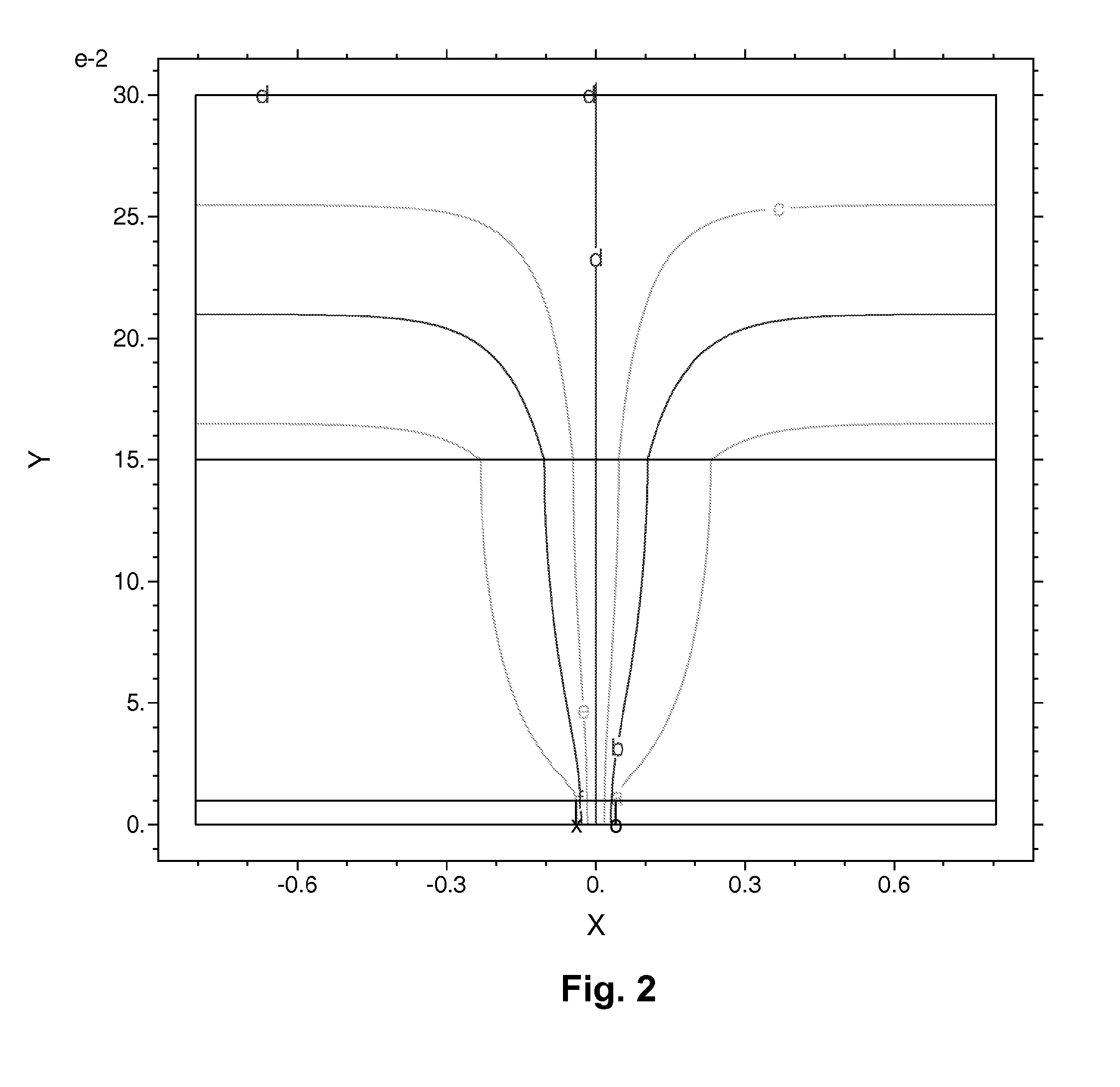
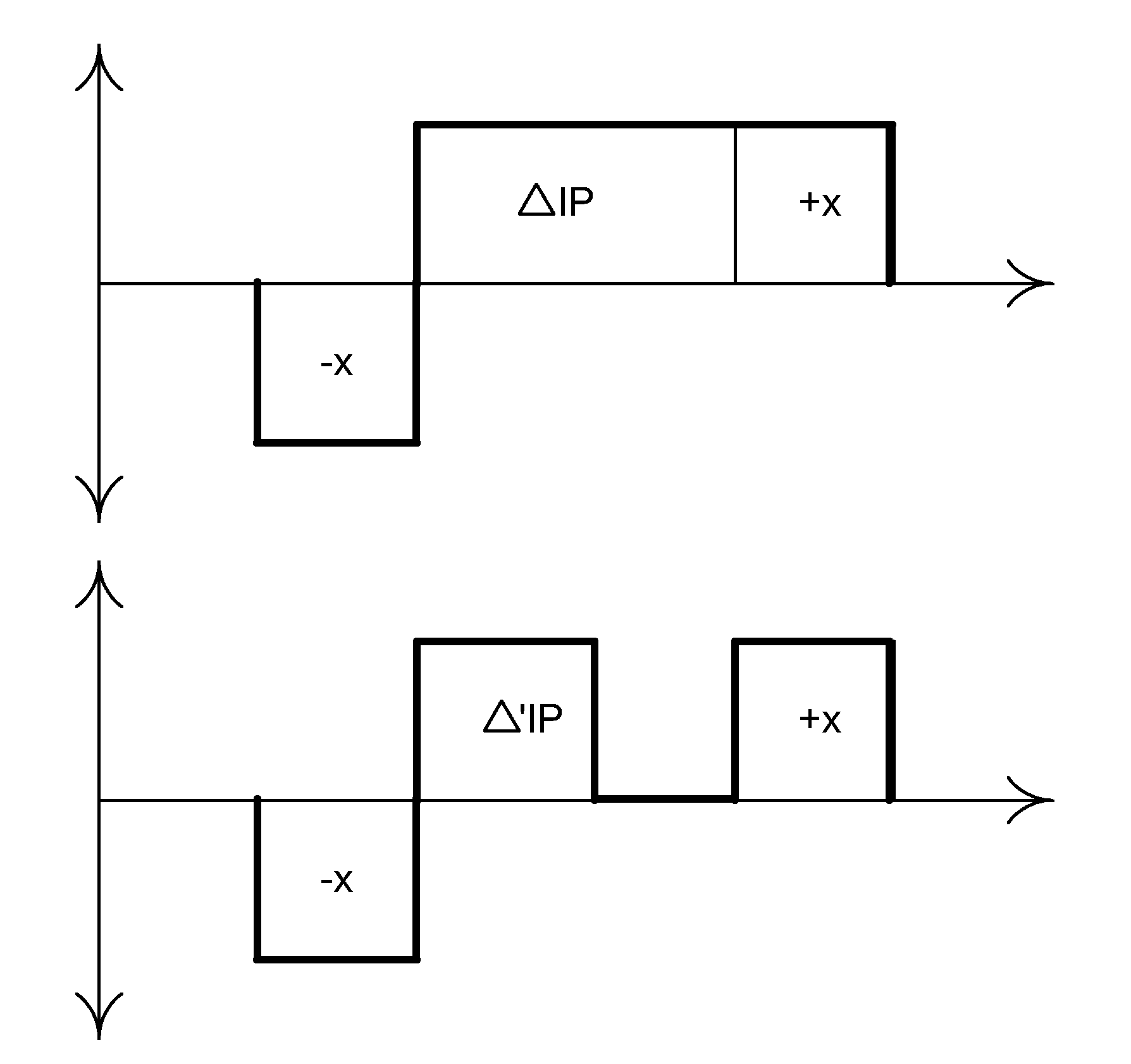
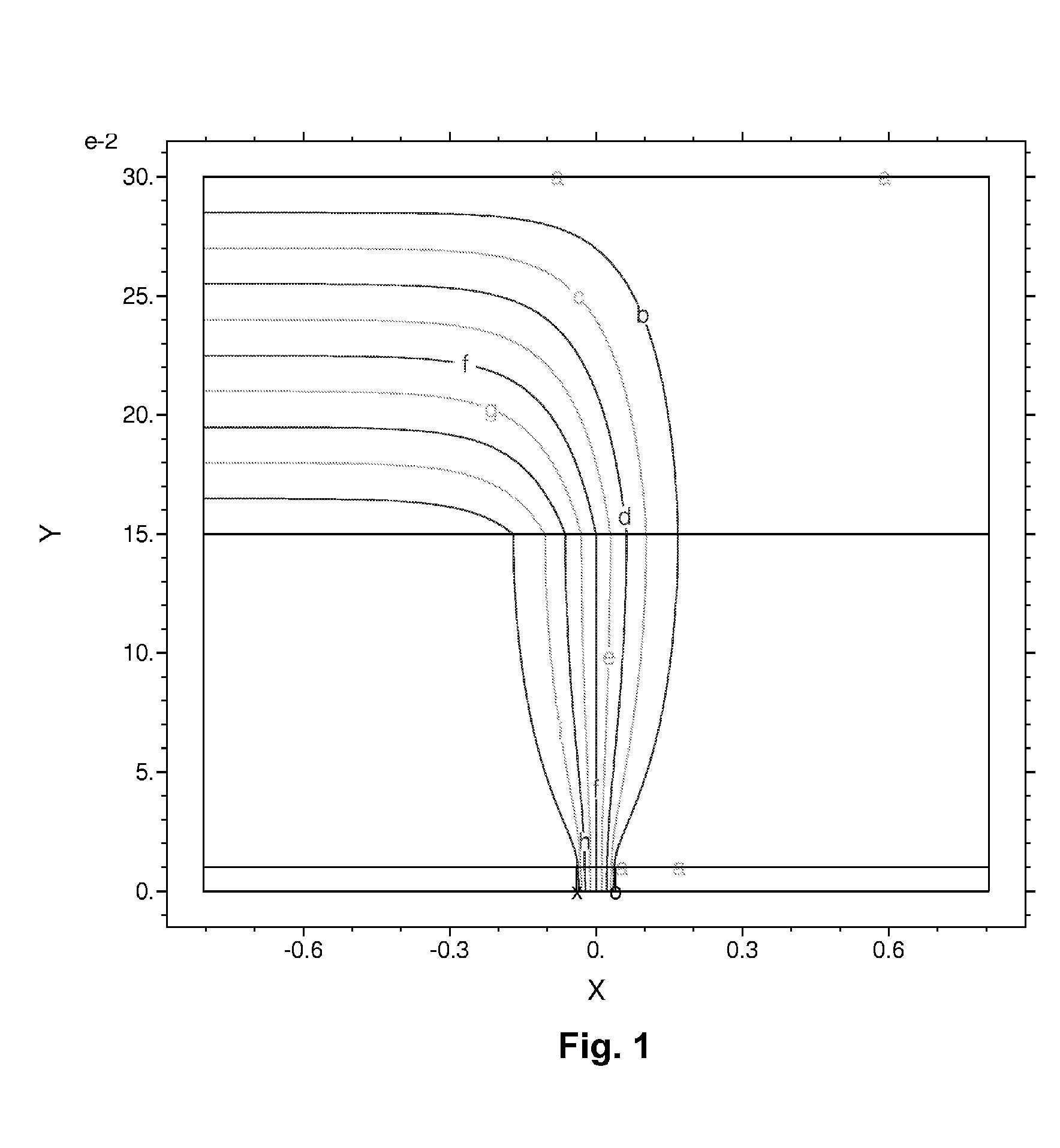
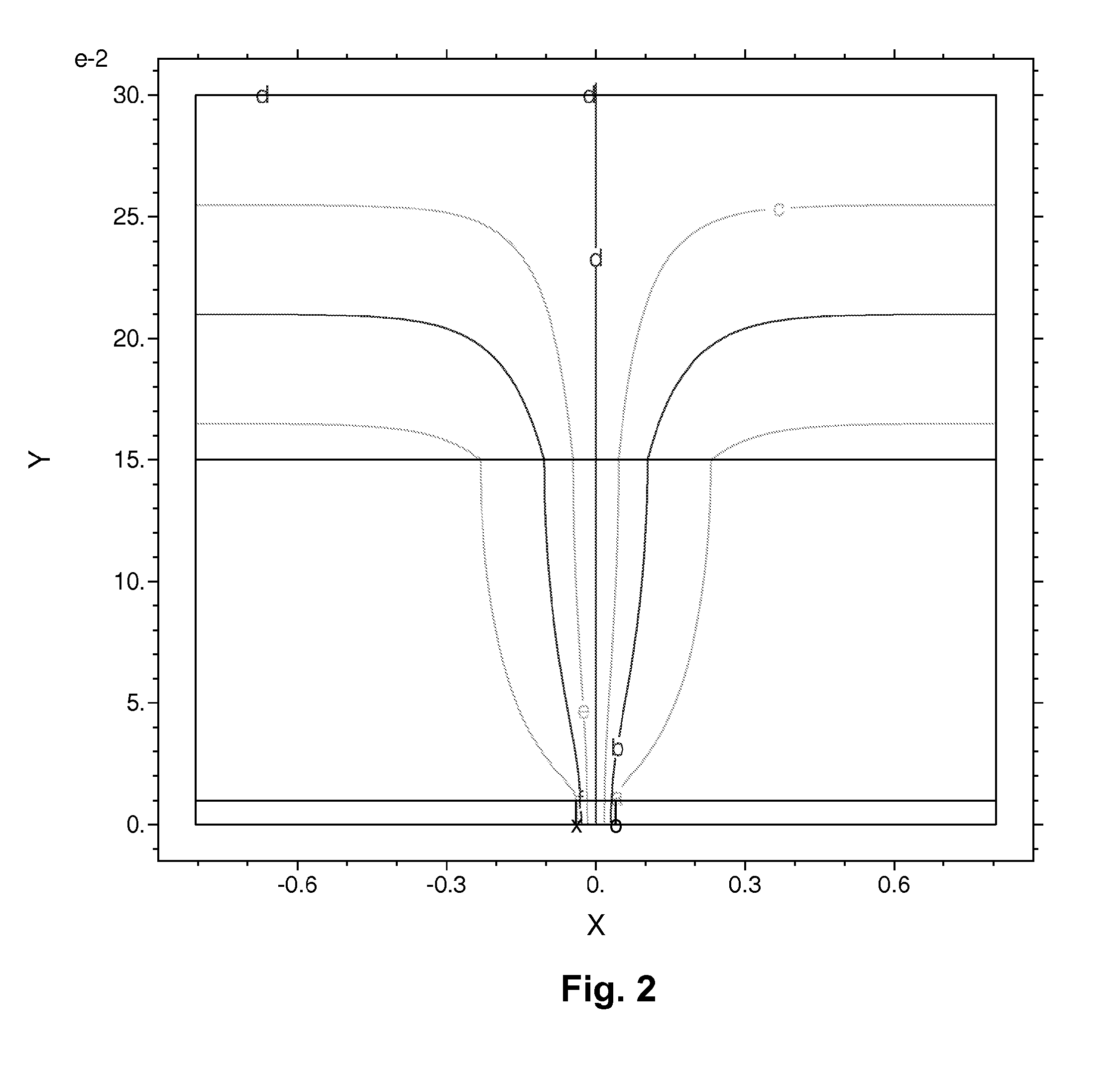
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2172 results about "Zero voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods and apparatus for driving electro-optic displays
ActiveUS7952557B2Shorten the overall cycleReduce data volumeCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingGray levelDisplay device
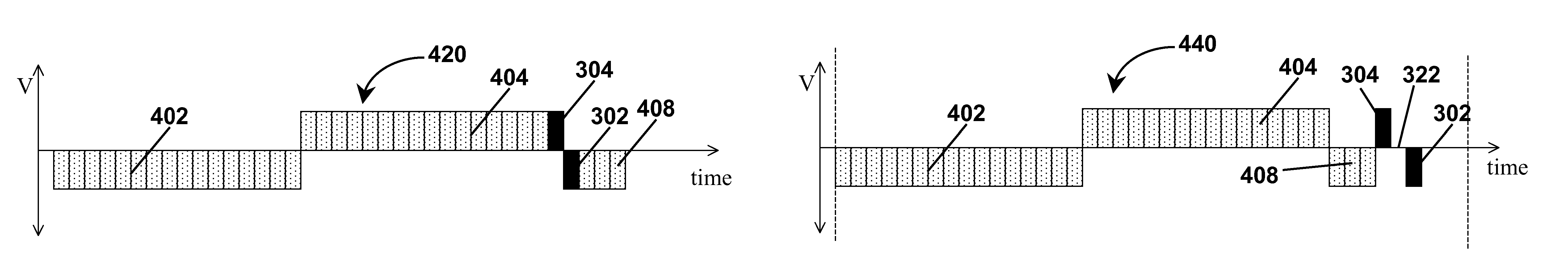
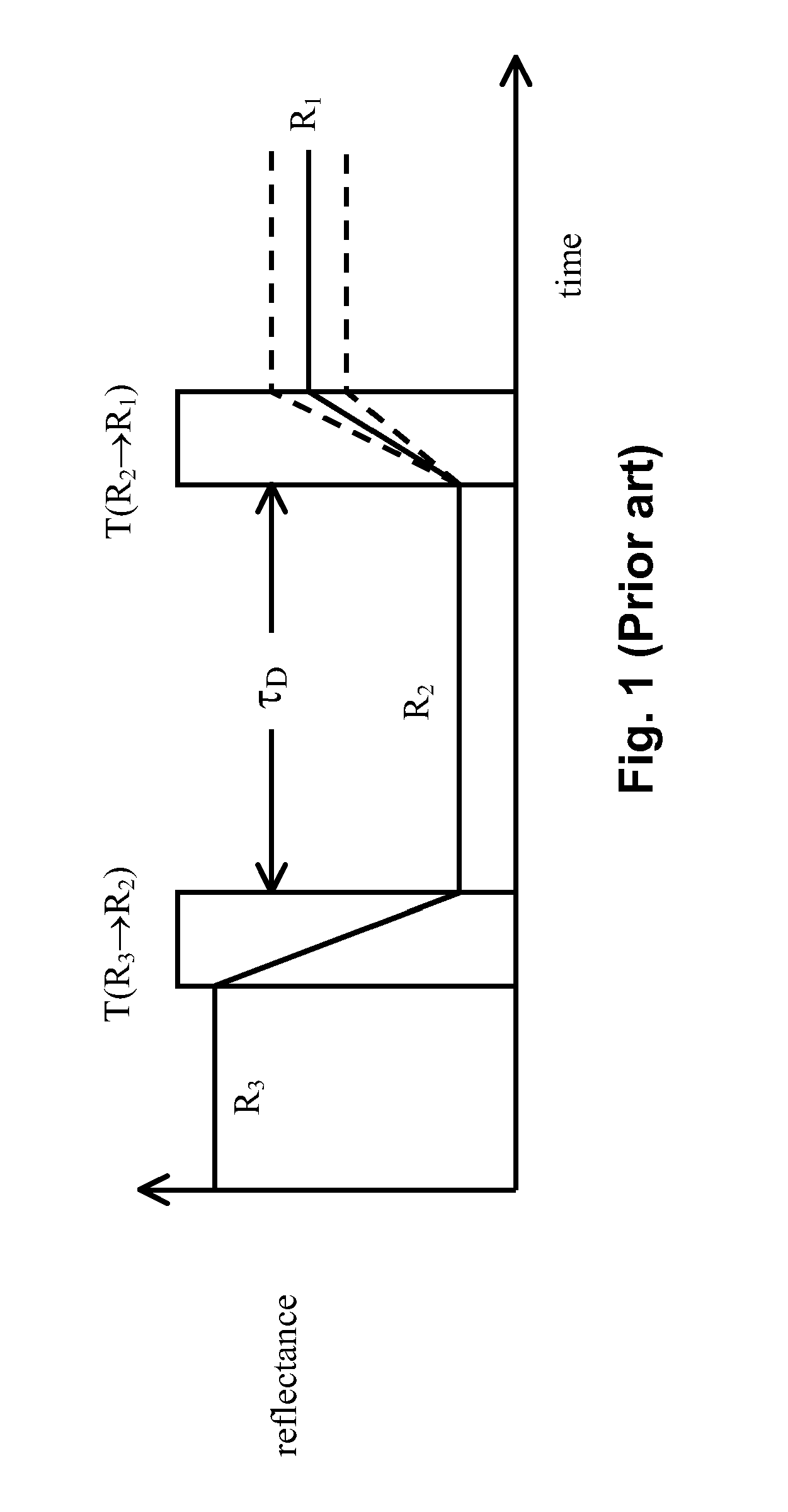
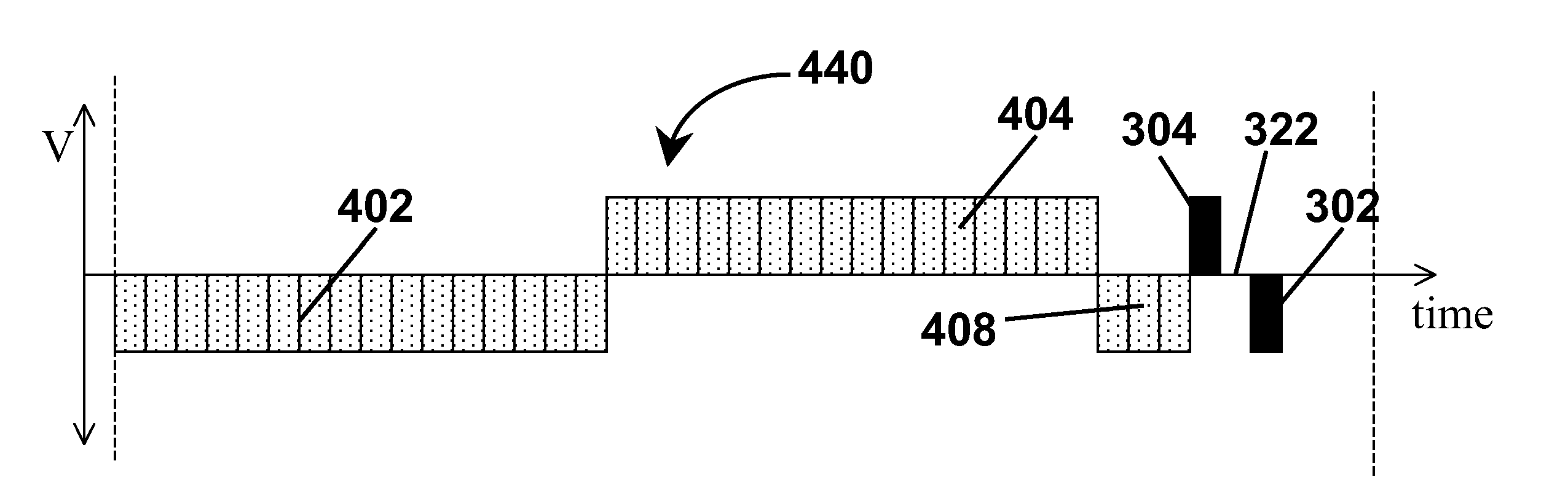
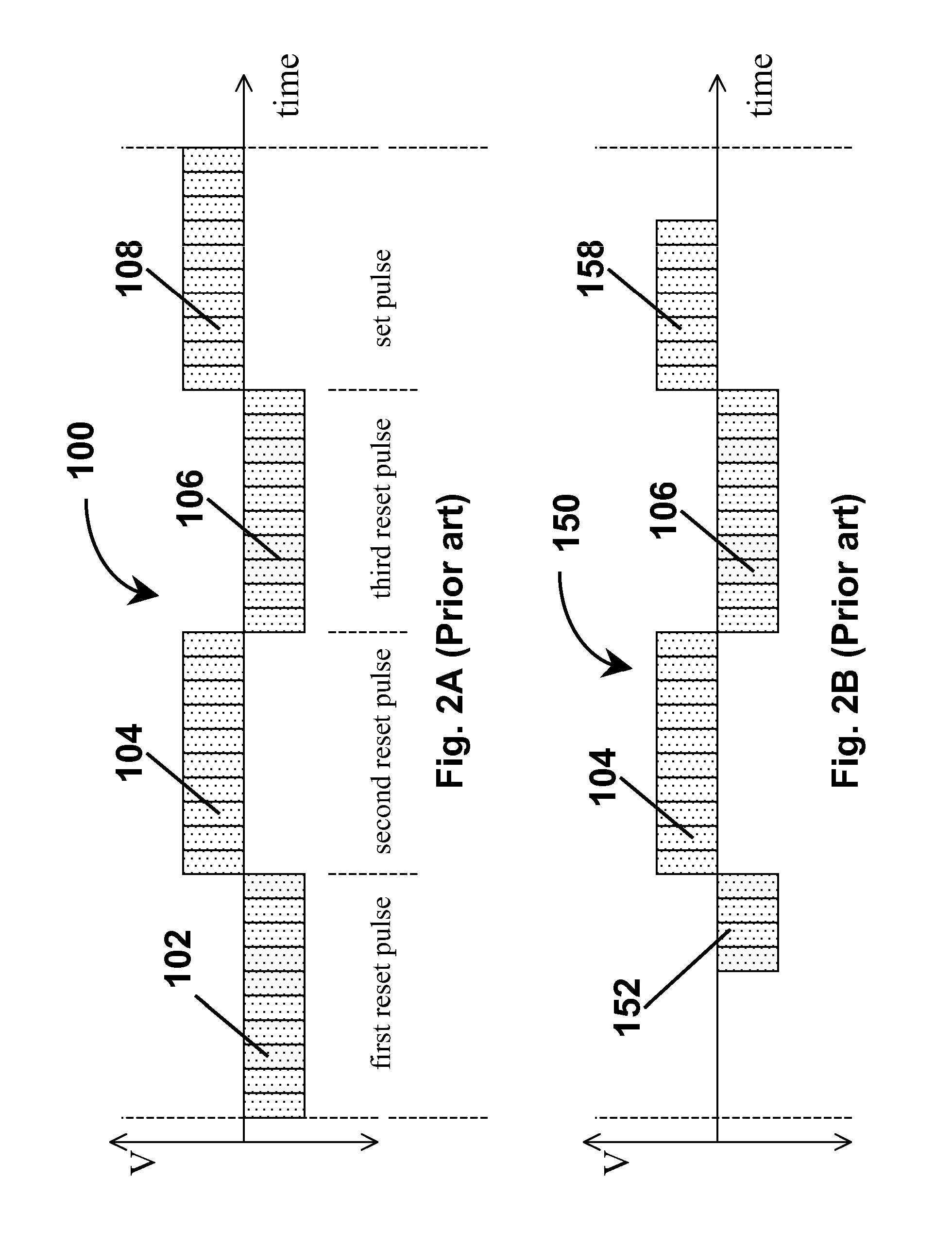
Waveforms for driving electro-optic displays, especially bistable electro-optic displays, are modified by one or more of insertion of at least one balanced pulse pair into a base waveform; excision of at least one balanced pulse pair from the base waveform; and insertion of at least one period of zero voltage into the base waveform. Such modifications permit fine control of gray levels.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
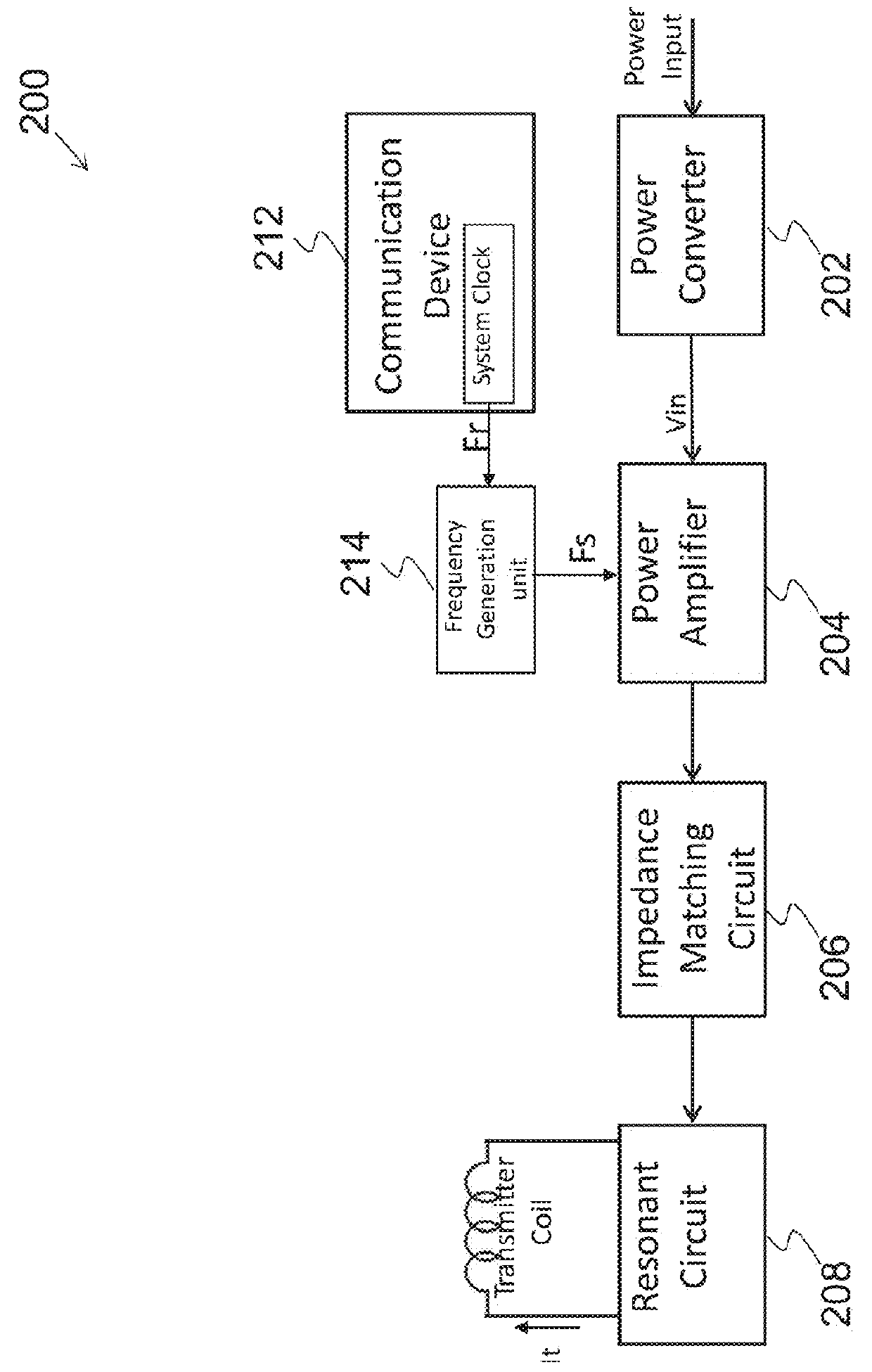
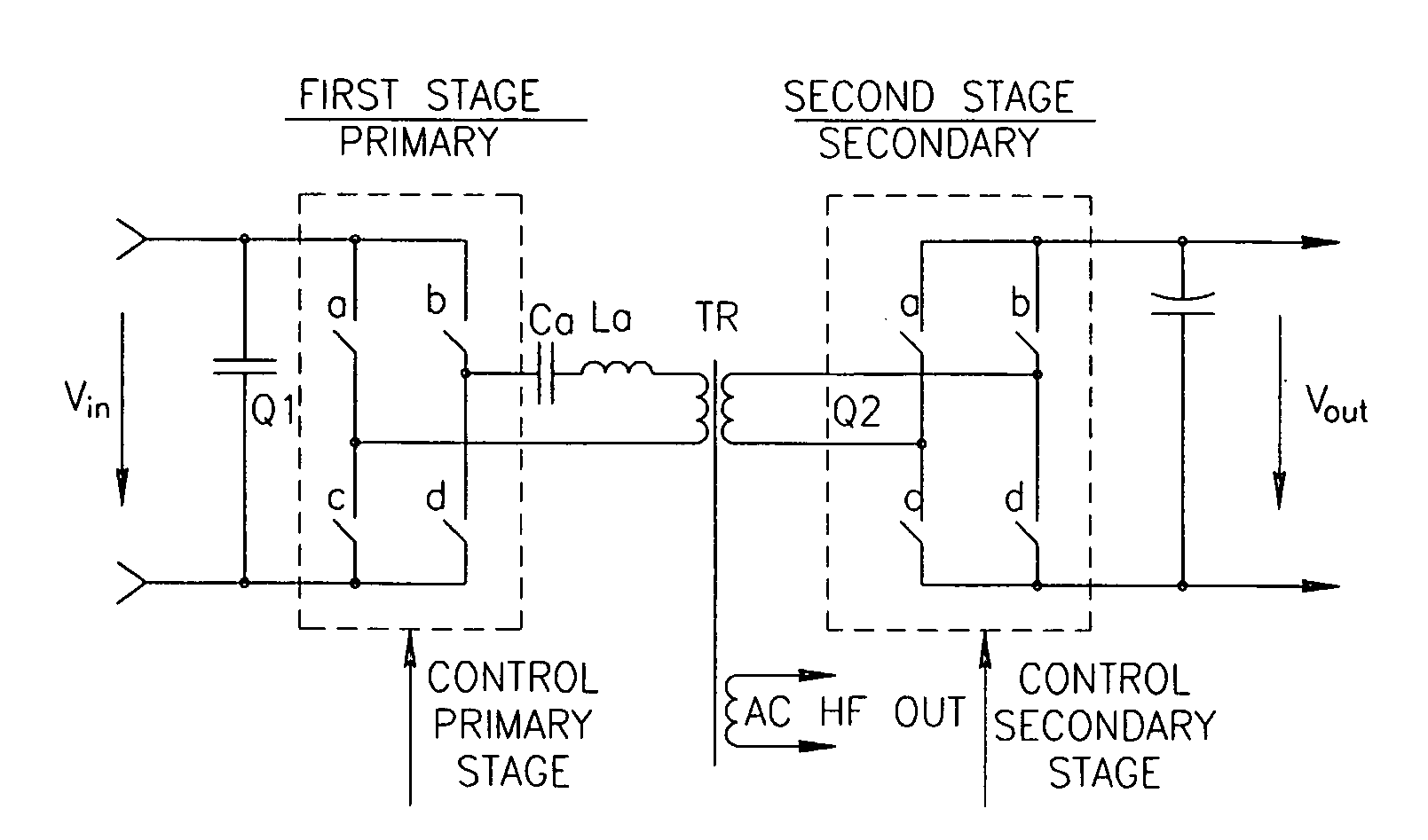
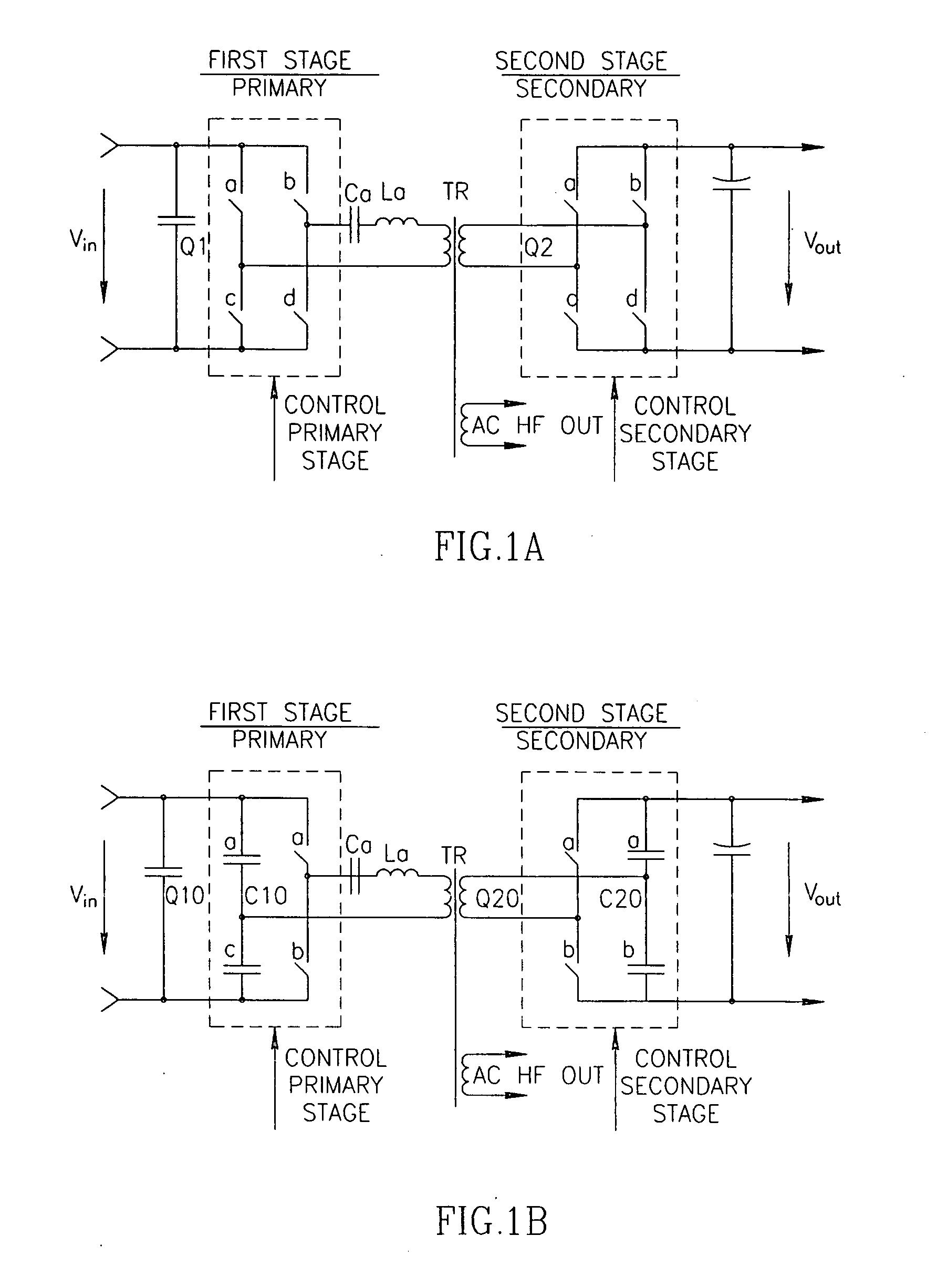
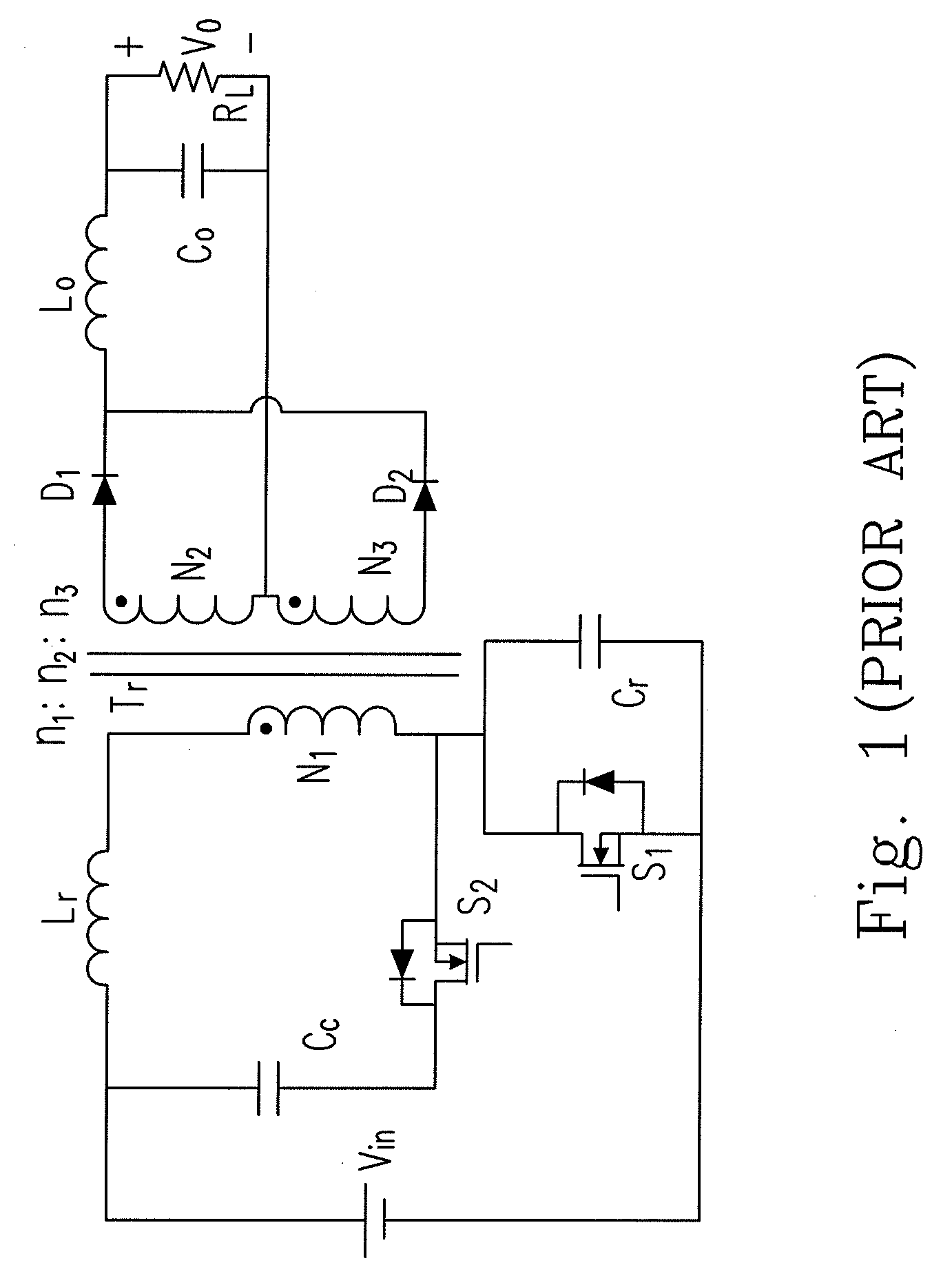
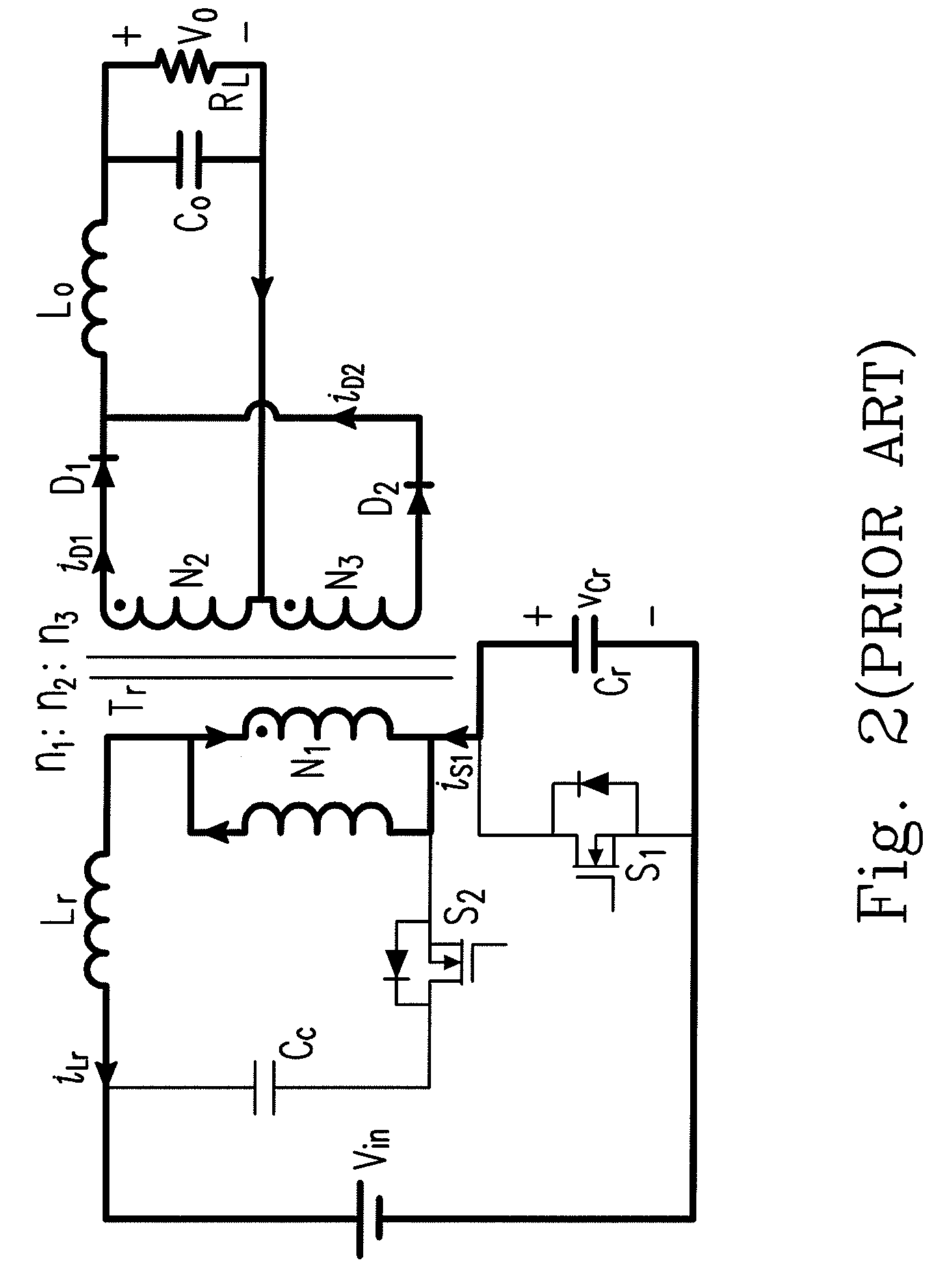
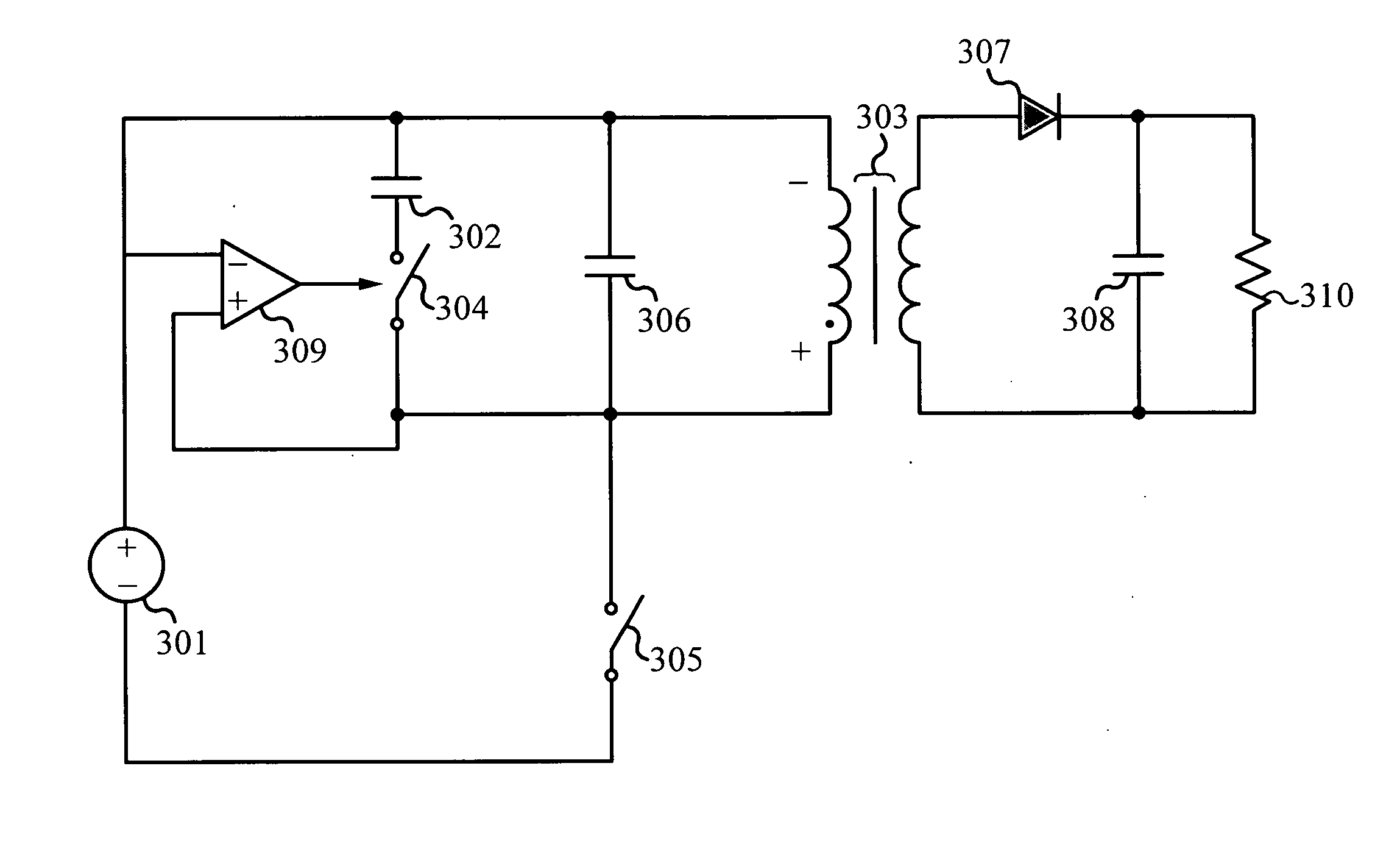
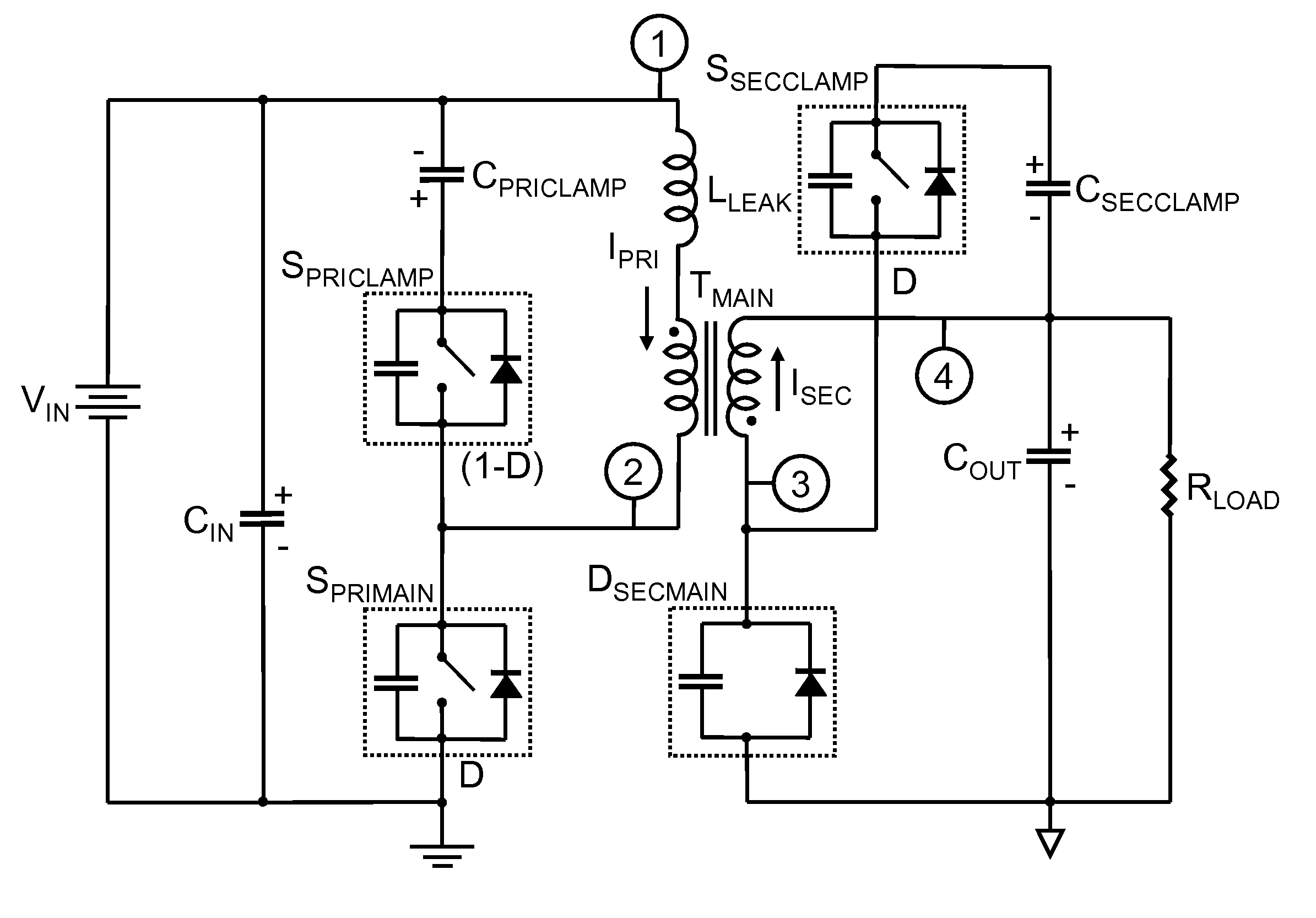
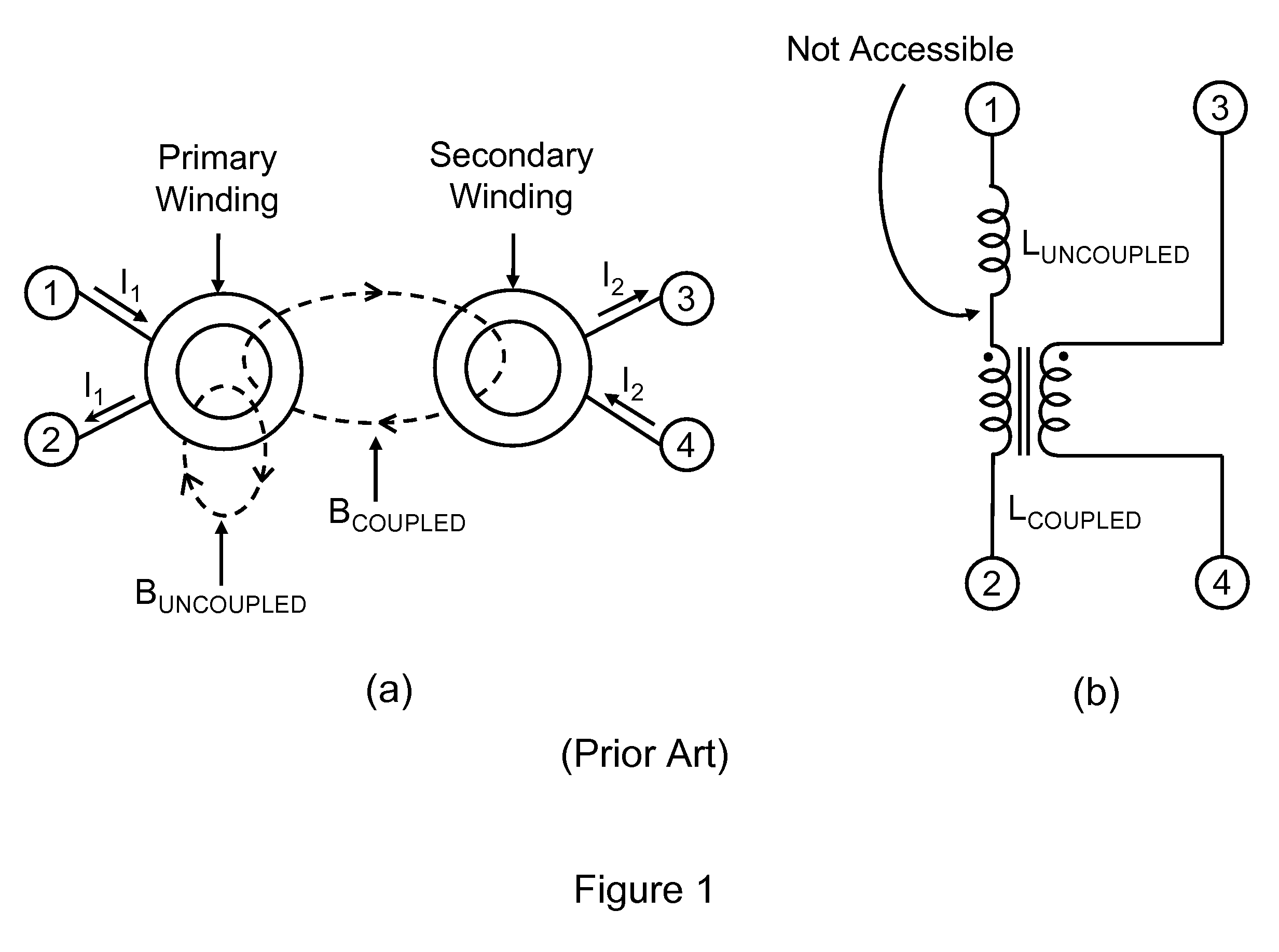
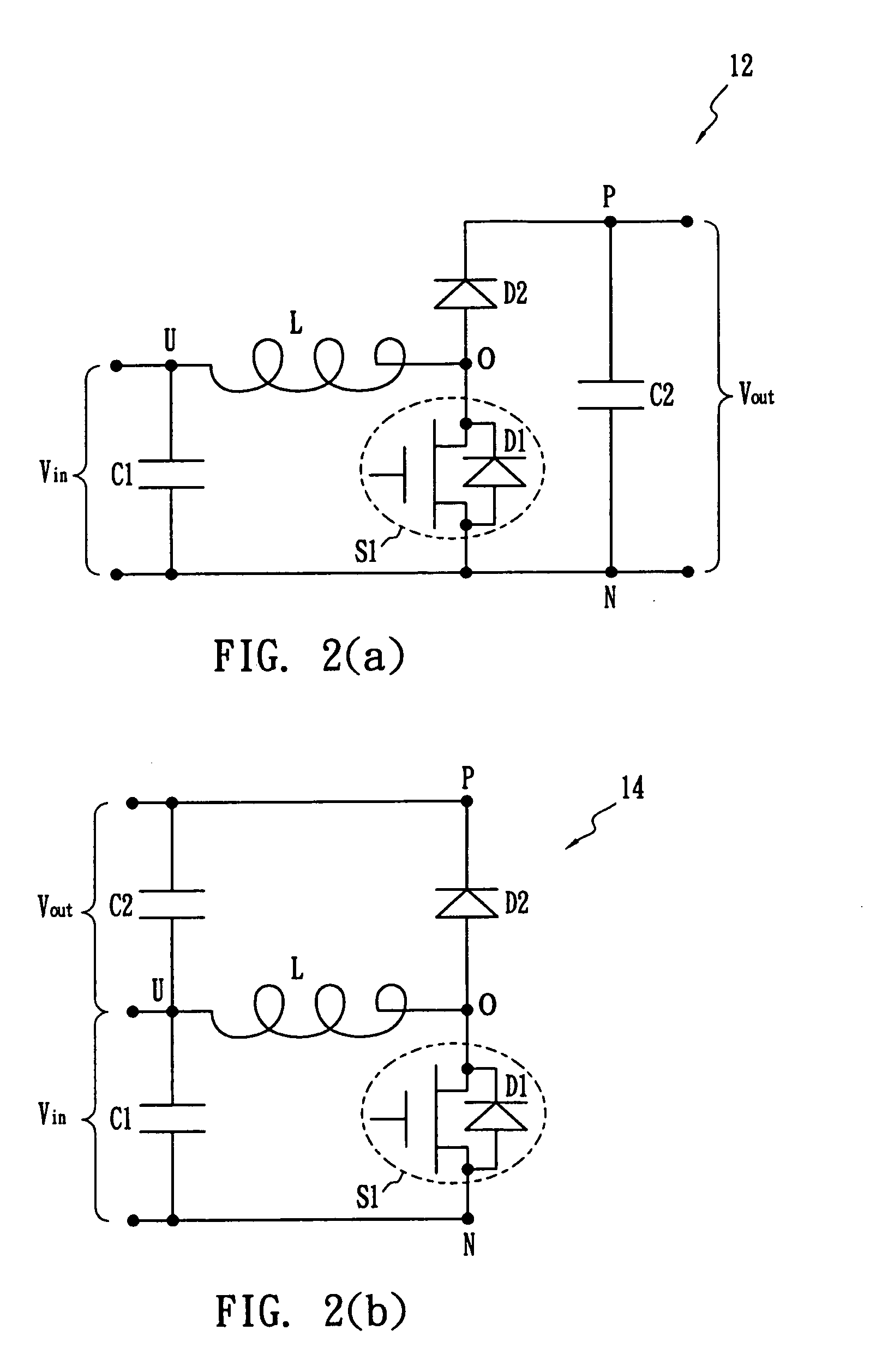
Zero Voltage Switching Half-Bridge Converters
ActiveUS20160056640A1Improve efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsElectromagnetic wave systemTransformerEngineering
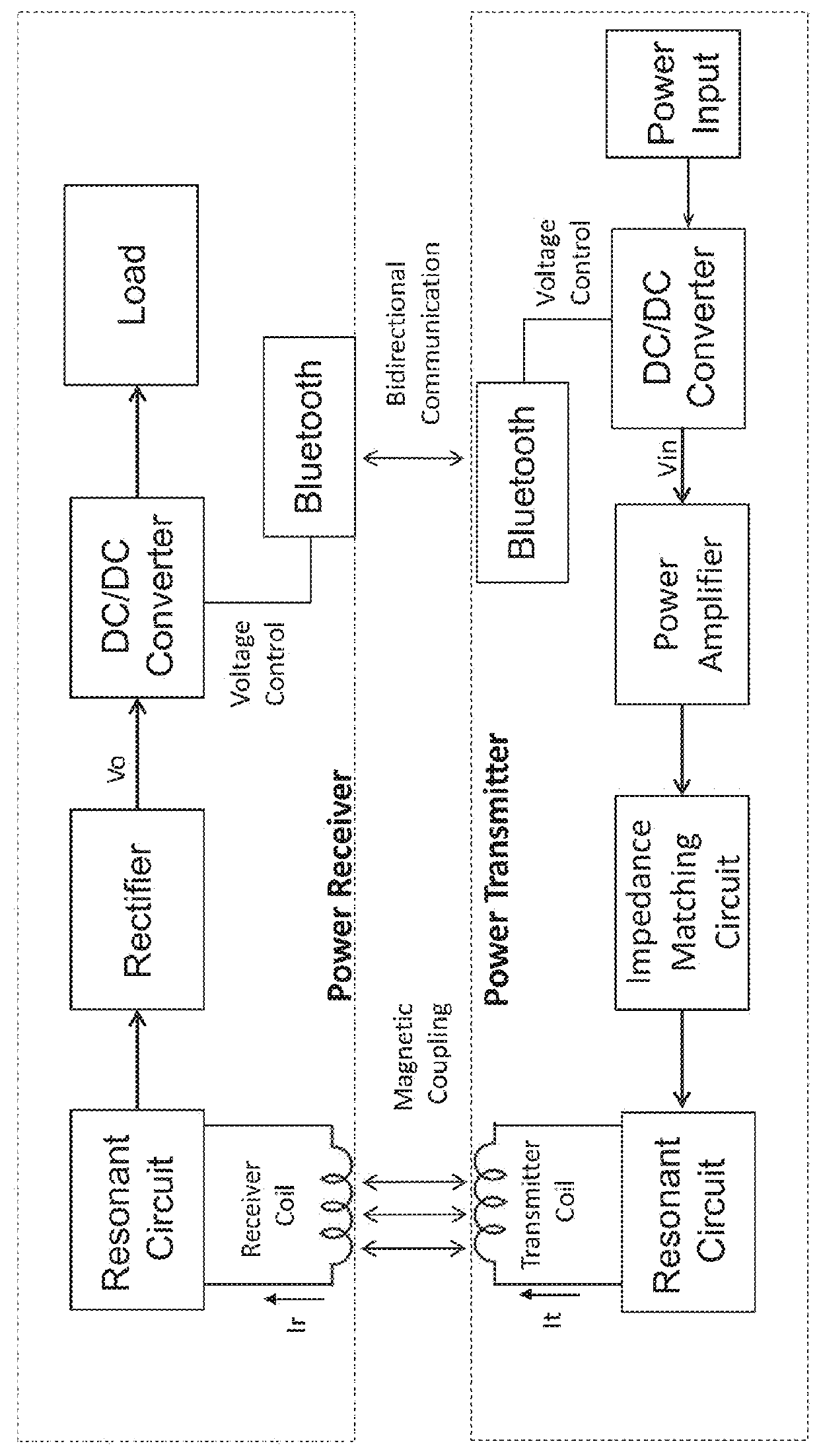
A power converter comprises a primary switch network coupled to a power source, wherein the primary switch network comprises a plurality of power switches, a controller configured to generate gate drive signals for the plurality of power switches, a secondary rectifier coupled to an output, a first transformer having a first winding coupled to the primary switch network, a second winding coupled to the secondary rectifier and a third winding coupled to the controller and a second transformer having a fourth winding coupled to the primary switch network, a fifth winding coupled to the secondary rectifier and a sixth winding coupled to the controller, wherein a voltage signal from the third winding and / or the sixth winding is processed to provide a feedback of a voltage at the output.
Owner:NUVOLTA TECH
Methods for reducing edge effects in electro-optic displays
InactiveUS20050062714A1Improve scanning rateReduce edge effectsCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingEdge effectsDisplay device
Edge effects in electro-optic displays are reduced by (a) ensuring that during rewriting of the display, the last period of non-zero voltage applied all pixels terminates at substantially the same time; and (b) scanning the display at a scan rate of at least 50 Hz.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Methods for reducing edge effects in electro-optic displays
InactiveUS7602374B2Reduce edge effectsCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingEdge effectsDisplay device
Edge effects in electro-optic displays are reduced by (a) ensuring that during rewriting of the display, the last period of non-zero voltage applied all pixels terminates at substantially the same time; and (b) scanning the display at a scan rate of at least 50 Hz.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Methods and apparatus for driving electro-optic displays
ActiveUS20050280626A1Reduce in quantityCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingGray levelDisplay device
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
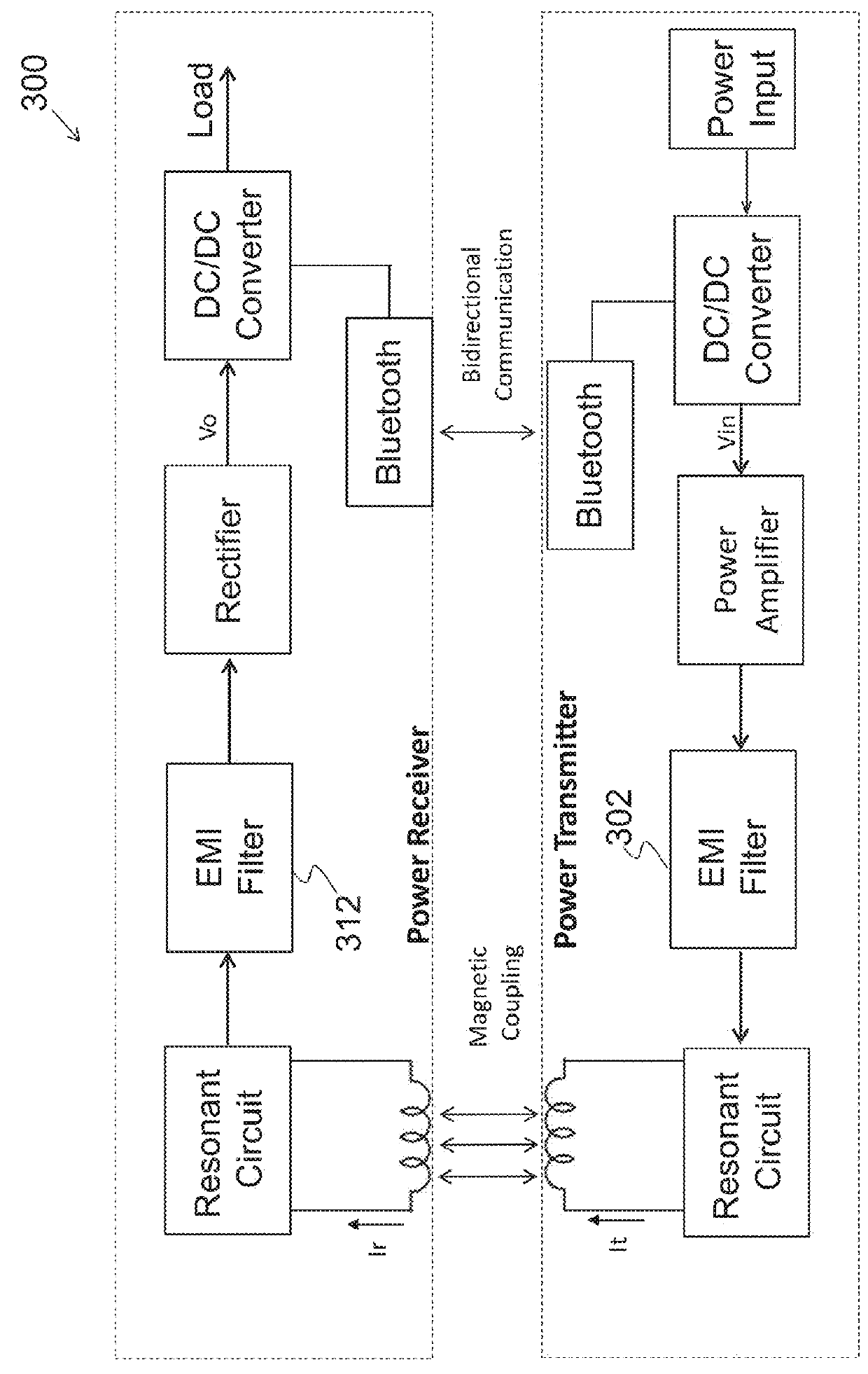
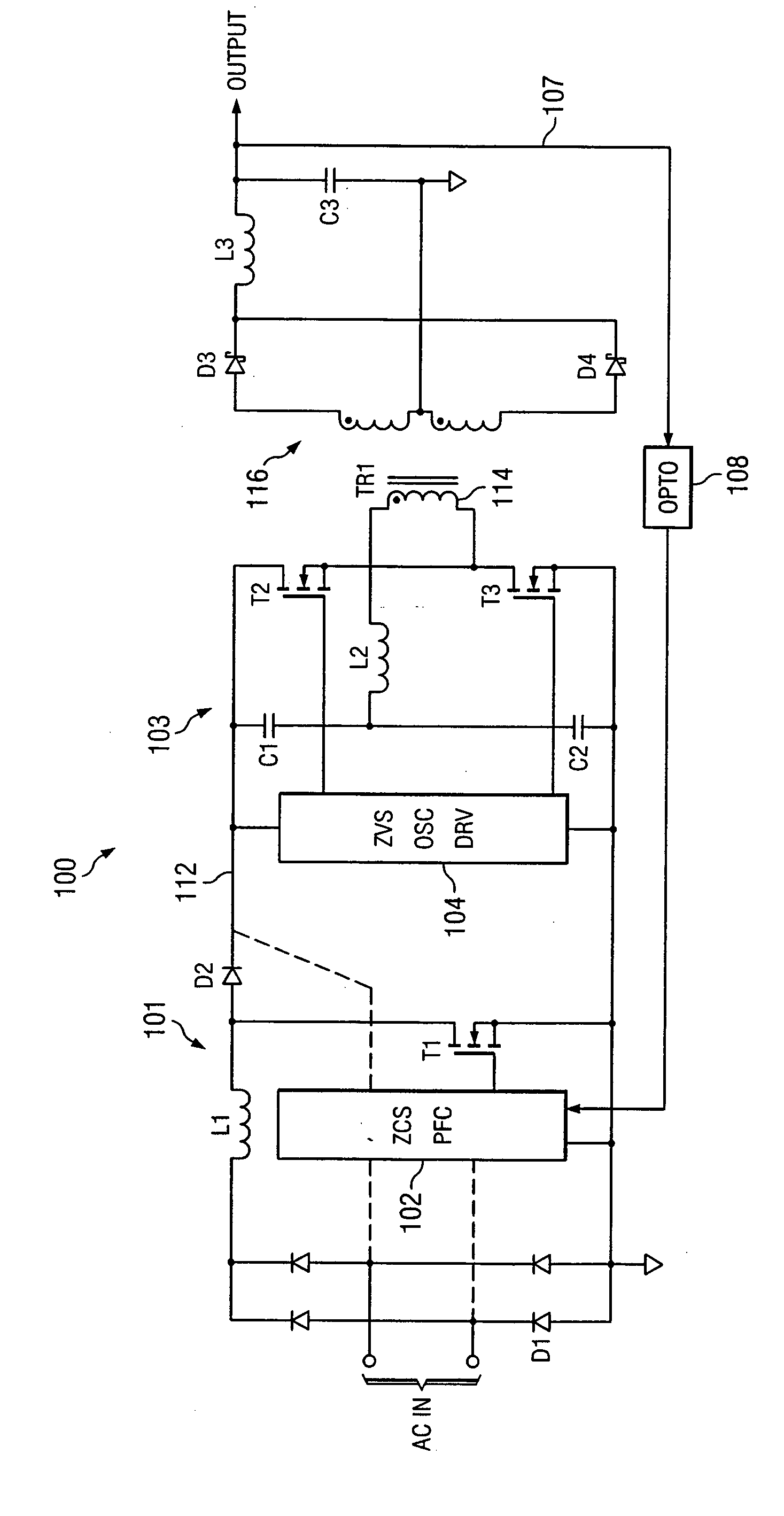
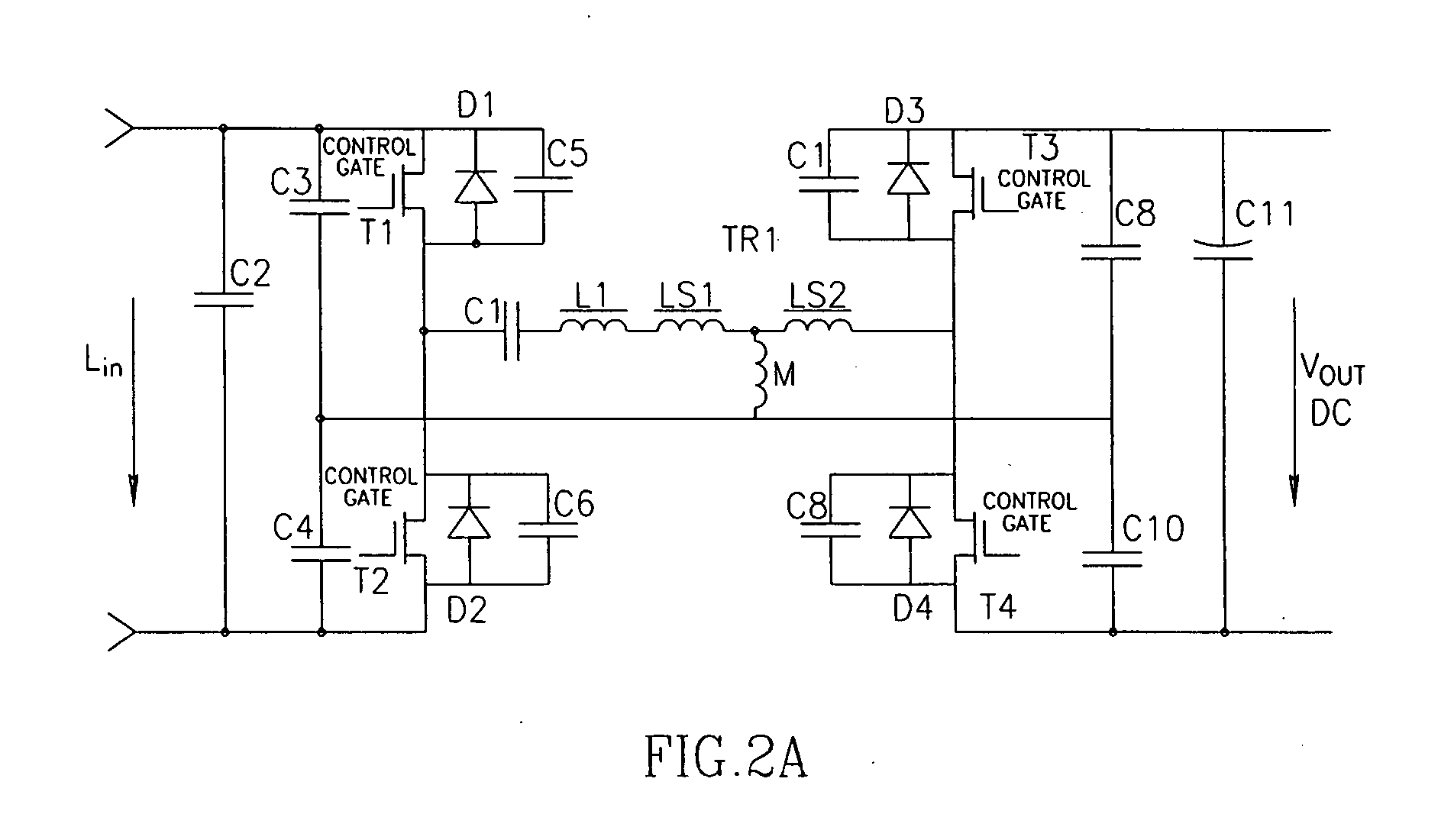
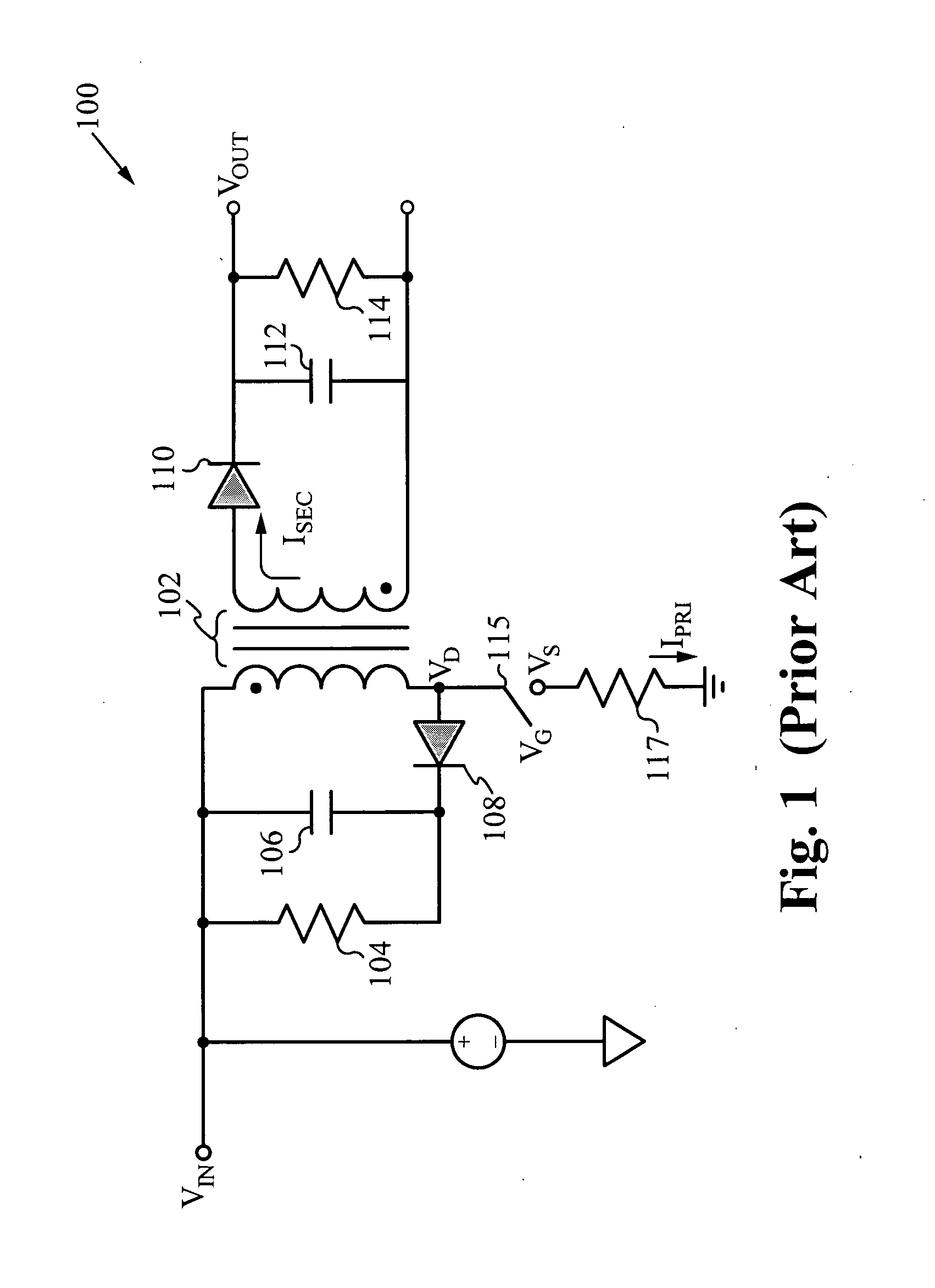
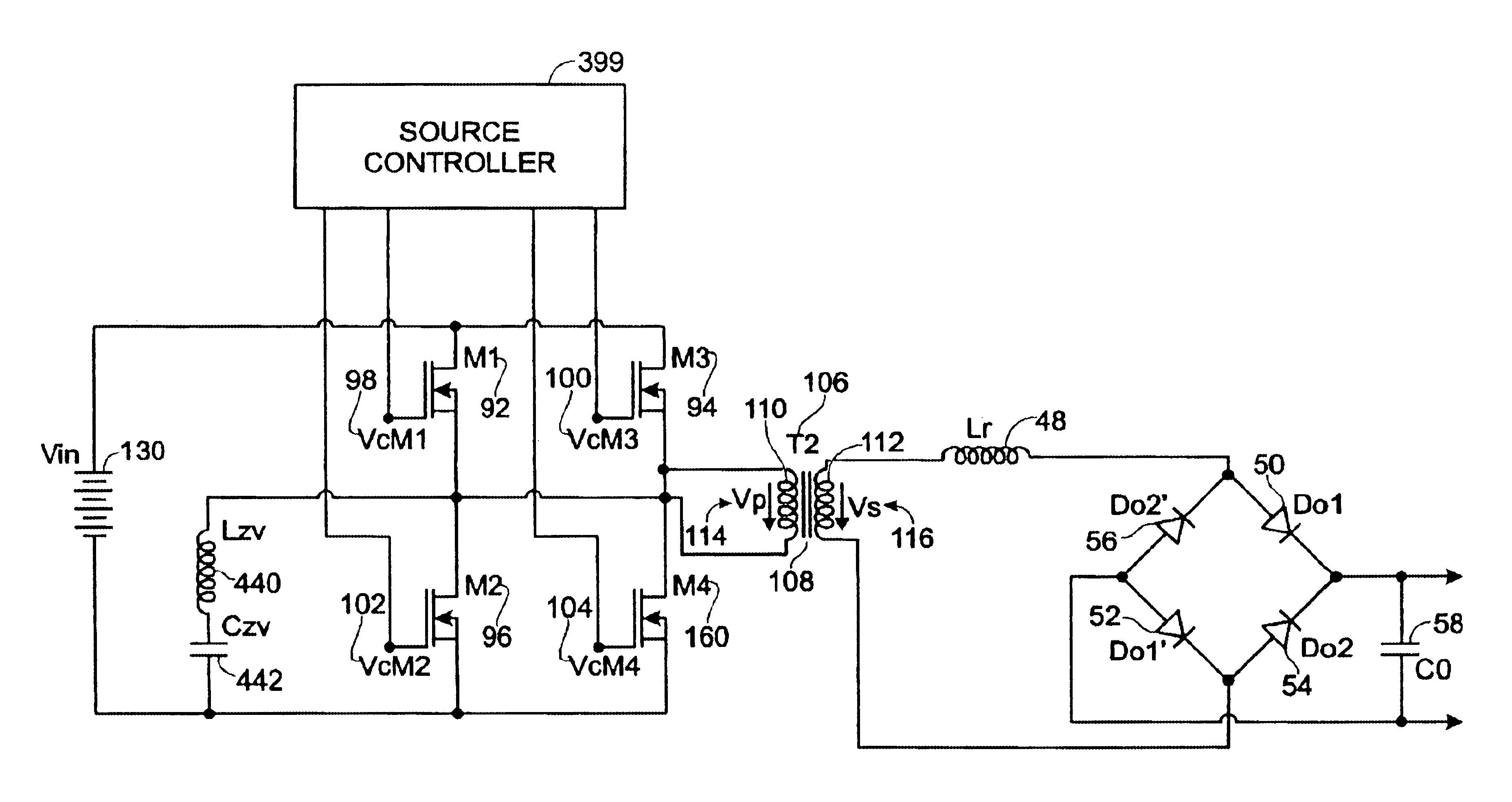
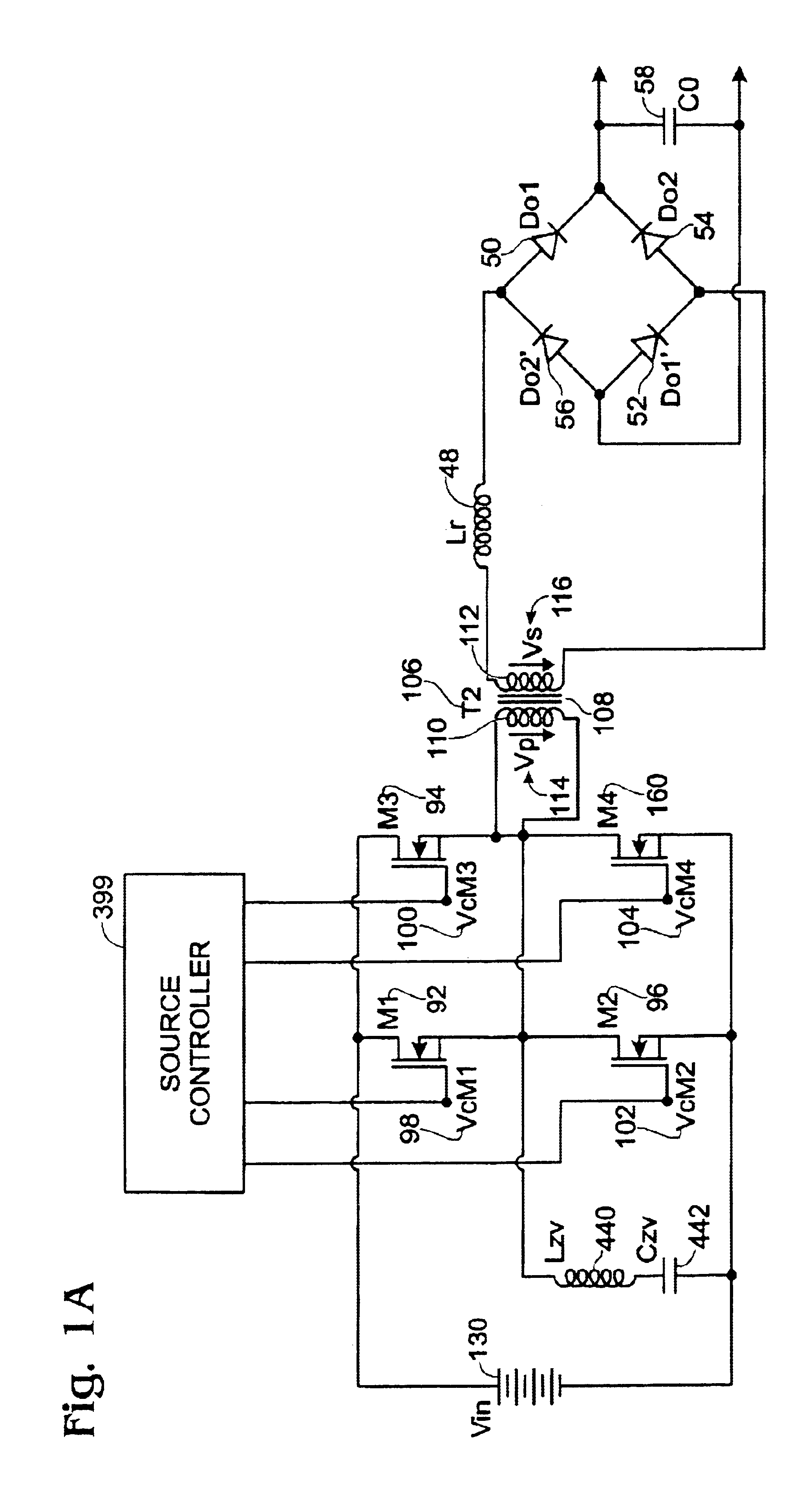
Highly efficient isolated AC/DC power conversion technique
ActiveUS20070081364A1Reduce circuit sizeReduce complexityAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionTransformerEngineering
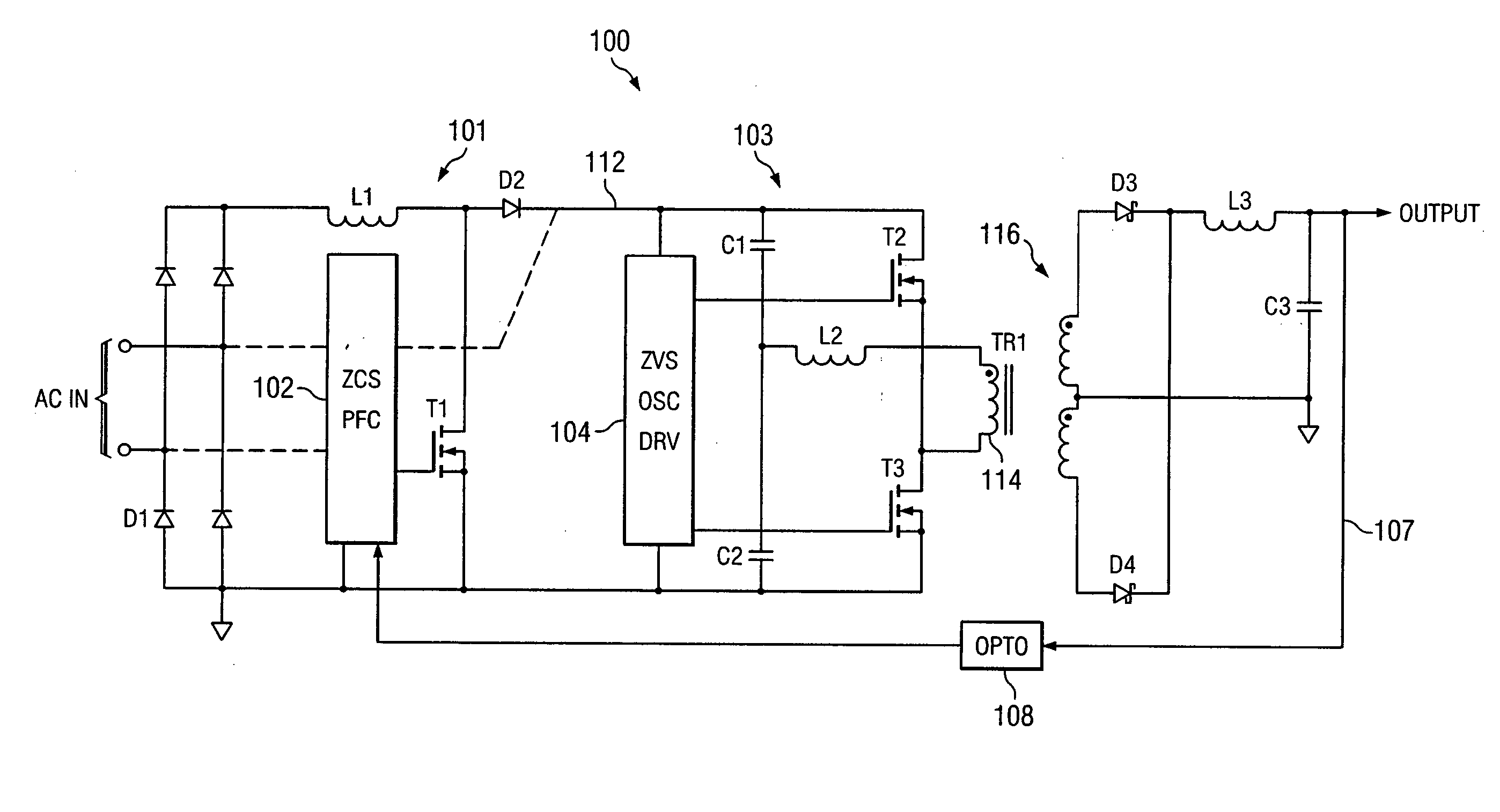
An AC-to-DC power converter that is capable of generating a regulated, isolated DC voltage output from a power factor corrected AC voltage input with improved efficiency. The AC-to-DC power converter is a two-stage power converter including a PFC stage connected in series to a power conversion stage. The PFC stage performs power factor correction using a zero current switching technique, and the power conversion stage includes a zero voltage switched half-bridge converter. The power conversion stage includes a transformer for providing the isolated DC voltage output. The AC-to-DC power converter includes a single feedback control loop for transferring error information from the DC voltage output to the PFC stage, thereby obtaining regulation of the DC voltage output.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
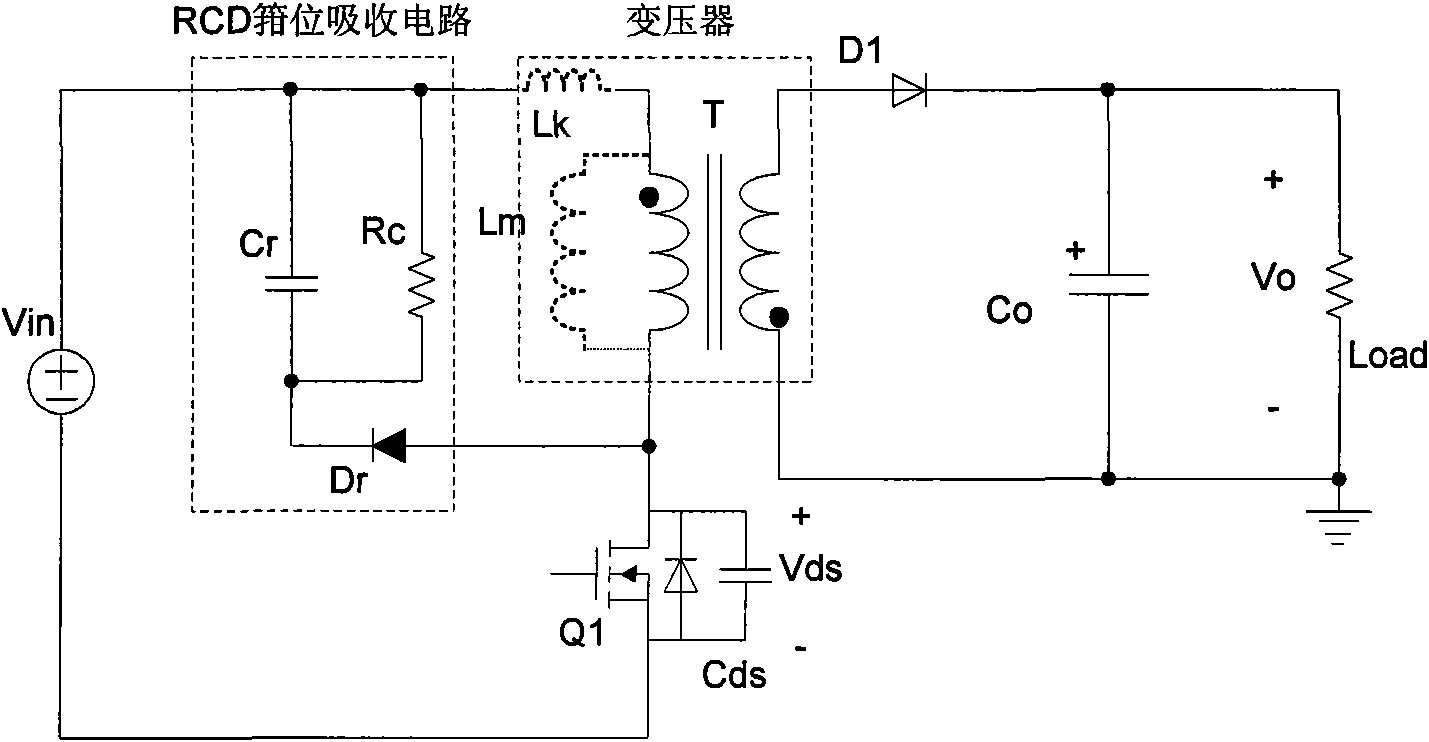
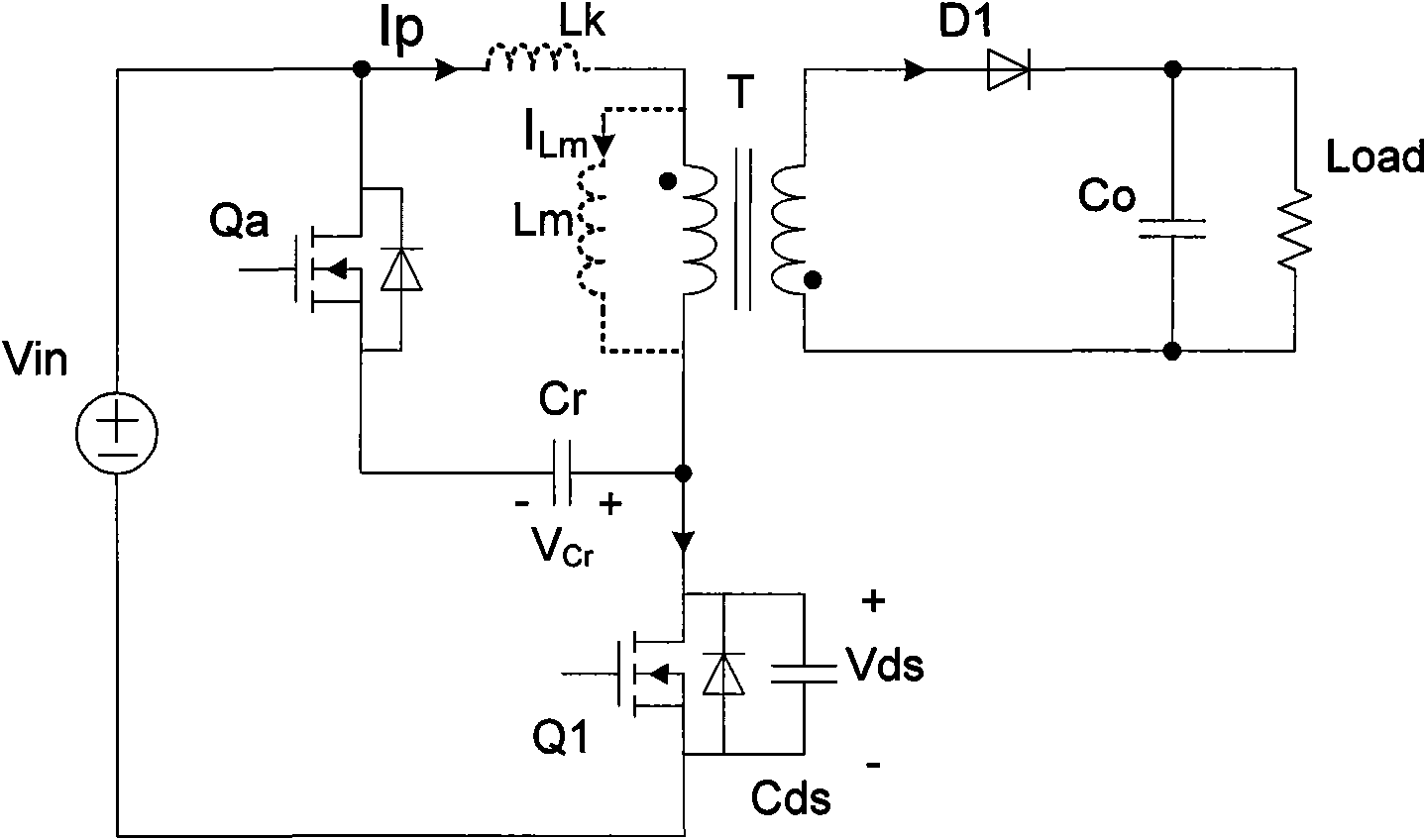
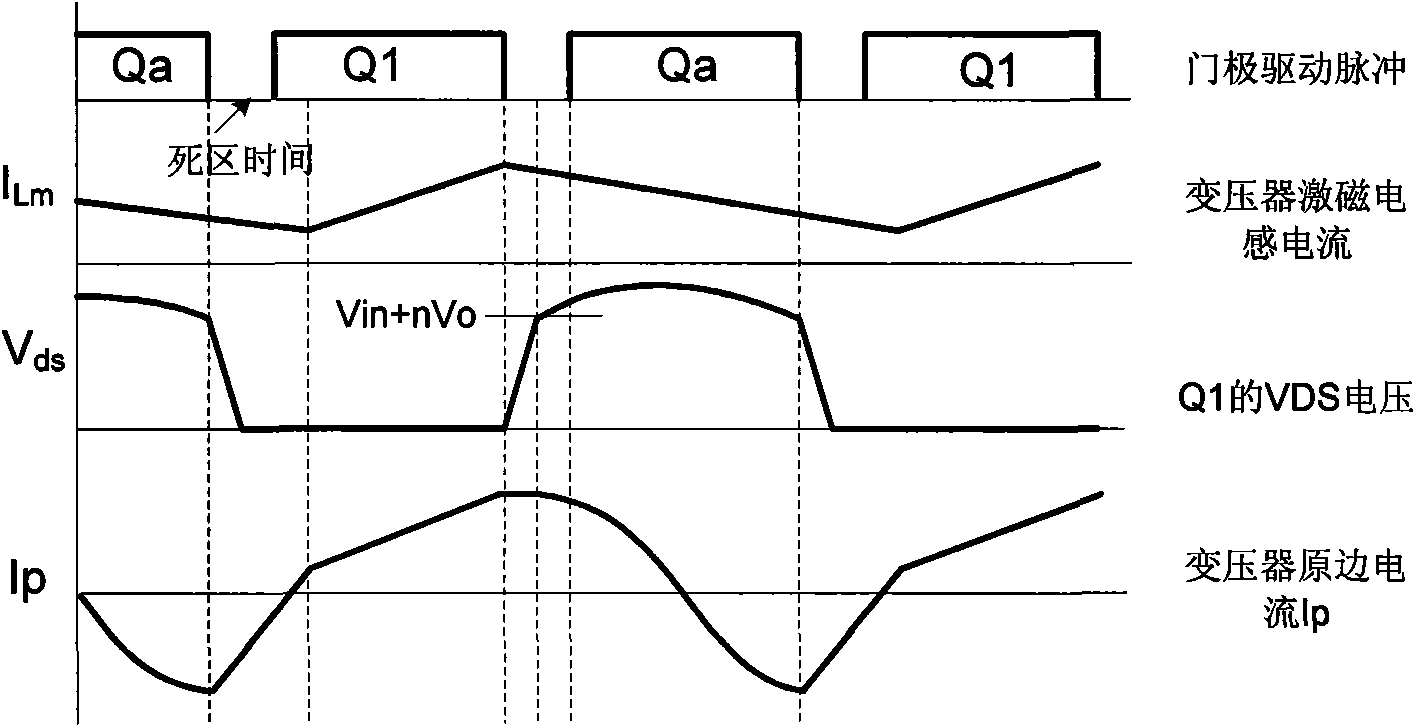
Zero-voltage switch flyback-type DC-DC power supply conversion device
ActiveCN101572490AEasy to controlImprove efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionCapacitanceTransformer
The invention relates to a DC-DC power supply conversion device, in particular to a zero-voltage switch (ZVS) flyback-type DC-DC power supply conversion device with efficient conversion, efficient light-load conversion and low standby power consumption. An auxiliary switch and an absorption capacitor are additionally arranged on the flyback circuit; the auxiliary switch and the absorption capacitor are connected in series so as to form an auxiliary branch circuit; the auxiliary branch circuit can be connected in parallel to the two ends of the primary winding of a transformer or alternatively connected in parallel to the two ends of a primary-side switch; and the auxiliary switch is conductive for a determined period of time before the primary-side switch is conductive. Compared with the prior art, the energy of the circuit leakage inductor can be absorbed and transferred to the output terminal and a soft switch for realizing the primary-side switch, so that the invention can greatly improve the circuit efficiency; the parasitic oscillation caused by the leakage inductor can be suppressed, so that the EMI (electromagnetic interference) characteristics of the circuit can be improved; and the circuit can be controlled more easily, thereby improving the light-load circuit efficiency and reducing the idle-load energy loss.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS SHANGHAI CO LTD
Apparatus and method for high efficiency isolated power converter
InactiveUS20090034299A1Improve efficiencyLow conductiveDc network circuit arrangementsEfficient power electronics conversionDc dc converterFull bridge
A DC-DC converter apparatus comprising half or full bridge, two-stage resonant converter, which may include series resonant (inductor, capacitor) devices. An isolated transformer having primary and secondary winding supplies current to full-wave secondary stage-bridge through the use of primary winding resonant devices employing primary stage-bridge. The magnetizing of said devices employs zero-current, zero-voltage resonant-transition switching technology, which reduces switching losses at all switching frequencies to almost zero. The regulation of output voltage at all loads and input voltages achieved by the control of the switching frequency and the phase between signals for primary and secondary stages. The proper intermittent of the frequency and the phase allows achieving the value of efficiency up to 97%.
Owner:LUMENIS LTD
Forward-flyback converter with active-clamp circuit
ActiveUS20100067259A1Improve conversion efficiencyAdditional drawbackEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsHeavy loadCenter tap
The present invention discloses a forward-flyback converter with active-clamp circuit. The secondary side of the proposed converter is of center-tapped configuration to integrate a forward circuit and a flyback circuit. The flyback sub-circuit operating continuous conduction mode is employed to directly transfer the reset energy of the transformer to the output load. The forward sub-circuit operating discontinuous conduction mode can correspondingly adjust the duty ratio with the output load change. Under the heavy load condition, the mechanism of active-clamp flyback sub-circuit can provide sufficient resonant current to facilitate the parasitic capacitance of the switches to be discharged to zero. Under the light load condition, the time interval in which the resonant current turns from negative into positive is prolonged to ensure zero voltage switching function. Meanwhile, the flyback sub-circuit wherein the rectifier diode is reverse biased is inactive in order to further reduce the power losses.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Methods and apparatus for driving electro-optic displays
InactiveUS8593396B2Shorten the overall cycleReduce data volumeCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsGray levelDisplay device
Waveforms for driving electro-optic displays, especially bistable electro-optic displays, are modified by one or more of insertion of at least one balanced pulse pair into a base waveform; excision of at least one balanced pulse pair from the base waveform; and insertion of at least one period of zero voltage into the base waveform. Such modifications permit fine control of gray levels.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Fast transition power supply
InactiveUS6121761AQuick transitionFacilitate rapid changeApparatus without intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationCapacitanceInductor
A fast transition power supply comprises three control functions, one to maintain steady state conditions, a voltage transition circuit that rapidly changes the charge on the output capacitor to effect a rapid step change in the output voltage, and a current control circuit that can switch a constant current in a pulse width modulation control from zero (or negative) current to any current less than the maximum rated current with no change of current in the inductors of the circuit. The power supply can thus go from zero volts, no current to full output voltage, full current very quickly, in the order of less than an micro-second. It can also transition from full voltage, full current to zero voltage, zero current just as fast, or transition from one voltage to another.
Owner:HERBERT EDWARD
Two terminals quasi resonant tank circuit
ActiveUS20070263415A1Efficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionResonanceParasitic capacitance
A power converter includes a transformer, a primary switch, an auxiliary switch, first and second resonance capacitors, and a secondary side rectification means. A switch mode power supply is formed to use reflected voltage and parasitic capacitance as an energy source for a transformer resonance. The auxiliary switch effectively exchanges energy between the primary inductance of the transformer and the first and second resonant capacitors. The auxiliary switch effectively switches the transformer resonance between two distinct frequencies. In one embodiment of the invention, the power converter can be, but is not limited to, a flyback converter and further includes a comparator and a driver. The comparator is for detecting the voltage across the second resonance capacitor and the driver is configured to drive the auxiliary switch based on the output state of the comparator. The resonant nature of the converter provides zero voltage (ZVS) for the primary switch as well as for the auxiliary switch.
Owner:MYPAQ HLDG LTD
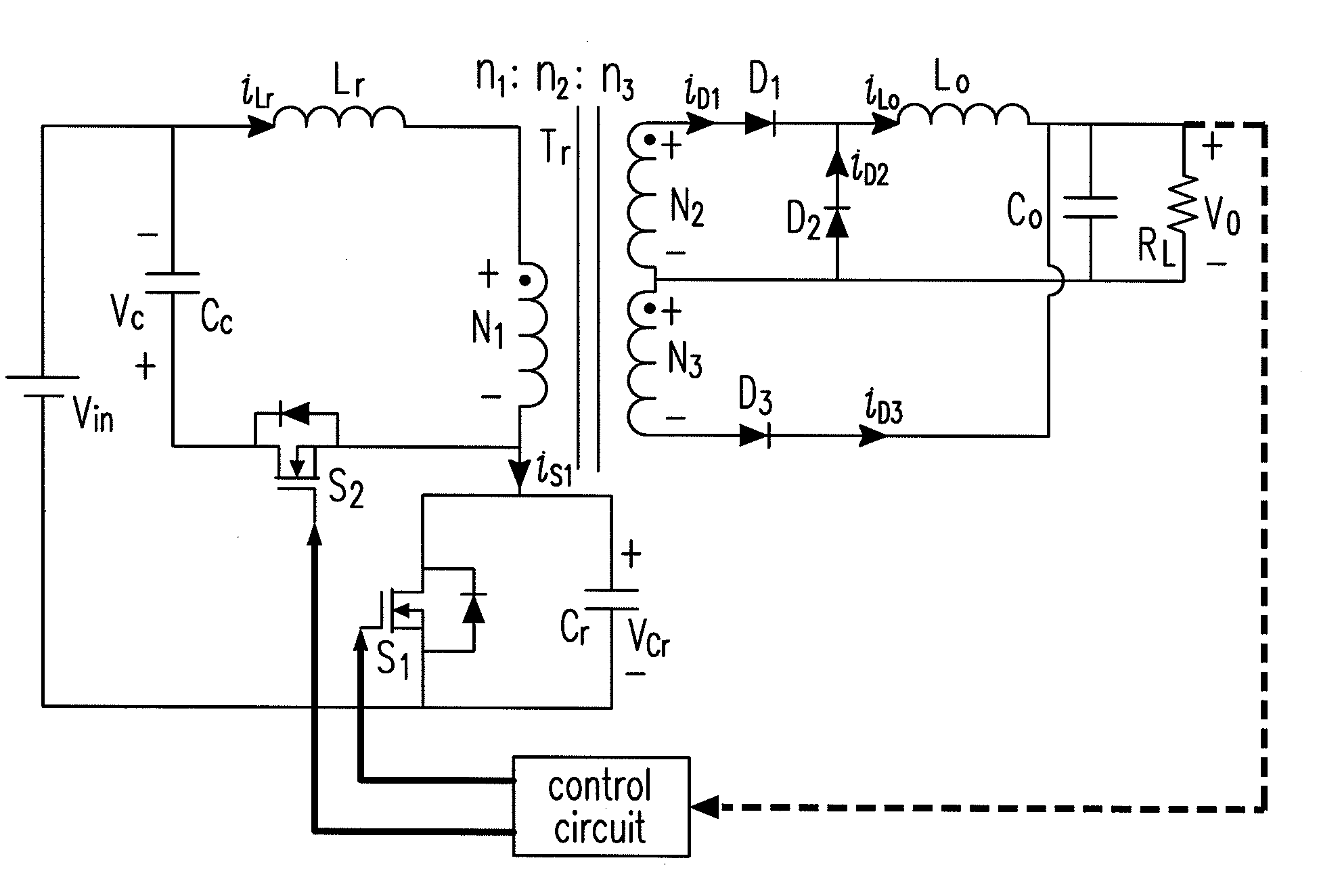
Zero-voltage-switched, full-bridge, phase-shifted DC-DC converter with improved light/no-load operation
InactiveUS6909617B1Operation efficiency is highImprove power supply efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcCapacitanceFull bridge
A zero-voltage-switched, full-bridge, phase-shifted DC-DC converter for use in a DC power supply or battery charger includes a power transformer, four switching transistors connected to form a full bridge, and a decoupling capacitor and resonant inductor connected in series to the primary winding of the power transformer. At high loads, i.e., high output voltages, the resonant inductor charges the stray and internal capacitance of the switching transistors. Under light loads or in a no-load condition, with the current through the resonant inductor insufficient to allow the inductor to recharge these capacitances, the combination of a second inductor connected at one end to the central tap of the power transformer's primary winding and at its second opposed end to the middle point of a capacitive voltage divider, permits the second inductor to store enough energy to effectively recharge the stray and internal capacitance of the switching transistors for improved operating efficiency.
Owner:LA MARCHE MFG
Modulation methods and apparatus for reducing common mode voltages
InactiveUS7164254B2Single-phase induction motor startersMotor/generator/converter stoppersPower inverterCarrier signal
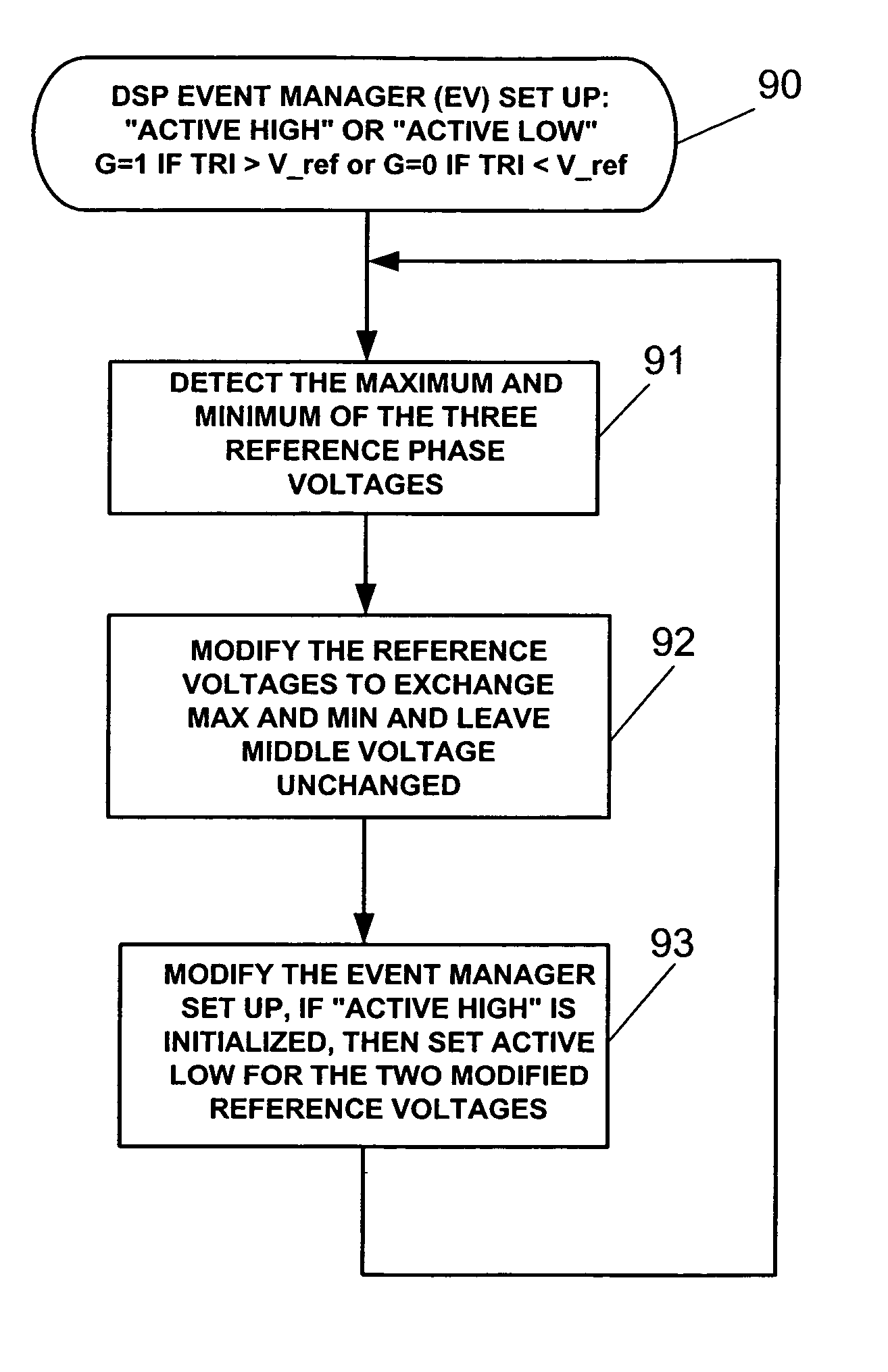
Methods and apparatus for reducing the common mode voltage generated by eliminating zero-voltage vectors in a rectifier / inverter variable frequency drive (VFD) system includes comparing three phase voltages to each other to determine a maximum voltage in one phase, a minimum voltage in another phase and a middle voltage in still another phase, inverting phase voltages for one phase having the maximum voltage and another phase having the minimum voltage, comparing the phase voltages to a carrier wave to determine gating signals for three respective phases of the inverter, and inverting gating signals for the one phase having the maximum voltage and for another phase having the minimum voltage to reduce the common mode voltage in the motor. In one embodiment, the zero-voltage vectors are removed by relating a first plurality of gating signals and a plurality of sector logic signals in a logic table to a second plurality of gating signals that are applied to phases of the inverter
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
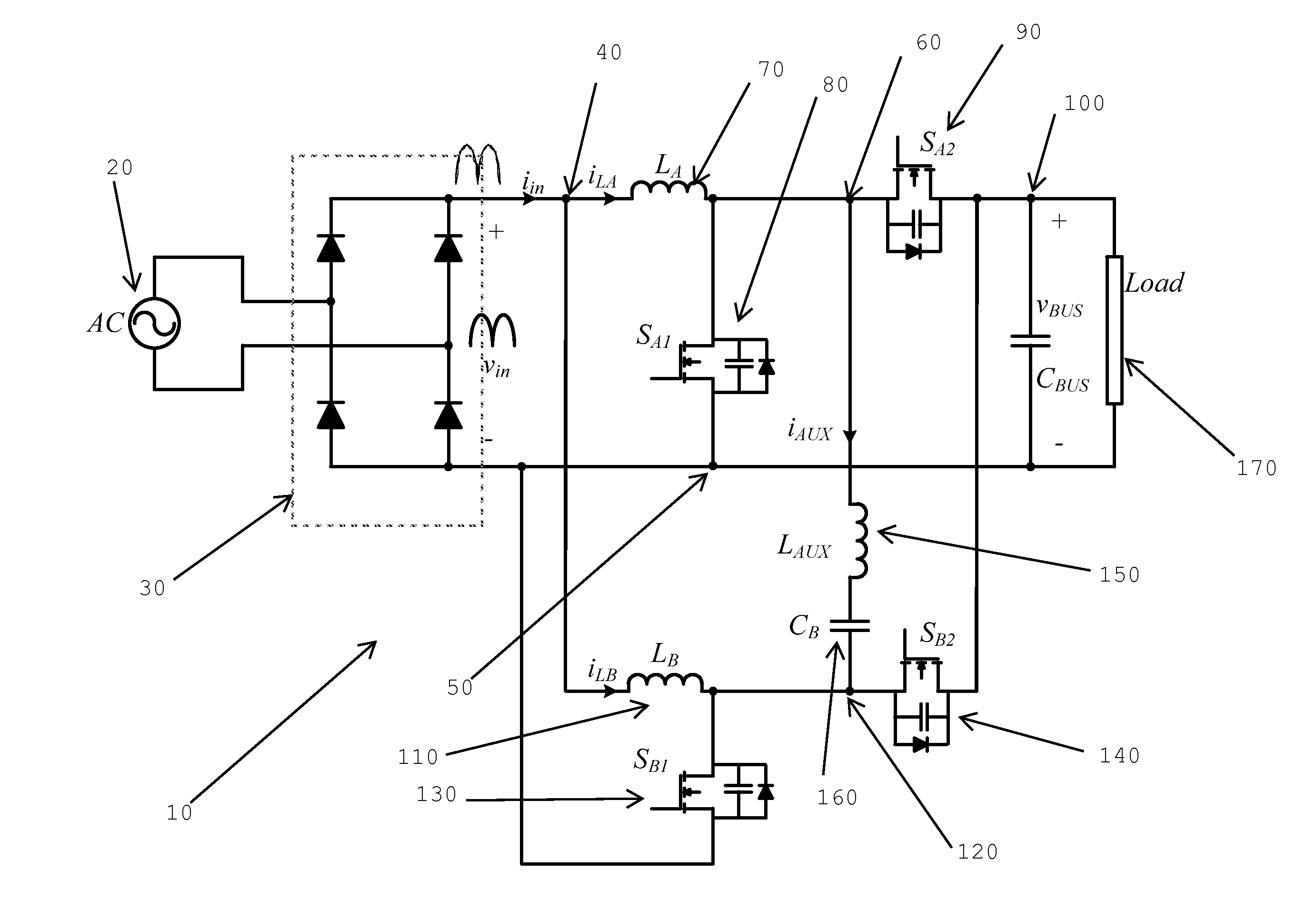
Zero voltage switching interleaved boost ac/dc converter
ActiveUS20130235631A1Ac-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionPhase shiftedPower factor
Circuits and methods relating to the provision of a reactive current to ensure zero voltage switching in a boost power factor correction converter. A simple passive circuit using a series connected inductor and capacitor are coupled between two phases of an interleaved boost PFC converter. The passive circuit takes advantage of the 180° phase-shift between the two phases to provide reactive current for zero voltage switching. A control system for adjusting and controlling the reactive current to ensure ZVS for different loads and line voltages is also provided.
Owner:SPARQ SYST INC
Three-Level Active Neutral Point Clamped Zero Voltage Switching Converter
ActiveUS20120218785A1Improve efficiencyHigh level conversionEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionThree levelSwitching cycle
A main circuit of a three-level active neutral point clamped voltage source converter having a pair of additional main switches provides two paths between an output node and a neutral point in which one of the paths involves only switches of an inner pair of switches that are operated at a high frequency. An auxiliary circuit operating at a high frequency for only a brief period during each high frequency switching cycle selects the path involving only the inner switches and provides operation with zero voltage switching and avoids reverse recovery of diodes connected antiparallel with the main and additional main switches. Accordingly, turn-on switching losses in the main switches is avoided and the voltage source converter can be operated at increased frequency to allow reduction in size of magnetic components and full potential power transfer to be achieved.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Power supply unit, hard disk drive and method of switching the power supply unit
InactiveUS20100232180A1Improve efficiencyBroadEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcCapacitanceHard disc drive
Zero volt switching during a light load is performed in such a manner that through an ON / OFF control of switches provided for a full bridge circuit and the synchronous rectifier switches in a rectifier and smoothing circuit, a resonant peak voltage necessary for the zero voltage switching determined by the output current flowing to output terminals, a resonant inductor and a resonant capacitor capacitance is ensured so that an energy accumulated in the rectifier and smoothing circuit is returned to the full bridge circuit so as to act as equivalent as when the output current is increased and to increase the current flowing through the full bridge circuit.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
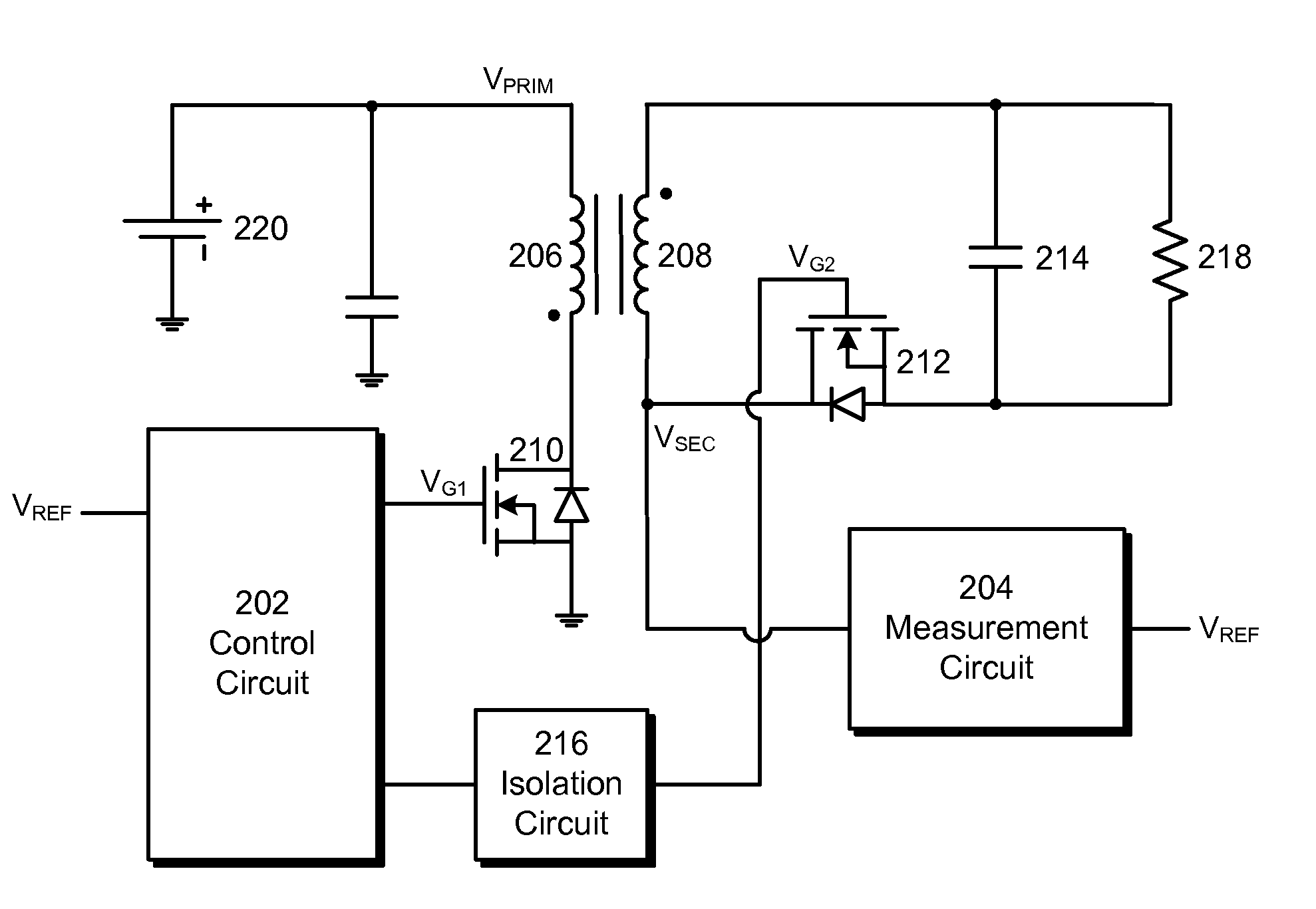
Switch controller, switch control method, and power supply device comprising the switch controller
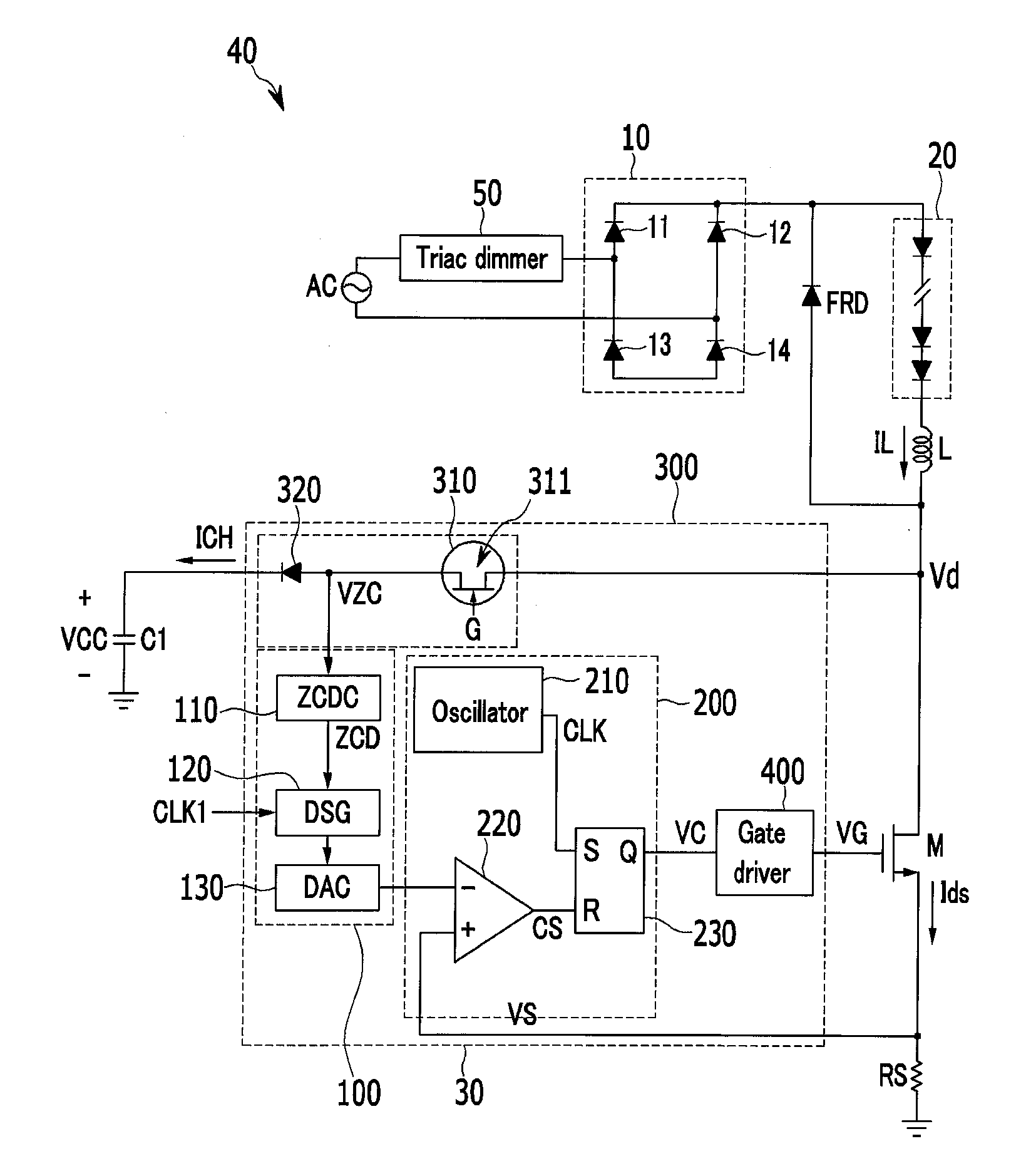
ActiveUS20130215655A1Enhanced digital signalAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcCharge currentPower flow
An exemplary embodiment of the present invention relates to a switch controller, a method for controlling a switch, and a power supply including the switch controller. According to the exemplary embodiment of the present invention, an AC input passed through a dimmer is rectified such that an input voltage is generated, and the input voltage is transmitted to the power switch. A charging current is generated using a voltage that depends on the input voltage, a zero cross-point at which the input voltage becomes zero voltage is detected using a detection voltage output from a current source, and a reference signal synchronized at the detected zero cross-point is generated.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
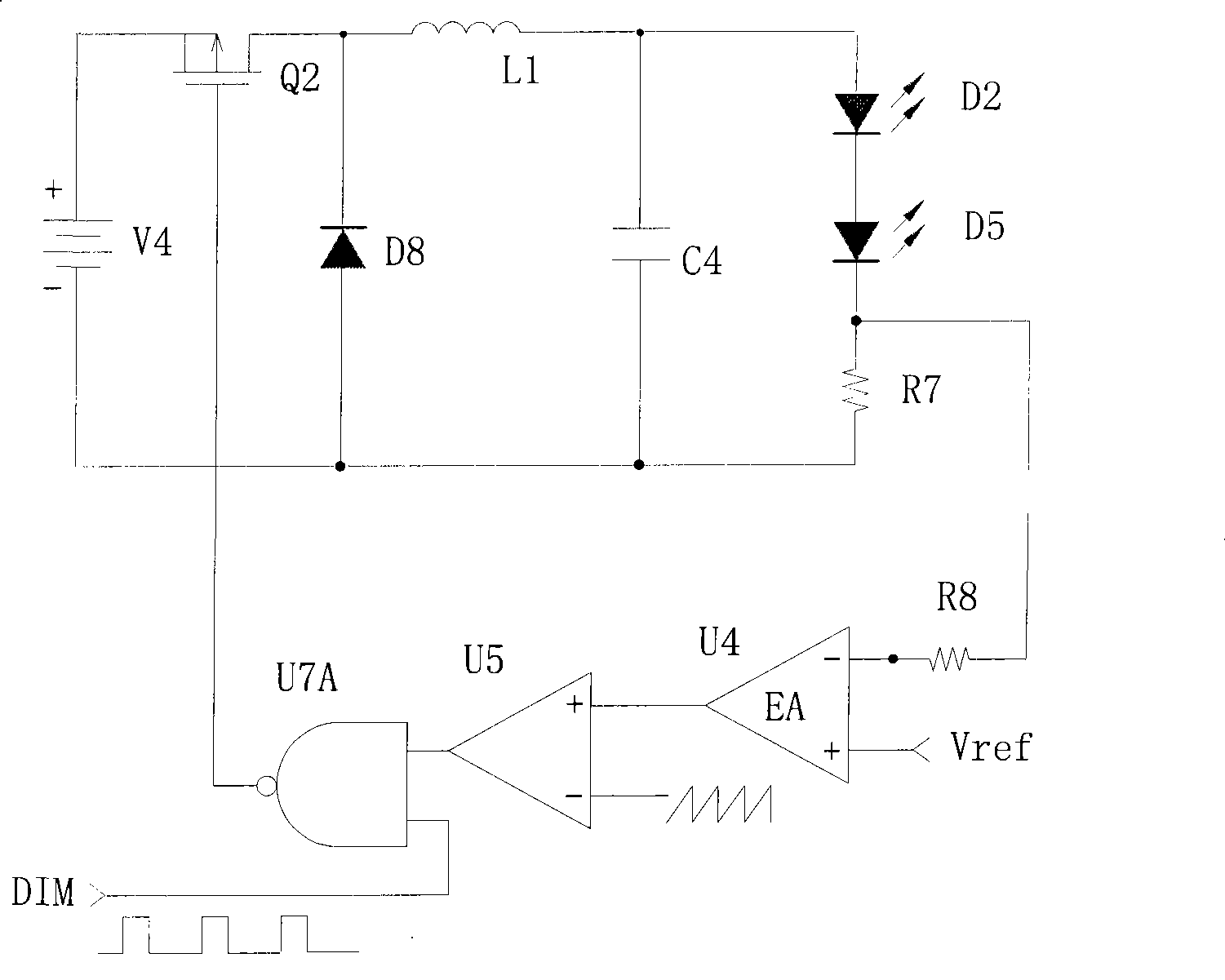
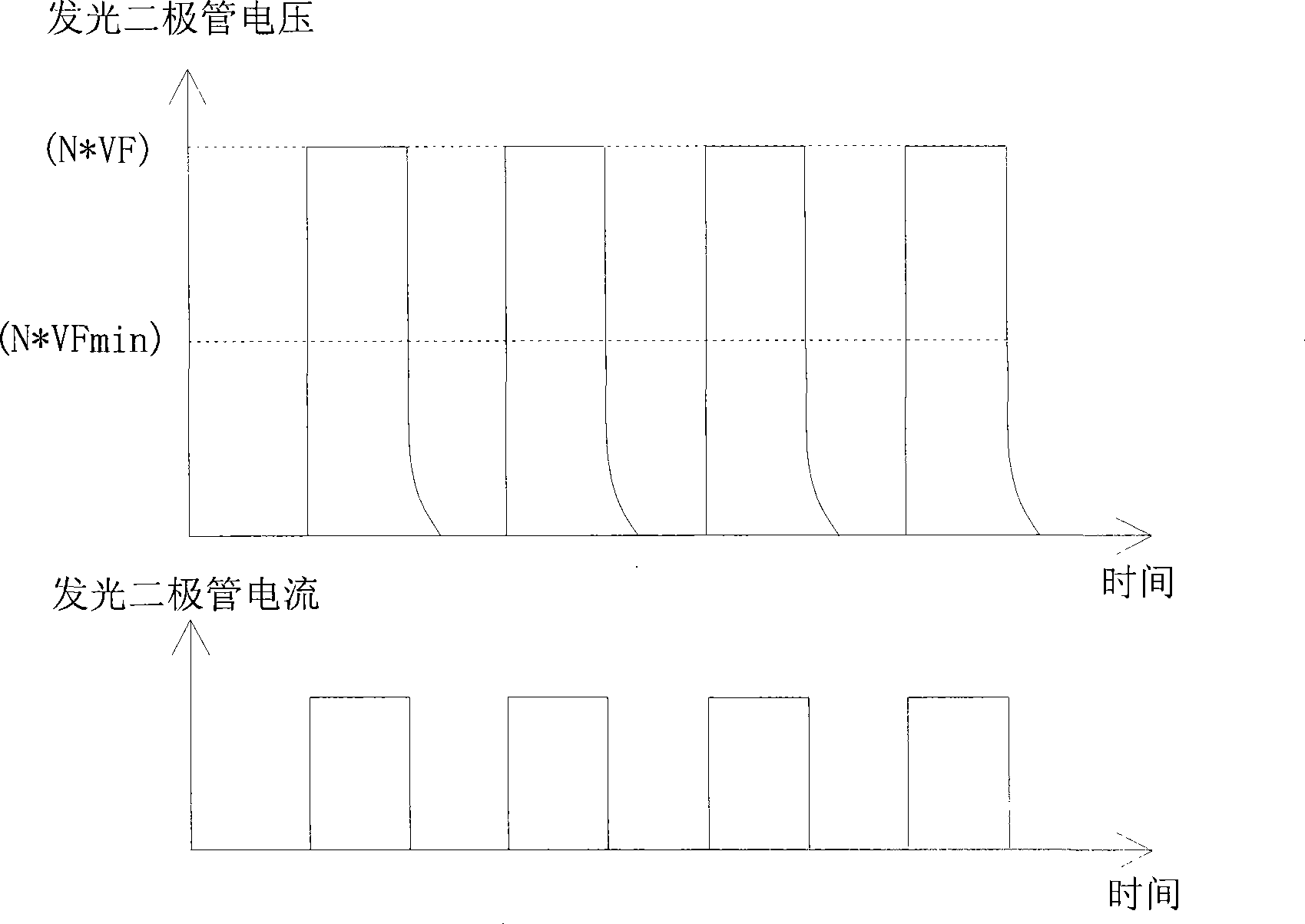
LED driving circuit and secondary side controller thereof
InactiveCN101489335ALow costOptimize layoutPoint-like light sourceElectric circuit arrangementsComputer moduleEngineering
A light emitting diode driving circuit of the invention and a secondary side controller control the output voltage to a first driving voltage or a second driving voltage. When the output voltage is in the first driving voltage, the light emitting diode module can be in a stable light emitting state. When the output voltage is in the second driving voltage, the output voltage is approximately in the threshold voltage (larger than zero voltage) of light emitting diode module so that the light emitting diode module hardly radiates. Thus the variation of voltage applied to the light emitting diode module is less than the present voltage variation in light modulation process, thereby avoiding the problem of overlarge voltage stress or inaccurate light modulation control of light emitting diodein prior art.
Owner:NIKO SEMICON
Fully clamped coupled inductors in power conversion circuits
InactiveUS7606051B1Improve electromagnetic compatibilitySmall sizeEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionActive clampLeakage inductance
The subject invention reveals improvement methods for circuits that use a coupled inductor wherein overshoot and ringing associated with leakage inductance of said coupled inductor is entirely eliminated by addition of non-dissipative active clamp networks that clamp each winding during each operating state of a power supply containing said coupled inductor. A further improvement applicable to zero voltage switching circuits that employ an inductor for driving a zero voltage turn on switching transition of a switch enables elimination of said inductor and preserves said zero voltage switching properties by adding leakage inductance to a coupled inductor without any adverse overshoot and ringing effects associated with said leakage inductance. The subject invention also reveals a coupled inductor with enhanced leakage inductance which can be used with said other improvements. Example circuits including zero voltage switching flyback and forward converters which require only one magnetic circuit element are revealed. Zero voltage switching tapped inductor buck and boost converters with a single magnetic circuit element are also revealed.
Owner:WITTENBREDER JR ERNEST HENRY
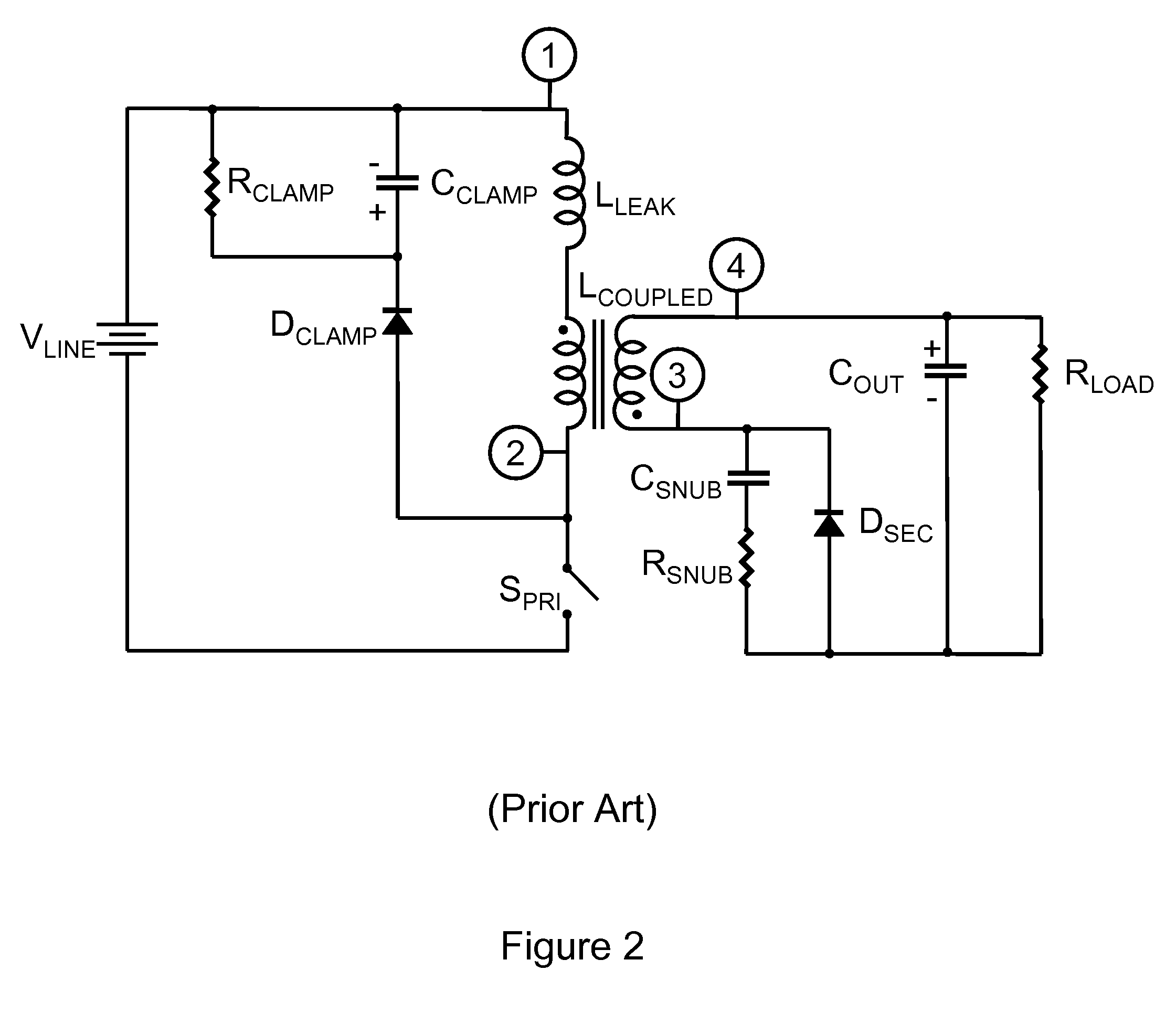
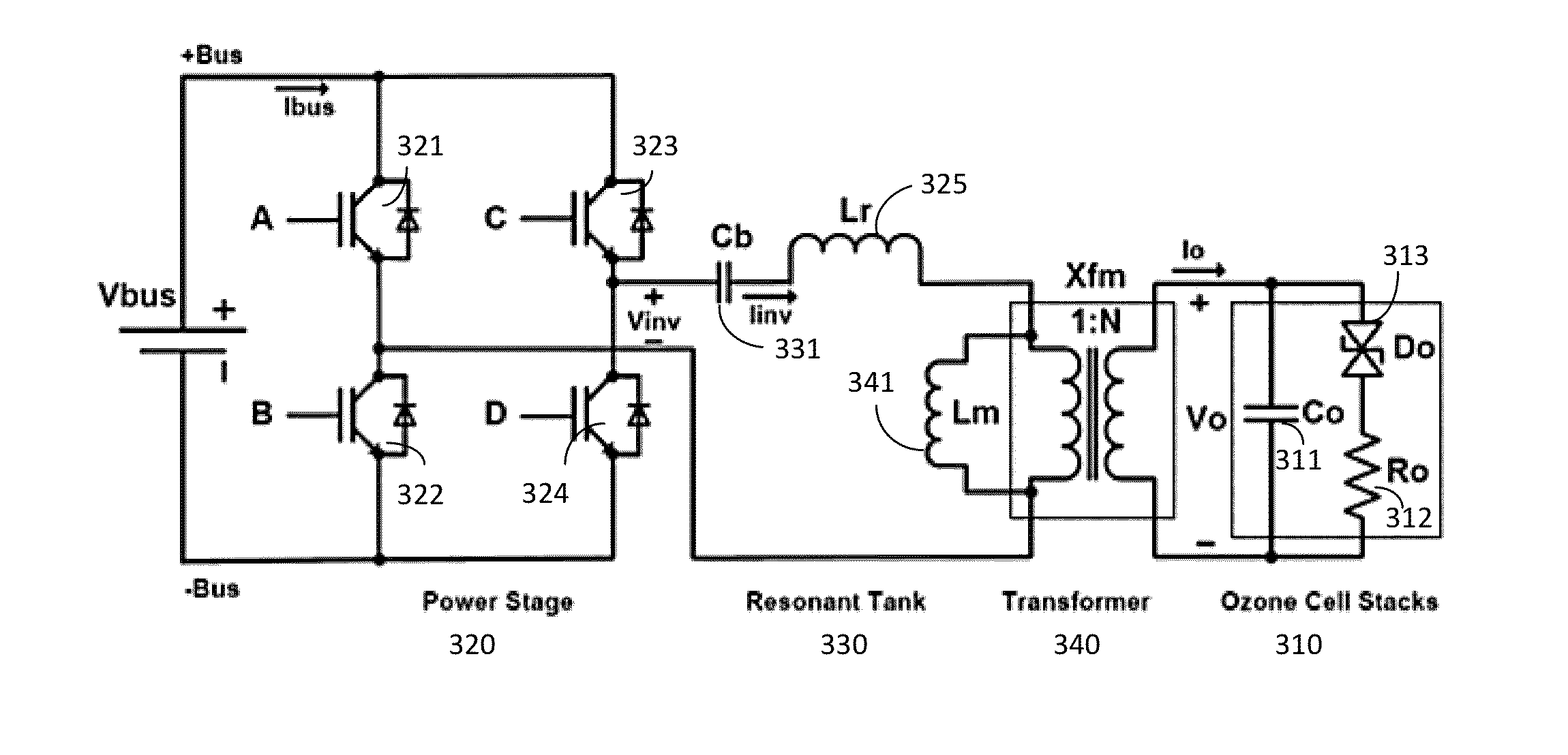
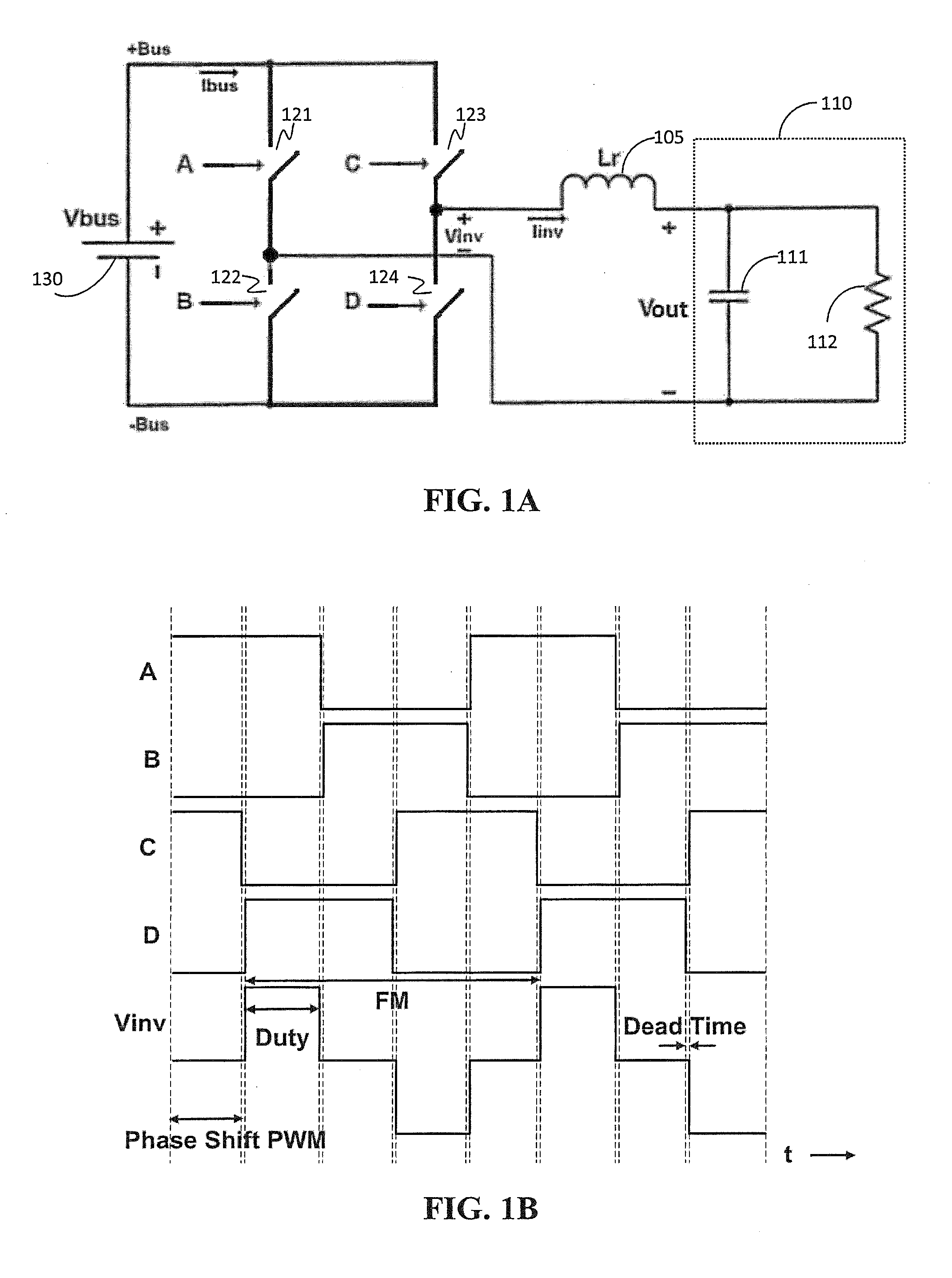
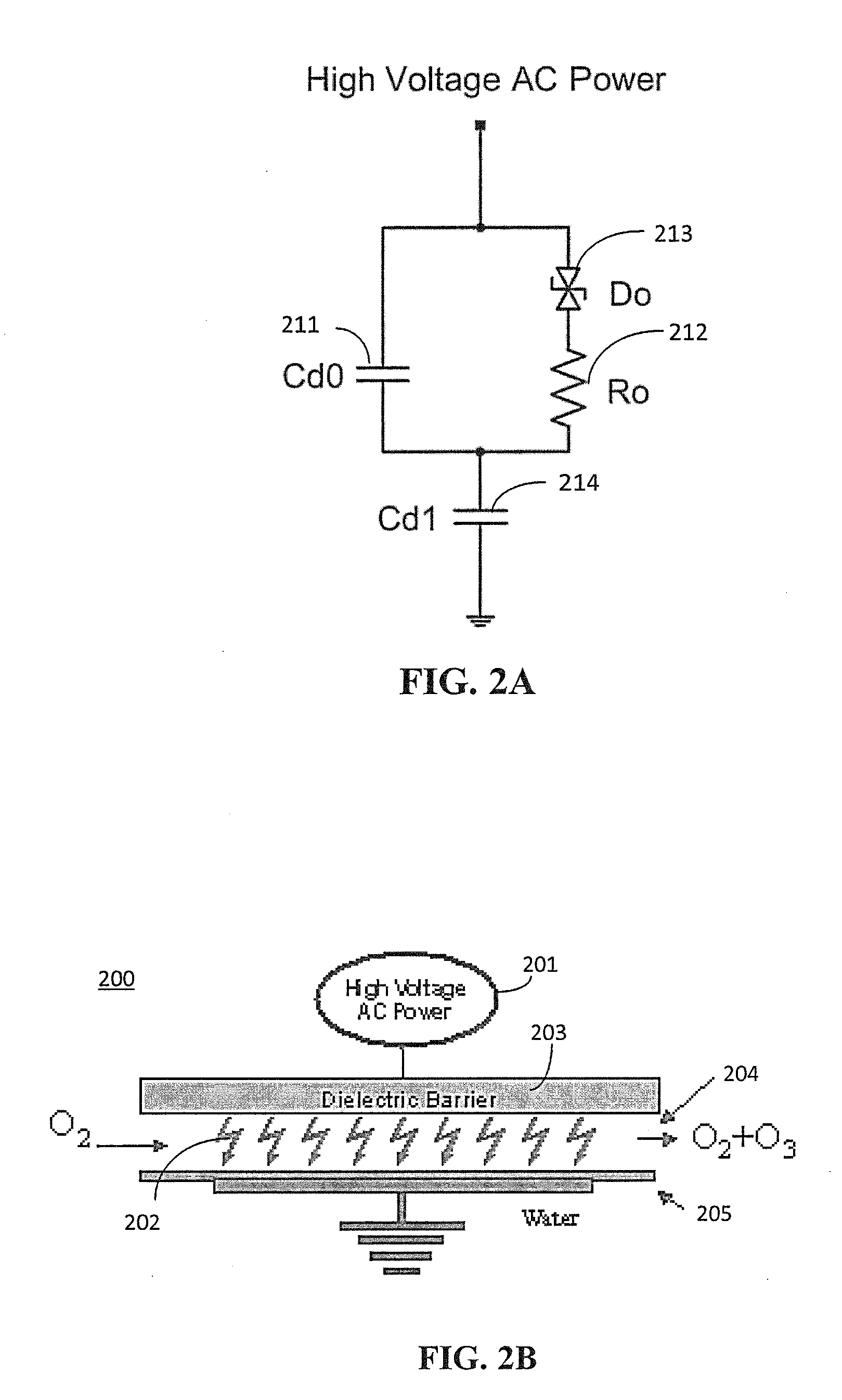
Versatile zero-voltage switch resonant inverter for industrial dielectric barrier discharge generator applications
ActiveUS20130257311A1Improve dynamic rangeImprove stabilityElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesResonant inverterSoft switching
A power system for a dielectric barrier discharge system, such as used for generating ozone, can include a full bridge inverter stage and parallel resonant tank outputting a signal for powering a dielectric barrier discharge cell stack. The inverter stage is controlled using a combination of pulse width modulation (PWM) and frequency modulation (FM) to enable soft switching through all load conditions—from full load to light load. A current control loop error amplifier compensator can provide a duty cycle adjustment signal to a phase shift PWM controller chip that generates the switching signals for the inverter stage. A feedback signal is also used to adjust a clock frequency time constant of the PWM controller chip to provide the FM. In one embodiment, the feedback signal is an output of an inverting amplifier connected at an output of the current control loop error amplifier compensator.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
High efficiency coupled inductor soft switching power converters
InactiveUS6272023B1Reduce switching lossesLow component part countEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcEngineeringVoltage source
The power converter of this invention accomplishes zero voltage switching at both turn on and turn off transitions of all primary switches. A pair of coupled inductors serve as both energy storage devices and isolation mechanisms. The placement of a small inductor in series with the coupled inductors enables the invariance of primary current direction throughout the switching transition which provides for zero voltage switching for all switches for all transitions. The power converter behaves as a pair of interleaved coupled inductor buck converters with oppositely directed magnetizing currents. During a first half cycle, while one inductor is coupled to the output, the other uncoupled inductor behaves as a current source, setting the primary winding currents for both inductors equal to the magnetizing current of the uncoupled inductor. The inductor which is coupled to the output appears as an output filter capacitor or voltage source to the uncoupled inductor during the first half cycle. During the alternate half cycle the roles of the two inductors are reversed.
Owner:TECHN WITTS
Zero voltage switch method for synchronous rectifier and inverter
InactiveUS20070109822A1Reduce switching lossesWithout compromising efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionLower limitReverse current
The zero voltage switch (ZVS) method for the synchronous rectifiers and inverter. The ZVS method for synchronous rectifier, in which the rectifier diode is replaced by a bi-directional-current one directional-voltage blocking capability switch, by allowing and terminating current flow in a reverse direction, achieves zero voltage turn-on on both inverter and rectifier switches. The ZVS method of the present invention includes: increasing an inductor current to a current upper limit with a first switch module active; decreasing the inductor current with the first switch module open and a second switch module passive; decreasing the inductor current with a second switch module active; turning the second switch module open when the inductor current turns negative; increasing the inductor current from a current lower limit with the first switch module passive; and increasing the inductor current with the first switch module active with zero voltage.
Owner:KUAN KAN SHENG
Soft transition converter
InactiveUS6862195B2Total current dropReduce reverse recovery lossEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcSoft switchingFull bridge
The present invention is a circuit and method for reducing switching and reverse recovery losses in the output rectifiers while creating zero voltage switching conditions for the primary switchers. There are described two output configurations, one employing a soft commutation inductor element a bridge rectifier and a output filter capacitor, the second using a soft commutation inductor element a rectification-filtering bridge composed by two capacitors and two capacitors. Both secondary circuits can be driven by three primary circuits. A first circuit is a full bridge with phase shift control, and a second circuit is a half bridge topology with an additional bydirectional switch which achieves two goals, on to get soft switching commutation across all the primary switches, the second to create the right waveforms in the secondary suitable with the claims in this invention. The third topology is a phase shifted two transistors forward. The circuits claimed in this invention can provide soft commutation across the primary switching elements and secondary rectifier means, clamping the voltage across the rectifiers to the output voltage eliminating the need for snubbers circuits both in primary and the secondary section.
Owner:DELTA ENERGY SYST SWITZERLAND
Zero voltage switching in flyback converters with variable input voltages
ActiveUS20130148385A1Reduce power lossEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionBuck converterPeak value
The disclosed embodiments provide a system that operates a flyback converter. During operation, the system senses an input voltage for the flyback converter. Next, the system uses the input voltage to determine a negative peak current that enables zero voltage switching for a primary switch in the flyback converter. Finally, the system uses the negative peak current to perform the zero voltage switching for the primary switch based on the input voltage, wherein the negative peak current reduces a power loss of the flyback converter.
Owner:APPLE INC
Adjustable resonant buck converter
ActiveUS20130043854A1Reduce power consumptionLower average currentEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionLoad circuitPower flow
A power converter includes first and second circuit modules, a first capacitor, a second diode and a control module. The first circuit module includes a switching element in parallel with a first diode. The second circuit module includes a first inductor and the first circuit module. The inductor is in series with the first circuit module. The first capacitor is in parallel with the second circuit module. The second diode includes a first terminal and a second terminal, where the first terminal is in series with the second circuit module and the first capacitor, and the second terminal is coupled to a second power terminal. The control module varies one or more of the first capacitor and the first inductor based on at least one of a current of a load circuit or an input voltage. A resonating waveform is generated by a resonant circuit of the second circuit and is used by the control module to turn off the switching element under zero-current and zero-voltage conditions.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
Highly efficient isolated AC/DC power conversion technique
ActiveUS7375994B2Improve efficiencyReduced Power RequirementsAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionTransformerEngineering
An AC-to-DC power converter that is capable of generating a regulated, isolated DC voltage output from a power factor corrected AC voltage input with improved efficiency. The AC-to-DC power converter is a two-stage power converter including a PFC stage connected in series to a power conversion stage. The PFC stage performs power factor correction using a zero current switching technique, and the power conversion stage includes a zero voltage switched half-bridge converter. The power conversion stage includes a transformer for providing the isolated DC voltage output. The AC-to-DC power converter includes a single feedback control loop for transferring error information from the DC voltage output to the PFC stage, thereby obtaining regulation of the DC voltage output.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Methods and apparatus for driving electro-optic displays
ActiveUS20110187684A1Reduce in quantityShorten the overall cycleCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsGray levelDisplay device
Waveforms for driving electro-optic displays, especially bistable electro-optic displays, are modified by one or more of insertion of at least one balanced pulse pair into a base waveform; excision of at least one balanced pulse pair from the base waveform; and insertion of at least one period of zero voltage into the base waveform. Such modifications permit fine control of gray levels.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Dynamic pulse plating for high aspect ratio features
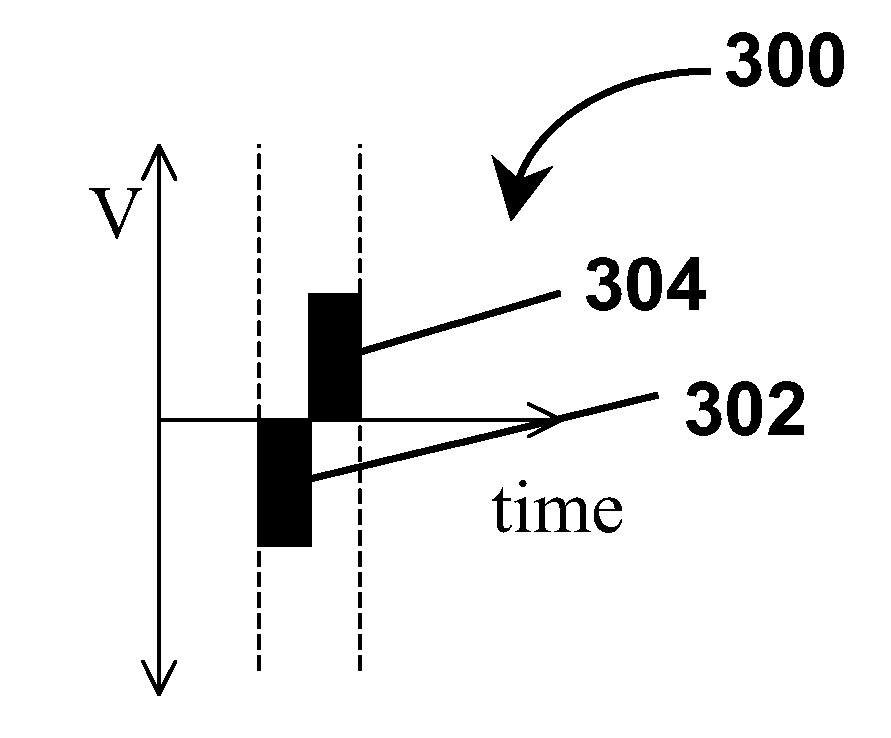
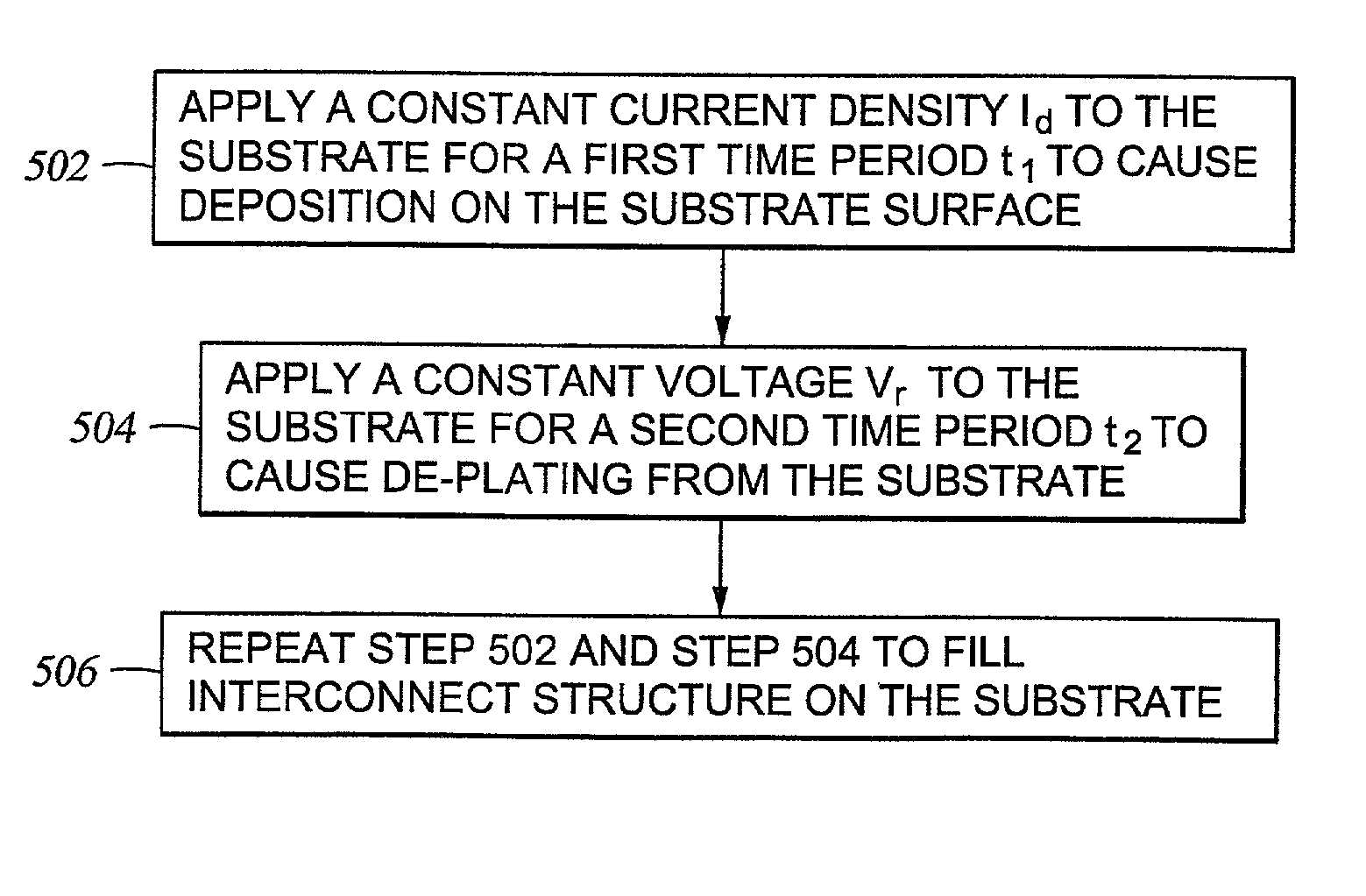
A method for depositing a metal on a substrate is provided. The metal is deposited by sequentially applying a electrodeposition pulse followed by an electrodissolution pulse to the substrate. After each electrodissolution pulse an before the next electrodeposition pulse there is provided at least one time interval of zero electrical voltage or current, also known as an "off-time", between the pulses. The first two electrodeposition pulses should preferably have the same time durations. Thereafter, the time durations of subsequent electrodeposition pulses are gradually decreased to provide a void-free and seam-free deposition of metal in high aspect ratio features.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Soft-switched power converters
ActiveUS20050226012A1Reduce switching lossesEffect efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsSnubberSoft switch
A soft-switched boost converter includes an active snubber to provide soft switching of all semiconductor components. Specifically, the current (“turn-off current”) in the rectifier is switched off at a controlled rate, the main switch is closed under zero-voltage switching (ZVS) condition, and the auxiliary switch in the active snubber is opened under zero-current switching (ZCS) condition. As a result, switching losses are reduced with beneficial effects on conversion efficiency and EMC performance.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com