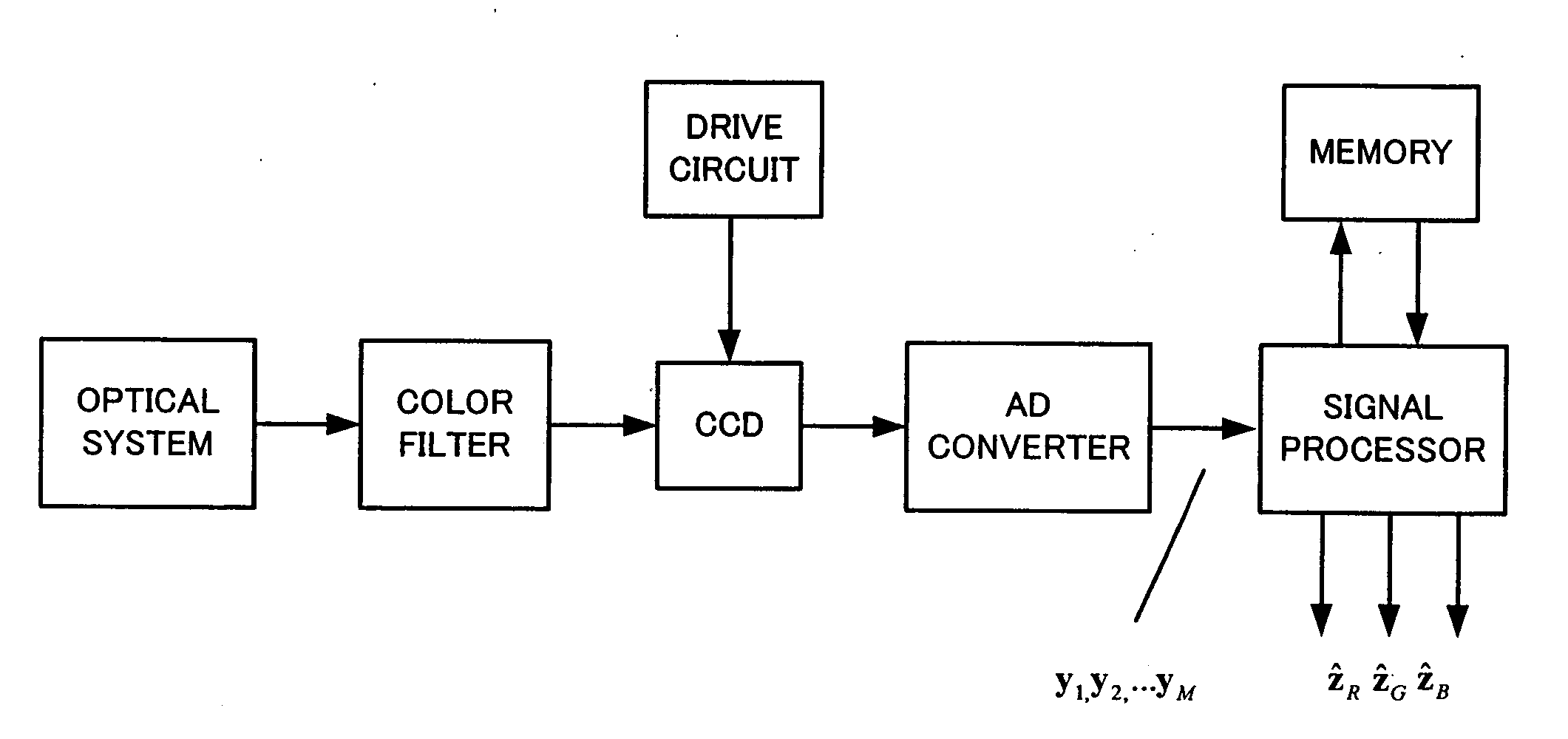
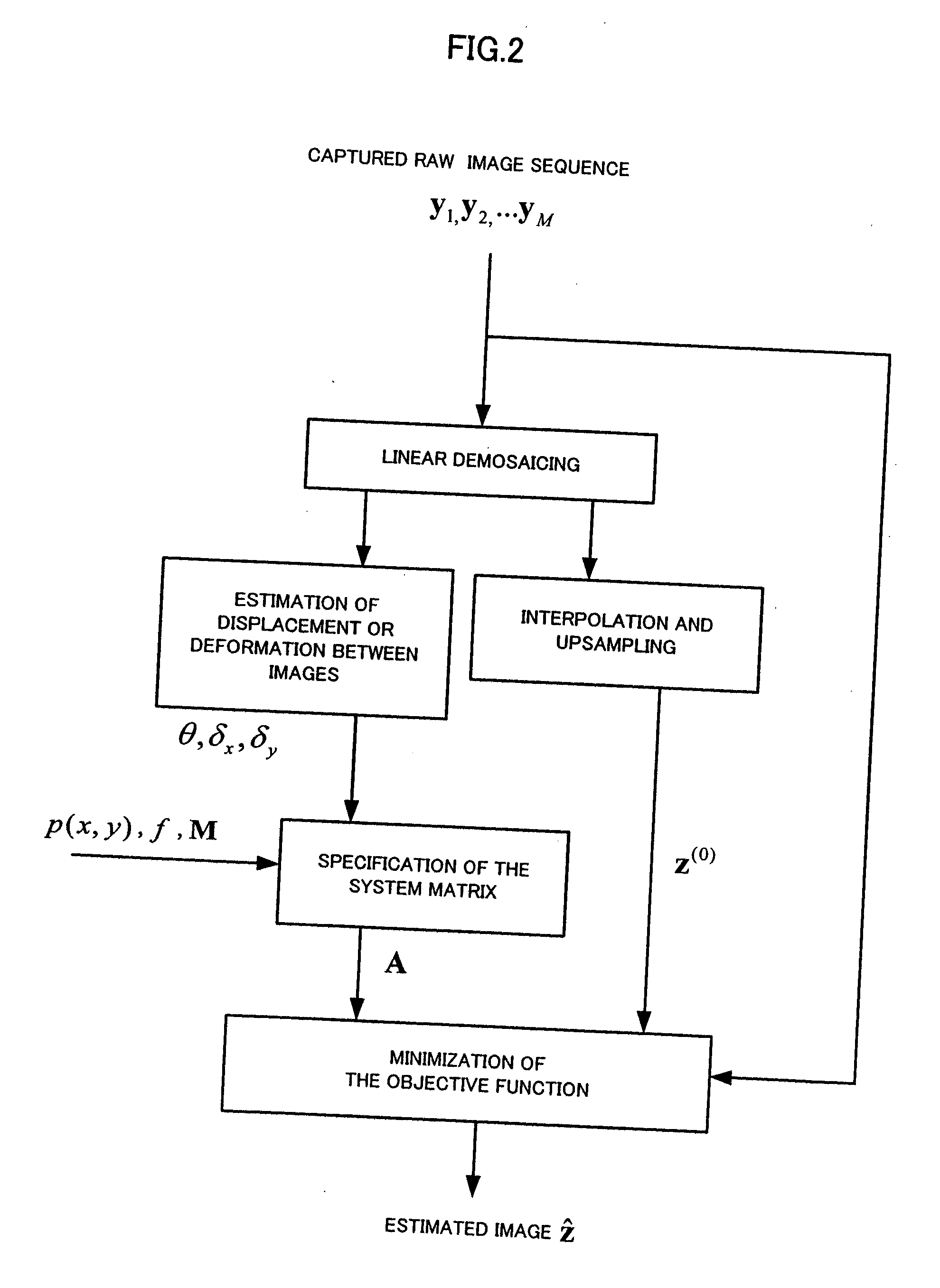
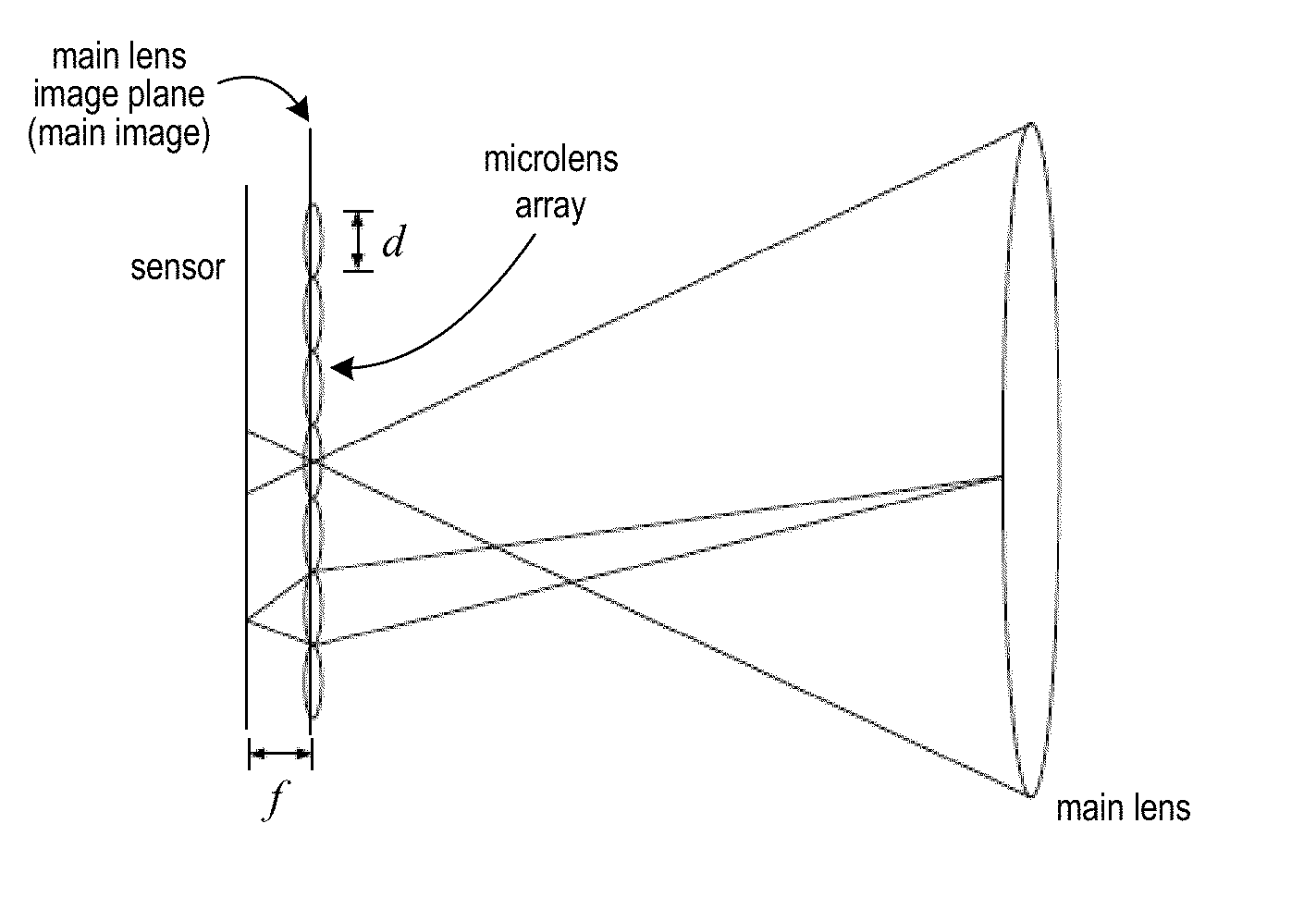
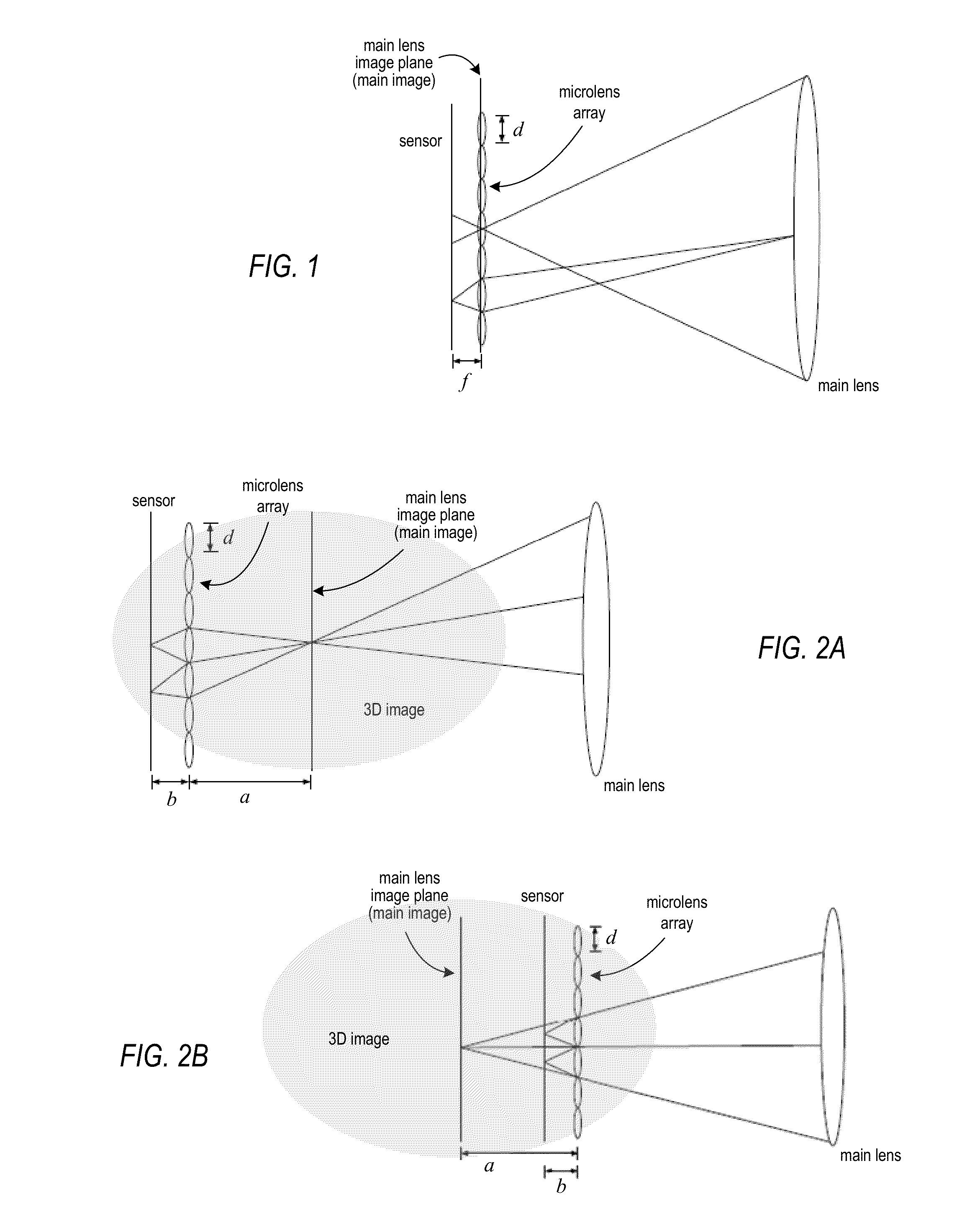
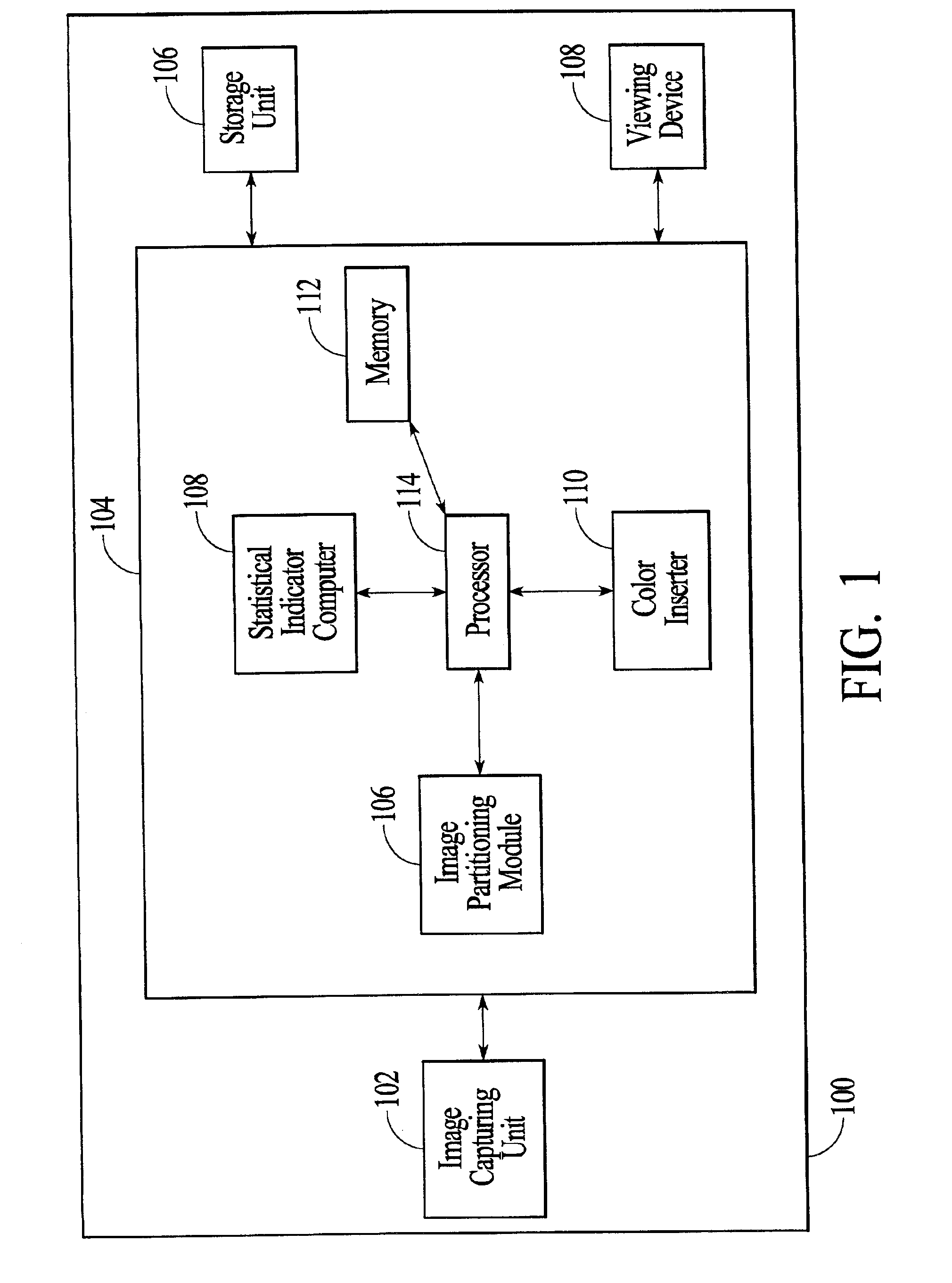
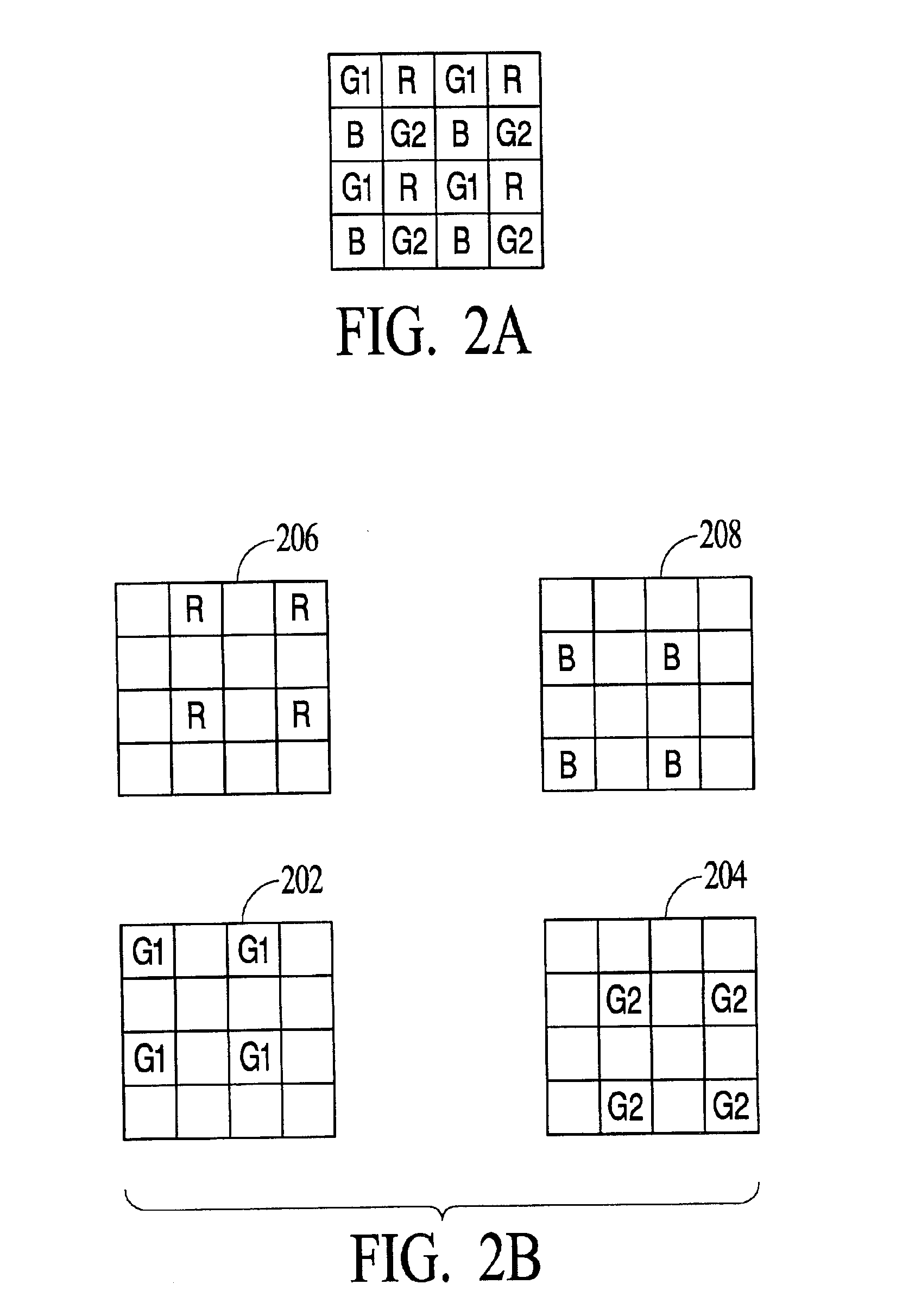
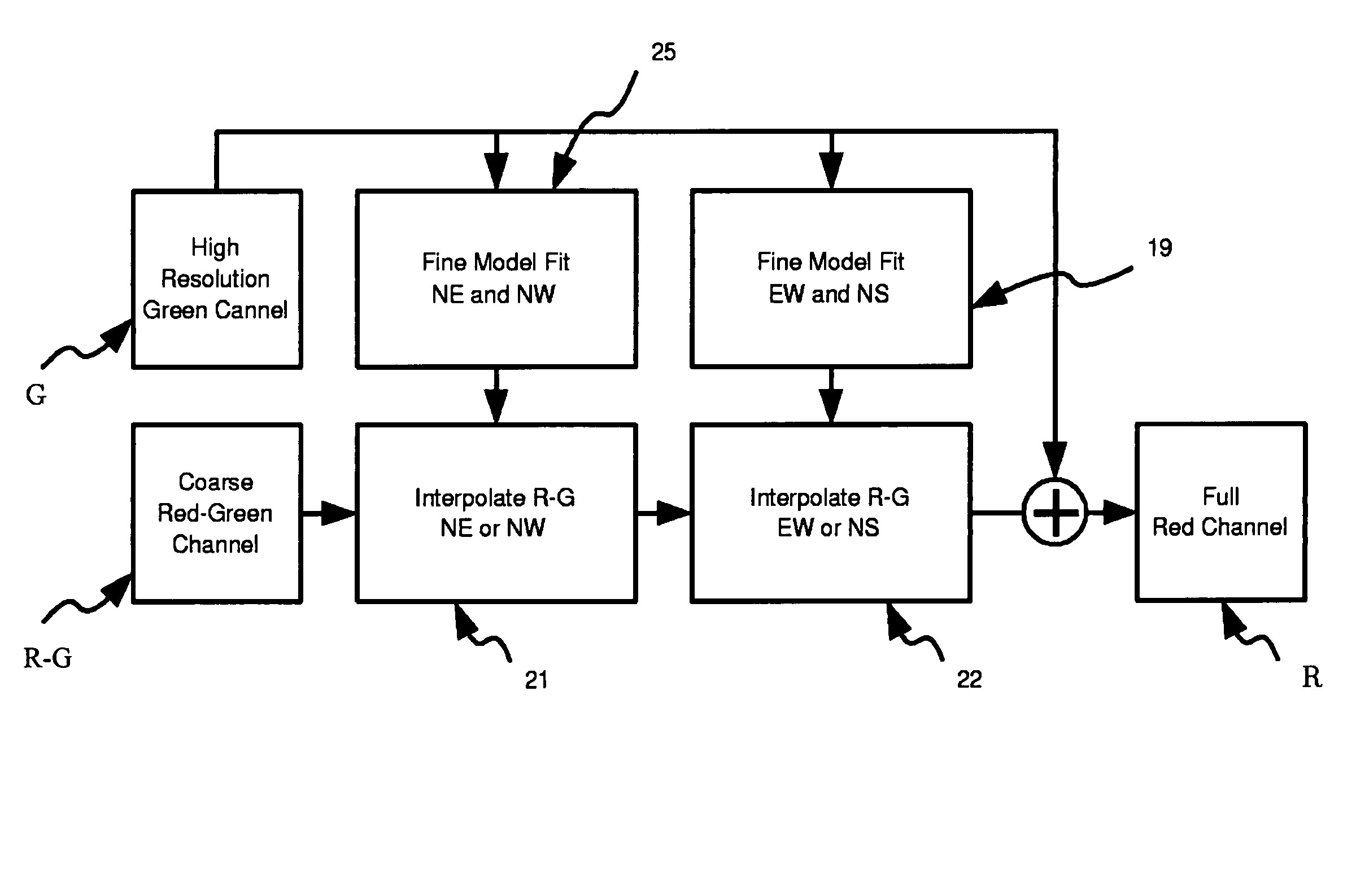
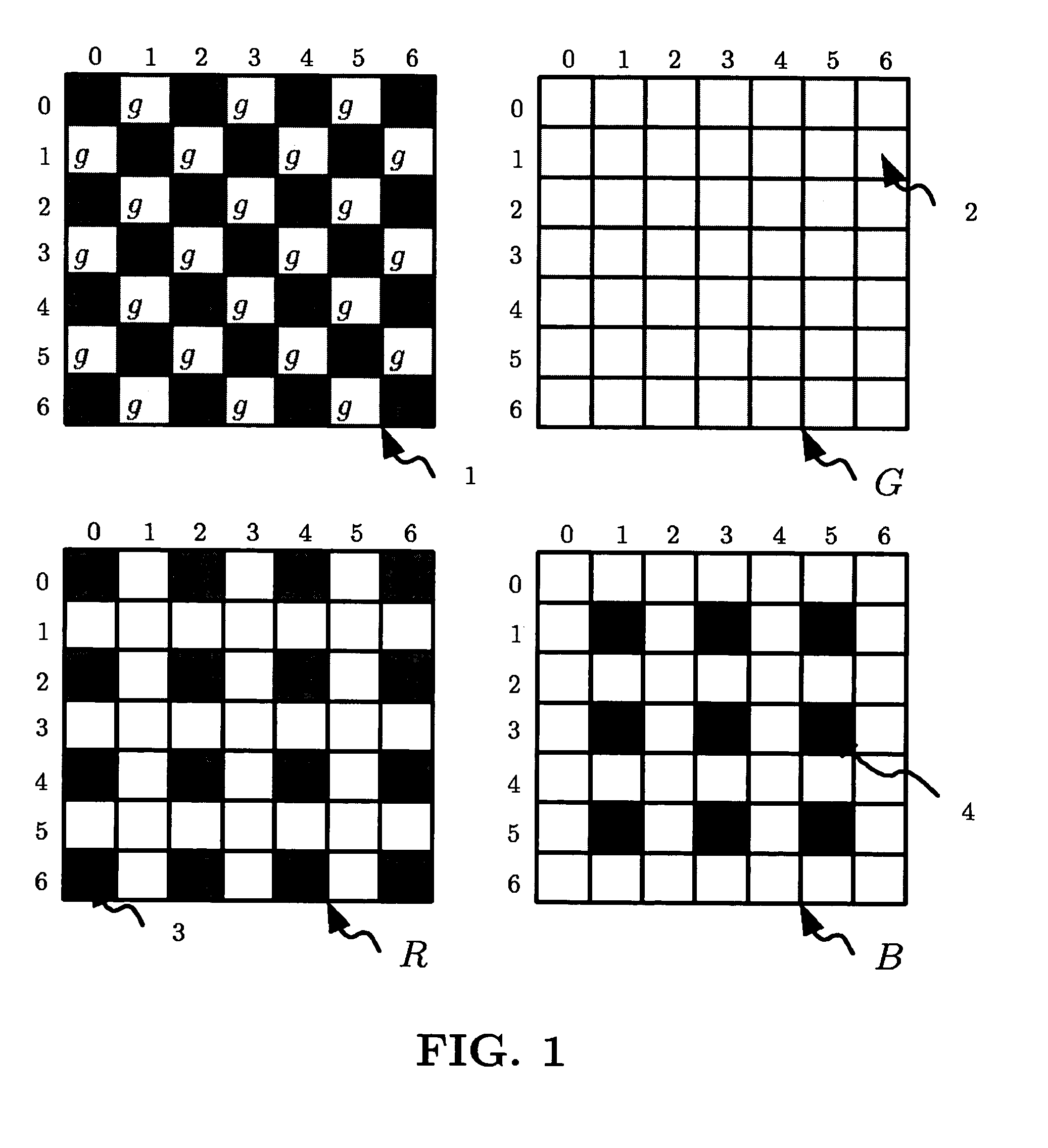
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
282 results about "Demosaicing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
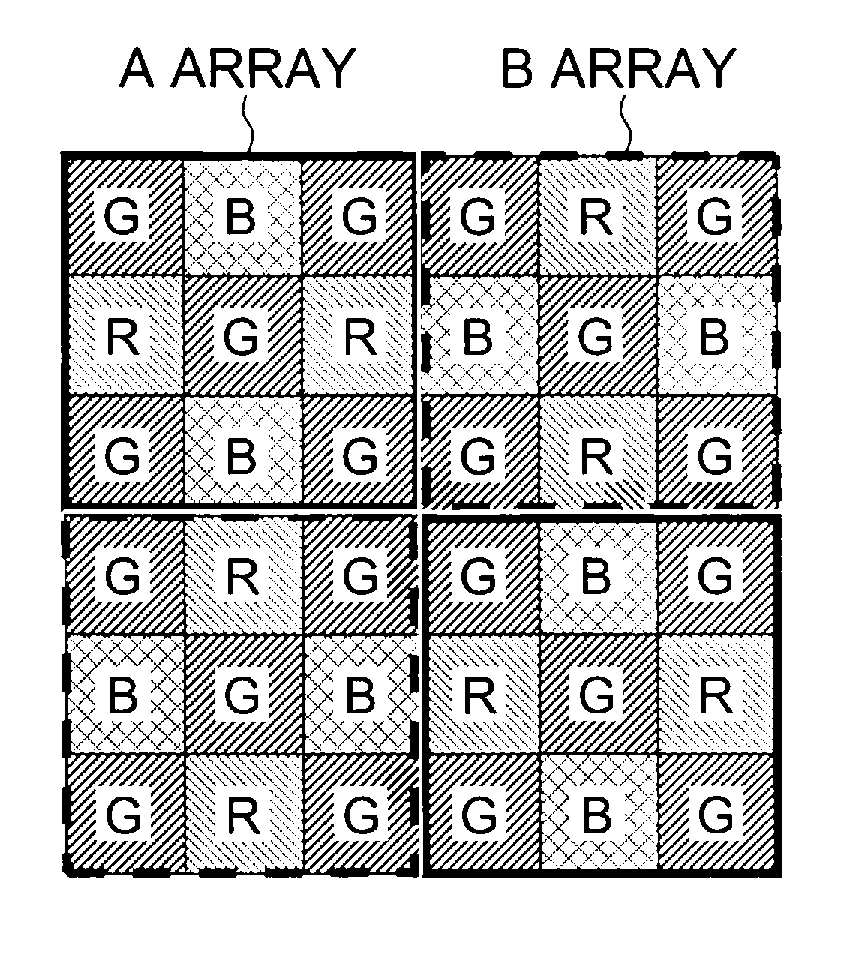
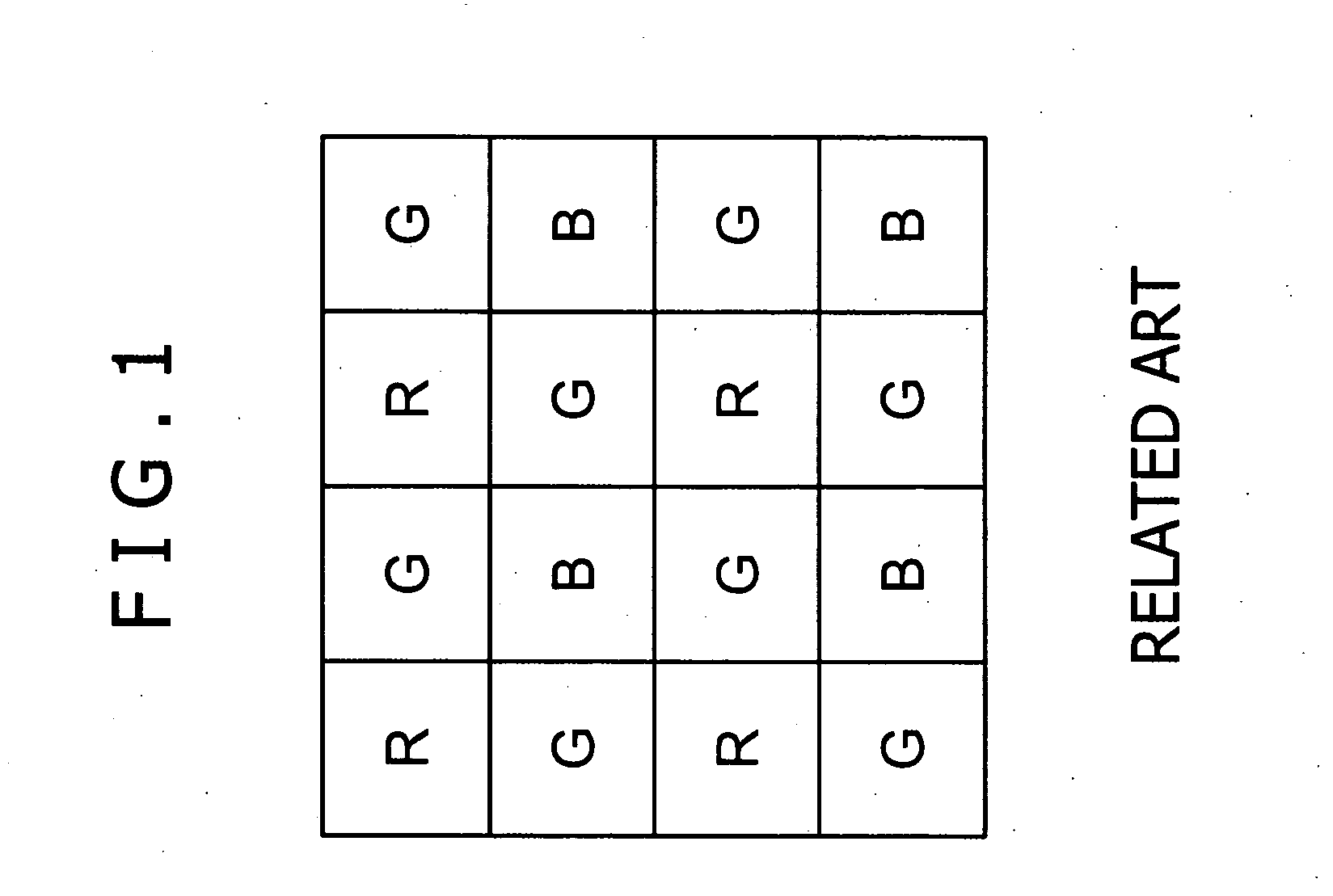
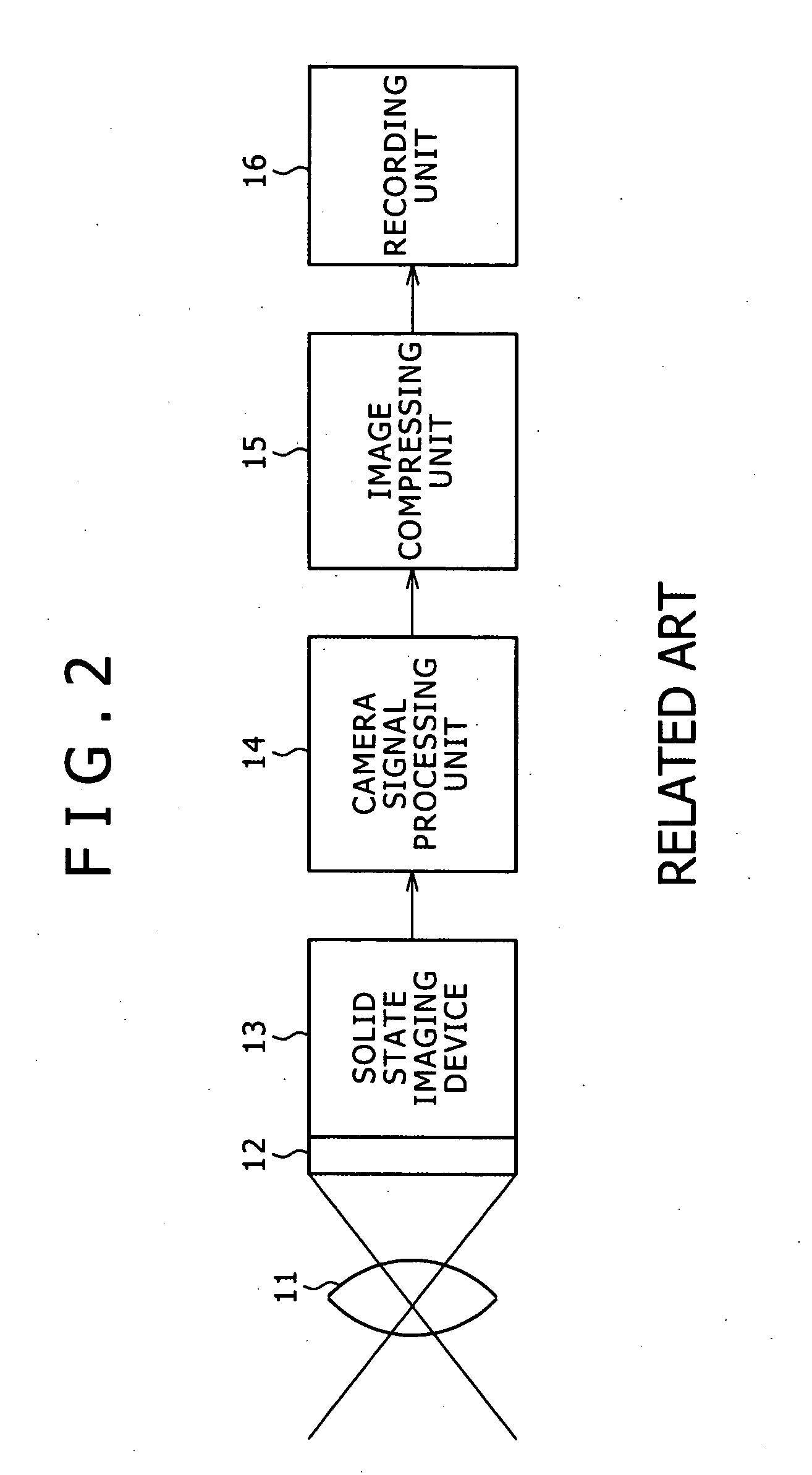
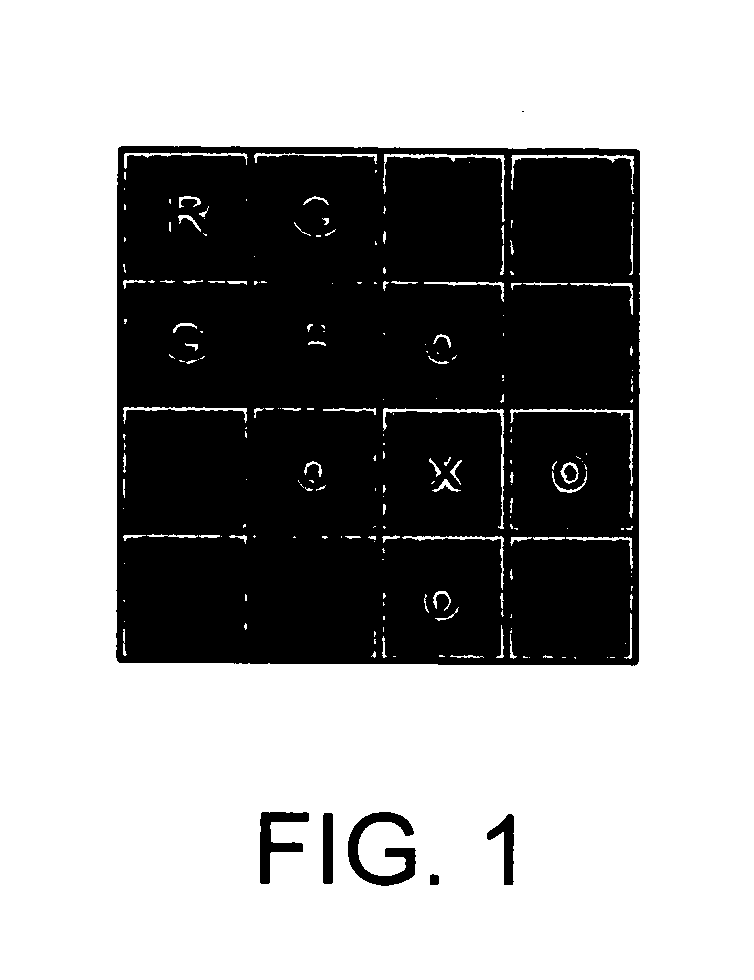
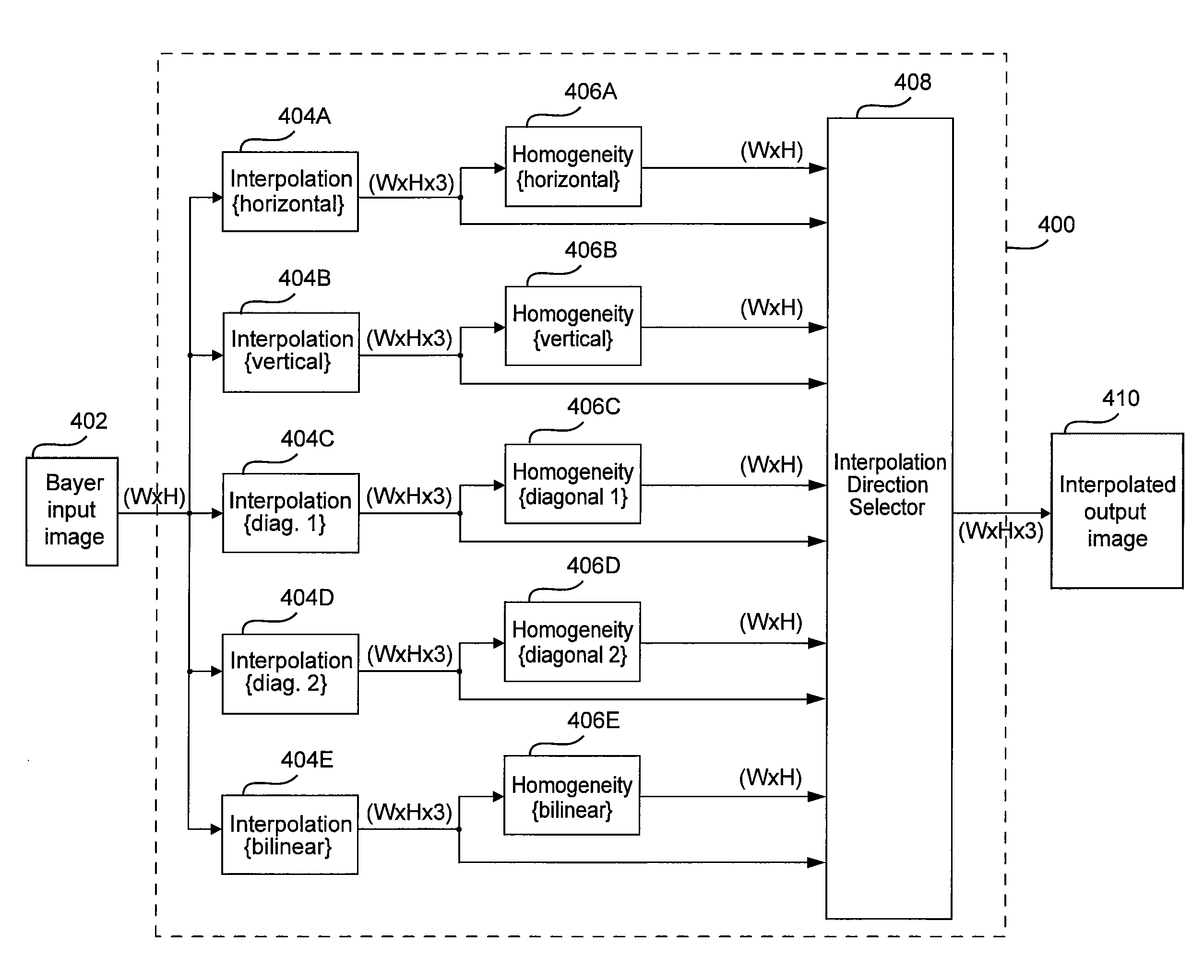
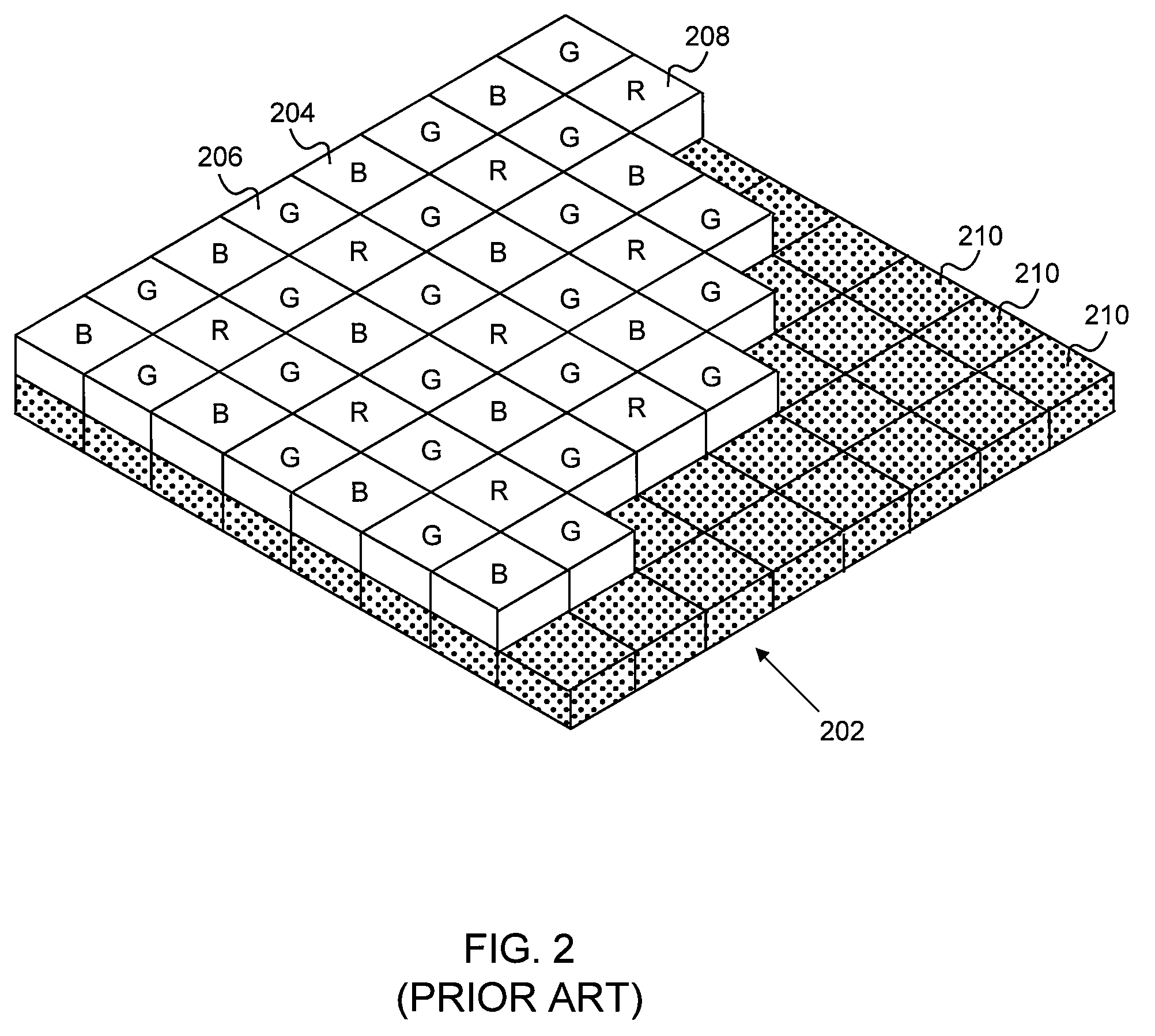
A demosaicing (also de-mosaicing, demosaicking or debayering) algorithm is a digital image process used to reconstruct a full color image from the incomplete color samples output from an image sensor overlaid with a color filter array (CFA). It is also known as CFA interpolation or color reconstruction.
Method for creating high resolution color image, system for creating high resolution color image and program creating high resolution color image
InactiveUS20060038891A1Evaluates smoothnessEfficient implementationTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionColor imageImage resolution
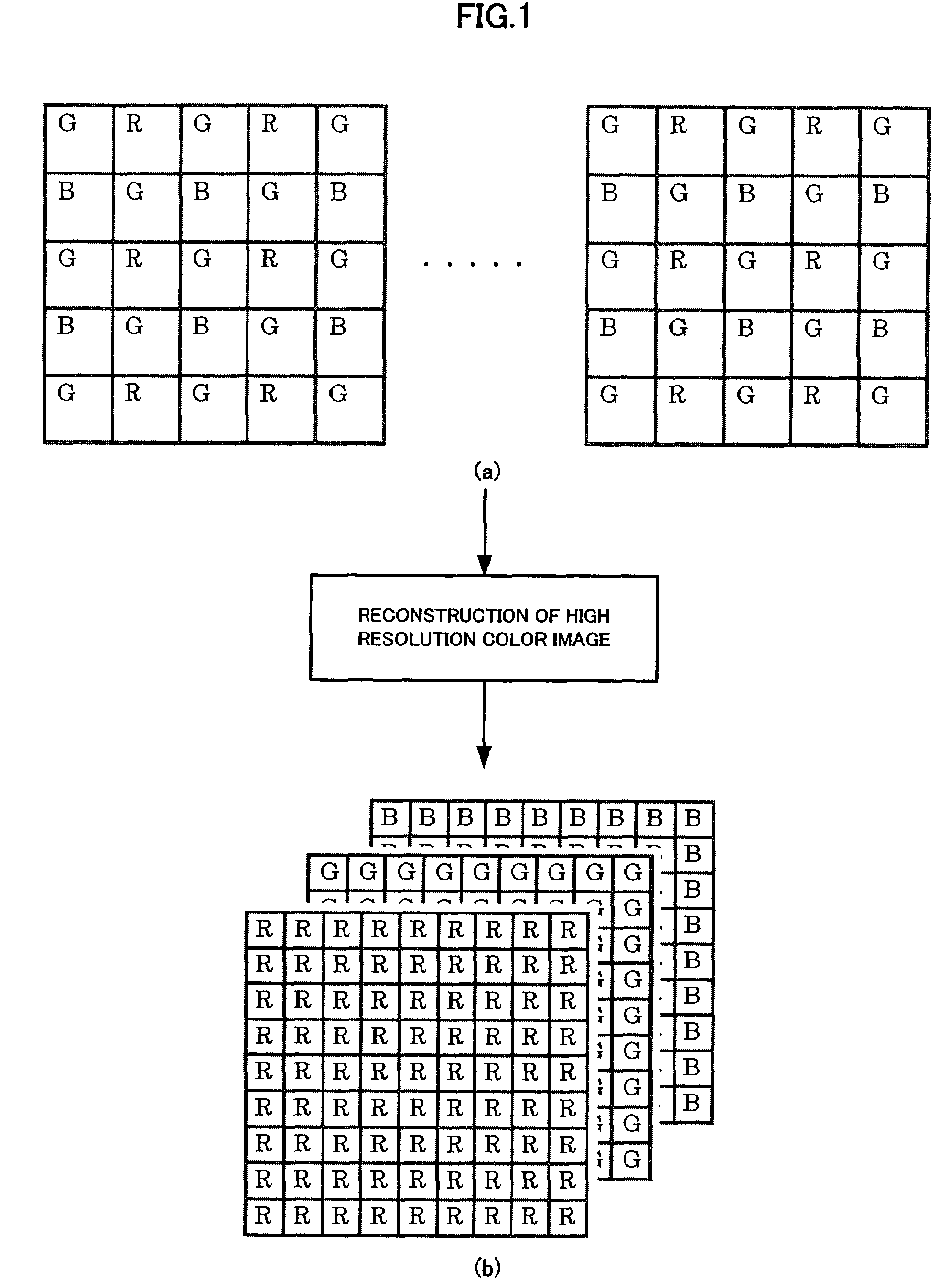
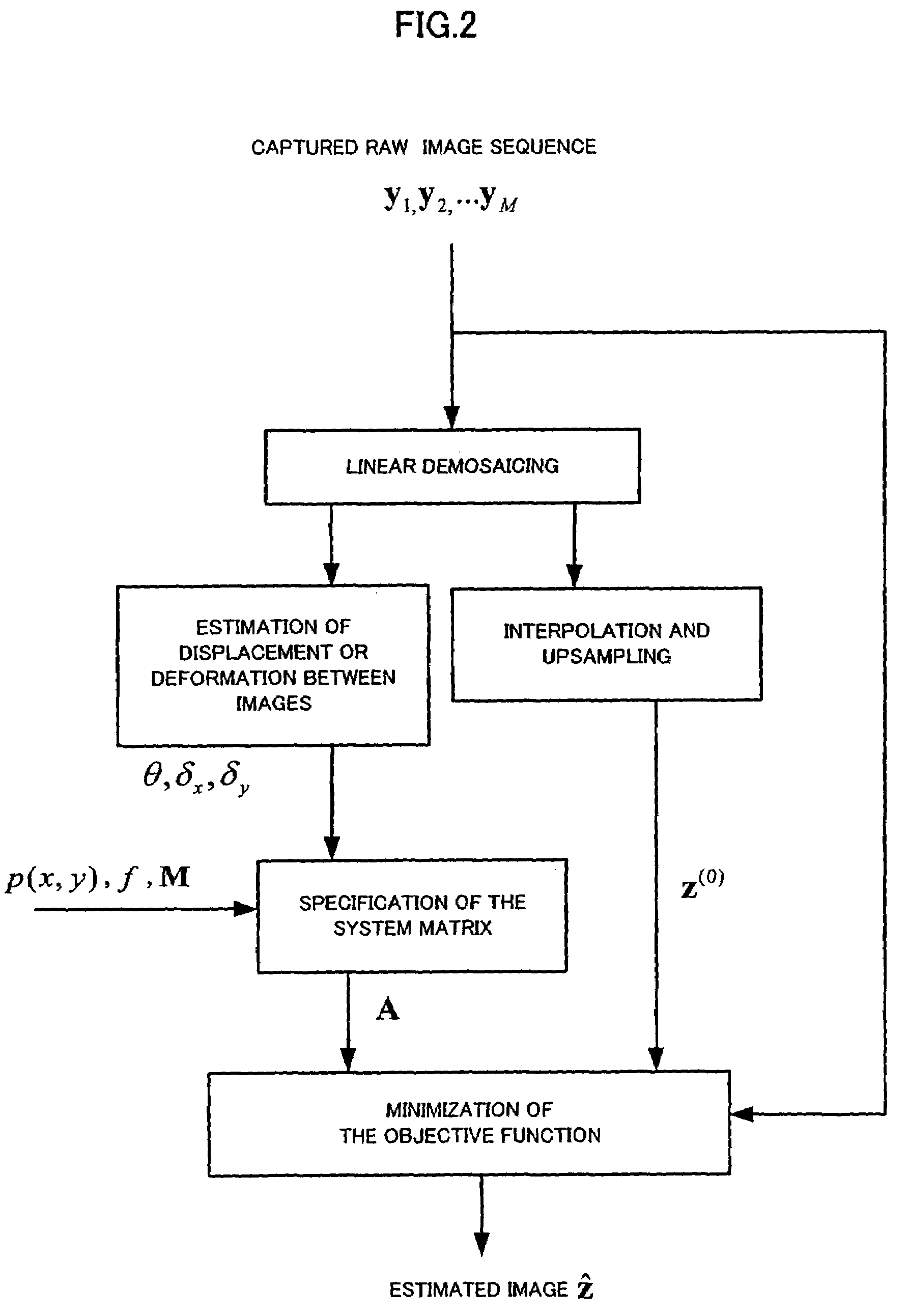
A limitation in the physical resolution of an image sensor offers a motivation to improve the resolution of an image. Super-resolution is mainly applied to gray scale images, and it has not been thoroughly investigated yet that a high resolution color image is reconstructed from an image sensor having a color filter array. An object of the invention is to directly reconstruct a high resolution color image from color mosaic obtained by an image sensor having a color filter array. A high resolution color image reconstruction method according to the invention is based on novel technique principles of color image reconstruction that an increase in resolution and demosaicing are performed at the same time. The verification and effective implement of the invention are also described.
Owner:TOKYO INST OF TECH
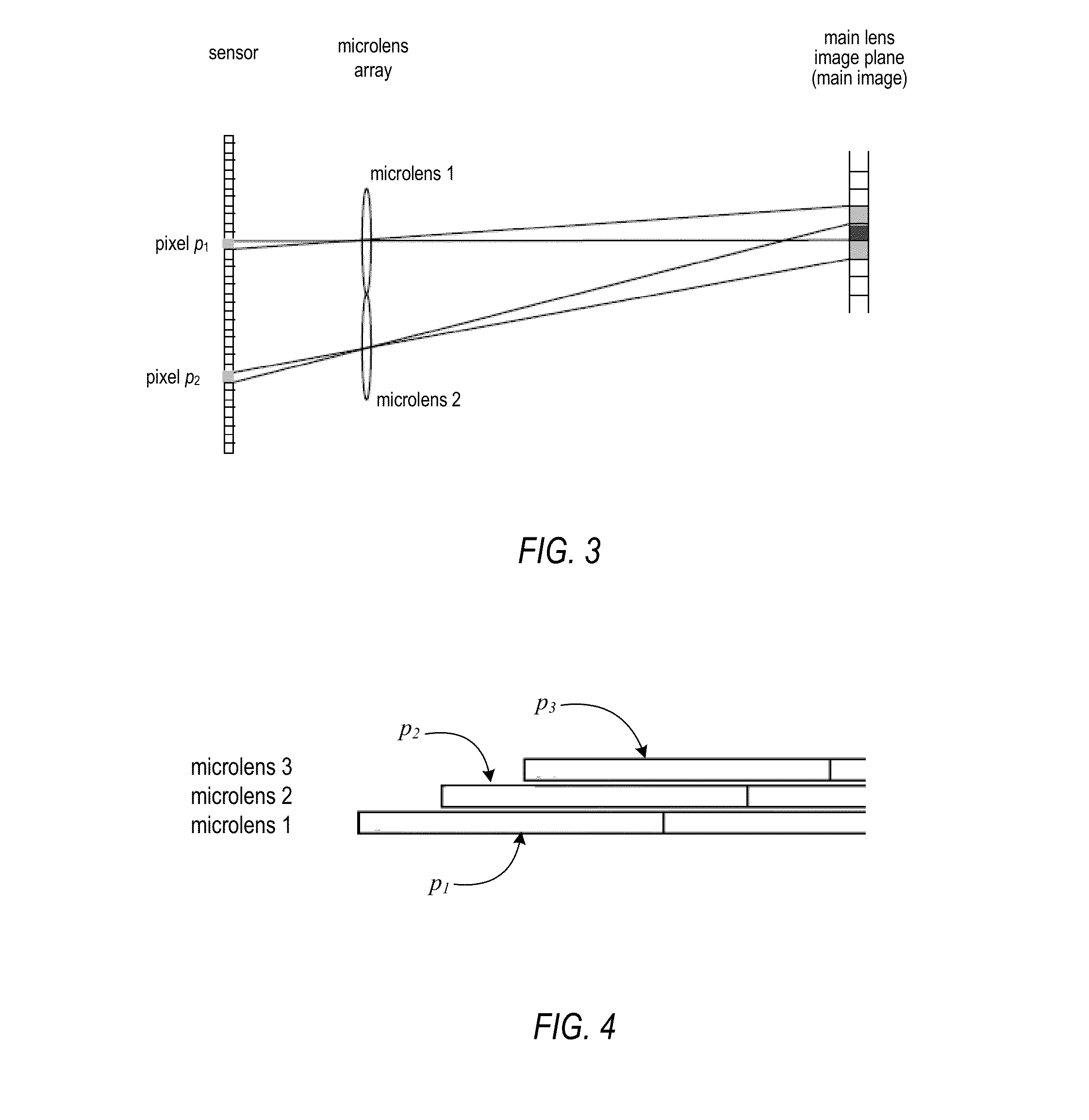
Methods and Apparatus for Rendering Focused Plenoptic Camera Data using Super-Resolved Demosaicing
ActiveUS20130128068A1Television system detailsSolid-state device signal generatorsCurrent pointDemosaicing
A super-resolved demosaicing technique for rendering focused plenoptic camera data performs simultaneous super-resolution and demosaicing. The technique renders a high-resolution output image from a plurality of separate microimages in an input image at a specified depth of focus. For each point on an image plane of the output image, the technique determines a line of projection through the microimages in optical phase space according to the current point and angle of projection determined from the depth of focus. For each microimage, the technique applies a kernel centered at a position on the current microimage intersected by the line of projection to accumulate, from pixels at each microimage covered by the kernel at the respective position, values for each color channel weighted according to the kernel. A value for a pixel at the current point in the output image is computed from the accumulated values for the color channels.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
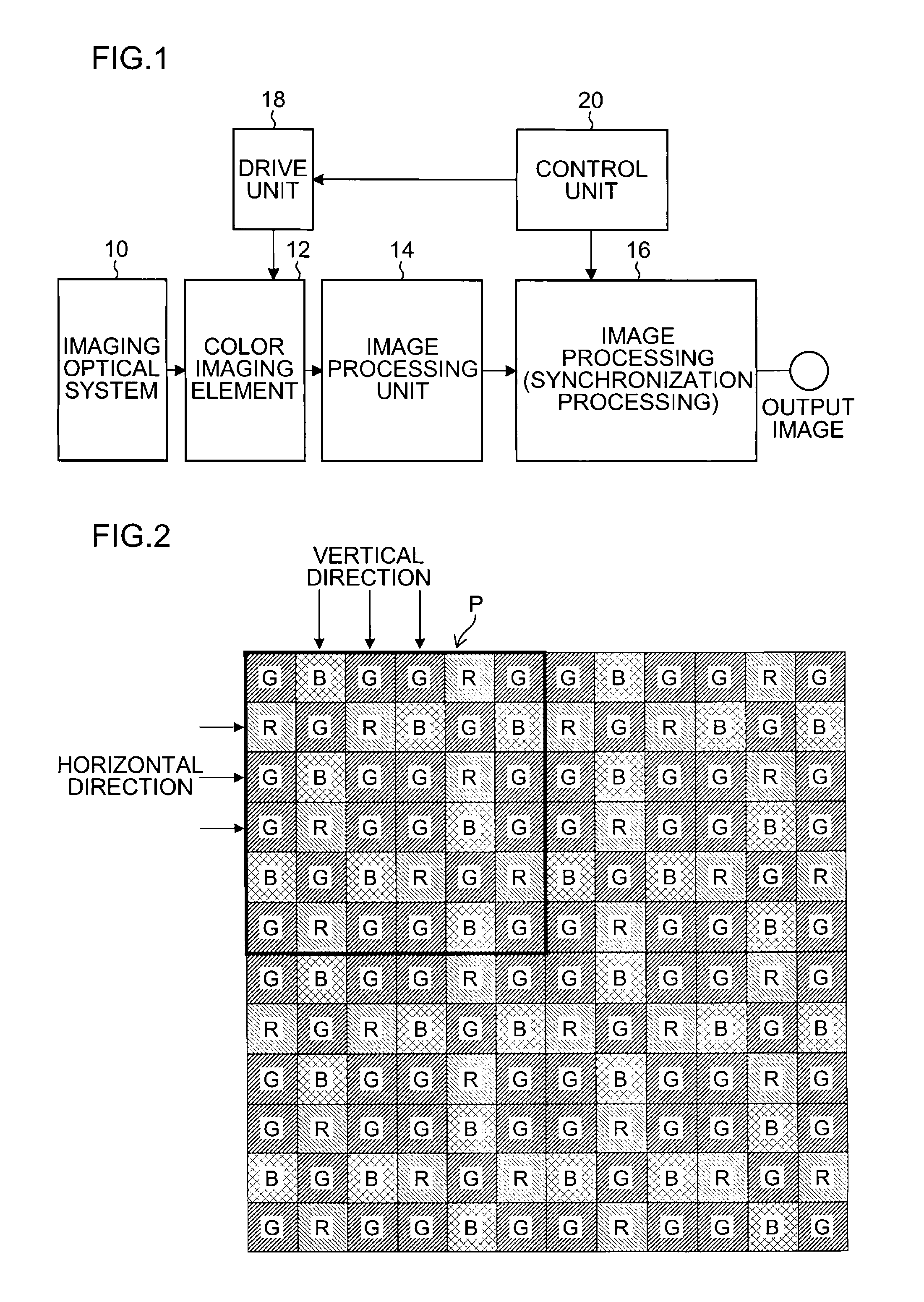
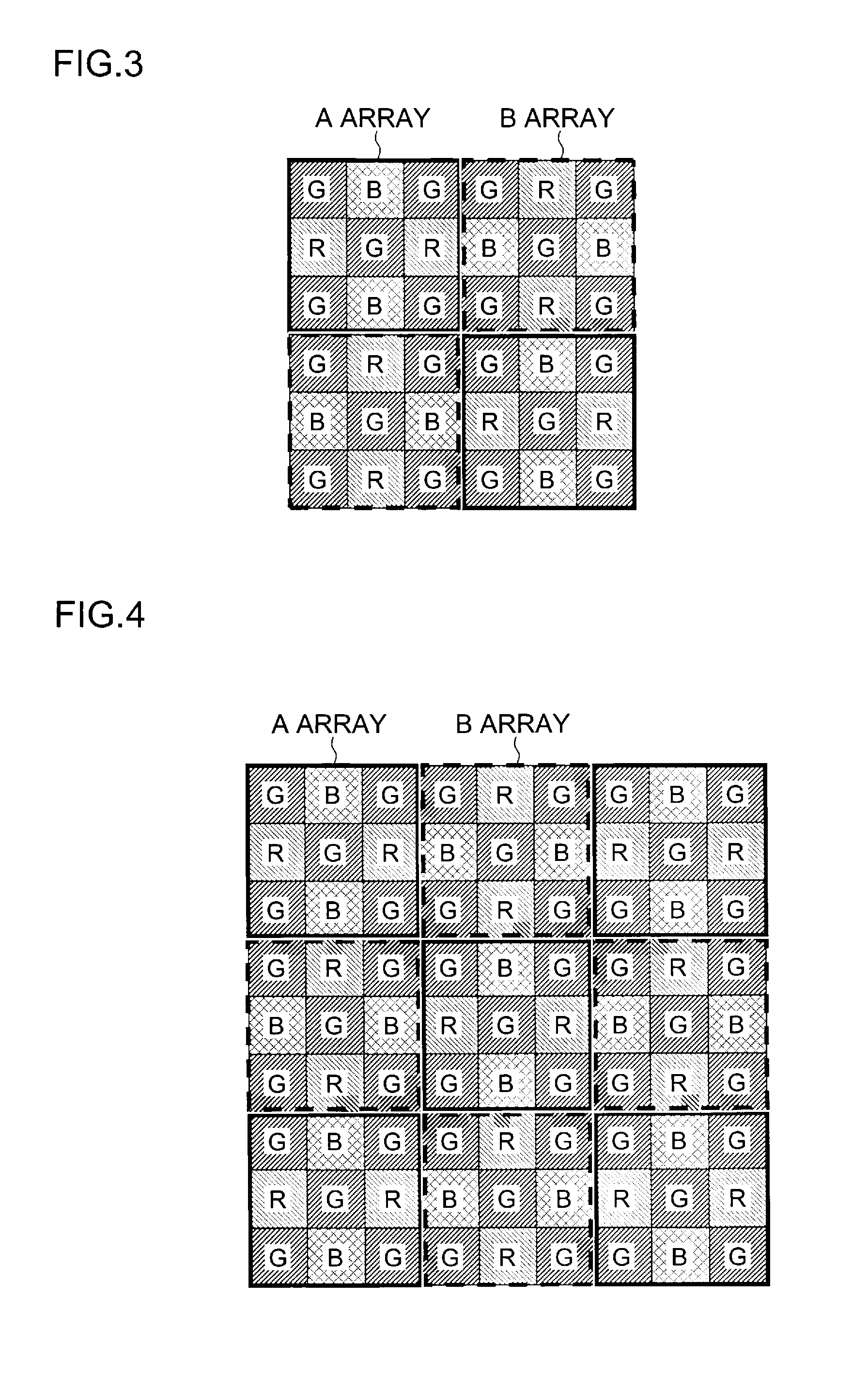
Color imaging apparatus
ActiveUS20120293695A1Accurate estimateSuppress generationTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsColor imageAverage filter
A color imaging apparatus comprising: a single-plate color imaging element including color filters arranged on pixels arranged in horizontal and vertical directions where all colors are arranged in each line in the directions; weighted average filters with filter coefficients set in a local area extracted from a mosaic image acquired from the color imaging element corresponding to the weighted average filters so that proportions of sums of the filter coefficients of each color in the lines in the horizontal and vertical directions are equal; a weighted average calculation unit that calculates weighted average values of each color; a demosaicking processing unit that calculates a pixel value of another color at a pixel position of a target pixel of demosaicking processing and that interpolates a pixel value of the target pixel based on a color ratio or a color difference of the calculated weighted average values to calculate the pixel value.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
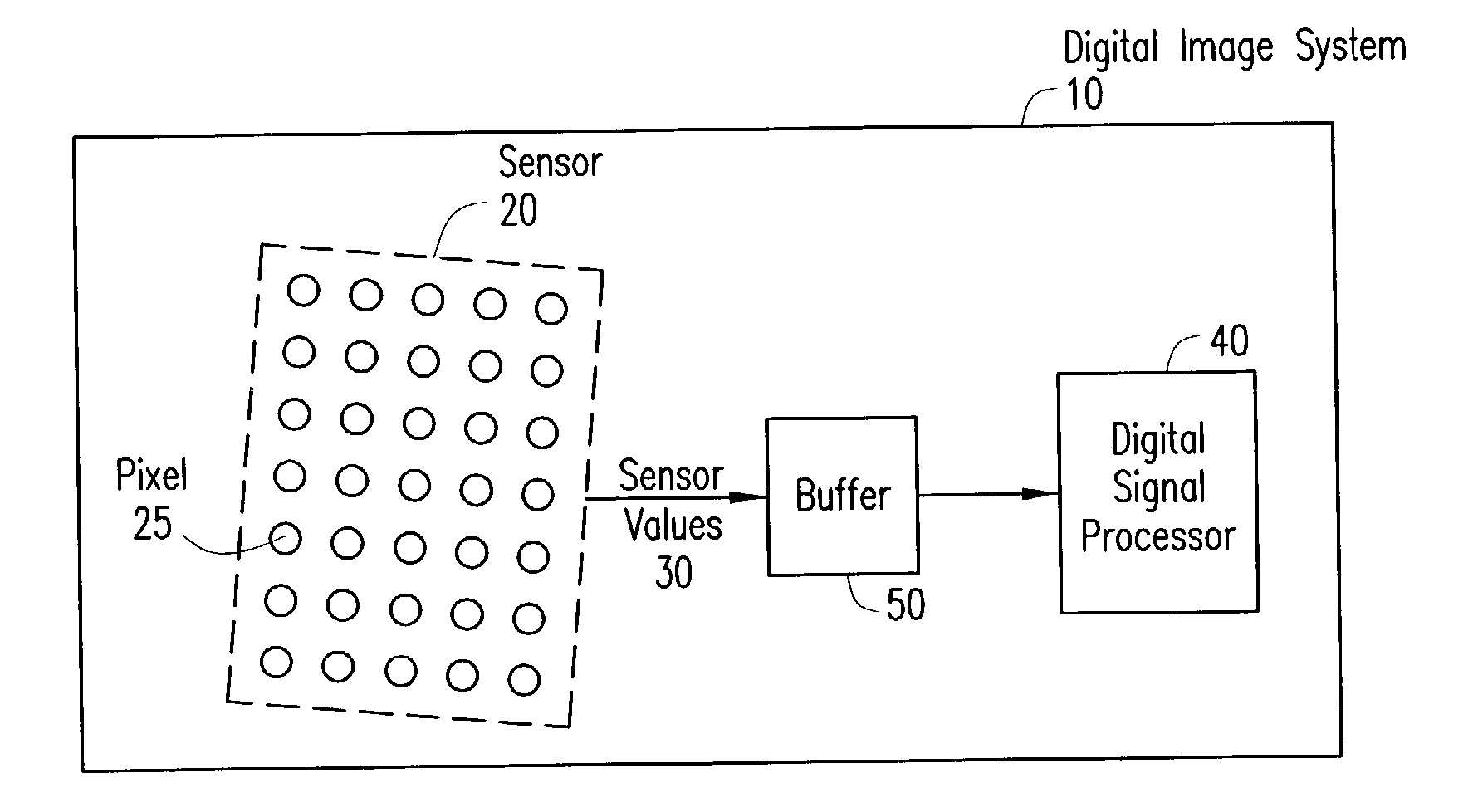
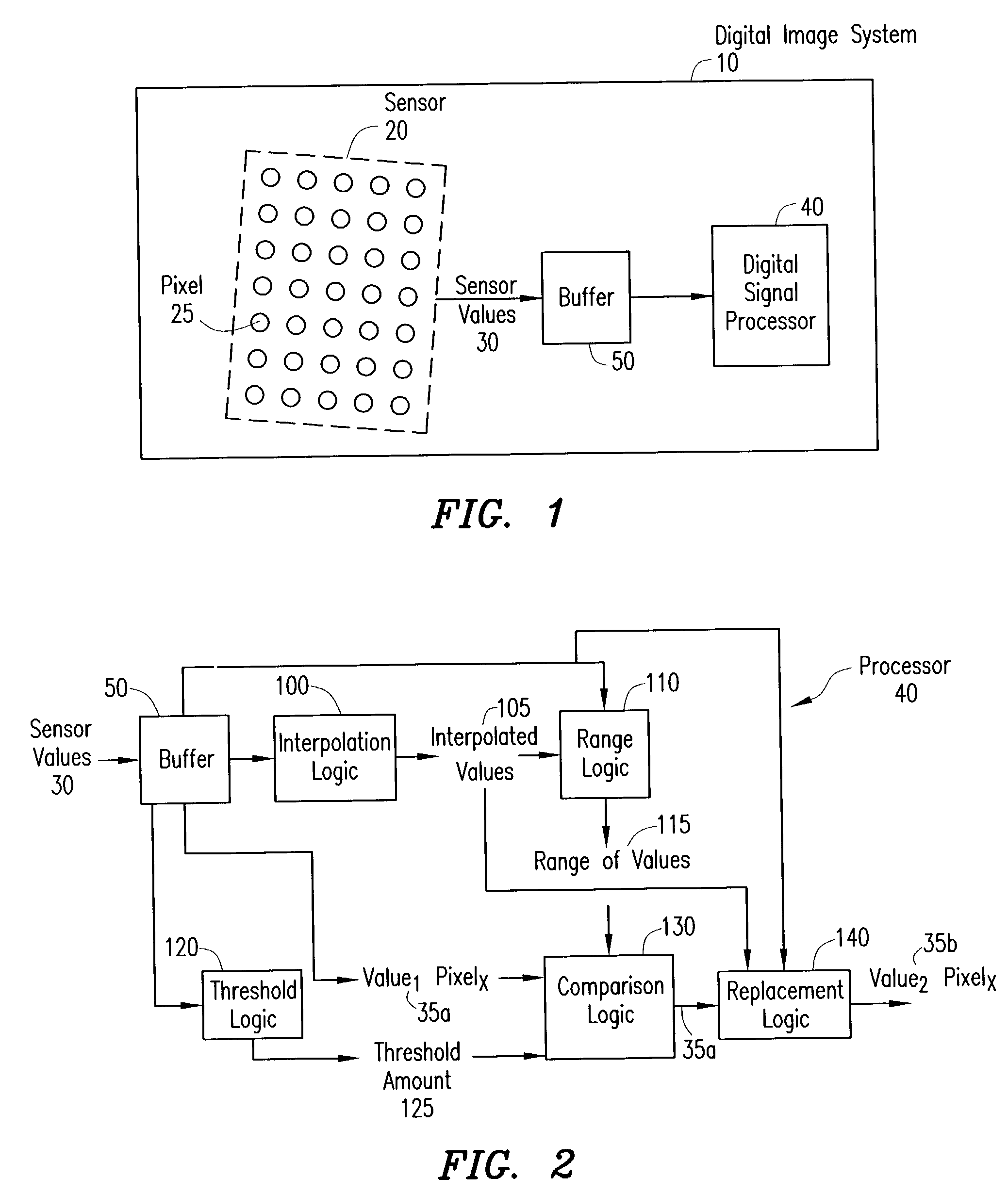
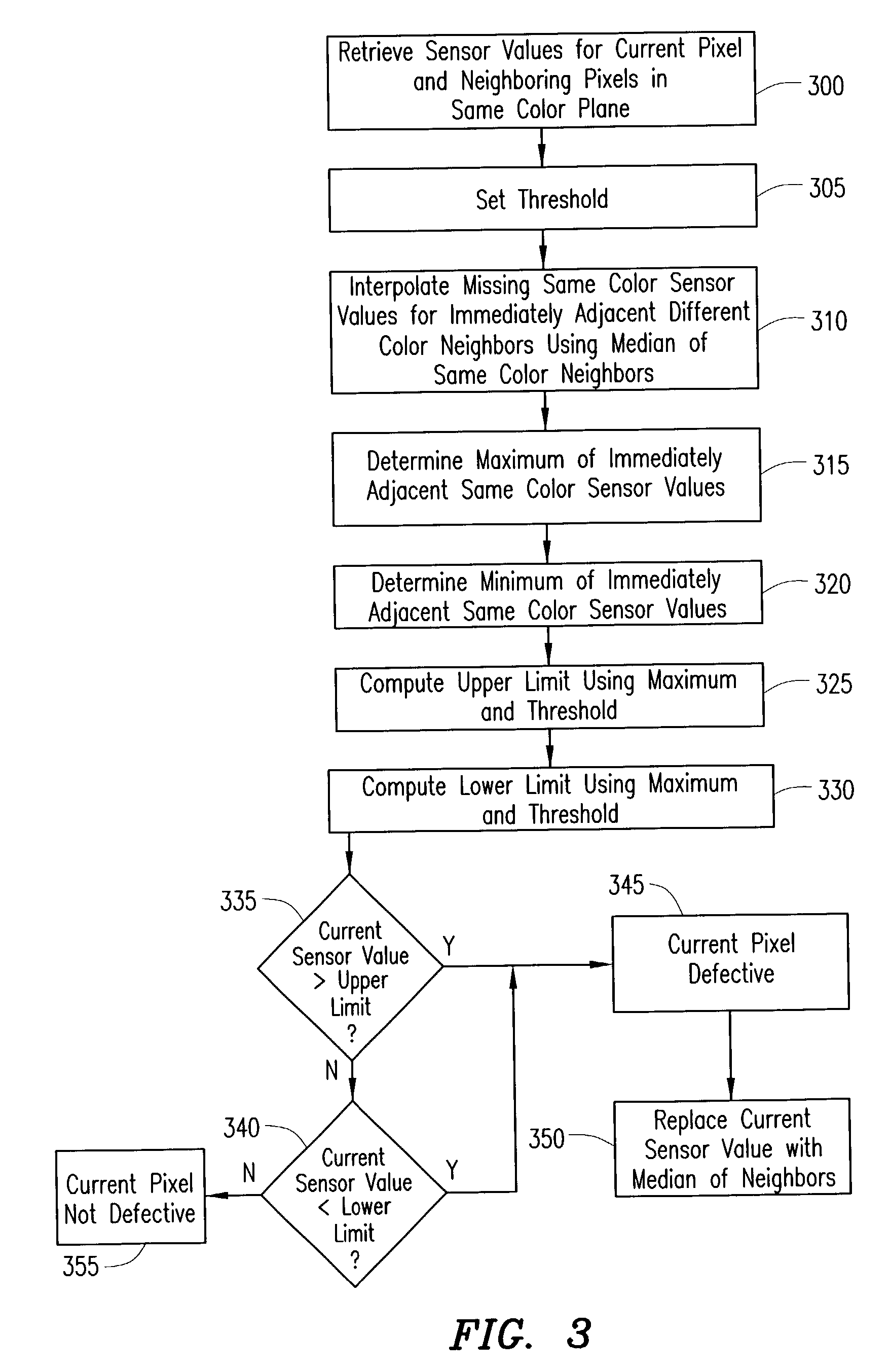
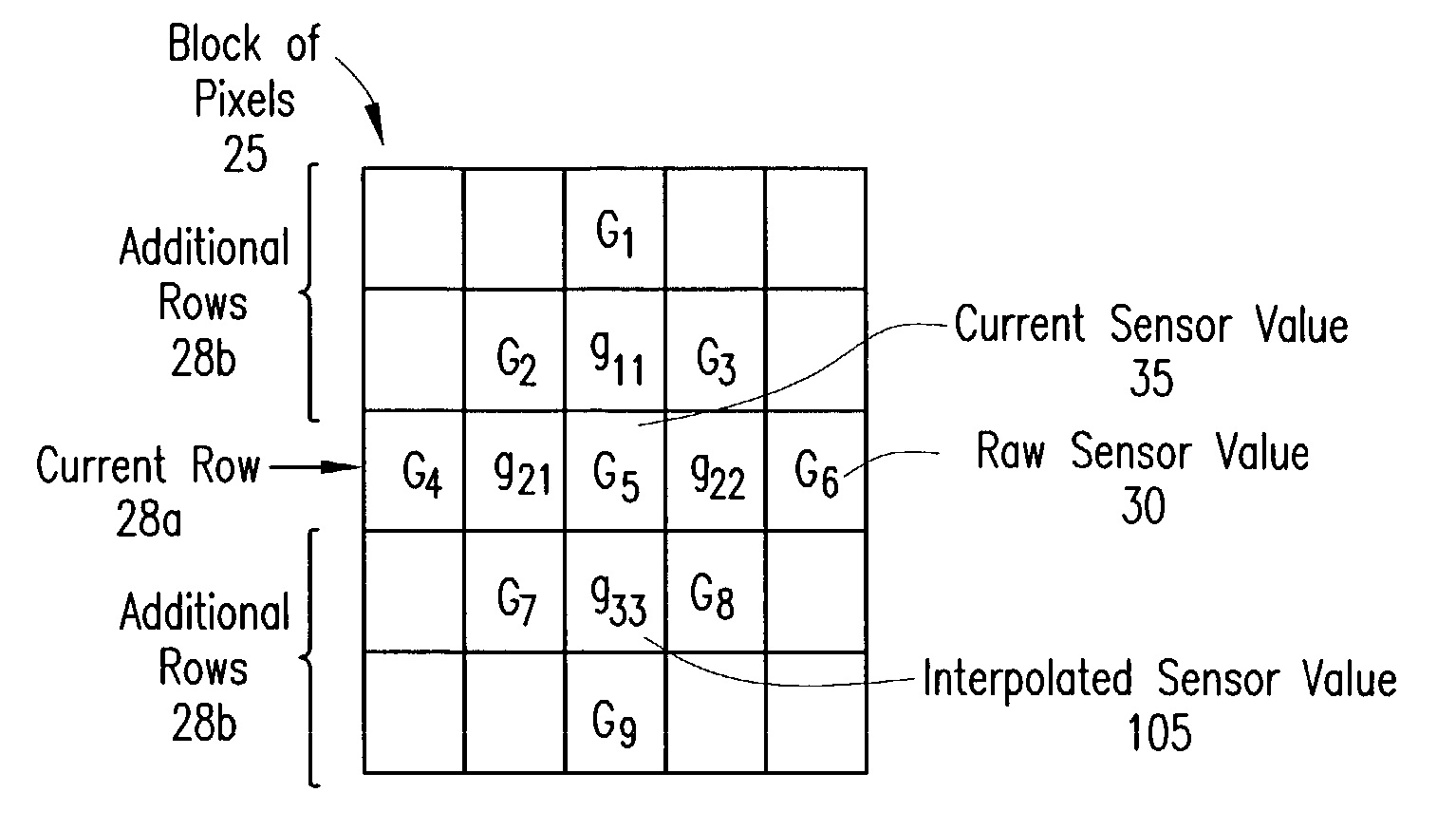
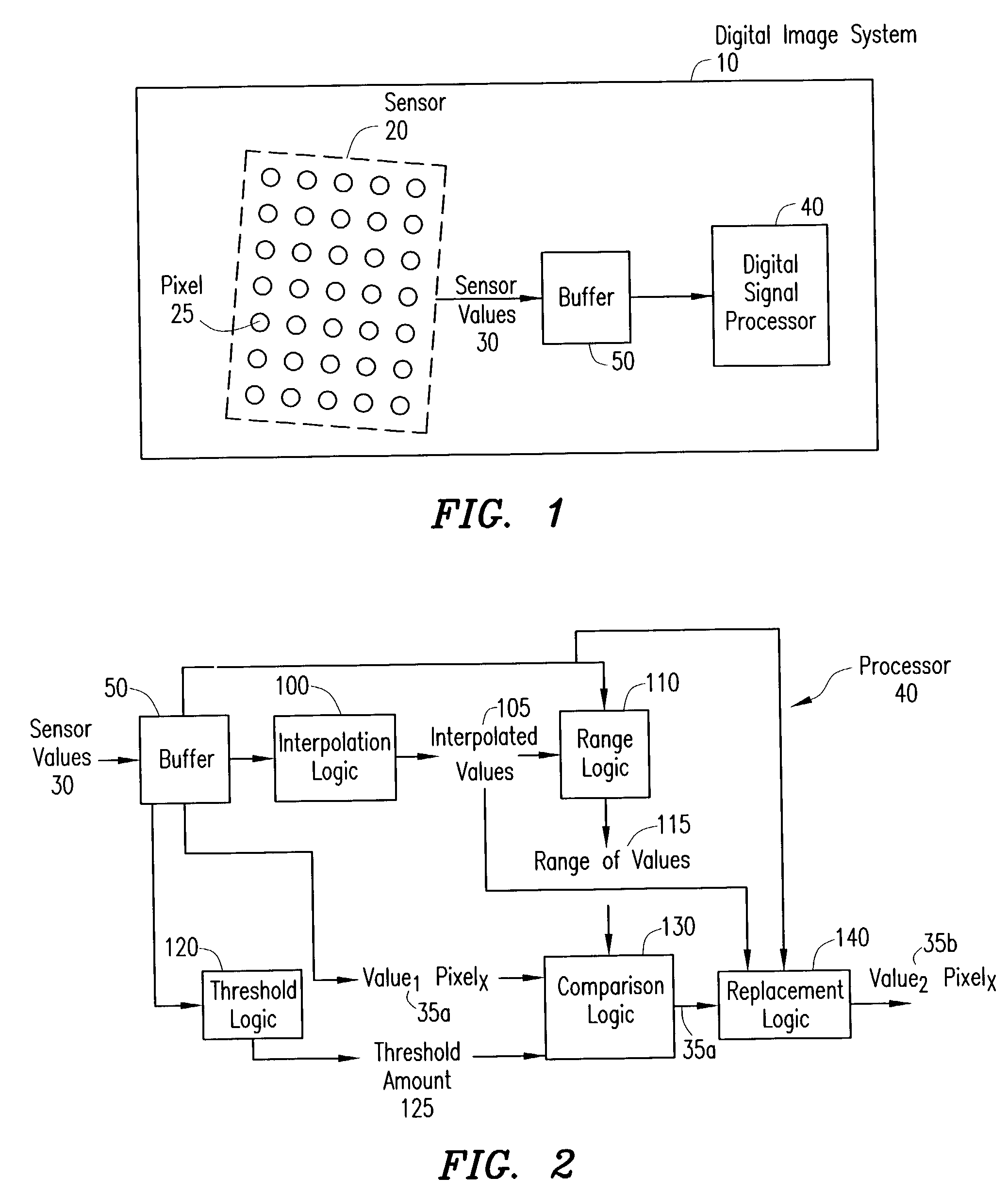
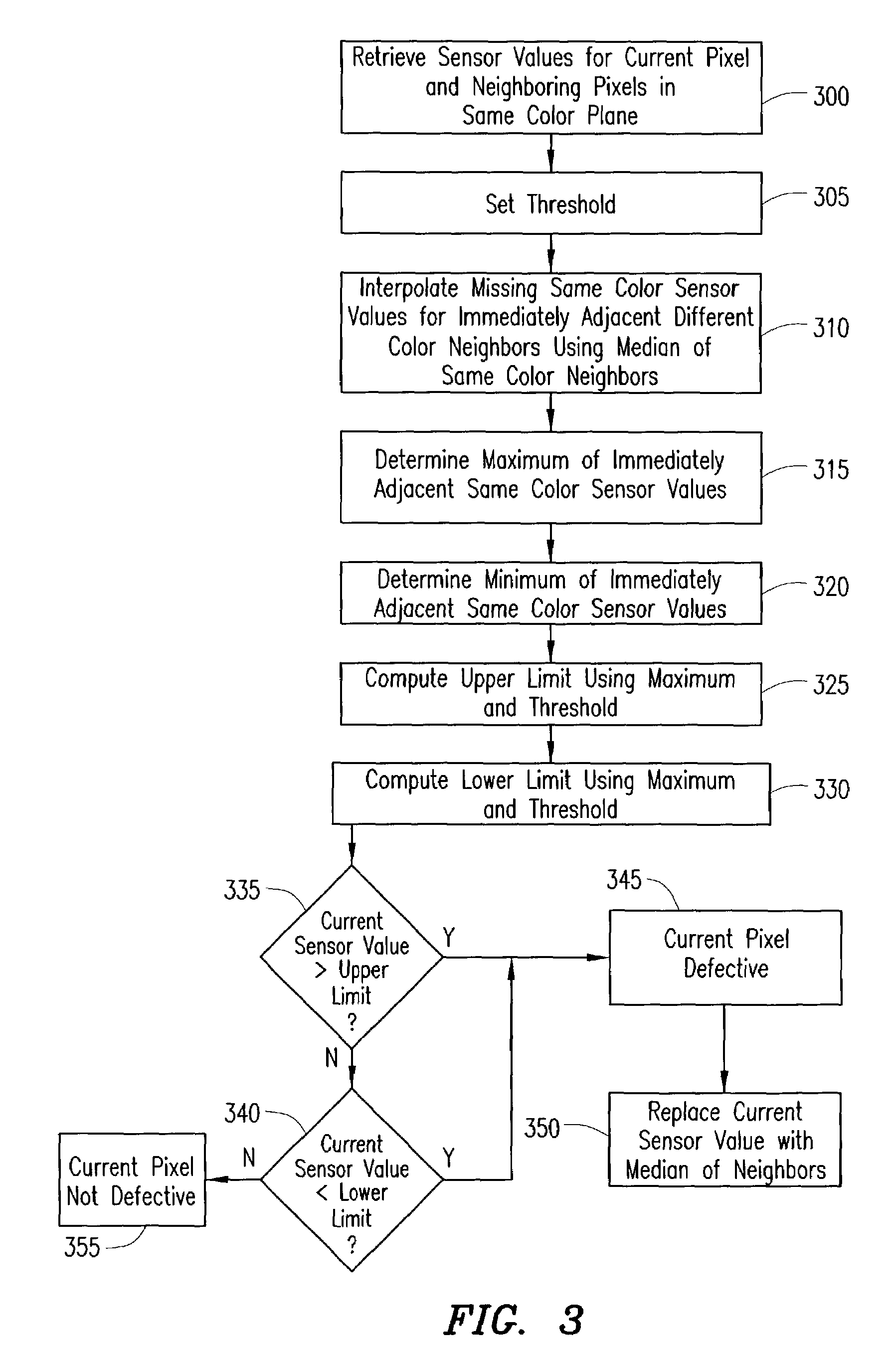
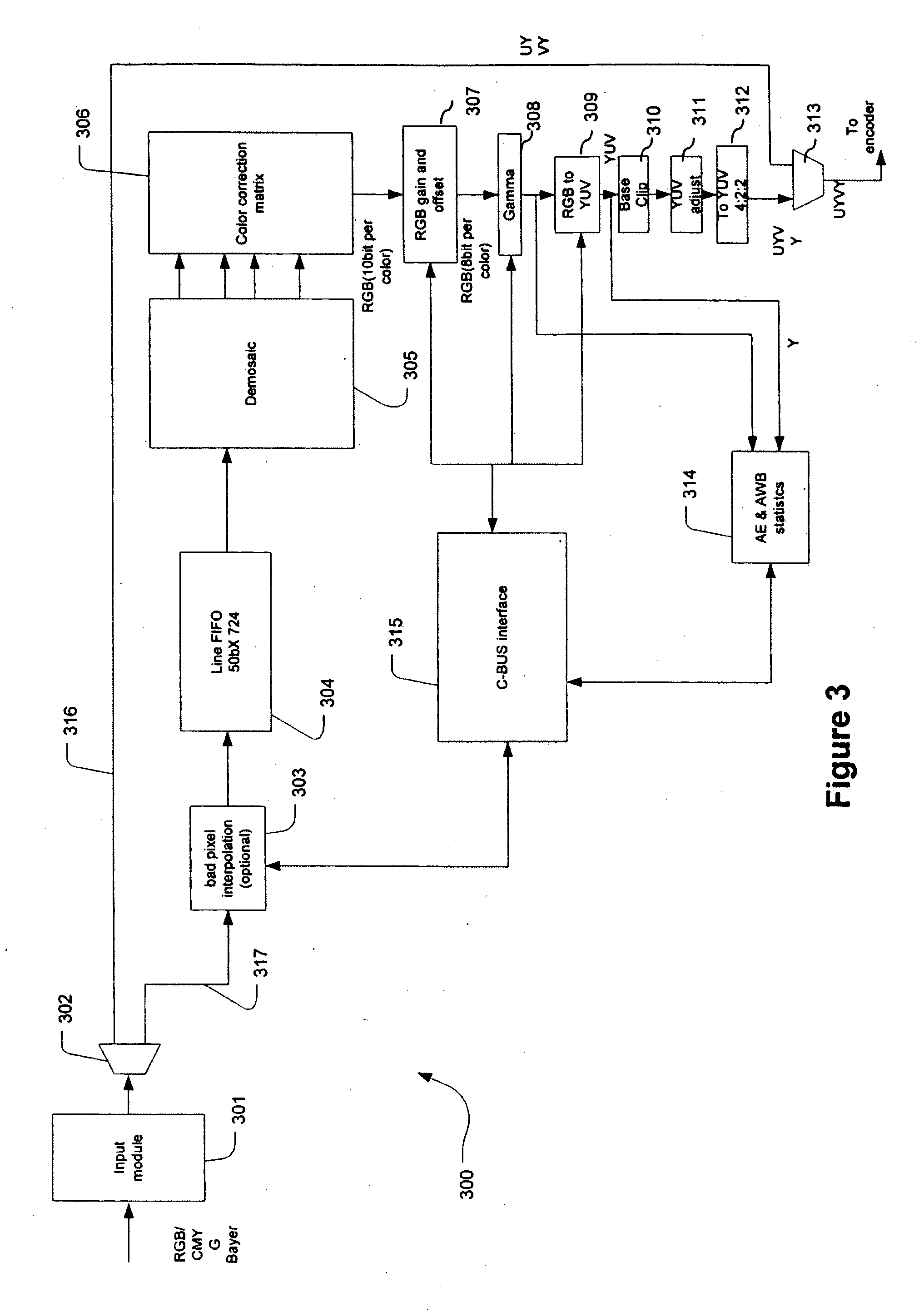
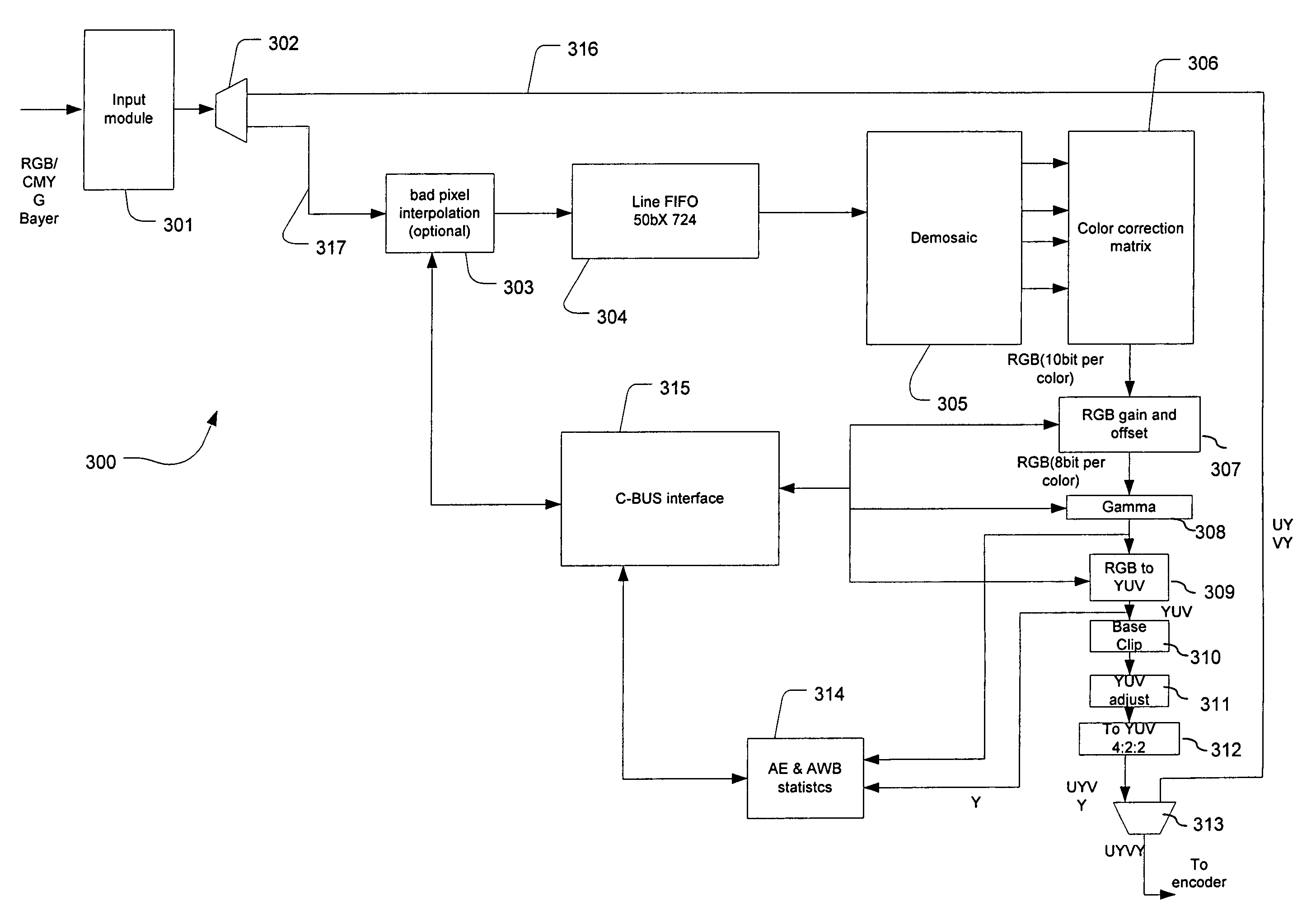
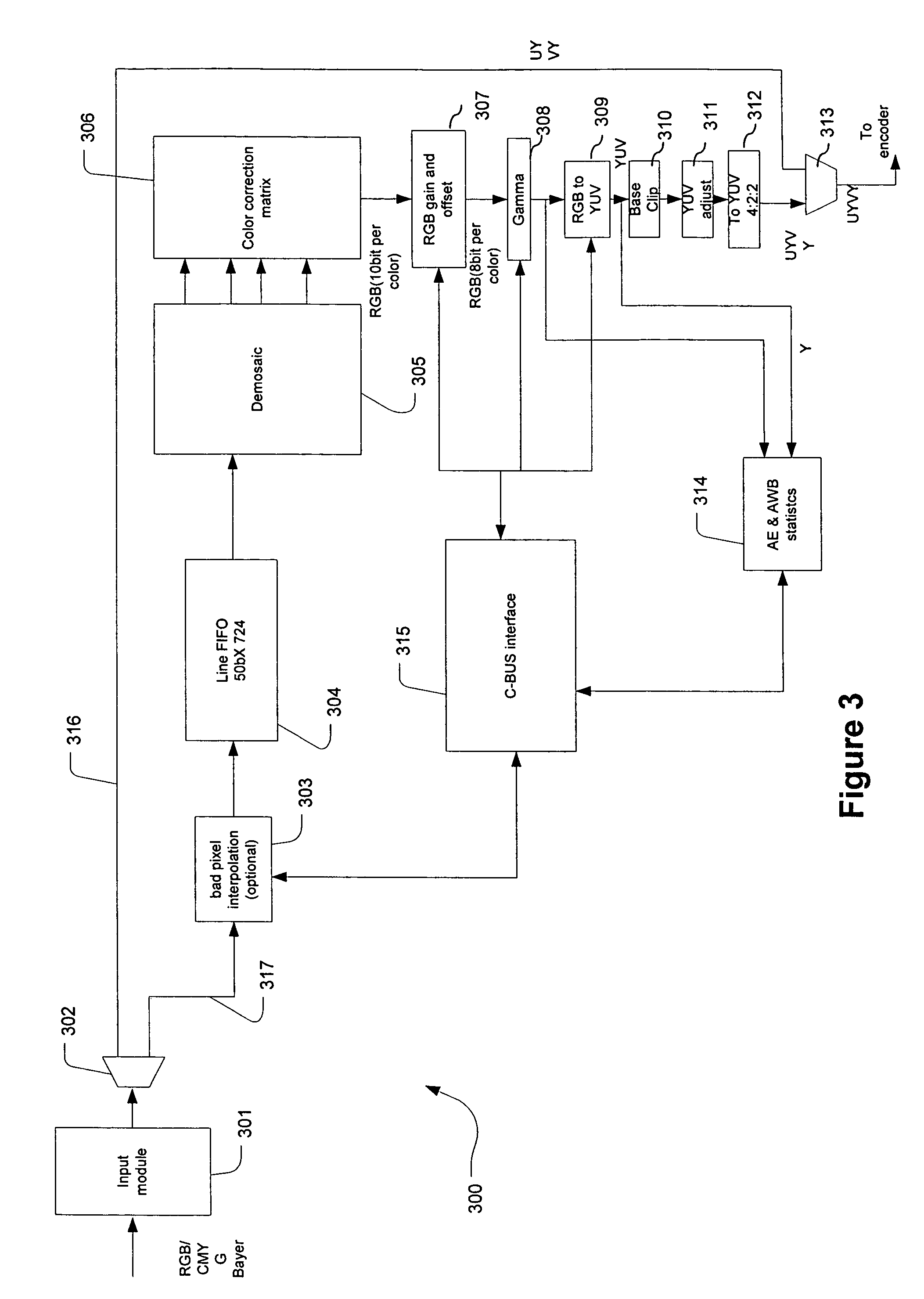
Digital image system and method for combining demosaicing and bad pixel correction
A digital image system and method for combining bad pixel correction and demosaicing in a single process is provided by interpolating sensor values for pixels immediately spatially adjacent to the current pixel being examined to detect defective pixels, and using the interpolated values for demosaicing. If the sensor value of the current pixel being examined is outside of a range of sensor values determined from the interpolated values by more than a configurable threshold amount, the current pixel is considered defective, and replaced using an estimated value from the neighboring pixels. The interpolated values calculated for use in detecting bad pixels can further be used as the interpolated values for demosaicing purposes
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Image signal processing apparatus, imaging apparatus, image signal processing method and computer program
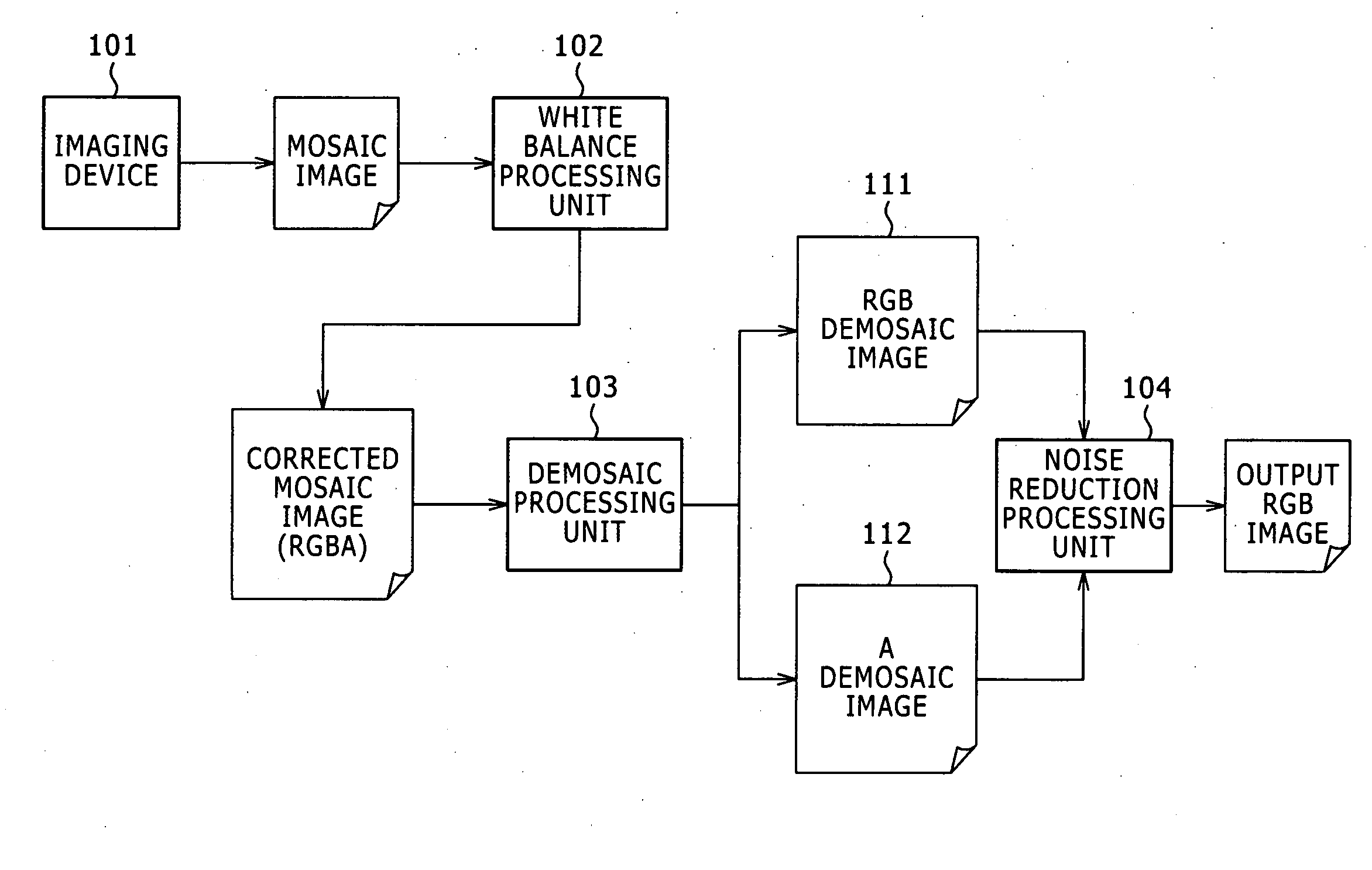
ActiveUS20070153335A1Improve image qualityReduce noiseImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersRadiologyNoise reduction
There is provided an image signal processing apparatus, comprising a demosaic processing unit receiving input of mosaic image data of each of signals obtained by a single plate imaging device having an element array composed of visible light obtaining elements obtaining visible light signals, and invisible light obtaining elements obtaining signals including invisible light components, and generating a demosaic image of each of the obtained signals; and a noise reduction processing unit receiving input of the demosaic image to execute correction of pixel values of the demosaic image obtained by the visible light obtaining elements on the basis of edge information extracted from the demosaic image of the signals obtained by the invisible light obtaining elements.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
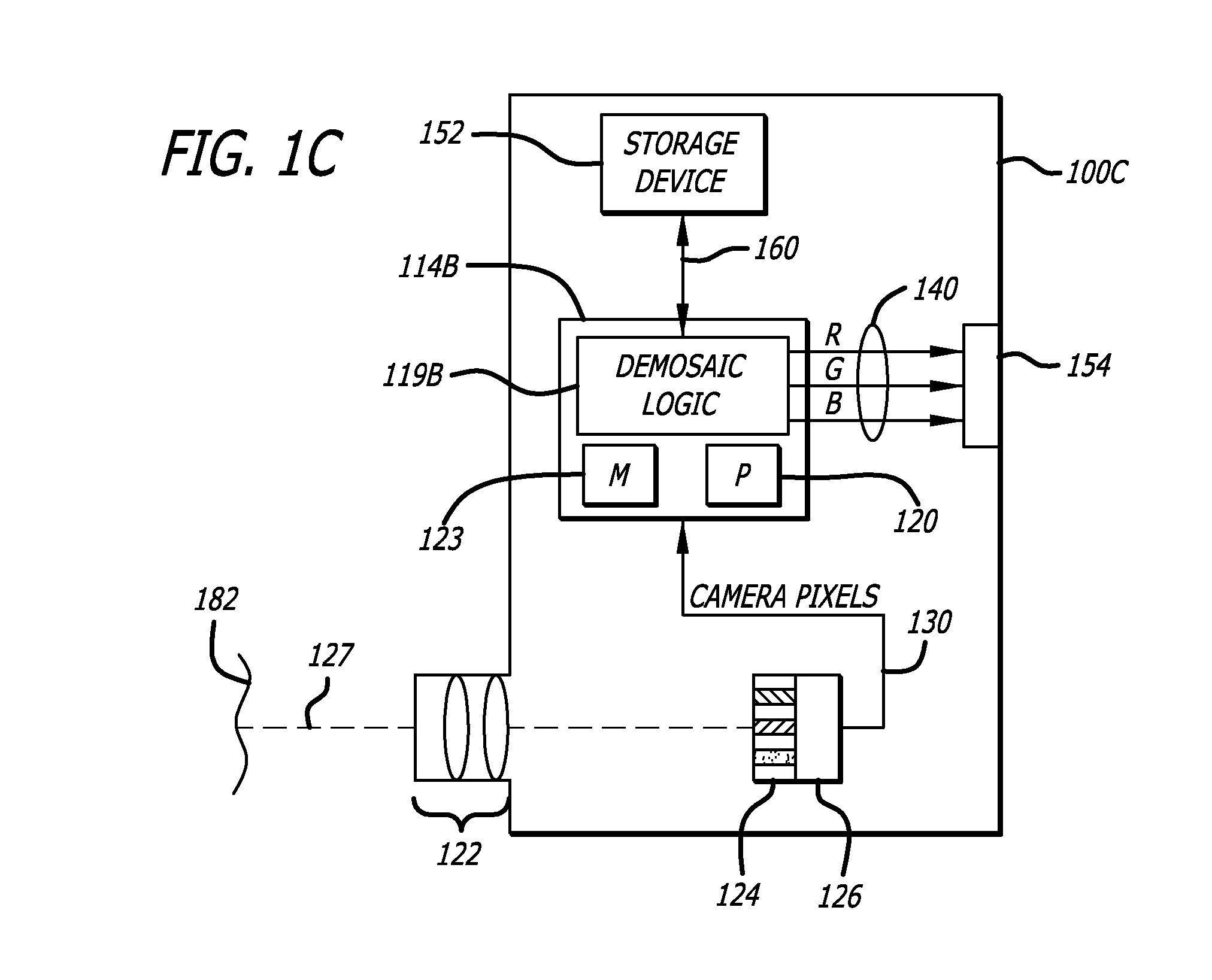
Methods and apparatus for demosaicing images with highly correlated color channels
ActiveUS20120206582A1Television system detailsGeometric image transformationSpatial correlationImage resolution
In one embodiment of the invention, an apparatus is disclosed including an image sensor, a color filter array, and an image processor. The image sensor has an active area with a matrix of camera pixels. The color filter array is in optical alignment over the matrix of the camera pixels. The color filter array assigns alternating single colors to each camera pixel. The image processor receives the camera pixels and includes a correlation detector to detect spatial correlation of color information between pairs of colors in the pixel data captured by the camera pixels. The correlation detector further controls demosaicing of the camera pixels into full color pixels with improved resolution. The apparatus may further include demosaicing logic to demosaic the camera pixels into the full color pixels with improved resolution in response to the spatial correlation of the color information between pairs of colors.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
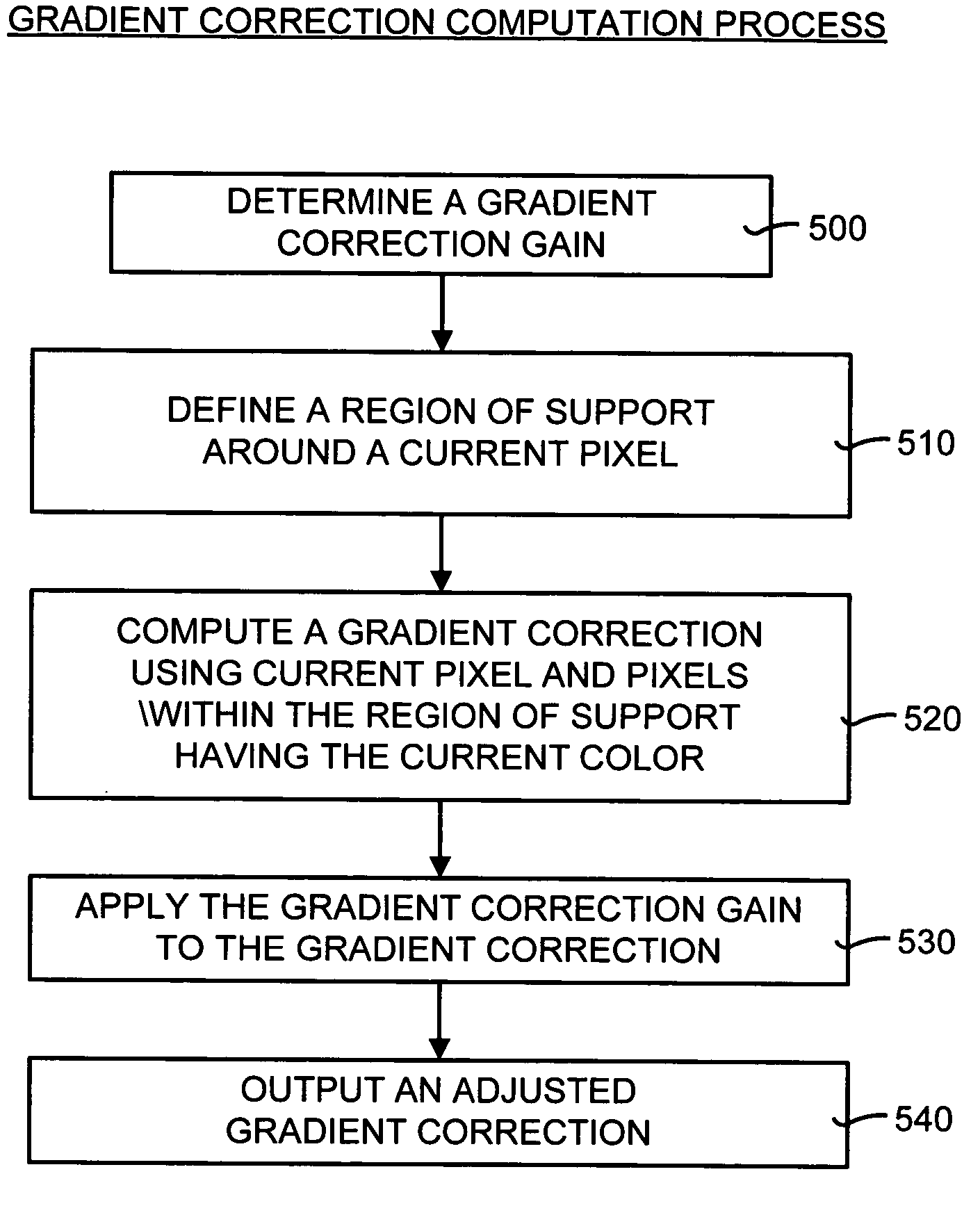
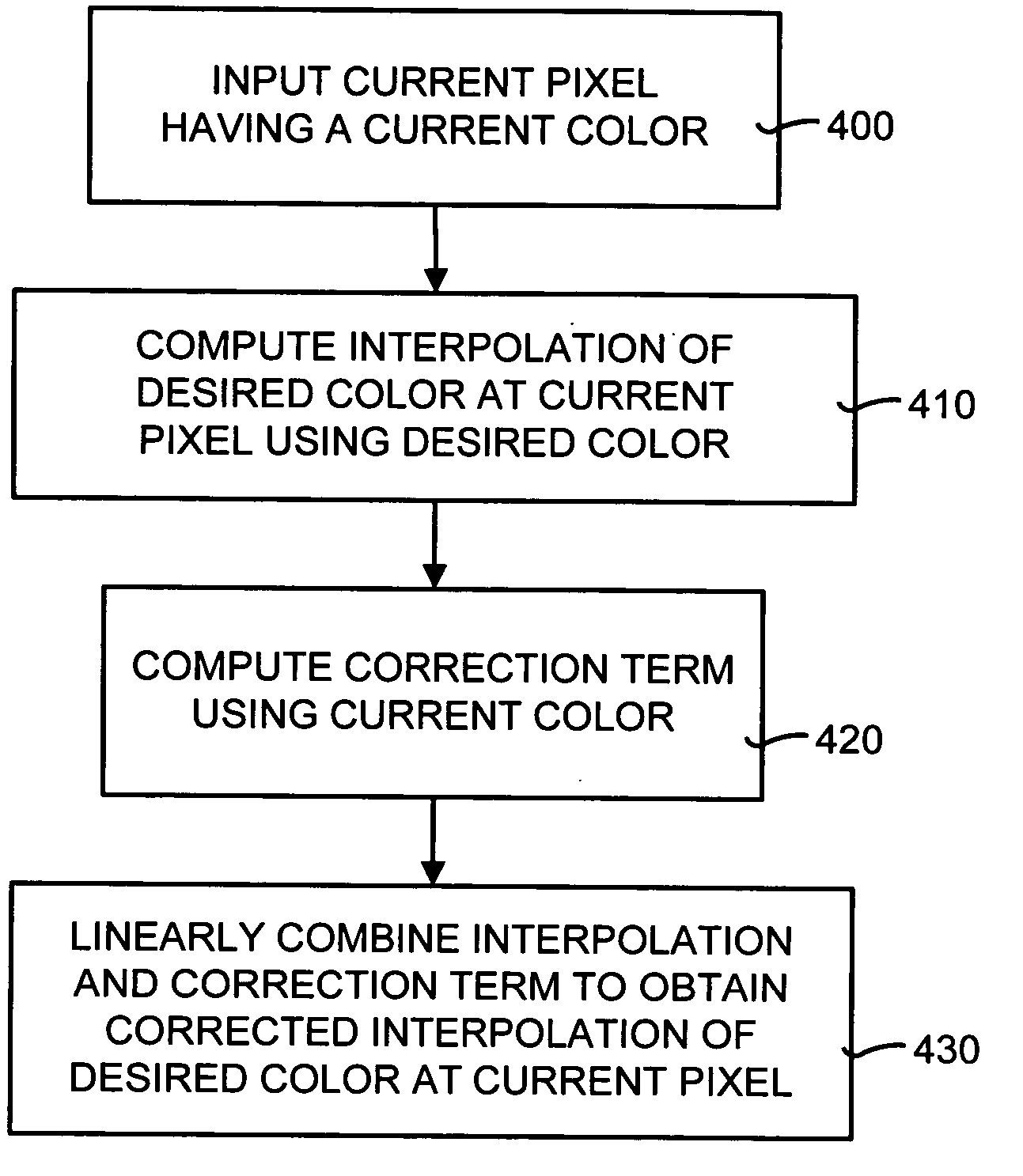
High-quality gradient-corrected linear interpolation for demosaicing of color images
ActiveUS7502505B2Improve performanceReduce complexityGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionColor imageAlgorithm
A gradient-corrected linear interpolation method and system for the demosaicing of color images. The method and system compute an interpolation using some a current technique (preferably a bilinear interpolation technique to reduce computational complexity), compute a correction term (such as a gradient of a desired color at a given pixel), and linearly combine the interpolation and the correction term to produce a corrected, high-quality interpolation of a missing color value at a pixel. The correction term may be a gradient correction term computed from the current color of the current pixel. This gradient is directly used to affect and correct the estimated color value produced by the prior art interpolation technique. The gradient-corrected linear interpolation method and system may also apply a gradient-correction gain to the gradient correction term. This gradient-correction gain affects the amount of gradient correction that is applied to the interpolation.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Digital image system and method for implementing an adaptive demosaicing method
InactiveUS7088392B2Reduce imbalanceAdaptive smoothingTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPattern recognitionSharpening
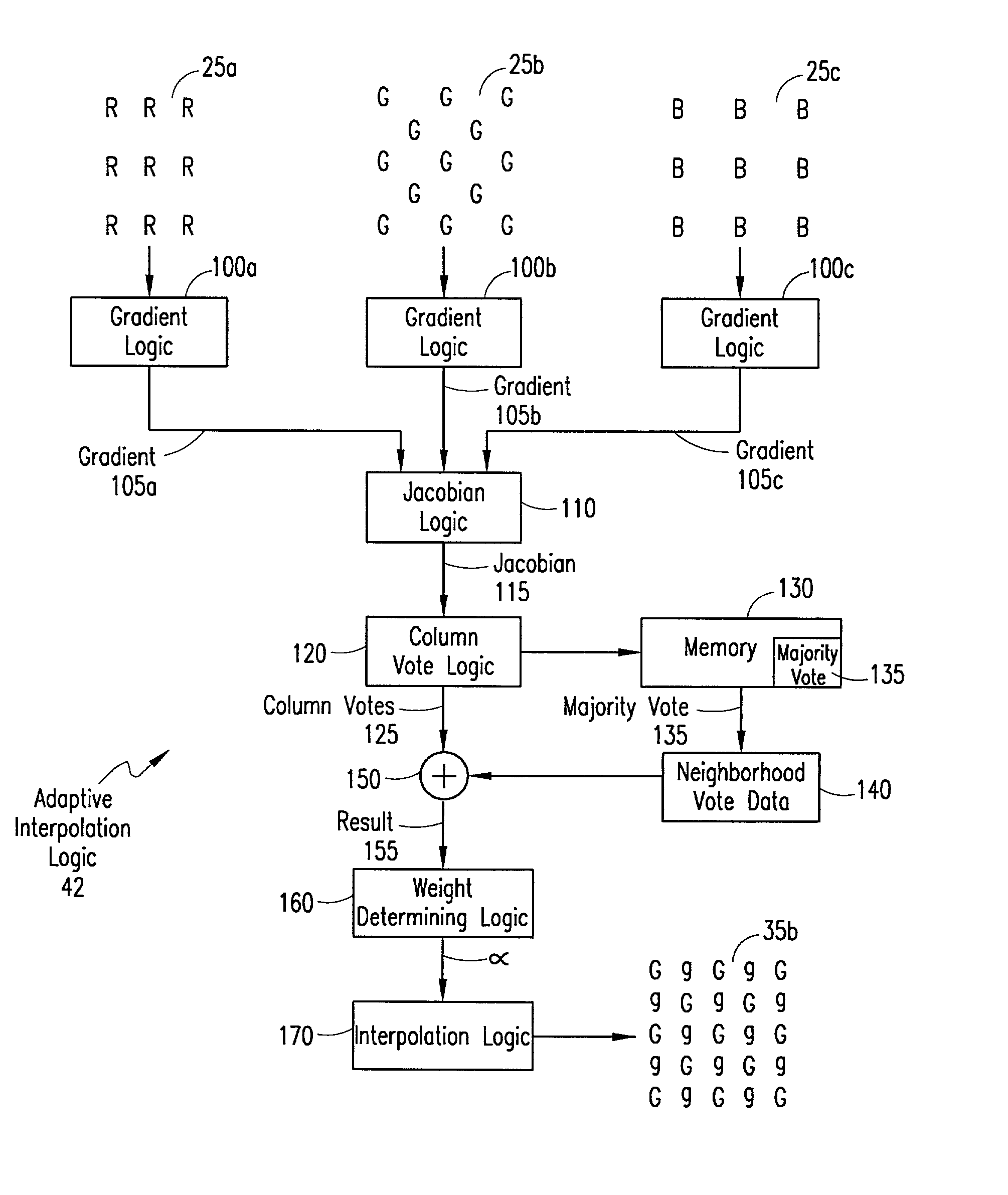
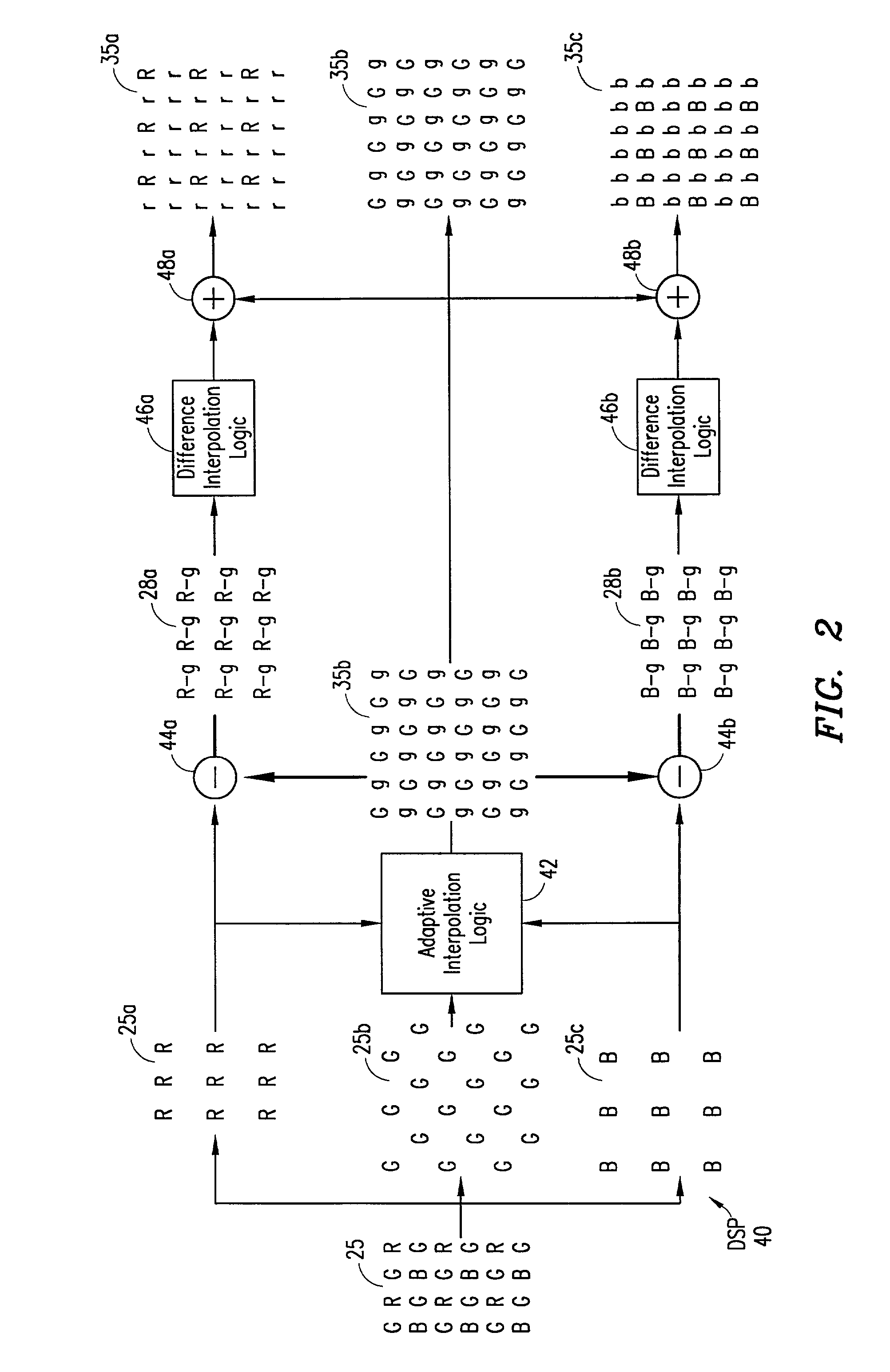
An adaptive demosaicing method interpolates images based on color edge detection and neighborhood voting. The adaptive demosaicing algorithm uses a voting scheme to determine the direction of interpolation at each missing luminance pixel location. Each color plane votes either horizontal or vertical based on a comparison between the horizontal and vertical components of the degree of change (i.e., gradient, Laplacian or other measure of the degree of change) in that color plane. Votes are counted from the neighborhood pixels as well as from measurements taken at the pixel location itself. Once the luminance plane is fully interpolated, the chrominance planes are filled in by simple bilinear or median interpolation of difference chrominance values. Enhancements to the adaptive demosaicing algorithm permit adaptive smoothing and sharpening.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
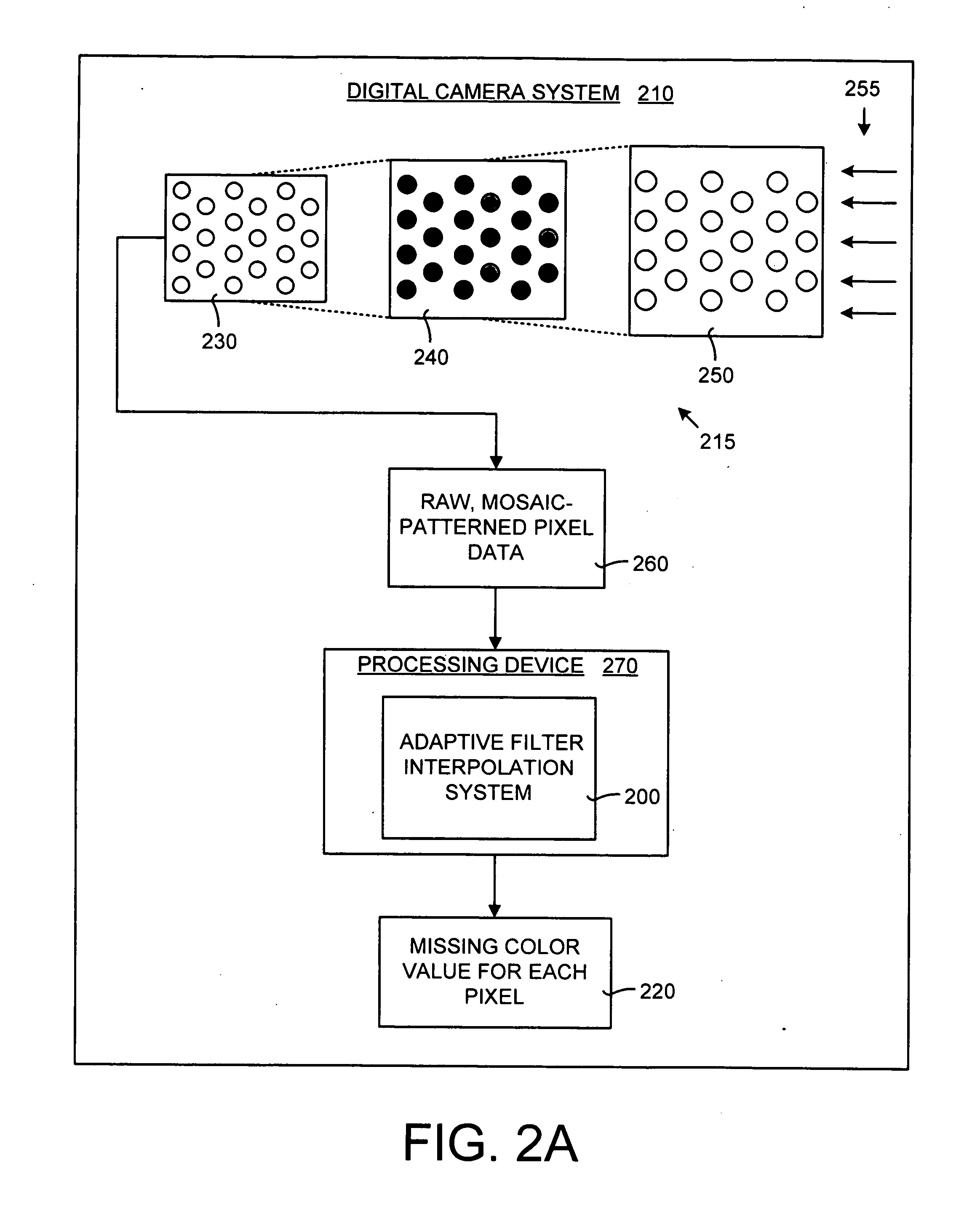
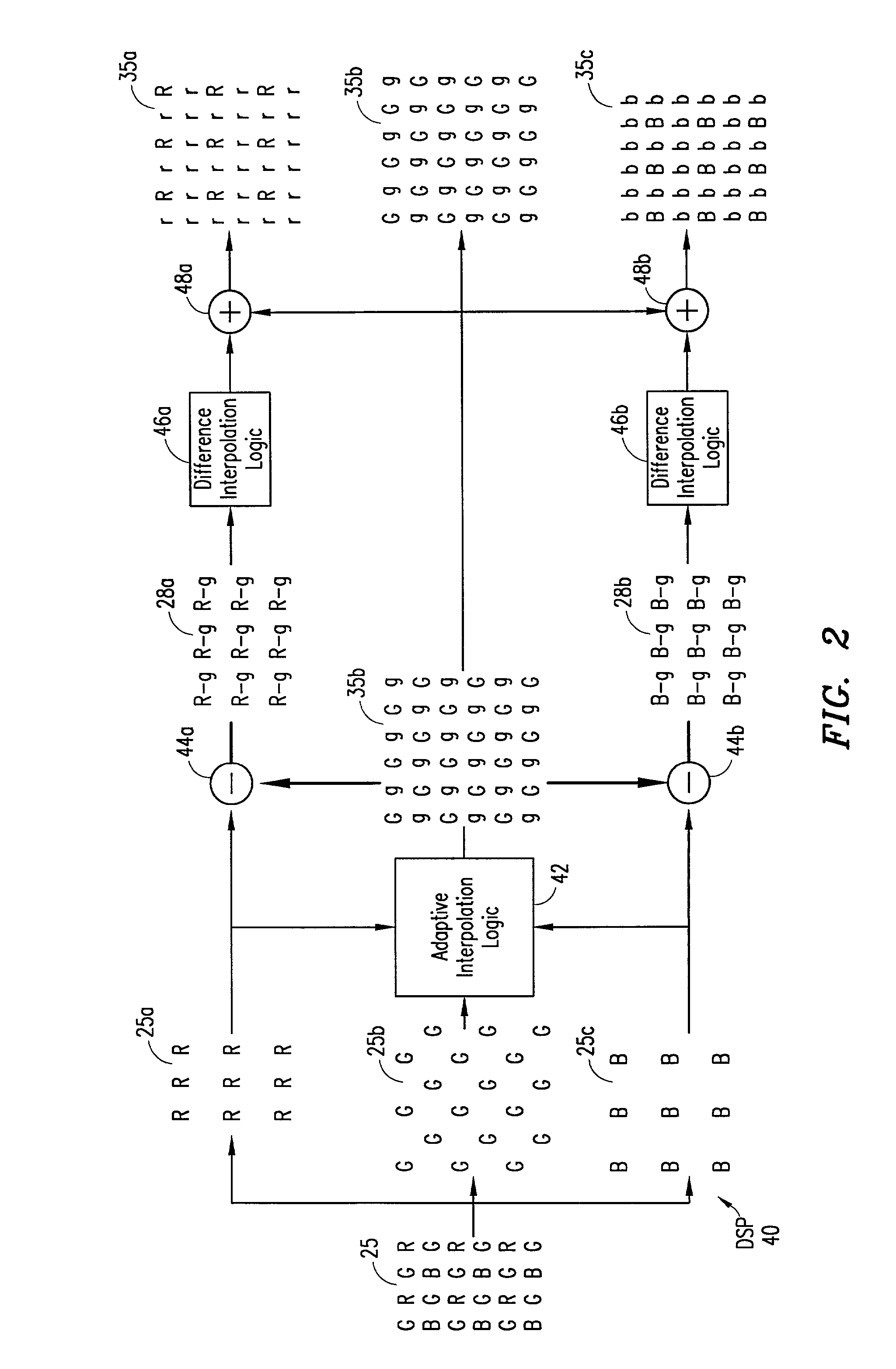
System and method for adaptive interpolation of images from patterned sensors
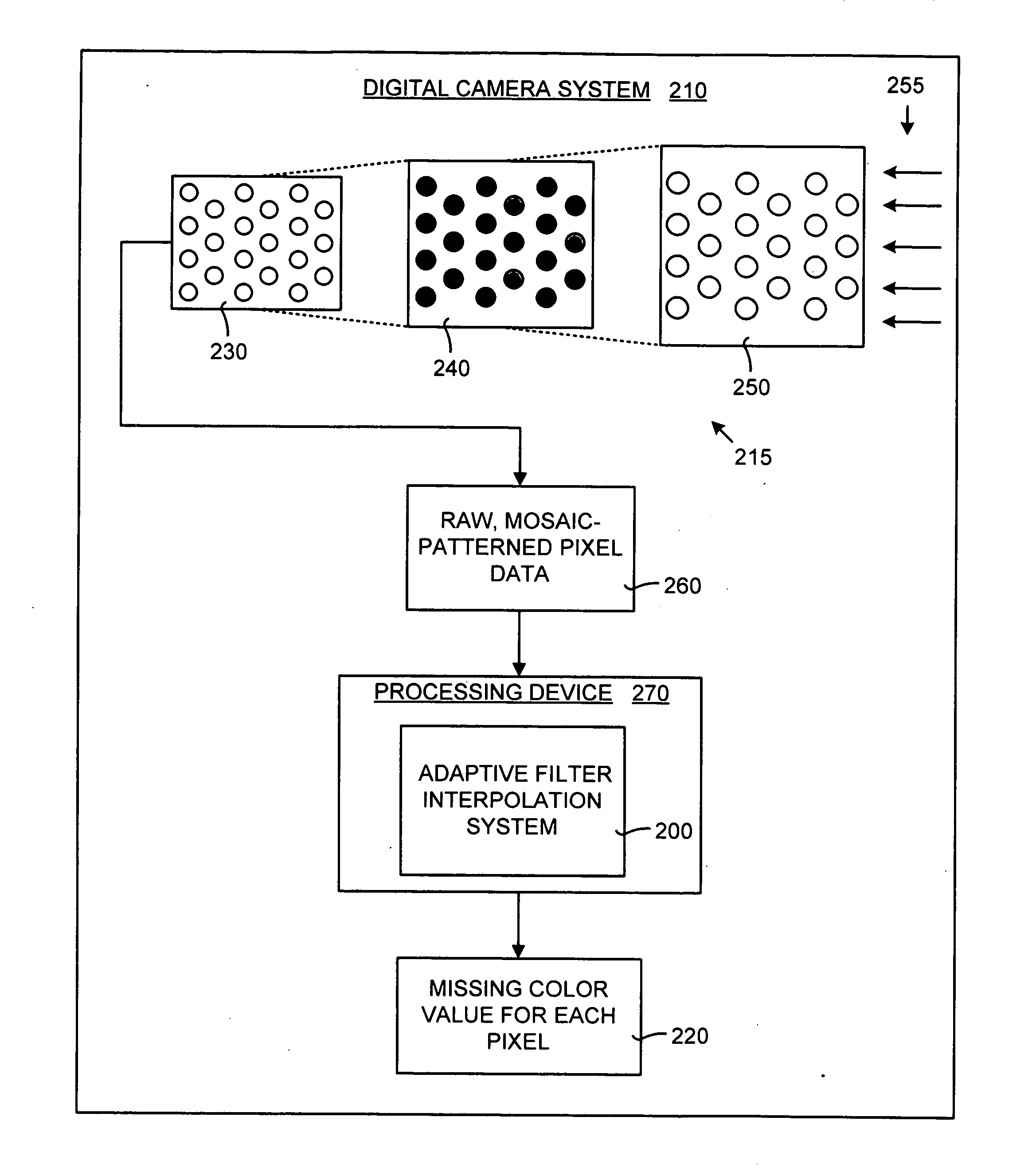
ActiveUS20050200733A1Computationally efficientImprove image qualityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsColor imageGrating
A adaptive filter interpolation method and system for the demosaicing of color images. In general, input pixels are input in a Bayer-mosaiced pattern (only one color per pixel), and output pixels are in full RGB mode (three color values per pixel). For each pixel location, in raster scan order, the processing steps can be summarized as follows. Following a regular raster scanning order (from left to right and top to bottom), for each pixel location horizontal and vertical gradients are first computed (whose computation depends on the available color for that pixel), and from those the appropriate interpolation filters are chosen from a small set of predetermined filters. Then, the chosen filters are applied to interpolate the missing data.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Digital image system and method for implementing an adaptive demosaicing method
InactiveUS20030052981A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPattern recognitionSharpening
An adaptive demosaicing method is disclosed that interpolates images based on color edge detection and neighborhood voting. The adaptive demosaicing algorithm uses a voting scheme to determine the direction of interpolation at each missing luminance pixel location. Each color plane votes either horizontal or vertical based on a comparison between the vertical and horizontal components of the degree of change (i.e., gradient, Laplacian or other measure of the degree of change) in that color plane. Votes are counted from the neighborhood pixels as well as from measurements taken at the pixel location itself. Once the luminance plane is fully interpolated, the chrominance planes are filled in by a simple bilinear or median interpolation of difference chrominance values. Enhancements to the adaptive demosaicing algorithm permit adaptive smoothing and sharpening.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
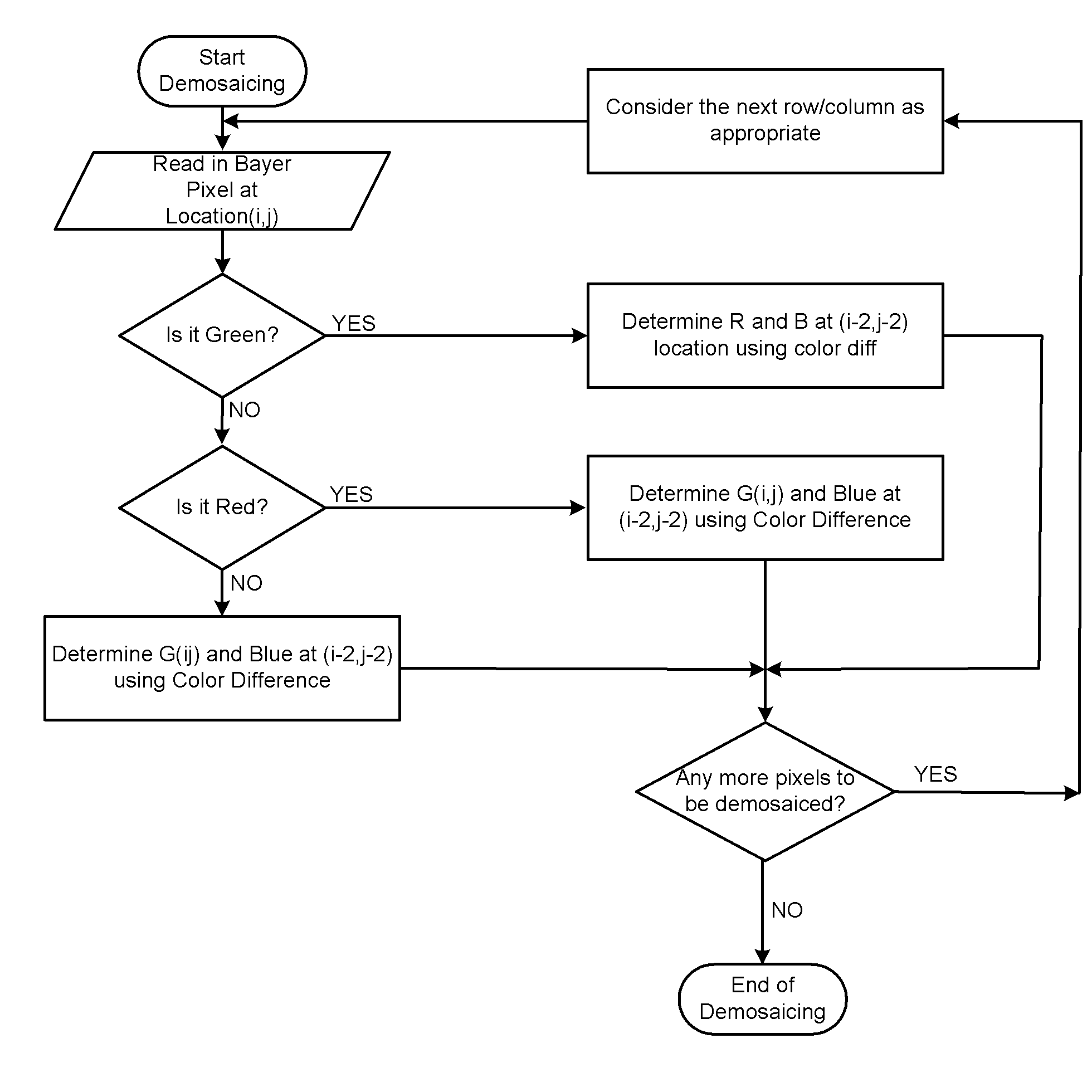
Method of demosaicing a digital mosaiced image
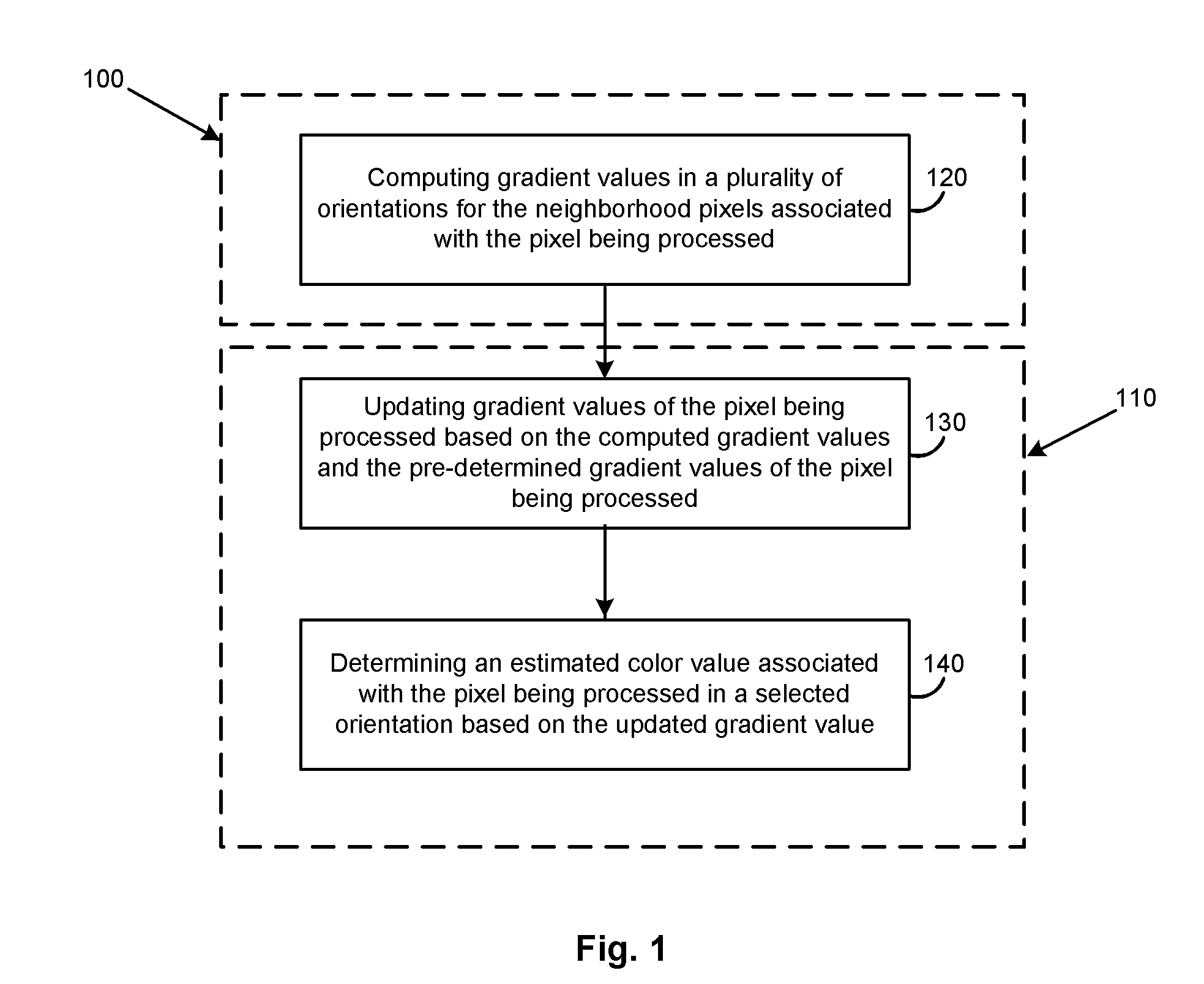
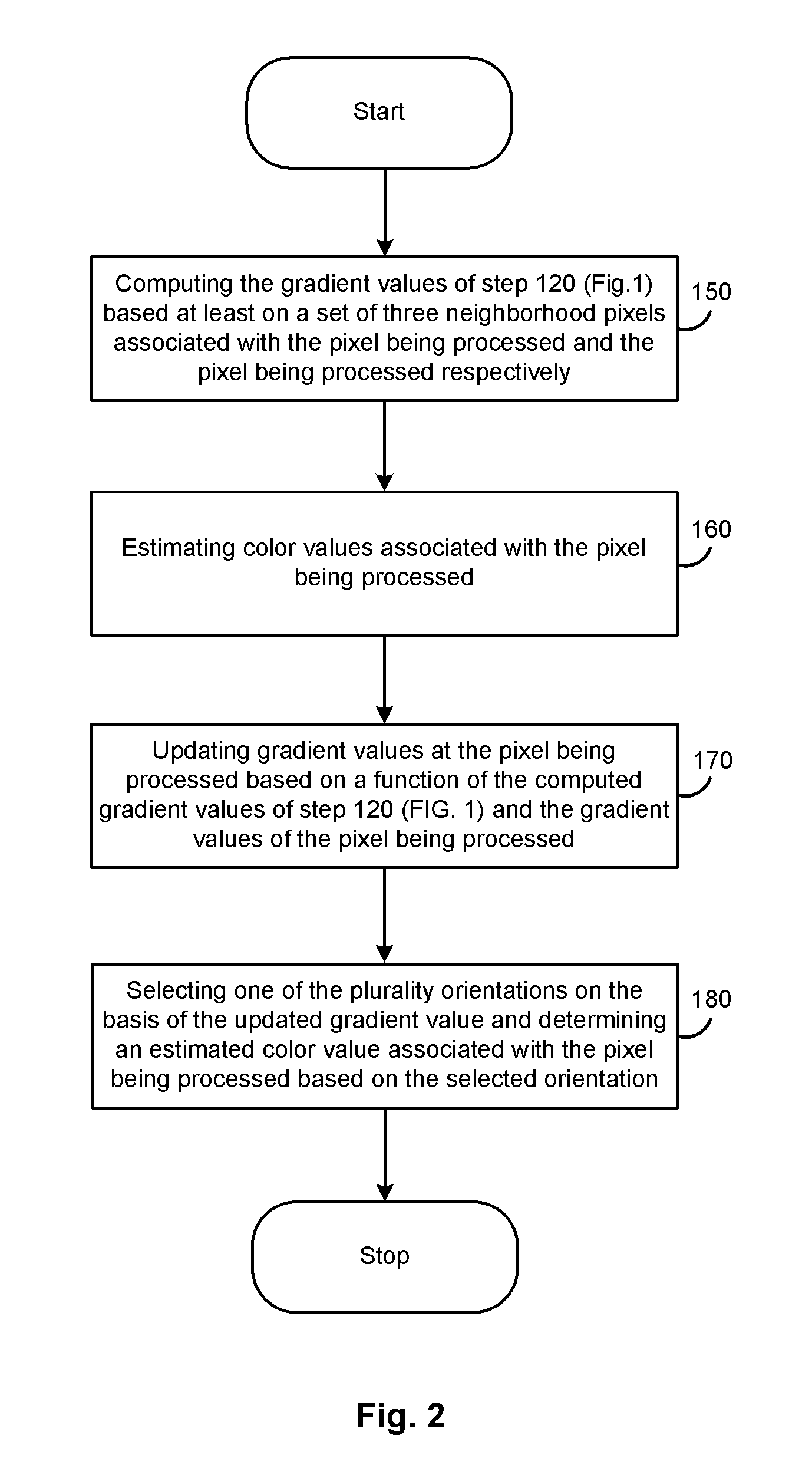
InactiveUS20080253652A1Geometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer visionPixel based
In one example embodiment, a method enables, computing, for a first pixel in the digital mosaiced image, the first pixel being characterized by a first color component and a first set of gradient values in a plurality of orientations, gradient values in the plurality of orientations for a second pixel in the neighborhood of the first pixel. Color values in the plurality of orientations corresponding to a second color component associated with the first pixel based on the set of first gradient values are estimated. The first set of gradient values based at least in part on the computed gradient values is updated. One of the plurality of orientations of the estimated color value based on the updated set of first gradient values is selected and one of the estimated color values corresponding to the selected orientation is determined.
Owner:ARICENT INC
System and method for capturing color images that extends the dynamic range of an image sensor using first and second groups of pixels
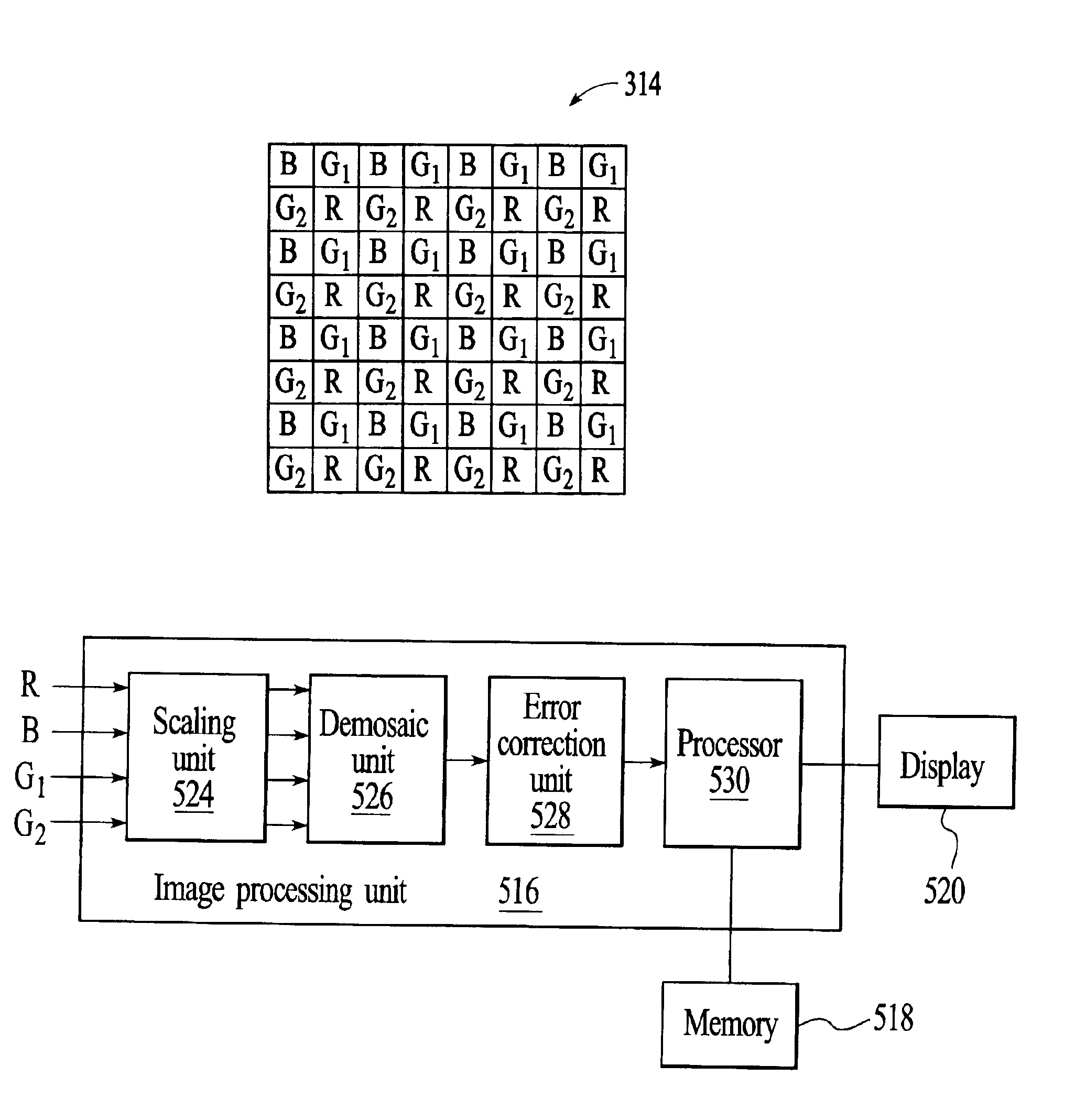
InactiveUS6924841B2Improve dynamic rangeLess powerImage enhancementTelevision system detailsColor imageDigital imaging
A technique for digitally capturing a high contrast color image involves simultaneously capturing image data from bright and dark areas using an image sensor with pixels of the same color that have different sensitivities to the bright and dark areas. The image data from the different sensitivity pixels is then used to generate a final image that includes features from both the bright and dark areas. An embodiment of a digital imaging system includes an image sensor with a first group of pixels that have a first sensitivity to a first color and a second group of pixels that have a second sensitivity to the same color. Image data that is captured by the two groups of pixels is brought to a common scale by a scaling unit before the image data is used to generate demosaiced image data. The scaled image data is used by a demosaic unit to determine intensity values for the first color at all of the pixel locations. Errors in the demosaiced intensity values that result from capturing the first color image data with pixels of two different sensitivities are corrected by an error correction unit to generate a final image that accurately depicts the original high contrast color image.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
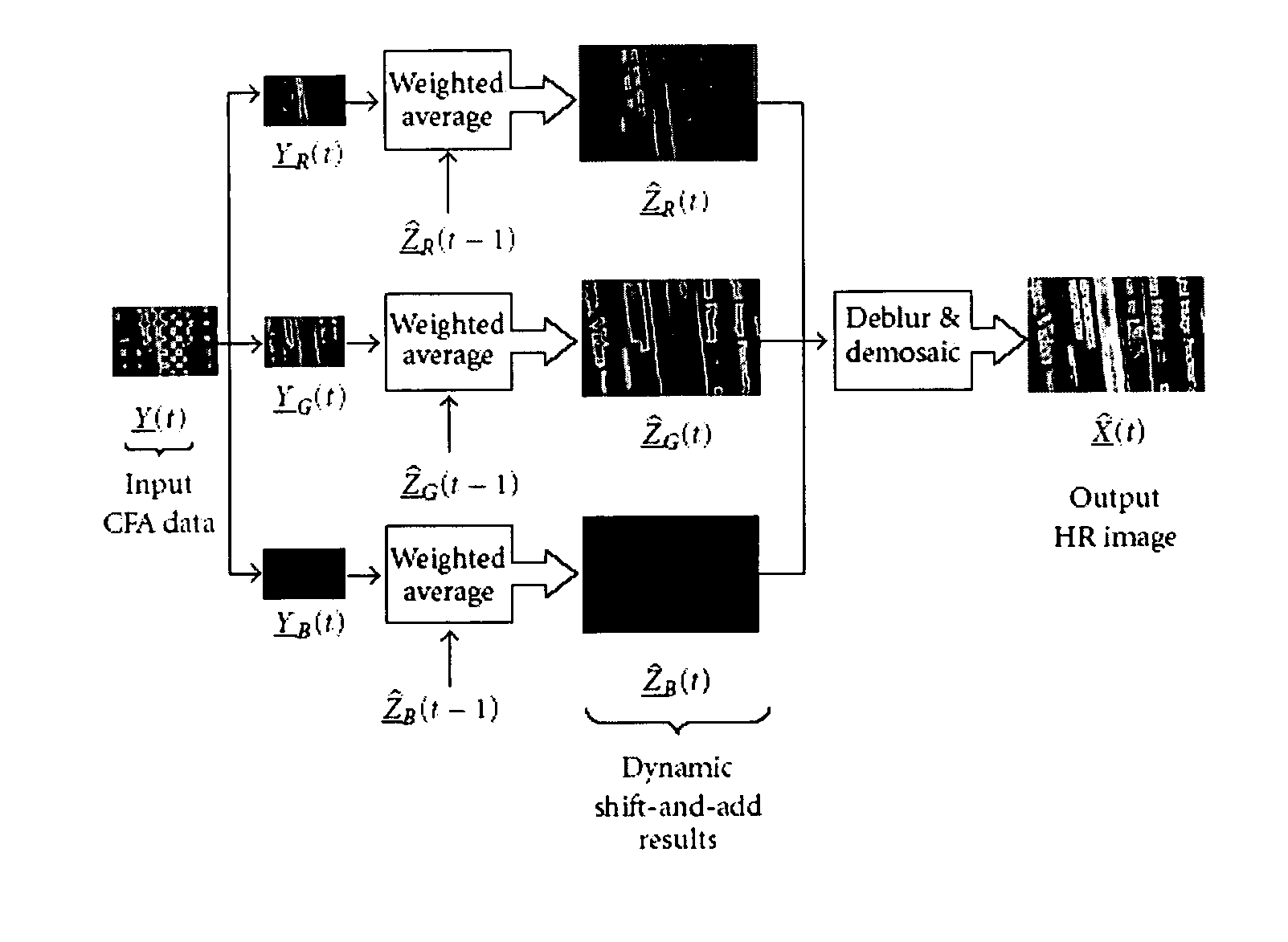
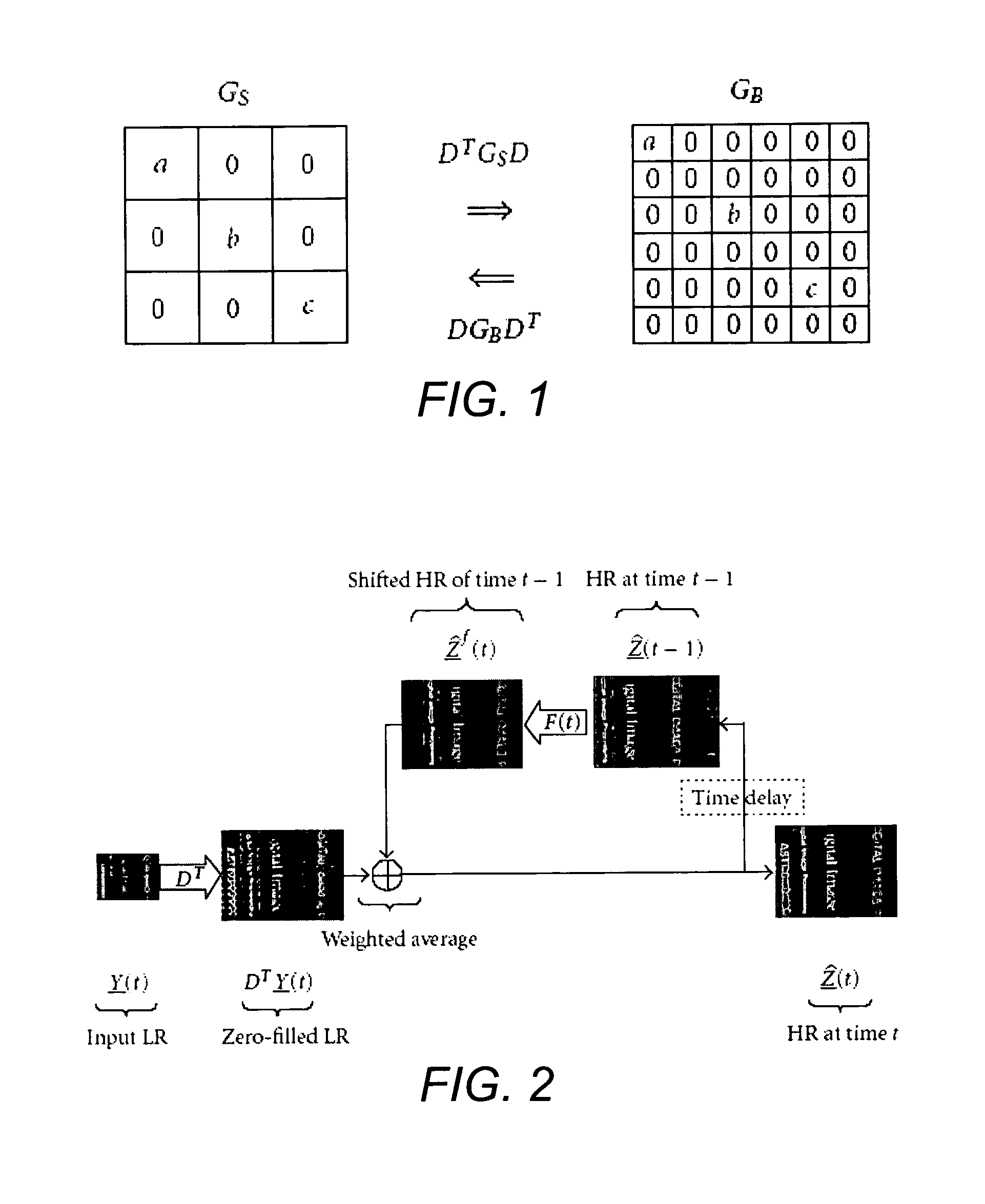
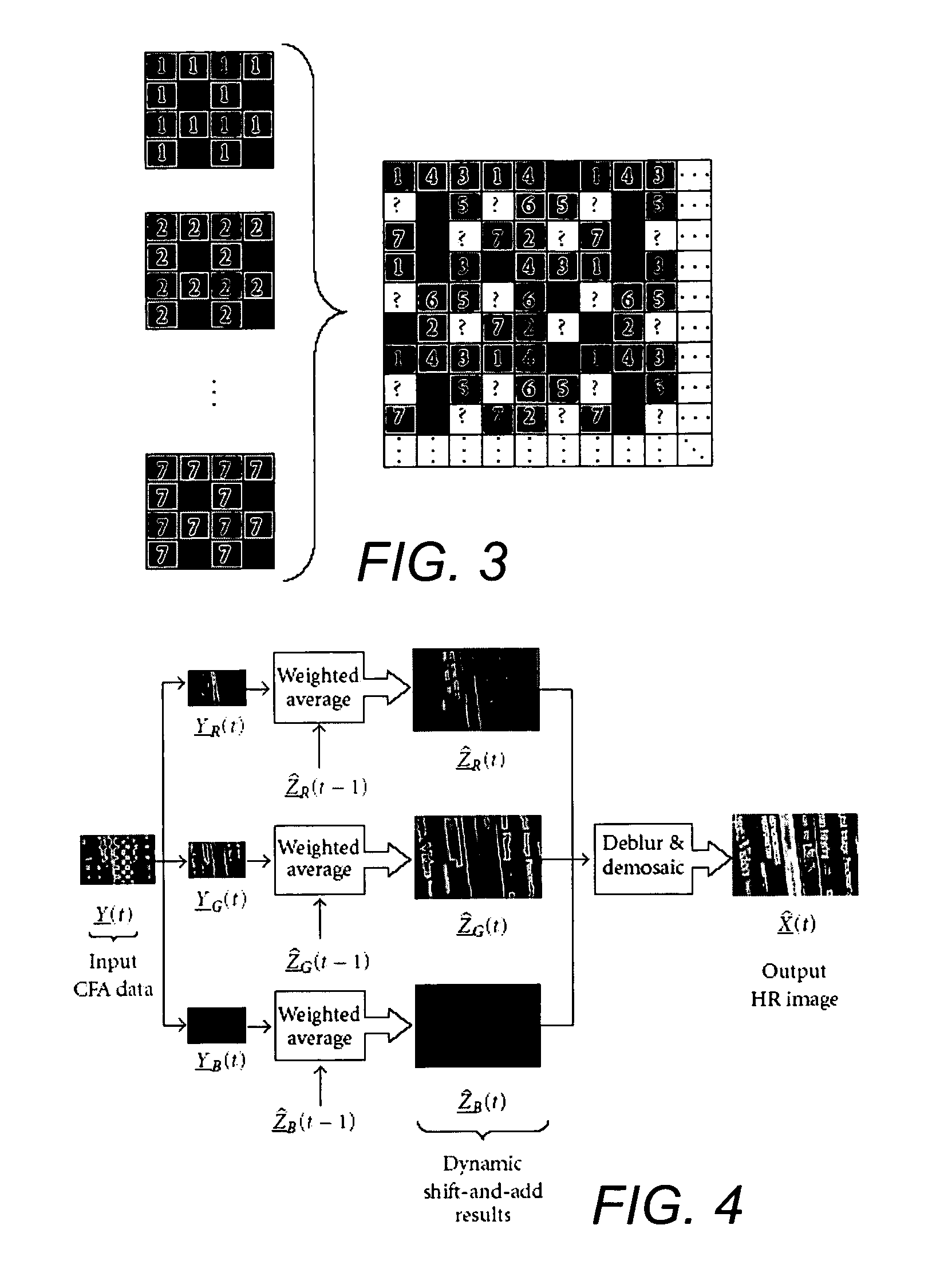
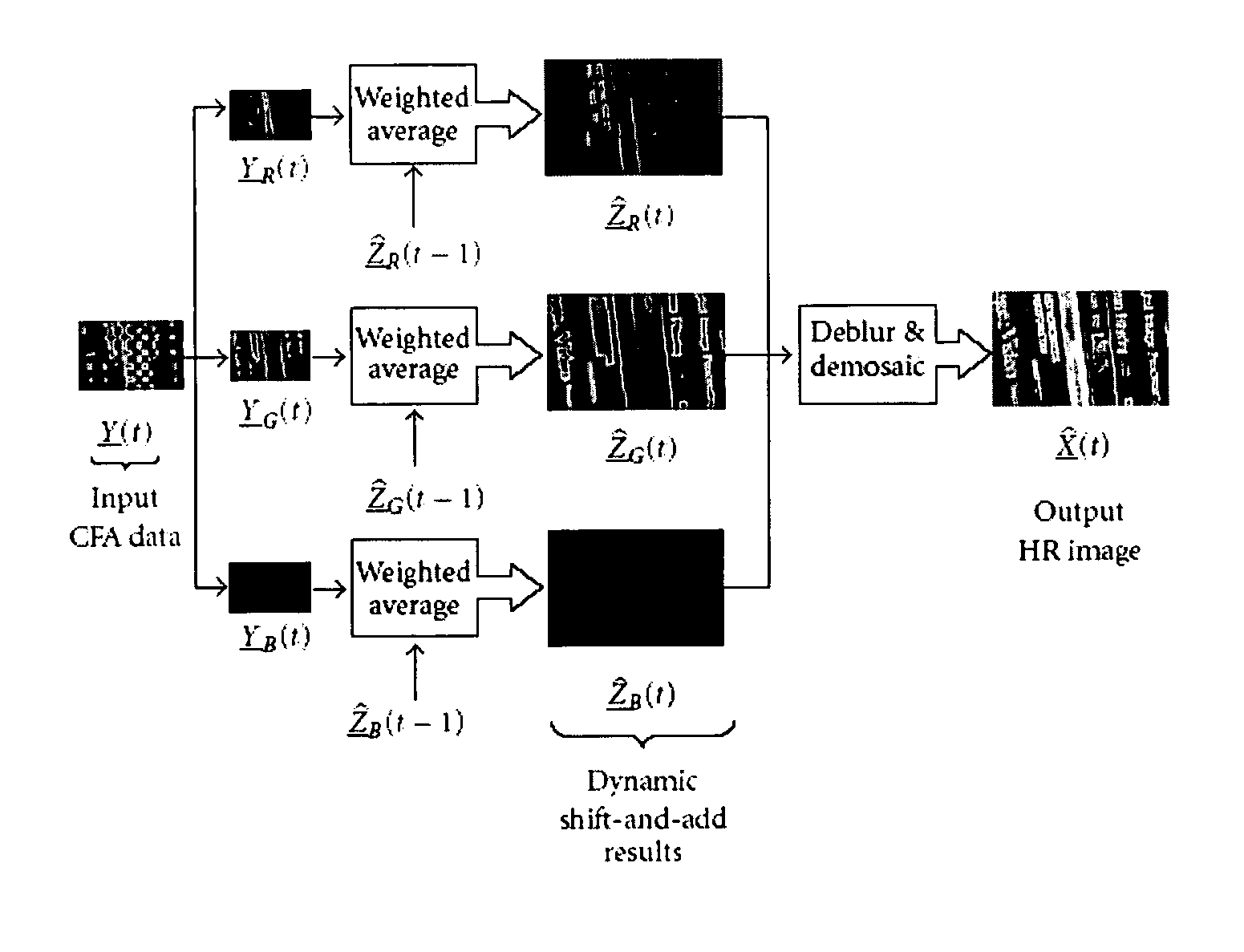
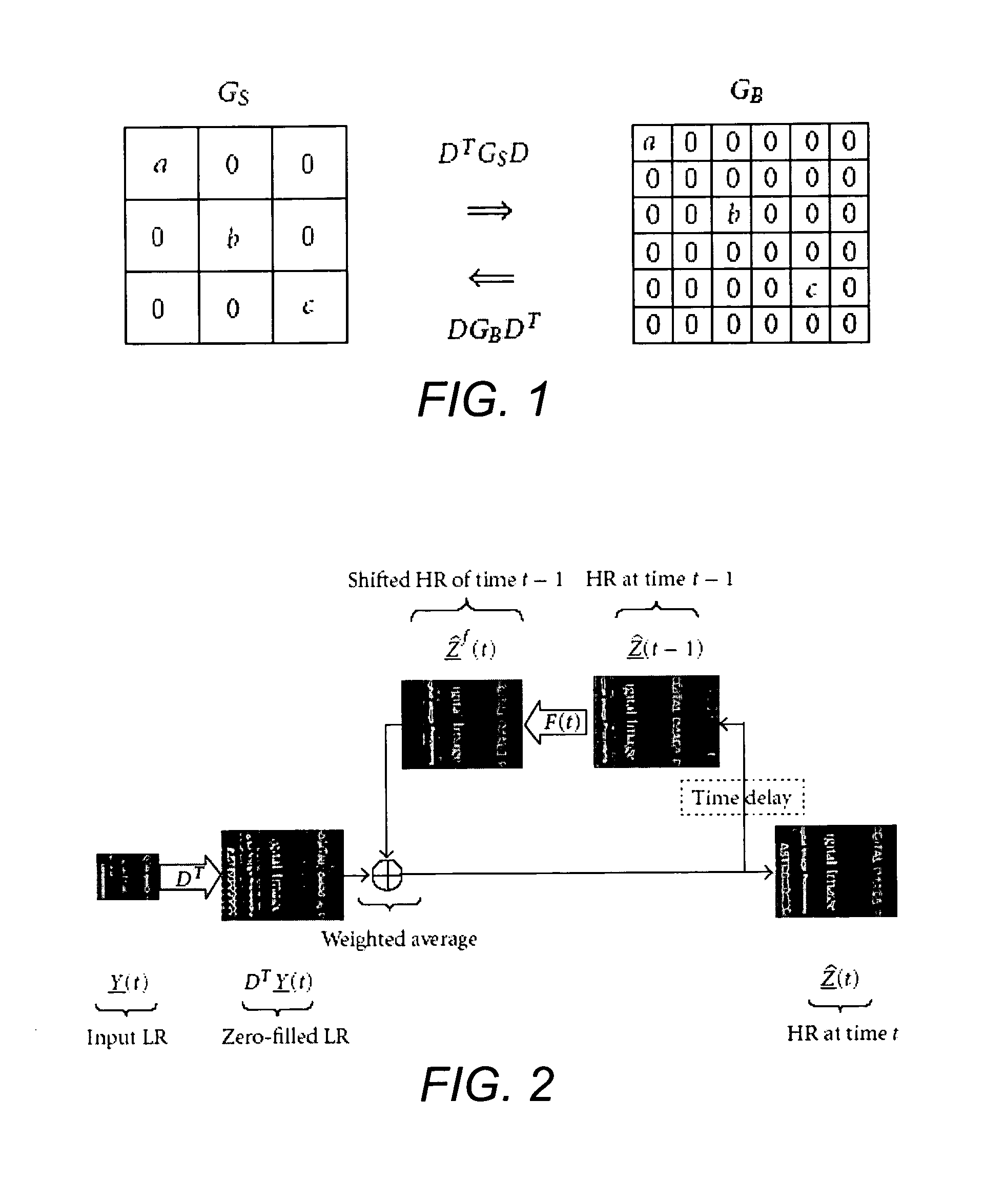
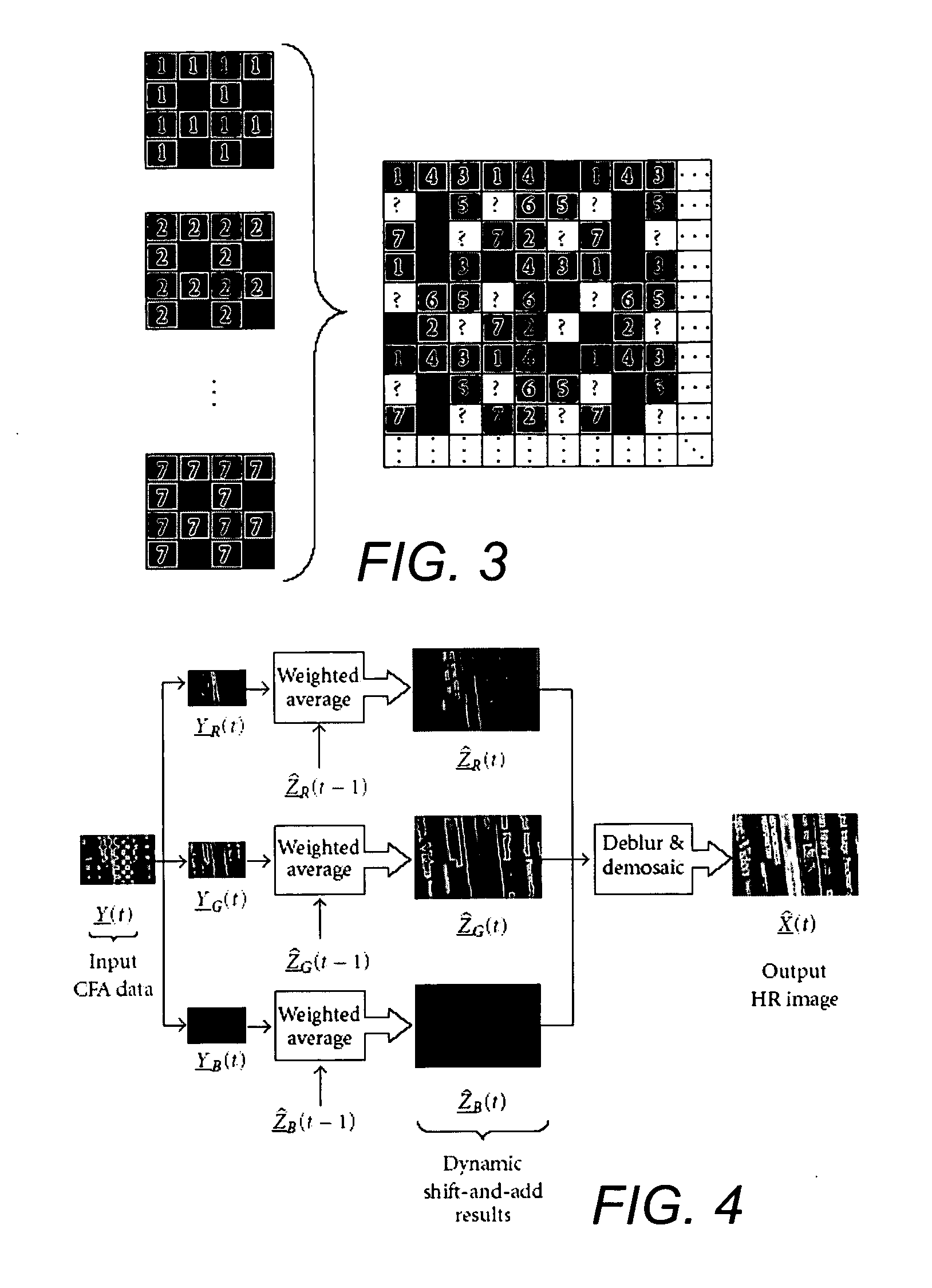
Dynamic reconstruction of high-resolution video from color-filtered low-resolution video-to-video super-resolution
ActiveUS7379612B2Quality improvementReduce memory requirementsGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionKaiman filterImage resolution
A method is provided of solving the dynamic super-resolution (SR) problem of reconstructing a high-quality set of monochromatic or color superresolved images from low-quality monochromatic, color, or mosaiced frames. The invention includes a joint method for simultaneous SR, deblurring, and demosaicing, this way taking into account practical color measurements encountered in video sequences. For the case of translational motion and common space-invariant blur, the proposed invention is based on a very fast and memory efficient approximation of the Kalman filter (KF). Experimental results on both simulated and real data are supplied, demonstrating the invention algorithms, and their strength.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
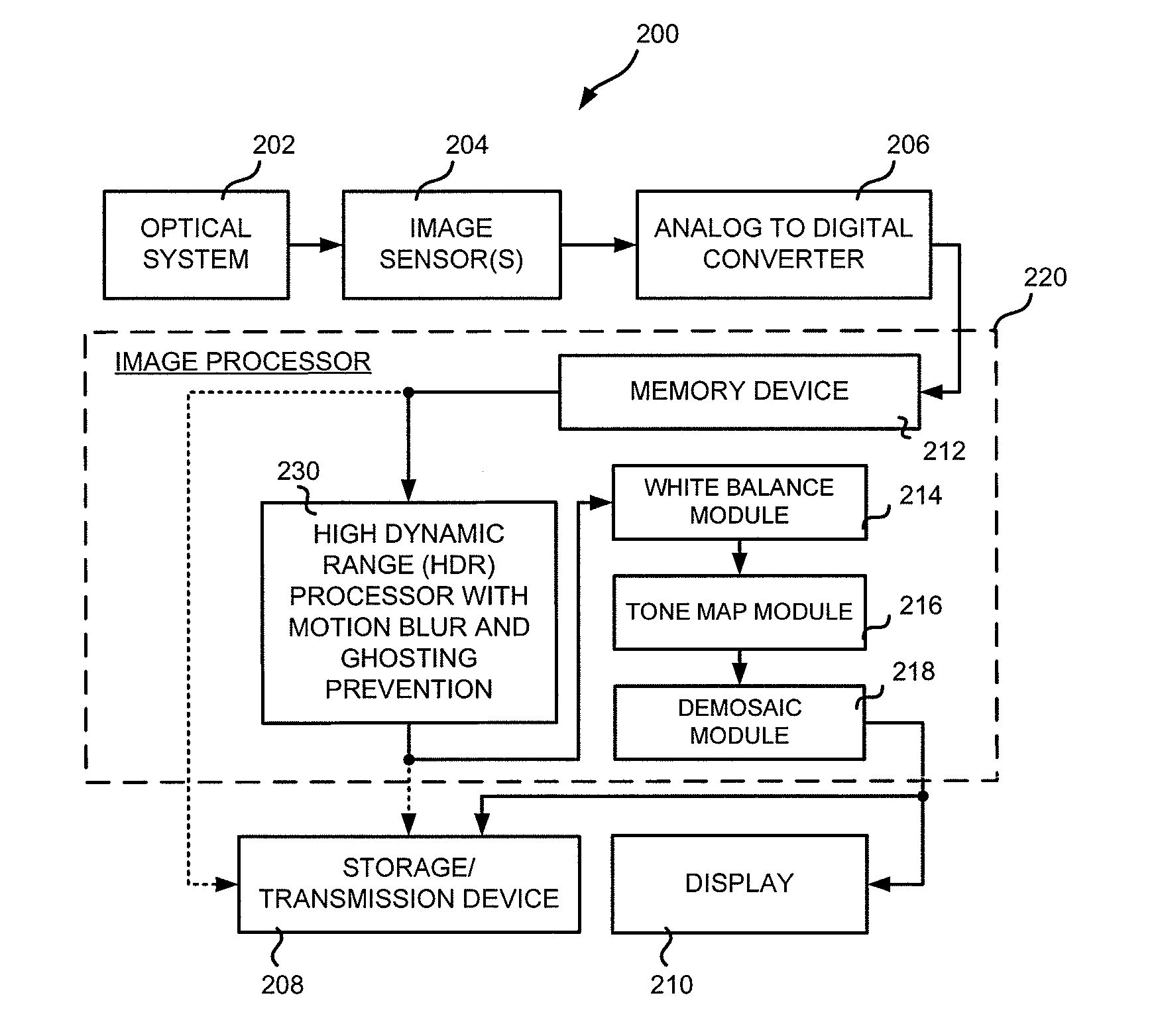
Method and apparatus for motion blur and ghosting prevention in imaging system
InactiveUS20110058050A1Noise robustPromote differentiationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsAlong edgeImage pair
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Image pickup apparatus, color noise reduction method, and color noise reduction program
InactiveUS20090160992A1Reduce color noiseReduce noiseImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionNoise reduction
An image pickup apparatus includes an image sensor including a color filter having pixels of different colors arranged in a predetermined order and a demosaic processor. The image sensor receives a subject image and outputs an image signal including color signals of the different colors. The demosaic processor generates color signals of the different colors for each of pixels of the image from the image signal. The demosaic processor includes a generation unit and a noise reduction unit. The generation unit performs computation using a target color signal representing a predetermined target color signal included in the image signal and a predetermined different color signal so as to generate a color-related signal that associates the target color signal with the predetermined different color signal for a pixel of the target color signal. The noise reduction unit performs a noise reduction process on the color-related signal generated by the generation unit.
Owner:SONY CORP
Dynamic reconstruction of high-resolution video from color-filtered low-resolution video-to-video super-resolution
ActiveUS20070071362A1Quality improvementReduce memory requirementsGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionKaiman filterImage resolution
A method is provided of solving the dynamic super-resolution (SR) problem of reconstructing a high-quality set of monochromatic or color superresolved images from low-quality monochromatic, color, or mosaiced frames. The invention includes a joint method for simultaneous SR, deblurring, and demosaicing, this way taking into account practical color measurements encountered in video sequences. For the case of translational motion and common space-invariant blur, the proposed invention is based on a very fast and memory efficient approximation of the Kalman filter (KF). Experimental results on both simulated and real data are supplied, demonstrating the invention algorithms, and their strength.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Digital image system and method for combining demosaicing and bad pixel correction
A digital image system and method for combining bad pixel correction and demosaicing in a single process is provided by interpolating sensor values for pixels immediately spatially adjacent to the current pixel being examined to detect defective pixels, and using the interpolated values for demosaicing. If the sensor value of the current pixel being examined is outside of a range of sensor values determined from the interpolated values by more than a configurable threshold amount, the current pixel is considered defective, and replaced using an estimated value from the neighboring pixels. The interpolated values calculated for use in detecting bad pixels can further be used as the interpolated values for demosaicing purposes
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
High-quality gradient-corrected linear interpolation for demosaicing of color images
ActiveUS20050201616A1Easy to implementImprove performanceGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionColor imageComputation complexity
A gradient-corrected linear interpolation method and system for the demosaicing of color images. The method and system compute an interpolation using some a current technique (preferably a bilinear interpolation technique to reduce computational complexity), compute a correction term (such as a gradient of a desired color at a given pixel), and linearly combine the interpolation and the correction term to produce a corrected, high-quality interpolation of a missing color value at a pixel. The correction term may be a gradient correction term computed from the current color of the current pixel. This gradient is directly used to affect and correct the estimated color value produced by the prior art interpolation technique. The gradient-corrected linear interpolation method and system may also apply a gradient-correction gain to the gradient correction term. This gradient-correction gain affects the amount of gradient correction that is applied to the interpolation.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for image demosaicing
ActiveUS8340407B2Improve image qualityReduce artifactsGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionParallel computingDemosaicing
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method for creating high resolution color image, system for creating high resolution color image and program creating high resolution color image
InactiveUS7515747B2Evaluates smoothnessEvaluates smoothness of chrominanceTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionColor imageImage resolution
A limitation in the physical resolution of an image sensor offers a motivation to improve the resolution of an image. Super-resolution is mainly applied to gray scale images, and it has not been thoroughly investigated yet that a high resolution color image is reconstructed from an image sensor having a color filter array. An object of the invention is to directly reconstruct a high resolution color image from color mosaic obtained by an image sensor having a color filter array. A high resolution color image reconstruction method according to the invention is based on novel technique principles of color image reconstruction that an increase in resolution and demosaicing are performed at the same time. The verification and effective implement of the invention are also described.
Owner:TOKYO INST OF TECH
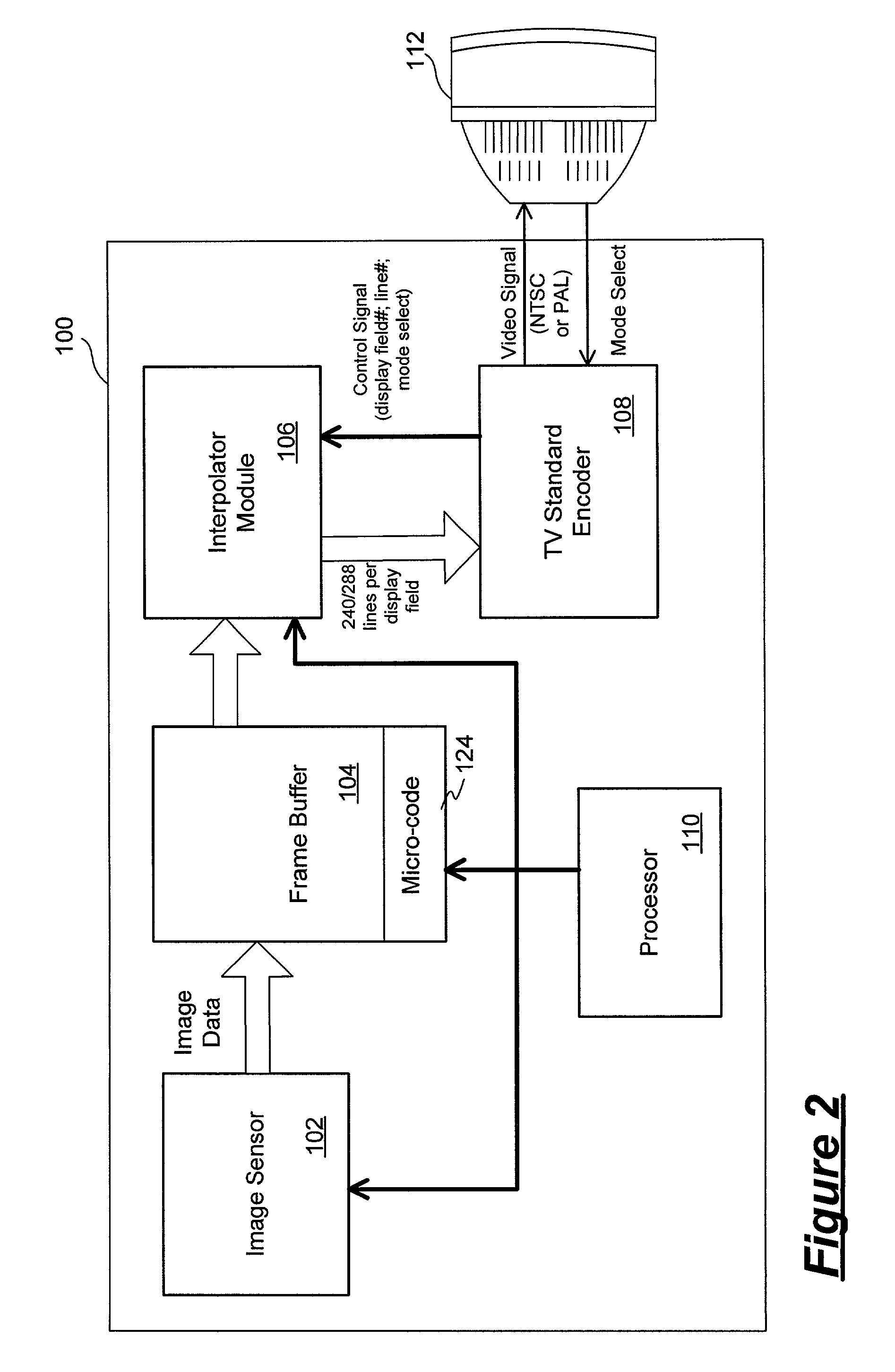
Multi-standard video image capture device using a single CMOS image sensor
InactiveUS7379105B1Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsCMOSComputer graphics (images)
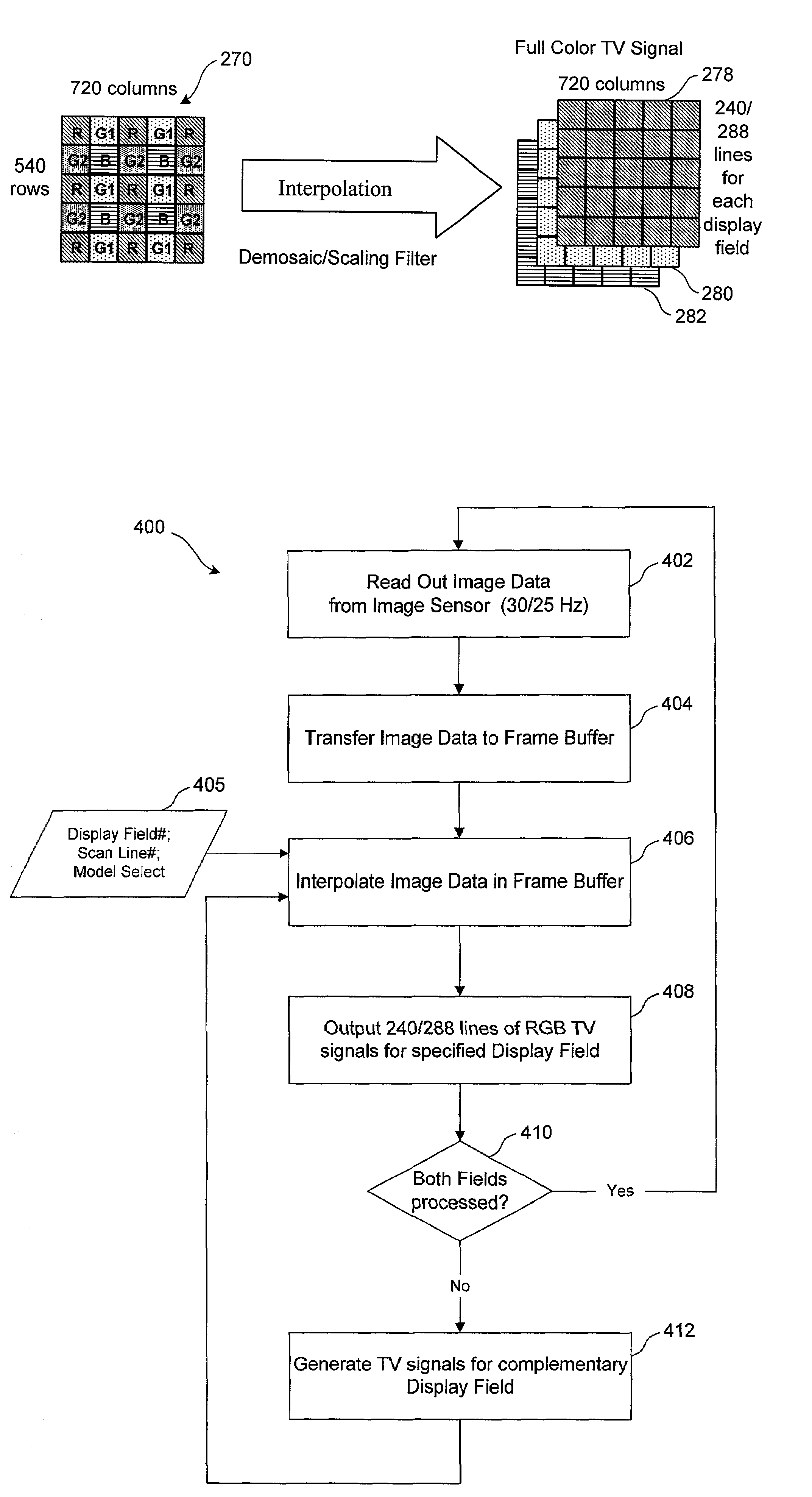
A video image capture device includes an image sensor including an two-dimensional array of pixel elements overlaid with a pattern of color filters and having a vertical resolution different from the vertical resolutions specified for a group of video formats, a frame buffer for storing digital pixel data outputted by the image sensor, and an interpolator module for interpolating the digital pixel data to generate video data in at least three color planes and having a vertical resolution corresponding to a video format selected from the group of video formats. In one embodiment, the group of video formats includes the NTSC and PAL video formats. The vertical resolution of the image sensor has a value between the vertical resolution of the NTSC and PAL video formats. The interpolator module performs interpolation using a set of combined filters, each of the combined filters incorporating a demosaic filter and a scaling filter.
Owner:PIXIM
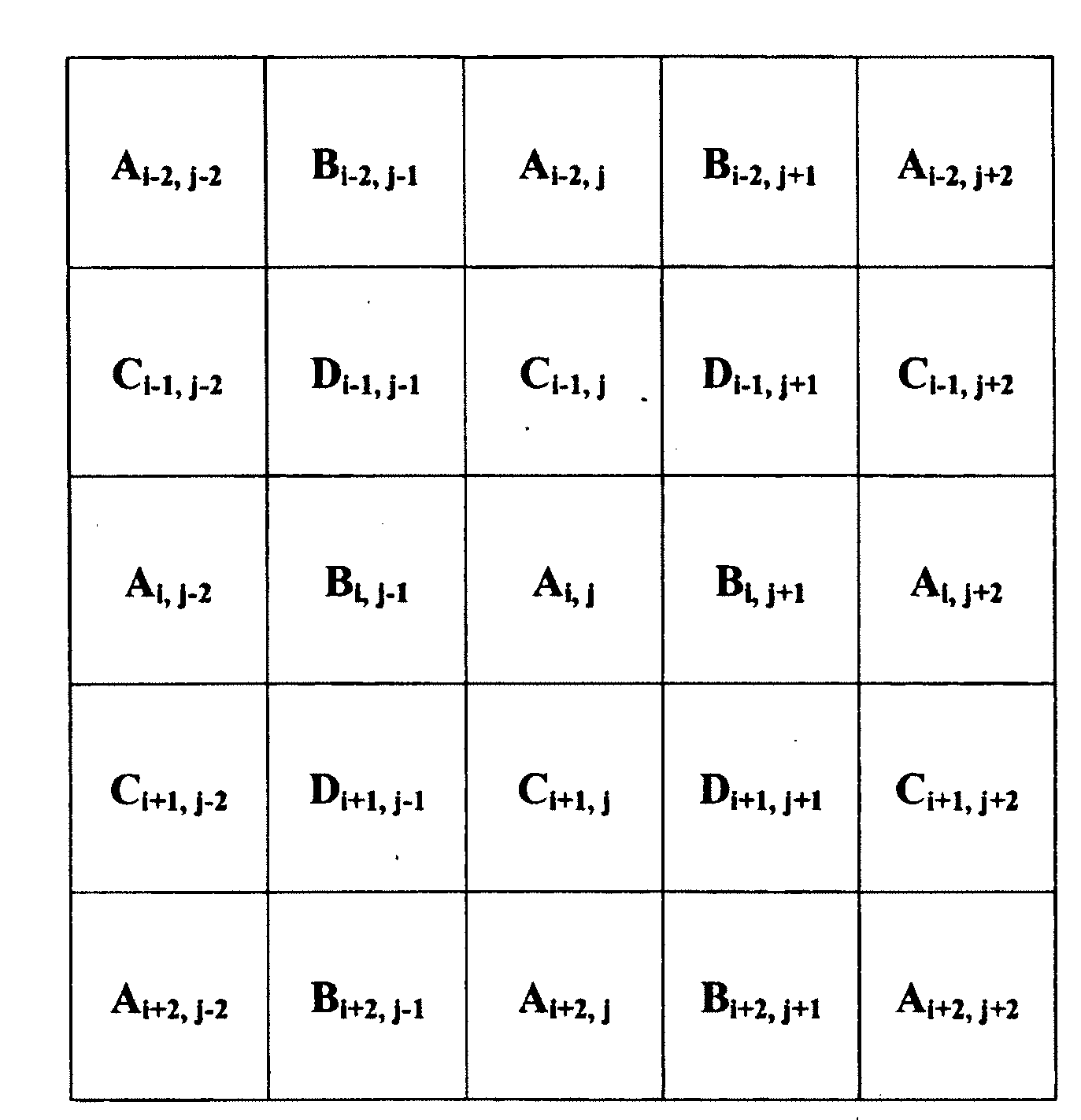
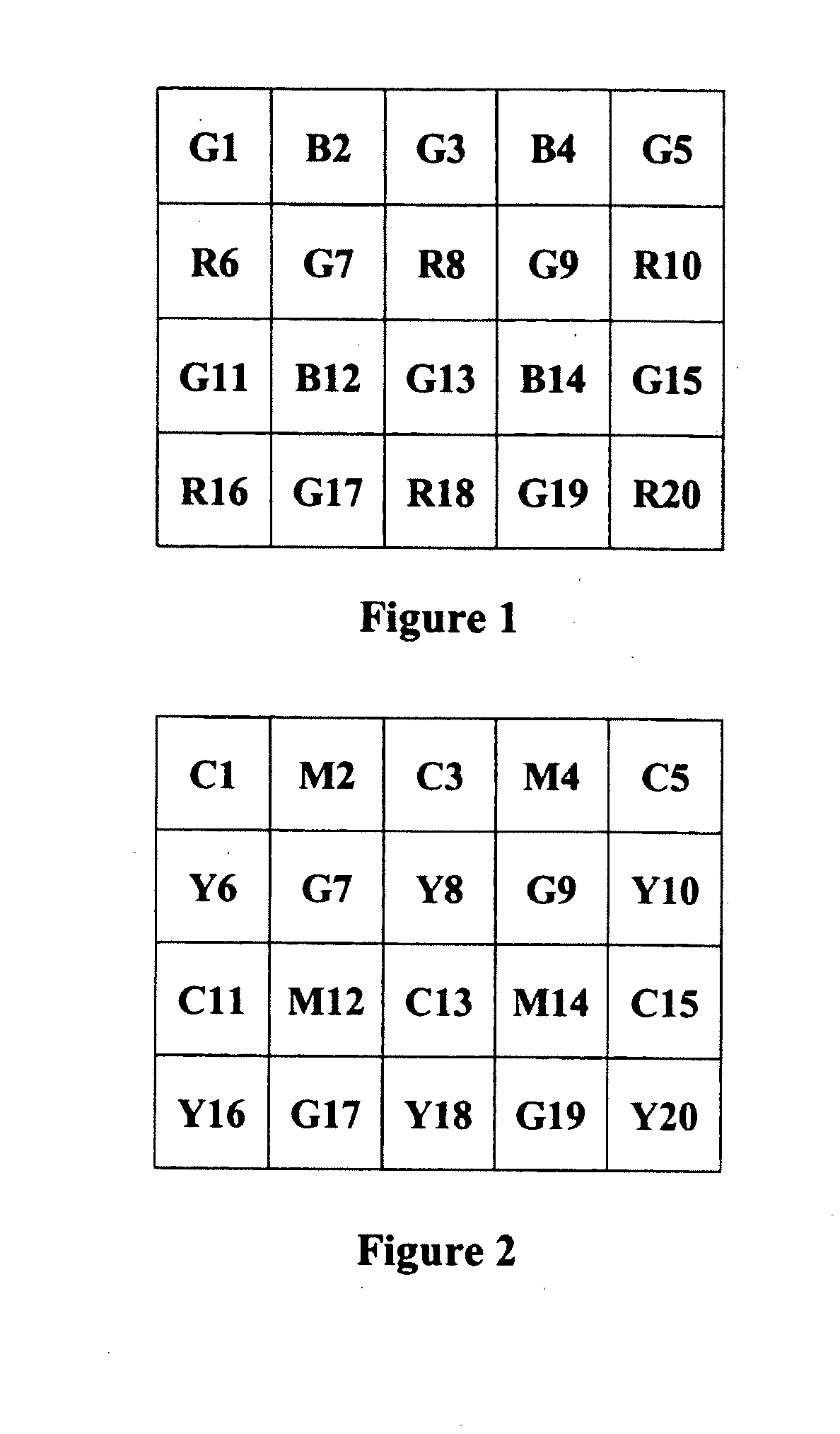
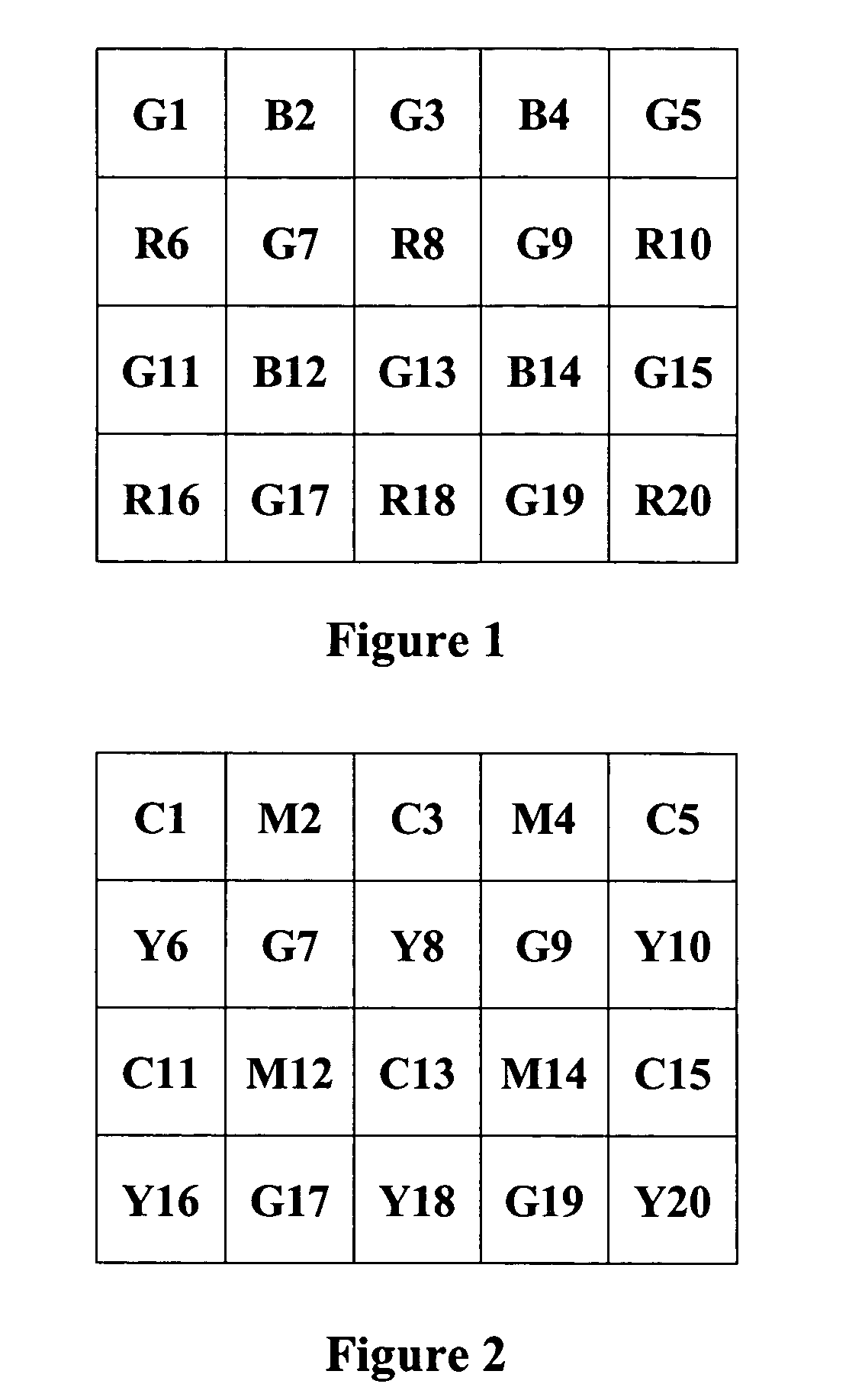
Edge adaptive demosaic system and method
InactiveUS20080075394A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPattern recognitionSystem usage
A demosaic system and method that supports multiple CFA pattern inputs is disclosed. The demosaic system is capable of handling both RGB Bayer input and CMYG input and perform demosaic operations on both inputs to recover full-color images from the raw input images. The system uses a variable number gradient demosiac process. The process uses a 5×5 neighborhood of sensor pixel data centered at the pixel under consideration. The process calculates a set of gradients corresponding to different directions within the neighborhood of the sensor pixel data. A threshold value is determined and a subset of gradients is selected from the set of gradients that fall below the threshold value. The system calculates estimation values for the missing color value and the actual measured center pixel color value obtained from the sensor data on directions that are within the subset of gradients below the threshold. The system then determines the sum of the missing color estimation values and the sum of the actual center pixel color estimation values. The system interpolates the missing color value by using the average difference of the summed estimation values for the missing color and the summed estimation values for the actual center measured pixel value from the sensor data.
Owner:MICRONAS
A system for multi- and hyperspectral imaging
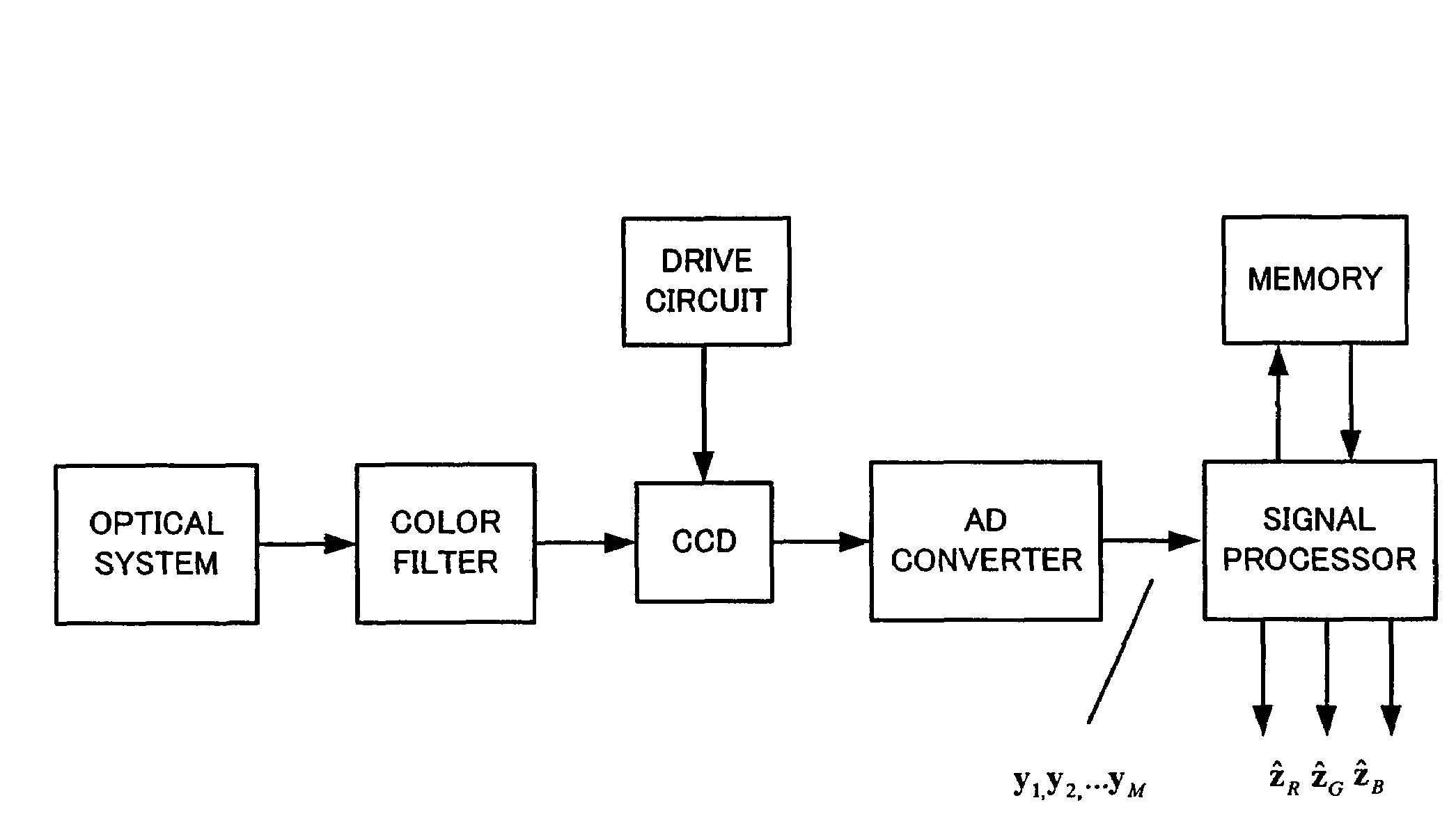
The present invention relates to the production of instantaneous multispectral or hyperspectral images, comprising light collecting means (11), an image sensor (12) with at least one two dimensional sensor array (121), an instantaneous colour separating means, positioned before said image sensor (12) in the optical path of said arrangement (1), and first uniform spectral filters (112) in said optical path, with the purpose of restricting imaging to certain parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. The present invention specifically teaches that at least one first colour mosaic filter (112) is interchangeably positioned before the colour separating means (122) in, or at least close to, converged light (B). The first colour mosaic filter (112) consists of a multitude of homogeneous filtering regions with transmission curves that are partly overlapping on the first colour mosaic (112) or between the first colour mosaic (112) and the colour separating means (122) and suitably spread out in the intervals of a spectrum to be studied. The combination of the colour separating means (122) and the first colour mosaic filter (112) produces different sets of linearly independent colour filter transmission curves.
Owner:RP VENTURES TECH OFFICE
Edge adaptive demosaic system and method
InactiveUS7333678B1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPattern recognitionSystem usage
A demosaic system and method that supports multiple CFA pattern inputs is disclosed. The demosaic system is capable of handling both RGB Bayer input and CMYG input and perform demosaic operations on both inputs to recover full-color images from the raw input images. The system uses a variable number gradient demosiac process. The process uses a 5×5 neighborhood of sensor pixel data centered at the pixel under consideration. The process calculates a set of gradients corresponding to different directions within the neighborhood of the sensor pixel data. A threshold value is determined and a subset of gradients is selected from the set of gradients that fall below the threshold value. The system calculates estimation values for the missing color value and the actual measured center pixel color value obtained from the sensor data on directions that are within the subset of gradients below the threshold. The system then determines the sum of the missing color estimation values and the sum of the actual center pixel color estimation values. The system interpolates the missing color value by using the average difference of the summed estimation values for the missing color and the summed estimation values for the actual center measured pixel value from the sensor data.
Owner:MICRONAS USA
System and method for concurrently demosaicing and resizing raw data images
InactiveUS6989862B2Improve efficiencyImprove image qualityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsComputer visionDemosaicing
A system and method for processing mosaiced or raw data images operates to concurrently demosaic and resize the mosaiced images in a combined process. The combined demosaic / resize process allows the system to perform demosaicing and resizing more efficiently than conventional systems, which perform these processes separately and sequentially. Furthermore, the combined demosaic / resize process allows the system to produce demosaiced and resized images of higher quality as compared to demosaiced and resized images produced by the conventional systems.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
System and method for processing demosaiced images to reduce color aliasing artifacts
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Fast edge directed demosaicing
ActiveUS20050146629A1High quality visual resultPromote reconstructionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsColor filter arrayErrors and residuals
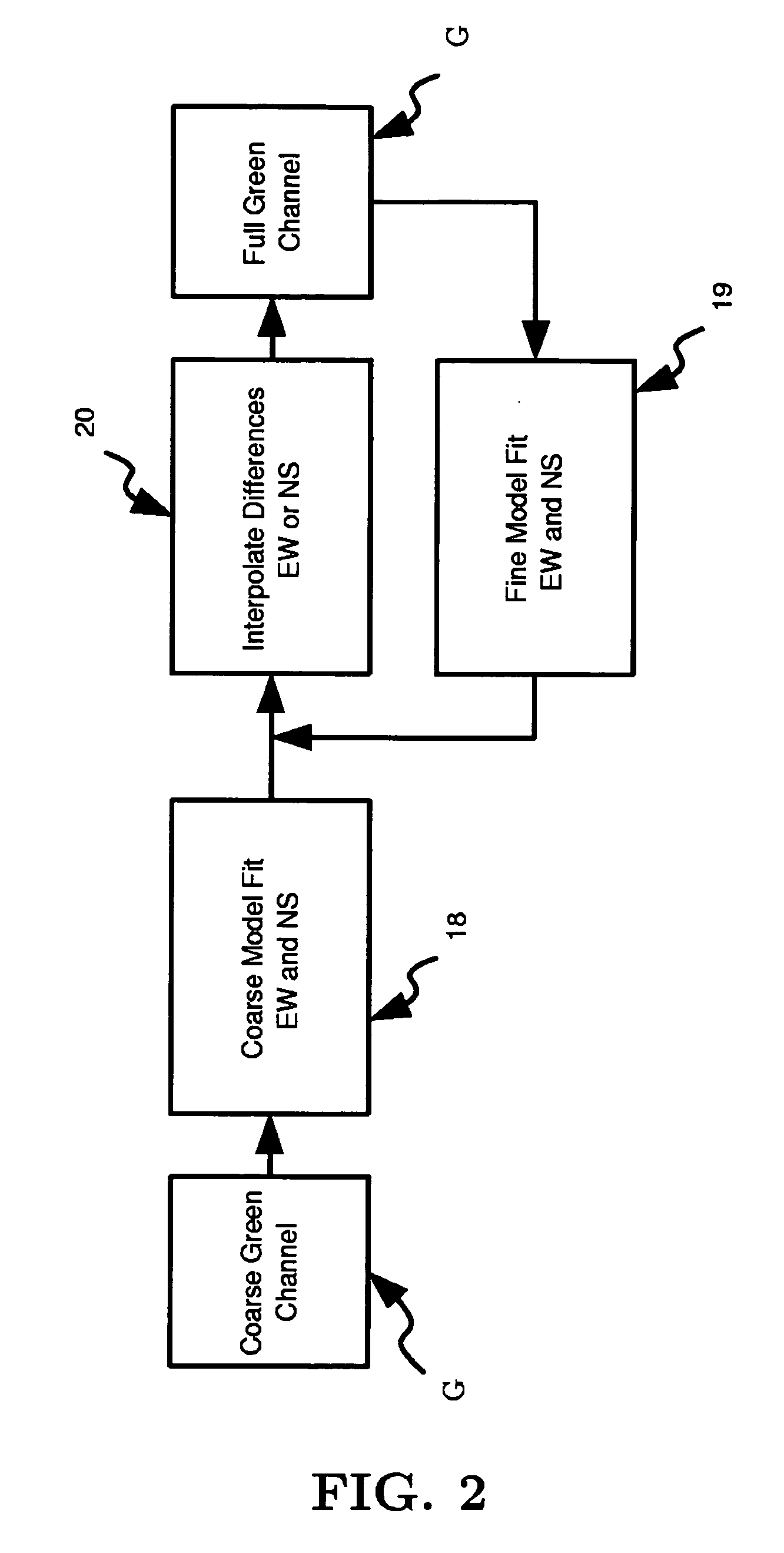
An edge directed demosaicing algorithm for determining an edge direction from an input color filter array (CFA) sampled image is disclosed. Aspects of the present invention include calculating for a current missing green pixel, interpolation errors in an East-West (EW) direction at known neighboring green pixels, and averaging the EW interpolation errors to obtain an EW error. Interpolation errors are also calculated for the current missing green pixel in a North-South (NS) direction at known neighboring green pixels, and the NS interpolation errors are averaged to obtain a NS error. An EW or NS direction indicated by a minimum of the EW error and the NS error is then selected as the edge direction.
Owner:LIFESIZE INC
Demosaicing method for CFA (color filter array) images based on edge-direction interpolation
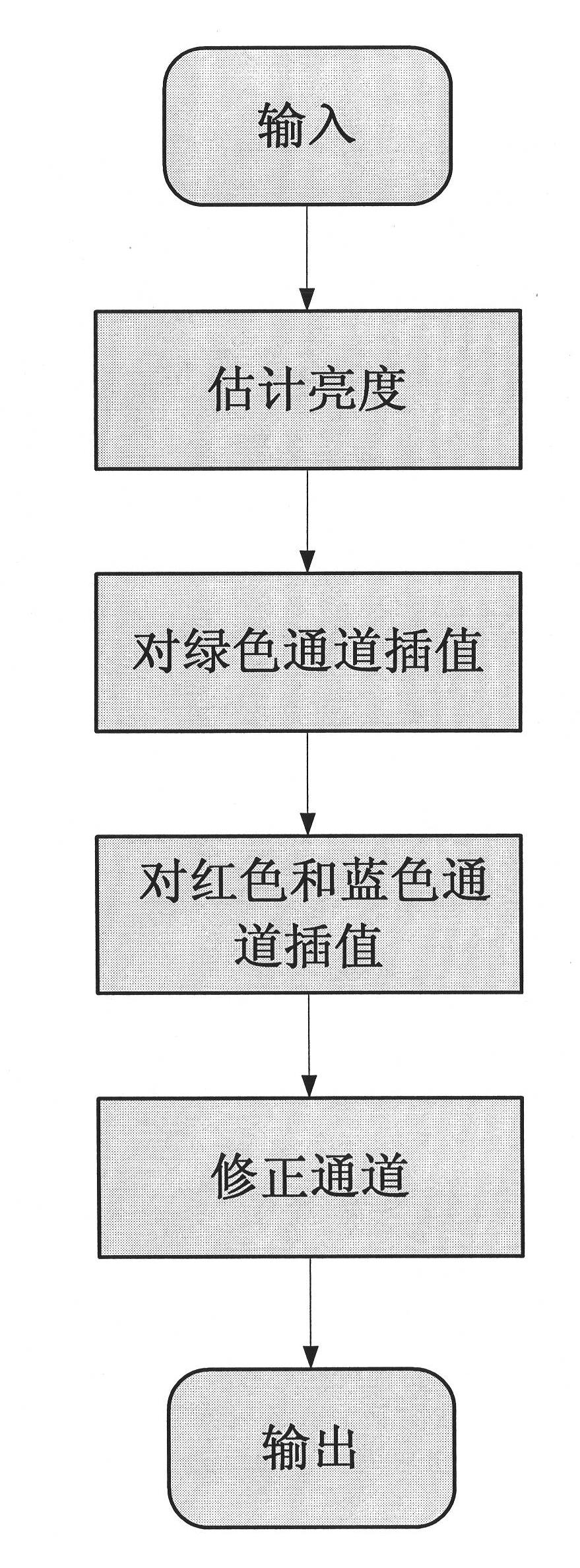
InactiveCN102254301AImprove interpolationSuppress false color effectsGeometric image transformationFalse colorRunning time
The invention discloses a demosaicing method for CFA (color filter array) images based on edge-direction interpolation. The demosaicing method for CFA images mainly solves the problems that the interpolation effect of the high-frequency part of an image is not good, and the false color effect is serious in the traditional demosaicing method. The demosaicing method for CFA images comprises the steps of: (1) inputting a CFA image to be demosaiced; (2) estimating the brightness; (3) interpolating a green channel; (4) respectively carrying out dual linear interpolation on a red channel and a bluechannel; (5) respectively correcting the red channel, a green channel and the blue channel; and (6) outputting a colorful image. The demosaicing method for CFA images has the advantages of capabilityof better maintaining high-frequency information of the image, inhibiting the false color effect effectively and improving the visual effect of the demosaiced CFA image has short running time.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
GAN (Generative Adversarial Nets)-based CFA (Color Filer Array) image demosaicing joint denoising method
InactiveCN108492265AOvercoming the problem of poor robustness to noiseImprove robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisColor imageColor filter array
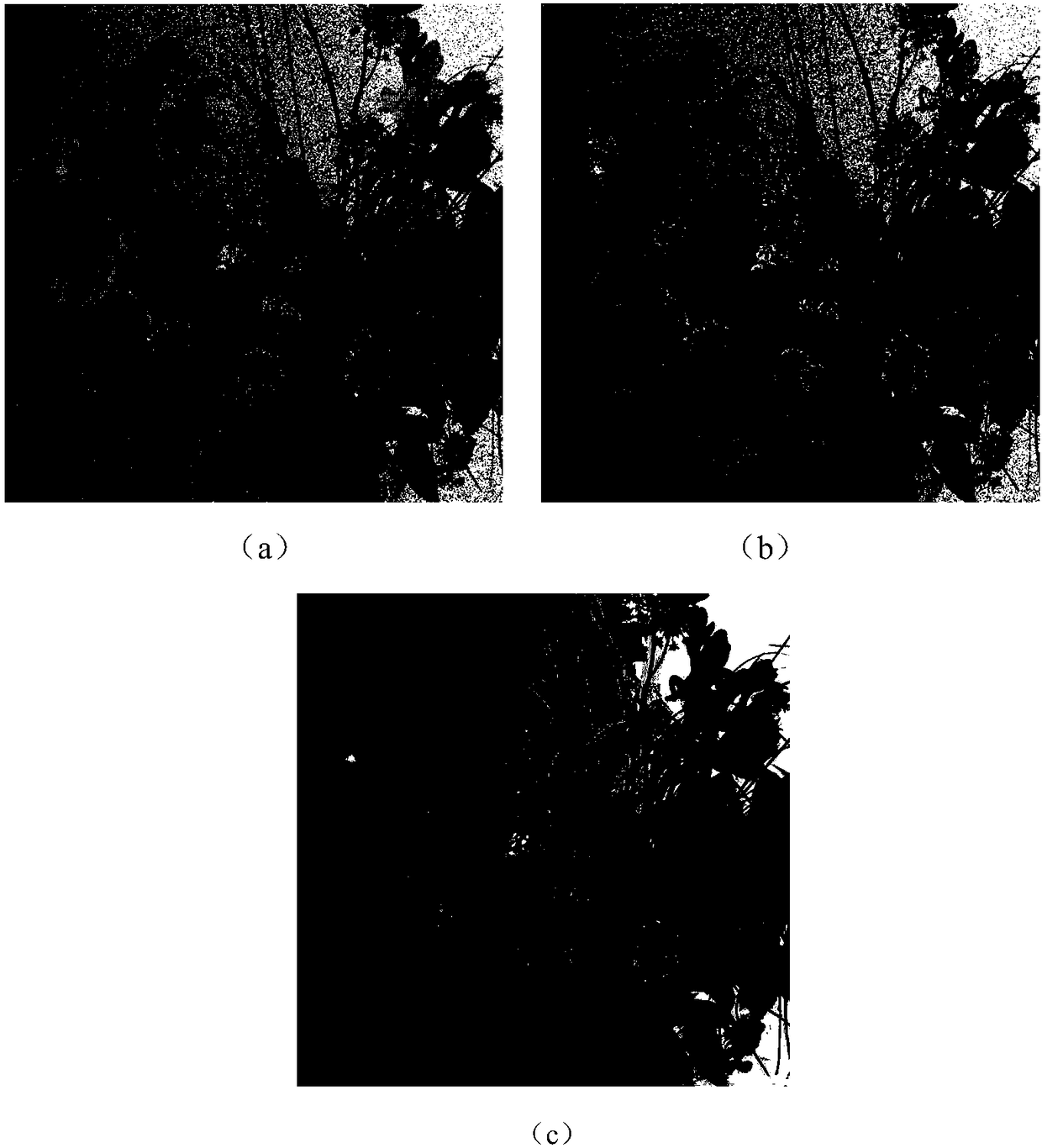
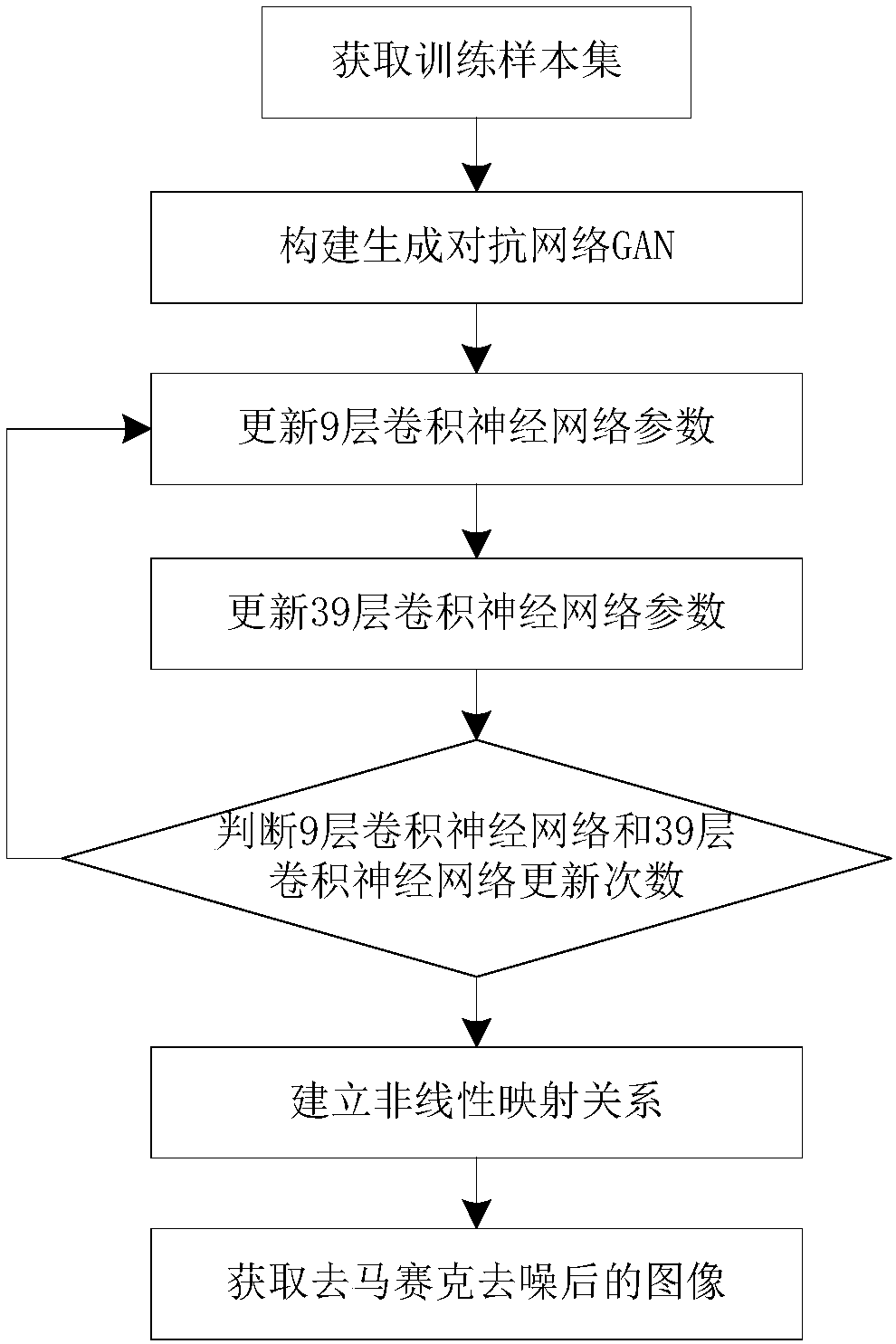
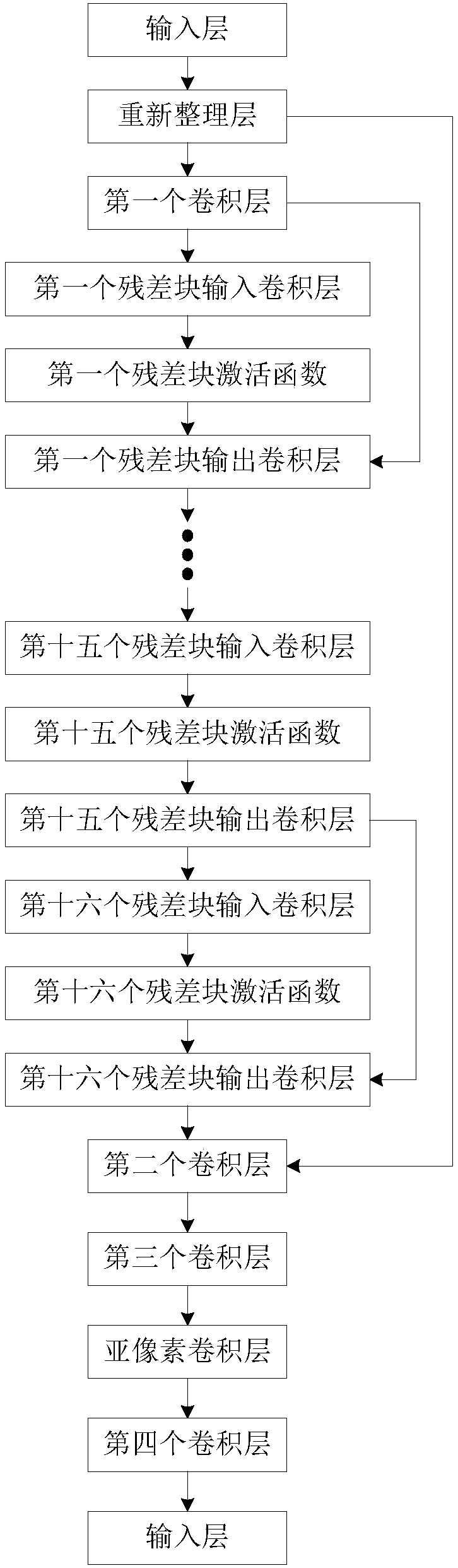
The invention discloses a GAN (Generative Adversarial Nets)-based CFA (Color Filer Array) image demosaicing joint denoising method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) a training sample setis acquired; (2) the GAN is built; (3) parameters of a 9-layer convolution neural network are updated; (4) parameters of a 39-layer convolution neural network are updated; (5) whether the updating times of the 39-layer convolution neural network and the 9-layer convolution neural network reach 200 times is judged, if yes, a step (6) is executed, or otherwise, the step (3) is executed; (6) a nonlinear mapping relationship is built; and (7) an image after demosaicing and denoising is acquired. The color information of a noisy CFA image obtained by a digital camera can be well recovered, the noise introduced during an image acquisition process of the digital camera can be effectively suppressed, the appearance of unnatural colors is reduced, and the visual effects of a color image are improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method and apparatus providing color interpolation in color filter arrays using edge detection and correction terms
ActiveUS20070153106A1Reduce lossesTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsColor planeColor interpolation
A method and apparatus for color plane interpolation are provided which interpolates the color values of pixels differently depending on an edge direction and whether a pixel is at an edge within an image. The use of the edge detection during the interpolation of each of the colors present in the color pattern helps reduce some of the disadvantages of the loss of image sharpness abundant in known demosaicing techniques.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com