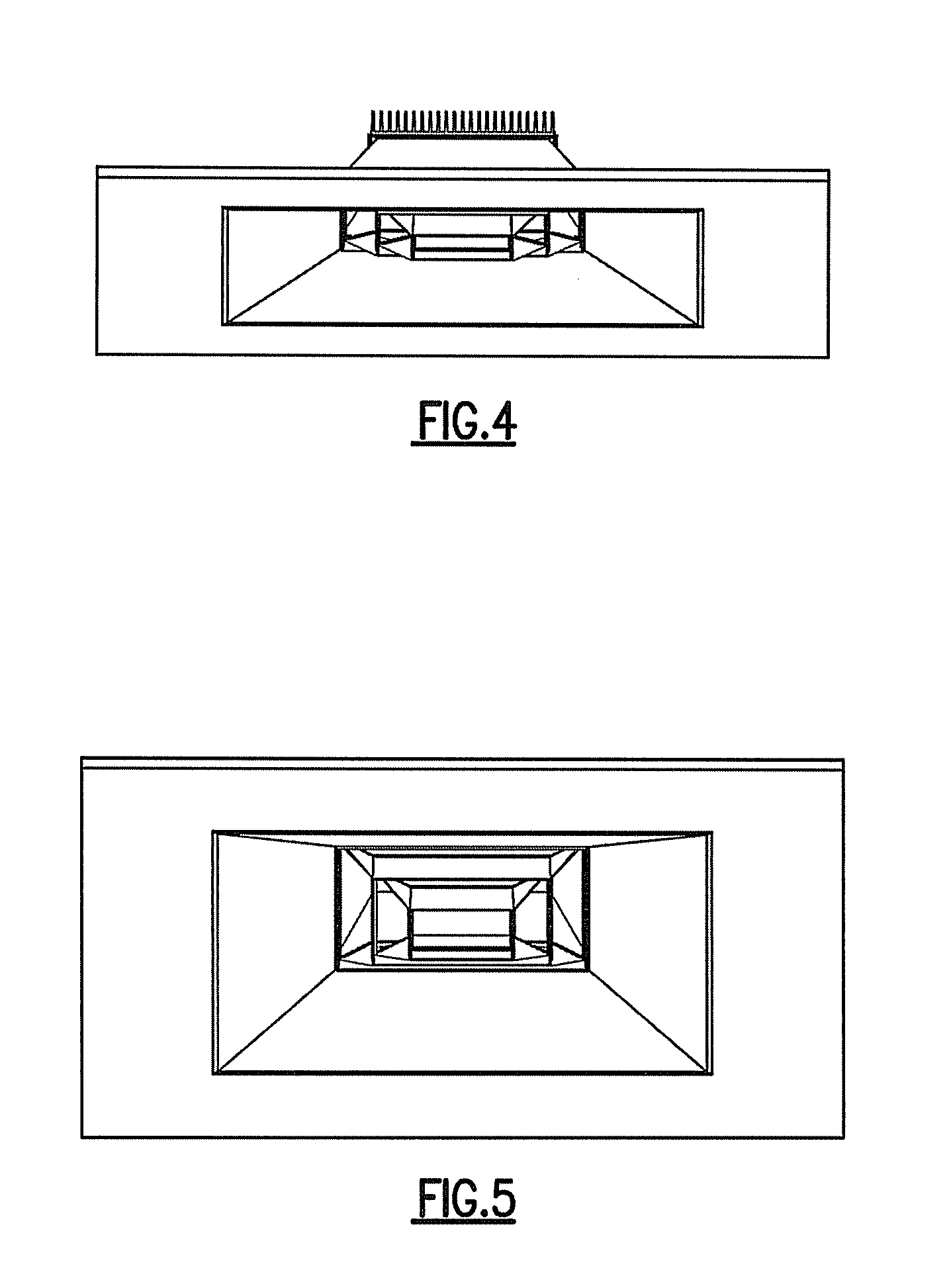
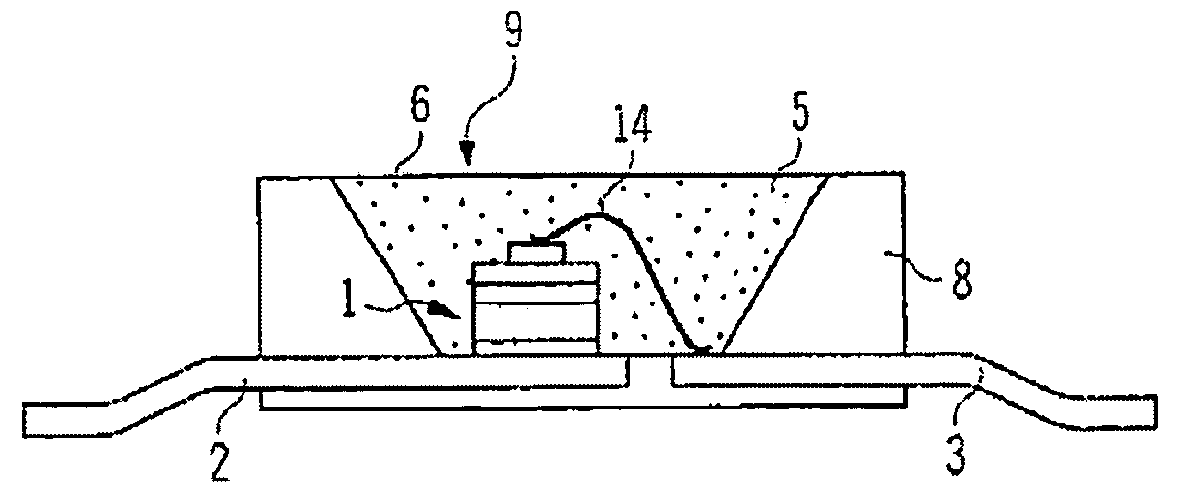
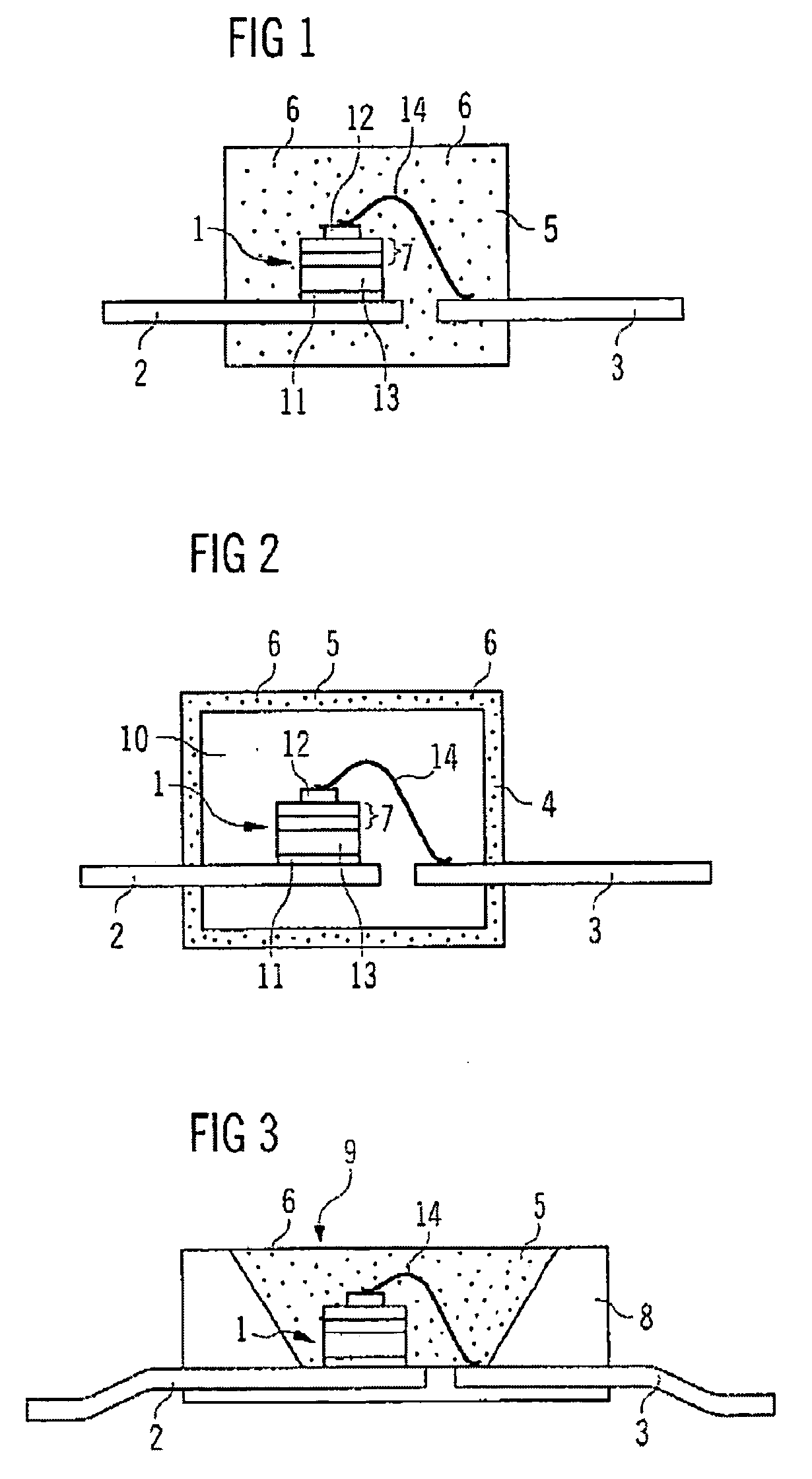
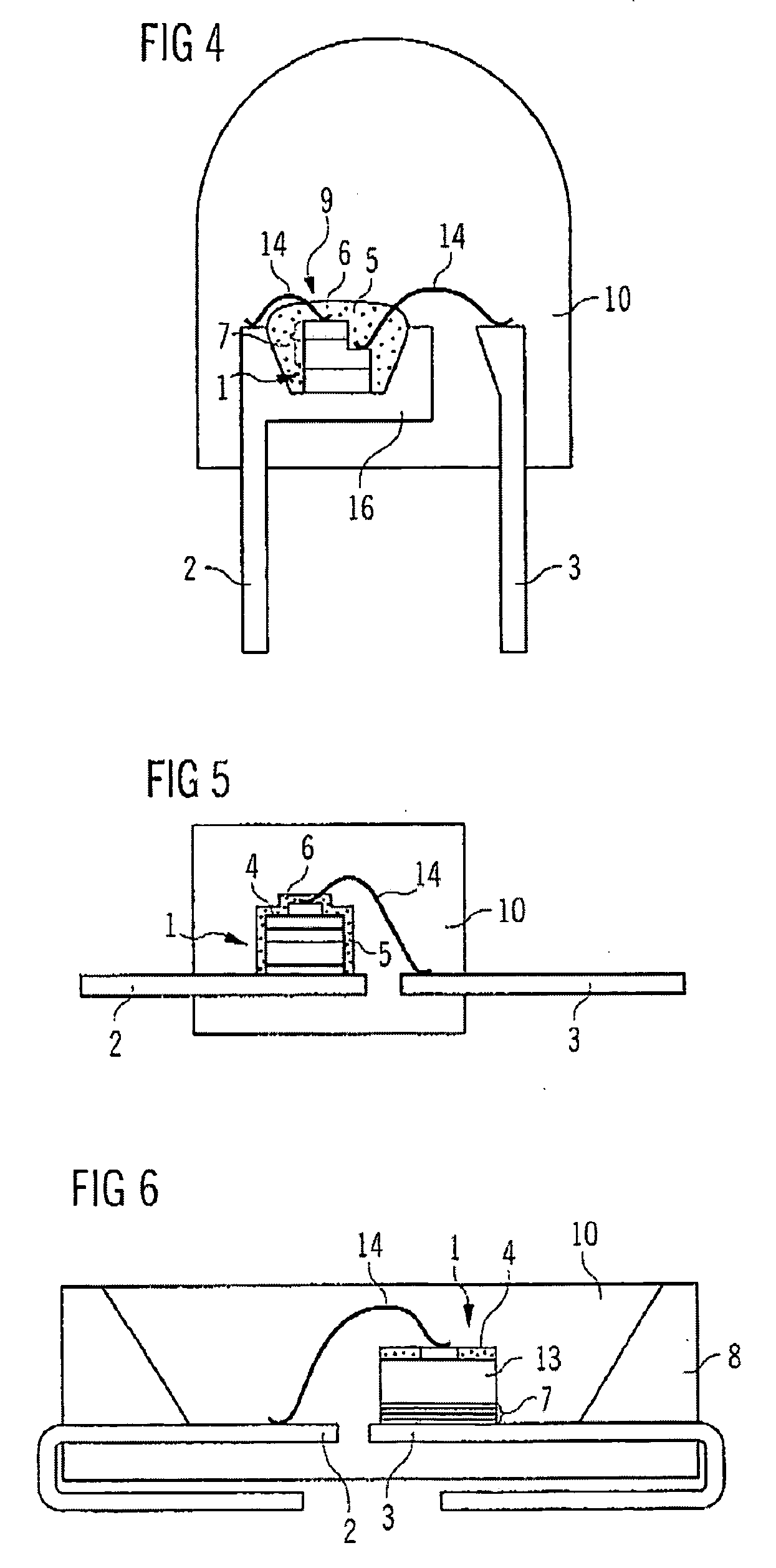
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3009results about How to "Reduce brightness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
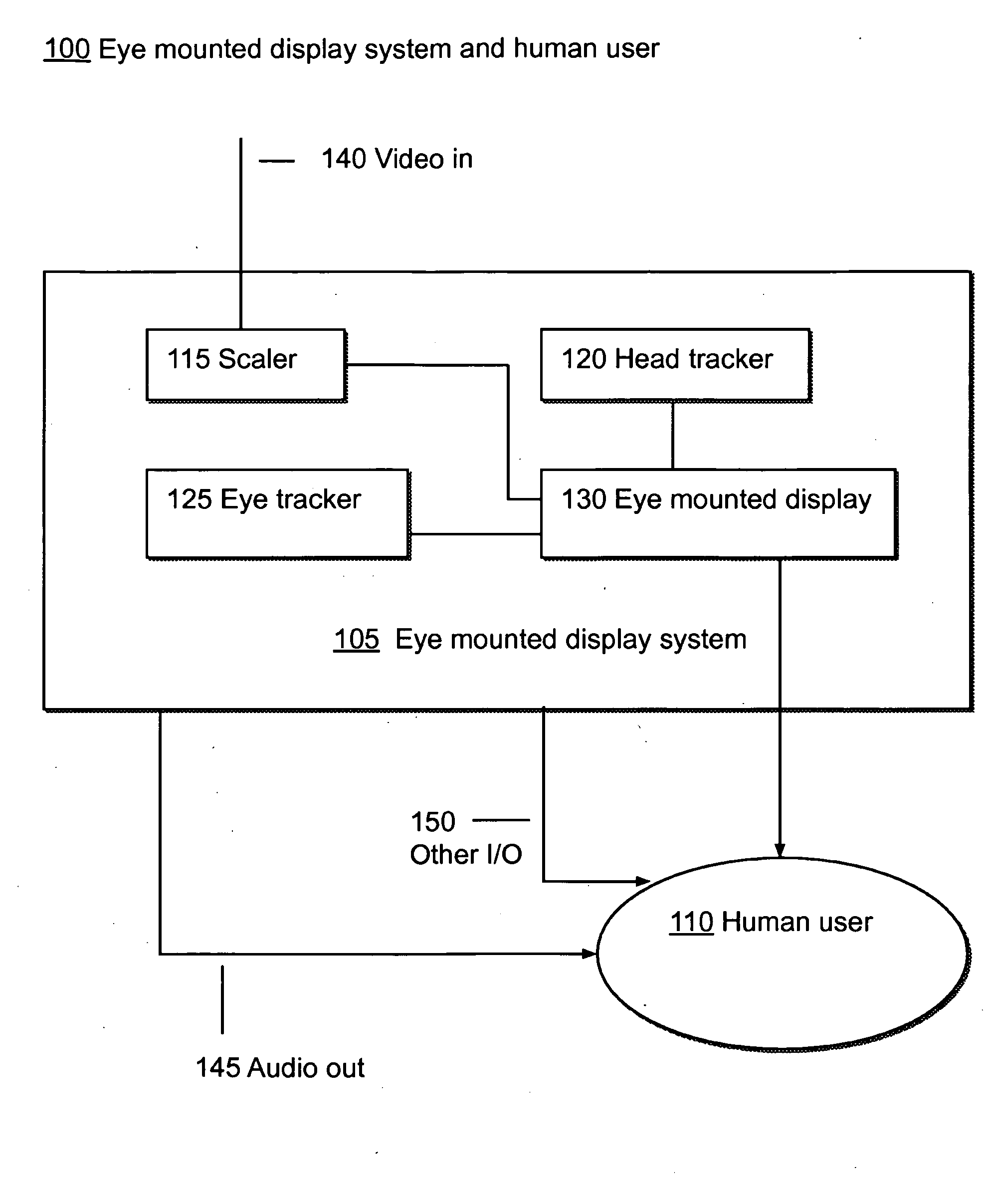
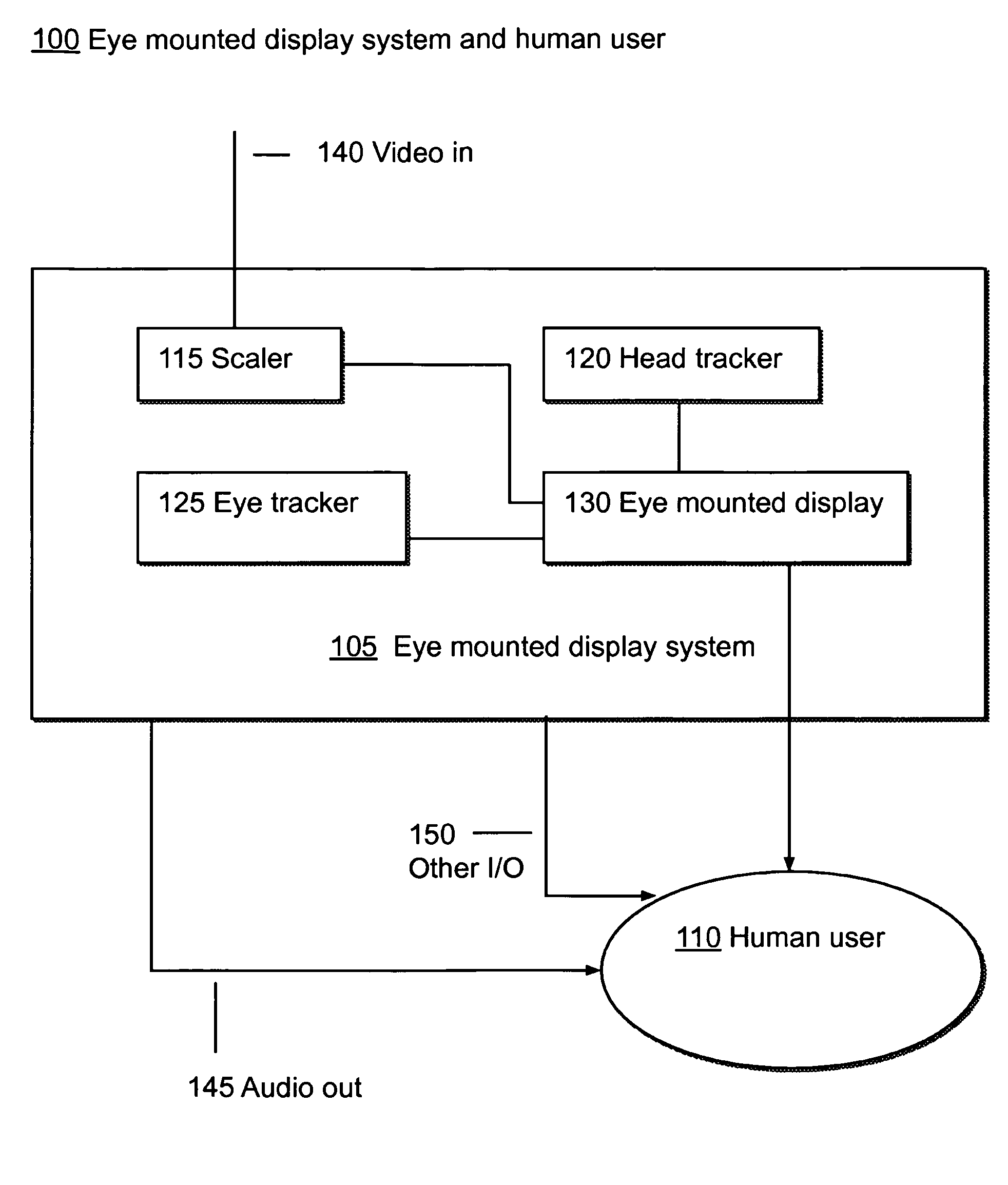
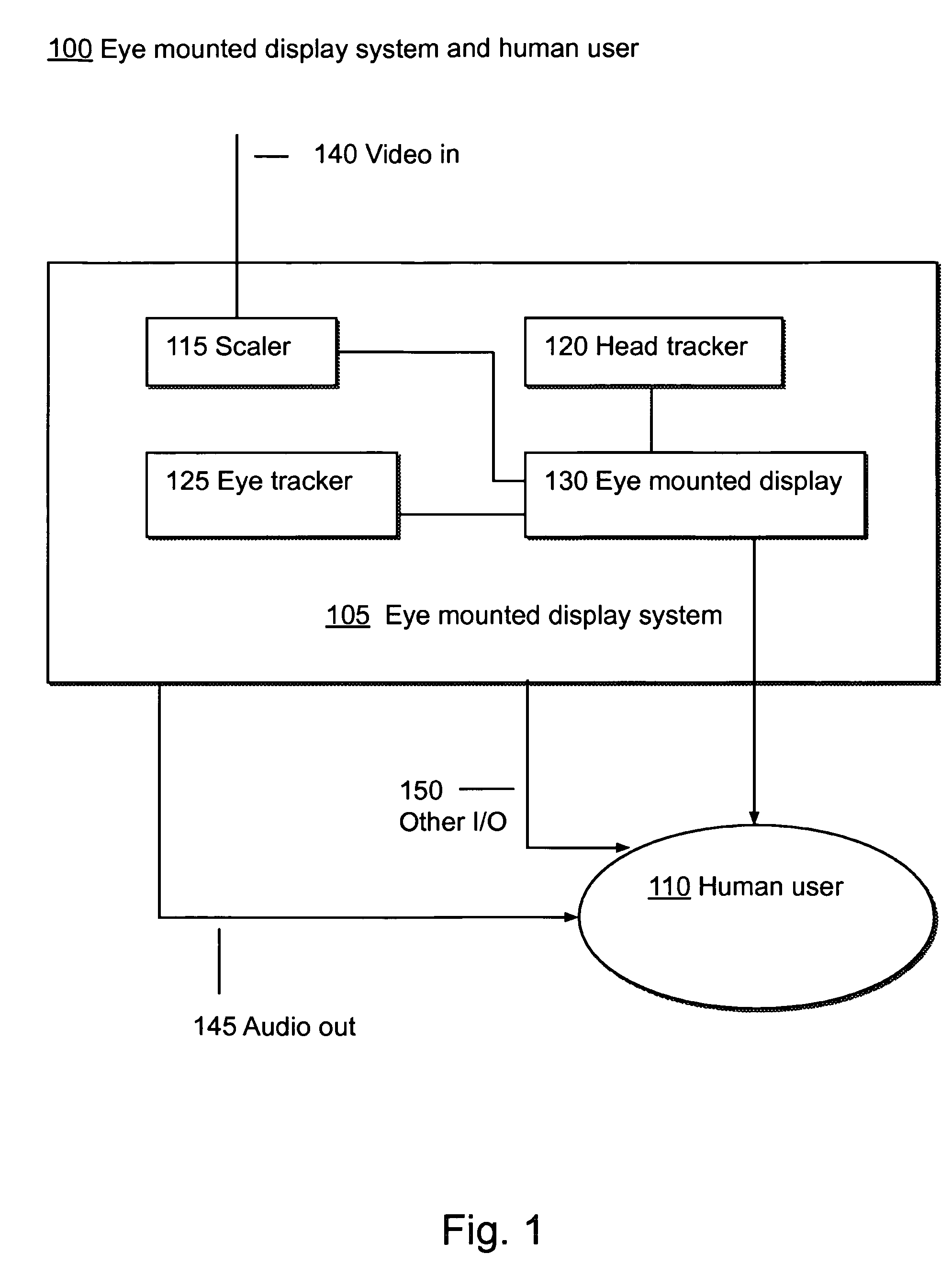
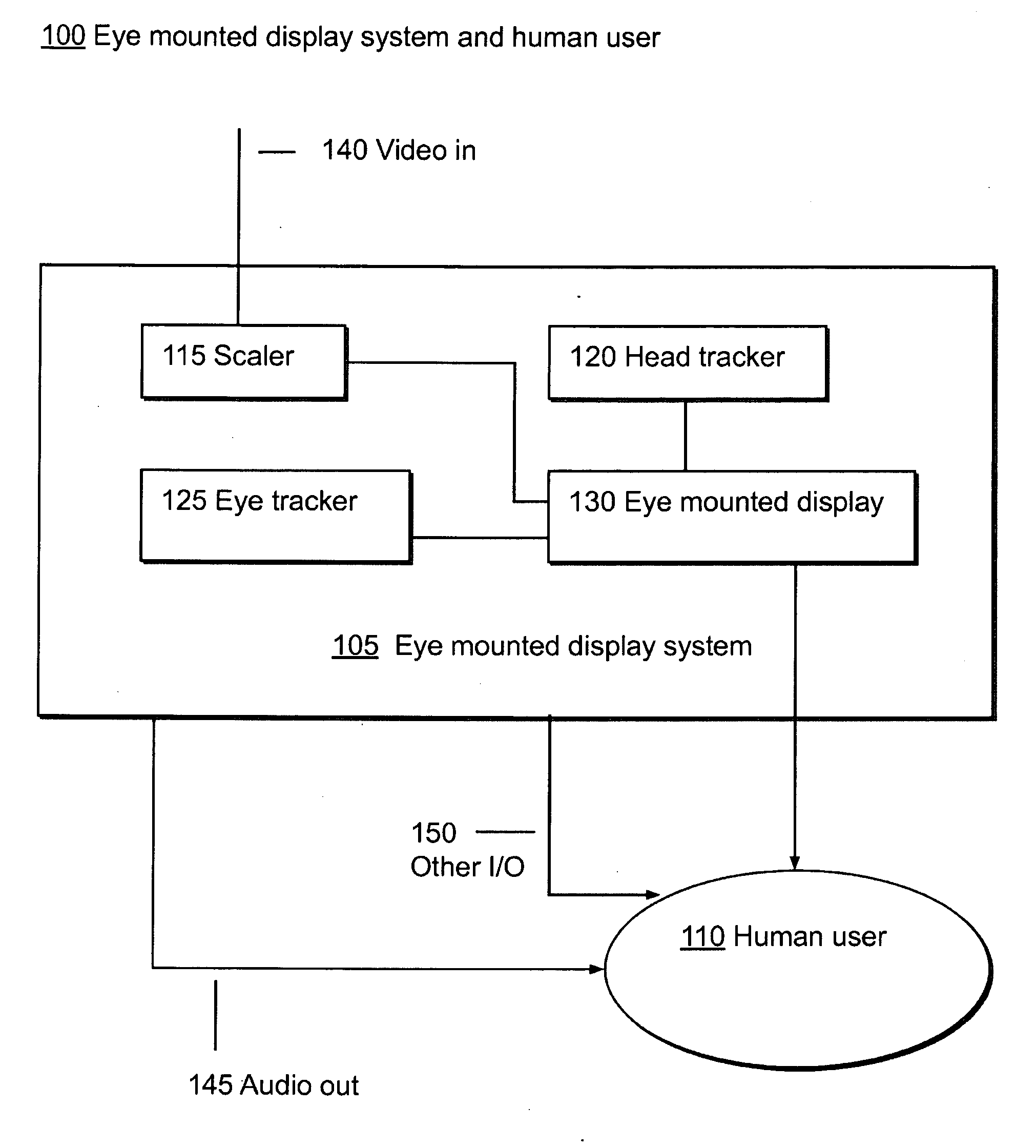
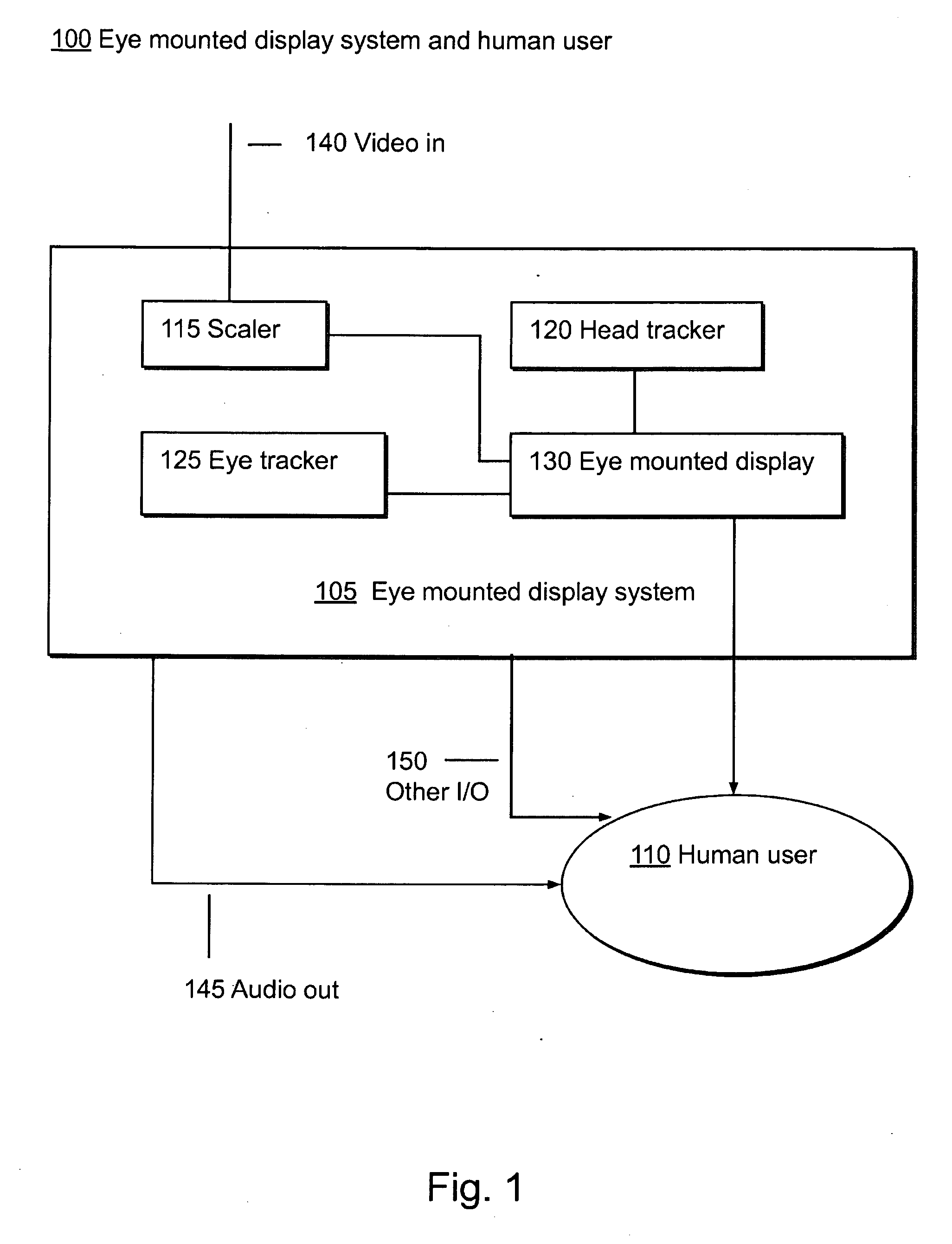
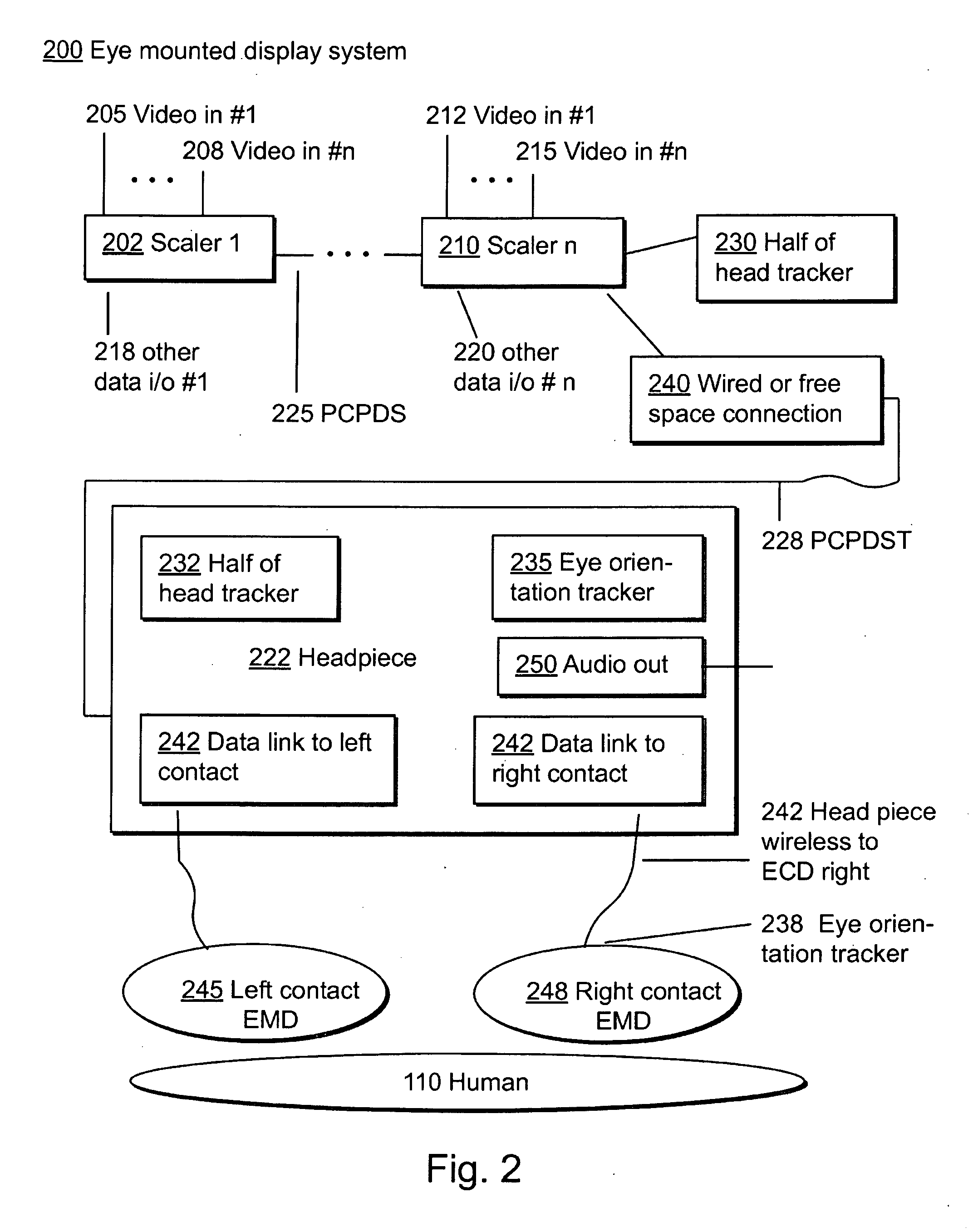
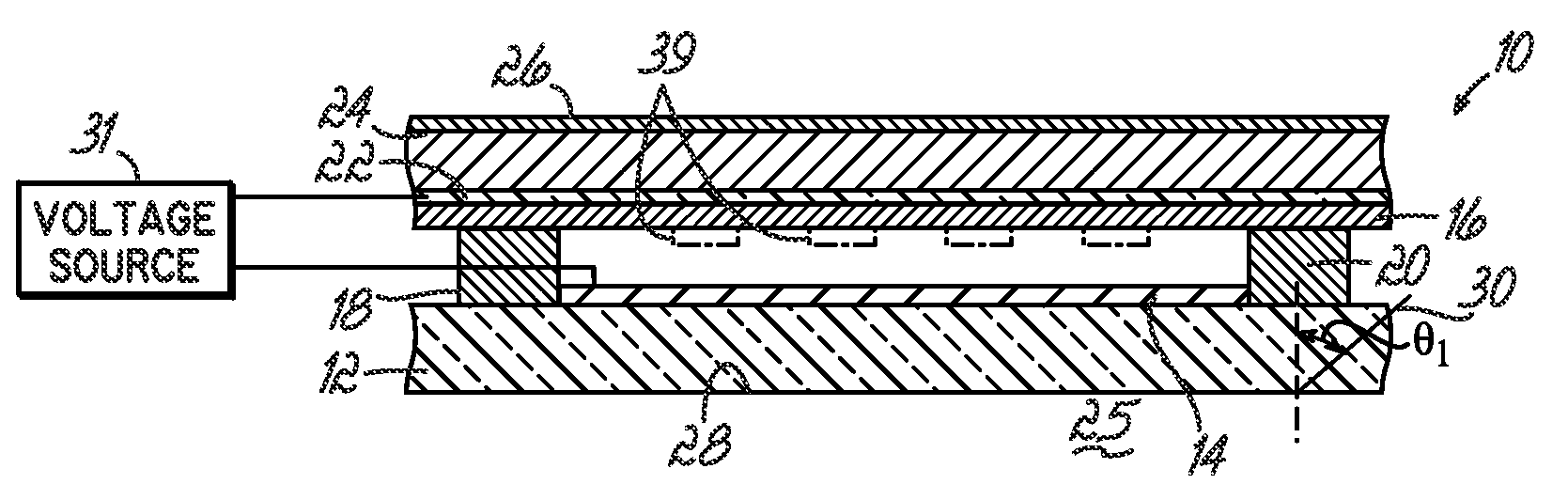
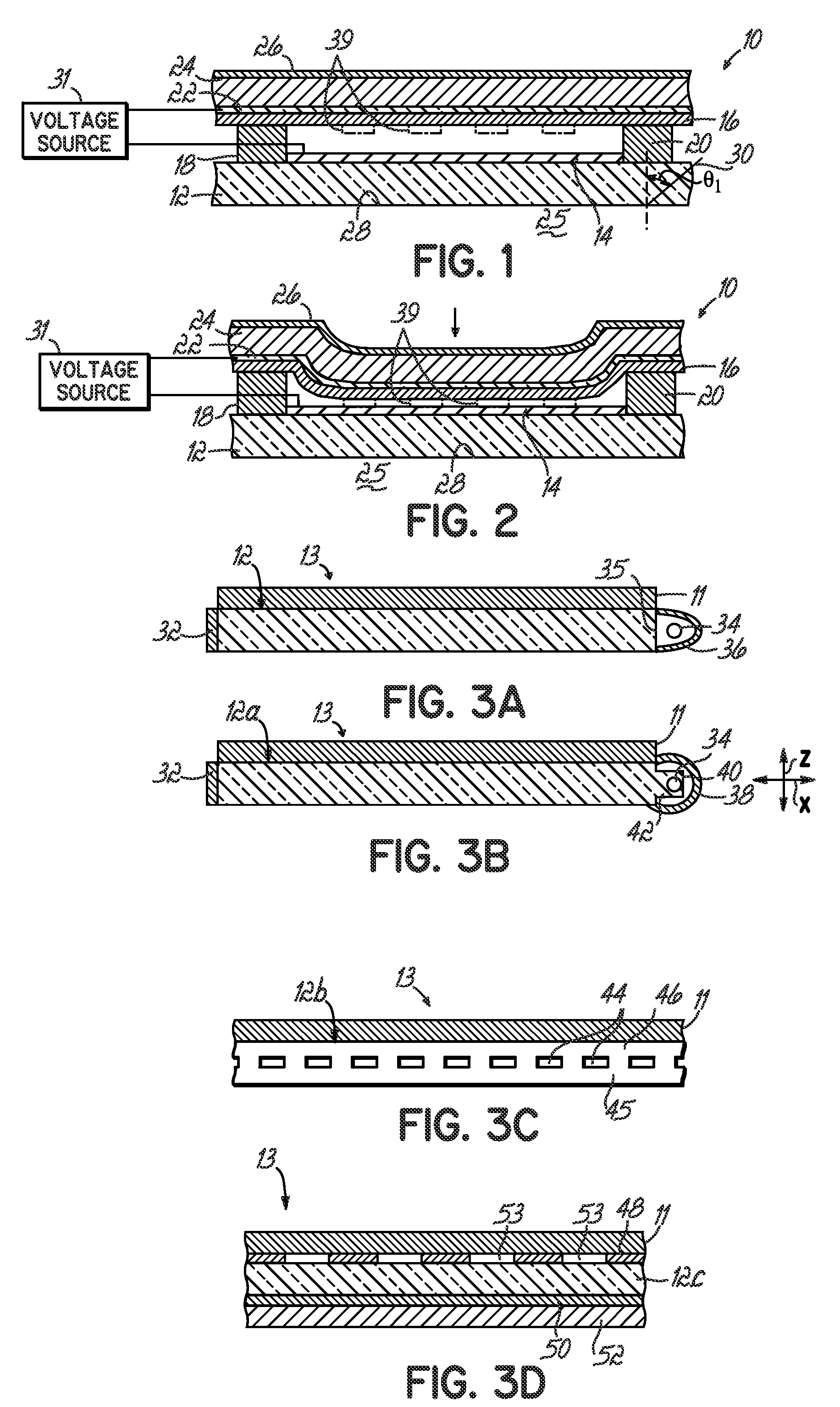
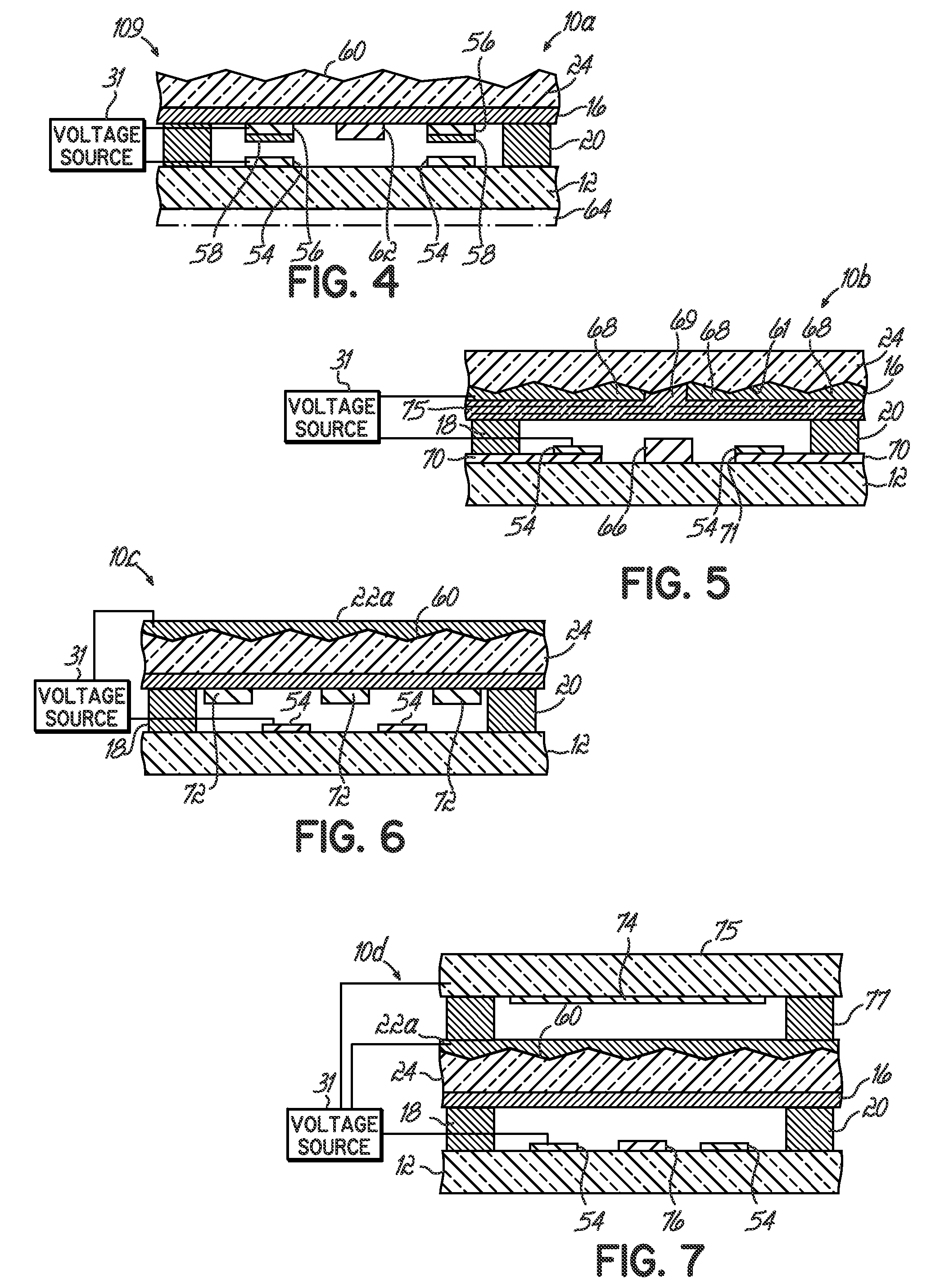
Systems Using Eye Mounted Displays
ActiveUS20090189974A1Avoid and reduce interferenceVarious limitationCathode-ray tube indicatorsSteroscopic systemsCorneal surfaceEntire pupil
A display device is mounted on and / or inside the eye. The eye mounted display contains multiple sub-displays, each of which projects light to different retinal positions within a portion of the retina corresponding to the sub-display. The projected light propagates through the pupil but does not fill the entire pupil. In this way, multiple sub-displays can project their light onto the relevant portion of the retina. Moving from the pupil to the cornea, the projection of the pupil onto the cornea will be referred to as the corneal aperture. The projected light propagates through less than the full corneal aperture. The sub-displays use spatial multiplexing at the corneal surface. Various electronic devices interface to the eye mounted display.
Owner:TECTUS CORP
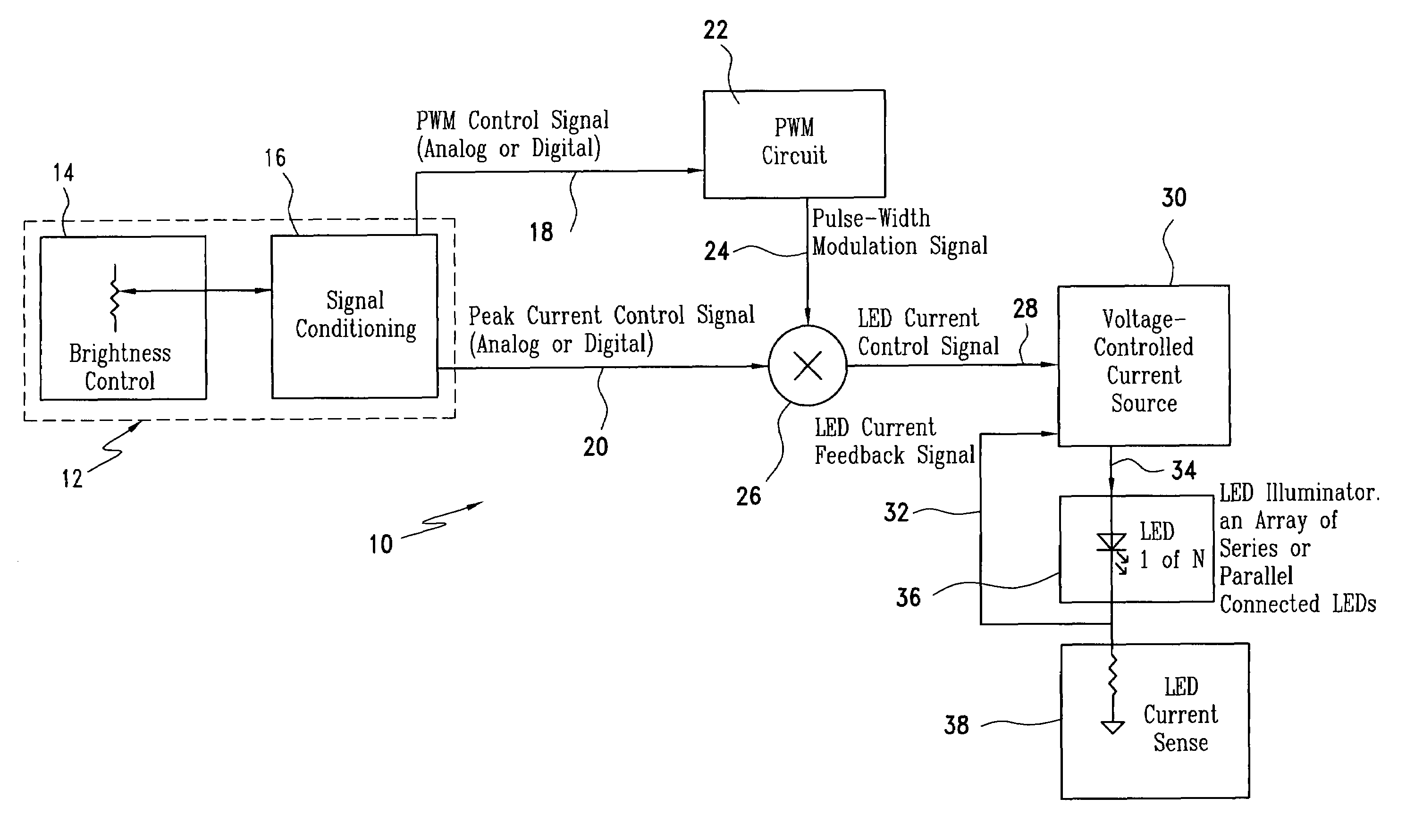
LED brightness control system for a wide-range of luminance control
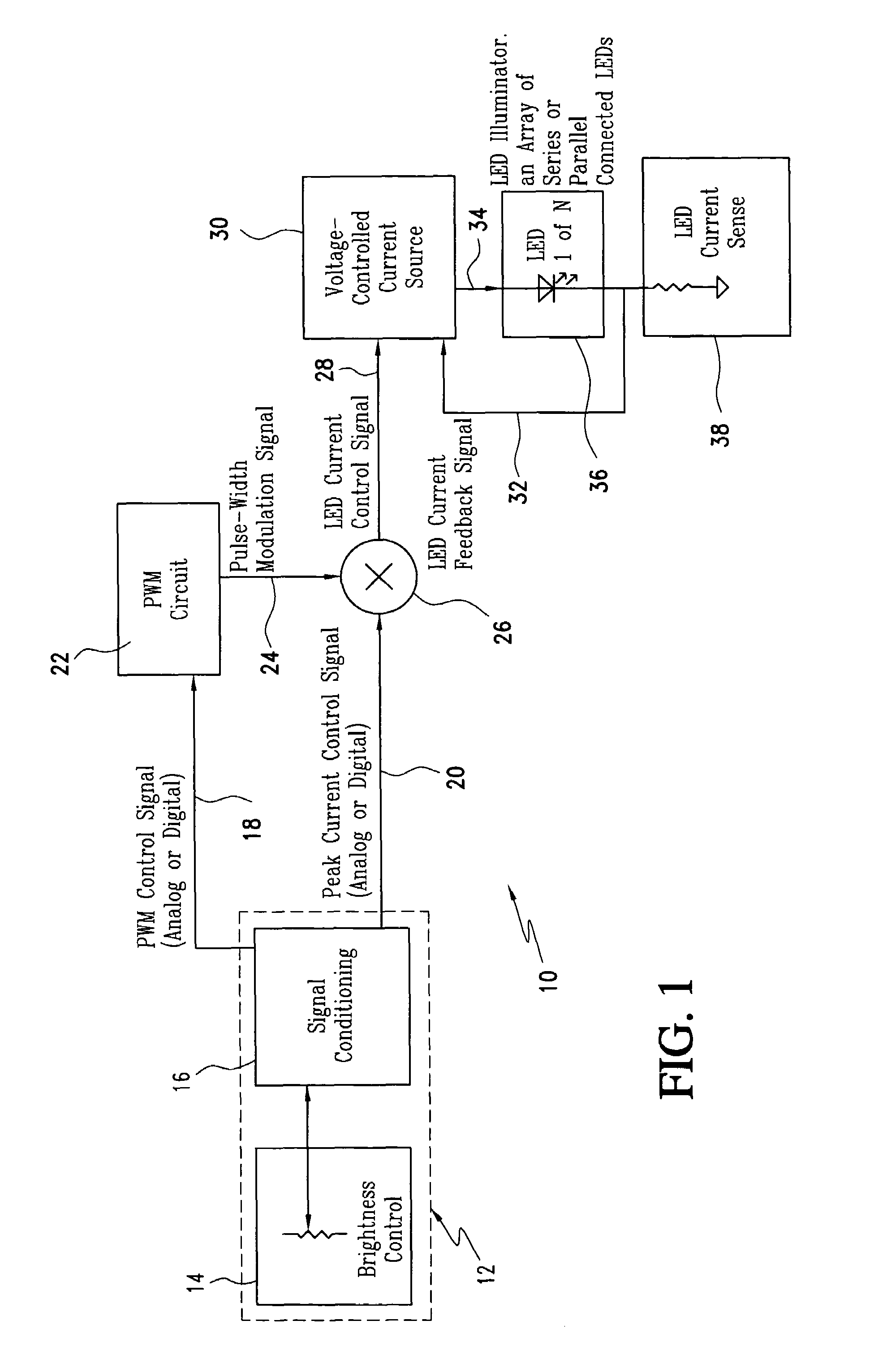
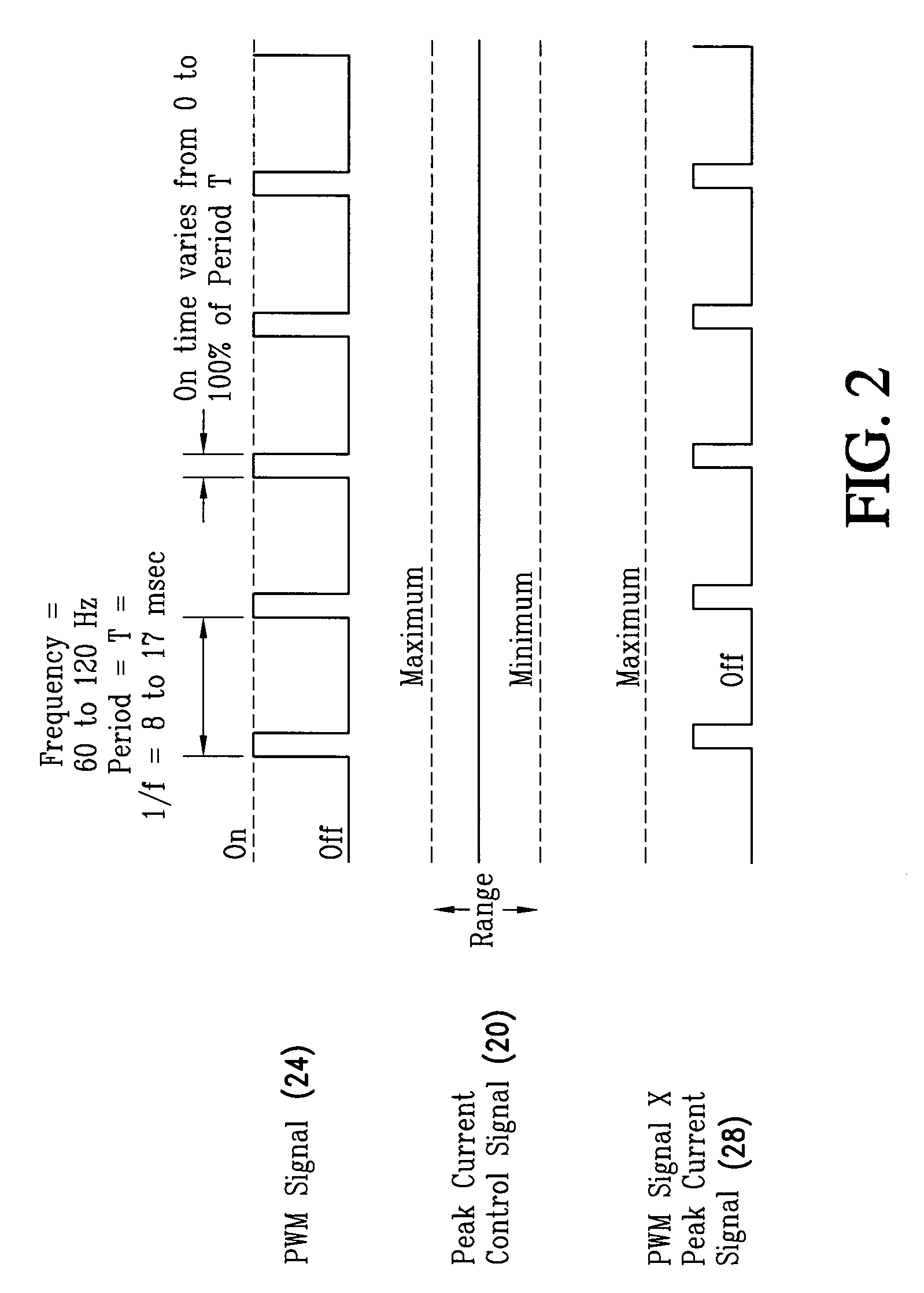
ActiveUS6987787B1Improve the level ofReduce brightnessLaser detailsElectroluminescent light sourcesControl signalControl system
The LED brightness control system for a wide range of luminance control includes a brightness control module that provides a pulse width modulation (PWM) control signal and a peak current control signal. A pulse width modulation (PWM) converter circuit receives the PWM control signal and converts it to a PWM signal. A multiplier receives the PWM signal and the peak current control signal from the brightness control module and multiplies the same to provide a light emitting diode (LED) current control signal with a variable “on” time as well as variable “on” level. A voltage-controlled current source utilizes the LED current control signal and an LED current feedback signal for providing an LED current. An LED illuminator array receives the LED current. A current sensing element connected to the LED illuminator array for providing an LED current feedback signal representing LED peak current. The voltage-controlled current source controls a drive voltage to the LED illuminator array at a commanded level.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
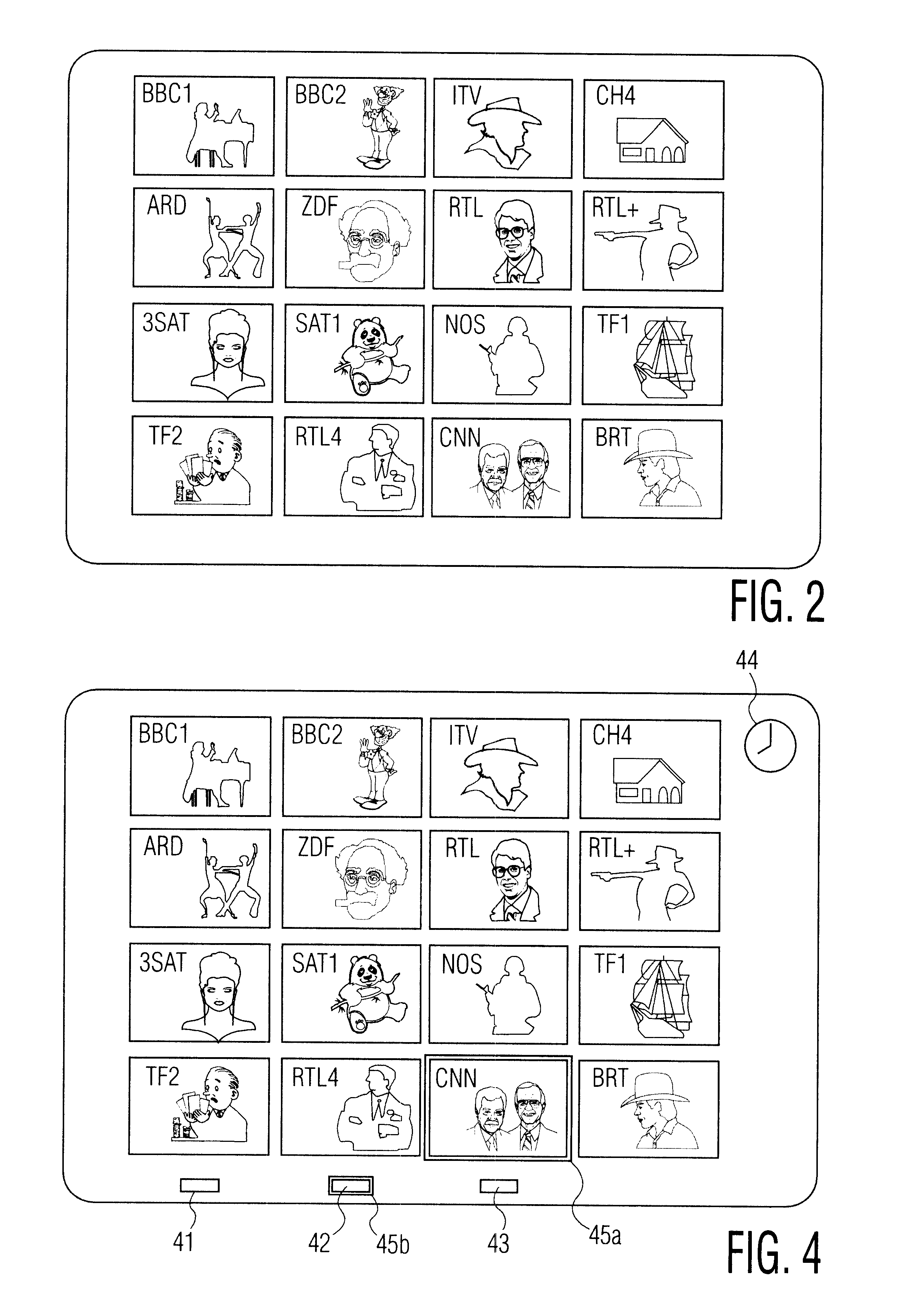
Navigating through television programs
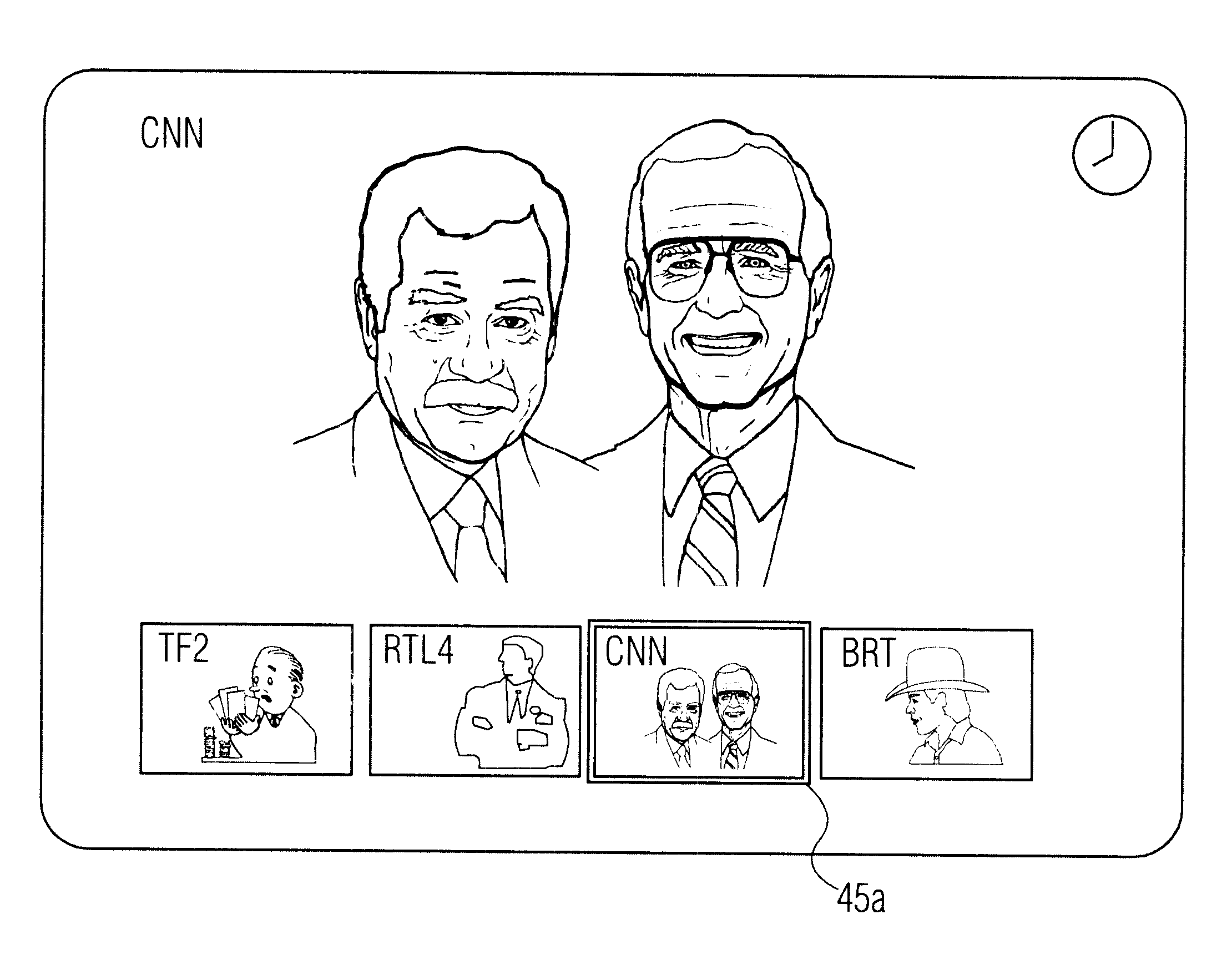
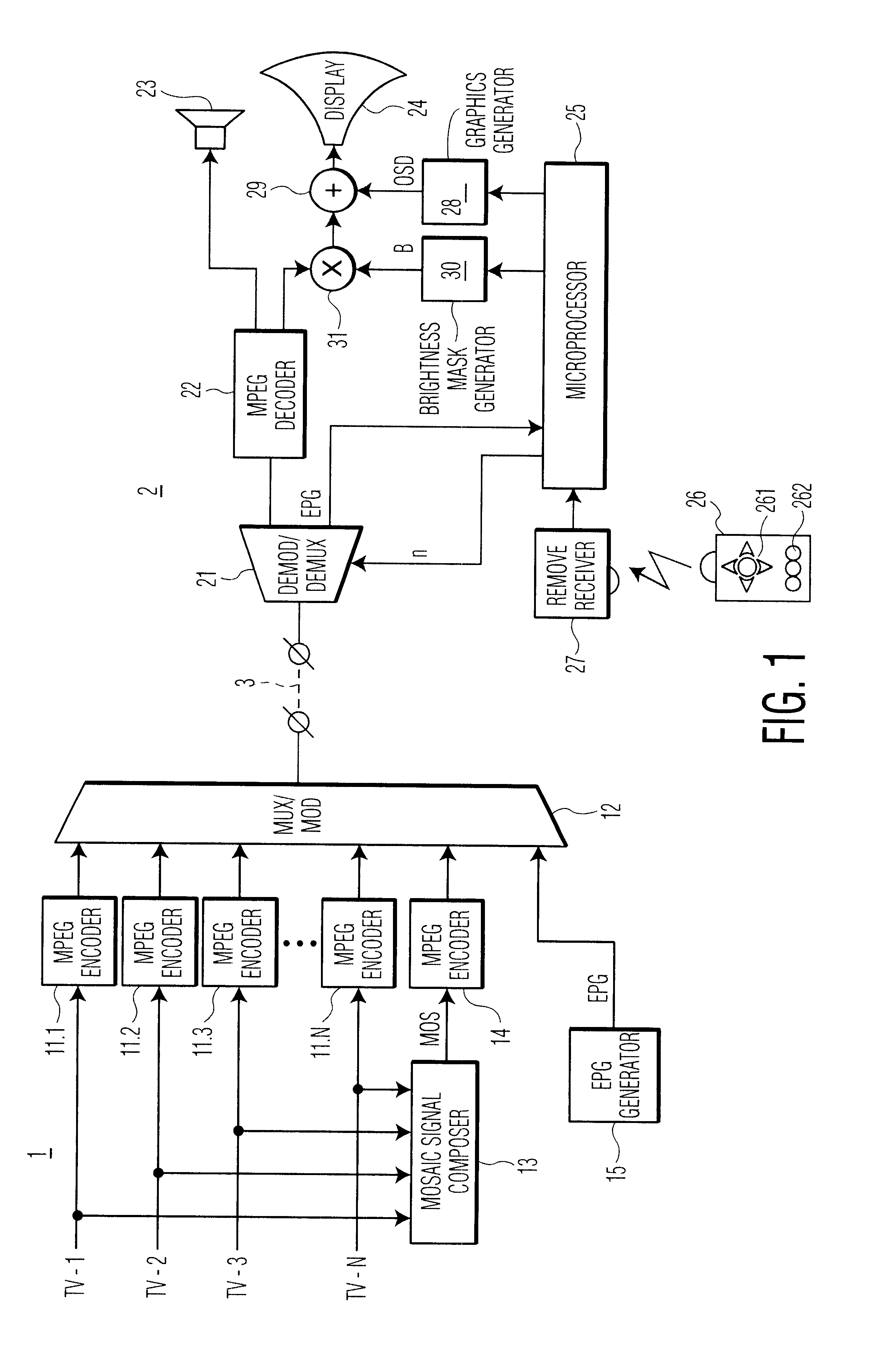
InactiveUS6405371B1Improve convenienceReduce brightnessTelevision system detailsColor television detailsTelevision receiversComputer science
A method of navigating through television programs is disclosed. A television receiver displays a mosaic image with sub-images representing the available programs. The receiver further receives an electronic program guide with program descriptions. Upon activating a "theme" button (42), the viewer can enter a desired program type, e.g. "movie". In response thereto, the brightness of the sub-images representing programs that are not desired is reduced. The user is thus assisted in navigating through programs he is interested in, while maintaining the mosaic structure he is familiar with, and without losing the association between channels and their positions on the mosaic screen.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Light Emissive Signage Devices Based on Lightwave Coupling
ActiveUS20070031097A1Low brightnessSupply legibilityCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideLight waveLight source
A signage device comprising one or more light sources, a waveguide or arrangement of waveguides and photoluminescent features coupled thereto. In one embodiment, a waveguide is adapted to receive light of a first wavelength and the photoluminescent features are adapted to emit light of a second wavelength in response to receiving light of the first wavelength.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
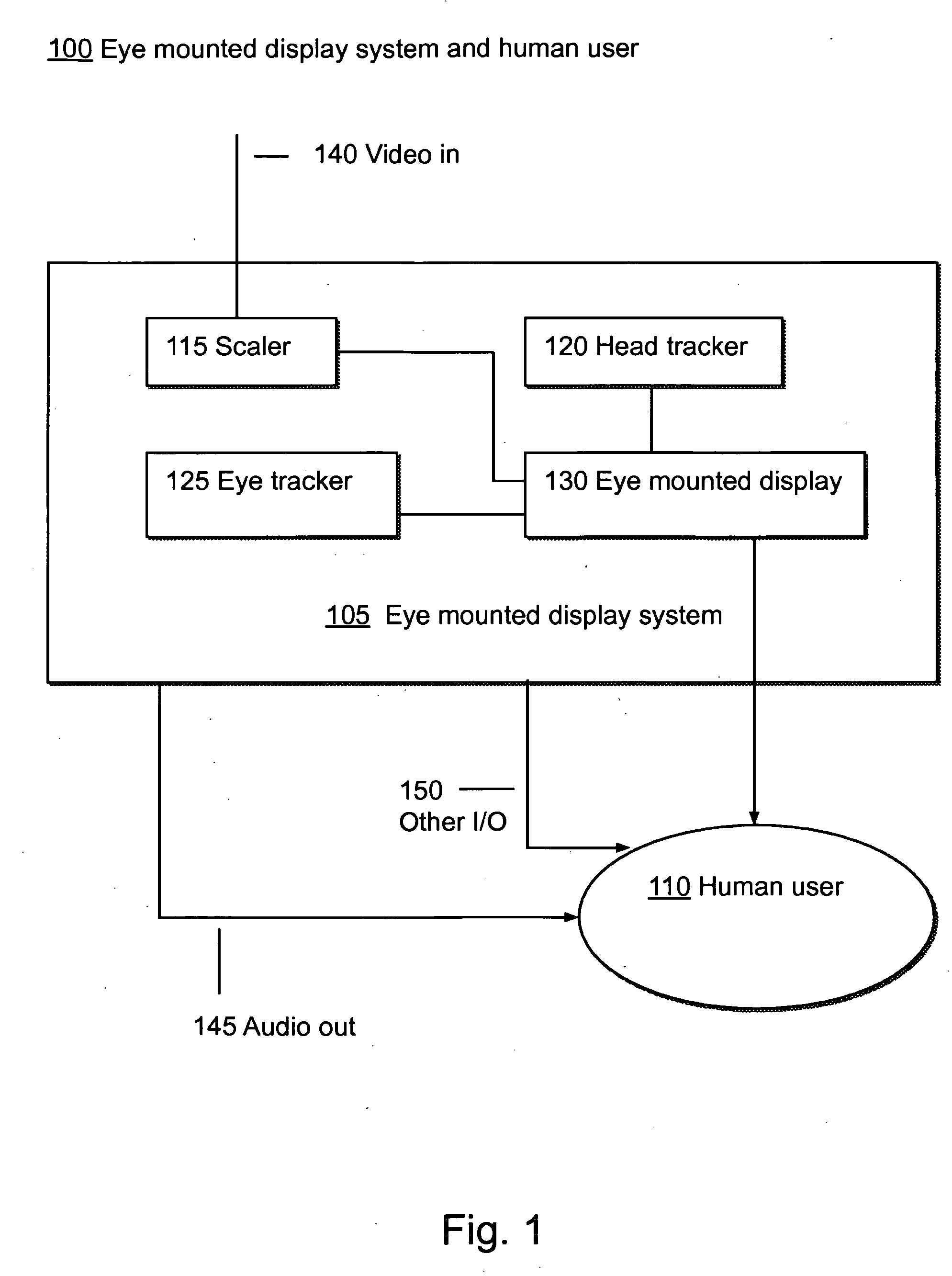
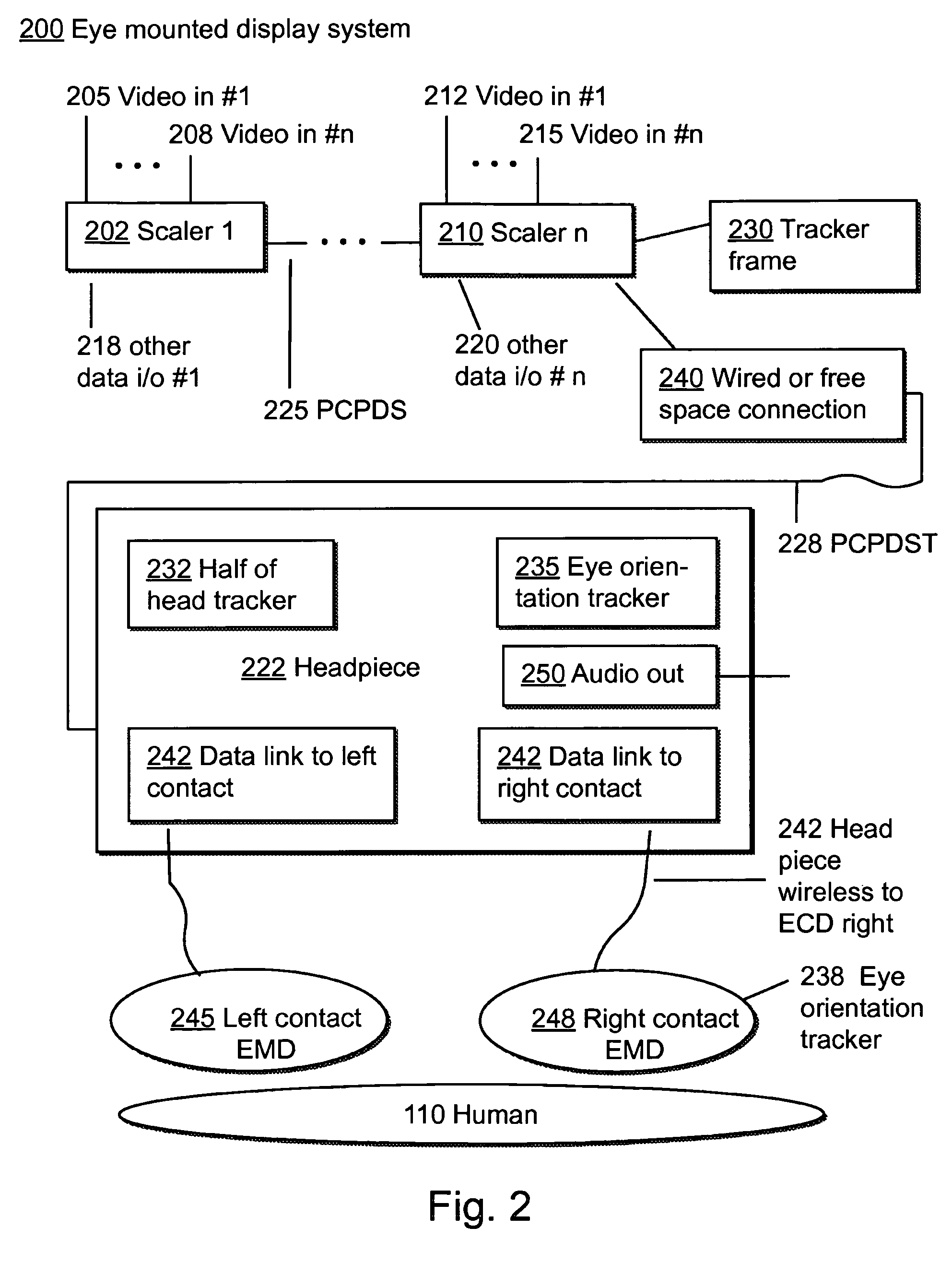
Systems using eye mounted displays
ActiveUS8786675B2Avoid and reduce interferenceVarious limitationNon-optical adjunctsCathode-ray tube indicatorsCorneal surfaceEntire pupil
A display device is mounted on and / or inside the eye. The eye mounted display contains multiple sub-displays, each of which projects light to different retinal positions within a portion of the retina corresponding to the sub-display. The projected light propagates through the pupil but does not fill the entire pupil. In this way, multiple sub-displays can project their light onto the relevant portion of the retina. Moving from the pupil to the cornea, the projection of the pupil onto the cornea will be referred to as the corneal aperture. The projected light propagates through less than the full corneal aperture. The sub-displays use spatial multiplexing at the corneal surface. Various electronic devices interface to the eye mounted display.
Owner:TECTUS CORP
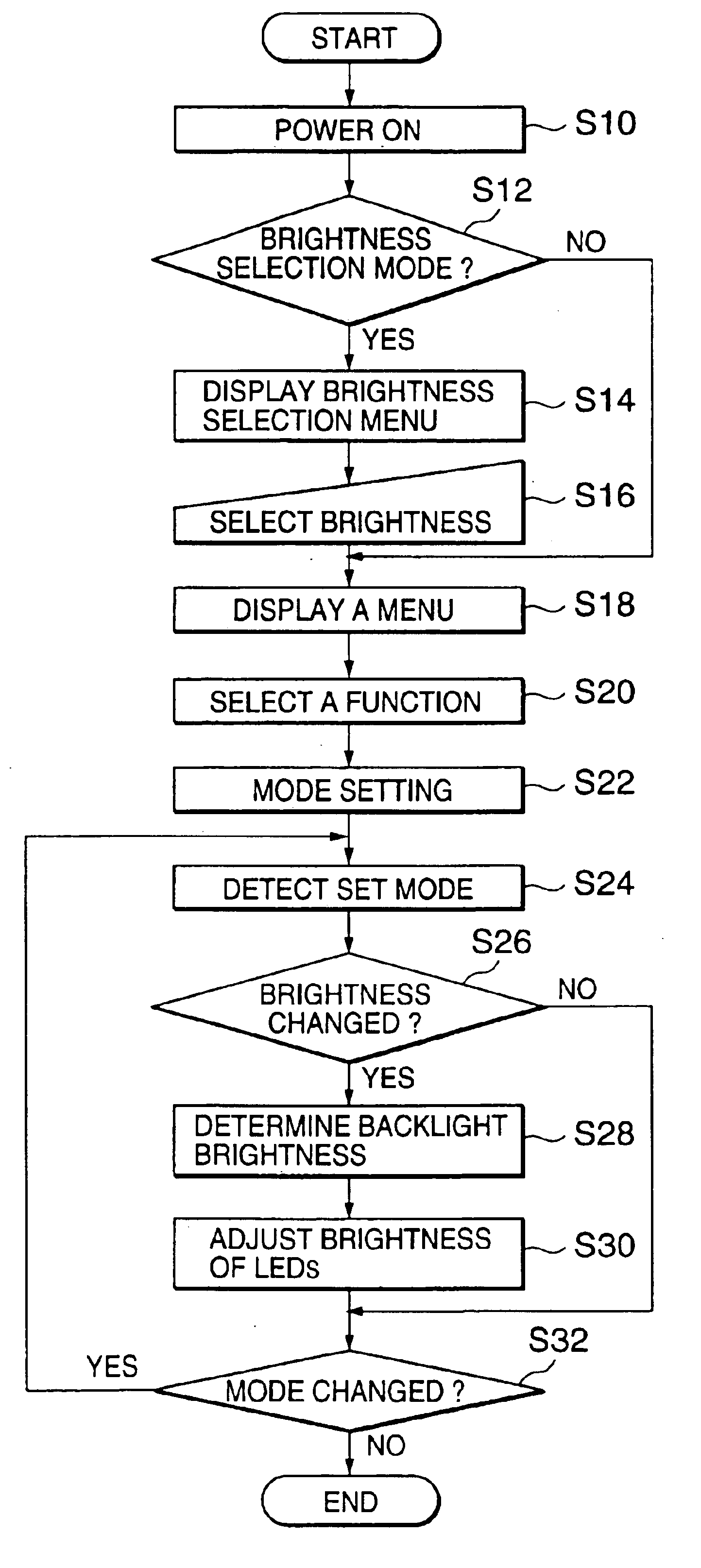
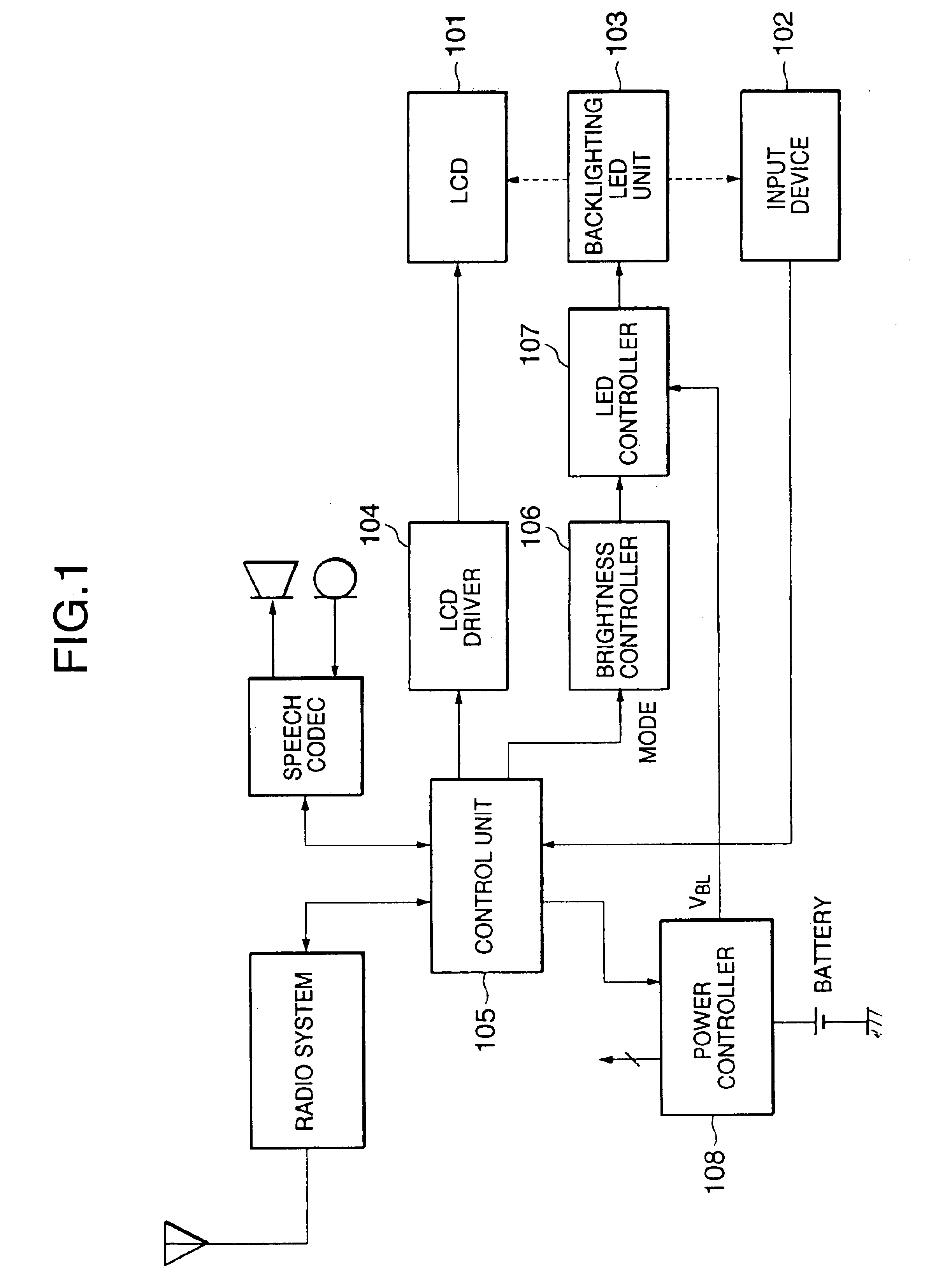
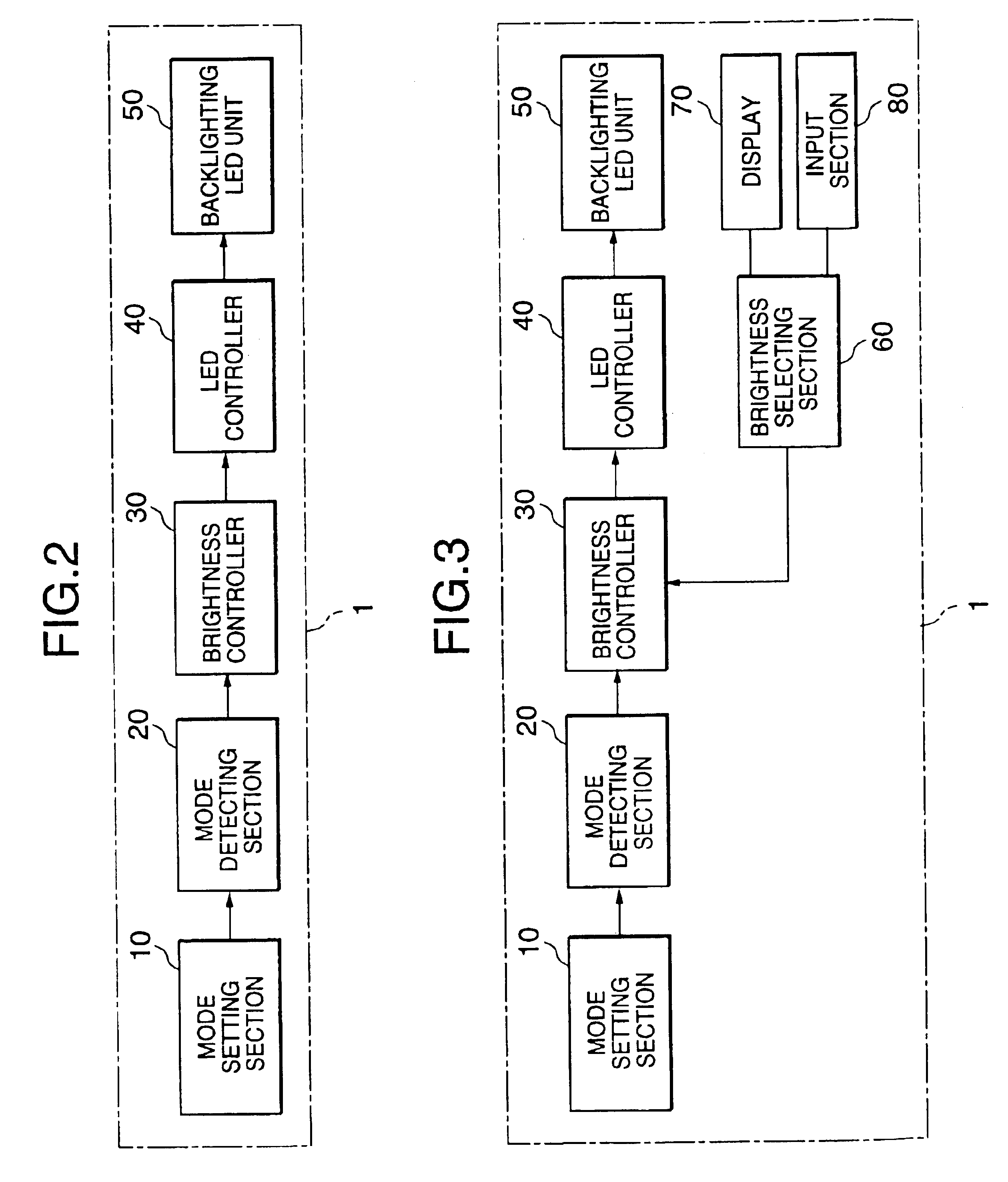
Electronic apparatus with backlighting device
InactiveUS6891525B2Suppressing excessive power consumptionMaintaining necessary brightnessCordless telephonesPower managementOperation modeBrightness perception
An electronic apparatus with backlit display and input device allowing reduced power consumption while maintaining necessary brightness is disclosed. A mode detecting section detects a currently set operation mode when performing a function. The brightness of the backlighting is controlled depending on the currently set operation mode. In the case of a data input mode, the brightness of the backlighting is reduced.
Owner:NEC CORP
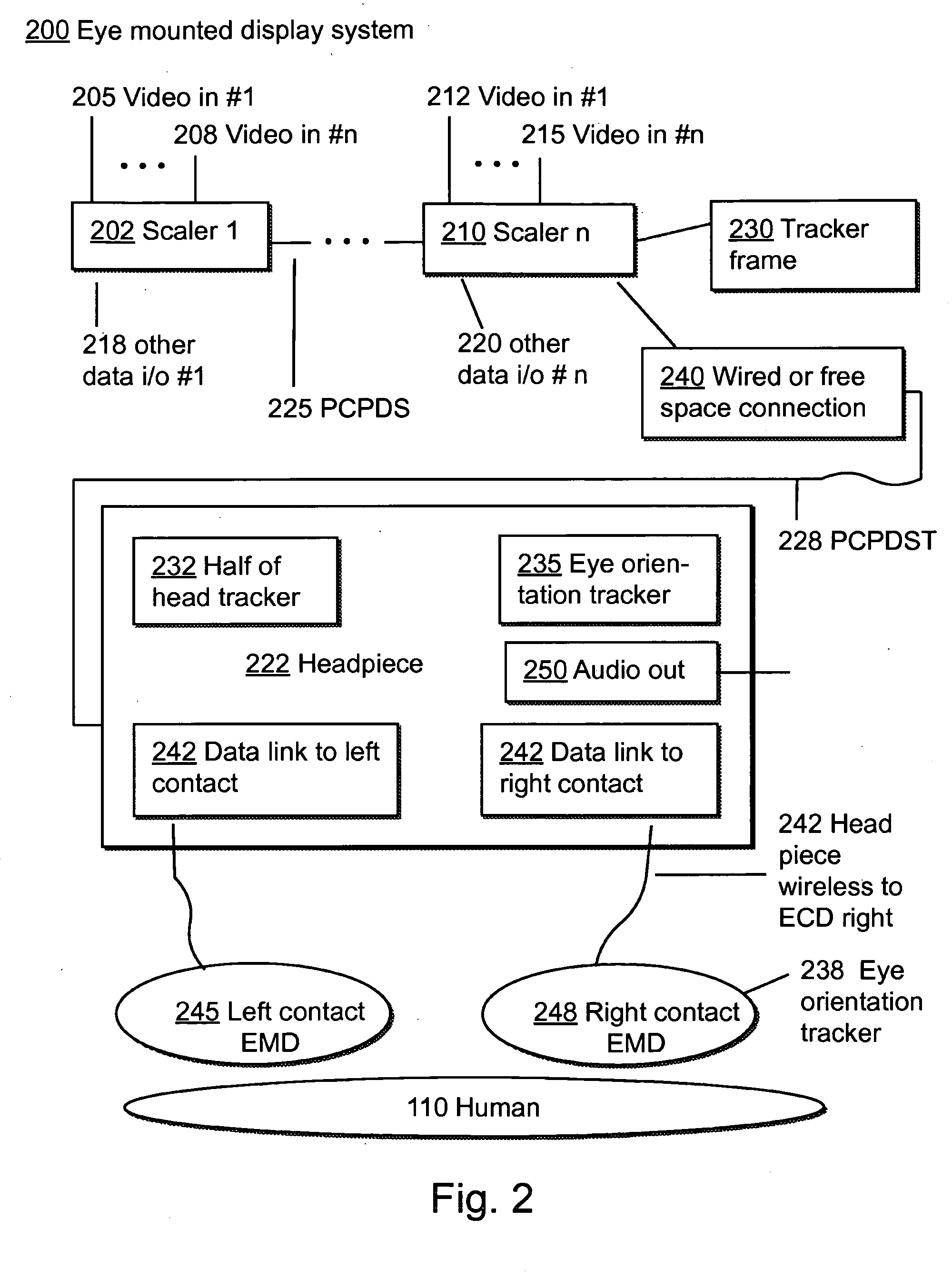
Eye Mounted Displays
InactiveUS20090189830A1Avoid and reduce interferenceVarious limitationCathode-ray tube indicatorsSteroscopic systemsCorneal surfaceEntire pupil
A display device is mounted on and / or inside the eye. The eye mounted display contains multiple sub-displays, each of which projects light to different retinal positions within a portion of the retina corresponding to the sub-display. The projected light propagates through the pupil but does not fill the entire pupil. In this way, multiple sub-displays can project their light onto the relevant portion of the retina. Moving from the pupil to the cornea, the projection of the pupil onto the cornea will be referred to as the corneal aperture. The projected light propagates through less than the full corneal aperture. The sub-displays use spatial multiplexing at the corneal surface.
Owner:TECTUS CORP
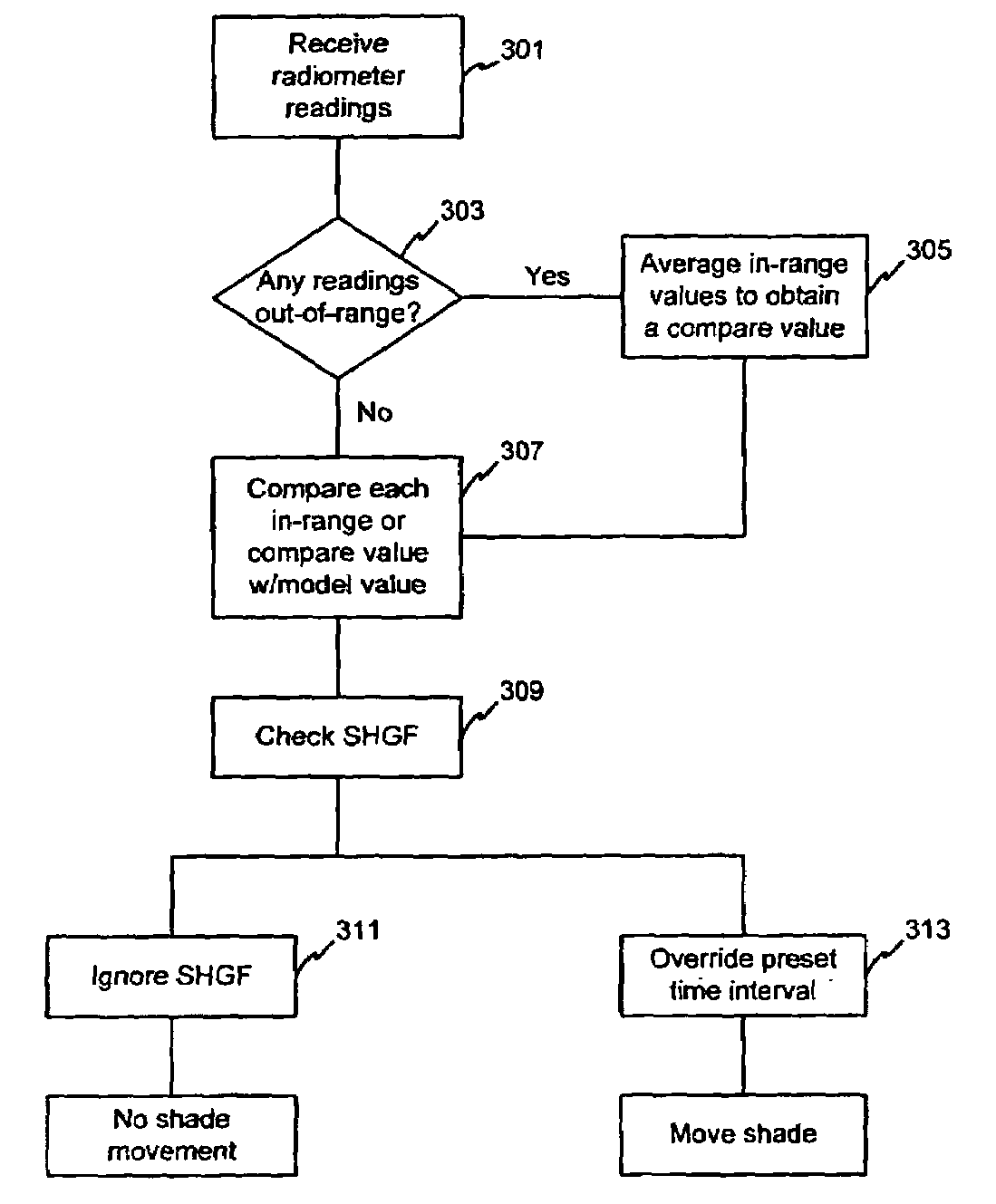
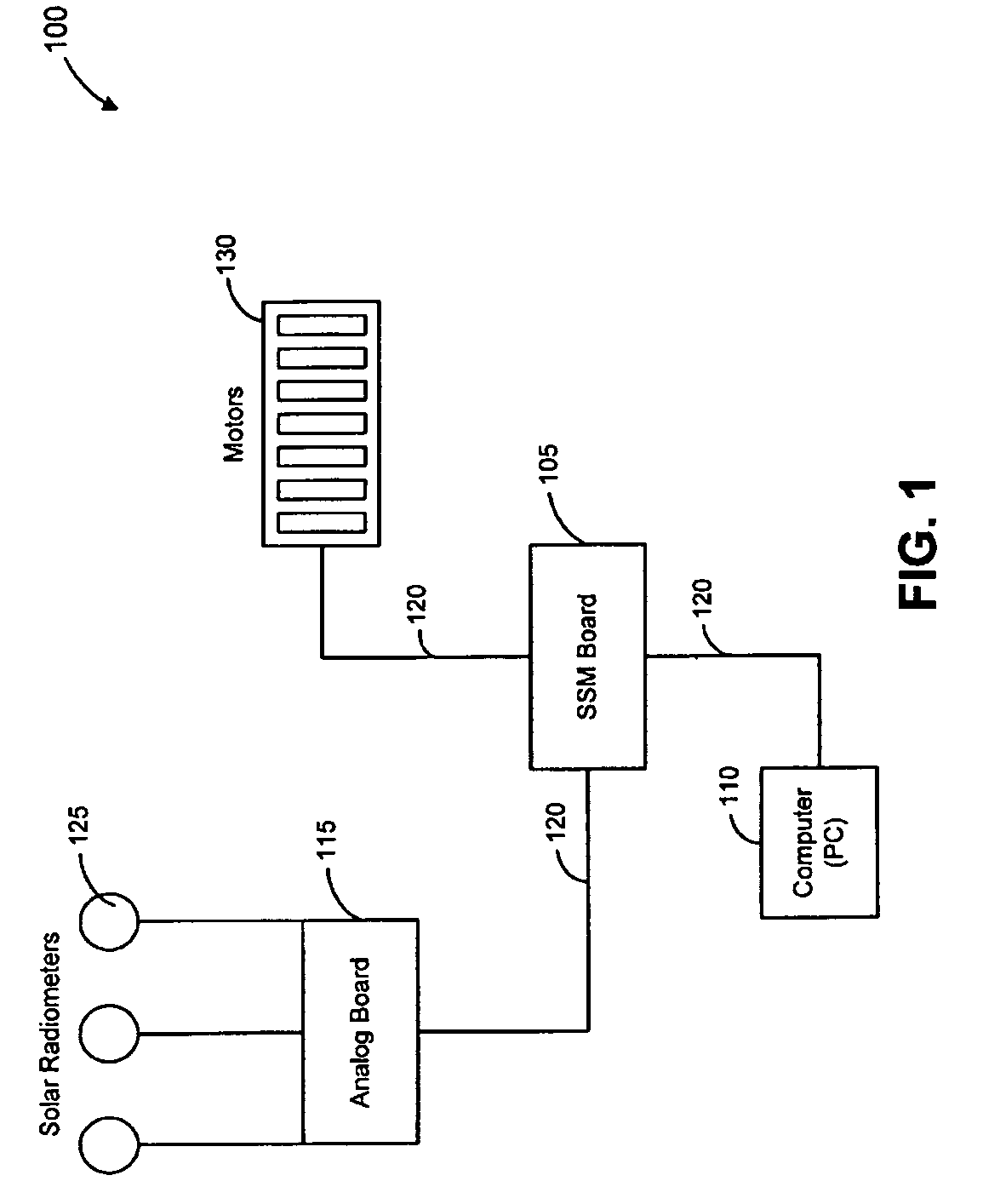
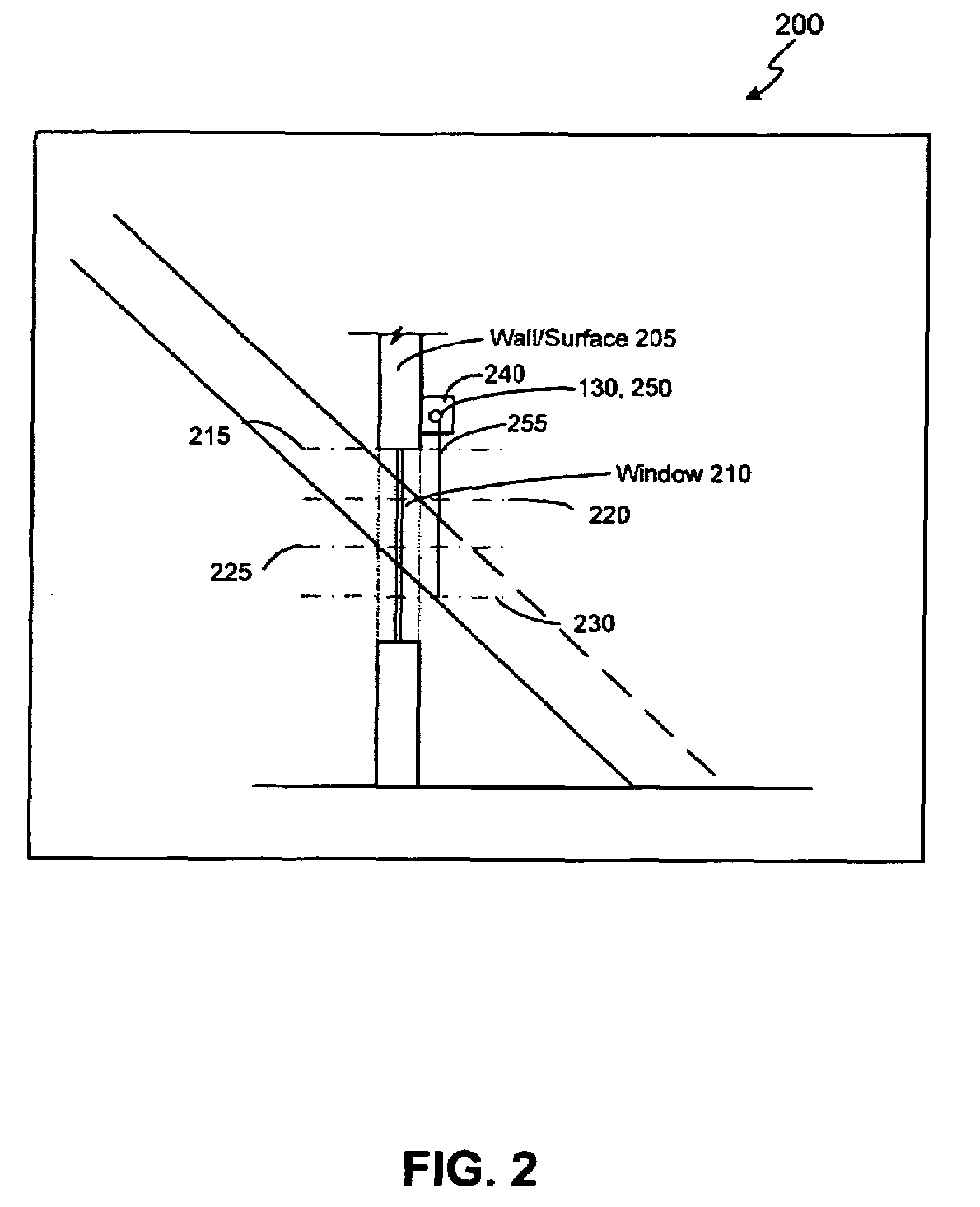
Automated shade control method and system
ActiveUS7417397B2Keep brightnessReduce brightnessLight dependant control systemsDC motor speed/torque controlRadiometerSolar angle
This invention generally relates to automated shade systems that employ one or more algorithms to provide appropriate solar protection from direct solar penetration; reduce solar heat gain; reduce radiant surface temperatures; control penetration of the solar ray, optimize the interior natural daylighting of a structure and optimize the efficiency of interior lighting systems. The invention additionally comprises a motorized window covering, radiometers, and a central control system that uses algorithms to optimize the interior lighting of a structure. These algorithms include information such as: geodesic coordinates of a building; solar position; solar angle solar radiation; solar penetration angles; solar intensity; the measured brightness and veiling glare across a surface; time, solar altitude, solar azimuth, detected sky conditions, ASHRAE sky models, sunrise and sunset times, surface orientations of windows, incidence angles of the sun striking windows, window covering positions, minimum BTU load and solar heat gain.
Owner:MECHOSHADE SYST LLC
Light emissive signage devices based on lightwave coupling
ActiveUS7430355B2Reduce brightnessSupply legibilityCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guidePhotoluminescenceCoupling
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
Display device and the driving method of the same
ActiveUS20060066533A1Restrict power consumptionProlonged life timeElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesPower circuitsEngineering
A plurality of organic EL elements which are arranged on a display panel lowers the brightness along with a lapse of light emitting time and hence, the power consumption is increased to maintain the brightness. However, the increase of the power consumption shortens a lifetime of the organic EL elements. To overcome this drawback, a power supply circuit which drives the display panel has a function of controlling an electric power supplied to the display panel to a fixed value or less in response to a detection signal from a detection part which detects a cathode current of the organic EL elements.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Light emissive display based on lightwave coupling
ActiveUS7123796B2Reduce brightnessSupply legibilityCoupling light guidesSpectral modifiersFluorescencePhotoluminescence
A light emissive display having a specular waveguide that propagates short wavelength light and photoluminescent features adjacent to the waveguide that fluoresce, for example, in visible red, green, blue, and mixed colors when selectively coupled with the short wavelength light. The photoluminescent layers emit light primarily and, therefore, efficiently in the direction of an observer only. This light emissive display may be utilized as a planar light source, as patterned information signage, or as a re-configurable information display containing intensity modulated pixels. The light emissive display may be enhanced optically such that only a small portion of ambient light is reflected from the display while preserving the majority of emitted display luminance.
Owner:CINCINNATI UNIV OF +1
Symmetric filter patterns for enhanced performance of single and concurrent driver assistance applications
InactiveUS20080043099A1Avoid saturationReduce intensityVehicle headlampsRoad vehicles traffic controlDriver/operatorReal time analysis
A system mounted on a vehicle for performing vehicle control applications and driver warning applications, the system including a camera configured to acquire a plurality of images of the environment in front of the camera. The camera includes a filter wherein the filter is installed at the focal plane of the camera and wherein designated portions of the filter transmit selective light wavelength. The preferred filter has a checkerboard pattern. The system further including an image processor capable of analyzing in real time a plurality of respective image sequences acquired from at least one of the portions of the filter and is capable of detecting yellow lane markings on a concrete road surface.
Owner:MOBILEYE TECH
Compact optical system for head-worn computer
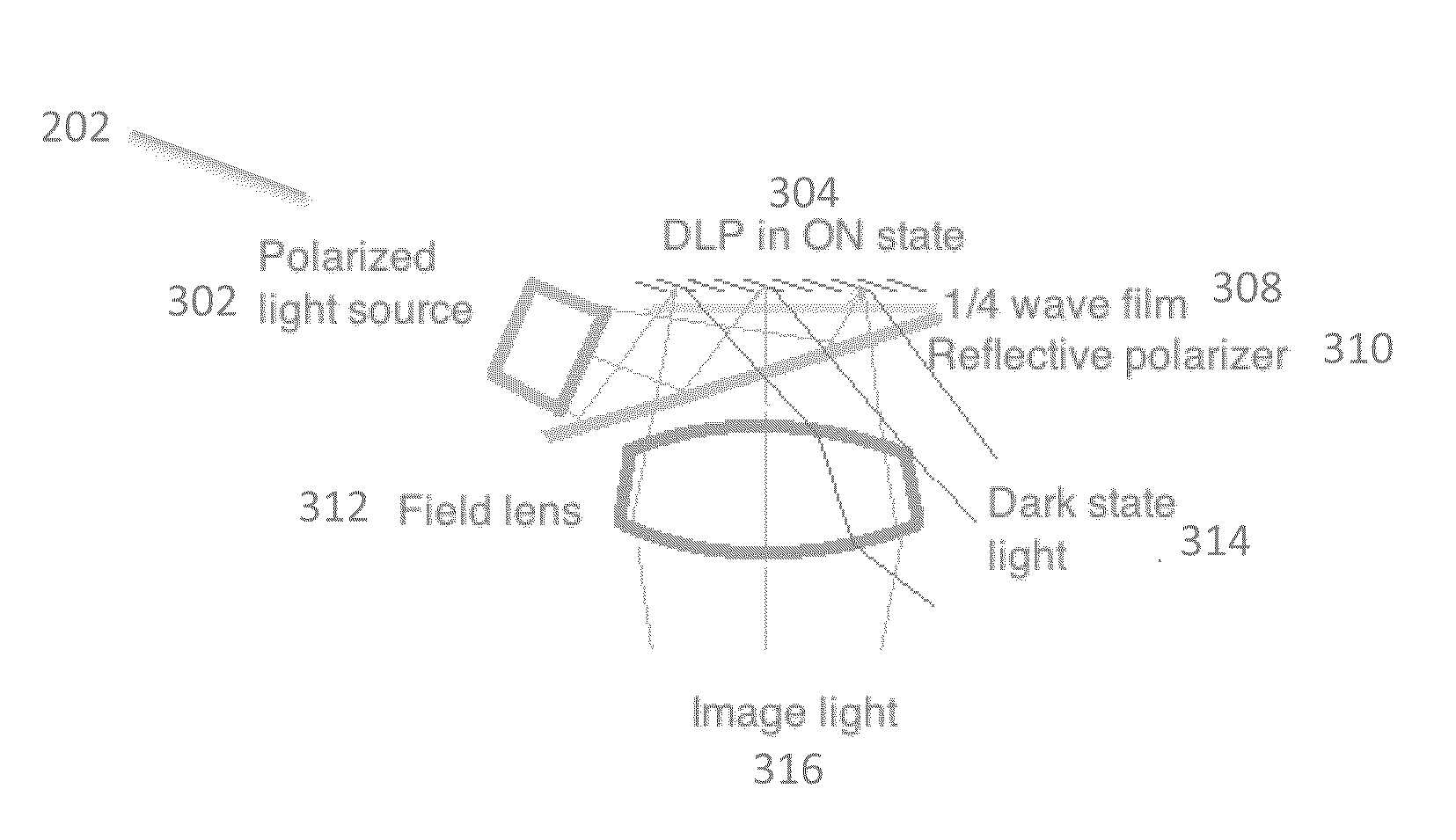
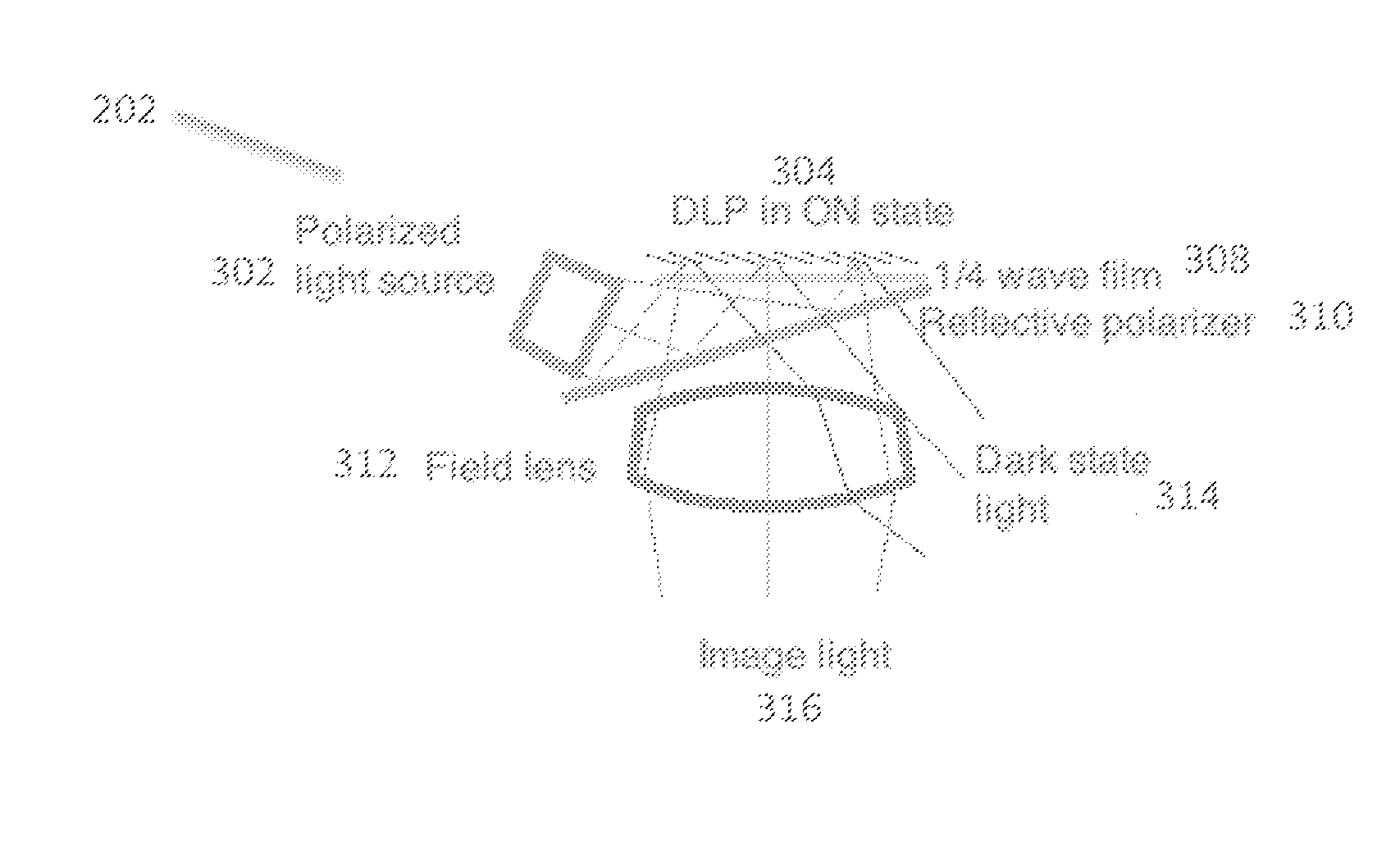
InactiveUS20160154244A1Reduce artifactsReduce brightnessElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesLight sourceDisplay device
An optical system for a head-worn computer includes a light source positioned within the head-worn computer and adapted to project polarized illuminating light towards a partially reflective partially transmissive surface such that the illuminating light reflects through a field lens and towards a reflective display. The illuminating light reflects off a surface of the reflective display, forming image light. The image light is then transmitted through the field lens and then through the partially reflective partially transmissive surface to a lower display optical system adapted to present the image light to an eye of a user wearing the head-worn computer.
Owner:OSTERHOUT GROUP INC
Light fixtures and lighting devices
ActiveUS20080278952A1Satisfies needCarefully balanced radiative couplingPoint-like light sourceElectric circuit arrangementsLight equipmentEffect light
There is provided a light fixture comprising a baffle system and a side reflector, the baffle system comprising at least an outer baffle structure and an inner baffle structure. Also, there is provided a light fixture which comprises at least two recessed concentric square elements, triangular connecting elements and lenses which are recessed from the faces of each of the square elements. In some embodiments, the lighting device comprises at least one solid state light emitter. In some embodiments, the light fixture further comprises at least one lens positioned between at least two respective baffle elements.
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC
Wavelength-converting converter material, light-emitting optical component, and method for the production thereof
ActiveUS20090173957A1Simple to executeGood reproducibilityIndividual molecule manipulationSynthetic resin layered productsNanoparticlePhosphor
Disclosed is a wavelength-converting converter material comprising at least one wavelength-converting phosphor comprising phosphor particles, wherein a portion of said phosphor or all of said phosphor is present in the form of nanoparticles. Also disclosed is a light-emitting optical component comprising such a converter material and a method for producing such components.
Owner:OSRAM OPTO SEMICON GMBH & CO OHG
Compact optical system with improved illumination
ActiveUS20160216517A1Increase contrastLow costElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesOptical powerDisplay device
A compact optical system with improved contrast for a head-worn computer includes a light source including a lens with positive optical power positioned within the head-worn computer and adapted to project converging illuminating light towards a partially reflective partially transmissive surface wherein the illuminating light forms a spot with an area smaller than the light source on the partially reflective partially transmissive surface prior to being reflected as diverging illuminating light that passes through a field lens and towards a reflective display. The illuminating light reflects off a surface of the reflective display, forming diverging image light which is transmitted through the field lens and then through the partially reflective partially transmissive surface to a lower display optical system adapted to present the image light to an eye of a user wearing the head-worn computer.
Owner:OSTERHOUT GROUP INC
Wiring Board for Light-Emitting Element
InactiveUS20080043444A1InhibitionHigh bonding strengthPrinted circuit aspectsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorHeat conducting
A wiring board for light-emitting element, comprising a ceramic insulating substrate, and a conductor layer formed on the surface or in the inside of the insulating substrate, and having a mounting region mounting a light-emitting element on one surface of the insulating substrate; wherein the insulating substrate is provided with a heat-conducting pole-like conductor having a thermal conductivity higher than that of said insulating substrate; and the heat-conducting pole-like conductor is extending through the insulating substrate in the direction of thickness thereof from the light-emitting element mounting region of the insulating substrate, and is formed by the co-firing with the insulating substrate. The wiring board is produced inexpensively by co-firing, features excellent heat-radiating performance, is capable of quickly radiating the heat from the light-emitting element when the light-emitting element is mounted, and effectively prevents a decrease in the brightness of the light-emitting element caused by the heat.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Compact optical system with improved contrast uniformity
ActiveUS20160216516A1Increase contrastLow costElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceOptic system
An optical system for a head-worn computer may include a light source positioned within the head-worn computer and adapted to project non-polarized illuminating light towards a partially reflective partially transmissive surface such that the illuminating light reflects through a field lens and towards a reflective display and a polarizing film adjacent to a surface of the reflective display that polarizes the illuminating light after it passes through the field lens. The illuminating light reflects off a surface of the reflective display, forming image light which is then analyzed by the polarizing film prior to being transmitted through the field lens and then through the partially reflective partially transmissive surface to a non-polarizing lower display optical system adapted to present the image light to an eye of a user wearing the head-worn computer.
Owner:OSTERHOUT GROUP INC
Light redirecting films and film systems
The light redirecting films of the present invention have a pattern of individual optical elements that may intersect and / or interlock each other to achieve substantially complete surface coverage of at least one of the surfaces occupied by the optical elements. At least some of the optical elements may have at least one flat surface and at least one curved surface that may intersect each other to a greater extent on the curved surface than on the flat surface to increase the relative percentage of flat surface area to curved surface area of the intersecting optical elements to increase the on axis gain of light passing through the film.
Owner:INNOVATIVE DISPLAY TECH
Image display device and image display method
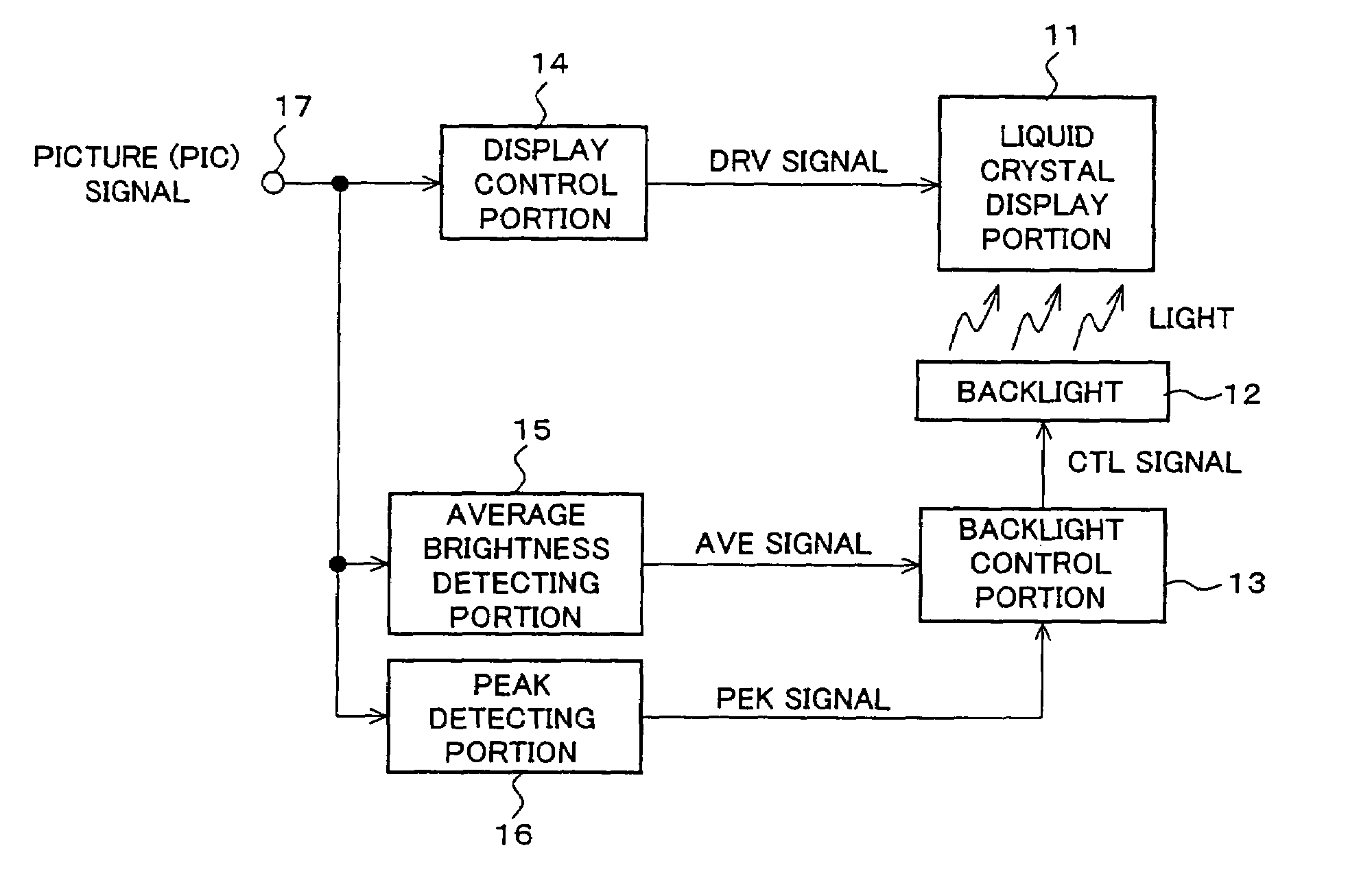
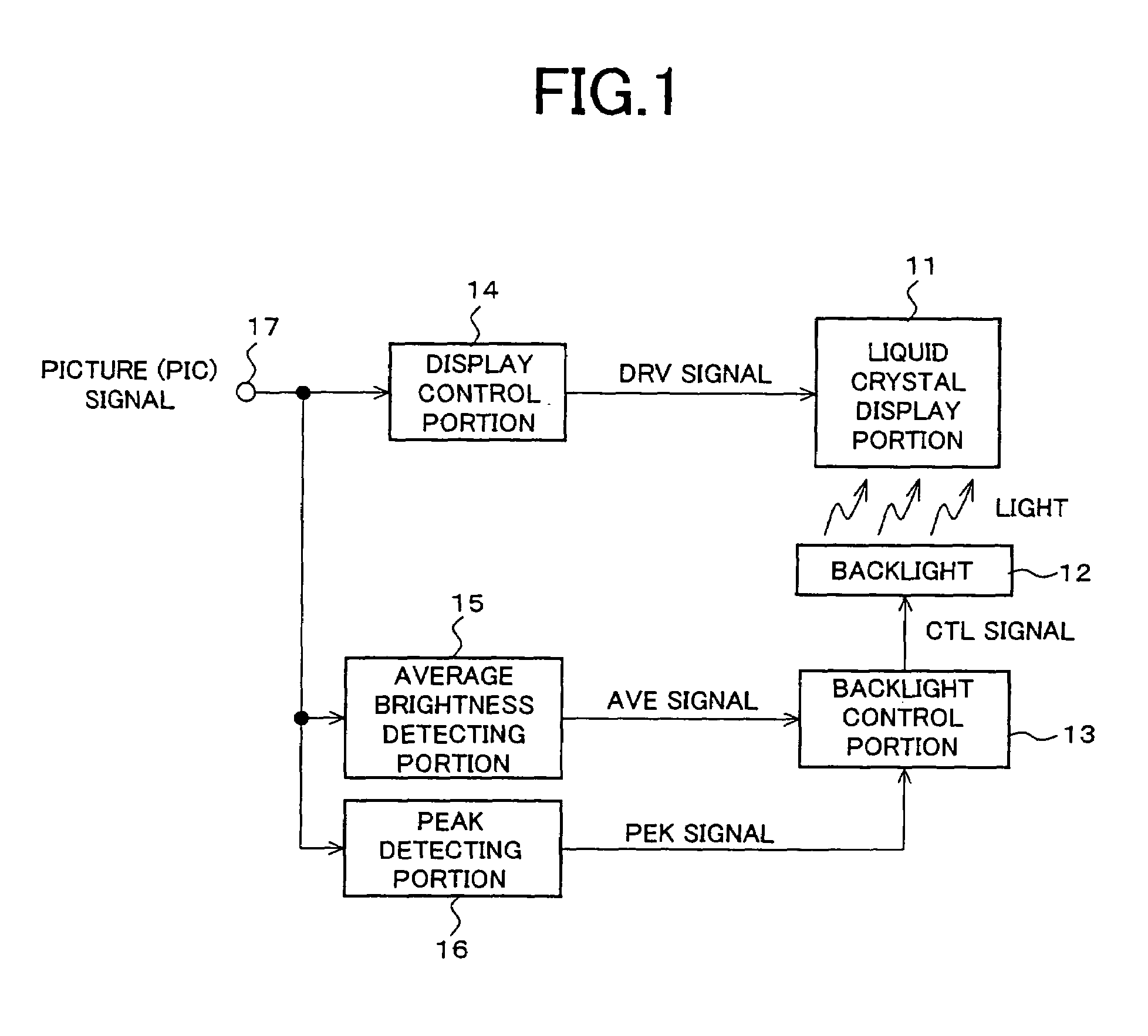
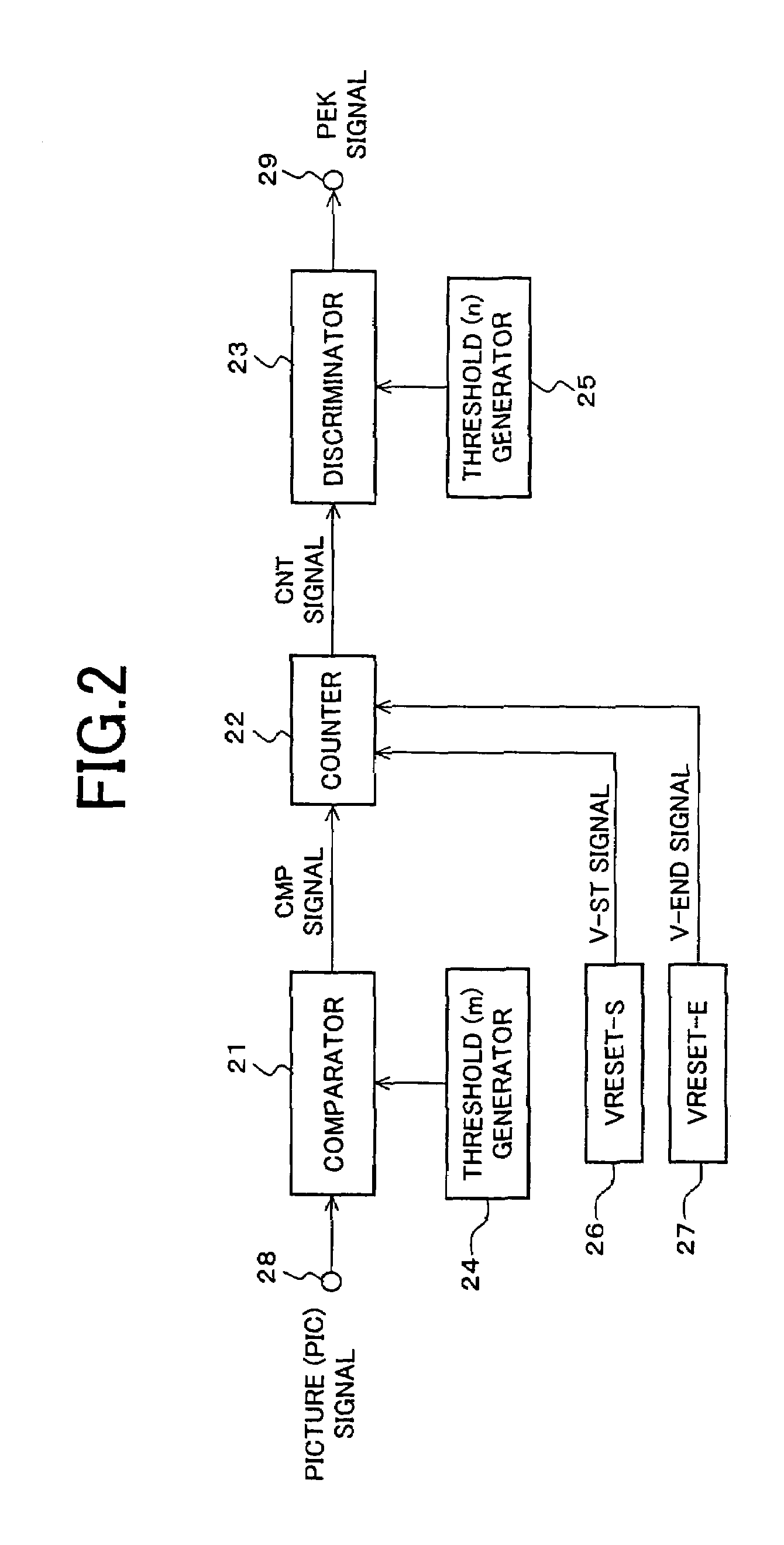
InactiveUS7053881B2Rule out the possibilityImprove dynamic contrastCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsDisplay devicePeak value
An image display device according to the present invention is capable of presenting to a viewer a high-quality lustrous video on a display screen with best screen brightness by increasing visual contrast and avoiding loss of true black elements without widening a dynamic range of a picture signal. The image display device is provided with a liquid crystal display portion (11), a display control portion (14), a backlight (12), a backlight control portion (13) and an average brightness detecting portion (15) and detects brightness of the light source in accordance with the average brightness of a picture signal to be displayed. It is further provided with a peak detecting portion (16) and corrects the control of the backlight control portion (13) in accordance with a detected peak value of a picture.
Owner:SHARP KK
Automotive head up display apparatus
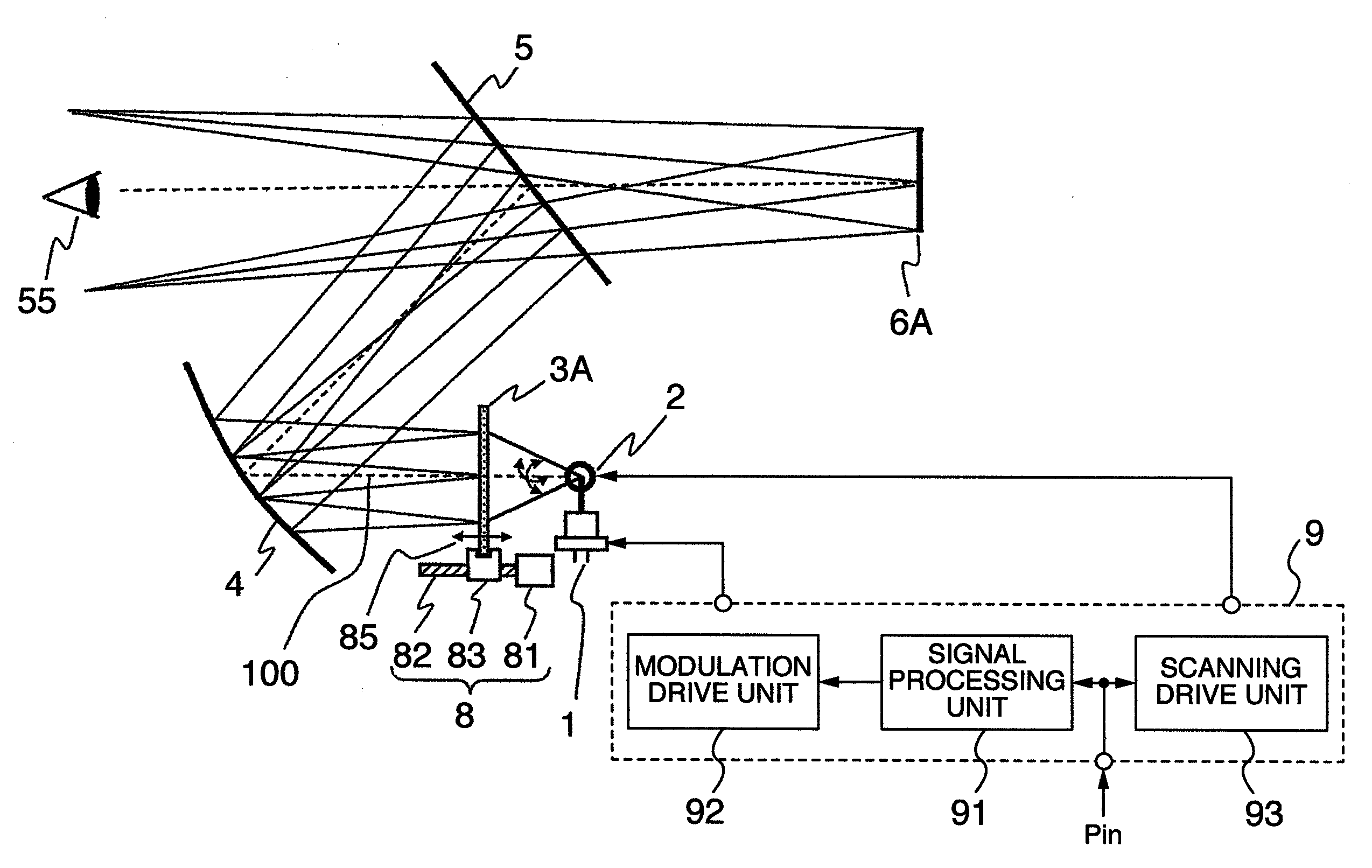
InactiveUS20090160736A1Less movementDisplay distance can be changedCathode-ray tube indicatorsOptical elementsHead-up displayOptoelectronics
A HUD apparatus for vehicles including a light source, a scanning unit for scanning light from the light source two-dimensionally, a screen to focus the scanned light on, and a projection unit for projecting the image on the screen. The apparatus further includes a moving mechanism for changing the position of the screen.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
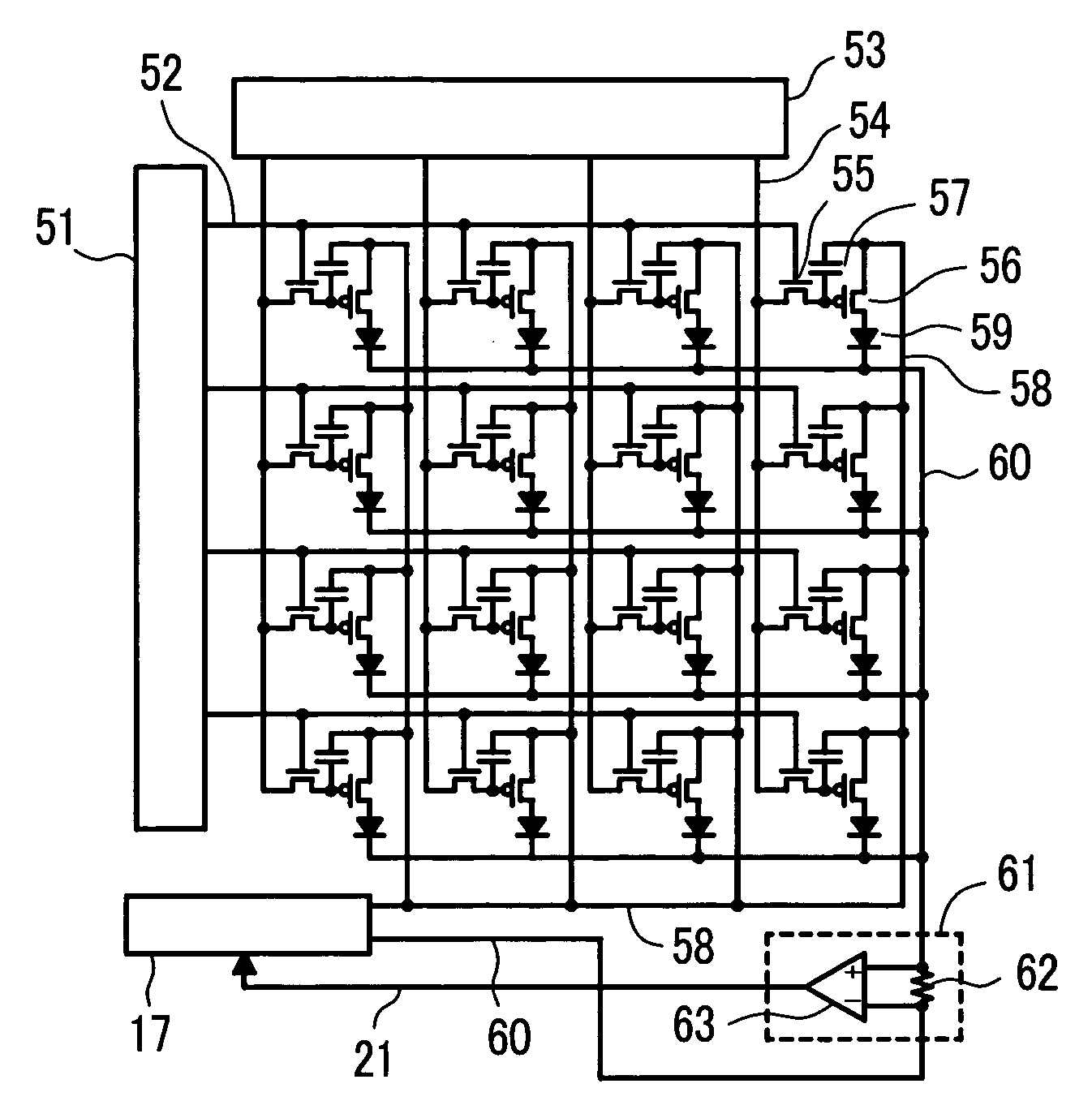
Control of electroluminescent displays
InactiveUS7119493B2Remove loadSmall voltage dropElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesElectricityControl signal
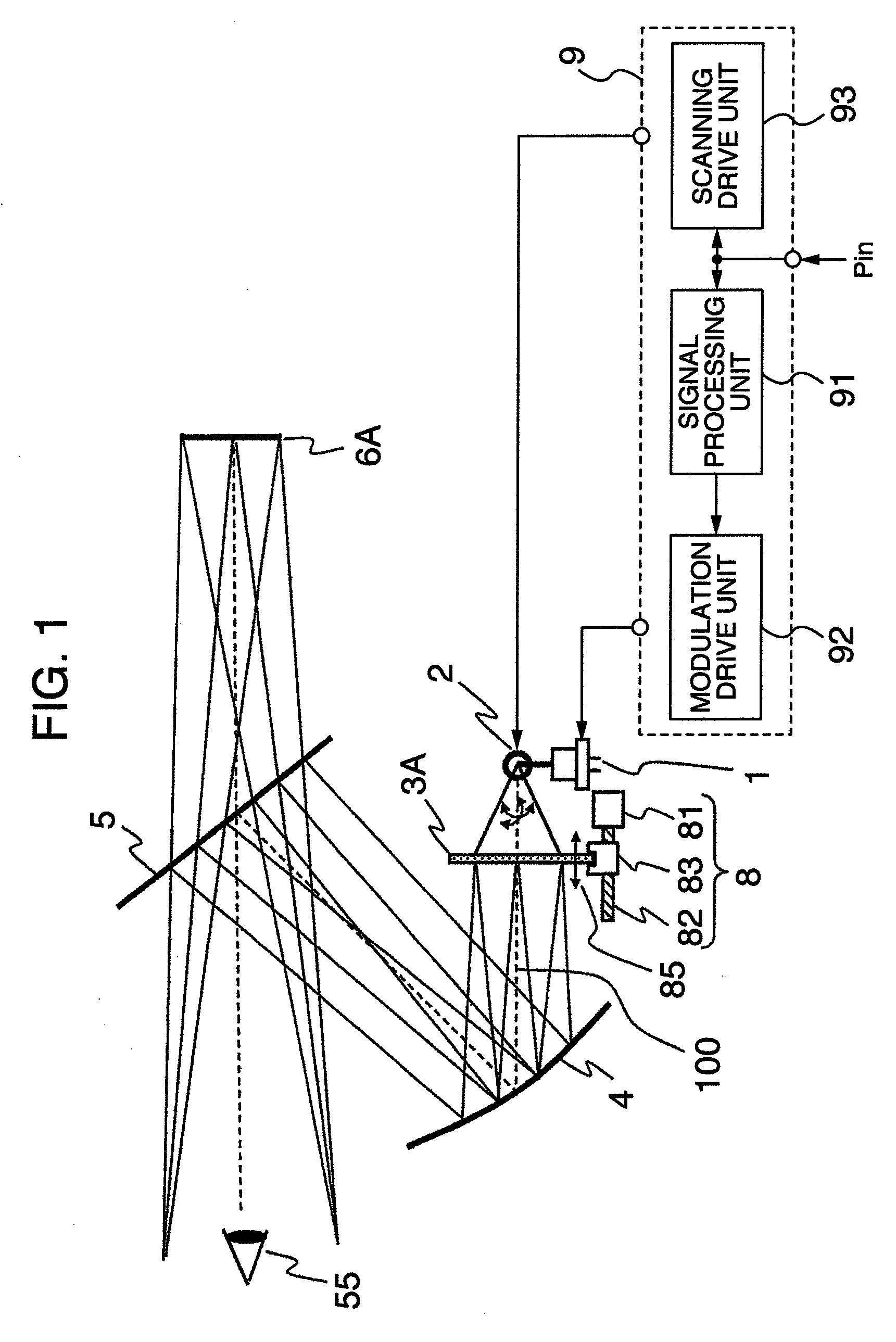
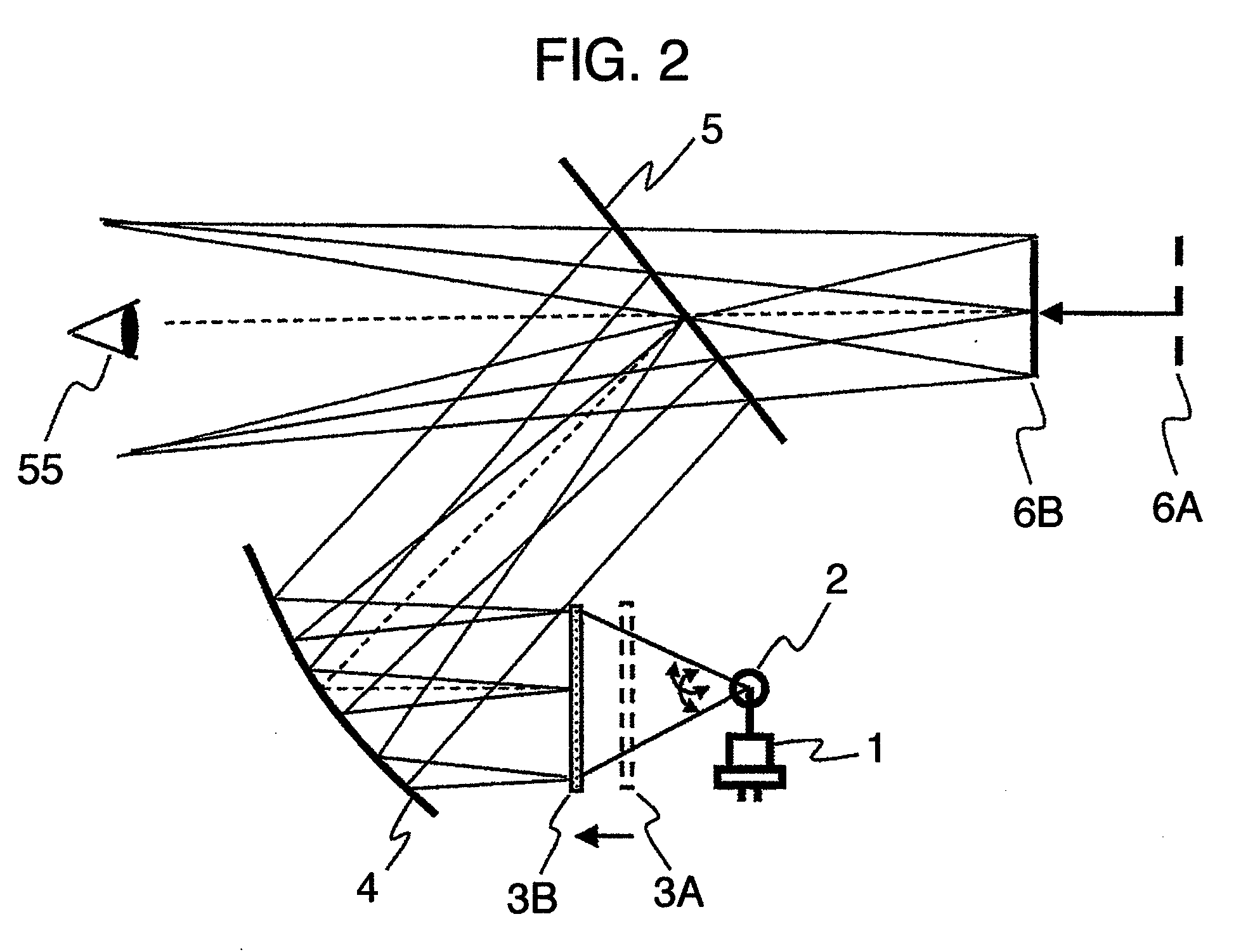
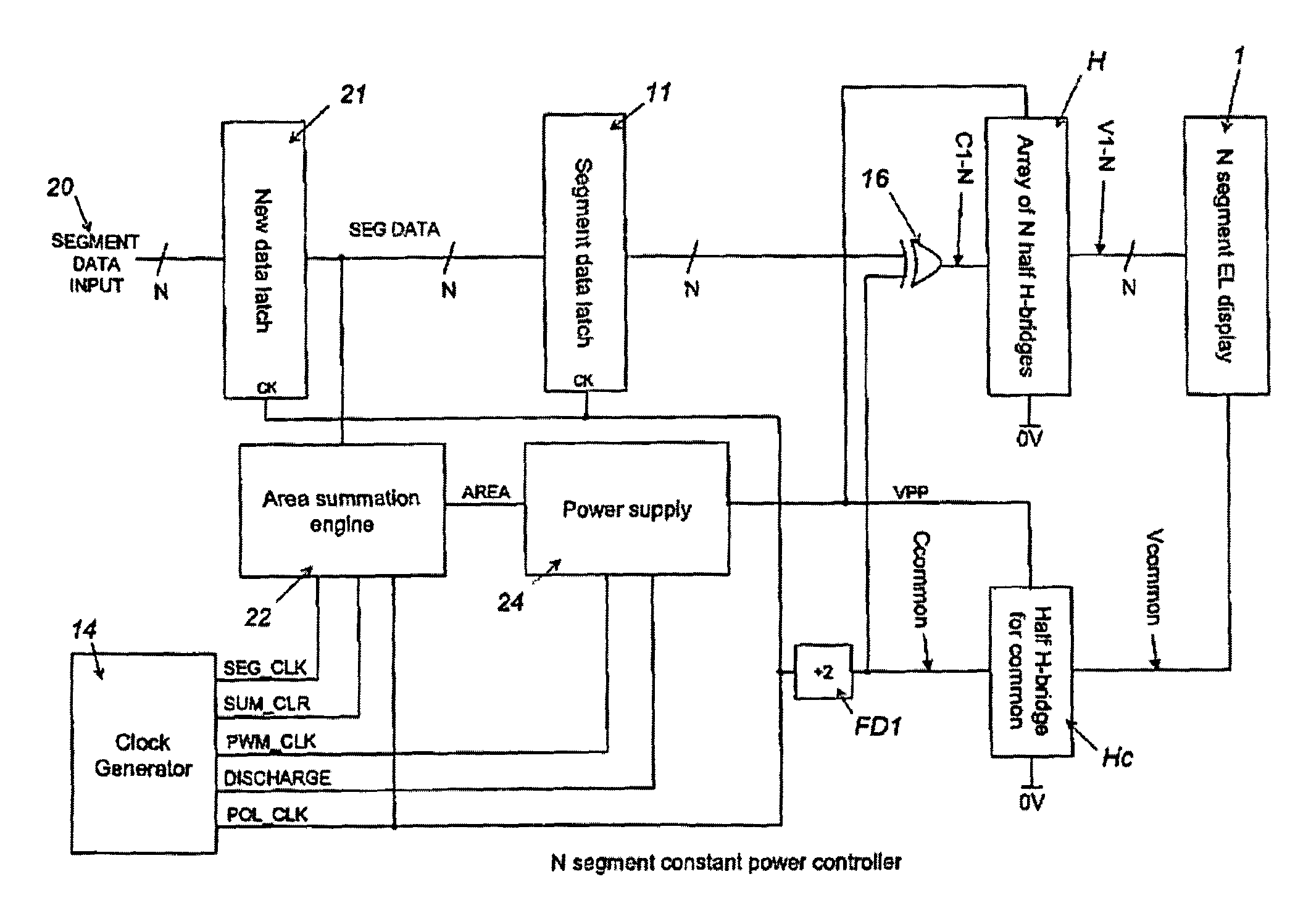
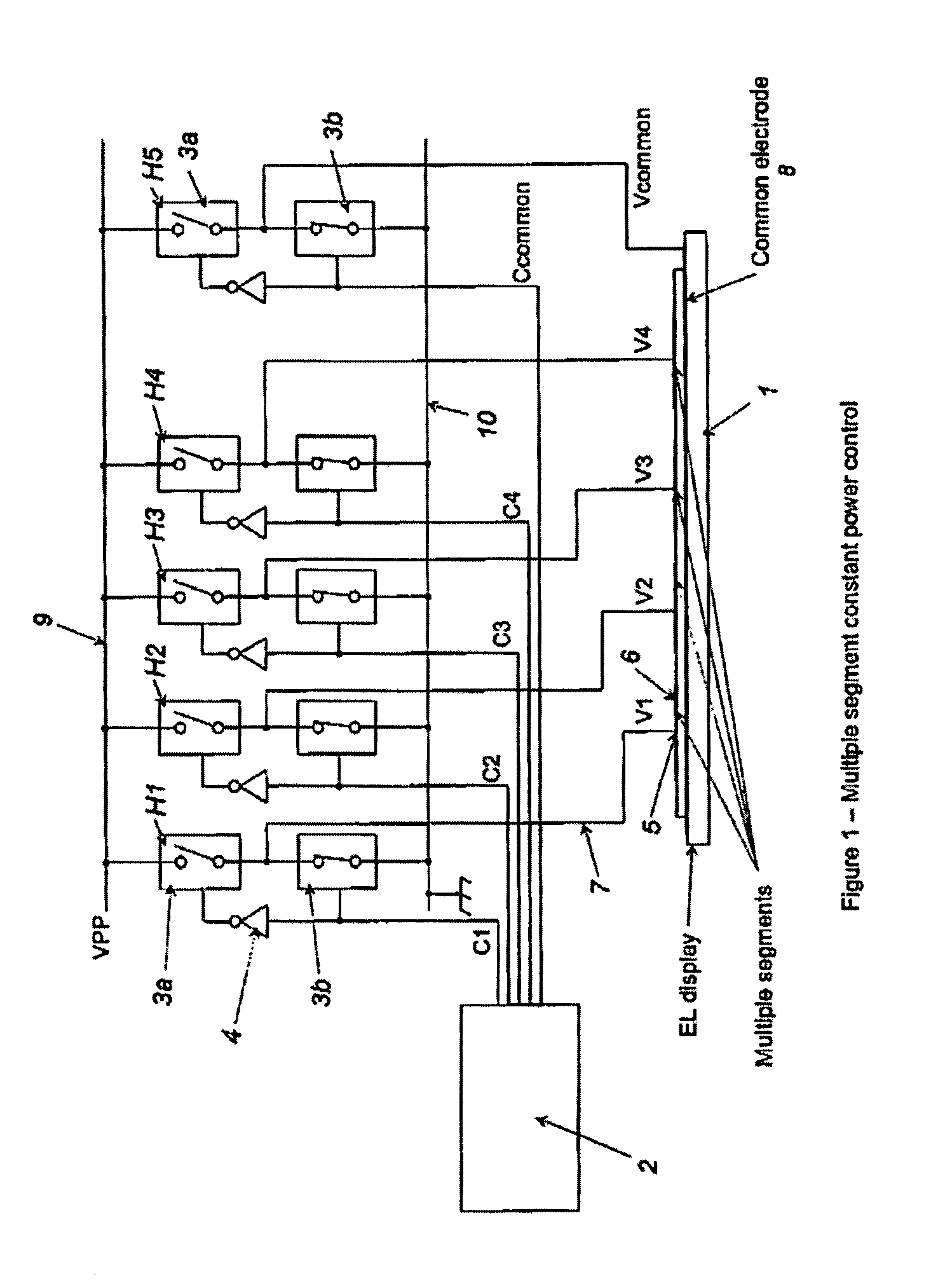
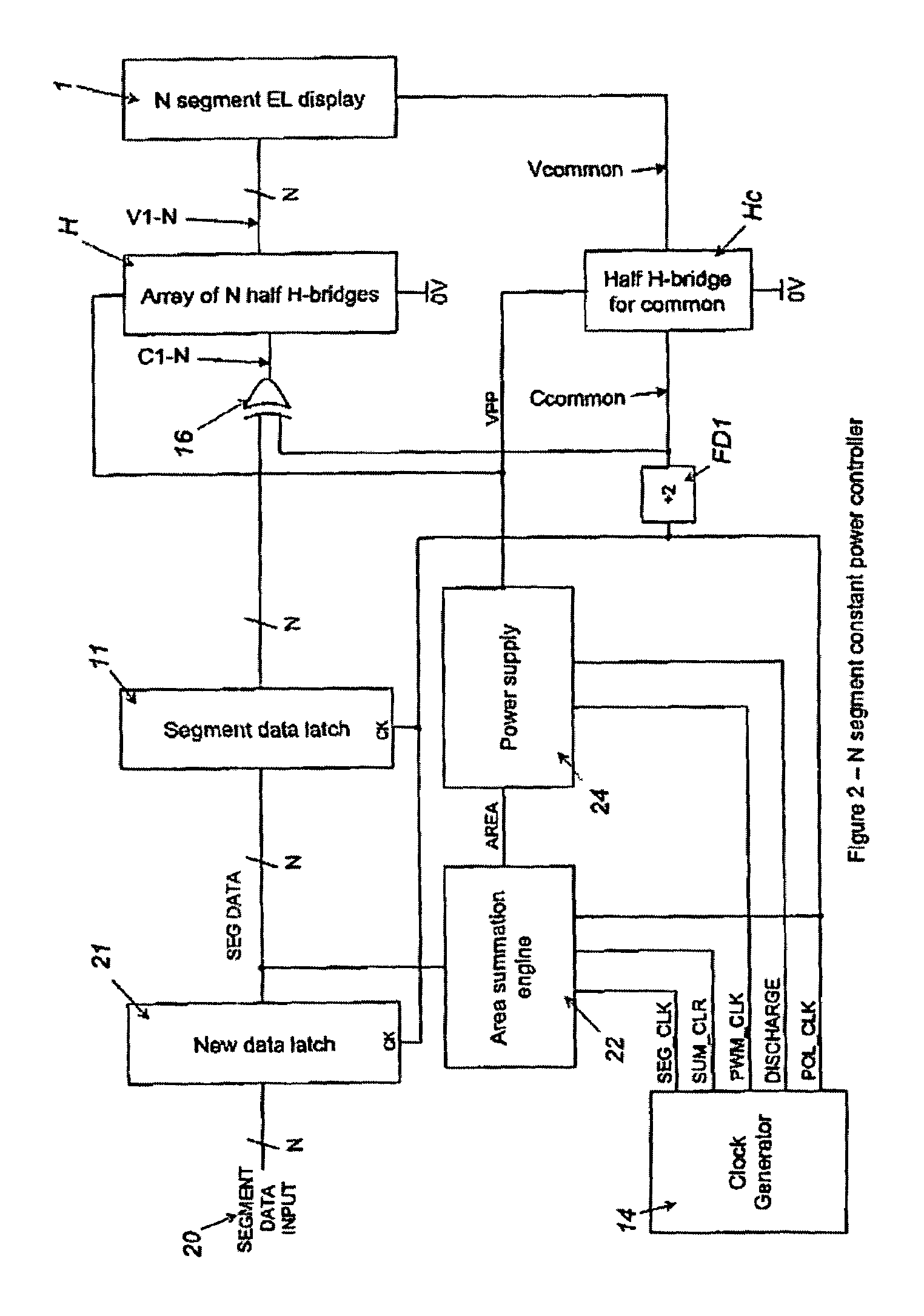
A controller for use with a multi-segment electroluminescent display 1. Control signals C1–CN control a plurality of half H-bridges H and Hc, the terminals of the half H-bridges being connected respectively to ground and to a high voltage DC supply 9. One of said half H-bridges provides a common output Vcommon and the remaining H-bridges provide drive voltages V1–VN for the segments of the display. The H bridges are driven by an oscillator 14 so that an AC voltage is selectively applied to the segments of the display. A power supply 24 provides a predetermined amount of power per unit area of the display. This is controlled by an area summation engine 22 having a segment data input, a segment counter and a memory containing area data corresponding to the segment(s) of the display. Based on the input from the segment data input, the area(s) of the segment(s) that are to be lit are obtained from the memory and summed to provide the total area to be lit. This is fed to the power supply 24, which then feeds the correct amount of power to display 1 via the half H-bridges.
Owner:PELIKON
Eye Mounted Displays and Systems Using Eye Mounted Displays
ActiveUS20150049004A1Avoid and reduce interferenceOvercome limitationsImage analysisGeometric image transformationCorneal surfaceEntire pupil
A display device is mounted on and / or inside the eye. The eye mounted display contains multiple sub-displays, each of which projects light to different retinal positions within a portion of the retina corresponding to the sub-display. The projected light propagates through the pupil but does not fill the entire pupil. In this way, multiple sub-displays can project their light onto the relevant portion of the retina. Moving from the pupil to the cornea, the projection of the pupil onto the cornea will be referred to as the corneal aperture. The projected light propagates through less than the full corneal aperture. The sub-displays use spatial multiplexing at the corneal surface. Various electronic devices interface to the eye mounted display.
Owner:TECTUS CORP
Liquid crystal display device achieving imaging with high s/n ratio using invisible light
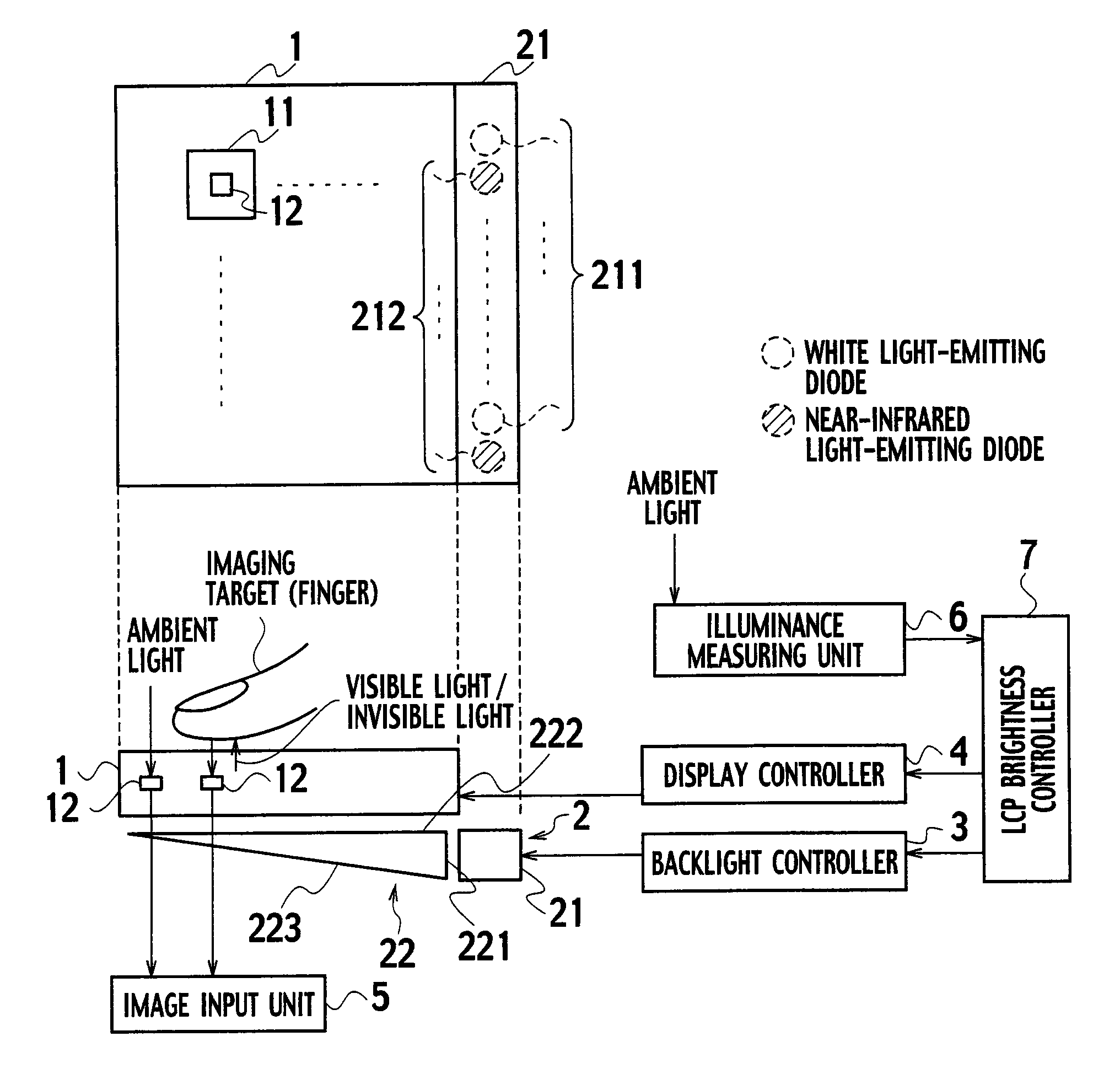
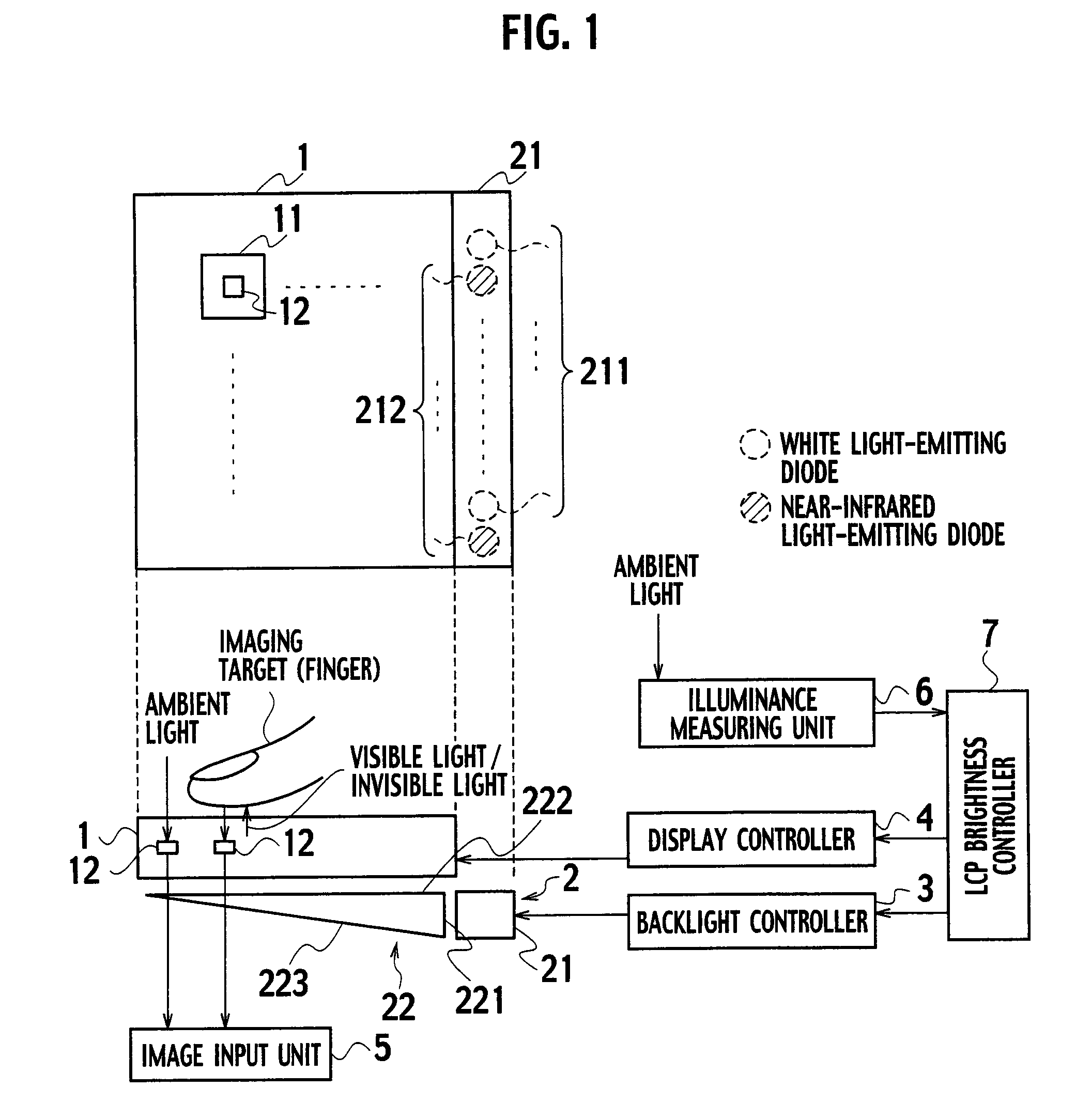
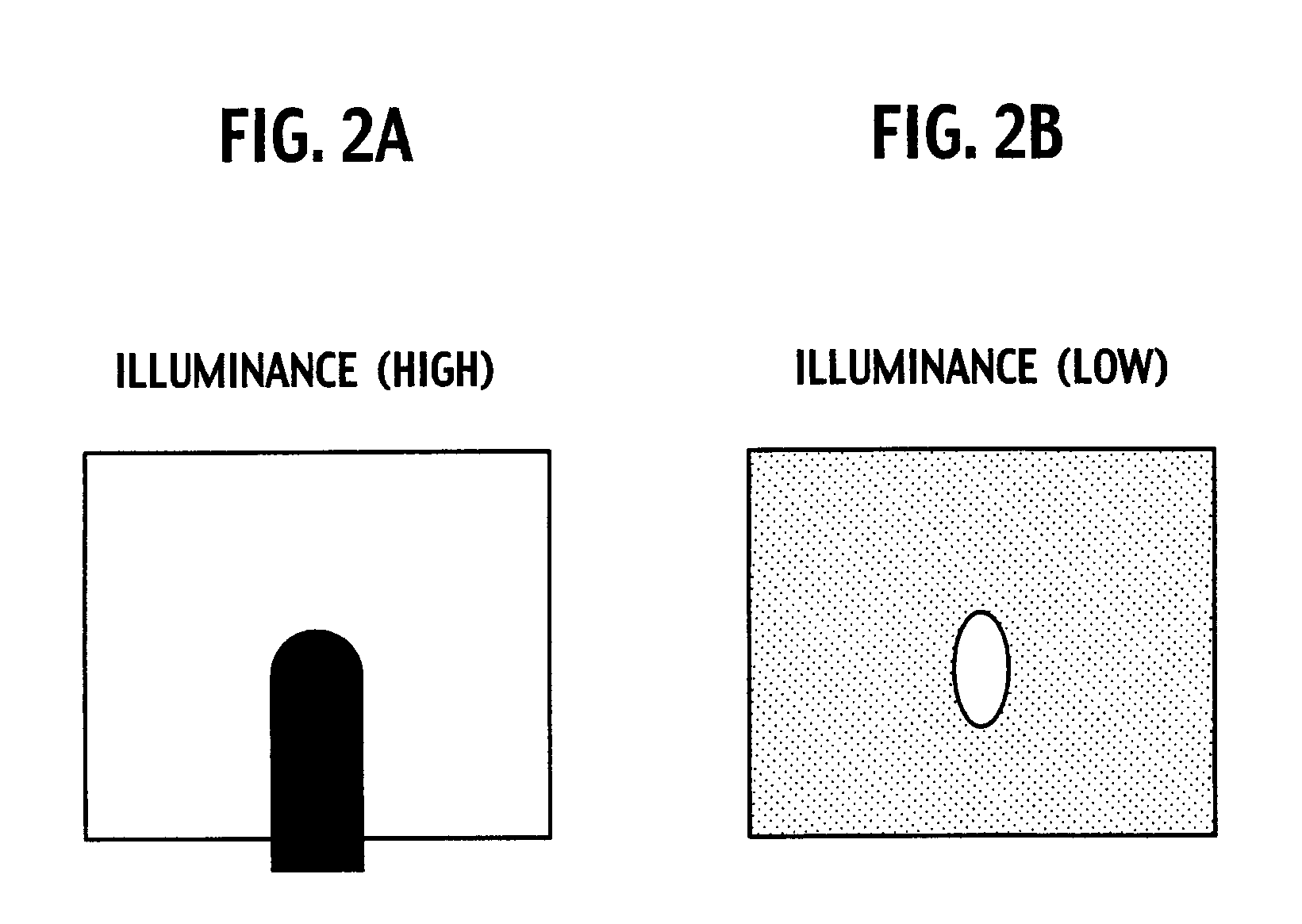
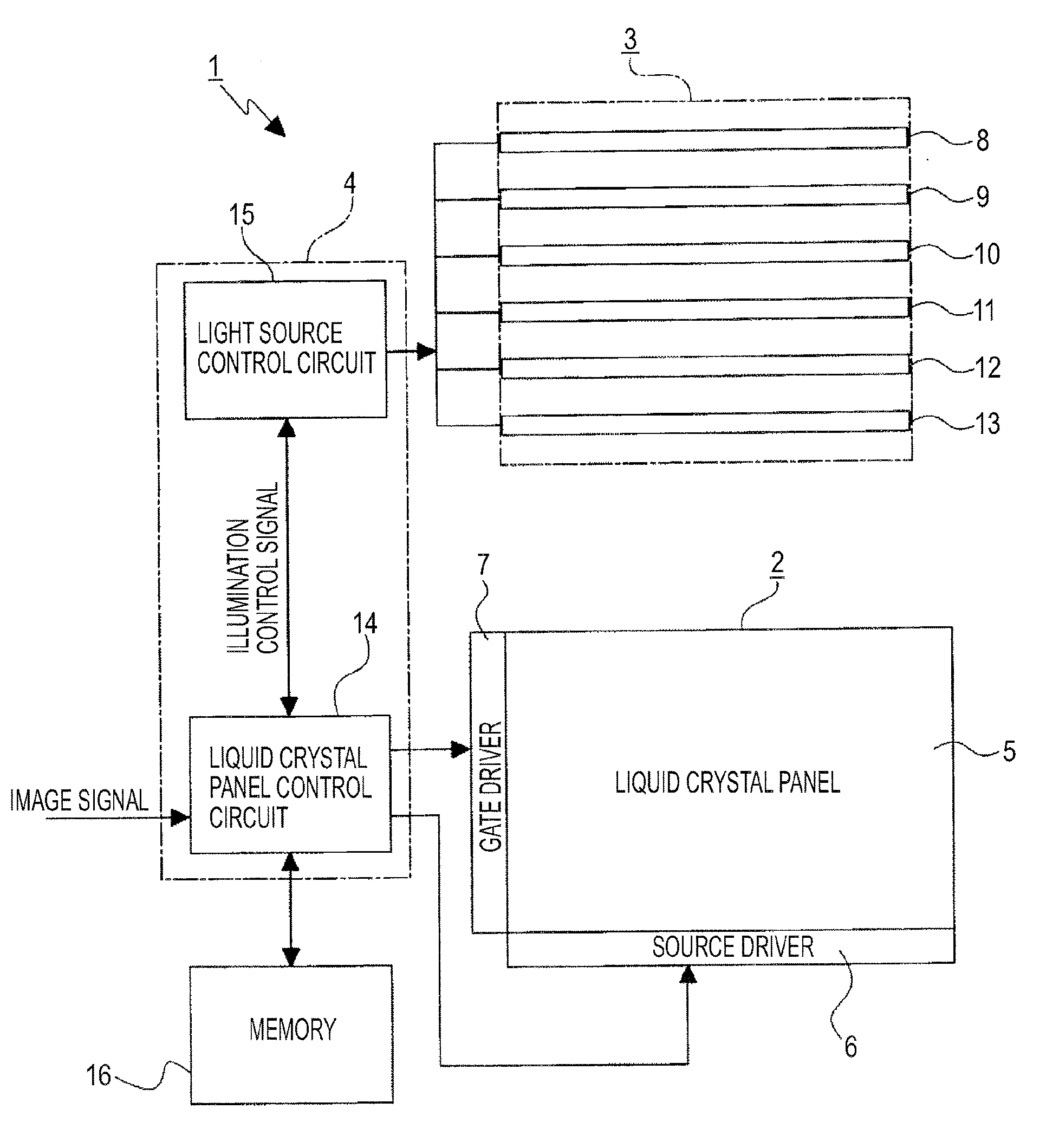
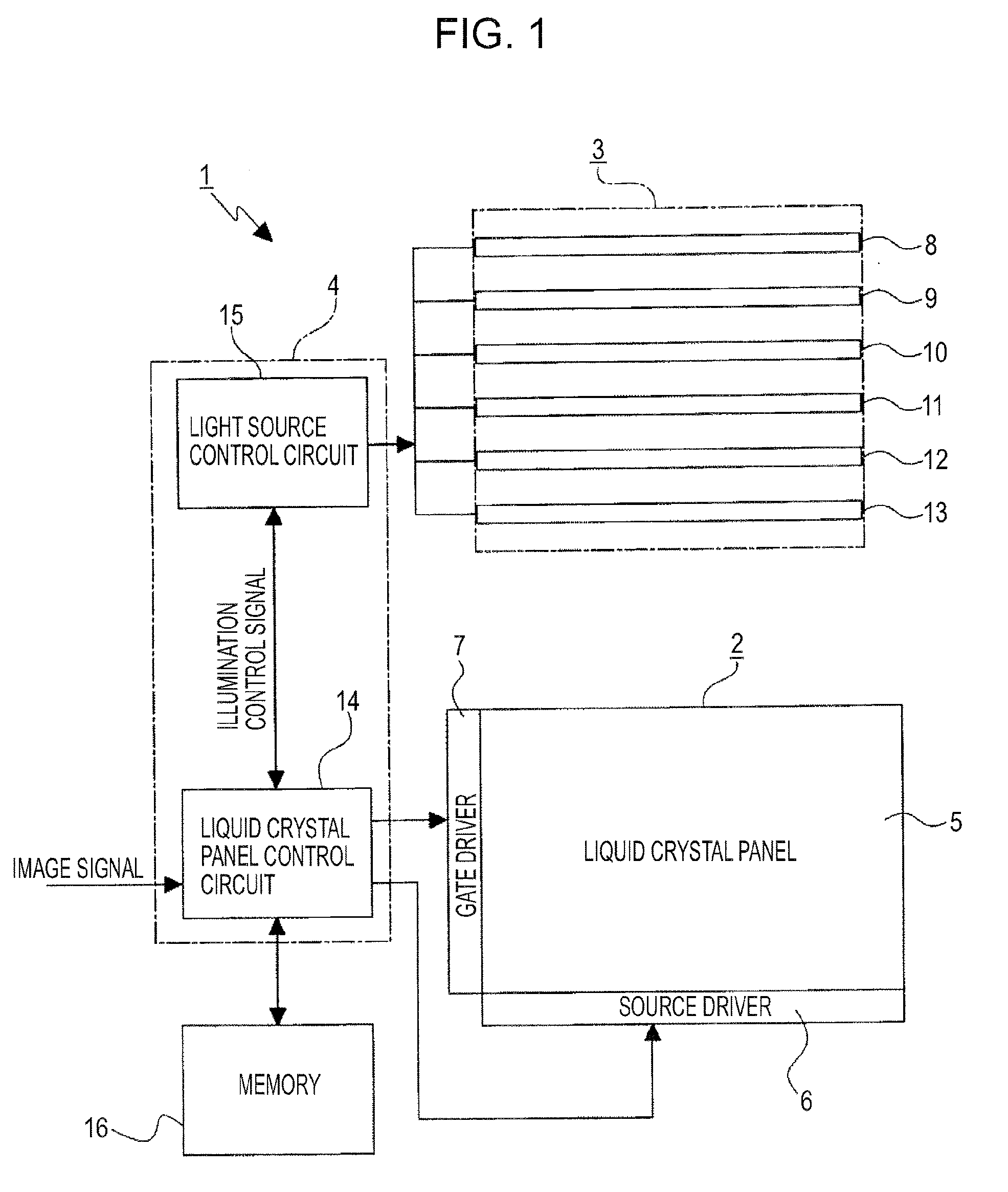
ActiveUS20070296688A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce brightnessTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesIlluminanceLiquid-crystal display
A liquid crystal panel brightness controller notifies a backlight controller that an illuminance of ambient light is equal to or less than a threshold value. Upon notification, the backlight controller causes invisible light emitted, for example. The invisible light passes through a liquid crystal panel and is reflected by an imaging target and is received by photosensors. Accordingly, the decrease in the amount of the visible light received by photosensors is compensated. As a result, an image with a high S / N ratio is obtained.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY CENTRAL CO LTD
Method for controlling LED-based backlight module
InactiveUS20070262732A1Reduce blurLessen flicker problemElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesEffect lightEngineering
The method of the present invention turns off the line of LEDs of a backlight module behind the currently enabled scanline of a LCD device so that the transient behavior of the liquid crystal molecules are less obvious, thereby enhancing the dynamic response of the LCD device. For one type of embodiments, in accordance with the top-down scanning of the LCD device, the corresponding horizontal lines of the LEDs of the backlight module are turned off in a certain manner so that they exhibit a lighting (or, more precisely, darkening) pattern as if they are also “scanned” from top to down. For another type of embodiments, the horizontal lines of the LEDs of the backlight module are turned off and on simultaneously so that the backlight module actually “flashes” the LCD device.
Owner:VASTVIEW TECH
Diagnosis assisting apparatus, diagnosis assisting method, and storage medium having a diagnosis assisting program recorded therein
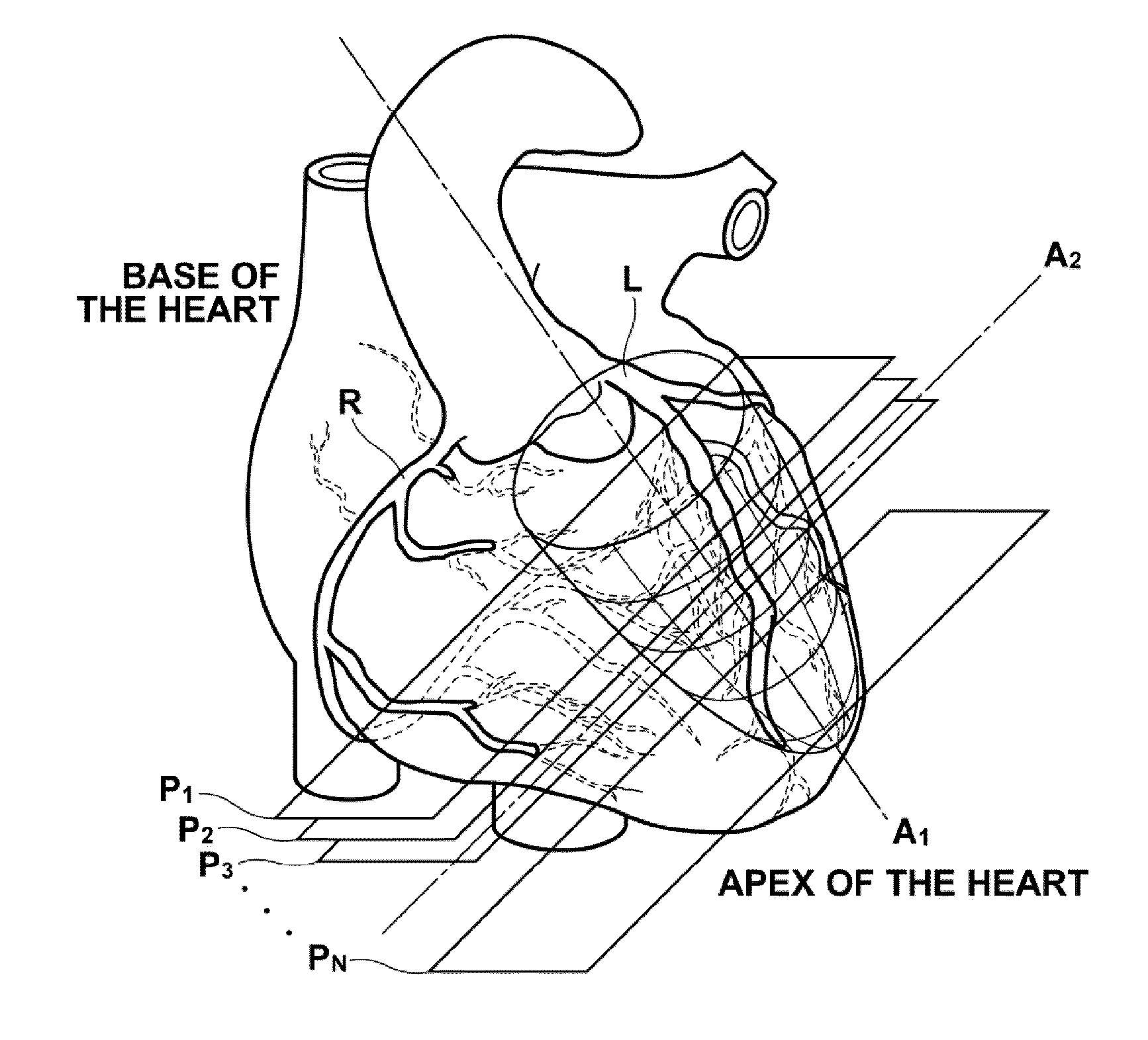
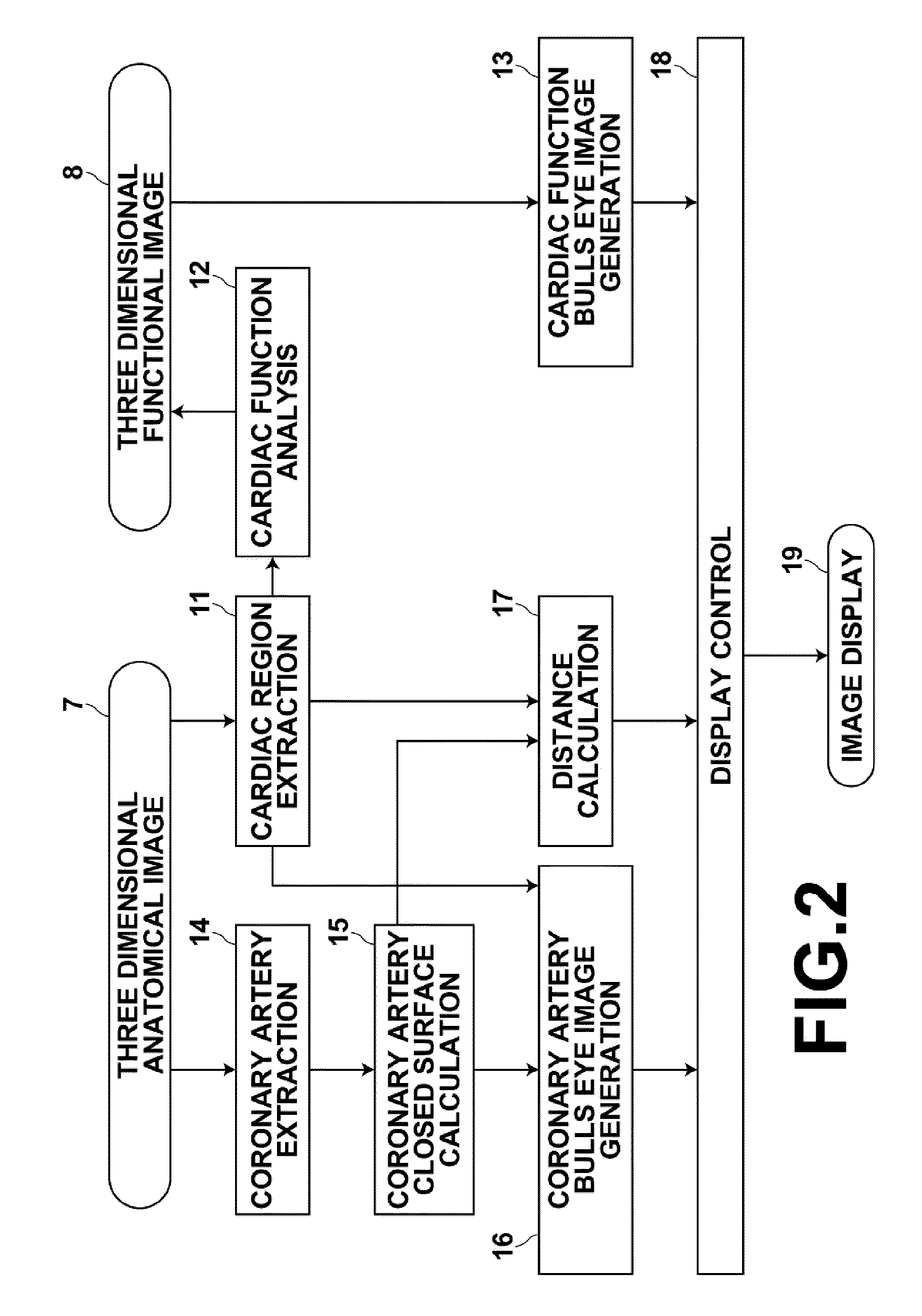
ActiveUS20100266176A1Brightness be lowerGreat distanceCharacter and pattern recognitionMedical imagesCoronary artery structureCoronary artery closure
A cardiac cavity region is extracted from a three dimensional functional image that represents evaluation index data of cardiac functions, and a cardiac function bulls eye image that represents the functions of the cardiac cavity is generated. Coronary artery image data are extracted from three dimensional anatomical images that represents the structures of the heart and the coronary artery, and coronary article closed surfaces that include the extracted coronary artery image data are calculated. A coronary artery bulls eye image is generated form the extracted coronary artery image data, and distances from the boundary surface of the cardiac cavity region to the coronary artery closed surfaces are calculated. Display output is controlled such that the cardiac function bulls eye image, the coronary artery bulls eye image, and data representing the distances are displayed simultaneously on the screen of a display device.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Display apparatus and display method
ActiveUS20060214904A1Reduce power consumptionIncrease qualityCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsLight sourceControl unit
A display apparatus includes a display unit having a display screen divided into a plurality of regions and controlled using an aperture ratio on a pixel-by-pixel basis, a backlight including a plurality of sets of light sources, each set being disposed so as to correspond to one of the regions, and a control unit for detecting display luminance in each region, computing the emission luminance of each light source on the basis of the detected display luminance while taking into account an effect on the region of the other light sources not corresponding to the region, and computing a correction value for each pixel on the basis of a shift amount between the set emission luminance and an optimal display luminance for one of the regions, and delivering a display driving signal generated on the basis of the correction value to each pixel so as to control the aperture ratio.
Owner:SATURN LICENSING LLC
Light emissive display based on lightwave coupling
ActiveUS20050123243A1Reduce luminance of backgroundImprove efficiencyCoupling light guidesWaveguidesPhotoluminescenceCoupling
A light emissive display having a specular waveguide that propagates short wavelength light and photoluminescent features adjacent to the waveguide that fluoresce, for example, in visible red, green, blue, and mixed colors when selectively coupled with the short wavelength light. The photoluminescent layers emit light primarily and, therefore, efficiently in the direction of an observer only. This light emissive display may be utilized as a planar light source, as patterned information signage, or as a re-configurable information display containing intensity modulated pixels. The light emissive display may be enhanced optically such that only a small portion of ambient light is reflected from the display while preserving the majority of emitted display luminance.
Owner:CINCINNATI UNIV OF +1
Liquid crystal display
ActiveUS20050140855A1Black luminance increaseContrast ratio is reducedNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayDepolarization
A normally-closed liquid crystal display includes a component to selectively absorb characteristic leakage light occurring at black representation. Therefore, when black is displayed, occurrence of unnecessary leakage light due to partial depolarization of polarized light caused by a component of an LCD panel can be suppressed. It is therefore possible to provide a liquid crystal display in which display performance of black is improved to clearly display black.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
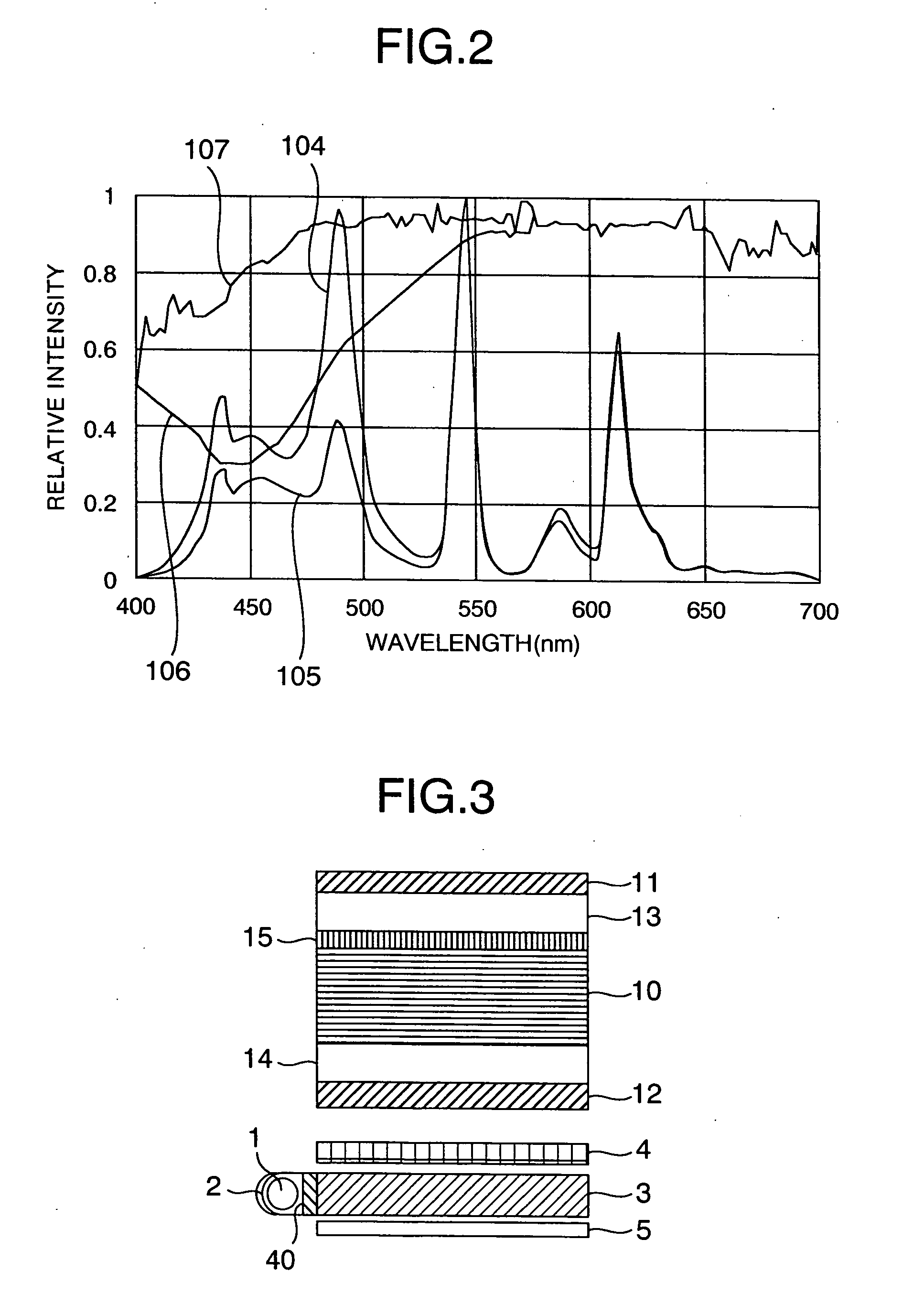
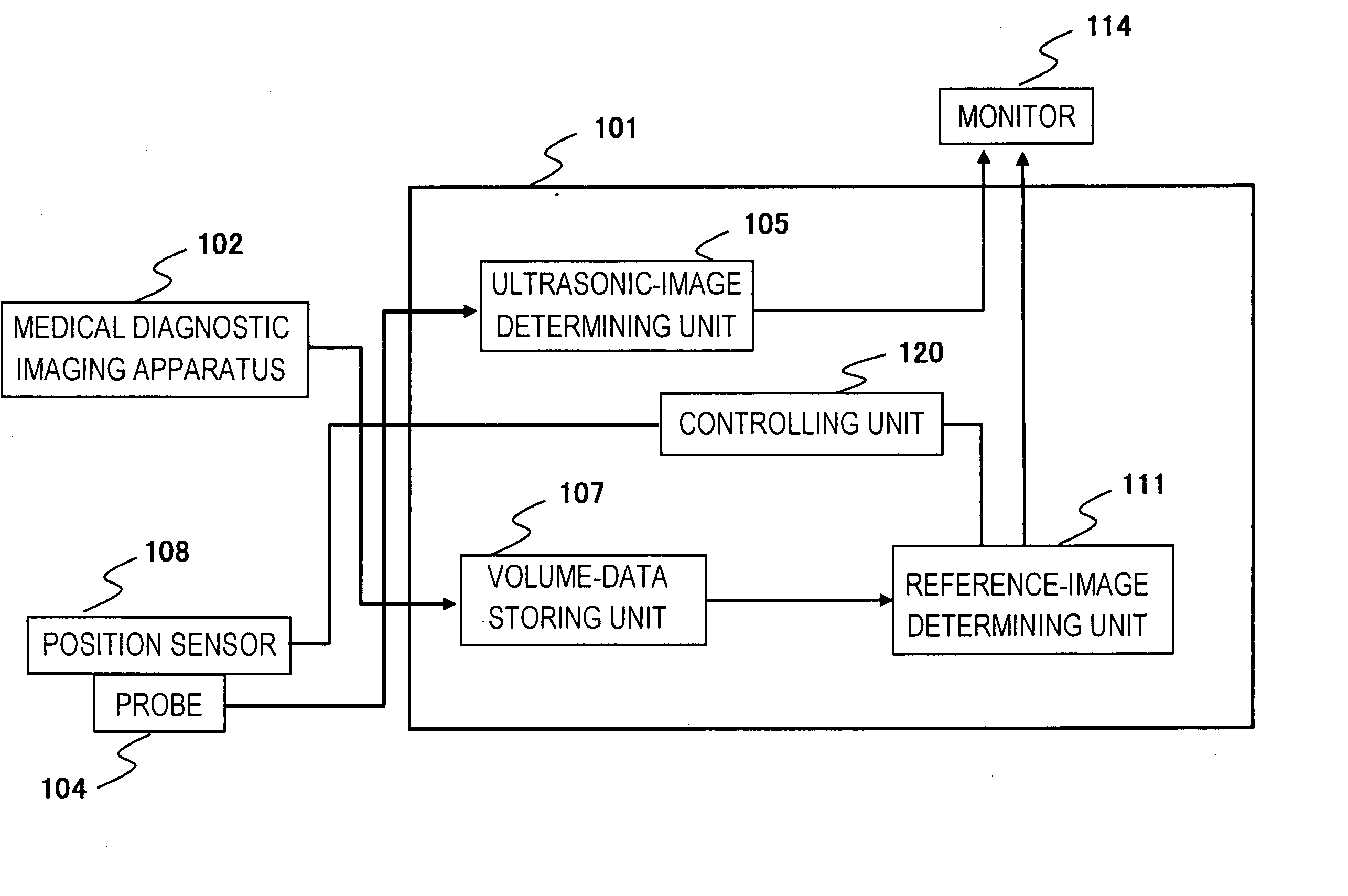
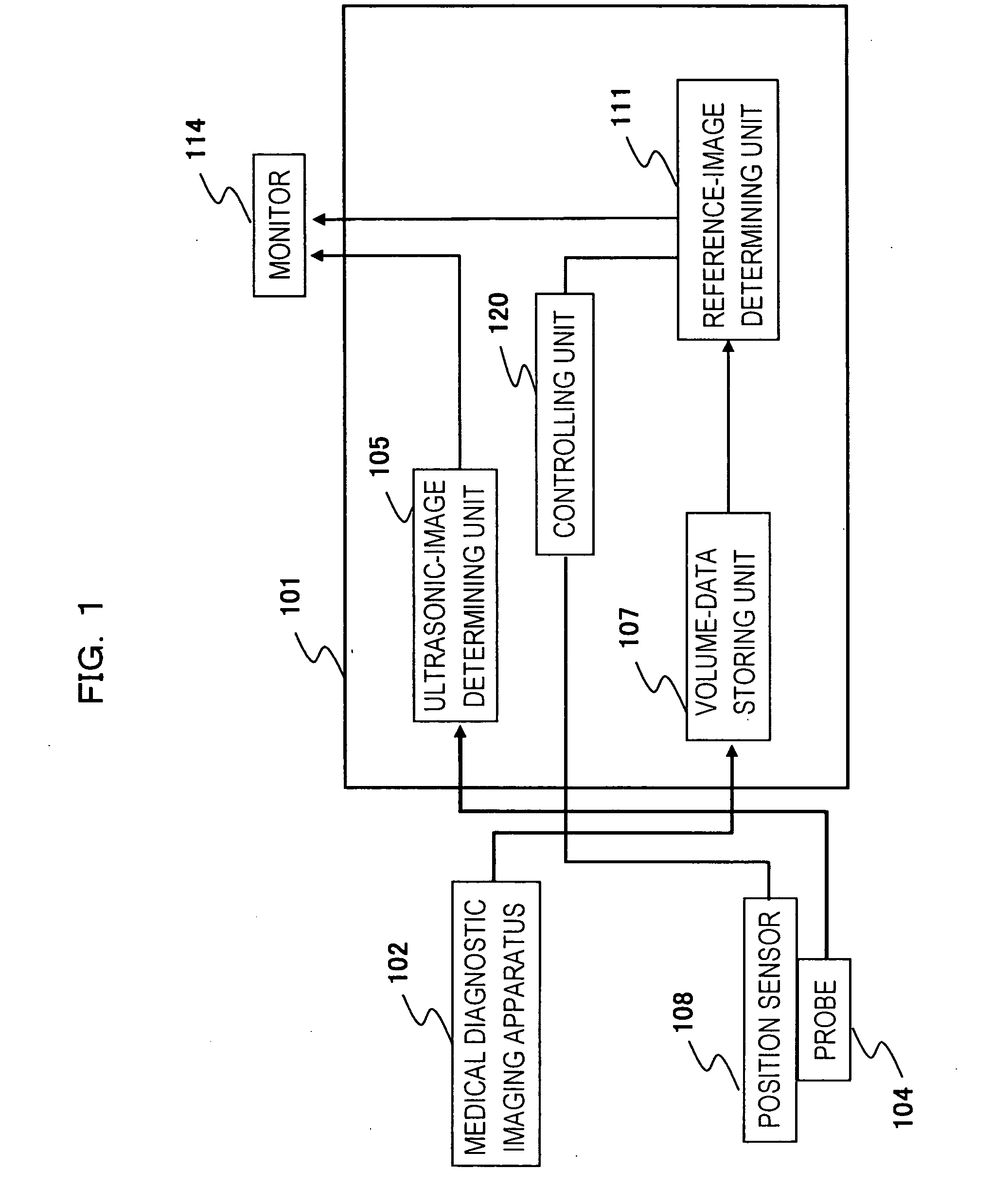
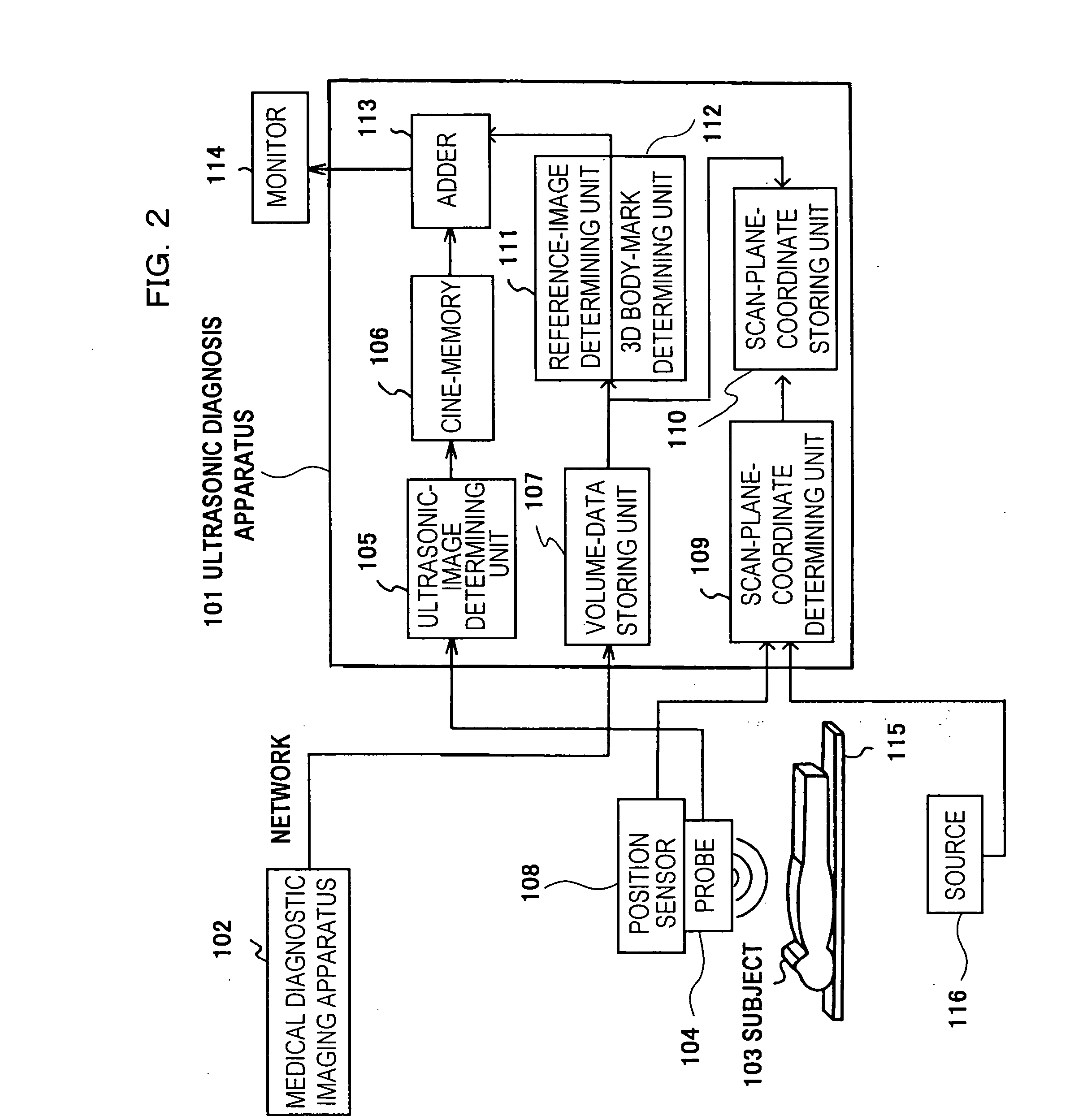
Reference image display method for ultrasonography and ultrasonograph
ActiveUS20070010743A1Increased freedom of settingImprove comparison accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementReference imageTomographic image
An ultrasonic image 105, 106 is captured by an ultrasonic probe 104. A reference image 111 is obtained by extracting a tomographic image corresponding to the scan plane of the ultrasonic image from volume image data that is pre-obtained by a diagnostic imaging apparatus 102 and that is stored in a volume-data storing unit 107. The ultrasonic image and the reference image 111 are displayed on the same screen 114. In this case, of the reference image, a portion corresponding to the view area of the ultrasonic image is extracted and the resulting reference image having the same region as the ultrasonic image is displayed as a fan-shaped image.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com