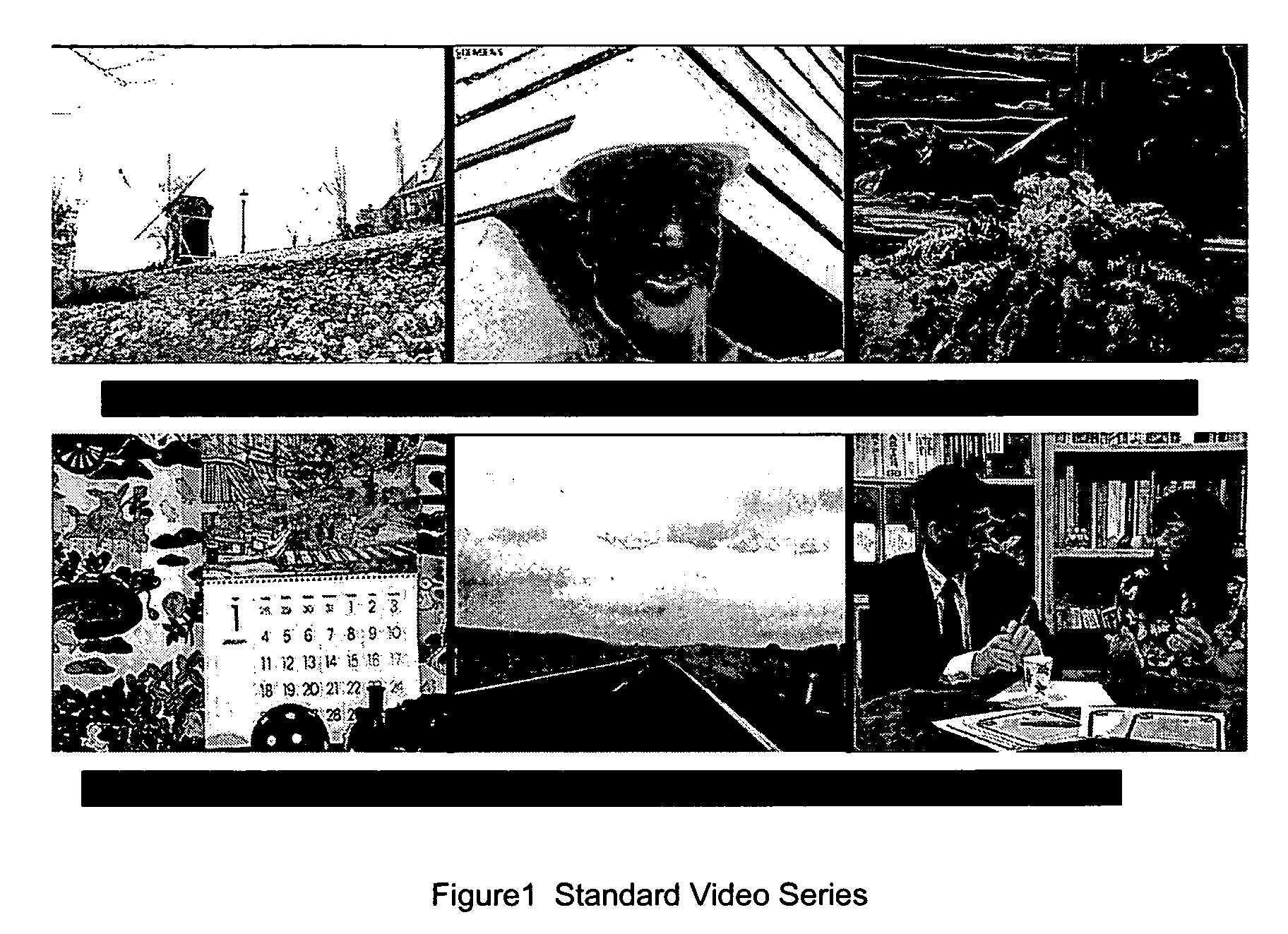
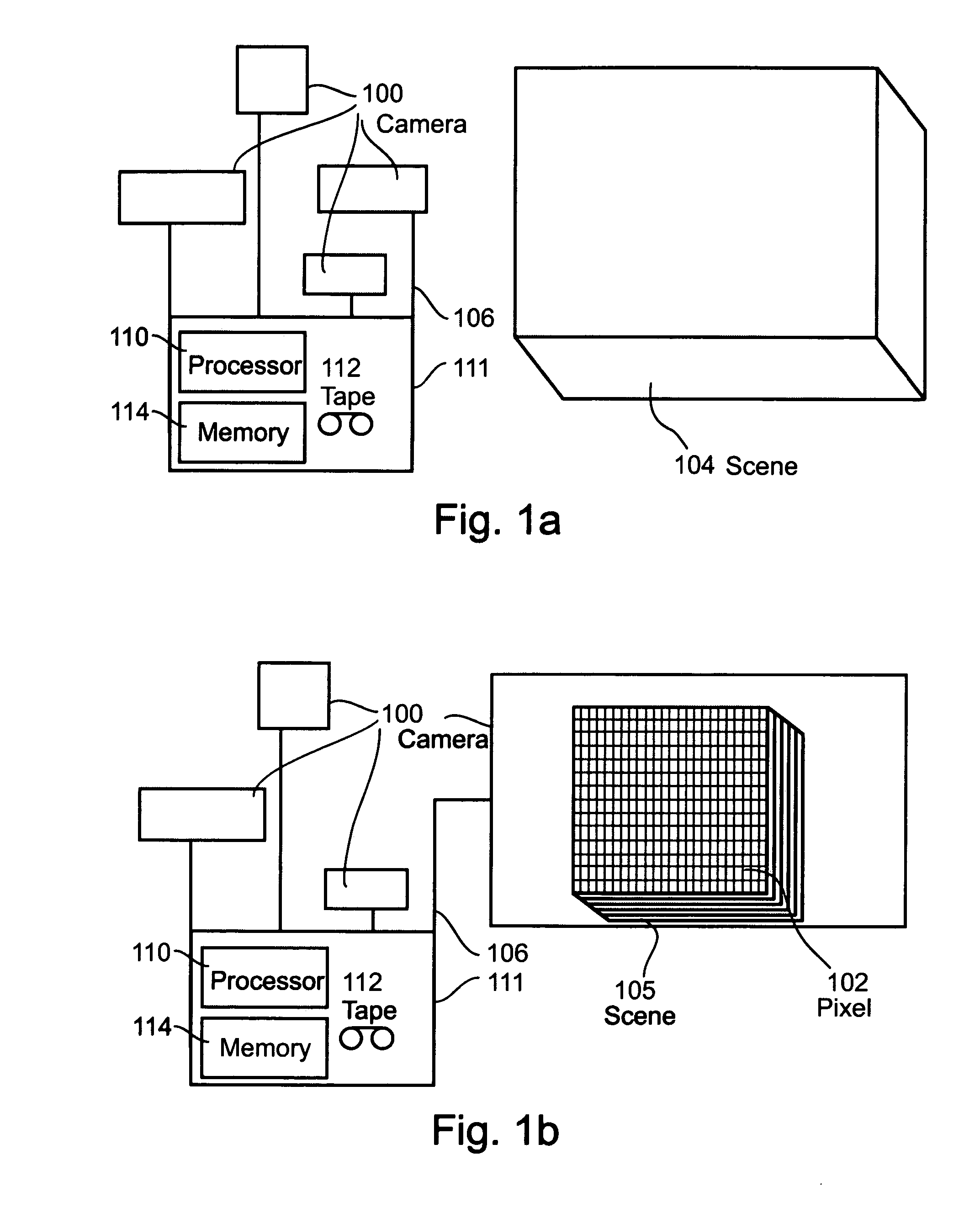
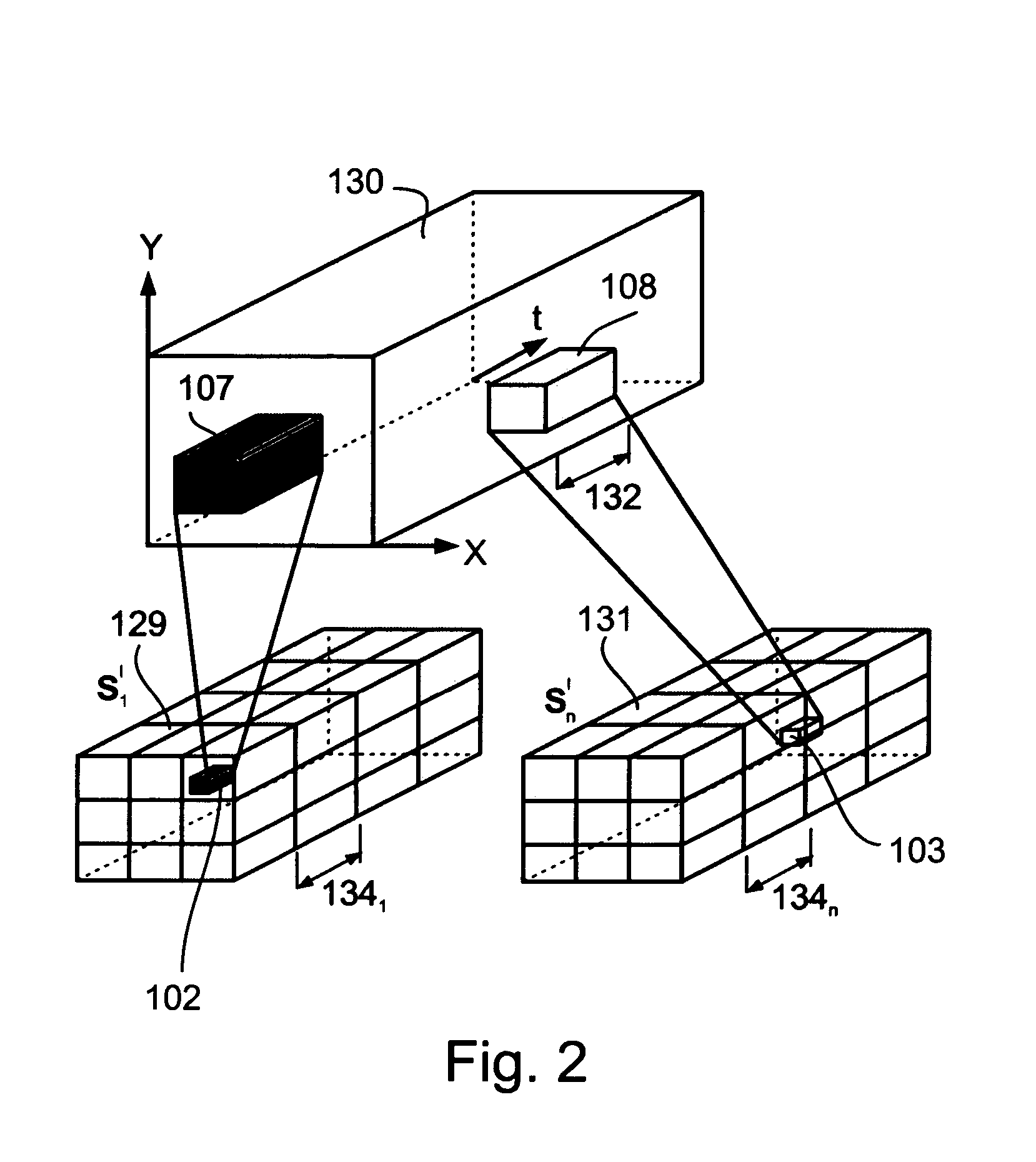
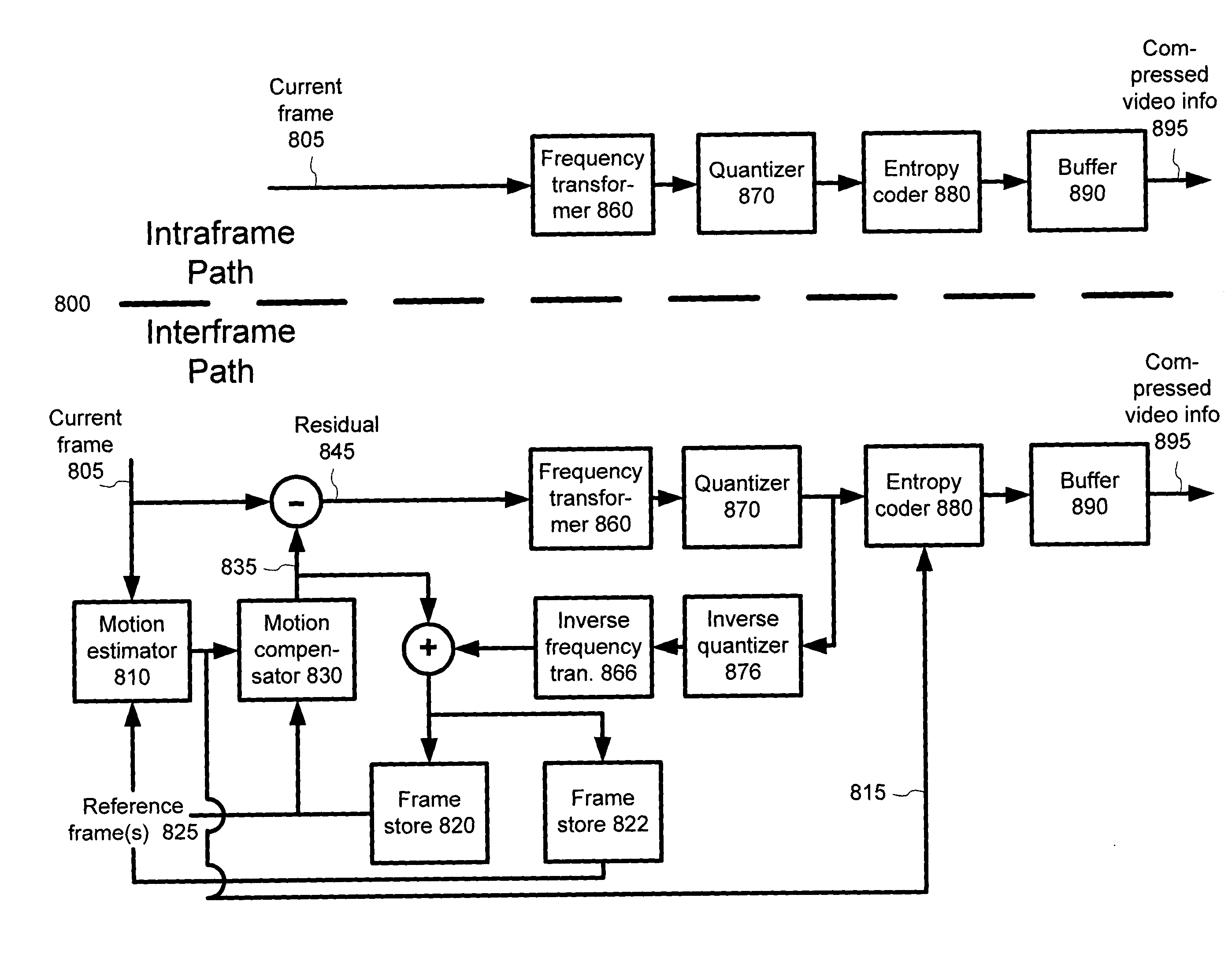
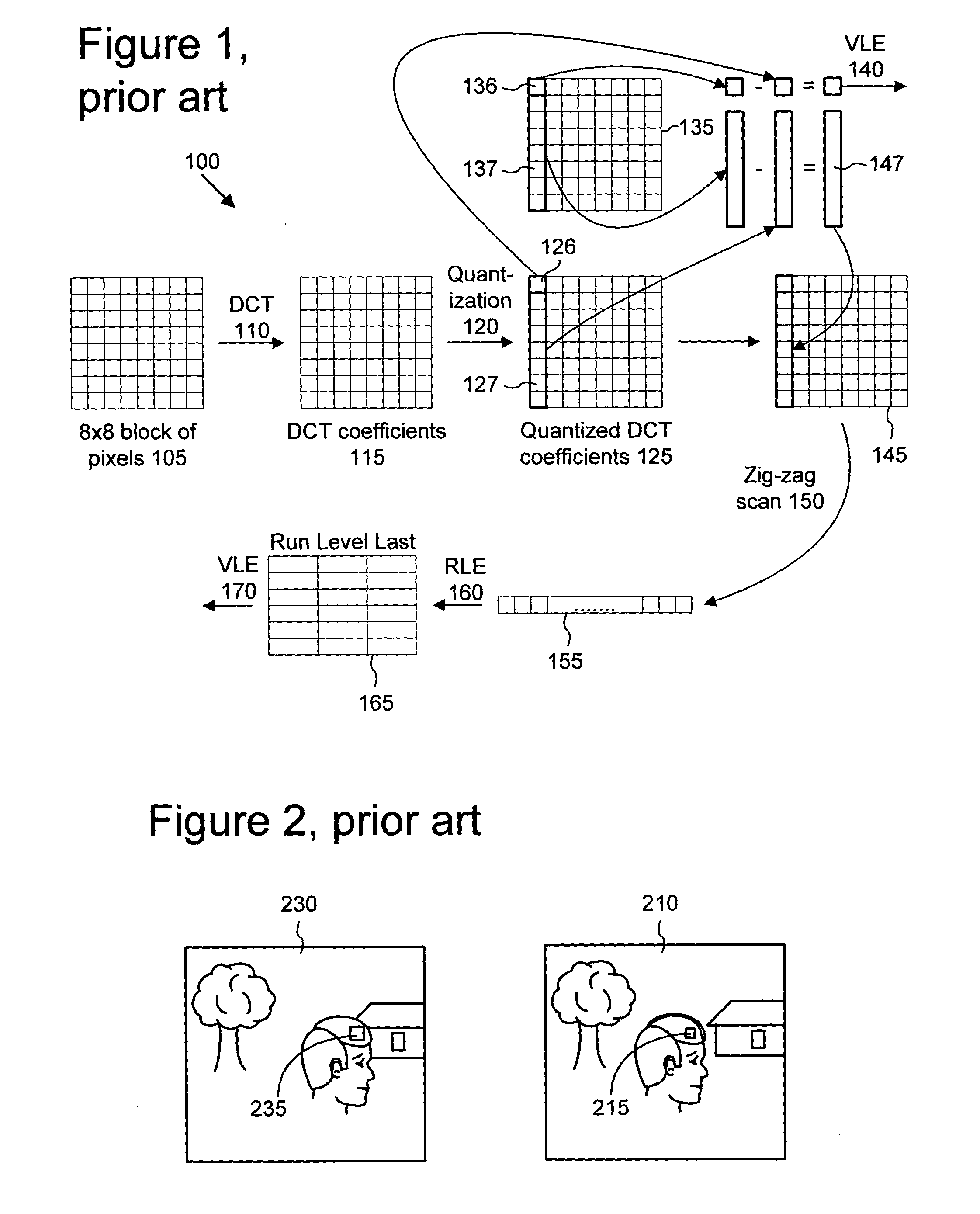
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
7360 results about "Motion vector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
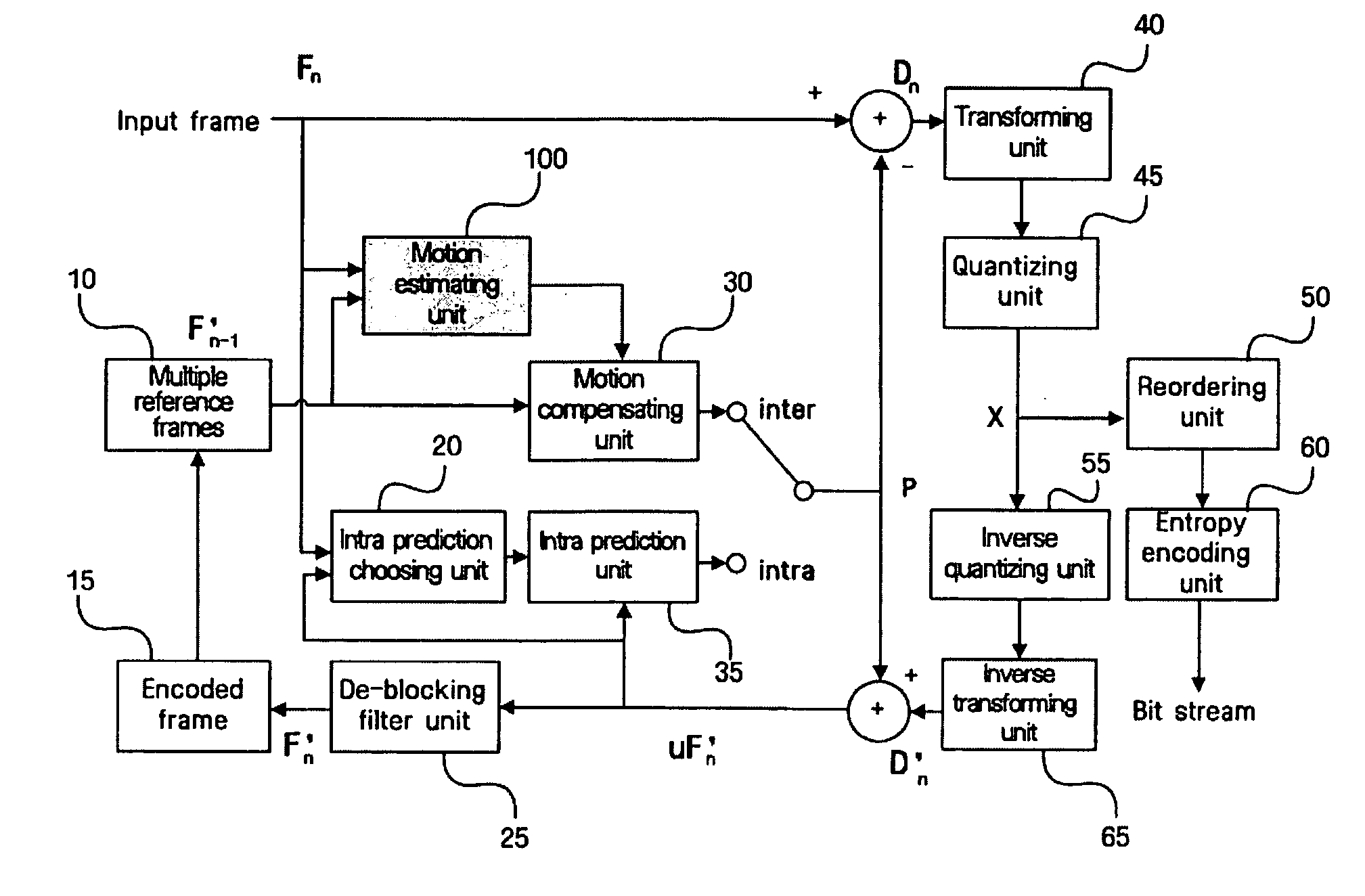
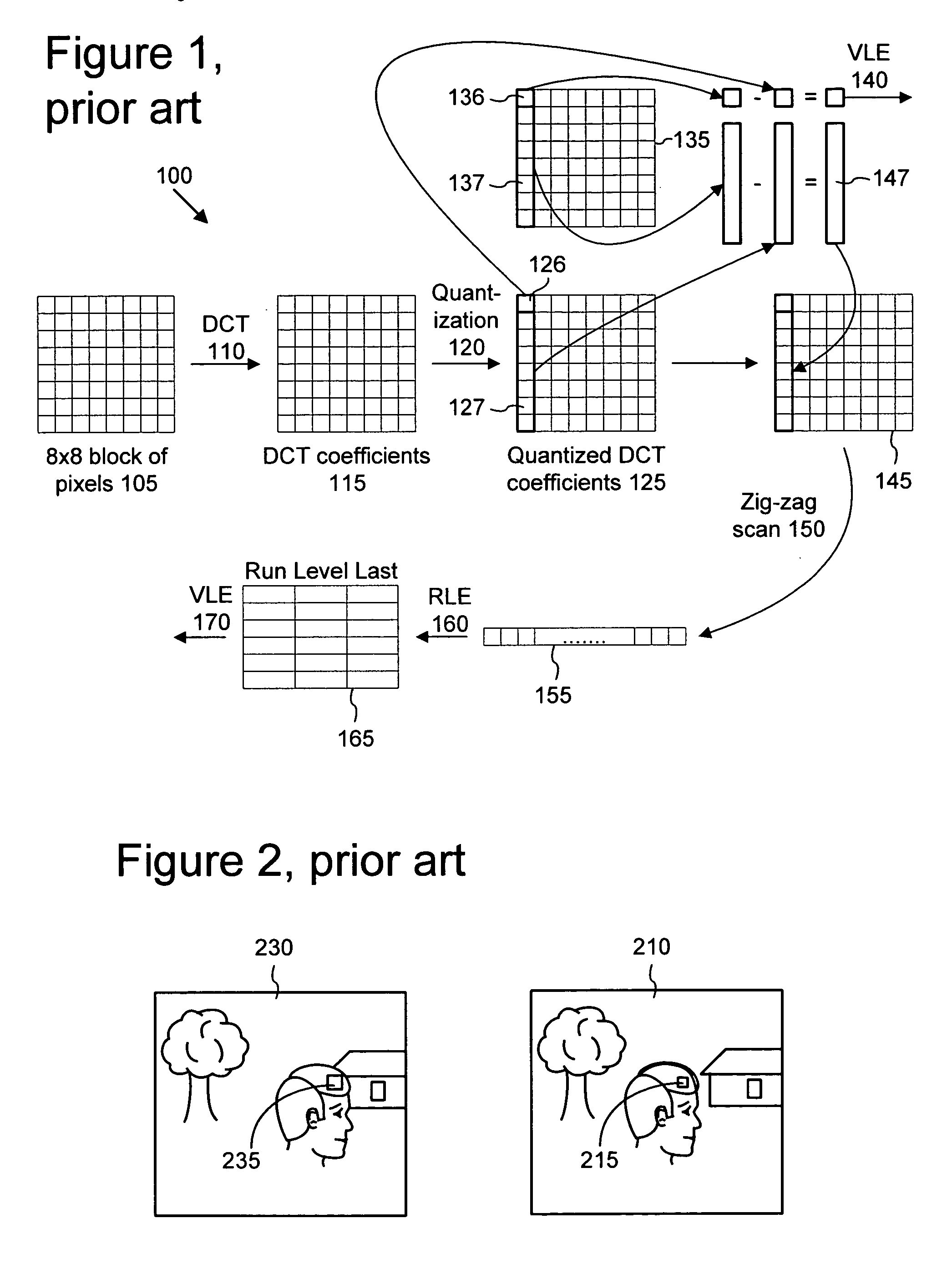
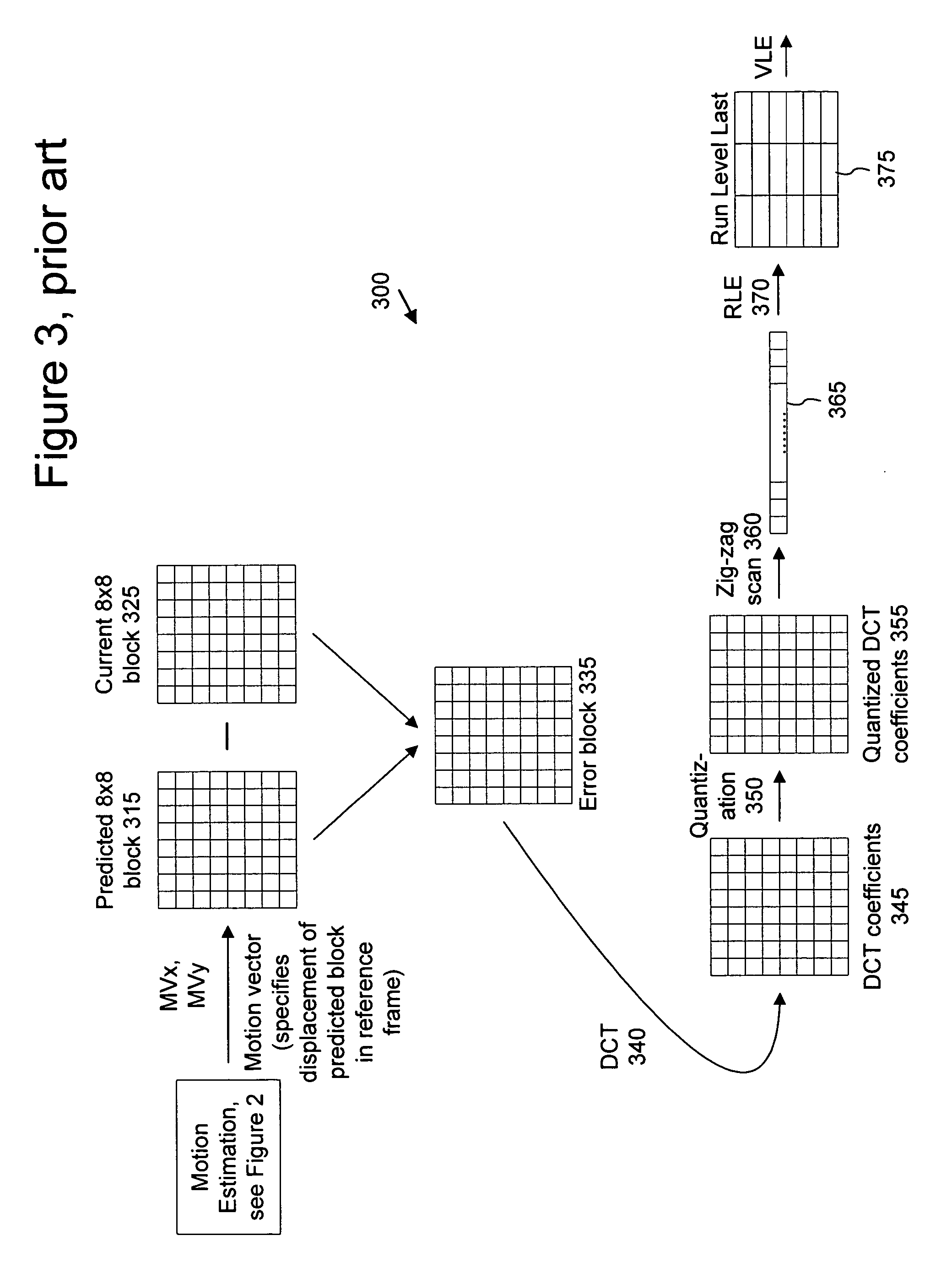
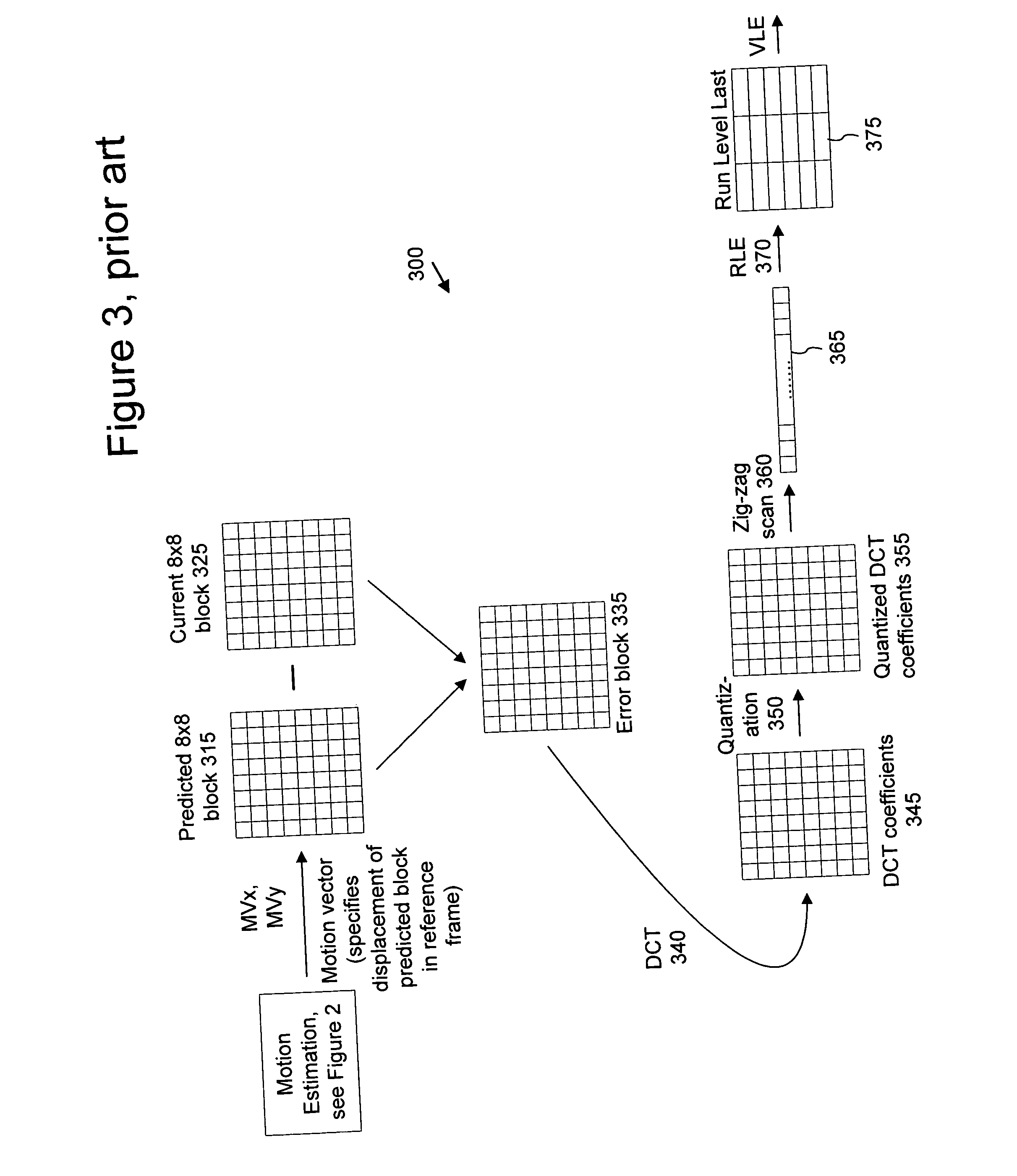
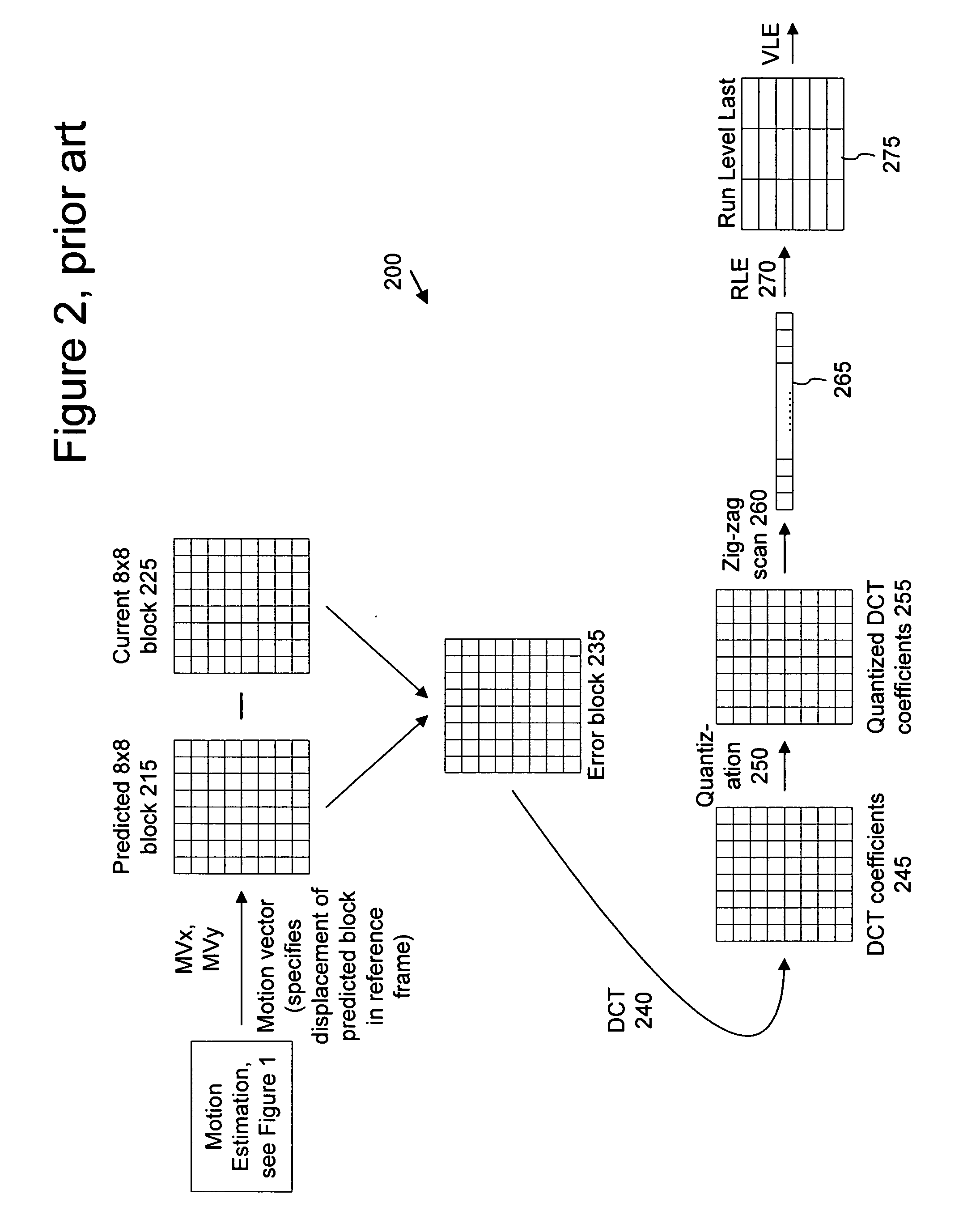
In video compression, a motion vector is the key element in the motion estimation process. It is used to represent a macroblock in a picture based on the position of this macroblock (or a similar one) in another picture, called the reference picture.
Combined motion vector and reference index prediction for video coding
ActiveUS20090304084A1Improve coding efficiencyImprove compression efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorVideo encoding
A system and method for improving the coding efficiency of motion vector information in video coding. According to various embodiments, a list of motion vector predictor candidates is arranged according to predefined rules. Each motion vector also has a reference index associated with it. One of the motion vector candidates is then selected as a predictor based on predefined rules, or the selection is explicitly signaled in the bitstream. The reference index associated with the selected motion vector is used as a reference index for the current block. The reference index is predicted along with the motion vector. Such embodiments can improve the compression efficiency of modern video codecs.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
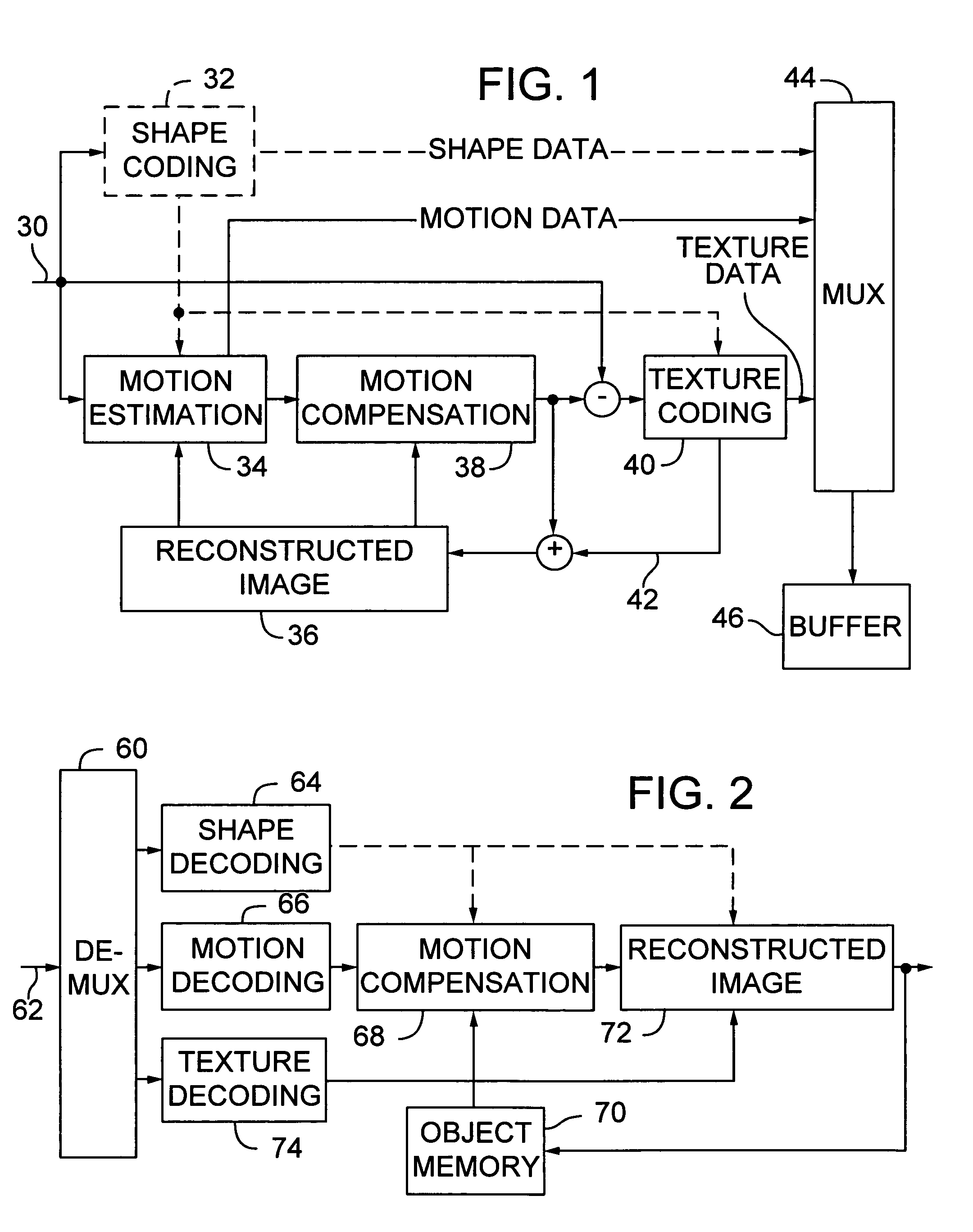
Image coding and decoding apparatus and methods thereof
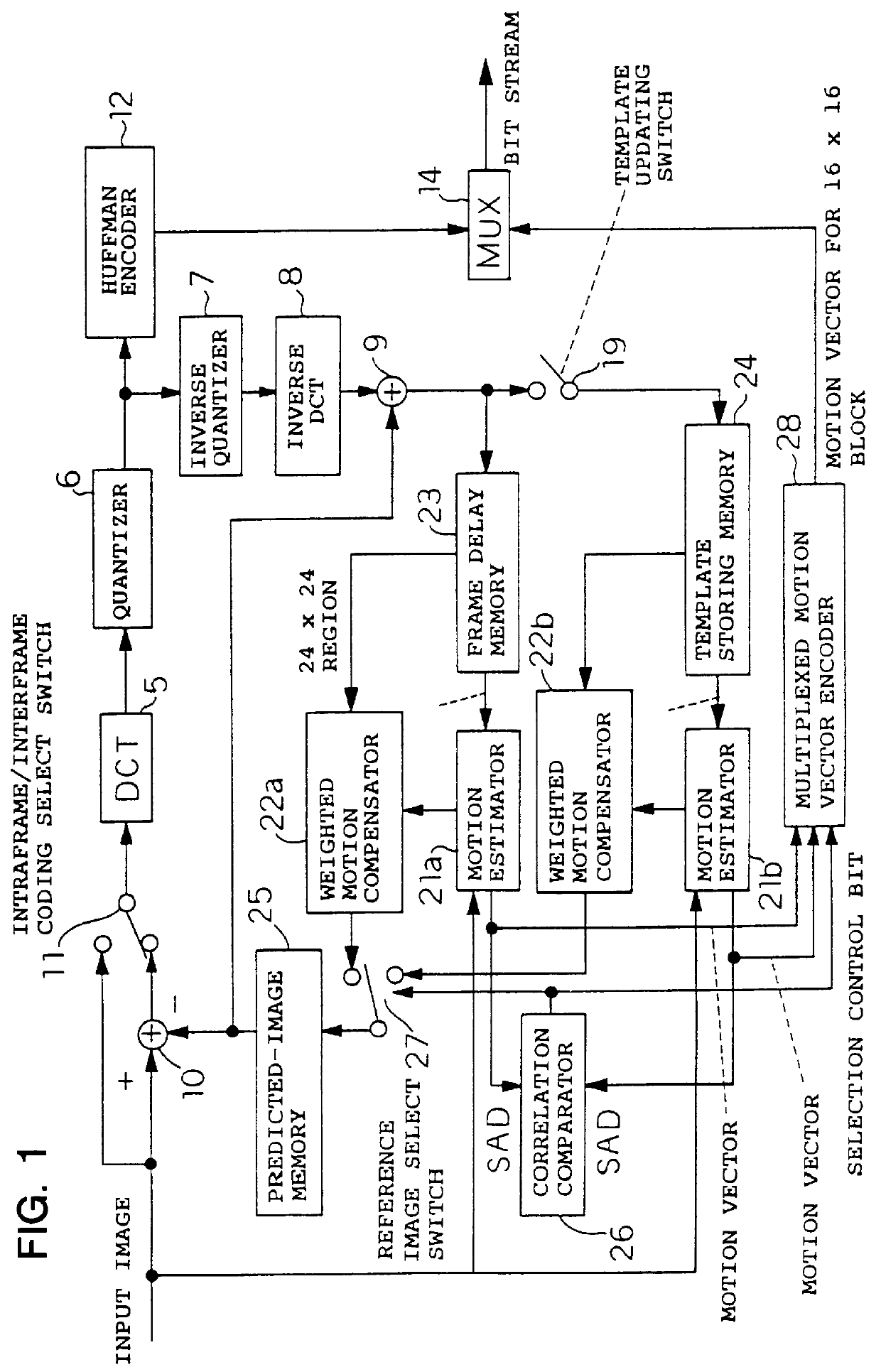
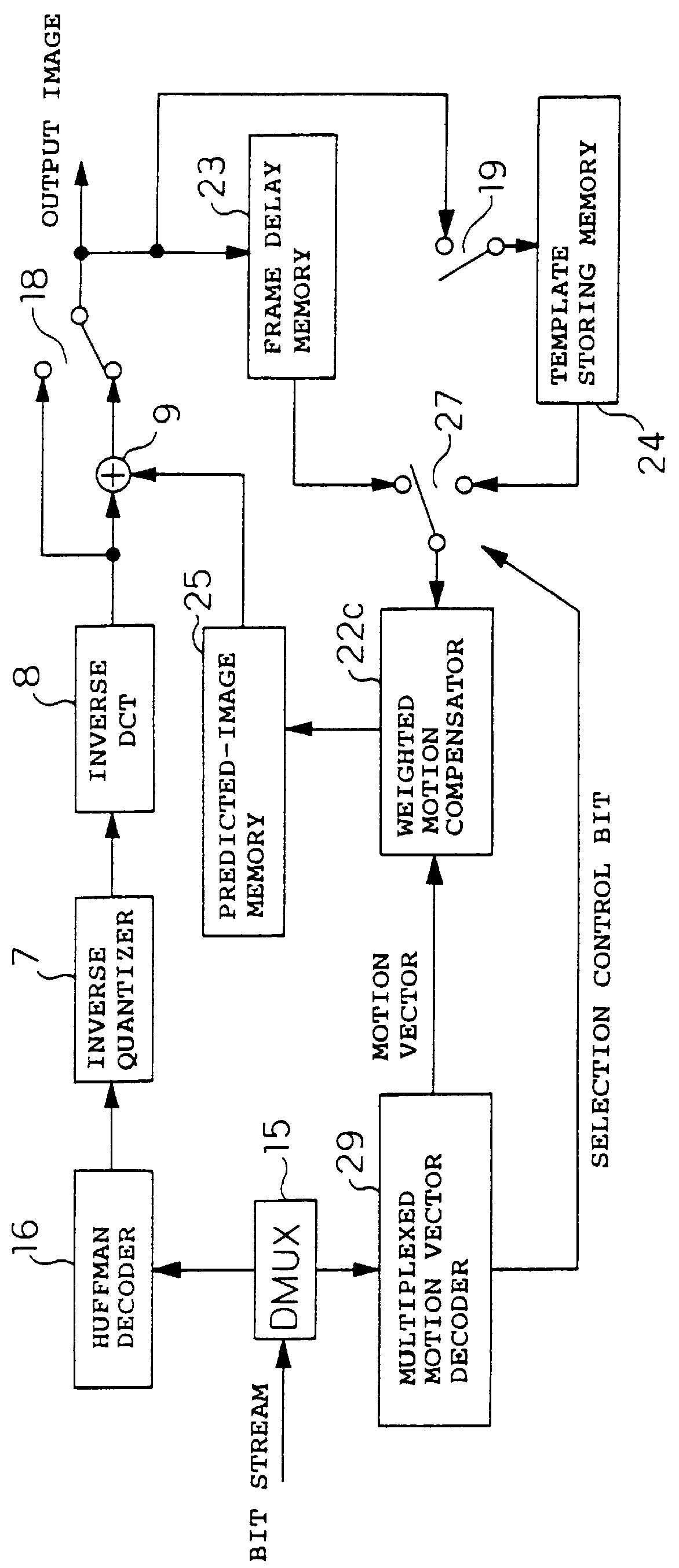
InactiveUS6081551APicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionExtensibilityMotion vector
To achieve an image encoding apparatus that has extensibility by not limiting an image to be referenced, and that can reduce processing time satisfactorily if the processing of an ordinary frame is skipped, the apparatus of the present invention comprises: motion detecting means for detecting a motion vector for each block of a prescribed size from a reference image and an input image; weighted motion-compensation means for, based on the detected motion vector, extracting from the reference image an area of a prescribed size which is wider than the prescribed block size and which contains an area corresponding to each block of the input image, and for creating a predicted image for the input image by applying a predetermined weight to each of pixels in the wider area and by using the weighted pixels of the wider area; a predicted-image memory for storing the predicted image; encoding means for taking a residual between the stored predicted image and the input image, and for encoding the residual; and decoding means for decoding the encoded image data and thereby obtaining a reference image.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
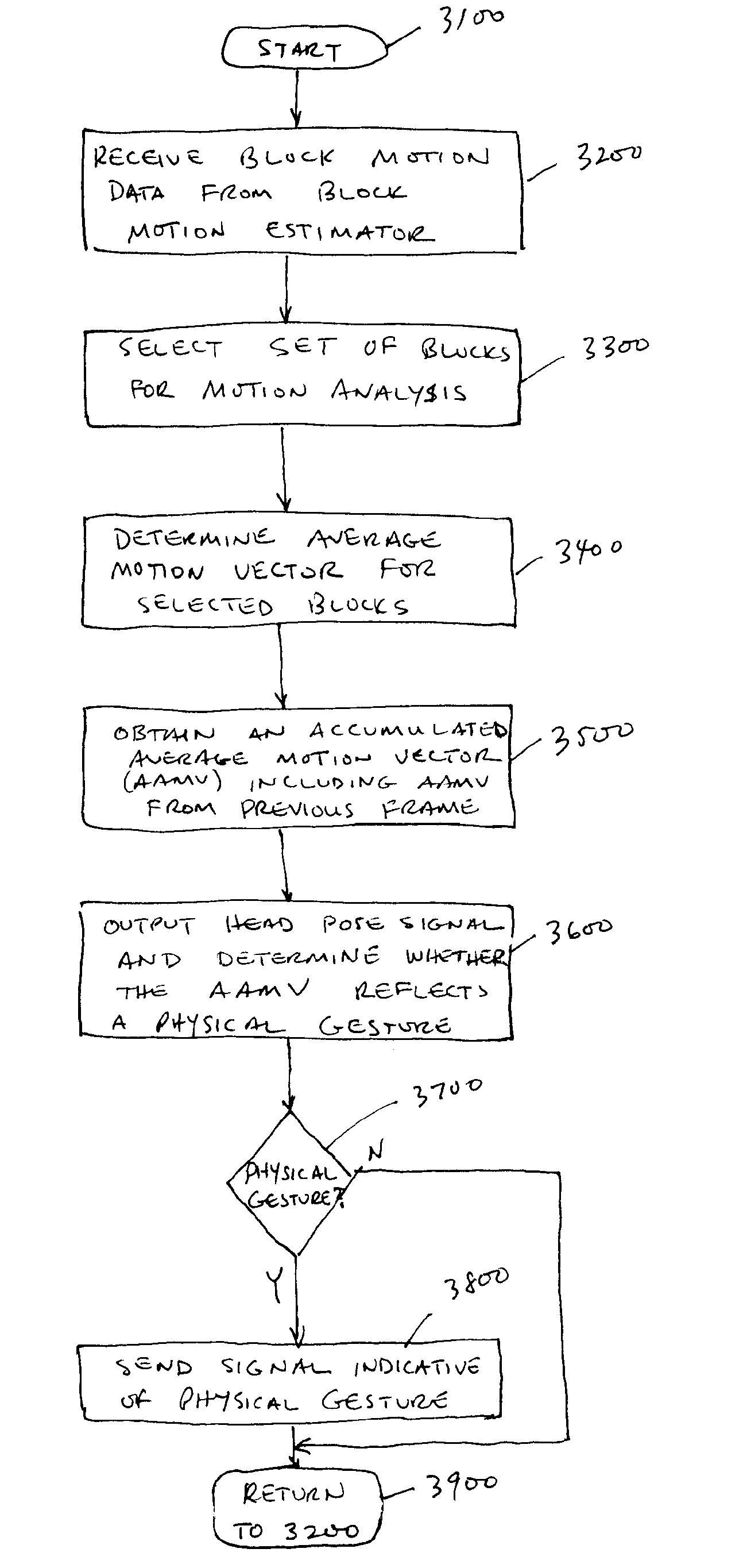
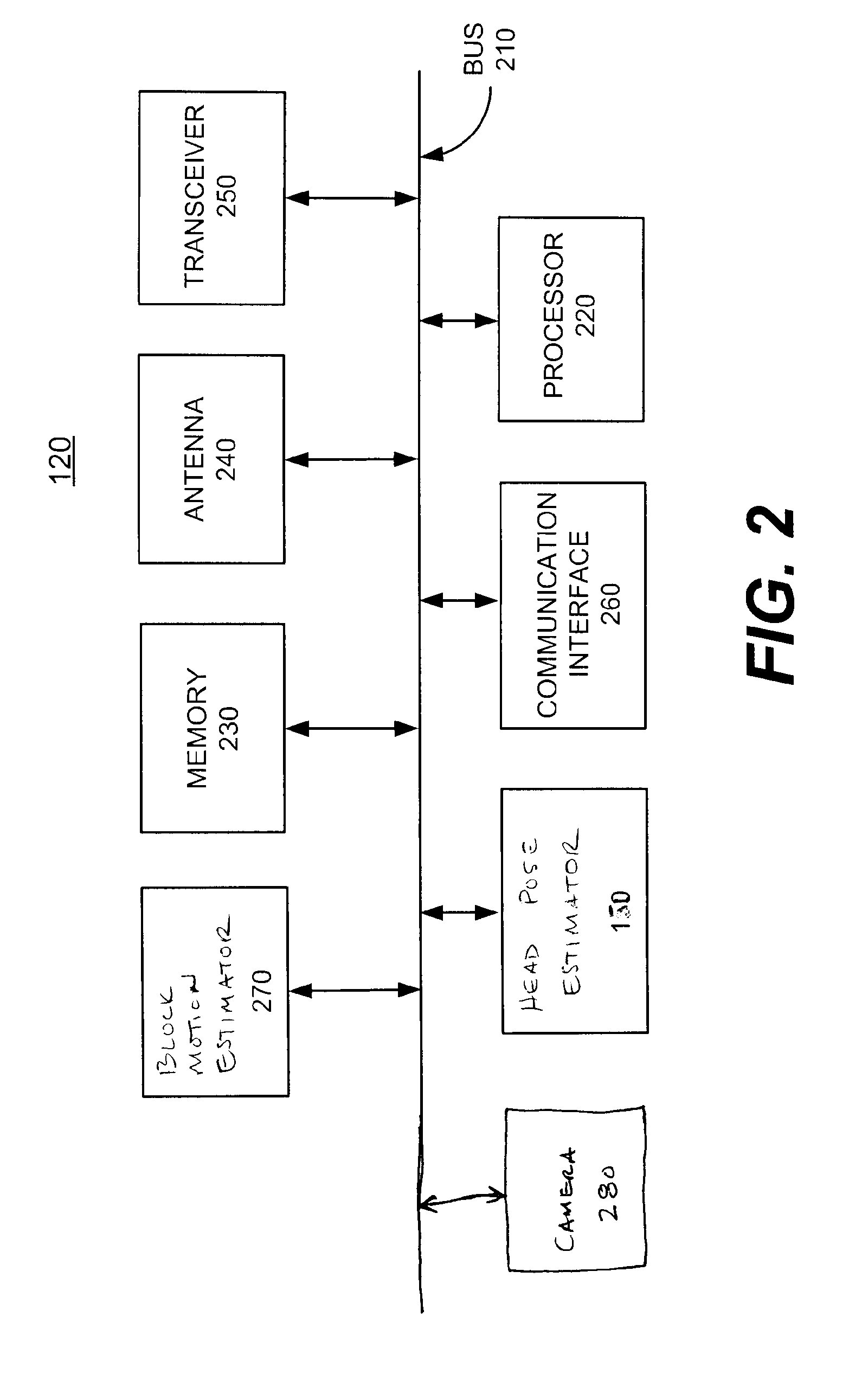
Apparatus and methods for head pose estimation and head gesture detection
InactiveUS7412077B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionFrame basedMotion vector
A method for head pose estimation may include receiving block motion vectors for a frame of video from a block motion estimator, selecting at least one block for analysis, determining an average motion vector for the at least one selected block, combining the average motion vectors over time (all past frames of video) to determine an accumulated average motion vector, estimating the orientation of a user's head in the video frame based on the accumulated average motion vector, and outputting at least one parameter indicative of the estimated orientation.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
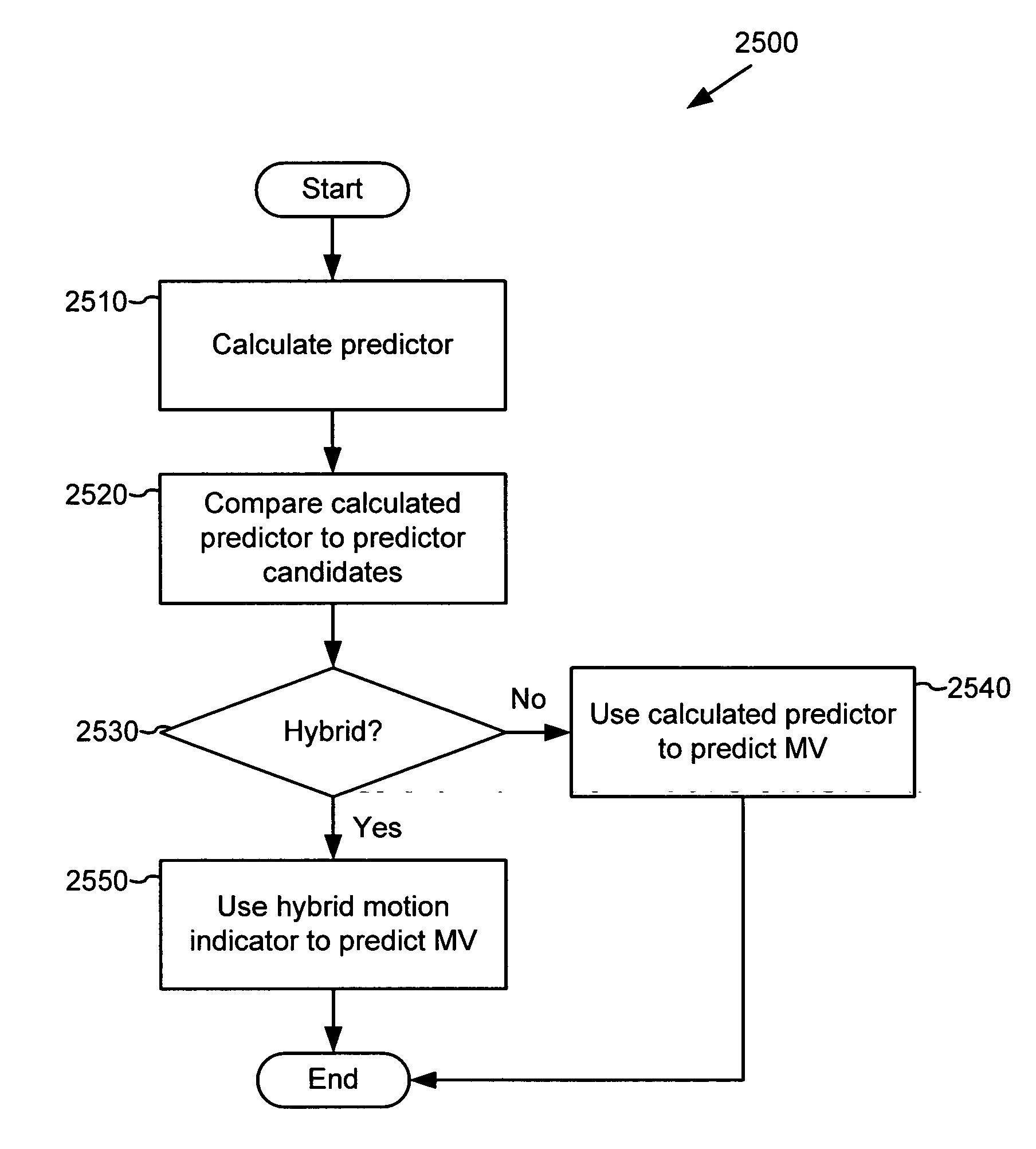
Coding of motion vector information
InactiveUS20050013498A1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionEncoder decoder
Techniques and tools for encoding and decoding motion vector information for video images are described. For example, a video encoder yields an extended motion vector code by jointly coding, for a set of pixels, a switch code, motion vector information, and a terminal symbol indicating whether subsequent data is encoded for the set of pixels. In another aspect, an encoder / decoder selects motion vector predictors for macroblocks. In another aspect, a video encoder / decoder uses hybrid motion vector prediction. In another aspect, a video encoder / decoder signals a motion vector mode for a predicted image. In another aspect, a video decoder decodes a set of pixels by receiving an extended motion vector code, which reflects joint encoding of motion information together with intra / inter-coding information and a terminal symbol. The decoder determines whether subsequent data exists for the set of pixels based on e.g., the terminal symbol.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus for motion estimation using variable block size of hierarchy structure
InactiveUS20050114093A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsMotion vectorComputer science
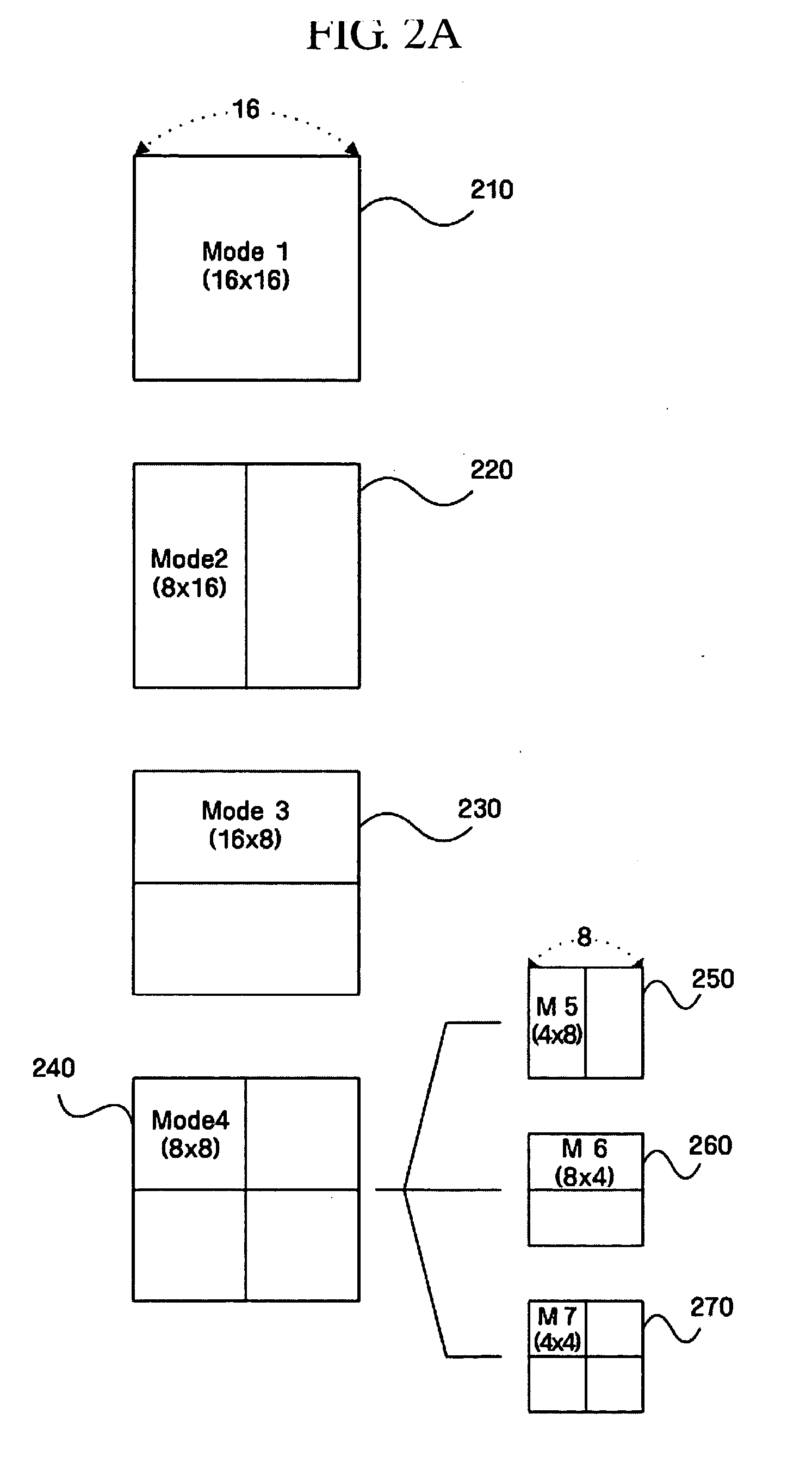
Disclosed is a method and apparatus for a motion estimation using a variable block size of a hierarchy structure. The method includes: calculating each of a motion vector of a desired minimum unit variable block; determining a similarity of the calculated motion vectors between the minimum unit variable blocks in a higher hierarchy including the minimum unit variable block; establishing a mode of the variable block according to the determined similarity; and deciding a motion vector with respect to the mode established variable block. The complexity of the method of compressing a motion picture of a hierarchy structure having a plurality of block sizes can be reduced by selecting a mode of the optimal block size on the basis of a motion vector with respect to the minimum unit and the cost occurred at that time without performing the motion estimation with respect to each mode each time.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Intraframe and interframe interlace coding and decoding
ActiveUS20050013497A1Facilitate decodingCharacter and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsInterlaced videoMotion vector
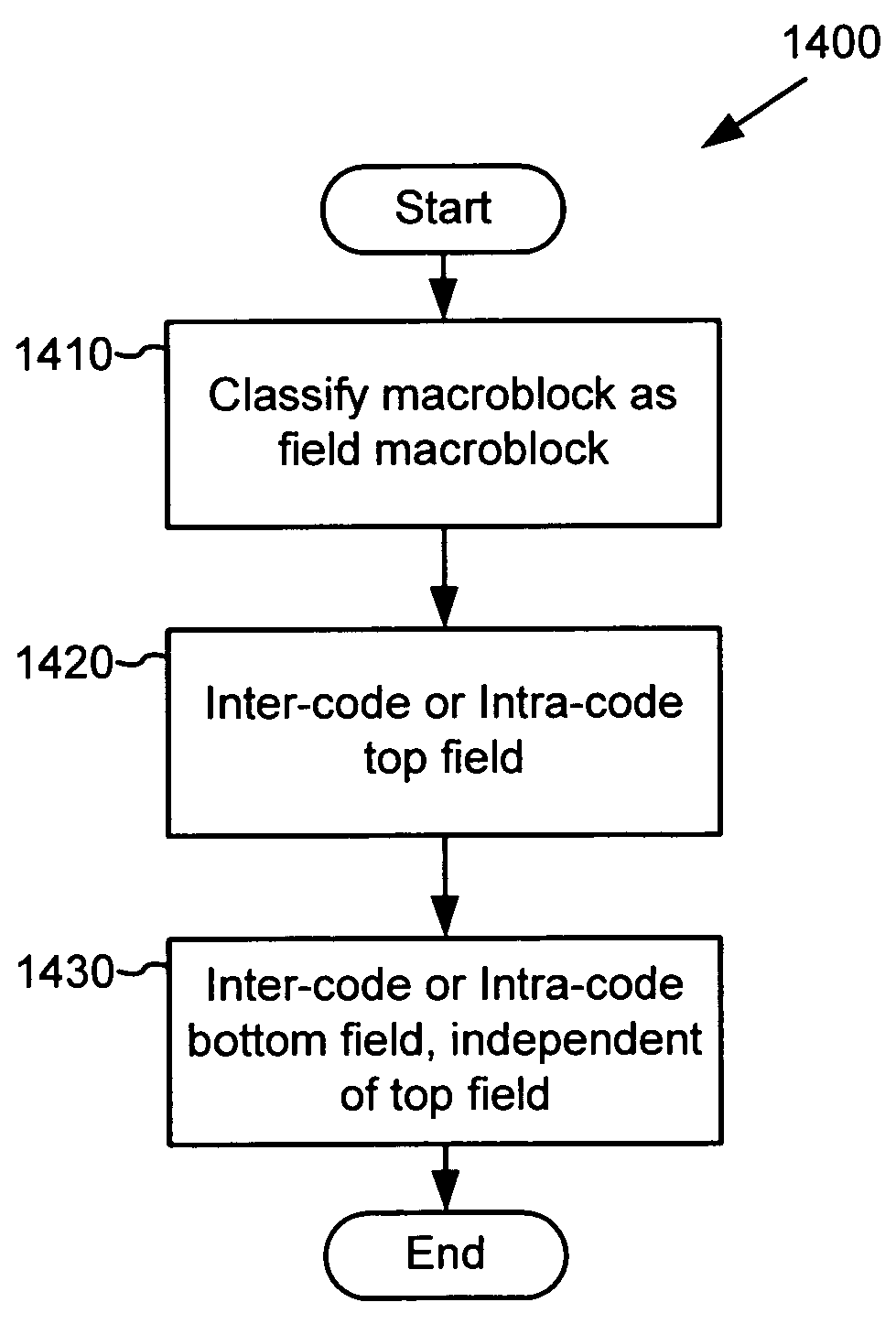
Techniques and tools for encoding and decoding video images (e.g., interlaced frames) are described. For example, a video encoder or decoder processes 4:1:1 format macroblocks comprising four 8×8 luminance blocks and four 4×8 chrominance blocks. In another aspect, fields in field-coded macroblocks are coded independently of one another (e.g., by sending encoded blocks in field order). Other aspects include DC / AC prediction techniques and motion vector prediction techniques for interlaced frames.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
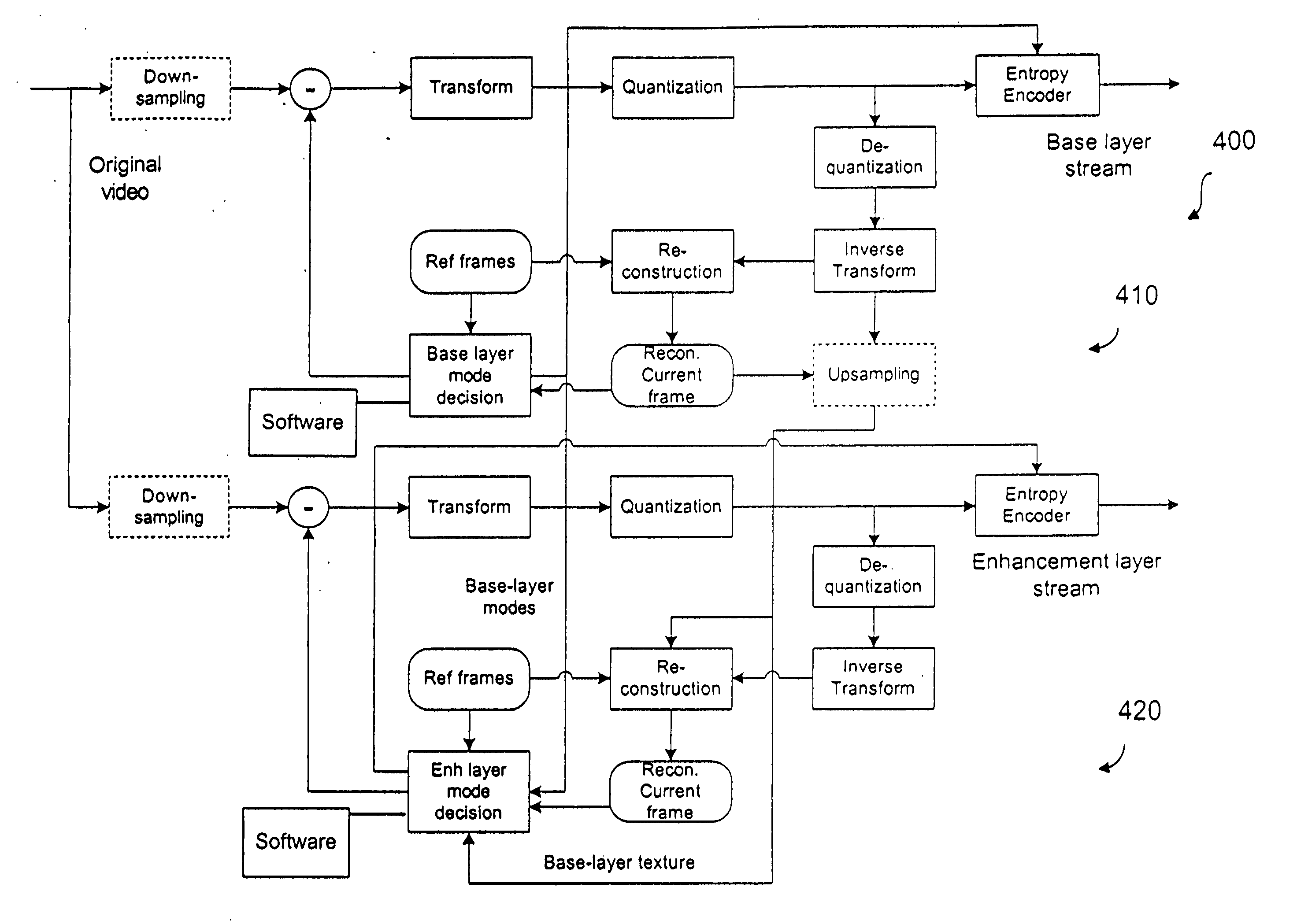
Inter-layer prediction for extended spatial scalability in video coding
ActiveUS20080165855A1Improving inter-layer predictionReduce computational complexityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionInter layerMotion vector
An improved system and method for providing improved inter-layer prediction for extended spatial scalability in video coding, as well as improving inter-layer prediction for motion vectors in the case of extended spatial scalability. In various embodiments, for the prediction of macroblock mode, the actual reference frame index and motion vectors from the base layer are used in determining if two blocks should be merged. Additionally, multiple representative pixels in a 4×4 block can be used to represent each 4×4 block in a virtual base layer macroblock. The partition and motion vector information for the relevant block in the virtual base layer macroblock can be derived from all of the partition information and motion vectors of those 4×4 blocks.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Moving picture encoding method and decoding method
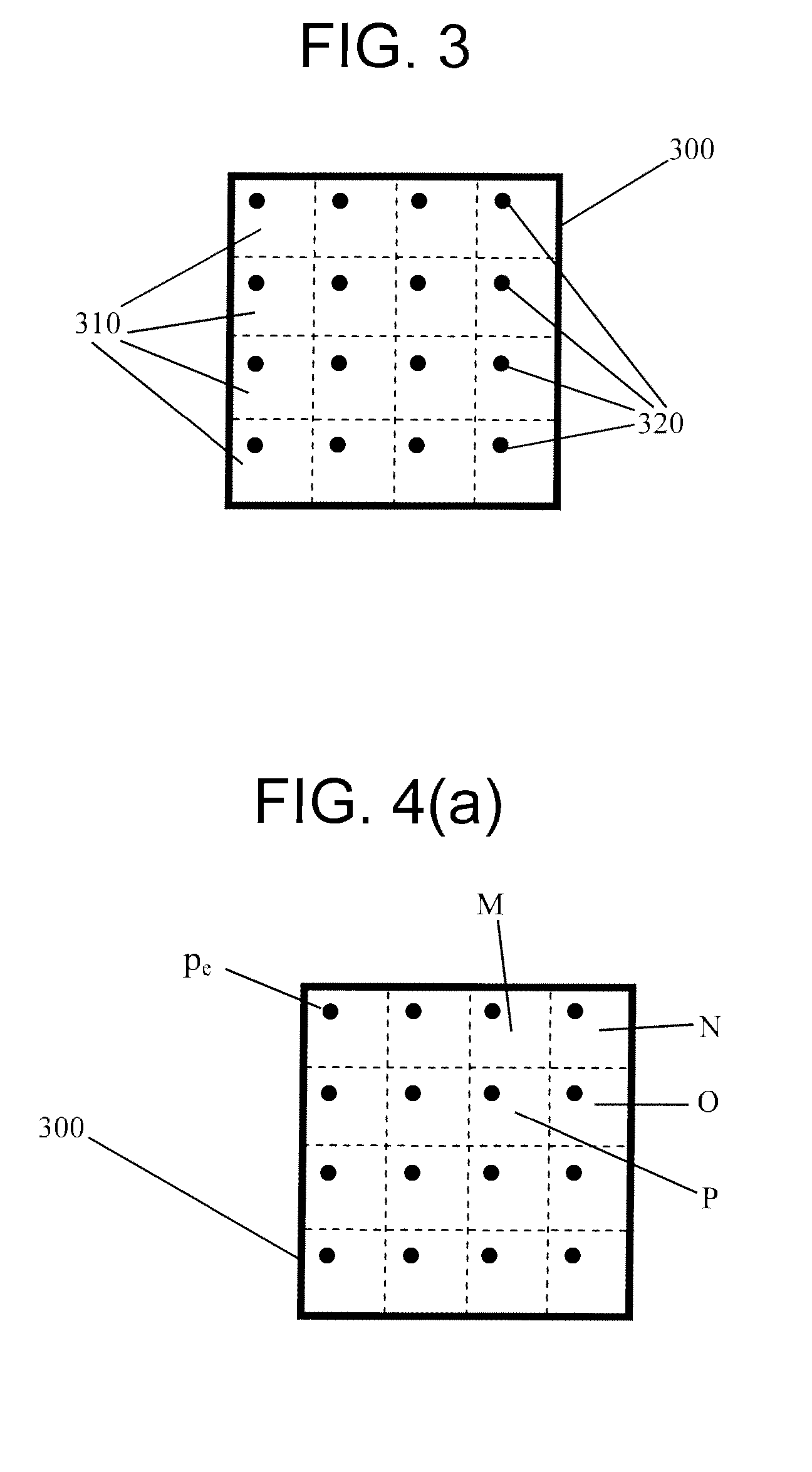
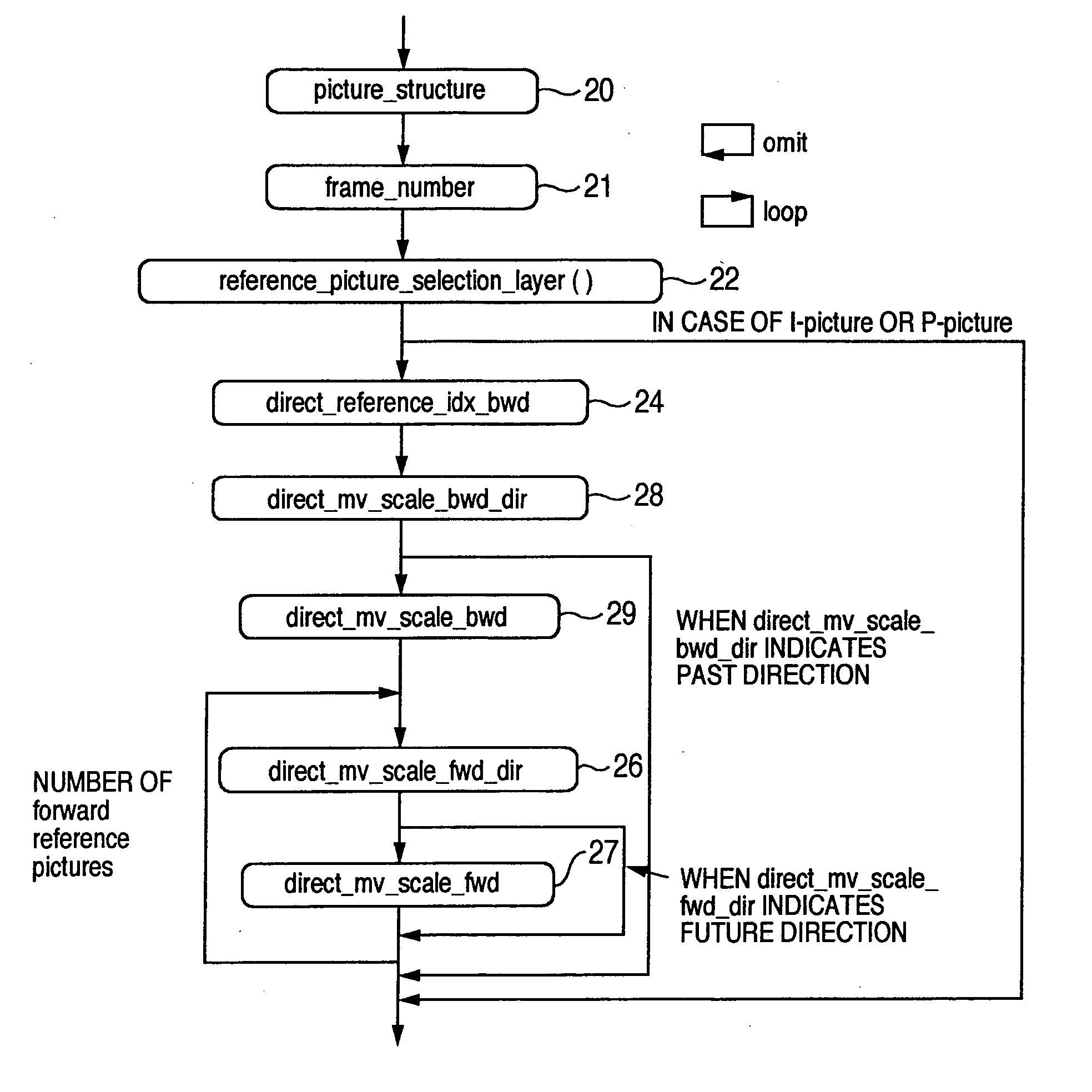
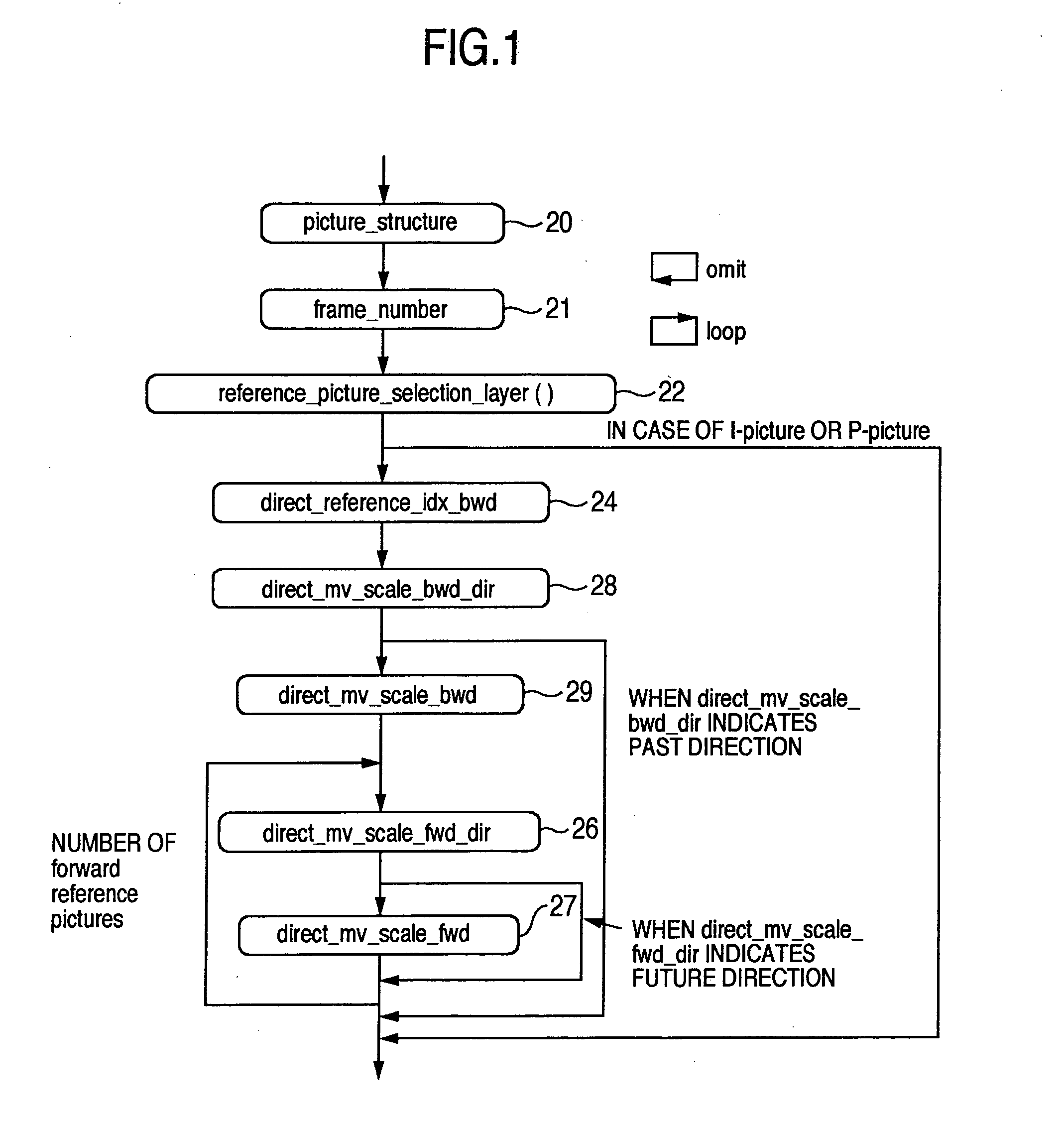
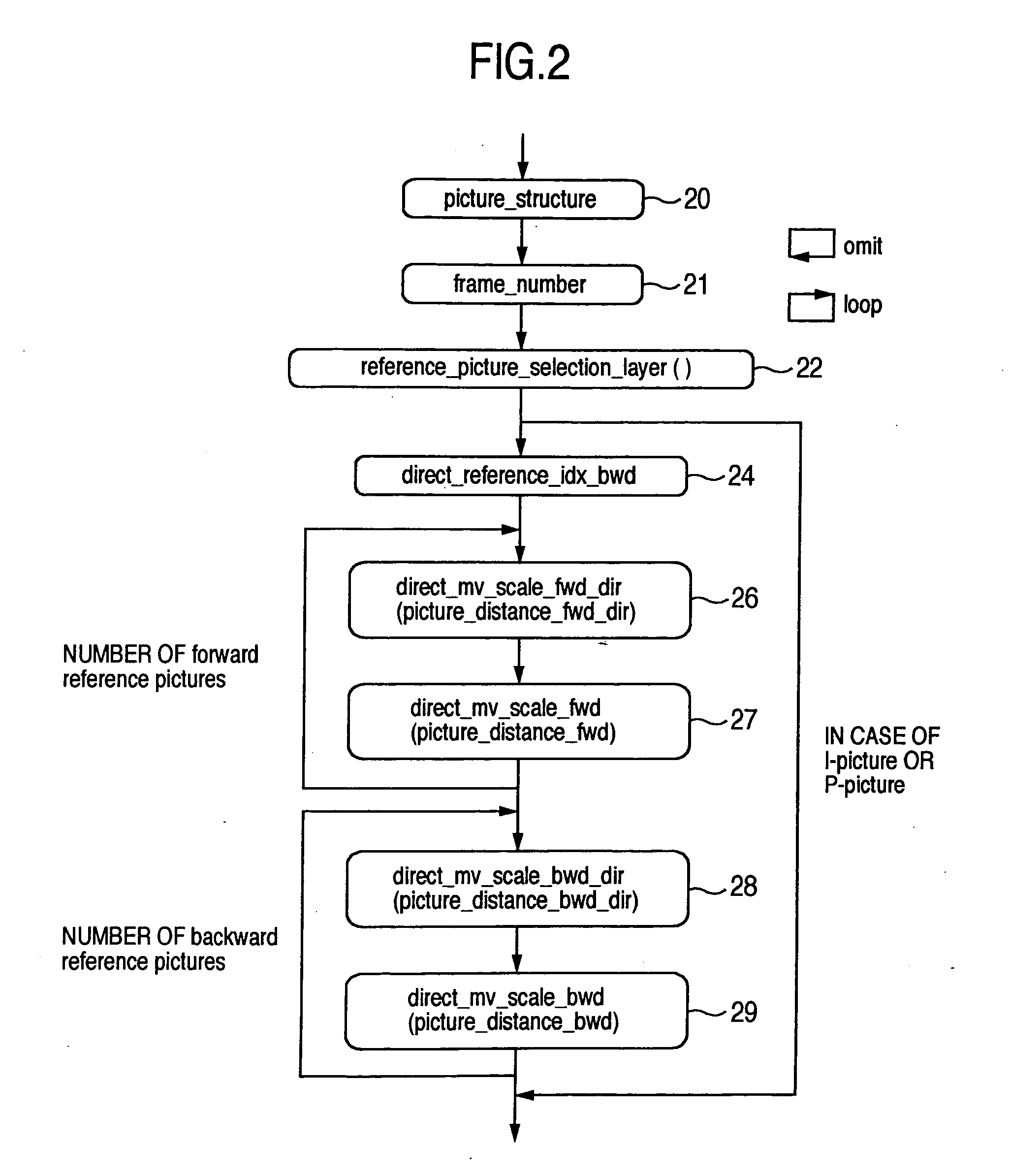
ActiveUS20050152452A1Prediction efficiency can be improvedReduce data volumePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningDecoding methodsTime information
Conventionally there has been a case that the direct mode cannot be applied effectively depending on the block. With such being the case, information indicating whether a backward reference frame set by default can be utilized in the direct mode is provided to a decoder. A switching procedure to switch to a compensation method applicable when a collocated block has no forward motion vector for effective use, and the compensation method are also provided to the decoder. Thus, it is possible to clearly determine whether the reference frame can be used in the direct mode. Further, when the frame number has no time information, it is possible to effectively send information indicating the relationship between the reference frame and the current frame. Furthermore, the alternative mode and its switching procedure of the present invention make it possible to improve the prediction performance when the direct mode cannot be applied.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
Device and method for converting two-dimensional video to three-dimensional video
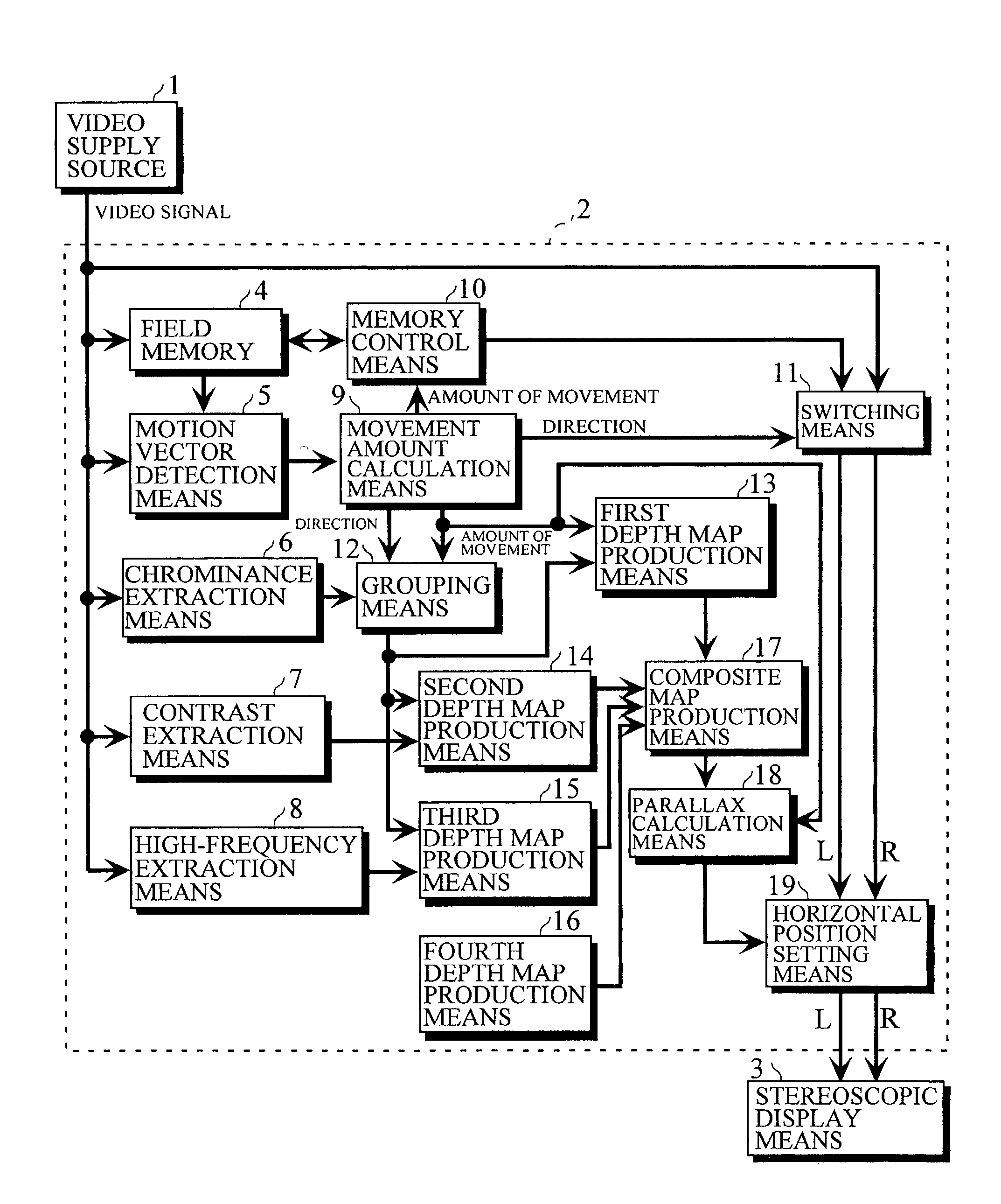
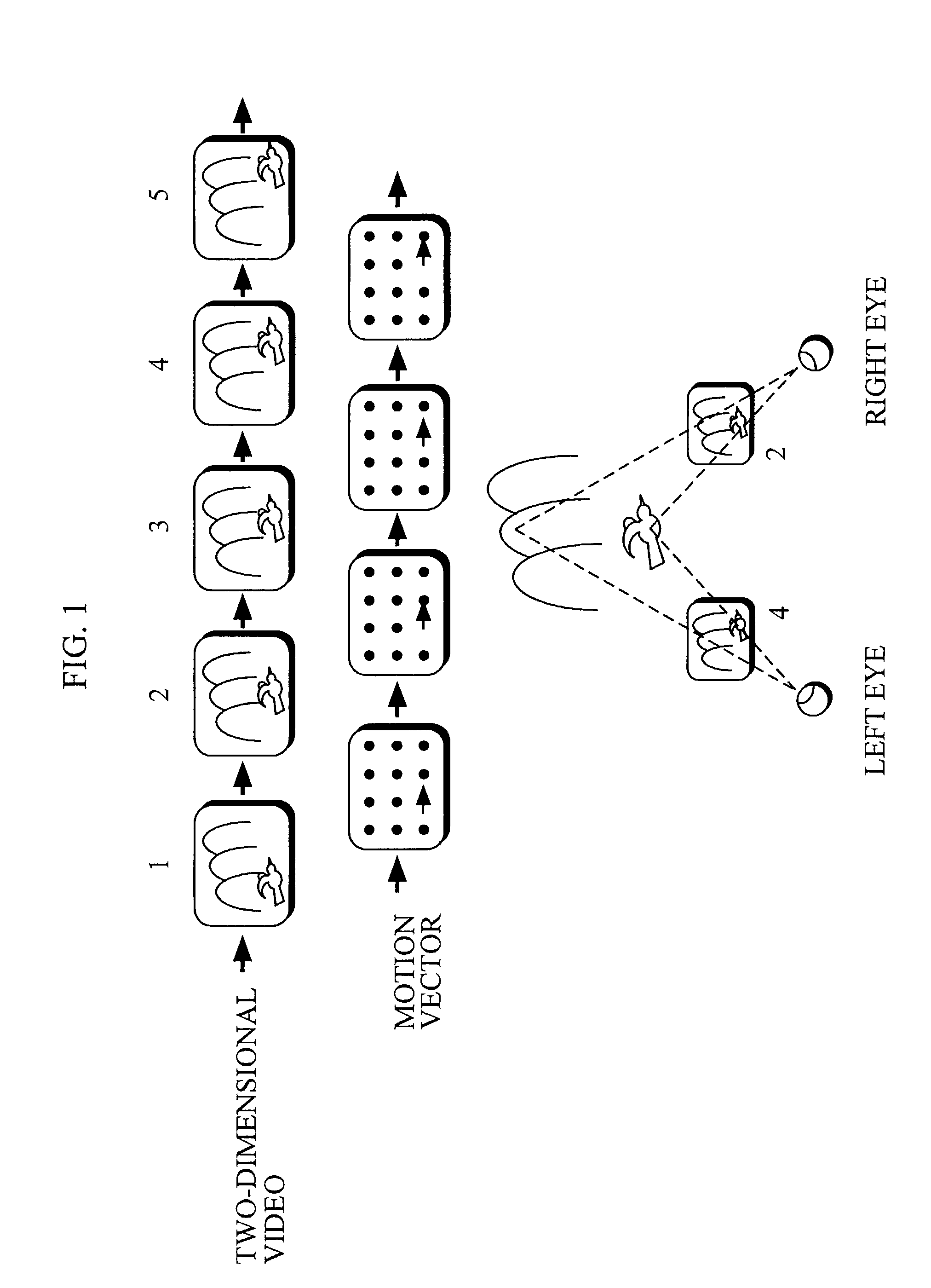
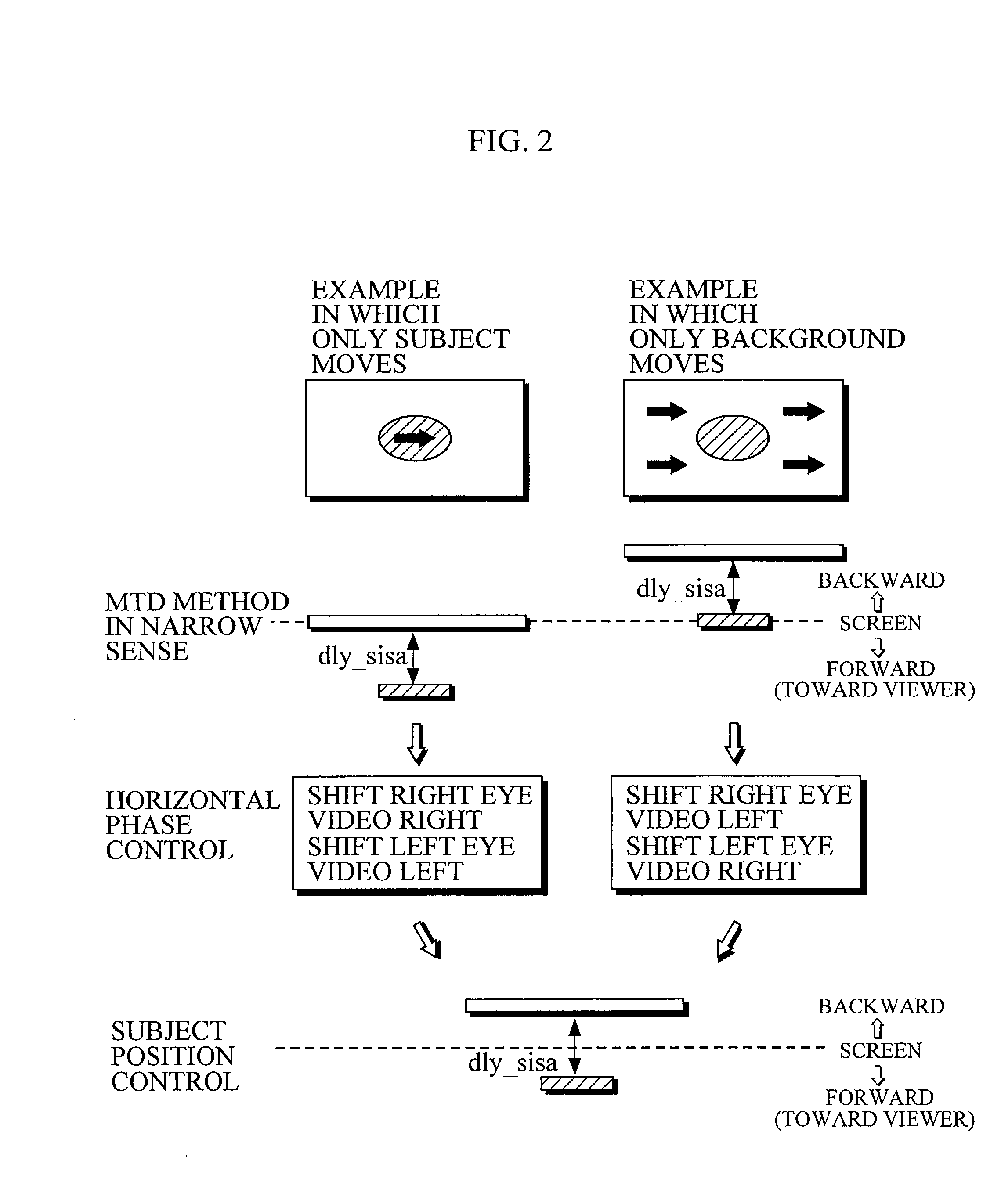
There is provided parallax correction means for correcting a parallax for each area calculated by parallax calculation means in accordance with the magnitude of a motion vector for the area detected by motion vector detection means in order to prevent the three-dimensional effect of a conversion video from greatly differing depending on an input video when the MTD method and the CID method are simultaneously used.When a depth estimate is converted into a parallax, the depth estimate is subjected to distance scale conversion in order to suppress the distortion of the conversion image, to find a tentative target phase for each parallax calculation area, and a dynamic range in which a phase difference between the parallax calculation areas is within a distortion allowable range is searched for and is subjected to distance scale conversion, to find a tentative target phase, which operations are repeated.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
System and method for increasing space or time resolution in video
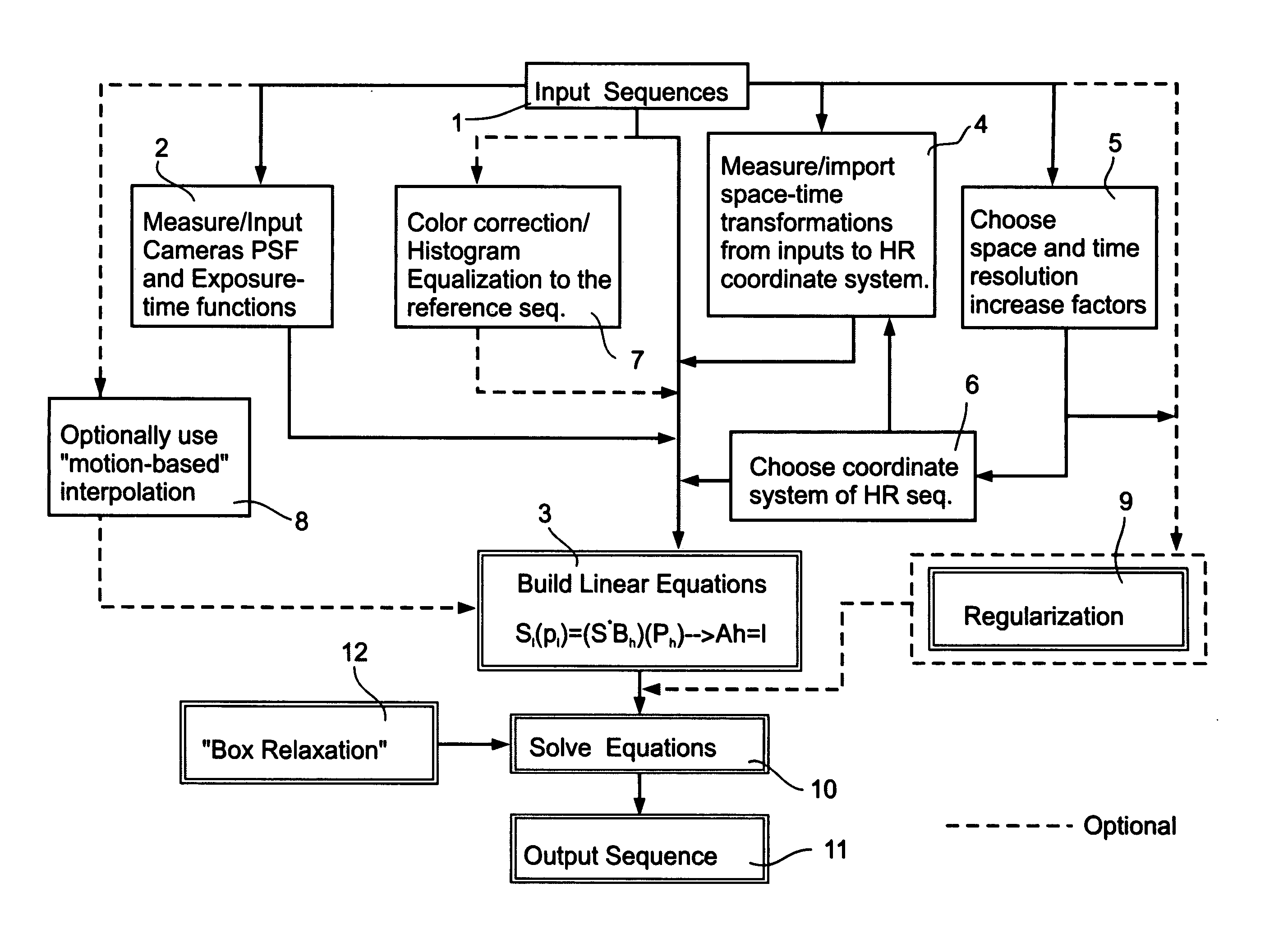
InactiveUS20050057687A1High temporalHigh spatial resolutionImage enhancementTelevision system detailsDigital videoMotion vector
A system and method for increasing space or time resolution of an image sequence by combination of a plurality input sources with different space-time resolutions such that the single output displays increased accuracy and clarity without the calculation of motion vectors. This system of enhancement may be used on any optical recording device, including but not limited to digital video, analog video, still pictures of any format and so forth. The present invention includes support for example for such features as single frame resolution increase, combination of a number of still pictures, the option to calibrate spatial or temporal enhancement or any combination thereof, increased video resolution by using high-resolution still cameras as enhancement additions and may optionally be implemented using a camera synchronization method.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Advanced bi-directional predictive coding of video frames
ActiveUS20050013365A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionEncoder decoderMotion vector
Techniques and tools for coding / decoding of video images, and in particular, B-frames, are described. In one aspect, a video encoder / decoder determines a fraction for a current image in a sequence. The fraction represents an estimated temporal distance position for the current image relative to an interval between a reference images for the current image. The video encoder / decoder processes the fraction along with a motion vector for a first reference image, resulting in a representation of motion (e.g., constant or variable velocity motion) in the current image. Other aspects are also described, including intra B-frames, forward and backward buffers for motion vector prediction, bitplane encoding of direct mode prediction information, multiple motion vector resolutions / interpolation filters for B-frames, proactive dropping of B-frames, and signaling of dropped predicted frames.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and system for motion vector prediction in scalable video coding
InactiveUS20060153300A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorVideo encoding
In scalable video coding where two predictive motion vectors are calculated: one from the current layer neighboring motion vectors and one from the co-located base layer motion vectors. One of the two predictive motion vectors is chosen as the predictive motion vector for current block. A flag bit is coded to indicate which predictive motion vector is chosen only if it is not possible to infer the layer from which the predictive motion vector for the current block comes. Such inference is possible in many situations, such as when both predictive motion vectors are substantially the same, or only one of the vectors is reliable or available.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Method and apparatus for video encoding and decoding using adaptive interpolation
ActiveUS20060294171A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo encodingMotion vector
A method and apparatus is disclosed herein for video encoding and / or decoding using adaptive interpolation is described. In one embodiment, the decoding method comprises decoding a reference index; decoding a motion vector; selecting a reference frame according to the reference index; selecting a filter according to the reference index; and filtering a set of samples of the reference frame using the filter to obtain the predicted block, wherein the set of samples of the reference frame is determined by the motion vector.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
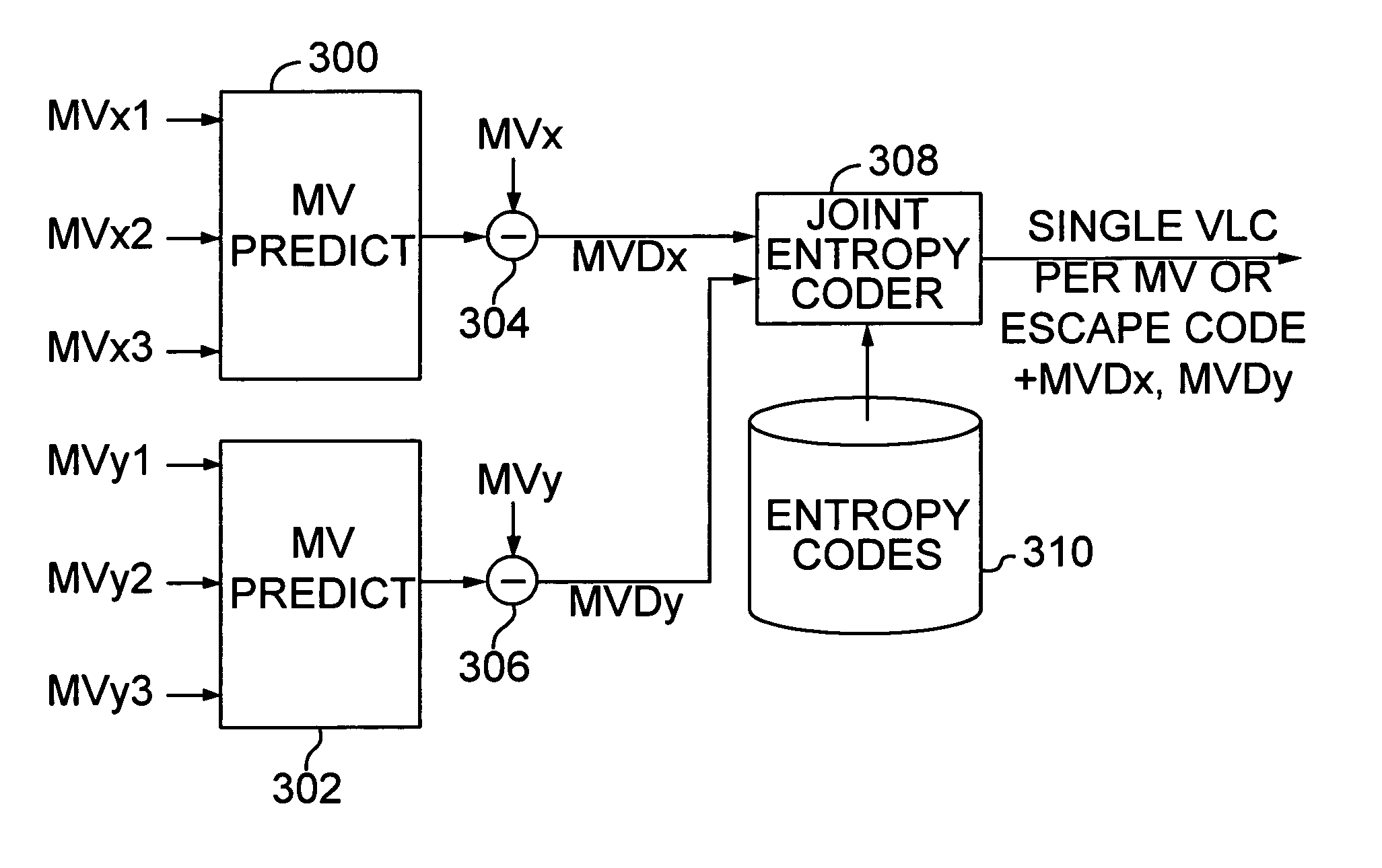
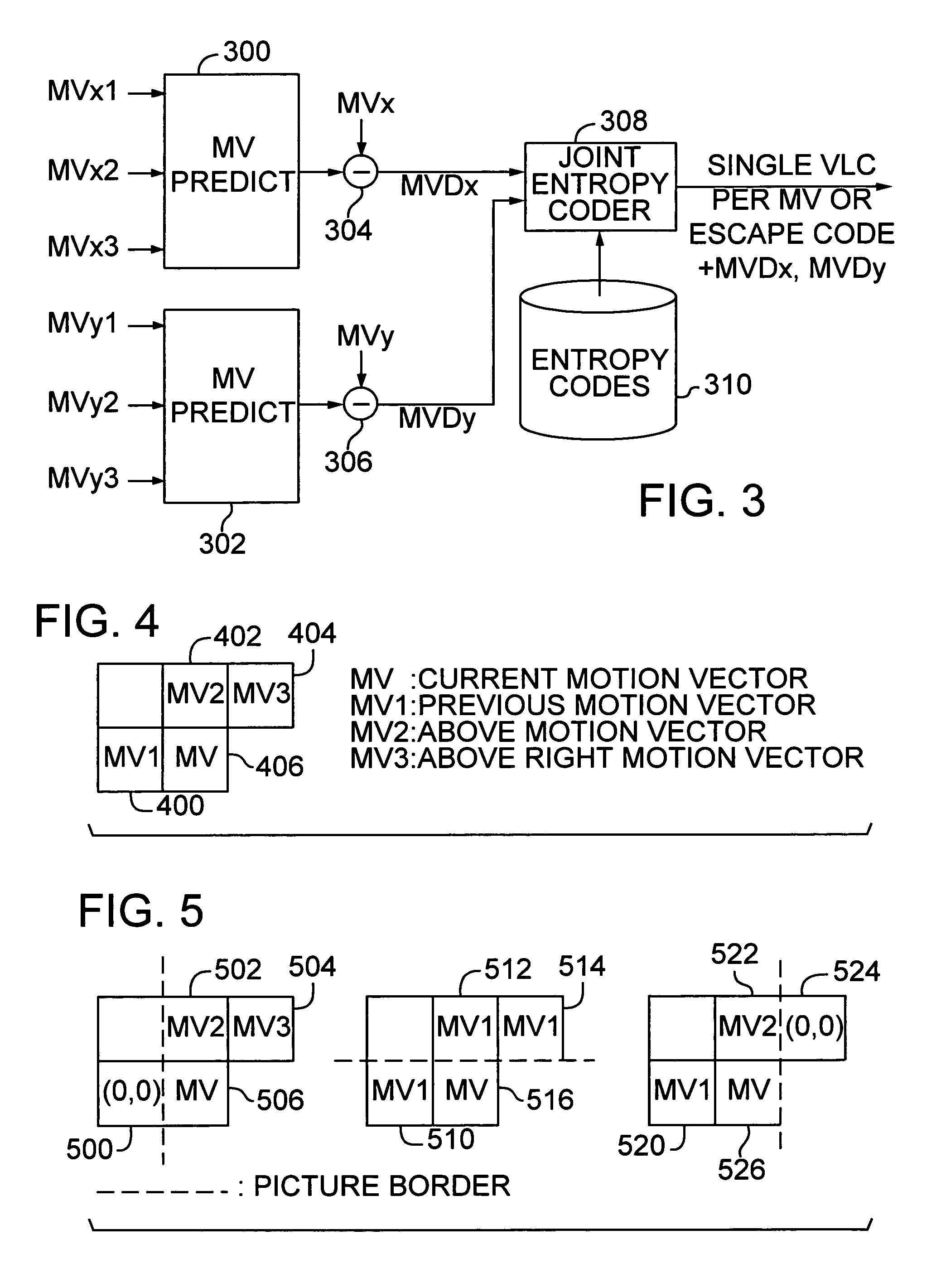
Efficient motion vector coding for video compression
InactiveUS6983018B1Code motion vectors more efficientlyLengthen codePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionVariable-length codeVideo encoding
Video coding efficiency is improved by jointly coding the x and y components of motion vectors with a single variable length code. The motion vector components for a block of pixels are predicted based on motion vectors of neighboring blocks of pixels. The predicted x and y components are then jointly coded by assigning a single variable length code corresponding to the pair of components, rather than a separate code for each component. If the x and y components do not have a corresponding entry in the coding table, they are coded with an escape code followed by fixed length codes.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
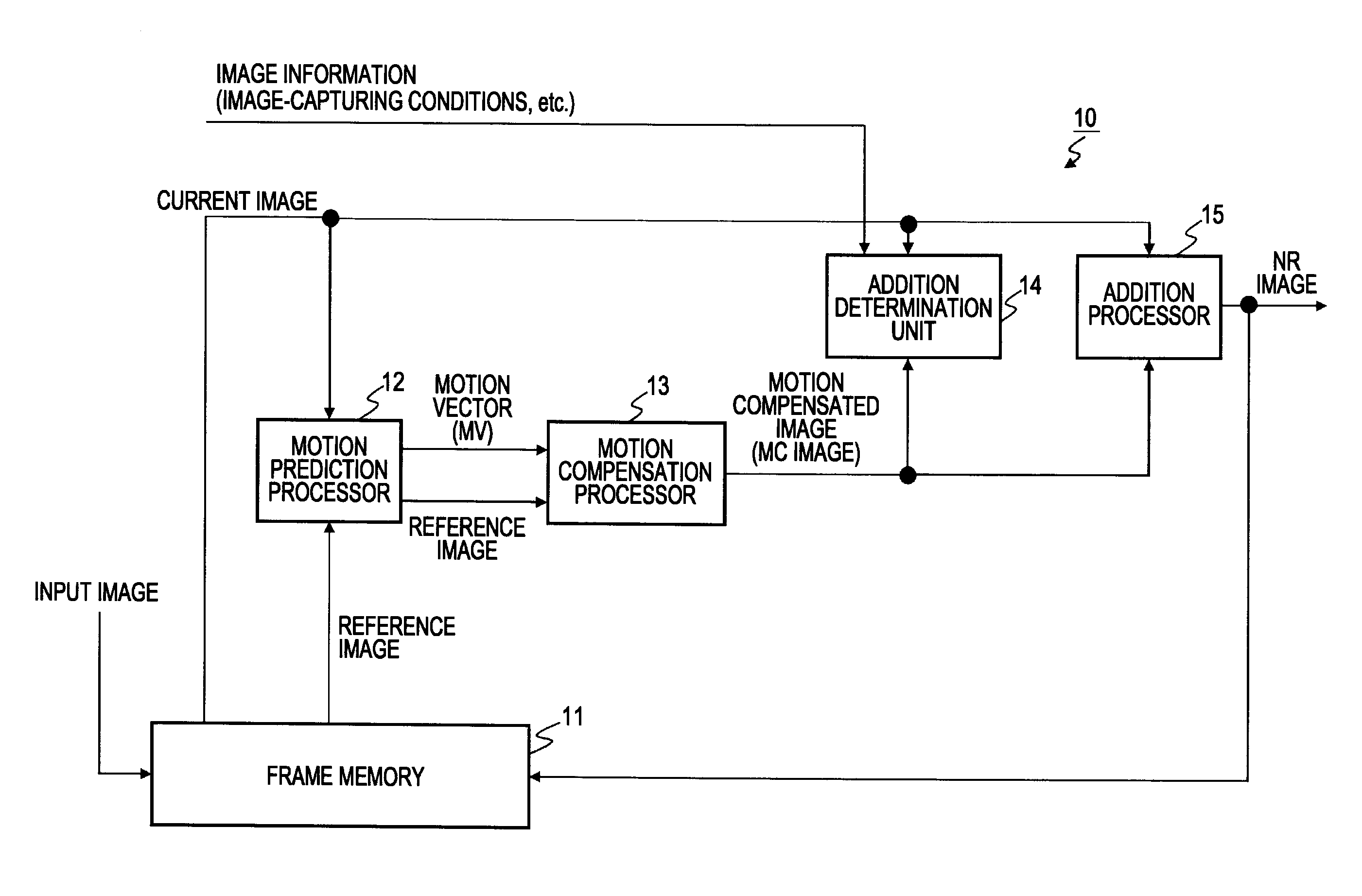
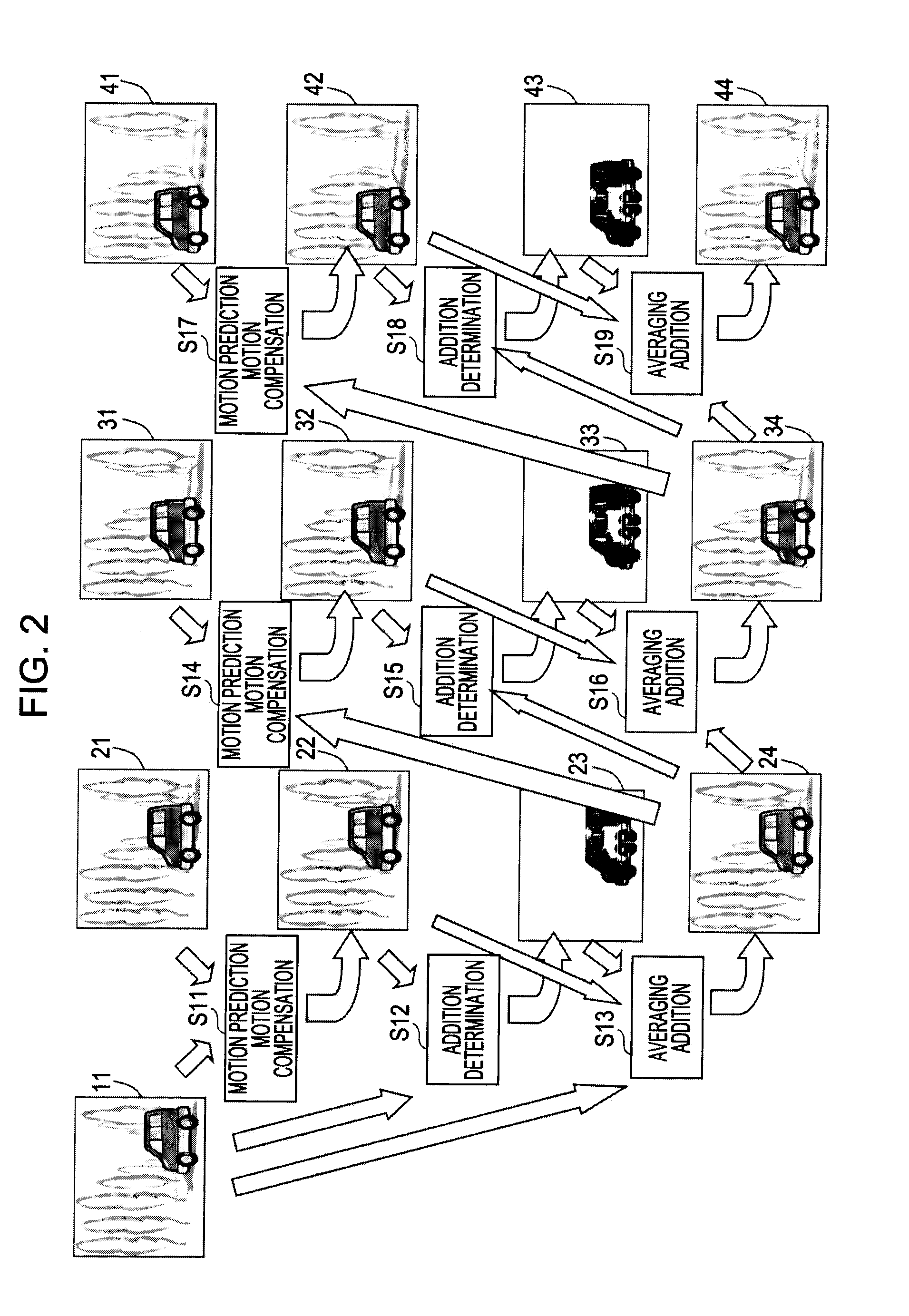
Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and program
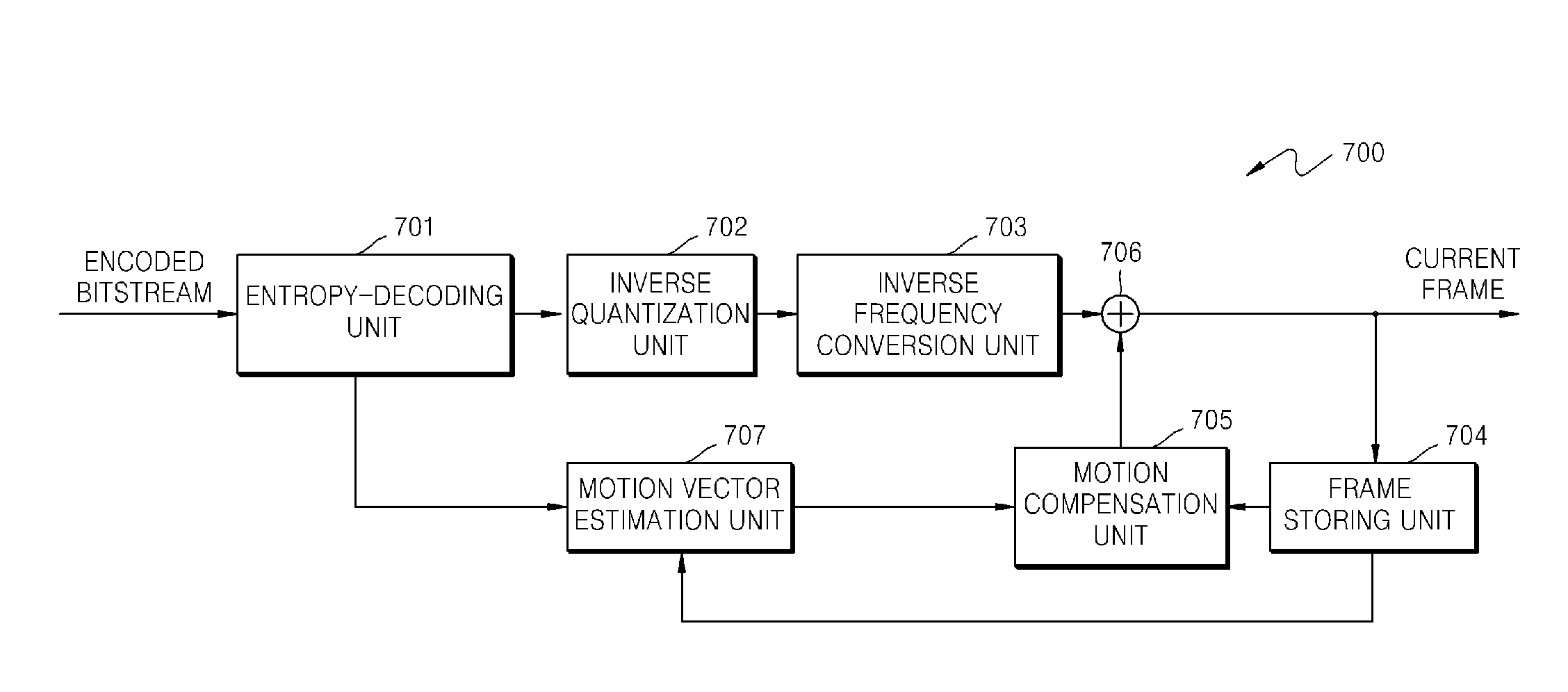
InactiveUS20100157073A1Television system detailsColor television detailsImaging processingMotion vector
An image processing apparatus includes a motion prediction processor configured to detect a motion vector that indicates inter-image motion between a current image and a reference image; a motion compensation processor configured to perform a motion compensation process for the reference image by using the motion vector and generate a motion compensated image; an addition processor configured to generate a noise reduced image in which noise of the current image is reduced by adding the current image and the motion compensated image; an addition determination unit configured to compute an addition weight in units of pixels of the motion compensated image; a down-sampling processor configured to perform a process for reducing the current image and the motion compensated image; and an up-sampling processor configured to perform a process for expanding an addition coefficient map that is an output of the addition determination unit.
Owner:SONY CORP
Motion skip and single-loop encoding for multi-view video content
InactiveUS20090116558A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionParallaxMotion vector
A system, method and computer program tangibly embodied in a memory medium for implementing motion skip and single-loop decoding for multi-view video coding. In various embodiments, a more efficient motion skip is used for the current JMVM arrangement by 8×8 or 4×4 pel disparity motion vector accuracy, while maintaining the motion compensation process that is compliant with the H.264 / AVC design regarding hierarchical macroblock partitioning. Adaptive referencing merging may be used in order achieve a more accurate motion skip from one inter-view reference picture. In order to indicate whether a picture is to be used for motion skip, a new syntax element or syntax modification in the NAL unit header may be used.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Real-time video coding/decoding
ActiveUS20050276323A1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionMotion vectorDownscaling
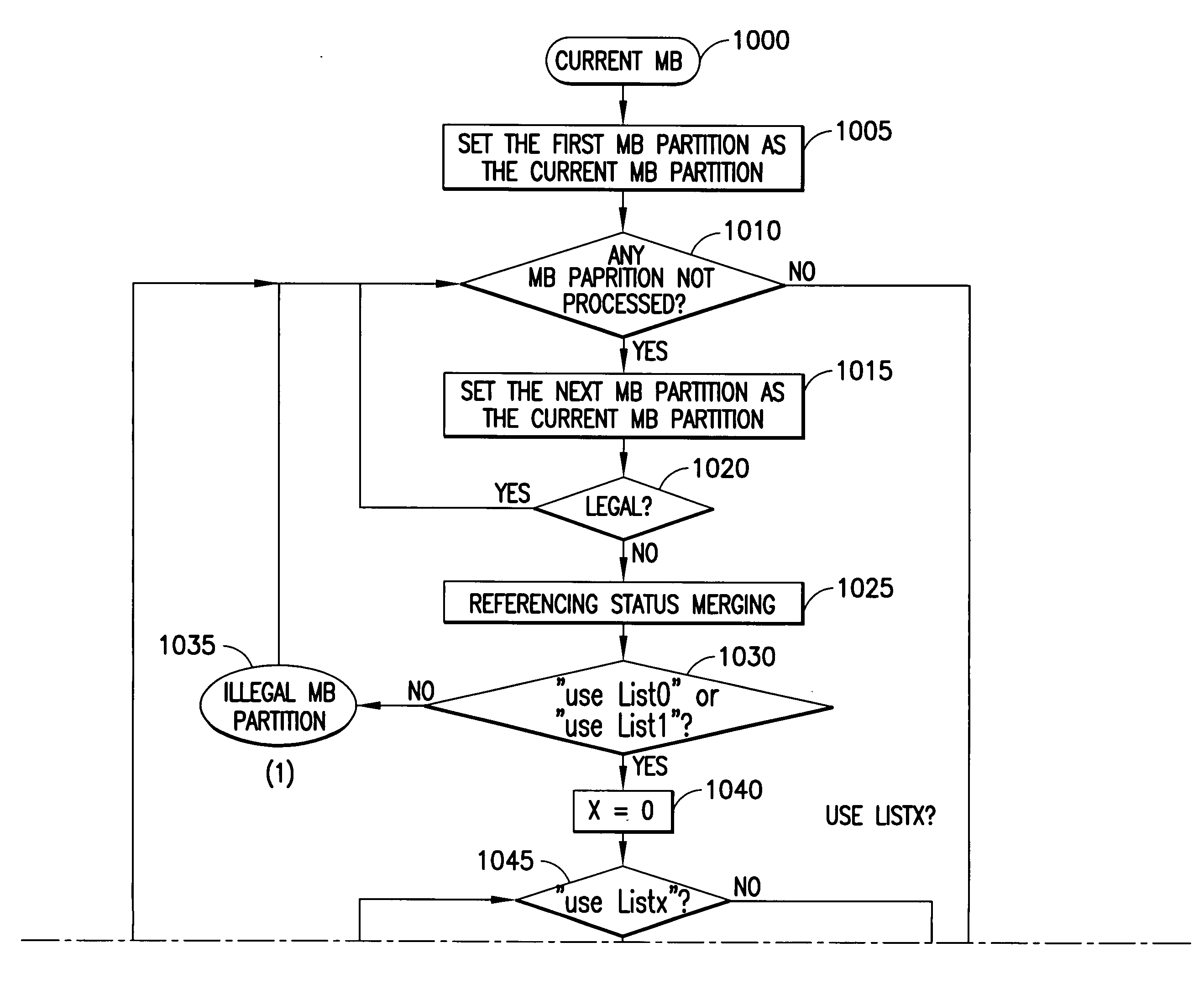
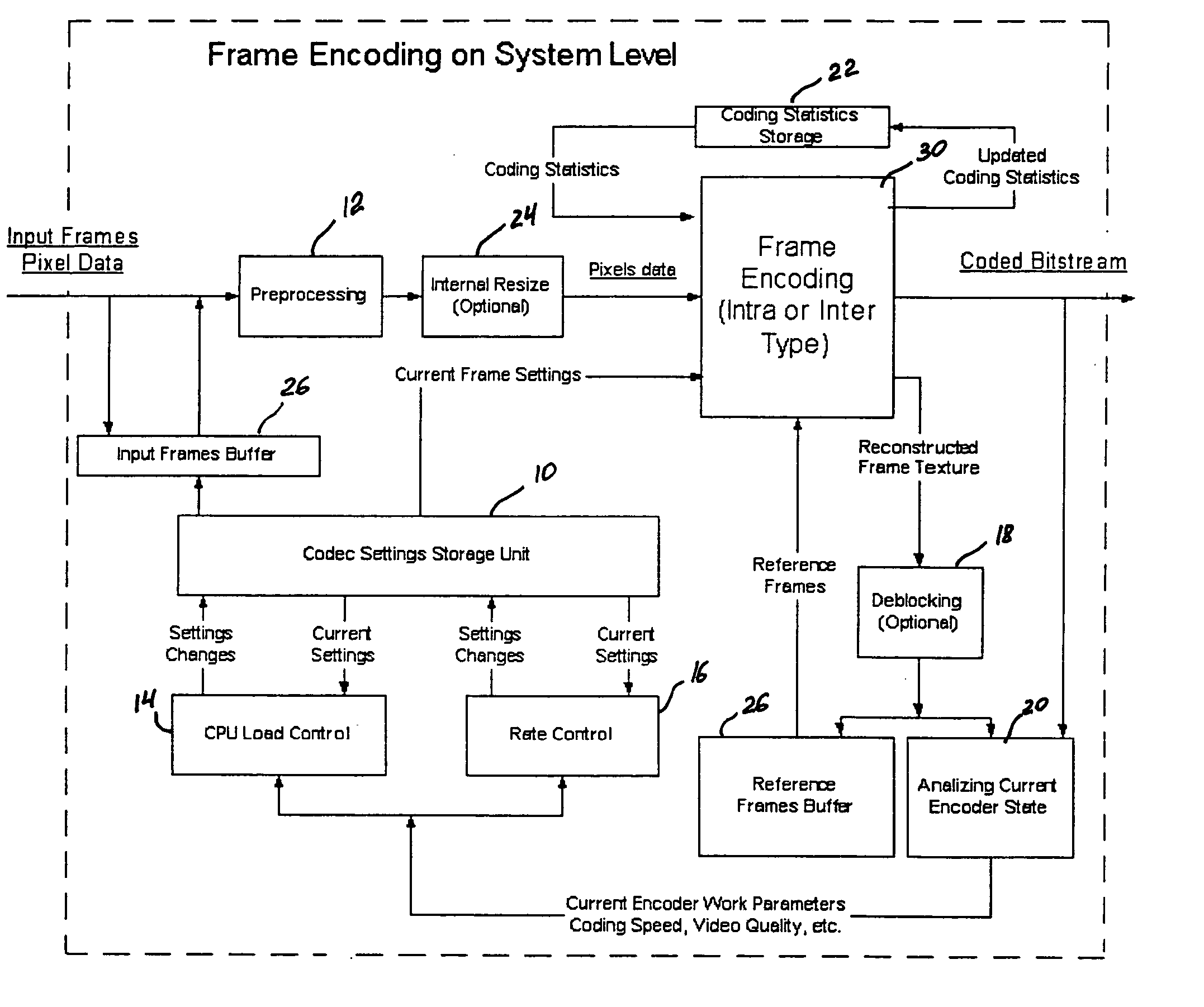
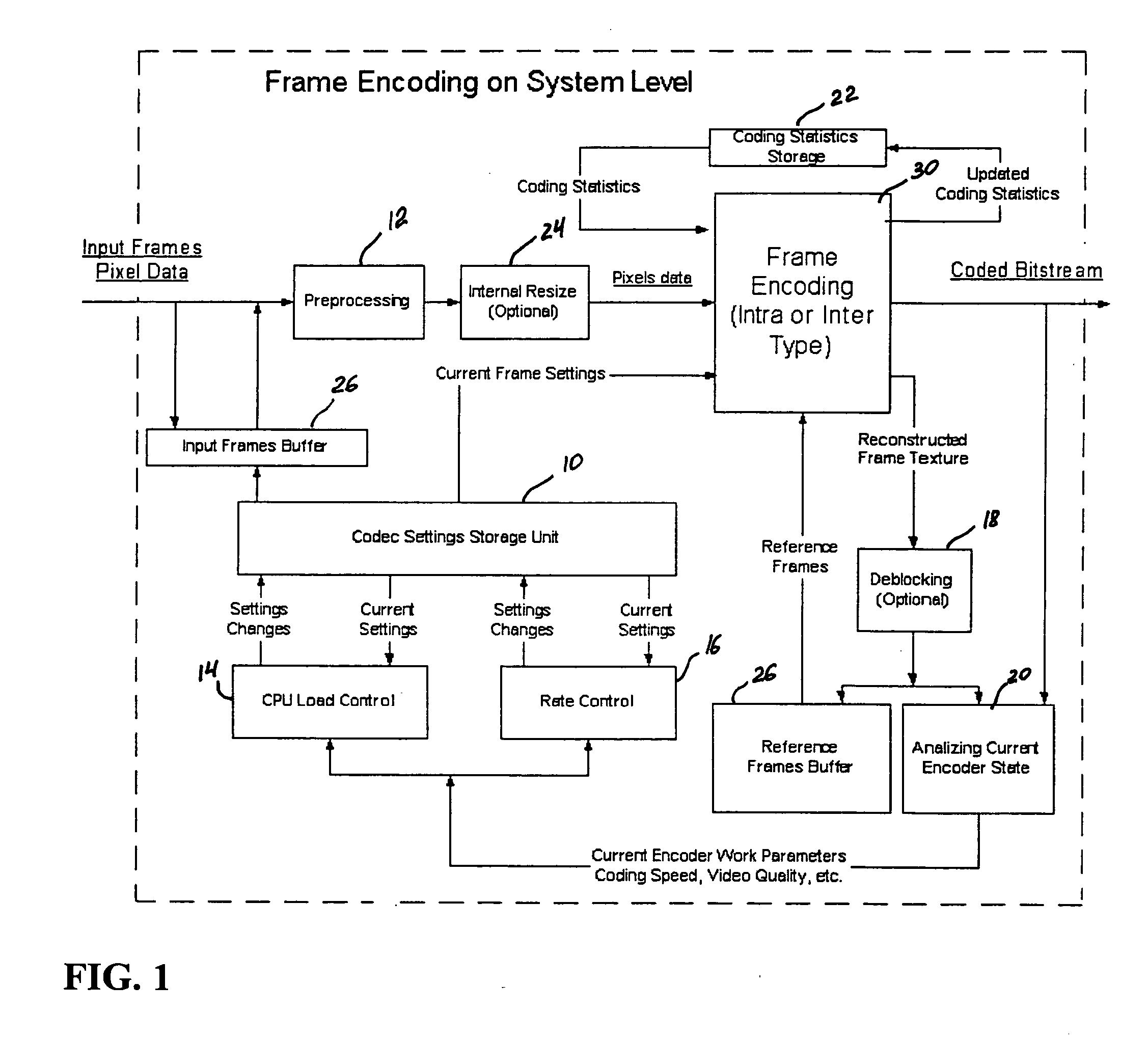
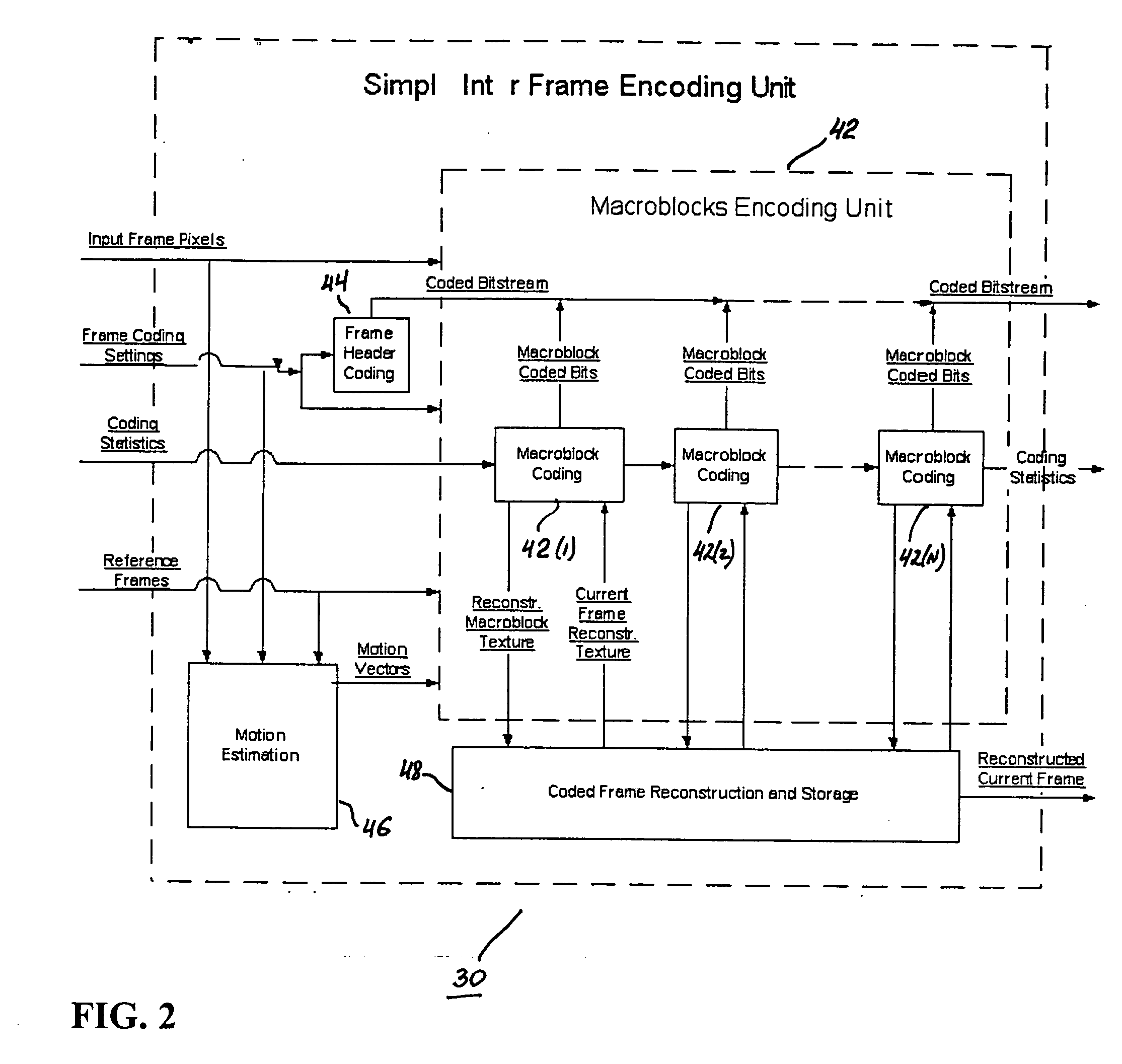
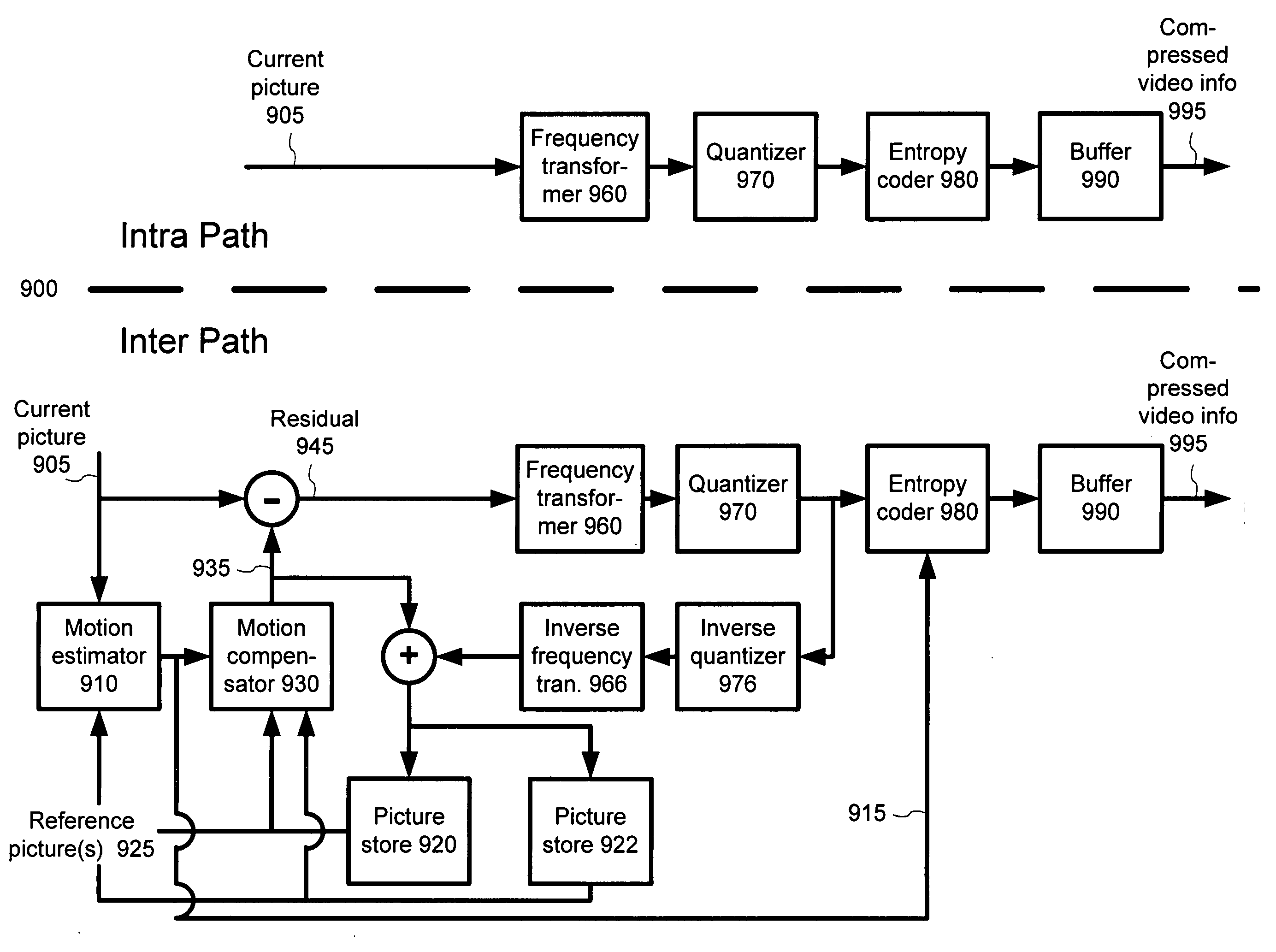
A video codec for real-time encoding / decoding of digitized video data with high compression efficiency, comprising a frame encoder receiving input frame pixels; a codec setting unit for setting and storing coding setting parameters; a CPU load controller for controlling desired frame encoding time and CPU loading; a rate controller for controlling frame size; a coding statistics memory for storing frequency tables for arithmetic coding of bitstream parameters and a reference frame buffer for storing reference frames. The frame encoder comprises a motion estimation unit, a frame head coding unit, a coded frame reconstruction and storage unit and a macroblock encoding unit. The macroblock encoding unit provides calculation of texture prediction and prediction error, transforming texture prediction error and quantization of transform coefficient, calculation of motion vector prediction and prediction error and arithmetic context modeling for motion vectors, header parameters and transform coefficients. The codec also includes a deblocking unit for processing video data to eliminate blocking effect from restored data encoded at high distortion level, which may be a part of encoder or decoder, an internal resize unit, providing matching downscaling of a frame before encoding and upscaling of decoded frame according to the coding setting parameters, and a noise suppression unit.
Owner:BEAMR IMAGING LTD
Apparatus and method of depth coding using prediction mode
InactiveUS20110317766A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorTemporal correlation
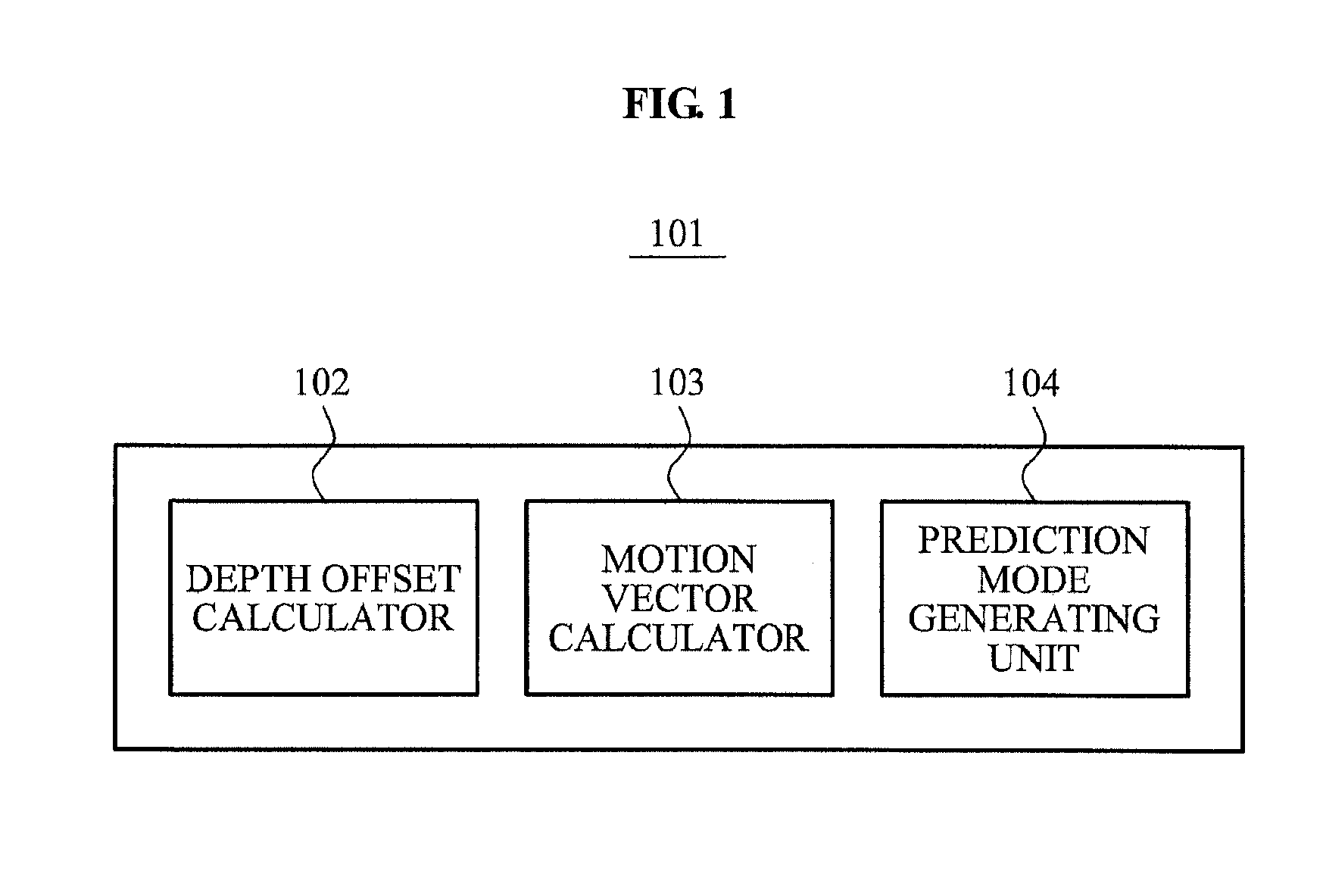
A depth image coding method may calculate a depth offset of a depth image, may generate a prediction mode based on the depth offset, may minimize a prediction error of the depth image having a low correlation between adjacent points of view and a low temporal correlation and may enhance a compression rate. The depth offset may be calculated based on a representative value of adjacent pixels included in a template as opposed to using a depth representative value of pixels in a block and header information may not be needed to encode an offset and the offset may be generated by a depth image decoding apparatus. When a plurality of objects is included in a block, a depth offset is calculated for each of the plurality of objects and a motion vector is calculated for each of the plurality of objects and the depth image may be accurately predicted.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
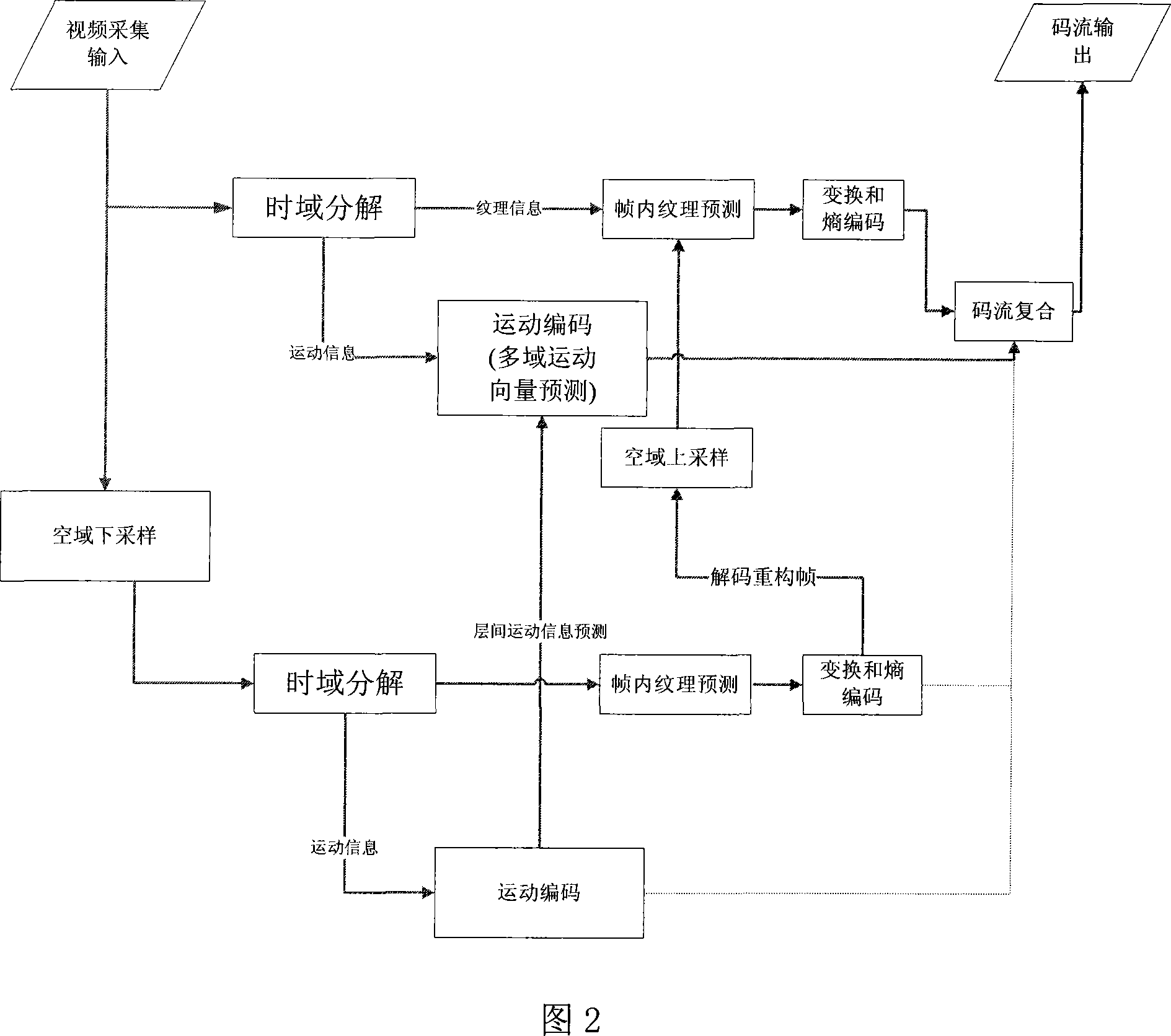
Movement vector prediction method in resolution demixing technology
InactiveCN101198064AReduce bit rateHigh gain performanceTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationTime domainMotion vector
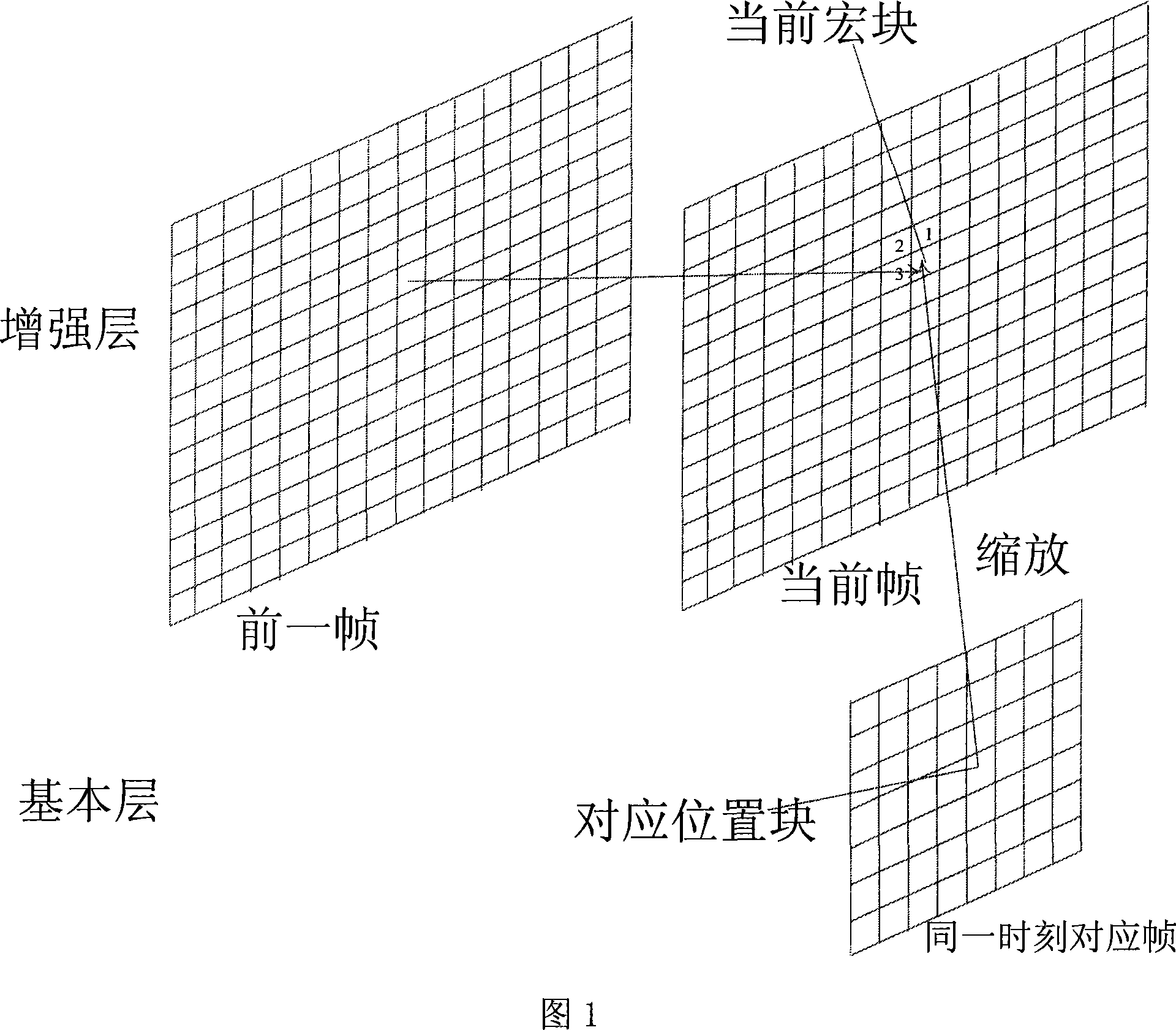
The invention discloses a motion vector forecasting method in a resolution quantizing structure, wherein, forecasting motion vectors of macro blocks in enhancement layers are acquired by utilization of relativity of motion vectors of a time domain, a space domain and an interlayer domain. The realization process is that: on the time domain, candidate motion vectors of the time domain are acquired from motion vectors of macro blocks with the same position with the prior frame; on the space domain, candidate motion vectors of the space domain are acquired from motion vectors of adjacent blocks; on the interlayer domain, candidate motion vectors of the interlayer domain are acquired from corresponding motion vectors with low space domain resolution hierarchy; candidate motion vectors with minimum motion estimation cost are selected to be forecasting motion vectors by selection among the candidate motion vectors of the time domain, the space domain and the interlayer domain. The invention has the advantages of capability of acquiring more accurate forecasting motion vectors, capability of compressing code rate of motion vectors, and obtaining of performance gain.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
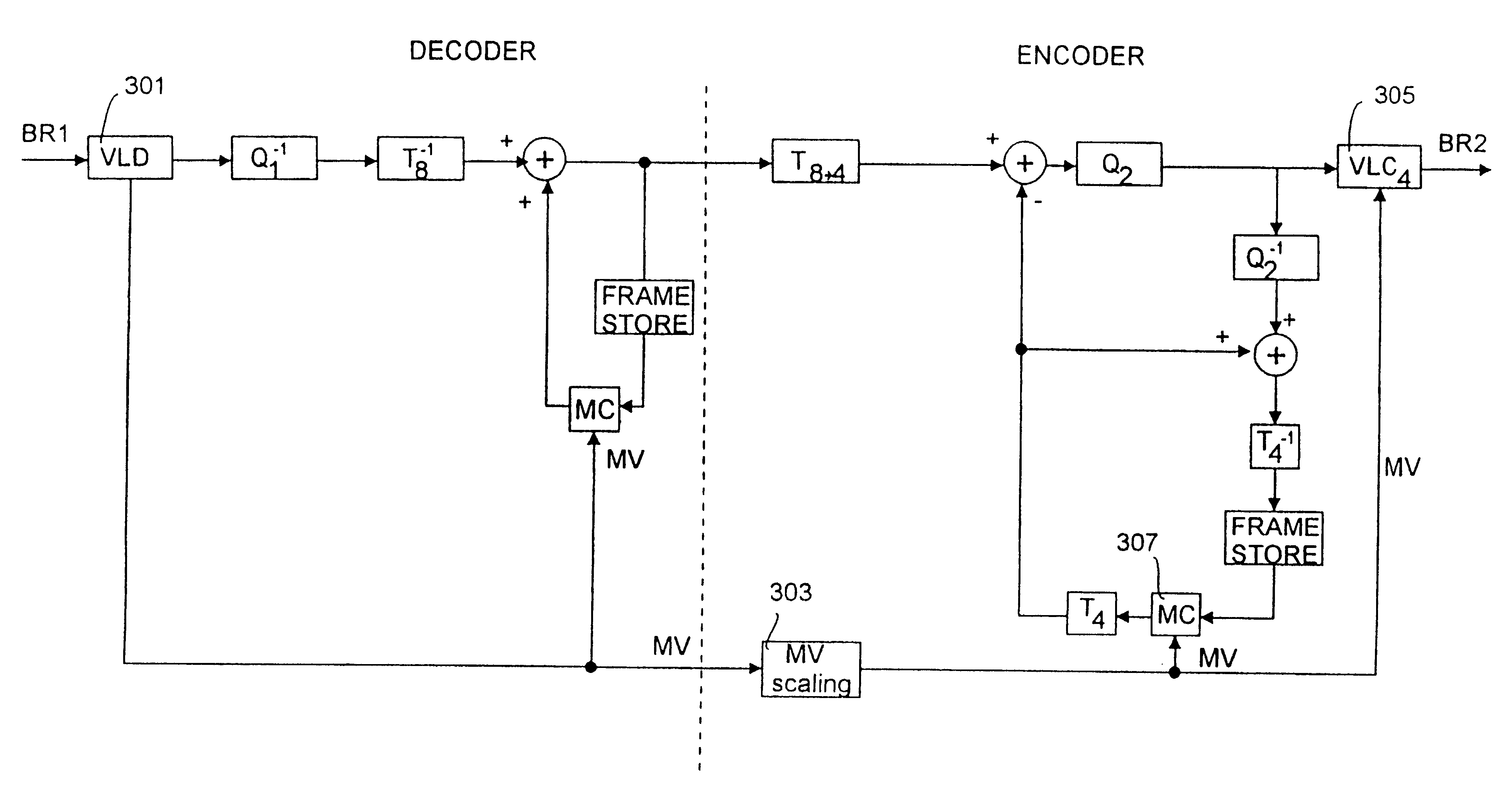
Transcoder
InactiveUS6526099B1Reduce complexityEasy to useColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorImage resolution
In a transcoder means are provided for implementing a simultaneous change in rate and in resolution. In a preferred embodiment means are also provided for transferring incoming motion vectors or the like directly to the output encoder. The transcoder architecture is both suited for implementation in the spatial as well as in the frequency domain.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Chroma motion vector derivation for interlaced forward-predicted fields
Techniques and tools for deriving chroma motion vectors for macroblocks of interlaced forward-predicted fields are described. For example, a video encoder or decoder determines a prevailing polarity among luma motion vectors for a macroblock. The encoder or decoder then determines a chroma motion vector for the macroblock based at least in part upon one or more of the luma motion vectors having the prevailing polarity.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Codec for IPTV
InactiveUS20070121728A1Easy to decodeOptimized for speedColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorSelf adaptive
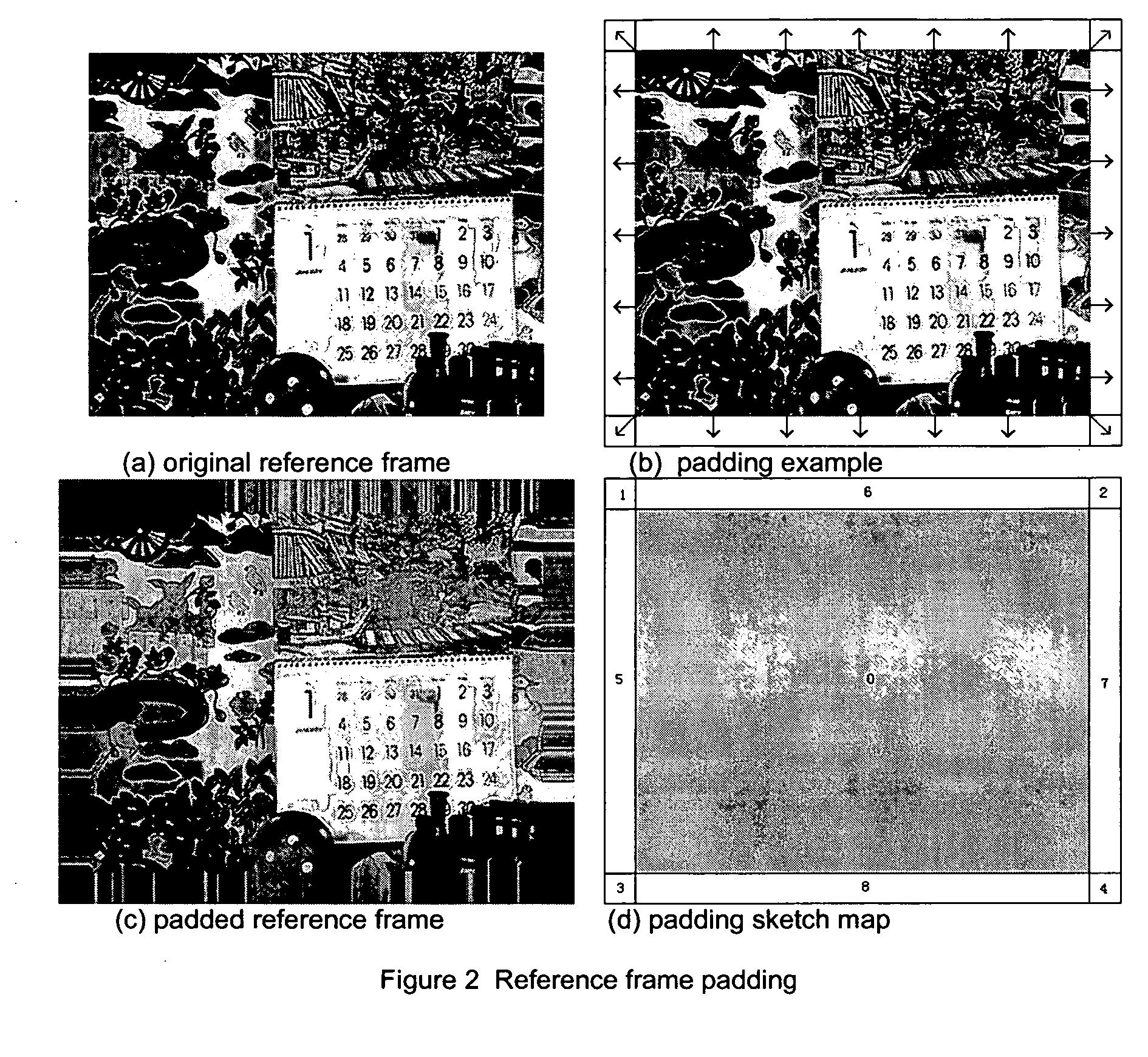
A method of optimizing decoding of MPEG4 compliant coded signals is provided, comprising: disabling processing for non-main profile sections; performing reference frame padding; performing adaptive motion compensation. The method of decoding further including performing fast IDCT wherein an IDCT process is performed on profile signals but no IDCT is performed based on whether a 4×4 block may be all zero, or only DC transform coefficient is non-zero, and including CAVLC encoding of residual data. Reference frame padding comprises compensating for motion vectors extending beyond a reference frame by adding to at least the length and width of the reference frame. Adaptive motion compensation includes original block size compensation processing for chroma up to block sizes of 16×16.
Owner:KYLINTV
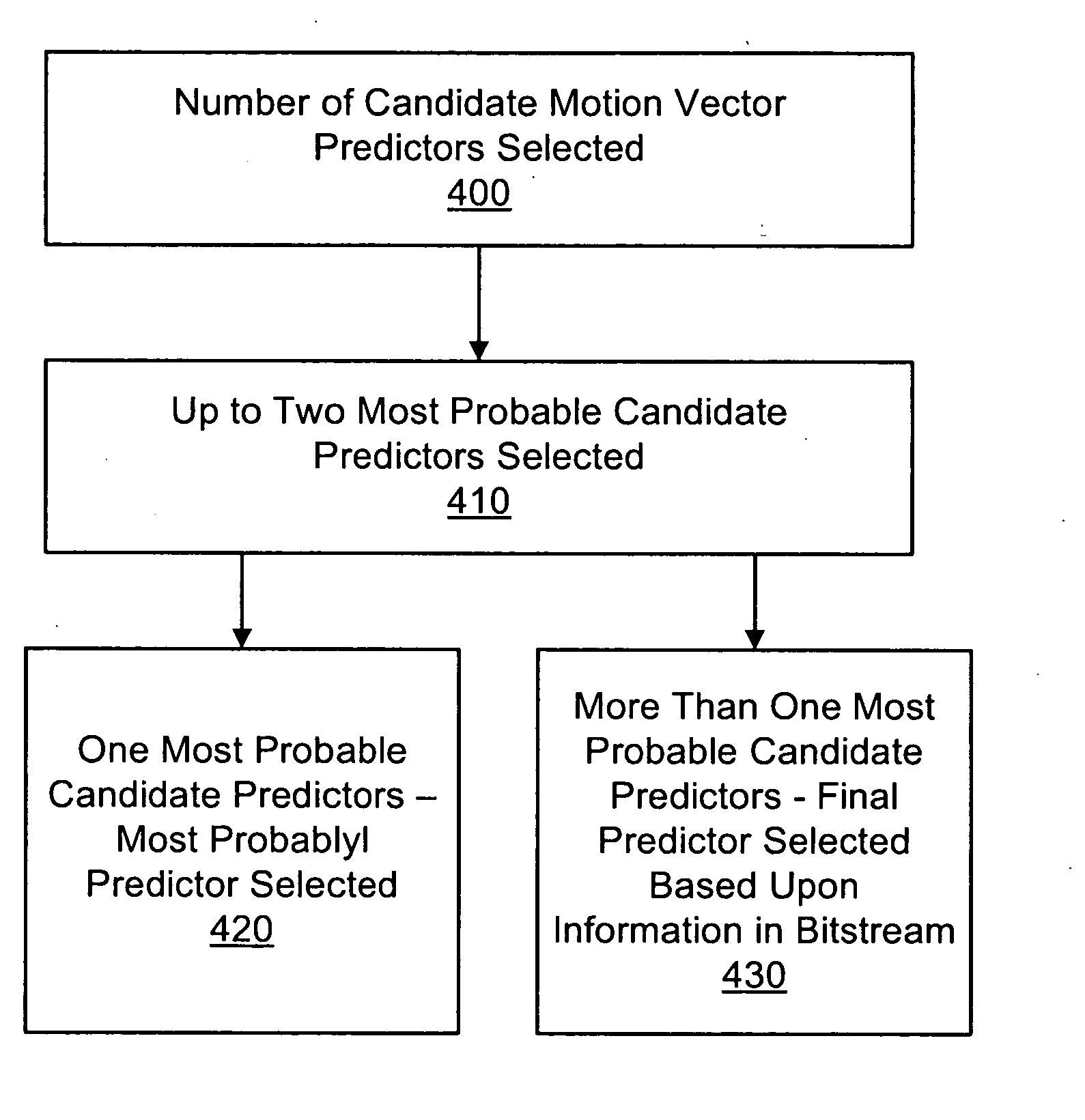
Method and apparatus for estimating motion vector using plurality of motion vector predictors, encoder, decoder, and decoding method
ActiveUS20080159401A1Color television with pulse code modulationPulse modulation television signal transmissionDecoding methodsMotion vector
Provided are a method and apparatus for estimating a motion vector using a plurality of motion vector predictors, an encoder, a decoder, and a decoding method. The method includes calculating spatial similarities between the current block and the plurality of neighboring partitions around the current block, selecting at least one of the neighboring partitions based on the calculated spatial similarities, and estimating a motion vector of the selected partition as the motion vector of the current block.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Format converter using bi-directional motion vector and method thereof
InactiveUS6900846B2Improve picture qualityEasy to implementTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesMotion vectorComputer science
A format converter which performs frame rate conversion and de-interlacing using a bi-directional motion vector and a method thereof are provided. The method includes the steps of (a) estimating a bi-directional motion vector between the current frame and the previous frame from a frame to be interpolated; setting the motion vector of a neighboring block that has the minimum error distortion, among motion vectors estimated in step (a), as the motion vector of the current block; and (c) forming a frame to be interpolated with the motion vector set in step (b).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
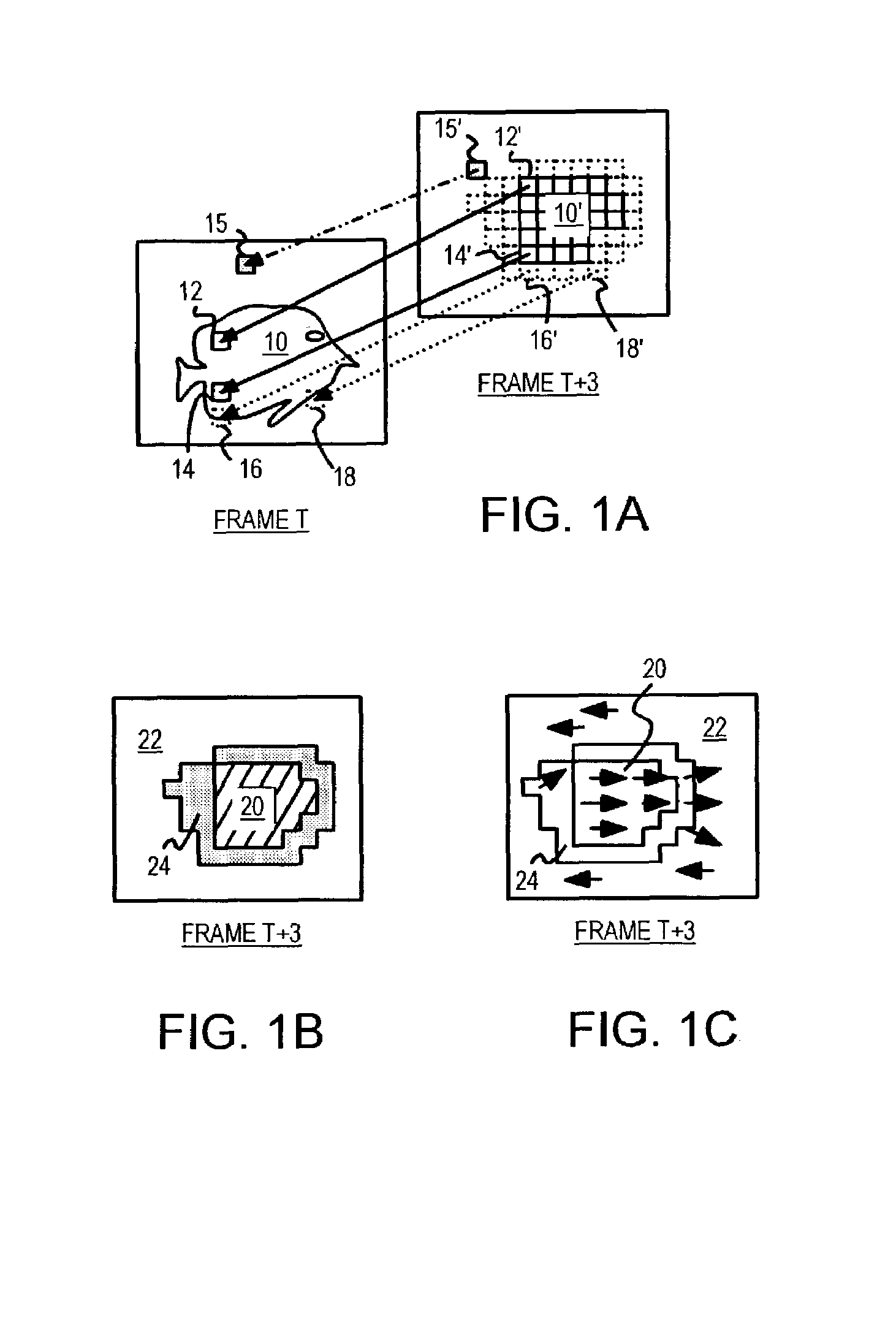
Occlusion/disocclusion detection using K-means clustering near object boundary with comparison of average motion of clusters to object and background motions
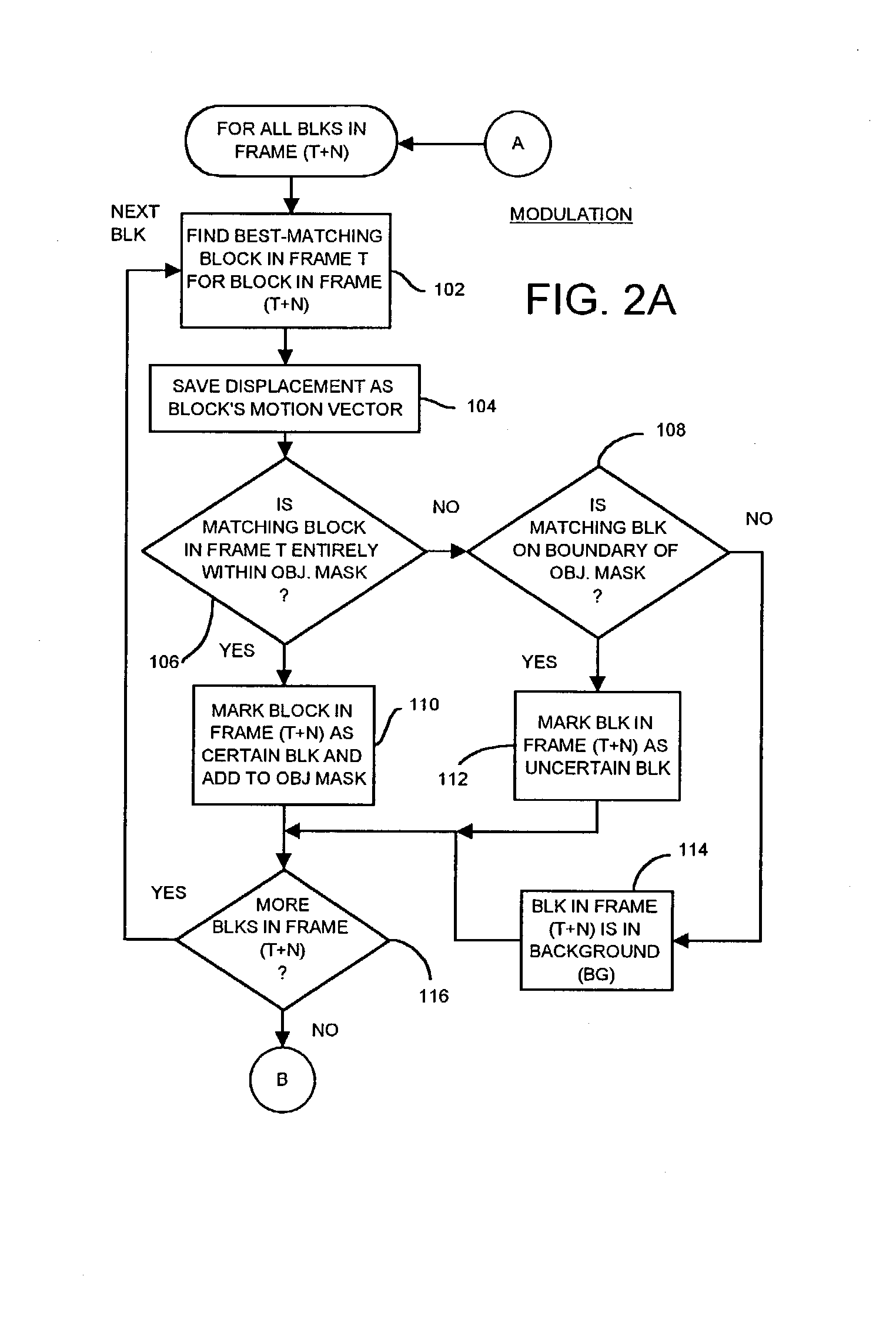
ActiveUS7142600B1Reduce varianceAccurate representationColor television with pulse code modulationImage analysisMotion vectorVideo sequence
An object in a video sequence is tracked by object masks generated for frames in the sequence. Macroblocks are motion compensated to predict the new object mask. Large differences between the next frame and the current frame detect suspect regions that may be obscured in the next frame. The motion vectors in the object are clustered using a K-means algorithm. The cluster centroid motion vectors are compared to an average motion vector of each suspect region. When the motion differences are small, the suspect region is considered part of the object and removed from the object mask as an occlusion. Large differences between the prior frame and the current frame detect suspected newly-uncovered regions. The average motion vector of each suspect region is compared to cluster centroid motion vectors. When the motion differences are small, the suspect region is added to the object mask as a disocclusion.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
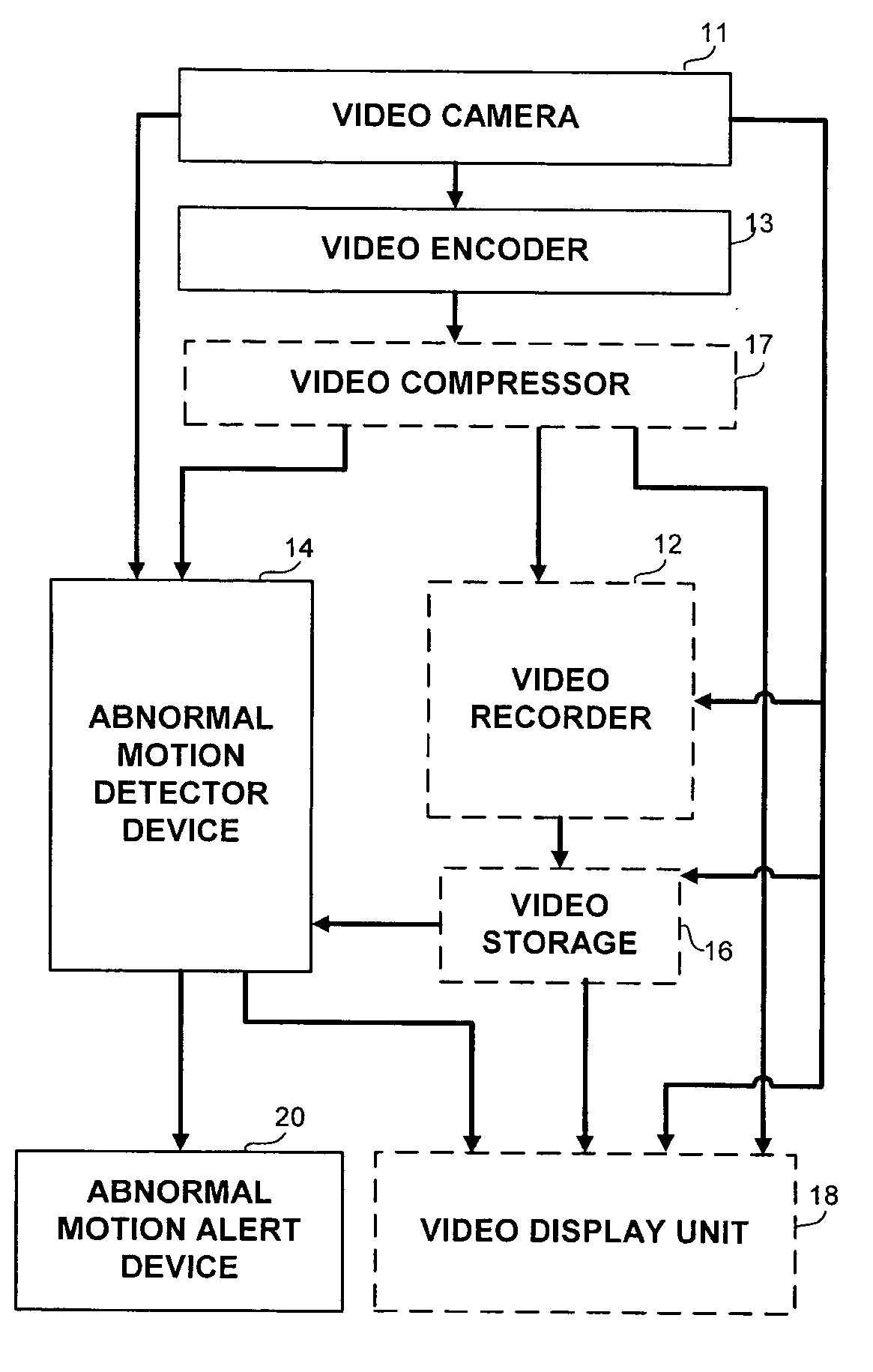
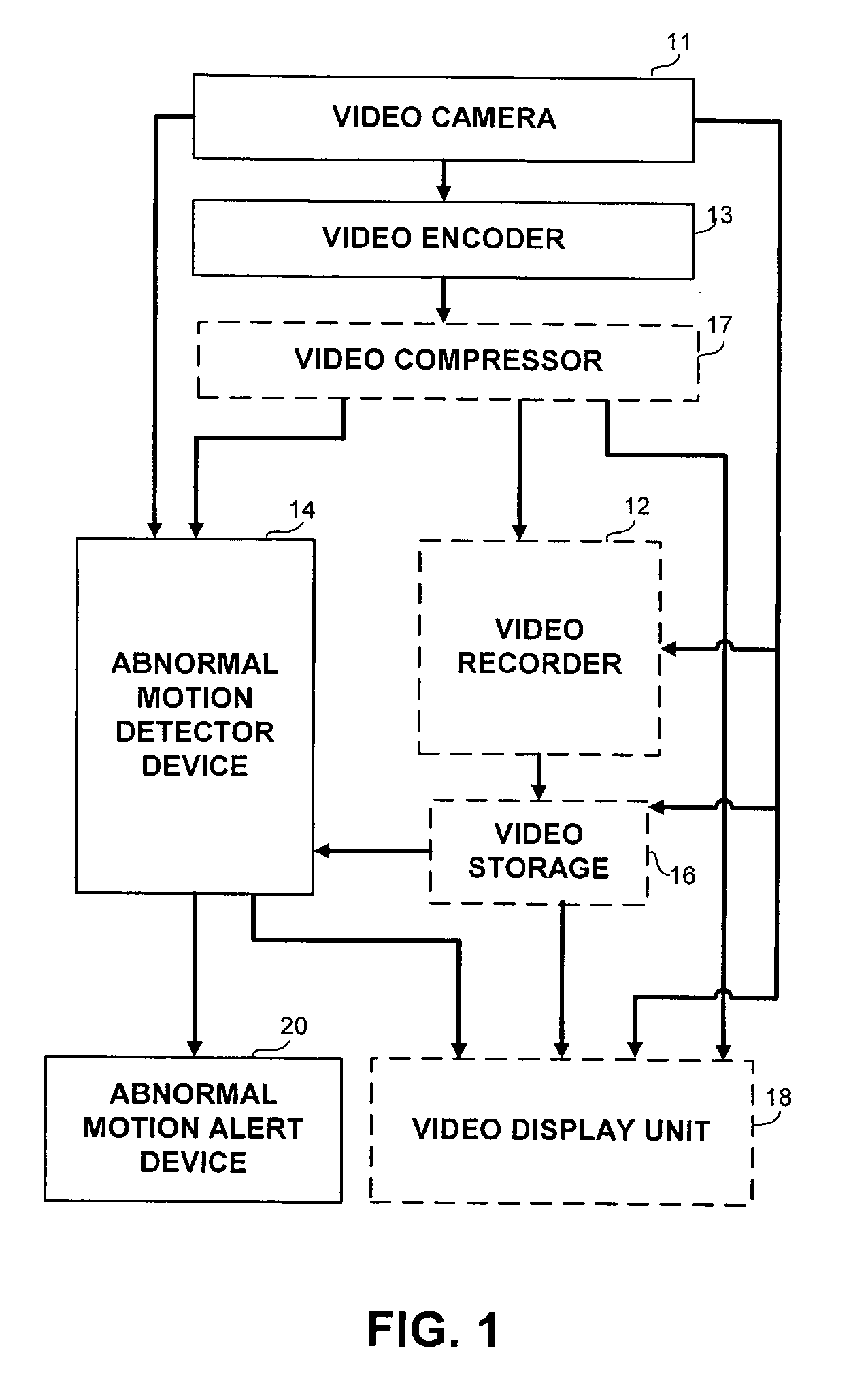
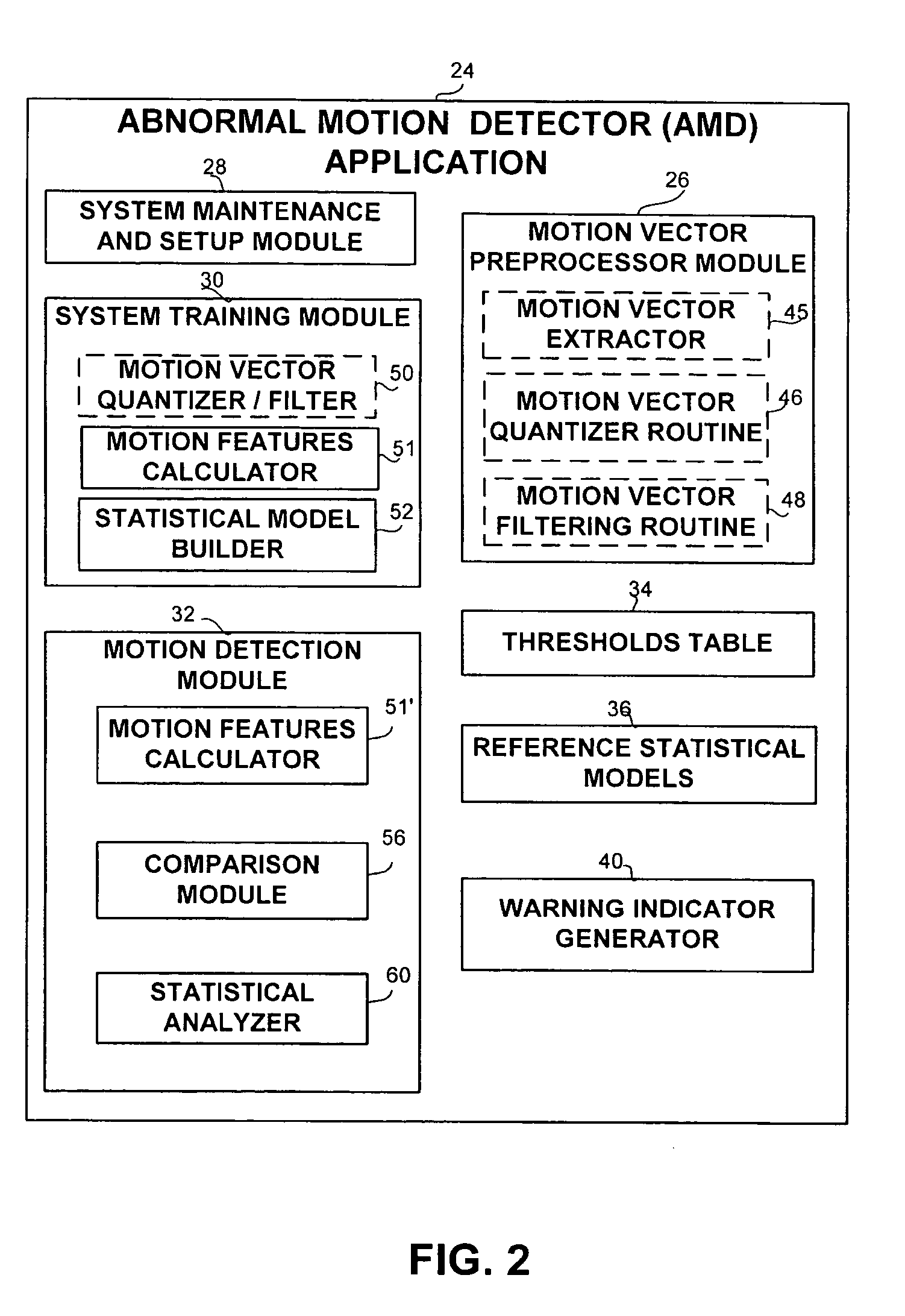
Apparatus and methods for the detection of abnormal motion in a video stream
An apparatus and method for detection of abnormal motion in video stream, comprising a training phase for defining normal motion and a detection phase for detecting abnormal motions in the video stream. Motion is detected according to motion vectors and motion features extracted from video frames.
Owner:MONROE CAPITAL MANAGEMENT ADVISORS +1
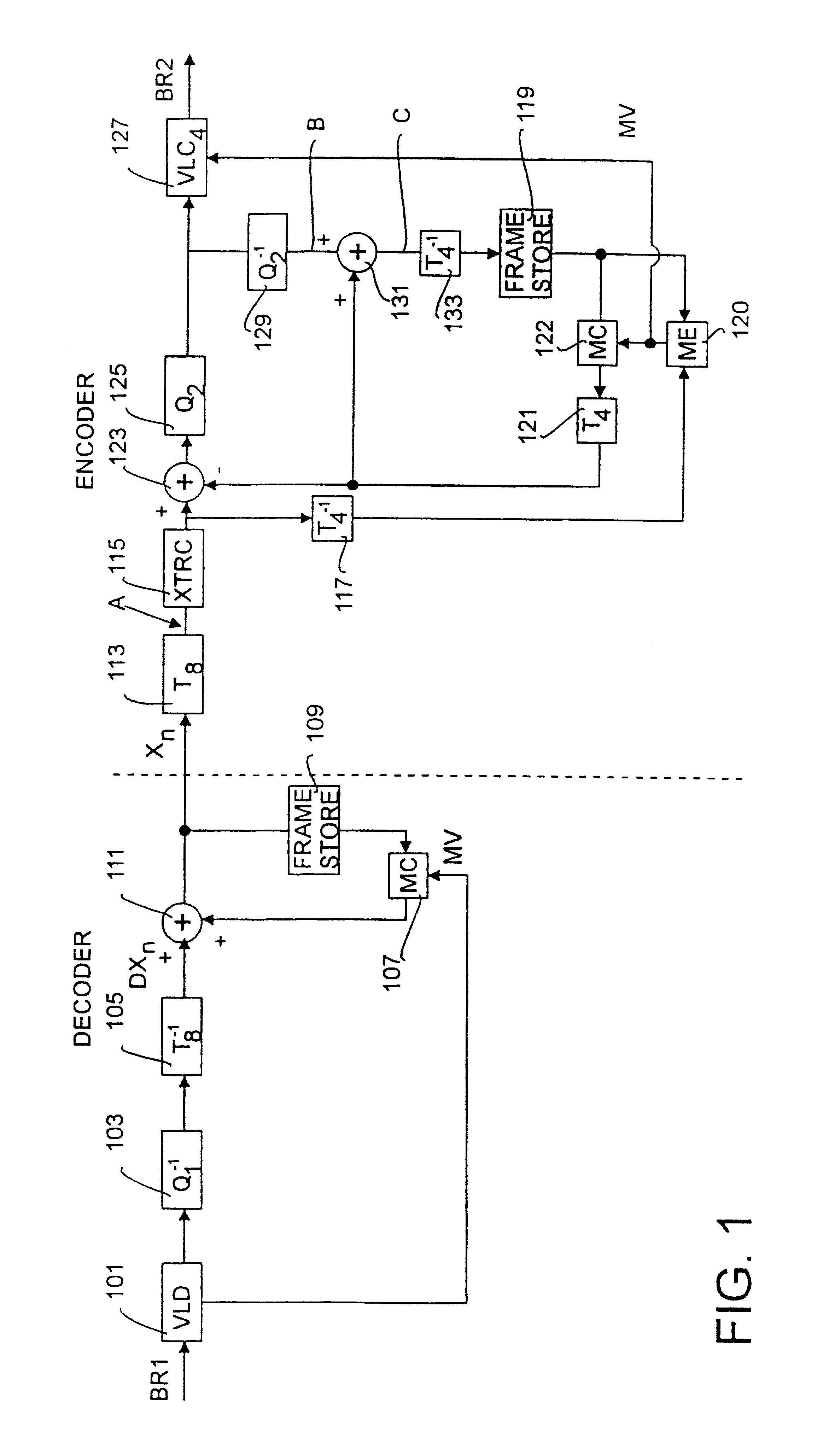
Transcoding
Transcoding is achieved by decoding a received video signal which has been coded according to a first coding scheme employing motion compensation and carries coded data and motion compensation information, and encoding the decoded according to a second coding scheme also employing motion compensation. Estimated motion vectors are generated for a current frame of the video signal, using vectors which, in the received signal, accompanying at least one other frame of the video signal. These may be used directly or used to define a search area for motion estimation.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Device and method for fast block-matching motion estimation in video encoders
InactiveUS20060245497A1Reduce complexityQuick estimateColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorVideo sequence
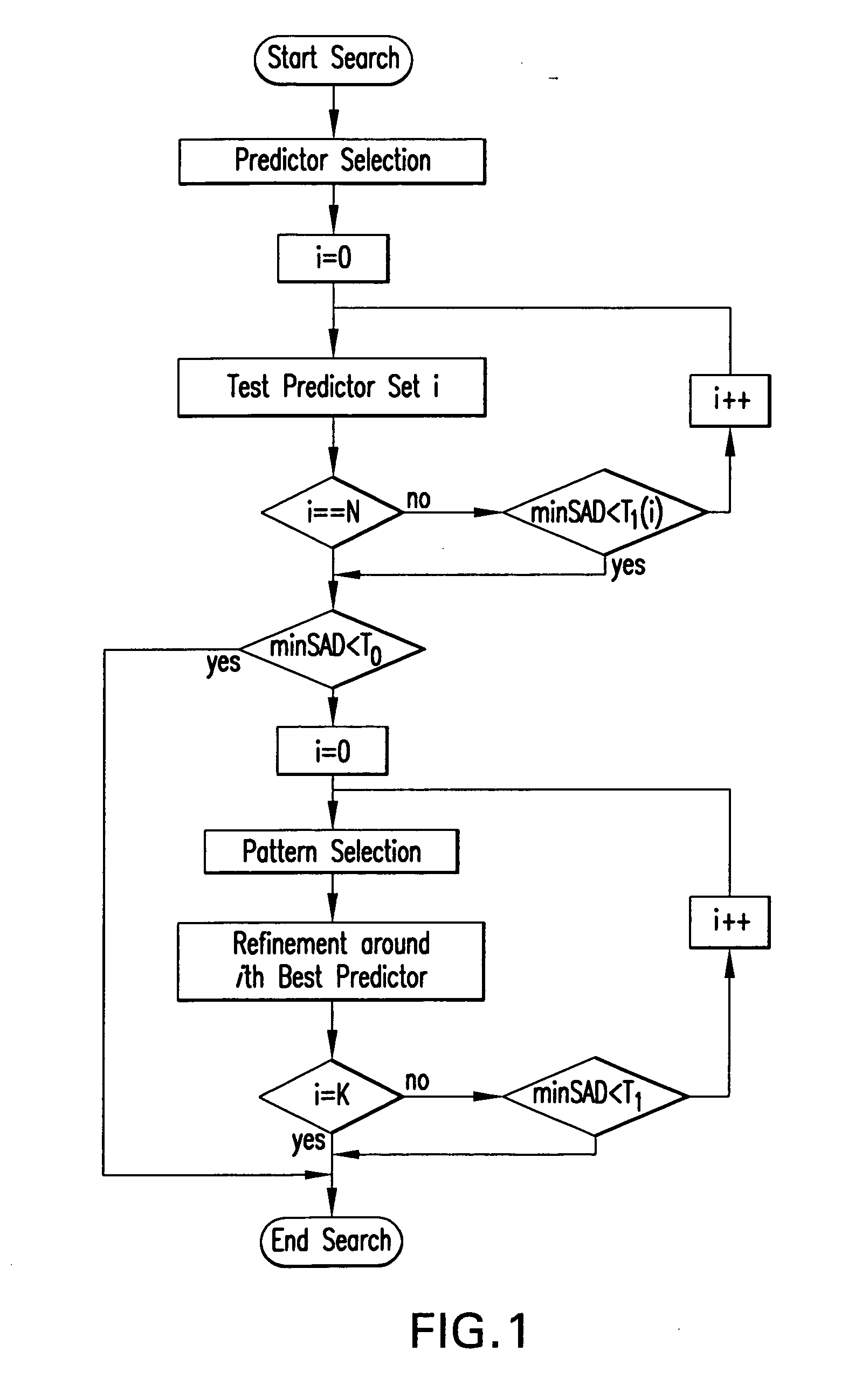
Motion estimation is the science of predicting the current frame in a video sequence from the past frame (or frames), by slicing it into rectangular blocks of pixels, and matching these to past such blocks. The displacement in the spatial position of the block in the current frame with respect to the past frame is called the motion vector. This method of temporally decorrelating the video sequence by finding the best matching blocks from past reference frames—motion estimation—makes up about 80% or more of the computation in a video encoder. That is, it is enormously expensive, and methods do so that are efficient are in high demand. Thus the field of motion estimation within video coding is rich in the breadth and diversity of approaches that have been put forward. Yet it is often the simplest methods that are the most effective. So it is in this case. While it is well-known that a full search over all possible positions within a fixed window is an optimal method in terms of performance, it is generally prohibitive in computation. In this patent disclosure, we define an efficient, new method of searching only a very sparse subset of possible displacement positions (or motion vectors) among all possible ones, to see if we can get a good enough match, and terminate early. This set of sparse subset of motion vectors is preselected, using a priori knowledge and extensive testing on video sequences, so that these “predictors” for the motion vector are essentially magic. The art of this method is the preselection of excellent sparse subsets of vectors, the smart thresholds for acceptance or rejection, and even in the order of the testing prior to decision.
Owner:FASTVDO
Predicting motion vectors for fields of forward-predicted interlaced video frames
ActiveUS20050053137A1Improve accuracyReduce bitratePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionInterlaced videoEncoder decoder
Techniques and tools for encoding and decoding predicted images in interlaced video are described. For example, a video encoder or decoder computes a motion vector predictor for a motion vector for a portion (e.g., a block or macroblock) of an interlaced P-field, including selecting between using a same polarity or opposite polarity motion vector predictor for the portion. The encoder / decoder processes the motion vector based at least in part on the motion vector predictor computed for the motion vector. The processing can comprise computing a motion vector differential between the motion vector and the motion vector predictor during encoding and reconstructing the motion vector from a motion vector differential and the motion vector predictor during decoding. The selecting can be based at least in part on a count of opposite polarity motion vectors for a neighborhood around the portion and / or a count of same polarity motion vectors.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Image encoding method and apparatus
InactiveUS6937773B1Without placing a burden upon the userColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorTransformation unit
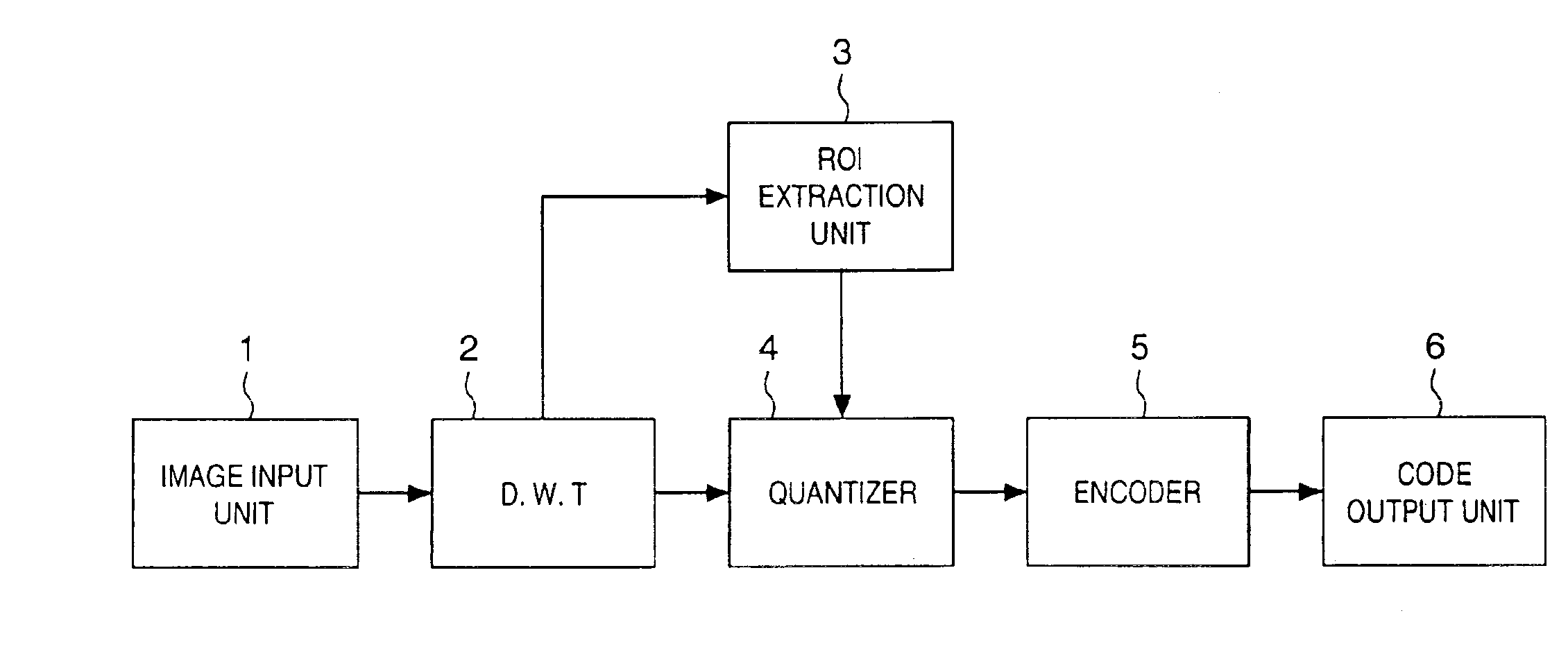
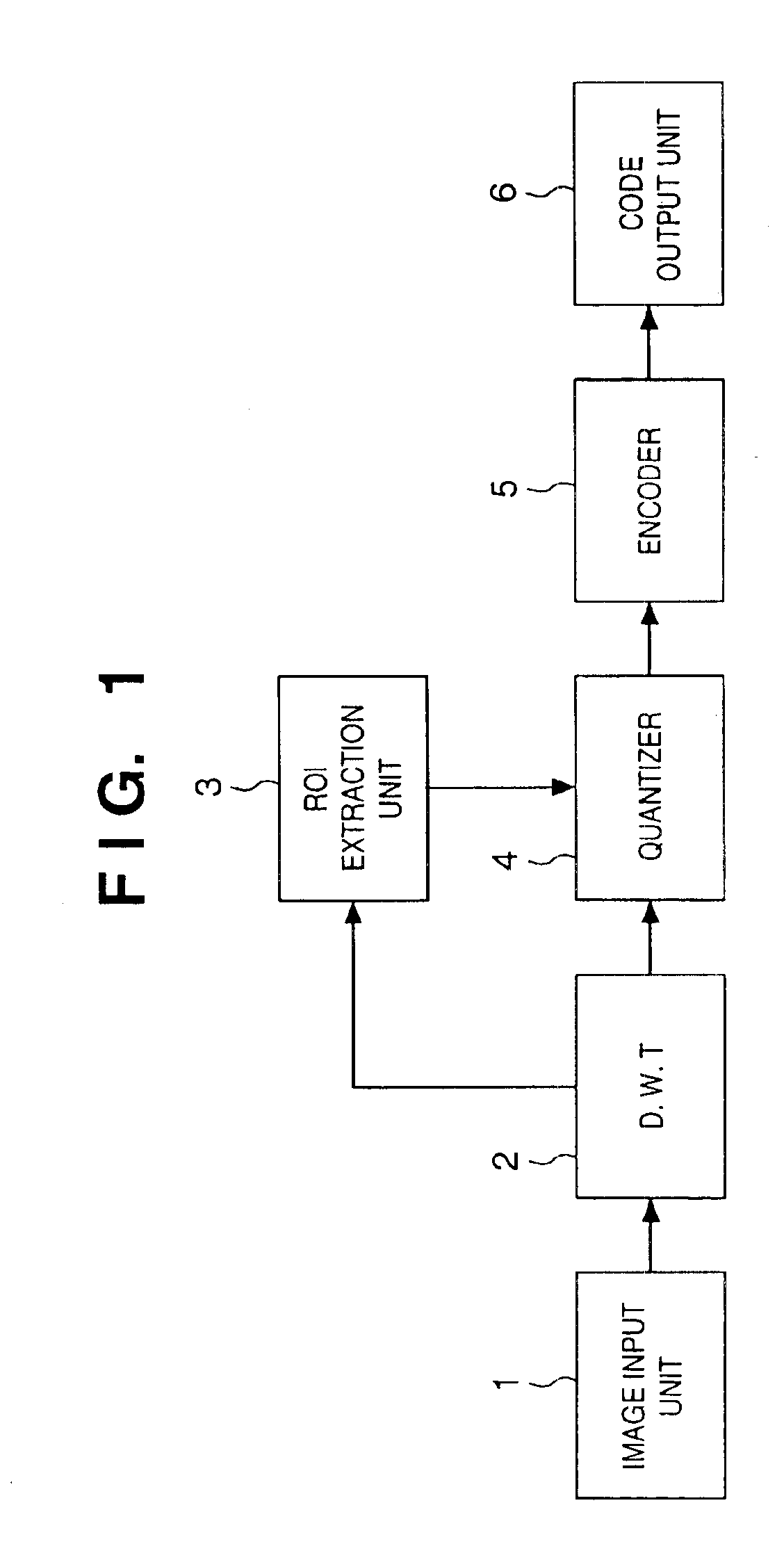
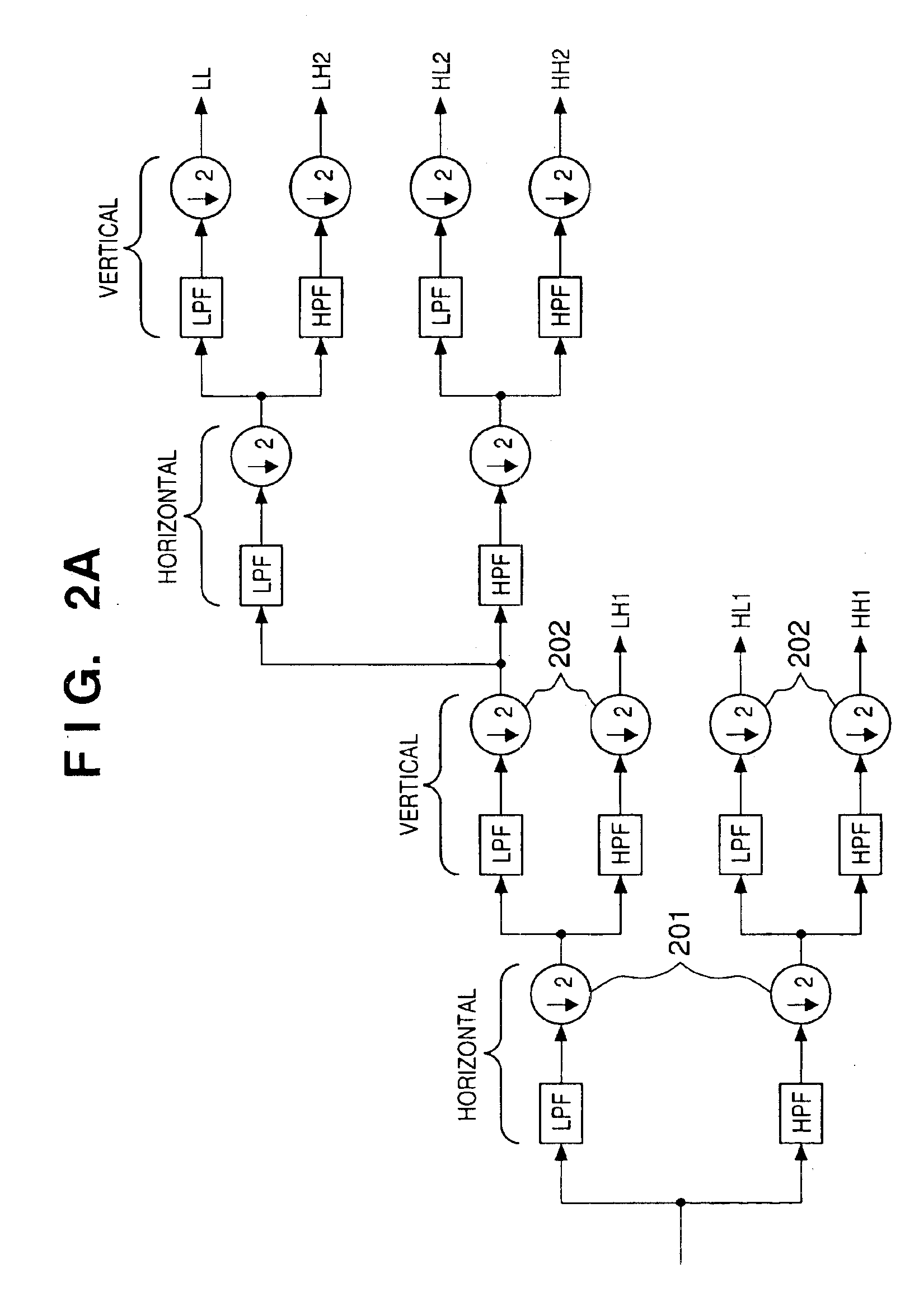
An image signal is input from an image input unit and is divided into different spatial frequency bands by applying a discrete wavelet transform thereto using a discrete wavelet transformation unit. On the basis of values of spatial frequency components, a region-of-interest extracts a region of interest by obtaining a distribution of motion vectors in the input image. A quantization unit applies quantization processing to the extracted region of interest and different quantization processing to other regions, and an encoder encodes the quantized image signal. Alternatively, motion of an image contained in the input image may be detected and the region of interest may be obtained based upon motion of this image.
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com