Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
483results about How to "Reduced life-time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
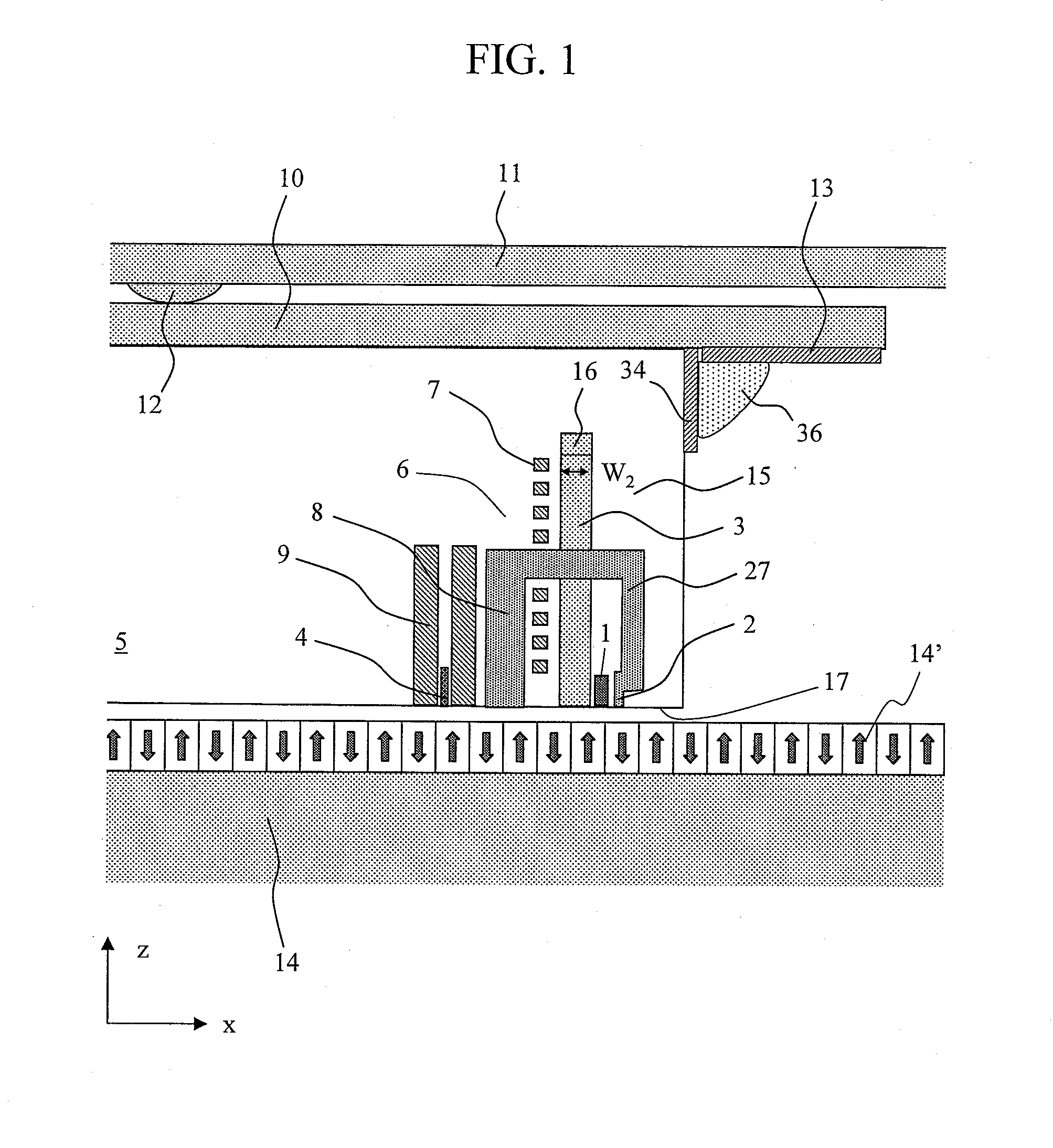
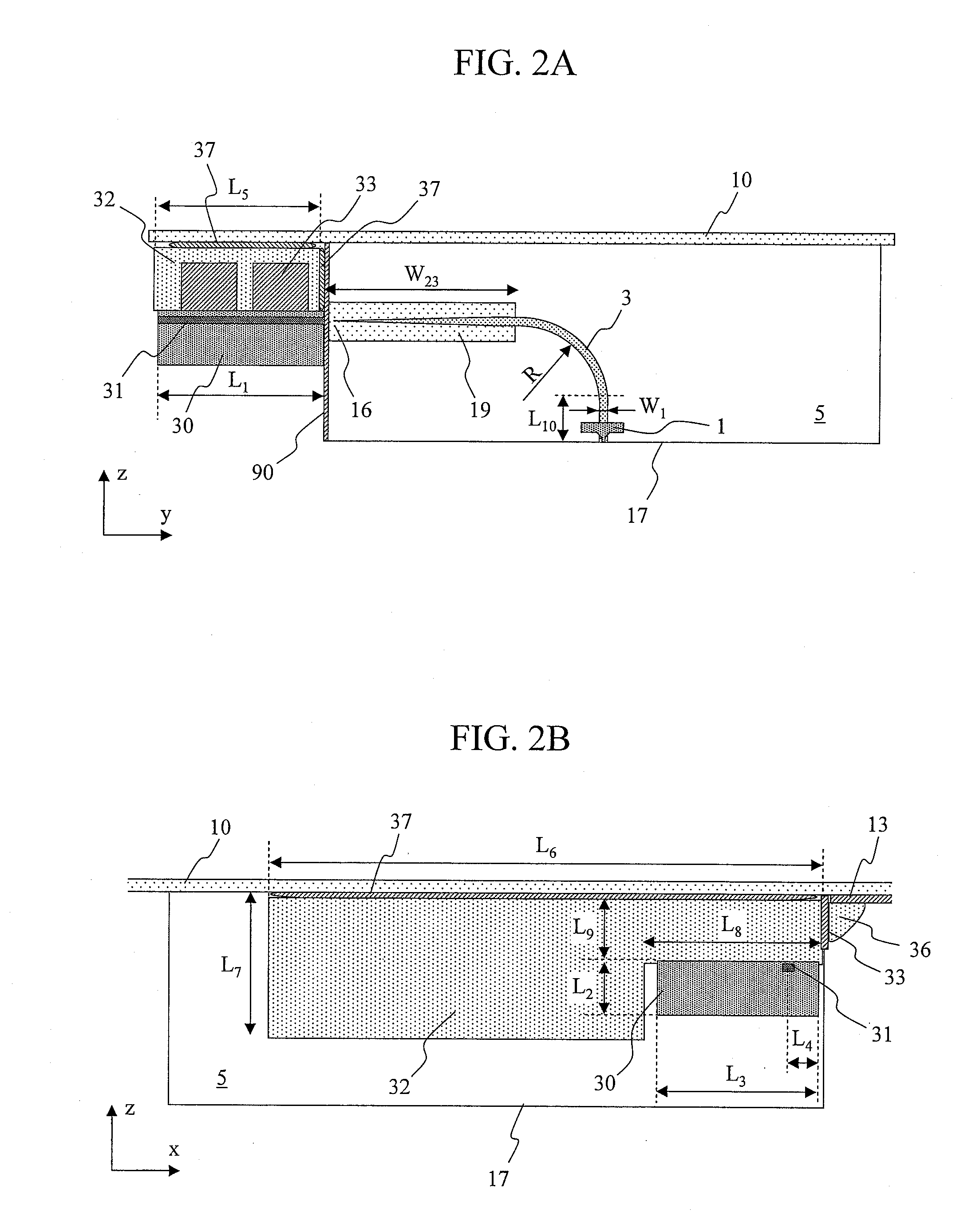
Low-carbon-doped silicon oxide film and damascene structure using same
ActiveUS20050260850A1Reduce electrical circuit lifetimeEnhance moisture intakeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMetal interconnectDevice material
A method of forming an interconnect for a semiconductor device using triple hard layers, comprises: forming a first hard layer serving as an etch stop layer on a metal interconnect-formed dielectric layer; forming a second hard layer on the first hard layer; forming a dielectric layer on the second hard layer; forming a third hard layer on the dielectric layer; forming a hole through the third and second hard layers, the dielectric layer, and the first hard layer; and filling the hole with metal to establish an interconnect. The second and third hard layers are each made of carbon-doped silicon oxide formed from a source gas and a redox gas, while controlling the carbon content in the second hard layer as a function of a flow rate of the redox gas.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
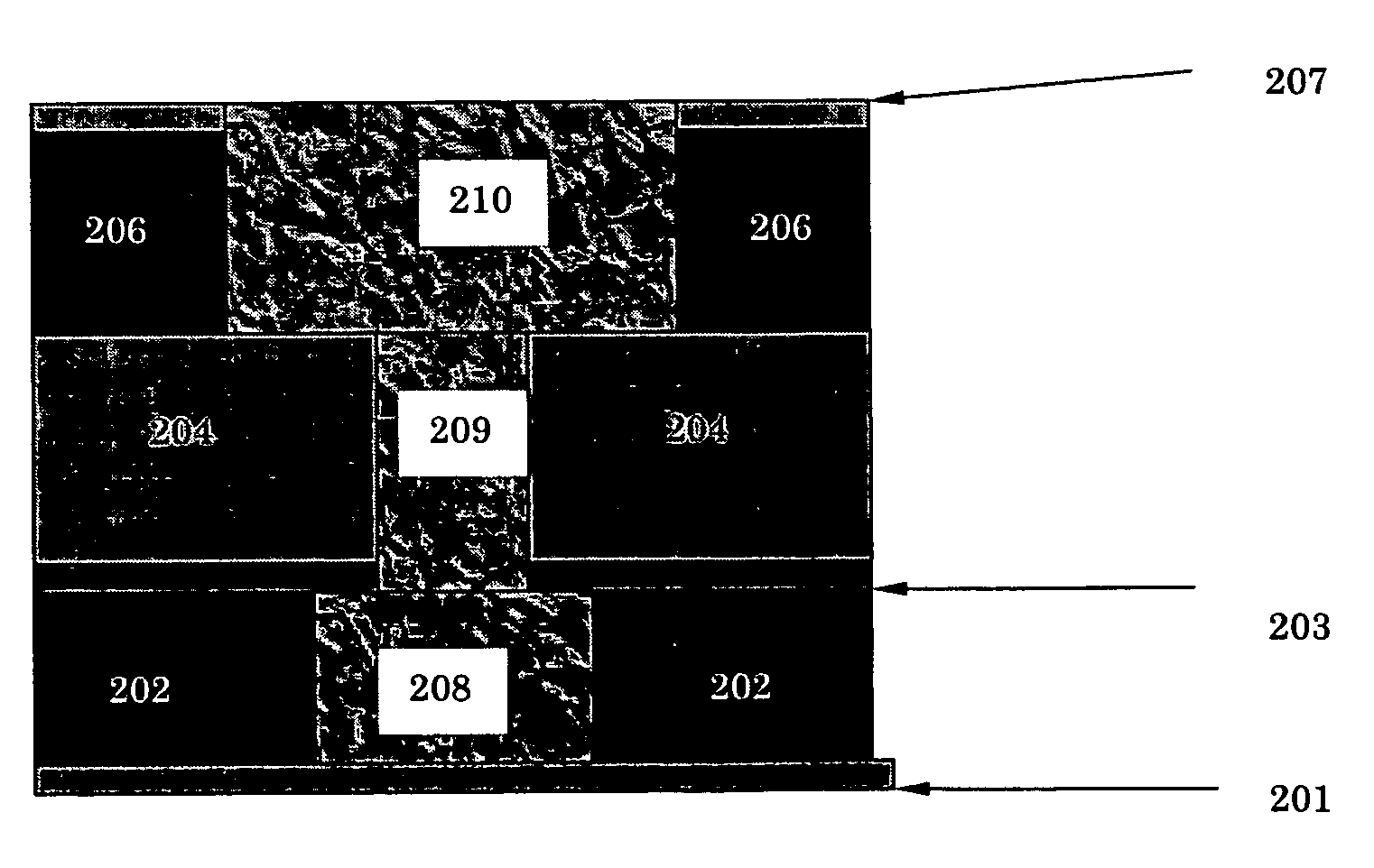
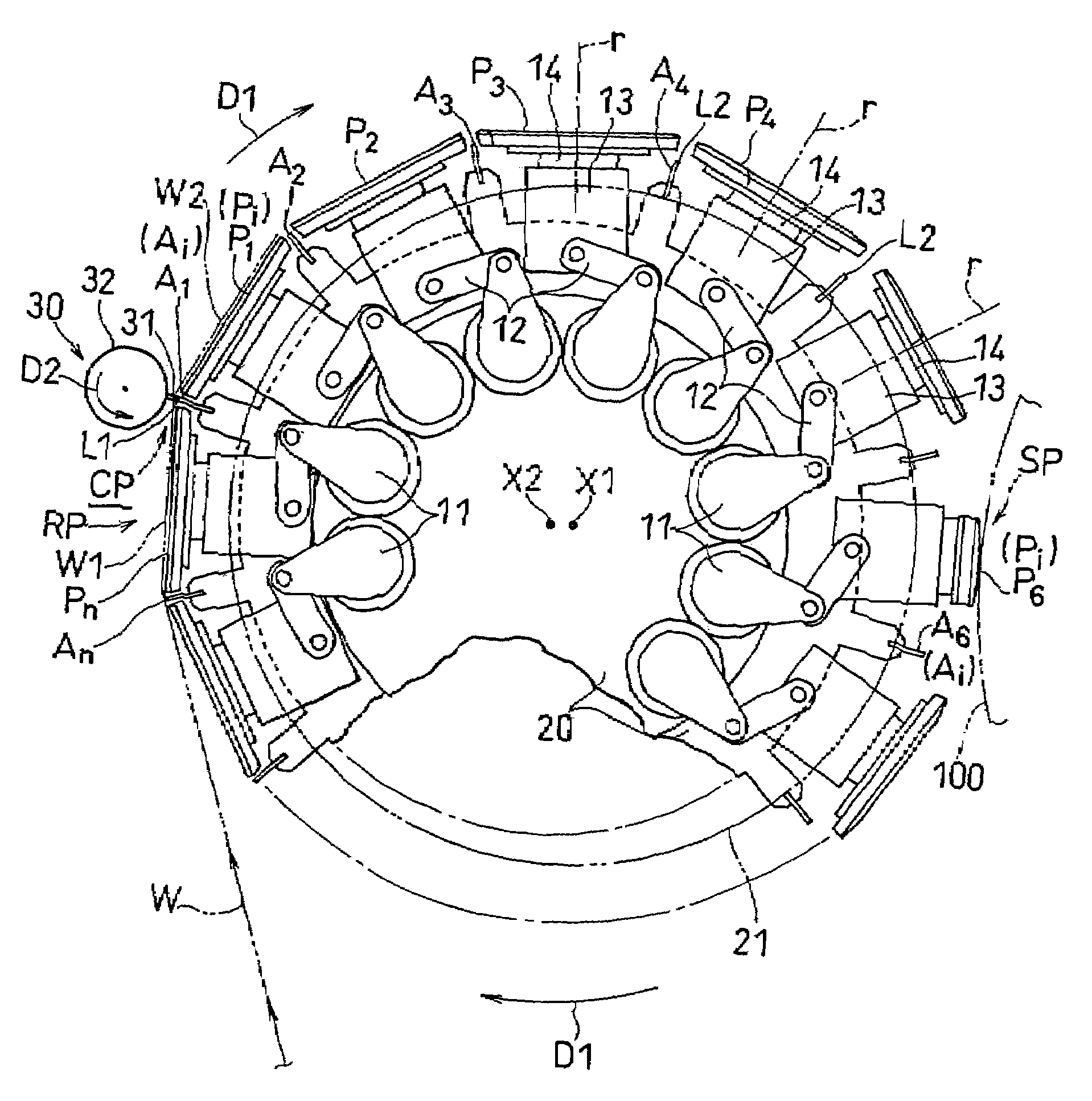
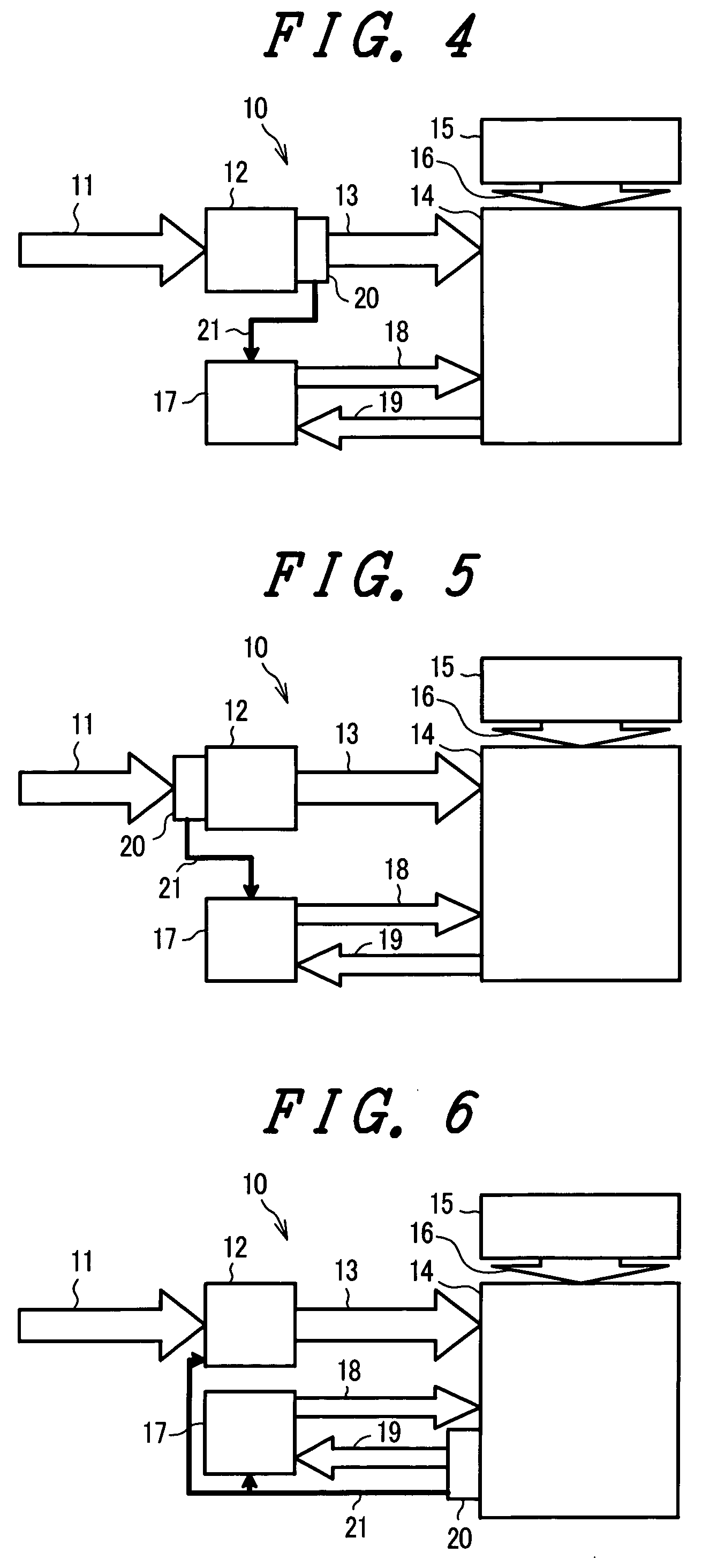
Web processing device and web processing method
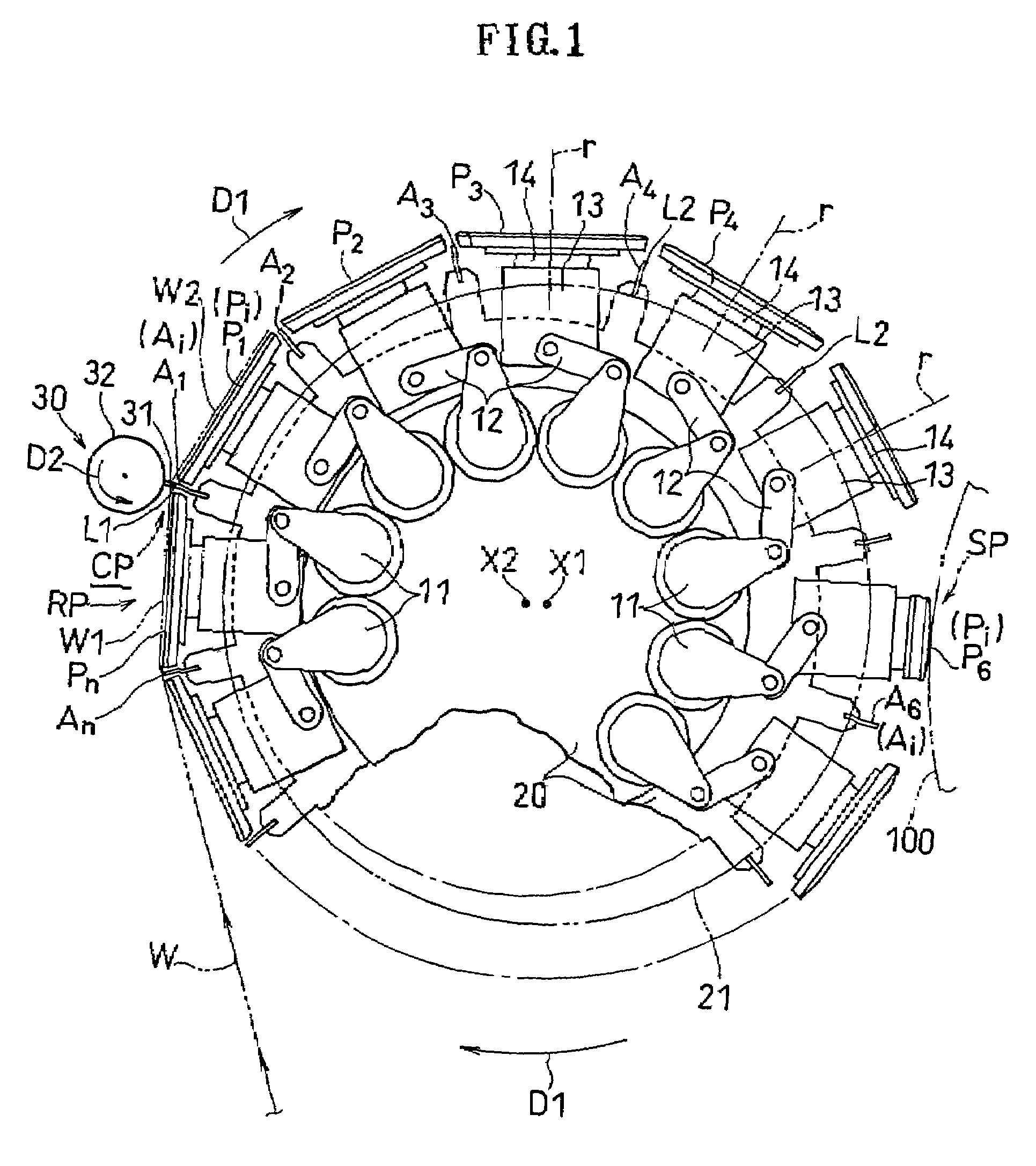
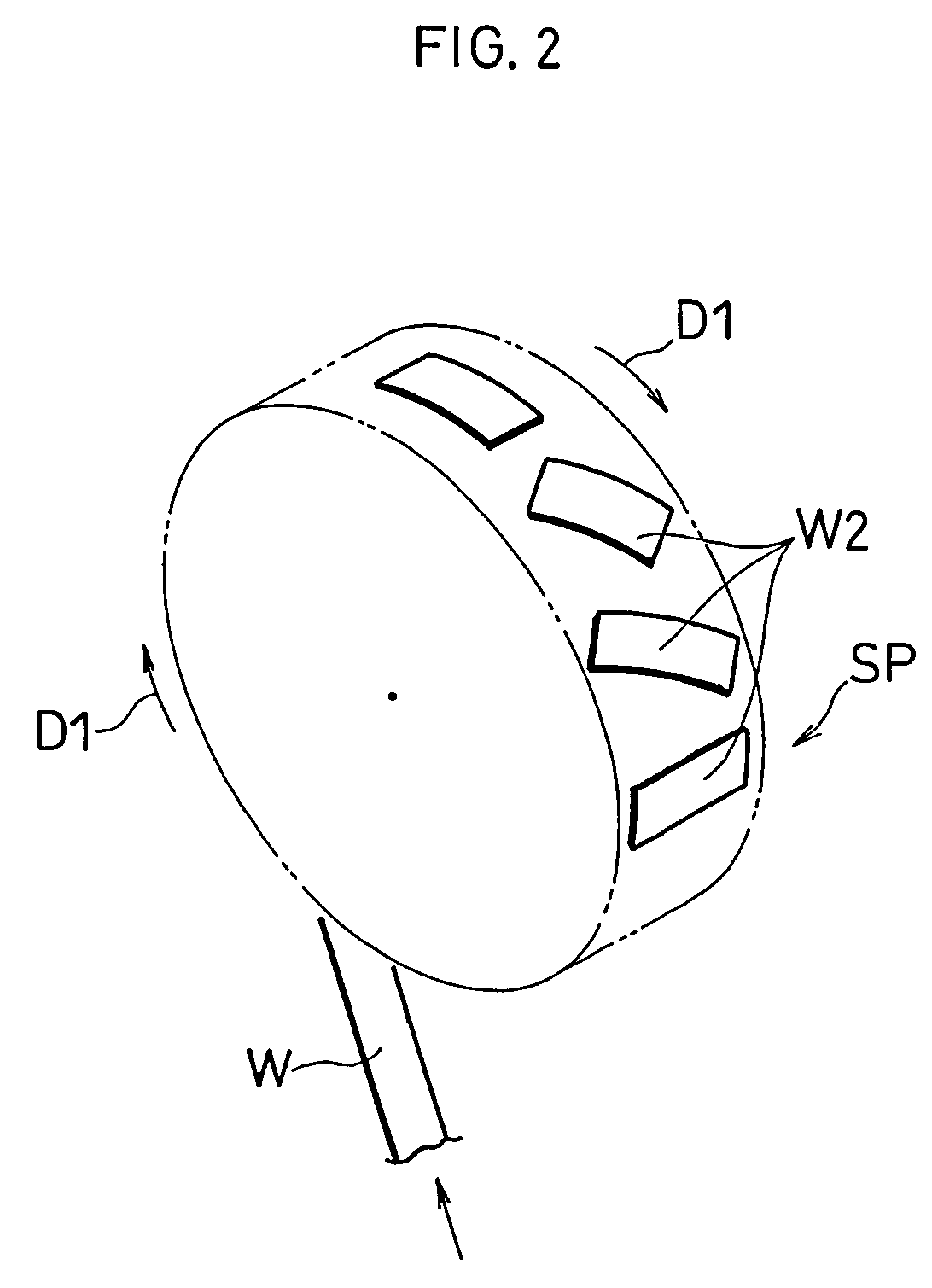
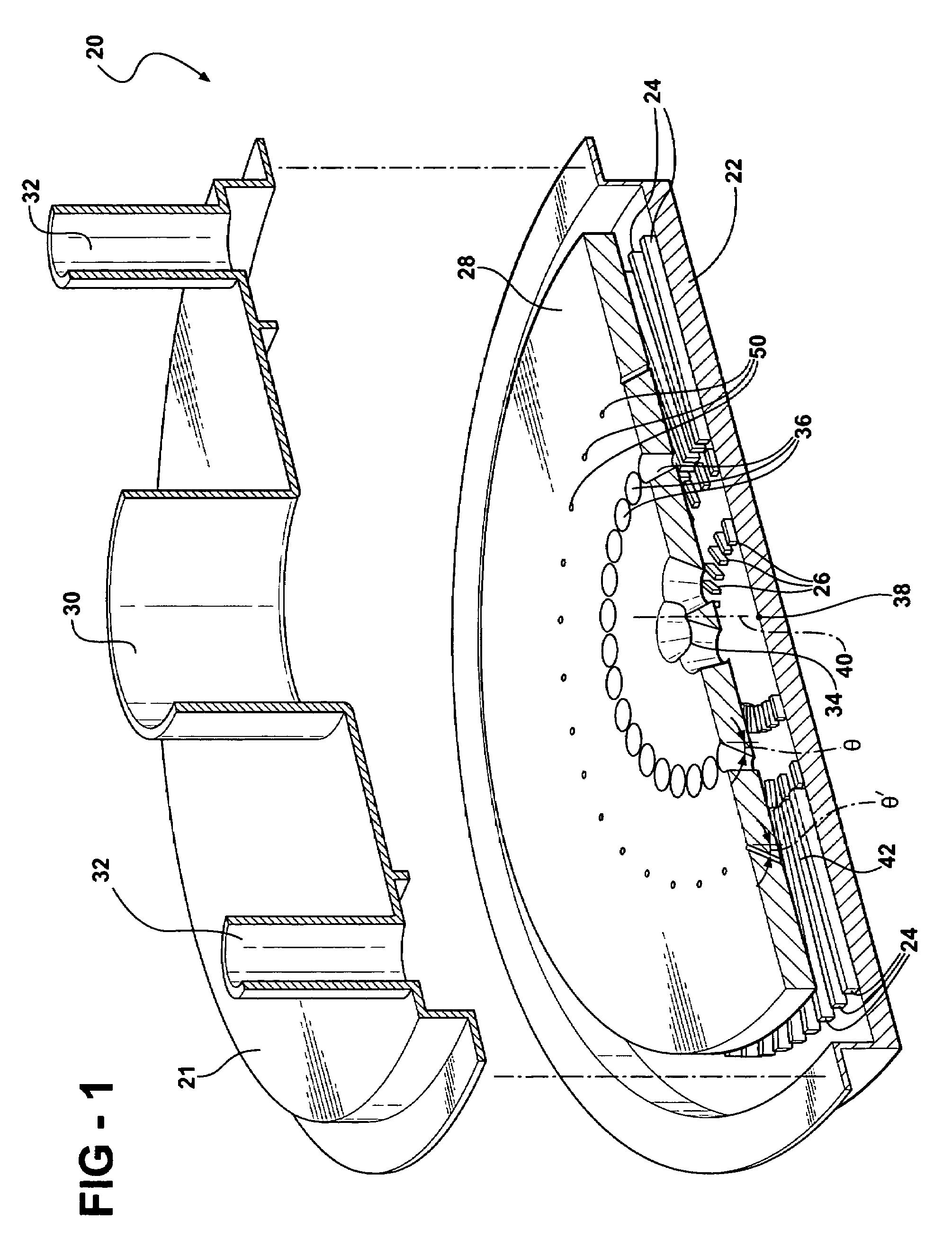
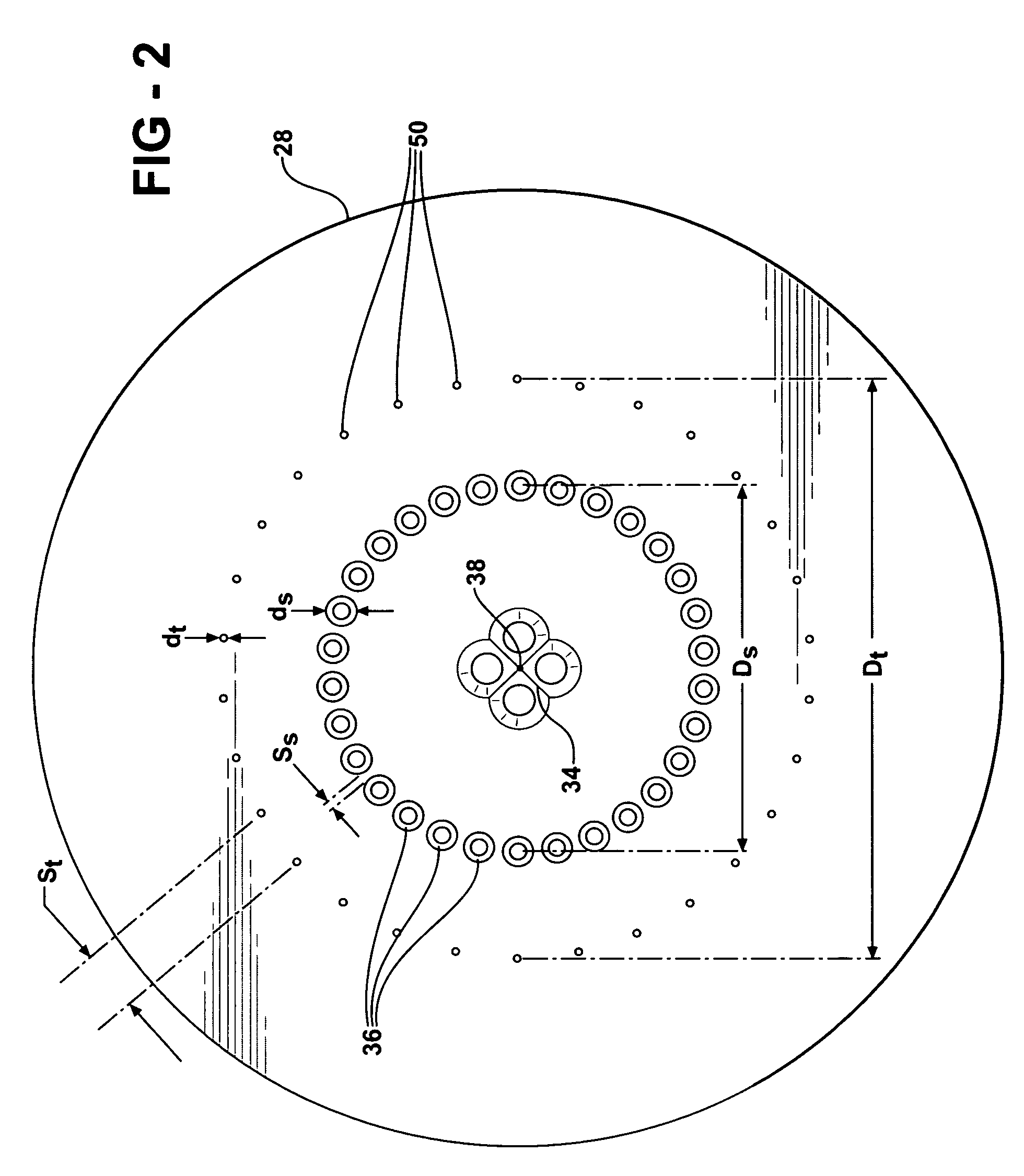
ActiveUS7587966B2Reduced life-timeInhibit attitude changesRegistering devicesStock shearing machinesEngineeringMechanical engineering
The present invention relates to a web processing device, comprising a plurality of pads Pi revolving around a axis X1, a cutter 30 for cutting a continuous web W, and a plurality of anvils Ai for receiving the cutter 30. The pads Pi receive the continuous web W, and the cutter 30 cuts the continuous web W into a cut-off web W2 together with the anvil Ai positioned at a first relative level L1. The pad Pi revolves around the axis X1 while changing an attitude of the pad Pi by turning about a line extending from the first axis toward the pad Pi, thereby carrying the cut-off web W2 while changing an attitude of the cut-off web W2. When the pad Pi changes its attitude, the anvil Ai relatively moves to a second relative level L2 so as not to hinder the pad Pi changing its attitude.
Owner:ZUIKO CORP
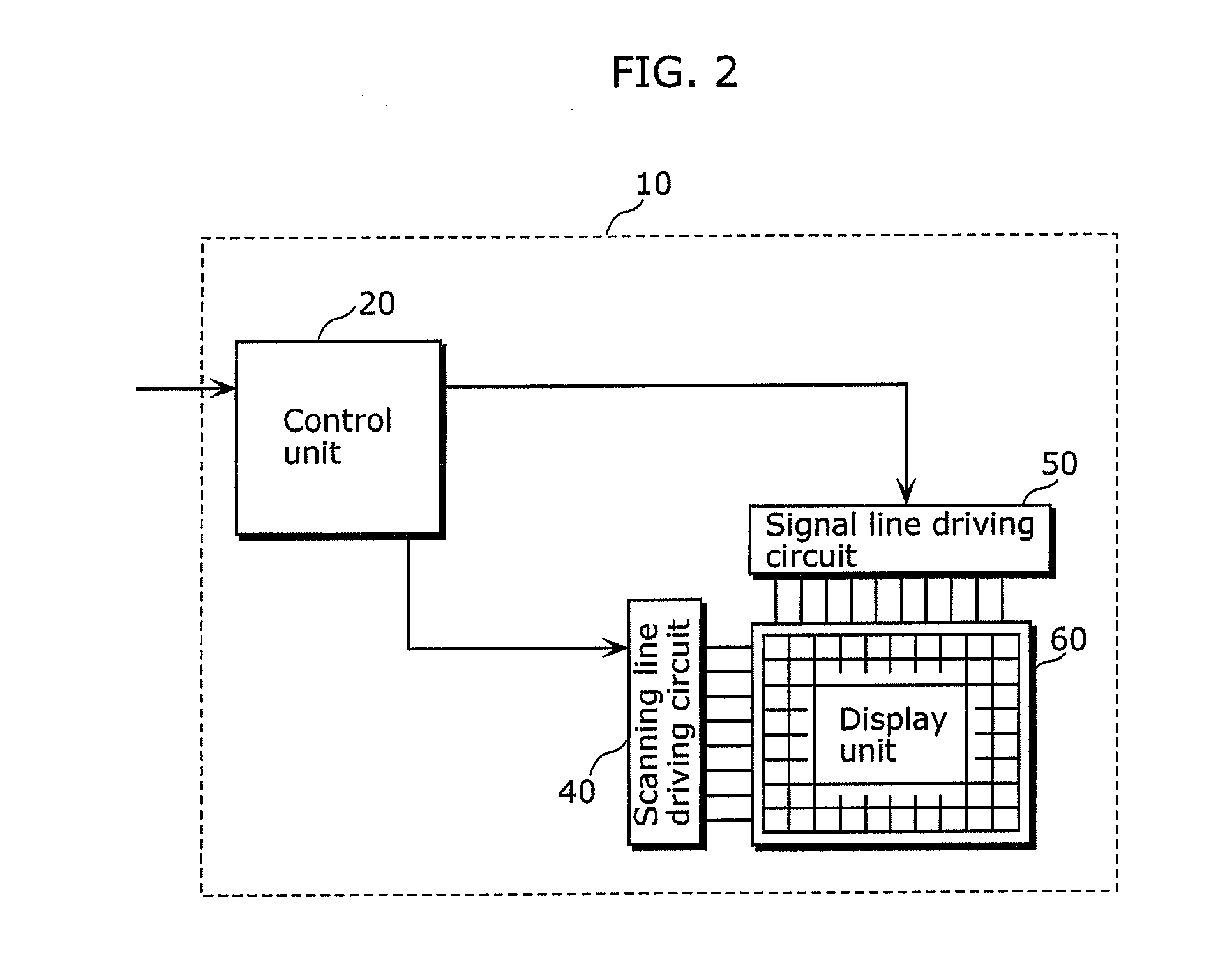
Display device and the driving method of the same
ActiveUS20060066533A1Restrict power consumptionProlonged life timeElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesPower circuitsEngineering
A plurality of organic EL elements which are arranged on a display panel lowers the brightness along with a lapse of light emitting time and hence, the power consumption is increased to maintain the brightness. However, the increase of the power consumption shortens a lifetime of the organic EL elements. To overcome this drawback, a power supply circuit which drives the display panel has a function of controlling an electric power supplied to the display panel to a fixed value or less in response to a detection signal from a detection part which detects a cathode current of the organic EL elements.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD +1
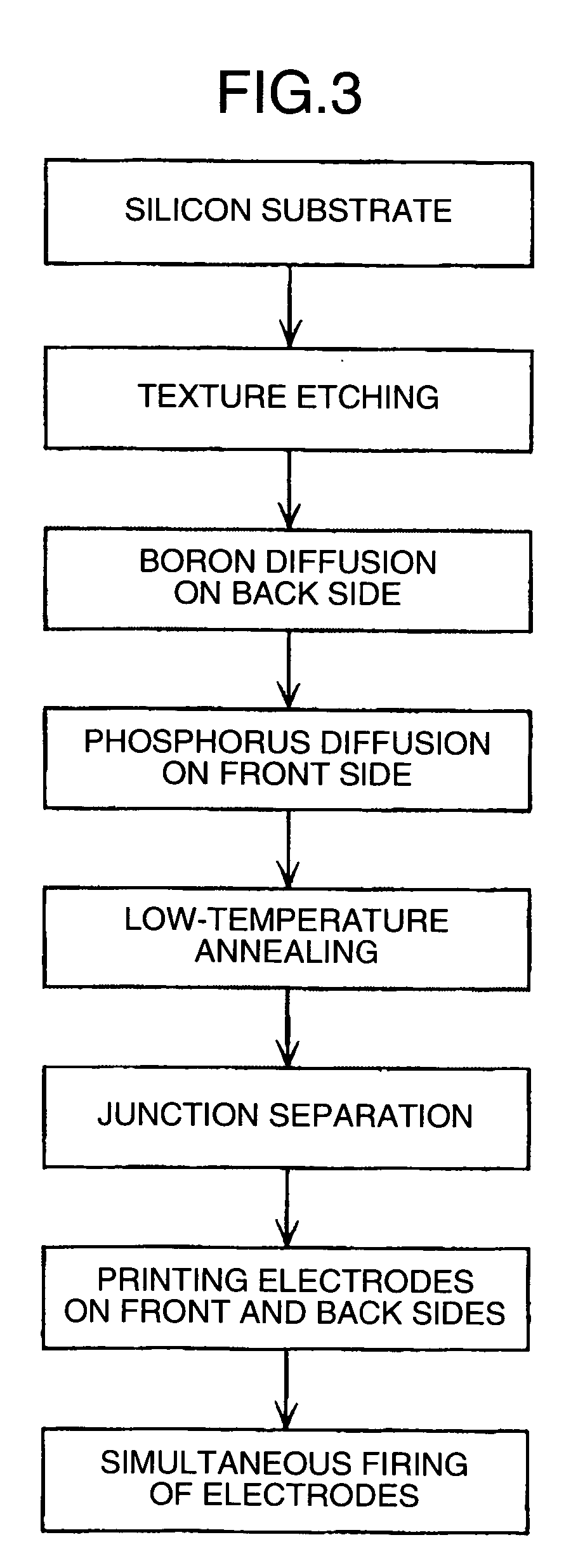
Silicon solar cell and production method thereof
InactiveUS20050133084A1Reduce life timeReduces its bulk effective life timePV power plantsSolid-state devicesBoron diffusionPeak value
It is an object of the present invention to provide a silicon solar cell with n+pp+ BSF structure using solar grade silicon substrate, having a life time close to the initial level of the substrate. The solar cell of the present invention is produced by a back side boron diffusion step for diffusing boron on a back side of the substrate, a front side phosphorus diffusion step for diffusing phosphorus on a front side of the substrate, a low-temperature annealing step for annealing the substrate at 600° C. or lower for 1 hour or more, and an electrode firing step carried out at a peak temperature of 700° C. or lower for 1 minute or less, carried out in this order.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
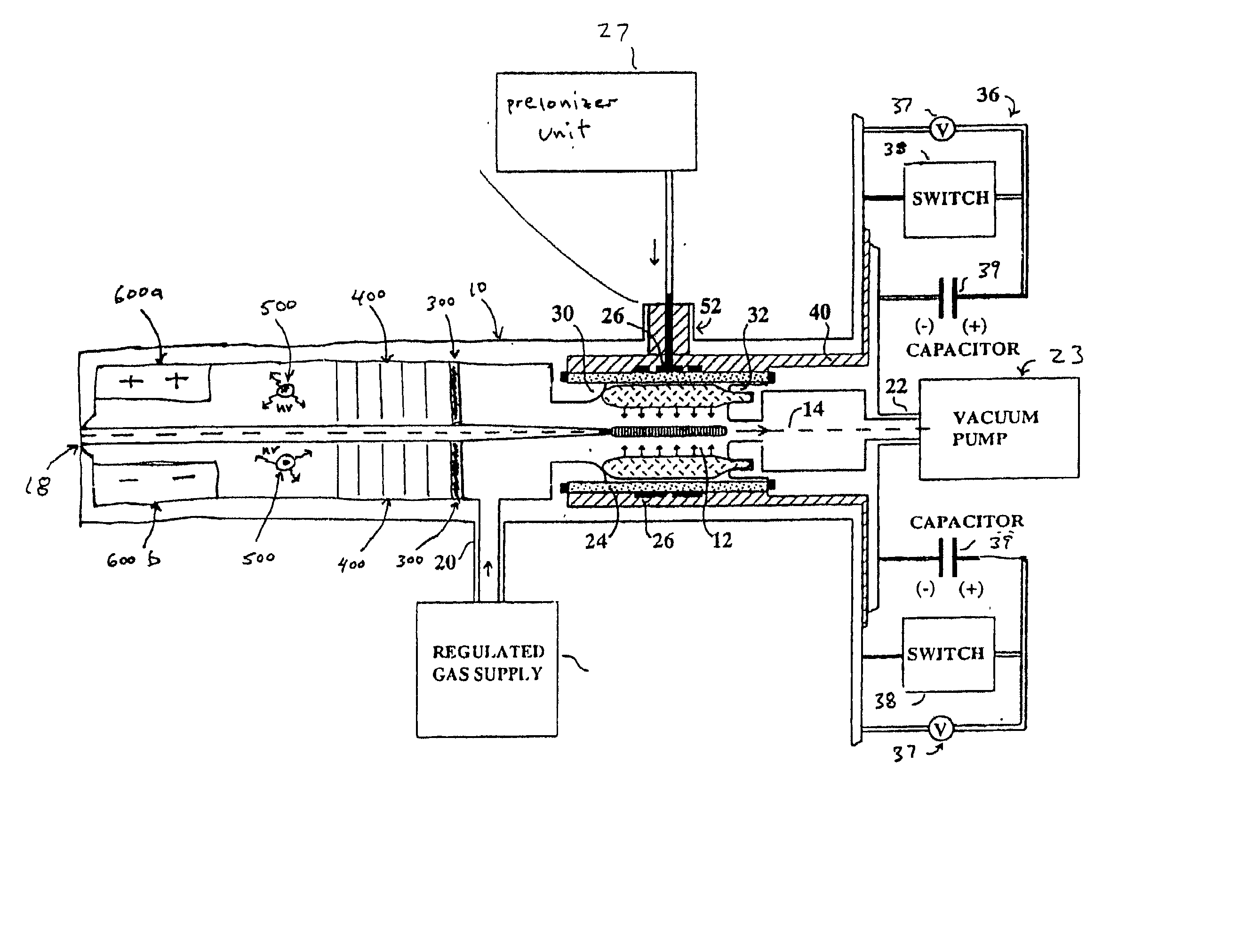
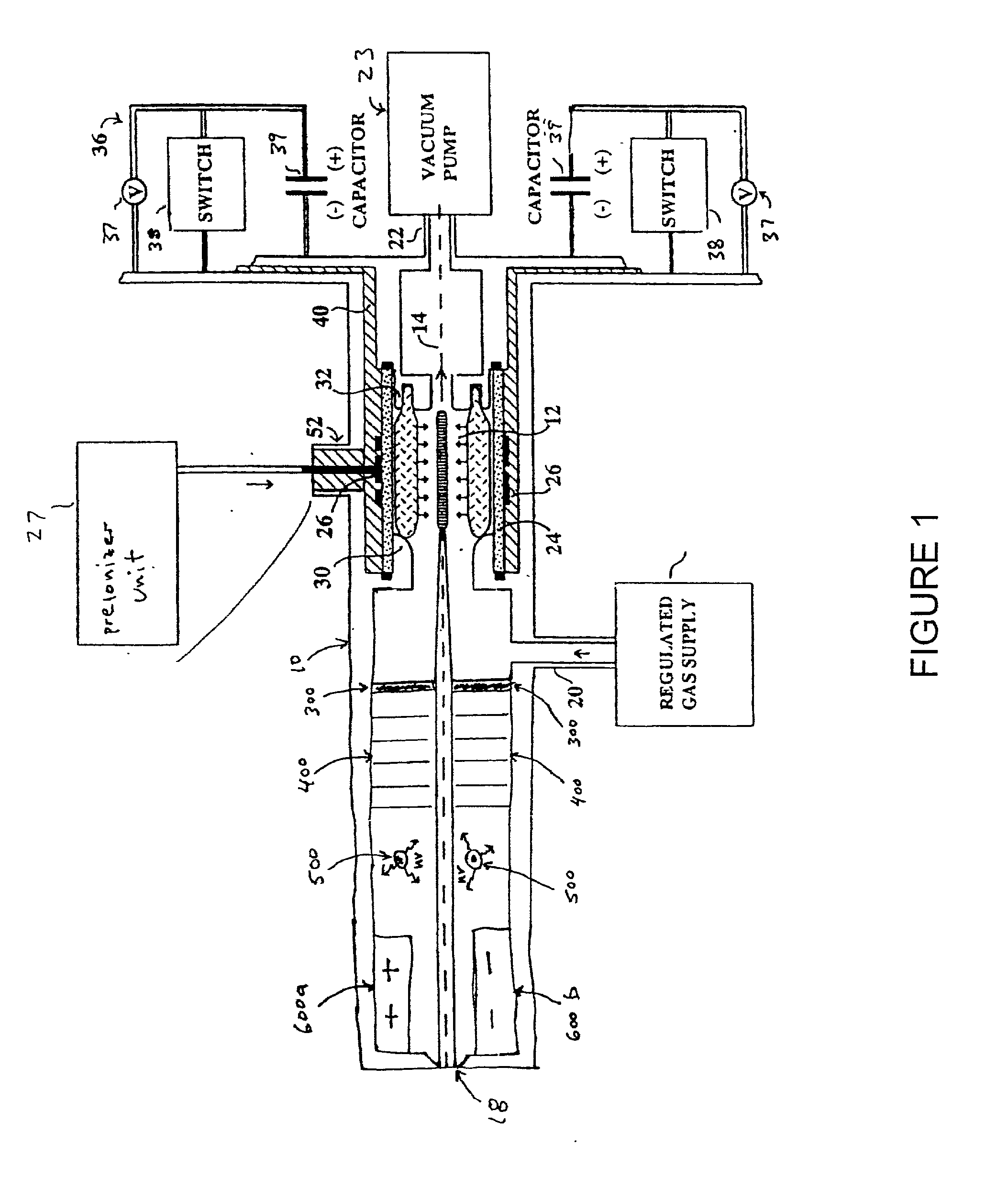
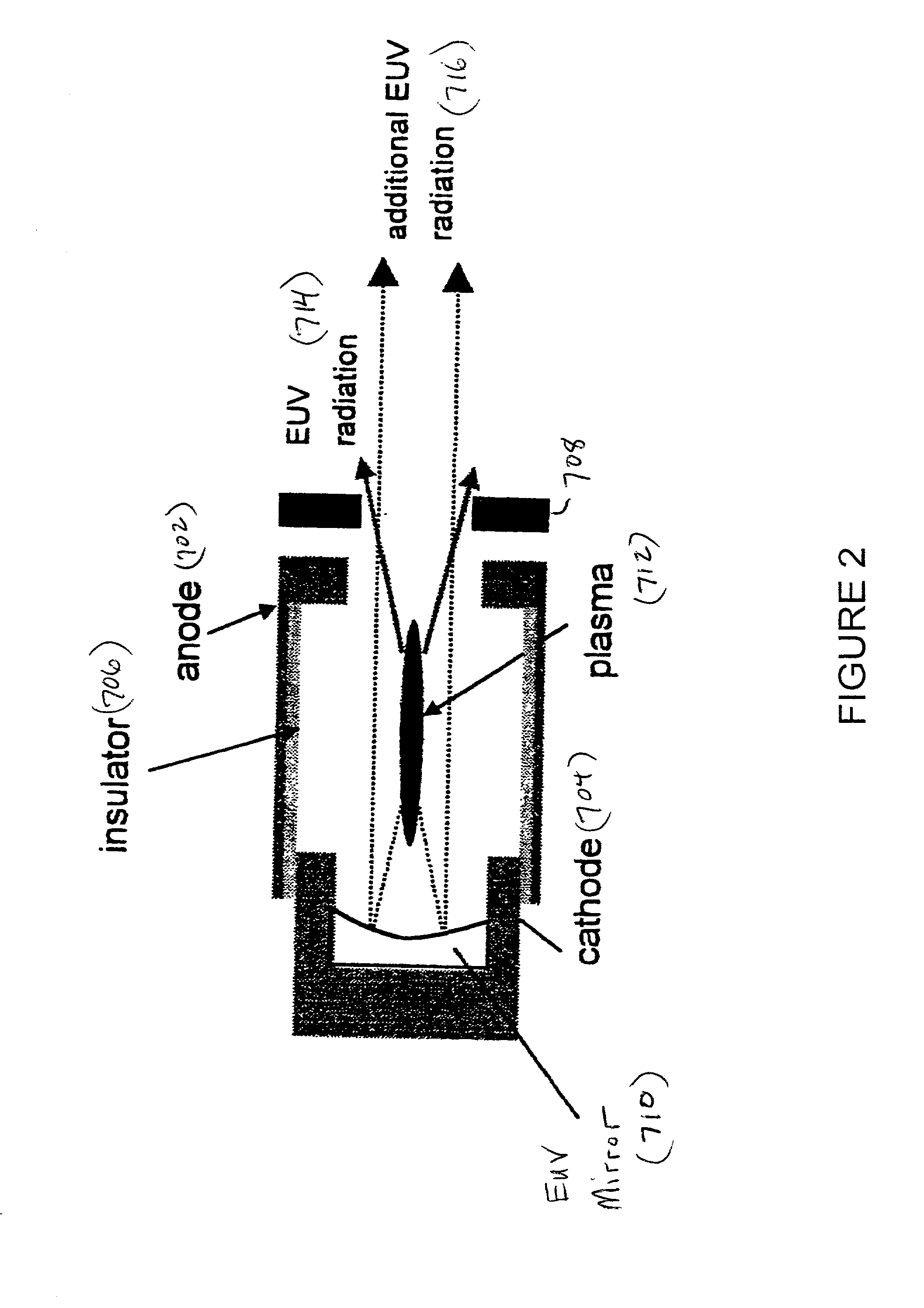
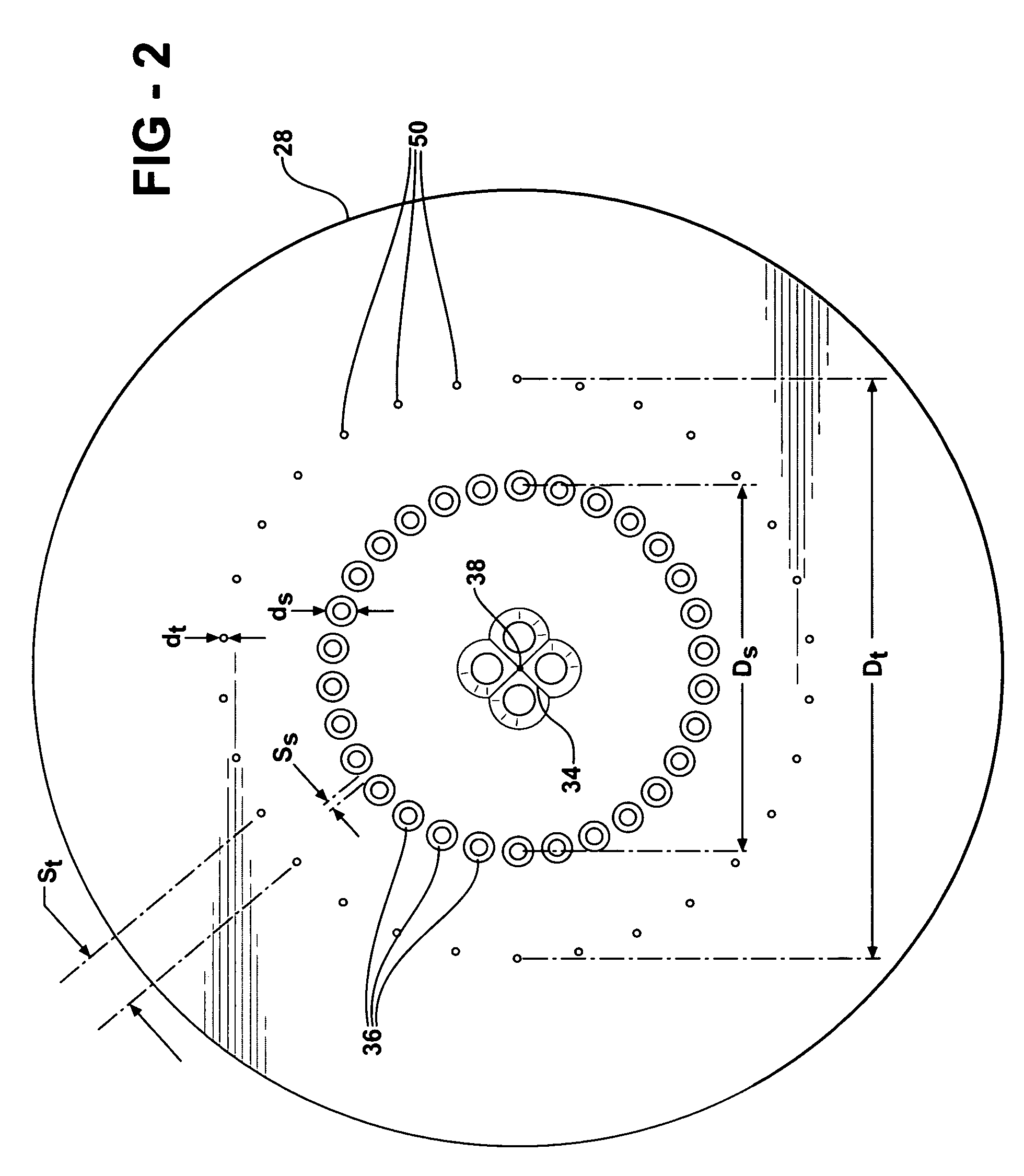
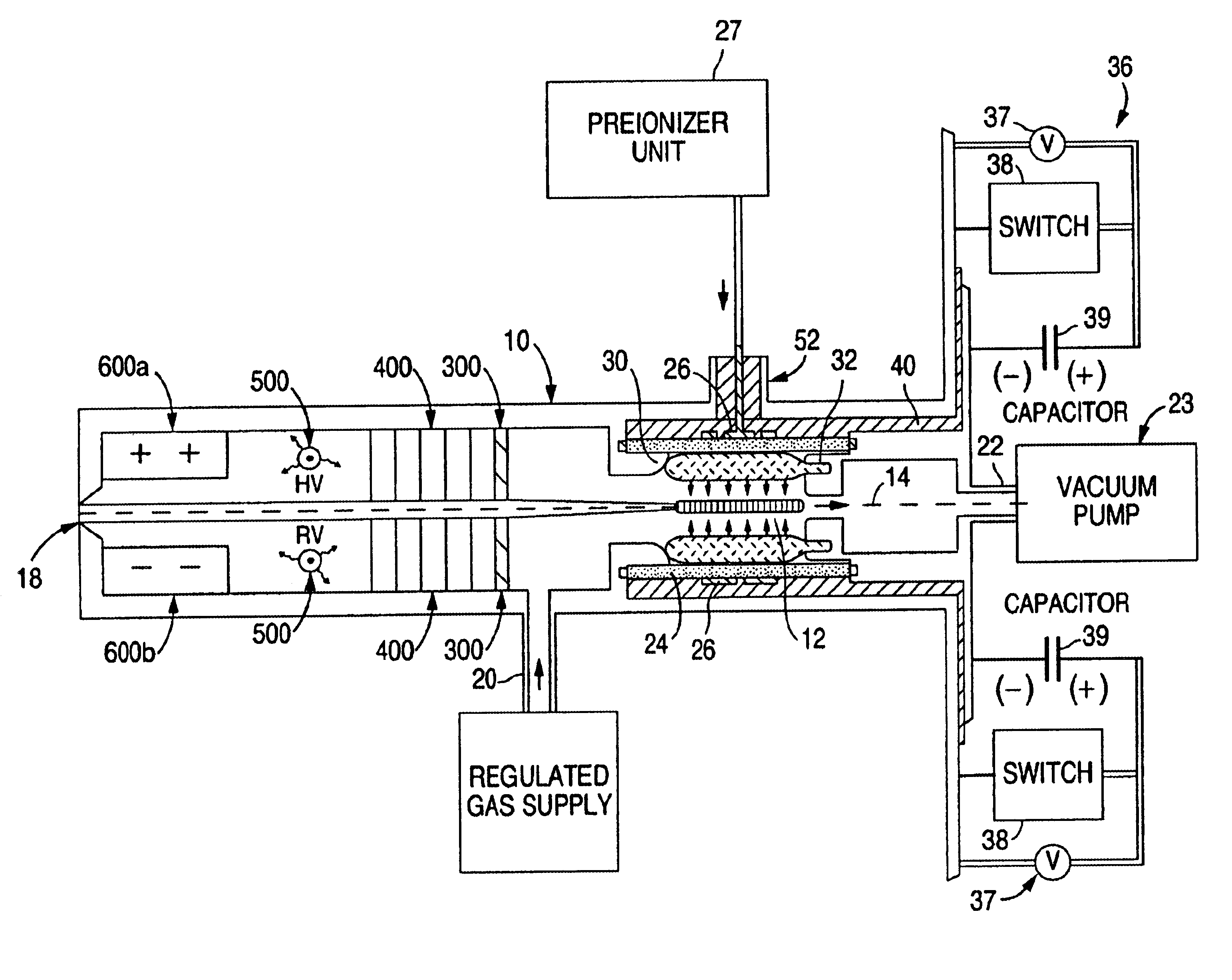
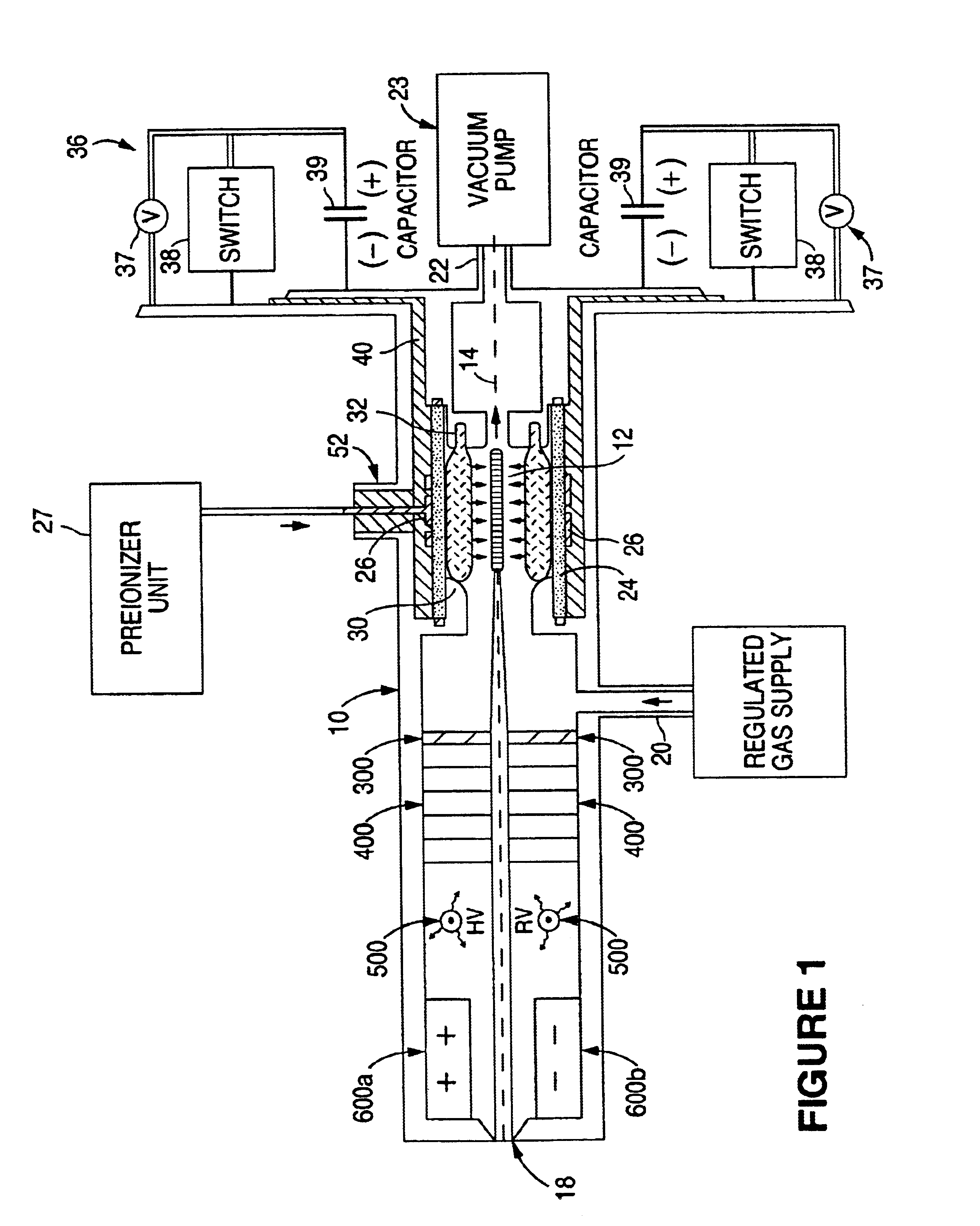
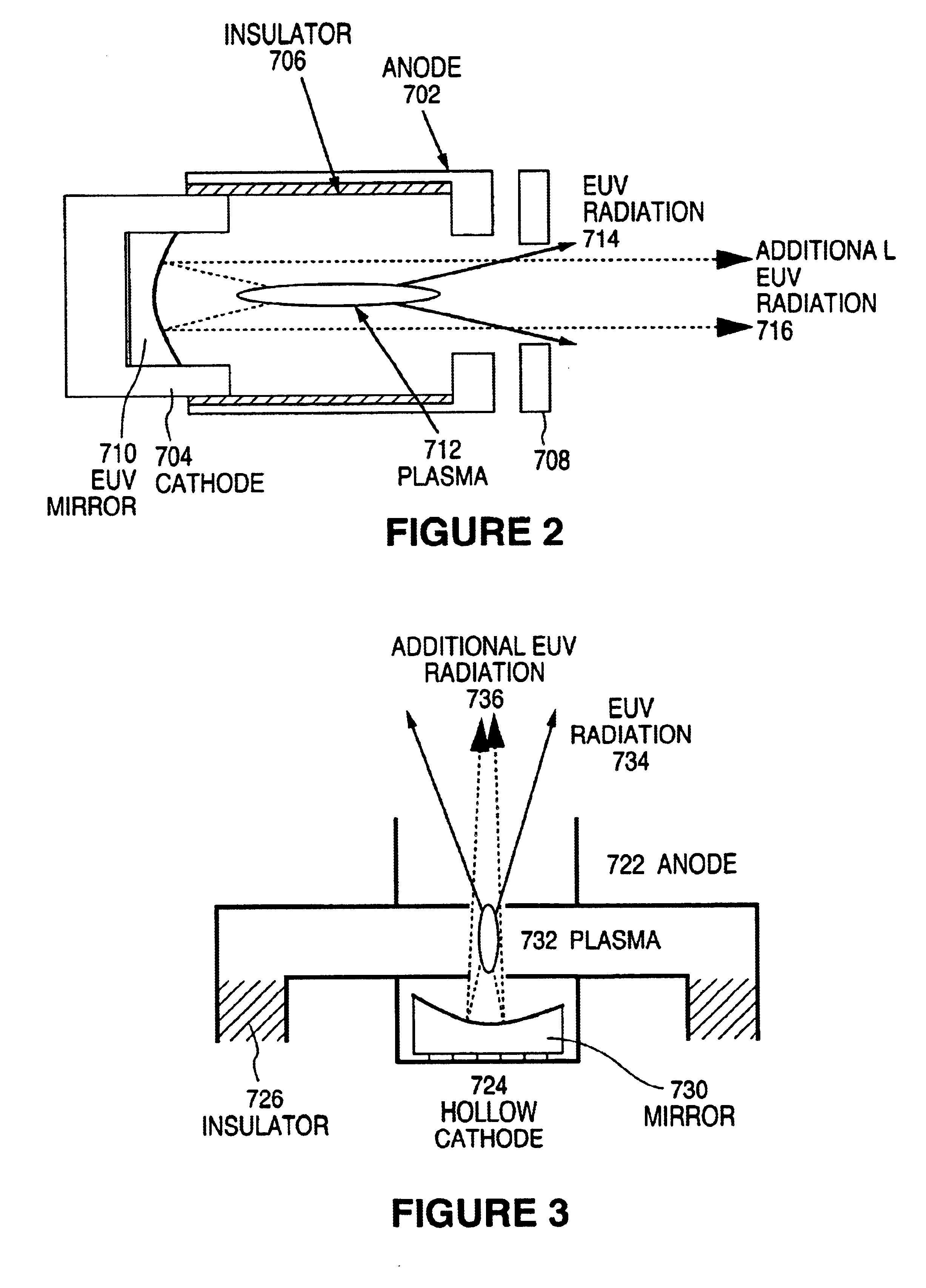
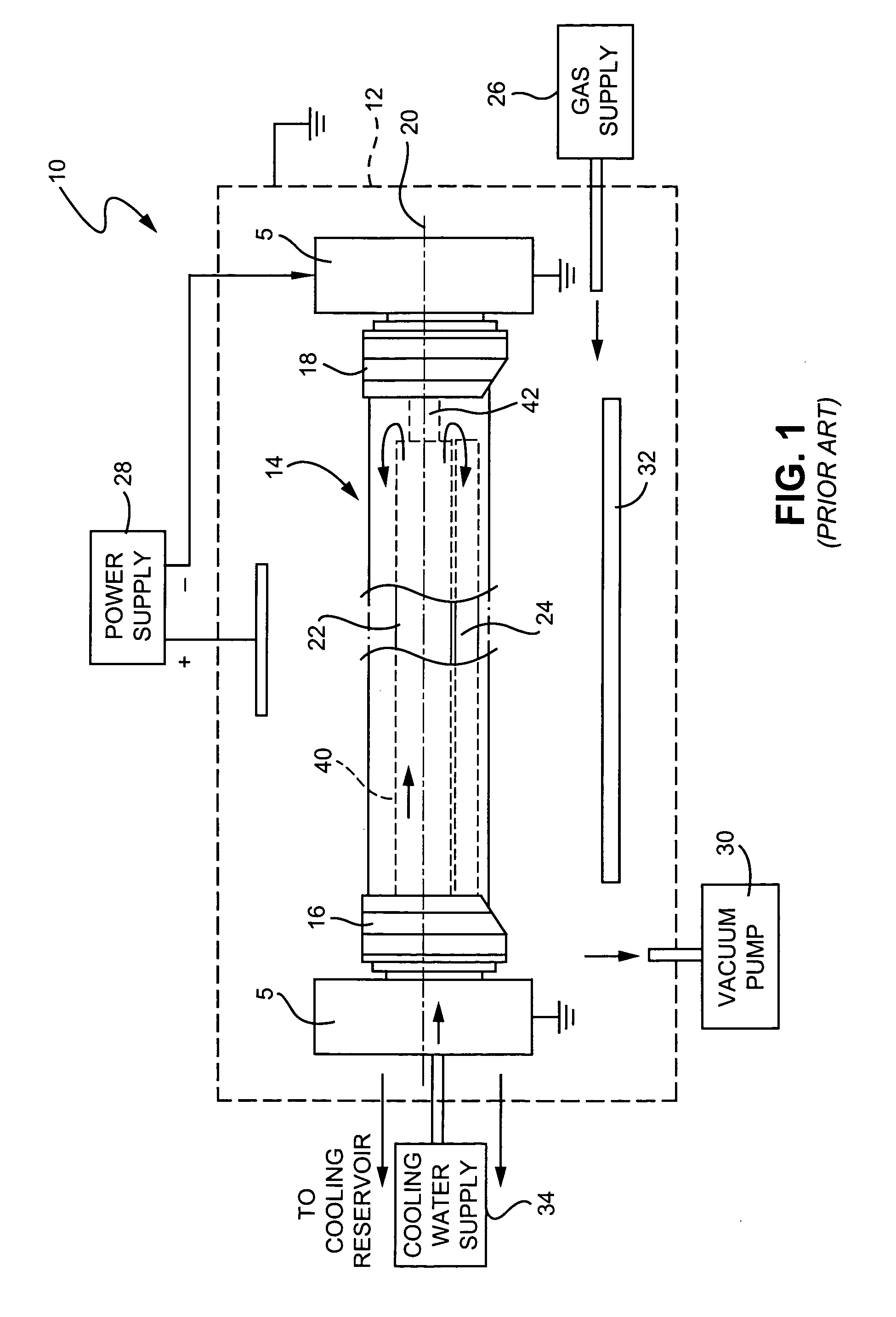
Method and apparatus for generating high output power gas discharge based source of extreme ultraviolet radiation and/or soft x-rays
InactiveUS20020168049A1Avoid reflectionsReduce reflectionRadiation/particle handlingNanoinformaticsSoft x rayUltraviolet radiation
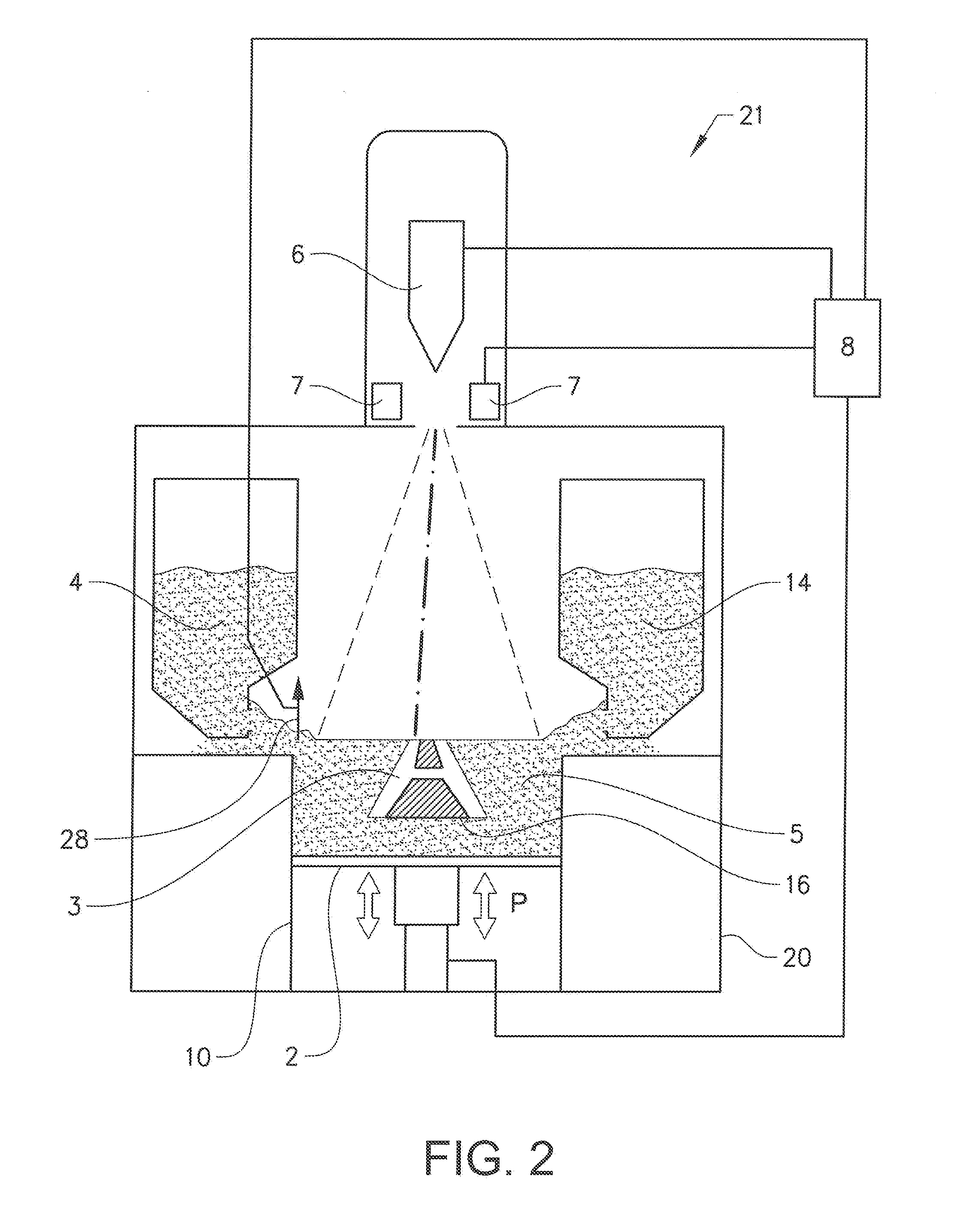
An EUV photon source includes a plasma chamber filled with a gas mixture, multiple electrodes within the plasma chamber defining a plasma region and a central axis, a power supply circuit connected to the electrodes for delivering a main pulse to the electrodes for energizing the plasma around the central axis to produce an EUV beam output along the central axis, and a preionizer for ionizing the gas mixture in preparing to form a dense plasma around the central axis upon application of the main pulse from the power supply circuit to the electrodes. The EUV source preferably includes an ionizing unit and precipitator for collecting contaminant particulates from the output beam path. A set of baffles may be disposed along the beam path outside of the pinch region to diffuse gaseous and contaminant particulate flow emanating from the pinch region and to absorb or reflect acoustic waves emanating from the pinch region away from the pinch region. A clipping aperture, preferably formed of ceramic and / or Al2O3, for at least partially defining an acceptance angle of the EUV beam. The power supply circuit may generates the main pulse and a relatively low energy prepulse for homogenizing the preionized plasma prior to the main pulse. A multi-layer EUV mirror is preferably disposed opposite a beam output side of the pinch region for reflecting radiation along the central axis for output along the beam path of the EUV beam. The EUV mirror preferably has a curved contour for substantially collimating or focusing the reflected radiation. In particular, the EUV mirror may preferably have a hyperbolic contour.
Owner:USHIO DENKI KK
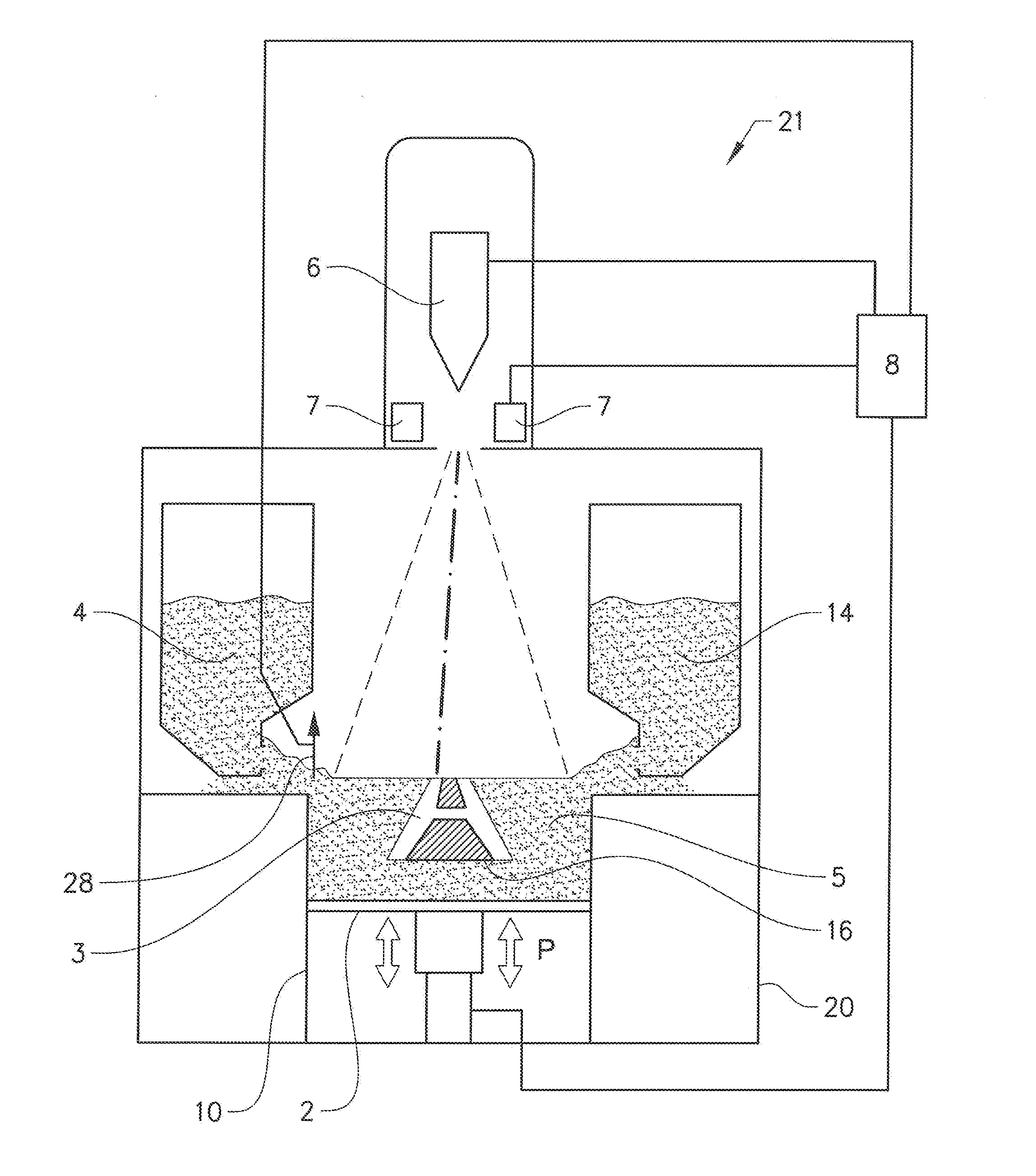
Method and apparatus for forming a three-dimensional article
ActiveUS20140314609A1Improve compactionIncrease flexibilityAdditive manufacturing apparatusElectric discharge tubesMetallurgyDistributor
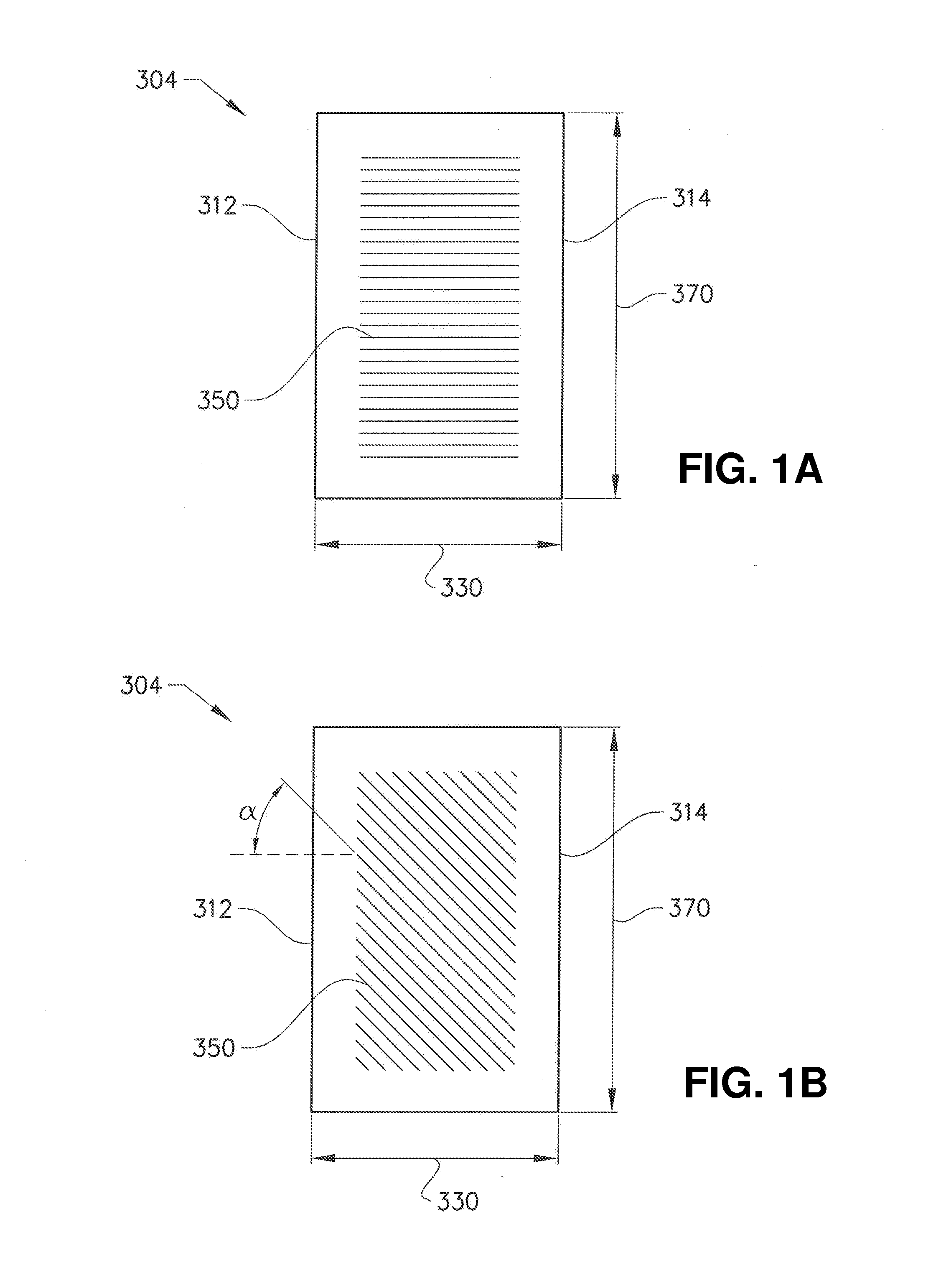
An apparatus for forming at least one three-dimensional article by fusing parts of a powder bed layer-wise. The apparatus comprising a powder distributor and an energy beam for fusing the powder layer. Said powder distributor comprises a first part being an elongated rod provided movable at a predetermined distance above the powder bed and with its central axis in parallel with a top surface of said work table and second part being a metal foil having at least a first and a second opposite edge portions. Said metal foil is provided between said elongated rod and said work table, said first and second opposite edge portions are attached to said elongated rod so that a distance between said first and second edge portions is smaller than the distance between said first and second edge portions of said metal foil when said metal foil is in a flat position.
Owner:ARCAM AB
High spatial resolution imaging of a structure of interest in a specimen
ActiveUS20090134342A1Reduces yield of fluorescent lightHigh resolutionMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationSensor arrayFluorescence
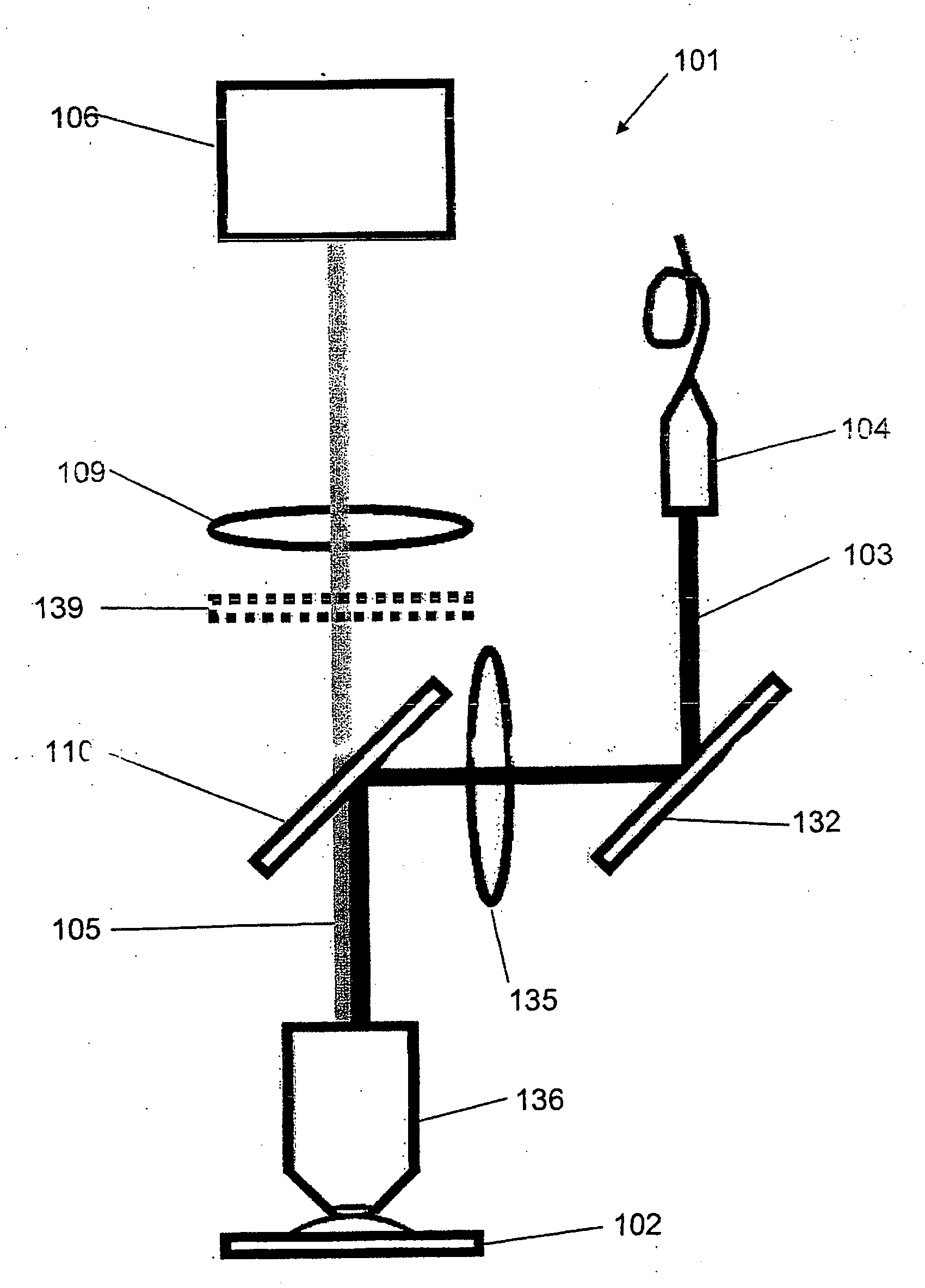
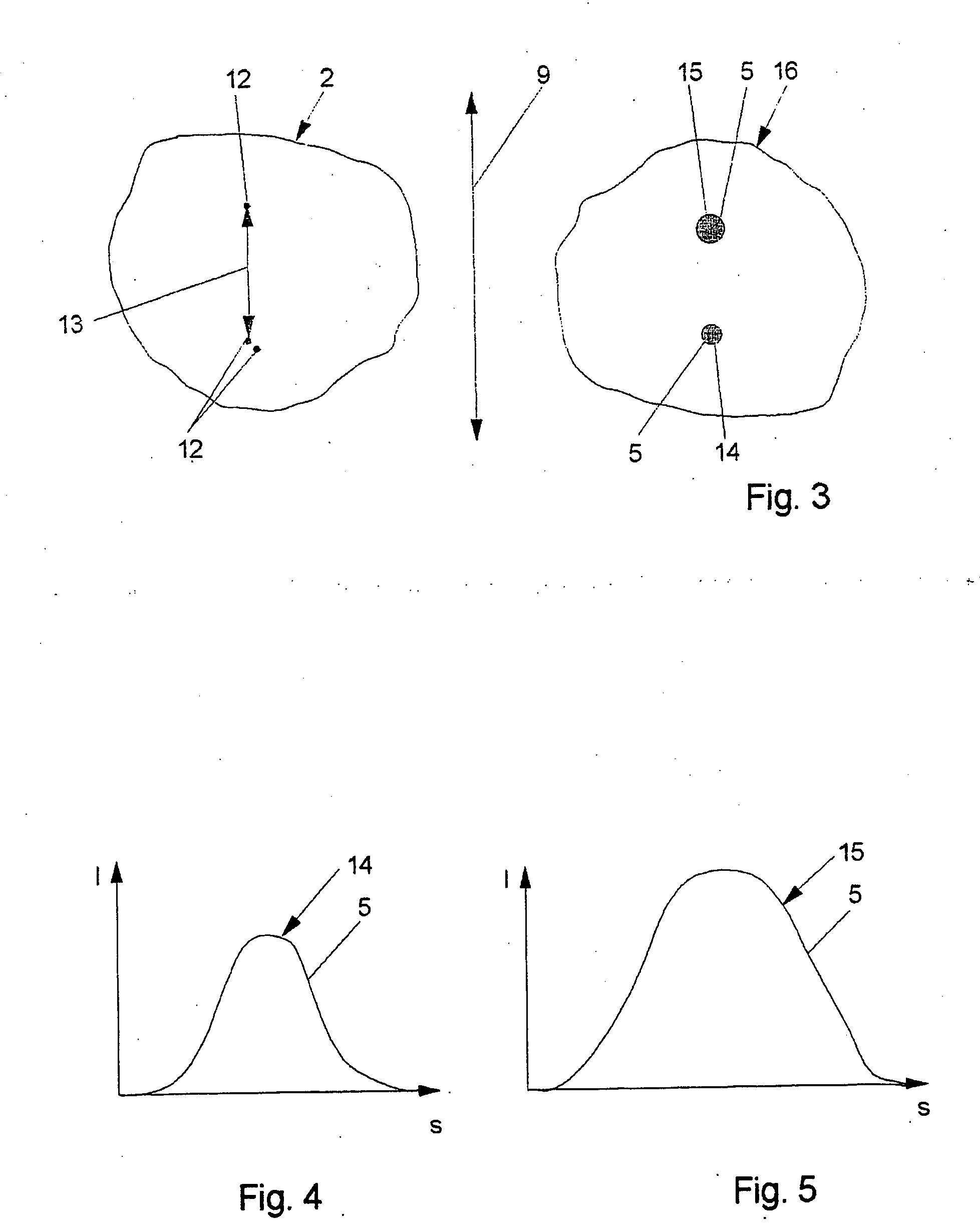
For the high spatial resolution imaging of a structure of interest in a specimen, a substance is selected from a group of substances which have a fluorescent first state and a nonfluorescent second state; which can be converted fractionally from their first state into their second state by light which excites them into fluorescence, and which return from their second state into their first state; the specimen's structure of interest is imaged onto a sensor array, a spatial resolution limit of the imaging being greater (i.e. worse) than an average spacing between closest neighboring molecules of the substance in the specimen; the specimen is exposed to light in a region which has dimensions larger than the spatial resolution limit, fractions of the substance alternately being excited by the light to emit fluorescent light and converted into their second state, and at least 10% of the molecules of the substance that are respectively in the first state lying at a distance from their closest neighboring molecules in the first state which is greater than the spatial resolution limit; and the fluorescent light, which is spontaneously emitted by the substance from the region, is registered in a plurality of images recorded by the sensor array during continued exposure of the specimen to the light.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Pt complexes as phosphorescent emitters in the fabrication of organic light emitting diodes
ActiveUS7002013B1Inhibit aggregationReduction of phosphorescence radiative lifetimeGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsGroup 1/11 element organic compoundsLight-emitting diodeCoordination complex
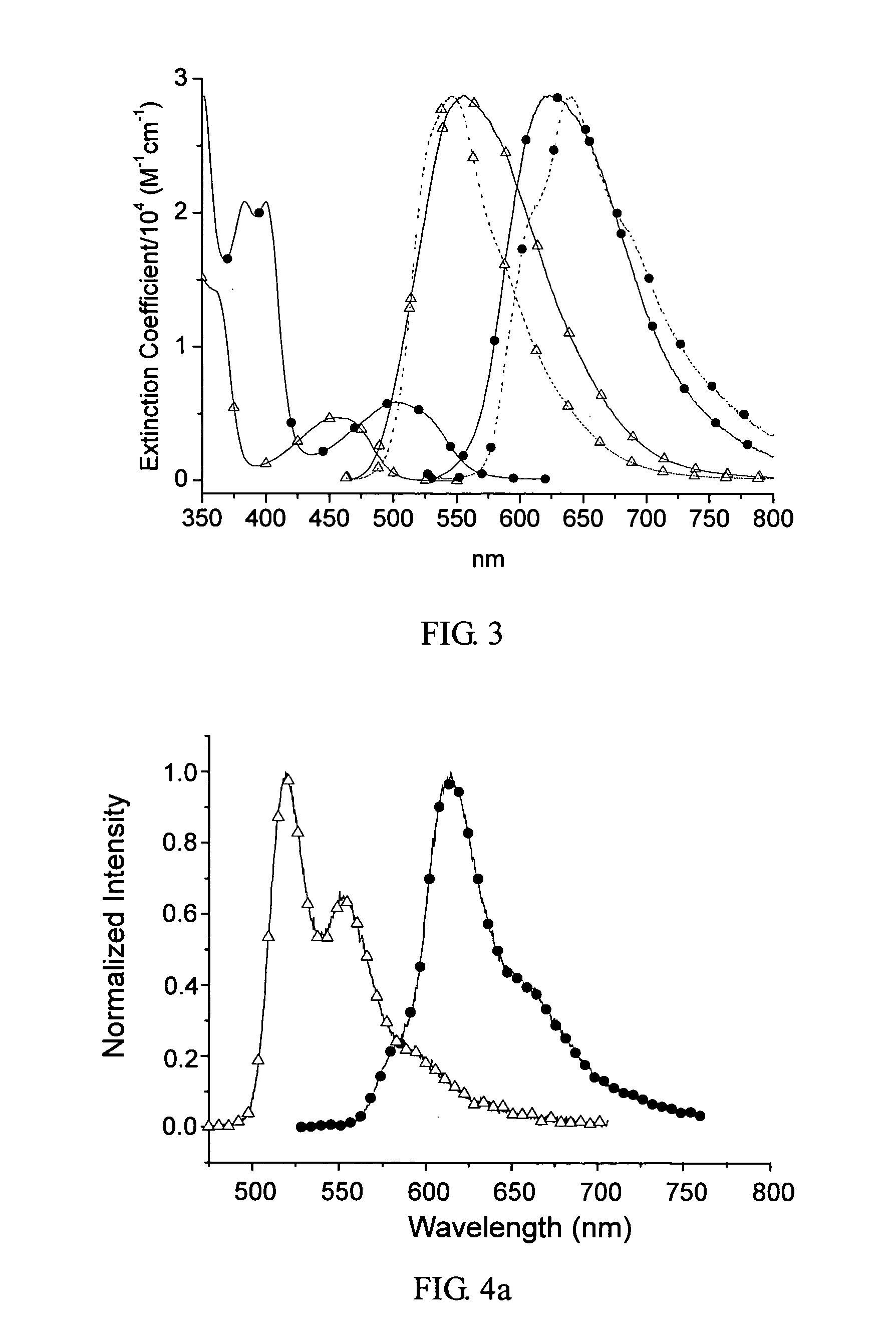
A series of Pt(II) complexes having the following formula are disclosed: X1 and X2 independently are C or N, X1 can also locate at another position of the hexagonal ring, when X1 is N;R1 is H, C1–C8 alkyl, or C1–C4 perfluoroalkyl, R2 is H, R1 and R2 together are C4–C8 alkylene, or R1 and R2 together are bridged carbocyclic C4–C12 alkylene, when X2 is C;R1 is H, C1–C8 alkyl, or C1–C4 perfluoroalkyl, and R2 is omitted, when X2 is N;R7 is H or methyl, and R8 is omitted, when X1 is N;R7 is H or methyl, R8 is H or methyl, or R7 and R8 together are when X1 is C.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
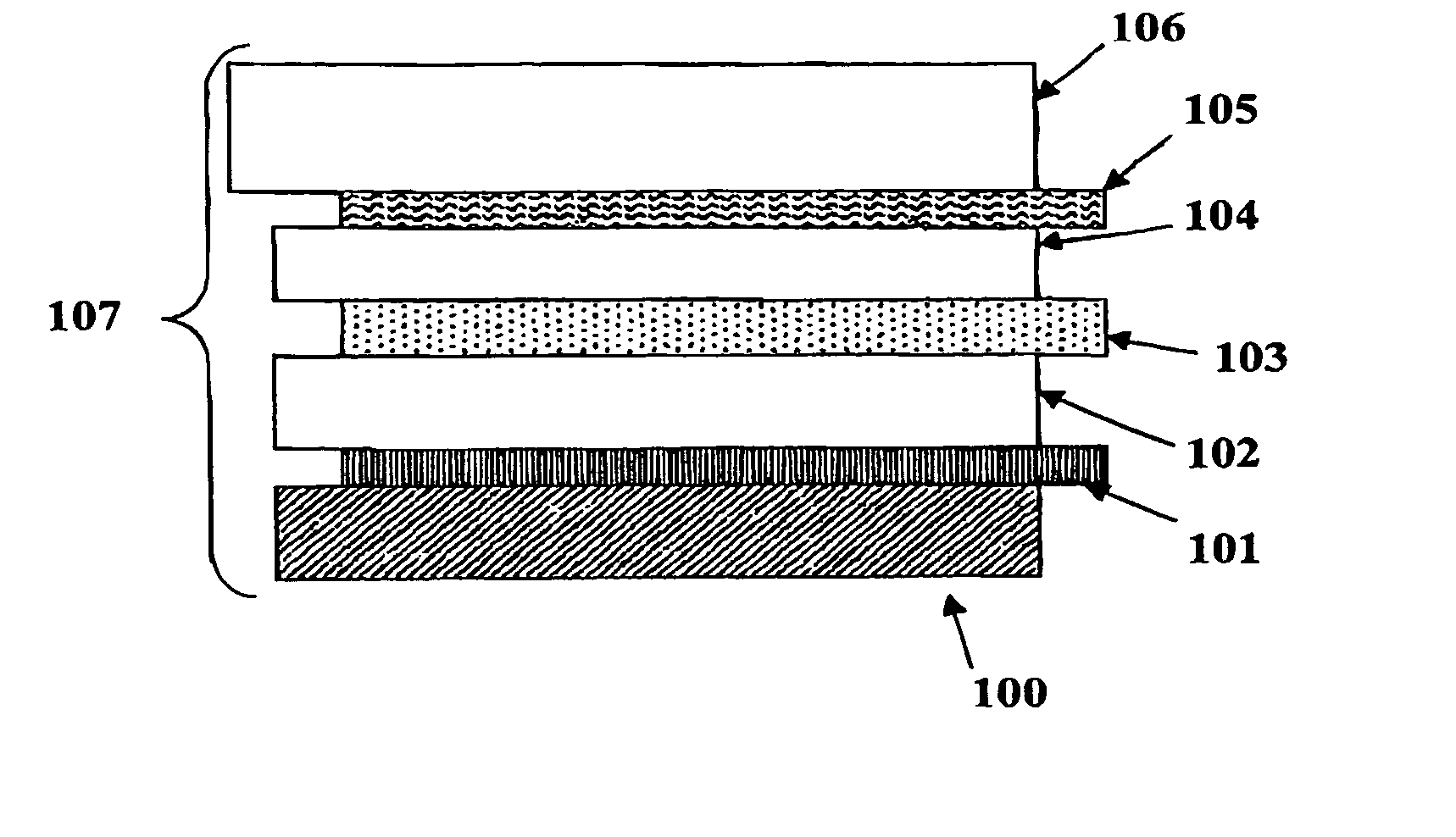
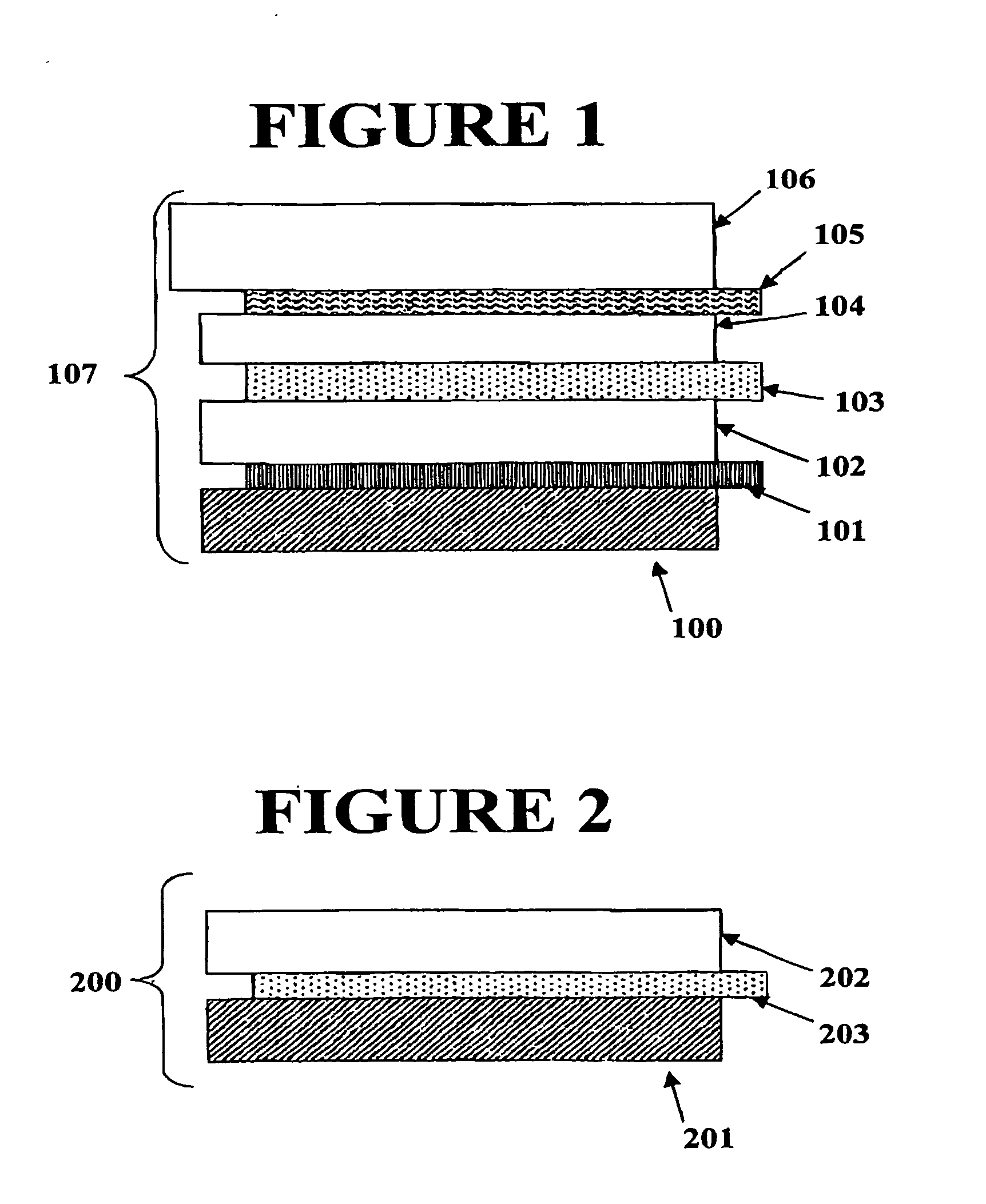
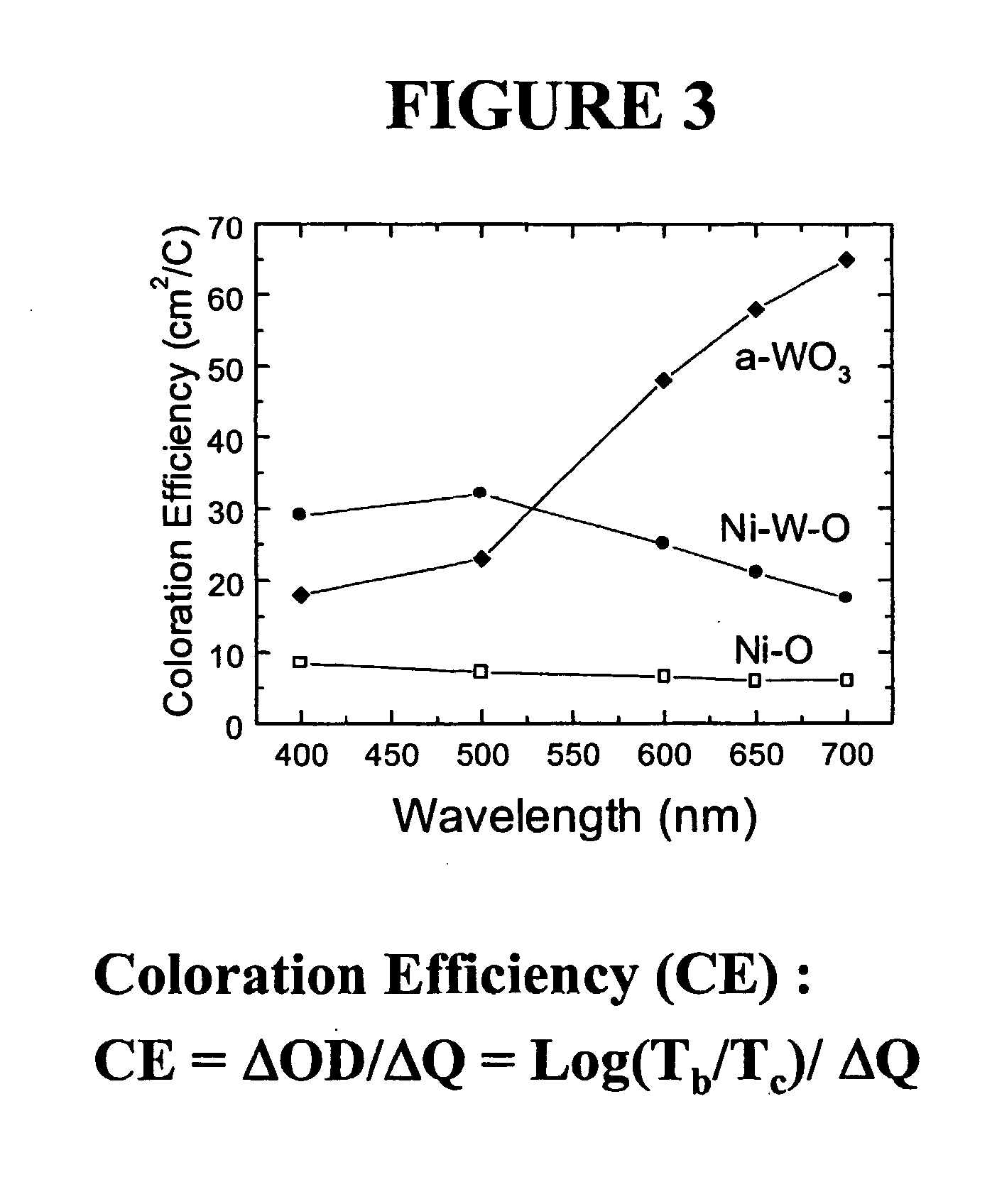
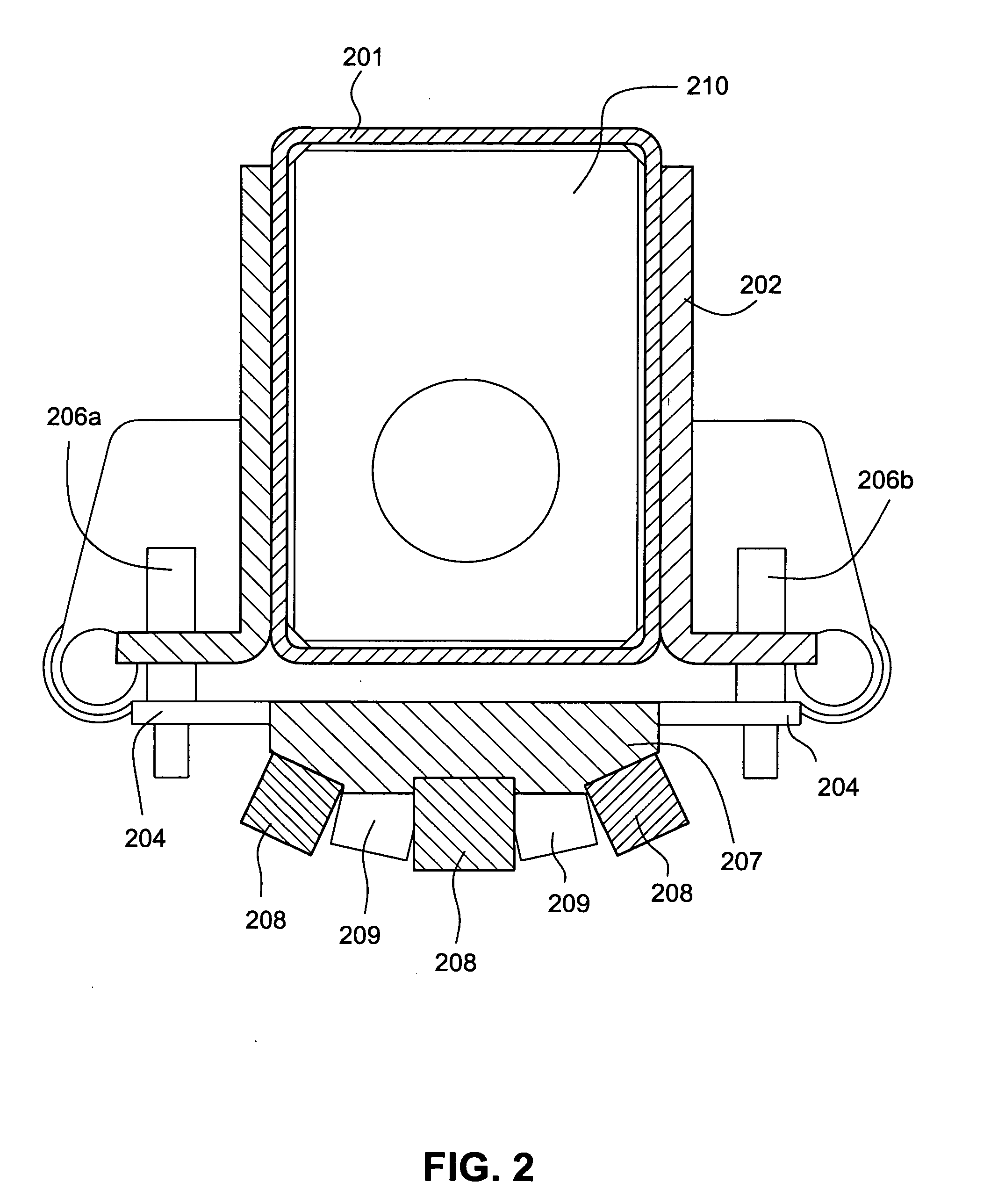
Electrochromic counter electrode
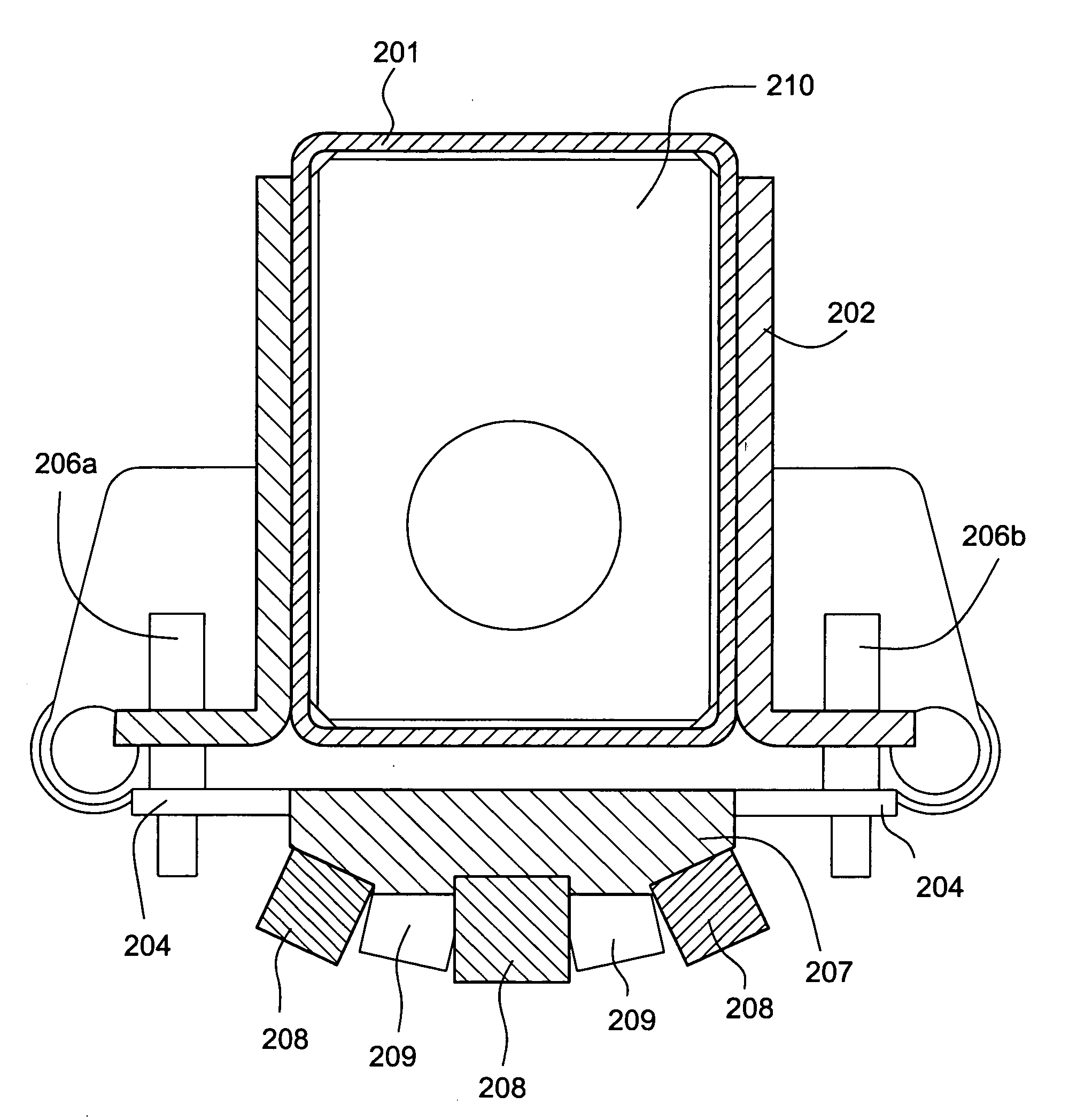
InactiveUS20040150867A1Easy to calculateSpeed of coloring/bleaching can be alteredNon-linear opticsElectricityElectrochromism
The present invention discloses an amorphous material comprising nickel oxide doped with tantalum that is an anodically coloring electrochromic material. The material of the present invention is prepared in the form of an electrode (200) having a thin film (202) of an electrochromic material of the present invention residing on a transparent conductive film (203). The material of the present invention is also incorporated into an electrochromic device (100) as a thin film (102) in conjunction with a cathodically coloring prior art electrochromic material layer (104) such that the devices contain both anodically coloring (102) and cathodically coloring (104) layers. The materials of the electrochromic layers in these devices exhibit broadband optical complimentary behavior, ionic species complimentary behavior, and coloration efficiency complimentary behavior in their operation.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY
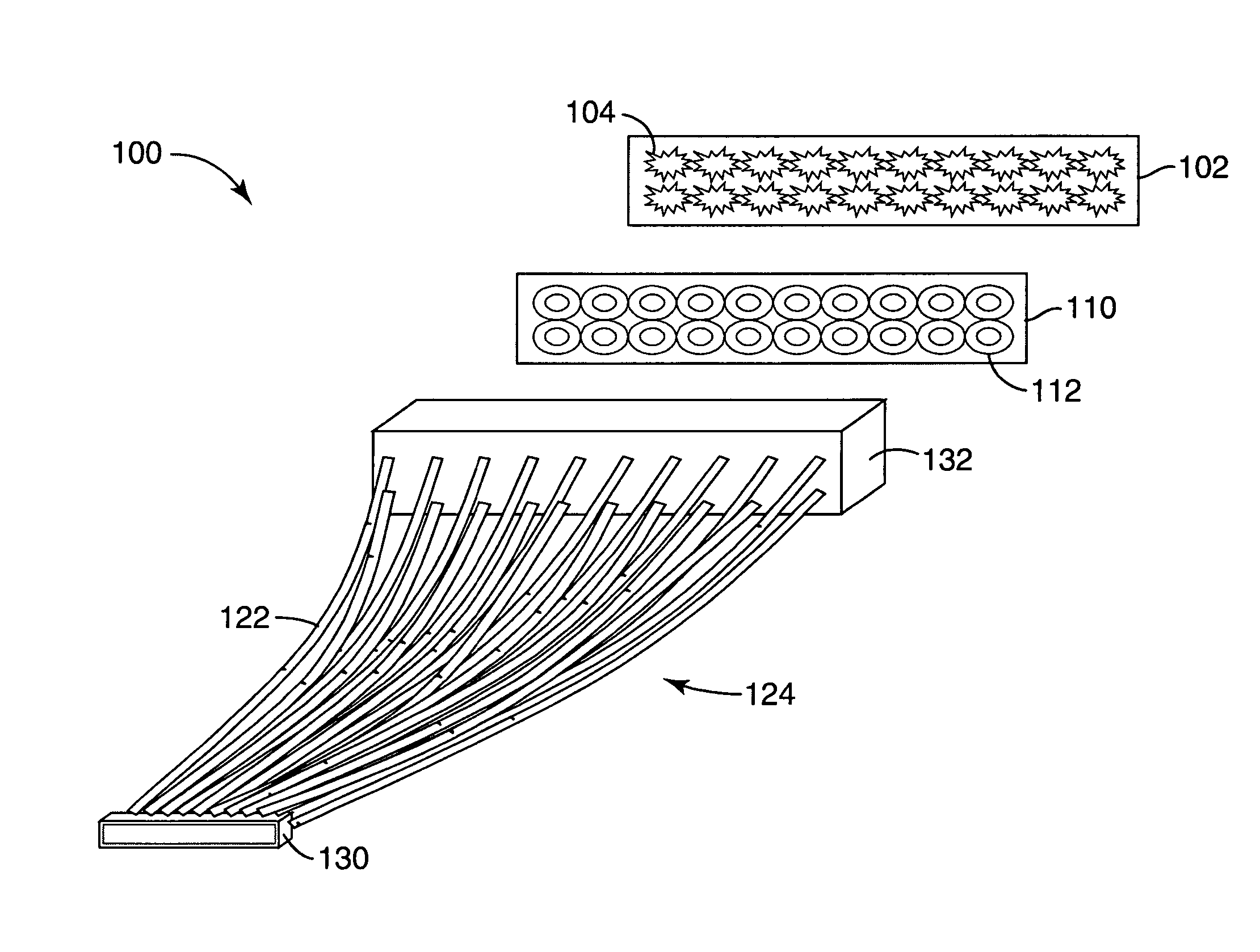
Illumination system using a plurality of light sources
InactiveUS7163327B2Reduce heat outputReduced life-timeMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceLighting systemOptical communication
An illumination system includes a plurality of radiation generating sources, such as LED dies. A corresponding plurality of optical waveguides is also provided, with each waveguide having a first and a second end, with each first end being in optical communication with the corresponding LED die. An array of corresponding passive optical elements is interposed between the plurality of LED dies and the corresponding first ends of the plurality of optical waveguides. The illumination system provides for substantially high light coupling efficiency and an incoherent light output that can appear to the human observer as arising from a single point of light. In addition, the light can be output remotely at one or more locations and in one or more directions.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Impingement cooled heat sink with low pressure drop
InactiveUS20070272392A1Reduced life-timeIncrease pressureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSystem pressureEngineering
Two embodiments of a heat exchanger assembly for cooling an electronic device are shown respectively in FIGS. 1 and 3 and each comprises a housing, a plurality of high fins, a plurality of low fins, a nozzle plate, an inlet, at least one outlet, a primary nozzle, and a plurality of secondary nozzles. In the first embodiment shown in FIG. 1, the housing and the nozzle plate are circular in shape. In the second embodiment shown in FIG. 3, the housing and the nozzle plate are rectangular in shape. Both embodiments include a plurality of secondary nozzles that are aligned outwardly of the primary nozzle and the center axis of the nozzle plate. The secondary nozzles direct the flow of the cooling liquid outwardly of the primary nozzle from the center thus creating an overall system pressure drop lower than that of other assemblies without a plurality of secondary nozzles.
Owner:COOLIT SYSTEMS INC
Method and apparatus for generating high output power gas discharge based source of extreme ultraviolet radiation and/or soft x-rays
InactiveUS6804327B2Reduce impactPreventing electrode burnoutRadiation/particle handlingNanoinformaticsSoft x rayLight beam
The method and system herein pertain to an EUV photon source which includes a plasma chamber filled with a gas mixture, multiple electrodes within the plasma chamber defining a plasma region and a central axis, a power supply circuit connected to the electrodes for delivering a main pulse to the electrodes for energizing the plasma around the central axis to produce an EUV beam. The system can also include a preionizer for ionizing the gas mixture in preparing to form a dense plasma around the central axis upon application of the main pulse from the power supply circuit to the electrodes. A set of baffles may be disposed along the beam path outside of the pinch region to diffuse gaseous and contaminant particulate flow emanating from the pinch region and to absorb or reflect acoustic waves emanating from the pinch region away from the pinch region.
Owner:USHIO DENKI KK
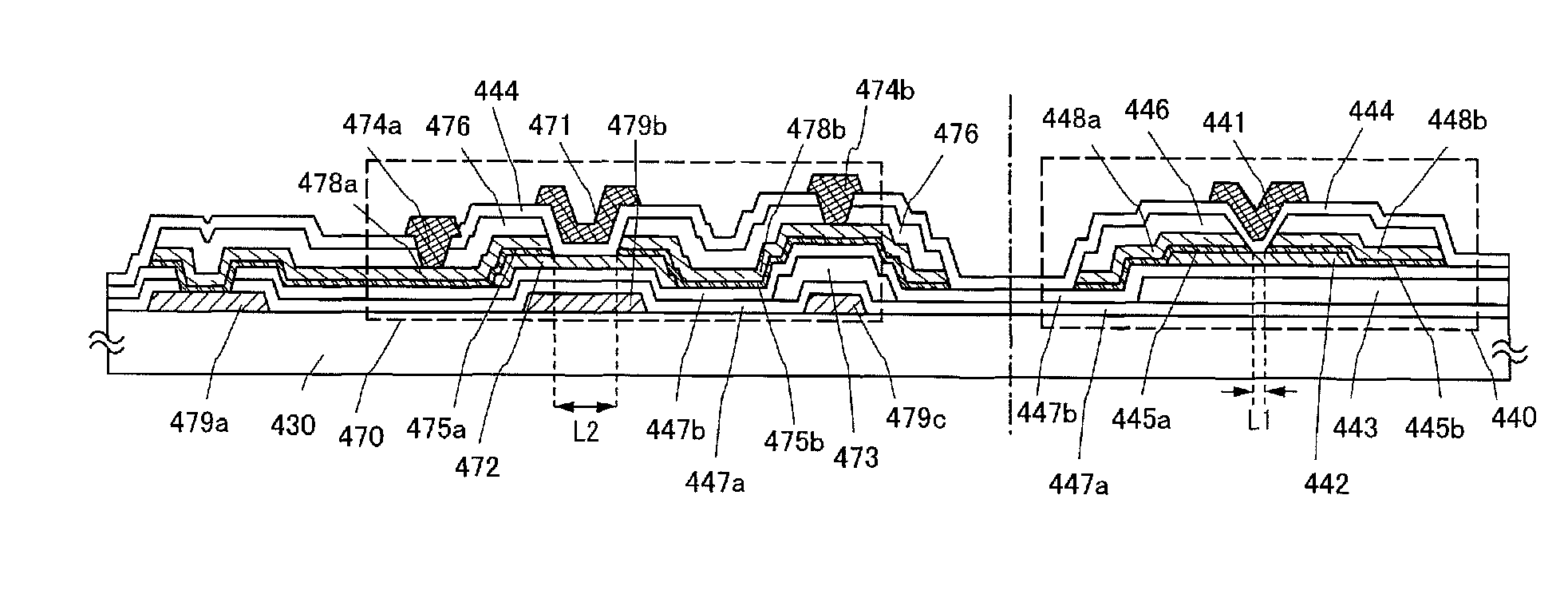
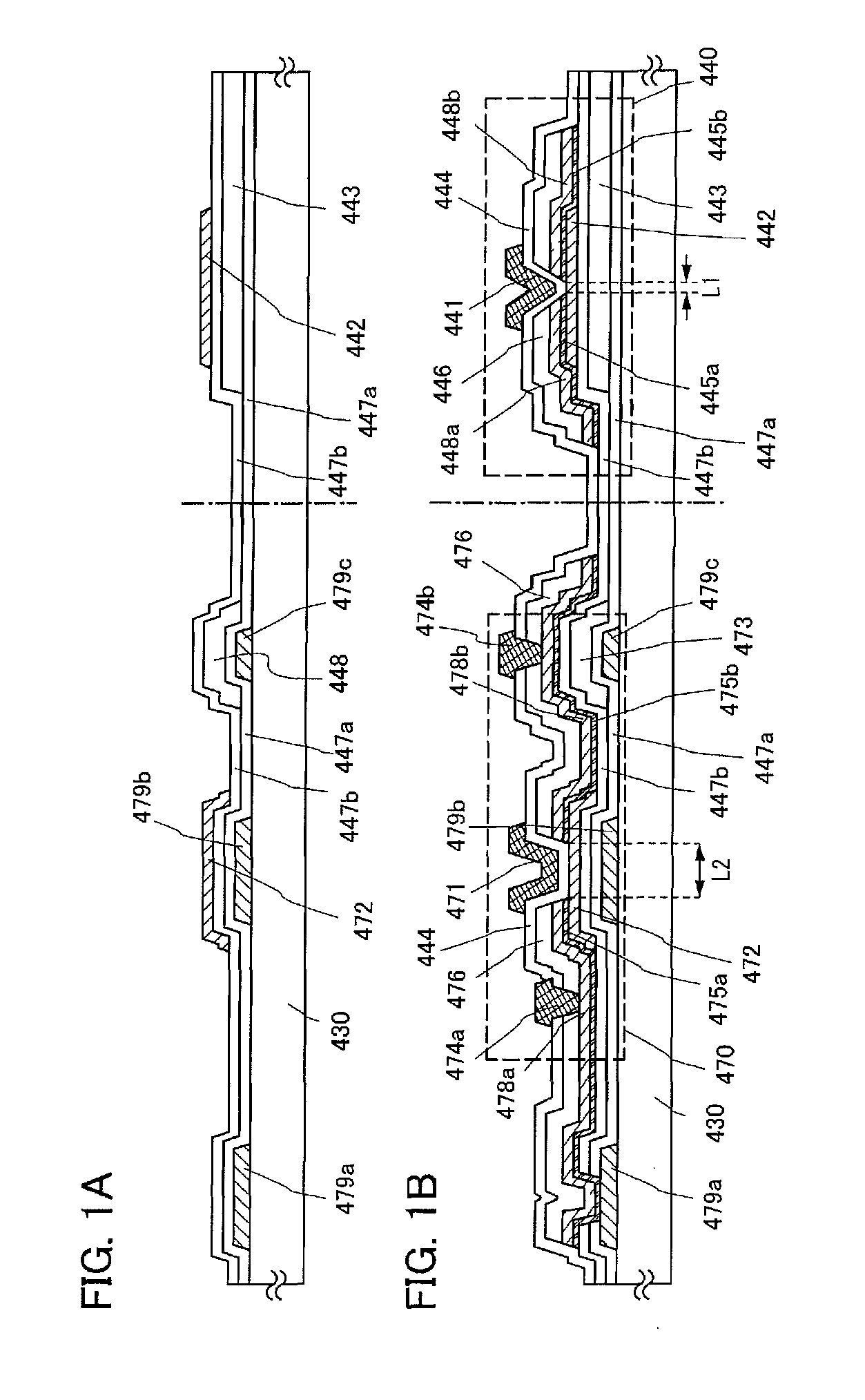
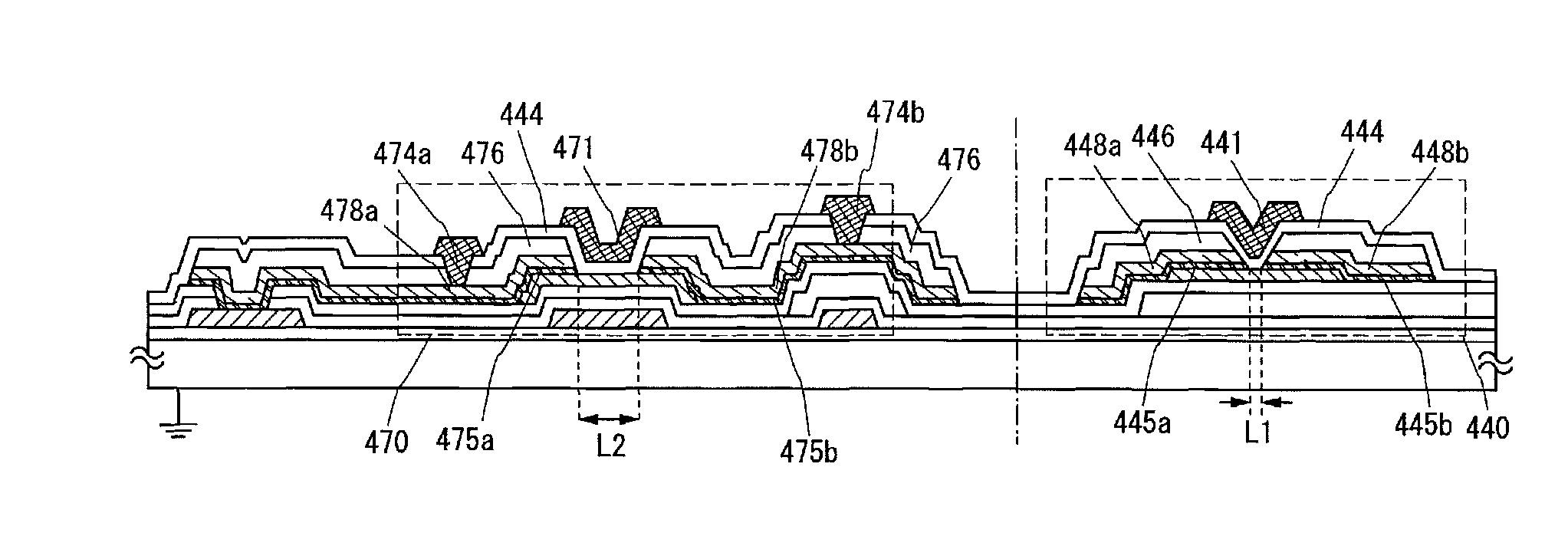
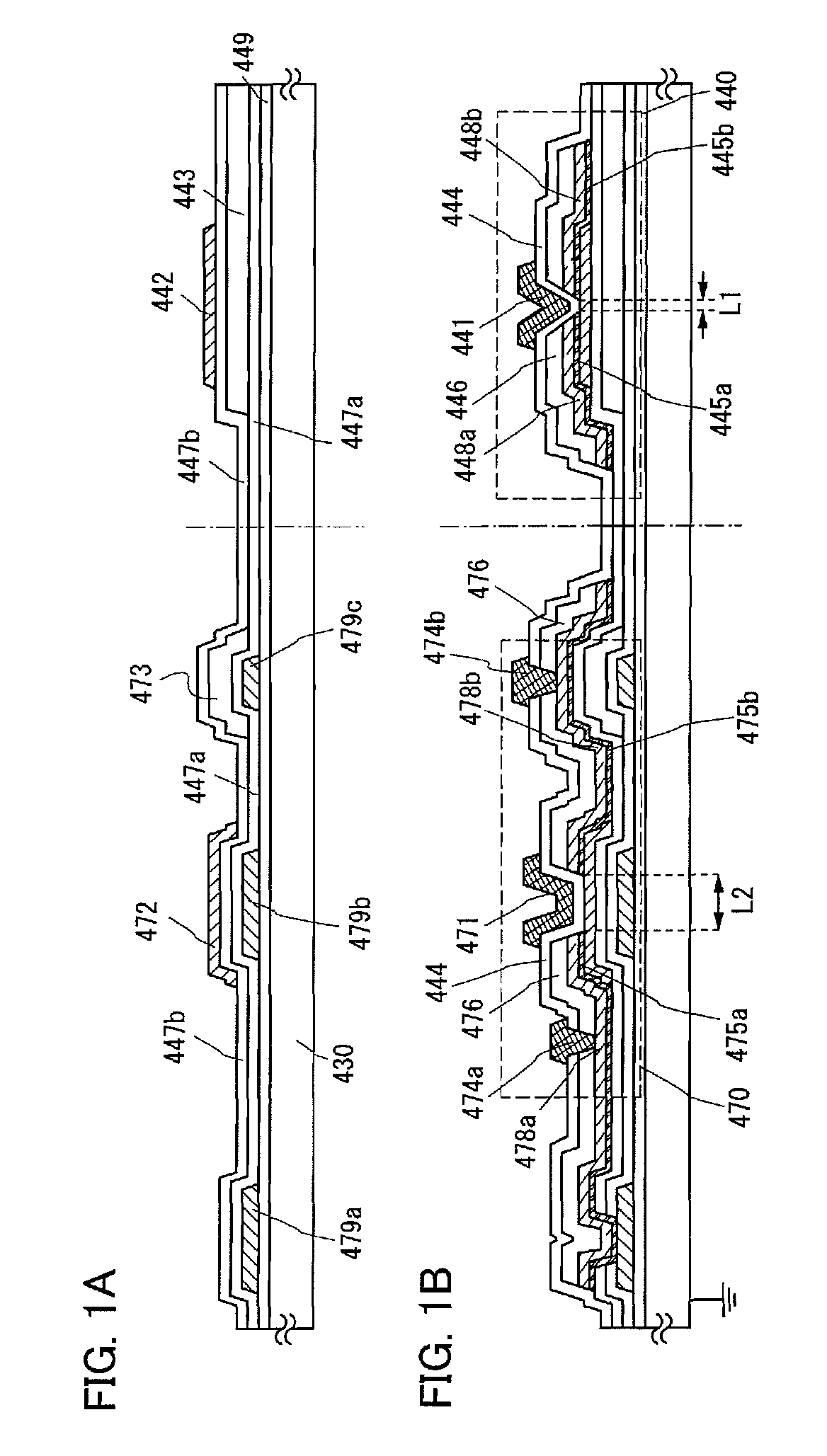
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS8421068B2Shorten driving distanceTimely controlSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectron donorElectron
An object is to reduce leakage current and parasitic capacitance of a transistor used for an LSI, a CPU, or a memory. A semiconductor integrated circuit such as an LSI, a CPU, or a memory is manufactured using a thin film transistor in which a channel formation region is formed using an oxide semiconductor which becomes an intrinsic or substantially intrinsic semiconductor by removing impurities which serve as electron donors (donors) from the oxide semiconductor and has larger energy gap than that of a silicon semiconductor. With use of a thin film transistor using a highly purified oxide semiconductor layer with sufficiently reduced hydrogen concentration, a semiconductor device with low power consumption due to leakage current can be realized.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
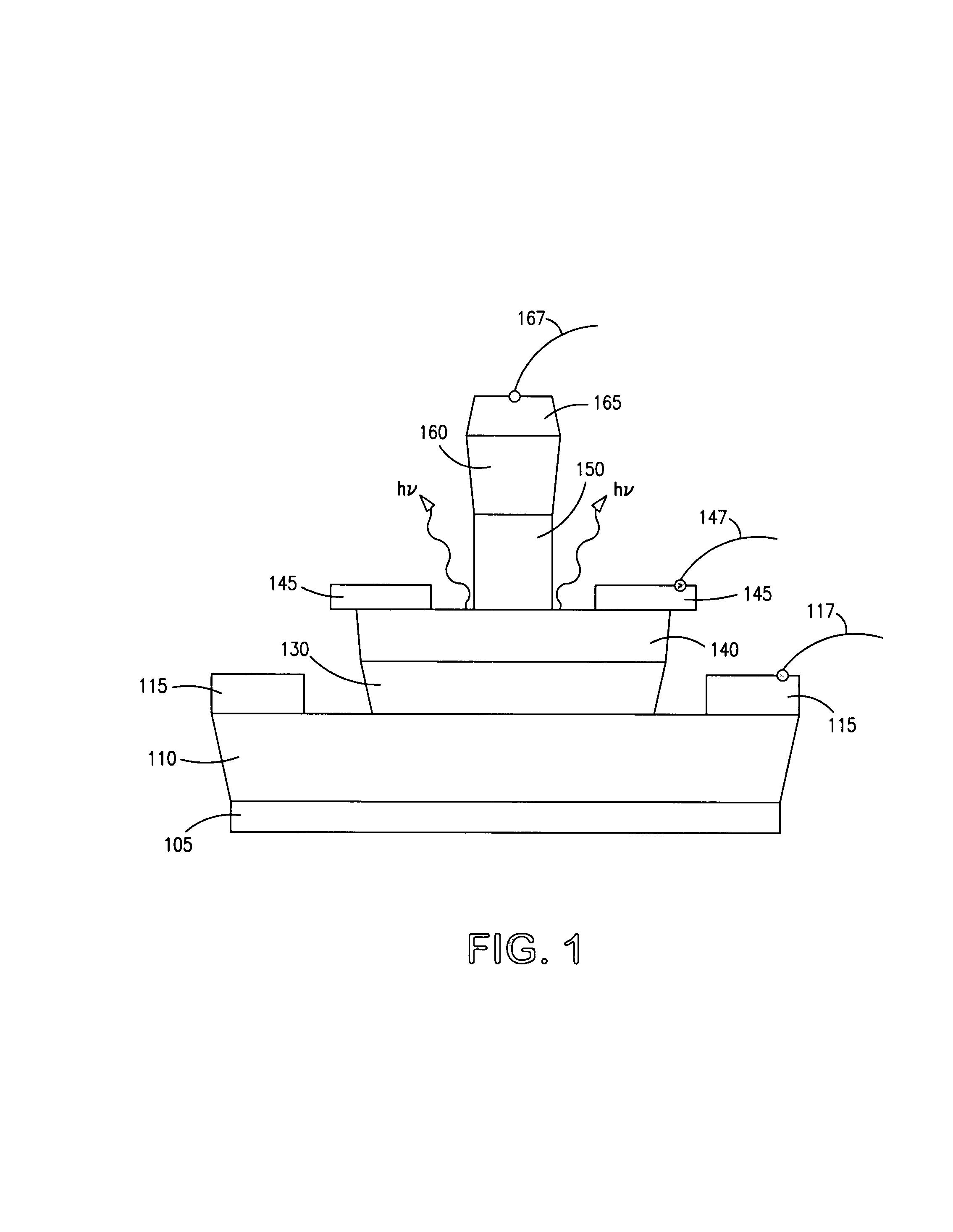
Head for thermal assisted magnetic recording device, and thermal assisted magnetic recording device
ActiveUS20110216635A1Increase head heightImprove floating stabilityCombination recordingRecord information storageHeat-assisted magnetic recordingEngineering
In a head for thermal assisted magnetic recording device, a semiconductor laser is mounted so that the total height of the head does not become larger and light power fluctuation due to wavelength fluctuation occurs less frequently. In addition, the rise in temperature of the mounted semiconductor laser is suppressed. A semiconductor laser is placed on a side surface which is different from surfaces on an inflow end side and a trailing side, of four side surfaces of a floating slider. An entrance of a waveguide is placed on the side surface of the floating slider, to thereby cause emitted light from the semiconductor laser to directly enter the waveguide. A curved line part or a reflective mirror is formed in the middle of the waveguide so that the light which has entered the waveguide travels toward an optical near-field generating element.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
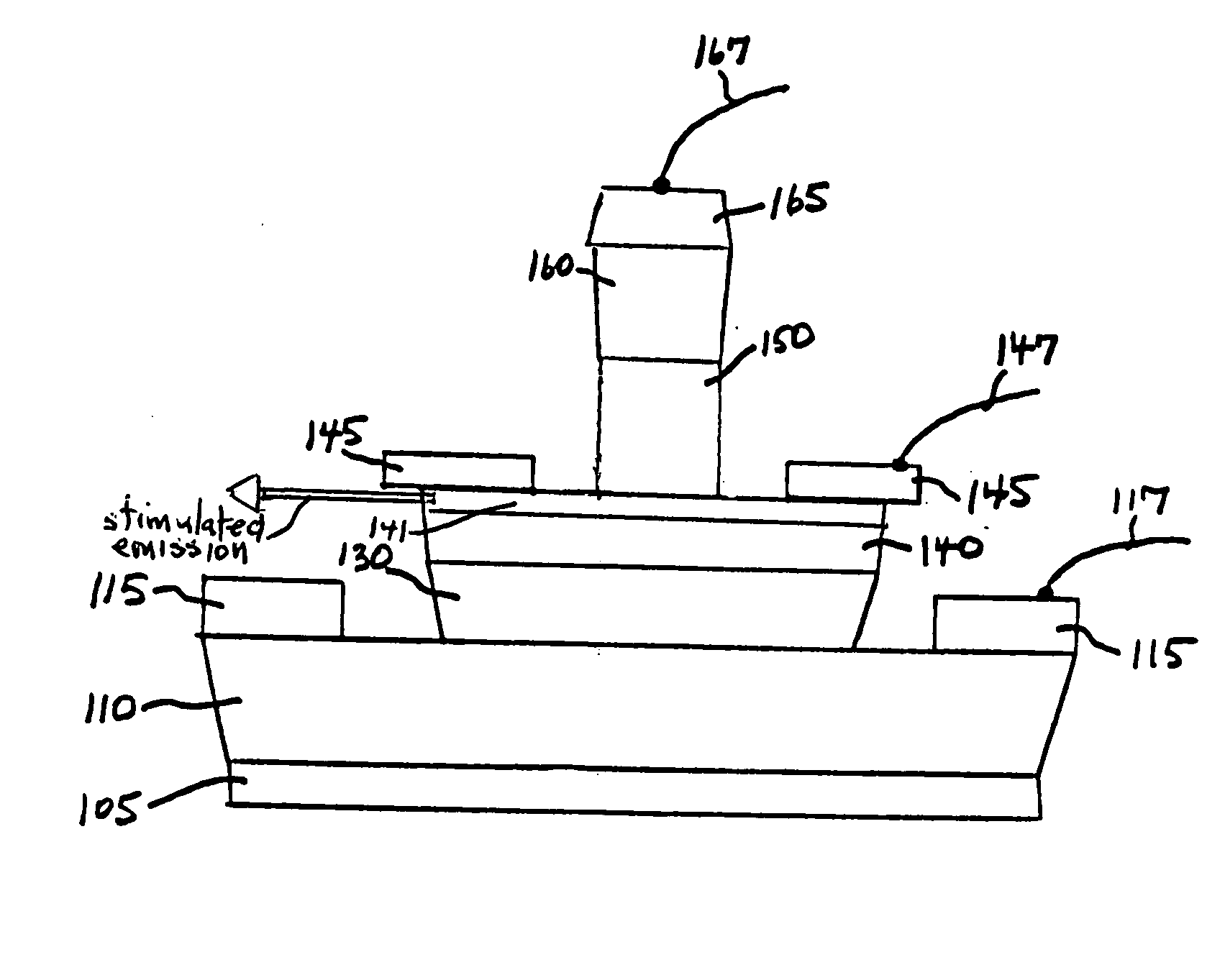
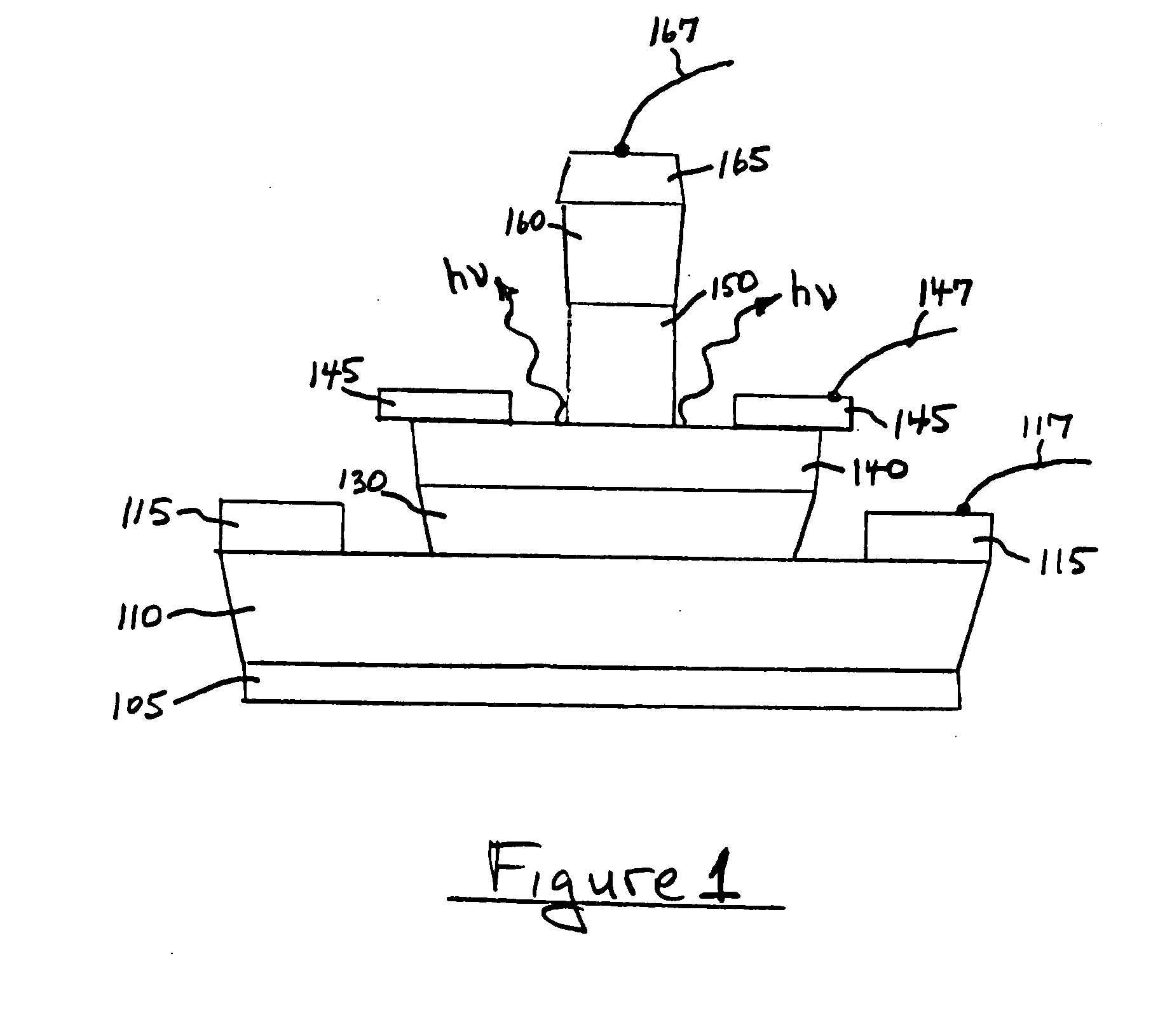
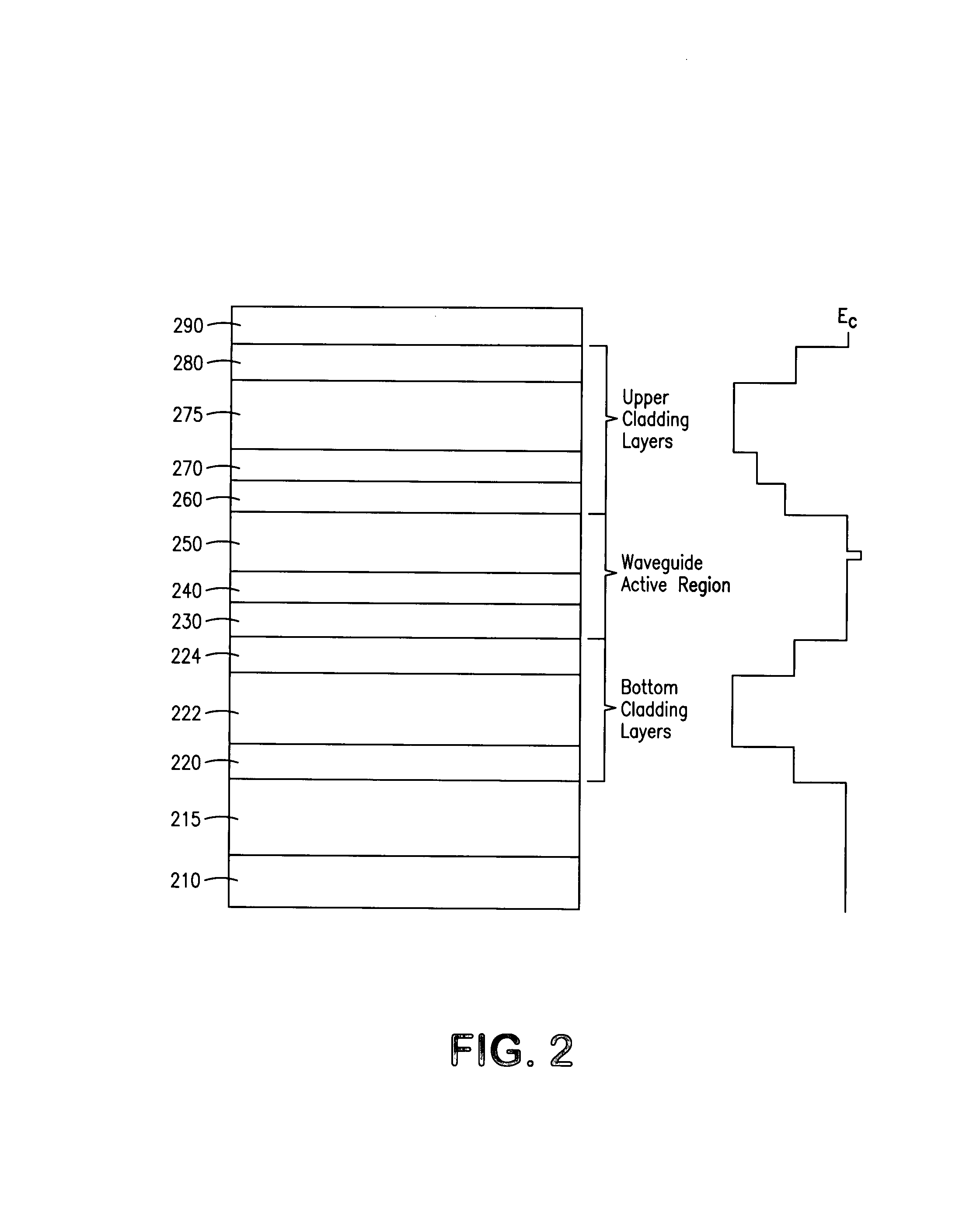
Semiconductor device and mehtod
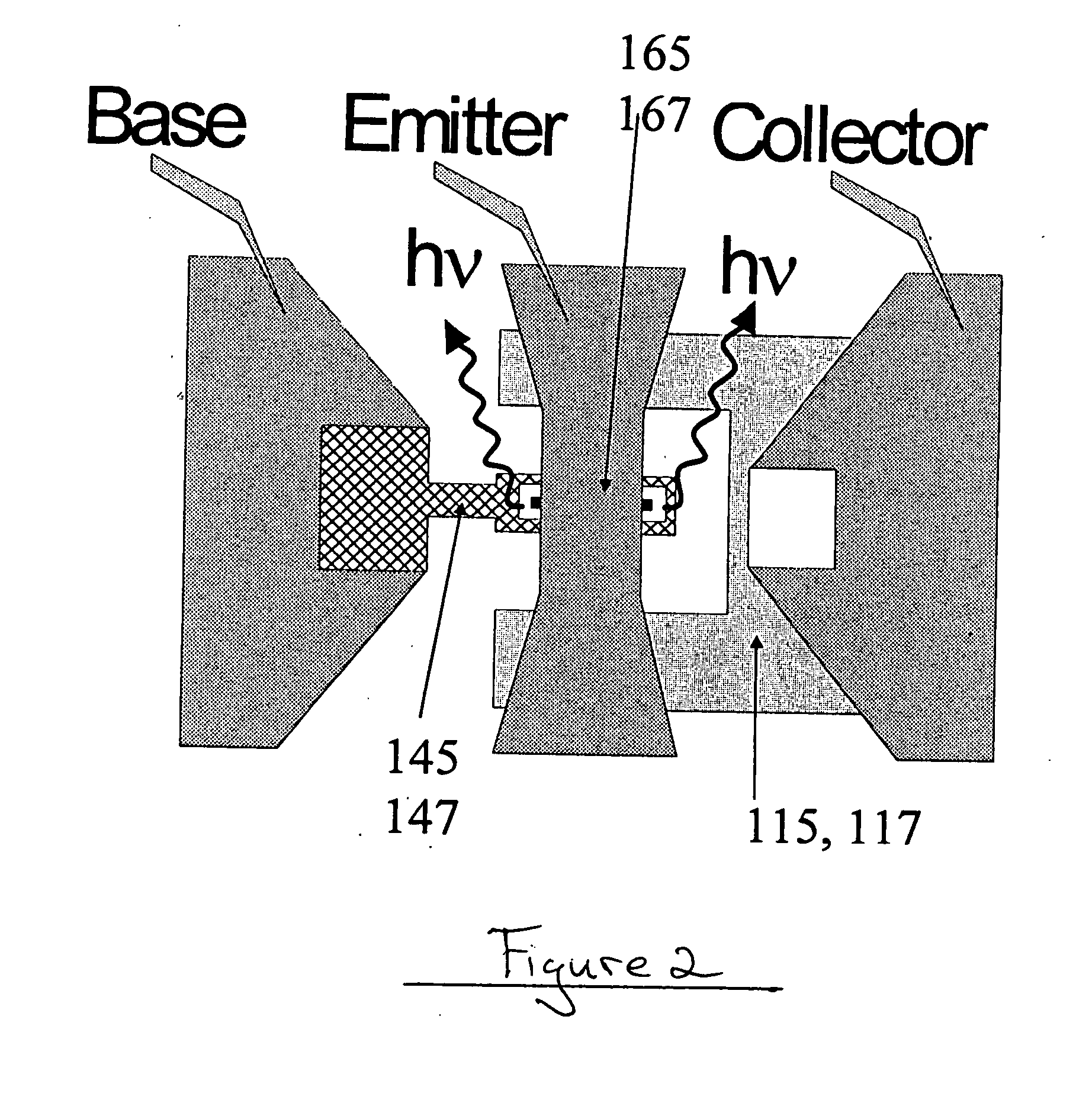
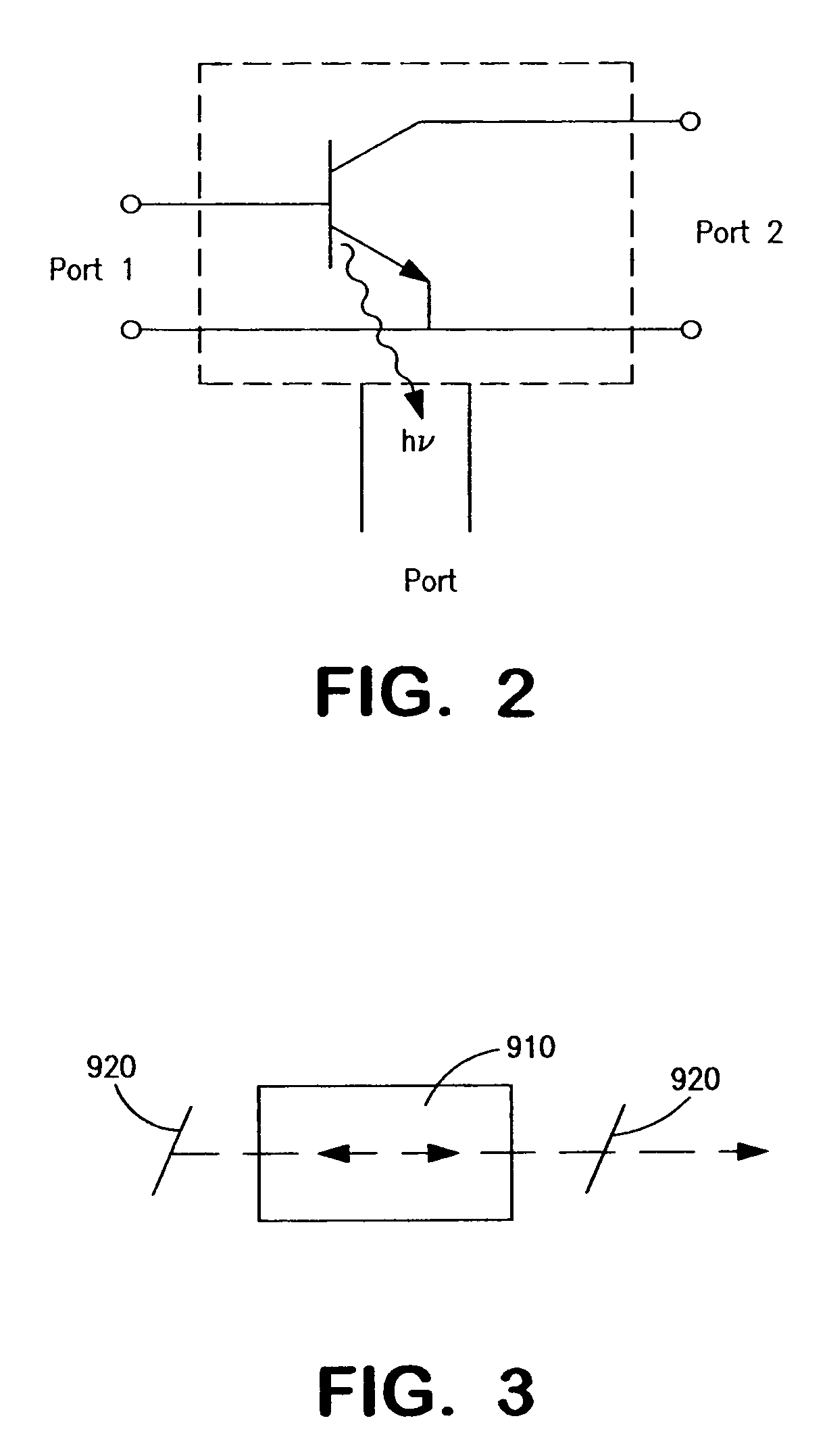
ActiveUS20050054172A1Increase speedImprove mobilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialStimulated emission
A method for increasing the speed of a bipolar transistor, includes the following steps: providing a bipolar transistor having emitter, base, and collector regions; providing electrodes for coupling electrical signals with the emitter, base, and collector regions; and adapting the base region to enhance stimulated emission to the detriment of spontaneous emission, so as to reduce carrier recombination lifetime in the base region.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20110089414A1Reduce leakage currentReduce power consumptionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectron donorElectron
An object is to reduce leakage current and parasitic capacitance of a transistor used for an LSI, a CPU, or a memory. A semiconductor integrated circuit such as an LSI, a CPU, or a memory is manufactured using a thin film transistor in which a channel formation region is formed using an oxide semiconductor which becomes an intrinsic or substantially intrinsic semiconductor by removing impurities which serve as electron donors (donors) from the oxide semiconductor and has larger energy gap than that of a silicon semiconductor. With use of a thin film transistor using a highly purified oxide semiconductor layer with sufficiently reduced hydrogen concentration, a semiconductor device with low power consumption due to leakage current can be realized.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Device containing non-blinking quantum dots
InactiveUS7777233B2Reduced life-timeShort radiative lifetime propertiesRadiation pyrometryDischarge tube luminescnet screensQuantum dotNanocrystal
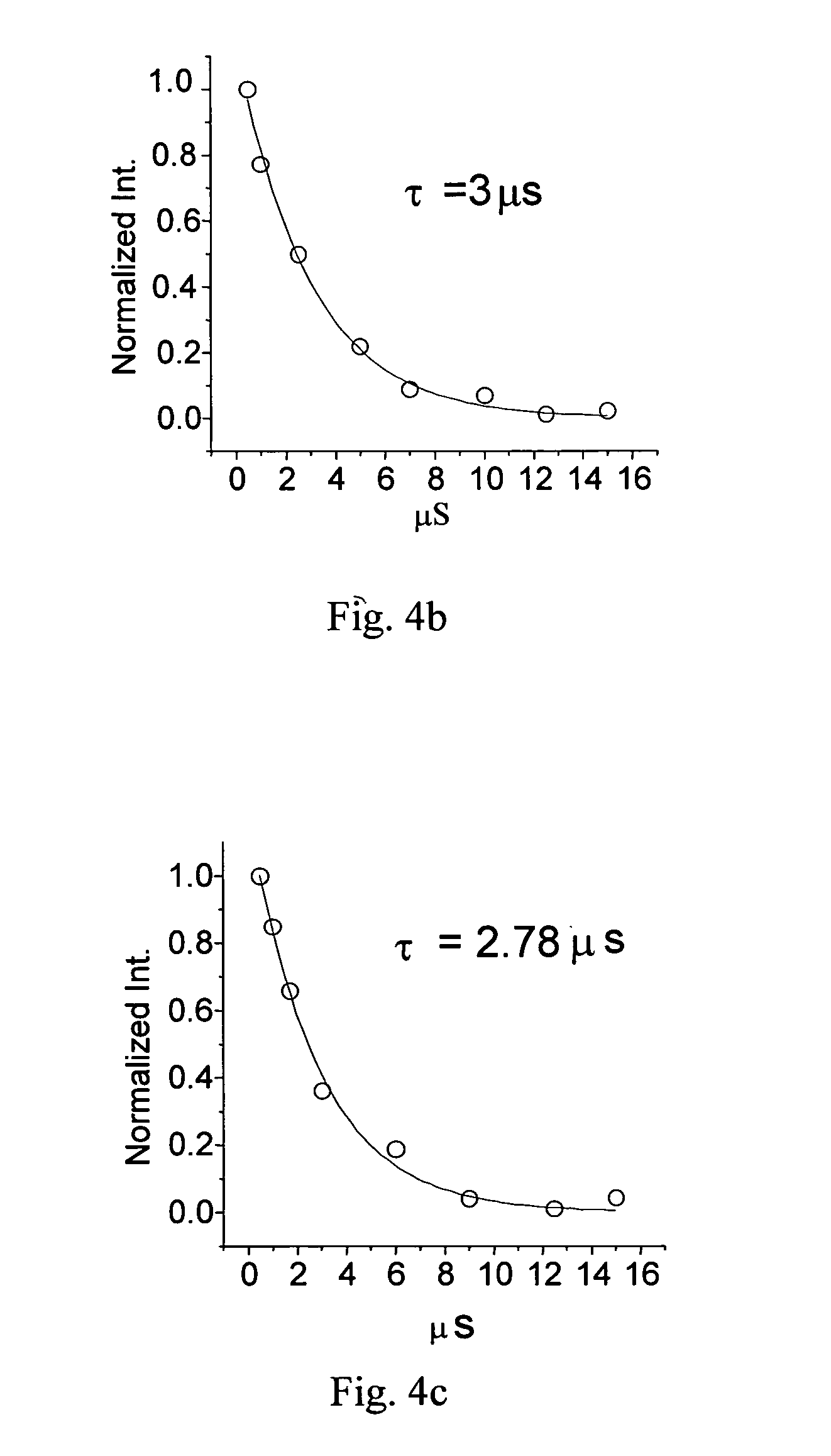
An optoelectronic device including two spaced apart electrodes; and at least one layer containing ternary core / shell nanocrystals disposed between the spaced electrodes and having ternary semiconductor cores containing a gradient in alloy composition and wherein the ternary core / shell nanocrystals exhibit single molecule non-blinking behavior characterized by on times greater than one minute or radiative lifetimes less than 10 ns.
Owner:NANOCO TECH LTD
Semiconductor laser devices and methods
InactiveUS7286583B2Increase speedImprove mobilityLaser detailsNanoopticsResonant cavitySemiconductor materials
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Connecting member and connector each having a slider adapted to displace contact portions
InactiveUS7503786B2Good adhesionEasy detachmentElectric discharge tubesIncorrect coupling preventionEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:JAPAN AVIATION ELECTRONICS IND LTD
Semiconductor device
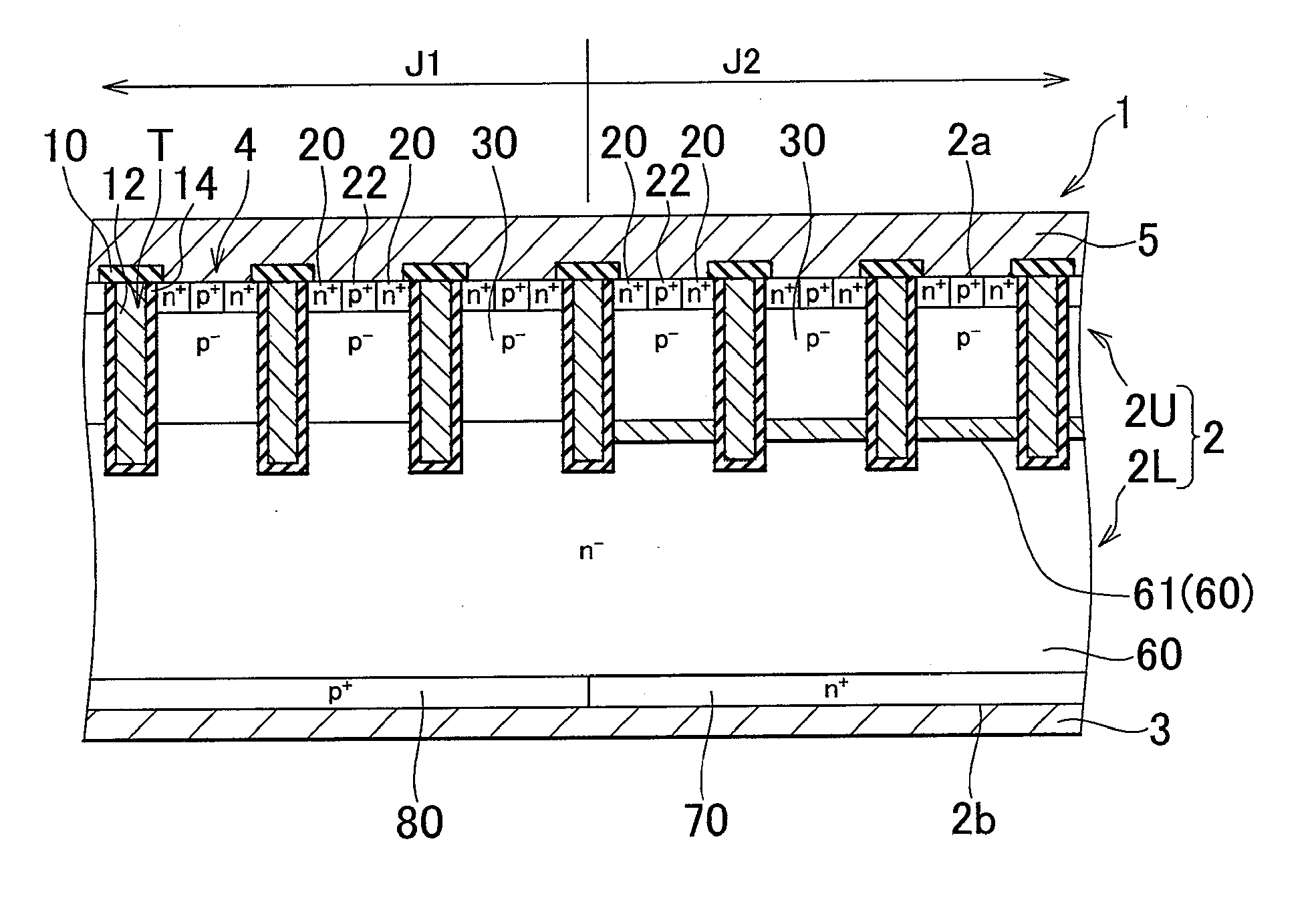
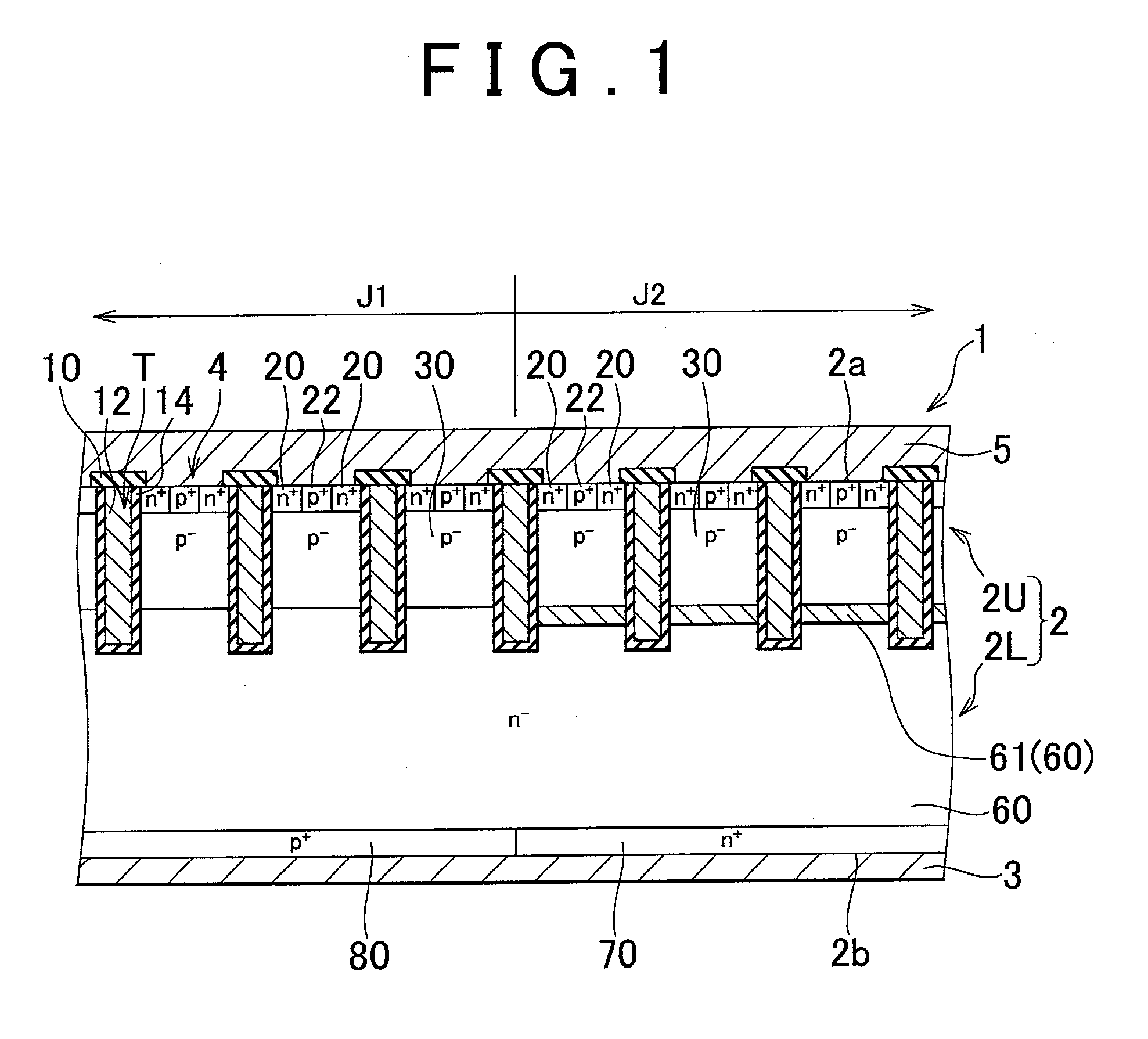
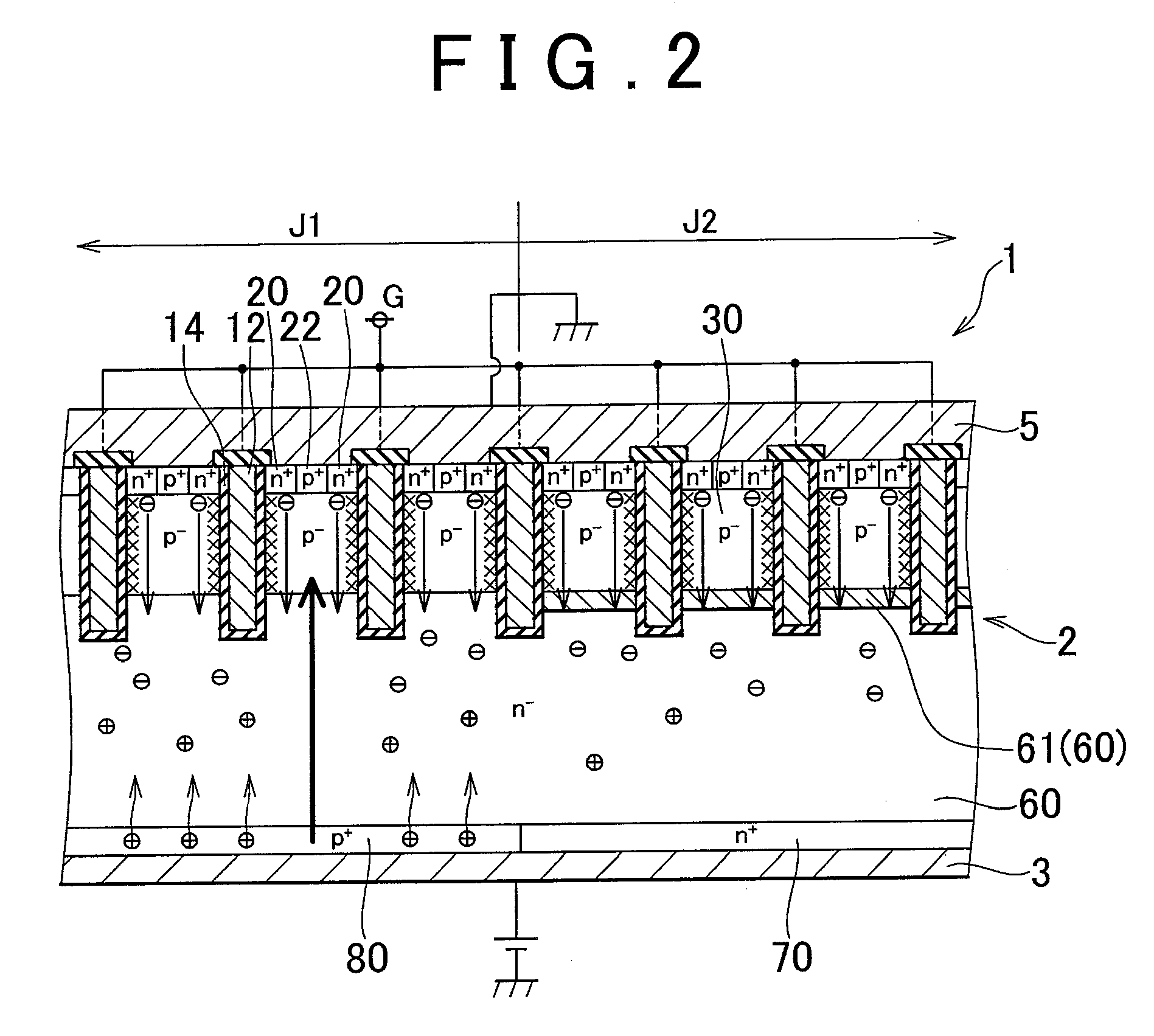
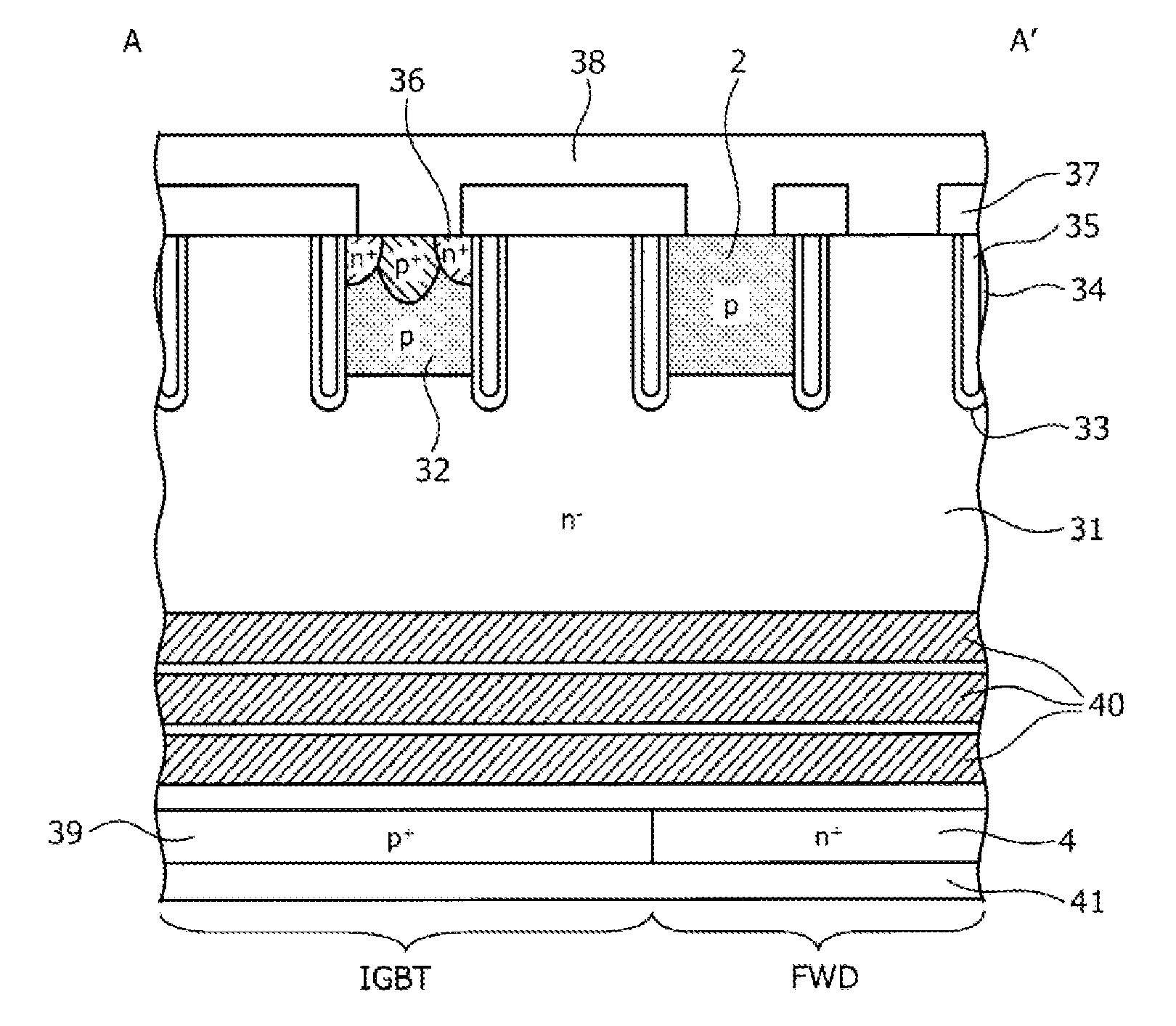
InactiveUS20090278166A1Reduce recovery lossReduced life-timeTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorSemiconductor device
A semiconductor device in which both an IGBT element region and a diode element region exist in the same semiconductor substrate includes a low lifetime region, which is formed in at least a part of a drift layer within the diode element region and shortens the lifetime of holes. A mean value of the lifetime of holes in the drift layer that includes the low lifetime region is shorter within the IGBT element region than within the diode element region.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
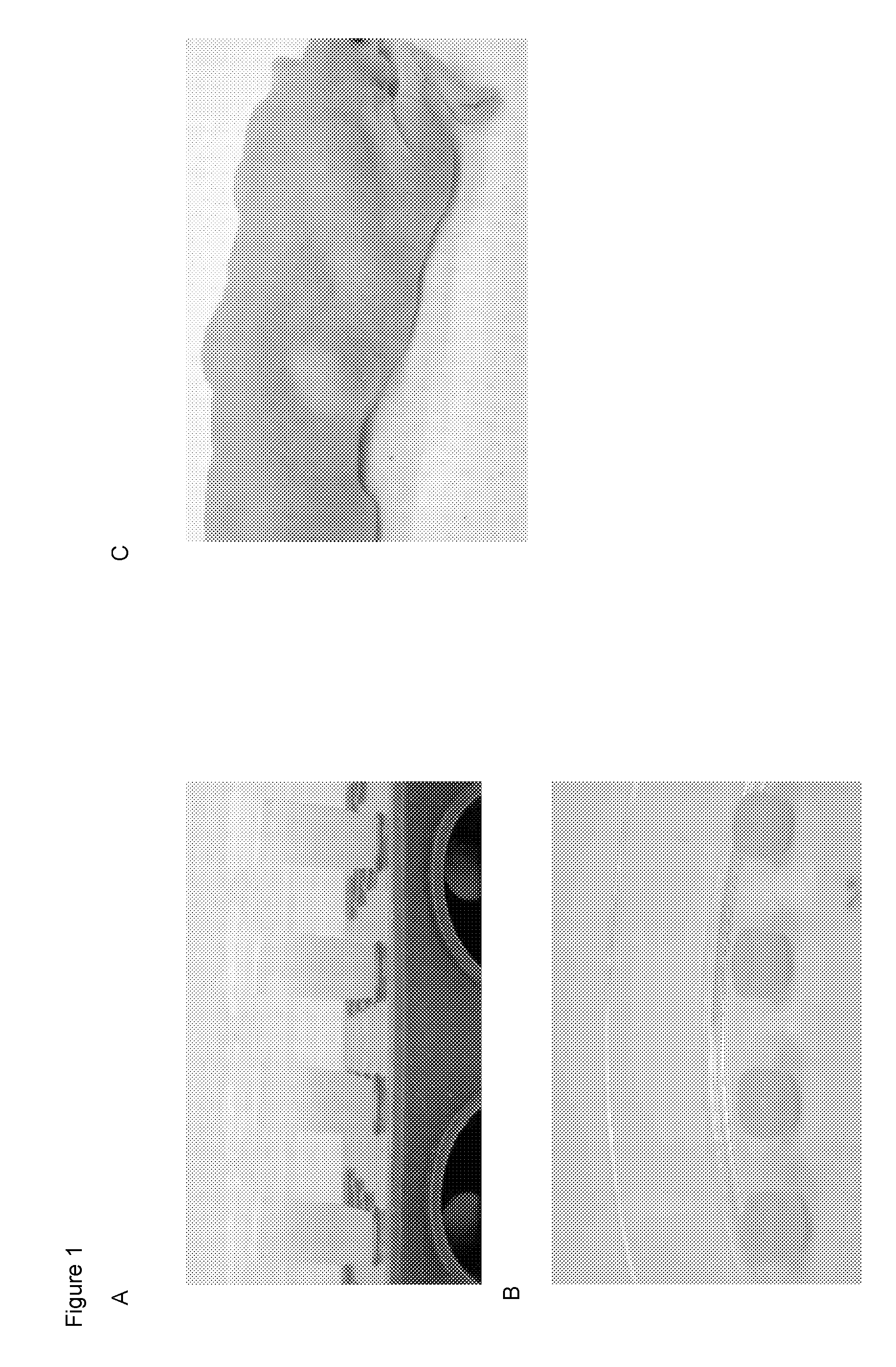
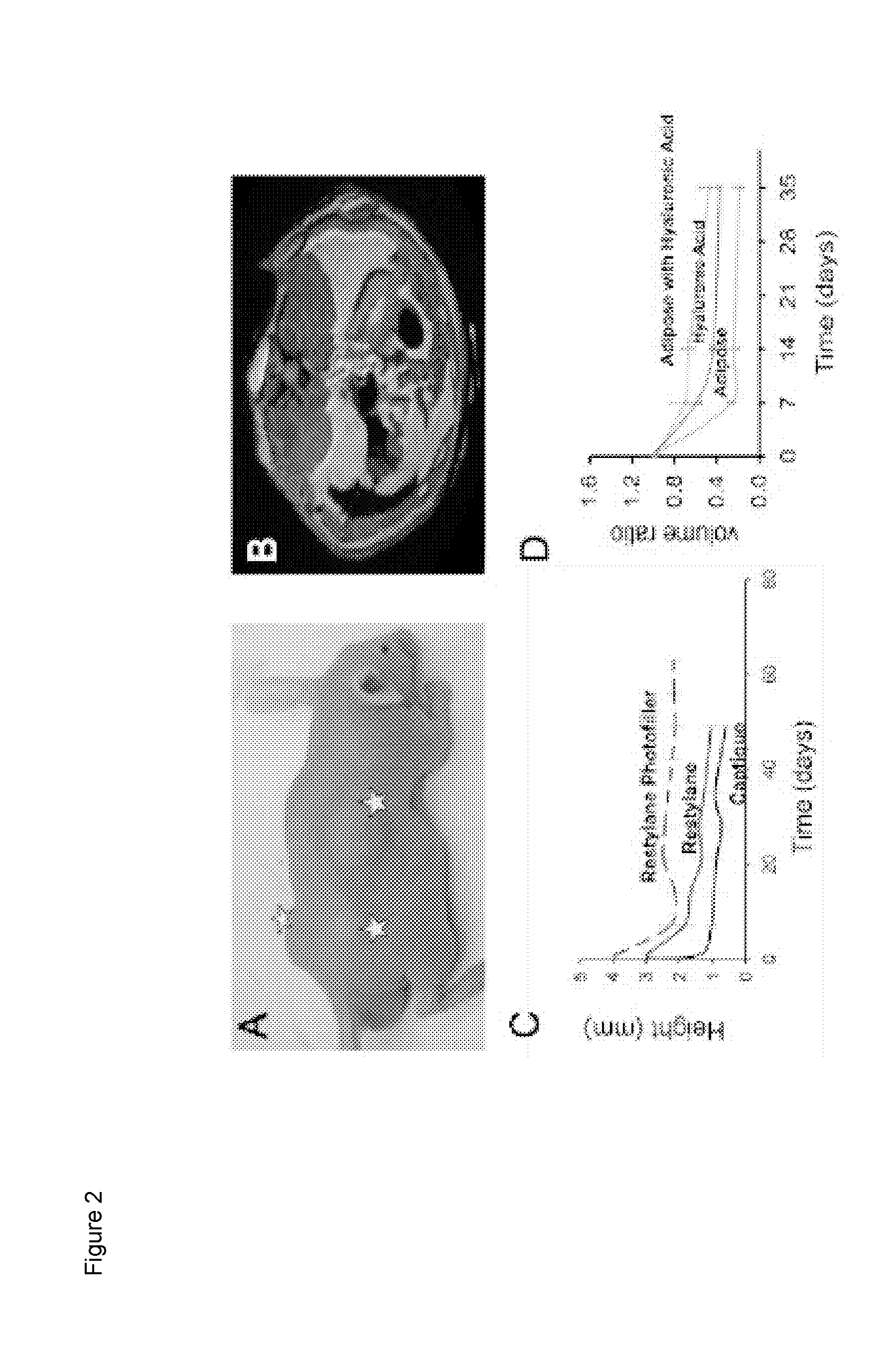
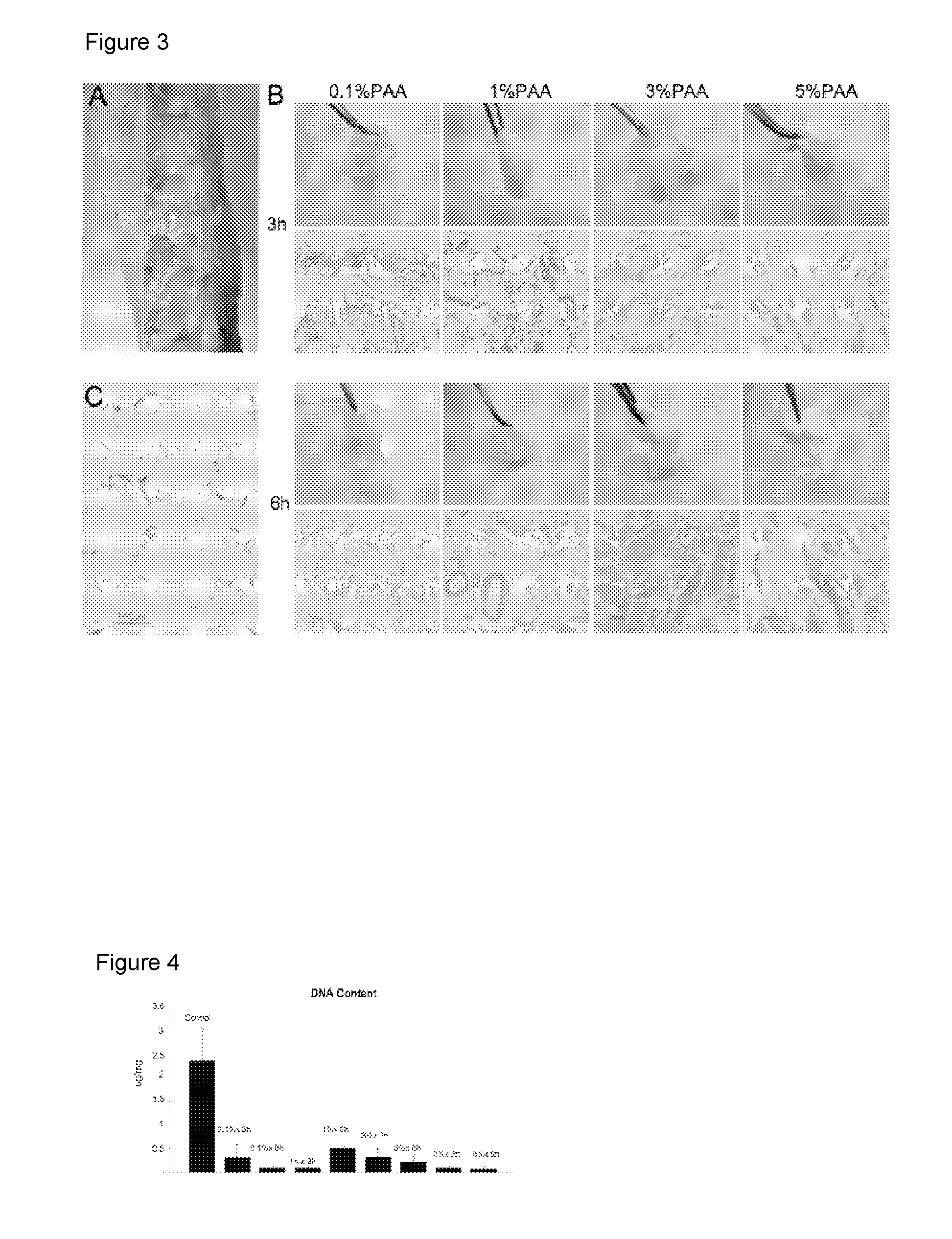
Compositions and Methods for Implantation of Processed Adipose Tissue and Processed Adipose Tissue Products
The invention provides compositions and methods for the preparation of processed adipose tissue. The invention further provides methods of use of the processed adipose tissue.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
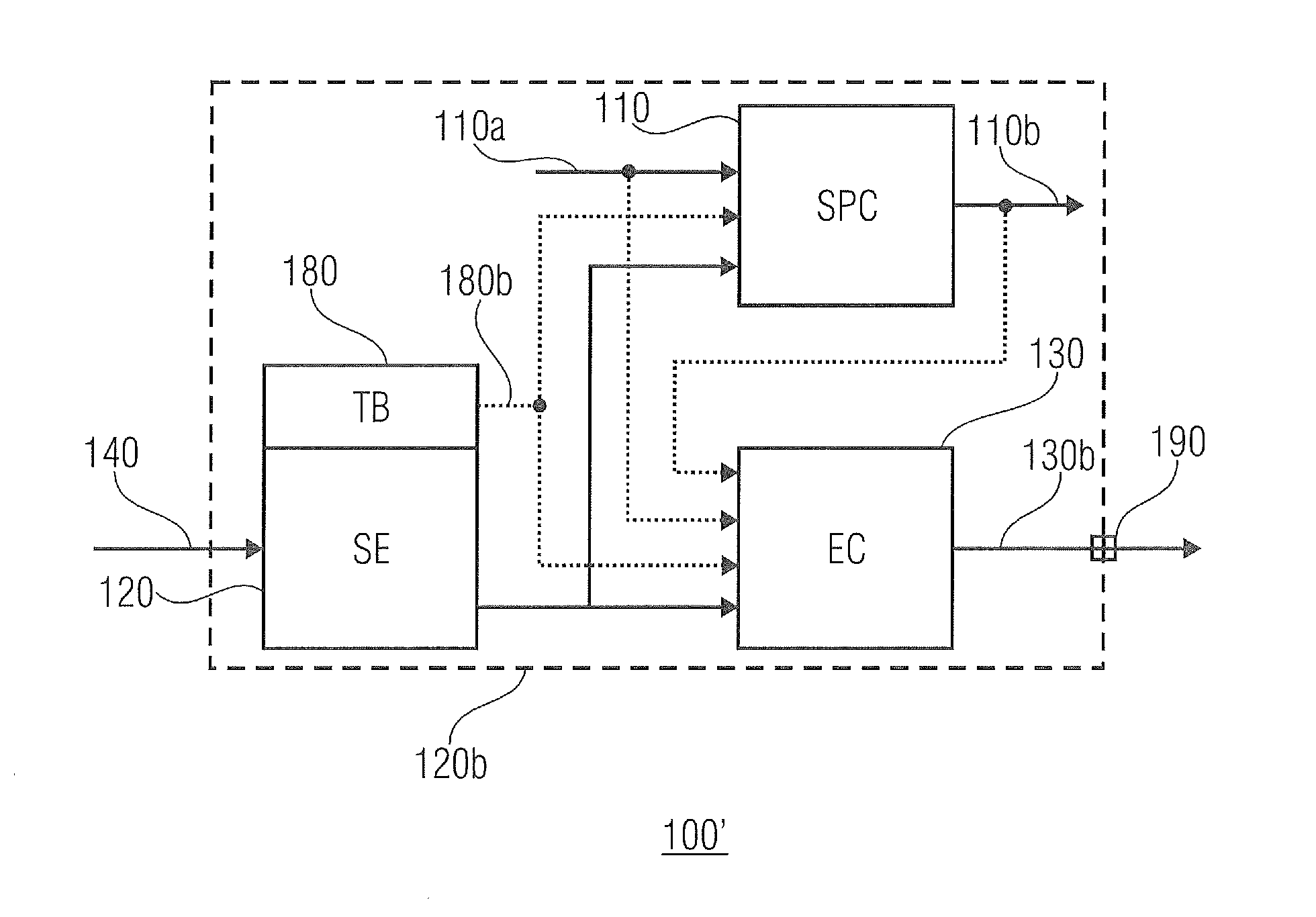
Apparatus, Sensor Circuit, and Method for Operating an Apparatus or a Sensor Circuit
ActiveUS20110270553A1Shorten speedQuality improvementMagnetic measurementsCurrent/voltage measurementSignal processing circuitsPhysical quantity
An apparatus is described, including: a signal processing circuit adapted to process an input signal to obtain an output signal; a sensor element for sensing a predetermined physical quantity, wherein the sensor element is adapted to generate a sensor signal in response to the predetermined physical quantity; wherein the signal processing unit is adapted to process the input signal to obtain the output signal depending on the sensor signal; and wherein the apparatus further comprises an evaluation circuit adapted to evaluate the sensor signal and to generate an indication signal indicating an abnormal operating condition in case the sensor signal does not fulfill a predetermined normal operation criterion.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Semiconductor light emitting devices and methods
InactiveUS7354780B2Increase speedImprove mobilityLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical communicationOptical coupling
A method for producing an optical output, including the following steps: providing first and second electrical signals; providing a bipolar light-emitting transistor device that includes collector, base, and emitter regions; providing a collector electrode coupled with the collector region and an emitter electrode coupled with the emitter region, and coupling electrical potentials with respect to the collector and emitter electrodes; providing an optical coupling in optical communication with the base region; providing first and second base electrodes coupled with the base region; and coupling the first and second electrical signals with the first and second base electrodes, respectively, to produce an optical output emitted from the base region and coupled into the optical coupling, the optical output being a function of the first and second electrical signals.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS8421069B2Shorten driving distanceTimely controlSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectron donorImpurity
An object is to reduce leakage current and parasitic capacitance of a transistor used for an LSI, a CPU, or a memory. A semiconductor integrated circuit included in an LSI, a CPU, or a memory is manufactured using the transistor which is formed using an oxide semiconductor which is an intrinsic or substantially intrinsic semiconductor obtained by removal of impurities which serve as electron donors (donors) from the oxide semiconductor and has larger energy gap than a silicon semiconductor, and is formed over a semiconductor substrate. With the transistor which is formed over the semiconductor substrate and includes the highly purified oxide semiconductor layer with sufficiently reduced hydrogen concentration, a semiconductor device whose power consumption due to leakage current is low can be realized.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
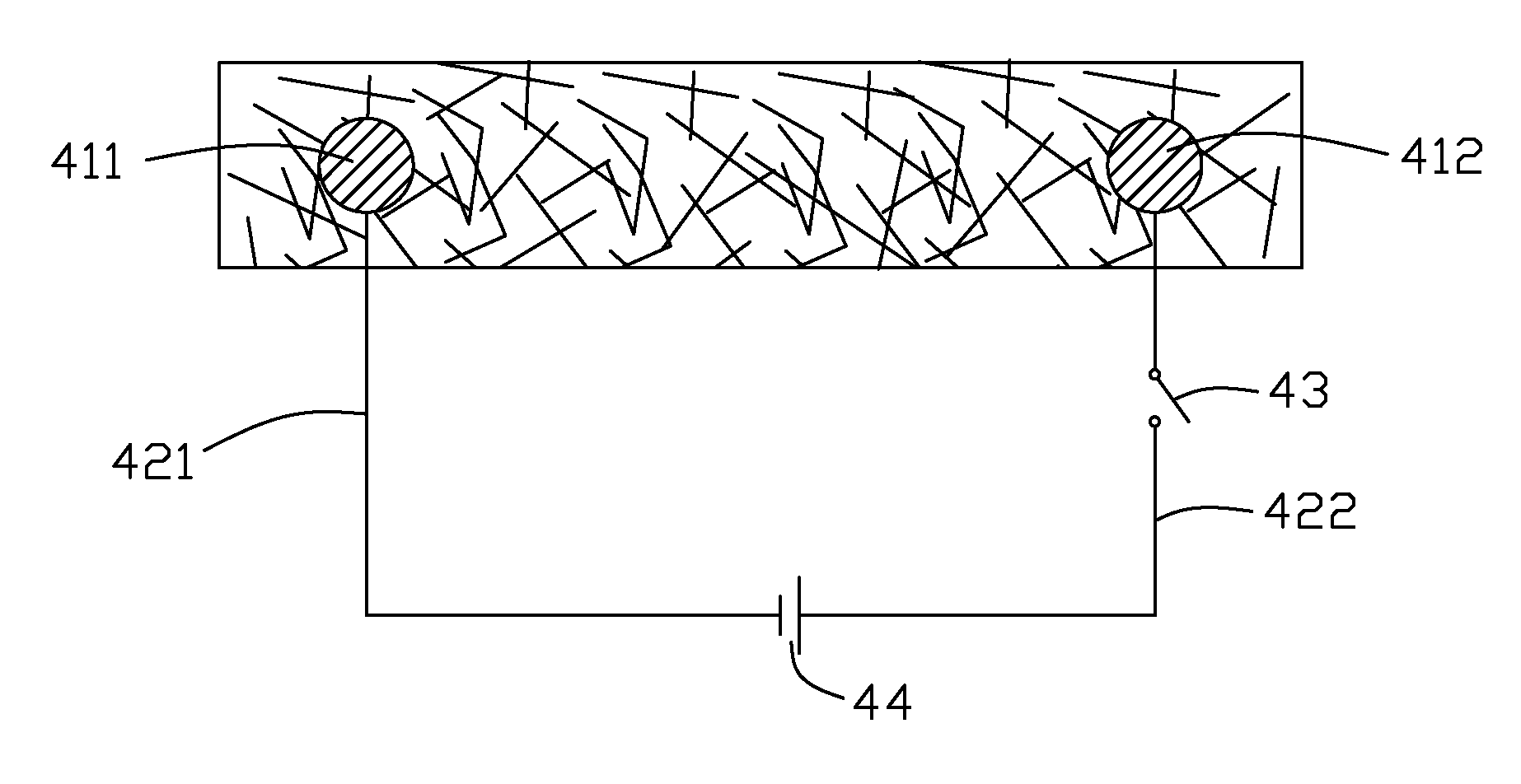
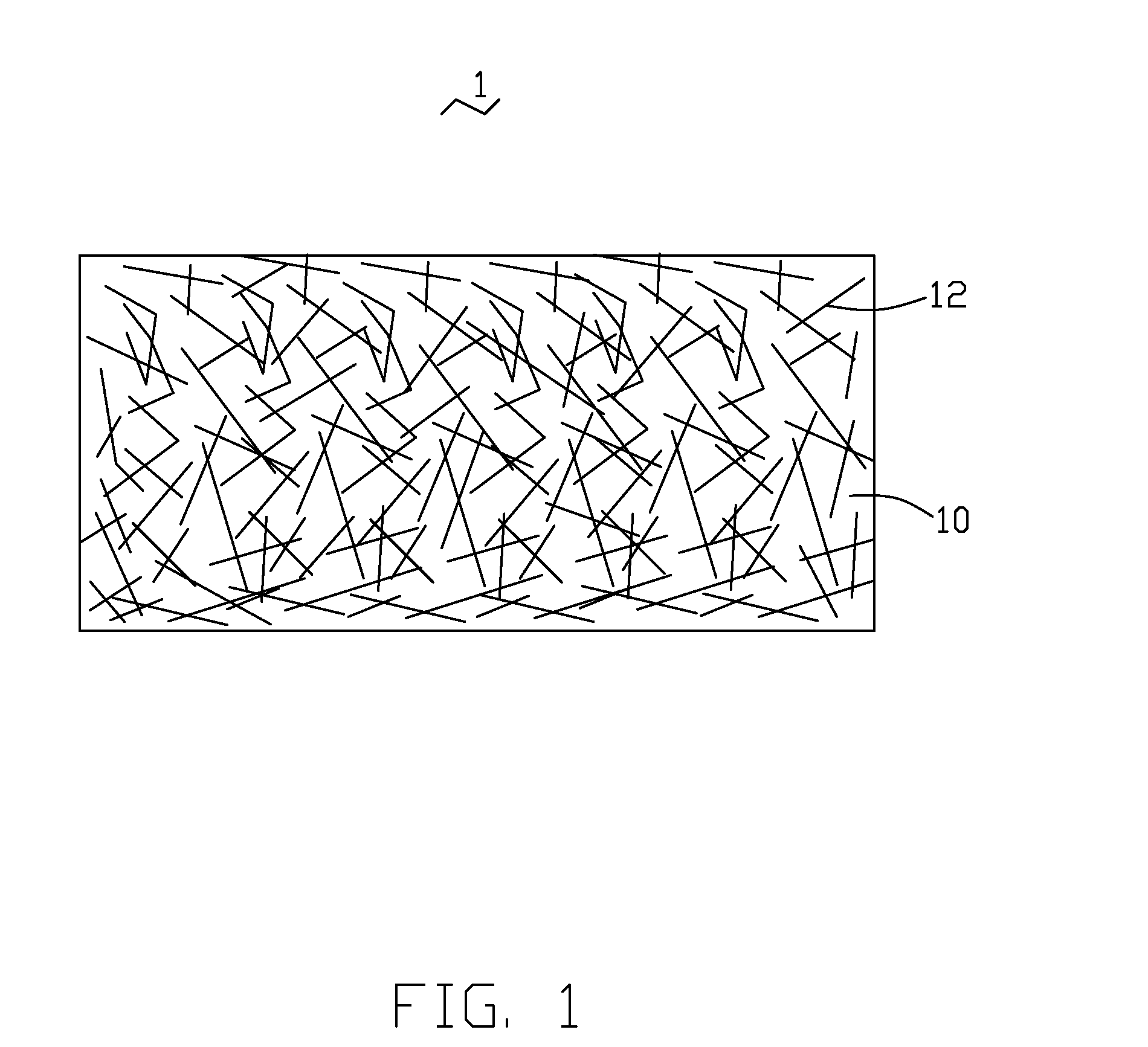
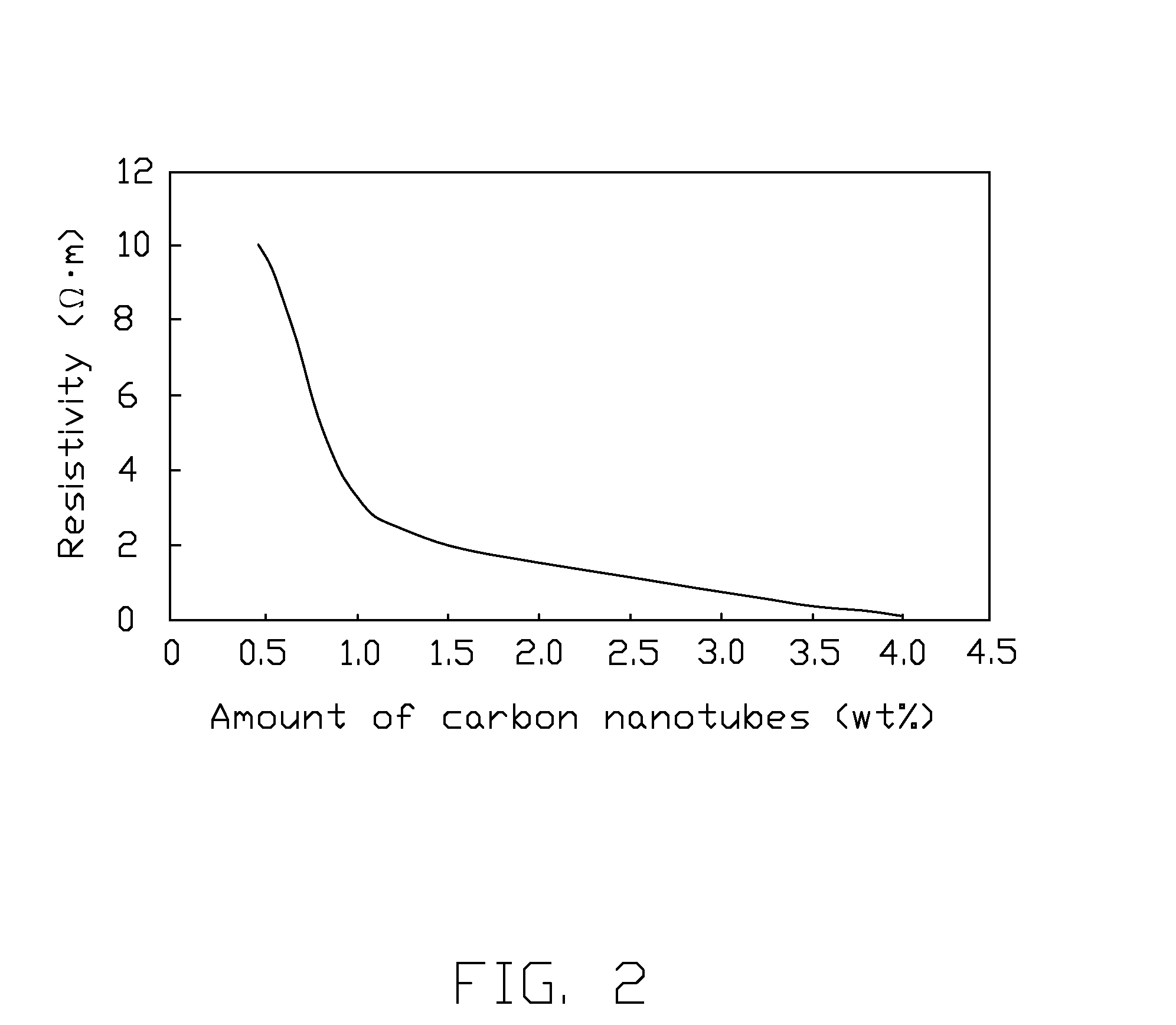
Flexible electrothermal composite and heating apparatus having the same
ActiveUS20070295714A1Increase flexibilityLow mechanical strengthLayered productsSpecial tyresCarbon nanotubePliability
The present invention relates to a flexible electrothermal composite. In one embodiment, a flexible electorthermal composite includes a flexible polymer matrix and a number of carbon nanotubes dispersed in the matrix, the carbon nanotubes forming a plurality of conductive network in the polymer. The flexible electrothermal composite has high flexibility, resistance and intensity.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Impingement cooled heat sink with low pressure drop
InactiveUS7597135B2Reduced life-timeIncrease pressureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSystem pressureHeat spreader
Owner:COOLIT SYSTEMS INC
Luminescent display device
ActiveUS20110128211A1Improve design flexibilityReduced life-timeStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
A luminescent display device includes a substrate and a thin-film transistor above the substrate. The thin-film transistor includes a semiconductor layer, a gate insulating film on the semiconductor layer, a gate electrode on the gate insulating film, a source electrode, and a drain electrode. The luminescent display device further includes an interlayer insulating film on the gate electrode, a first capacitor electrode on the interlayer insulating film in a region above the gate electrode, and a luminescent element configured to be driven by a driver to produce luminescence. The driver includes the thin-film transistor, and the first capacitor electrode and the gate electrode constitute a capacitor.
Owner:JOLED INC
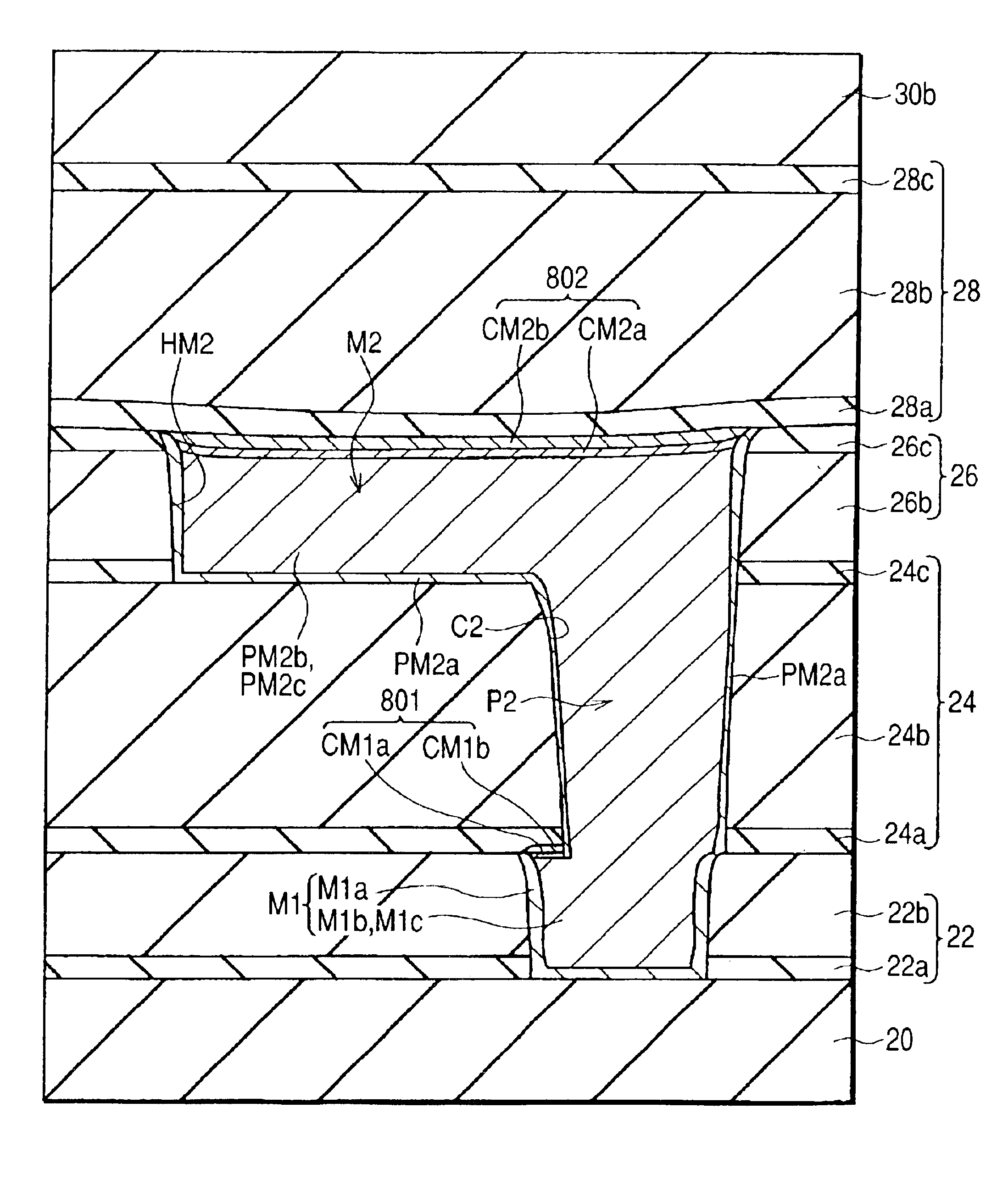
Method of manufacturing a semiconductor device having an interconnect embedded in an insulating film
InactiveUS6908847B2Reduced life-timeReduce contact areaSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorEngineering
A semiconductor device has first interlayer insulating film having a wiring trench; a wiring portion having a first barrier metal layer formed over side walls and bottom surface of the wiring trench, a first conductor layer formed over the first barrier metal layer to embed the wiring trench, and a capping barrier metal film formed over the first conductor layer; second interlayer insulating film formed over the first interlayer insulating film and having a connecting hole; and a connecting portion having a second barrier metal layer formed over side walls and bottom surface of the connecting hole, and a second conductor layer formed over the second barrier metal layer to embed the connecting hole; wherein, at a joint between the connecting portion and wiring portion, at least one of the second barrier metal layer and capping barrier metal film on the bottom surface of the connecting hole is removed.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor device and semiconductor device manufacturing method
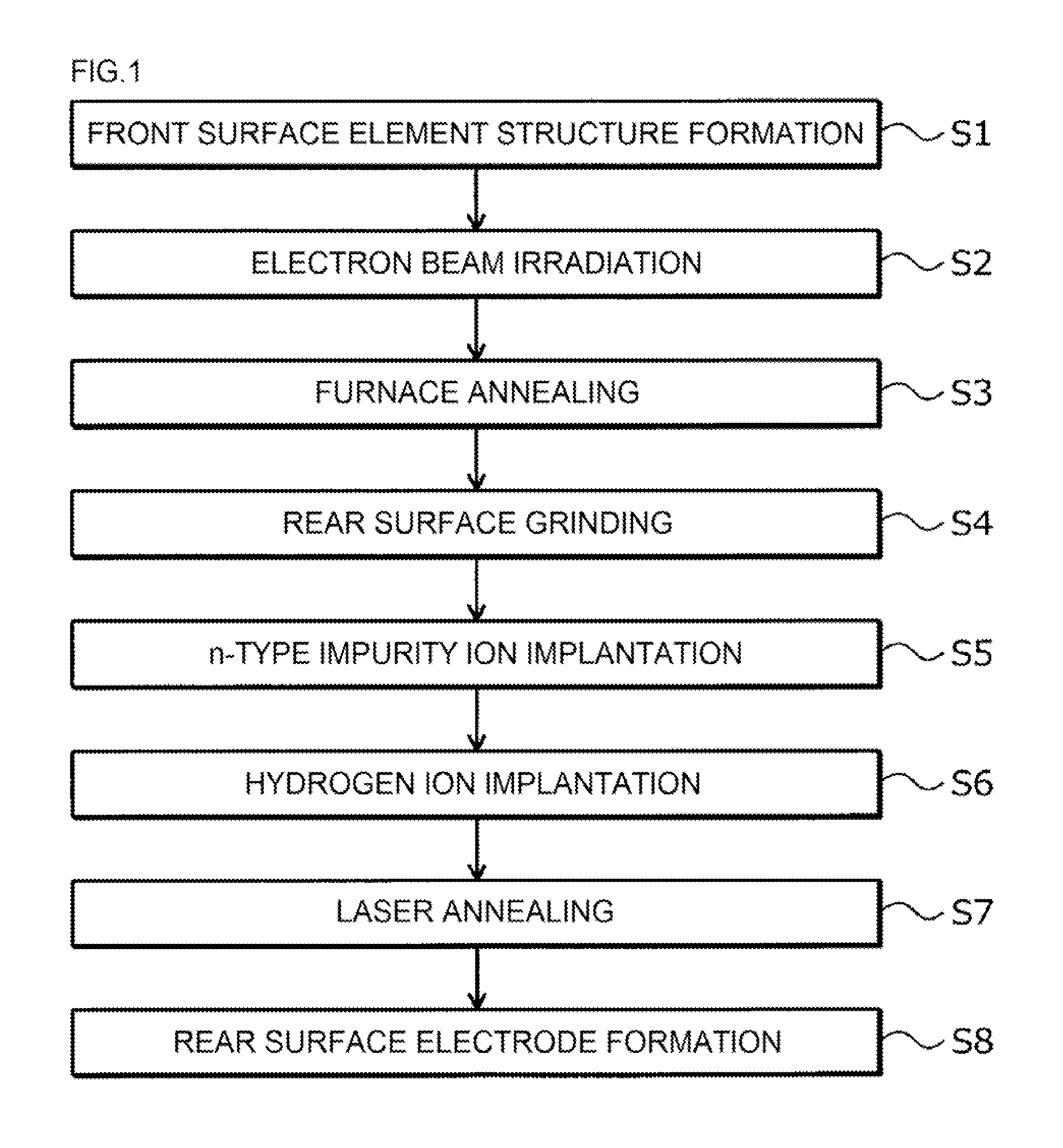
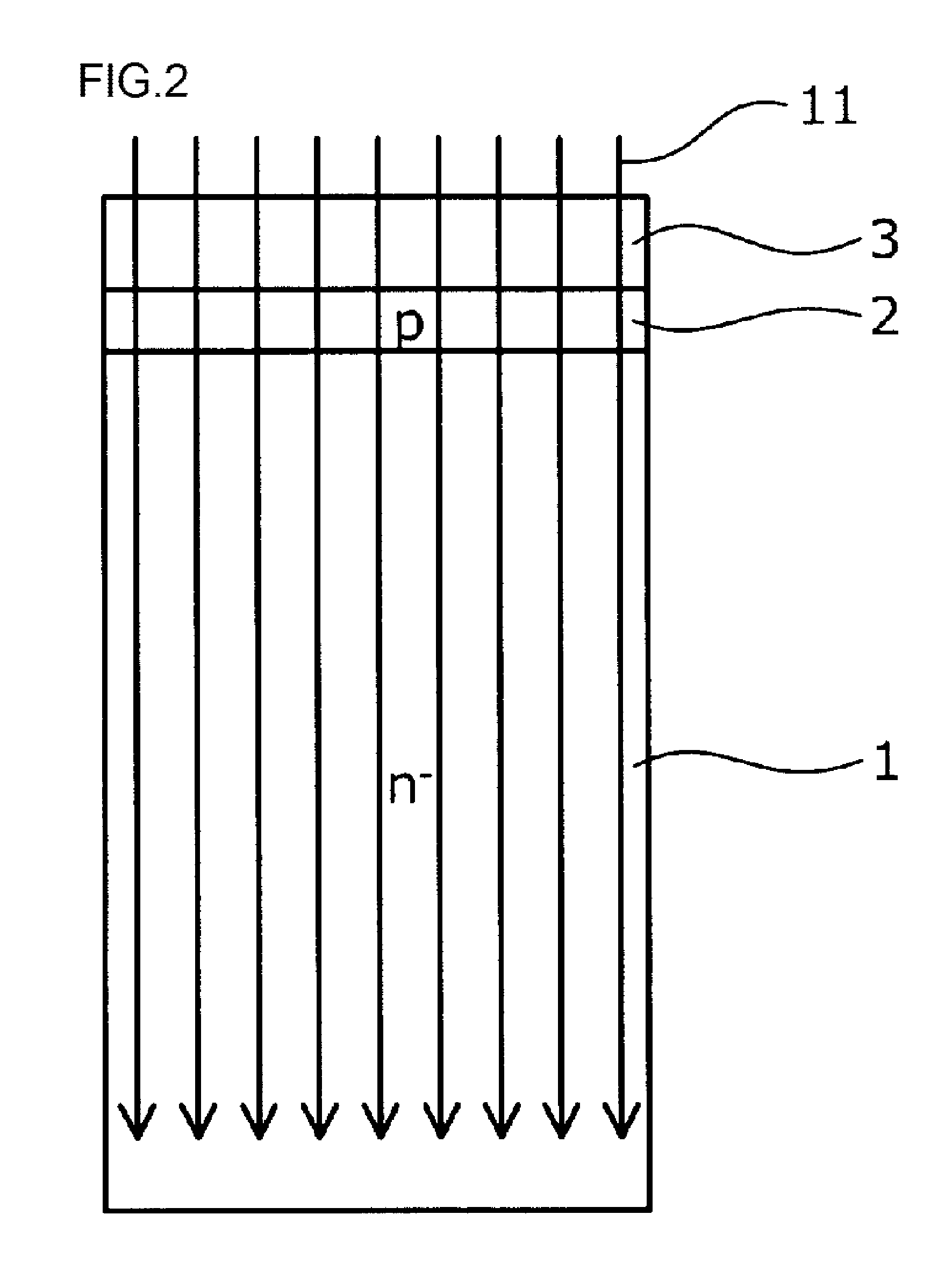
ActiveUS20150311279A1Longer lifetime of carrier particlesLimit drastically carrier lifetimeTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogen concentrationSurface layer
A front surface element structure is formed on the front surface side of an n−-type semiconductor substrate. Then defects are formed throughout an n−-type semiconductor substrate to adjust a carrier lifetime. Hydrogen ions are ion-implanted from a rear surface side of the n−-type semiconductor substrate, and a hydrogen implanted region having a hydrogen concentration higher than a hydrogen concentration of a bulk substrate is formed in the surface layer of a rear surface side of the n−-type semiconductor substrate.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Segmented/modular magnet bars for sputtering target
InactiveUS20080047831A1Easy and efficient adjustmentEasy and more cost-effective replacementCellsElectric discharge tubesMagnetMagnetic field
A modular and / or segmented magnetic bar for magnetron sputtering targets is provided. A magnet bar is made up of a plurality of magnet segments aligned in a substantially linear manner. One or more magnet bars may be provided. The positions of the magnet segments may be selectively adjusted to, for example, adjust magnetic field(s), replace magnet segment(s) that have been broken or damaged, and so forth.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com