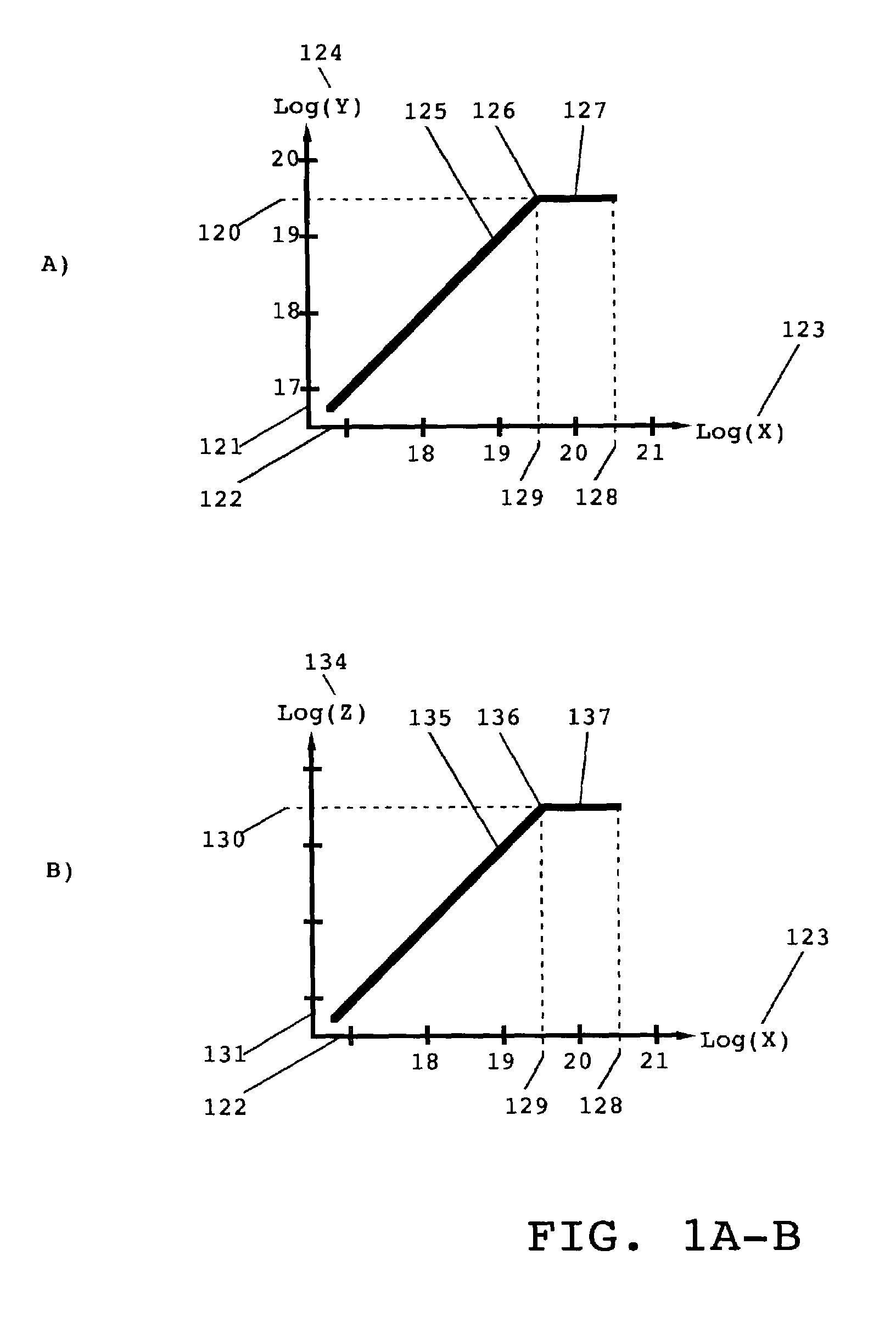
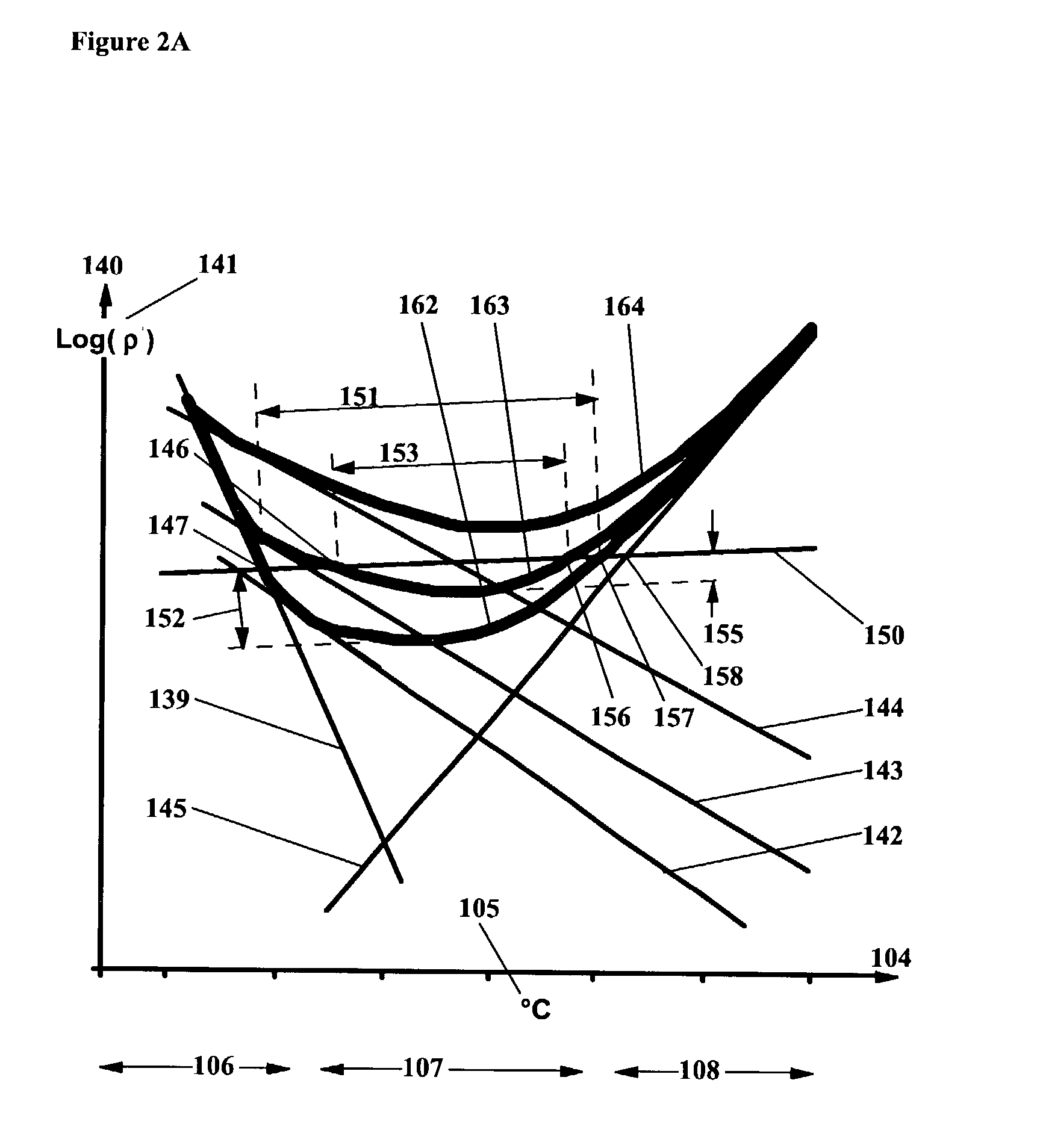
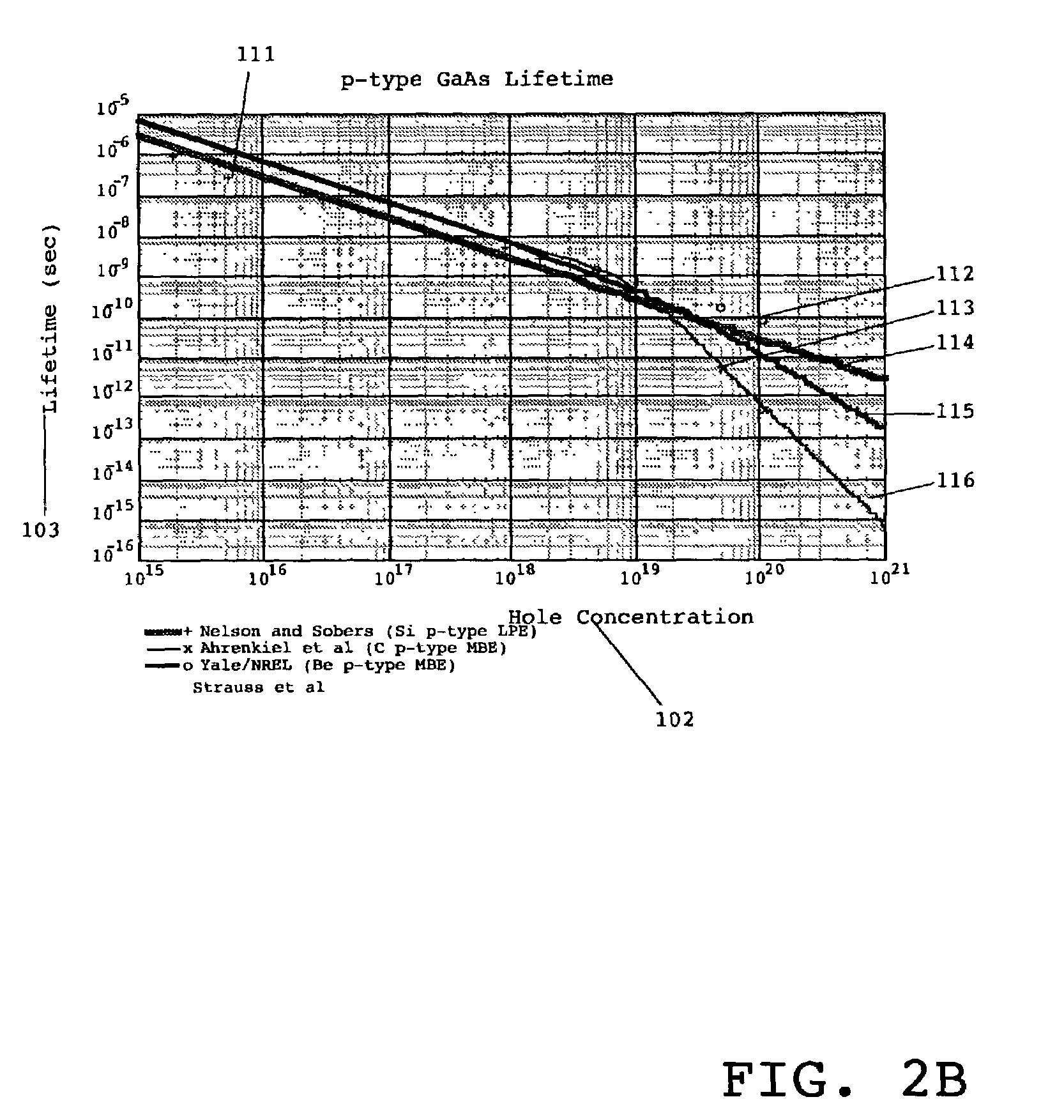
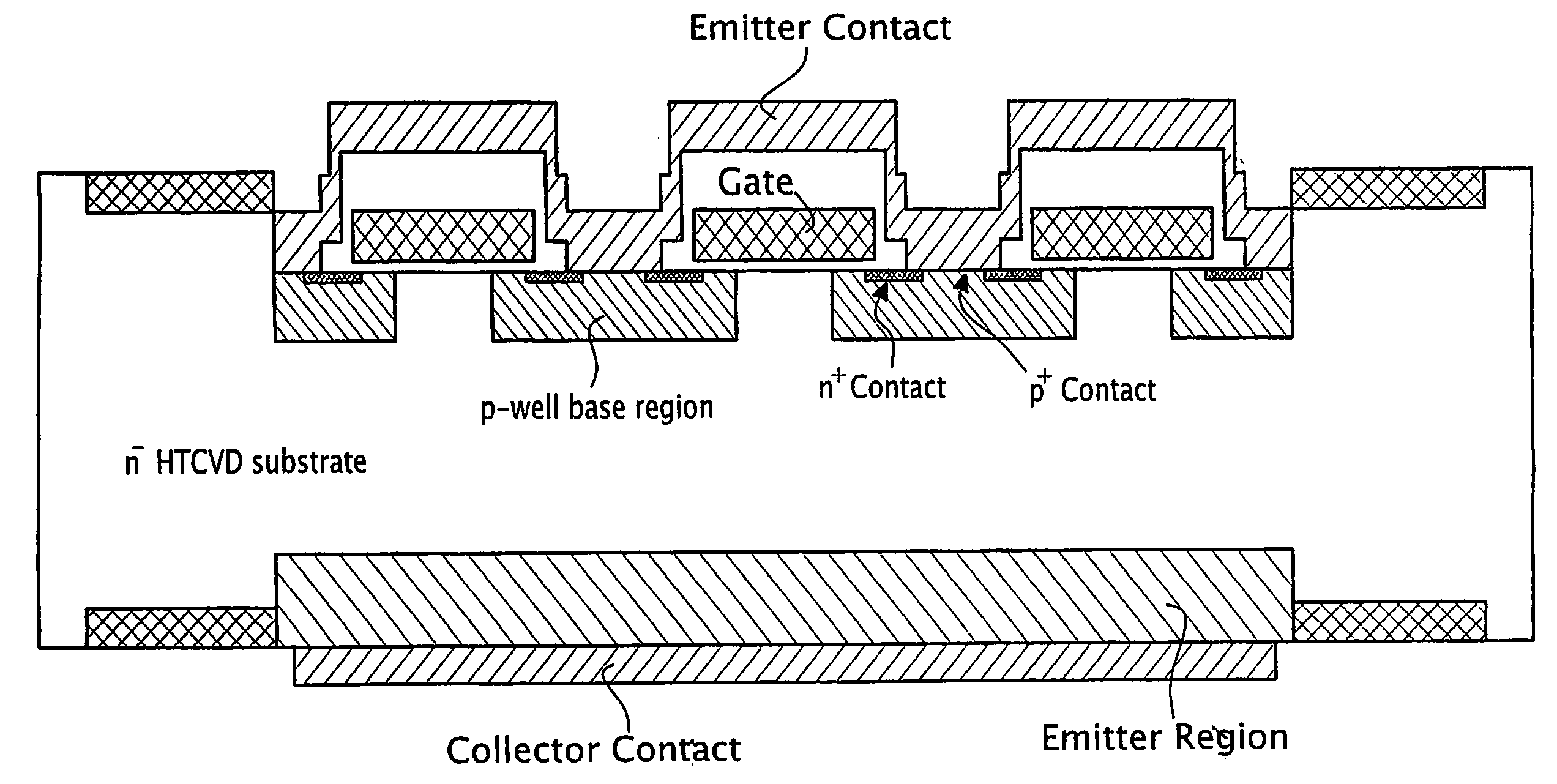
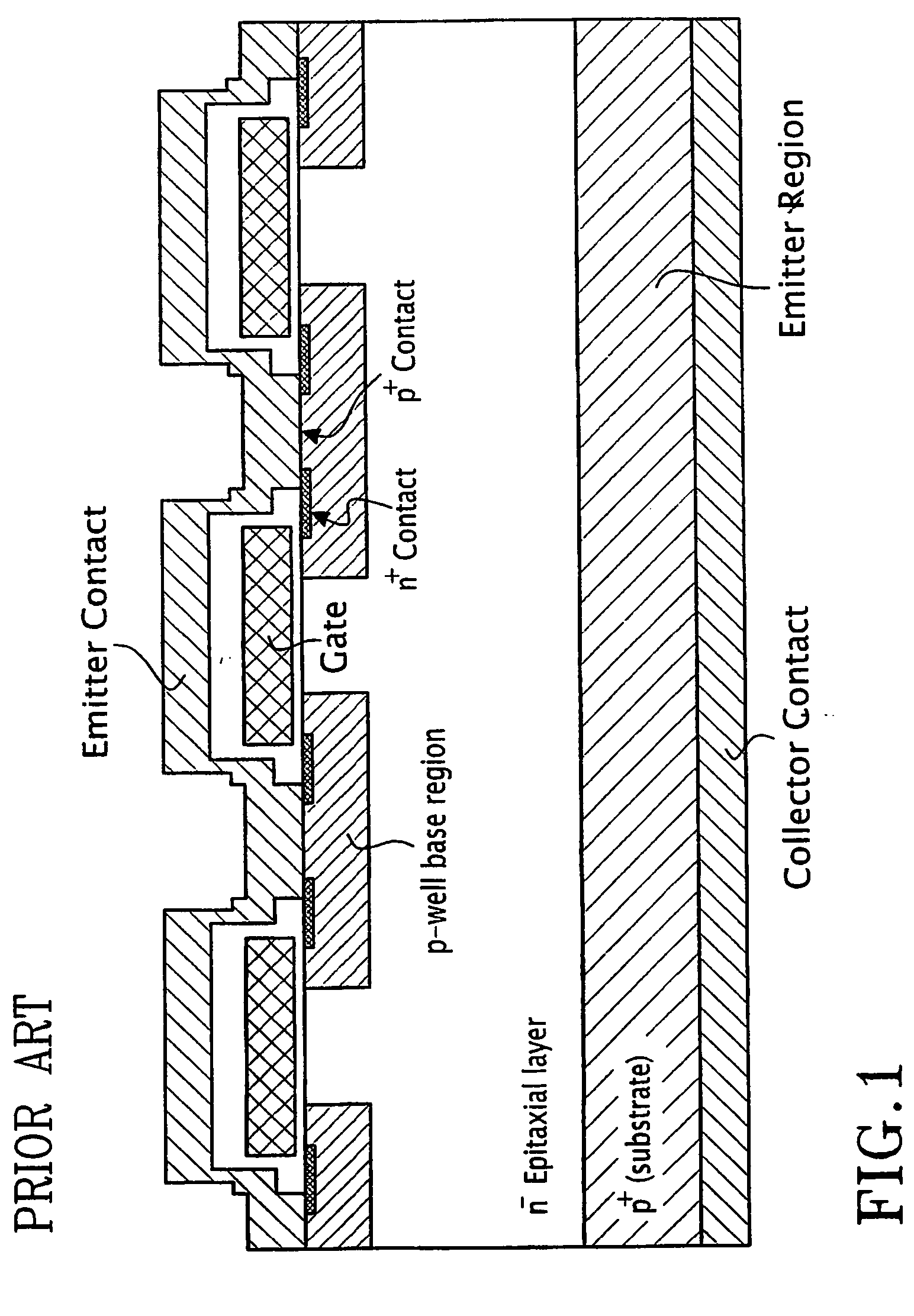
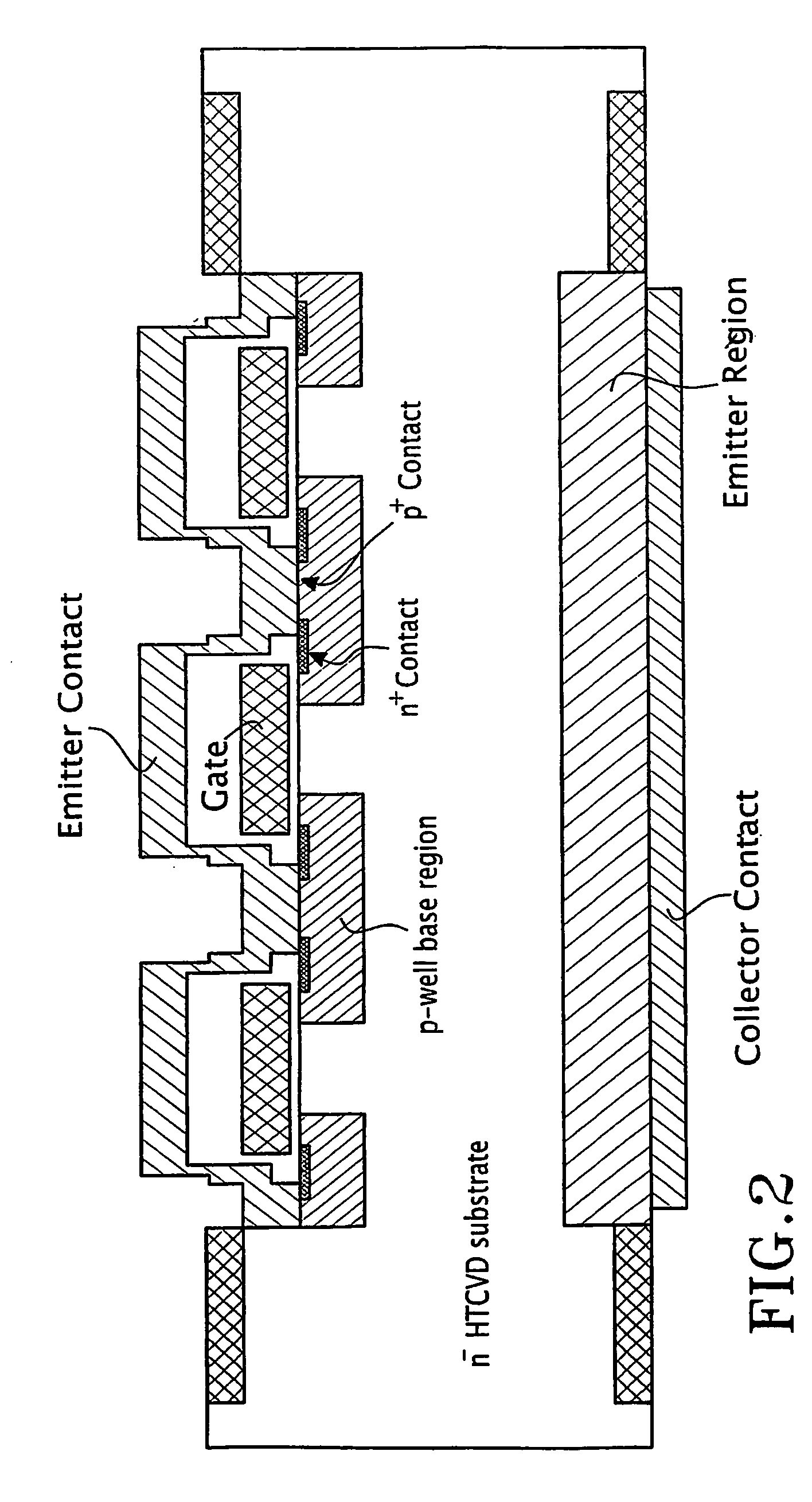
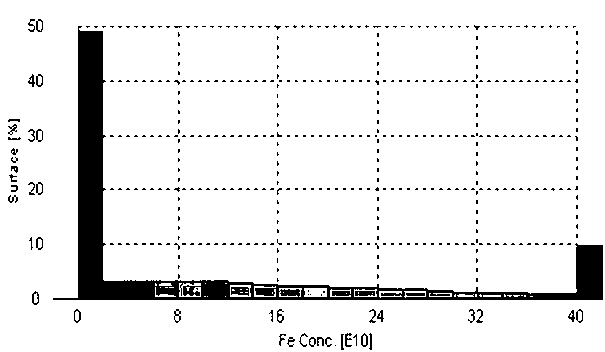
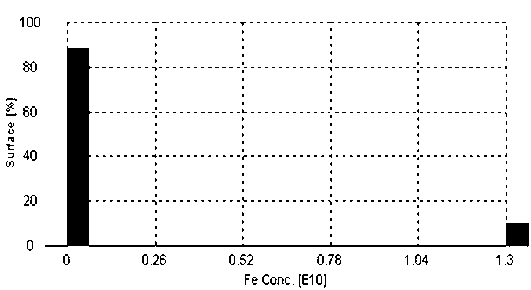
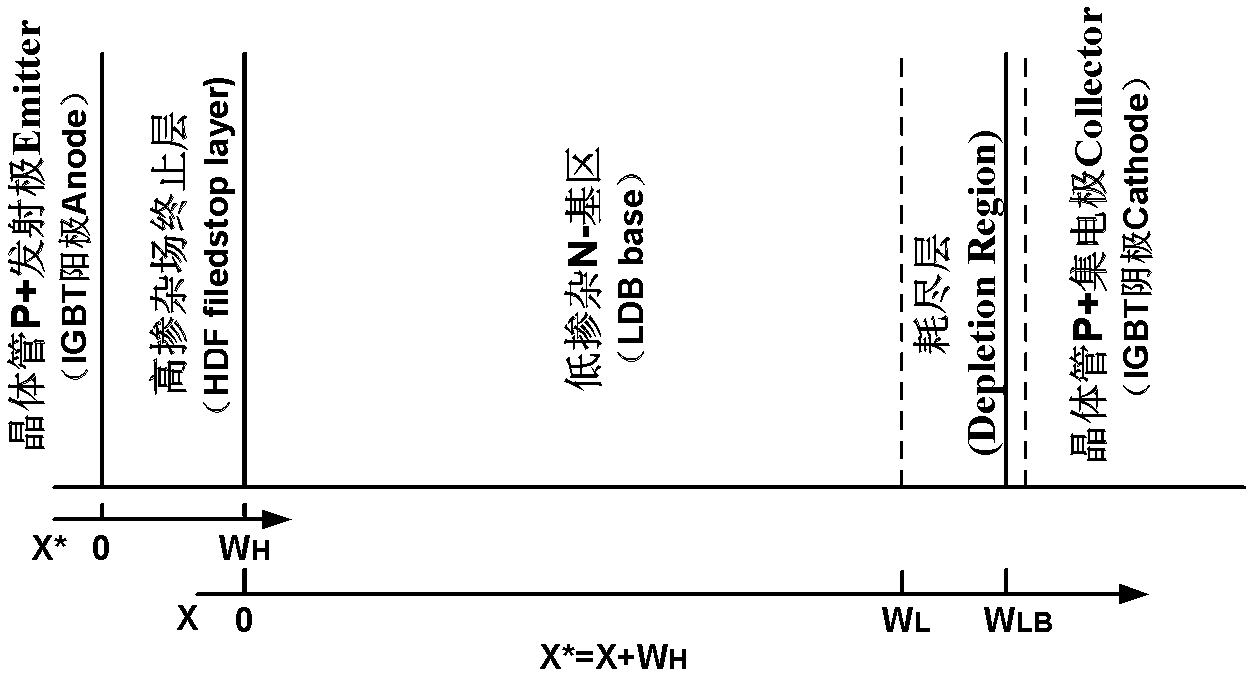
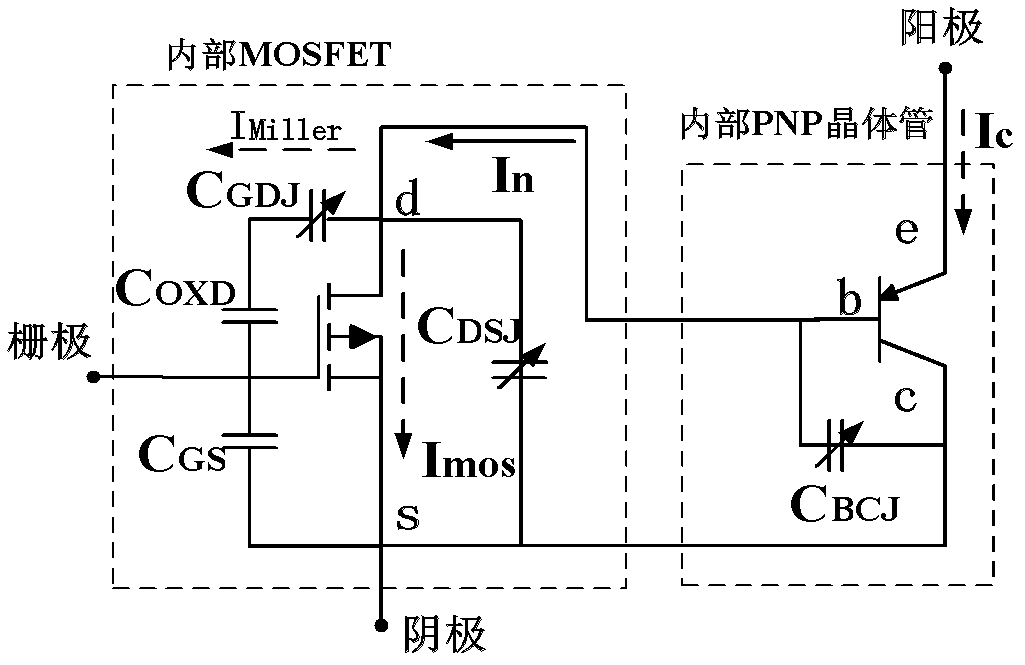
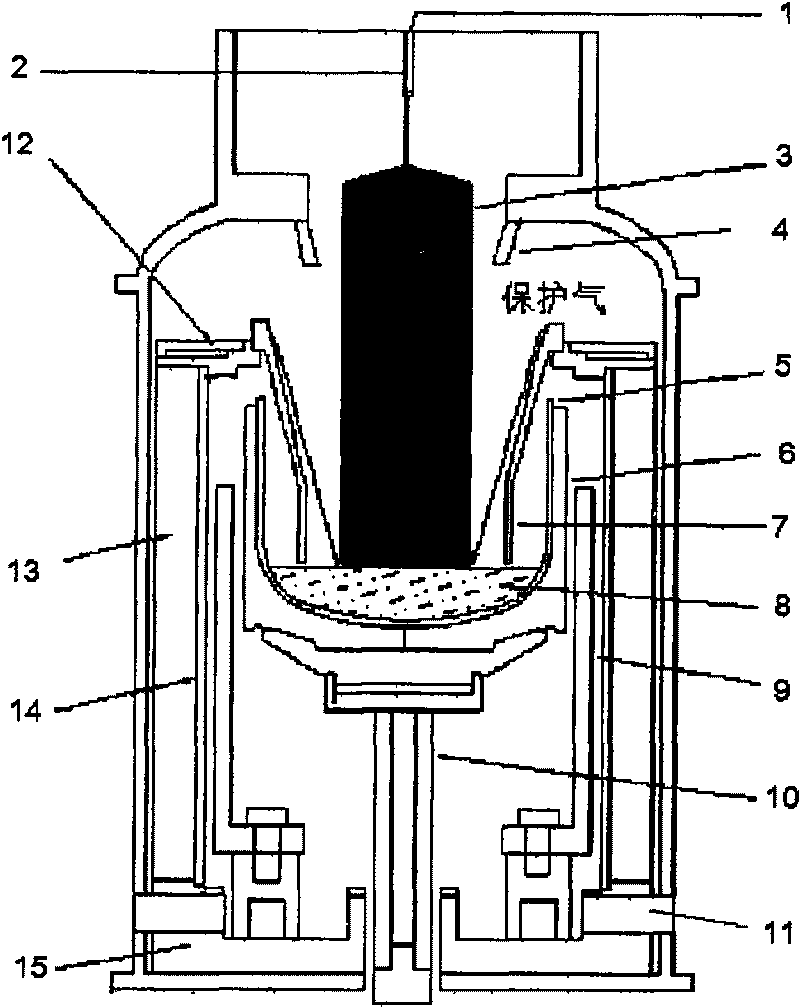
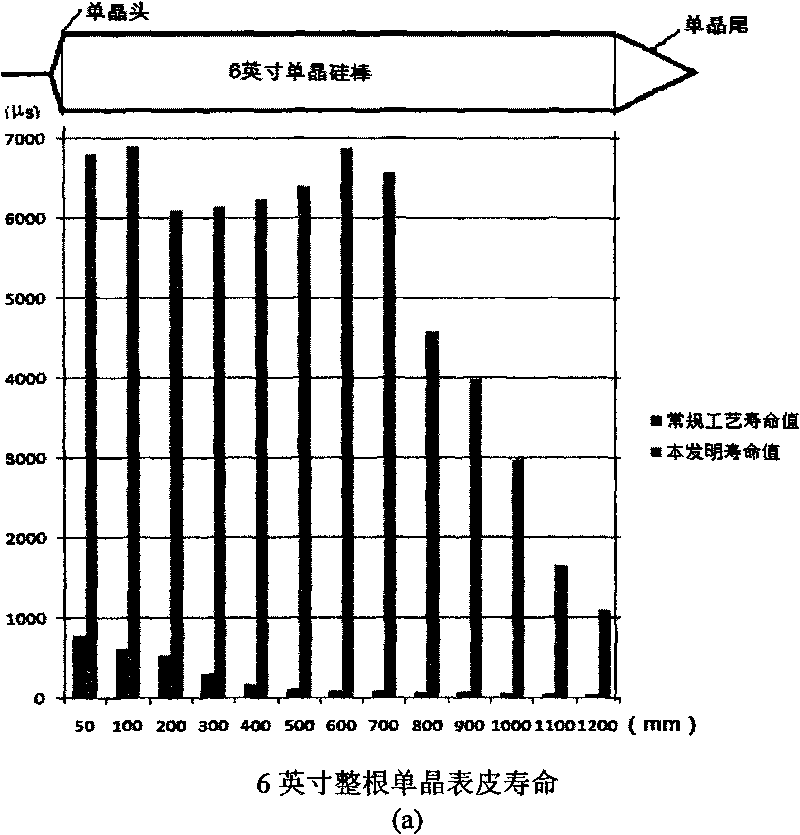
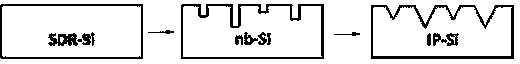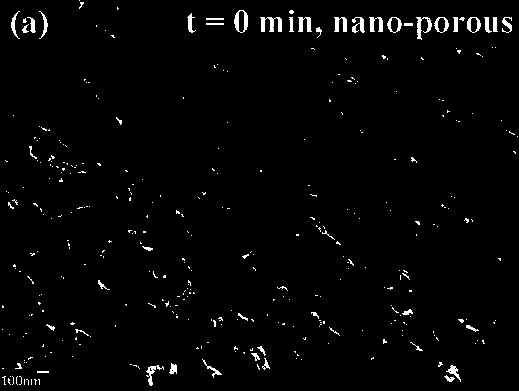Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
769 results about "Carrier lifetime" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A definition in semiconductor physics, carrier lifetime is defined as the average time it takes for a minority carrier to recombine. The process through which this is done is typically known as minority carrier recombination.
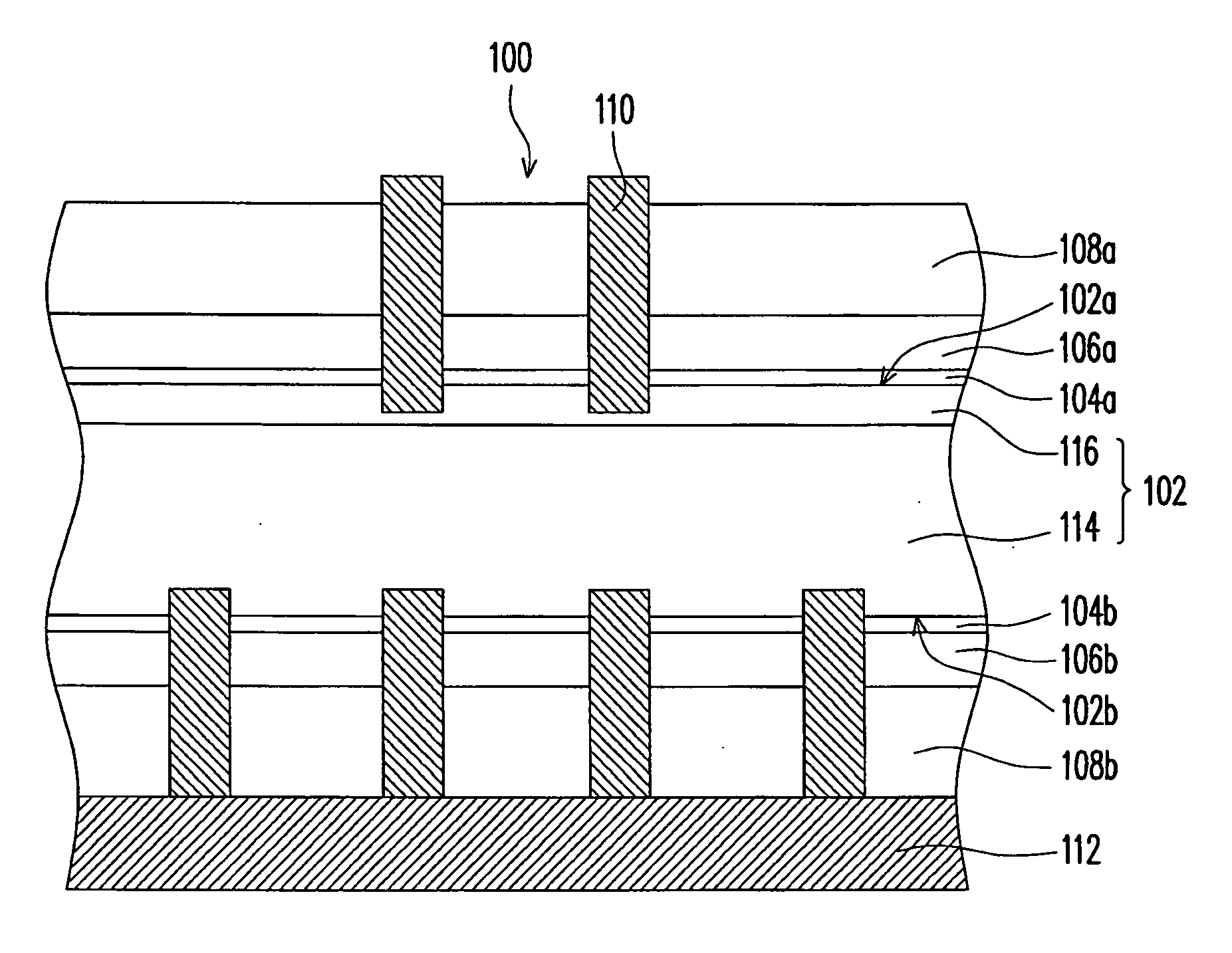
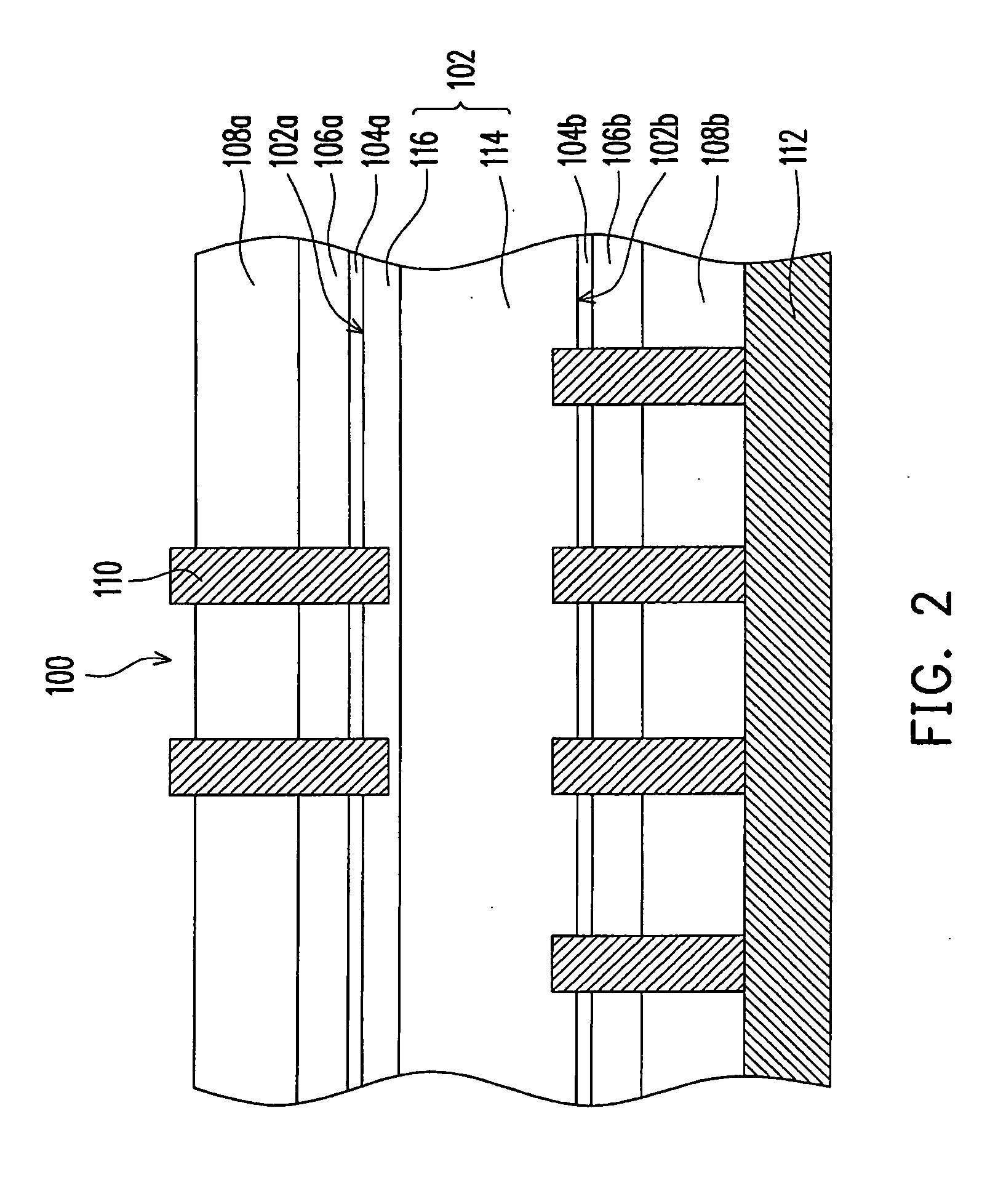
Passivation layer structure of solar cell and fabricating method thereof
InactiveUS20090165855A1Improve passivation effectImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyFinal product manufactureCoatingsCarrier lifetimePhotoelectric conversion efficiency
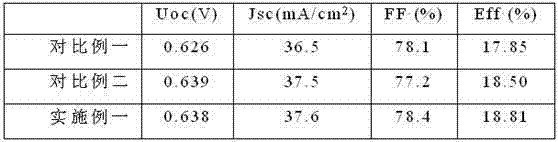
A passivation layer structure of a solar cell, disposed on a substrate, is provided. The passivation layer structure has a first passivation layer and a second passivation layer. The first passivation layer is disposed on the substrate. The second passivation layer is disposed between the substrate and the first passivation layer, and the material of the second passivation layer is an oxide of the material of the substrate. Since the second passivation layer is disposed between the substrate and the first passivation layer, the surface passivation effect and carrier lifetime of a photoelectric device are enhanced, and a photoelectric conversion efficiency of the solar cell is increased as well.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Methods of hyperdoping semiconductor materials and hyperdoped semiconductor materials and devices
InactiveUS20030121468A1Avoiding and mitigating formationEasy to operateTransistorPolycrystalline material growthSide effectSemiconductor materials
Methods are disclosed for producing highly doped semiconductor materials. Using the invention, one can achieve doping densities that exceed traditional, established carrier saturation limits without deleterious side effects. Additionally, highly doped semiconductor materials are disclosed, as well as improved electronic and optoelectronic devices / components using said materials. The innovative materials and processes enabled by the invention yield significant performance improvements and / or cost reductions for a wide variety of semiconductor-based microelectronic and optoelectronic devices / systems. Materials are grown in an anion-rich environment, which, in the preferred embodiment, are produced by moderate substrate temperatures during growth in an oxygen-poor environment. The materials exhibit fewer non-radiative recombination centers at higher doping concentrations than prior art materials, and the highly doped state of matter can exhibit a minority carrier lifetime dominated by radiative recombination at higher doping levels and higher majority carrier concentrations than achieved in prior art materials. Important applications enabled by these novel materials include high performance electronic or optoelectronic devices, which can be smaller and faster, yet still capture or emit light efficiently, and high performance electronics, such as transistors, which can be smaller and faster, yet cooler.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Silicon carbide for crystalline silicon solar cell surface passivation
InactiveUS20090250108A1Increases optical pathHigh internal reflection interfaceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationSilicon oxideCrystalline silicon
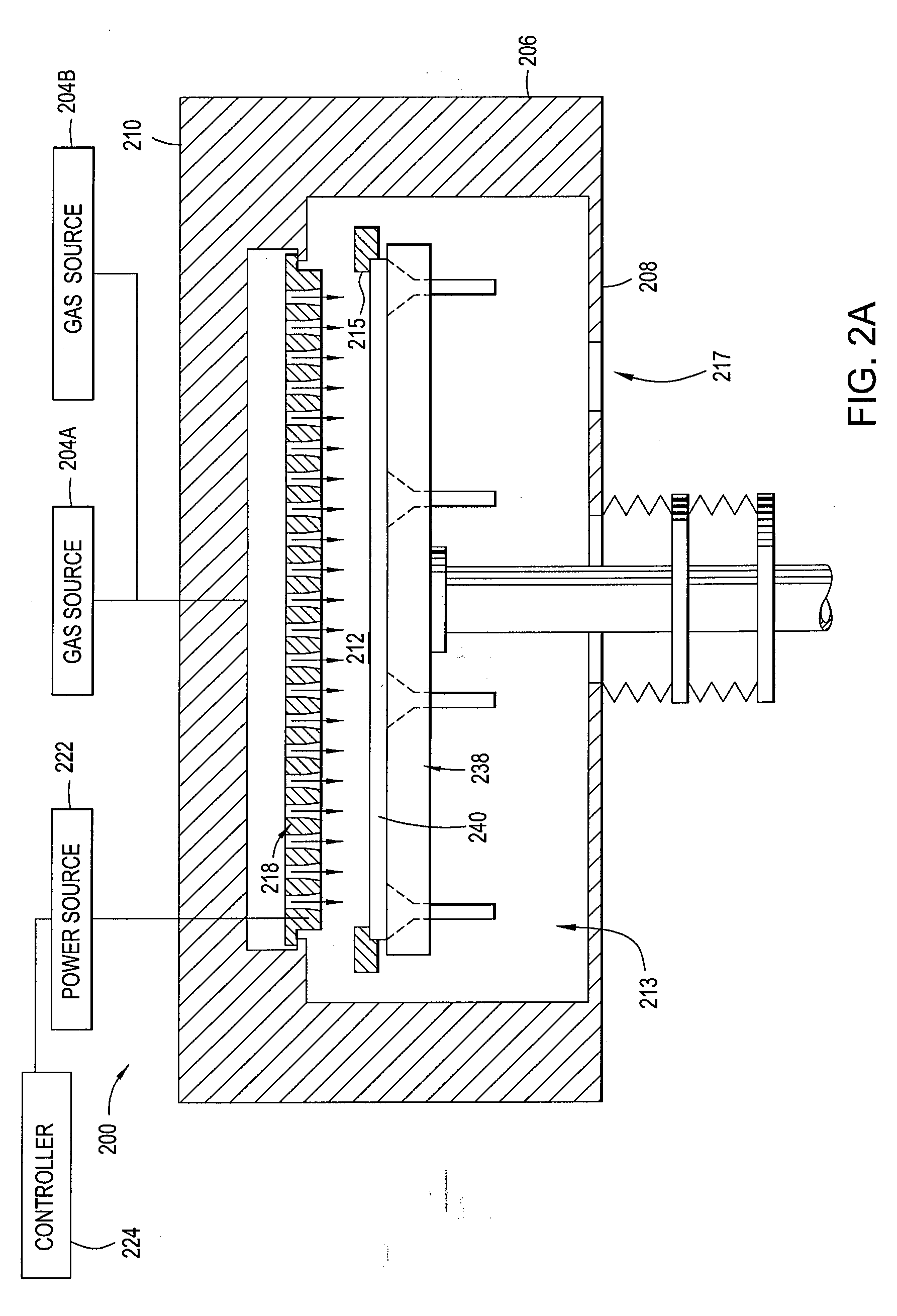
Embodiments of the present invention generally provide methods for depositing a silicon carbide (SiC) passivation layer that may act as a high-quality passivation layer for solar cells. Embodiments of the invention also provide methods for depositing a silicon carbide / silicon oxide passivation layer that acts as a high-quality rear surface passivation layer for solar cells. The methods described herein enable the use of deposition systems configured for processing large-area substrates for solar cell processing. According to embodiments of the invention, a SiC passivation layer may be formed with improved minority carrier lifetime measurements. The SiC passivation layer may be formed at a temperature between about 150° C. and 450° C., which is much lower than temperatures for thermal oxide passivation.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Semiconductor device
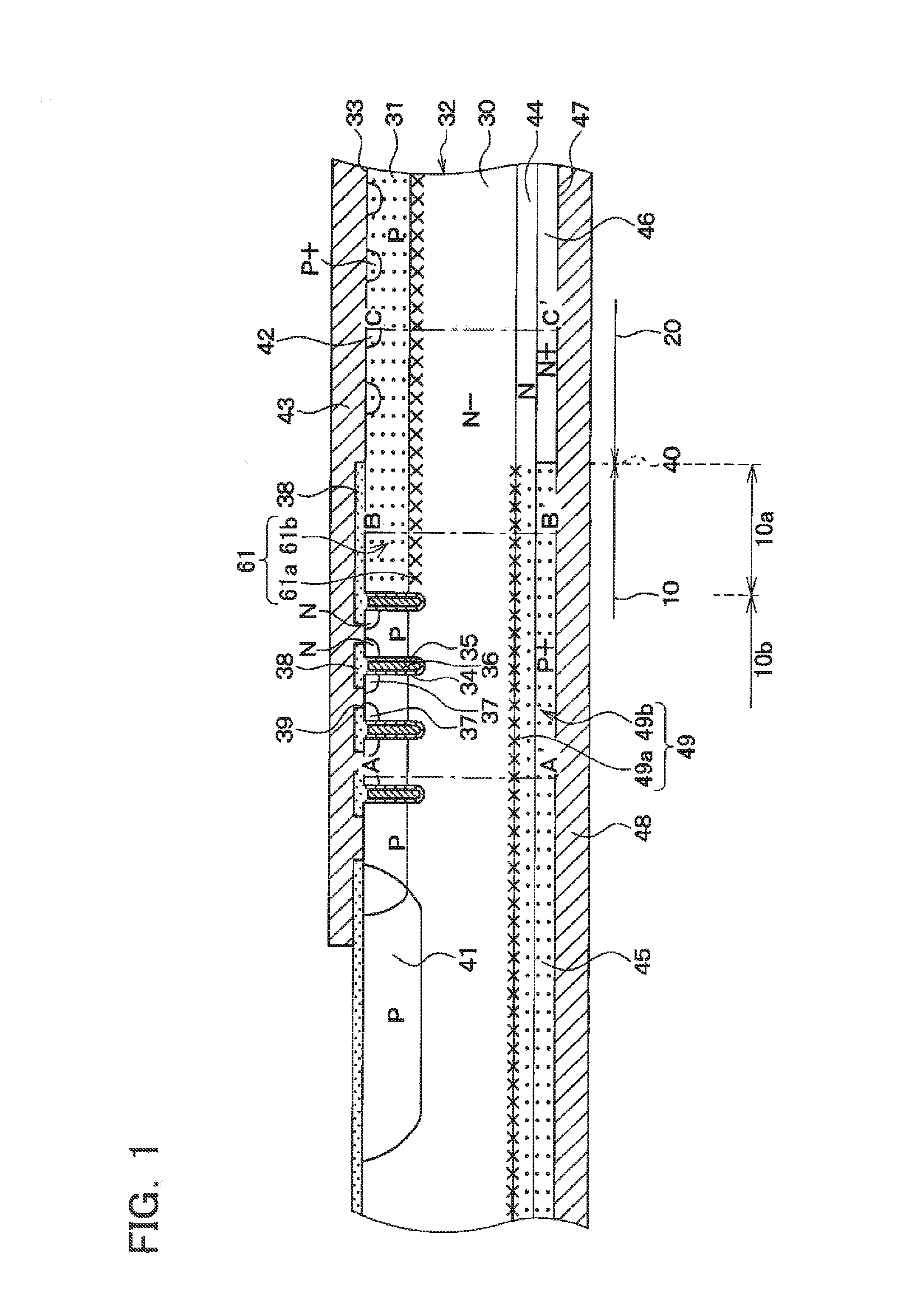
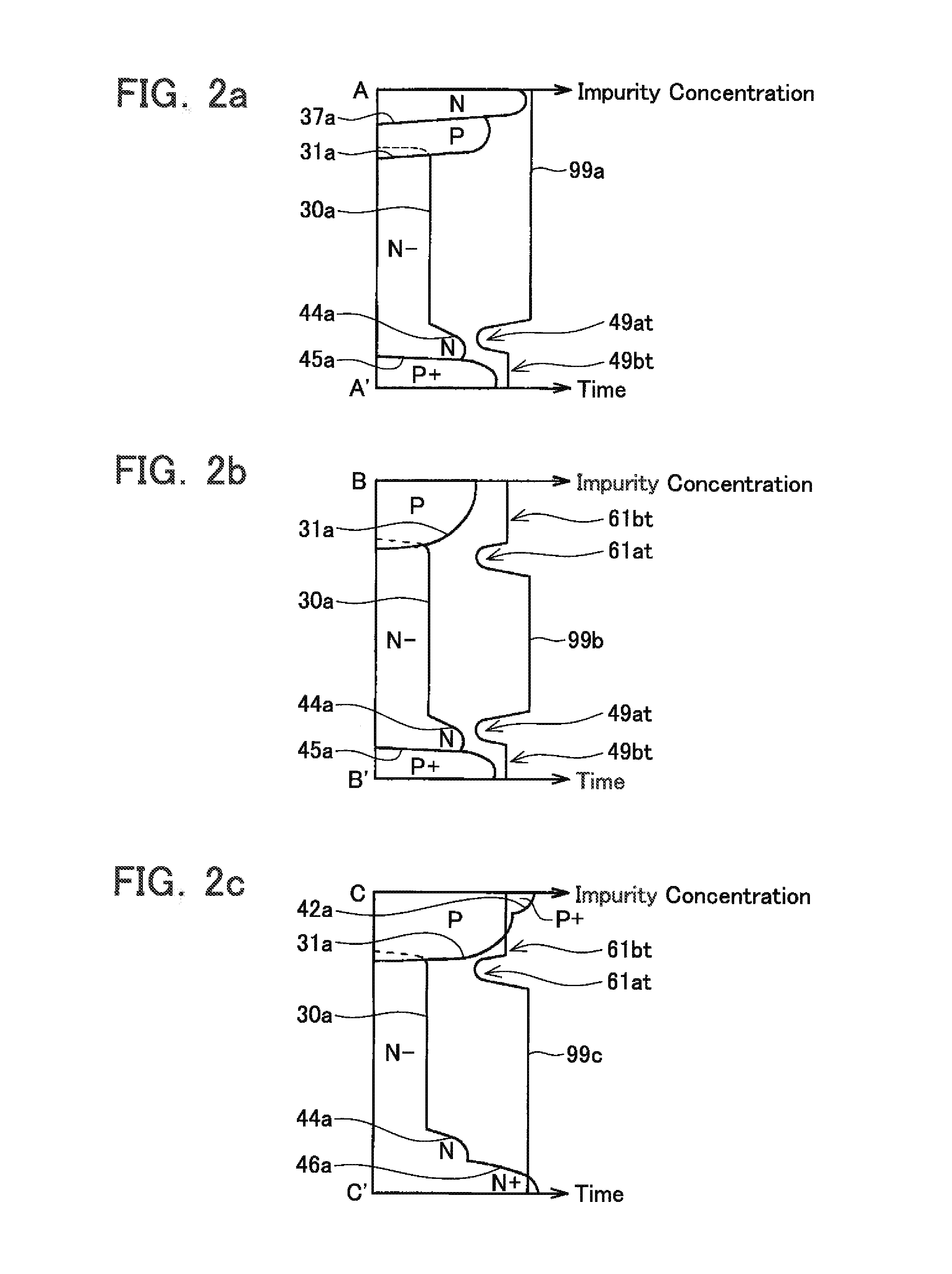
InactiveUS20080315297A1Increase resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectrical conductorCharge carrier
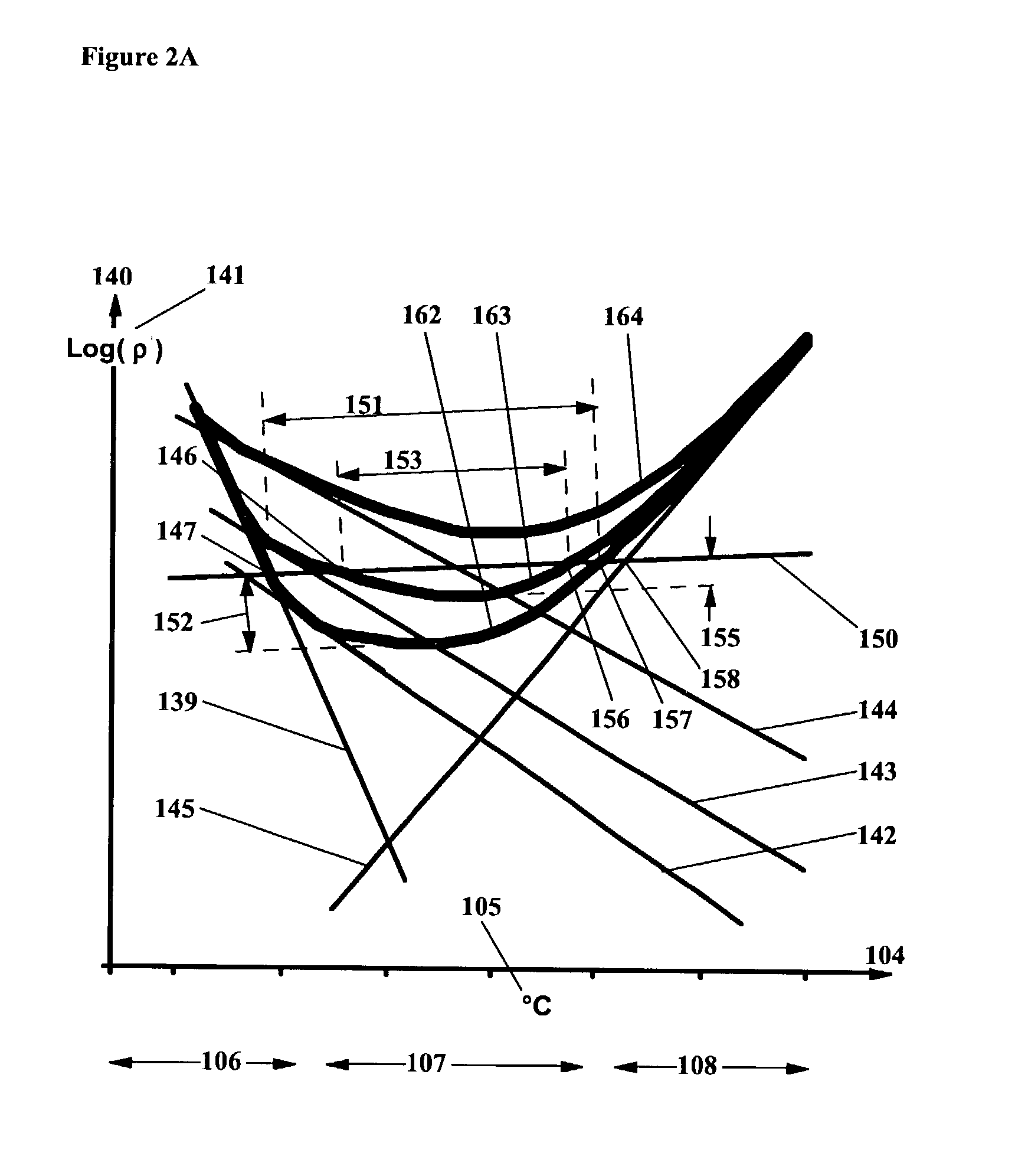
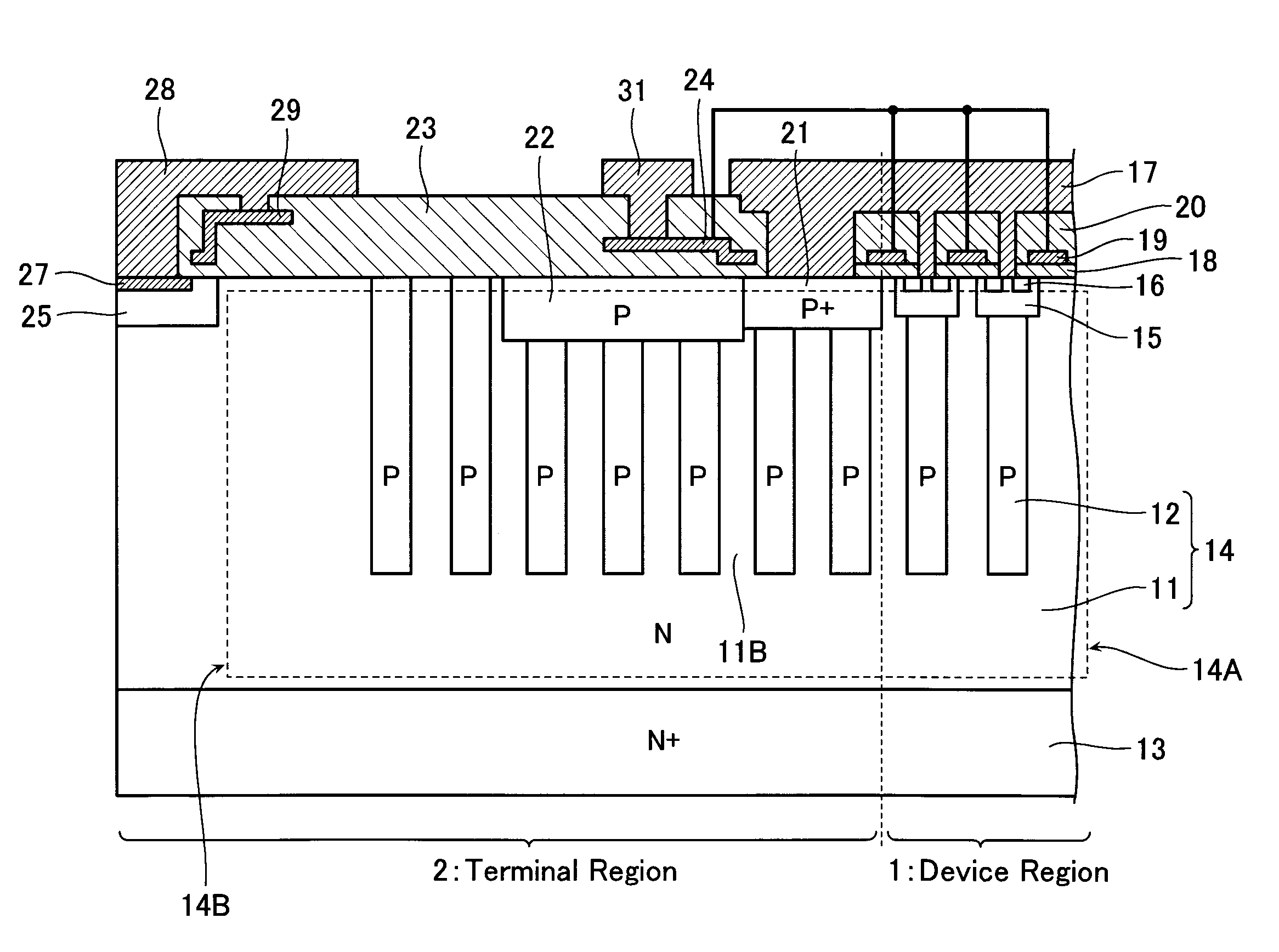
There is provided a semiconductor device having a drift layer with a pillar structure including first semiconductor layer portions of the first conduction type and second semiconductor layer portions of the second conduction type formed in pillars alternately and periodically on a semiconductor substrate. A device region includes a plurality of arrayed transistors composed of the first semiconductor layer portions and the second semiconductor layer portions. A terminal region is formed at the periphery of the device region without the transistors formed therein. The drift layer in the terminal region has a carrier lifetime lower than ⅕ the carrier lifetime in the drift layer in the device region.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
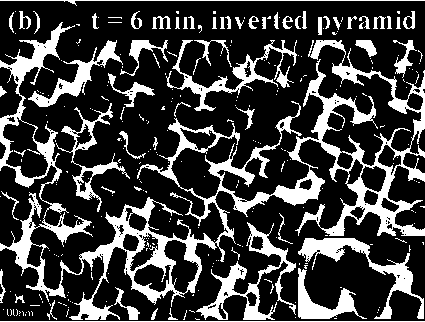
Method for forming inverted-pyramid porous surface nanometer texture on polycrystalline silicon and method for manufacturing short-wave reinforcing solar cell
InactiveCN103456804AExtend your lifeUniform and smooth microstructureFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationCharge carrierSolar cell
The invention discloses a method for forming an inverted-pyramid porous surface nanometer texture on polycrystalline silicon and a method for manufacturing a short-wave reinforcing solar cell. The method for forming the inverted-pyramid porous surface nanometer texture on the polycrystalline silicon and the method for manufacturing the short-wave reinforcing solar cell are suitable for the technical field of solar photovoltaic batteries. By means of a metal catalytic chemical corrosion method, a nanometer porous surface structure is formed on the polycrystalline silicon through HF, AgNO3, H2O2, HNO3 and other solutions, then partial samples are placed in a NaOH corrosive liquid with the concentration of 0.1-1% for surface modification of a nanometer inverted pyramid, a nanometer inverted pyramid silicon structure is formed, and the micro structure appearance of the nanometer inverted pyramid silicon structure is even and smooth, so that service life of a few effective charge carriers is greatly prolonged, and ultimately, in the nanometer texture surface structure, by means of changes of the thickness of a silicon nitride layer in the solar cell manufacturing process, a nanometer inverted pyramid silicon solar photovoltaic cell which is low in surface reflection rate and high in short wave spectrum response is prepared. The method for forming the inverted-pyramid porous surface nanometer texture on the polycrystalline silicon and the method for manufacturing the short-wave reinforcing solar cell are simple in process, convenient to operate, low in cost and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
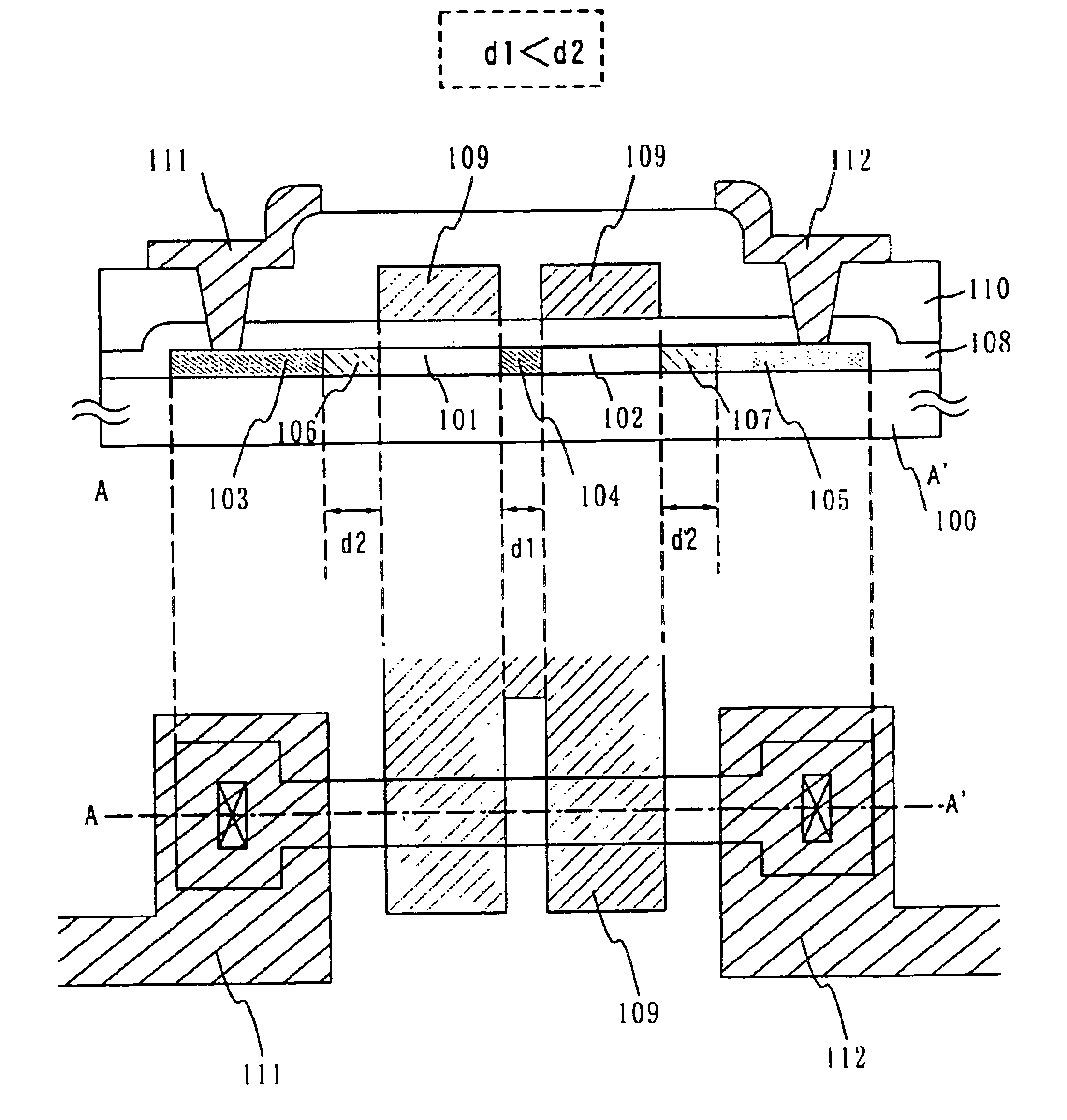
Semiconductor device, manufacturing method thereof, and display device
InactiveUS6897477B2Suppress mutationAvoid alternationTransistorSolid-state devicesHigh concentrationCharge carrier
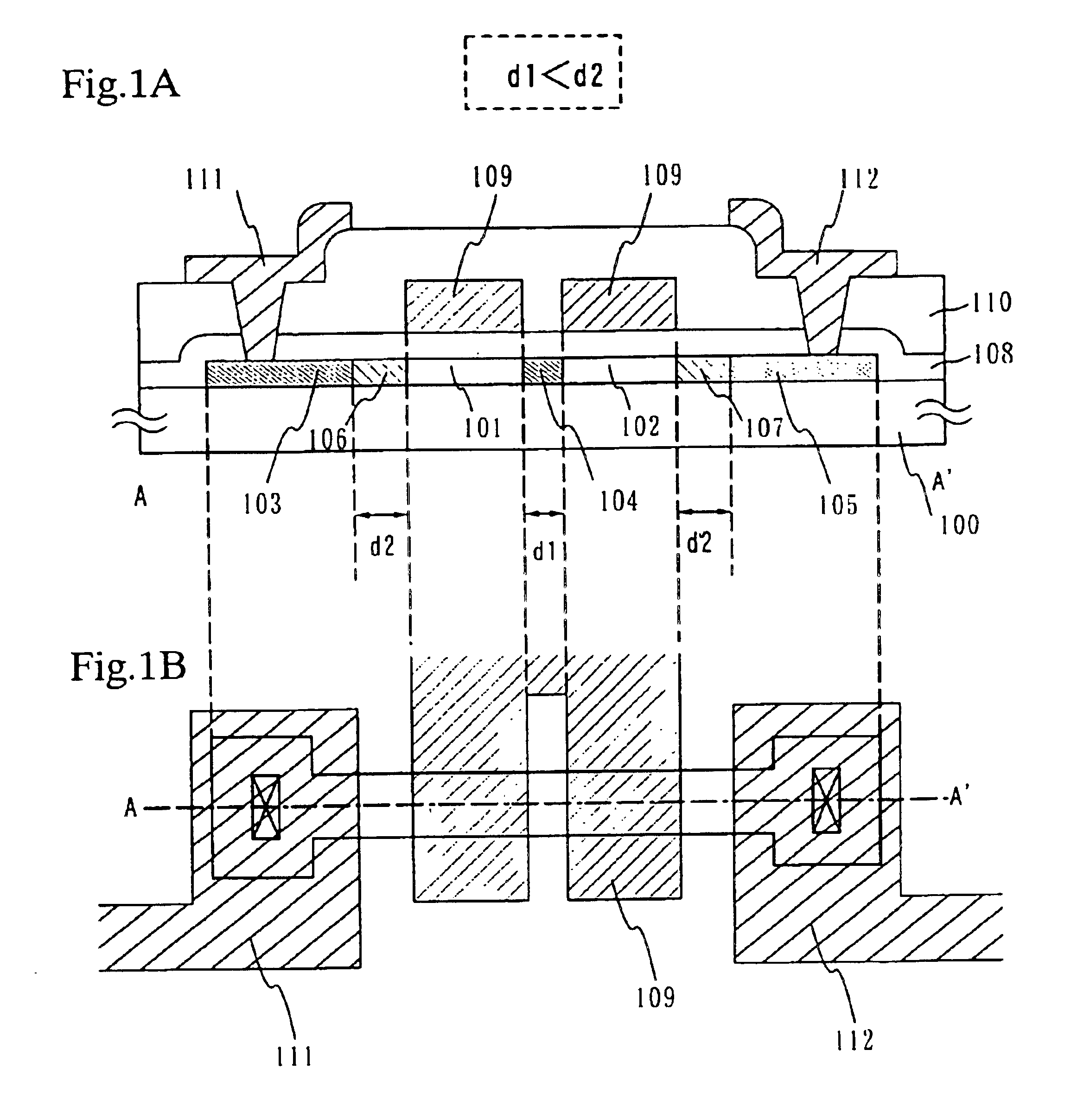
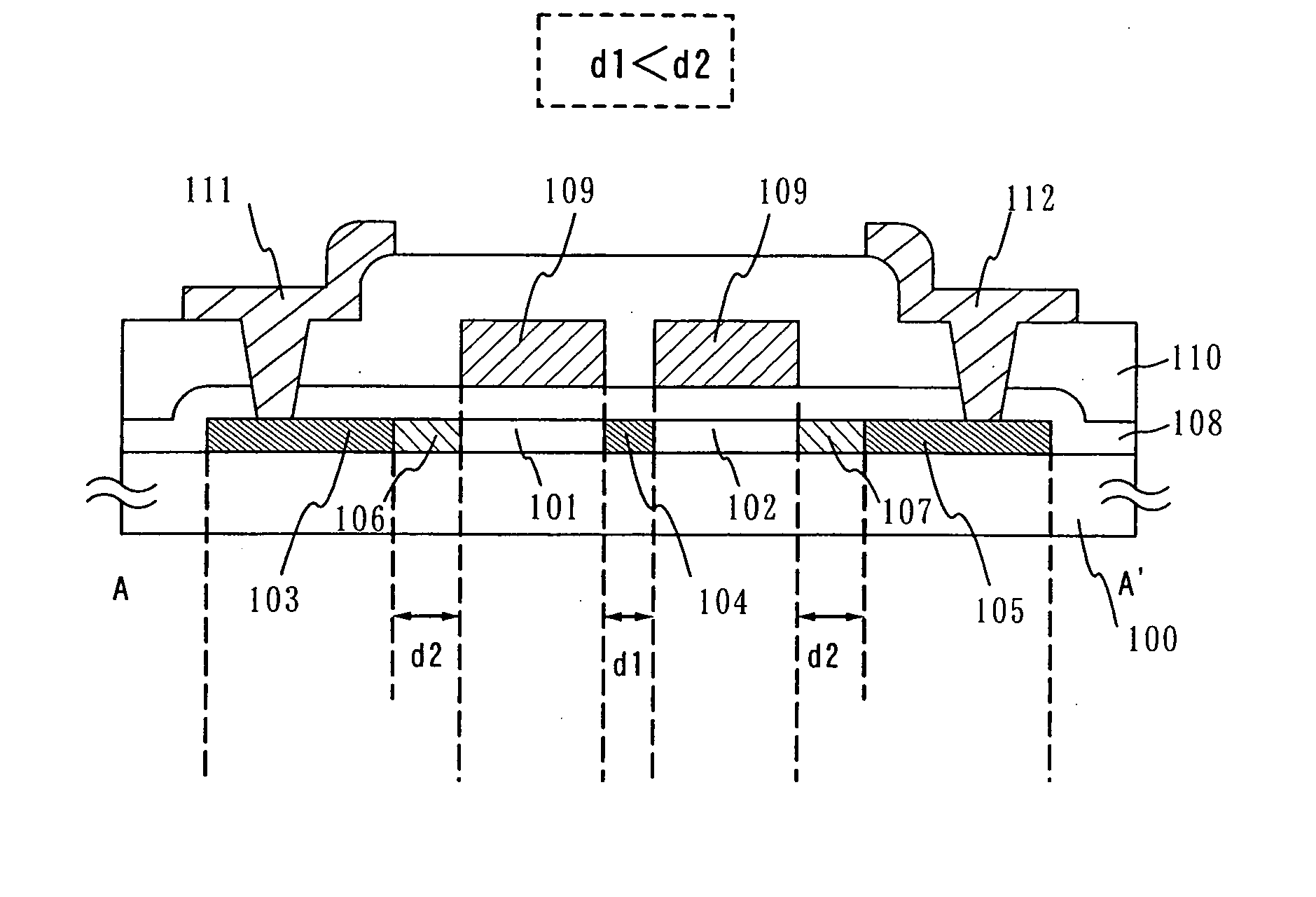
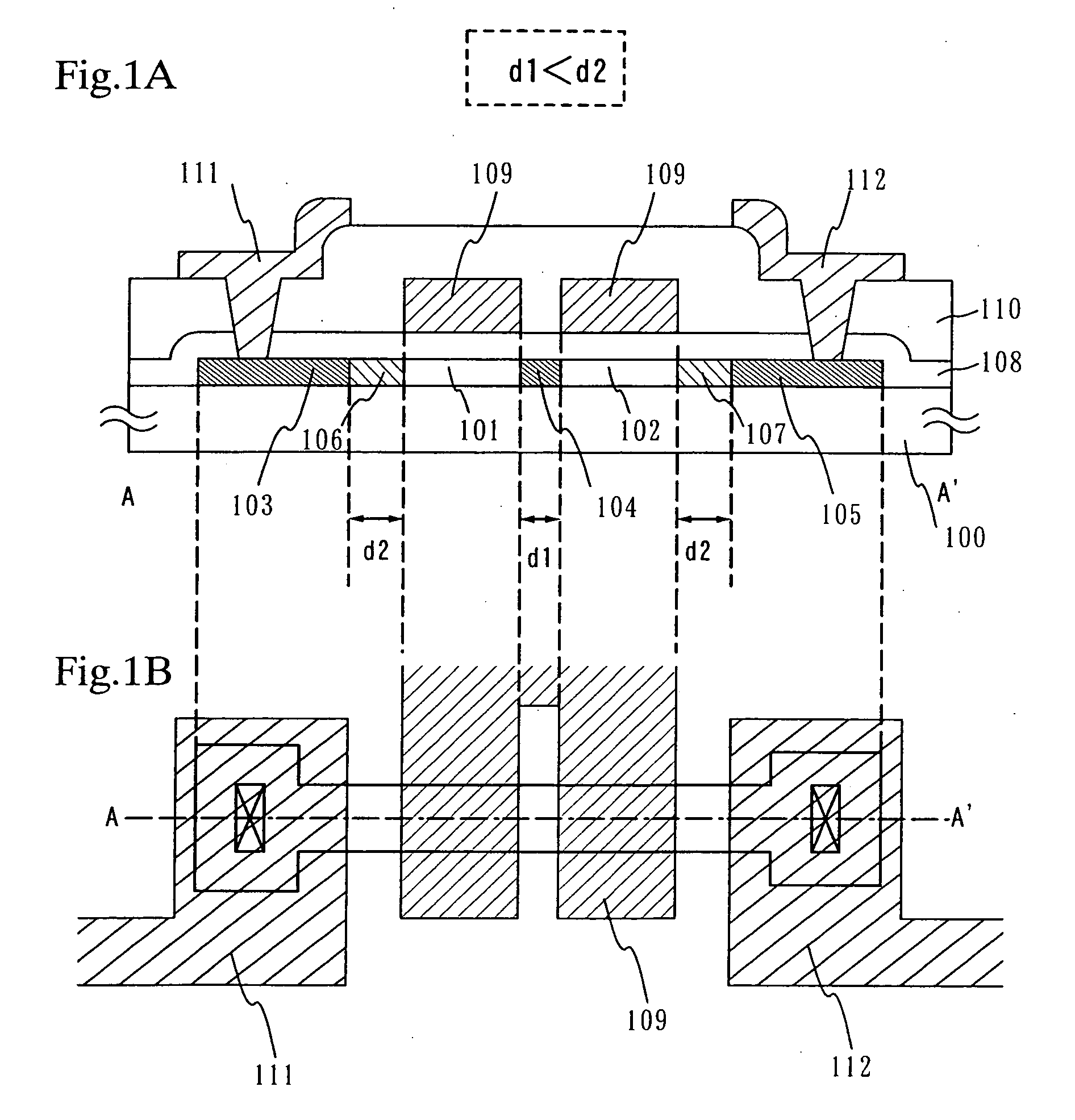
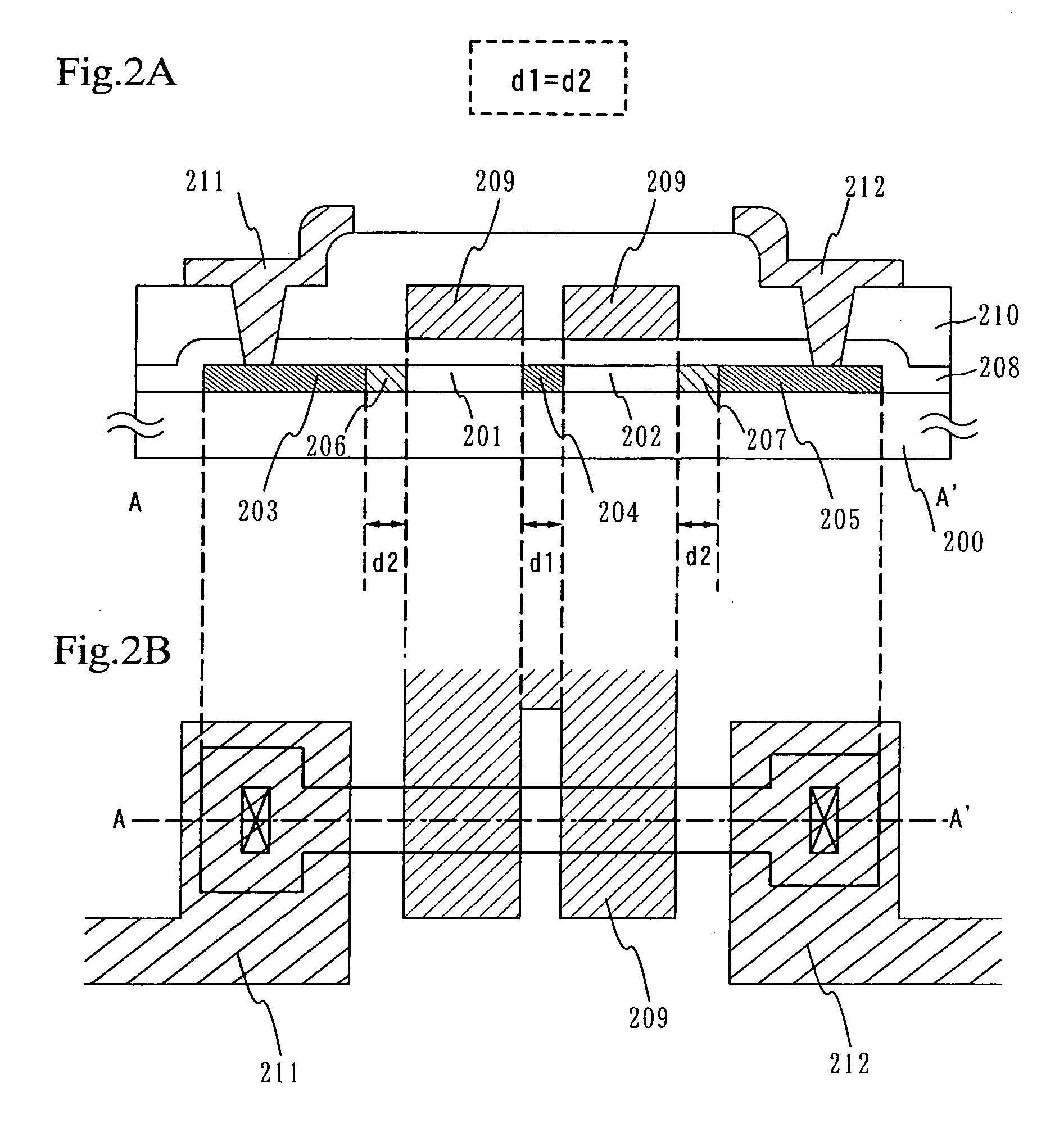
A multi-gate structure is used and a width (d1) of a high concentration impurity region sandwiched by two channel forming regions in a channel length direction is set to be shorter than a width (d2) of low concentration impurity regions in the channel length direction. Thus, a resistance of the entire semiconductor layer of a TFT which is in an on state is reduced to increase an on current. In addition, a carrier life time due to photoexcitation produced in the high concentration impurity region can be shortened to reduce light sensitivity.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device and semiconductor device manufacturing method
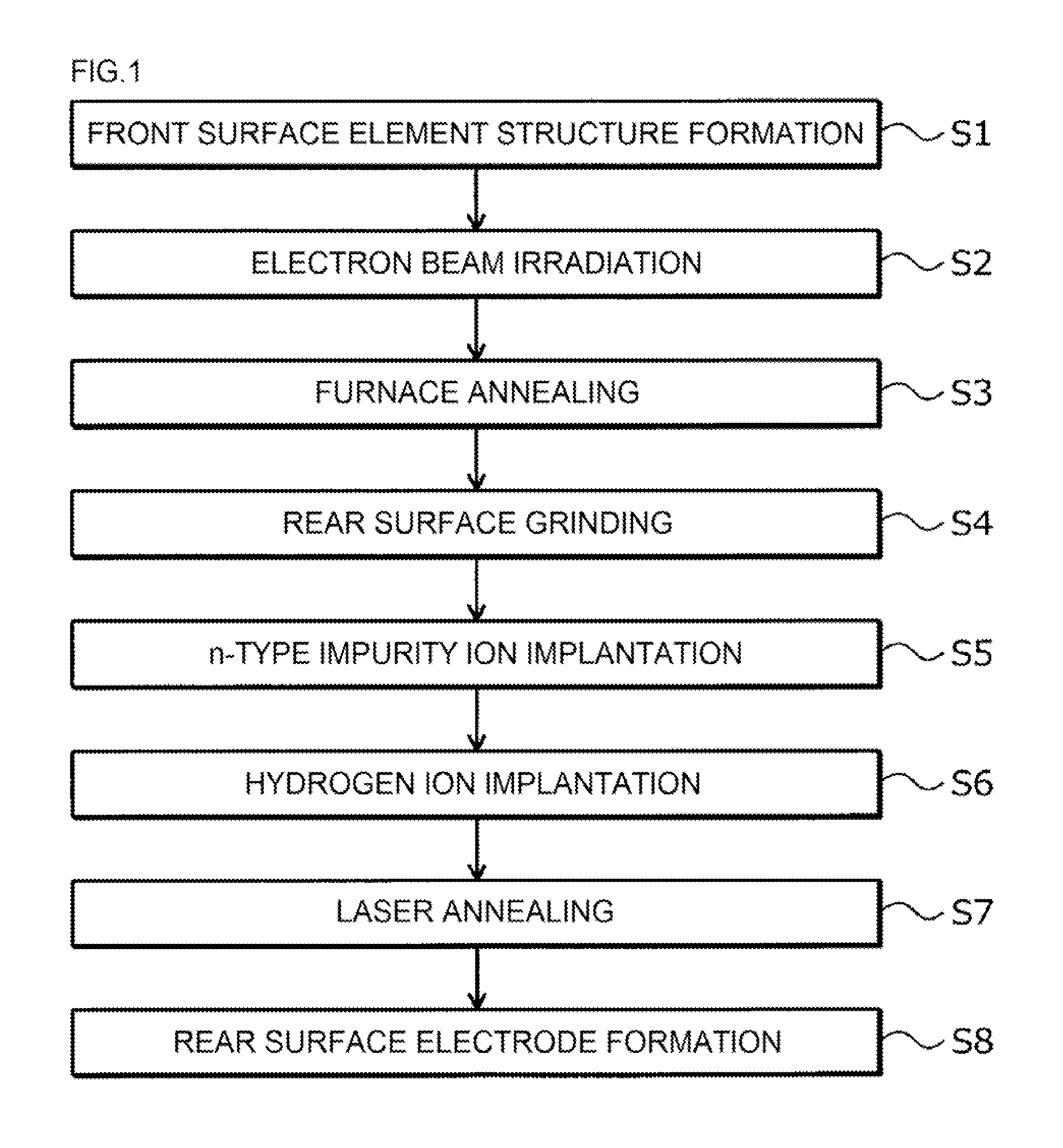
ActiveUS20150311279A1Longer lifetime of carrier particlesLimit drastically carrier lifetimeTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogen concentrationSurface layer
A front surface element structure is formed on the front surface side of an n−-type semiconductor substrate. Then defects are formed throughout an n−-type semiconductor substrate to adjust a carrier lifetime. Hydrogen ions are ion-implanted from a rear surface side of the n−-type semiconductor substrate, and a hydrogen implanted region having a hydrogen concentration higher than a hydrogen concentration of a bulk substrate is formed in the surface layer of a rear surface side of the n−-type semiconductor substrate.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Photovoltaic solar module comprising bifacial solar cells
InactiveUS20110132423A1Without compromising structural integrityLess costly bifacial solar cellsPV power plantsSoldering apparatusDiffusion methodsPhotovoltaic solar energy
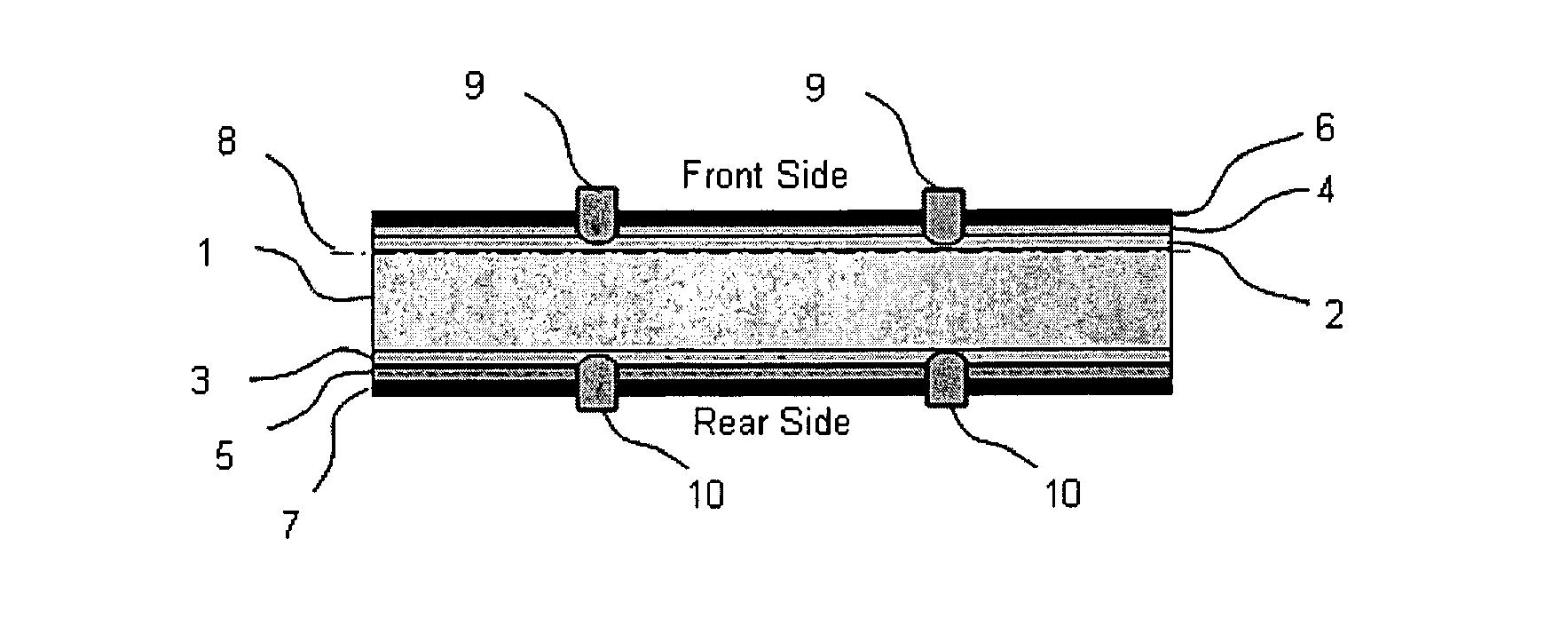
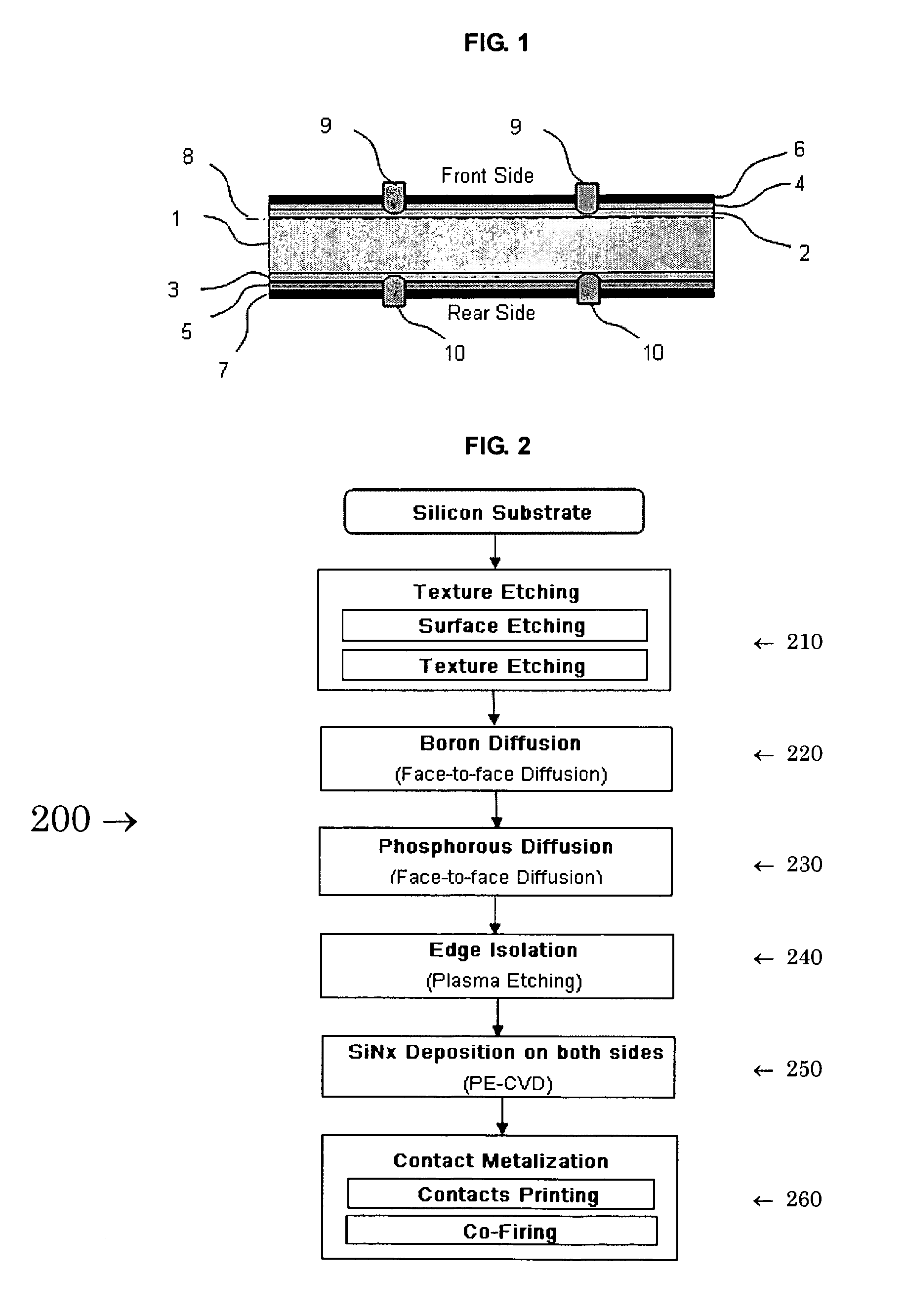
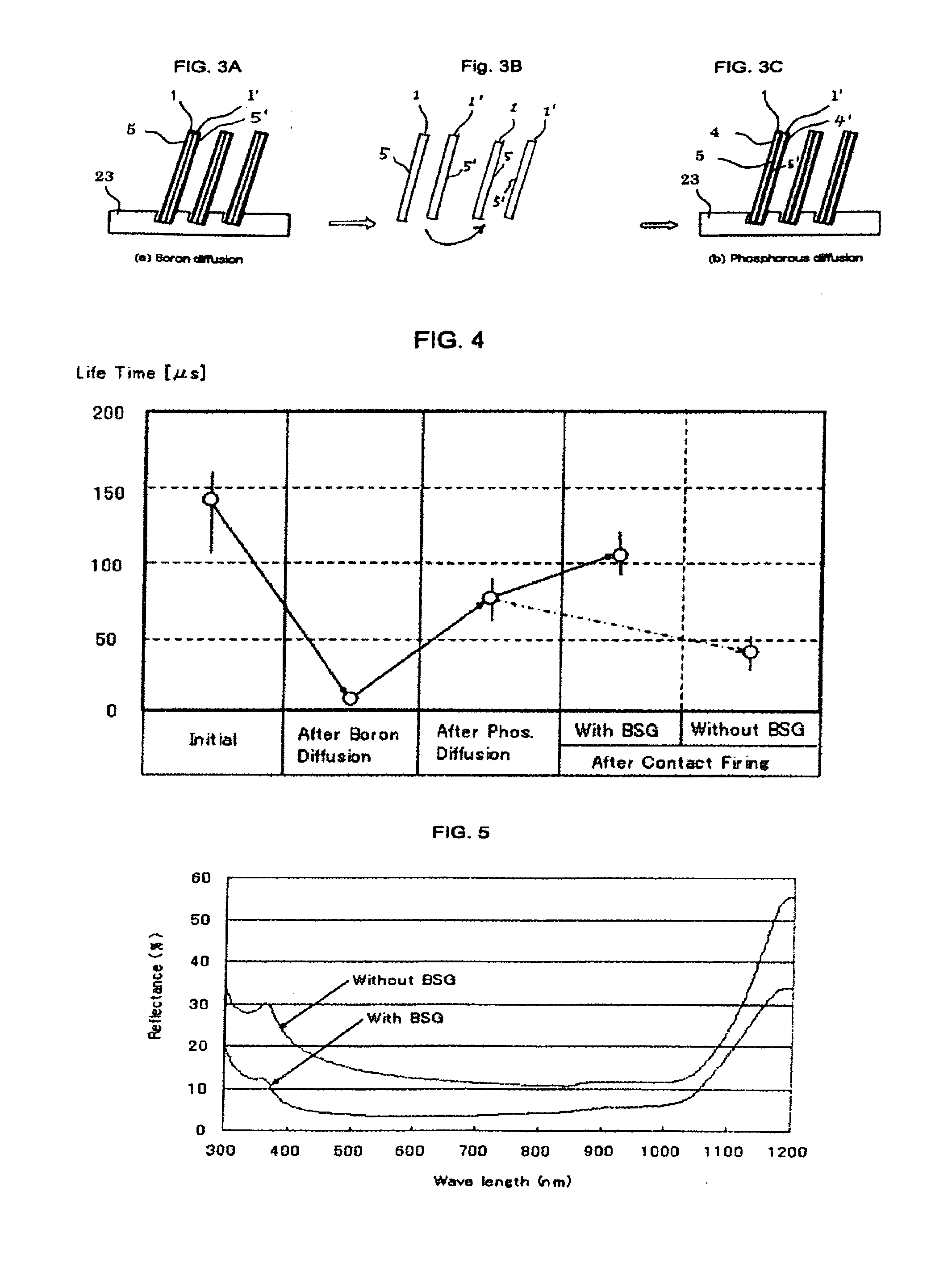
A photovoltaic solar cell module comprises a plurality of bifacial solar cells and electrical conductors. Each bifacial solar cell comprises a plurality of bus-bar contacts. A phosphorous silicon glass layer is formed on one side of the bifacial cell by phosphorous diffusion, and a boron silicon glass layer is formed on the other side of the bifacial cell by boron diffusion. The phosphorous diffusion and the boron diffusion are conducted by a face-to-face diffusion method. The combination of the two gettering methods substantially increases the minority carrier life time of the bifacial solar cell.
Owner:GAMMA SOLAR
Phosphorus gettering process of silicon chip
InactiveCN101667605AImprove electrical performance parametersIncreased average life expectancyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesEtchingSurface oxidation
The invention relates to a phosphorus gettering process of silicon chips in the manufacture of solar cells, which comprises the following steps: putting sueded silicon chips into a diffusion furnace for pre-deposition, removing a phosphorosilicate glass layer after diffusion, soaking the silicon chips through distributed processing in a hydrofluoric acid solution, and removing oxide layers from the surfaces of the silicon chips; then putting the silicon chips after washing into the diffusion furnace for secondary diffusion processing, taking the silicon chips out from the diffusion furnace after the processing of the secondary diffusion working procedure, cooling the silicon chips to room temperature, and measuring the square resistance of the silicon chips. The invention can effectively decrease heavily doped 'dead layers' and greatly prolong the average minority carrier lifetime of the silicon chips; after the processes including etching, PECVD, silk screen sintering and the like arefinished according to the normal process of a cell chip, the average transformation efficiency of the made cell chip is further improved, and the cell chip has better electrical performance parameters.
Owner:无锡尚品太阳能电力科技有限公司
Semiconductor device having both IGBT area and diode area
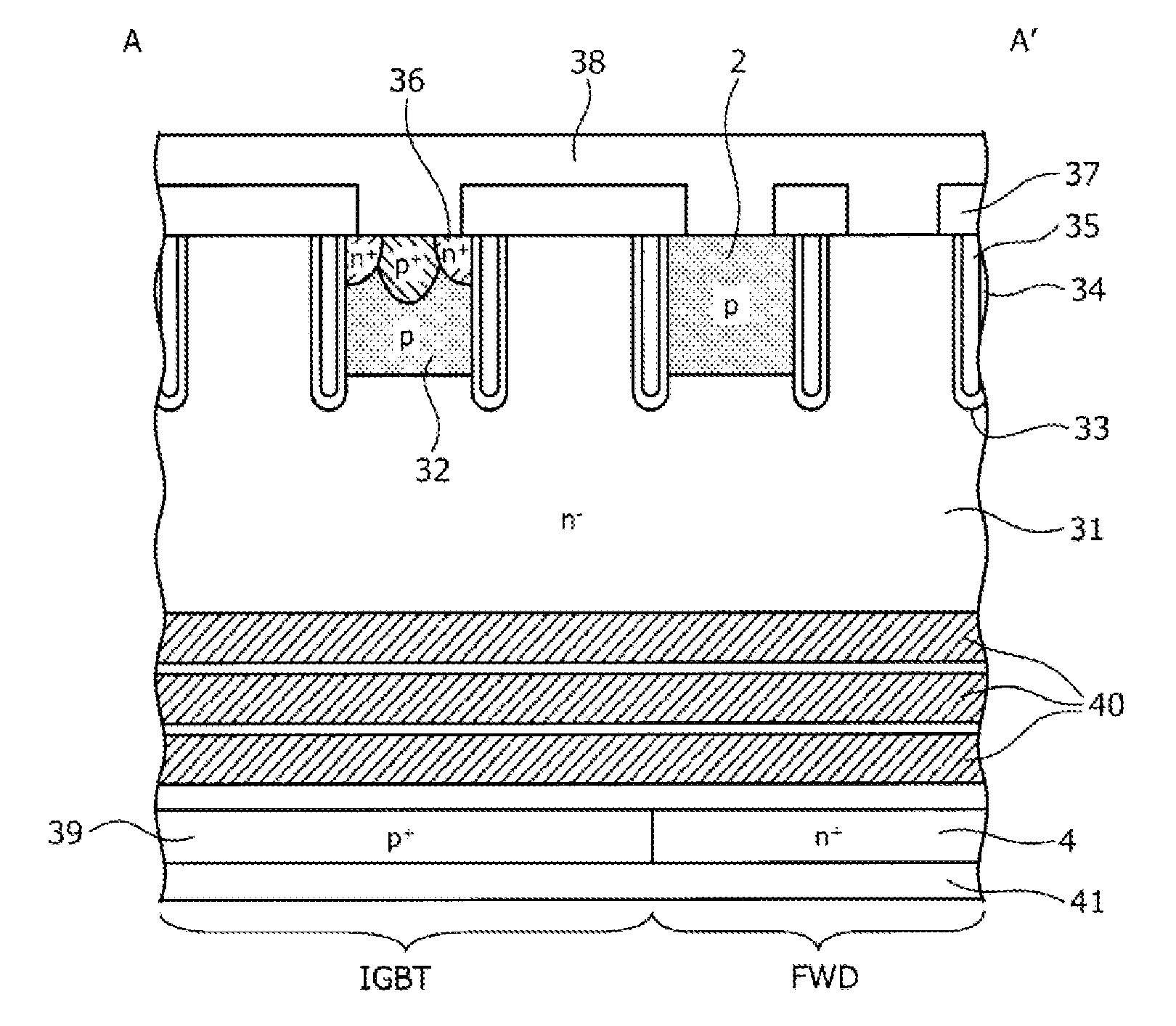
ActiveUS20120043582A1Promote recoveryImprove suppression propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCharge carrierSemiconductor
There is known a semiconductor device in which an IGBT structure is provided in an IGBT area and a diode structure is provided in a diode area, the IGBT area and the diode area are both located within a same substrate, and the IGBT area is adjacent to the diode area. In this type of semiconductor device, a phenomenon that carriers accumulated within the IGBT area flow into the diode area when the IGBT structure is turned off. In order to prevent this phenomenon, a region of shortening lifetime of carriers is provided at least in a sub-area that is within said IGBT area and adjacent to said diode area. In the sub-area, emitter of IGBT structure is omitted.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
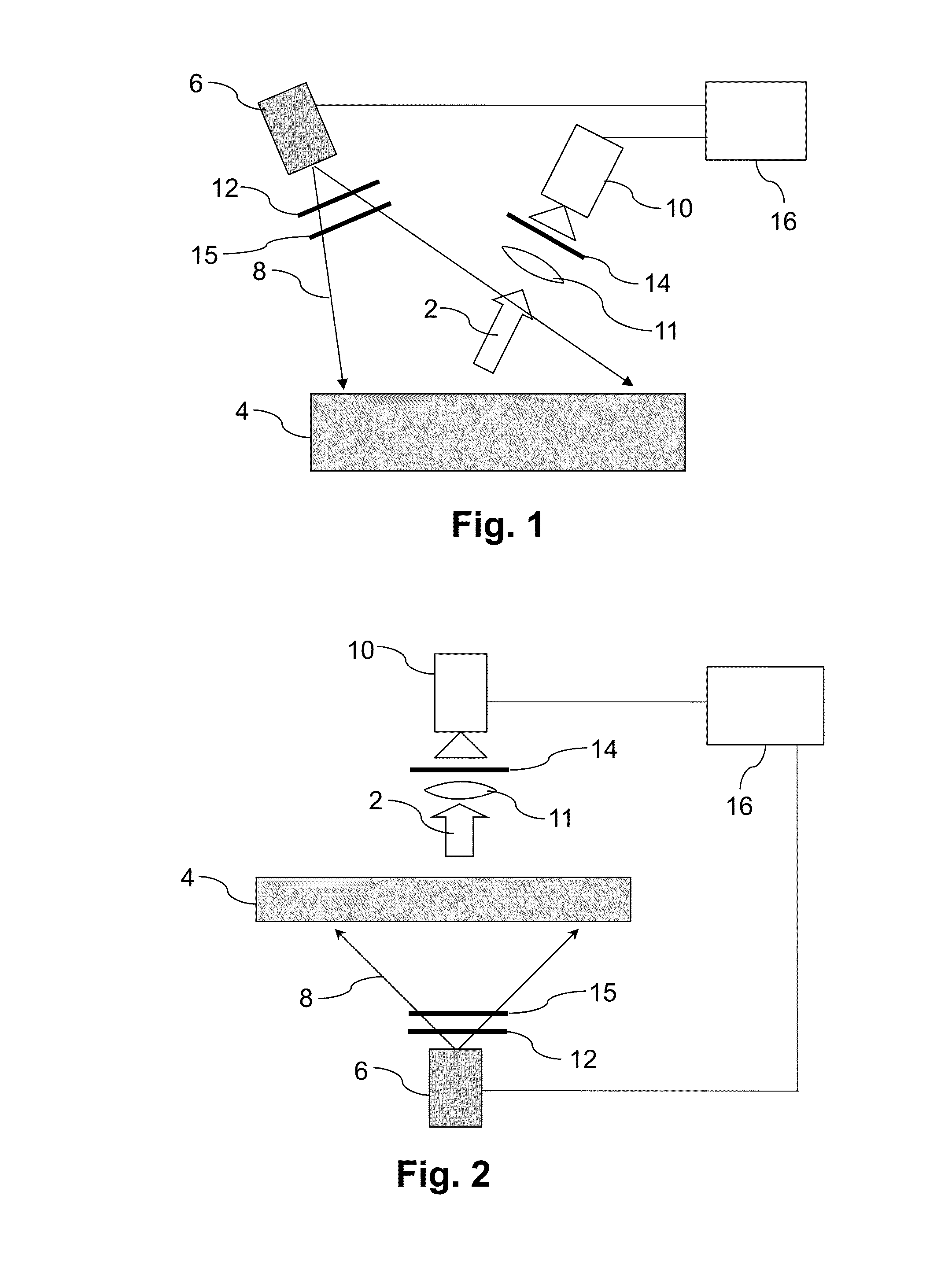
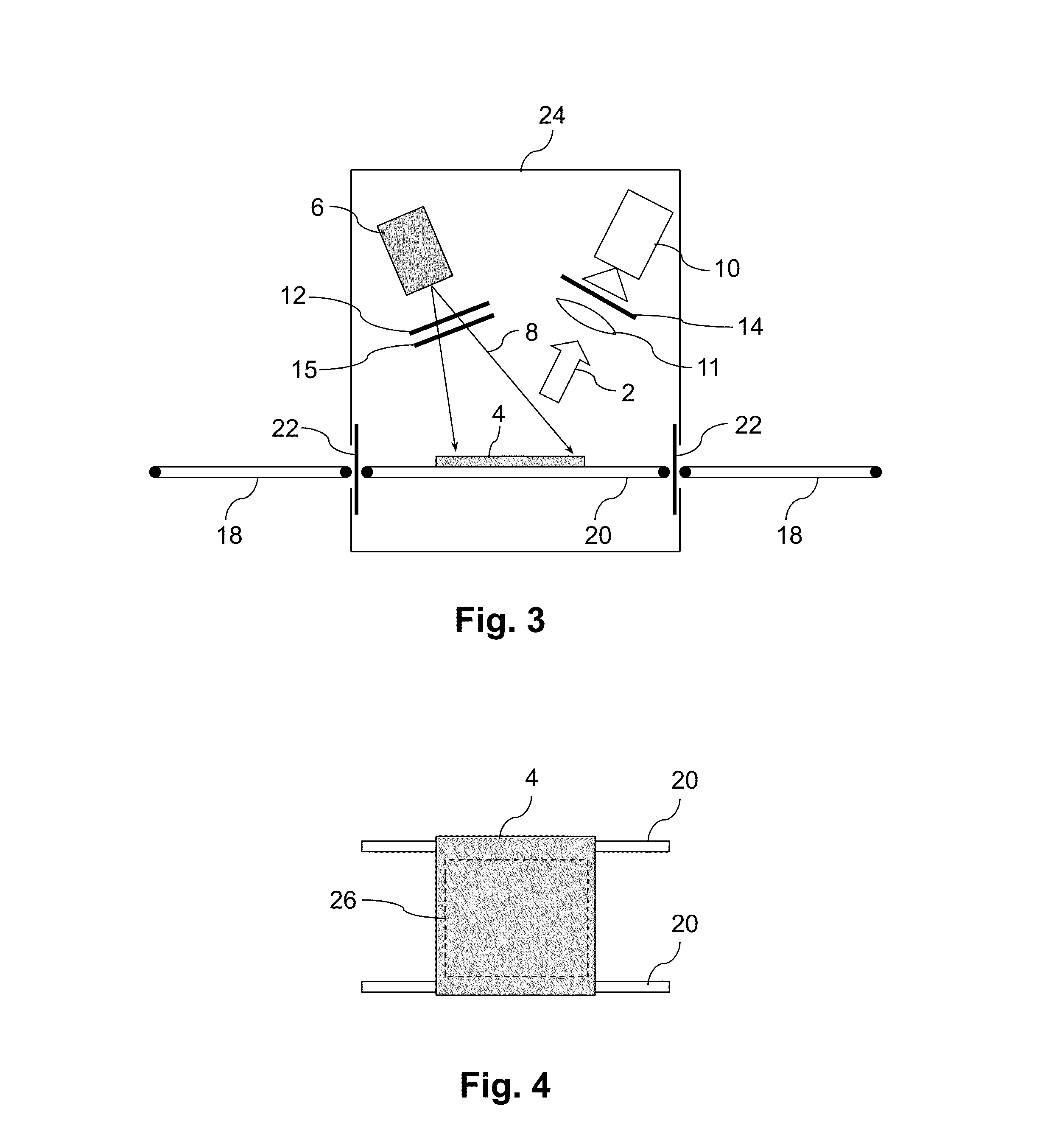
In-Line Photoluminescence Imaging of Semiconductor Devices
ActiveUS20130043405A1Provide usageAvoid blurPhotometrySolid-state devicesPhotoluminescenceSilicon solar cell
Methods and systems are presented for acquiring photoluminescence images (2) of silicon solar cells and wafers (4) as they progress along a manufacturing line (36). In preferred embodiments the images are acquired while maintaining motion of the samples. In certain embodiments photoluminescence is generated with short pulse, high intensity excitation, (8) for instance by a flash lamp (50) while in other embodiments images are acquired in line scanning fashion. The photoluminescence images can be analysed to obtain information on average or spatially resolved values of one or more sample properties such as minority carrier diffusion length, minority carrier lifetime, dislocation defects, impurities and shunts, or information on the incidence or growth of cracks in a sample.
Owner:BT IMAGING PTY LTD
Methods of hyperdoping semiconductor materials and hyperdoped semiconductor materials and devices
InactiveUS7179329B2Easy to operateIncrease computing speedTransistorPolycrystalline material growthSide effectSemiconductor materials
Methods are disclosed for producing highly doped semiconductor materials. Using the invention, one can achieve doping densities that exceed traditional, established carrier saturation limits without deleterious side effects. Additionally, highly doped semiconductor materials are disclosed, as well as improved electronic and optoelectronic devices / components using said materials. The innovative materials and processes enabled by the invention yield significant performance improvements and / or cost reductions for a wide variety of semiconductor-based microelectronic and optoelectronic devices / systems.Materials are grown in an anion-rich environment, which, in the preferred embodiment, are produced by moderate substrate temperatures during growth in an oxygen-poor environment. The materials exhibit fewer non-radiative recombination centers at higher doping concentrations than prior art materials, and the highly doped state of matter can exhibit a minority carrier lifetime dominated by radiative recombination at higher doping levels and higher majority carrier concentrations than achieved in prior art materials. Important applications enabled by these novel materials include high performance electronic or optoelectronic devices, which can be smaller and faster, yet still capture or emit light efficiently, and high performance electronics, such as transistors, which can be smaller and faster, yet cooler.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Lightly doped silicon carbide wafer and use thereof in high power devices
ActiveUS20060137600A1Low resistivityImprove the immunityPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRoom temperatureSingle crystal
A uniform silicon carbide single crystal with either an n-type or a p-type conductivity. The crystal has a net carrier concentration less than 1015 cm−3 and a carrier lifetime of at least 50 ns at room temperature.
Owner:SICED ELECTRONICS DEV +1
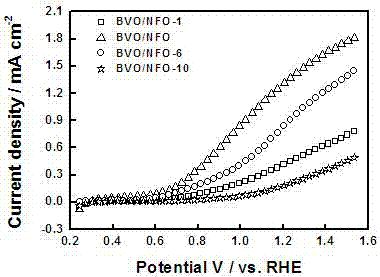
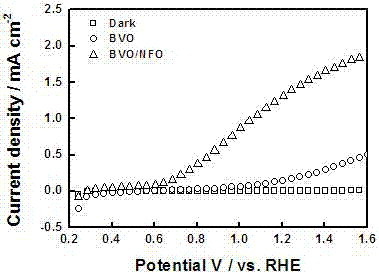
Ferro-nickel oxyhydroxide-modified bismuth vanadate photoelectrode and preparation method and application thereof
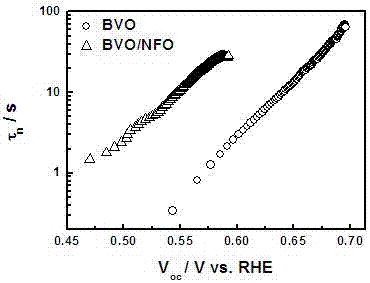
ActiveCN107324441AInhibitory complexPromote oxygen evolution reactionWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment by oxidationBismuth vanadateDecomposition
The invention discloses a ferro-nickel oxyhydroxide-modified bismuth vanadate photoelectrode and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, depositing bismuth oxyiodide on the surface of conductive glass, then coating the surface with the deposited bismuth oxyiodide with a dimethyl sulfoxide solution of vanadyl acetylacetonate, annealing, performing alkali soaking and rinsing with water to remove excessive vanadium pentoxide, and then drying to obtain a bismuth vanadate photoelectrode, and modifying ferro-nickel oxyhydroxide on the surface of the bismuth vanadate photoelectrode by adopting a cyclic voltammetry method in a three-electrode system, thus obtaining the ferro-nickel oxyhydroxide-modified bismuth vanadate photoelectrode. The invention further discloses applications of the ferro-nickel oxyhydroxide-modified bismuth vanadate photoelectrode in photoelectrocatalytic decomposition water. The prepared photoelectrode is used for producing hydrogen from photoelectrocatalytic decomposition water, can inhibit the compounding of photon-generated carriers, the service life of carriers generated by a BiVO4 photoelectrode can be effectively prolonged, and the oxygen evolution reaction on the surface of the photoelectrode can be promoted, so that the solar optic hydrogen conversion efficiency of a semiconductor photoelectrode can be improved.
Owner:HUANGHE S & T COLLEGE
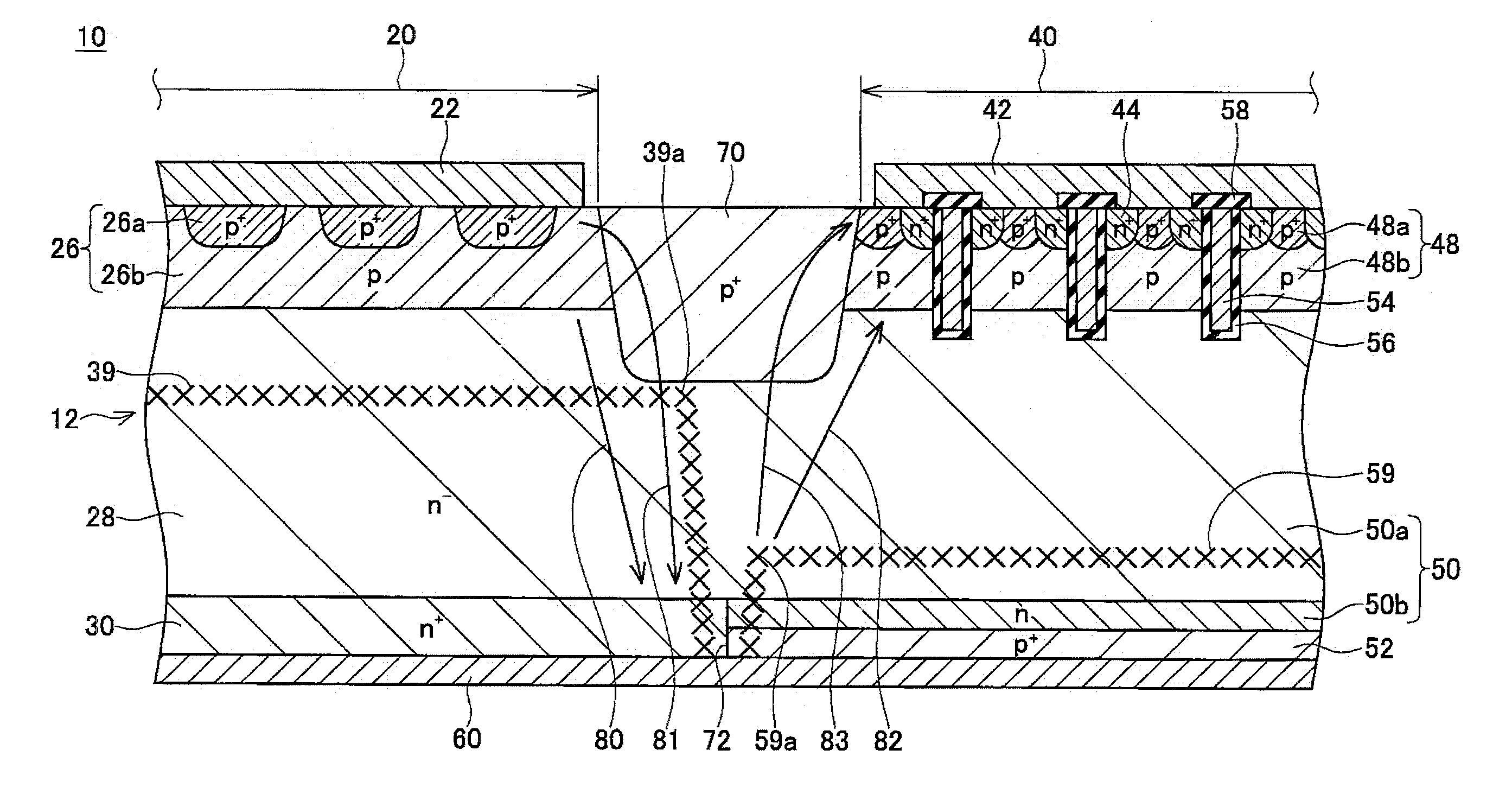
Semiconductor device
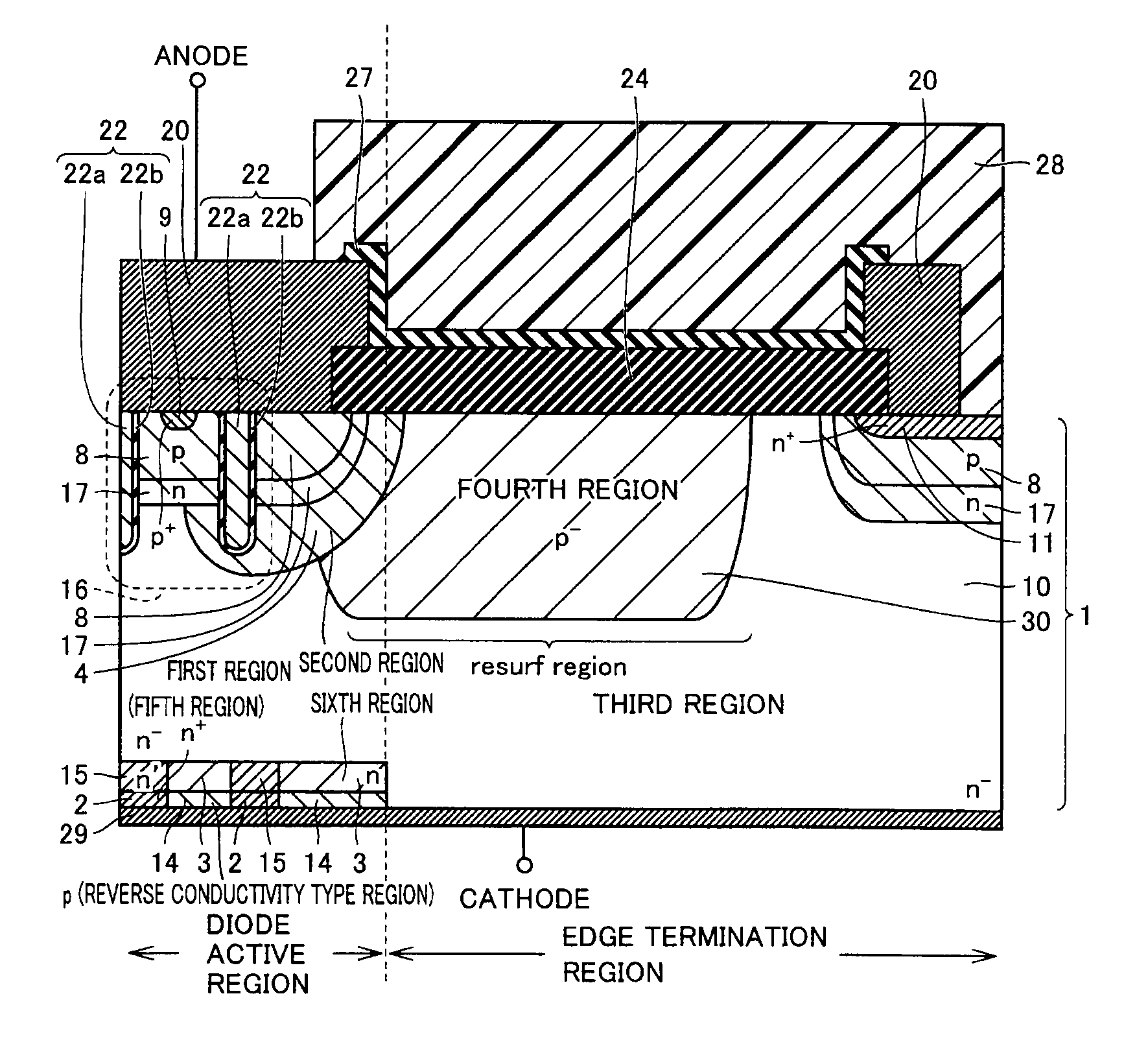
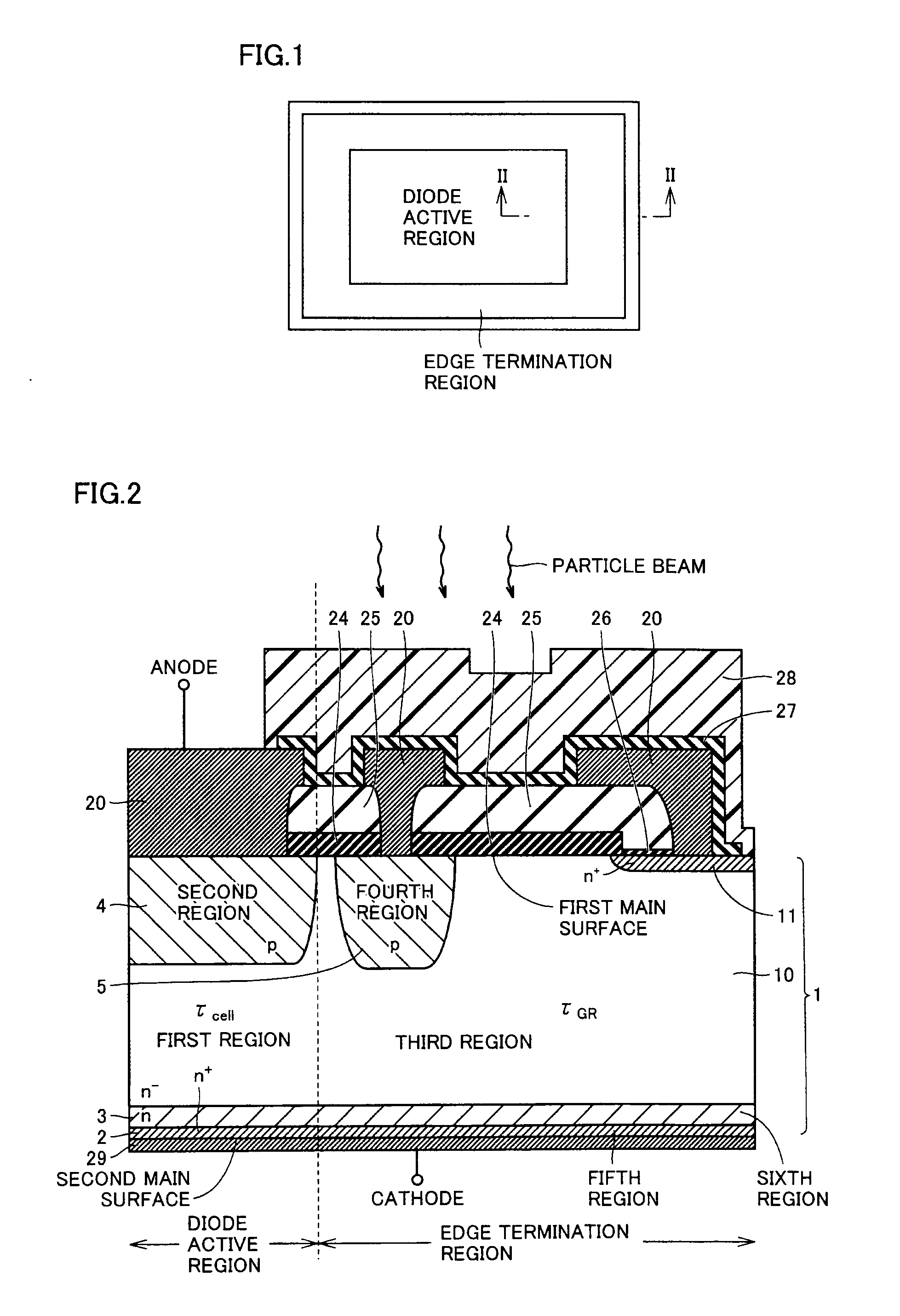
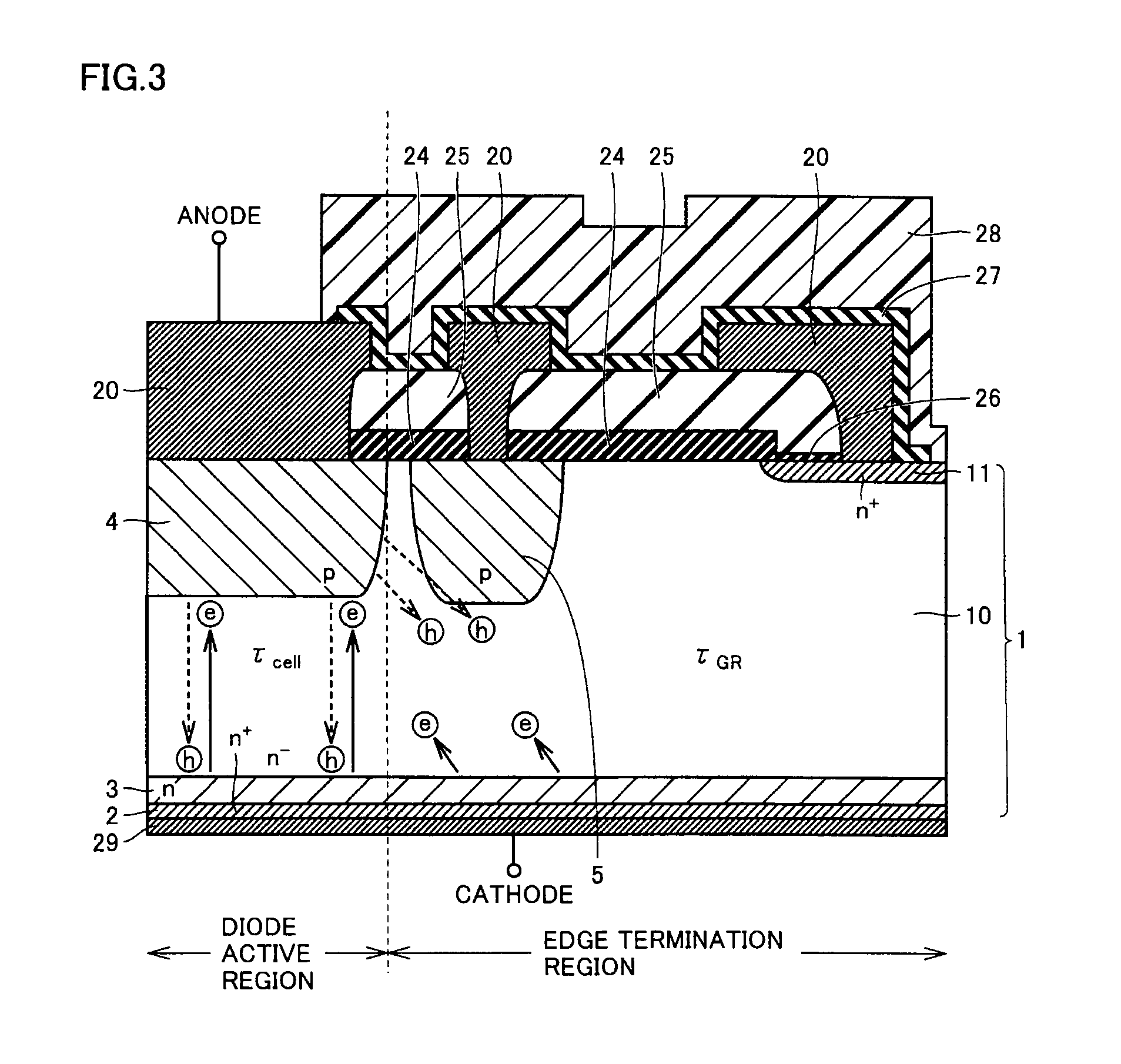
ActiveUS20110291223A1Increase in current densityImprove breakdown voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceCharge carrier
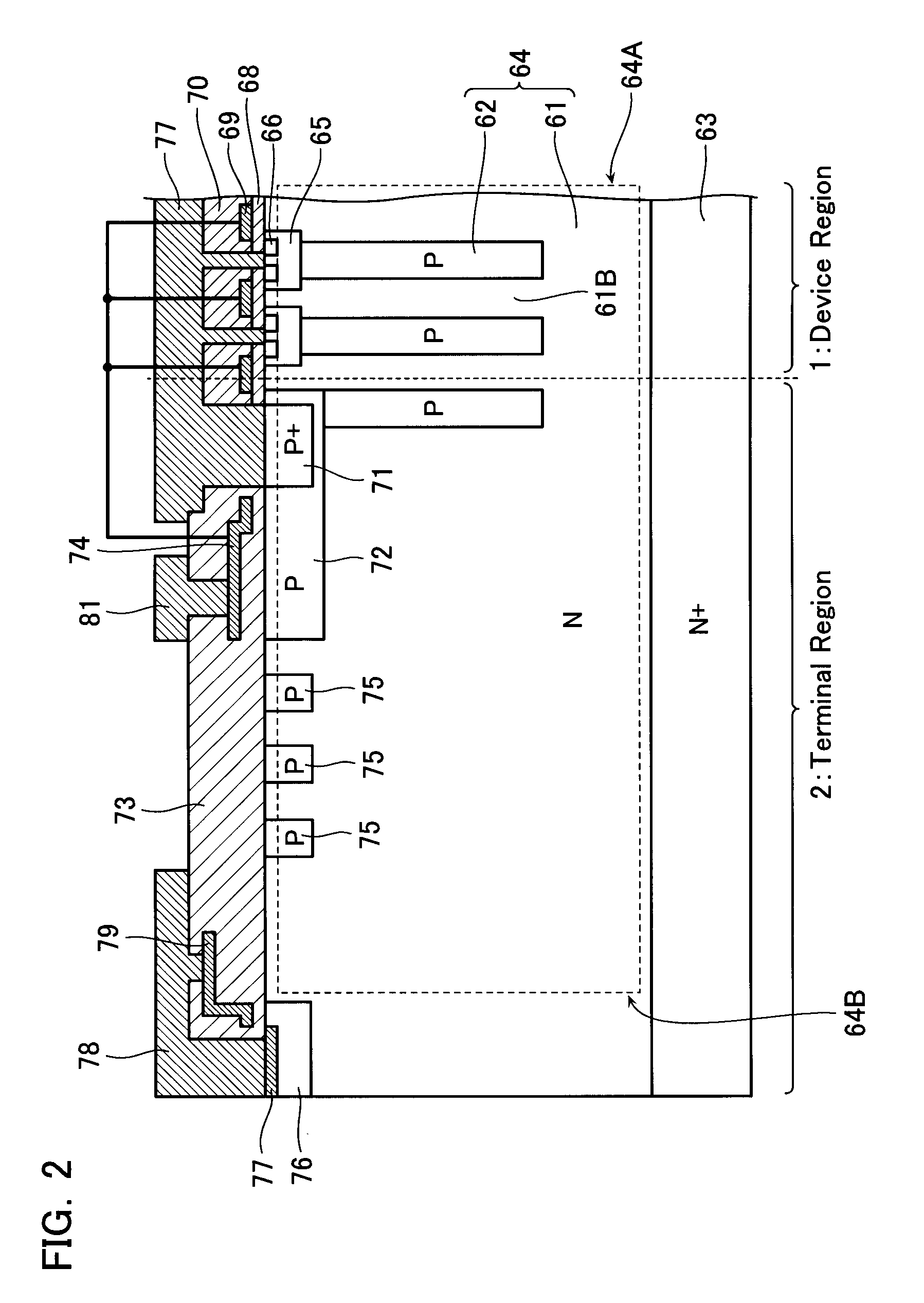
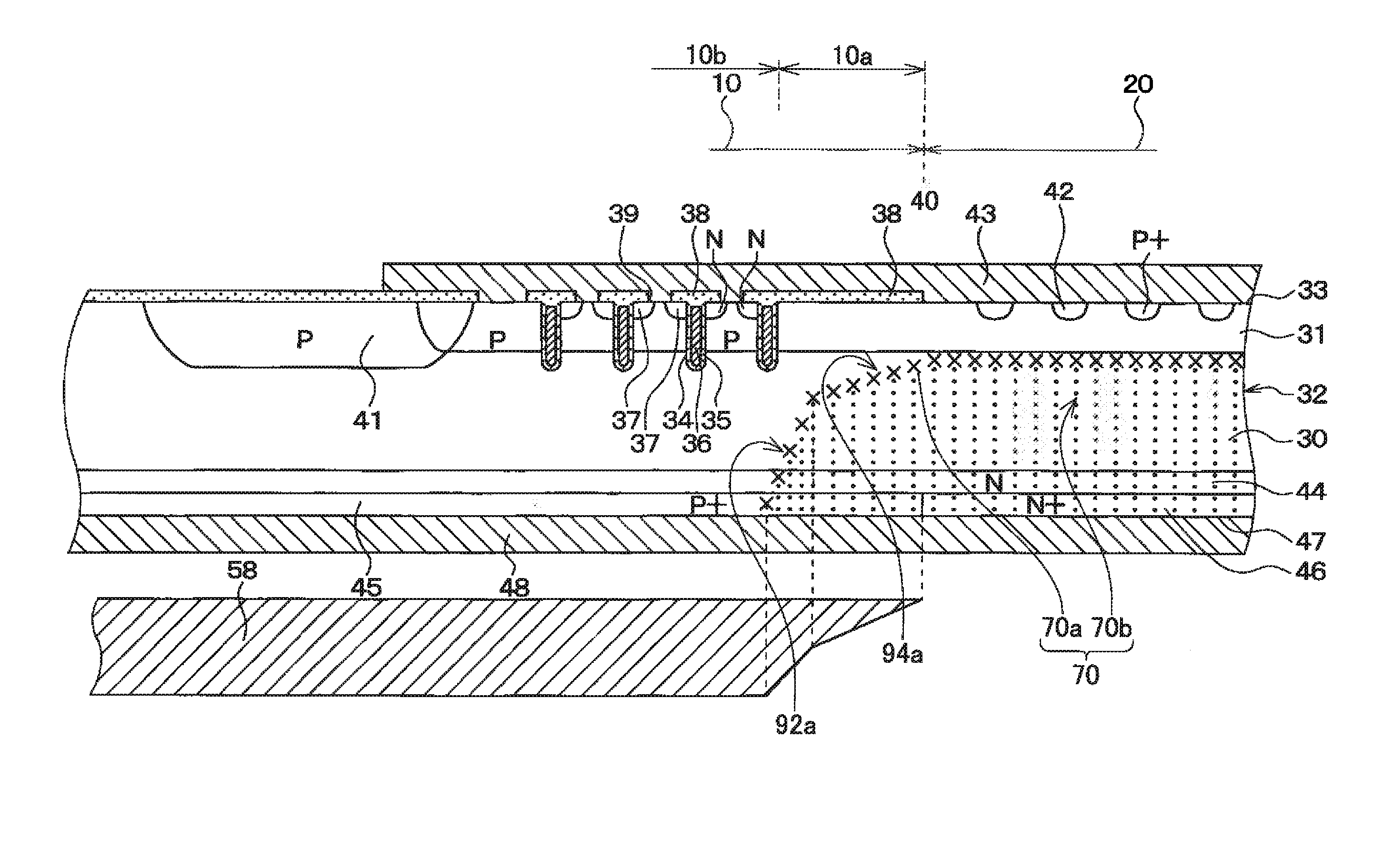
A semiconductor device includes a semiconductor substrate having a diode active region and an edge termination region adjacent to each other, a first region of a first conductivity type in the diode active region, a second region of a second conductivity type, a third region of the first conductivity type in the edge termination region, and a fourth region of the second conductivity type. The first region and the third region share a drift region of the first conductivity type. The first region and the third region share a fifth region of the first conductivity type. The drift region in the third region is greater in number of crystal defects per unit volume than the drift region in the first region in order that the drift region in the third region is shorter in carrier lifetime than the drift region in the first region.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
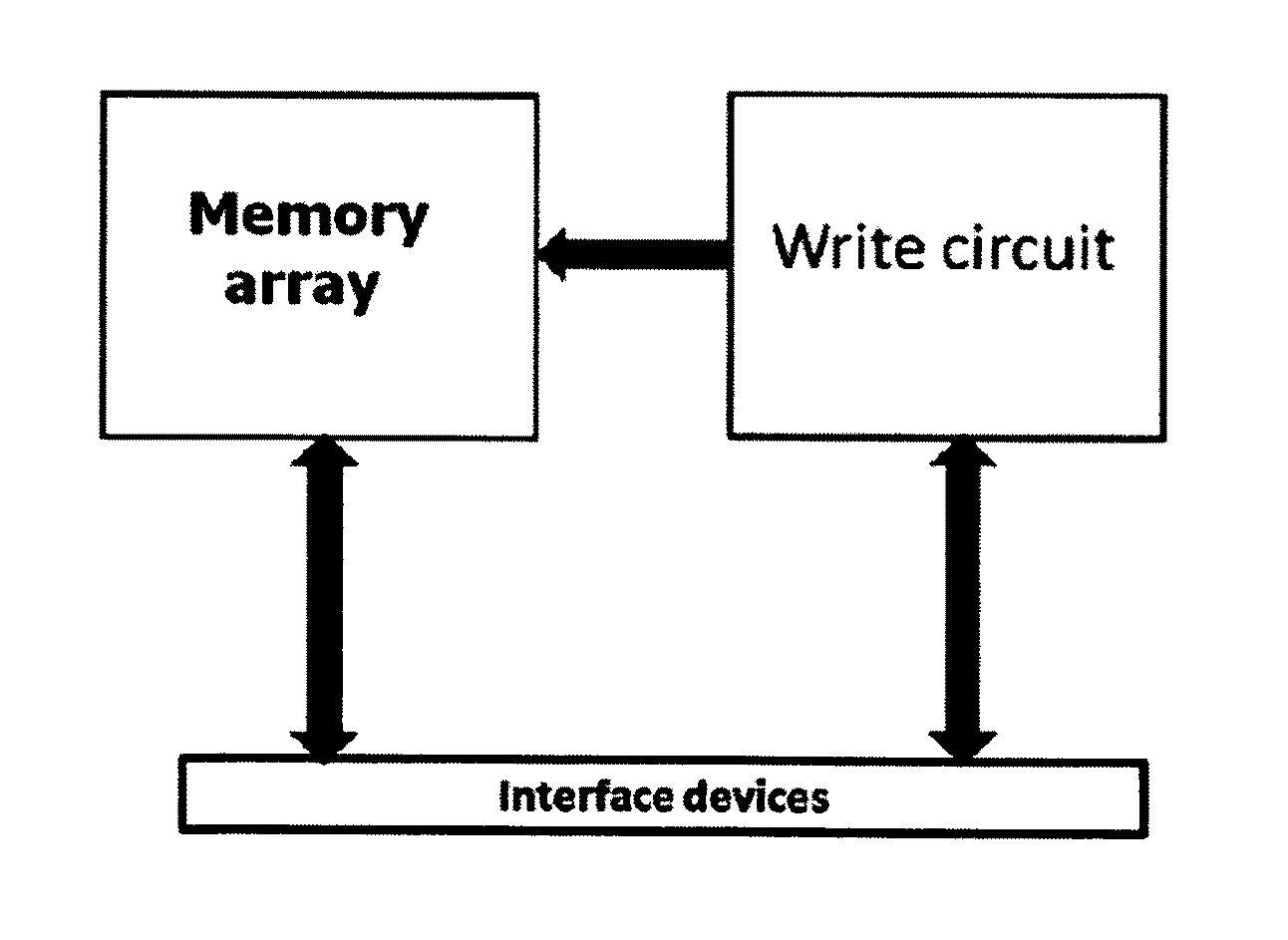
Method of cross-point memory programming and related devices
A reverse recovery current of a diode is used for programming a cross-point memory. Programming of a crossbar memory device, comprising a diode with preferably short charge carriers lifetime and a storage element by keeping the device at one polarity for a period of time and then switching it from first polarity to second polarity (e.g., forward to reverse polarity of the diode). Programming occurs due to diode's reverse recovery current. The value and duration of the recovery current pulse are selected to program the storage element into one of plurality of electrically distinguish states by variation of the level of current flowing through the device in the first polarity of applied bias voltage, by variation of the speed for changing the bias voltage from first polarity to second polarity, and by steady state value of the second polarity voltage applied to the device in one or more embodiments.
Owner:SAVRANSKY SEMYON D
Semiconductor device having semiconductor substrate including diode region and IGBT region
ActiveUS20120007142A1Easily recombinedDifficult to characterizeTransistorSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceCharge carrier
Provided is a semiconductor device including a semiconductor substrate in which a diode region and an IGBT region are formed. A separation region formed of a p-type semiconductor is formed in a range between the diode region and the IGBT region and extending from an upper surface of the semiconductor substrate to a position deeper than both a lower end of an anode region and a lower end of a body region. A diode lifetime control region is formed within a diode drift region. A carrier lifetime in the diode lifetime control region is shorter than that in the diode drift region outside the diode lifetime control region. An end of the diode lifetime control region on an IGBT region side is located right below the separation region.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Electrical passivation of silicon-containing surfaces using organic layers
InactiveUS7491642B2Improve electrical performanceImprove electronic efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsElectrical devices
Electrical structures and devices may be formed and include an organic passivating layer that is chemically bonded to a silicon-containing semiconductor material to improve the electrical properties of electrical devices. In different embodiments, the organic passivating layer may remain within finished devices to reduce dangling bonds, improve carrier lifetimes, decrease surface recombination velocities, increase electronic efficiencies, or the like. In other embodiments, the organic passivating layer may be used as a protective sacrificial layer and reduce contact resistance or reduce resistance of doped regions. The organic passivation layer may be formed without the need for high-temperature processing.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Low-temperature phosphorus gettering diffusion process based on removal of metal impurities in polycrystalline silicon
InactiveCN102703987AGet rid ofImprove battery efficiencyFinal product manufactureDiffusion/dopingMetal impuritiesPolycrystalline silicon
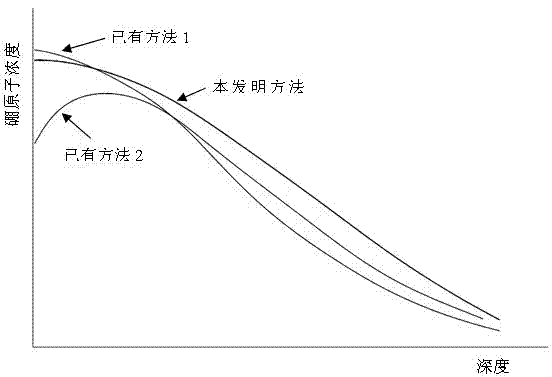
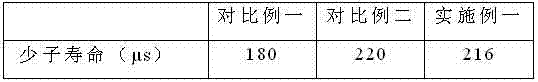
The invention discloses a low-temperature phosphorus gettering diffusion process based on removal of metal impurities in polycrystalline silicon. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: (1) feeding into a boat; (2) stably heating; (3) performing first-step deposition; (4) performing second-step deposition; (5) propelling; (6) absorbing impurities; (7) propelling once again at a low temperature; and (8) cooling, annealing and discharging out of the boat. Through innovation of a polycrystalline silicon diffusion process in a solar industrial production process, the removal of metal ions in a type B polycrystalline silicon wafer with short minority carrier lifetime and improvement on the structure of a silicon wafer crystal are realized, the photoelectric conversion efficiency of a solar cell produced by using the type B wafer with short minority carrier lifetime is increased, the average value of the minority carrier lifetime of the type silicon wafer is not less than 12mus, and the efficiency of a battery produced by using the type silicon wafer is 0.2 percent higher than that of a battery produced by using a normal process.
Owner:TIANWEI NEW ENERGY HLDG +1
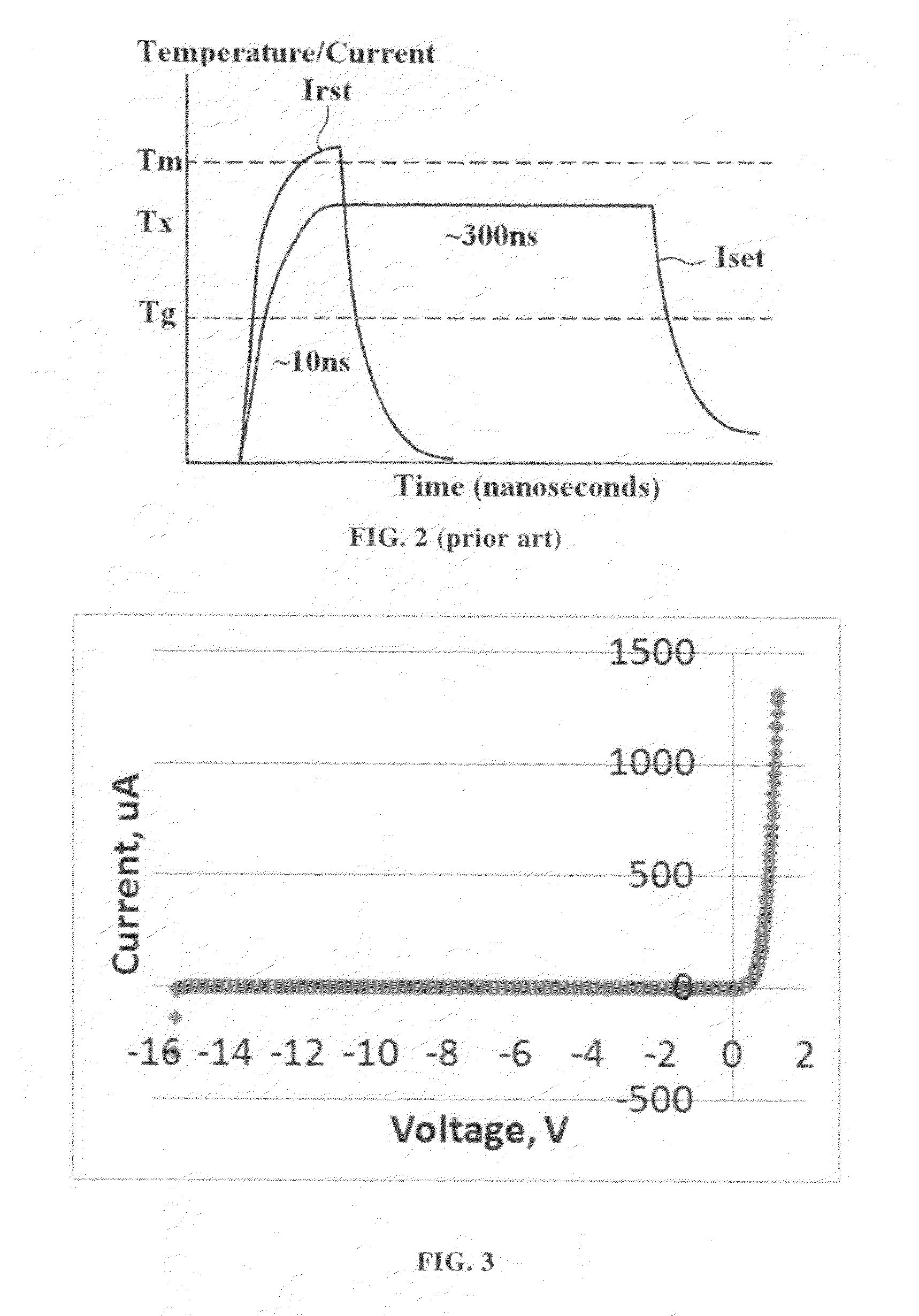
Electro-thermal simulation method for FS (Field Stop) type IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) transient temperature characteristic
ActiveCN102368274AEasy to buildHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsTransconductanceThermal simulation
The invention provides an electro-thermal simulation method for FS (Field Stop) type IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) transient temperature characteristic. An FS type IGBT switching transient working process is actually tested and is analyzed by being combined with an IGBT working principle and a semiconductor physical principle to determine that the IGBT transient temperature characteristic is mainly influenced by life of internal excess carrier, so that the electro-thermal simulation method is established. The method comprises the following steps of: actually testing carrier life values extracted at different temperatures to acquire a relational expression of the carrier life and temperature; calculating through an empirical value formula to acquire a relational expression amongthreshold voltage, transconductance, emitter saturation and current as well as the temperature; and adding temperature related parameters into an FS type IGBT current tailing stage current analyticalexpression and a switching transient model equation set and calculating to acquire transient working waveform of the FS type IGBT at different temperatures. The electro-thermal model simulation method provided by the invention simultaneously has the advantages of simple parameter calculation and high accuracy.
Owner:NAVAL UNIV OF ENG PLA
Quartz crucible and method for casting quasi-single crystal
InactiveCN101979718AQuality improvementImprove electrical performanceFrom frozen solutionsConventional castingElectrical performance
The invention discloses a quartz crucible. The bottom of the quartz crucible is provided with a pit which is spontaneously generated by inducing seed crystal. The invention also discloses a method for casting quasi-single crystal by using the quartz crucible. By using the quartz crucible of the invention, the quality of grown cast crystalline silicon is effectively improved so as to improve the electrical performance of a solar cell. By the method for casting the quasi-single crystal in the invention, the diameter of the obtained crystal grain is about 5 to 10cm, tests show that the dislocation density is about 10<3>cm<-2> which is far less than a number range of 10<4> to 10<5>cm<-2> of silicon crystal obtained by the conventional casting method under the same condition; and accordingly, the minority carrier lifetime value of a silicon slice obtained by the method of the invention is about 18us which is greater than the minority carrier lifetime value of 11us of the silicon slice prepared from the same raw material by the conventional casting method.
Owner:ALTUSVIA ENERGY TAICANG
Semiconductor device, manufacturing method thereof, and display device
InactiveUS20050247940A1Deterioration of image qualitySmall off current valueTransistorSolid-state devicesHigh concentrationDevice material
A multi-gate structure is used and a width (d1) of a high concentration impurity region sandwiched by two channel forming regions in a channel length direction is set to be shorter than a width (d2) of low concentration impurity regions in the channel length direction. Thus, a resistance of the entire semiconductor layer of a TFT which is in an on state is reduced to increase an on current. In addition, a carrier life time due to photoexcitation produced in the high concentration impurity region can be shortened to reduce light sensitivity.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Germanium-doped directionally solidified casting monocrystalline silicon and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101591808AHigh mechanical strengthReduce dislocation densityPolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsSolar cellDislocation free
The invention discloses germanium-doped directionally solidified casting monocrystalline silicon, which contains boron, gallium or phosphorus with the concentration of between 1*10 and 1*10 / cm and germanium with the concentration of between 1*10 and 5*10 / cm. The invention also discloses a preparation method for the germanium-doped directionally solidified casting monocrystalline silicon, which comprises the following steps: placing polycrystalline silicon, the germanium and an electroactive doping agent on a dislocation-free monocrystalline silicon block paved on the bottom of a crucible; completely melting the polycrystalline silicon, the germanium and the doping agent and partially melting the dislocation-free monocrystalline silicon block by thermal field regulation; and performing directional solidification by heat exchange, and using a part of unmelted dislocation-free momocrystalline silicon block as a seed crystal to induce to grow the germanium-doped casting monocrystalline silicon from bottom to top. The product has strong mechanical strength and long minority carrier lifetime, can be used for preparing a high efficiency wafer solar cell, and greatly reduces the production cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Boron diffusion method of crystalline silicon solar cell
ActiveCN102769069AImprove life expectancyDiffusion avoid or reduceFinal product manufactureDiffusion/dopingHigh surfaceNitrogen gas
The invention discloses a boron diffusion method of a crystalline silicon solar cell. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) putting a silicon chip which is felted and cleaned into a diffusion furnace tube, raising temperature to 800 to 1,000 DEG C, filling oxygen, and oxidizing for 1 to 30 min; (2) keeping the temperature in the step (1), or raising the temperature to 900 to 1,100 DEG C, and filling a boron source, the oxygen and nitrogen for boron diffusion; (3) stopping filling the source, keeping the temperature or reducing the temperature to 800 to 900 DEG C, and keeping the temperature for 5 to 50 min in the nitrogen atmosphere; and (4) reducing the temperature, taking out the silicon chip, and finishing the diffusion process. By adoption of the method, the uniformity of the boron diffusion can be improved, formation of a boron-rich layer is avoided or reduced, and the minority carrier lifetime of the silicon chip is prolonged; and meanwhile, high surface impurity concentration can be kept, and high ohmic contact is formed, so the performance of the cell is improved.
Owner:CSI CELLS CO LTD +1
Method for preparing vacuum zone melting high resistant silicon single crystal
ActiveCN101525764AHigh resistivityEnhanced ultra-high purityPolycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsZone meltingSingle crystal
The invention discloses a method for preparing vacuum zone melting high resistant silicon single crystal, comprising the two sequential major processes: polysilicon purification and crystal forming of silicon single crystal, wherein, the process of polysilicon purification comprises the steps of cleaning fire, charging, evacuating, preheating, melting materials heat sealing, growing narrow necks, shouldering, shoulder circuiting, equating diameter, ending and repeating; the process of crystal forming of silicon single crystal comprises the steps of cleaning fire, charging, evacuating, preheating, processing of chemicals, crystal seeding, shouldering, shoulder circuiting, equating diameter, ending and blowing out. With the method of the invention adopted to prepare silicon single crystal, electric resistivity, ultra-high purity, resistivity profile, uniformity of cross-section electric resistivity and minority carrier lifetime are greatly improved; purity of the silicon single crystal is above 11N, electric resistivity reaches 8000 omega / cm-30000omega / cm, uniformity of cross-section electric resistivity is less than 15%, and minority carrier lifetime is more than 600-1000Mus, thus greatly improving performance, stability and safety of the devices while realizing mass production of vacuum zone melting high resistant silicon single crystal.
Owner:峨嵋半导体材料研究所
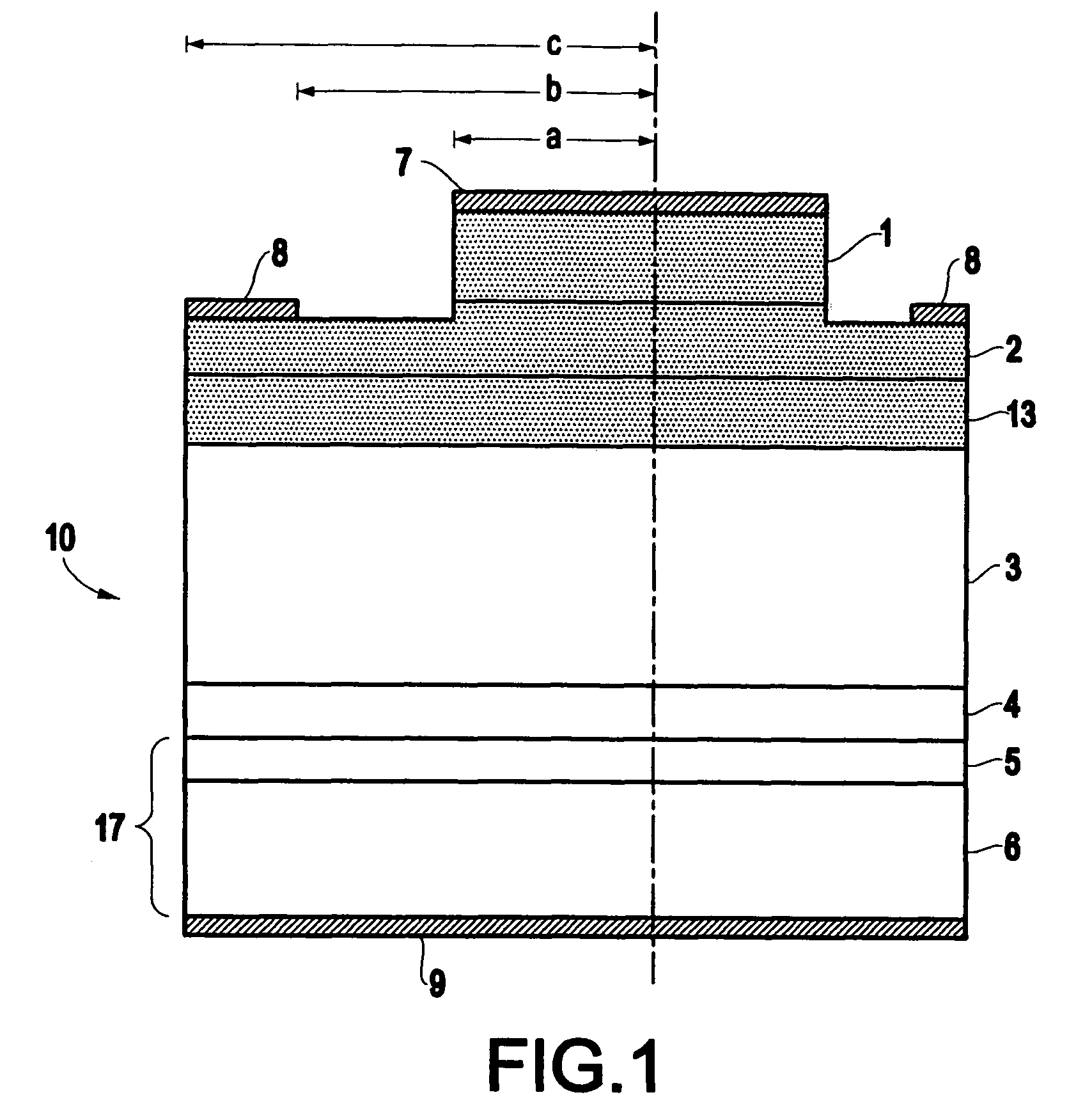
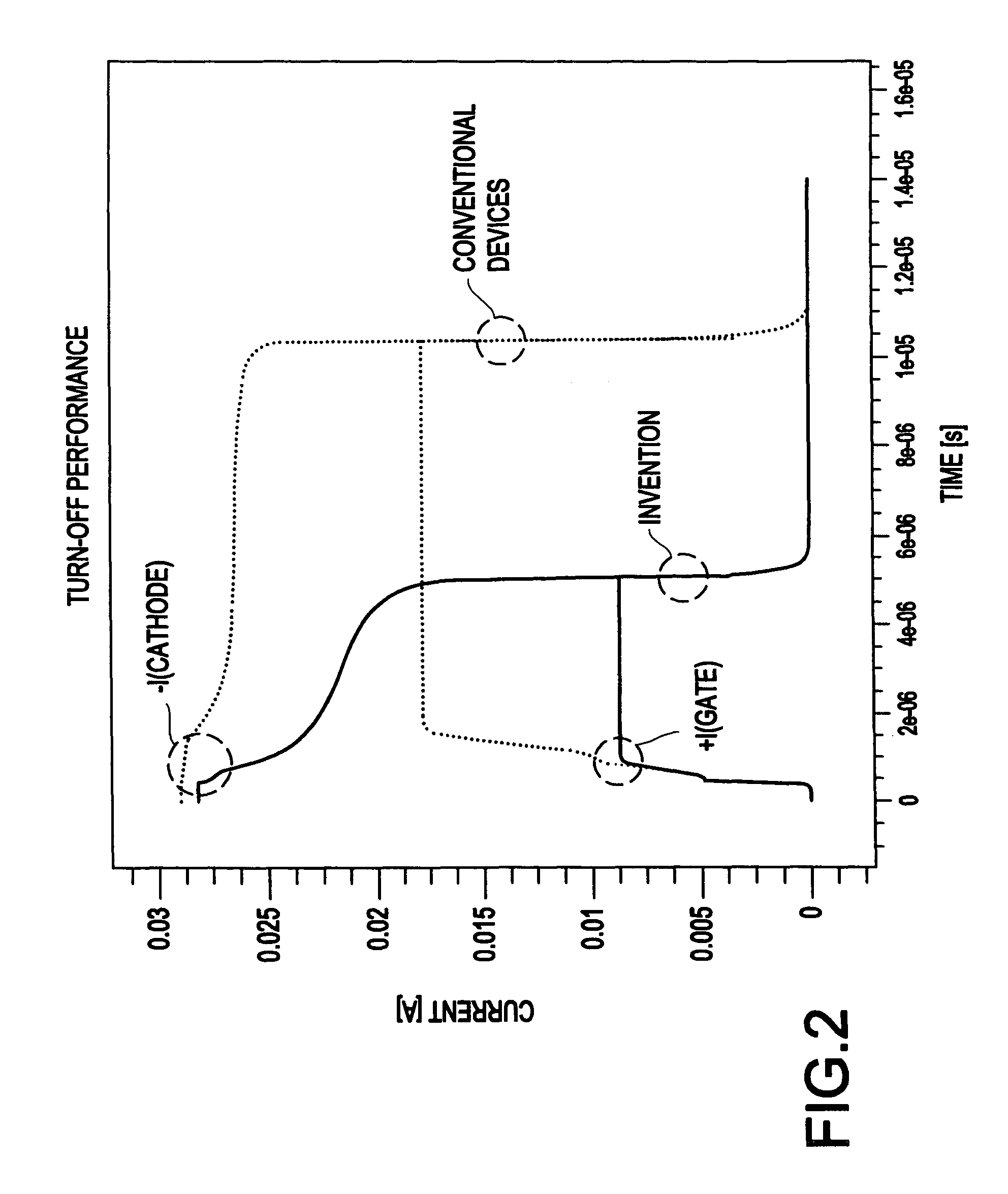
Processing technique to improve the turn-off gain of a silicon carbide gate turn-off thyristor
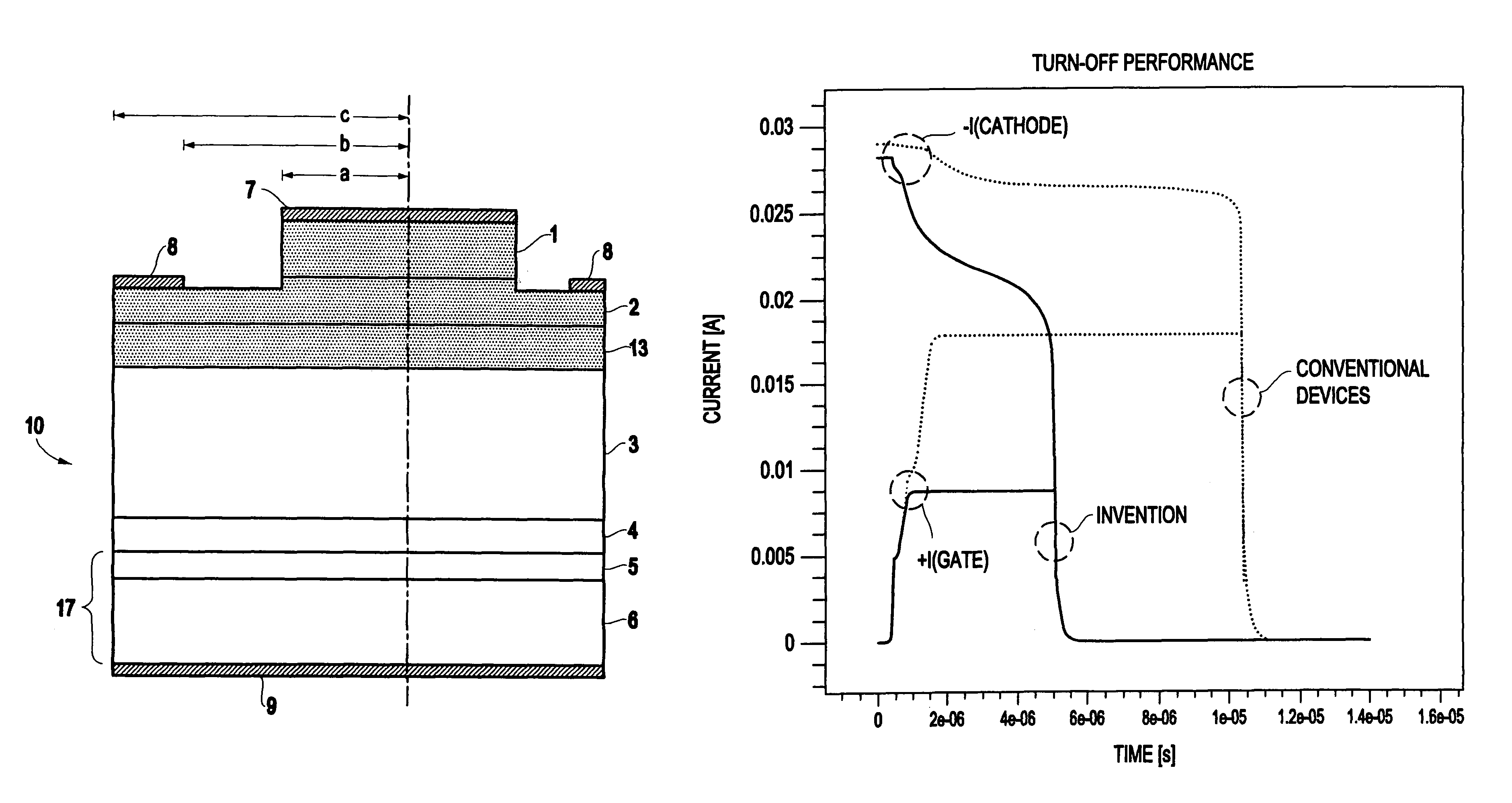
ActiveUS7851274B1Increased turnLow mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate turn-off thyristorNanosecond
A structure and method for a silicon carbide (SiC) gate turn-off (GTO) thyristor device operable to provide an increased turn-off gain comprises a cathode region, a drift region having an upper portion and a lower portion, wherein the drift region overlies the cathode region, a gate region overlying the drift region, an anode region overlying the gate, and at least one ohmic contact positioned on each of the gate region, anode region, and cathode region, wherein the upper portion of the drift region, the gate region, and the anode region have a free carrier lifetime and mobility lower than a comparable SiC GTO thyristor for providing the device with an increased turn-off gain, wherein the free carrier lifetime is approximately 10 nanoseconds. The reduced free carrier lifetime and mobility are affected by altering the growth conditions, such as temperature under which epitaxy occurs.
Owner:ARMY US SEC THE
Fabrication process of crystalline silicon solar cell
ActiveCN105870249AImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyExtend your lifeFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCell fabricationMetallurgy
The invention relates to the field of fabrication of a solar cell, in particular to a surface passivation and anti-reflection technology of crystalline silicon cell for improving photoelectric conversion efficiency. Aiming at the existing cell technology process flow, nanometer lamination of a material such as SiO2, Al2O3 and SiNx and a composite material are fabricated by atomic layer deposition and plasma atomic layer deposition, passivation layer plating is carried out on the front surface and the back surface of the crystalline silicon cell, so that the minority carrier lifetime is prolonged, and the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the cell is improved; and SiNx anti-reflection layer plating can be continuously carried out after passivation layer plating, so that passivation and anti-reflection processes can be integrated in the same flow, the cost is reduced, and the yield is improved. The fabrication method is particularly and suitably used for combining with a black silicon technology, and multiple processes are avoided; and moreover, for a double-sided battery, the fact that double-sided passivation is carried out by using the fabrication method is a necessary choice.
Owner:JIANGSU MICROVIA NANO EQUIP TECH CO LTD
Semiconductor device having an electrode overlaps a short carrier lifetime region
InactiveUS6870199B1Improving reverse-recovery withstanding capabilityThyristorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingParticle beamReverse recovery
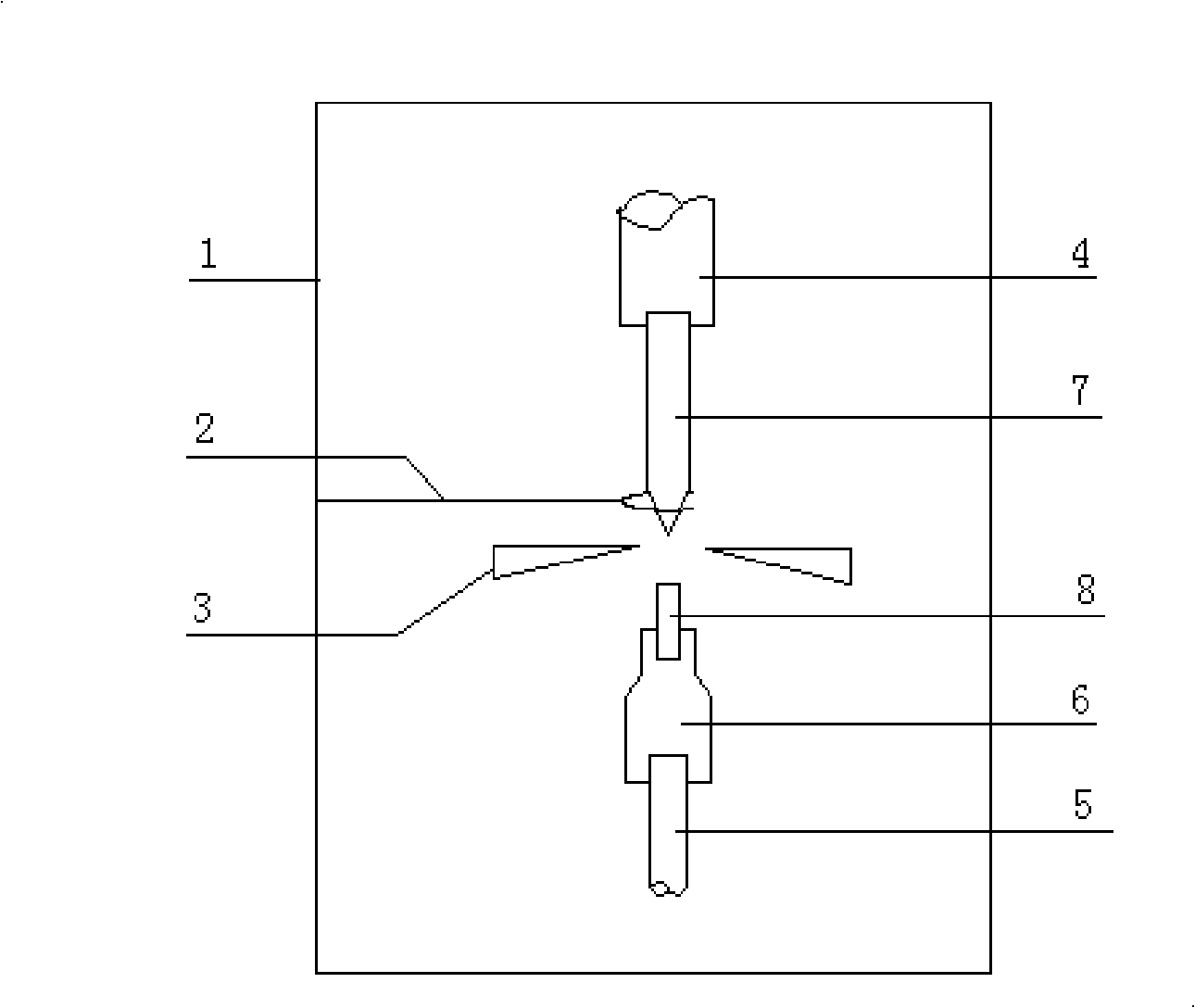
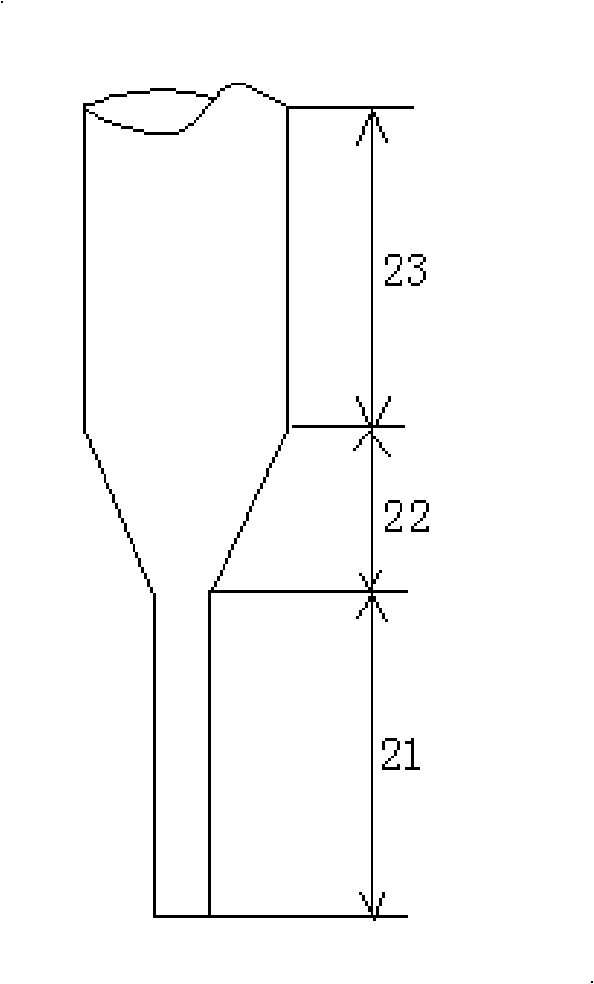
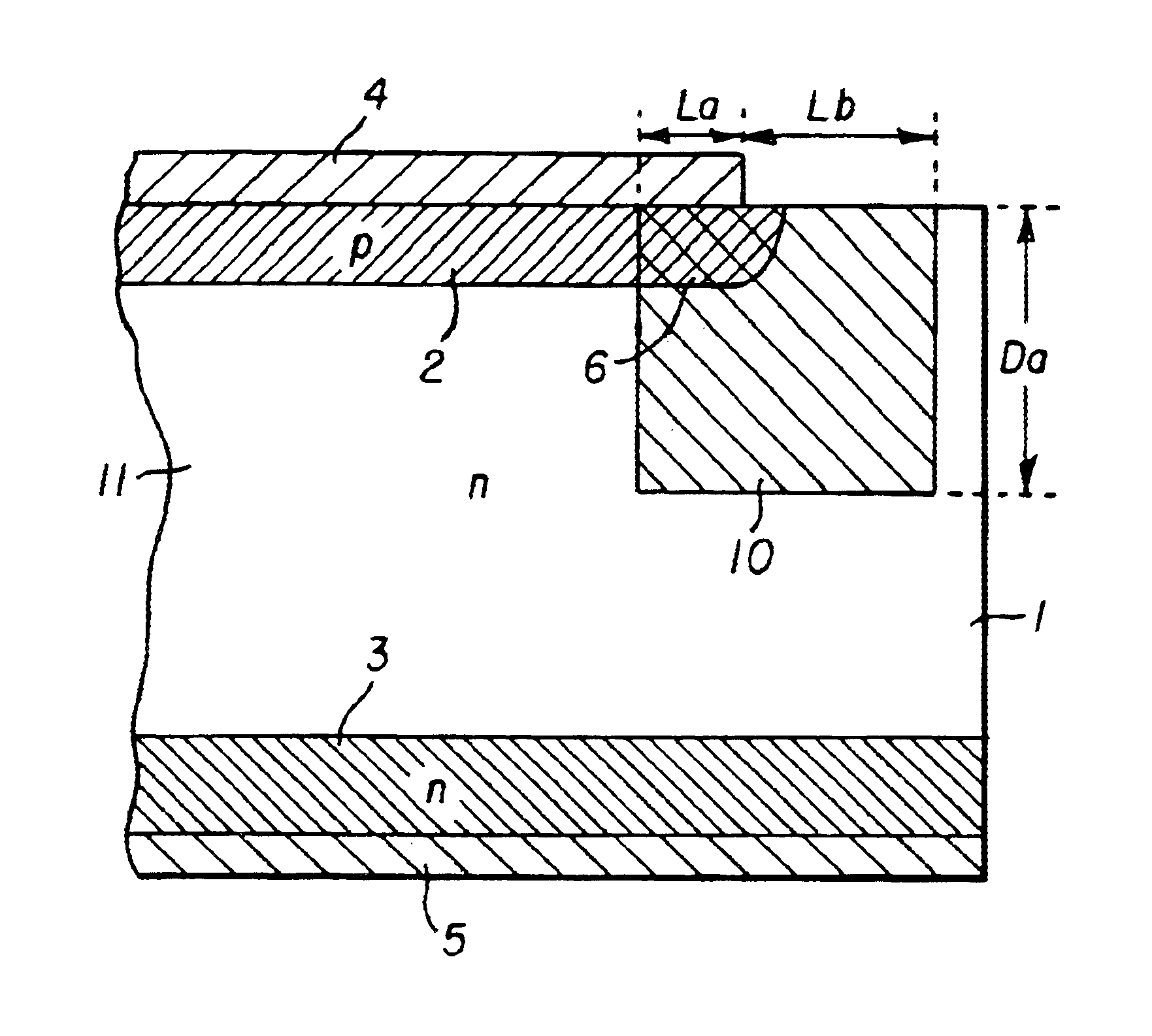
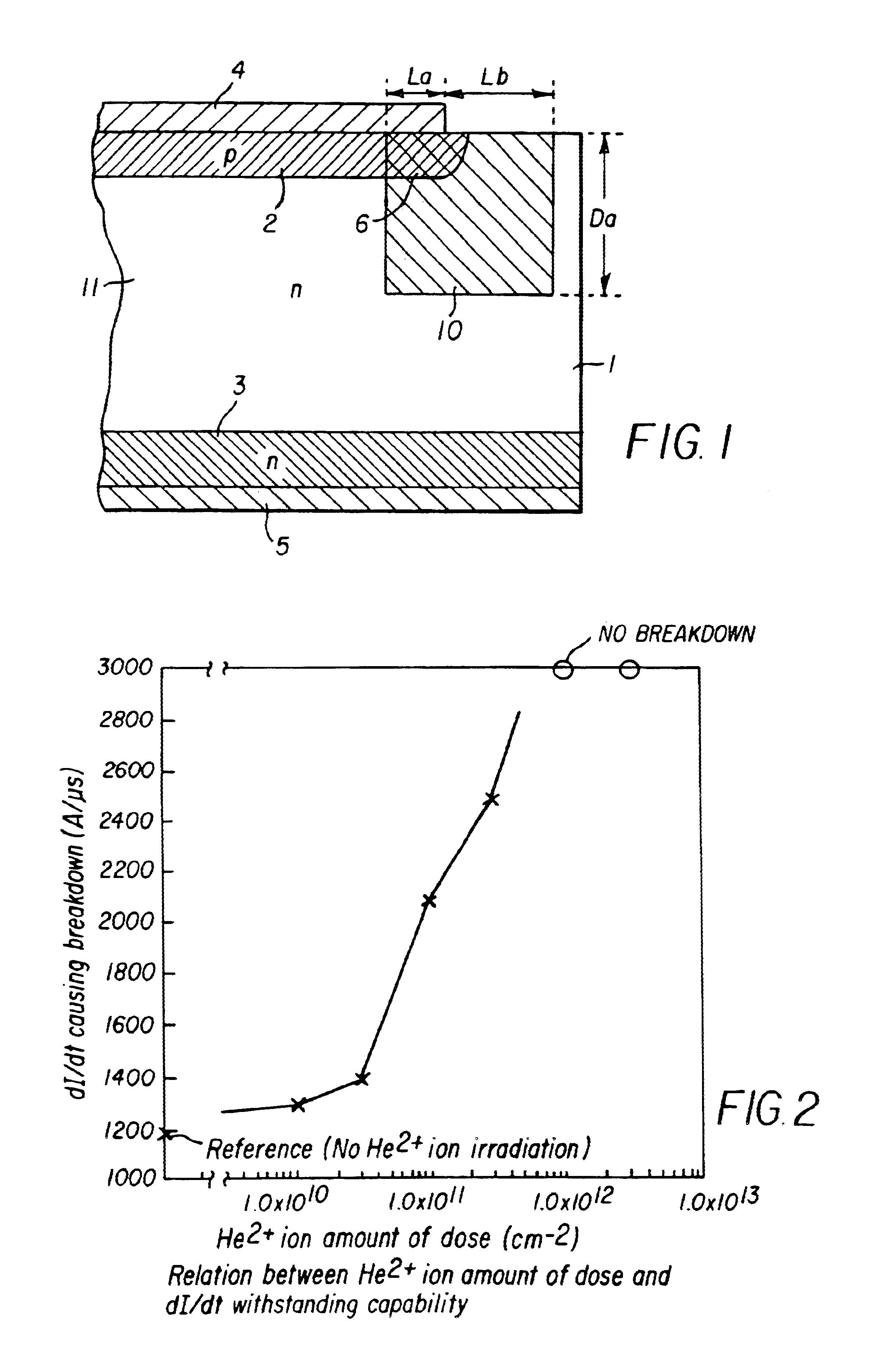
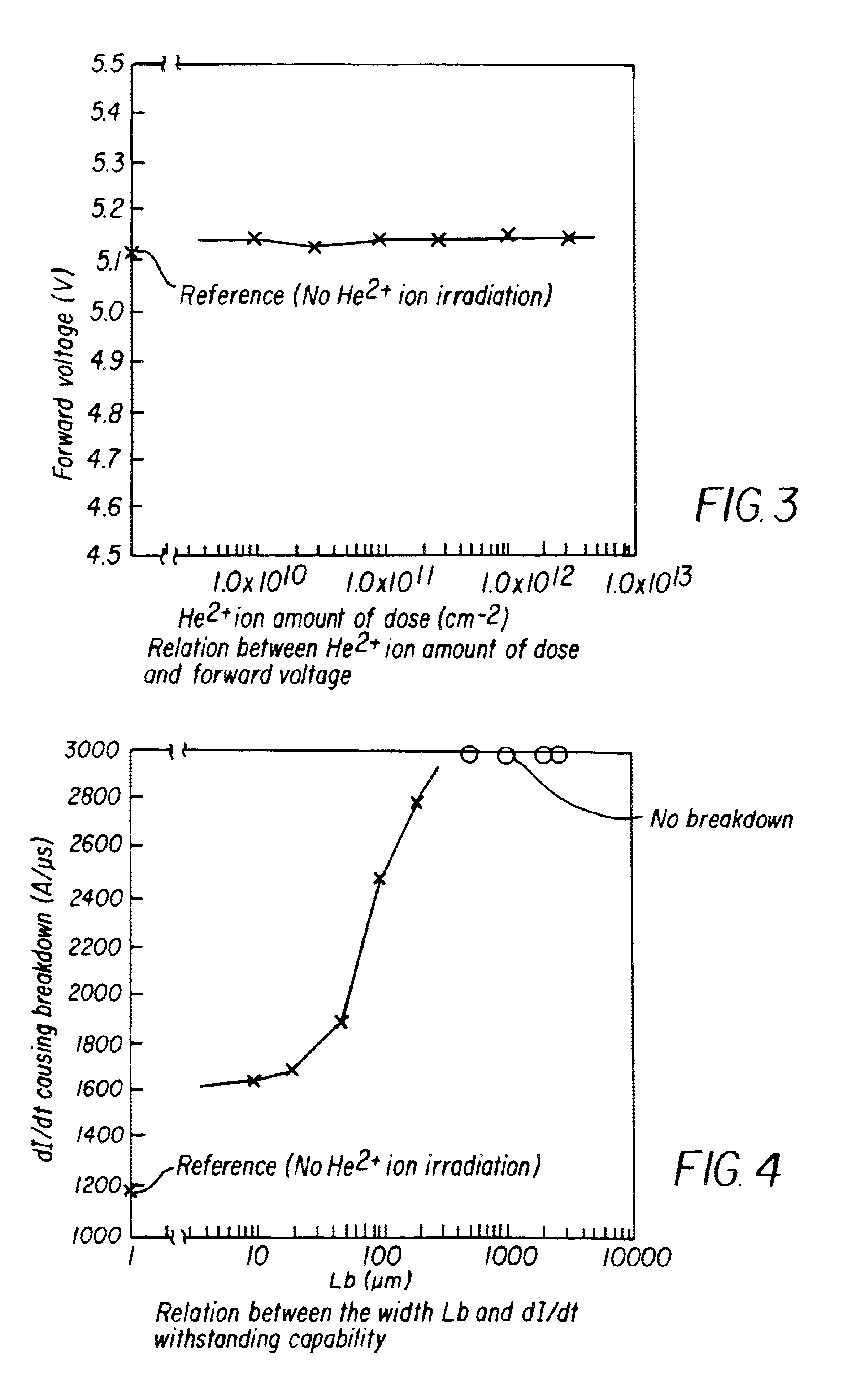
A semiconductor device that helps to prevent the occurrence of current localization in the vicinity of an electrode edge and improves the reverse-recovery withstanding capability. The semiconductor device according to the invention includes a first carrier lifetime region, in which the carrier lifetime is short, formed in such a configuration that the first carrier lifetime region extends across the edge area of an anode electrode projection, which projects the anode electrode vertically into a semiconductor substrate. The first carrier lifetime region also includes a vertical boundary area spreading nearly vertically between a heavily doped p-type anode layer and a lightly doped semiconductor layer. The first carrier lifetime region of the invention is formed by irradiating with a particle beam, such as a He2+ ion beam or a proton beam.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method to realize fast silicon-on-insulator (SOI) optical device
A fast silicon-on-insulator (SOI) waveguide-based optical device enhanced with minority charge carrier lifetime modifiers enables faster modulation speeds in optical attenuators, optical intensity / phase-modulators, and optical switches whose operation principles are based on free-carrier injection into a waveguide. The waveguide is doped with gold (Au) or platinum (Pt) such that when a drive voltage (applied to the device) is turned off, the minority charge carriers rapidly annihilate because gold doping reduces the minority carrier lifetime, which improves transient characteristics of the optical device. Integration of the fast active device with passive devices such as WDM demultiplexers / multiplexers on the SOI optical waveguide platform enables realization of monolithic integrated optical components for advanced functionality such as dynamic spectral equalization.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Growth process for N-type solar energy silicon single crystal with minority carrier service life of larger than or equal to 1,000 microseconds
InactiveCN101724899ASolve the problem of low lifespanPractical growing methodPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltCrystal orientationSingle crystal
The invention relates to a growth process for N-type solar energy silicon single crystal with minority carrier service life of larger than or equal to 1,000 microseconds. The appearance is in 6-8 inches, the (100) crystal orientation resistivity range is between 1 omega.cm and 20 omega.cm, the minority carrier service life of the surface and the section is larger than or equal to 1,000 microseconds, the clearance oxygen content [Oi] is smaller than or equal to 17.5ppma, and the substituted carbon content [Cs] is smaller than or equal to 0.5ppma. Phosphorus-doped block-shaped polycrystalline silicon is used as a raw material to prepare the N-type solar energy silicon single crystal. The process comprises the steps of: charging, heating, leading diameter, maintaining equal diameter, collecting, cooling, heating by a program, stably heating and melting the material; after a thermal field in melting silicon is stable, leading the thin diameter, lifting the tail part of a single crystal to the upper edge of a guide cylinder with the cooling time of not larger than three hours. The crystal growth process is practical, has high efficiency and low cost, can prepare the N-type single crystal silicon which is completely larger than or equal to 1,000 microseconds from the head part to the tail part by a CZ method, and creates an industrialized foundation for efficiency improvement of an efficient solar battery.
Owner:任丙彦 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com