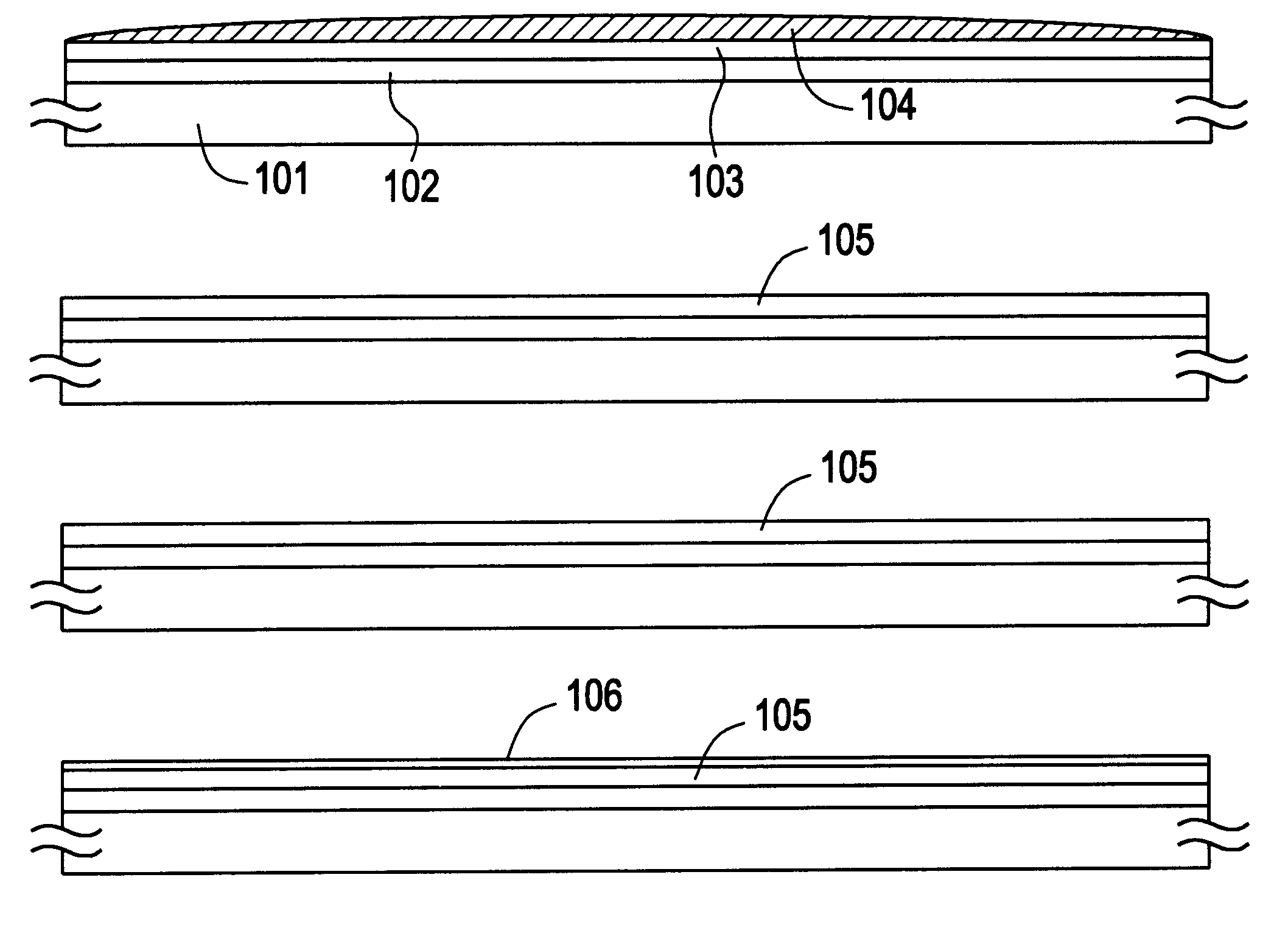
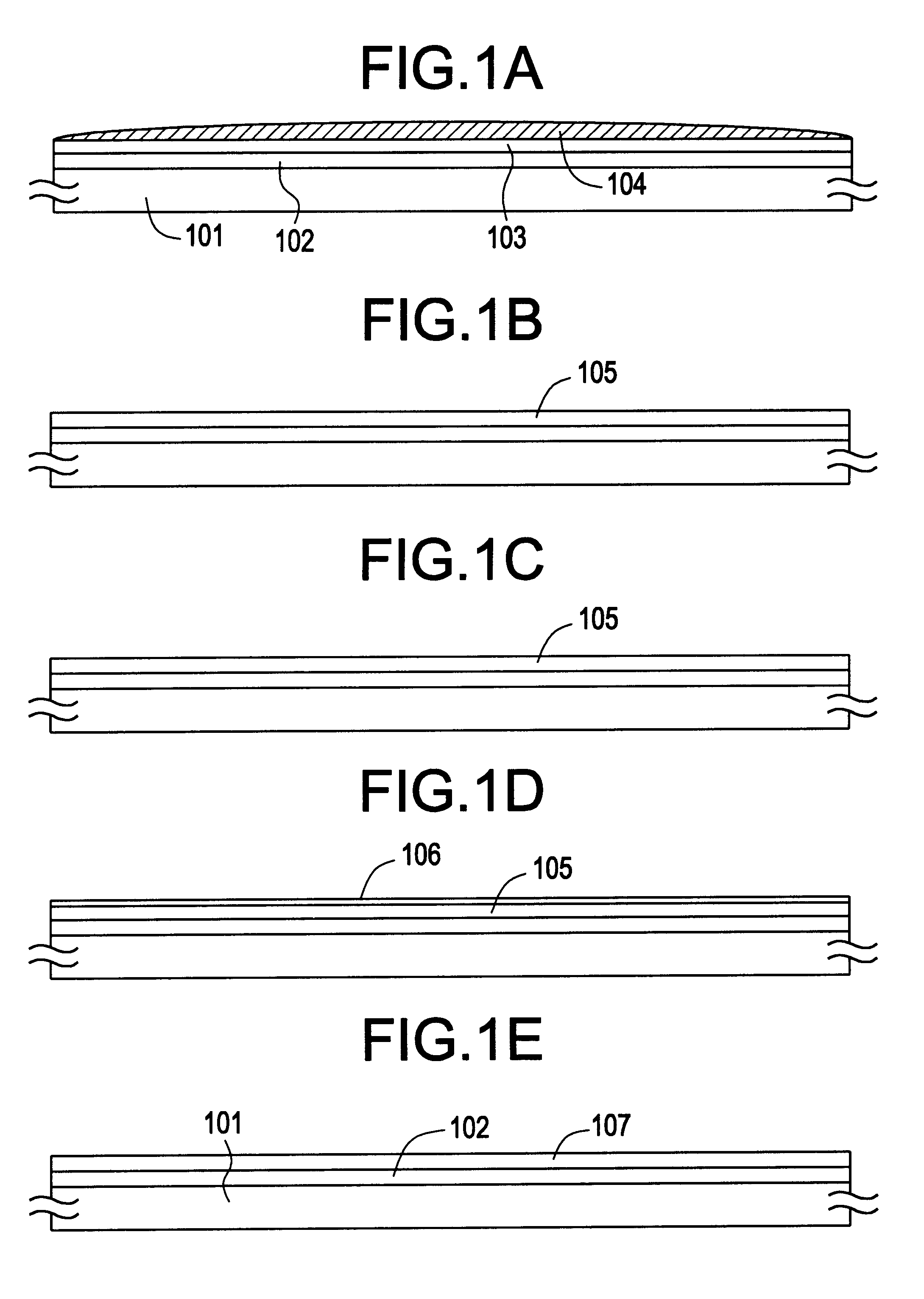
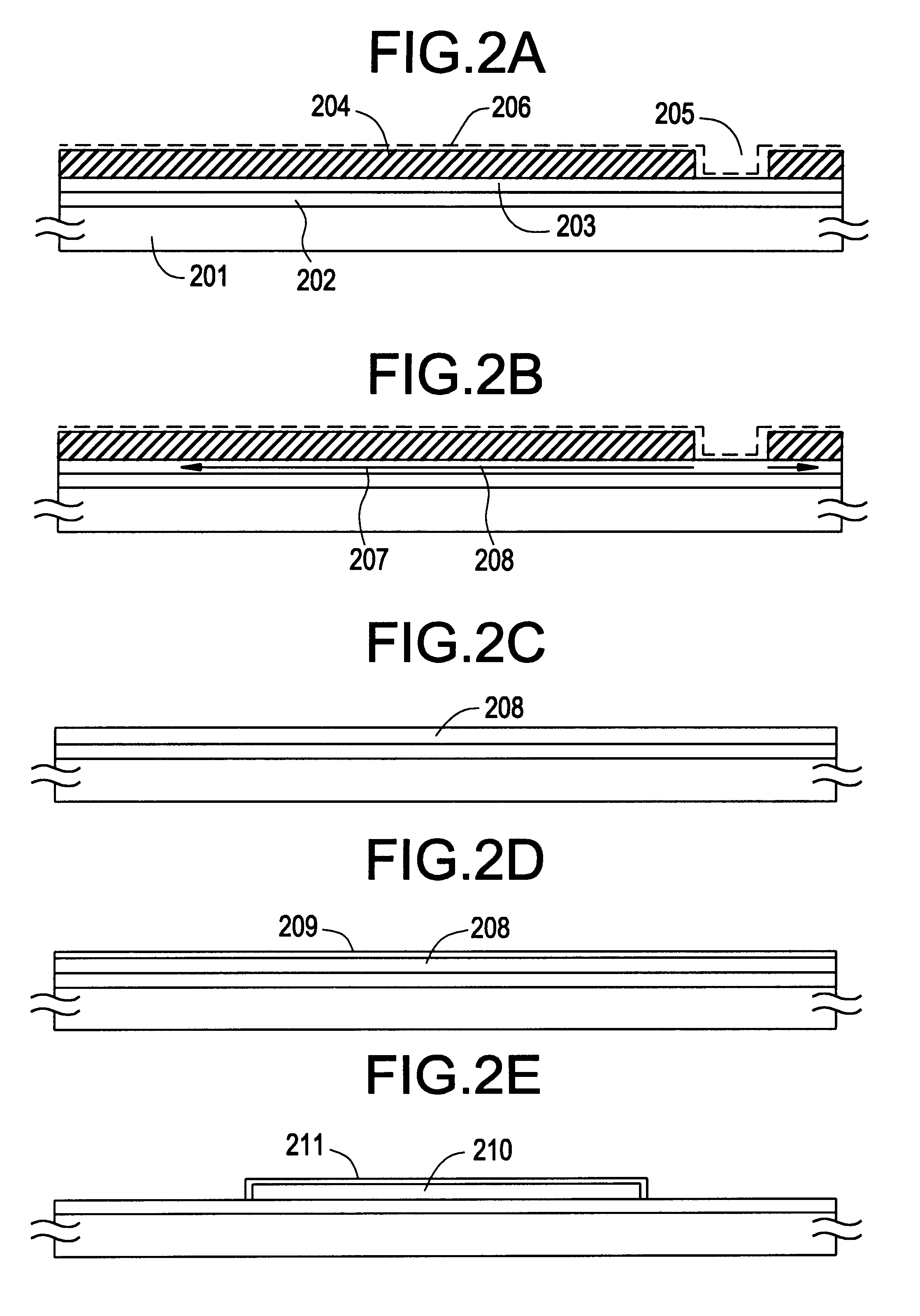
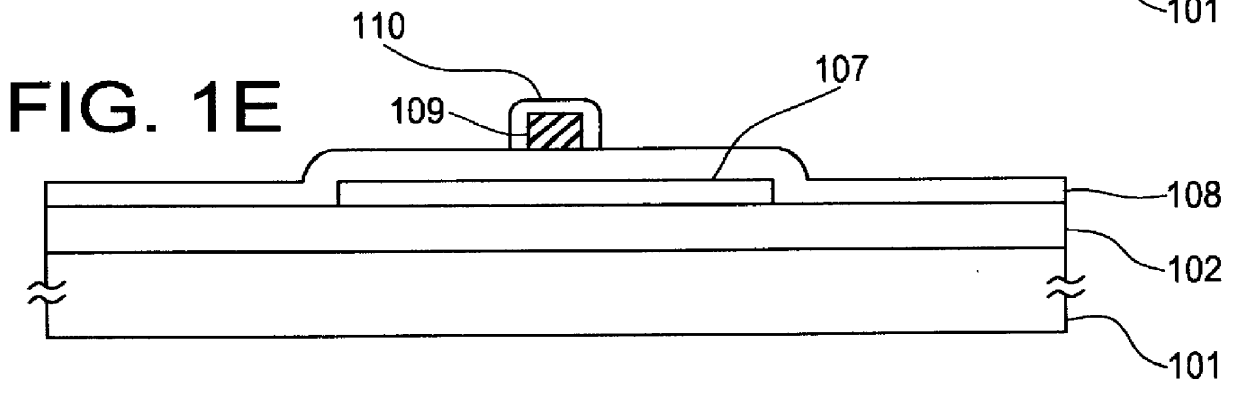
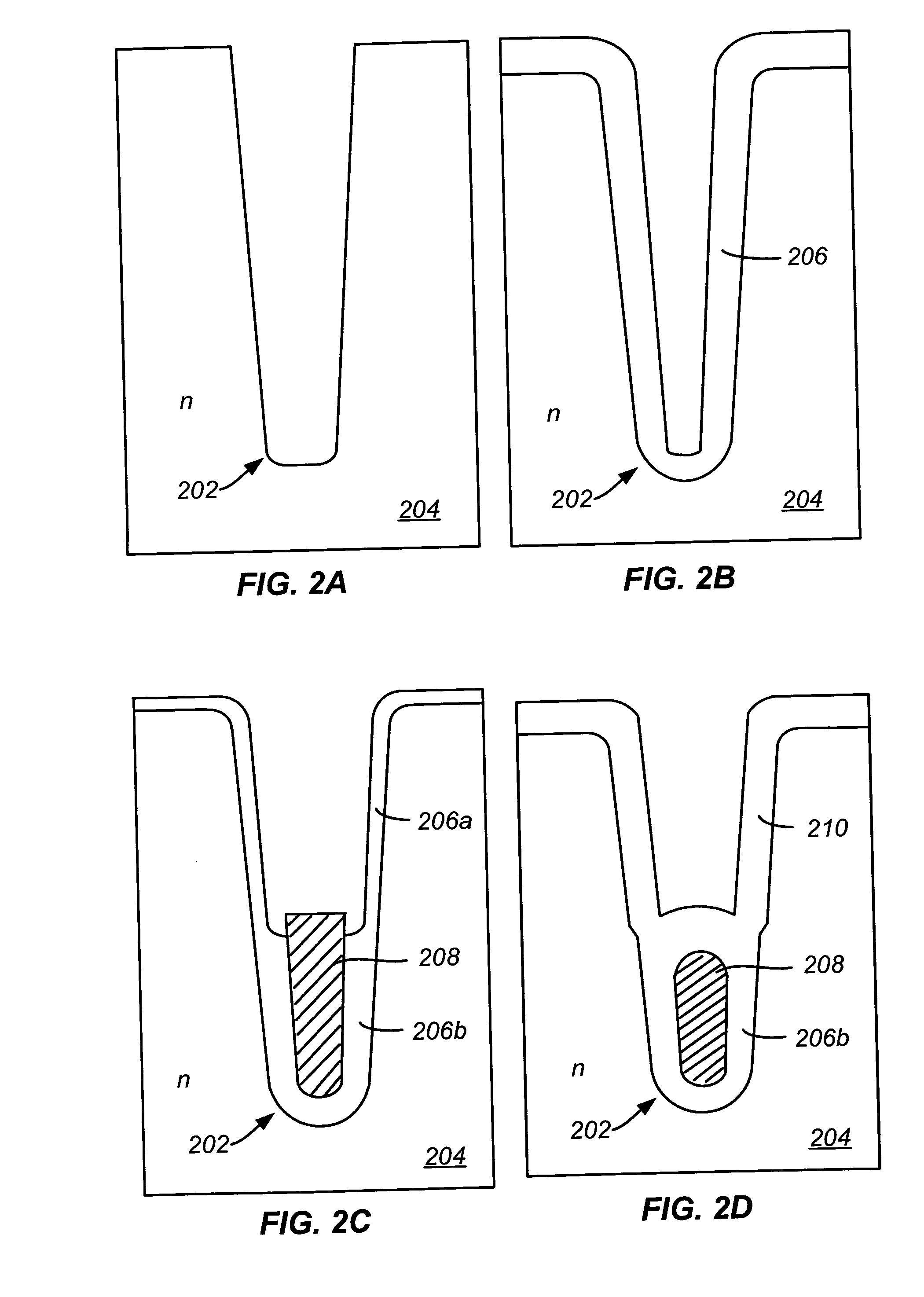
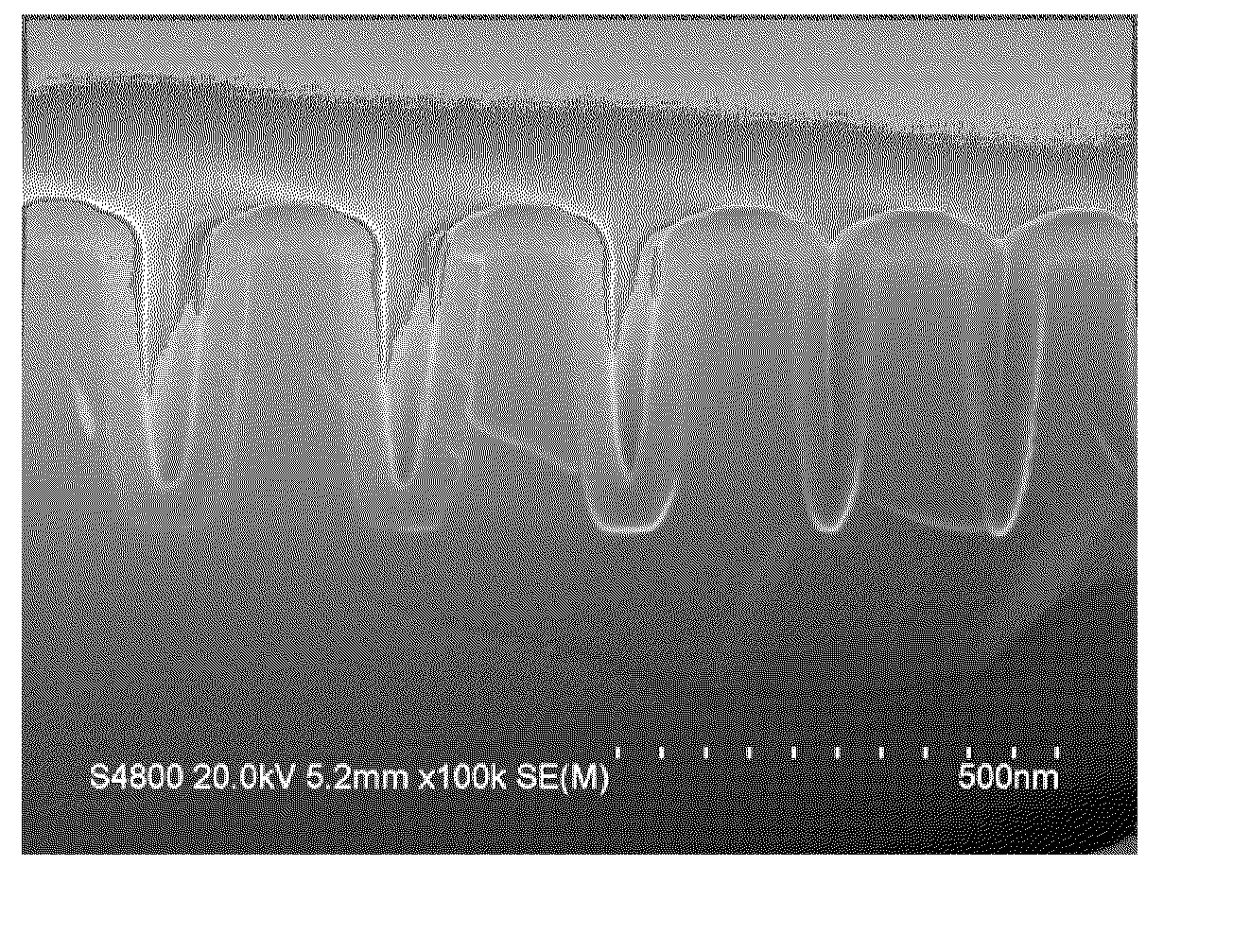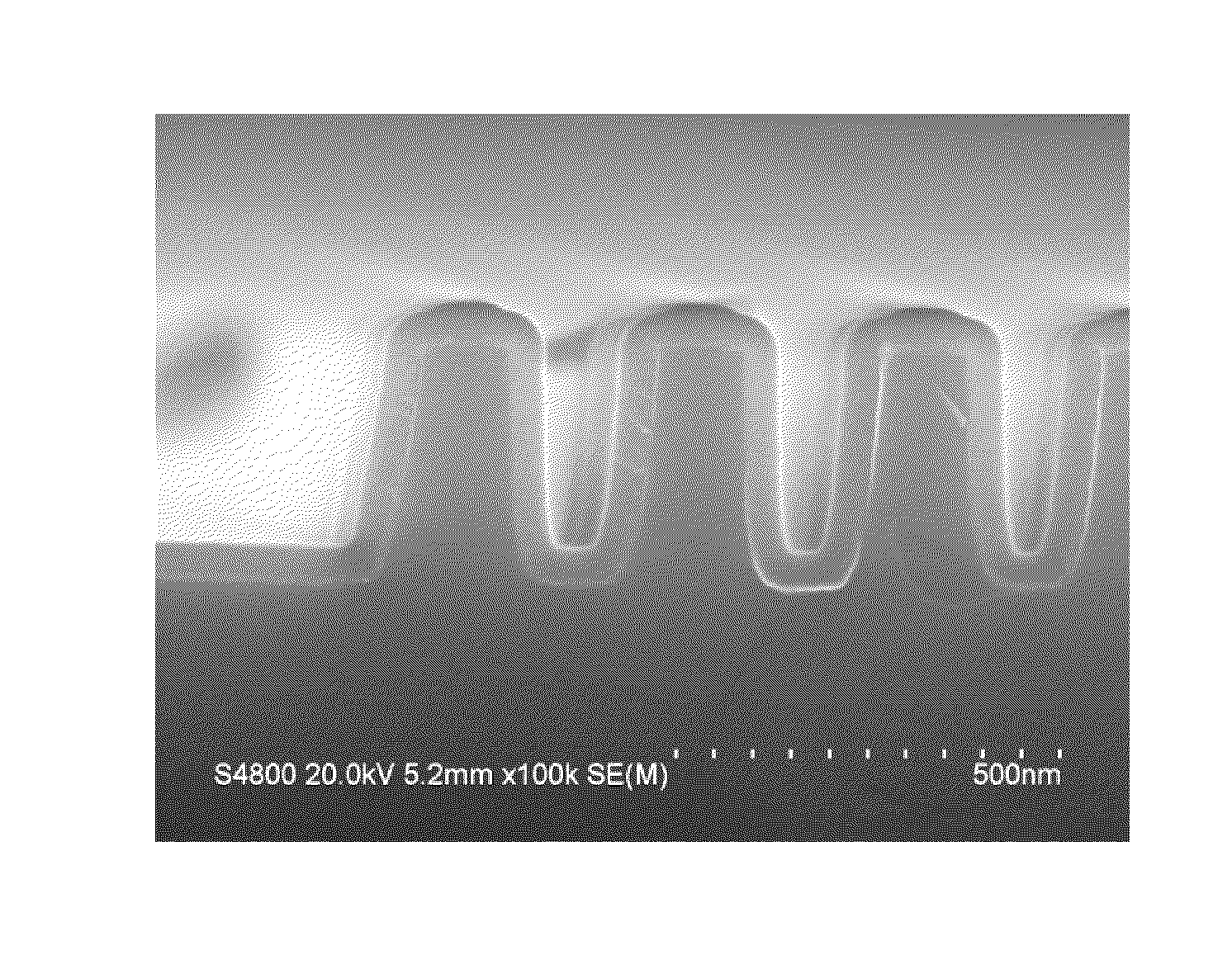Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
543 results about "Thermal oxide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
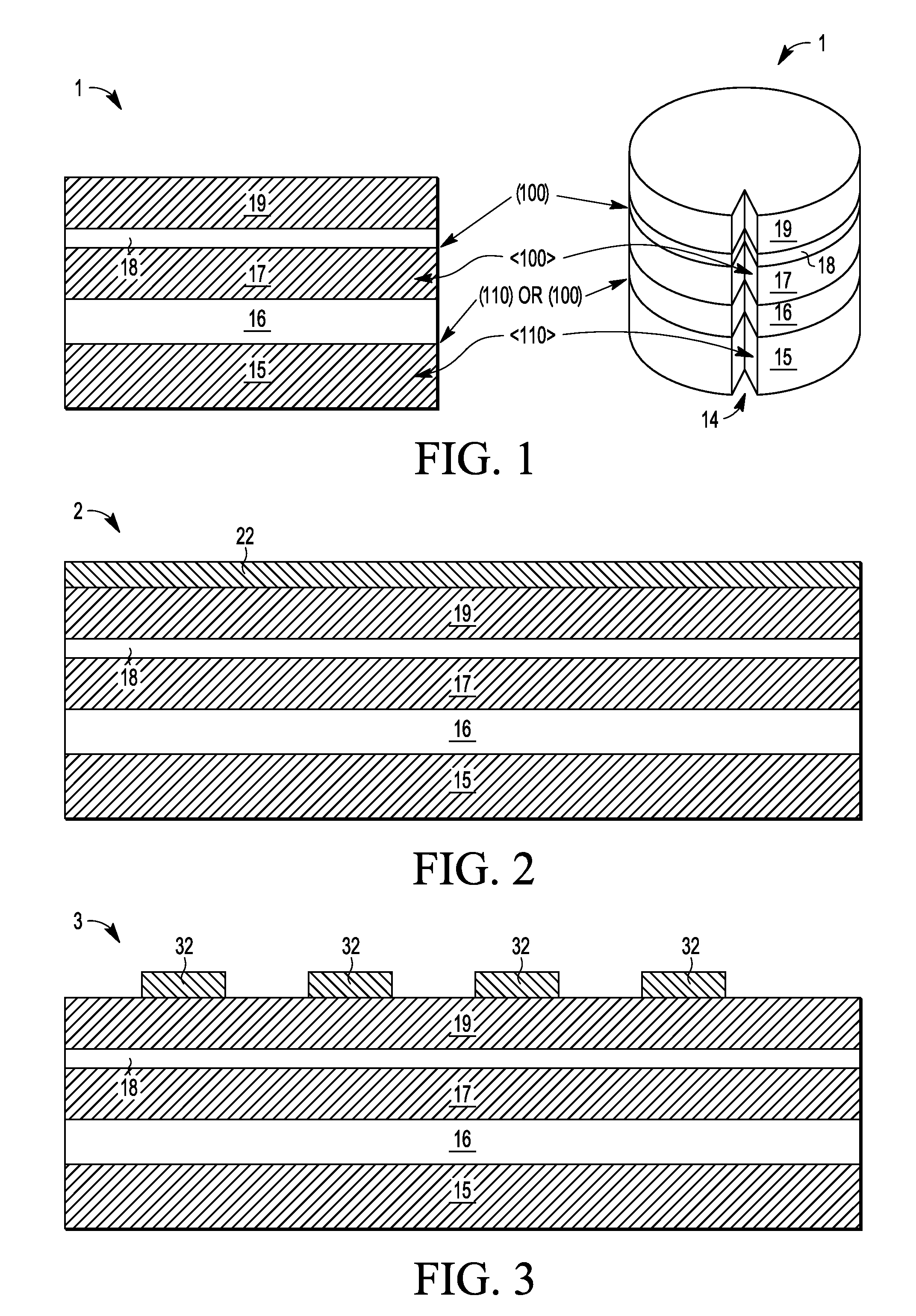
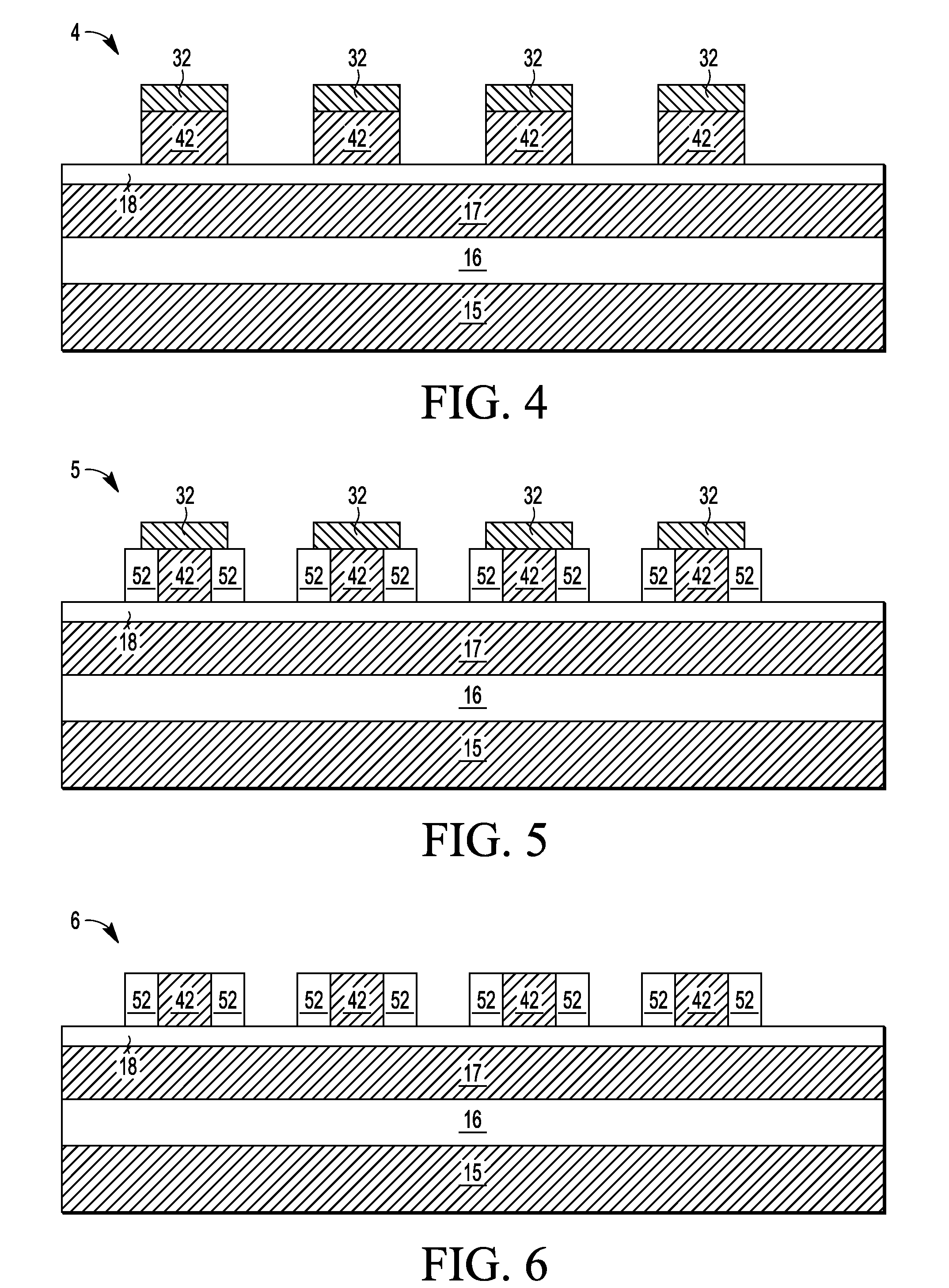
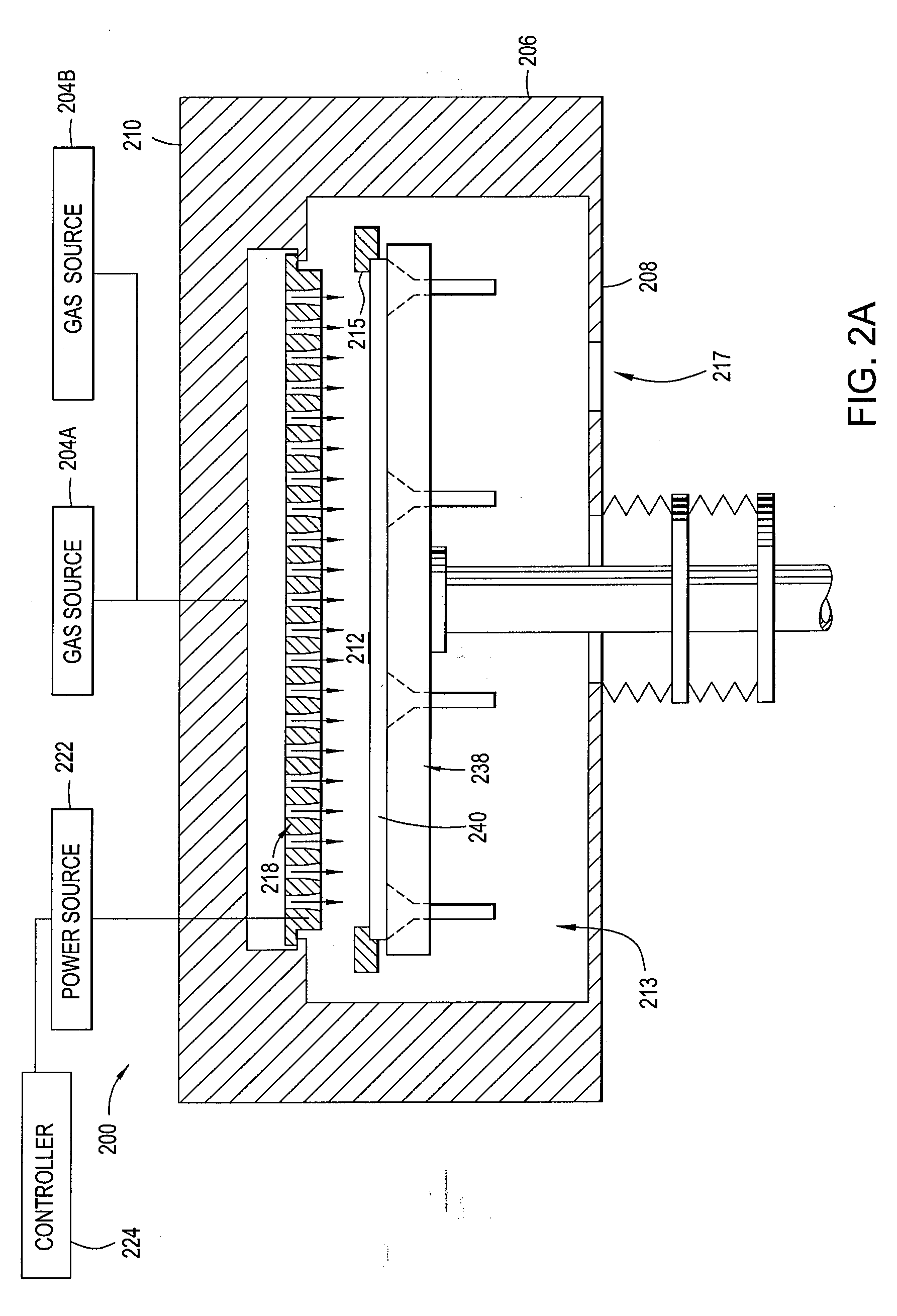
Thermal Oxide or SiO2 is one of the "building block" films used in making both simple and complex semiconductor devices. Thermal oxide is grown at high temperatures from 800°C - 1100°C using either a "Wet" or "Dry" growth method.
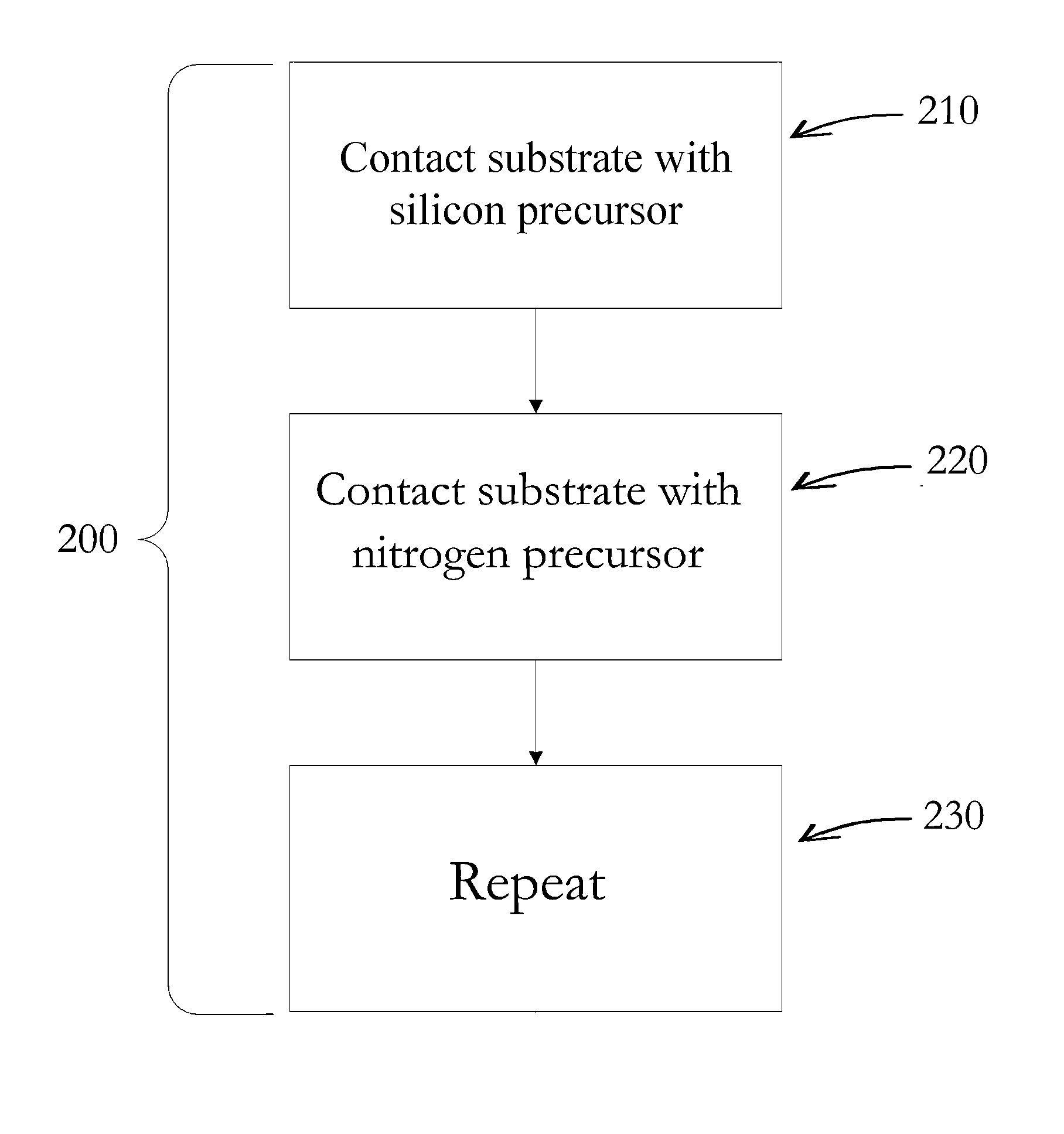
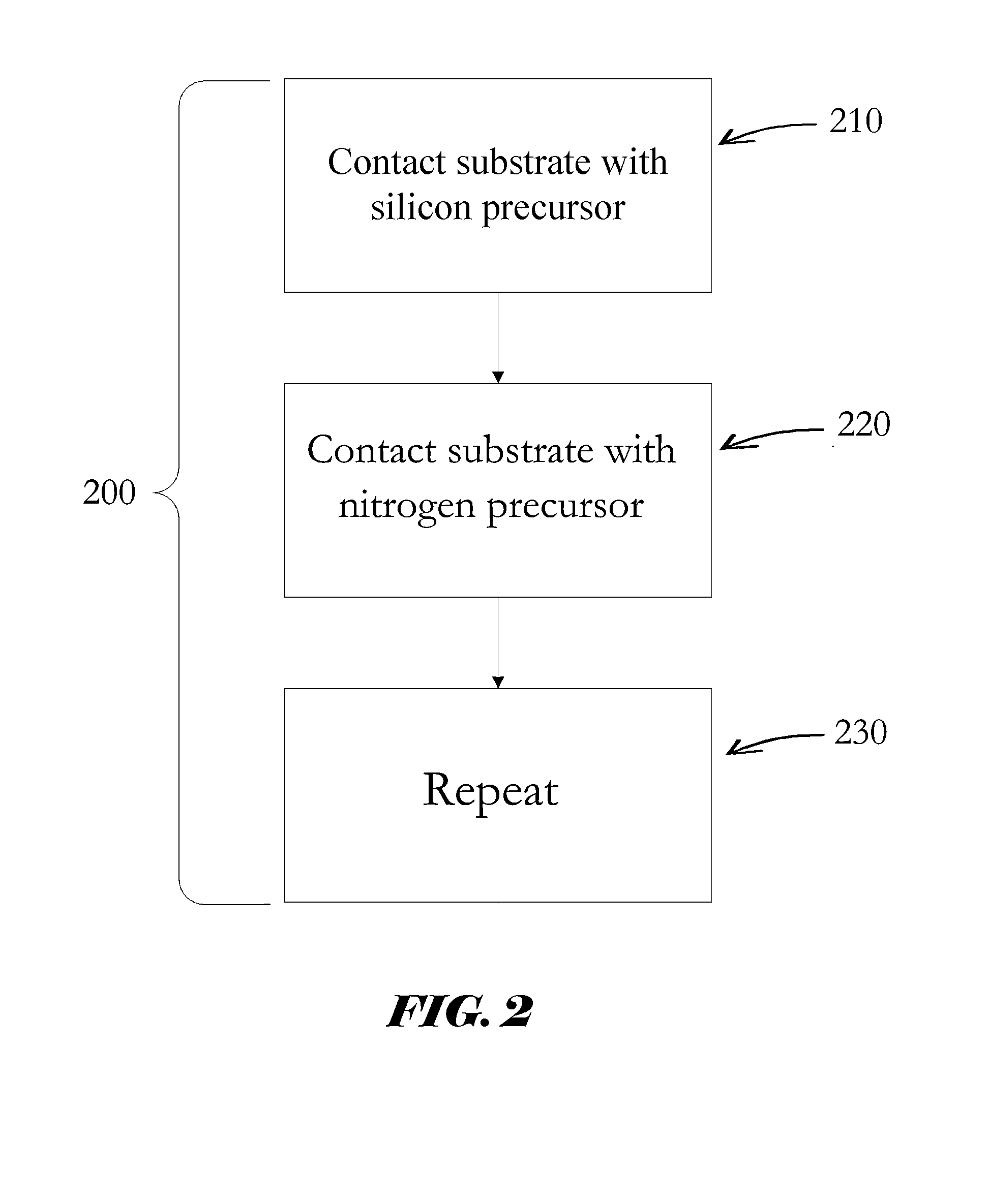
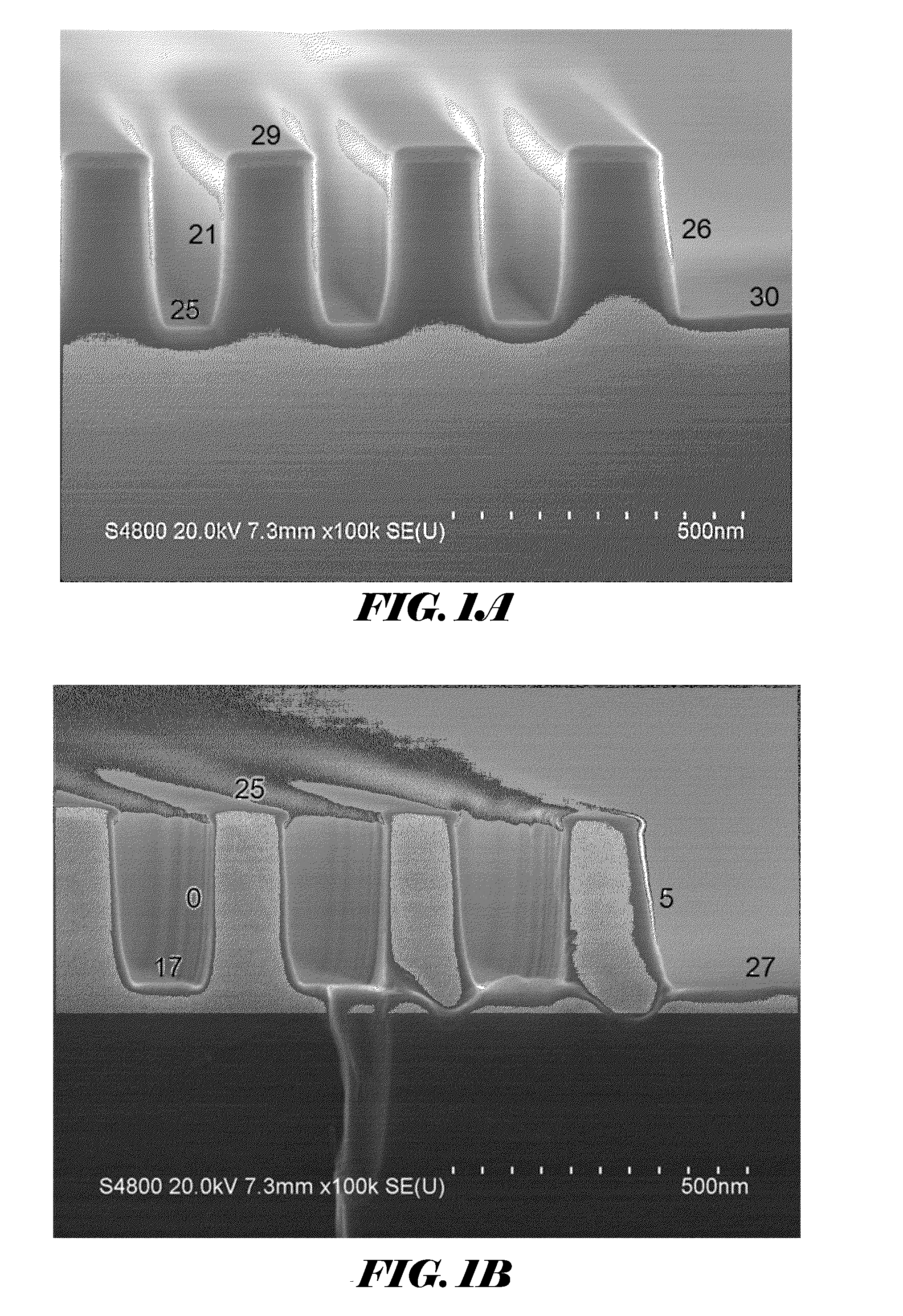
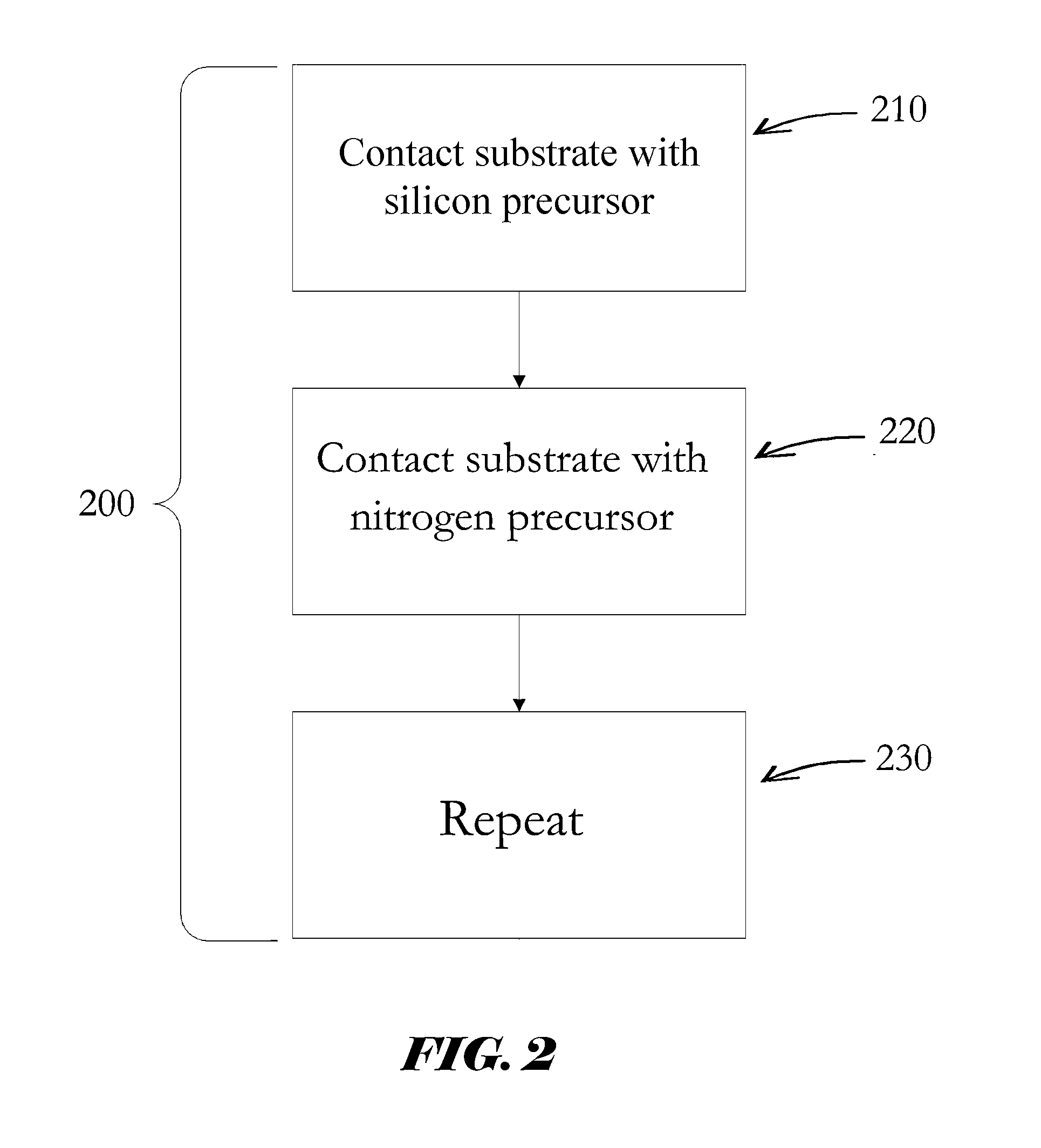
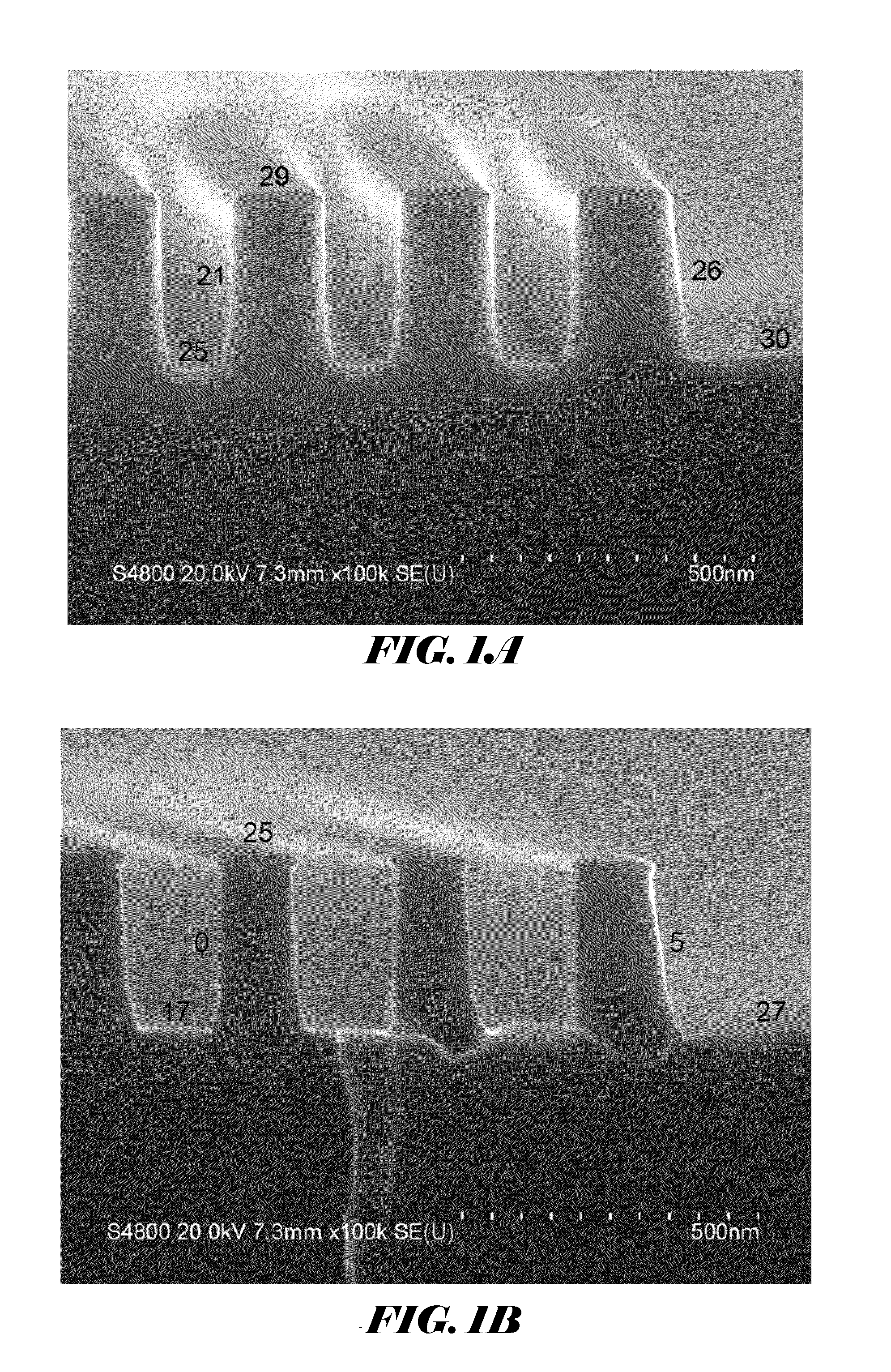
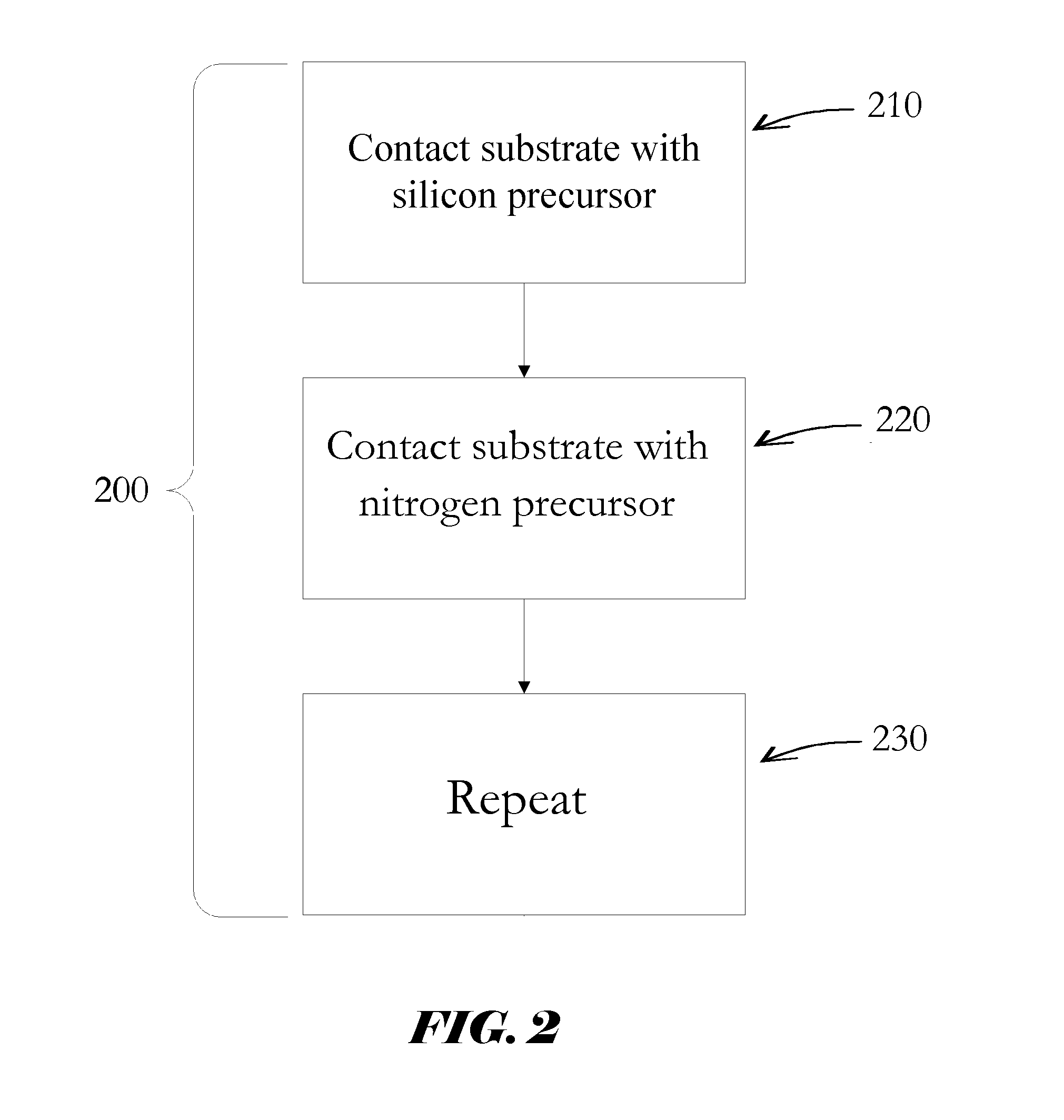
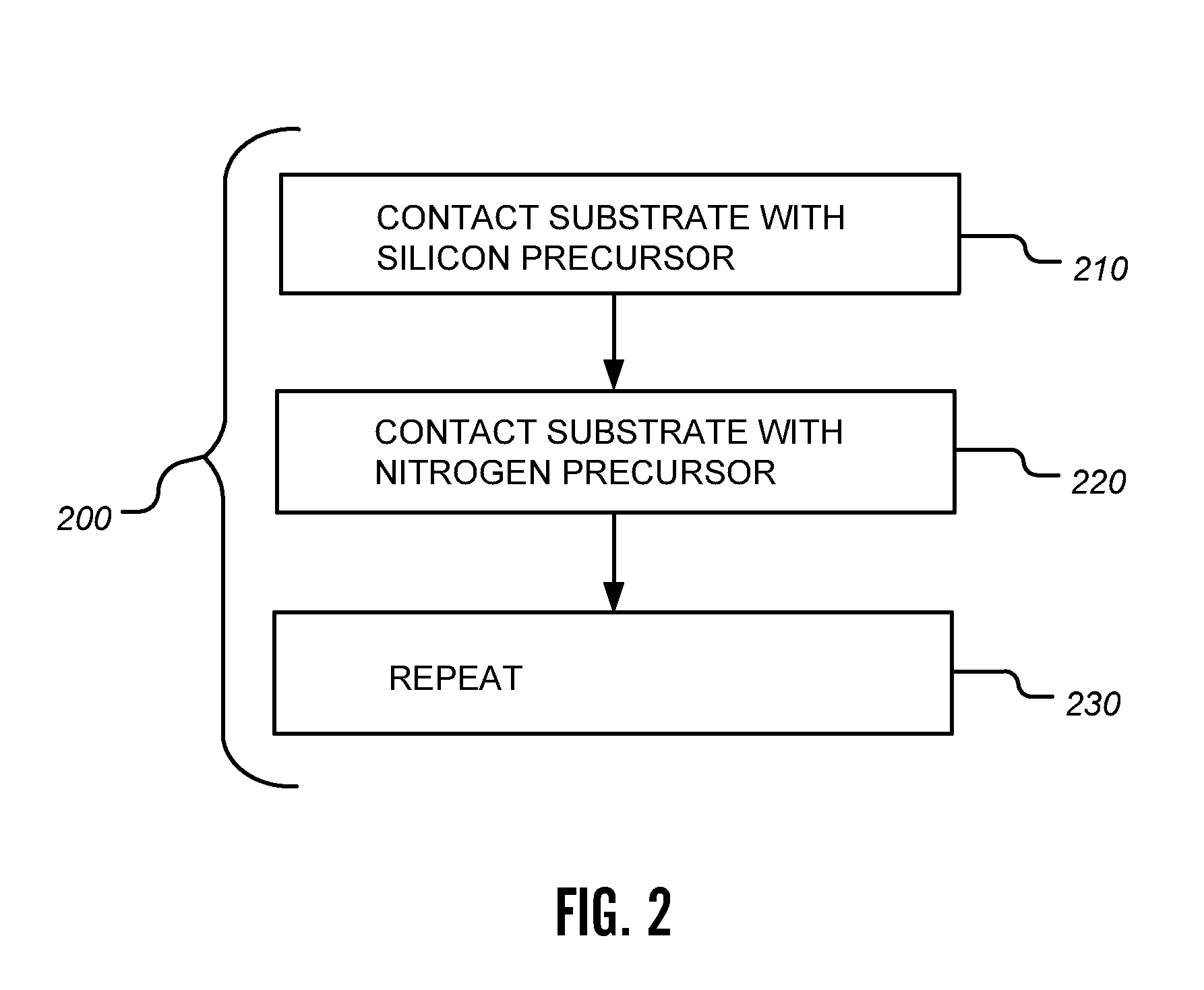
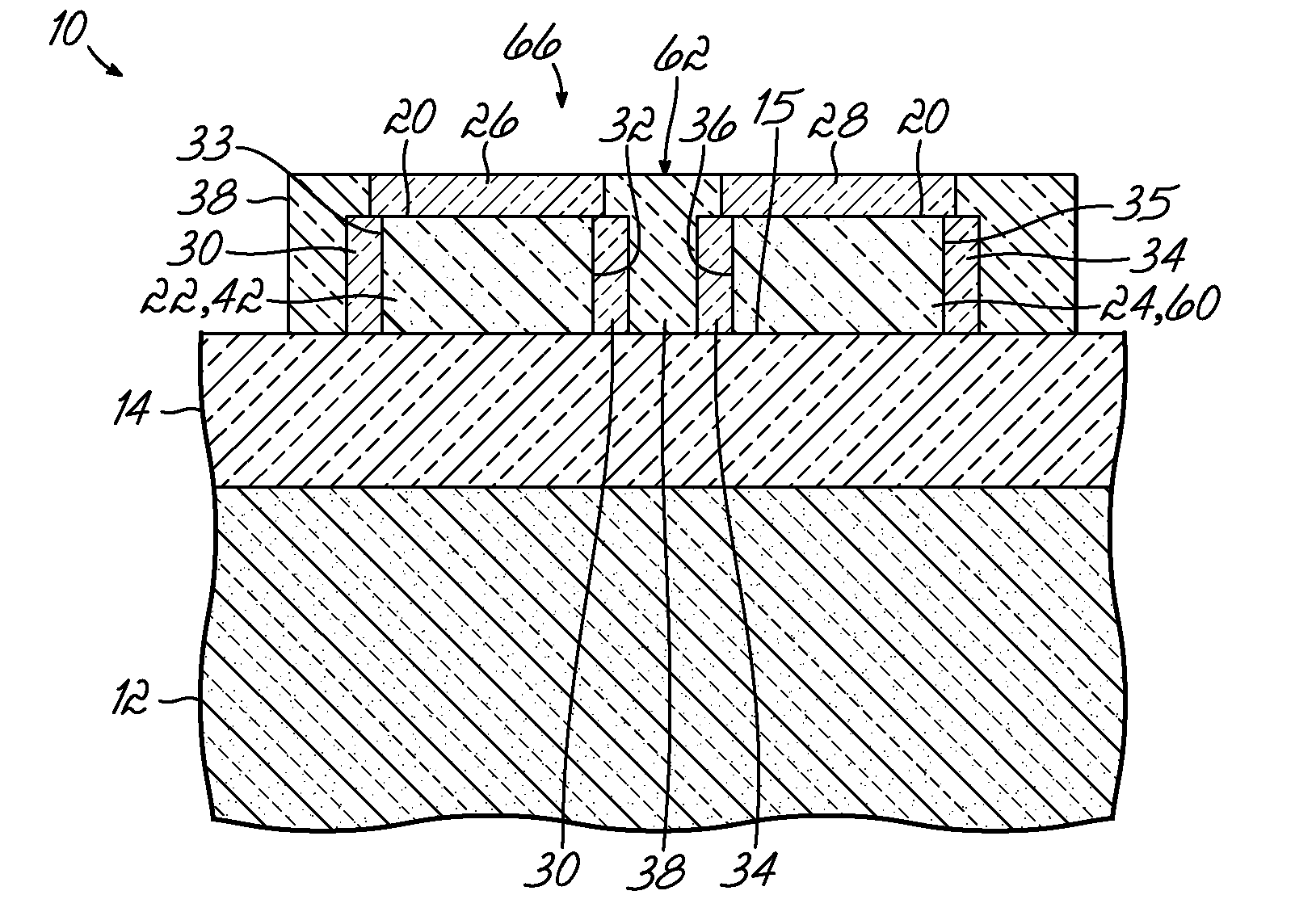
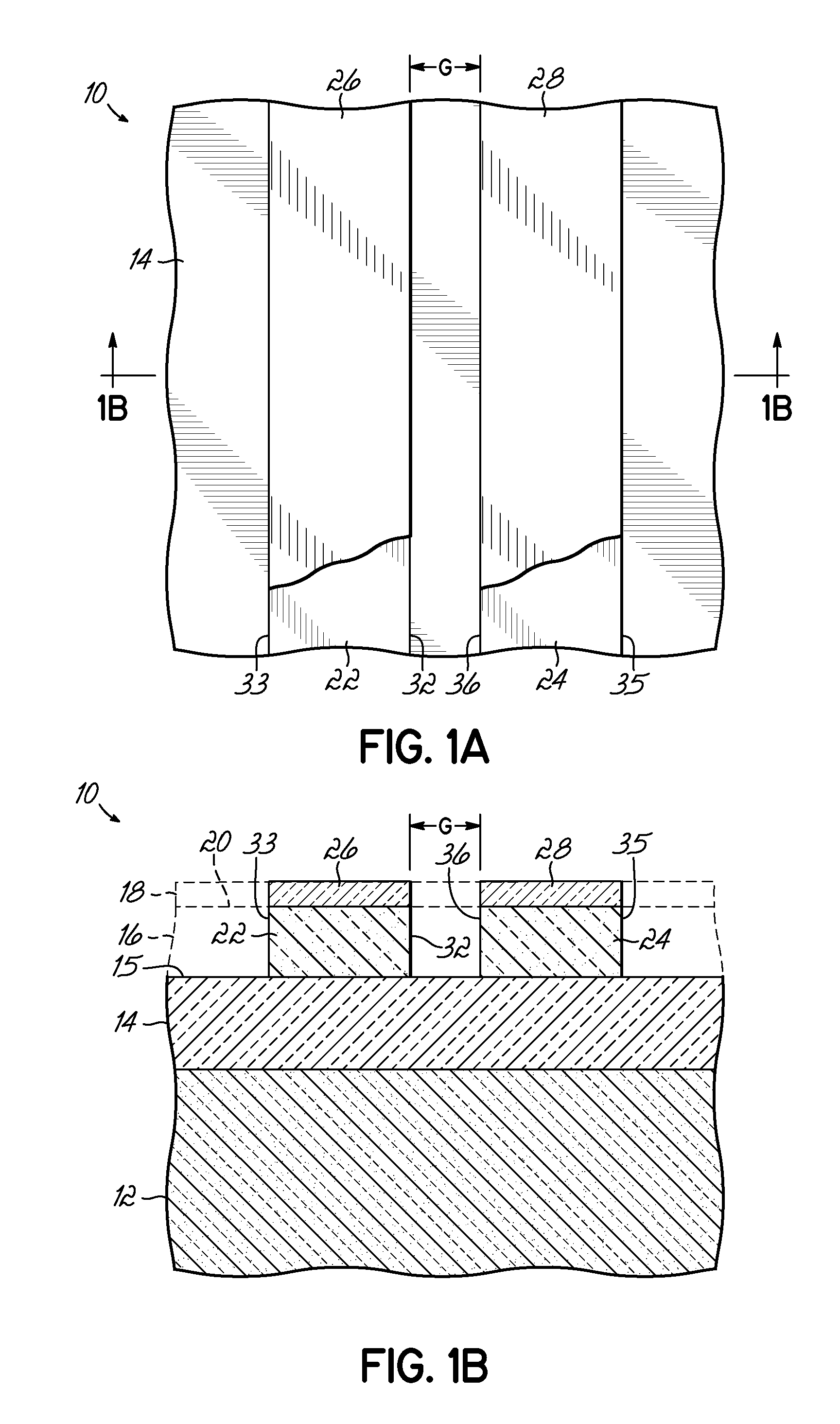
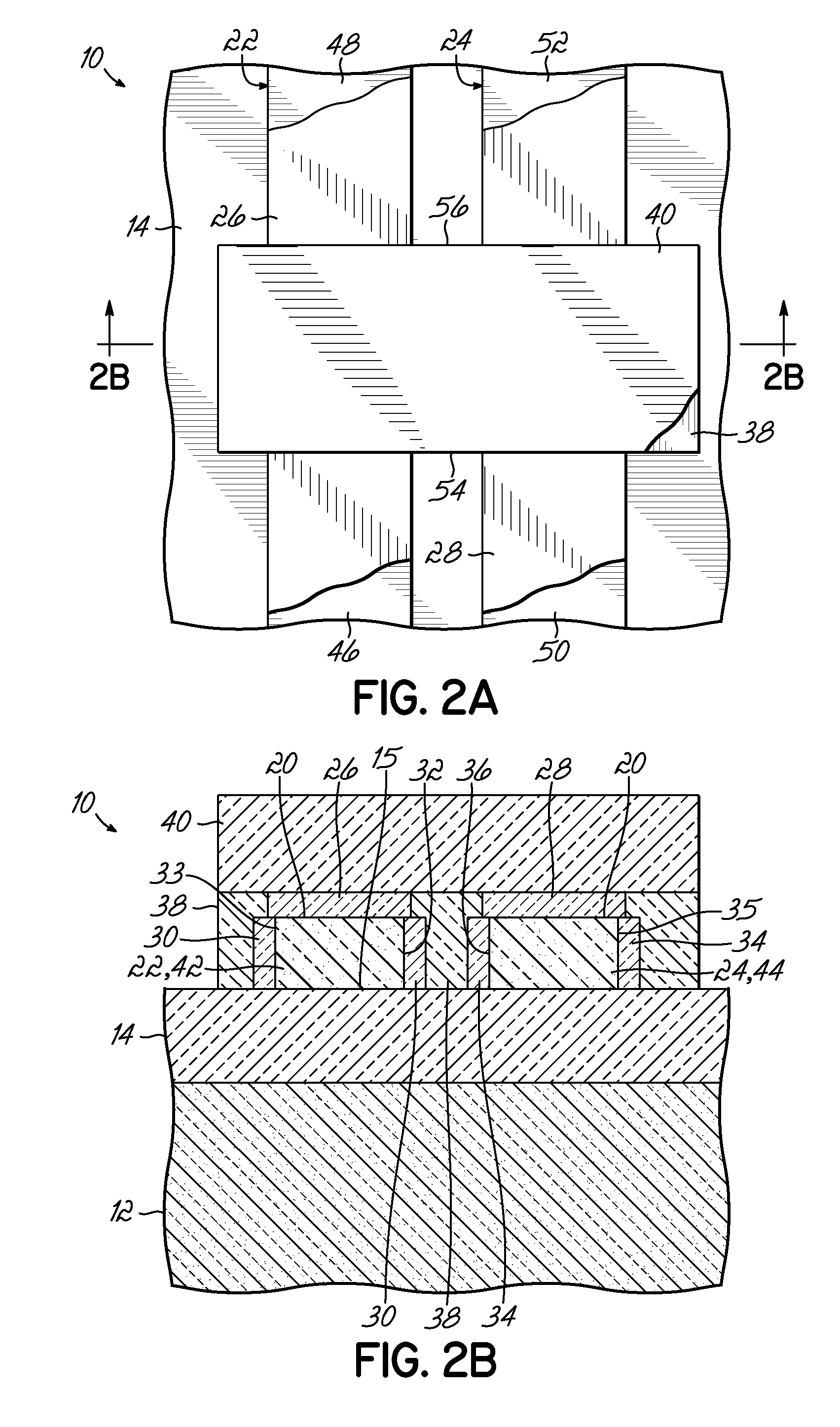
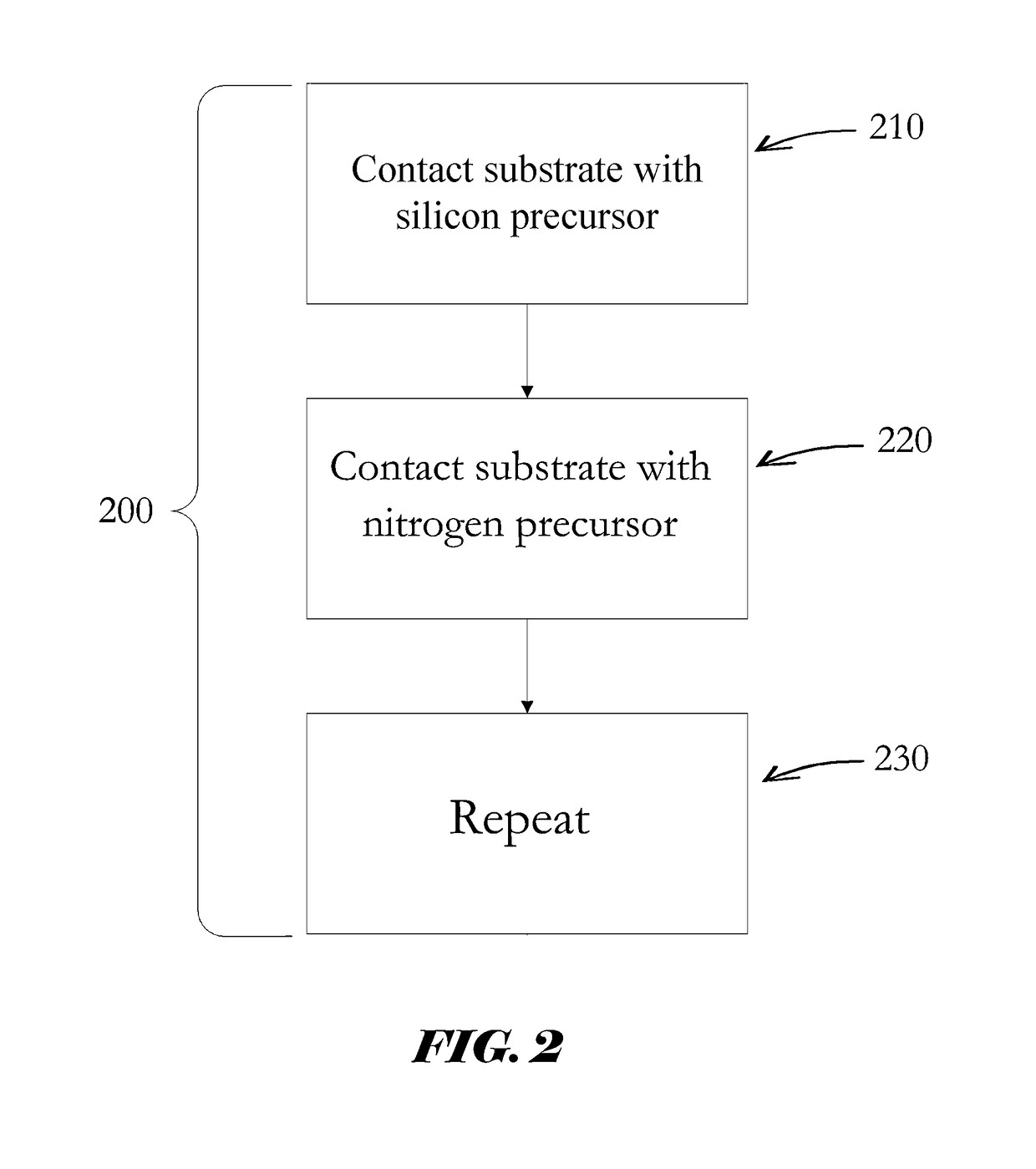
Si PRECURSORS FOR DEPOSITION OF SiN AT LOW TEMPERATURES
ActiveUS20140273528A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingMetallurgyAtomic layer deposition
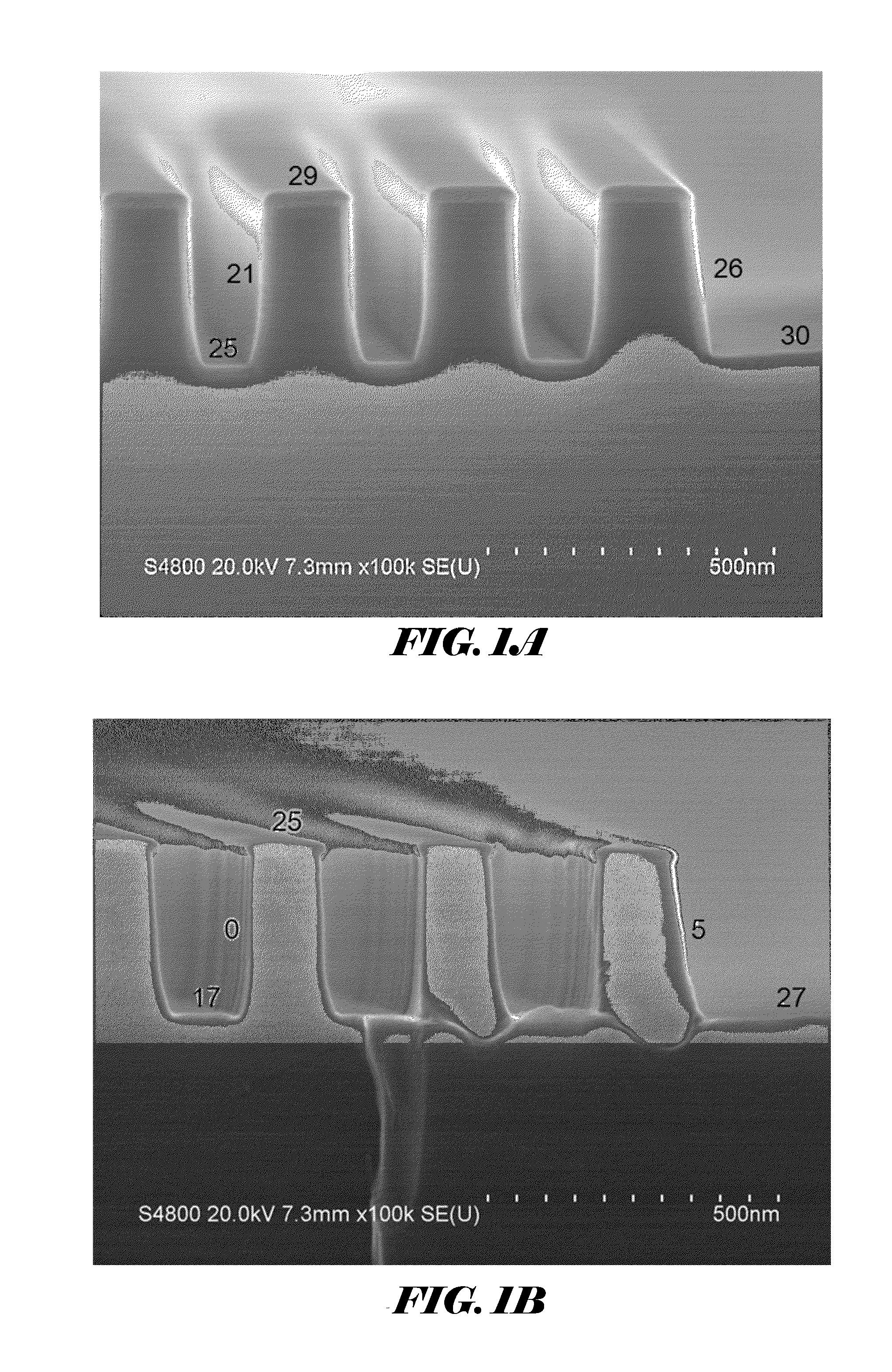
Methods and precursors for depositing silicon nitride films by atomic layer deposition (ALD) are provided. In some embodiments the silicon precursors comprise an iodine ligand. The silicon nitride films may have a relatively uniform etch rate for both vertical and the horizontal portions when deposited onto three-dimensional structures such as FinFETS or other types of multiple gate FETs. In some embodiments, various silicon nitride films of the present disclosure have an etch rate of less than half the thermal oxide removal rate with diluted HF (0.5%).
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Si PRECURSORS FOR DEPOSITION OF SiN AT LOW TEMPERATURES
ActiveUS20140273477A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAtomic layer depositionThermal oxide
Methods and precursors for depositing silicon nitride films by atomic layer deposition (ALD) are provided. In some embodiments the silicon precursors comprise an iodine ligand. The silicon nitride films may have a relatively uniform etch rate for both vertical and the horizontal portions when deposited onto three-dimensional structures such as FinFETS or other types of multiple gate FETs. In some embodiments, various silicon nitride films of the present disclosure have an etch rate of less than half the thermal oxide removal rate with diluted HF (0.5%).
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Si PRECURSORS FOR DEPOSITION OF SiN AT LOW TEMPERATURES
InactiveUS20140273531A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingAtomic layer depositionThermal oxide
Methods and precursors for depositing silicon nitride films by atomic layer deposition (ALD) are provided. In some embodiments the silicon precursors comprise an iodine ligand. The silicon nitride films may have a relatively uniform etch rate for both vertical and the horizontal portions when deposited onto three-dimensional structures such as FinFETS or other types of multiple gate FETs. In some embodiments, various silicon nitride films of the present disclosure have an etch rate of less than half the thermal oxide removal rate with diluted HF (0.5%).
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
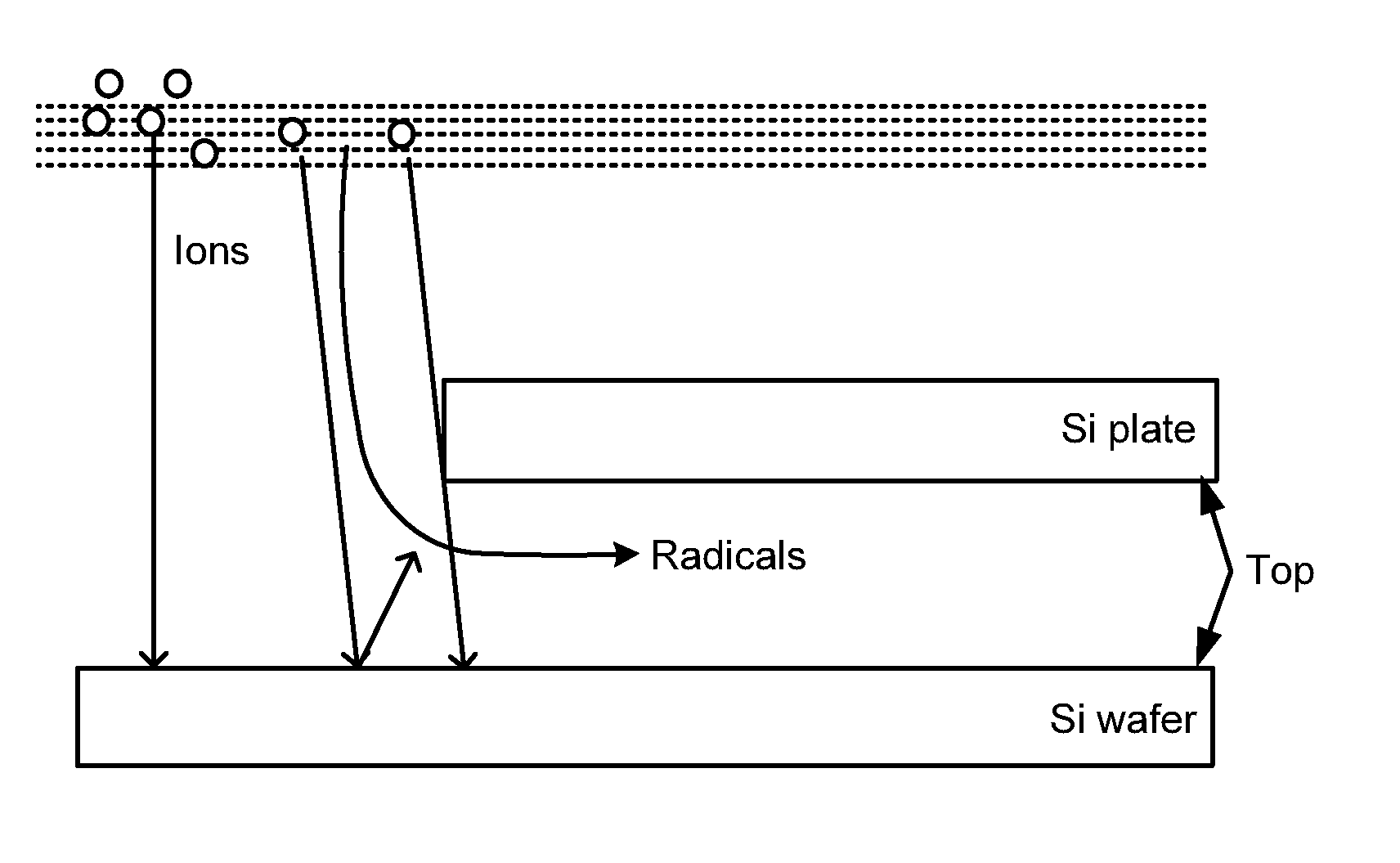
Deposition of SiN
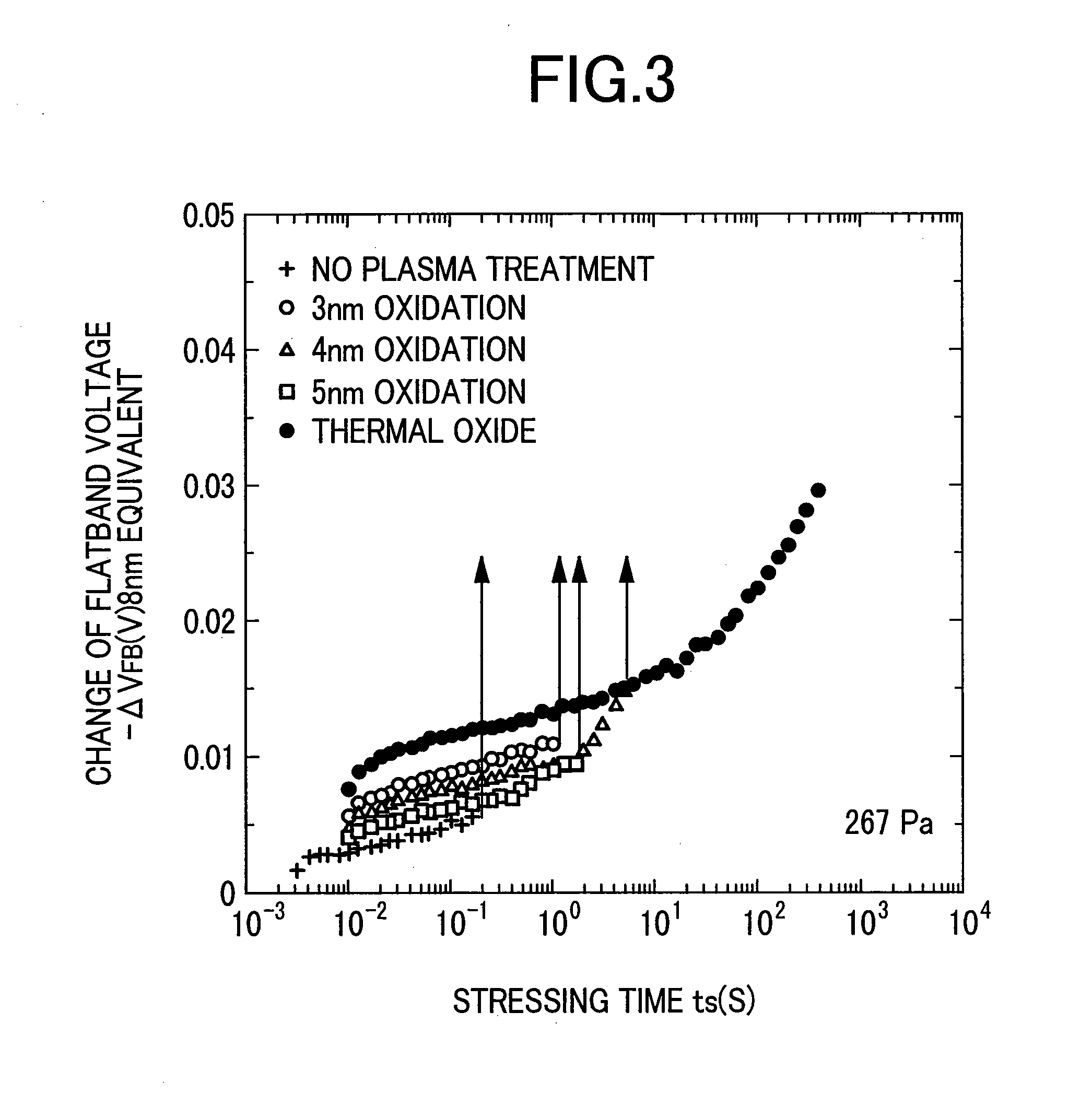
ActiveUS20160079054A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingNitrogen plasmaAtomic layer deposition
Methods and precursors for forming silicon nitride films are provided. In some embodiments, silicon nitride can be deposited by atomic layer deposition (ALD), such as plasma enhanced ALD. In some embodiments, deposited silicon nitride can be treated with a plasma treatment. The plasma treatment can be a nitrogen plasma treatment. In some embodiments the silicon precursors for depositing the silicon nitride comprise an iodine ligand. The silicon nitride films may have a relatively uniform etch rate for both vertical and the horizontal portions when deposited onto three-dimensional structures such as FinFETS or other types of multiple gate FETs. In some embodiments, various silicon nitride films of the present disclosure have an etch rate of less than half the thermal oxide removal rate with diluted HF (0.5%). In some embodiments, a method for depositing silicon nitride films comprises a multi-step plasma treatment.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
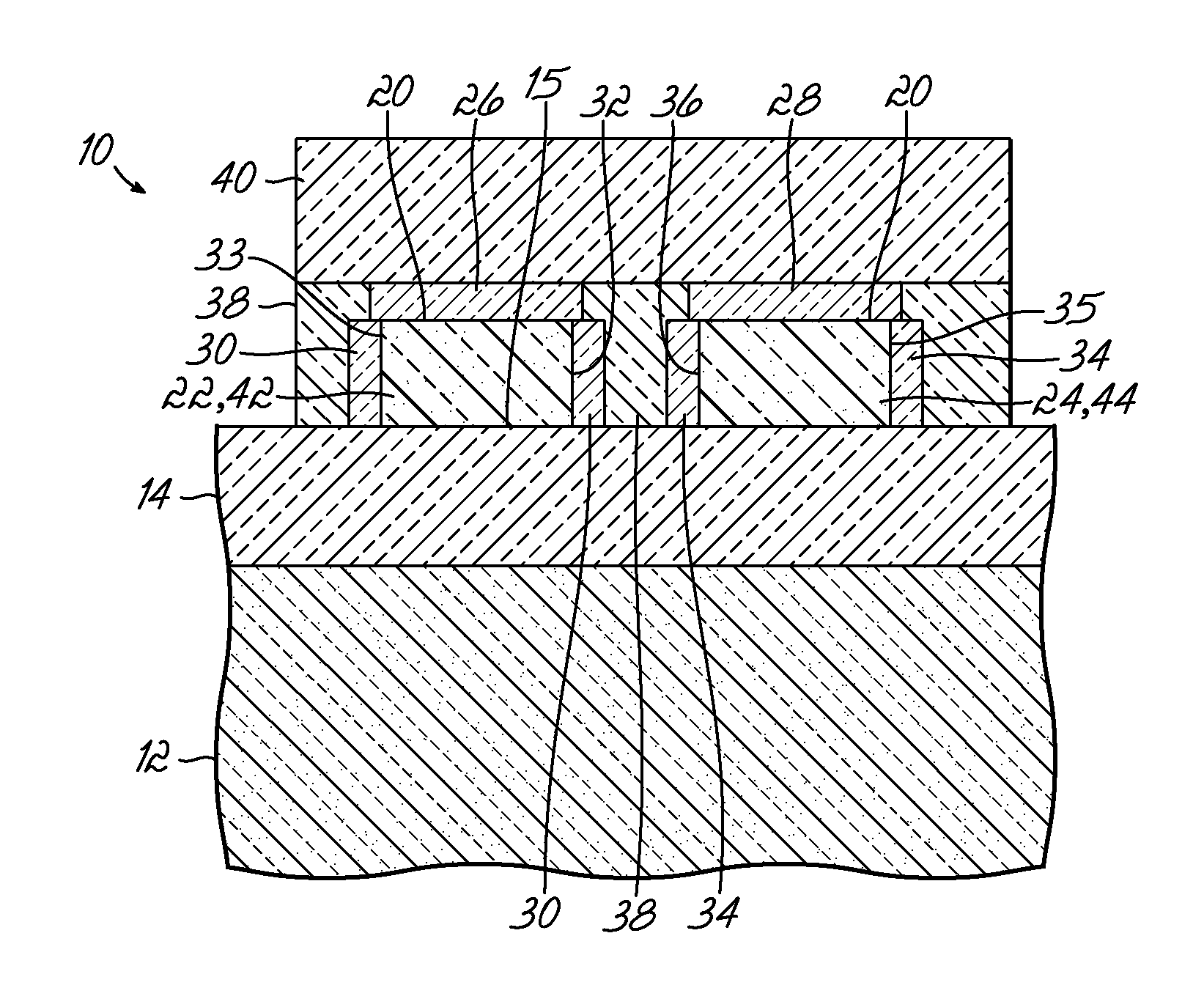
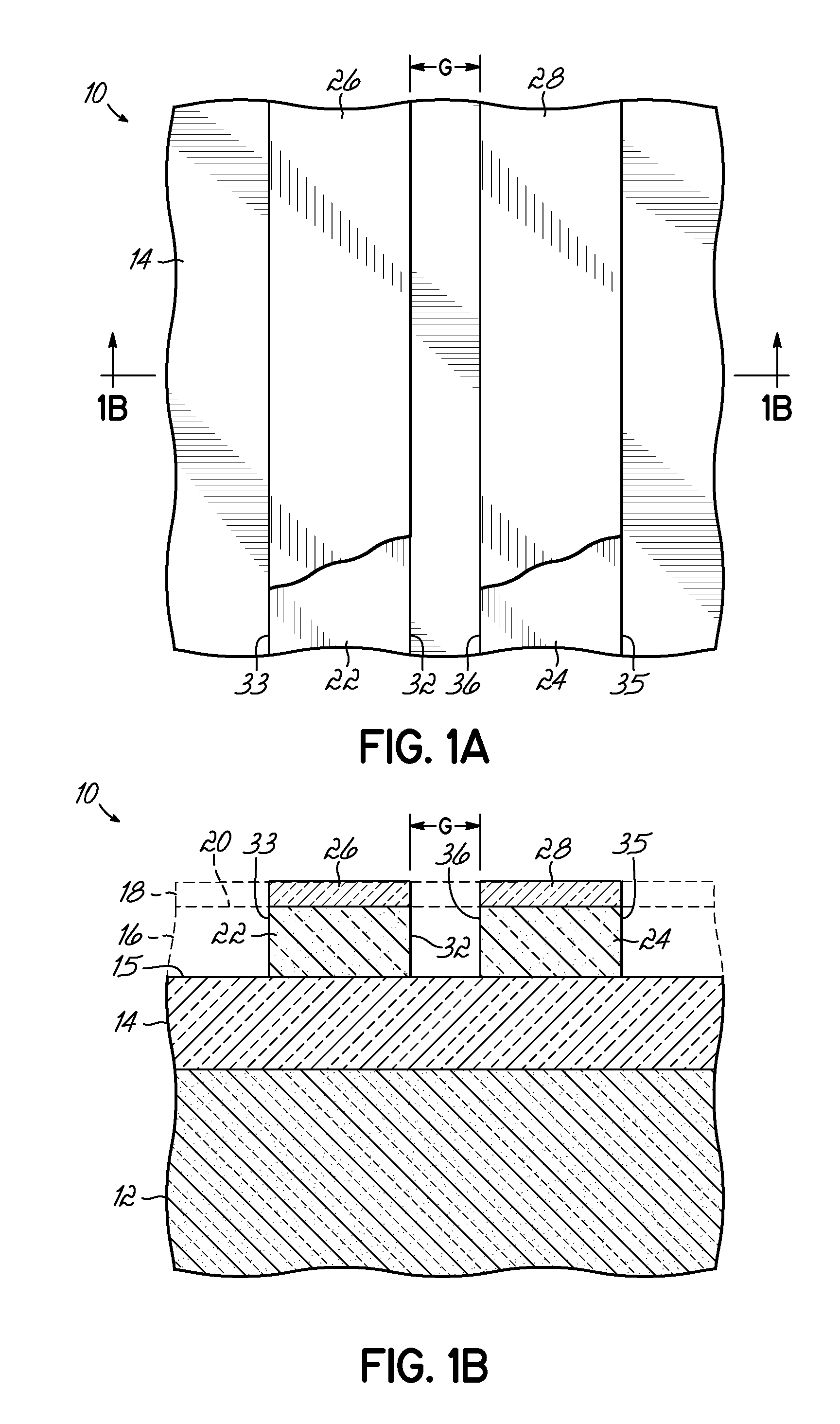
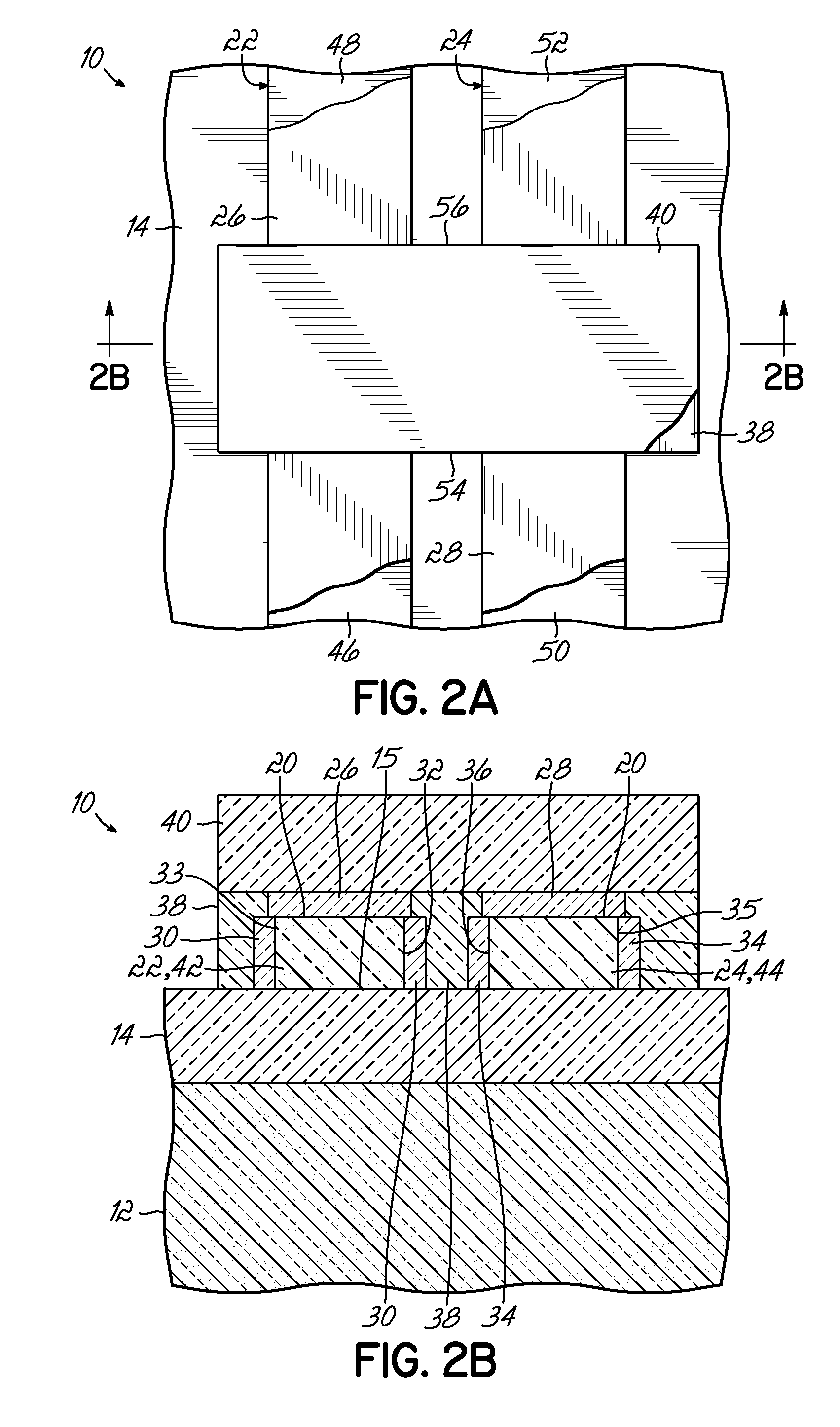
Thermal oxide equivalent low temperature ALD oxide for dual purpose gate oxide and method for producing the same
ActiveUS10106892B1Nitrogen-metal/silicon/boron binary compoundsSolid-state devicesNitrideThermal oxide
Methods of forming conformal low temperature gate oxides on a HV I / O and a core logic and the resulting devices are provided. Embodiments include providing a HV I / O and core logic laterally separated on a Si substrate, each having a fin; forming a gate oxide layer over each fin and the Si substrate; forming a silicon oxy-nitride layer over the gate oxide layer; forming a sacrificial oxide layer over the silicon oxy-nitride layer; removing the sacrificial oxide and silicon oxy-nitride layers and thinning the gate oxide layer; forming a second gate oxide layer over the thinned gate oxide layer; forming a silicon oxy-nitride layer over the second gate oxide layer; removing the silicon oxy-nitride and second gate oxide layers over the core logic fin portion; forming an IL over the core logic fin portion; and forming a HfOx layer over the second silicon oxy-nitride layer and ILs.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
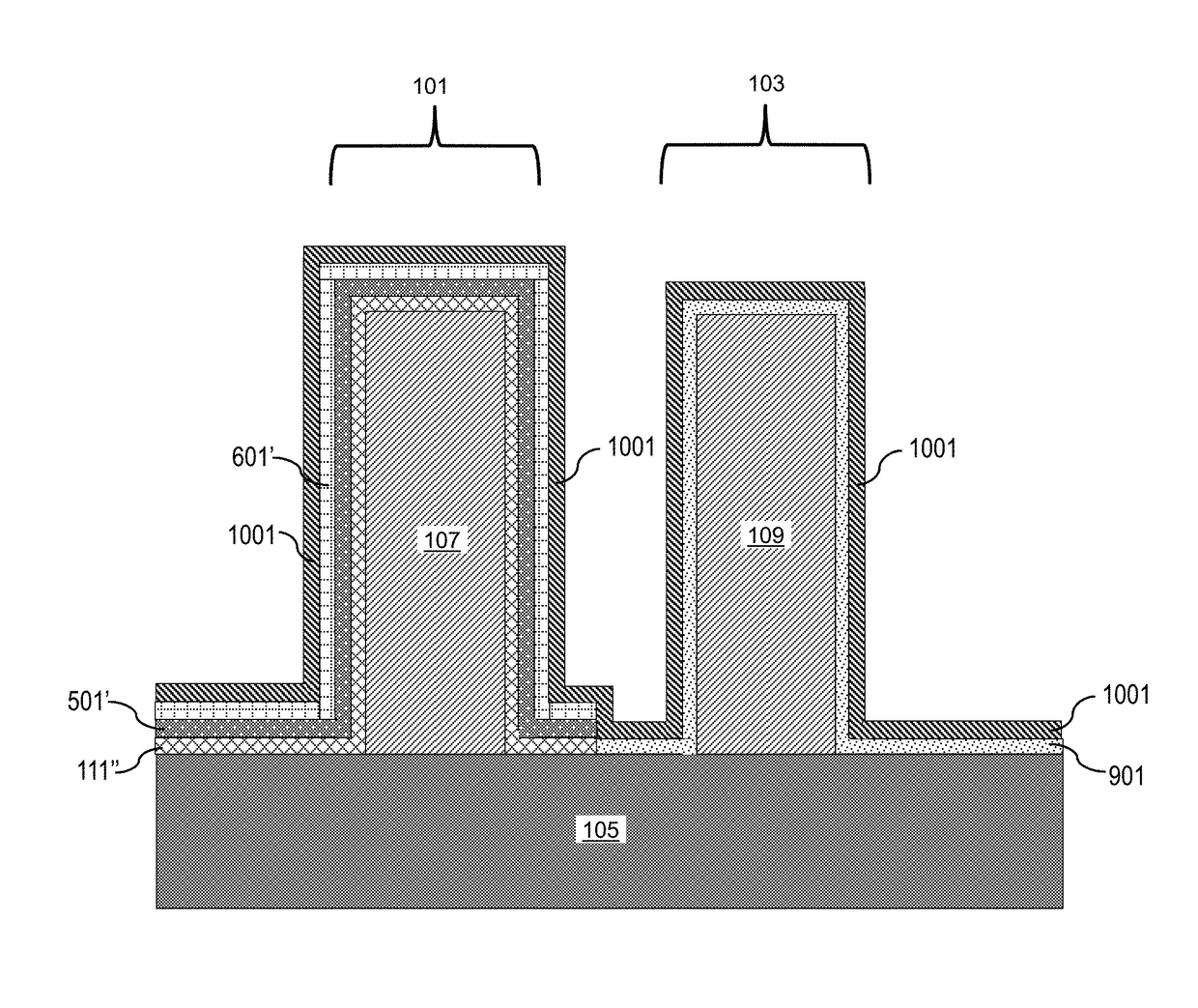
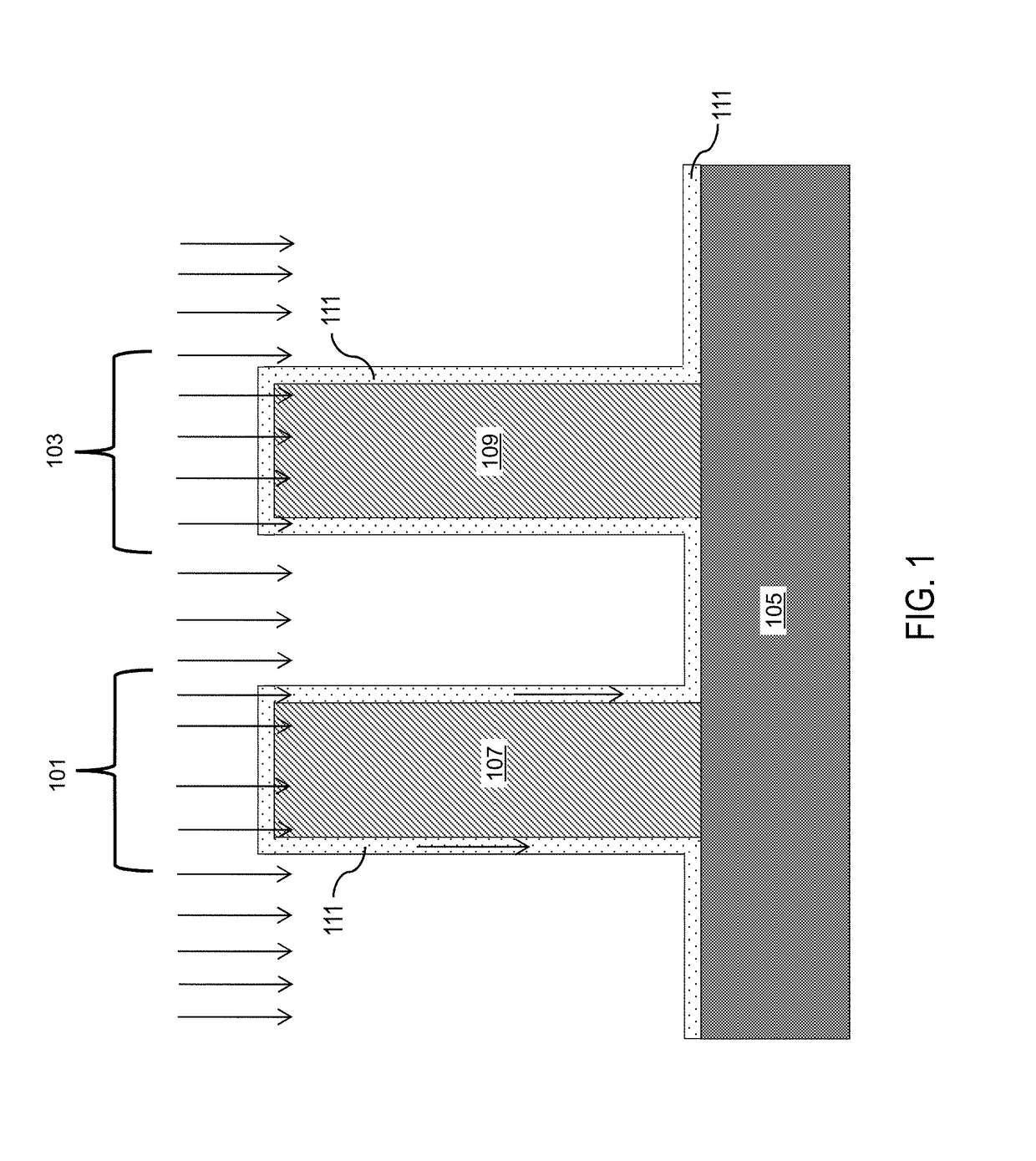
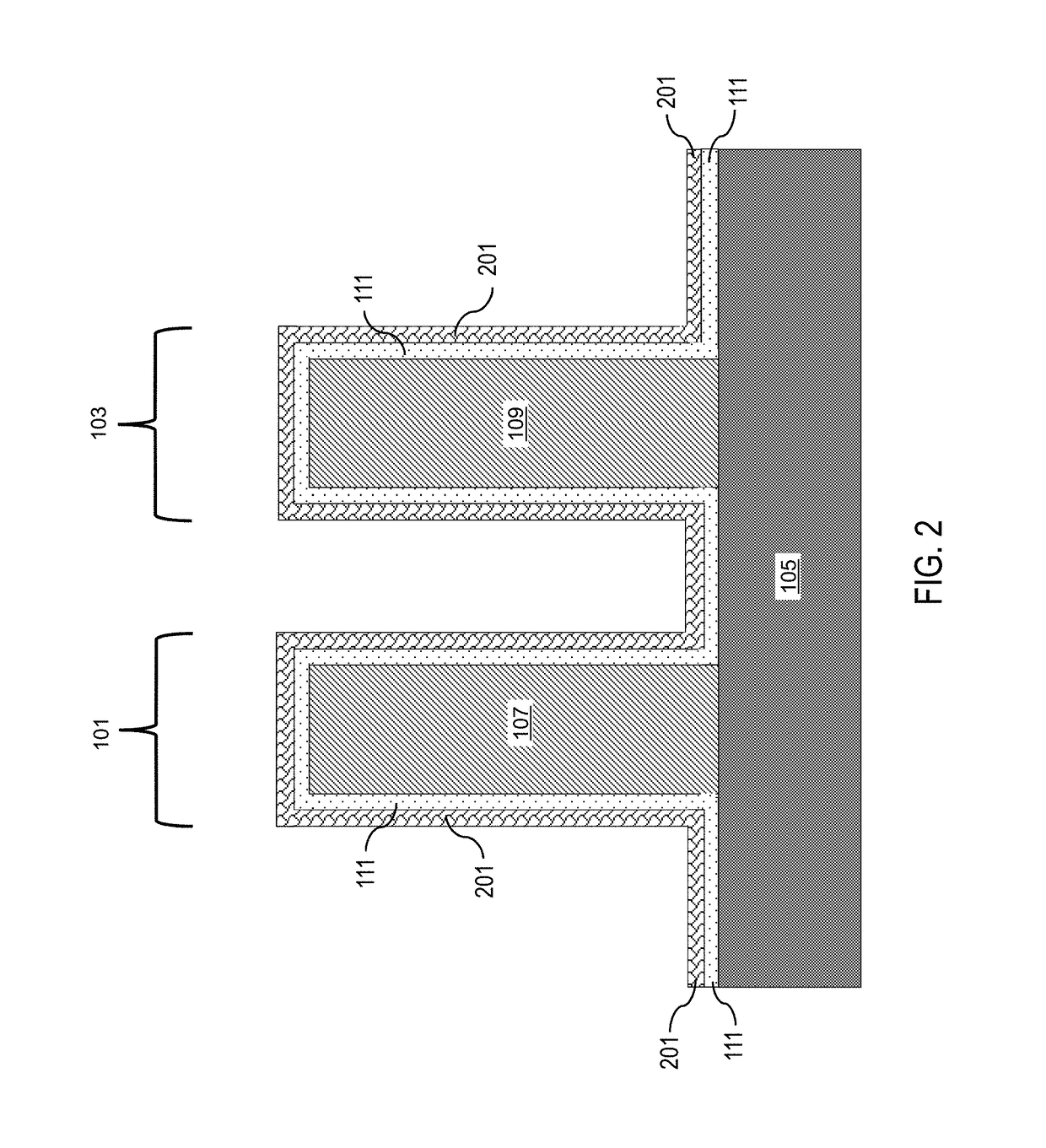
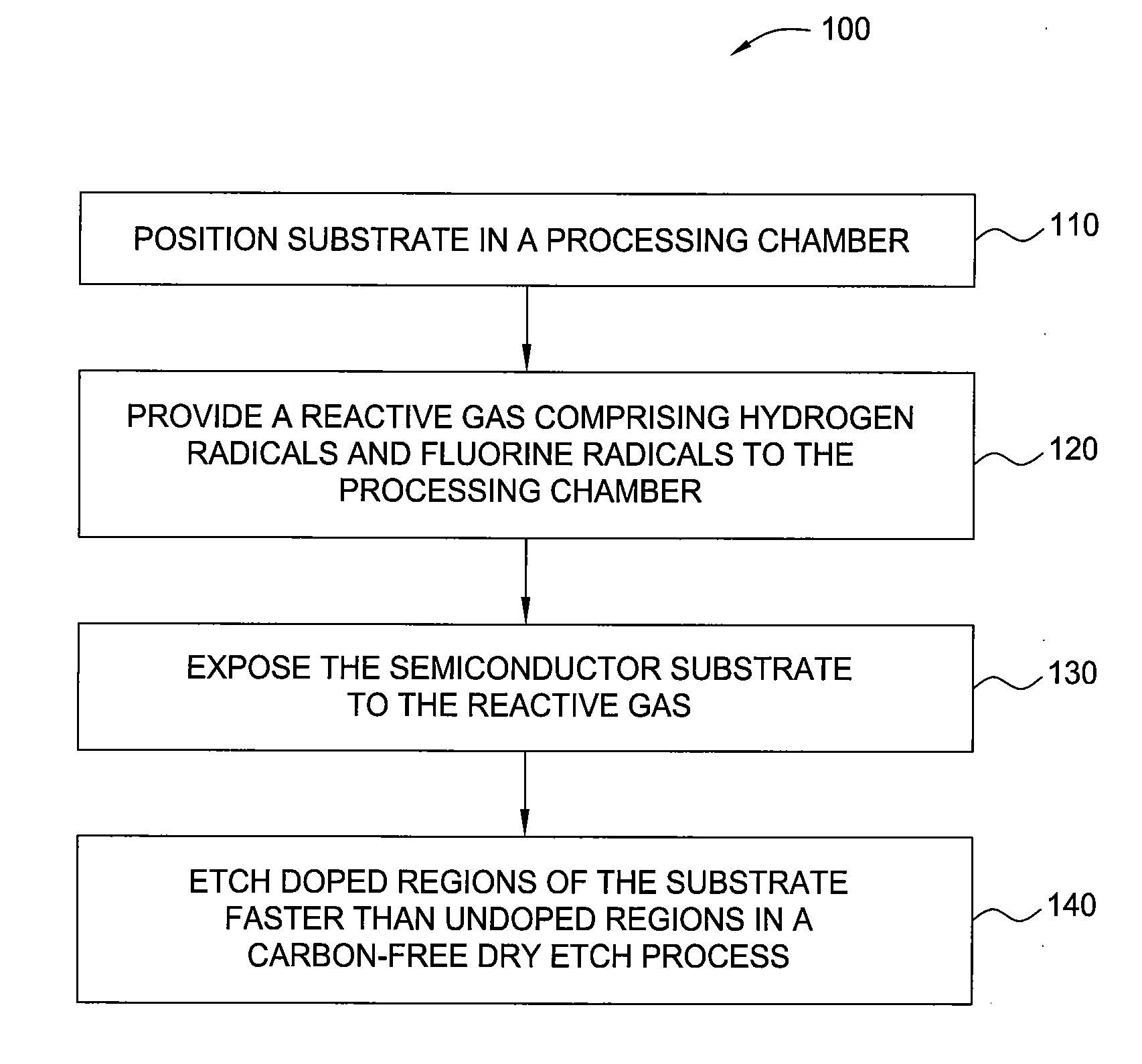
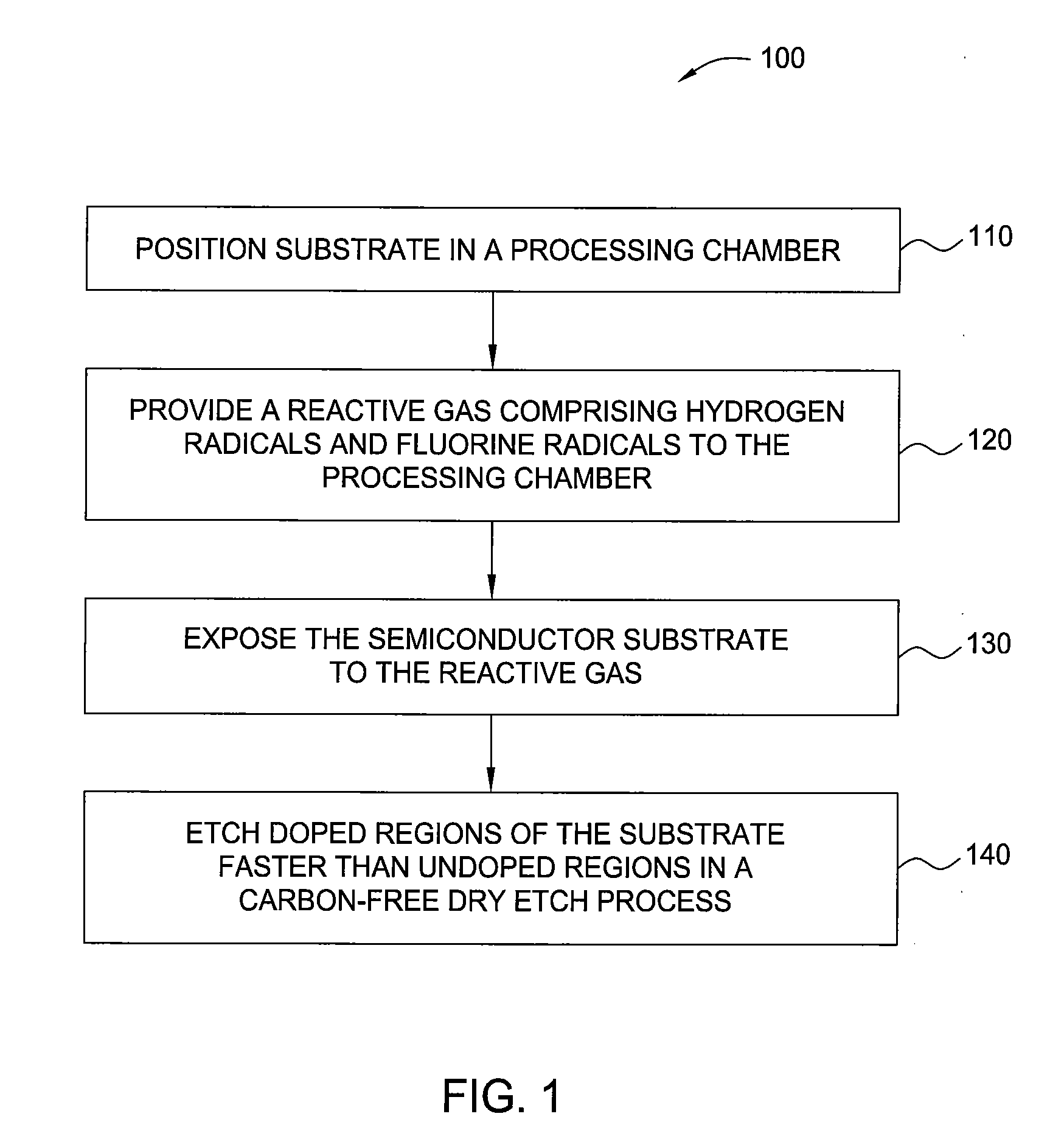
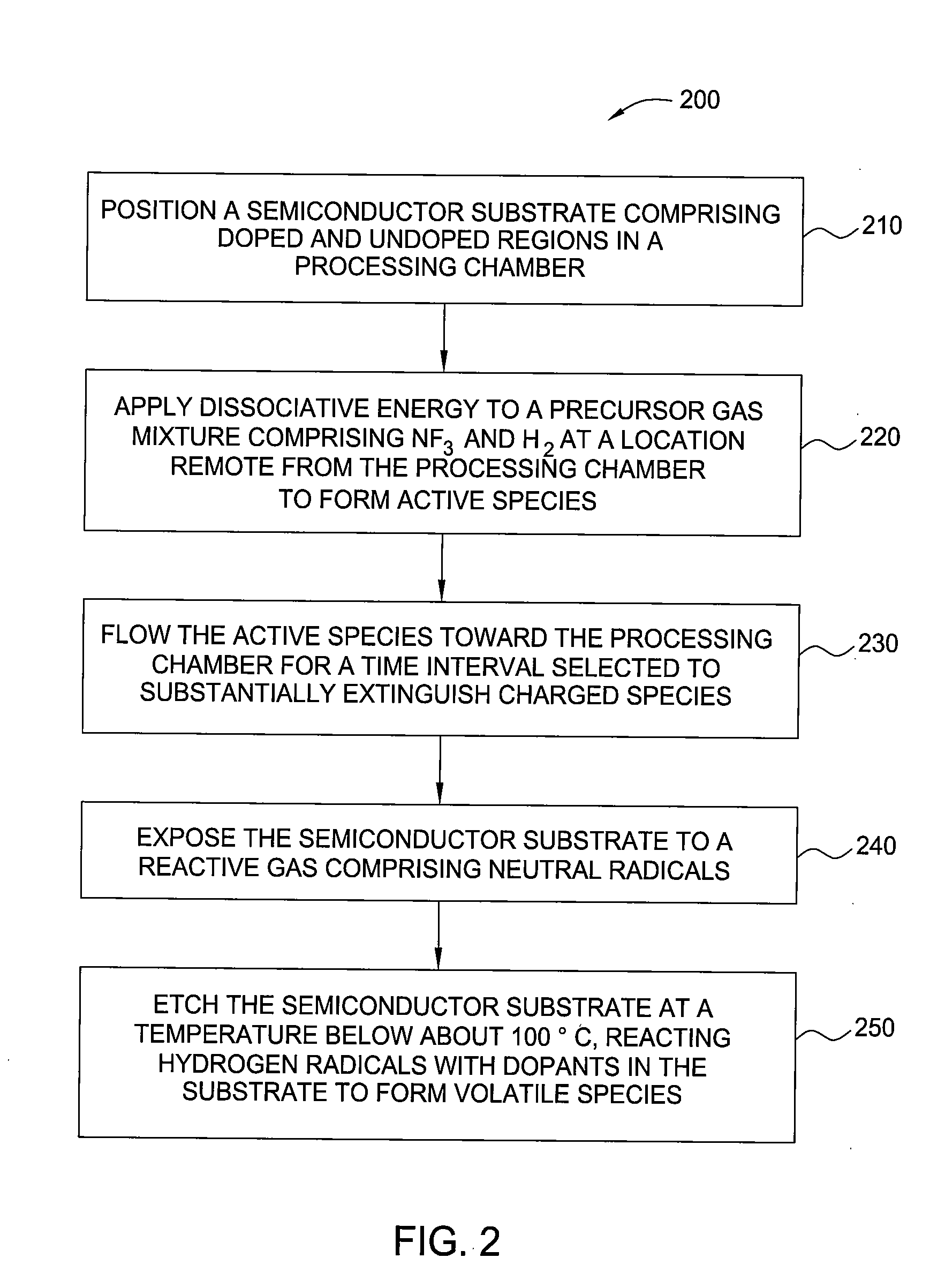
Nf3/h2 remote plasma process with high etch selectivity of psg/bpsg over thermal oxide and low density surface defects
InactiveUS20100099263A1Fast etchElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenRemote plasma
A method and apparatus for selectively etching doped semiconductor oxides faster than undoped oxides. The method comprises applying dissociative energy to a mixture of nitrogen trifluoride and hydrogen gas remotely, flowing the activated gas toward a processing chamber to allow time for charged species to be extinguished, and applying the activated gas to the substrate. Reducing the ratio of hydrogen to nitrogen trifluoride increases etch selectivity. A similar process may be used to smooth surface defects in a silicon surface.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
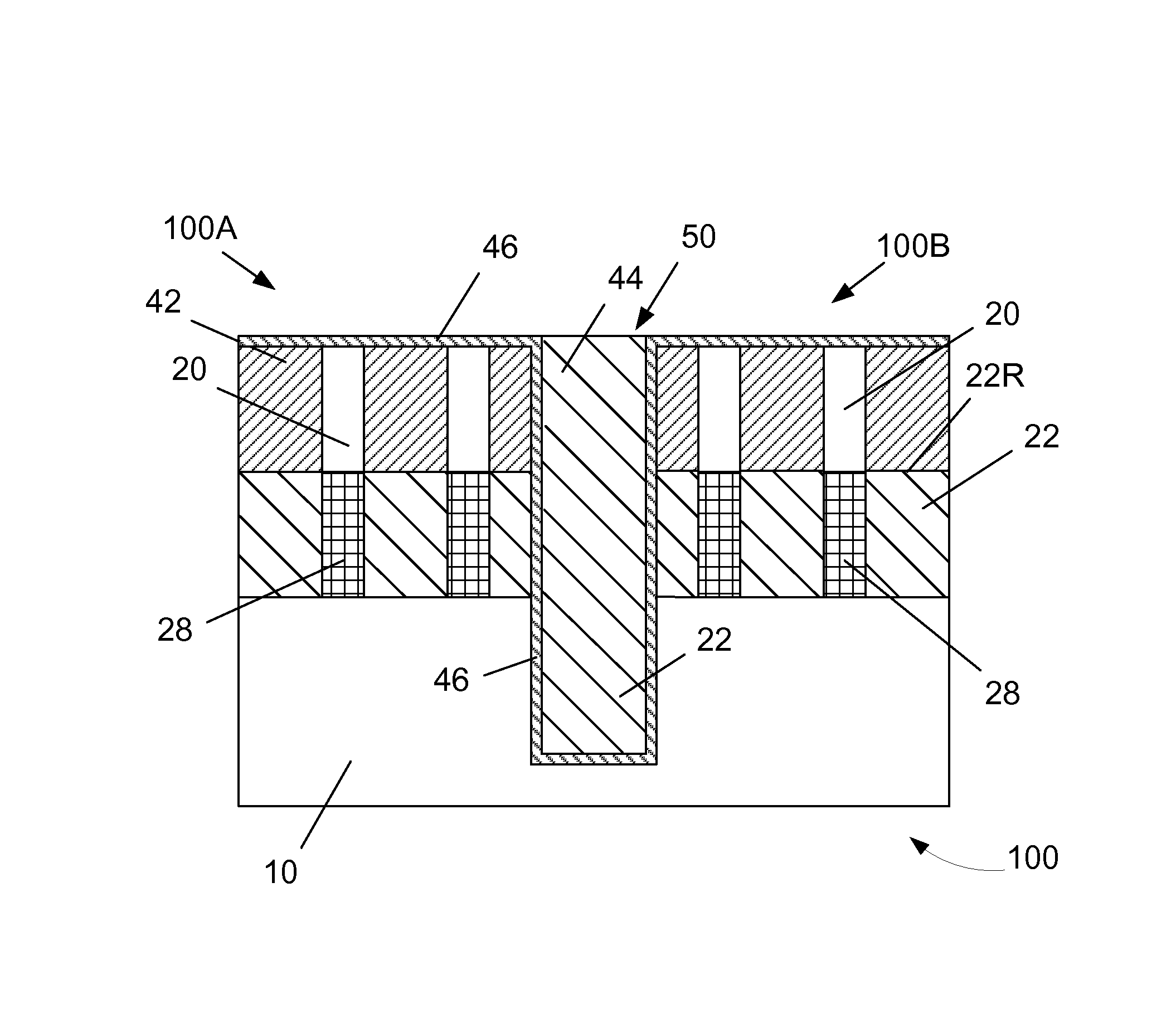
Small Area, Robust Silicon Via Structure and Process
ActiveUS20090032951A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor structureMaterials science
A semiconductor structure includes: at least one silicon surface wherein the surface can be a substrate, wafer or other device. The structure further includes at least one electronic circuit formed on each side of the at least one surface; and at least one conductive high aspect ratio through silicon via running through the at least one surface. Each through silicon via is fabricated from at least one etch step and includes: at least one thermal oxide dielectric for coating at least some of a sidewall of the through silicon via for a later etch stop in fabrication of the through silicon via.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
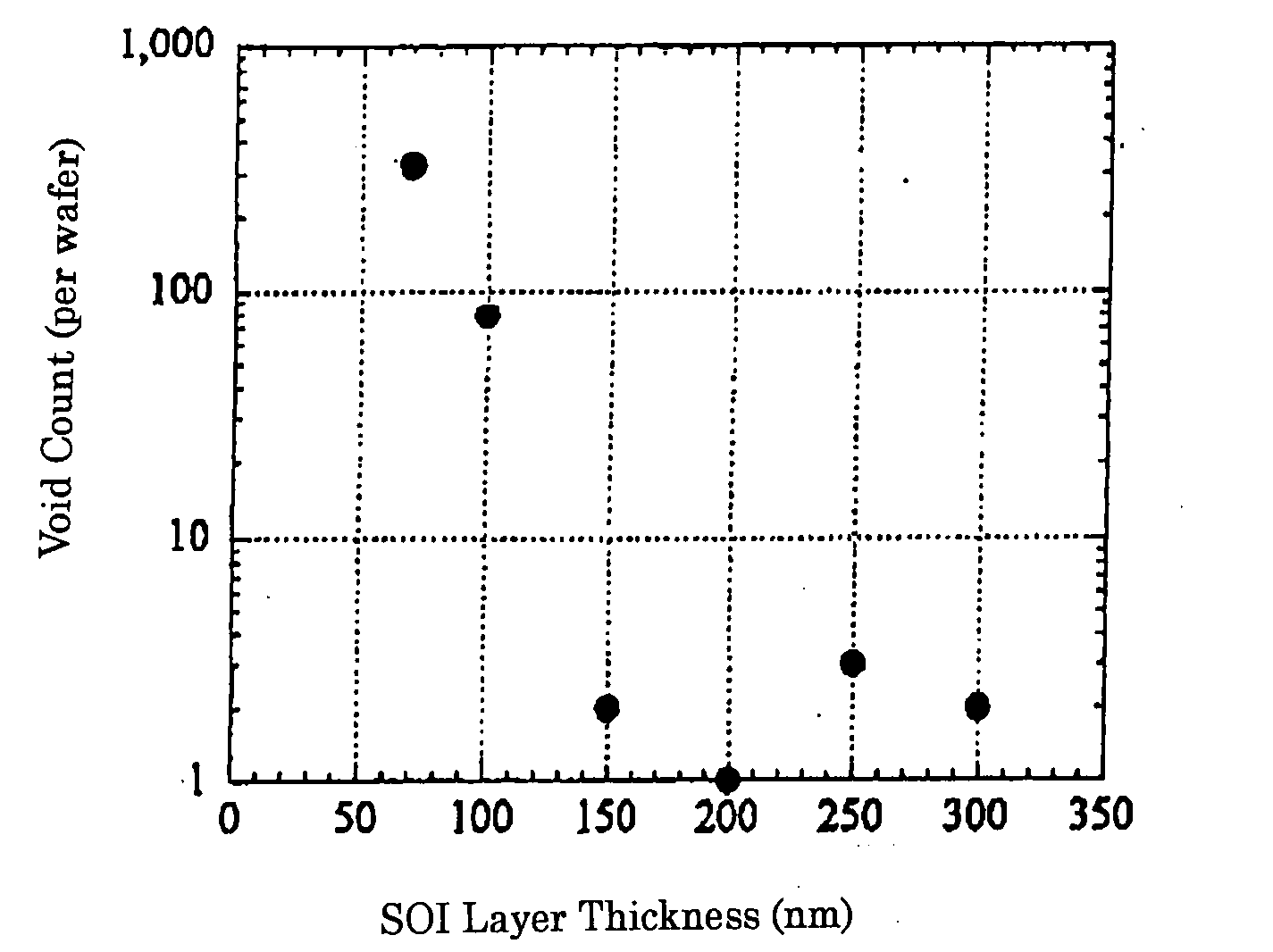
Method for Producing Direct Bonded Wafer and Direct Bonded Wafer
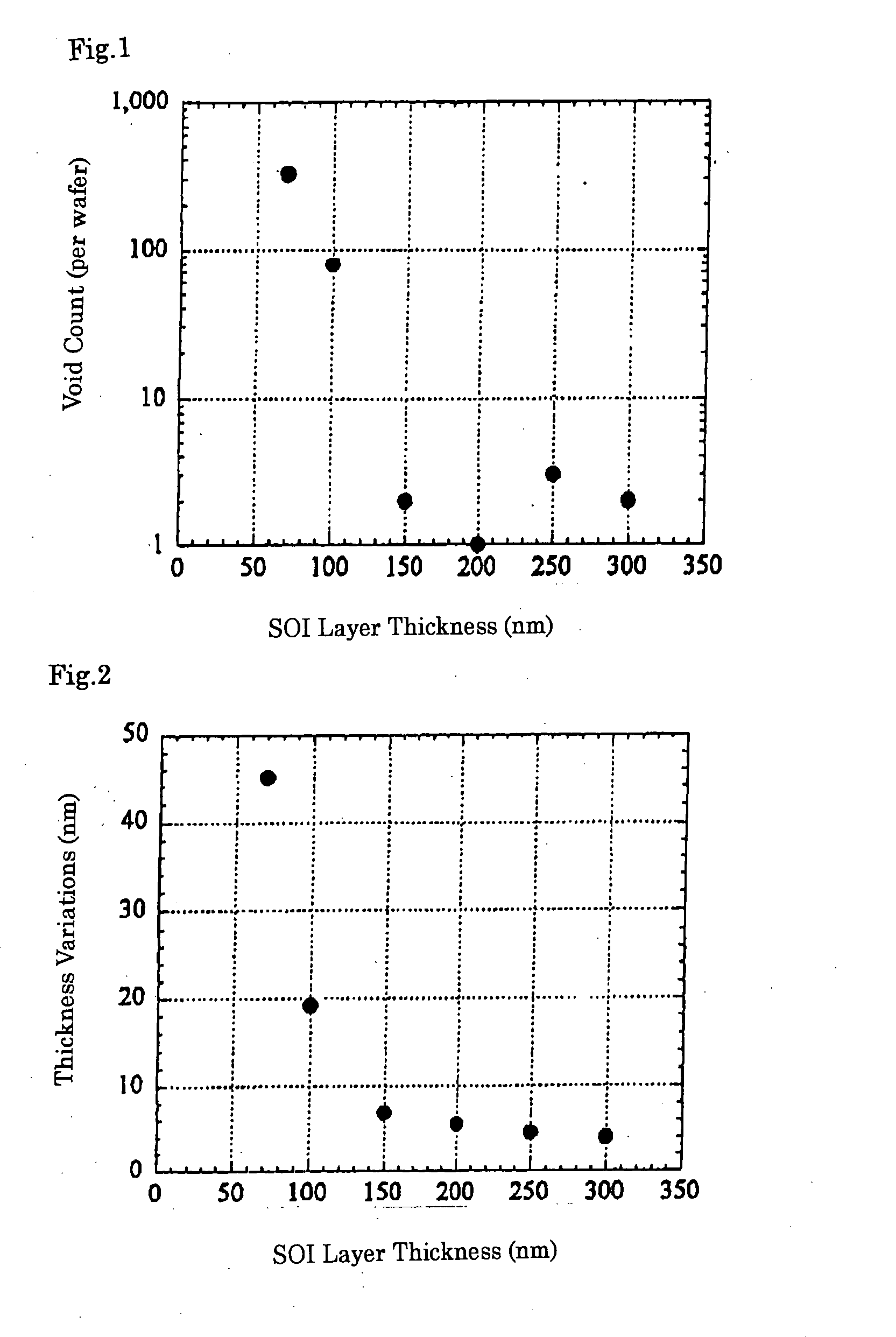
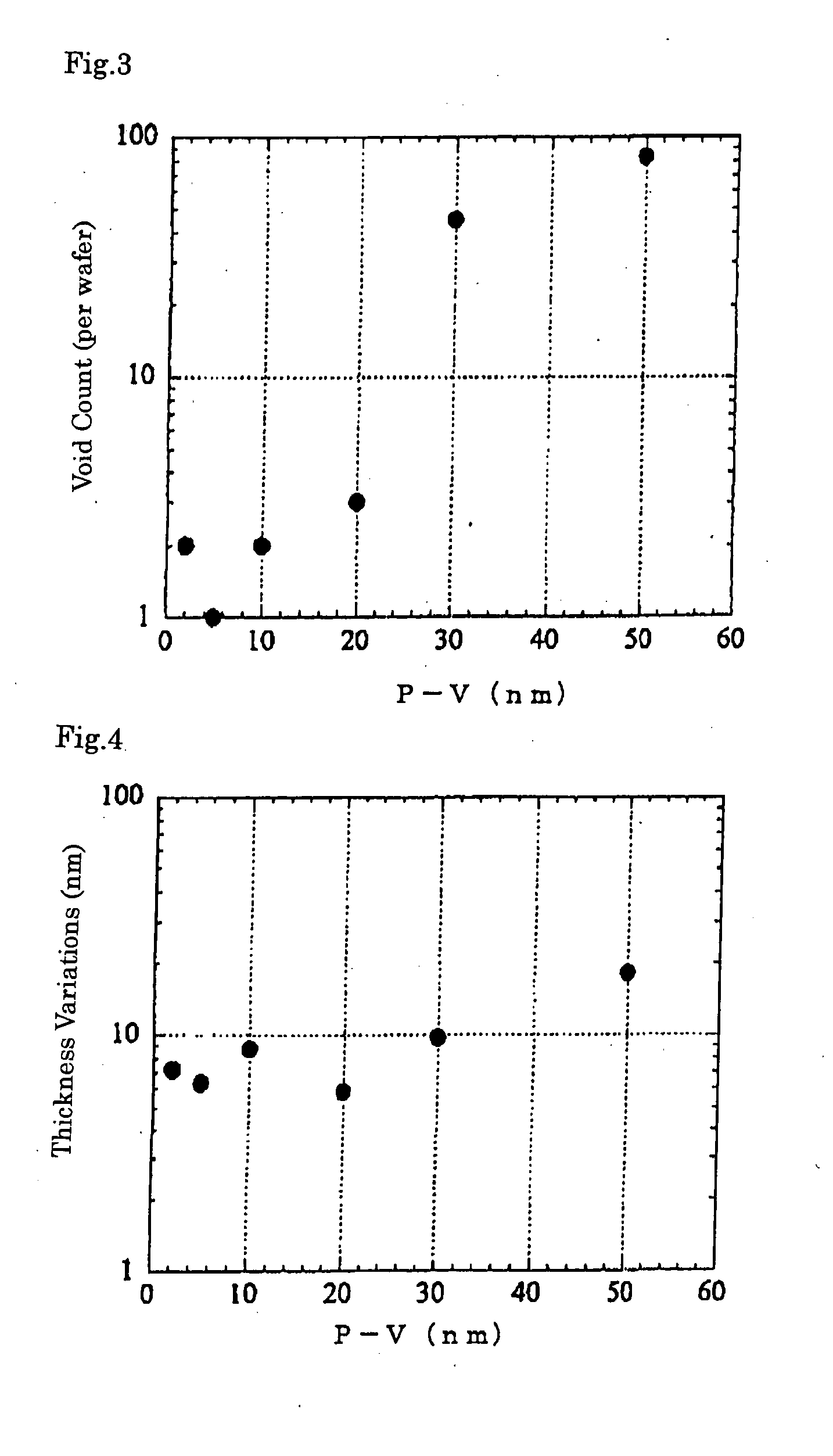
ActiveUS20080102603A1Reduce porosityReduce the generation of voidsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenWafering
A method for producing a direct bonded wafer comprising: forming a thermal oxide film or a CVD oxide film on a surface of at least one of a bond wafer and a base wafer, and bonding the wafer to the other wafer via the oxide film; subsequently thinning the bond wafer to prepare a bonded wafer; and thereafter conducting a process of annealing the bonded wafer under an atmosphere including any one of an inert gas, hydrogen and a mixed gas of an inert gas and hydrogen so that the oxide film between the bond wafer and the base wafer is removed to bond the bond wafer directly to the base wafer. Thereby, there is provided a method for producing a direct bonded wafer in which generation of voids is reduced, and a direct bonded wafer with a low void count.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
Method for fabricating semiconductor devices
InactiveUS20070190744A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsOxygen plasmaGate insulator
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
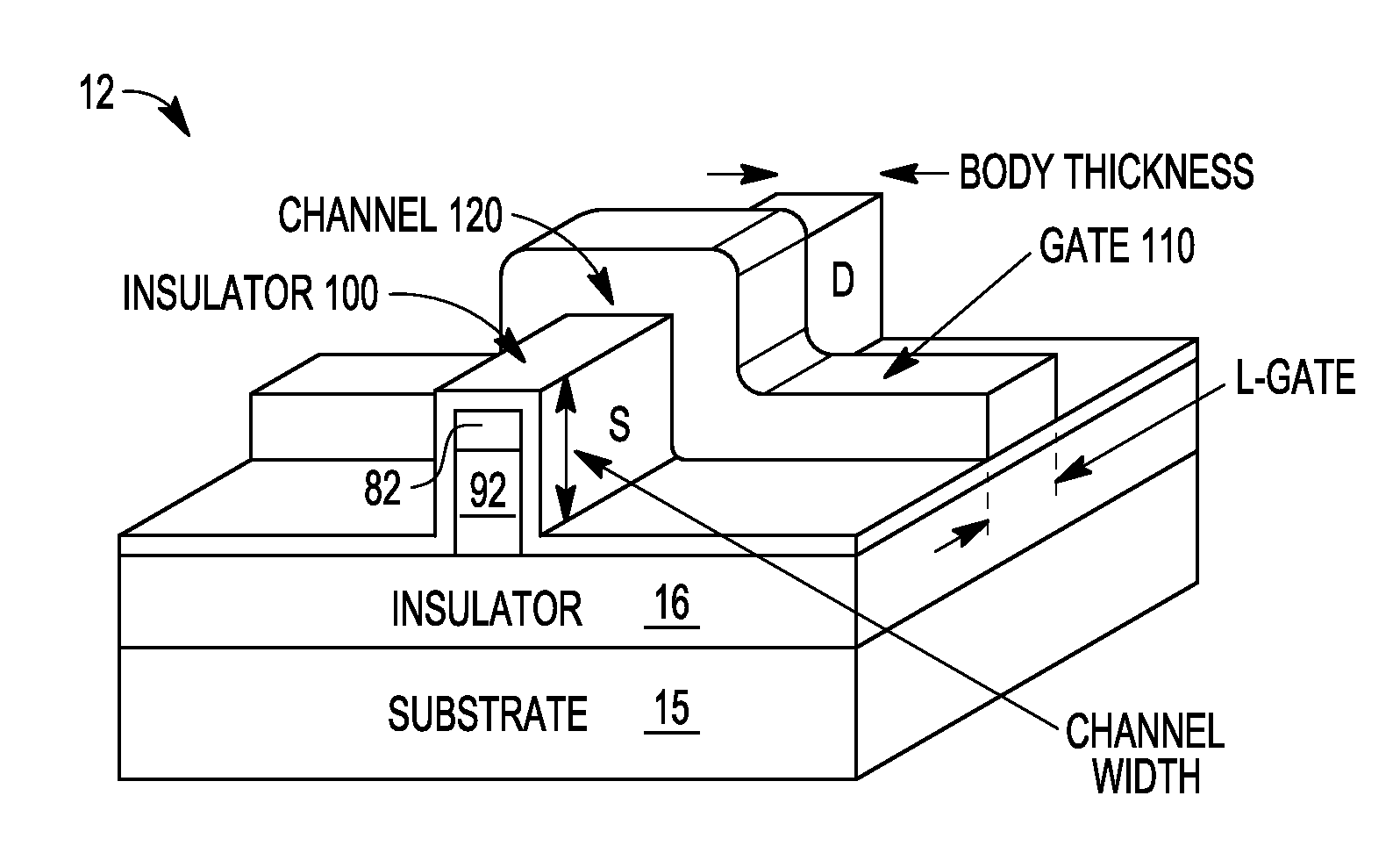
Device structures for a metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor and methods of fabricating such device structures
InactiveUS7790543B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETGate dielectric
Device structures for a metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) that is suitable for operation at relatively high voltages and methods of forming same. The MOSFET, which is formed using a semiconductor-on-insulator (SOI) substrate, includes a channel in a semiconductor body that is self-aligned with a gate electrode. The gate electrode and semiconductor body, which are both formed from the monocrystalline SOI layer of the SOI substrate, are separated by a gap that is filled by a gate dielectric layer. The gate dielectric layer may be composed of thermal oxide layers grown on adjacent sidewalls of the semiconductor body and gate electrode, in combination with an optional deposited dielectric material that fills the remaining gap between the thermal oxide layers.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Device structures for a metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor and methods of fabricating such device structures
InactiveUS20090179266A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETGate dielectric
Device structures for a metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) that is suitable for operation at relatively high voltages and methods of forming same. The MOSFET, which is formed using a semiconductor-on-insulator (SOI) substrate, includes a channel in a semiconductor body that is self-aligned with a gate electrode. The gate electrode and semiconductor body, which are both formed from the monocrystalline SOI layer of the SOI substrate, are separated by a gap that is filled by a gate dielectric layer. The gate dielectric layer may be composed of thermal oxide layers grown on adjacent sidewalls of the semiconductor body and gate electrode, in combination with an optional deposited dielectric material that fills the remaining gap between the thermal oxide layers.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Si precursors for deposition of SiN at low temperatures
ActiveUS9824881B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingAtomic layer depositionThermal oxide
Methods and precursors for depositing silicon nitride films by atomic layer deposition (ALD) are provided. In some embodiments the silicon precursors comprise an iodine ligand. The silicon nitride films may have a relatively uniform etch rate for both vertical and the horizontal portions when deposited onto three-dimensional structures such as FinFETS or other types of multiple gate FETs. In some embodiments, various silicon nitride films of the present disclosure have an etch rate of less than half the thermal oxide removal rate with diluted HF (0.5%).
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method for fabricating a semiconductor device
InactiveUS6180439B1Promote crystallizationReduce concentrationTransistorSolid-state devicesAtmospheric airLaser light
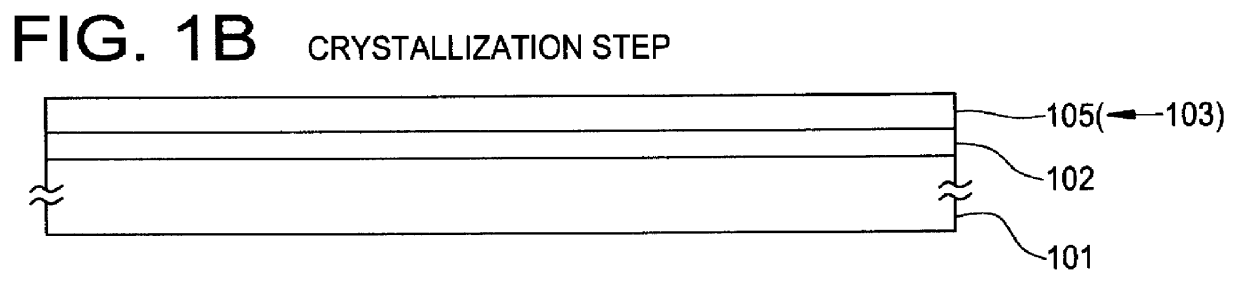
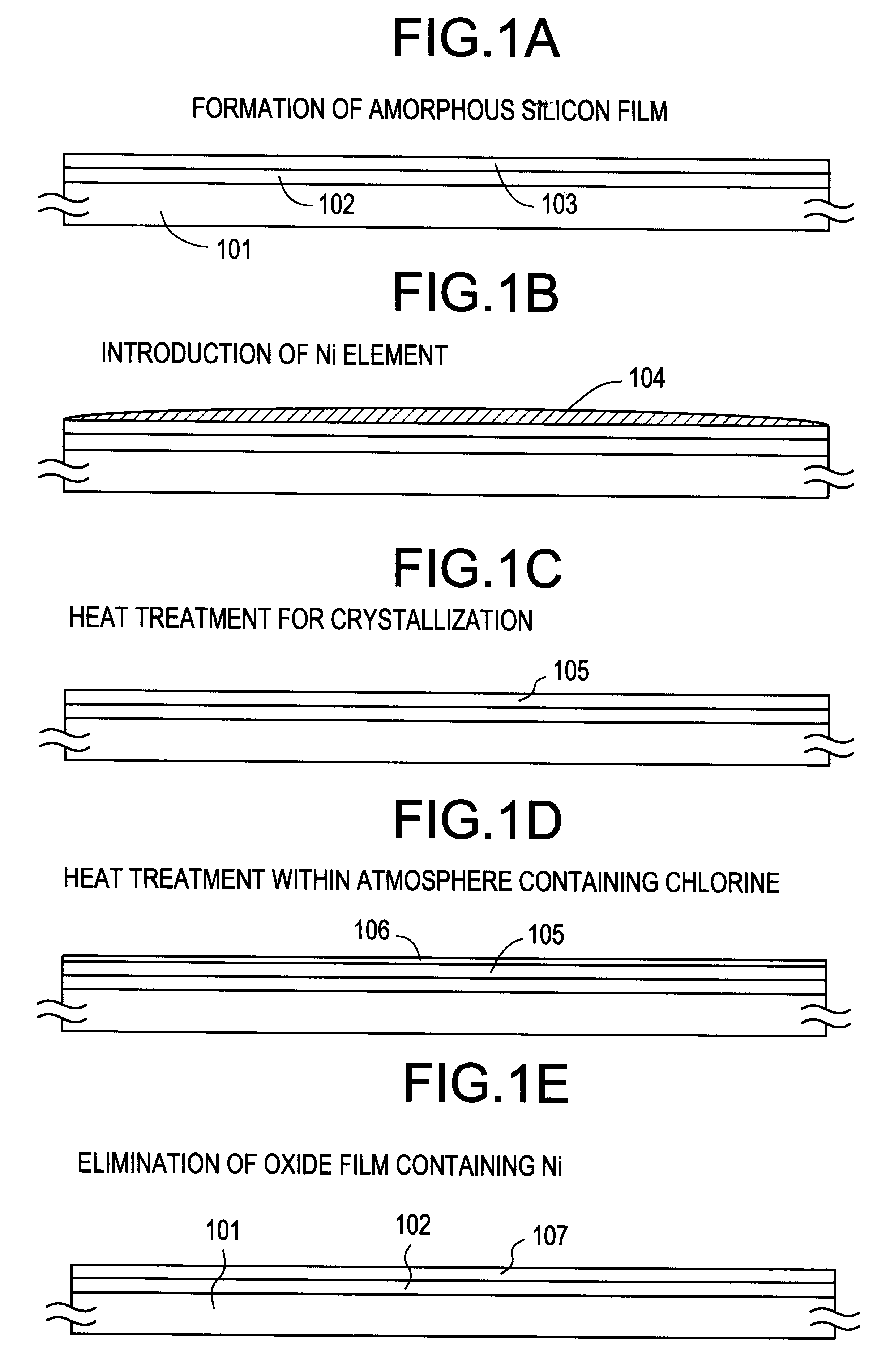
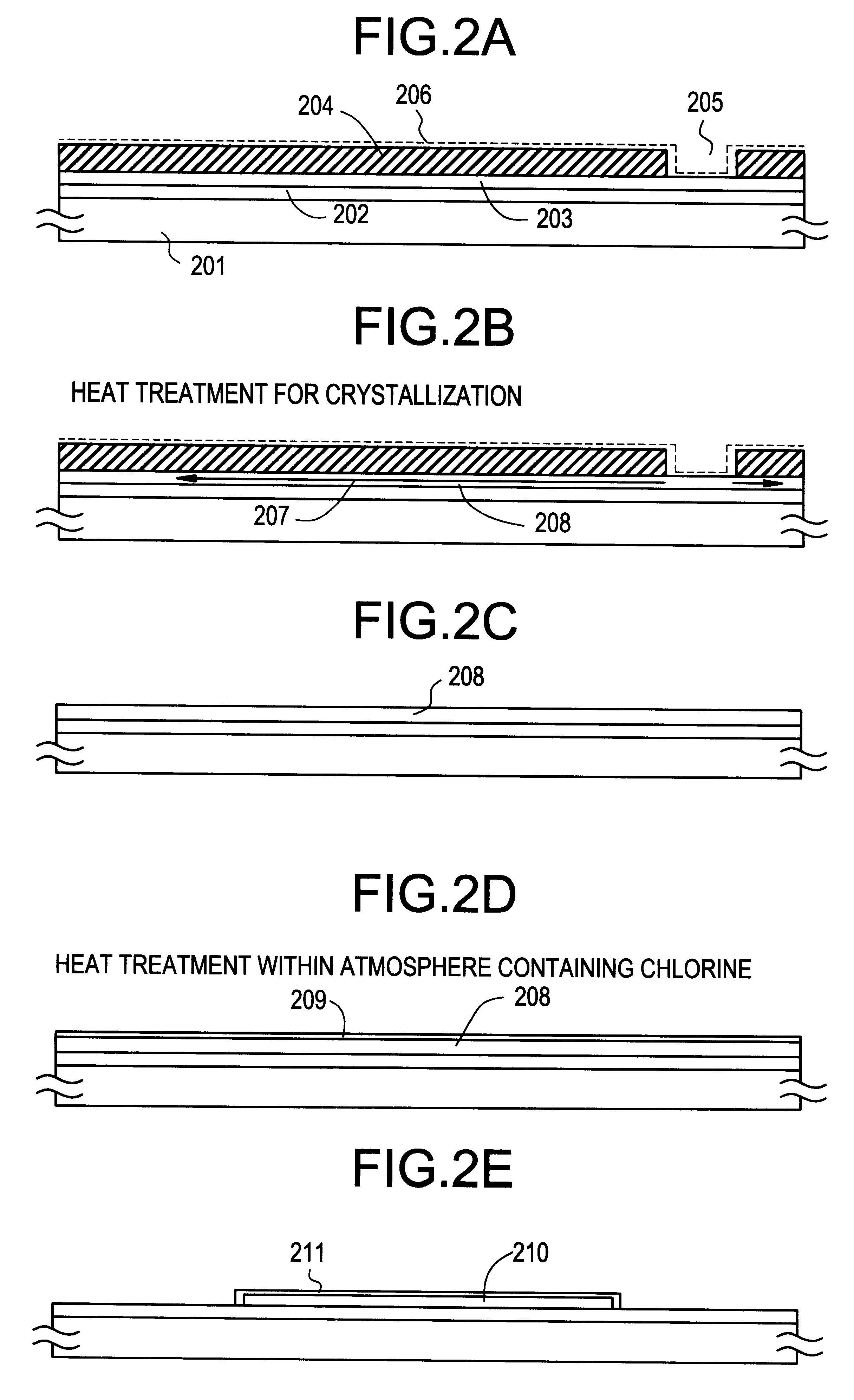
Concentration of metal element which promotes crystallization of silicon and which exists within a crystalline silicon film obtained by utilizing the metal element is reduced. A first heat treatment for crystallization is performed after introducing nickel to an amorphous silicon film 103. Then, laser light is irradiated to diffuse nickel element which is concentrated locally. After that, another heat treatment is performed within an oxidizing atmosphere at a temperature higher than that of the previous heat treatment. At this time, HCl or the like is added to the atmosphere. A thermal oxide film 106 is formed in this step. At this time, gettering of the nickel element into the thermal oxide film 106 takes place. Then, the thermal oxide film 106 is removed. Thereby, a crystalline silicon film 107 having low concentration of the metal element and a high crystallinity can be obtained.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method of manufacturing a thin film transistor involving laser treatment
InactiveUS6063654AImprove reliabilityEnhancing reliability and characteristicTransistorSolid-state devicesHydrogenAmorphous silicon
Defects at the grain boundaries of a crystal silicon film, which has been crystallized from an amorphous silicon film, are passivated without using a hydrogen plasma treatment. An underlying film and a crystal silicon film which has been crystallized from an amorphous silicon film are formed on a glass substrate. A thermal oxide film is grown on the surface of the crystal silicon film by heating in an oxygen atmosphere into which NF3 gas has been added. As the thermal oxide film is grown, non-coupled Si is generated. The defects at the grain boundaries of the crystal silicon film are passivated by the additional Si. Then, the thermal oxide film is removed and the crystal silicon film is patterned into an island shape to form an active layer of a TFT. A gate insulating film, a gate electrode and the like are then formed sequentially to complete the TFT.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Display switch with double layered gate insulation and resinous interlayer dielectric
InactiveUS6316810B1Reduce concentrationPromote crystallizationTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectricAtmospheric air
Concentration of metal element which promotes crystallization of silicon and which exists within a crystal silicon film obtained by utilizing the metal element is reduced. A first heat treatment for crystallization is implemented after introducing nickel element to an amorphous silicon film 103. Then, after obtaining the crystal silicon film, another heat treatment is implemented within an oxidizing atmosphere at a temperature higher than that of the previous heat treatment. At this time, HCl or the like is added to the atmosphere. A thermal oxide film 106 is formed in this step. At this time, gettering of the nickel element into the thermal oxide film 106 takes place. Next, the thermal oxide film 106 is removed. Thereby, a crystal silicon film 107 having low concentration of the metal element and a high crystalinity can be obtained.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
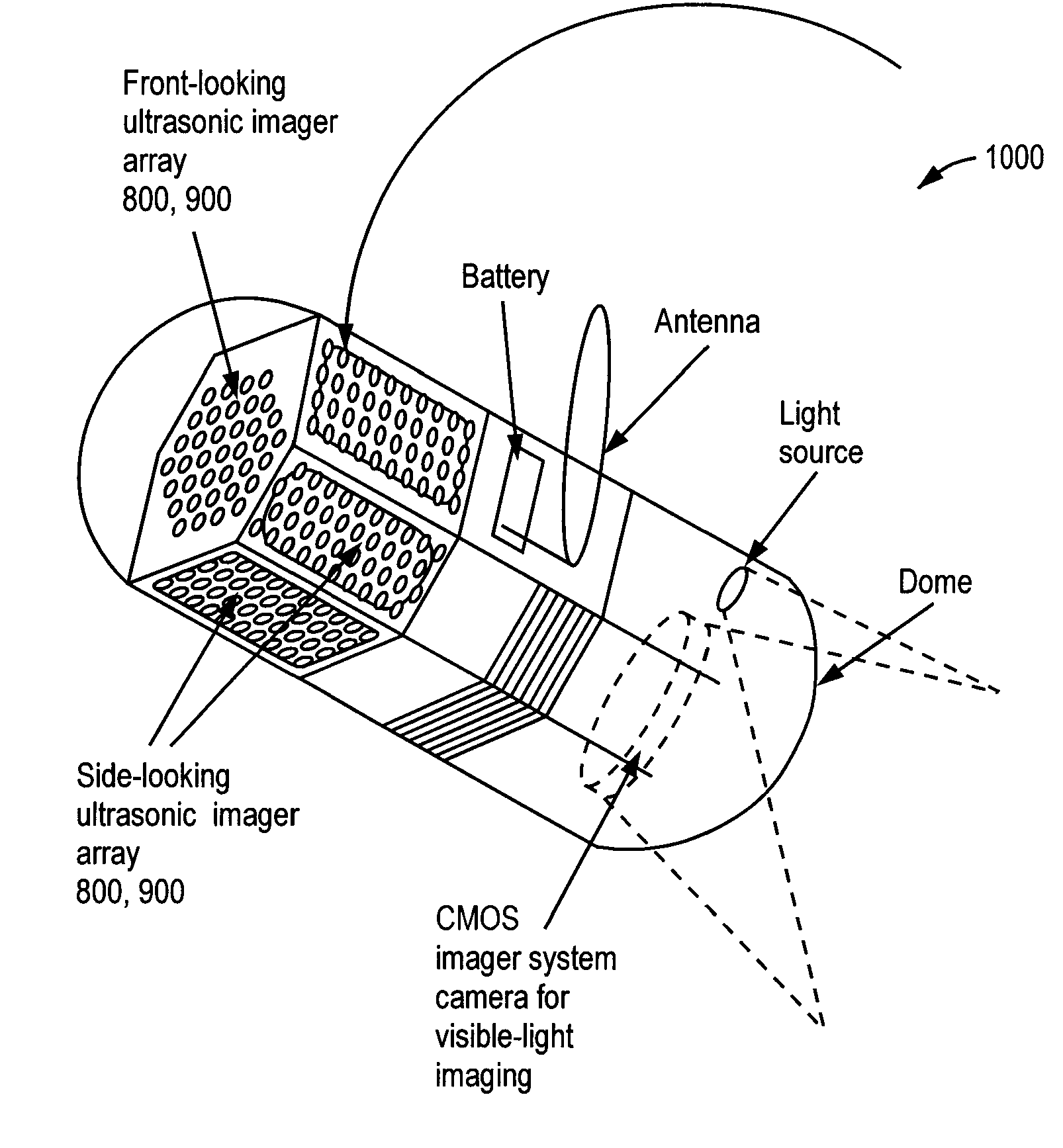
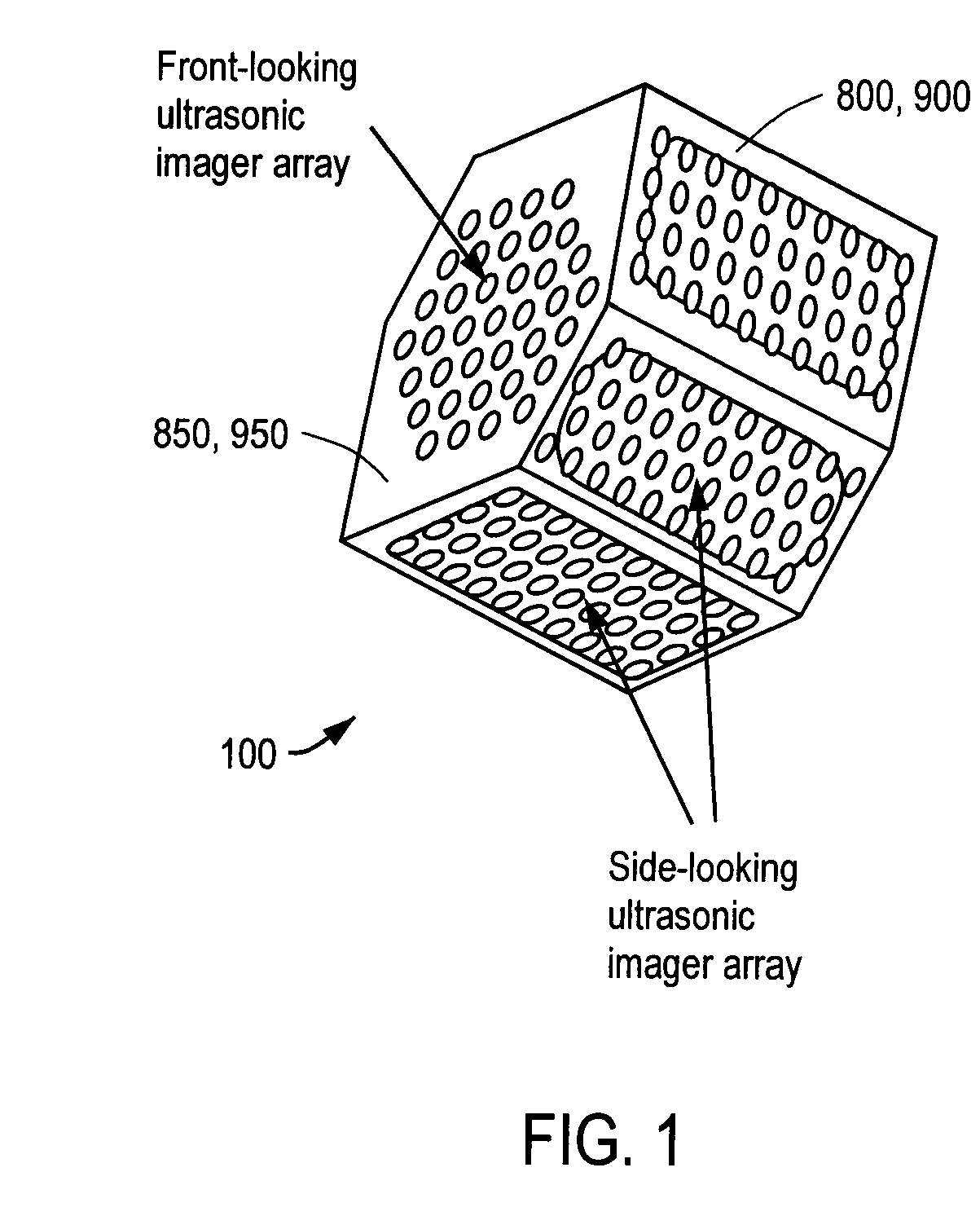
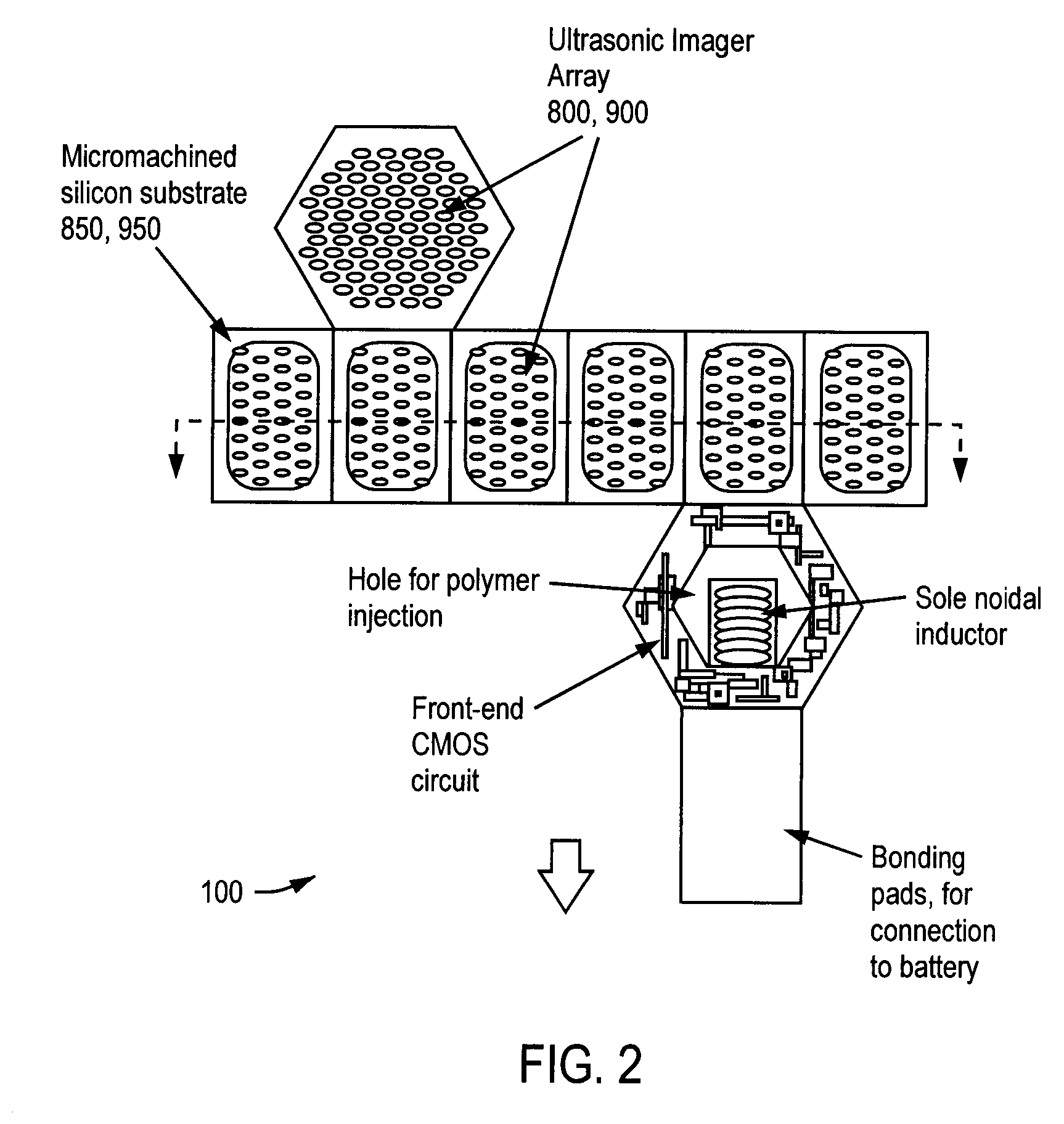
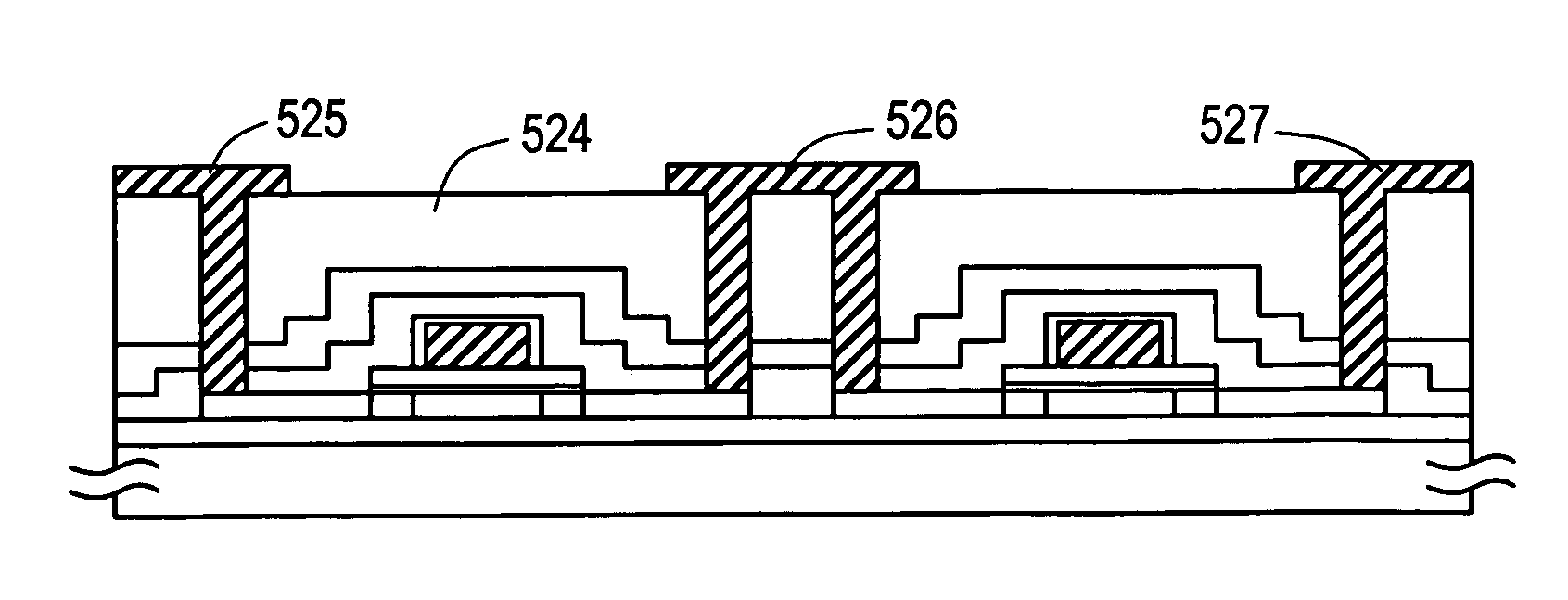
Three-Dimensional, Ultrasonic Transducer Arrays, Methods of Making Ultrasonic Transducer Arrays, and Devices Including Ultrasonic Transducer Arrays
ActiveUS20070264732A1Avoid cavitiesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsEndoscopesSurface layerMedical imaging
Medical imaging devices may comprise an array of ultrasonic transducer elements. Each transducer element may comprise a substrate having a doped surface creating a highly conducting surface layer, a layer of thermal oxide on the substrate, a layer of silicon nitride on the layer of thermal oxide, a layer of silicon dioxide on the layer of silicon nitride, and a layer of conducting thin film on the layer of silicon dioxide. The layers of silicon dioxide and thermal oxide may sandwich the layer of silicon nitride, and the layer of conducting thin film may be separated from the layer of silicon nitride by the layer of silicon dioxide.
Owner:STC UNM
Fabrication method of semiconductor device
InactiveUS7056381B1Metal concentration be relatively lowerHigh crystallinityPolycrystalline material growthSolid-state devicesLaser lightCrystallinity
Concentration of metal element which promotes crystallization of silicon and which exists within a crystal silicon film obtained by utilizing the metal element is reduced. A first heat treatment for crystallization is implemented after introducing nickel to an amorphous silicon film 103. Then, laser light is irradiated to diffuse the nickel element concentrated locally. After that, another heat treatment is implemented within an oxidizing atmosphere at a temperature higher than that of the previous heat treatment. A thermal oxide film 106 is formed in this step. At this time, the nickel element is gettered to the thermal oxide film 106. Then, the thermal oxide film 106 is removed. Thereby, a crystal silicon film 107 having low concentration of the metal element and a high crystallinity can be obtained.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Formulations for cleaning memory device structures
InactiveUS20080125342A1Inorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic detergent compounding agentsBorophosphosilicate glassSilicon oxide
A removal composition and process for removing silicon-containing layers from a microelectronic device having said layers thereon. The removal composition selectively removes layers including, but not limited to, silicon oxide, plasma enhanced tetraethyl orthosilicate (P-TEOS), borophosphosilicate glass (BPSG), plasma enhanced oxide (PEOX), high density plasma oxide (HDP), phosphosilicate glass (PSG), spin-on-dielectrics (SOD), thermal oxide, updoped silicate glass, sacrificial oxides, silicon-containing organic polymers, silicon-containing hybrid organic / inorganic materials, organosilicate glass (OSG), TEOS, fluorinated silicate glass (FSG), hemispherical grain (HSQ), carbon-doped oxide (CDO) glass, and combinations thereof, relative to lower electrode, device substrate, and / or etch stop layer materials.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH MATERIALS INC
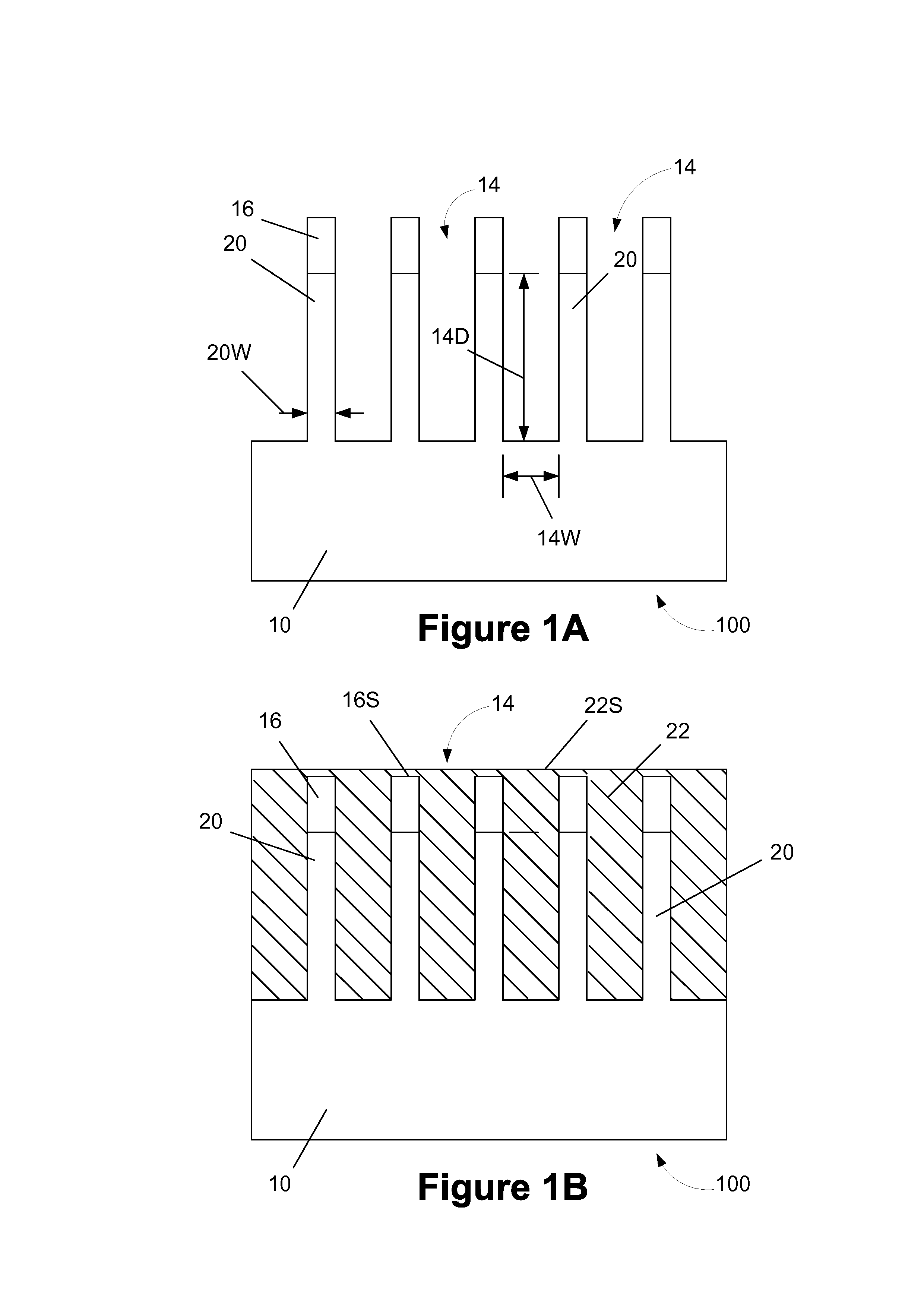
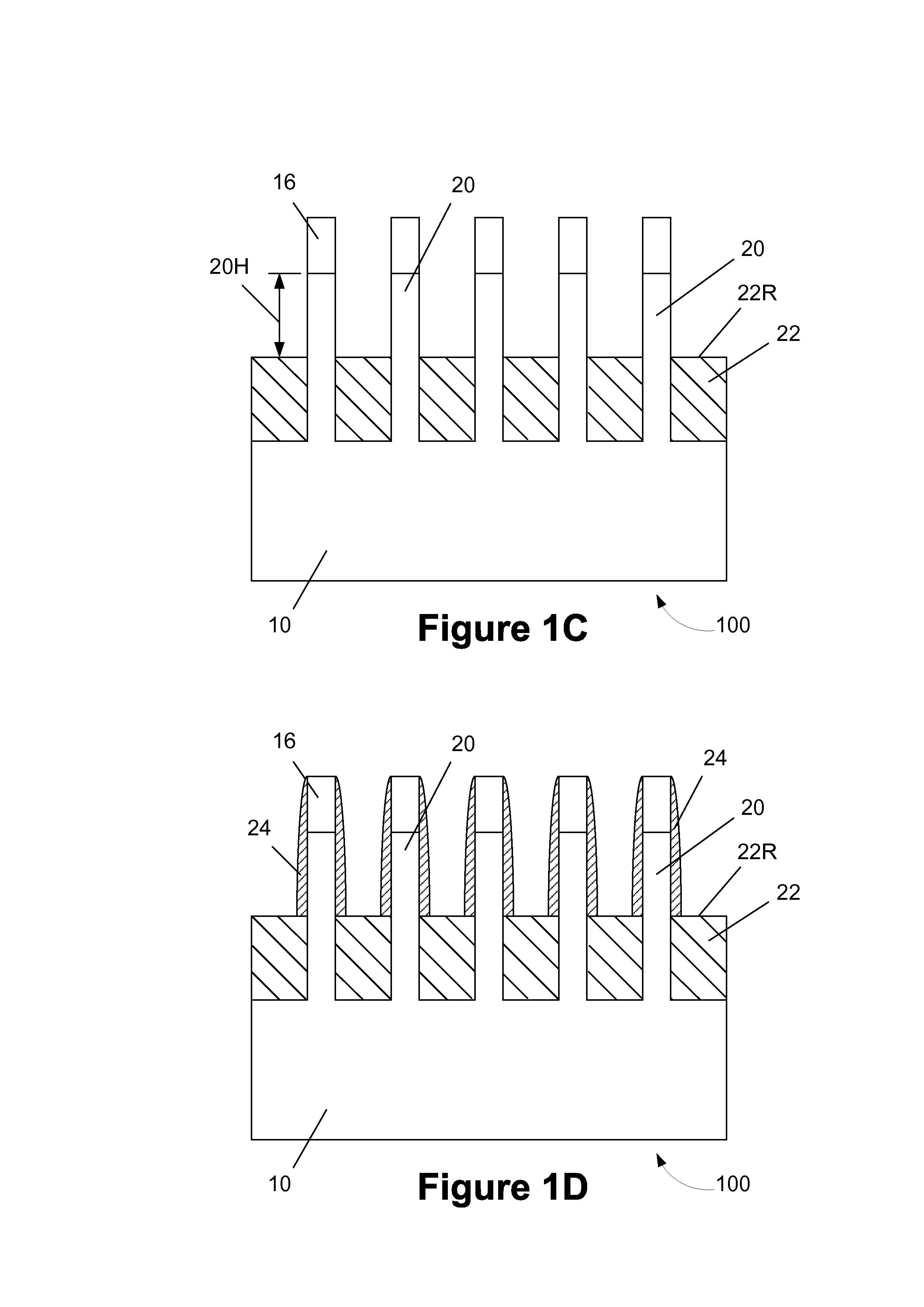
Semiconductor devices having a convex active region and methods of forming the same
ActiveUS20080057644A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialEngineering
Methods of forming a semiconductor device include forming a trench mask pattern on a semiconductor substrate having active regions and device isolation regions. A thermal oxidation process is performed using the trench mask pattern as a diffusion mask to form a thermal oxide layer defining a convex upper surface of the active regions. The thermal oxide layer and the semiconductor substrate are etched using the trench mask pattern as an etch mask to form trenches defining convex upper surfaces of the active regions. The trench mask pattern is removed to expose the convex upper surfaces of the active regions. Gate patterns are formed extending over the active regions.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High speed piezoelectric optical system with tunable focal length
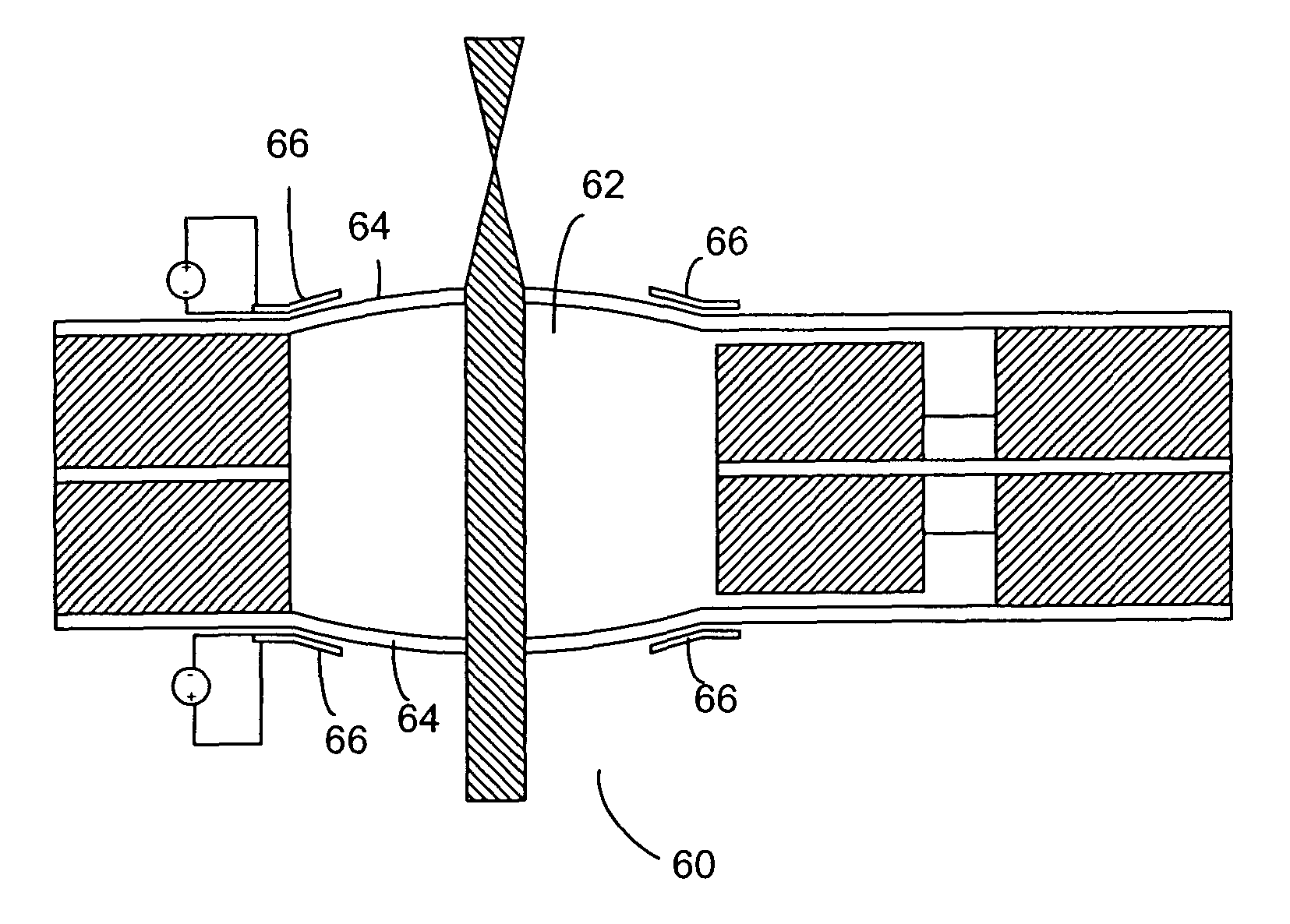
ActiveUS7369723B1Curvature can be modifiedAltering focal length of lensCoupling light guidesLensOptical storageLens plate
A varifocal optical system includes a substantially circular membrane deposited on a substrate, and a ring-shaped PZT thin film deposited on the outer portion of the circular membrane. The membrane may be a MEMS-micromachined membrane, made of thermal oxide, polysilicon, ZrO2 and SiO2. The membrane is initially in a buckled state, and may function as a mirror or a lens. Application of an electric voltage between an inner and outer electrode on the piezoelectric thin film induces a lateral strain on the PZT thin film, thereby altering the curvature of the membrane, and thus its focal length. Focal length tuning speeds as high as 1 MHz have been demonstrated. Tuning ranges of several hundred microns have been attained. The varifocal optical system can be used in many applications that require rapid focal length tuning, such as optical switching, scanning confocal microscopy, and vibration compensation in optical storage disks.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Structure and method for forming inter-poly dielectric in a shielded gate field effect transistor
ActiveUS20070037327A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDielectricGate dielectric
A shielded gate trench FET is formed as follows. A trench is formed in a silicon region of a first conductivity type, the trench including a shield electrode insulated from the silicon region by a shield dielectric. An inter-poly dielectric (IPD) including a layer of thermal oxide and a layer of conformal dielectric is formed along an upper surface of the shield electrode. A gate dielectric lining at least upper trench sidewalls is formed. A gate electrode is formed in the trench such that the gate electrode is insulated from the shield electrode by the IPD.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Shallow trench isolation (STI) with bilayer of oxide-nitride for VLSI applications
A reduction in parasitic leakages of shallow trench isolation vias is disclosed wherein the distance between the silicon nitride liner and the active silicon sidewalls is increased by depositing an insulating oxide layer prior to deposition of the silicon nitride liner. Preferably, the insulating oxide layer comprises tetraethylorthosilicate. The method comprises of etching one or more shallow trench isolations into a semiconductor wafer; depositing an insulating oxide layer into the trench; growing a thermal oxide in the trench; and depositing a silicon nitride liner in the trench. The thermal oxide may be grown prior to or after deposition of the insulating oxide layer.
Owner:QIMONDA +1
Selective silicon oxide etchant formulation including fluoride salt, chelating agent, and glycol solvent
InactiveUS6280651B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface treatment compositionsSilicon oxideFluoride
The formulations of the present invention etch doped silicon oxide compounds, such as BPSG and PSG layers, at rates greater than or equal to the etch rate of undoped silicon oxide such as thermal oxide. The formulations have the general composition of a chelating agent, preferably weakly to moderately acidic (0.1-10%; preferably 0.2-2.8%); a fluoride salt, which may be ammonium fluoride or an organic derivative of either ammonium fluoride or a polyammonium fluoride (1.65-7%; preferably 2.25-7%); a glycol solvent (71-98%; preferably 90-98%); and optionally, an amine.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Methods of Forming a Dielectric Cap Layer on a Metal Gate Structure
ActiveUS20130181263A1Well formedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
Disclosed herein are various methods of forming isolation structures on FinFETs and other semiconductor devices, and the resulting devices that have such isolation structures. In one example, the method includes forming a plurality of spaced-apart trenches in a semiconducting substrate, wherein the trenches define a fin for a FinFET device, forming a layer of insulating material in the trenches, wherein the layer of insulating material covers a lower portion of the fin but not an upper portion of the fin, forming a protective material on the upper portion of the fin, and performing a heating process in an oxidizing ambient to form a thermal oxide region on the covered lower portion of the fin.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
FinFET Formation with a Thermal Oxide Spacer Hard Mask Formed from Crystalline Silicon Layer
InactiveUS20110053361A1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsSingle crystal
A semiconductor process and apparatus provide a FinFET device by forming a second single crystal semiconductor layer (19) that is isolated from an underlying first single crystal semiconductor layer (17) by a buried insulator layer (18); patterning and etching the second single crystal semiconductor layer (19) to form a single crystal mandrel (42) having vertical sidewalls; thermally oxidizing the vertical sidewalls of the single crystal mandrel to grow oxide spacers (52) having a substantially uniform thickness; selectively removing any remaining portion of the single crystal mandrel (42) while substantially retaining the oxide spacers (52); and selectively etching the first single crystal semiconductor layer (17) using the oxide spacers (52) to form one or more FinFET channel regions (92).
Owner:NXP USA INC +1
Silicon carbide for crystalline silicon solar cell surface passivation
InactiveUS20090250108A1Increases optical pathHigh internal reflection interfaceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationSilicon oxideCrystalline silicon
Embodiments of the present invention generally provide methods for depositing a silicon carbide (SiC) passivation layer that may act as a high-quality passivation layer for solar cells. Embodiments of the invention also provide methods for depositing a silicon carbide / silicon oxide passivation layer that acts as a high-quality rear surface passivation layer for solar cells. The methods described herein enable the use of deposition systems configured for processing large-area substrates for solar cell processing. According to embodiments of the invention, a SiC passivation layer may be formed with improved minority carrier lifetime measurements. The SiC passivation layer may be formed at a temperature between about 150° C. and 450° C., which is much lower than temperatures for thermal oxide passivation.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Semiconductor device structure and methods of making
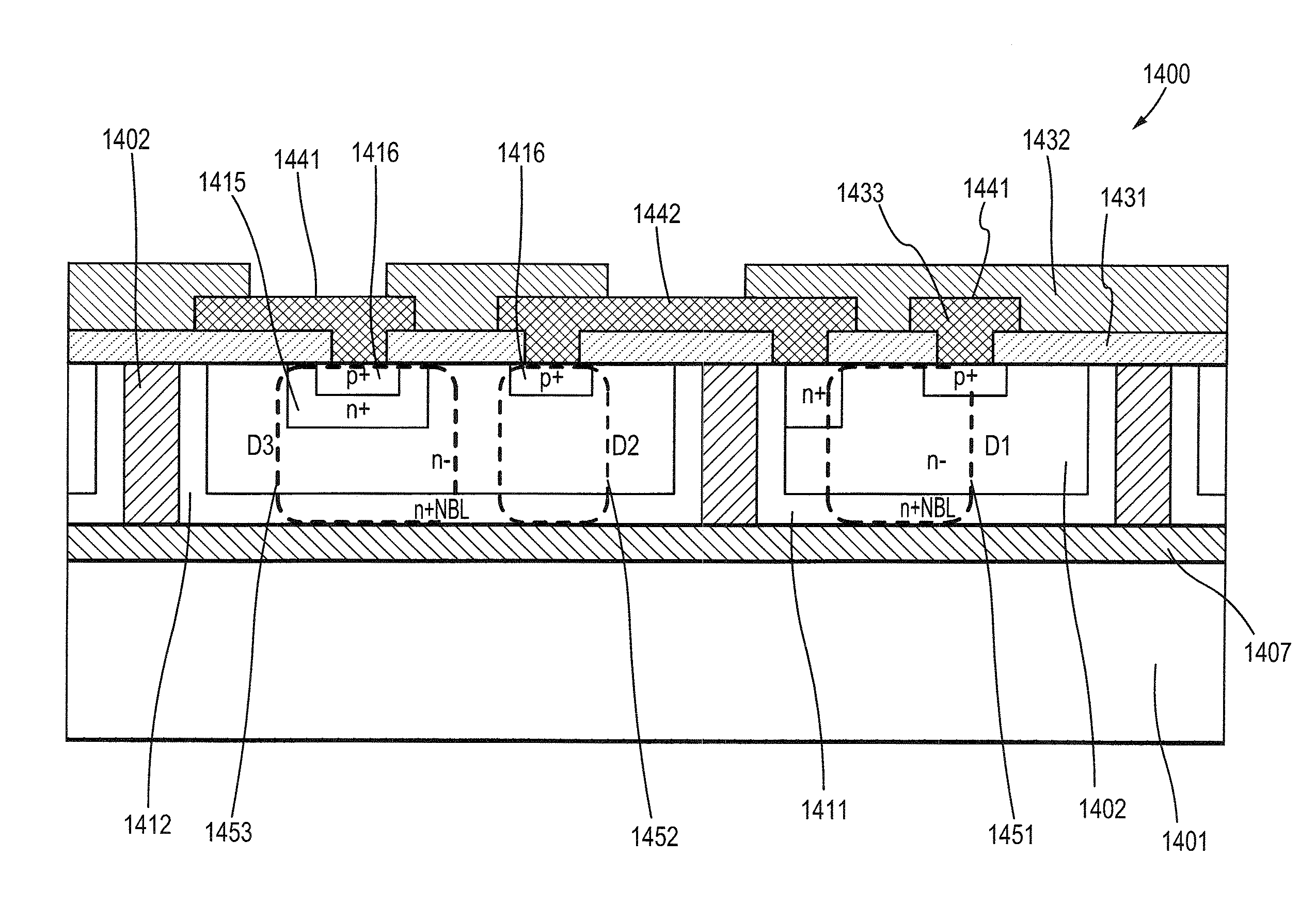
InactiveUS20110212595A1Reduce doping concentrationReduce thermal cyclesThyristorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceGas phase
A process for fabricating a semiconductor device having reduced capacitance for high frequency circuit protection is disclosed that comprises first forming an n+ buried layer in a p-type substrate by depositing n-type dopant on the top surface of the substrate and then drive in or by implanting n-type material into the substrate, and then growing an n-type epitaxial layer atop the n+ buried layer as the device layer. Trenches that surrounds the device region with depth extending from the top surface, going through the n+ buried layer and reaching down to the substrate are then formed and then an n+ layer on the sidewalls of the trenches is formed by diffusion or ion implantation. The trenches are then filled by growing a layer of thermal oxide on the sidewalls of the trenches and followed by deposition of plasma enhanced oxide, nitride, TEOS oxide CVD oxide, or polysilicon into the trenches and then planarizing the top surface by plasma etch back or polishing. Then n+ region of the device is formed by forming an oxide layer on the top surface of the device layer and then etching the oxide by photolithography, then depositing n-type dopant material and then driving in by high temperature diffusion. Finally p+ region of the device is formed by etching the oxide using photolithography, then depositing p-type dopant material by solid or gas phase deposition or ion implantation and then driving in by high temperature diffusion so that the breakdown voltage between cathode and anode of the device is set to a targeted voltage for high frequency circuit protection.
Owner:HU JERRY +2
Semiconductor device having trench isolation layer and a method of forming the same
A semiconductor device having a trench isolation layer in a semiconductor substrate is provided, wherein the trench isolation layer includes a silicon nitride liner, a silicon oxide liner; and a buried layer, wherein the buried layer includes a first buried layer for filling a lower part of the trench isolation layer and a second buried layer for filling an upper part of the trench isolation layer. A semiconductor device preferably further includes a silicon oxide layer disposed between the semiconductor substrate and the silicon nitride liner. The silicon oxide layer includes a thermal oxide layer densified at a temperature over about 800.degree. C.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
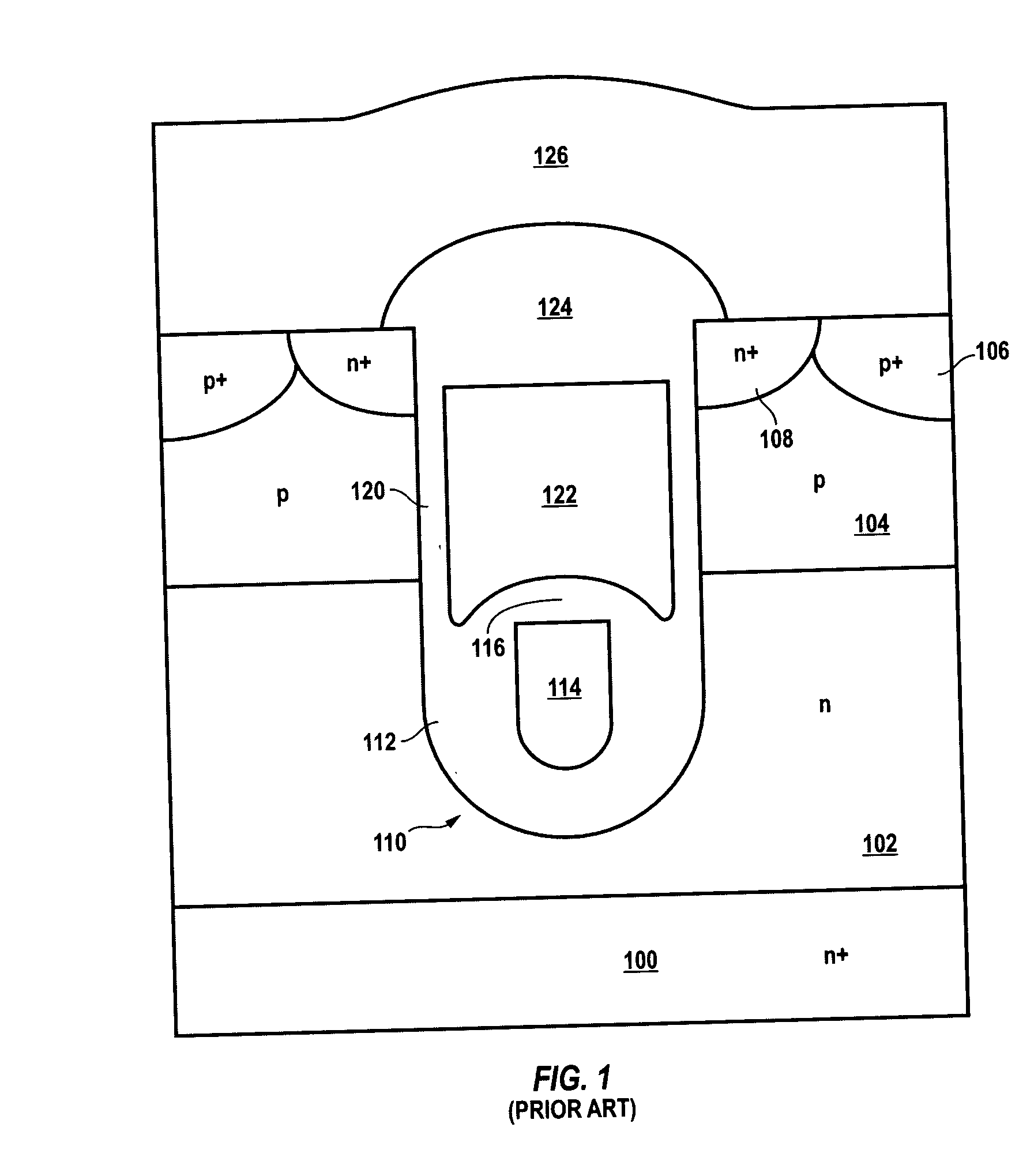
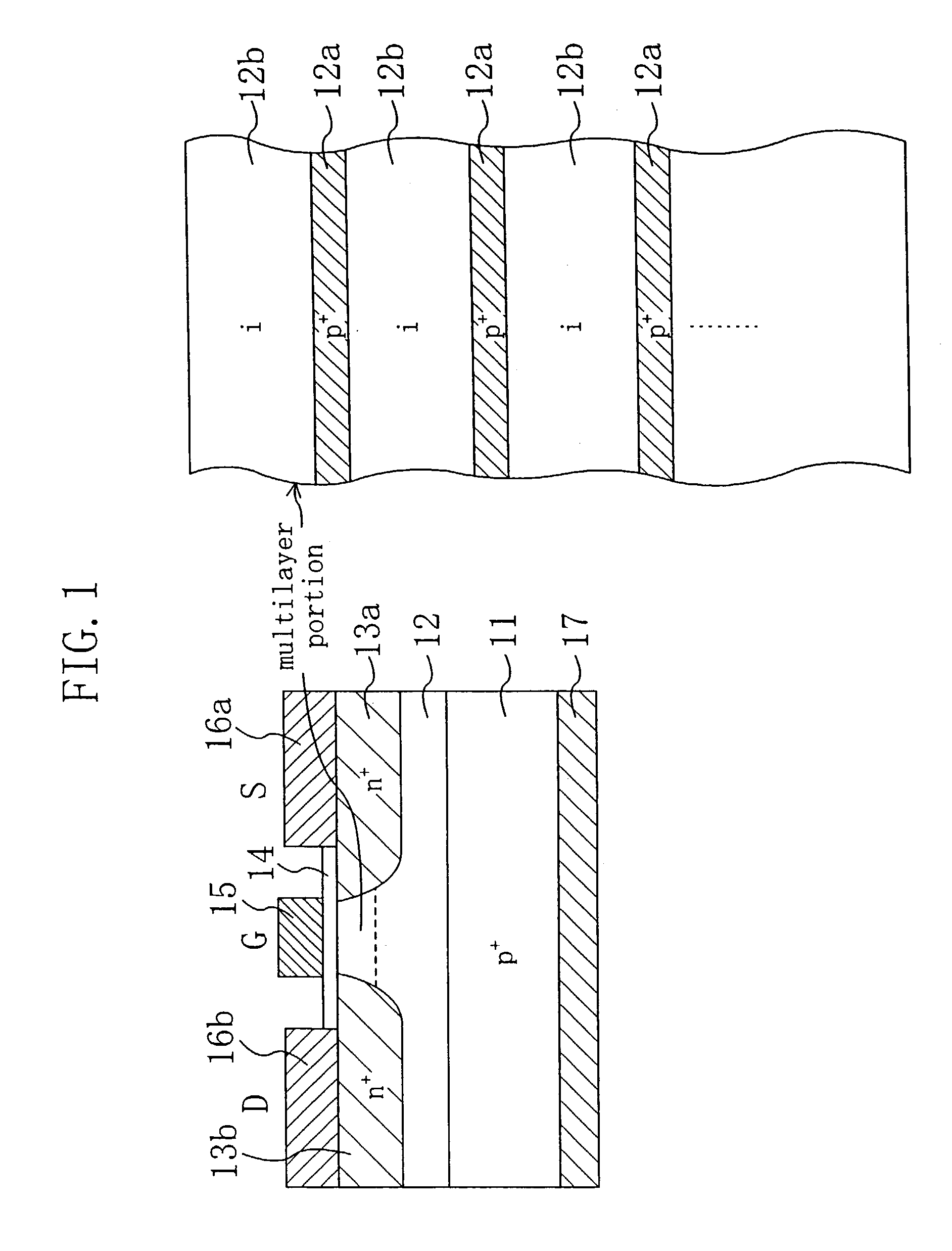
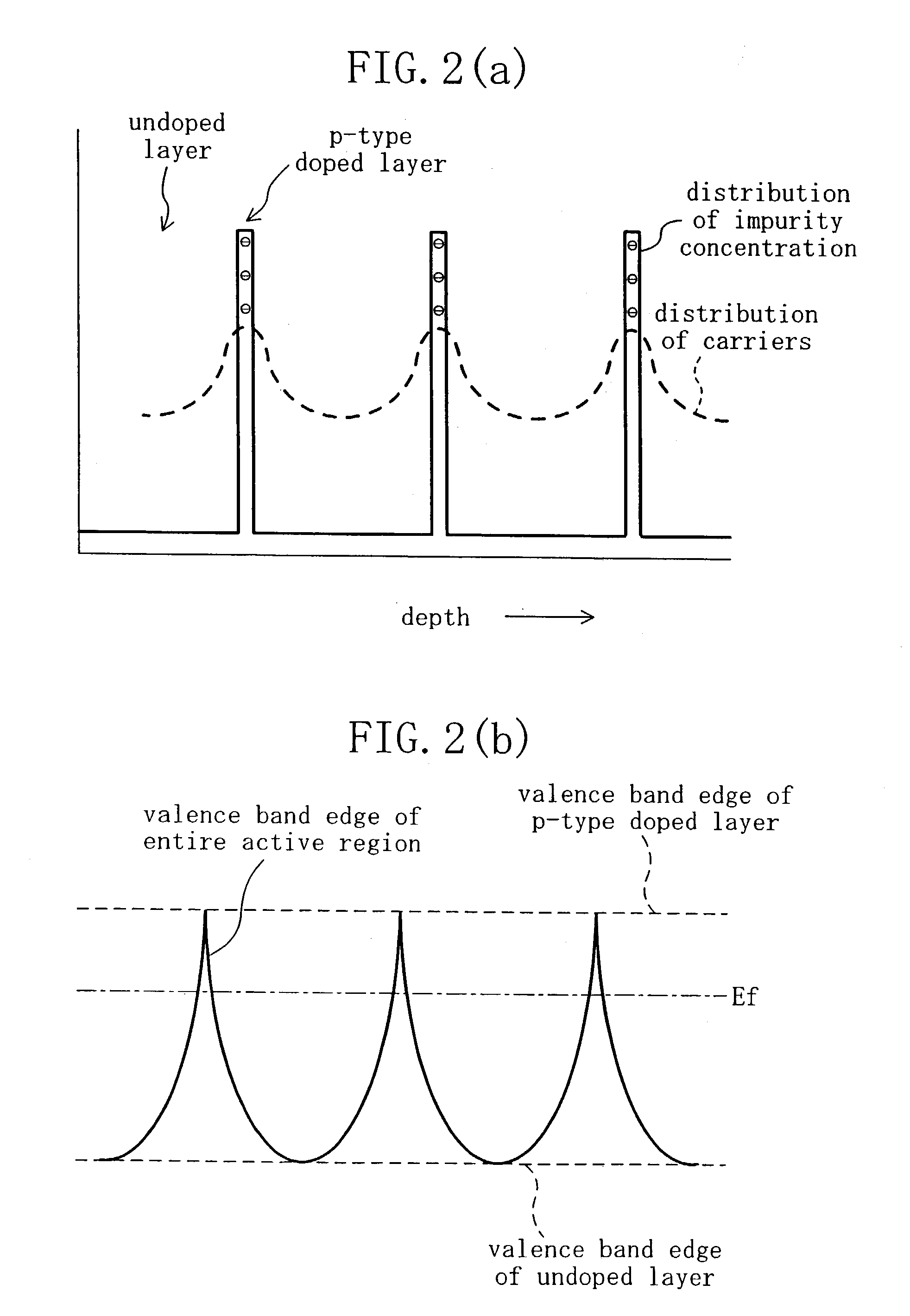
Misfet
InactiveUS20030227061A1Improve electronic propertiesAvoid harmful effectsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingImpurity ionsSic substrate
P-type active region 12; n-type source / drain regions 13a and 13b; gate insulating film 14 made of a thermal oxide film; gate electrode 15; source / drain electrodes 16a and 16b, are provided over a p-type SiC substrate 11. In the active region 12, p-type heavily doped layers 12a, which are thin enough to create a quantum effect, and thick undoped layers 12b are alternately stacked. When carriers flow, scattering of impurity ions in the active region is reduced, and the channel mobility increases. In the OFF state, a depletion layer expands throughout the active region, and the breakdown voltage increases. As a result of reduction in charges trapped in the gate insulating film or near the interface between the gate insulating film and the active region, the channel mobility further increases.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Programmable via structure and method of fabricating same
ActiveUS20080142775A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBulk negative resistance effect devicesConductive materialsDiffusion barrier
A programmable via structure is provided as well as a method of fabricating the same. The inventive programmable via a semiconductor substrate. An oxide layer such as a thermal oxide is located on a surface of the semiconductor substrate. A patterned heating material is located on a surface of the oxide layer. The inventive structure also includes a patterned dielectric material having a least one via filled with a phase change material (PCM). The patterned dielectric material including the PCM filled via is located on a surface of the patterned heating material. A patterned diffusion barrier is located on an exposed surface of said at least one via filled with the phase change material. The inventive structure also includes contact vias that extend through the patterned dielectric material. The contact vias are filled with a conductive material which also extends onto the upper surface of the patterned dielectric material. A conductive material which serves as the input of the device is located atop the patterned diffusion barrier that is located directly above the via that is filled with the phase change material.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com