Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1272 results about "Diagnostic information" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
What is Diagnostic Information. 1. Information that helps to understand why a particular consequence happened or did not happen.
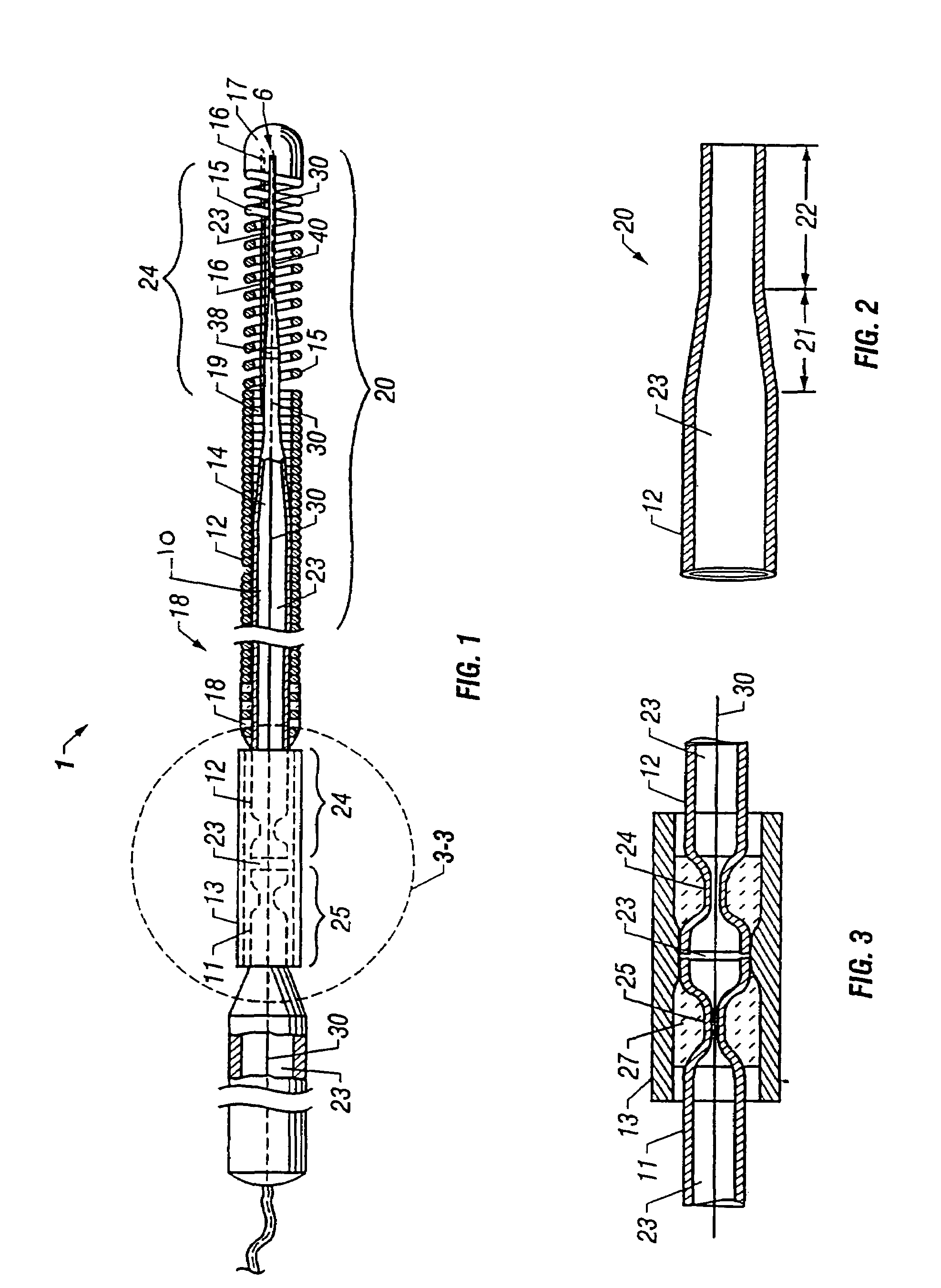
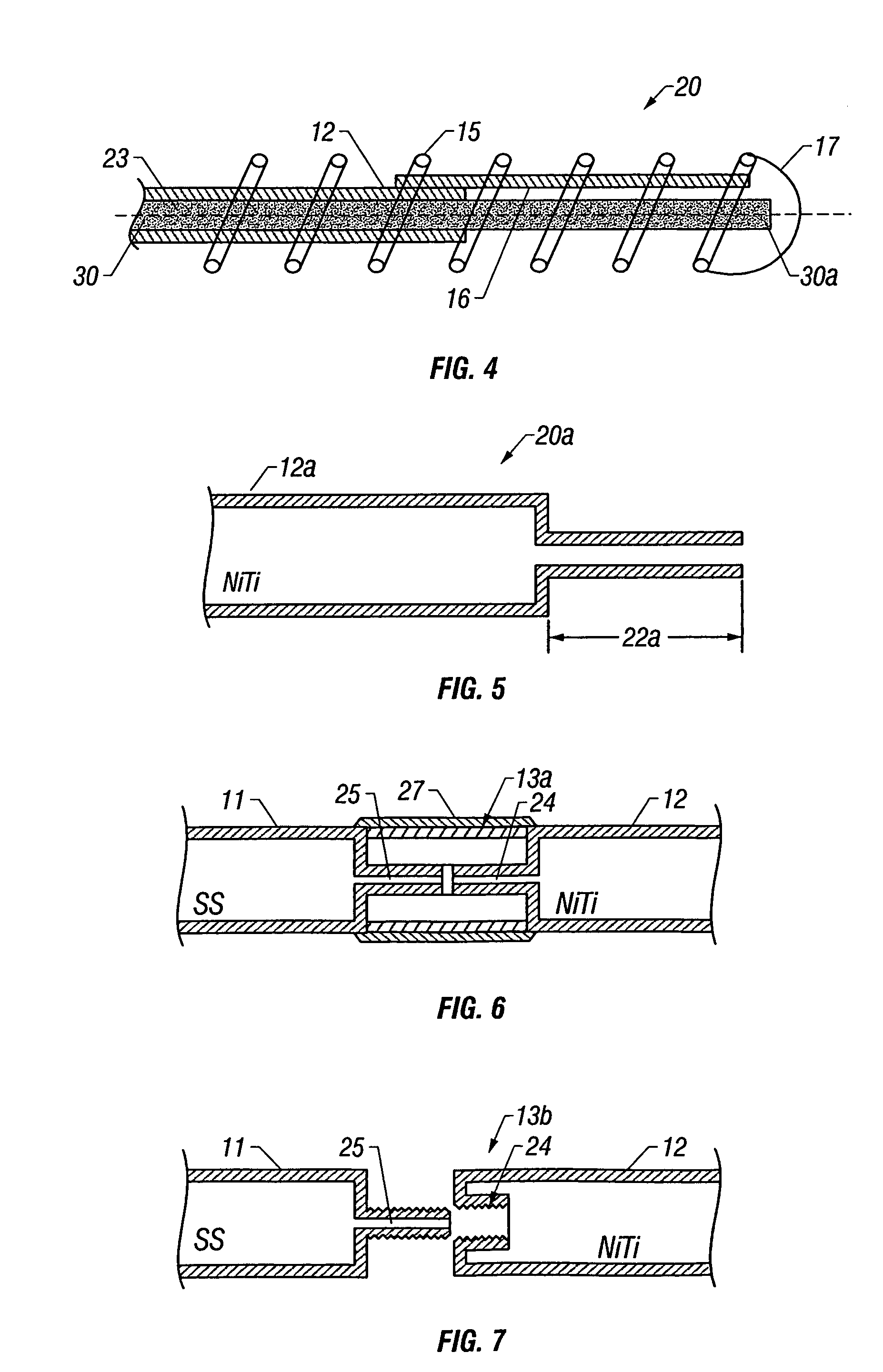
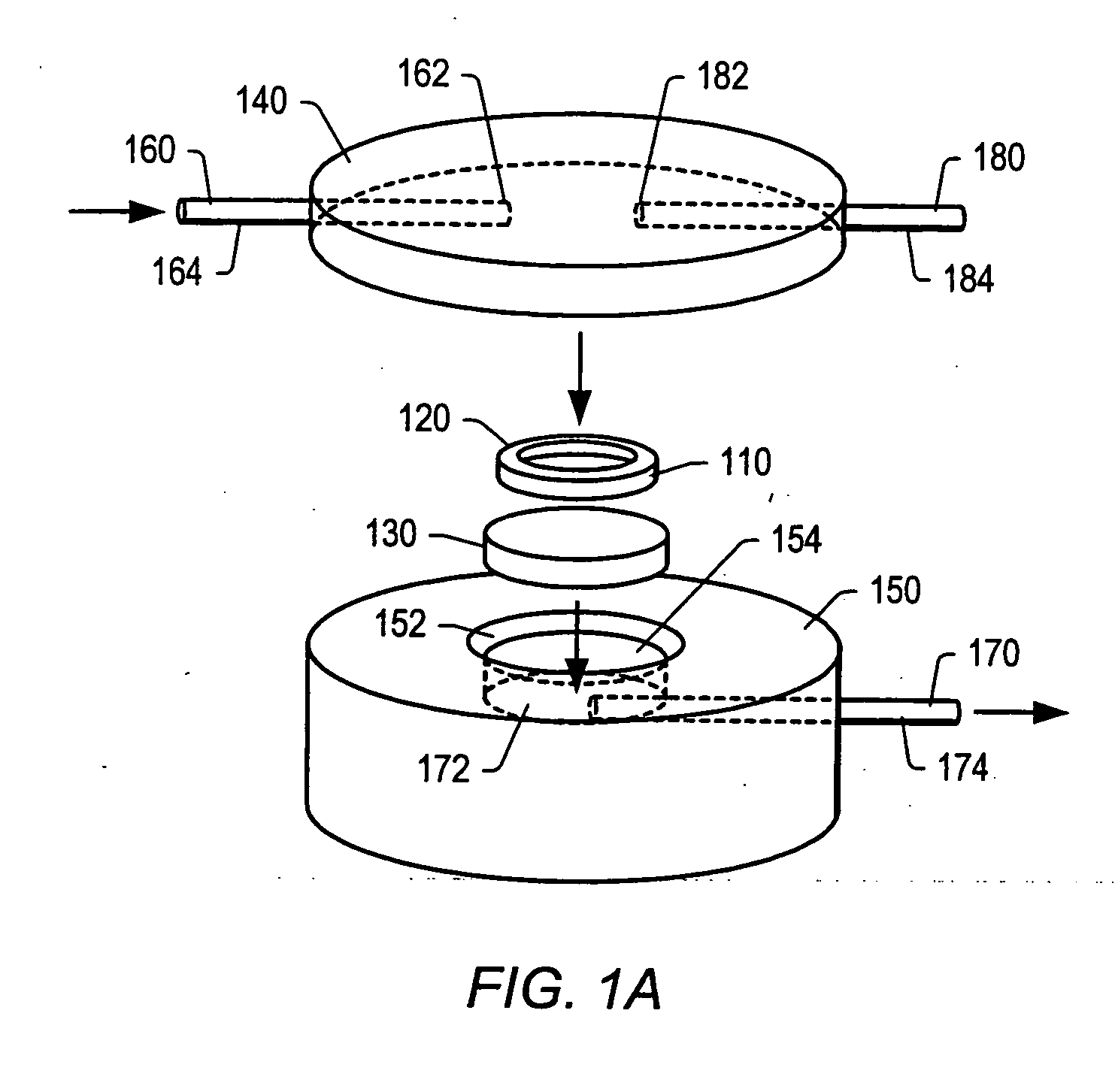
Apparatus and method for altering generator functions in an ultrasonic surgical system
InactiveUS6908472B2Avoid mistakesNew system functionalityIncision instrumentsDiagnosticsDriving currentElectricity
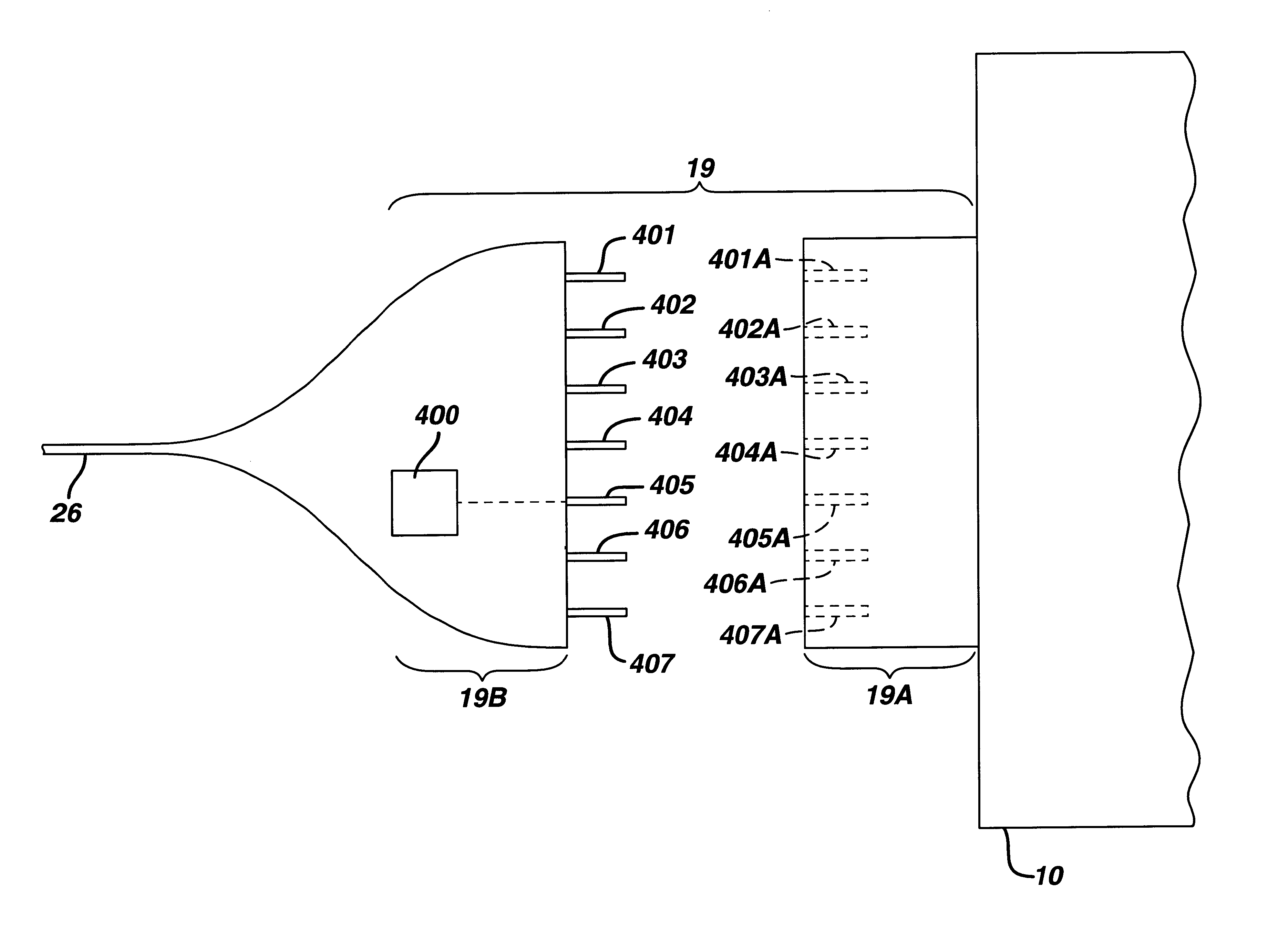
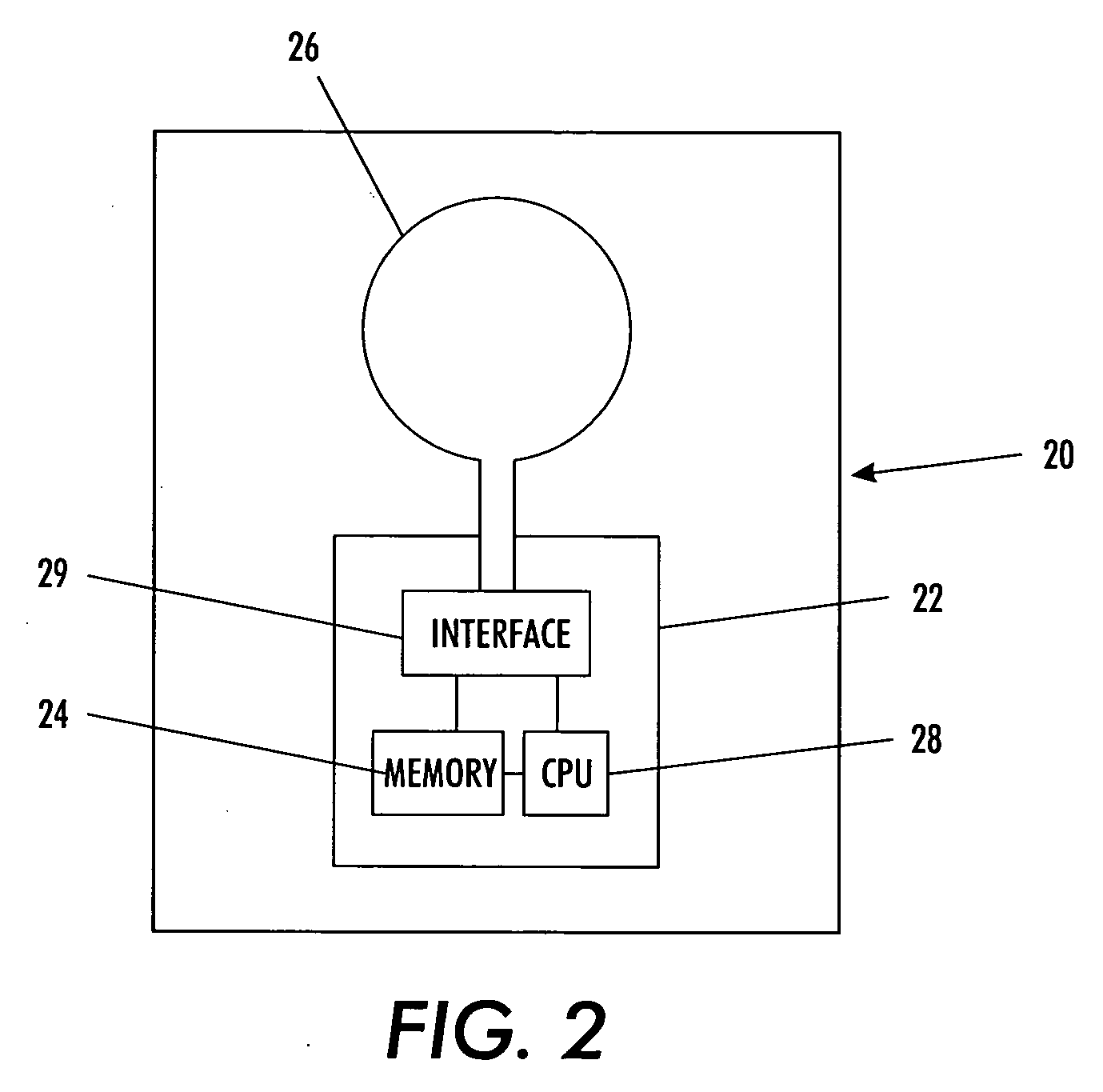
The present invention provides a system for implementing surgical procedures which includes an ultrasonic surgical hand piece having an end-effector, a console having a digital signal processor (DSP) for controlling the hand piece, an electrical connection connecting the hand piece and the console, and a memory, such as an EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory), disposed in the electrical connection. The console sends a drive current to drive the hand piece which imparts ultrasonic longitudinal movement to the blade. The console reads the memory and authenticates the hand piece for use with the console if particular or proprietary data are present in the memory. Moreover, to prevent errors in operating the hand piece, the memory can store certain diagnostic information which the console can utilize in determining whether the operation of the hand piece should be handicapped or disabled. Furthermore, the memory can be used to reprogram the console, if needed.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
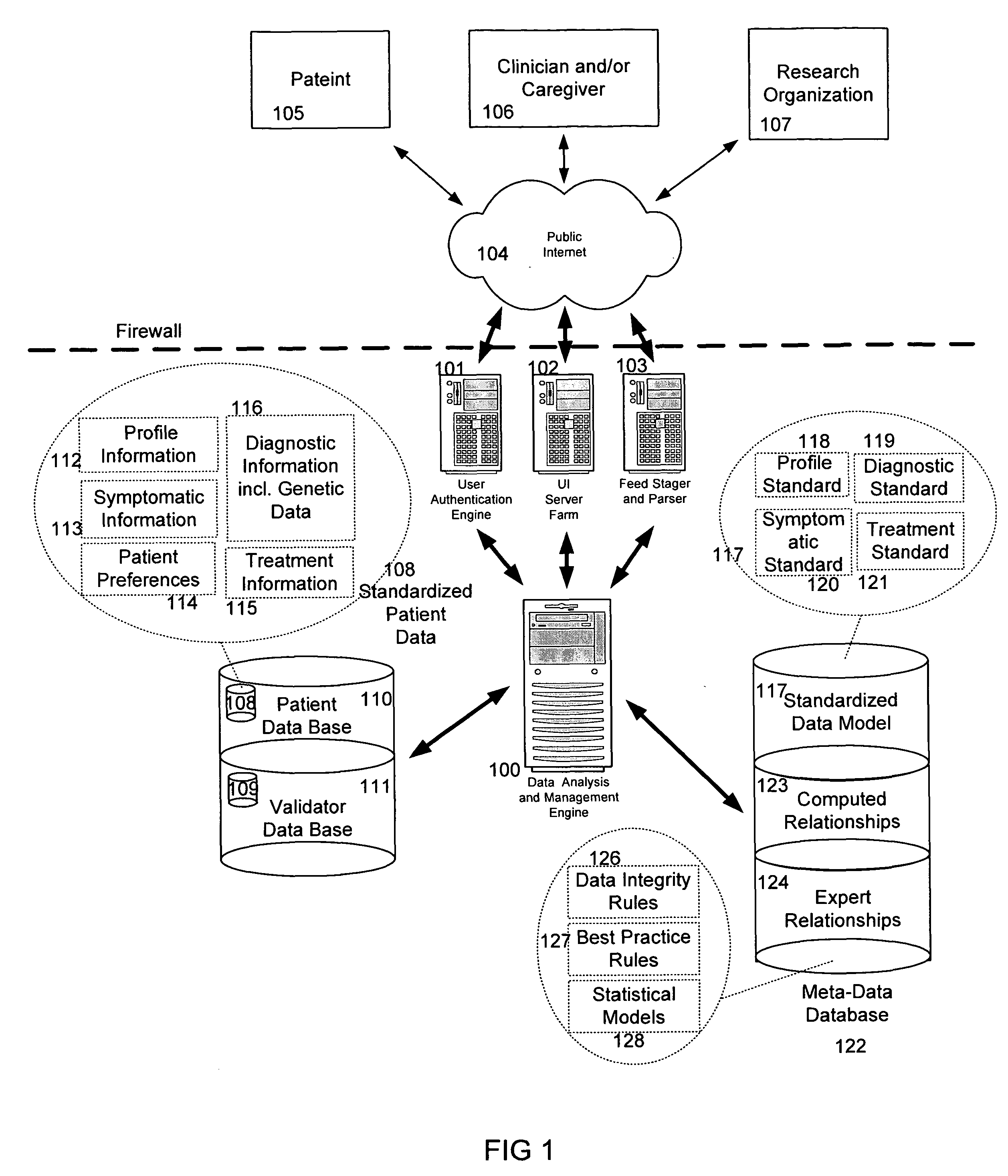
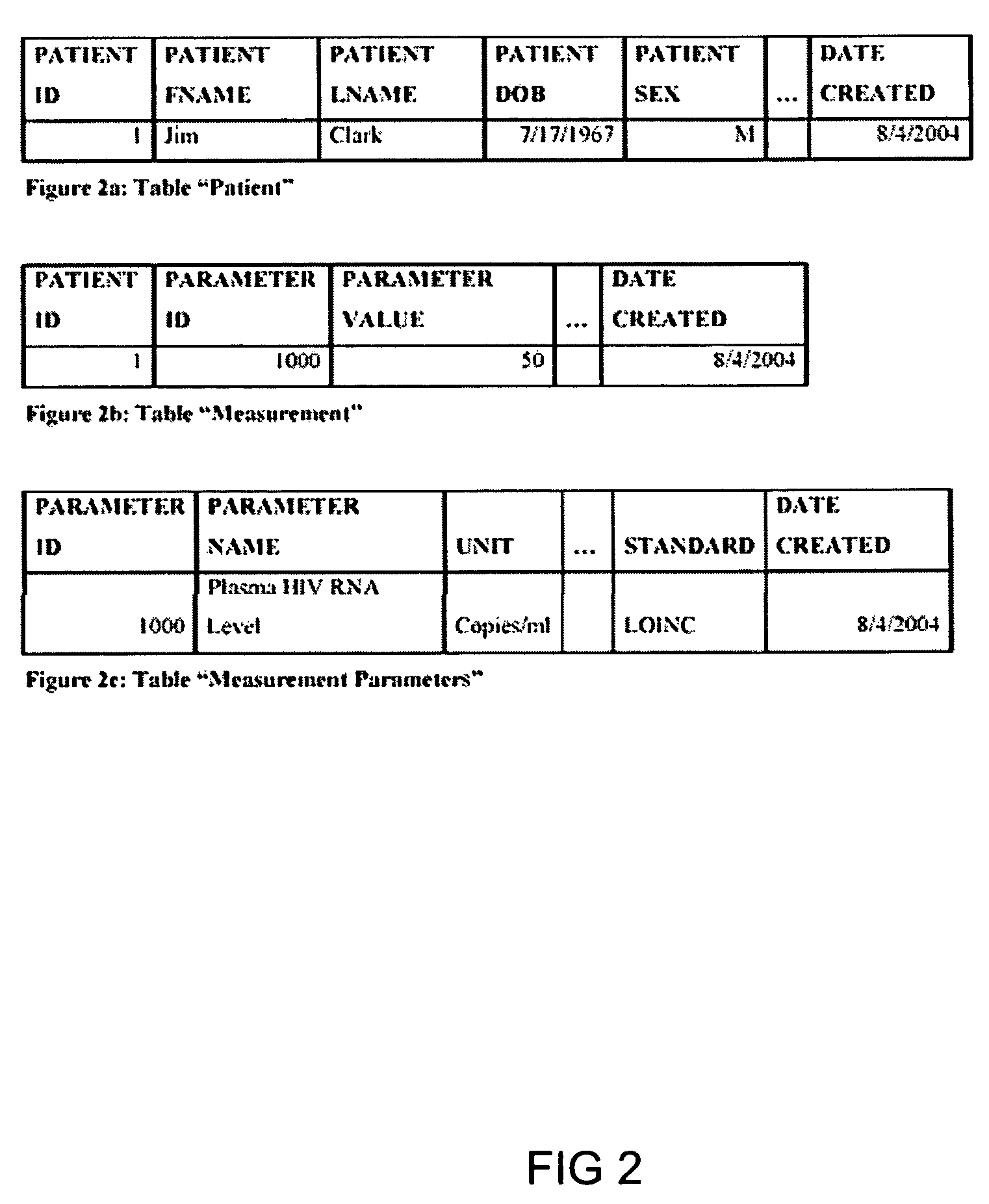
System and method for improving clinical decisions by aggregating, validating and analysing genetic and phenotypic data
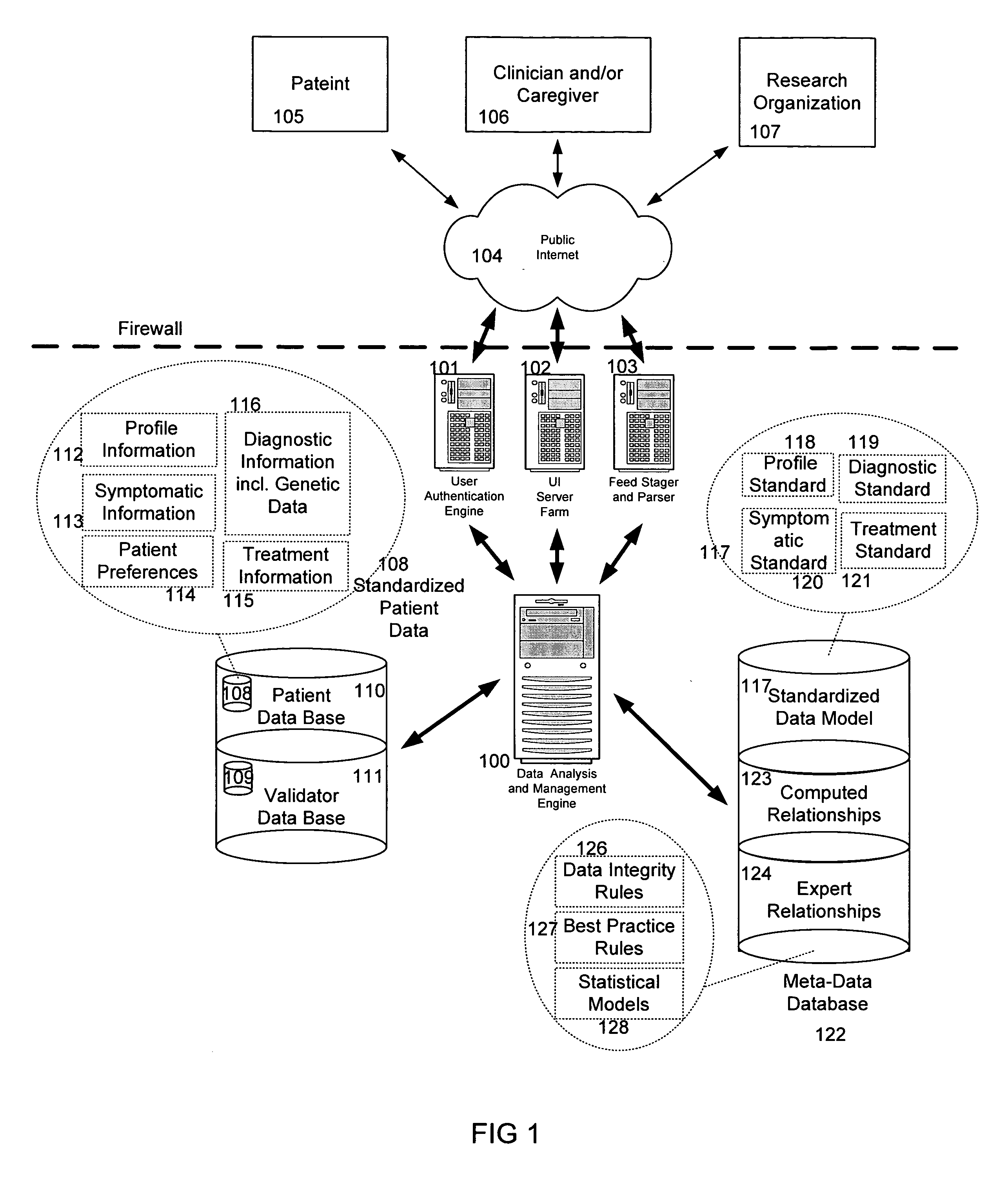
The information management system disclosed enables caregivers to make better decisions, faster, using aggregated genetic and phenotypic data. The system enables the integration, validation and analysis of genetic, phenotypic and clinical data from multiple subjects who may be at distributed facilities. A standardized data model stores a range of patient data in standardized data classes that encompass patient profile information, patient symptomatic information, patient treatment information, and patient diagnostic information including genetic information. Data from other systems is converted into the format of the standardized data classes using a data parser, or cartridge, specifically tailored to the source system. Relationships exist between standardized data classes that are based on expert rules and statistical models. The relationships are used both to validate new data, and to predict phenotypic outcomes based on available data. The prediction may relate to a clinical outcome in response to a proposed intervention by a caregiver. The statistical models may be inhaled into the system from electronic publications that define statistical models and methods for training those models, according to a standardized template. Methods are described for selecting, creating and training the statistical models to operate on genetic, phenotypic and clinical data, in particular for underdetermined data sets that are typical of genetic information. The disclosure also describes how security of the data is maintained by means of a robust security architecture, and robust user authentication such as biometric authentication, combined with application-level and data-level access privileges.
Owner:NATERA
Diagnosis of programmable modules
InactiveUS20050258963A1Memory record carrier reading problemsDetecting faulty computer hardwareComputer hardwareDiagnostic data
An electronic diagnostic device for testing electronic monitoring tags for devices such as replaceable modules for a printing apparatus includes a tag reader with a reader wireless communication element. The tag reader is adapted to read tag diagnostic information from an electronic monitoring tag. The electronic diagnostic device further includes a data processor in communication with the tag reader. The data processor is adapted to determine from the tag diagnostic data whether the electronic monitoring tag is operating within predetermined parameters, to identify one of a predetermined set of error categories if the electronic monitoring tag is operating outside the predetermined parameters, and to generate error category information. The electronic diagnostic device further includes a results communication element adapted to communicate the error category information generated by the data processor. The diagnostic device may also communicate correction information to the electronic monitoring tag.
Owner:XEROX CORP
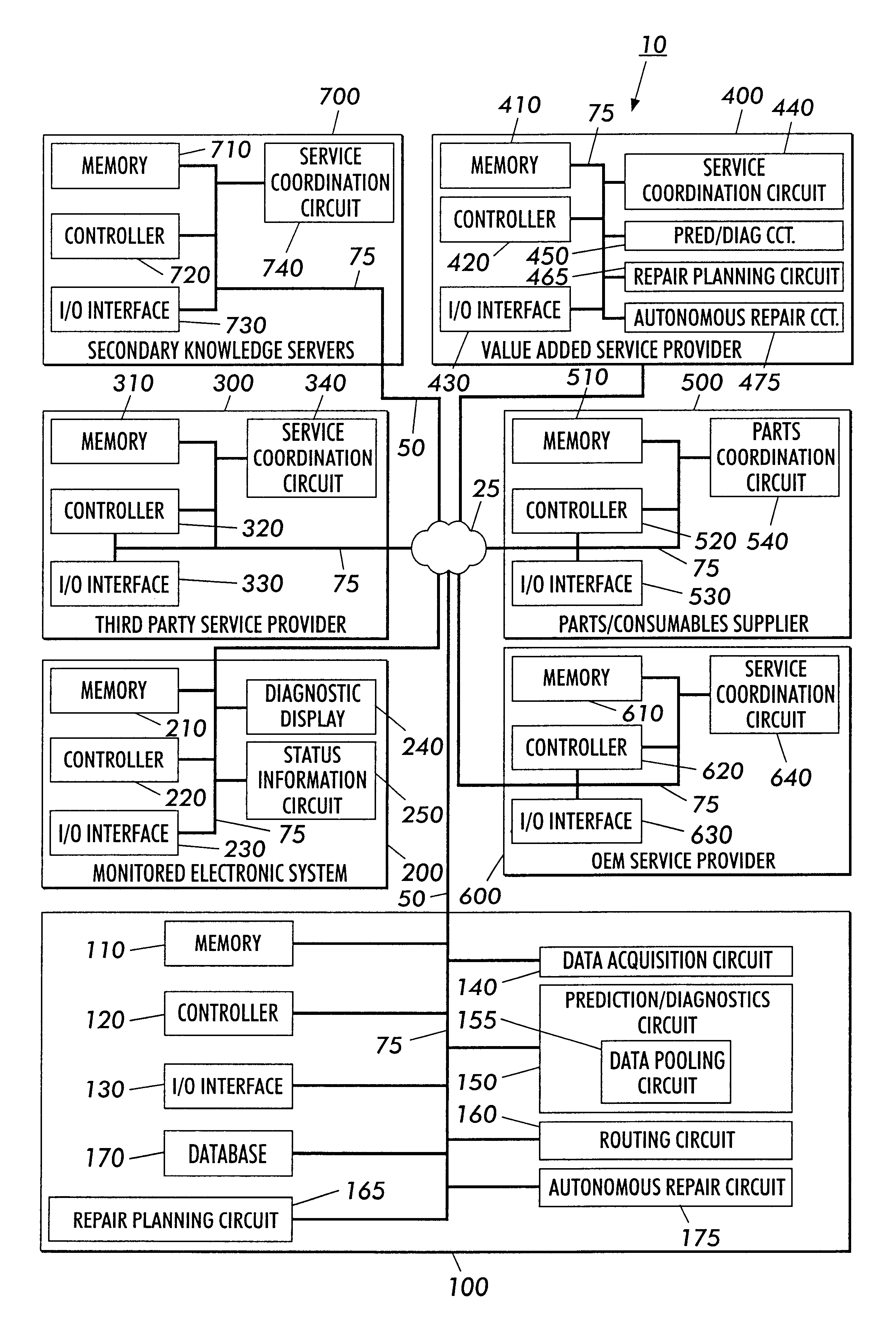
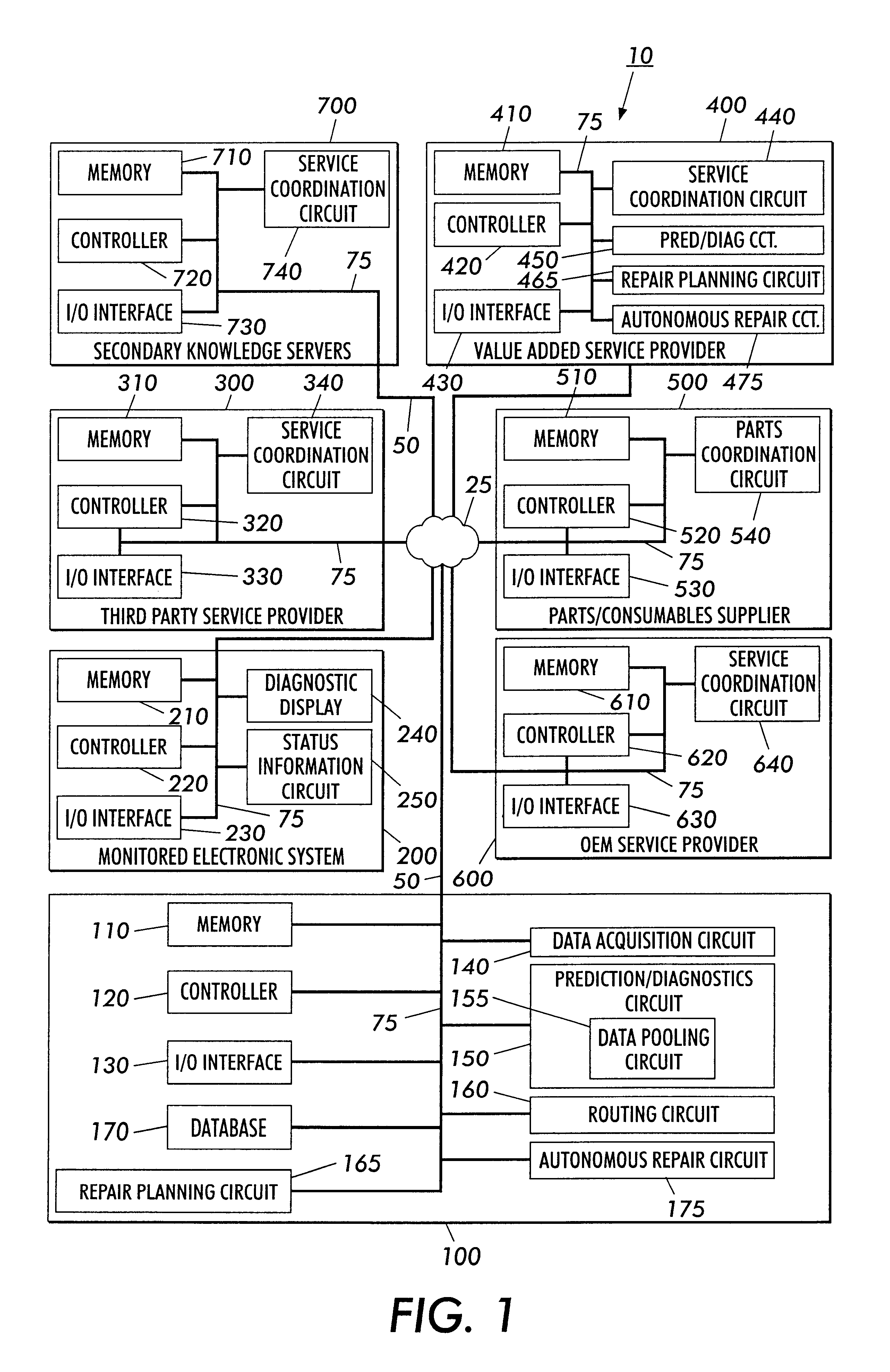
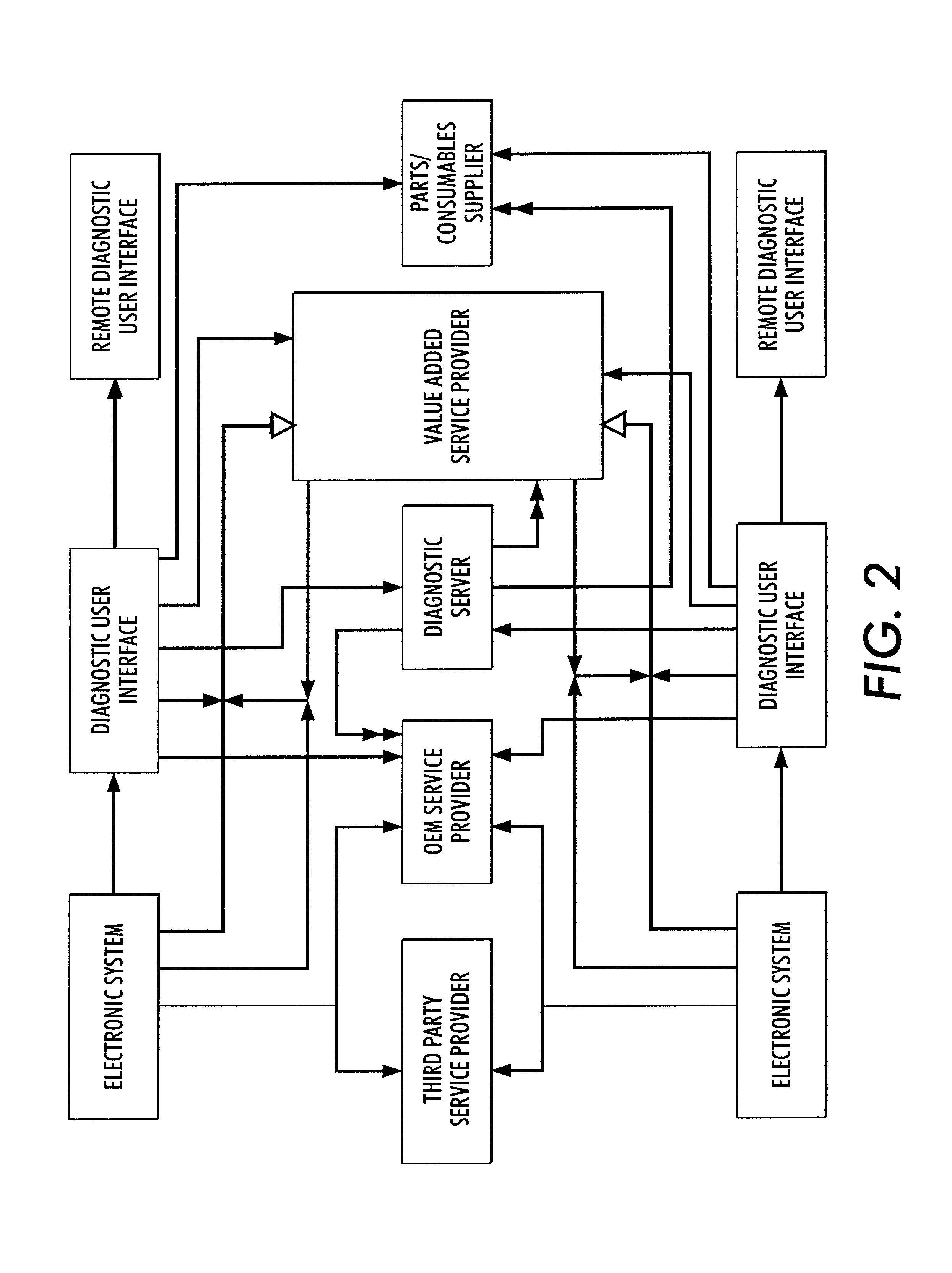
Systems and methods for failure prediction, diagnosis and remediation using data acquisition and feedback for a distributed electronic system
InactiveUS6892317B1Highly reliable actionHighly reliable responseData processing applicationsLogical operation testingPredictive systemsElectronic systems
By using monitoring data, feedback data, and pooling of failure data from a plurality of electronic devices, real-time failure prediction and diagnoses of electronic systems operating in a network environment can be achieved. First, the diagnostic system requests data on the state of a machine and / or its components and collections thereof as part of the machine's normal operation. Secondly, real-time processing of the data either at the machine site or elsewhere in the distributed network allows for predicting or diagnosing system failures. Having determined and / or predicted a system failure, a communication to one or more remote observers in the network allows the remote observers to view the diagnostic information and / or required action to repair the failure. Furthermore, interrogation of either the particular electronic system, or a database containing data on similar electronic systems by the diagnostic server allows the diagnostic server to refine original diagnoses based on this population data to achieve a comprehensive failure predication / diagnosing system.
Owner:LONGHORN HD LLC
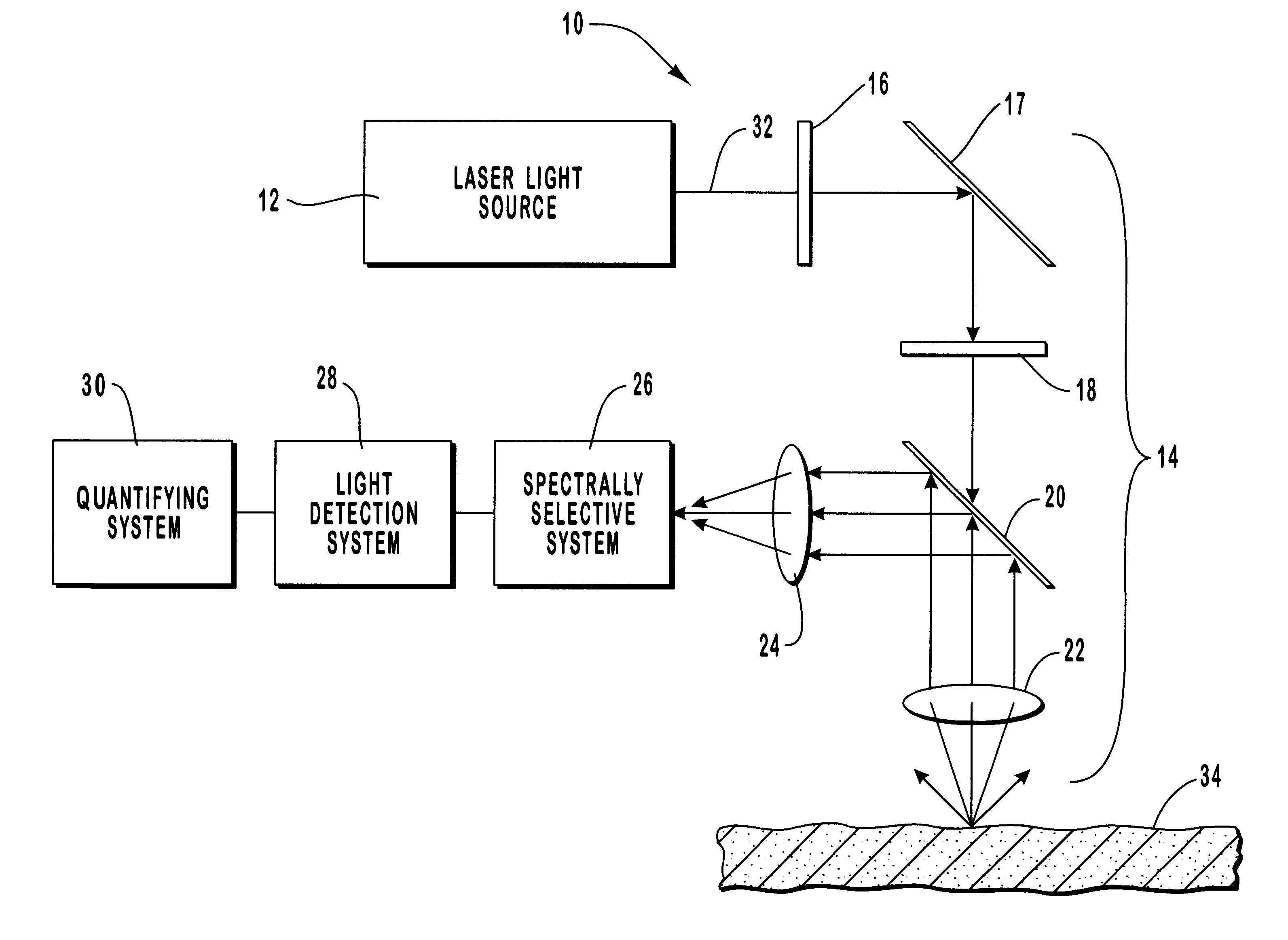
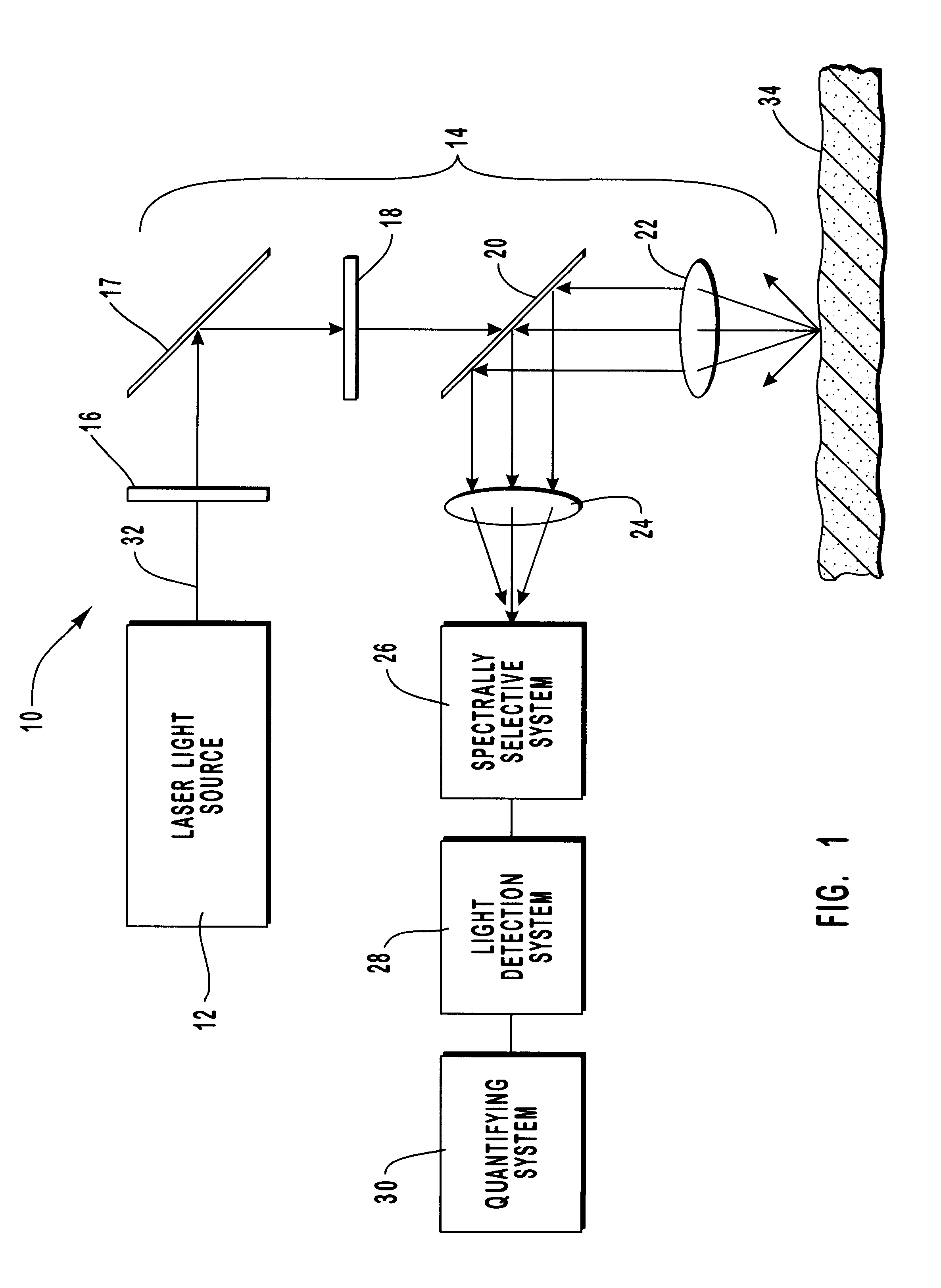
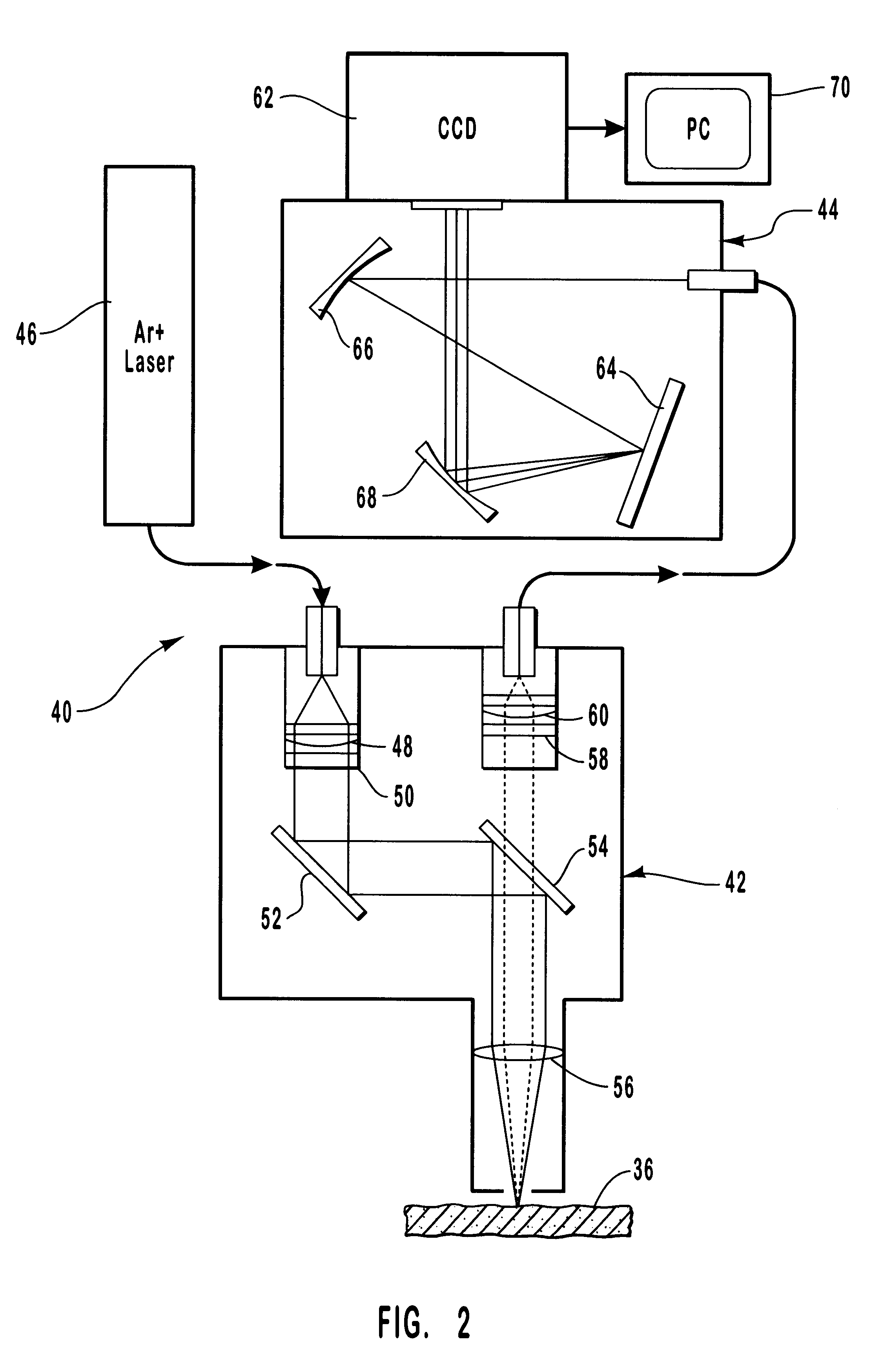
Method and apparatus for noninvasive measurement of carotenoids and related chemical substances in biological tissue
InactiveUS6205354B1Rapid and noninvasive and quantitative measurementRiskRadiation pyrometrySurgeryResonance Raman spectroscopyAntioxidant
A method and apparatus are provided for the determination of levels of carotenoids and similar chemical compounds in biological tissue such as living skin. The method and apparatus provide a noninvasive, rapid, accurate, and safe determination of carotenoid levels which in turn can provide diagnostic information regarding cancer risk, or can be a marker for conditions where carotenoids or other antioxidant compounds may provide diagnostic information. Such early diagnostic information allows for the possibility of preventative intervention. The method and apparatus utilize the technique of resonance Raman spectroscopy to measure the levels of carotenoids and similar substances in tissue. In this technique, laser light is directed upon the area of tissue which is of interest. A small fraction of the scattered light is scattered inelastically, producing the carotenoid Raman signal which is at a different frequency than the incident laser light, and the Raman signal is collected, filtered, and measured. The resulting Raman signal can be analyzed such that the background fluorescence signal is subtracted and the results displayed and compared with known calibration standards.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
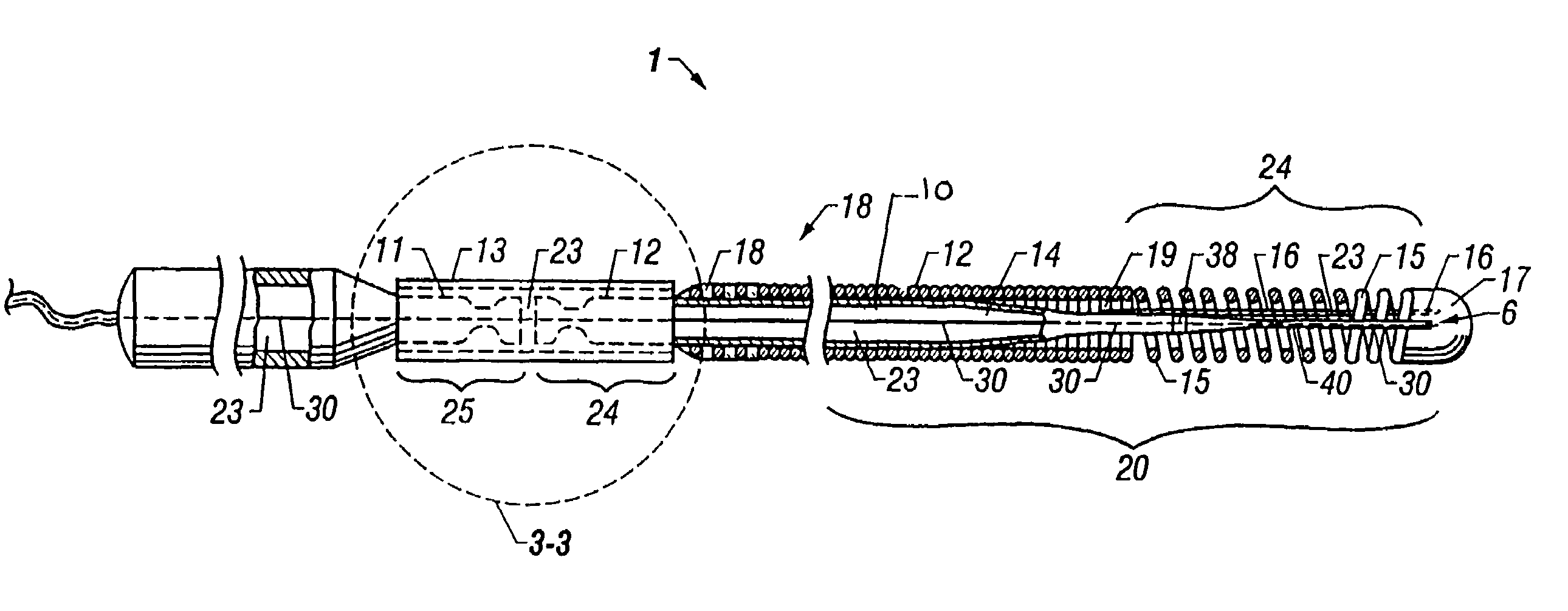
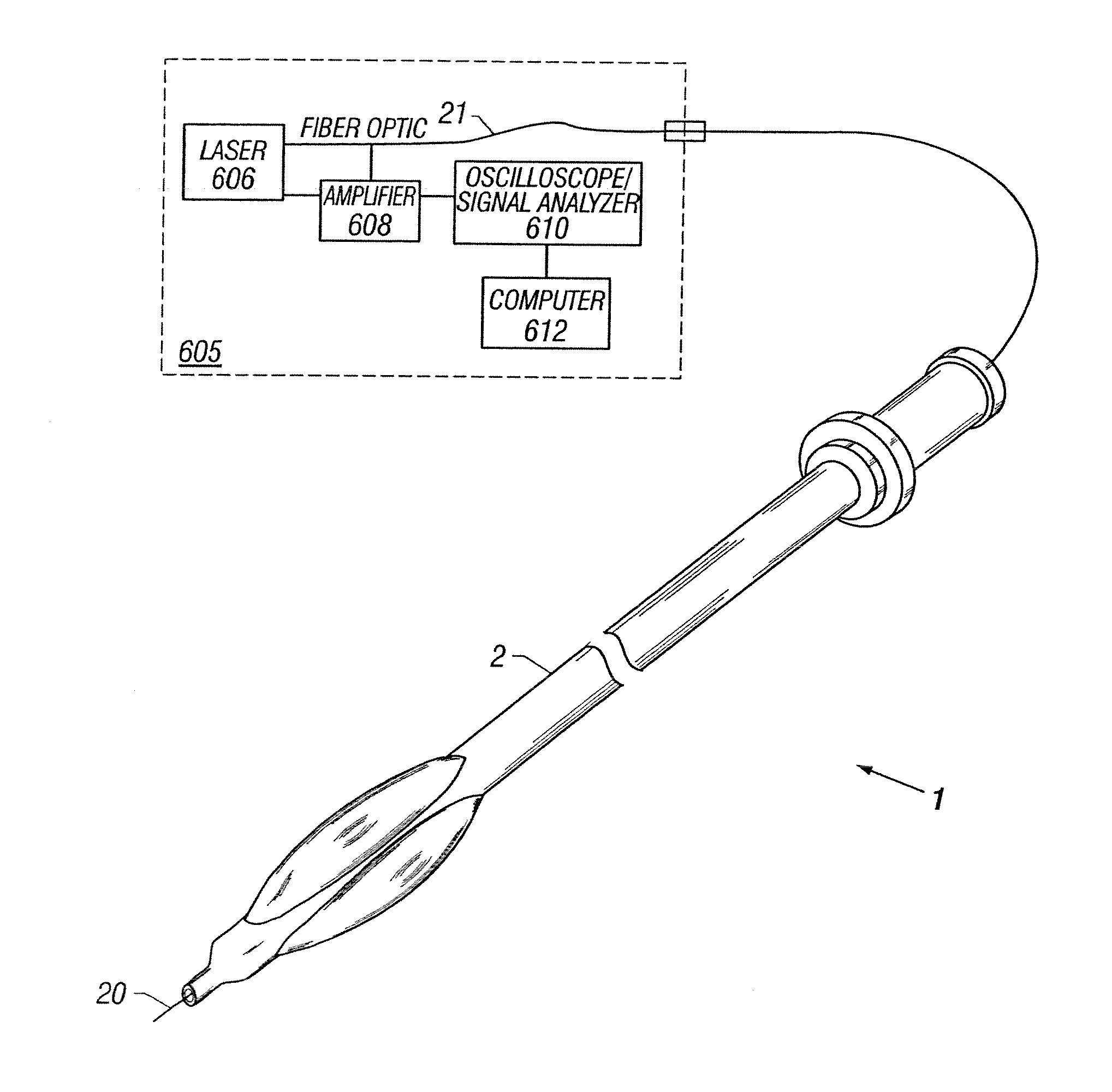
Guidewire with optical fiber
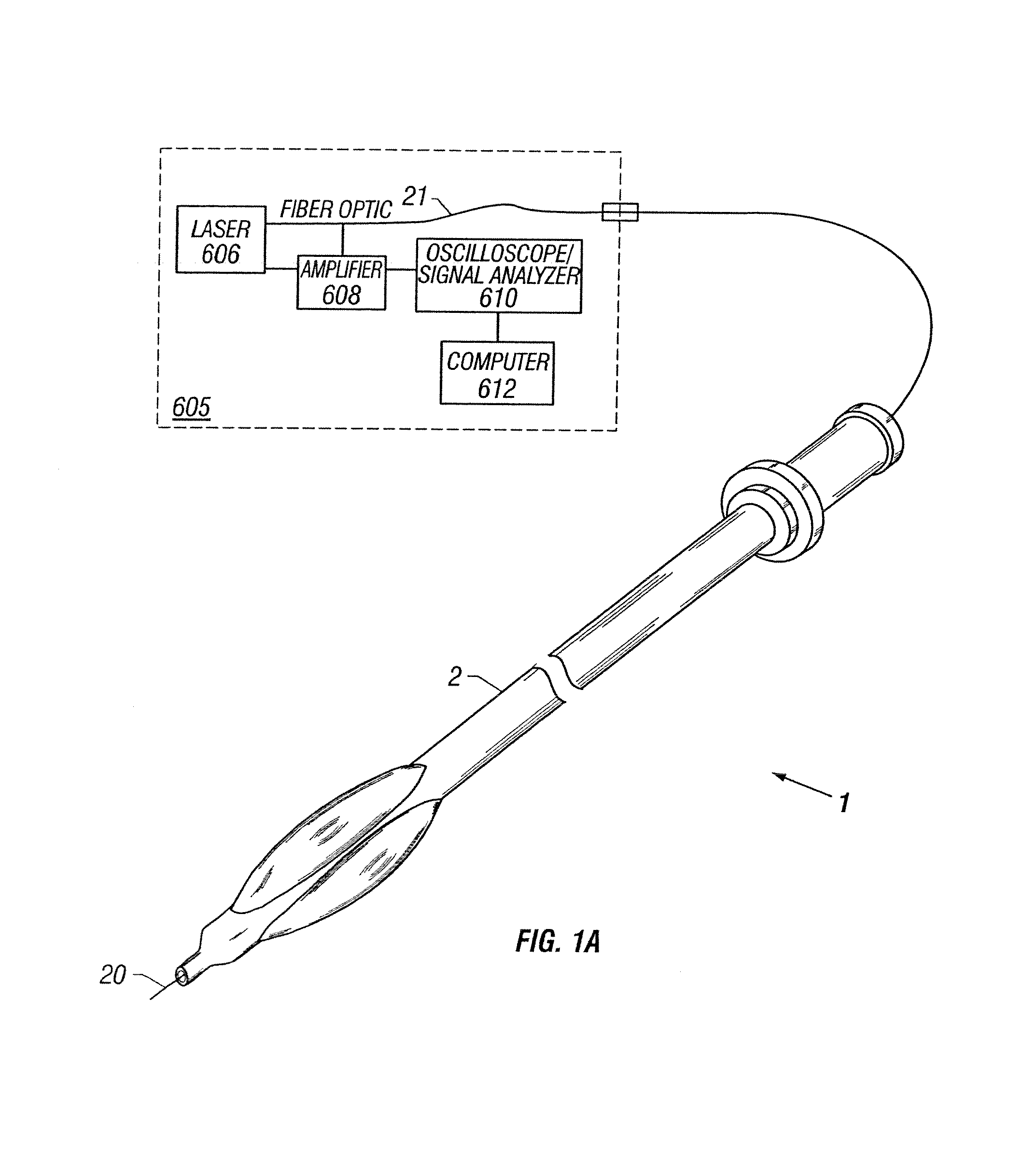
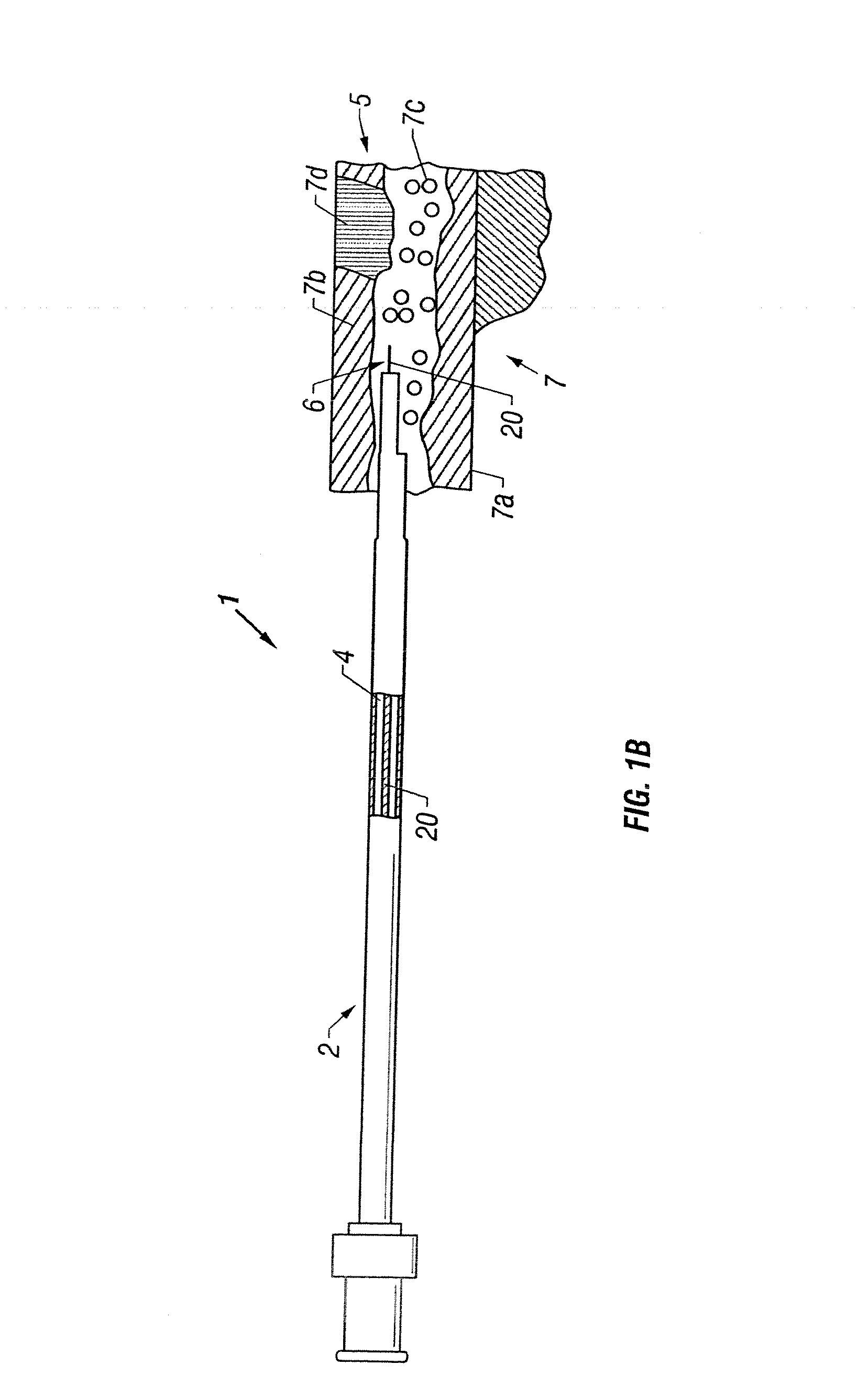
Apparatus and method to perform therapeutic treatment and diagnosis of a patient's vasculature through the use of an intravascular device having an optical fiber disposed therein. In an embodiment of this invention, the apparatus includes a therapeutic guidewire and at least one optical fiber disposed through the therapeutic guidewire, the optical fiber capable of providing diagnostic information before, during, and after the therapeutic treatment. In an embodiment, diagnostic information includes vessel and blood characteristics such as hemodynamic characteristics, hematological parameters related to blood and blood components, and thermal parameters of the vasculature.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Integration of fluids and reagents into self-contained cartridges containing sensor elements
InactiveUS20060257993A1Facilitate digital/optical acquisition of fluorescent signalBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPoint of careAnalyte
Described herein is an analyte detection device and method related to a portable instrument suitable for point-of-care analyses. In some embodiments, a portable instrument may include a disposable cartridge, an optical detector, a sample collection device and / or sample reservoir, reagent delivery systems, fluid delivery systems, one or more channels, and / or waste reservoirs. Use of a portable instrument may reduce the hazard to an operator by reducing an operator's contact with a sample for analysis. The device is capable of obtaining diagnostic information using cellular- and / or particle-based analyses and may be used in conjunction with membrane- and / or particle-based analysis cartridges. Analytes, including proteins and cells and / or microbes may be detected using the membrane and / or particle based analysis system.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
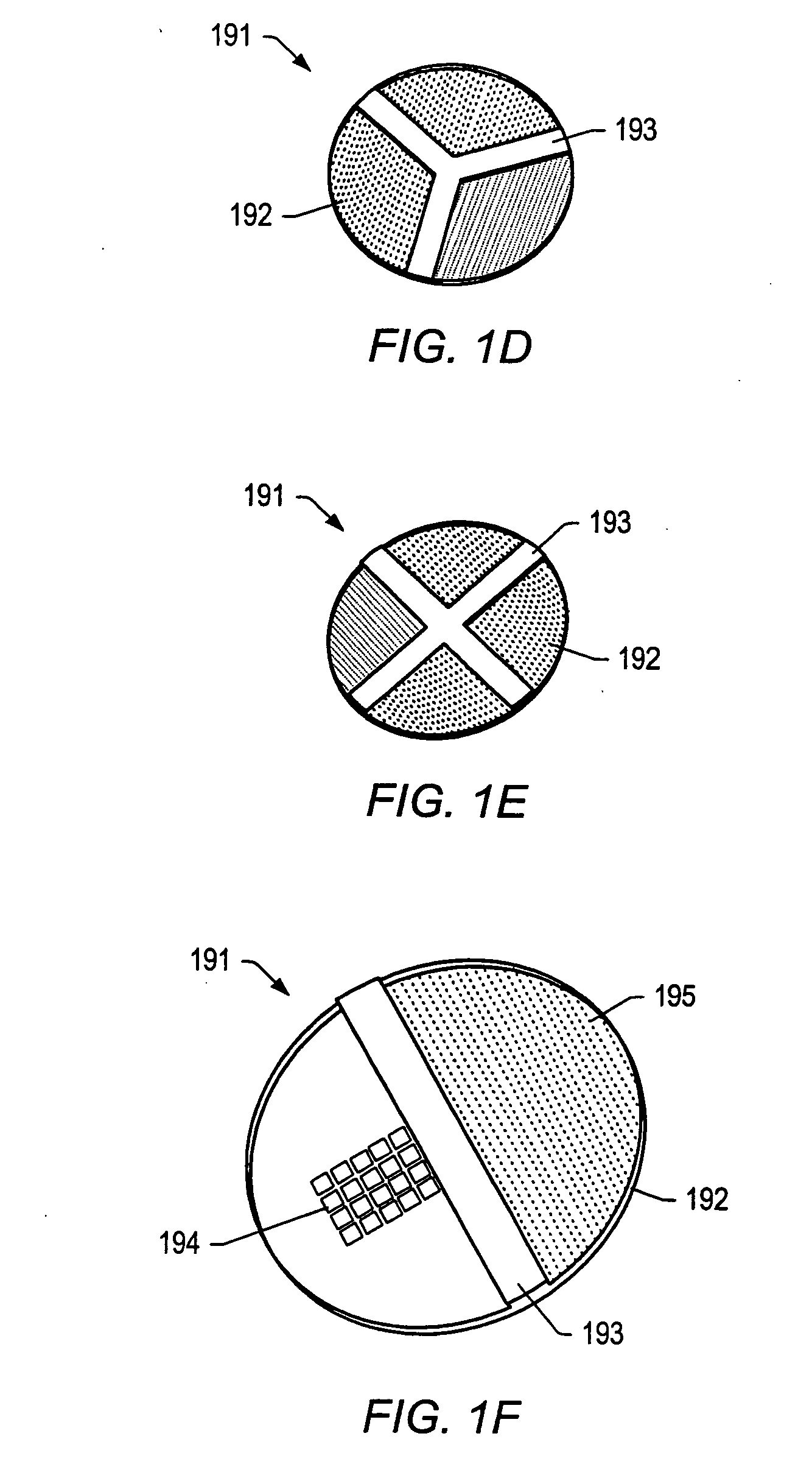
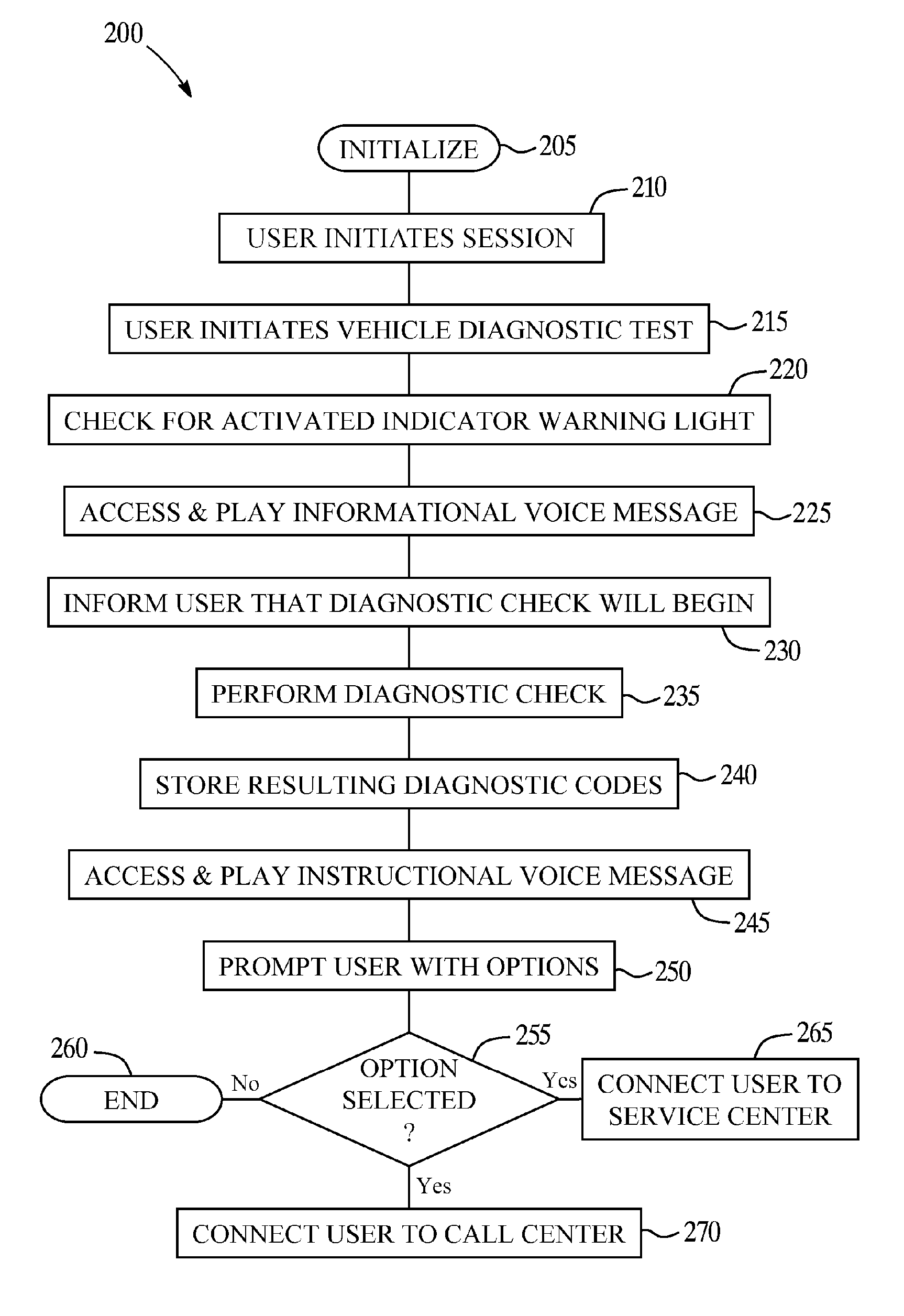
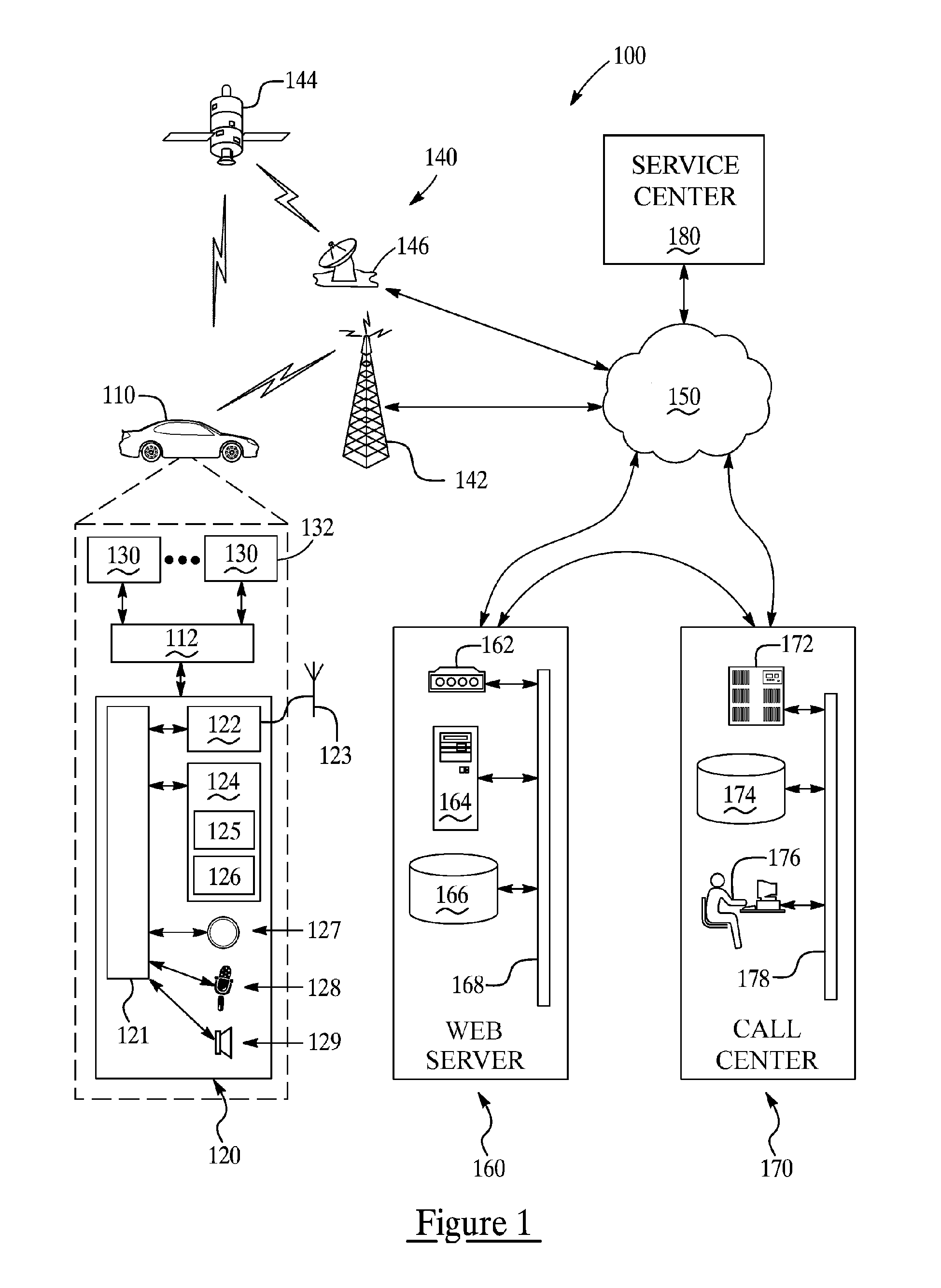
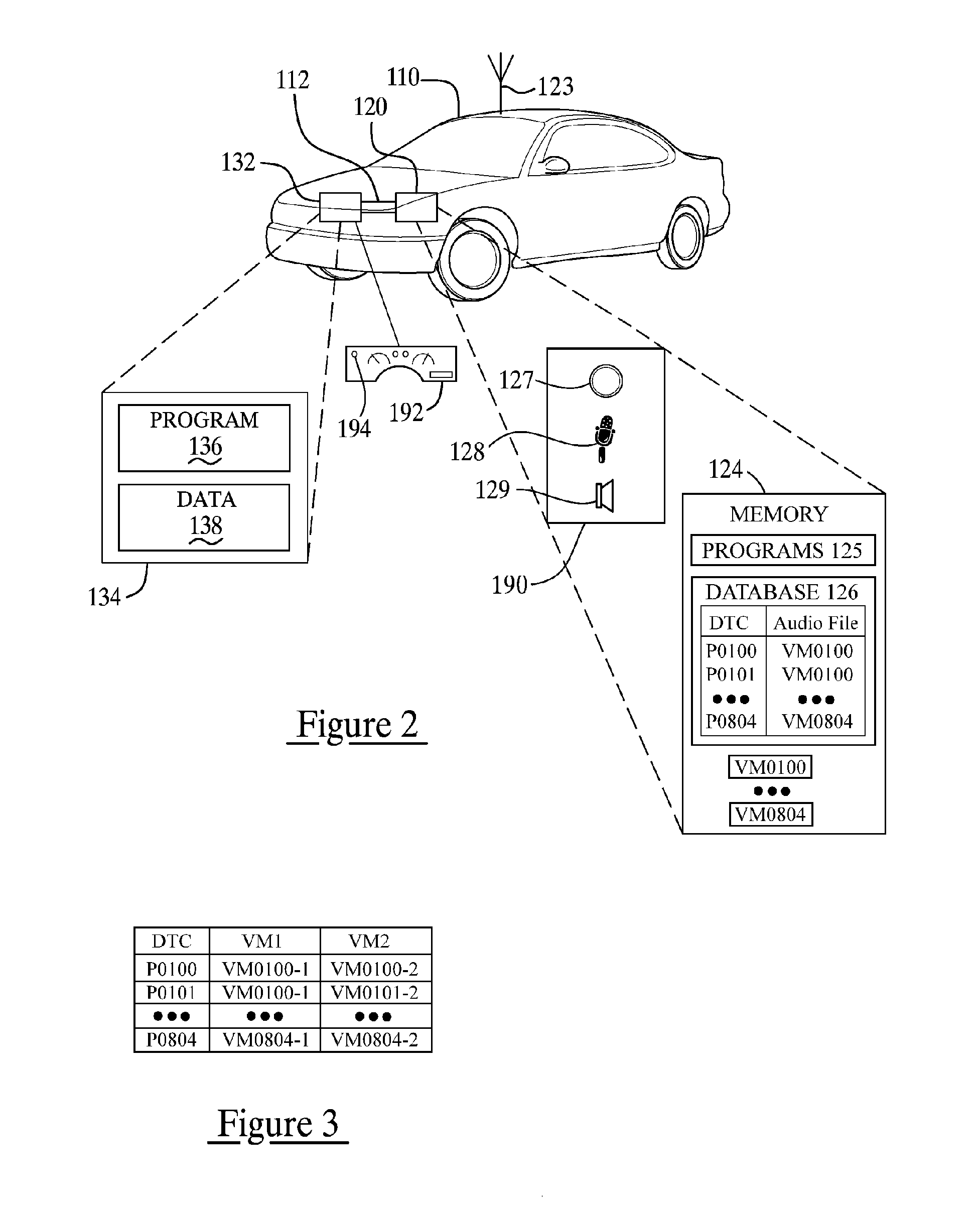
Vehicle diagnostic test and reporting method
ActiveUS20070093947A1Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesInformation processingDriver/operator
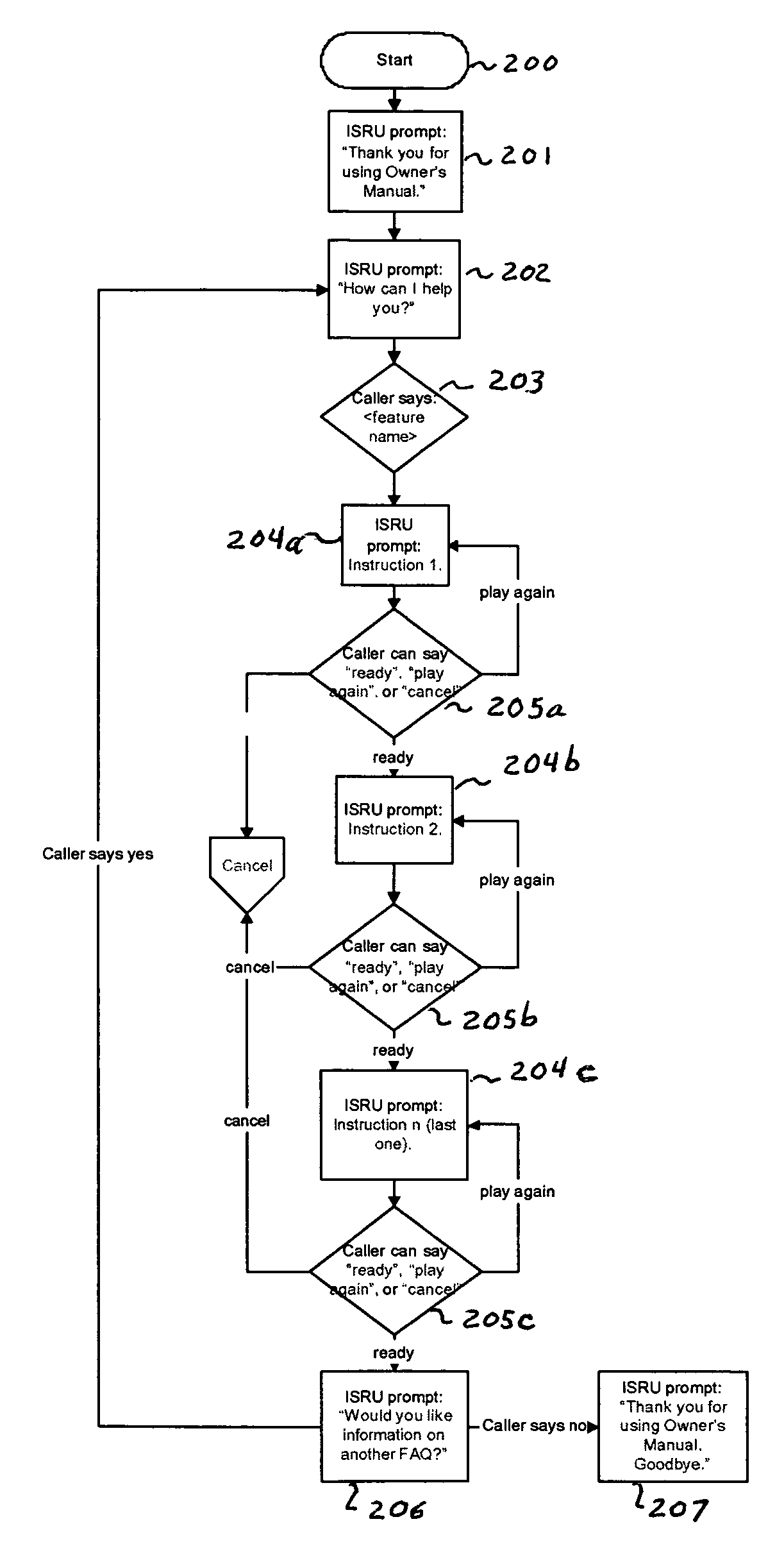
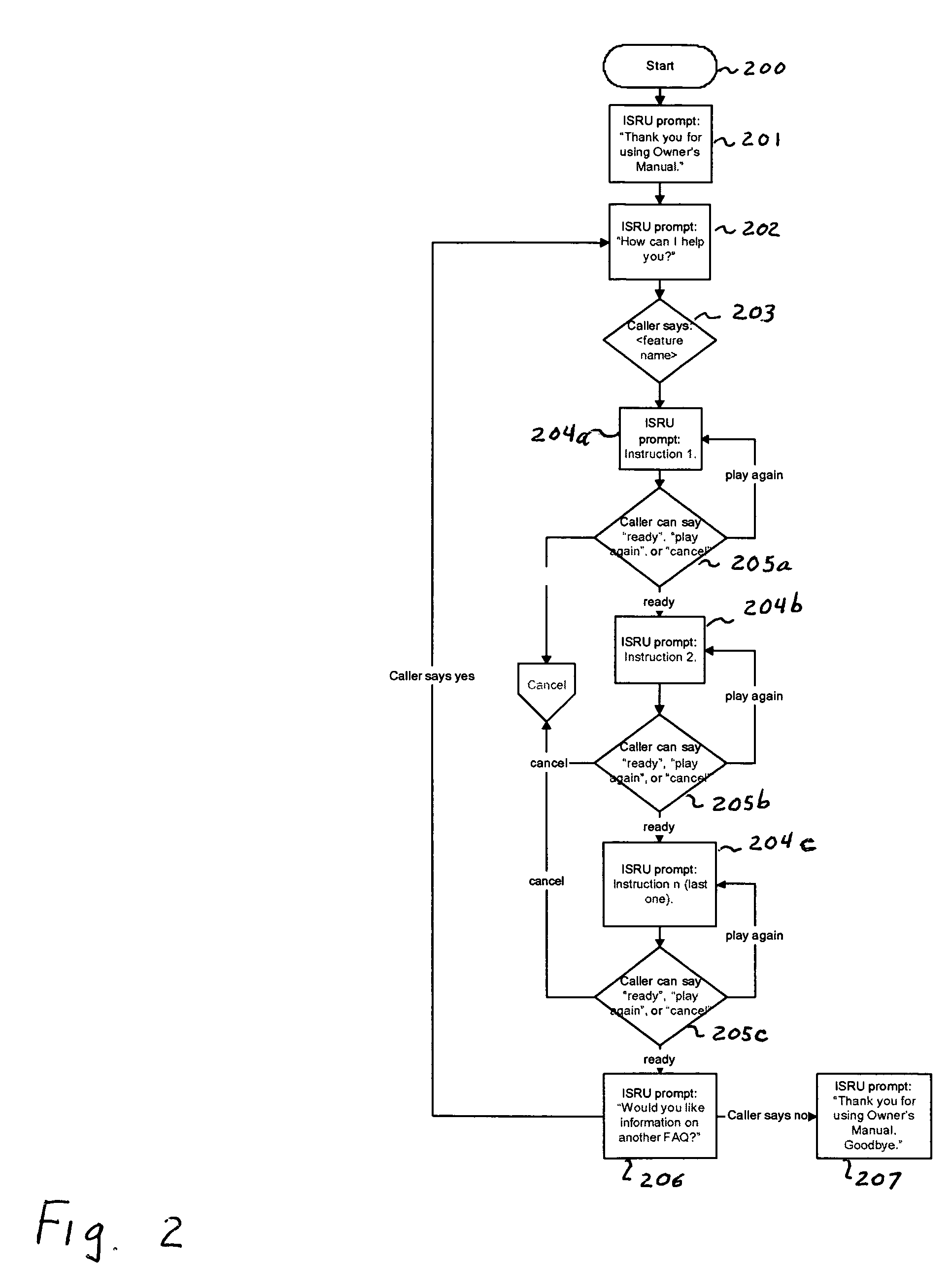
A system and method for providing user-initiated vehicle diagnostic testing and reporting in a telematics-enabled vehicle. In the method, a request for a vehicle diagnostic test is received from the driver through a user interface of a telematics unit on the vehicle. A simplified initial diagnostic check is made and a first voice message is played for the driver that provides information concerning any detected vehicle problem. The method then undergoes a more complete diagnostic check and the resulting diagnostic information is used to select and play a second voice message that provides instructions for taking corrective action to fix the detected problem. Communication with a live advisor is also provided by way of a cellular or other wireless carrier system.
Owner:GENERA MOTORS LLC
Wirelessly delivered owner's manual
ActiveUS7219063B2Easy accessInstrument arrangements/adaptationsSpecial service for subscribersData centerDiagnostic information
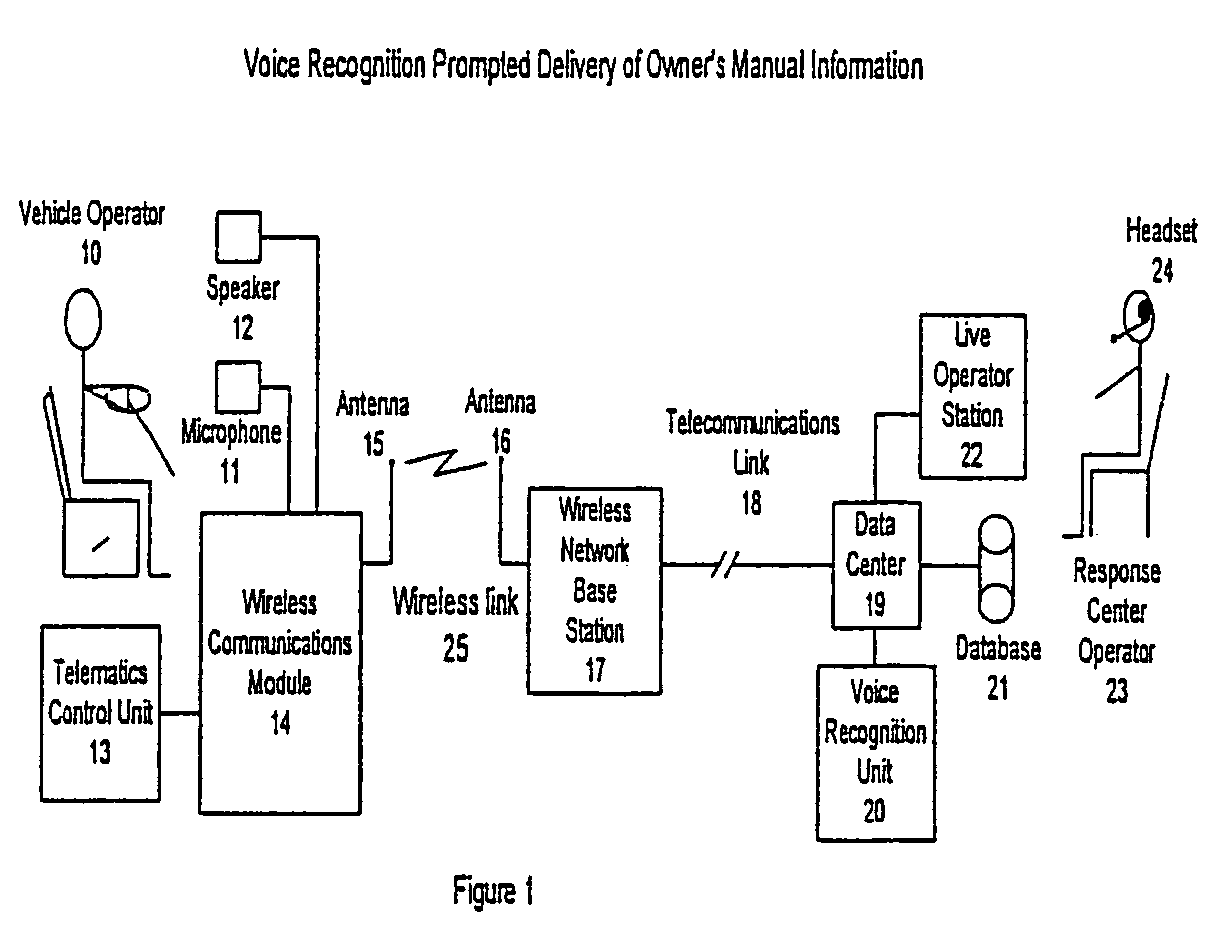
This invention is directed to a method of delivering vehicle owner's manual or other vehicle-specific information to the vehicle operator from a remote data center and associated vehicle information database by utilizing a voice recognition system at the remote data center and delivering the information to the vehicle operator in audible speech. The vehicle operator speaks his request in the vehicle and the data center recognizes the request, perhaps asks more questions, leads the vehicle operator through a spoken menu, and then provides the answer vocally to the vehicle operator over the speaker(s) located in the vehicle. The invention includes methodology for obtaining vehicle diagnostic information and controlling certain vehicle functions automatically via an embedded telematics control unit. The invention further includes remote telephone access outside the vehicle.
Owner:SIRIUS XM CONNECTED VEHICLE SERVICES
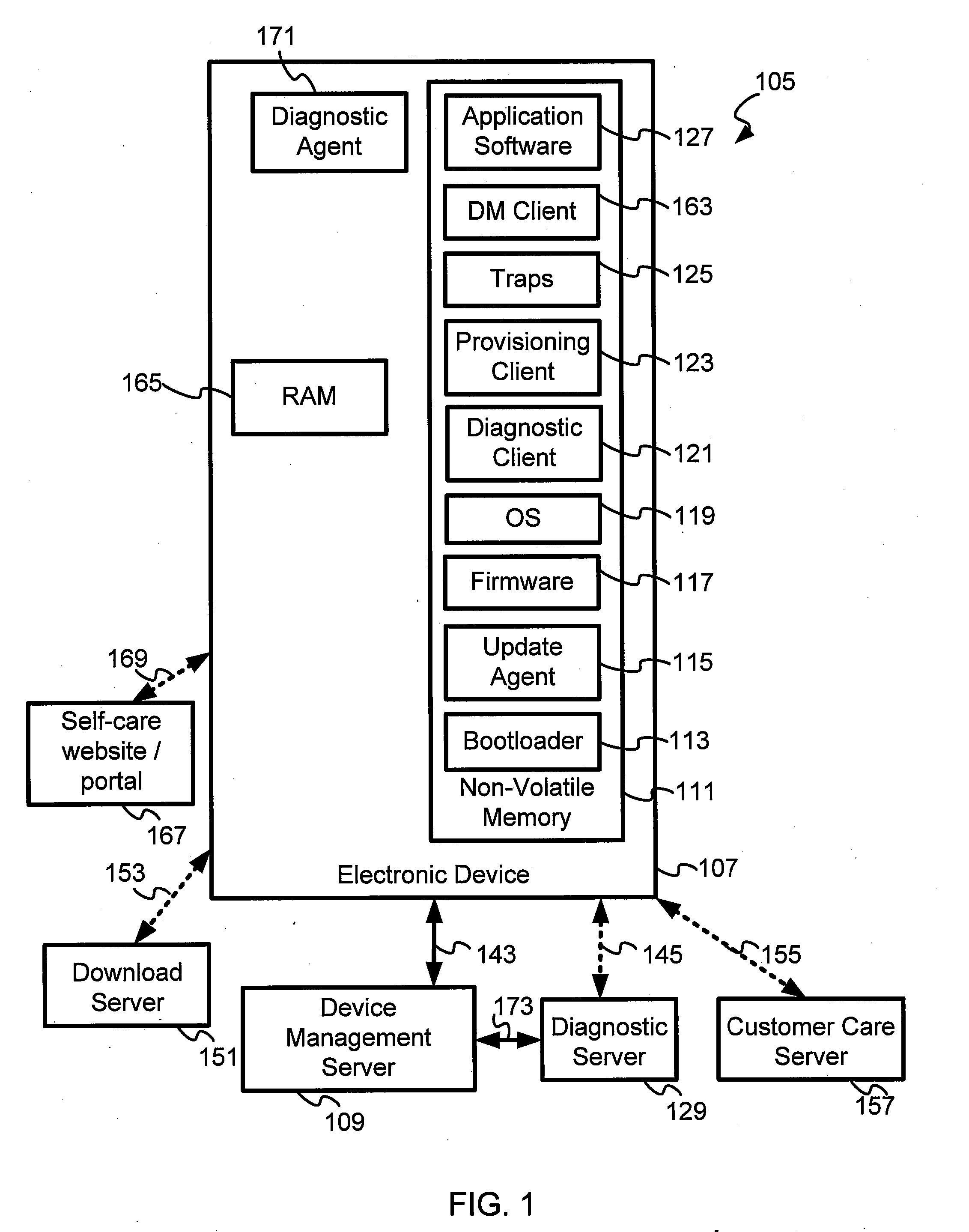
Diagnostics And Monitoring Services In A Mobile Network For A Mobile Device
InactiveUS20070207800A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsData switching networksPagerMobile electronics
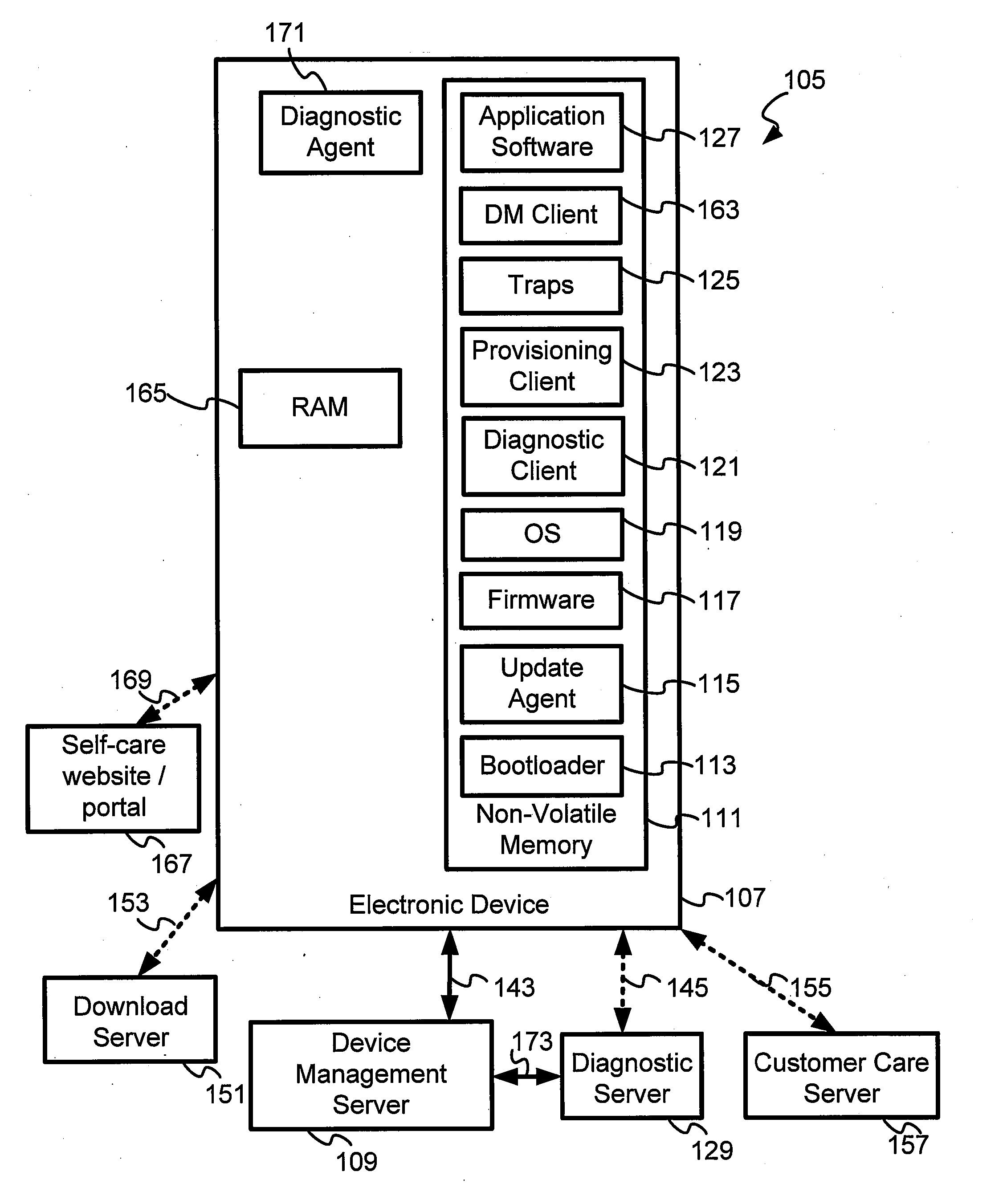
The present invention makes it possible to obtain debug- and other diagnostic information from mobile electronic devices in a system operator network. A Log Management object provides support for logging diagnostic data. A log file is employed to collect information on various device features for which tracing or debugging is turned on in a mobile electronic device such as, for example, a mobile handset, cellular phone, a personal digital assistant, a pager and a personal computer. It is also used to selectively collect information on specific events that are monitored, device specific data being collected, and network performance data, among other items. The diagnostic agent in the mobile device is a client side application that may run on the mobile device when required, or continuously as a monitoring application, and which manages and collects tracing information wirelessly to a server using a cellular data network. A diagnostic client may also be downloaded and executed to collect diagnostic data from applications, for example. Traps may also be set and data collected from them. The Log file may be retrieved from the server side in pull or push mode.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
System and method for improving clinical decisions by aggregating, validating and analysing genetic and phenotypic data
The information management system disclosed enables caregivers to make better decisions by using aggregated data. The system enables the integration, validation and analysis of genetic, phenotypic and clinical data from multiple subjects. A standardized data model stores a range of patient data in standardized data classes comprising patient profile, genetic, symptomatic, treatment and diagnostic information. Data is converted into standardized data classes using a data parser specifically tailored to the source system. Relationships exist between standardized data classes, based on expert rules and statistical models, and are used to validate new data and predict phenotypic outcomes. The prediction may comprise a clinical outcome in response to a proposed intervention. The statistical models and methods for training those models may be input according to a standardized template. Methods are described for selecting, creating and training the statistical models to operate on genetic, phenotypic, clinical and undetermined data sets.
Owner:NATERA
System and method for evaluating monitored computer systems
InactiveUS6237114B1Hardware monitoringEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionImage resolutionComputerized system
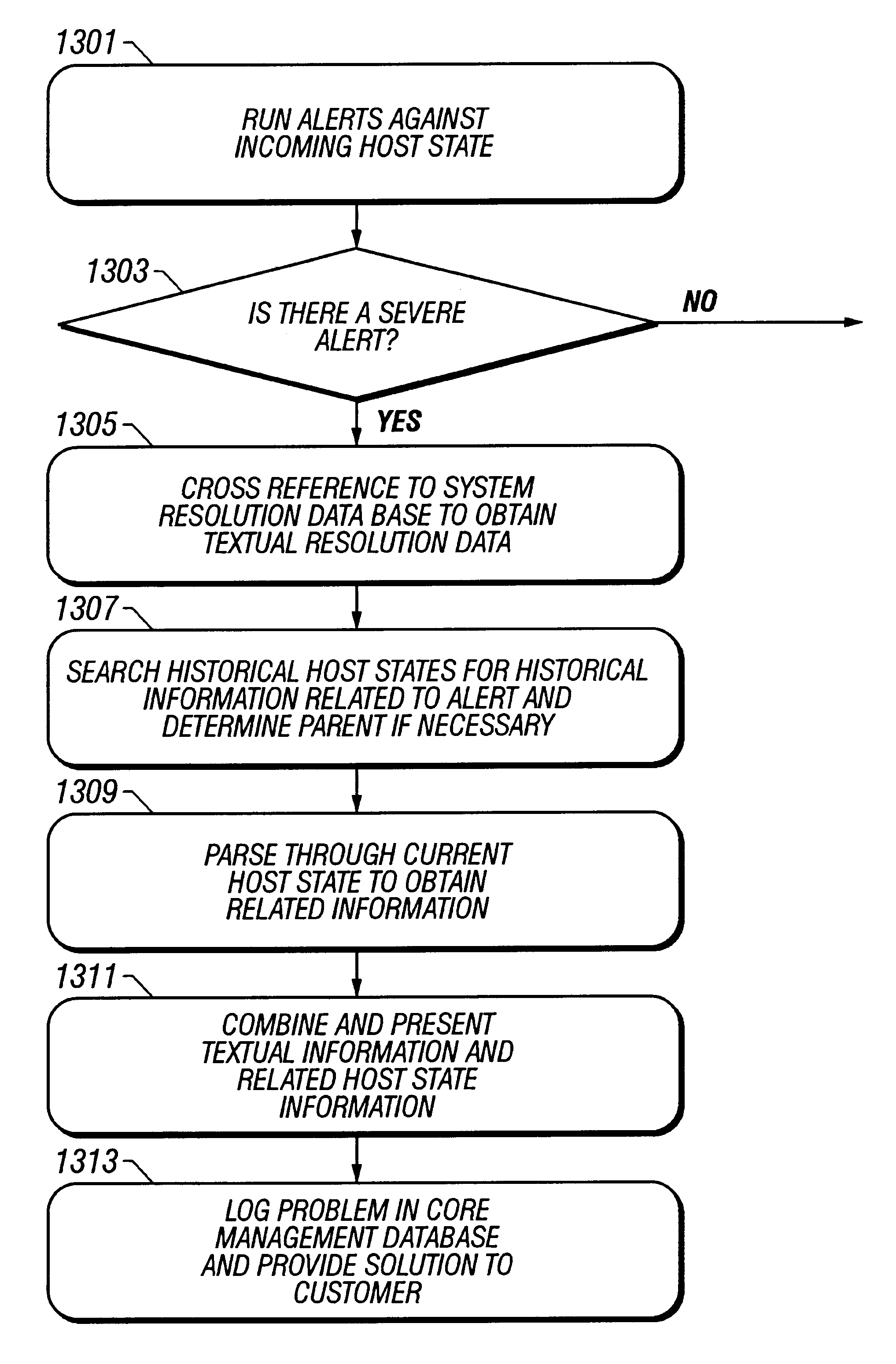
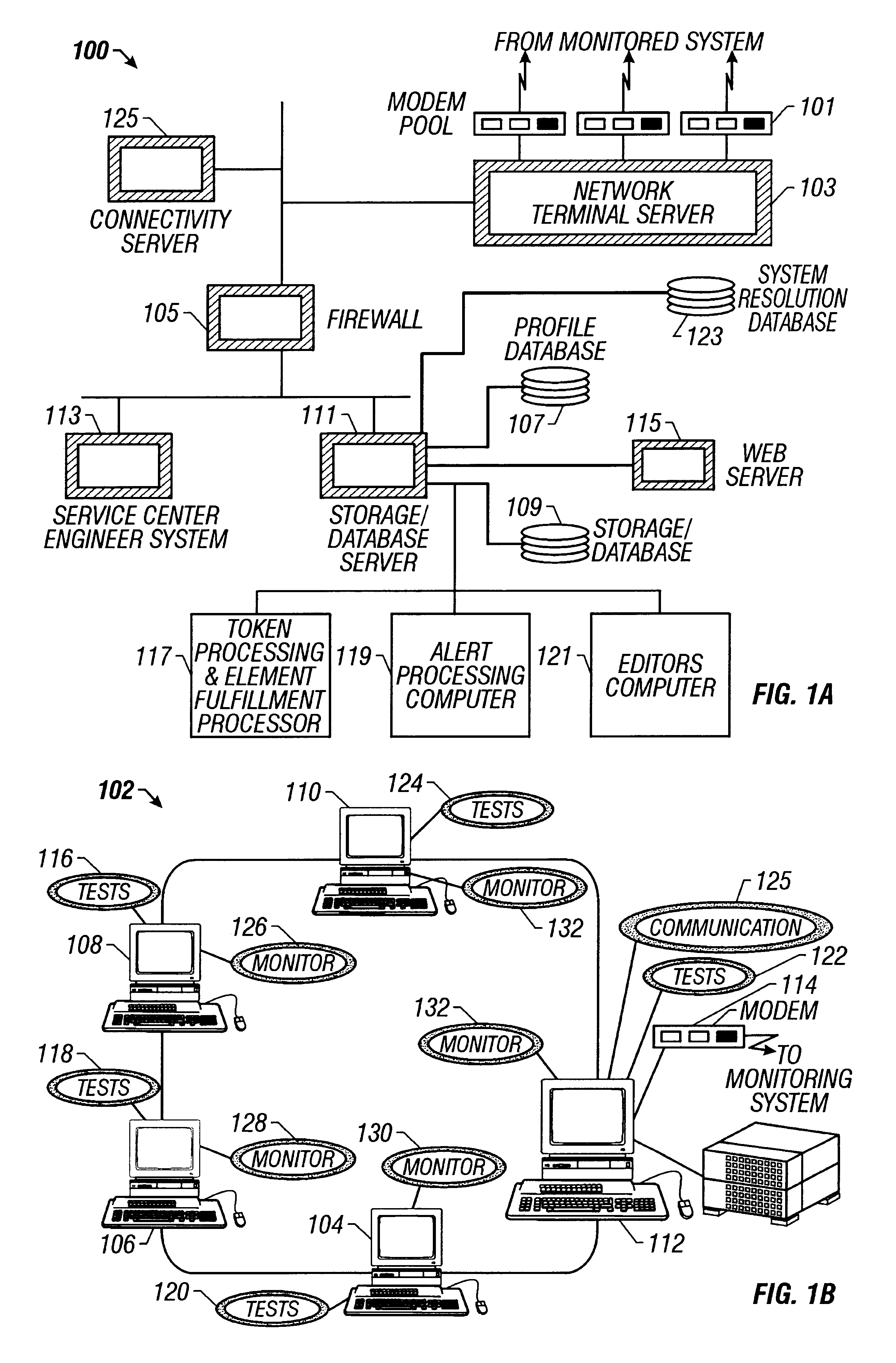
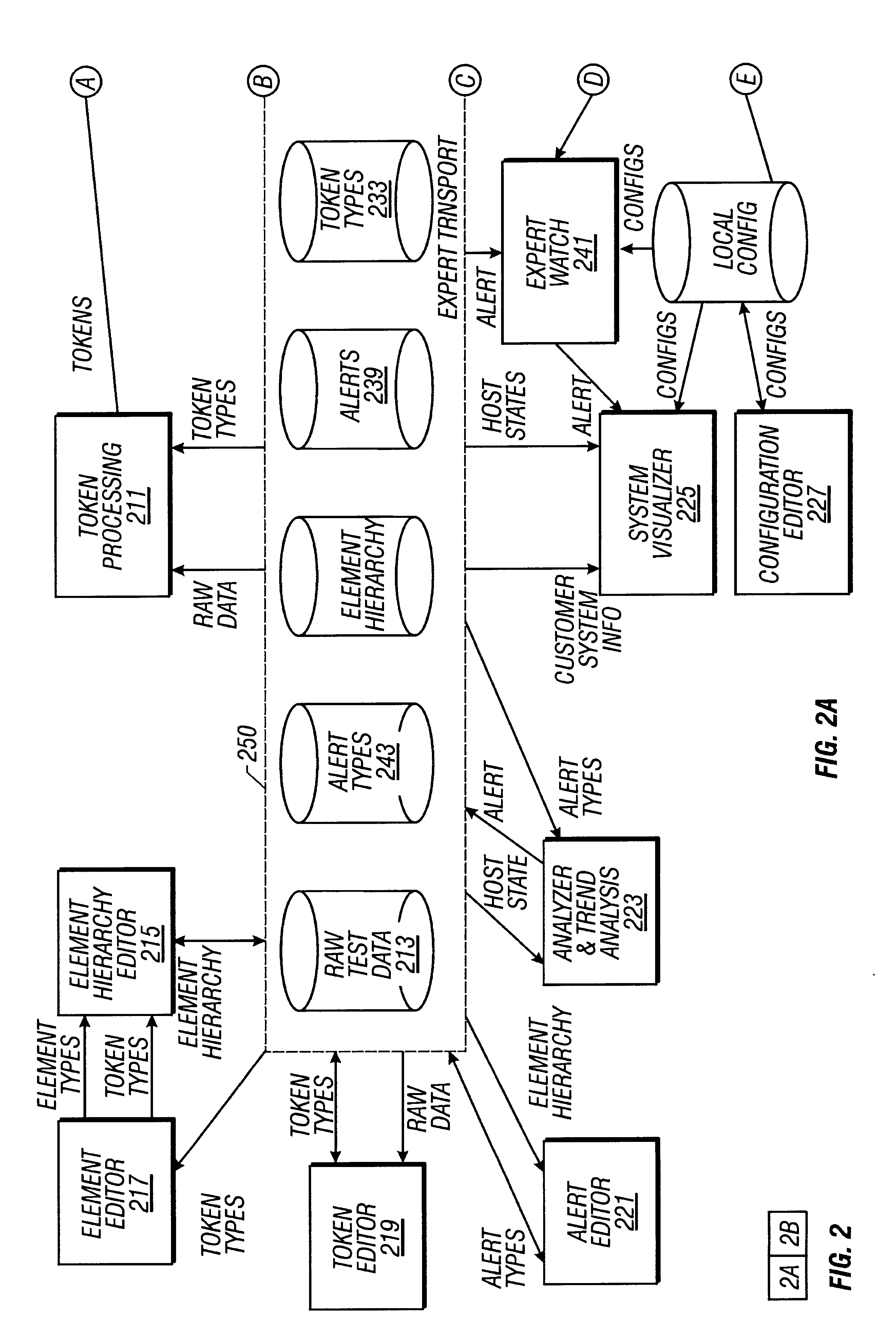
A computer system used in monitoring another computer system provides both textual resolution information describing a likely solution for a problem encountered in the monitored computer system as well as component information that relates to the particular problem. The component information includes the various hardware, software and operating conditions found in the monitored computer system. The monitoring computer system determines if a condition of a predetermined severity exists in the monitored computer system according to diagnostic information provided from the monitored computer system. The diagnostic information is represented in the monitoring computer system as a hierarchical representation of the monitored computer system. The hierarchical representation provides present state information indicating the state of hardware and software components and operating conditions of the monitored computer system. The resolution information relating to the condition is retrieved from a resolution database and relevant component information is retrieved from the hierarchical representation of the computer system and presented to a support engineer to assist them in diagnosing the problem in the monitored computer system.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Computer interface system for tracking of radio frequency identification tags
ActiveUS7102509B1Electric signal transmission systemsMultiple keys/algorithms usageTransceiverDiagnostic information
A method for operating with multiple protocols for handling communications comprising the steps of obtaining information from sensors and related input devices utilizing specialized tamper resistant passive transceivers working with active pulse type transceivers to create historical maps of information on people or objects. This includes steps of: a) identifying recording information, b) sending and receiving prompts, c) associating the call with timers, d) monitoring passive transceivers with low level diagnostic information, e) monitoring the transceivers with voice recognition software, f) recording associated data, g) identifying the users, the key words or phrases within the recorded data, h) naming the recording and i) saving the data in a protected format.
Owner:GLOBAL TELLINK
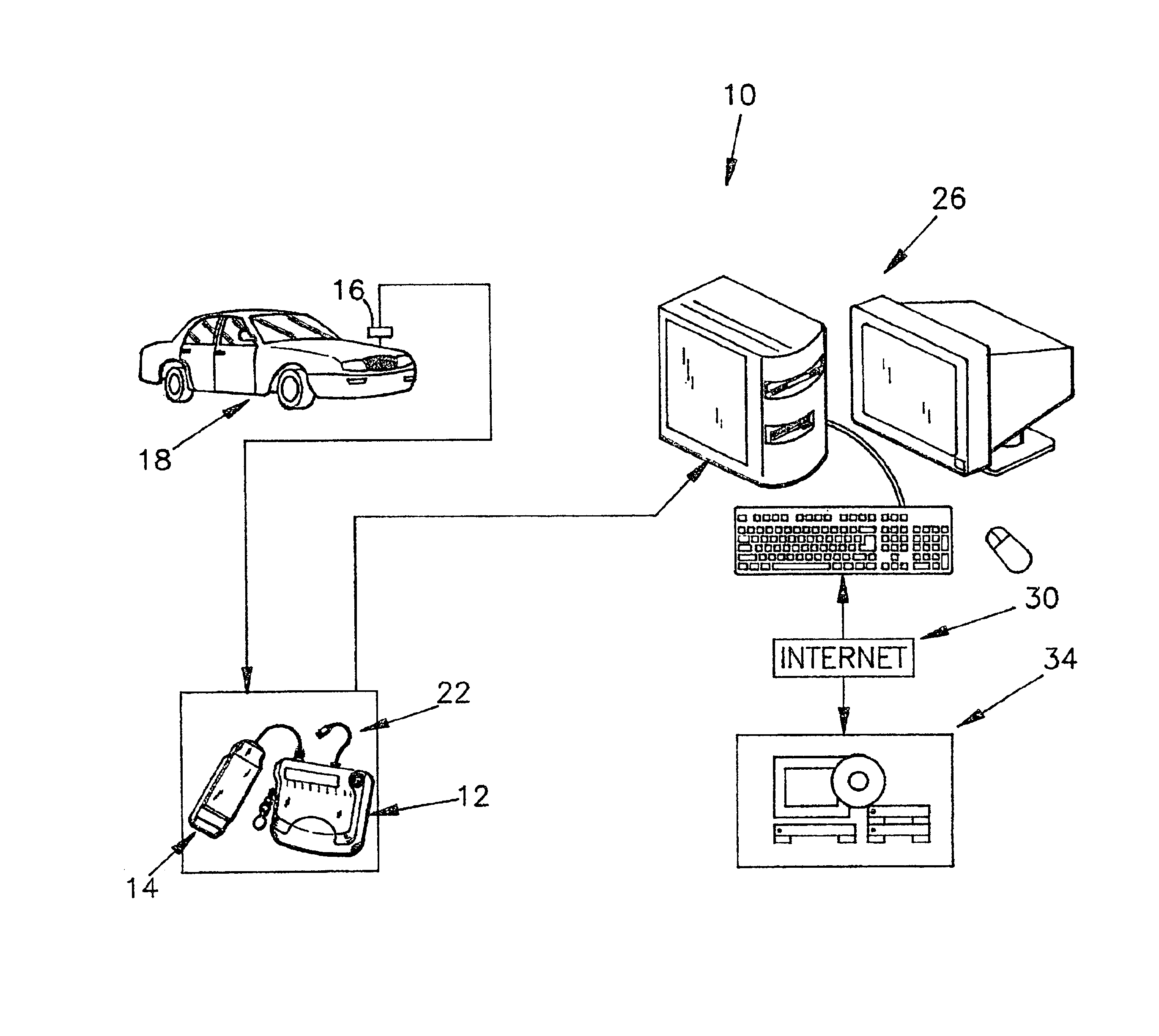
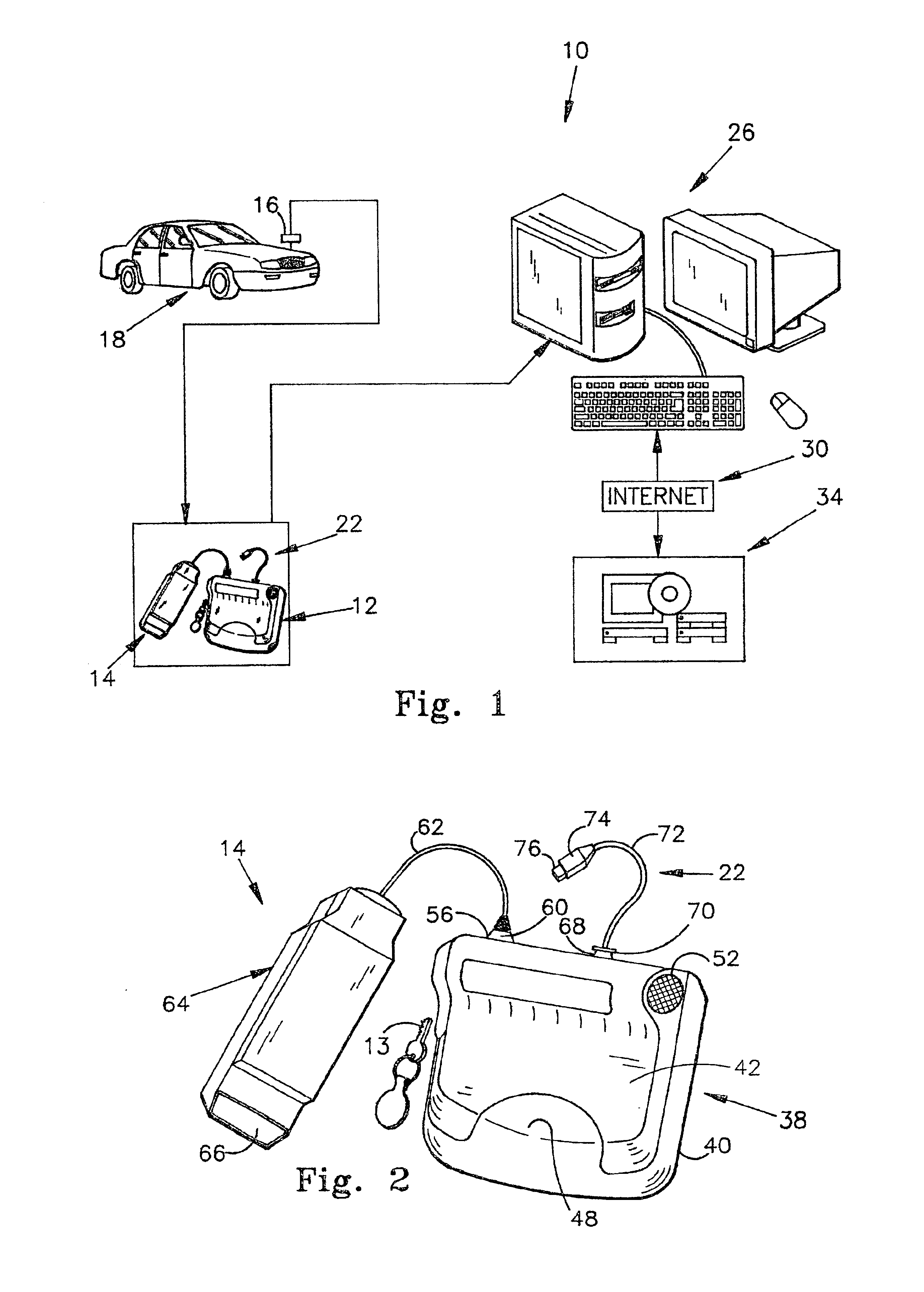
Auto diagnostic method and device
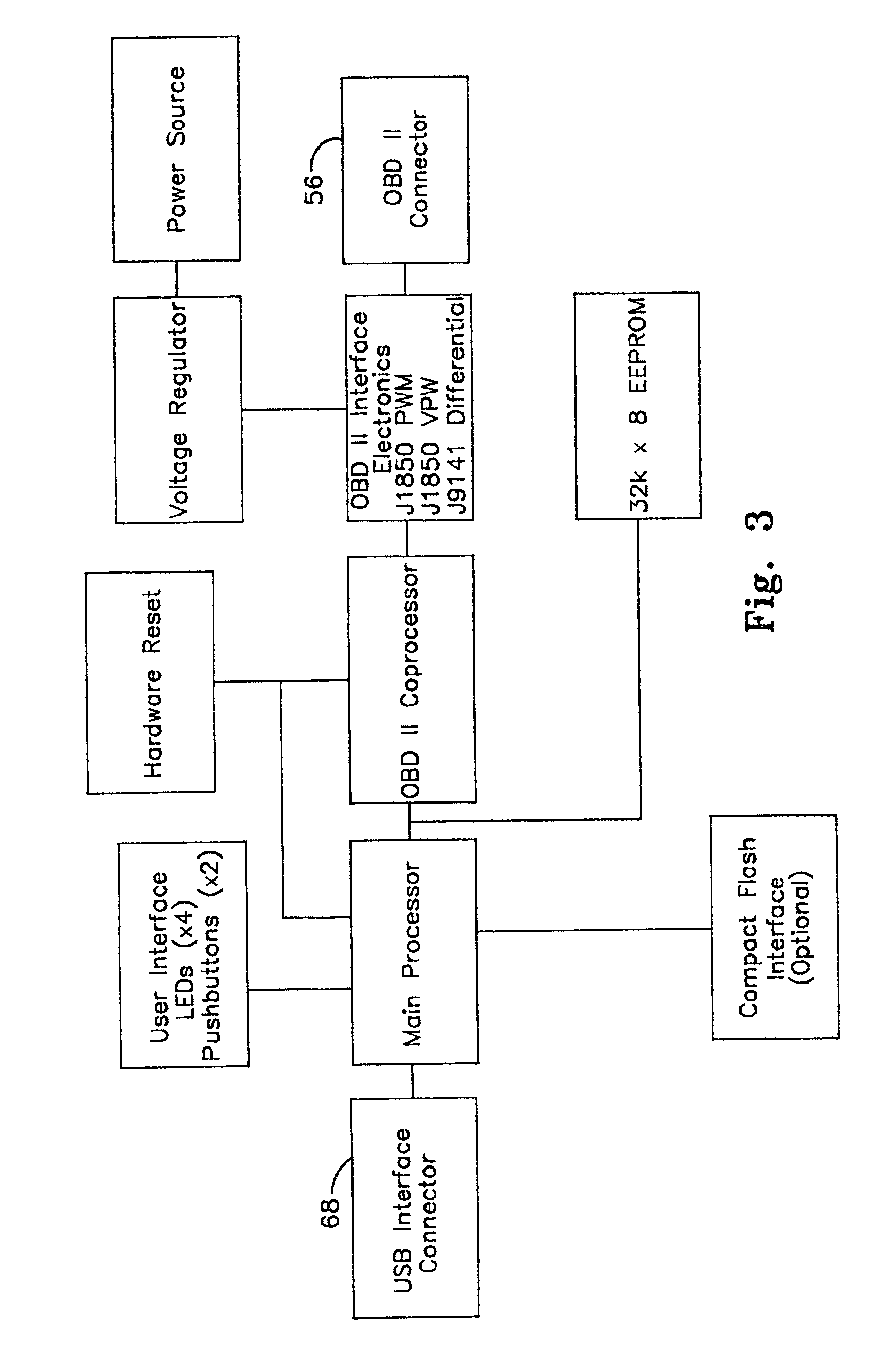
InactiveUS6807469B2Reduce manufacturing costReduces component investmentVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDiagnostic dataData acquisition
According to the present invention, a vehicle monitoring and maintenance device capable of being connected to a diagnostic port of a vehicle is provided. The monitoring and maintenance device comprises a hand holdable, data acquisition and transfer device. The data acquisition and transfer device includes a first data link connectable to a diagnostic port of a vehicle for retrieving diagnostic data from the vehicle; and a second data link connectable to a global computer network communicable device. The data acquisition and transfer device also includes a processor and memory unit capable of retrieving unprocessed diagnostic data containing error codes from the vehicle via the first data link, storing unprocessed diagnostic data for a limited time, and transferring the unprocessed data to the global computer network communicable device, to the second data link. The hand holdable data acquisition and transfer device lacks sufficient data processing capability to fully process the unprocessed diagnostic data into human useable diagnostic information.
Owner:INNOVA ELECTRONICS
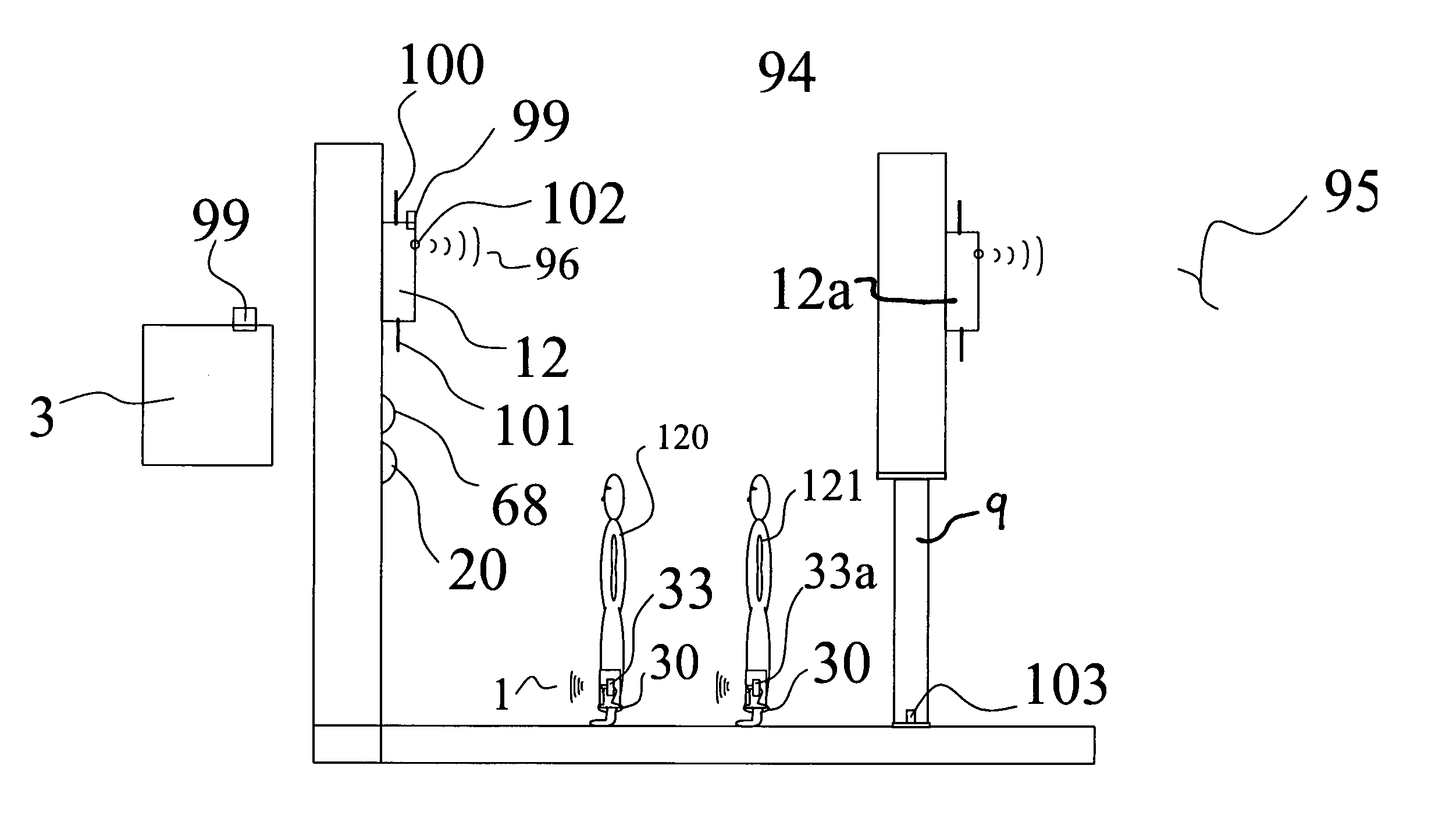
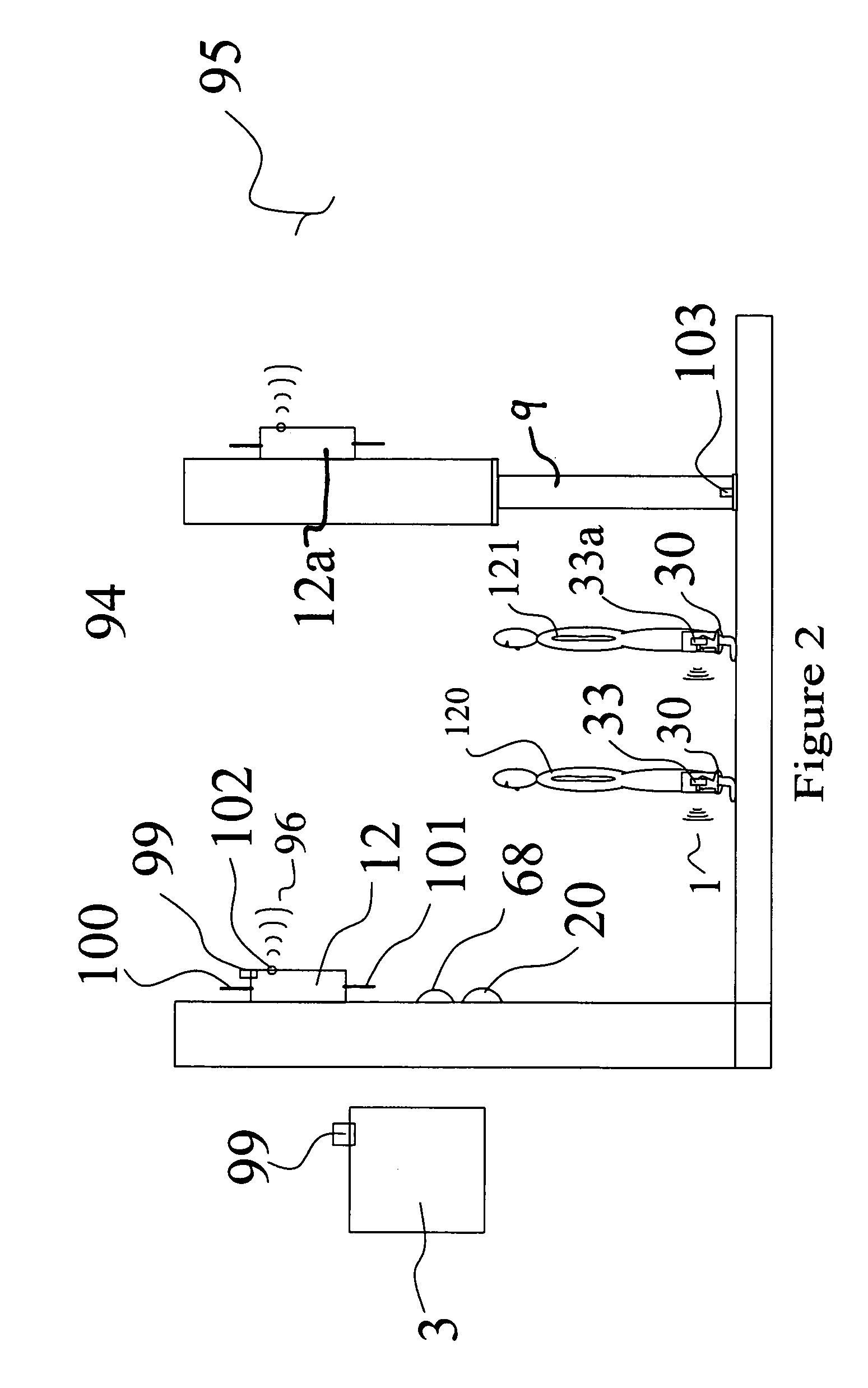
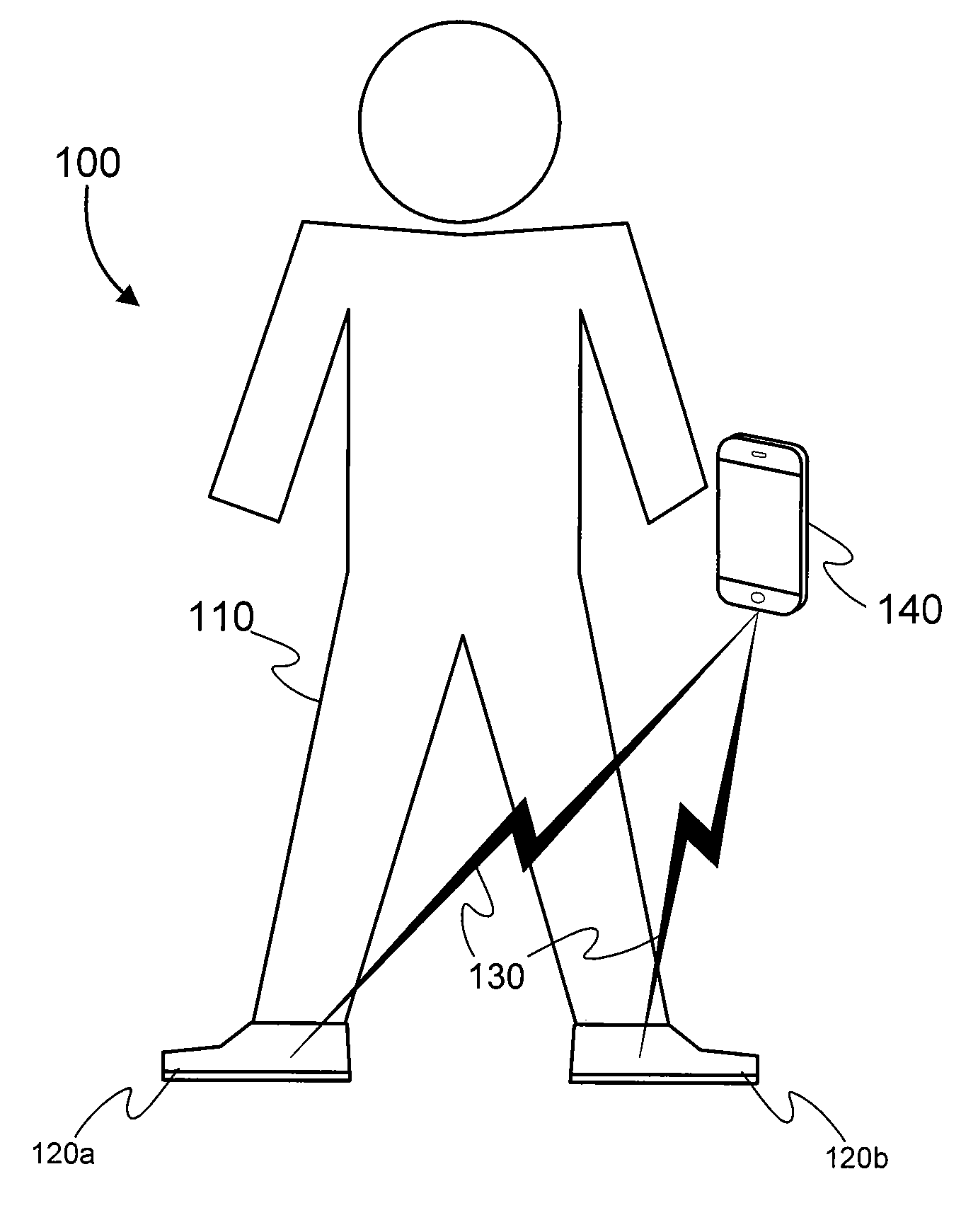
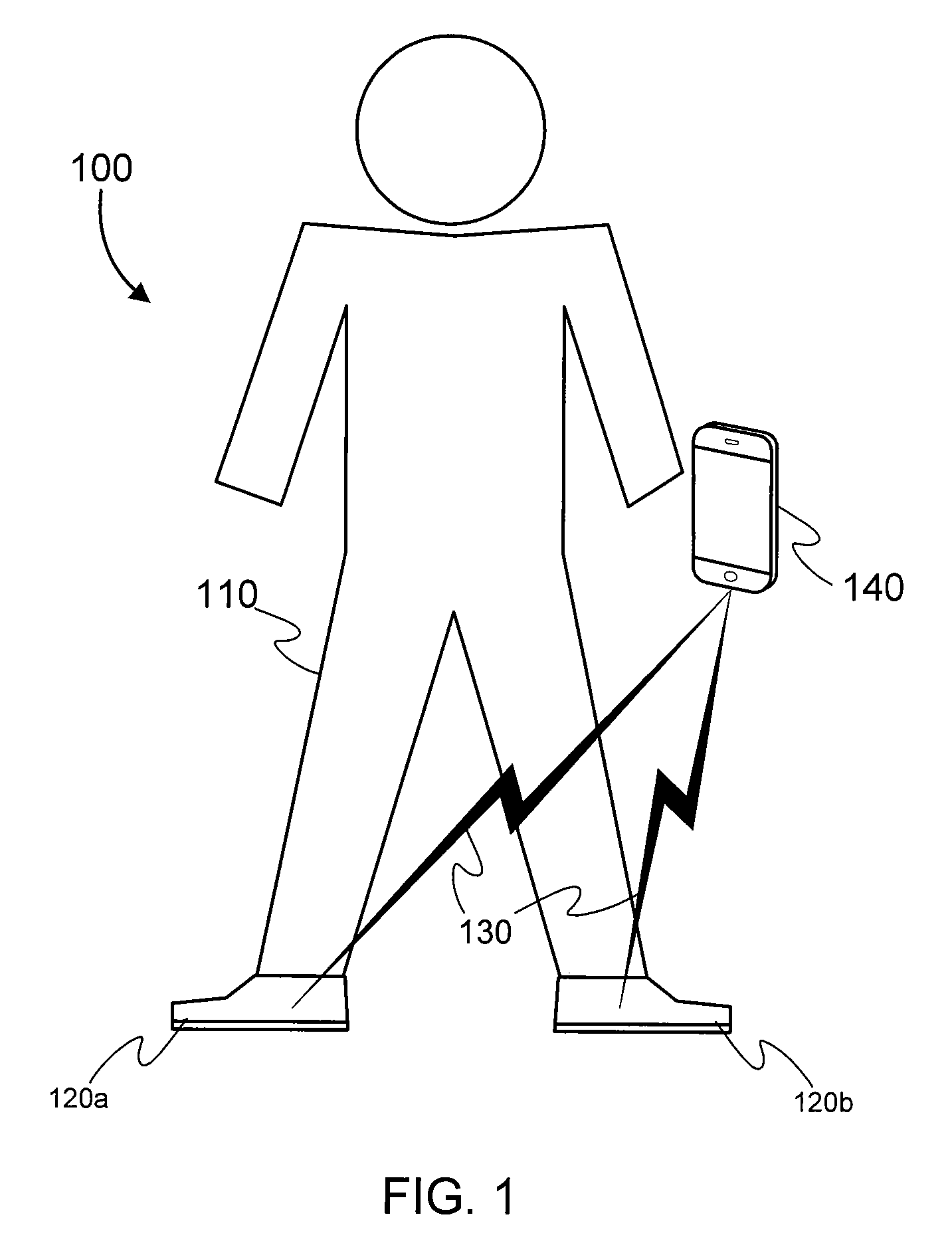
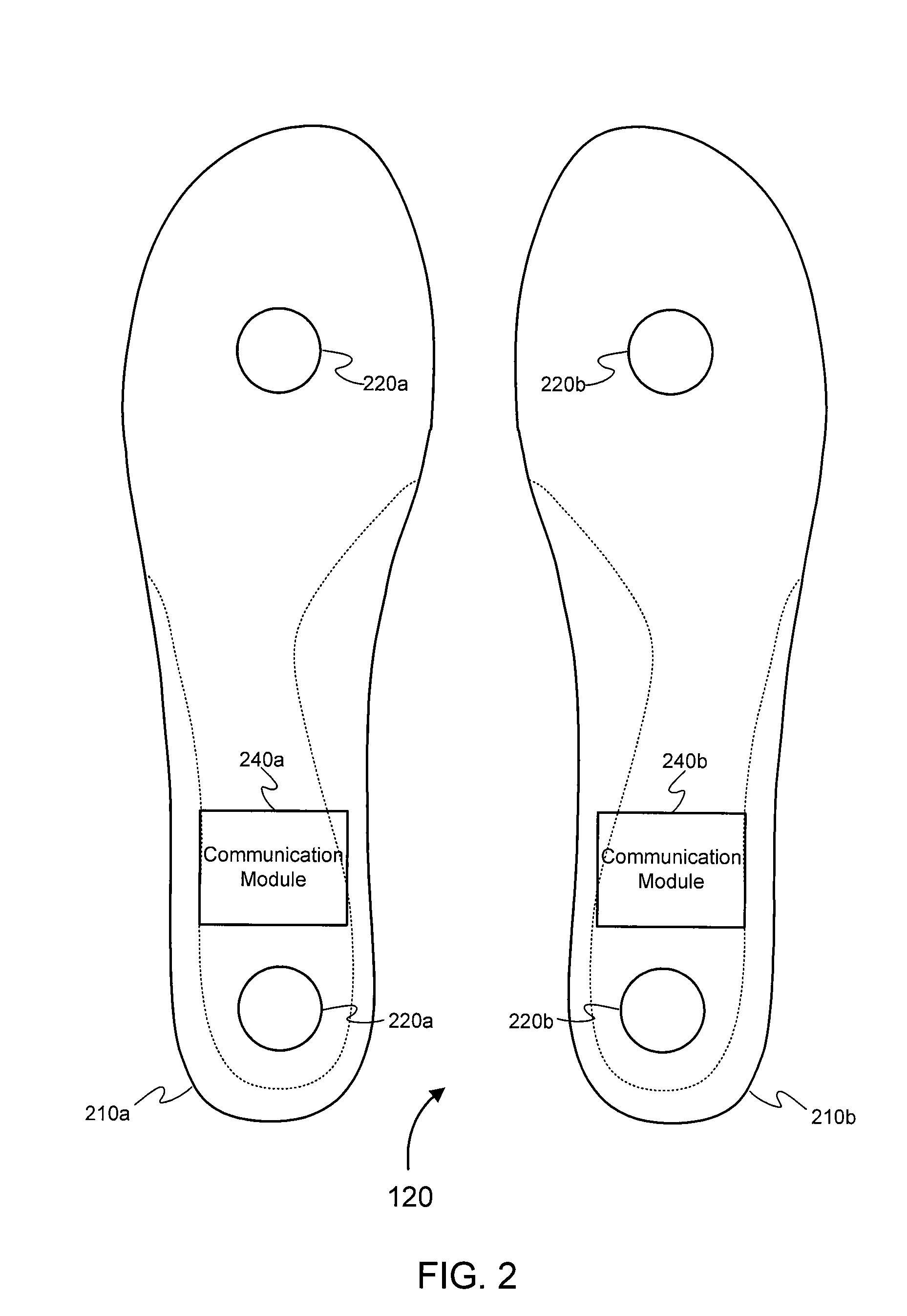
Methods and systems for sensing equilibrium
Systems and methods for monitoring equilibrium of a user are presented. A stability monitoring device in a shoe insole area utilizes pressure sensors to measure pressure information in real-time. The pressure information is transmitted over an RF network to a device for analyzing the pressure information and calculating postural state information including the current postural state, next postural state, and / or a range of postural stability. The person or a third party may be notified if the postural state information indicates an unstable state. Additionally, the postural state information may be analyzed to determine activity level of the user, diagnostic information, or performance information. Metrics may be displayed by the system for assisting physical therapy or training regimens.
Owner:ISHOE
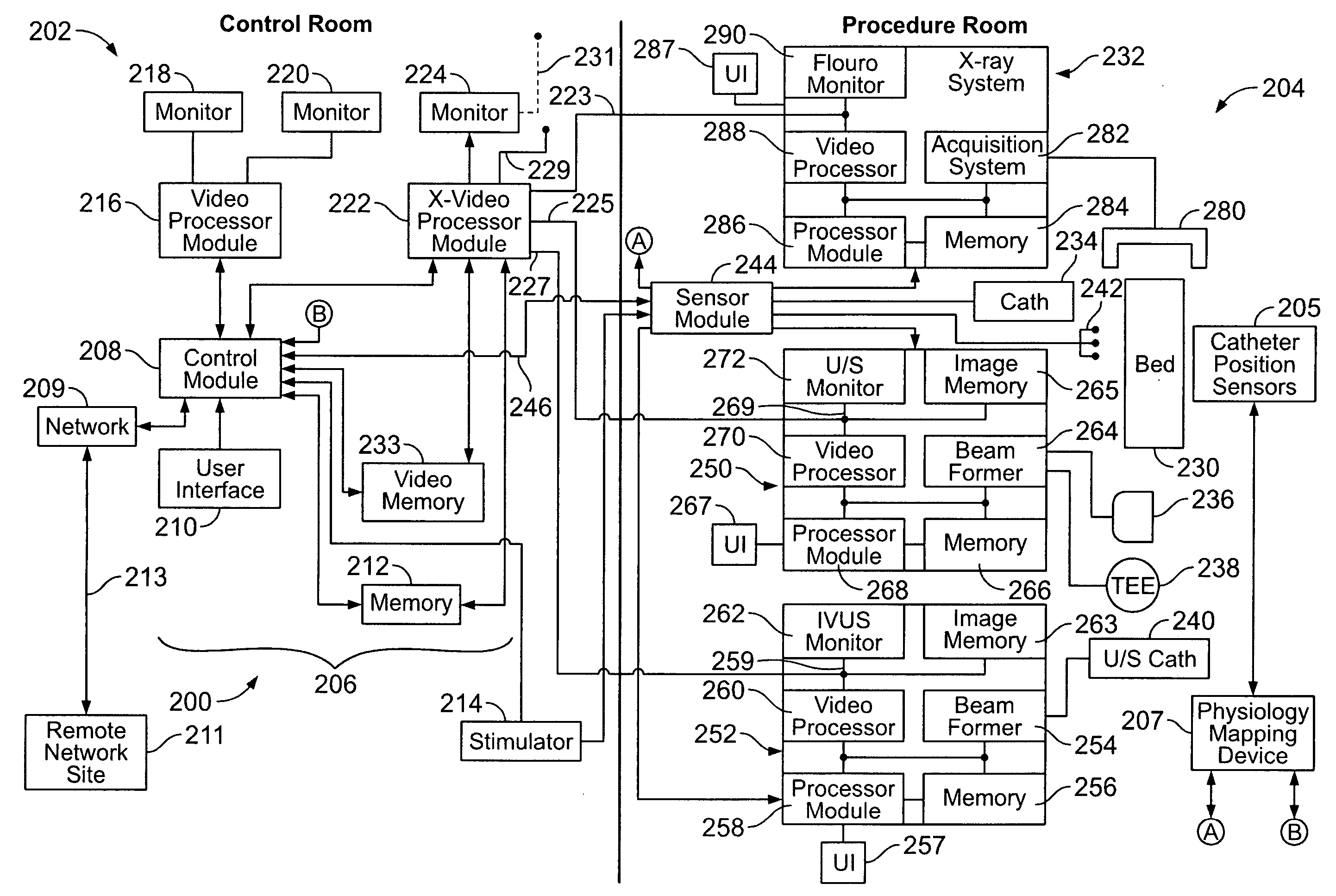
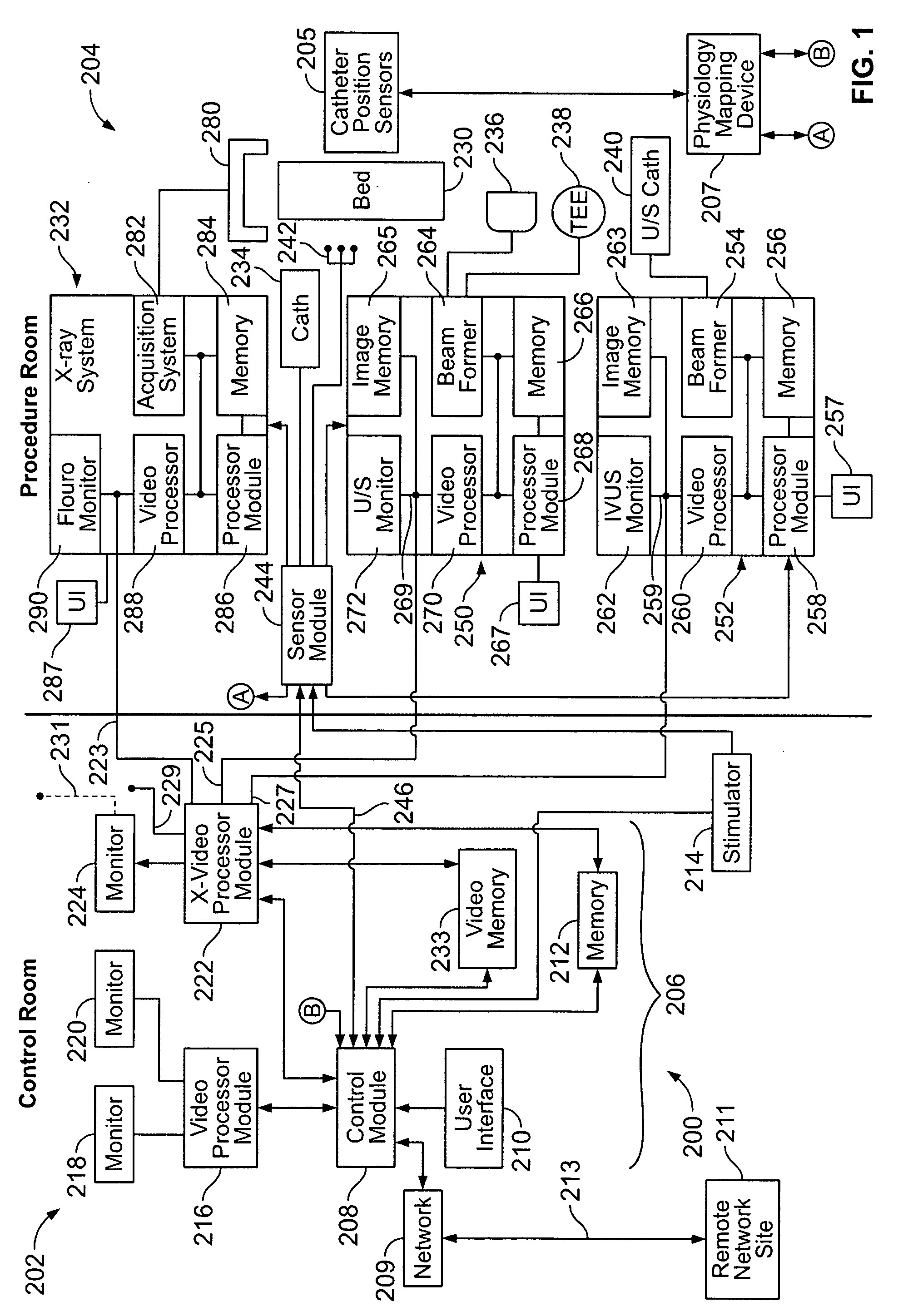
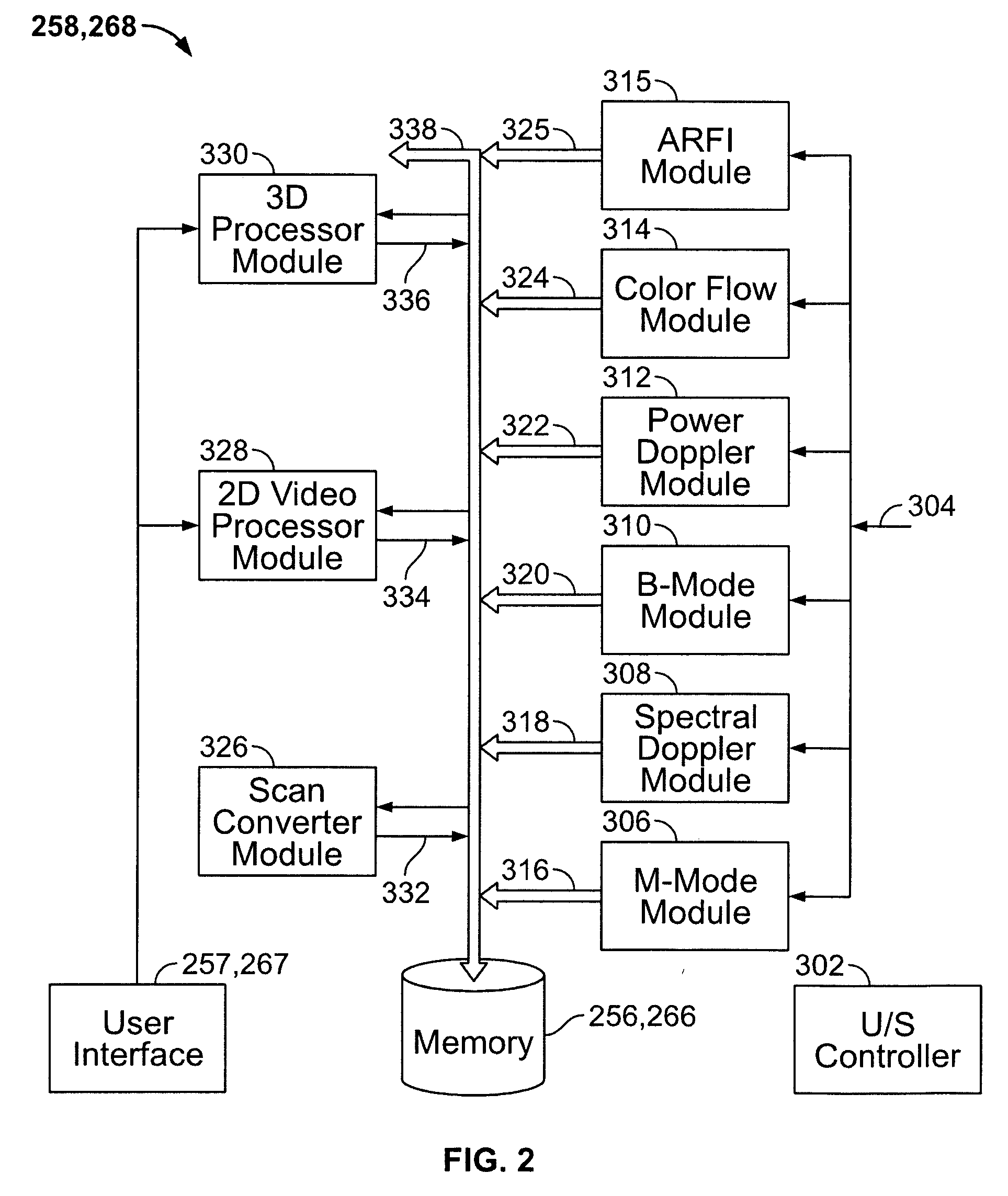
Physiology workstation with real-time fluoroscopy and ultrasound imaging
A physiology workstation is provided that comprises an physiology input configured to receive physiology signals from at least one of an intracardiac (IC) catheter inserted in a subject and surface ECG leads provided on the subject. The physiology signals are obtained during a procedure. A video input is configured to receive image frames, in real-time during the procedure. The image frames contain diagnostic information representative of data samples obtained from the subject during the procedure. A control module controls physiology operations based on user inputs. A display module is controlled by the physiology control module. The display module displays the physiology signals and the image frames simultaneously, in real-time, during the procedure. Optionally, the workstation may include a video processor module that formats the physiology signals into a display format. The video processor module may include an video processor and an external video processor that receive and control display of the physiology signals and image frames, respectively. The image frames may include at least one of ultrasound images obtained from a surface ultrasound probe, intravenous ultrasound images obtained from an ultrasound catheter and fluoroscopy images obtained from a fluoroscopy system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
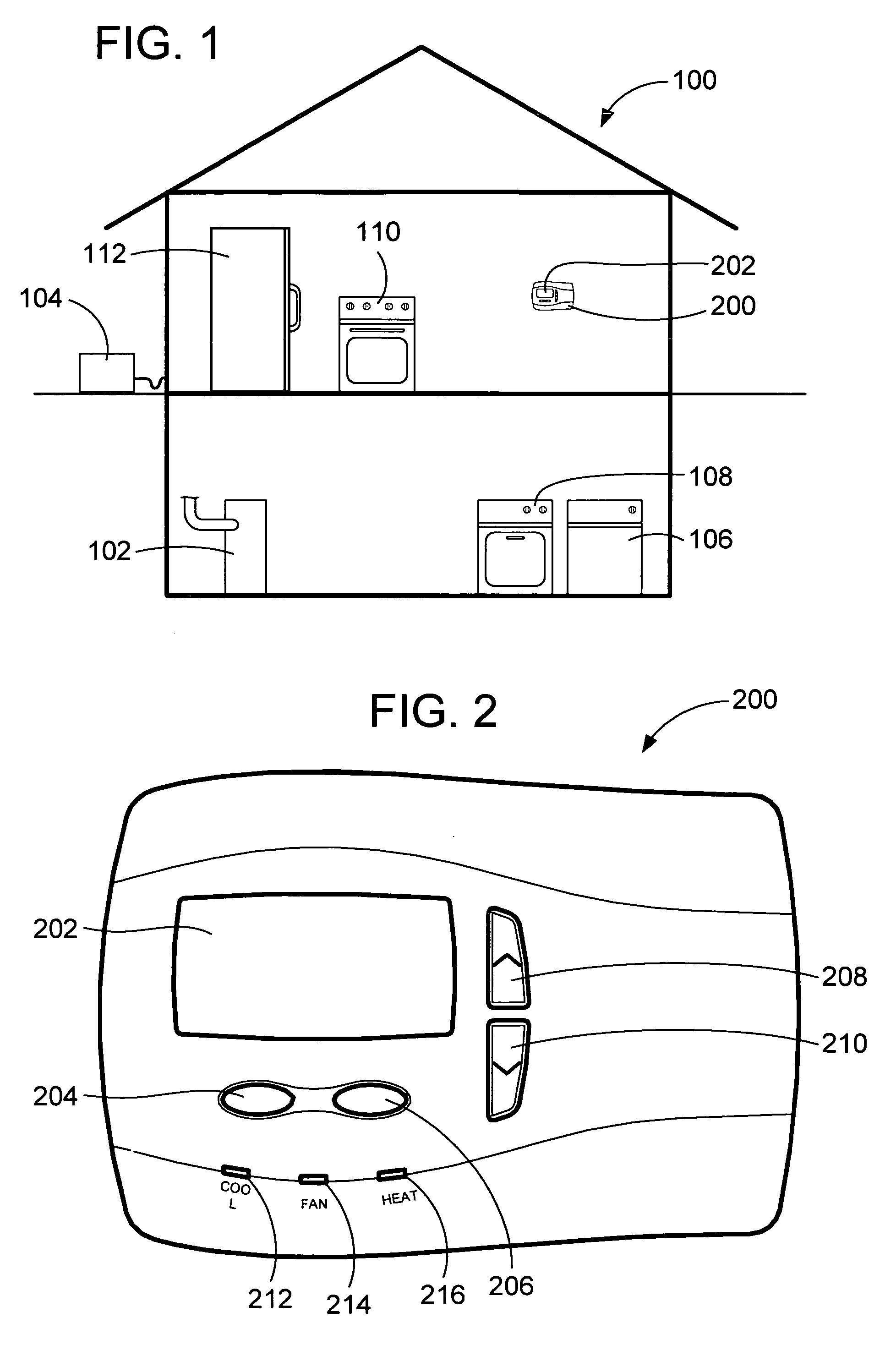
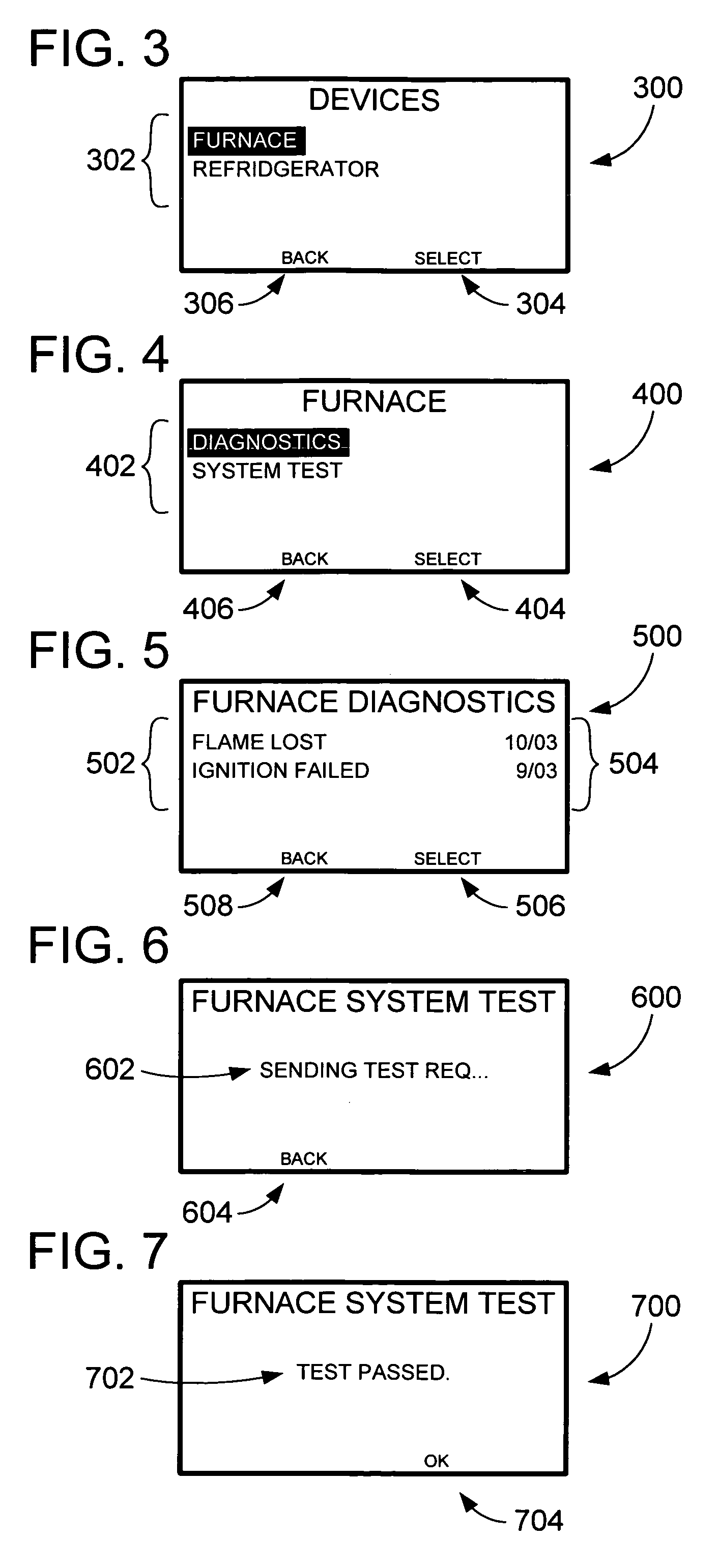
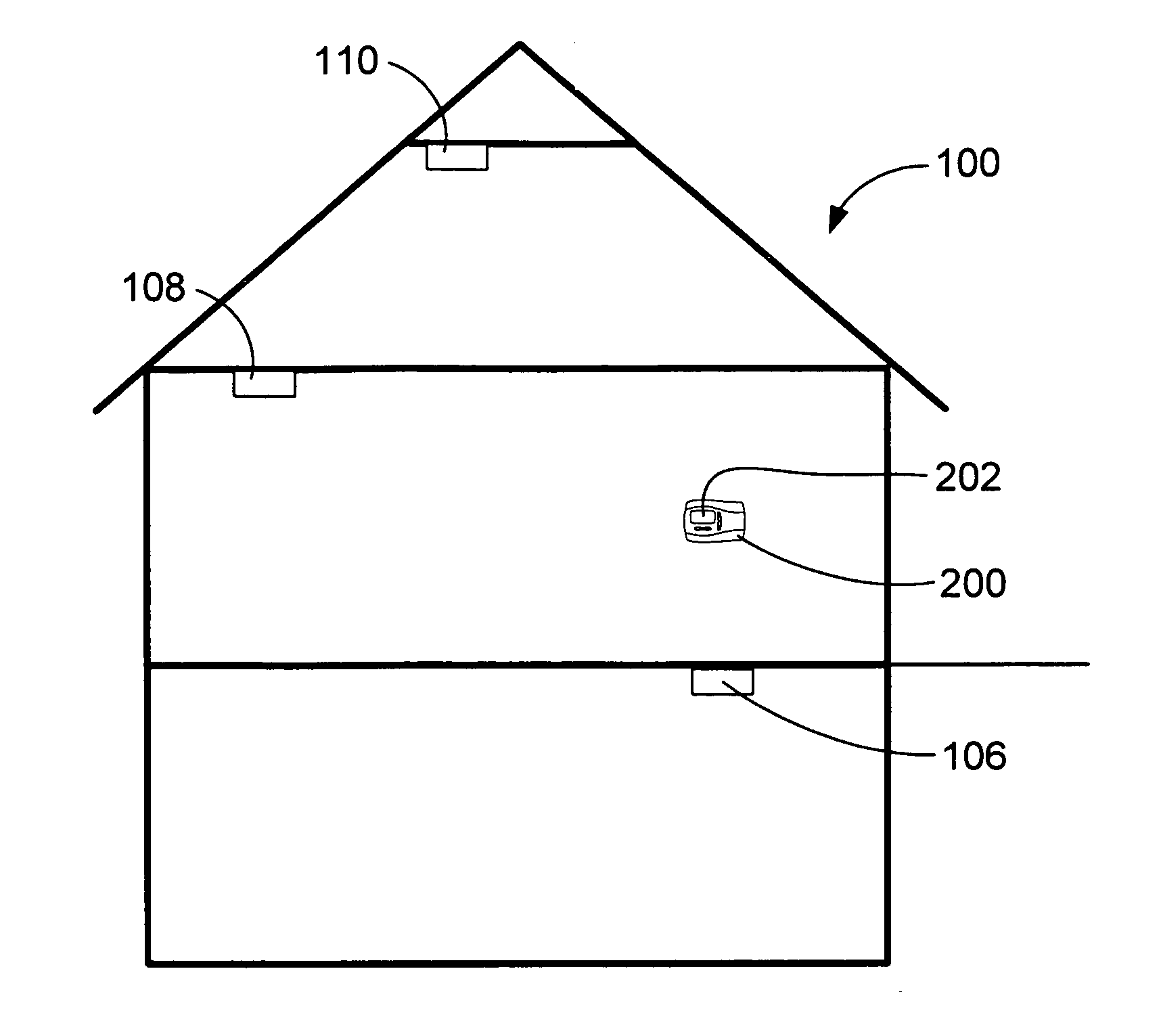
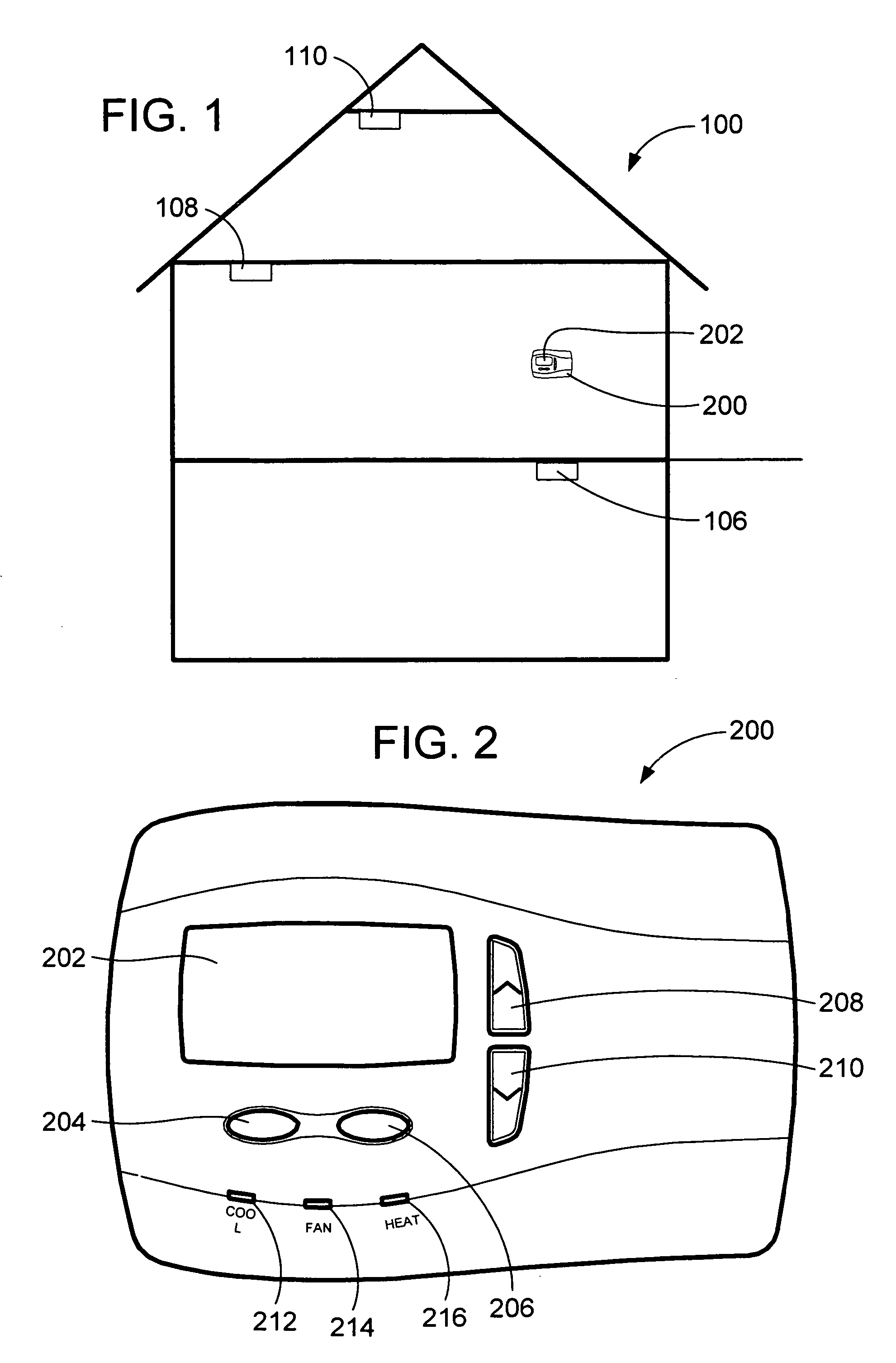
Appliance diagnostic display apparatus and network incorporating same
InactiveUS7188002B2Easy to testSpace heating and ventilationTemperatue controlWired communicationSystem testing
An appliance diagnostic display and interface system providing a centralized user interface for appliance diagnostic information and control of system self-tests is provided. This centralized user interface is provided via an intelligent thermostat that includes an LCD display. The intelligent thermostat interfaces, via wireless or wired communications, with the appliances installed in the home. The intelligent thermostat then generates and displays various user interface screens that allow particular appliances to be selected. Separate appliance specific screens are then generated that allow the user to access the diagnostic information in system test functionality provided by the individual appliance. Soft function keys provided on the intelligent thermostat allow multi-functional access to the features of the invention depending on which screen is currently being displayed.
Owner:INVENSYS SYST INC
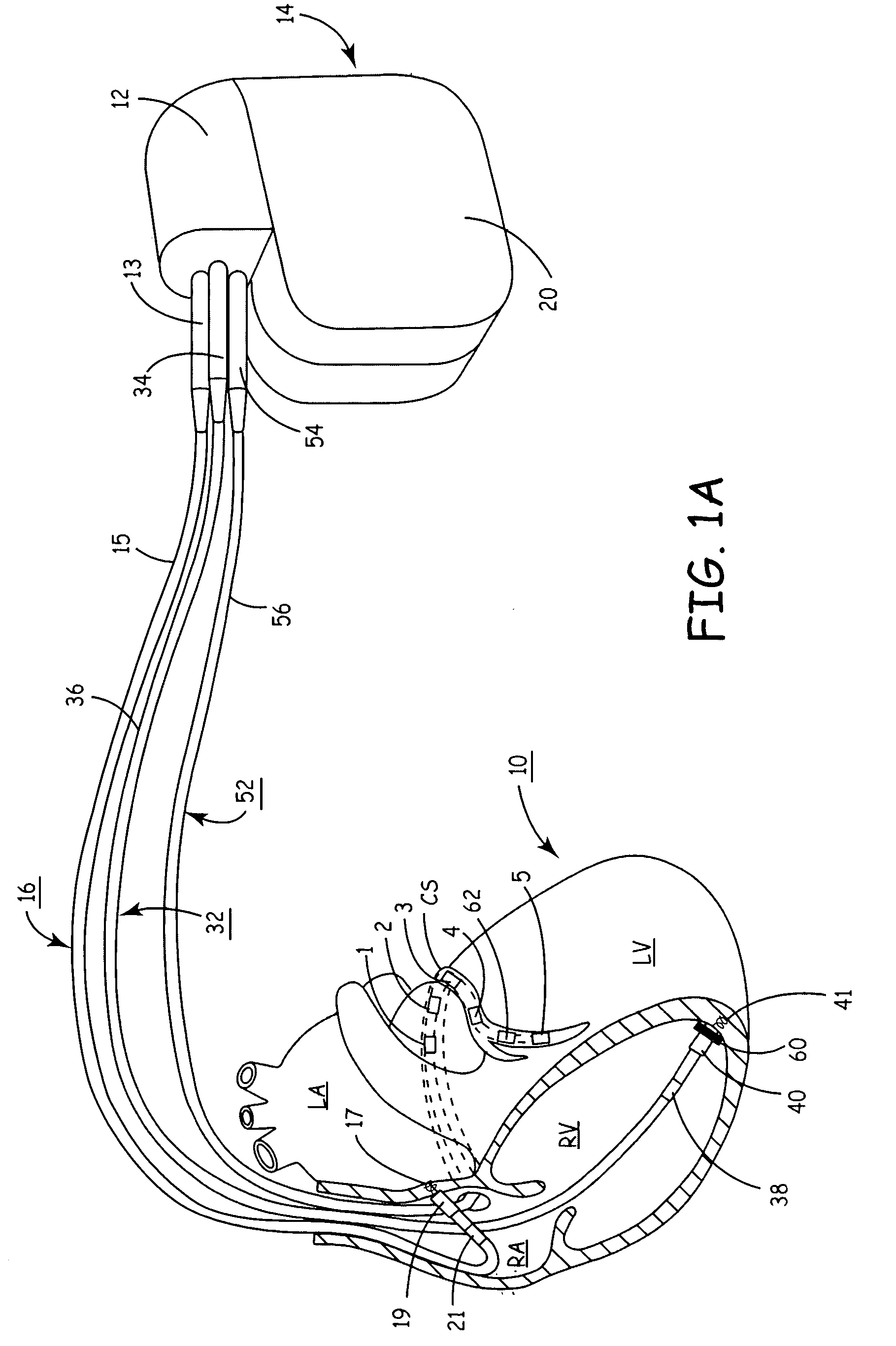
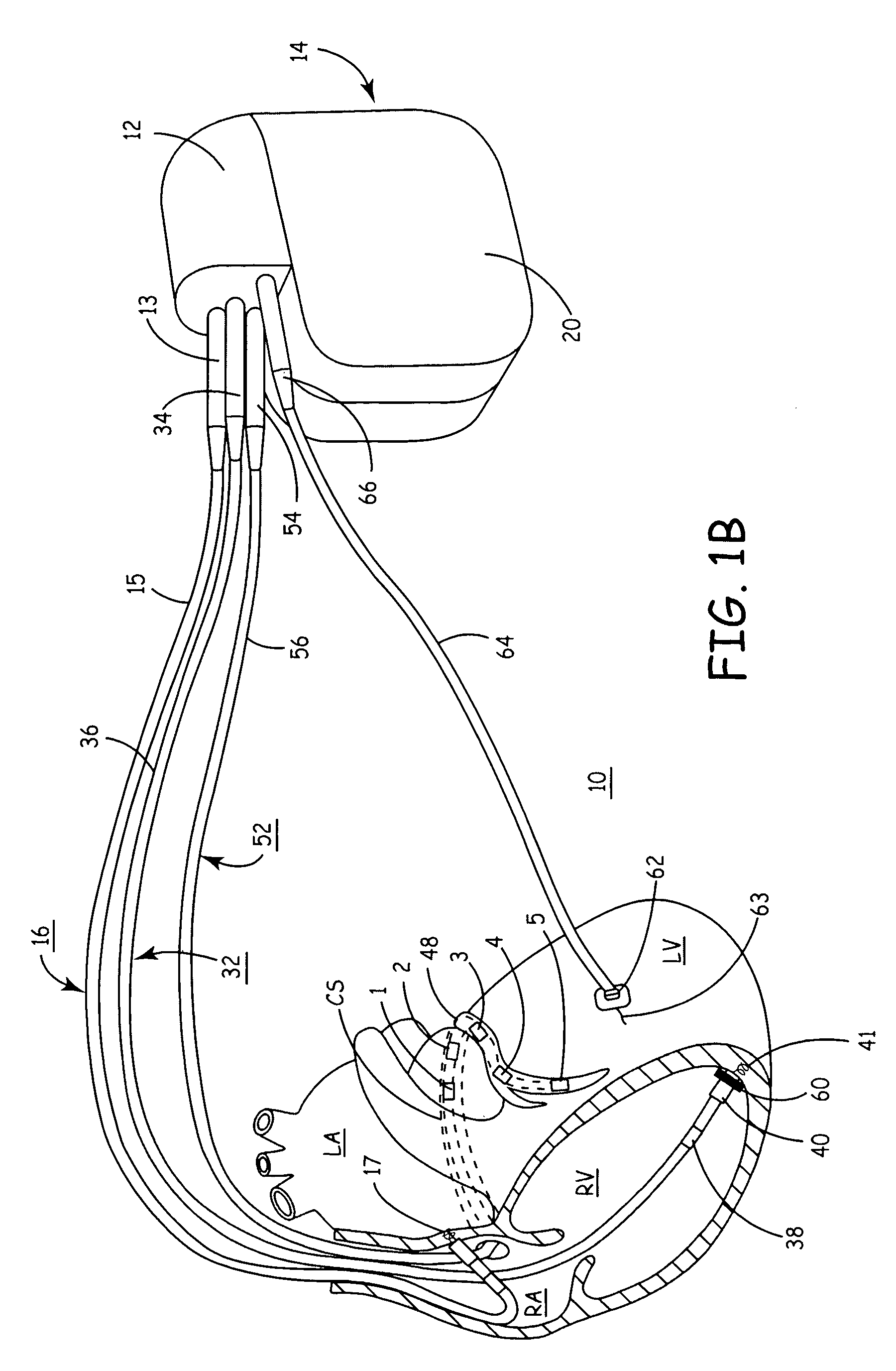
Reconfigurable, fault tolerant multiple-electrode cardiac lead systems
InactiveUS20050090870A1Easy to detectEfficient deliveryElectrocardiographyEpicardial electrodesLead systemVentricular tissue
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for assessing ventricular function on a chronic basis using a plurality of electrodes disposed on or about a left ventricle and / or a right ventricle—and optionally, at least one mechanical or metabolic sensor—all operatively electrically coupled to an implantable medical device. The plurality of electrodes are preferably spaced-apart so that at least one electrode is disposed electrical communication with a discrete volume of ventricular tissue. In one embodiment, the discrete volume of tissue is defined by multiple longitudinal and axial planes as known and used in the medical arts. Thus, according to the present invention, at least one electrode couples to appropriate sensing circuitry and essentially provides a localized electrogram (EGM) that, when compared to other EGMs, provides for configurable, localized delivery of therapeutic pacing stimulus, diverse impedance-sensing vectors, various diagnostic information regarding myocardial function and / or anti-tachycardia pacing.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
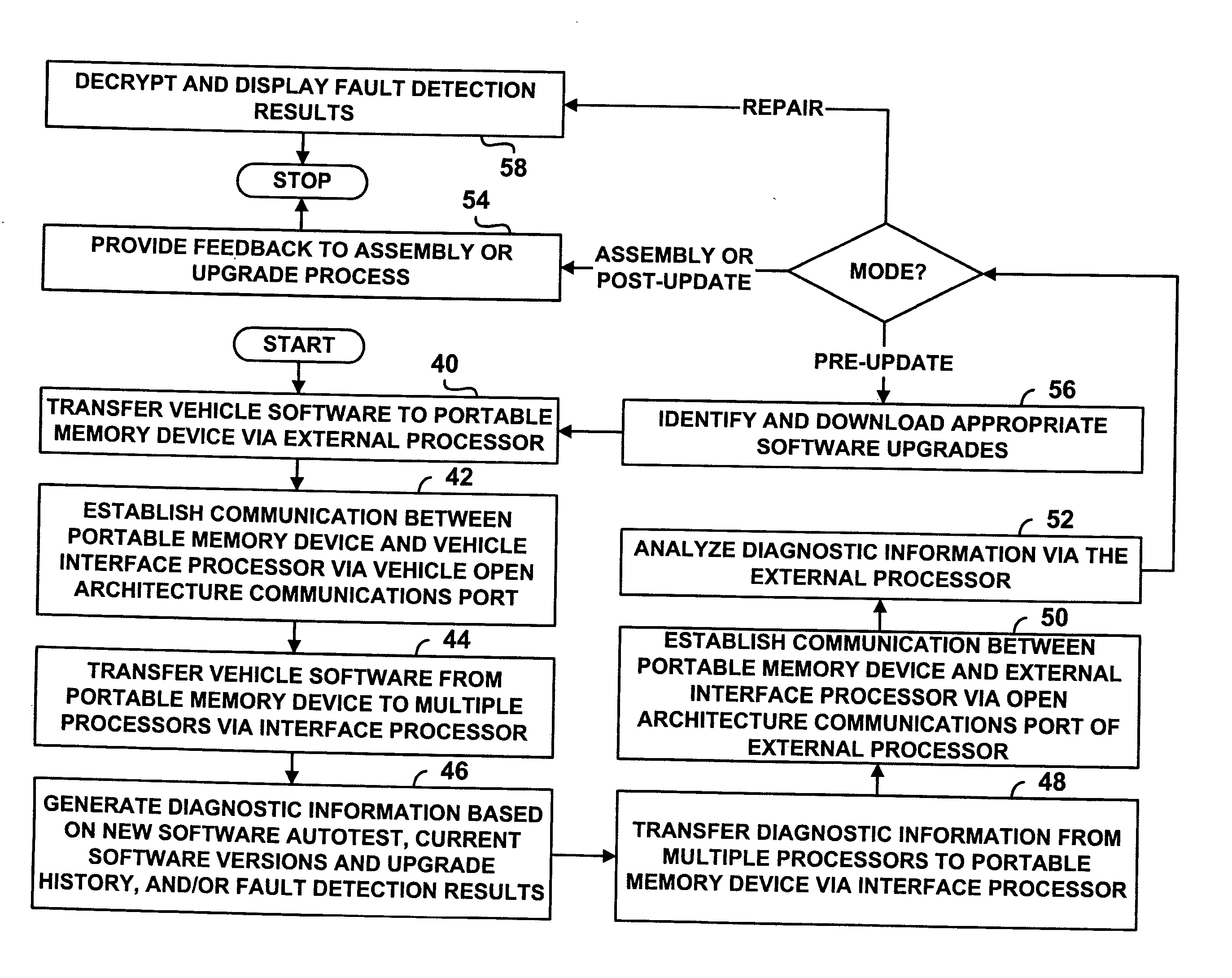
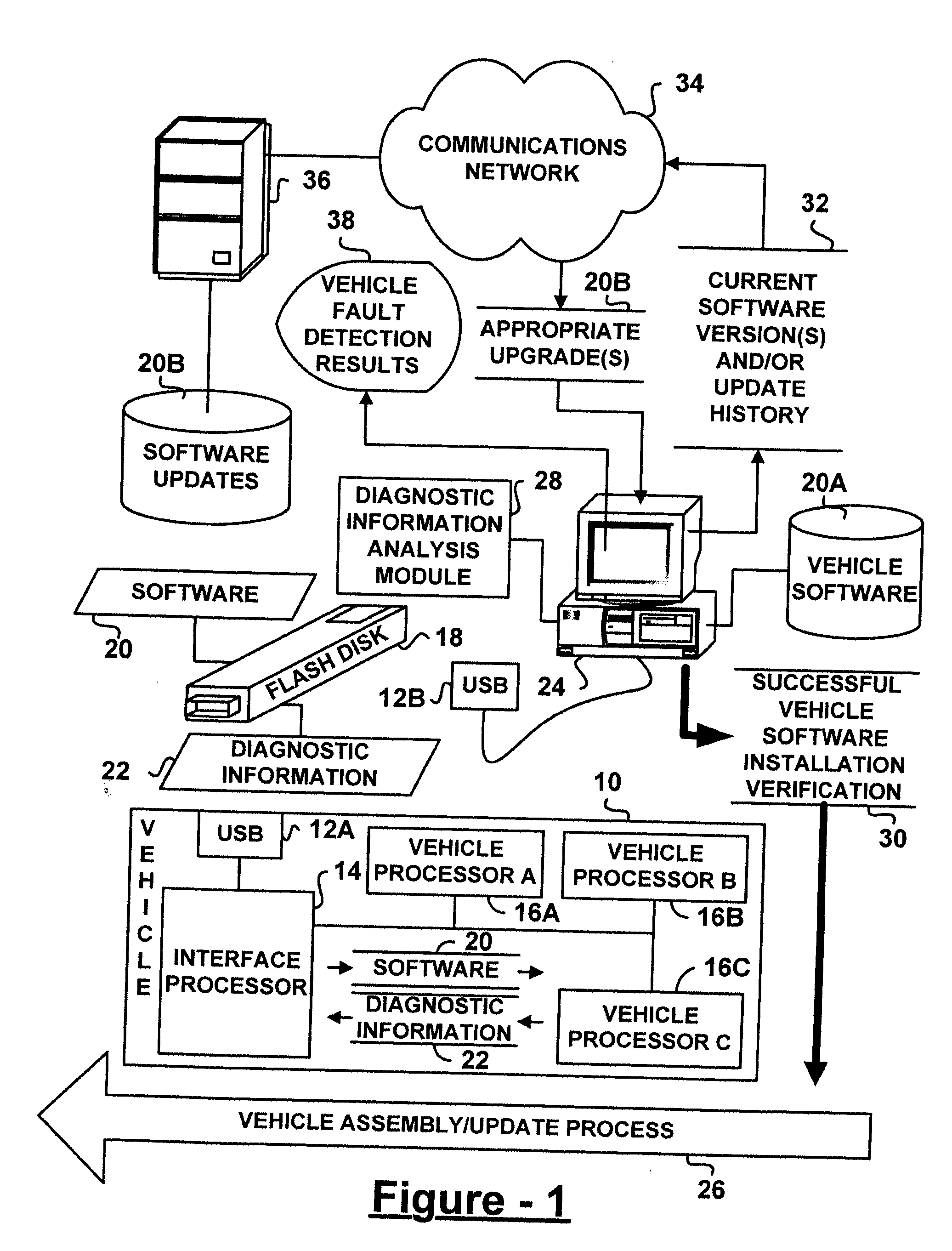
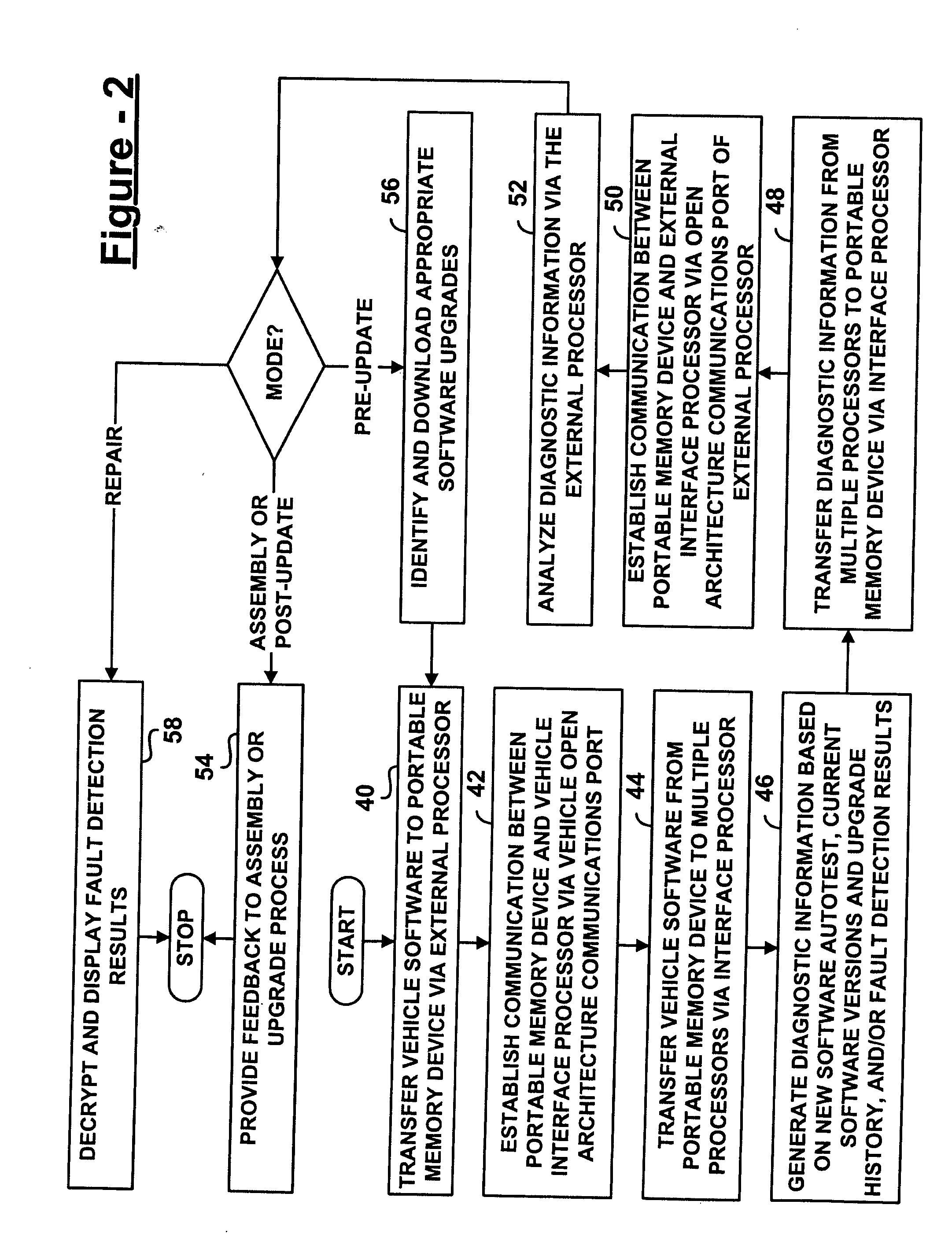
Low cost, open approach for vehicle software installation/updating and on-board diagnostics
ActiveUS20050097541A1Digital data processing detailsProgram loading/initiatingIn vehicleDiagnostic information
A vehicle software installation, upgrade, and diagnostic system for use in vehicle assembly, upgrade, and repair, includes a portable memory device, such as a USB flash disk. The device receives diagnostic information via an open architecture communications port of a vehicle, such as a USB port. An external processor has a complimentary open architecture communications port and is adapted to receive and analyze the diagnostic information from the portable device. According to various aspects, analysis of the diagnostic information verifies successful installation and testing of vehicle software transferred from the portable device to vehicle processors, identifies software versions resident on the vehicle and related upgrade history for download and installation of an appropriate software upgrade, and / or diagnoses vehicle problems in accordance with sensed vehicle conditions and predetermined fault detection criteria.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
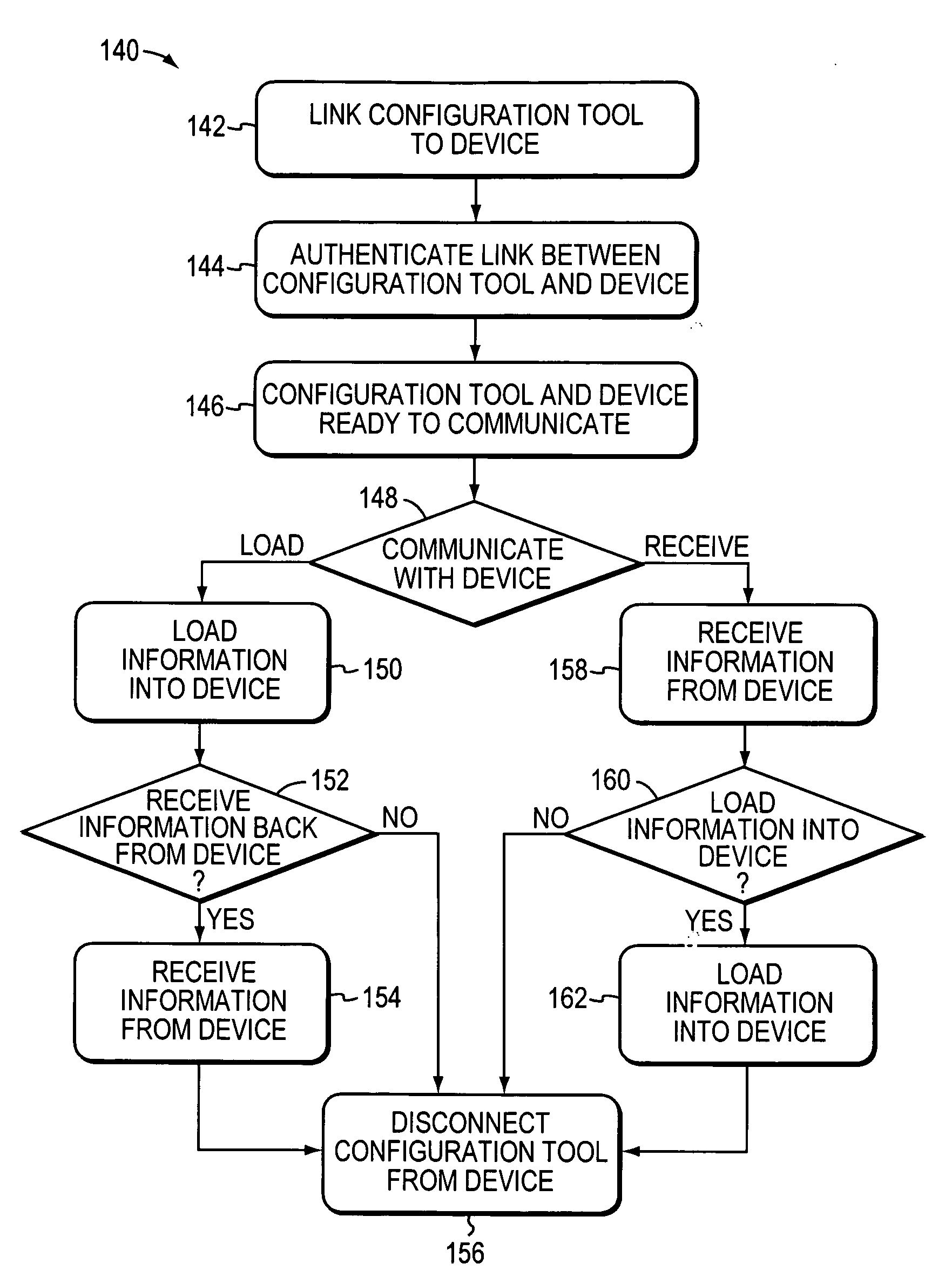
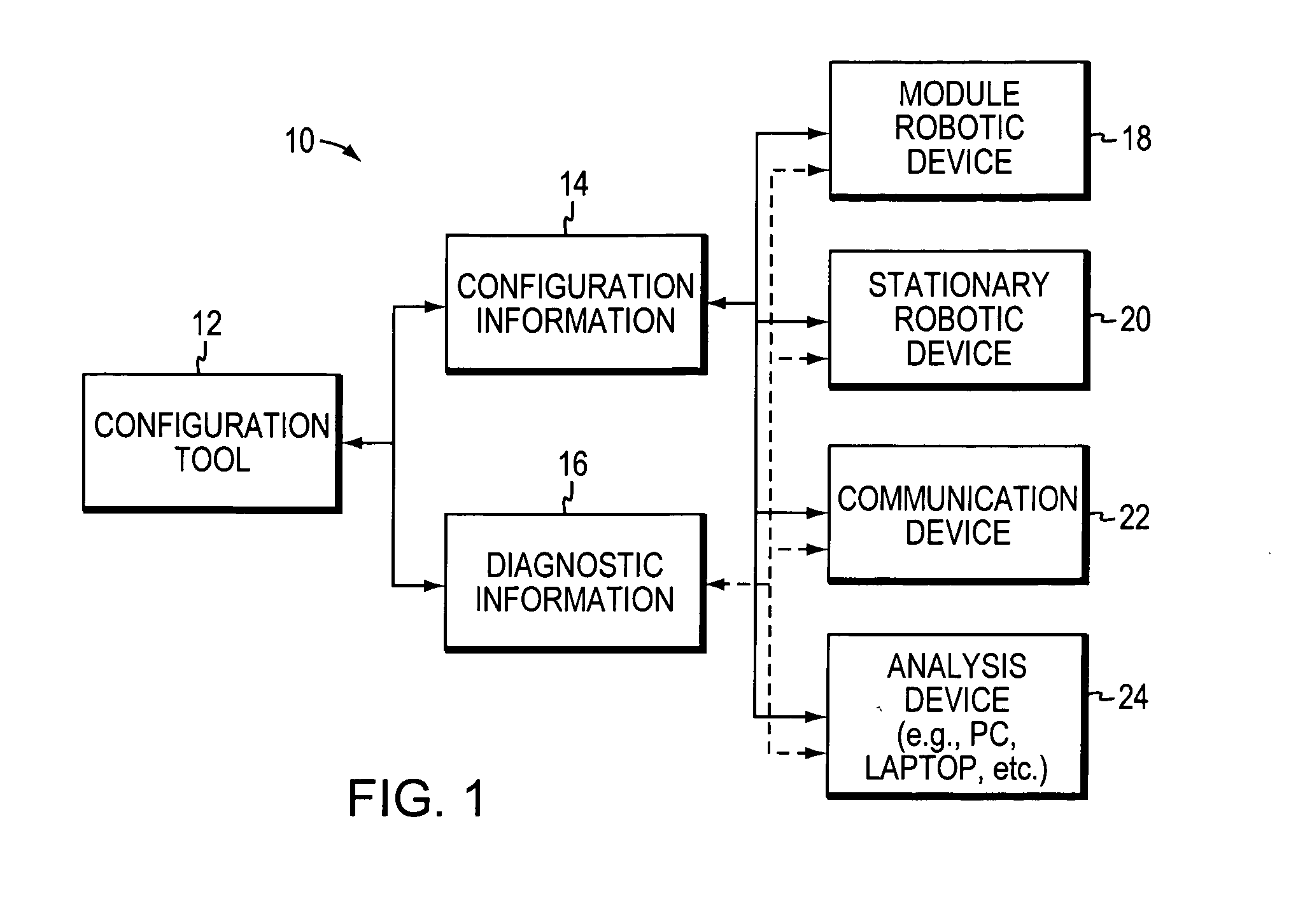
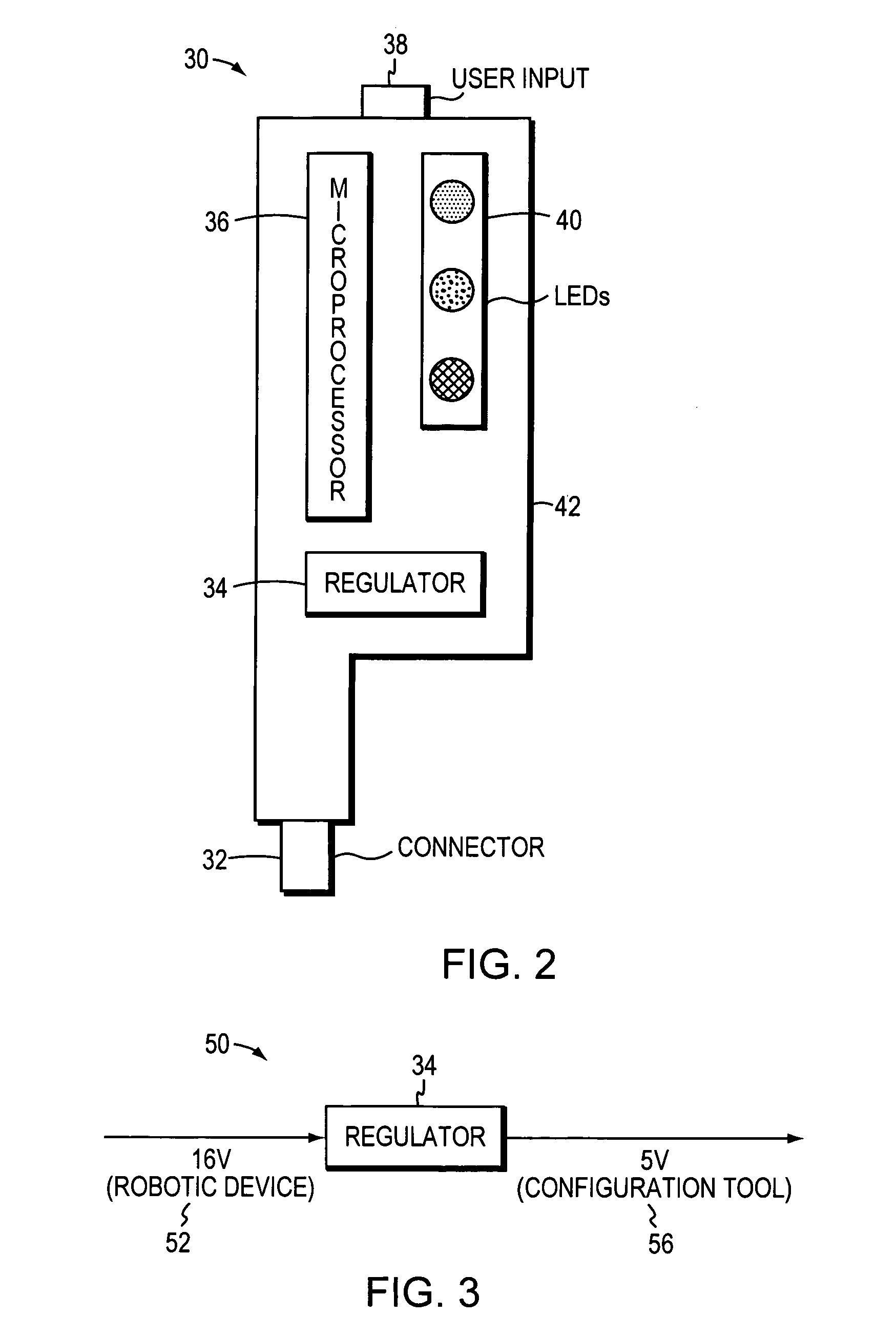
Programming and diagnostic tool for a mobile robot
InactiveUS20060009879A1Programme-controlled manipulatorAutonomous decision making processSimulationHand held
Owner:IROBOT CORP
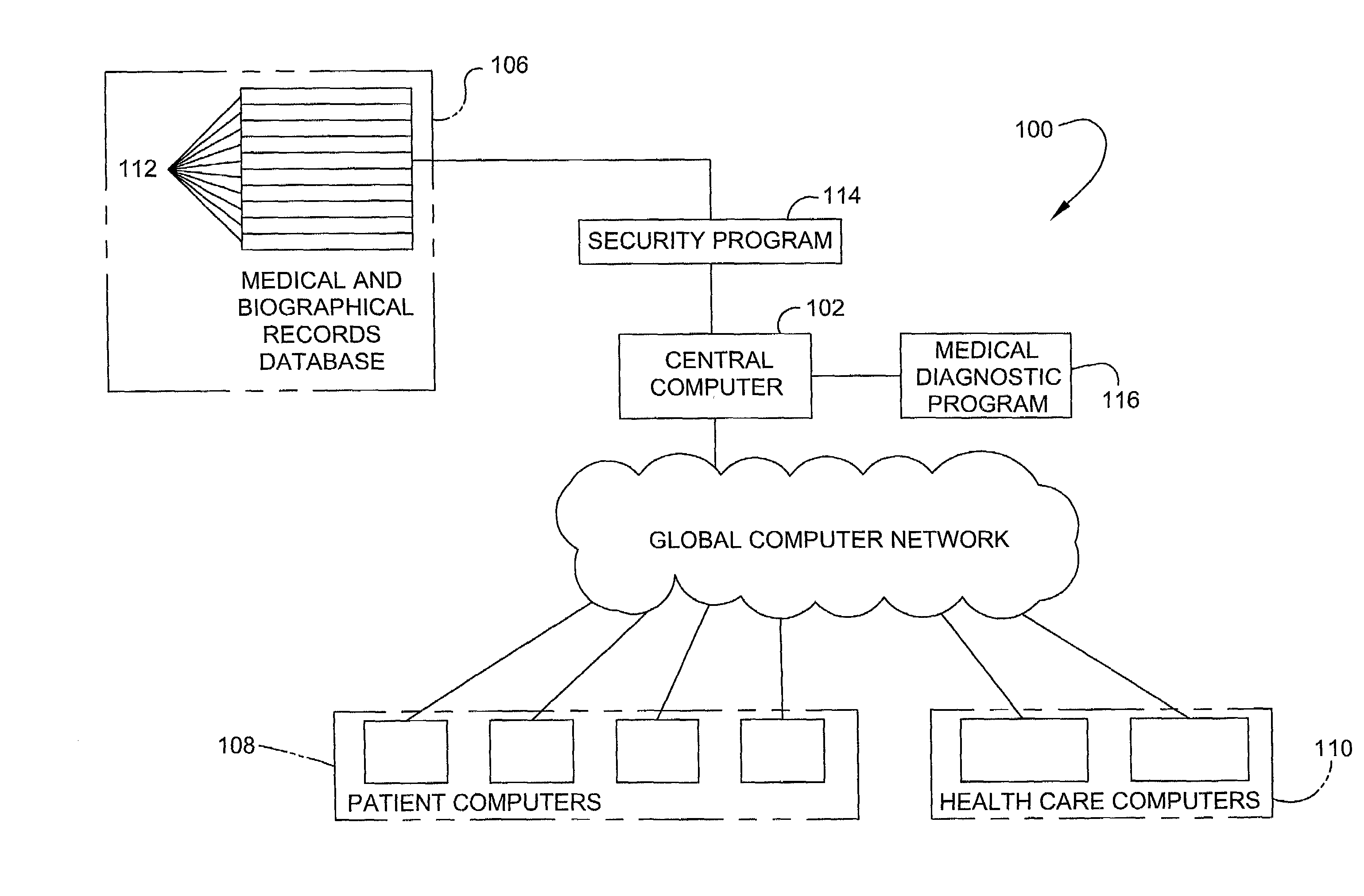
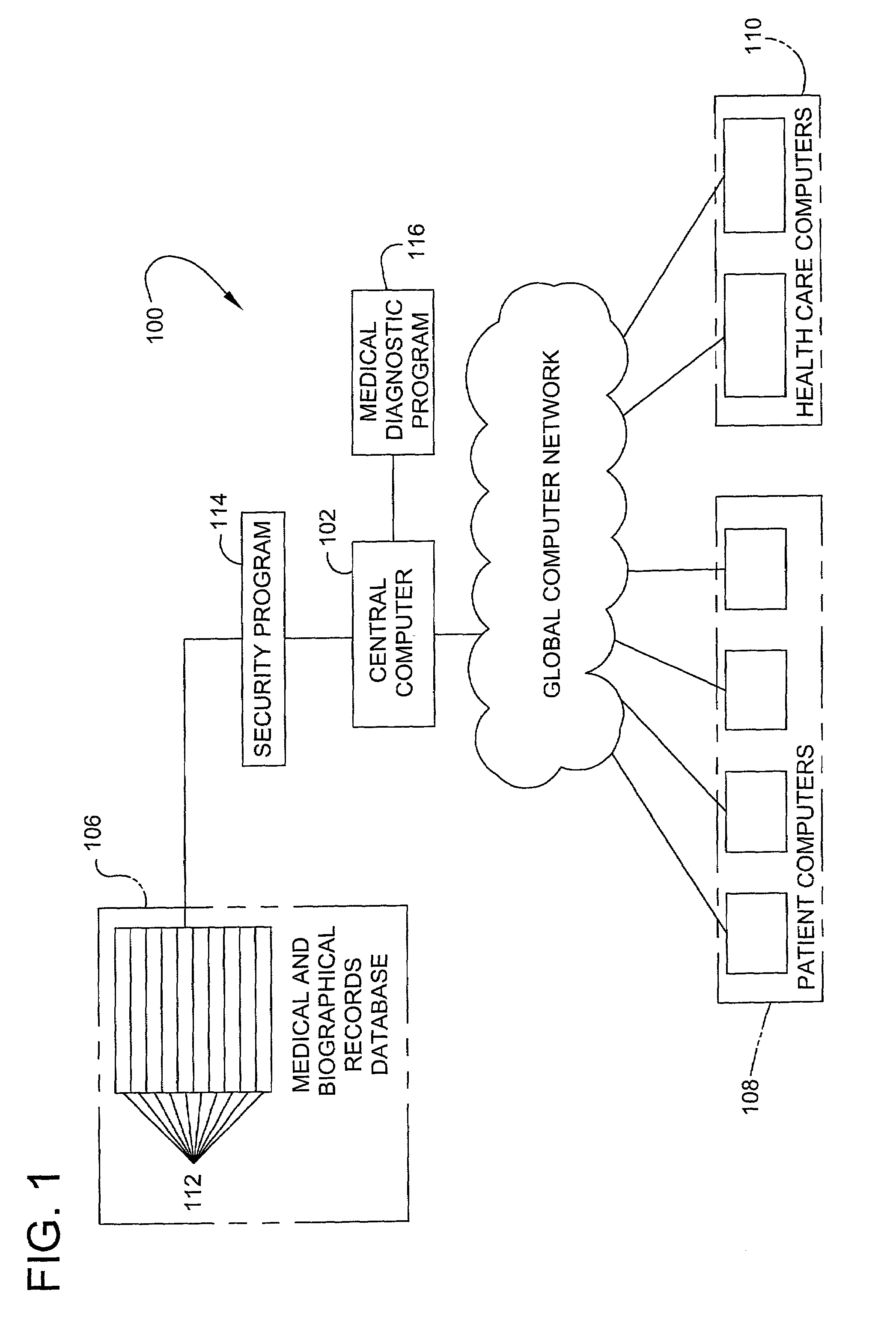
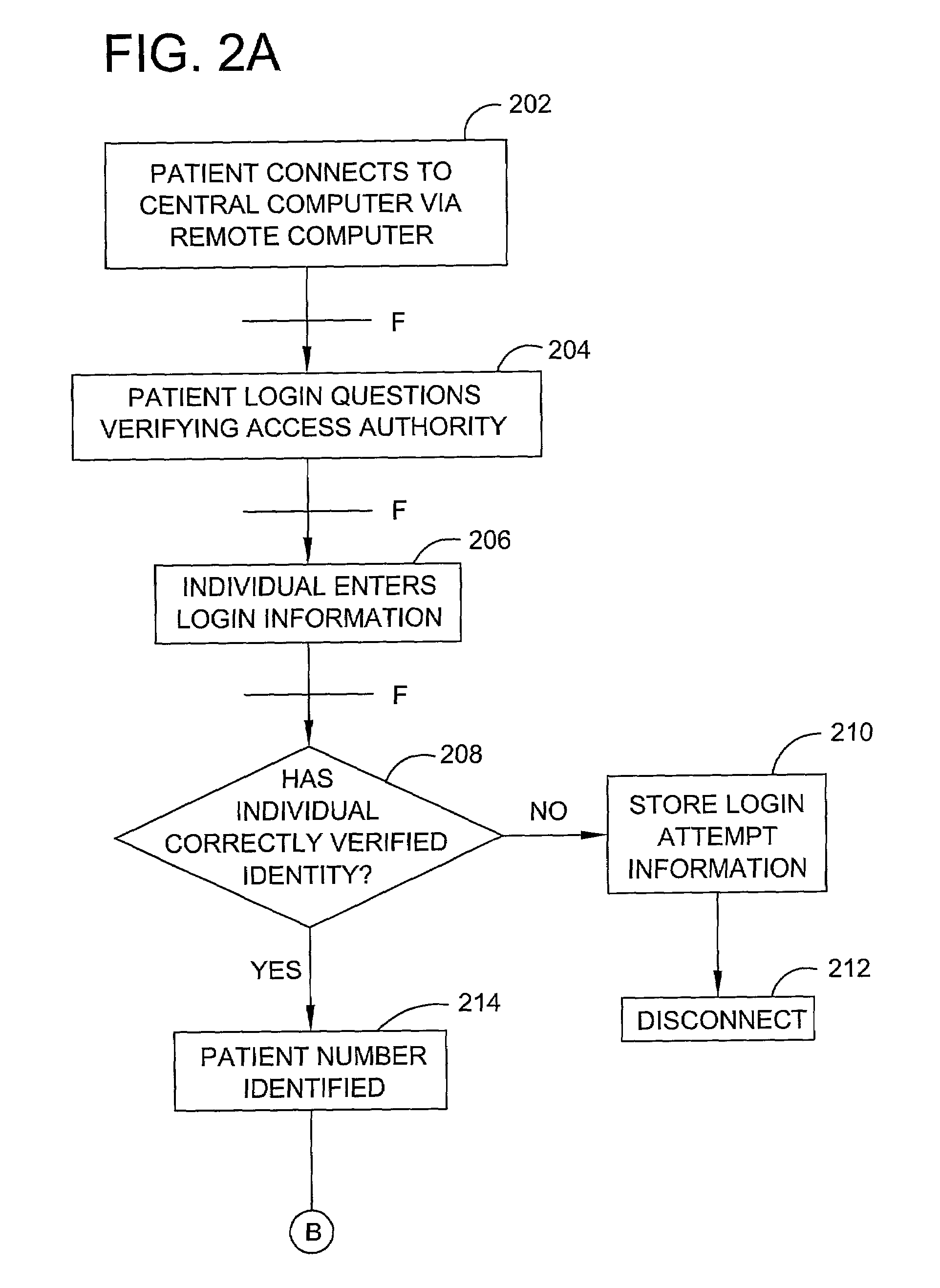
Patient-controlled automated medical record, diagnosis, and treatment system and method
A system and process for providing a computerized medical and biographical records database and diagnostic information. A medical records database and diagnostic program is stored on a central computer that is accessible to individuals using remotely situated computers connected to a computer network. Individual patient medical and biographical records are owned by individual patients who can enter information in their record as well as grant or deny authorization to others, such as health care professionals, insurance providers and other entities, to review part or all of their record. The diagnostic program provides a series of diagnostic questions to an individual who must respond either “yes” or “no” to each question. Each potential response is weighted relative to its importance to a particular disease diagnosis. Relative weights for all responses to diagnostic questions are summed to identify potential diagnoses to connected to the answered questions. The diagnostic program provides the individual with a list of potential diagnoses as well as permitting the individual to save the information to his or her individual medical and biographical record. The information maintained in the above system and process is utilized for health care financing and insurance.
Owner:MARFLY 1 LP
Particle on membrane assay system
InactiveUS20050191620A1Facilitate digital/optical acquisition of fluorescent signalBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAssayAnalyte
Described herein is an analyte detection device and method related to a portable instrument suitable for point-of-care analyses. In some embodiments, a portable instrument may include a disposable cartridge, an optical detector, a sample collection device and / or sample reservoir, reagent delivery systems, fluid delivery systems, one or more channels, and / or waste reservoirs. Use of a portable instrument may reduce the hazard to an operator by reducing an operator's contact with a sample for analysis. The device is capable of obtaining diagnostic information using cellular- and / or particle-based analyses and may be used in conjunction with membrane- and / or particle-based analysis cartridges. Analytes, including proteins and cells and / or microbes may be detected using the membrane and / or particle based analysis system.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS
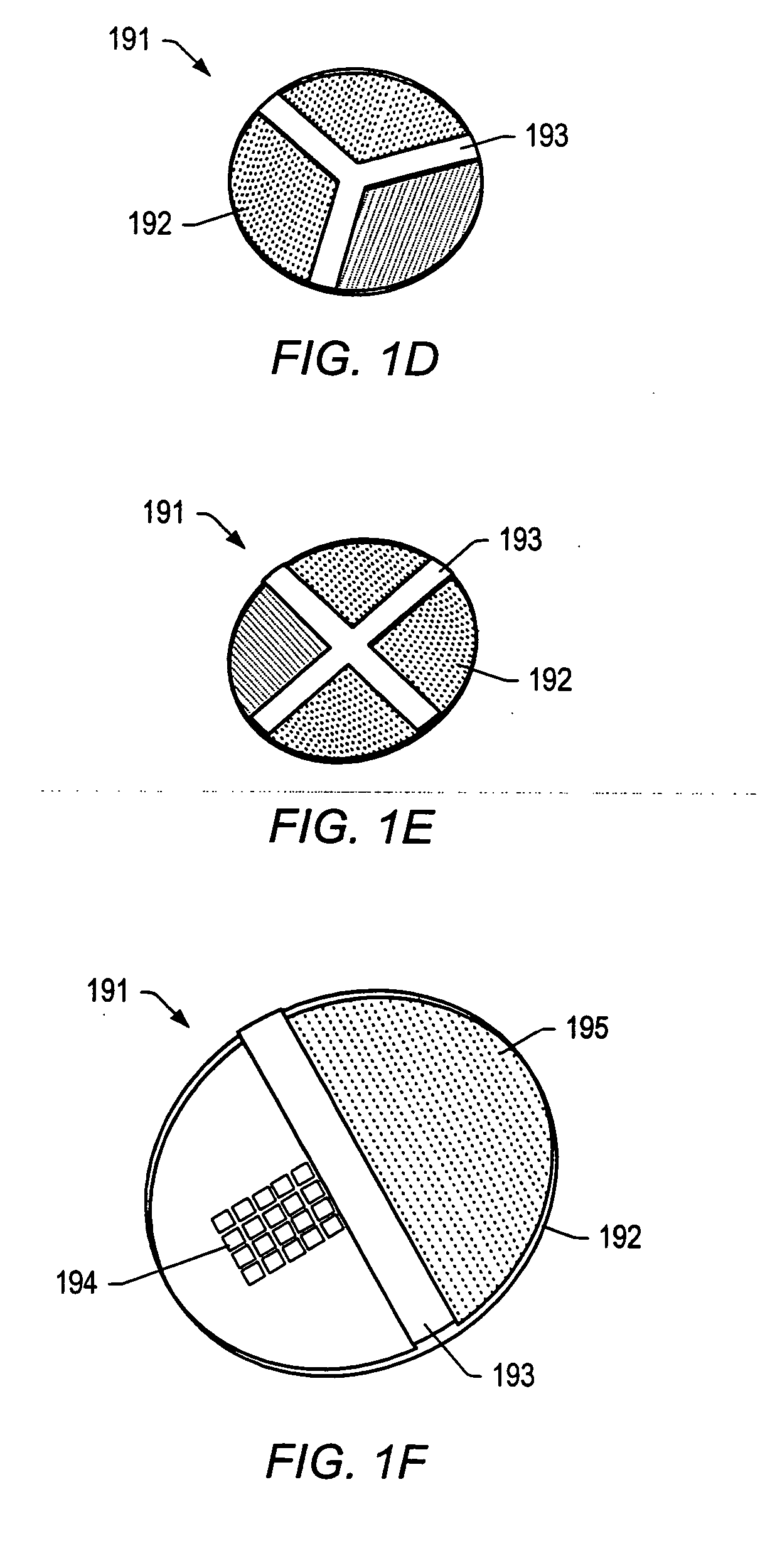
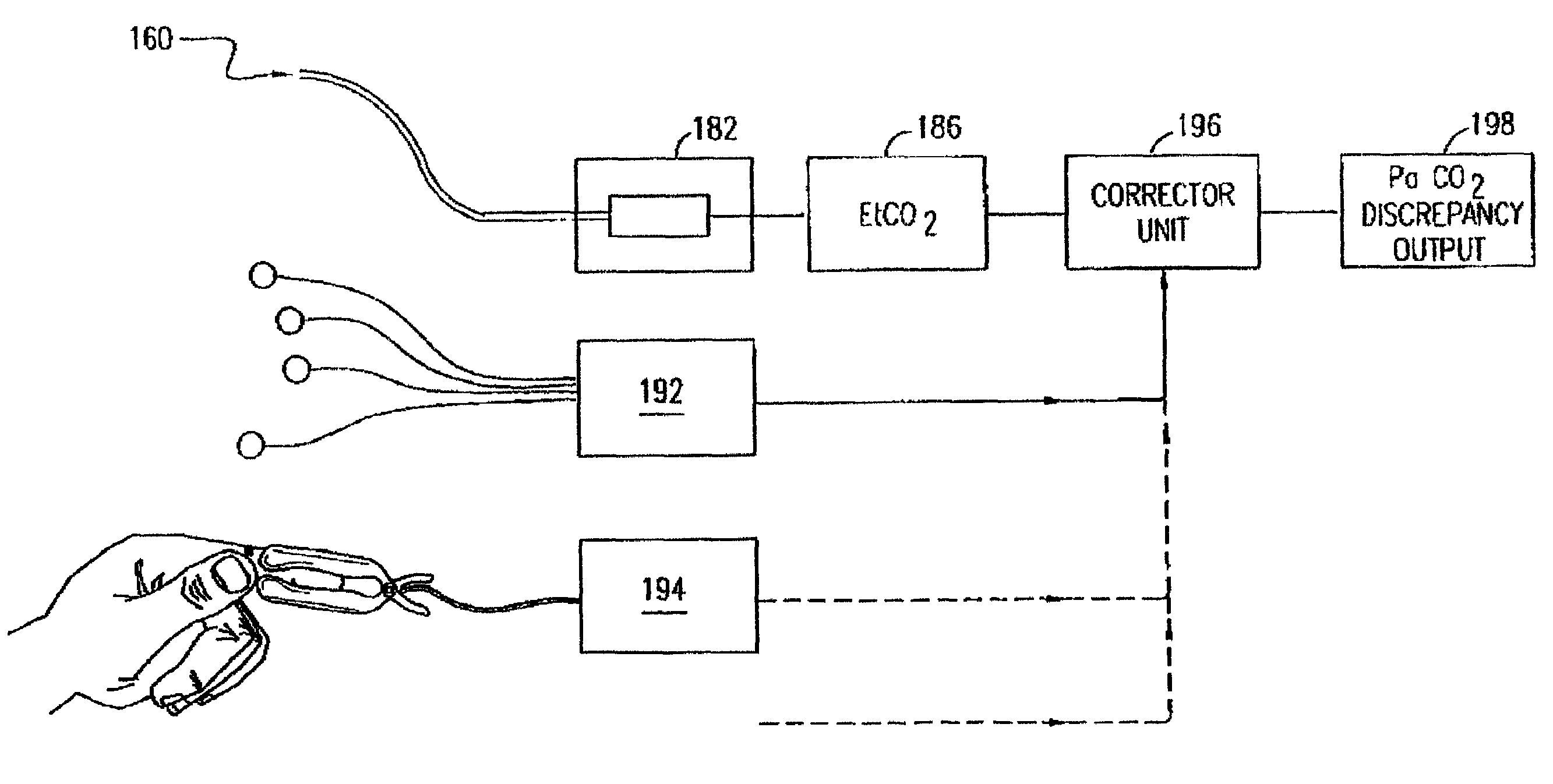
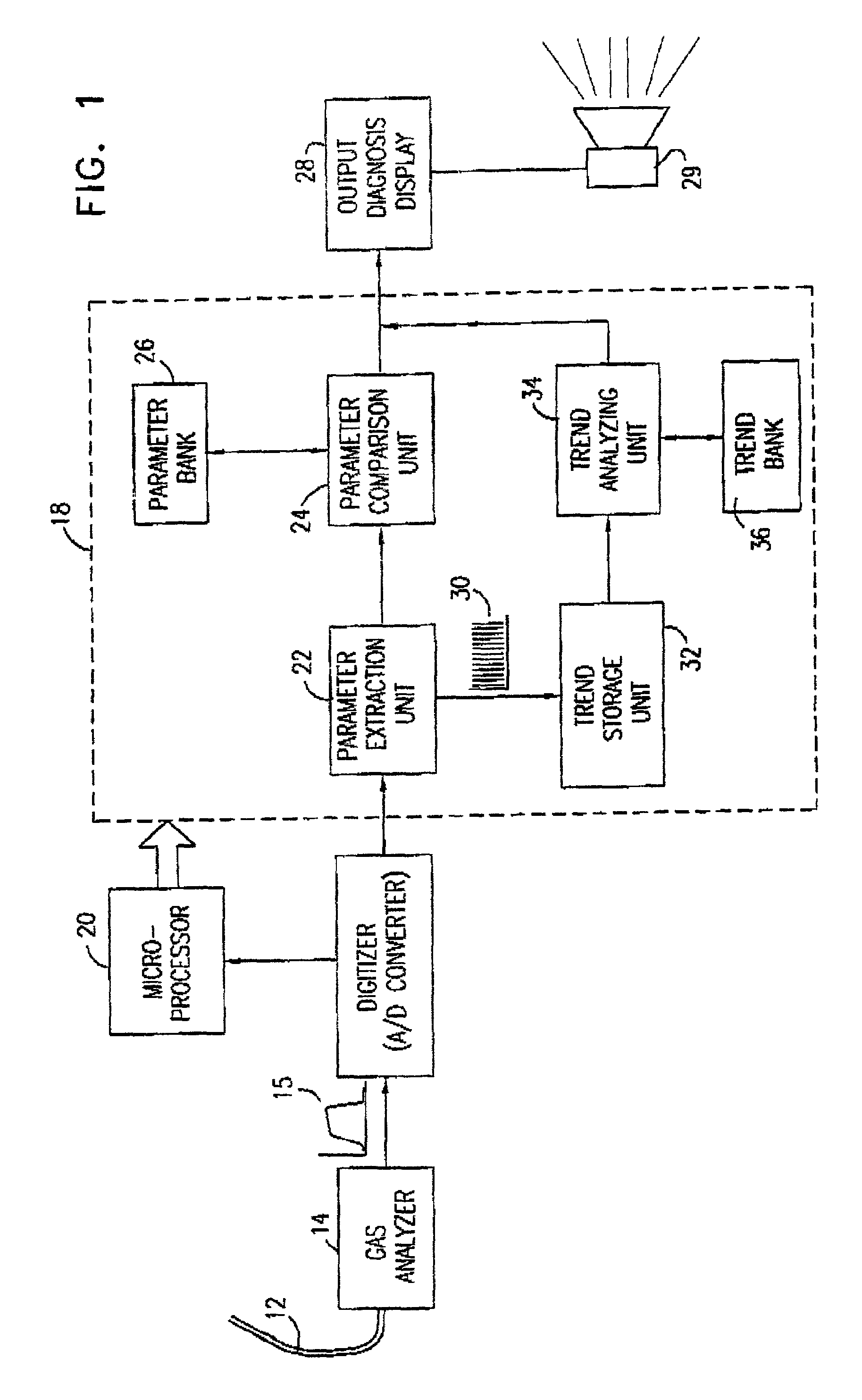
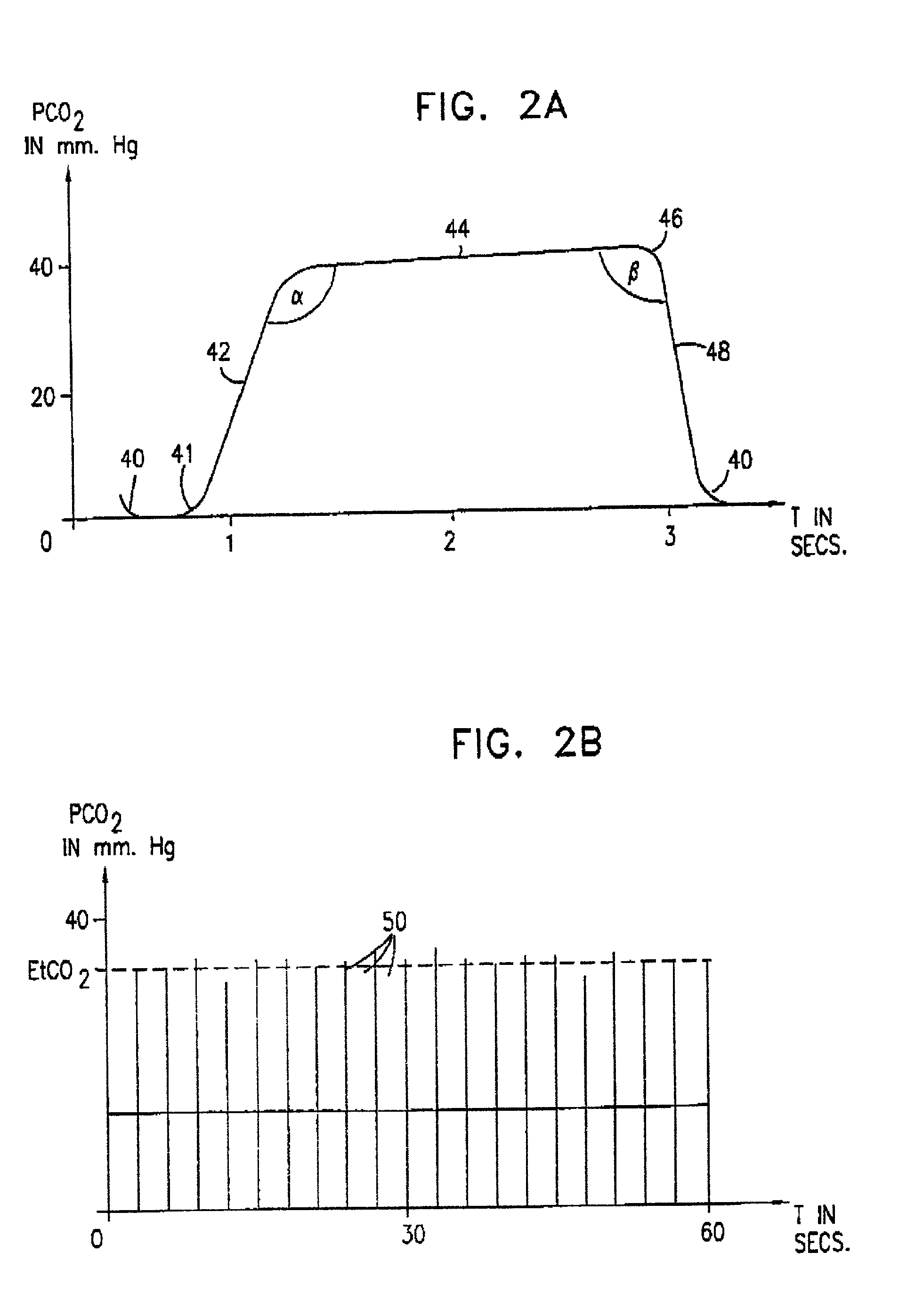
Waveform interpreter for respiratory analysis
InactiveUS6997880B2More informationAccurate diagnosisRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsWaveform analysisTime domain
A capnograph which performs an analysis of the breath waveforms measured by the carbon dioxide sensor, interprets the results of this analysis, and outputs to the operator diagnostic information about the respiratory status of the patient, or about the adequacy of the breathing support provided to the patient. The instrument compares a number of parameters characteristic of the waveforms of the patient's breath with an internal library of the values of those parameters expected from normal waveforms stored in its memory. These parameters may either relate to specific features of the waveform in the time domain, or may characterize spectral components of the waveform in the frequency domain. The capnographic waveform analysis may be combined with further non-invasive measurements in order to provide an indication of the deviation of the value of EtCO2 from PaCO2.
Owner:ORIDION MEDICAL 1987
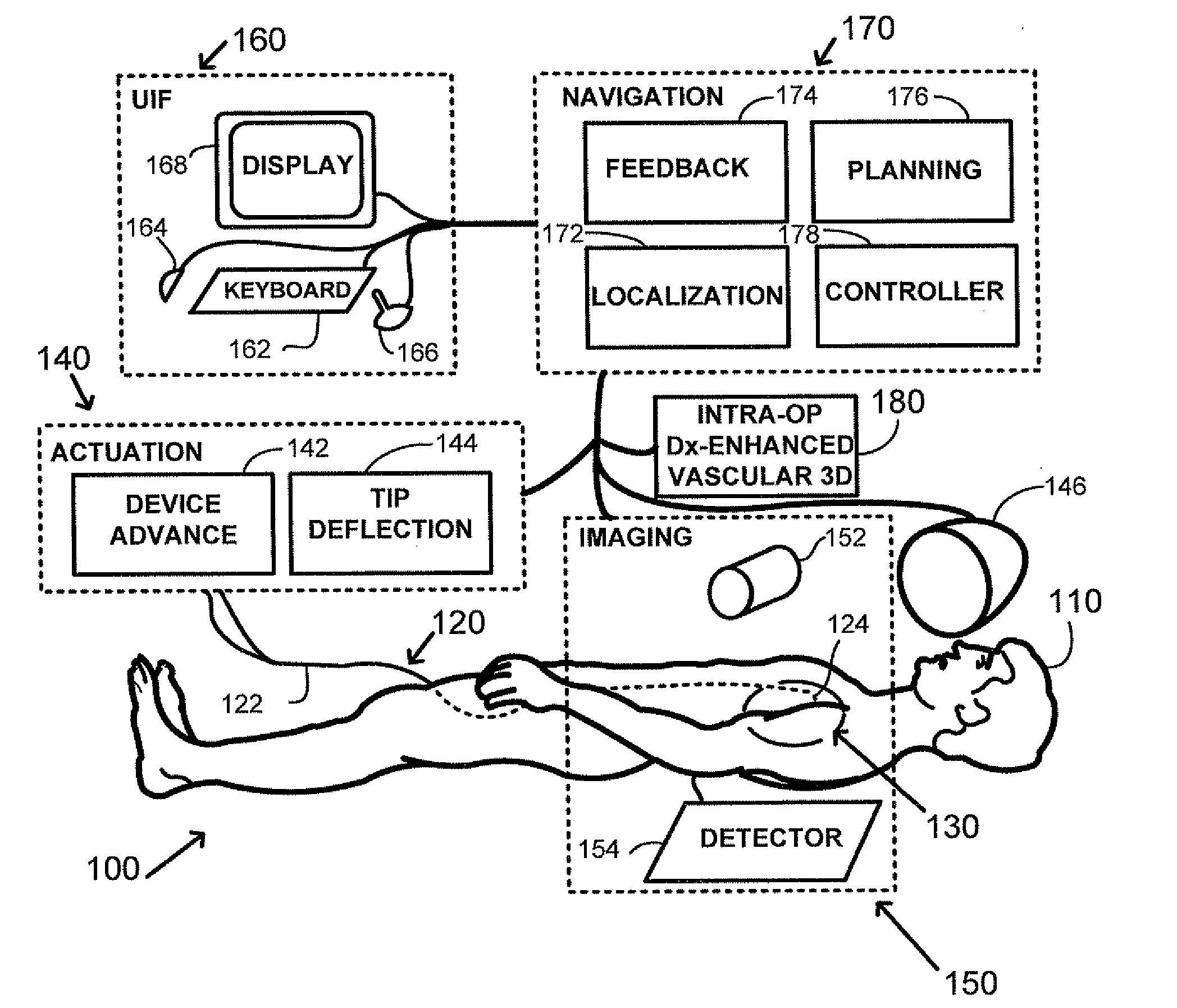
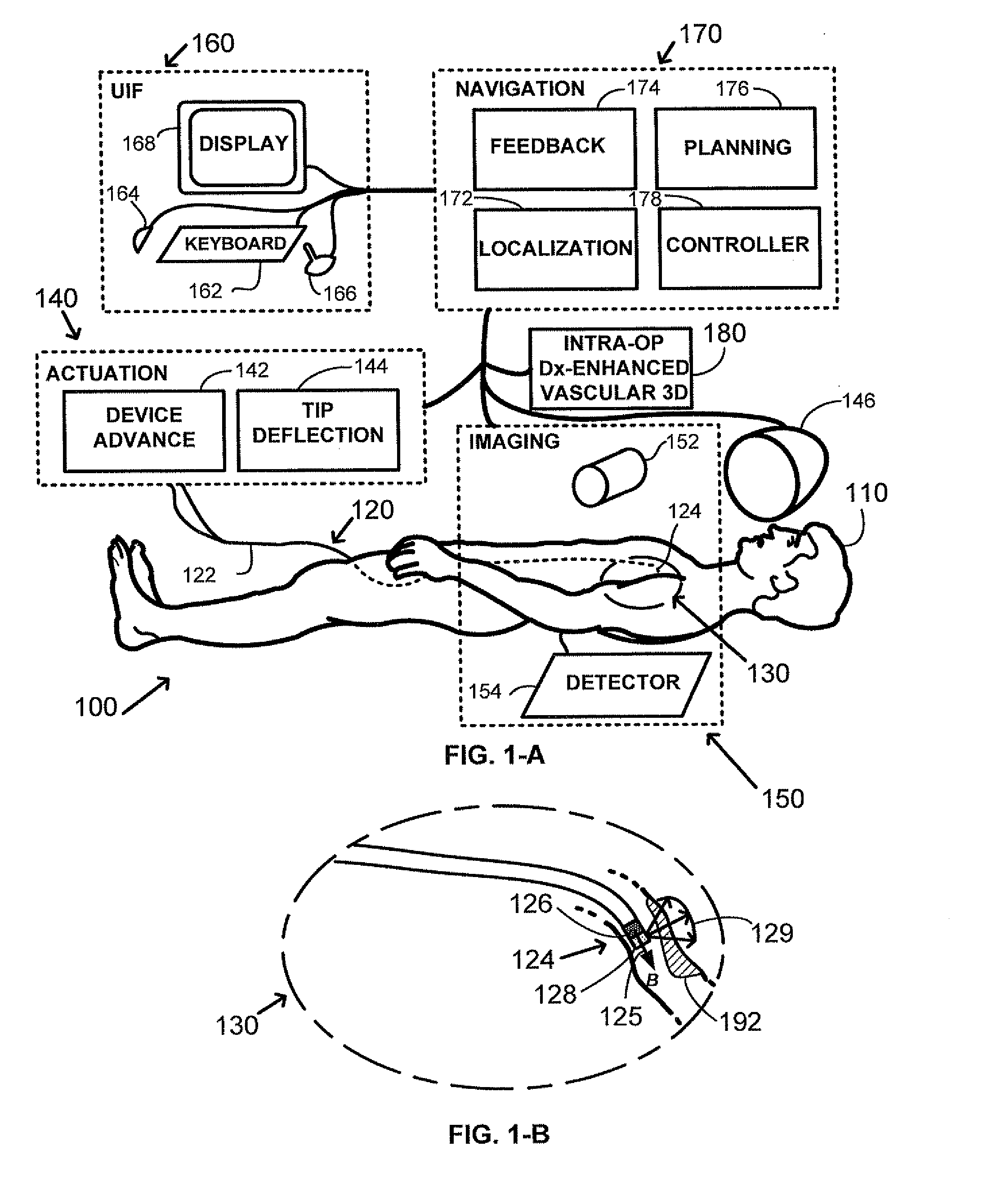
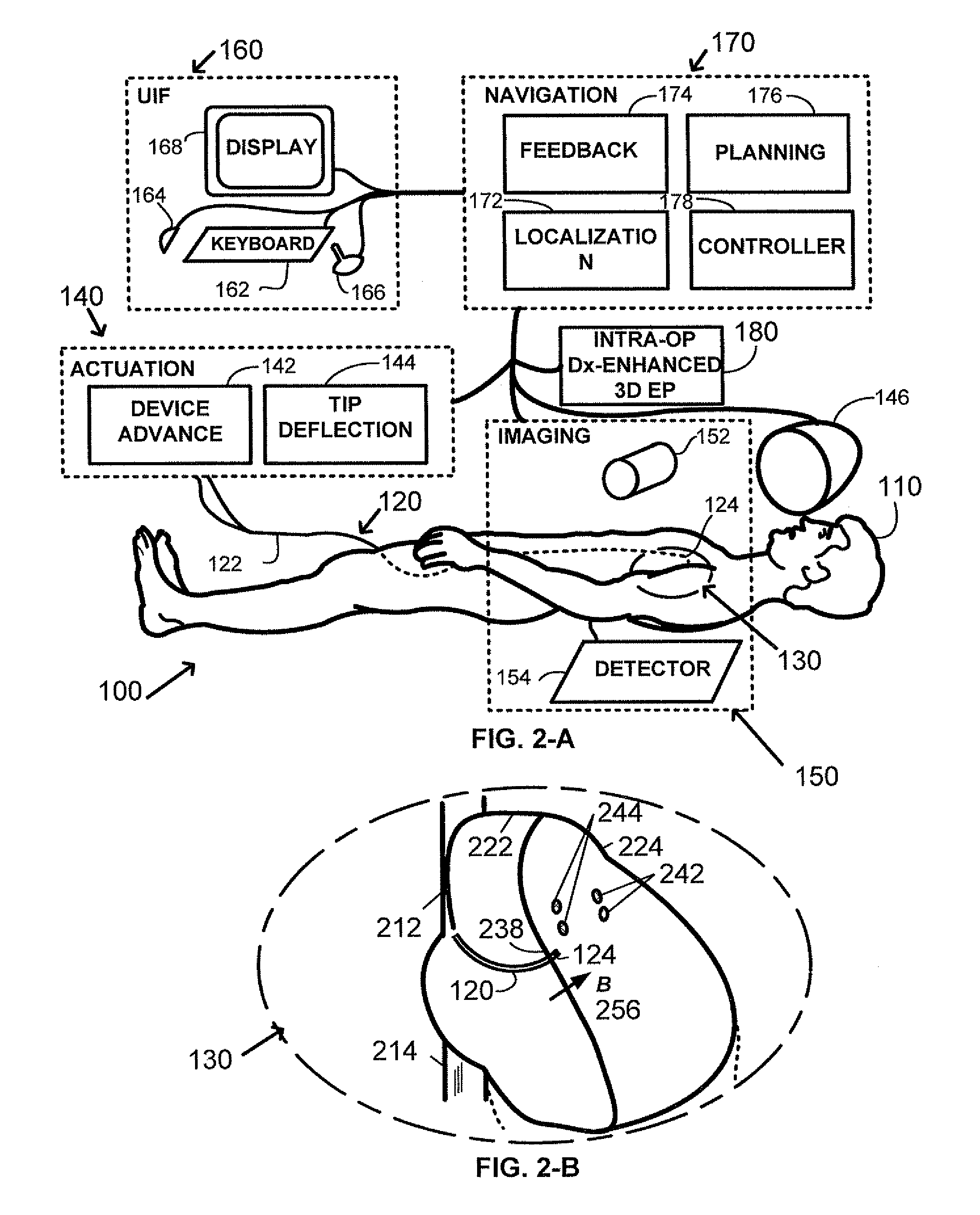
Method and apparatus for remotely controlled navigation using diagnostically enhanced intra-operative three-dimensional image data
InactiveUS20090105579A1Effective diagnosisUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementVascular diseaseRadiology
A method of performing intra-operative three-dimensional imaging and registering diagnostic functional information to the three-dimensional anatomical data is introduced. The availability of co-registered diagnostic information to intra-operative data enables fast and efficient navigation to pre-selected target areas, and allows automatic or semi-automatic treatment of cardiac cavity or vascular disease.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
System, method and computer program product for diagnostic supervision of internet connections
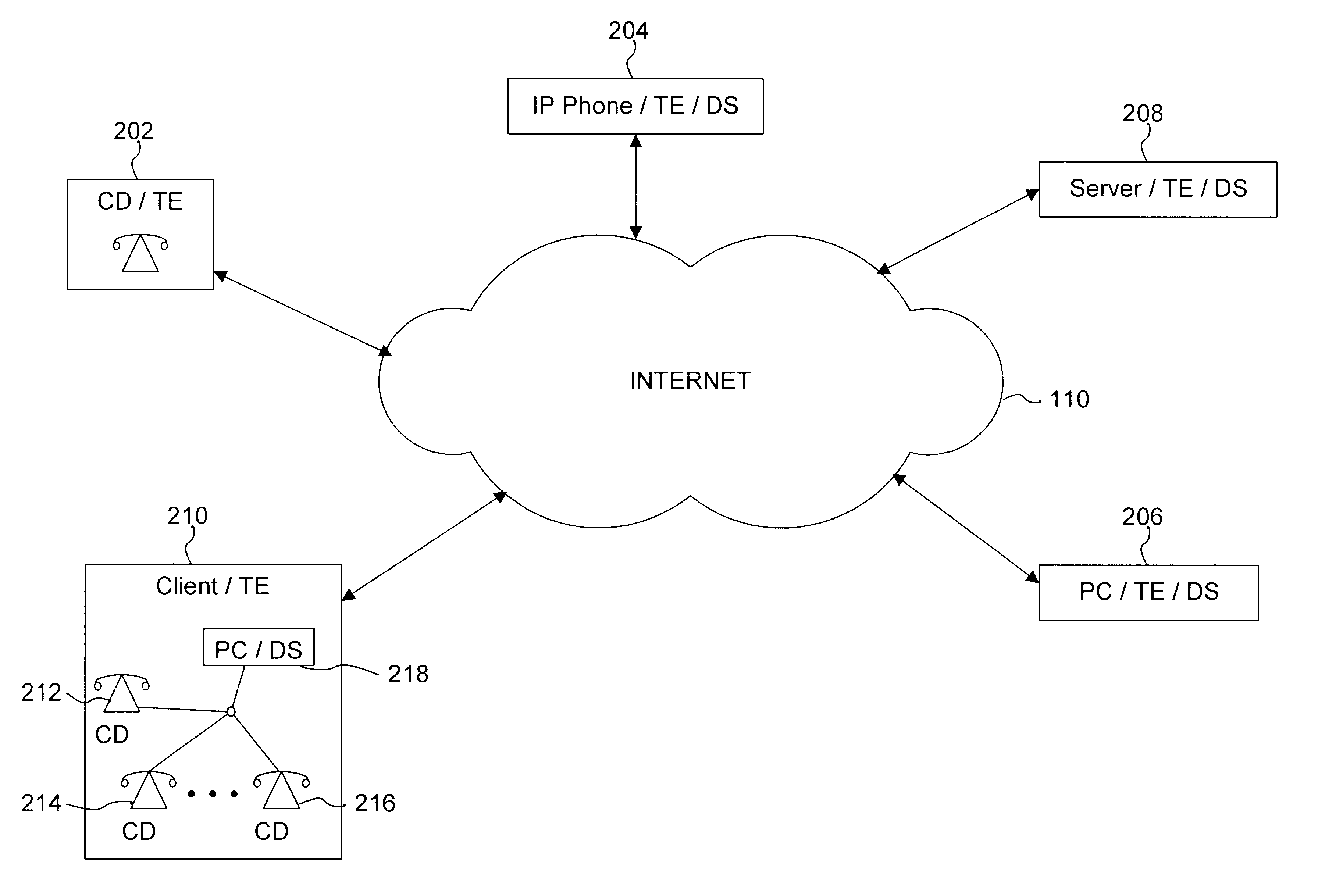
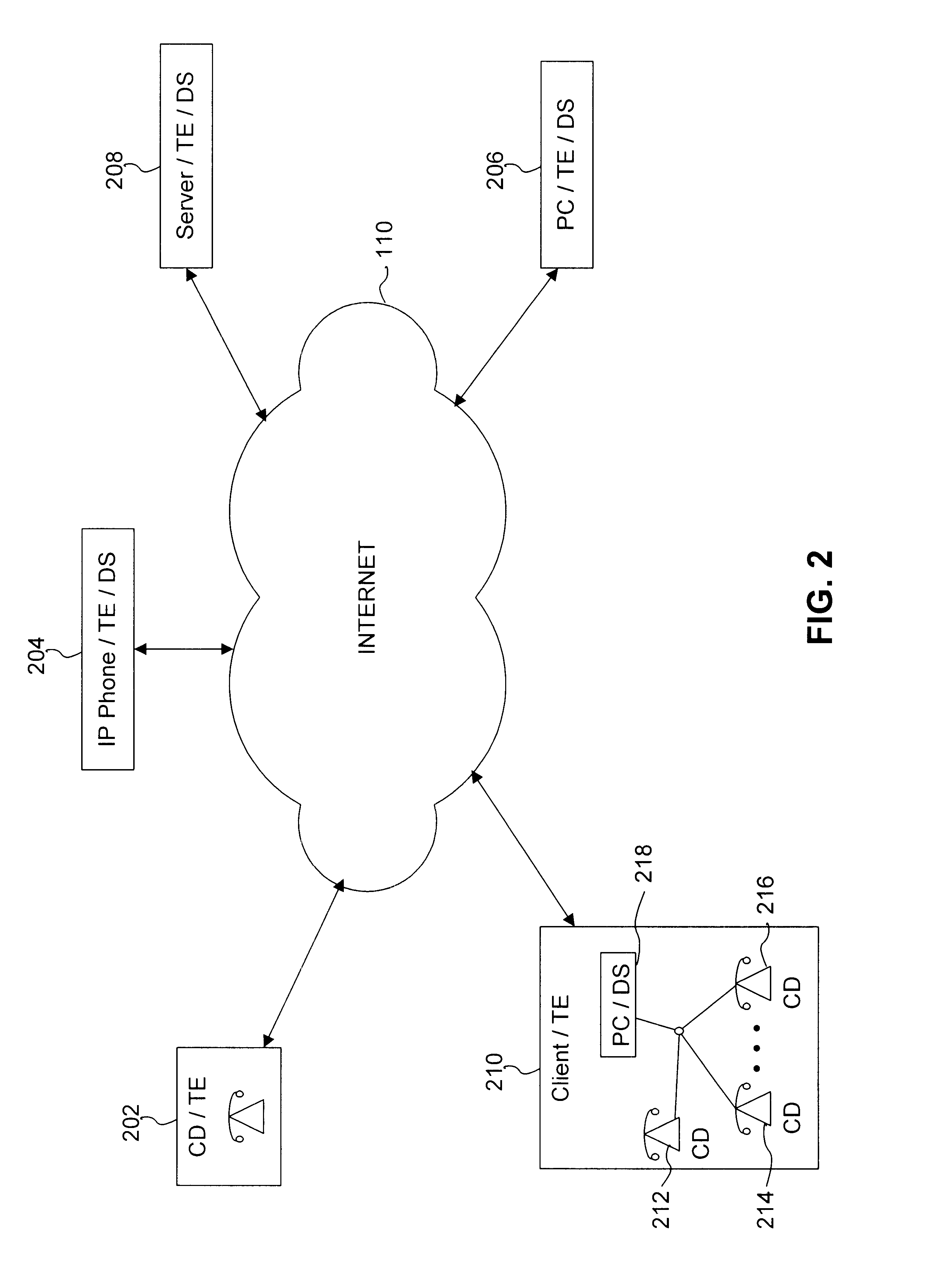
InactiveUS6553515B1Error detection/correctionDigital computer detailsModem deviceCommunications system
A system, method and computer program product for managing diagnostic and performance information for communications system terminal endpoints (TEs) communicating over an Internet Protocol (IP) network. The TEs communicate by connections that are voice, modem, facsimile, video, data transmissions, or the like. A Diagnostic Supervisor (DS) transmits Diagnostic Configuration Messages (DCMs) to the TEs. The TE's generate Diagnostic Messages (DMs) based on diagnostic information, including error statistics, voice statistics, facsimile statistics, video statistics, data statistics, or the like, concerning IP network connections in which the TEs participate. The DCMs instructs the TEs how to format and when to transmit DMs. The DMs are transmitted by the TEs to the DS. In a system with more that one DS, the TEs can transmit DMs to the plural DSs, other TEs or any network devices. The DS can be programmed locally or remotely to send various types of DCMs. The DS can also be programmed locally or remotely to provide diagnostic reports based on DMs to network users or to the network administrator. Diagnostic information is used for disconnect supervision, answer detection, attendant supervision, billing management, rerouting of IP connections to the PSTN, and the like.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
Retrieving diagnostic information from an HVAC component
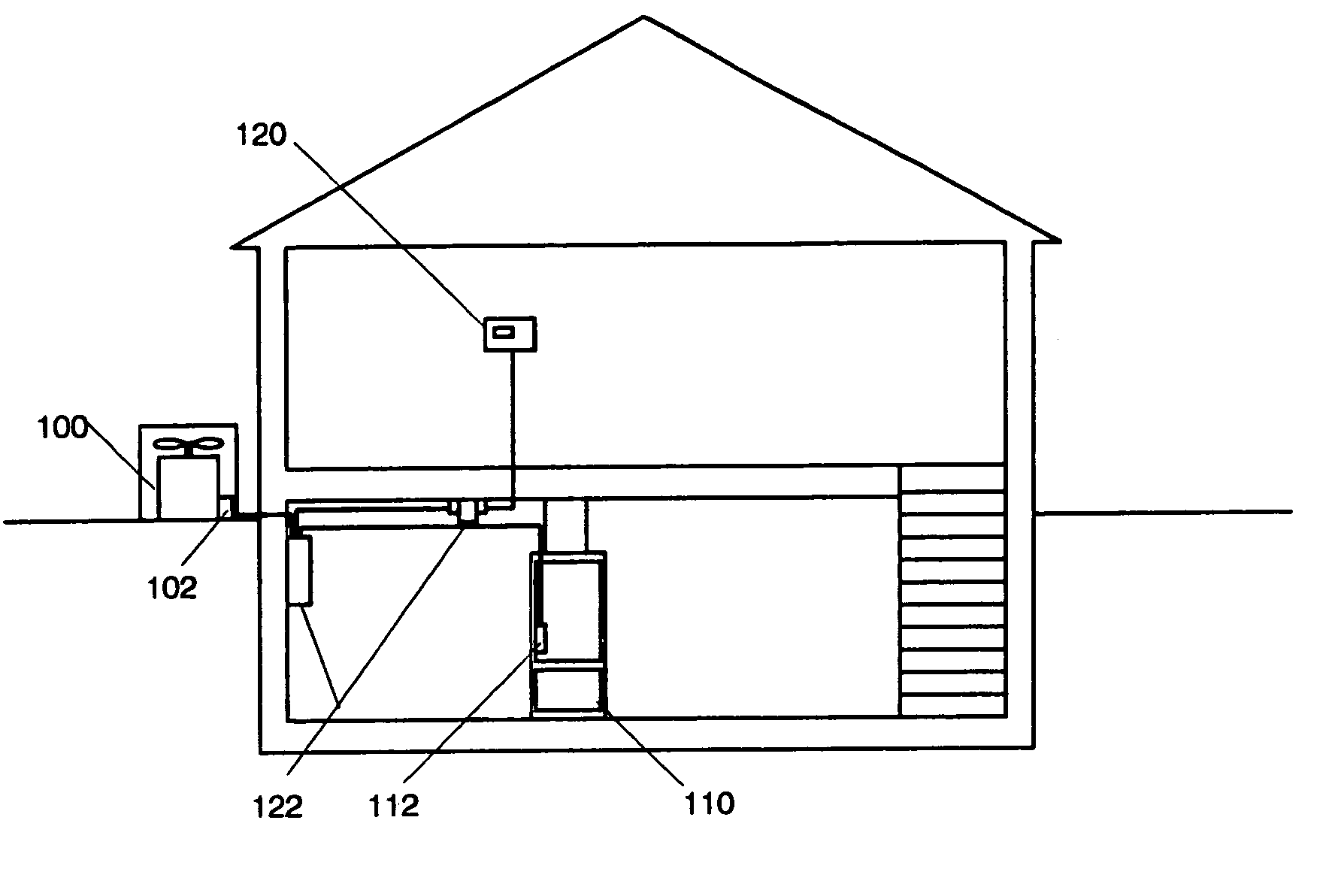
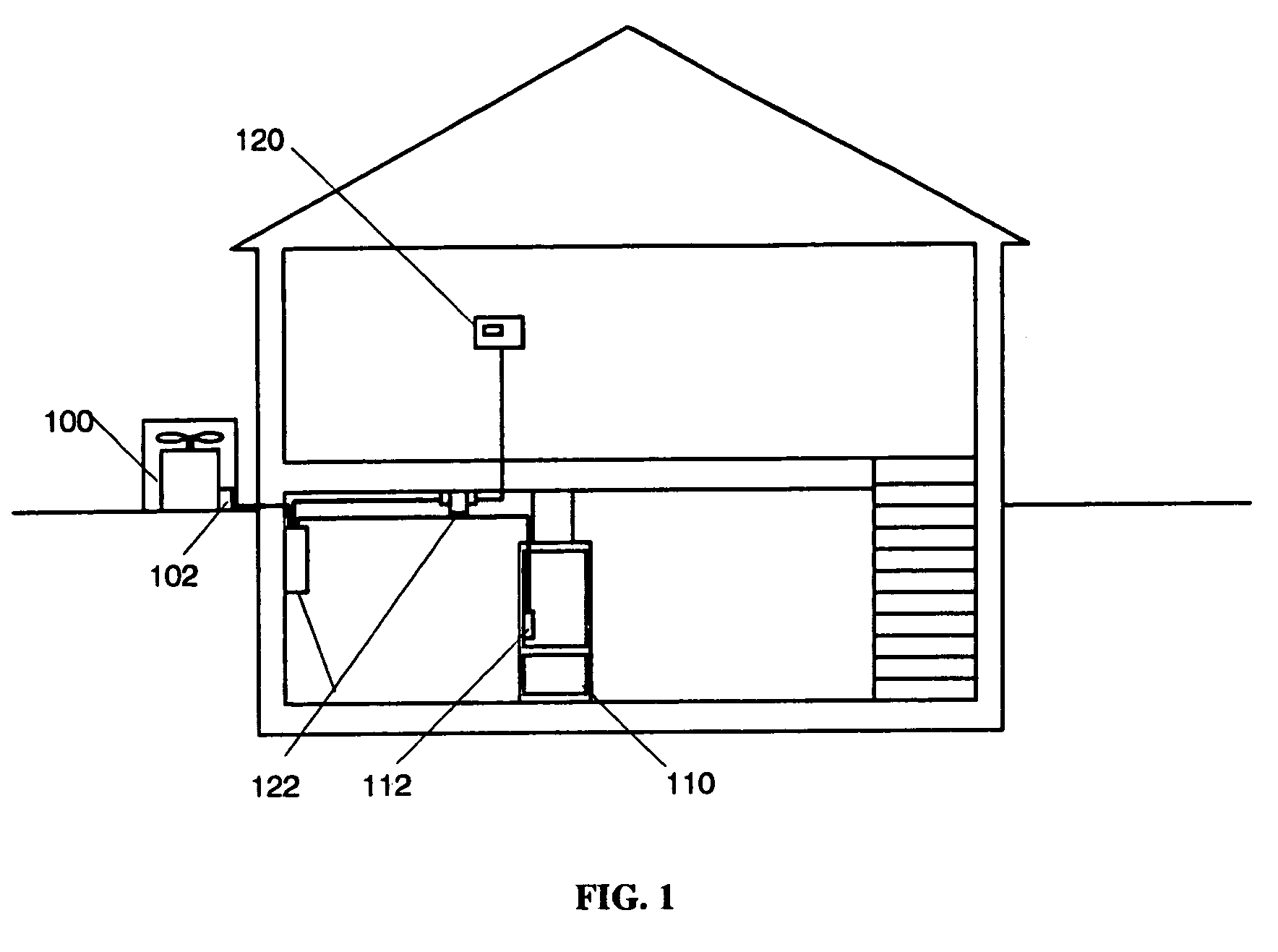
ActiveUS7174239B2Temperature control without auxillary powerTemperature control with auxillary non-electric powerLow voltageControl system
A control is provided for controlling the operation of a climate control system, which includes a processor that is capable of receiving power from a low voltage power supply adapted to be connected to an external alternating current power source, or a second external low voltage power supply. The processor is capable of storing diagnostic information pertaining to the operating status of at least one component of the climate control system. The processor is configured to retrieve stored diagnostic information from memory pertaining to the climate control system and send the diagnostic information to the display means when the processor receives power from the external low voltage power supply and detects the absence of a connection to an external alternating current power source.
Owner:COPELAND COMFORT CONTROL LP
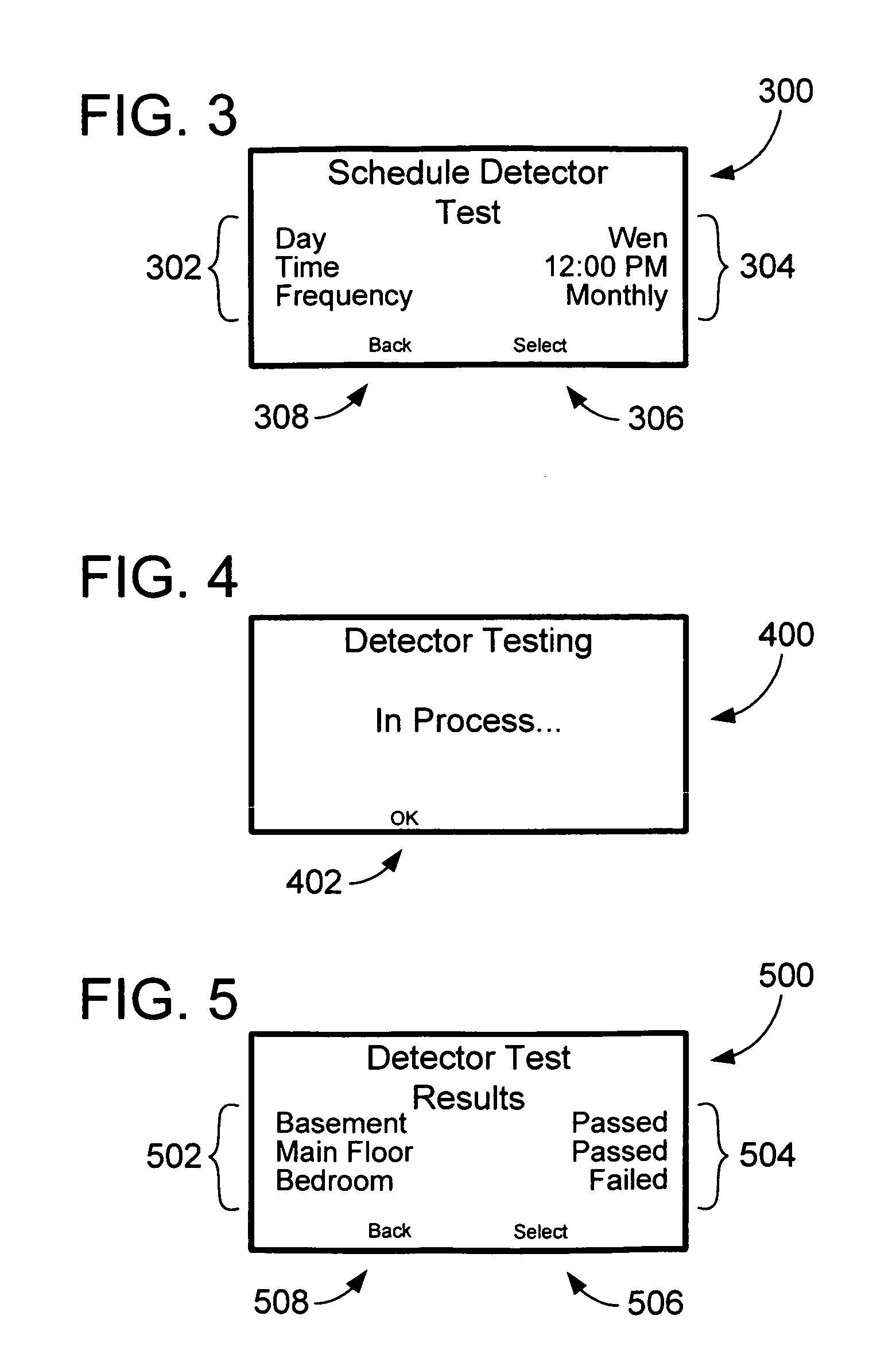
Hazardous condition detection system and method and thermostat for use therewith
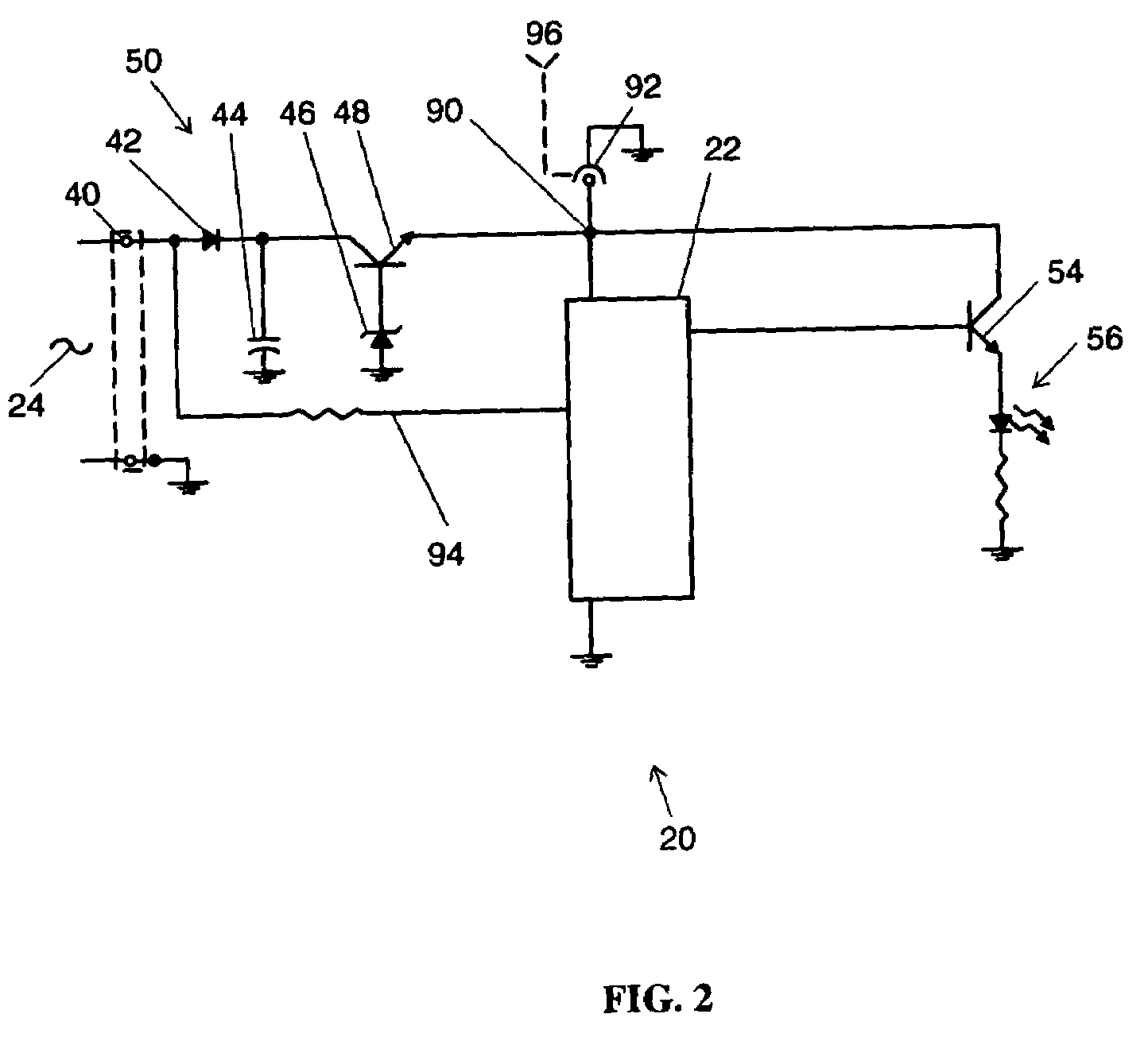
ActiveUS7135965B2Electric signal transmission systemsMechanical apparatusReal-time clockControl signal
An intelligent thermostat communicates with threat detectors to allow periodic remote testing of the detector. The real-time clock and calendar functions of the thermostat allow the consumer to program the day, time, and frequency of the testing. The thermostat then communicates a test control signal to each of the detectors to initiate the self-test. The communication may be wired or wireless. During testing the thermostat displays a detector test screen. Upon completion of the self-test, the thermostat displays a test results screen for user confirmation. This results screen will indicate that the test passed or failed along with any diagnostic information provided by the detector. The thermostat also provides a test initiation screen from which the consumer may initiate a detector self-test manually. Loss of communications with a detector is also communicated to the user, as is the location of the detector that first identified a threat.
Owner:INVENSYS SYST INC
Catheter with optical fiber sensor
An apparatus and method to perform therapeutic treatment and diagnosis of a patient's vasculature through the use of an intravascular device having an optical fiber disposed therein. In an embodiment, the apparatus includes an intravascular device to perform a therapeutic treatment and at least one optical fiber disposed through the intravascular device. The optical fiber is configured to provide diagnostic information before, during, and after the therapeutic treatment. In an embodiment, diagnostic information includes vessel and blood characteristics such as hemodynamic characteristics, hematological parameters related to blood and blood components, and thermal parameters of the vasculature.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
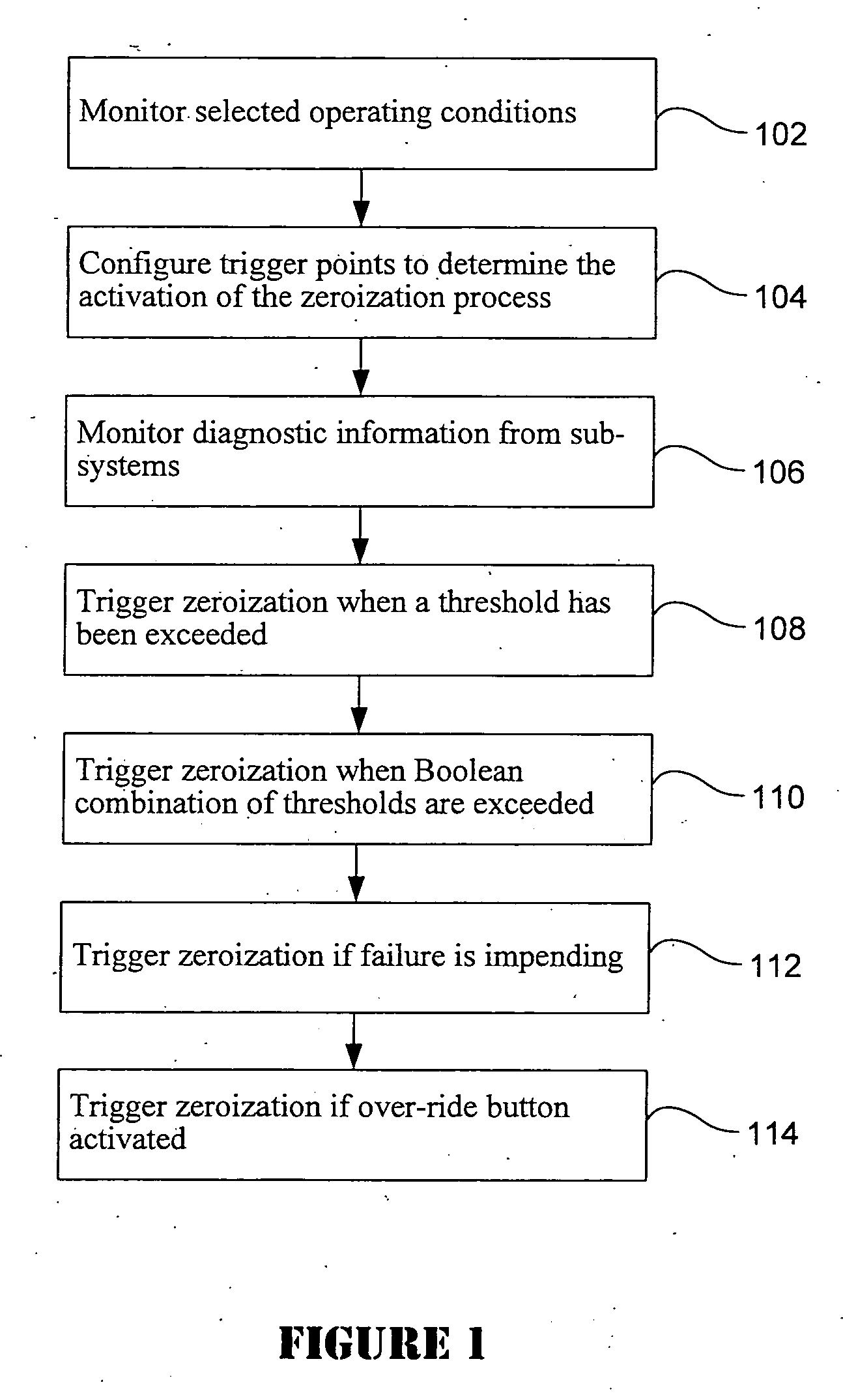
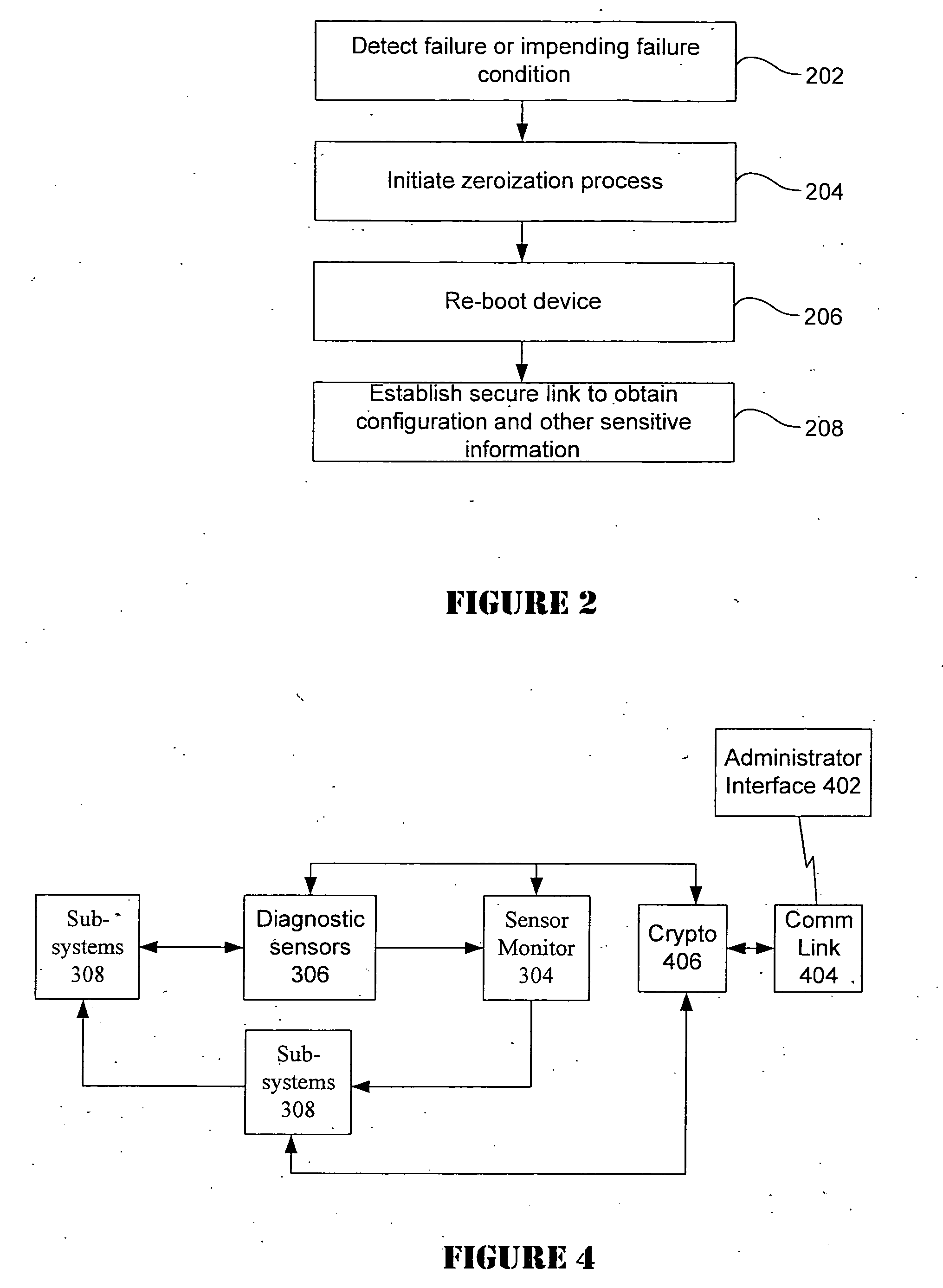
Method and electronic device for triggering zeroization in a electronic device
A method and apparatus for initiating a zeroization process in an electronic device is provided. Diagnostic information is provided by a plurality of sub-systems such that when one or more conditions are detected that are expected to cause the electronic device to experience a failure in the near future or if the electronic device appears to have been compromised, then the zeroization process is triggered.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Integration of fluids and reagents into self-contained cartridges containing particle and membrane sensor elements
InactiveUS20060257941A1Facilitate digital/optical acquisition of fluorescent signalSamplingMaterial analysis by optical meansPoint of careAnalyte
Described herein is an analyte detection device and method related to a portable instrument suitable for point-of-care analyses. In some embodiments, a portable instrument may include a disposable cartridge, an optical detector, a sample collection device and / or sample reservoir, reagent delivery systems, fluid delivery systems, one or more channels, and / or waste reservoirs. Use of a portable instrument may reduce the hazard to an operator by reducing an operator's contact with a sample for analysis. The device is capable of obtaining diagnostic information using cellular- and / or particle-based analyses and may be used in conjunction with membrane- and / or particle-based analysis cartridges. Analytes, including proteins and cells and / or microbes may be detected using the membrane and / or particle based analysis system.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com