Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32852results about "Hollow article cleaning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
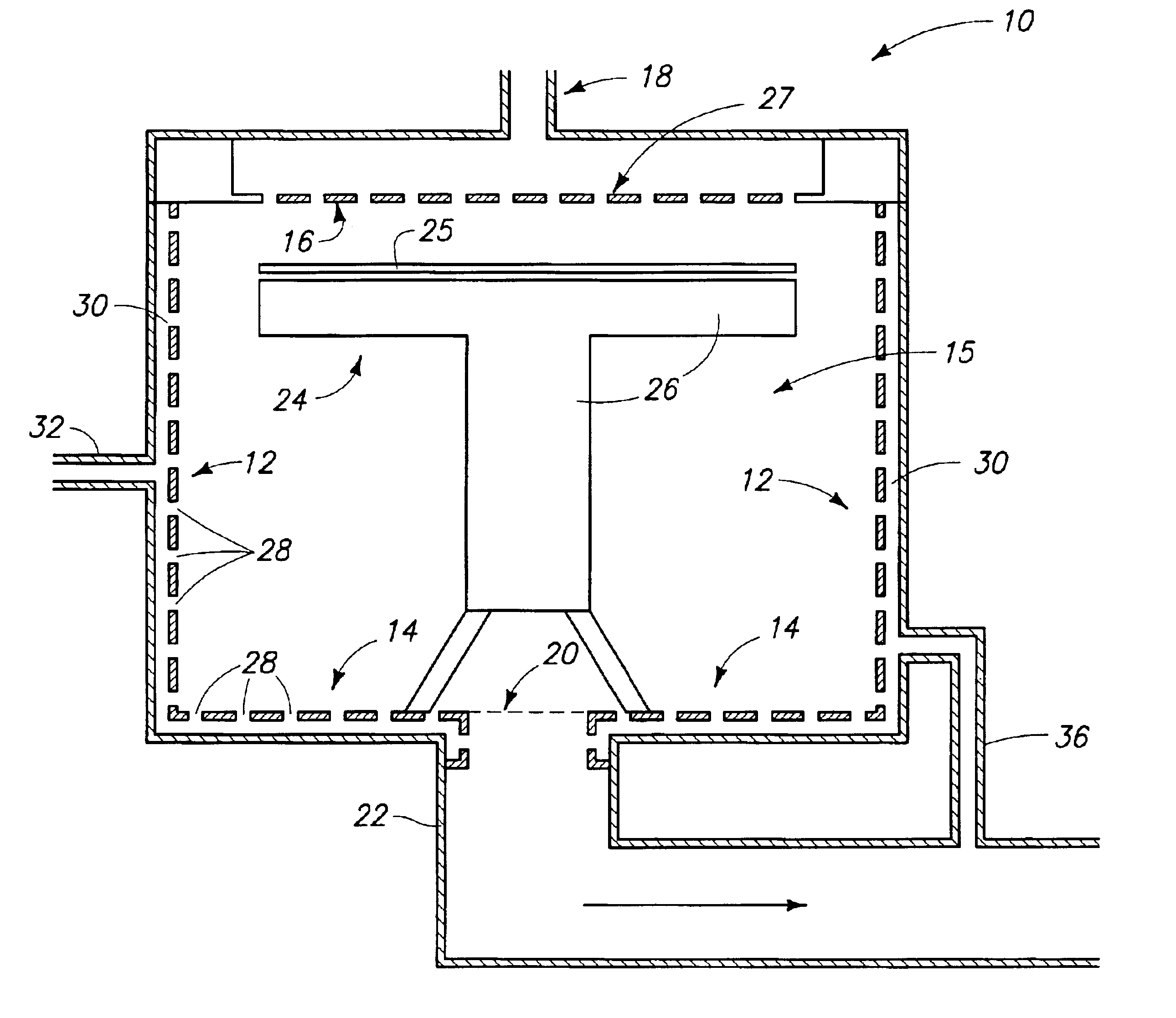
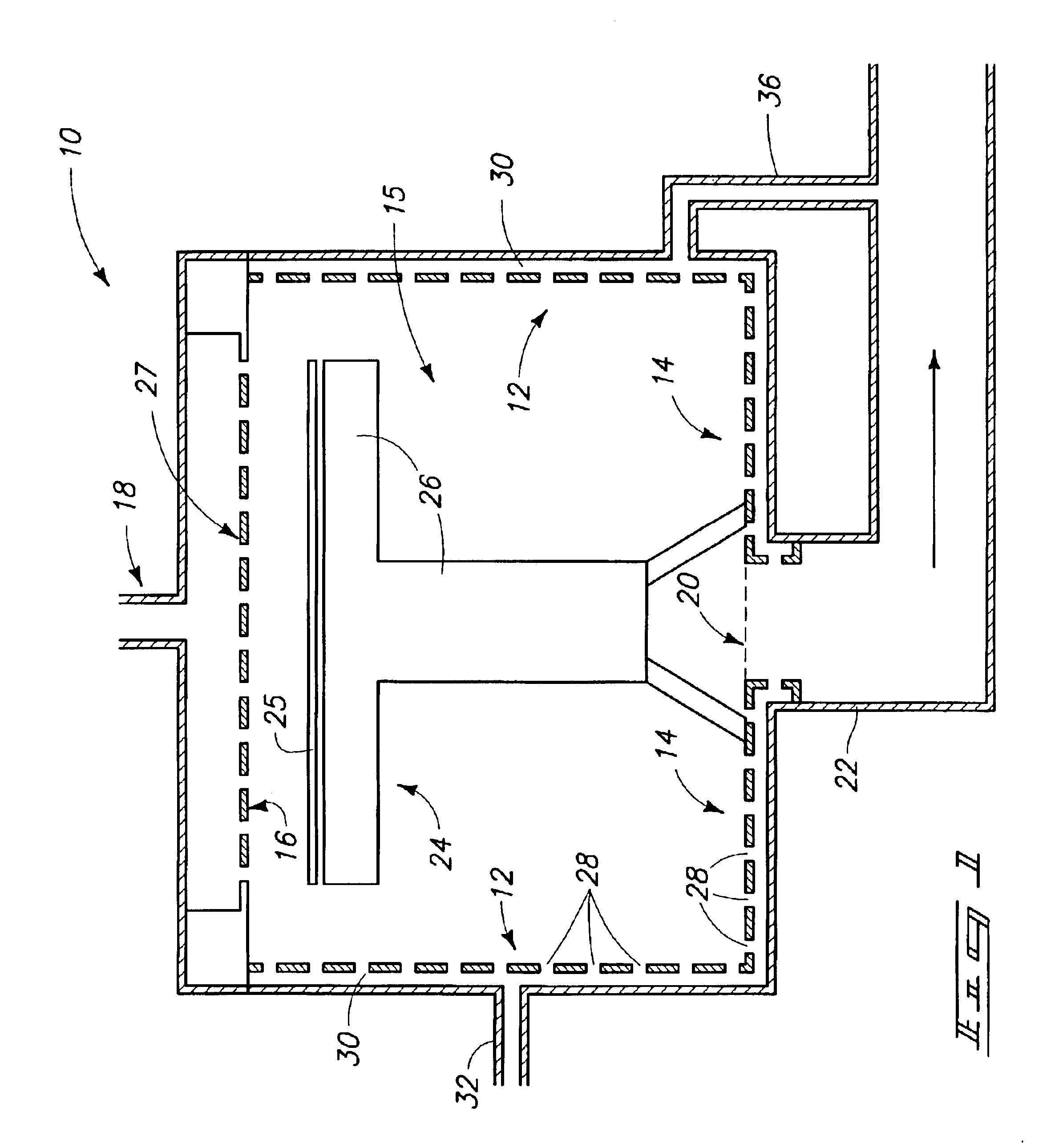
Robot for surgical applications
The present invention provides a micro-robot for use inside the body during minimally-invasive surgery. The micro-robot includes an imaging devices, a manipulator, and in some embodiments a sensor.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
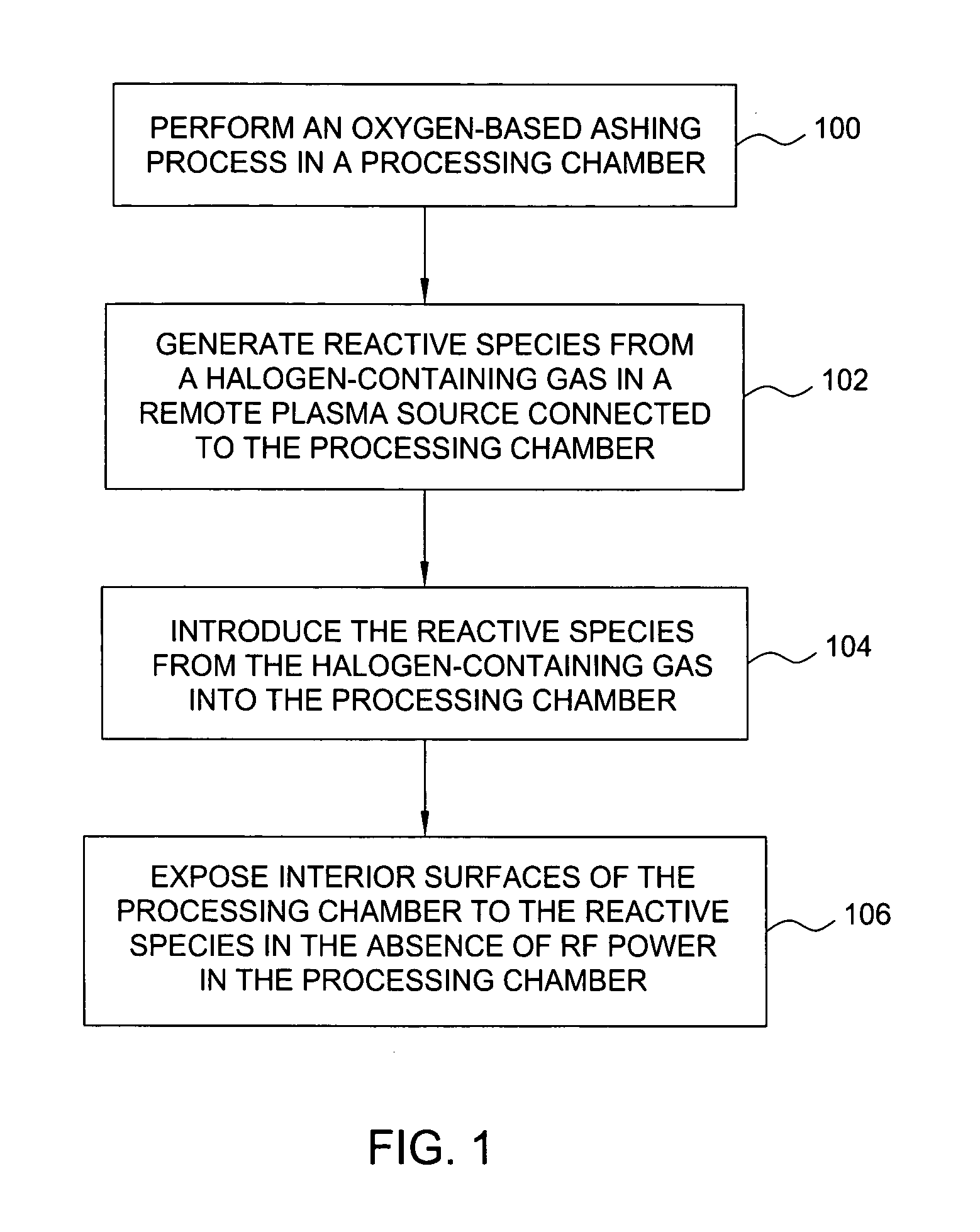
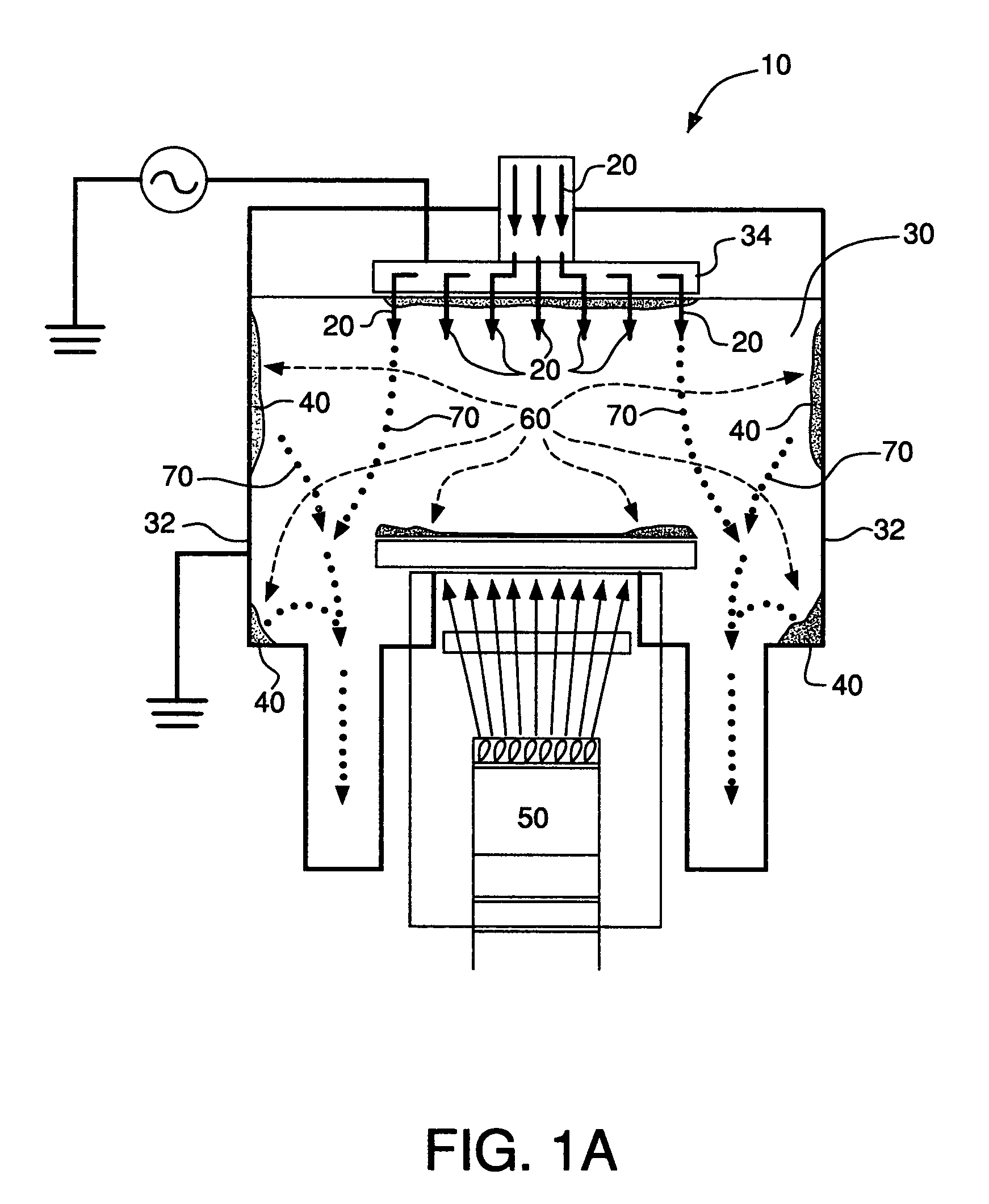
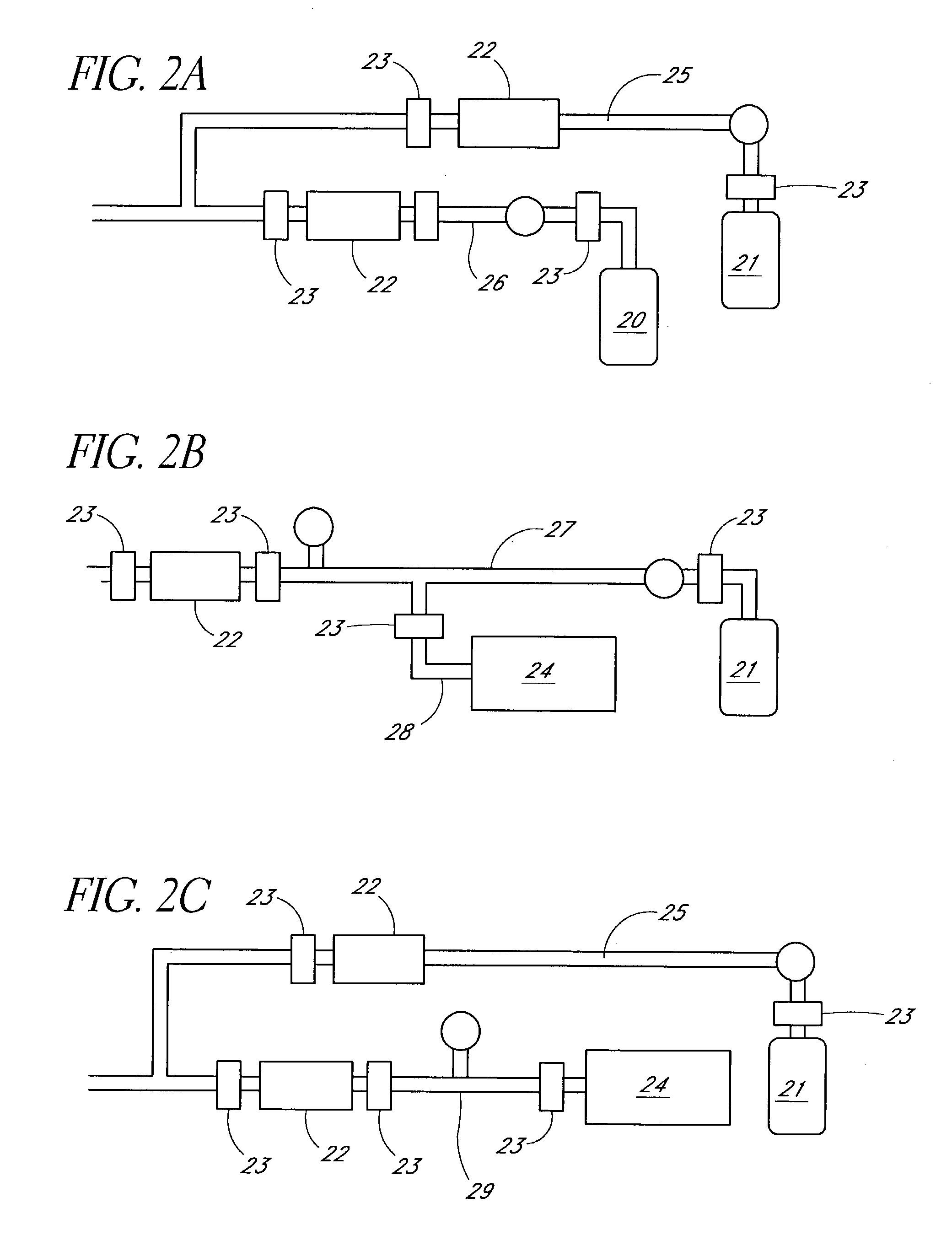
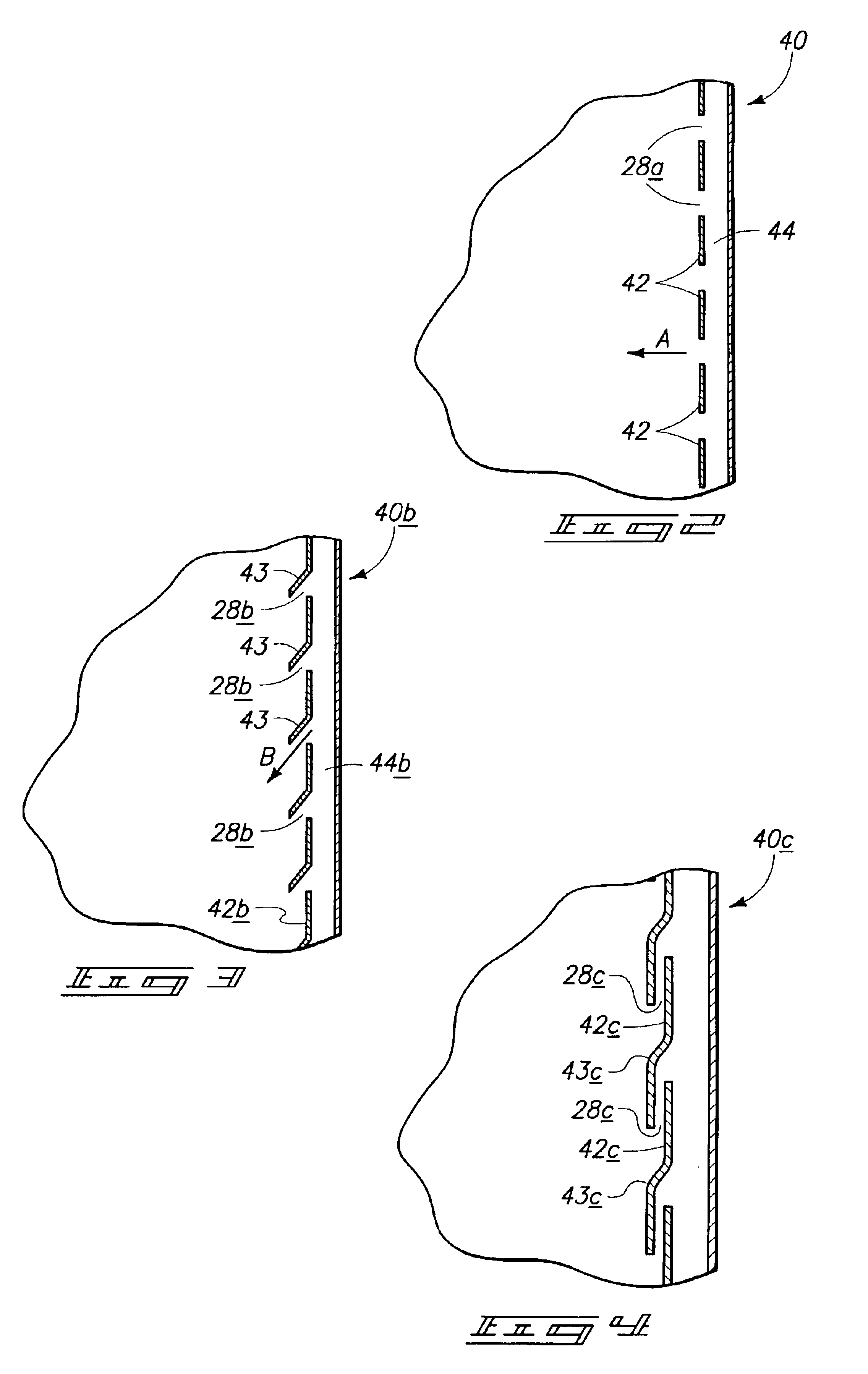
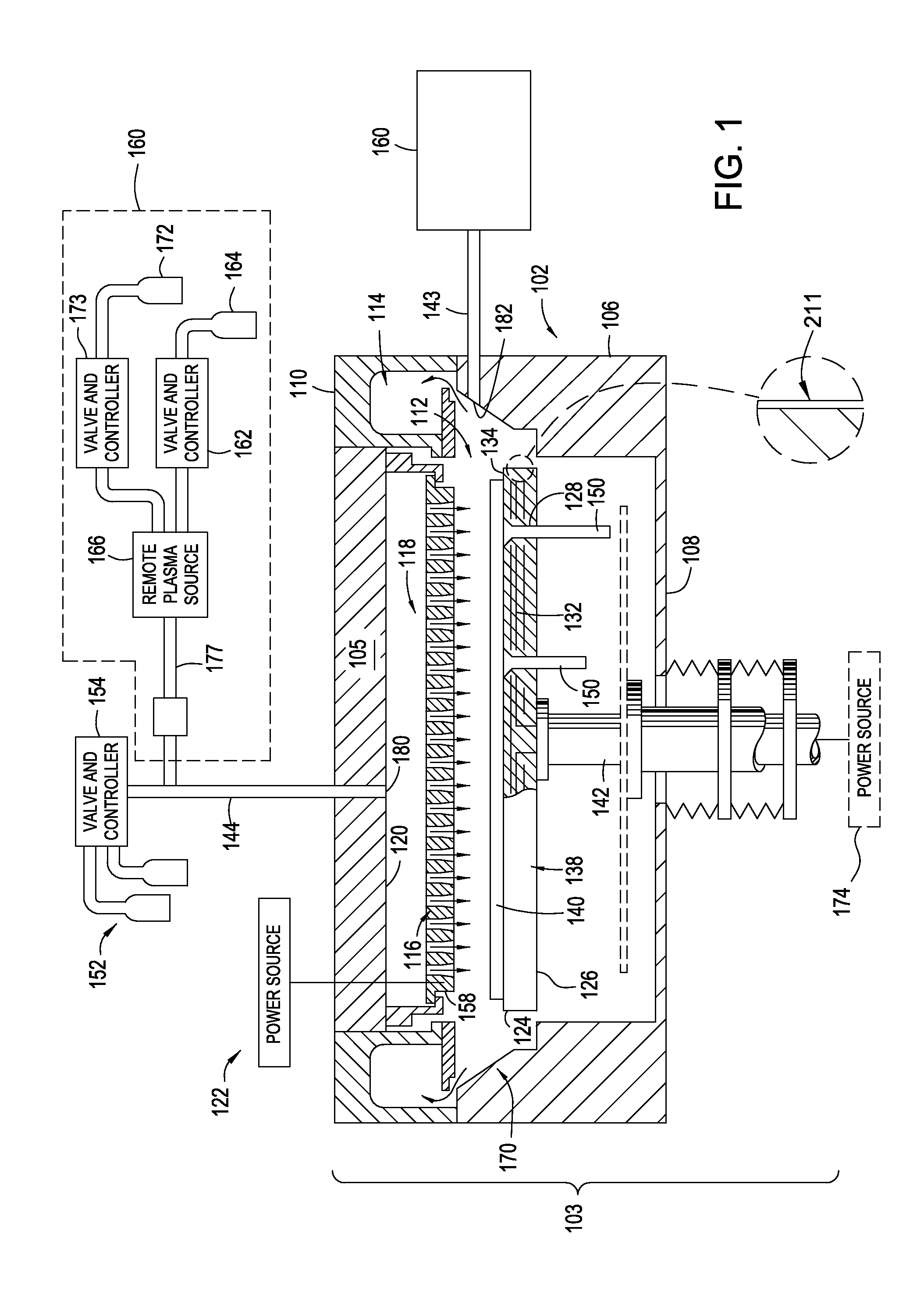
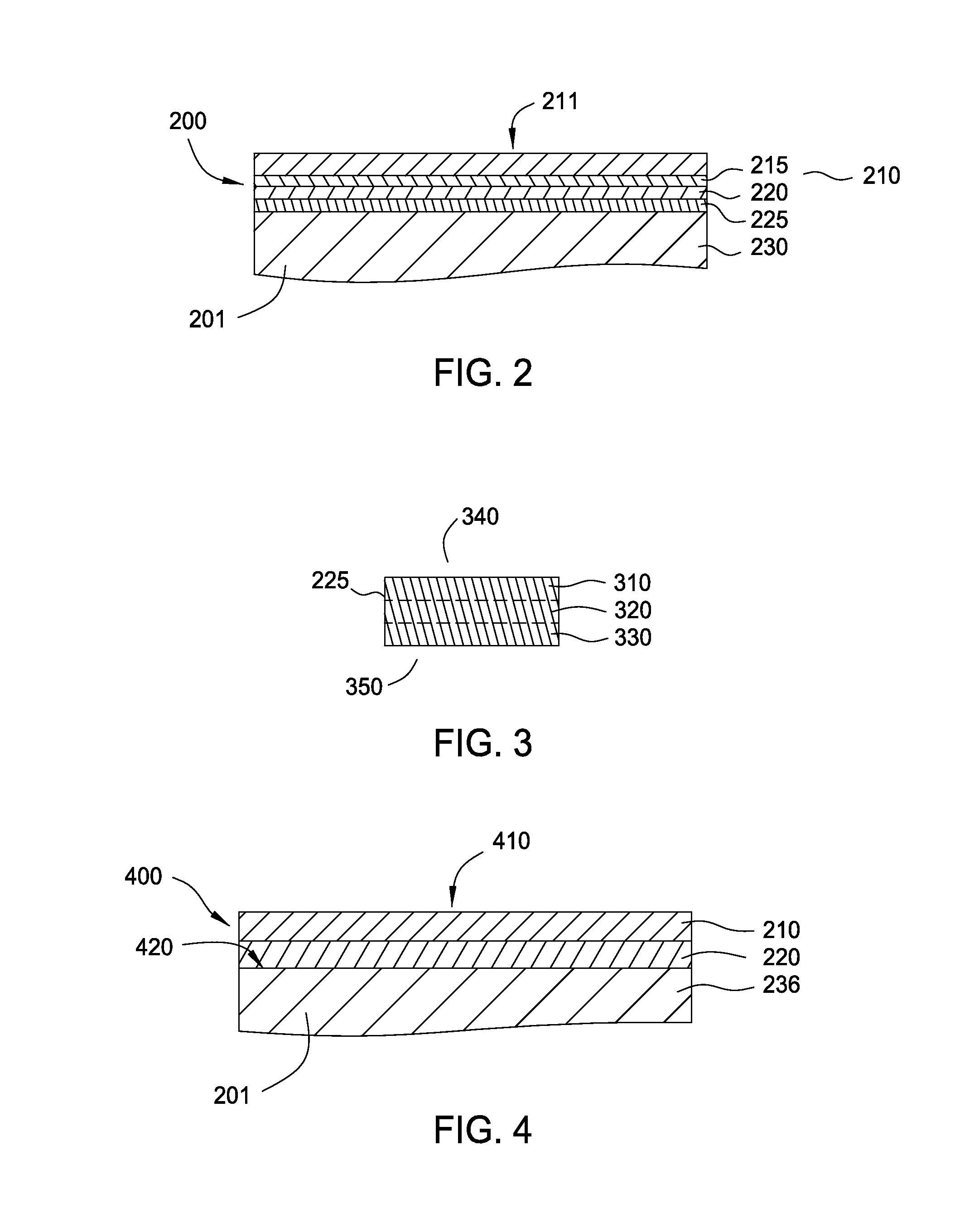
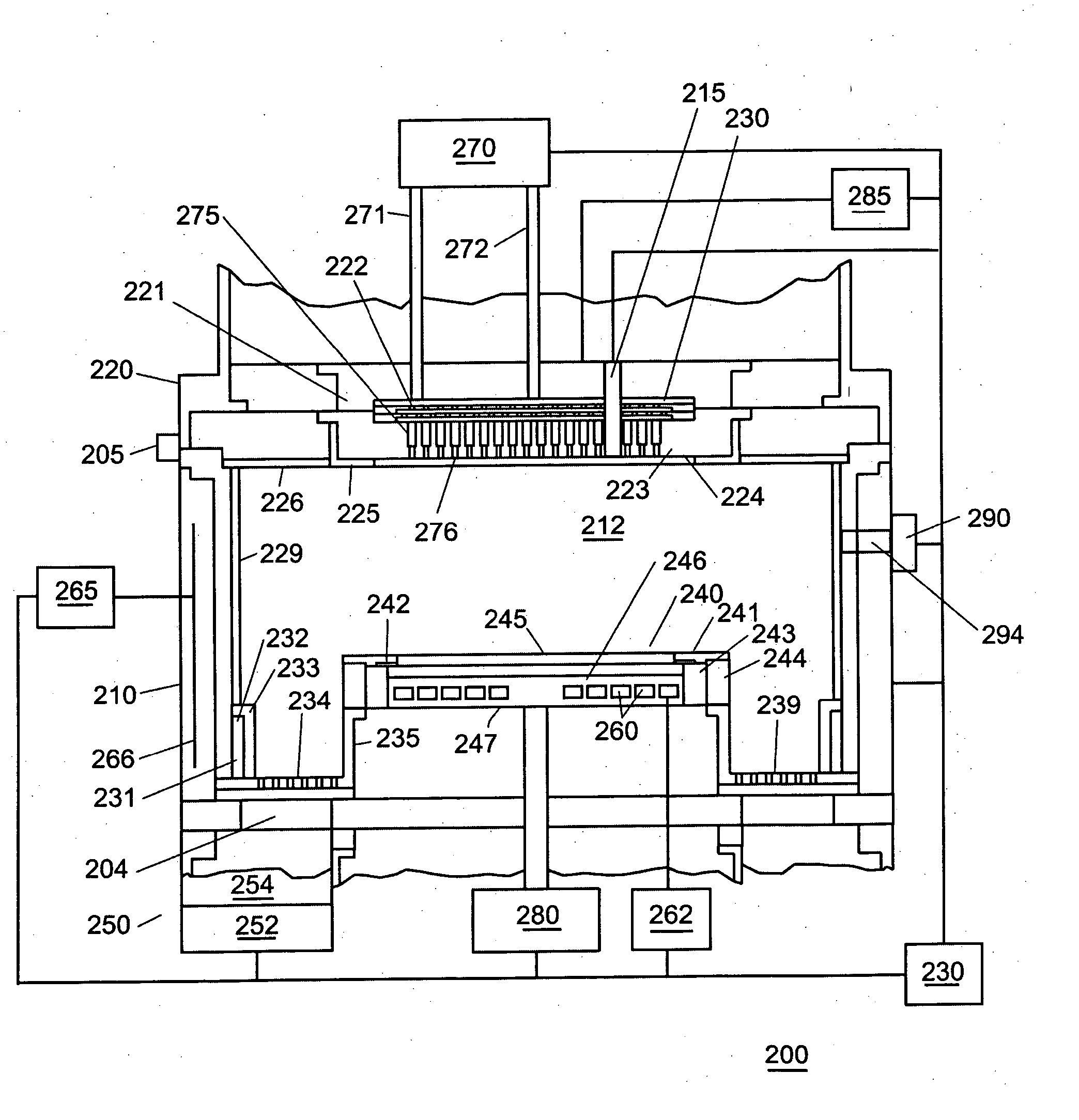
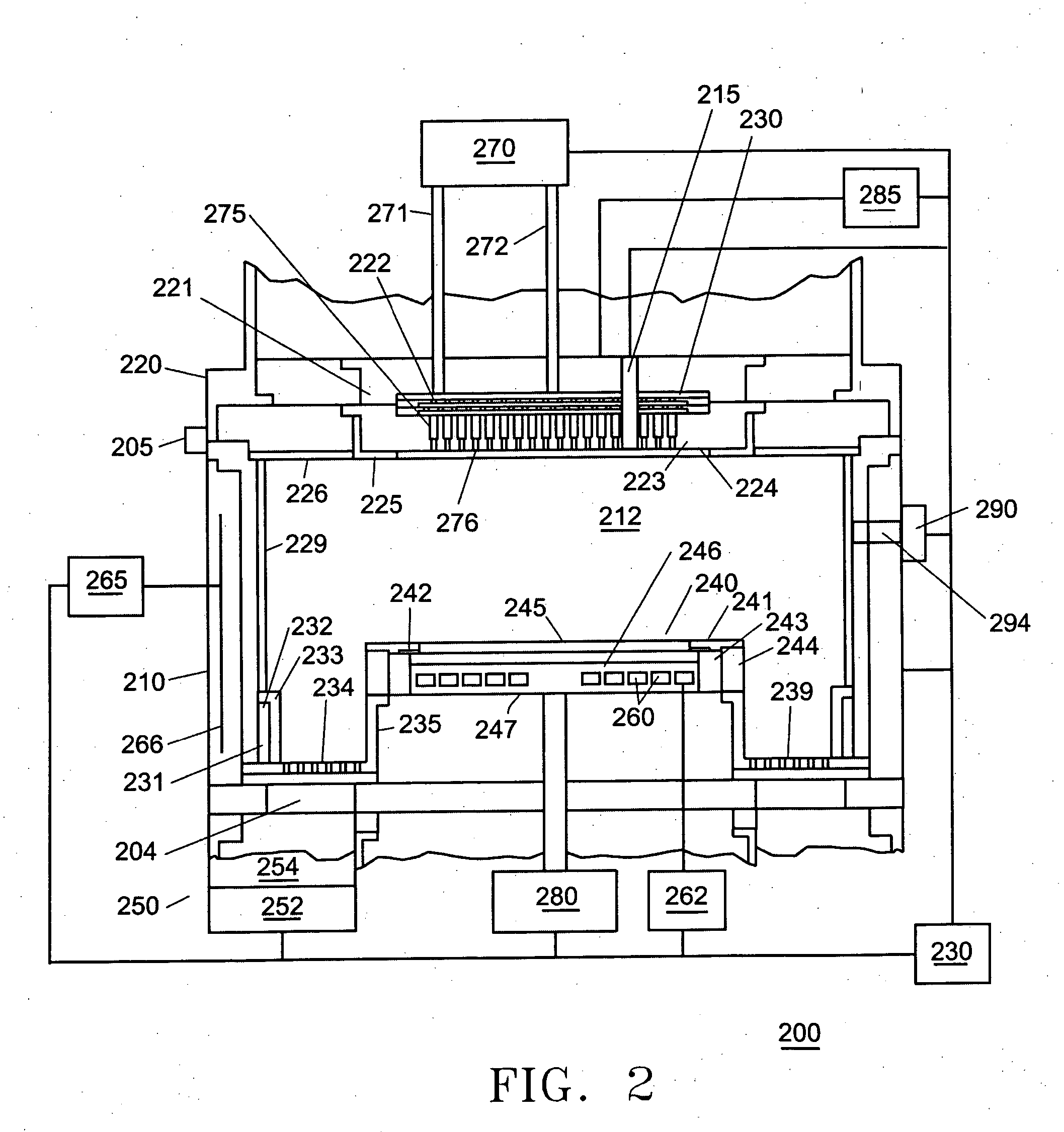
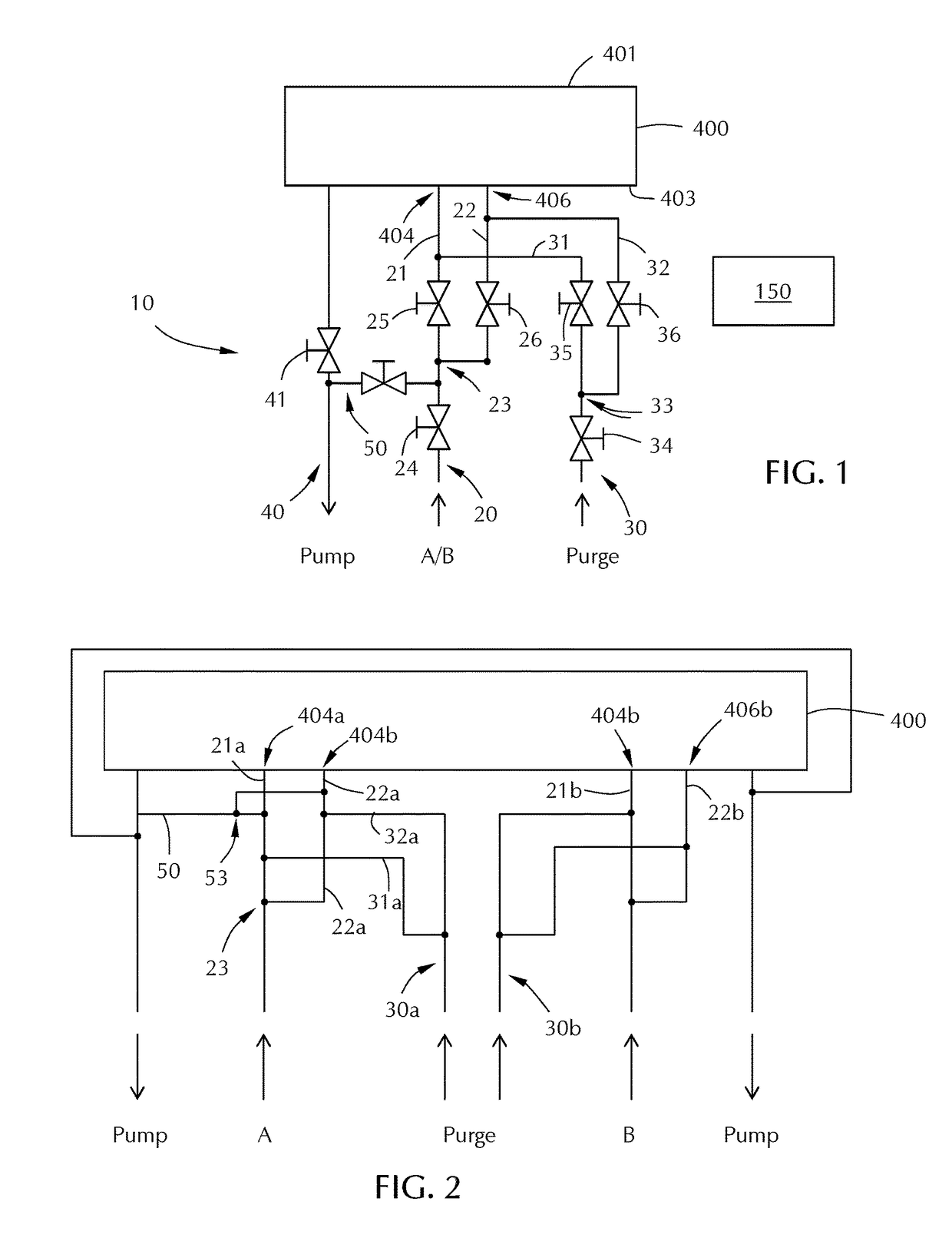
Enhancement of remote plasma source clean for dielectric films
Methods for cleaning semiconductor processing chambers used to process carbon-containing films, such as amorphous carbon films, barrier films comprising silicon and carbon, and low dielectric constant films including silicon, oxygen, and carbon are provided. The methods include using a remote plasma source to generate reactive species that clean interior surfaces of a processing chamber in the absence of RF power in the chamber. The reactive species are generated from an oxygen-containing gas, such as O2, and / or a halogen-containing gas, such as NF3. An oxygen-based ashing process may also be used to remove carbon deposits from the interior surfaces of the chamber before the chamber is exposed to the reactive species from the remote plasma source.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
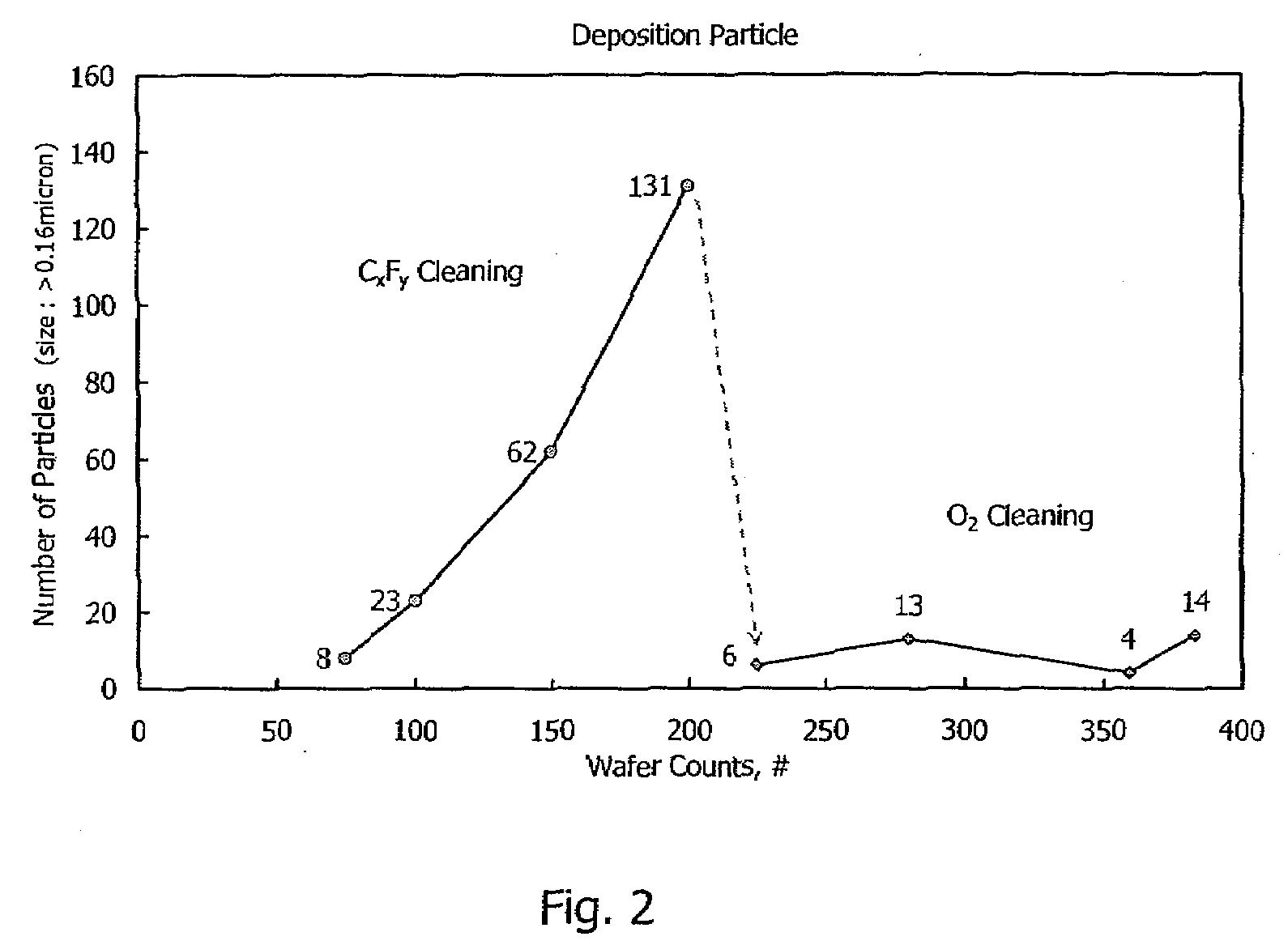
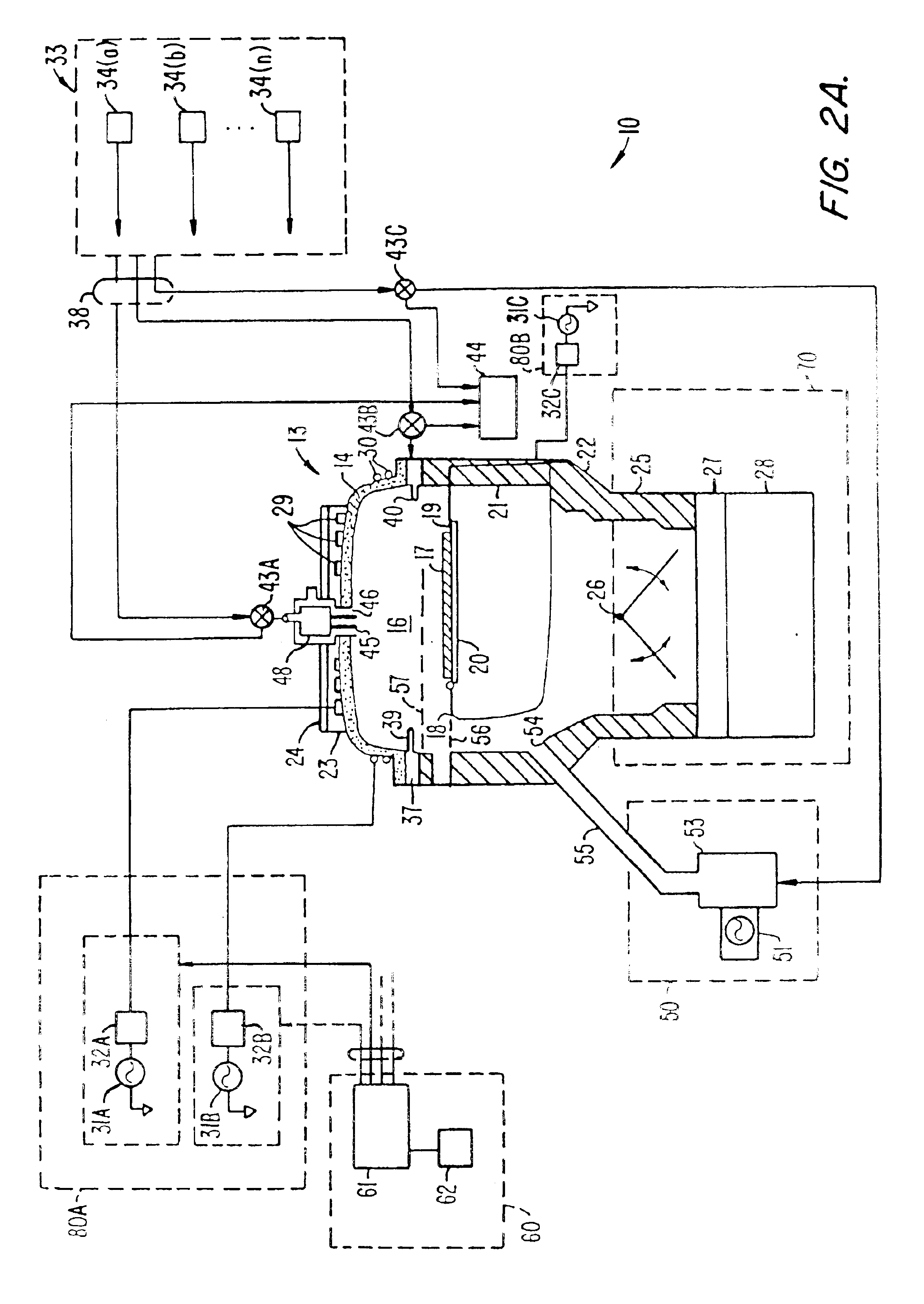
Method of cleaning etching apparatus
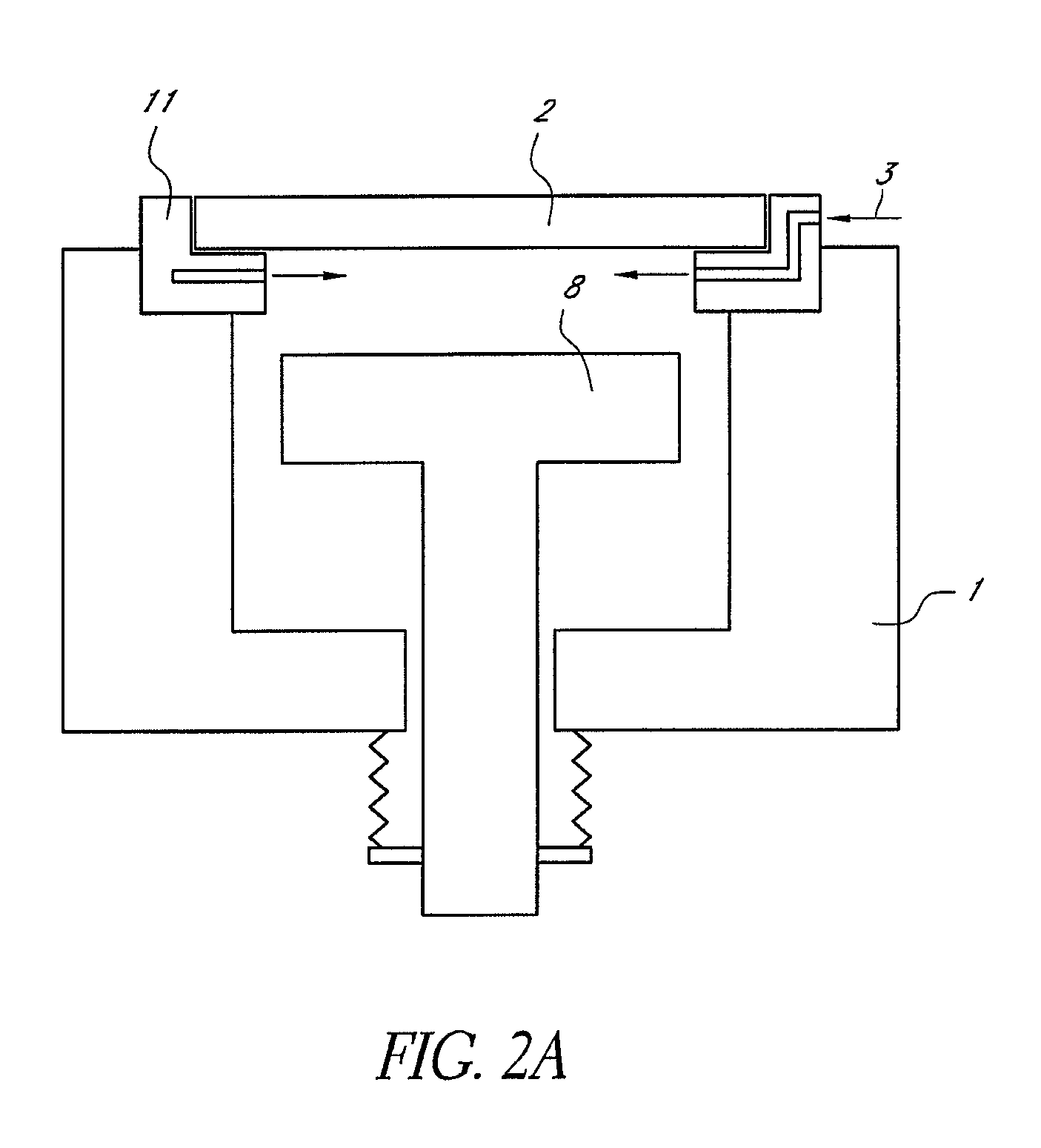
ActiveUS20060191555A1Clean interiorMaintain repeatabilityHollow article cleaningElectrostatic cleaningBoron trichlorideOxygen
To provide a cleaning method for an etching apparatus for a metal film that efficiently removes an etching residue deposited in an etching process chamber, assures the reproducibility of the etching performance, and keeps the etching process chamber in a low-dust-emission condition. Each time one workpiece with a metal film is etched (S1), the interior of the vacuum chamber is cleaned by replacing the workpiece with a dummy substrate (S2), performing a first step of plasma processing using oxygen (O2) and carbon tetrafluoride (CF4) to remove a carbon-based deposit pile (S3), and performing a second step of plasma processing using boron trichloride (BCl3) and chlorine (Cl2) to remove a residue that could not be removed by the first step and an etching residue of the metal film (S4).
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
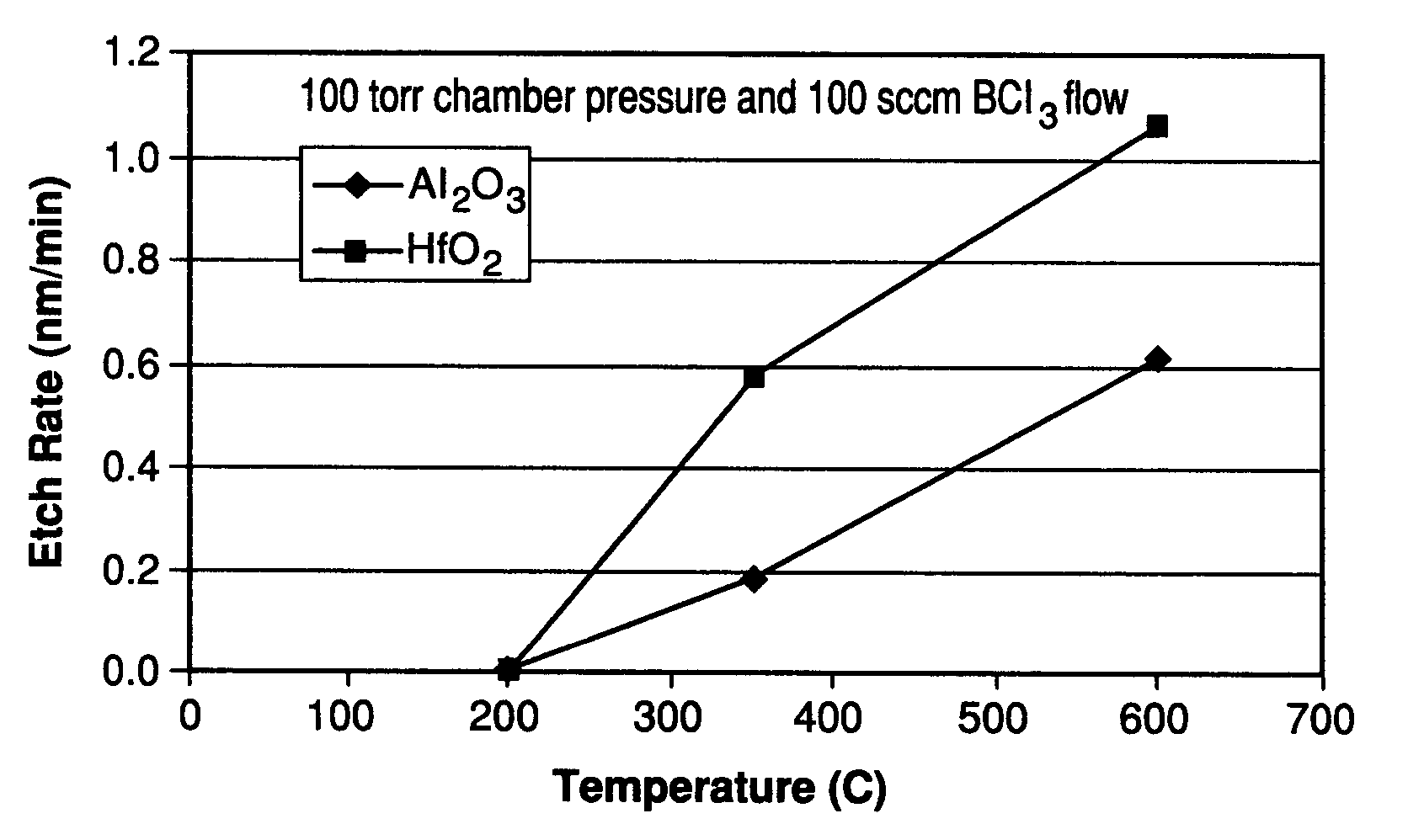
Method for etching high dielectric constant materials and for cleaning deposition chambers for high dielectric constant materials
A process for the removal of a substance from a substrate for etching and / or cleaning applications is disclosed herein. In one embodiment, there is provided a process for removing a substance having a dielectric constant greater than silicon dioxide from a substrate by reacting the substance with a reactive agent that comprises at least one member from the group consisting a halogen-containing compound, a boron-containing compound, a hydrogen-containing compound, nitrogen-containing compound, a chelating compound, a carbon-containing compound, a chlorosilane, a hydrochlorosilane, or an organochlorosilane to form a volatile product and removing the volatile product from the substrate to thereby remove the substance from the substrate.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Method of cleaning a chemical vapor deposition chamber
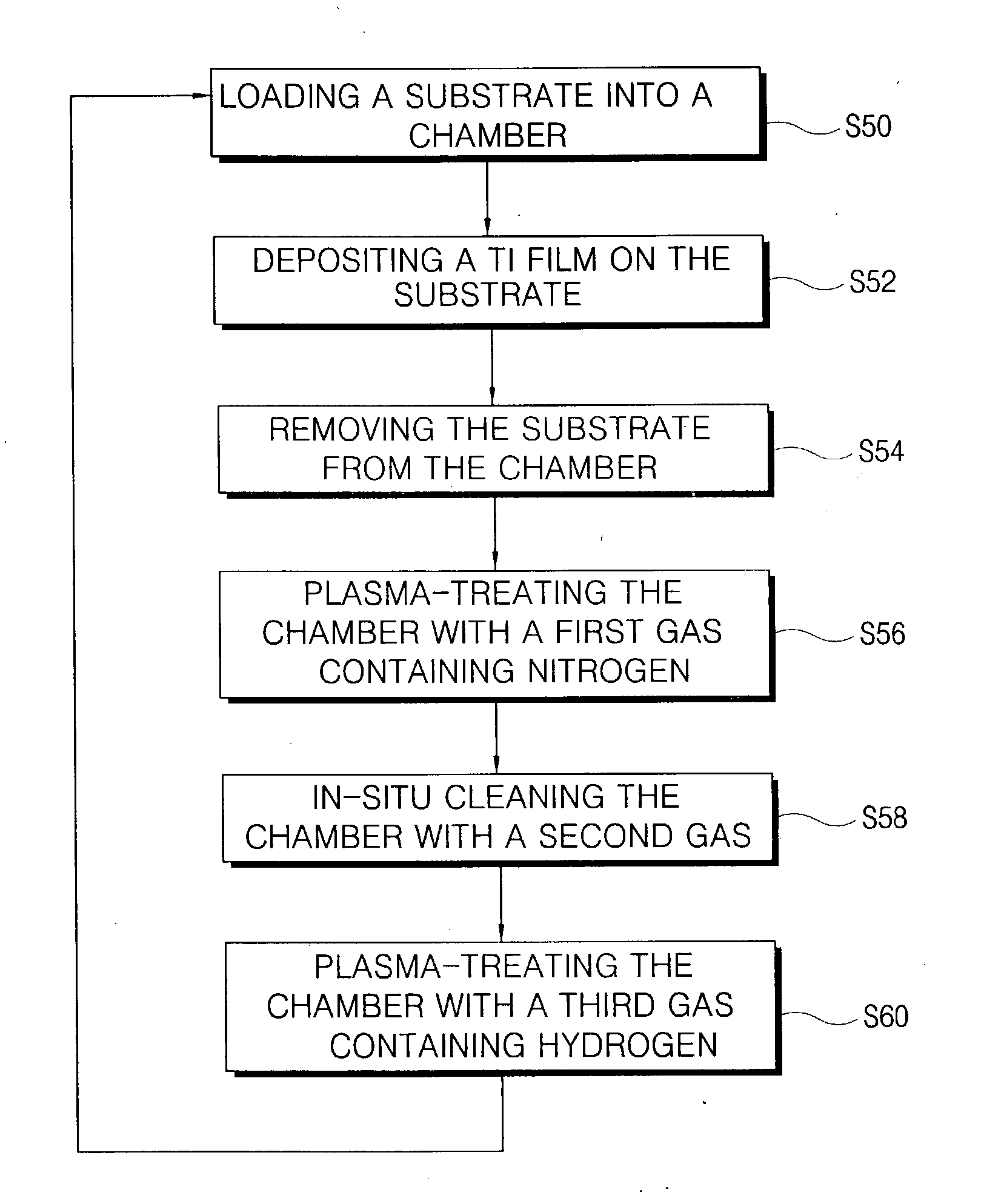
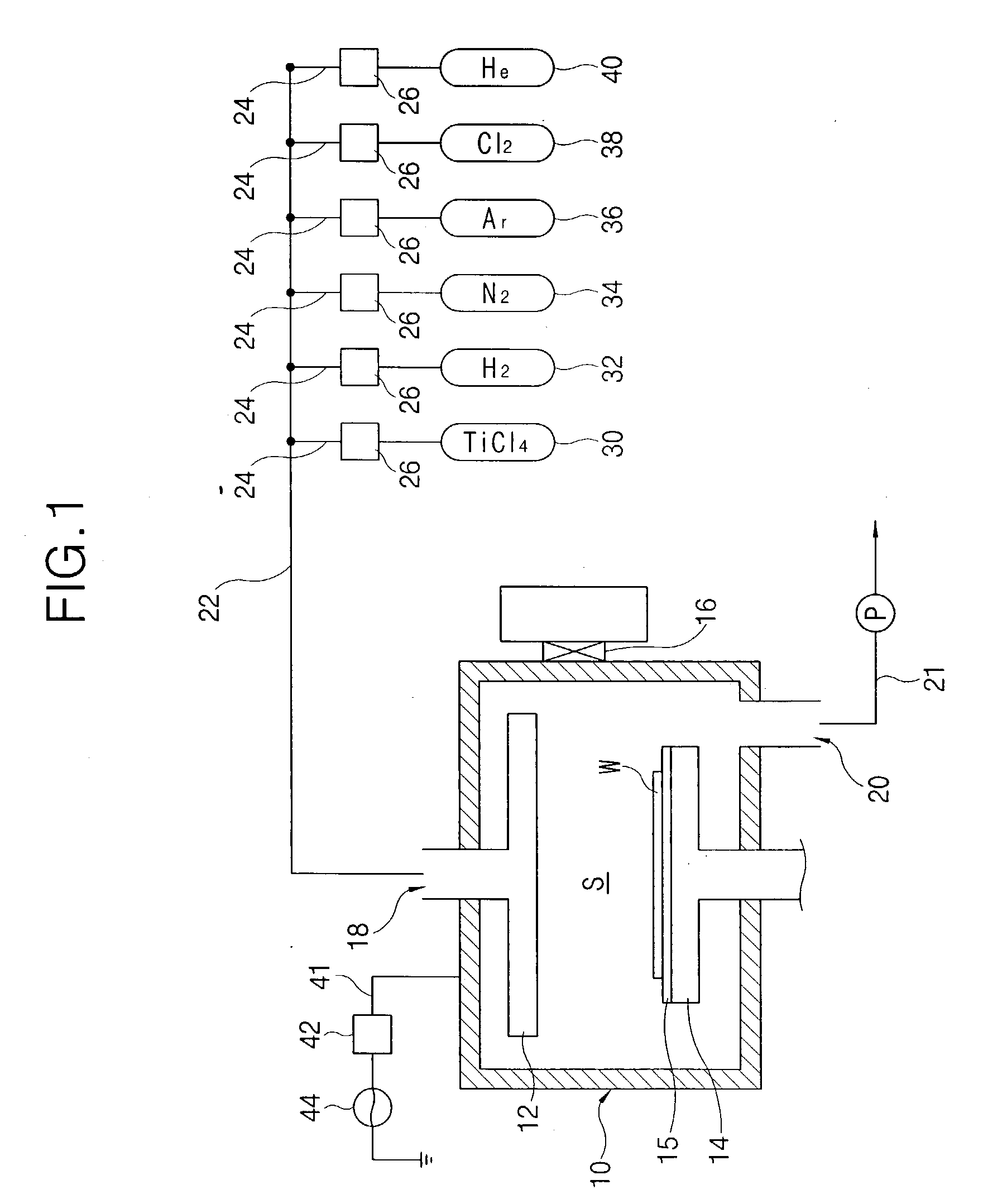
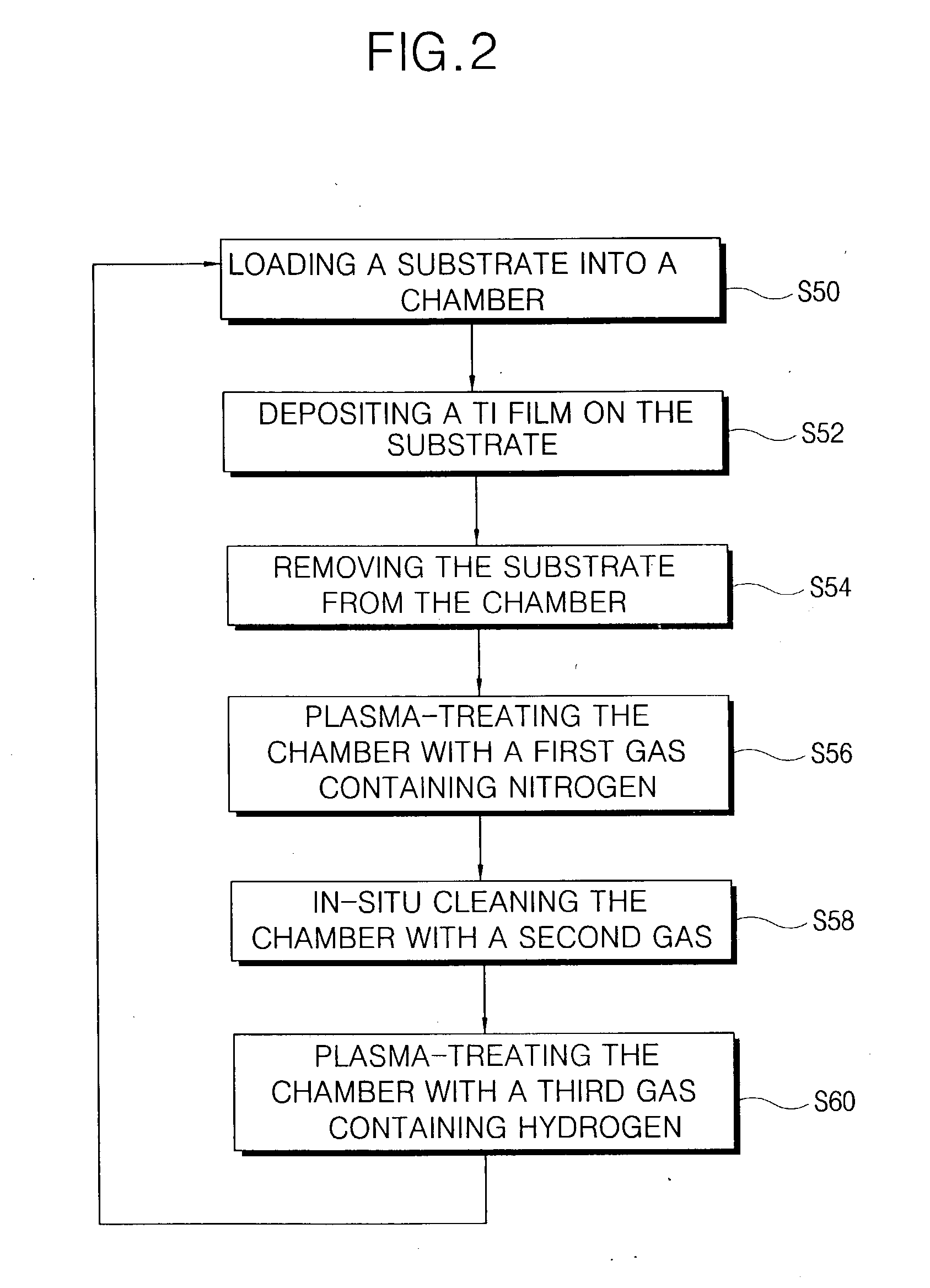
InactiveUS20040013818A1Reduce the amount requiredIncrease resistanceHollow article cleaningElectrostatic cleaningHydrogenNitrogen
After a processing chamber is used to deposit a refractory metal film on a substrate, the chamber is plasma-treated with a gas including either nitrogen and / or hydrogen and in-situ cleaned. By plasma-treating the chamber with a gas including nitrogen, the refractory metal film that forms on interior surfaces of the chamber during substrate processing is nitrided. The nitrided refractory metal film can be removed from the chamber during the in-situ cleaning. By plasma-treating the chamber with a gas including hydrogen, reaction by-products generated in the chamber is diluted and removed. The chamber may be plasma-treated in a gas ambient including both nitrogen and hydrogen. Also, the plasma treatment may be performed before and after the in-situ cleaning.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Plasma clean method for deposition chamber
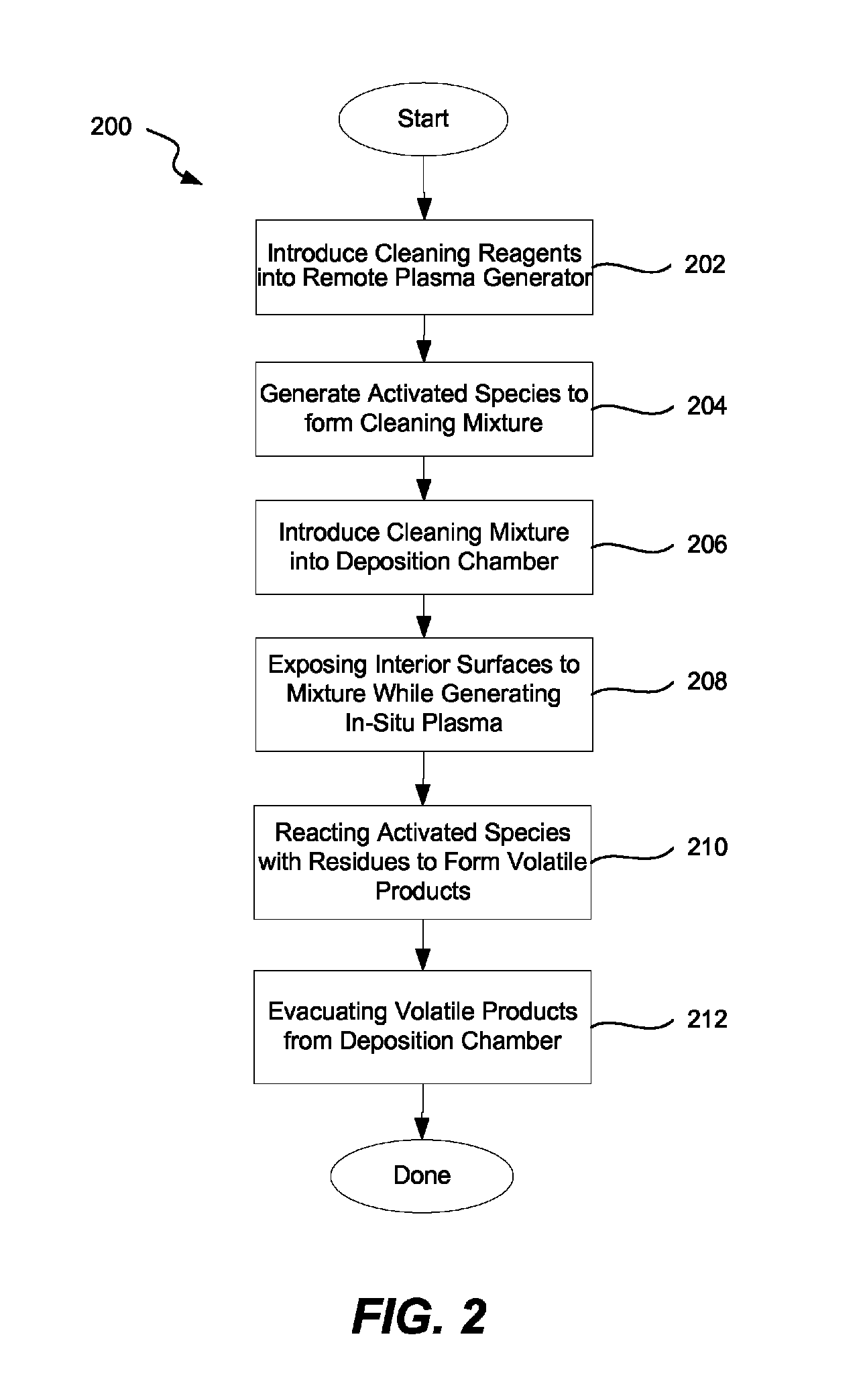
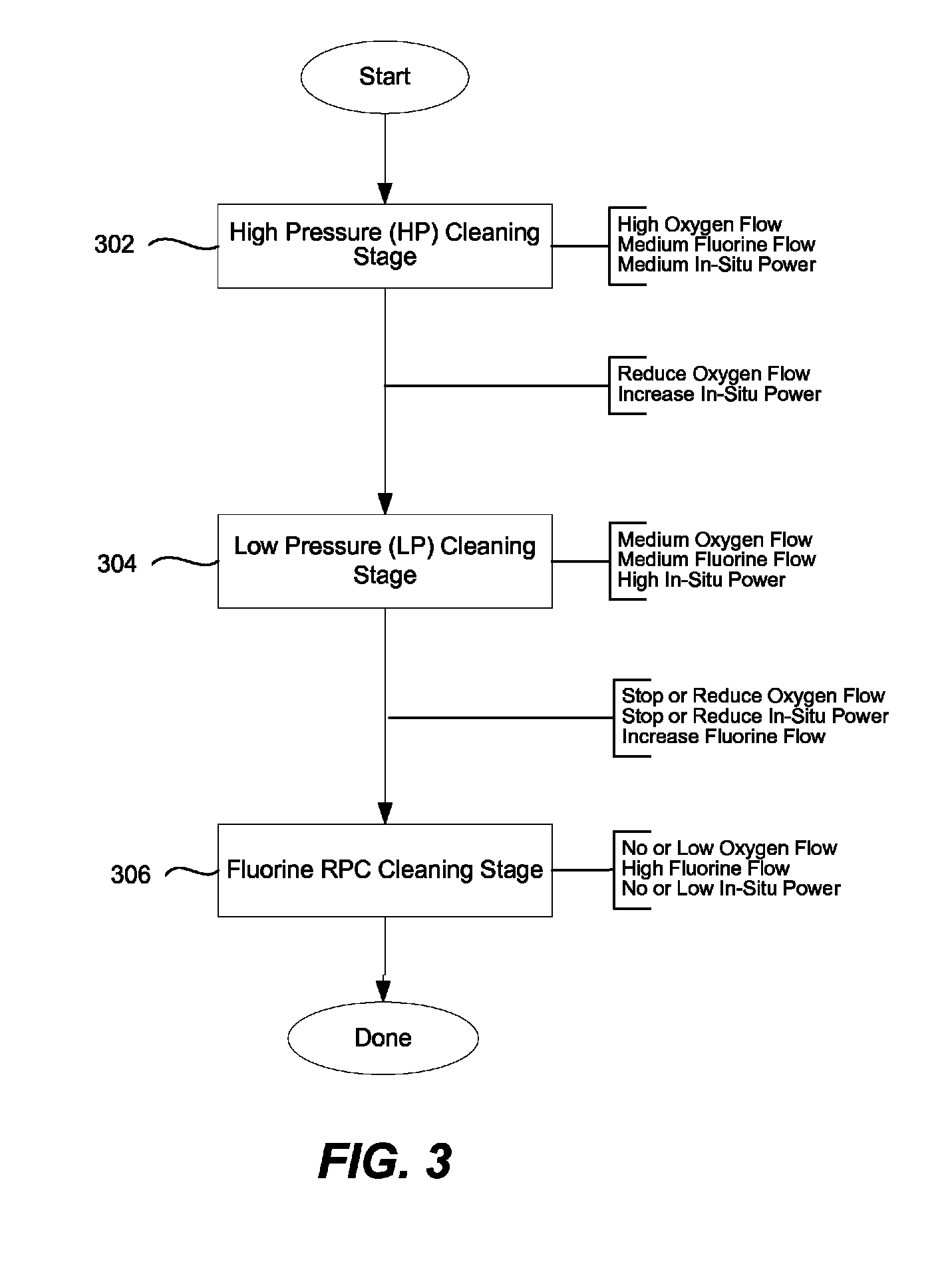
ActiveUS8591659B1Improve cleaning efficiencyEasy to cleanElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsRemote plasmaImproved method
Improved methods and apparatuses for removing residue from the interior surfaces of the deposition reactor are provided. The methods involve increasing availability of cleaning reagent radicals inside the deposition chamber by generating cleaning reagent radicals in a remote plasma generator and then further delivering in-situ plasma energy while the cleaning reagent mixture is introduced into the deposition chamber. Certain embodiments involve a multi-stage process including a stage in which the cleaning reagent mixture is introduced at a high pressure (e.g., about 0.6 Torr or more) and a stage the cleaning reagent mixture is introduced at a low pressure (e.g., about 0.6 Torr or less).
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Method of cleaning UV irradiation chamber
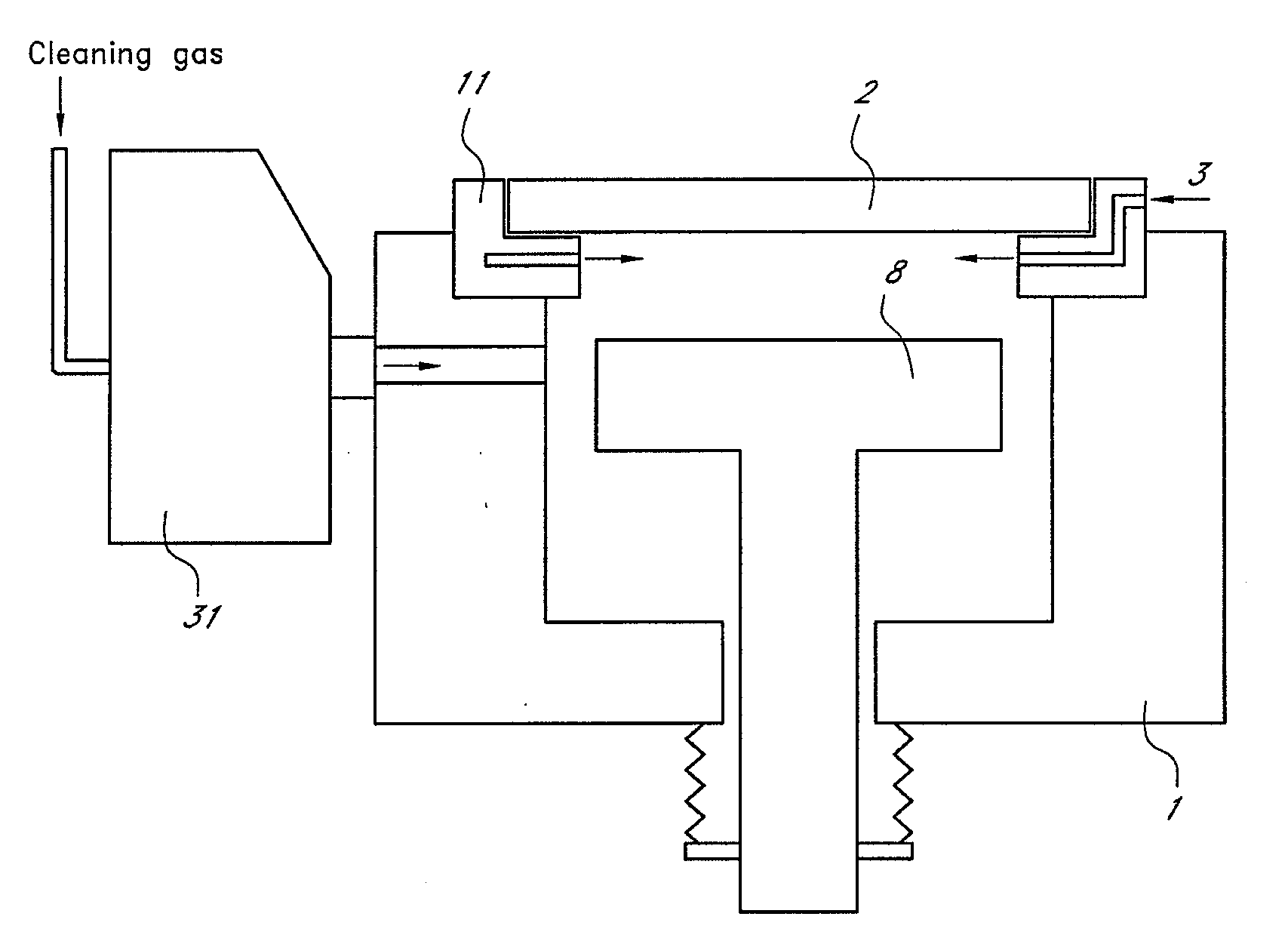
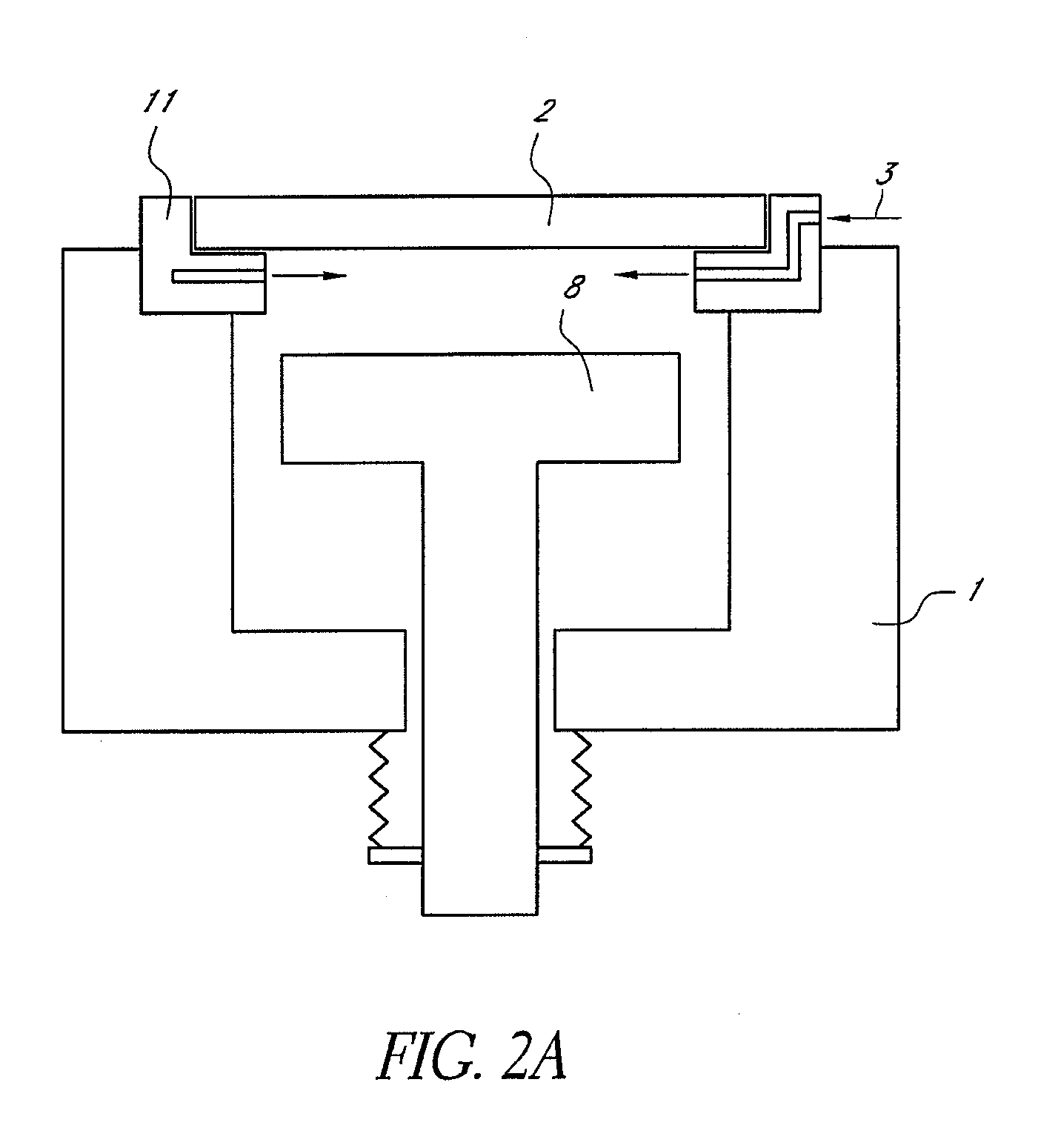
ActiveUS7789965B2Improve efficiencyKeep for a long timeLighting and heating apparatusHollow article cleaningIrradiationPhotochemistry
A method of cleaning a UV irradiation chamber includes steps of: (i) after completion of irradiating a substrate with UV light transmitted through an optical transmitted window provided in the UV irradiation chamber, generating radical species of a cleaning gas outside the UV irradiation chamber; and (ii) introducing the radical species from the outside of the UV irradiation chamber into the UV irradiation chamber, thereby cleaning the optical transmitted window.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
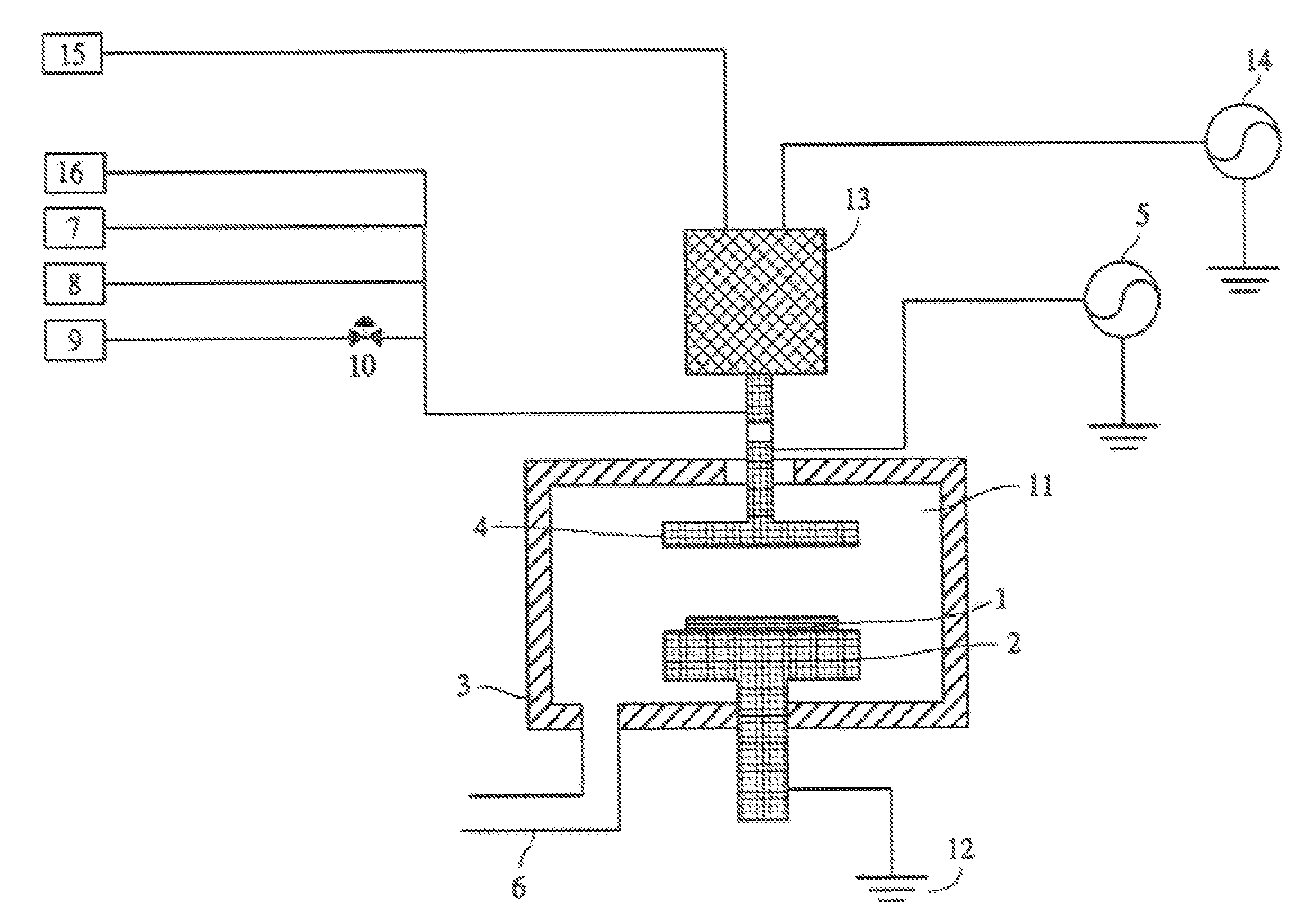
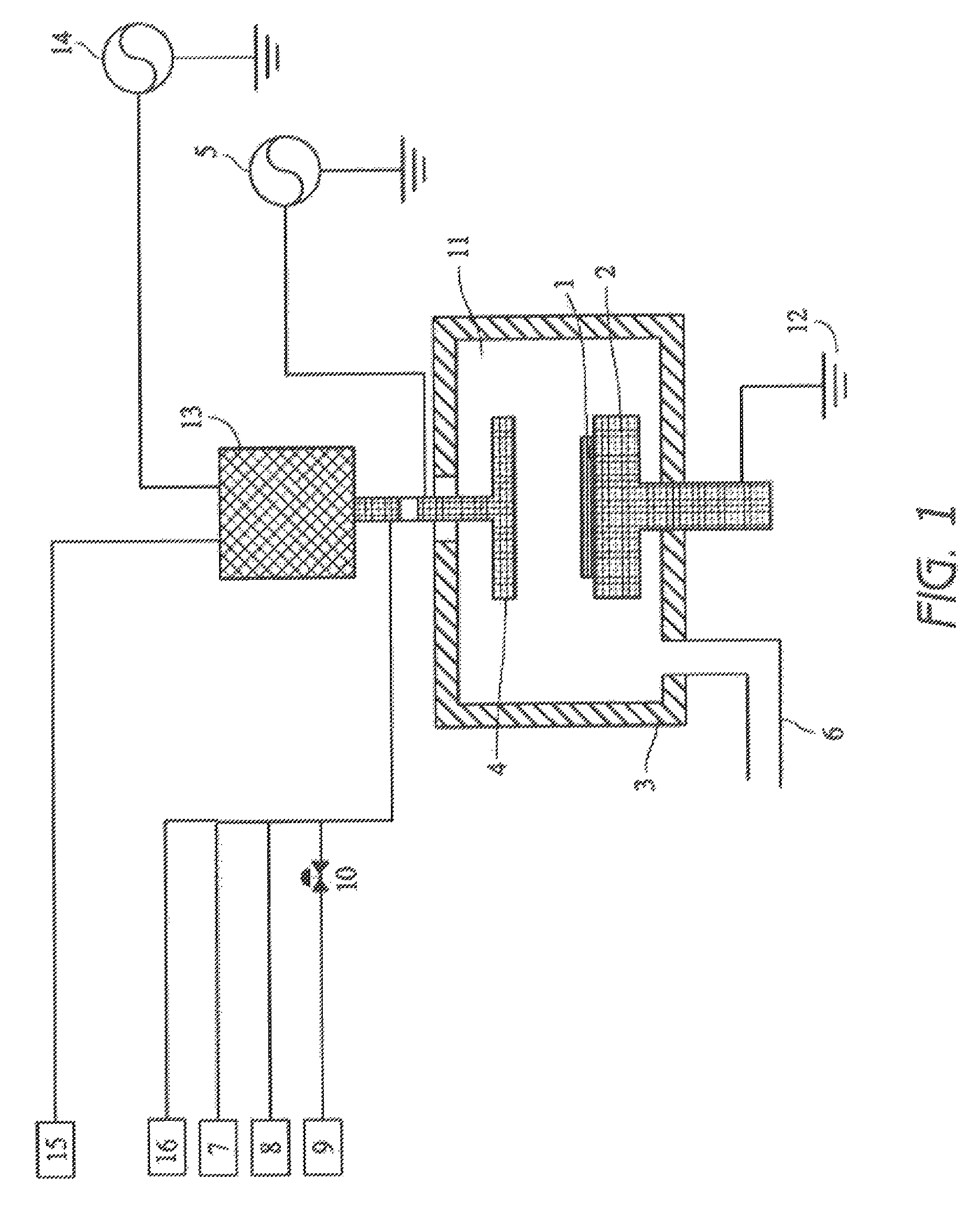
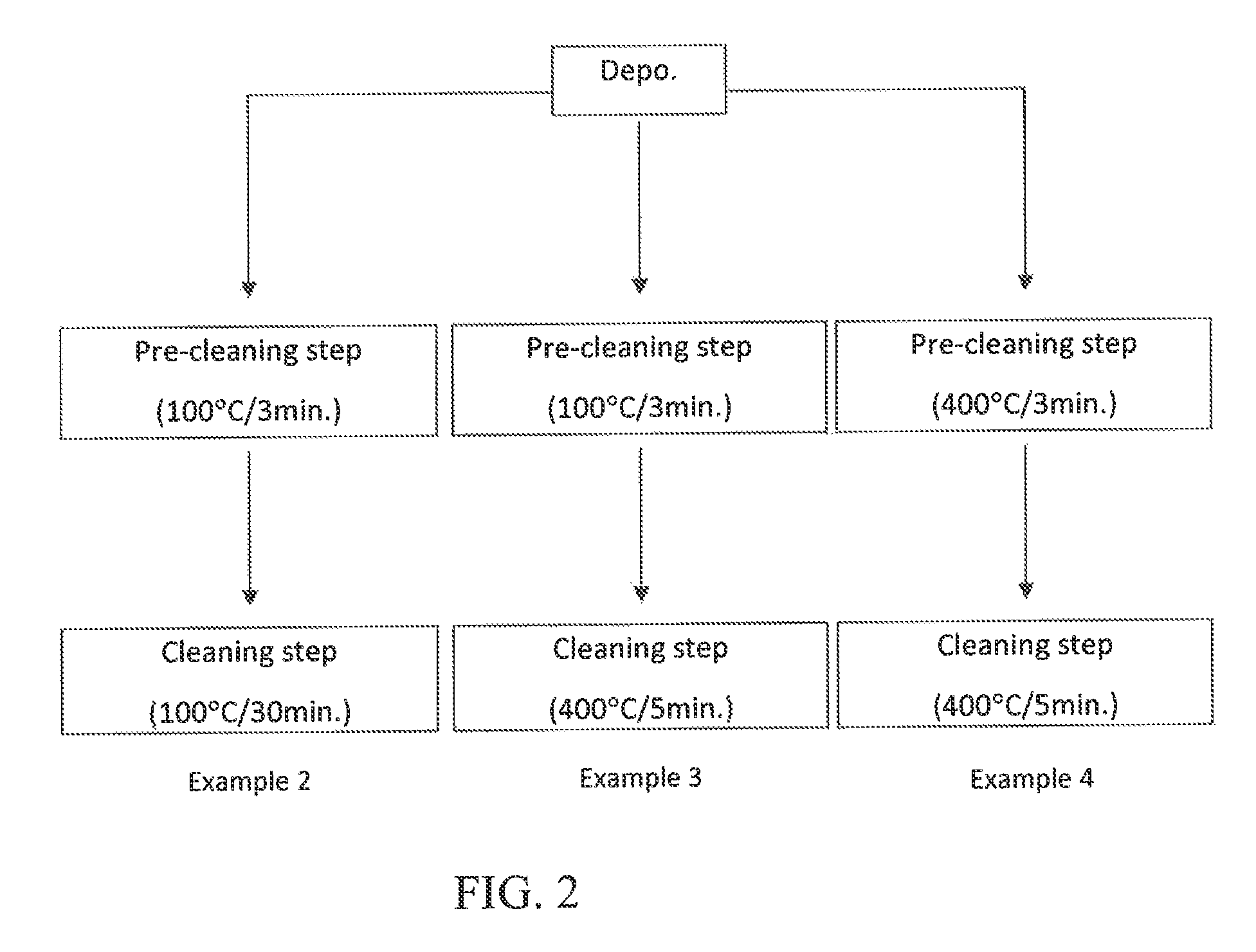
Method for cleaning reaction chamber using pre-cleaning process
ActiveUS9142393B2Improve efficiencyElectric discharge tubesHollow article cleaningNitrogenSilicon oxide
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method of cleaning UV irradiation chamber
ActiveUS20080066778A1Improve efficiencyLong cleaning timeLighting and heating apparatusHollow article cleaningIrradiationPhotochemistry
A method of cleaning a UV irradiation chamber includes steps of: (i) after completion of irradiating a substrate with UV light transmitted through an optical transmitted window provided in the UV irradiation chamber, generating radical species of a cleaning gas outside the UV irradiation chamber; and (ii) introducing the radical species from the outside of the UV irradiation chamber into the UV irradiation chamber, thereby cleaning the optical transmitted window.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Method of self-cleaning of carbon-based film
InactiveUS20070248767A1Hollow article cleaningVacuum evaporation coatingNitrogen oxidePlasma reactor
A method of self-cleaning a plasma reactor upon depositing a carbon-based film on a substrate a pre-selected number of times, includes: (i) exciting oxygen gas and / or nitrogen oxide gas to generate a plasma; and (ii) exposing to the plasma a carbon-based film accumulated on an upper electrode provided in the reactor and a carbon-based film accumulated on an inner wall of the reactor.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
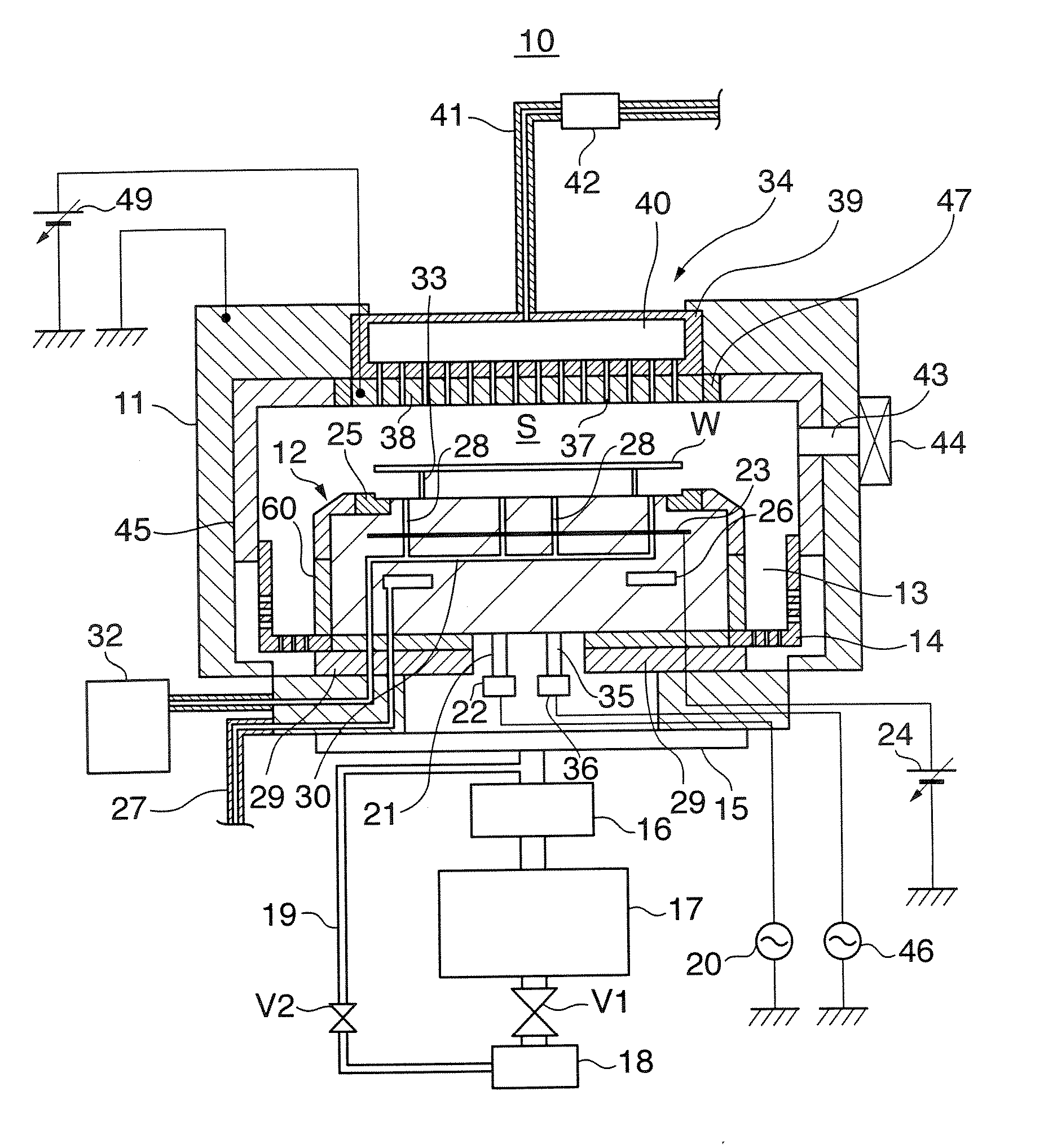
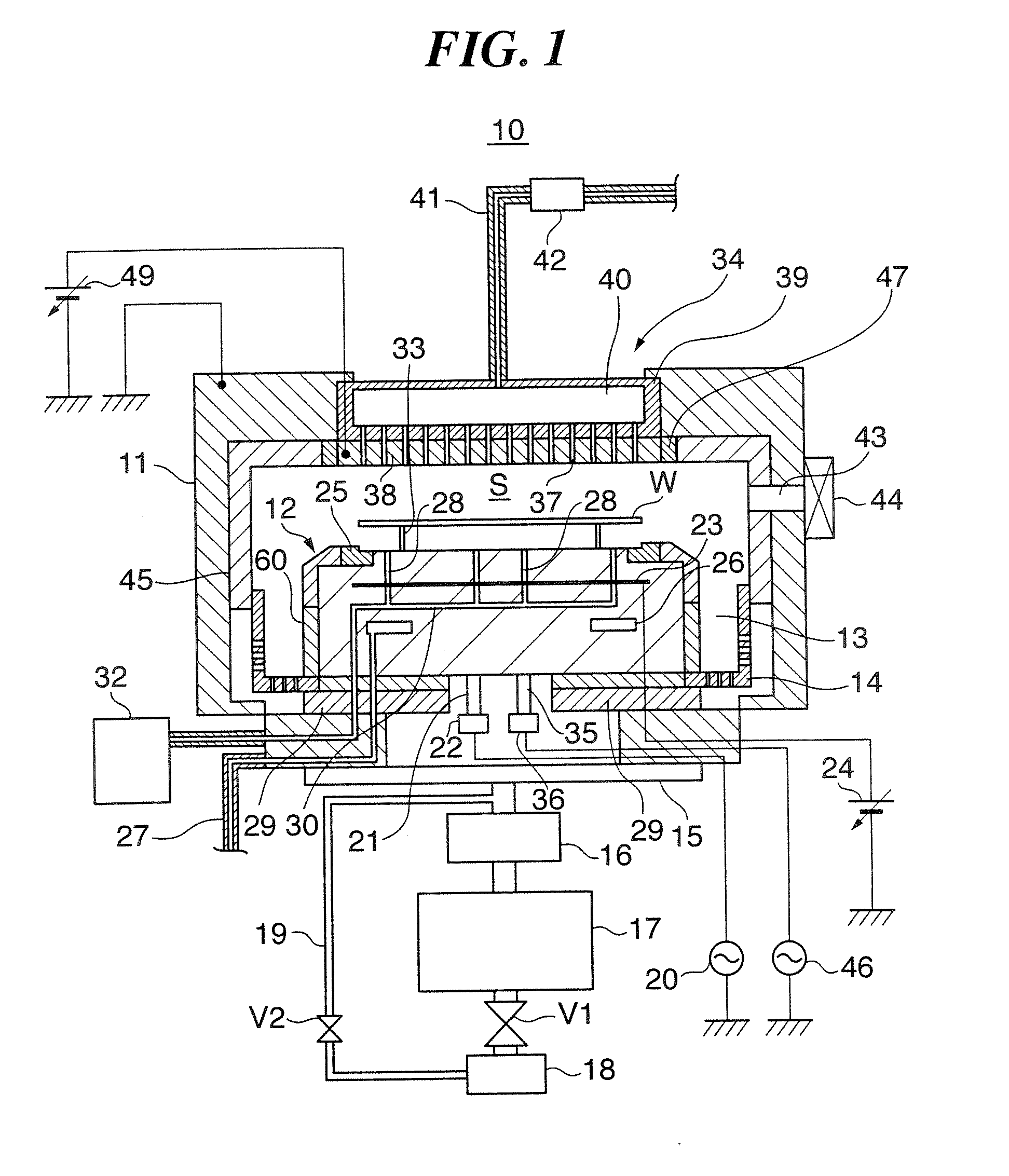
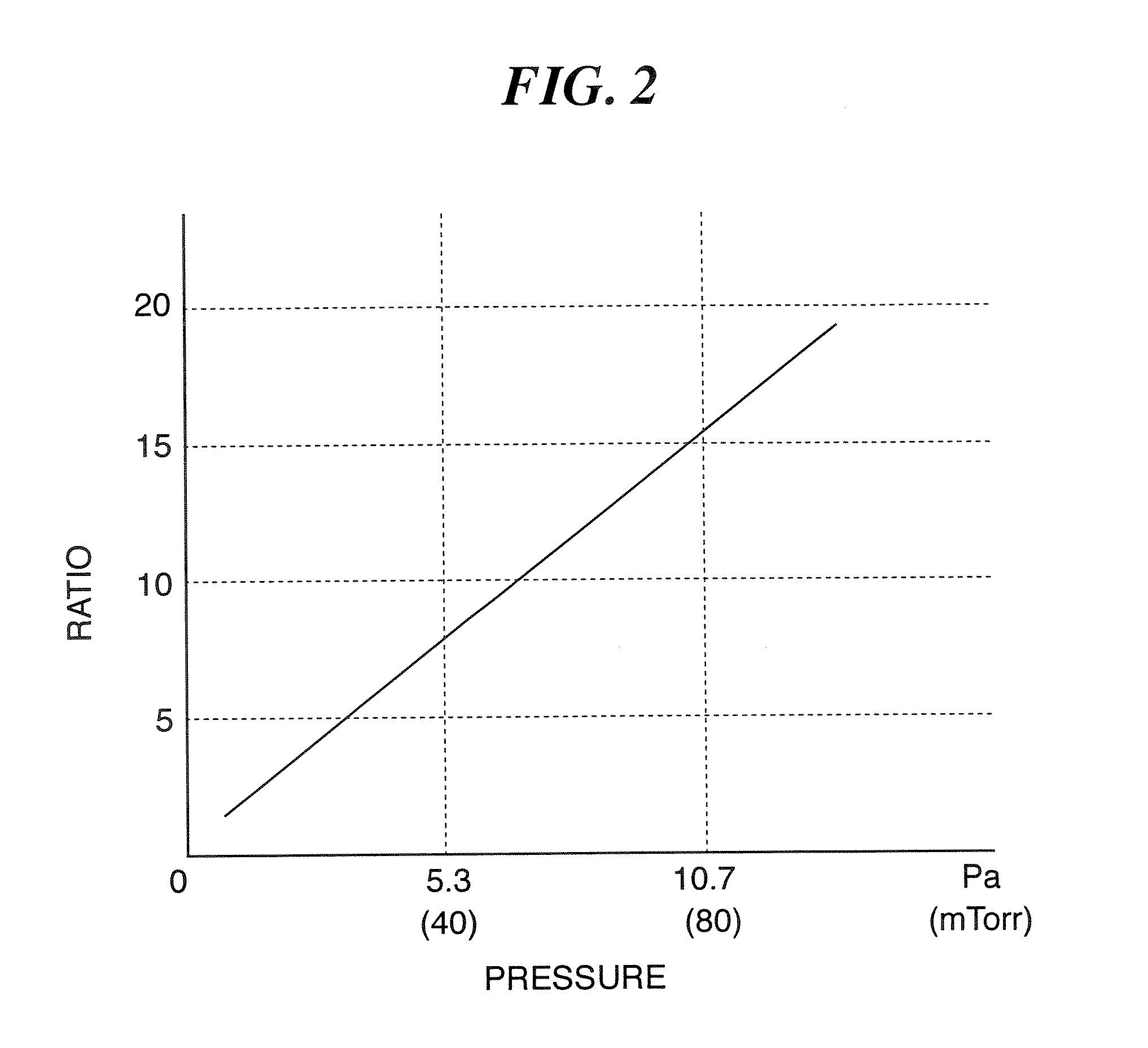
Method of cleaning substrate processing chamber, storage medium, and substrate processing chamber
ActiveUS20070186952A1Inhibition formationElectric discharge tubesHollow article cleaningElectricityReactive-ion etching
A method of cleaning a substrate processing chamber that enables formation of an oxide film on a surface of a processing chamber inside component to be prevented. A substrate processing chamber 11 has therein a processing space S into which a wafer W is transferred and carries out reactive ion etching on the wafer W in the processing space S. The substrate processing chamber 11 has an upper electrode plate 38 that comprises silicon and a lower surface of which is exposed to the processing space S. A dry cleaning is carried out on the upper electrode plate 38 using oxygen radicals produced from oxygen gas introduced into the processing space S. An oxide removal processing is carried out on the upper electrode plate 38 using fluorine ions and fluorine radicals produced from carbon tetrafluoride gas introduced into the processing space S.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
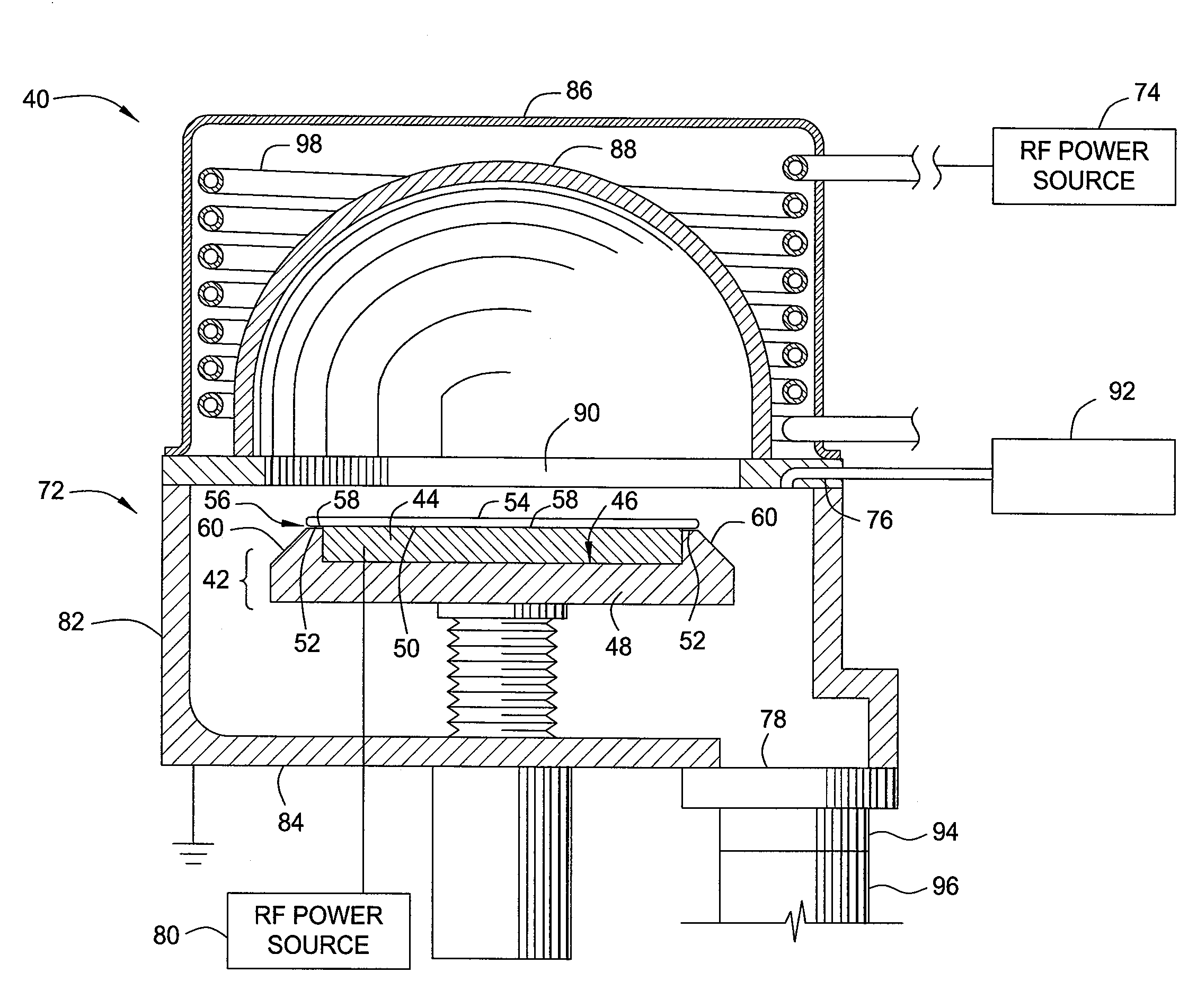
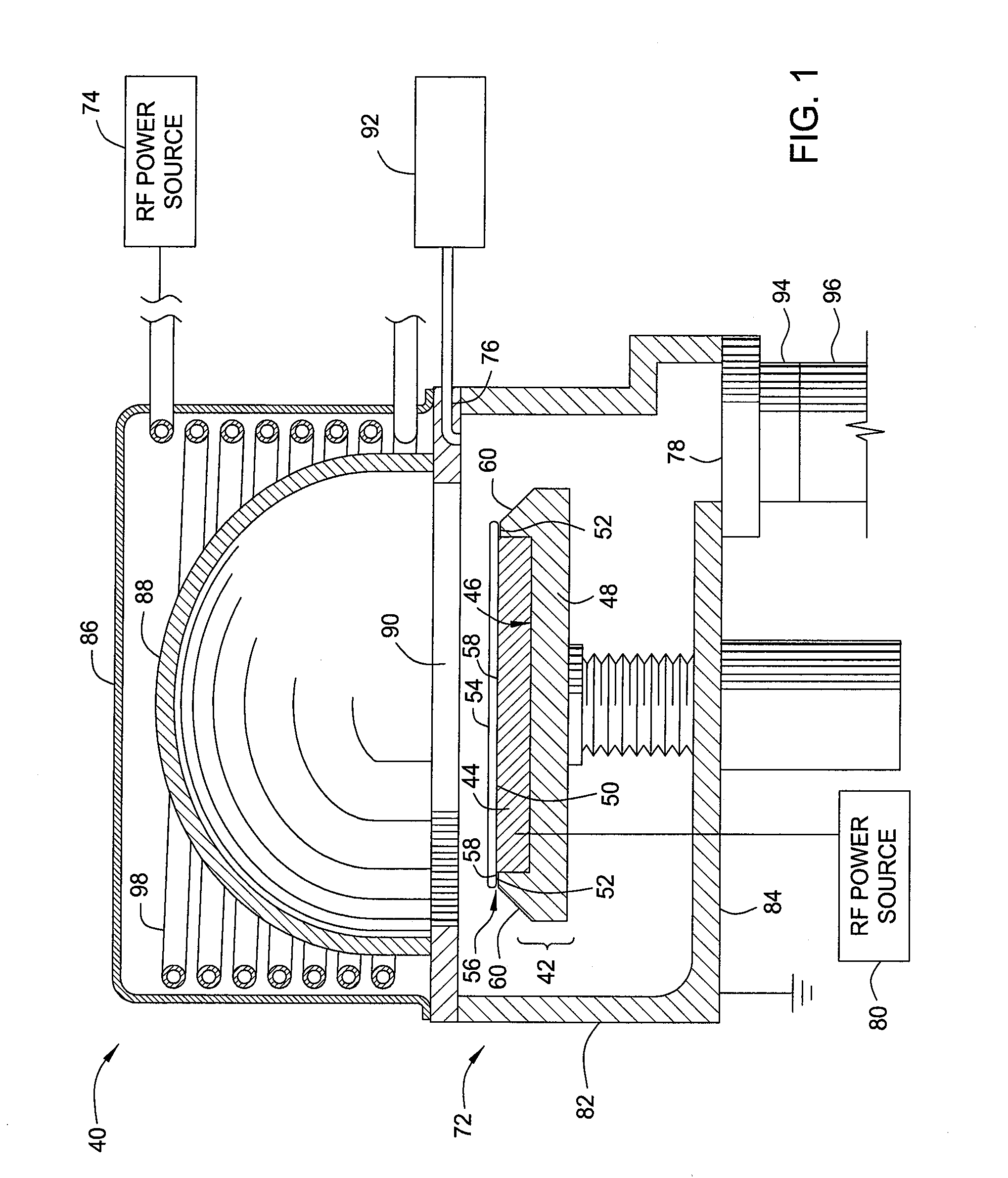
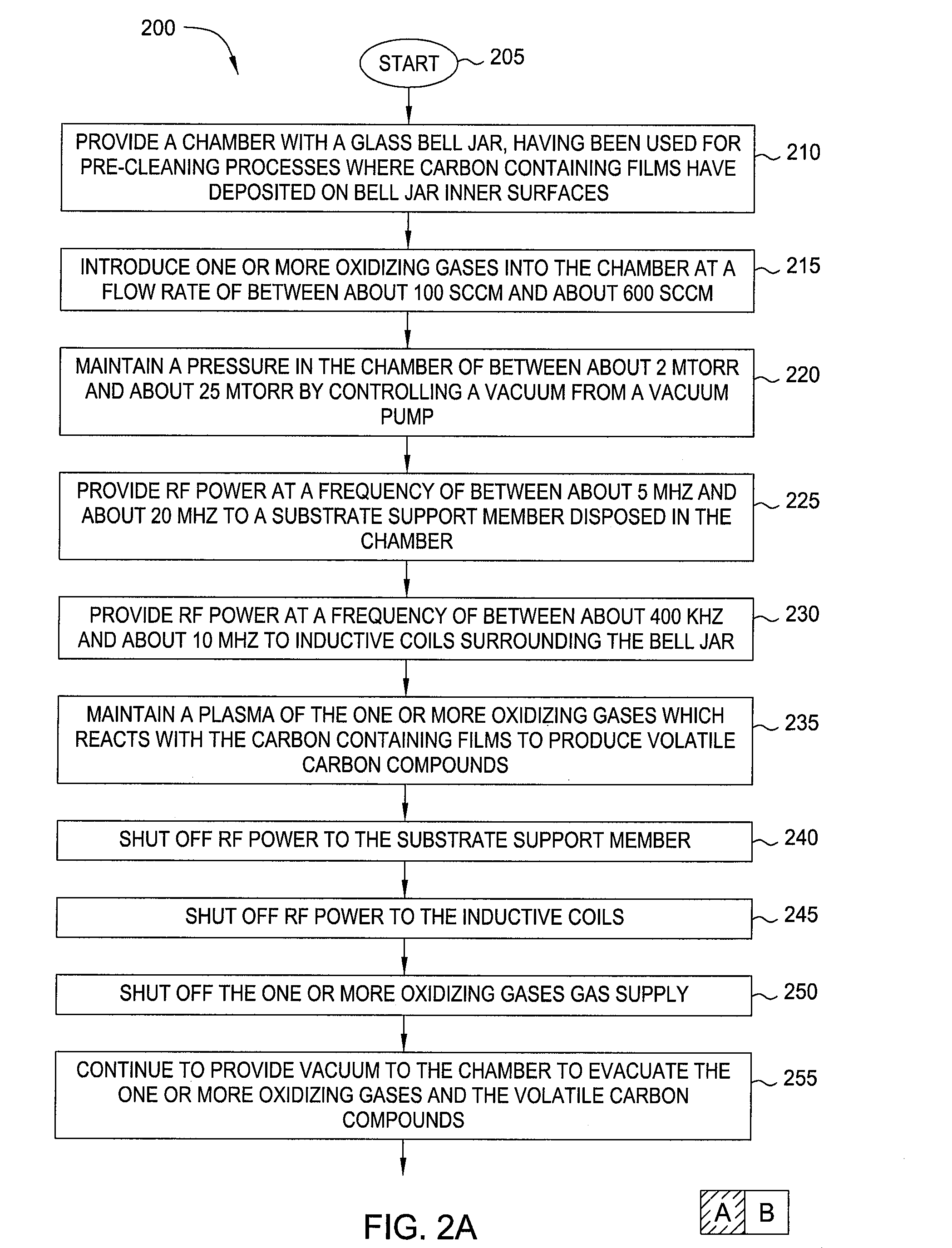
Oxygen plasma clean to remove carbon species deposited on a glass dome surface
InactiveUS20080173326A1Decorative surface effectsHollow article cleaningChemical compoundOxygen plasma
A method for in-situ cleaning of a dielectric dome surface having been used in pre-clean processes is provided. Carbon containing deposits are removed by providing a plasma of one or more oxidizing gases which react with the carbon containing films to form volatile carbon containing compounds.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method of cleaning CVD equipment processing chamber
ActiveUS7234476B2Reduce operating costsImprove efficiencyElectric discharge tubesHollow article cleaningRemote plasmaOperational costs
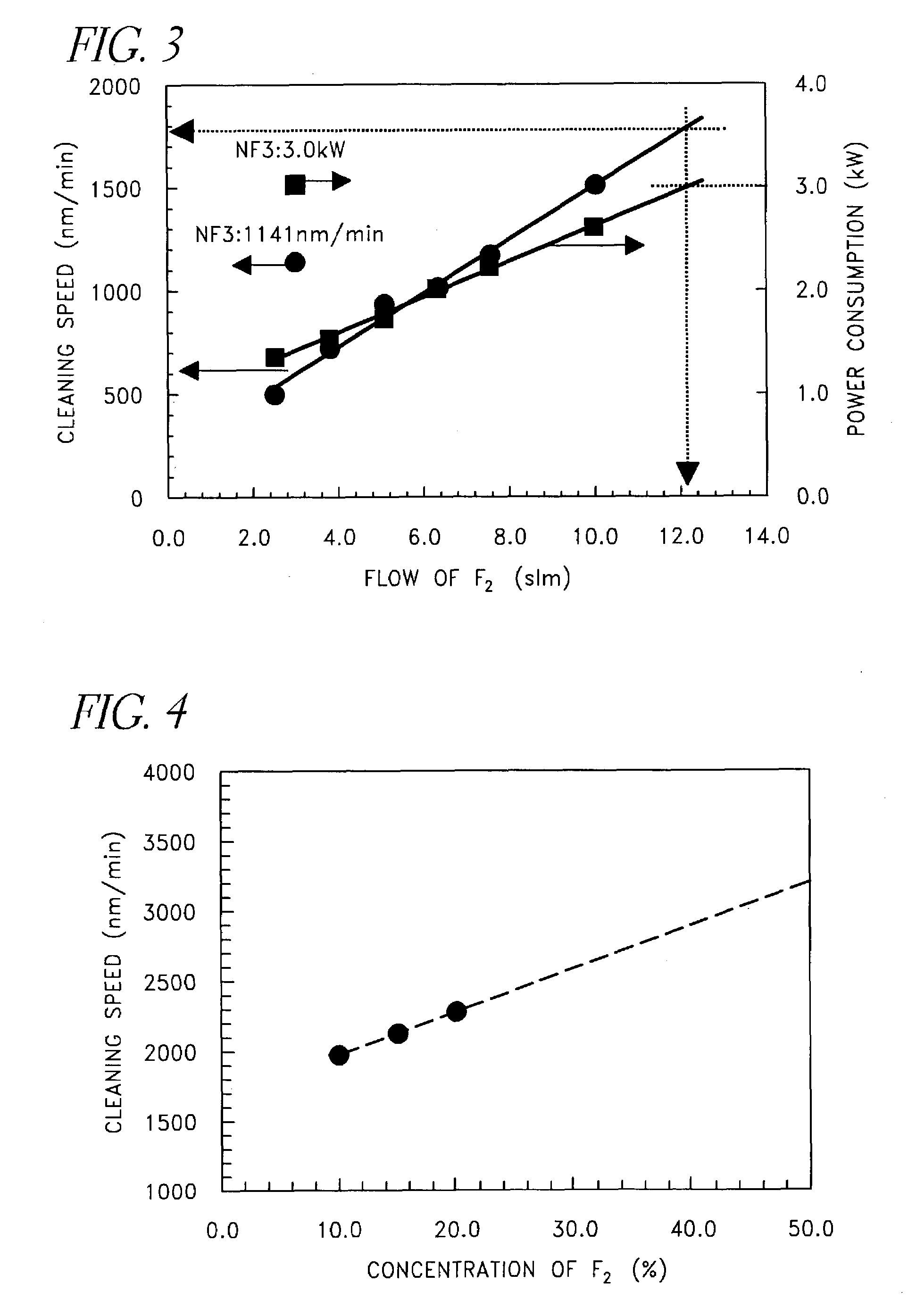
A method of remote plasma cleaning a processing chamber of CVD equipment, which has high cleaning rates, low cleaning operational cost and high efficiency, is provided. The method comprises supplying cleaning gas to the remote plasma-discharge device; activating the cleaning gas inside the remote plasma-discharge device; and bringing the activated cleaning gas into the processing chamber and which is characterized in that a mixed gas of F2 gas and an inert gas are used as the cleaning gas. A concentration of the F2 gas is 10% or higher. The F2 gas, which is a cleaning gas, is supplied to the remote plasma-discharge device from an F2 gas cylinder by diluting F2 gas at a given concentration by an inert gas.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
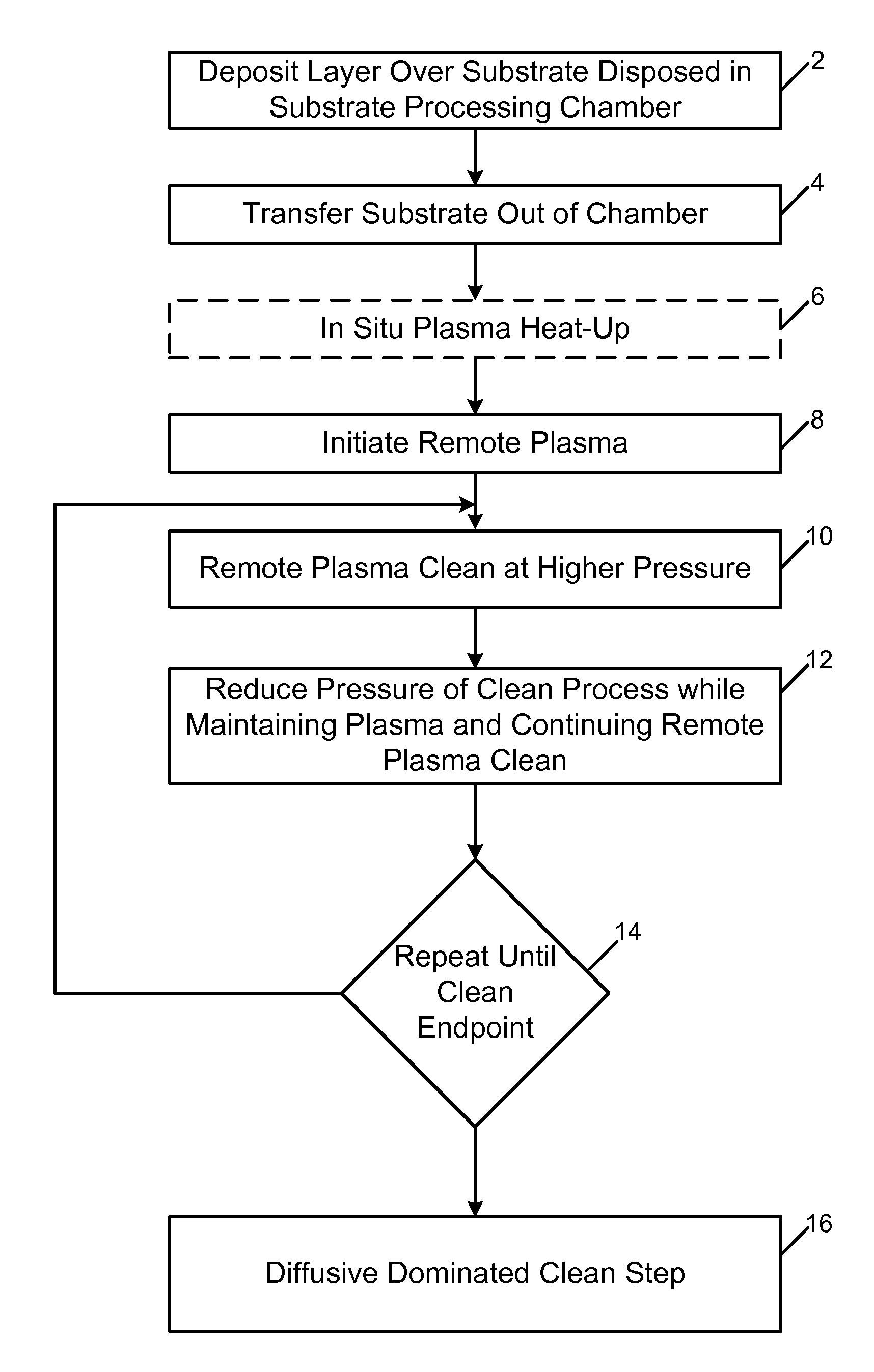
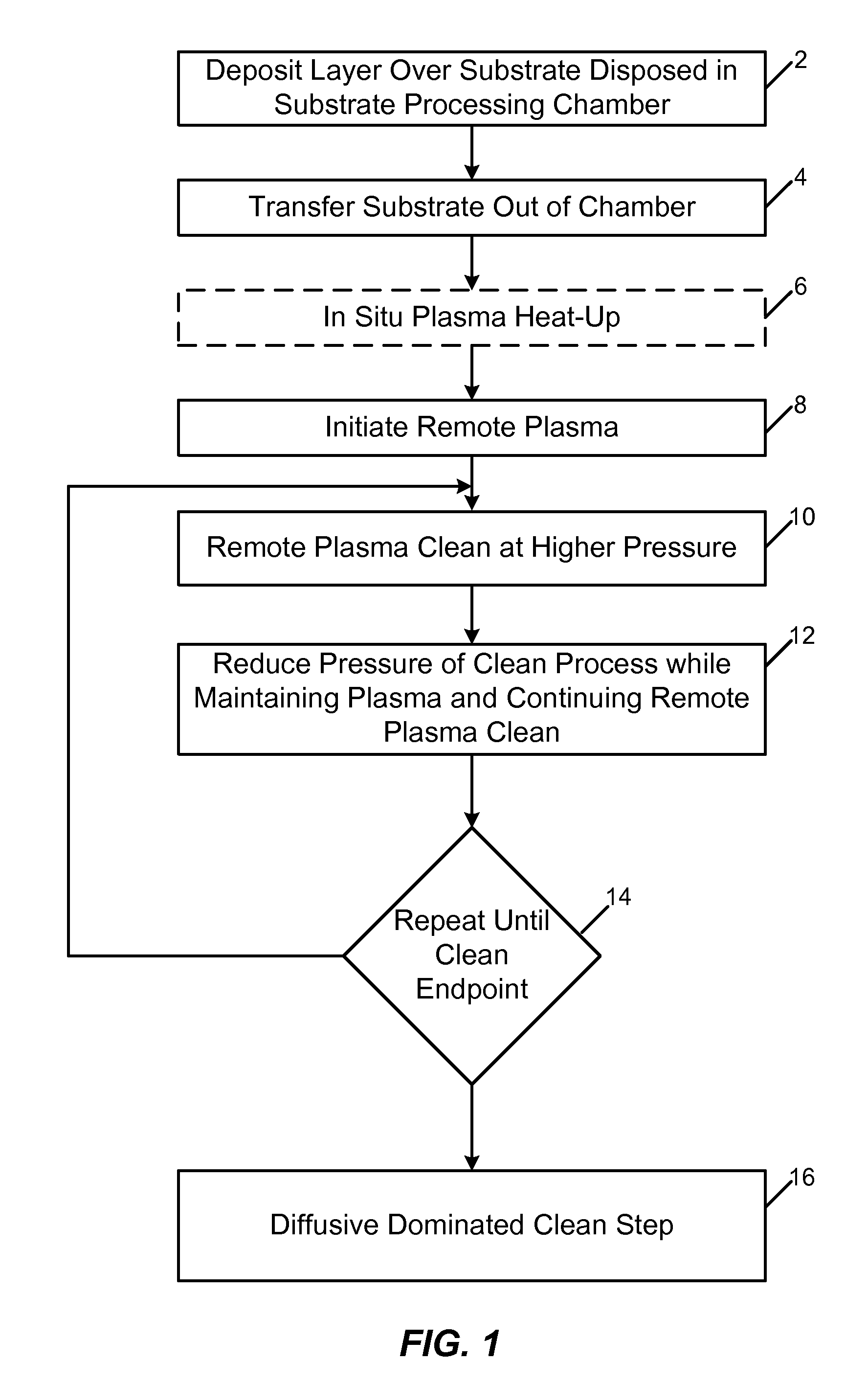
Remote plasma clean process with cycled high and low pressure clean steps
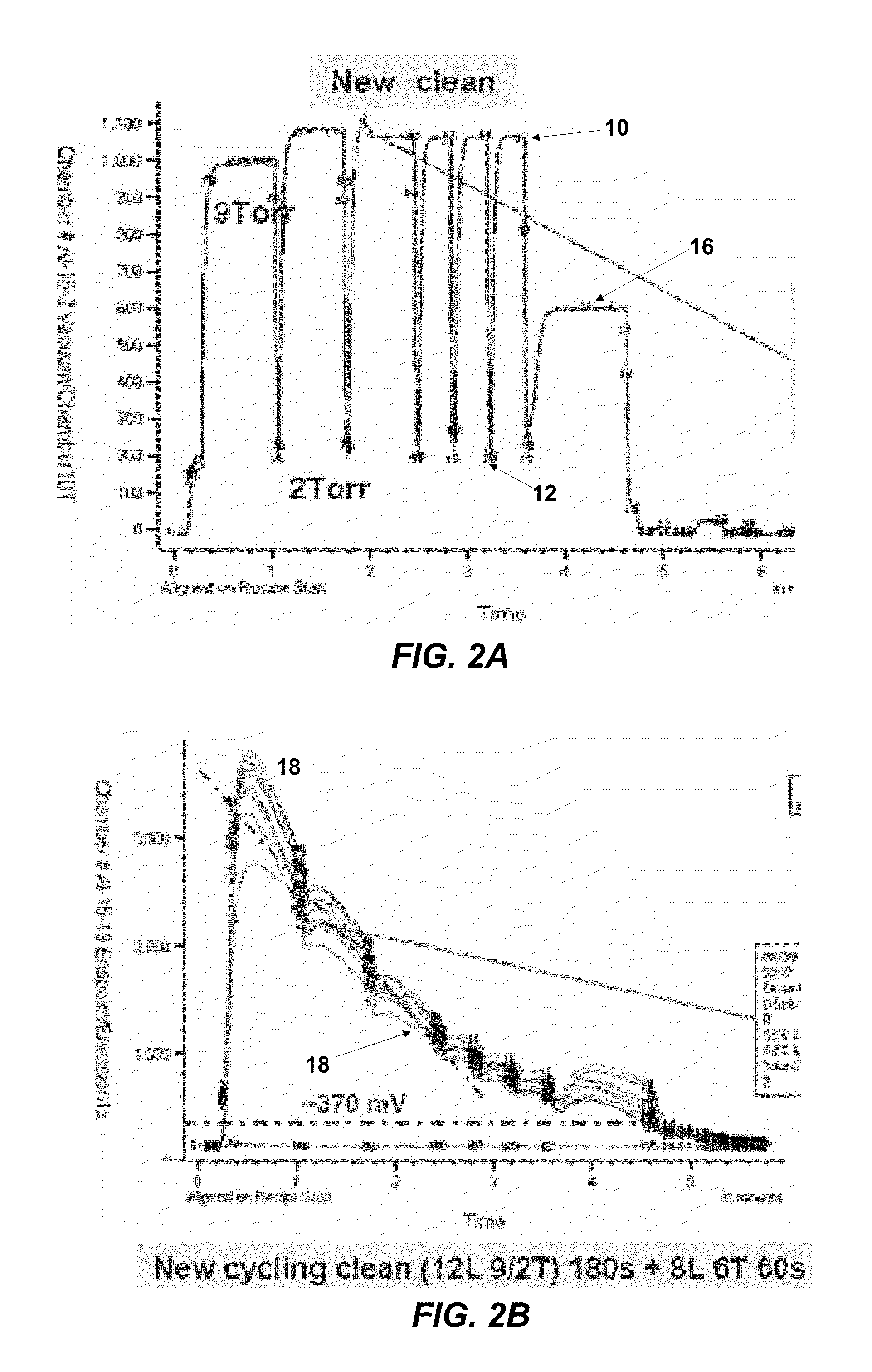
InactiveUS7967913B2Hollow article cleaningSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRemote plasmaContinuous flow
A remote plasma process for removing unwanted deposition build-up from one or more interior surfaces of a substrate processing chamber after processing a substrate disposed in the substrate processing chamber. In one embodiment, the substrate is transferred out of the substrate processing chamber and a flow of a fluorine-containing etchant gas is introduced into a remote plasma source where reactive species are formed. A continuous flow of the reactive species from the remote plasmas source to the substrate processing chamber is generated while a cycle of high and low pressure clean steps is repeated. During the high pressure clean step, reactive species are flown into the substrate processing chamber while pressure within the substrate processing chamber is maintained between 4-15 Torr. During the low pressure clean step, reactive species are flown into the substrate processing chamber while reducing the pressure of the substrate processing chamber by at least 50 percent of a high pressure reached in the high pressure clean step.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method of cleaning a semiconductor device processing chamber after a copper etch process
The present invention is a method for removing deposited etch byproducts from surfaces of a semiconductor processing chamber after a copper etch process. The method of the invention comprises the following general steps: (a) an oxidation step, in which interior surfaces of the processing chamber are contacted with an oxidizing plasma; (b) a first non-plasma cleaning step, in which interior surfaces of the processing chamber are contacted with an H+hfac-comprising gas; and (c) a second cleaning step, in which interior surfaces of the processing chamber are contacted with a plasma containing reactive fluorine species, whereby at least a portion of the copper etch byproducts remaining after step (b) are volatilized into gaseous species, which are removed from the processing chamber. The method of the invention is preferably performed at a chamber wall temperature of at least 150° C. in order to achieve optimum cleaning of the chamber at the chamber operating pressures typically used during the cleaning process. The dry cleaning method of the invention can be performed between wafer processing runs without opening the processing chamber, thereby minimizing potential contamination to the chamber as well as chamber downtime.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Deposition methods
A deposition method includes positioning a substrate within a deposition chamber defined at least in part by chamber walls. At least one of the chamber walls comprises a chamber surface having a plurality of purge gas inlets to the chamber therein. A process gas is provided over the substrate effective to deposit a layer onto the substrate. During such providing, a material adheres to the chamber surface. Reactive purge gas is emitted to the deposition chamber from the purge gas inlets effective to form a reactive gas curtain over the chamber surface and away from the substrate, with such reactive gas reacting with such adhering material. Further implementations are contemplated.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
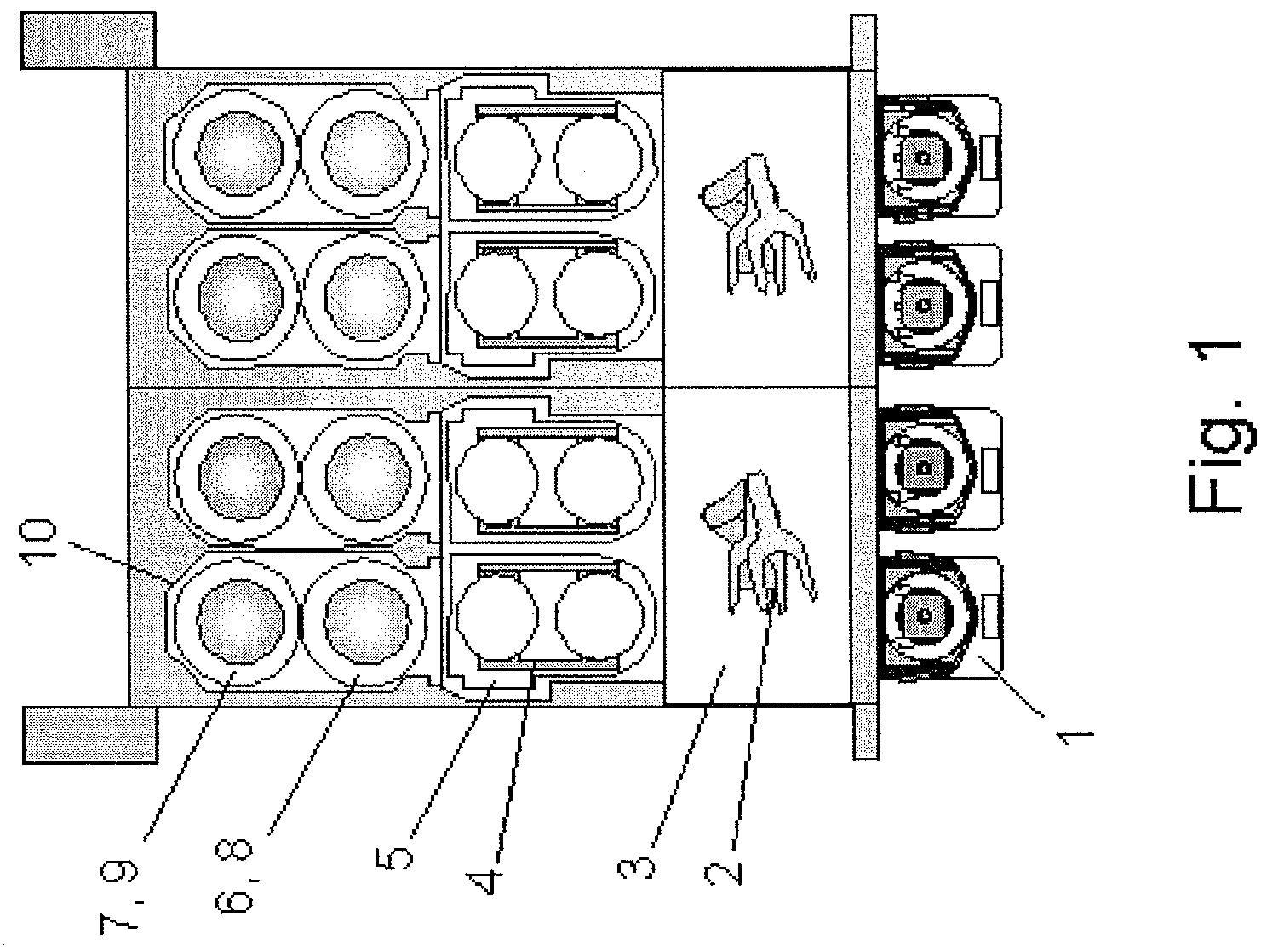
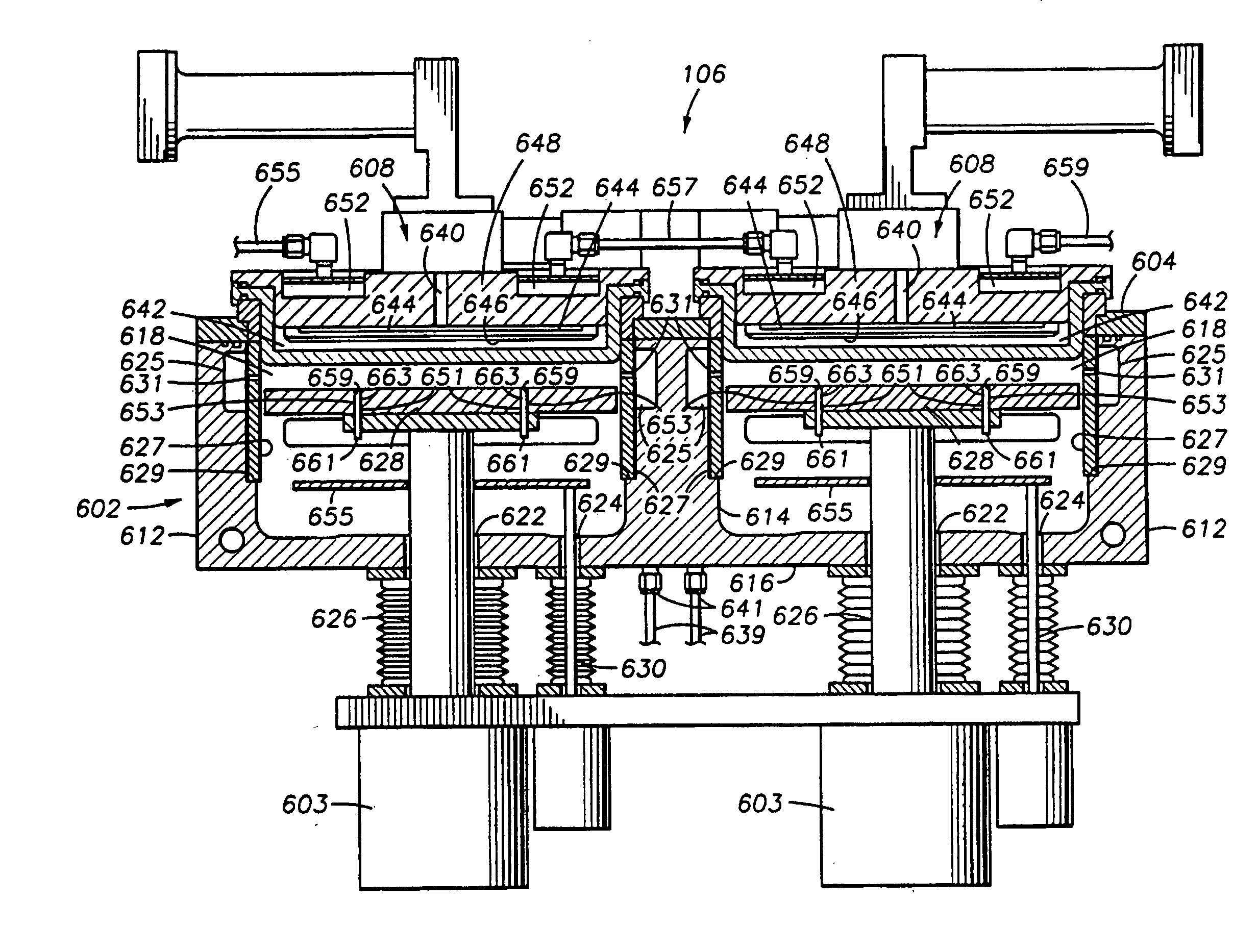
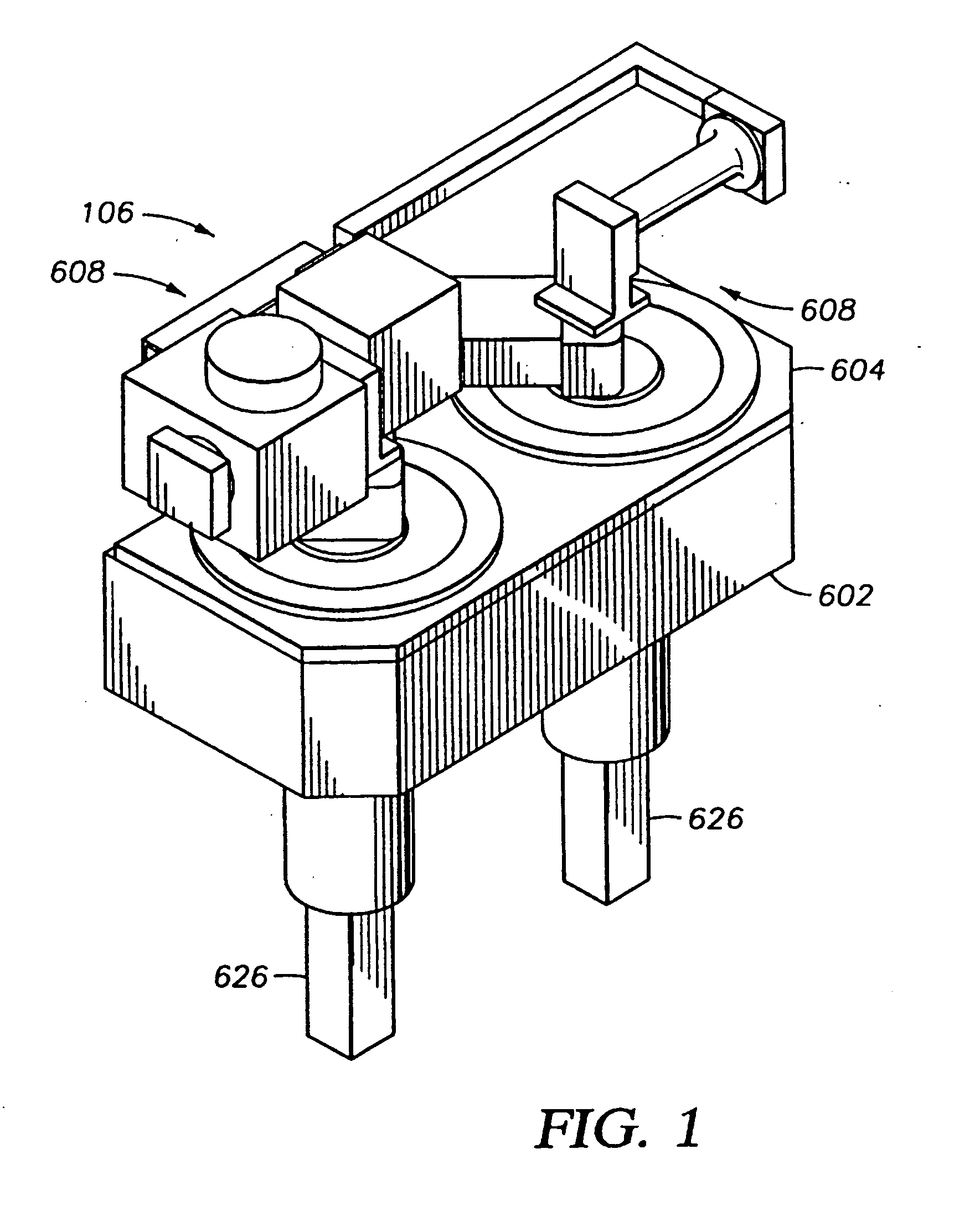
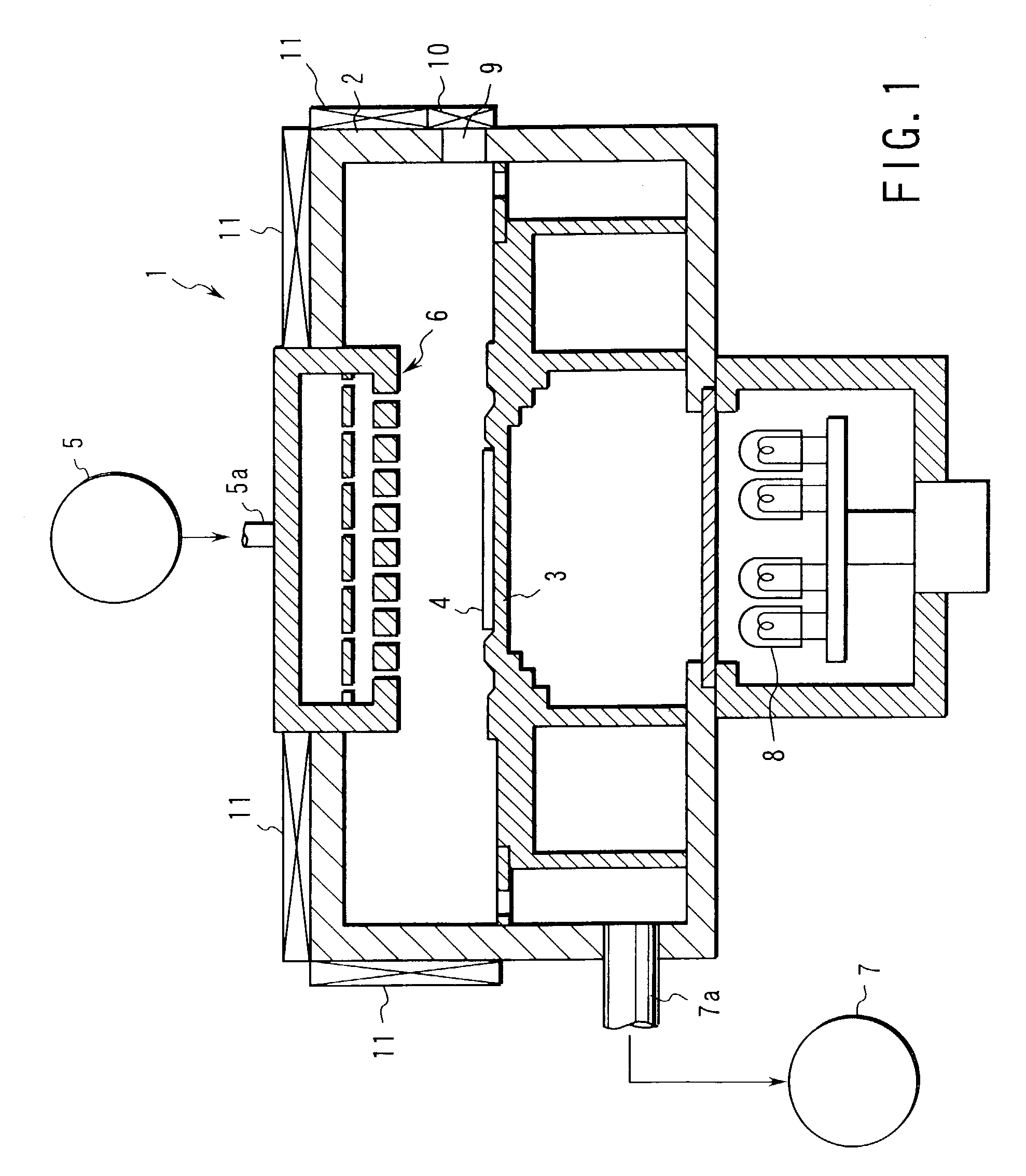
Multiple-Substrate Transfer Apparatus and Multiple-Substrate Processing Apparatus
InactiveUS20100147396A1Cost per throughputSmall footprintHollow article cleaningCombustion enginesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A multiple-substrate processing apparatus includes: a reaction chamber comprised of two discrete reaction stations aligned one behind the other for simultaneously processing two substrates; a transfer chamber disposed underneath the reaction chamber, for loading and unloading substrates to and from the reaction stations simultaneously; and a load lock chamber disposed next to the transfer chamber. The transfer arm includes one or more end-effectors for simultaneously supporting two substrates one behind the other as viewed in the substrate-loading / unloading direction.
Owner:ASM JAPAN +1
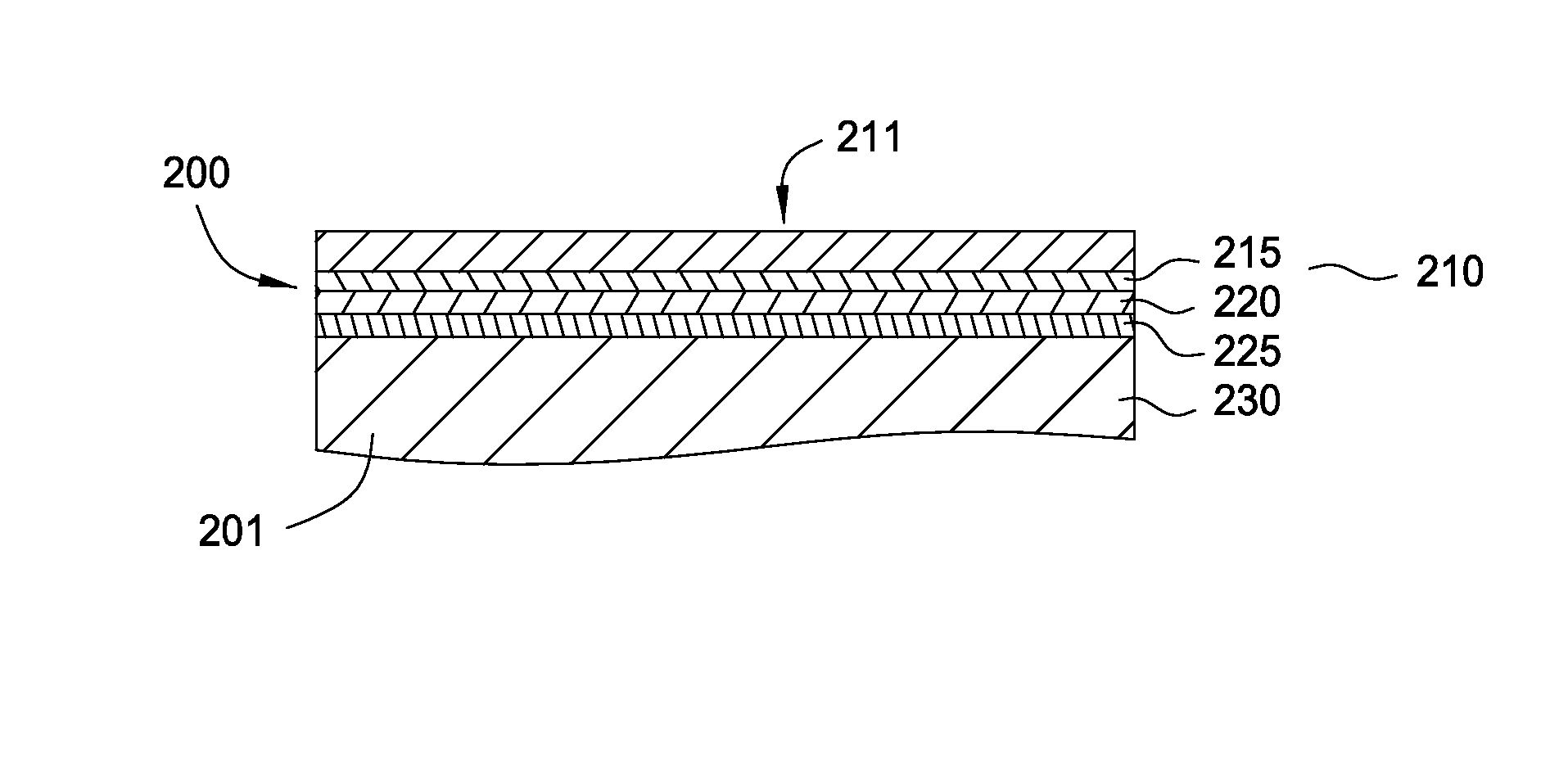
Thermal treated sandwich structure layer to improve adhesive strength
InactiveUS20140272341A1Improve integrityElectric discharge tubesLayered productsRemote plasmaDistribution system
A method and apparatus for cleaning a process chamber are provided. In one embodiment, a process chamber is provided that includes a remote plasma source and a processing chamber. The processing chamber includes a substrate support assembly disposed in the bottom portion of the processing chamber, a gas distribution system configured to provide gas into the processing chamber above the substrate support assembly, a removable liner layer the chamber interior walls. An adhesion layer is disposed on the substrate support. A protective layer is disposed on the adhesion layer. Pluralities of intermediate layers are created between the substrate support layer and the adhesion layer, and the adhesion layer and the protective layer through a thermal treatment in a non-reactive environment.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for conditioning a process chamber
A method of conditioning a processing chamber for a production process includes performing a conditioning step at a conditioning process recipe substantially different than a process recipe of the production process, and performing a warm-up process at a warm-up process recipe substantially the same as the process recipe of the production process. The method can be performed after a wet-cleaning process has been performed. The conditioning procedure can allow the maintenance time to be decreased and can cause the etched features to be more accurate.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Stable solid block metal protecting warewashing detergent composition
InactiveUS6156715AFit tightlyEasy to cleanInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic detergent compounding agentsAlkalinityIndustrial setting
The dimensionally stable alkaline solid block warewashing detergent uses an E-form binder forming a solid comprising a sodium carbonate source of alkalinity, a metal corrosion protecting alkali metal silicate composition, a sequestrant, a surfactant package and other optional material. The solid block is dimensionally stable and highly effective in removing soil from the surfaces of dishware in the institutional and industrial environment. The E-form hydrate comprises an organic phosphonate and a hydrated carbonate.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
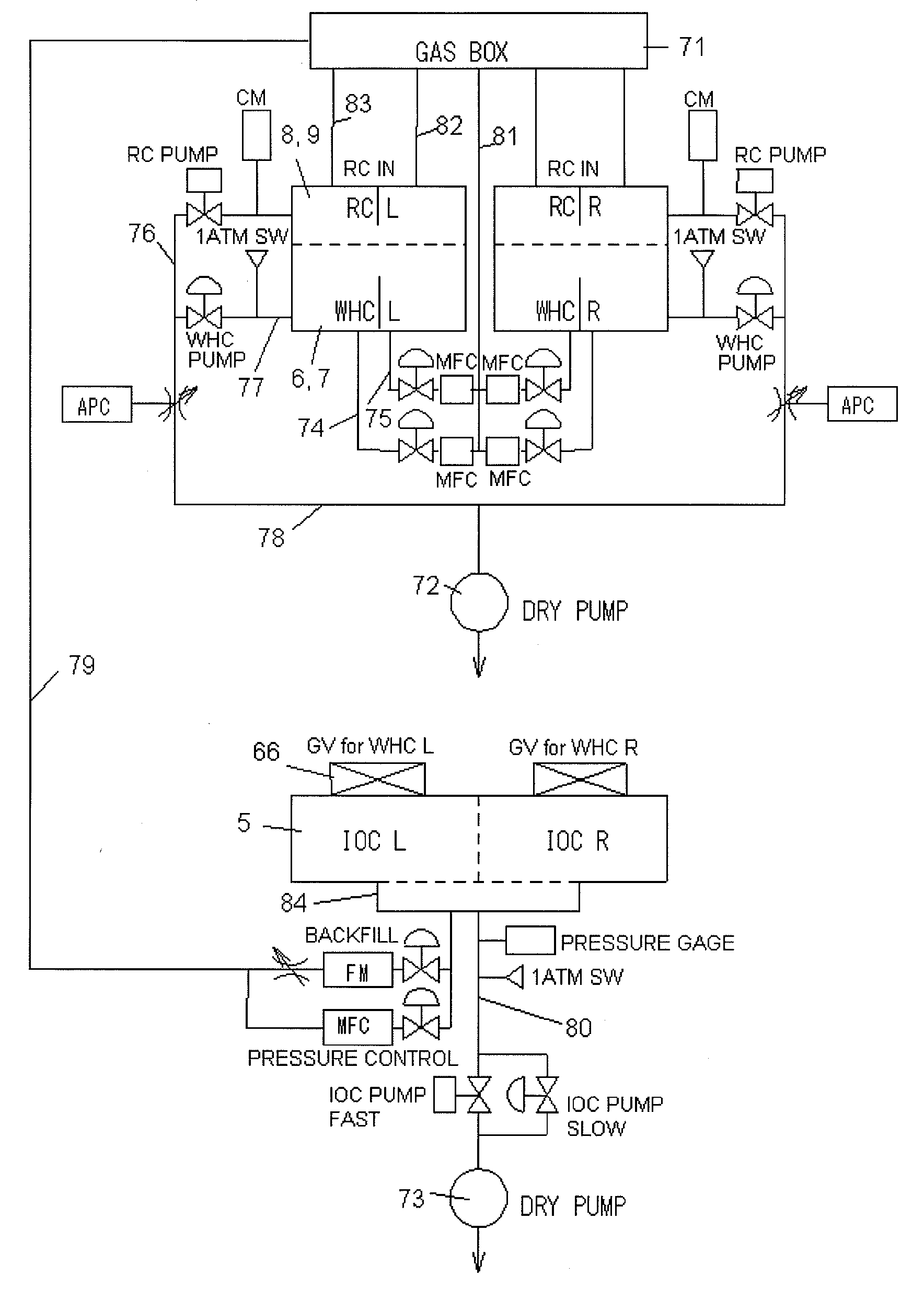
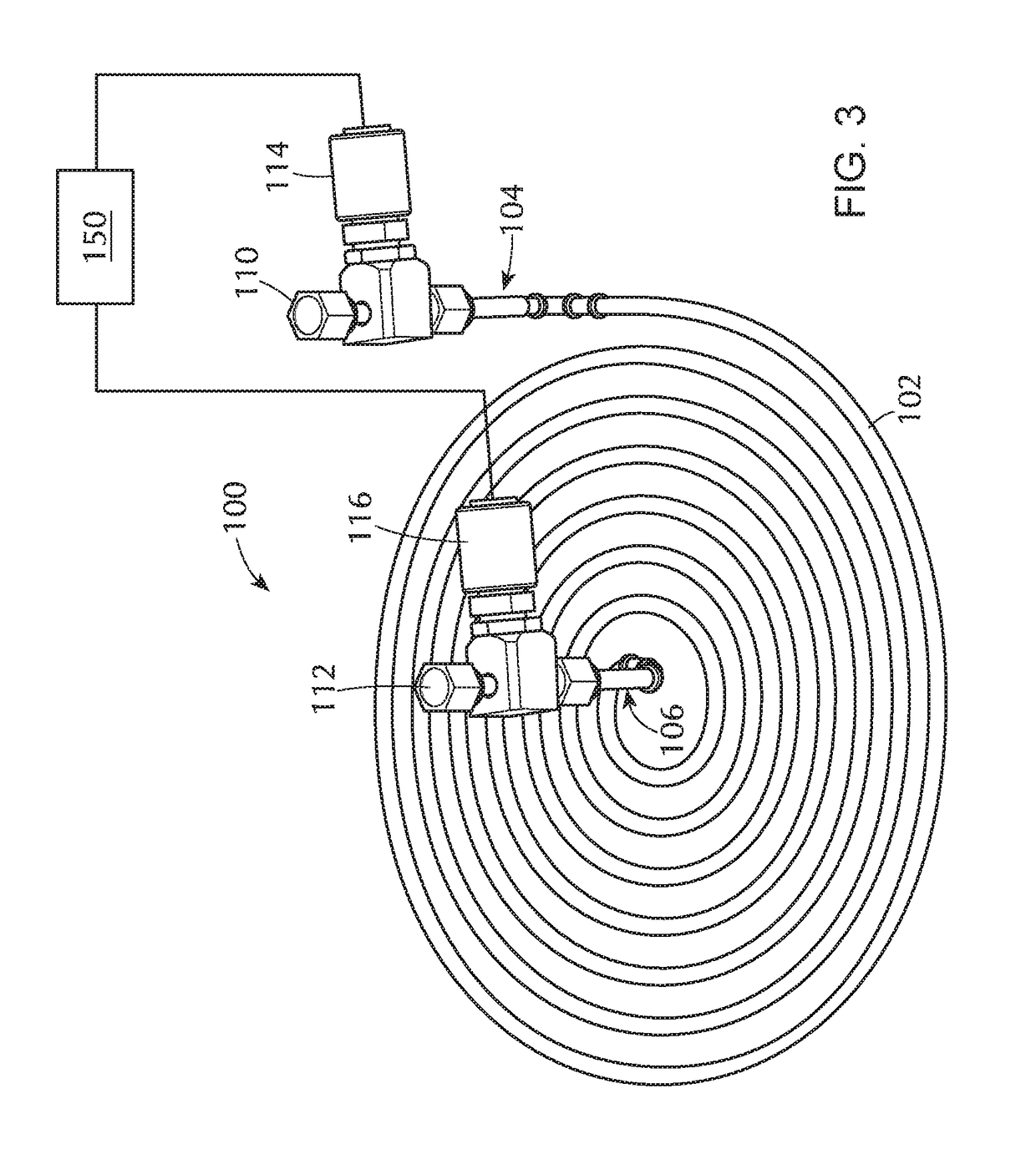
Multi-port pumping system for substrate processing chambers
InactiveUS20090120464A1Improve pumping capacityImprove rendering capabilitiesFrozen sweetsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringMulti port
An exhaust foreline for purging fluids from a semiconductor fabrication chamber is described. The foreline may include a first, second and third ports independently coupled to the chamber. A semiconductor fabrication system is also described that includes a substrate chamber that has a first, second and third interface port. The system may also include a multi-port foreline that has a first, second and third port, where the first foreline port is coupled to the first interface port, the second foreline port is coupled to the second interface port, and the third foreline port is coupled to the third interface port. The system may further include an exhaust vacuum coupled to the multi-port foreline.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Water vapor passivation of a wall facing a plasma
InactiveUS20070190266A1Easy to cleanHollow article cleaningVacuum evaporation coatingChemistryLow-k dielectric
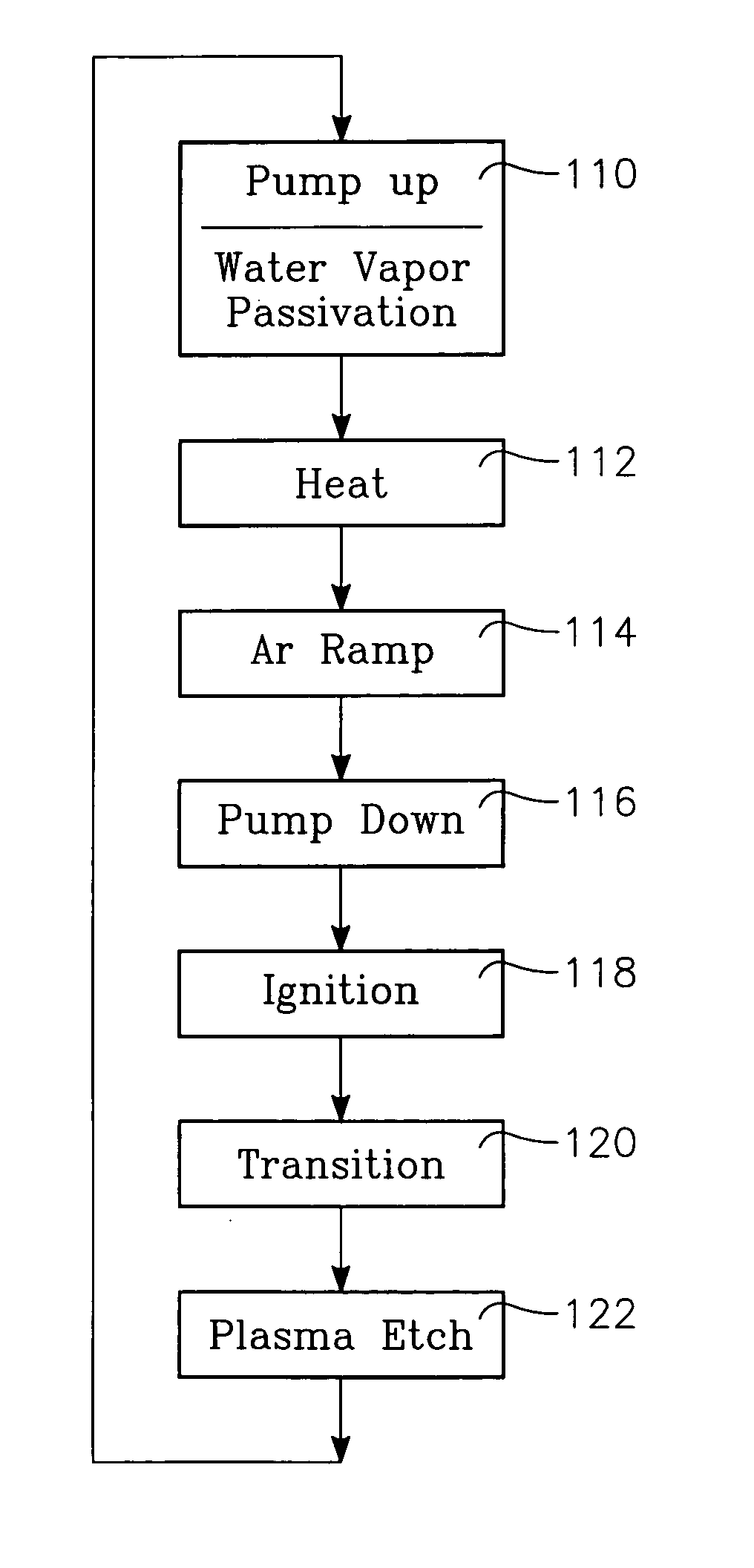
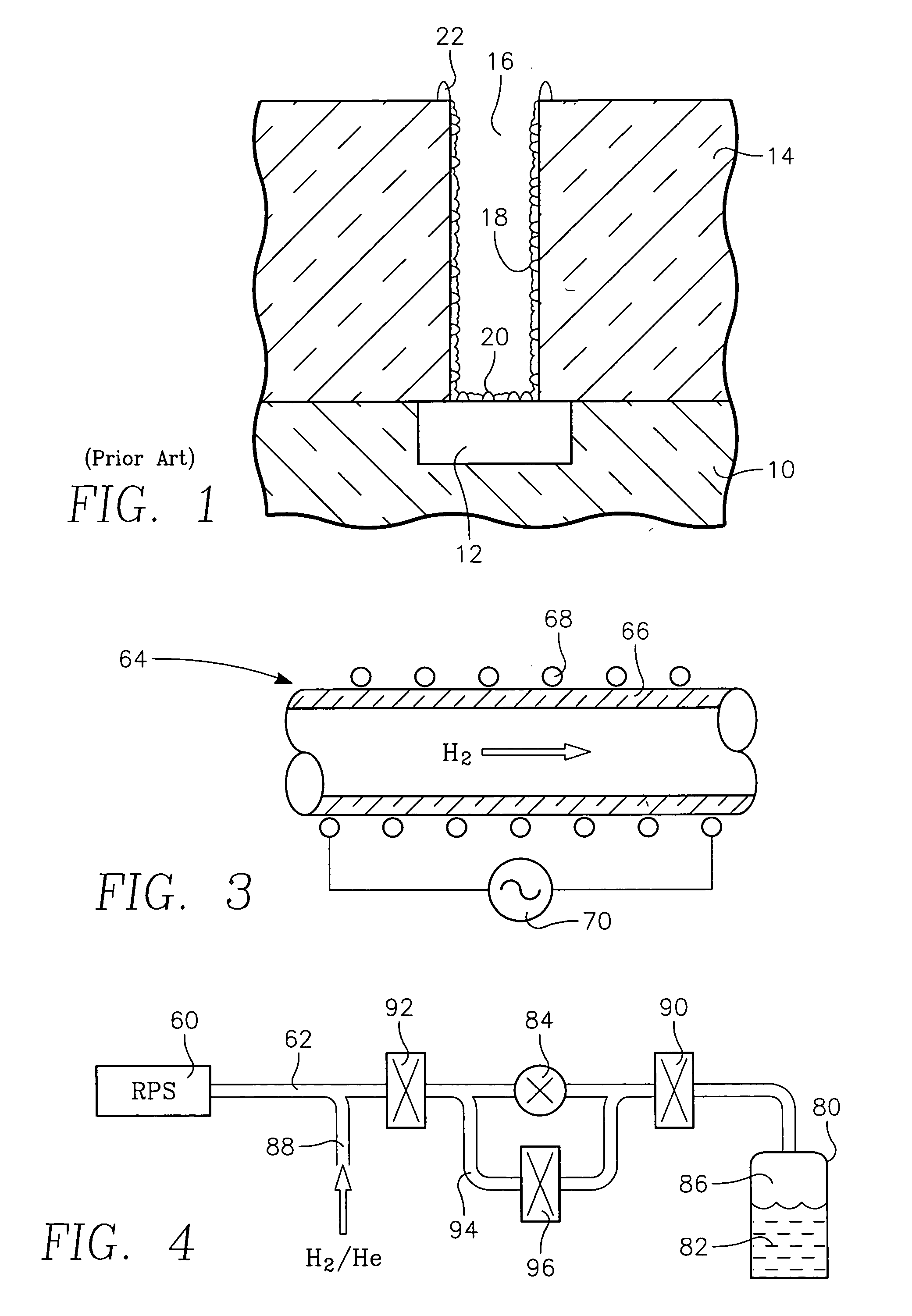
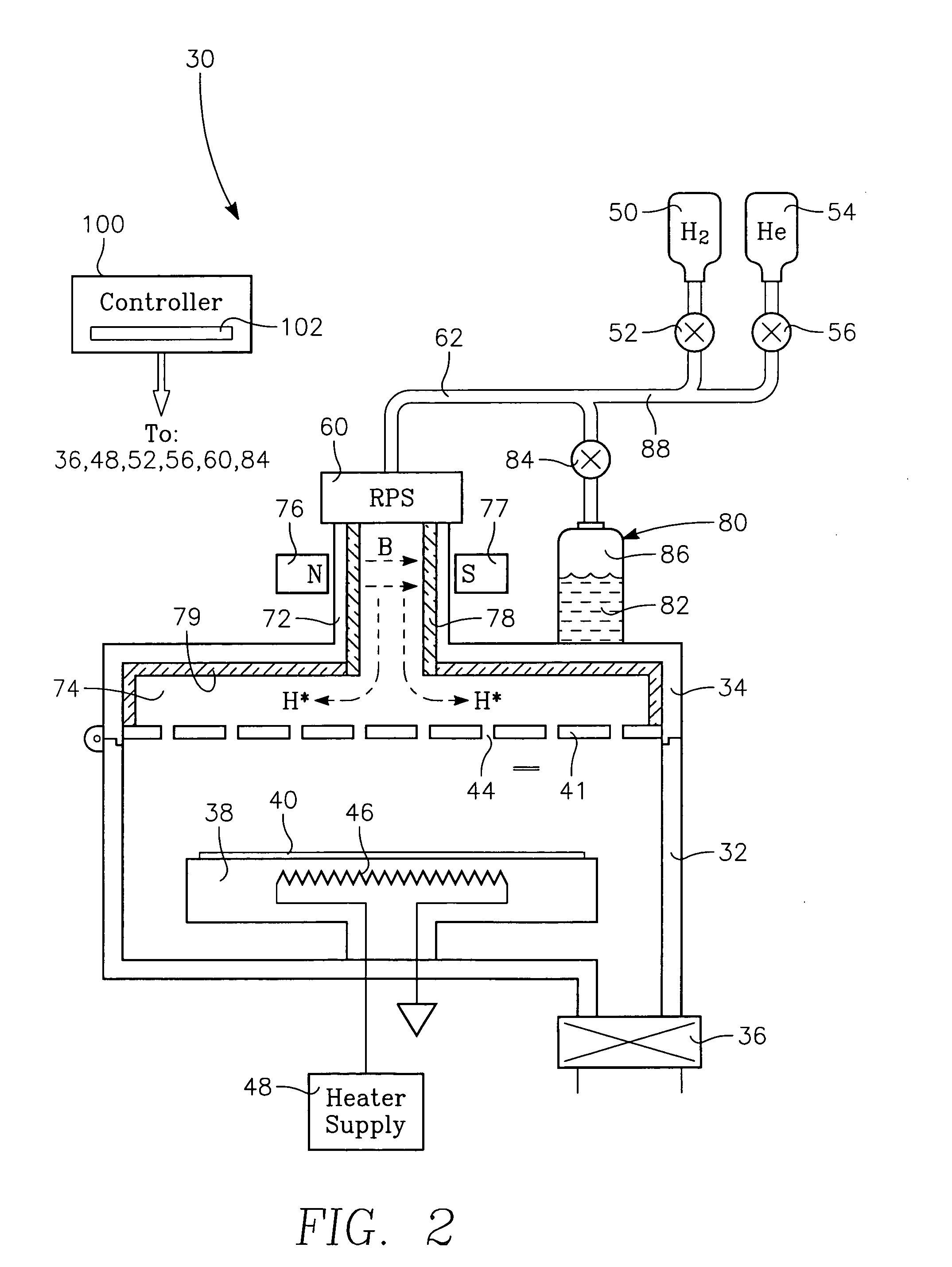
A chamber passivation method particularly useful for hydrogen plasma cleaning of low-k dielectrics prior to coating a barrier layer into a via hole with hydrogen radicals are provided from a remote plasma source. For each wafer, the chamber is passivated with water vapor (or other gas even more chemabsorbed on plasma facing walls) passed through the remote plasma source prior to the ignition of the hydrogen plasma. The water vapor is absorbed on walls, such as alumina and quartz parts of the remote plasma source, and forms a protective mono-layer that endures sufficiently long to protect the walls during the generation of the hydrogen plasma. Thereby, the plasma facing walls, particularly of a dielectric such as alumina, are protected from etching.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Dual-direction chemical delivery system for ALD/CVD chambers
ActiveUS9765432B2Control flowHollow article cleaningVacuum evaporation coatingCompound (substance)Engineering
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Reduction of reactive gas attack on substrate heater
InactiveUS20060005856A1Reduce harmReduce the amount requiredElectric discharge tubesHollow article cleaningAluminum fluorideReactive gas
Embodiments of the present invention provide a method of reducing damage to the substrate support by the cleaning gas during a cleaning process of the processing chamber, such as by reducing aluminum fluoride formation on the substrate support. In one embodiment, a method of cleaning a semiconductor process chamber which is used for processing a substrate disposed on a surface of a substrate support comprises introducing a cleaning gas into a process chamber through an inlet facing a surface of a substrate support. The inlet is spaced from the surface of the substrate support by a clean spacing. Reactive species are provided from the cleaning gas to clean the process chamber. The clean spacing is substantially greater than a process spacing between the inlet and the surface of the substrate support during processing of a substrate on the substrate support in the process chamber.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Microrobot for surgical applications
InactiveUS7042184B2Programme-controlled manipulatorAdditive manufacturing apparatusLess invasive surgeryReoperative surgery
The present invention provides a micro-robot for use inside the body during minimally-invasive surgery. The micro-robot may include various sensors, imaging devices or manipulators.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
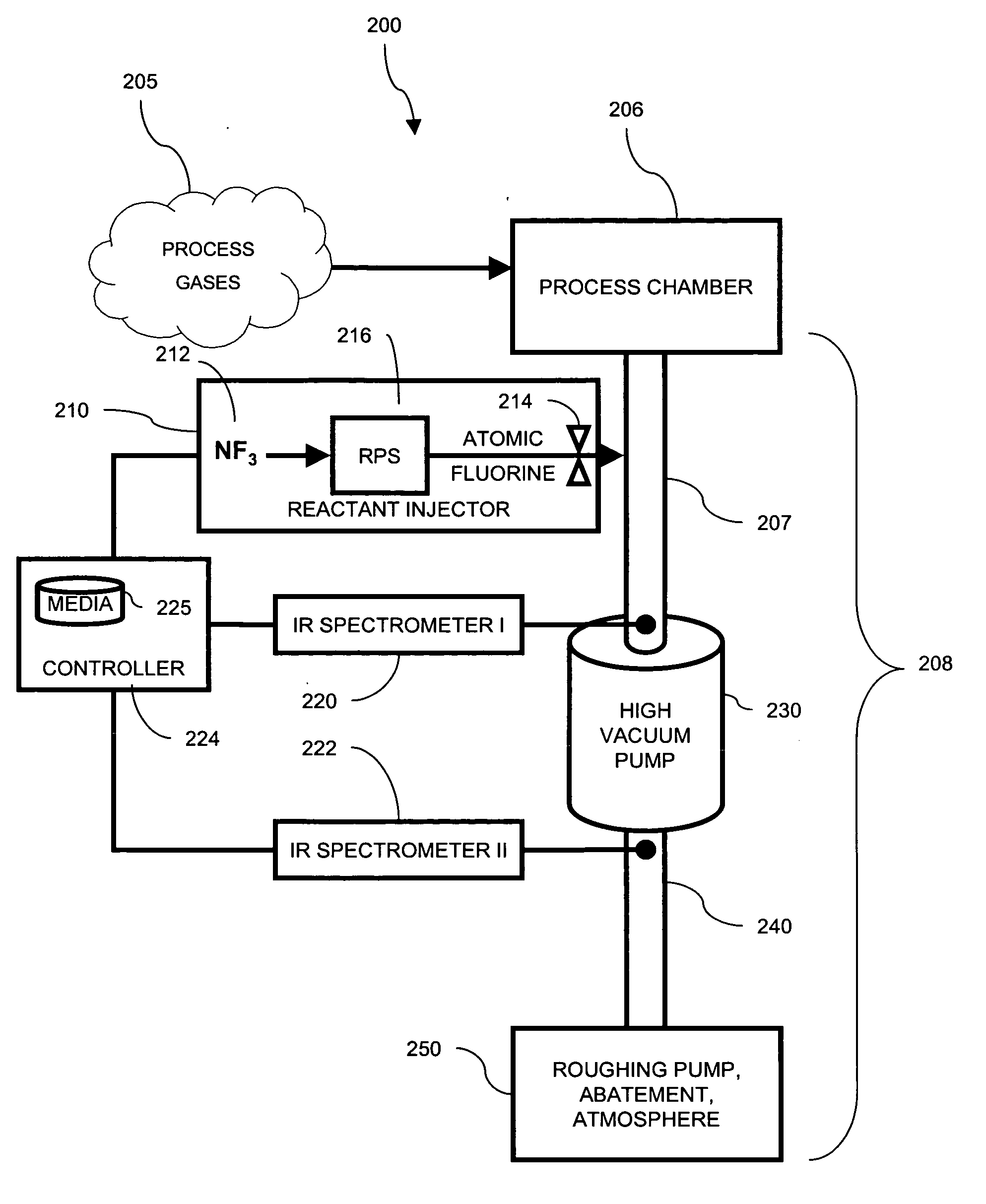
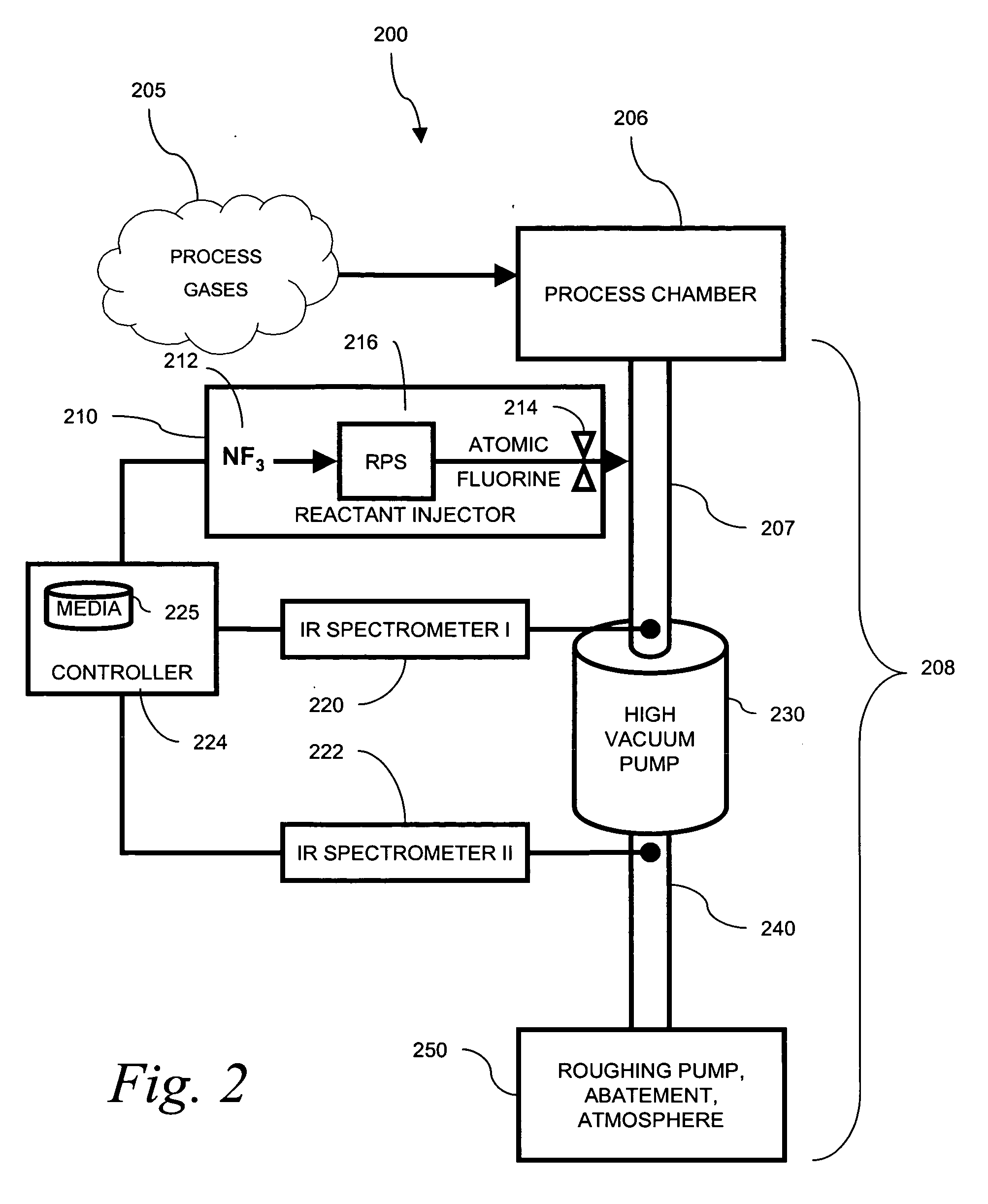
Use of spectroscopic techniques to monitor and control reactant gas input into a pre-pump reactive gas injection system
ActiveUS20090320881A1Produce some attenuationTrend downRotary/oscillating piston combinations for elastic fluidsHollow article cleaningGas phaseReactive gas
The present invention relates to vacuum processing systems in which process gases are introduced in a process chamber and are exhausted through a vacuum processing system exhaust path. Deposits made by the exhausted gas are reduced or eliminated by introducing a reactive gas upstream of the device affected by deposits. The amount of introduced reactive gas is controlled by measuring gas phase concentrations of exhausted gas components upstream and downstream of the affected device, and, from those measurements, determining whether the components are being consumed in deposits on the affected device.
Owner:EDWARDS VACUUM LLC
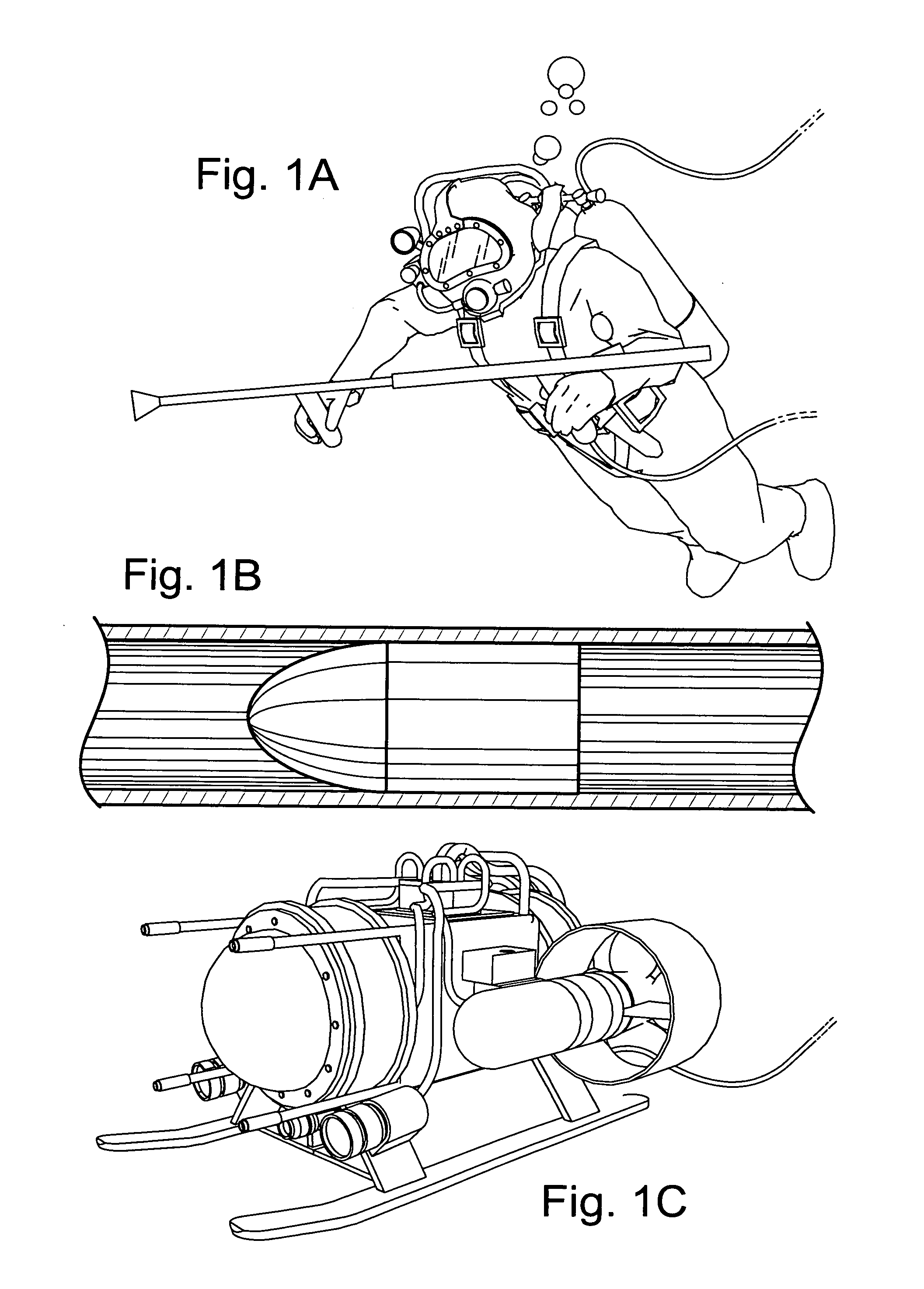
Submersible robotically operable vehicle system for infrastructure maintenance and inspection
InactiveUS20120215348A1Programme-controlled manipulatorDigital data processing detailsElectric powerInstrumentation
A configurable robotic apparatus and system is disclosed that is remotely operable in difficult, hazardous, subterranean, or submerged environs. The apparatus merges diverse disciplines to effect inspecting, cleaning, treating, repairing or otherwise maintaining a wide variety of materials and conditions. Deployment environments include power, municipal water and wastewater plants, surface and submerged infrastructures (pipes, lines, conduits), and like industrial applications. Extensible and articulating modules, configurable through standardized and interchangeable connectors, provide unique flexibility, scalability and versatility to accommodate a wide range of shapes, surfaces, and obstacles. In-module intelligence and instrumentation eliminates the need for constant manual control through autonomous operation capable of simultaneous optimization and synchronization of multiple work processes, but manual override and remote control is provided to overcome unanticipated limitations. Benefits include improved efficiency, cost, and safety over prior art. High-performance, one-pass operation reduces facility downtime while incorporating environmentally responsible debris recovery.
Owner:SKRINDE RICHARD ARTHUR
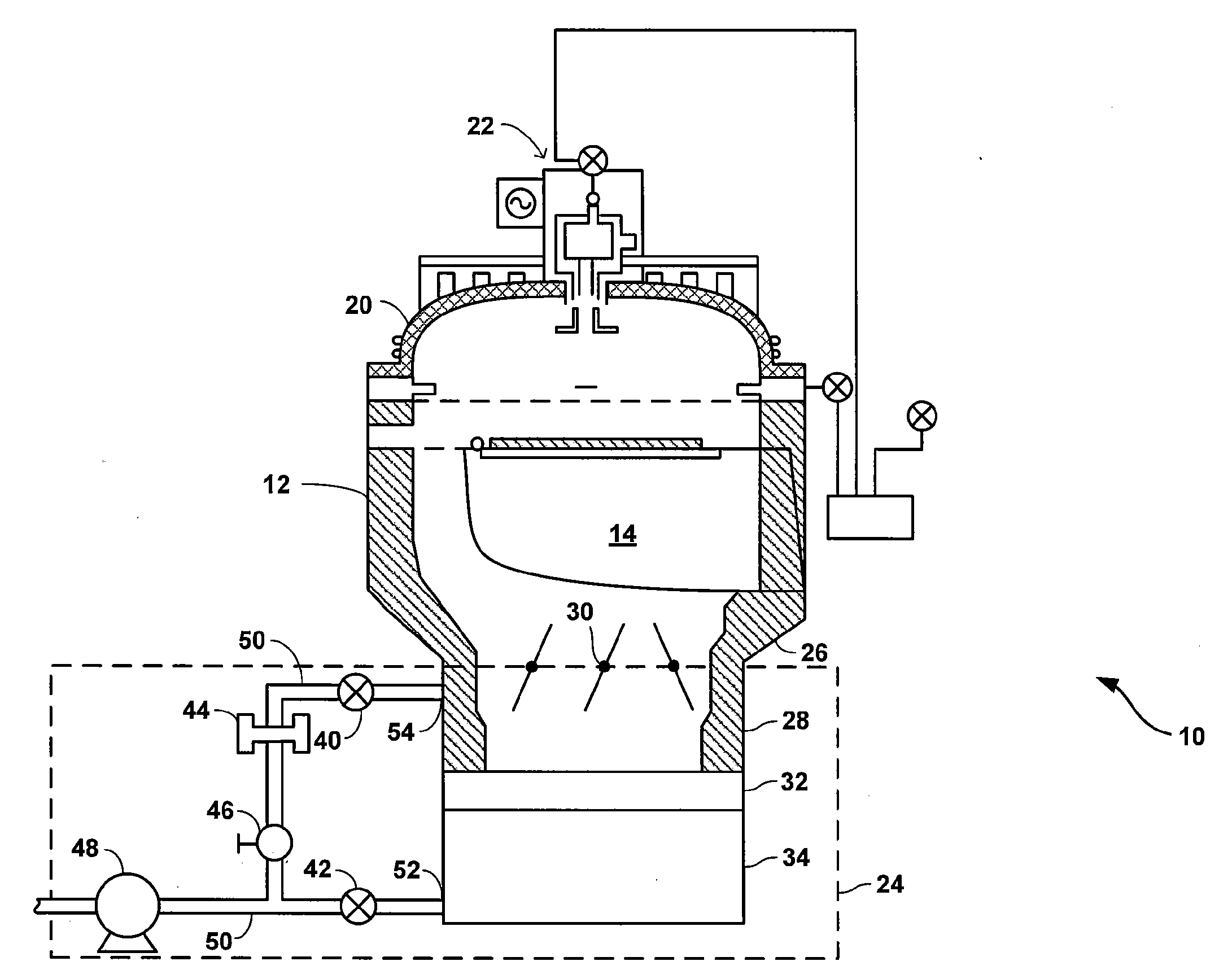
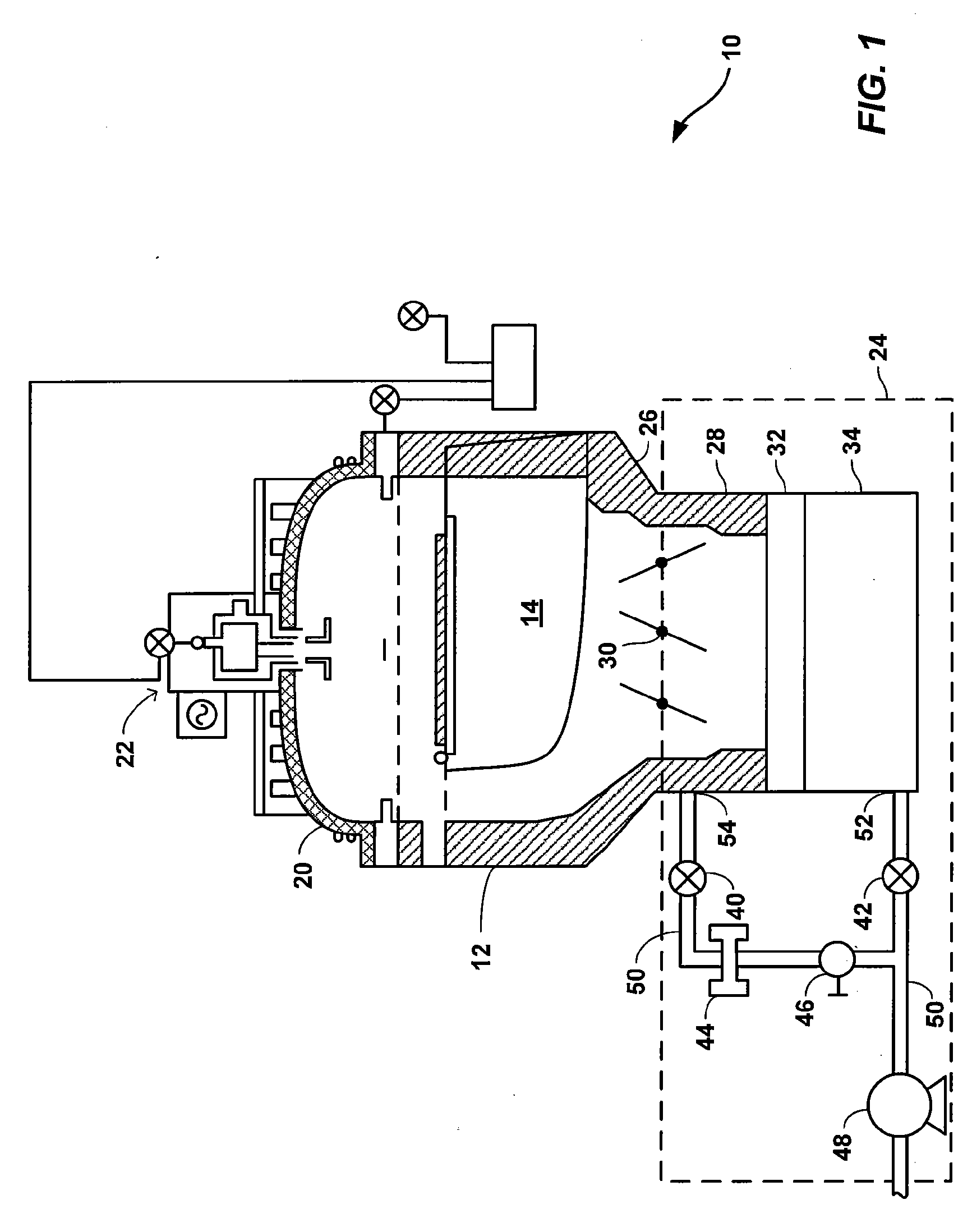
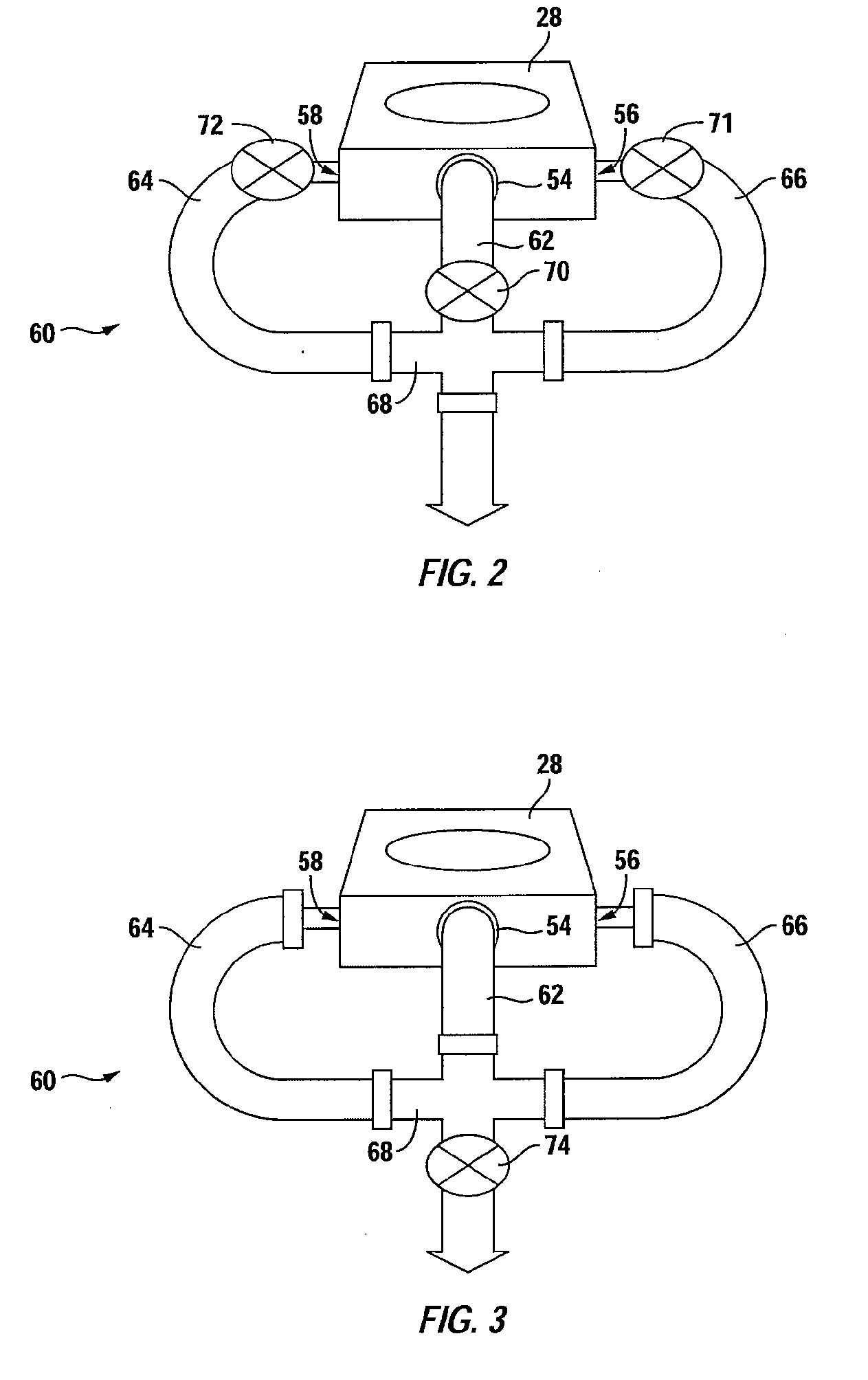
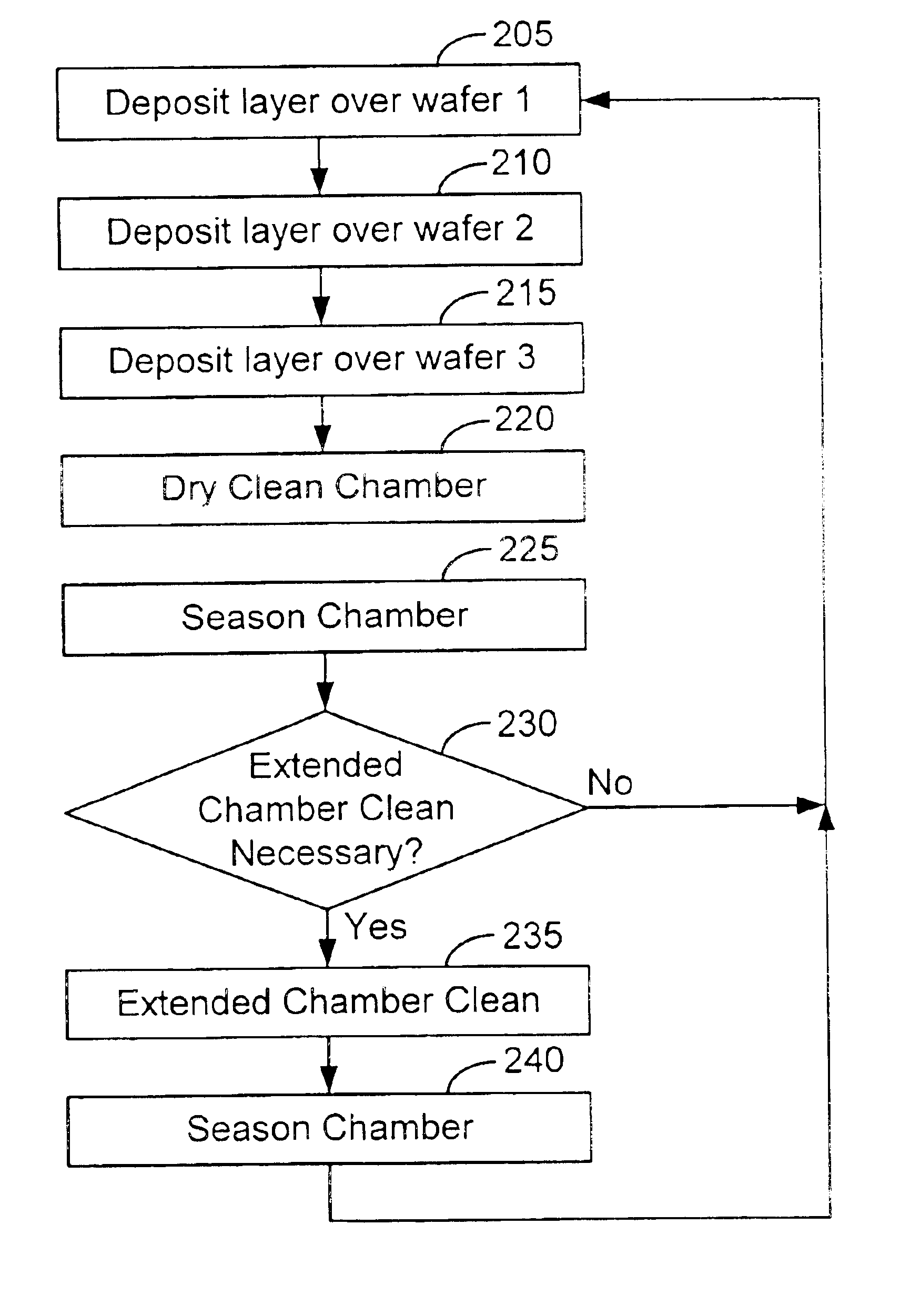
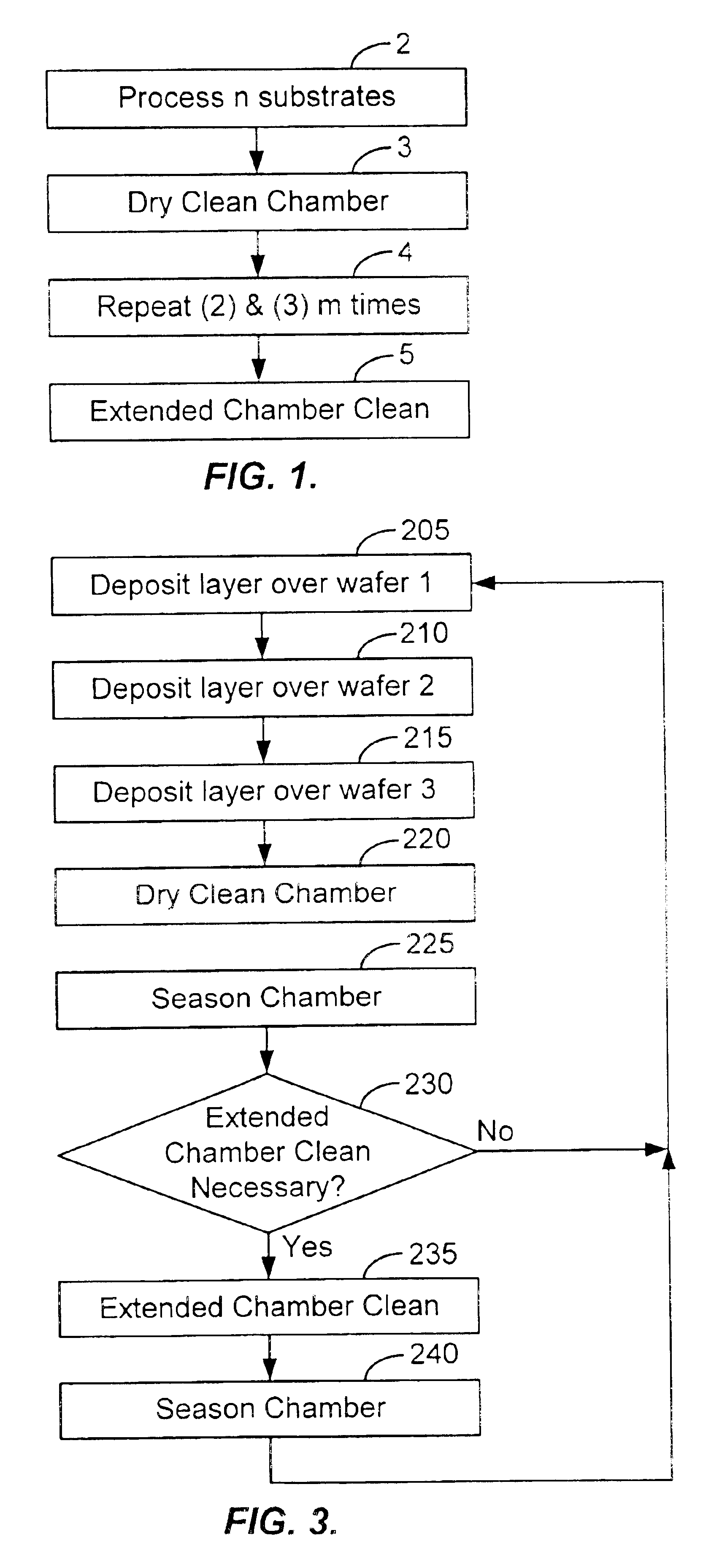
Method of cleaning a semiconductor processing chamber
A method of operating a substrate processing chamber. In one embodiment the method includes processing one or more substrates in the substrate processing chamber and subsequently cleaning the chamber using a dry cleaning process. This substrate processing and dry cleaning sequence is then repeated multiple times before chamber is further cleaned by flowing a cleaning gas into the chamber and forming a plasma within the chamber from the cleaning gas in an extended cleaning process. During the extended cleaning process the plasma is maintained within the chamber for a total of at least 5 minutes before the chamber is reused to process a substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
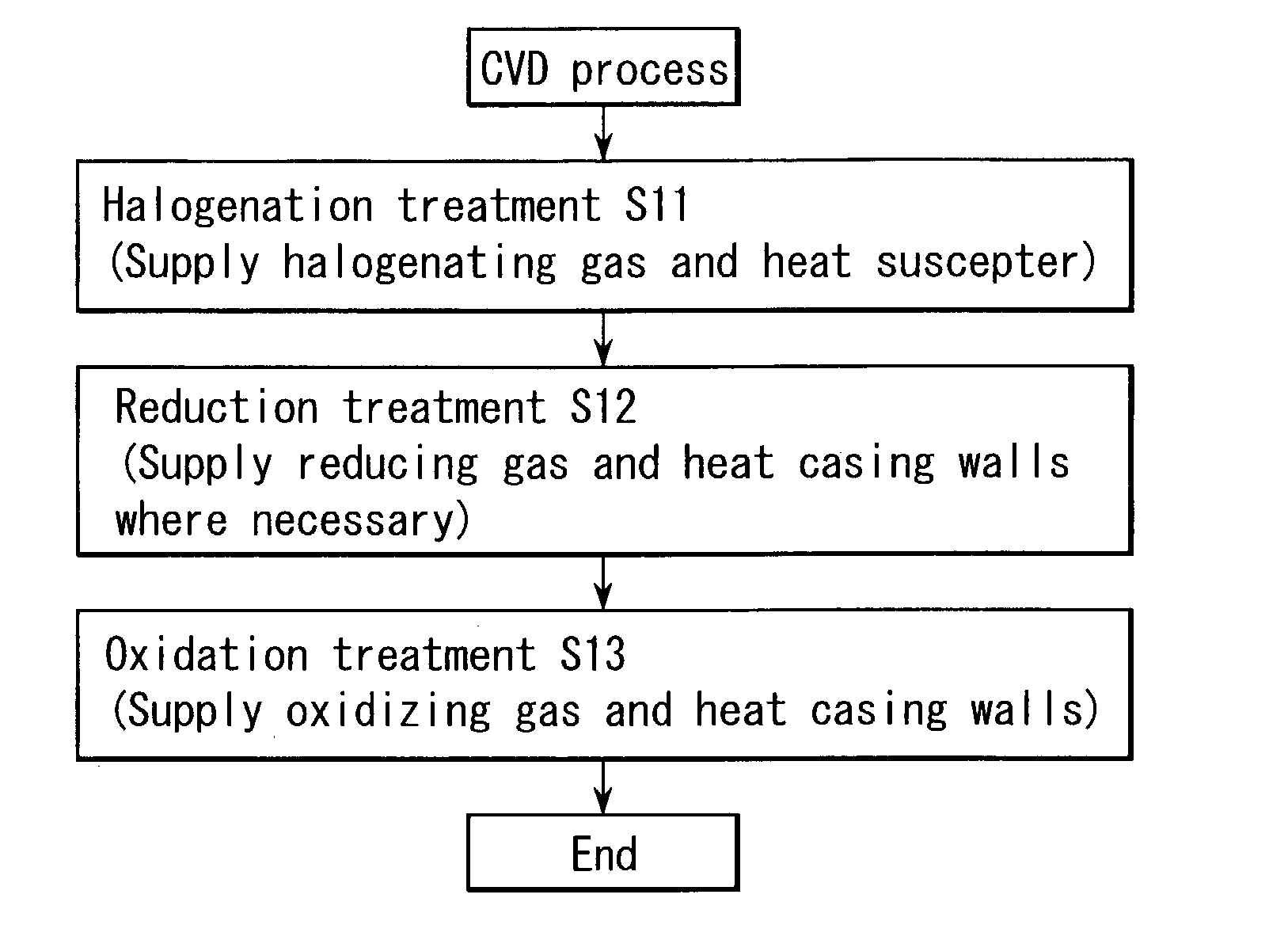
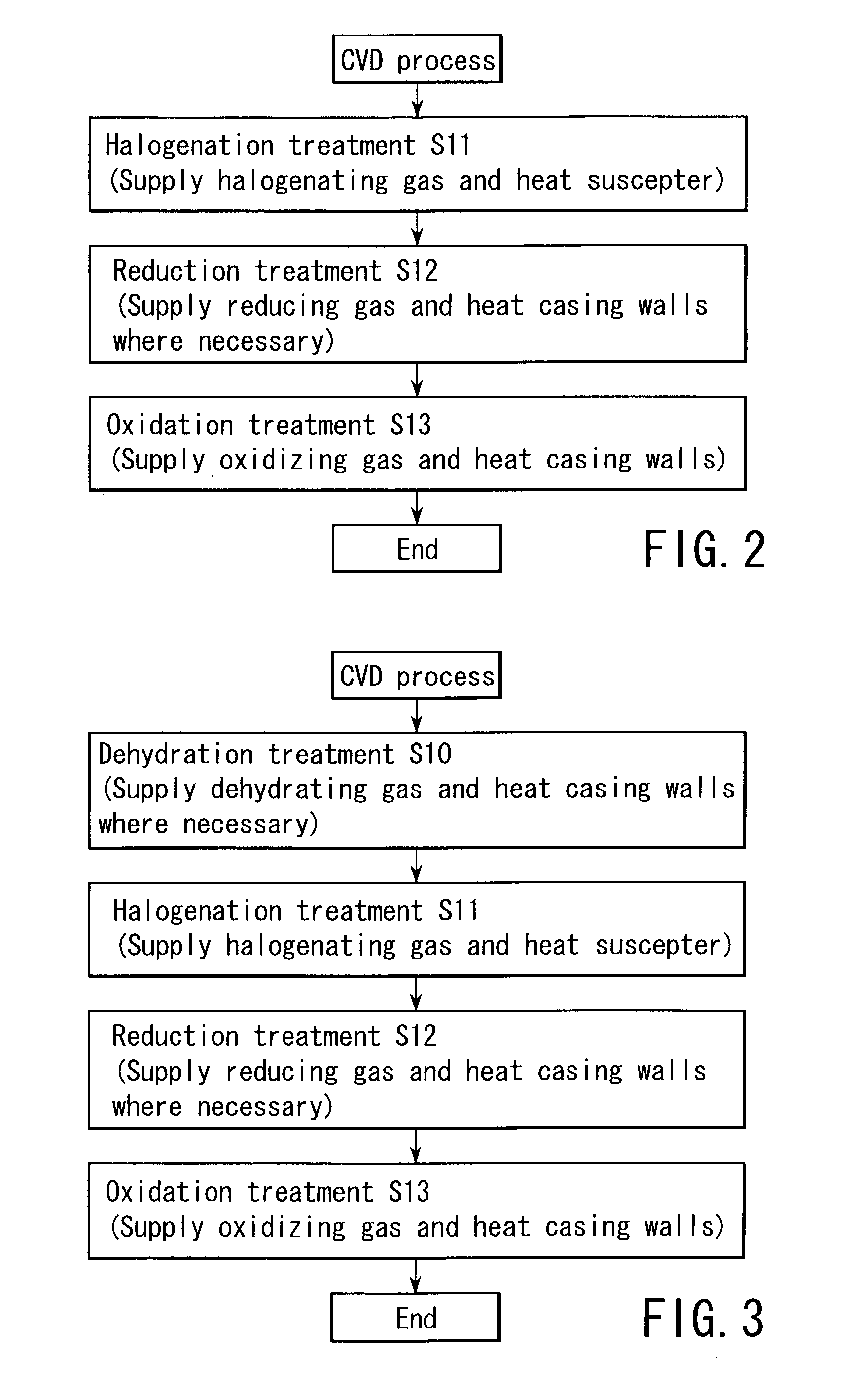
Method of cleaning processing chamber of semiconductor processing apparatus
InactiveUS20030205237A1Hollow article cleaningElectrostatic cleaningReduction treatmentSemiconductor
A method of cleaning the interior of a processing chamber first performs a halogenation treatment by supplying a treatment gas containing a halogenating gas into the processing chamber and heating a support member for a target substrate, thereby halogenating a metal element in a by-product film. A reduction treatment is then performed by supplying a treatment gas containing a reducing gas into the processing chamber, thereby reducing a halide of the metal element and liberating the metal element. An oxidation treatment is then performed by supplying a treatment gas containing an oxidizing gas into the processing chamber and heating the casing walls of the processing chamber, thereby passivating the liberated metal element by oxidation.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
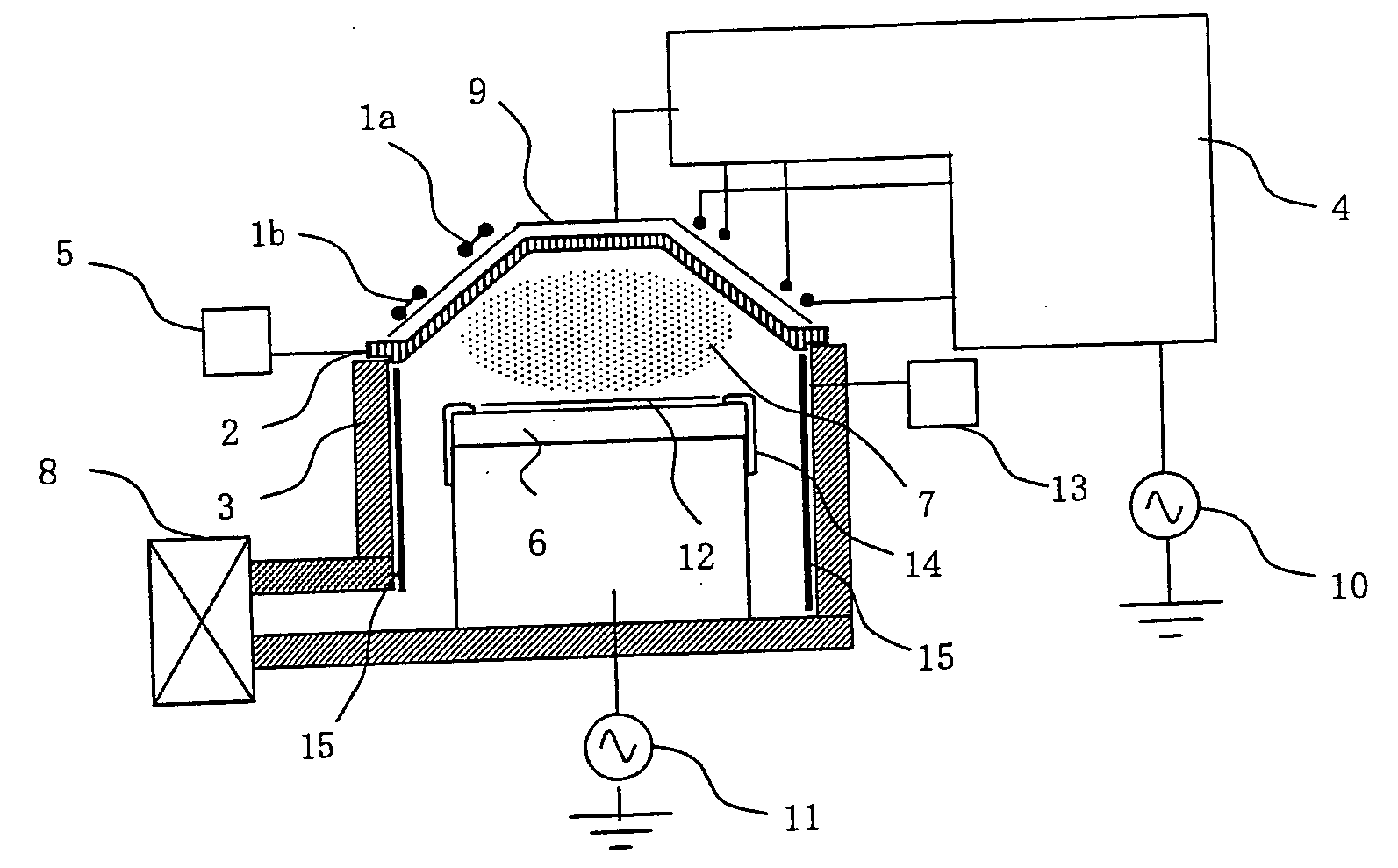
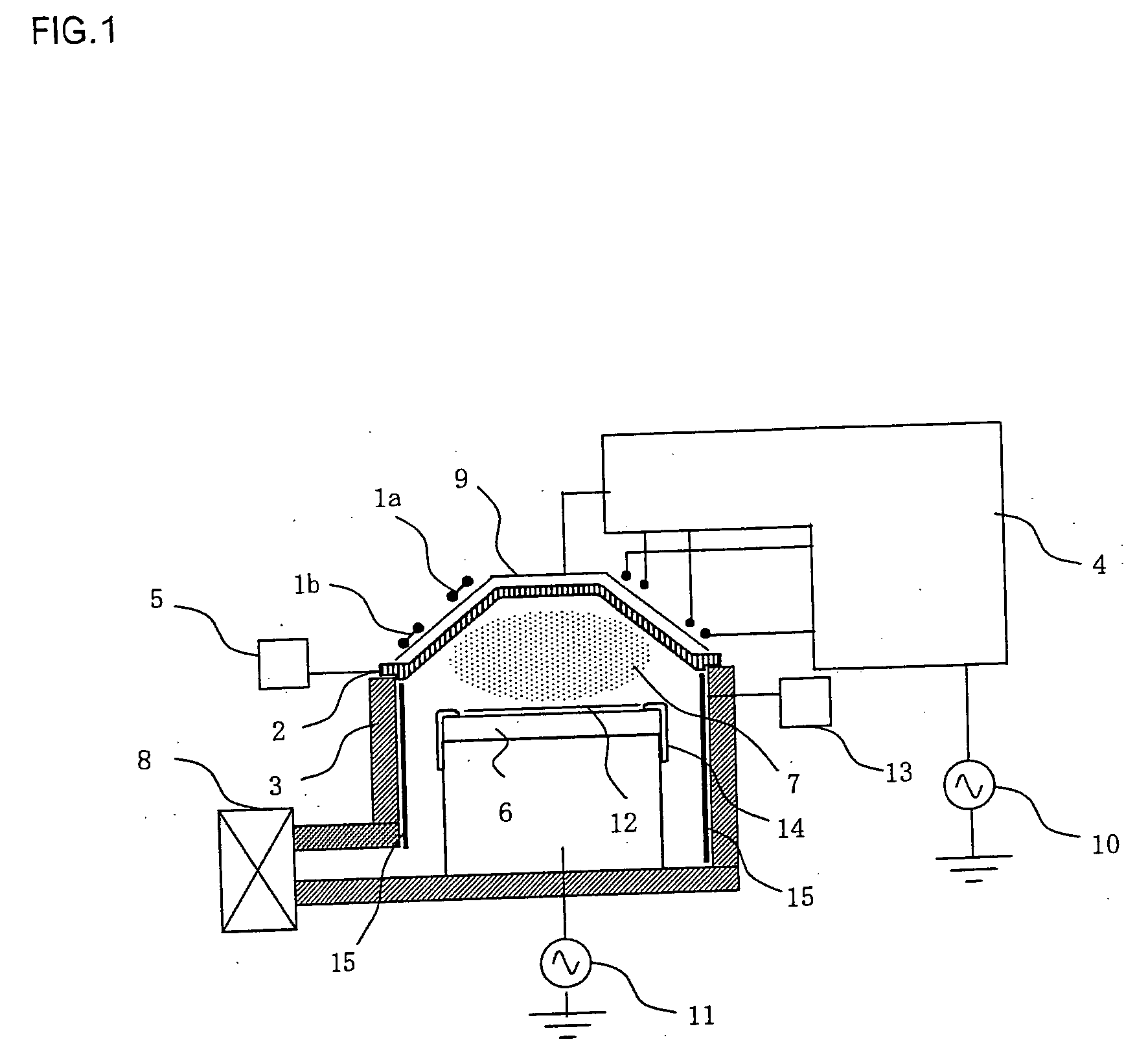
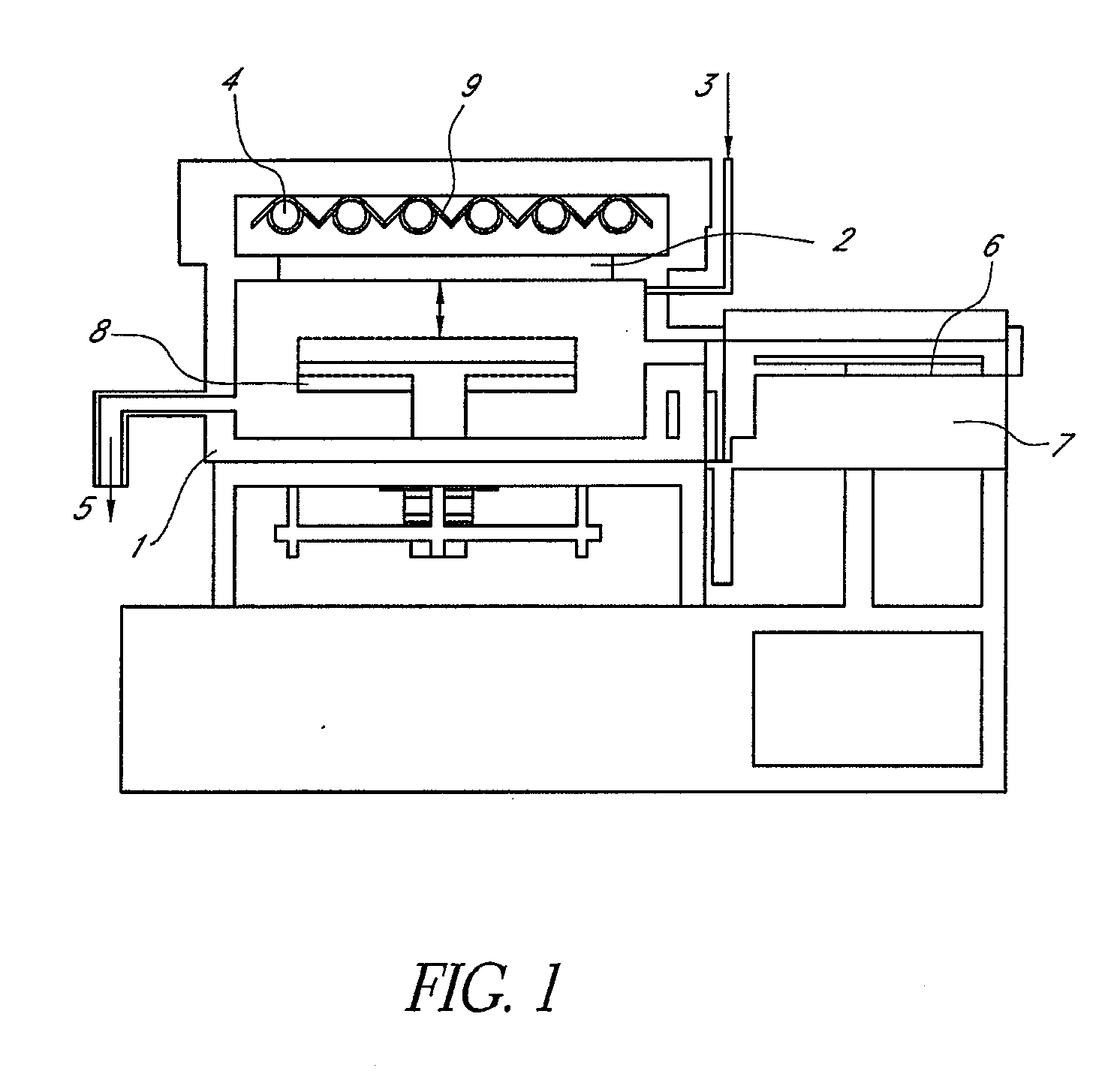
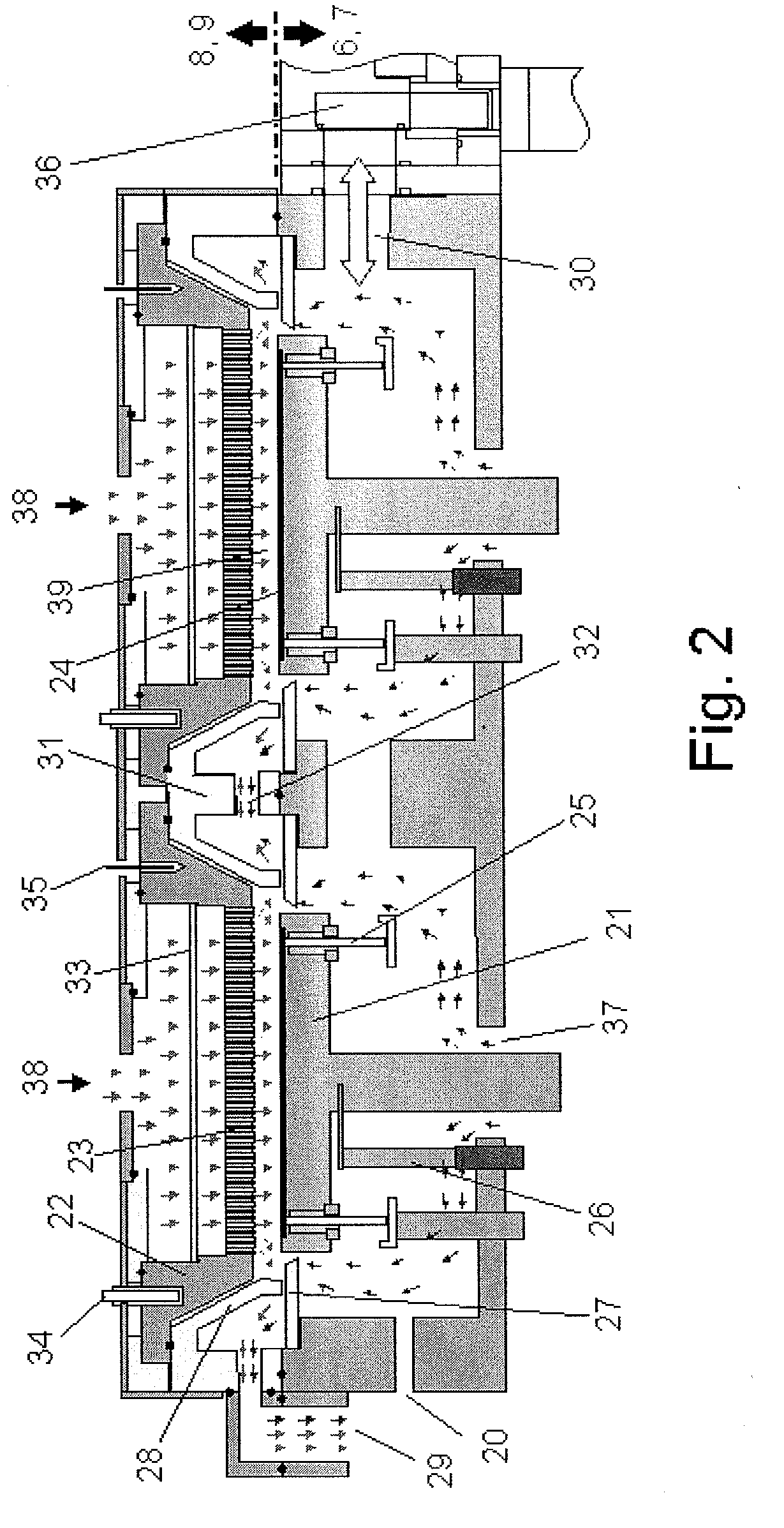
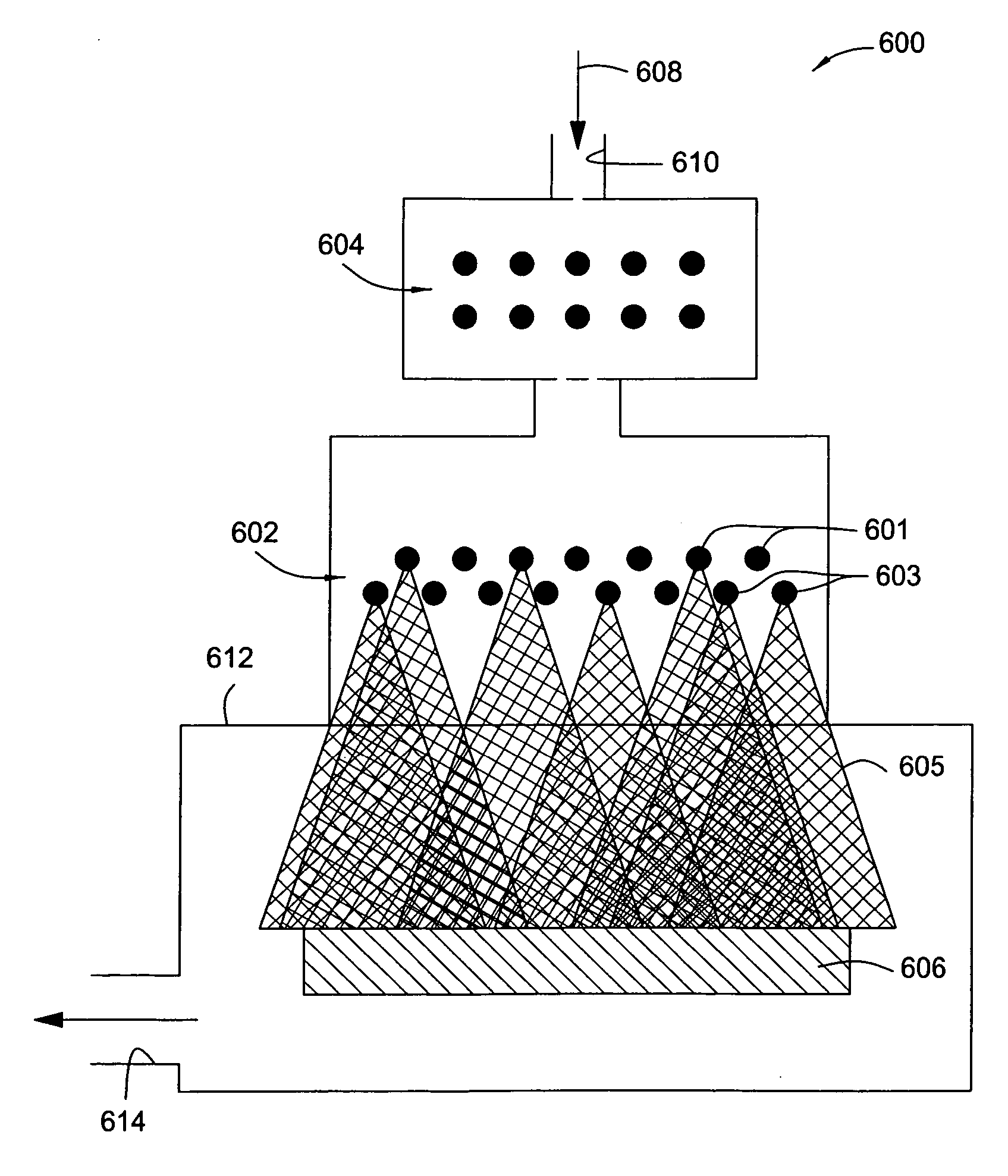
High efficiency UV curing system
InactiveUS20060249175A1Improve uniformityLighting and heating apparatusHollow article cleaningUV curingUltraviolet
An ultraviolet (UV) cure chamber enables curing a dielectric material disposed on a substrate and in situ cleaning thereof. A tandem process chamber provides two separate and adjacent process regions defined by a body covered with a lid having windows aligned respectively above each process region. One or more UV bulbs per process region that are covered by housings coupled to the lid emit UV light directed through the windows onto substrates located within the process regions. The UV bulbs can be an array of light emitting diodes or bulbs utilizing a source such as microwave or radio frequency. The UV light can be pulsed during a cure process. Using oxygen radical / ozone generated remotely and / or in-situ accomplishes cleaning of the chamber. Use of lamp arrays, relative motion of the substrate and lamp head, and real-time modification of lamp reflector shape and / or position can enhance uniformity of substrate illumination.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com