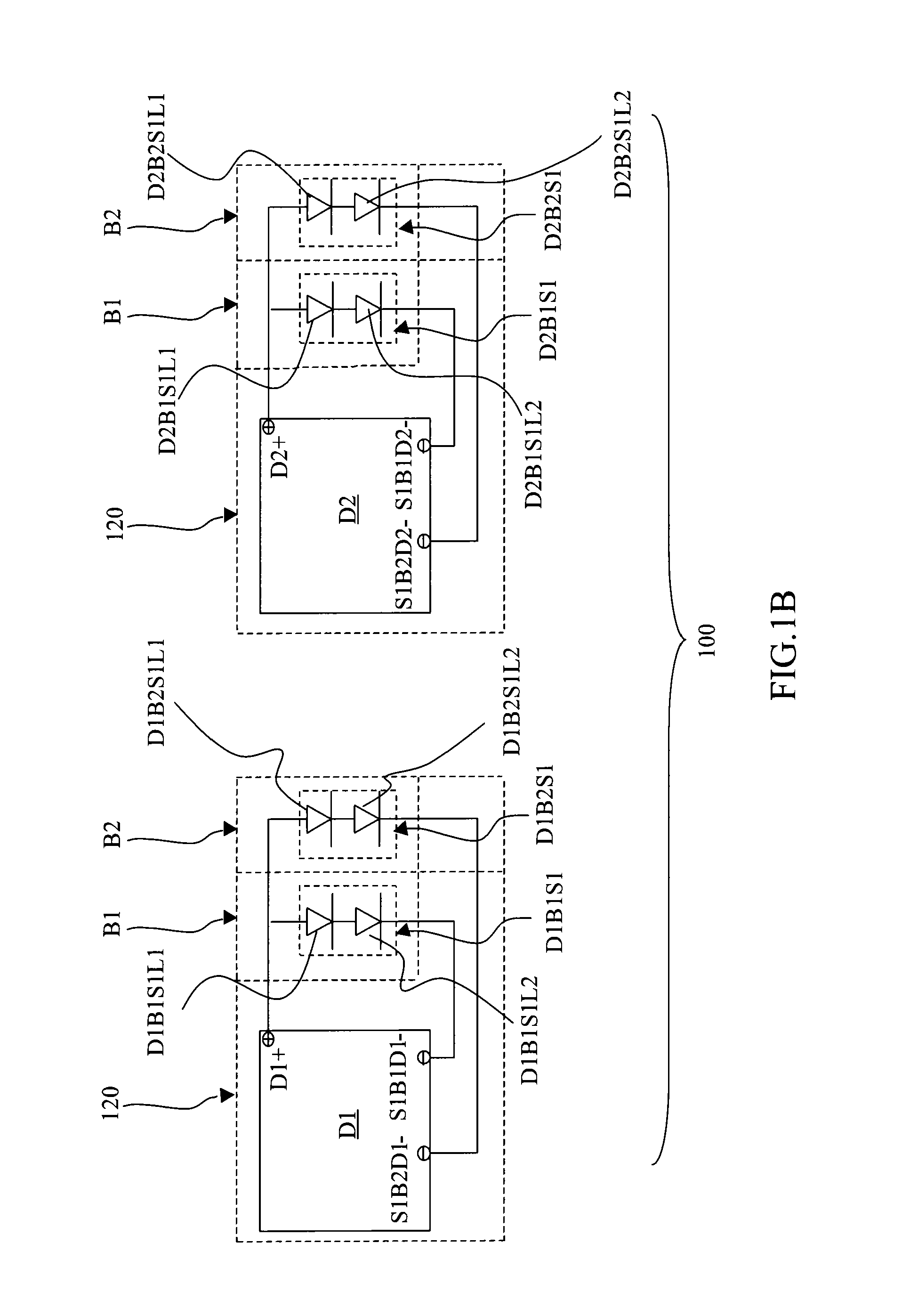
Display device, liquid crystal display device, electronic apparatus, and display device manufacturing method
ActiveUS20090256820A1Low costIssue to overcomeVessels or leading-in conductors manufactureConductive pattern formationLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
To provide a low-cost display device which can accurately detect a position touched by a finger. A display device displays an image by having display elements capable of performing electro-optic responses formed between conductible first and second substrates, and detects a contact position touched by a contact body by having a conductive impedance surface formed on the second substrate side. The display device includes: linearization pattern sections formed on the first substrate, which include a plurality of electrodes capable of detecting electric currents on a conductive impedance surface; and a conductive member which electrically connects the linearization pattern sections with the conductive impedance surface on the second substrate.
Owner:NEC LCD TECH CORP
Model construction in a neural network for object detection
InactiveUS20190156202A1Shorten the timeLow costImage analysisNeural learning methodsNerve networkCollective model
Exemplary computer-implemented method and system can be provided for constructing a model in a neural network for object detection in an unprocessed image, where the construction can be performed based on at least one image training batch. The exemplary model can be constructed by training one or more collective model variables in the neural network to classify the individual annotated objects as a member of an object class. The exemplary model, e.g., in combination with the set of specifications when implemented in a neural network, can perform object detection in an unprocessed image with probability of the object detection.
Owner:SCOPITO APS
Stroboscopic interferometry with frequency domain analysis
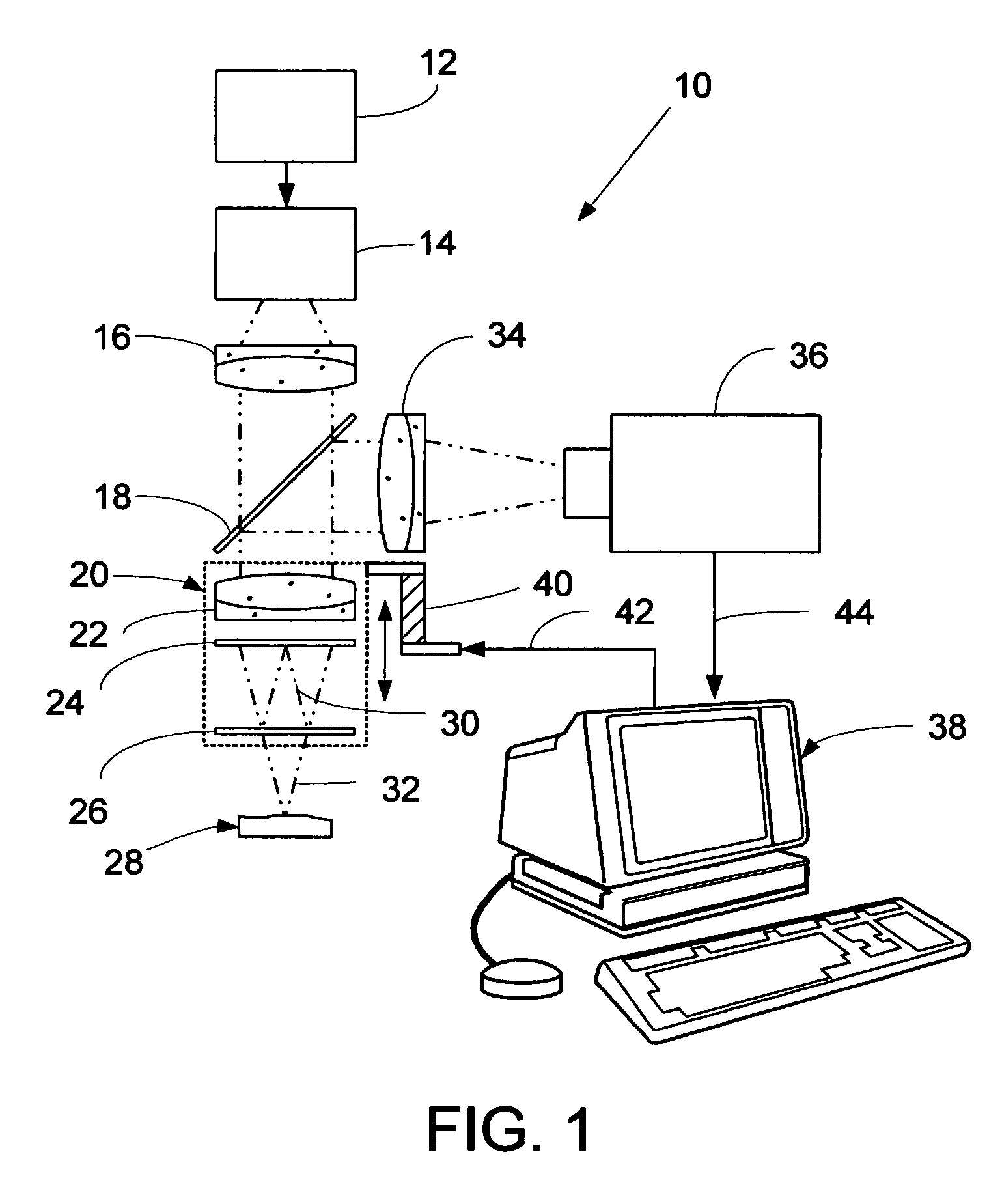
ActiveUS7177029B2Issue to overcomeSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing optical meansDigital signal processingTwo dimensional detector
A computer-based stroboscopic interferometric microscope system for measuring the topography of a microscopic vibratory object includes an interferometric microscope equipped with a multiple-color (e.g., LED) or white-light source, a mechanical scanning apparatus for varying the optical path difference between the vibratory object and a reference surface, a camera having a two-dimensional detector array, and digital signal processing apparatus for determining surface height from interference data. Interferograms for each of the detector image points in the field of view are generated simultaneously by scanning the object in a direction approximately perpendicular to the object surface illuminated stroboscopically while recording detector data in digital memory. Recorded interferograms for each image point are then transformed into the spatial frequency domain by Fourier analysis, and the surface height for each corresponding object surface point is obtained by examination of the complex phase as a function of spatial frequency. A complete three-dimensional image of the object surface is then constructed from the height data and corresponding image plane coordinates. The three-dimensional image may be presented on a display or hard copy or written to a storage medium.
Owner:ZYGO CORPORATION
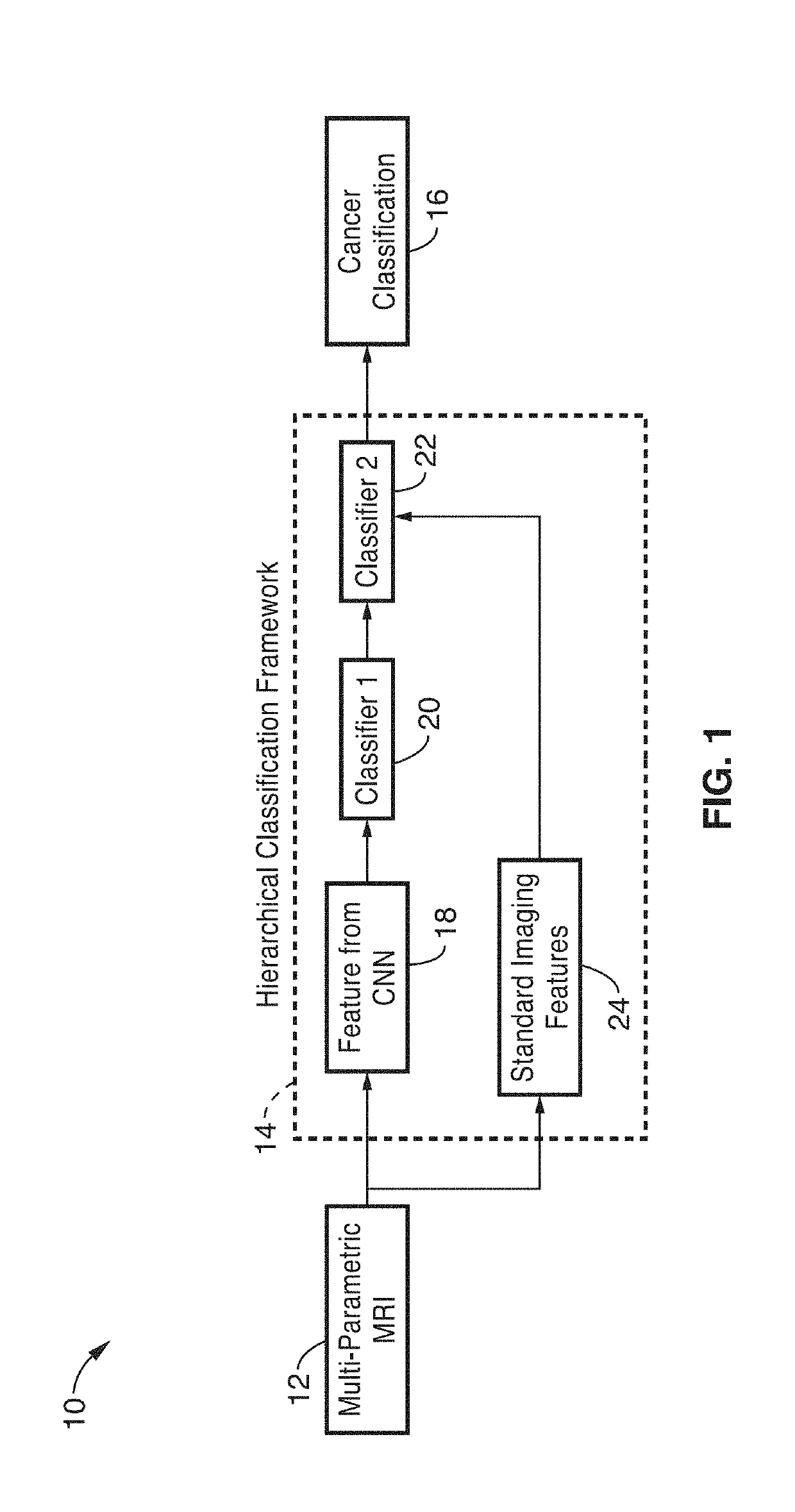
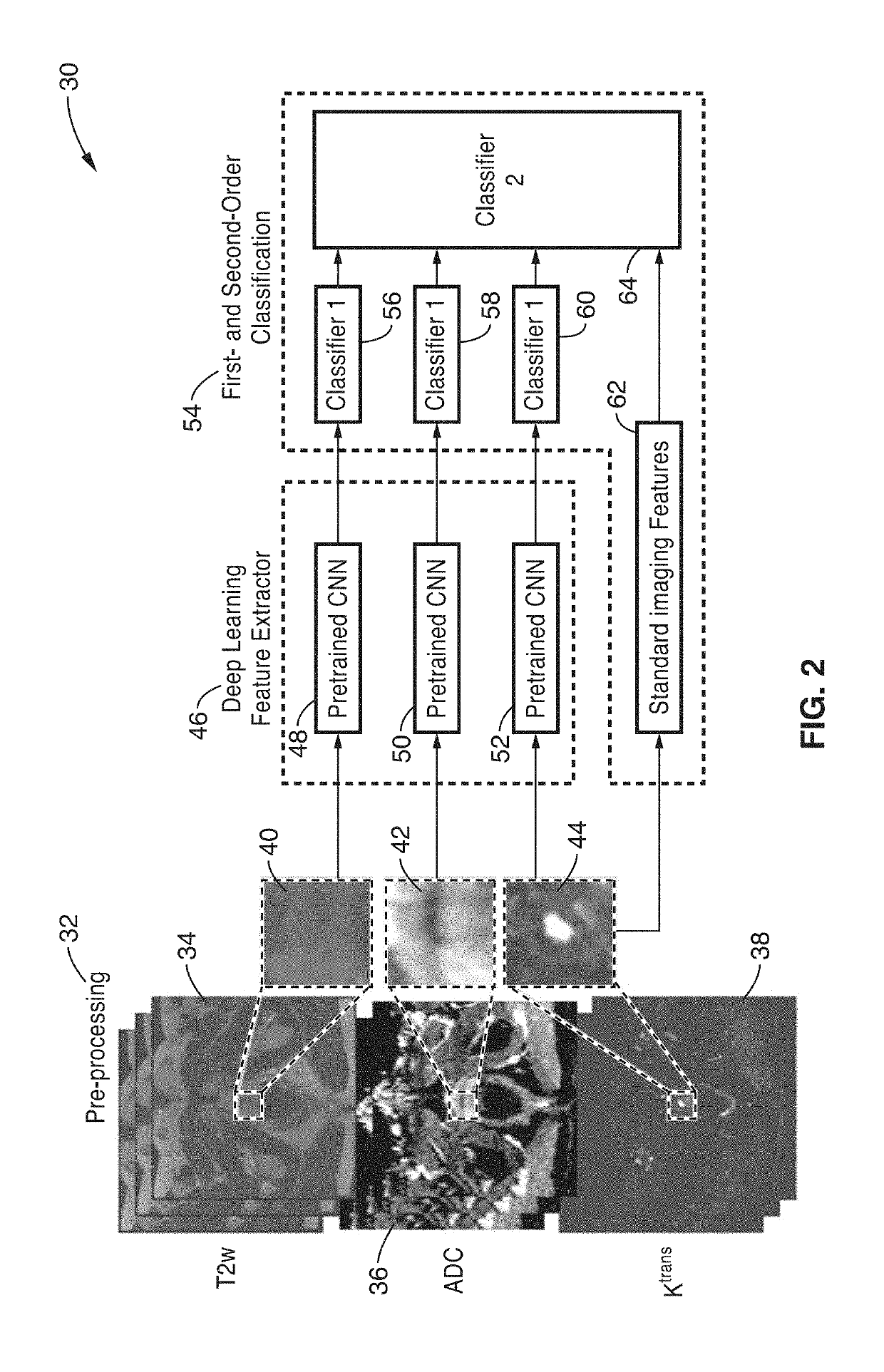
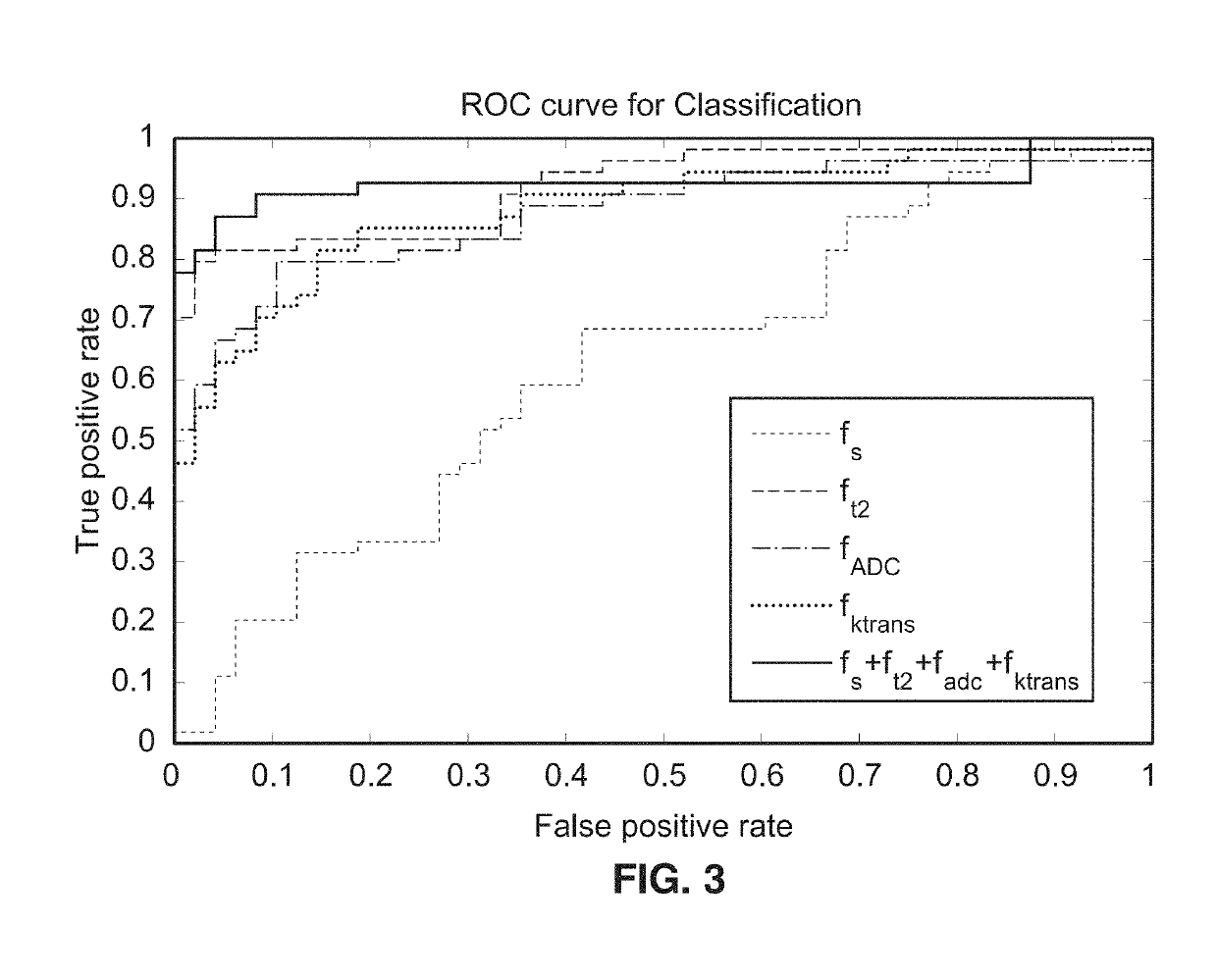
Deep-learning-based cancer classification using a hierarchical classification framework
ActiveUS20190183429A1Alleviate learning requirementExtra featureImage enhancementMedical data miningLearning basedClassification methods
An automatic classification method for distinguishing between indolent and clinically significant carcinoma using multiparametric MRI (mp-MRI) imaging is provided. By utilizing a convolutional neural network (CNN), which automatically extracts deep features, the hierarchical classification framework avoids deficiencies in current schemes in the art such as the need to provide handcrafted features predefined by a domain expert and the precise delineation of lesion boundaries by a human or computerized algorithm. This hierarchical classification framework is trained using previously acquired mp-MRI data with known cancer classification characteristics and the framework is applied to mp-MRI images of new patients to provide identification and computerized cancer classification results of a suspicious lesion.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method of, and system for, real estate index generation
ActiveUS20100057538A1Improve efficiencyLack of liquidityFinanceFuzzy logic based systemsSystem usageComputer science
A method and system for generating a real estate property index uses real estate data including price data, property data and time of sale data that are entered into a computing apparatus. The time of sale data is manipulated to provide consecutive triple times giving two consecutive time periods (e.g., March, April, May 2007 and April, May, June 2007). A transform function, preferably a log function, is generated with two time dummy variables, and the coefficients of the two time dummy variables are extracted and added to generate a transformed growth rate. The reverse transform function, preferably an anti-log function, is generated to provide the desired untransformed growth rate.
Owner:RP DATA PTY LTD
Non-contact RF strain sensor
InactiveUS20070186677A1Good adhesionEasy to readForce measurementMaterial strength using steady bending forcesAcousticsRadio frequency
A passive, non-contact radio frequency (RF) strain sensor changes resonant frequency as it is deformed. The sensor's resonant frequency can be determined by monitoring the signals transmitted and / or reflected therefrom upon illumination of the sensor by a known RF signal source. The sensor can be implemented using thin film techniques on a flexible thin substrate that can be attached to the surface of a structural member of interest.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY +1
Split-path color switching system and method
InactiveUS7195356B1Improve transmittanceQuick switchProjectorsColor photographyPhysicsSingle polarization
The present application describes a retarder stack color switch using a single polarization analyzer for reflective-mode projection displays. The single polarization analyzer permits additive mode switching, which optimizes the chrominance of the additive primary outputs and the black state. Moreover, the single analyzer color switch provides a white state, which is frequently used in sequential systems. The single analyzer color switch overcomes some of the cost and manufacturing challenges associated with conventional transmissive full color switches based on retarder-stack-filters. The single analyzer color switch according to an embodiment uses a split-path so that relatively weak colors can follow a “high-efficiency” path.
Owner:REAID INC
System and method to selectively combine video frame image data
ActiveUS8111300B2Reduce hand jitterReduce ghostingImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImaging dataImage sensor
Systems and methods to selectively combine video frame image data are disclosed. First image data corresponding to a first video frame and second image data corresponding to a second video frame are received from an image sensor. The second image data is adjusted by at least partially compensating for offsets between portions of the first image data with respect to corresponding portions of the second image data to produce adjusted second image data. Combined image data corresponding to a combined video frame is generated by performing a hierarchical combining operation on the first image data and the adjusted second image data.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
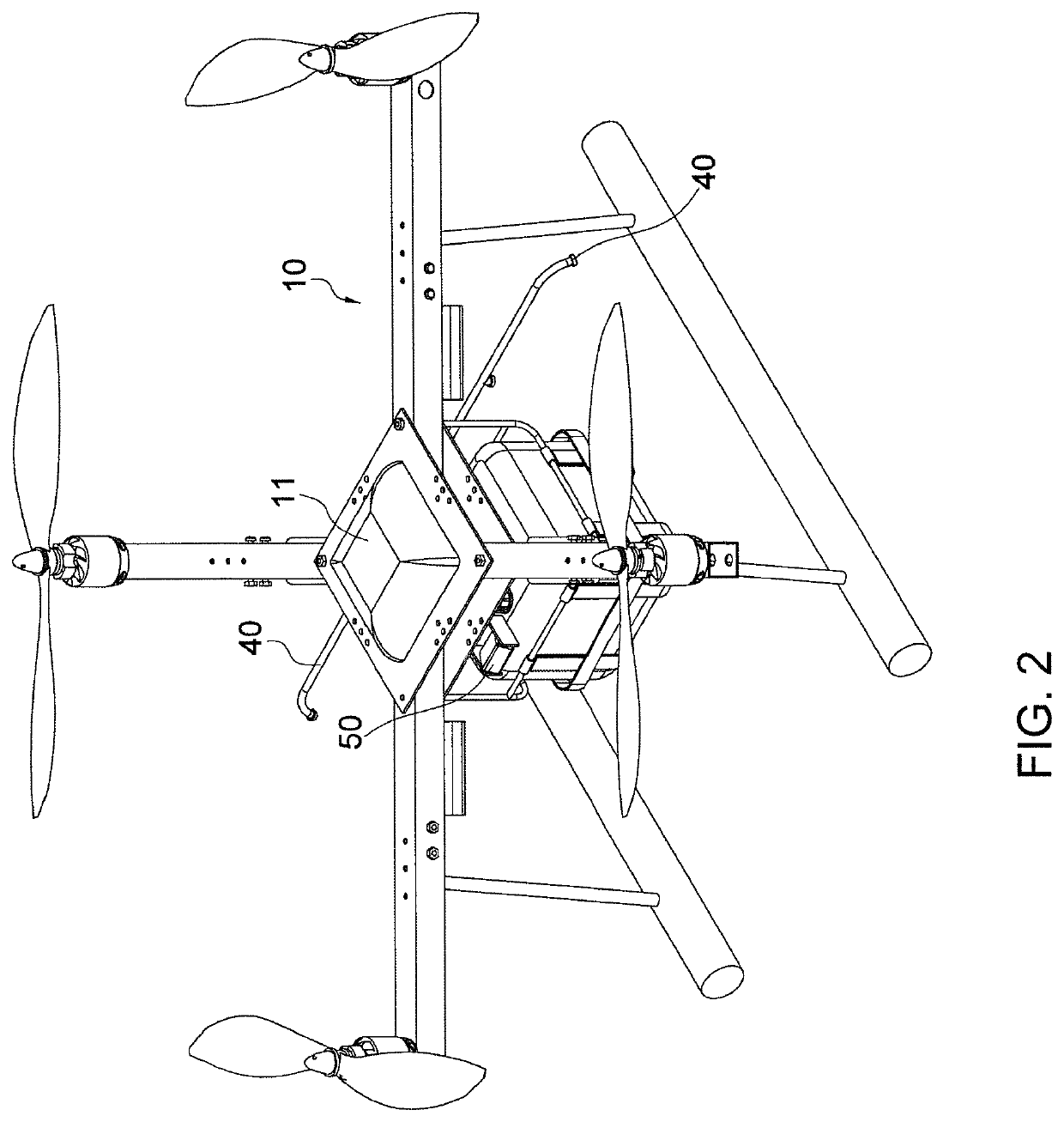
Precision agriculture implementation method by UAV systems and artificial intelligence image processing technologies
ActiveUS20210078706A1Agricultural planting costImprove efficiencyAircraft componentsUnmanned aerial vehiclesAgricultural engineeringControl cell
A precision agriculture implementation method by UAV systems and artificial intelligence image processing technologies provides an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), a wireless communication device, a central control unit, and a spray device and a multispectral camera installed to the UAV. The farming area is divided into an array of blocks. The central control unit controls the UAV to fly over the blocks according to navigation parameters and the multispectral camera to capture a multispectral image of each block. A projected leaf area index (PLAI) and a normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) of each block are calculated by the multispectral image, and a spray control mode of the spray device of the corresponding block is set according to the PLAI and NDVI. The spray device is controlled to spray a water solution, salt solution, fertilizer solution, and / or pesticide solution to the corresponding block according to the spray control mode.
Owner:NAT FORMOSA UNIV
System and method for vascular segmentation by Monte-Carlo sampling
InactiveUS20060239541A1Reduce in quantityIssue to overcomeImage enhancementImage analysisDigital imageConditional probability
A method of segmenting tubular structures in digital images includes selecting a point in an image of a tubular object to be segmented, defining an initial state of the selected point, initializing measurement weights, a conditional probability distribution and a prior probability distribution of a feature space of the initial state, sampling the feature space from the prior probability distribution, estimating a posterior probability distribution by summing sample measurements weighted by the measurement weights, and segmenting a cross section of the tubular object from the posterior probability distribution.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Touch panel
InactiveUS20130201116A1Quality improvementIssue to overcomeInput/output processes for data processingOptoelectronicsTouch panel
A touch panel includes a substrate, at least one first axis sensing electrode, at least one second axis sensing electrode, and a compensating pattern. The substrate has a top surface and a bottom surface disposed oppositely to each other. The first axis sensing electrode and the second axis sensing electrode are disposed on the top surface of the substrate. A slit exists between the first axis sensing electrode and the second axis sensing electrode. The compensating pattern is disposed on the bottom surface of the substrate. The compensating pattern at least partially overlaps the slit between the first axis sensing electrode and the second axis sensing electrode in a vertical projective direction.
Owner:CHUNGHWA PICTURE TUBES LTD
System and method to selectively combine images
InactiveUS20130251283A1Reduce ghostingAdd depthImage enhancementImage analysisMotion vectorControl circuit
Systems and methods to selectively combine images are disclosed. In a particular embodiment, an apparatus includes a registration circuit configured to generate a set of motion vector data based on first image data corresponding to a first image and second image data corresponding to a second image. The apparatus includes a combination circuit to selectively combine the first image data and adjusted second image data that corresponds to the second image data adjusted according to the motion vector data. The apparatus further includes a control circuit to control the combination circuit to generate third image data.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Exercise device
ActiveUS8007417B2Effective exerciseEfficient and effectiveStiltsMuscle exercising devicesButtocksWorking environment
An exercise device for strengthening the core or midsection of the body that is suitable for use in a professional work environment. The exercise device comprises a domed seat positioned atop a plurality of baffled sections. The domed seat is deformable, allowing it to support and conform to the buttocks of a user when sitting on the device. The baffled sections are also deformable, allowing the seat to shift in all directions along a horizontal plane as a user's weight naturally shifts while sitting on the device. As the baffled sections deform and the seat persistently shifts over the course of a given period of time, a user's core muscles repeatedly tense in order to stabilize the body. The constant tension of the muscles over that period of time simulates a workout, particularly in the midsection of the body.
Owner:ERGOERGO
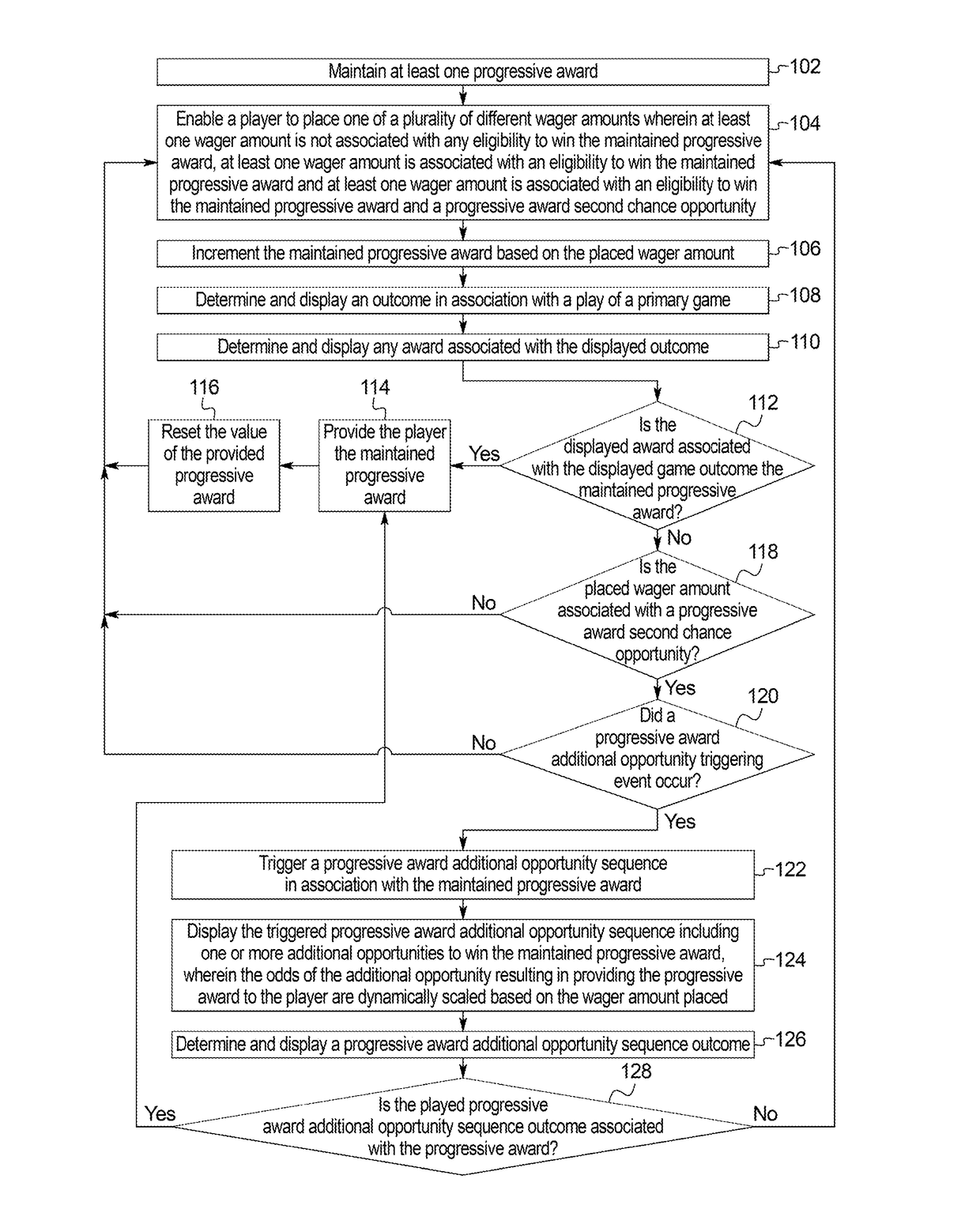
Gaming system and method for providing a plurality of chances of winning a progressive award with dynamically scalable progressive award odds
ActiveUS20180082533A1Better oddsIncrease opportunitiesApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingMultimedia
Owner:IGT
Display device, liquid crystal display device, electronic apparatus, and display device manufacturing method
ActiveUS20140132859A1Low costIssue to overcomeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
To provide a low-cost display device which can accurately detect a position touched by a finger. A display device displays an image by having display elements capable of performing electro-optic responses formed between conductible first and second substrates, and detects a contact position touched by a contact body by having a conductive impedance surface formed on the second substrate side. The display device includes: linearization pattern sections formed on the first substrate, which include a plurality of electrodes capable of detecting electric currents on a conductive impedance surface; and a conductive member which electrically connects the linearization pattern sections with the conductive impedance surface on the second substrate.
Owner:TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
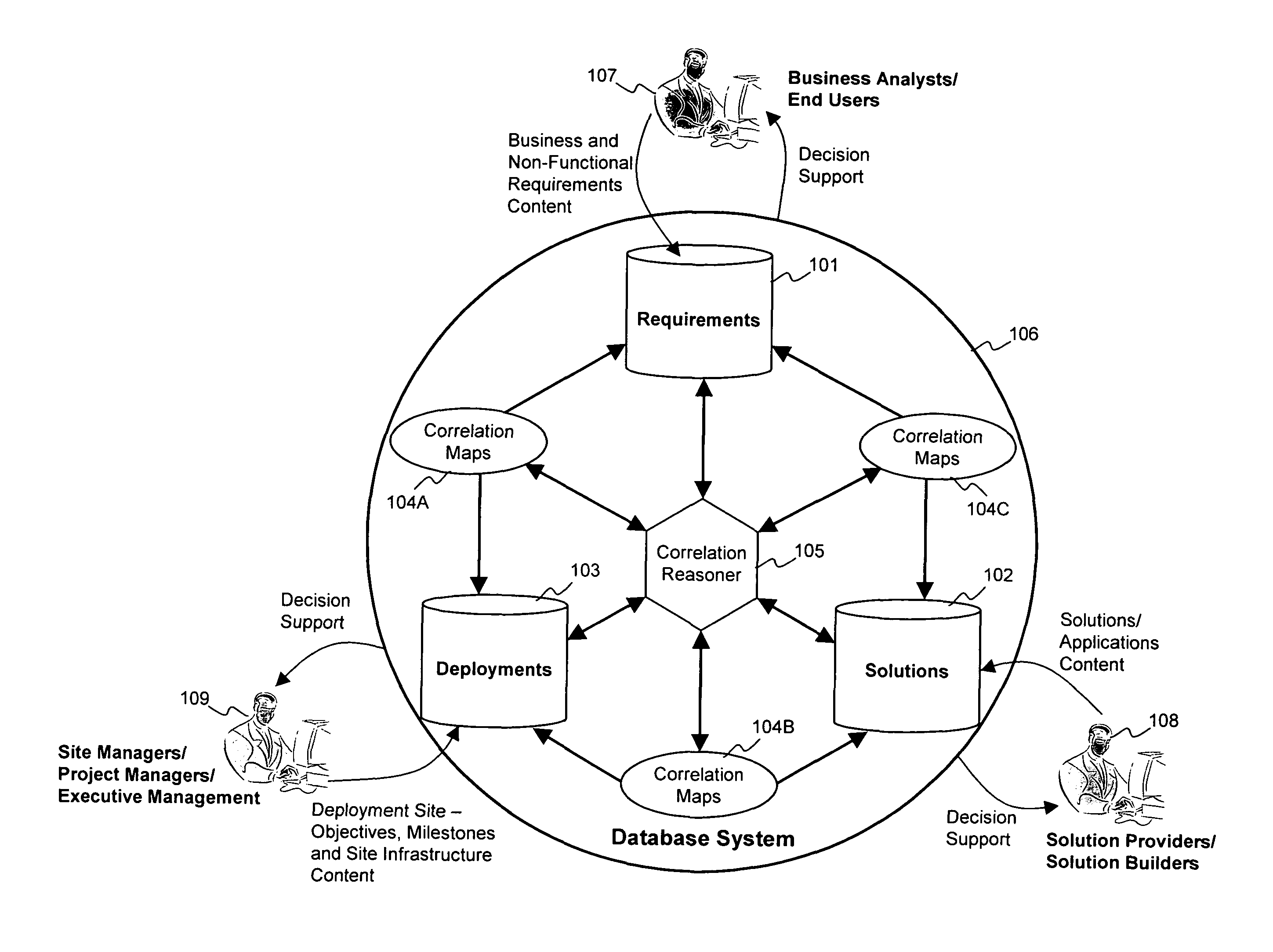
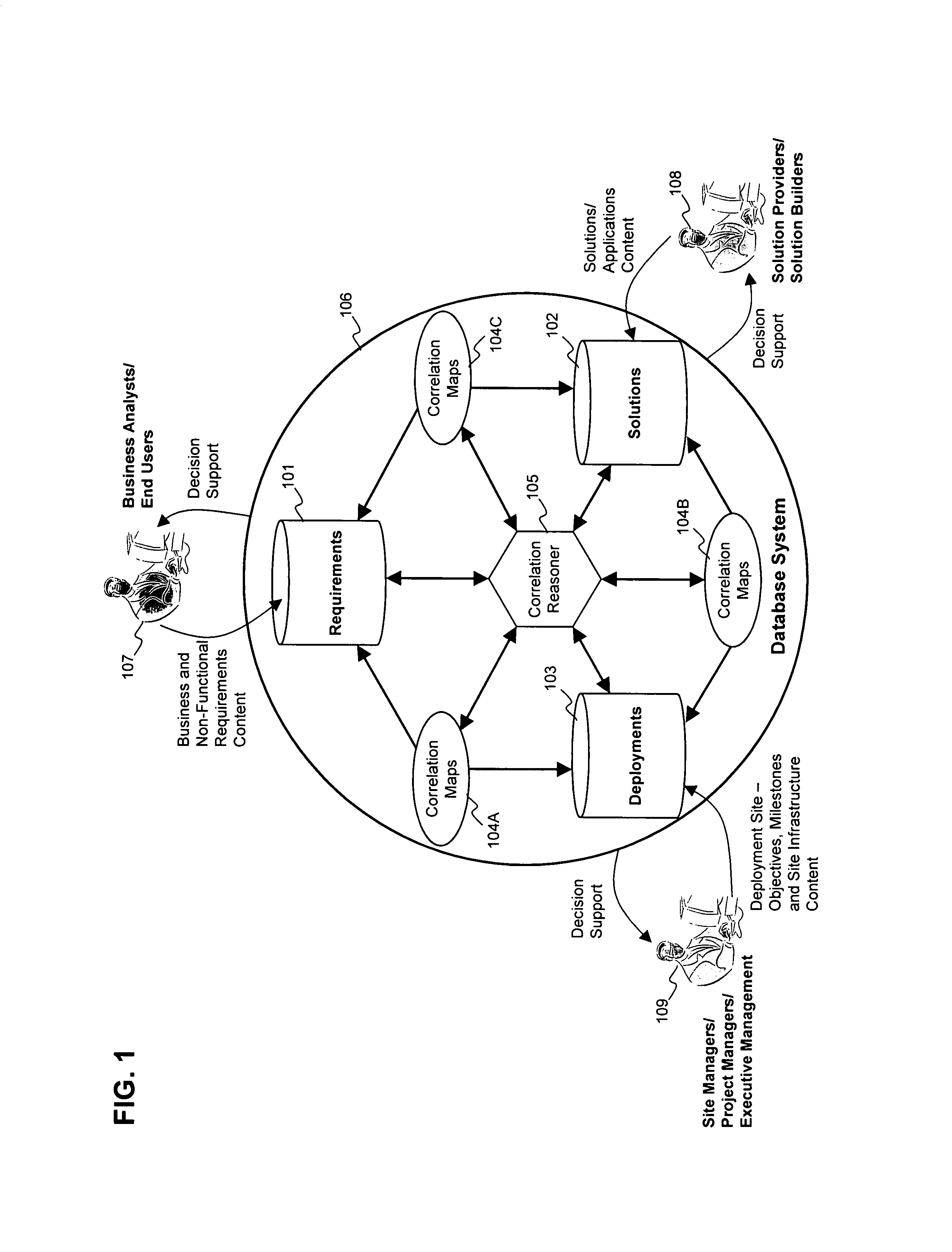
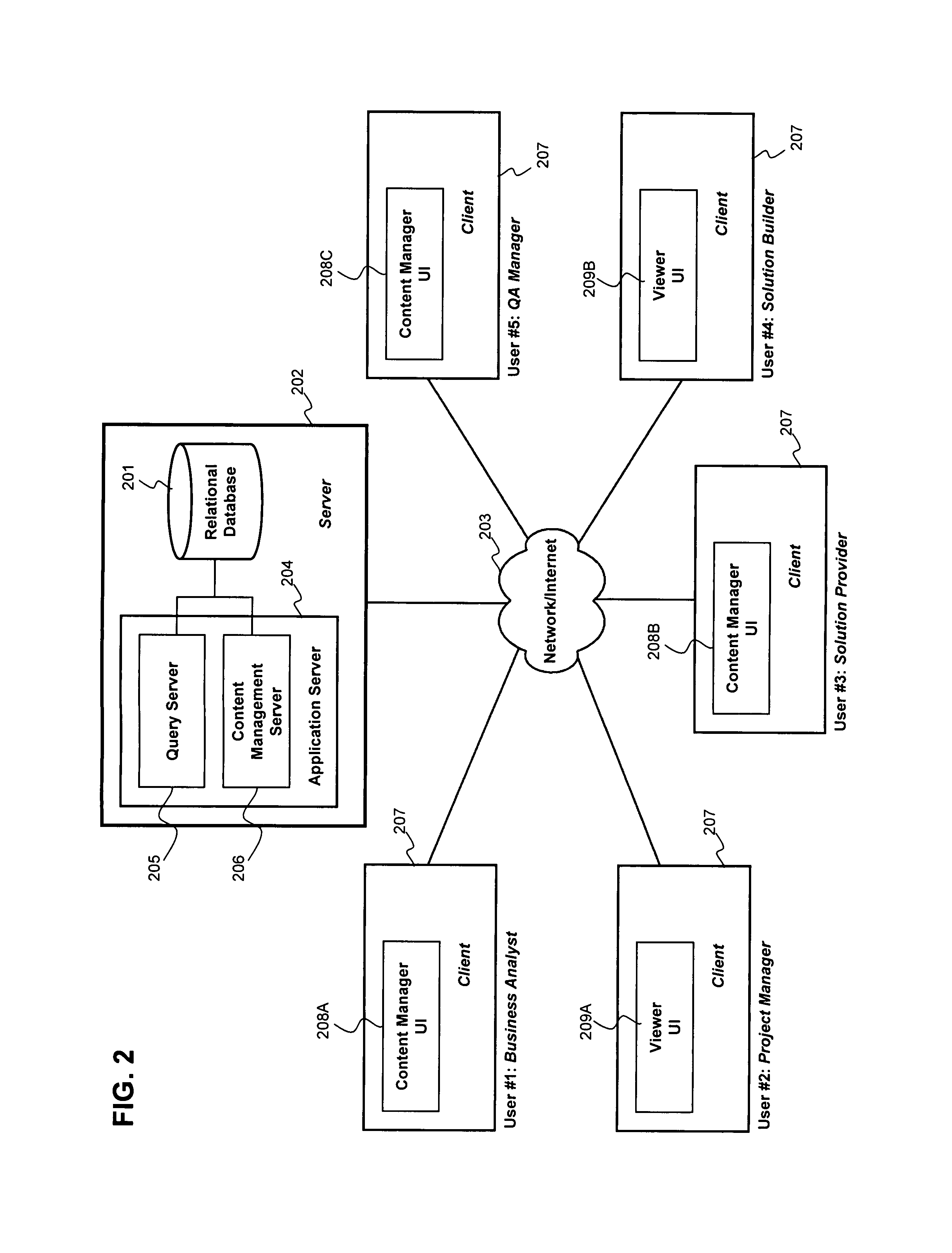
Methods and tools to support strategic decision making by specifying, relating and analyzing requirements, solutions, and deployments
ActiveUS8160913B2Disadvantages and and reduced eliminatedProblems and reduced eliminatedResourcesGraphicsData combination
Owner:AWARE SOFTWARE
Exercise device
ActiveUS20100285931A1Effective exerciseEfficient and effectiveStiltsMuscle exercising devicesButtocksWorking environment
An exercise device for strengthening the core or midsection of the body that is suitable for use in a professional work environment. The exercise device comprises a domed seat positioned atop a plurality of baffled sections. The domed seat is deformable, allowing it to support and conform to the buttocks of a user when sitting on the device. The baffled sections are also deformable, allowing the seat to shift in all directions along a horizontal plane as a user's weight naturally shifts while sitting on the device. As the baffled sections deform and the seat persistently shifts over the course of a given period of time, a user's core muscles repeatedly tense in order to stabilize the body. The constant tension of the muscles over that period of time simulates a workout, particularly in the midsection of the body.
Owner:ERGOERGO
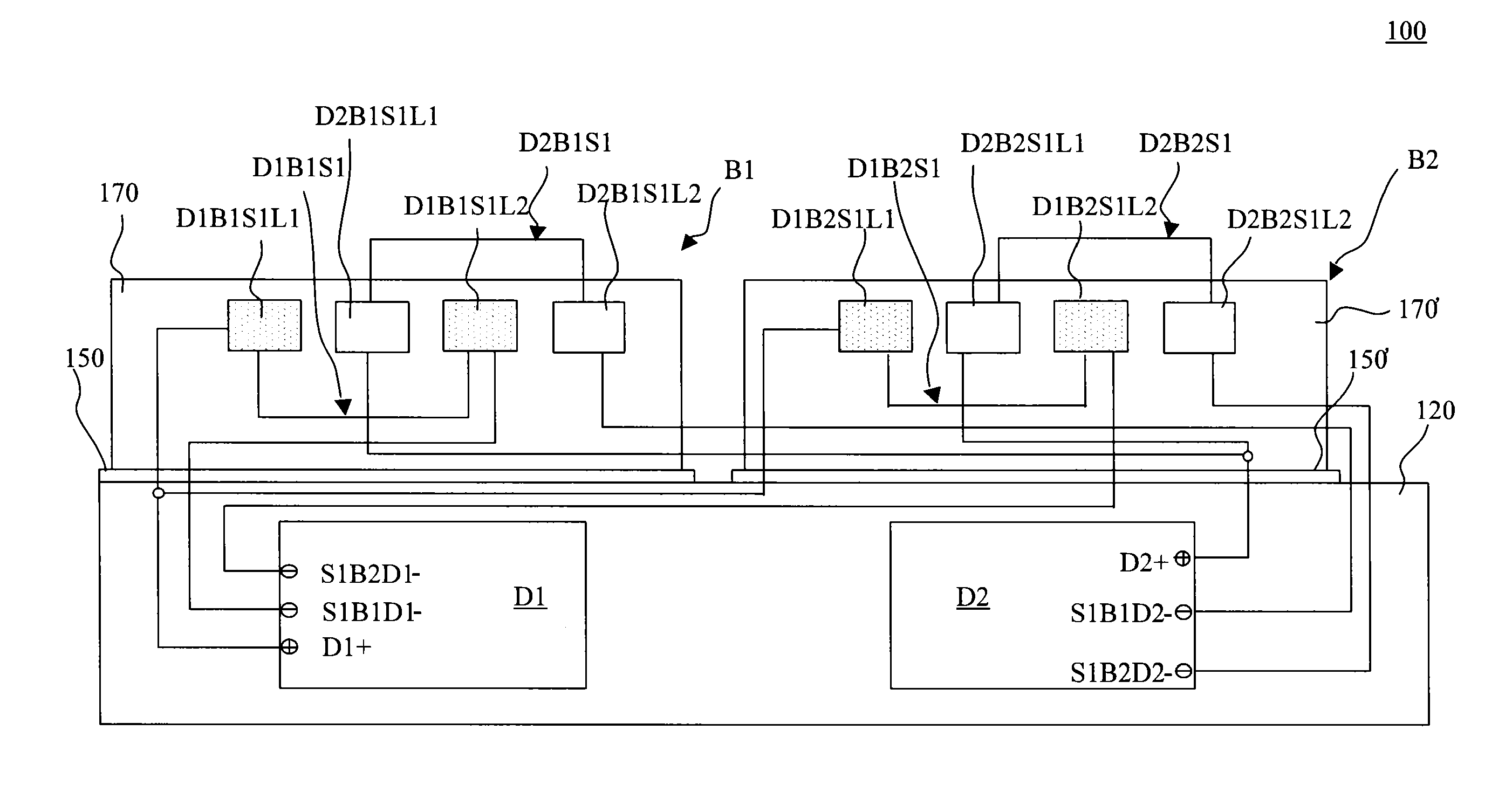
Liquid Crystal Display Device and Back Light Module of the Liquid Crystal Display Device
InactiveUS20110050682A1Cut down manufacturing cost costCut down cost substitution costCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
A back light module of a liquid crystal display device and the liquid crystal display device are provided. The back light module includes a printed circuit board (PCB), a light emitting diode (LED) driver, and a plurality of LED light bars. Each LED light bar has a plurality of LED series. The LED driver simultaneously electrically connects the LED series of different LED light bars via tracks of the PCB.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
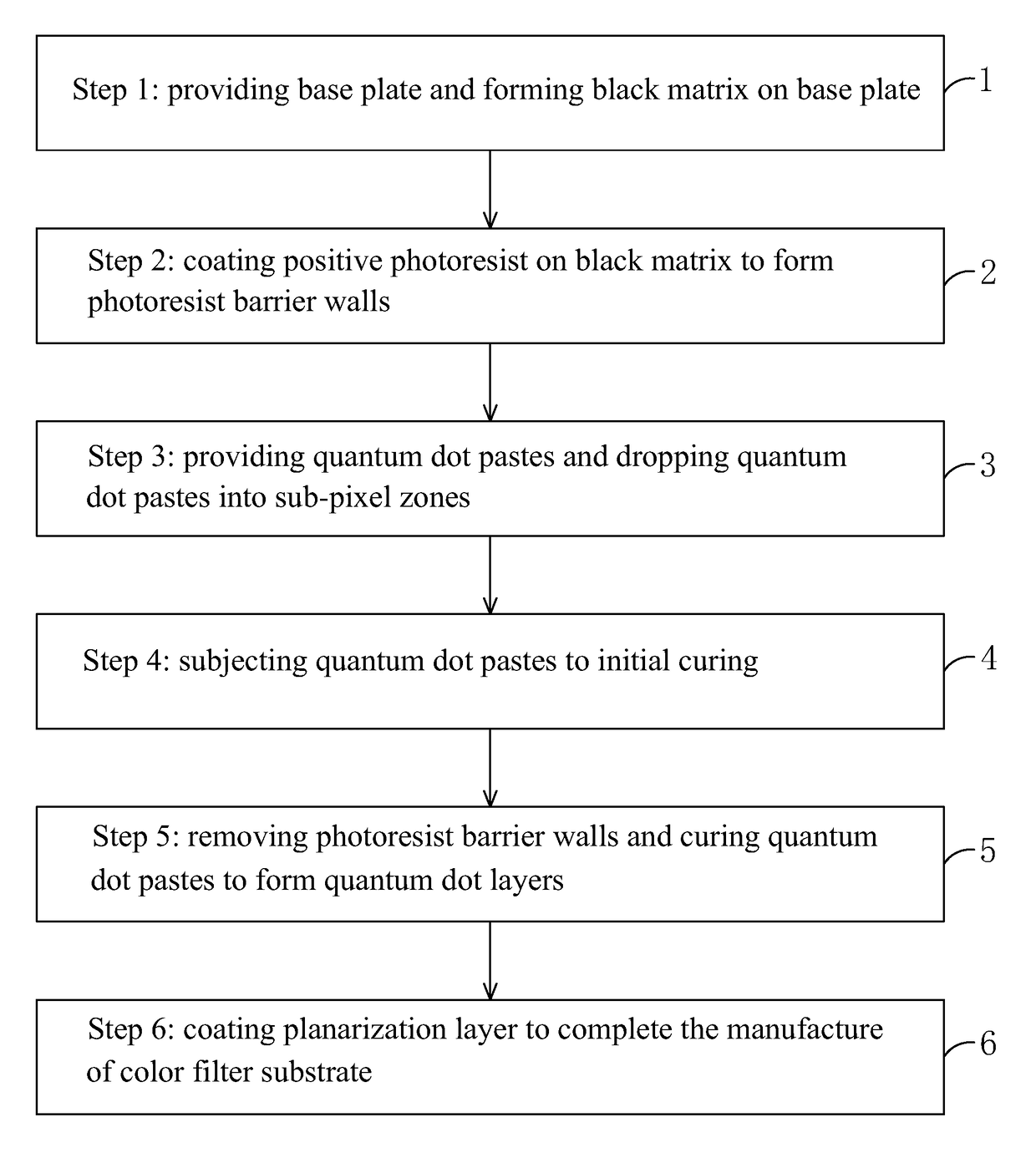
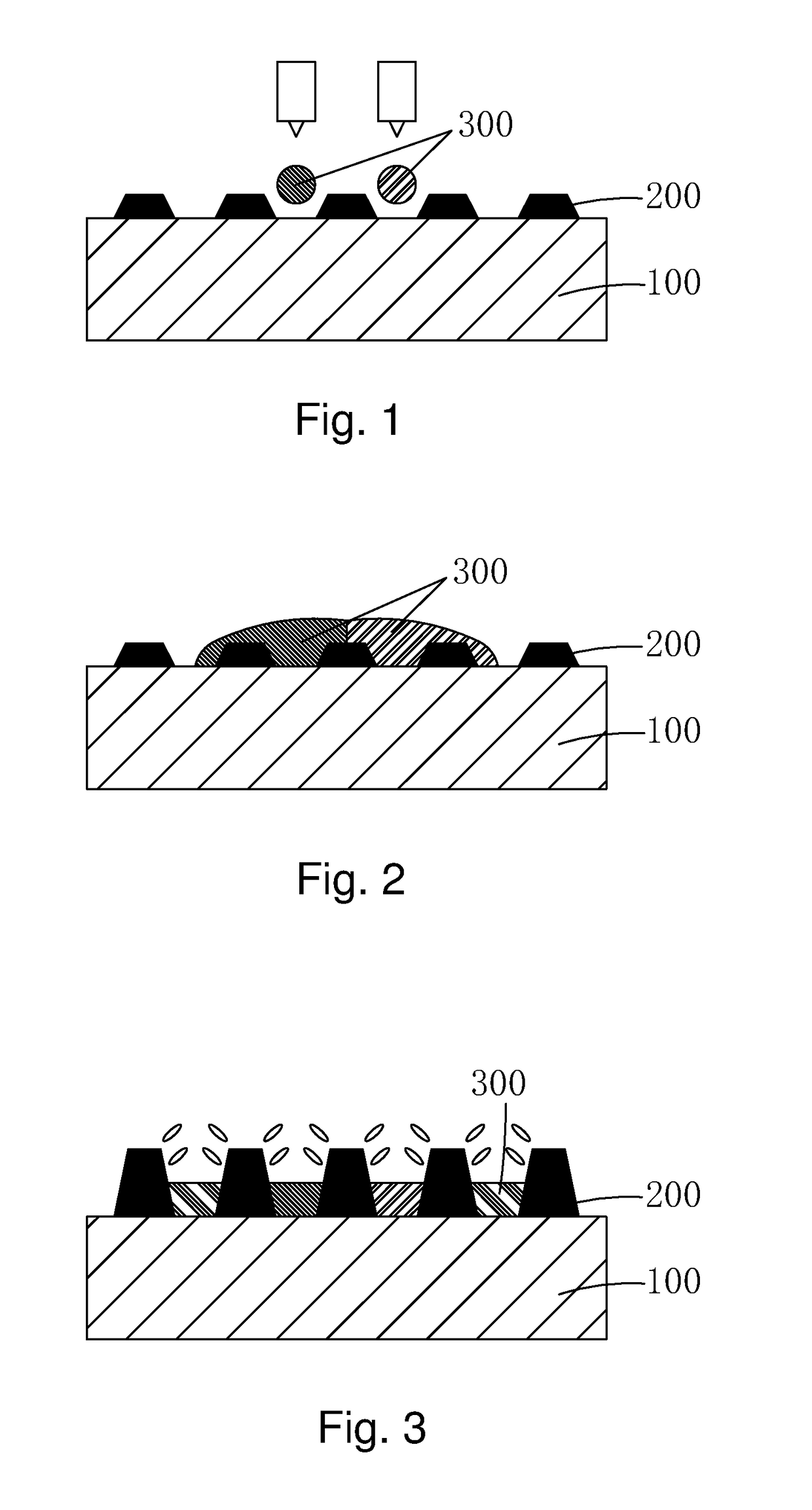
Method for manufacturing color filter substrate
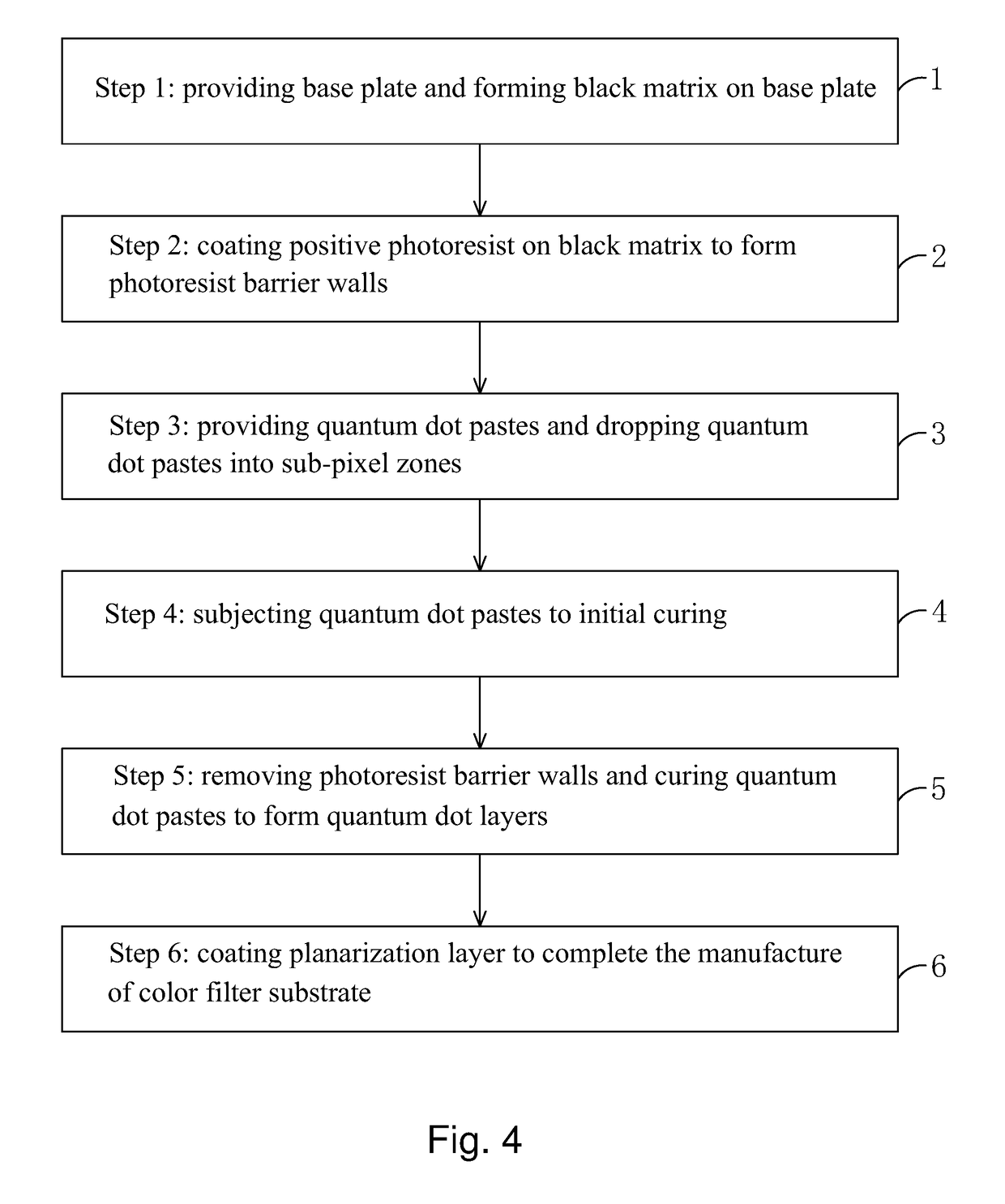
InactiveUS20170261849A1Improve flatnessIssue to overcomePhotomechanical apparatusTypewritersQuantum dotLight filter
The present invention provides a method for manufacturing a color filter substrate. In the method for manufacturing a color filter substrate of the present invention, before quantum dot pastes are dropped into sub-pixel zones, photoresist barrier walls are first formed on a black matrix by means of positive photoresist to provide an effect of barrier in dropping the quantum dot paste. After the effect of barrier has been completed, the photoresist barrier walls are removed to prevent the problems of the convention color filter substrate manufacturing method that color mixture may result due to free flowing of quantum dot pastes caused by an excessively small height of the barrier walls and light leakage may result due to disorderly arrangement of liquid crystal caused by an excessively large height of barrier walls. The operation is easy and the color filter substrate so manufactured exhibits better flatness.
Owner:TCL CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Stirred tank bioreactor
ActiveUS8999702B2Issue to overcomeGood flexibilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCholesterol bindingAir interface
The present invention is a disposable bioreactor formed of molded plastic. The bioreactor is presterilized and has a top and body sealed to each other. One or more ports are formed in the top and side of the housing. Preferably at least one port is below the liquid / air level for the housing. The one or more ports that are below the liquid / air interface level may be used as sampling ports or access ports for probes or drains or supply ports for liquids or gases. The bioreactor provides a direct retrofit for the existing glass or steel assembly that utilizes the existing support structures and controls. The molded design overcomes issues of discontinuity, dead spots and the like due to its fixed dimensions that are built in by the molding process. Reproducible probe and other equipment location is also guaranteed through the use of the molded port features. The molded plastic allows for greater flexibility in material selection to reduce or eliminate lipid or cholesterol binding.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com