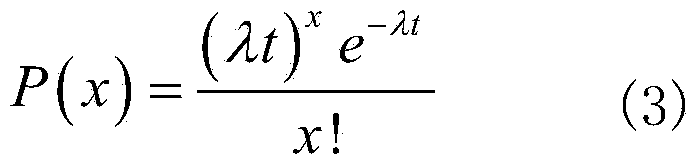Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
425 results about "Temporal correlation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Temporal correlation is important for modeling the channel for terminals in motion, and this subject is well known from SISO channels. Spatial correlation, on the other hand, is a feature that entered the scene by the application of array antennas in MISO or SIMO situations.
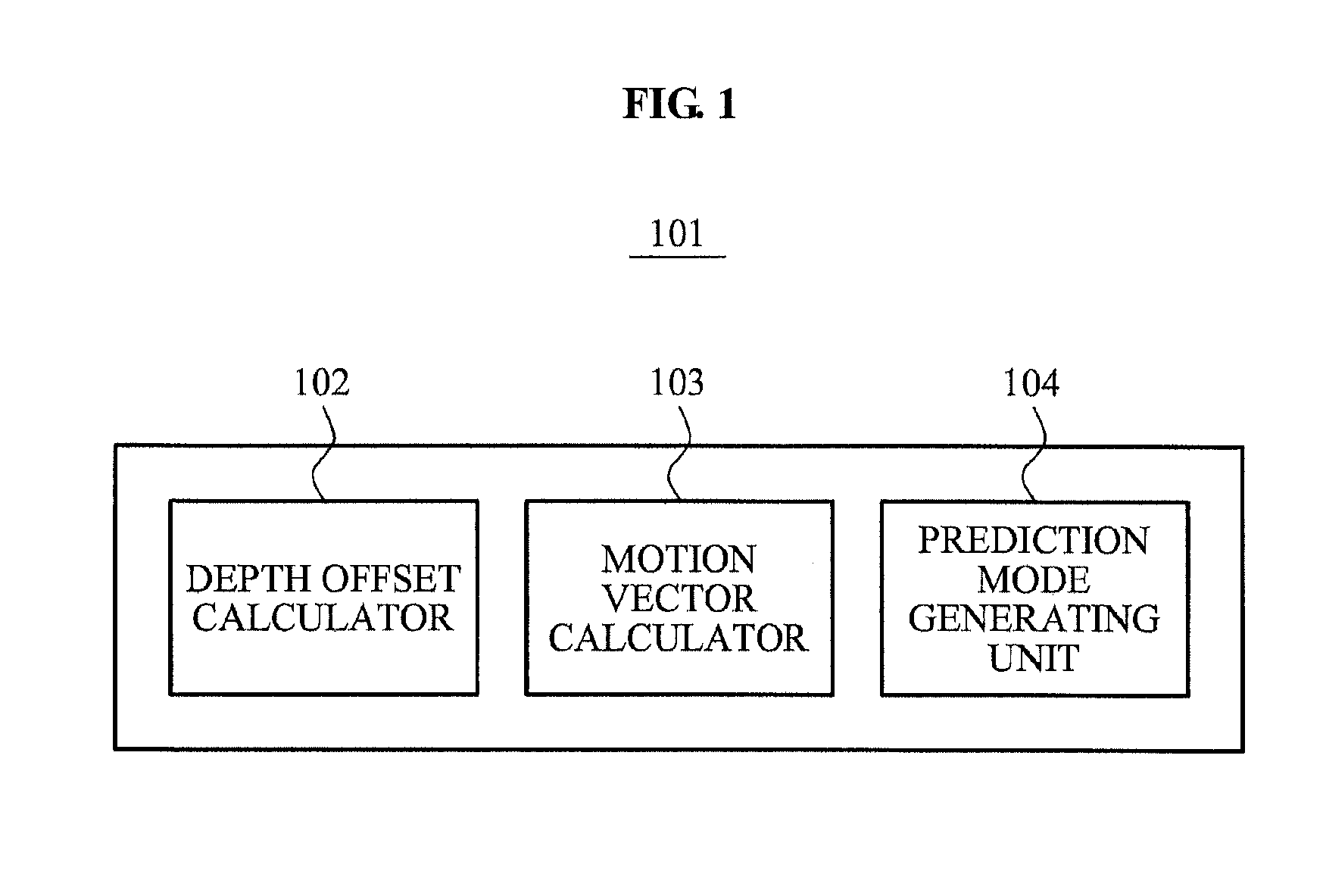
Apparatus and method of depth coding using prediction mode
InactiveUS20110317766A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorTemporal correlation
A depth image coding method may calculate a depth offset of a depth image, may generate a prediction mode based on the depth offset, may minimize a prediction error of the depth image having a low correlation between adjacent points of view and a low temporal correlation and may enhance a compression rate. The depth offset may be calculated based on a representative value of adjacent pixels included in a template as opposed to using a depth representative value of pixels in a block and header information may not be needed to encode an offset and the offset may be generated by a depth image decoding apparatus. When a plurality of objects is included in a block, a depth offset is calculated for each of the plurality of objects and a motion vector is calculated for each of the plurality of objects and the depth image may be accurately predicted.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
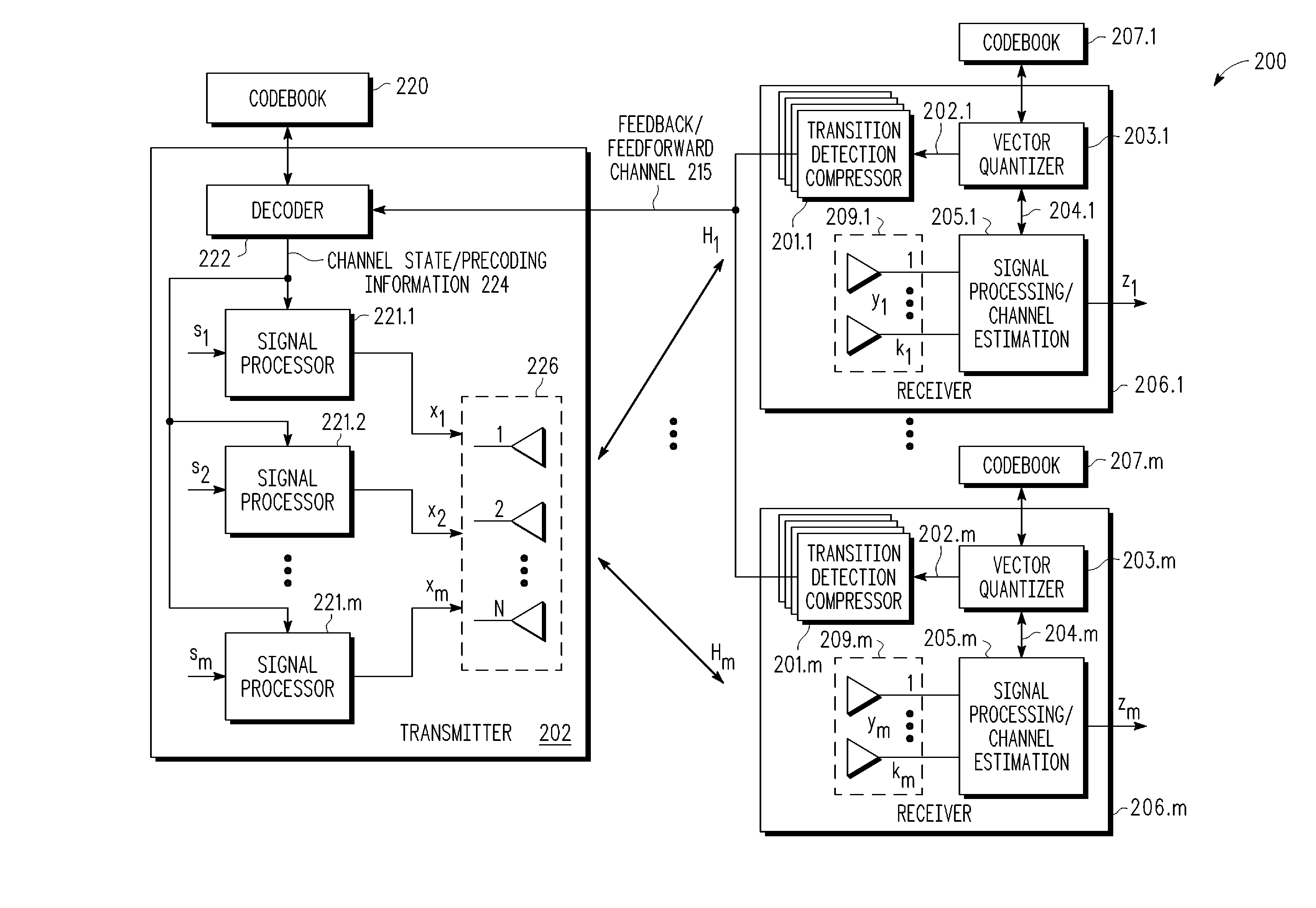
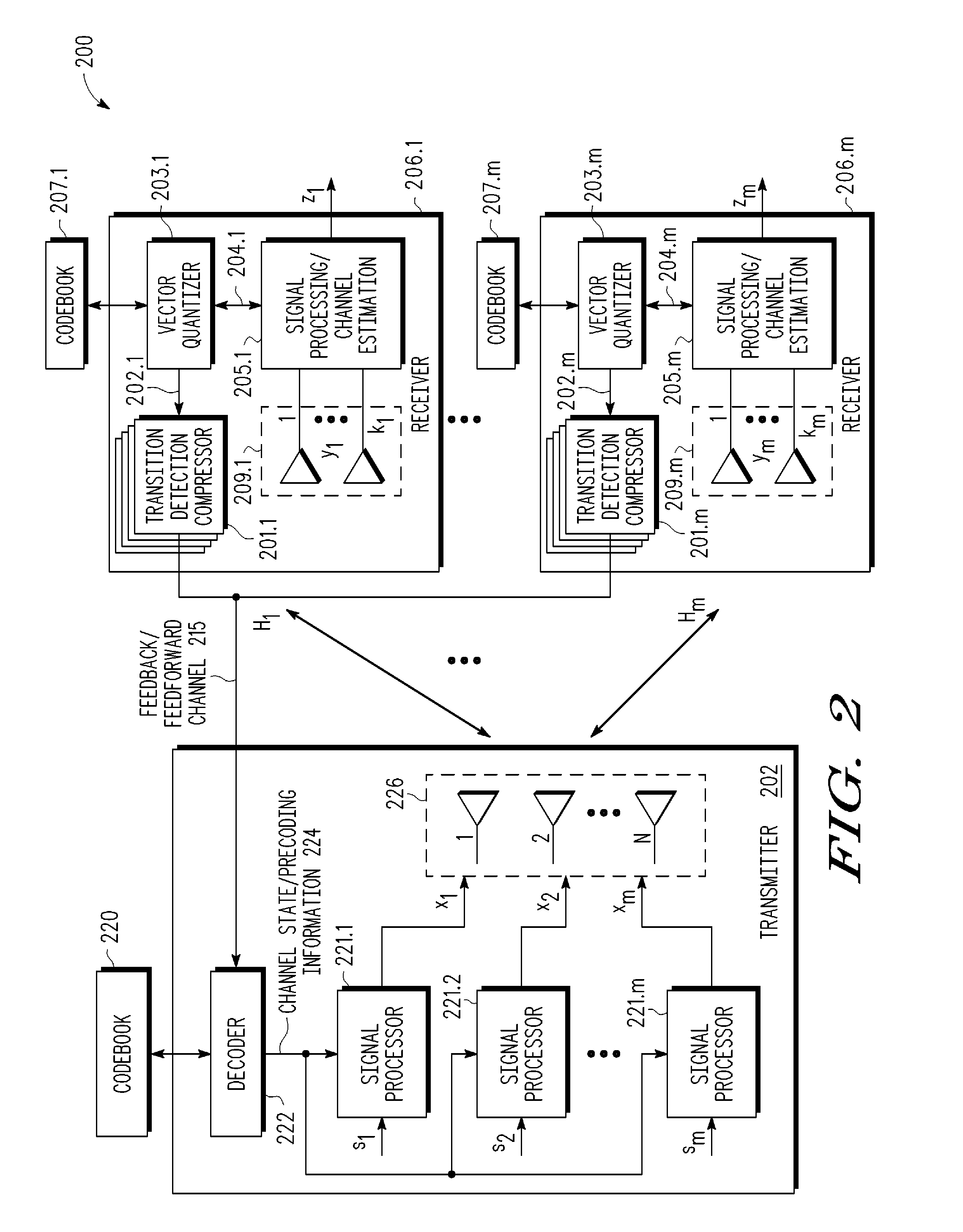
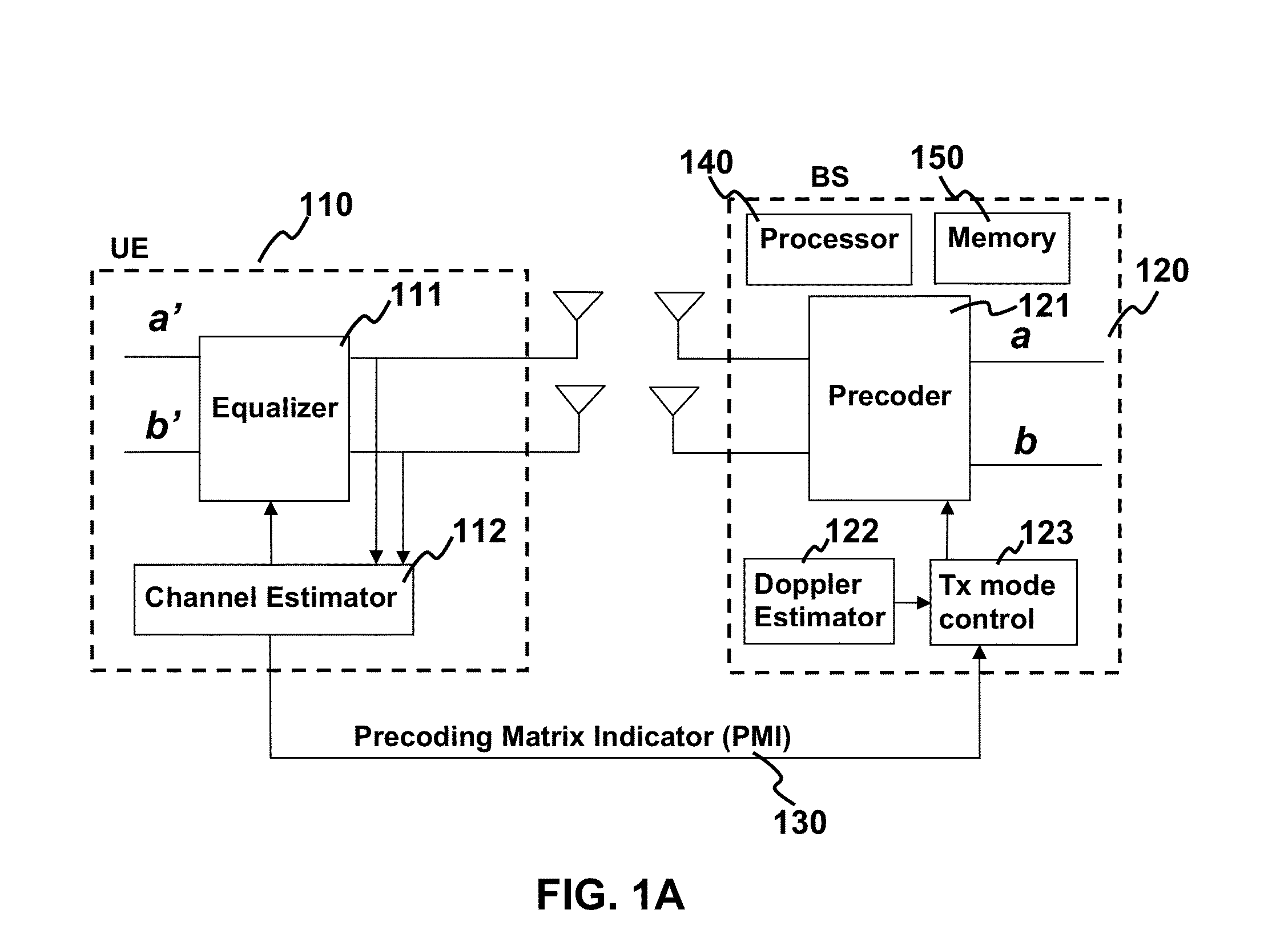
Feedback reduction for MIMO precoded system by exploiting channel correlation
ActiveUS20080080459A1Special service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsPrecodingCommunications system
In a closed-loop wireless communication system, a codebook-based precoding feedback compression mechanism is provided to remove redundancy from the precoding feedback that is caused by channel correlation in time and frequency. Redundancy due to temporal correlation of the transmission channel is removed by sending precoding feedback only if there is a change in the precoder state for the channel to the receiver. Redundancy due to frequency correlation is removed by run length encoding the precoding feedback, thereby compressing the precoding feedback prior in the frequency domain. By compressing the precoding feedback, the average rate of precoder feedback is reduced.
Owner:NXP USA INC
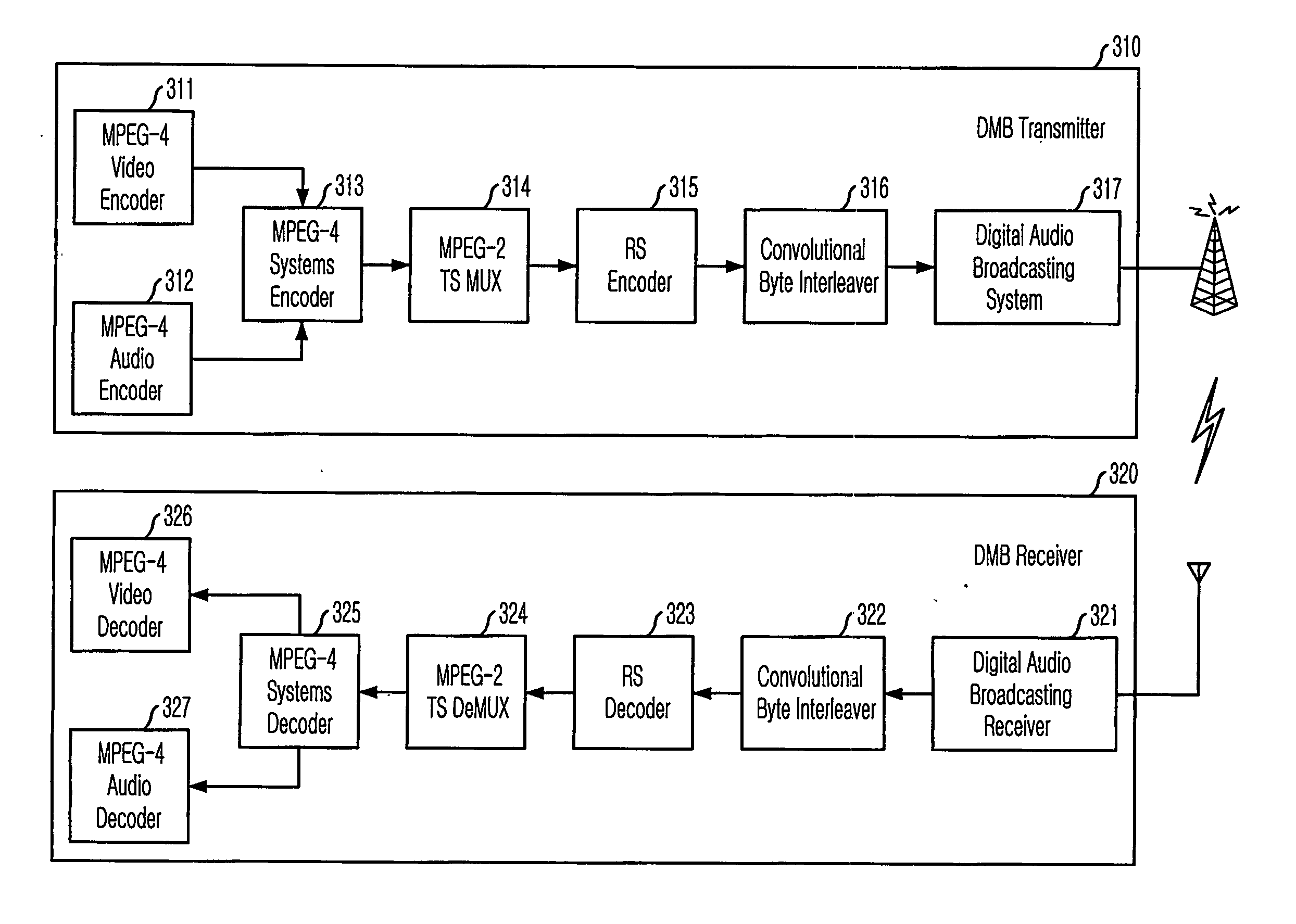
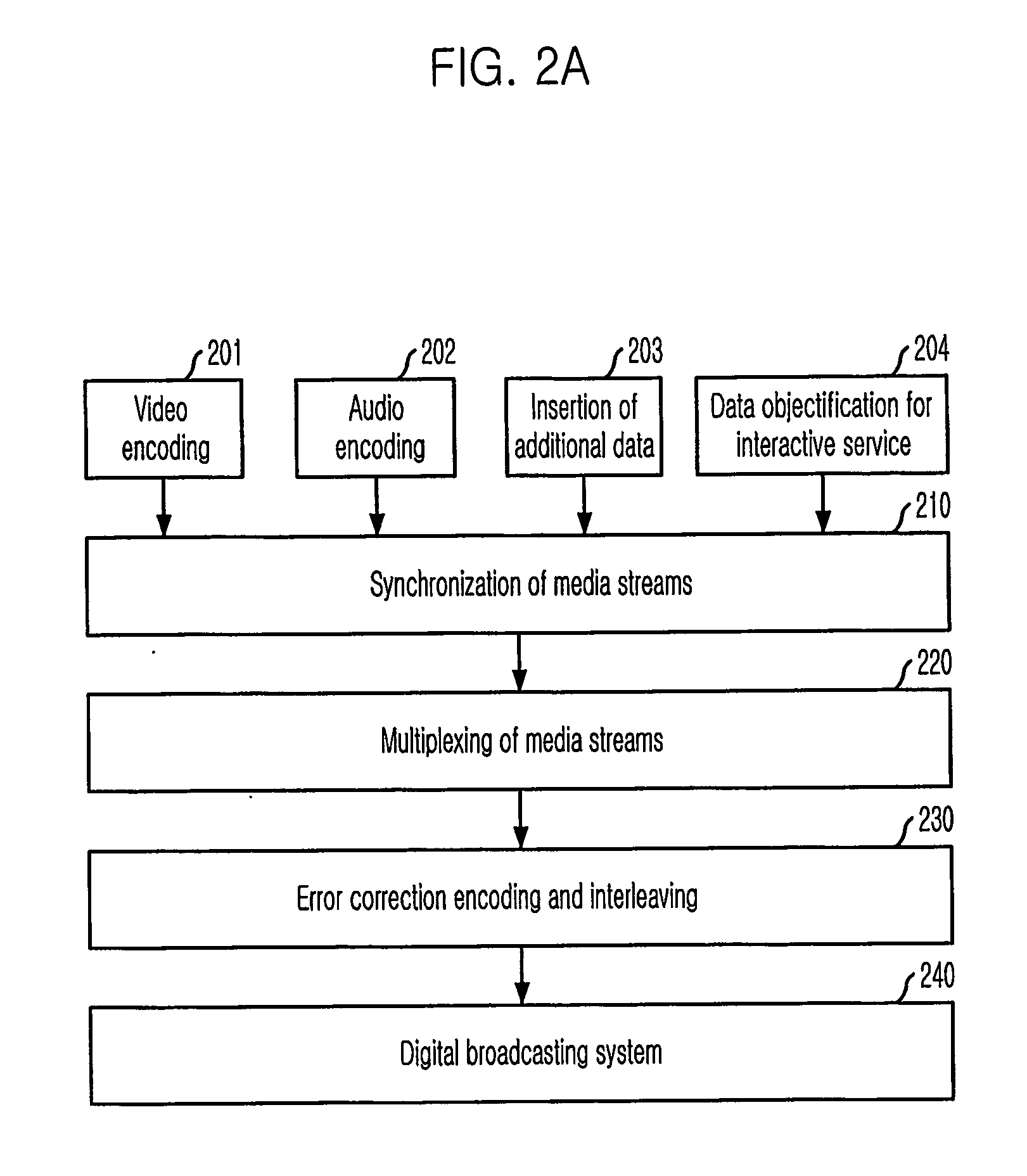
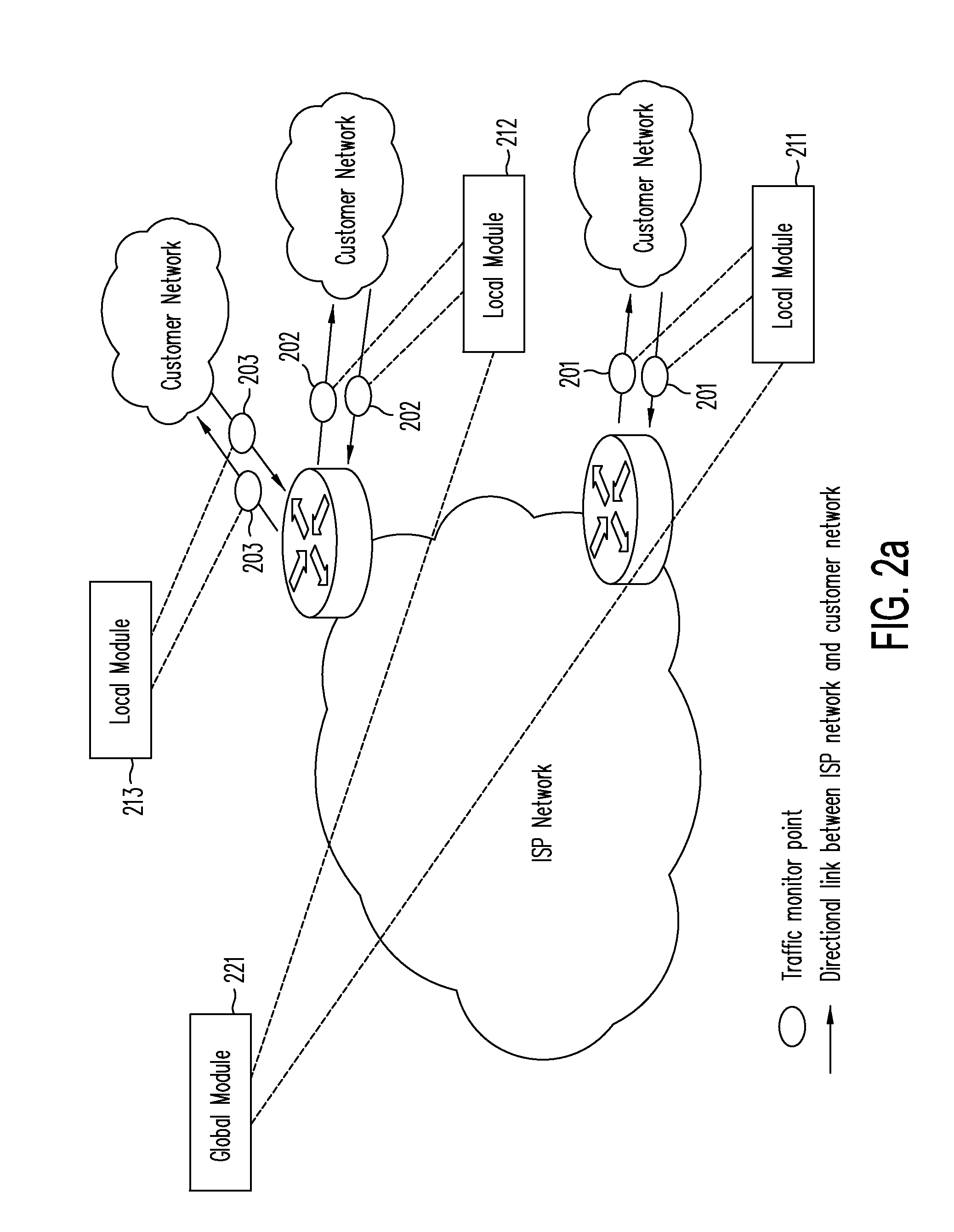
System and method for digital multimedia broadcasting
InactiveUS20060262227A1Improve reception qualityEfficient compressionTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionMultiplexingData stream
Provided is a digital multimedia broadcasting (DMB) system that can provide a multimedia data broadcasting service having an excellent reception quality, a method thereof, and a computer-readable recording medium for recording a program that implements the method. The DMB system includes an encoding unit for encoding an inputted audio / video signal; a synchronizing unit for synchronizing media stream, additional data, interactive service objectifying data that are outputted from the encoding unit; a multiplexing unit for multiplexing the media stream outputted from the synchronizing unit; an error correction encoding unit for performing additional error correction encoding on the media stream outputted from the multiplexing unit; an interleaving unit for removing temporal correlation between adjacent byte units within a data stream outputted from the error correction encoding unit; and a transmitting unit for transmitting a DMB media stream outputted from the interleaving unit to the conventional DAB system and other digital broadcasting systems.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
System and method to create a collaborative web-based multimedia layered platform
InactiveUS20070198534A1Multimedia data browsing/visualisationMultiple digital computer combinationsFile descriptorTemporal correlation
The present invention relates to a system and method to allow multiple users to collaborate on tasks and interact in a shared space session within a network in real-time; using a media application to manage media-layers. Each media-layer serves as a container for multimedia programs or plug-ins. The invention allows which media-layer to display via organization metaphors and filtering criteria. When multiple users are logged into the same shared space, each user can invoke and observe modifications to media-layers with the browser based or client based application. All events are synchronized among all users in that shared space, where the system is a communication conduit. The media-layers in the shared space maintains spatial and temporal correlation by a media application stage manager tool and described as a collection file descriptor such as an XML file. The ability to invoke events that affect media-layers can be supported in a synched or non synched mode on demand.
Owner:SIMULAT
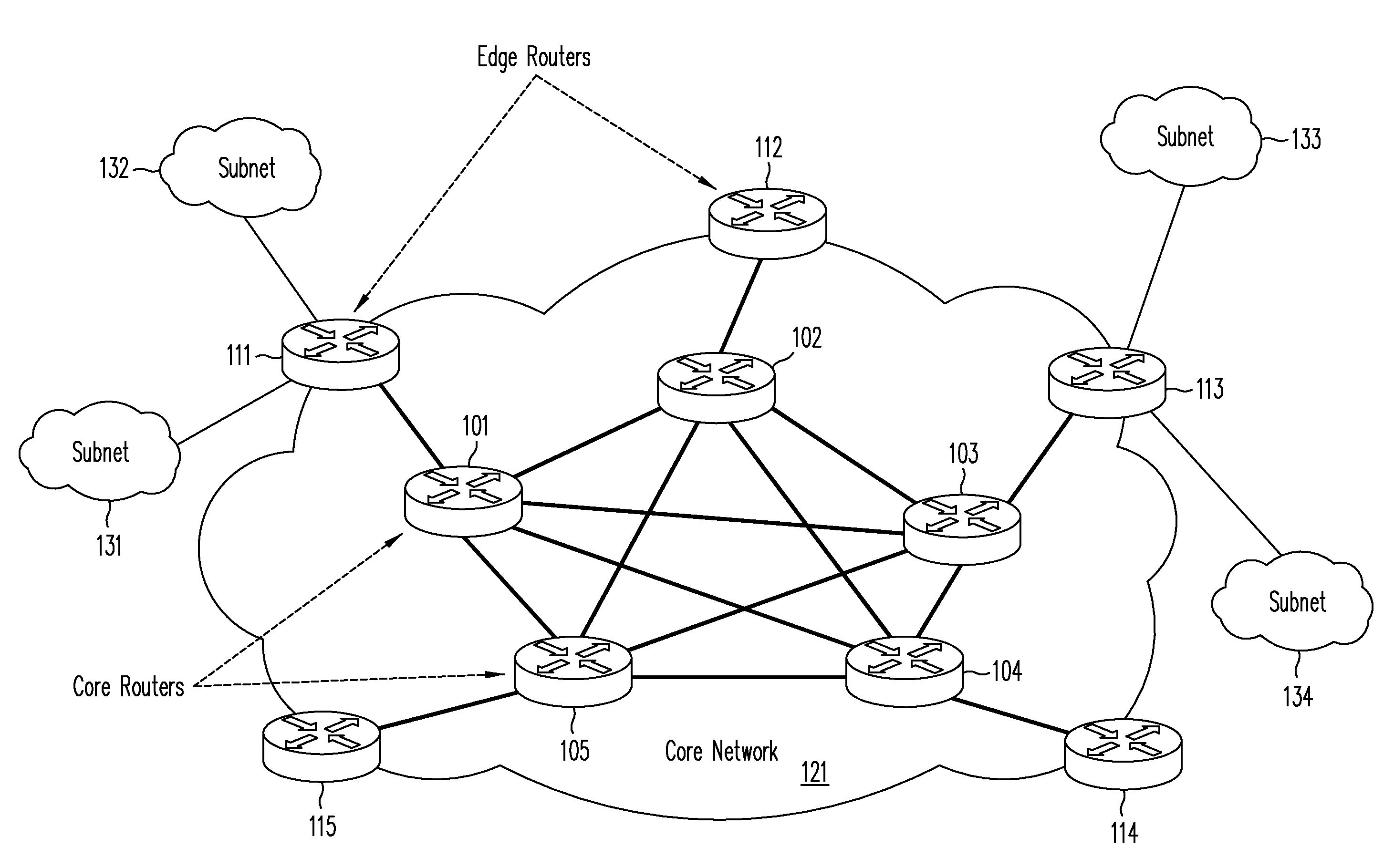
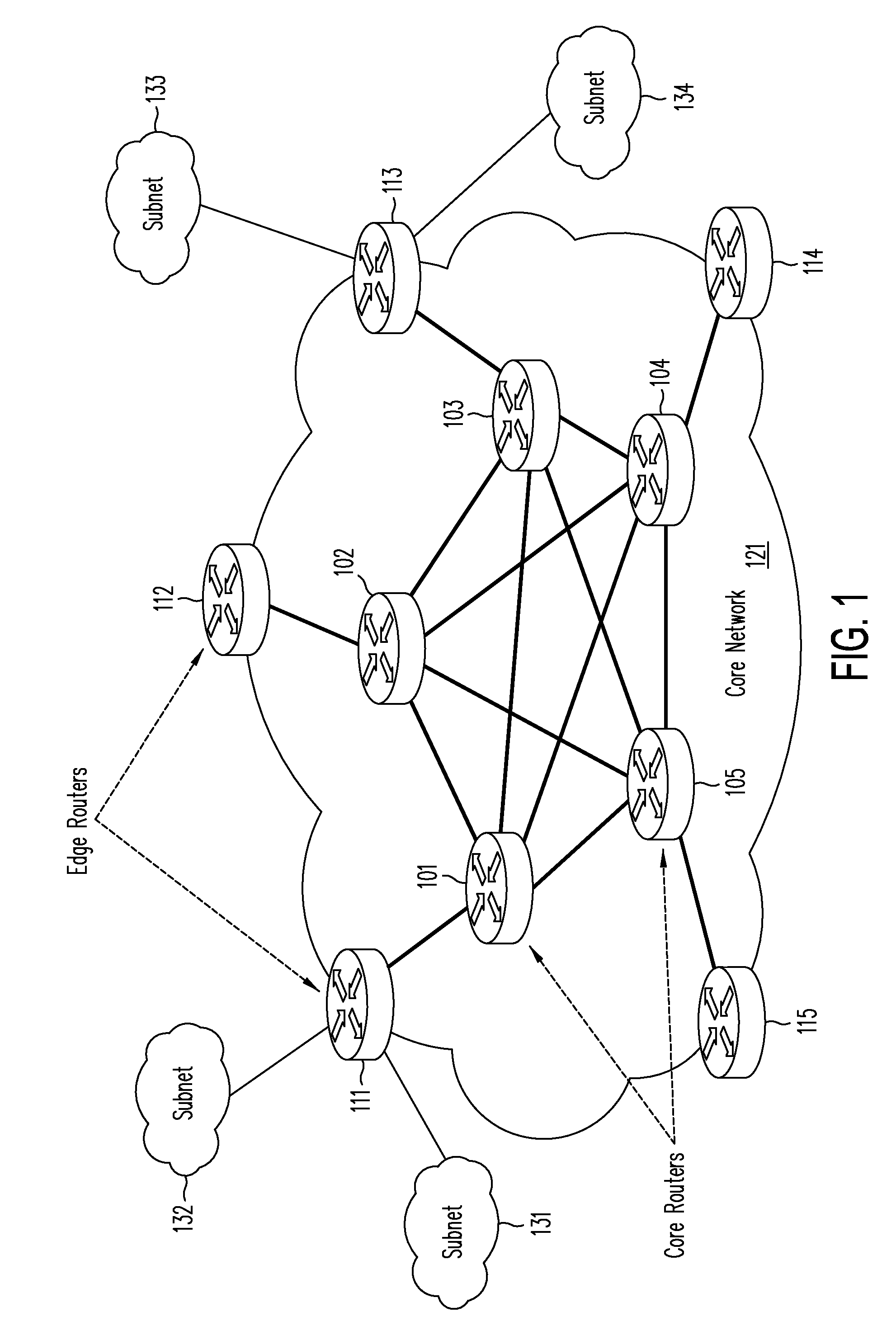
Architecture, systems and methods to detect efficiently DoS and DDoS attacks for large scale internet
ActiveUS7584507B1Efficient identificationMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionSpatial correlationThe Internet
The present invention efficiently detects various DDoS attacks for large scale Internet with the temporal correlation of traffic flows on the two directions of a single link, the spatial correlation of DDoS attack traffic at different locations and powerful machine learning algorithms. With these techniques, the present invention effectively detects and identifies attack sources without modifying existing IP forwarding mechanisms and without a global upgrade to Internet backbone routers. More importantly, the present invention can detect synchronized DDoS attacks even if the volume of attack traffic is extremely small at the location that is close to the attack source.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
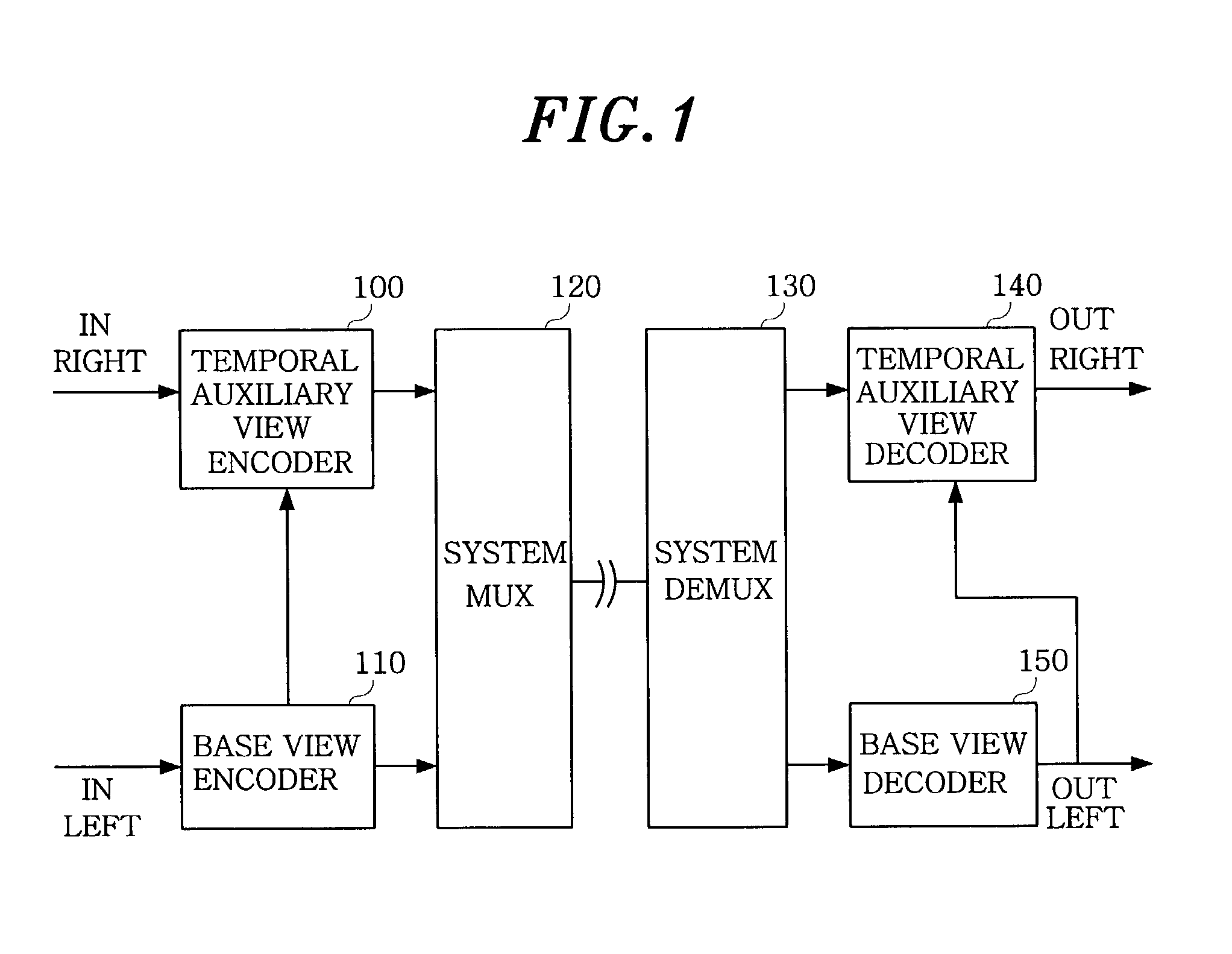
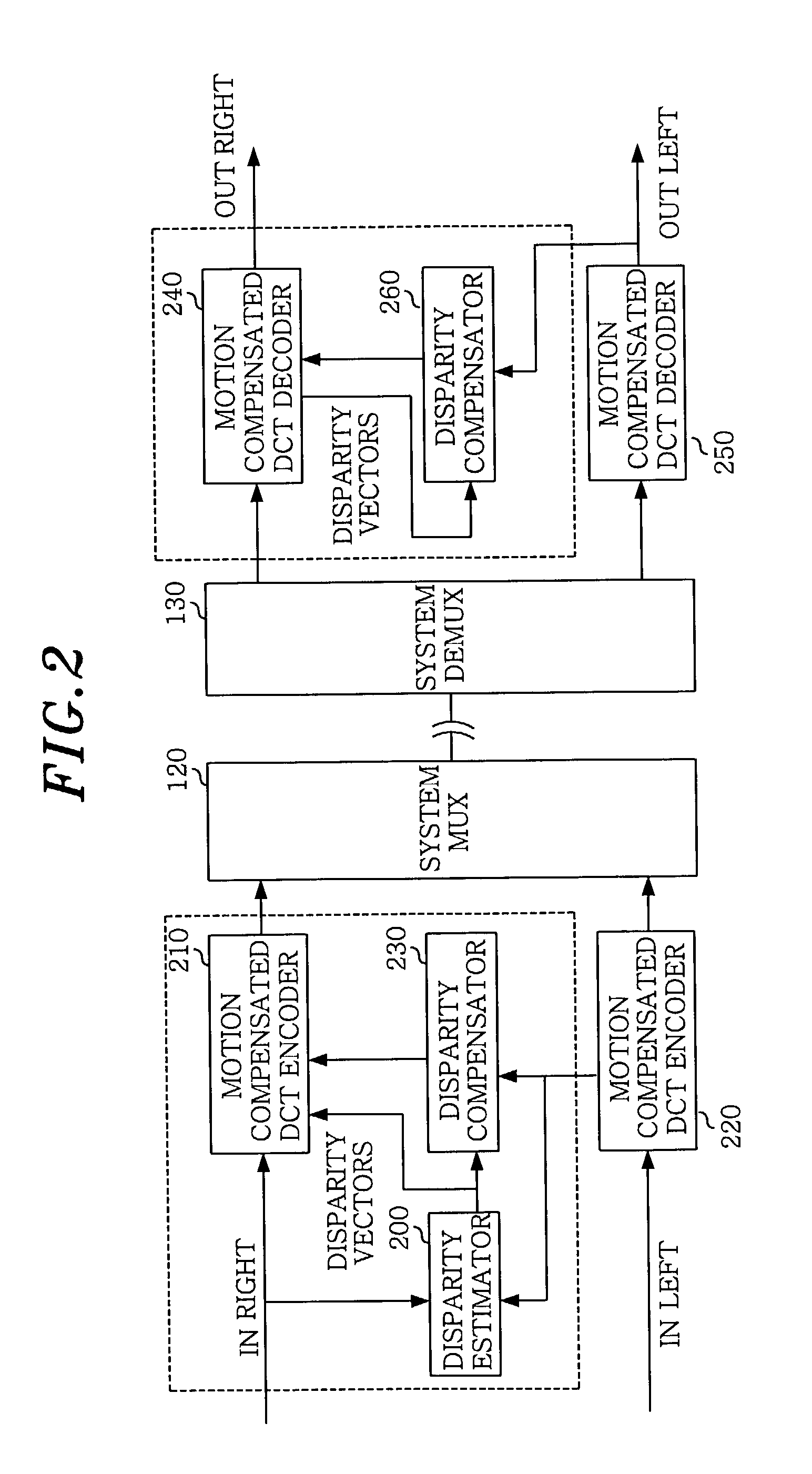
Apparatus for encoding a multi-view moving picture
ActiveUS6999513B2Minimize informationImprove picture qualityPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningParallaxMotion vector
A disparity prediction stage and a motion prediction stage predict a disparity vector and a motion vector by extending a MPEG-2 structure into a view axis and using spatial / temporal correlation. A disparity / motion compensation stage compensates an image reconstructed by the disparity prediction stage and the motion prediction stage by using a sub-pixel compensation method. A residual image encoding stage performs an encoding to provide a better visual quality and a three-dimensional effect of an original image and the reconstructed image. A bit rate control stage controls a bit rate for assigning an effective amount of bit to each frame on the reconstructed image according to a bit rate. An entropy encoding stage generates a bit stream on multi-view video source data according to the bit rate.
Owner:KOREA ELECTRONICS TECH INST
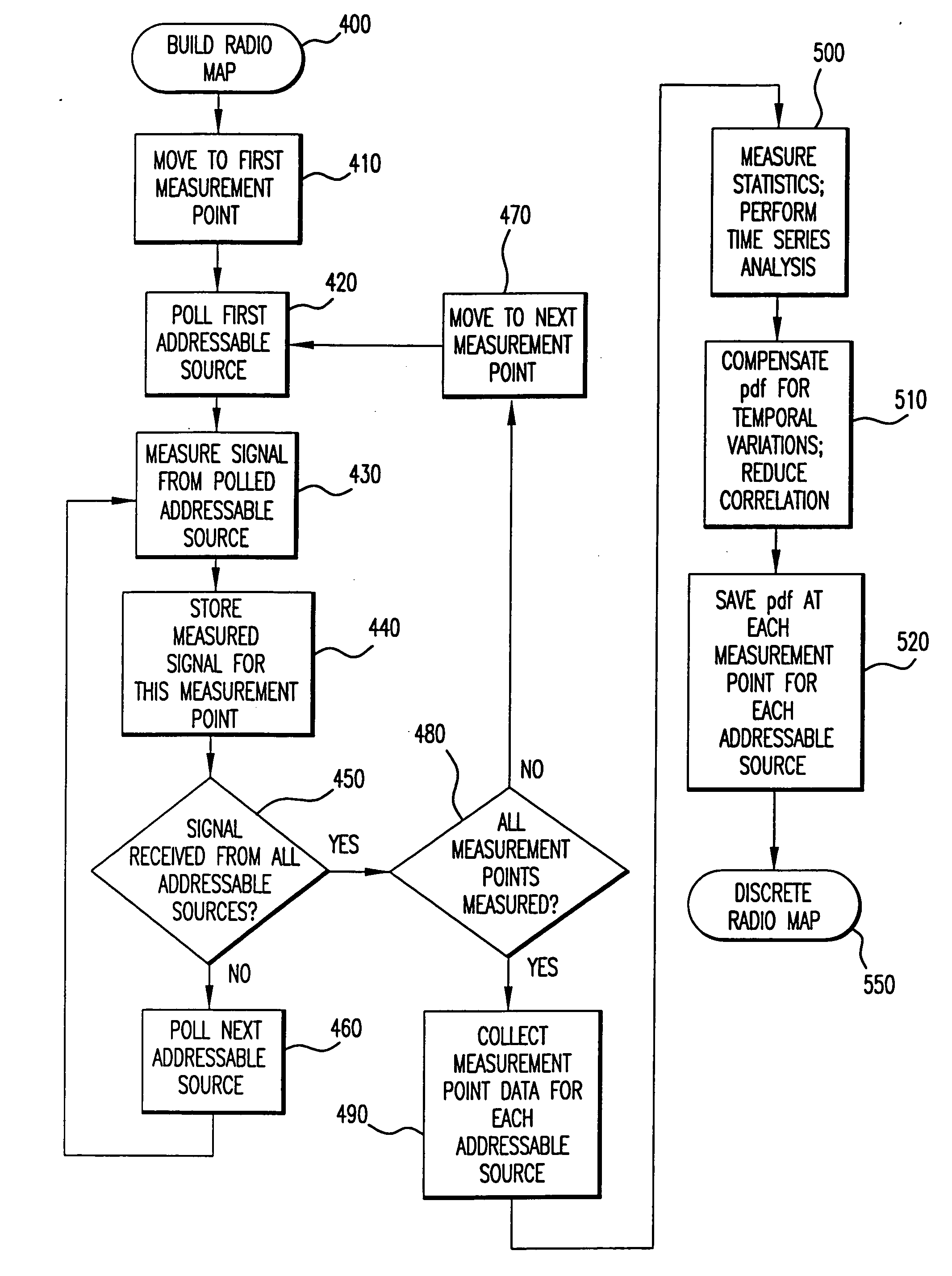
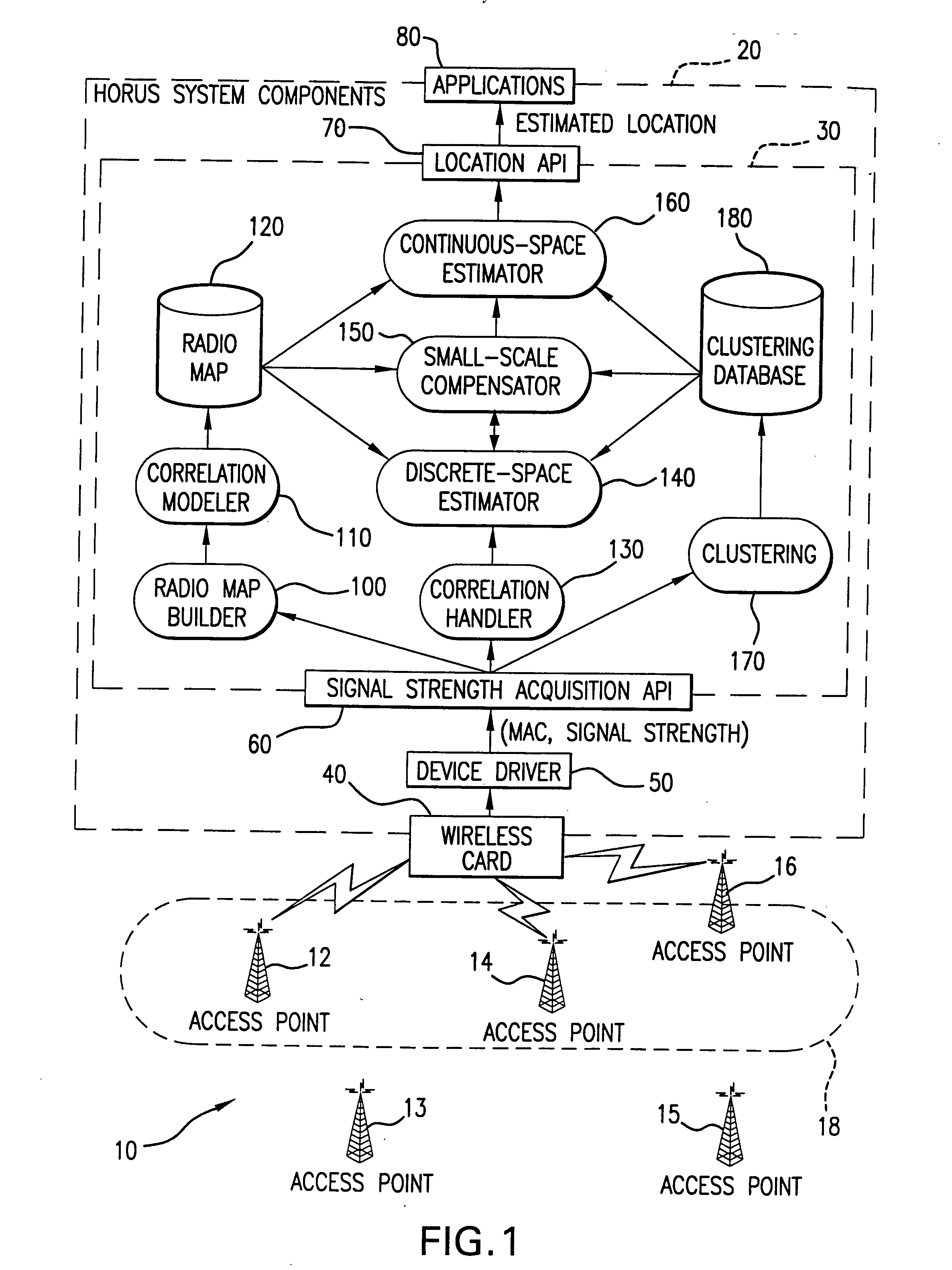
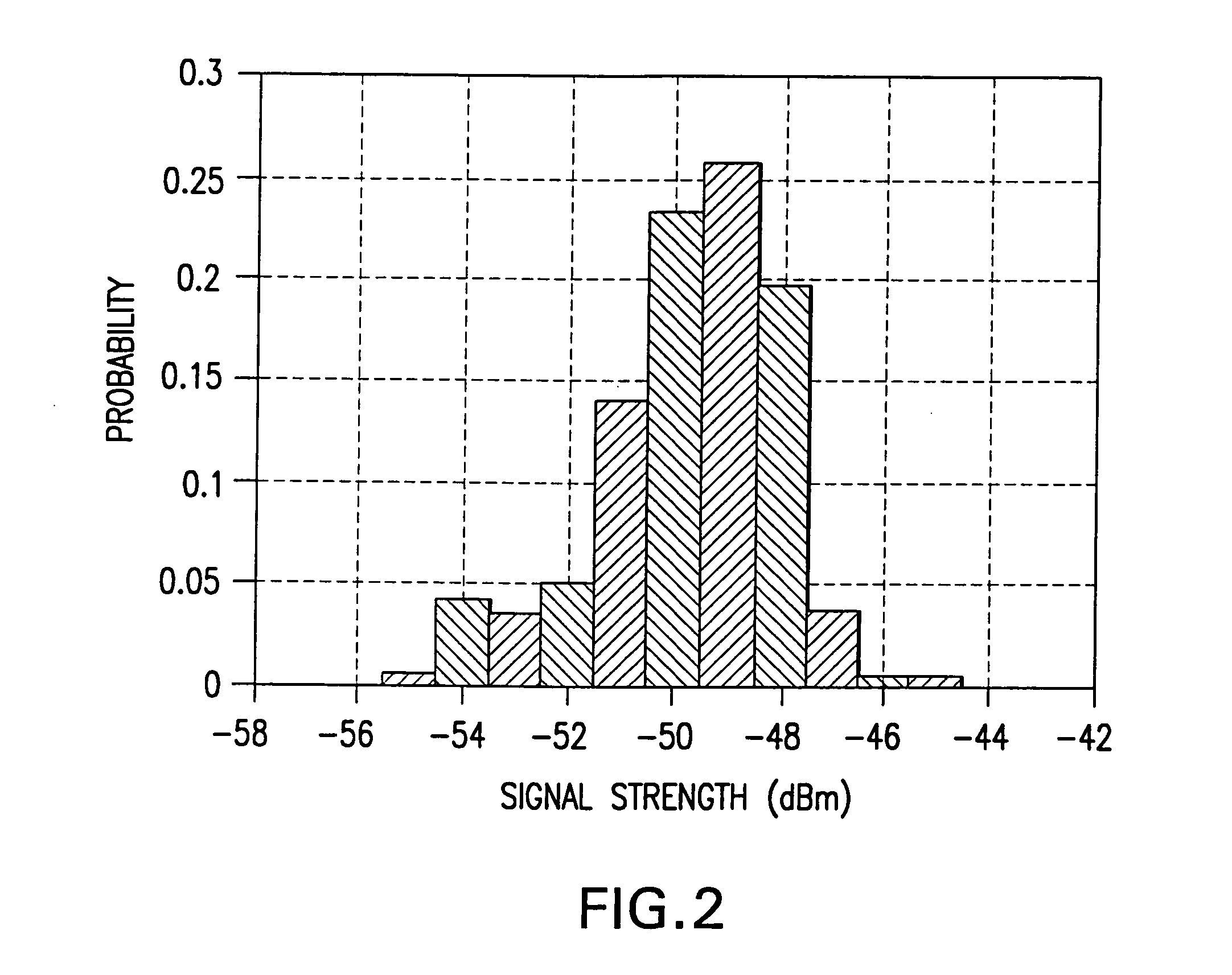
Method and system for determining user location in a wireless communication network
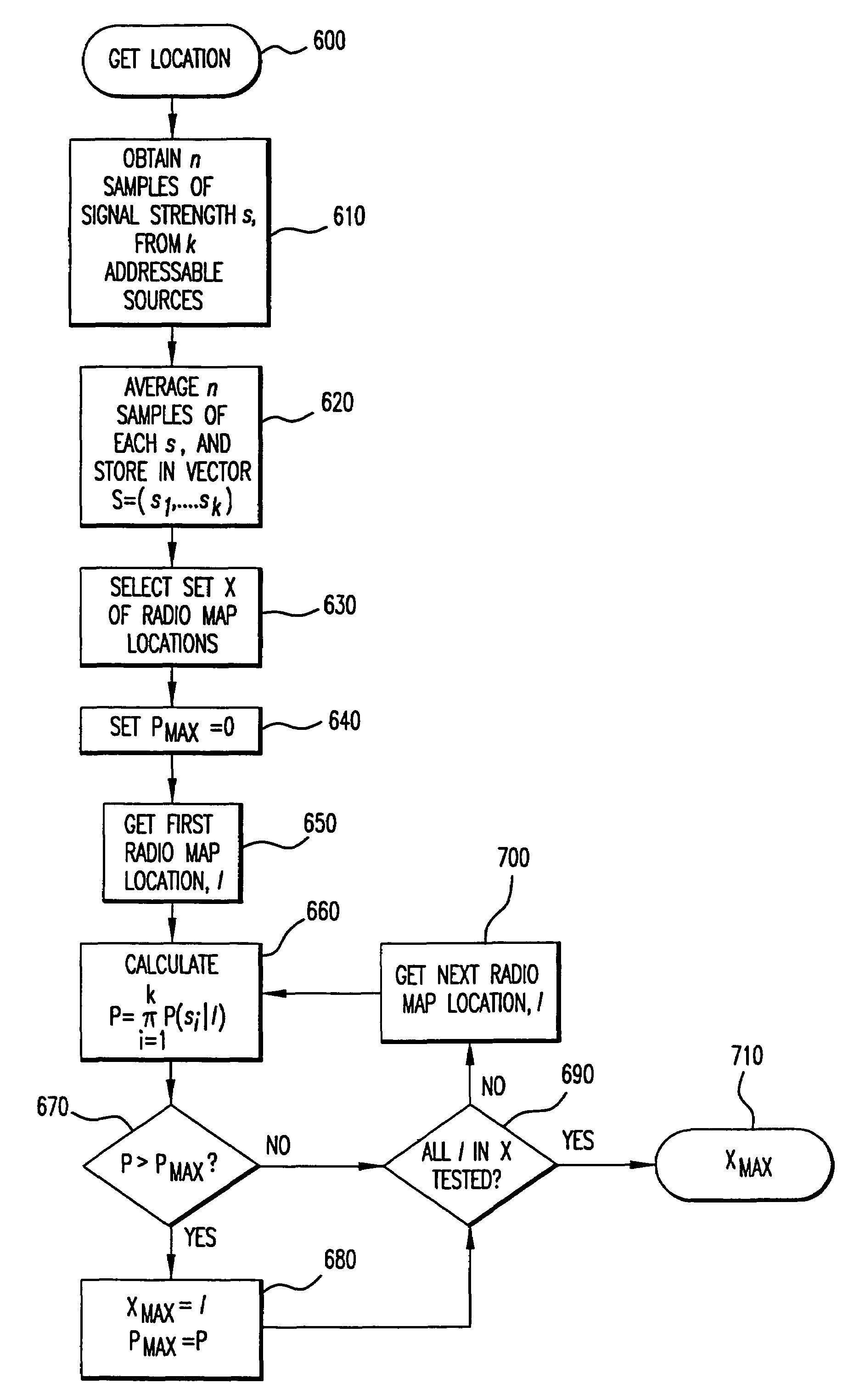
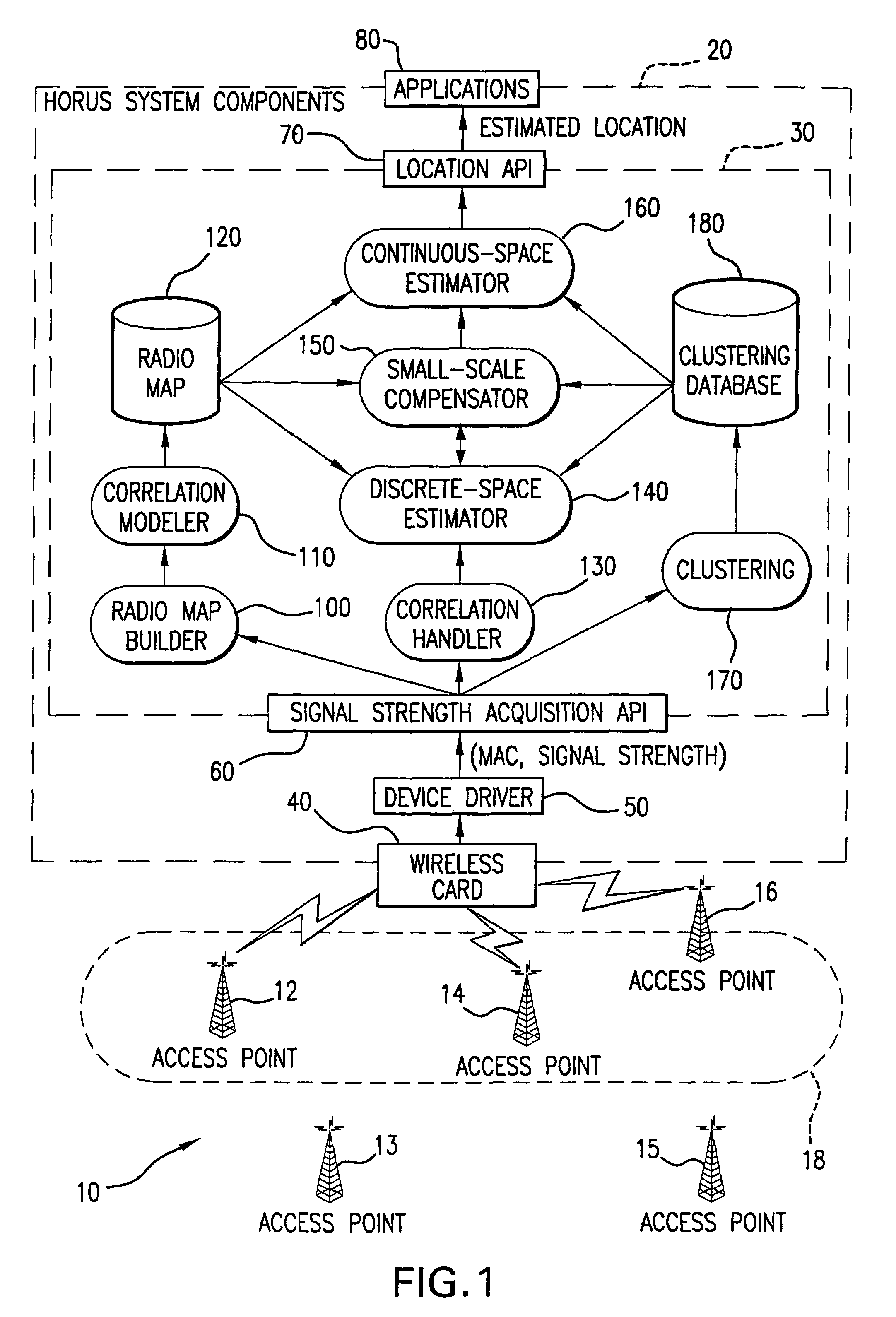
InactiveUS20050243936A1Maximize probabilityAccurate measurementData switching by path configurationSatellite radio beaconingProbit modelRadio map
In a wireless communication network, the location of an addressable receiver relative to the locations of a plurality of addressable sources of electromagnetic radiation is found using probabilistic models of the signal strength measured at the addressable receiver. The inventive method provides location determination on a finer spatial scale than was heretofore available. A region of interest is calibrated via a discrete-space radio map storing probability distributions of received signal strength at the measurement locations. The stored probability distributions are compensated for temporal variability and biases, such as through temporal correlations of the sampled received signal strength. A measurement of the signal strength at the addressable receiver from each of the plurality of addressable sources is used in conjunction with the discrete-space radio map to identify one of the coordinates thereof that maximizes the conditional probability P(x|s), where x is the radio map location and s is a vector of measured signal strengths. Small spatial scale variability can be compensated for using a perturbation technique. The method further implements a continuous-space estimator to return an estimated user location that falls between discrete-space radio map locations.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
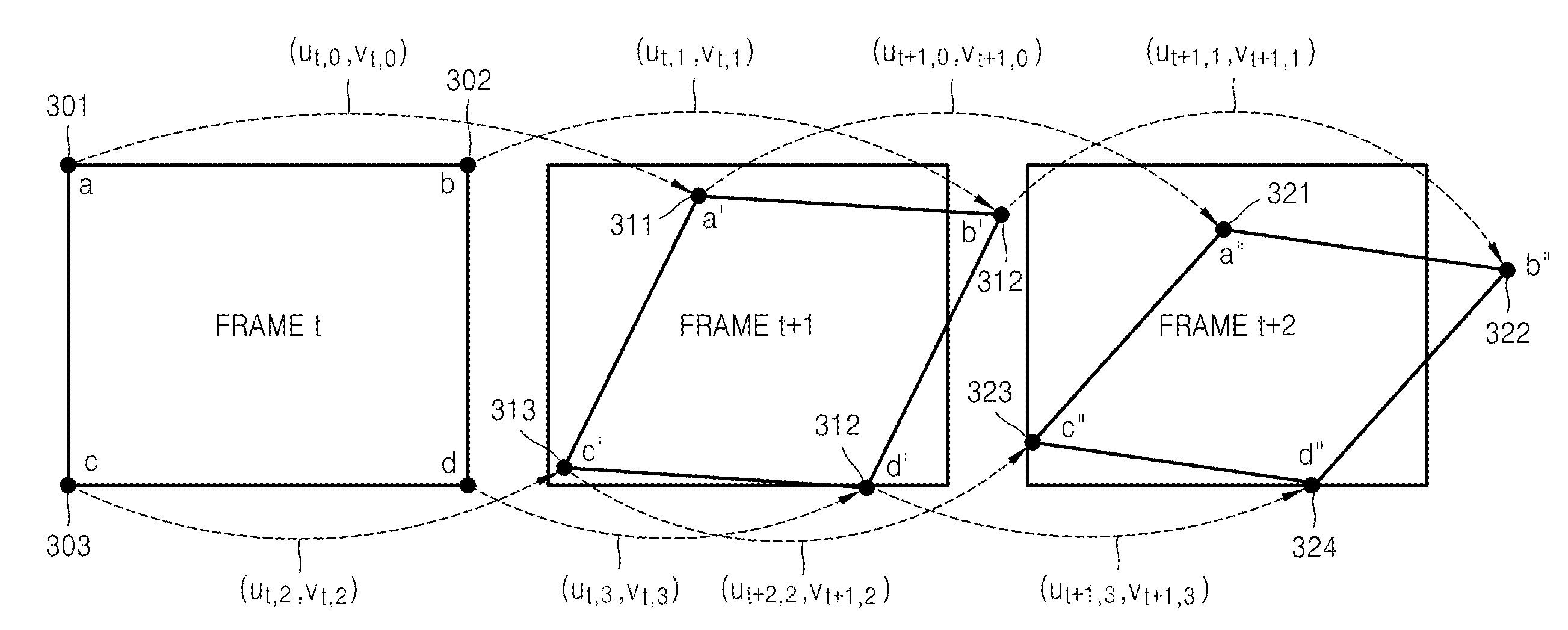
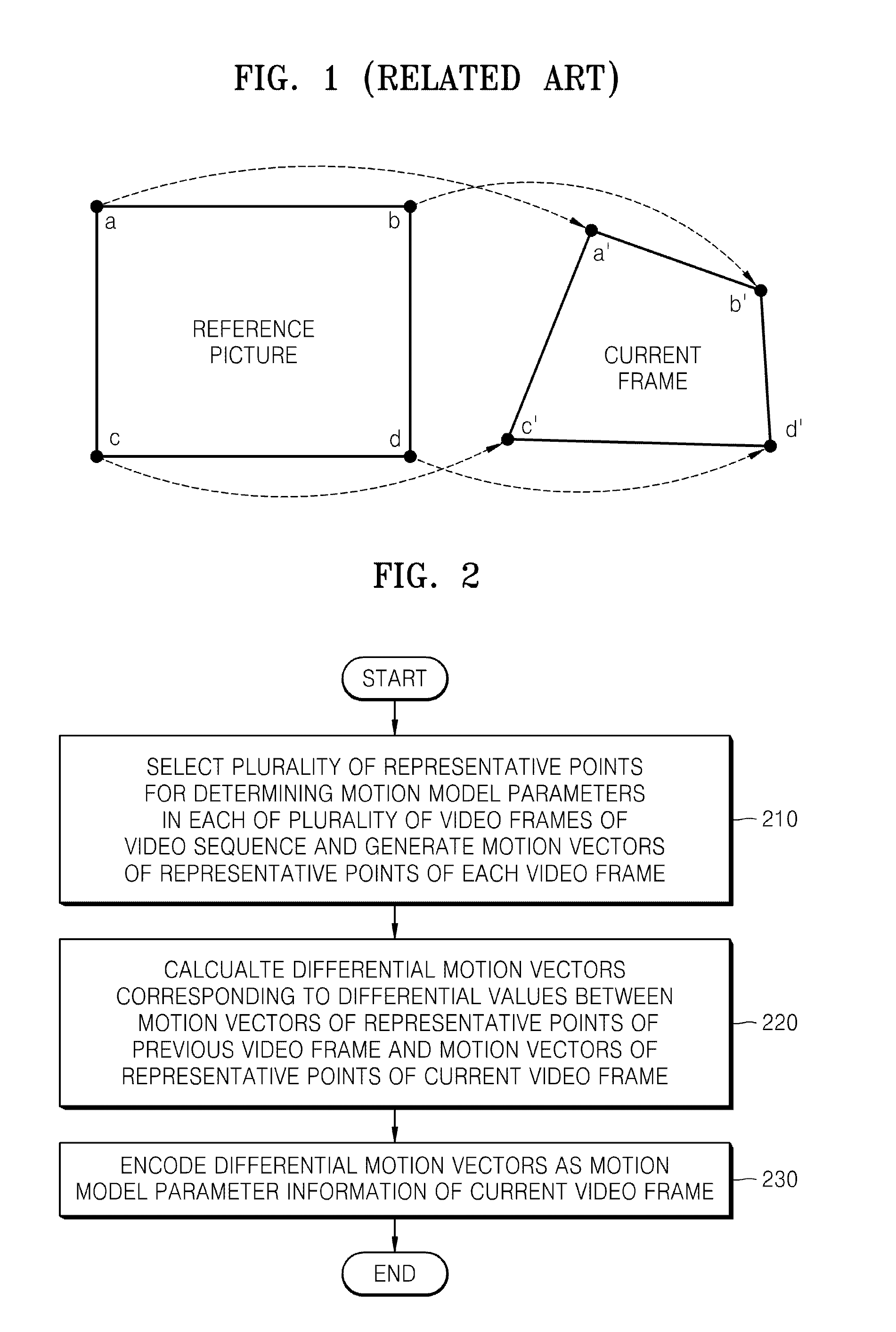
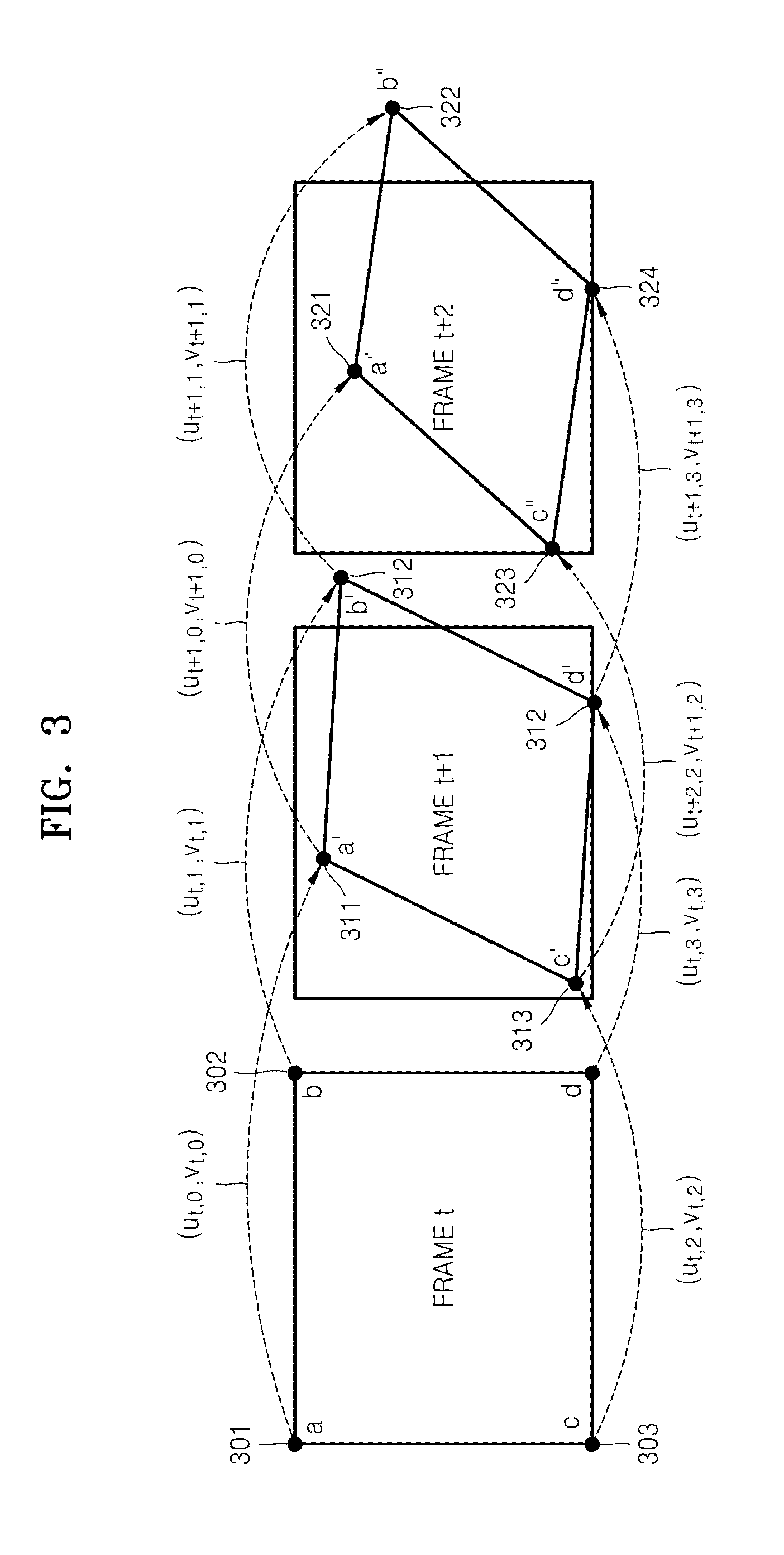
Method of encoding and decoding motion model parameters and video encoding and decoding method and apparatus using motion model parameters
InactiveUS20080240247A1Efficient codingImproving video compression efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionMotion vector
Provided are a method of efficiently transmitting motion model parameters using temporal correlation between video frames and a video encoding and decoding method and apparatus, in which motion estimation and motion compensation are performed by generating a plurality of reference pictures that are motion-compensated using motion model parameters. Motion model parameters are encoded based on temporal correlation between motion vectors of representative points expressing the motion model parameters, global motion compensation is performed on a previous reference video frame using motion model parameters in order to generate a plurality of transformation reference pictures, and a current video frame is encoded using the plurality of transformation reference pictures.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
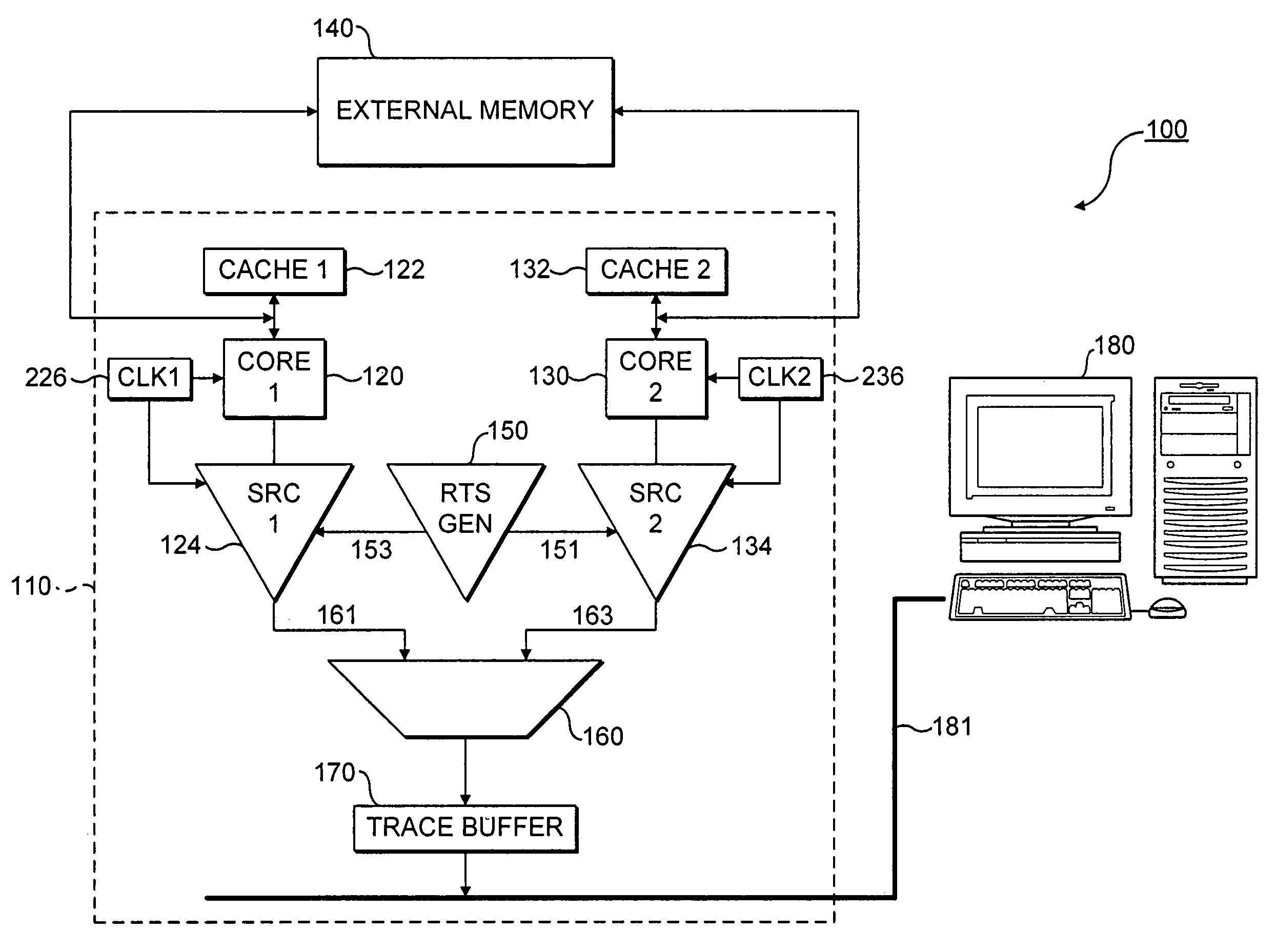
Trace source correlation in a data processing apparatus
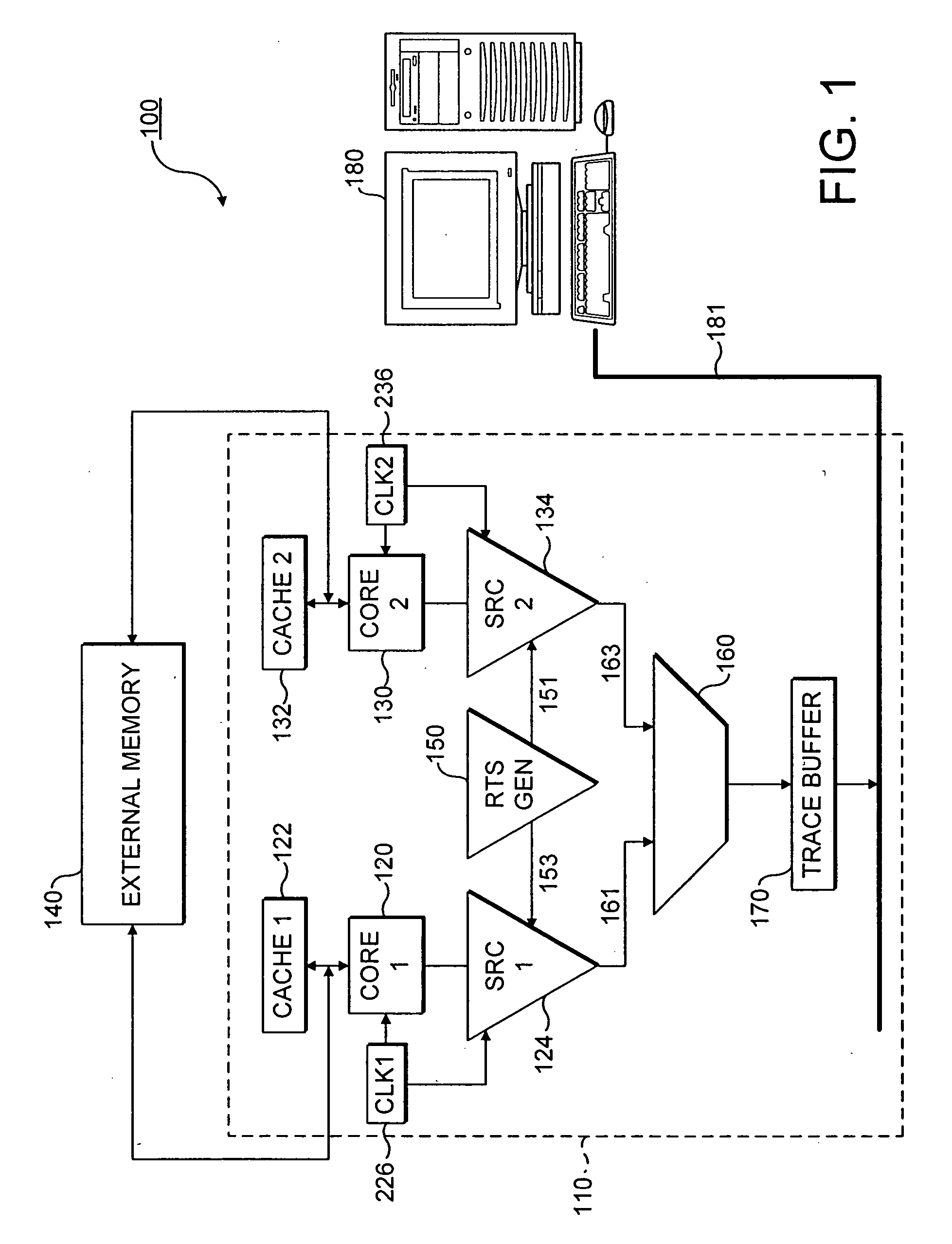
ActiveUS7069176B2Efficiently enableAvoid the needTime indicationSynchronous motors for clocksData streamTimestamp
An integrated circuit is provided with multiple data processing components associated with respective sources which generate trace data streams. A reference timestamp generator is provided and the trace data streams are annotated such that they are output off-chip together with reference timestamp data. Outputting the reference timestamp data together with the trace data streams enables temporal correlation between points in different trace data streams by trace analysis tools.
Owner:ARM LTD
Coding of animated 3-D wireframe models for internet streaming applications: methods, systems and program products
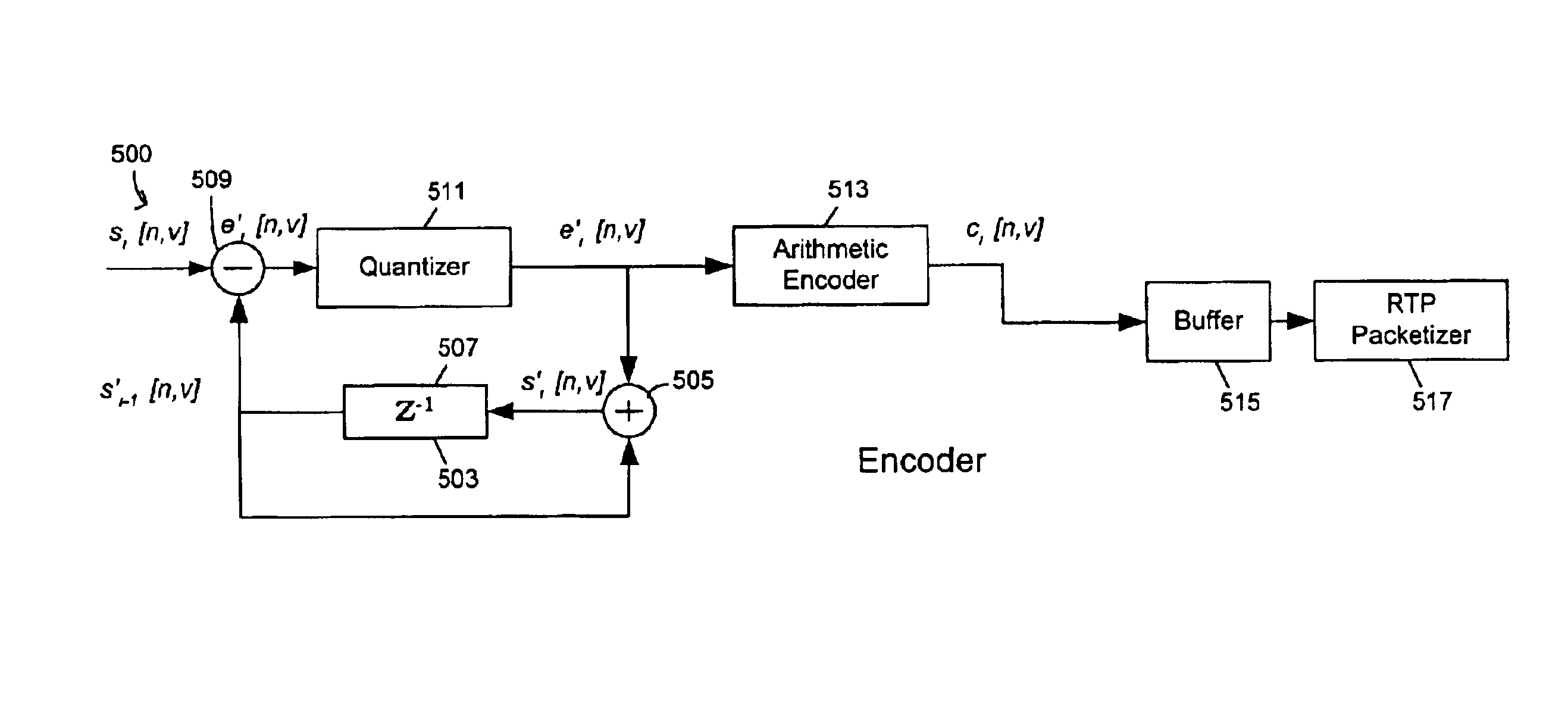
A 3-D wireframe model expressed in terms of nodes and vertices receives a 3-D video or like signal representative of a scene expressed in terms of a reference model, I frames and P frames. A DPCM coder takes advantage of the temporal correlation of the displacement of each vertex along every axis in the 3-D space. The 3-D signal is a set of non-zero displacements of all vertices and all nodes (sl[n, v]) at time tl. The decoded set (animation frame) of the previous instance is used as the predicted value (si-l[n, v]). The prediction error el[n, v], i.e. the difference between the current displacement set and the predicted one, is computed and quantised (el[n, v]). Finally, the quantised samples are entropy coded (ci[n, v]) using an adaptive arithmetic coding algorithm to handle the unknown data statistics. The predictive scheme described above prevents quantization error accumulation. A DPCM decoder first decodes arithmetically the received samples (‘e’ [n, v]) and computers the decoded samples (si′ [n, v]).
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
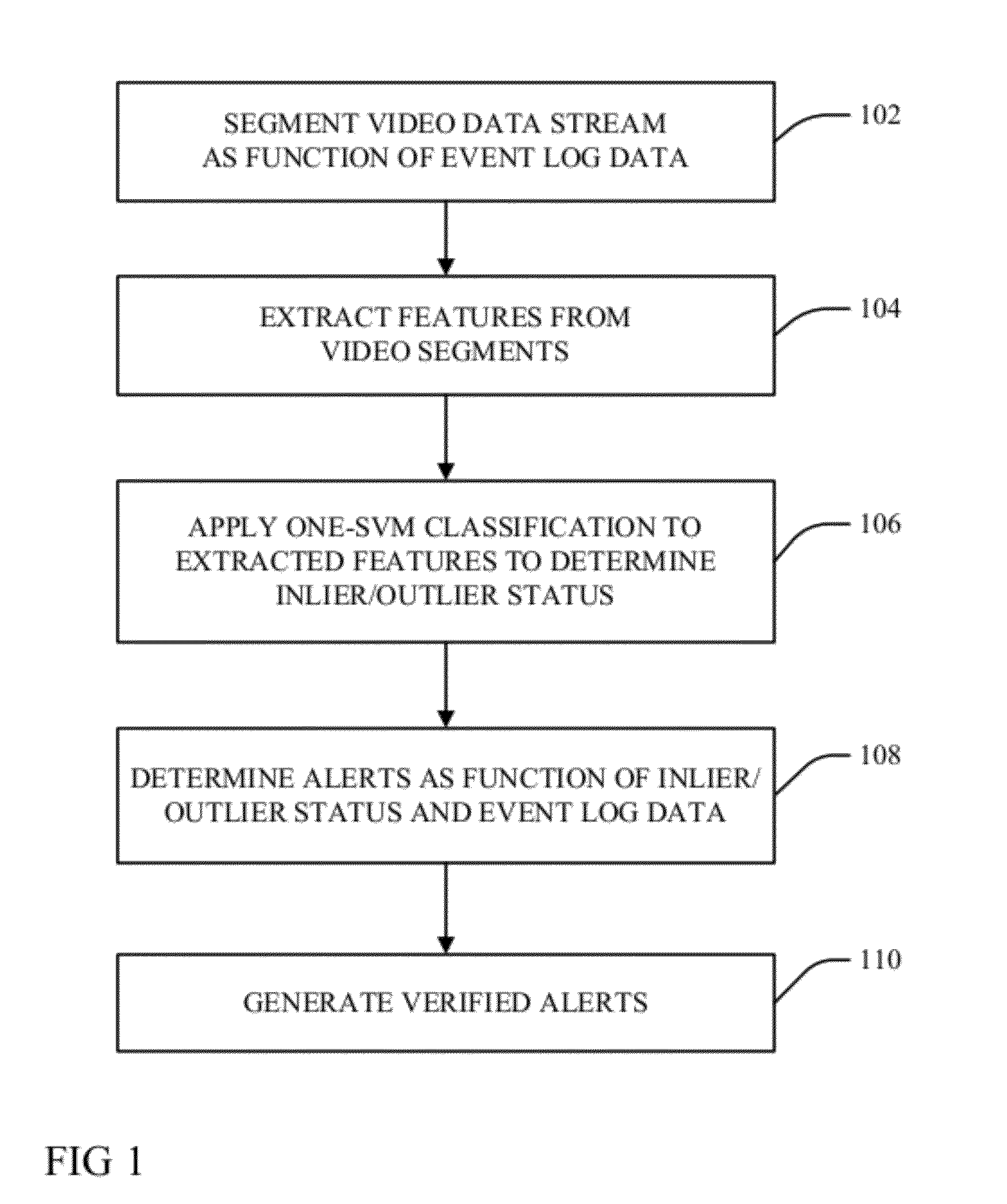
Activity determination as function of transaction log
ActiveUS20120075450A1Character and pattern recognitionColor television detailsHuman behaviorImaging analysis
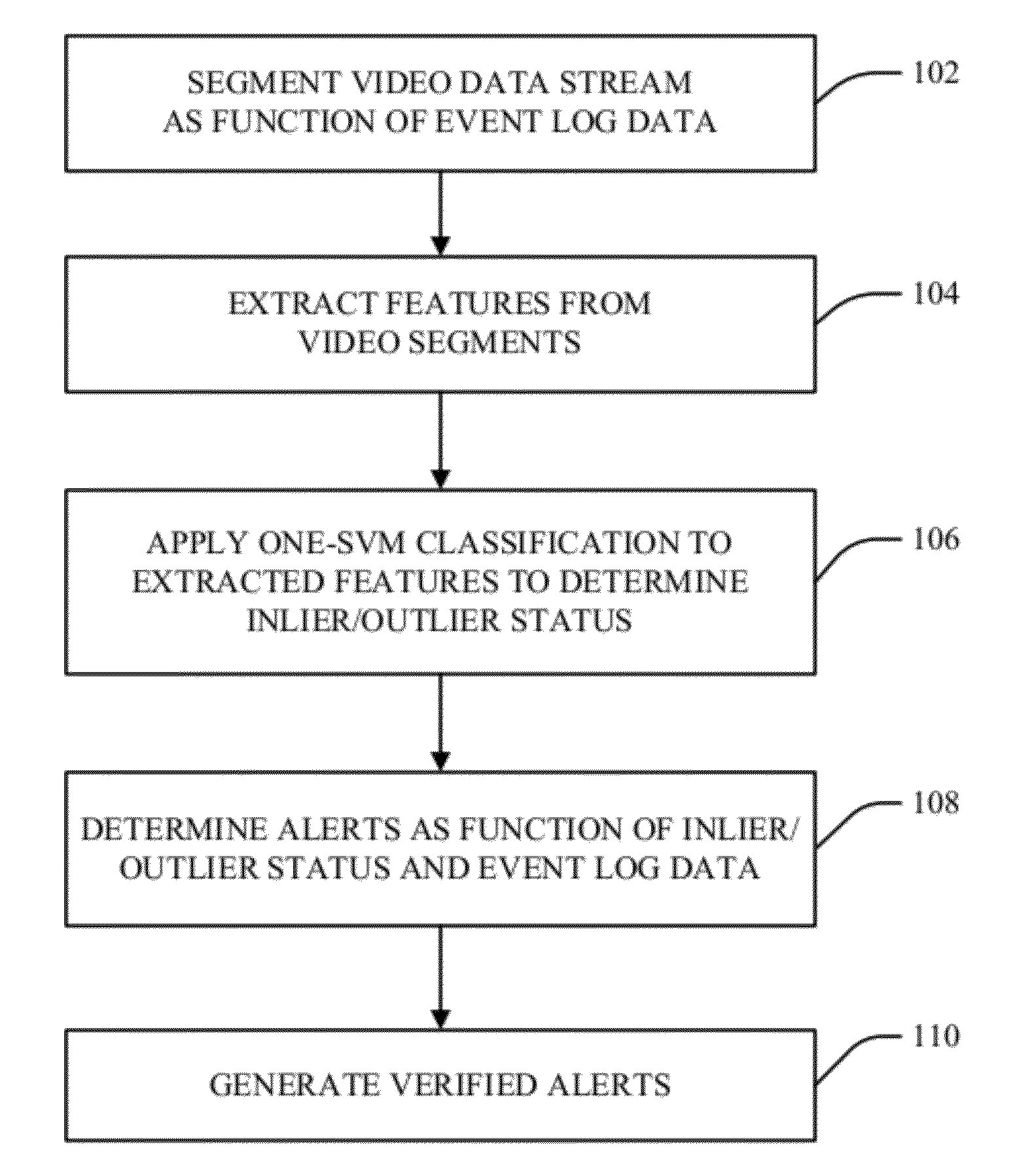
Human behavior alerts are determined from a video stream through application of video analytics that parse a video stream into a plurality of segments, wherein each of the segments are either temporally related to at least one of a plurality of temporally distinct transactions in an event data log; or they are each associated with a pseudo transaction marker if not temporally related to at least one of the temporally distinct transactions and an image analysis indicates a temporal correlation with at least one of the distinct transactions is expected. Visual image features are extracted from the segments and one-SVM classification is performed on the extracted features to categorize segments into inliers or outliers relative to a threshold boundary. Event of concern alerts are issued with respect to the inlier segments associated with the associated pseudo transaction marker.
Owner:SERVICENOW INC +1
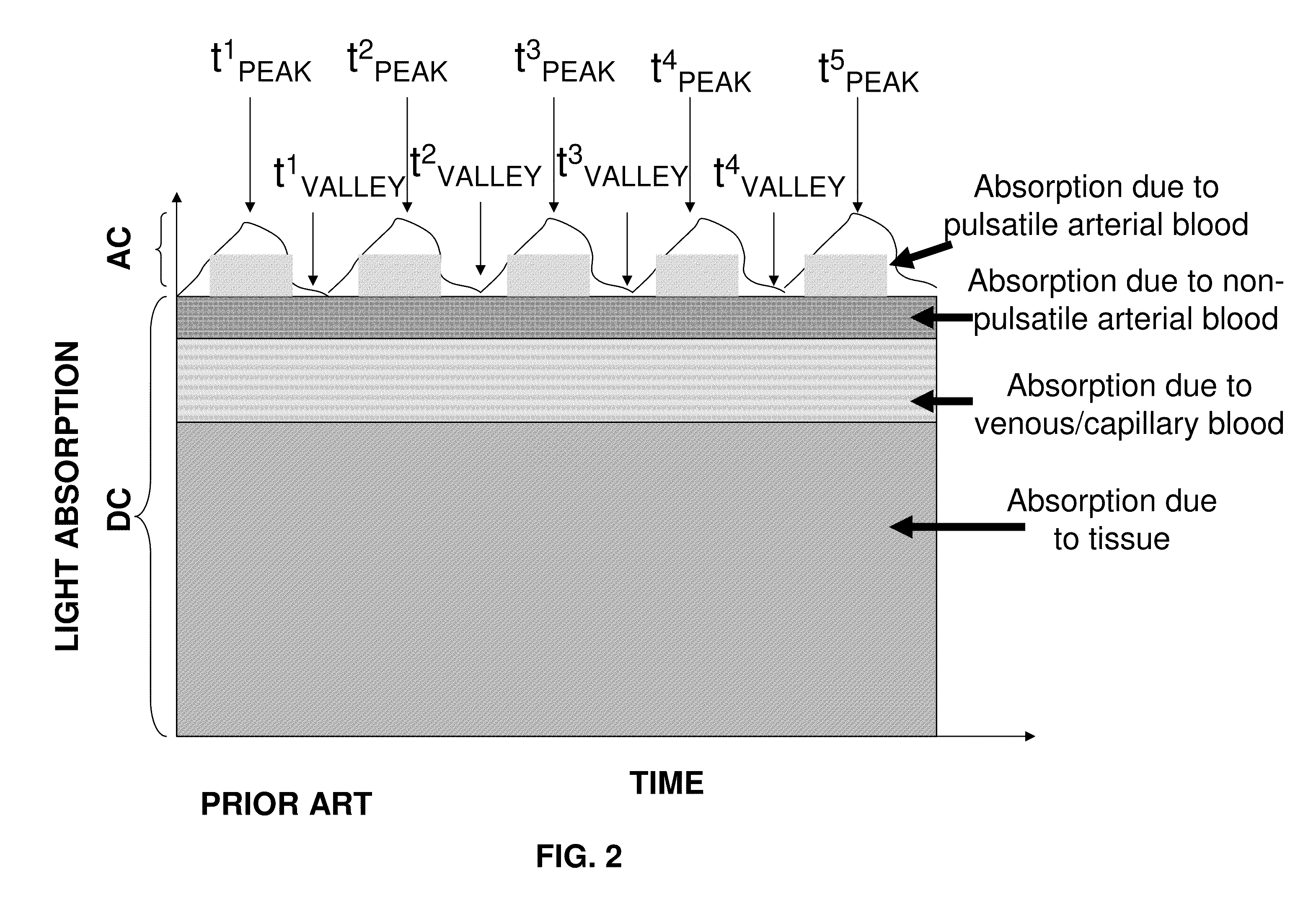
Photoplethysmography device and method
InactiveUS20110082355A1Accurate descriptionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAnalytePulse parameter
A system and method for measuring one or more light-absorption related blood analyte concentration parameters of a mammalian subject, is disclosed. In some embodiments, the system comprises: a) a photoplethysmography (PPG) device configured to effect a PPG measurement by illuminating skin of the subject with at least two distinct wavelengths of light and determining relative absorbance at each of the wavelengths; b) a dynamic light scattering measurement (DLS) device configured to effect a DLS measurement of the subject to rheologically measure a pulse parameter of the subject; and c) electronic circuitry configured to: i) temporally correlating the results of the PPG and DLS measurements; and ii) accordance with the temporal correlation between the PPG and DLS measurements, assessing value(s) of the one or more light-absorption related blood analyte concentration parameter(s).
Owner:OXITONE MEDICAL
Method of controlling a communications link
ActiveUS20040027994A1Limited feedback capacityQuantity minimizationFrequency-division multiplex detailsWireless commuication servicesTelecommunications linkControl communications
The present invention is directed to a method of controlling a communications link and apparatus configured to perform this method. This invention is particularly related to but in no way limited to MIMO (multiple inputs multiple outputs) wireless communications systems. The method comprises the steps of determining at the receiver the quality of the communications link and based on this, selecting a group of transmission parameters and an element from this group. These selections are then communicated to the transmitter. The transmission parameter may be the transmission configuration such as the modulation and coding scheme. The invention minimises the required feedback signalling from the receiver to the transmitter by exploiting temporal correlation of the parameter being controlled, whilst allowing rapid selection of the parameter.
Owner:APPLE INC
System and method to create a collaborative web-based multimedia layered platform
InactiveUS7933956B2Multimedia data browsing/visualisationMultiple digital computer combinationsFile descriptorApplication software
Owner:SIMULAT
Electronic medical information system, electronic medical information programs, and computer-readable recording media for storing the electronic medical information
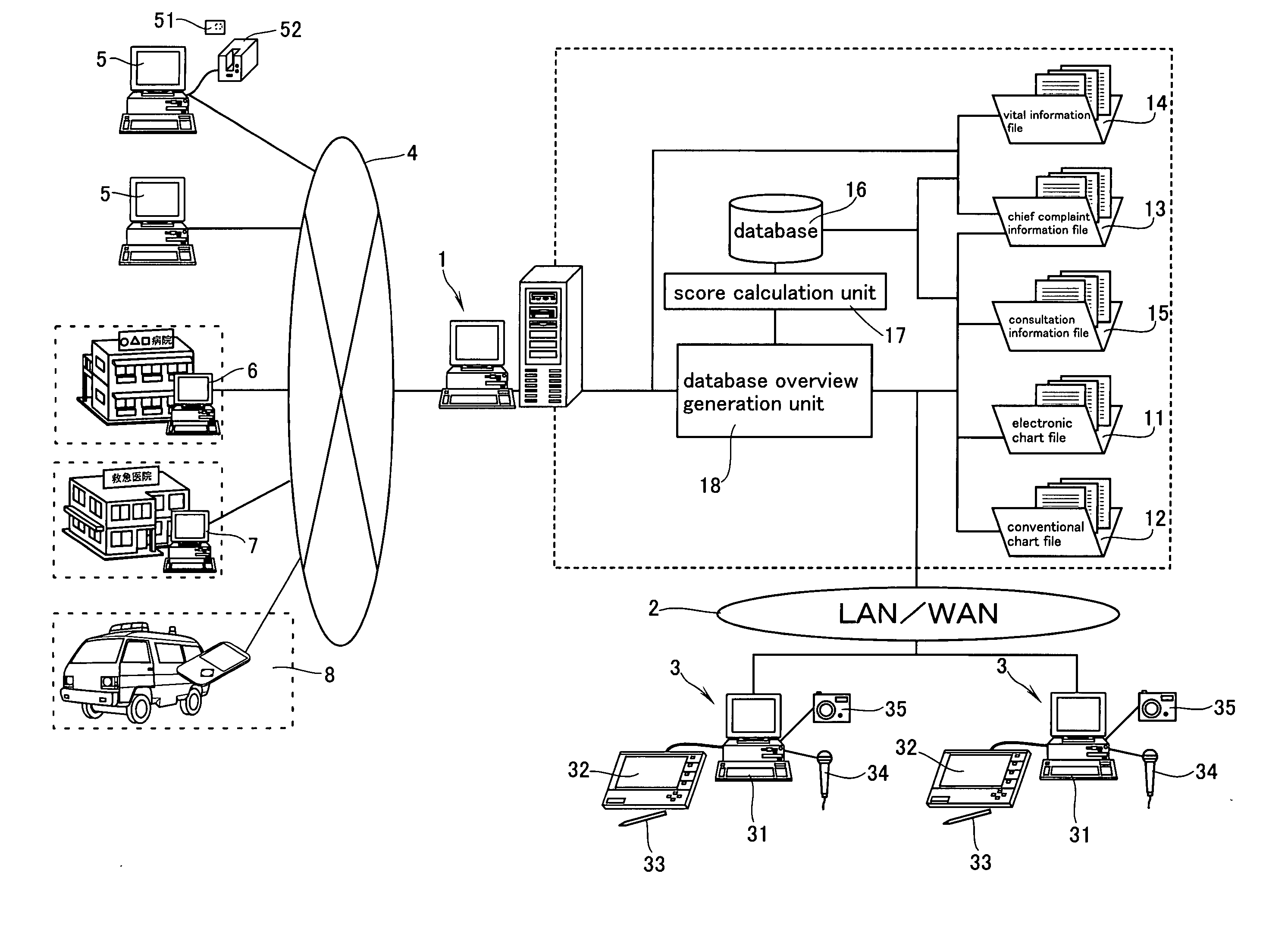
InactiveUS20070106535A1Quick medical servicePreventing medical errorLocal control/monitoringHealth-index calculationTemporal correlationComputer science
Problem The problem is to facilitate viewing of temporal correlation between patient's chief complaint and doctor's interview results associated with the patient's chief complaint. Means of Solution The temporal correlation can be viewed by providing an electronic medical information system equipped with a control server comprising an input means for inputting, among the information written on the chart, the patient's chief complaint information into a chief complaint information file and for inputting the doctor's consultation information associated with the patient's chief complaint information into a consultation information file; an accumulation means for accumulating the chief complaint information and consultation information; a calculation means for scoring, with respect to each date of consultation, the latest chief complaint information and consultation information input by the input means, and the past chief complaint information and consultation information accumulated by the accumulation means, respectively; a generation means for automatically generating, based on the scores, a list by which the temporal variation of the chief complaint information and consultation information can be viewed.
Owner:PROACTIVE LIFETIME HEALTH
Apparatus and method for event correlation and problem reporting
InactiveUS6868367B2Effective monitoringImprove efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceLogical operation testingProblem identificationAmbiguity
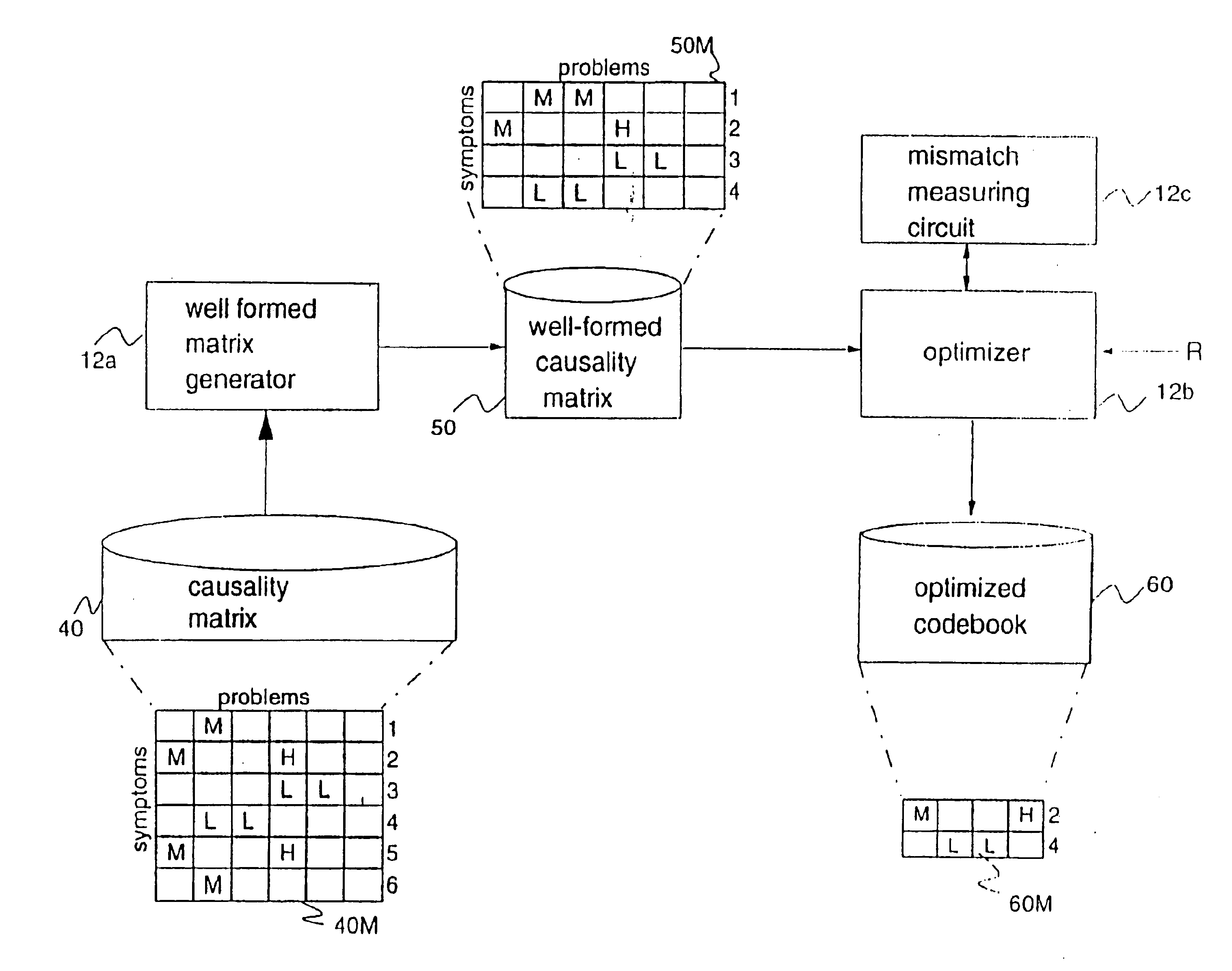
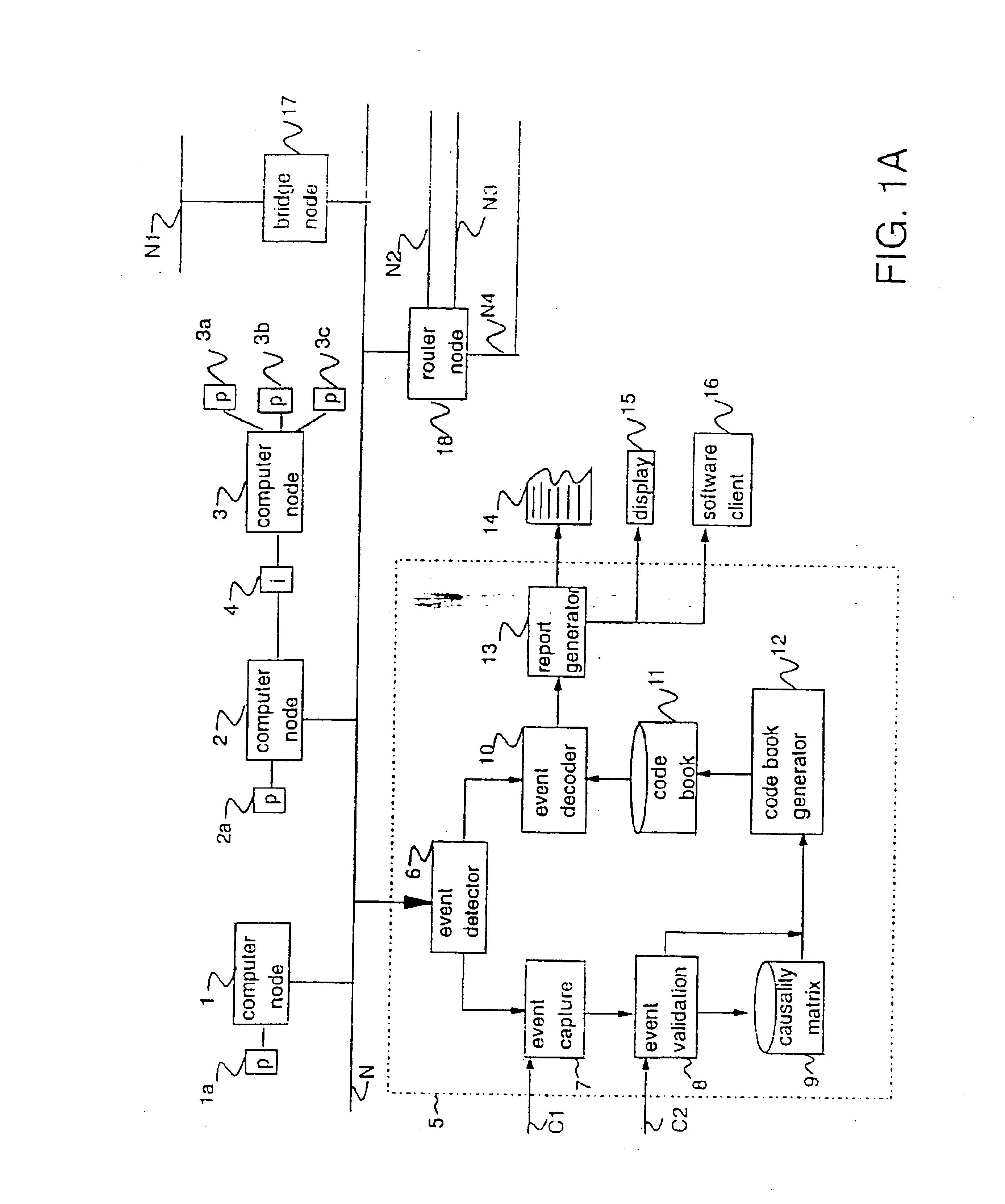
An apparatus and method is provided for efficiently determining the source of problems in a complex system based on observable events. By splitting the problem identification process into two separate activities of (1) generating efficient codes for problem identification and (2) decoding the problems at runtime, the efficiency of the problem identification process is significantly increased. Various embodiments of the invention contemplate creating a causality matrix which relates observable symptoms to likely problems in the system, reducing the causality matrix into a minimal codebook by eliminating redundant or unnecessary information, monitoring the observable symptoms, and decoding problems by comparing the observable symptoms against the minimal codebook using various best-fit approaches. The minimal codebook also identifies those observable symptoms for which the greatest benefit will be gained if they were monitored as compared to others.By defining a distance measure between symptoms and codes in the codebook, the invention can tolerate a loss of symptoms or spurious symptoms without failure. Changing the radius of the codebook allows the ambiguity of problem identification to be adjusted easily. The invention also allows probabilistic and temporal correlations to be monitored. Due to the degree of data reduction prior to runtime, extremely large and complex systems involving many observable events can be efficiently monitored with much smaller computing resources than would otherwise be possible.
Owner:VMWARE INC
System and method for improved real-time cine imaging
ActiveUS20090263001A1Reduce noiseRedundancy is limitedImage enhancementImage analysisCine imagingNoise reduction
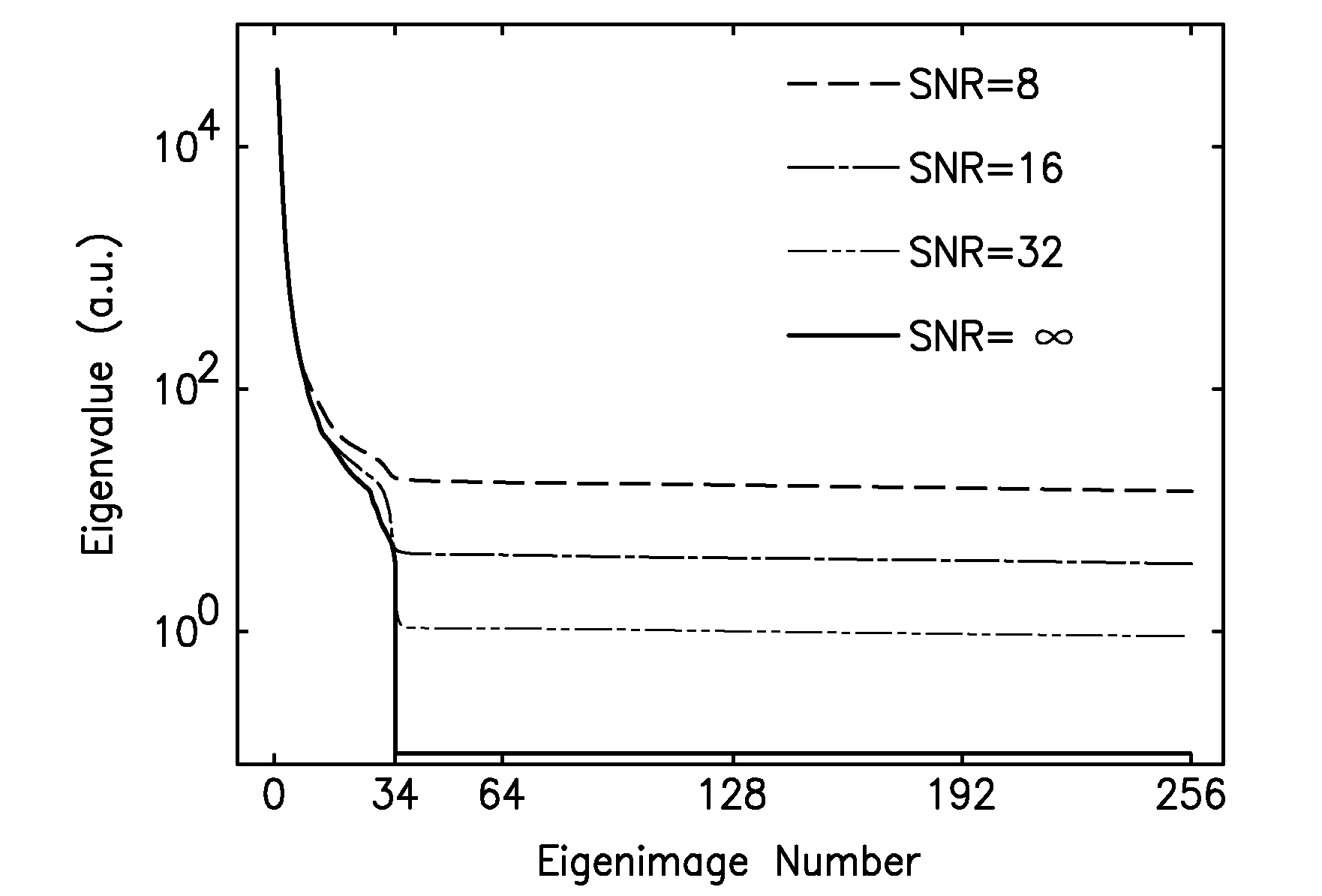
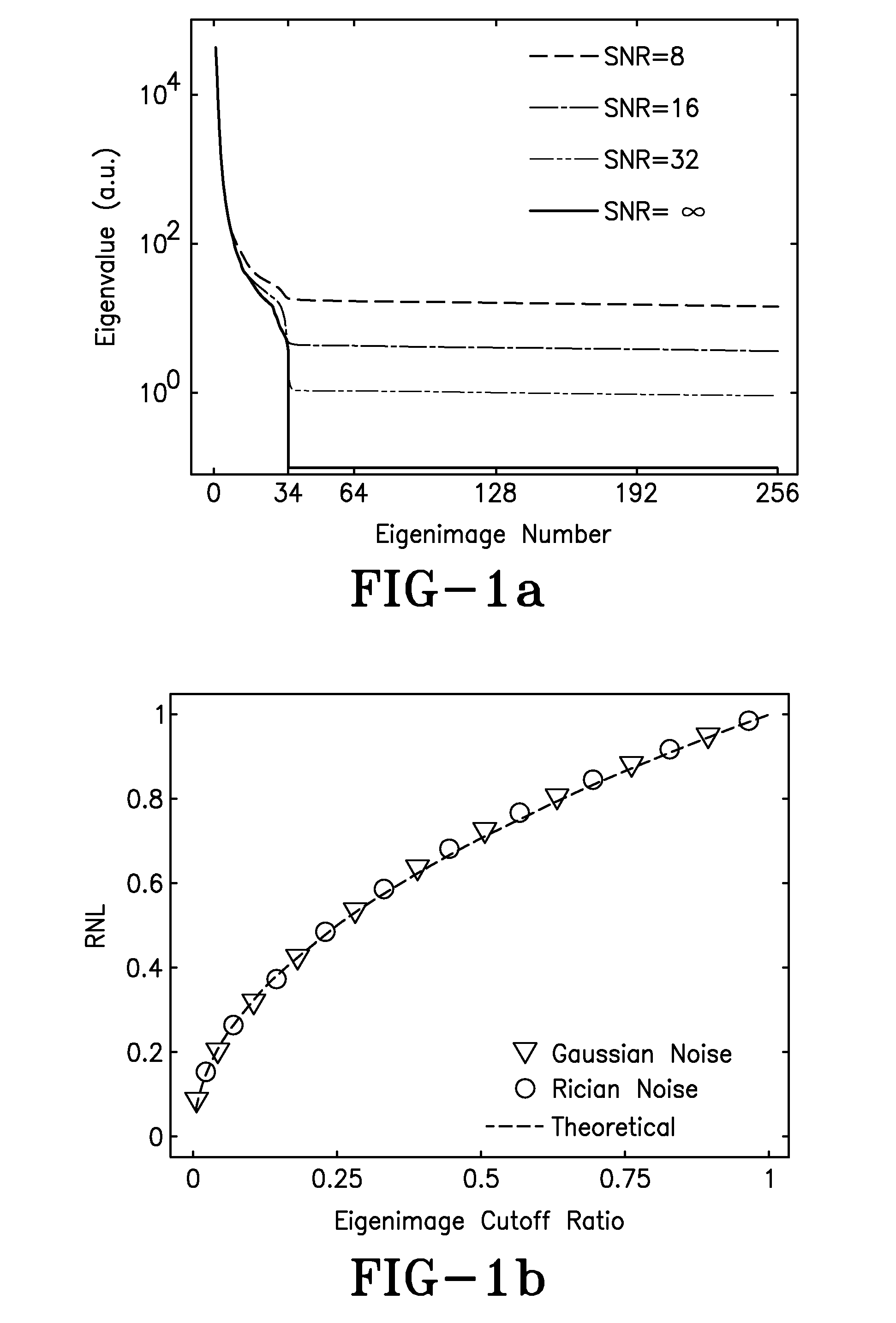
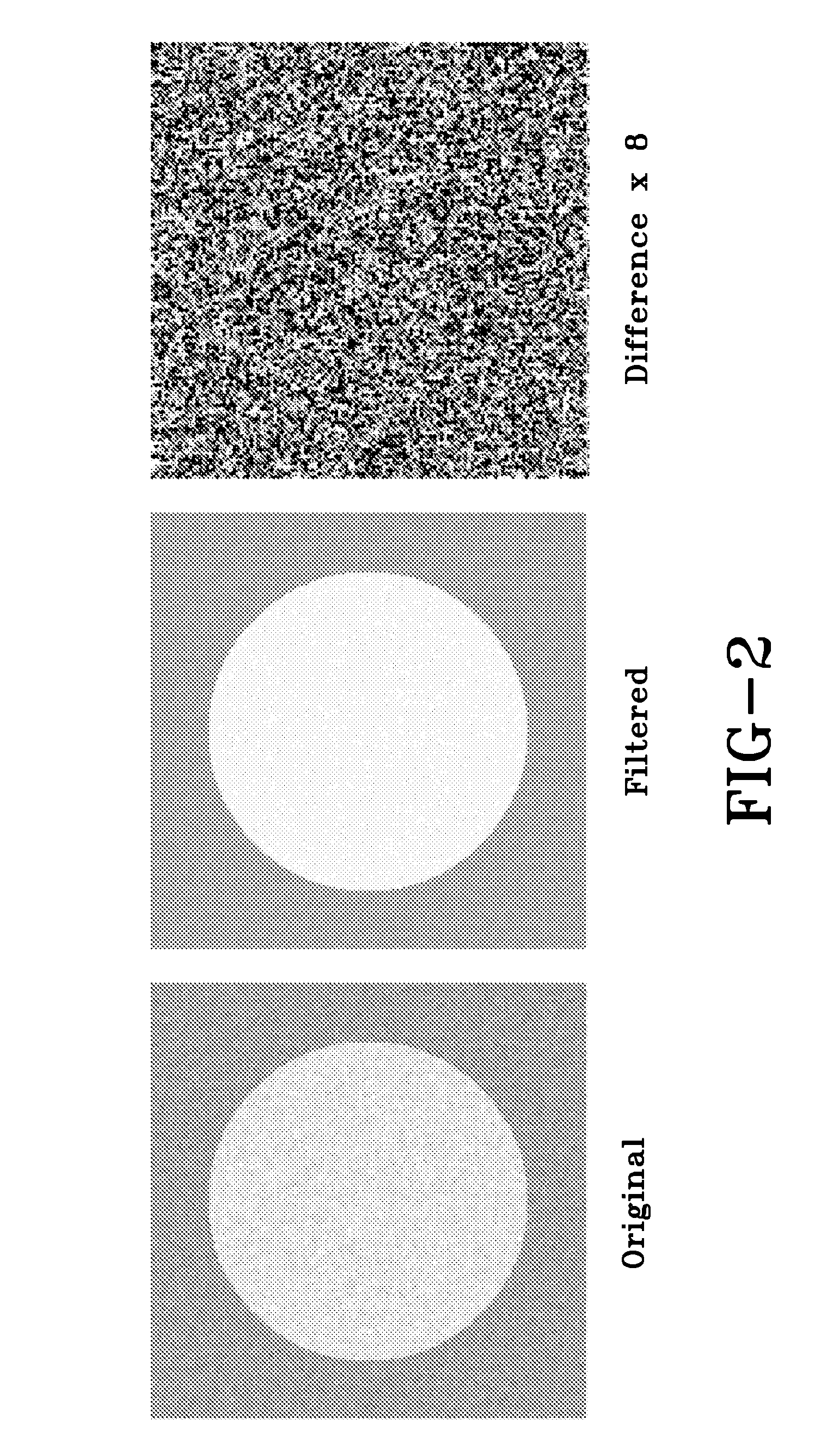
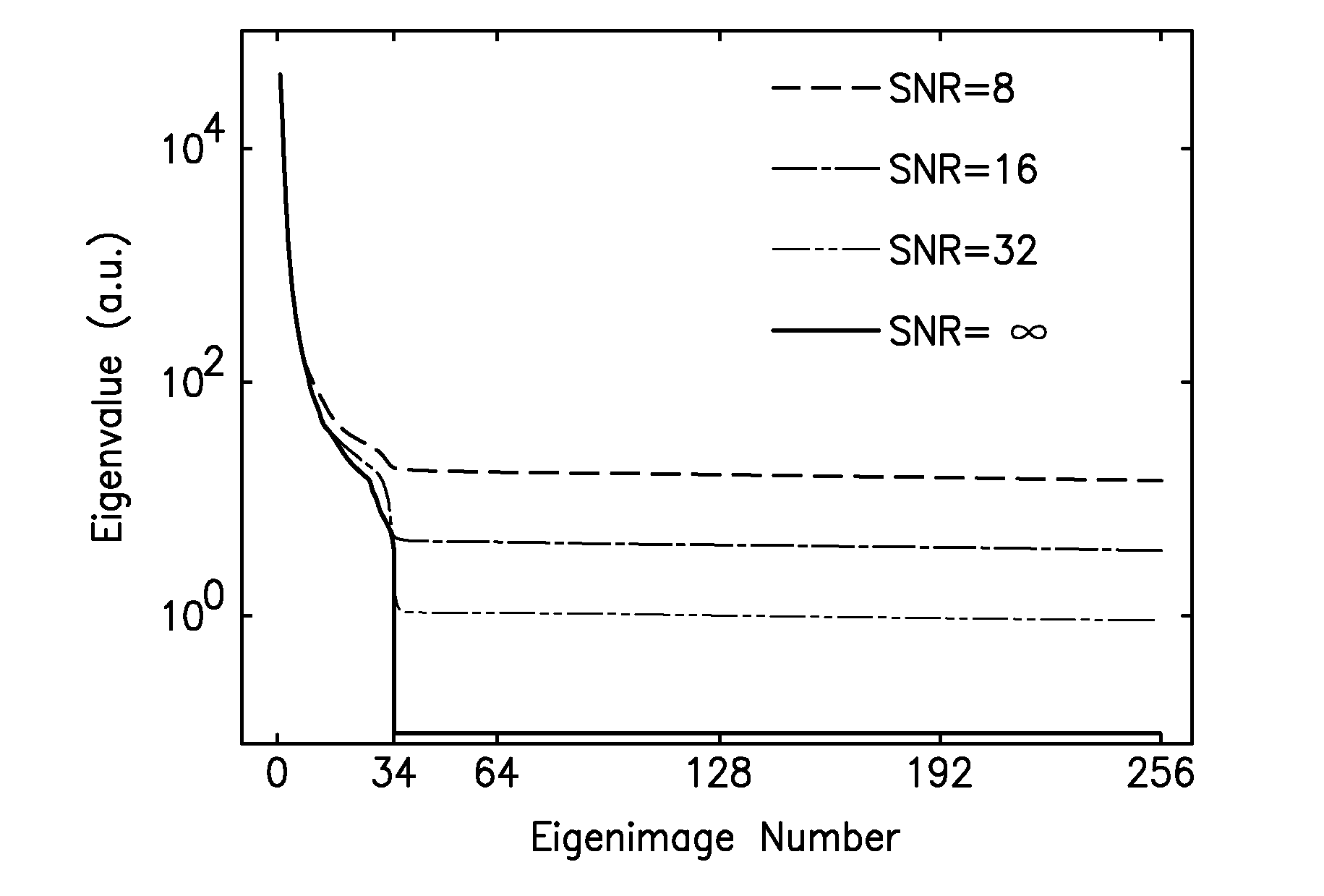
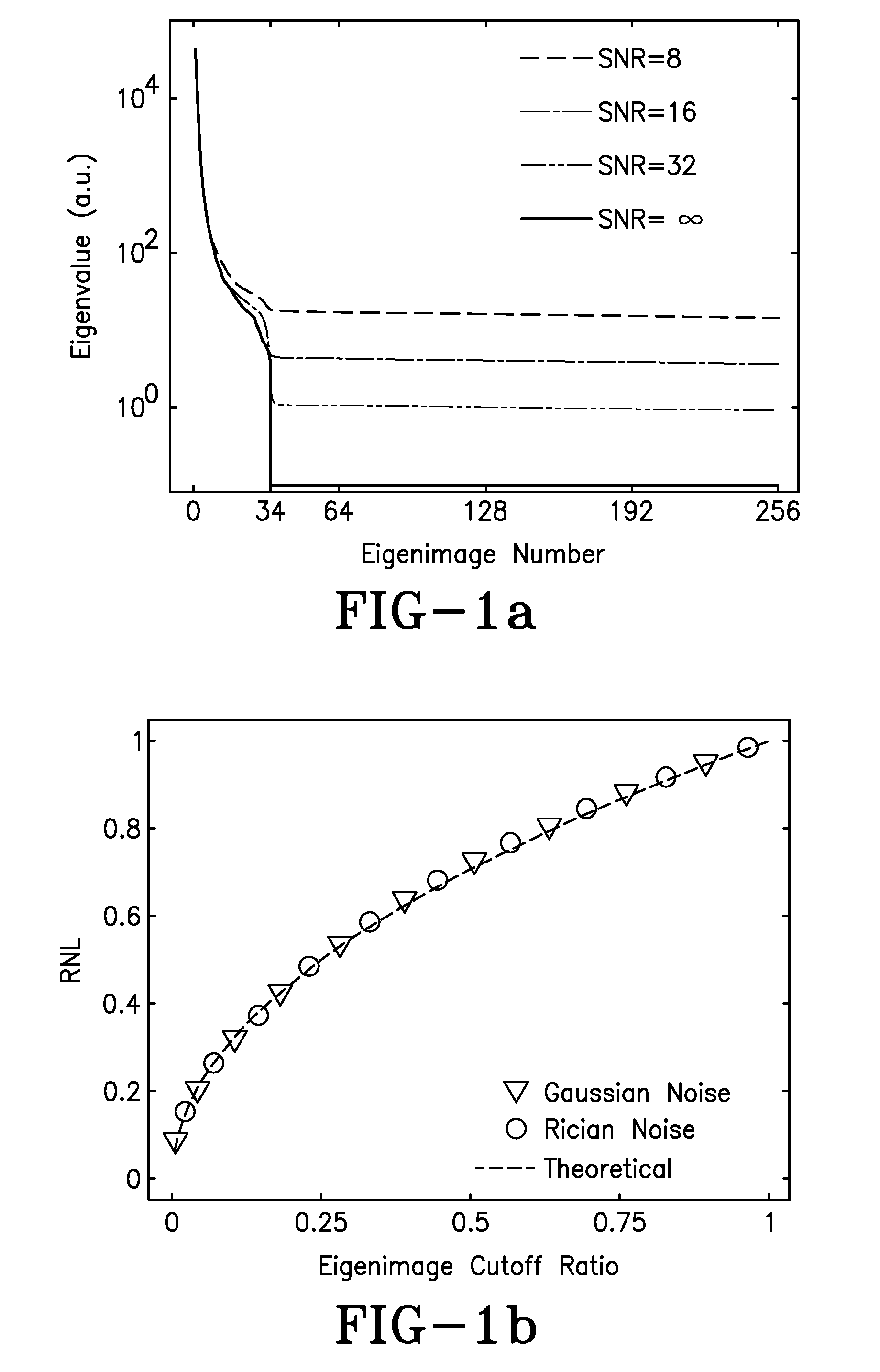
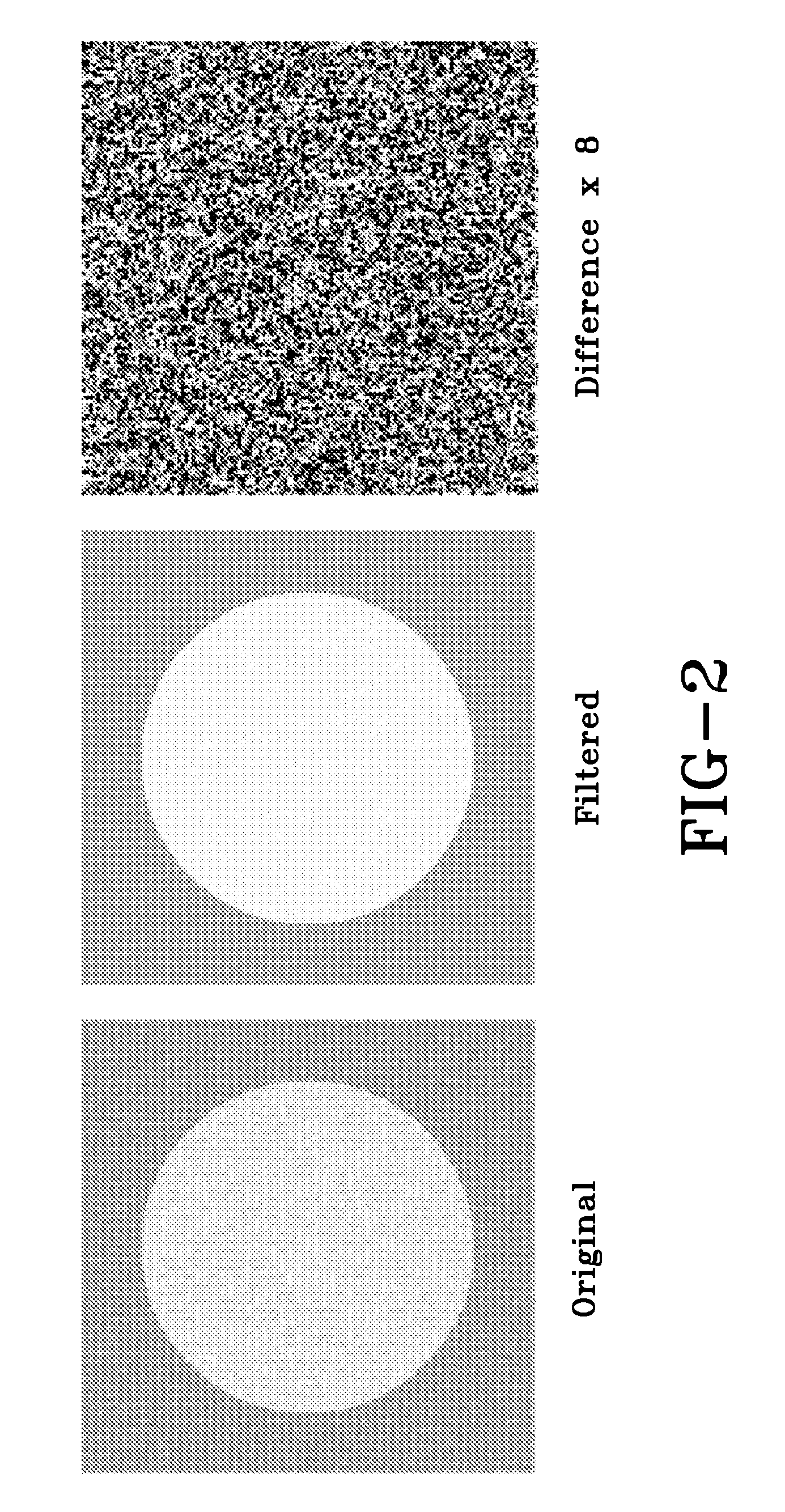
A cine imaging filter and method of use that includes a denoising image-filter based on the Karhunen-Loeve transform along the temporal direction to take advantage of the high temporal correlation among images. The cine imaging filter may further include the application of a simple formula describing the quantitative noise reduction capabilities of the KLT filter as a function of eigenimage cutoff. Additionally, the filter may validate its accuracy in numerical simulation and in in-vivo real time cine images. Furthermore, exemplary embodiments of the cine imaging filter may employ a technique to automatically select the optimal eigenimage cutoff to maximize noise reduction with minimal effect on image information.
Owner:THE OHIO STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Trace source correlation in a data processing apparatus
ActiveUS20050033553A1Efficiently enableAvoid the needTime indicationSynchronous motors for clocksTimestampData stream
An integrated circuit is provided with multiple data processing components associated with respective sources which generate trace data streams. A reference timestamp generator is provided and the trace data streams are annotated such that they are output off-chip together with reference timestamp data. Outputting the reference timestamp data together with the trace data streams enables temporal correlation between points in different trace data streams by trace analysis tools.
Owner:ARM LTD
Feedback reduction for MIMO precoded system by exploiting channel correlation
ActiveUS8023457B2Special service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsPrecodingCommunications system
In a closed-loop wireless communication system, a codebook-based precoding feedback compression mechanism is provided to remove redundancy from the precoding feedback that is caused by channel correlation in time and frequency. Redundancy due to temporal correlation of the transmission channel is removed by sending precoding feedback only if there is a change in the precoder state for the channel to the receiver. Redundancy due to frequency correlation is removed by run length encoding the precoding feedback, thereby compressing the precoding feedback prior in the frequency domain. By compressing the precoding feedback, the average rate of precoder feedback is reduced.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Method and system for determining user location in a wireless communication network
InactiveUS7406116B2Maximize probabilityAccurate measurementData switching by path configurationRadio transmissionProbit modelRadio map
In a wireless communication network, the location of an addressable receiver relative to the locations of a plurality of addressable sources of electromagnetic radiation is found using probabilistic models of the signal strength measured at the addressable receiver. The inventive method provides location determination on a finer spatial scale than was heretofore available. A region of interest is calibrated via a discrete-space radio map storing probability distributions of received signal strength at the measurement locations. The stored probability distributions are compensated for temporal variability and biases, such as through temporal correlations of the sampled received signal strength. A measurement of the signal strength at the addressable receiver from each of the plurality of addressable sources is used in conjunction with the discrete-space radio map to identify one of the coordinates thereof that maximizes the conditional probability P(xls), where x is the radio map location and s is a vector of measured signal strengths.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
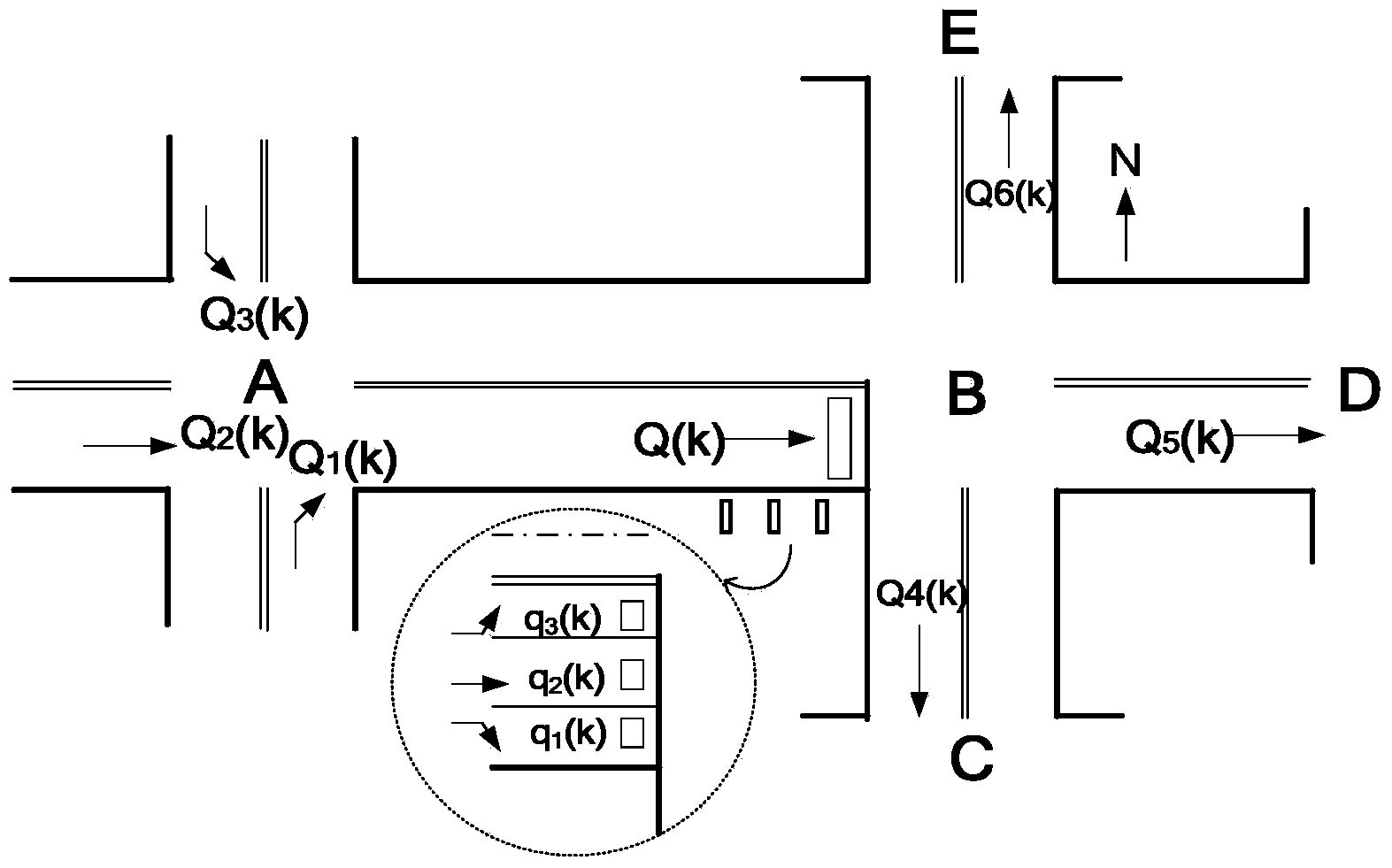
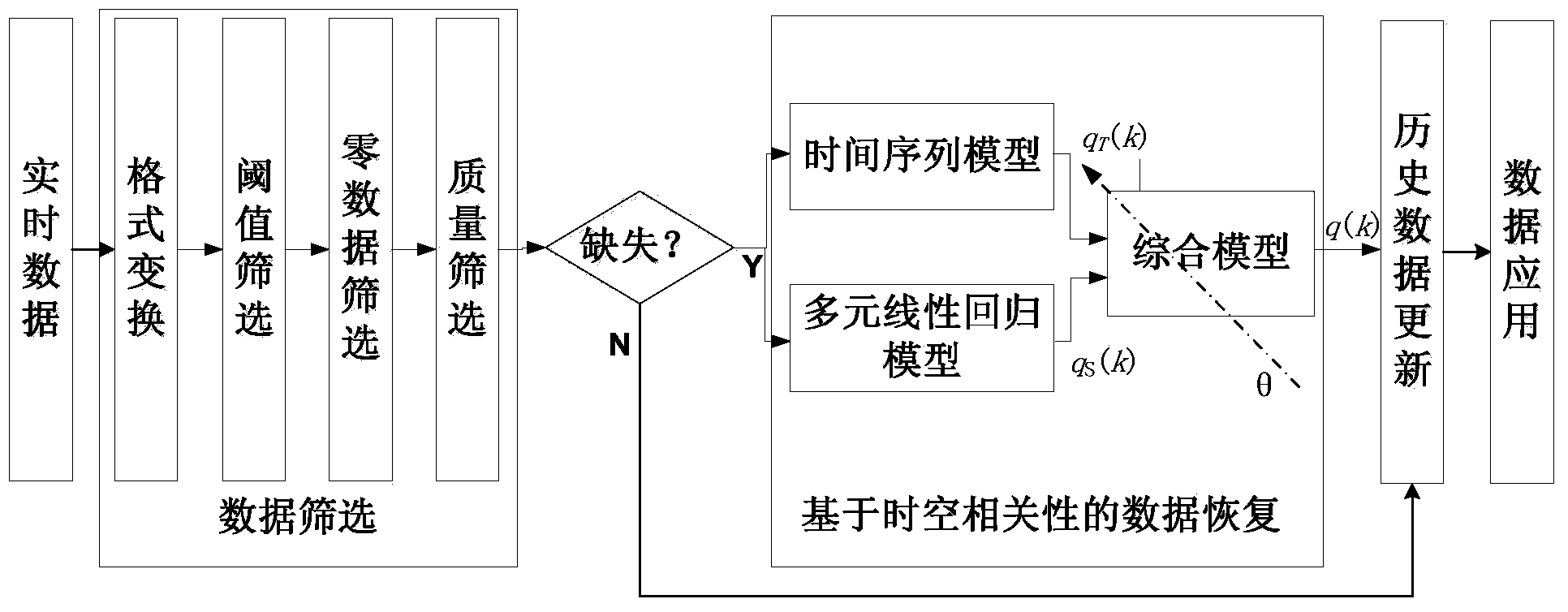
Traffic flow data recovery method based on space-time correlation
InactiveCN103971520AAccuracy is not lostMeet the requirements of real-time processingDetection of traffic movementSpecial data processing applicationsScreening methodLinear regression
The invention discloses a traffic flow data recovery method based on space-time correlation. The method includes a front-stage traffic data conversion and abnormal data screening method and a follow-up traffic flow data recovery method. The data screening method relates to a threshold value screening method, a zero data screening method and a quality screening method according to the abnormal condition of actual traffic flow data. According to time correlation and space correlation of traffic flow data, by the combination of a time sequence method and a multiple linear regression method, namely the data recovery method based on temporal correlation and spatial correlation, the comprehensive traffic flow data recovery method based on space-time correlation is designed. The method is simple and quick, the real-time processing requirement can be met, and an acquired result is high in accuracy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
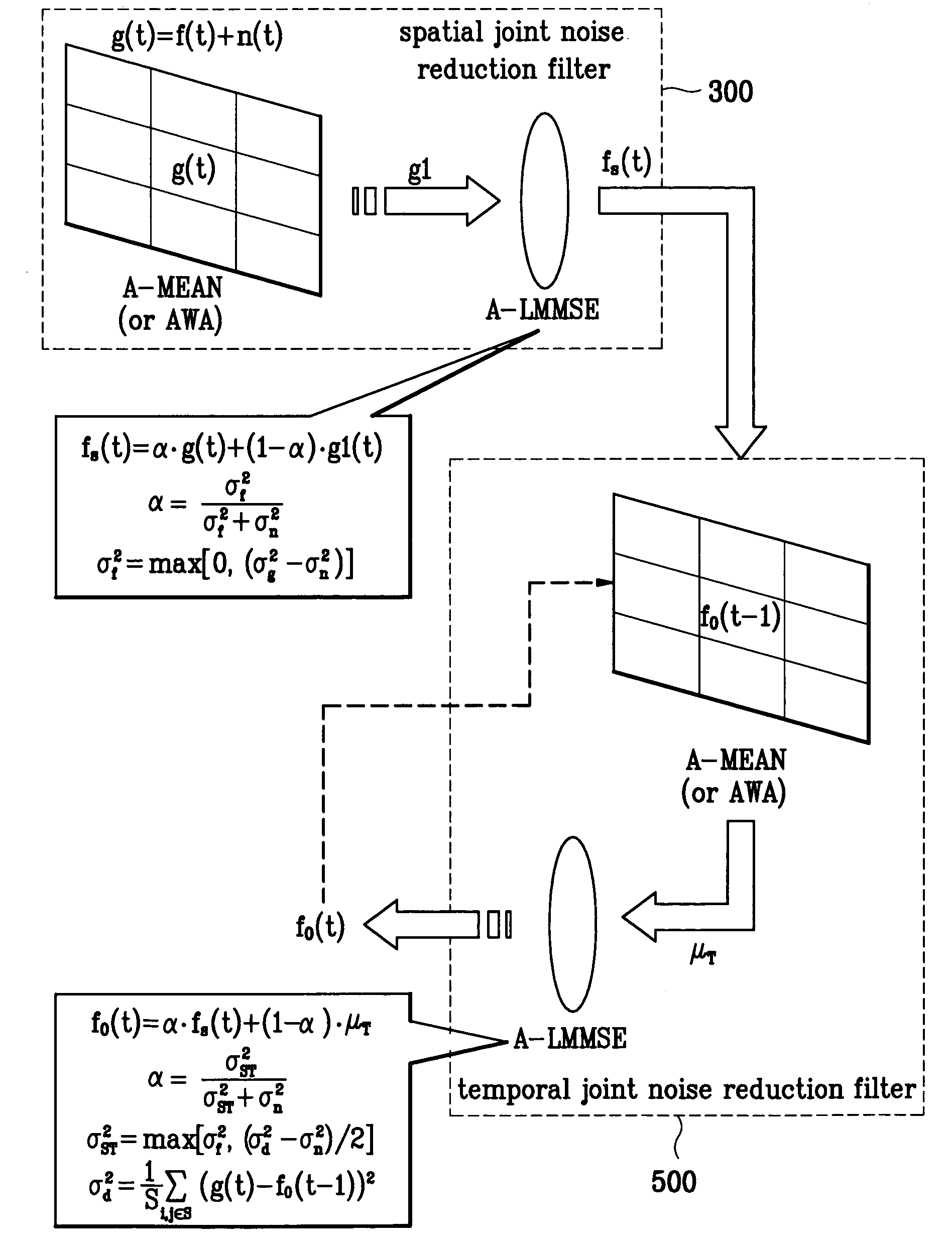
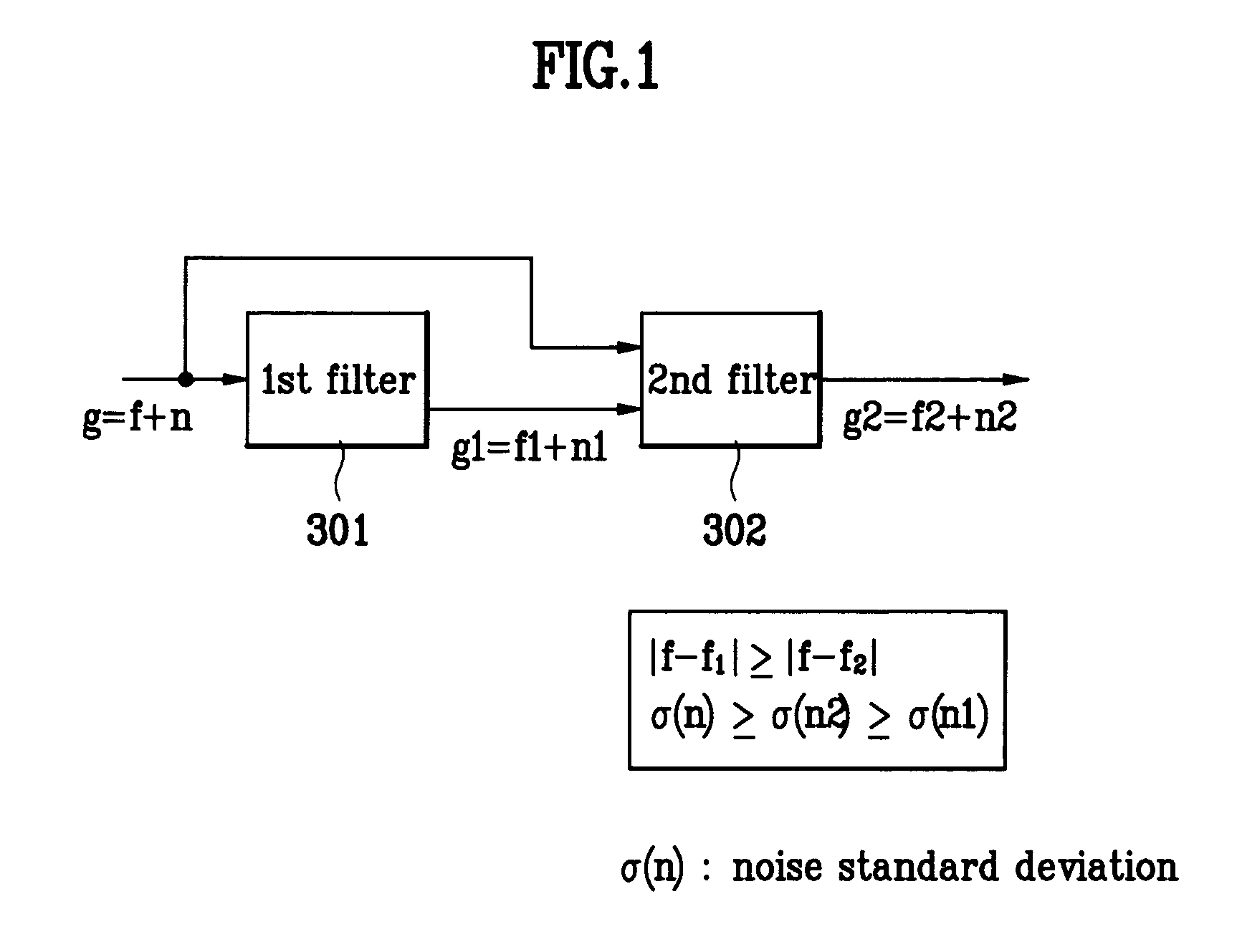
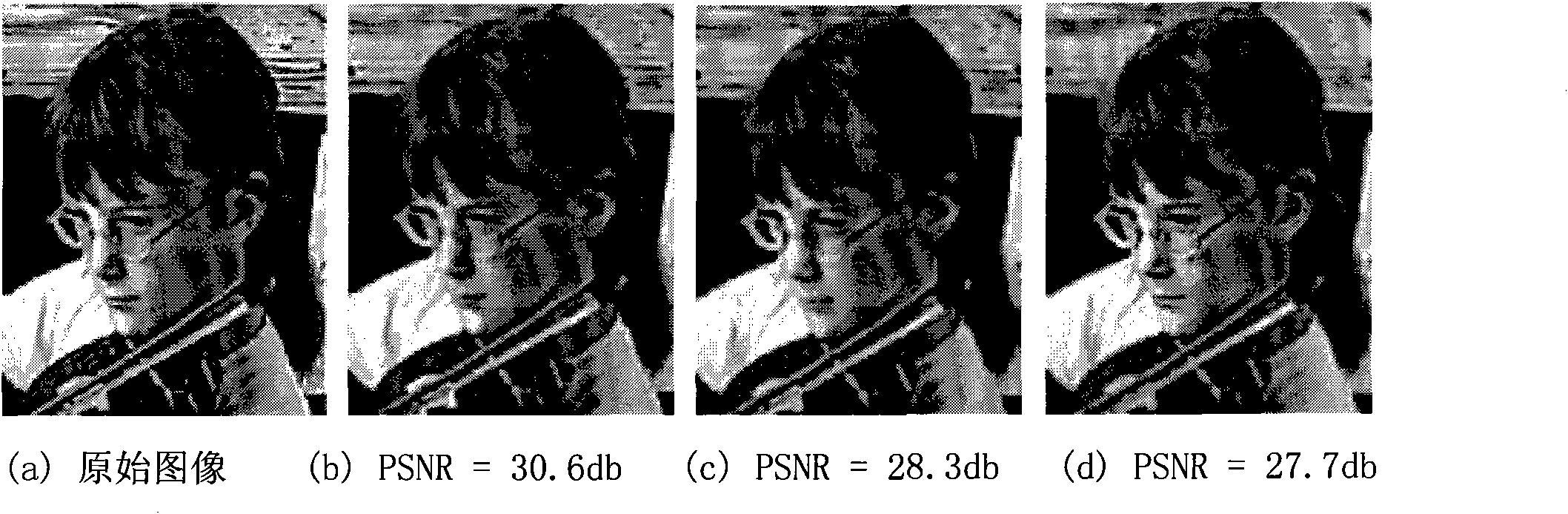
Spatio-temporal joint filter for noise reduction
InactiveUS6999634B2Reduce noiseEliminates temporal flickerImage enhancementTelevision system detailsCompensation effectEngineering
A spatio-temporal joint filter and a spatial joint filter for noise reduction are disclosed. The spatio-temporal joint filter includes a spatial joint filter including the first and second sub filters having different characteristics and includes a temporal joint filter. When the present invention is adequately used, an edge / detail region of an image is well preserved, an aggressive noise reduction is performed on a flat region, and the temporal flicker problems are eliminated. Additionally, it has an intrinsic motion compensation effect by using the spatio-temporal correlation between the adjacent frames.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method, device and system for regional division/coding of image
InactiveCN101882316AQuality improvementImprove subjective qualityImage enhancementImage analysisSpatial correlationMotion vector
The invention discloses a method, a device and a system for regional division / coding of an image. By extracting a motion vector of the image in a video sequence, judging the image as an interest region or a non-interest region according to the complexity of the motion vector, and performing further accurate judgment on the image after regional division according to spatial correlation and temporal correlation of a macro block, the accurate division of a foreground region and a background region is performed on the image. A smaller quantization parameter is adopted for the interest region to improve the quality of a video, and a higher quantization parameter is adopted for the non-interest region to balance the overall bit consumption to be unchanged, and finally achieve the effect of improving the subjective quality of the video.
Owner:SHENZHEN TEMOBI SCI &TECH
Method and apparatus for estimation of channel temporal correlation and MIMO mode selection in LTE system
ActiveUS20130044610A1Improve structural propertiesMaintain good propertiesError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsEngineeringTemporal correlation
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for channel temporal correlation estimation and MIMO mode selection. An embodiment of the invention under LTE system utilizes SRS symbols for temporal correlation estimation and performs MIMO mode selection based on the said temporal correlation estimation.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
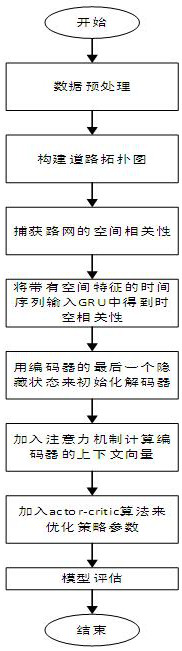
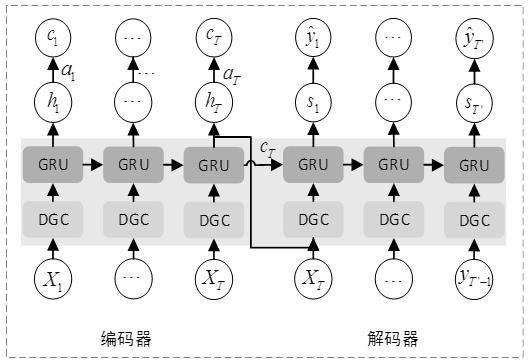
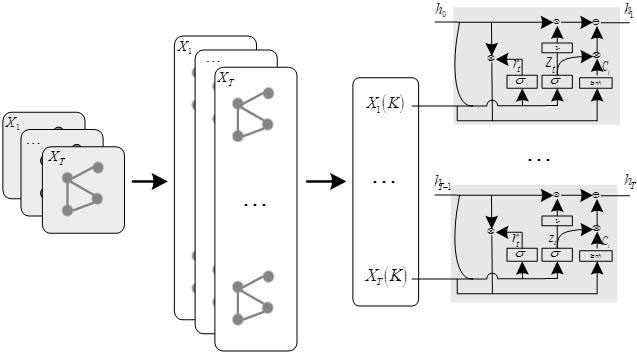
Traffic prediction method based on enhanced space-time diagram neural network
ActiveCN112241814AImprove forecast accuracyDetection of traffic movementForecastingTraffic predictionTopological graph
The invention provides a traffic prediction method based on an enhanced space-time diagram neural network, and the method comprises the steps: modeling the time correlation and spatial correlation ofa road network based on a traffic prediction framework from a sequence to a sequence model, and constructing a directed weighted graph for the whole road network according to the upstream and downstream relationship of the road network; spatial correlation of a road network is captured through a diffusion graph convolutional network, spatial correlation characteristics of the road network are extracted, a time sequence with the spatial correlation characteristics is input into a recurrent neural network to capture time correlation of the road network, and then a prediction result is optimizedin the decoding process by an actor-critic algorithm in reinforcement learning; regarding A road network relation topological graph captured by each time slice as an actor in an intelligent agent anda recurrent neural network as a random strategy of a next action selected by the actor, judging the action selected by the actor by using critic, feeding back a dominance function, and enabling the actor to update strategy parameters according to the fed-back dominance function, so that prediction precision is greatly improved compared with a traditional method.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Traffic prediction method based on adaptive spatial self-attention map convolution
The invention discloses a traffic prediction method based on adaptive spatial self-attention map convolution, belongs to the traffic field and the deep learning field, and provides an adaptive spatial self-attention graph convolution network (ASSAGCN) for traffic prediction. The ASSAGCN is formed by stacking two residual error blocks. Each residual block is composed of a graph convolution module (GCN), a multi-head spatial self-attention module (MHSSA), a gating fusion module (GF) and a multi-receptive-field cavity causal convolution module (MRDCC), Wherein the GCN performs modeling on local spatial correlation of a road network based on connectivity; the MHSSA is used for capturing implicit spatial correlation of a road network and aggregating information of each node globally; the GF fuses the output of the GCN and the output of the MHSSA; and the MRDCC is used to model temporal correlation. An input layer adopts a simple full-connection layer to map input to a high-dimensional space to improve the expression ability of the model, and an output layer adopts two 1 * 1 convolutional layers. The method can capture the potential spatial correlation in the road network, and adapts to the dynamic change of the road network structure.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
System and method for improved real-time cine imaging
ActiveUS8208709B2Reduce noiseRedundancy is limitedImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionCine imaging
A cine imaging filter and method of use that includes a denoising image-filter based on the Karhunen-Loeve transform along the temporal direction to take advantage of the high temporal correlation among images. The cine imaging filter may further include the application of a simple formula describing the quantitative noise reduction capabilities of the KLT filter as a function of eigenimage cutoff. Additionally, the filter may validate its accuracy in numerical simulation and in in-vivo real time cine images. Furthermore, exemplary embodiments of the cine imaging filter may employ a technique to automatically select the optimal eigenimage cutoff to maximize noise reduction with minimal effect on image information.
Owner:THE OHIO STATE UNIV RES FOUND
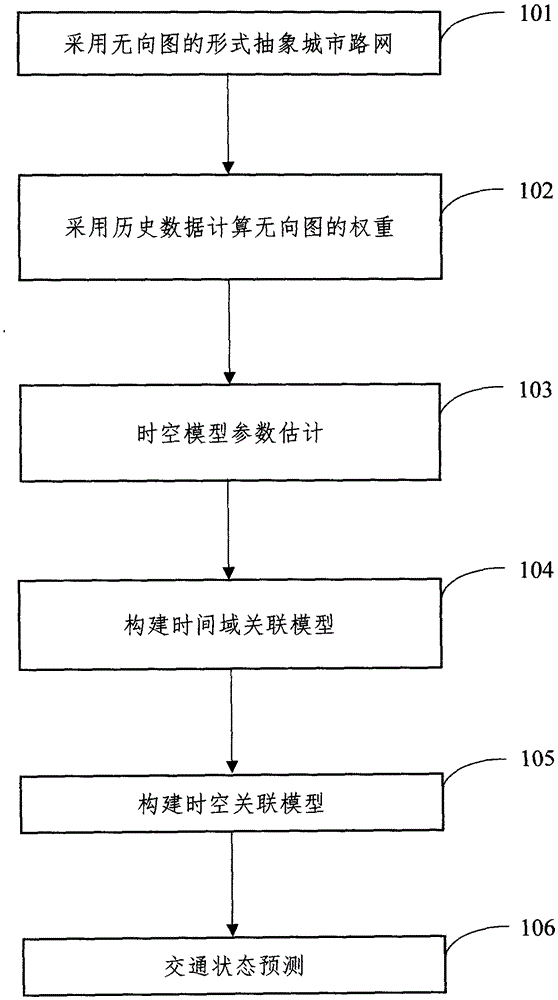
Urban road traffic condition prediction method based on spatial-temporal data
The invention discloses an urban road traffic condition prediction method based on spatial-temporal data. The method comprises the following steps: calculating the parameters of a spatial-temporal correlation model using historical traffic data; abstracting an urban road network in the form of undirected graph; calculating the weight of the undirected graph using historical data; building a time domain correlation model; building a spatial-temporal correlation model; and predicting the traffic condition of a road section through use of real-time traffic data and based on a time-space domain model. A more accurate urban road traffic condition prediction method is provided.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
Spatio-temporal speech enhancement technique based on generalized eigenvalue decomposition
InactiveUS20100076756A1Reduce computational complexityEliminate the effects ofSpeech recognitionEuclidean vectorSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
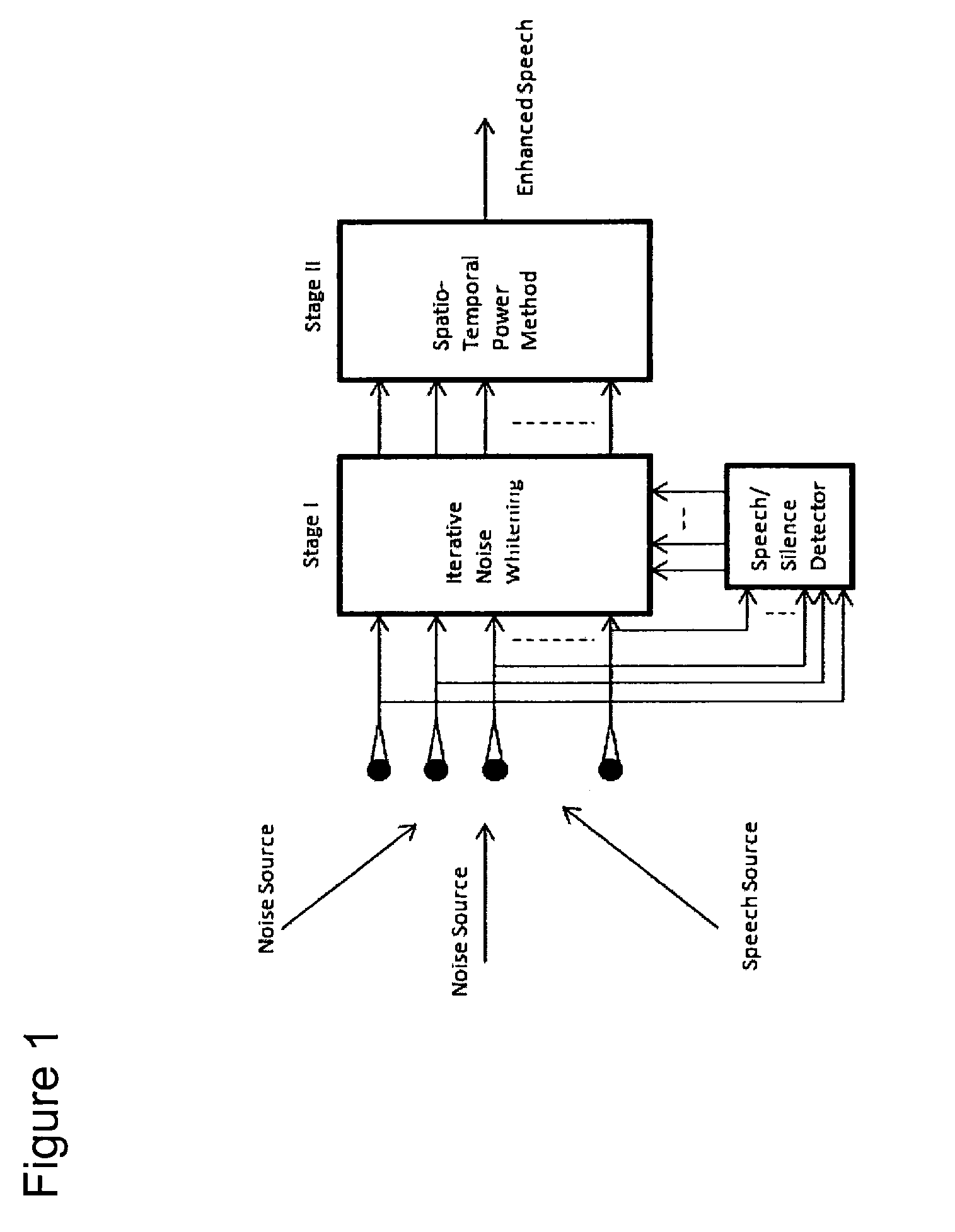
The present invention describes a speech enhancement method using microphone arrays and a new iterative technique for enhancing noisy speech signals under low signal-to-noise-ratio (SNR) environments. A first embodiment involves the processing of the observed noisy speech both in the spatial- and the temporal-domains to enhance the desired signal component speech and an iterative technique to compute the generalized eigenvectors of the multichannel data derived from the microphone array. The entire processing is done on the spatio-temporal correlation coefficient sequence of the observed data in order to avoid large matrix-vector multiplications. A further embodiment relates to a speech enhancement system that is composed of two stages. In the first stage, the noise component of the observed signal is whitened, and in the second stage a spatio-temporal power method is used to extract the most dominant speech component. In both the stages, the filters are adapted using the multichannel spatio-temporal correlation coefficients of the data and hence avoid large matrix vector multiplications.
Owner:SOUTHERN METHODIST UNIVERSITY
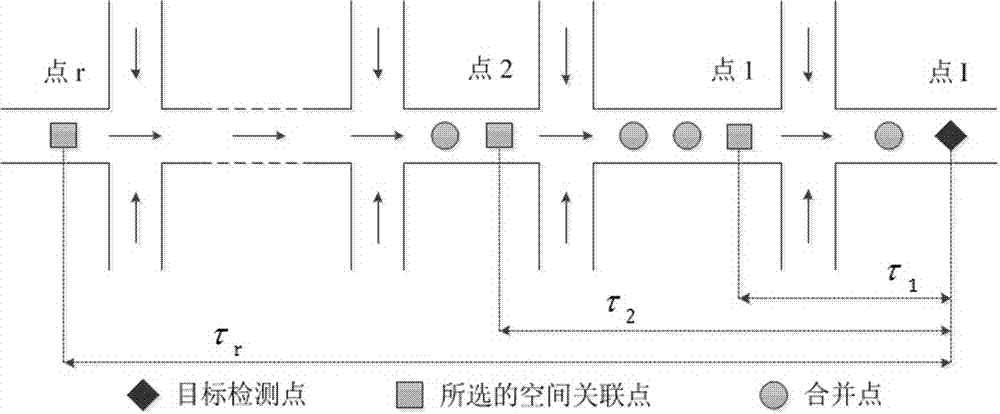
Short-time traffic flow prediction method considering spatial-temporal correlation
ActiveCN106971547AImprove accuracyOvercome the inadequacy of not being able to make full use of spatio-temporal featuresDetection of traffic movementSpatial correlationPresent method
The invention relates to a short-time traffic flow prediction method considering spatial-temporal correlation. The influence of temporal correlation on the traffic flow of a target detection point is considered, and a short-time traffic flow temporal correlation prediction value is acquired; the spatial correlation of the object traffic flow is analyzed and researched by using a hierarchical clustering method, and multiple key spatial correlation points are determined; the influence of the traffic flow of the spatial correlation points on the traffic flow of the target detection point is considered, and a short-time traffic flow spatial correlation prediction value is acquired; the temporal correlation prediction value, the spatial correlation prediction value and the prediction value of the present method are integrated by using an "entropy method" so that the final prediction result of the short-time traffic flow of the target detection point is generated; and the prediction error is evaluated and analyzed according to the prediction result of the traffic flow and the actual traffic data. According to the method, the defect of the present method that the spatial-temporal characteristics cannot be fully utilized can be overcome, and the spatial-temporal correlation prediction result and the prediction result of the present method can be further integrated so that the accuracy of the short-time traffic flow prediction result can be effectively enhanced.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com