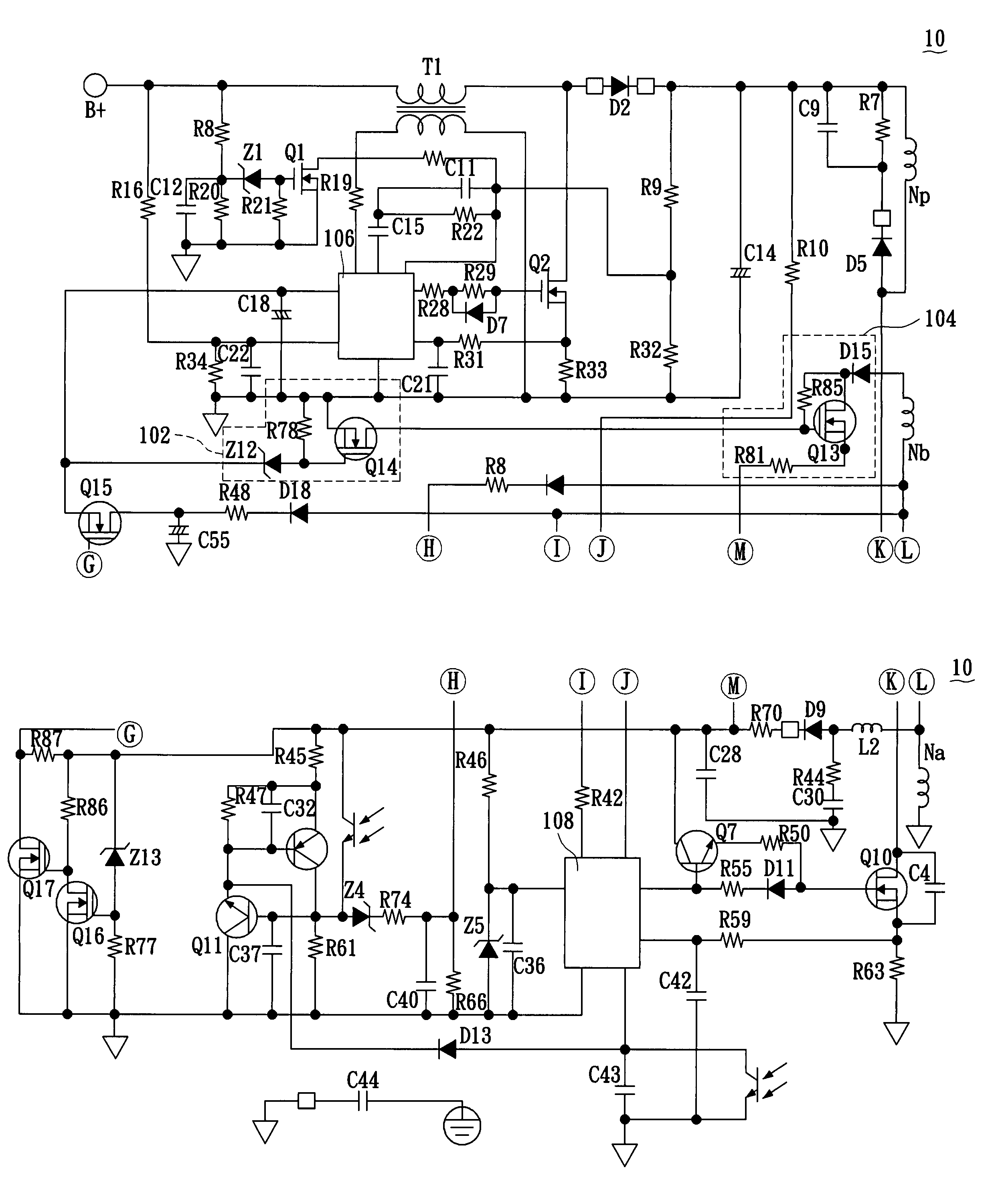
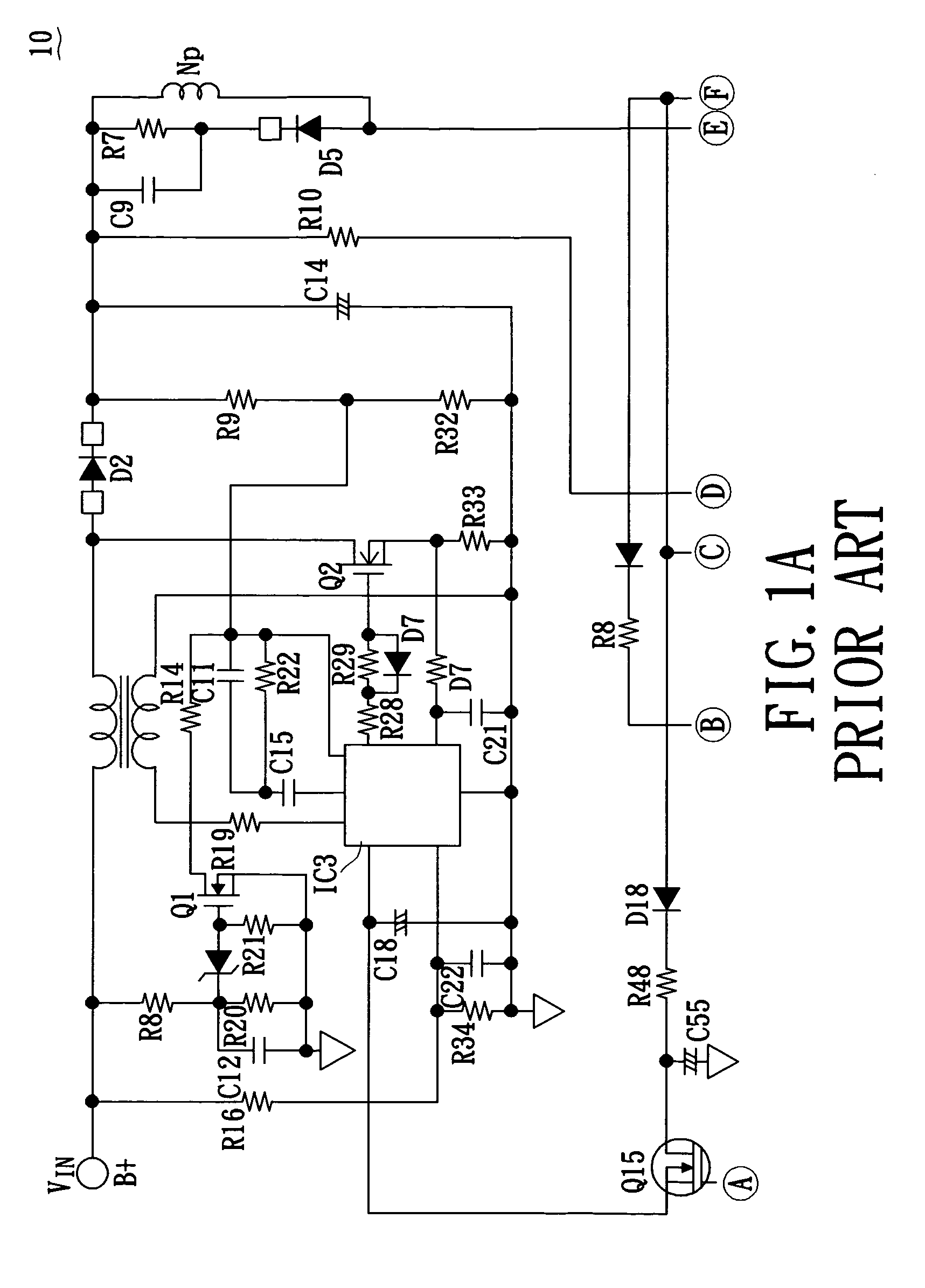
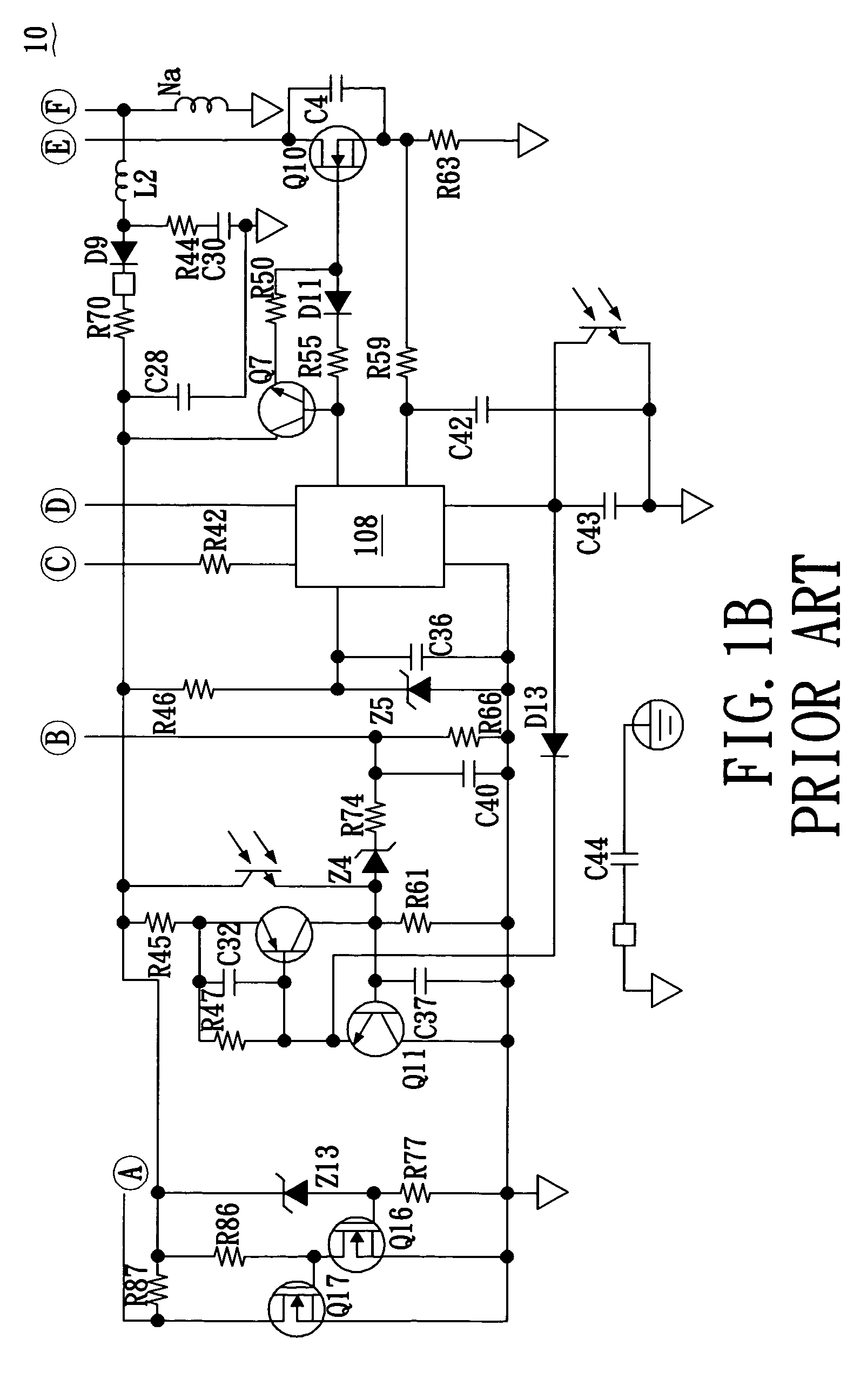
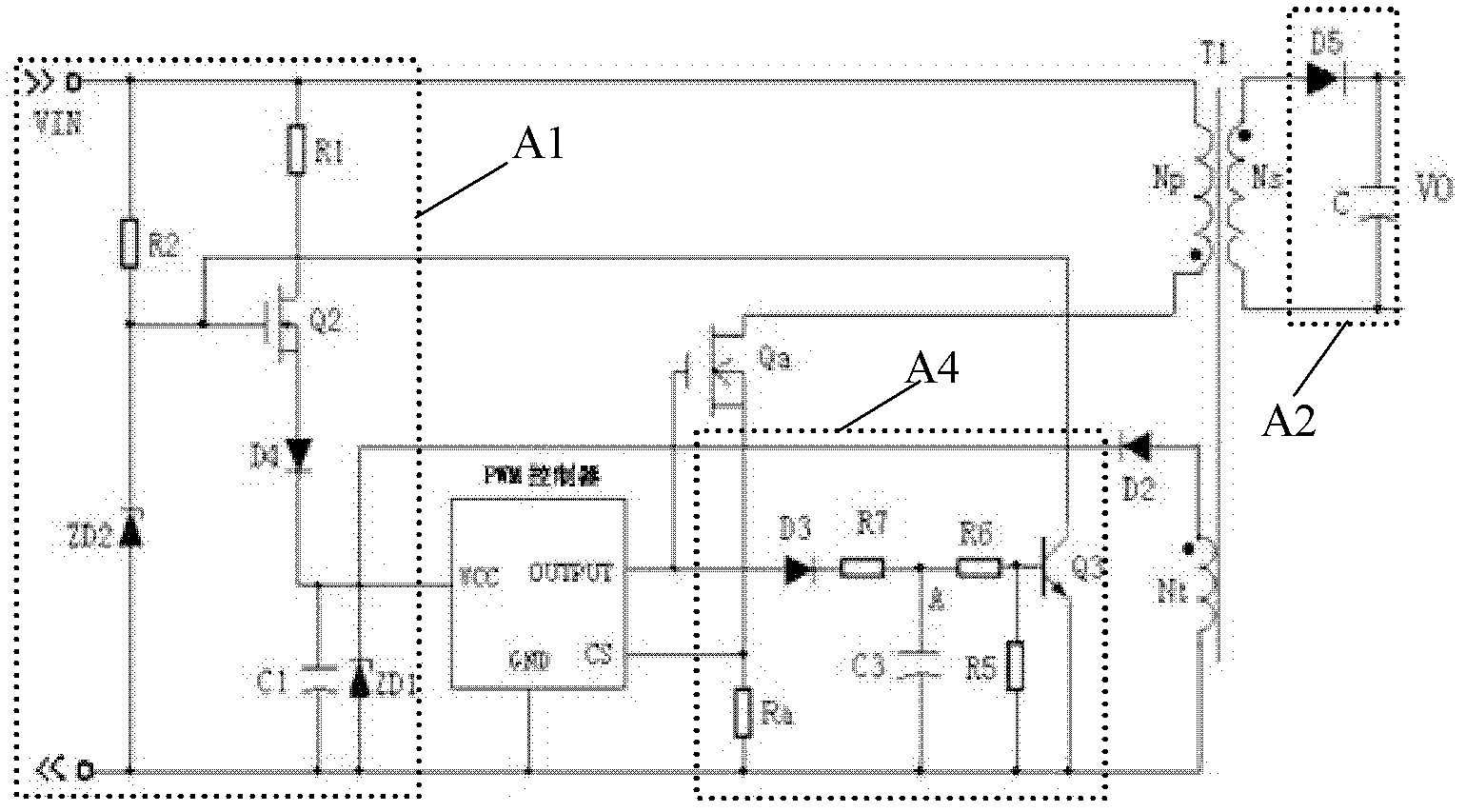
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1231 results about "Pwm controller" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
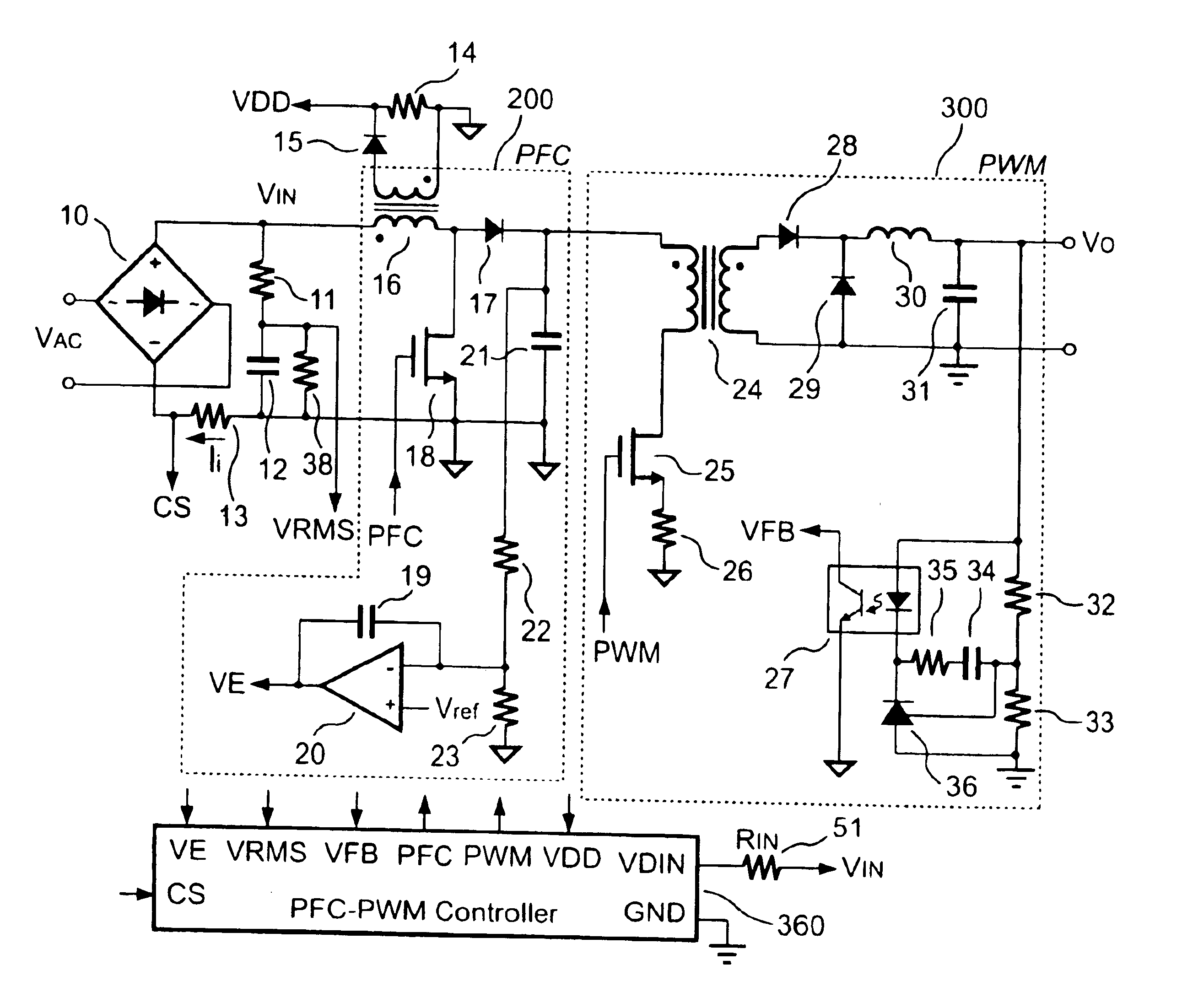
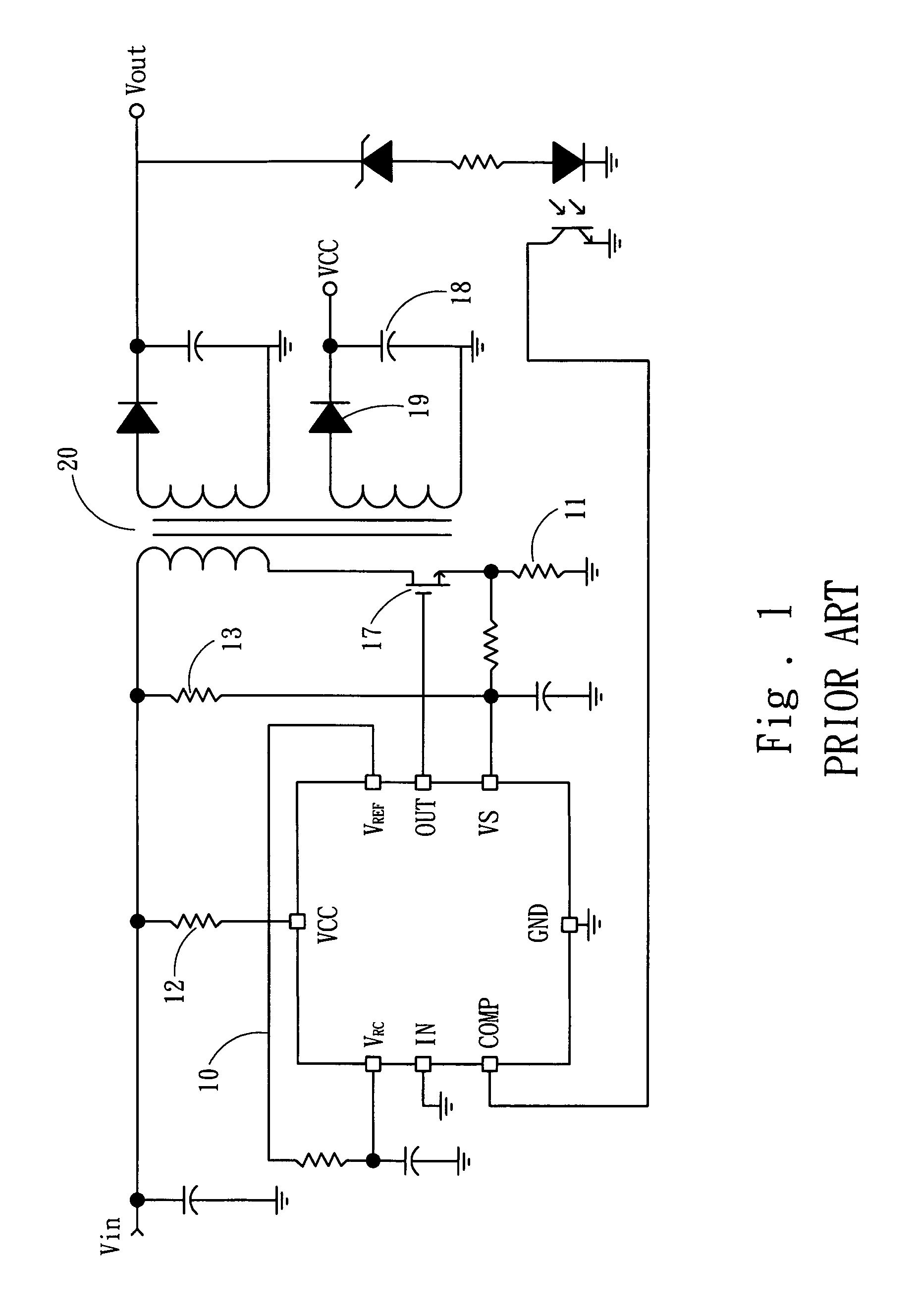
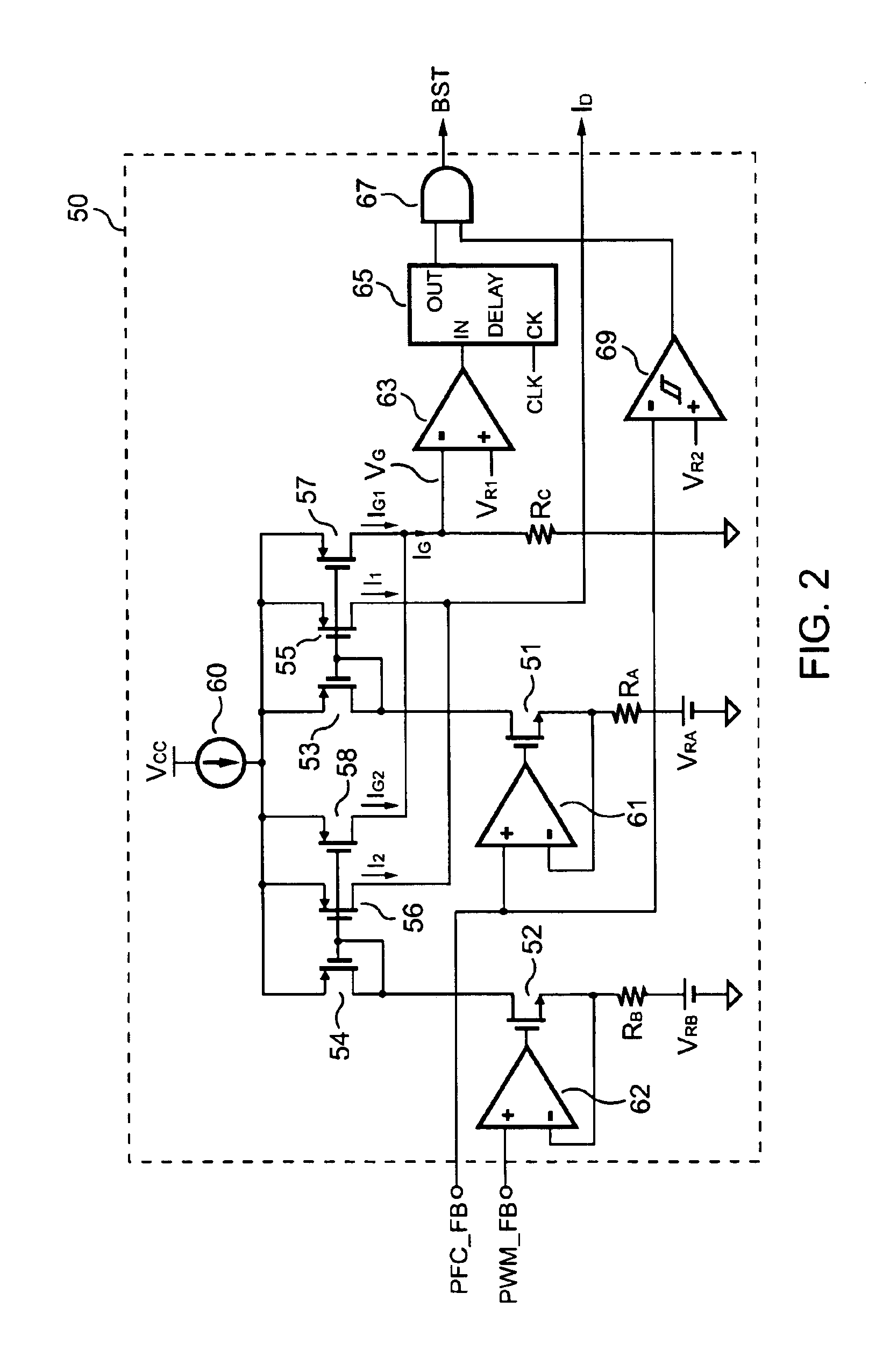
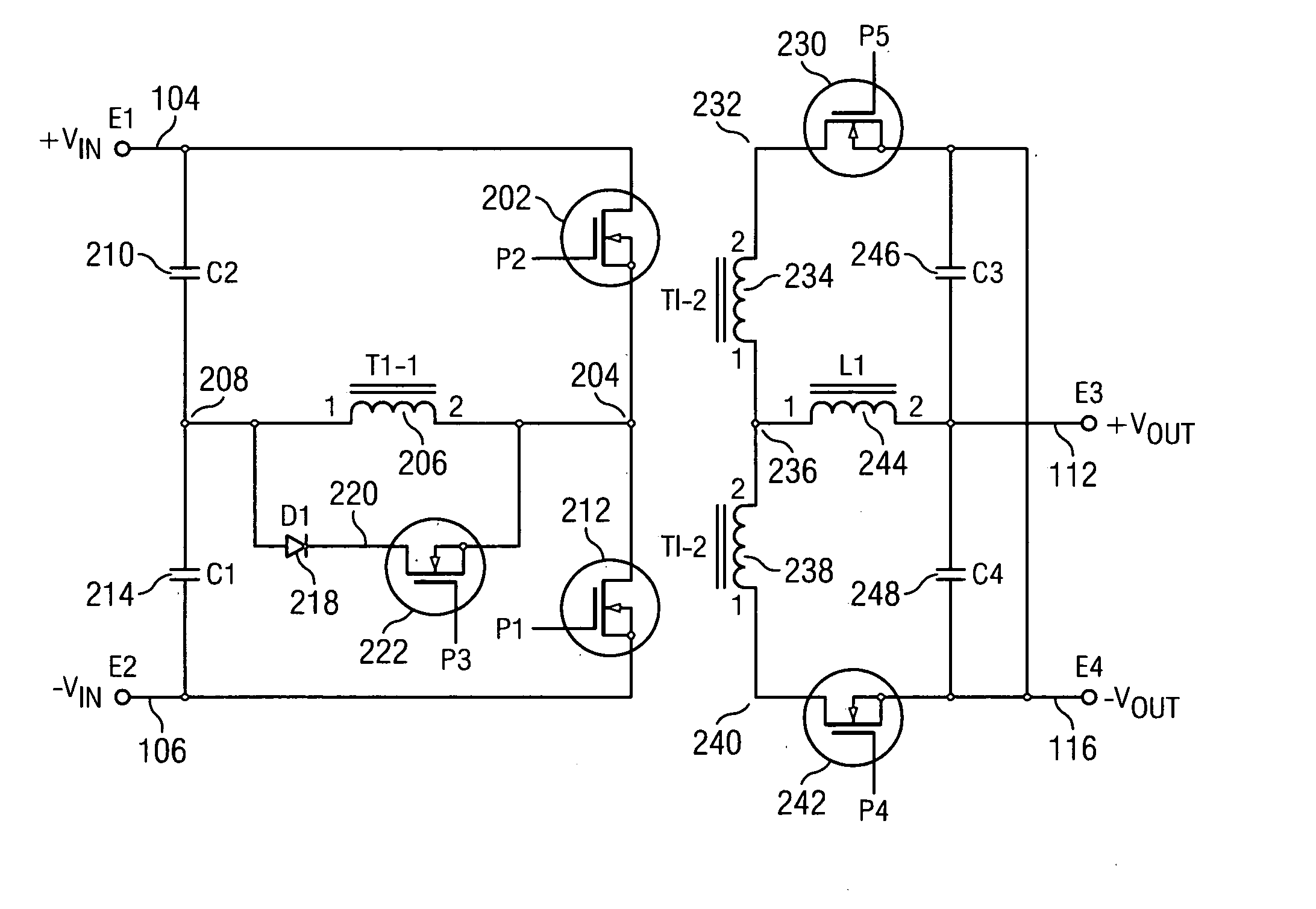
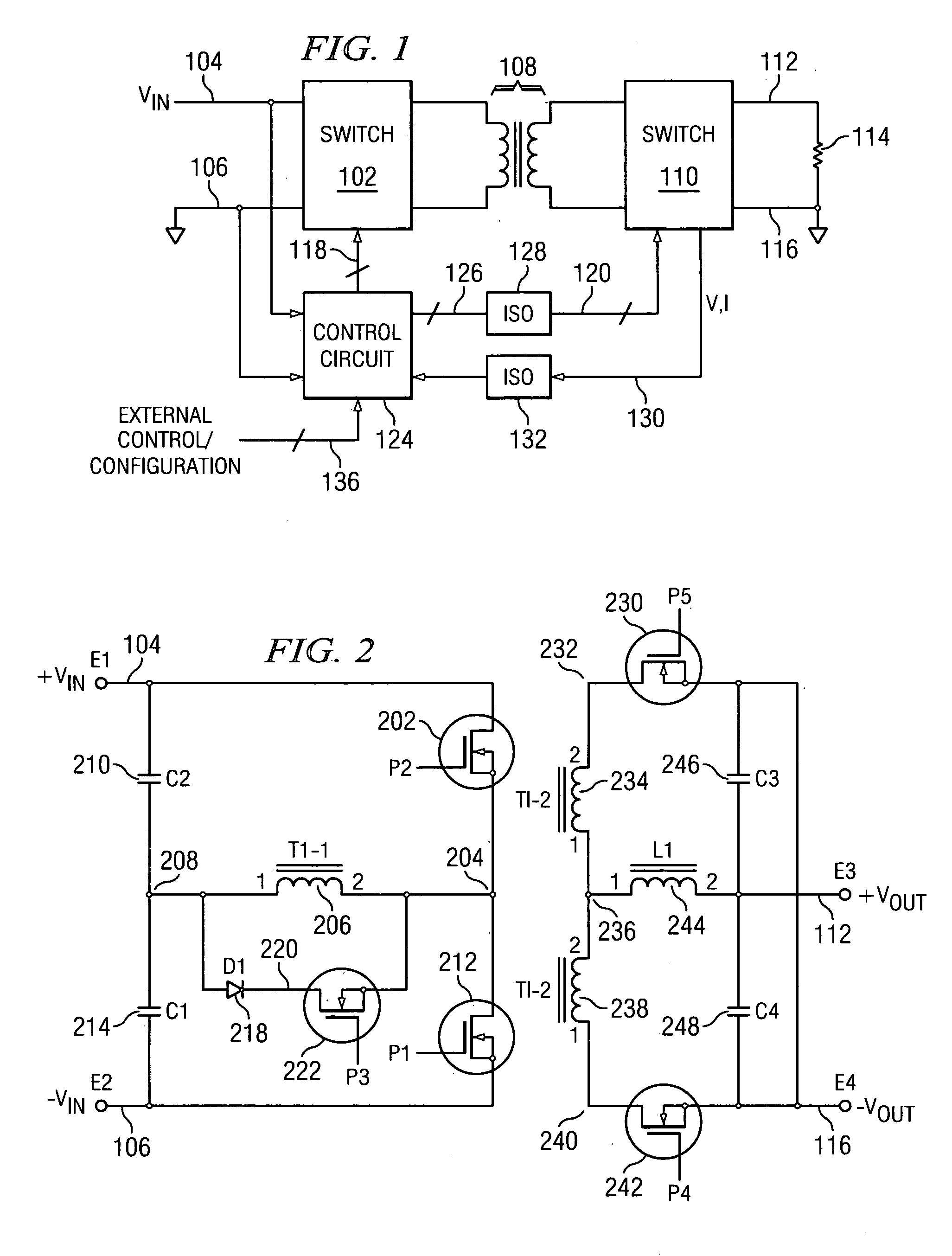
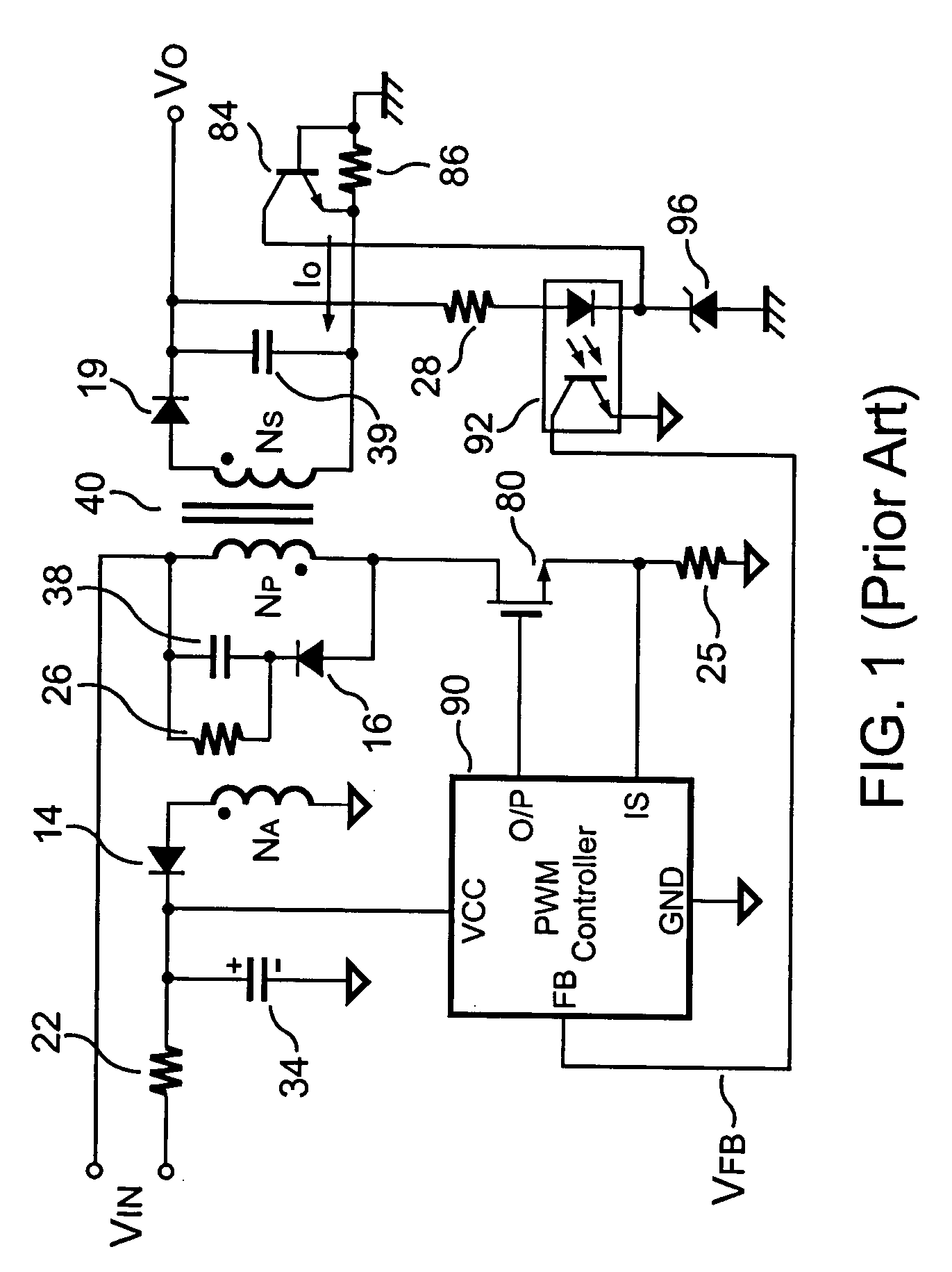
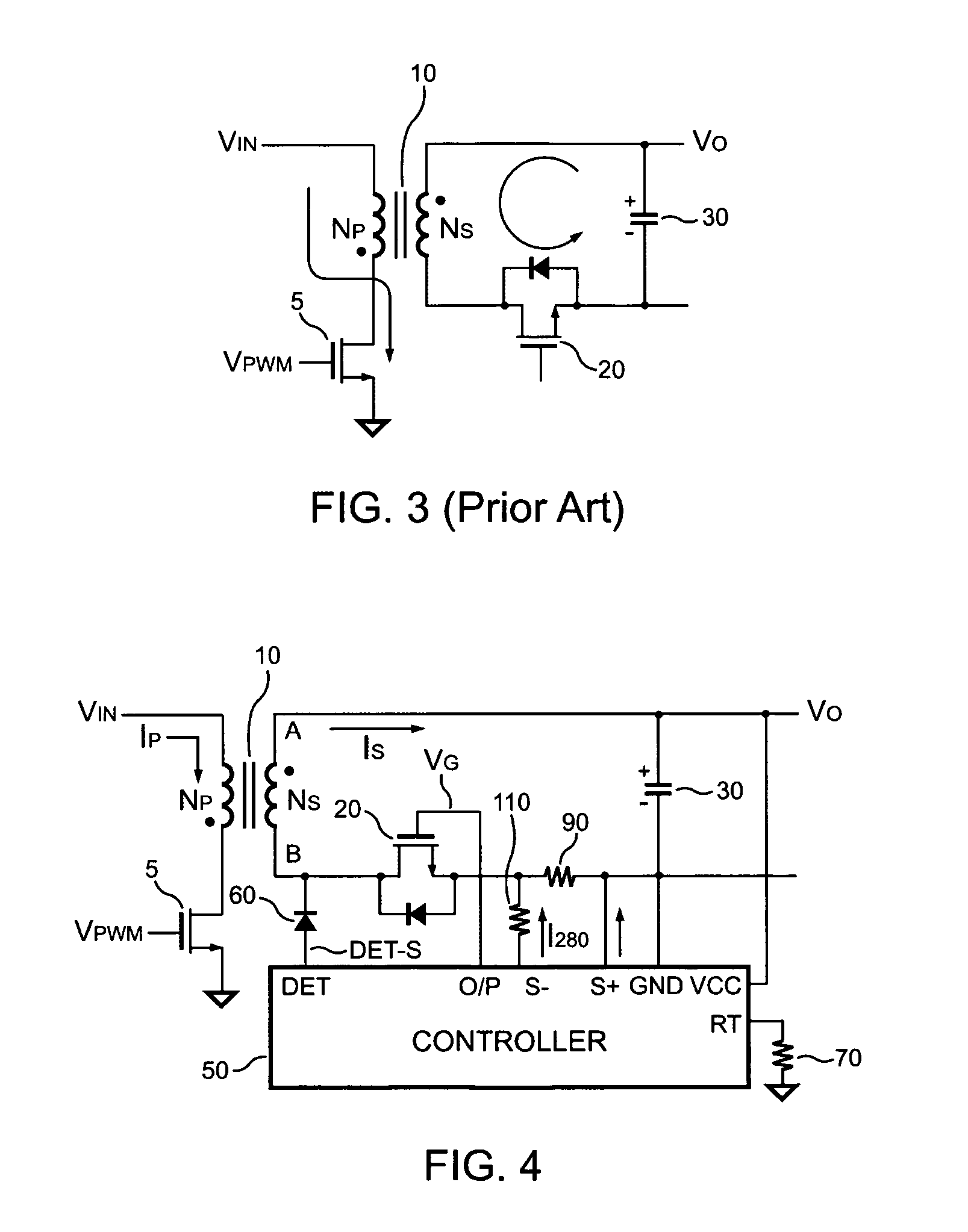
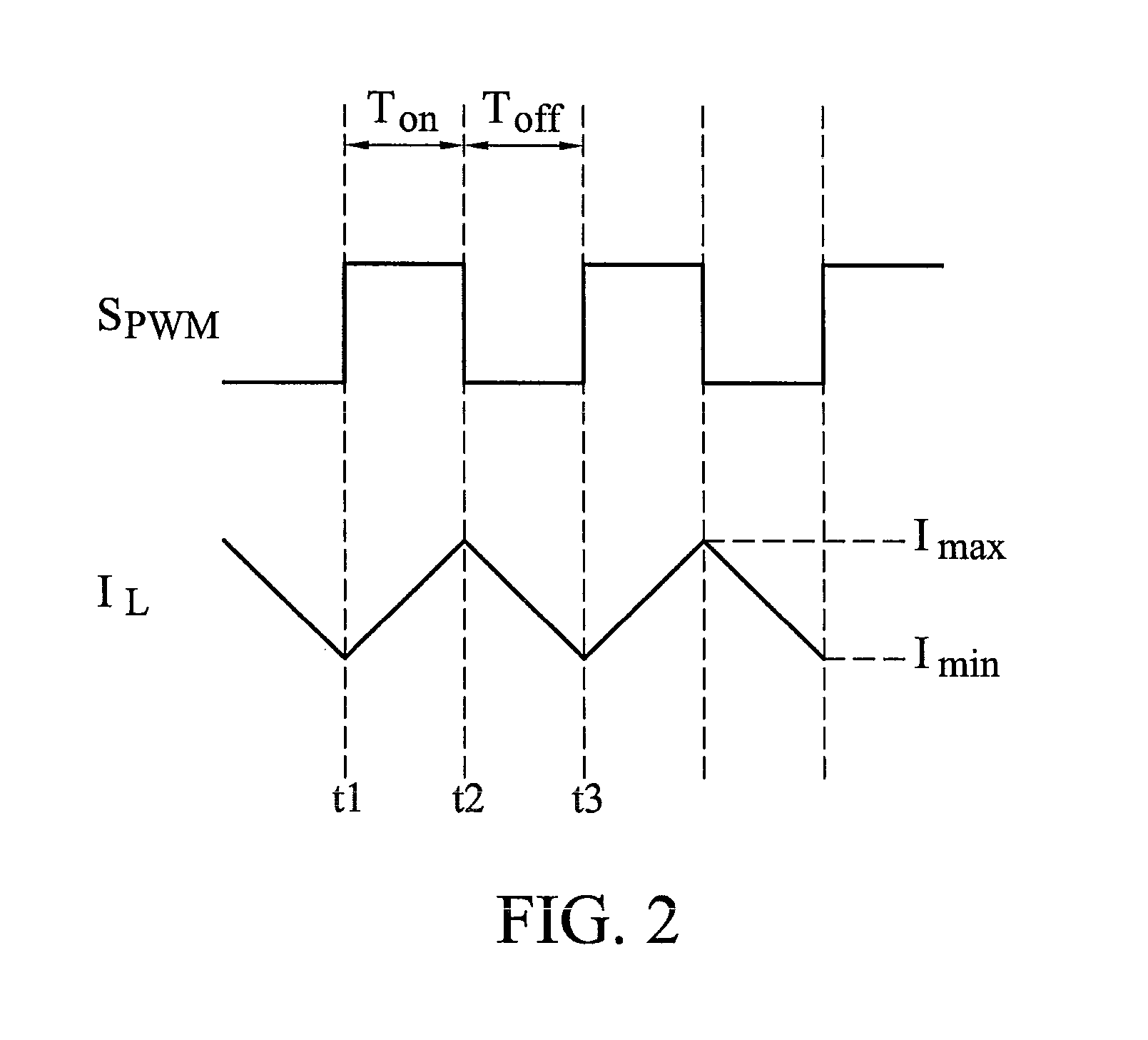
PFC-PWM controller having a power saving means
InactiveUS6839247B1Stable deliveryImprove transmission efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcSwitching signalEngineering
A PFC-PWM controller with a power saving means is disclosed. A built-in current synthesizer generates a bias current in response to feedback voltages sampled from the PWM circuit and the PFC circuit. The bias current modulates the oscillation frequency to further reduce the switching frequencies of the PWM signal and the PFC signal under light-load and zero-load conditions. Thus, power consumption is greatly reduced. The PFC and the PWM switching signals interleave each other, so that power can be transferred more smoothly from the PFC circuit to the PWM circuit. The saturation of the switching components can be avoided by limiting the maximum on-time of the PWM signal. Further, an external resistor is used to start up the PFC-PWM controller and provide an AC template signal for PFC control.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
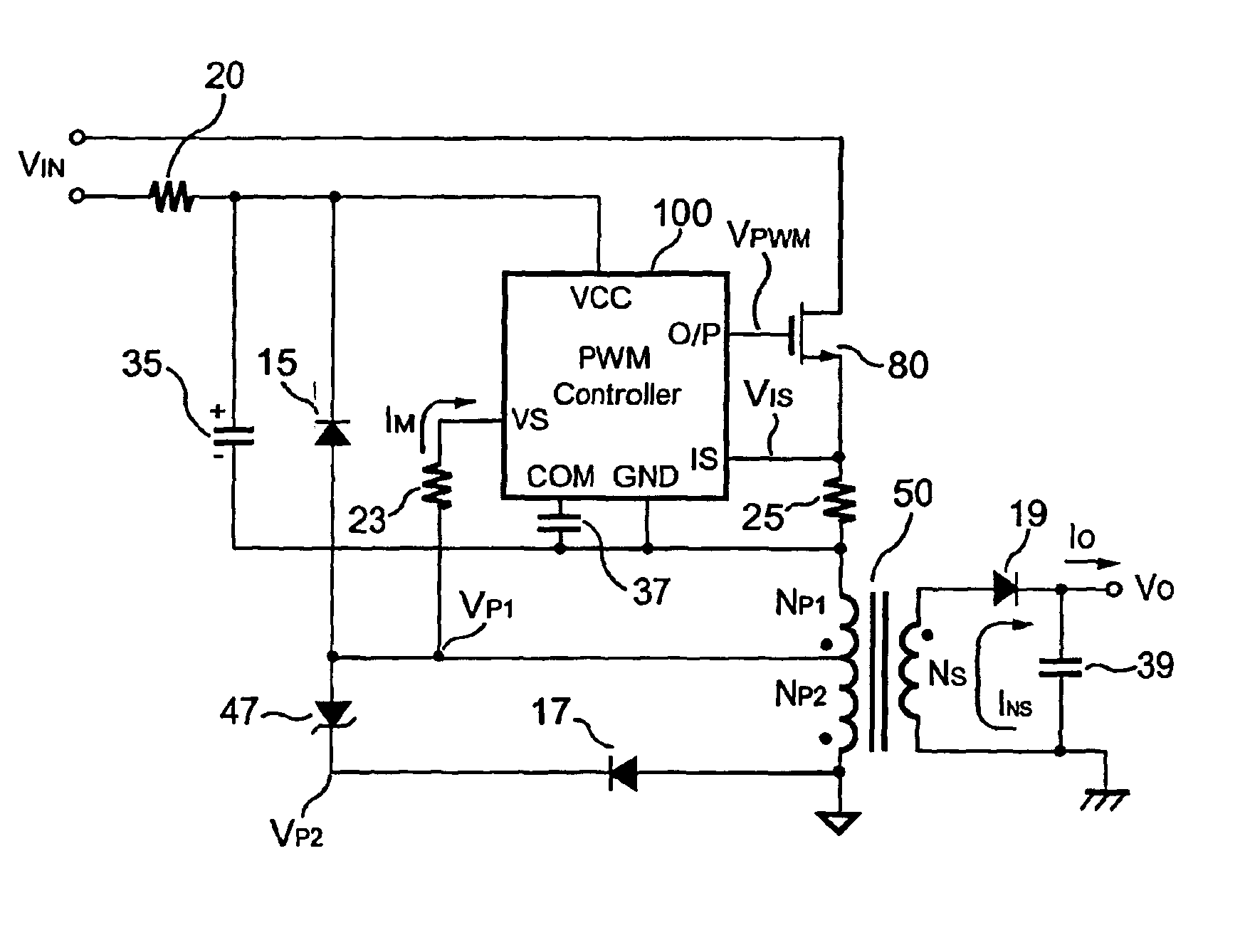
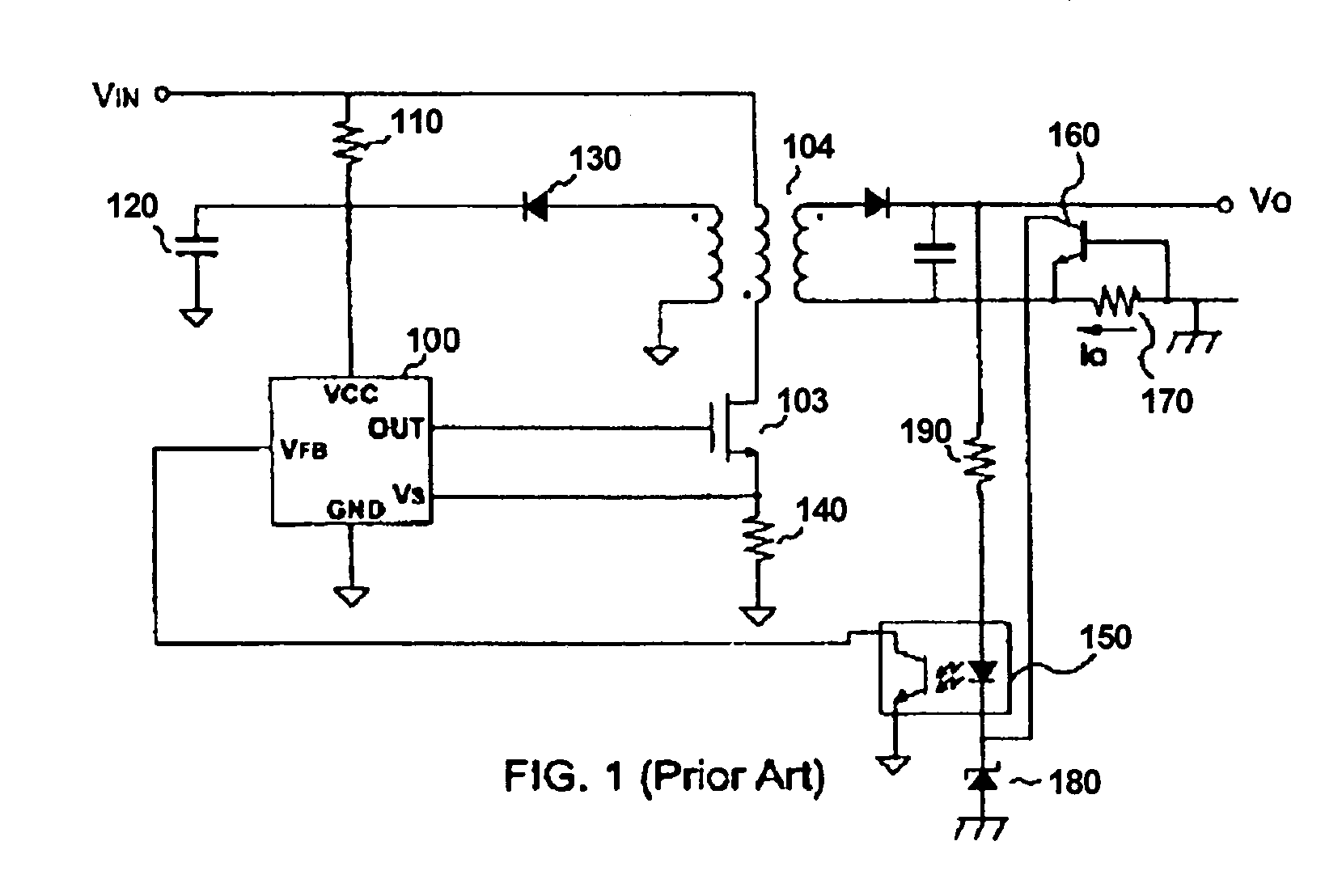
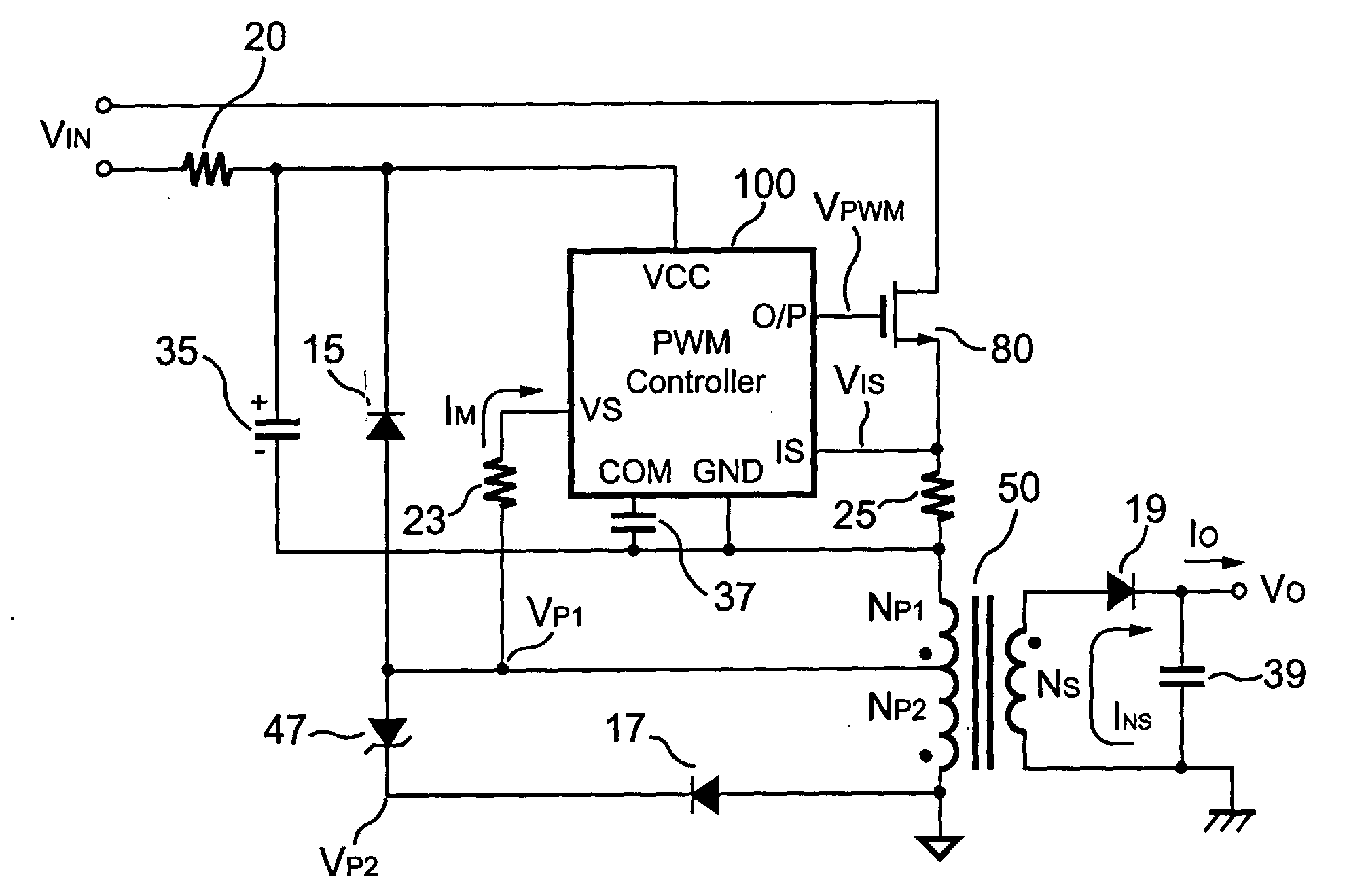
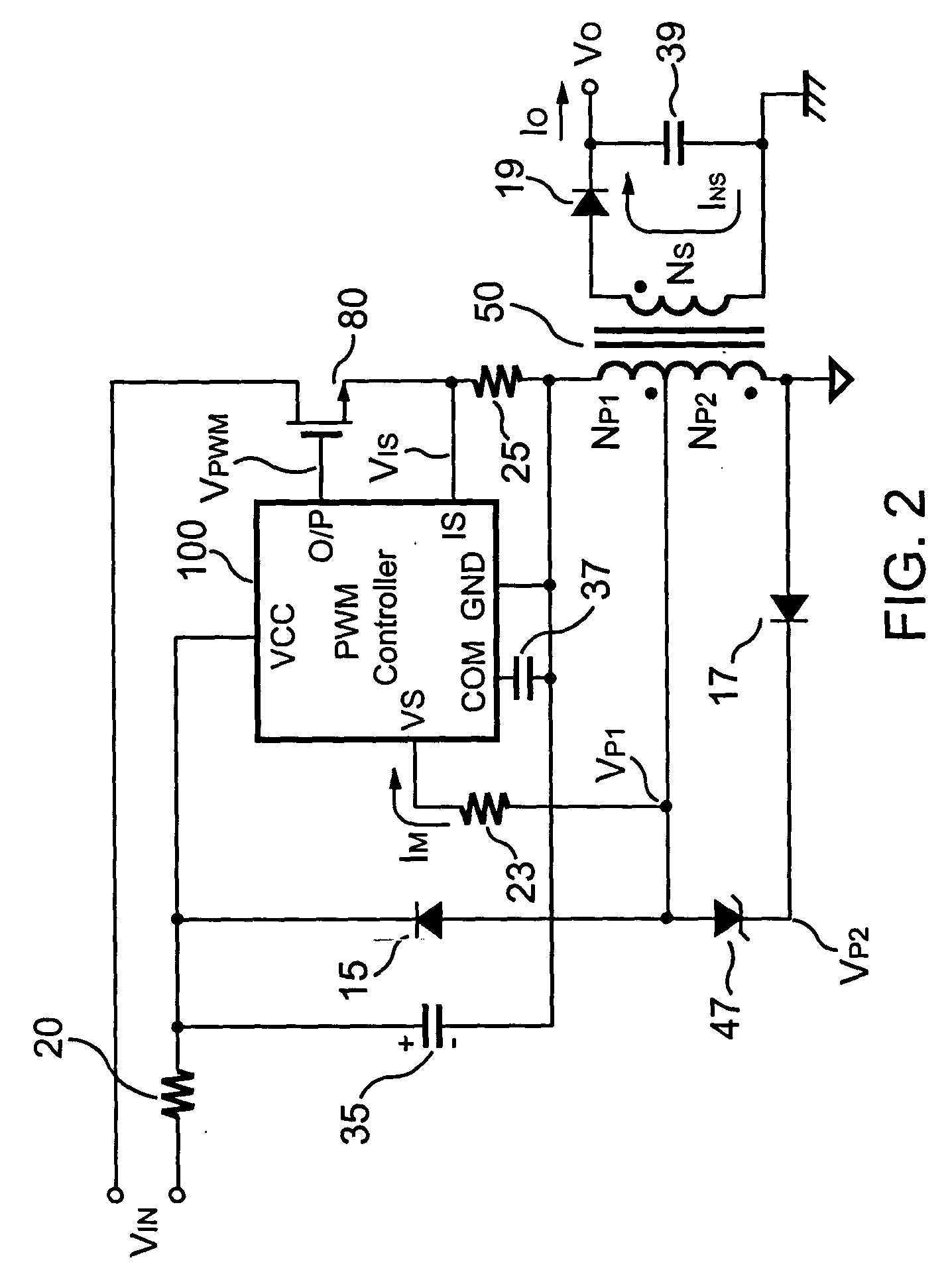
Primary-side controlled flyback power converter
InactiveUS6853563B1Low costSmall sizeEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionTransformerSwitching frequency
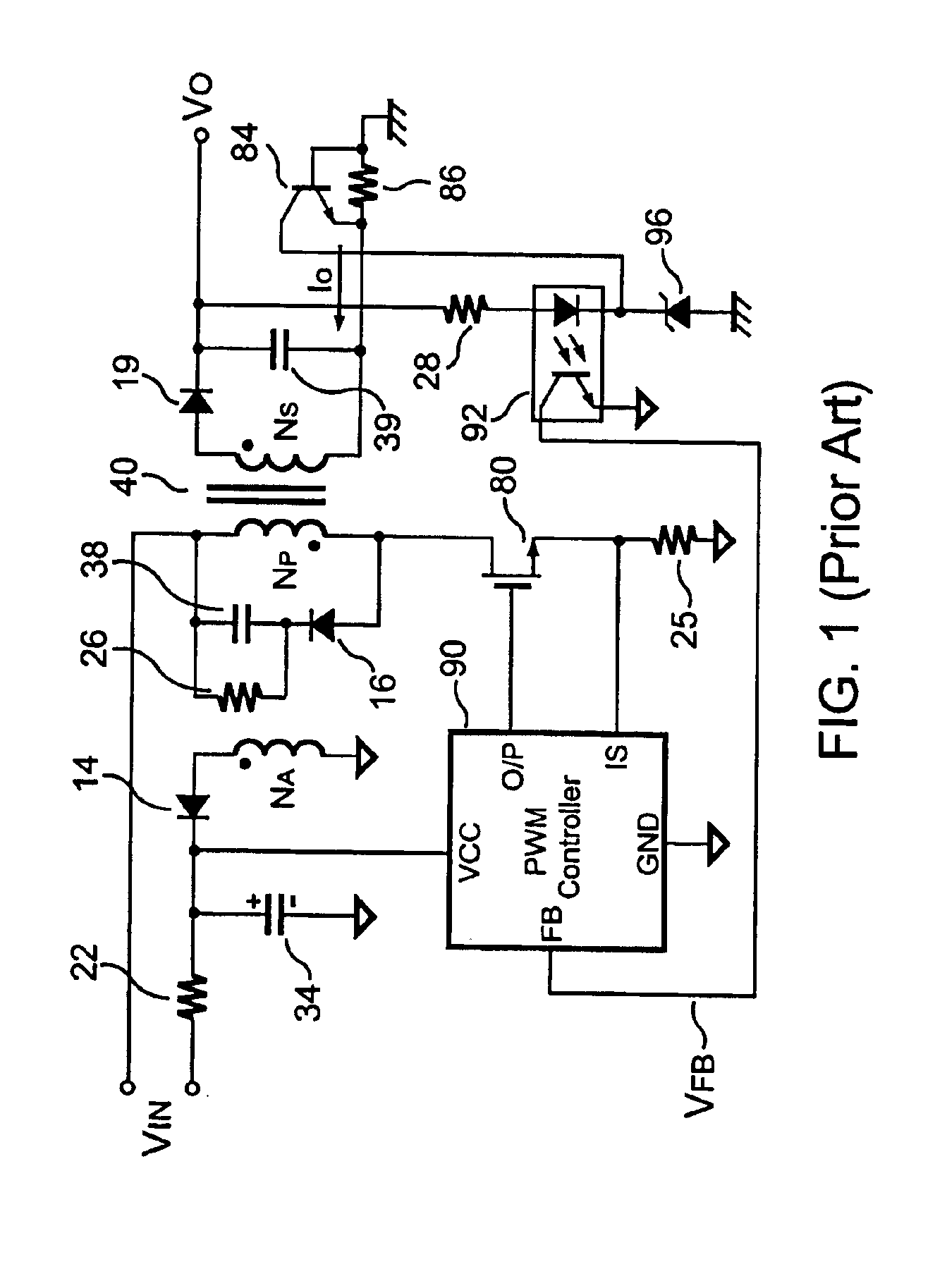
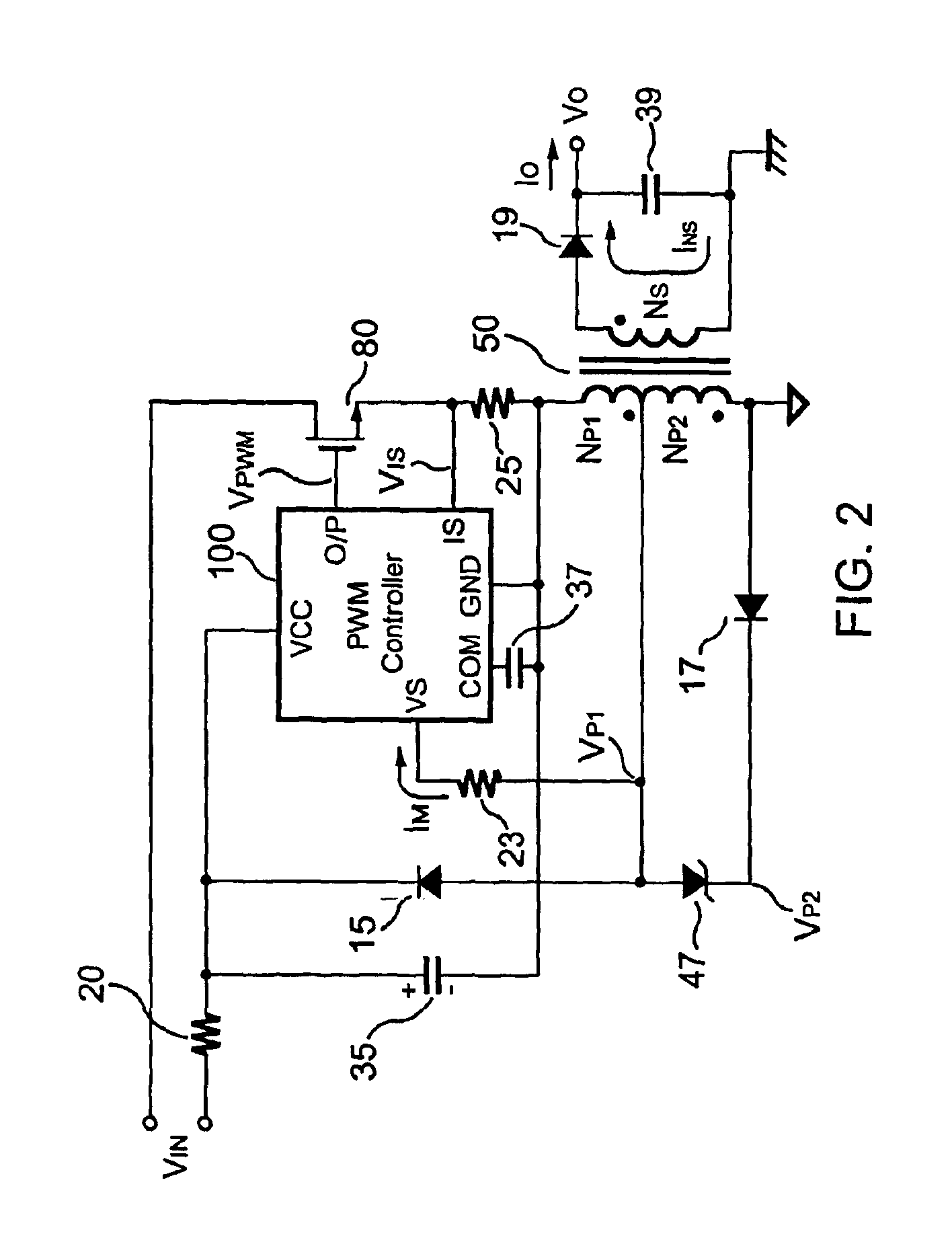
The present invention provides a primary-side flyback power converter that supplies a constant voltage output and a constant current output. To generate a well-regulated output voltage under varying load conditions, a PWM controller is included in the power converter in order to generate a PWM signal controlling a switching transistor in response to a flyback voltage sampled from a first primary winding of the power supply transformer. Several improvements are included in this present invention to overcome the disadvantages of prior-art flyback power converters. Firstly, the flyback energy of the first primary winding is used as a DC power source for the PWM controller in order to reduce power consumption. A double sample amplifier samples the flyback voltage just before the transformer current drops to zero. Moreover, an offset current is pulled from a detection input of the double sample amplifier in order to generate a more accurate DC output voltage. The offset current is generated in response to the temperature in order to compensate for temperature-induced voltage fluctuations across the output rectifier. Ultimately, in order to maintain a constant output current, the PWM controller modulates the switching frequency in response to the output voltage.
Owner:FAIRCHILD TAIWAN
LED driving circuit having dimming circuit
InactiveUS20060261754A1Increases ‘Decreases ‘Static indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesControl signalEngineering
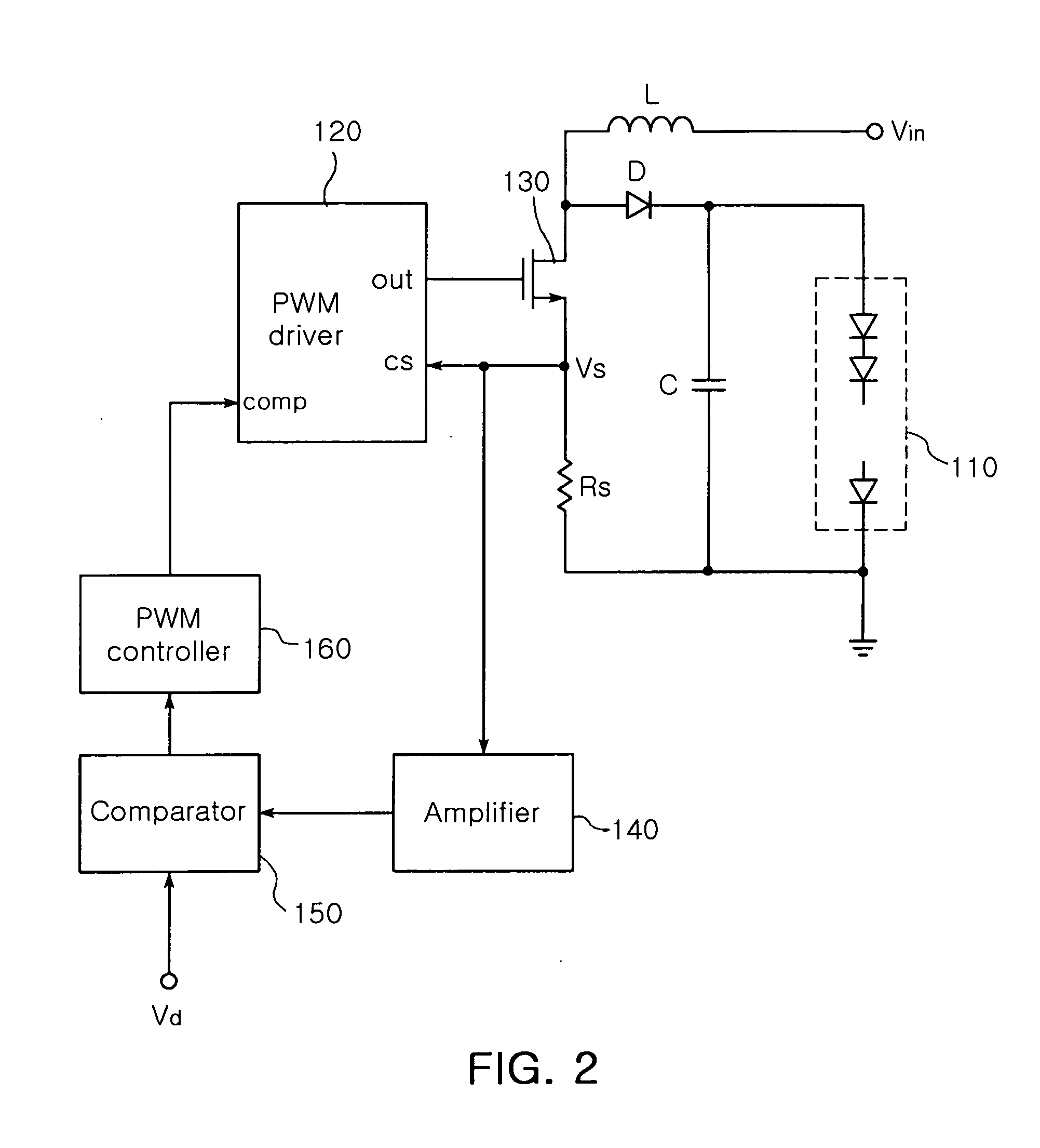
The invention relates to an LED driving circuit having a dimming circuit, which includes a PWM driver for providing a switching pulse having a width adjustable according to a voltage value detected by a voltage detecting resistor to control on / off durations of a switch. The circuit also includes a comparator for comparing the voltage value detected from the voltage detection resistor with a predetermined dimming voltage value, and a PWM controller for generating a control signal to increase the ‘on’ duration of the switching pulse outputted from the PWM driver if a comparison value from the comparator is increased, and to decrease the ‘on’ duration of the switching pulse outputted from the PWM driver if the comparison value from the comparator is decreased. The width of the switching pulse outputted from the PWM driver is controlled according to the predetermined dimming voltage value to adjust luminance of an LED.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Circuit for controlling LED with temperature compensation
ActiveUS7330002B2Low production costStatic indicating devicesElectric light circuit arrangementWave shapeLinearity
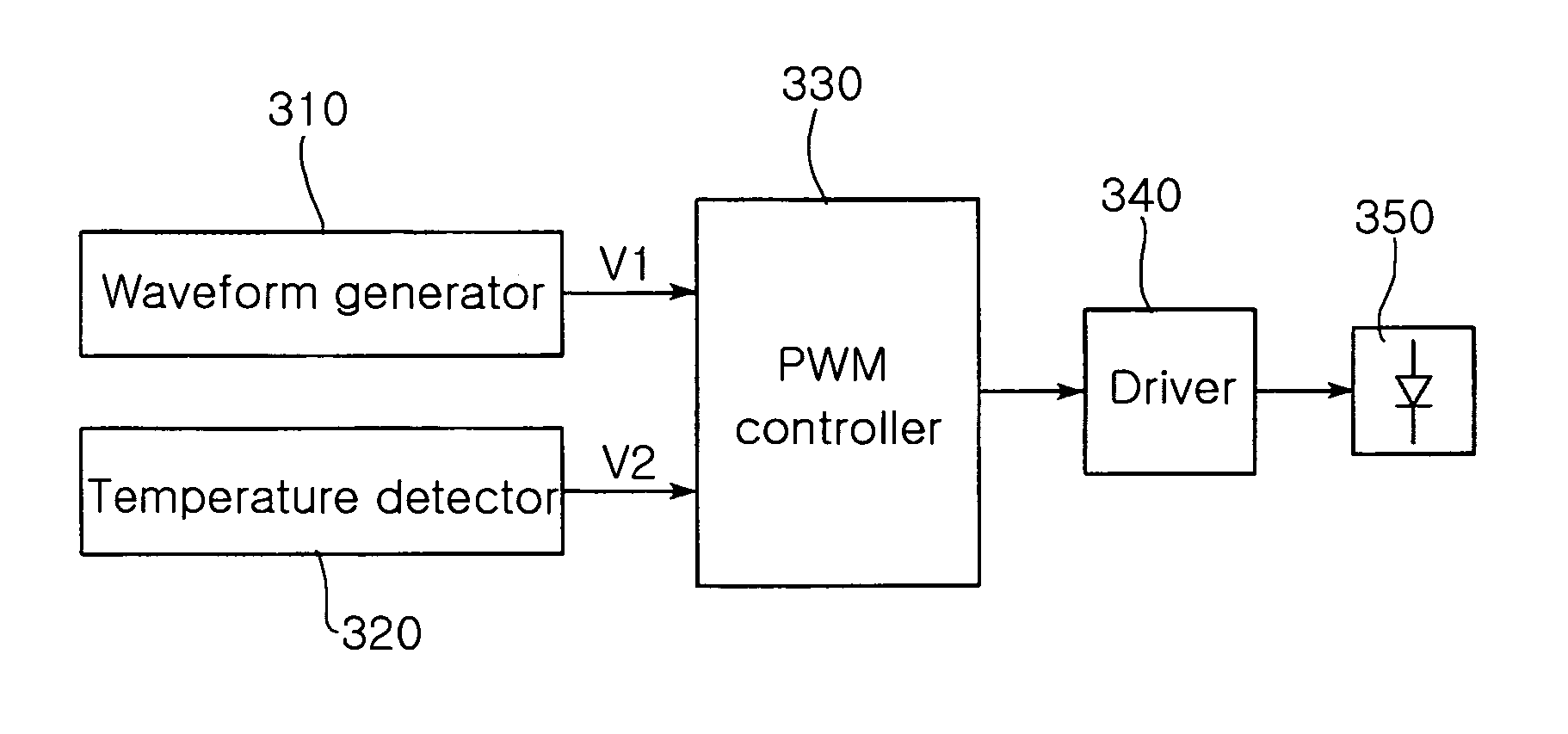
A circuit for controlling an LED with temperature compensation is employed in the LED-based system. The circuit of the invention linearly controls luminance and color of the LED according to temperature change and more precisely compensates for temperature-related variations in LED properties. Also, the circuit saves the cost of the product due to no requirement of a microprocessor. In the circuit, a waveform generator generates a sawtooth wave for Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) control. A temperature detector detects a voltage via a resistance value which is linearly variable according to changes in an ambient temperature. A PWM controller compares the sawtooth wave from the wave generator with the detection voltage from the temperature detector and generates a PWM voltage having a duty determined by the comparison result.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Flyback power converter having a constant voltage and a constant current output under primary-side PWM control
InactiveUS6862194B2Accurate supervisionSmall sizeAc-dc conversion without reversalEmergency protective circuit arrangementsConductor CoilPwm signals
A primary-side flyback power converter supplies a constant voltage and a constant current output. To generate a well-regulated output voltage under varying load conditions, the power converter includes a PWM controller. The PWM controller generates a PWM signal to control a switching transistor in response to a flyback voltage detected from the first primary winding of the power supply transformer. To reduce power consumption, the flyback energy of the first primary winding is used as a DC power source for the PWM controller. The flyback voltage is sampled following a delay time to reduce interference from the inductance leakage of the transformer. To generate a more accurate DC output voltage, a bias current is pulled from the detection input to form a voltage drop across a detection resistor for compensating for the voltage drop of the output rectifying diode.
Owner:FAIRCHILD TAIWAN
PWM controller with constant output power limit for a power supply
ActiveUS7099163B1Save power consumptionEase PCB layoutDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationReference currentEngineering
A PWM controller has a line voltage input that allows using a start-up resistor for both start-up and power-limit compensations so that it can save the power consumption, ease the PCB layout, and shrink the power supply size. In the integrated circuit, a current switch used for both start-up and line voltage sensing is composed of a diode and a switch transistor. A current multiplier is used to improve the precise by canceling the impact of the integrated resistor's absolute value, which is composed of a transistor loop, a constant current and a reference current. Thus, by properly selecting the value of the start-up resistor, an identical output power limit for low line and high line voltage input can be achieved.
Owner:BCD SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
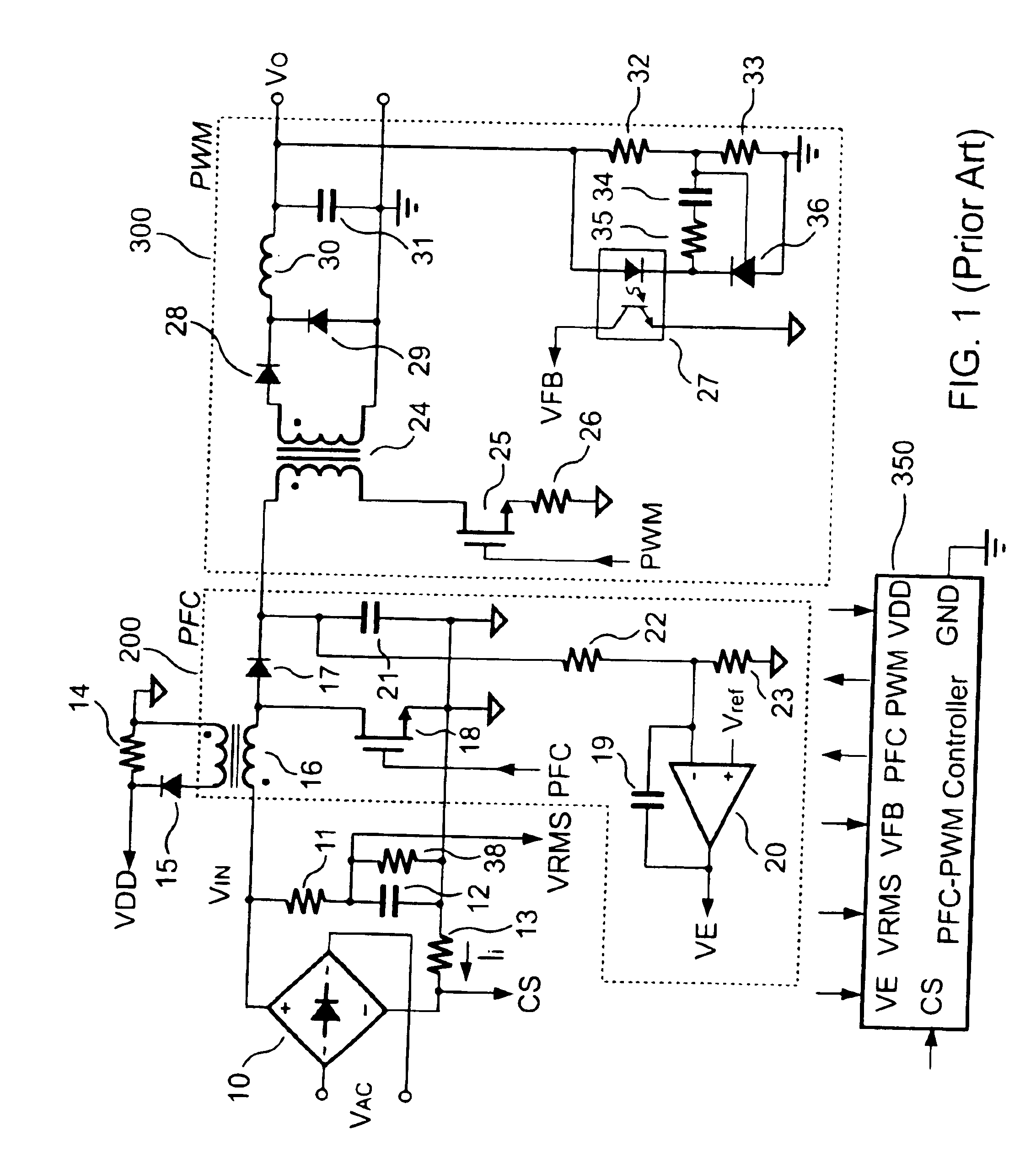
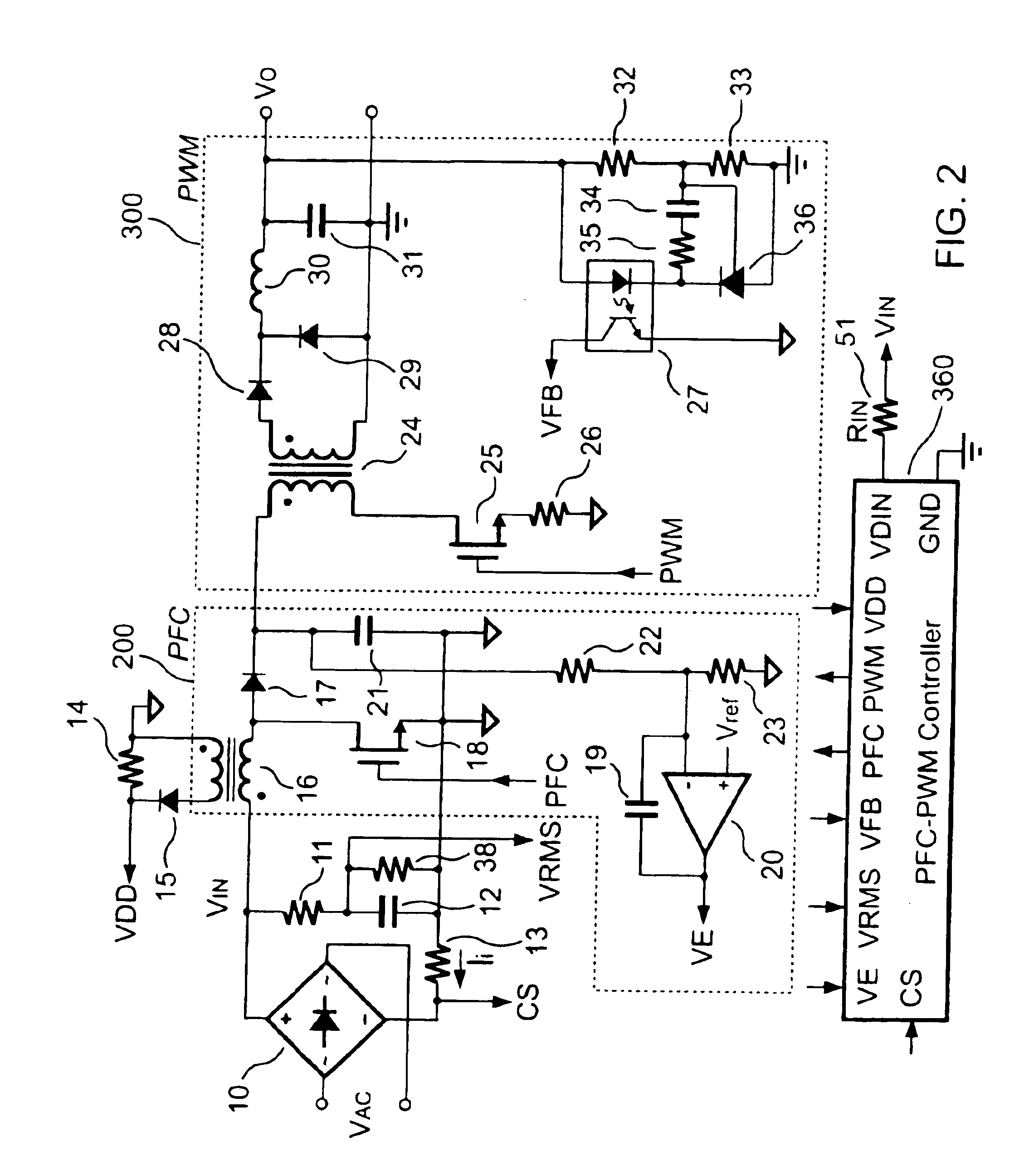
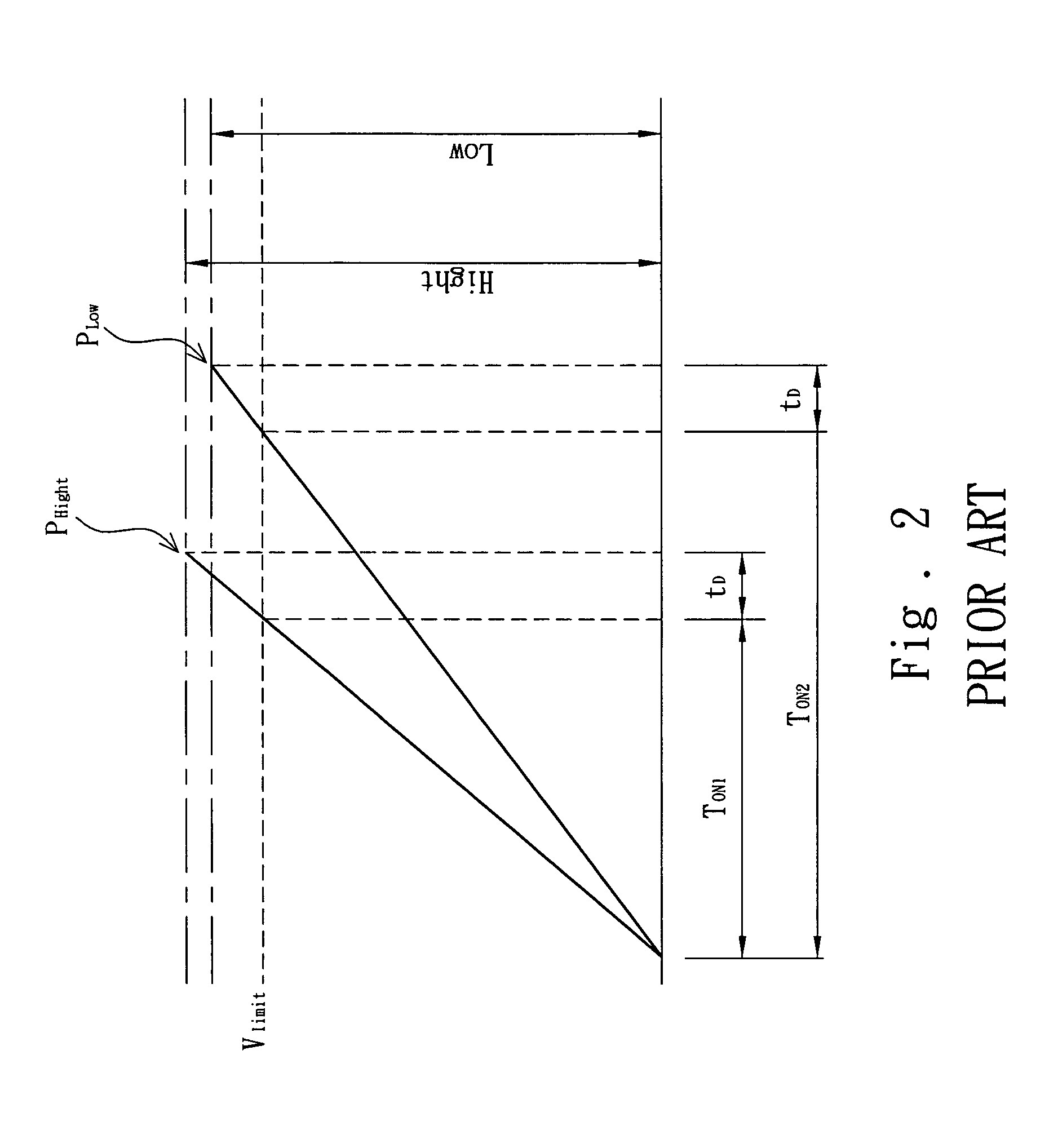
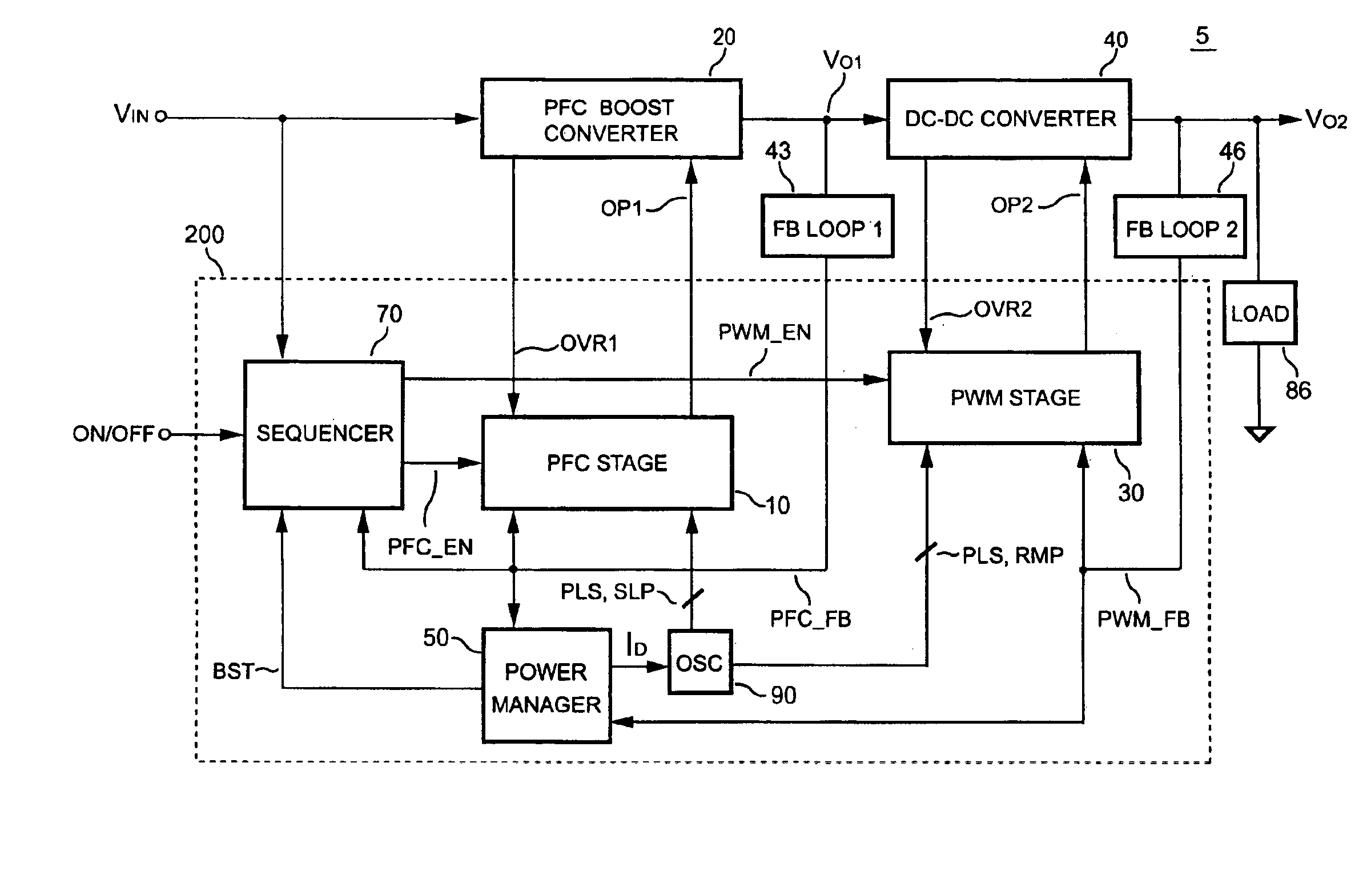
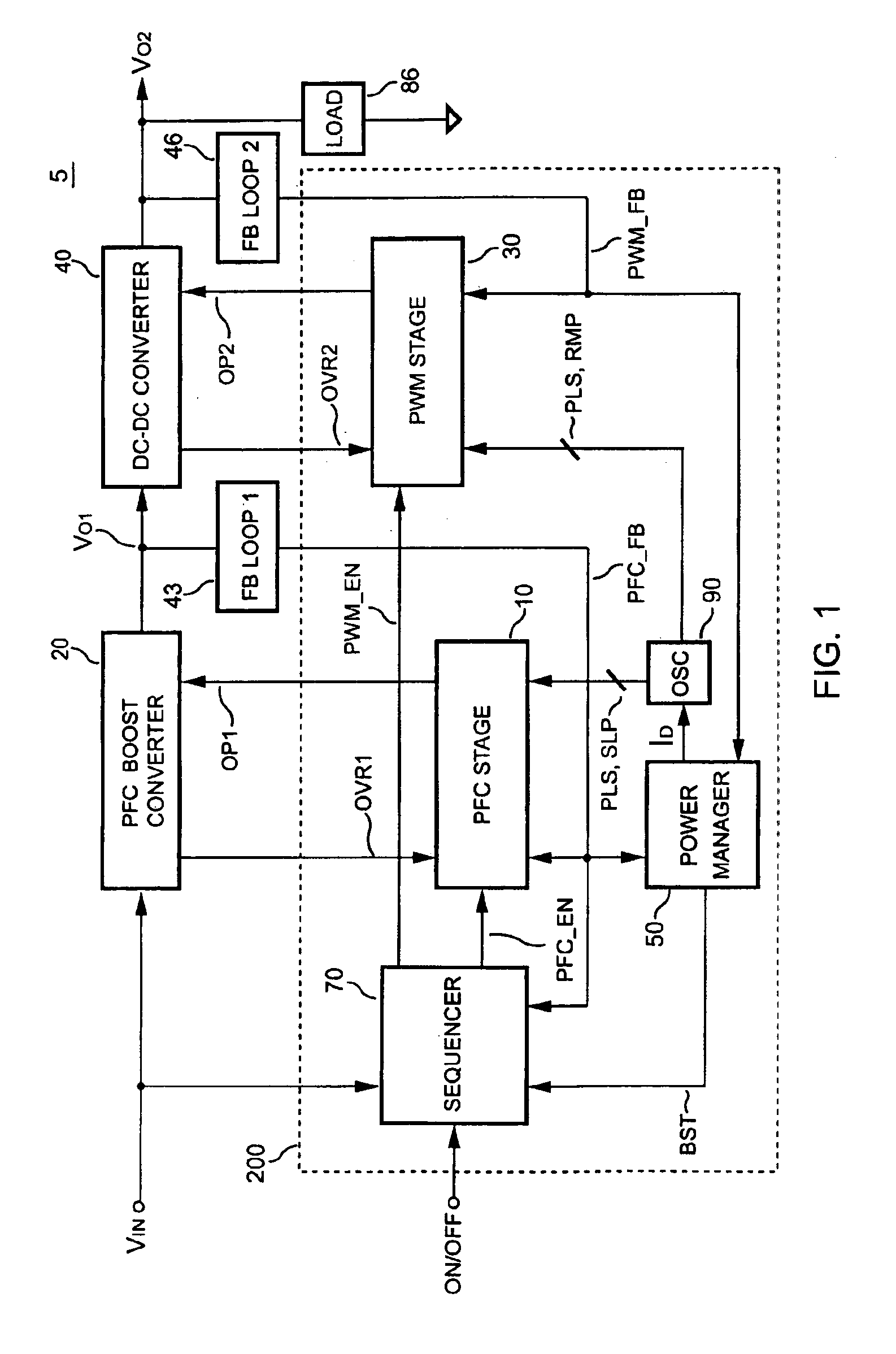
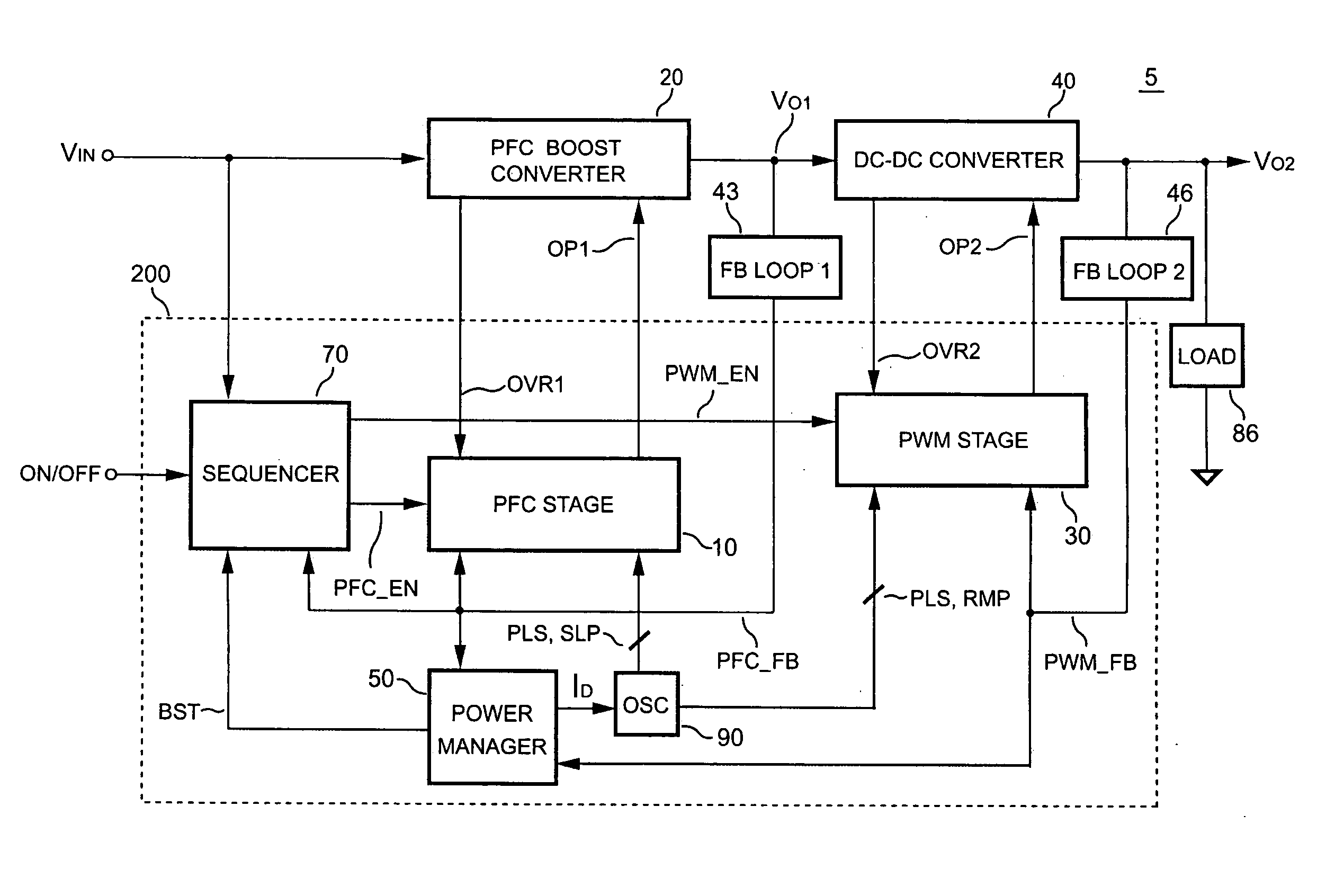
PFC-PWM controller having interleaved switching
InactiveUS6903536B2Reduce switching noiseIncrease the pulse widthEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDead timeSwitching signal
The present invention discloses a PFC-PWM controller having interleaved switching. A PFC stage generates a PFC signal for switching a PFC boost converter of a power converter. A PWM stage generates a PWM signal for switching a DC-to-DC converter of the power converter. The PFC-PWM controller includes a power manager for generating a discharge current and a burst-signal. Under light-load conditions, the discharge current decreases in proportion to a load of the power converter. The burst signal is utilized to disable the PFC signal in a suspended condition for power saving. A pulse width of the pulse-signal ensures a dead time to spread switching signals, such as the PFC and PWM signals, and reduces switching noise. When the discharge current decreases, the pulse width of the pulse-signal will increase and a frequency of the pulse-signal will decrease correspondingly. This further reduces power consumption under light-load and zero-load conditions.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
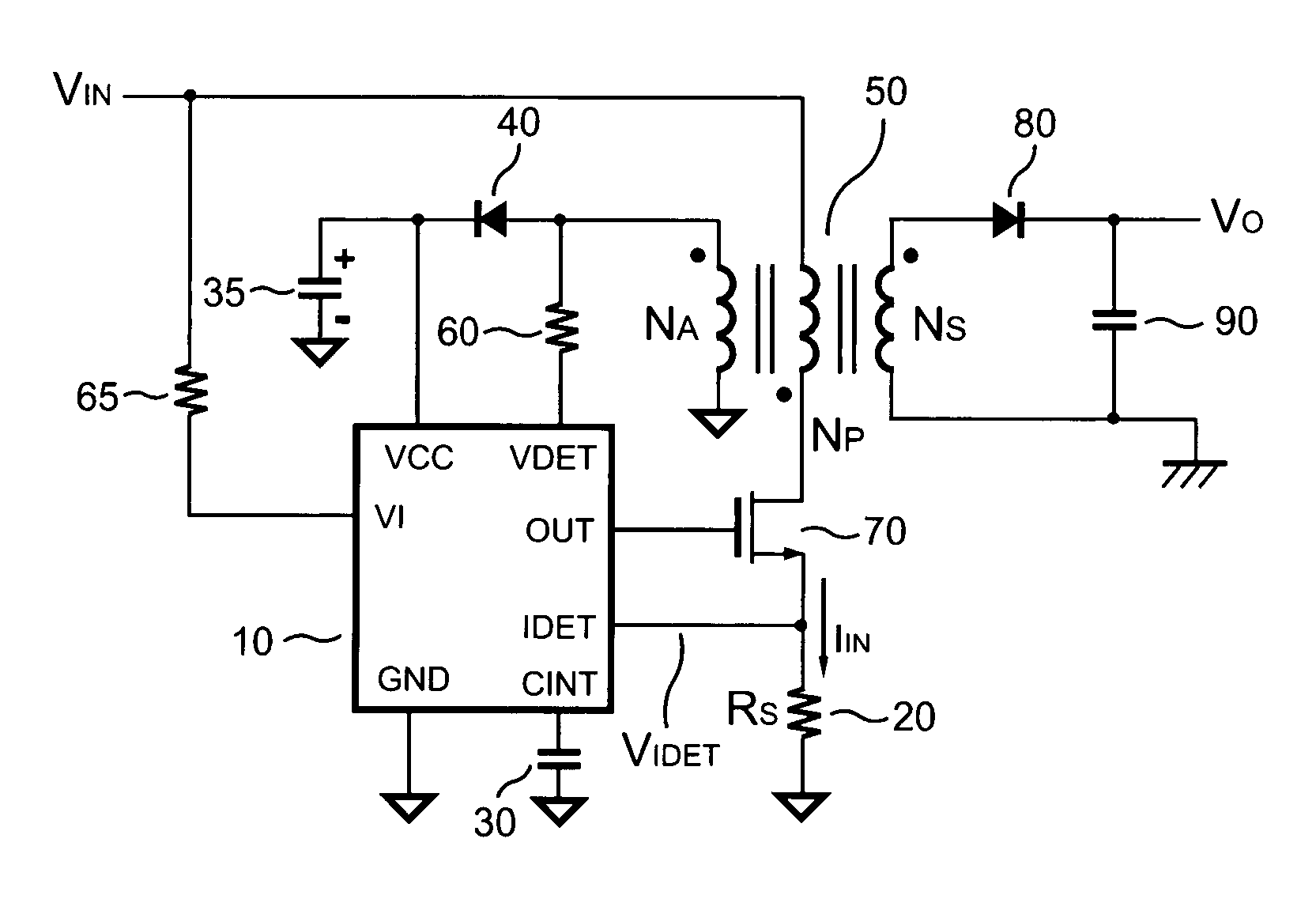
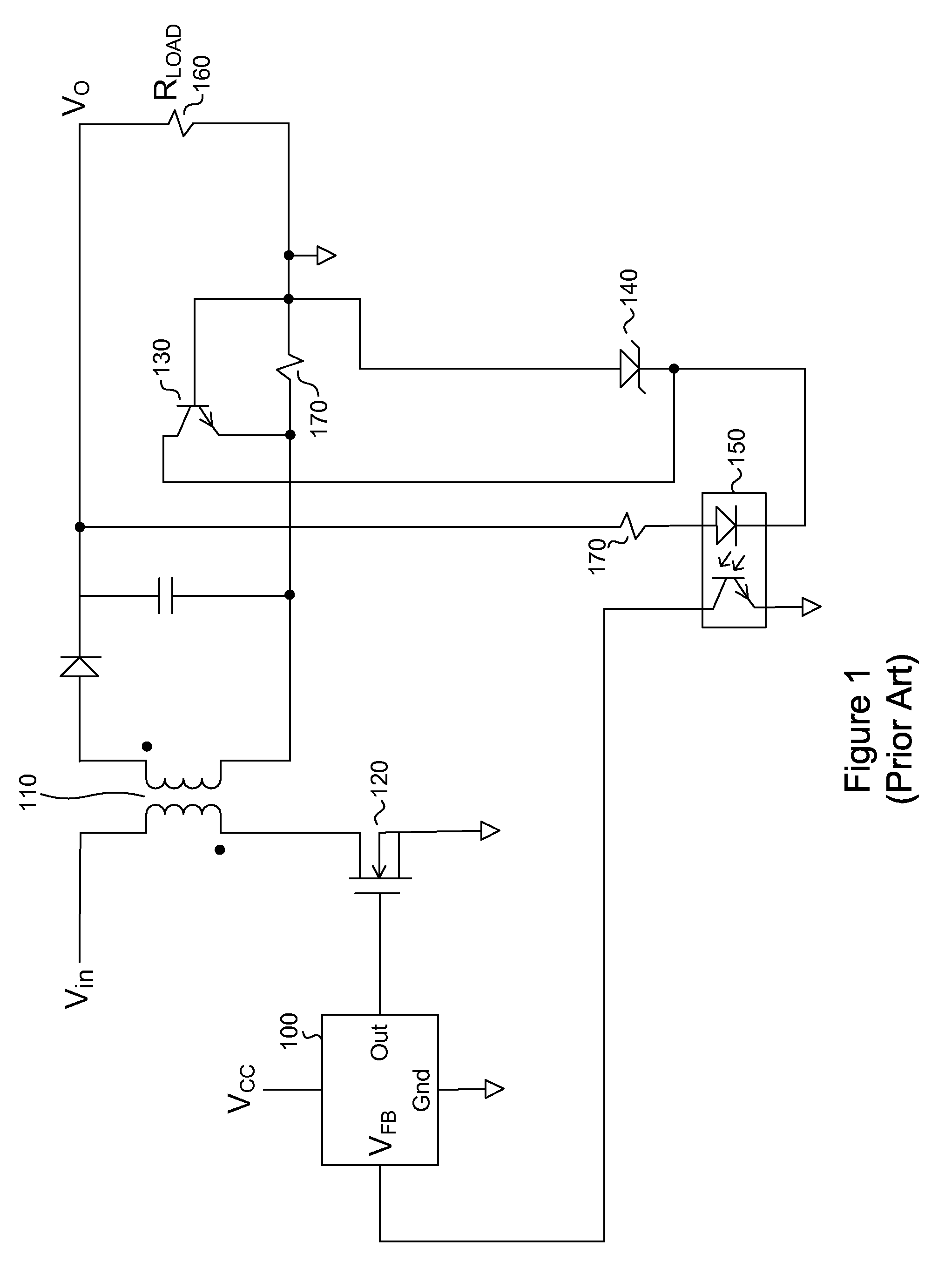
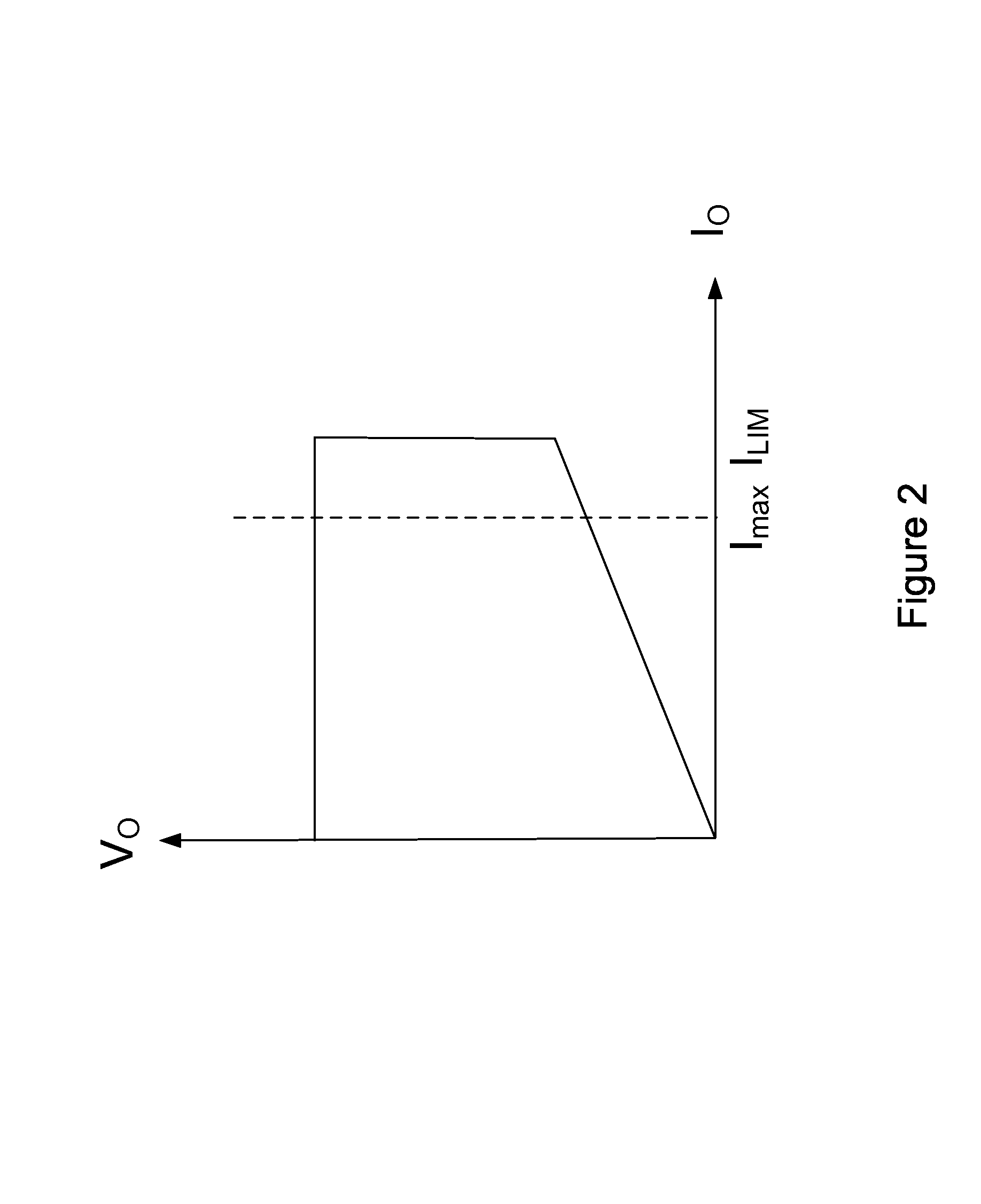
System and method for controlling current limit with primary side sensing
InactiveUS6972969B1Small rangeConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionCurrent limitingControl system
A primary side sensing power control system and method that controls the current limit such that it is maintained within a small range for any acceptable input voltages and causes the output voltage of a PWM controller to drop as the output load increases when the current limit is reached.
Owner:HERCULES TECH GROWTH CAPITAL +1
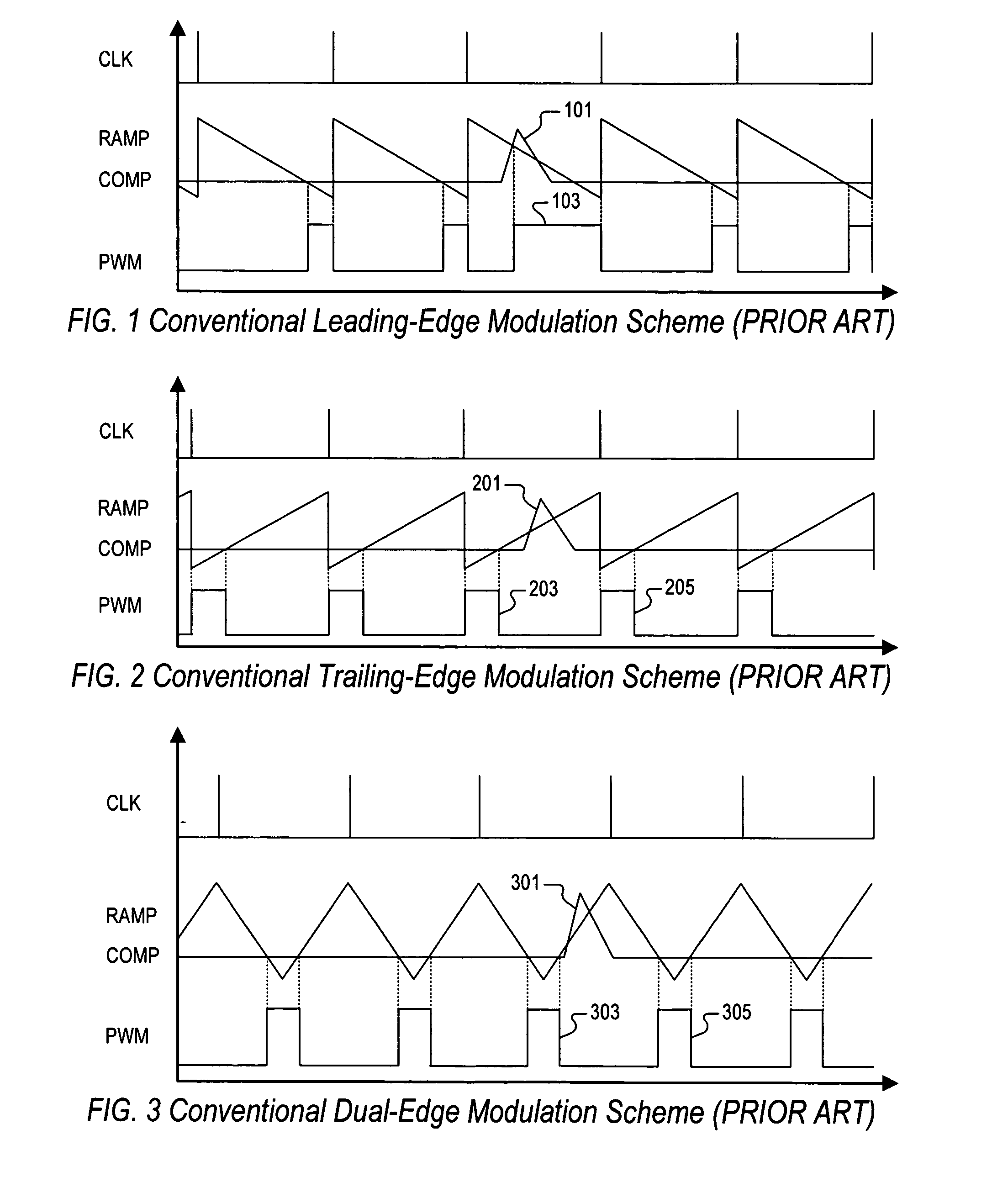
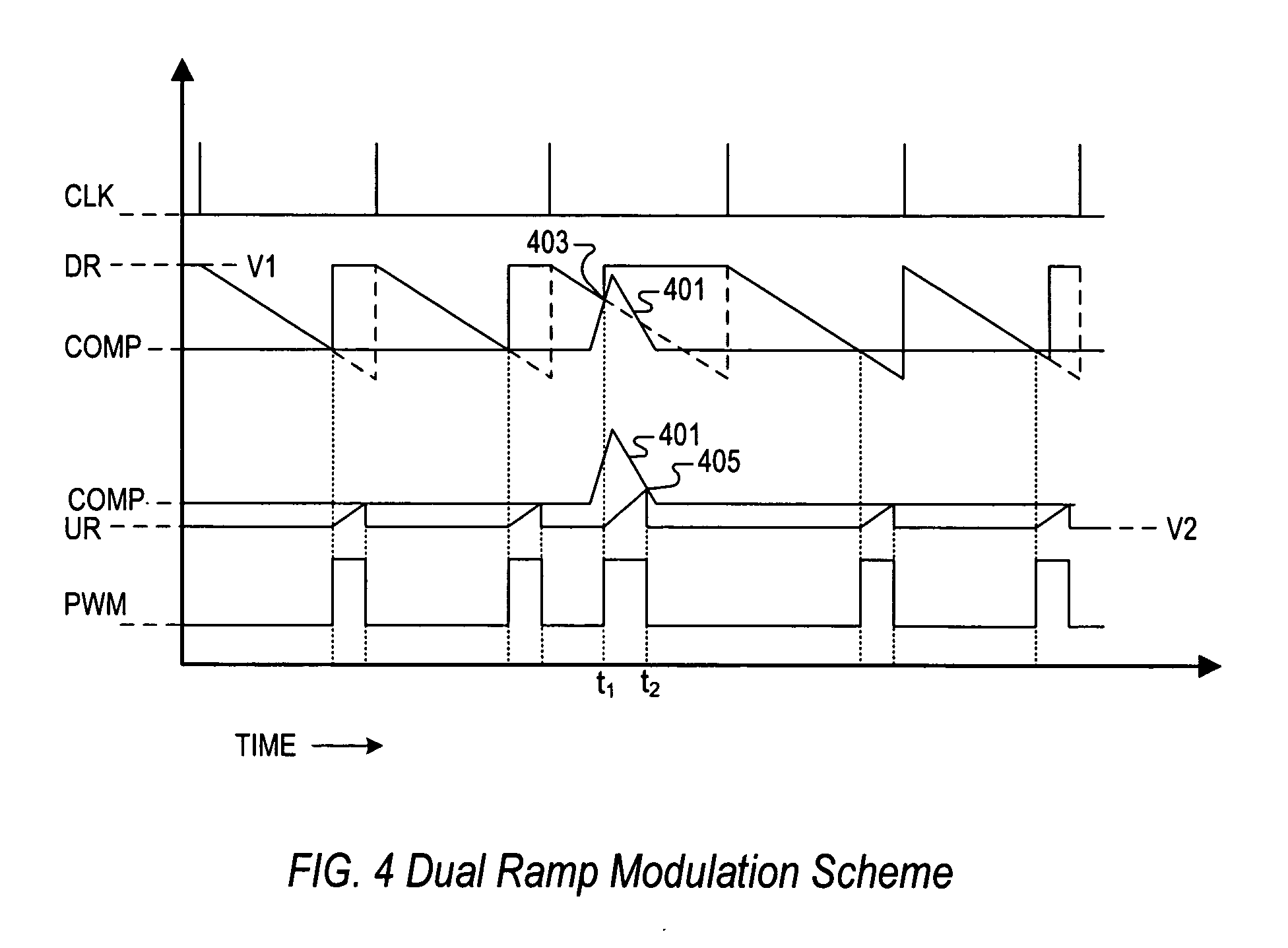
PWM controller with dual-edge modulation using dual ramps
ActiveUS20070013356A1Efficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionLeading edgePulse control
A dual-edge modulation controller including first and second ramp circuits, first and second comparators, an error amplifier and pulse control logic. The first ramp circuit provides a leading-edge ramp synchronous with a clock. The error amplifier compares a feedback signal with a reference and provides a compensation signal. The first comparator compares the leading-edge ramp with the compensation signal and asserts a set signal. The second ramp circuit provides a trailing-edge ramp that begins ramping when the set signal is asserted. The second comparator compares the trailing-edge ramp with the compensation signal and asserts a reset signal. The pulse control logic asserts a PWM signal when the set signal is asserted and de-asserts the PWM signal when the reset signal is asserted. The controller may control multiple phases with current balancing. The slew rate of the ramps may be adjusted based on the number of PWM signal asserted.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
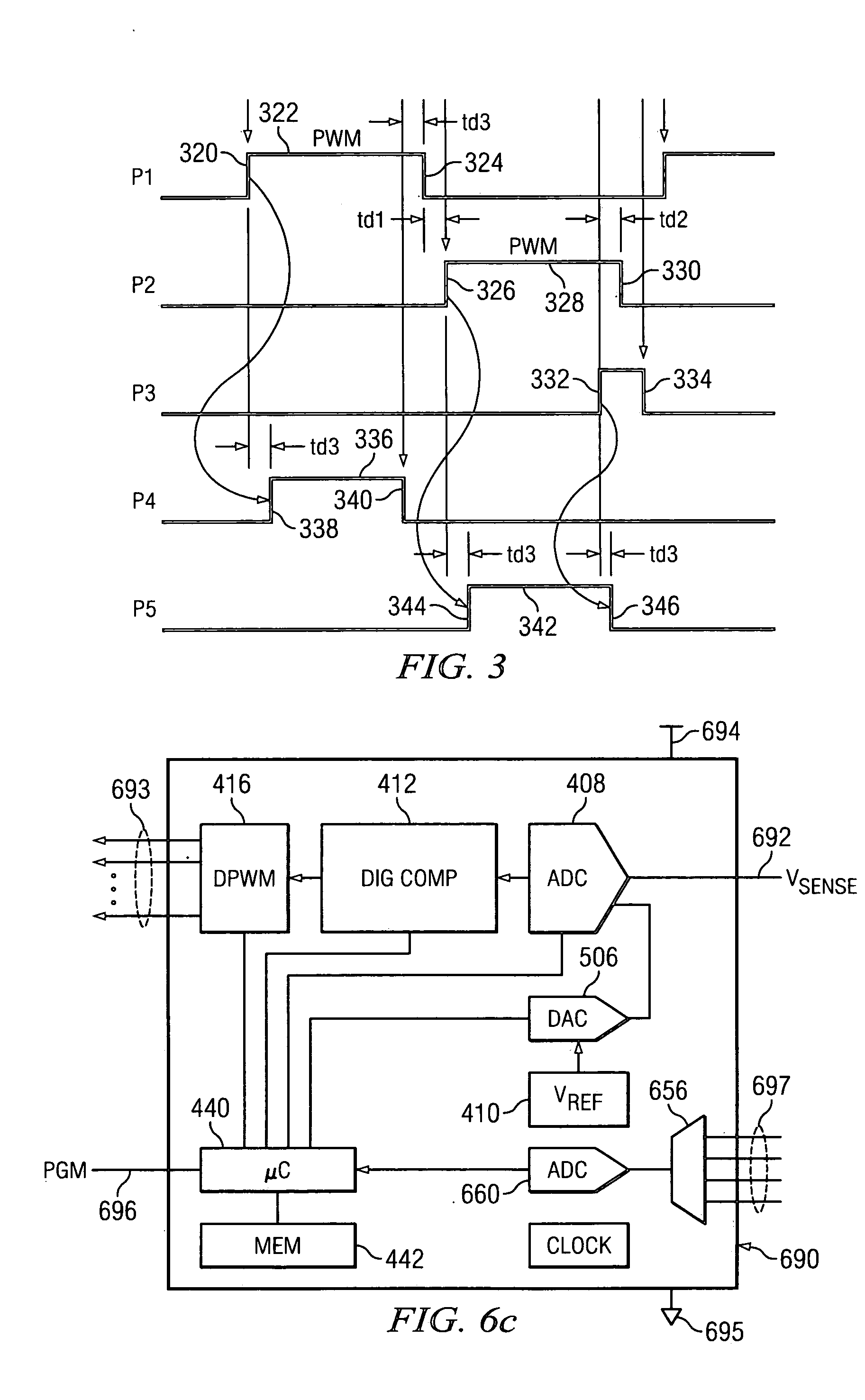
Digital PWM controller for digital power supply having programmable dead times
A system for controlling a switching power converter and includes a digital controller that receives an analog signal representing the output DC voltage of the power converter for comparison to a desired output voltage level and generates switching control signals to control the operation of the power supply to regulate the output DC voltage to said desired output voltage level. At least two of the switching control signals having a dead time between a first edge of a first control signal and a second edge of a second control signal. The dead time is programmable such that the second edge of the second control signal may occur at a selected point in time either before or after the first edge of the first control signal.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
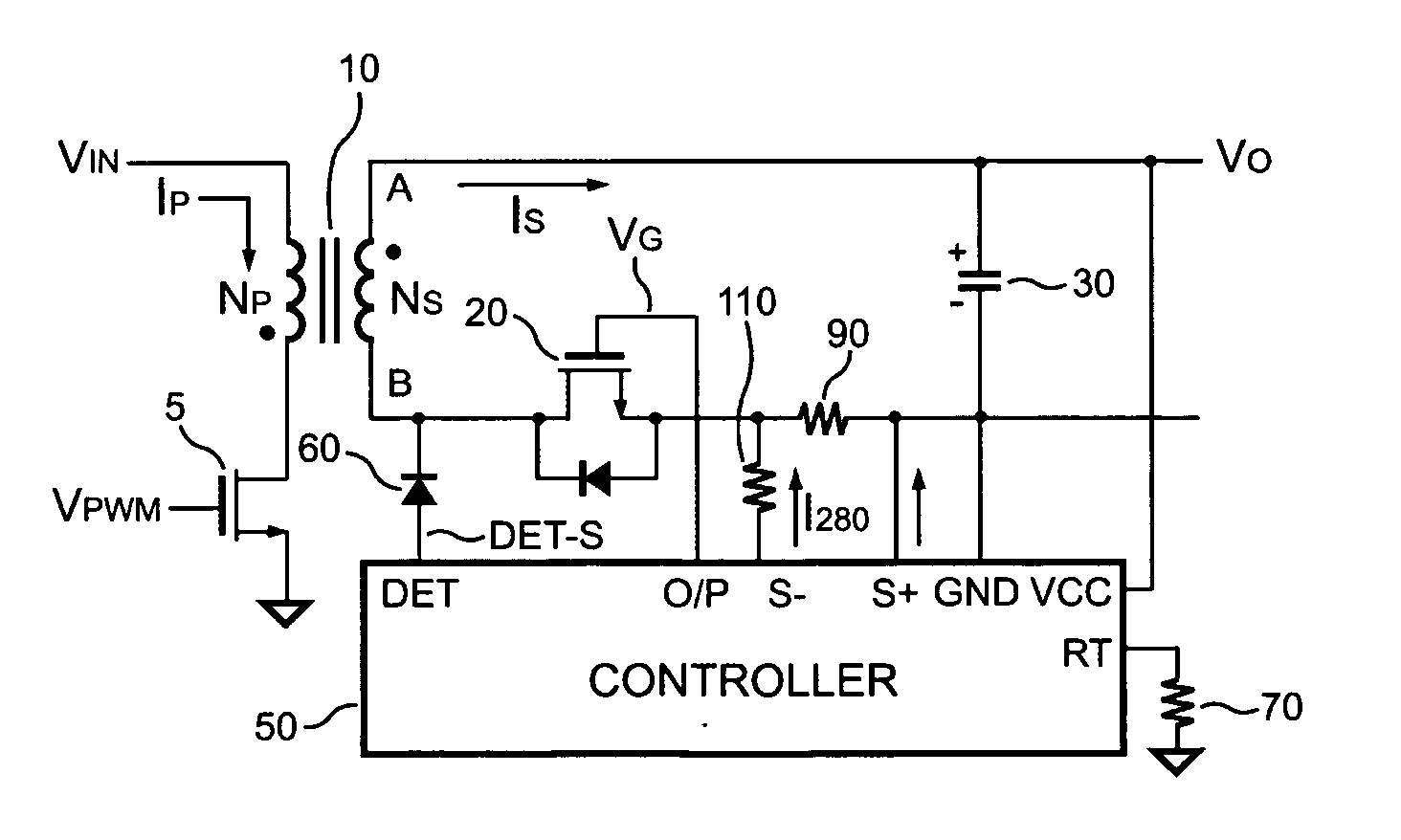
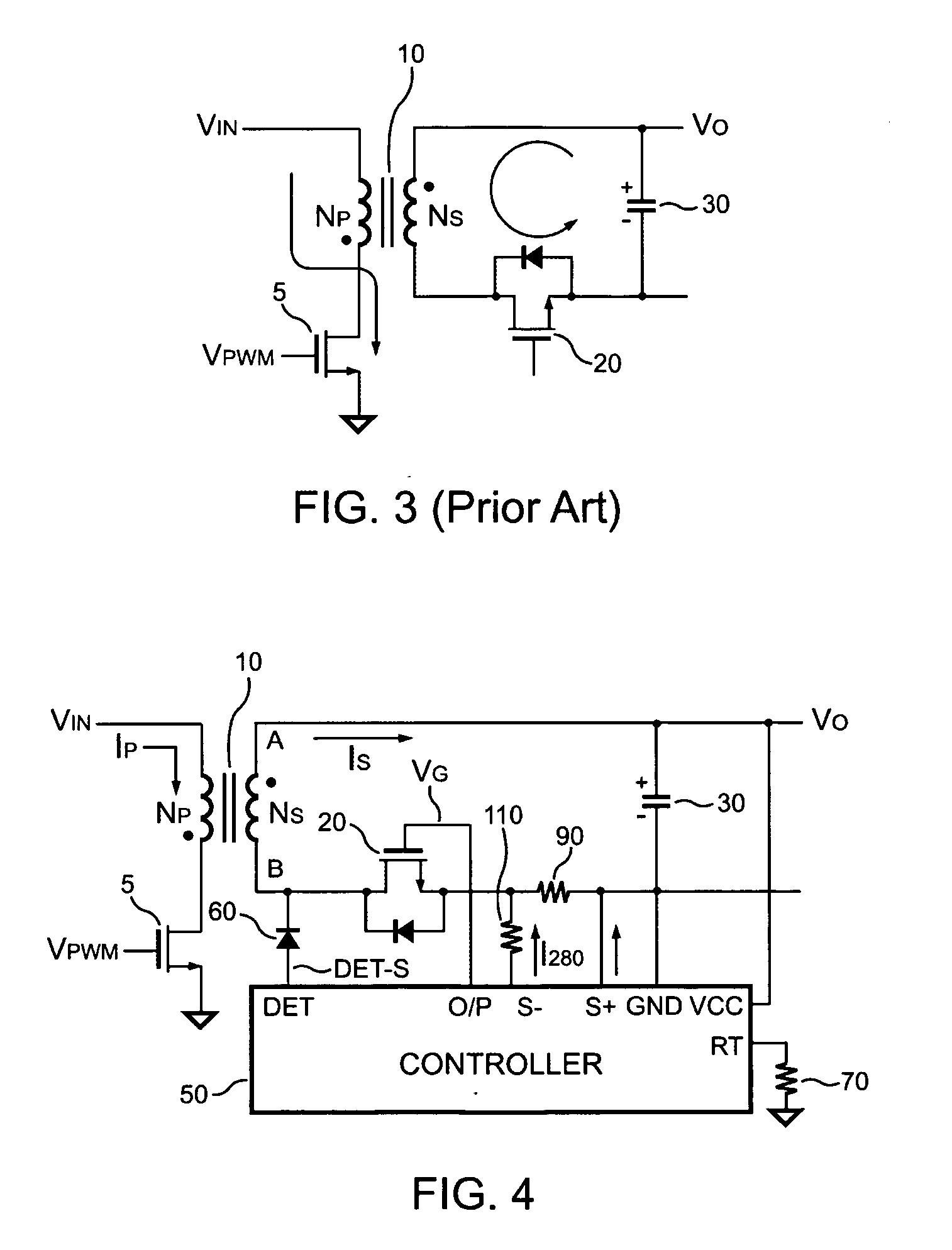
Pwm controller for synchronous rectifier of flyback power converter
A synchronous rectifier PWM (SR-PWM) controller controls a MOSFET in response to the value of a secondary current and the status of a synchronous signal for both discontinuous and continuous operation mode. The secondary current is generated in a secondary circuit and is detected by two threshold-detection terminals of the SR-PWM controller. The SR-PWM controller produces the synchronous signal by detecting a switching signal of the transformer via a detection terminal of the SR-PWM controller. Furthermore, a delay-time is inserted after the MOSFET is turned off and before the next switching cycle starts to ensure a proper operation of the MOSFET. In one embodiment, an equivalent series resistance (ESR) of an output capacitor can be used as a sensor to detect the secondary current. Therefore, no additional current sensor is required and the efficiency can be improved.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Primary-side controlled flyback power converter
InactiveUS20050024898A1Save power costSmall sizeEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionTransformerSwitching frequency
The present invention provides a primary-side flyback power converter that supplies a constant voltage output and a constant current output. To generate a well-regulated output voltage under varying load conditions, a PWM controller is included in the power converter in order to generate a PWM signal controlling a switching transistor in response to a flyback voltage sampled from a first primary winding of the power supply transformer. Several improvements are included in this present invention to overcome the disadvantages of prior-art flyback power converters. Firstly, the flyback energy of the first primary winding is used as a DC power source for the PWM controller in order to reduce power consumption. A double sample amplifier samples the flyback voltage just before the transformer current drops to zero. Moreover, an offset current is pulled from a detection input of the double sample amplifier in order to generate a more accurate DC output voltage. The offset current is generated in response to the temperature in order to compensate for temperature-induced voltage fluctuations across the output rectifier. Ultimately, in order to maintain a constant output current, the PWM controller modulates the switching frequency in response to the output voltage.
Owner:FAIRCHILD TAIWAN
Power-mode controlled power converter
A power-mode controlled power converter is capable of supplying a constant output voltage and output current. A PWM controller generates a PWM signal in response to a voltage sampled from a transformer auxiliary winding. A programmable current-sink and a detection resistor compensate for a voltage drop of an output rectifier. A low-pass filter integrates a switching-current voltage to an average-current signal. An attenuator produces an input-voltage signal from a line-voltage input signal. The PWM controller multiplies the average-current signal with the input-voltage signal to generate a power-control signal. An error-amplifier compares the power-control signal with a power-reference voltage to generate a limit voltage. The limit voltage controls the power delivered from a primary-side circuit to a secondary-side circuit of the power-mode controlled power converter. Since the power-reference voltage varies in proportional to output voltage variations, a constant output current is therefore achieved.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
PWM controller for synchronous rectifier of flyback power converter
A synchronous rectifier PWM (SR-PWM) controller controls a MOSFET in response to the value of a secondary current and the status of a synchronous signal for both discontinuous and continuous operation mode. The secondary current is generated in a secondary circuit and is detected by two threshold-detection terminals of the SR-PWM controller. The SR-PWM controller produces the synchronous signal by detecting a switching signal of the transformer via a detection terminal of the SR-PWM controller. Furthermore, a delay-time is inserted after the MOSFET is turned off and before the next switching cycle starts to ensure a proper operation of the MOSFET. In one embodiment, an equivalent series resistance (ESR) of an output capacitor can be used as a sensor to detect the secondary current. Therefore, no additional current sensor is required.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Pfc-pwm controller having interleaved switching
ActiveUS20050099164A1Reduce switching noiseImproper operationEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionEngineeringPwm signals
The present invention discloses a PFC-PWM controller having interleaved switching. A PFC stage generates a PFC signal for switching a PFC boost converter of a power converter. A PWM stage generates a PWM signal for switching a DC-to-DC converter of the power converter. The PFC-PWM controller includes a power manager for generating a discharge current and a burst-signal. Under light-load conditions, the discharge current decreases in proportion to a load of the power converter. The burst signal is utilized to disable the PFC signal in a suspended condition for power saving. A pulse width of the pulse-signal ensures a dead time to spread switching signals, such as the PFC and PWM signals, and reduces switching noise. When the discharge current decreases, the pulse width of the pulse-signal will increase and a frequency of the pulse-signal will decrease correspondingly. This further reduces power consumption under light-load and zero-load conditions.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Non-linear PWM controller for dc-to-dc converters
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
Liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20060221047A1Shorten the timeReduce brightnessCathode-ray tube indicatorsElectric light circuit arrangementSpectral transmittanceEngineering
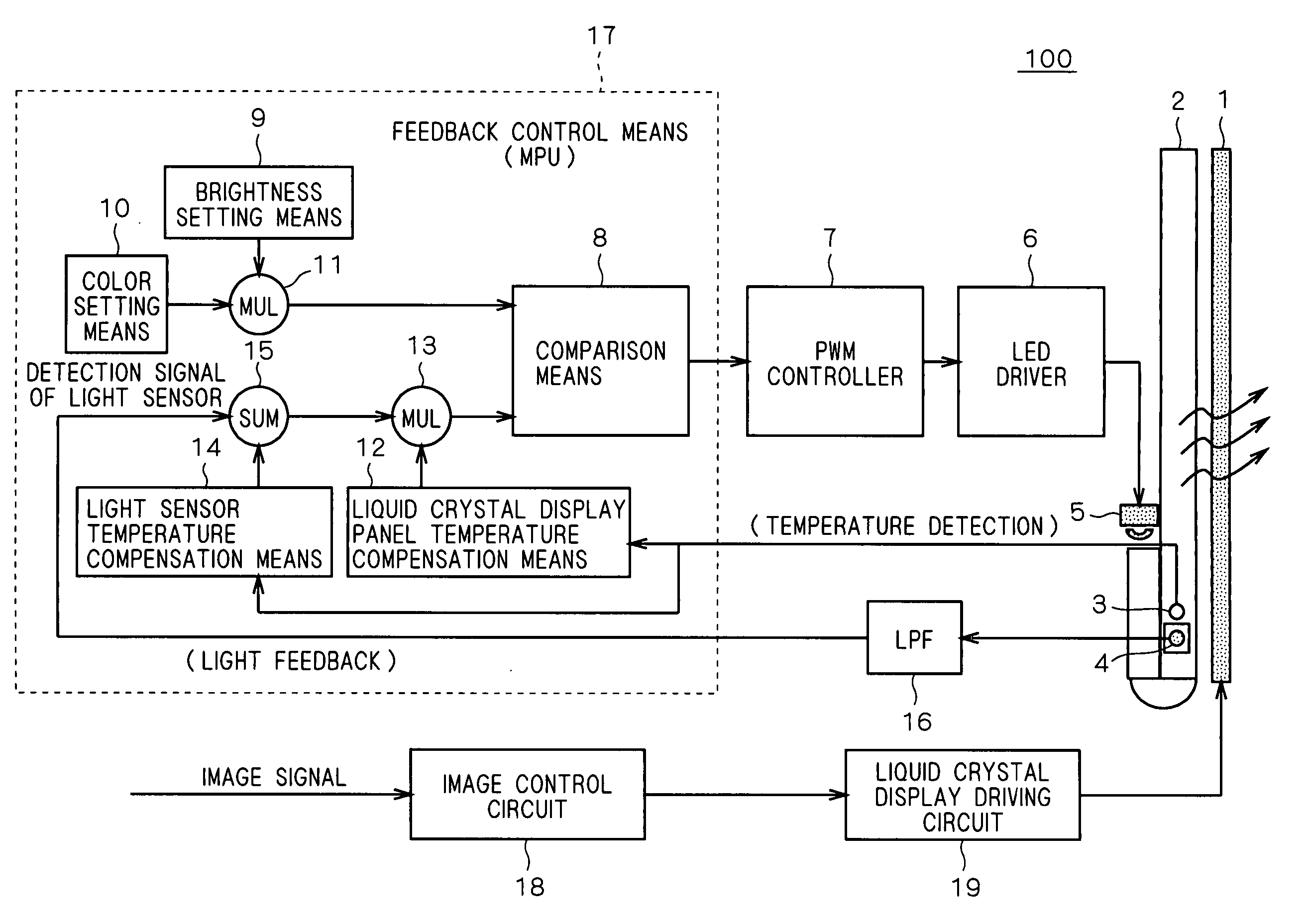
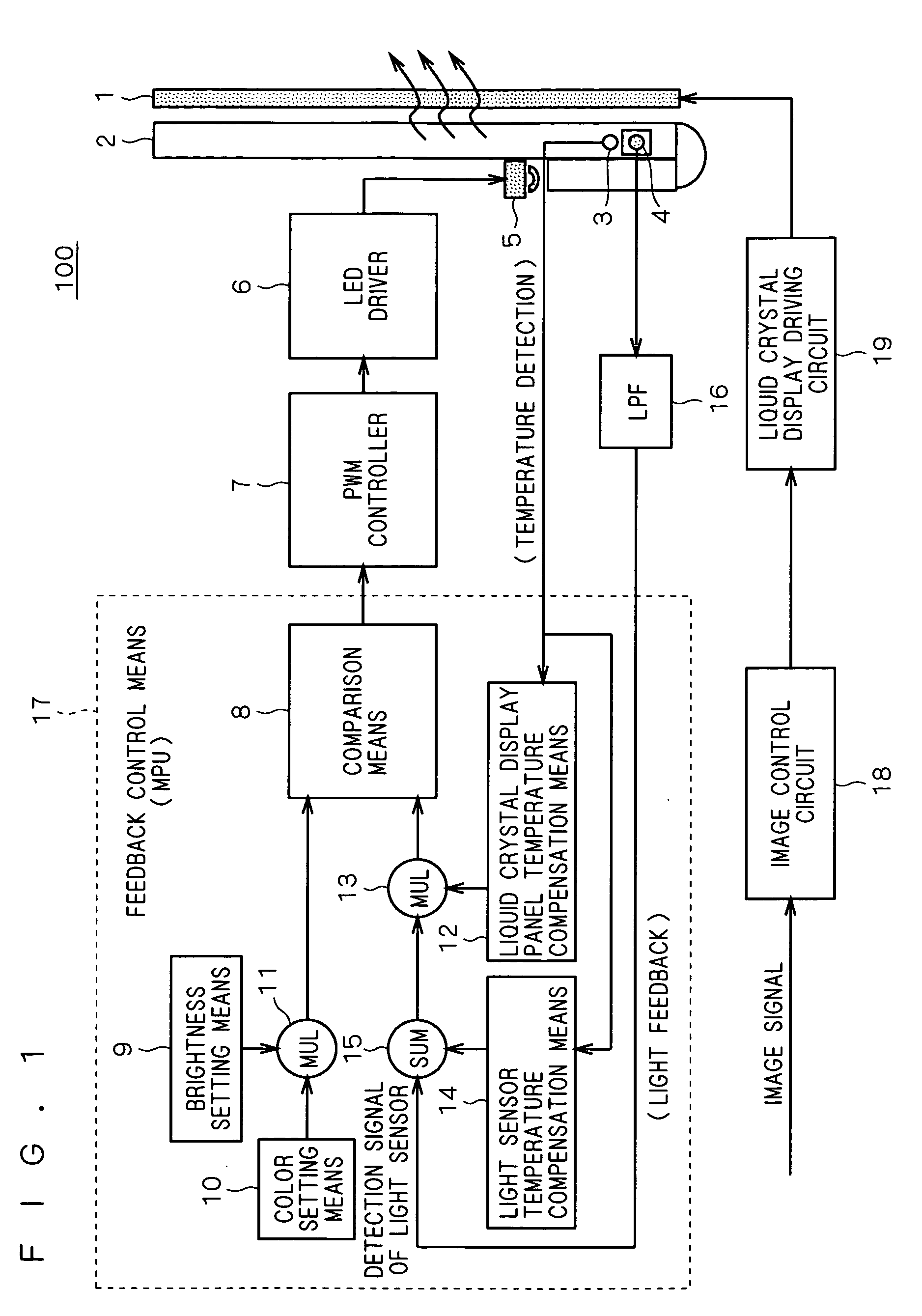
The present invention provides a liquid crystal display device capable of shortening the time required for stabilizing the brightness and the chromaticity to the temperature change. The input of an LED driver is connected to the output of a PWM controller, so that the electric power supplied to the respective LED groups of red, green and blue are controlled with a PWM method. A feedback control means for controlling the PWM controller includes a brightness setting means, a color setting means, a multiplication means for receiving the outputs from the brightness setting means and the color setting means, a comparison means fed with the output of the multiplication means at one of the inputs thereof, a light sensor temperature compensation means for compensating for fluctuations of the output of the light detection means due to temperature changes, a liquid crystal display panel temperature compensation means for compensating for fluctuations of the spectral transmittance of the liquid crystal display panel due to temperature changes, an addition means for summing the result of detection by the light detection means and the output of the light sensor temperature compensation means, and a multiplication means for multiplying the output of the addition means by the output of the liquid crystal display panel temperature compensation means.
Owner:NEC DISPLAY SOLUTIONS LTD
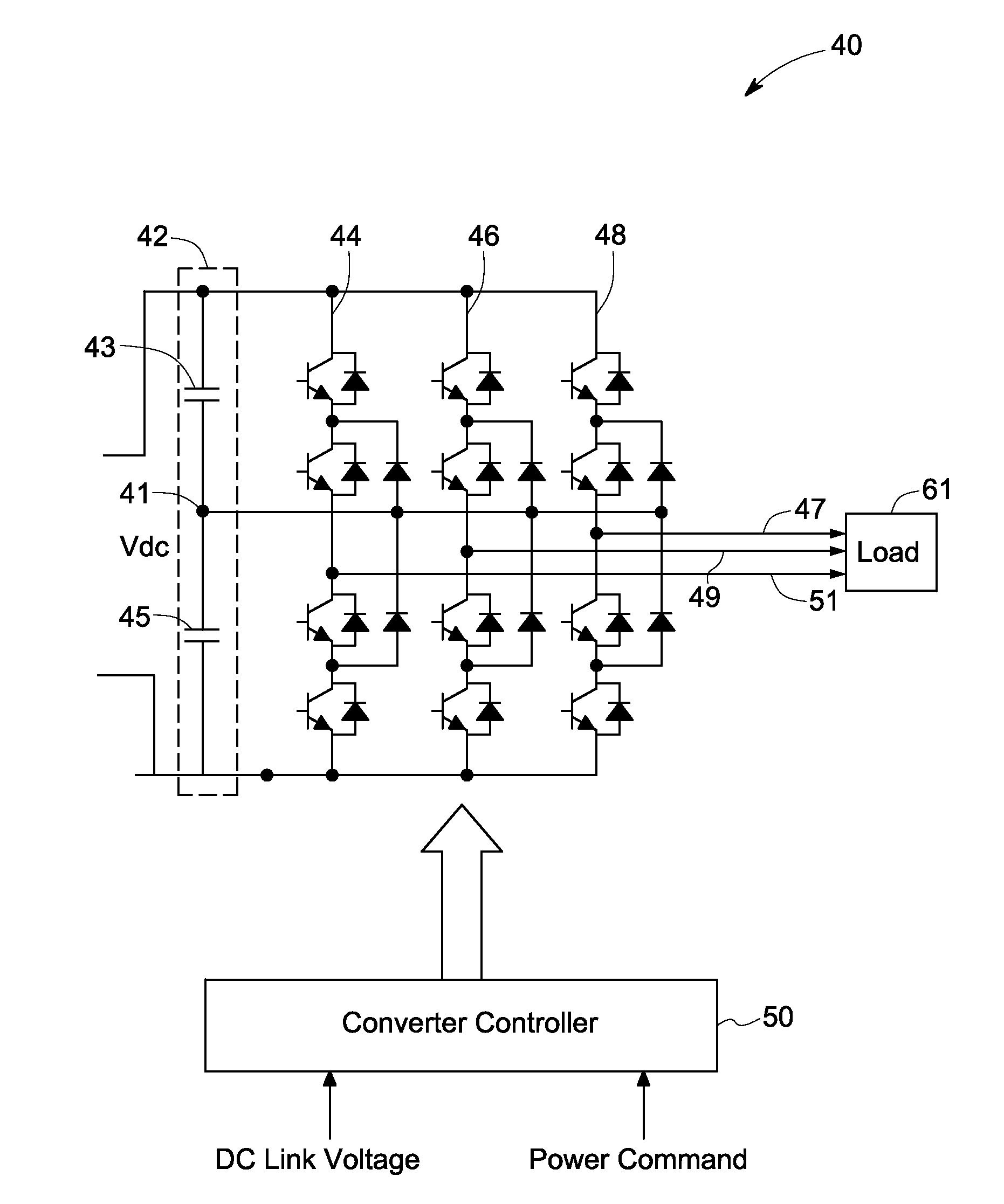
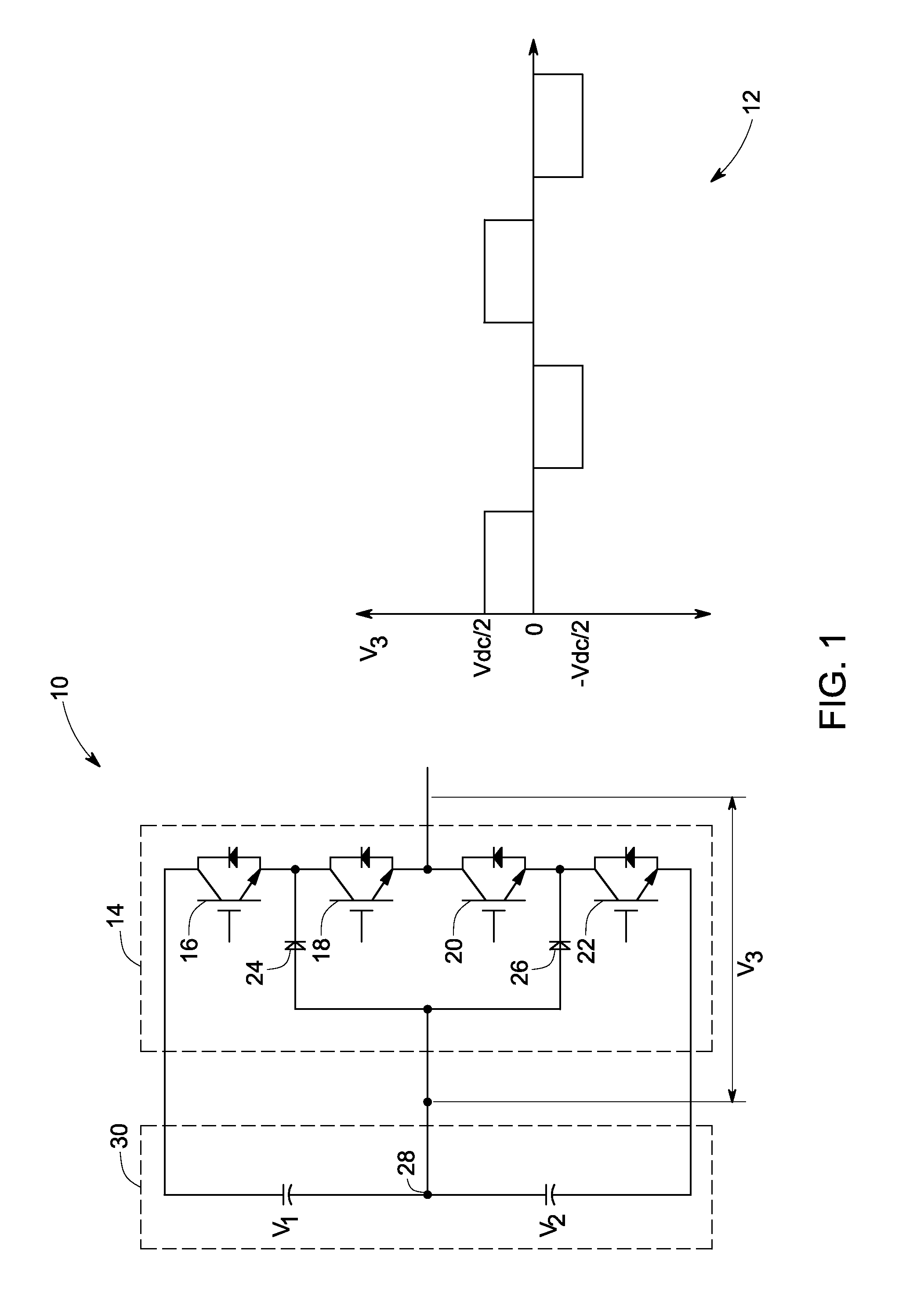
Dc-link voltage balancing system and method for multilevel converters
ActiveUS20110141786A1Emergency protective circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversionReference currentControl system
A control system for a multilevel converter includes a differential mode current regulator, a neutral point (NP) controller and a PWM controller for generating switching pulses for the multilevel converter. The differential mode current regulator generates reference voltage command signals based on a difference between reference current command signals and actual current command signals, and the NP controller determines a modified neutral point current signal in response to a DC link voltage unbalance. The NP controller utilizes the modified neutral point current signal to generate a common mode reference voltage signal. The switching pulses are generated by the PWM controller based on the reference voltage command signals and the common mode reference voltage signal.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
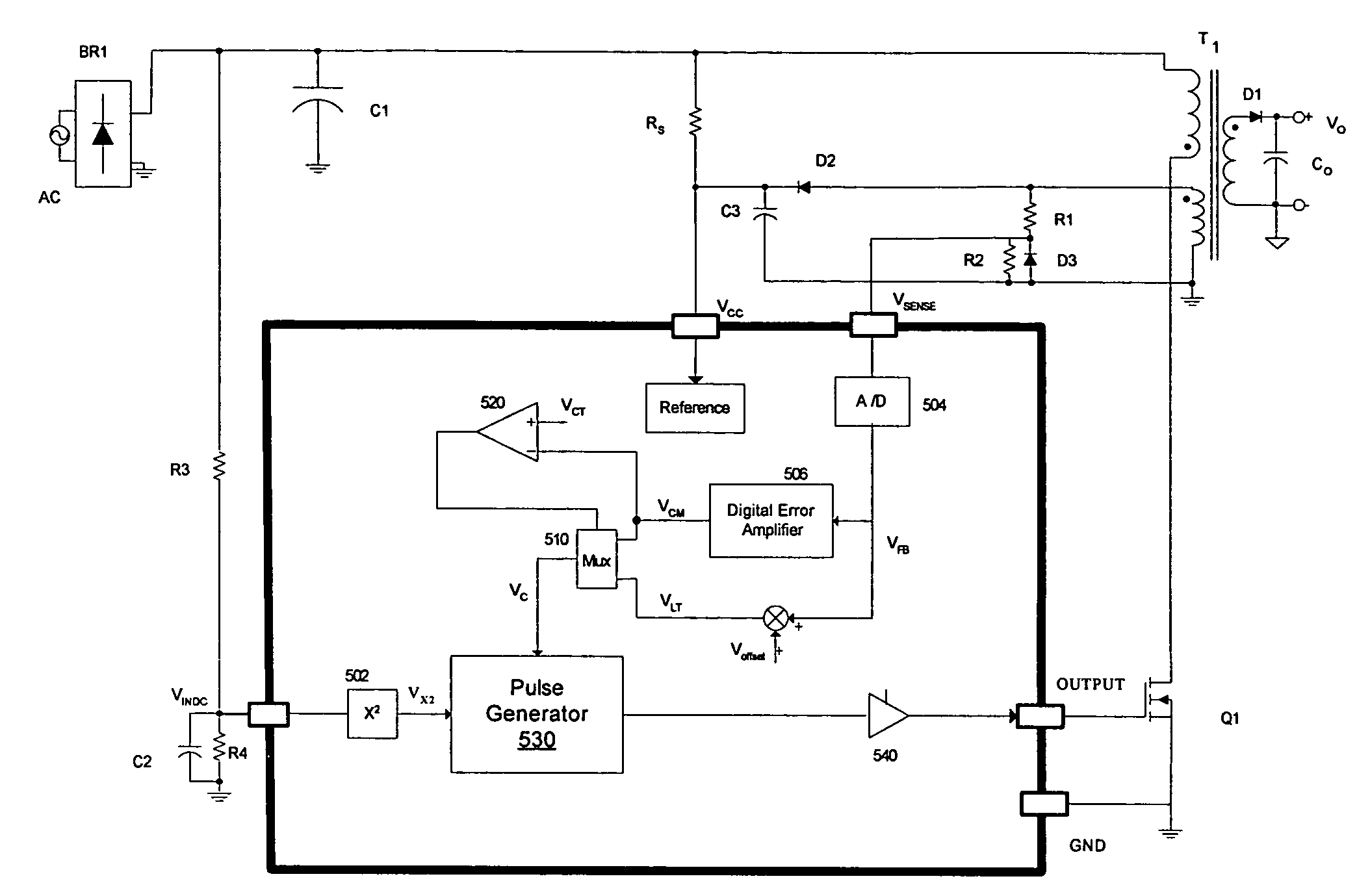
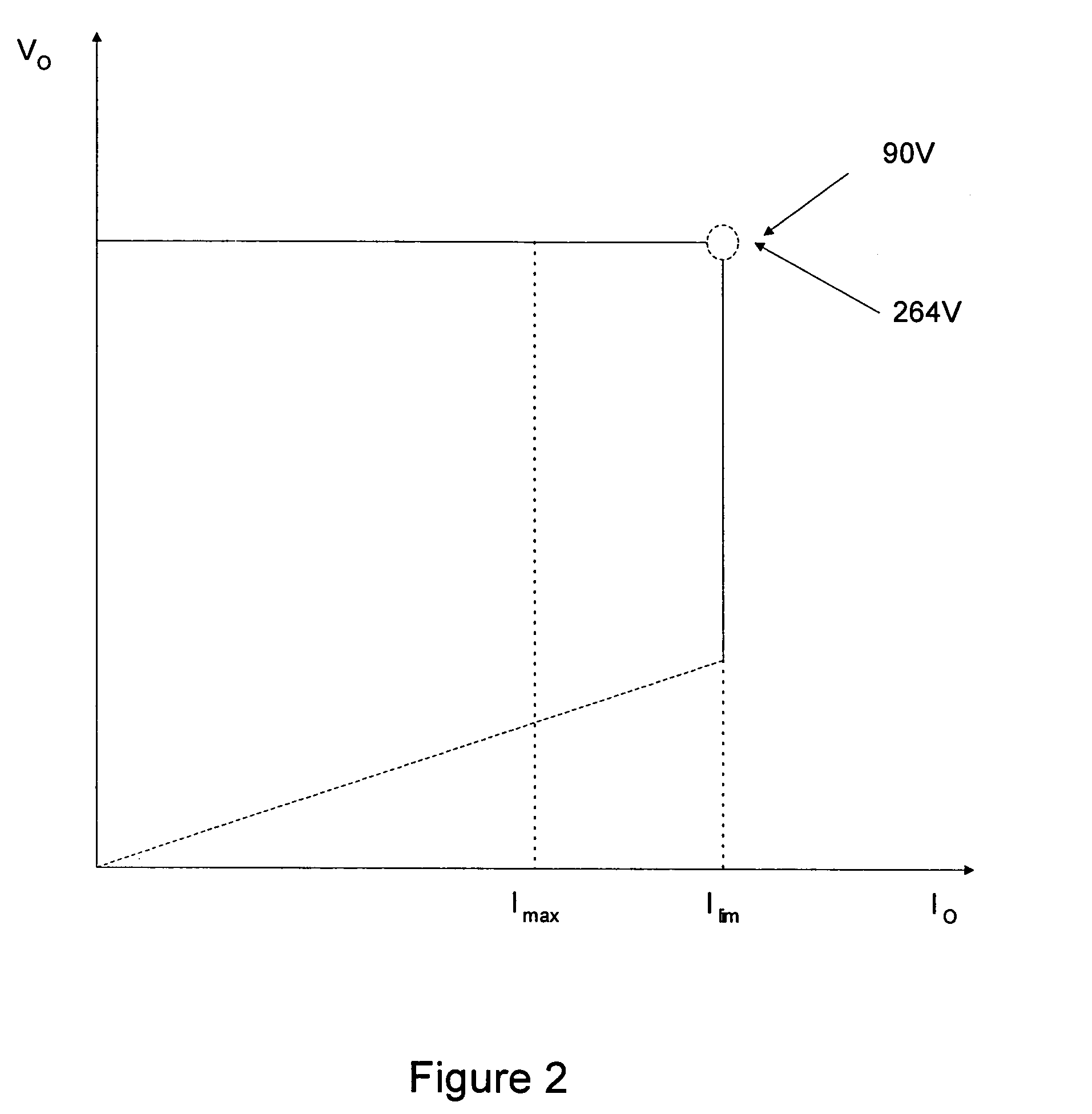
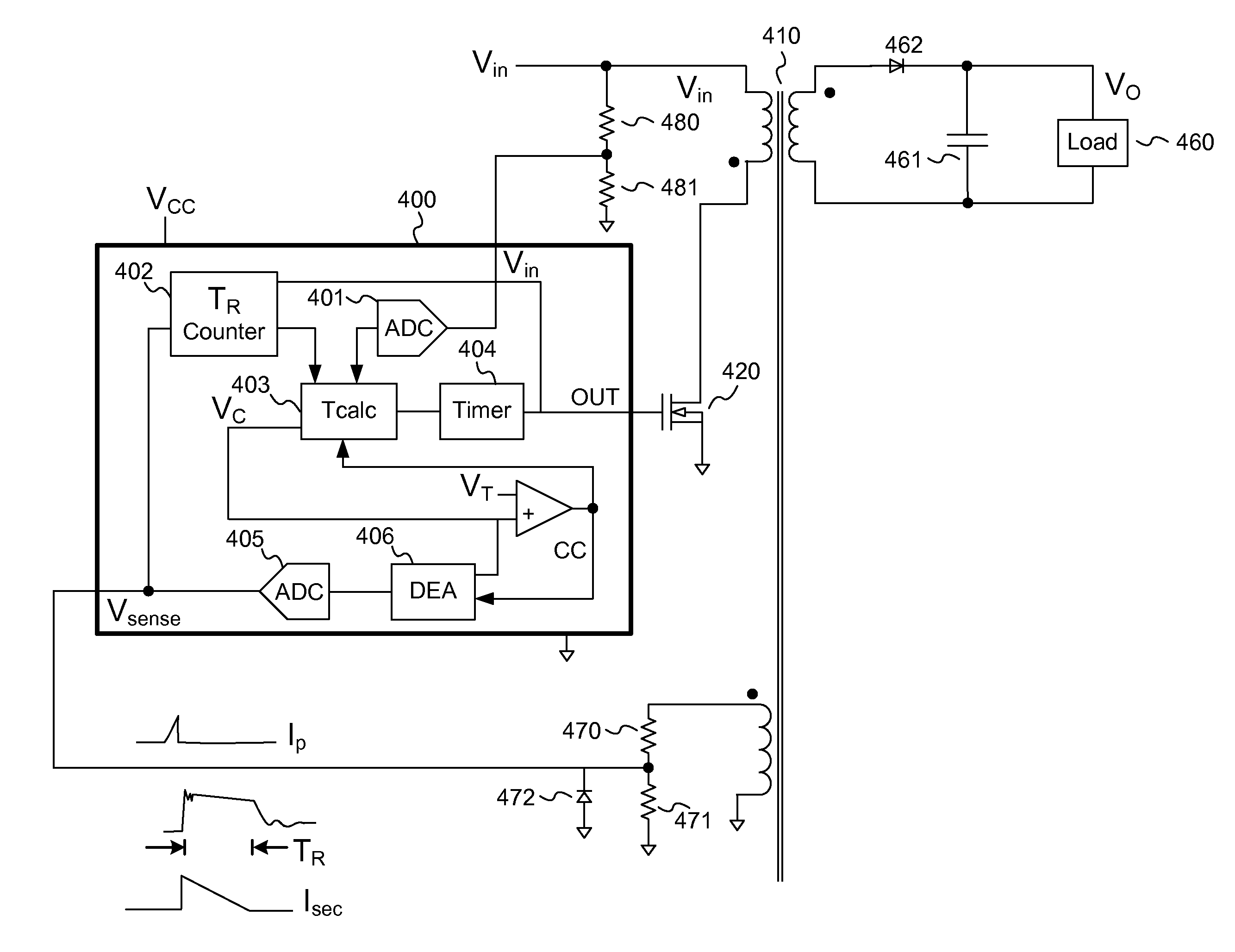
On-time control for constant current mode in a flyback power supply
ActiveUS7505287B1Easy to implementDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationLoop filterCurrent limiting
The present invention is a system and a method that controls the current limit such that it is maintained within a small range for any acceptable input voltages, e.g., 90 to 264 Volts RMS, causes the output voltage of a PWM controller to drop as the output load increases so as to maintain a constant current output, and does cycle by cycle calculation compensating for the VIN ripple output from the bridge and bulk filter capacitor so that no loop filter is required in the constant current mode.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR INC
DC-DC converter having protective function of over-voltage and over-current and led driving circuit using the same
ActiveUS20060261752A1Avoid damageDischarge tube incandescent screensElectric discharge tubesMicrocontrollerDc dc converter
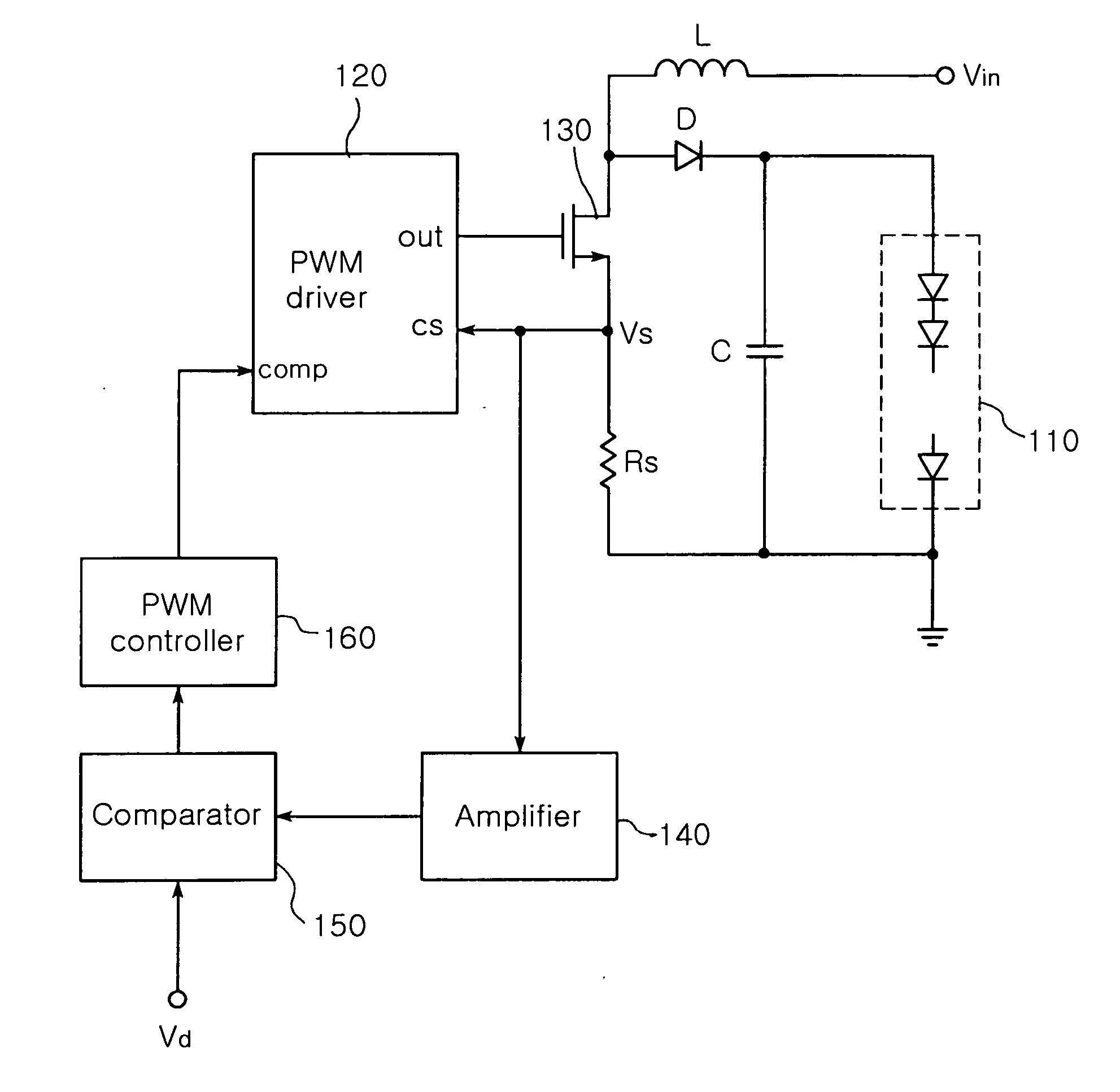
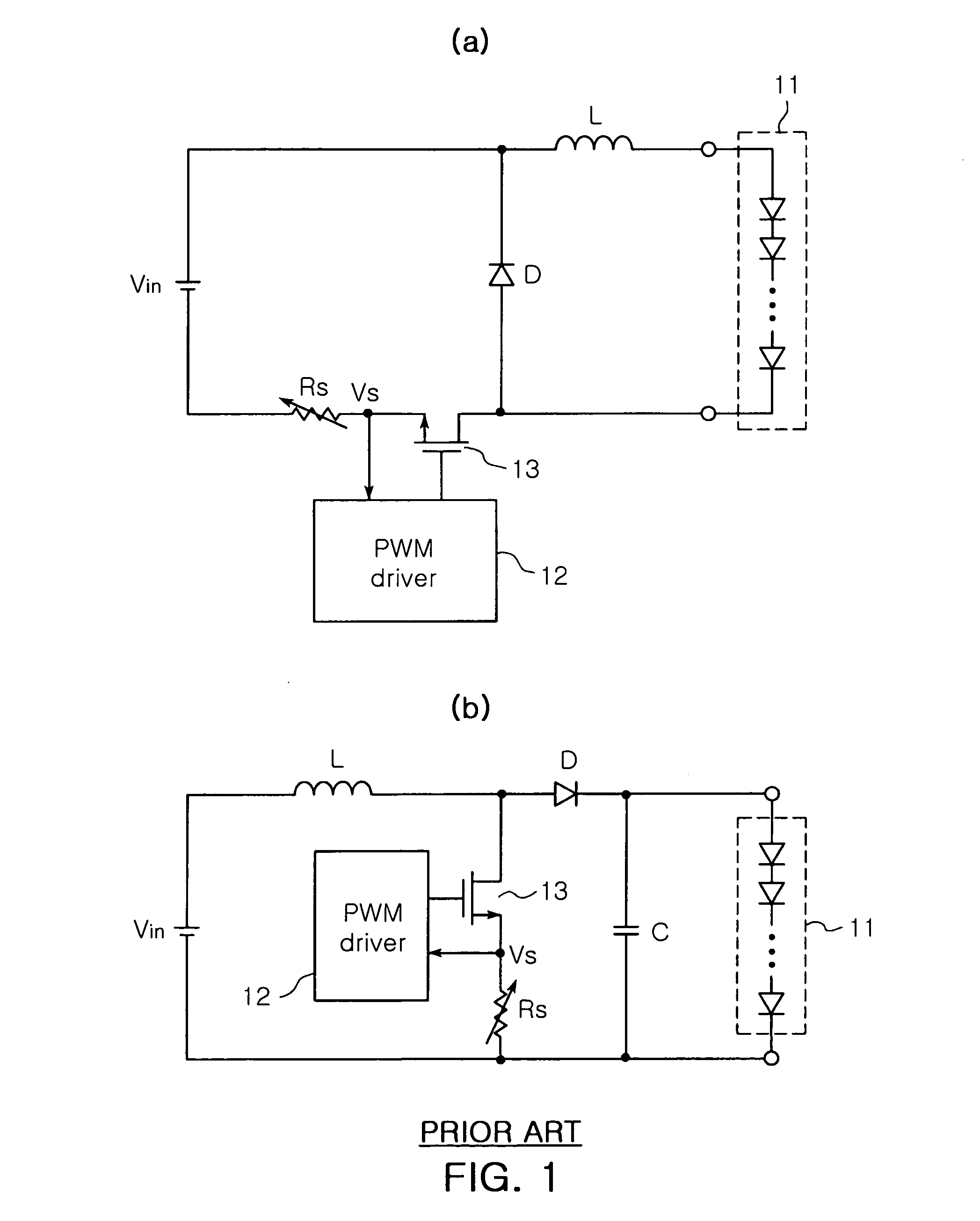
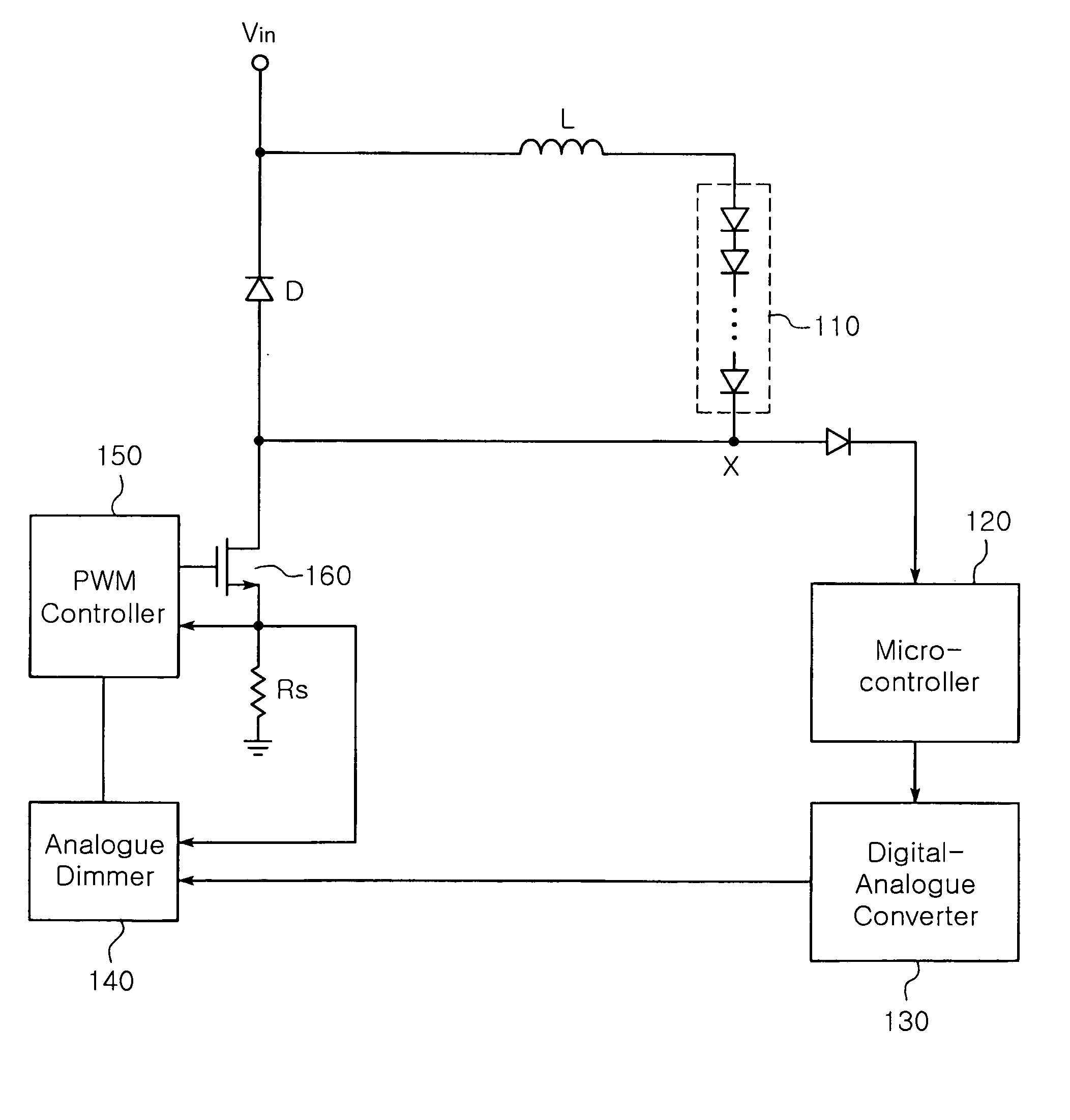
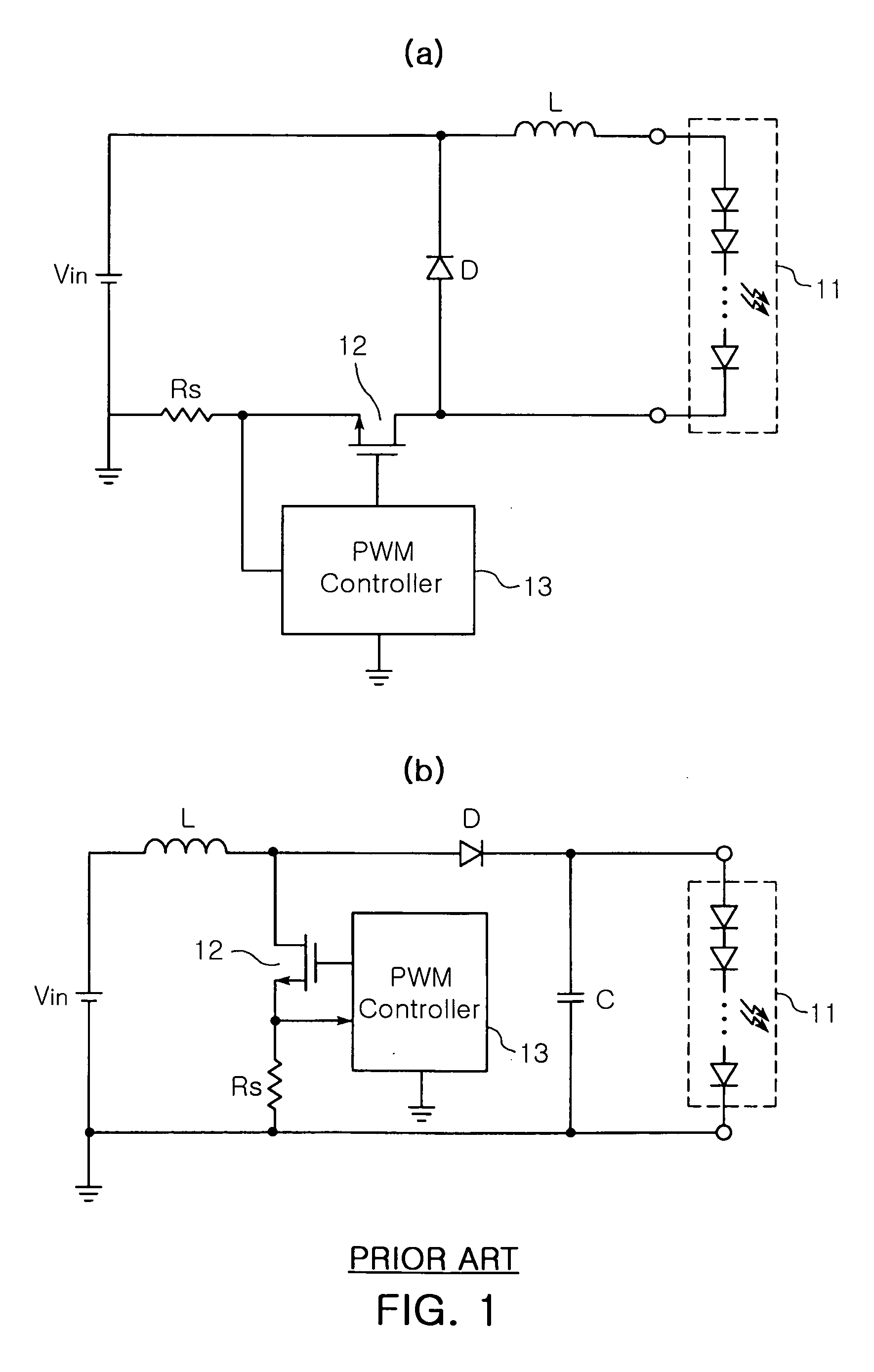
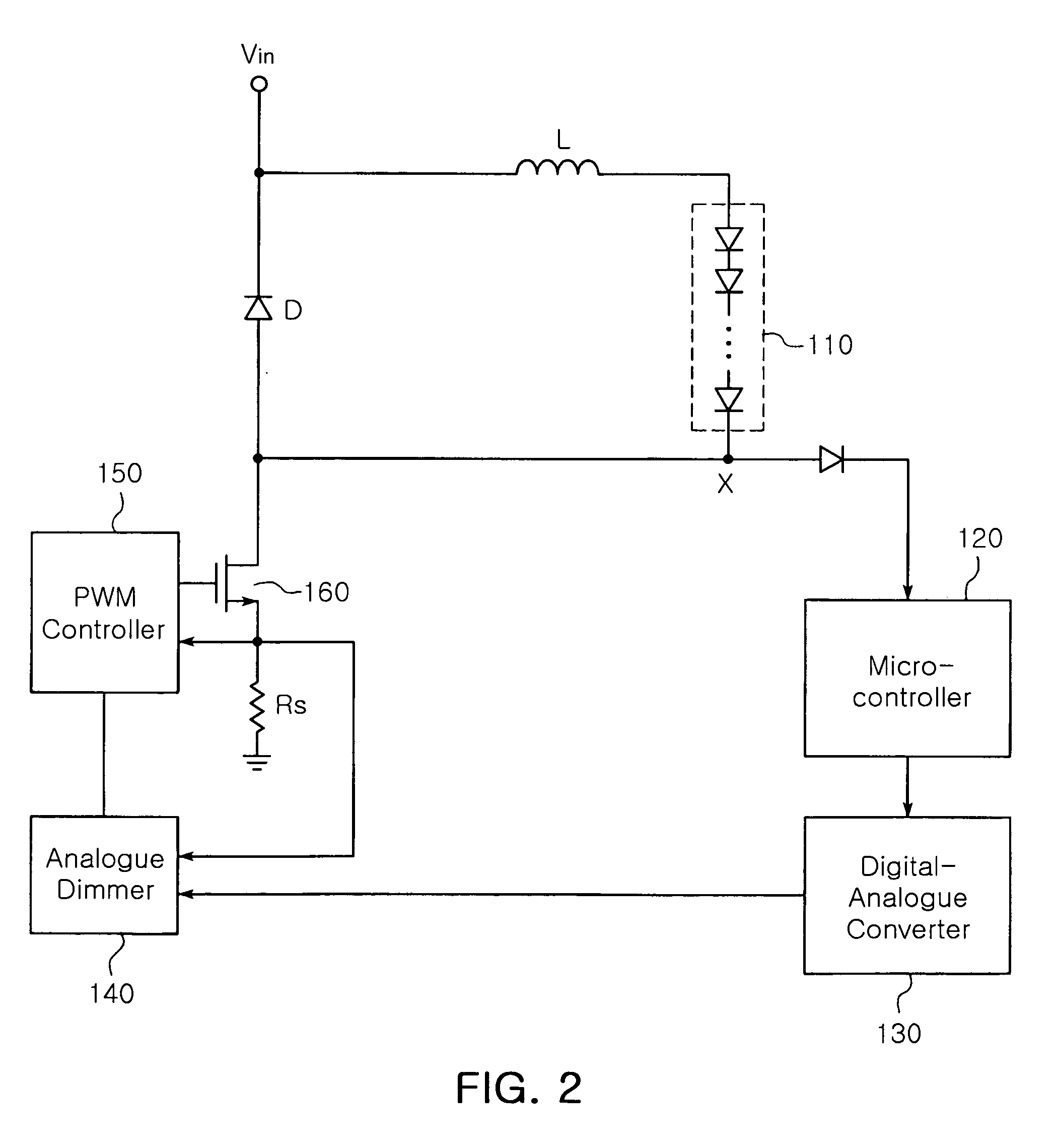
The invention relates to a DC-DC converter having over-current / over-voltage protection function and an LED driving circuit using the same. The DC-DC converter adjusts a width of a switching pulse outputted from a Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) controller to control on / off durations of a switch, thereby providing a controlled level of voltage to a load. The DC-DC converter includes a microcontroller for detecting a voltage, and if the detected voltage is greater than a reference voltage, generating an alarm signal. The DC-DC converter further includes a digital-analogue converter for outputting a voltage of 0V and an analogue dimmer for generating a control signal that changes an ‘on’ duration of the switching pulse outputted from the PWM controller to 0 and providing the control signal to the PWM controller.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Power-factor correction constant current controller and control method
ActiveCN103296904AImprove efficiencyImprove conversion efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionControl signalPeak value
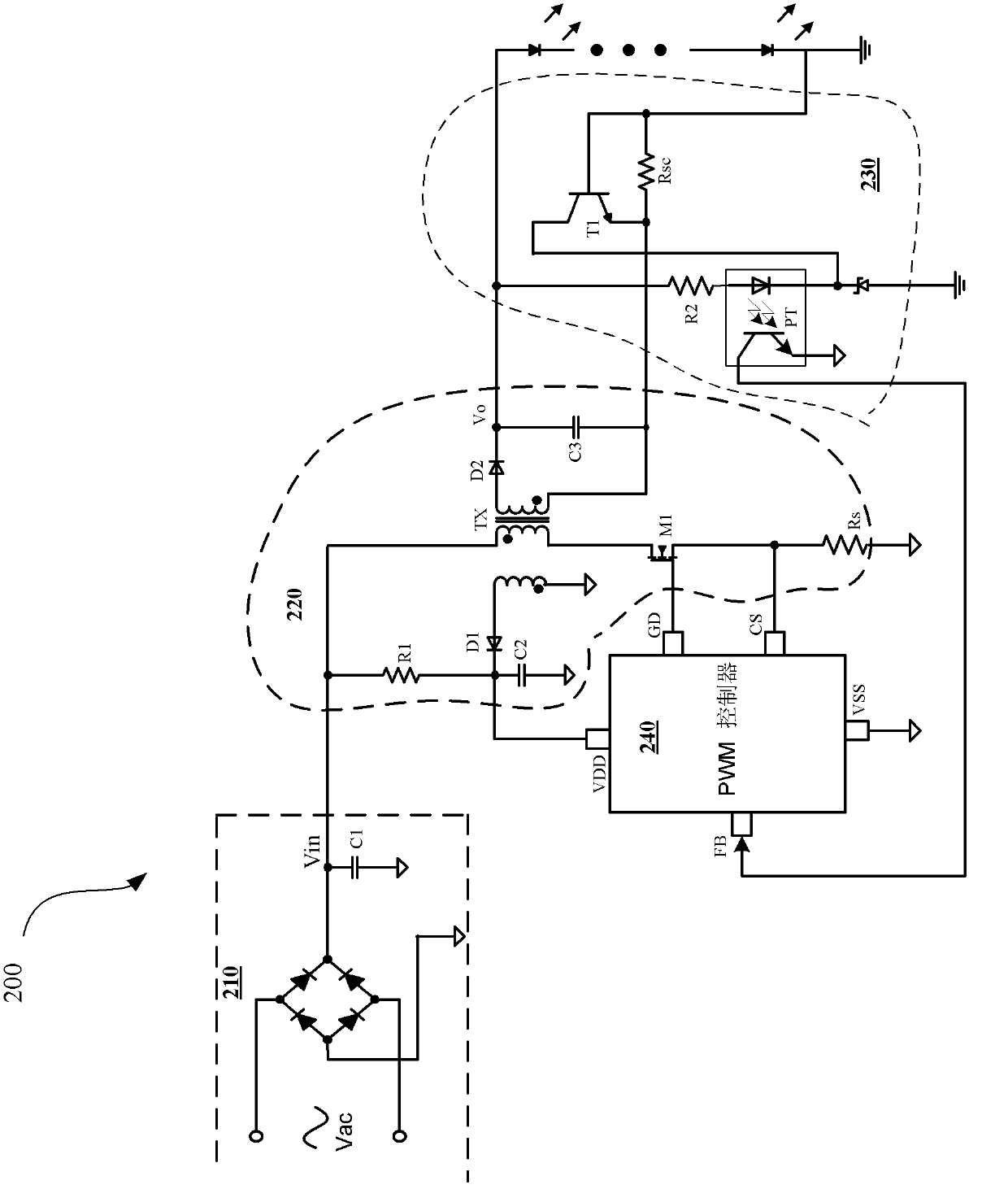
The invention relates to a PFC constant current controller and a control method of the PFC constant current controller. Unlike the traditional mode of additionally adding a PFC circuit besides a PWM controller, the PFC constant current controller integrates a single-stage PFC circuit and the PWM controller. The PFC constant current controller comprises a peak value sampling device, a feedback signal detector, a sigma delta modulator, a digital signal processor, a digital to analog converter, a comparator, a PWM generator and a power switch driver. The PFC constant current controller can obtain sampled signals of current output by a flyback switching power supply system, and the sampled signals serve as feedback signals to generate a constant-current control signal to be used for controlling averagely-output current. Therefore, the averagely-output currents are limited within a preset reference value, and accordingly the target of constant-current control is achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI BRIGHT POWER SEMICONDUCTOR CO LTD
Switch-mode self-coupling auxiliary power device
InactiveUS7106603B1Solve problemsEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcEngineeringHigh pressure
A switch-mode self-coupling power device additionally increases a set of high voltage auxiliary winding in the transformer and increases a control circuit and an energy transmitting circuit in the primary side circuit of the conventional circuit. When the load is too low, the control circuit may control the energy transmitting circuit according to the variation of the load so that the voltage of the high voltage auxiliary winding can be transmitted to a controller for operation through the energy transmitting circuit. Therefore, the design of PWM controller (pulse width modulation controller) auxiliary power circuit according to the present invention, which is not limited by the magnitude of a dummy load at the secondary side of the transformer, can conform to international regulations and is a product with industrial purpose and conforming to green mode.
Owner:TAMIRAS PER PTE LTD LLC
Switching power supply circuit
ActiveCN102361402AReduce power consumptionConforms to the short-circuit power consumption indexDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCapacitancePower flow
The invention discloses a switching power supply circuit, which comprises a starting circuit, a pulse width modulation (PWM) controller, a starting turn-off circuit, a main power tube and a main transformer, wherein the starting turn-off circuit comprises a first resistor, a turn-off triode, a charging capacitor, a first voltage sharing resistor and a second voltage sharing resistor; a connection point between the current sampling end of the PWM controller and a source of the main power tube is connected to the voltage reference end of the starting circuit through the first resistor; one circuit of the output end of the PWM controller is connected to the voltage reference end of the starting circuit through the charging capacitor and the other circuit of the output end of the PWM controller is connected to the voltage reference end of the starting circuit through the first voltage sharing resistor and the second voltage sharing resistor sequentially; a connection point between the first voltage sharing resistor and the second voltage sharing resistor is connected to a base of the turn-off triode; a collector of the turn-off triode is connected to the control end of the starting circuit; and an emitter of the turn-off triode is connected to the voltage reference end of the starting circuit.
Owner:MORNSUN GUANGZHOU SCI & TECH
Dc-dc converter
ActiveUS20110031948A1Efficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDc dc converterEngineering
A DC-DC converter including a Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) controller for converting an input voltage into an output voltage is provided. The PWM controller includes an error amplifier, a comparator, a PWM generator and a ramp generator. The error amplifier generates an error signal according to a difference between a reference voltage and the output voltage. The comparator compares the error signal with a ramp signal to generate a trigger signal. The PWM generator generates a PWM signal with a fixed turn-on time, wherein a frequency of the PWM signal is adjusted according to the trigger signal, the input and output voltages. The ramp generator generates the ramp signal according to the PWM signal, the input voltage and the output voltage.
Owner:UPI SEMICON CORP
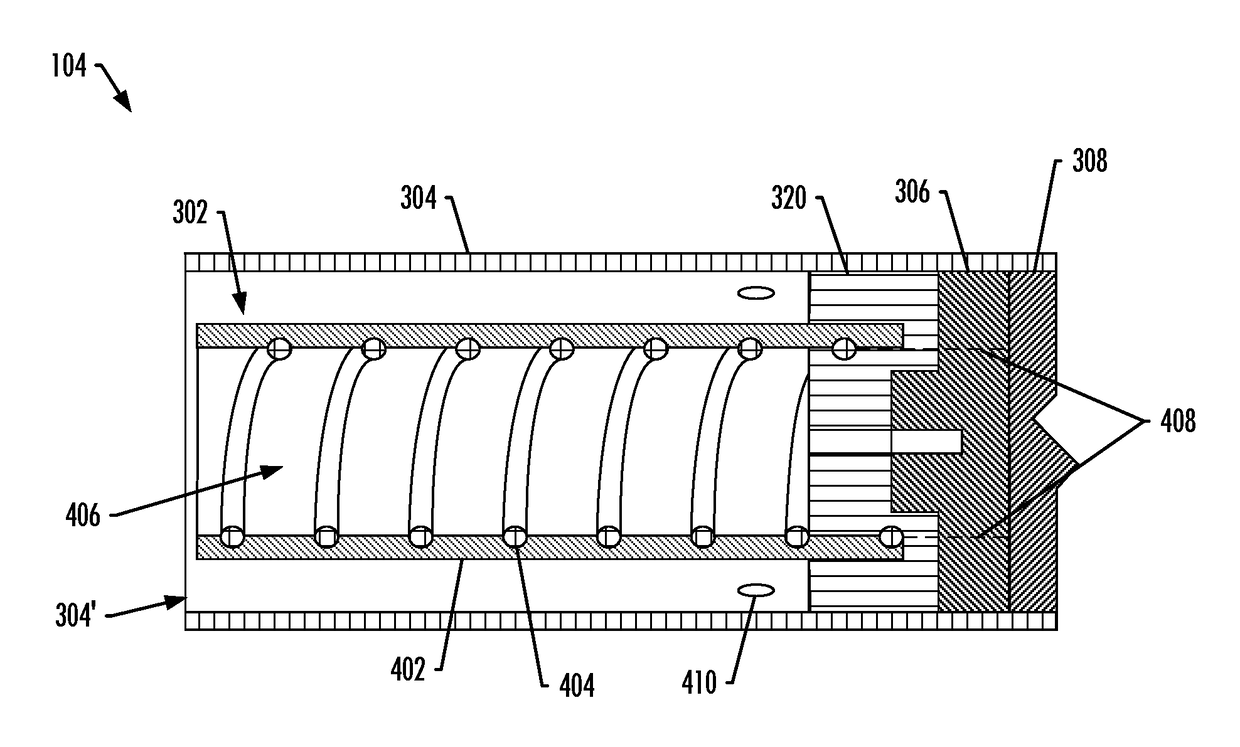
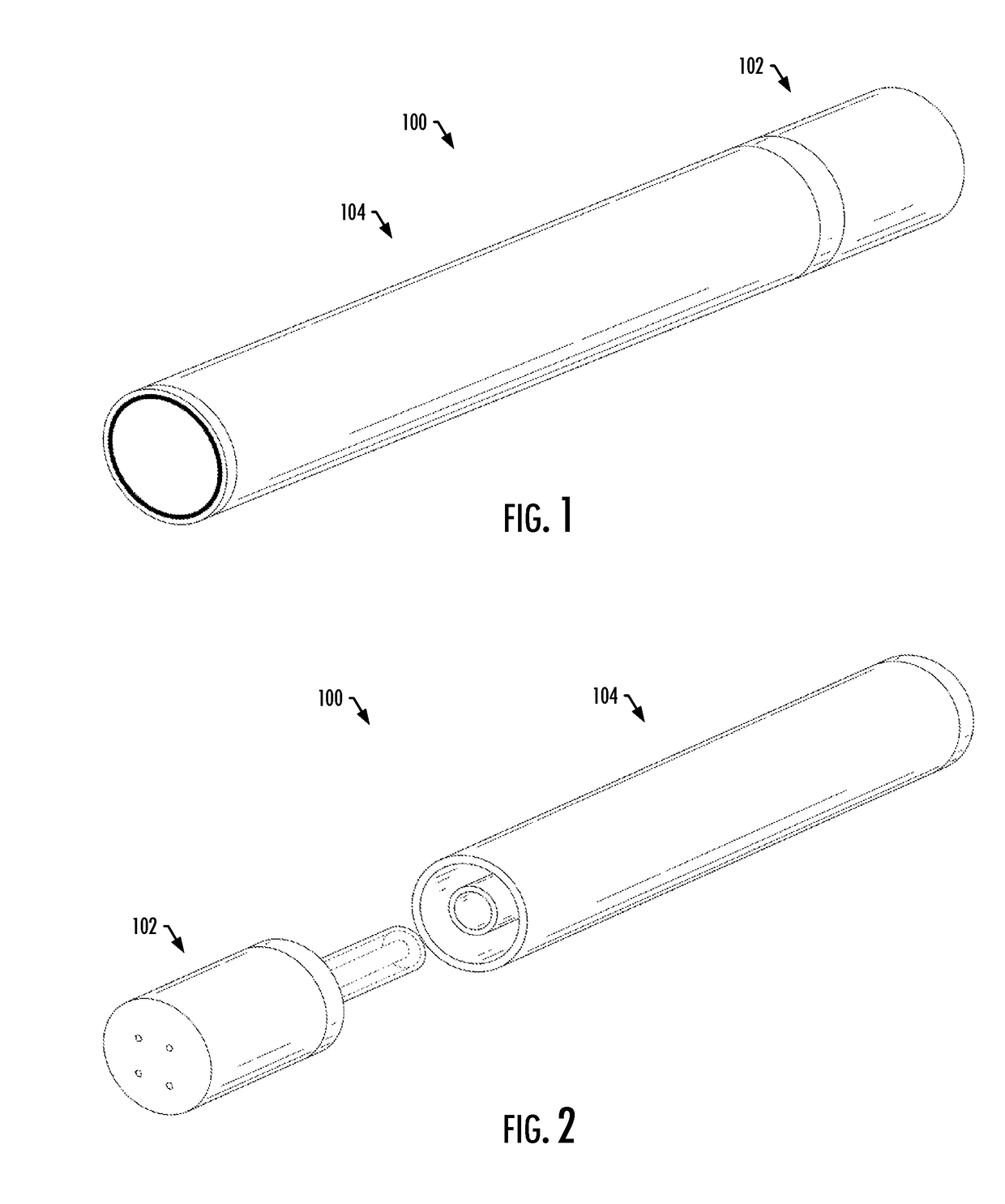
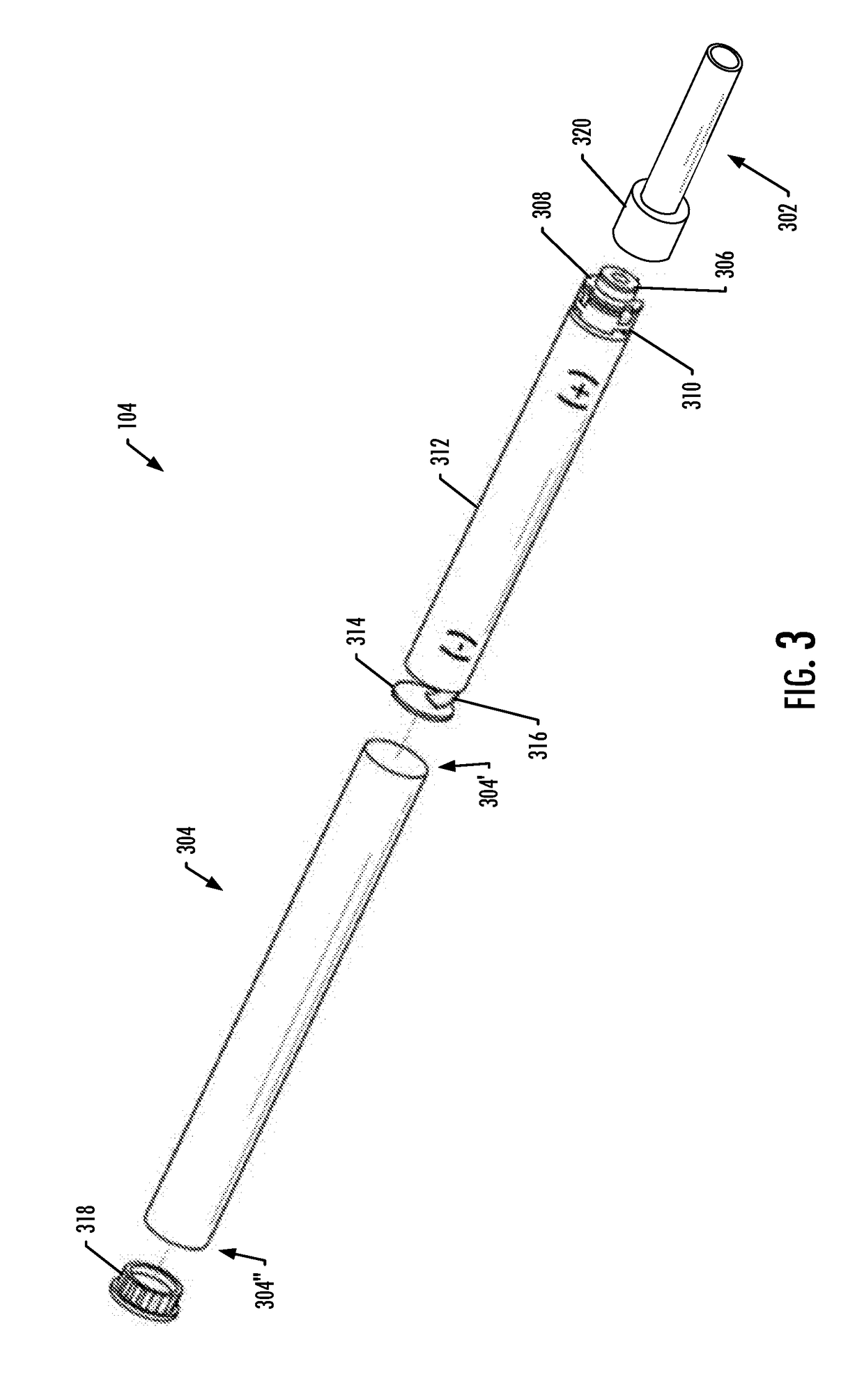
Induction-based aerosol delivery device
An aerosol delivery device is provided that includes a substrate configured to carry an aerosol precursor composition, and a resonant transformer including a transmitter coupling device and a resonant receiver coupling device that is positioned in proximity to the substrate. The aerosol delivery device also includes a pulse width modulation (PWM) inverter configured to drive the resonant transformer. The PWM inverter includes a bridge circuit coupled to the transmitter coupling device, and a PWM controller embodied as an integrated circuit and configured to output a PWM signal to the bridge circuit configured to drive the transmitter coupling device to generate an oscillating magnetic field and induce an alternating voltage in the resonant receiver coupling device when exposed to the oscillating magnetic field. The alternating voltage causes the resonant receiver coupling device to generate heat and thereby vaporize components of the aerosol precursor composition.
Owner:RAI STRATEGIC HLDG INC
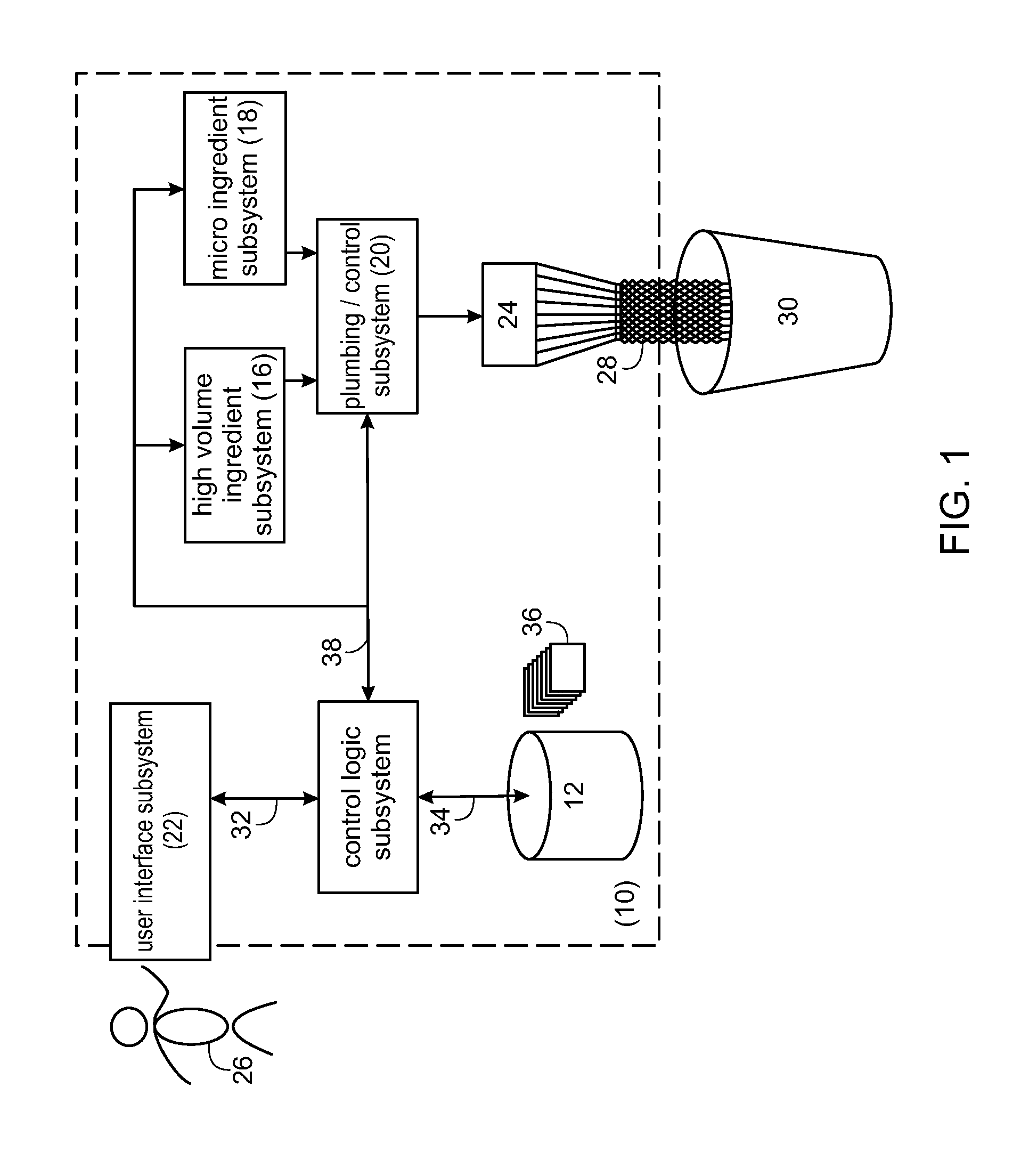
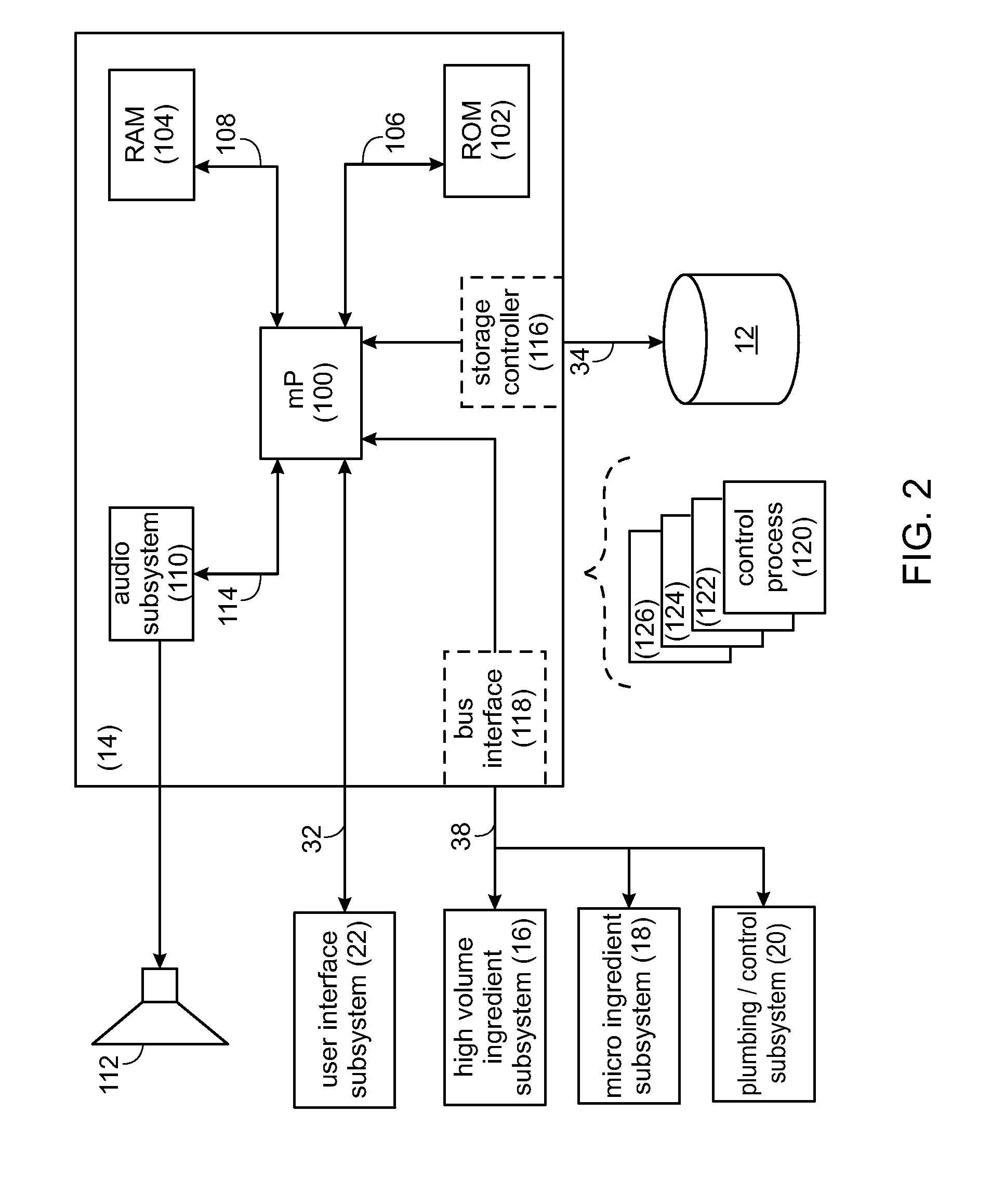
Product Dispensing System
A system for monitoring flow conditions of fluid flowing from a product container through a solenoid pump. The system includes at least one solenoid pump comprising a solenoid coil, which, when energized, produces a stroke of the solenoid pump, at least one product container connected to the at least one solenoid pump wherein the at least one solenoid pump pumps fluid from the at least one product container during each stroke, at least one PWM controller configured to energize the at least one solenoid pump, at least one current sensor for sensing the current flow through the solenoid coil and producing an output of the sensed current flow, and a control logic subsystem for controlling the flow of fluids through the solenoid pump by commanding the PWM controller and for monitoring the current through the solenoid pump by receiving the output from the current sensor, wherein the control logic subsystem uses the measured current flow through the solenoid coil to determine whether the stroke of the solenoid pump is functional.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
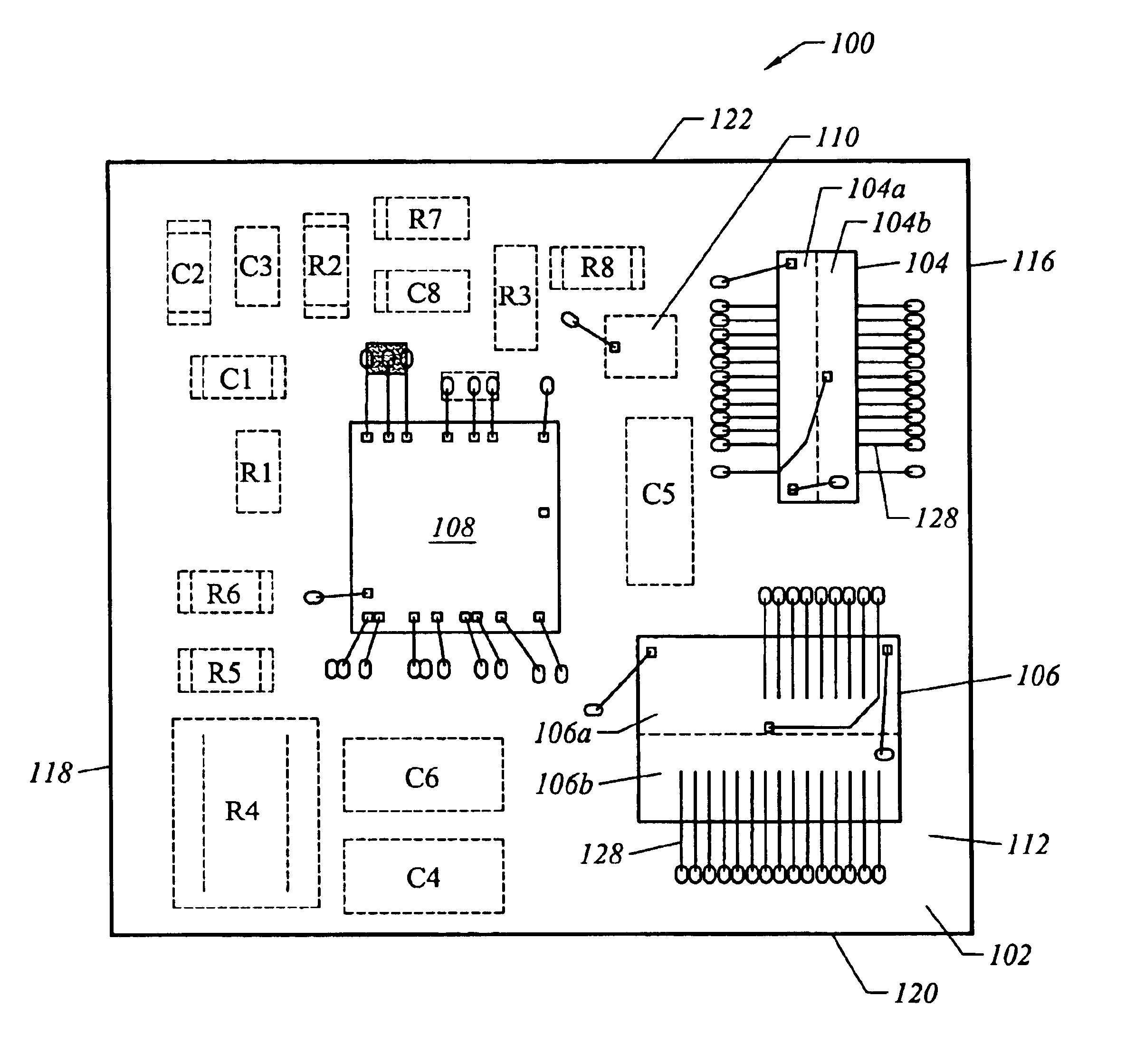
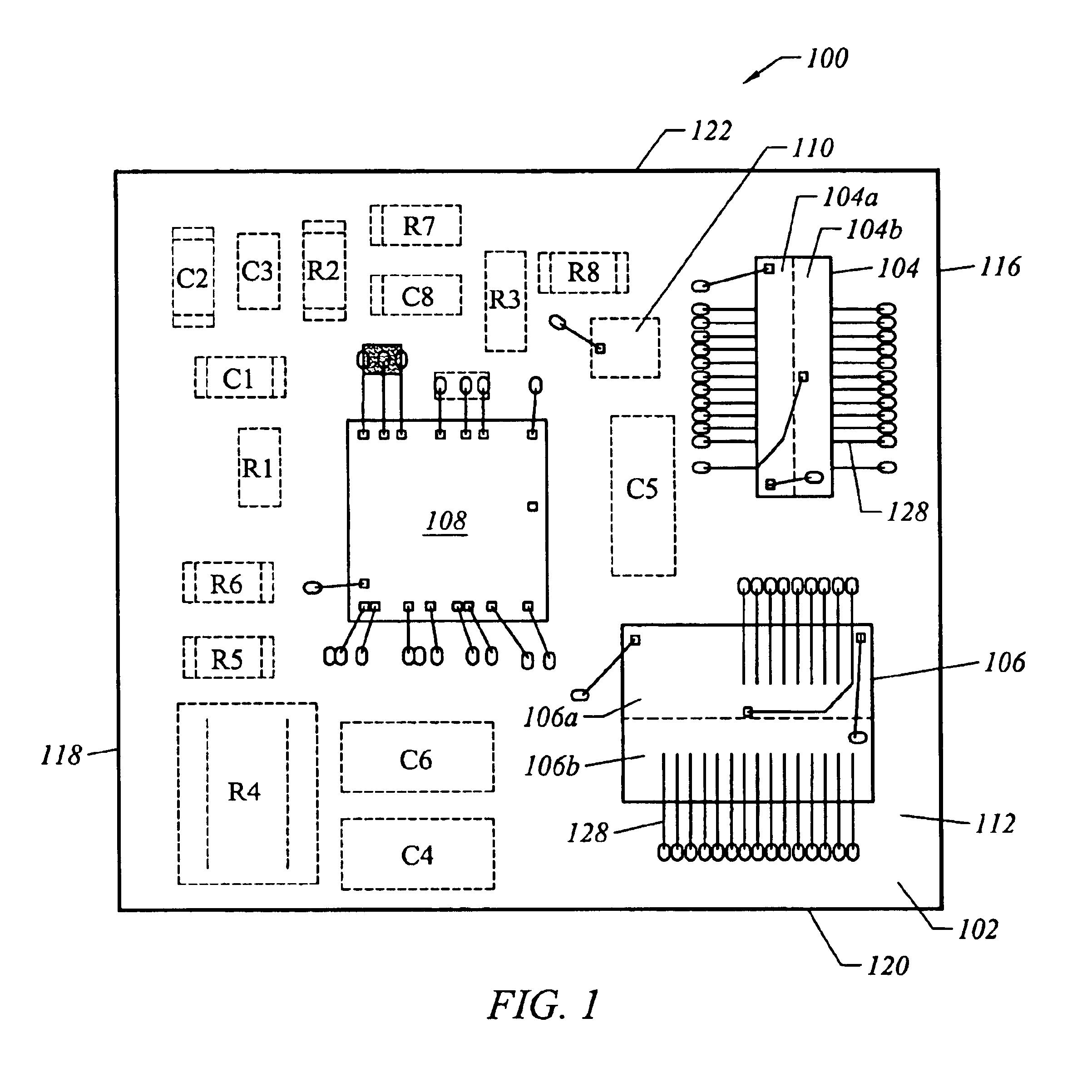
DC-DC converter implemented in a land grid array package
InactiveUS6940724B2Improve heat dissipation characteristicsHigh densityEfficient power electronics conversionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMOSFETSemiconductor chip
A semiconductor chip package that includes a DC—DC converter implemented with a land grid array (LGA) package for interconnection and surface mounting to a printed circuit board. The LGA package integrates all required active components of the DC—DC power converter, including a synchronous buck PWM controller, driver circuits, and MOSFET devices. In particular, the LGA package comprises a substrate having a top surface and a bottom surface, with a DC—DC converter provided on the substrate. The DC—DC converter including at least one power silicon die disposed on the top surface of the substrate. A plurality of electrically and thermally conductive pads are provided on the bottom surface of the substrate in electrical communication with the DC—DC converter through respective conductive vias. The plurality of pads include first pads having a first surface area and second pads having a second surface area, the second surface area being substantially larger than the first surface area. Heat generated by the DC—DC converter is conducted out of the LGA package through the plurality of pads.
Owner:PWER BRIDGE
PWM controller having frequency jitter for power supplies
ActiveUS7026851B2Undesired ripple signal can be eliminatedLower impedanceDc-dc conversionElectric pulse generatorUltrasound attenuationAttenuation ratio
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Versatile zero-voltage switch resonant inverter for industrial dielectric barrier discharge generator applications
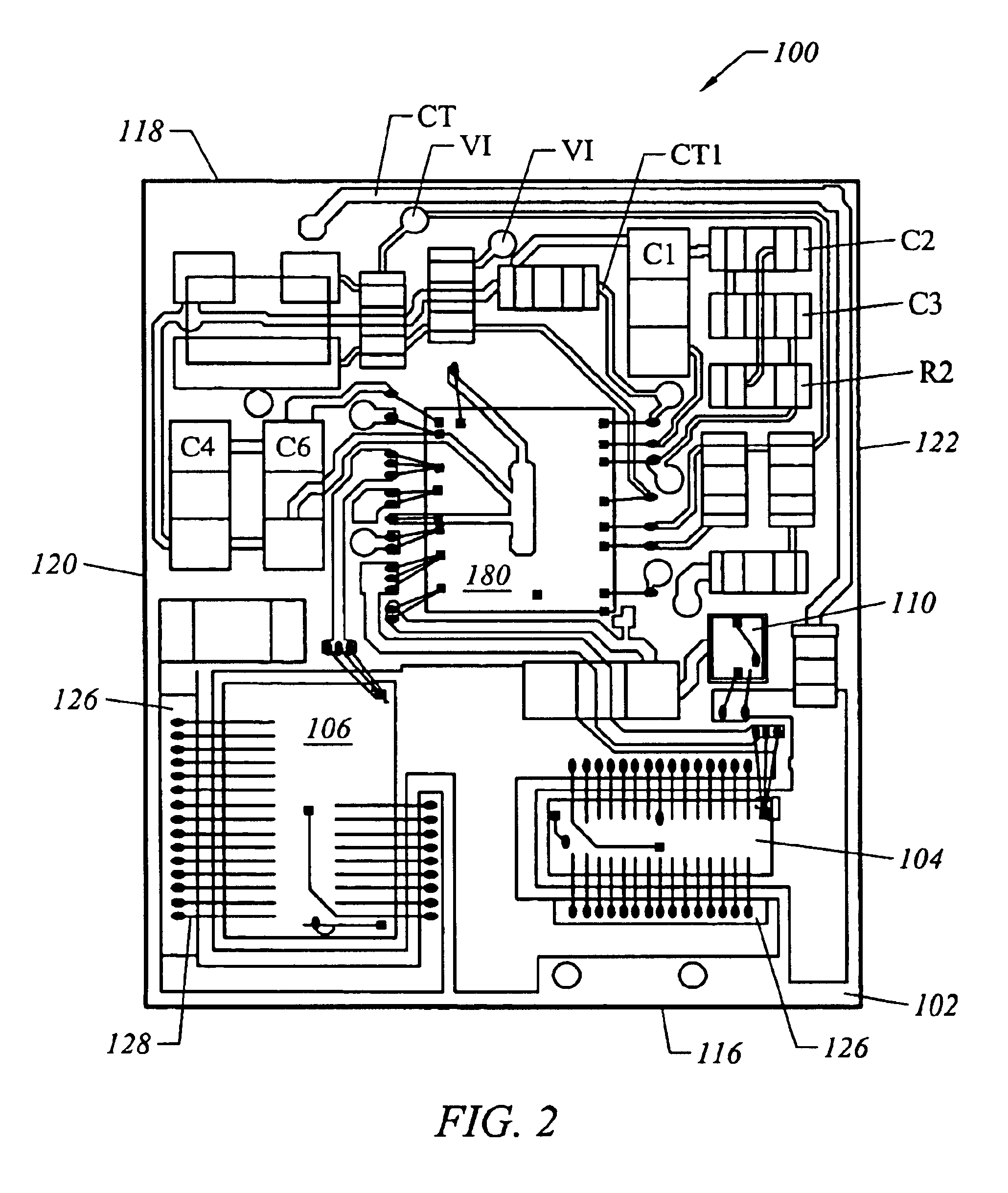
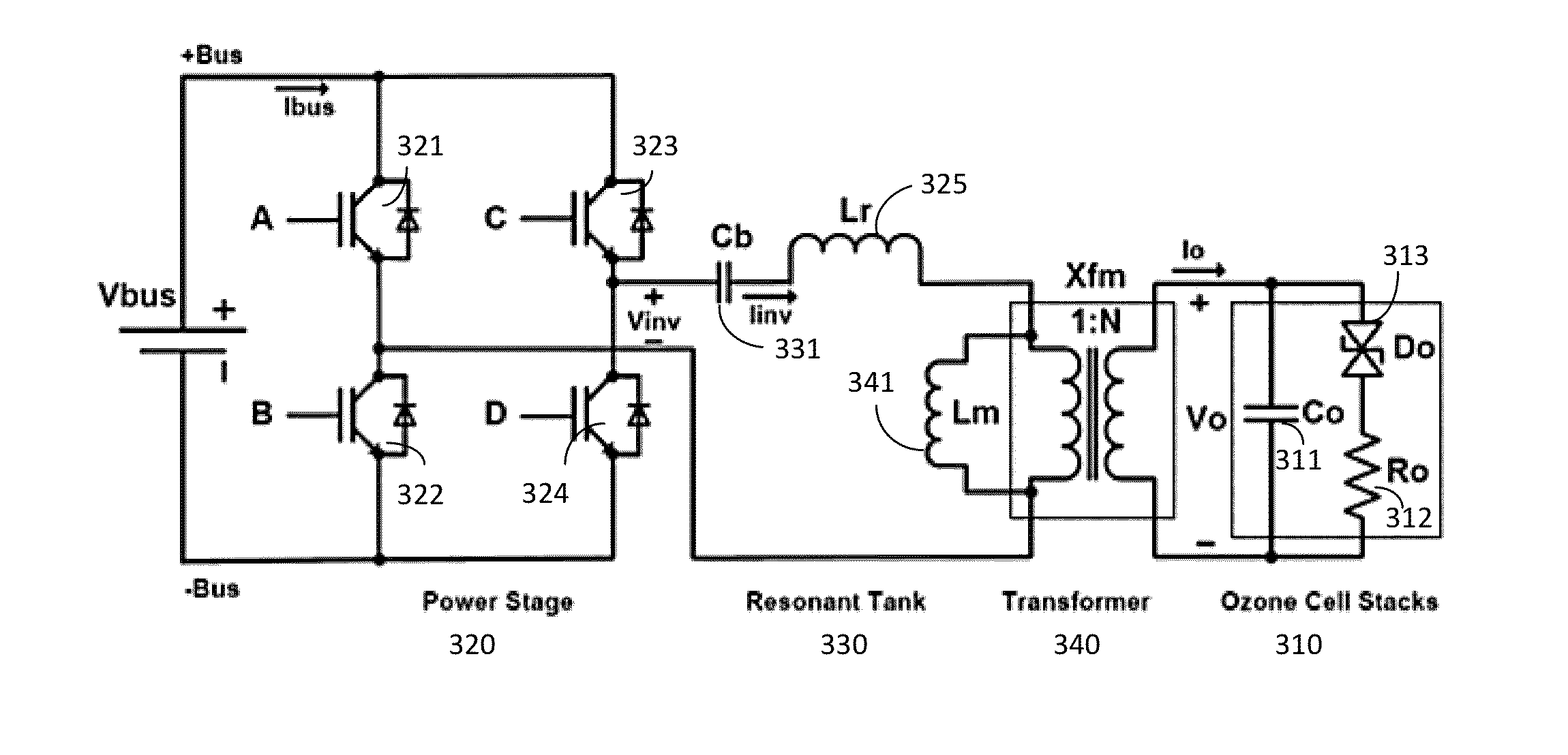
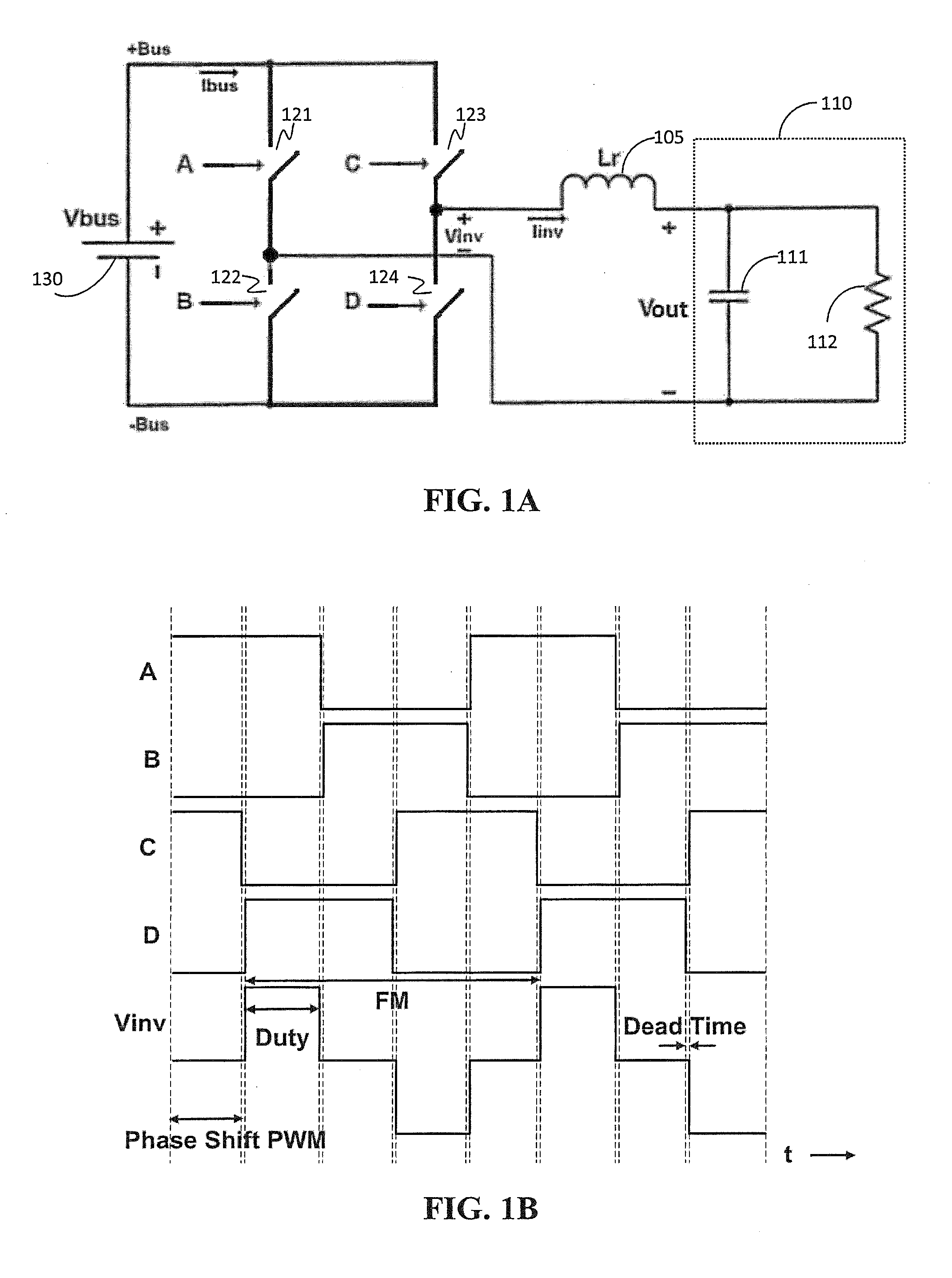
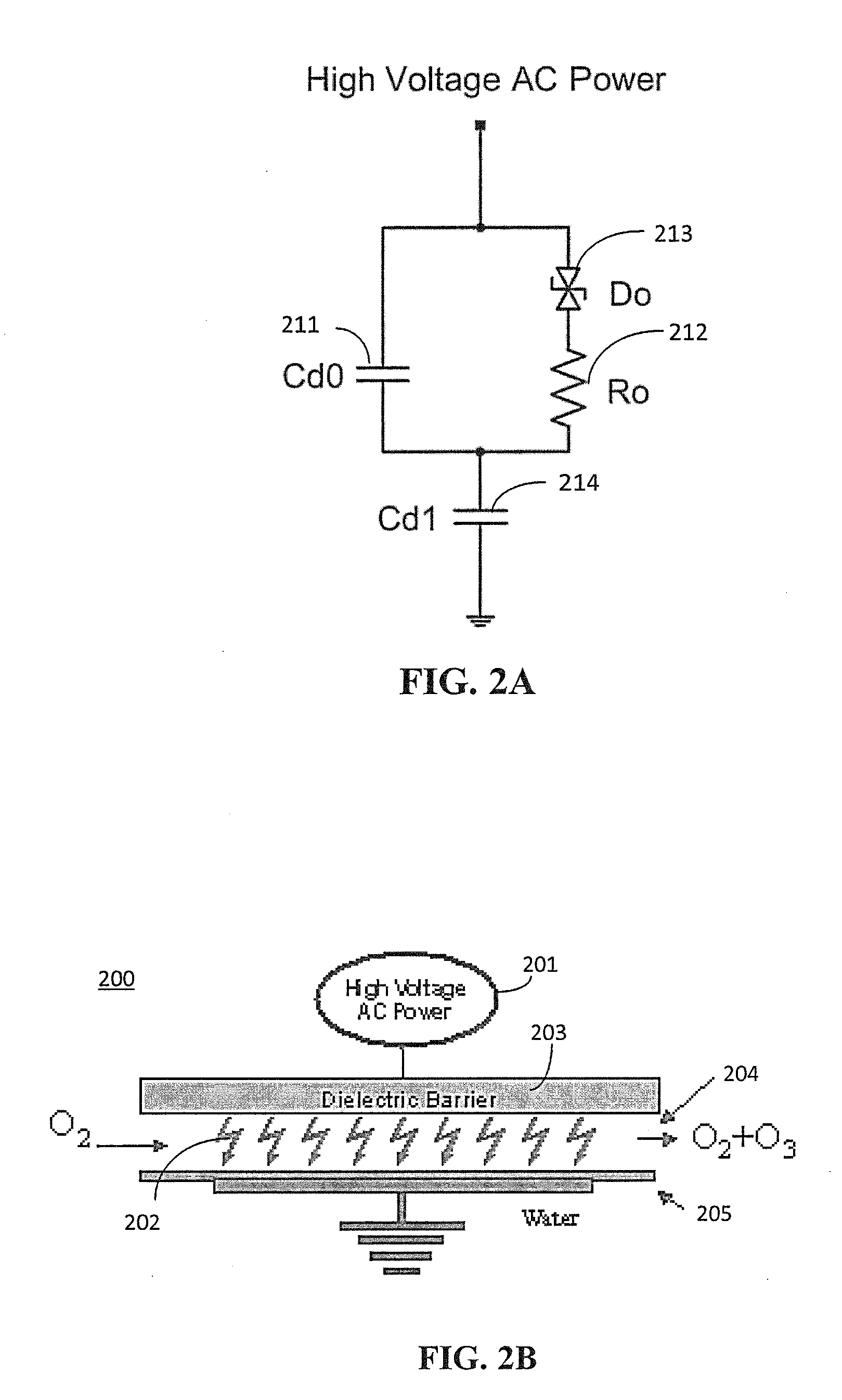
ActiveUS20130257311A1Improve dynamic rangeImprove stabilityElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesResonant inverterSoft switching
A power system for a dielectric barrier discharge system, such as used for generating ozone, can include a full bridge inverter stage and parallel resonant tank outputting a signal for powering a dielectric barrier discharge cell stack. The inverter stage is controlled using a combination of pulse width modulation (PWM) and frequency modulation (FM) to enable soft switching through all load conditions—from full load to light load. A current control loop error amplifier compensator can provide a duty cycle adjustment signal to a phase shift PWM controller chip that generates the switching signals for the inverter stage. A feedback signal is also used to adjust a clock frequency time constant of the PWM controller chip to provide the FM. In one embodiment, the feedback signal is an output of an inverting amplifier connected at an output of the current control loop error amplifier compensator.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
Multi-Phase Power Block For a Switching Regulator for use with a Single-Phase PWM Controller
A multi-phase power block for a switching regulator includes a phase control circuit, N power cells and a current sharing control circuit. The phase control circuit is configured to receive a single phase PWM clock signal and generate N clock signals in N phases. Each of the N power cells includes a pair of power switches, gate drivers, a control circuit receiving one of the N clock signals and generating gate drive signals for the gate drivers, and an inductor. The current sharing control circuit is configured to assess the inductor current at the inductor of the N power cells and to generate duty cycle control signals for the N power cells. The duty cycle control signals are applied to the control circuits to adjust the duty cycle of one or more clock signals supplied to the power cells to balance a current loading among the N power cells.
Owner:MICREL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com