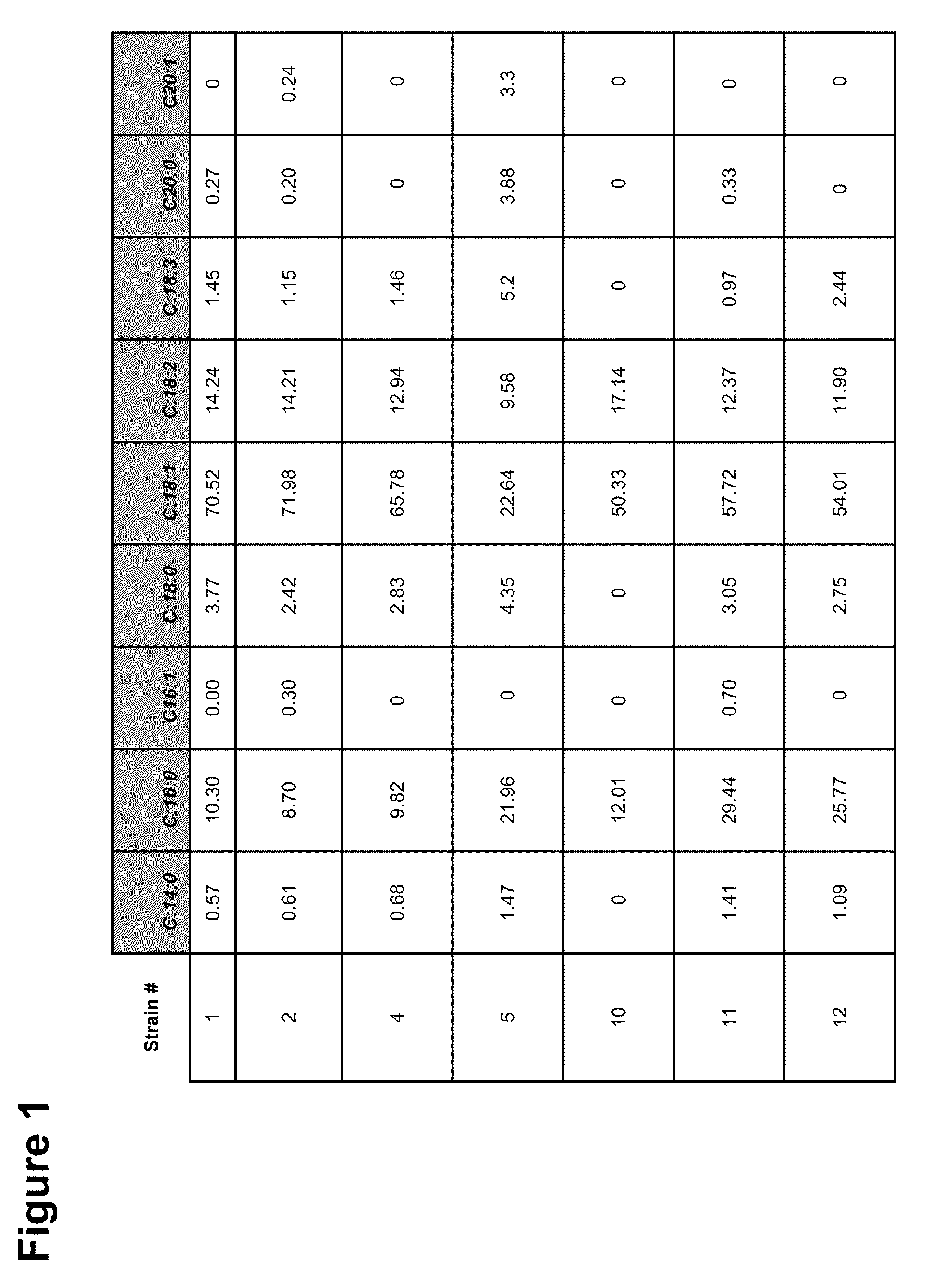
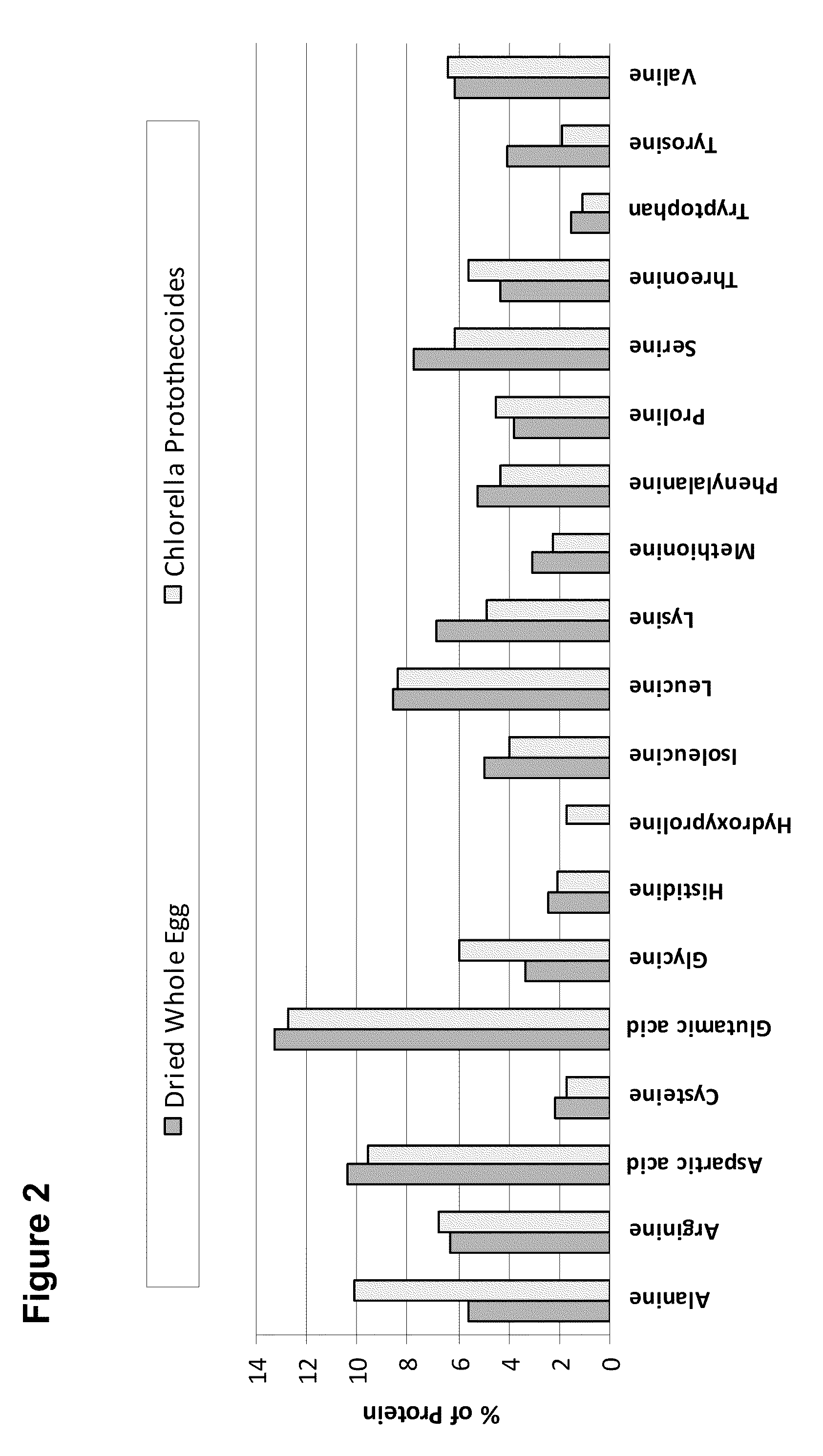
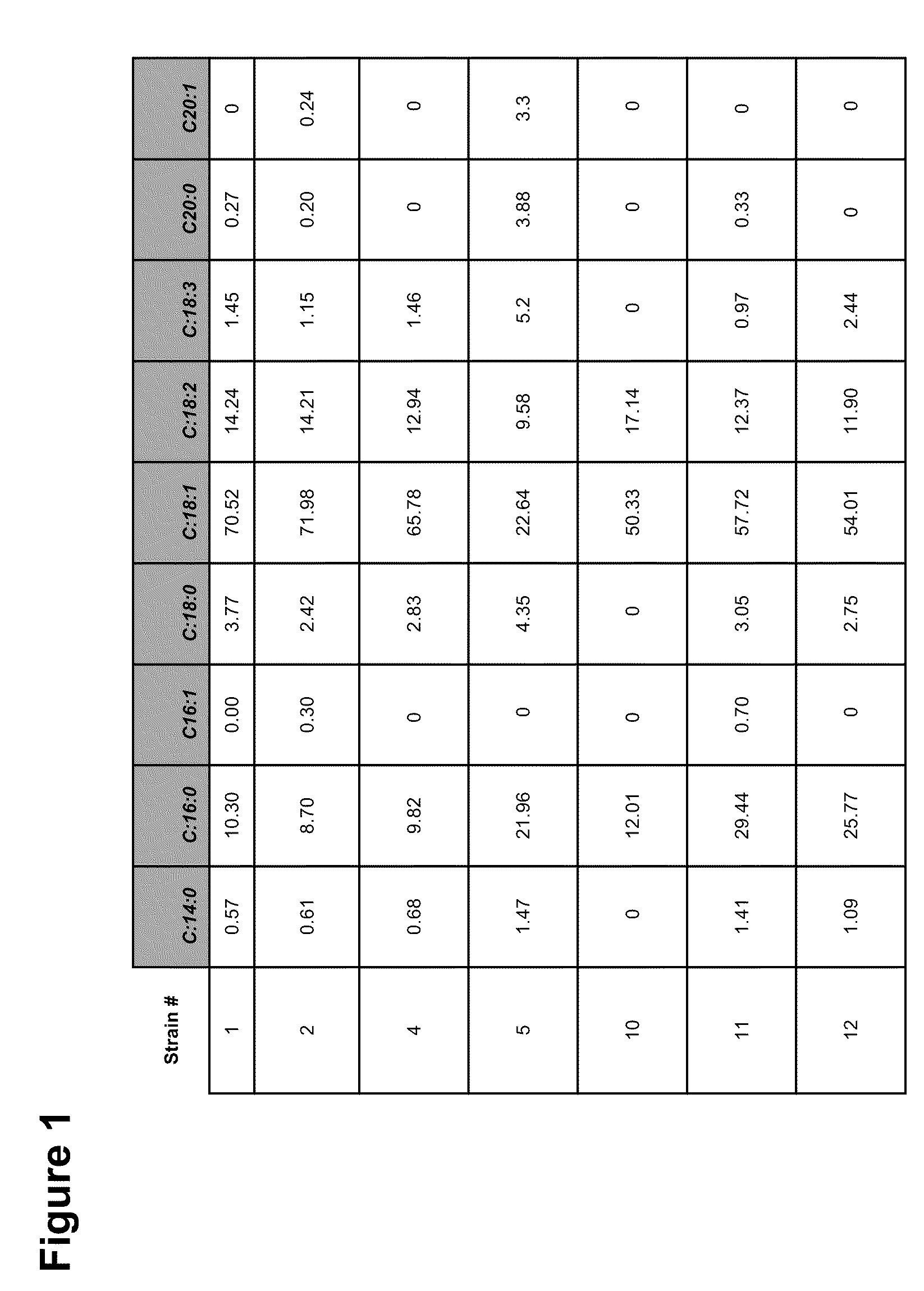
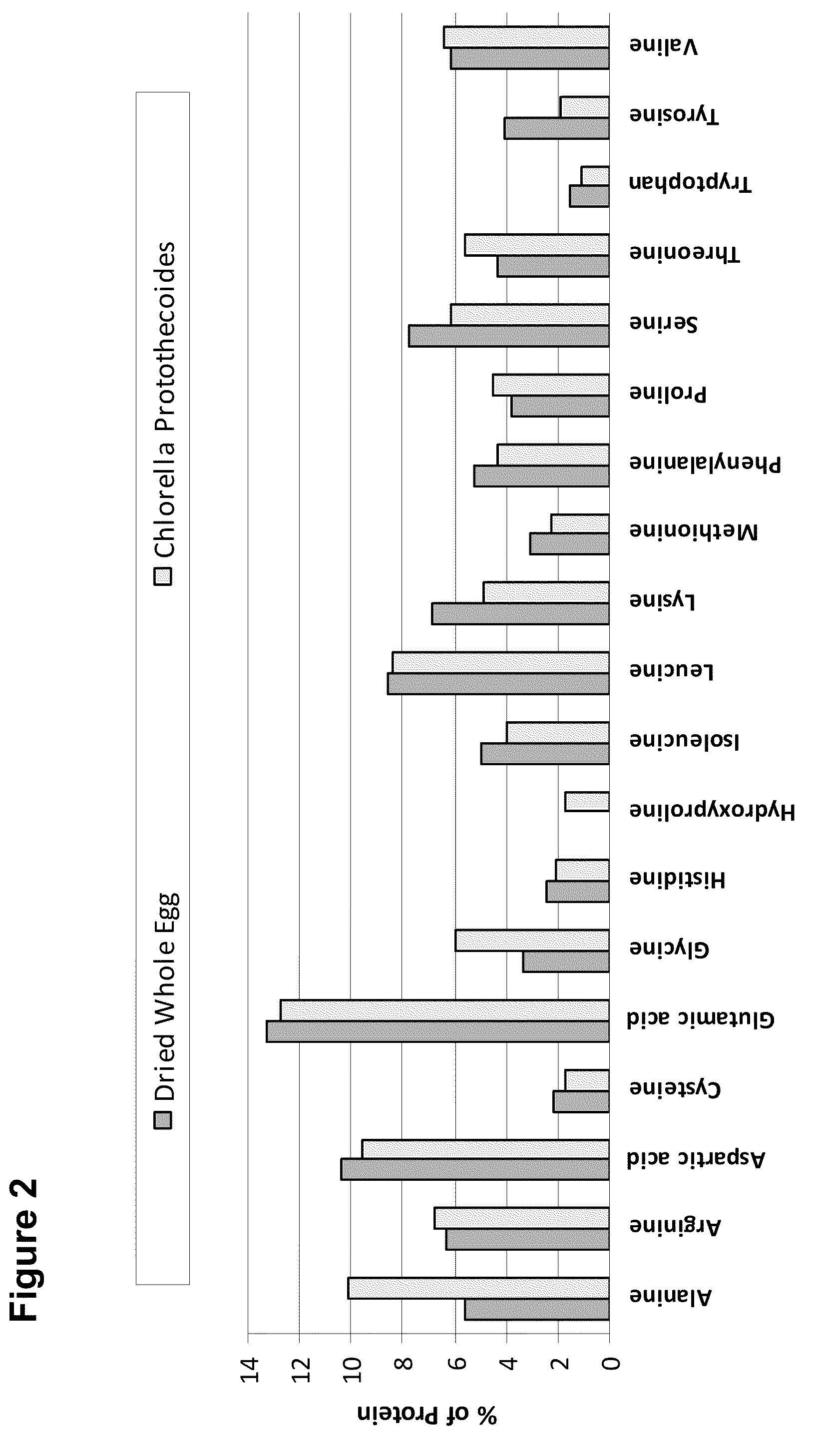
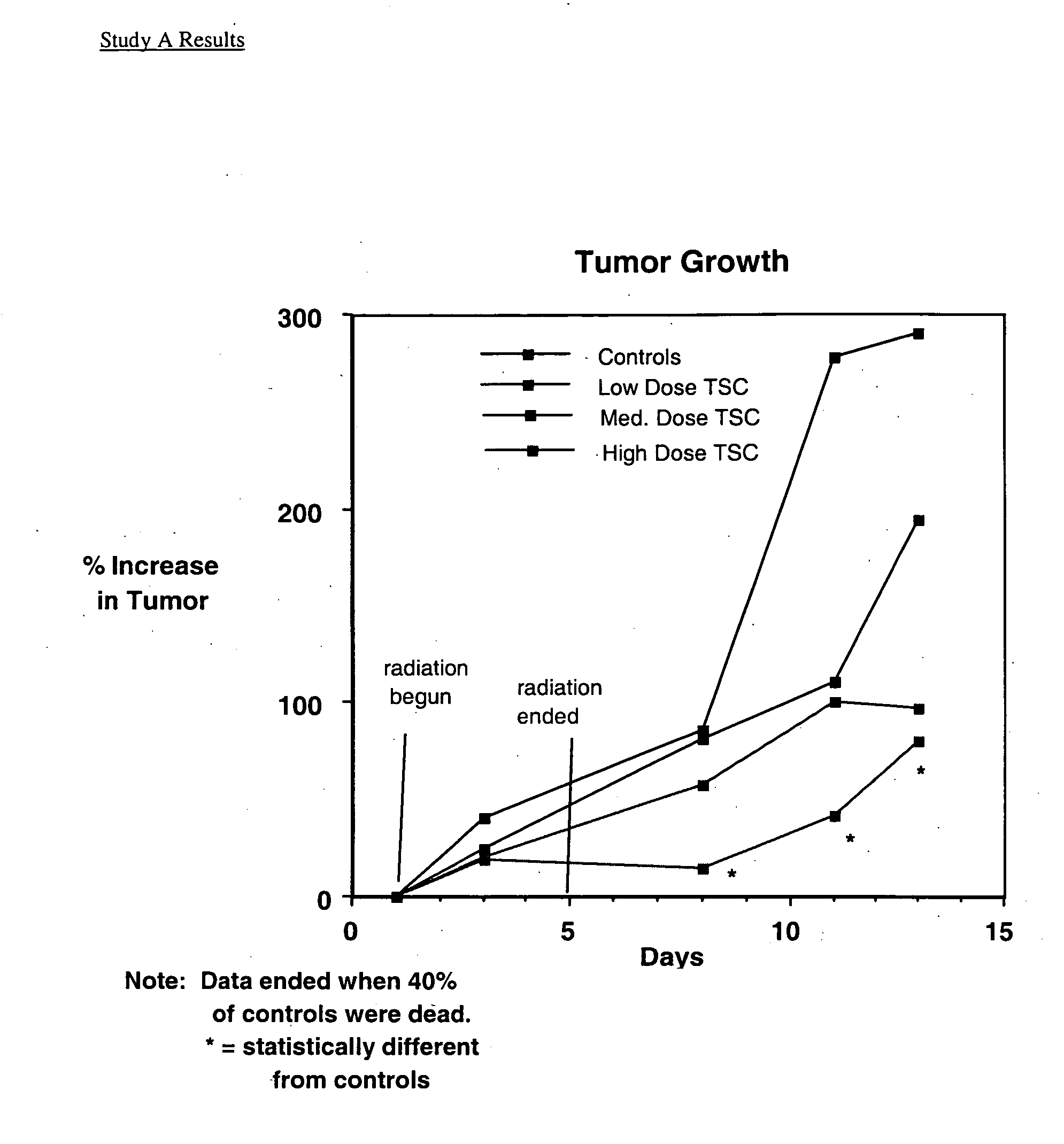
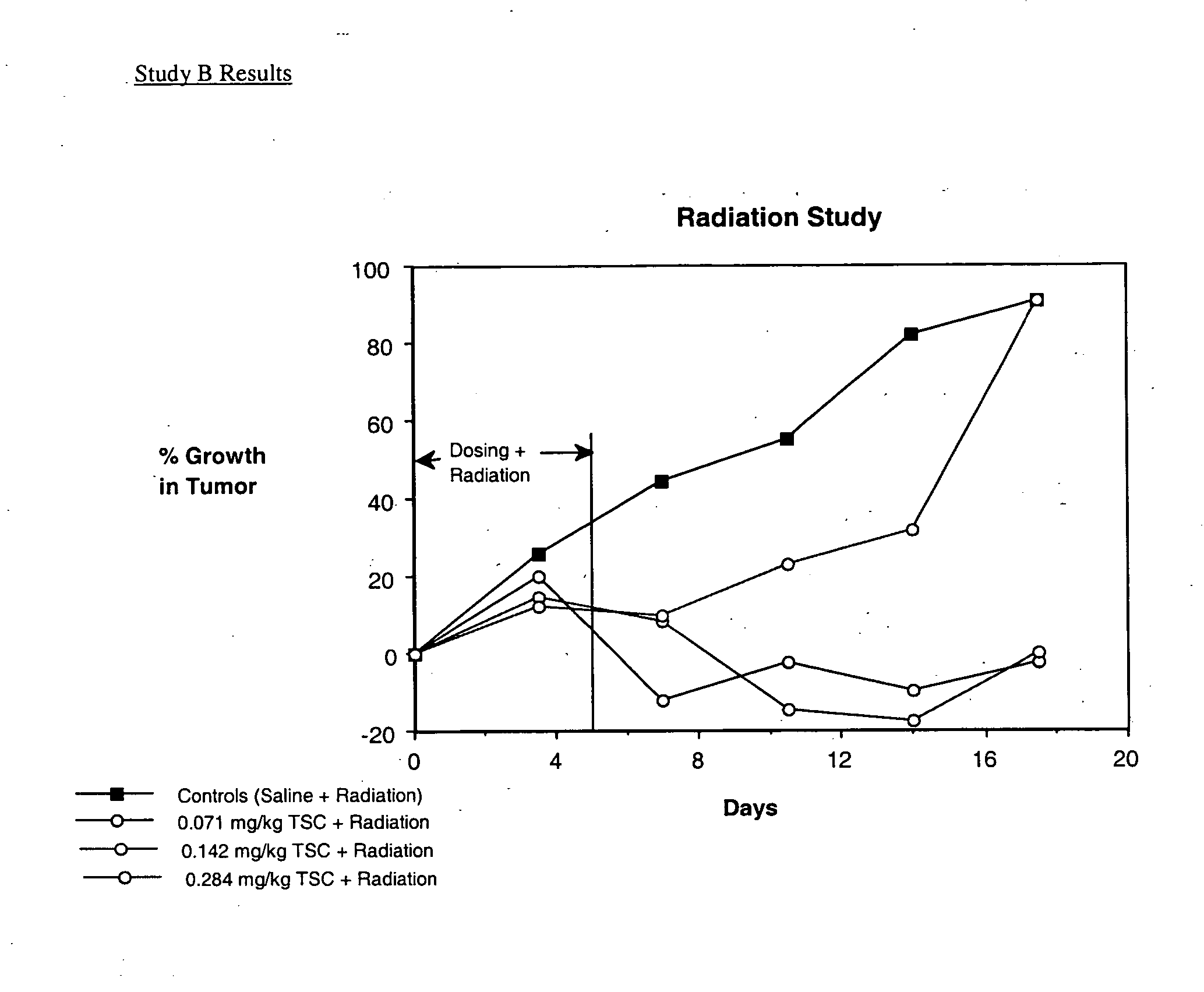
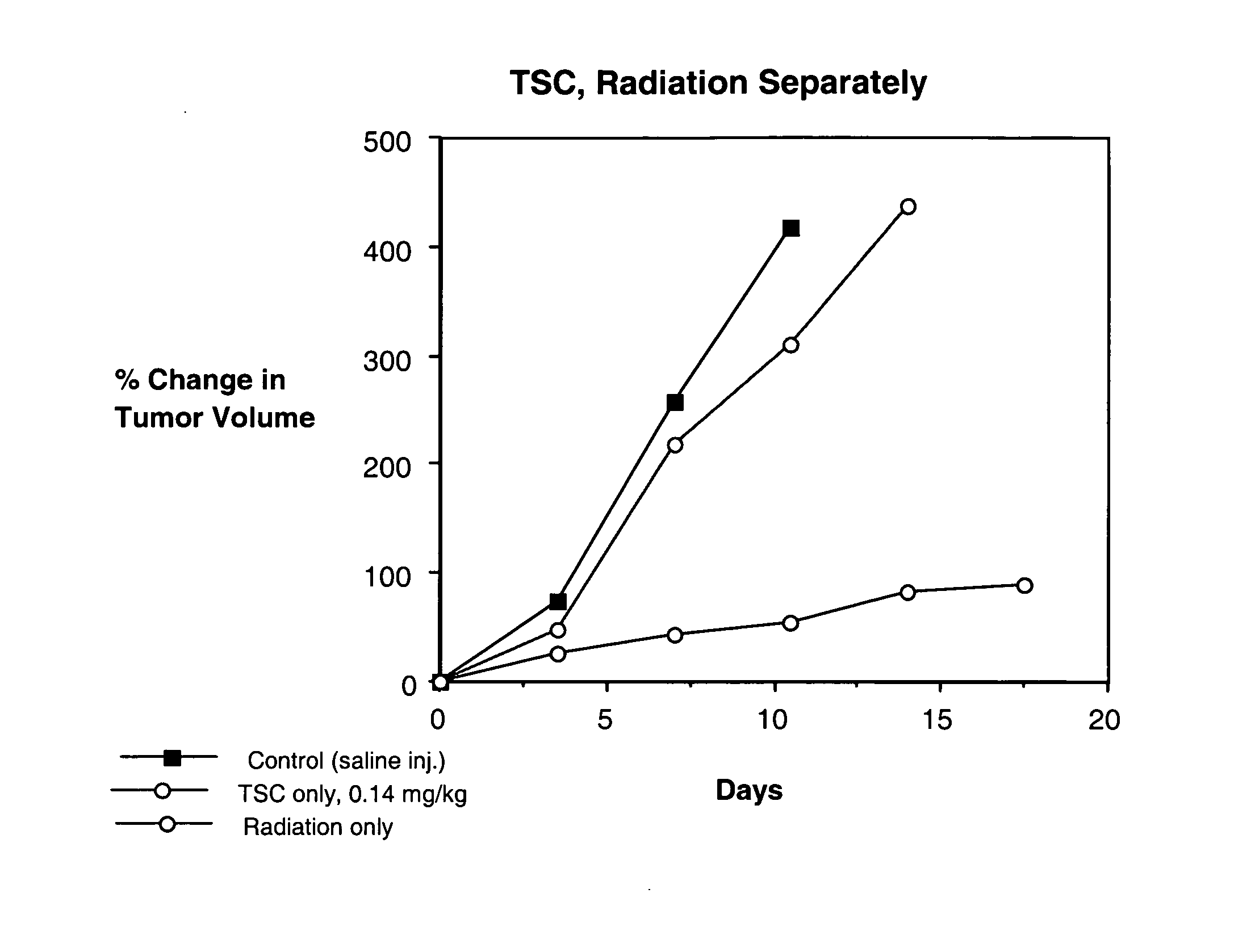
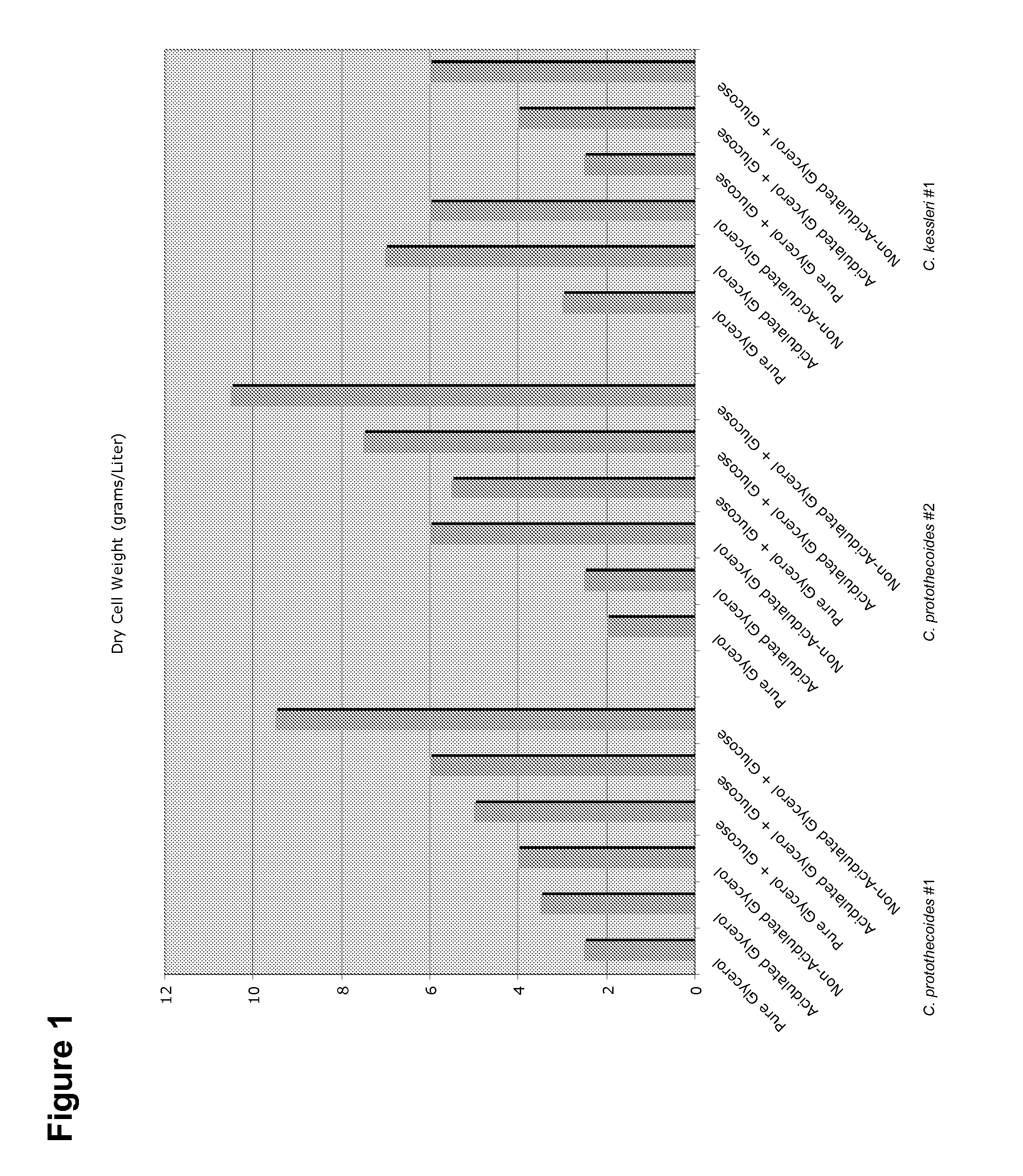
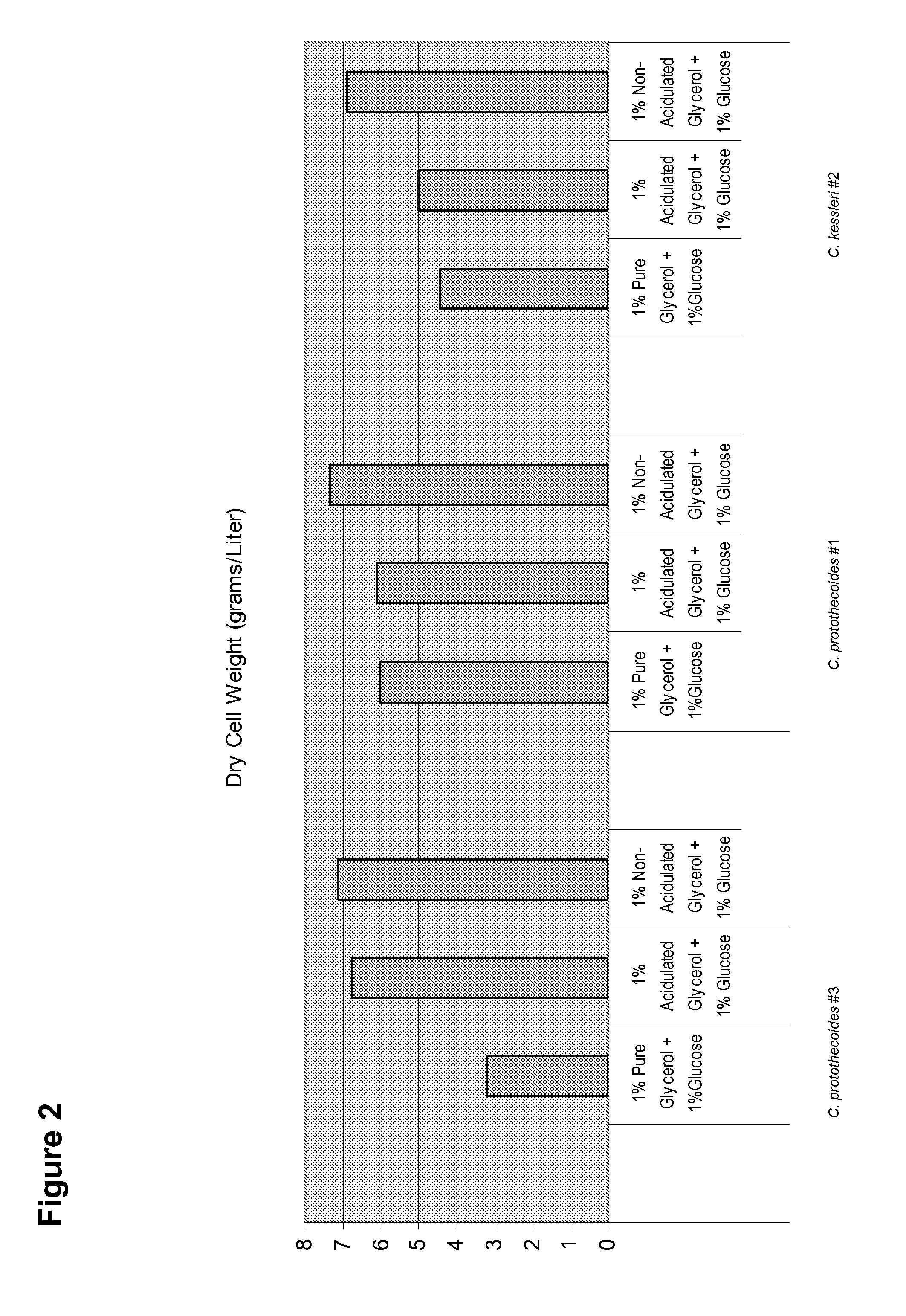
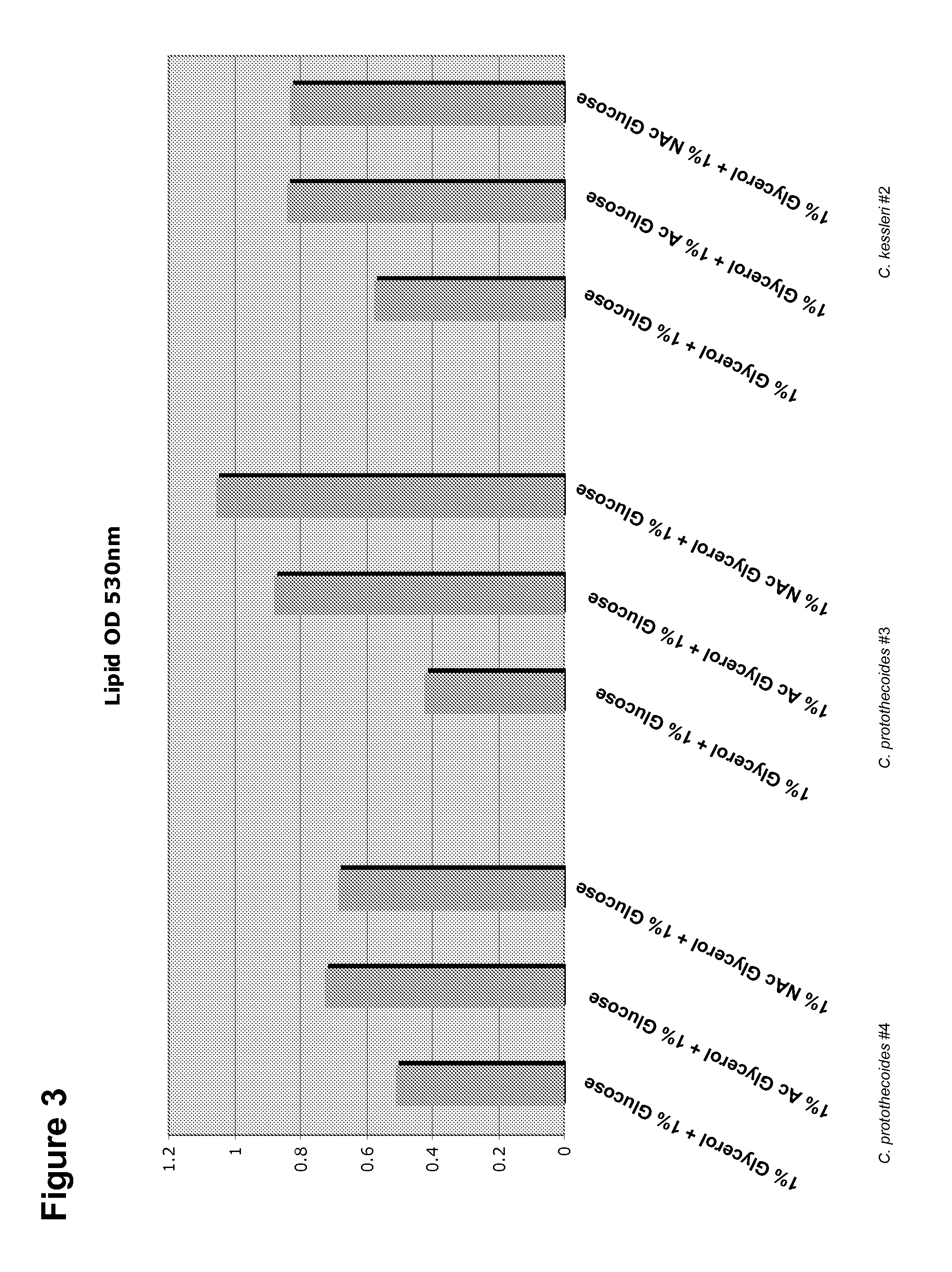
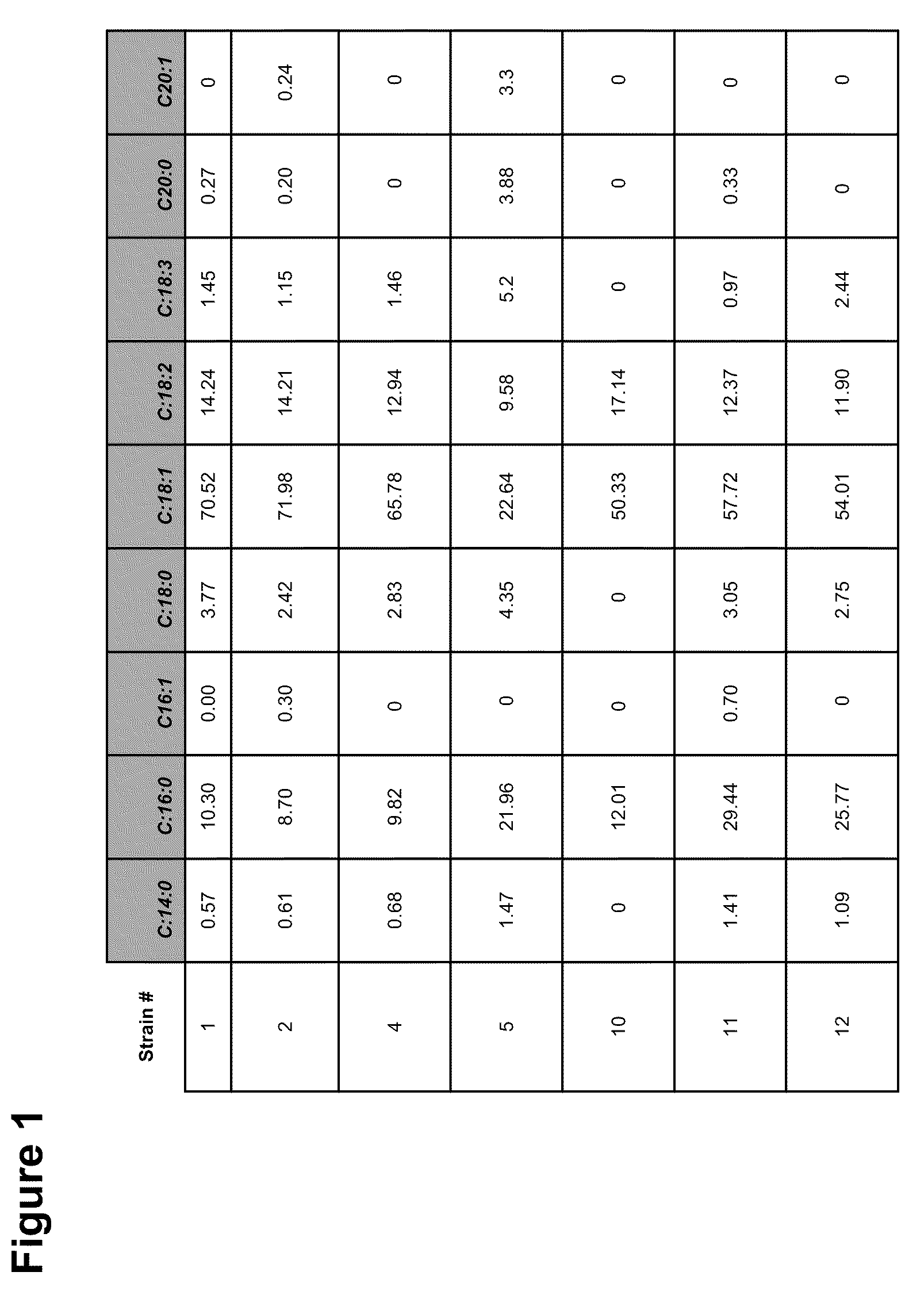
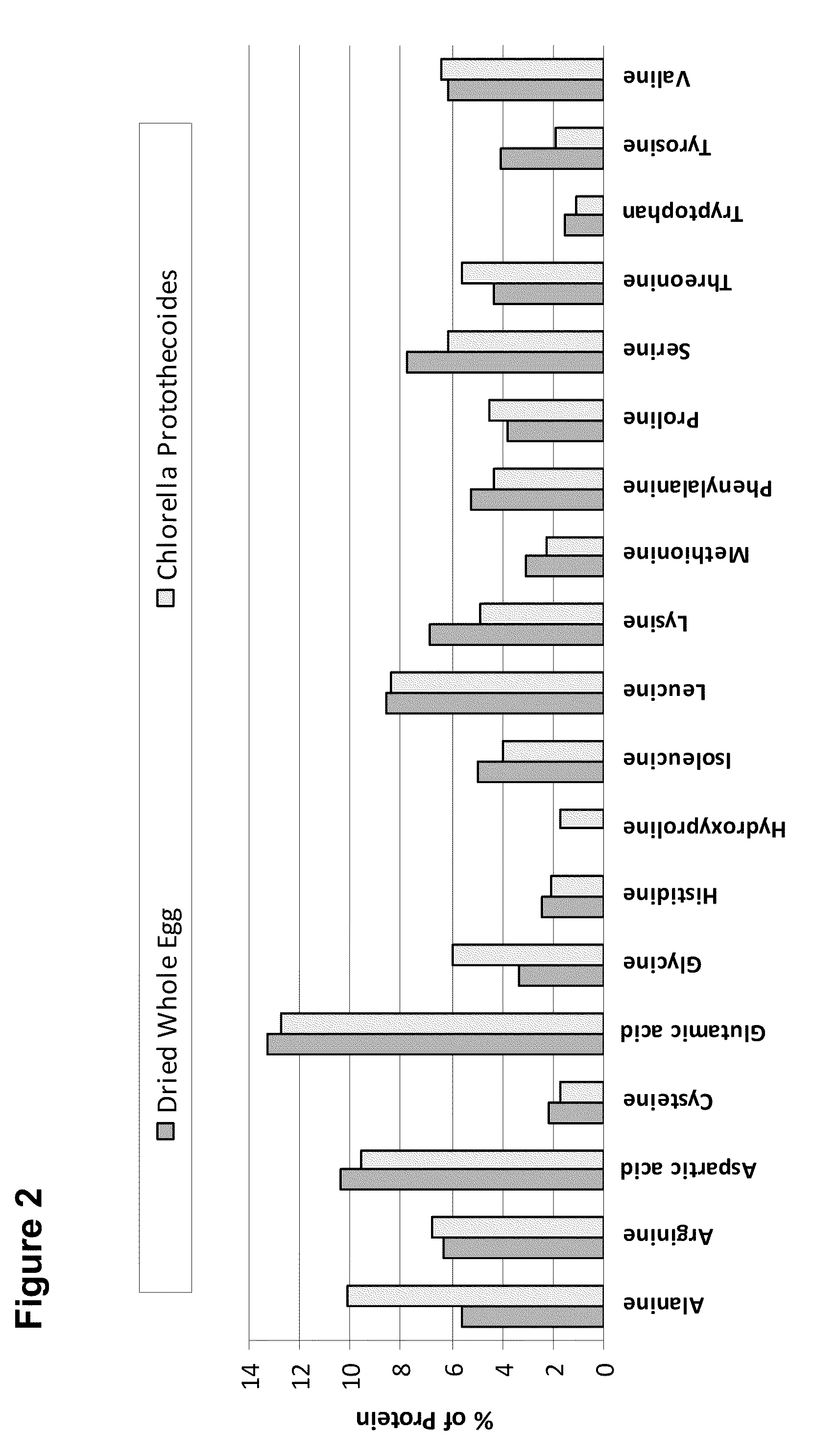
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1211 results about "Carotenoid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Carotenoids (/kəˈrɒtɪnɔɪd/), also called tetraterpenoids, are yellow, orange, and red organic pigments that are produced by plants and algae, as well as several bacteria and fungi. Carotenoids give the characteristic color to pumpkins, carrots, corn, tomatoes, canaries, flamingos, and daffodils. Carotenoids can be produced from fats and other basic organic metabolic building blocks by all these organisms. The only animals known to produce carotenoids are aphids and spider mites, which acquired the ability and genes from fungi or it is produced by endosymbiotic bacteria in whiteflies. Carotenoids from the diet are stored in the fatty tissues of animals, and exclusively carnivorous animals obtain the compounds from animal fat. In the human diet, absorption of carotenoids is improved when consumed with fat in a meal. Cooking carotenoid-containing vegetables in oil increases carotenoid bioavailability.
Breed-specific canine food formulations
InactiveUS6156355AUnique shapeManaged fat levelMilk preparationAnimal feeding stuffFood formulationAdditive ingredient
Breed-specific dog food formulations that comprise chicken meat as the major ingredient, rice as the predominant (or sole) grain source, fruit and / or vegetable fiber as the primary or sole fiber source, unique fat and antioxidant blend, vitamins, herbs and spices, carotenoids, and no corn or artificial colors, preservatives, flavors or sugars are provided.
Owner:BIG HEART PET INC
Method and apparatus for noninvasive measurement of carotenoids and related chemical substances in biological tissue
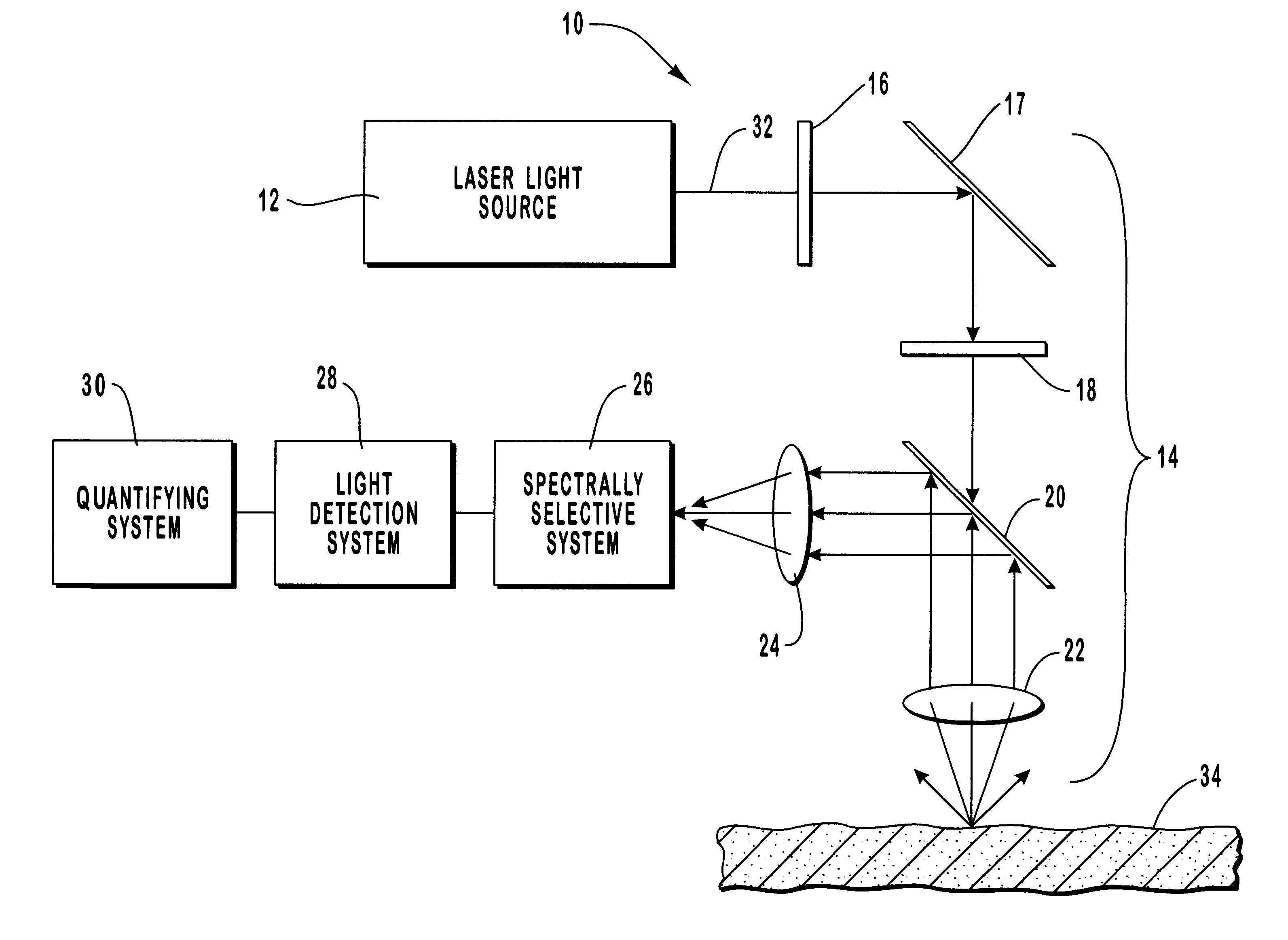
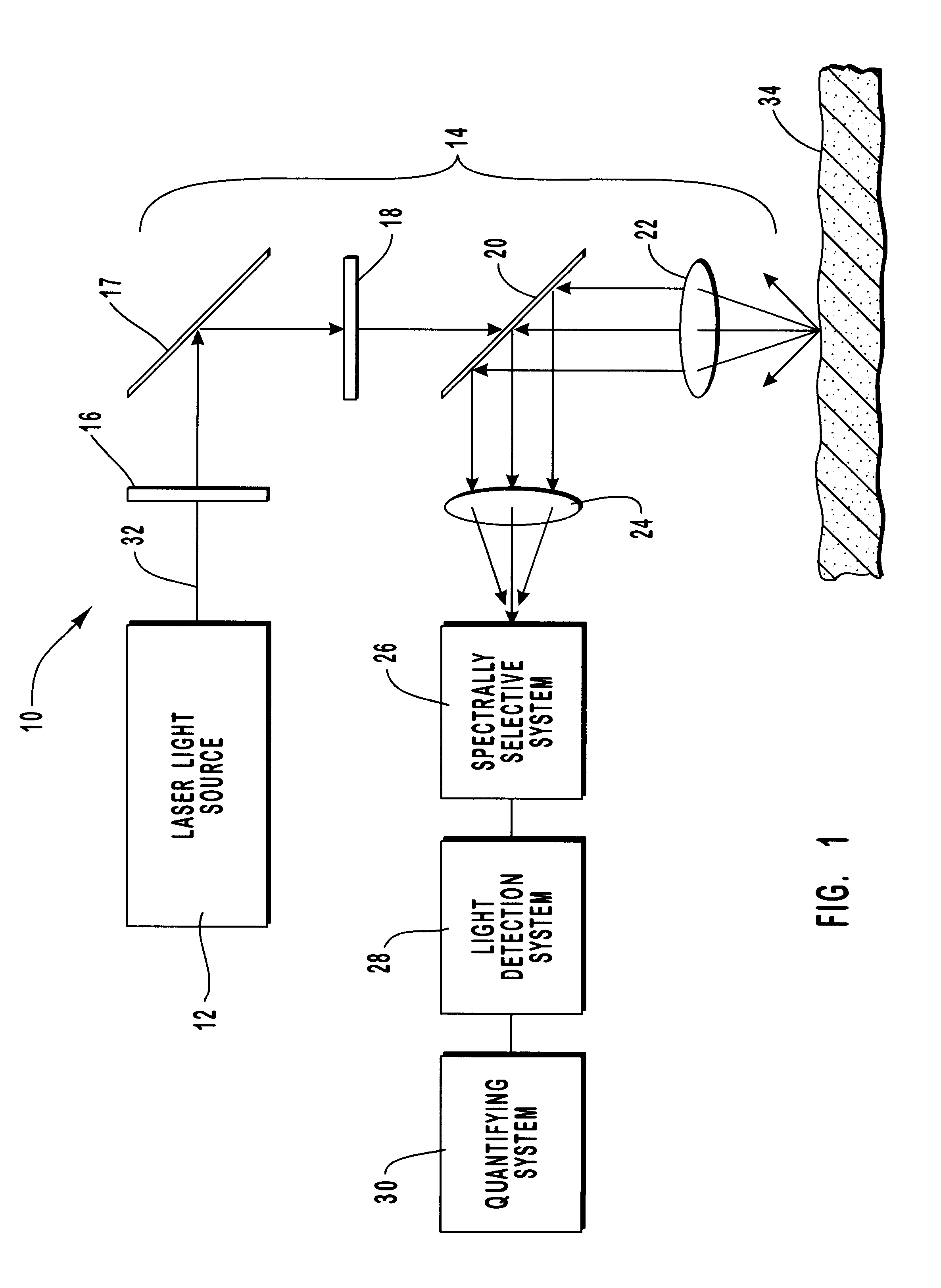
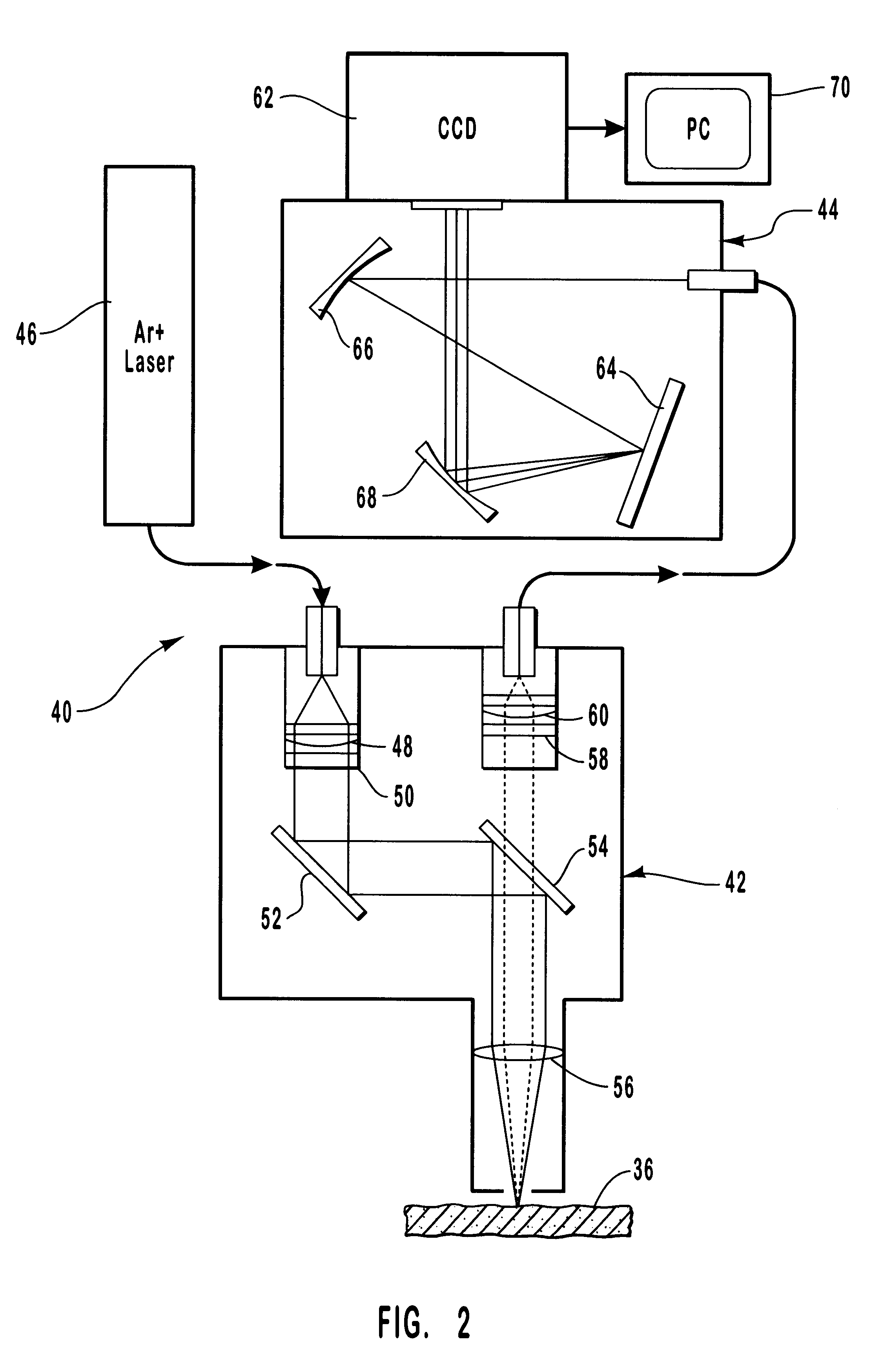
InactiveUS6205354B1Rapid and noninvasive and quantitative measurementRiskRadiation pyrometrySurgeryResonance Raman spectroscopyAntioxidant
A method and apparatus are provided for the determination of levels of carotenoids and similar chemical compounds in biological tissue such as living skin. The method and apparatus provide a noninvasive, rapid, accurate, and safe determination of carotenoid levels which in turn can provide diagnostic information regarding cancer risk, or can be a marker for conditions where carotenoids or other antioxidant compounds may provide diagnostic information. Such early diagnostic information allows for the possibility of preventative intervention. The method and apparatus utilize the technique of resonance Raman spectroscopy to measure the levels of carotenoids and similar substances in tissue. In this technique, laser light is directed upon the area of tissue which is of interest. A small fraction of the scattered light is scattered inelastically, producing the carotenoid Raman signal which is at a different frequency than the incident laser light, and the Raman signal is collected, filtered, and measured. The resulting Raman signal can be analyzed such that the background fluorescence signal is subtracted and the results displayed and compared with known calibration standards.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Method for supplementing the diet
InactiveUS6579544B1Increased susceptibilityPrevent diseaseHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideDietary supplementAlpha-Lipoic Acid
A dietary supplement blend composition is disclosed, the basic formulation of the composition containing vitamins, minerals, and carotenoids. The composition can also contain bioflavonoids, cartilage protectors such as glucosamine or chondroitin, alpha-lipoic acid, coenzyme Q10, and a source of omega-3 fatty acids such as flax seed oil. The composition is beneficial for improving health and preventing disease, particularly for degenerative conditions. A method for supplementing the diet is also disclosed, wherein the quantity of daily rations of the dietary supplement blend composition is determined based on the person's age, body weight, and quality of diet.
Owner:NUTRIEX
Microparticles for Oral Delivery
The invention provides microbeads containing oil-associated biologically active compounds and methods for their manufacture and use. The microbeads consist of a soluble complex of non-digestible polymer and emulsifier with oil-associated biologically active compounds embedded in a matrix of digestible polymer. The disclosed microbead complex protects the biologically active compounds, such as vitamins, fish oil and carotenoids, from oxidation, taste and odor degradation. The disclosed microbeads also provide protection from the stomach digestive distraction, and allows for the delivery of the biologically active compounds in the intestine.
Owner:INTERVET INC
Soaps Produced from Oil-Bearing Microbial Biomass and Oils
ActiveUS20090305942A1Improve efficiencyLow costSoap detergents with organic compounding agentsBiofuelsMicroorganismMicrobial oil
Soap and cosmetic products can be made from oil-bearing microbial biomass via the alkaline hydrolysis of glycerolipids and fatty acid esters to fatty acid salts. The saponified microbial oils / lipids can be combined with a variety of additives to produce compositions for use as soaps and other cosmetic products, which may also contain other constituents of the biomass, including unsaponified oils, glycerol and carotenoids, among others.
Owner:CORBION BIOTECH INC
Microalgae-Based Beverages
InactiveUS20100297295A1Great tasteLower levelMilk preparationDough treatmentEmulsionAdditive ingredient
The invention provides novel beverages and raw materials for the manufacture thereof, such beverage and raw materials containing microalgae of various species with varying components. Attributes of the microalgal biomass used in the invention include nutrition-providing materials such as carotenoids, dietary fiber, tocotrienols and tocopherols, and varying lipid compositions, particularly low levels of saturated lipids. Attributes of the microalgal biomass used in the invention include structural attributes such as improved mouth feel compared to alternative milk products such as soy milk and rice milk. The novel beverages provide delivery systems for high nutrition materials found in microalgae. The invention provides a new category of finished beverages based on microalgae (such as refrigerated and shelf stable liquids and emulsions) as well as compositions for augmenting properties of current beverages through inclusion of novel microalgae-based materials as ingredients.
Owner:TERRAVIA HLDG INC
Reduced Pigmentation Microalgae Strains and Products Therefrom
InactiveUS20100297292A1Reduced colorationIncrease rangeMilk preparationDough treatmentHypopigmentationCarotenoid
The invention provides unique and novel strains of microalgae that have been subjected to non-transgenic methods of mutation sufficient to reduce the coloration of biomass produced by the strains. Biomass produced from such strains can be used in the manufacture of baked goods, gluten free foods, beverages, high lipid algal flours, and other foods. Pigments such as carotenoids and chlorophyll can be undesirable for consumer acceptance when incorporated into foods such as mayonnaise, yogurt, and white sauces that are not traditionally associated with colors such as yellow, red, orange and green. Some pigments, such as chlorophyll, can also create undesirable taste profiles. Use of reduced pigment microalgal biomass expands the range of food products that can be manufactured with healthy lipid profiles. High protein containing biomass of the invention, also reduced in pigmentation, is also incorporated into products such as meat analogues, nutritional bars and meal replacement beverages. The reduced pigmentation microalgae also allow for incorporation of higher amounts of biomass into certain food products that could otherwise be achieved using highly pigmented microalgal biomass. Methods of generating novel reduced pigment microalgae are disclosed herein. The strains provided by the invention are also useful in the manufacture of healthy, neutral colored extracted triglyceride oils.
Owner:TERRAVIA HLDG INC
Production of carotenoids in oleaginous yeast and fungi
ActiveUS7851199B2Improve oilinessAlter their carotenoid-producing capabilitiesSenses disorderFungiYeastCarotenoid
The present invention provides systems for producing engineered oleaginous yeast or fungi that express carotenoids.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Trans carotenoids, their synthesis, formulation and uses
The invention relates to trans carotenoid compounds and salts thereof as well as compositions thereof, methods for making them, and uses thereof. These compounds are useful in improving diffusivity of oxygen between red blood cells and body tissues in mammals including humans.
Owner:DIFFUSION PHARMA LLC
Soaps produced from oil-bearing microbial biomass and oils
ActiveUS8119583B2Low costImprove efficiencySoap detergents with organic compounding agentsCosmetic preparationsMicrobial oilGlycerol
Soap and cosmetic products can be made from oil-bearing microbial biomass via the alkaline hydrolysis of glycerolipids and fatty acid esters to fatty acid salts. The saponified microbial oils / lipids can be combined with a variety of additives to produce compositions for use as soaps and other cosmetic products, which may also contain other constituents of the biomass, including unsaponified oils, glycerol and carotenoids, among others.
Owner:CORBION BIOTECH INC
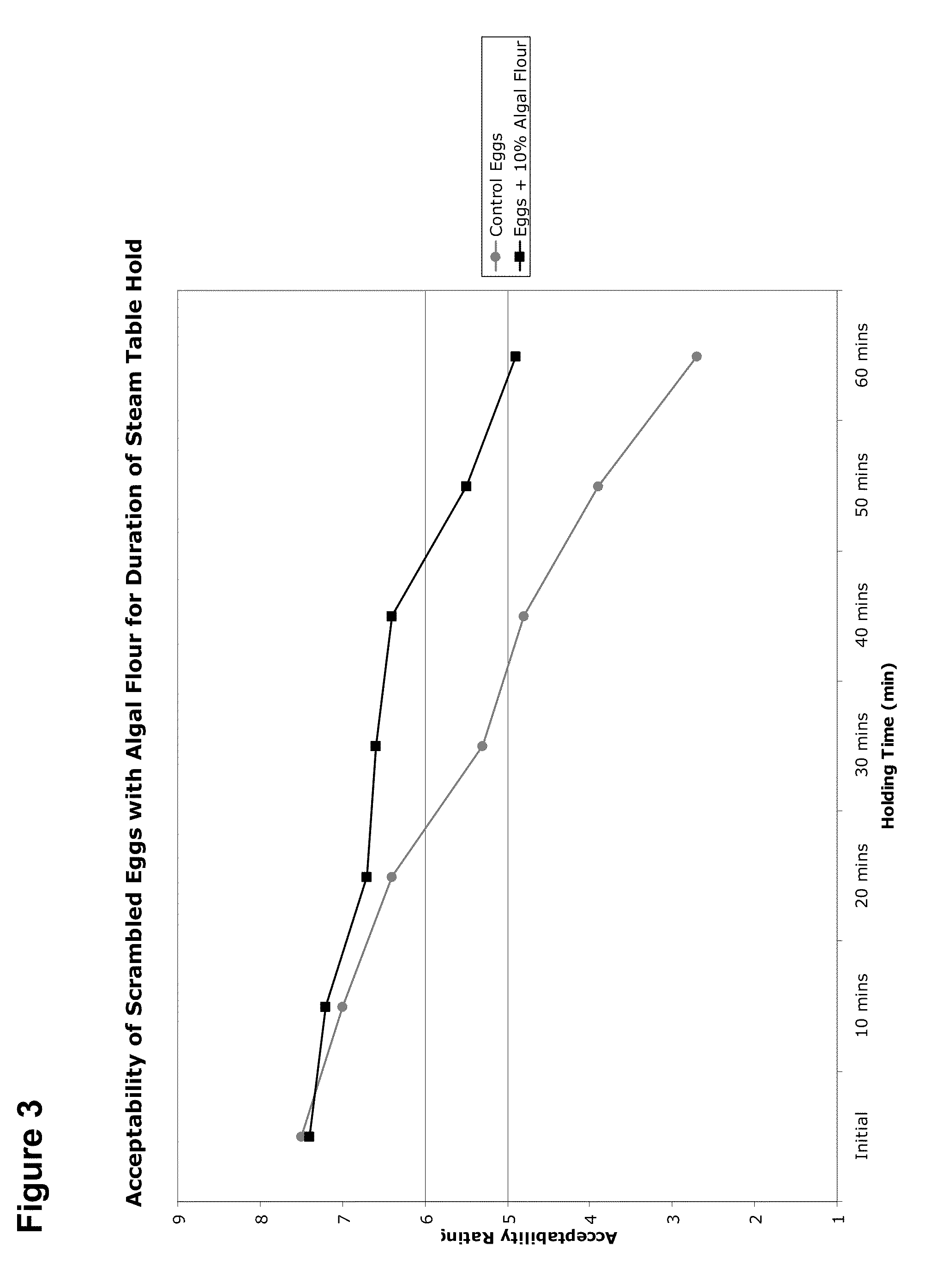
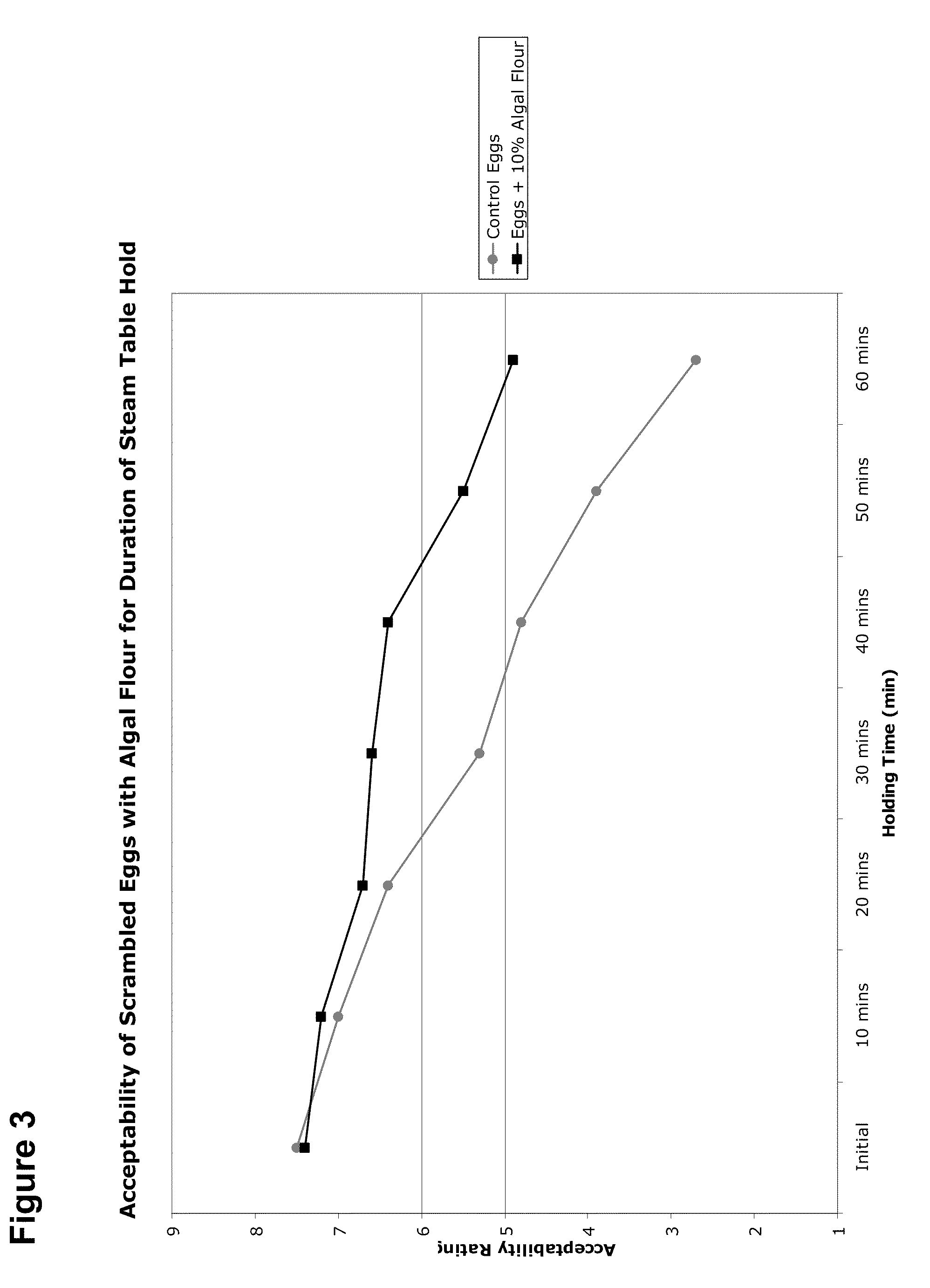
Egg Products Containing Microalgae
The compositions and methods of the invention relate to the creation of food products based on eggs, wherein the productions contain various raw materials made from microalgae in different forms. Some forms include high levels of monounsaturated oil, dietary fiber, carotenoids, and digestible crude protein. Provided herein are methods and compositions for enhancing food stability at elevated temperature during extended periods of storage in hydrated egg products. The microalgae-derived materials are provided as dry or hydrated homogenates made from heterotrophically produced microalgae of varying genera, species and strain. Weight / weight levels of saturated fats and cholesterol are reduced in egg products of the invention, while dietary fiber is increased. Blends of liquid or dried egg with liquid or dried algae are provided, as well as methods of manufacturing and formulating the blends. Unique combinations of egg whites and microalgae are also provided for manufacture of very low cholesterol egg products. In some embodiments, the textural characteristics of powdered eggs are altered to be more like the textural characteristics of liquid eggs through the inclusion of dietary fiber and other moisture-retaining properties of microalgal biomass.
Owner:TERRAVIA HLDG INC
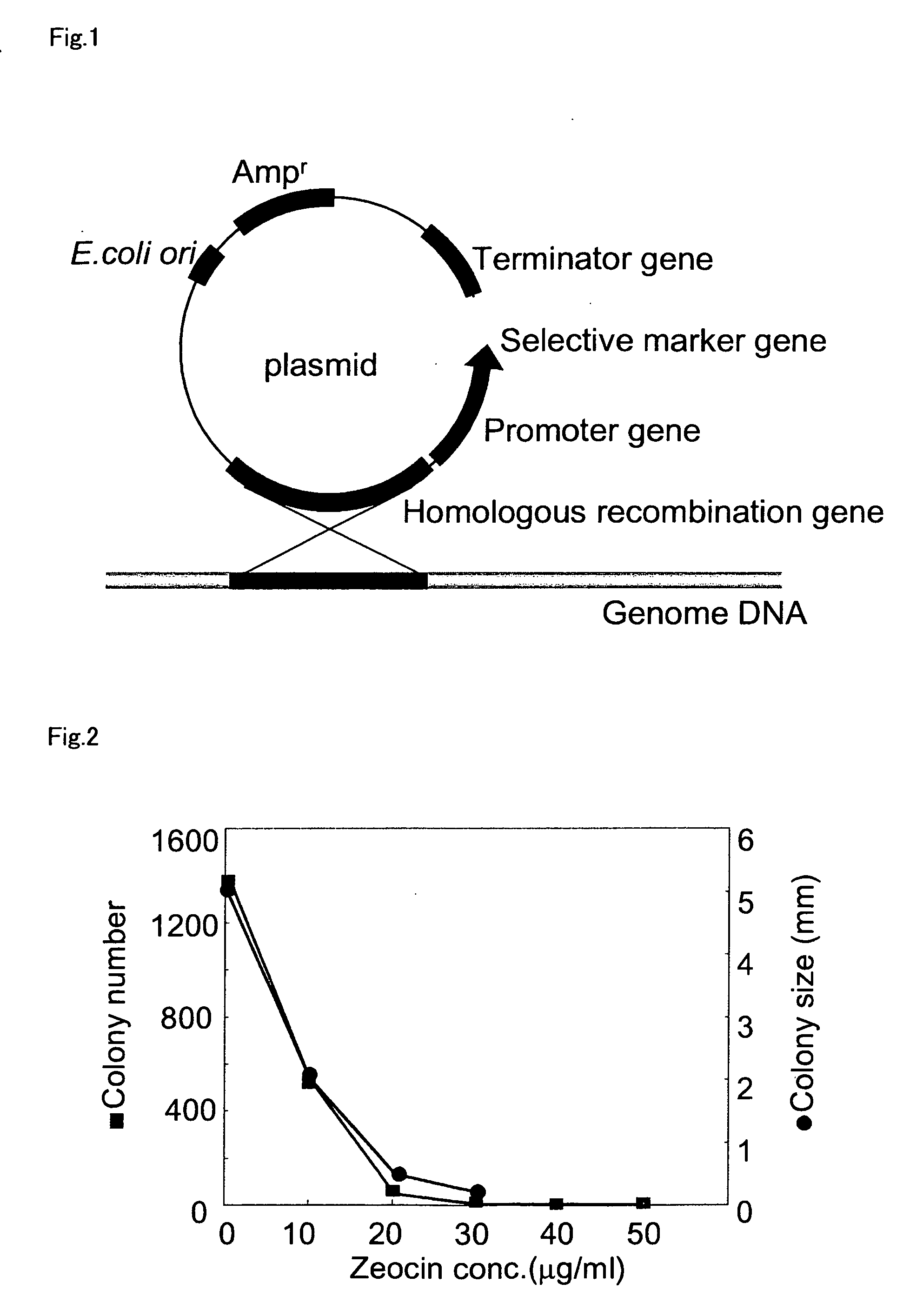
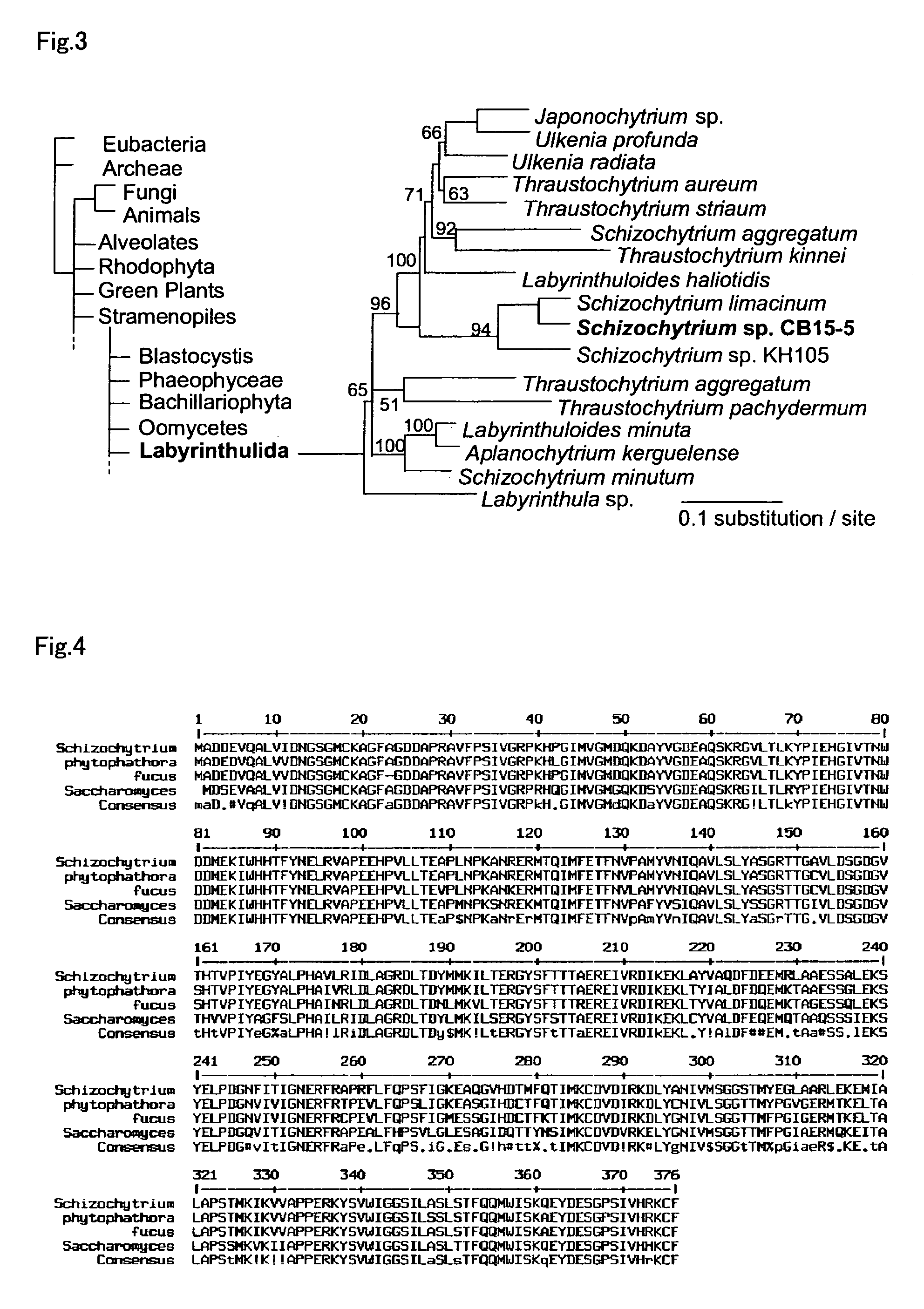
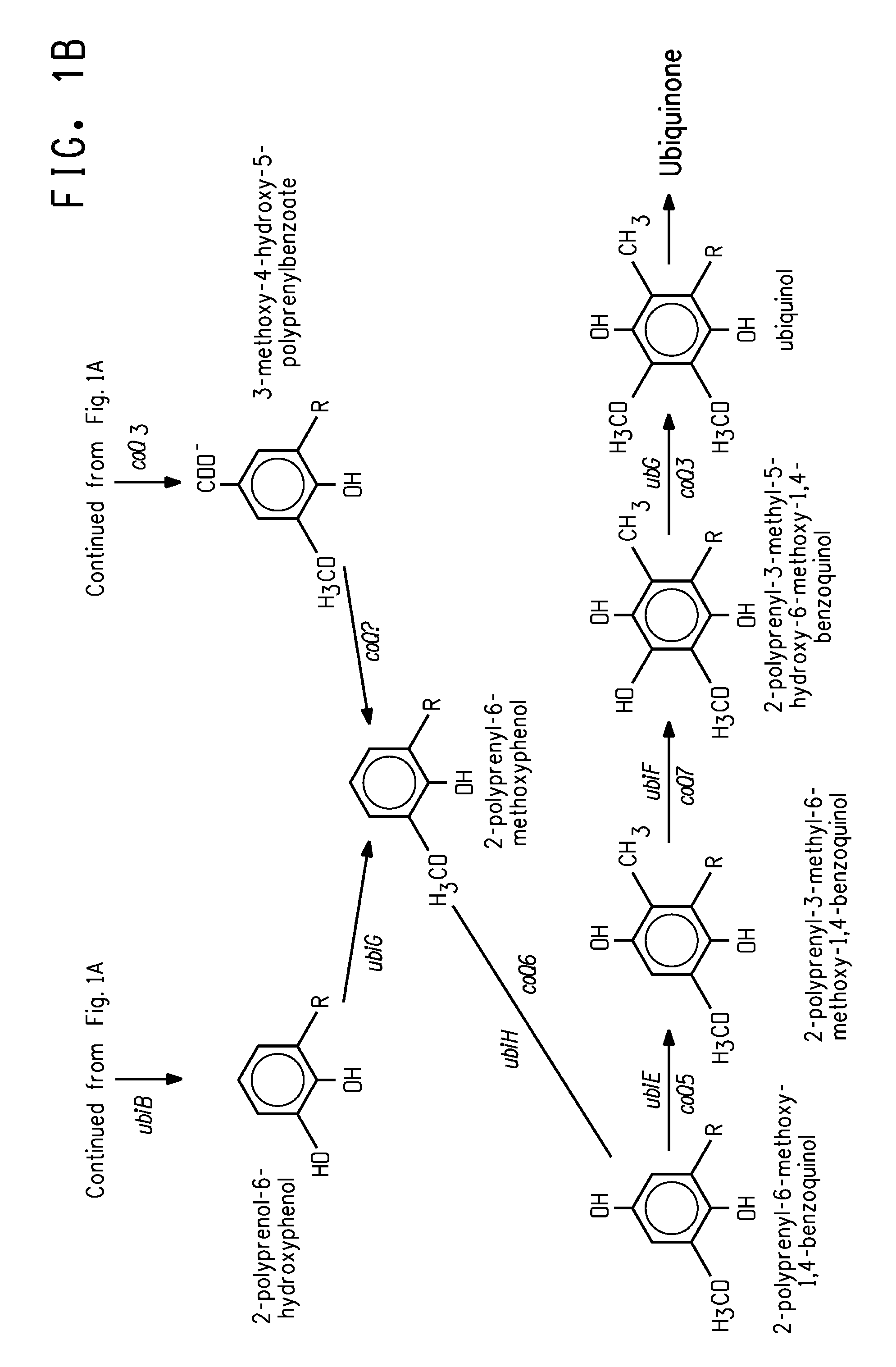
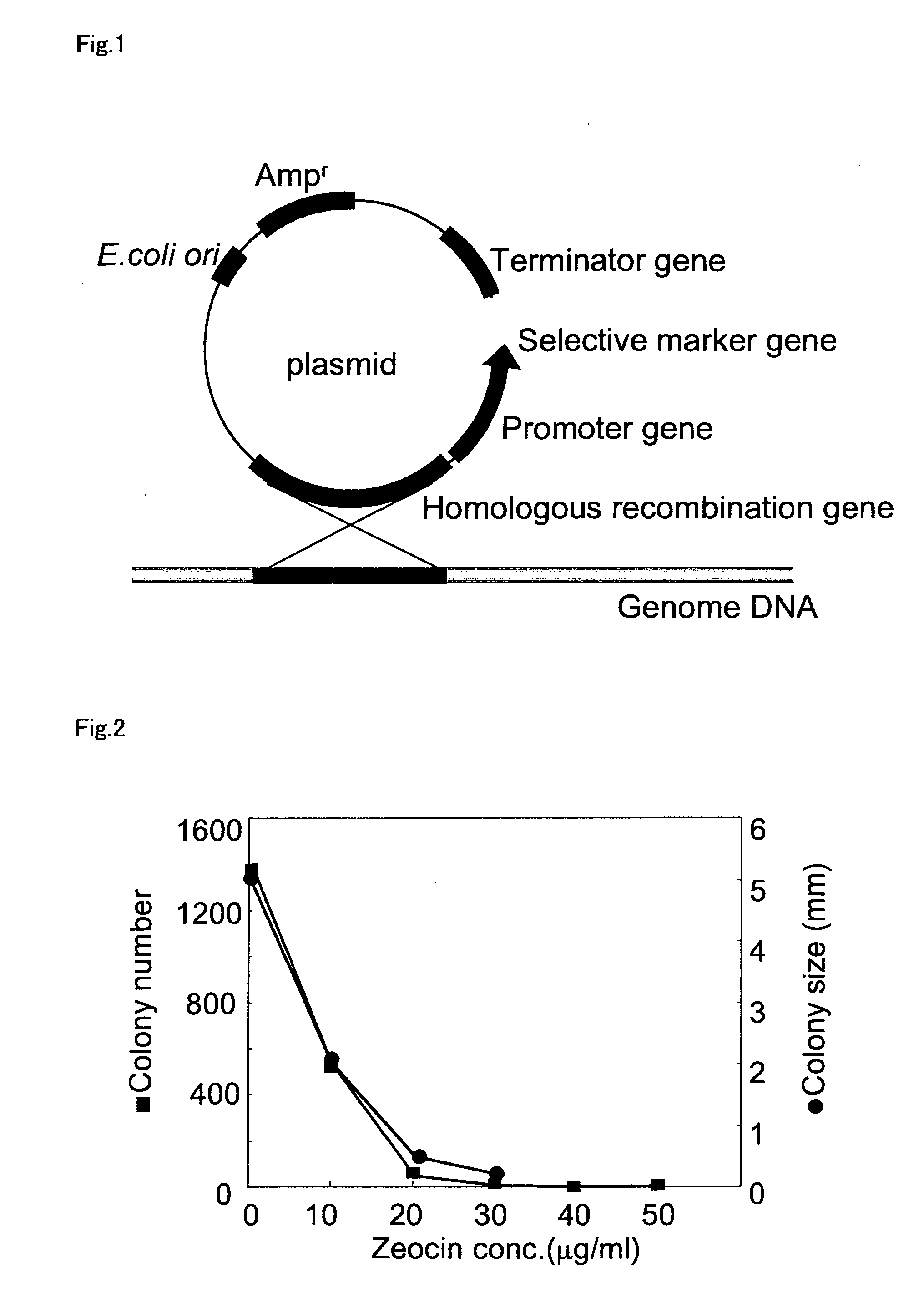
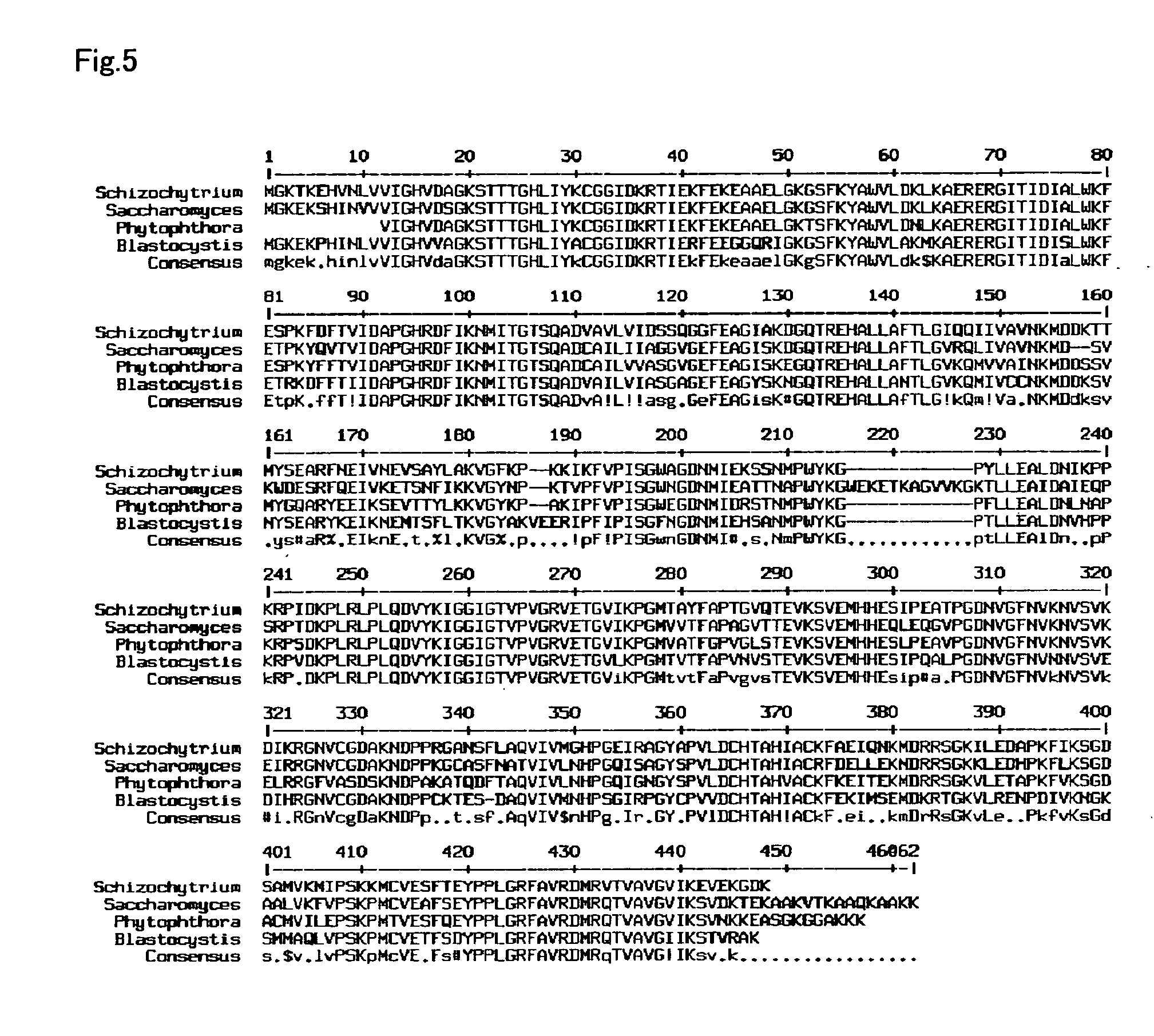
Method for introducing a gene into Labyrinthulomycota
An object of the present invention is to provide a transformation system for Labyrinthulomycota that allows the elucidation of biosynthetic mechanisms of lipids such as PUFA and carotenoids as well as for the construction of a high production system and the design and development of novel functional lipid molecules by the control of the mechanisms. The present invention provides a method for introducing a transgene into a cell of Labyrinthulomycota, which comprises introducing into a cell of Labyrinthulomycota a recombinant vector comprising a transgene and a nucleotide sequence which is homologous to a part of chromosomal DNA of Labyrinthulomycota and is capable of homologous recombination with the chromosomal DNA, and then inducing homologous recombination in this homologous nucleotide sequence.
Owner:HIROSHIMA UNIVERSITY +1
Methods of producing biofuels, chlorophylls and carotenoids
InactiveUS20110263886A1Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationWater insolubleBiofuel
A method for producing biofuels along with valuable food and neutraceutical products is provided. A method of making biofuels includes dewatering substantially intact algal cells to make an algal biomass, extracting neutral lipids along with carotenoids and chlorophylls from the algal biomass, and separation of the carotenoids and chlorophylls using adsorption or membrane diafiltration or other methods. The remaining neutral lipids are esterified with a catalyst in the presence of an alcohol. The method also includes separating a water soluble fraction comprising glycerin from a water insoluble fraction comprising fuel esters and distilling the fuel esters under vacuum to obtain a C16 or shorter fuel esters fraction, a C16 or longer fuel ester fraction, and a residue comprising omega-3 fatty acids esters and remaining carotenoids. The method further includes hydrogenating and deoxygenating at least one of (i) the C16 or shorter fuel esters to obtain a jet fuel blend stock and (ii) the C16 or longer fuel esters to obtain a diesel blend stock.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Coenzyme Q10 Production in a Recombinant Oleaginous Yeast
Engineered strains of the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica capable of co-producing coenzyme Q10 and at least one ω-3 / ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid are provided. The strains may also be engineered to co-produce at least one C40 carotenoid. Methods of using the antioxidant products obtained (e.g., biomass and / or pigmented oils) in food and feed applications are also provided.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
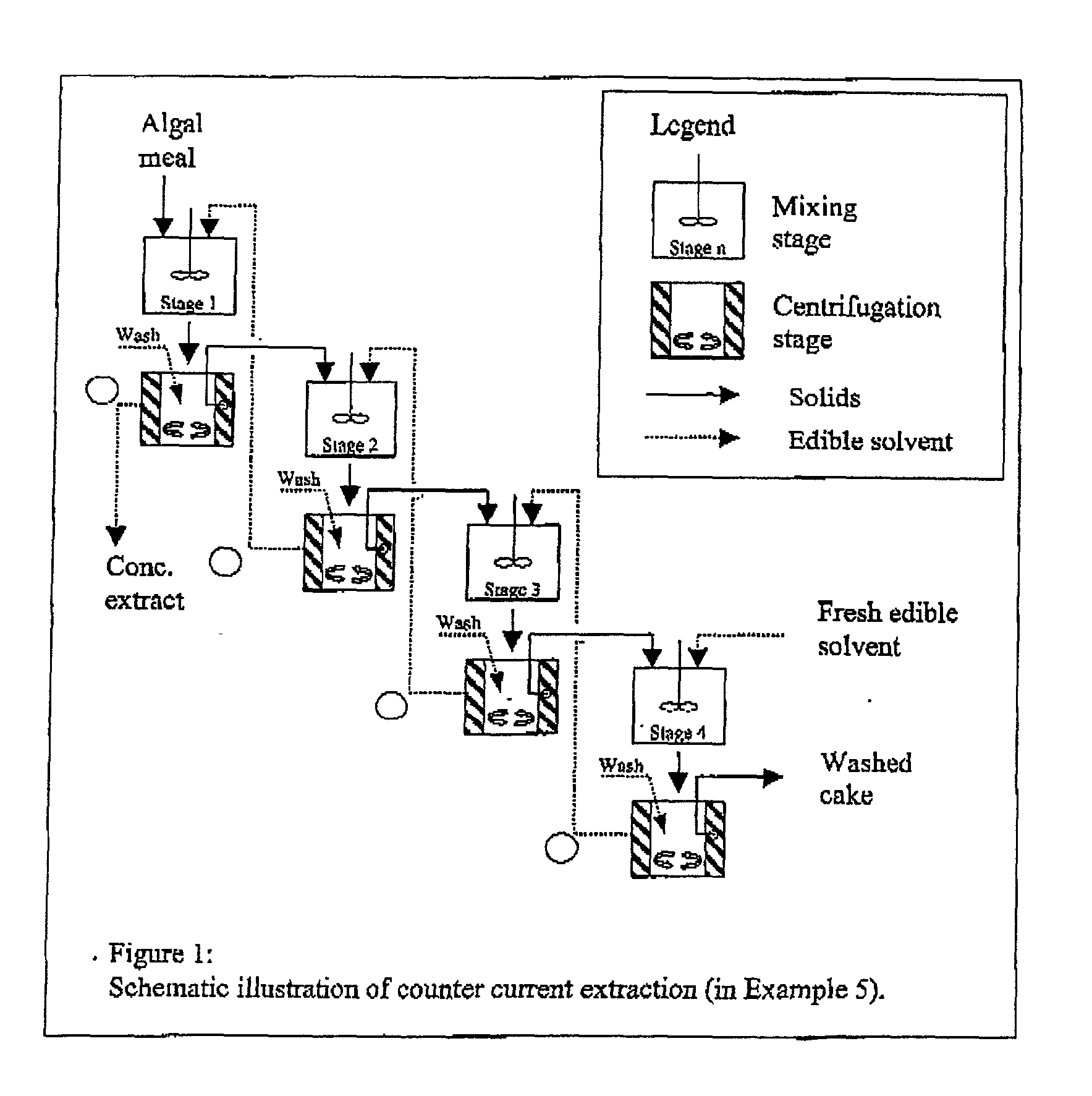
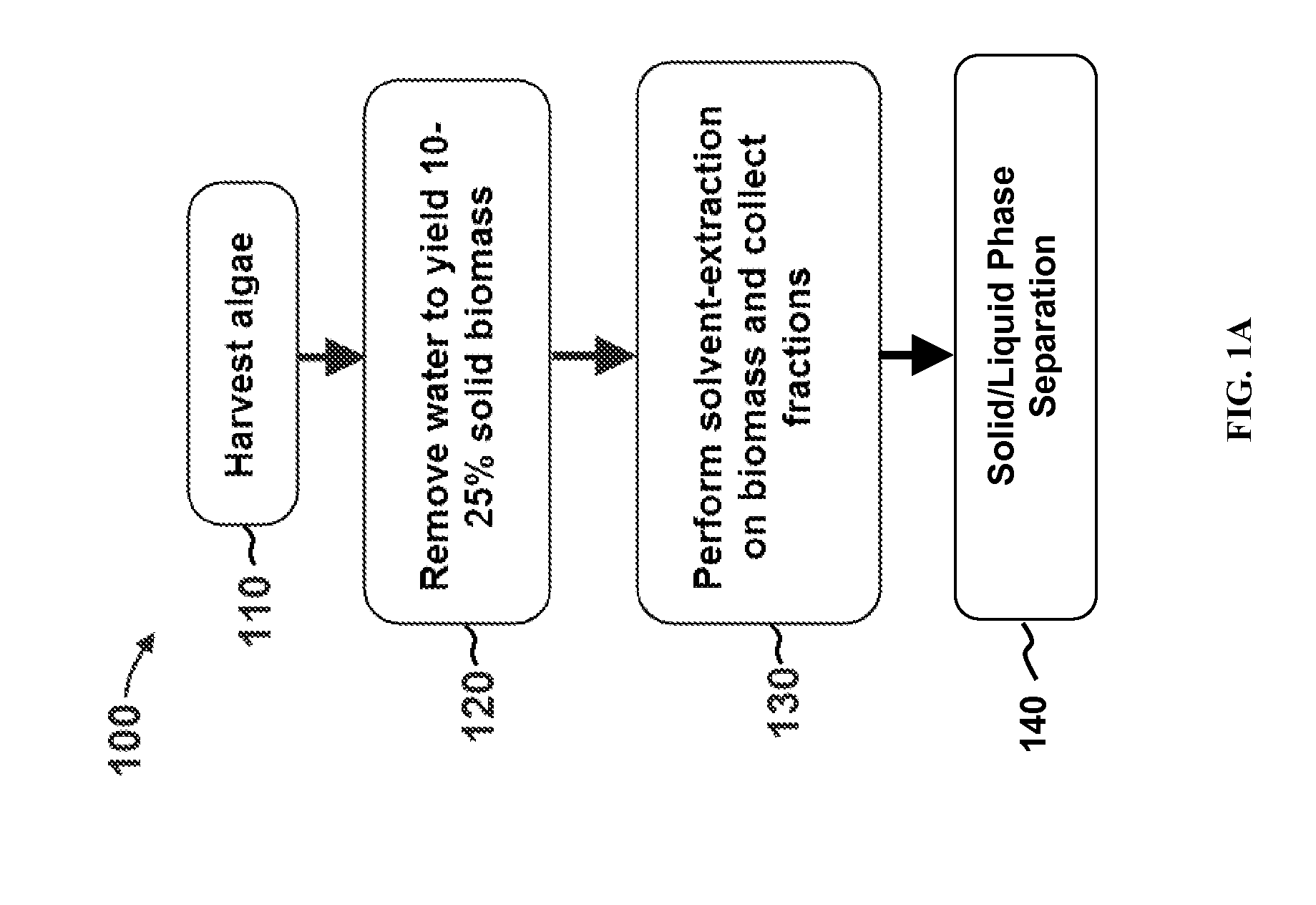
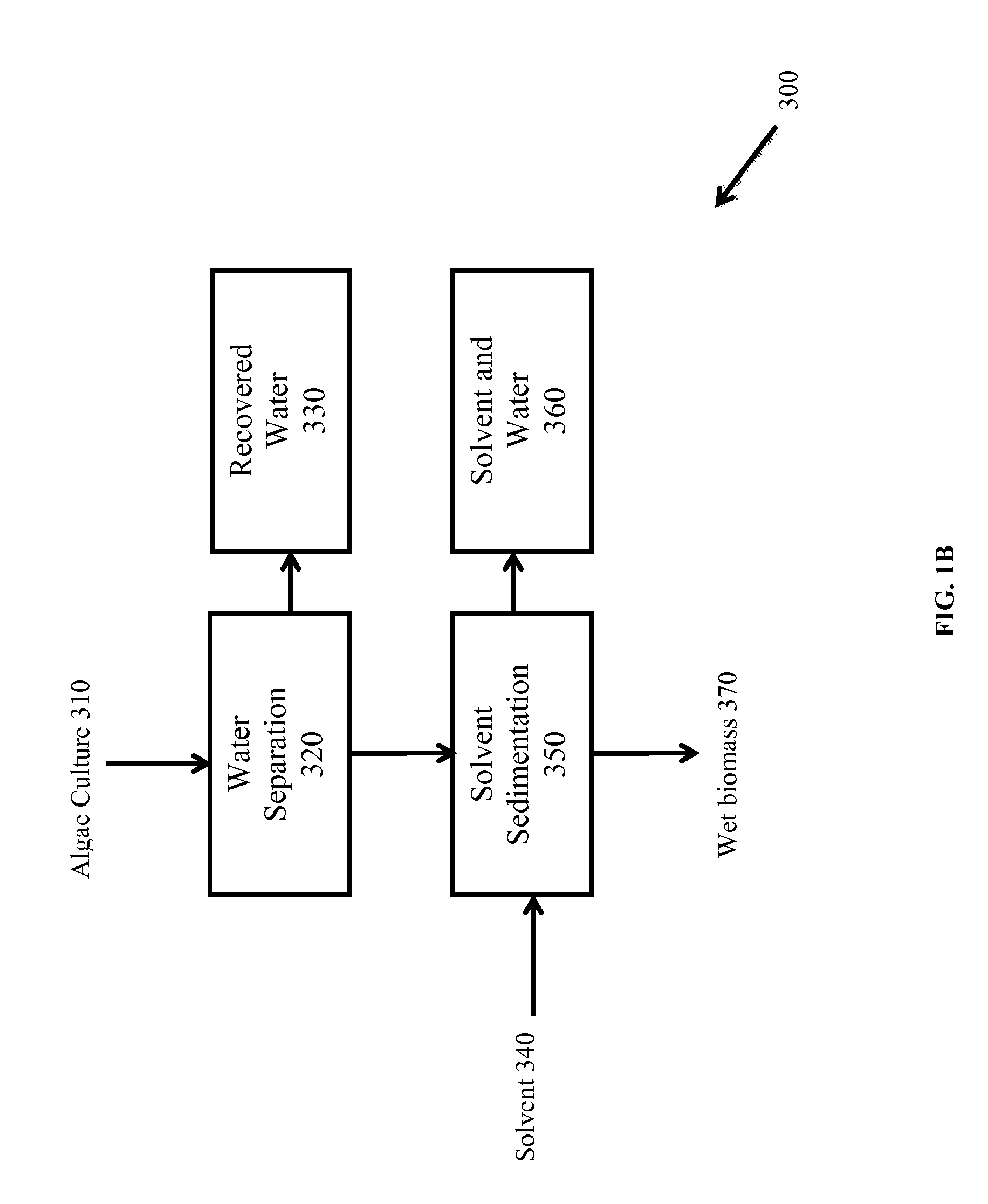
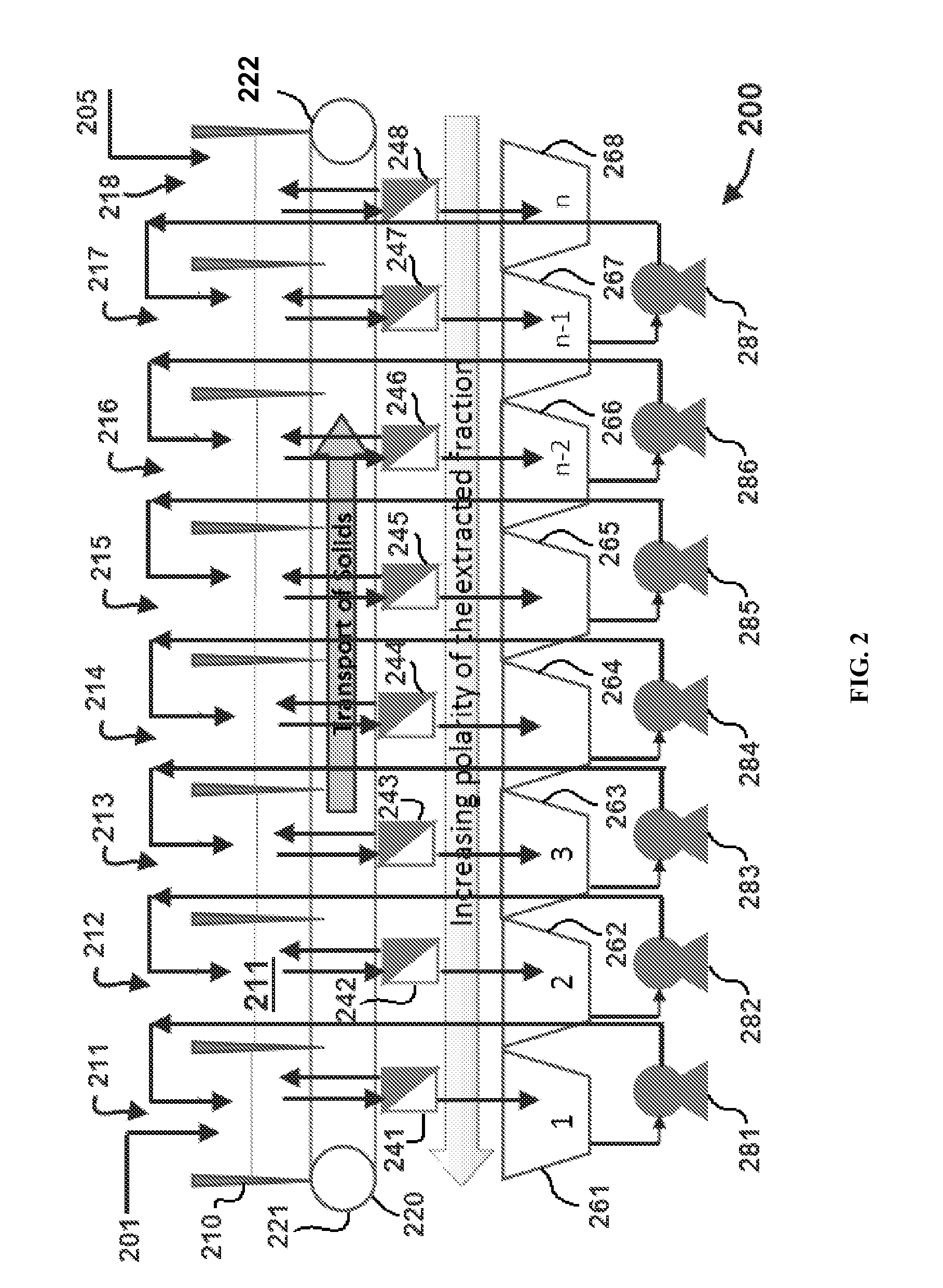
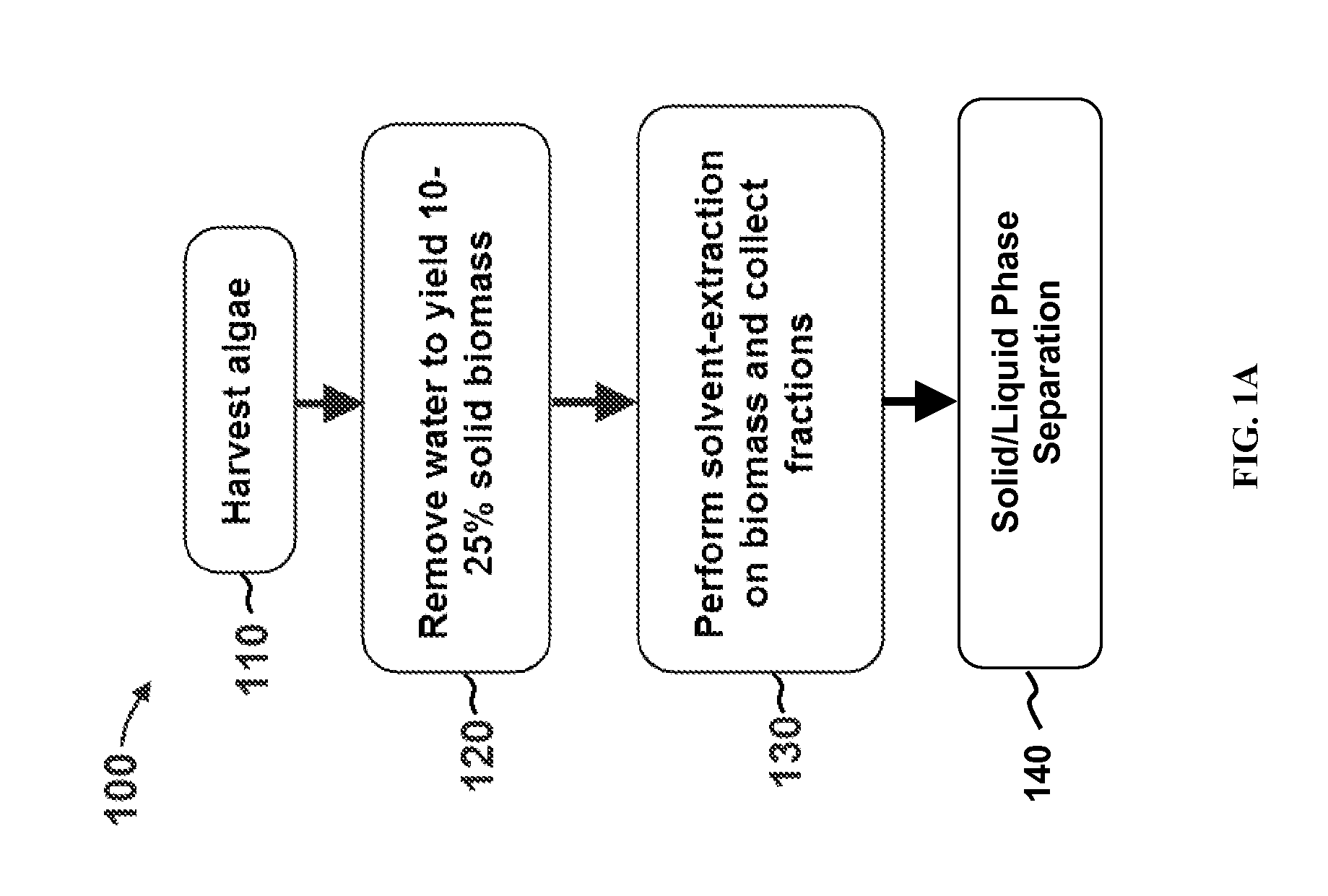
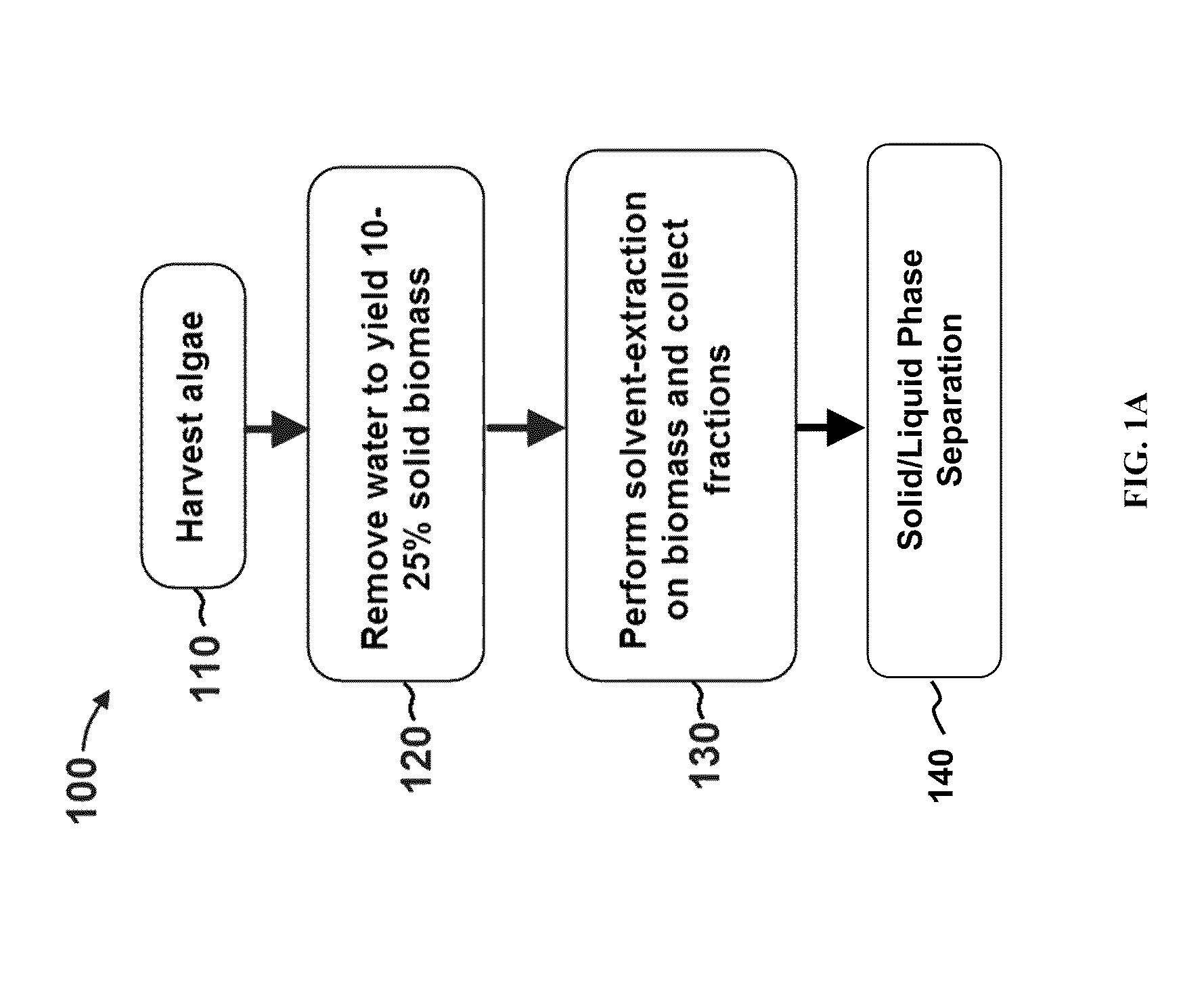
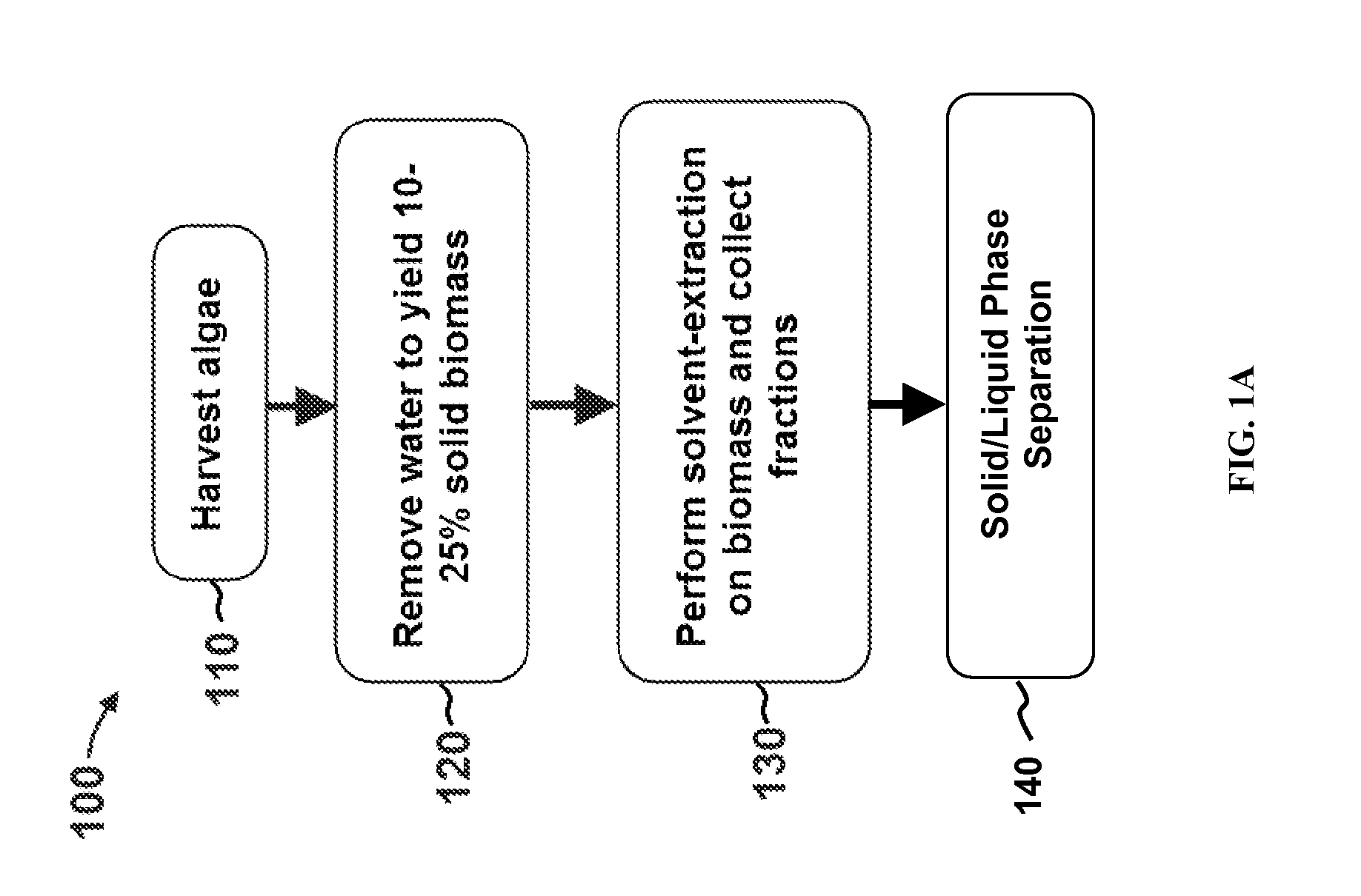
Edible solvent extraction of carotenoids from microorganisms
InactiveUS20030054070A1Efficient extractionEnriching carotenoid contentLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionHydrocarbonsParticulatesAnimal food
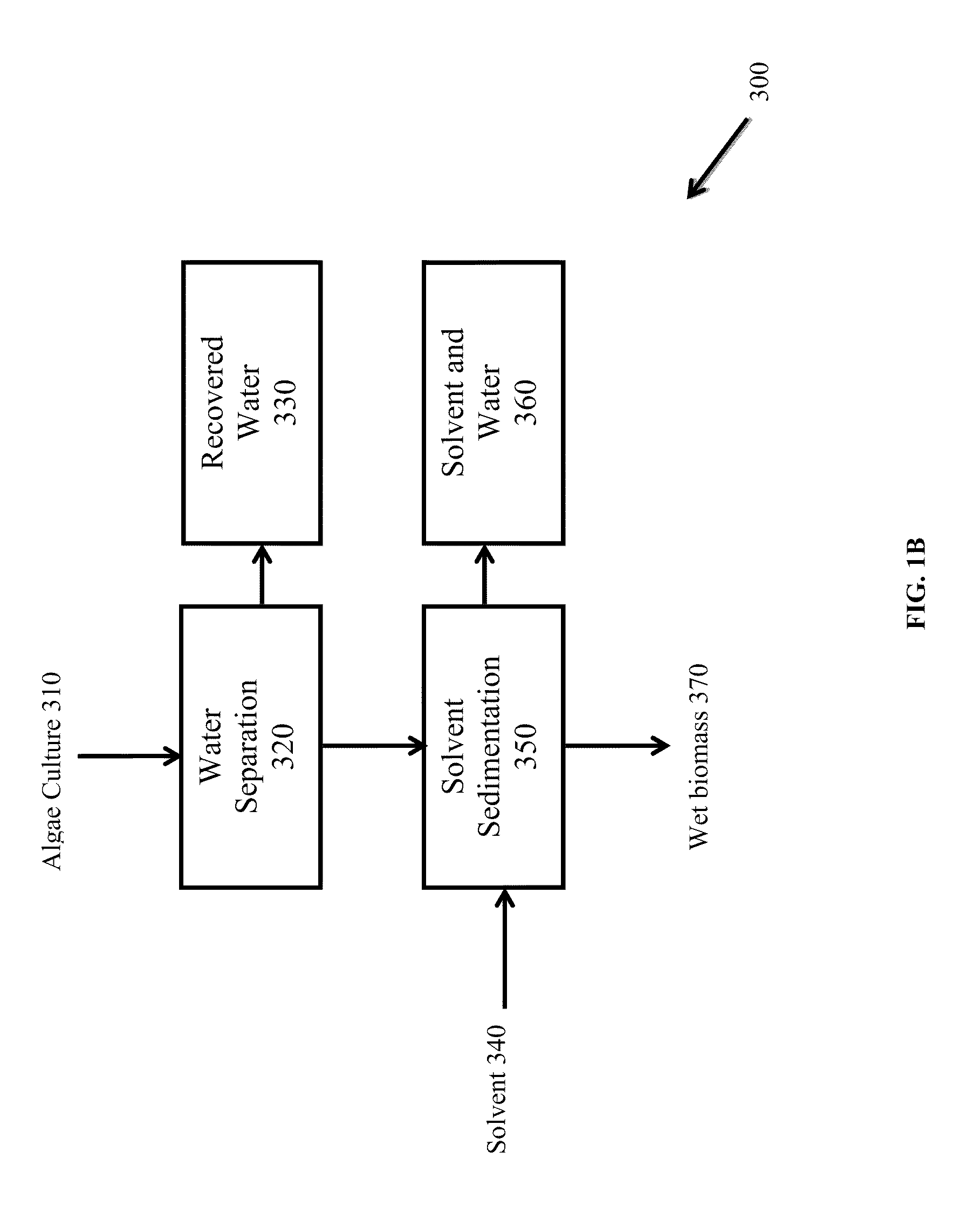
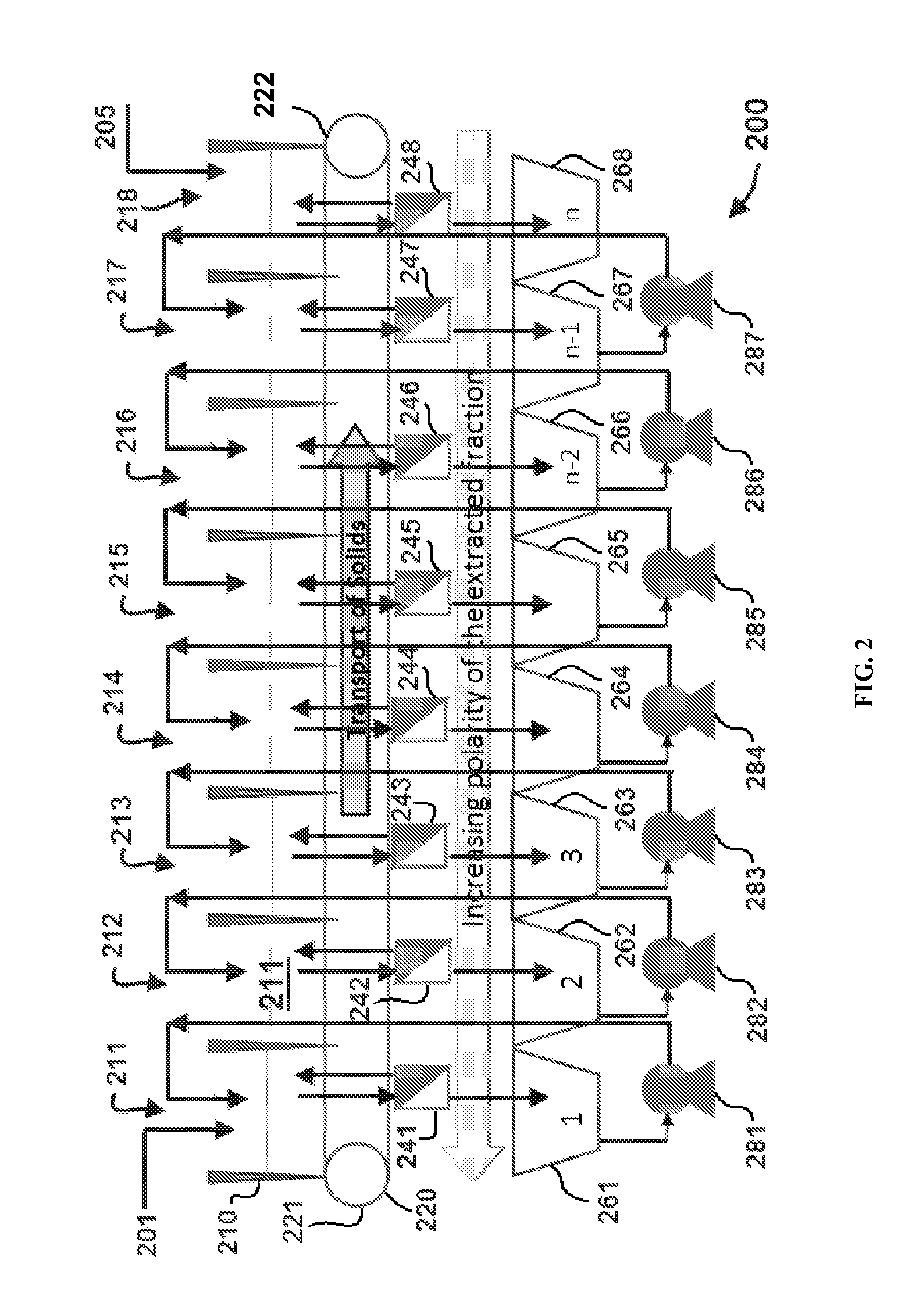
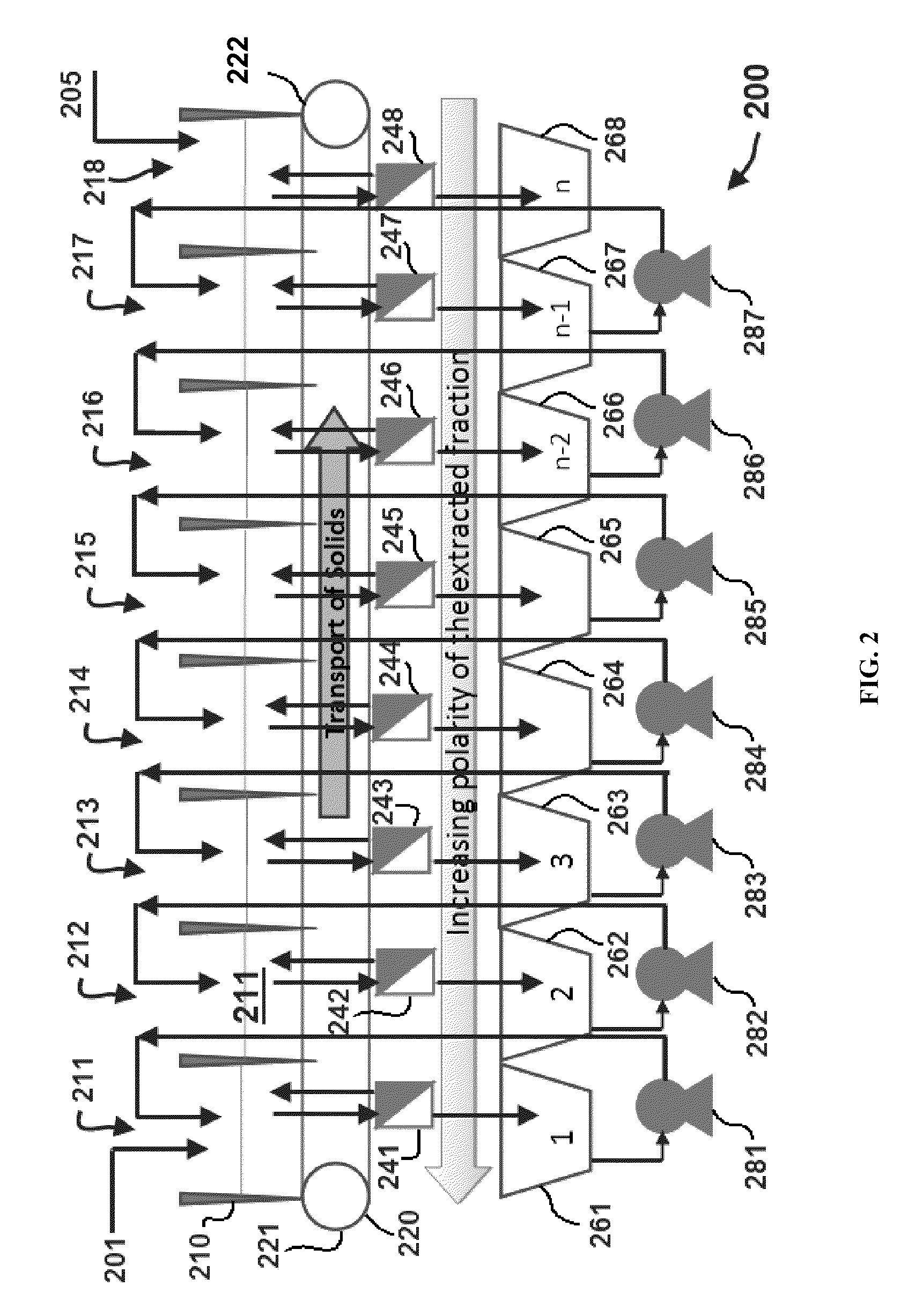
A process for extracting carotenoids from a carotenoid-containing starting material produced by microorganisms is described. Said starting material is admixed with edible solvent to effectuate the transfer of carotenoids. Separation of the carotenoid-enriched edible solvent is improved by the formation of a "cake", composed of said carotenoid-containing particulate solids, and, as required, a certain quantity of suitable filtration aid to modify the cake's consistency. Mechanical aids accelerate the separation of the carotenoid-enriched edible solvent. Said mixture may be hydrated to aid the removal of solids and gums from the carotenoid containing edible solvent. The carotenoid-enriched edible solvent is filtered though said cake to reduce the particulate load including any undesirable microbial load. A counter-current process increases the carotenoid concentration of the extract. The carotenoid-enriched edible solvent can be used as an ingredient in human and animal foodstuffs and dietary supplements for the possible prevention and treatment of illnesses and diseases.
Owner:AQUSRCH
Vector capable for transformation of labyrinthulomycota
An object of the present invention is to provide a transformation system for Labyrinthulomycota that allows the elucidation of biosynthetic mechanisms of lipids such as PUFA and carotenoids as well as for the construction of a high production system and the design and development of novel functional lipid molecules by the control of the mechanisms. The present invention provides a vector for the transformation of Labyrinthulomycota with a transgene, which comprises at least (1) a nucleotide sequence which is homologous to a part of chromosomal DNA of Labyrinthulomycota and is capable of homologous recombination with the chromosomal DNA, (2) a selection marker gene having a promoter sequence located upstream and a terminator sequence located downstream, and (3) a cloning site for transgene insertion having a promoter sequence located upstream and a terminator sequence located downstream.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Pharmaceutical composition and method for the transdermal delivery of magnesium
InactiveUS20050196434A1Reduce disadvantagesBiocideAerosol deliveryAutonomic bladder dysfunctionMagnesium salt
The present invention relates to a method and transdermal pharmaceutical composition for preventing magnesium deficiency or imbalances associated with magnesium deficiency including diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol, cardiac arrhythmias, acute myocardial infarction, arteriosclerosis, atherosclerosis, preeclampsia, dysautonomia, mitral valve prolapse, asthma, constipation, irritable bowel syndrome, migraines, muscle spasms and cramping, premenstrual syndrome, osteoporosis, kidney stones, chronic fatigue syndrome, and fibromyalgia. The transdermal pharmaceutical composition includes a therapeutically effective amount of a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of magnesium and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. A therapeutically effective amount of a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of zinc a vitamin such as B-complex vitamin, a carotenoid, a mineral, or a combination thereof may also be included in the transdermal pharmaceutical composition. A therapeutically effective amount of progesterone may also be included in the transdermal pharmaceutical composition. The transdermal pharmaceutical composition may be topically administered to prevent magnesium deficiency or imbalances caused by magnesium deficiency.
Owner:BRIERRE BARBARA T
Methods of and Systems for Producing Biofuels
A method for producing biofuels is provided. A method of making biofuels includes dewatering substantially intact algal cells to make an algal biomass, extracting neutral lipids from the algal biomass, and esterifying the neutral lipids with a catalyst in the presence of an alcohol. The method also includes separating a water soluble fraction comprising glycerin from a water insoluble fraction comprising fuel esters and distilling the fuel esters under vacuum to obtain a C16 or shorter fuel esters fraction, a C16 or longer fuel ester fraction, and a residue comprising carotenoids and omega-3 fatty acids. The method further includes hydrogenating and deoxygenating at least one of (i) the C16 or shorter fuel esters to obtain a jet fuel blend stock and (ii) the C16 or longer fuel esters to obtain a diesel blend stock.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Composition for the treatment and/or prevention of macular degeneration, method for its manufacture, and its use for treating the eye
Negatively charged phospholipids, as well as compositions including negatively charged phospholipids and possibly carotenoids and / or antioxidants, for treating the eye are disclosed. In a preferred embodiment, a composition comprising at least one negatively charged phospholipid except cardiolipin is used to treat age-related macular degeneration. Methods for producing the negatively charged phospholipids, as well as methods for producing the compositions including negatively charged phospholipids and possibly carotenoids and / or antioxidants for treating age-related macular degeneration, are also disclosed.
Owner:MULTIGENE BIOTECH
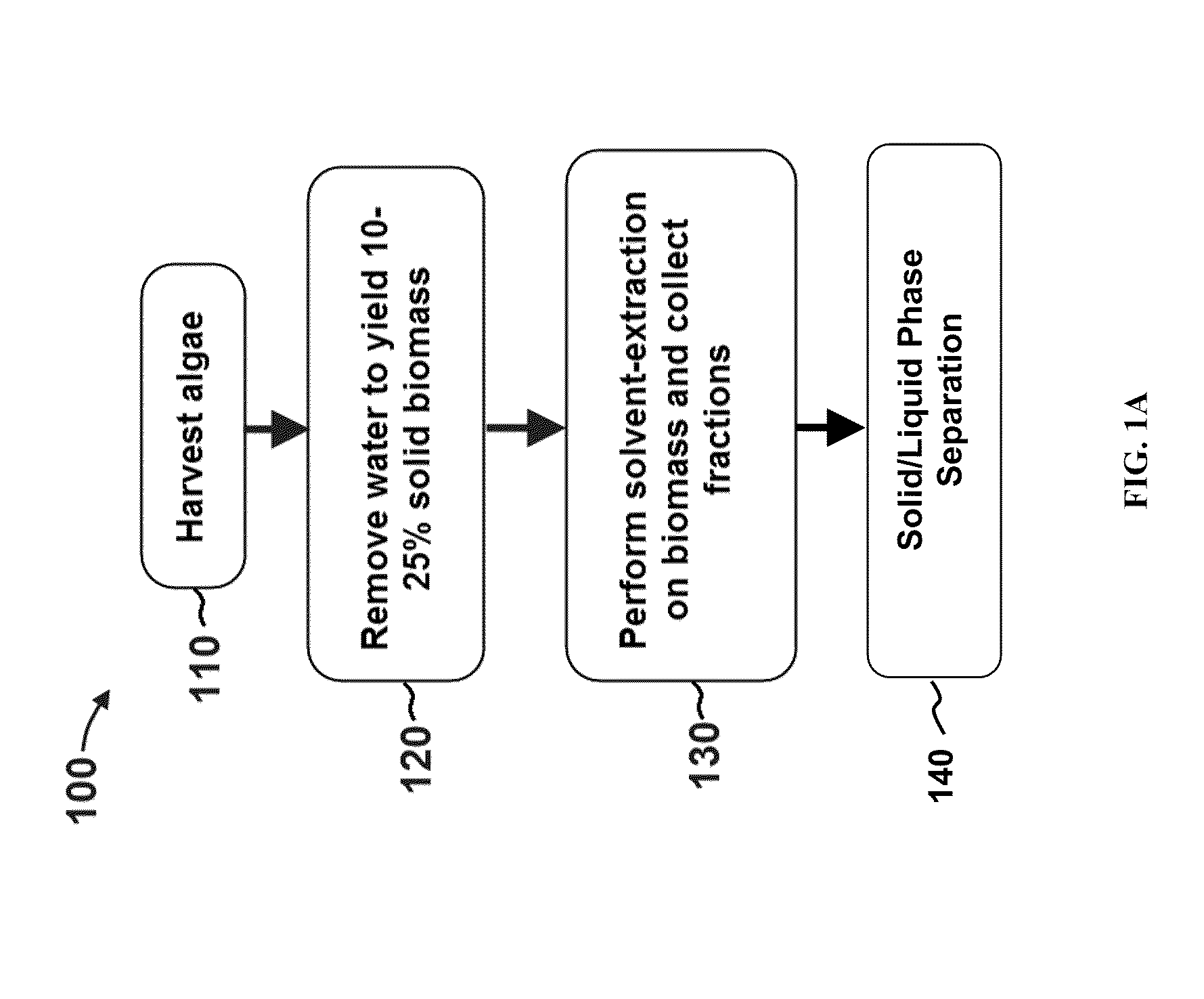
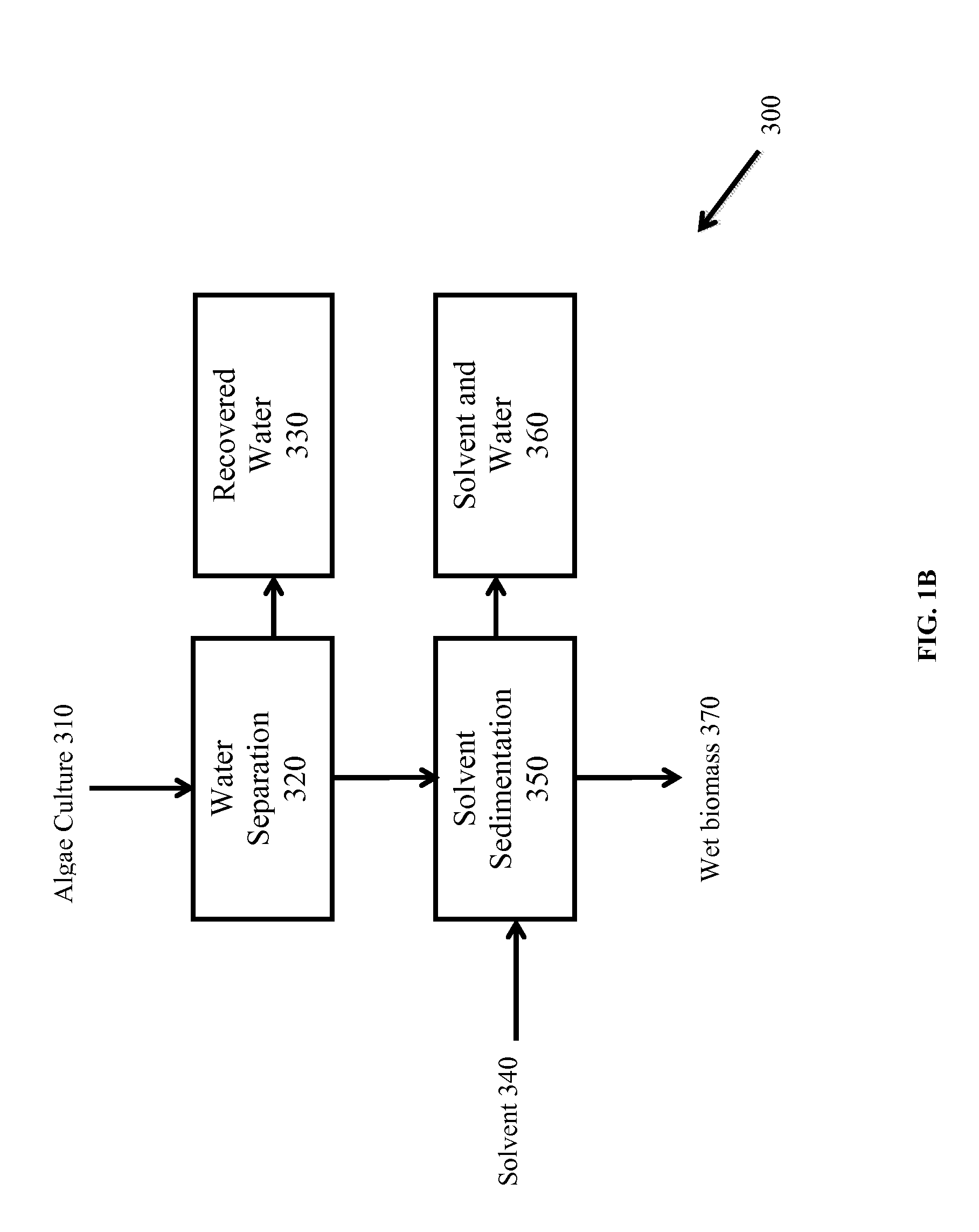
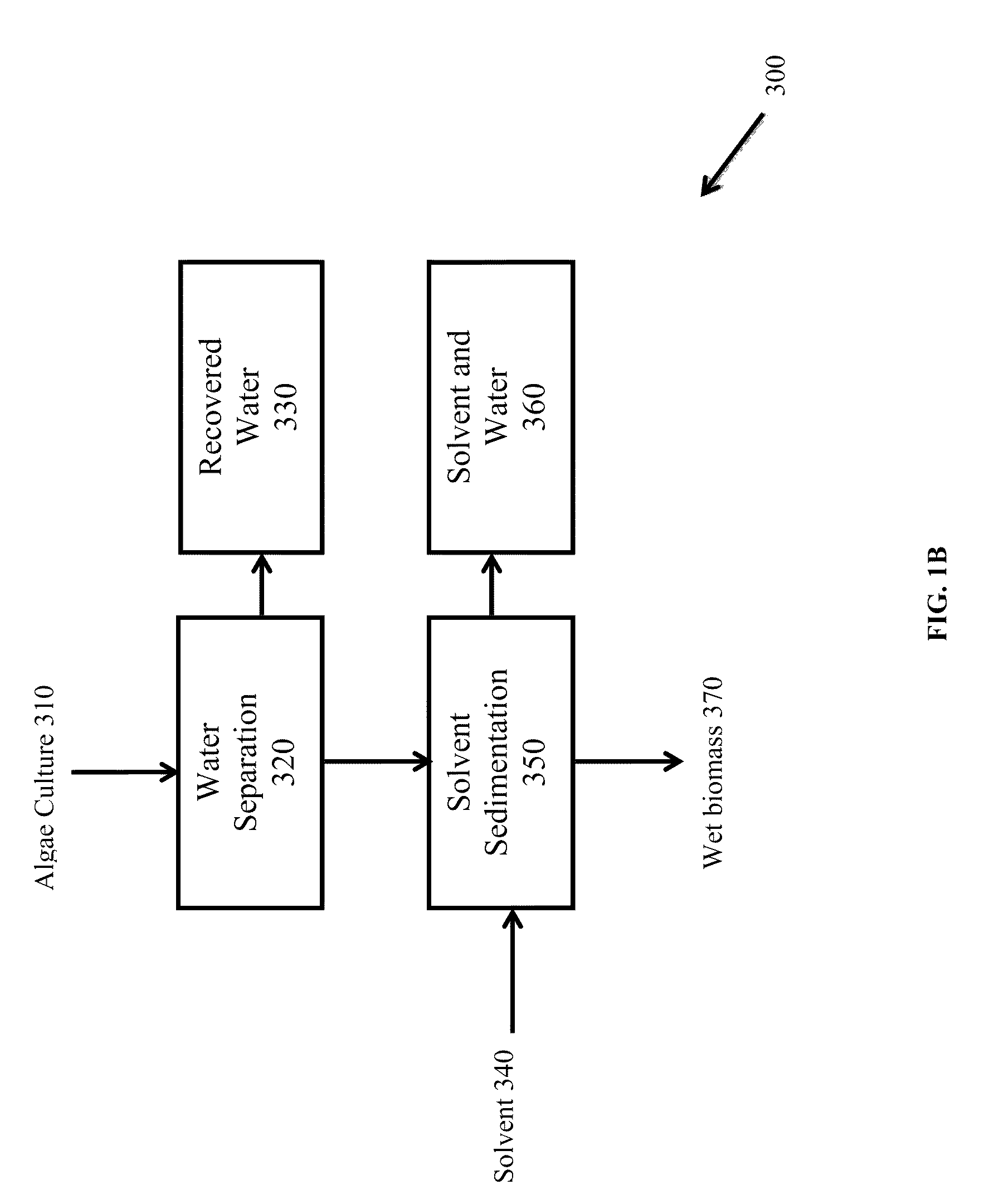
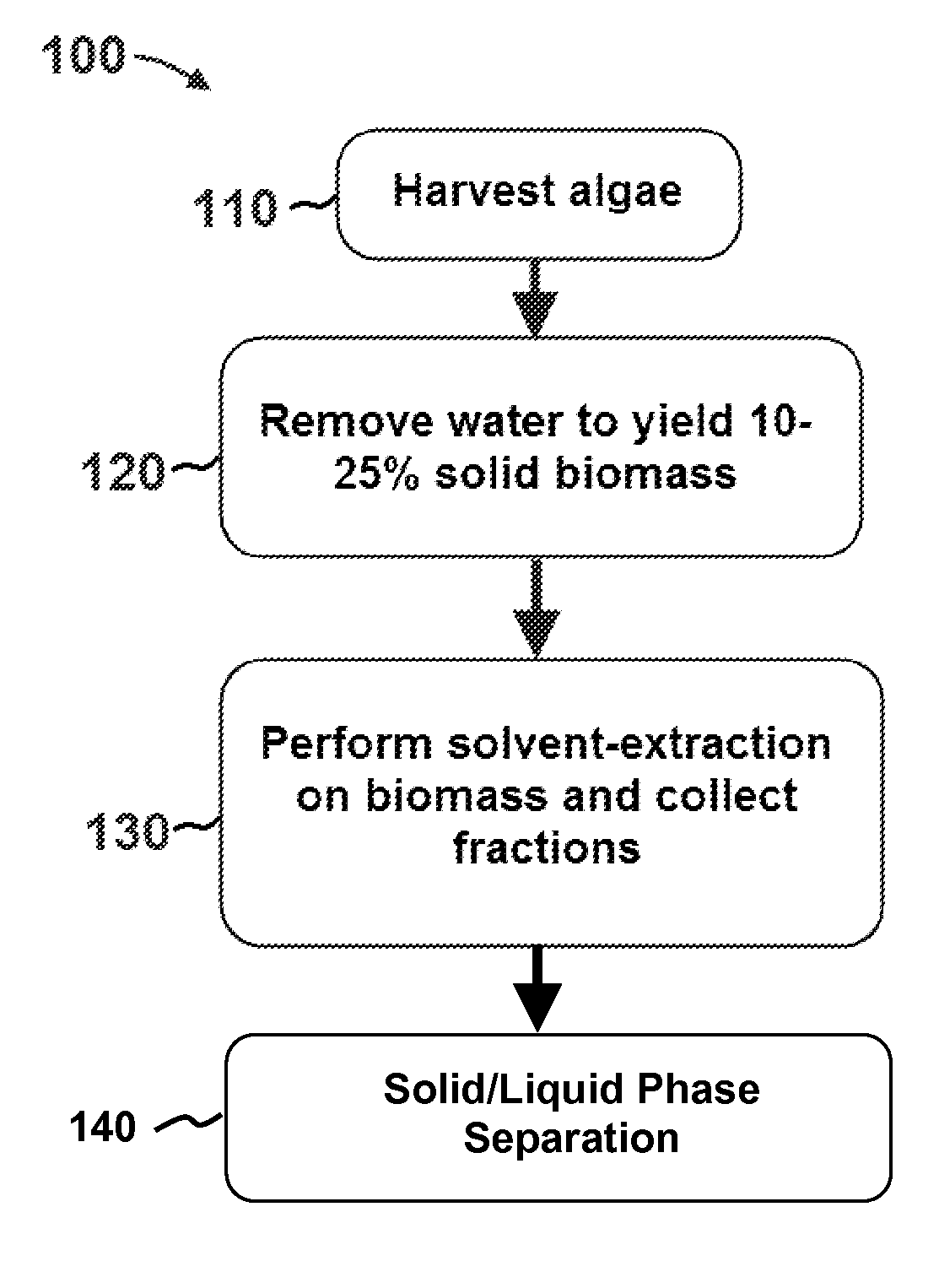
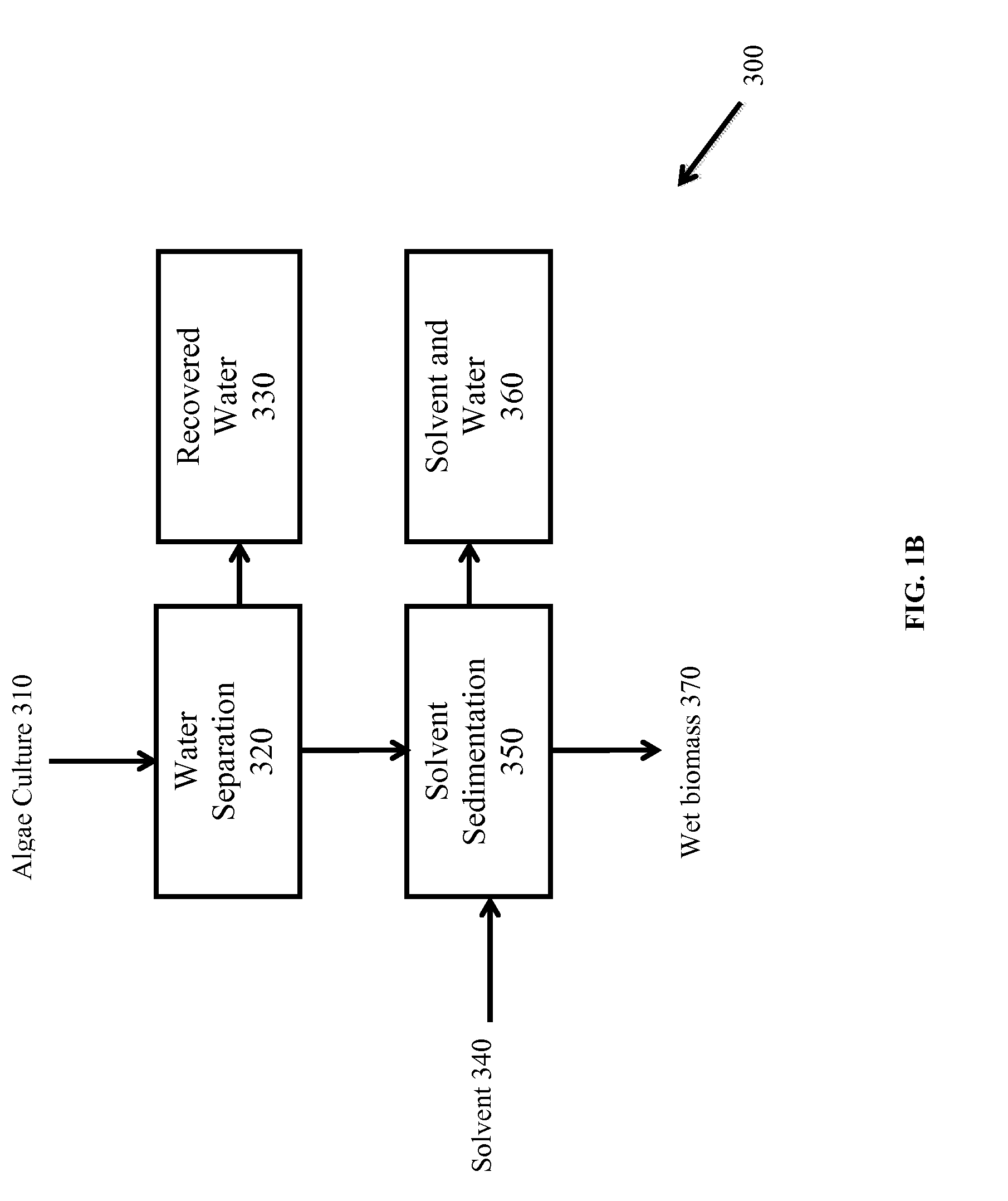
Methods of and Systems for Isolating Nutraceutical Products from Algae
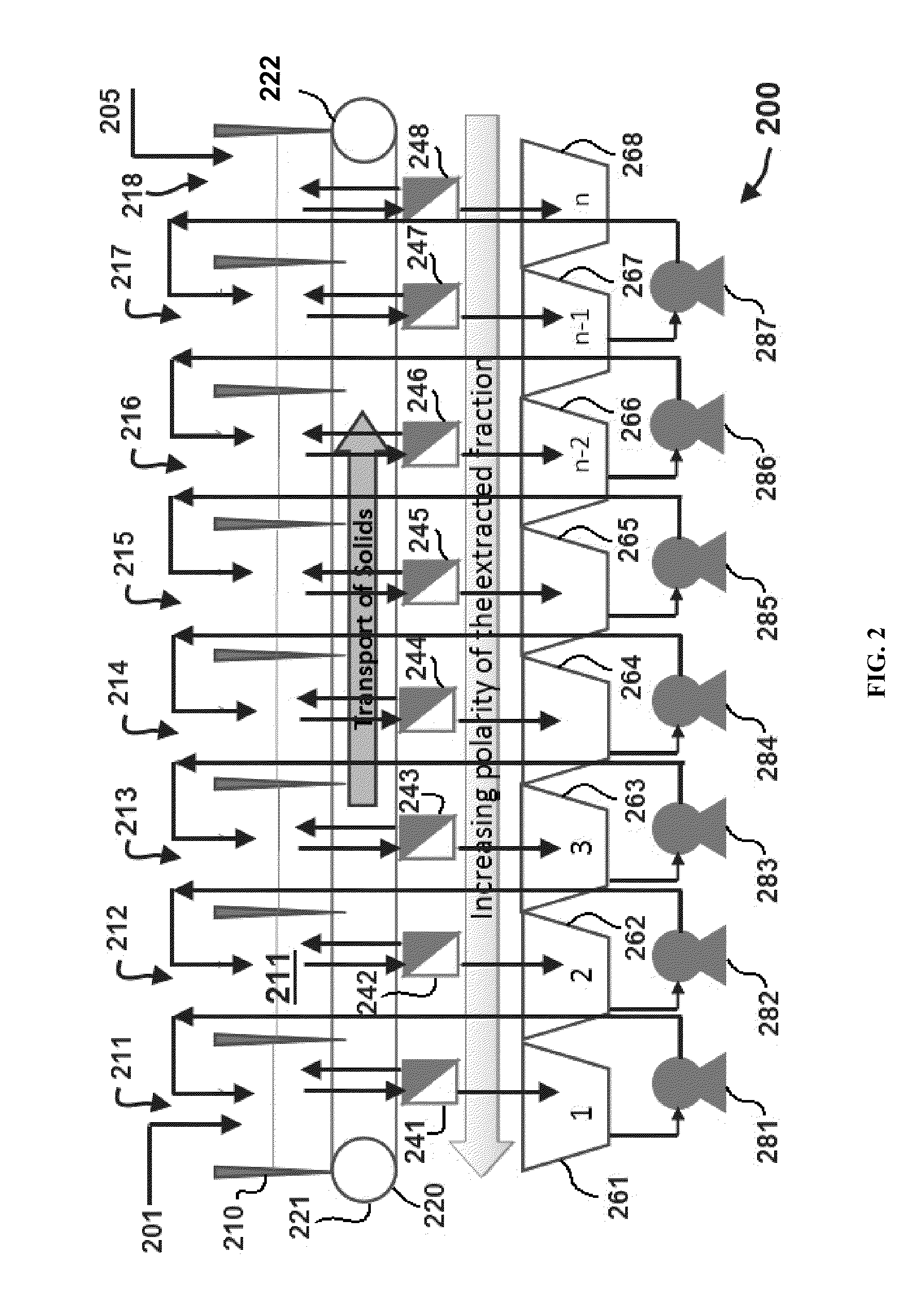
A method of isolating nutraceuticals products from algae is provided. A method of isolating carotenoids and omega-3 rich oil from algae includes dewatering substantially intact algal cells to make an algal biomass and adding a first ethanol fraction to the algal biomass. The method also includes separating a first substantially solid biomass fraction from a first substantially liquid fraction comprising proteins and combining the first substantially solid biomass fraction with a second ethanol fraction. The method further includes separating a second substantially solid biomass fraction from a second substantially liquid fraction comprising polar lipids and combining the second substantially solid biomass fraction with a third ethanol solvent fraction. The method also includes separating a third substantially solid biomass fraction from a third substantially liquid fraction comprising neutral lipids, wherein the third substantially solid biomass fraction comprises carbohydrates and separating the neutral lipids into carotenoids and omega-3 rich oil.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Methods of producing biofuels, chlorophylls and carotenoids
InactiveUS8115022B2Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationWater insolubleBiofuel
A method for producing biofuels along with valuable food and neutraceutical products is provided. A method of making biofuels includes dewatering substantially intact algal cells to make an algal biomass, extracting neutral lipids along with carotenoids and chlorophylls from the algal biomass, and separation of the carotenoids and chlorophylls using adsorption or membrane diafiltration or other methods. The remaining neutral lipids are esterified with a catalyst in the presence of an alcohol. The method also includes separating a water soluble fraction comprising glycerin from a water insoluble fraction comprising fuel esters and distilling the fuel esters under vacuum to obtain a C16 or shorter fuel esters fraction, a C16 or longer fuel ester fraction, and a residue comprising omega-3 fatty acids esters and remaining carotenoids. The method further includes hydrogenating and deoxygenating at least one of (i) the C16 or shorter fuel esters to obtain a jet fuel blend stock and (ii) the C16 or longer fuel esters to obtain a diesel blend stock.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Methods of and systems for isolating nutraceutical products from algae
A method of isolating nutraceuticals products from algae is provided. A method of isolating carotenoids and omega-3 rich oil from algae includes dewatering substantially intact algal cells to make an algal biomass and adding a first ethanol fraction to the algal biomass. The method also includes separating a first substantially solid biomass fraction from a first substantially liquid fraction comprising proteins and combining the first substantially solid biomass fraction with a second ethanol fraction. The method further includes separating a second substantially solid biomass fraction from a second substantially liquid fraction comprising polar lipids and combining the second substantially solid biomass fraction with a third ethanol solvent fraction. The method also includes separating a third substantially solid biomass fraction from a third substantially liquid fraction comprising neutral lipids, wherein the third substantially solid biomass fraction comprises carbohydrates and separating the neutral lipids into carotenoids and omega-3 rich oil.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Preparation method of carotenoid emulsion and microcapsules
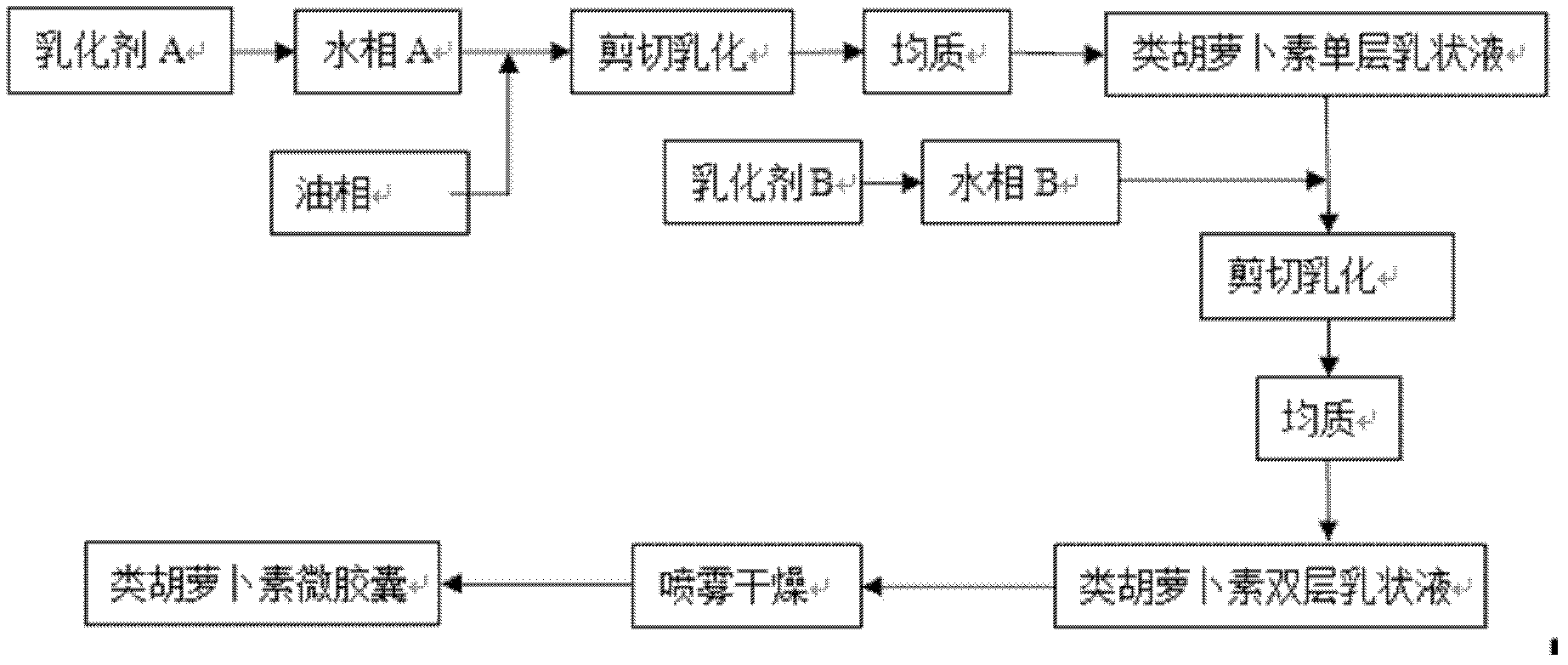
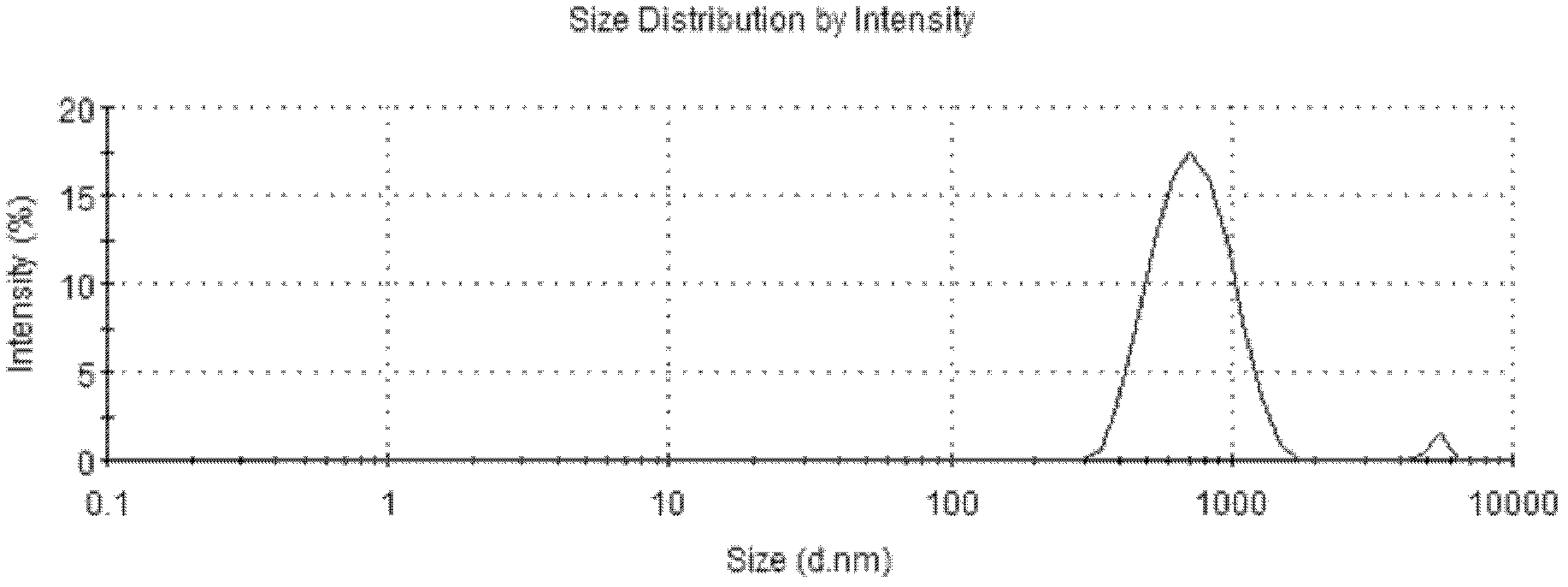
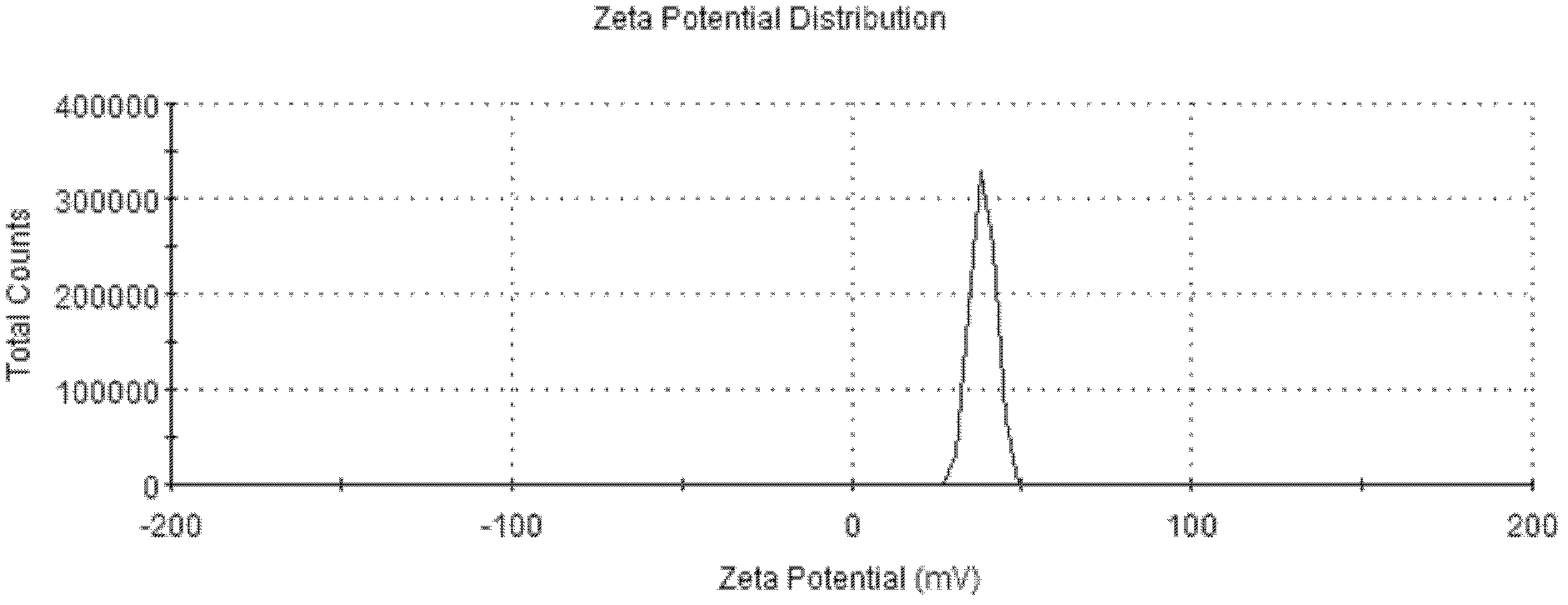
InactiveCN102525923AReduce lossesGood biocompatibilityOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsEmulsionBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a preparation method of carotenoid emulsion and microcapsules. The method is characterized in that the electrostatic force interaction of emulsifier molecules on an emulsion interface is utilized, and a two-step homogenization method is applied to preparing carotenoid bilayer emulsion which can be further dried to prepare carotenoid microcapsules. The method disclosed by the invention is simple, convenient and feasible for preparation, the used emulsifier and microcapsule wall materials have favorable biocompatibility and can be biodegraded, and a material source range is wide; and the carotenoid emulsion and microcapsules have the characteristics of good physical and chemical stability, long shelf life and the like, the carotenoid loading capacity of the emulsion can reach 2%, and the carotenoid loading capacity of the microcapsules can reach 10%.
Owner:宁波威龙香精香料有限公司
Methods of and Systems for Producing Biofuels
A method for producing biofuels is provided. A method of making biofuels includes dewatering substantially intact algal cells to make an algal biomass, sequentially adding solvent sets to the algal biomass, and sequentially separating solid biomass fractions from liquid fractions to arrive at a liquid fraction comprising neutral lipids. The method also includes esterifying the neutral lipids, separating a water miscible fraction comprising glycerin from a water immiscible fraction comprising fuel esters, carotenoids, and omega-3 fatty acids. The method also includes obtaining a C16 or shorter fuel esters fraction, a C16 or longer fuel ester fraction, and a residue comprising carotenoids and omega-3 fatty acids. The method includes hydrogenating and deoxygenating at least one of (i) the C16 or shorter fuel esters to obtain a jet fuel blend stock and (ii) the C16 or longer fuel esters to obtain a diesel blend stock.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
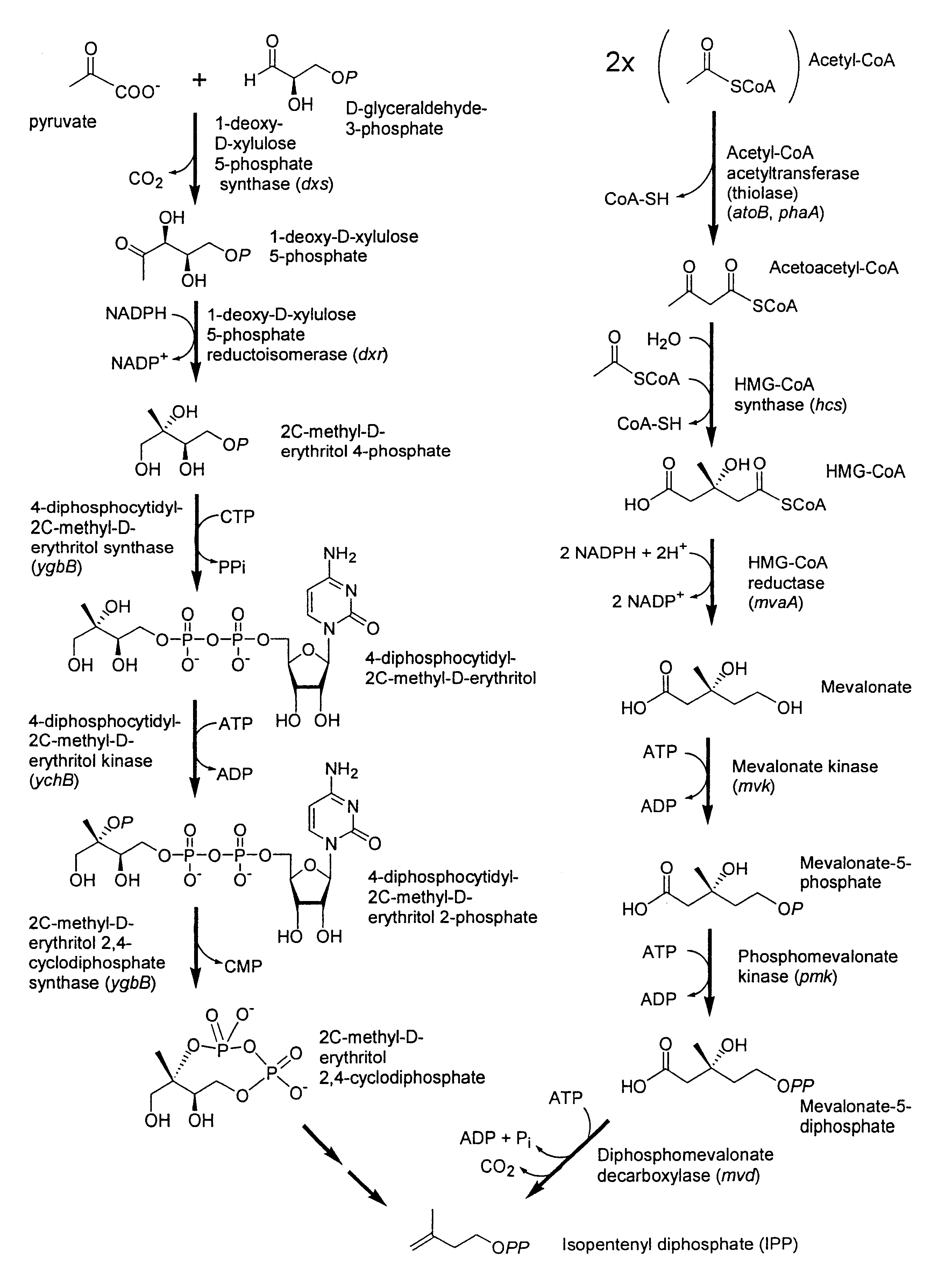
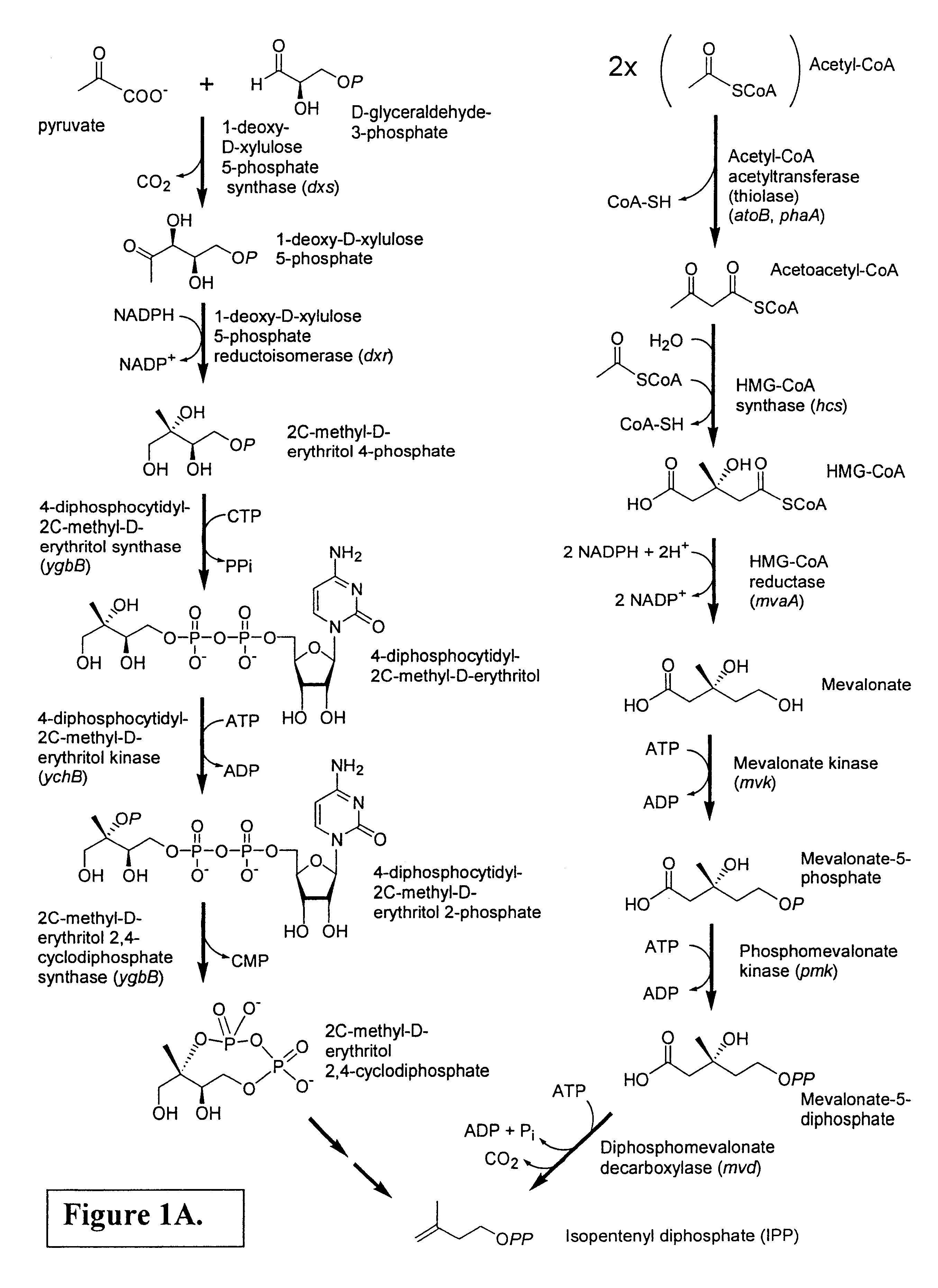
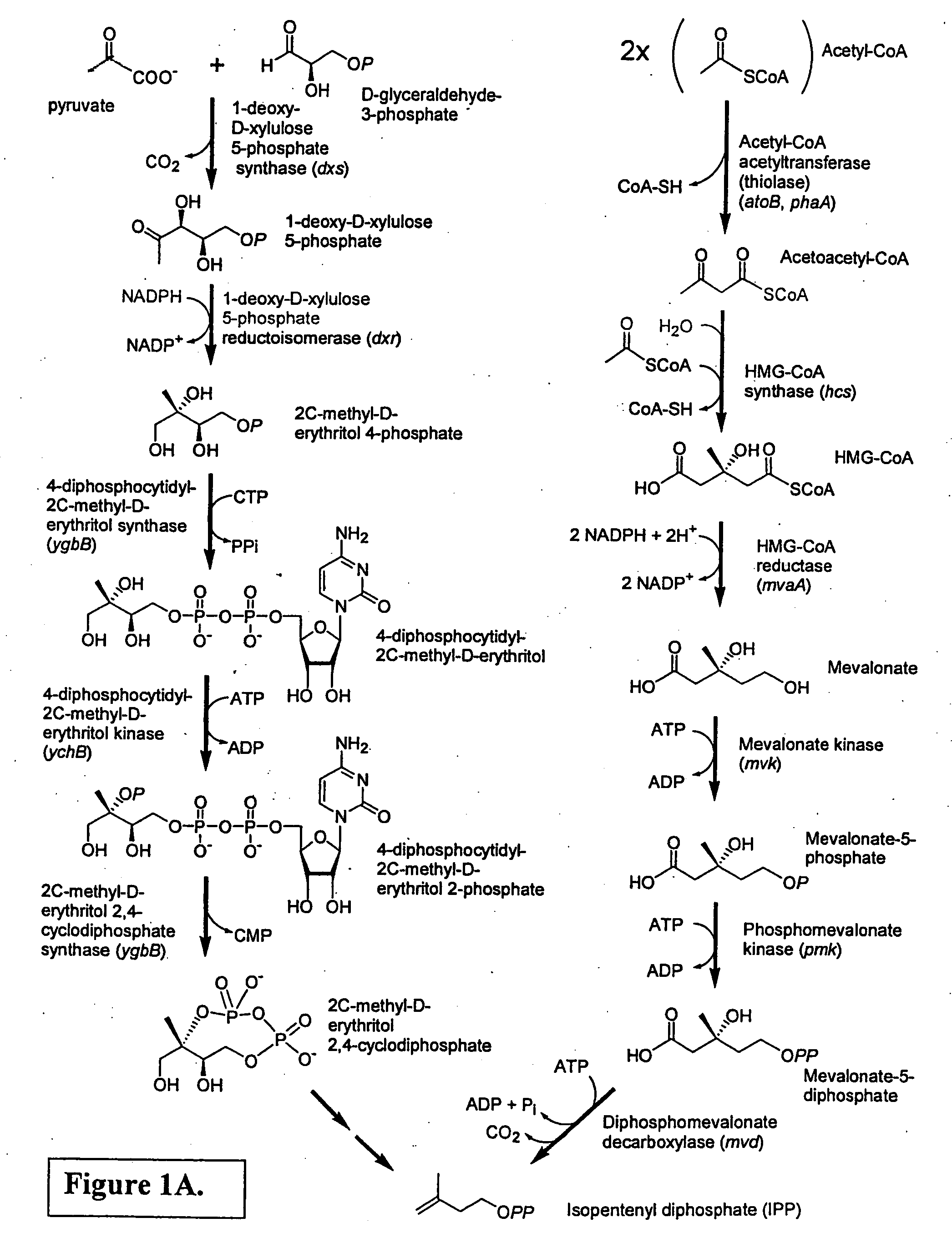
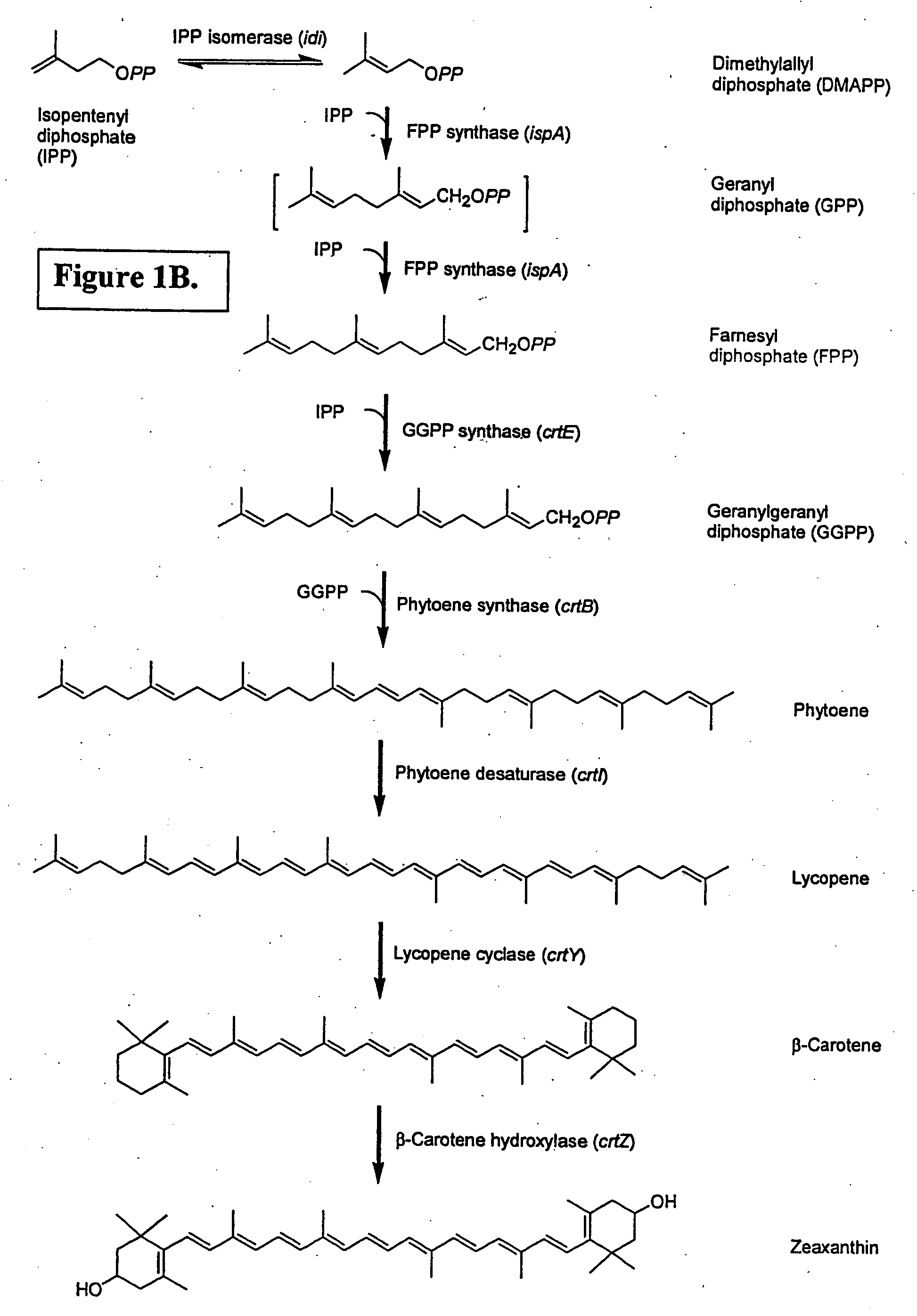
Isoprenoid production
Owner:DSM NUTRITIONAL PROD +1
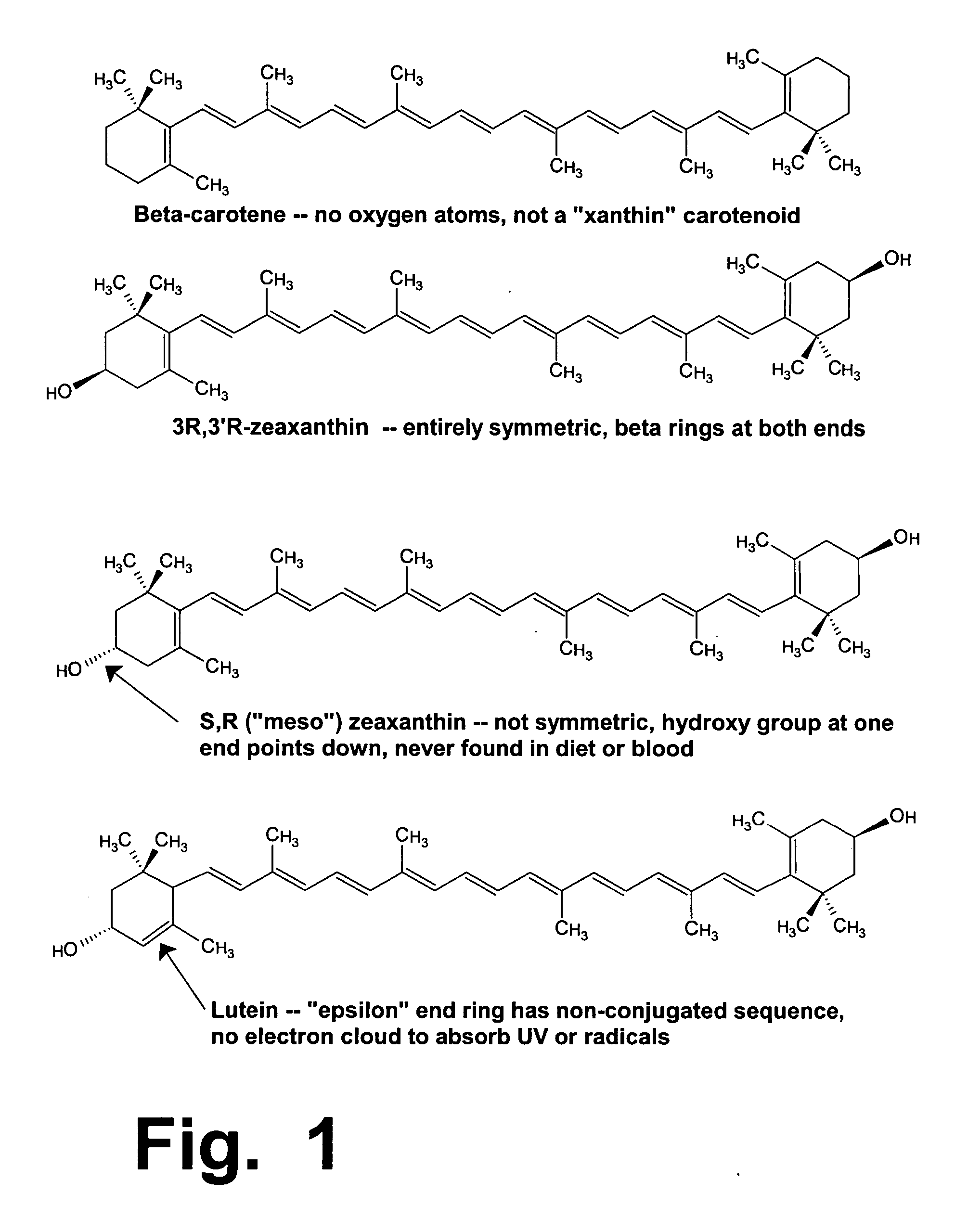
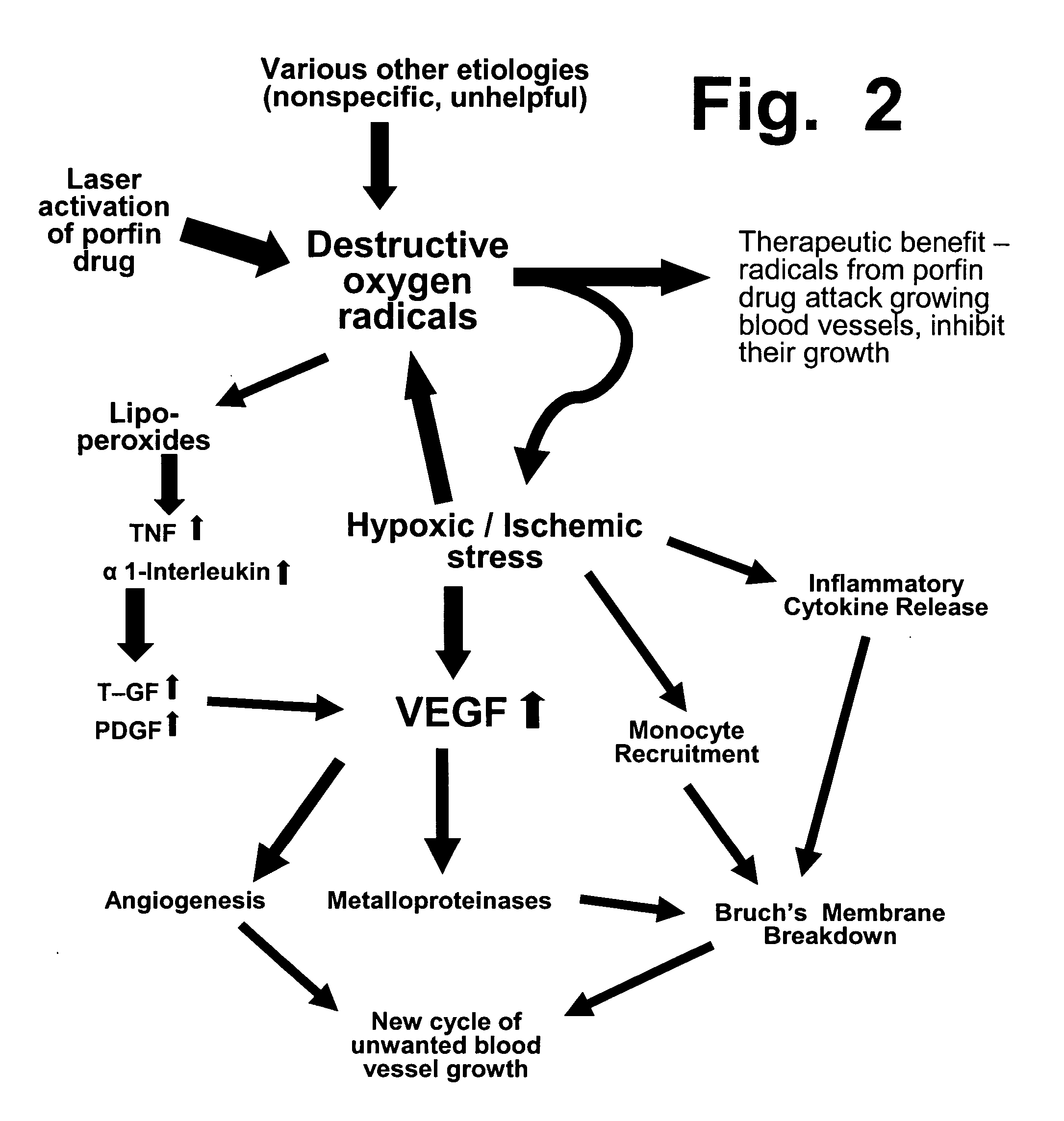
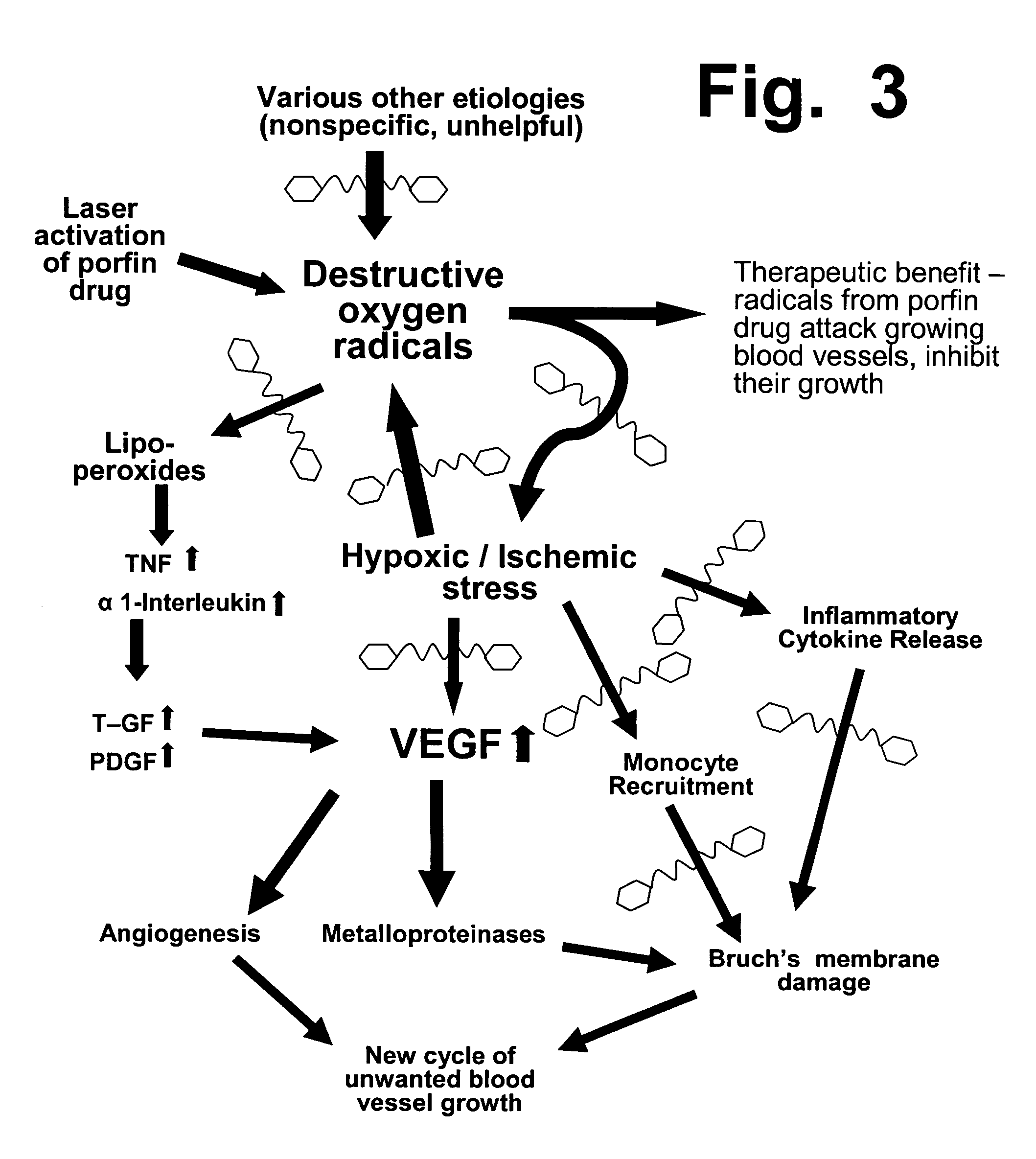
Preloading with macular pigment to improve photodynamic treatment of retinal vascular disorders
Pre-treatment using a xanthin carotenoid (preferably 3R,3′R-zeaxanthin) can improve the benefits and efficacy of photodynamic therapy (PDT), which uses a light-activated drug (such as verteporfin) in patients who suffer from unwanted retinal blood vessel growth, including the “wet” (exudative) form of macular degeneration. Before a PDT treatment, patients are given a regimen of orally-ingested zeaxanthin for a period of at least 1 and preferably at least 2 to 3 weeks, at dosages of at least 3 and preferably at least 10 milligrams per day. Since zeaxanthin imparts a yellowish color to the macula, a preferred dosage should increase a patient's macular pigment density before the PDT treatment is performed.
Owner:ZEAVISION LLC
Sea cucumber carotenoid lipid fractions and process
InactiveUS6055936AThe material is lowPromote recoveryNervous disorderHydrolysed protein ingredientsLipid formationCarotenoid
Processing methods and compositions of matter are disclosed for lipid fractions of sea cucumber intestinal mass and body wall tissue suitable for the healthfood industry and aquaculture feed pigment industry. A process and composition of matter description for obtaining a high protein de-lipidized, de-odorized meal is also disclosed.
Owner:COLLIN PETER DONALD
Carotenoid analogs or derivatives for the inhibition and amelioration of disease
ActiveUS20050113372A1Increase connexin expressionAmeliorate proliferationBiocideHydrocarbon active ingredientsSolubilityDisease
A method for inhibiting and / or ameliorating the occurrence of diseases associated with reactive oxygen species, reactive nitrogen species, radicals and / or non-radicals in a subject whereby a subject is administered a carotenoid analog or derivative, either alone or in combination with another carotenoid analog or derivative, or co-antioxidant formulation. The analog or derivative is administered such that the subject's risk of experiencing diseases associated with reactive oxygen species, reactive nitrogen species, radicals and / or non-radicals may be thereby reduced. The analog or analog combination may be administered to a subject for the inhibition and / or amelioration of any disease that involves production of reactive oxygen species, reactive nitrogen species, radicals and / or non-radicals. In some embodiments, the invention may include a chemical compound including an analog or derivative of a carotenoid. The carotenoid analog or derivative may be synthetic. The carotenoid analog may include a conjugated polyene with between 7 to 14 double bonds. The conjugated polyene may include an acyclic alkene including at least one substituent and / or a cyclic ring including at least one substituent. In some embodiments, a carotenoid analog or derivative may include at least one substituent. The substituent may enhance the solubility of the carotenoid analog or derivative such that the carotenoid analog or derivative at least partially dissolves in water.
Owner:CARDAX PHARMA
Isoprenoid production
Isolated polynucleotides encoding polypeptides having the activity of enzymes in the mevalonate pathway are provided. These sequences are useful for recombinantly producing isoprenoid compounds, such as carotenoids, in particular zeaxanthin. Expression vectors, cultured cells, and methods of making isoprenoid compounds are also provided.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Fucoidan compositions and methods
InactiveUS20080089941A1Effective treatmentPromote healingOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsAdditive ingredientDietary supplement
Compositions and methods relating to partially hydrolyzed fucoidan for use in dietary supplements and skin-care products are described. Fucoidan from brown seaweeds is partially hydrolyzed and / or sulfonated and then mixed with other ingredients for use as a dietary supplement in beverage, capsule, or tablet form or for use as a skin-care product. Other ingredients that can be included in the dietary supplements include vitamins, minerals, amino acids, carotenoids, flavonoids, antioxidants, aminosugars, glycosaminoglycans, and botanicals. Skin care products according to the present invention comprise partially hydrolyzed fucoidan and a base.
Owner:SAKURA PROPERTIES LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com