Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
6112 results about "Gray level" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
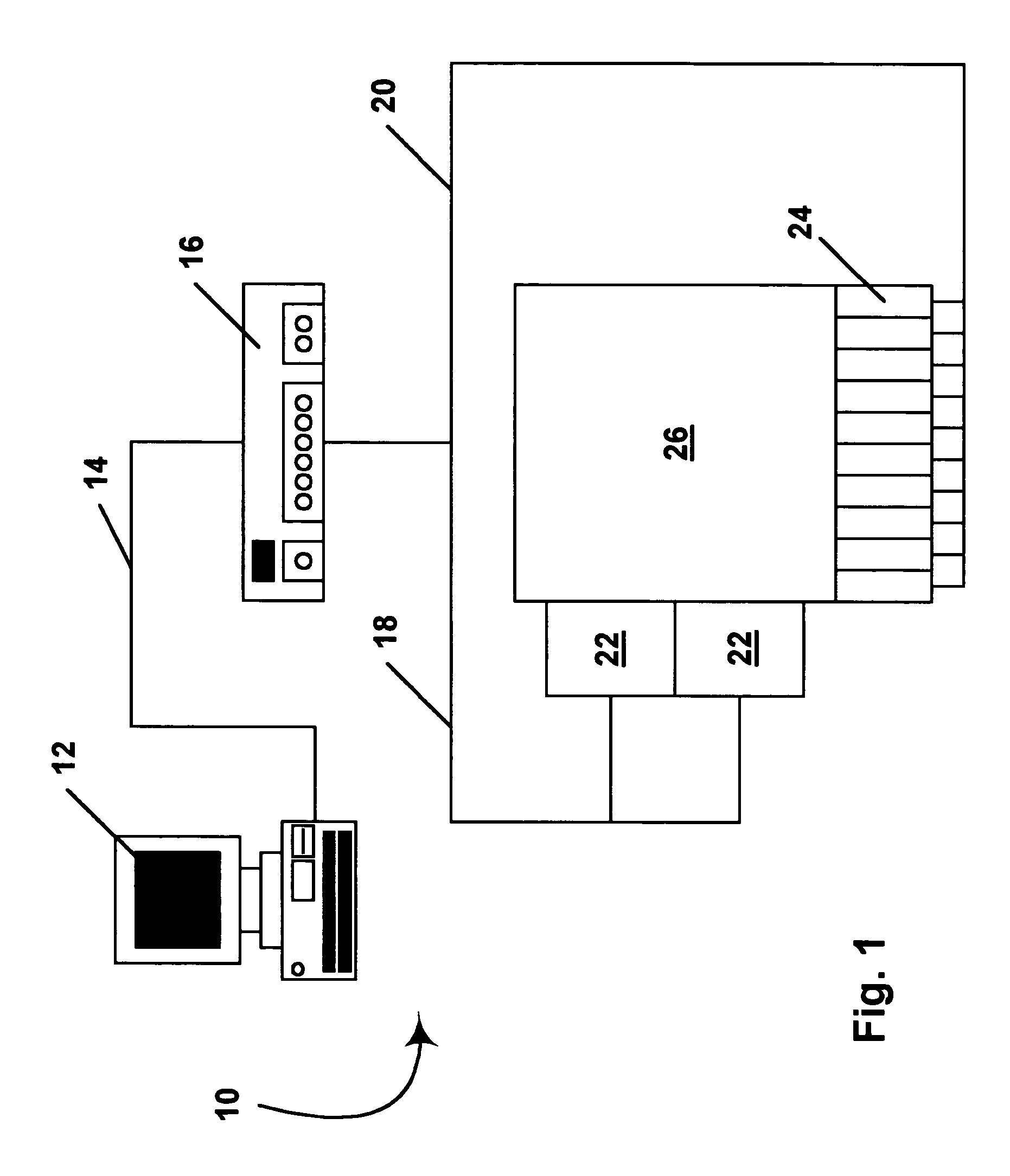
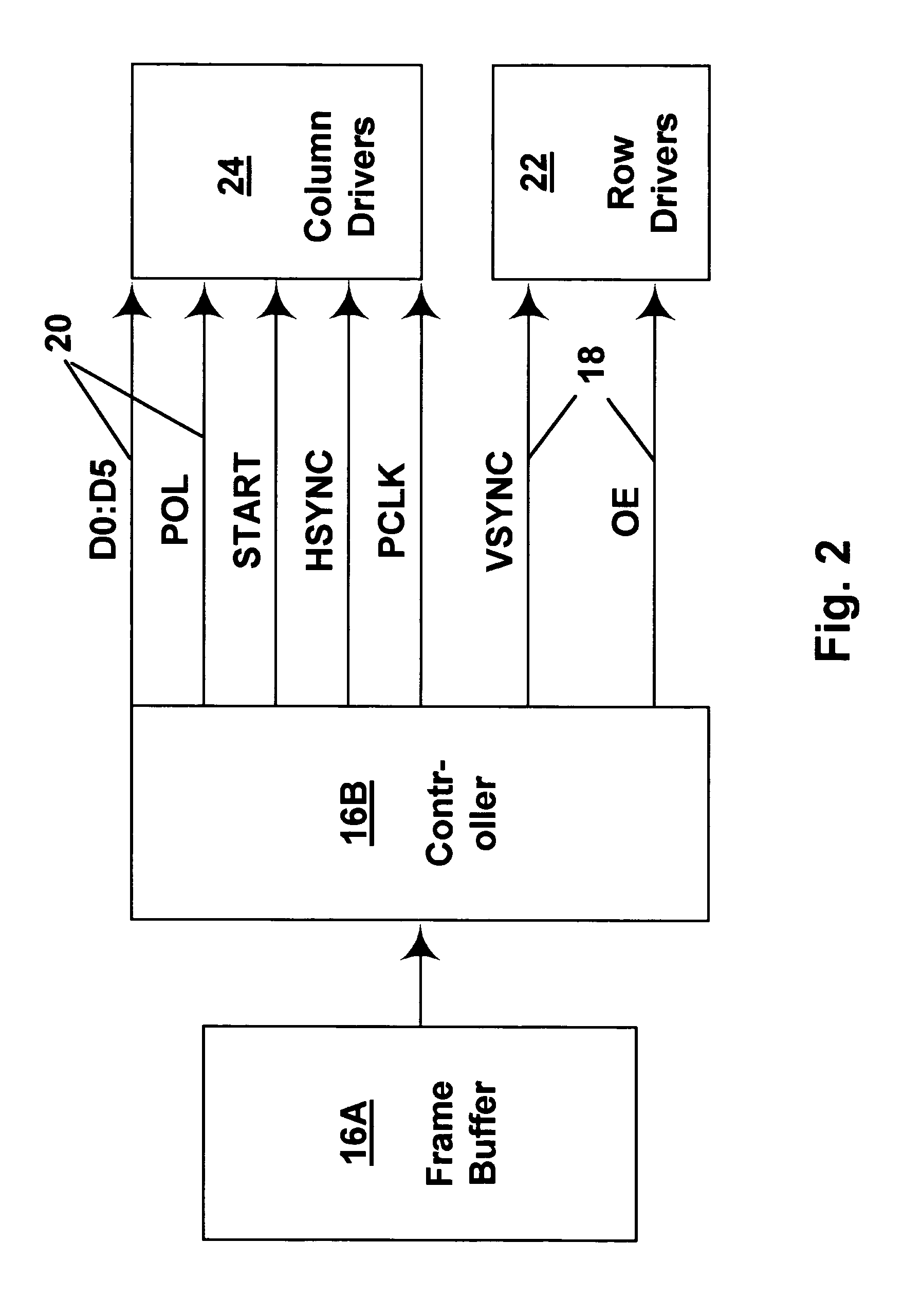
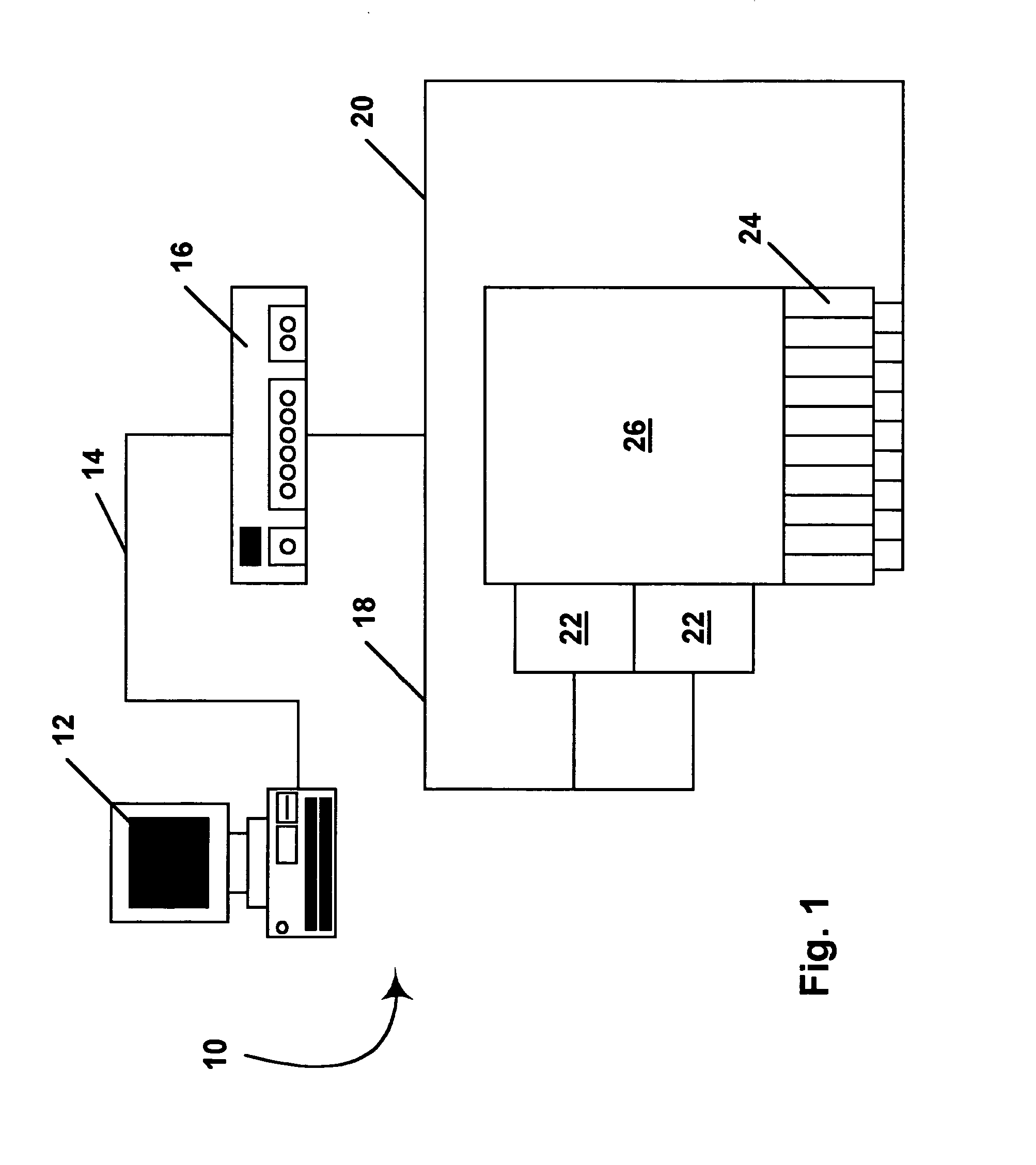
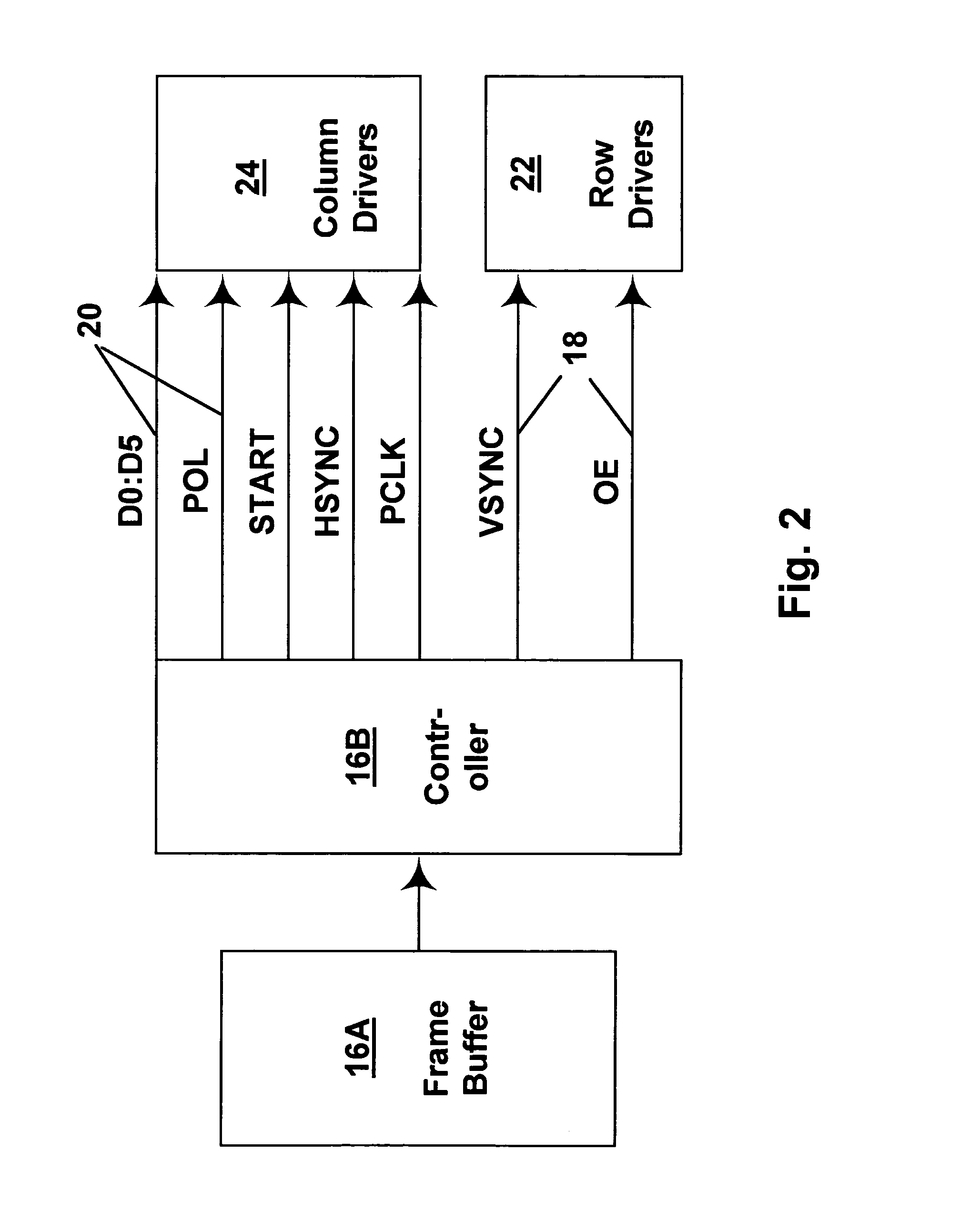
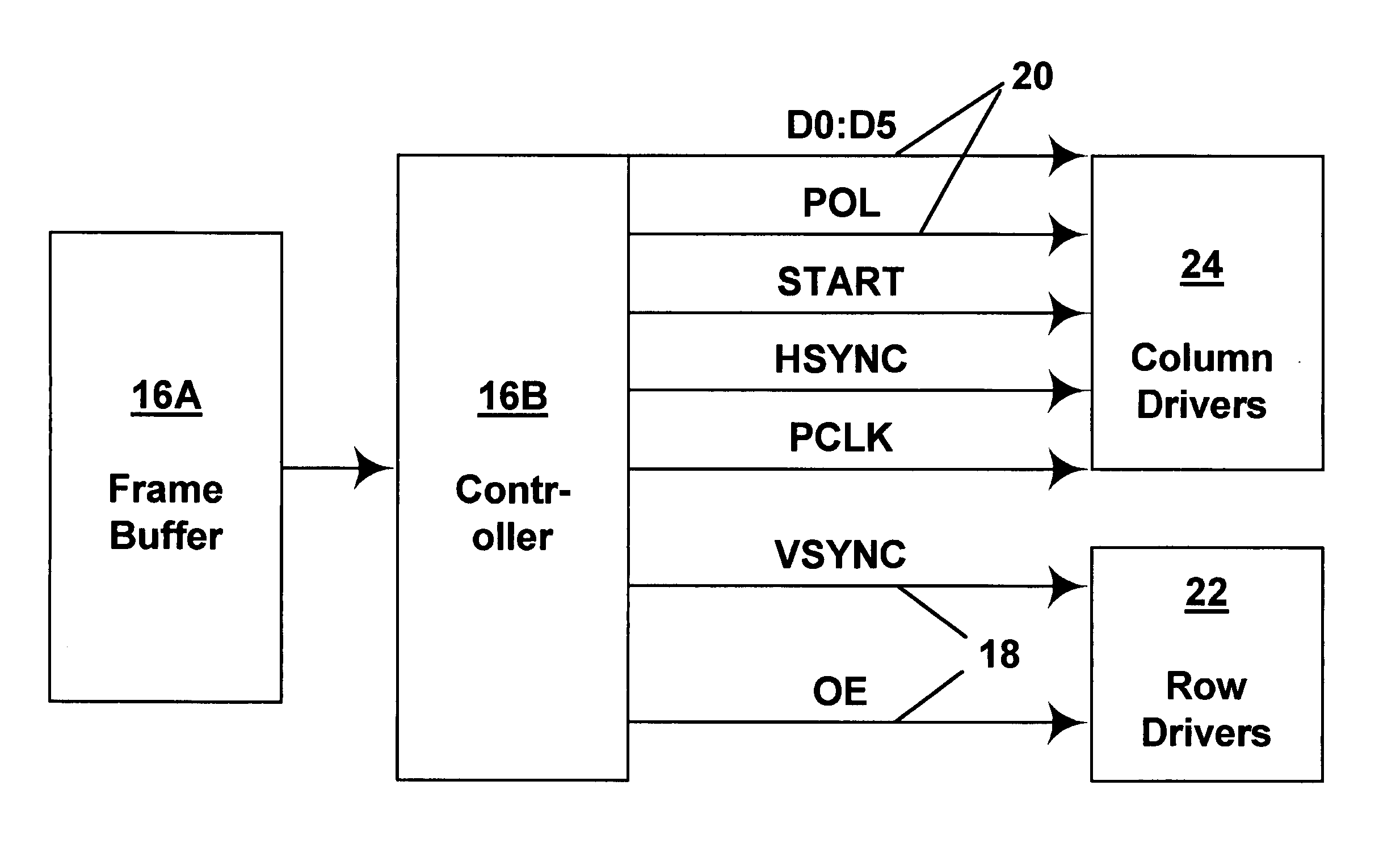
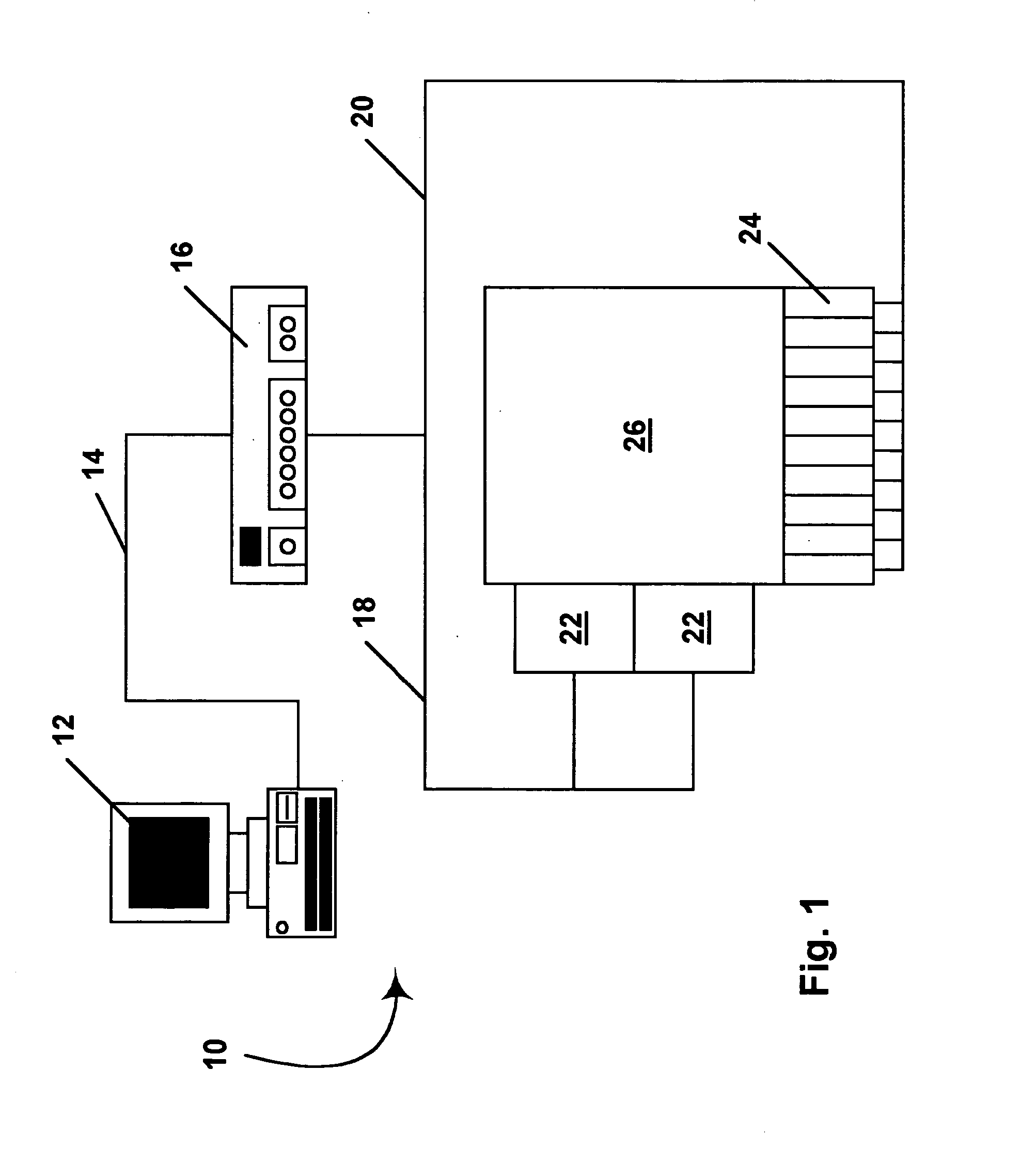
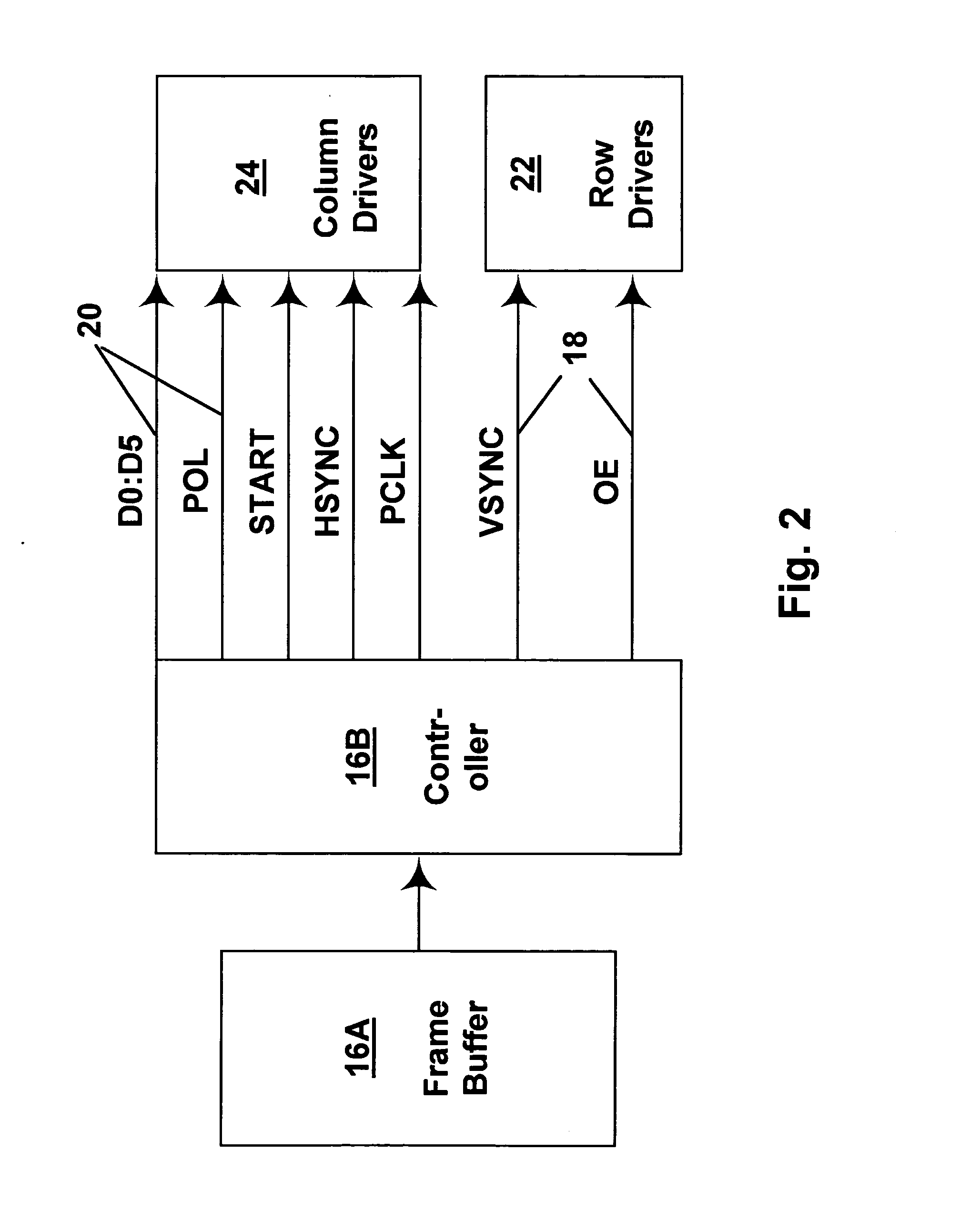
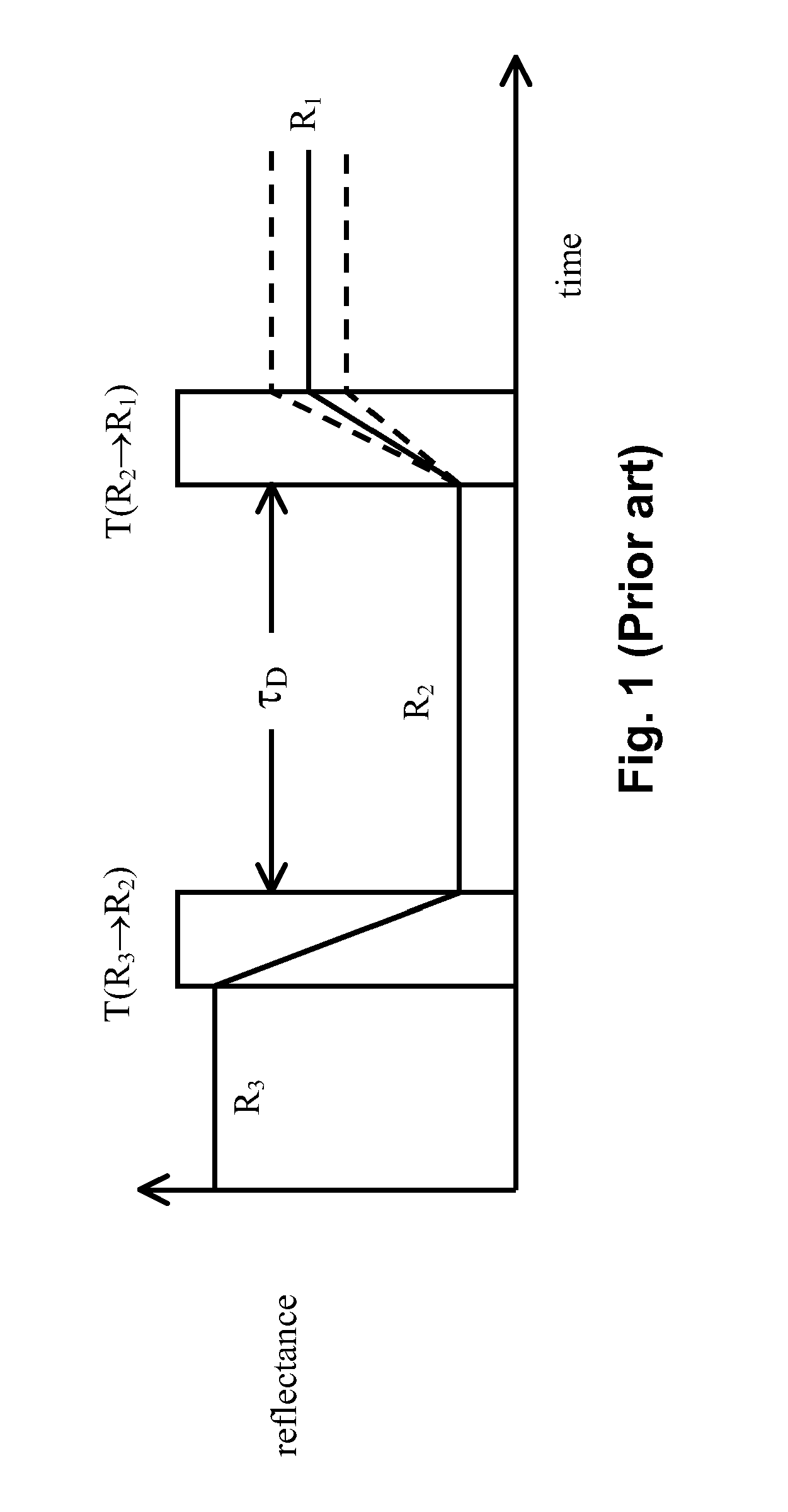
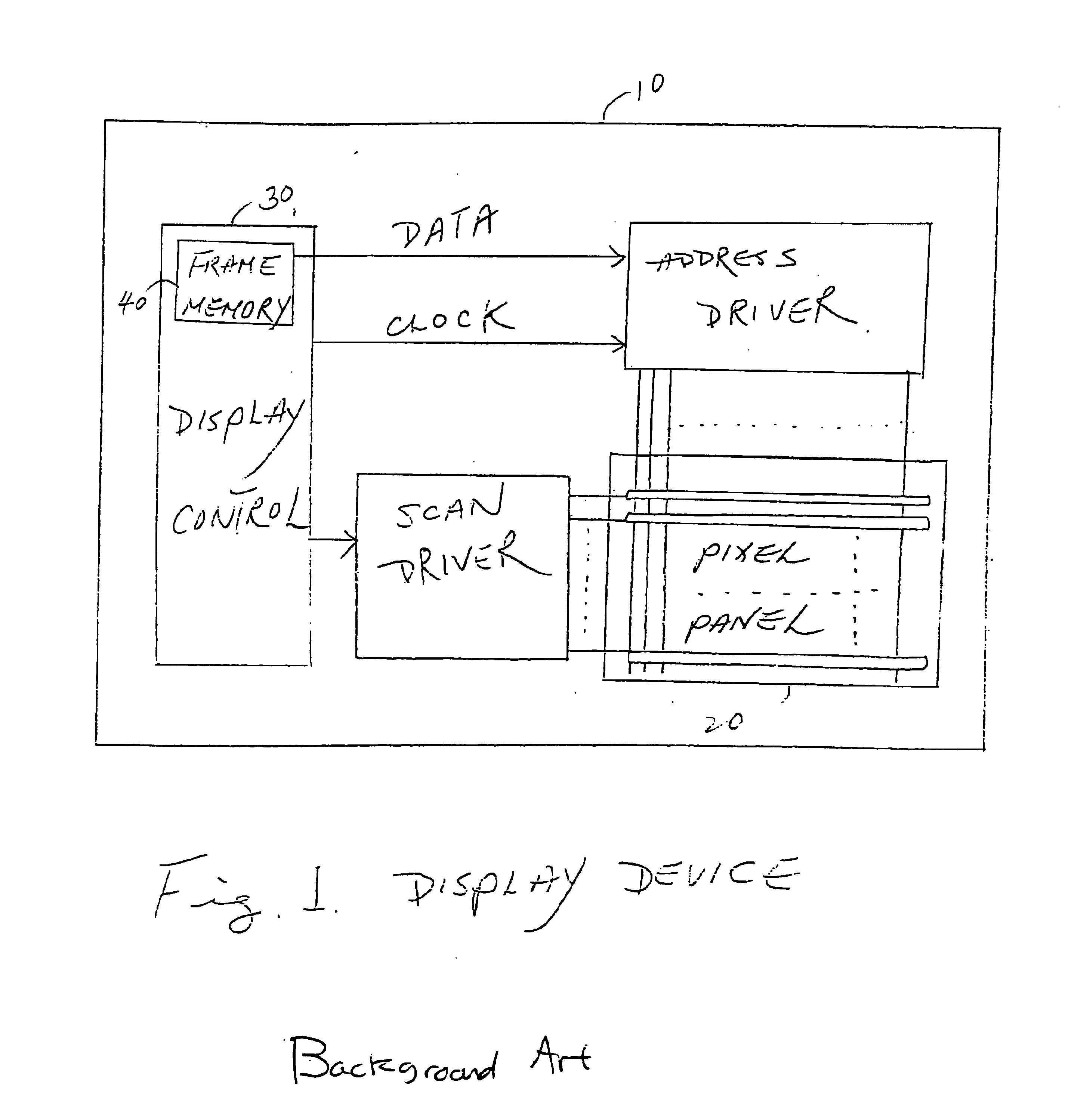
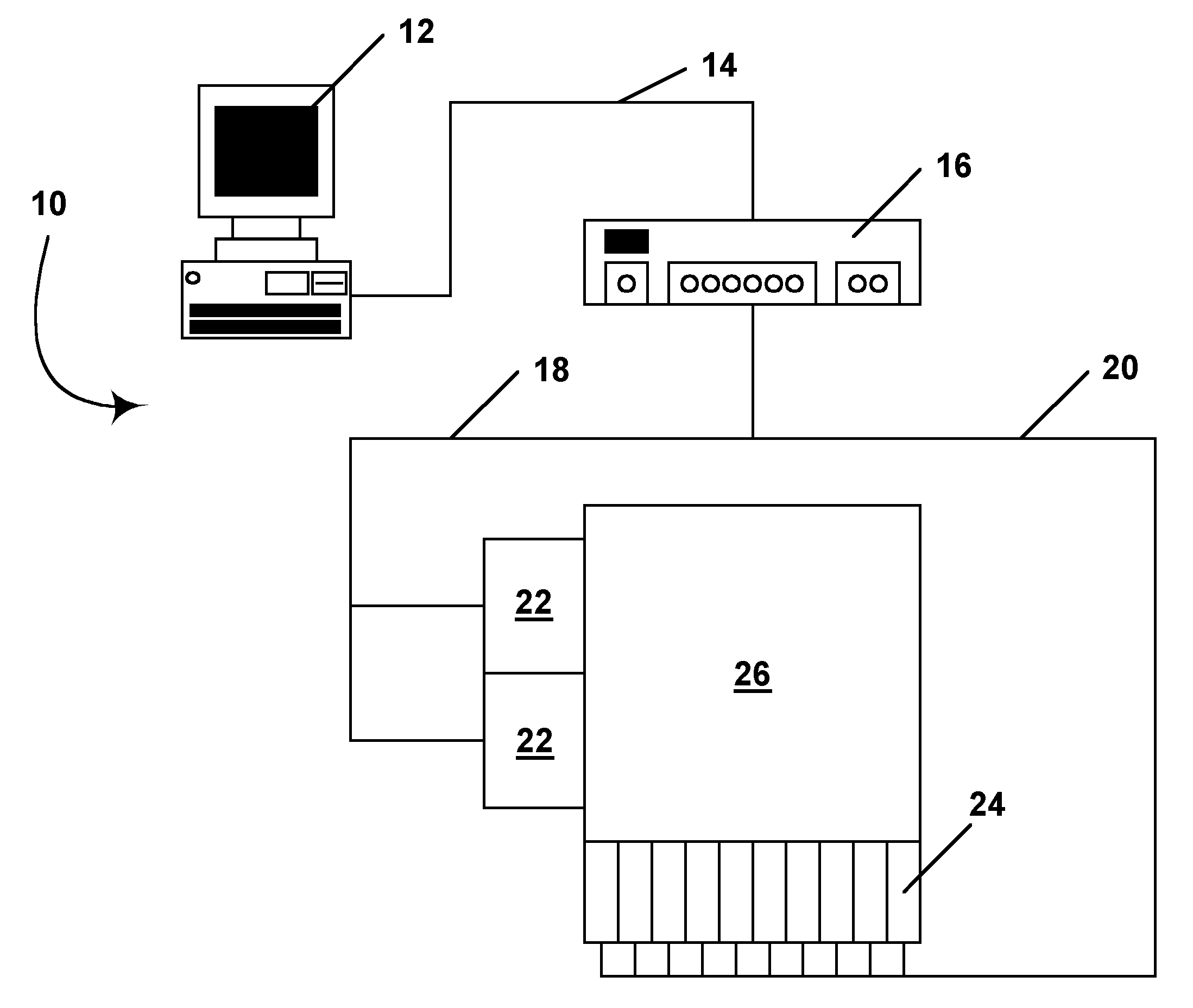
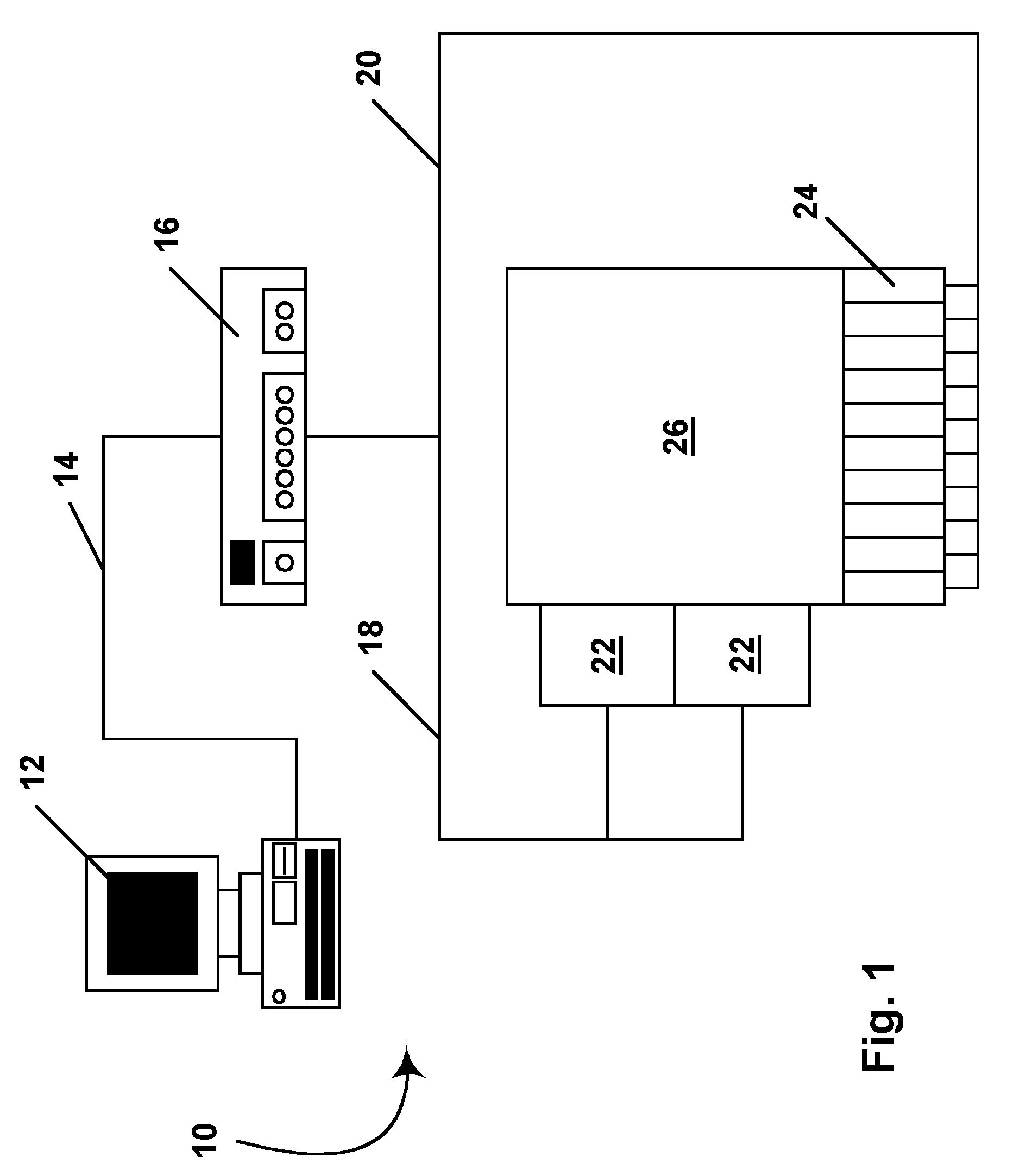
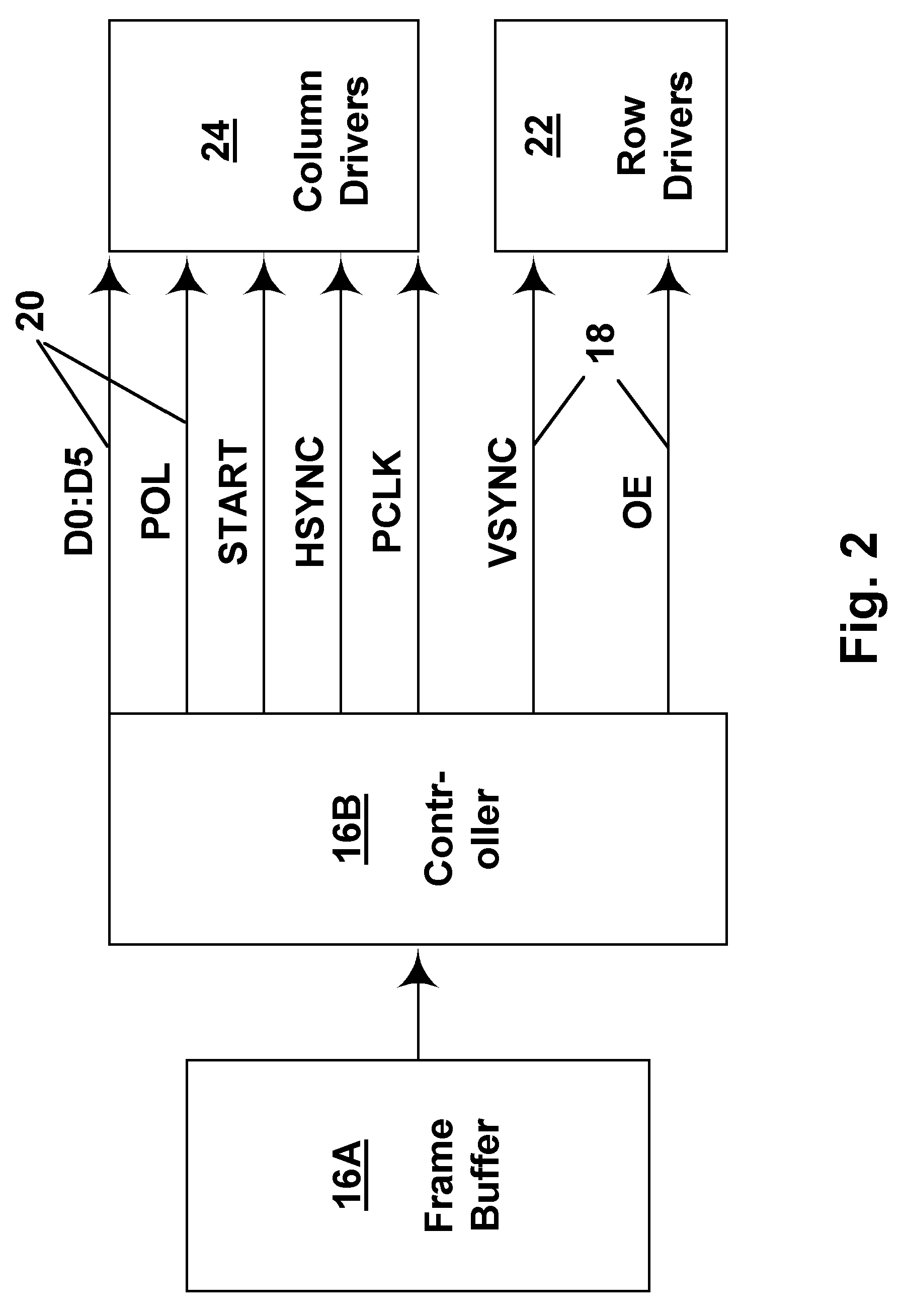
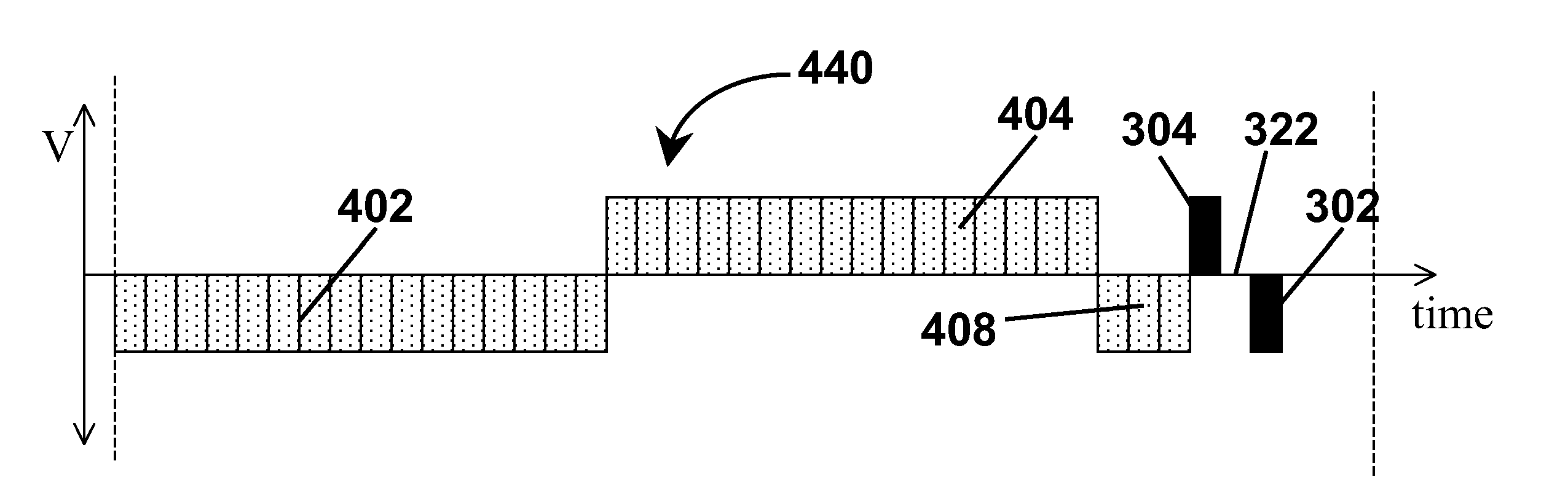
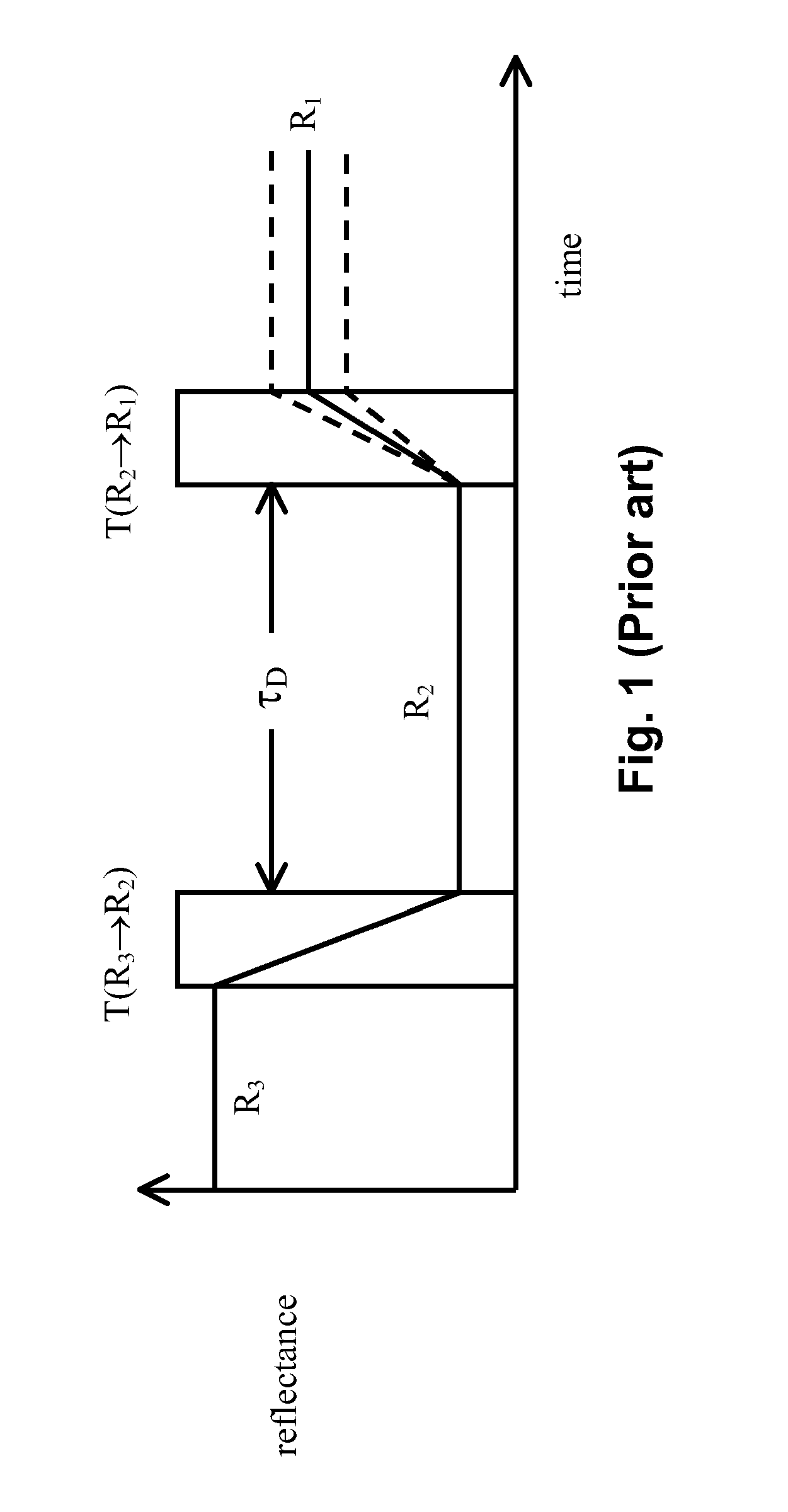
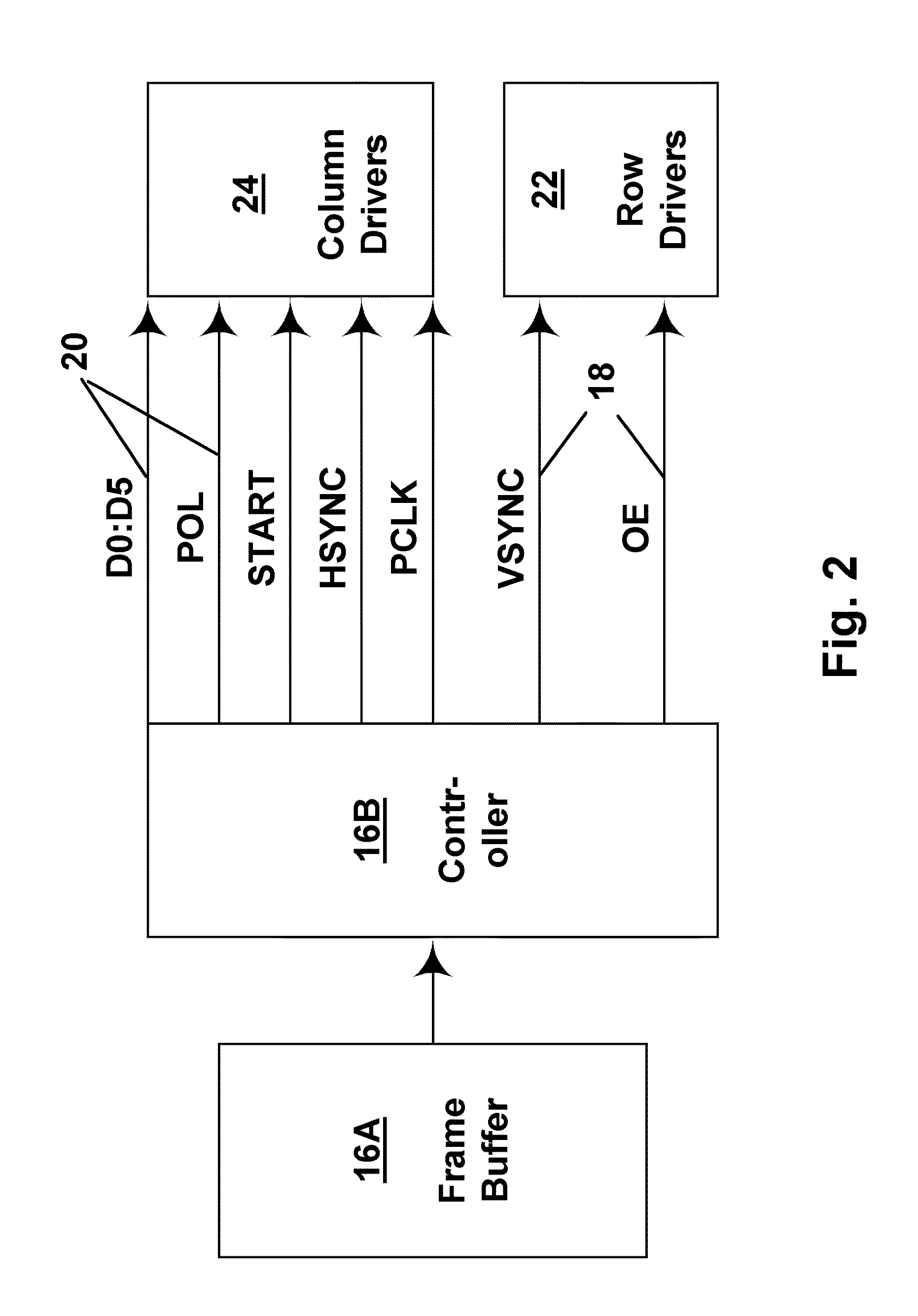
Methods for driving bistable electro-optic displays, and apparatus for use therein
InactiveUS7012600B2Character and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGray levelDisplay device
A bistable electro-optic display has a plurality of pixels, each of which is capable of displaying at least three gray levels. The display is driven by a method comprising: storing a look-up table containing data representing the impulses necessary to convert an initial gray level to a final gray level; storing data representing at least an initial state of each pixel of the display; receiving an input signal representing a desired final state of at least one pixel of the display; and generating an output signal representing the impulse necessary to convert the initial state of said one pixel to the desired final state thereof, as determined from said look-up table. The invention also provides a method for reducing the remnant voltage of an electro-optic display.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Methods for driving bistable electro-optic displays, and apparatus for use therein
A gray scale bistable electro-optic display is driven by storing a look-up table containing data representing the impulses necessary for transitions, storing data representing at least an initial state of each pixel of the display, storing data representing temporal and gray level prior states of each pixel, receiving an input signal representing a desired final state of at least one pixel of the display; and generating an output signal representing the impulse necessary for a transition, as determined from the look-up table, dependent upon the temporal and gray level prior states. Other similar methods for driving such displays are also disclosed.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Methods for driving electro-optic displays
An electro-optic display, having at least one pixel capable of achieving any one of at least four different gray levels including two extreme optical states, is driven by displaying a first image on the display, and rewriting the display to display a second image thereon, wherein, during the rewriting of the display, any pixel which has undergone a number of transitions exceeding a predetermined value without touching an extreme optical state, is driven to at least one extreme optical state before driving that pixel to its final optical state in the second image.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Methods for driving electro-optic displays
ActiveUS20050024353A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsGray levelComputer graphics (images)
An electro-optic display, having at least one pixel capable of achieving any one of at least four different gray levels including two extreme optical states, is driven by displaying a first image on the display, and rewriting the display to display a second image thereon, wherein, during the rewriting of the display, any pixel which has undergone a number of transitions exceeding a predetermined value without touching an extreme optical state, is driven to at least one extreme optical state before driving that pixel to its final optical state in the second image.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
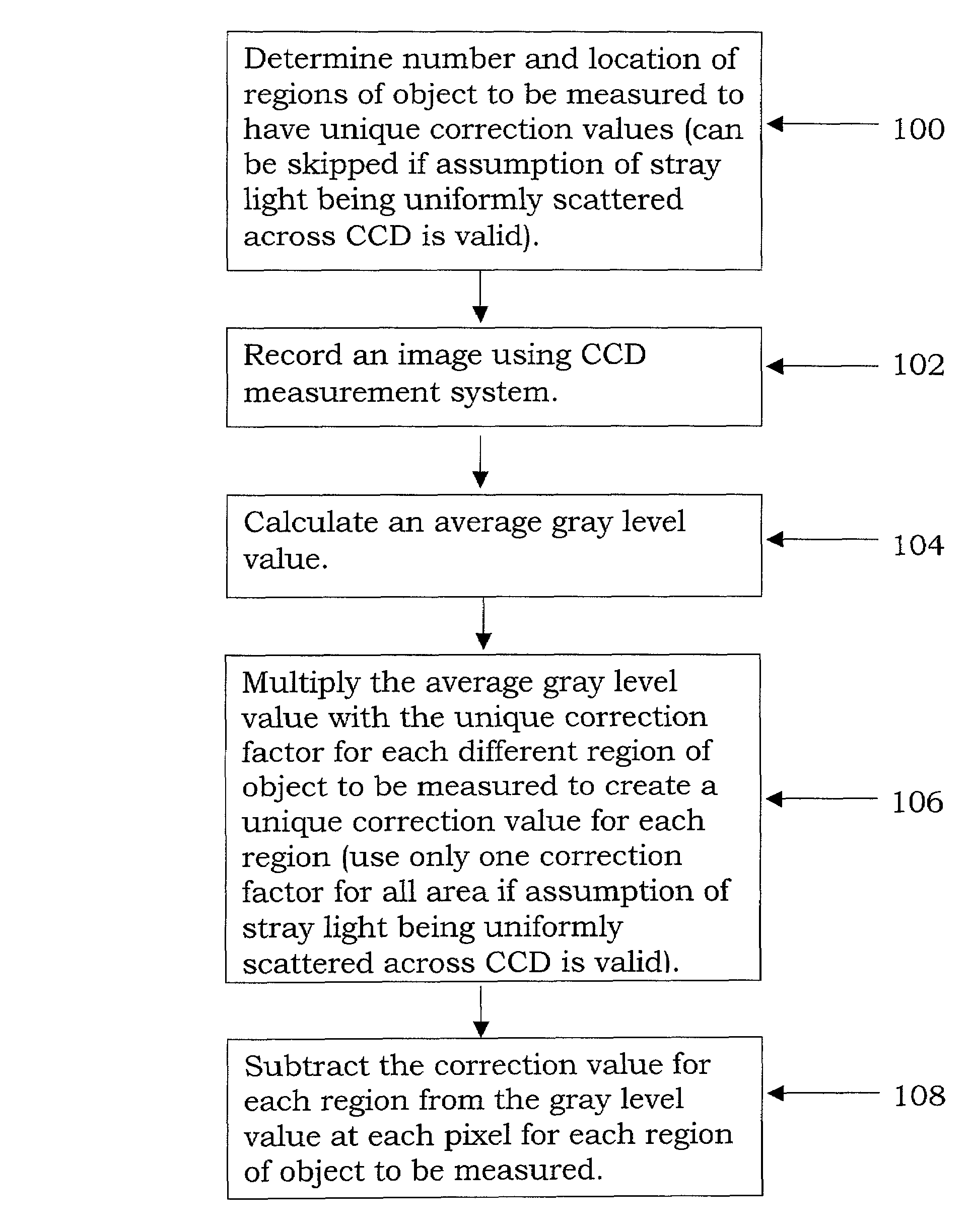
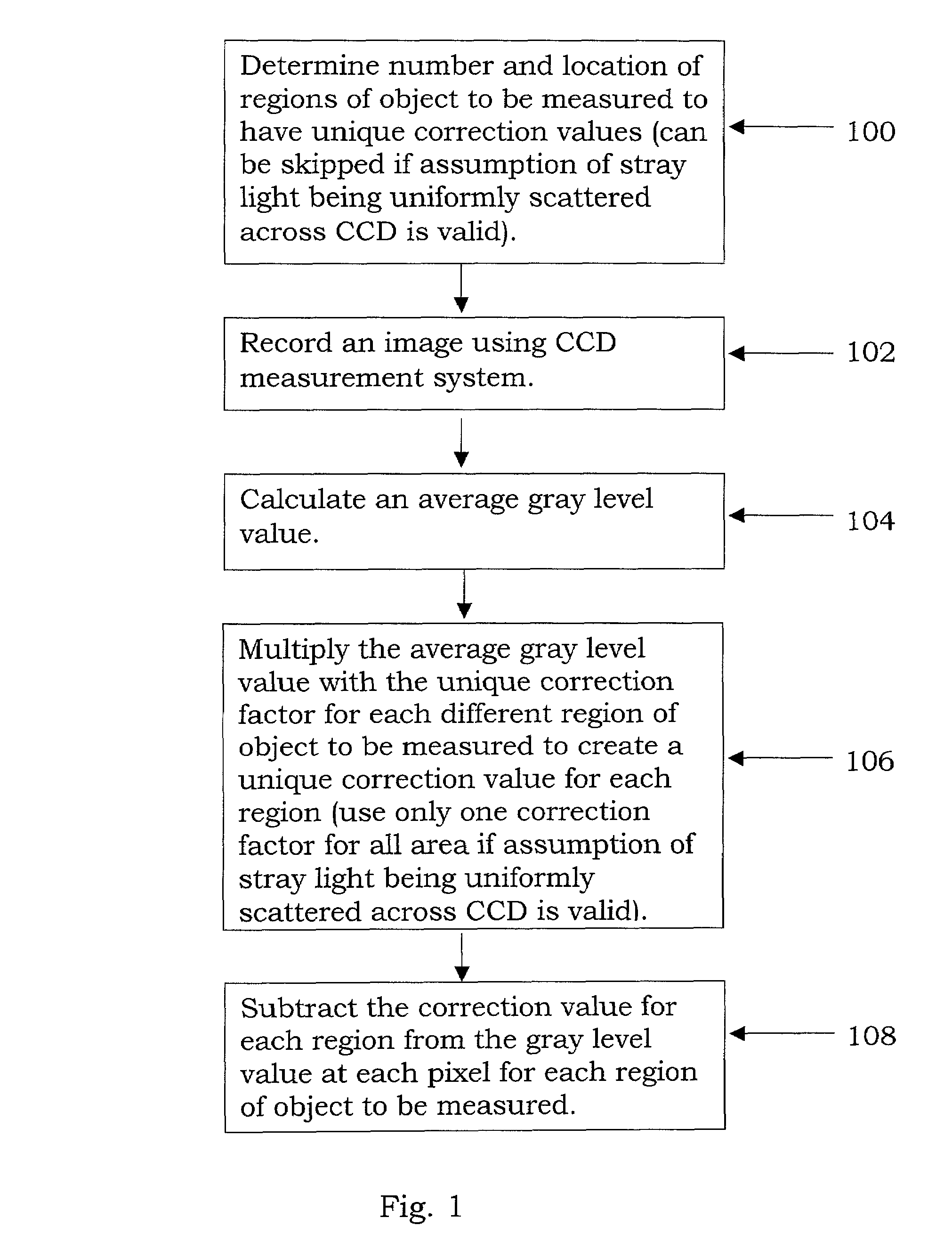
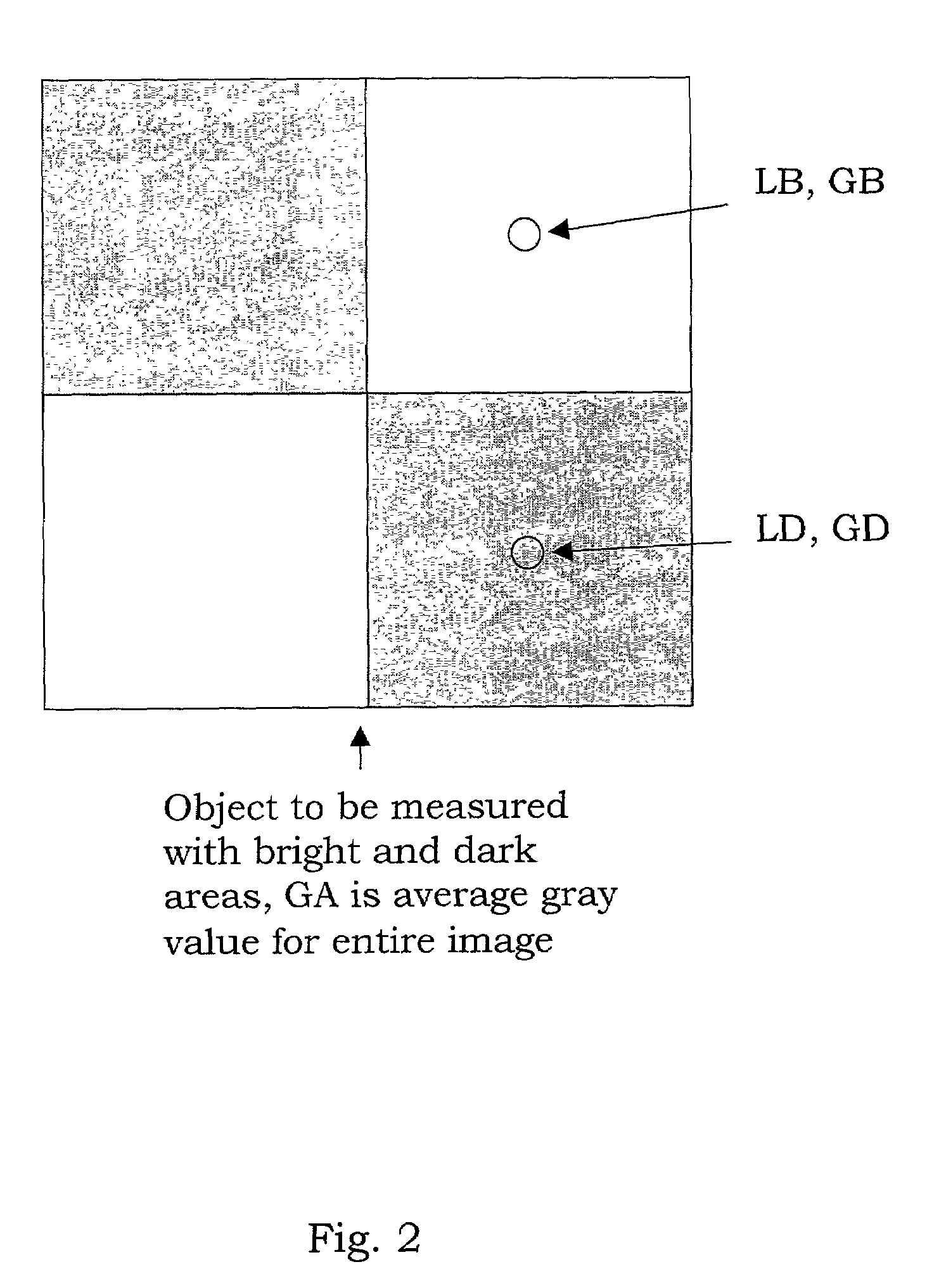
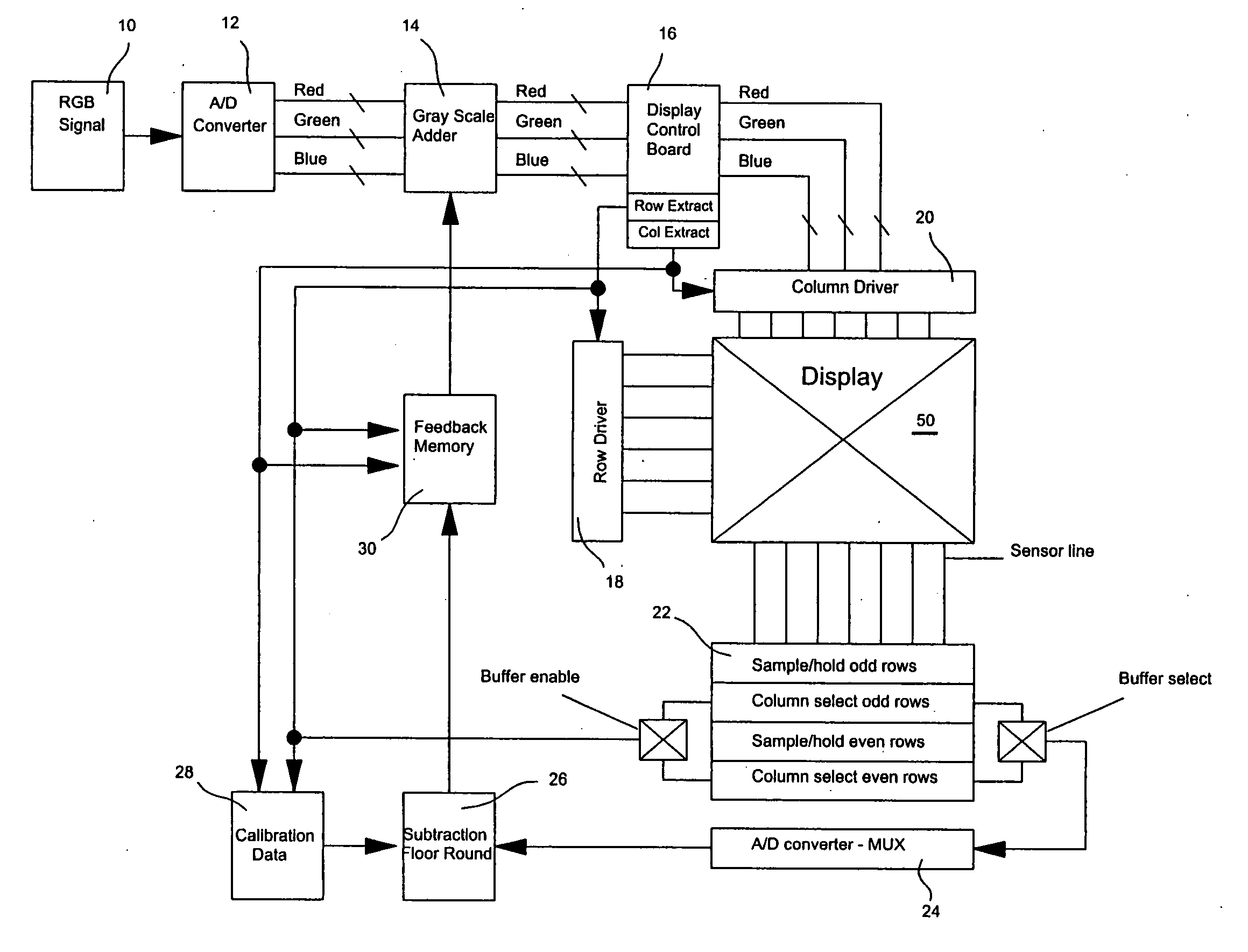
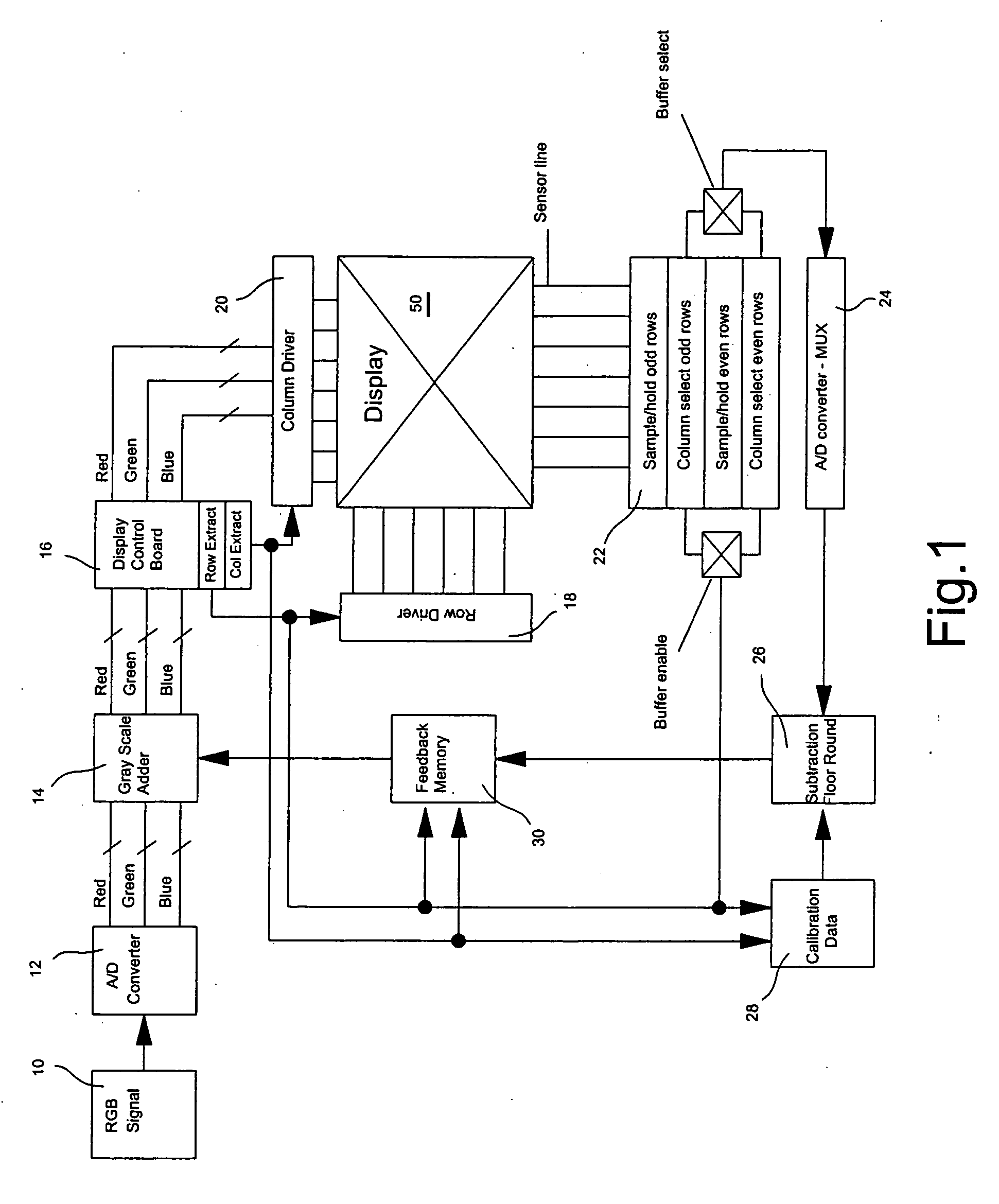
Stray light correction method for imaging light and color measurement system
ActiveUS6975775B2Eliminate the effects ofIncrease grayscaleTelevision system detailsImage enhancementGray levelOptoelectronics
A stray light correction method for image light and color measurement system, uses a solid-state light detector array such as a charge-coupled device to record an image, so that a gray level value for each pixel of the solid-state light detector array is obtained. An average gray level value of the solid-state light detector array is calculated based on the gray level value for each pixel. The average gray level value is further multiplied with a stray light factor to obtain a correction value. The gray level value of each pixel is then subtracted with the correction value, such that the stray light effect can be eliminated.
Owner:RADIANT ZEMAX
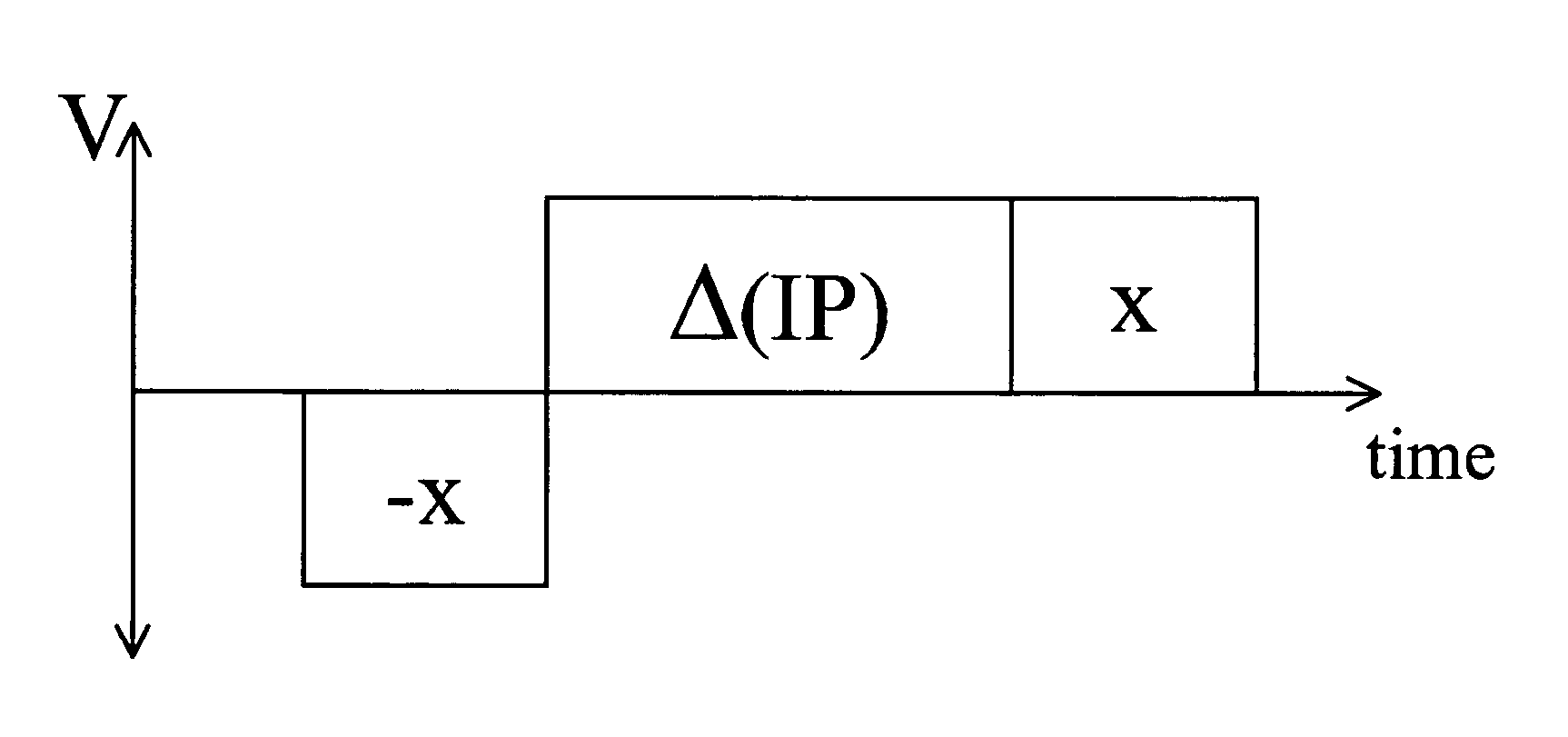
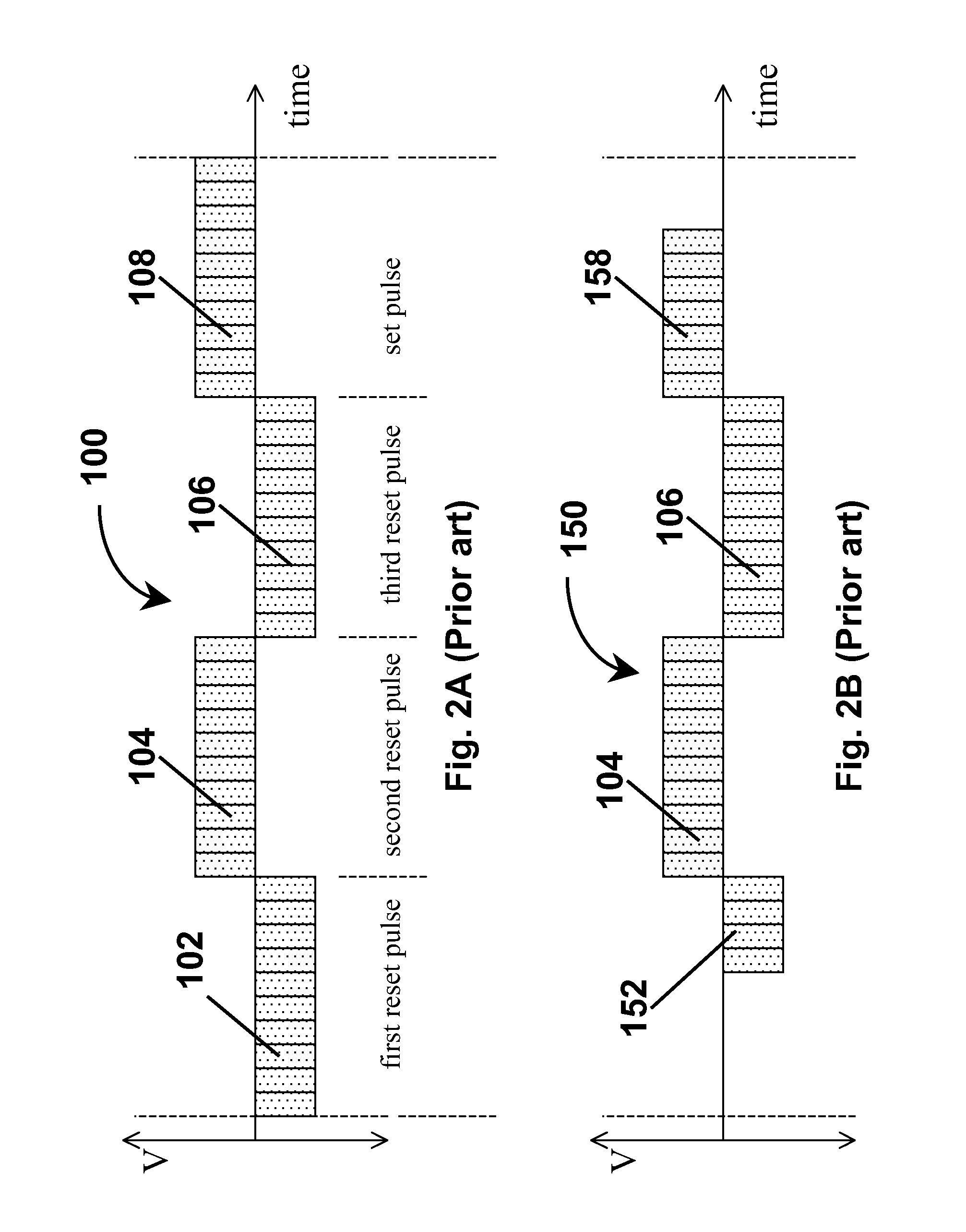
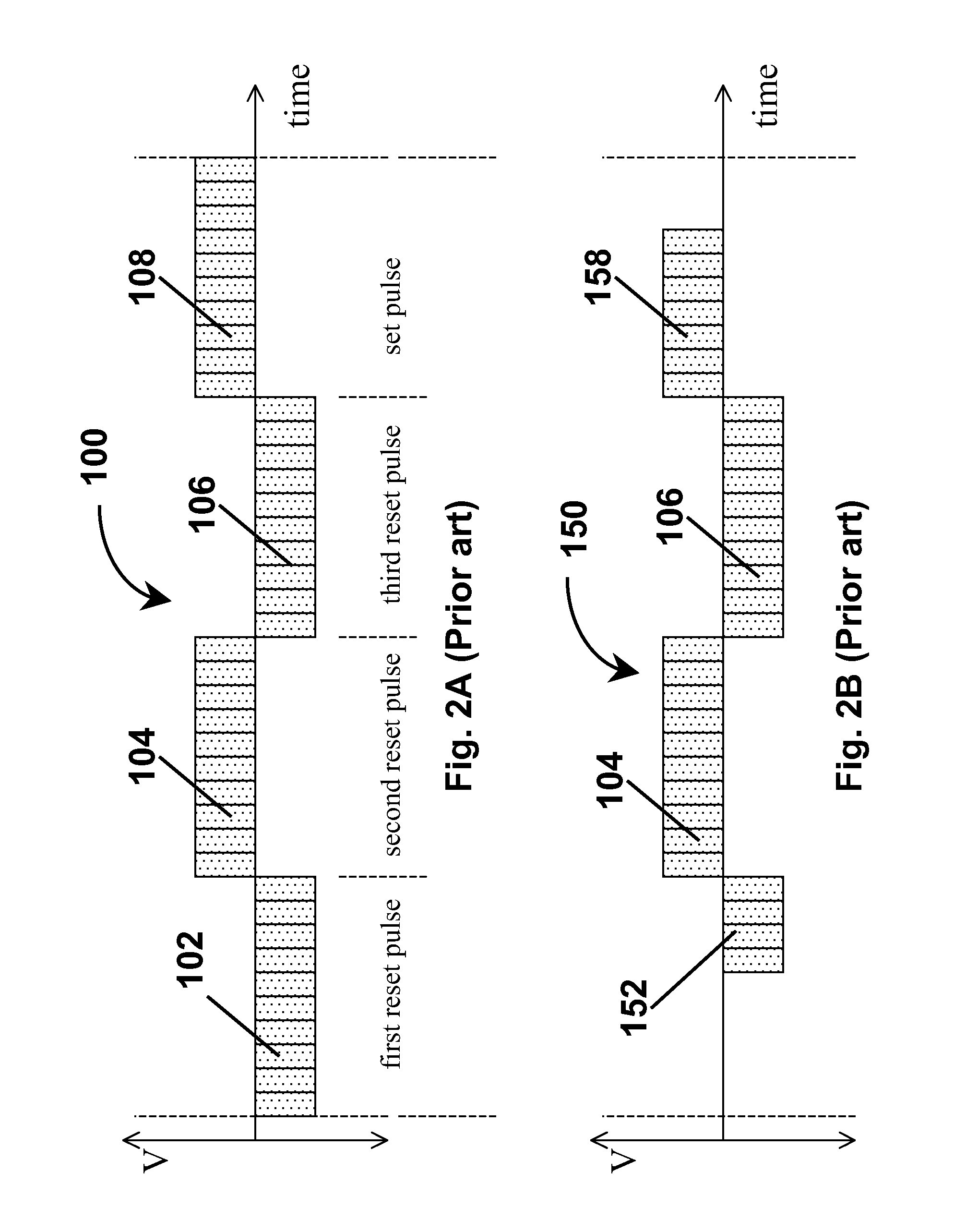
Methods and apparatus for driving electro-optic displays
ActiveUS7952557B2Shorten the overall cycleReduce data volumeCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingGray levelDisplay device
Waveforms for driving electro-optic displays, especially bistable electro-optic displays, are modified by one or more of insertion of at least one balanced pulse pair into a base waveform; excision of at least one balanced pulse pair from the base waveform; and insertion of at least one period of zero voltage into the base waveform. Such modifications permit fine control of gray levels.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Methods for driving bistable electro-optic displays, and apparatus for use therein
InactiveUS20050001812A1Reduce residual voltageTelevision system detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsGray levelDisplay device
A gray scale bistable electro-optic display is driven by storing a look-up table containing data representing the impulses necessary for transitions, storing data representing at least an initial state of each pixel of the display, storing data representing temporal and gray level prior states of each pixel, receiving an input signal representing a desired final state of at least one pixel of the display; and generating an output signal representing the impulse necessary for a transition, as determined from the look-up table, dependent upon the temporal and gray level prior states. Other similar methods for driving such displays are also disclosed.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Methods for driving electro-optic displays
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Methods for driving electro-optic displays
ActiveUS20090195568A1Short transition timeCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingGray levelDisplay device
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
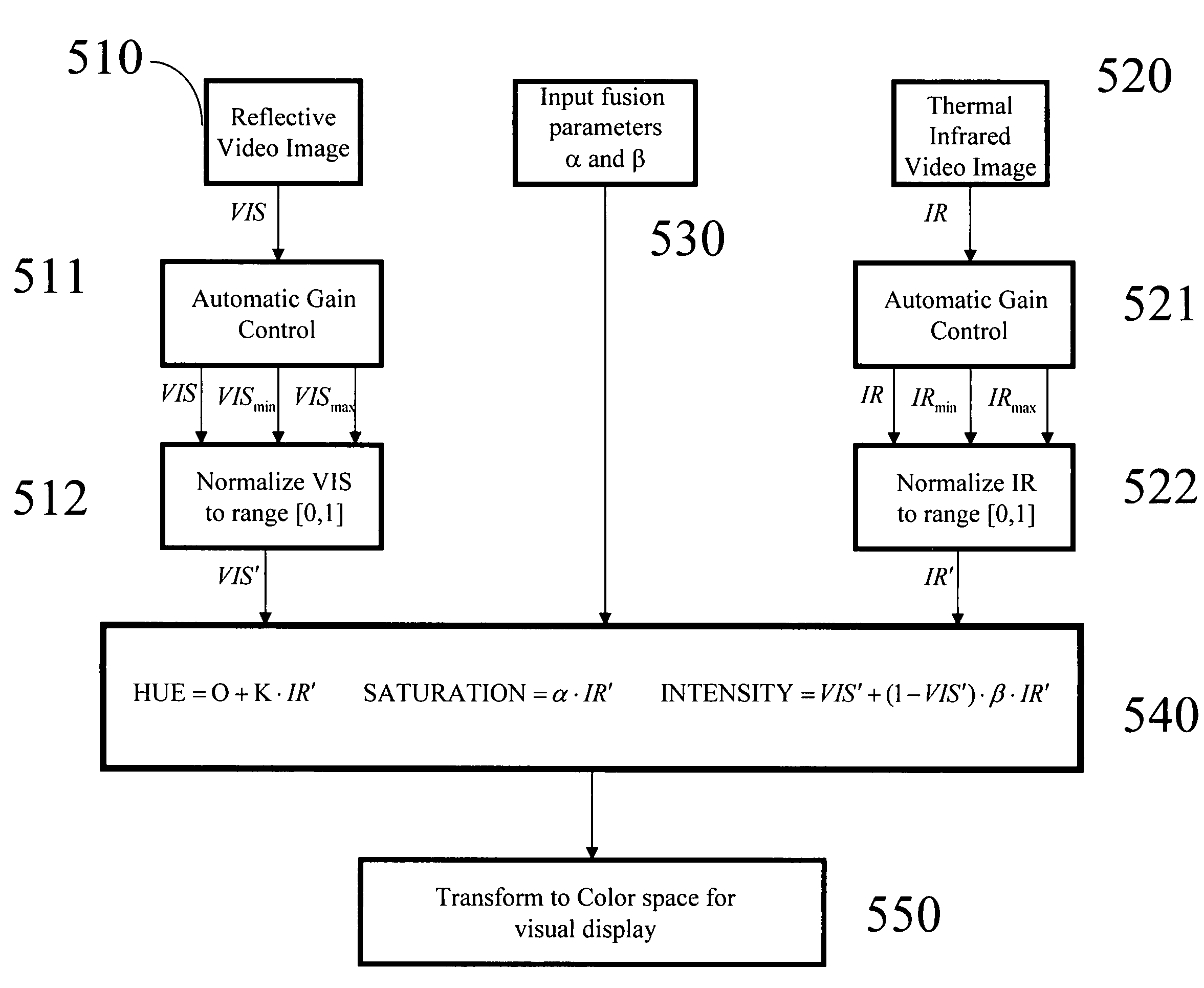
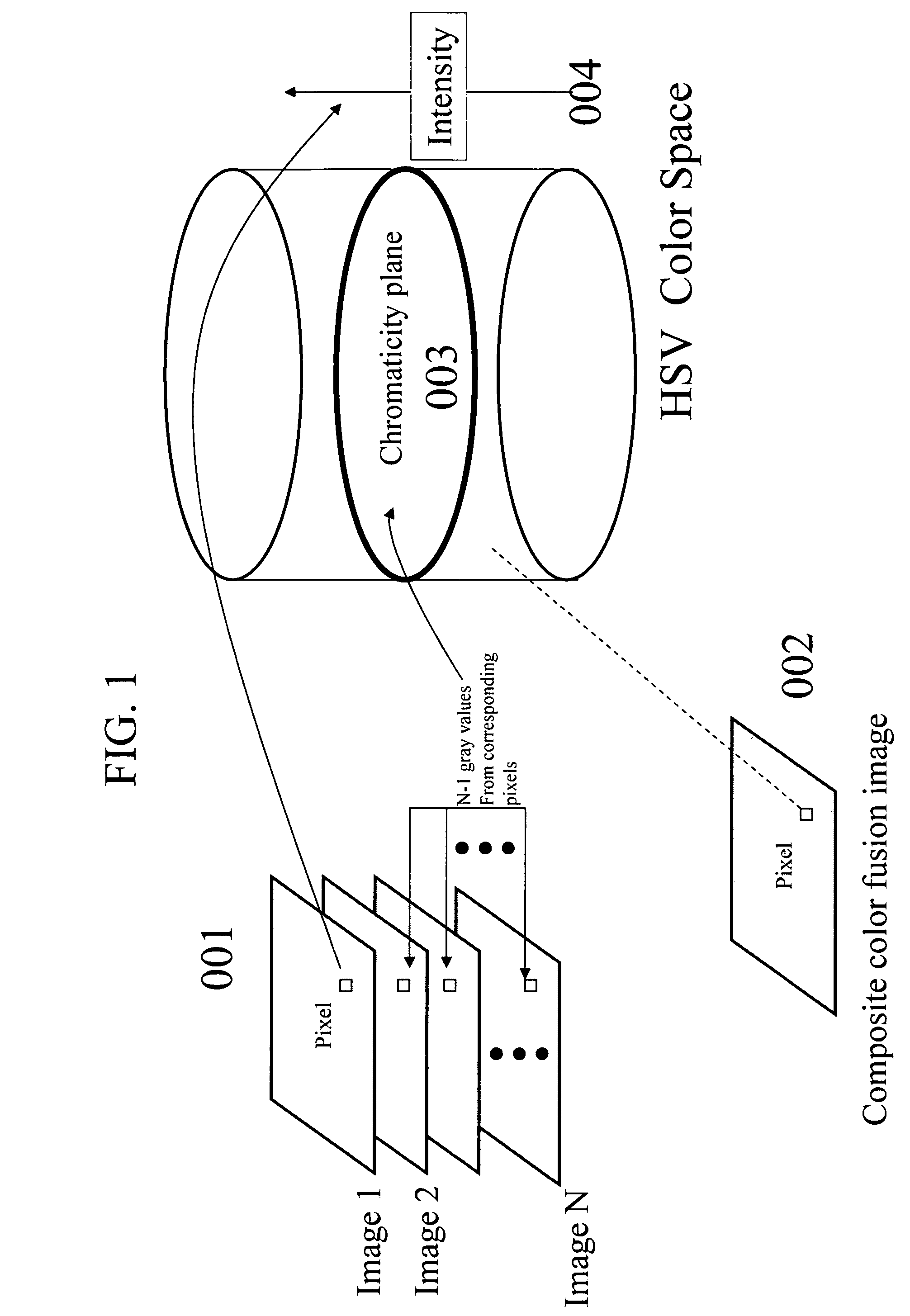
Color invariant image fusion of visible and thermal infrared video
A methodology for forming a composite color image fusion from a set of N gray level images takes advantage of the natural decomposition of color spaces into 2-D chromaticity planes and 1-D intensity. This is applied to the color fusion of thermal infrared and reflective domain (e.g., visible) images whereby chromaticity representation of this fusion is invariant to changes in reflective illumination.
Owner:EQUINOX CORP
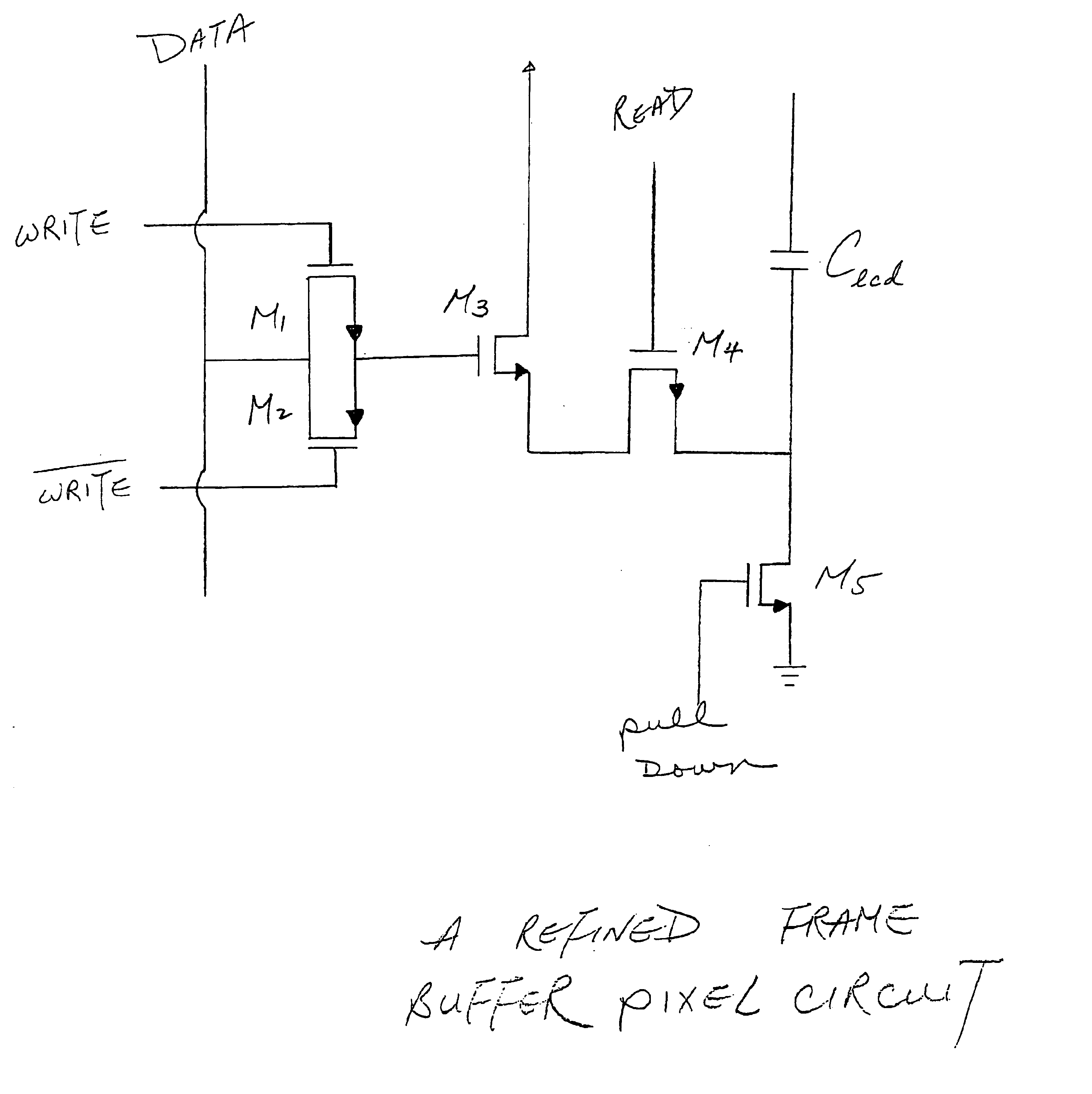
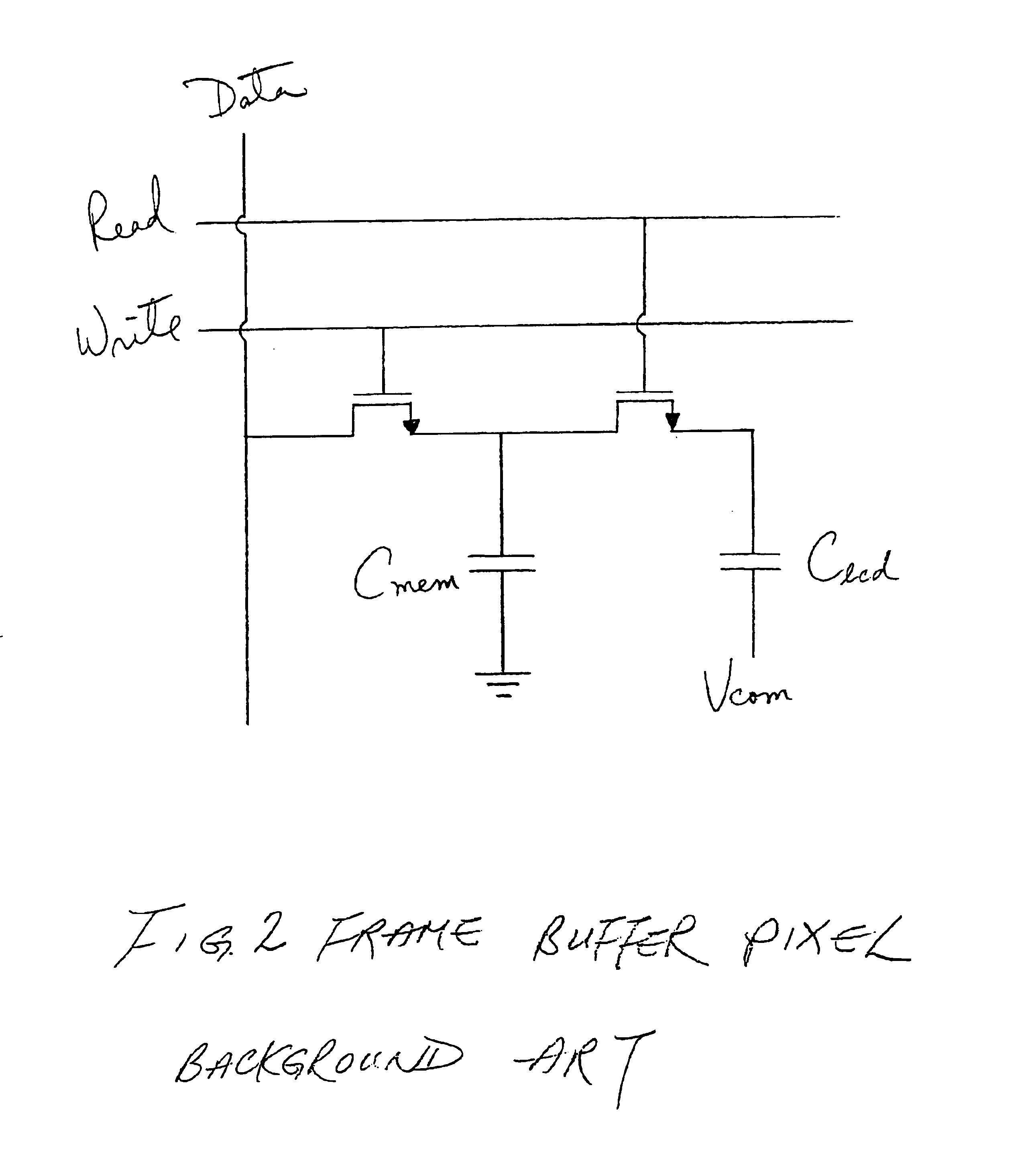
Frame buffer pixel circuit for liquid crystal display
InactiveUS6911964B2Enhanced frame buffer pixelIncrease contrastStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsCMOSLiquid-crystal display
An enhanced frame buffer pixel circuit with two control transistors and a separate capacitor put in as a memory capacitor before the memory transistor yields a high contrast ratio by removing induced charge and solving a charge sharing problem between the memory capacitor and the liquid crystal display (LCD) capacitor. The memory transistor may be made of either CMOS or PMOS. The frame buffer pixel can be used to drive binary displays which expresses ON and OFF only if a comparator is put in after the pixel electrode circuit to represent gray levels with reduced sub-frame frequency.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
Methods for driving electro-optic displays
InactiveUS20090179923A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsGray levelComputer graphics (images)
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Methods for driving electro-optic displays, and apparatus for use therein
InactiveUS20050219184A1Reduce residual voltageCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsGray levelDisplay device
A bistable electro-optic display has a plurality of pixels, each of which is capable of displaying at least three gray levels. The display is driven by a method comprising: storing a look-up table containing data representing the impulses necessary to convert an initial gray level to a final gray level; storing data representing at least an initial state of each pixel of the display; receiving an input signal representing a desired final state of at least one pixel of the display; and generating an output signal representing the impulse necessary to convert the initial state of said one pixel to the desired final state thereof, as determined from said look-up table. The invention also provides a method for reducing the remnant voltage of an electro-optic display.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Methods and apparatus for driving electro-optic displays
ActiveUS20050280626A1Reduce in quantityCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingGray levelDisplay device
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
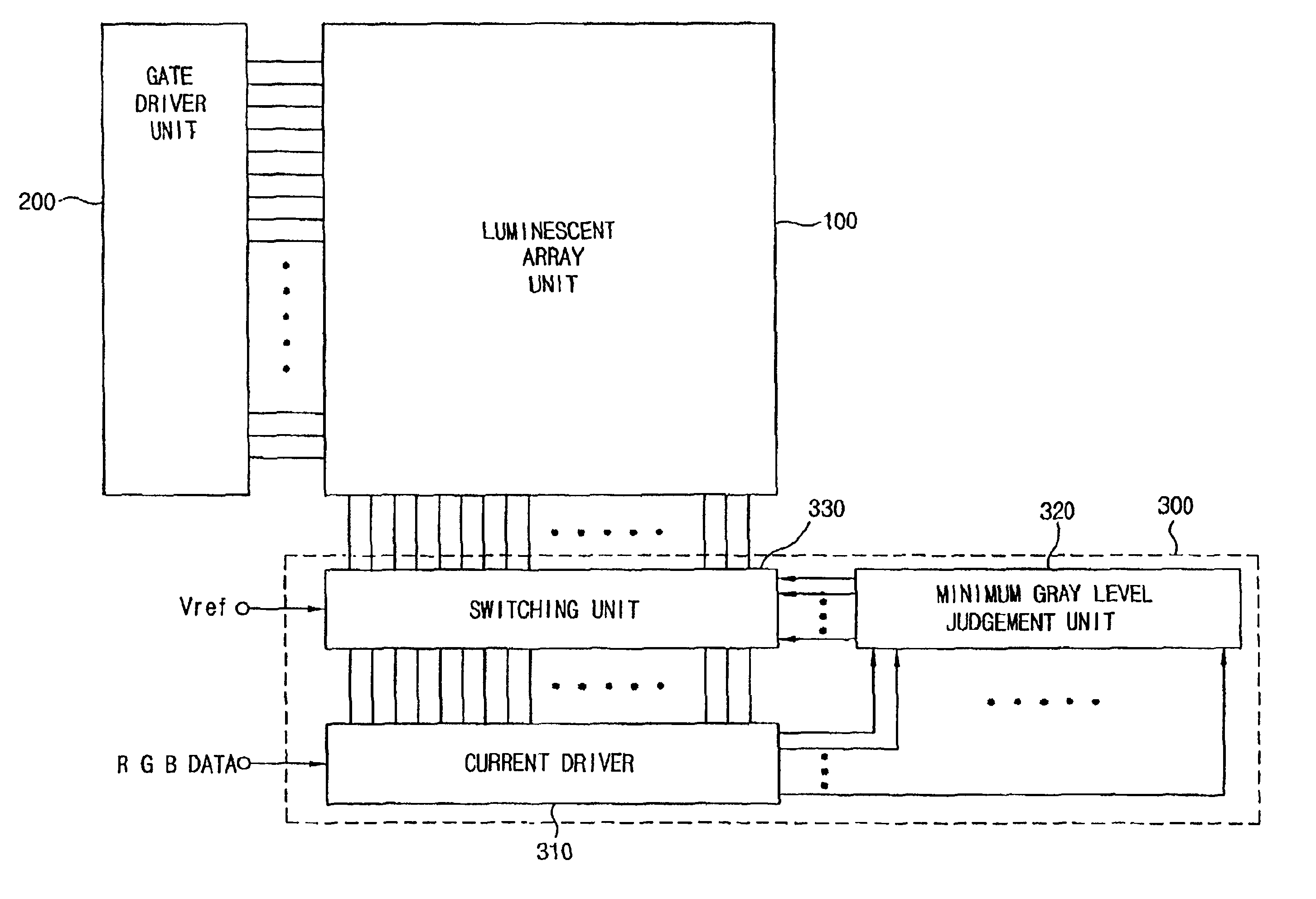
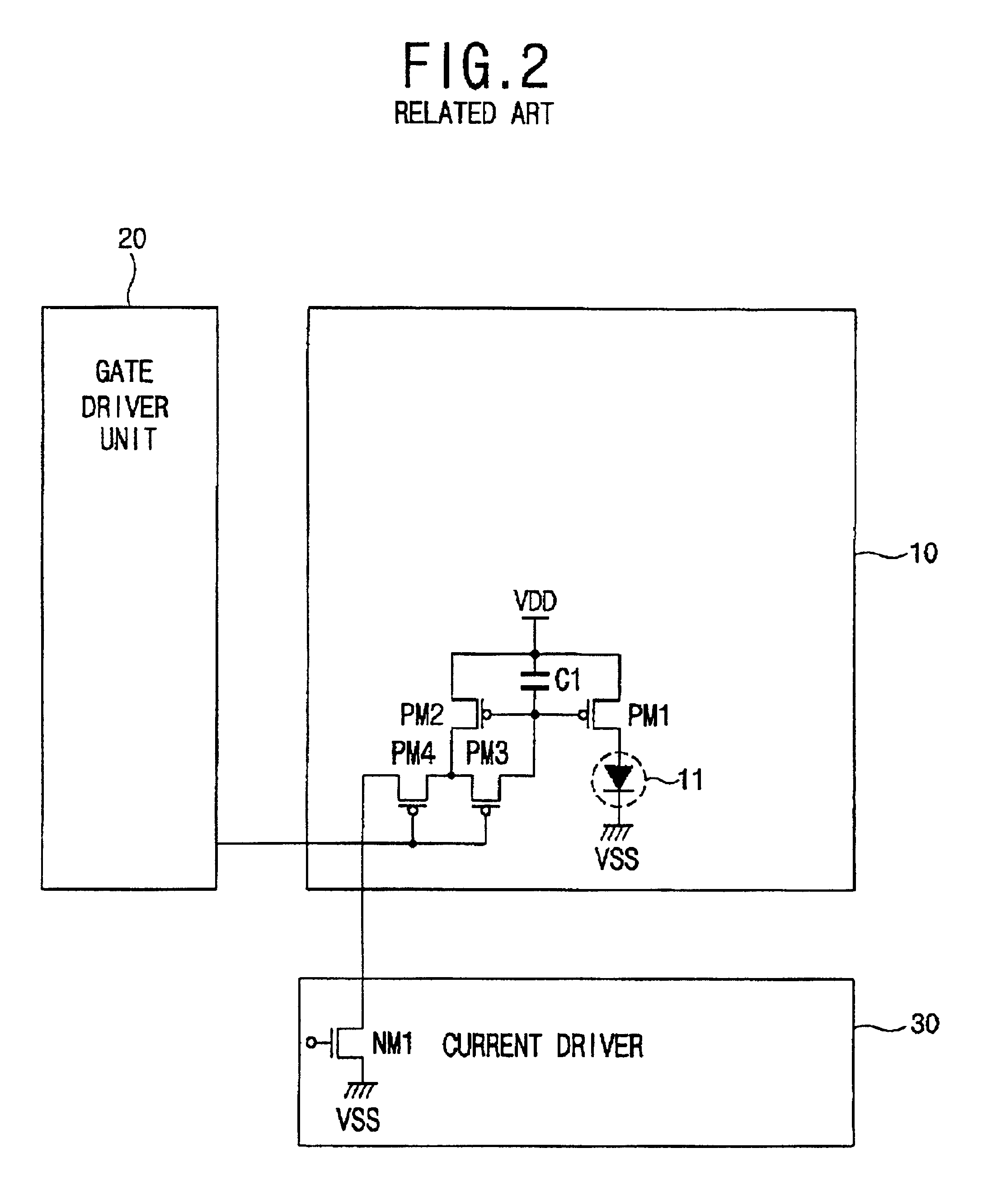
Driving circuit and method of driving an organic electroluminescence device
ActiveUS6956547B2Shorten the timeCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingReference currentControl signal
A driving circuit in an organic electroluminescent device includes a gate driver unit for sequentially outputting a control signal to select gate lines in a luminescent array unit and a current driver unit for supplying picture data to a data lines in the luminescent array unit corresponding to the gate lines selected by the gate driver unit and selectively driving organic electroluminescent devices of the selected line. The driving circuit includes a minimum gray level judgment unit for determining whether the picture data is of a predetermined minimum gray level; and a switching unit for receiving a control signal according to the determination made by the minimum gray level judgment unit and for selectively supplying a reference voltage or a reference current to the selectively driven organic electroluminescent devices.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
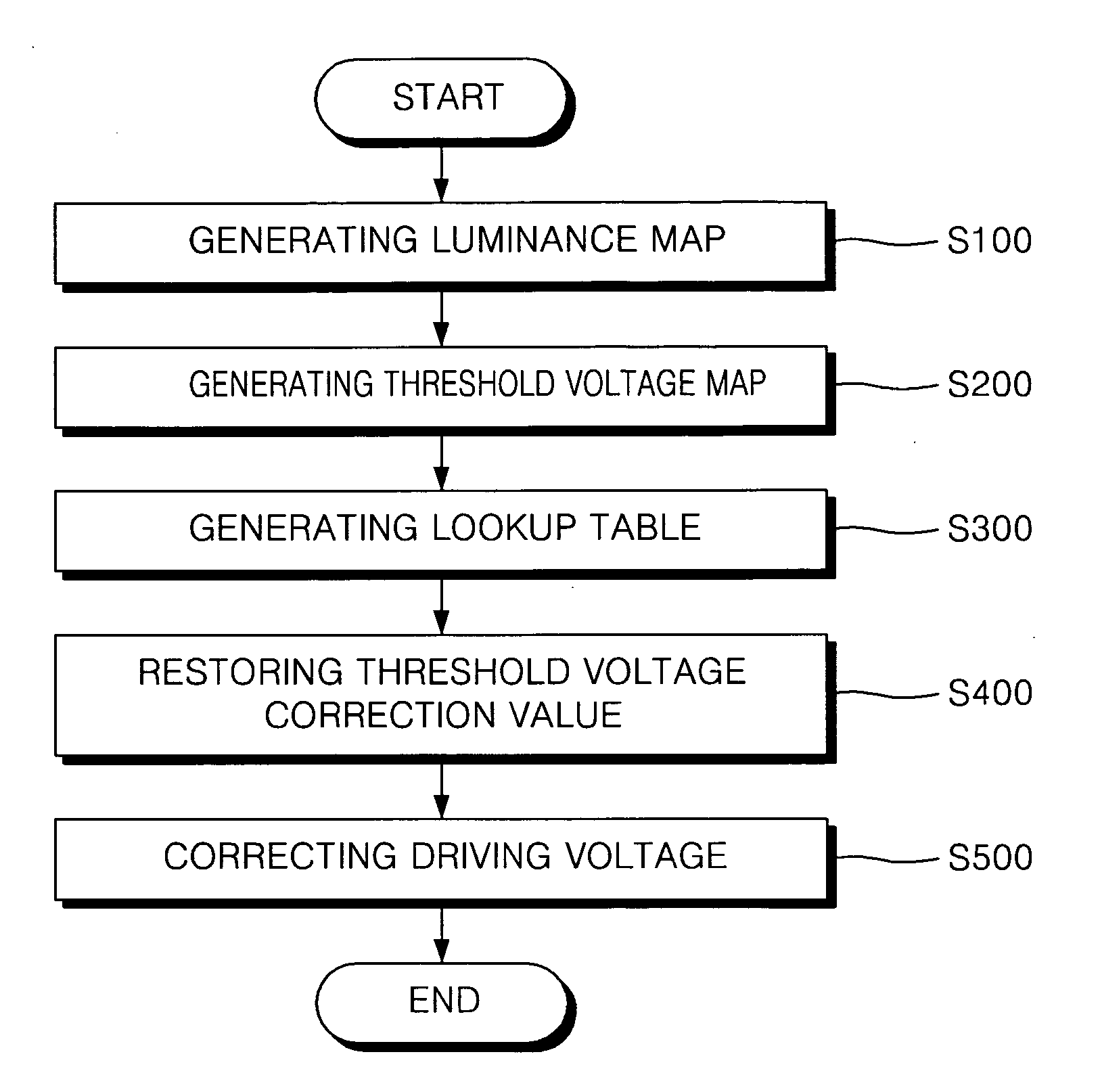
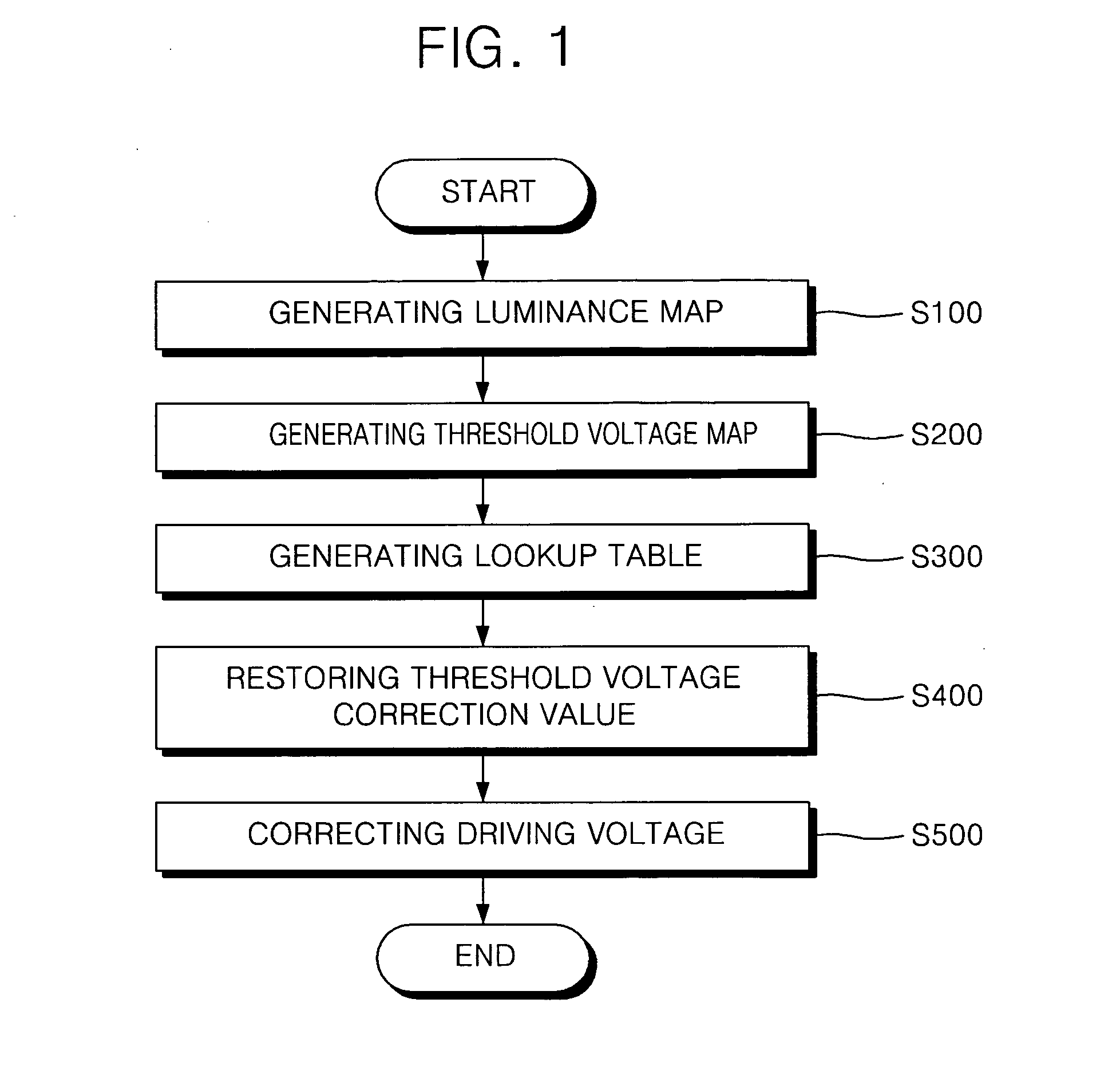
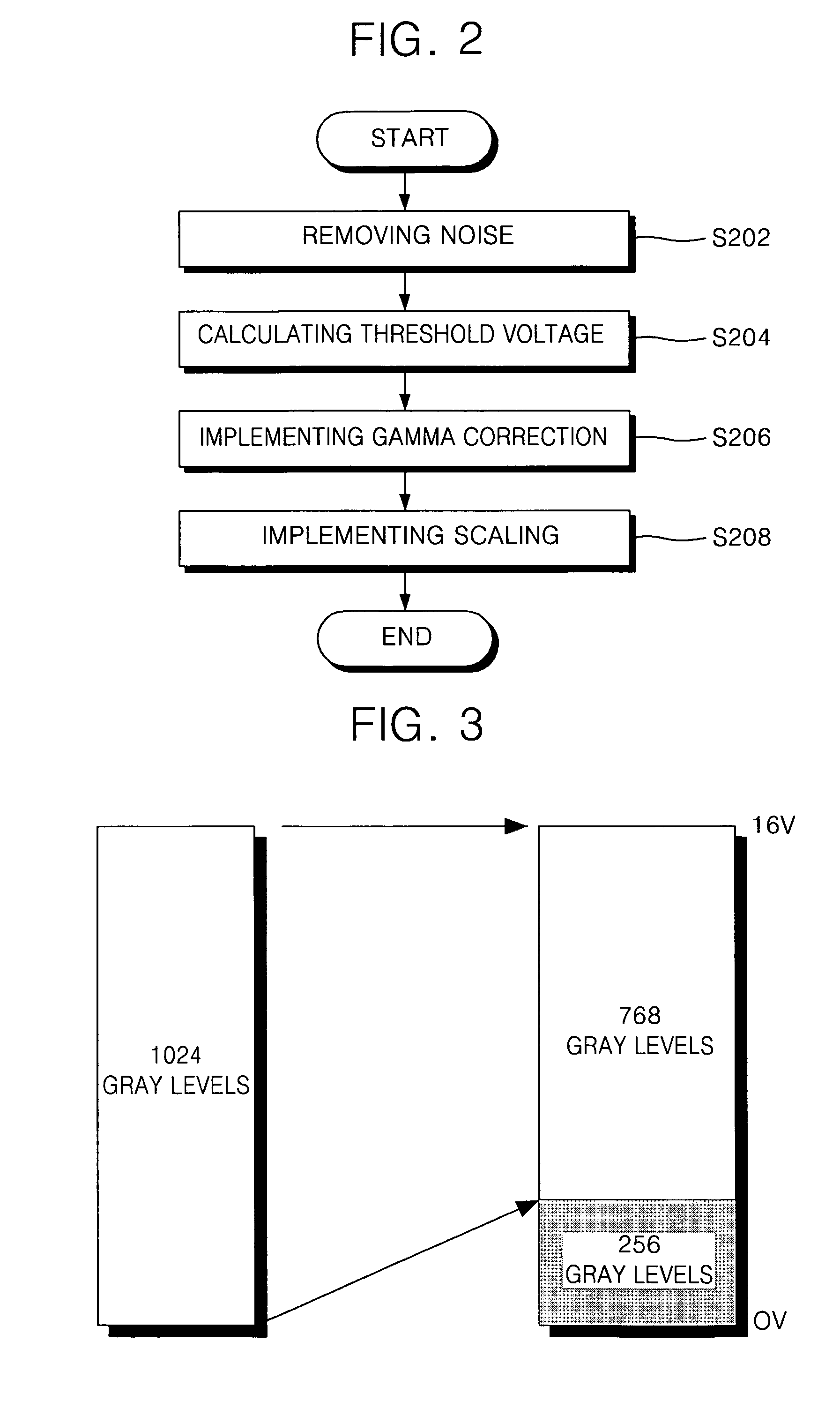
Organic light emitting display and method for driving the same
A method of driving an organic light emitting display device includes generating a luminance map for a plurality of pixels by applying the same driving voltage to driving transistors formed in the plurality of pixels of a panel and by capturing luminances of the pixels, generating a threshold voltage map by calculating threshold voltage correction values that compensate for threshold voltages of the driving transistors associated with the luminances of the pixels. A lookup table is generated by sampling the threshold voltage correction values stored in the threshold voltage map. Threshold voltage correction values are restored by interpolating the sampled threshold voltage correction values, and correcting a driving voltage by adding the restored threshold voltage correction values to input gray level data and by providing the added value to the panel.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Feedback based apparatus, systems and methods for controlling emissive pixels using pulse width modulation and voltage modulation techniques
The present invention provides techniques for emissive pixels of flat panel displays. Specifically, pixel feedback and a combination of voltage modulation and pulse width modulation are used to improve the quality and consistency of aging pixels. Based on feedback, an image frame is divided into sub-frames of various time periods. Also based on feedback, a voltage, or voltages of different voltage levels, is (are) applied to the selected sub-frames to generate an image frame of a particular gray level. The human eye integrates the effects of the voltage and pulse width modulation techniques that are applied to the various sub-frames of the image frame, over the duration of the image frame.
Owner:LEADIS TECH
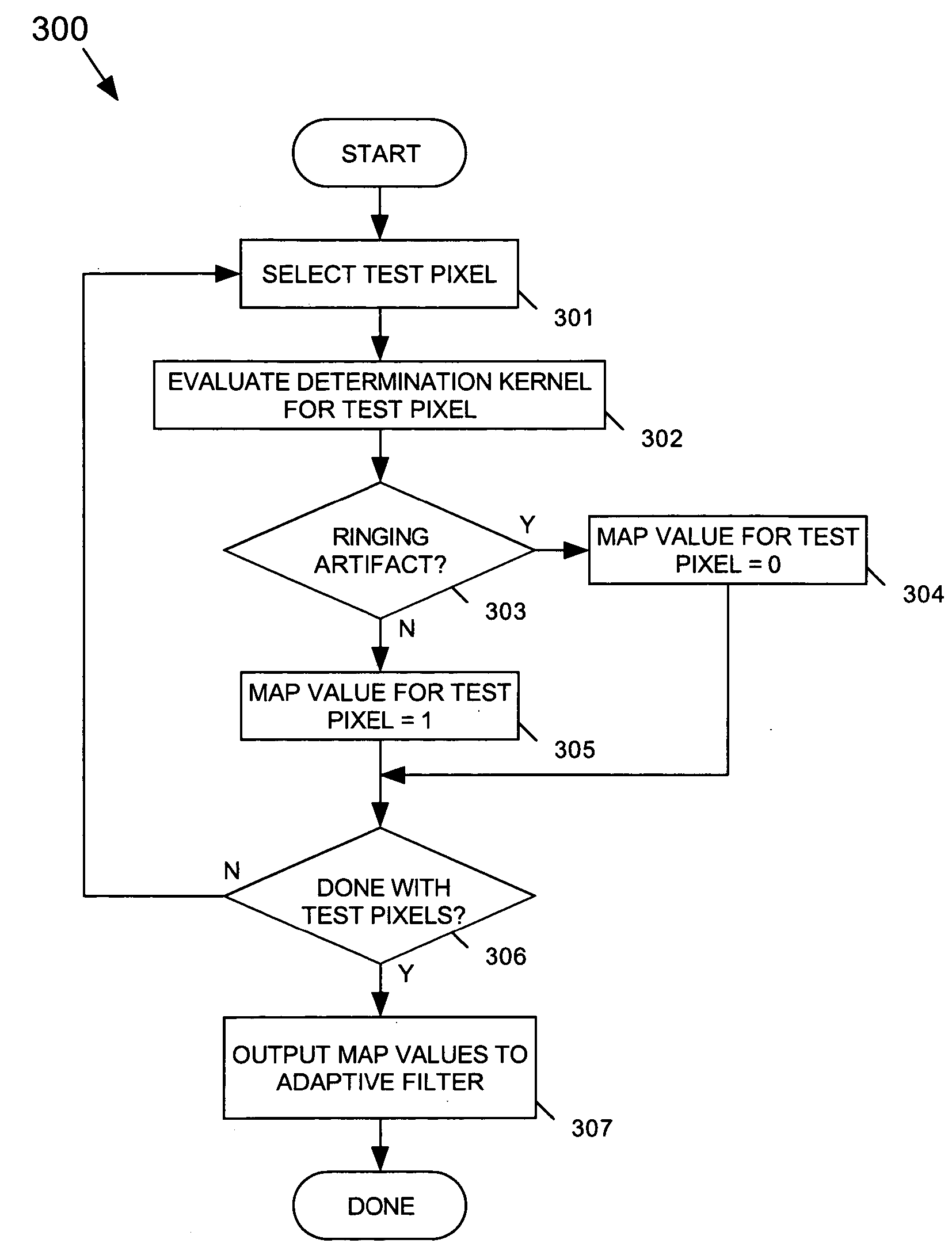
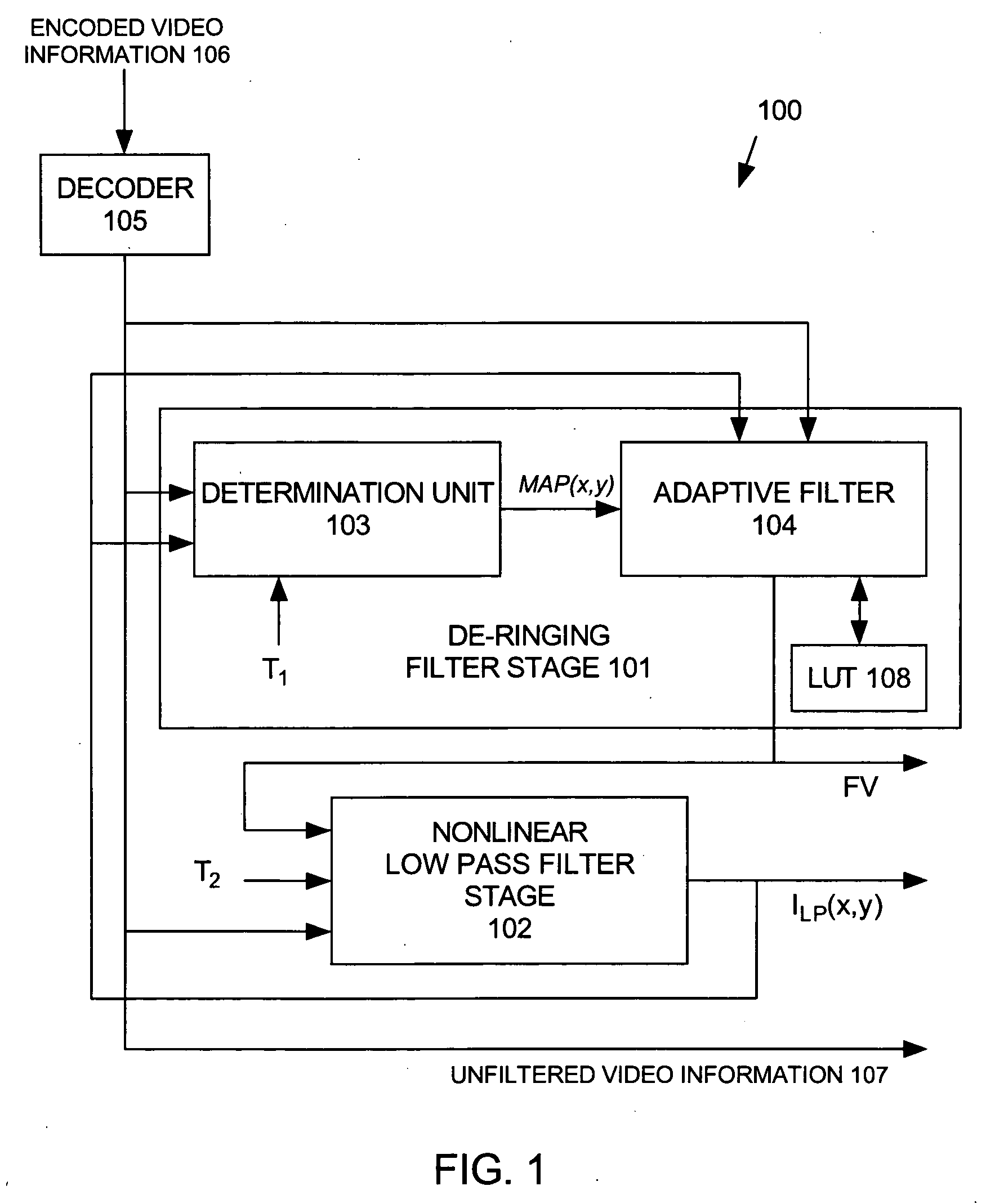
System and method for removing ringing artifacts
InactiveUS20050147319A1Reduce complexityTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionAdaptive filterGray level
Ringing artifacts are removed from a quantized image by an image de-ringing filter that includes a determination unit, an adaptive filter and a nonlinear low-pass filter. The determination unit determines whether each selected pixel of a first set of selected pixels of an image contains a ringing artifact based on, for example, gray-level values of selected pixels within a determination kernel of pixels relating to the selected pixel. The adaptive filter generates a filtered gray-level value for each pixel determined by the determination unit to contain a ringing artifact based on, for example, gray-level values of selected pixels within a filtering kernel of pixels relating to the pixel. The nonlinear low-pass filter generates a low-pass-filtered gray-level value for each selected pixel of a second set of selected pixels of the image.
Owner:SHARP KK
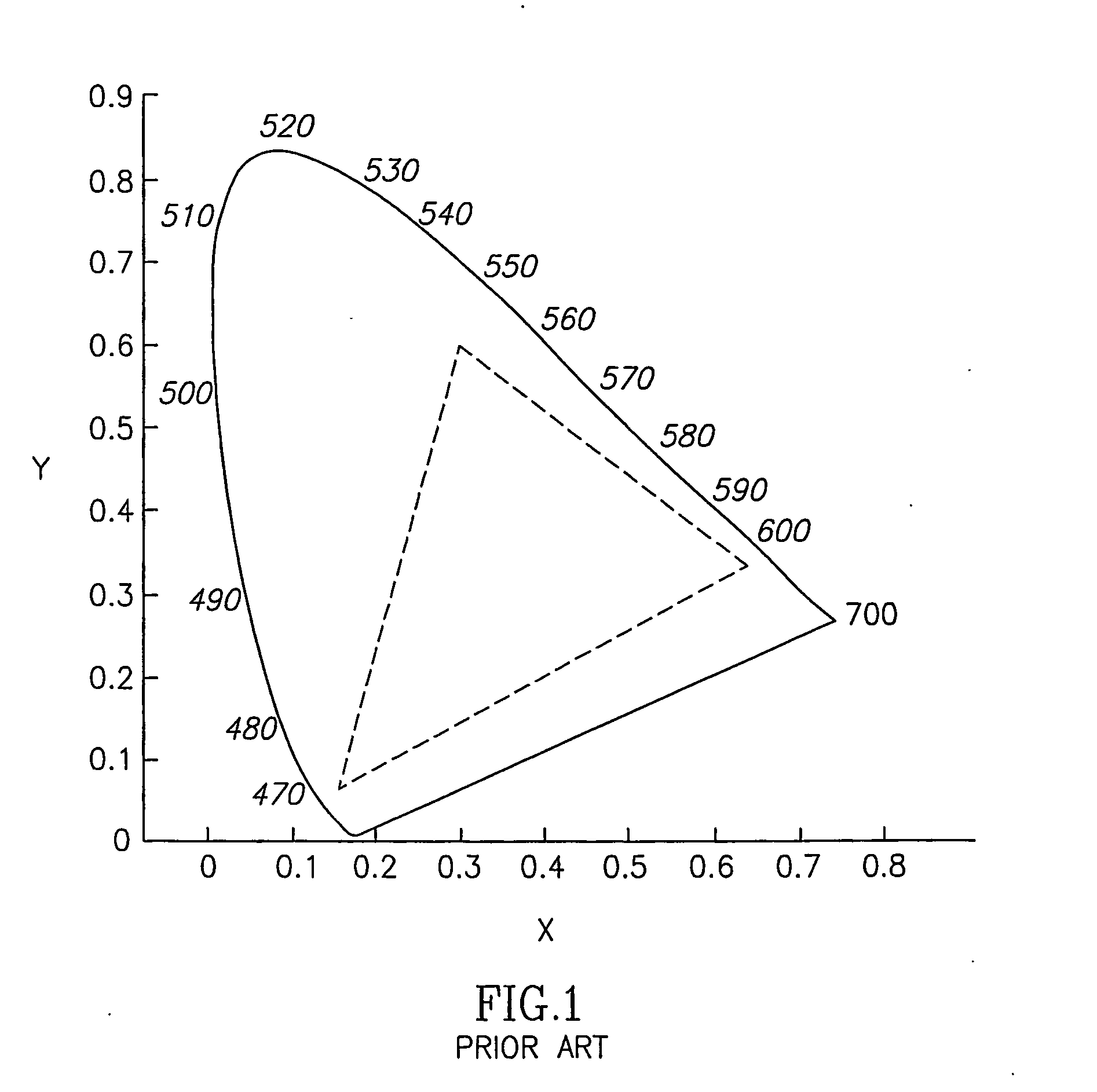
Method and system for automatically calibrating a color display
InactiveUS20070052735A1Improve image qualityExact reproductionColor signal processing circuitsCathode-ray tube indicatorsGray levelImaging quality
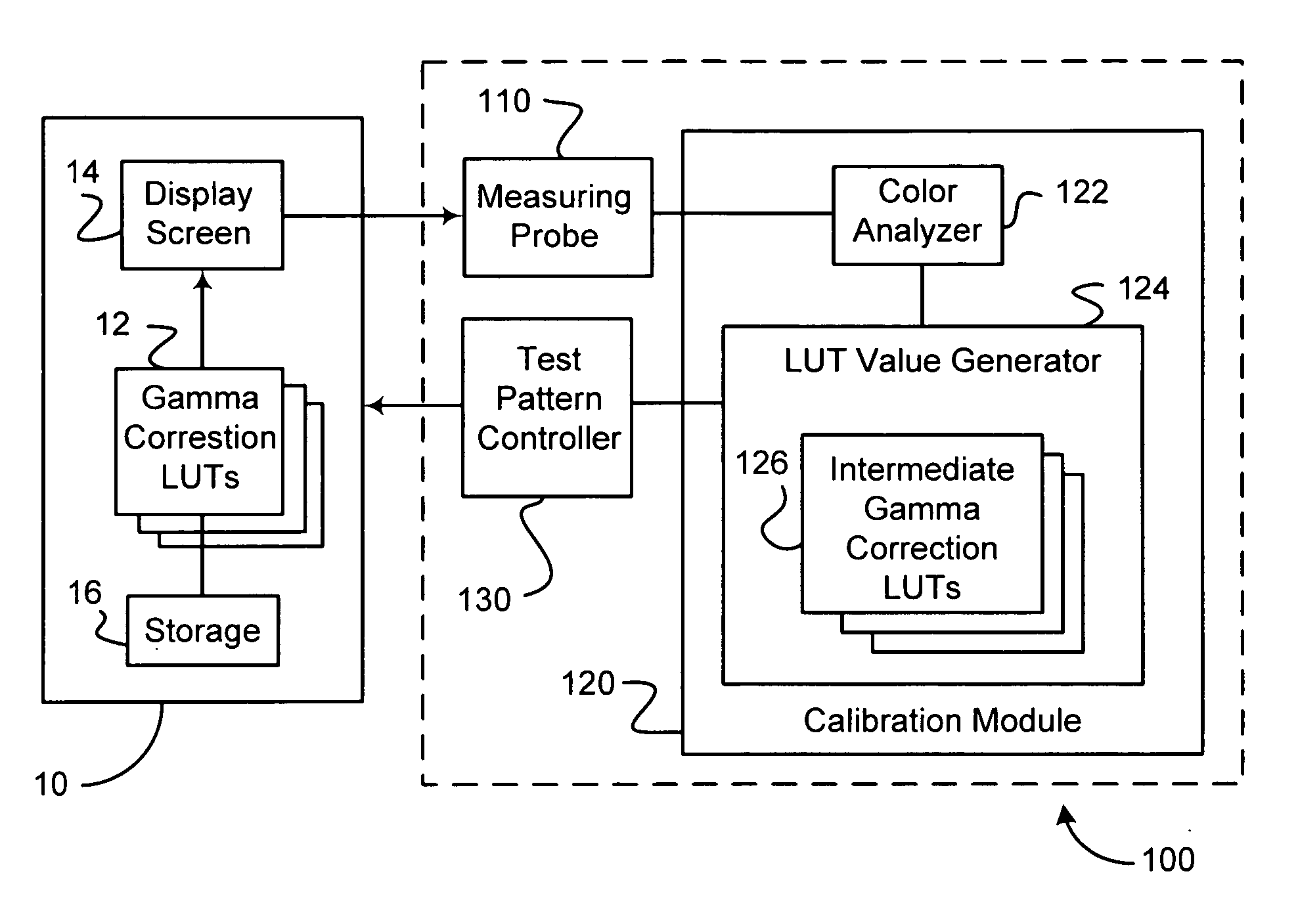
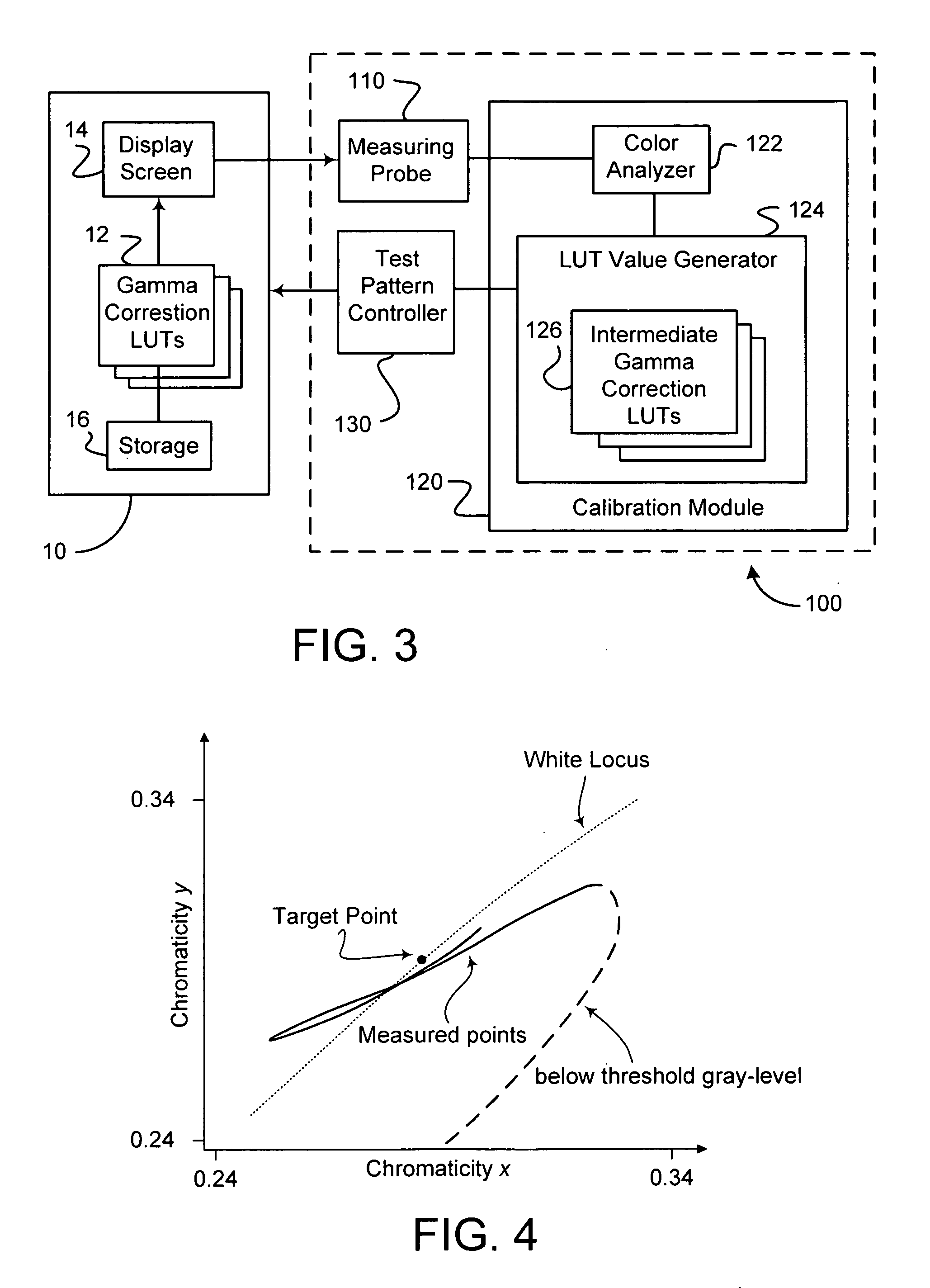
A system for calibrating a display device to improve its perceived image quality includes a calibration module that is configured to determine, for each of a plurality of white colors associated with a plurality of gray levels displayed sequentially by the display device, a measured chromaticity point on a chromaticity diagram and a measured luminance level. The calibration module calculates, for each gray level, a differential change in each primary color component that simultaneously moves the measured chromaticity point to a target chromaticity point and adjusts the measured luminance level to a target luminance level on a predetermined luminance curve having a target gamma value, and calculates correction values for each primary color component and each gray level based on the calculated differential changes. The system also includes means for outputting the calculated correction values to the display device. The display device corrects the primary color components of a color video signal based on the calculated correction values such that the display device accurately reproduces luminance and color properties of the color video signal.
Owner:CORONA
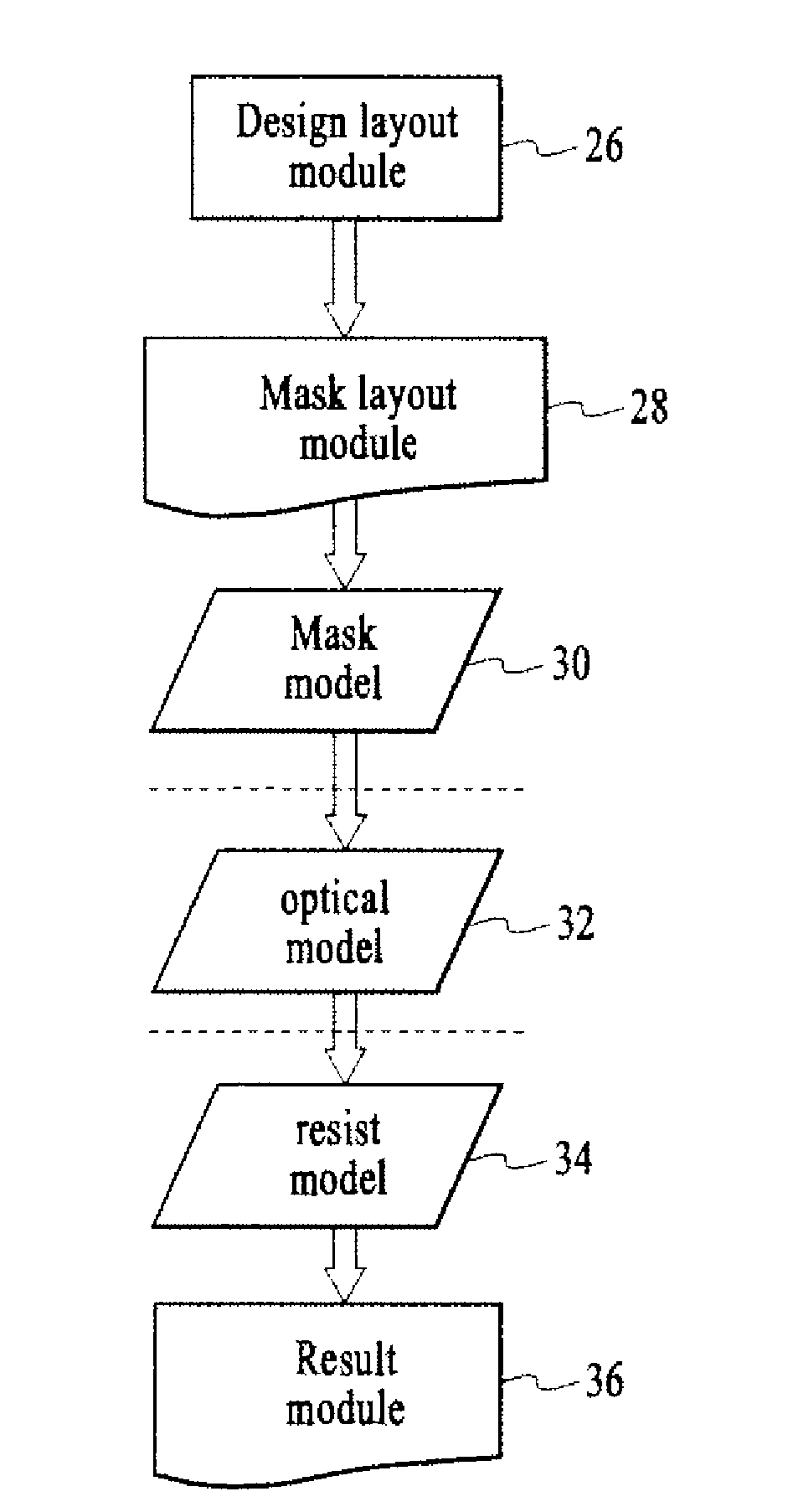
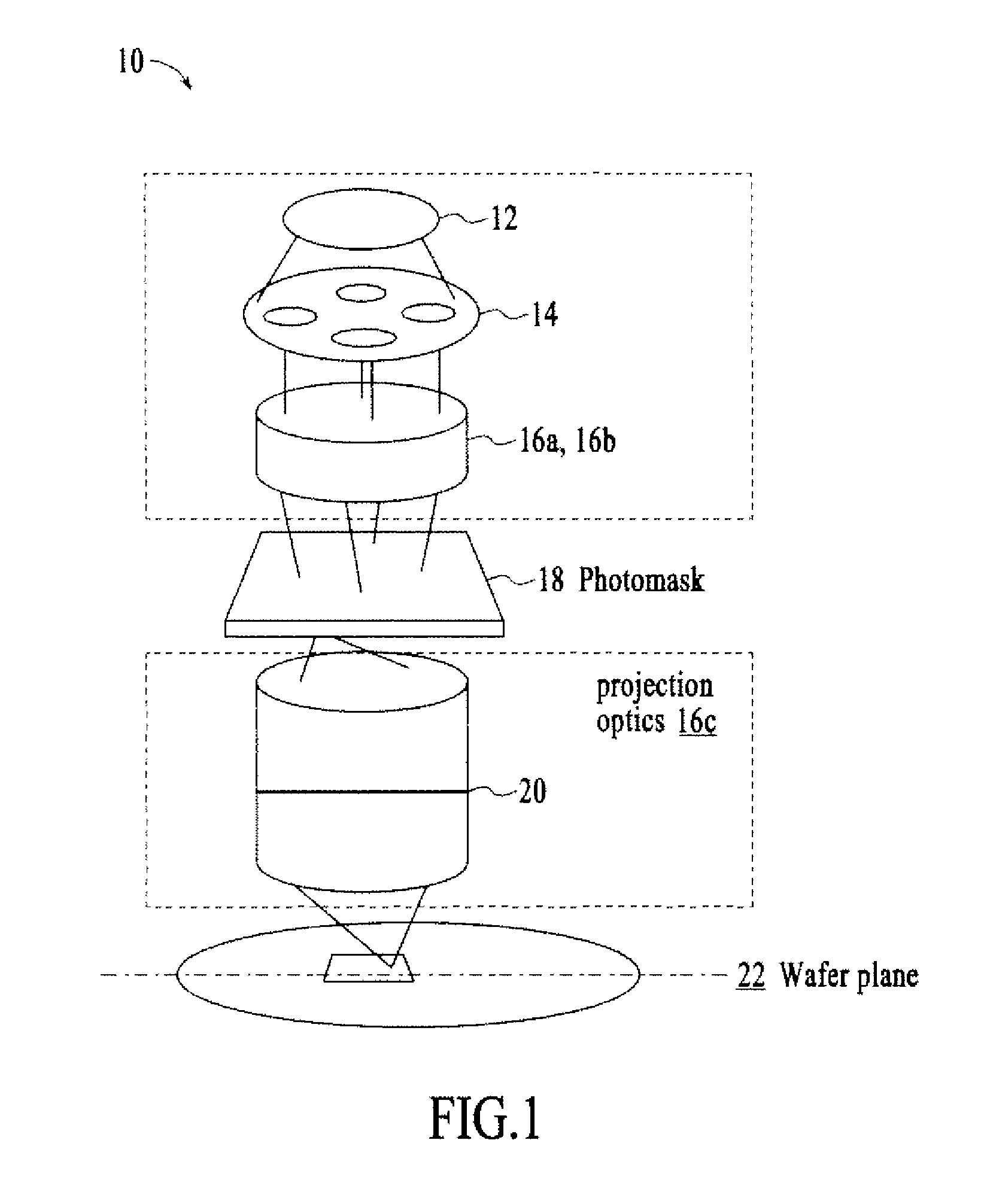
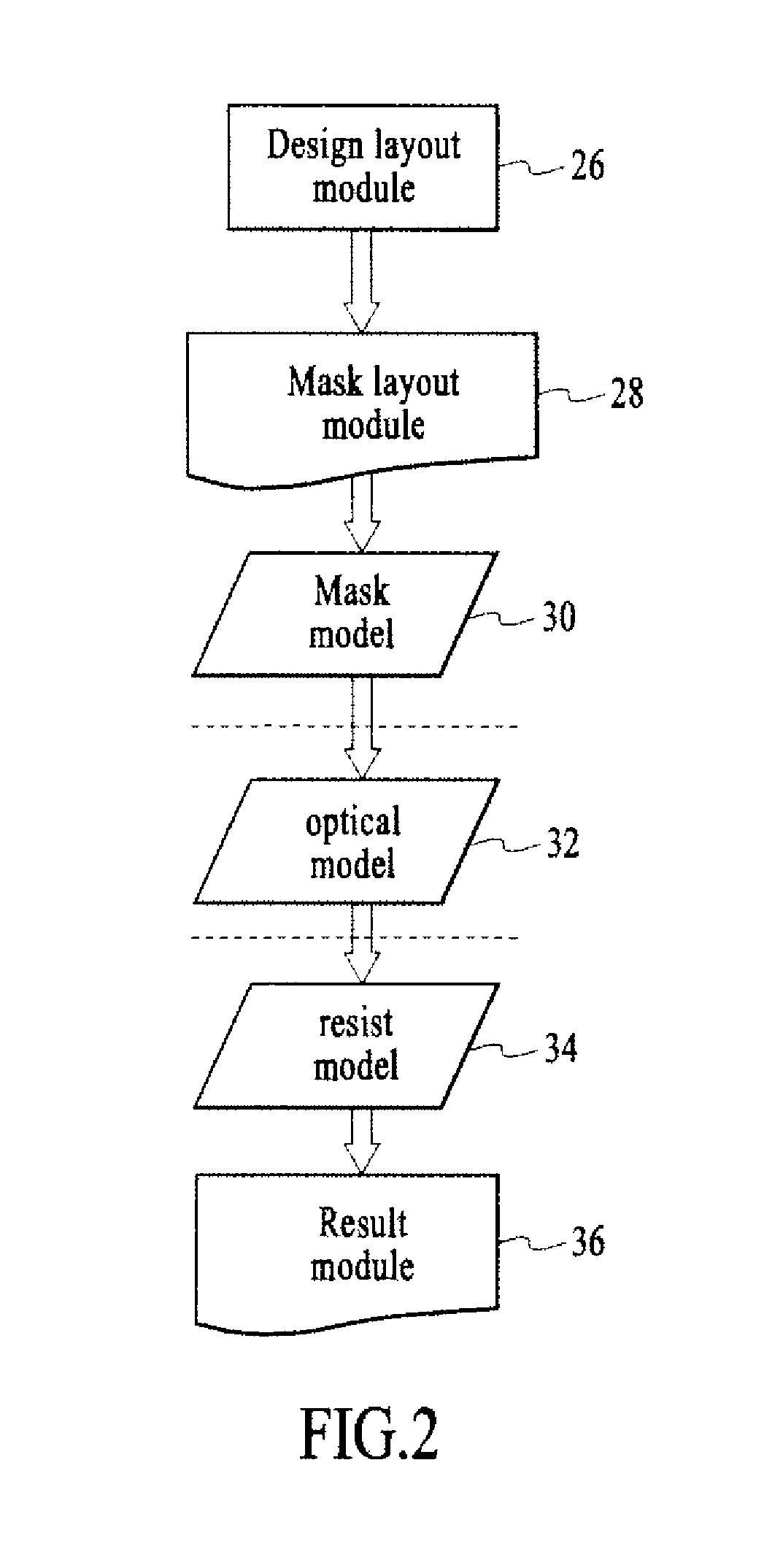
Method and system for lithography process-window-maximixing optical proximity correction
ActiveUS20100162197A1MaximizesOvercome deficienciesPhotomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentLithography processGray level
The present invention relates to an efficient OPC method of increasing imaging performance of a lithographic process utilized to image a target design having a plurality of features. The method includes the steps of determining a function for generating a simulated image, where the function accounts for process variations associated with the lithographic process; and optimizing target gray level for each evaluation point in each OPC iteration based on this function. In one given embodiment, the function is approximated as a polynomial function of focus and exposure, R(ε, f)=P0+f2·Pb with a threshold of T+Vε for contours, where P0 represents image intensity at nominal focus, f represents the defocus value relative to the nominal focus, ε represents the exposure change, V represents the scaling of exposure change, and parameter “Pb” represents second order derivative images. In another given embodiment, the analytical optimal gray level is given for best focus with the assumption that the probability distribution of focus and exposure variation is Gaussian.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
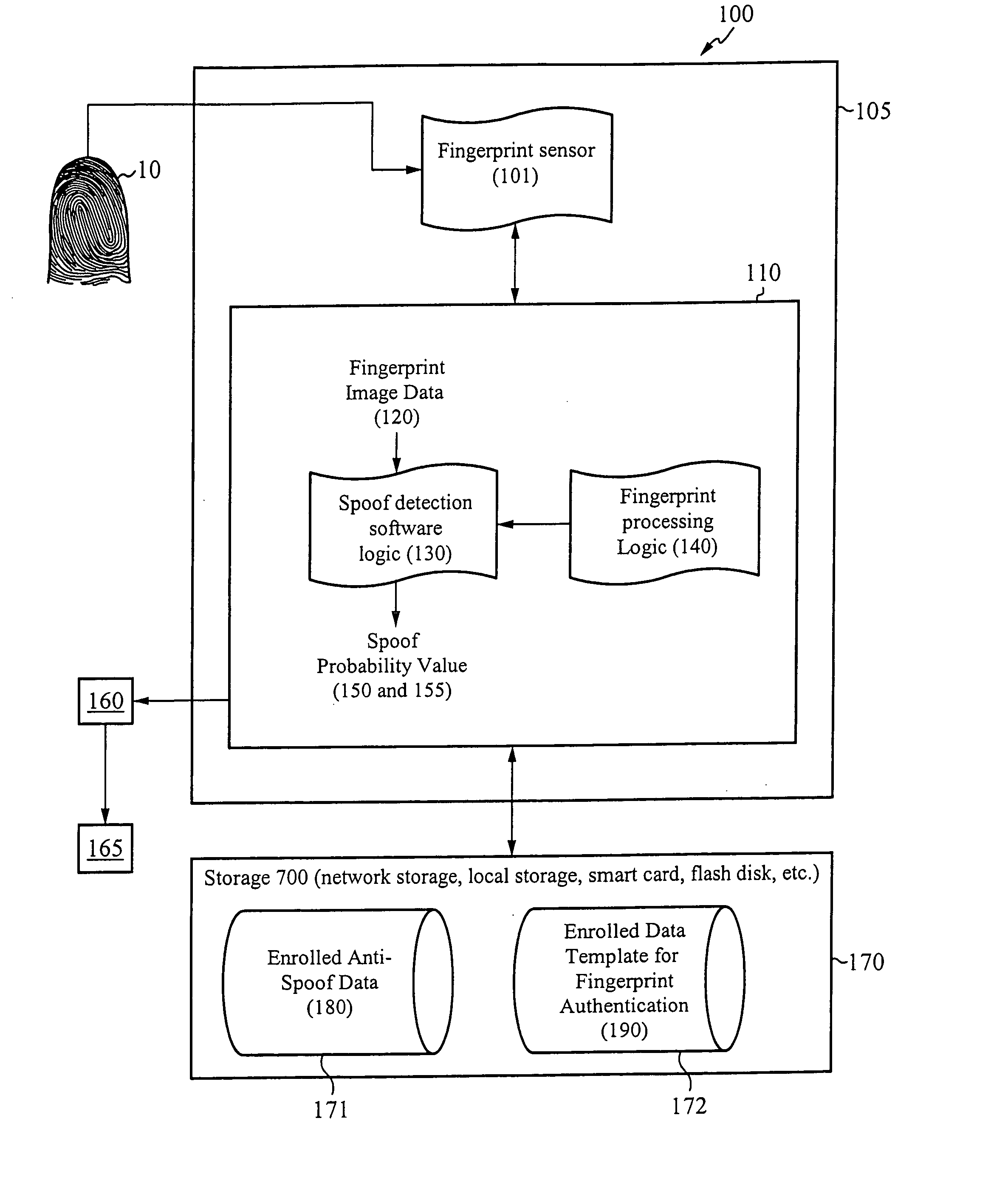
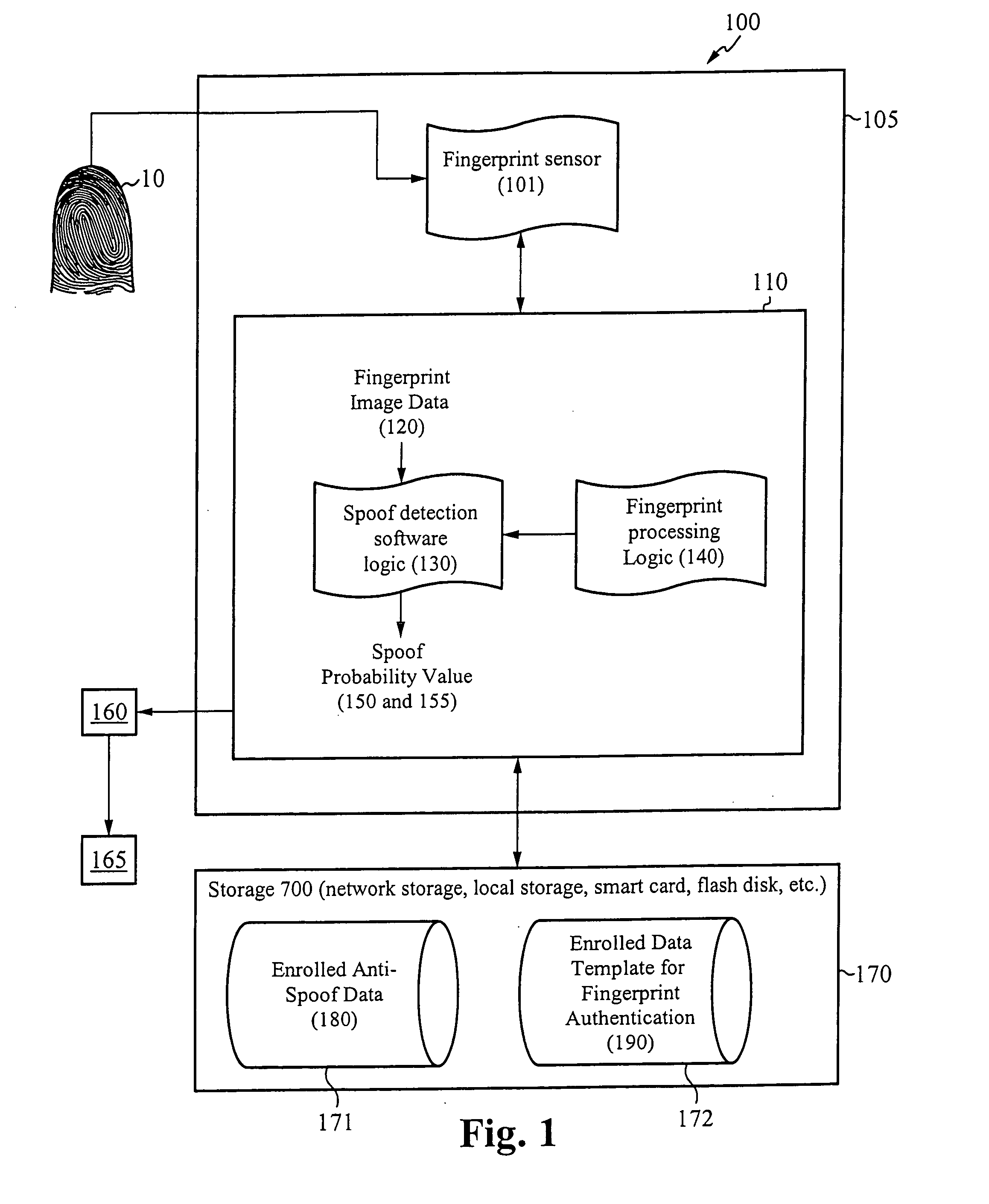
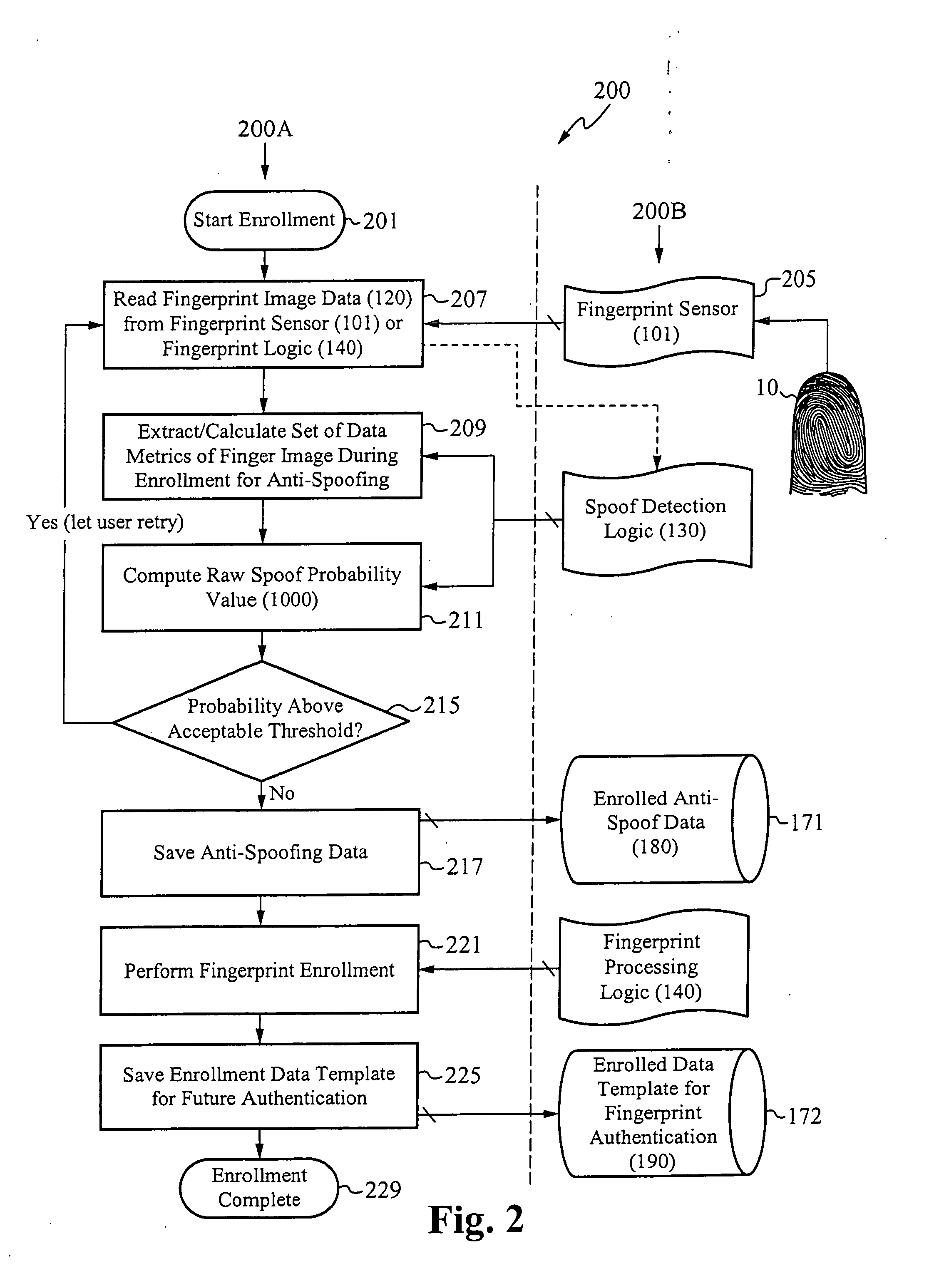
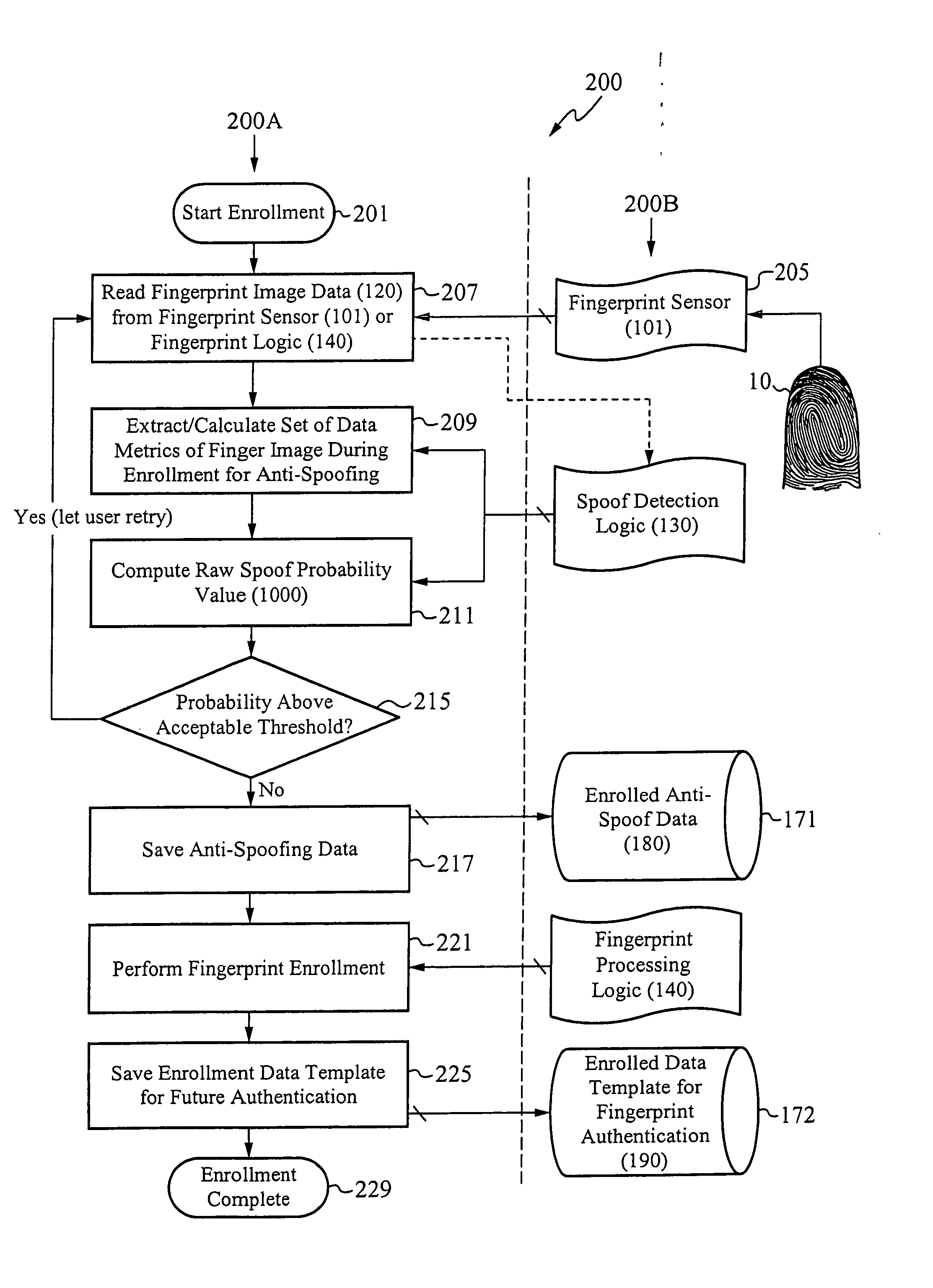
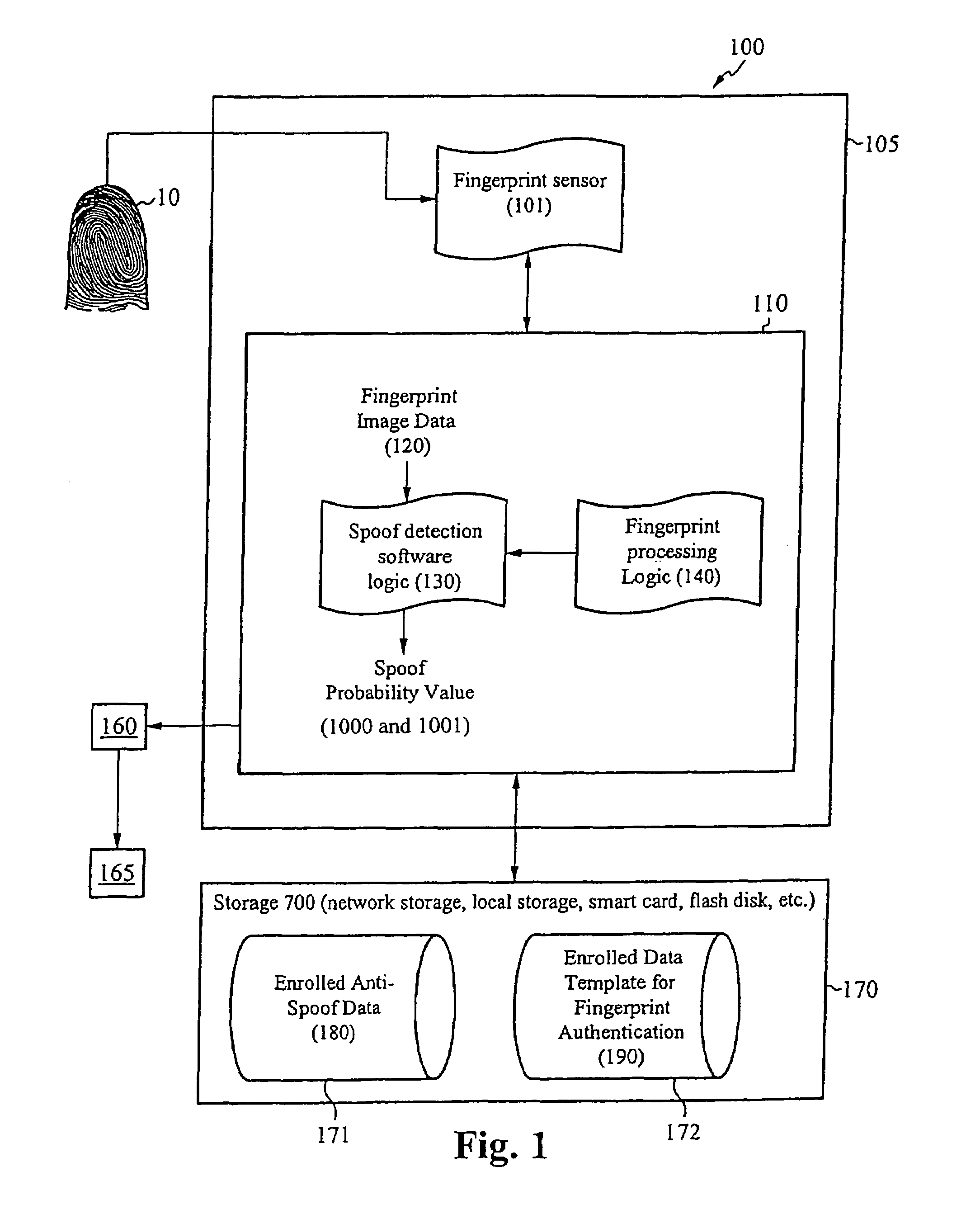
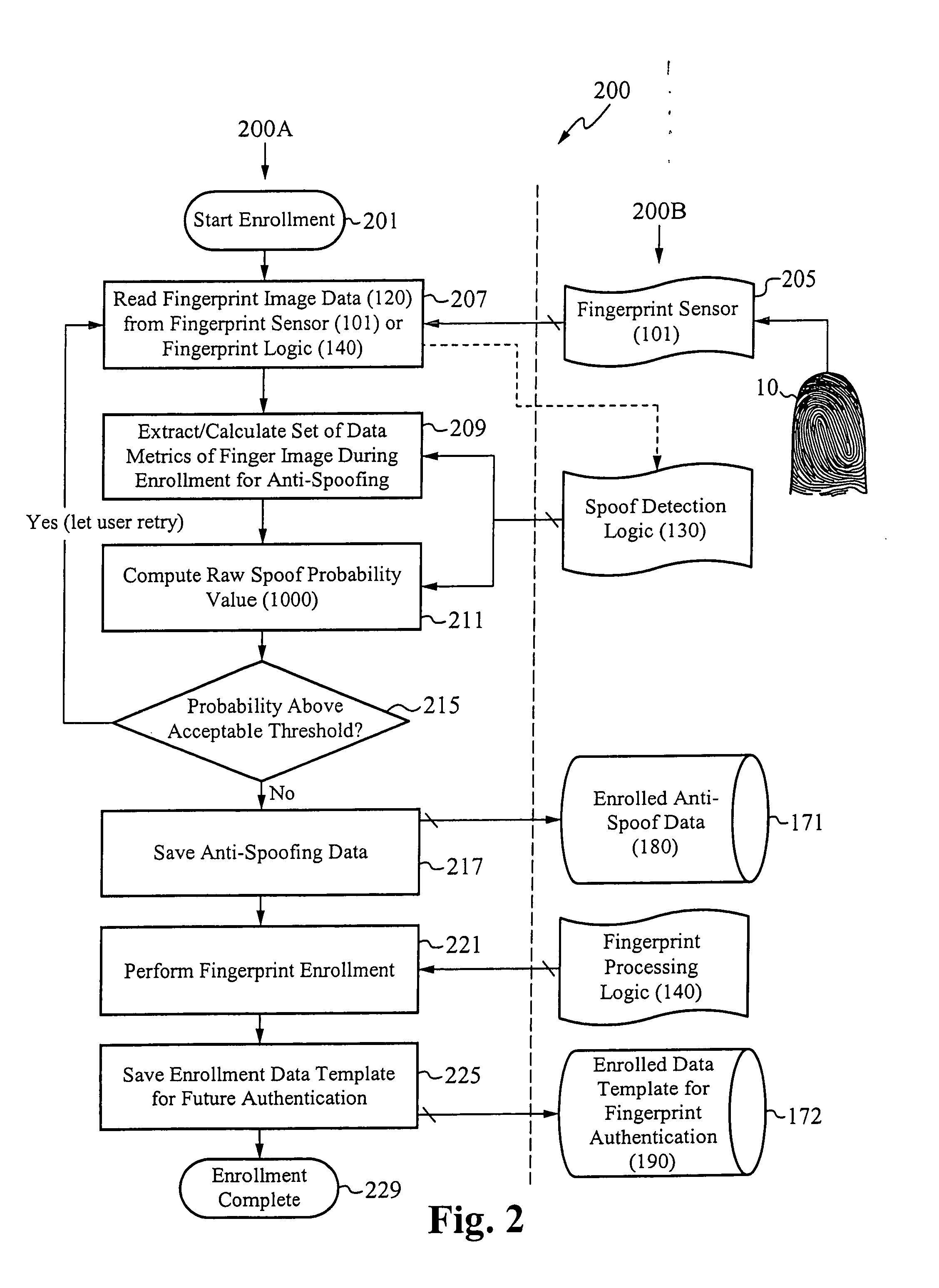
System for and method of securing fingerprint biometric systems against fake-finger spoofing
ActiveUS20070014443A1Easy to predictElectric signal transmission systemsImage analysisPattern recognitionGray level
A biometric secured system grants a user access to a host system by classifying a fingerprint used to verify or authorize the user to the system as real or fake. The classification is based on a probability that fingerprint image data corresponds to characteristics that reliably identify the finger as real. The system includes a fingerprint sensor for capturing fingerprint image data coupled to a spoof detection module. In one embodiment, the spoof detection module is programmed to determine spoof probability based on a combination of metrics that include, among other metrics, pixel gray level average and the variance of pixels corresponding to a fingerprint ridge, pixel gray level average and the variance of pixels corresponding to a fingerprint valley, density of sweat pores, and density of sweat streaks, to name a few metrics.
Owner:APPLE INC
Methods for driving electro-optic displays
An electro-optic display, having at least one pixel capable of achieving any one of at least four different gray levels including two extreme optical states, is driven by displaying a first image on the display, and rewriting the display to display a second image thereon, wherein, during the rewriting of the display, any pixel which has undergone a number of transitions exceeding a predetermined value without touching an extreme optical state, is driven to at least one extreme optical state before driving that pixel to its final optical state in the second image.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
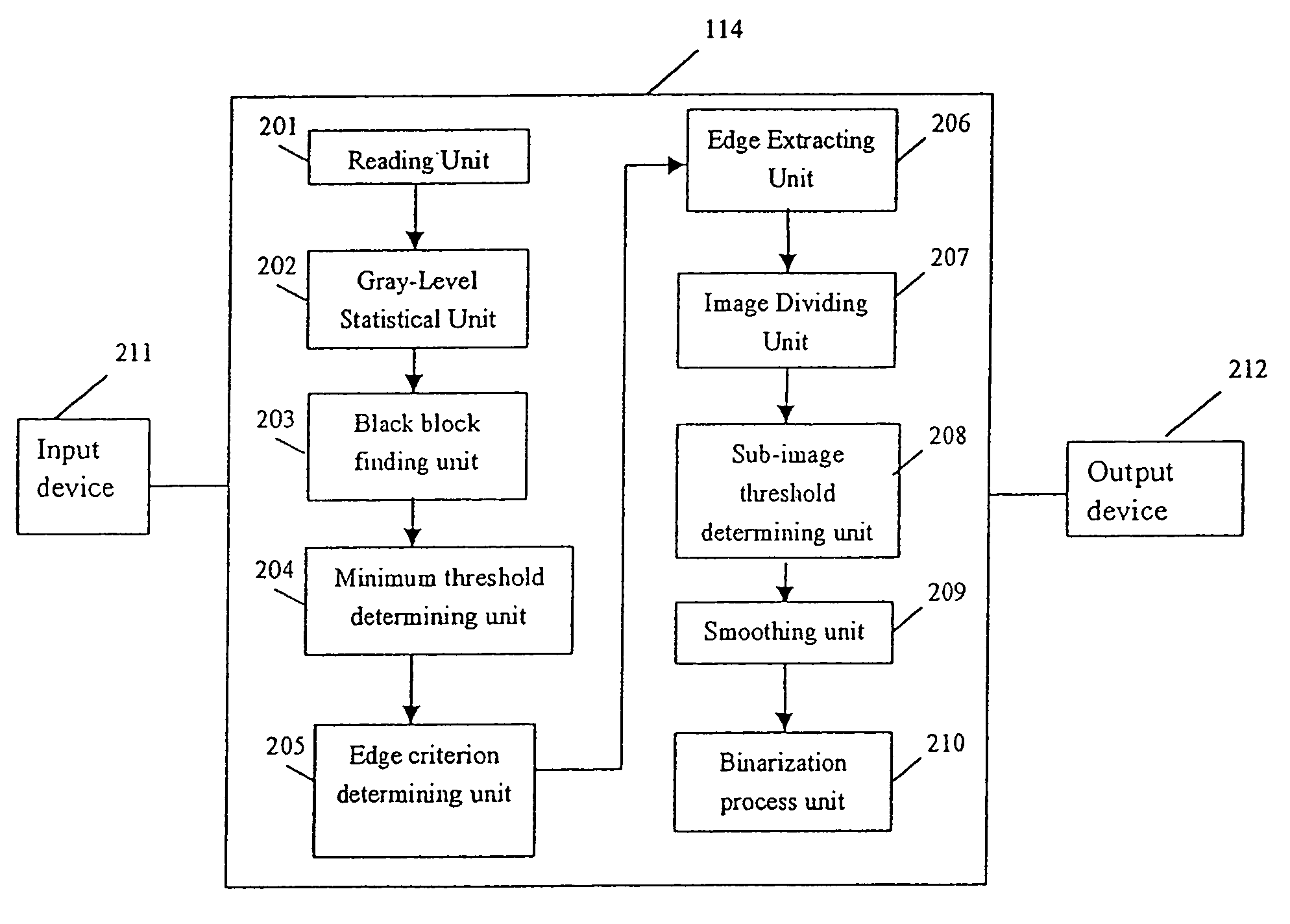
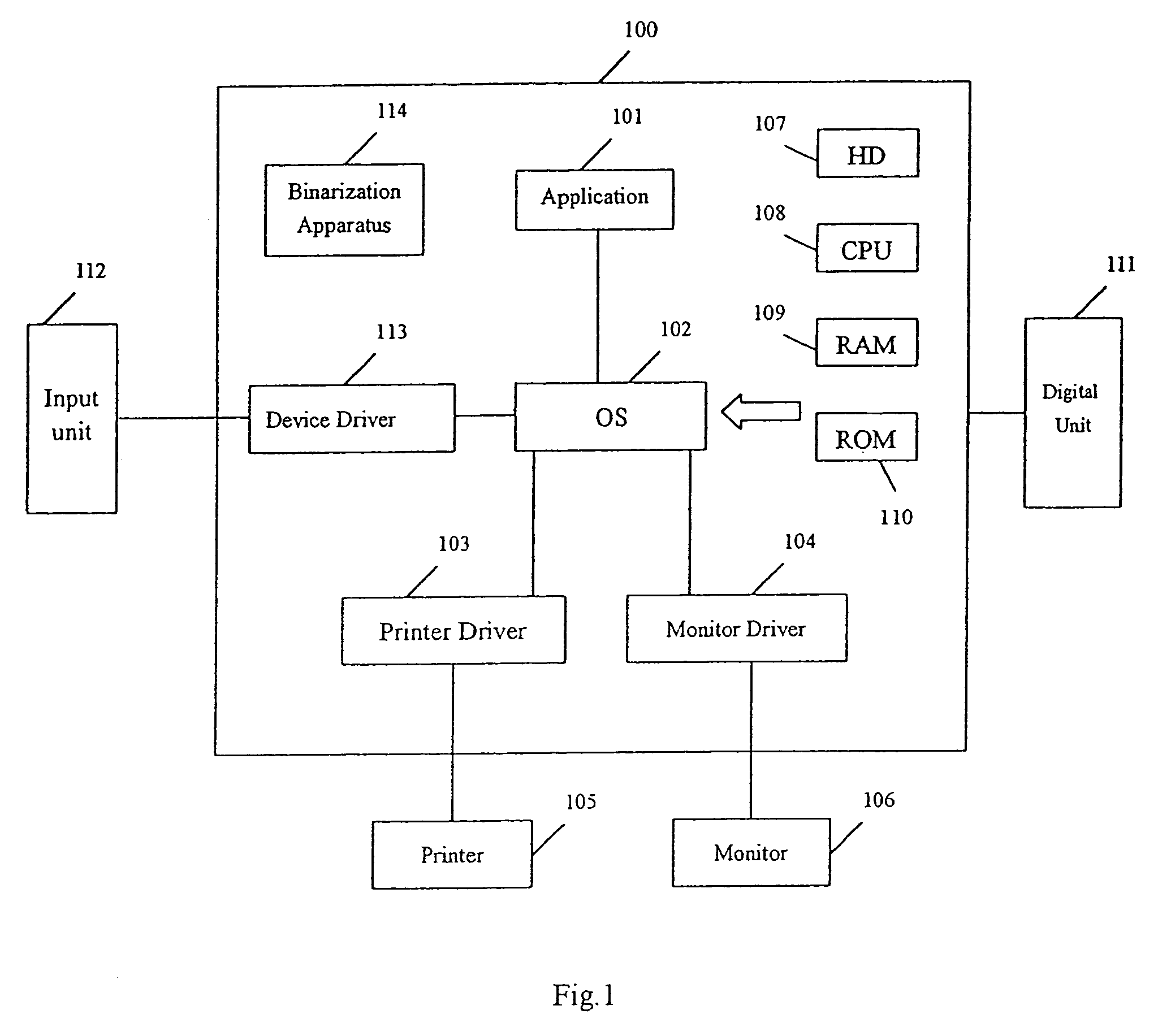
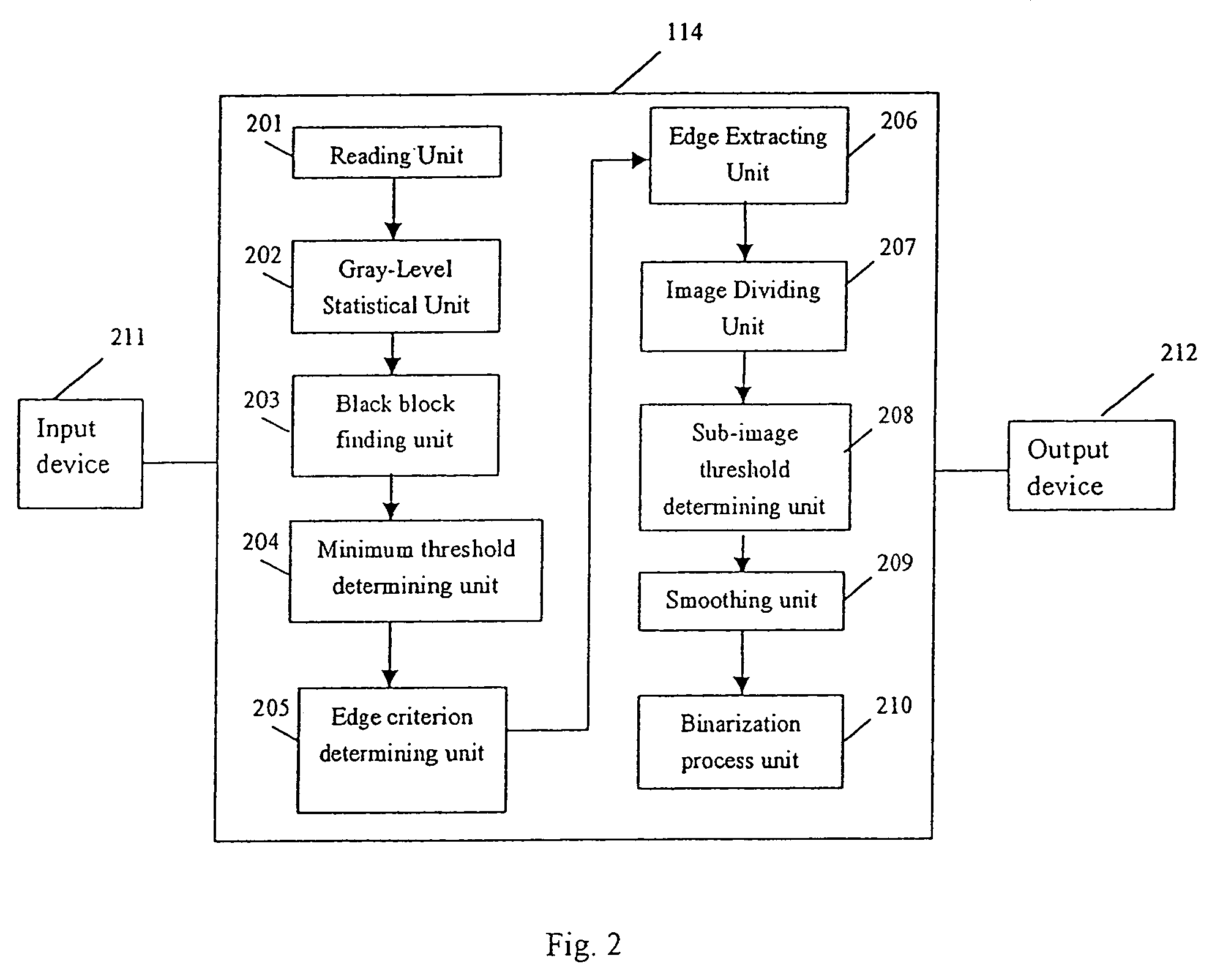
Image processing method and apparatus using self-adaptive binarization
ActiveUS7062099B2Fast and effective binarization processImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging processing
The present invention provides a unique method, apparatus, system and storage medium for image binarization process, wherein an image to be processed is divided into a plurality of sub-images and an binarization threshold for each of the sub-images is determined based on the gray-levels of the edge pixels detected in respective sub-image. The image processing method of the present invention comprises: calculating a gray-level statistical distribution of pixels of an image, detecting edge pixels in an image based on an edge criterion corresponding to the gray-level statistical distribution, dividing the image into a plurality of sub-images; determining a binarization threshold for each of the sub-images based on the gray-levels of edge pixels detected in the sub-image; and performing binarization process for each of the sub-images based on the binarization threshold of the sub-image.
Owner:CANON KK
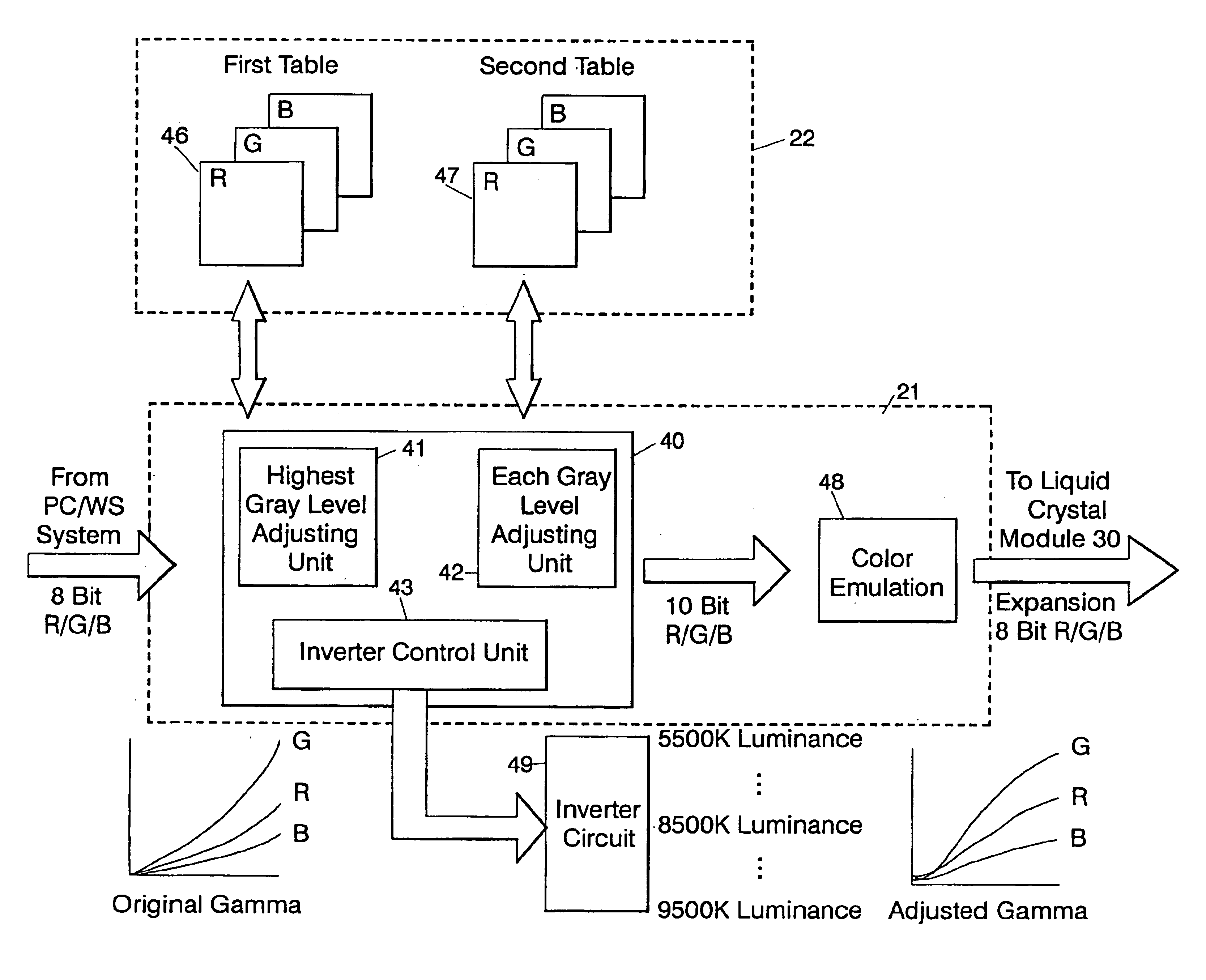
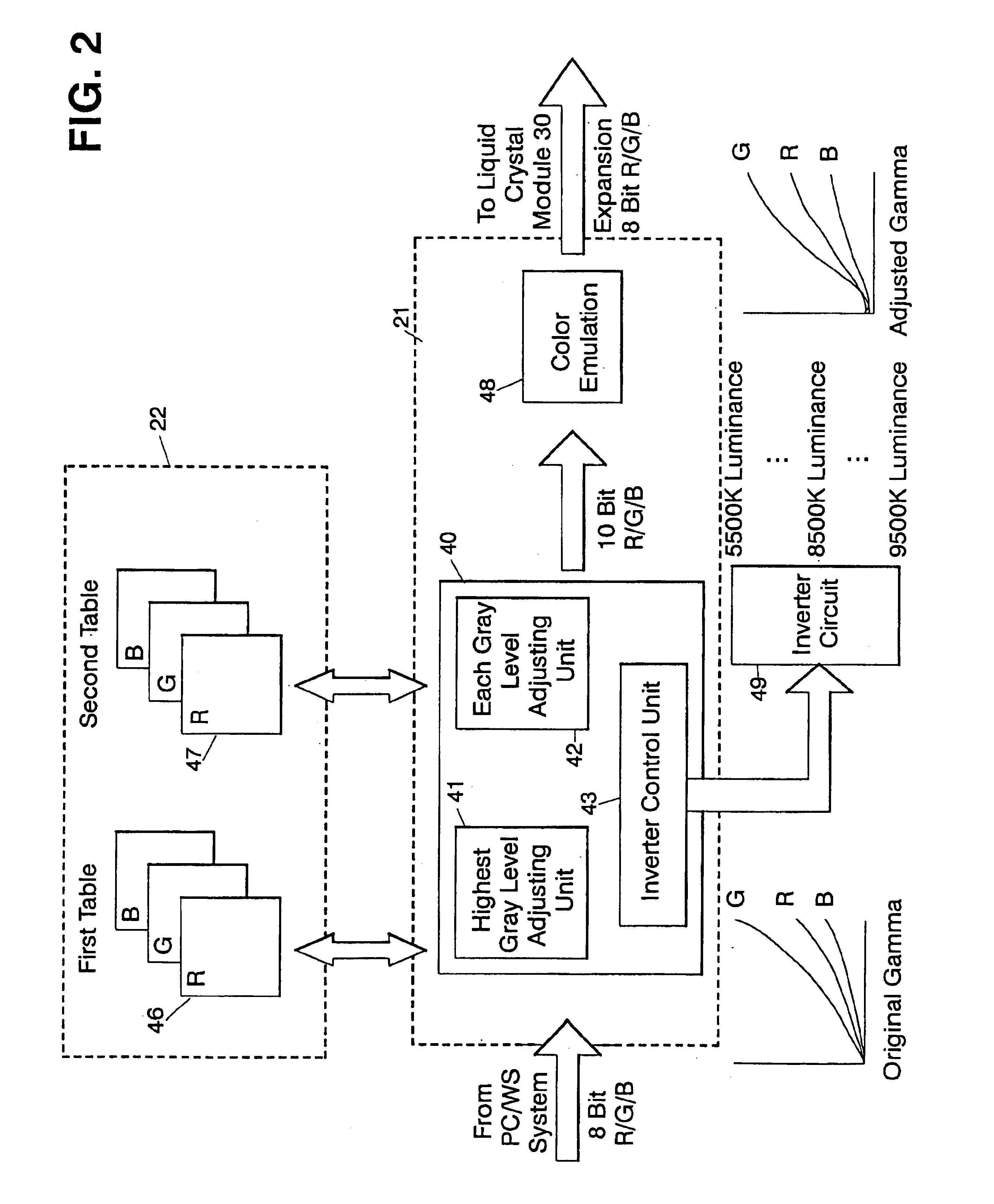
White point adjusting method, color image processing method, white point adjusting apparatus and liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS6862012B1Highly accurate convergenceImprove accuracyColor signal processing circuitsCathode-ray tube indicatorsLiquid-crystal displayComputer graphics (images)
A white point adjusting apparatus is provided to adjust an achromatic color level for an input video signal including a plurality of color signals, and display an adjusted image on a liquid crystal module. This adjusting apparatus comprises: a first table for setting a white point by deciding an offset quantity of at least one color signal from a highest gray level for each color temperature; a second table for setting an offset quantity of the color signal to converge a halftone white point for each color temperature set by the first table; and a white point adjusting unit for adding the offset quantities set by the first and second tables and to the input video signal.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
System for and method of securing fingerprint biometric systems against fake-finger spoofing
ActiveUS7505613B2Easy to predictElectric signal transmission systemsImage analysisPattern recognitionGray level
A biometric secured system grants a user access to a host system by classifying a fingerprint used to verify or authorize the user to the system as real or fake. The classification is based on a probability that fingerprint image data corresponds to characteristics that reliably identify the finger as real. The system includes a fingerprint sensor for capturing fingerprint image data coupled to a spoof detection module. In one embodiment, the spoof detection module is programmed to determine spoof probability based on a combination of metrics that include, among other metrics, pixel gray level average and the variance of pixels corresponding to a fingerprint ridge, pixel gray level average and the variance of pixels corresponding to a fingerprint valley, density of sweat pores, and density of sweat streaks, to name a few metrics.
Owner:APPLE INC
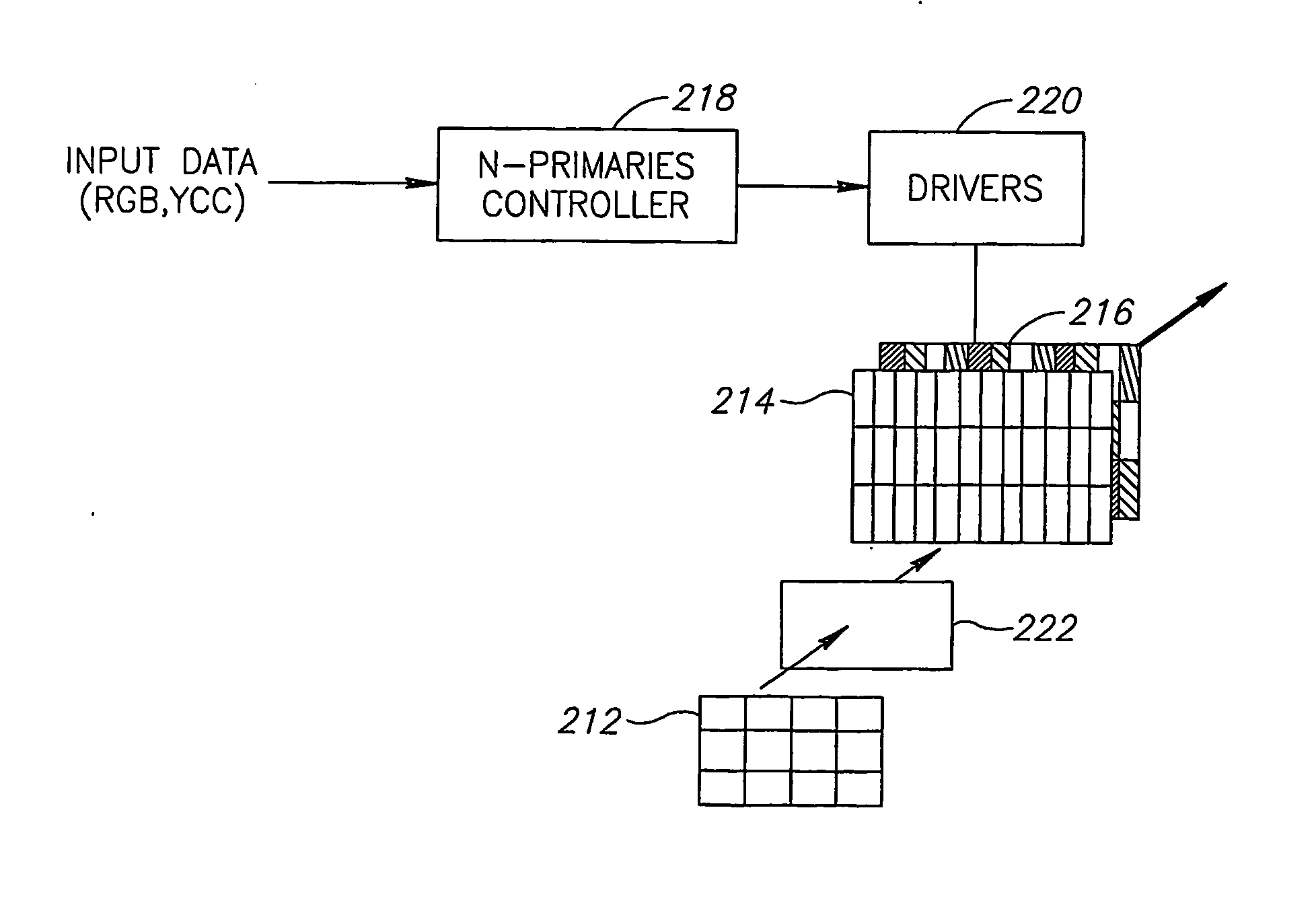
Multi-primary display with spectrally adapted back-illumination
ActiveUS20070001994A1Addressing Insufficient CoverageMaximizing brightness levelColor signal processing circuitsOpticsColor imageUltrasound attenuation
Some embodiments of the invention provide a device, system and method for displaying a color image. According to some exemplary embodiments of the invention a device for displaying a color image may include an illumination source including a plurality of light-producing elements able to produce light of each of m different wavelength spectra, wherein m is equal to or greater than three. The device may also include an array of attenuating elements able to spatially selectively attenuate the light produced by the illumination source according to an attenuation pattern corresponding to a gray-level representation of the color image, and an array of color sub-pixel filter elements able to receive selectively attenuated light from the array of attenuating elements, each sub-pixel filter element able to transmit light of one of n different primary colors, wherein n is equal to or greater than four.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
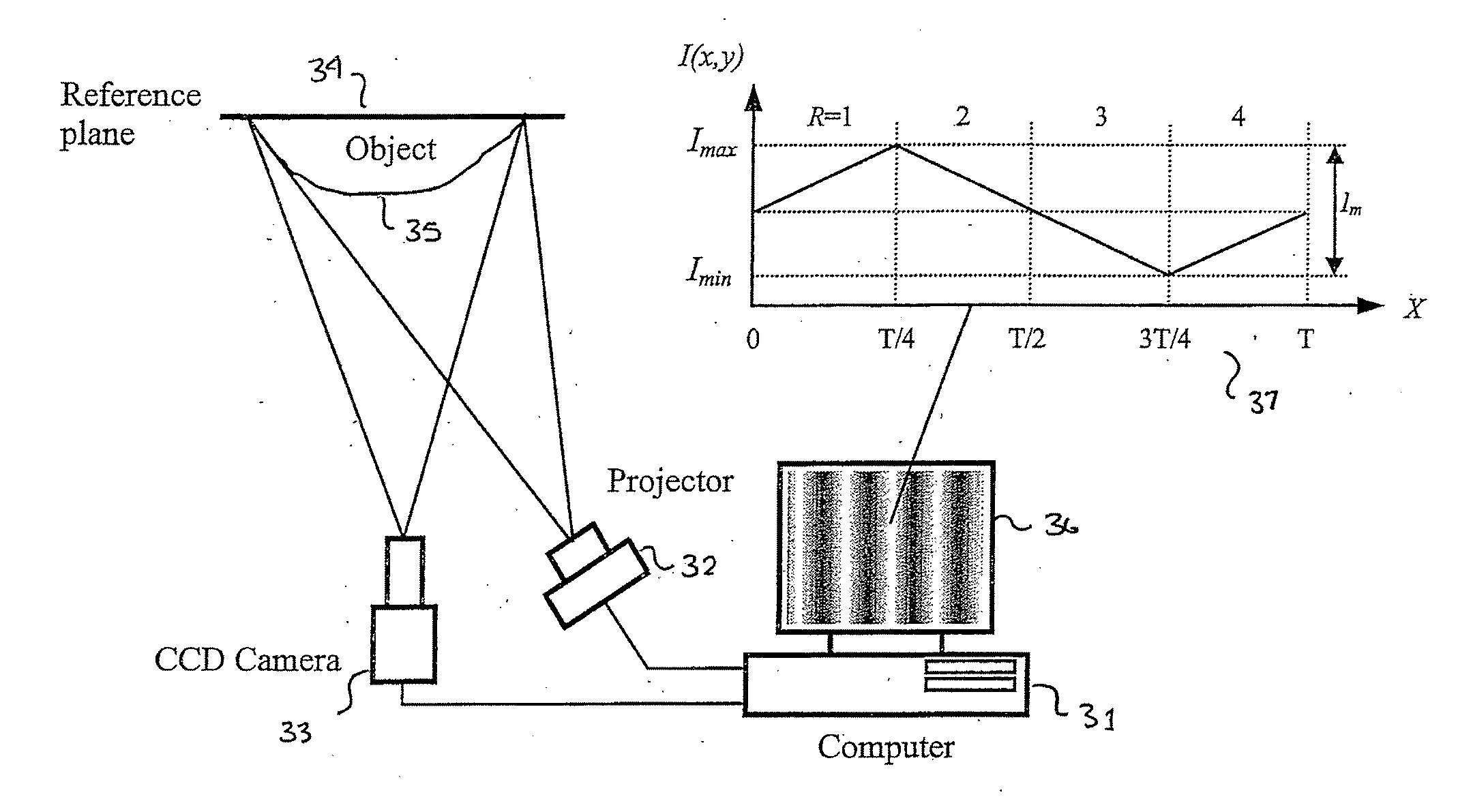
Full-field three-dimensional measurement method
InactiveUS20070206204A1Improve processing speedSimple calculationUsing optical meansTriangulationFull field
A method and system for full-field fringe-projection for 3-D surface-geometry measurement, referred to as “triangular-pattern phase-shifting” is disclosed. A triangular grey-scale-level-coded fringe pattern is computer generated, projected along a first direction onto an object or scene surface and distorted according to the surface geometry. The 3-D coordinates of points on the surface are calculated by triangulation from distorted triangular fringe-pattern images acquired by a CCD camera along a second direction and a triangular-shape intensity-ratio distribution is obtained from calculation of the captured distorted triangular fringe-pattern images. Removal of the triangular shape of the intensity ratio over each pattern pitch generates a wrapped intensity-ratio distribution obtained by removing the discontinuity of the wrapped image with a modified unwrapping method. Intensity ratio-to-height conversion is used to reconstruct the 3-D surface coordinates of the object. Intensity-ratio error compensation involves estimating intensity-ratio error in a simulation of the measurement process with both real and ideal captured triangular-pattern images obtained from real and ideal gamma non-linearity functions. A look-up table relating the measure intensity-ratio to the corresponding intensity-ratio error is constructed and used for intensity-ratio error compensation. The inventive system is based on two-step phase-shifting but can be extended for multiple-step phase-shifting.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO
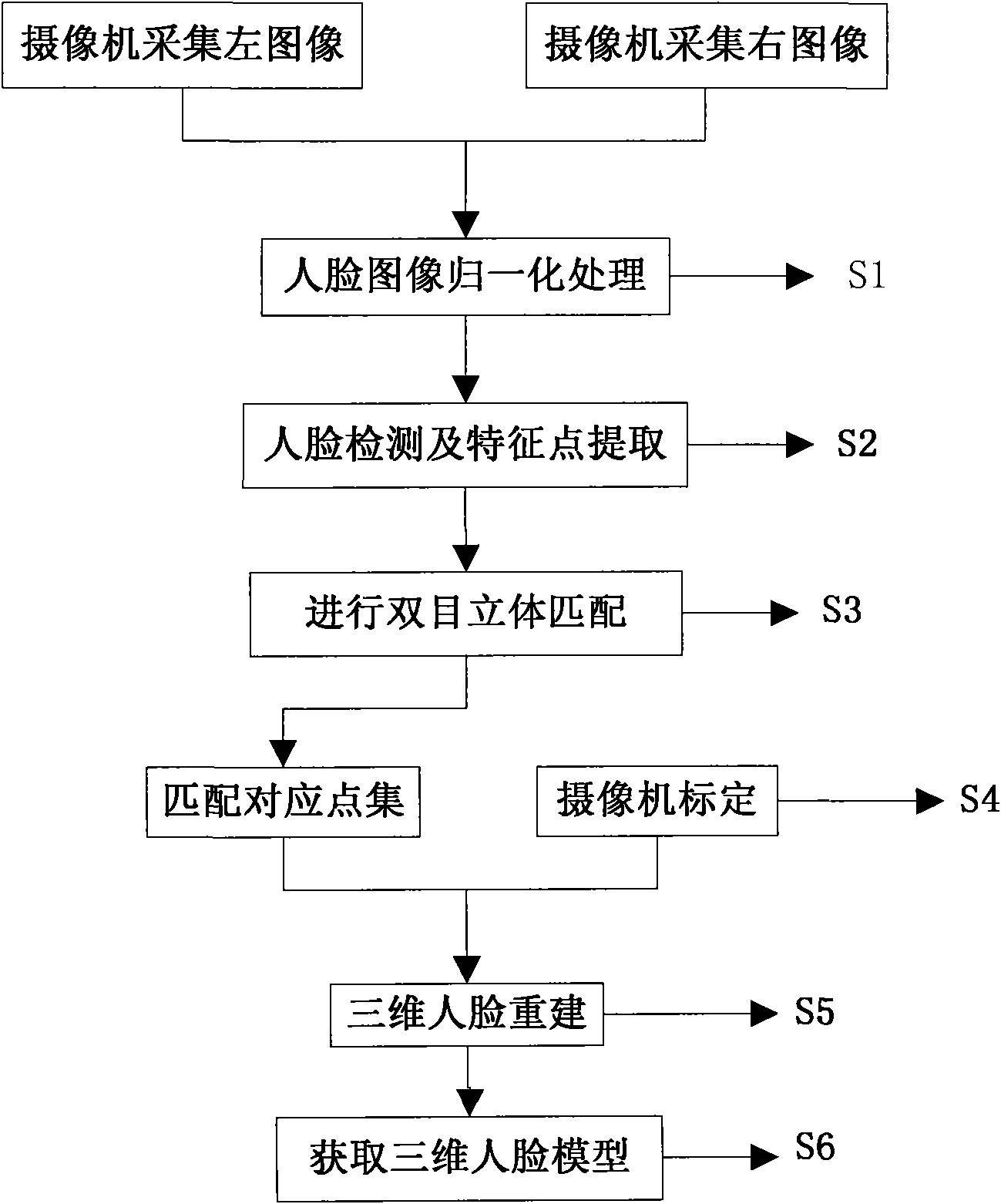
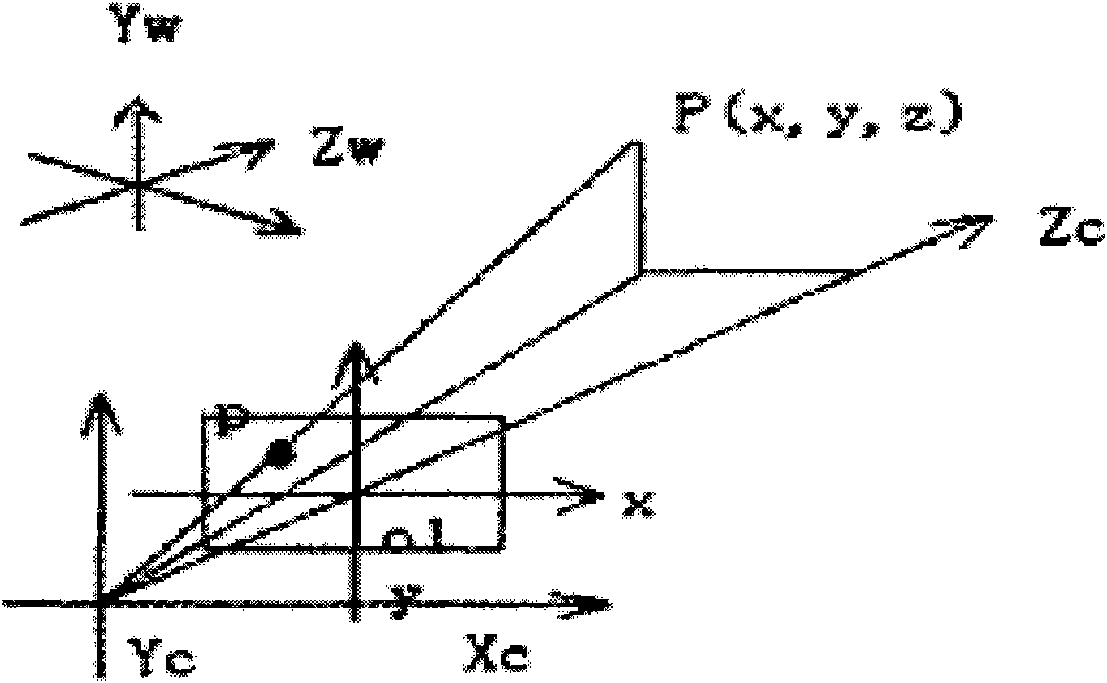
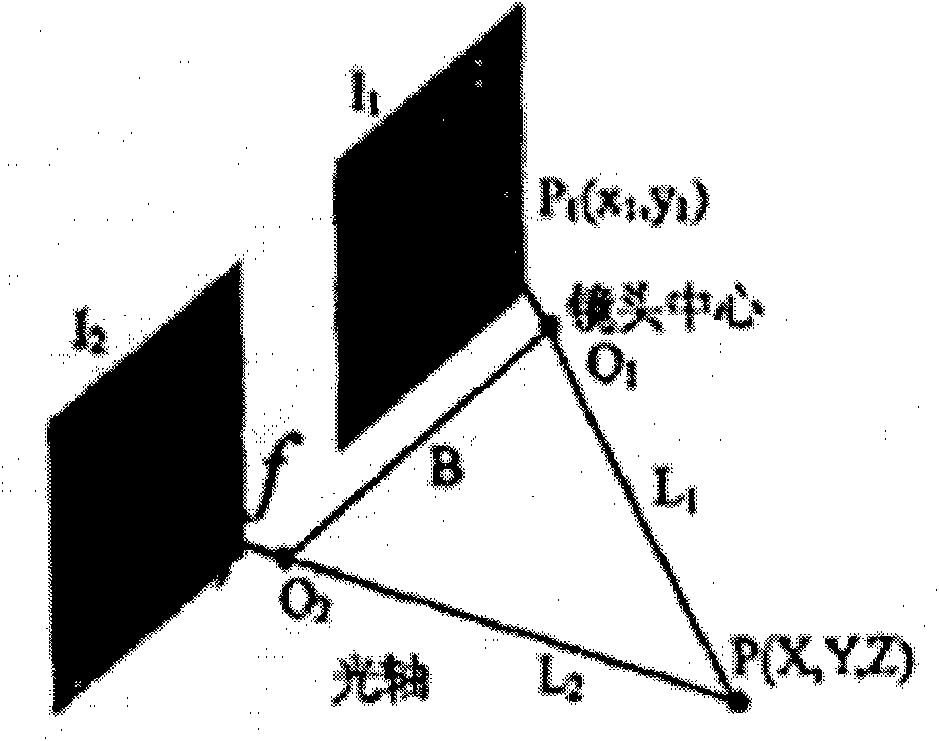
Binocular stereo vision based intelligent three-dimensional human face rebuilding method and system
The invention discloses a binocular stereo vision based intelligent three-dimensional human face rebuilding method and a system; the method comprises: preprocessing operations including image normalization, brightness normalization and image correction are carried out to a human face image; a human face area in the human face image which is preprocessed is obtained and human face characteristic points are extracted; the object is rebuilt by projection matrix, so as to obtain internal and external parameters of a vidicon; based on the human face characteristic points, gray level cross-correlation matching operators are expanded to color information, and a parallax image generated by stereo matching is calculated according to information including polar line restraining, human face area restraining and human face geometric conditions; a three-dimensional coordinate of a human face spatial hashing point cloud is calculated according to the vidicon calibration result and the parallax image generated by stereo matching, so as to generate a three-dimensional human face model. By adopting the steps, more smooth and vivid three-dimensional human face model is rebuilt in the invention.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
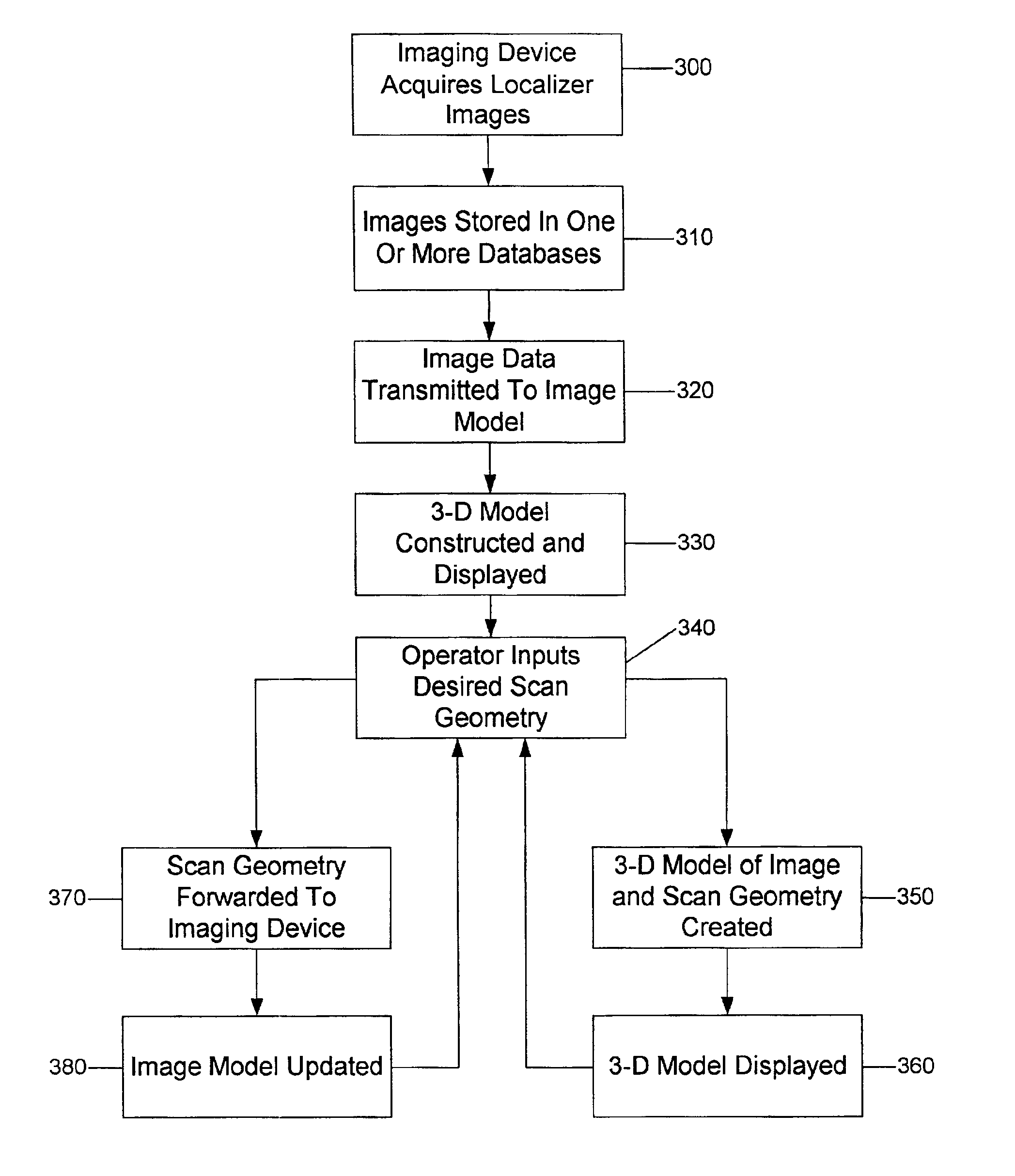
Systems, methods and computer program products for the display and visually driven definition of tomographic image planes in three-dimensional space
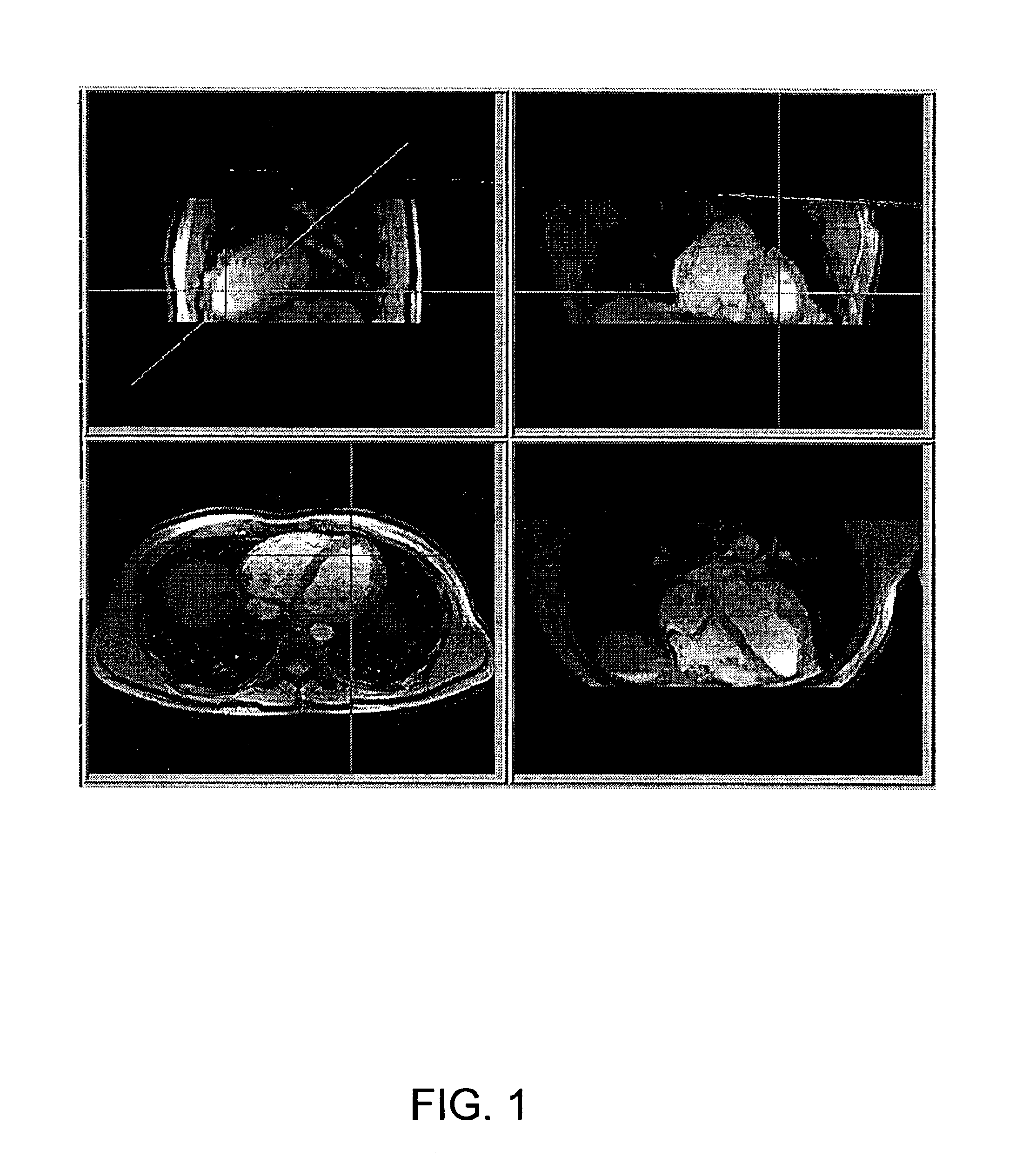
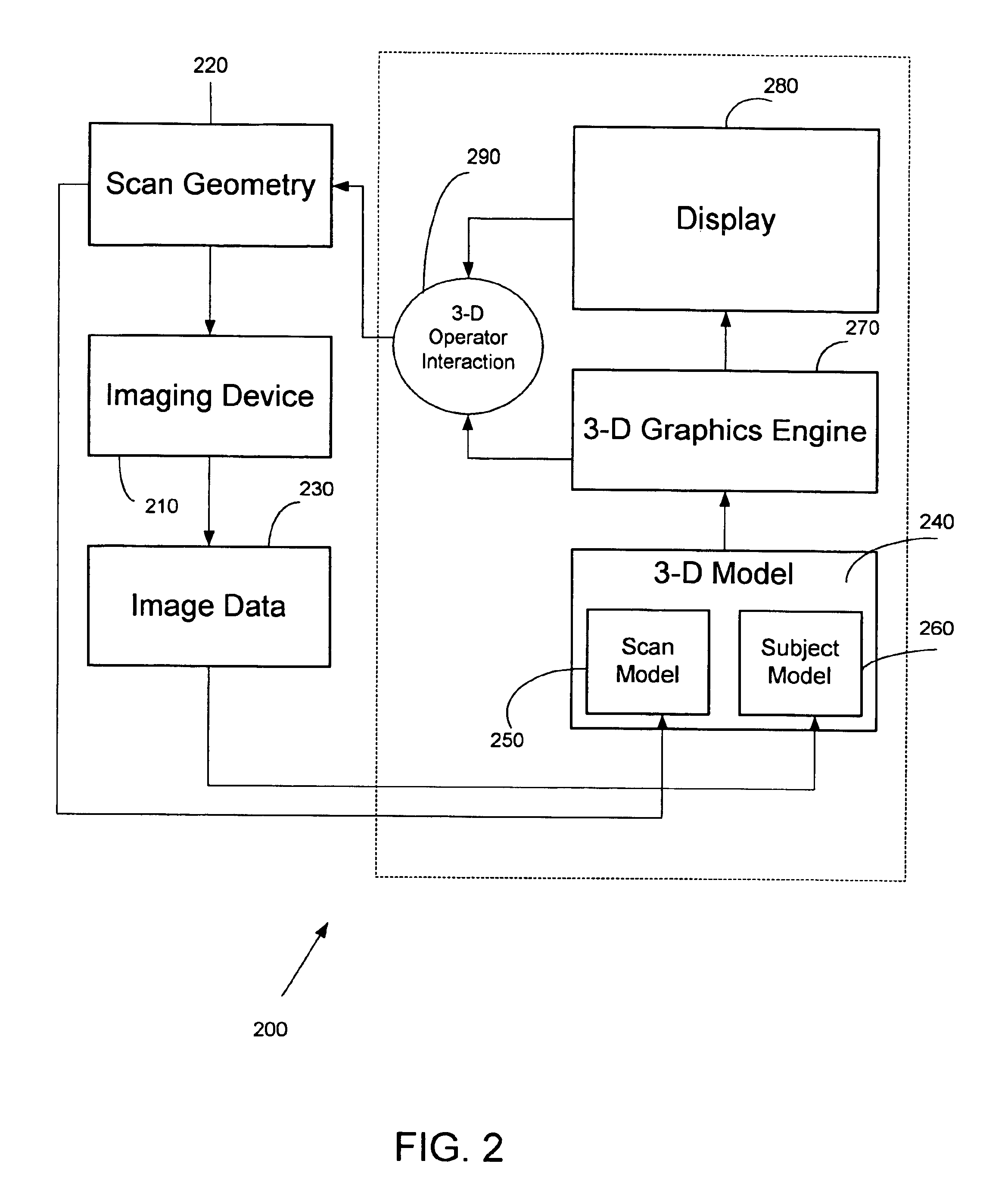
InactiveUS6898302B1Easy and more comprehensive understandingEasy to detectCharacter and pattern recognitionImage generationDisplay deviceData acquisition
Apparatuses, methods and computer program products for scan plane geometry definition in tomographic data acquisition via an interactive three-dimensional (3-D) graphical operator interface. The apparatuses, methods and computer program products are initially proposed for use in cardiac MRI, but have a much broader area of application. The apparatuses and methods utilize 3-D computer graphics aspect views of slice planes to show a new scan, represented as semi-transparent uniformly-colored planes. Intersections of these planes with opaque texture-mapped gray-level views of previously acquired images enable the orientation of a new scan to be viewed in a much more intuitive fashion. Advantageously, the apparatuses and methods of the present invention provide for more efficient elimination of positional ambiguity that is often associated with conventional 2-D intersection line views. In addition, any misregistration between localizer scans can be detected immediately in the integrated 3-D display by misalignment of anatomy in the previously acquires image planes.
Owner:UNIV EMORY
Embedding hidden auxiliary code signals in media
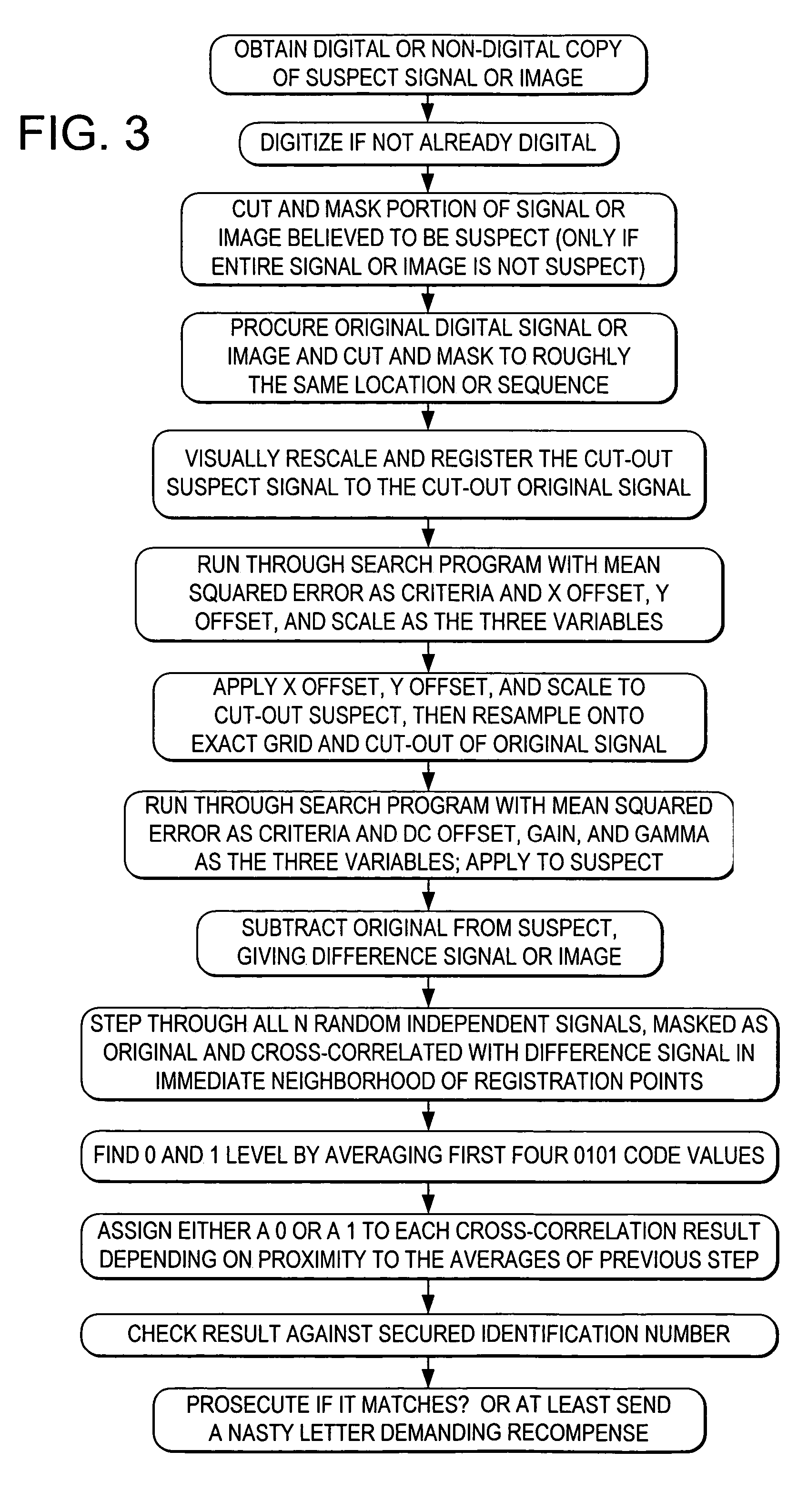
InactiveUS7003132B2Better pinpointEfficient and reliableTelevision system detailsRecord information storageGray levelImage signal
Methods for embedding and reading auxiliary messages from image signals use embedded code signals modulated with the auxiliary message. These embedded ode signals may be used to convey hidden tracking codes in images, video and printed objects. The embedded code signals are embedded by varying characteristics of the image signal, including, for example, gray-level, reflective properties, photo-reactive properties, etc.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com