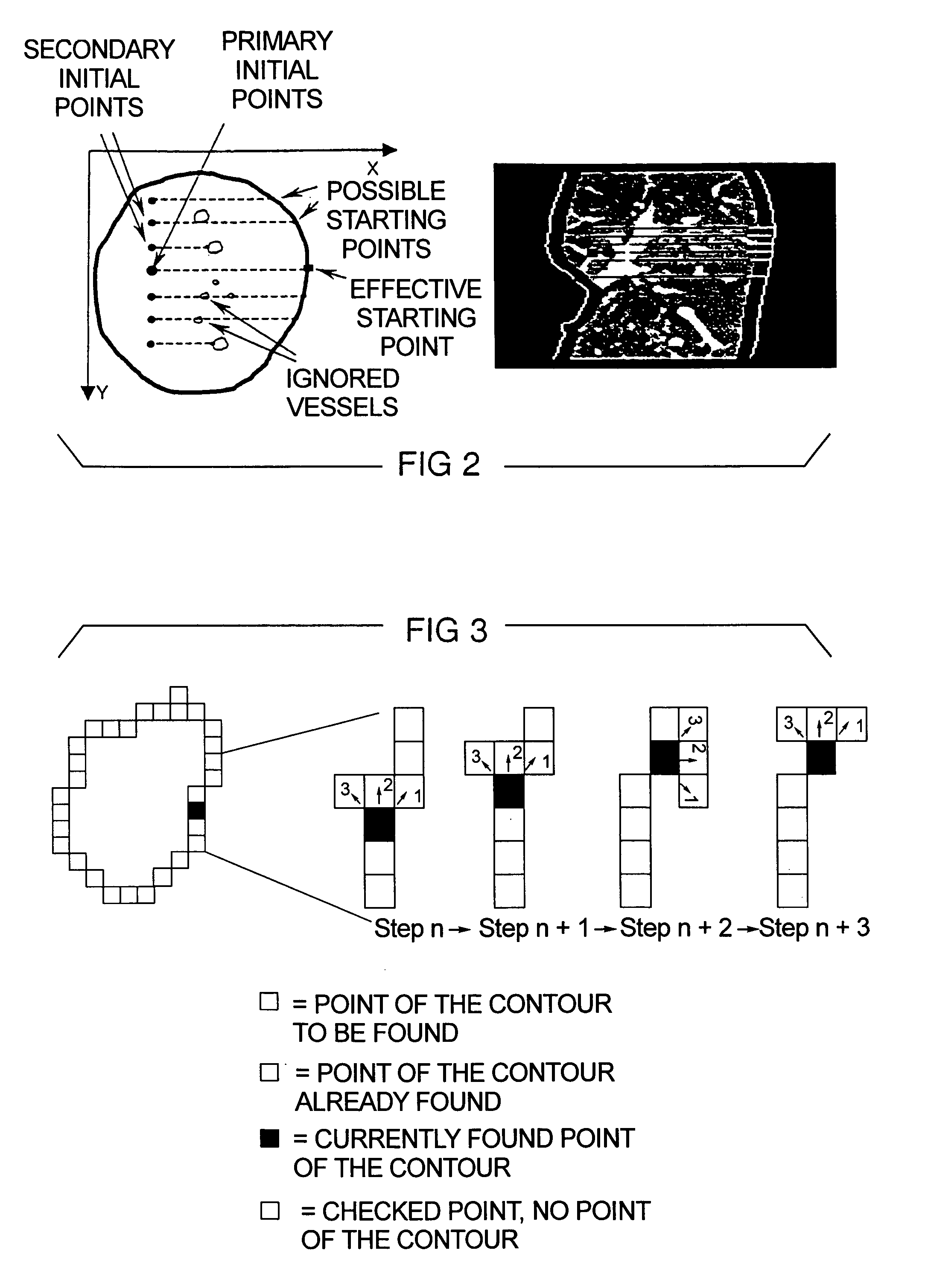
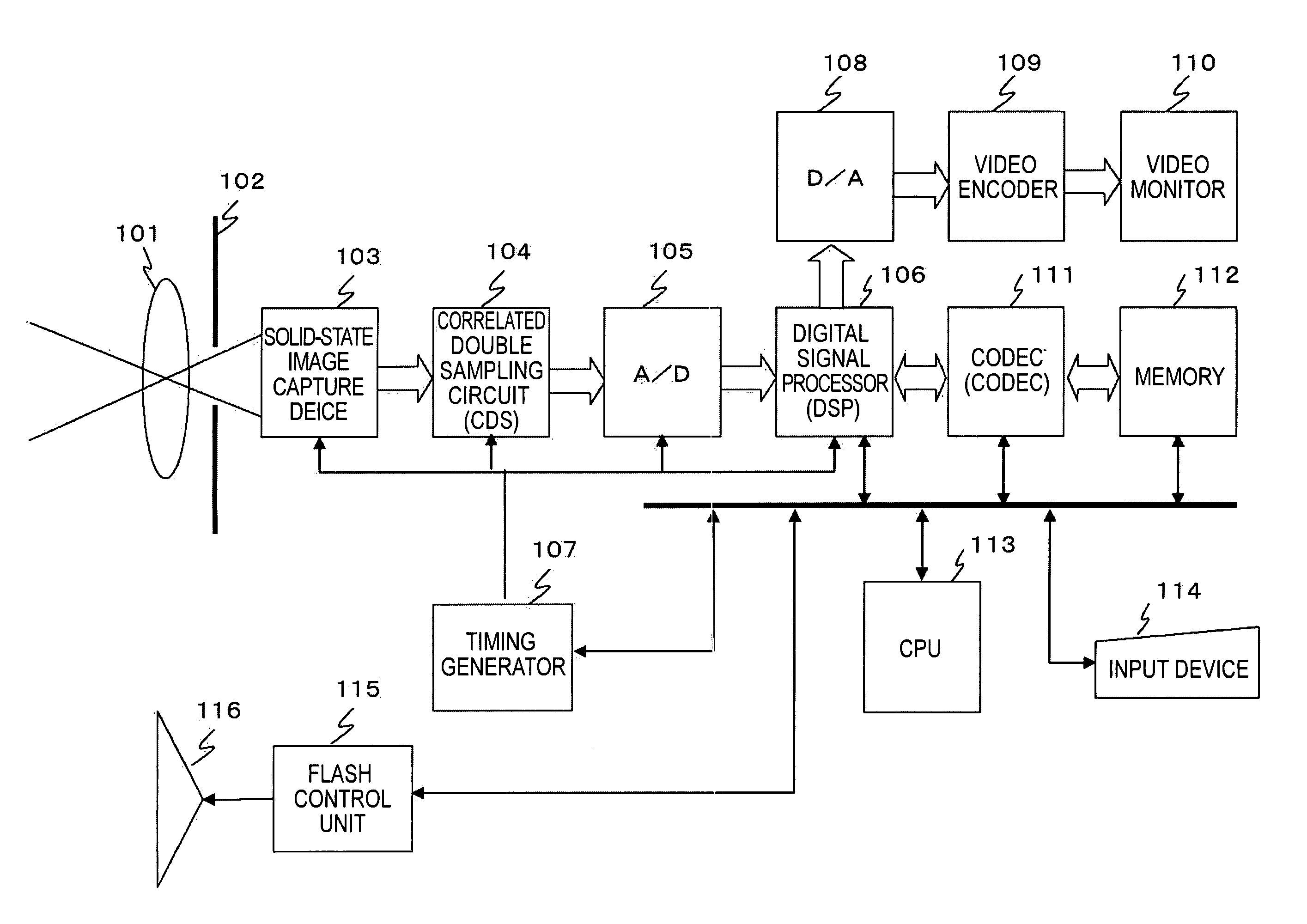
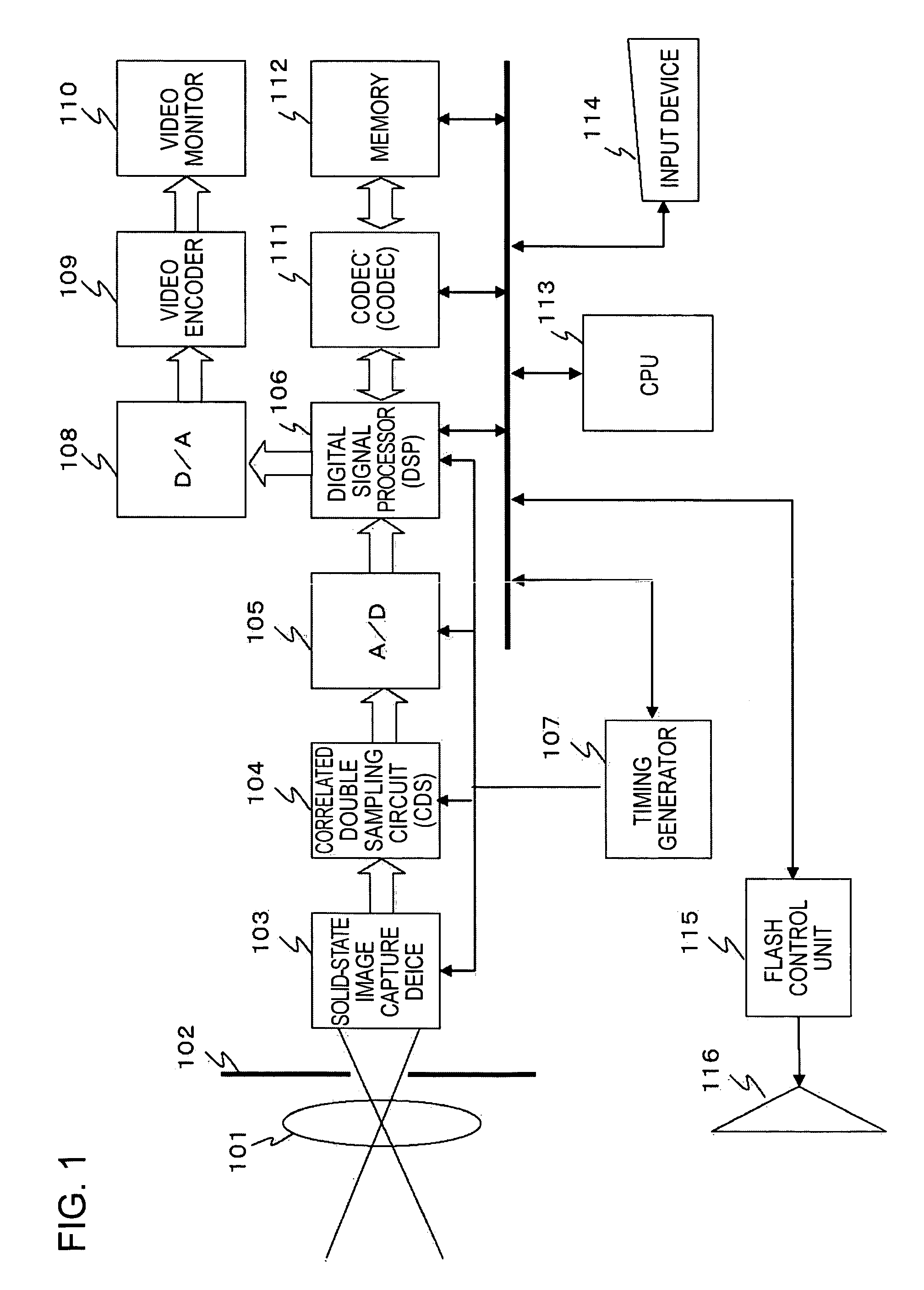
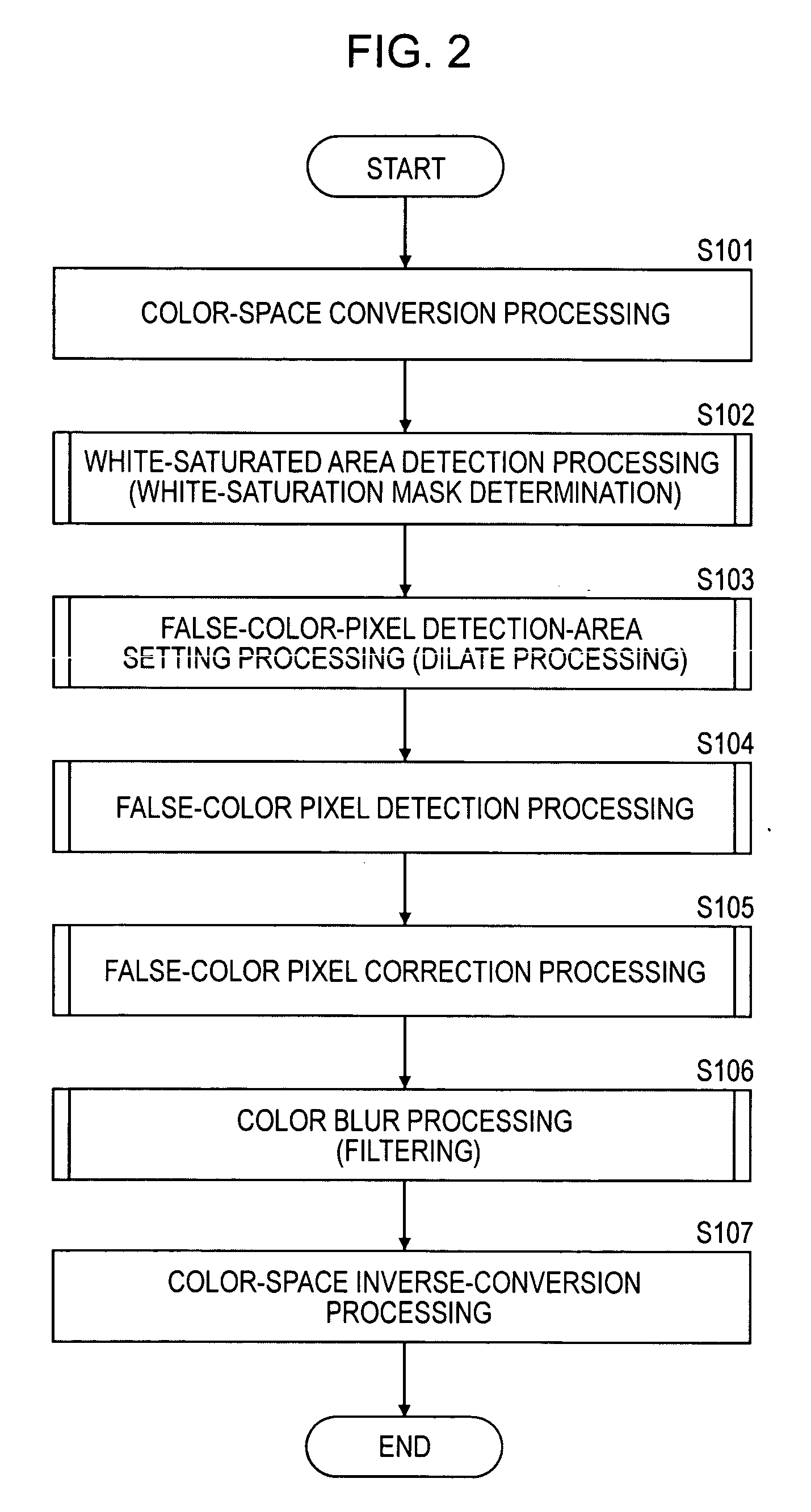
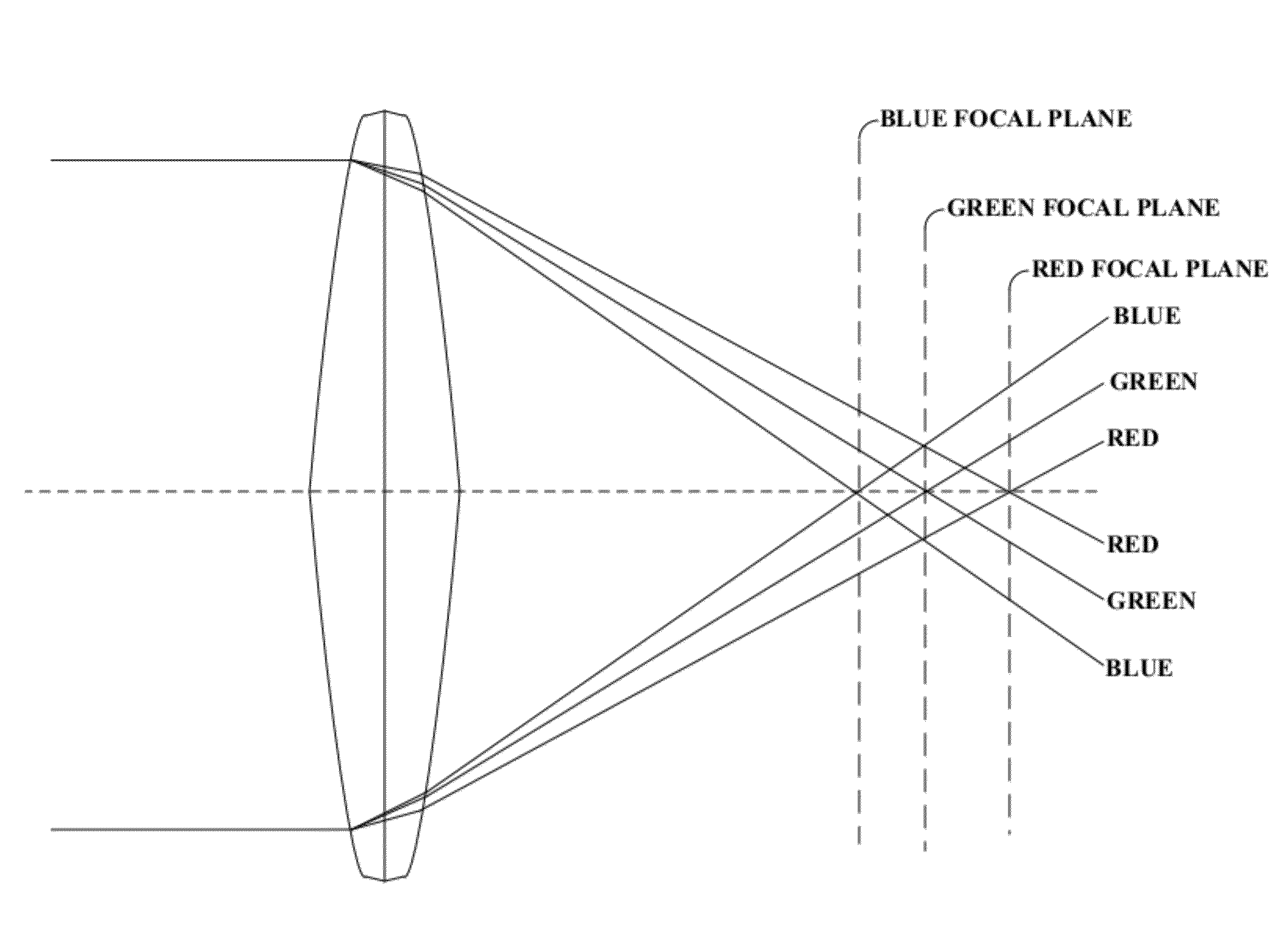
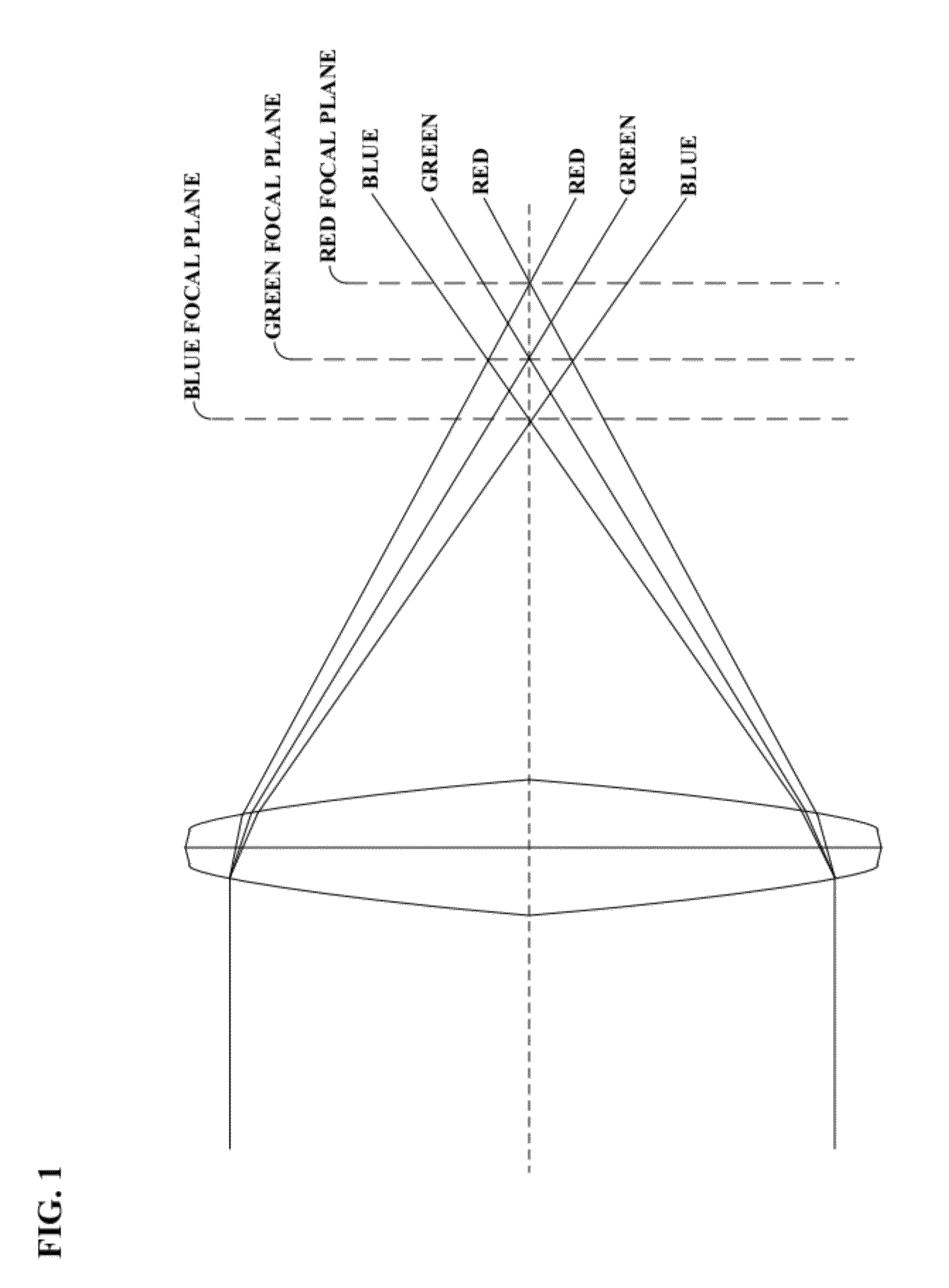
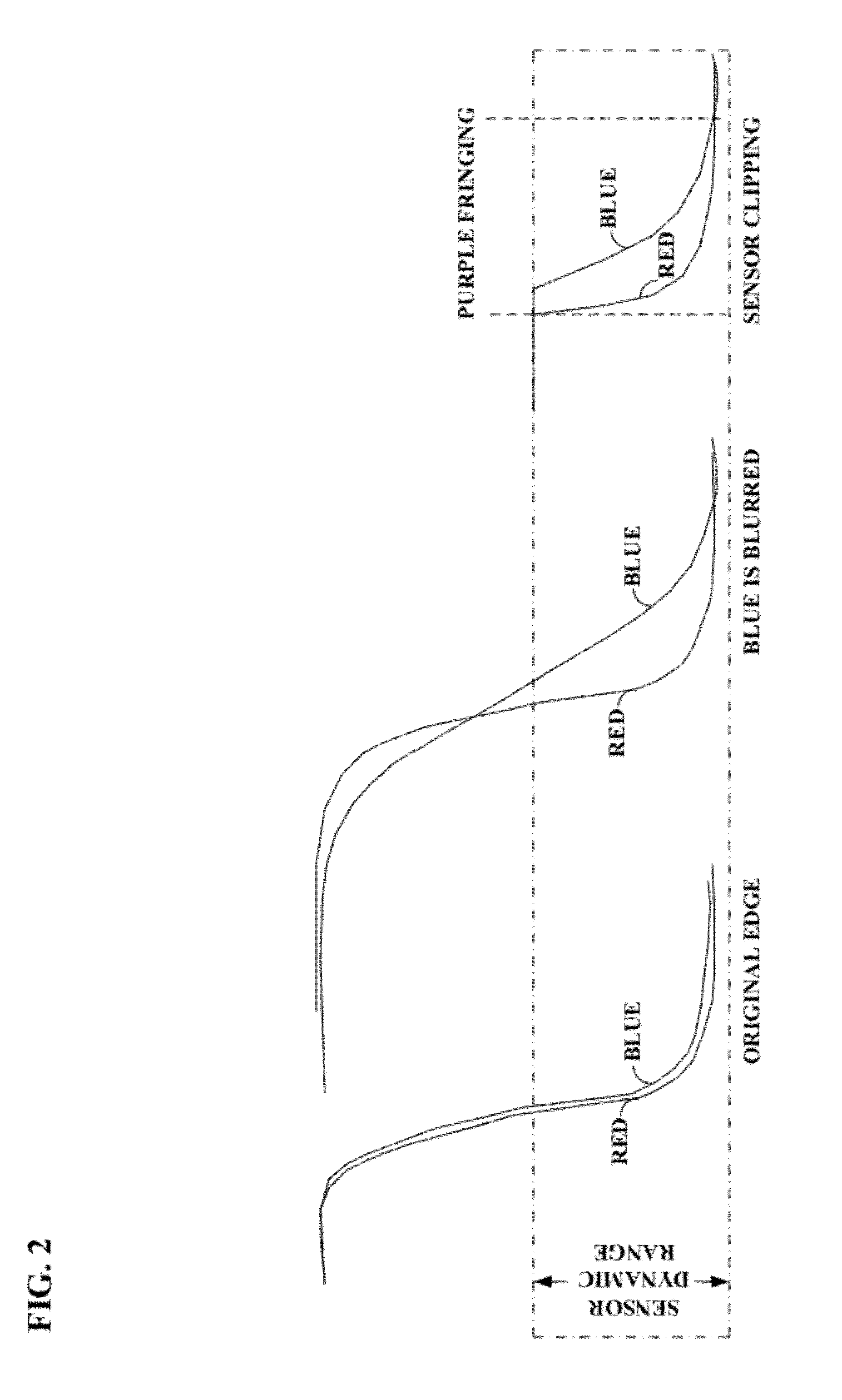
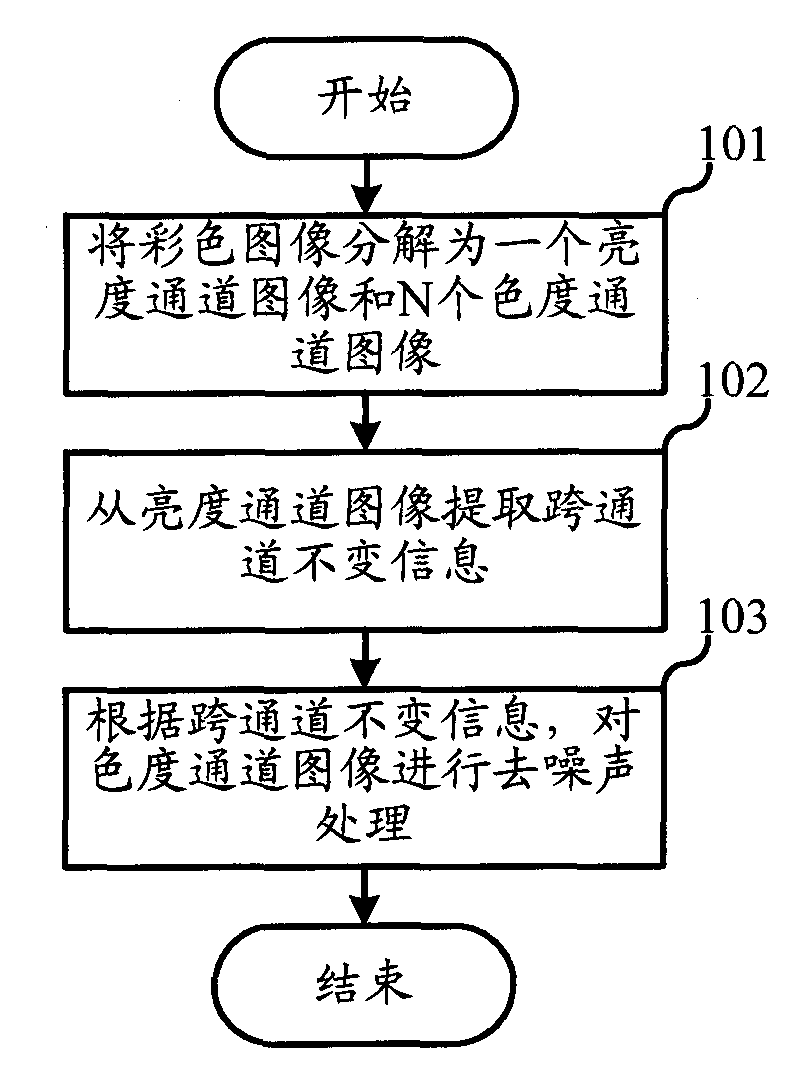
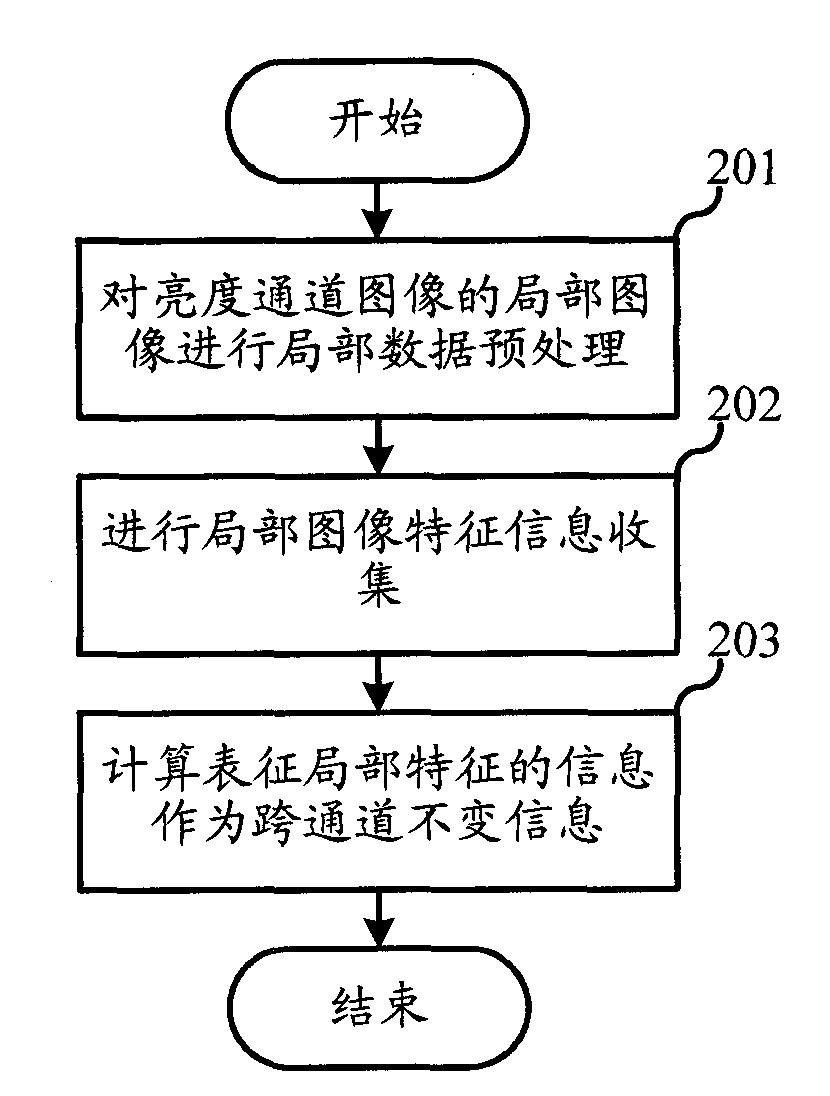
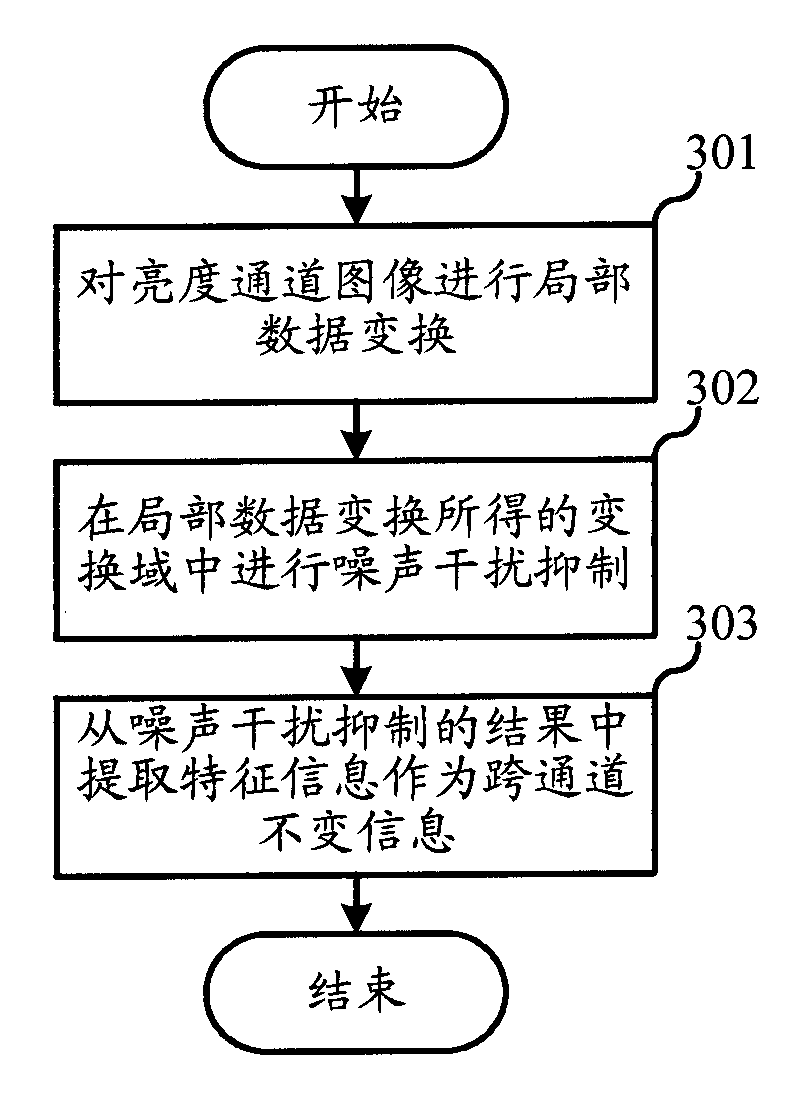
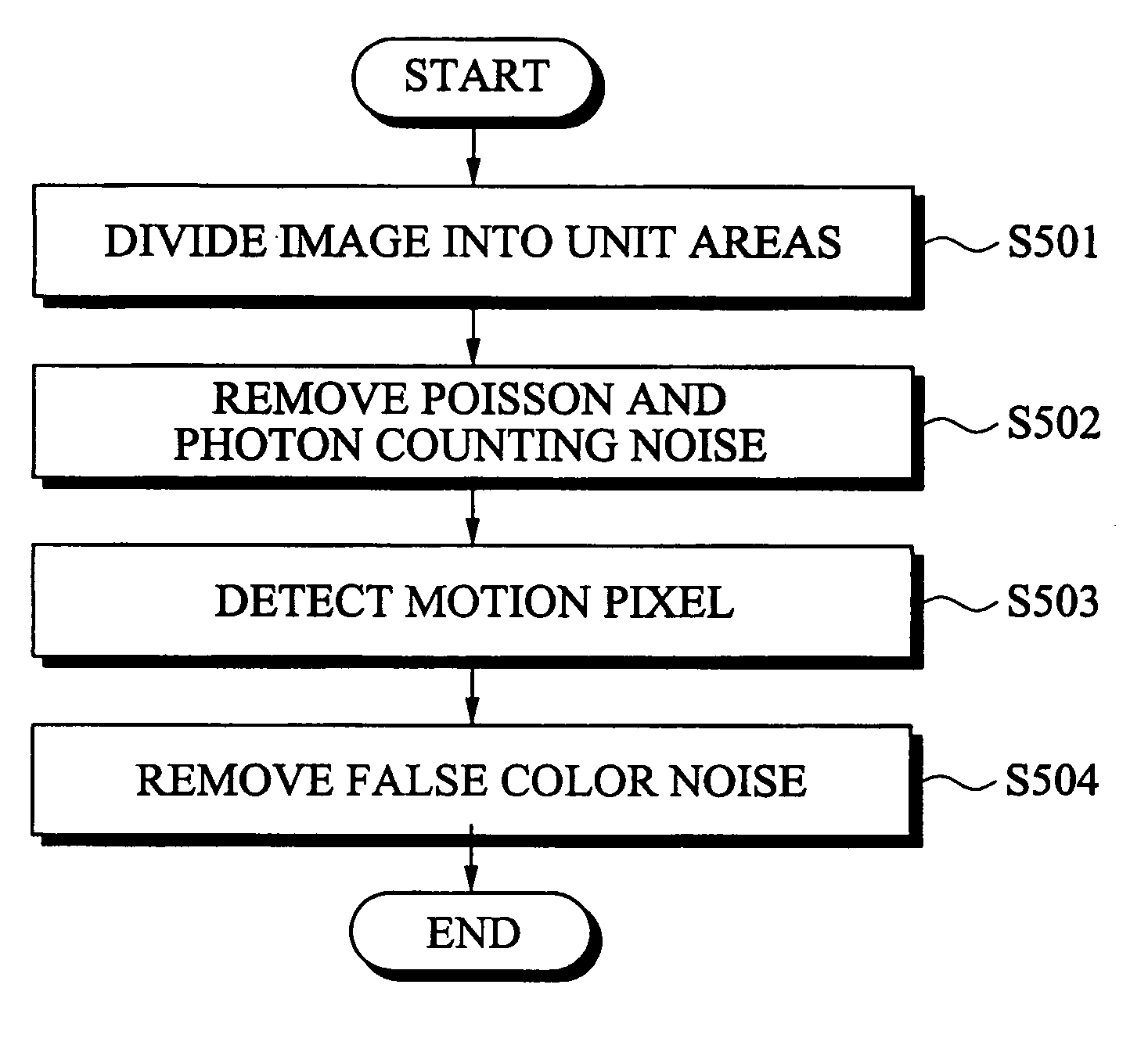
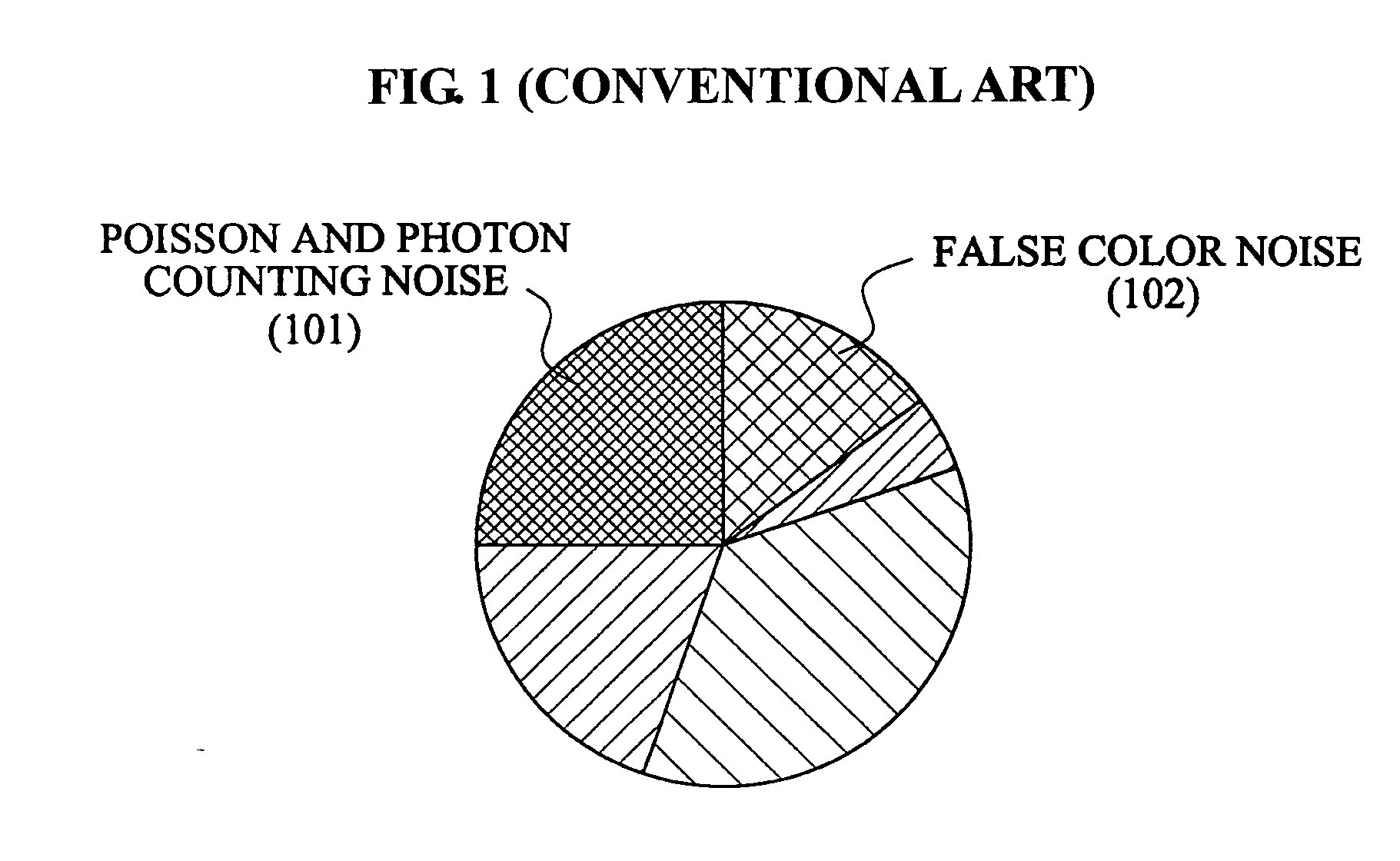
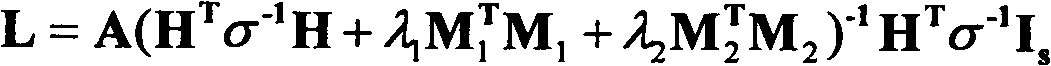Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
277 results about "False color" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
False color (or pseudo color) refers to a group of color rendering methods used to display images in color which were recorded in the visible or non-visible parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. A false-color image is an image that depicts an object in colors that differ from those a photograph (a true-color image) would show.
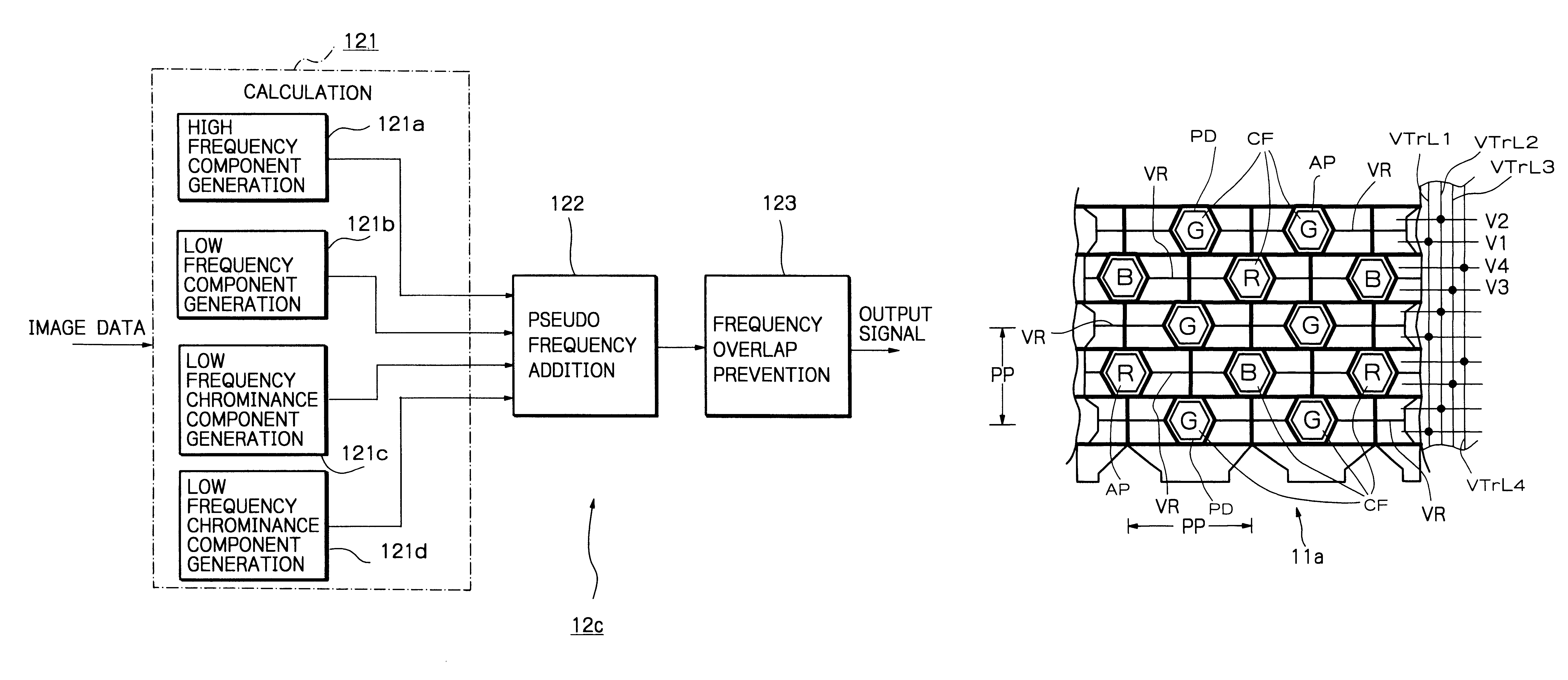
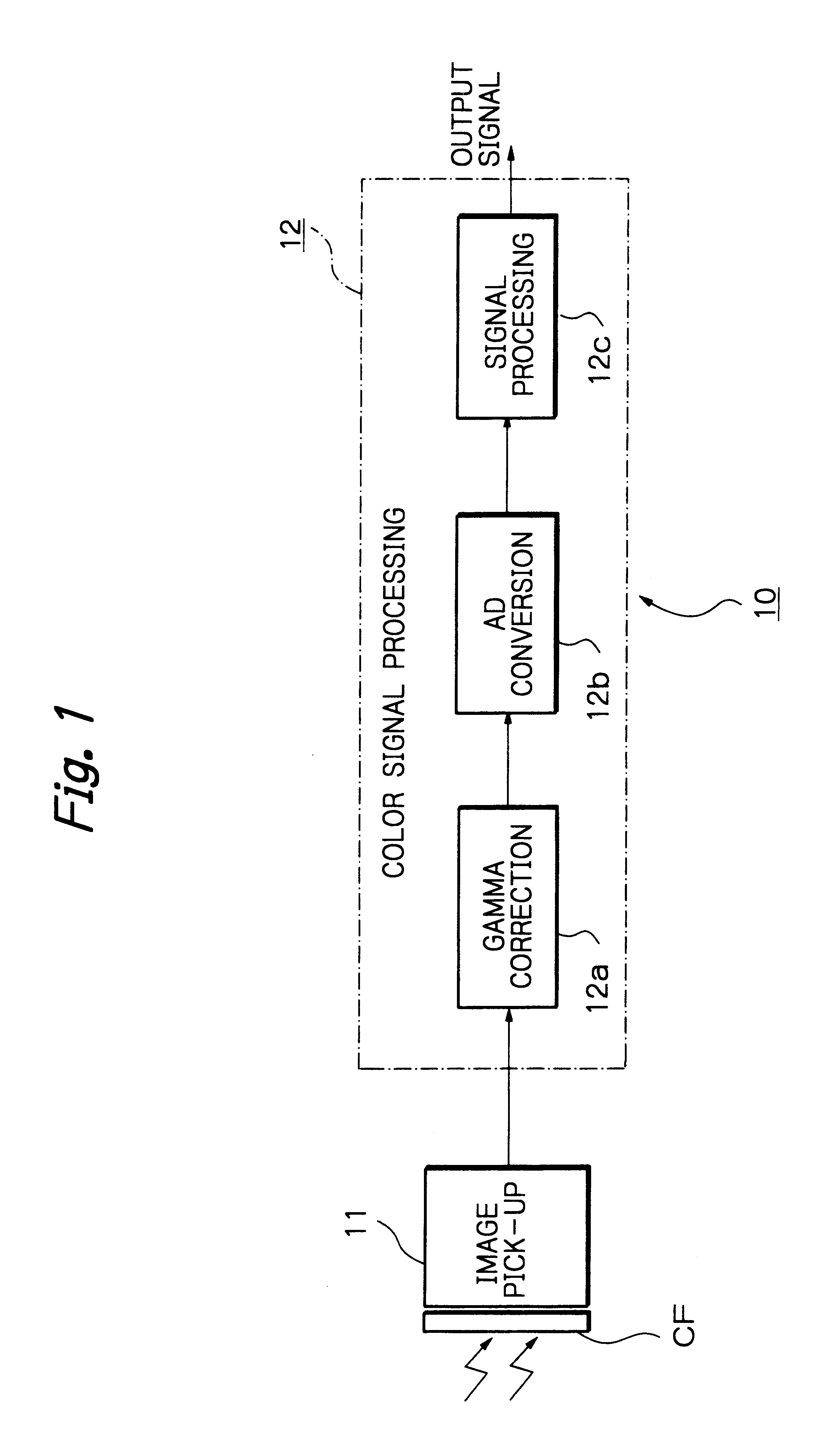
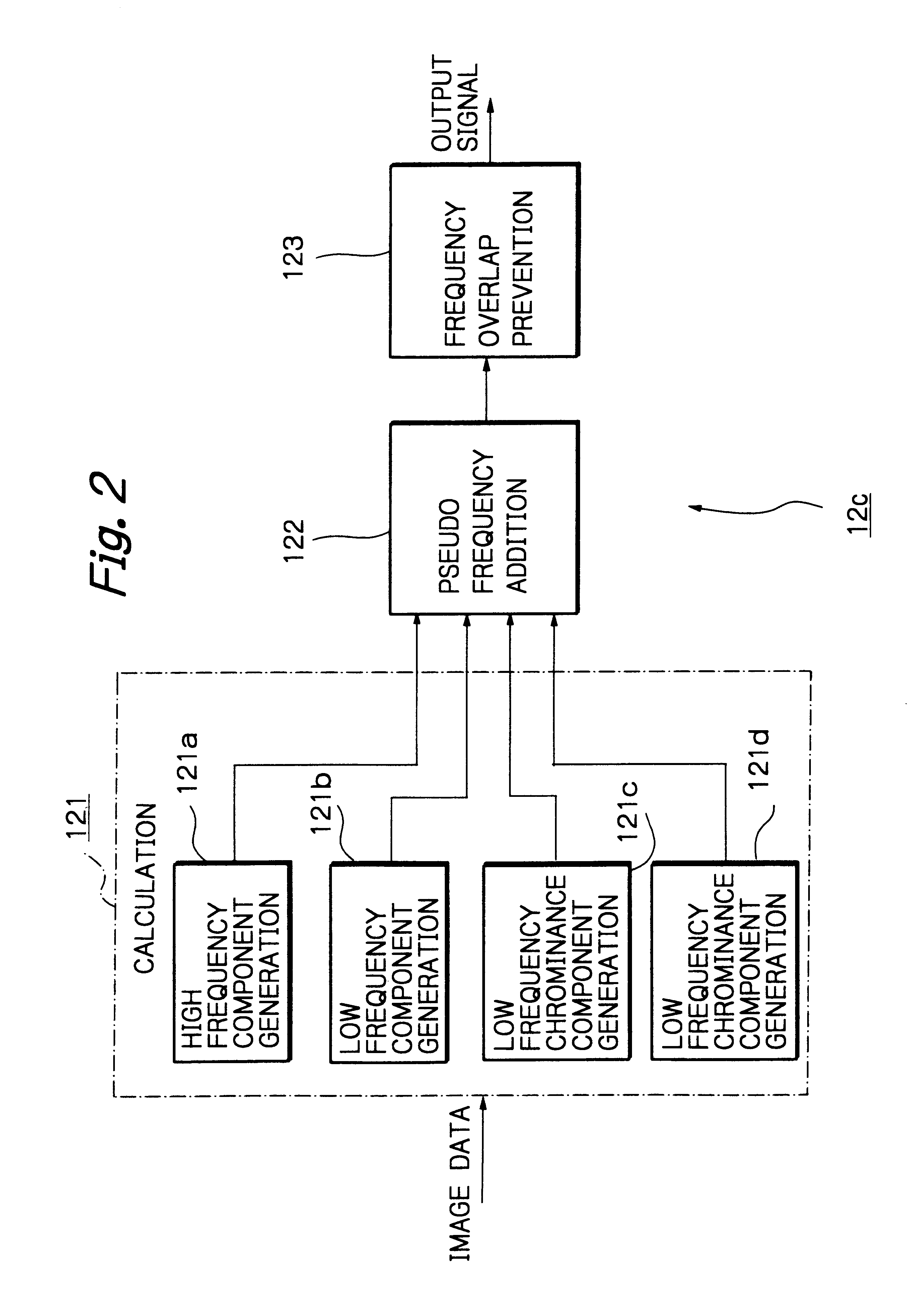
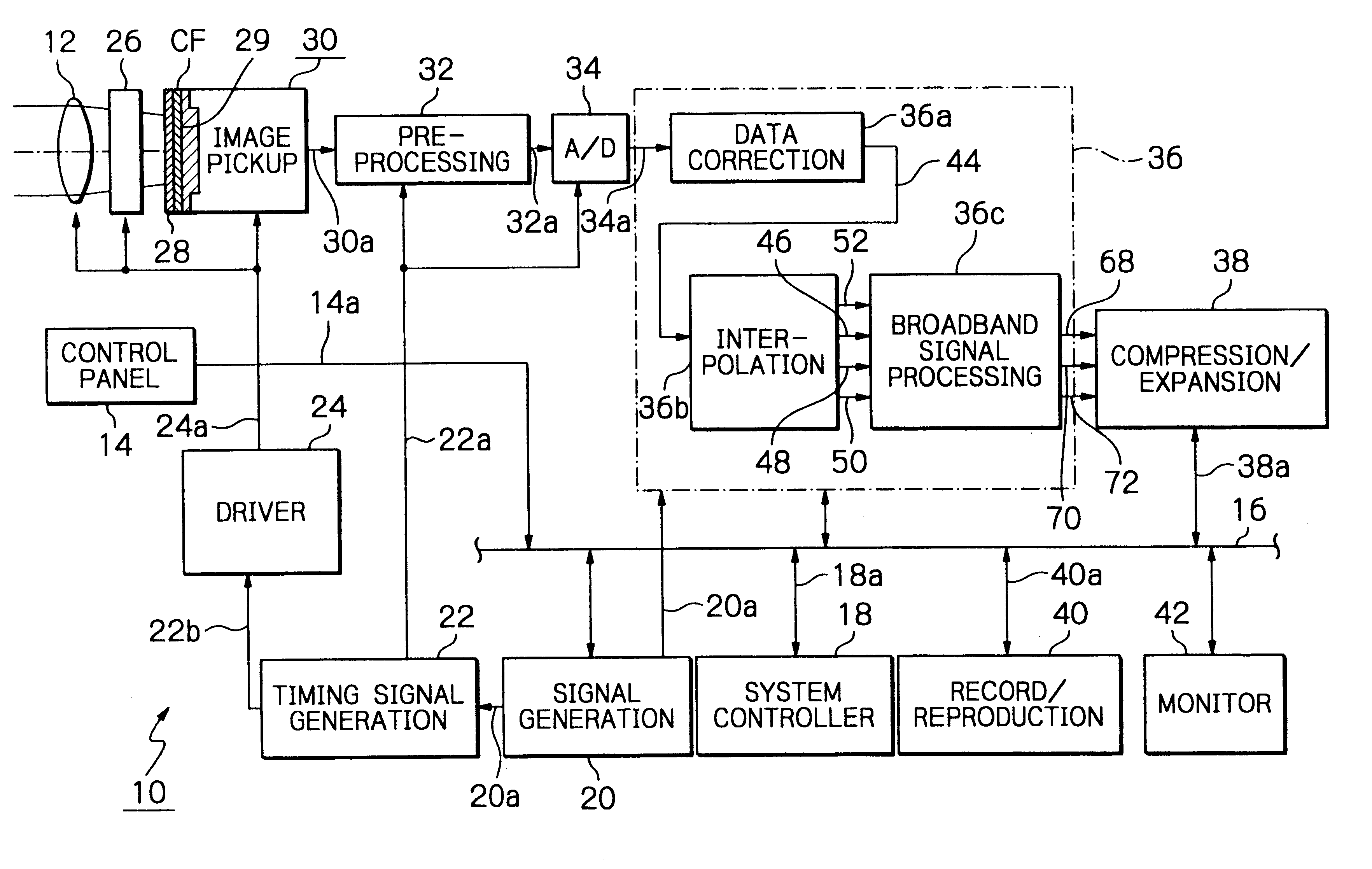
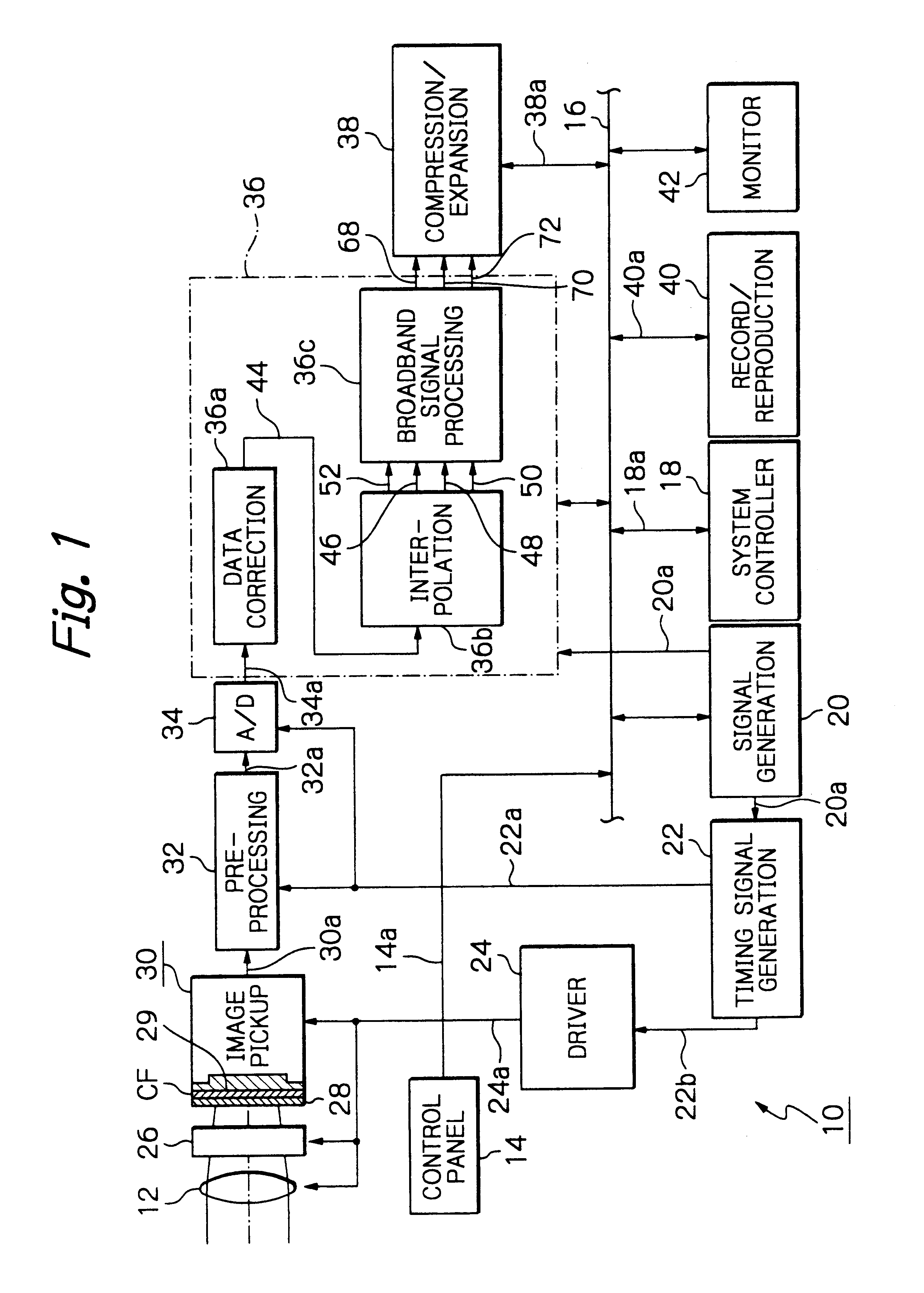
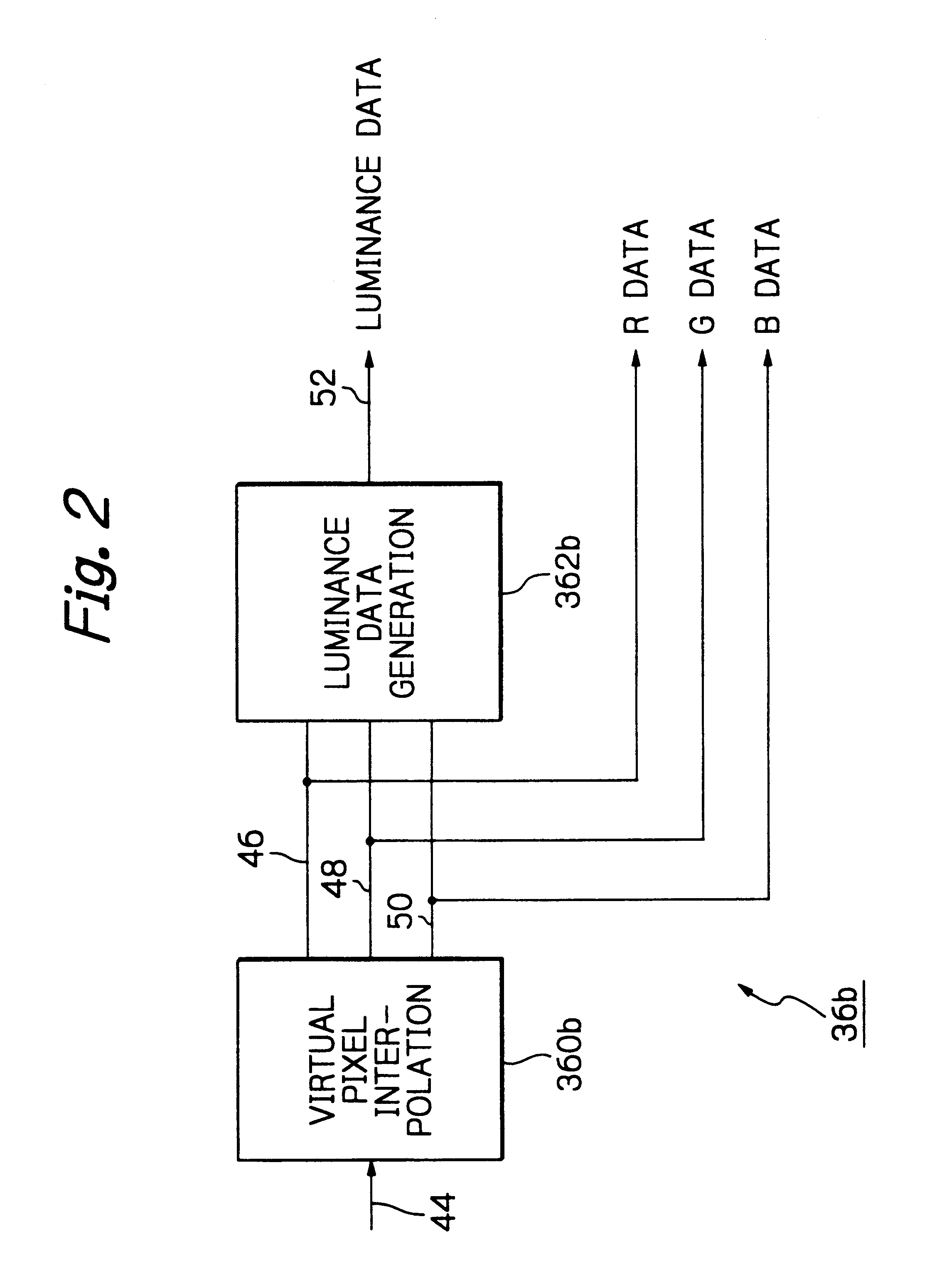
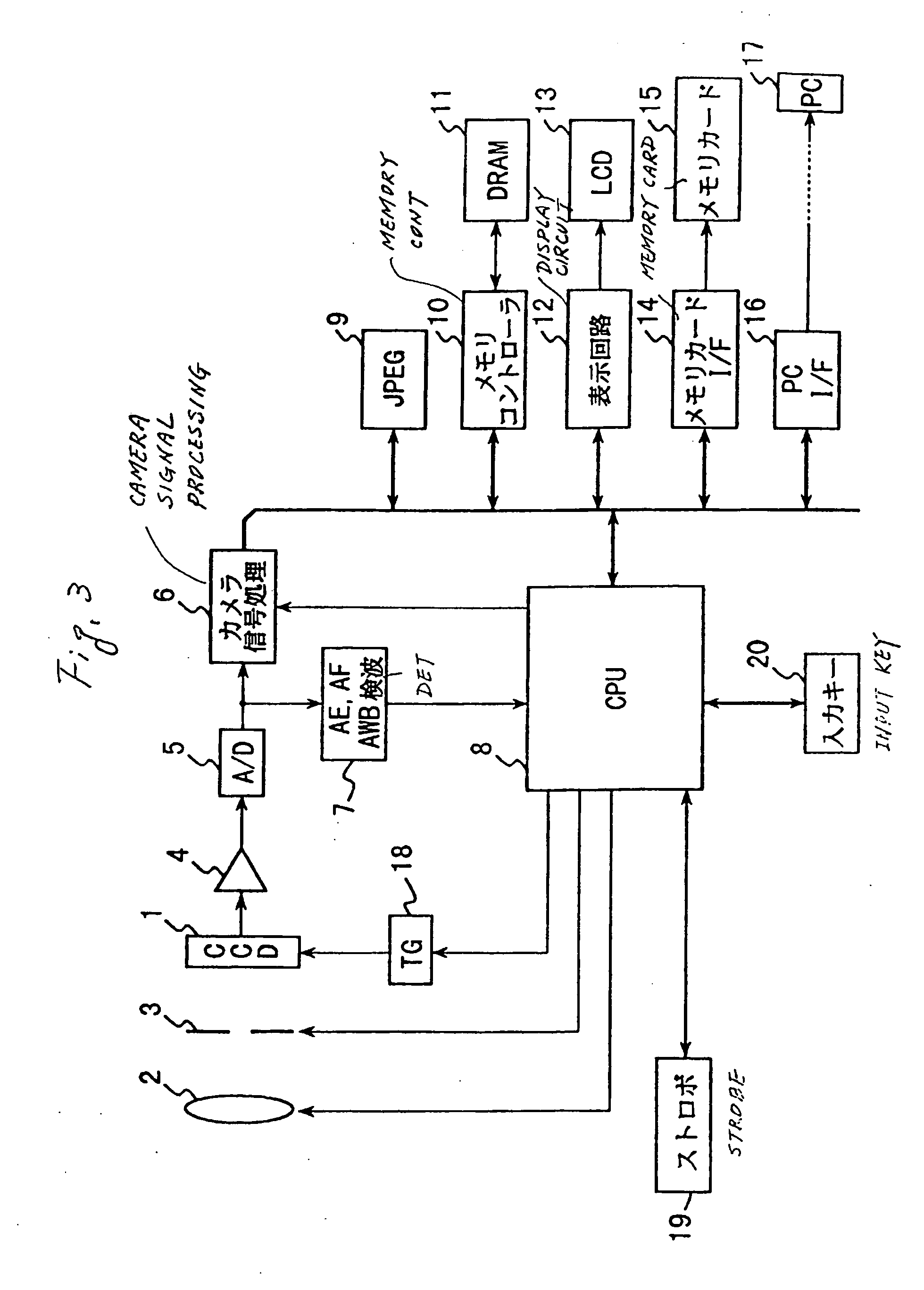
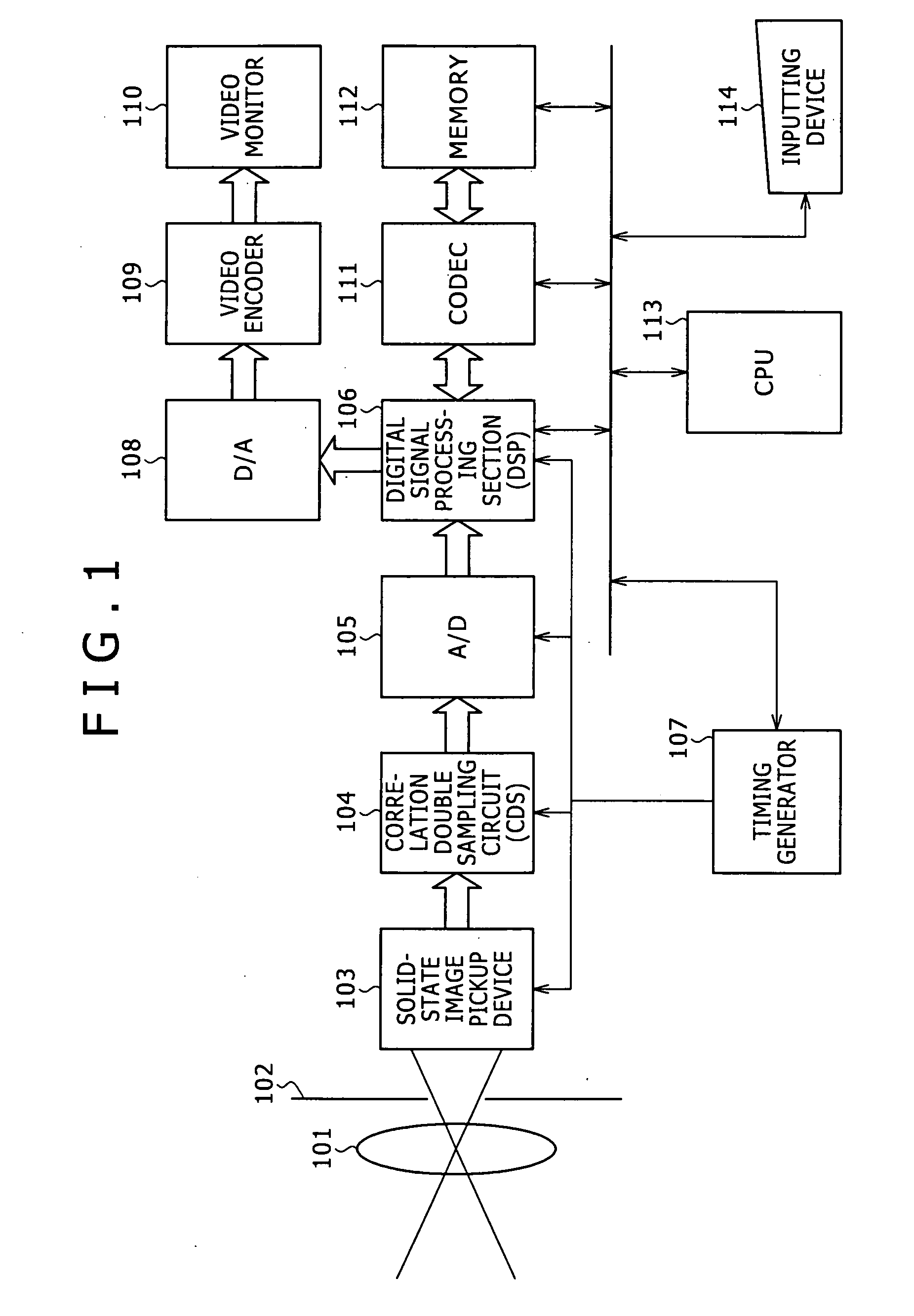
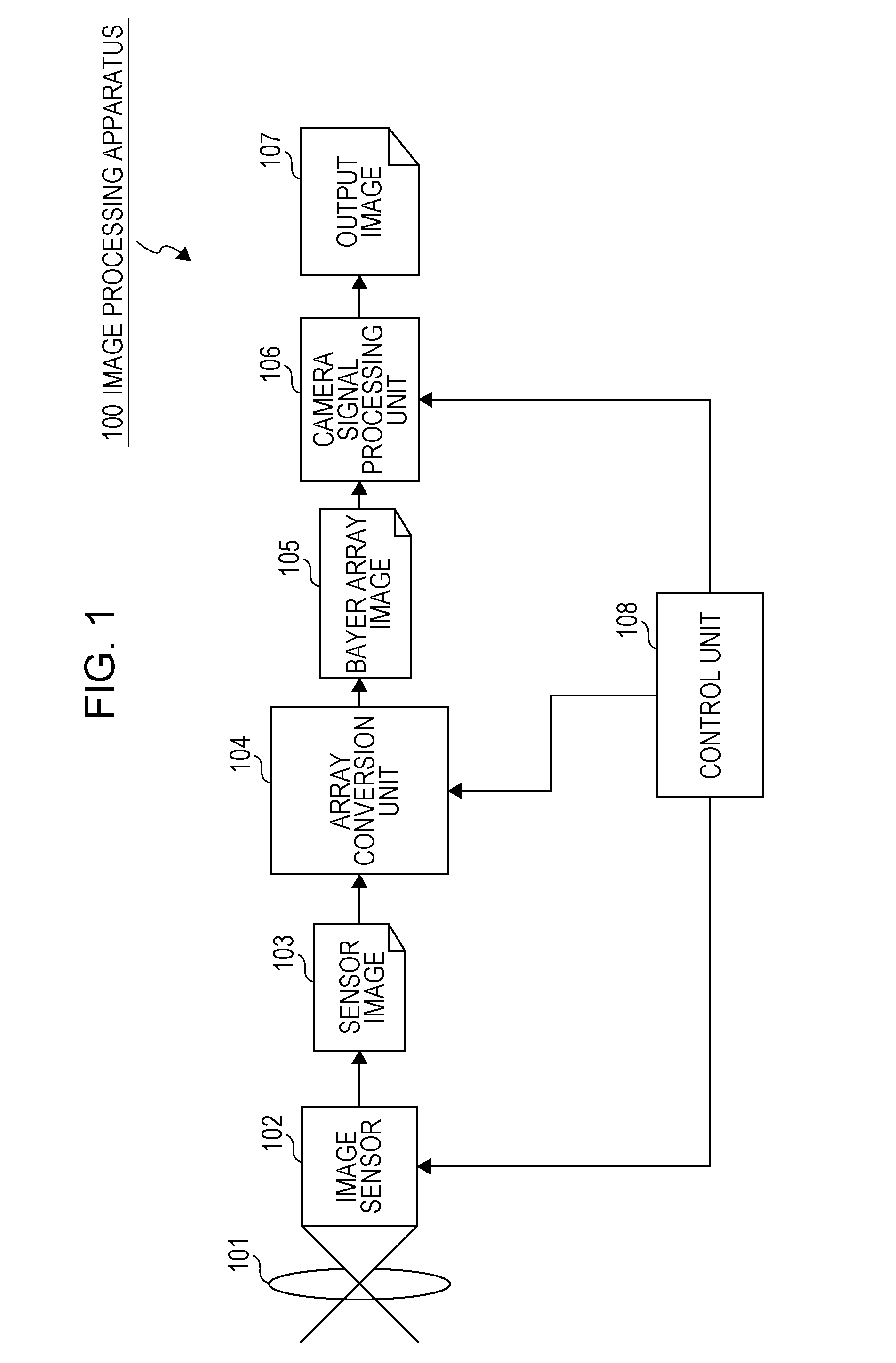
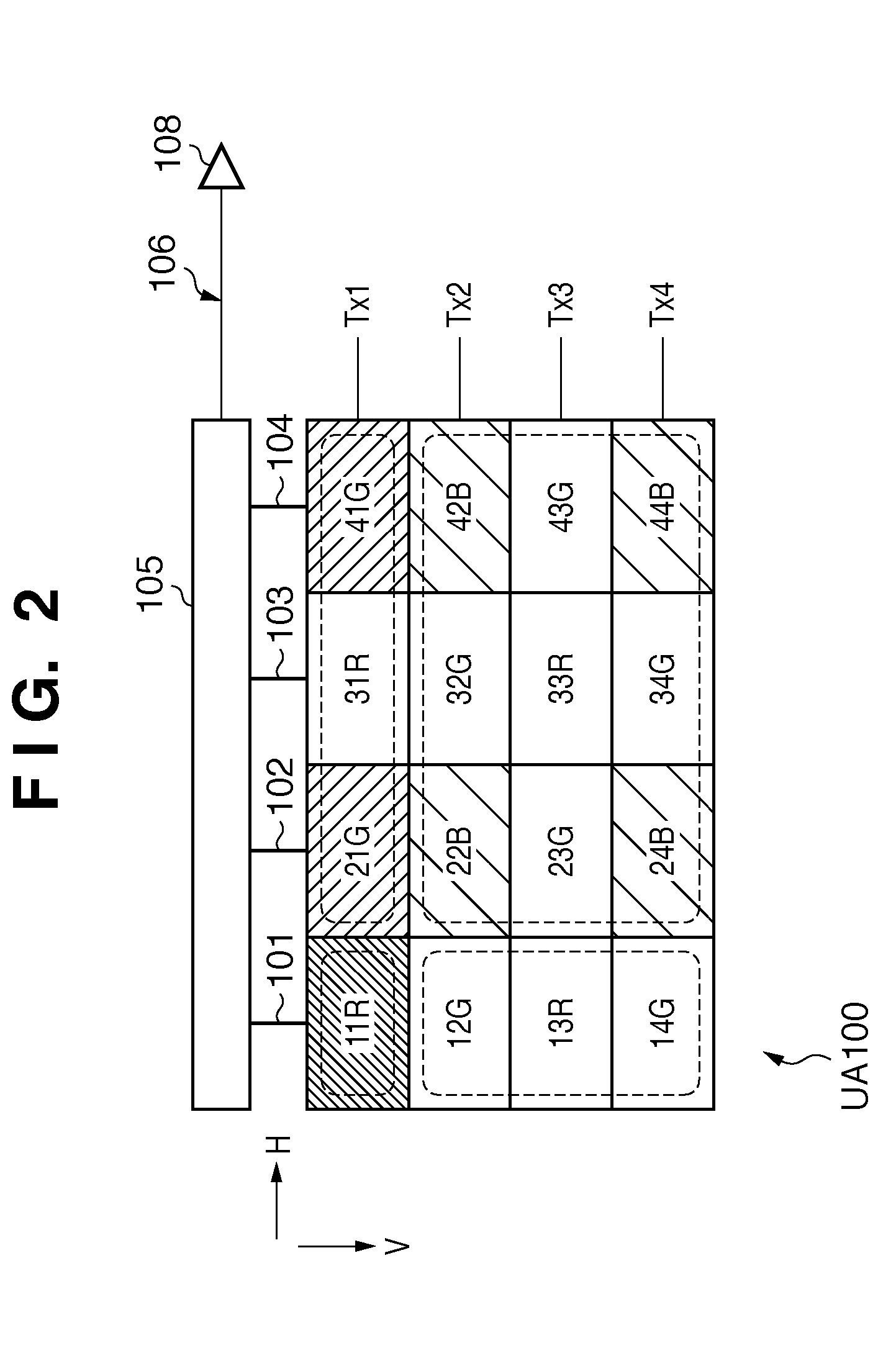
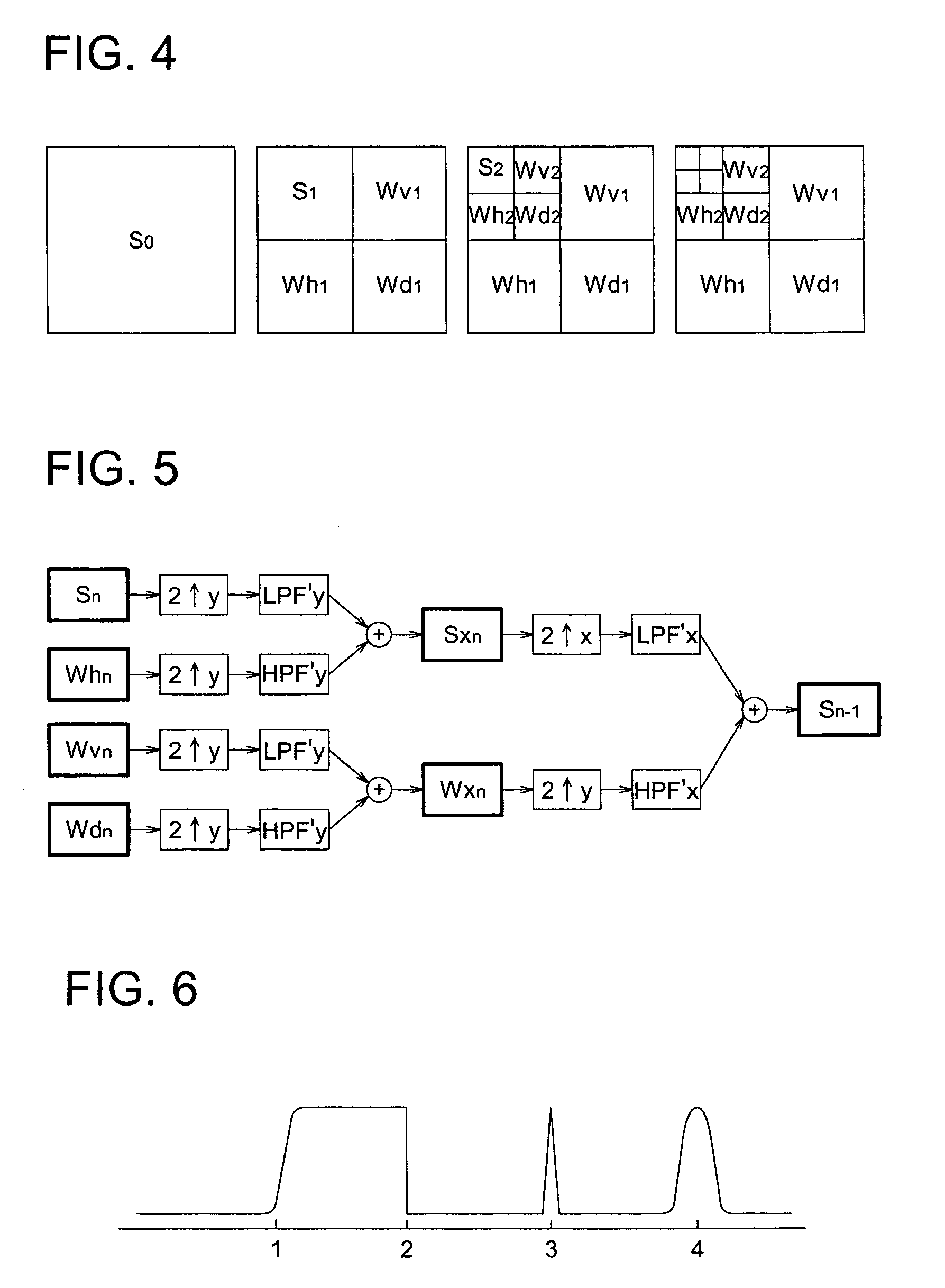
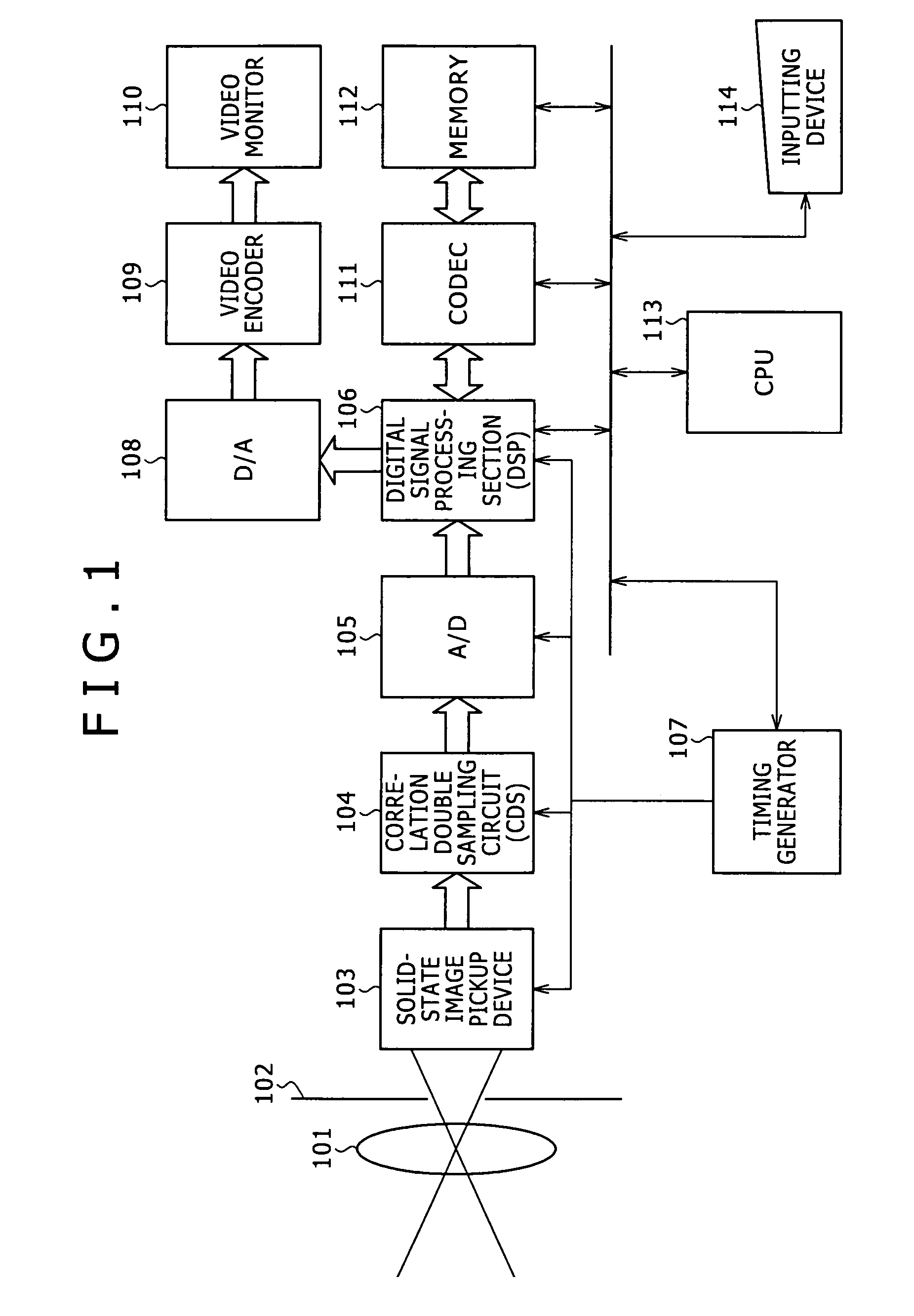
Solid-state imaging apparatus and signal processing method for transforming image signals output from a honeycomb arrangement to high quality video signals
InactiveUS6882364B1High outputWithout delayTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsLow-pass filterFalse color
A solid-state imaging apparatus includes an image pick-up section in which photosensitive devices are arranged in, e.g., a honeycomb G square lattice, RB full-checker pattern due to shifted pixels. Regions void of the photosensitive devices are assumed to be virtual photosensitive devices. A signal processing section generates data for the virtual photosensitive devices by using the data of surrounding photosensitive devices while attaching importance to accurate color reproduction and horizontal and / or vertical resolution. As a result, the number of pixel data are increased in a square lattice arrangement. Therefore, high quality image signals are readily achievable with a smaller number of photosensitive devices than conventional with a conventional apparatus. Interpolation can be executed with the high quality signals to the limit of resolution with an adequate circuit scale. The honeycomb arrangement guarantees the required size of the individual pixel and thereby the sensitivity of the entire apparatus while increasing yield on a production line. False colors particular to a single photosensitive portion can be reduced by, e.g., uniform interpolation. Particularly, when a digital camera is constructed by using an imaging apparatus including optics operable with a silver halide sensitive type of film, false colors can be reduced without resorting to an optical low pass filter.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
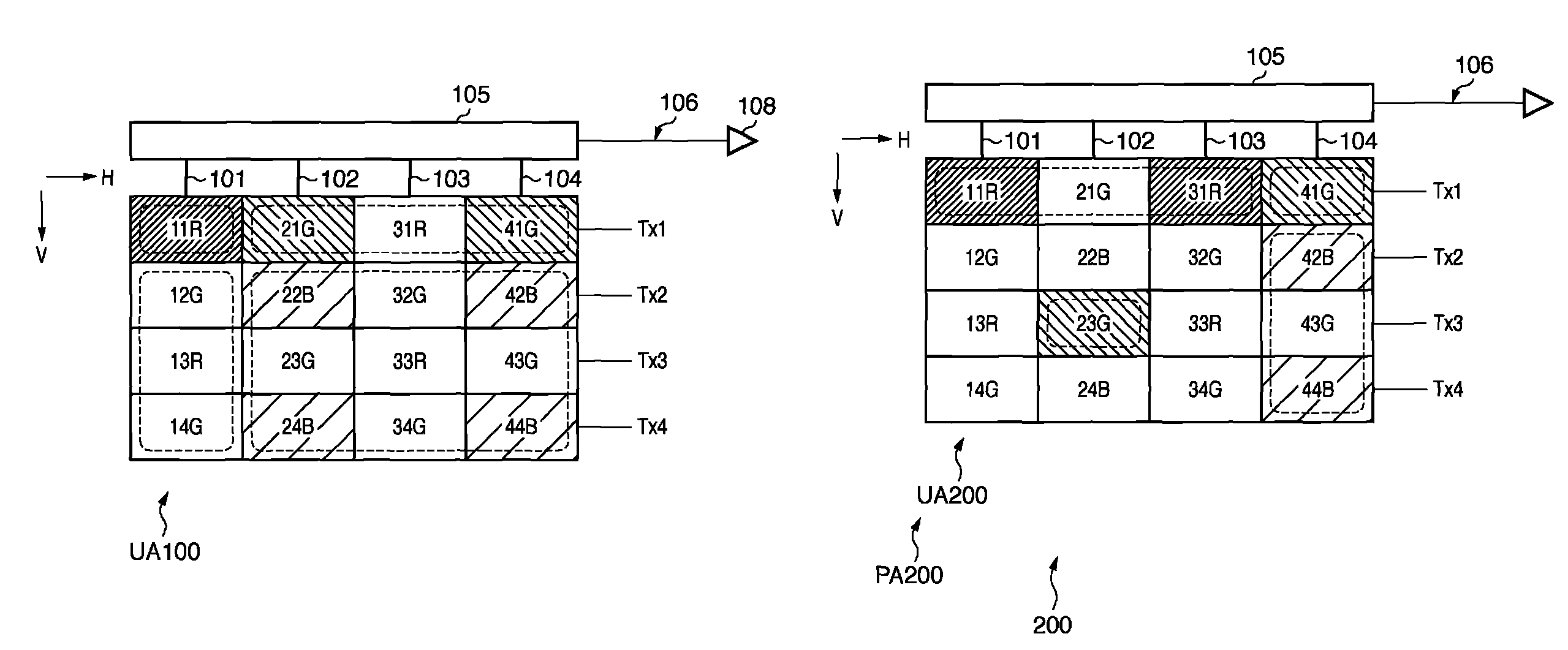
Solid-state image sensor having pixels shifted and complementary-color filter and signal processing method therefor
InactiveUS6847397B1Guaranteed effective useImprove imaging resolutionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImaging qualityFalse color
A solid-state image sensor capable of enhancing efficient use of incident light and increasing the resolution of an image and a signal processing method therefore are disclosed. A digital camera includes an image pickup section having a photosensitive array in which photosensitive cells or photodiodes are arranged. Signal charges, or pixel data, are read out of the photodiodes, two lines at a time, three lines at a time, or three lines at a time with line-by-line shift in accordance with a color filter using complementary colors. A signal processing section includes a data correcting circuit for correcting the pixel data. Pixel data of one of three primary colors R, G and B is interpolated in the position of each virtual photosensitive cell or that of each real photosensitive cell. The above color filer uses more efficiently incident light than a filter using the primary colors and improves the sensitivity of the photosensitive cells in a dense pixel arrangement, thereby contributing to the enhancement of image quality. Further, the generated pixel data are used to interpolate pixel data in the real photosensitive cells or the virtual photosensitive cells. This is successful to broaden the frequency band of the pixel data of the real photosensitive cells or those of the virtual photosensitive cells and therefore to improve image quality while obviating false colors.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Electronic Camera
InactiveUS20090147102A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsElectronic shutterFalse color
Disclosed herein is an electronic camera for generating an image having a wide dynamic range by synthesizing two image pickup signals of different exposure amount generated by using an electronic shutter function and means for shutting off light, shading of image pickup signals resulting from difference in charge accumulating time among the pixels of image pickup device due to operation from opened state to closed state of the means for shutting off light being corrected by a shading correction means to form a synthesized image without an occurrence of false color due to shading. Also provided is an electronic camera generating two image pickup signals of different exposure amount by two shots of picture taking each using a flash emission in combination, at least one of an electronic shutter of image pickup device and means for shutting off light, as well as an emission of the flash emission means, being controlled to equalize between the two shots of picture taking ratio of exposure by normal light excluding light from the flash emission means and ratio of emission amount by the light from the flash emission means so that the two image pickup signals can be readily generated as having a predetermined exposure amount ratio in every part of a frame of picture even when a flash emission is used in combination.
Owner:OLYMPUS OPTICAL CO LTD
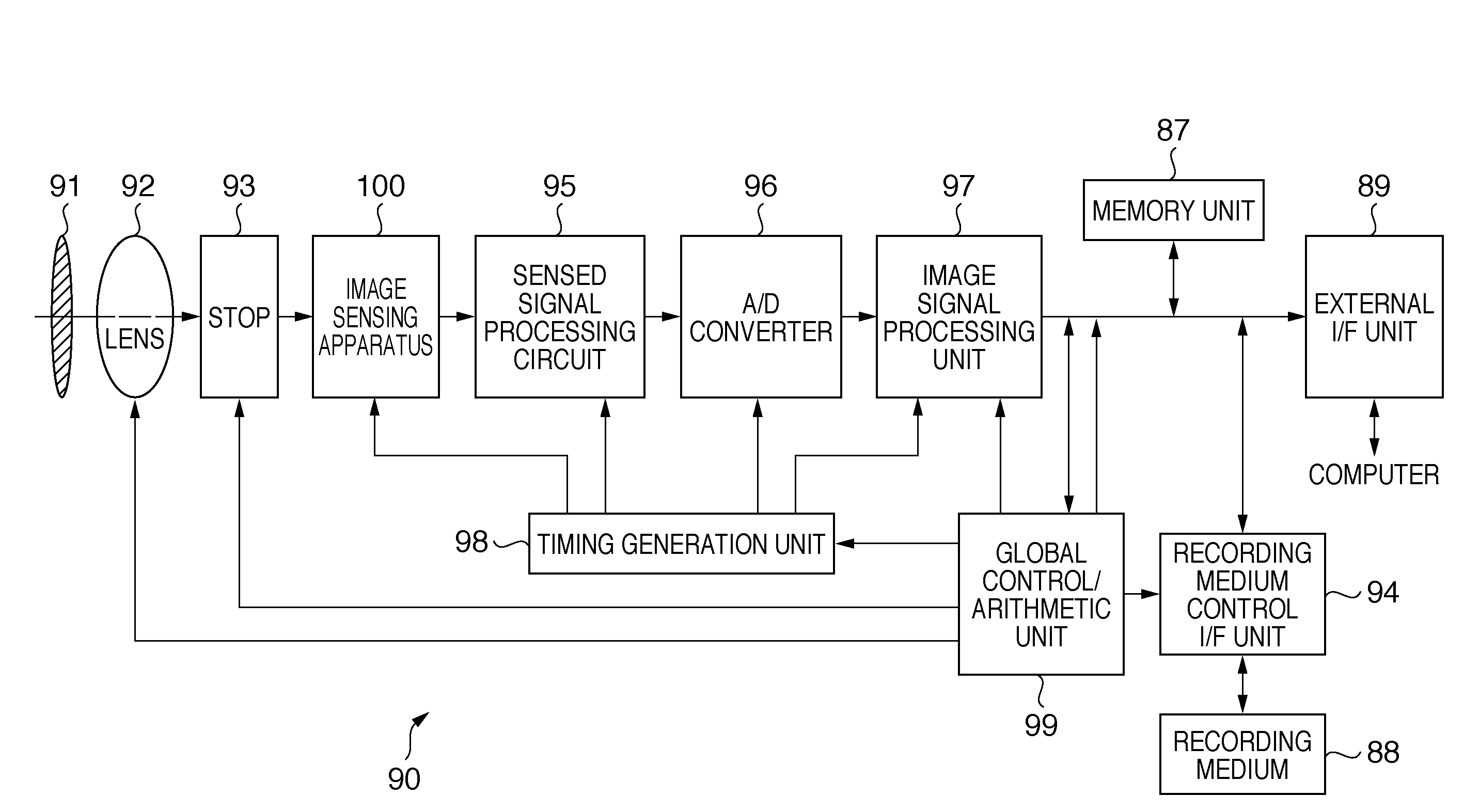
Image sensing apparatus driving method, image sensing apparatus, and image sensing system
InactiveUS7982789B2Reduce generationSufficient frame rateTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImage resolutionFalse color
Since pixel signals are not only added in the row direction but also averaged in the column direction, it is possible to sufficiently increase the frame rate even when the number of pixels increases. Additionally, since the spatial centers of gravity of the added or averaged signals are arranged at equal intervals in a Bayer array, it is possible to reduce false color (moiré) generation and suppress the decrease in the spatial resolution.
Owner:CANON KK
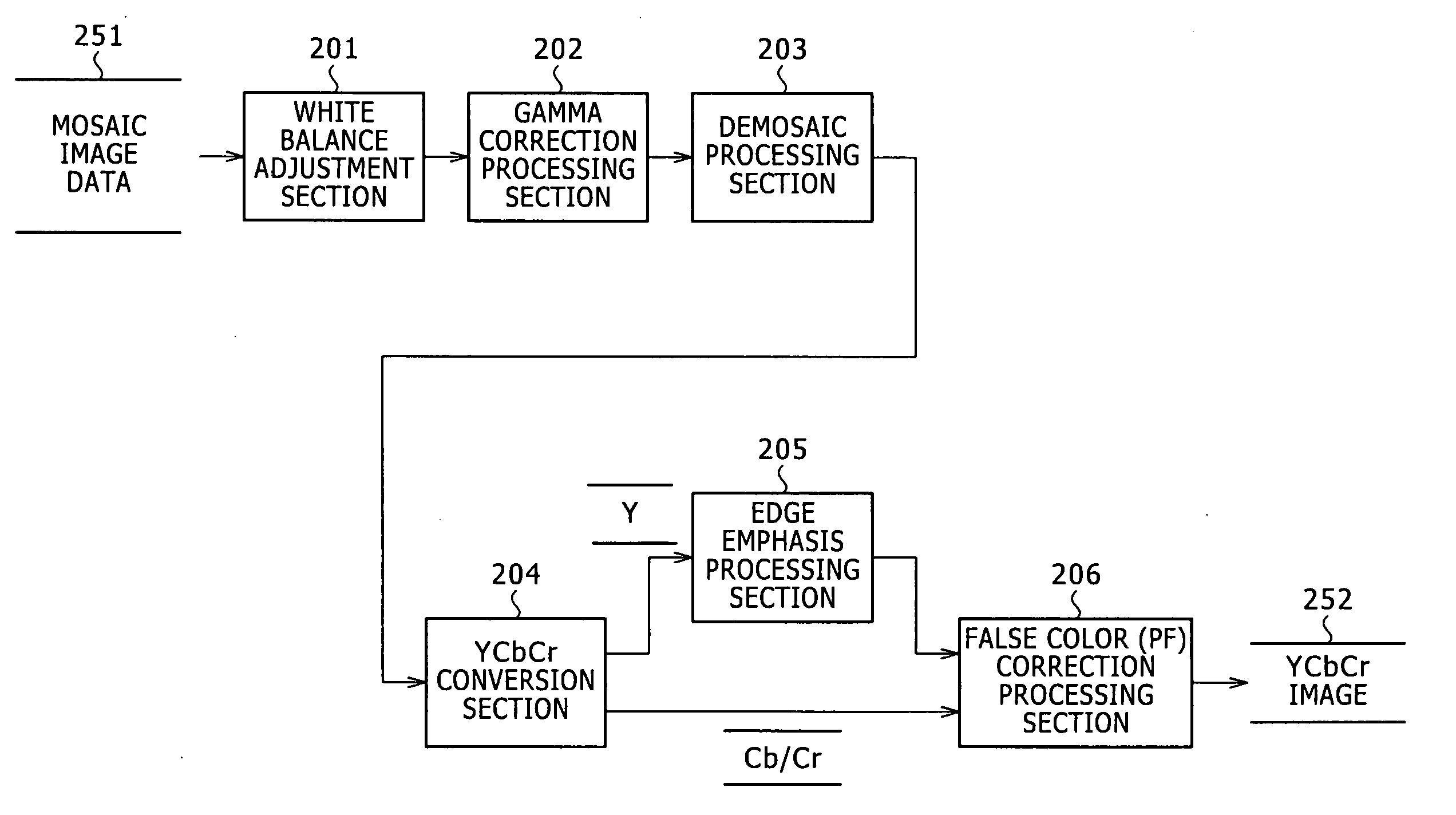
Image processing apparatus and image processing method as well as computer program
InactiveUS20060098253A1Excessive of saturation can be preventedQuality improvementImage enhancementTelevision system detailsReduction rateImaging processing
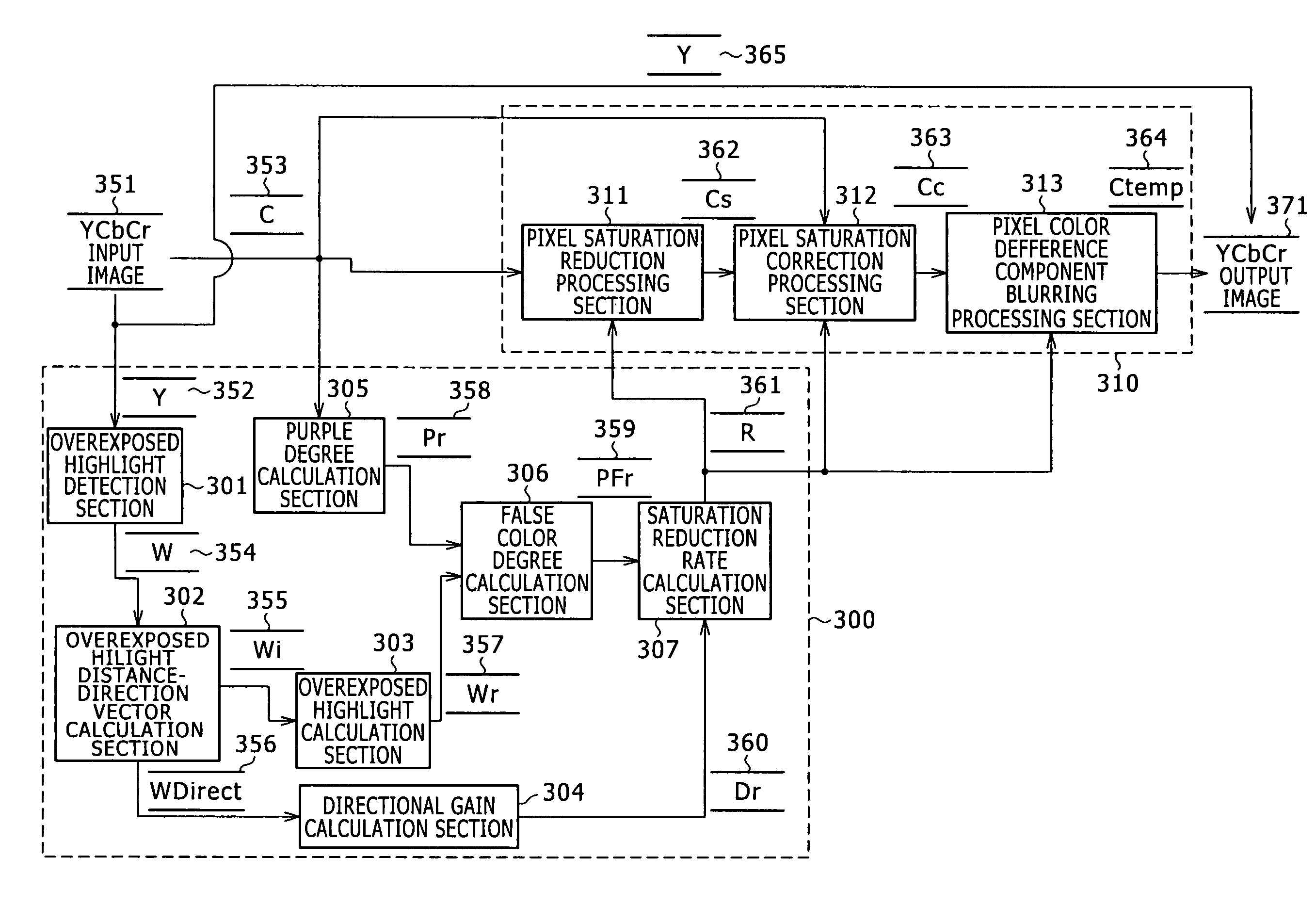
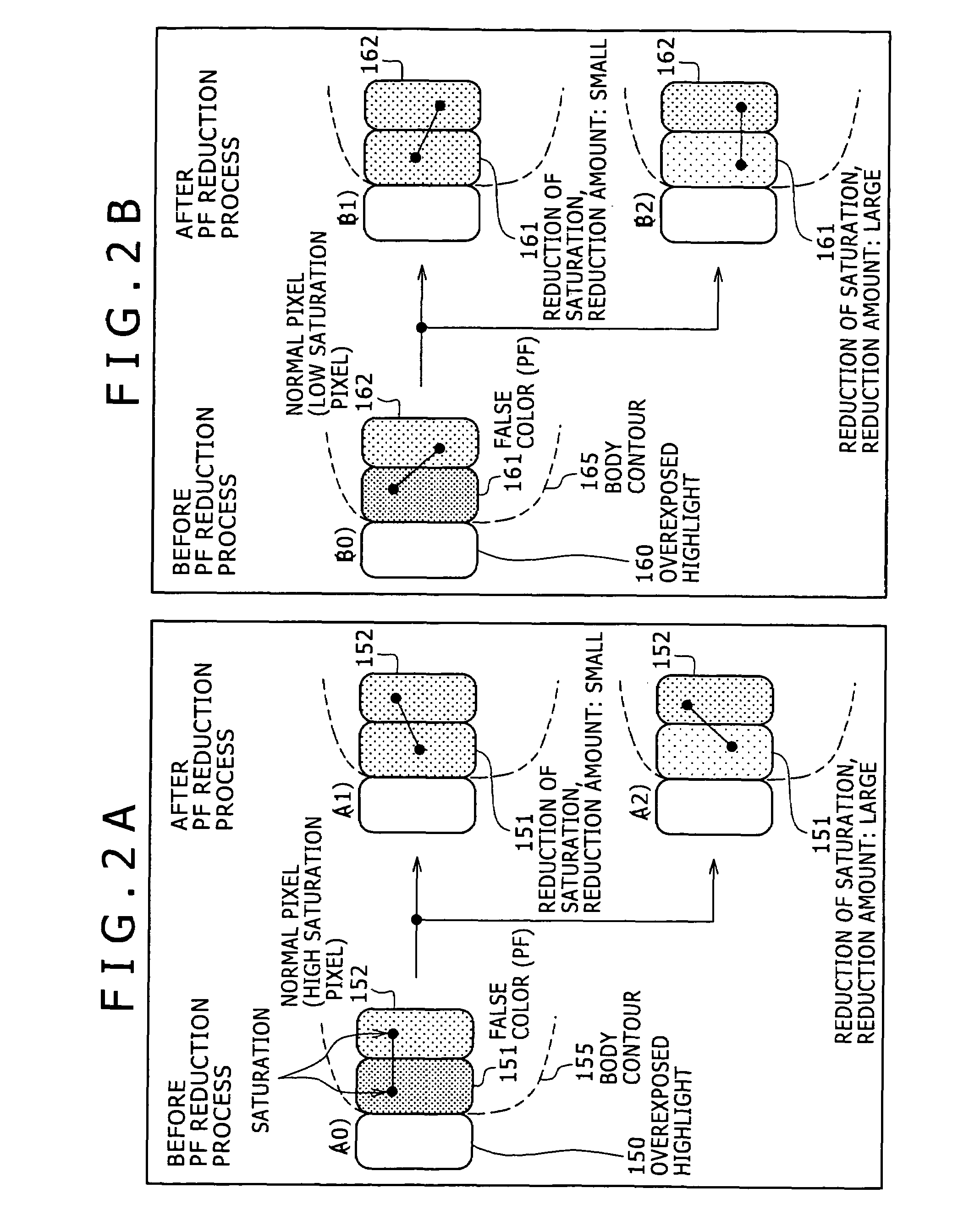
An image processing apparatus and an image processing method are disclosed by which an image correction process for a false color such as a purple fringe can be executed efficiently while excessive reduction of the saturation is prevented to produce image data of a high quality. A saturation reduction rate corresponding to each pixel is calculated, and saturation reduction of the pixel is executed based on the saturation reduction rate. Then, saturation correction is executed so that the difference between the hue of the pixel whose saturation has been reduced and a surrounding reference pixel may be reduced. Further, a surrounding pixel to be referred to in the saturation correction process is selected along a scanning line.
Owner:SONY CORP
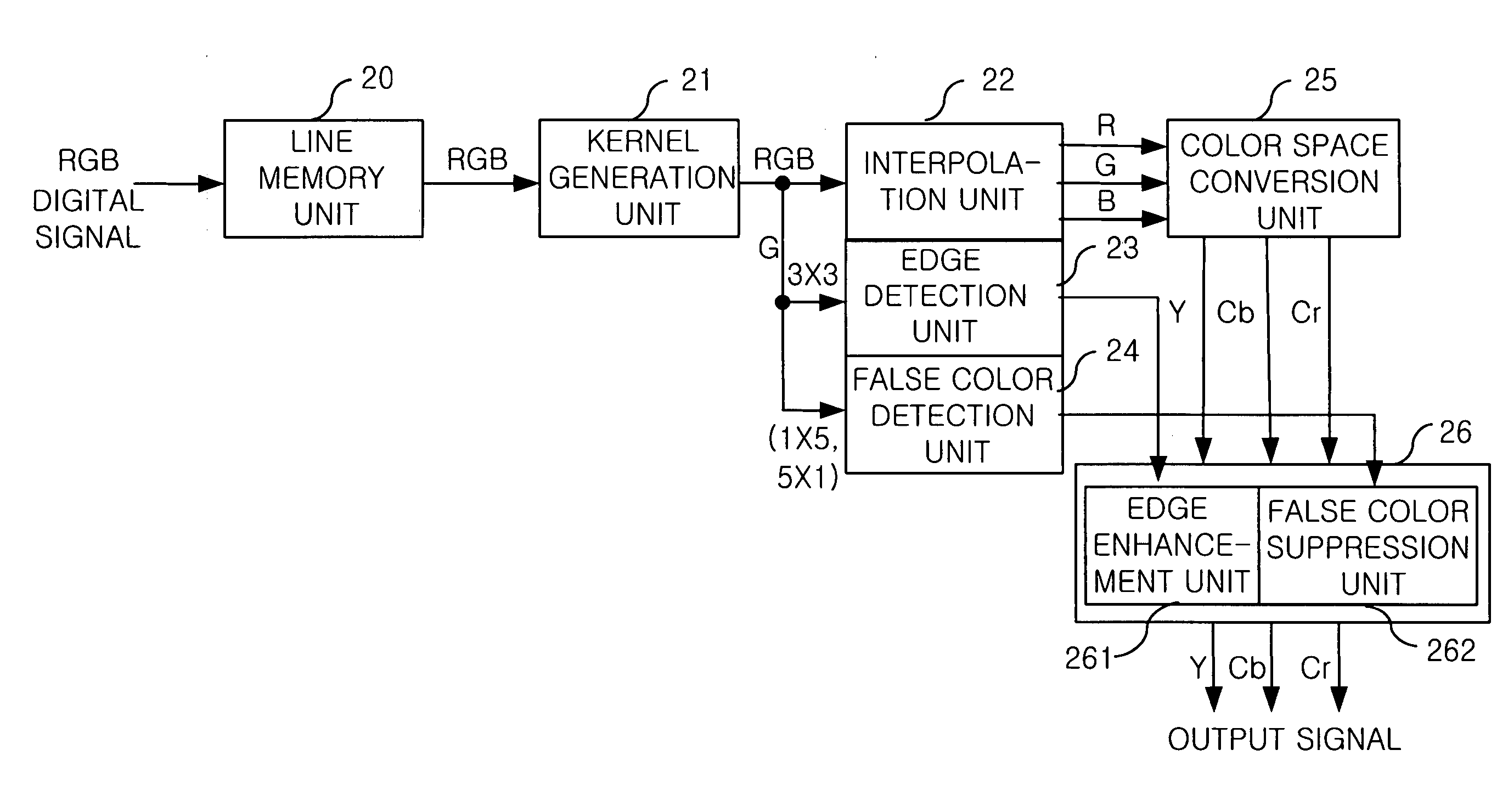
Digital signal processing apparatus in image sensor
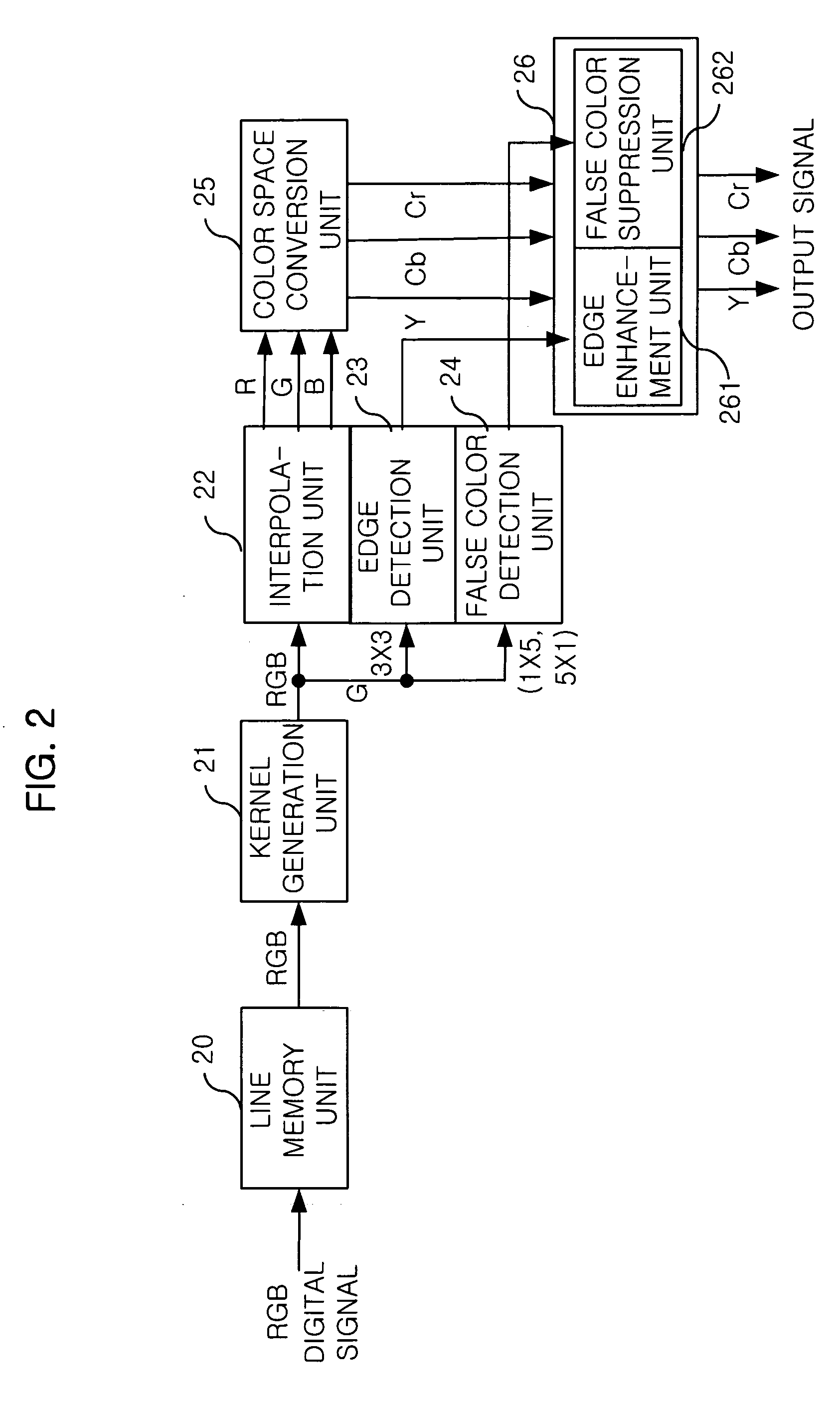
InactiveUS20050238225A1Image enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionDigital signal processing
Disclosed is an apparatus for processing a digital signal in an image sensor. The apparatus includes: a line memory unit for storing an inputted digital signal of red (R), green (G) and blue (B); a kernel generation unit for generating a plurality of kernels after receiving the RGB digital signal from the line memory unit; a false color detection unit for detecting false colors by using the plurality of kernels; an edge detection unit for detecting edges by using the plurality of kernels; an interpolation unit for interpolating the RGB digital signal from the line memory unit; a color space conversion unit for converting the interpolated RGB digital signal into a YCbCr signal; and an image enhancement unit for suppressing the false colors and enhancing the edges in the YCbCr signal in response to outputs of the false color detection unit and the edge detection unit.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES II
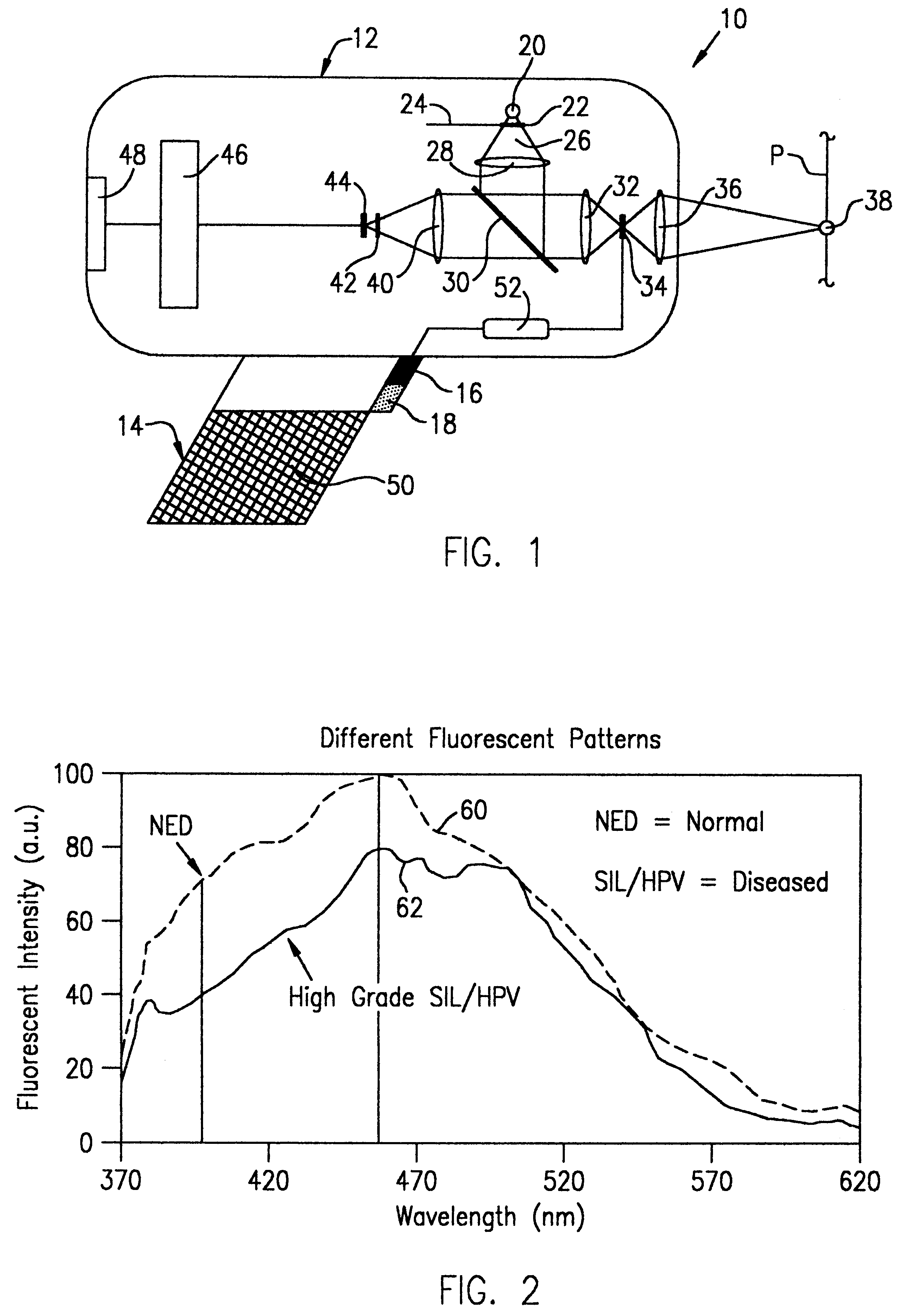
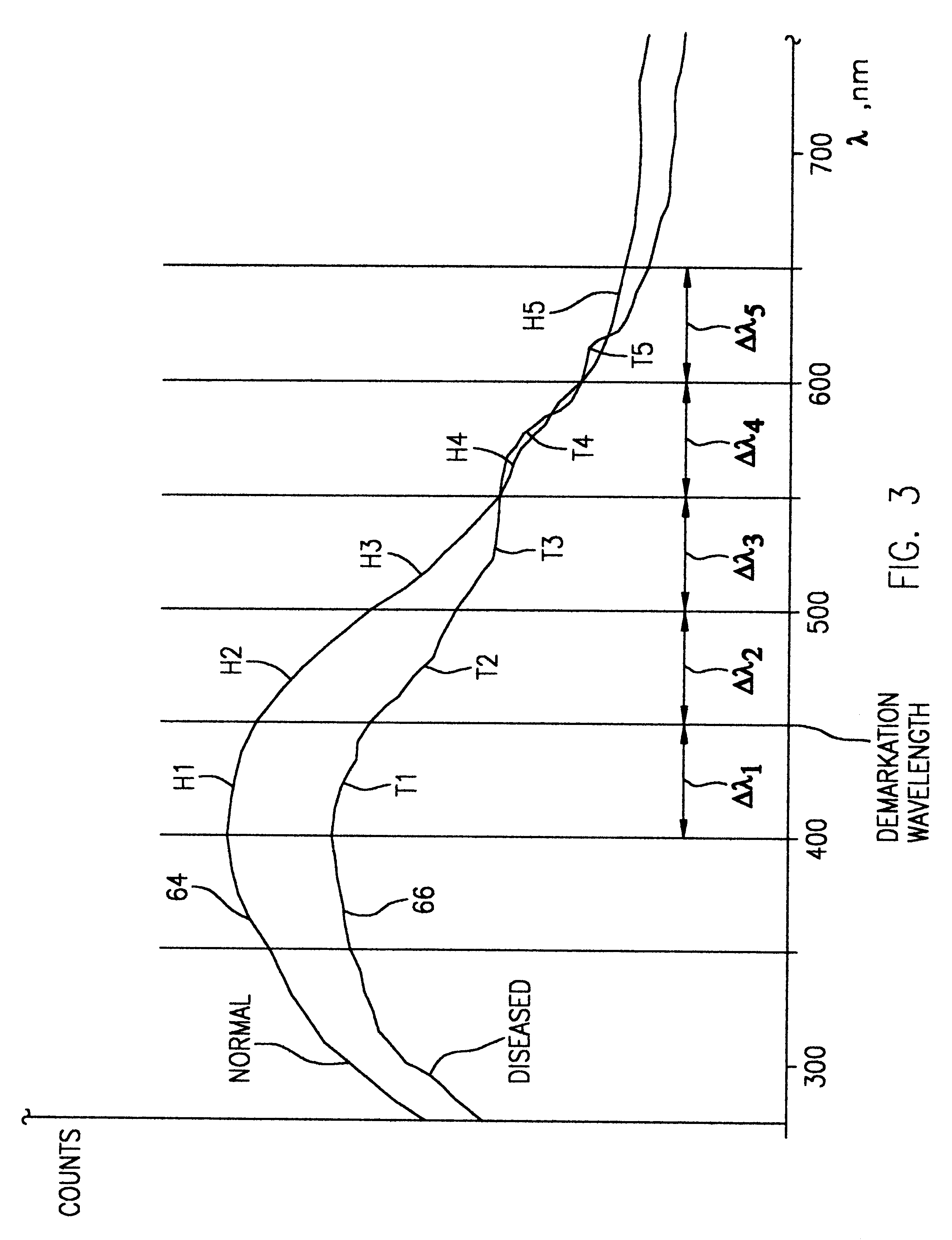
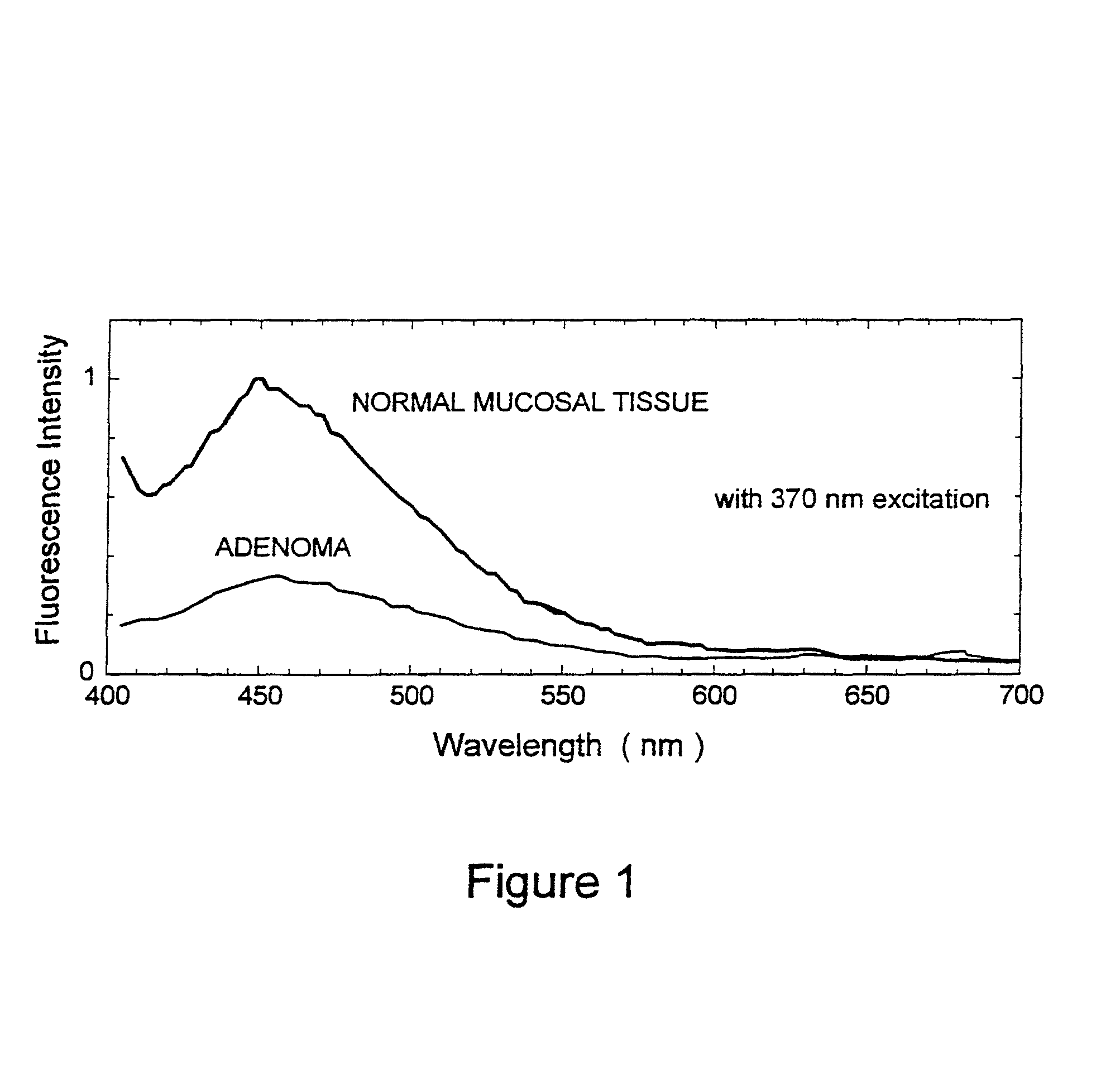
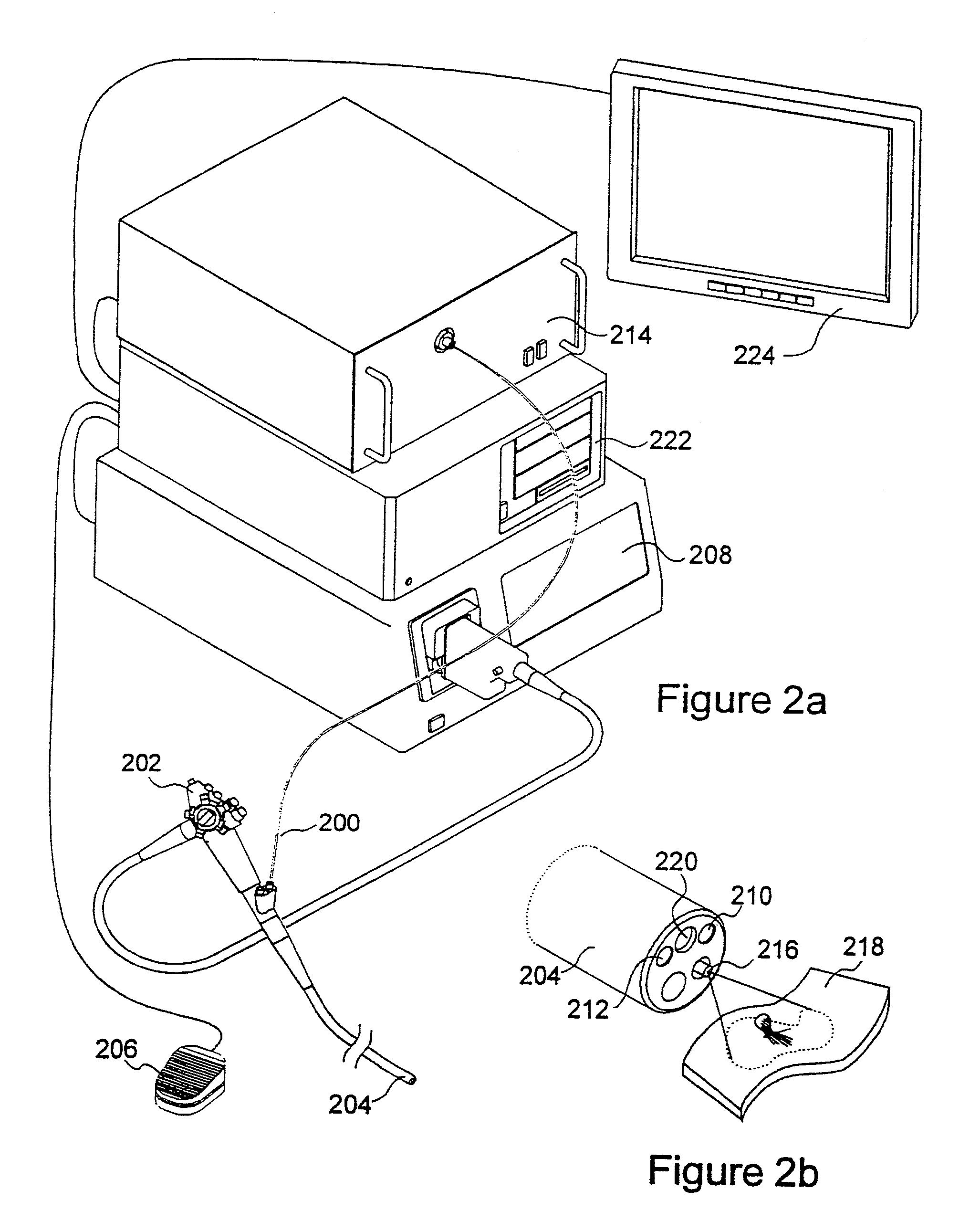
Optical instrument and technique for cancer diagnosis using in-vivo fluorescence emission of test tissue
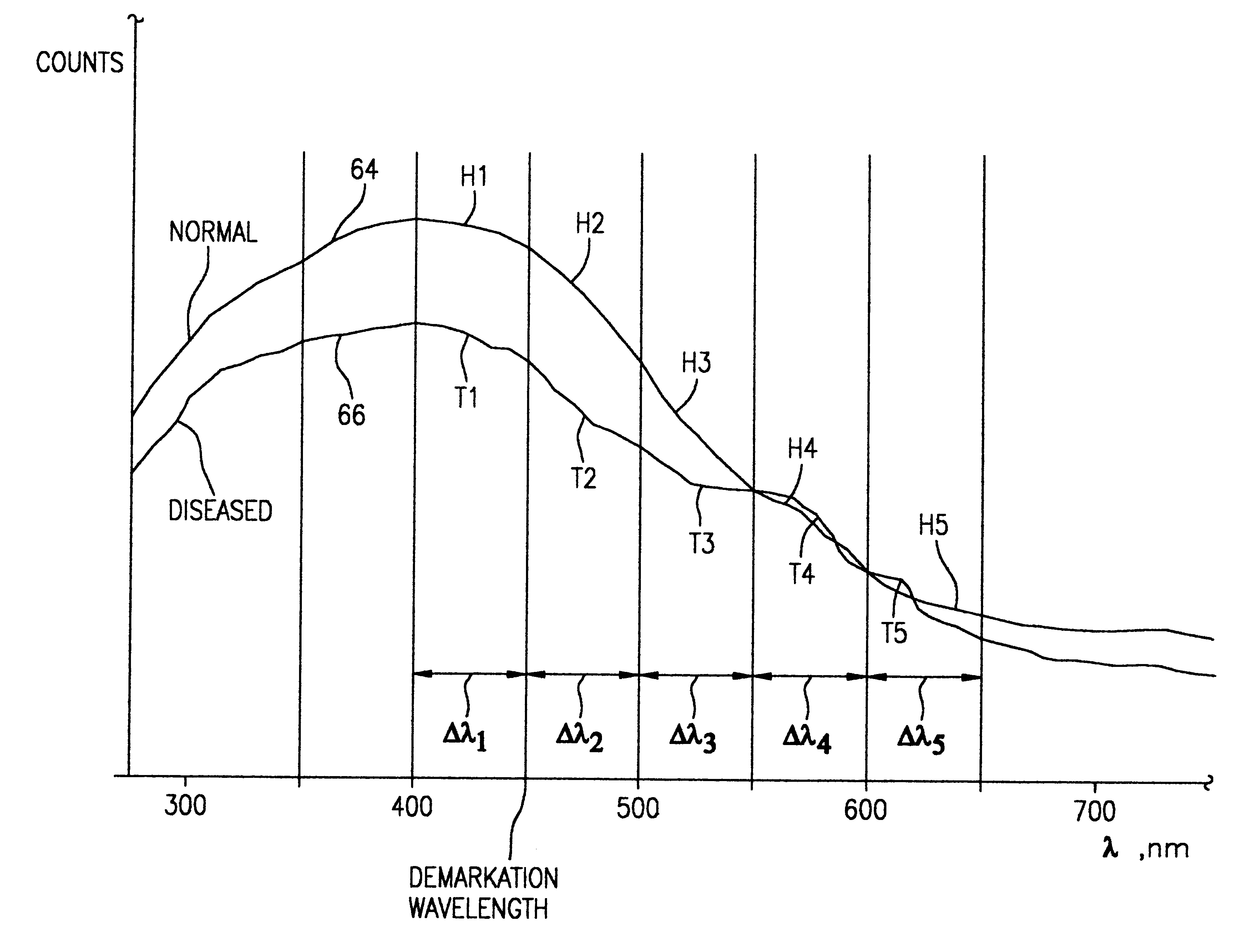
A hand-held, small, lightweight instrument is disclosed that contains a light source capable of producing radiant energy in the spectral range between approximately 370 and approximately 410 nm, and an optical direction system for irradiating a target tissue by producing an illuminated spot thereon. A collection system is provided for receiving and directing fluorescent emissions in the frequency range between 450 and 700 nm returned from the target area to a detector. A processing system is used to determine the state of the tissue by using at least two and up to five spectral bands, preferably each being larger than 45 nm. Pairs of ratios of fluorescent intensities are compared to identify cancerous cells. An alphanumeric, false-color image and / or audio signal is immediately provided to inform a user of the state of the tissue.
Owner:WOLFE WILLIAM L
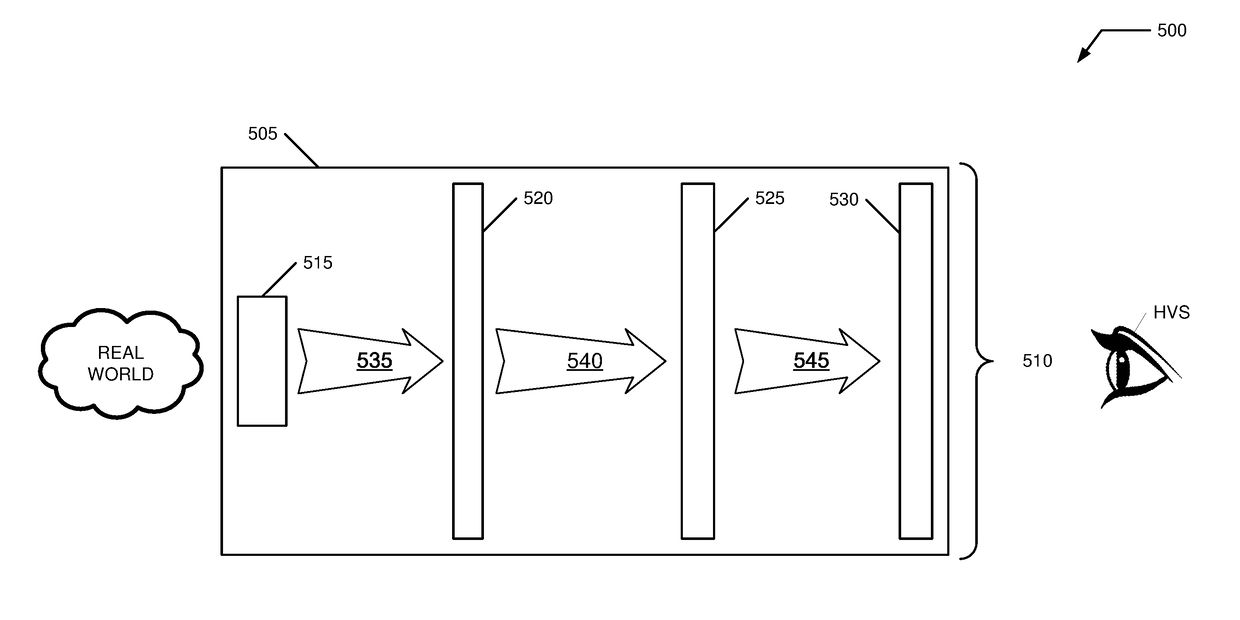
Hybrid photonic vr/ar systems
InactiveUS20180122143A1Need for goodEasy to handleImage enhancementImage analysisPhotonicsComputer vision
A VR / AR system, method, architecture includes an augmentor that concurrently receives and processes real world image constituent signals while producing synthetic world image constituent signals and then interleaves / augments these signals for further processing. In some implementations, the real world signals (pass through with possibility of processing by the augmentor) are converted to IR (using, for example, a false color map) and interleaved with the synthetic world signals (produced in IR) for continued processing including visualization (conversion to visible spectrum), amplitude / bandwidth processing, and output shaping for production of a set of display image precursors intended for a HVS.
Owner:PHOTONICA
Image processing apparatus, imaging device, image processing method, and program
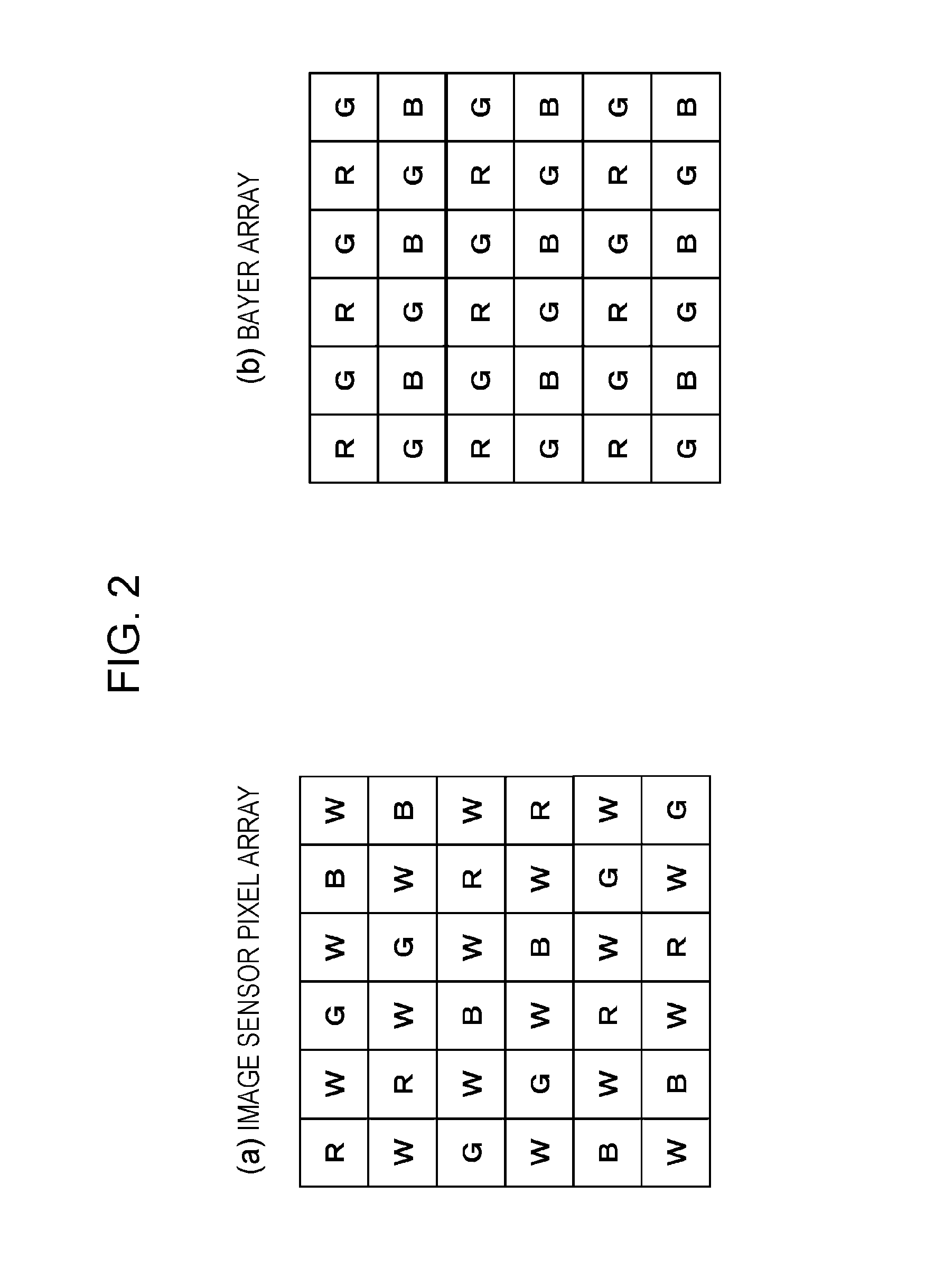
ActiveUS20150029358A1Less color noiseFalse colorTelevision system detailsImage enhancementImaging processingRgb image
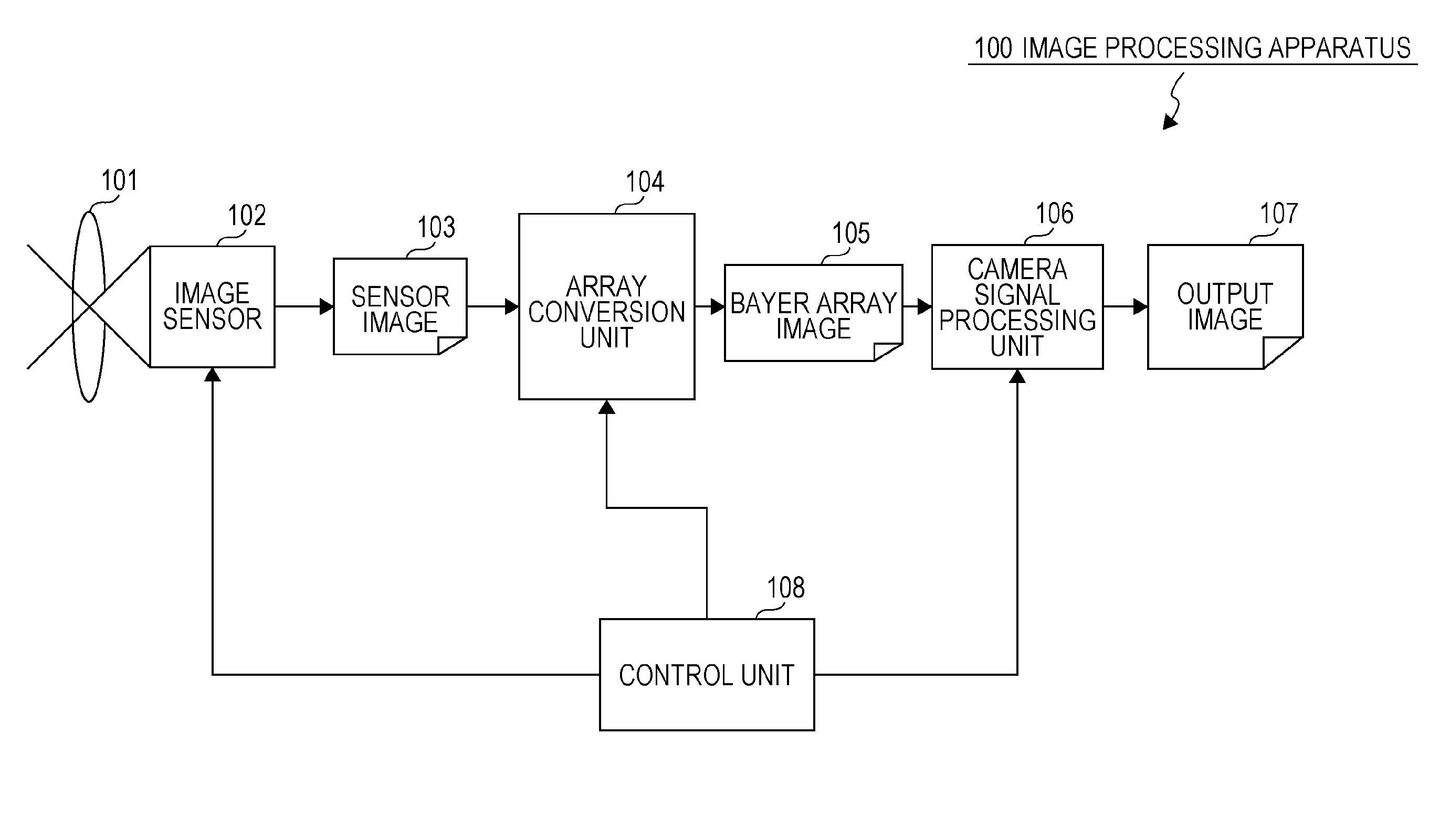
There are provided an apparatus and a method which generate an RGB image having less color noise and fewer false colors by inputting an RGBW image. The apparatus has an image sensor having an RGBW array, and an image processing unit which performs image processing by inputting a sensor image formed of an RGBW pixel signal output from the image sensor. The image sensor has a periodic array of a unit composition formed of each RGBW pixel, and has an array in which composition ratios of each RGB pixel within the unit composition are adapted to be the same as each other. The image processing unit converts a pixel array of the sensor image formed of the RGBW pixel signal, and performs at least either array conversion processing for generating an RGB array image or signal processing for generating each RGB image signal in which all RGB pixel values are set for each pixel position of the sensor image.
Owner:SONY CORP
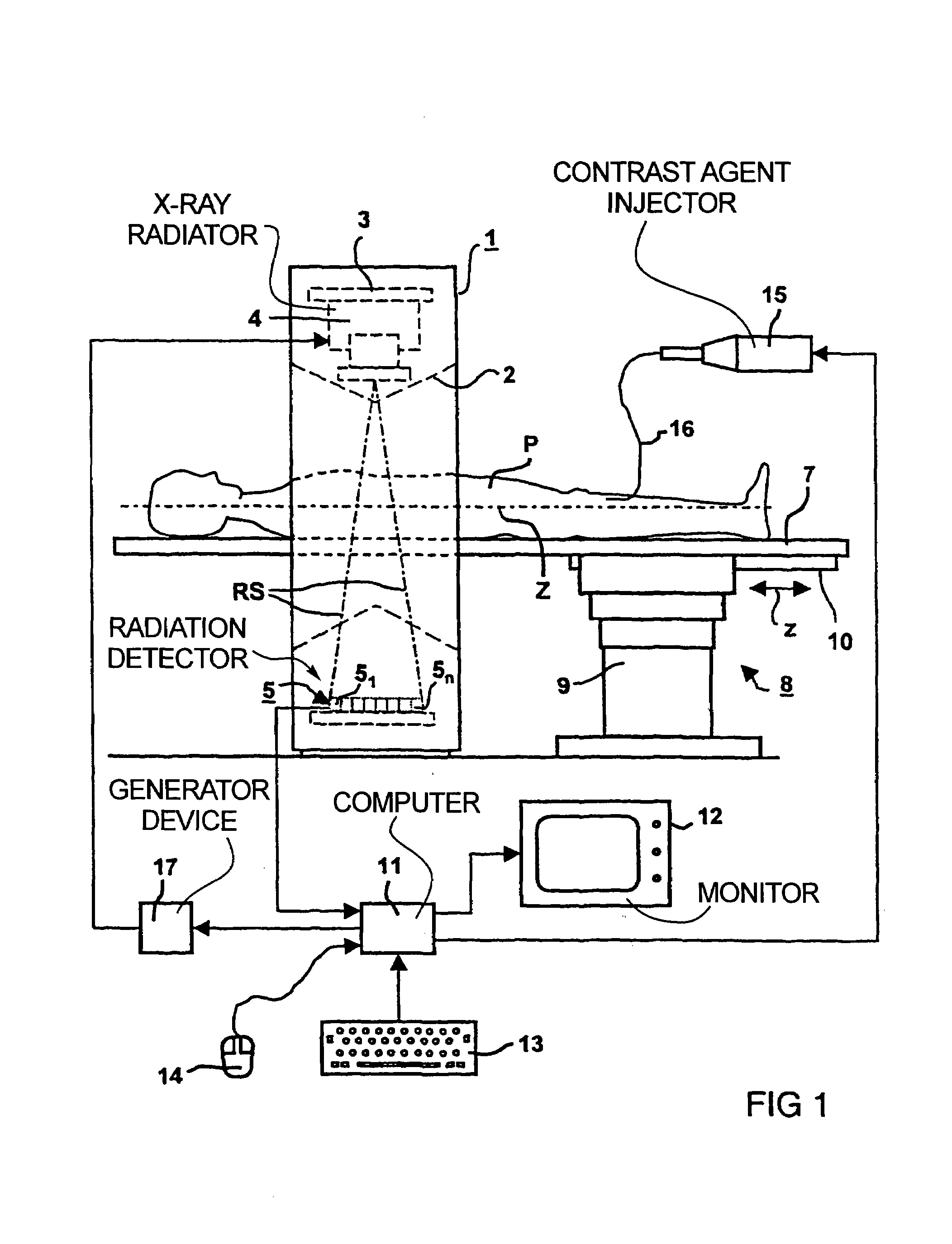
Method and apparatus for processing a computed tomography image of a lung obtained using contrast agent
ActiveUS7203353B2Improve diagnostic reliabilityImprove reliabilityImage analysisSurgeryPulmonary parenchymaComputed tomography
In a method and apparatus for image processing proceeding from a computed tomography (CT) image of a lung as an original image that is registered using a contrast agent, pulmonary parenchyma pixels are determined, the pulmonary parenchyma pixels are presented in false colors, and the remaining image regions are presented in the gray scale values of the original image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and computer program
InactiveUS20070035641A1Efficient detectionHigh-quality image dataTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsImaging processingFalse color
An apparatus and a method for efficiently executing correction of false color, such as purple fringe, caused by chromatic aberration and for generating and outputting high-quality image data are provided. A white-saturated pixel is detected from image data, a false-color-pixel detection area is set around the detected white-saturated pixel, and pixels having color corresponding to false color such as purple fringe are detected from the set area. The detected pixels are determined as false-color pixels and correction processing based on the values of the surrounding pixels is performed on the determined false-color pixels. With this configuration, an area of false color such as purple fringe generated in the neighborhood of a white-saturated pixel can be efficiently detected, pixel values can be partially corrected, and high-quality image data can be generated and output without affecting the entire image.
Owner:SONY CORP
Color image generating method and device
InactiveCN104079904AHigh resolutionSolve the problem of prone to false colorTelevision system detailsPicture signal generatorsCamera lensColor image
The invention is suitable for the technical field of digital photographing, and provides a color image generating method and device. The color image generating method includes the steps of controlling a camera lens to conduct exposure multiple times when shooting request information is received to obtain monochrome values of pixel points in exposed color images each time; combining the monochrome values of the pixel points obtained after exposure each time to obtain RGB color values of the pixel points, and generating the color images through the RGB color values of the pixel points. The false color problem caused when the color images are output in the traditional Bayer array color interpolation mode is accordingly solved, and the resolution ratio of the obtained color images is improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
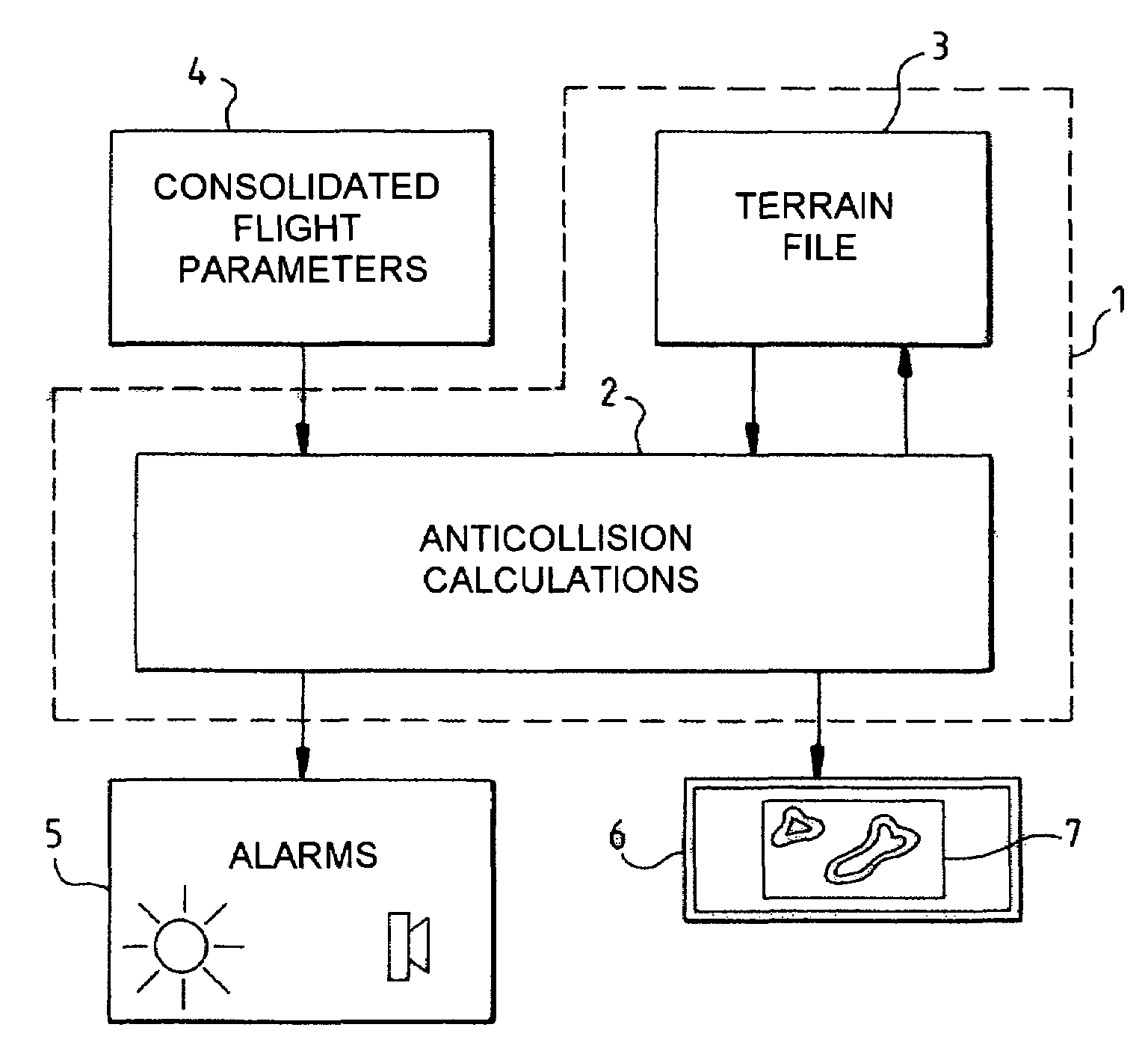
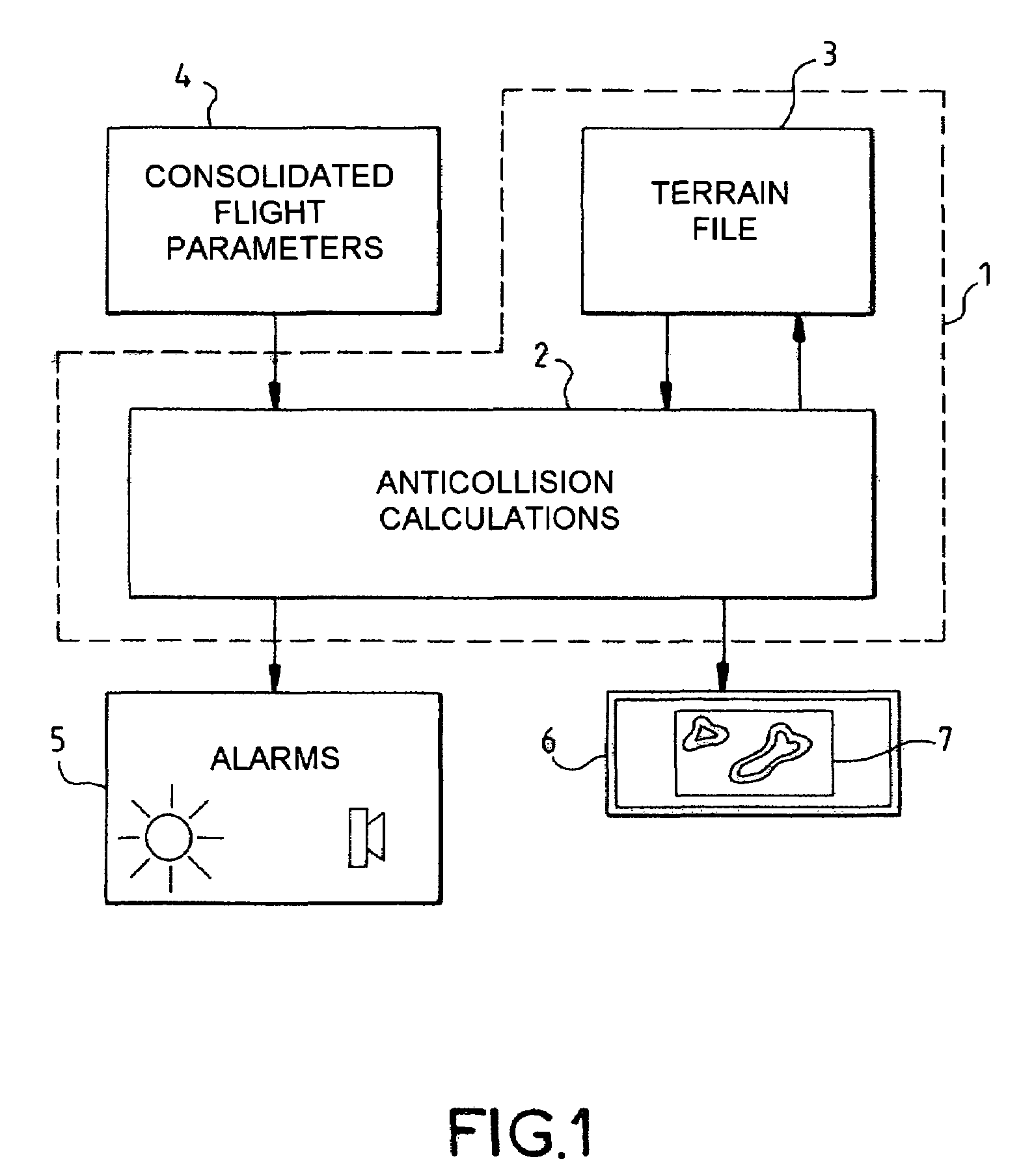
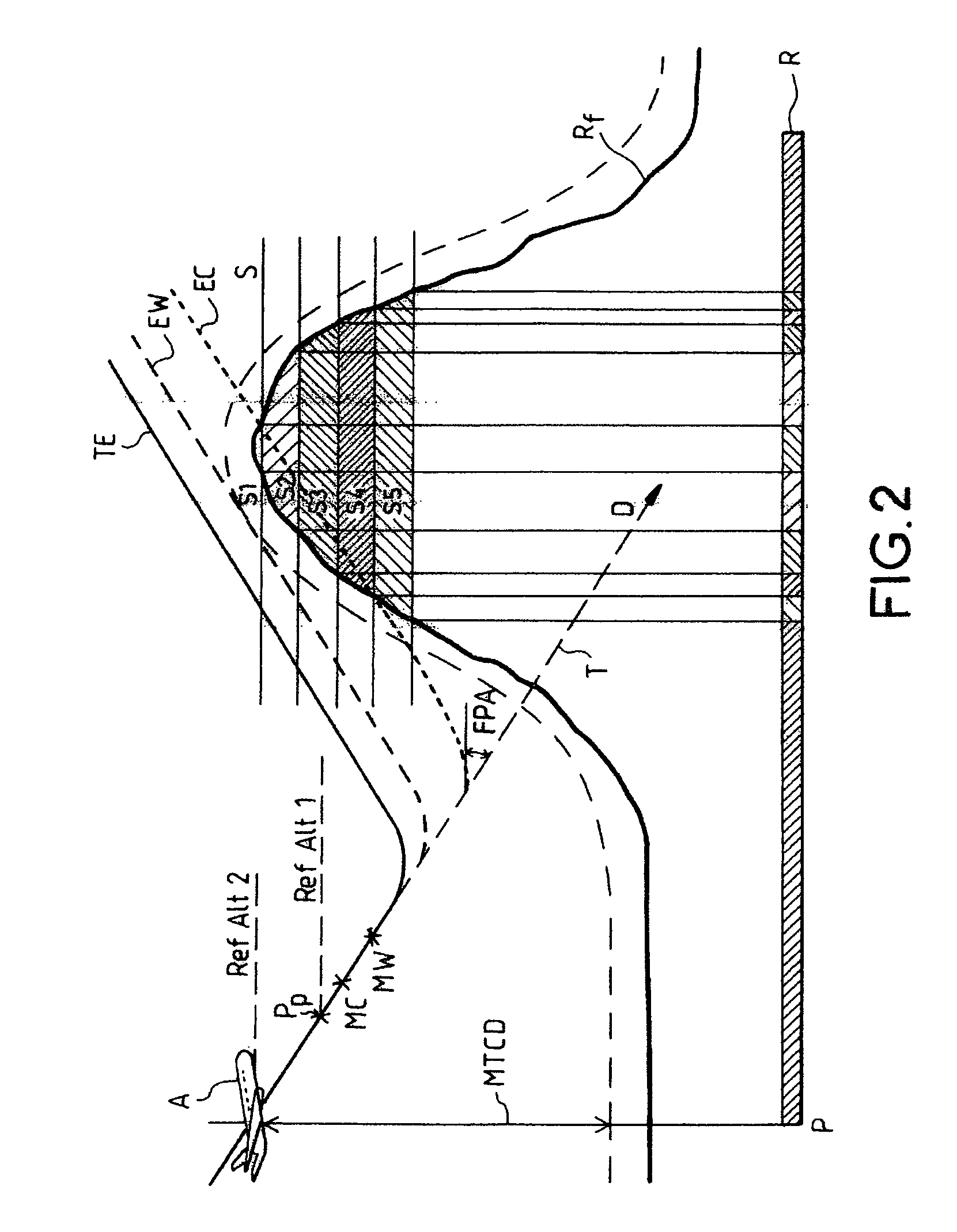
Onboard terrain anticollision display device
ActiveUS7120540B2Alleviating the aforesaid drawbackHinders maneuveringInstruments for road network navigationDigital data processing detailsTerrainAircrew
Terrain anticollision equipment generally uses a display device showing a two-dimensional synthetic map of the terrain overflown by the aircraft and in which the relief is shown by superposed slices assigned false colors representative of the magnitude of the risk of collisions. The allocation of the false colors and / or the positions of the slices is referenced with respect to a reference display altitude related to the instantaneous altitude of the aircraft or to a short term forecast altitude for the aircraft, each of the referencings having its own advantages as a function of the situation in progress for the aircraft. Here it is proposed that the reference display altitude be made to vary, with gentle transitions, with no visible jerks on the screen, as a function of the aircraft's situation deduced from the flight parameters so as to have, at any moment for the crew, the most pertinent possible and the most useful possible map having regard to the instantaneous situation vis à vis the risks of collision.
Owner:THALES SA +1
Autofluorescence imaging system for endoscopy
InactiveUS7846091B2Improve featuresAccurate and diagnostically usefulSurgeryEndoscopesFalse colorLight source
A system and method for imaging tissue autofluorescence through a video endoscope is described, comprising a light source capable of providing both ultraviolet light capable of inducing tissue autofluorescence and visible light which induces little or no autofluorescence, an optical system to deliver both wavelength bands to the tissue with the same apparent spatial and angular intensity distribution, a means for digitally acquiring the resulting, visible fluorescence and visible reflectance images using a single imaging detector at the distal tip of the endoscope and a means for digitally processing said images to generate a final, false-color image for display which indicates regions of tissue dysplasia. This system can either be added on to an existing video endoscope or integrated into its structure. The combined system can be electronically switched between normal white light imaging and fluorescence imaging.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Image sensing apparatus driving method, image sensing apparatus, and image sensing system
InactiveUS20090015699A1Generation of false color can be reducedSufficient frame rateTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImage resolutionFalse color
Since pixel signals are not only added in the row direction but also averaged in the column direction, it is possible to sufficiently increase the frame rate even when the number of pixels increases. Additionally, since the spatial centers of gravity of the added or averaged signals are arranged at equal intervals in a Bayer array, it is possible to reduce false color (moiré) generation and suppress the decrease in the spatial resolution.
Owner:CANON KK
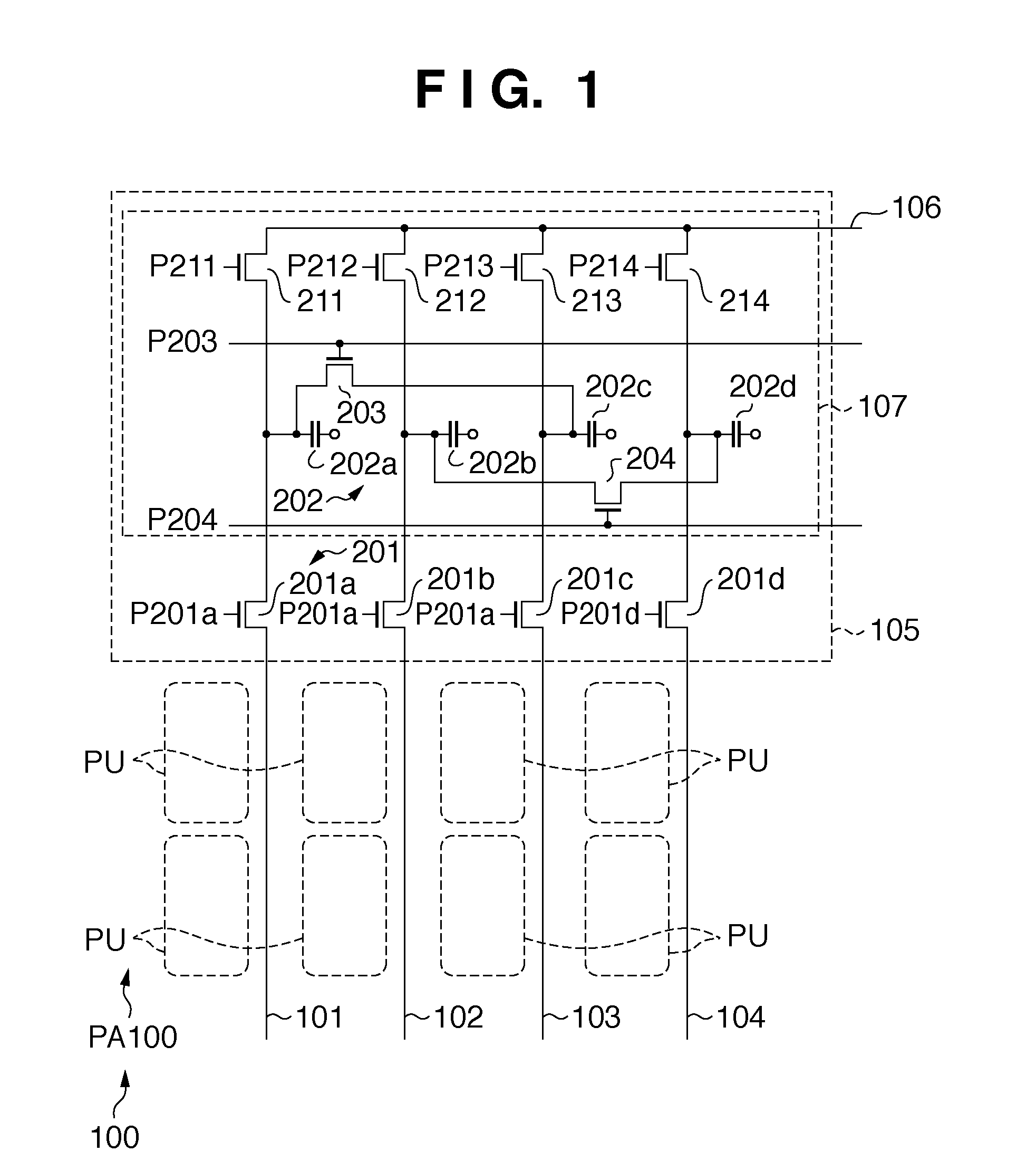
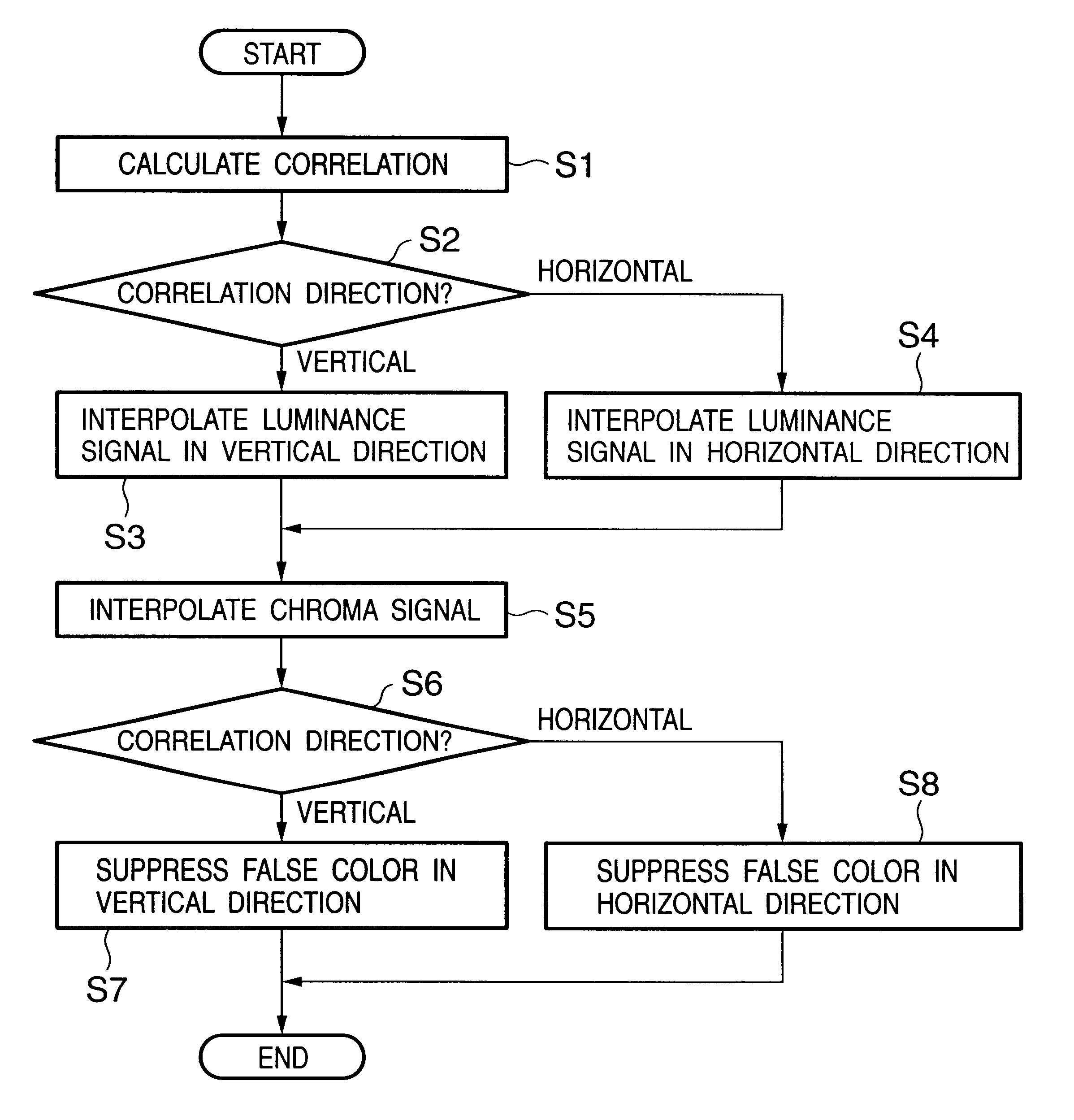
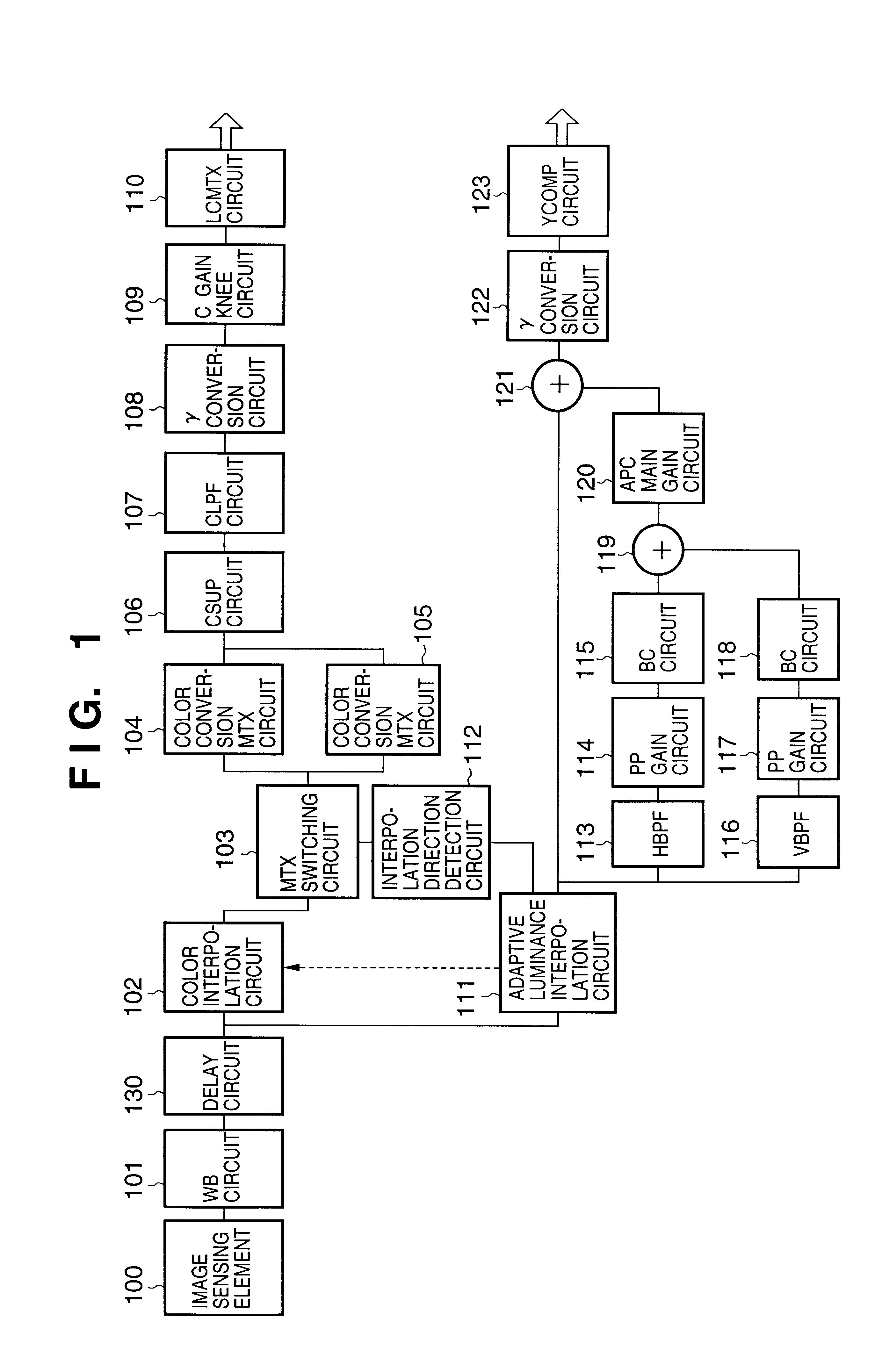
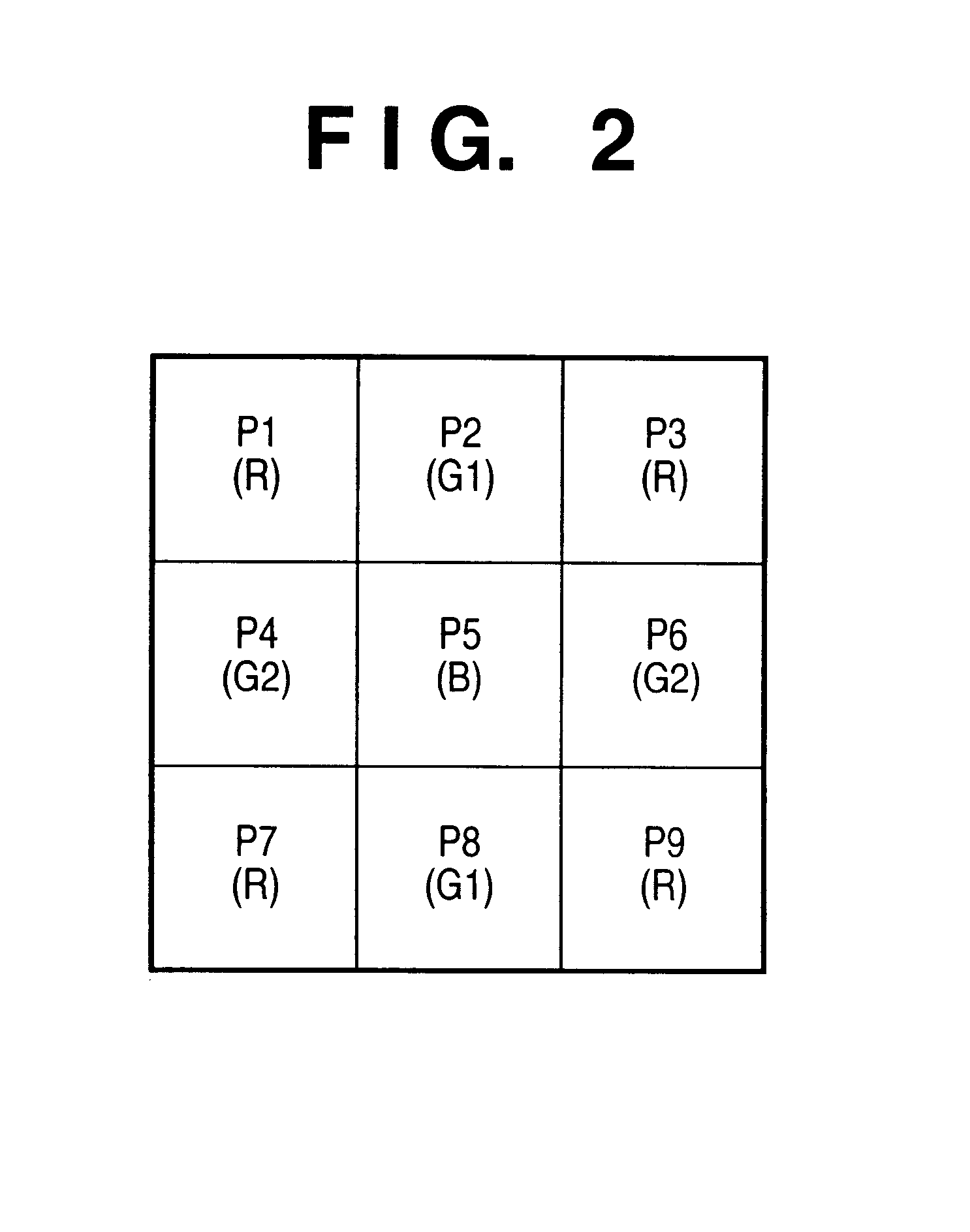
Signal processing apparatus and method for reducing generation of false color by adaptive luminance interpolation
InactiveUS6853748B2Reduce colorWithout decreasing resolutionImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionFalse color
Adaptive luminance interpolation processing in a signal processing apparatus for acquiring an image signal from an image sensing element having color filters and processing the image signal is described. An adaptive luminance interpolation circuit determines the correlation of the image signal in the vertical and horizontal directions, and interpolates the luminance signal of the image signal in a direction in which the correlation is higher. The chroma signal of the image signal is interpolated regardless of the correlation direction. The chroma signal is processed by a color conversion matrix circuit for performing signal processing of suppressing a false color in the vertical direction or a color conversion matrix circuit for performing signal processing of suppressing a false color in the horizontal direction, switched by a matrix switching circuit based on the interpolation direction.
Owner:CANON KK
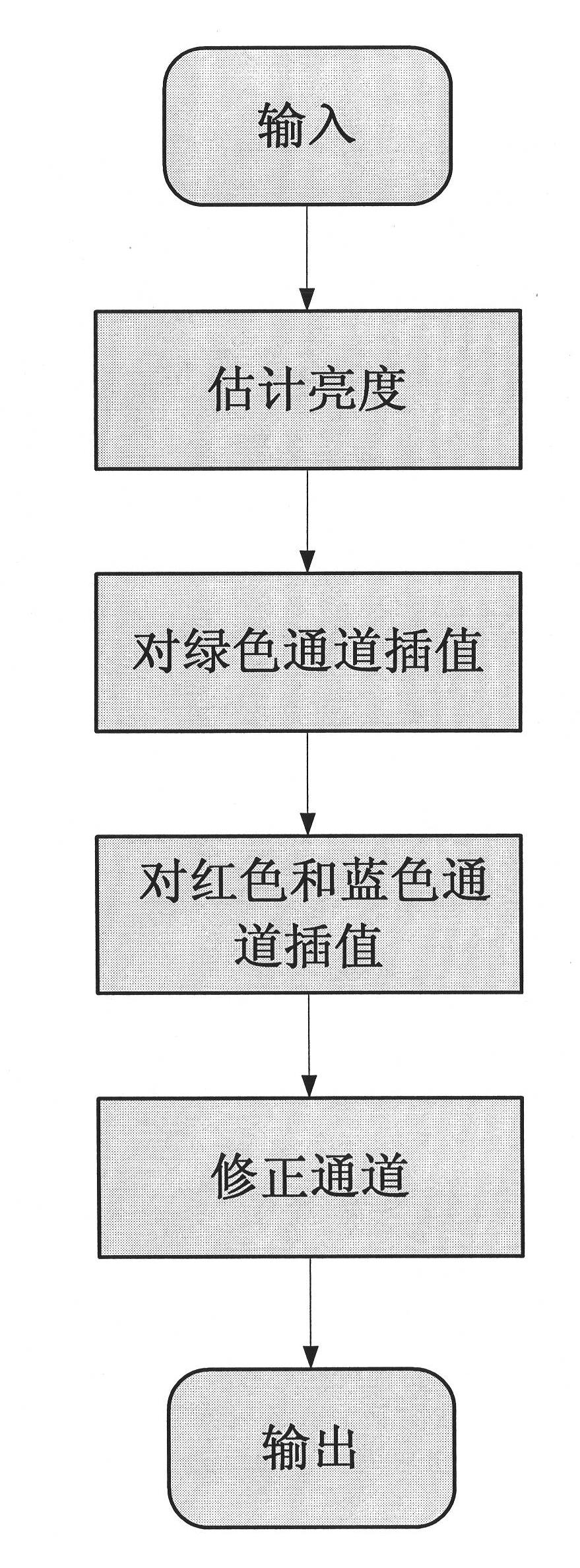
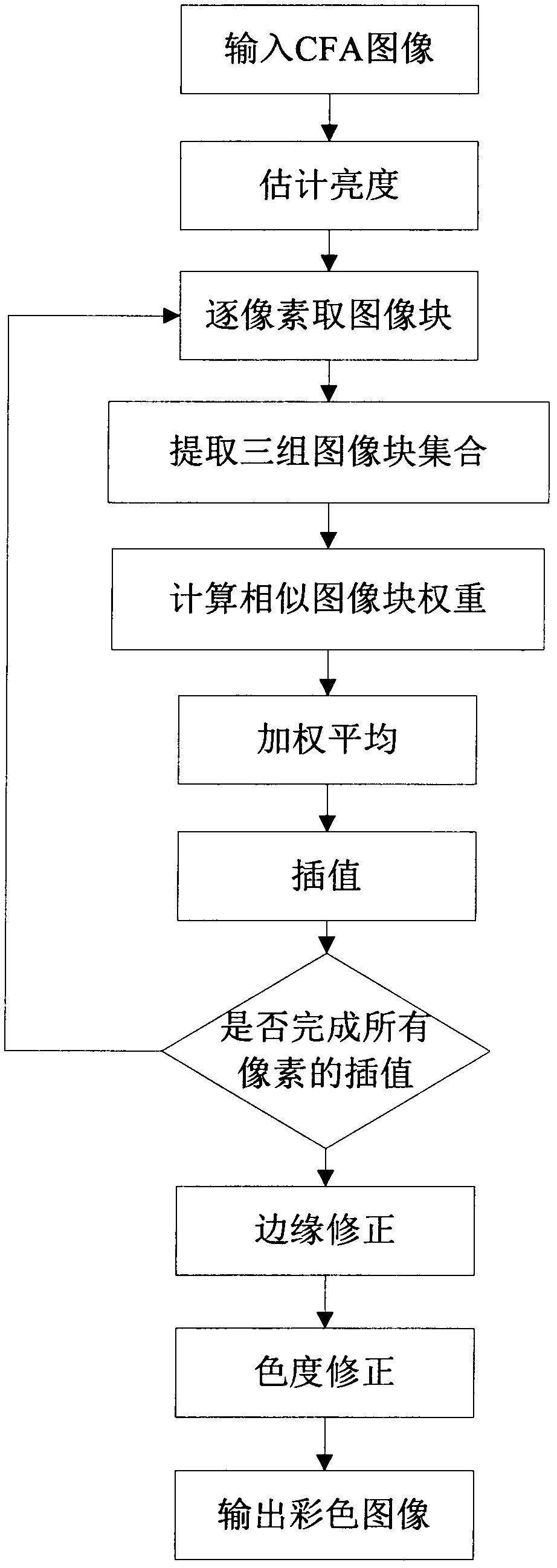
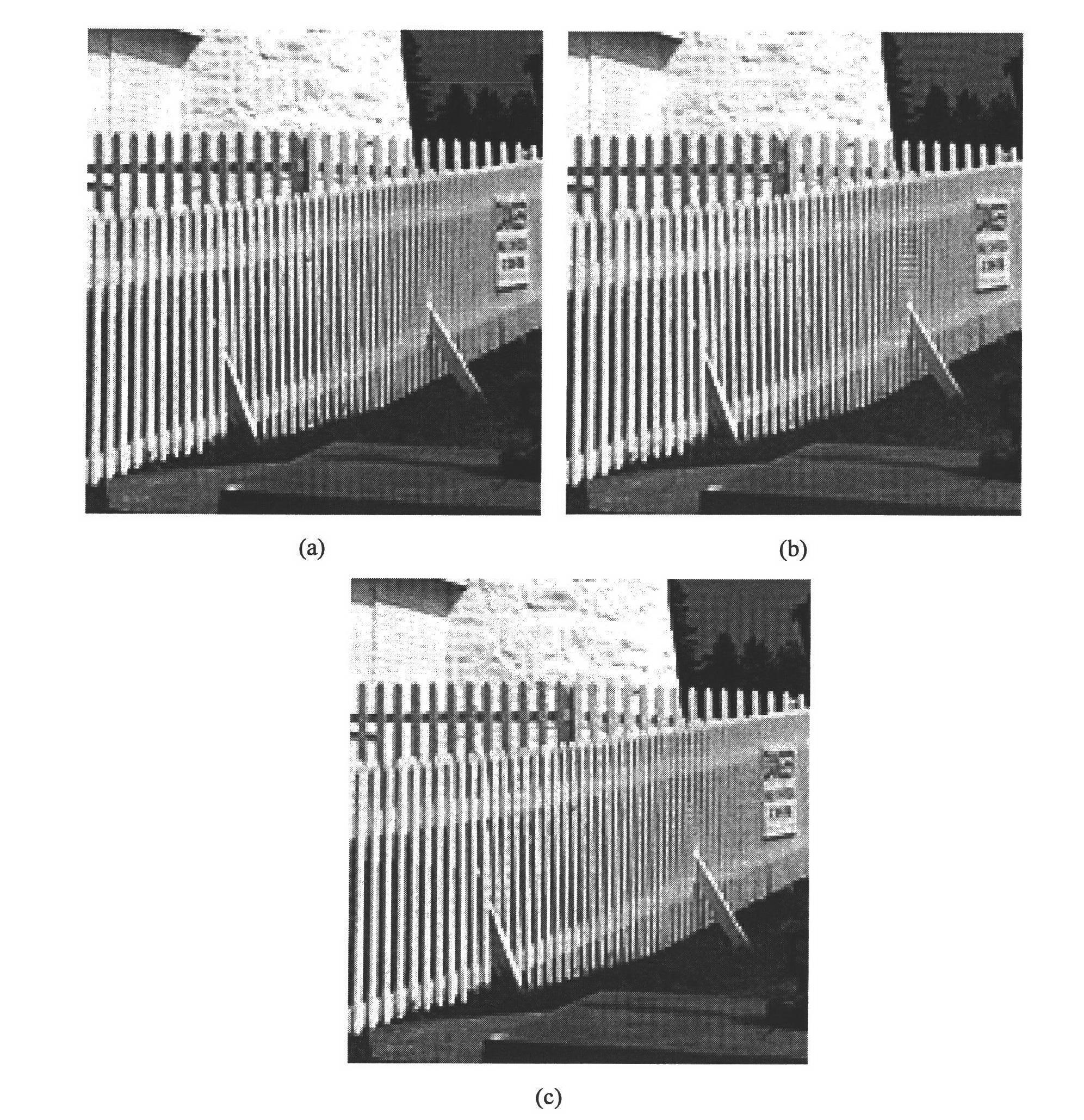
Demosaicing method for CFA (color filter array) images based on edge-direction interpolation
InactiveCN102254301AImprove interpolationSuppress false color effectsGeometric image transformationFalse colorRunning time
The invention discloses a demosaicing method for CFA (color filter array) images based on edge-direction interpolation. The demosaicing method for CFA images mainly solves the problems that the interpolation effect of the high-frequency part of an image is not good, and the false color effect is serious in the traditional demosaicing method. The demosaicing method for CFA images comprises the steps of: (1) inputting a CFA image to be demosaiced; (2) estimating the brightness; (3) interpolating a green channel; (4) respectively carrying out dual linear interpolation on a red channel and a bluechannel; (5) respectively correcting the red channel, a green channel and the blue channel; and (6) outputting a colorful image. The demosaicing method for CFA images has the advantages of capabilityof better maintaining high-frequency information of the image, inhibiting the false color effect effectively and improving the visual effect of the demosaiced CFA image has short running time.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
A method of processing pseudo color of medical gray image signals
InactiveCN101080024ARich color saturationIncrease contrastTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsPattern recognitionGradient operators
This invention discloses a method for false color process to medical grey image signals, which first of all utilizes a Gauss low-pass filter to eliminate noises of a polluted medical image, then utilizes a cross gradient operator to acquire the gradient value of each pixel of the image then to determine a threshold value based on the gradient value, then carries out false color coding in two modes based on the comparison of gradient value and threshold value, if the gradient value is greater than the threshold value, it applies red to false-code, otherwise, it applies a non-linear coding method based on the grey value, and medical images process by this method meets vision character of man-eye.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
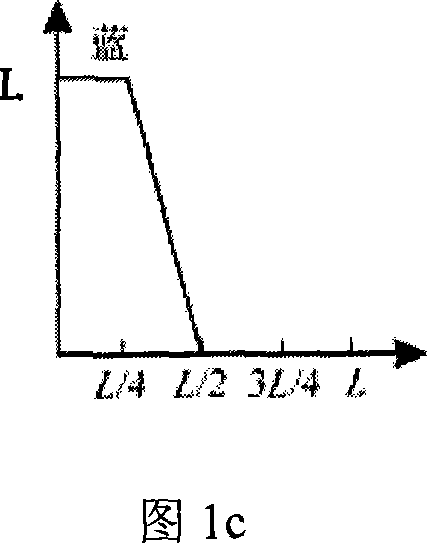
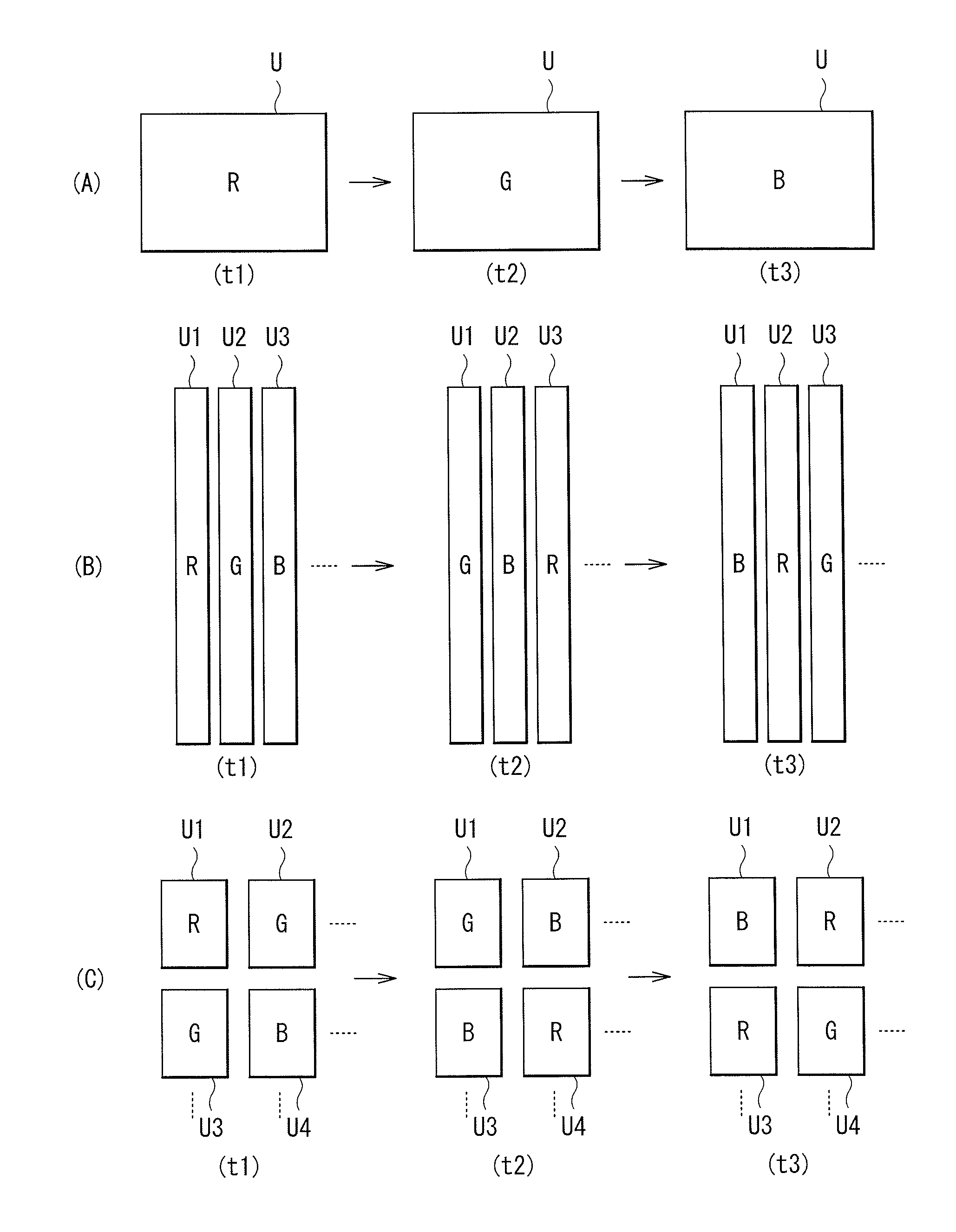
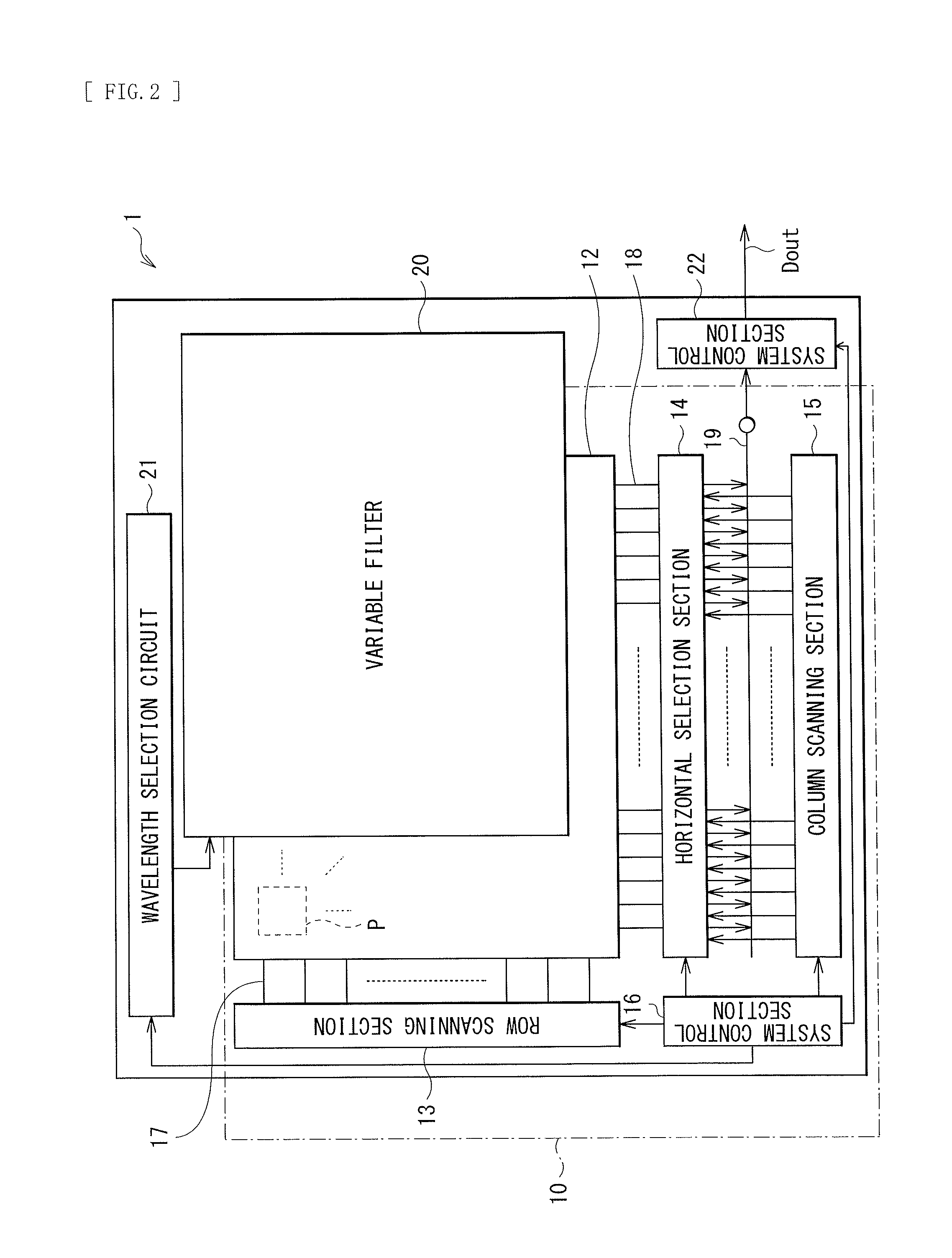
Image pickup unit and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20140232912A1InhibitionImprove image qualityImage enhancementTelevision system detailsColor imageImaging quality
There is provided an image pickup unit capable of suppressing occurrence of false color and color mixture and acquiring a color image with high image quality. The image pickup unit includes: an image sensor including a plurality of pixels and acquiring an image pickup data; a variable filter provided on a light receiving face of the image sensor, and transmitting a selective wavelength; and a filter drive section (a wavelength selection circuit and a system control section) driving the variable filter and thereby setting its transmission wavelength. By acquiring the image pickup data while time-divisionally switching the transmission wavelength of the variable filter, pixel data corresponding to the transmission wavelength of the variable filter are acquired in a temporally-successive manner.
Owner:SONY CORP
Process and apparatus for segregation and testing by spectral analysis of solid deposits derived from liquid mixtures
InactiveUS20050275837A1Limiting and controlling spreadAvoid spreadingMaterial nanotechnologyRadiation pyrometrySolubilitySpectroscopy
Micro-droplets of liquid confining organic molecules of interest are dried on selected planar solvo-phobic substrates under conditions facilitating segregated precipitation of the larger, less soluable analytes toward edge portions of the deposit. Micro-spectrometer imaging using white light and FTIR false color can identify points of interest, and the same optics generally directed perpendicularly to the substrates selectively captures normal Raman spectra from selected points in the deposit. The spectra are manipulated using various data techniques to extract reliable information concerning analytes present at pico-Molar levels. The selected spots can also be subjected to FTIR spectroscopy followed by MALDI mass spectroscopy to obtain a variety of information from the identical specimen.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Image sensor and digital camera
InactiveUS7742088B2High-sensitivity, high-resolution, and faithful color reproductionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImage resolutionPhotoelectric conversion
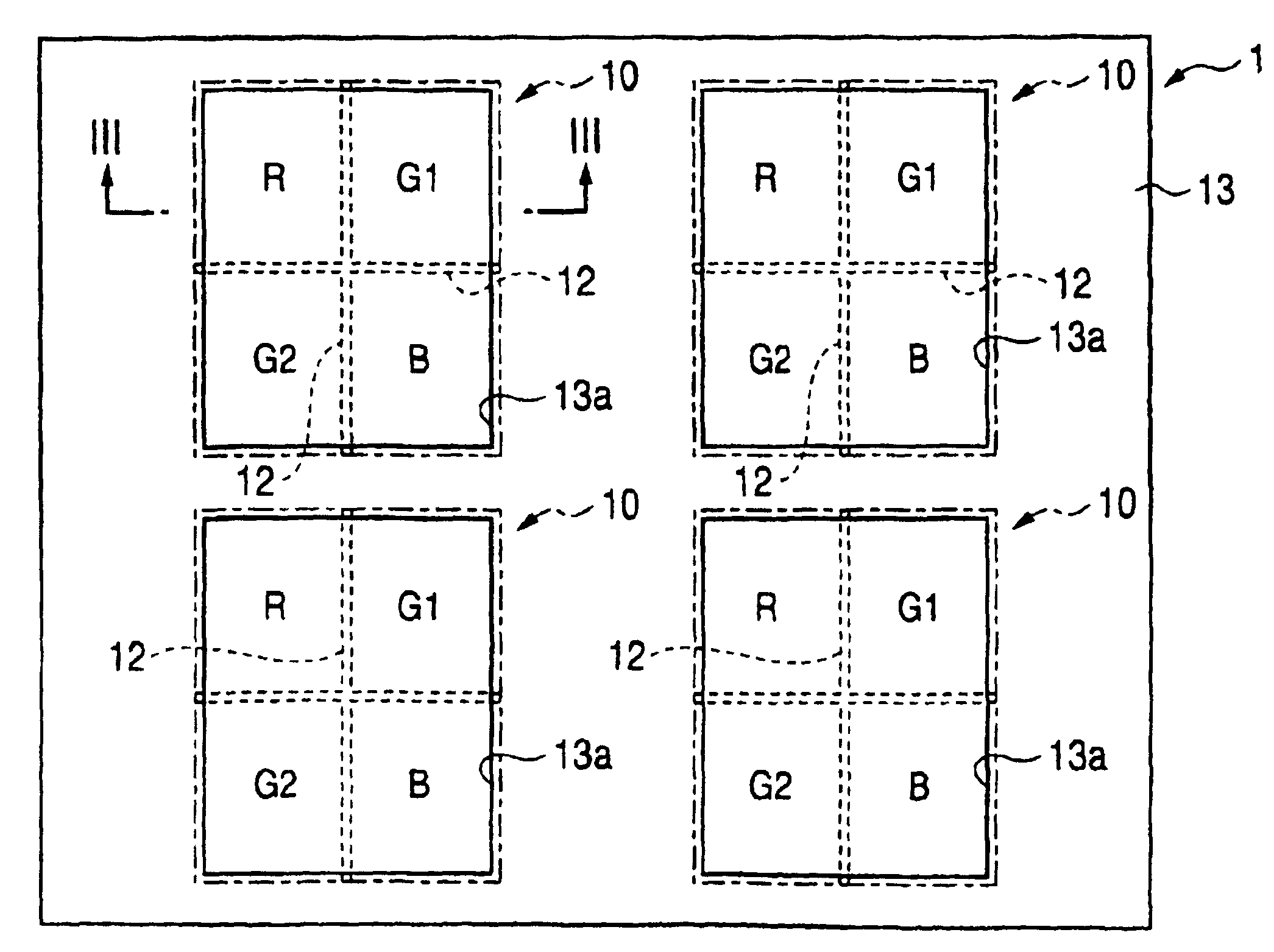
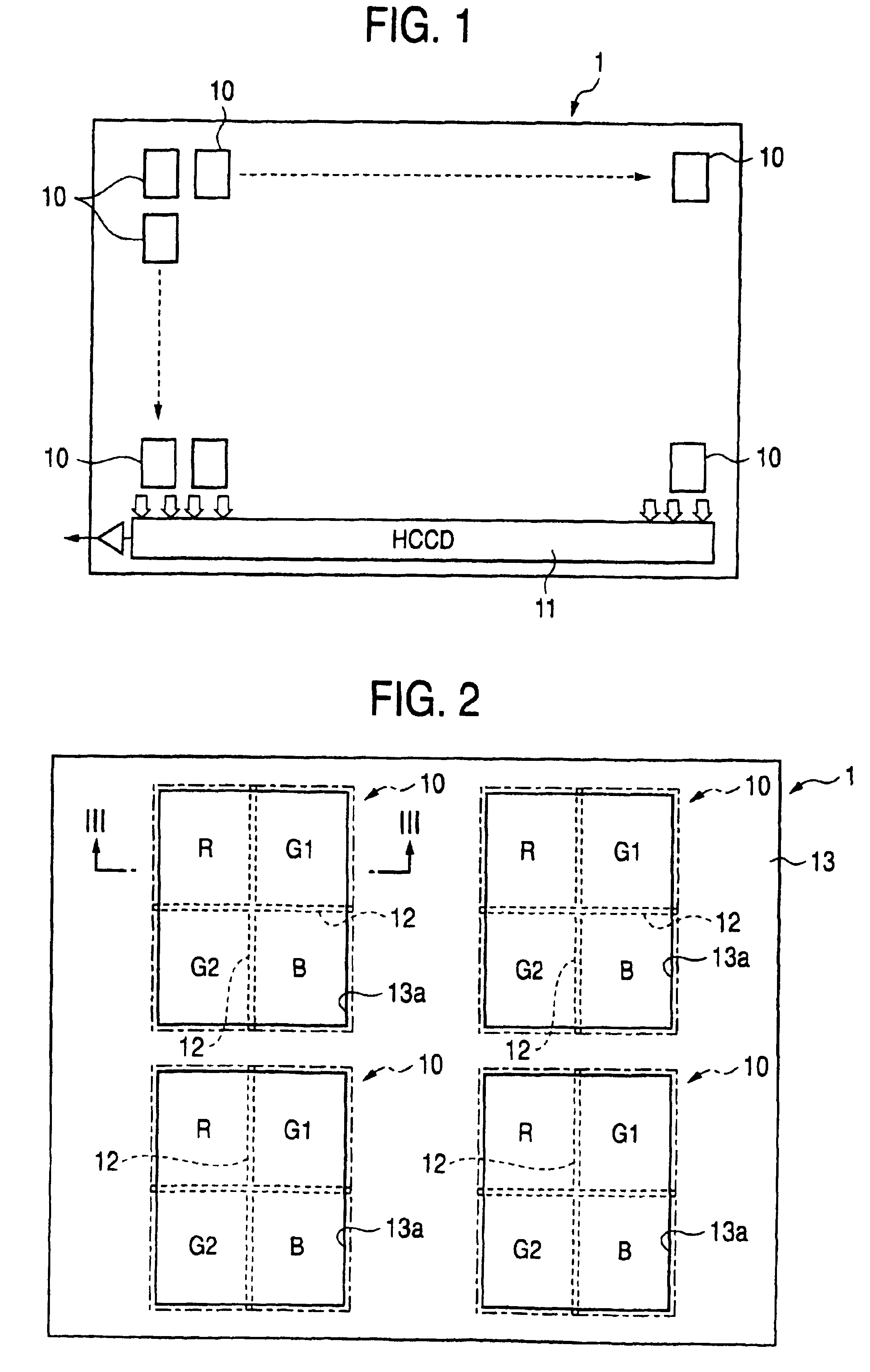
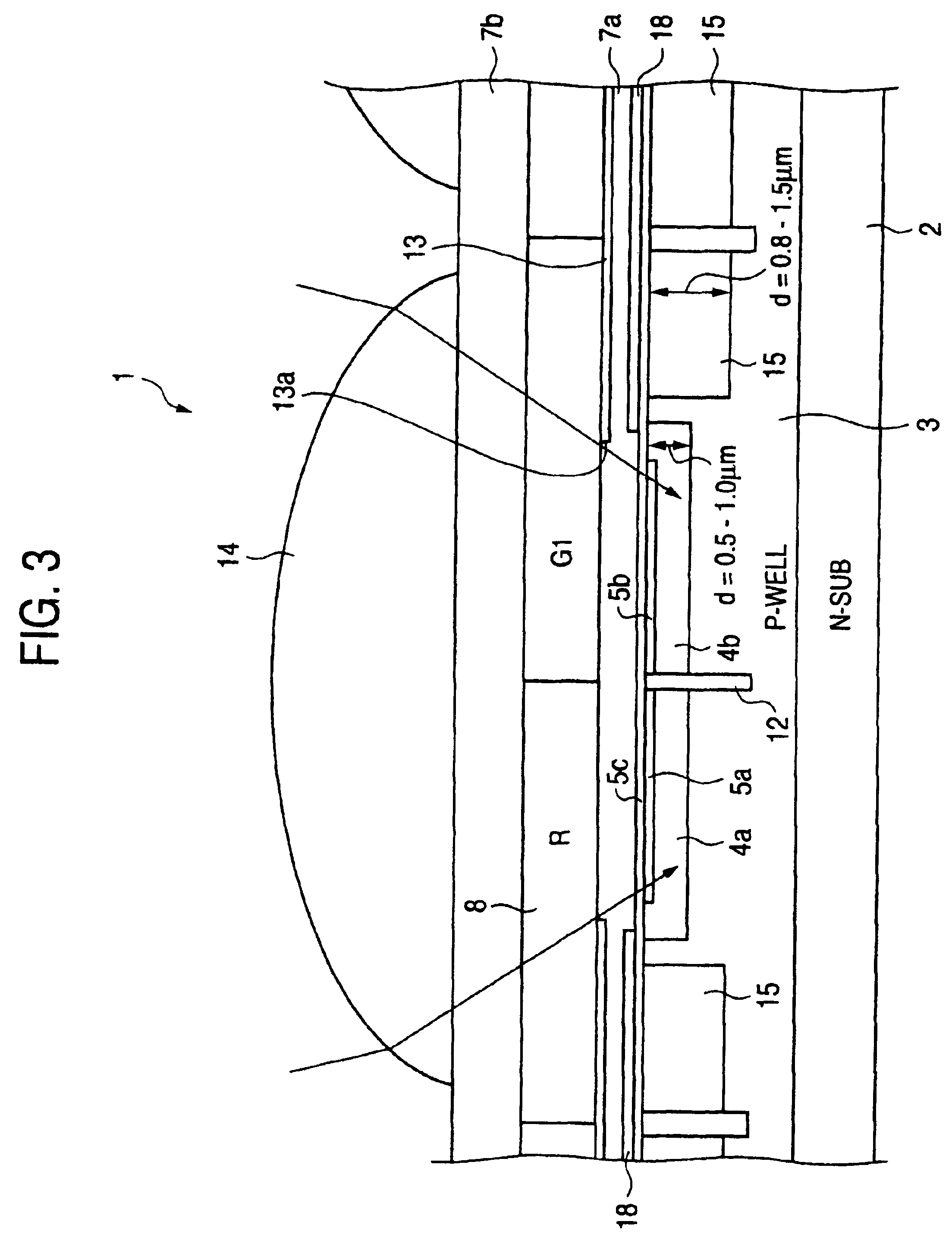
A color solid-state image pickup device includes a plurality of photoelectric conversion areas provided in an array pattern on a surface of a semiconductor substrate. The inside of each of photoelectric conversion areas 10 is two-dimensionally partitioned into a plurality of segments R, G1, G2, and B which output a plurality of photoelectric conversion signals of different spectral sensitivities. As a result, occurrence of a false signal and a false color is suppressed, and high-sensitivity, high-resolution image data having superior color reproducibility can be obtained.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Image processing method, image processing apparatus, image processing program and image recording apparatus
InactiveUS7260266B2Reduce computing loadSuppressing mottled granular noiseImage enhancementImage analysisColor imageFalse color
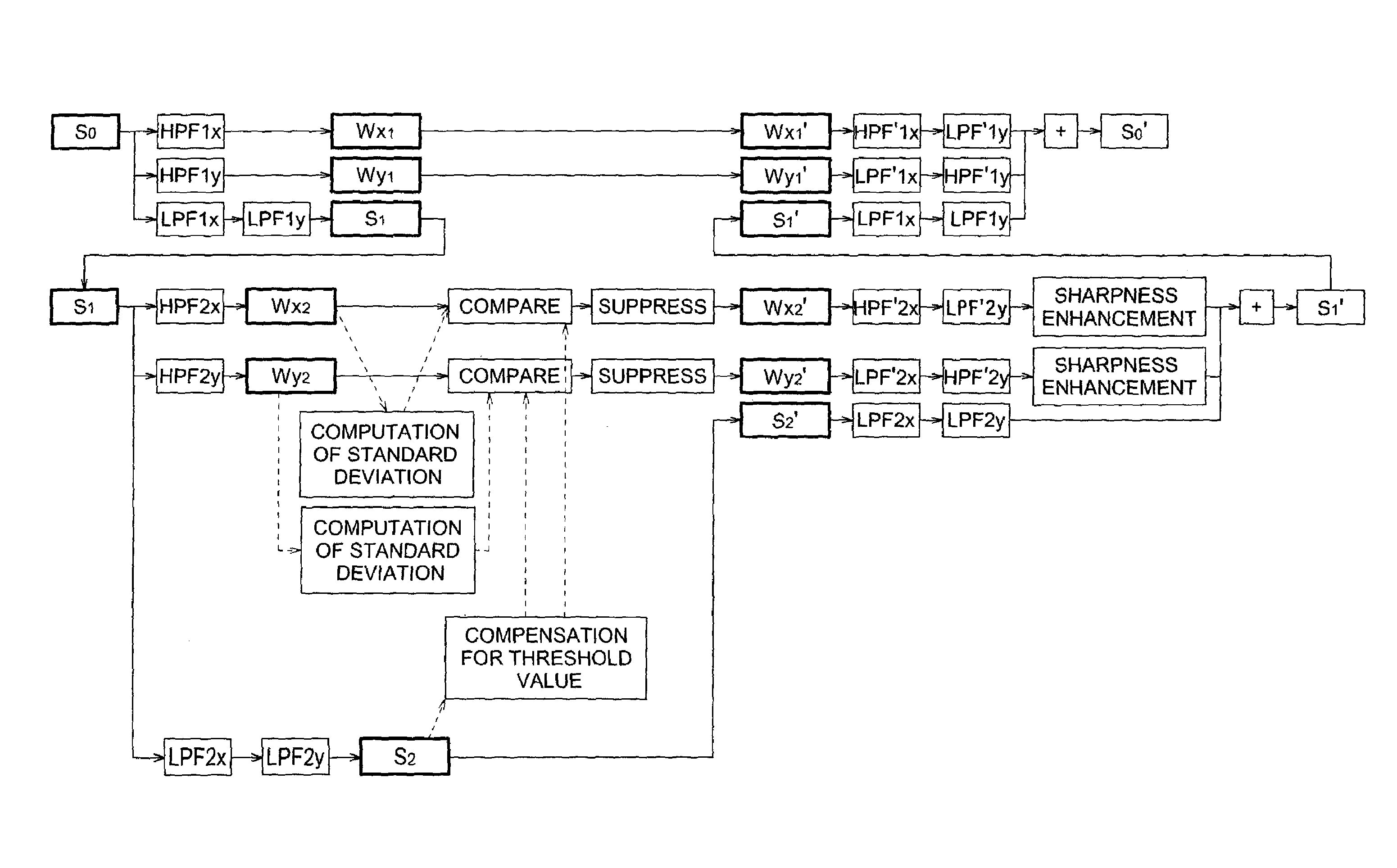
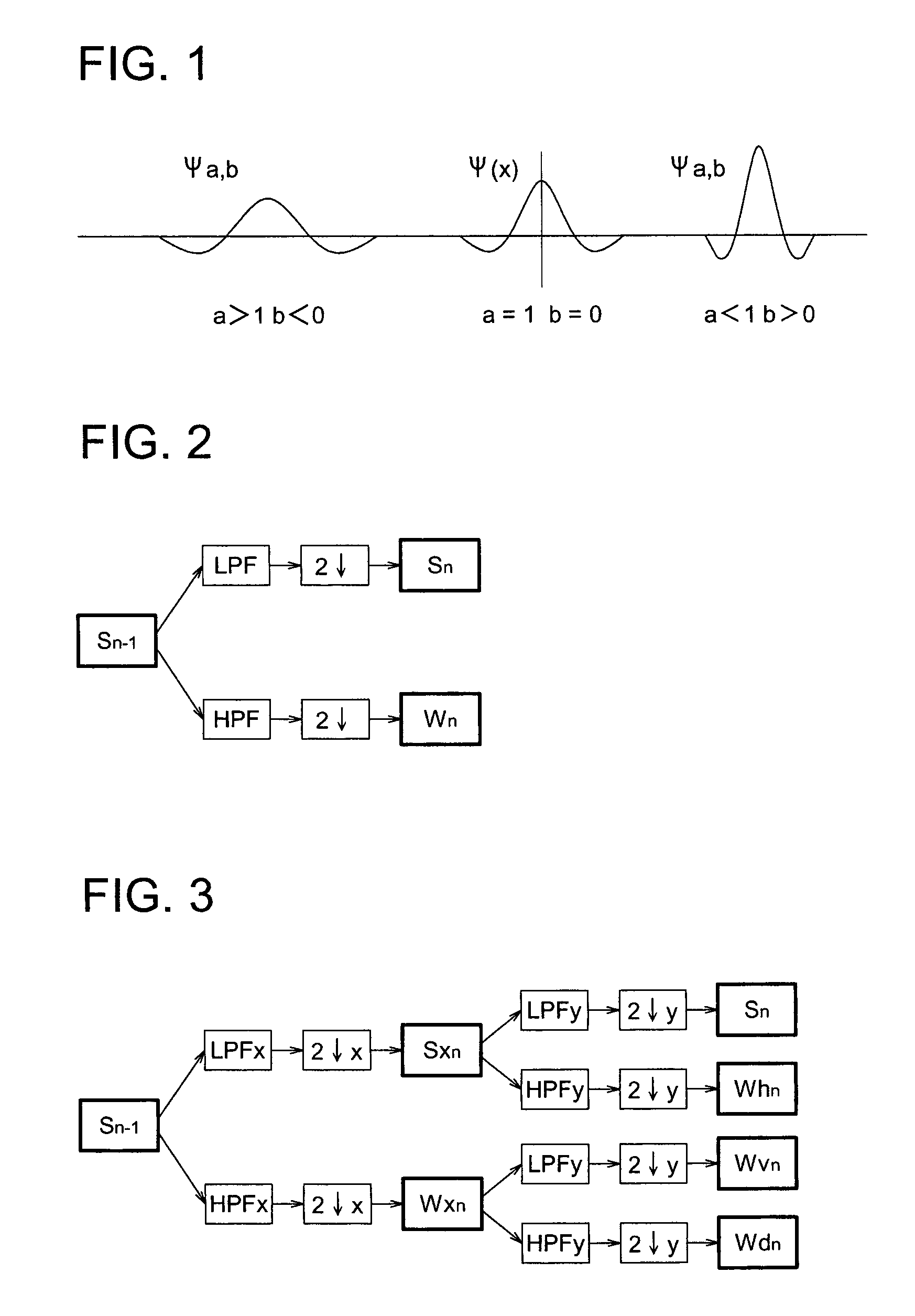
There are described an image processing method, an image processing apparatus, an image processing program and an image recording apparatus characterized by reduced computation loads and capable of suppressing the mottled granular noise contained in color image signals and enhancing the sharpness of the image, without generating noises similar to color misregistration and false color contour appearing close to the edge. The image processing method includes the steps of: converting the image signals to luminance signals and chrominance signals; applying a Dyadic Wavelet transform processing to at least the luminance signals; suppressing a signal intensity of a high-frequency luminance component at P-th level, when the intensity of the high-frequency luminance component conforms to a specific condition; applying a Dyadic Wavelet inverse-transform processing to transformed and processed signals; and synthesizing processed luminance signals and the chrominance signals with each other to generate processed image signals.
Owner:KONICA CORP
Bayer-pattern CFA image demosaicking method based on non-local mean
InactiveCN102663719AImprove interpolationSuppress false color effectsImage enhancementImage analysisColor imageFalse color
The invention discloses a bayer-pattern CFA image demosaicking method based on a non-local mean, mainly solving the problem of poor effect of interpolation on a small fringe part of an image in the prior art, comprising the following steps:(1) inputting a Bayer-pattern CFA image; (2) estimating brightness; (3) adopting an image block pixel by pixel as a current to-be-demosaicked image block; (4) extracting three image block sets; (5) calculating weights of the image blocks; (6) performing weighted average on the similar image blocks; (7) performing interpolation on the current to-be-demosaicked image block; (8) determining whether interpolation on all pixels is completed, if yes, executing step (9), if not shifting to step (3); (9) correcting an edge; (10) correcting a color; and (11) outputting a color image. By adopting the method provided in the invention small fringe area information of an image can well restored, and false color effects can be effectively inhibited; and the method is especially suitable for a CFA image with more textures.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Mass spectrometric differentiation of tissue states
ActiveUS20060063145A1Easy to doMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSpatially resolvedGray level
The invention relates to the determination and visualization of the spatial distribution of tissue states in histologic tissue sections on the basis of mass spectrometric signals acquired so as to be spatially resolved. The invention provides a method which determines the tissue state for the tissue spots as a state characteristic, which is calculated as a mathematical or logical expression from at least two mass signals of this tissue spot, and which indicates the tissue state as a gray-level or false-color image in one or two dimensions.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
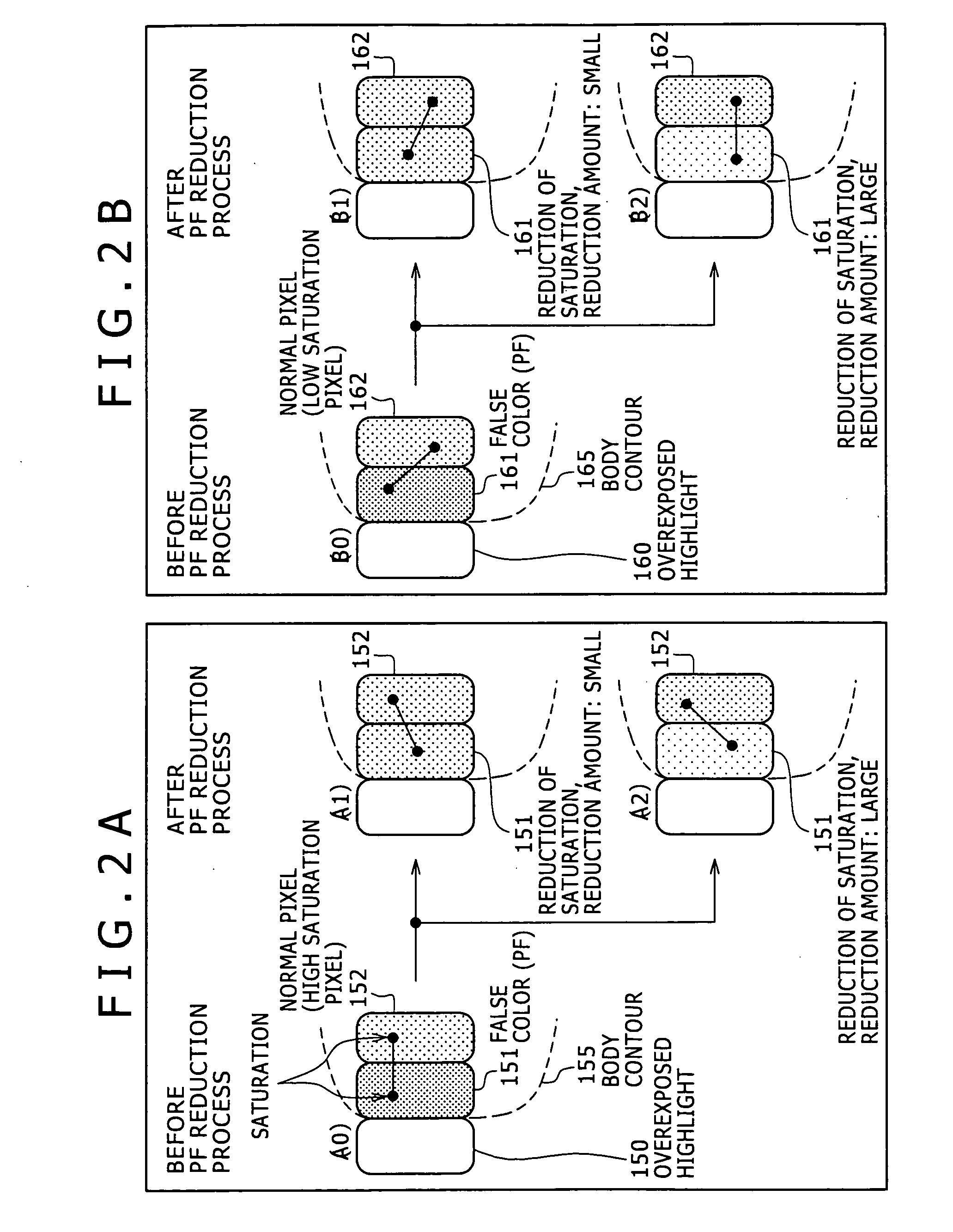
System and method for providing multi resolution purple fringing detection and correction
A system, method, and computer program product for automatically detecting and correcting the “purple fringing” effect, typically due to axial chromatic aberration in imaging devices, are disclosed and claimed. A chromaticity score is computed, denoting the amount of false color related to a purple fringing artifact. A locality score is computed, denoting the similarity of the purple fringing region to a shape of a narrow ridge, which is typical for purple fringing artifacts. A saturation score is also computed, denoting the proximity of a pixel to saturated pixels. These scores are then combined into a detection score, denoting pixels having strong indications they share properties common to pixels of purple fringing artifacts. The detected pixels are then correspondingly corrected, e.g. by chroma suppression. The scoring and correction may be performed over combinations of image resolutions, e.g. an original version and potentially numerous downscaled versions.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Color image denoising method and system thereof
ActiveCN102156964AGood denoising effectGood noise removalImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionColor image denoising
The invention relates to the field of video processing, and discloses a color image denoising method and a system thereof. In the method and the system thereof, cross-channel invariable information is extracted from a luminance channel image for the denoising treatment on a chrominance channel image, so that a false color edge or texture can be eliminated, the fuzzyness of the edge part can be reduced, and better integral denoising effect can be obtained. The cross-channel invariable information can be edge information, texture information, noise intensity and the like. The luminance channel may be firstly processed with local data conversion; the cross-channel invariable information is extracted from a conversion domain; and characteristic information, such as edge texture and the like can be extracted from local image data more effectively based on different characteristics of a signal represented in the conversion domain, and consequently, the chrominance channel image can be denoised better based on the information.
Owner:HANGZHOU HIKVISION DIGITAL TECH
Method for removing noise in image using statistical information and system thereof
ActiveUS20080144958A1Quickly and effectively removingCancel noiseImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionImaging processing
Disclosed are an image processing method capable of effectively removing noise contained in an image photographed in a low light environment by using statistical information, and a system thereof. There is provided an image processing method for an image consecutively inputted per frame unit, the method comprising: a step of segmenting the image into unit areas comprising a predetermined number of pixels; a first step of dividing each unit area into a low light region or a high light region by using the brightness of image data contained in said each unit area; a second step of outputting statistical information from image data contained in at least one unit area divided into the low light region, and detecting and removing Poisson and photon counting noise on the basis of the statistical information, the statistical information being the mean of the unit area; a third step of detecting a motion pixel from the image data; and a fourth step of detecting and removing false color noise from the image data on the basis of the detected motion pixel and the statistical information.
Owner:NEXTCHIP
Mass spectrometric differentiation of tissue states
ActiveUS7873478B2Easy to doMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSpatially resolvedGray level
The invention relates to the determination and visualization of the spatial distribution of tissue states in histologic tissue sections on the basis of mass spectrometric signals acquired so as to be spatially resolved. The invention provides a method which determines the tissue state for the tissue spots as a state characteristic, which is calculated as a mathematical or logical expression from at least two mass signals of this tissue spot, and which indicates the tissue state as a gray-level or false-color image in one or two dimensions.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
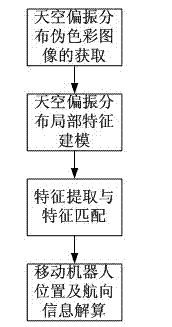
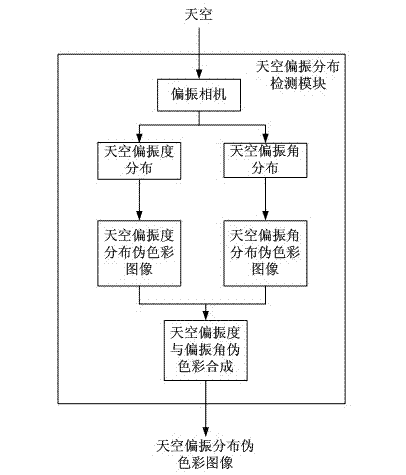
Navigational positioning method based on sky polarization distribution model matching
InactiveCN102967311AImprove adaptabilityImprove accuracyNavigation by astronomical meansPicture interpretationSkyFalse color
The invention relates to a navigational positioning method based on sky polarization distribution model matching. The method comprises the following steps: taking a positive direction of a mobile robot as a 0-degree reference direction, photographing the sky above the mobile robot in real time by employing a polarization camera, acquiring a real-time sky polarization distribution false color image through calculation and synthesis; performing local feature modeling on the sky polarization distribution false color image; performing stable feature point extraction and feature matching on the local features of the sky polarization distribution false color image, and obtaining an affine transformation relationship between the sky polarization distribution model diagrams; and calculating the position and navigational direction of the mobile robot. According to the method, the polarization distribution of the whole sky is not required to be obtained; the local feature information of the sky polarization distribution is utilized, so that the navigational direction of the mobile robot can be acquired from the sky polarization distribution, and the position of the mobile robot can be acquired; and the method is not required to depend on prior knowledge and is high in environmental adaptivity and high in accuracy.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Image processing apparatus and image processing method as well as computer program
InactiveUS7529405B2Reduce the differenceImage enhancementTelevision system detailsReduction rateImaging processing
An image processing apparatus and an image processing method are disclosed by which an image correction process for a false color such as a purple fringe can be executed efficiently while excessive reduction of the saturation is prevented to produce image data of a high quality. A saturation reduction rate corresponding to each pixel is calculated, and saturation reduction of the pixel is executed based on the saturation reduction rate. Then, saturation correction is executed so that the difference between the hue of the pixel whose saturation has been reduced and a surrounding reference pixel may be reduced. Further, a surrounding pixel to be referred to in the saturation correction process is selected along a scanning line.
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com