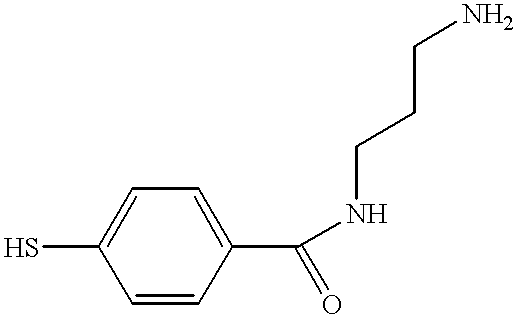
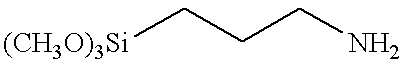
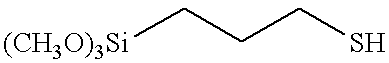
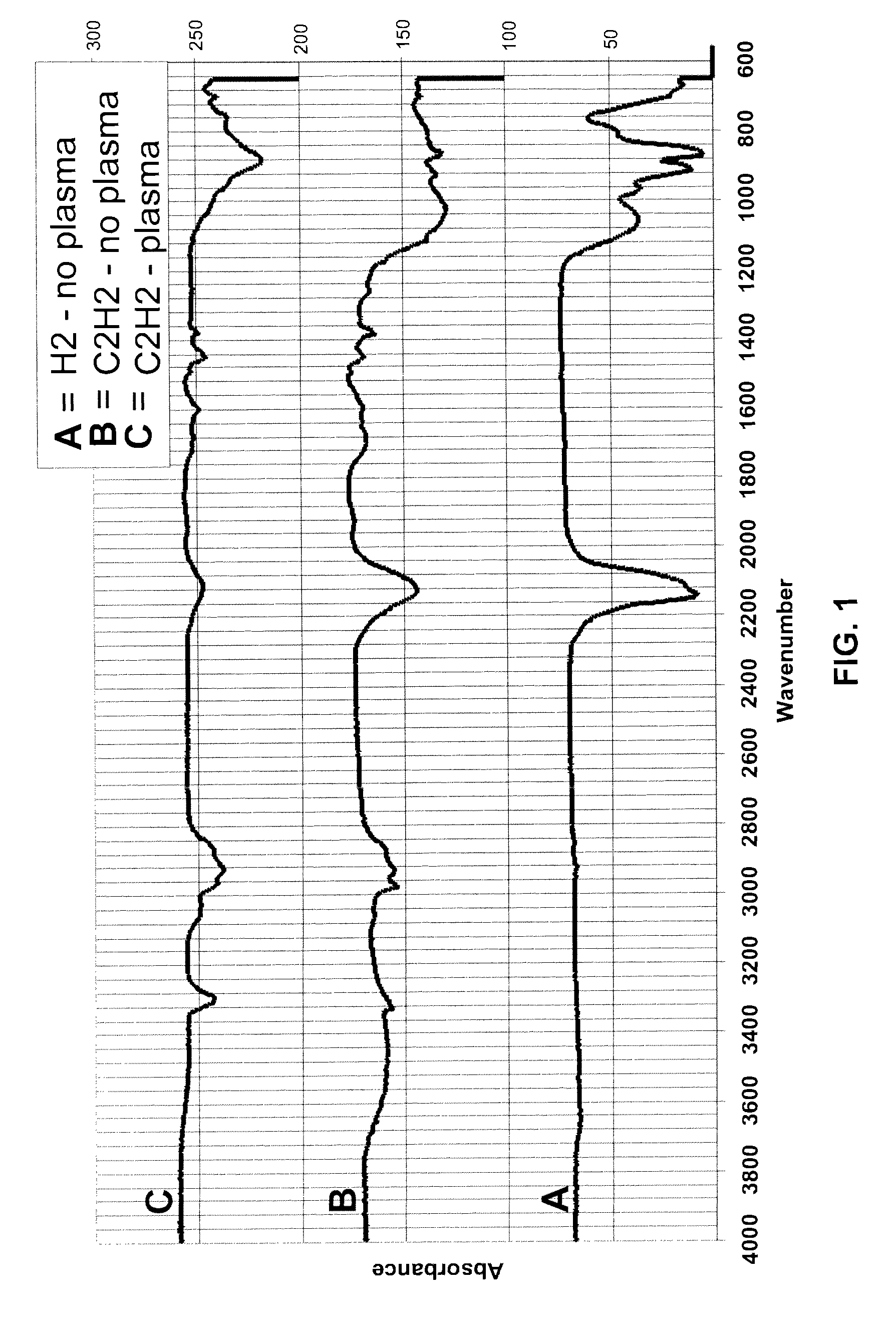
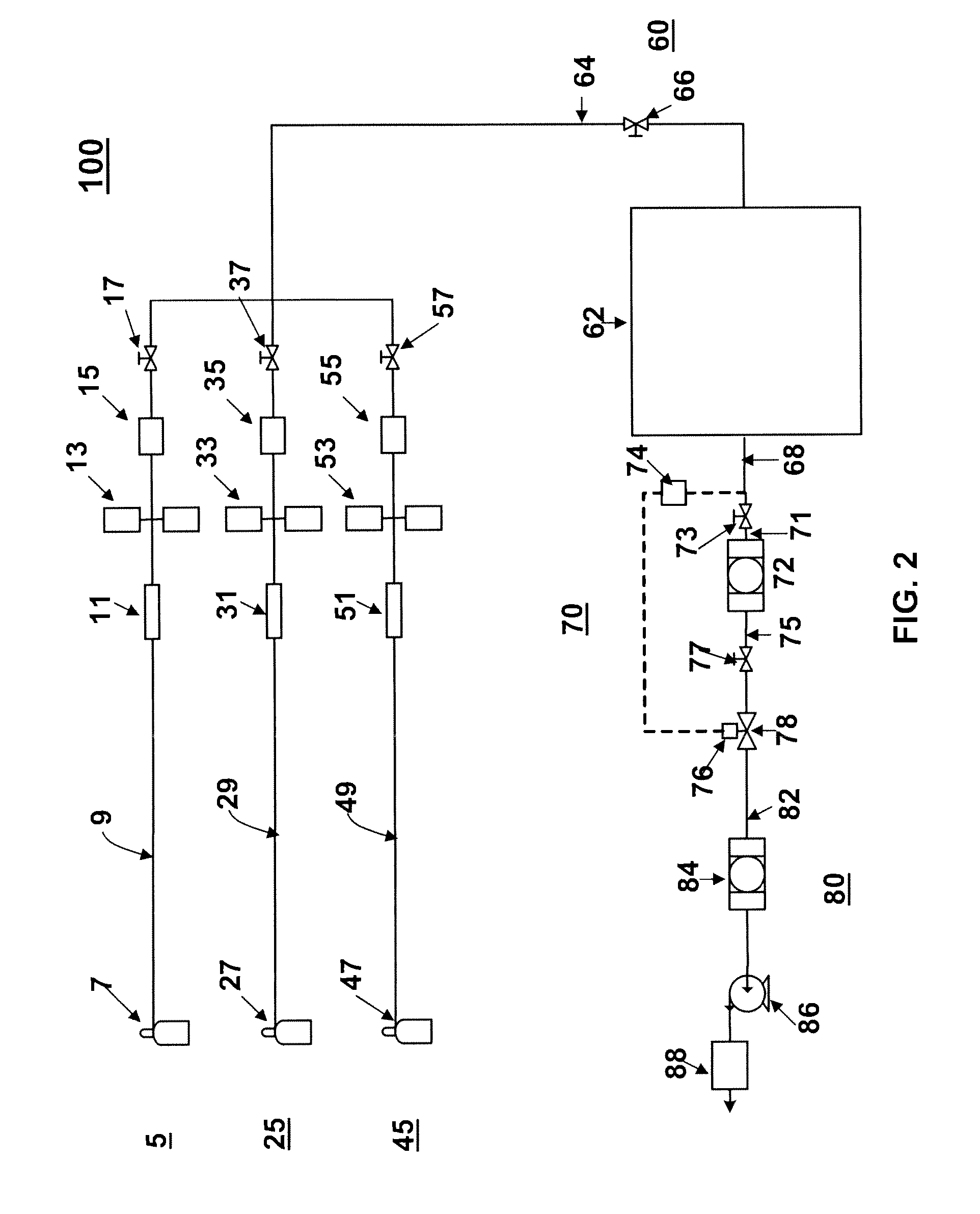
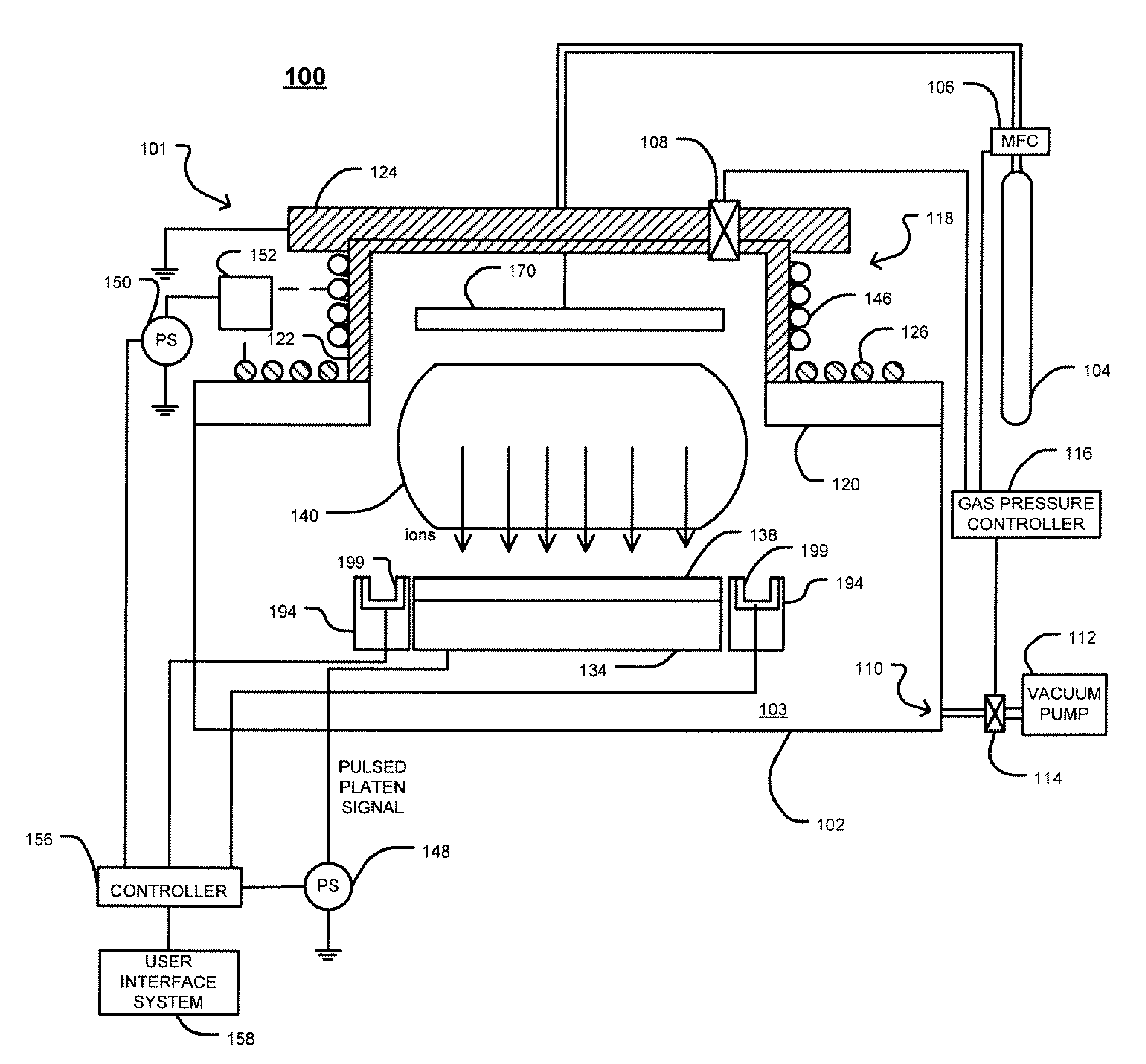
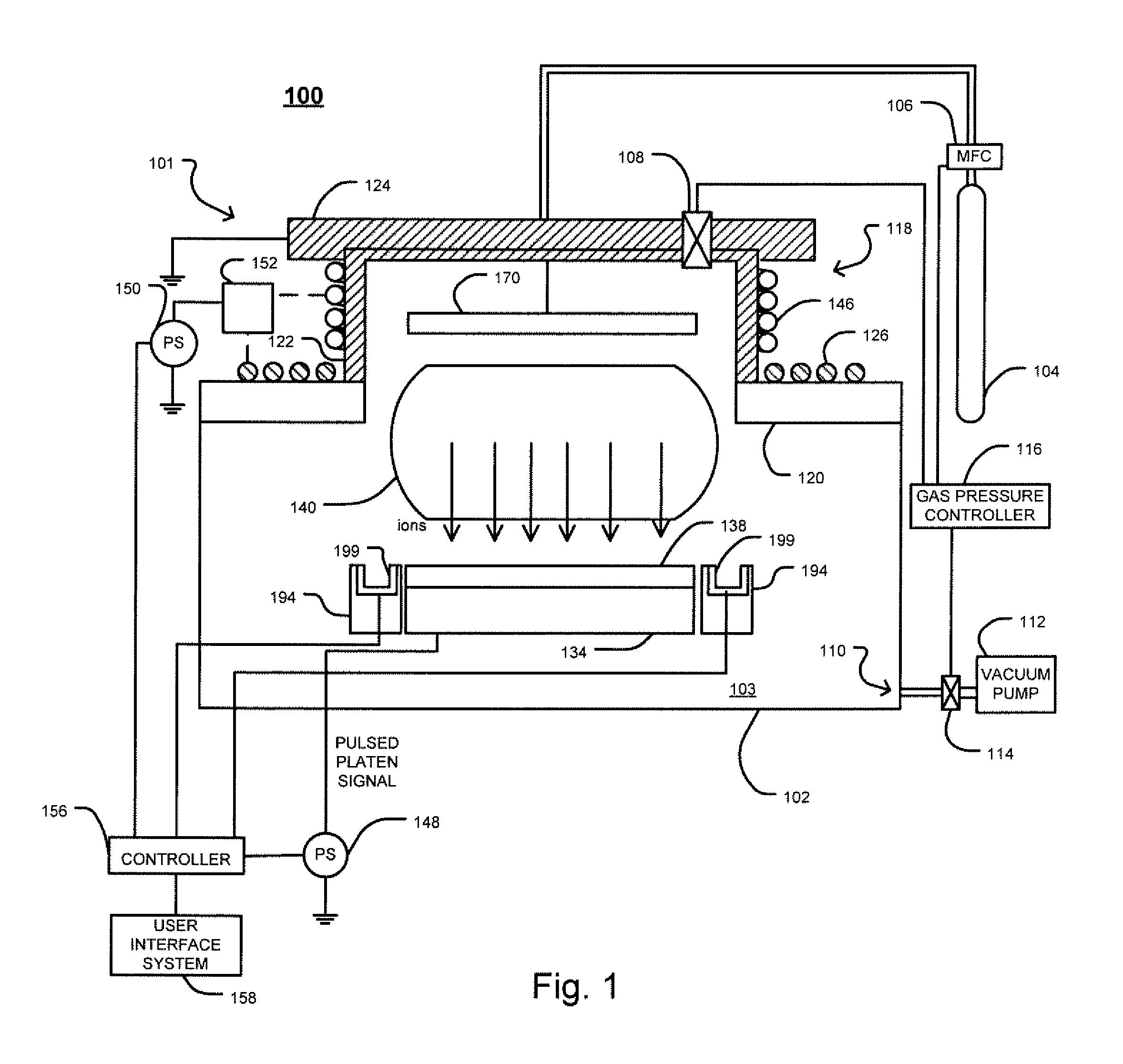
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
10424 results about "Amount of substance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In chemistry, the amount of substance in a given sample of matter is the number of discrete atomic-scale particles in it; where the particles may be molecules, atoms, ions, electrons, or other, depending on the context. It is sometimes referred to as the chemical amount.
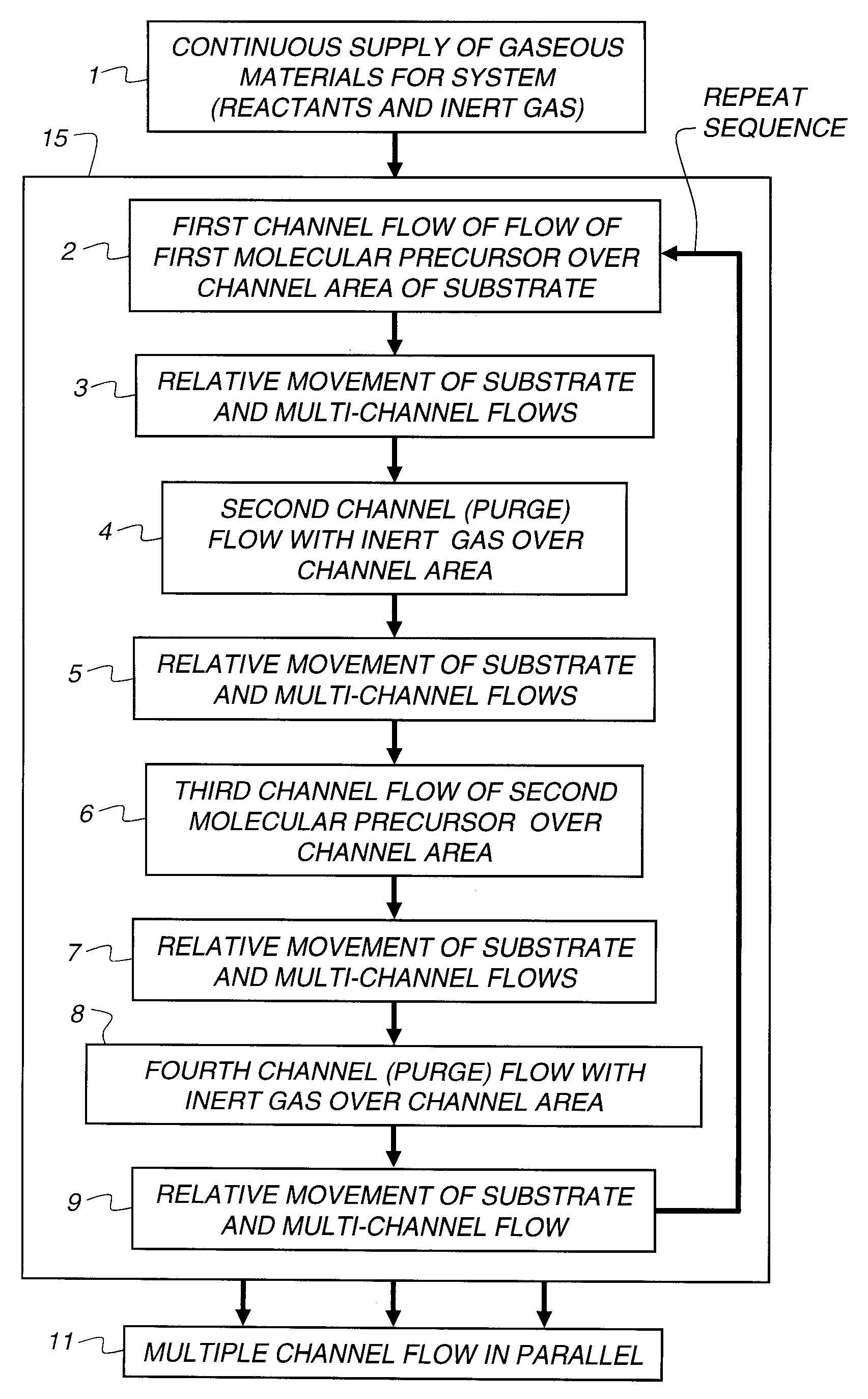
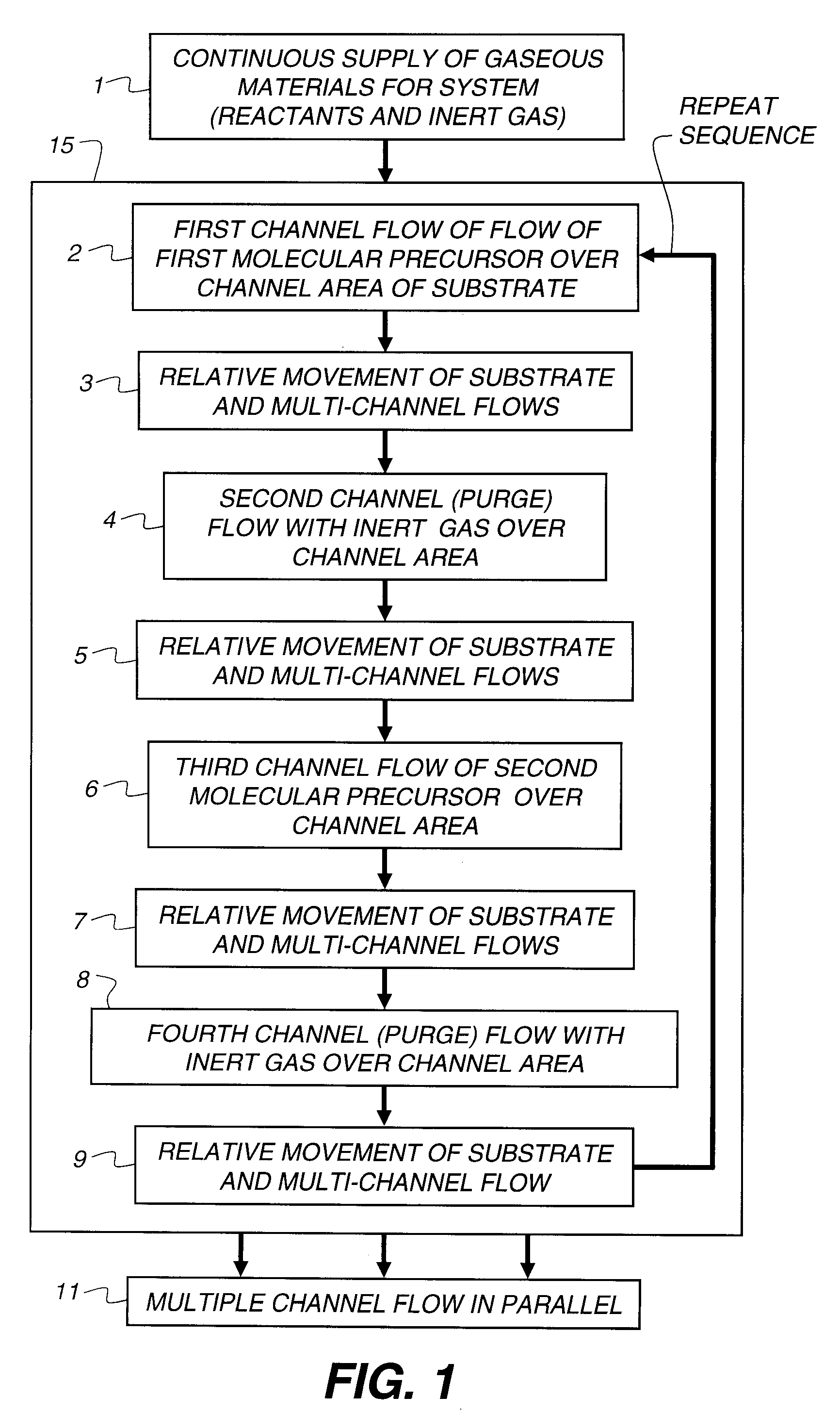
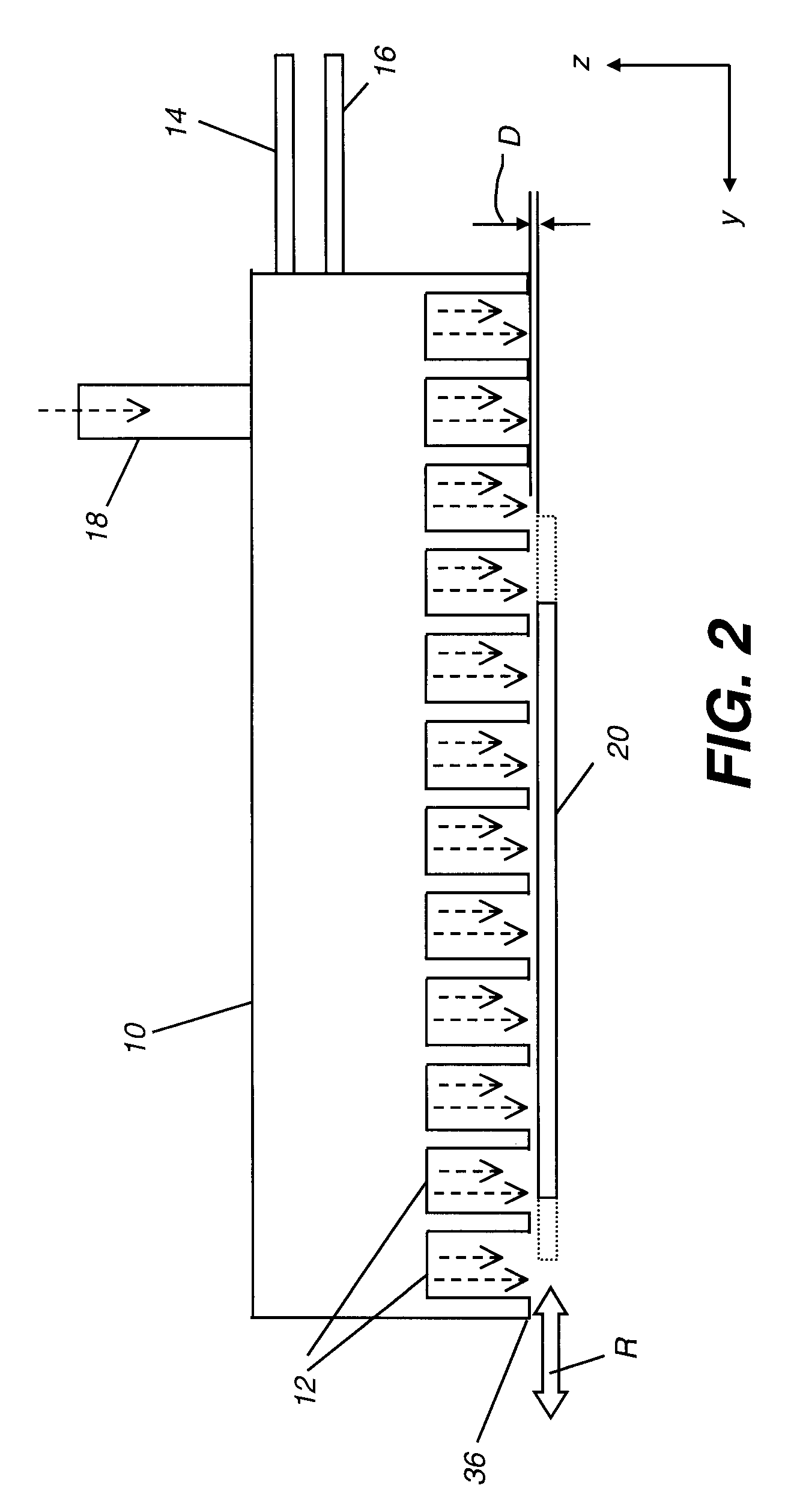
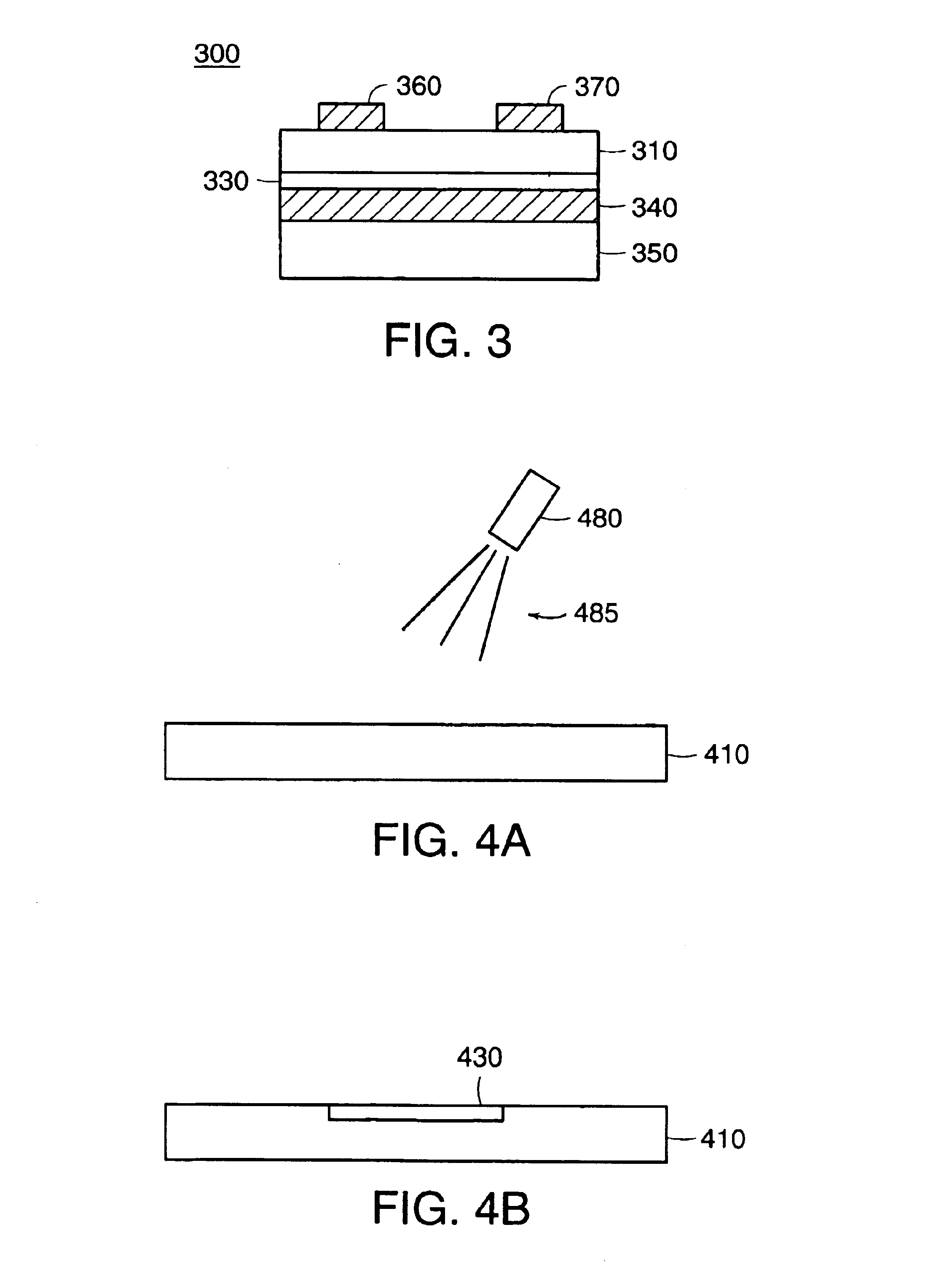
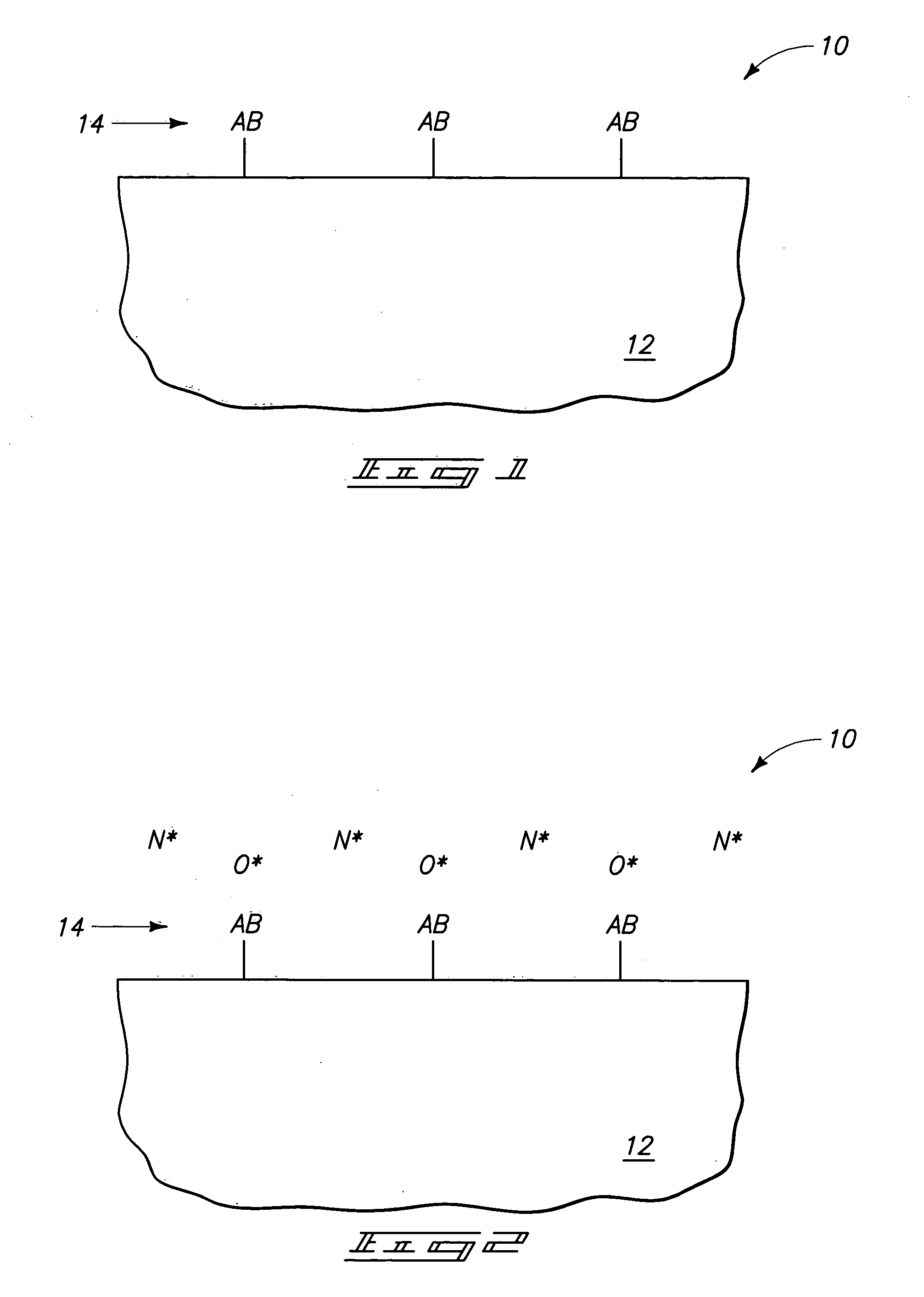
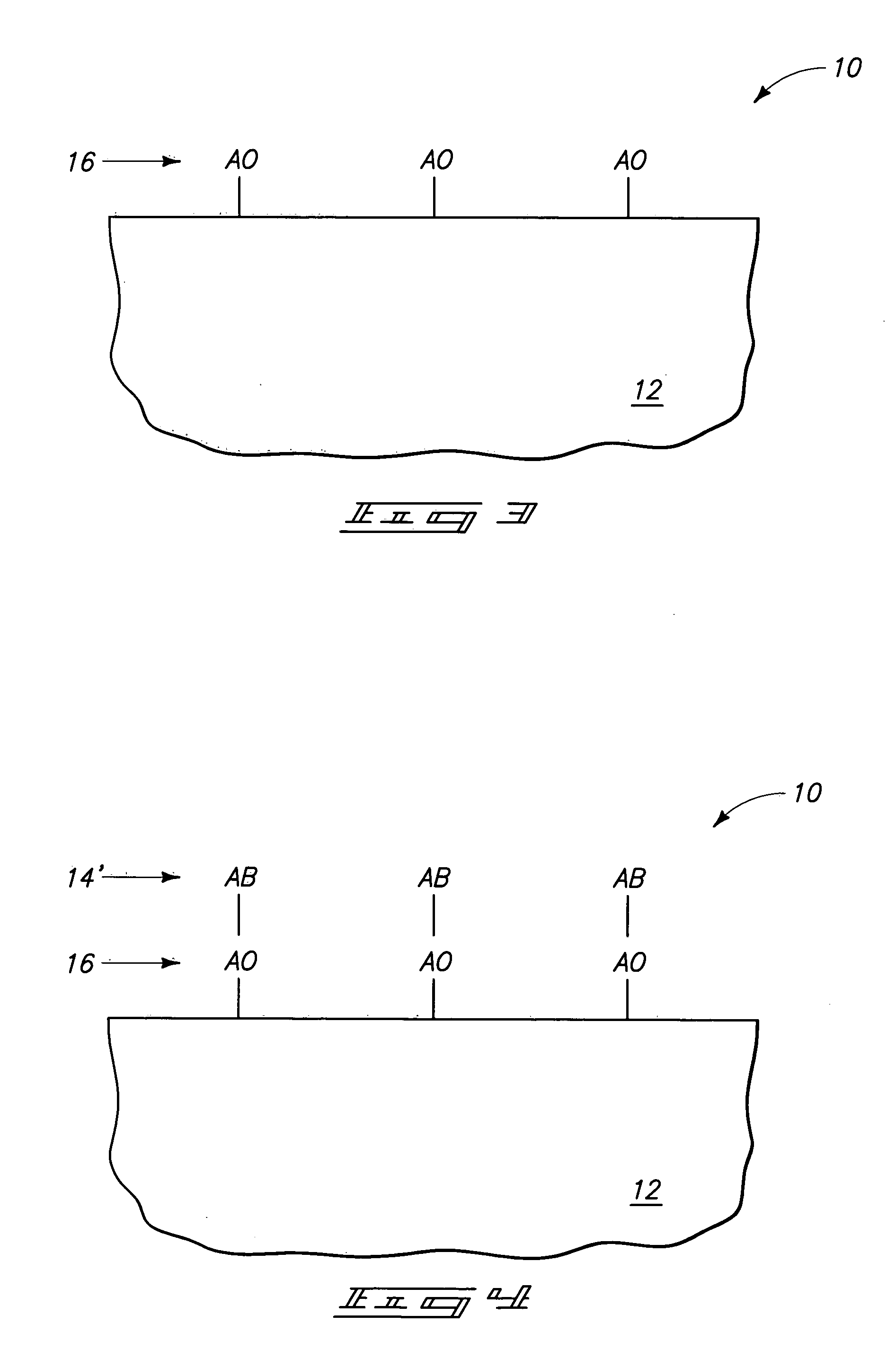
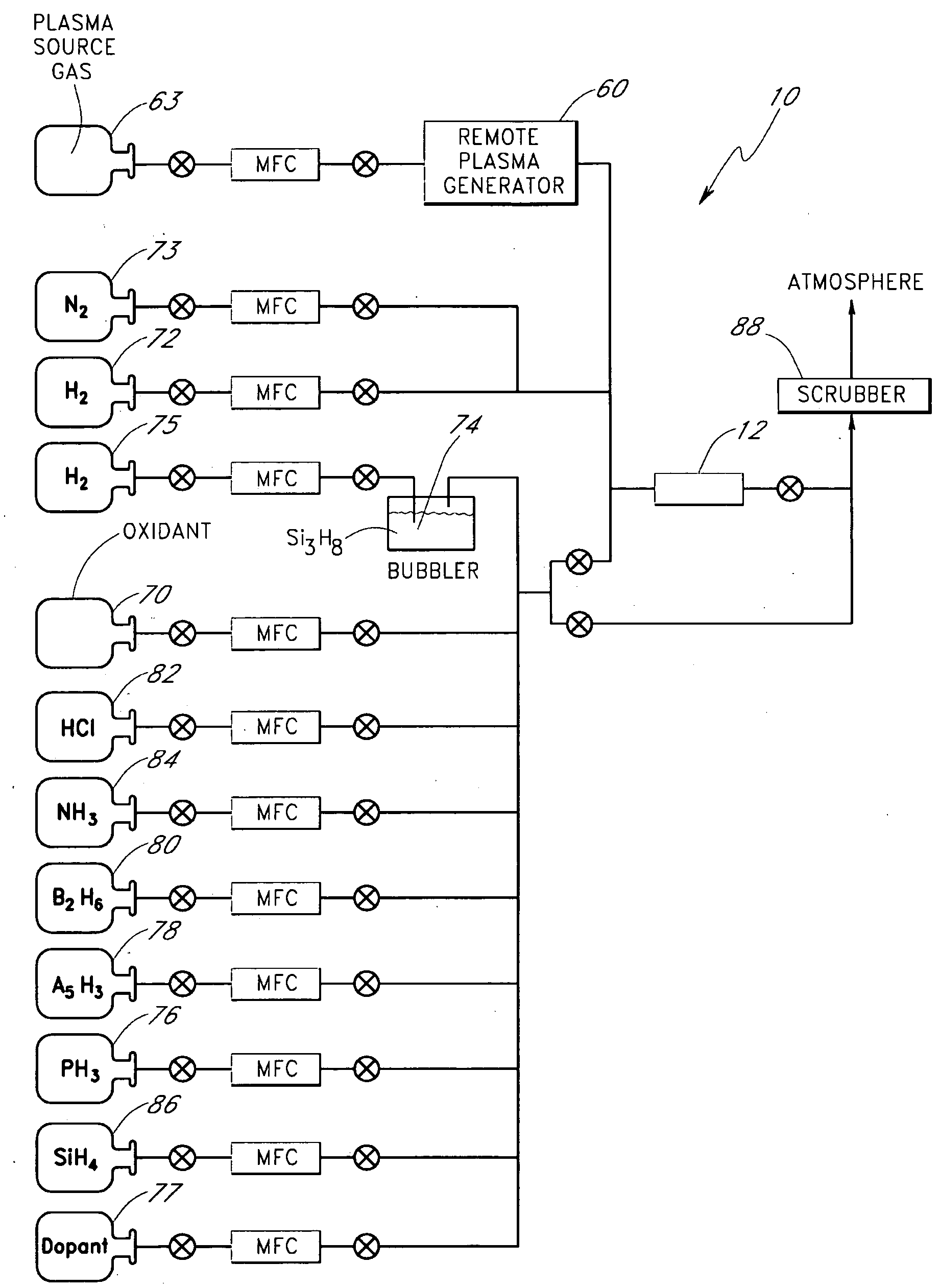
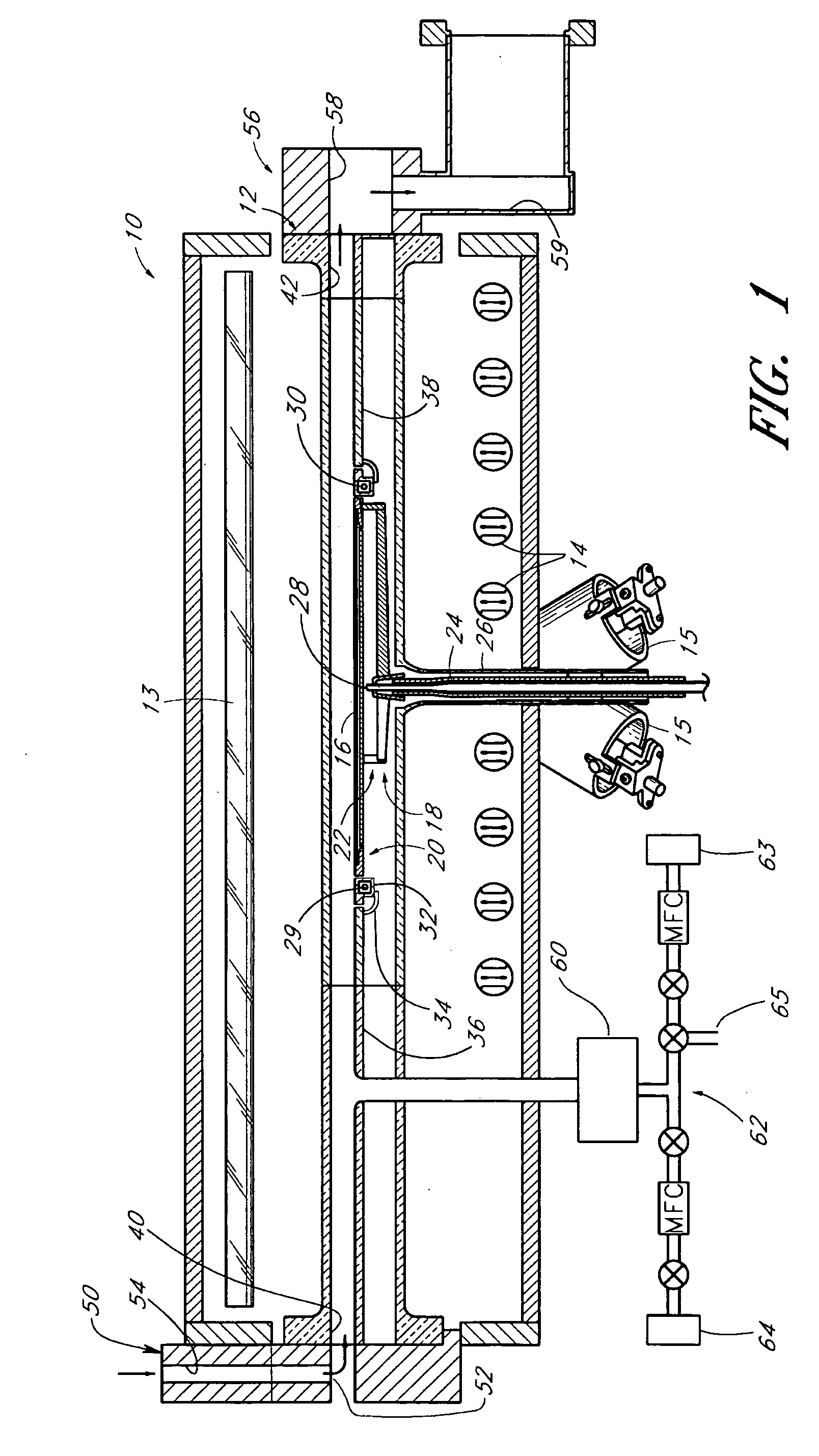
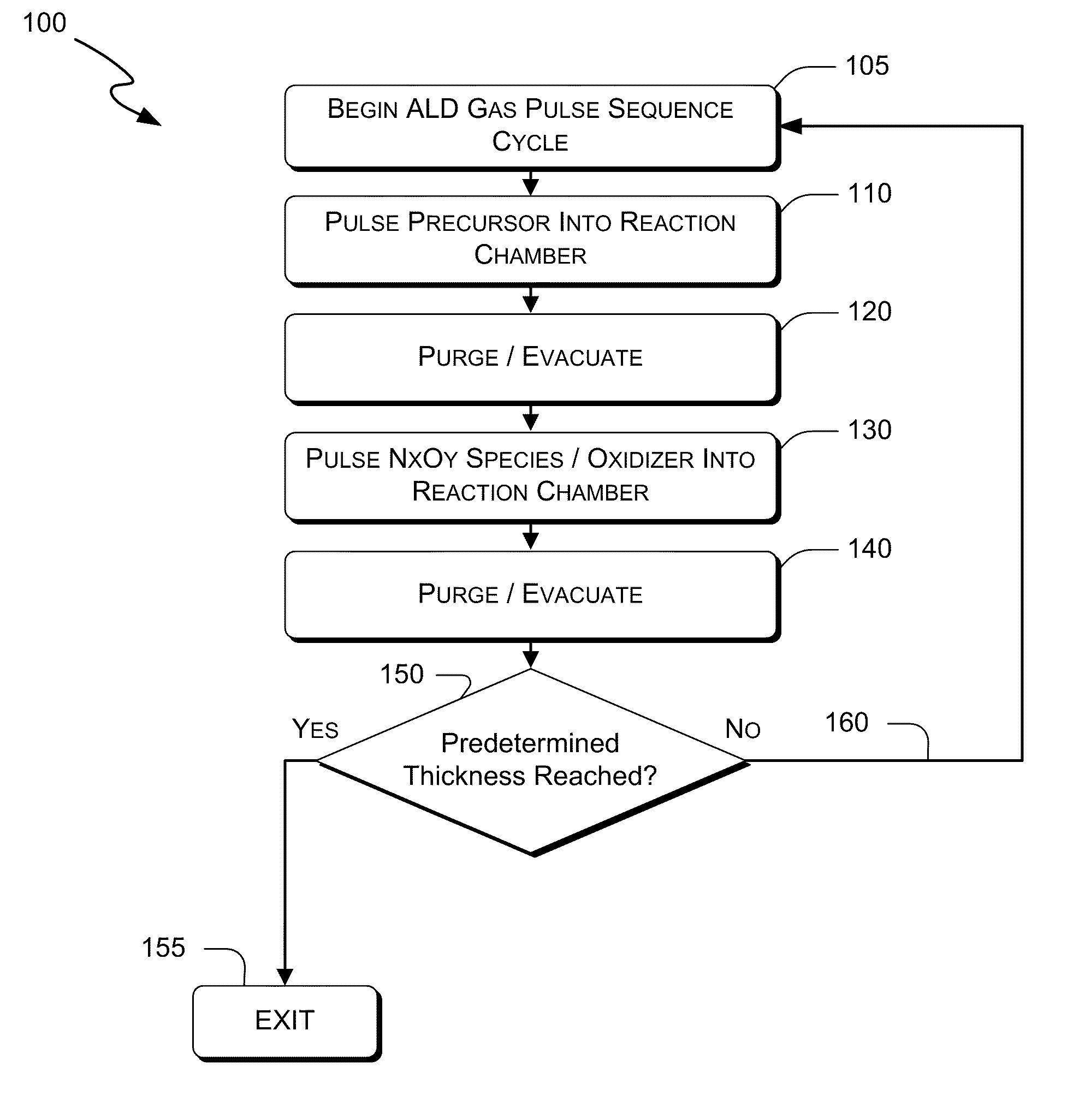
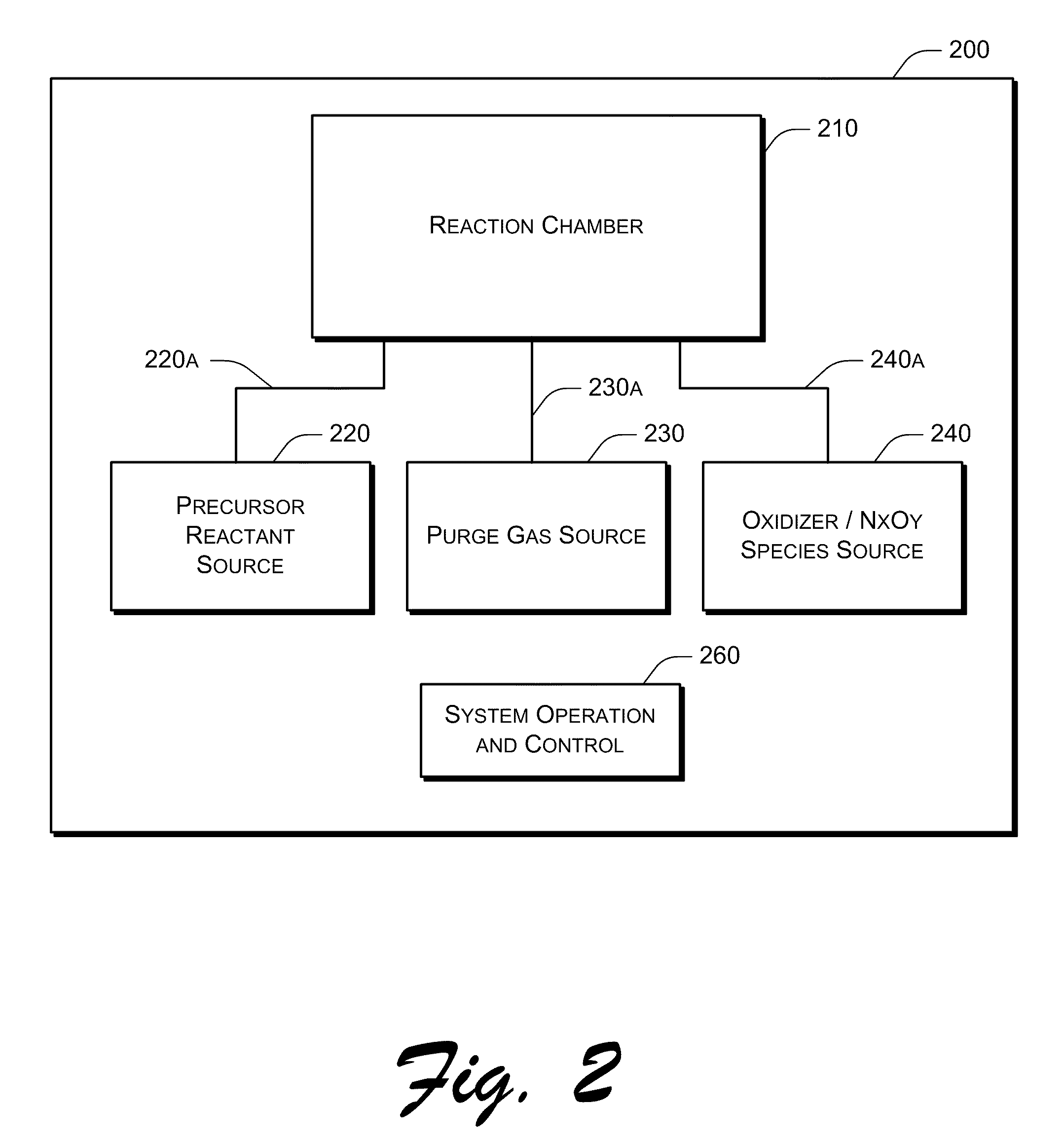
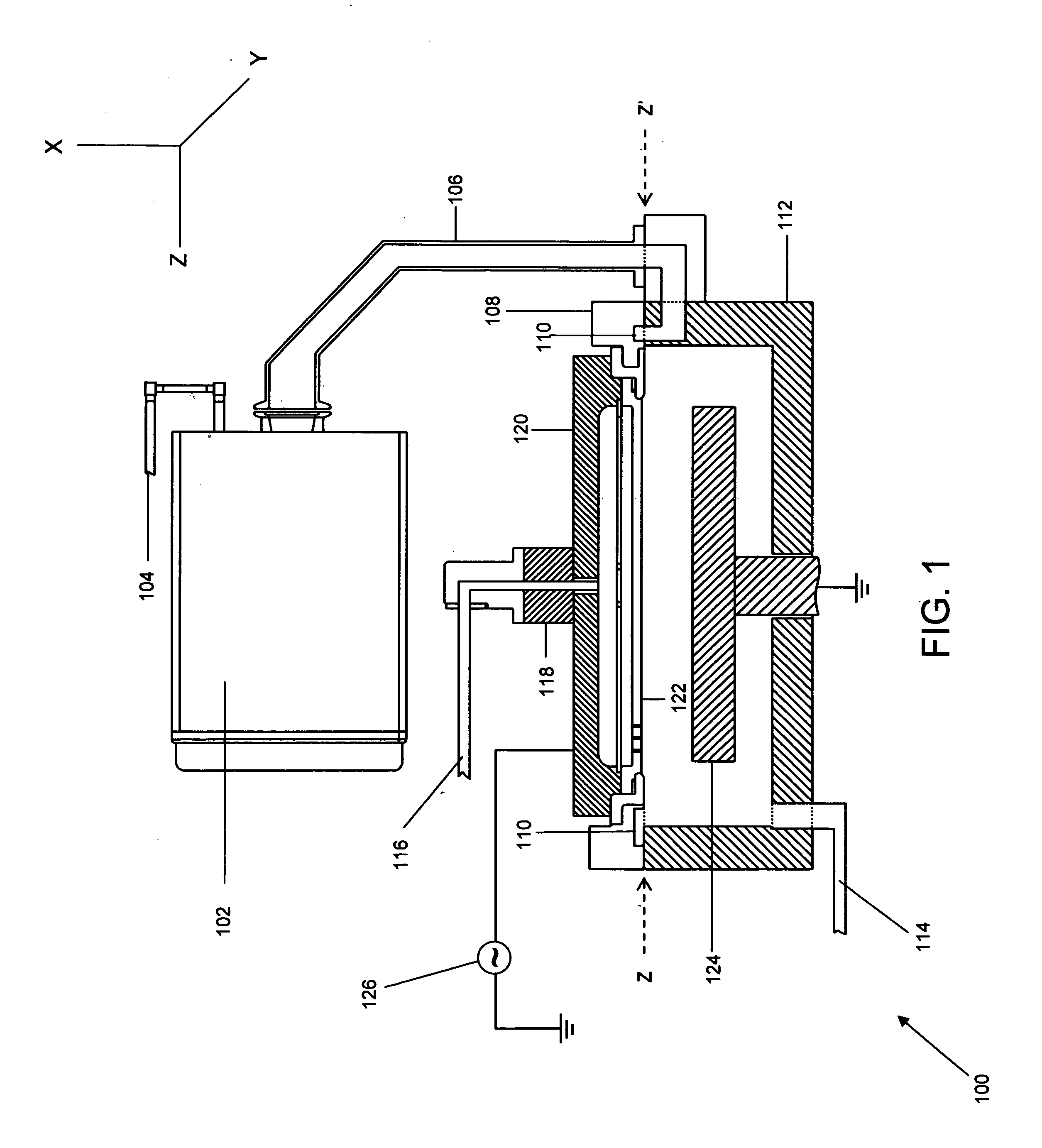
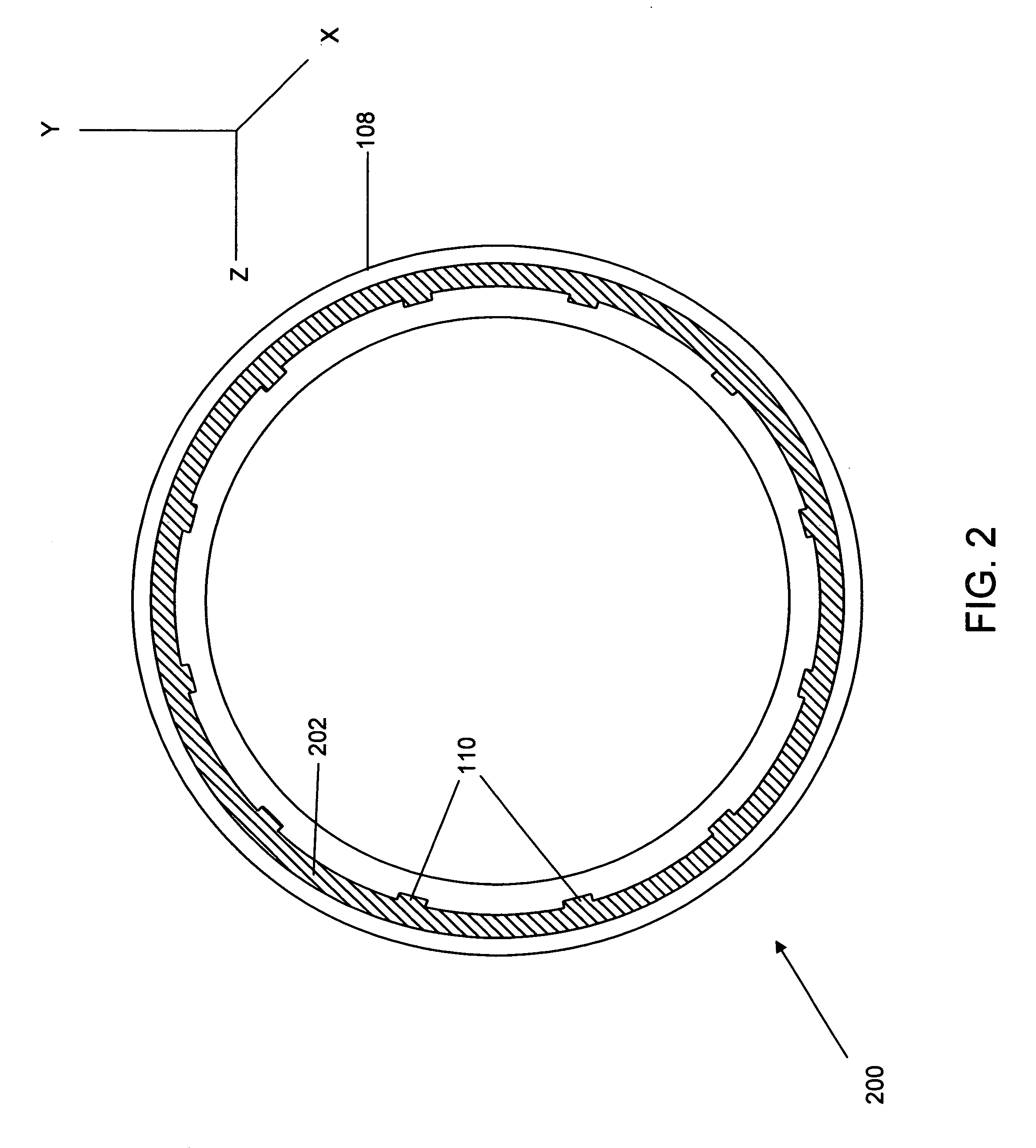
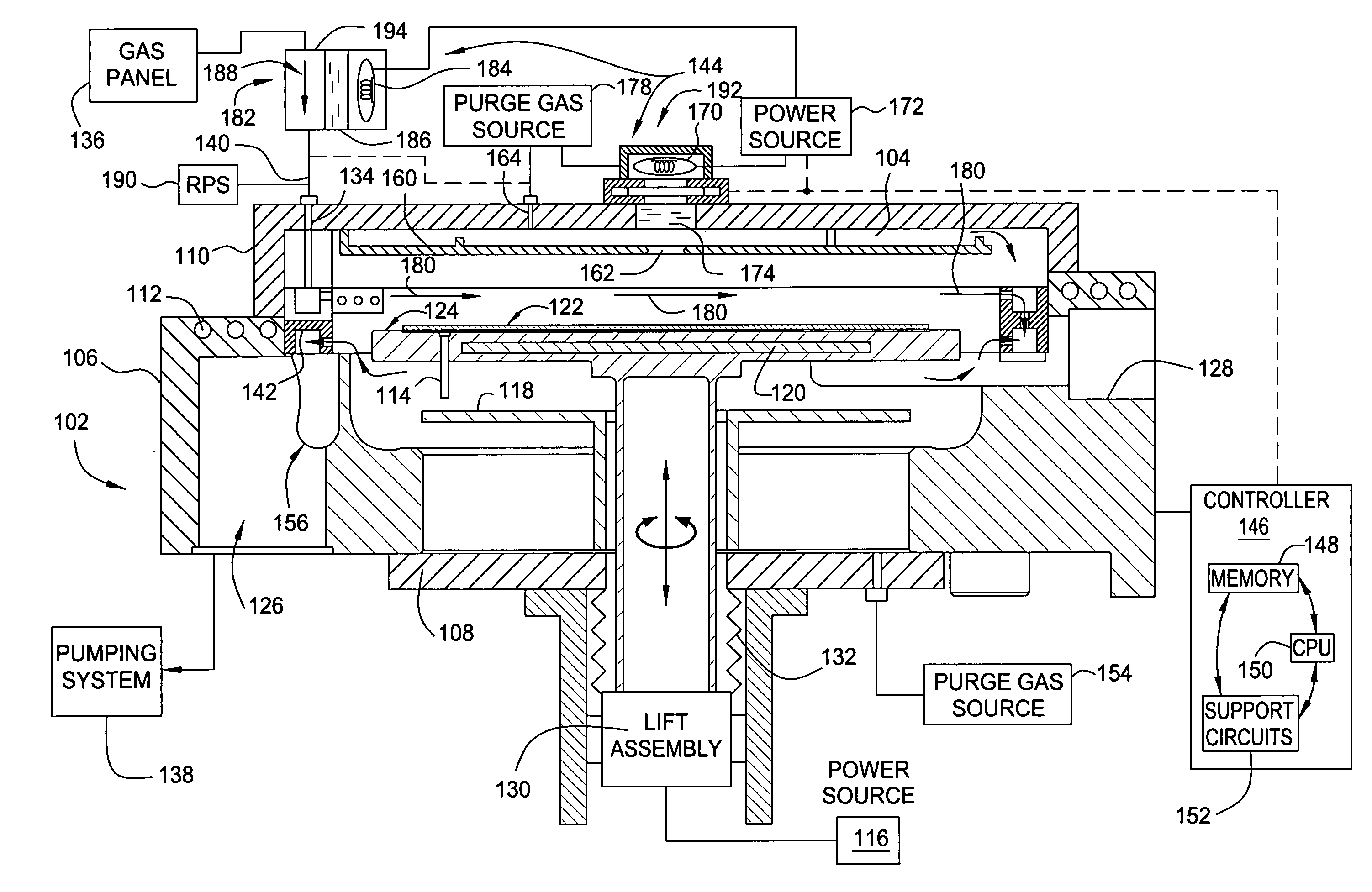
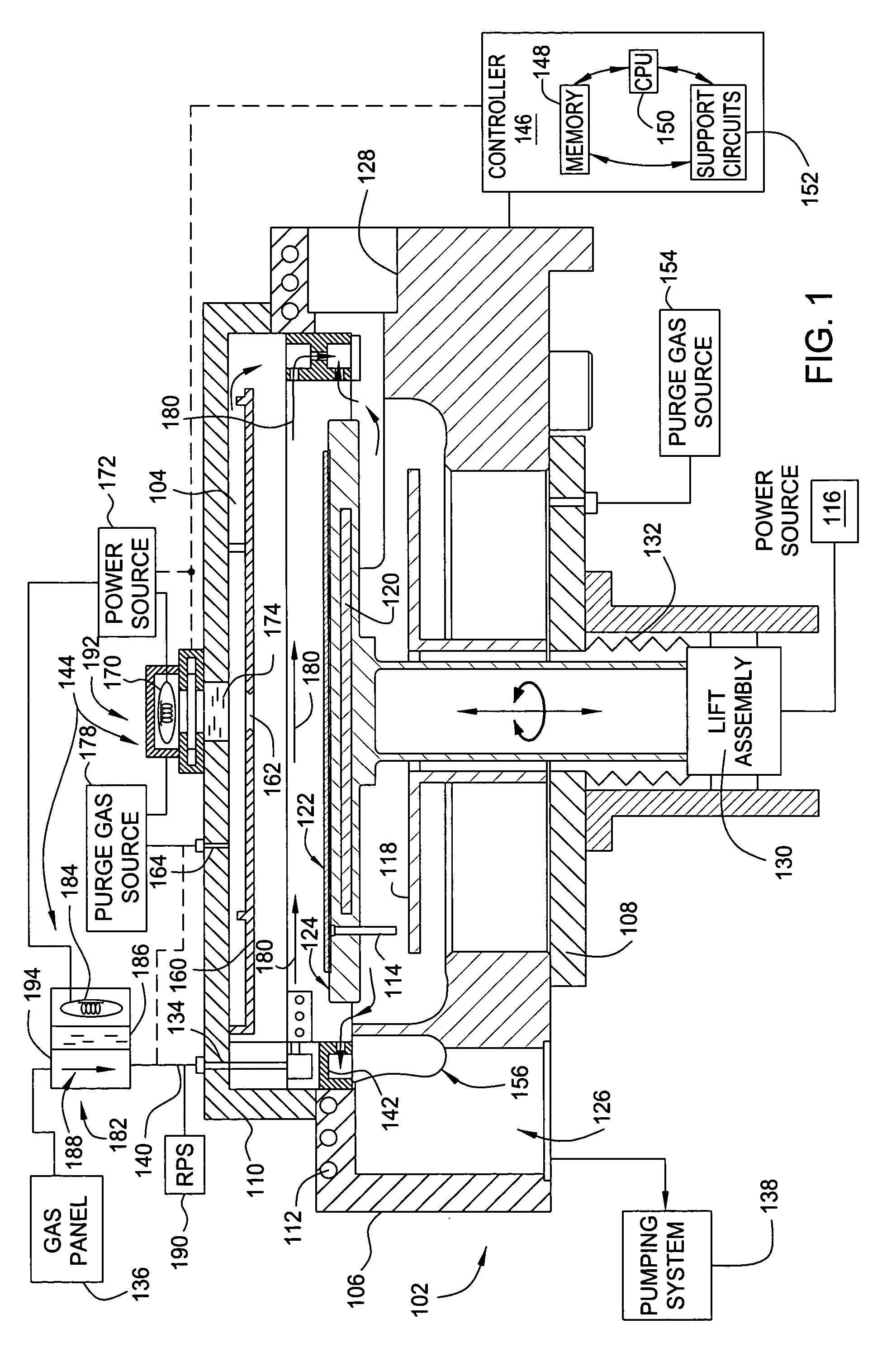
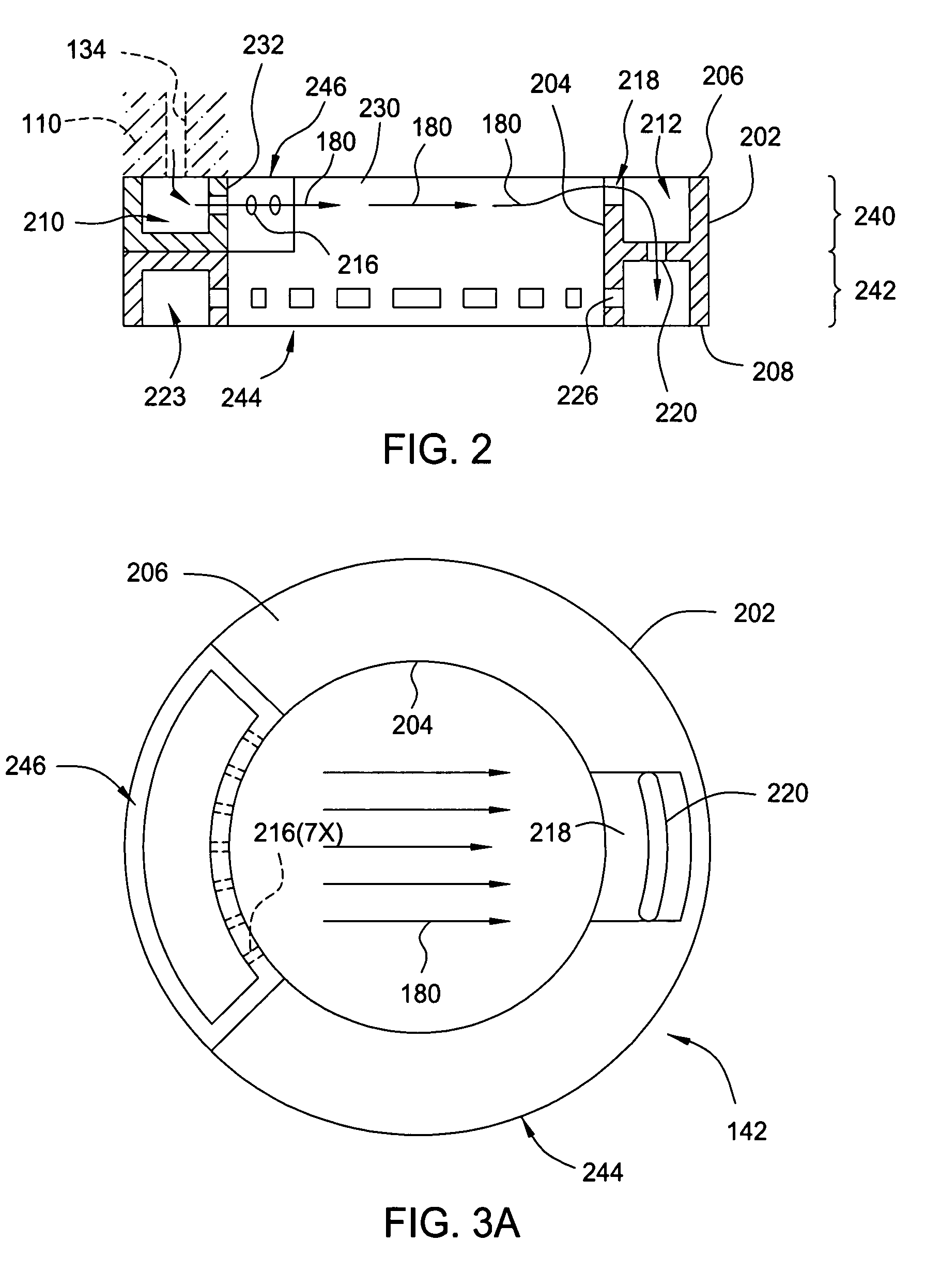
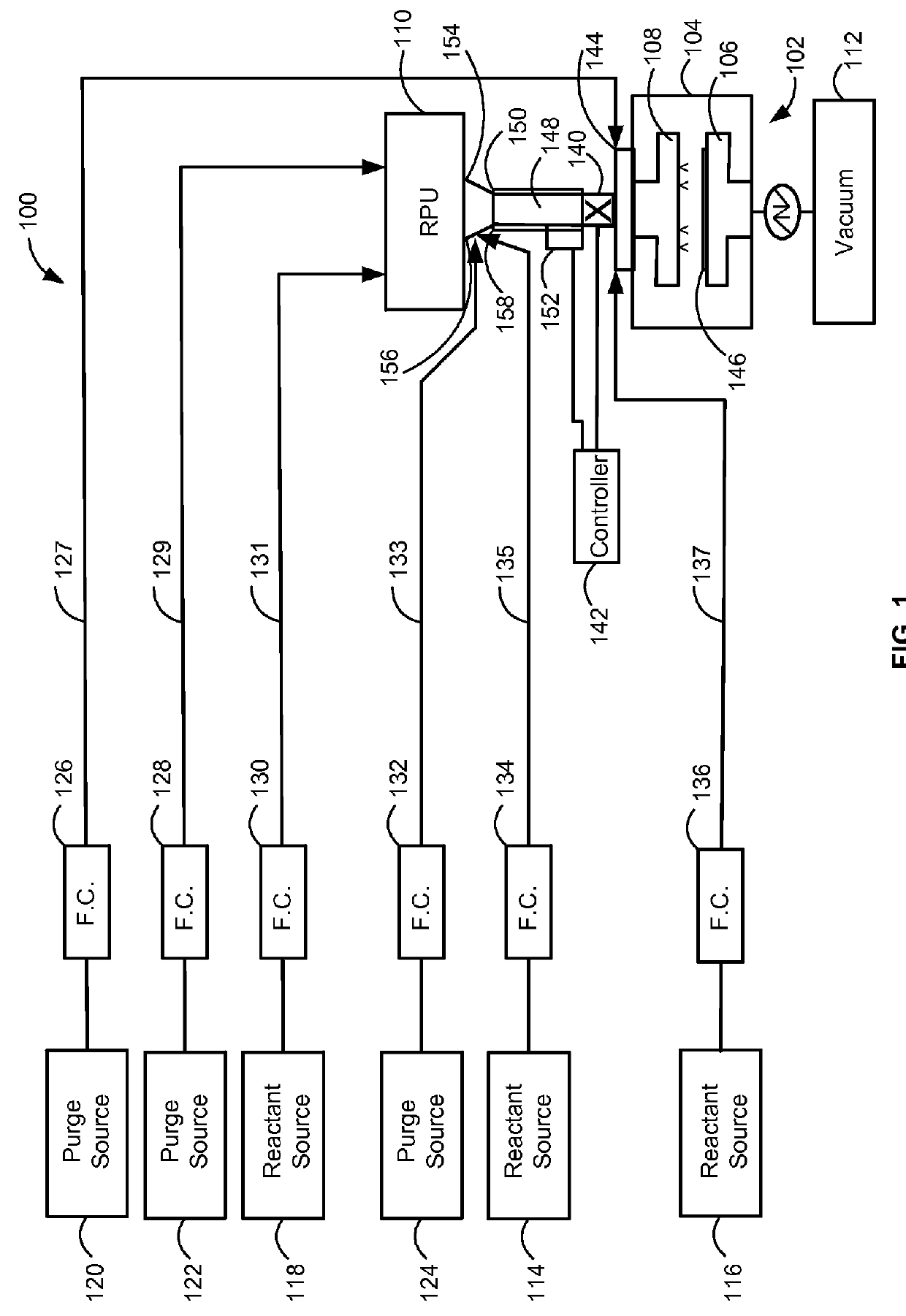
Process for atomic layer deposition
ActiveUS20080182358A1Suitable for processingAllowed to operateAdditive manufacturing apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingZincAtomic layer deposition
The present invention relates to a process of making a zinc-oxide-based thin film semiconductor, for use in a transistor, comprising thin film deposition onto a substrate comprising providing a plurality of gaseous materials comprising at least first, second, and third gaseous materials, wherein the first gaseous material is a zinc-containing volatile material and the second gaseous material is reactive therewith such that when one of the first or second gaseous materials are on the surface of the substrate the other of the first or second gaseous materials will react to deposit a layer of material on the substrate and wherein the third gaseous material is inert with respect to reacting with the first or second gaseous materials.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
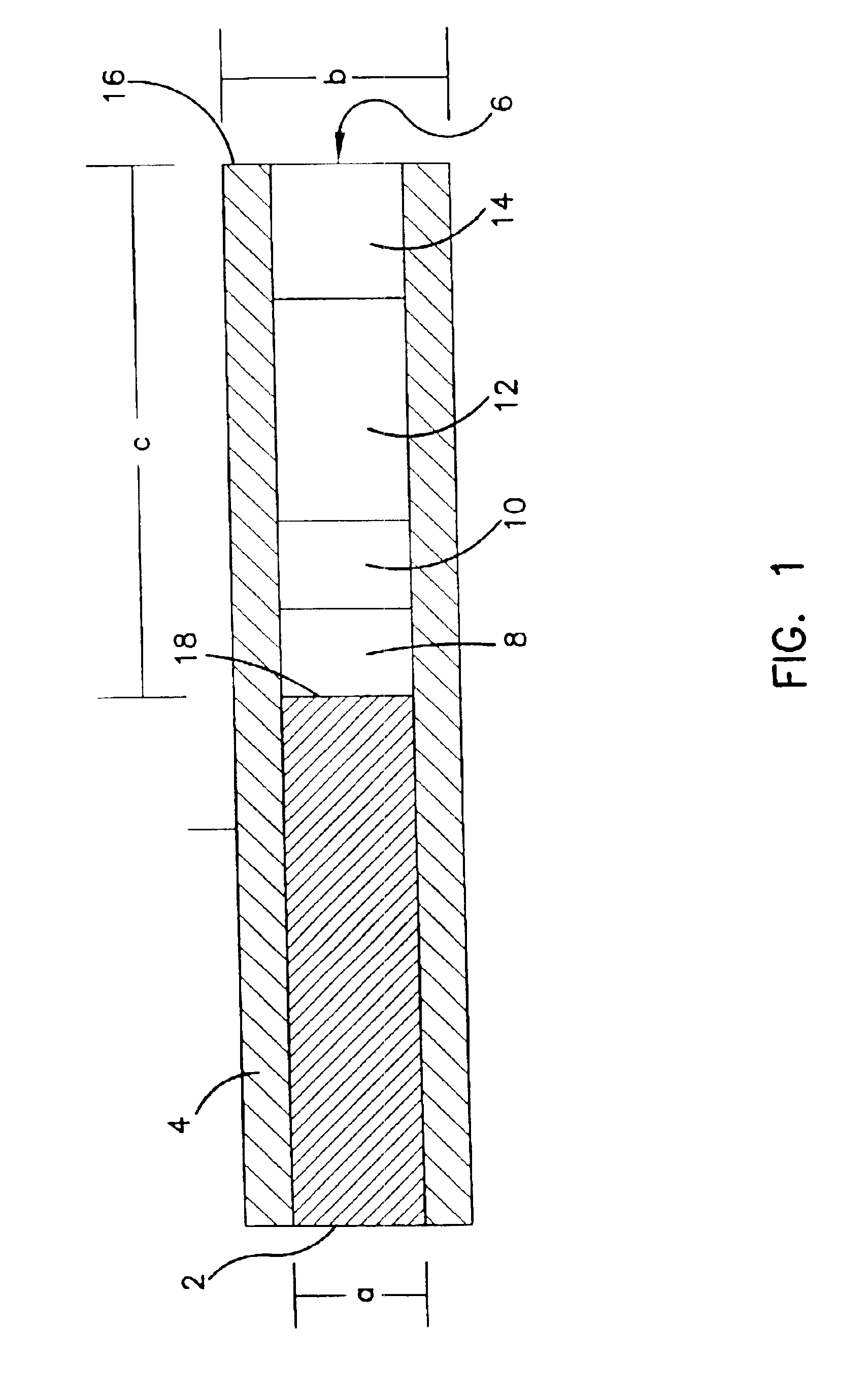
Subcutaneous glucose electrode
InactiveUS6881551B2Reduce transportationAccurate measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsConcentrations glucosePolyamide
A small diameter flexible electrode designed for subcutaneous in vivo amperometric monitoring of glucose is described. The electrode is designed to allow “one-point” in vivo calibration, i.e., to have zero output current at zero glucose concentration, even in the presence of other electroreactive species of serum or blood. The electrode is preferably three or four-layered, with the layers serially deposited within a recess upon the tip of a polyamide insulated gold wire. A first glucose concentration-to-current transducing layer is overcoated with an electrically insulating and glucose flux limiting layer (second layer) on which, optionally, an immobilized interference-eliminating horseradish peroxidase based film is deposited (third layer). An outer (fourth) layer is biocompatible.
Owner:THERASENSE
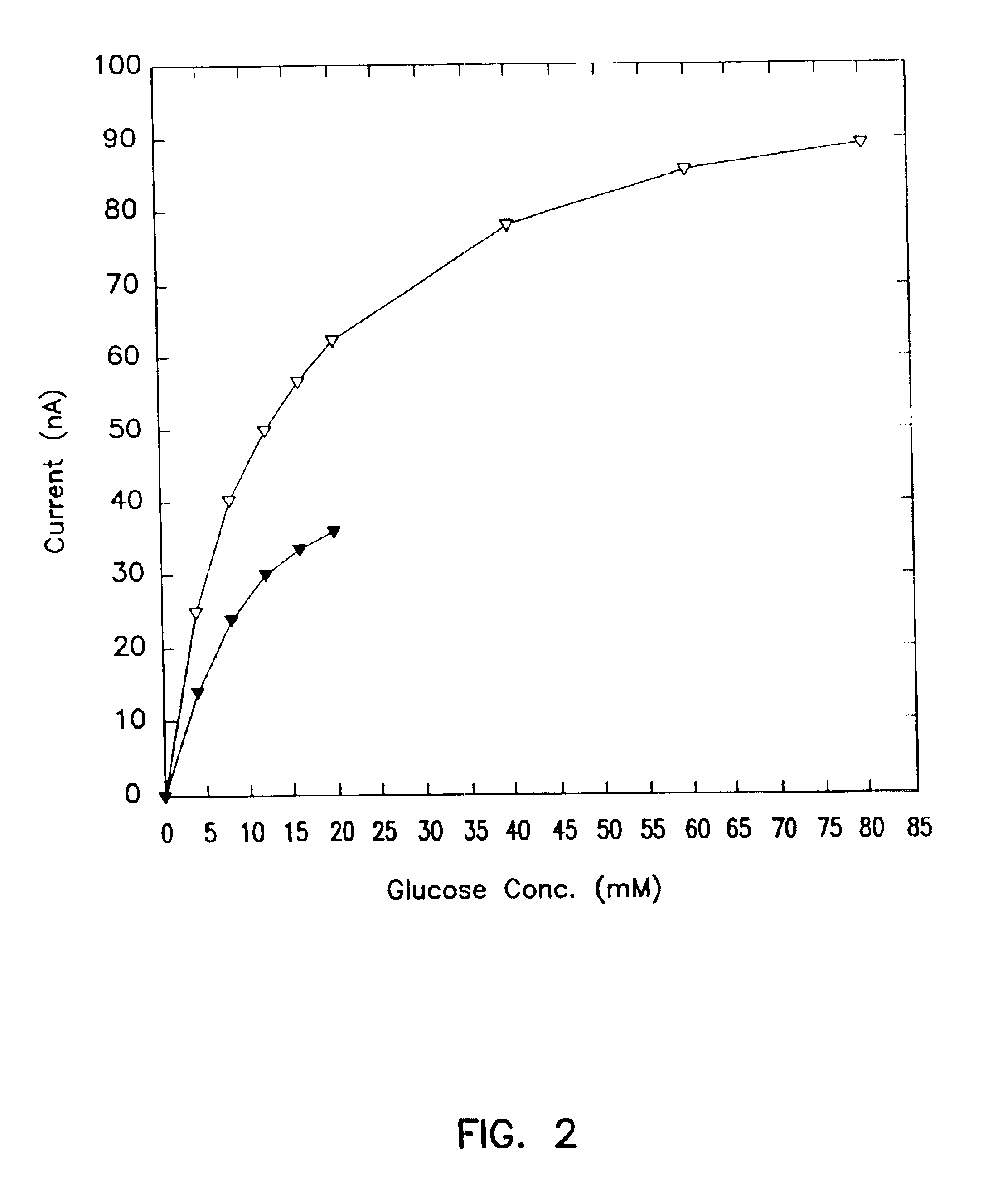
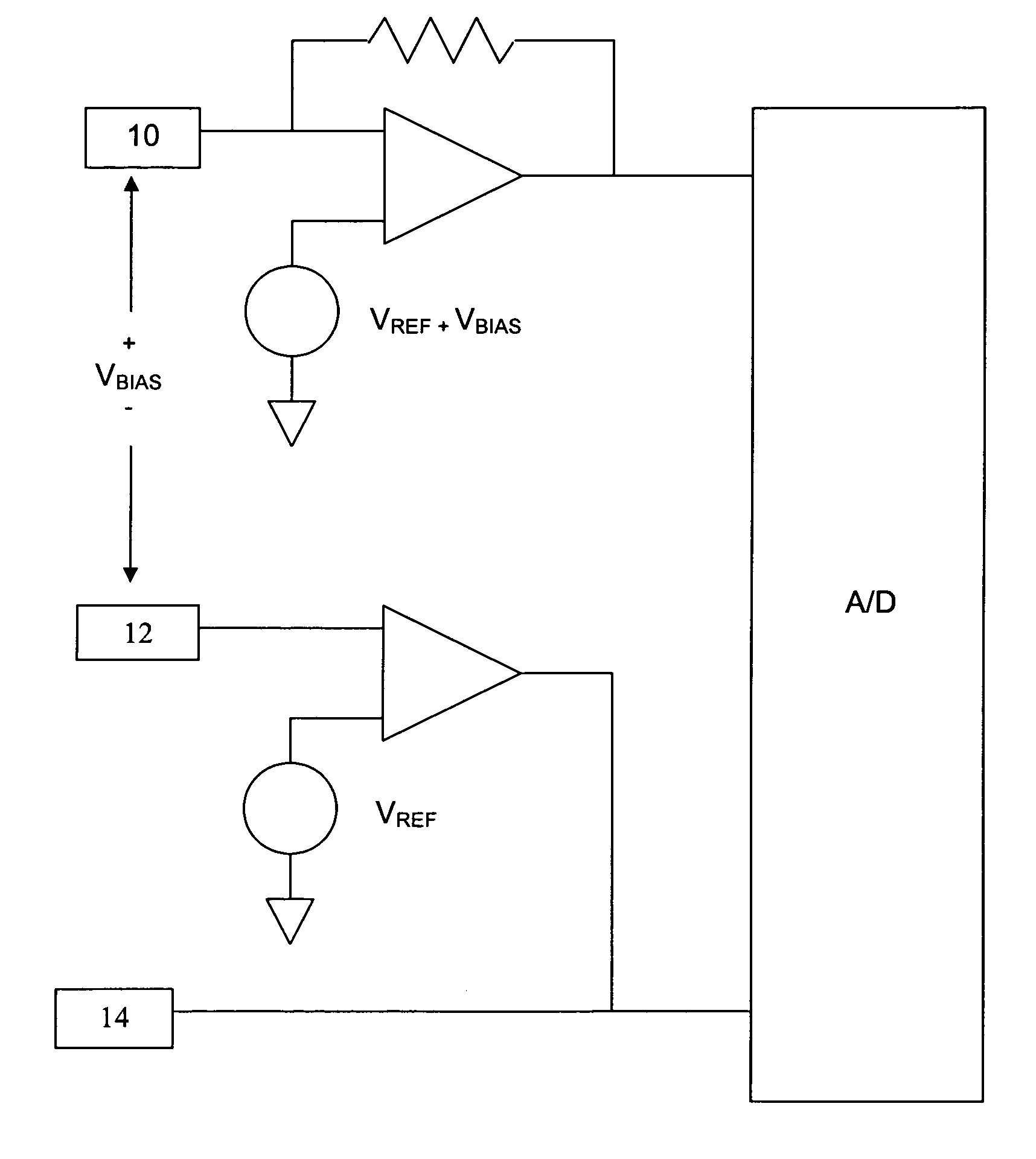
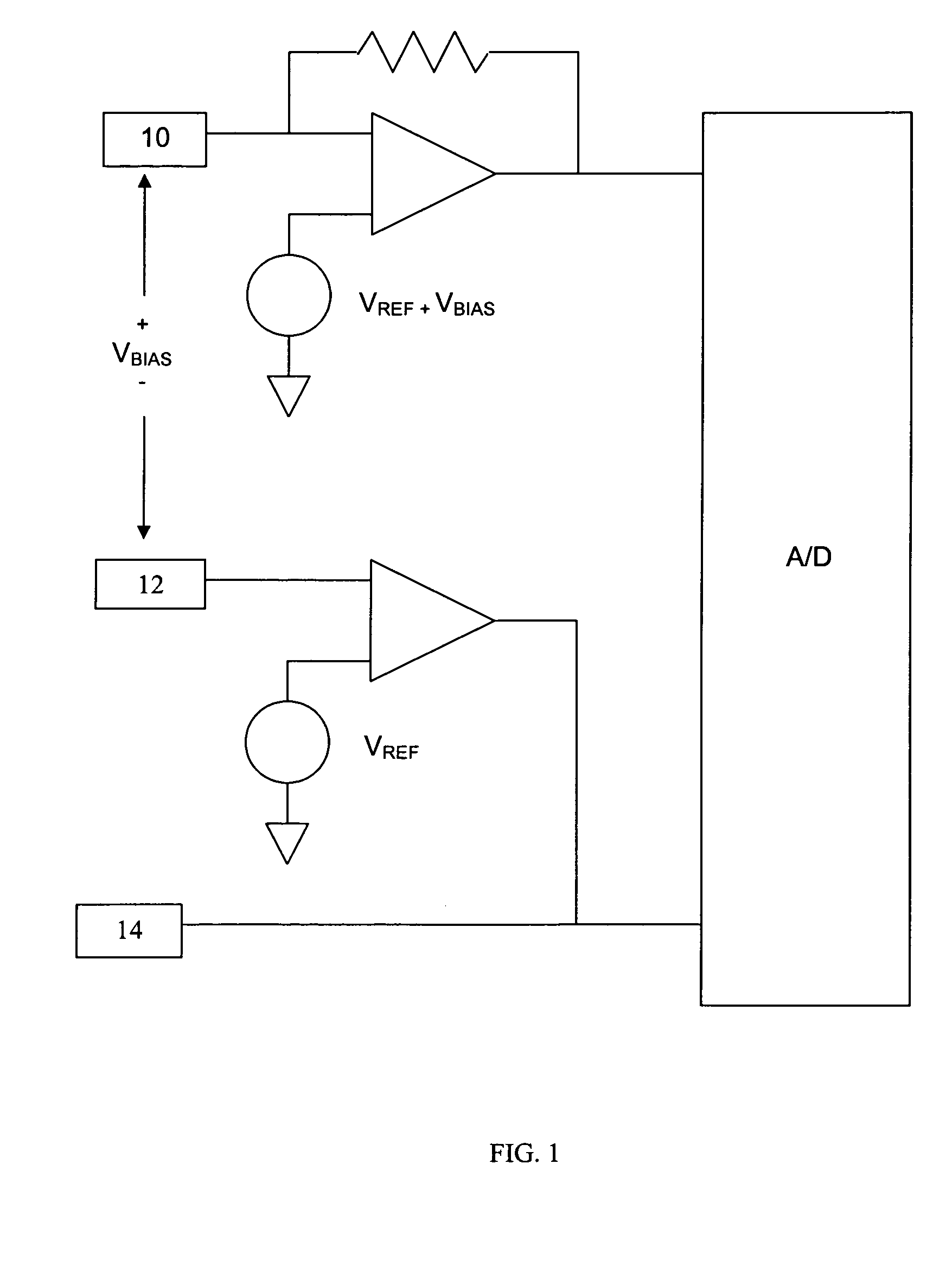
Systems and methods for improving electrochemical analyte sensors
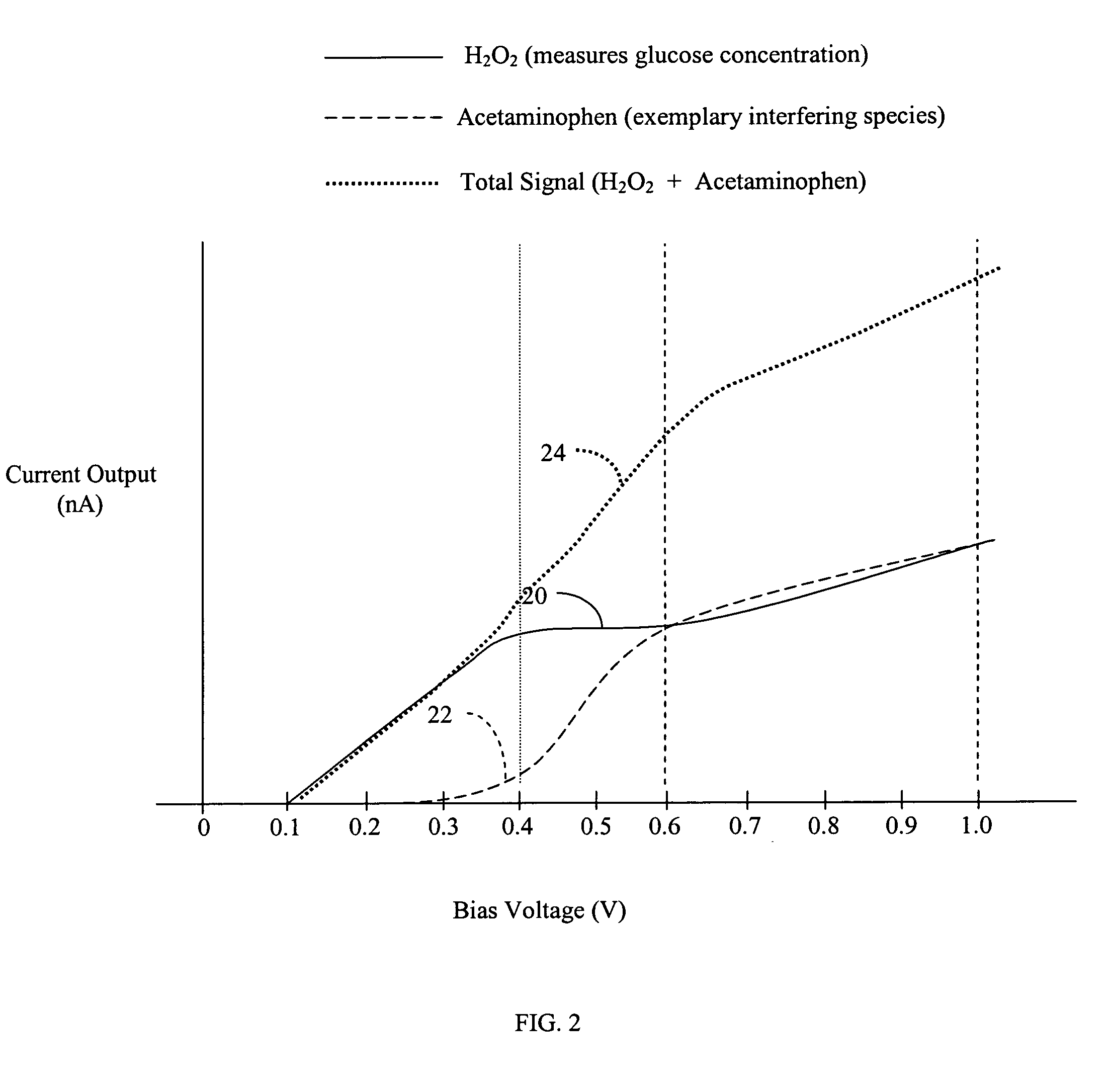
ActiveUS7081195B2Quality improvementReducing and eliminating effectImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteD-Glucose
An analyte-measuring device, particularly an electrochemical sensor, is provided for measuring current values at multiple bias potential settings to assess the quality of the analyte measurement, identify interference in the signal, and calculate substantially interference-free analyte concentration measurements. The device and method are suitable for calculating substantially interference-free analyte concentration measurements when glucose is the analyte and acetaminophen is an interfering species.
Owner:DEXCOM
In vivo biosensor apparatus and method of use
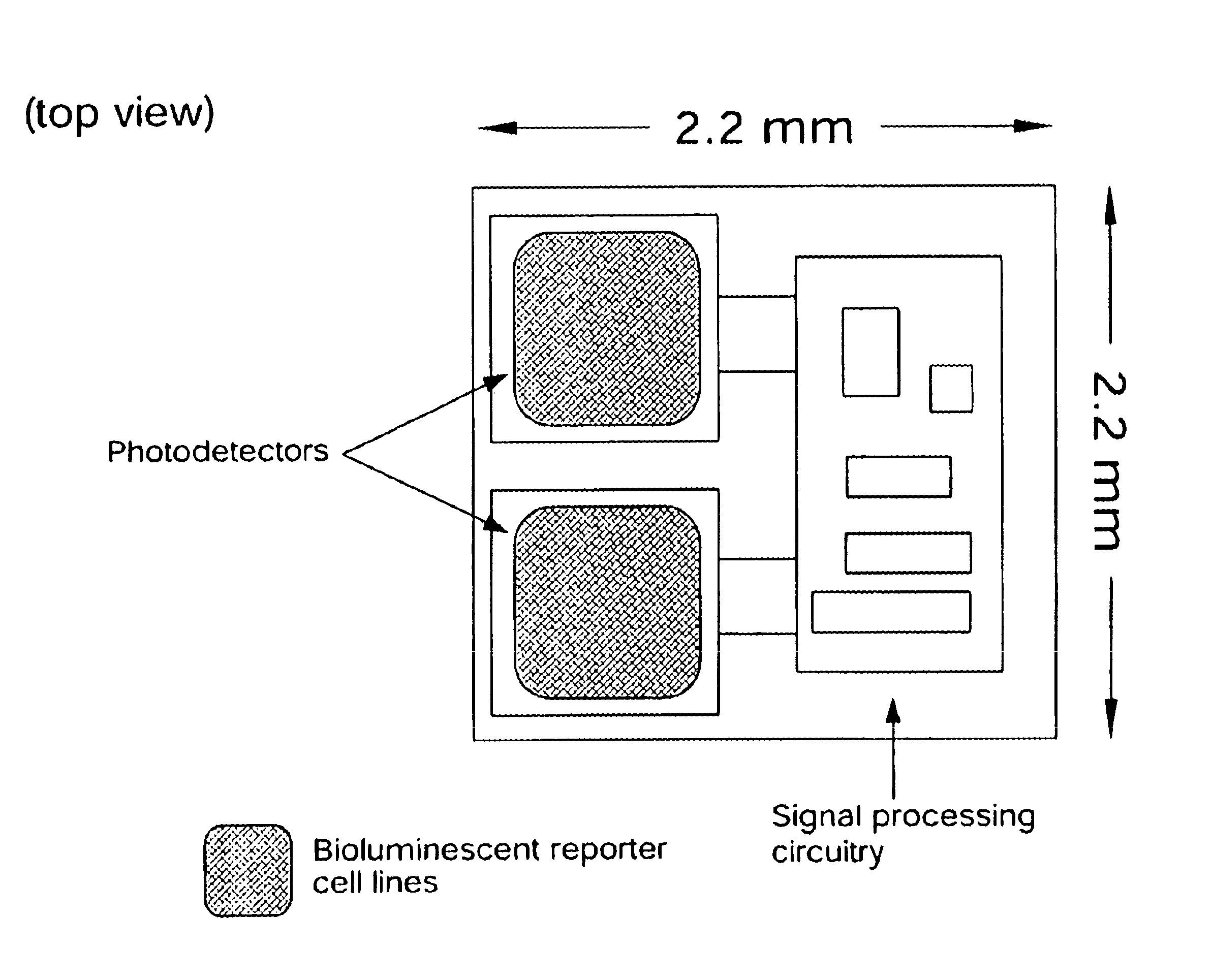
InactiveUS6673596B1Less can be administeredCost-effective administration of drugBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsIn vivoGenetically engineered
Disclosed are bioluminescent bioreporter integrated circuit devices that detect selected analytes in fluids when implanted in the body of an animal. The device comprises a bioreporter that has been genetically engineered to contain a nucleic acid segment that comprises a cis-activating response element that is responsive to the selected substance operably linked to a gene encoding a bioluminescent reporter polypeptide. In preferred embodiments, the target analyte is glucose, glucagons, or insulin. Exposure of the bioreporter to the target substance causes the response element to up-regulate the nucleic acid sequence encoding the reporter polypeptide to produce a luminescent response that is detected and quantitated. In illustrative embodiments, the bioreporter device is encapsulated on an integrated circuit that is capable of detecting the emitted light, processing the resultant signal, and then remotely reporting the results. Also disclosed are controlled drug delivery systems capable of being directly or indirectly controlled by the detection device that provide drugs such as insulin to the animal in reponse to the amount of target analyte present in the body fluids.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND +1
Organo luminescent semiconductor nanocrystal probes for biological applications and process for making and using such probes
A semiconductor nanocrystal compound is described capable of linking to an affinity molecule. The compound comprises (1) a semiconductor nanocrystal capable of emitting electromagnetic radiation and / or absorbing energy, and / or scattering or diffracting electromagnetic radiation-when excited by an electromagnetic radiation source or a particle beam; and (2) at least one linking agent, having a first portion linked to the semiconductor nanocrystal and a second portion capable of linking to an affity molecule. The compound is linked to an affinity molecule to form a semiconductor nanocrystal probe capable of bonding with a detectable substance. Subsequent exposure to excitation energy will excite the semiconductor nanocrystal in he probe, causing the emission of electromagnetic radiation. Further described are processes for respectively: making the semiconductor nanocrystal compound; making the semiconductor nanocrystal probe; and using the probe to determine the presence of a detectable substance in a material.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method of etching patterned layers useful as masking during subsequent etching or for damascene structures
InactiveUS6080529APhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConductive polymerOrganic base
A first embodiment of the present invention pertains to a method of patterning a semiconductor device conductive feature while permitting easy removal of any residual masking layer which remains after completion of the etching process. A multi-layered masking structure is used which includes a layer of high-temperature organic-based masking material overlaid by either a patterned layer of inorganic masking material or by a layer of patterned high-temperature imageable organic masking material. The inorganic masking material is used to transfer a pattern to the high-temperature organic-based masking material and is then removed. The high-temperature organic-based masking material is used to transfer the pattern and then may be removed if desired. This method is also useful in the pattern etching of aluminum, even though aluminum can be etched at lower temperatures. A second embodiment of the present invention pertains to a specialized etch chemistry useful in the patterning of organic polymeric layers such as low k dielectrics, or other organic polymeric interfacial layers. This etch chemistry is useful for mask opening during the etch of a conductive layer or is useful in etching damascene structures where a metal fill layer is applied over the surface of a patterned organic-based dielectric layer. The etch chemistry provides for the use of etchant plasma species which minimize oxygen, fluorine, chlorine, and bromine content.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Reactive formation of dielectric layers and protection of organic layers in organic semiconductor device fabrication
InactiveUS6842657B1Use is harmfulDamage is causedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic layerOrganic semiconductor
In one embodiment of the invention, a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device comprises the steps of: a) providing an organic semiconductor layer; b) depositing a reactive species on a portion of the organic semiconductor layer; and c) reacting the reactive species with the portion of the organic layer to form a dielectric layer.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Optical fiber with quantum dots
Holey optical fibers (e.g. photonic fibers, random-hole fibers) are fabricated with quantum dots disposed in the holes. The quantum dots can provide light amplification and sensing functions, for example. When used for sensing, the dots will experience altered optical properties (e.g. altered fluorescence or absorption wavelength) in response to certain chemicals, biological elements, radiation, high energy particles, electrical or magnetic fields, or thermal / mechanical deformations. Since the dots are disposed in the holes, the dots interact with the evanescent field of core-confined light. Quantum dots can be damaged by high heat, and so typically cannot be embedded within conventional silica optical fibers. In the present invention, dots can be carried into the holes by a solvent at room temperature. The present invention also includes solid glass fibers made of low melting point materials (e.g. phosphate glass, lead oxide glass) with embedded quantum dots.
Owner:LAMBDA LABORATORY INSTRUMENTS +1
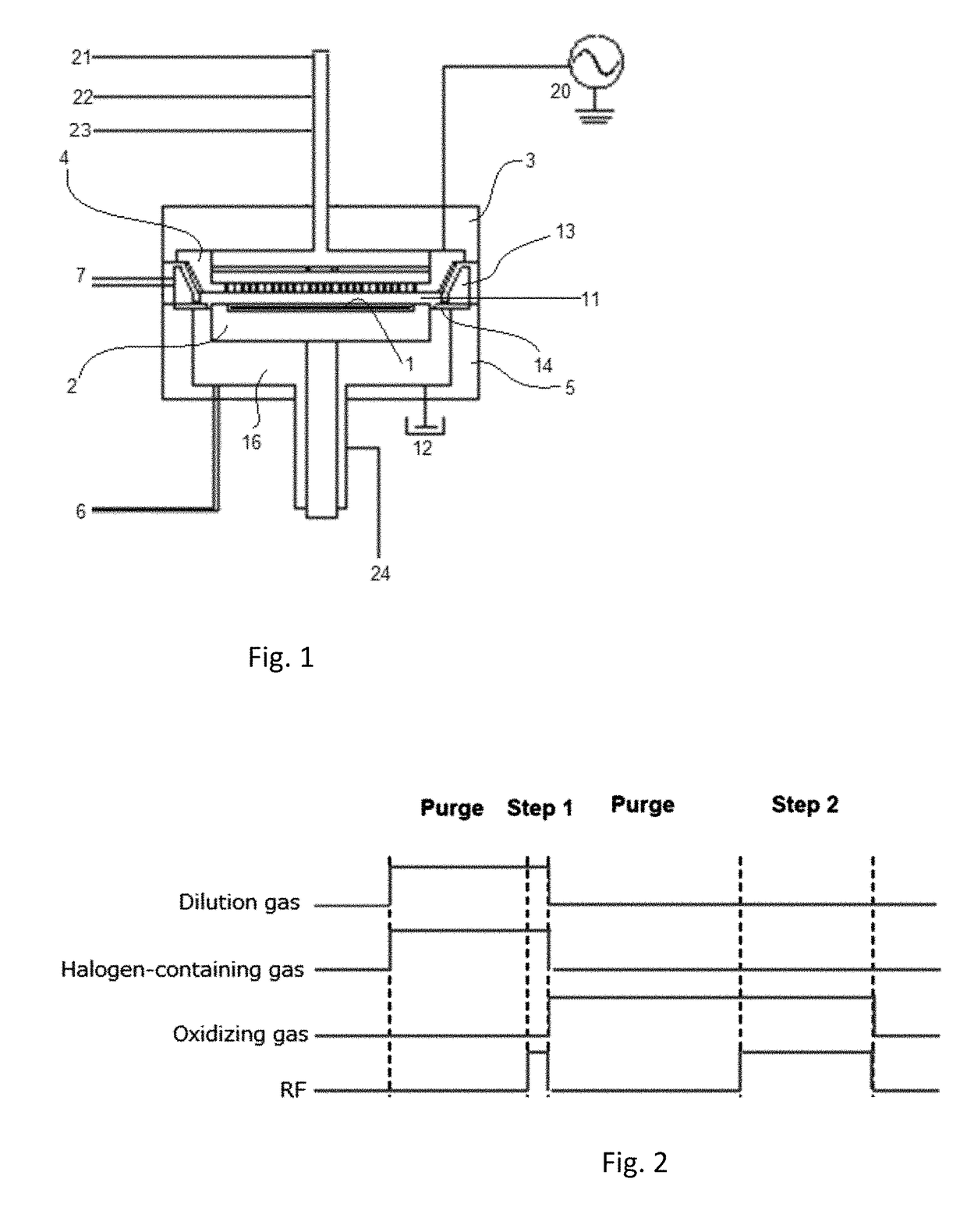
Enhancement of remote plasma source clean for dielectric films
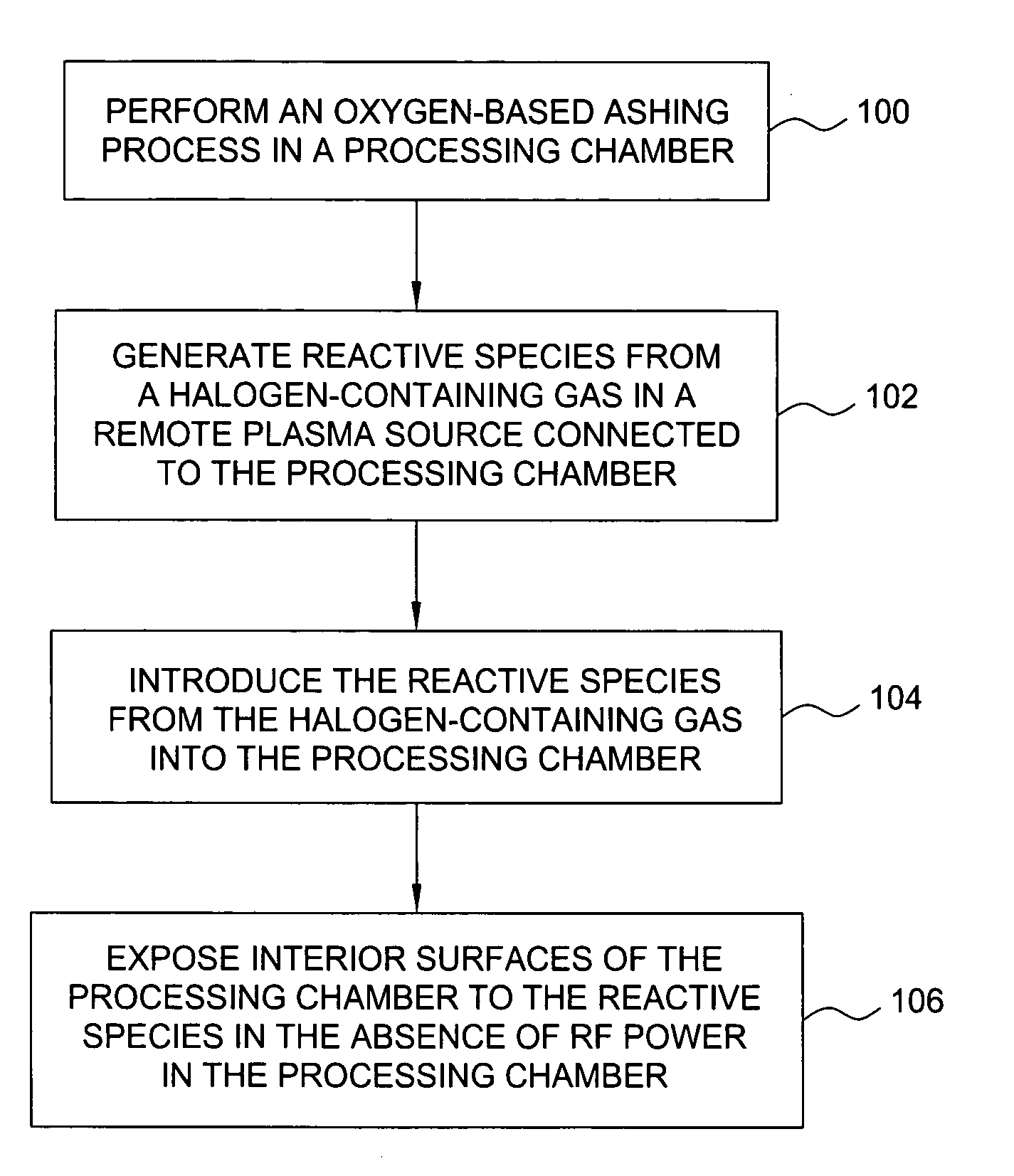
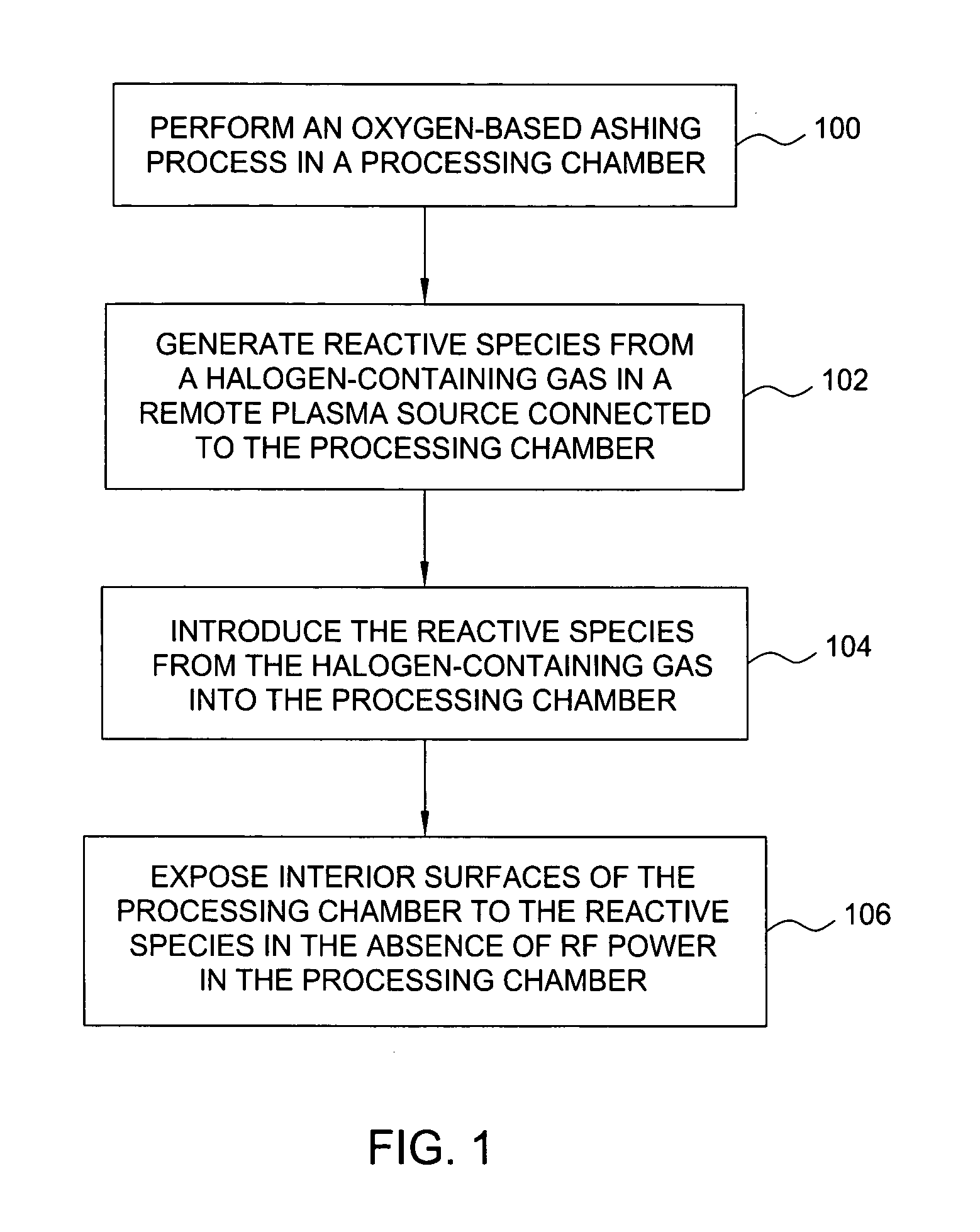
Methods for cleaning semiconductor processing chambers used to process carbon-containing films, such as amorphous carbon films, barrier films comprising silicon and carbon, and low dielectric constant films including silicon, oxygen, and carbon are provided. The methods include using a remote plasma source to generate reactive species that clean interior surfaces of a processing chamber in the absence of RF power in the chamber. The reactive species are generated from an oxygen-containing gas, such as O2, and / or a halogen-containing gas, such as NF3. An oxygen-based ashing process may also be used to remove carbon deposits from the interior surfaces of the chamber before the chamber is exposed to the reactive species from the remote plasma source.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Atomic layer deposition method of depositing an oxide on a substrate
The invention includes atomic layer deposition methods of depositing an oxide on a substrate. In one implementation, a substrate is positioned within a deposition chamber. A first species is chemisorbed onto the substrate to form a first species monolayer within the deposition chamber from a gaseous precursor. The chemisorbed first species is contacted with remote plasma oxygen derived at least in part from at least one of O2 and O3 and with remote plasma nitrogen effective to react with the first species to form a monolayer comprising an oxide of a component of the first species monolayer. The chemisorbing and the contacting with remote plasma oxygen and with remote plasma nitrogen are successively repeated effective to form porous oxide on the substrate. Other aspects and implementations are contemplated.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
High stress nitride film and method for formation thereof
ActiveUS20060199357A1Increase the tensile stressSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDopantNitrogen
A silicon nitride film is formed on a substrate in a reaction chamber by introducing trisilane and a reactive nitrogen species into the chamber in separate pulses. A carbon precursor gas is also flowed into the chamber during introduction of the trisilane and / or during introduction of the reactive nitrogen species, or in pulses separate from the trisilane and reactive nitrogen species pulses. The carbon is used as a dopant in the silicon nitride film and advantageously allows a high stress silicon nitride film to be formed.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Curing methods for silicon dioxide thin films deposited from alkoxysilane precursor with harp ii process
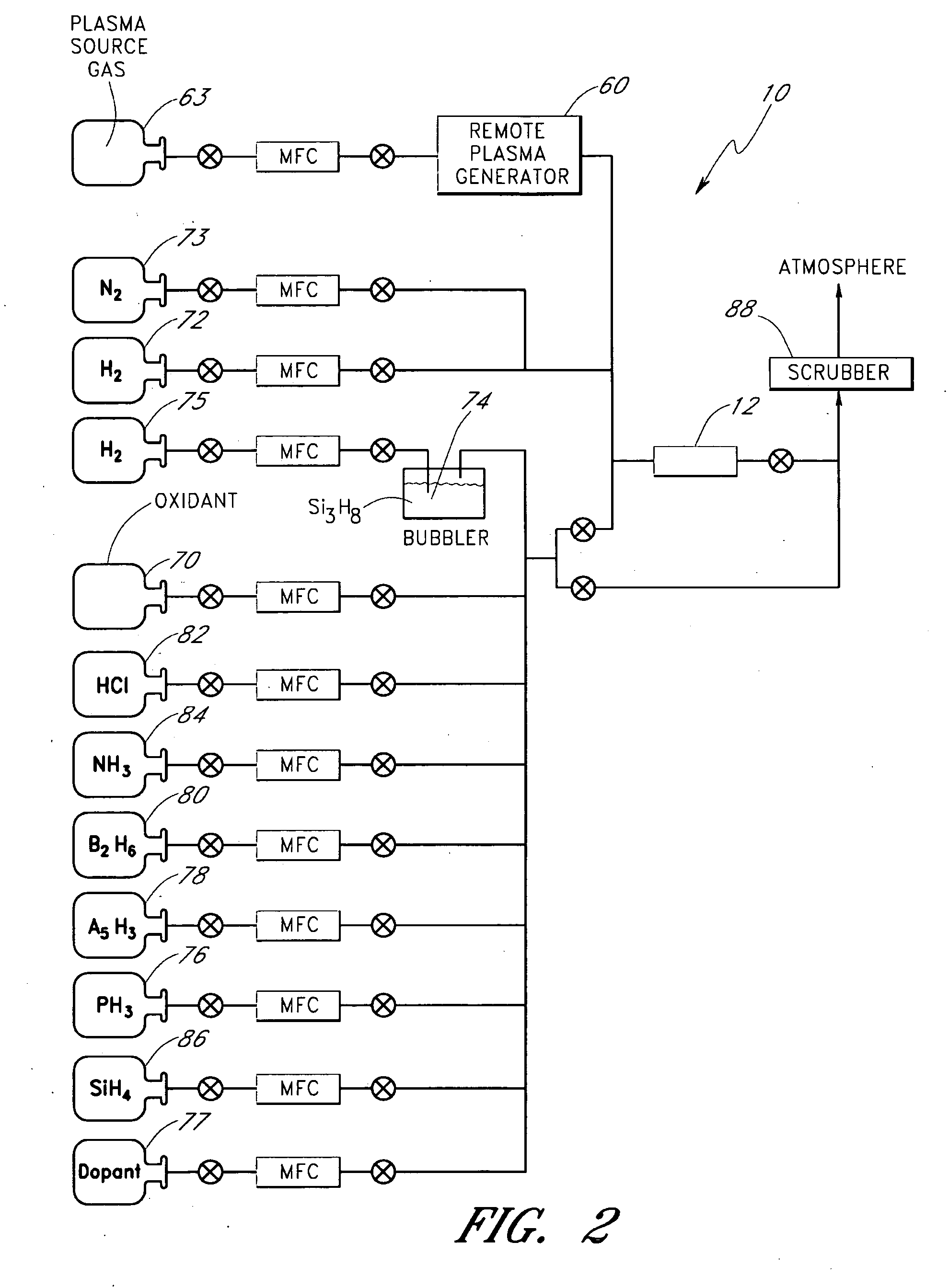
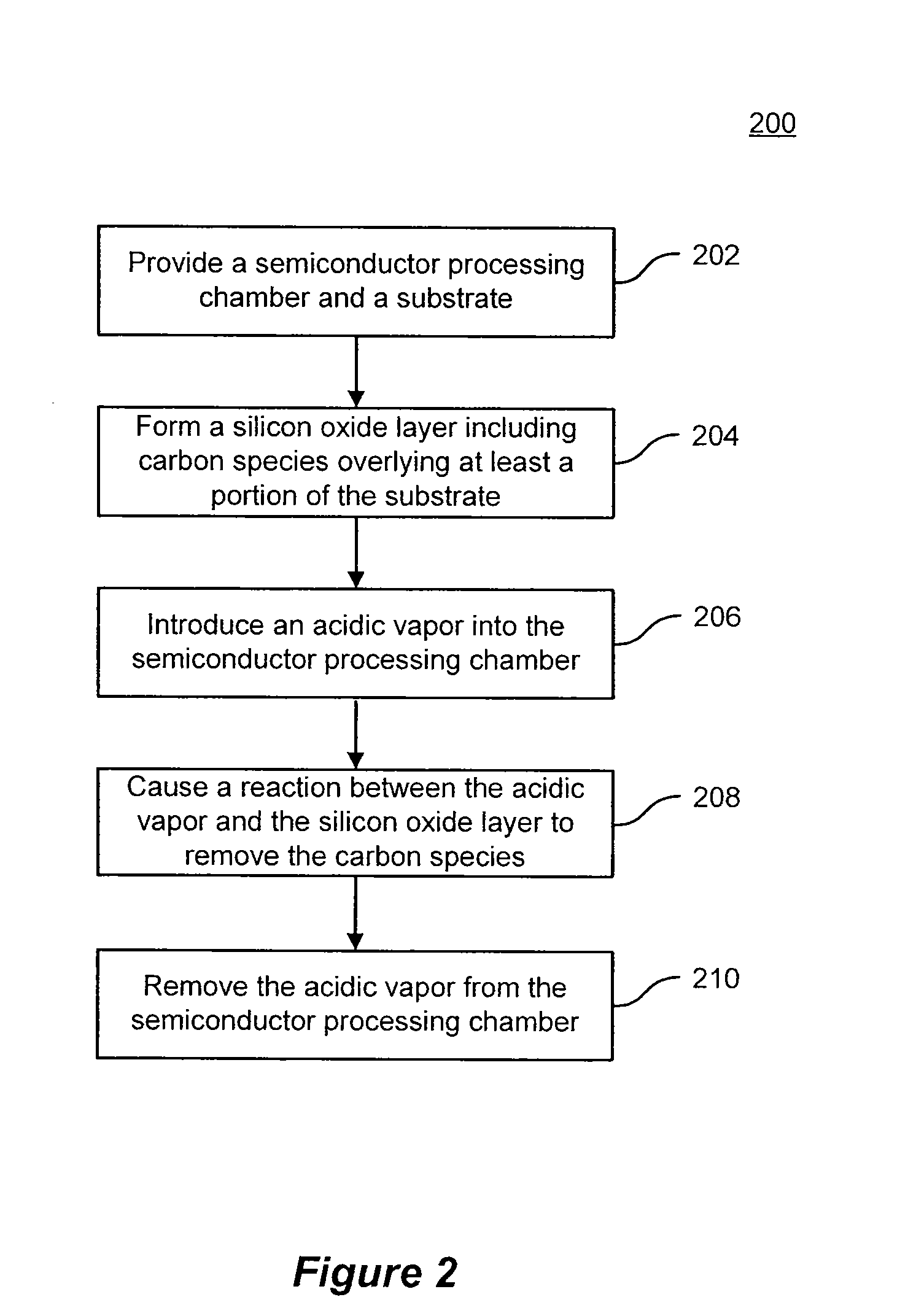
Methods of curing a silicon oxide layer on a substrate are provided. The methods may include the processes of providing a semiconductor processing chamber and a substrate and forming an silicon oxide layer overlying at least a portion of the substrate, the silicon oxide layer including carbon species as a byproduct of formation. The methods may also include introducing an acidic vapor into the semiconductor processing chamber, the acidic vapor reacting with the silicon oxide layer to remove the carbon species from the silicon oxide layer. The methods may also include removing the acidic vapor from the semiconductor processing chamber. Systems to deposit a silicon oxide layer on a substrate are also described.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Systems and methods for thin-film deposition of metal oxides using excited nitrogen-oxygen species
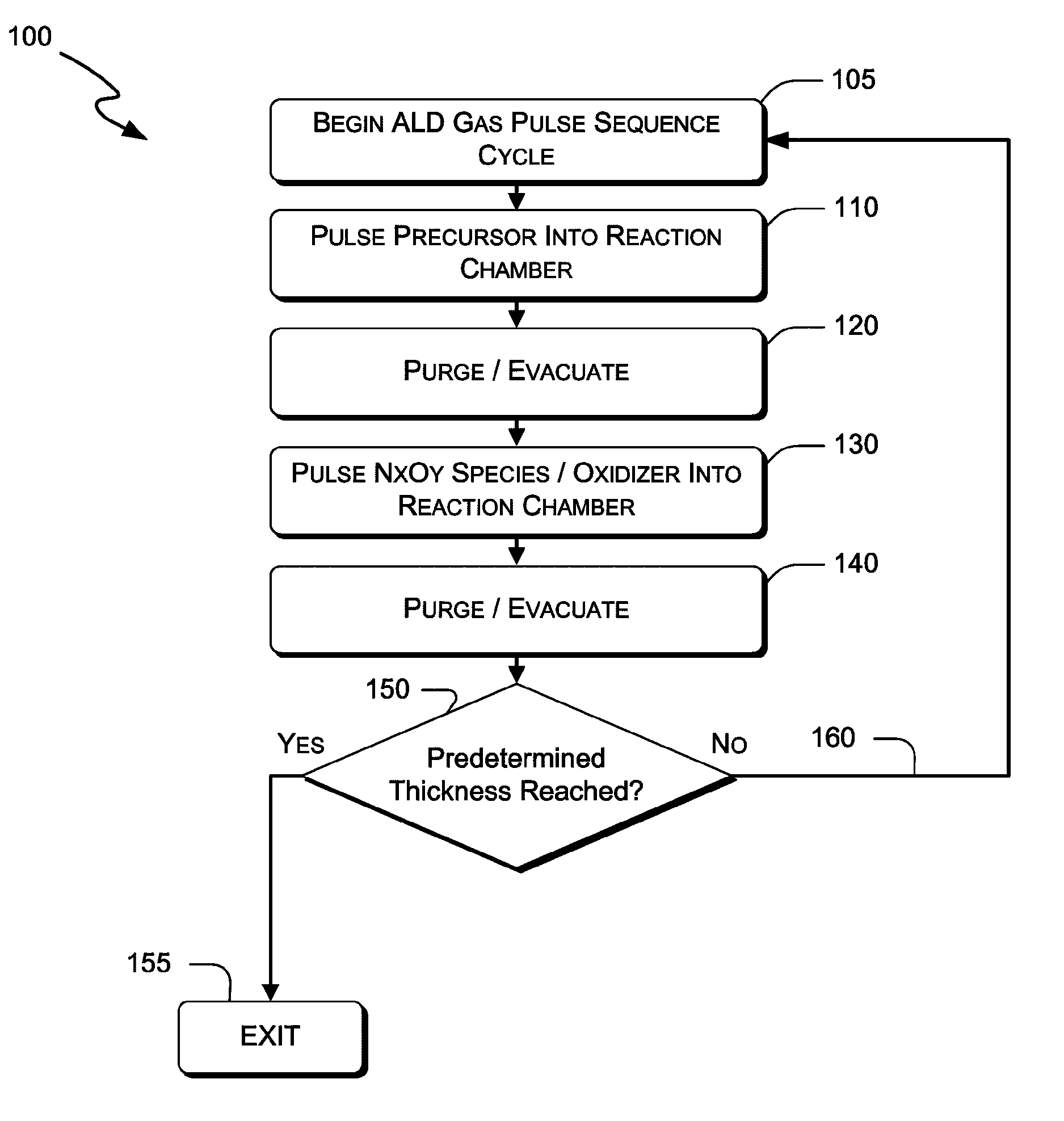
ActiveUS20110070380A1Improve deposition efficiencyImprove uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical discharge ozone preparationNitrogenOxygen
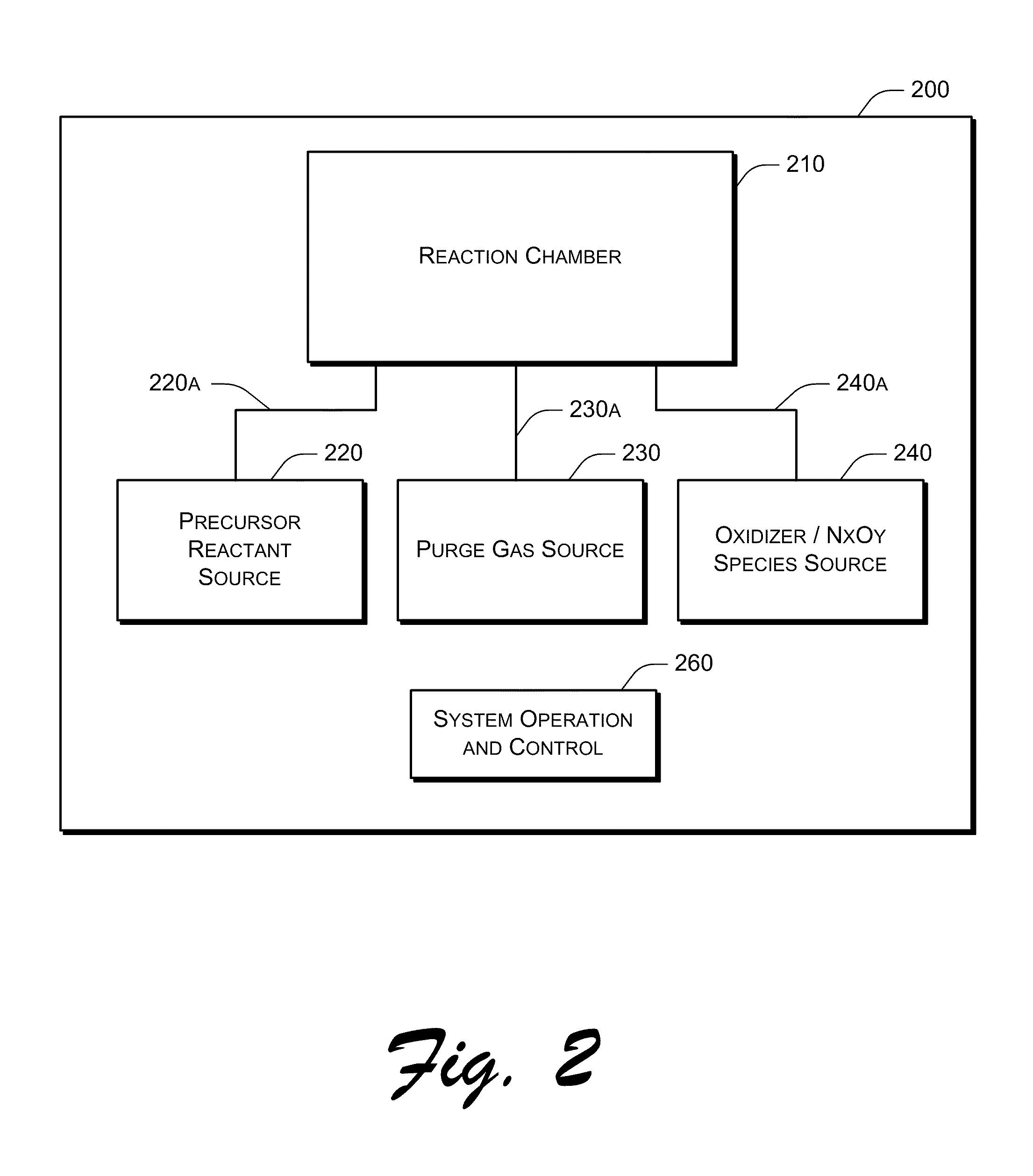
Systems and methods are delineated which, among other things, are for depositing a film on a substrate that is within a reaction chamber. In an exemplary method, the method may comprise applying an atomic layer deposition cycle to the substrate, wherein the cycle may comprise exposing the substrate to a precursor gas for a precursor pulse interval and then removing the precursor gas thereafter, and exposing the substrate to an oxidizer comprising an oxidant gas and a nitrogen-containing species gas for an oxidation pulse interval and then removing the oxidizer thereafter. Aspects of the present invention utilize molecular and excited nitrogen-oxygen radical / ionic species in possible further combination with oxidizers such as ozone. Embodiments of the present invention also include electronic components and systems that include devices fabricated with methods consistent with the present invention.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
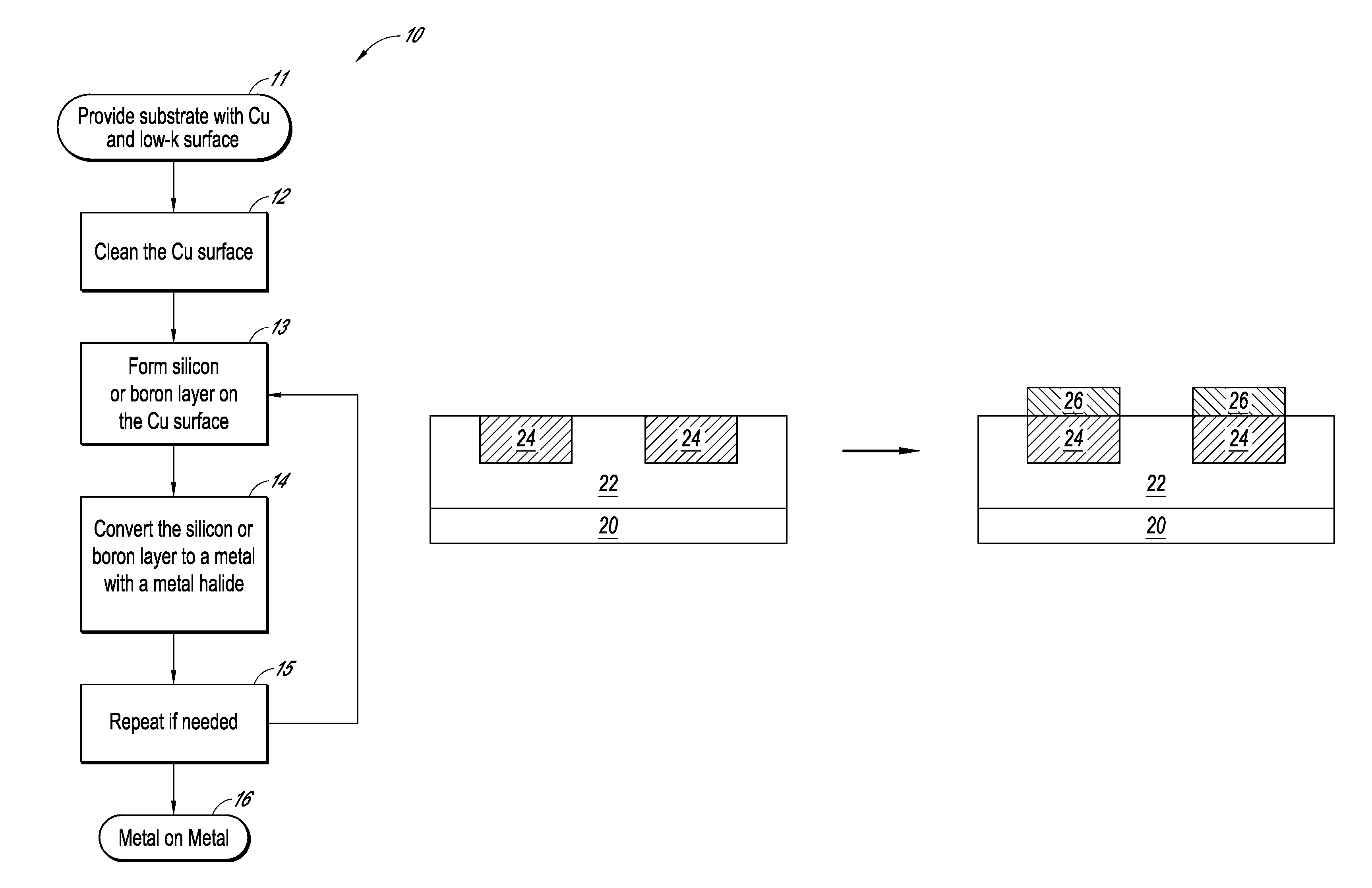
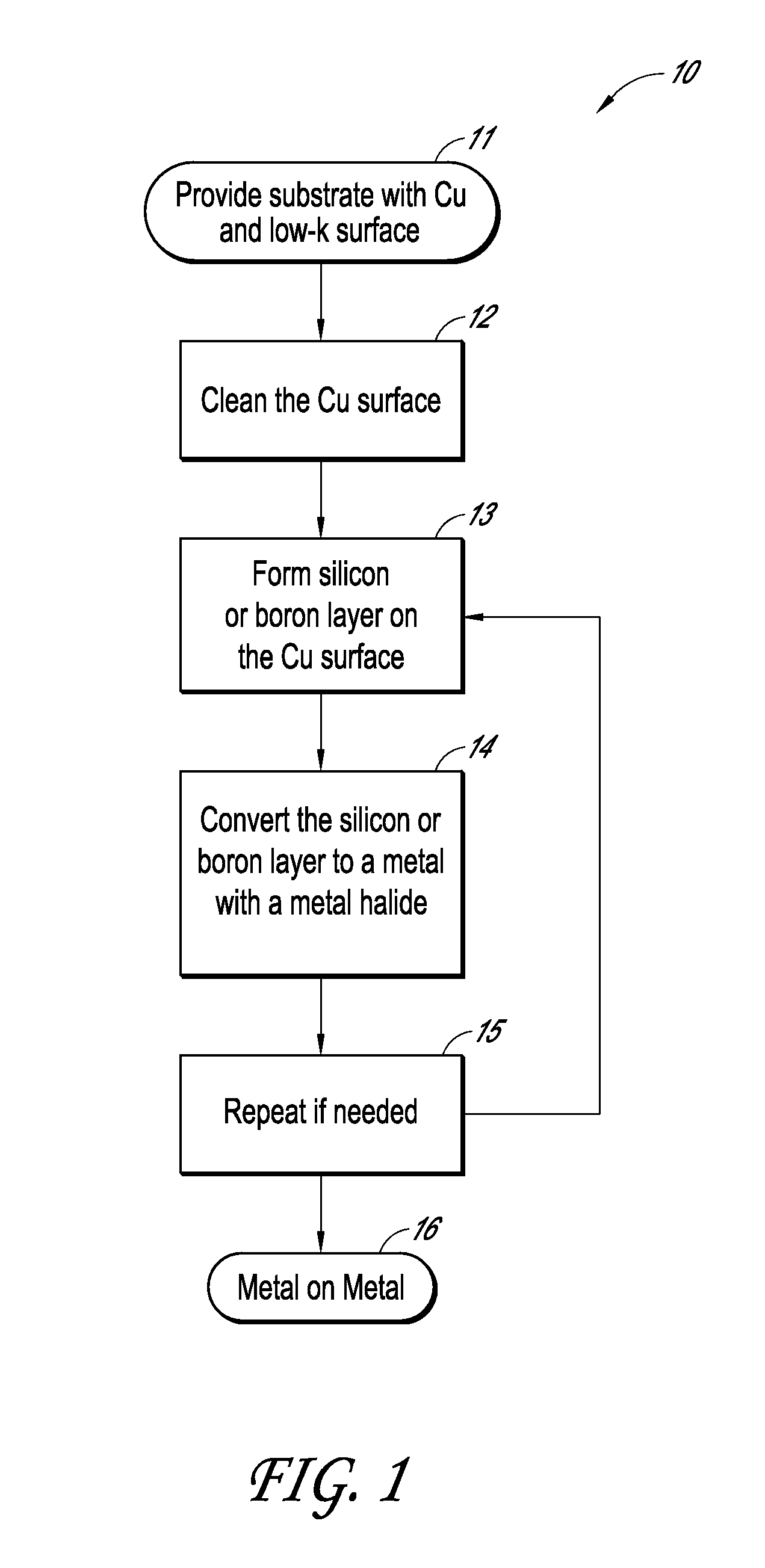
Selective formation of metallic films on metallic surfaces
ActiveUS8956971B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDeposition temperatureCopper
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
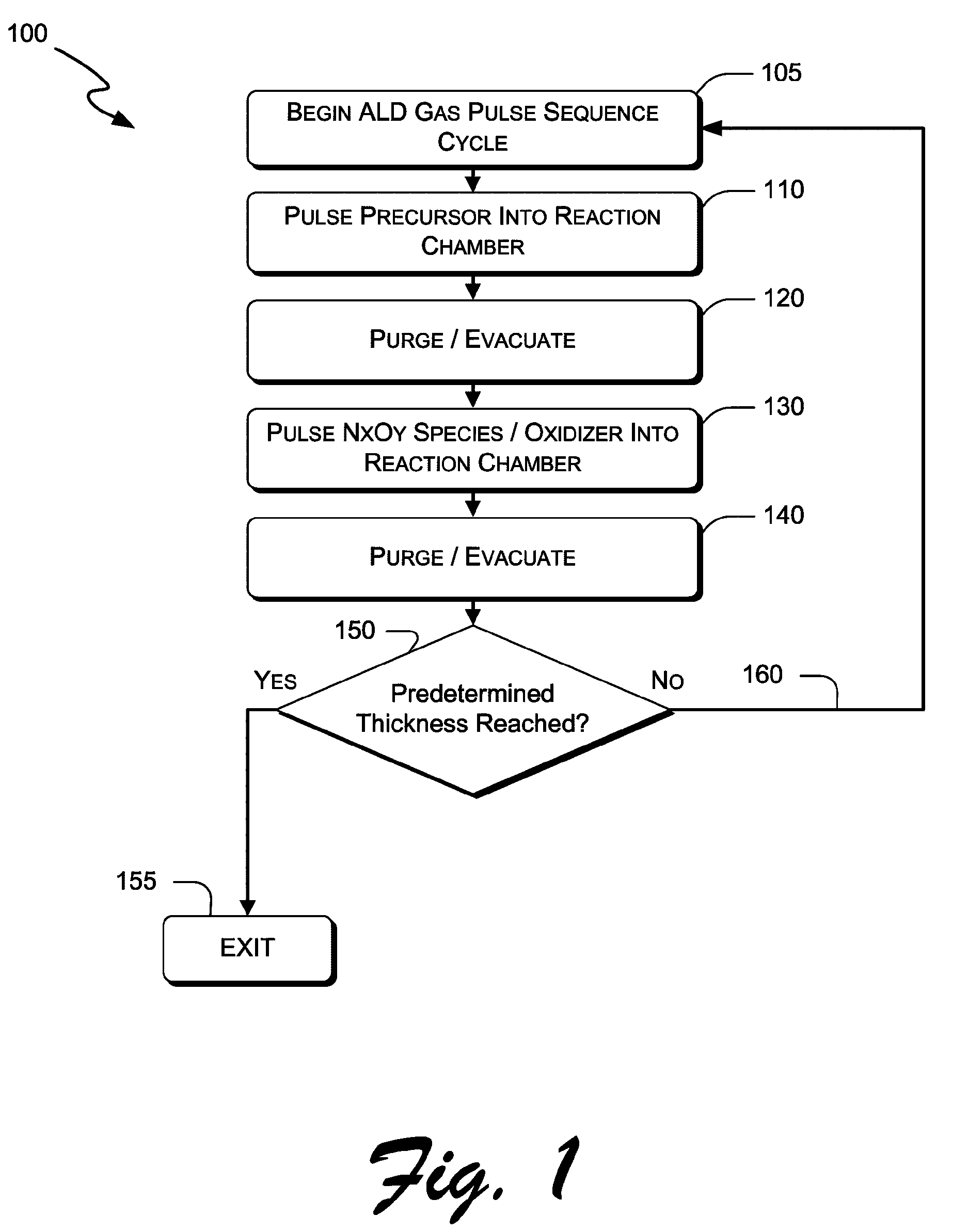
Systems and methods for thin-film deposition of metal oxides using excited nitrogen—oxygen species
ActiveUS8883270B2Improve deposition efficiencyEnhance growth rate and uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical discharge ozone preparationOxygenAtomic layer deposition
Systems and methods are delineated which, among other things, are for depositing a film on a substrate that is within a reaction chamber. In an exemplary method, the method may comprise applying an atomic layer deposition cycle to the substrate, wherein the cycle may comprise exposing the substrate to a precursor gas for a precursor pulse interval and then removing the precursor gas thereafter, and exposing the substrate to an oxidizer comprising an oxidant gas and a nitrogen-containing species gas for an oxidation pulse interval and then removing the oxidizer thereafter. Aspects of the present invention utilize molecular and excited nitrogen-oxygen radical / ionic species in possible further combination with oxidizers such as ozone. Embodiments of the present invention also include electronic components and systems that include devices fabricated with methods consistent with the present invention.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
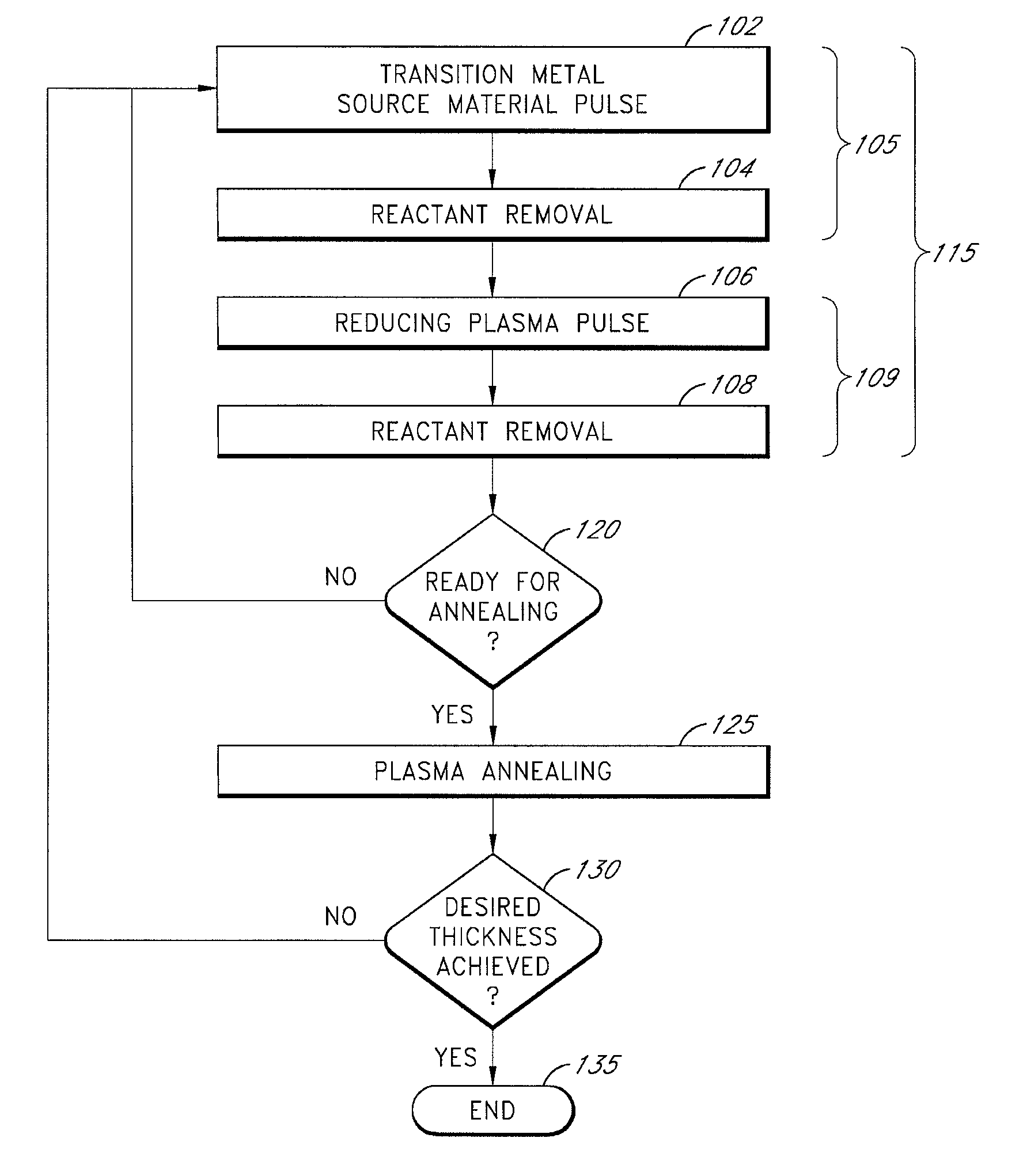
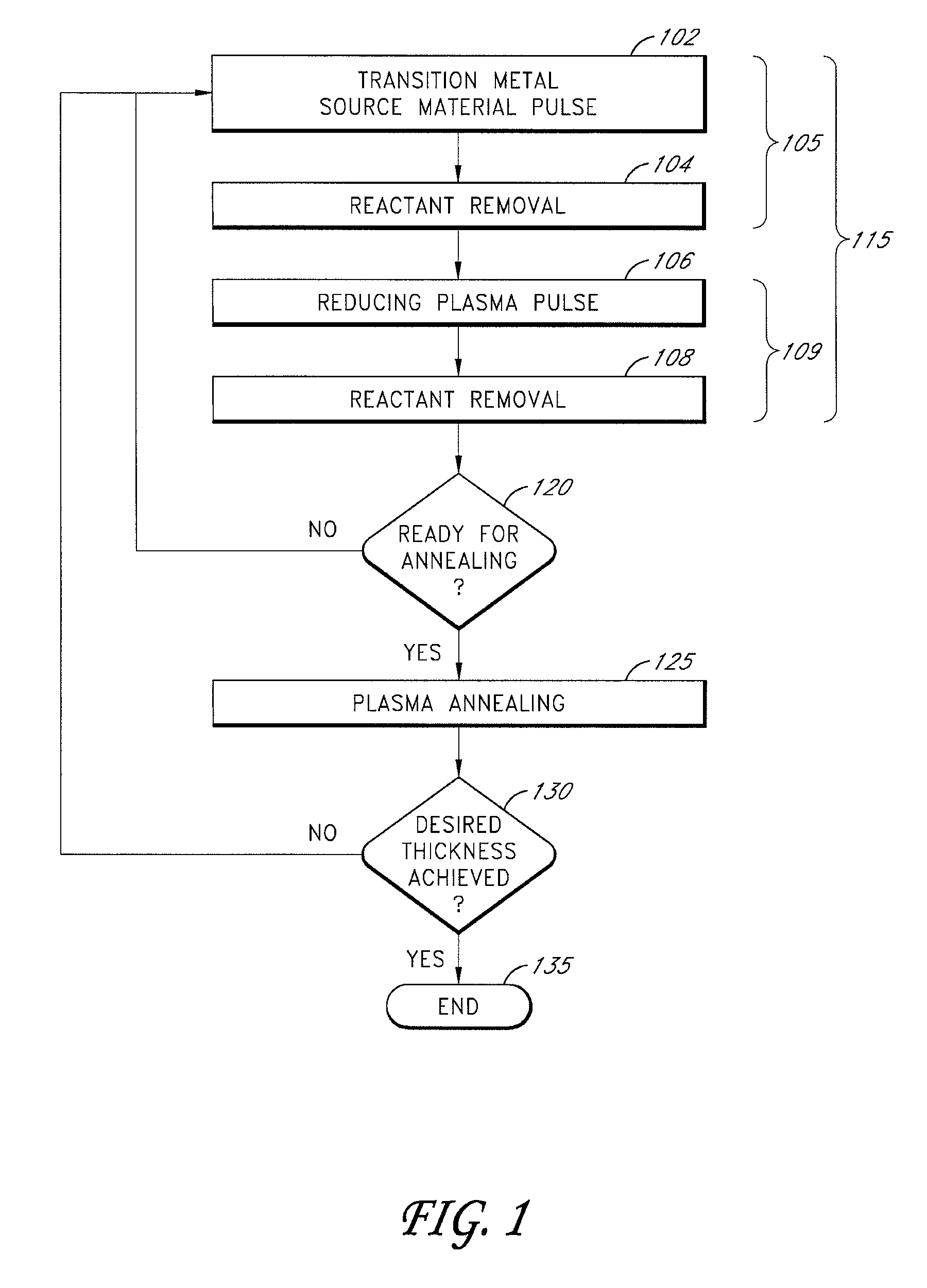
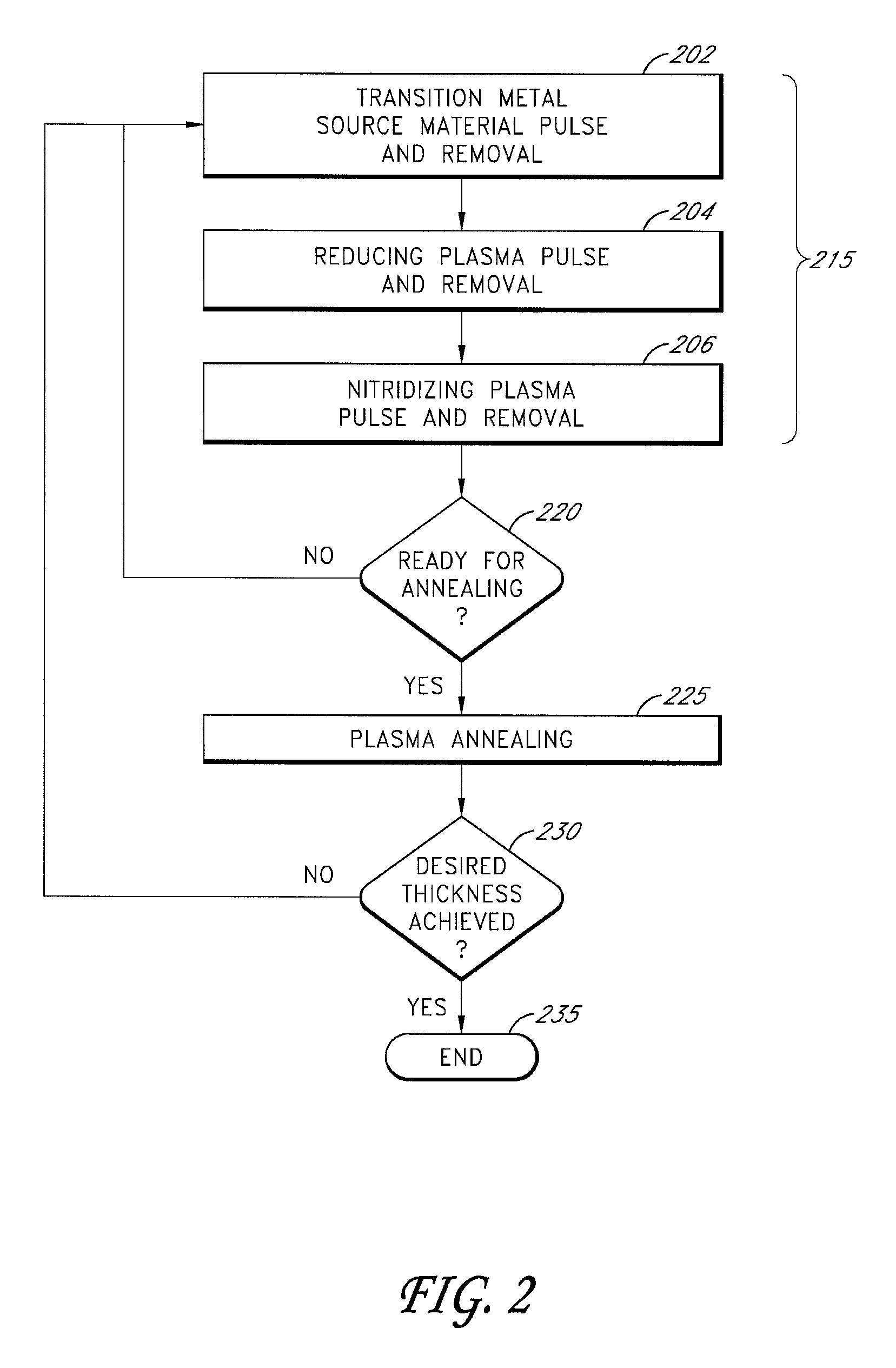
Periodic plasma annealing in an ALD-type process
ActiveUS7713874B2Increase probabilityReduce susceptibility to oxidationPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseVapor phase
Methods for performing periodic plasma annealing during atomic layer deposition are provided along with structures produced by such methods. The methods include contacting a substrate with a vapor-phase pulse of a metal source chemical and one or more plasma-excited reducing species for a period of time. Periodically, the substrate is contacted with a vapor phase pulse of one or more plasma-excited reducing species for a longer period of time. The steps are repeated until a metal thin film of a desired thickness is formed over the substrate.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method for silicon based dielectric chemical vapor deposition
InactiveUS20060286818A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricCelsius Degree
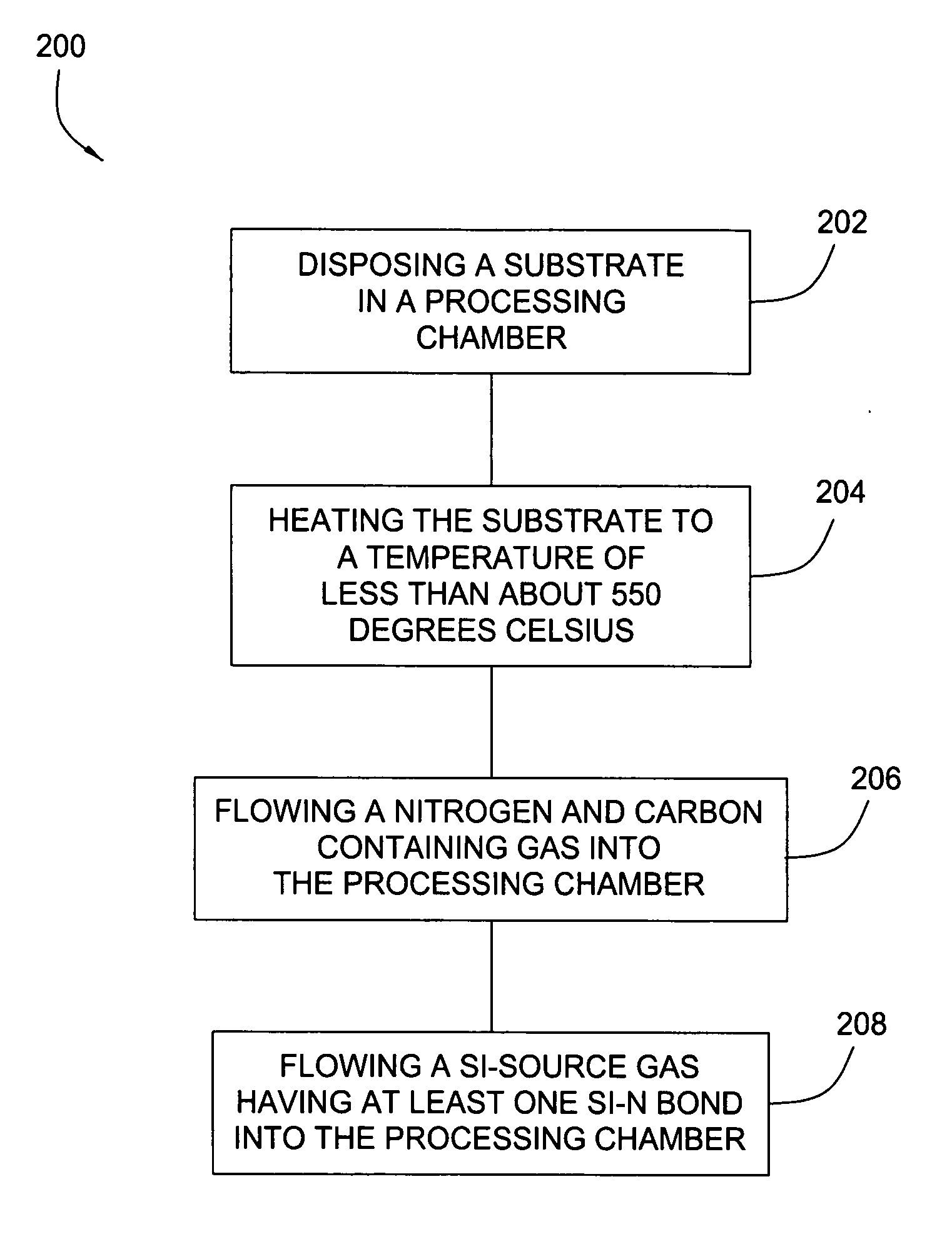
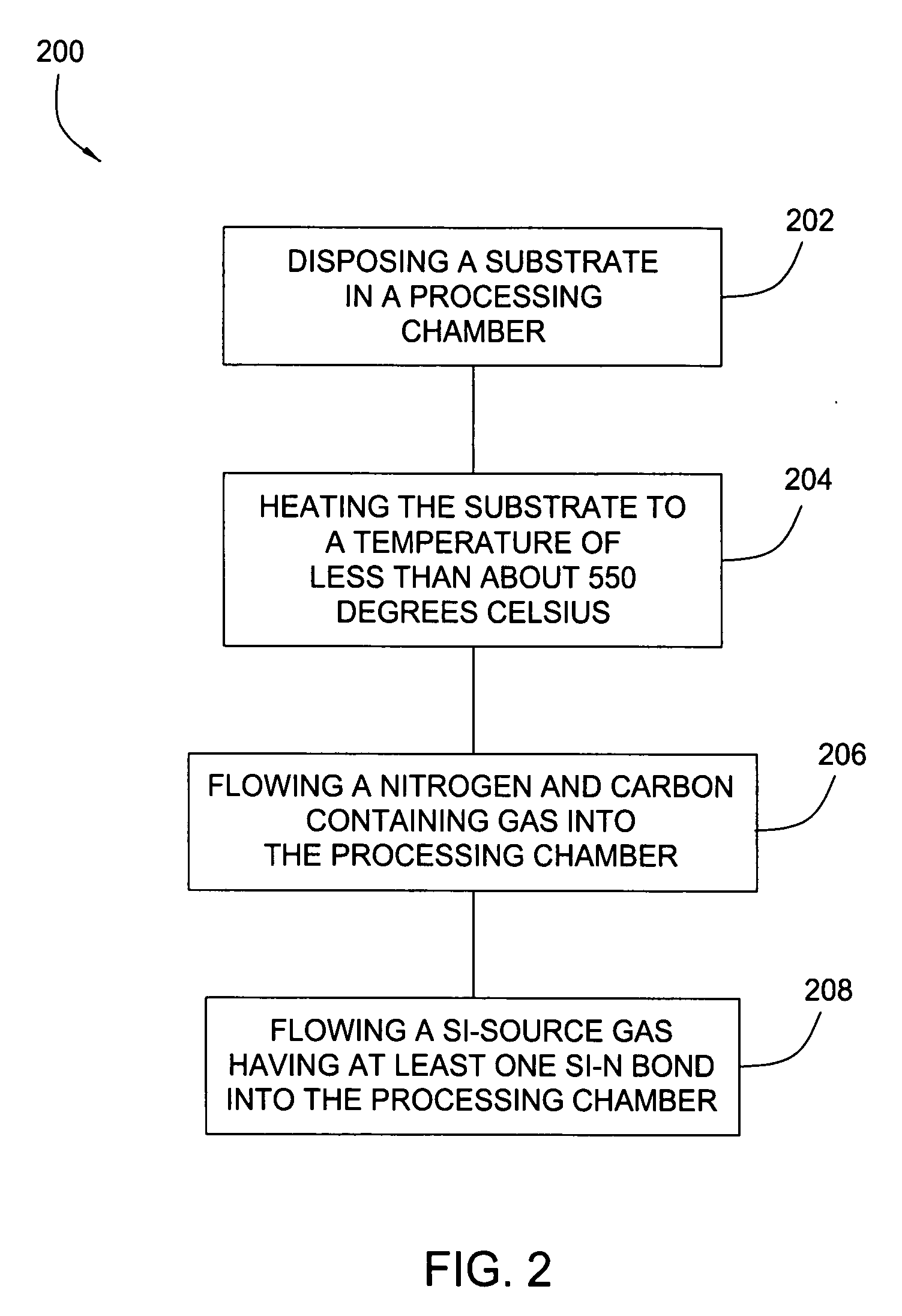
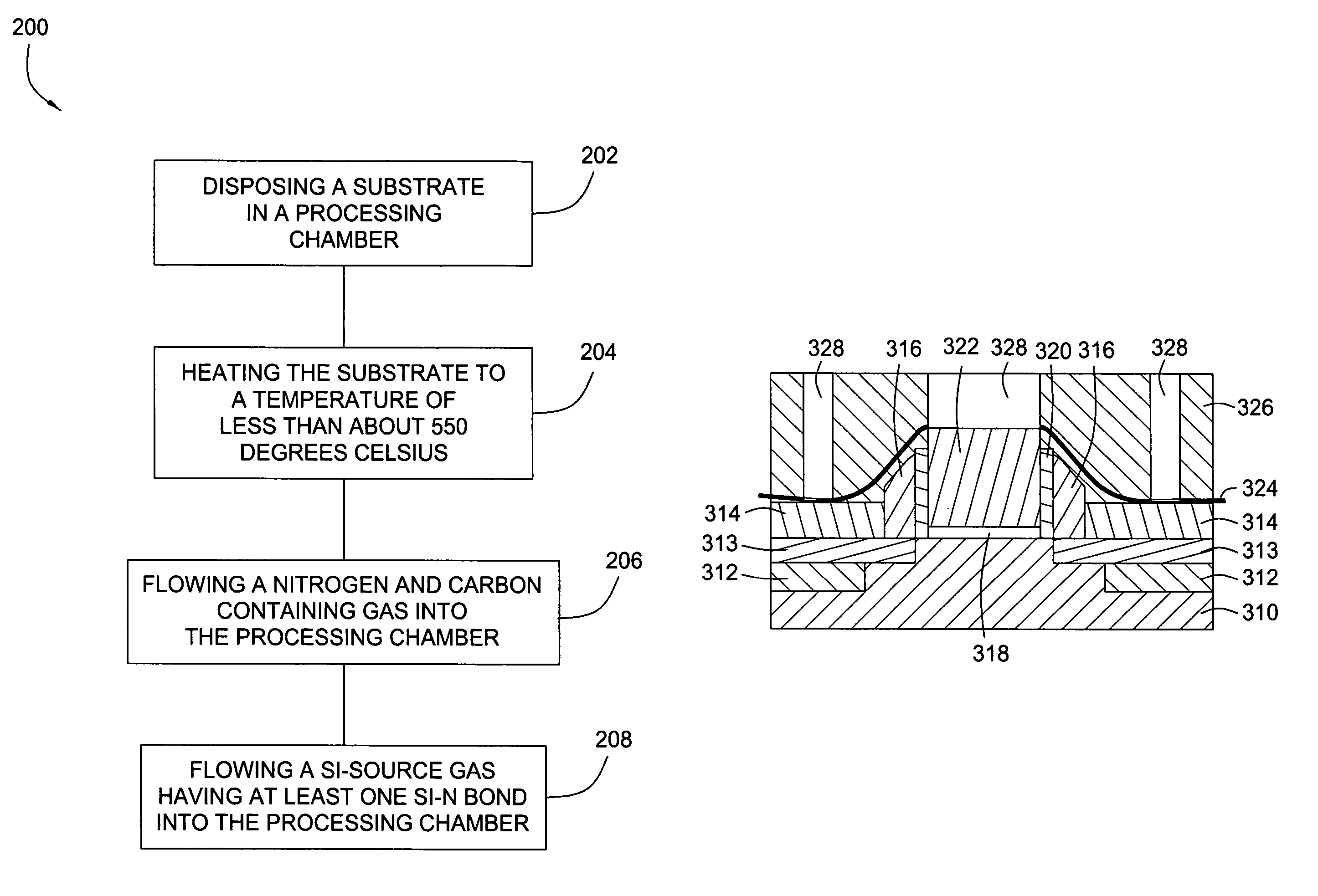
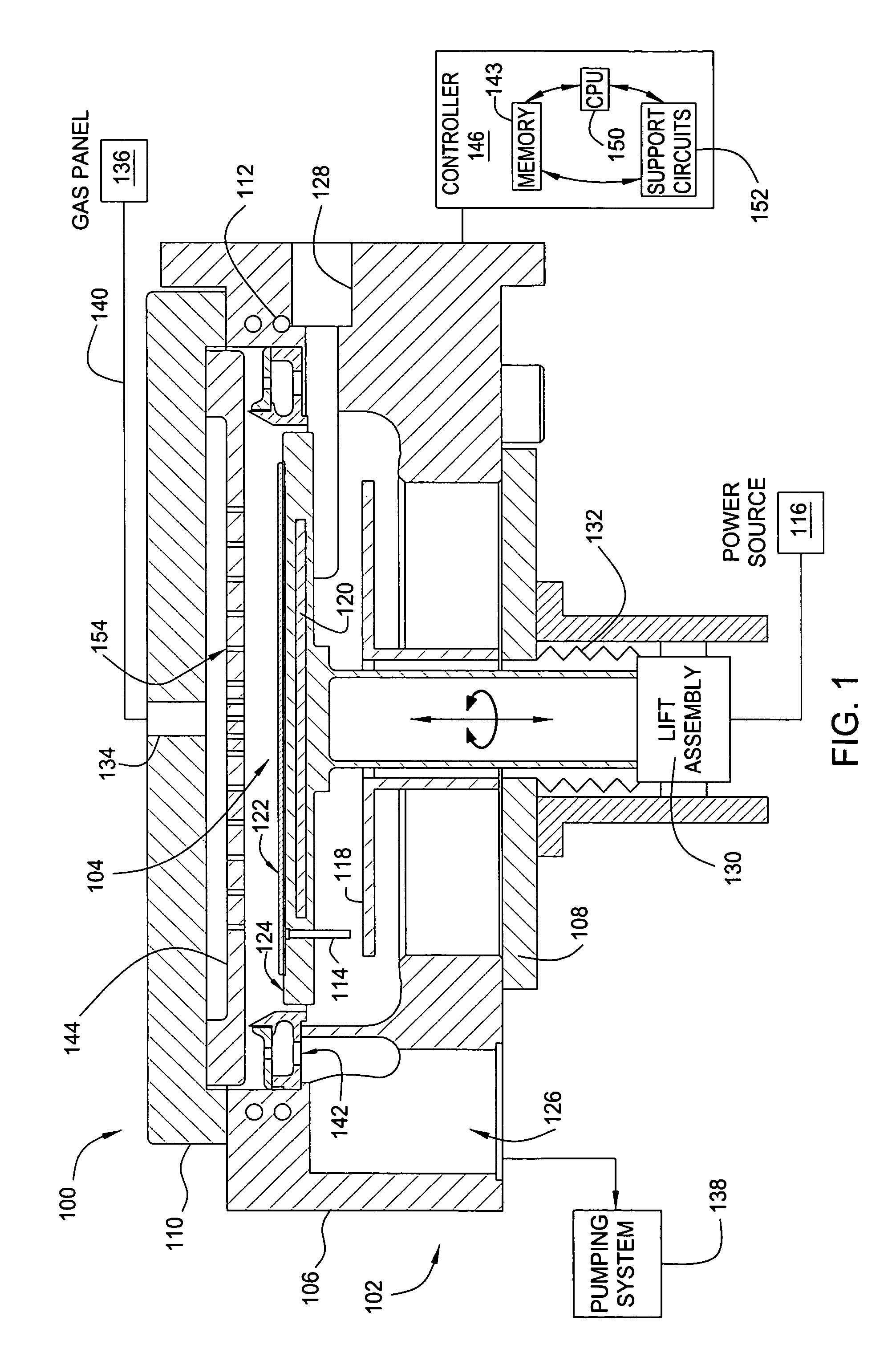
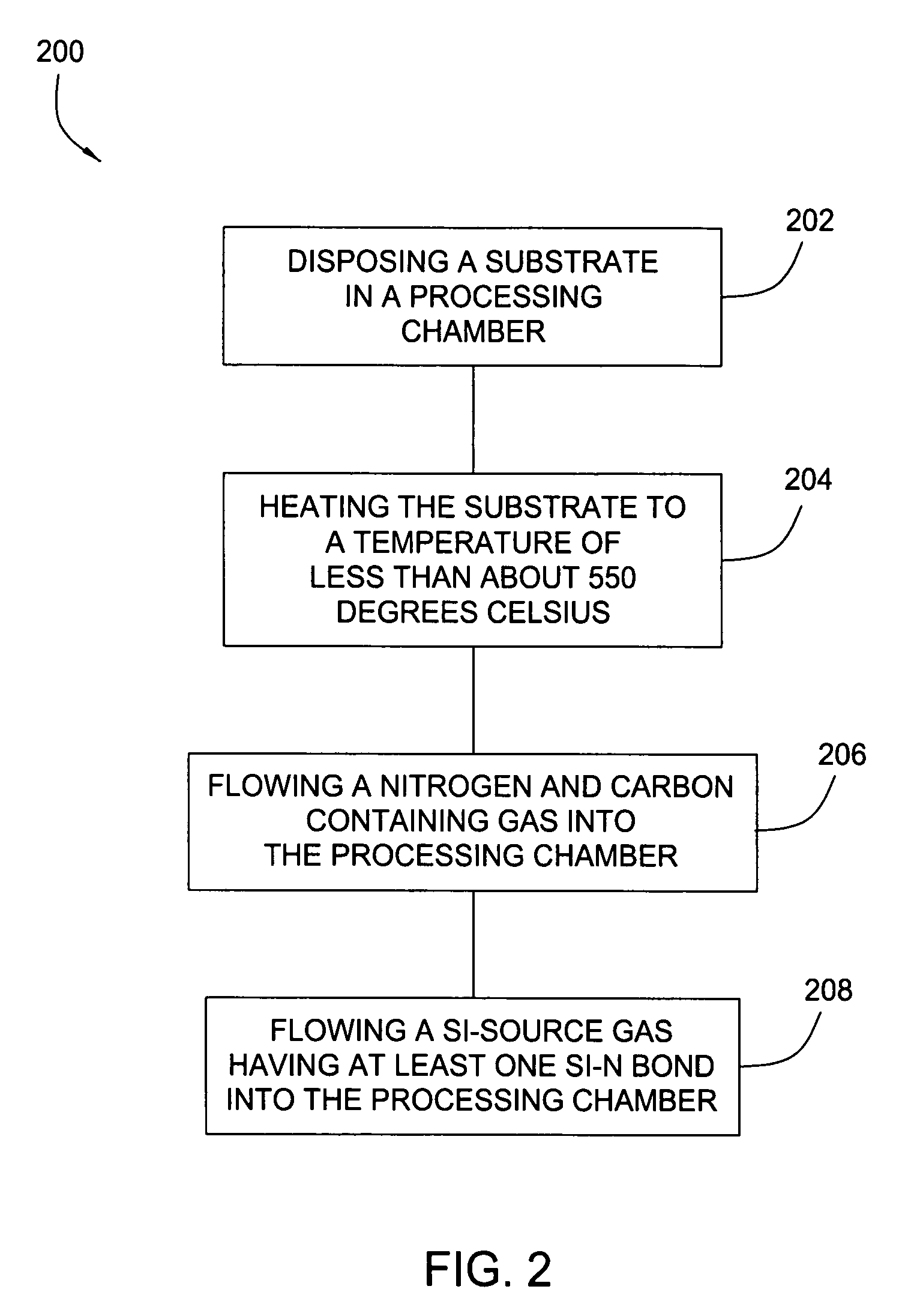
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a method for depositing silicon-containing films. In one embodiment, a method for depositing silicon-containing material film on a substrate includes flowing a nitrogen and carbon containing chemical into a deposition chamber, flowing a silicon-containing source chemical having silicon-nitrogen bonds into the processing chamber, and heating the substrate disposed in the chamber to a temperature less than about 550 degrees Celsius. In another embodiment, the silicon containing chemical is trisilylamine and the nitrogen and carbon containing chemical is (CH3)3—N.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
In situ modification of group iv nanoparticles using gas phase nanoparticle reactors
A method for creating an organically capped Group IV semiconductor nanoparticle is disclosed. The method includes flowing a Group IV semiconductor precursor gas into a chamber. The method also includes generating a set of Group IV semiconductor precursor radical species from the Group IV semiconductor precursor gas with a laser pyrolysis apparatus, wherein the set of the Group IV semiconductor precursor radical species nucleate to form the Group IV semiconductor nanoparticle; and flowing an organic capping agent precursor gas into the chamber. The method further includes generating a set of organic capping agent radical species from the organic capping agent precursor gas, wherein the set of organic capping agent radical species reacts with a surface of the Group IV semiconductor nanoparticle and forms the organically capped Group IV semiconductor nanoparticle.
Owner:LI XUEGENG +3
Techniques for cold implantation of carbon-containing species
InactiveUS20090200494A1Increase strainElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIon implantationMaterials science
Techniques for cold implantation of carbon-containing species are disclosed. In one particular exemplary embodiment, the techniques may be realized as an apparatus for ion implantation including a cooling device for cooling a target material to a predetermined temperature, and an ion implanter for implanting the target material with a carbon-containing species at the predetermined temperature to improve at least one of strain and amorphization.
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
Organic species that facilitate charge transfer to or from nanostructures
InactiveUS6949206B2Facilitates injection and extractionMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureOligomerNanocrystal
The present invention provides compositions (small molecules, oligomers and polymers) that can be used to modify charge transport across a nanocrystal surface or within a nanocrystal-containing matrix, as well as methods for making and using the novel compositions.
Owner:SHOEI CHEM IND CO LTD
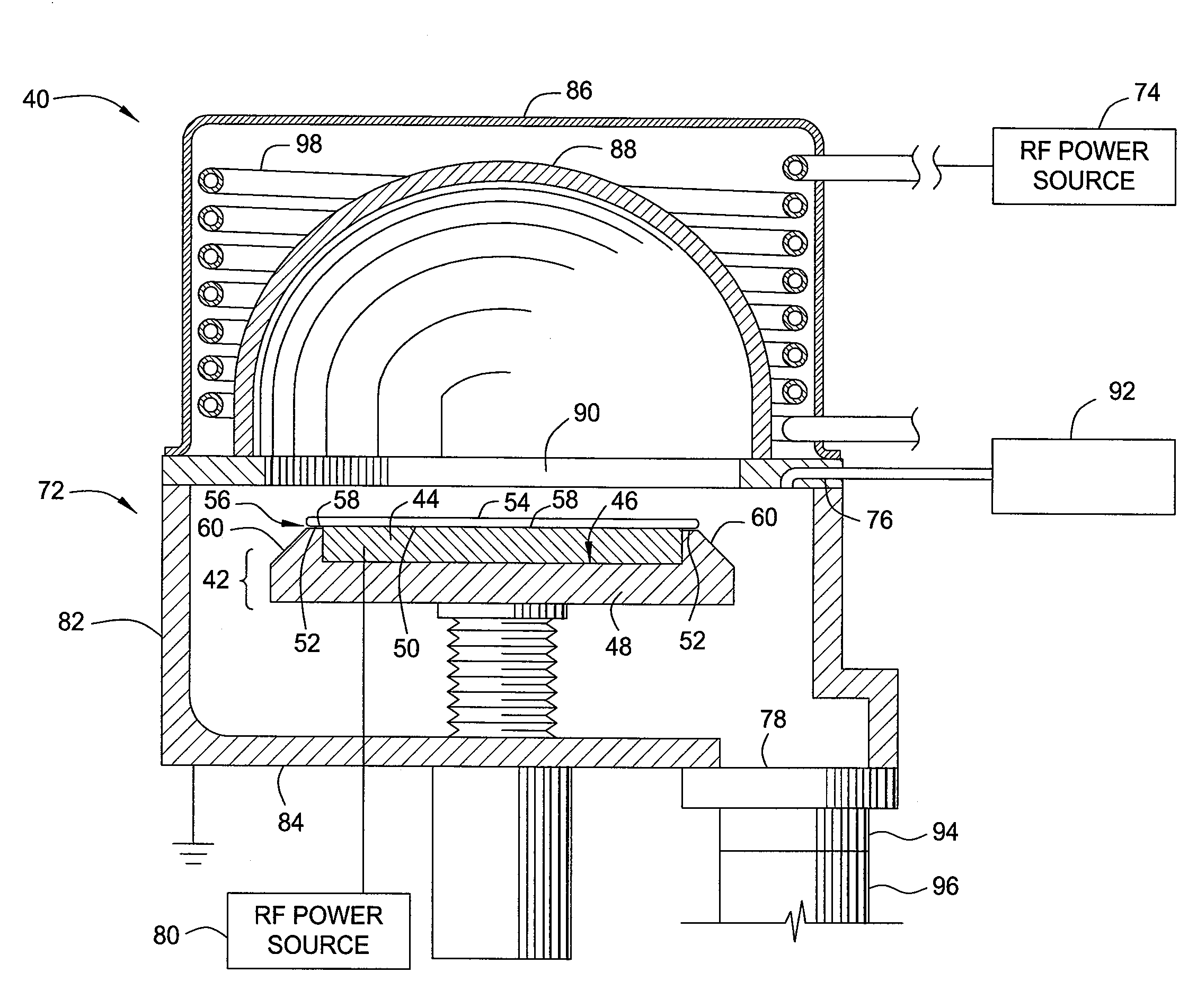
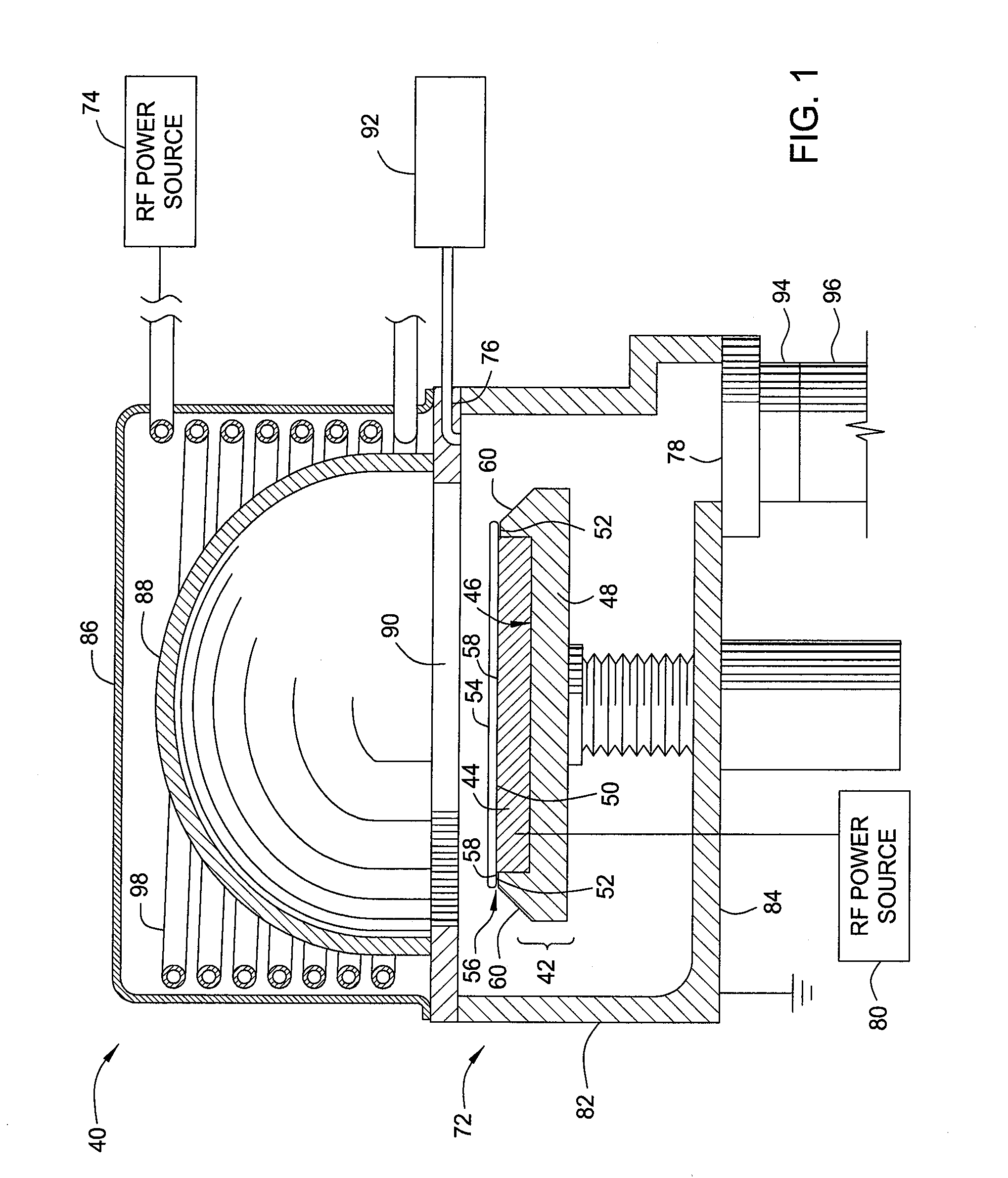
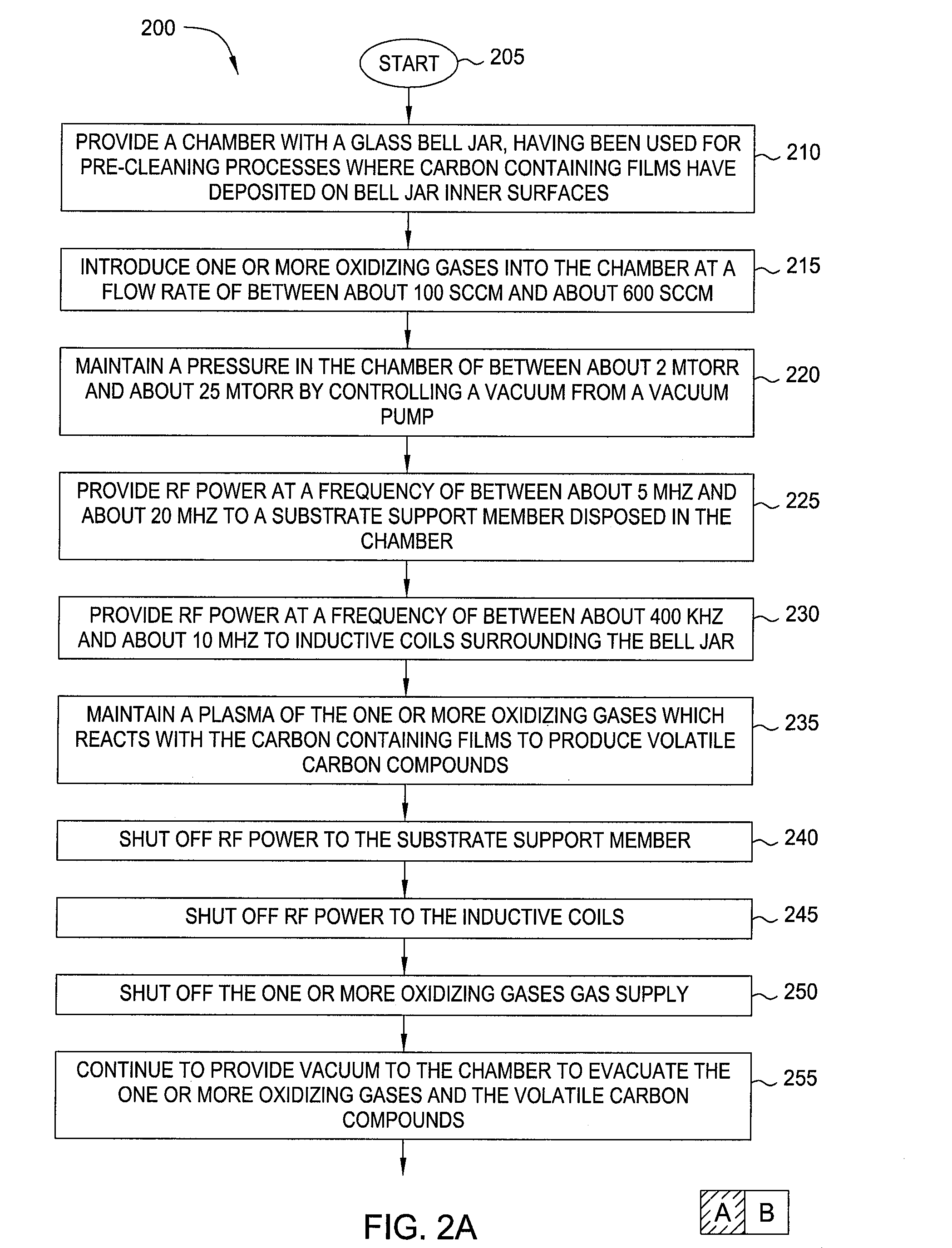
Oxygen plasma clean to remove carbon species deposited on a glass dome surface
InactiveUS20080173326A1Decorative surface effectsHollow article cleaningChemical compoundOxygen plasma
A method for in-situ cleaning of a dielectric dome surface having been used in pre-clean processes is provided. Carbon containing deposits are removed by providing a plasma of one or more oxidizing gases which react with the carbon containing films to form volatile carbon containing compounds.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
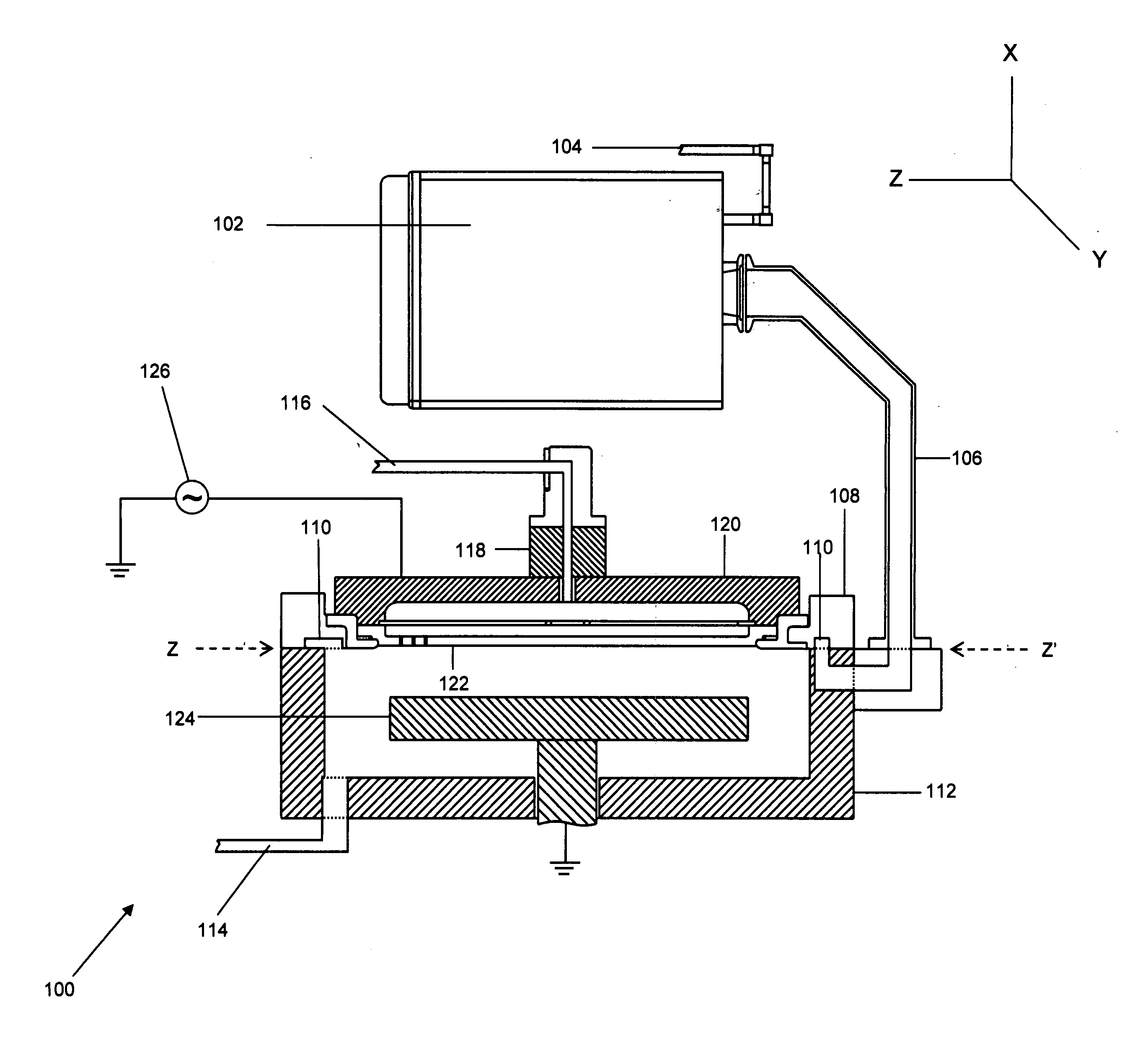
Method and apparatus for cleaning of a CVD reactor
InactiveUS20090269506A1Efficient and uniform remote plasma cleaningImprove efficiencyVacuum evaporation coatingElectrostatic cleaningRemote plasmaOxygen
The present invention provides a process and an apparatus for remote plasma cleaning of a process chamber of a chemical vapor deposition (CVD) reactor. The reactive species are generated in a remote plasma unit and are introduced into the process chamber through a plurality of inlet holes. The reactive species are free radicals such as oxygen radicals, fluorine radicals, and the like. These reactive species react with the unwanted residues in the process chamber and generate volatile products. The invention also provides a method for controlling the flow rate of the reactive species.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
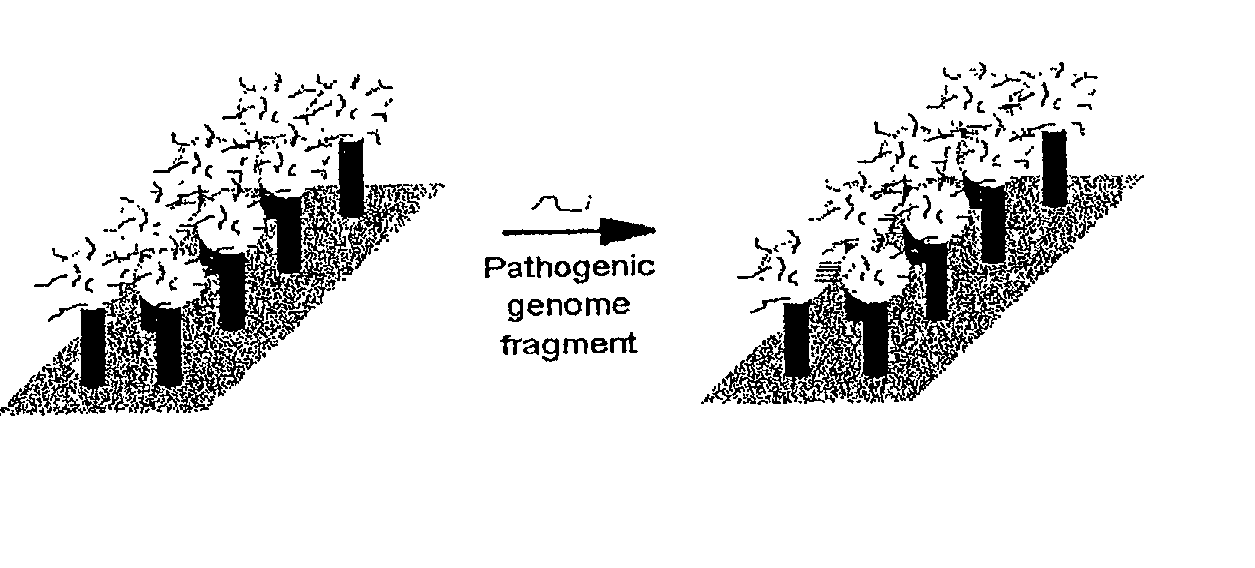
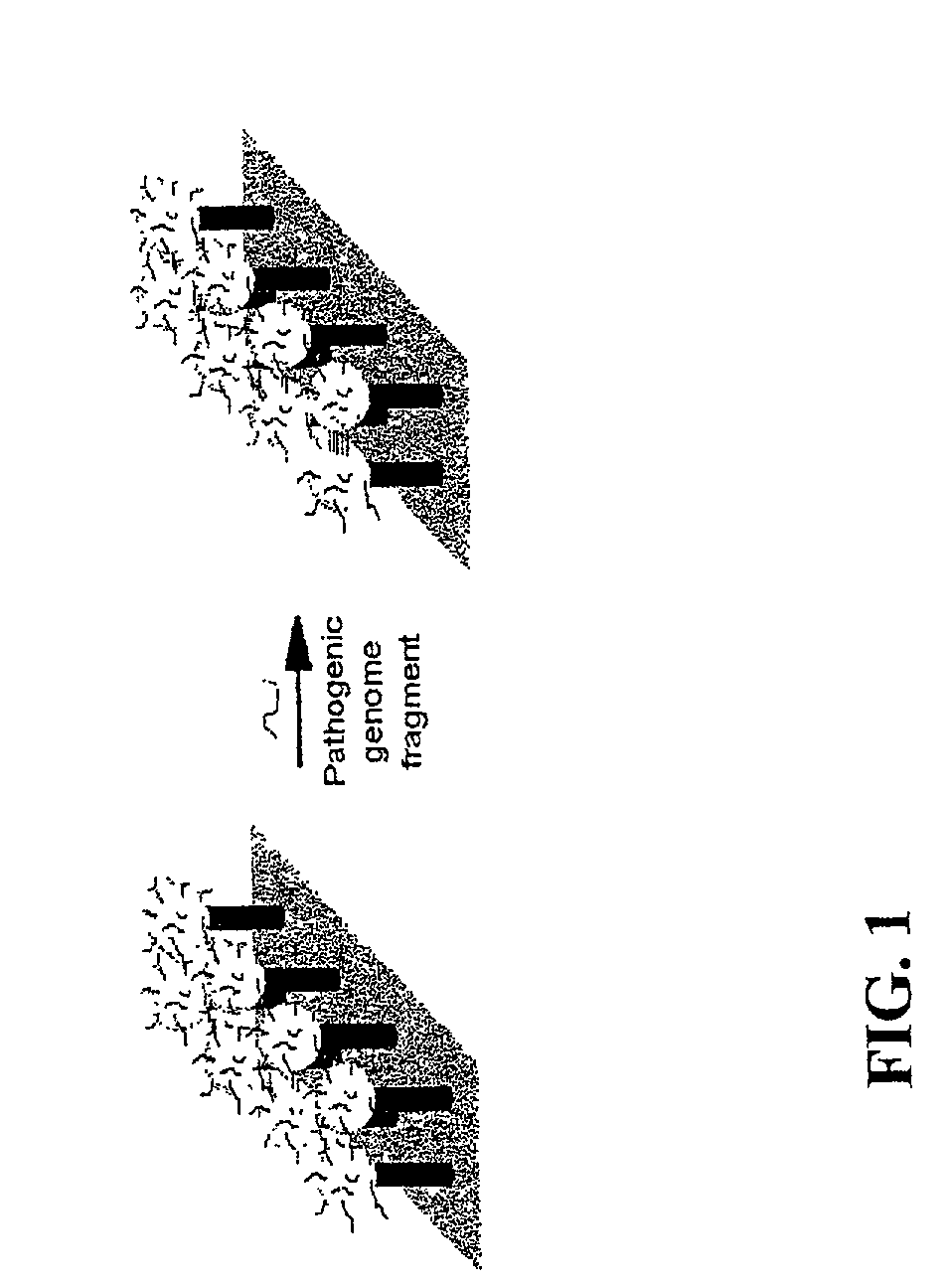
DNA-bridged carbon nanotube arrays
InactiveUS20020172963A1High precisionHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyChemical ligationElectron transfer reactions
A class of biological sensing devices that include a substrate comprising an array of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) to which are chemically attached biological molecules is disclosed. The attached biological molecules are capable of electrical conductivity that is responsive to chemical changes occurring as a result of their interaction with target species. A means for means for using DNA as a material of potential in molecular electronic sensor devices, being primarily based on molecular electron-transfer reaction processes between DNA-binding donors and acceptors is also disclosed, including composition, method of manufacture and their use are described.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON COLLEGE THE
Method for treating substrates and films with photoexcitation
InactiveUS7601652B2Easy to cleanSpeed up the processSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingNitrogenCompound (substance)
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a method for depositing films using photoexcitation. The photoexcitation may be utilized for at least one of treating the substrate prior to deposition, treating substrate and / or gases during deposition, treating a deposited film, or for enhancing chamber cleaning. In one embodiment, a method for depositing silicon and nitrogen-containing film on a substrate includes heating a substrate disposed in a processing chamber, generating a beam of energy of between about 1 to about 10 eV, transferring the energy to a surface of the substrate; flowing a nitrogen-containing chemical into the processing chamber, flowing a silicon-containing chemical with silicon-nitrogen bonds into the processing chamber, and depositing a silicon and nitrogen-containing film on the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method and system for in situ formation of gas-phase compounds
ActiveUS20160051964A1Process can be usedProcess control/regulationCell electrodesCompound aGas phase
A system and method for providing intermediate reactive species to a reaction chamber are disclosed. The system includes an intermediate reactive species formation chamber fluidly coupled to the reaction chamber to provide intermediate reactive species to the reaction chamber. A pressure control device can be used to control an operating pressure of the intermediate reactive species formation chamber, and a heater can be used to heat the intermediate reactive species formation chamber to a desired temperature.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
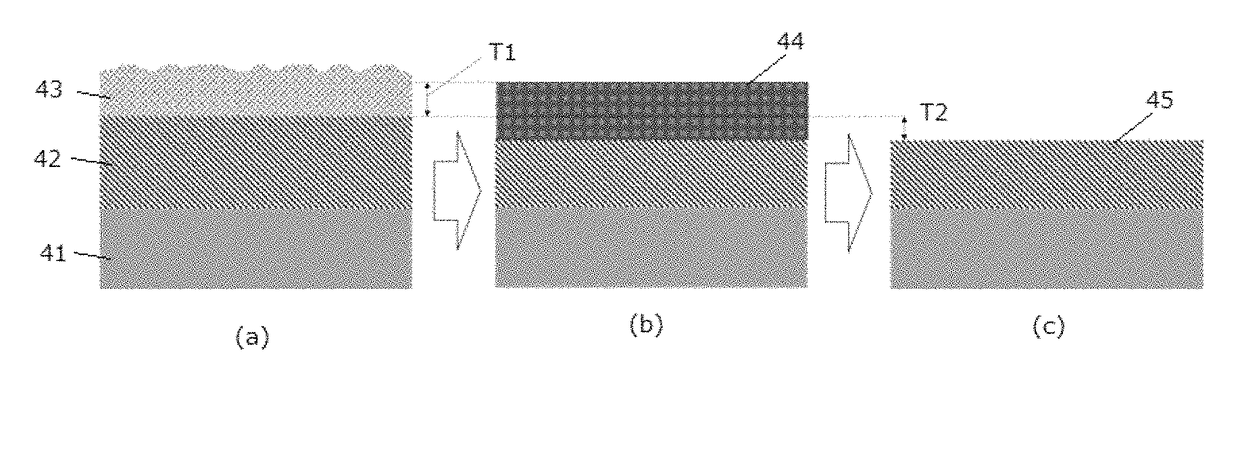
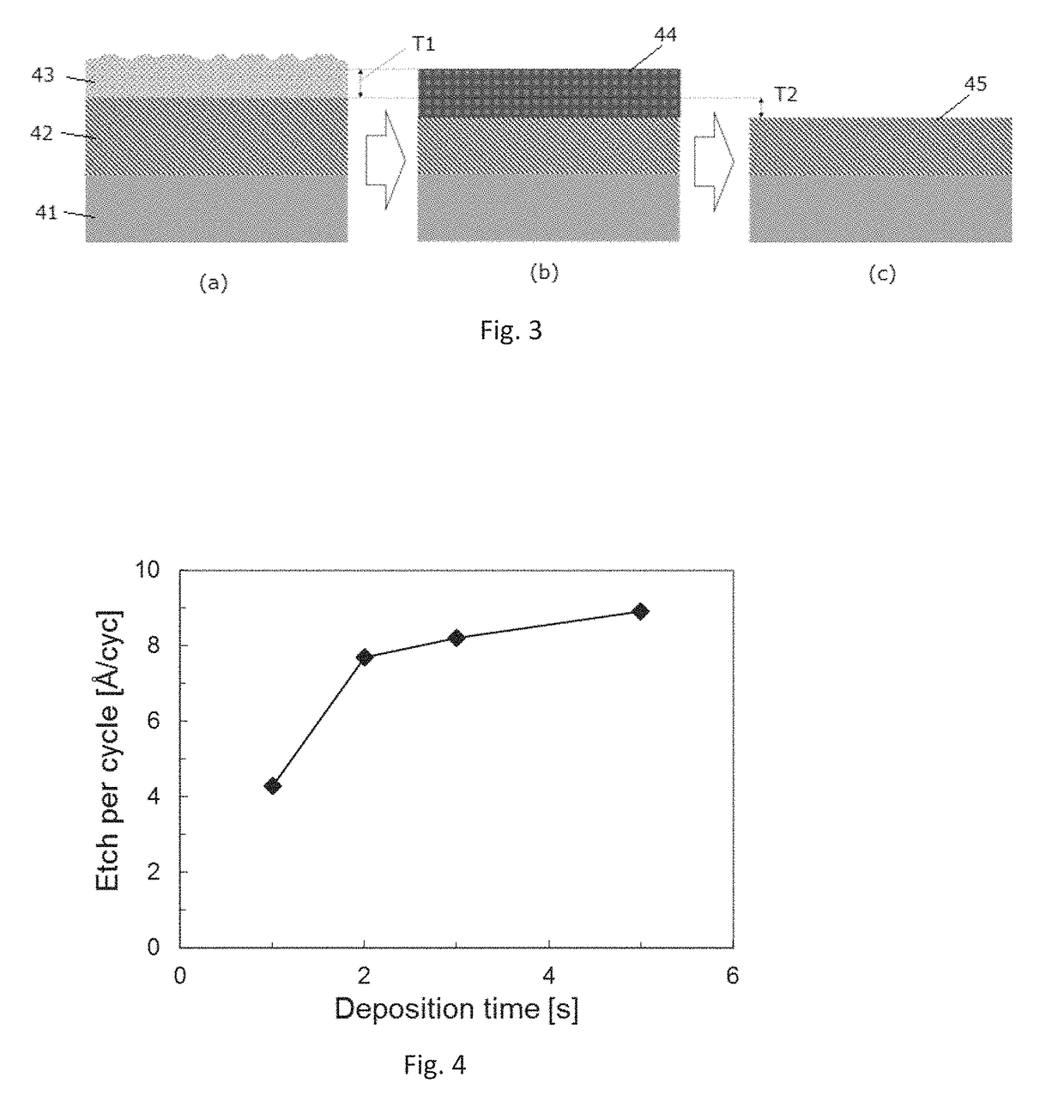
Method of cyclic dry etching using etchant film
ActiveUS9793135B1Improve controllabilityEasy to operateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsBoundary region
A method for etching a target layer on a substrate by a dry etching process includes at least one etching cycle, wherein an etching cycle includes: depositing a halogen-containing film using reactive species on the target layer on the substrate; and etching the halogen-containing film using a plasma of a non-halogen etching gas, which plasma alone does not substantially etch the target layer, to generate etchant species at a boundary region of the halogen-containing film and the target layer, thereby etching a portion of the target layer in the boundary region.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method for silicon based dielectric chemical vapor deposition
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a method for depositing silicon-containing films. In one embodiment, a method for depositing silicon-containing material film on a substrate includes flowing a nitrogen and carbon containing chemical into a deposition chamber, flowing a silicon-containing source chemical having silicon-nitrogen bonds into the processing chamber, and heating the substrate disposed in the chamber to a temperature less than about 550 degrees Celsius. In another embodiment, the silicon containing chemical is trisilylamine and the nitrogen and carbon containing chemical is (CH3)3—N.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
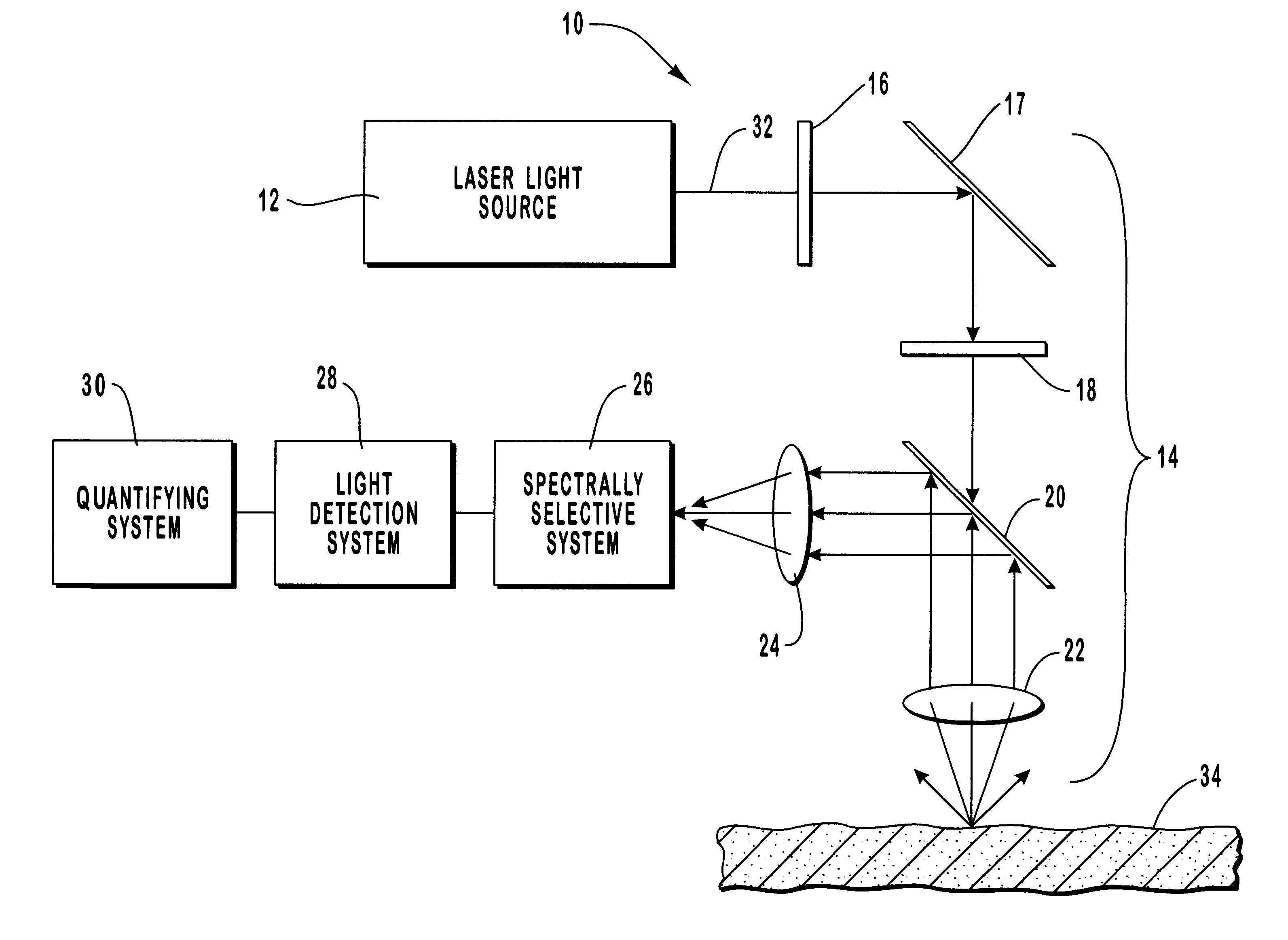
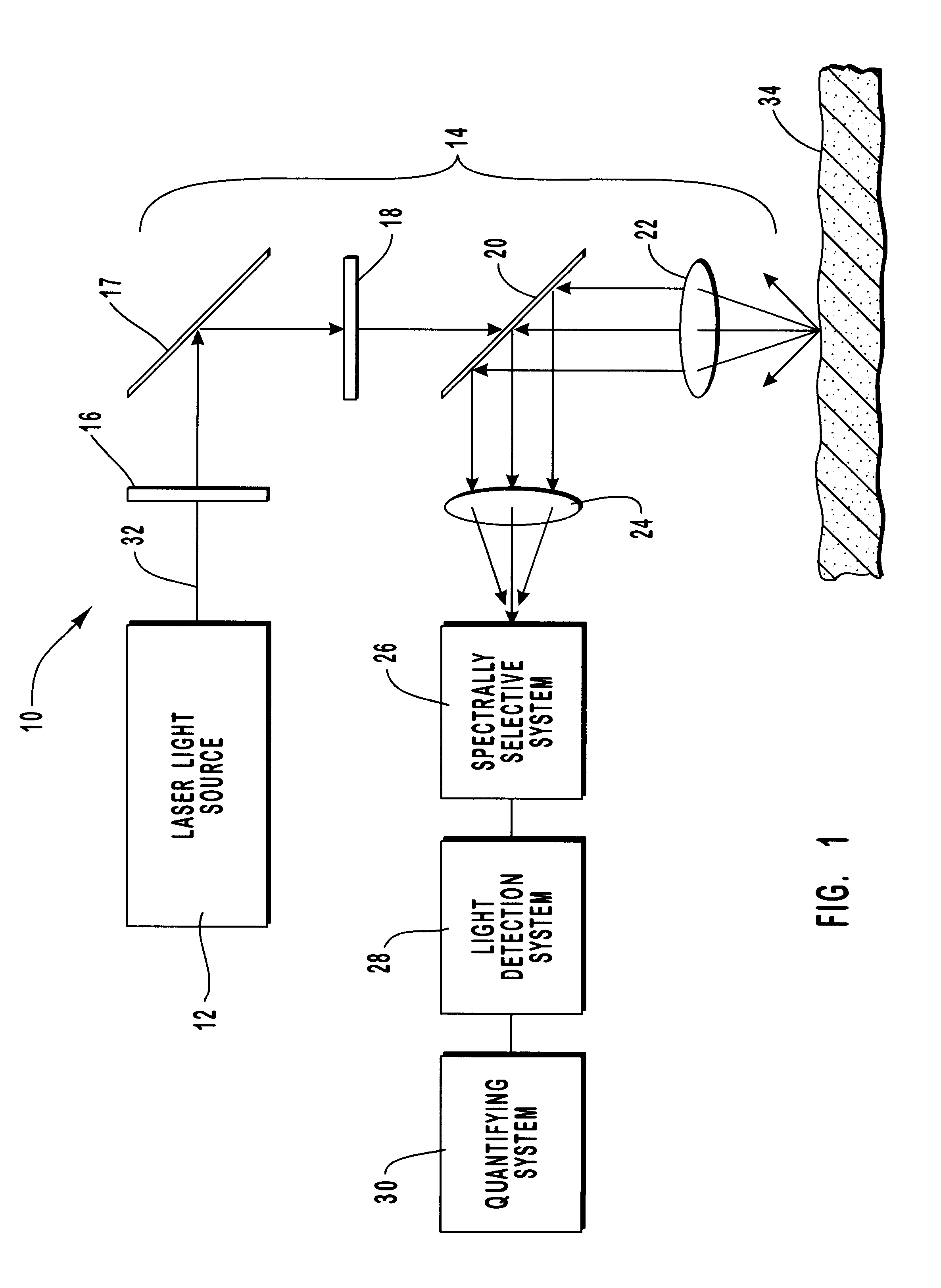
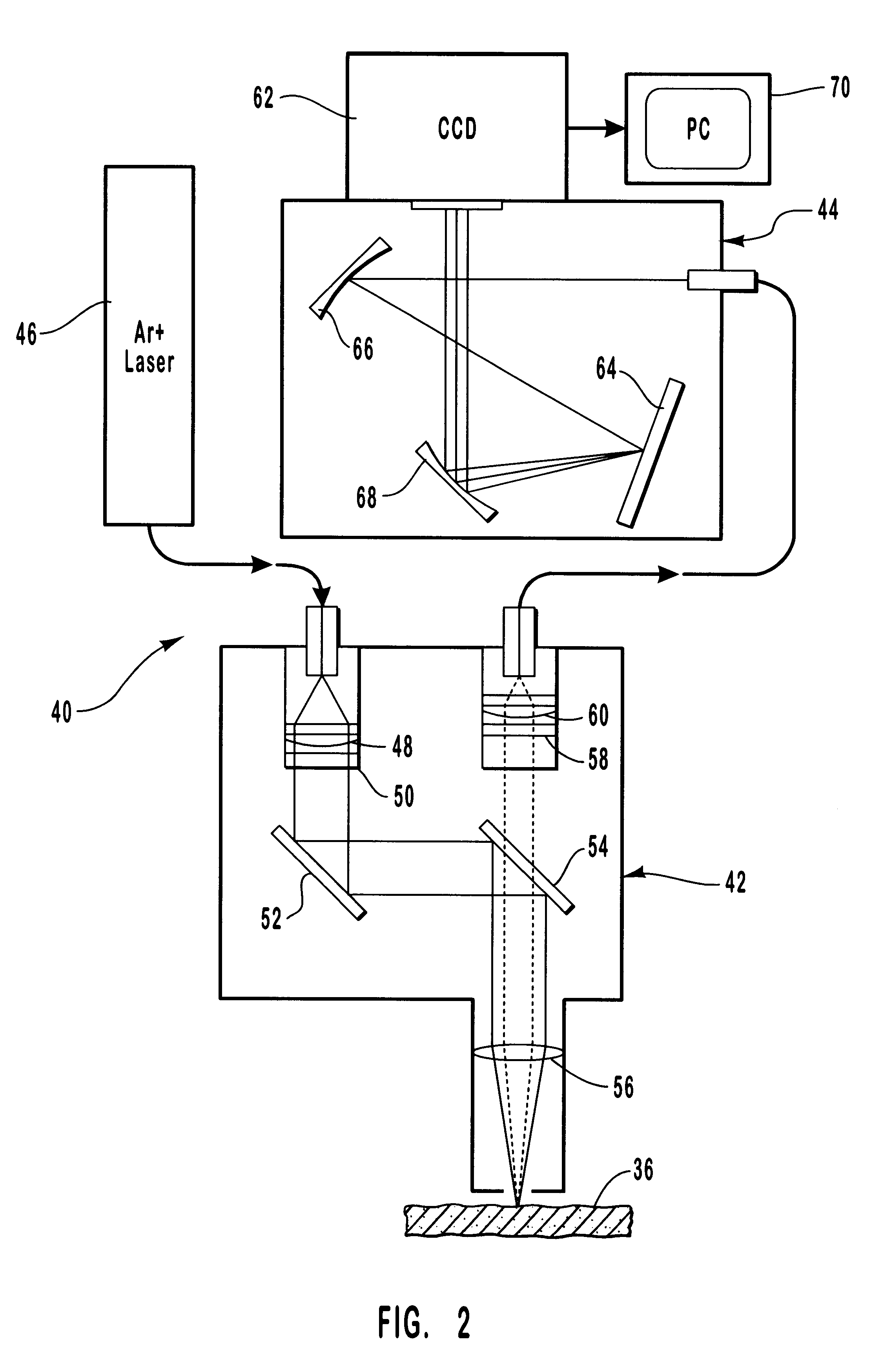
Method and apparatus for noninvasive measurement of carotenoids and related chemical substances in biological tissue
InactiveUS6205354B1Rapid and noninvasive and quantitative measurementRiskRadiation pyrometrySurgeryResonance Raman spectroscopyAntioxidant
A method and apparatus are provided for the determination of levels of carotenoids and similar chemical compounds in biological tissue such as living skin. The method and apparatus provide a noninvasive, rapid, accurate, and safe determination of carotenoid levels which in turn can provide diagnostic information regarding cancer risk, or can be a marker for conditions where carotenoids or other antioxidant compounds may provide diagnostic information. Such early diagnostic information allows for the possibility of preventative intervention. The method and apparatus utilize the technique of resonance Raman spectroscopy to measure the levels of carotenoids and similar substances in tissue. In this technique, laser light is directed upon the area of tissue which is of interest. A small fraction of the scattered light is scattered inelastically, producing the carotenoid Raman signal which is at a different frequency than the incident laser light, and the Raman signal is collected, filtered, and measured. The resulting Raman signal can be analyzed such that the background fluorescence signal is subtracted and the results displayed and compared with known calibration standards.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Monitoring a physiological analytes
InactiveUS7174199B2Minimize impactReduce presenceElectrotherapyMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteEngineering
Methods and devices are provided for measuring the concentration of target chemical analytes present in a biological system. Device configuration and / or measurement techniques are employed in order to reduce the effect of interfering species on sensor sensitivity. One important application of the invention involves a method and device for monitoring blood glucose values.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC +1
Droplet-based surface modification and washing
ActiveUS20070243634A1Reduces and eliminates build-upImprove efficiencyHeating or cooling apparatusTransportation and packagingSurface modificationAmount of substance
The present invention relates to droplet-based surface modification and washing. According to one embodiment, a method of providing a droplet in contact with a surface with a reduced concentration of a substance is provided, wherein the method includes: (a) providing a droplet microactuator comprising a surface in contact with a droplet comprising a starting concentration and starting quantity of the substance and having a starting volume; (b) conducting one or more droplet operations to merge a wash droplet with the droplet provided in step (a) to yield a combined droplet; and (c) conducting one or more droplet operations to divide the combined droplet to yield a set of droplets comprising: (i) a droplet in contact with the surface having a decreased concentration of the substance relative to the starting concentration; and (ii) a droplet which is separated from the surface.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com