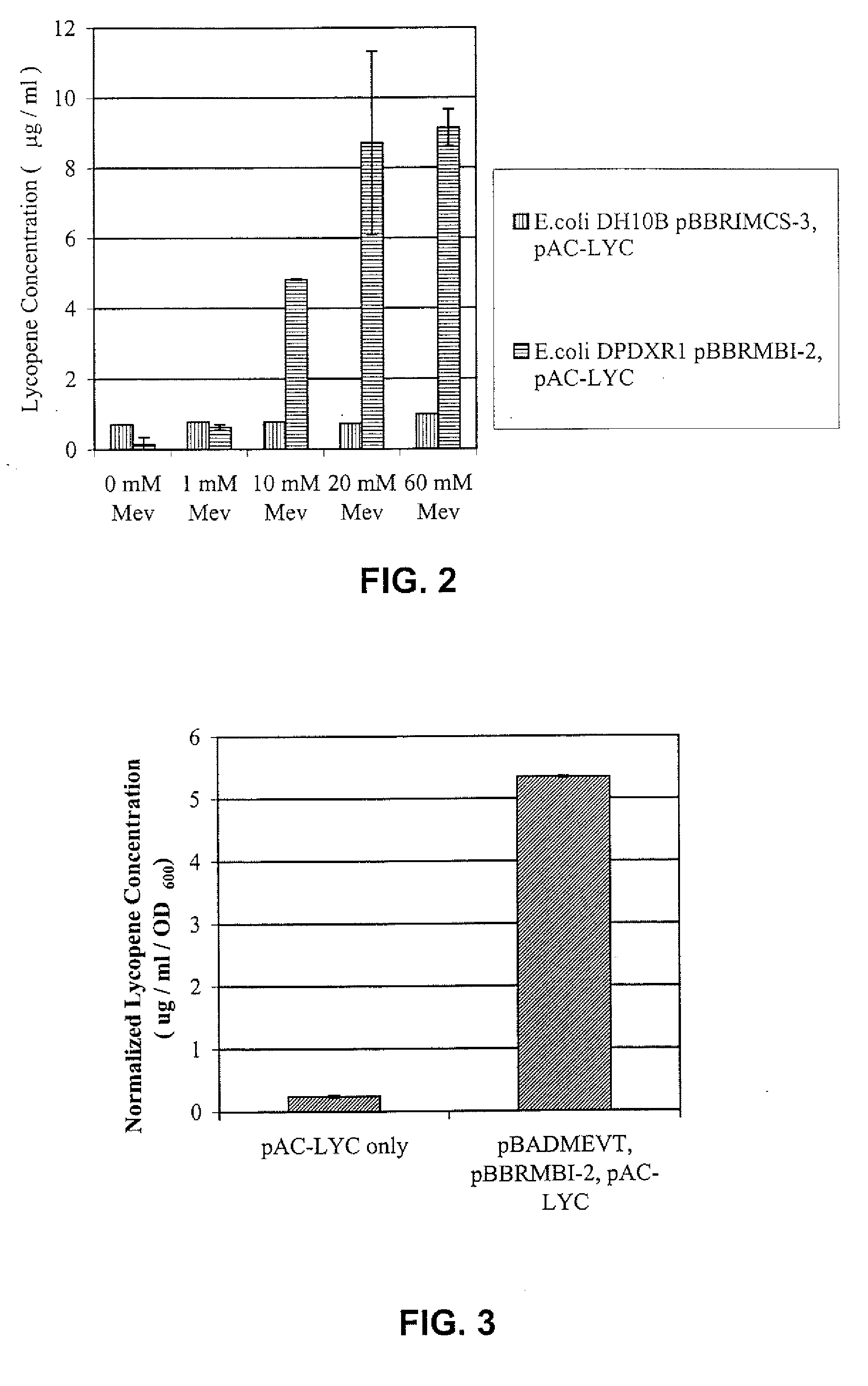
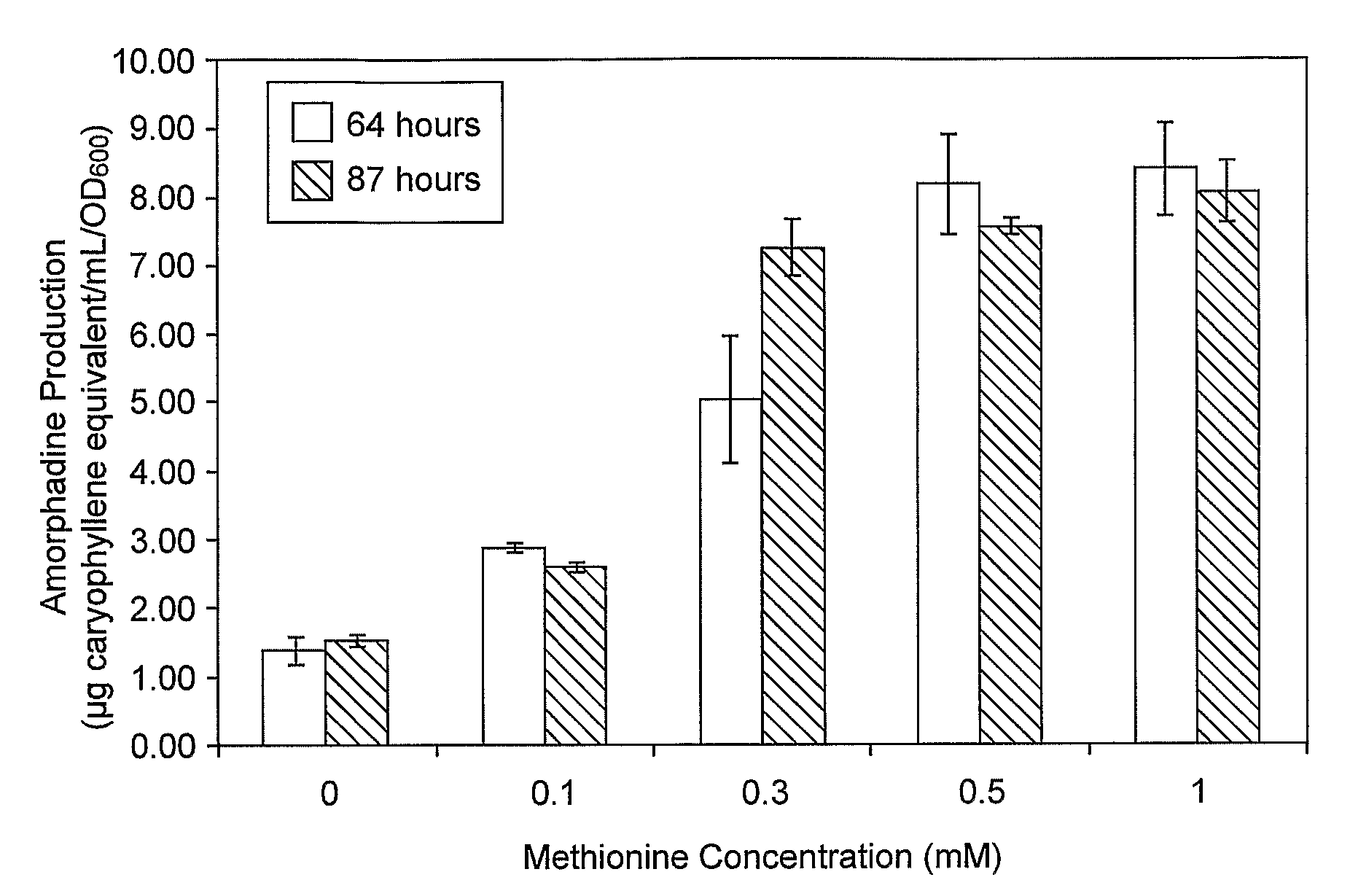
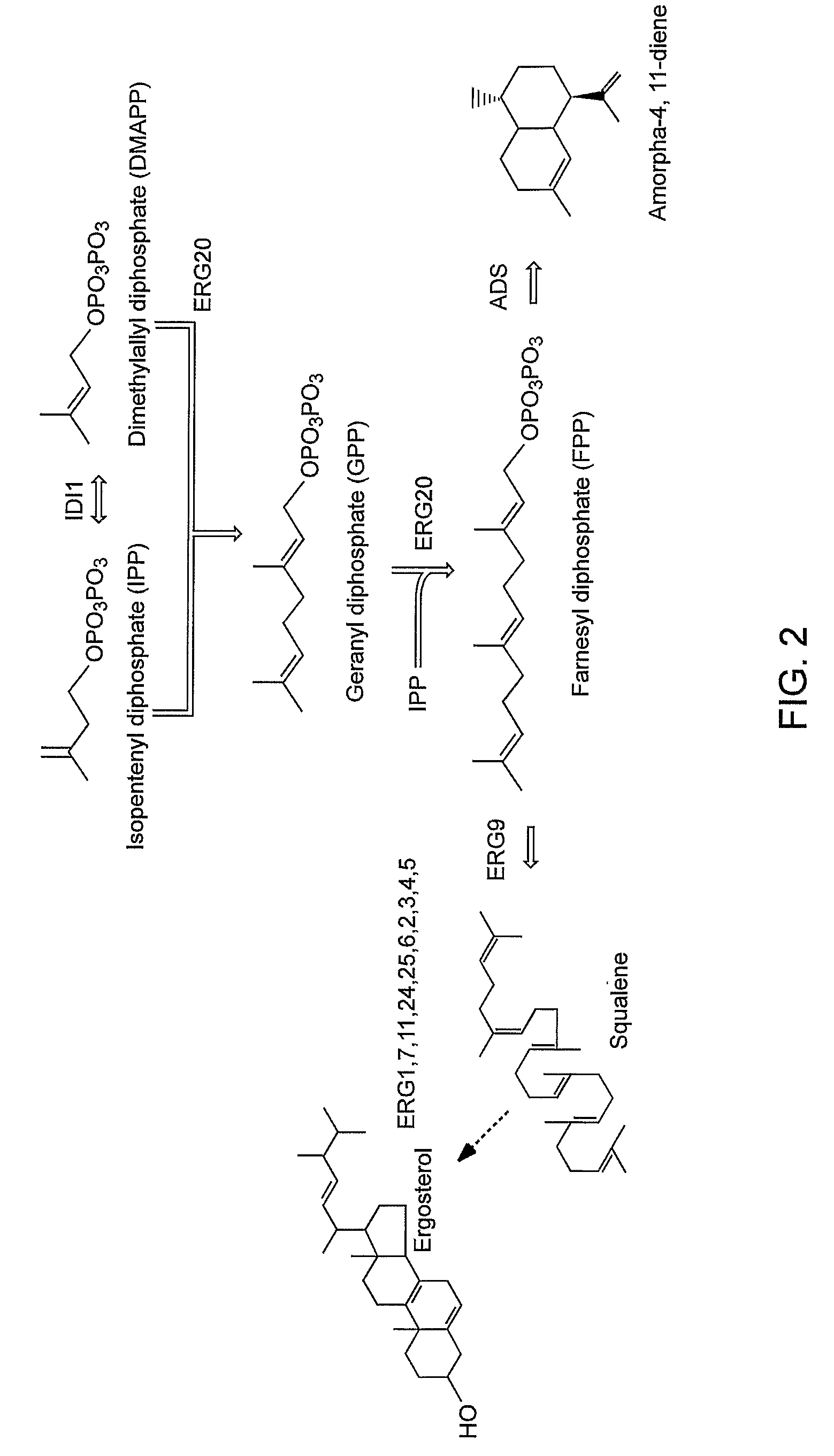
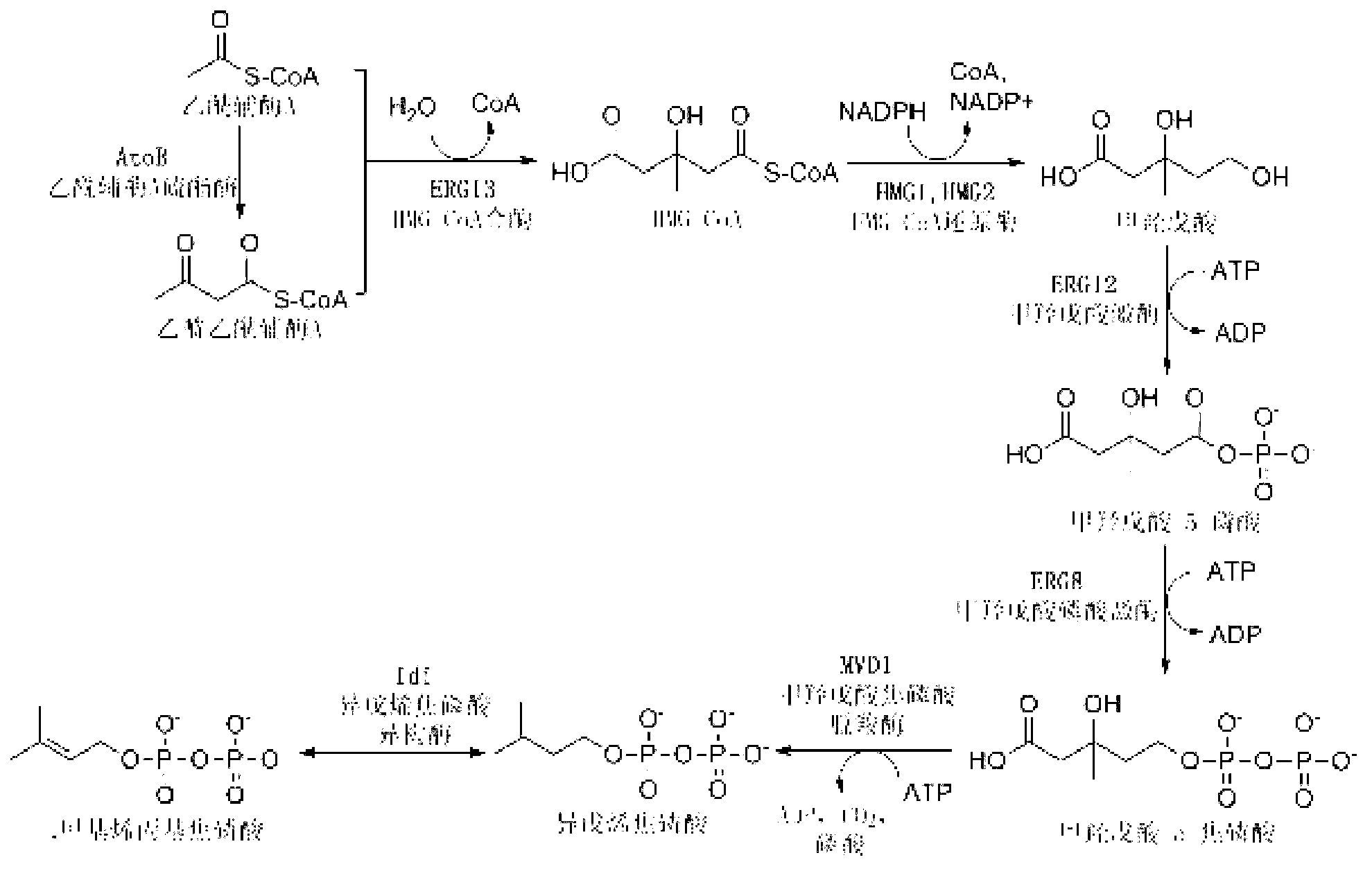
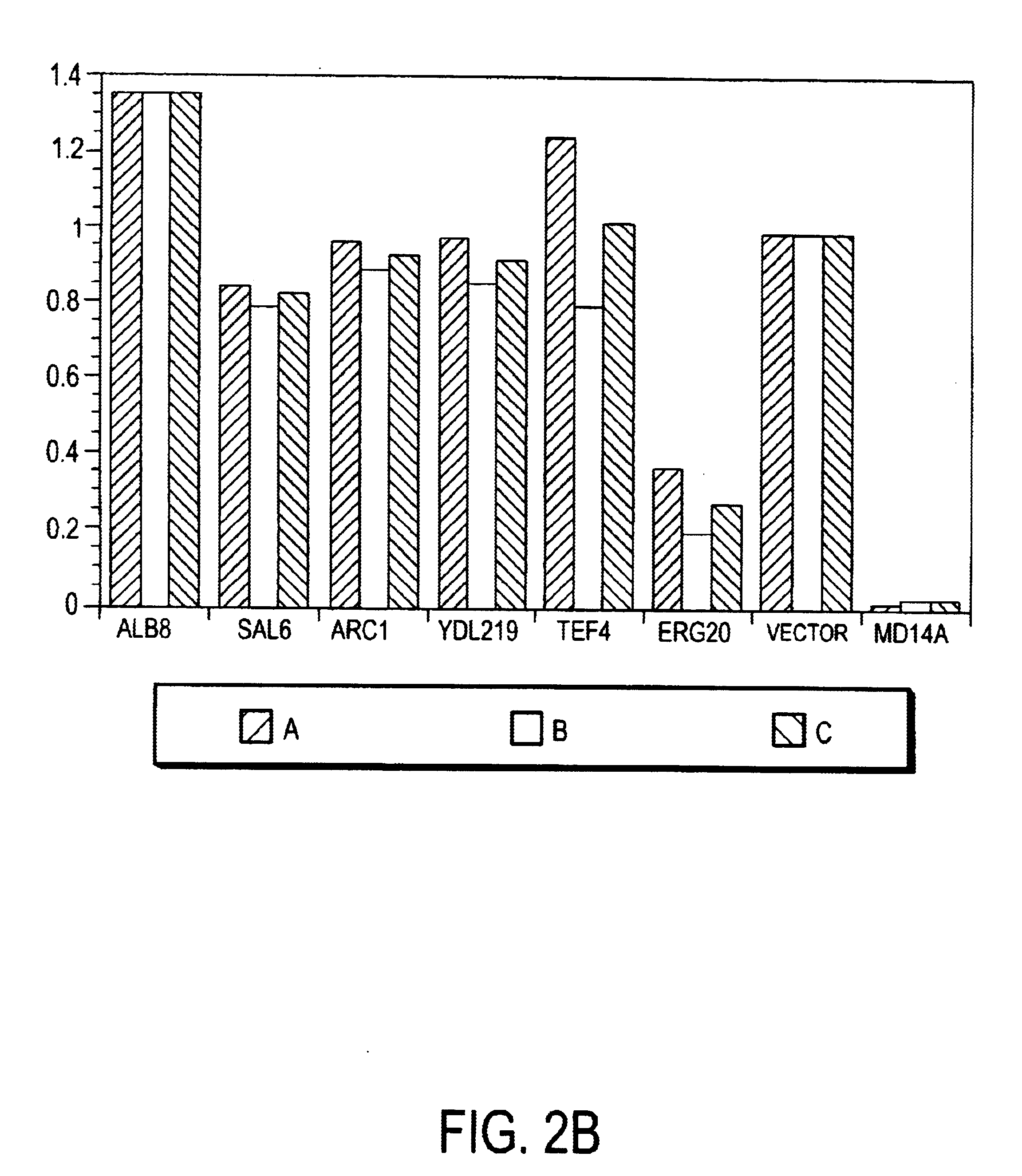
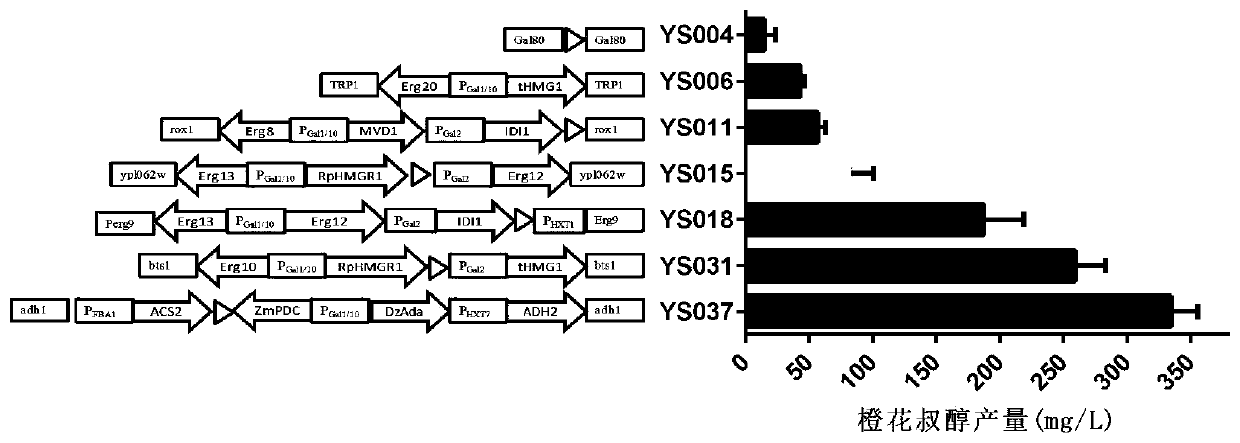
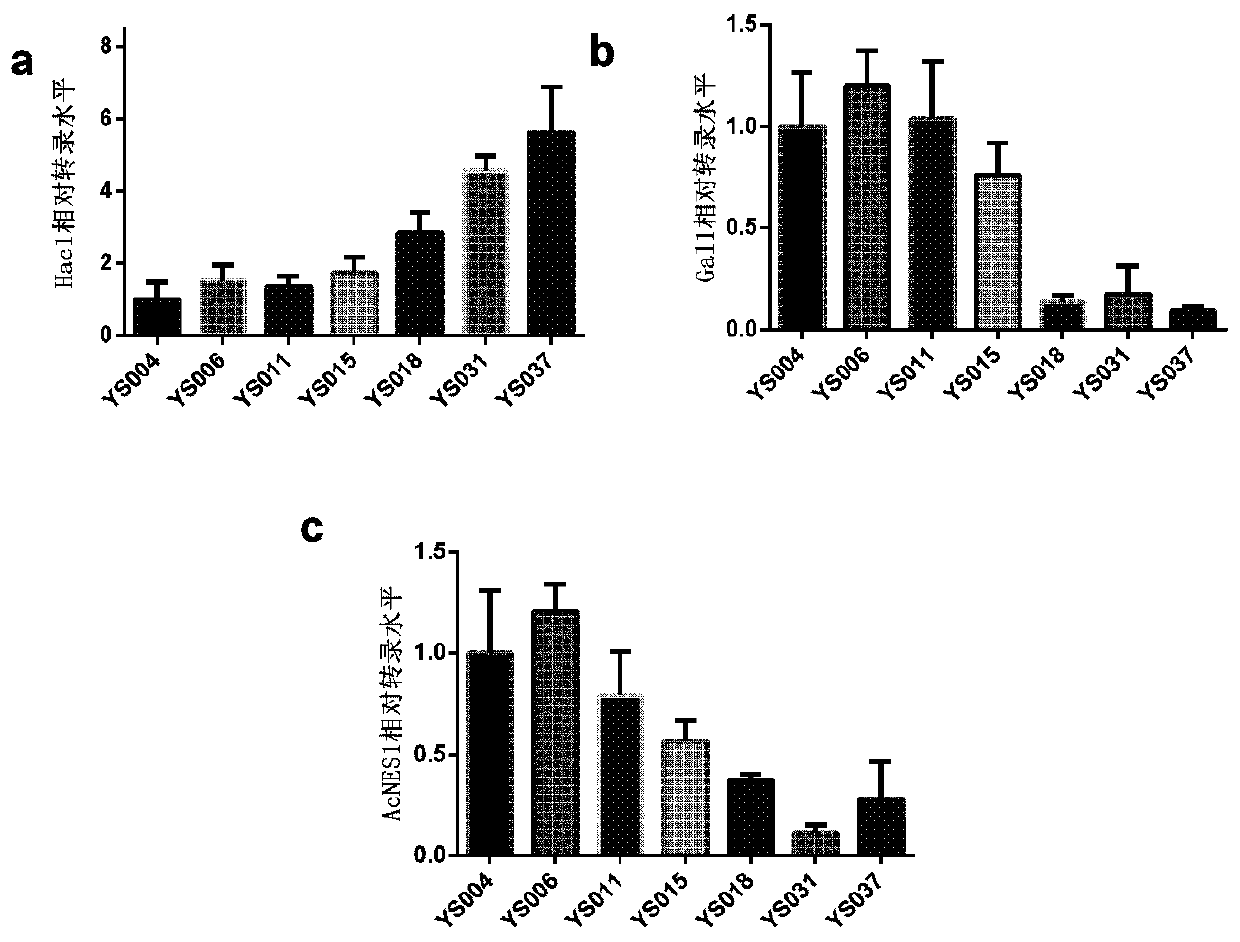
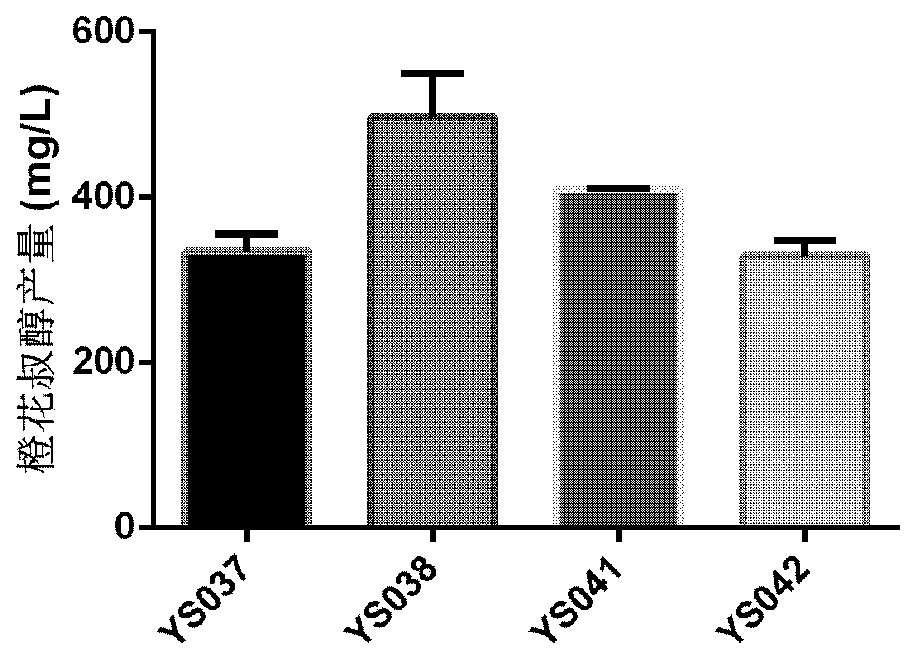
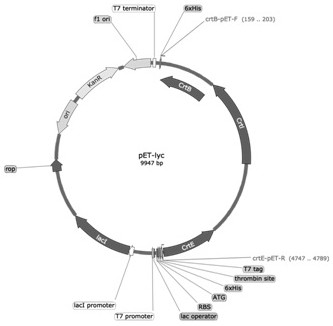
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
86 results about "Mevalonate pathway" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
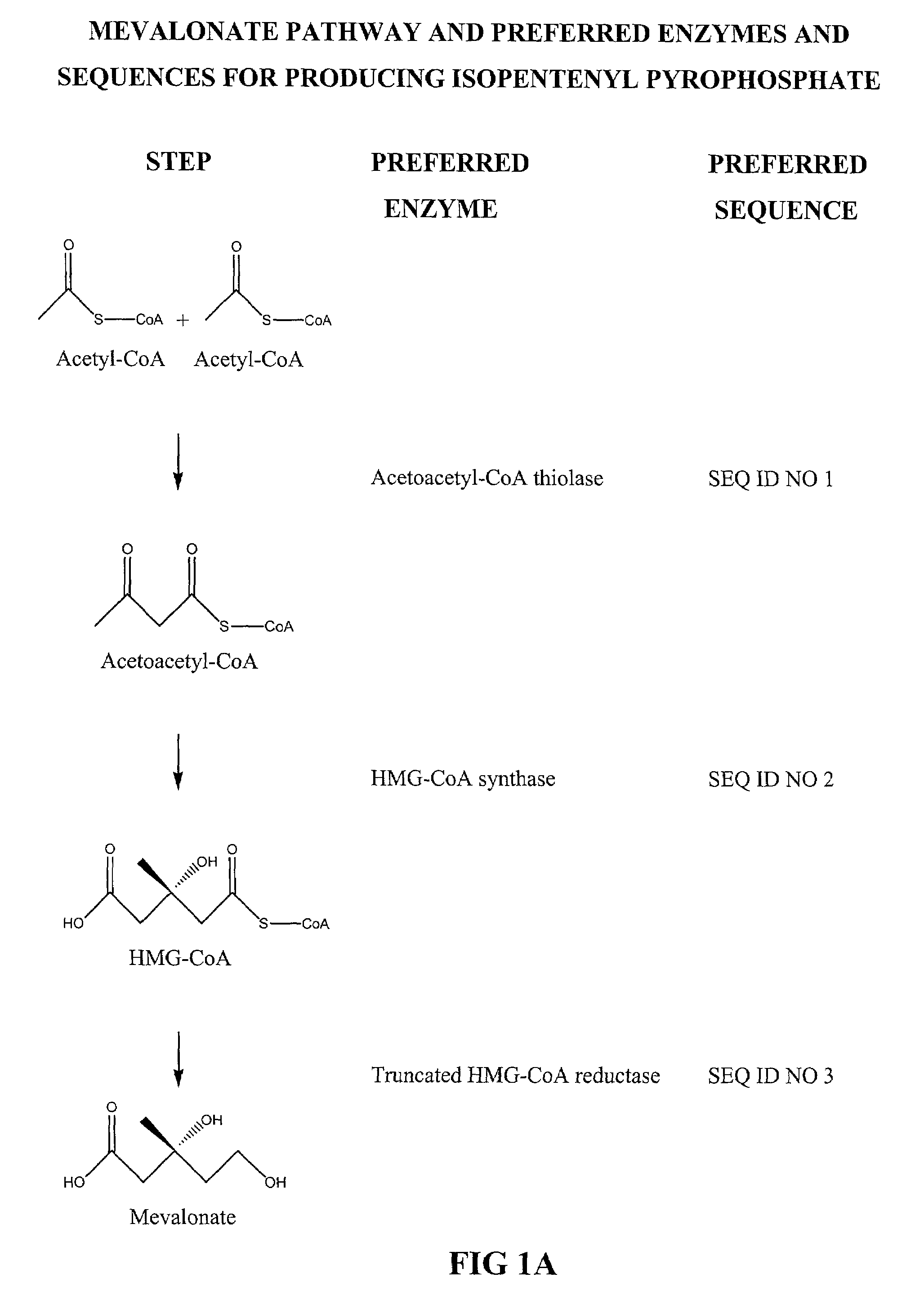
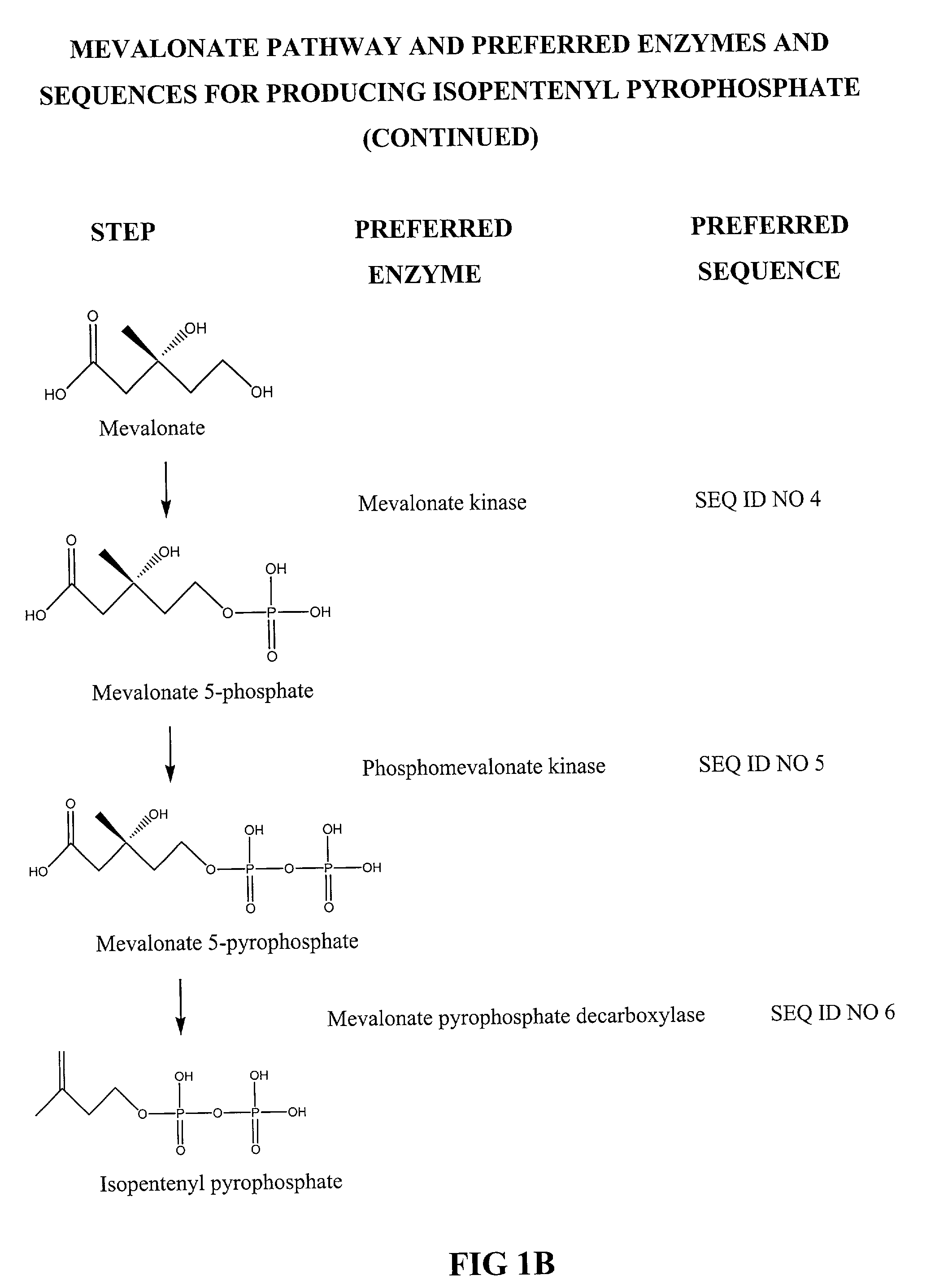
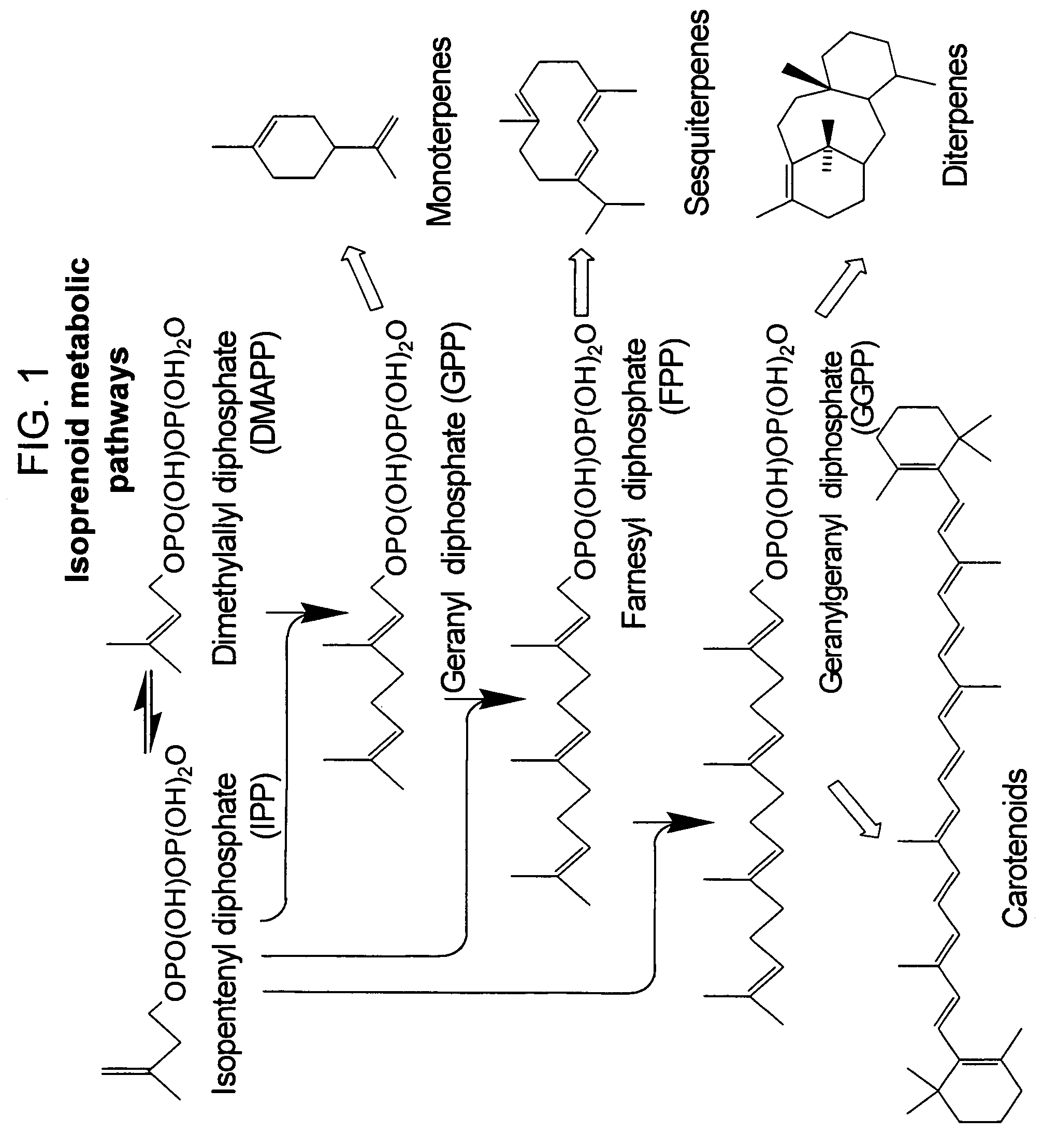
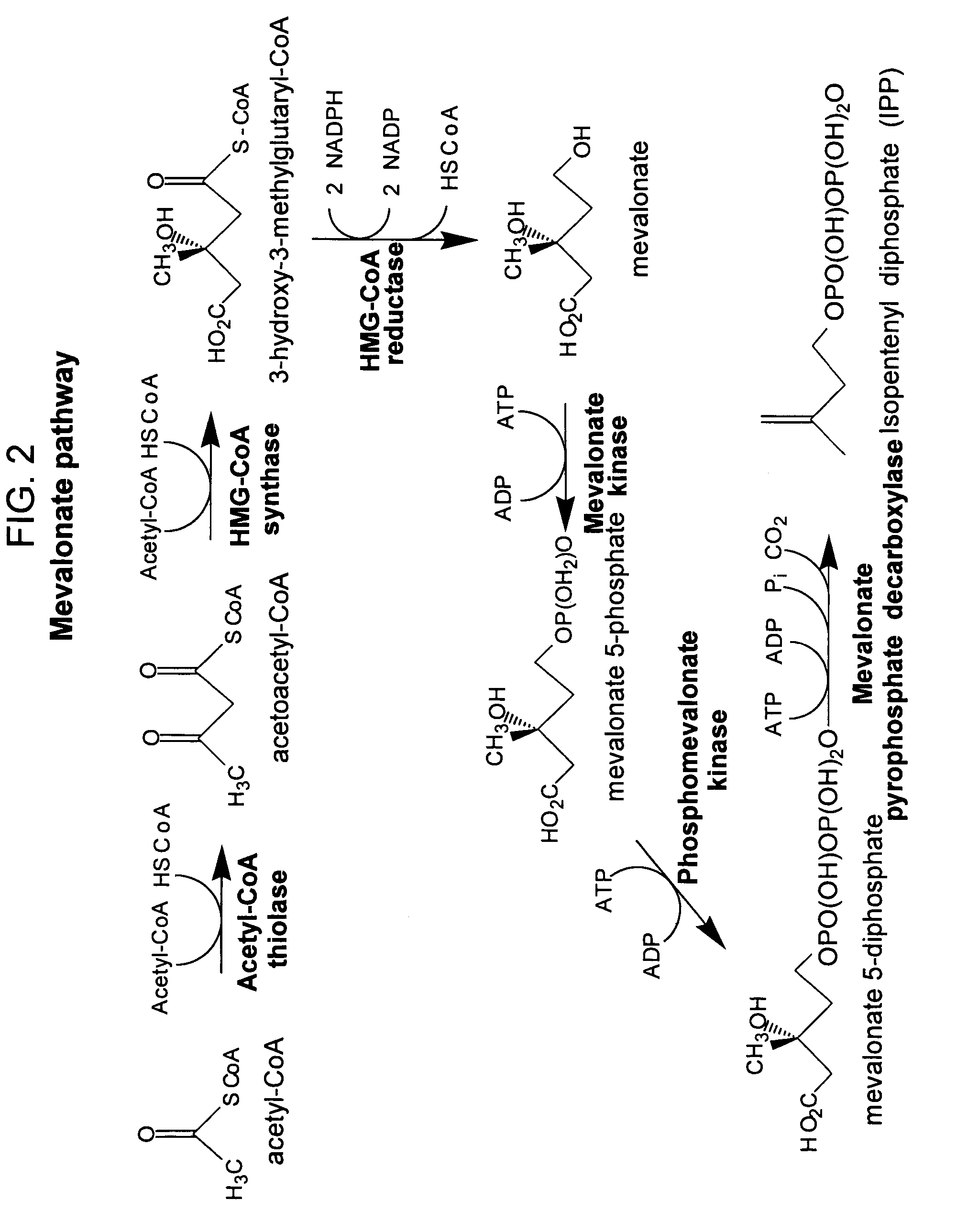
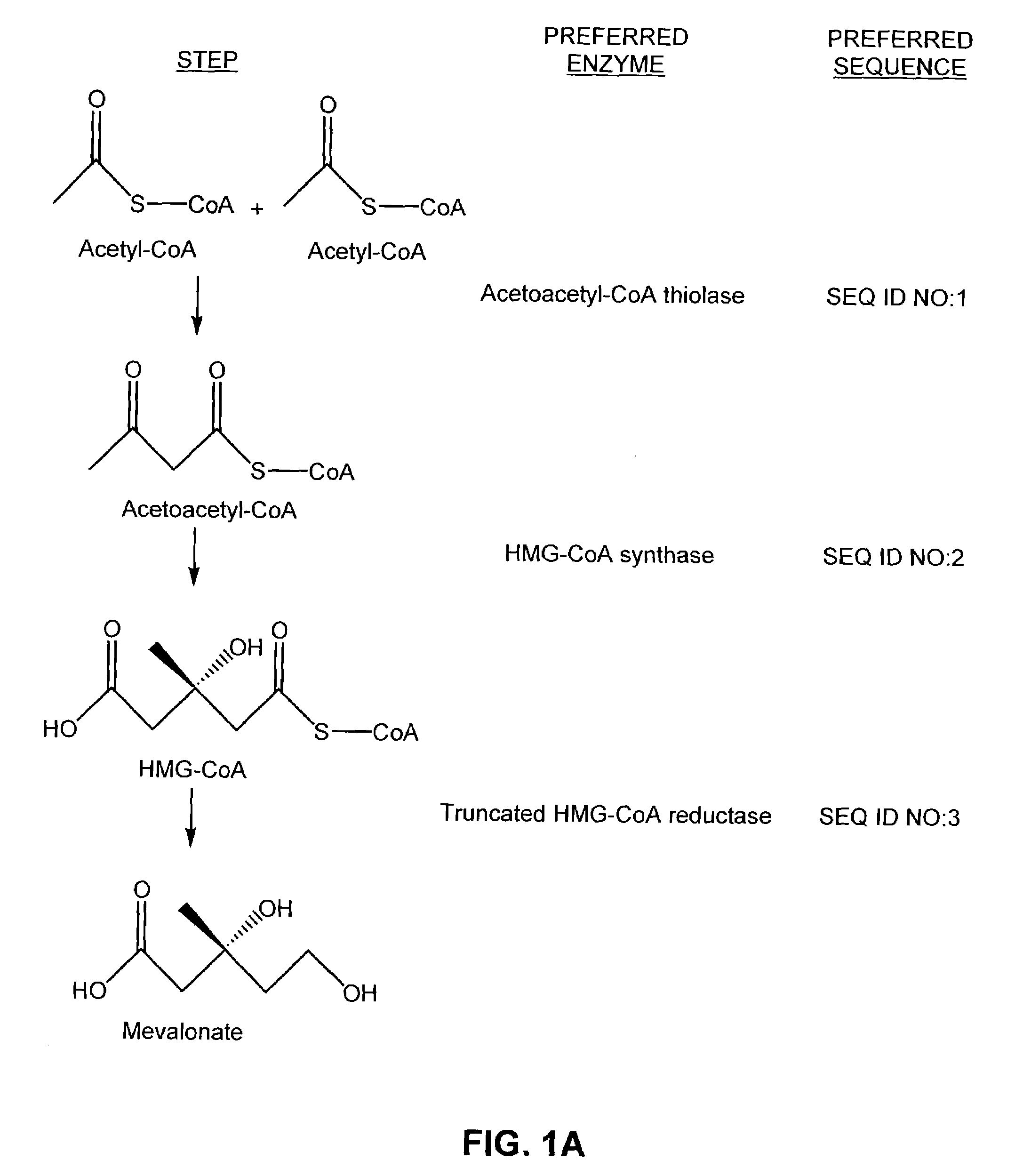
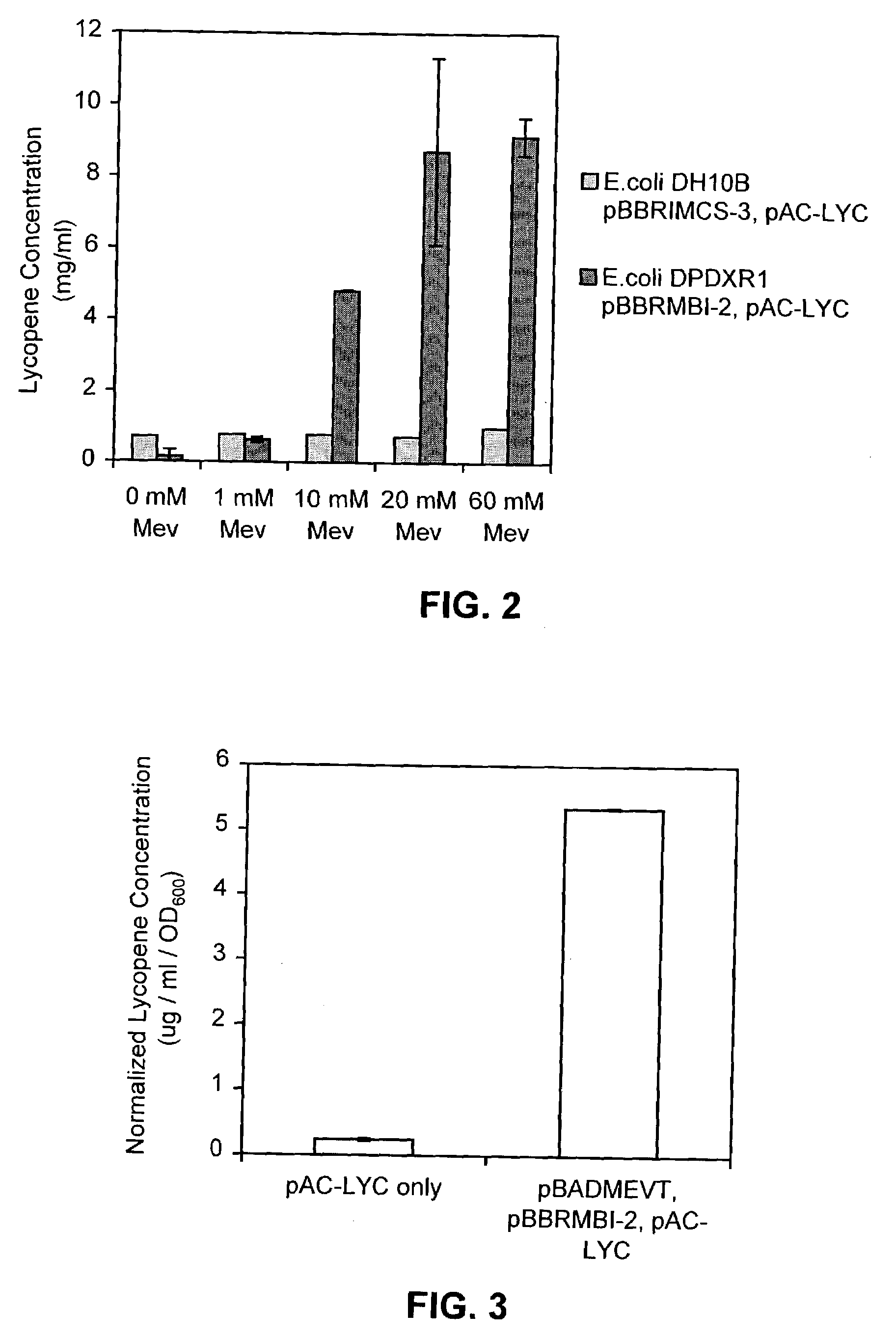
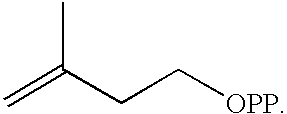
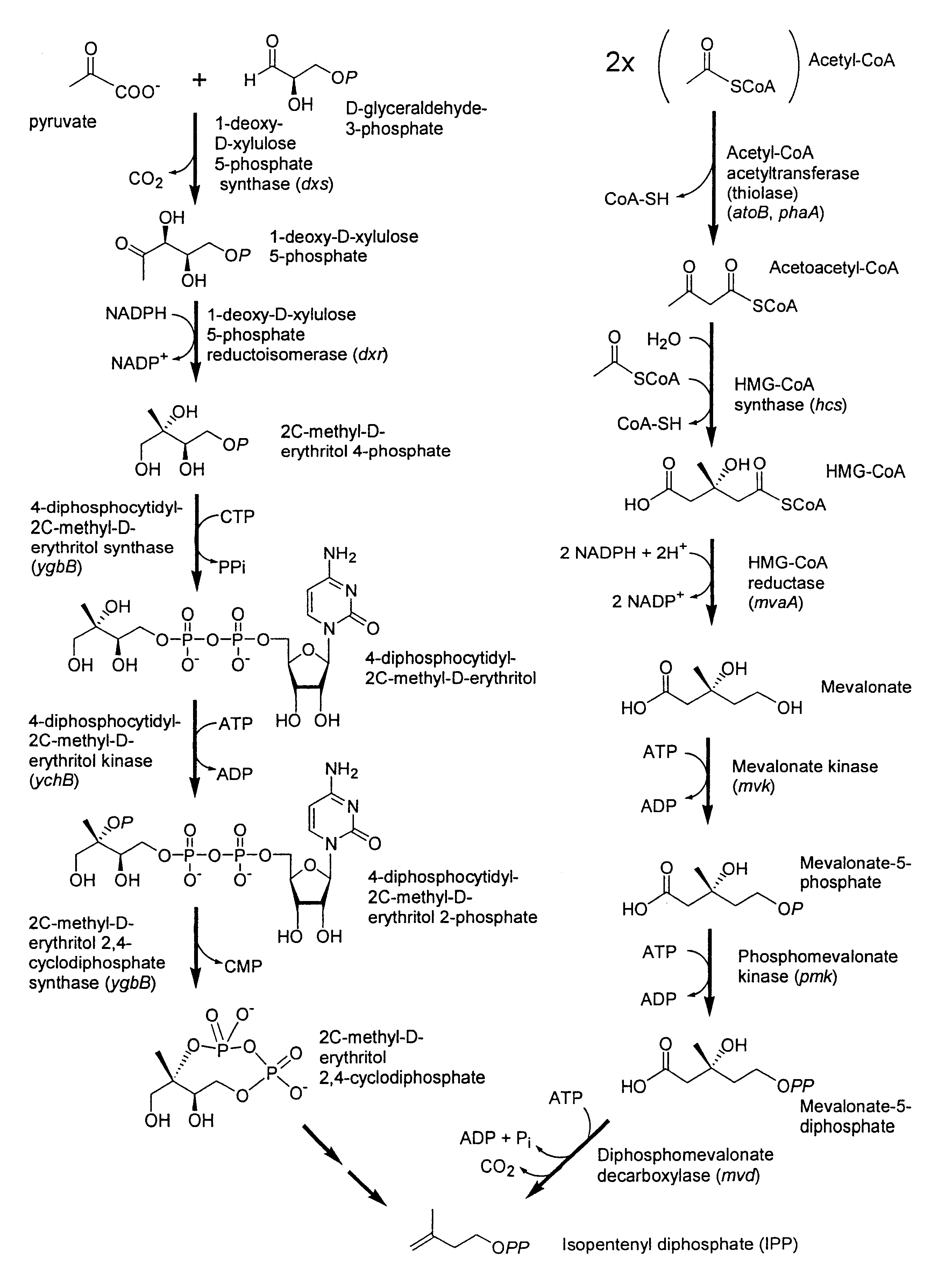
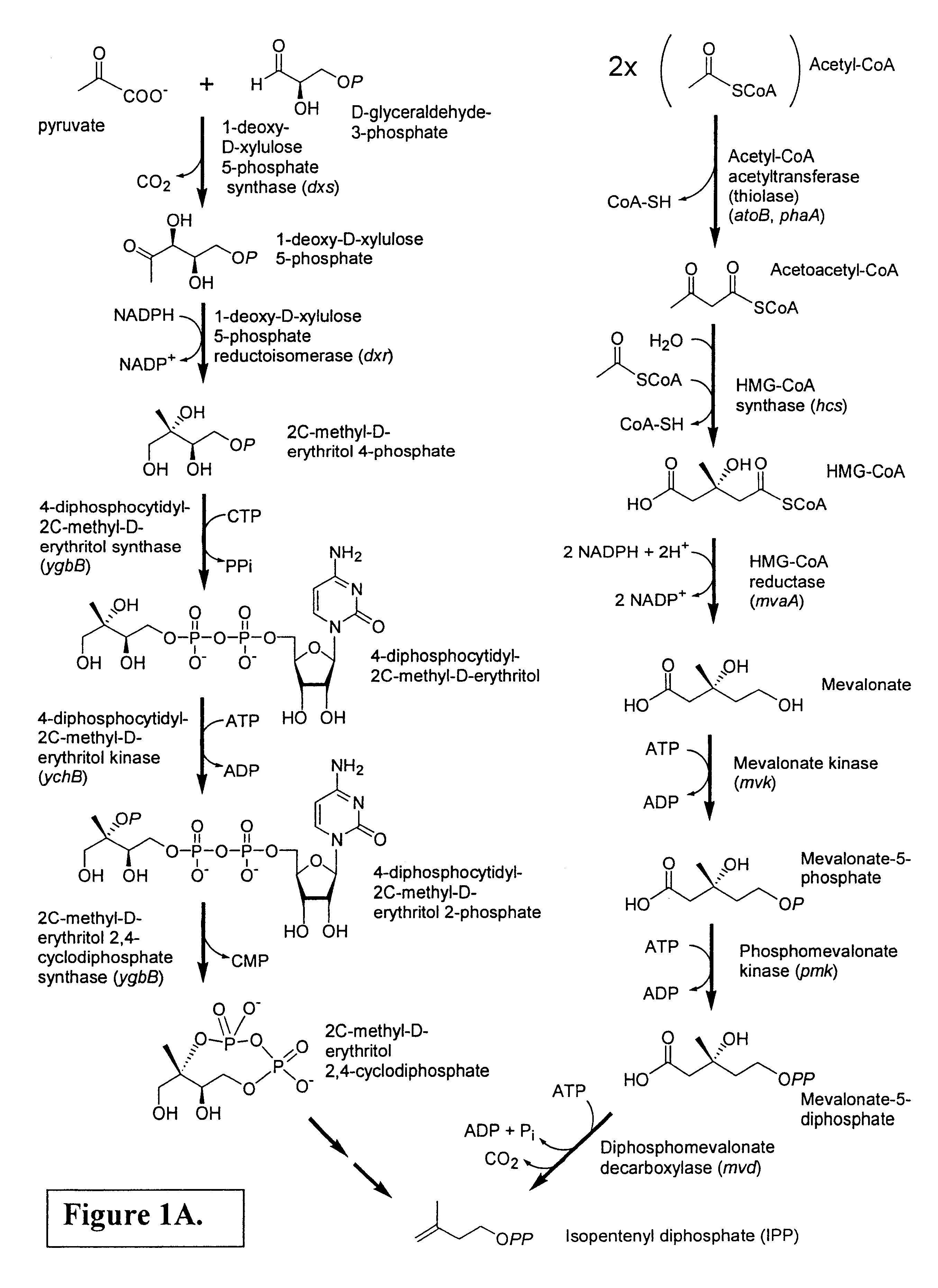
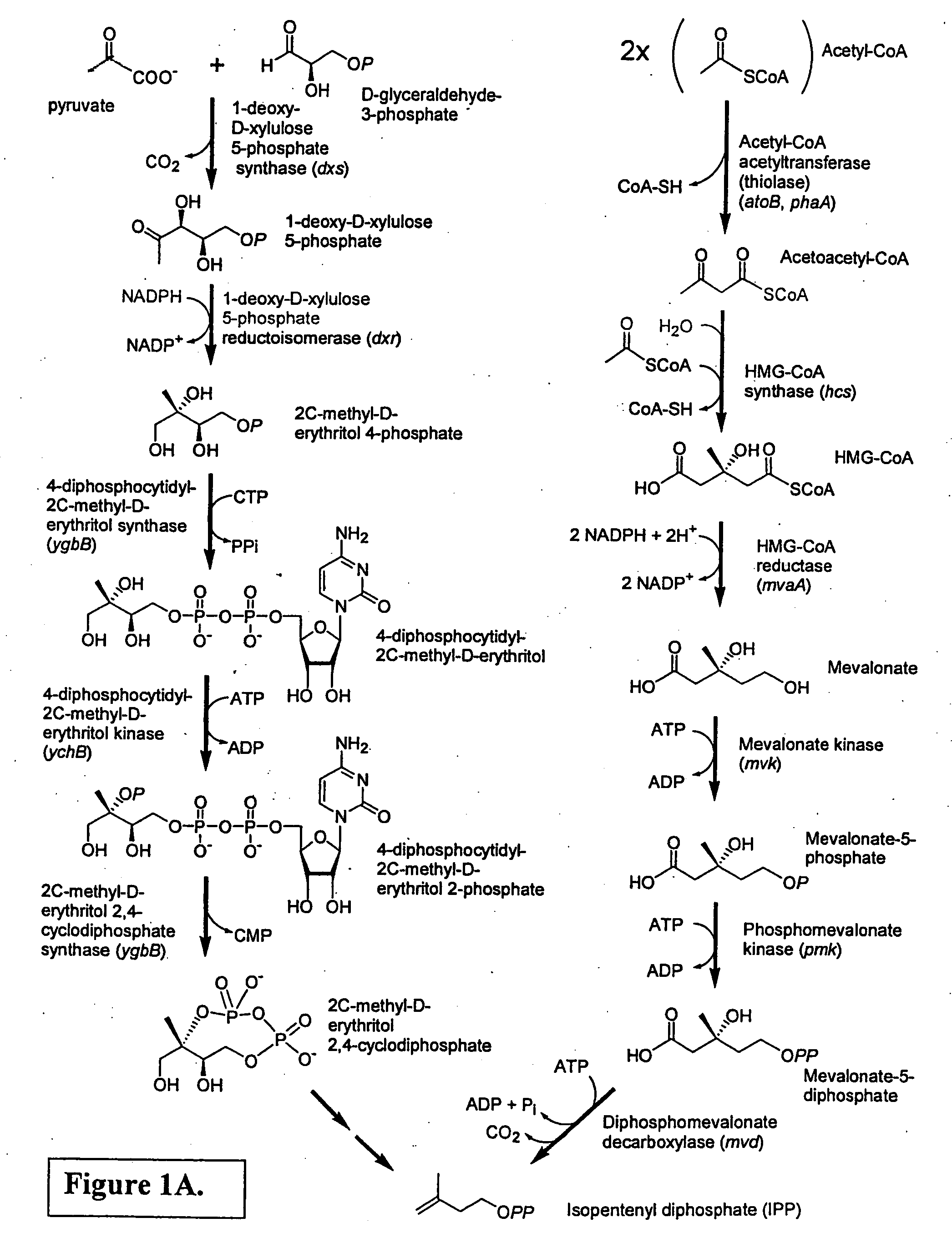
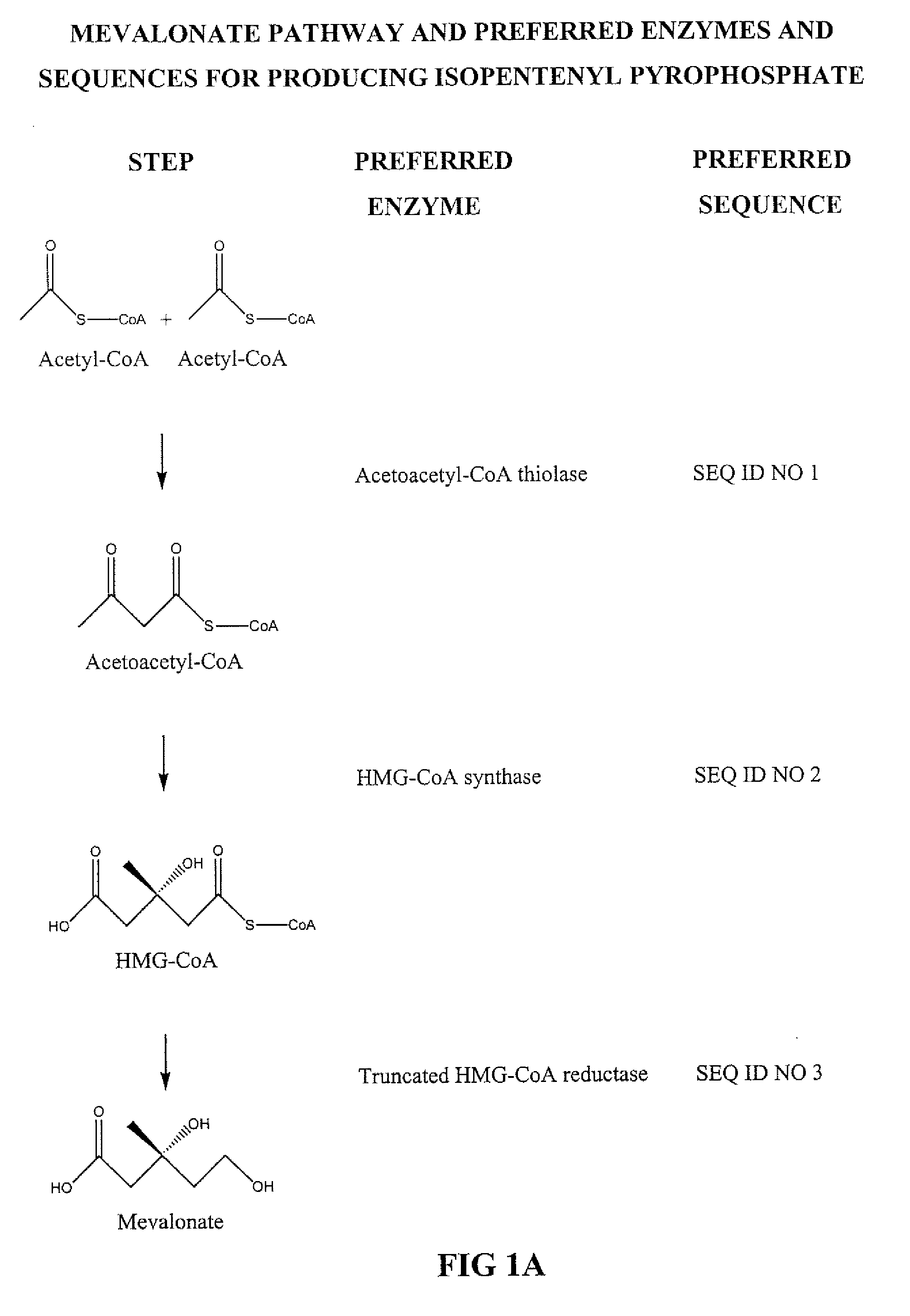
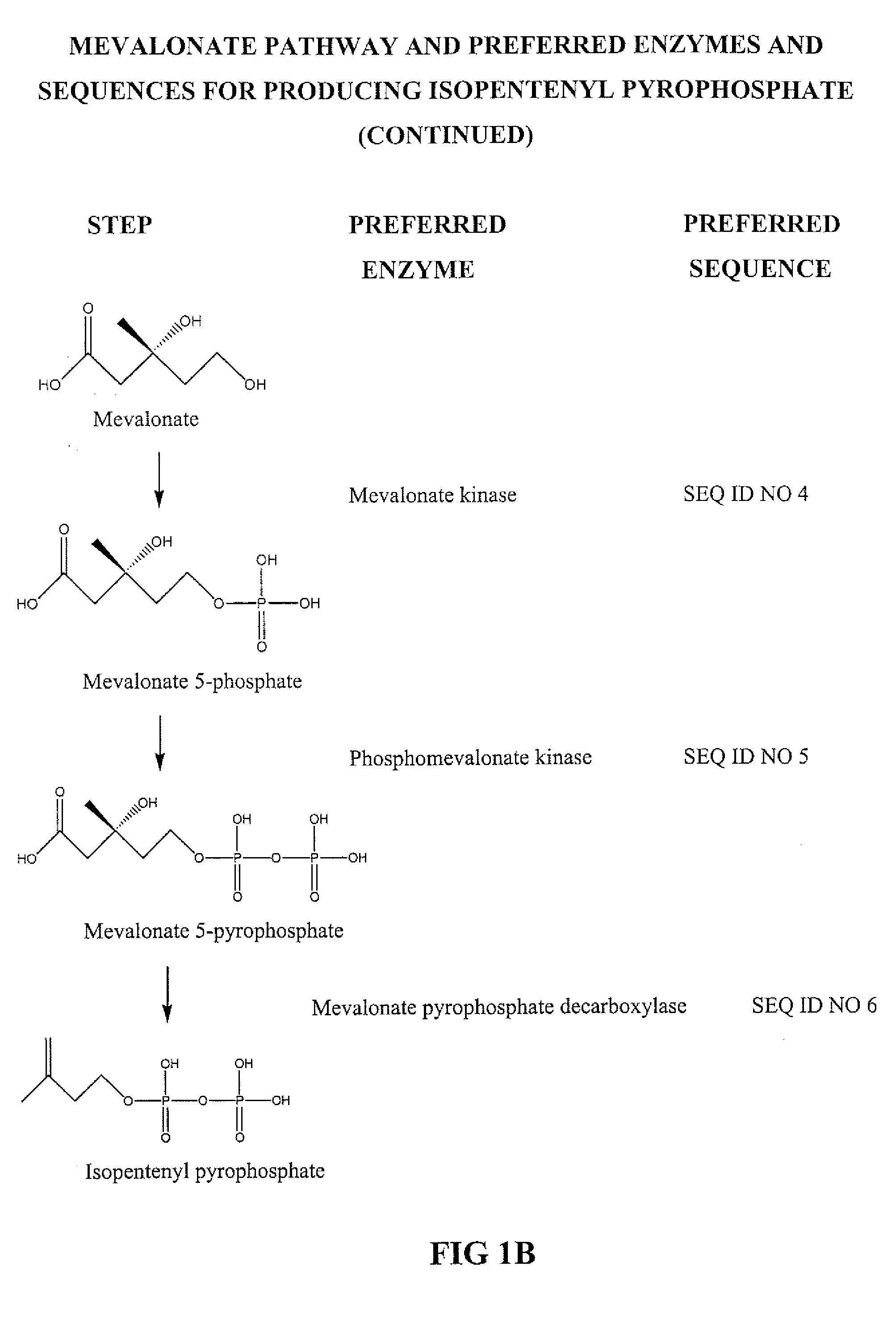
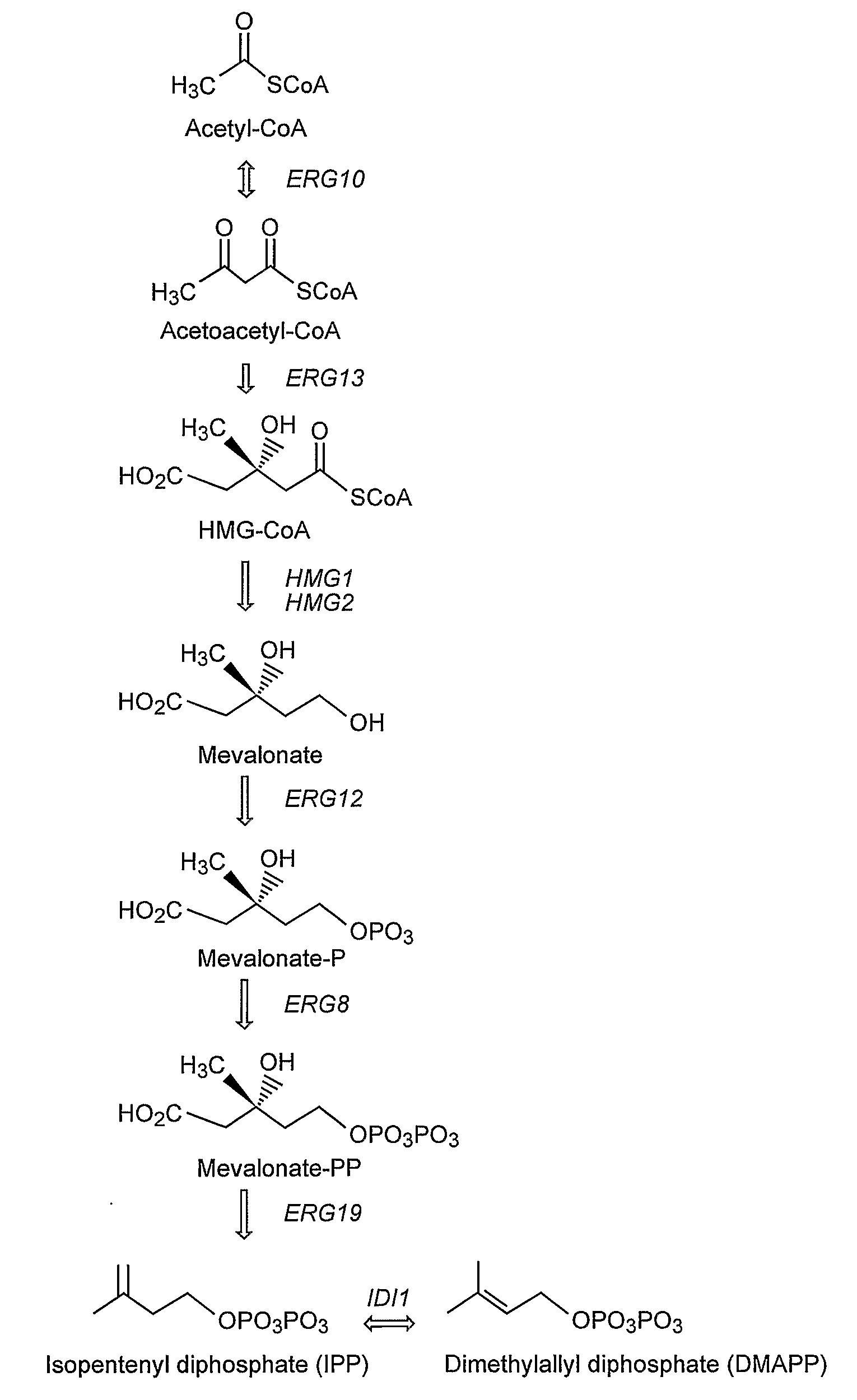
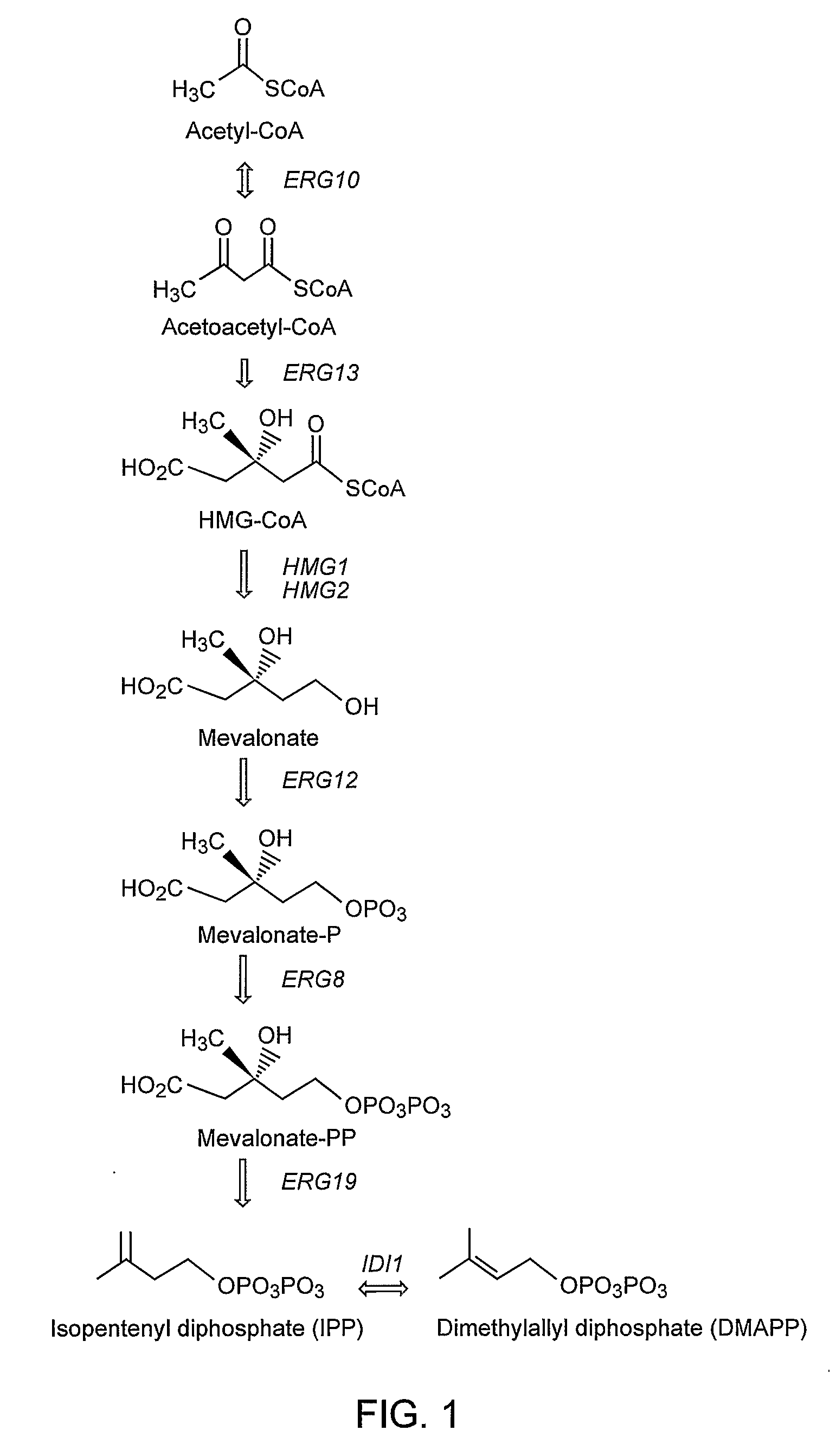
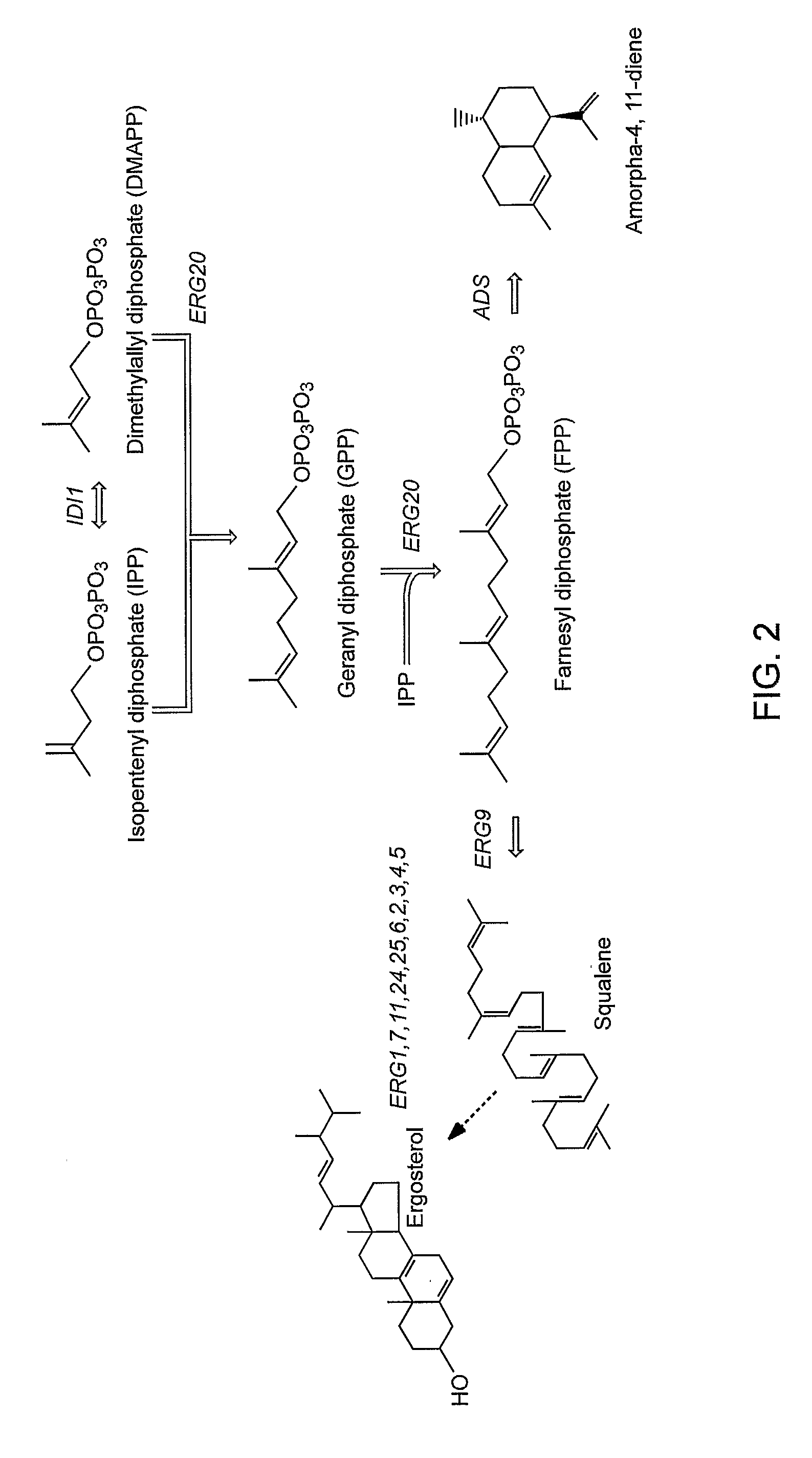
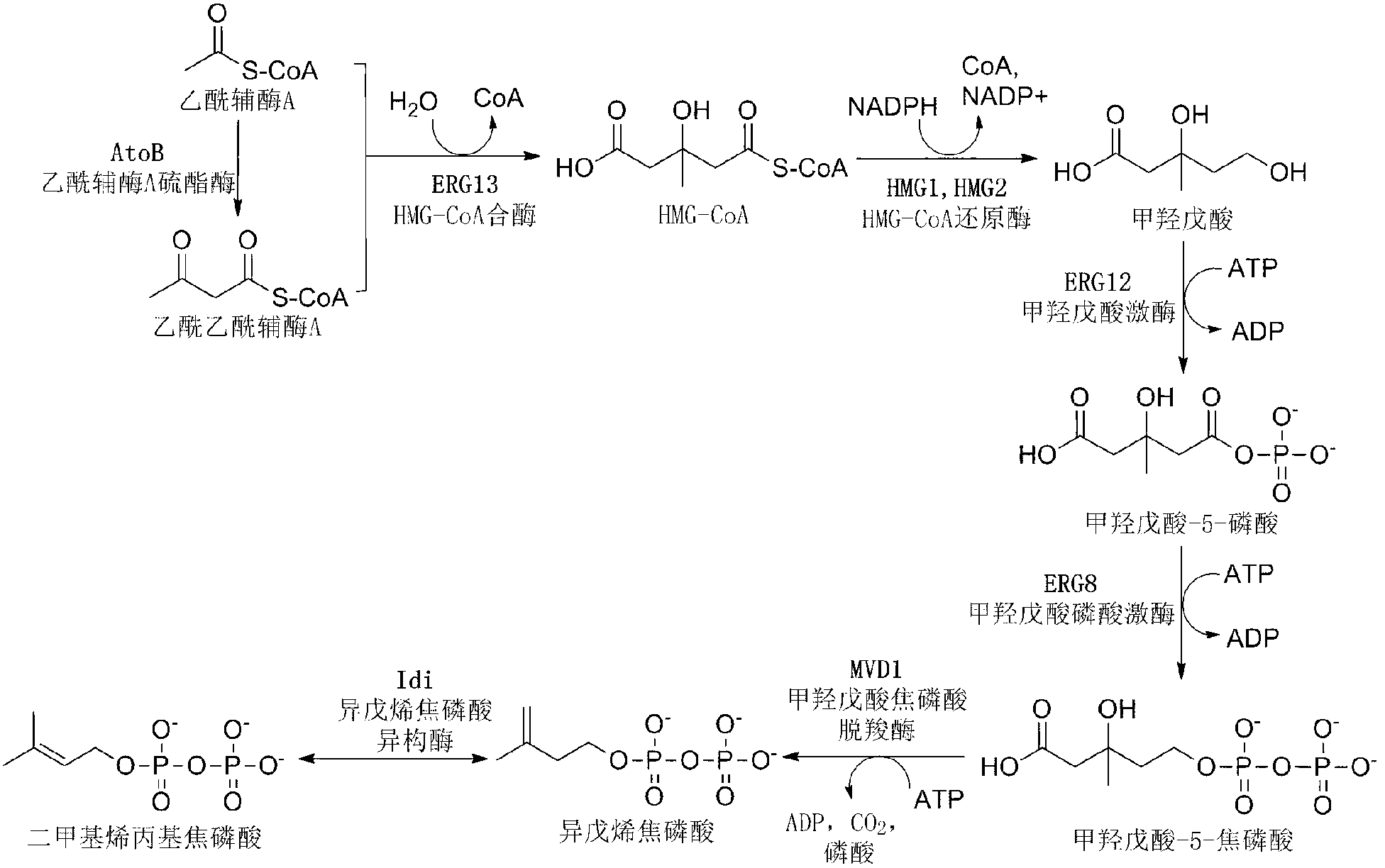
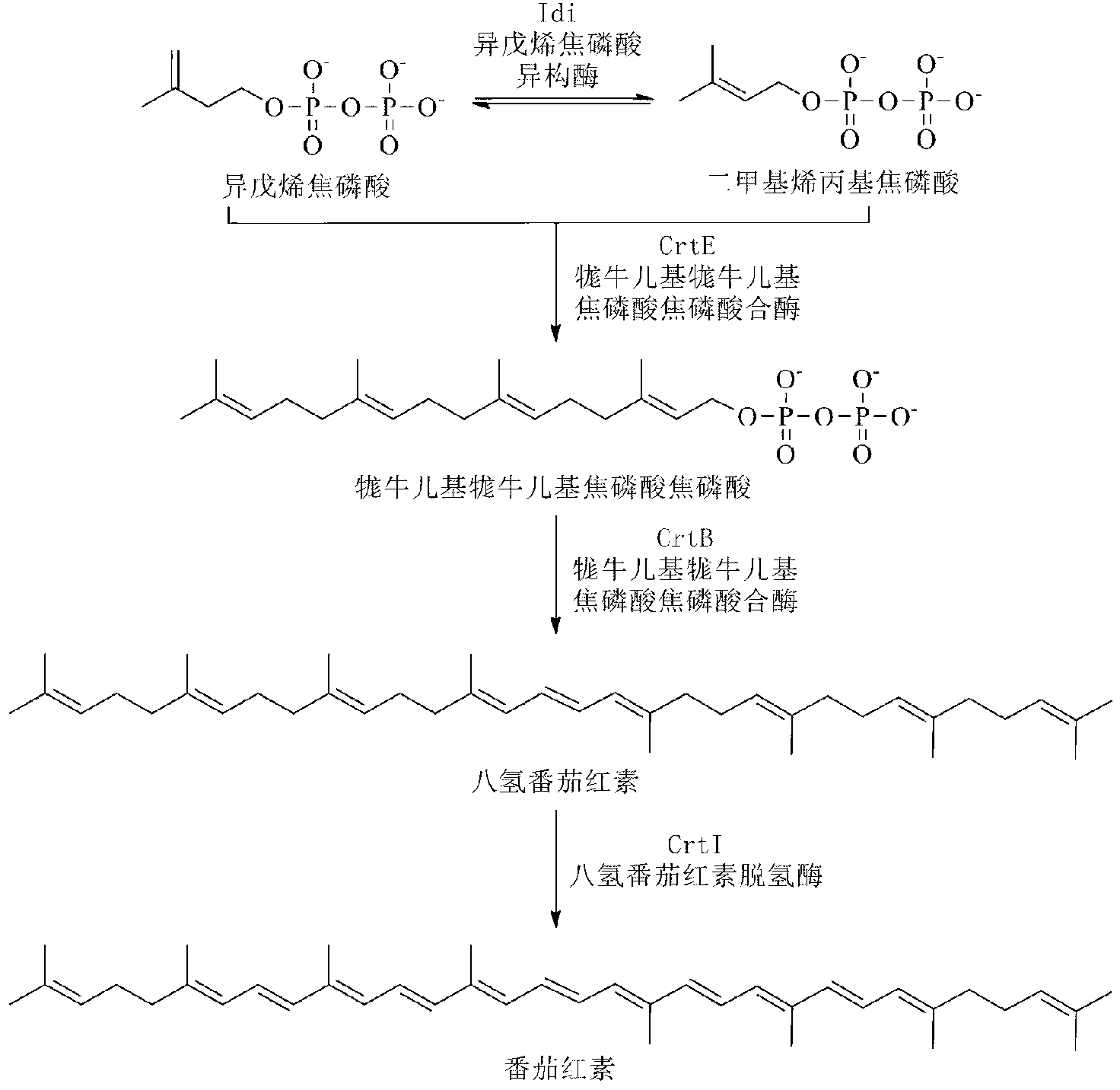
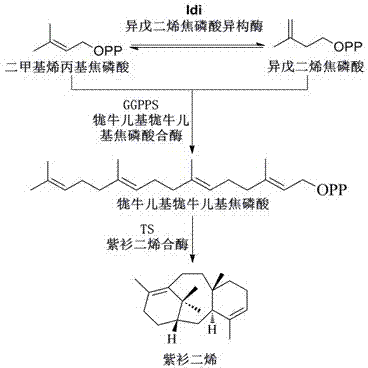
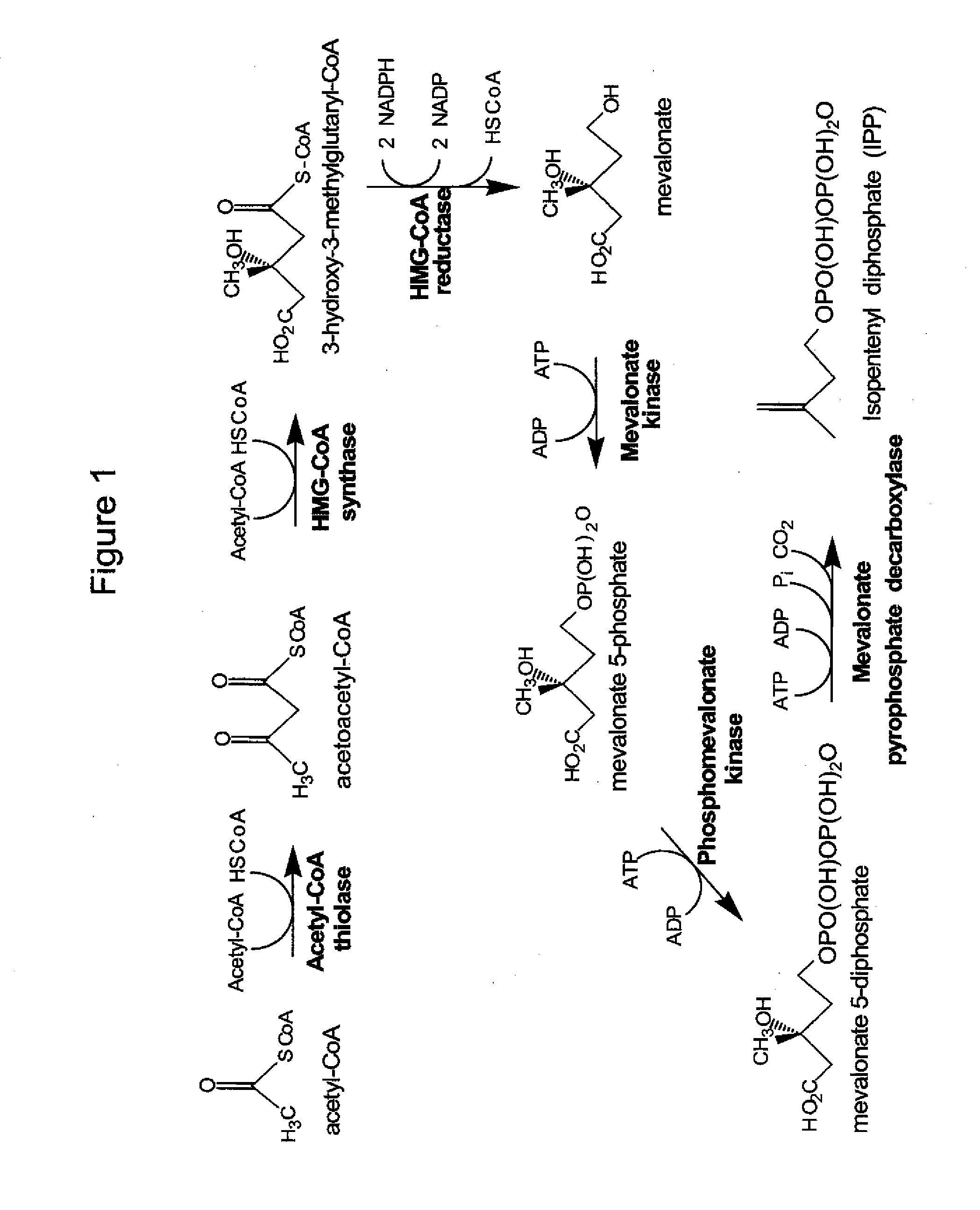
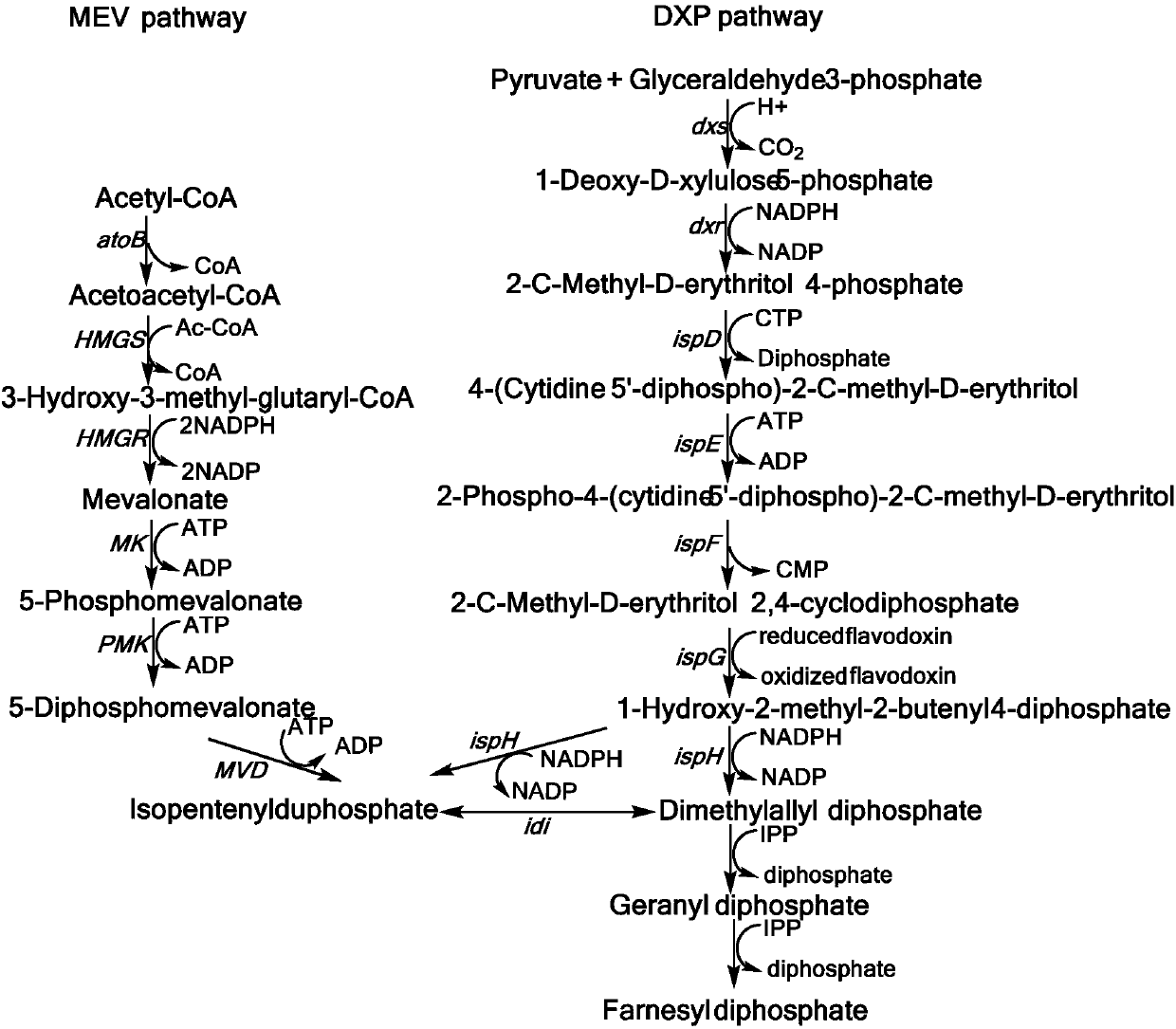
The mevalonate pathway, also known as the isoprenoid pathway or HMG-CoA reductase pathway is an essential metabolic pathway present in eukaryotes, archaea, and some bacteria. The pathway produces two five-carbon building blocks called isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP), which are used to make isoprenoids, a diverse class of over 30,000 biomolecules such as cholesterol, vitamin K, coenzyme Q10, and all steroid hormones.
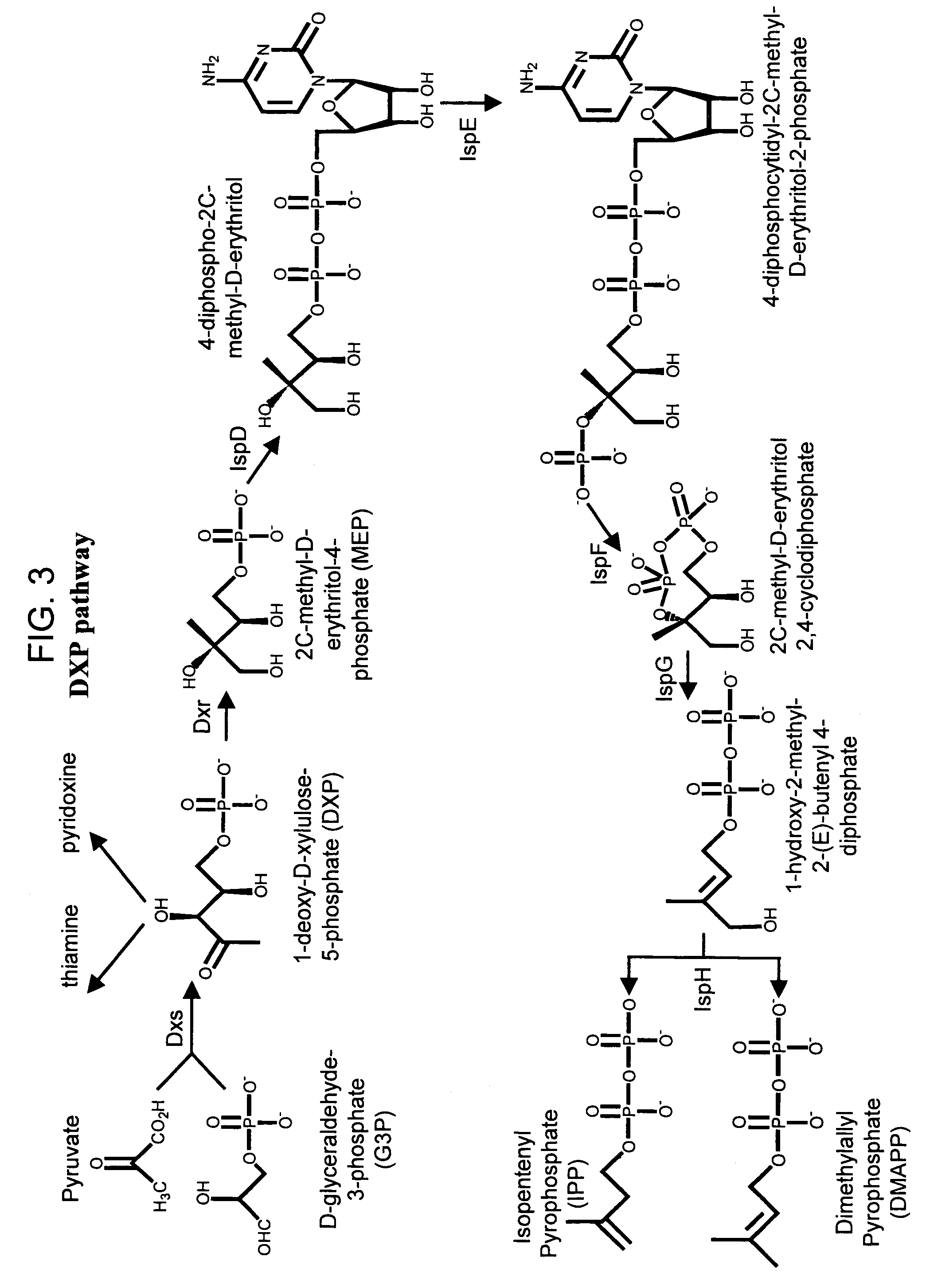
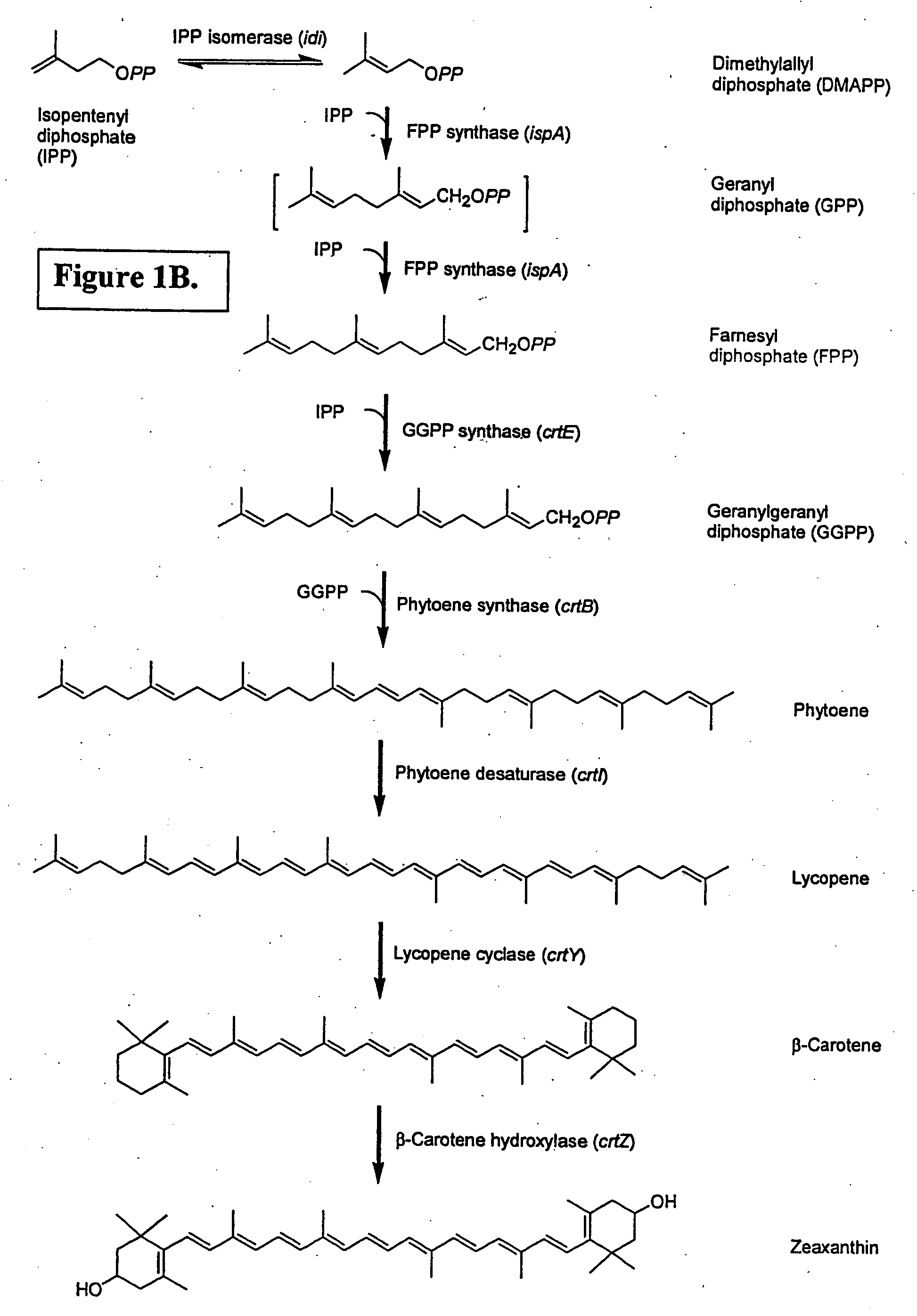
Biosynthesis of isopentenyl pyrophosphate
InactiveUS7172886B2High yieldImprove efficiencySugar derivativesBacteriaMicroorganismIsopentenyl pyrophosphate
Methods for synthesizing isopentenyl pyrophosphate are provided. A first method comprises introducing into a host microorganism a plurality of heterologous nucleic acid sequences, each coding for a different enzyme in the mevalonate pathway for producing isopentenyl pyrophosphate. A related method comprises introducing into a host microorganism an intermediate in the mevalonate pathway and at least one heterologous nucleic acid sequence, each sequence coding for an enzyme in the mevalonate pathway necessary for converting the intermediate into isopentenyl pyrophosphate. The invention also provides nucleic acid sequences, enzymes, expression vectors, and transformed host cells for carrying out the methods.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for enhancing production of isoprenoid compounds
The present invention provides methods of producing an isoprenoid or an isoprenoid precursor in a genetically modified host cell. The methods generally involve modulating the level of hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA) in the cell, such that the level of HMG-CoA is not toxic to the cell and / or does not substantially inhibit cell growth, but is maintained at a level that provides for high-level production of mevalonate, IPP, and other downstream products of an isoprenoid or isoprenoid pathway, e.g., polyprenyl diphosphates and isoprenoid compounds. The present invention further provides genetically modified host cells that are suitable for use in a subject method. The present invention further provides recombinant nucleic acid constructs for use in generating a subject genetically modified host cell, including recombinant nucleic acid constructs comprising nucleotide sequences encoding one or more mevalonate pathway enzymes, and recombinant vectors (e.g., recombinant expression vectors) comprising same. The present invention further provides methods for identifying nucleic acids that encode HMG-CoA reductase (HMGR) variants that provide for relief of HMG-CoA accumulation-induced toxicity. The present invention further provides methods for identifying agents that reduce intracellular accumulation of HMG-CoA.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Increased isoprene production using the archaeal lower mevalonate pathway
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
Biosynthesis of amorpha-4,11-diene
InactiveUS7192751B2High yieldImprove efficiencySugar derivativesBacteriaMicroorganismIsopentenyl pyrophosphate
Methods for synthesizing amorpha-4,11-diene synthase from isopentenyl pyrophosphate are provided. A first method comprises introducing into a host microorganism a plurality of heterologous nucleic acid sequences, each coding for a different enzyme in the mevalonate pathway for producing isopentenyl pyrophosphate. Amorpha-4,11-diene synthase is then produced using an optimized amorpha-4,11-diene synthase gene. The invention also provides nucleic acid sequences, enzymes, expression vectors, and transformed host cells for carrying out the methods.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Isoprenoid production
Owner:DSM NUTRITIONAL PROD +1
Isoprenoid production
Isolated polynucleotides encoding polypeptides having the activity of enzymes in the mevalonate pathway are provided. These sequences are useful for recombinantly producing isoprenoid compounds, such as carotenoids, in particular zeaxanthin. Expression vectors, cultured cells, and methods of making isoprenoid compounds are also provided.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Biosynthesis of isopentenyl pyrophosphate
InactiveUS20070077616A1Enhancing yield and efficiencyReduce side effectsBacteriaSugar derivativesHeterologousMicroorganism
Methods for synthesizing isopentenyl pyrophosphate are provided. A first method comprises introducing into a host microorganism a plurality of heterologous nucleic acid sequences, each coding for a different enzyme in the mevalonate pathway for producing isopentenyl pyrophosphate. A related method comprises introducing into a host microorganism an intermediate in the mevalonate pathway and at least one heterologous nucleic acid sequence, each sequence coding for an enzyme in the mevalonate pathway necessary for converting the intermediate into isopentenyl pyrophosphate. The invention also provides nucleic acid sequences, enzymes, expression vectors, and transformed host cells for carrying out the methods.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Genetically modified host cells and use of same for producing isoprenoid compounds
The present invention provides genetically modified eukaryotic host cells exhibiting increased activity levels of one or more enzymes that generate precursors to be utilized by the mevalonate pathway enzymes, increased activity levels of one or more mevalonate pathway enzymes, prenyl transferase, and / or decreased levels of squalene synthase activity; such cells are useful for producing isoprenoid compounds. The present invention provides genetically modified eukaryotic host cells that produce higher levels of acetyl-CoA than a control cell; such cells are useful for producing a variety of products, including isoprenoid compounds. Methods are provided for the production of an isoprenoid compound or an isoprenoid precursor in a subject genetically modified eukaryotic host cell. The methods generally involve culturing a subject genetically modified host cell under conditions that promote production of high levels of an isoprenoid or isoprenoid precursor compound.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Bacterial strain for producing farnesene and application of bacterial strain
ActiveCN103243065AIncrease productionRational experimentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacterial strainCulture mediums
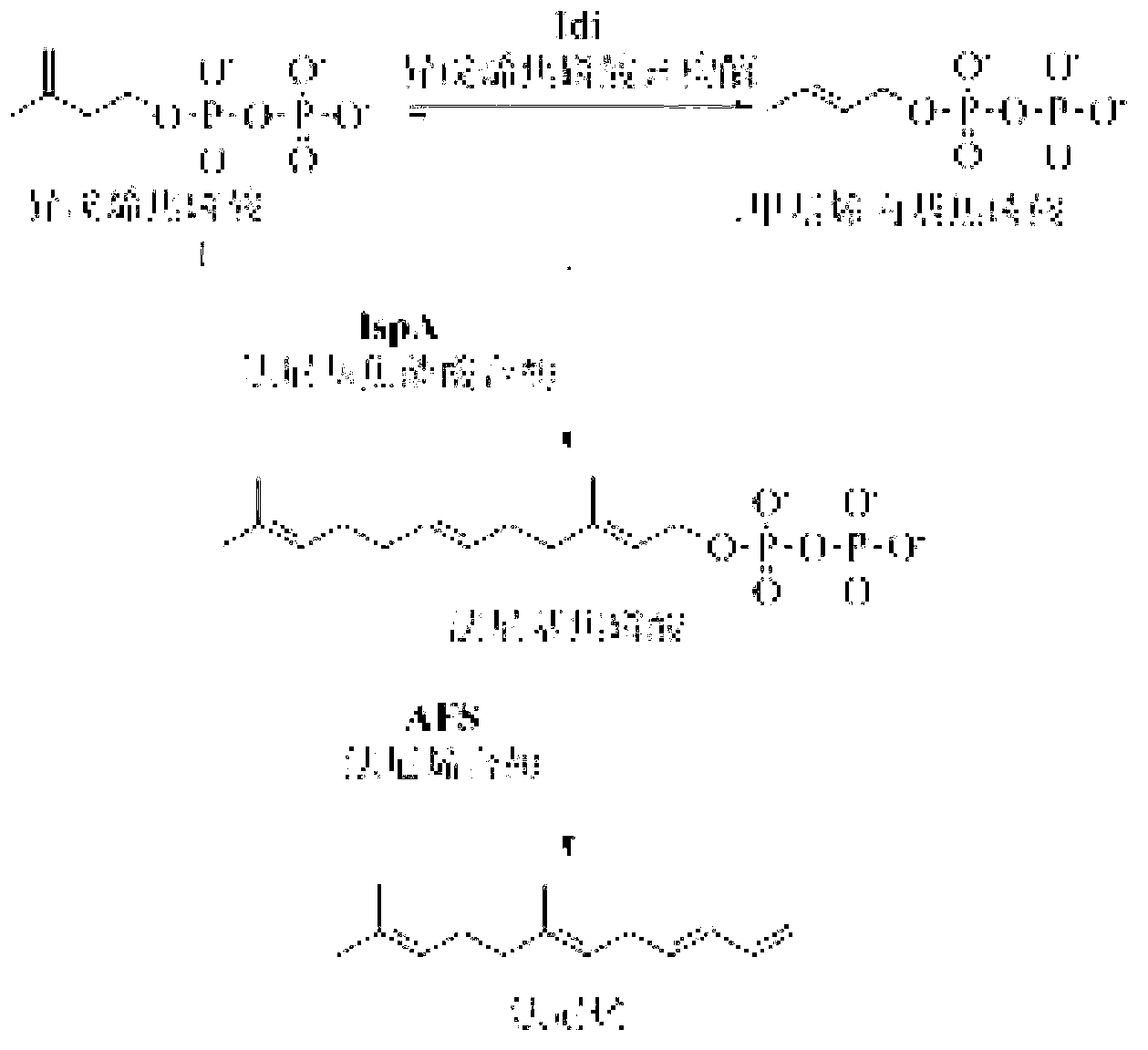
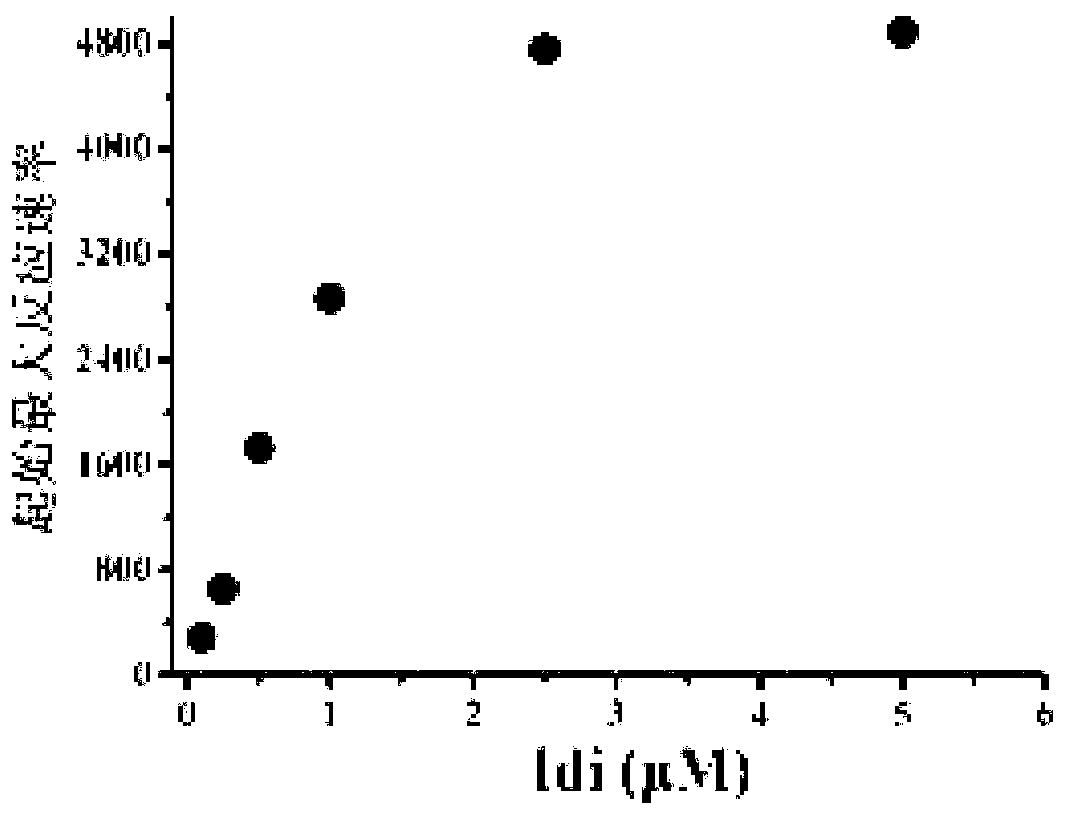
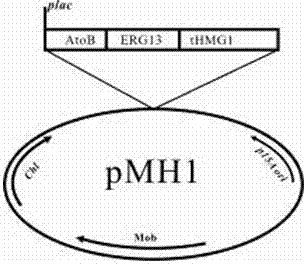
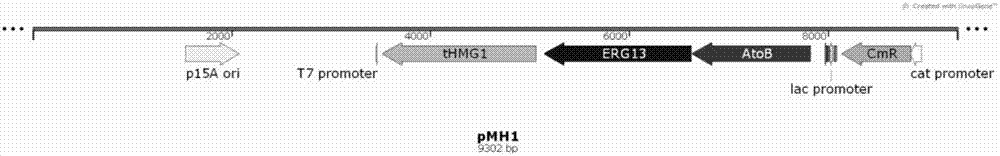
The invention discloses a bacterial strain for producing farnesene and an application of the bacterial strain, belonging to the field of synthetic biology. The bacterial strain for producing the farnesene contains related genes for synthesizing the farnesene through a mevalonic acid pathway and codon optimization; and the sequence of a farnesene synthetic gene afs optimized by codons is as shown by SEQ ID NO.1. The bacterial strain can be used for producing the farnesene, and a seed solution of the bacterial strain is inoculated into a culture medium containing a carbon source to carry out prokaryotic expression to obtain the farnesene. The gene for synthesizing the farnesene is subjected to codon optimization or the farnesene is synthesized by using the mevalonic acid pathway to ensure that each protein is closer to a ratio of AtoB:ERG13:tHMG1:ERG12:ERG8:MVD1:Idi:IspA:AFS=1:10:2:5:5:2:5:2:2, so that the production of the farnesene can be further promoted. By adopting the bacterial strain, the output of the farnesene is greatly improved to be more than 1g / L.
Owner:SHENZHEN ACTION TECH CO LTD
Genetically Modified Host Cells And Use Of Same For Producing Isoprenoid Compounds
ActiveUS20080171378A1Improve the level ofLower Level RequirementsMicroorganismsTransferasesPrenylationSqualene synthase activity
The present invention provides genetically modified eukaryotic host cells that produce isoprenoid precursors or isoprenoid compounds. A subject genetically modified host cell comprises increased activity levels of one or more of mevalonate pathway enzymes, increased levels of prenyltransferase activity, and decreased levels of squalene synthase activity. Methods are provided for the production of an isoprenoid compound or an isoprenoid precursor in a subject genetically modified eukaryotic host cell. The methods generally involve culturing a subject genetically modified host cell under conditions that promote production of high levels of an isoprenoid or isoprenoid precursor compound.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Process for producing isoprenoid compounds by microorganisms and a method for screening compounds with antibiotic or weeding activity
InactiveUS20070004000A1Improve efficiencyImprove productivityBiocideBacteriaPrenylationAnti-fouling paint
The present invention provides a process for producing isoprenoid compounds or proteins encoded by DNA using DNA that contains one or more of the DNA encoding proteins having activity to improve efficiency in the biosynthesis of isoprenoid compounds effective in pharmaceuticals for cardiac diseases, osteoporosis, homeostasis, prevention of cancer, and immunopotentiation, health food and anti-fouling paint products against barnacles; the DNA; the protein; and a method for screening a substance with antibiotic and weeding activities comprising screening a substance inhibiting enzymatic reaction on the non-mevalonate pathway.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KOGYO CO LTD
Bacterial strain for producing lycopene and application of bacterial strain
ActiveCN103243066AImprove the ability to produce lycopeneIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLycopene synthesisBacterial strain
The invention discloses a bacterial strain for producing lycopene and an application of the bacterial strain, and belongs to the field of synthetic biology. The bacterial strain for producing lycopene contains a mevalonate pathway and a related gene which is synthetized by the lycopene optimized by a codon; and the synthetic gene sequence of the lycopene optimized by the codon is shown in SEQ ID NO.1-3. The bacterial strain can be used for producing the lycopene; and a seed solution of the bacterial strain is inoculated into a culture medium containing a carbon source to carry out prokaryotic expression, so as to obtain the lycopene. The gene synthetized by the lycopene is optimized by the codon or each protein of the mevalonate pathway is closer to A to B:ERG13:tHMG1:ERG12:ERG8:MVD1:Idi=1:10:2:5:5:2:5; and production of the lycopene can be further promoted. By adopting the bacterial strain, the yield of the lycopene can be greatly improved to over 1g / L; and the fermentation cycle is shortened by over 50%.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Methods to identify modulators of the mevalonate pathway in sterol synthesis
InactiveUS6803193B1Avoid injuryPrevent rejectionMicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementSterol synthesisCell biology
An assay for the detection of substances agonistic or antagonistic to the mevalonate pathway are disclosed.
Owner:PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIVERSITY
High-yield s-linalool genetic engineering strain and building method thereof
InactiveCN102071155AReduce feedback inhibitionEasy to buildFungiMicroorganism based processesHeterologousLinalool
The invention discloses a high-yield s-linalool genetic engineering strain and a building method, which belong to the field of genetic engineering. Through the metabolic engineering reformation, linalool synthetase from actinidiaarguta is expressed in saccharomyces cerevisiae CEN.PK2-1 in a heterologous way, the terpene synthesis path-mevalonic acid (MVA) path carbon metabolizing flow is increased, and the high-yield s-linalool genetic engineering strain CEN. PK2 linalool is obtained. Compared with an initial strain CEN. PK2-1C, the modified genetic engineering strain CEN. PK2 linalool can metabolize and produce s-linalool, in addition, the feedback inhibition of the s-linalool is obviously reduced, the yield of the s-linalool can reach 12 mg / L, and the genetic engineering strain has good application prospects.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for preparing farnesene by using biodiesel by-product
ActiveCN107418978ABroaden raw material selectionConducive to sustainable large-scale productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiodieselIsopentenyl pyrophosphate
The invention discloses a method for preparing farnesene by using a biodiesel by-product. The method comprises the steps of purification of the biodiesel by-product, wherein the purity of the purified glycerin reaches 63.8% (w / w), building of a recombinant host cell for preparing farnesene from the purified glycerin as the raw material, wherein the recombinant host cell comprises related genes in a mevalonate pathway or deoxymutulose-5-hexose monophosphate pathway, an isopentene pyrophosphate isomerase gene, a farnesene isopentenyl pyrophosphate synthetase gene and a farnesene synthetase gene. The method also comprises fermentation of the purified glycerin as the raw material in the recombinant host cell to prepare the farnesene, wherein the concentration of the obtained farnesene is 0.025g / L; and optimum construction of the recombinant host cell capable of improving the yield of the farnesene by employing the purified glycerin as the raw material, wherein the concentration of the obtained farnesene reaches 2.9g / L, and the concentration is improved by 115 times in comparison with that before optimization.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Construction method for high-yield sclareol strain
InactiveCN103387944AEfficient productionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCoenzyme A biosynthesis
The invention discloses a method for constructing a high-yield sclareol engineering strain by a synthetic biology methdo, and an application thereof. The construction method for the strain relates to express plant sourced key enzymes for synthesizing sclareol, wherein the key enzymes comprise a pyrophosphoric acid ladanum enediol ester synthase and a sclareol synthase; and overexpress a combination of one or more yeast endogenous enzyme-based genes, wherein the enzyme-based genes comprise a key enzyme of a mevalonic acid approach-(hydroxymethyl) coenzyme A reductase, and two enzymes of an isopentenylpyrophosphate approach-a farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase and a geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase. The method can efficiently produce sclareol, with a shake flask fermentation level reaches 9 mg / l, and has industrial application prospects.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Terpenoid synthase for producing nerolidol and application thereof
ActiveCN106906201ASpecificEfficientBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliSynthetic biology
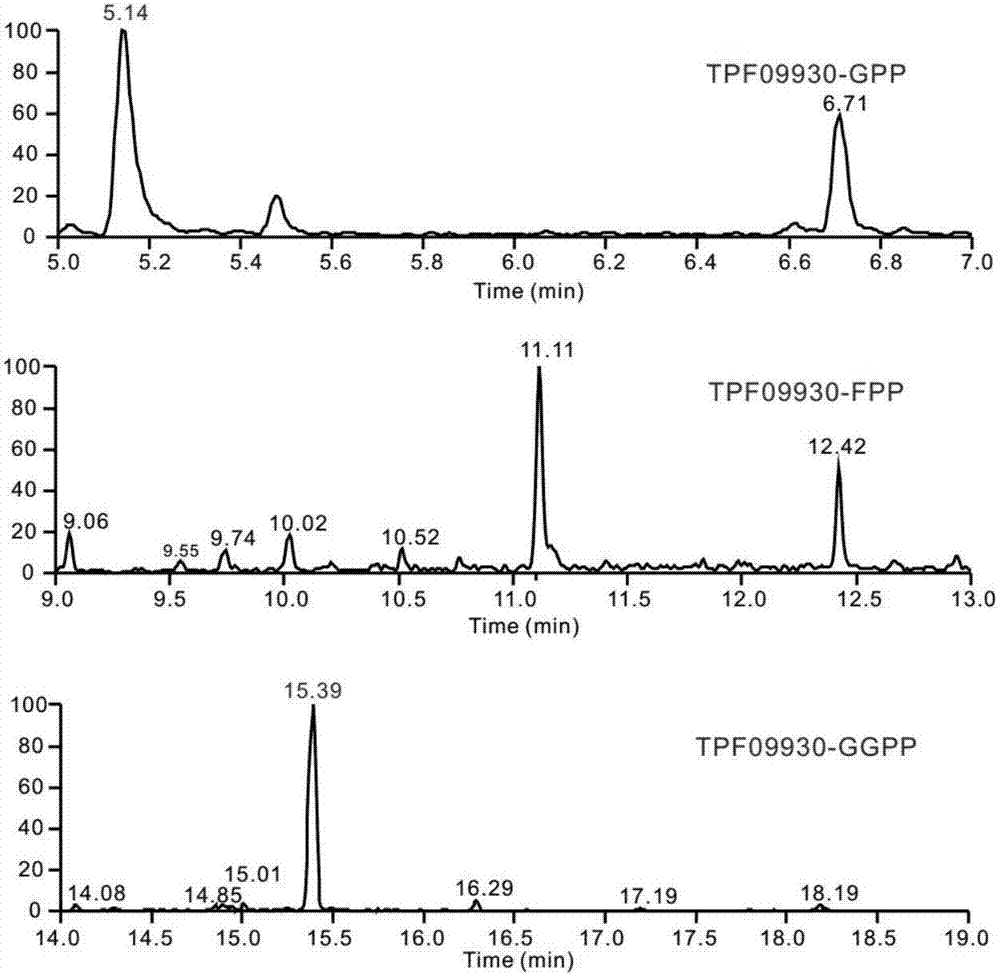
The invention discloses a terpenoid synthase for producing nerolidol and application thereof, and belongs to the field of synthetic biology. Terpene synthase TPF09930 for producing the nerolidol is provided, a nucleotide sequence of the terpene synthase TPF09930 is as shown in SEQIDNO:2, the terpene synthase TPF09930 is combined with mevalonic acid pathway related genes to construct a strain for producing the nerolidol. By overexpression of Escherichia coli XL1 blue-derived atoB gene or idi gene of mevalonic acid pathway, catalytic substrate Farnesyl pyrophosphate can be synthesized in large scale, and producing of the nerolidol can be further promoted. The terpene synthase has specificity and high efficiency, can improve the nerolidol yield, greatly overcomes the defects of a large amount of raw materials and a low nerolidol yield, reduces study cost, and ensures greenness and environmental friendliness.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
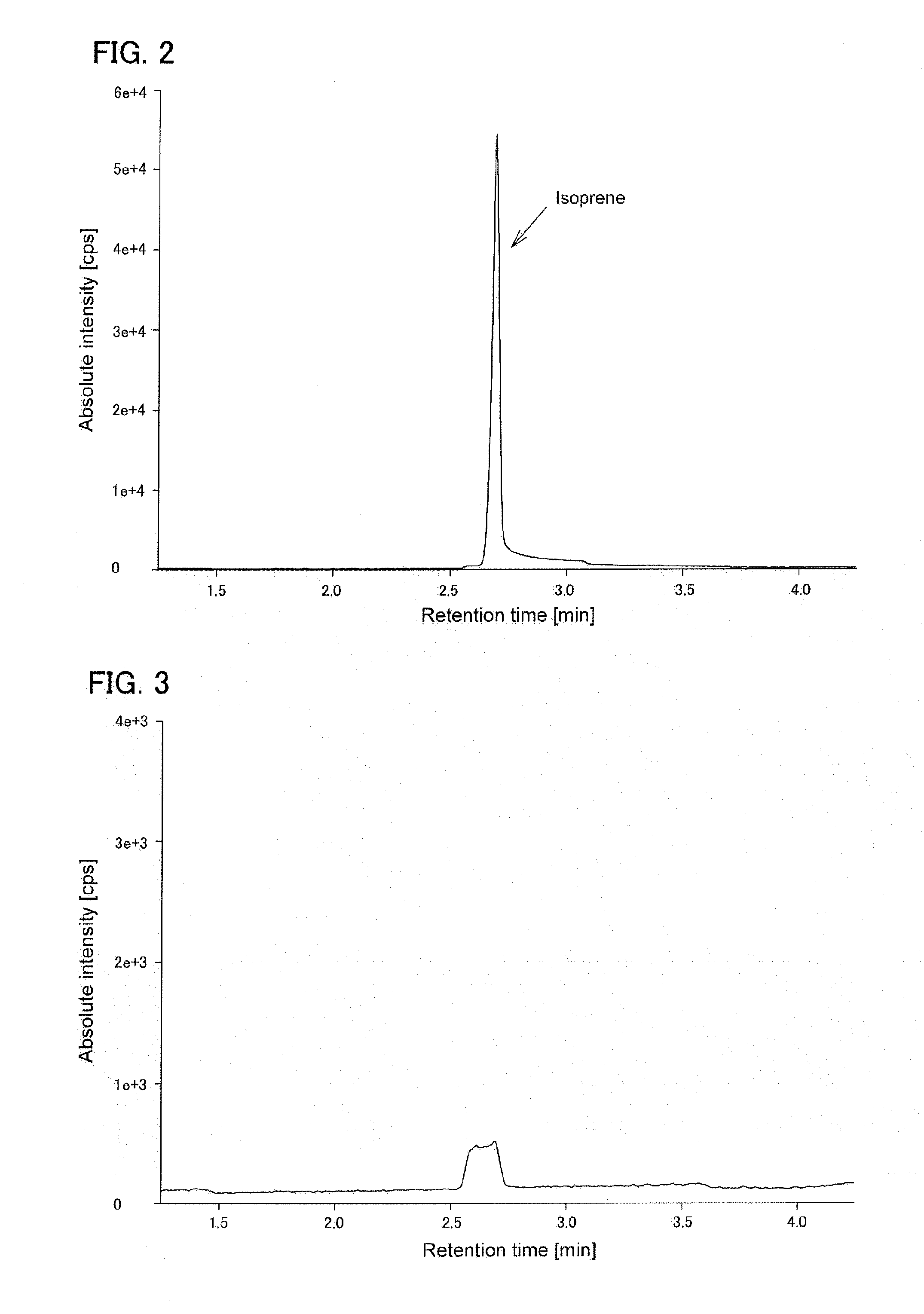
Recombinant cell, and method for producing isoprene
InactiveUS20150284742A1Efficient supplyImprove synthesis abilityBacteriaWaste based fuelIsoprene synthaseIsopentadiene
To provide a series of techniques capable of producing isoprene from syngas or the like.Provided is a recombinant cell prepared by introducing a nucleic acid encoding isoprene synthase into a host cell having an isopentenyl diphosphate synthesis ability by a non-mevalonate pathway, wherein the nucleic acid is expressed in the host cell, and the recombinant cell is capable of producing isoprene from at least one C1 compound selected from the group consisting of carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, formic acid, and methanol. As the host cell, a Clostridium bacterium or a Moorella bacterium is exemplified. Also provided is a method for producing isoprene using the recombinant cell.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV +1
System and microorganism for producing taxadiene, and application of system or microorganism
The invention discloses a system and microorganism for producing taxadiene, and application of the system or the microorganism, and belongs to the field of synthetic biology. The system for producing the taxadiene comprises mevalonate pathway related genes or functional equivalents thereof, and taxadiene synthetized related genes or functional equivalents thereof. The mevalonate pathway related genes are selected from atoB and idi of escherichia coli BL21, and erg13, thmg1, erg12, erg8, and mvd1 of brewer's yeast INVSC1; gene nucleotide sequences of the taxadiene synthetized related genes ggpps are shown by SEQID No.1 and SEQID No.2. The microorganism for producing the taxadiene is the microorganism containing the system for producing the taxadiene, by applying the system into the microorganism, the microorganism for producing the taxadiene is obtained. The microorganism produced in the invention can produce culture for the taxadiene stably, lays a foundation for further using the microorganism to produce paclitaxel, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
USE OF FATOSTATIN FOR TREATING CANCER HAVING A p53 MUTATION
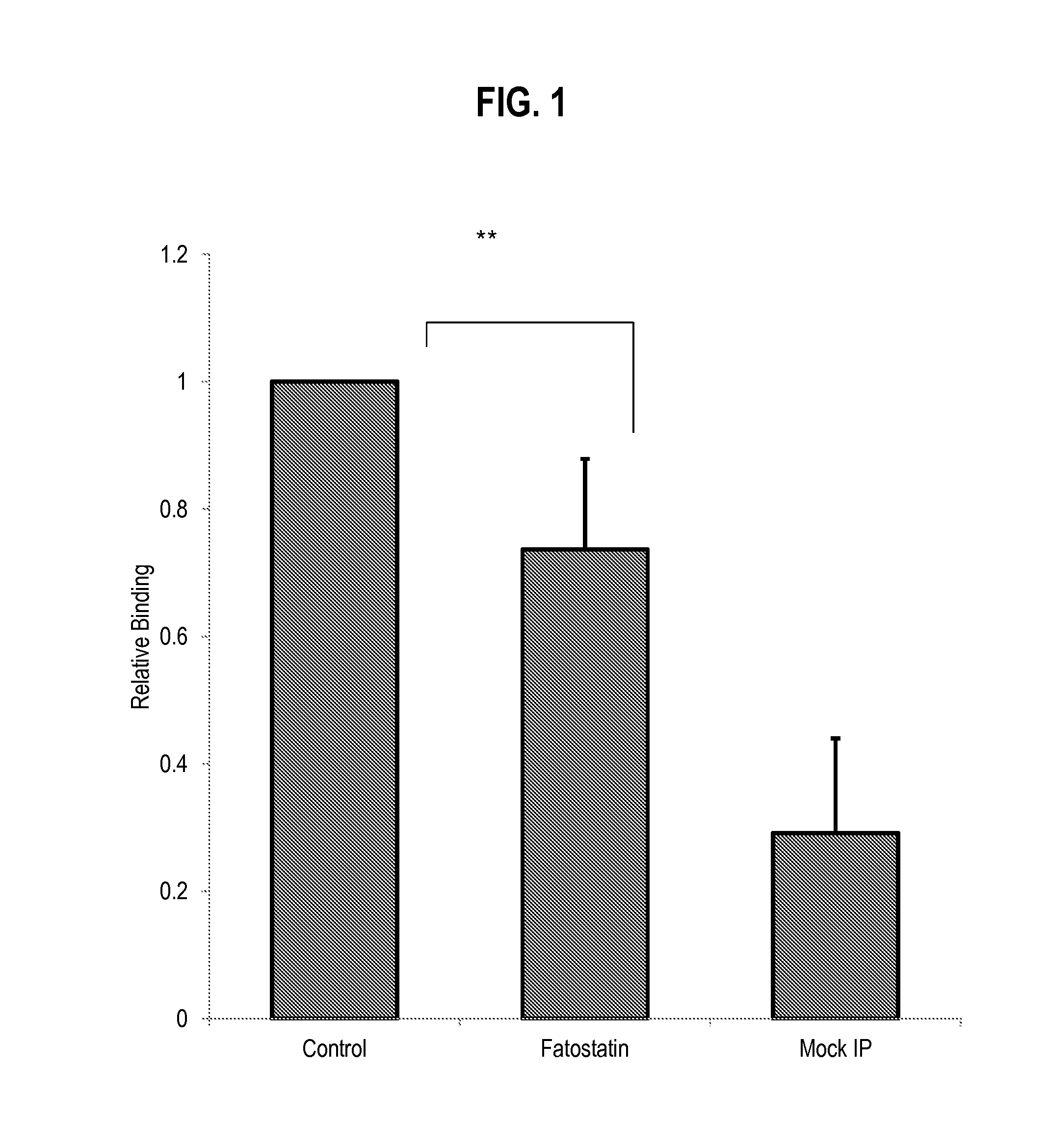
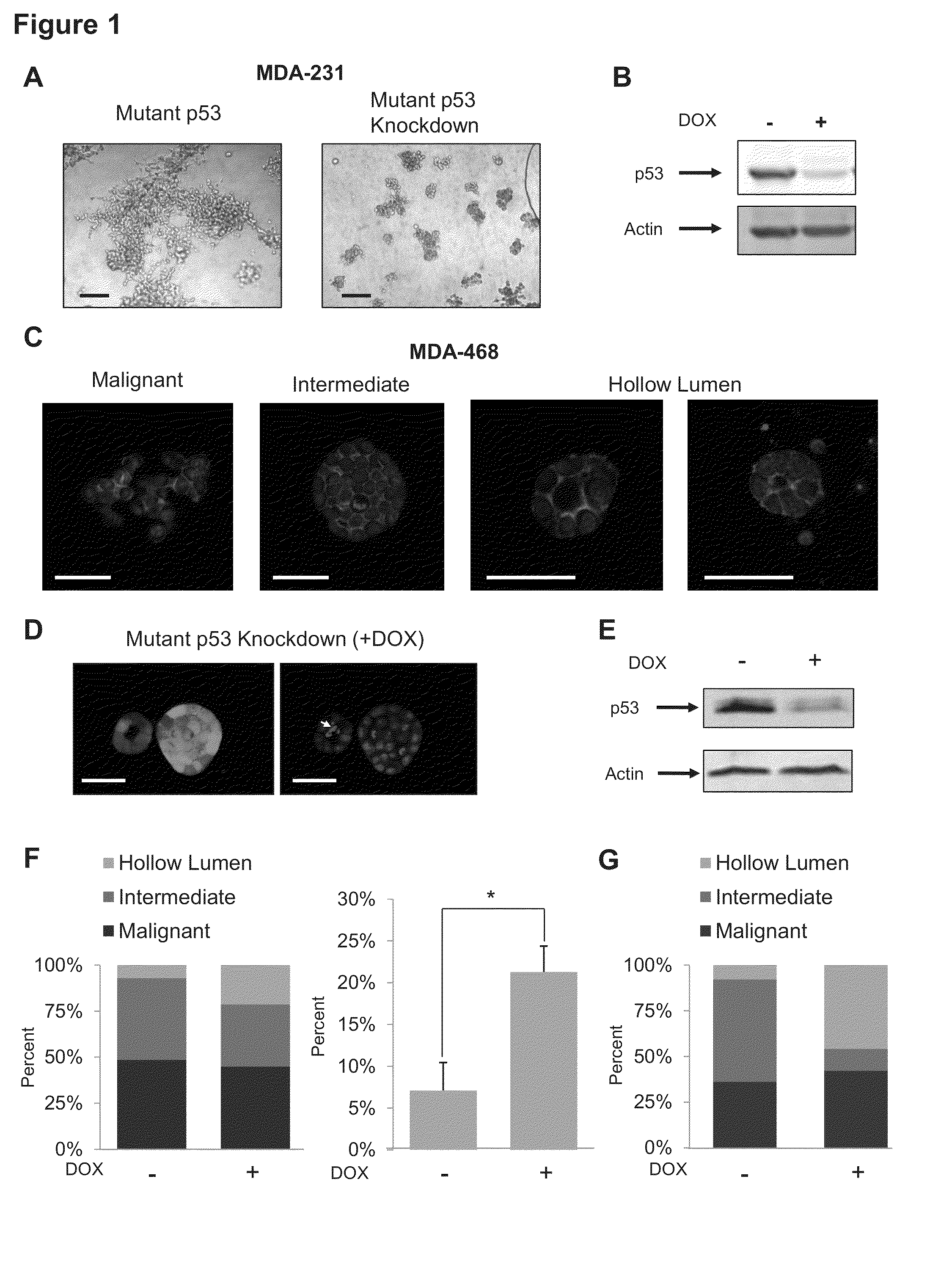
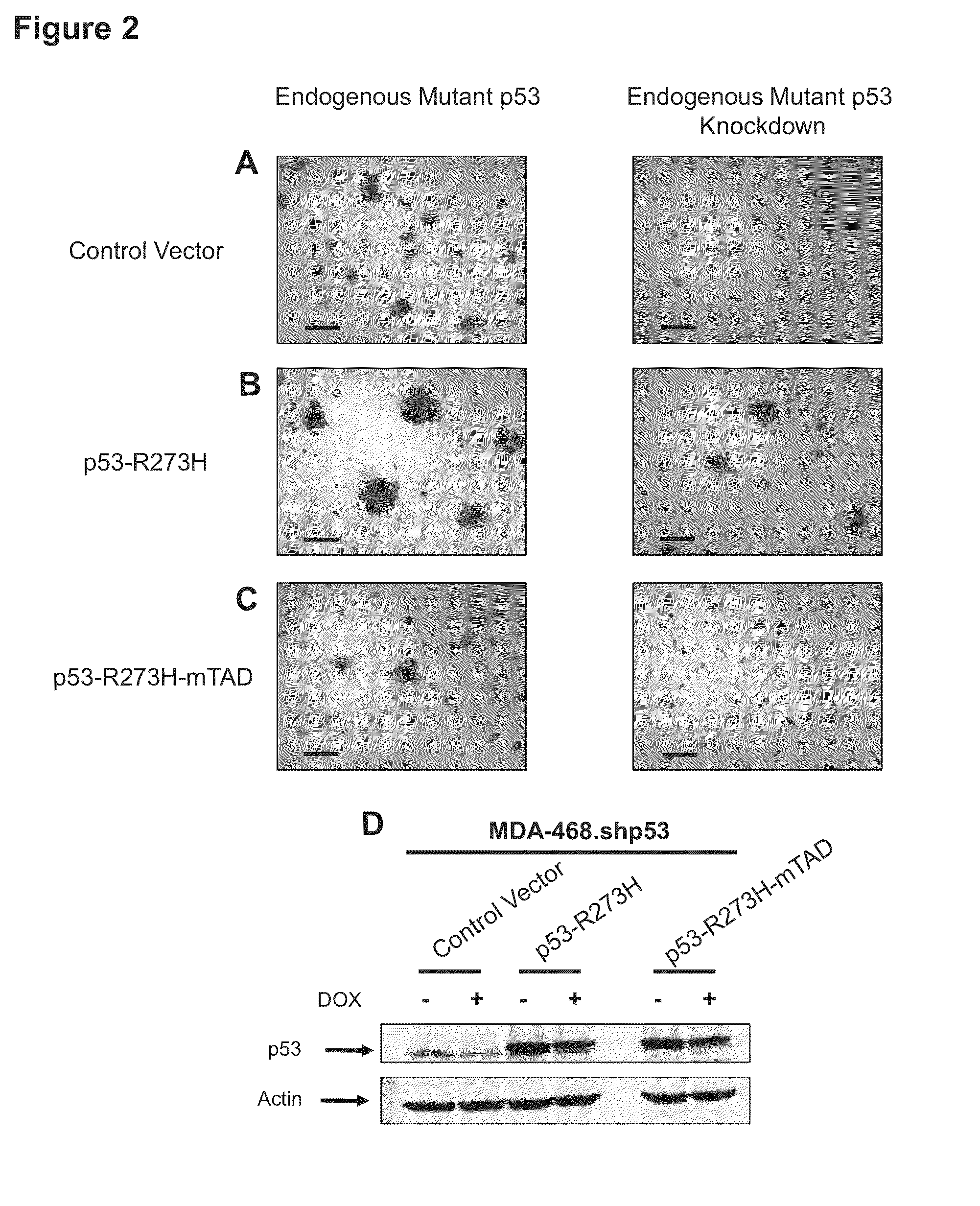
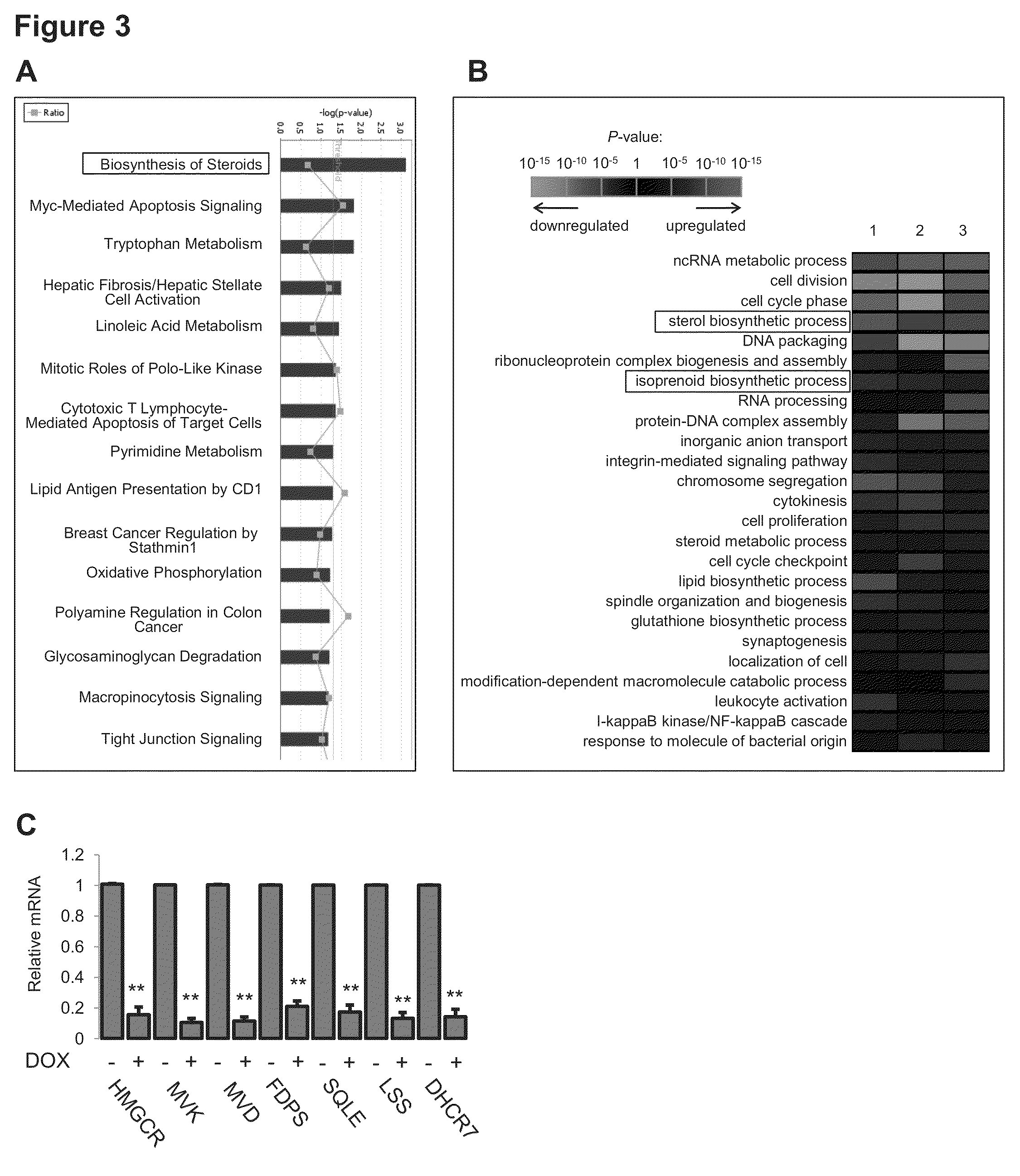
Fatostatin, a recently described inhibitor of SREBP activation, significantly reduces the level of mutant p53 binding to the HMG-CoA reductase gene promoter. Further, fatostatin treatment had a dramatic effect on normalizing the abnormal 3D morphology of 3 strains of breast cancer cells: MDA-468 cells, MDA-231 cells, and SKBR3 cells. The results show a functional interaction with SREBPs as being critical for mutant p53-mediated upregulation of the mevalonate pathway genes. At a clinical level, inhibition of the mevalonate pathway, either alone or in combination with other therapies, offers a novel, safe and much needed therapeutic option for tumors bearing mutant p53.
Owner:NIH DEITR
Method for Treating Cancer Harboring a p53 Mutation
InactiveUS20130281493A1Preventing or delaying the onset (or reoccurrence)Reduce the possibilityBiocideOrganic chemistryCancer cellFhit gene
A method for determining if a subject with cancer or precancerous lesions or a benign tumor, will respond to treatment with an inhibitor selected from the group comprising an inhibitor of one or more enzymes in the mevalonate pathway, an inhibitor of geranylgeranyl transferase, an inhibitor of farnesyl transferase or an inhibitor of squalene synthase, by (i) obtaining a sample of the cancer cells, precancerous cells or benign tumor cells from the subject, (ii) assaying the cells in the sample for the presence of a mutated p53 gene or a mutant form of p53 protein or a biologically active fragment thereof, and (iii) if the cells have the mutated p53 gene or mutant form of the p53 protein, then determining that the subject will respond to treatment with the inhibitor or combinations thereof. Some embodiments are directed to treatment with the inhibitors.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Method for increasing nerolidol yield of saccharomyces cerevisiae
ActiveCN110484572ADecreased transcriptional activityHigh activityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNerolidol
The invention discloses a method for increasing the yield of nerolidol of saccharomyces cerevisiae. According to the method, in the saccharomyces cerevisiae whose Gal80 gene is knocked out, a Gal promoter is used for driving the expression of a mevalonate pathway metabolizing enzyme and a nerolidol synthase to form a secondary growth induction system, and meanwhile a transcription factor hac1 geneis overexpressed to construct a yeast engineered strain for synthesizing nerolidol. In the method, a yeast secondary growth induction system is used for metabolic transformation; when a large numberof expression cassettes driven by the GAL promoter are integrated on a genome, the transcriptional activity of the GAL promoter is greatly reduced; however, an overexpressed transcription factor Hac1in the method can increase the transcriptional activity and strain viability of the GAL promoter and accordingly promote the synthesis of the target metabolite product in the secondary growth induction system; the yield of nerolidol is increased by 48.4% to 497 mg / L.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Preparation method for synthesizing biosensor by using lycopene operon as well as corresponding biosensor and application thereof
ActiveCN112877342AEasy to useHigh synthesis efficiencyBacteriaMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLycoperseneNucleotide
The invention discloses a preparation method for synthesizing a biosensor by using a lycopene operon as well as the corresponding biosensor and application thereof. The biosensor comprises a recombinant plasmid containing a lycopene operon, a mevalonic acid pathway upstream expression vector and a mevalonic acid pathway downstream expression vector; the recombinant plasmid contains a lycopene operon and a promoter, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the lycopene operon is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 or the lycopene operon is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, has more than 90% of homology with the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and can synthesize the nucleotide sequence of lycopene, and the promoter is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The biosensor can sense explosive molecules with different concentrations to synthesize lycopene with different yields, the concentration of the explosive molecules and the yield of the lycopene are coupled, visual detection of the explosive molecules is achieved, the detection operation is simple and convenient, and the safety is high.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV +1
Method for synthesizing 3-geranyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid and xiamenmycin by utilizing escherichia coli
ActiveCN108865961AIncrease productionAchieve biosynthesisBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliGeranyl pyrophosphate
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing 3-geranyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid and xiamenmycin by utilizing escherichia coli. According to the method, an adopted escherichia coli strain contains xiamenmycin synthesis related genes and mevalonic acid pathway related genes which are partially or entirely subjected to codon optimization; three genes required by synthesis of the xiamenmycin are imported into the escherichia coli; the three genes are subjected to inducible expression, and GBA and the xiamenmycin are synthesized in the escherichia coli; the feed of intracellular geranyl pyrophosphate of the escherichia coli is further improved by introducing a mevalonic acid synthesis pathway, and the yield of the GBA is further increased by adding 4-hydroxybenzoic acid into a fermentation medium; the yield of the synthesized 3-geranyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid reaches 94 mg / L, and the yield of the xiamenmycin reaches 11 mg / L; and the biosynthesis of the 3-geranyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid and the xiamenmycin in the escherichia coli is realized for the first time.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Methods of Monitoring Metabolic Pathways
ActiveUS20090203019A1High productMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMetaboliteMevalonic acid
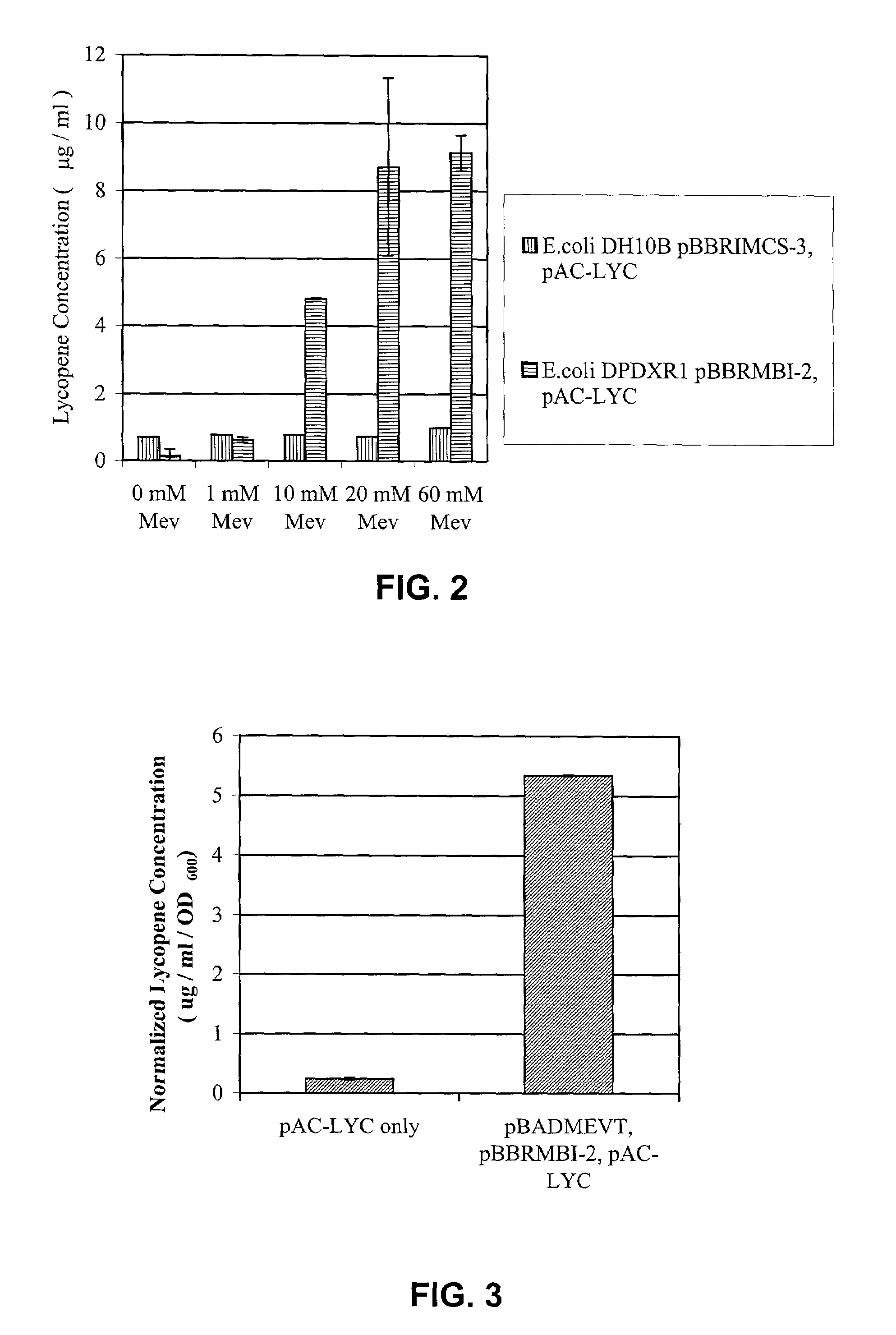
The present invention provides methods and compositions for monitoring cofactors and metabolites of a metabolic pathway of interest. The subject compositions and methods are particularly suited for monitoring the mevalonate pathway in a variety of cells. The invention also provides fermentation methods for the production of isoprenoids.
Owner:AMYRIS INC
Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria for producing farnesene and application thereof
PendingCN112080440AConducive to continuous synthesis and accumulationPromote accumulationFungiMicroorganism based processesSynthetic biologyTransformation efficiency
The invention discloses saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria for producing farnesene and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of synthetic biology. According to the saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria, farnesene synthetase Fsso with high conversion efficiency in saccharomyces cerevisiae is obtained through screening; all gene-enhanced farnesene synthetic strains with different copy numbers of HMG1 and mevalonic acid paths are constructed, and that single-copy and double-copy HMG1 are most beneficial to continuous synthesis and accumulation of farnesene isconfirmed; and the accumulation amount of farnesene can be further increased by simultaneously controlling expression of HMG1 and Fsso through a GAL promoter. The constructed farnesene synthetic strains are easy in gene operation, and 1.11g / L farnesene can be accumulated at most through shake flask fermentation.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
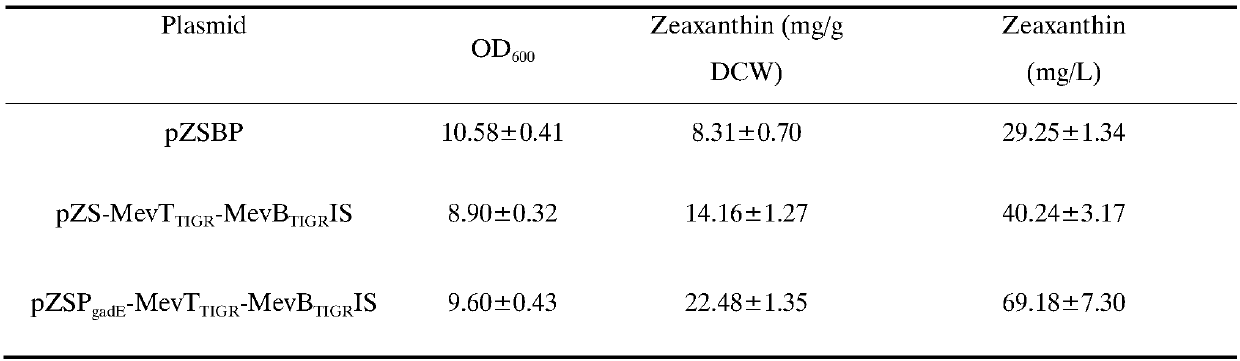
Mevalonic acid pathway tuned by TIGR
InactiveCN107190004AIncrease productionAvoid toxicityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliZeaxanthin
The invention belongs to the field of biochemistry, and relates to an MEV (mevalonic acid) pathway tuned by TIGR (tunable intergenic regions) to produce isopentene compounds, especially zeaxanthin. In particular, the exogenous MEV pathway is introduced into the engineered escherichia coli (ZEAX) for producing zeaxanthin, especially an upstream pathway and a downstream pathway of MEV tuned by the TIGR are introduced to coordinate the production of intermediate products and reduce the toxicity to cells due to the accumulation of intermediate products, and finally the yield of zeaxanthin is increased.
Owner:辛珉
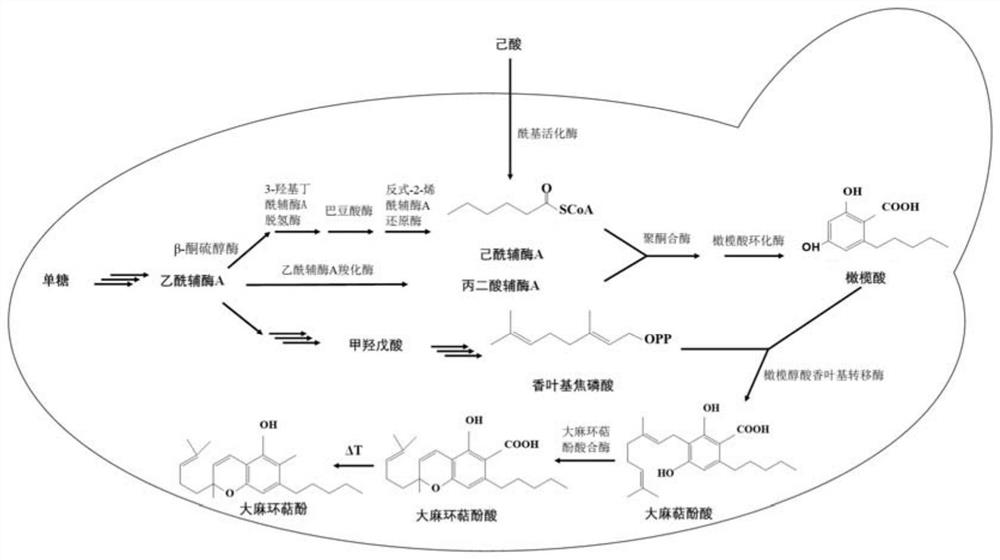
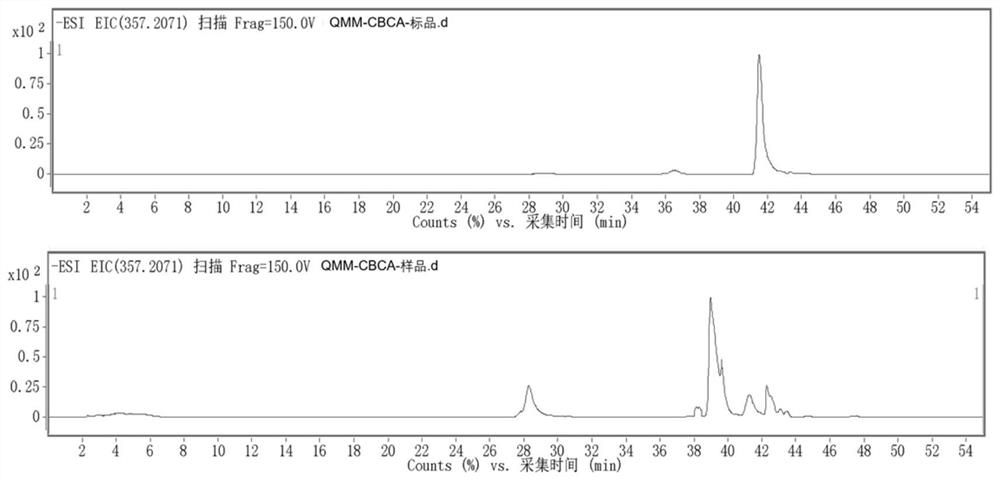
Method for producing heterocannabinoid phenol by using saccharomyces cerevisiae
ActiveCN112795495AIncrease added valueThe method is accurate and efficientFungiCarbon-sulfur lyasesHeterologousPhenol
The invention discloses a recombinant host cell capable of biosynthesizing cannabinoid phenolic acid, a construction method of the recombinant host cell and a method for biosynthesizing the cannabinoid phenolic acid through the recombinant host cell, and belongs to the field of biotechnology and medicine. The saccharomyces cerevisiae is used as a host, firstly, cannabinoid synthase and cannabinoid phenolic acid synthase are over-expressed in the host, then a metabolic pathway for synthesizing a precursor compound oleylic acid of cannabinoid phenolic acid by using saccharides is constructed in the host, and a metabolic pathway from caproic acid to oleylic acid is further constructed in the host; finally, an endogenous mevalonic acid pathway of a host and a metabolic pathway of acetyl coenzyme A are optimized, the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae capable of biologically synthesizing cannabinoid phenolic acid is obtained, a new pathway for producing cannabinoid phenolic acid with high additional value from a cheap carbon source is provided, the production efficiency is high, the period is short, the cost is low, and large-scale production of cannabinoid phenolic acid is facilitated.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH +1
Use of nitrine phlorizin in preparing drug for treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
InactiveCN108721308AReduce lipid accumulationReduce fatty degenerationOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemIsrapafantMevalonate pathway
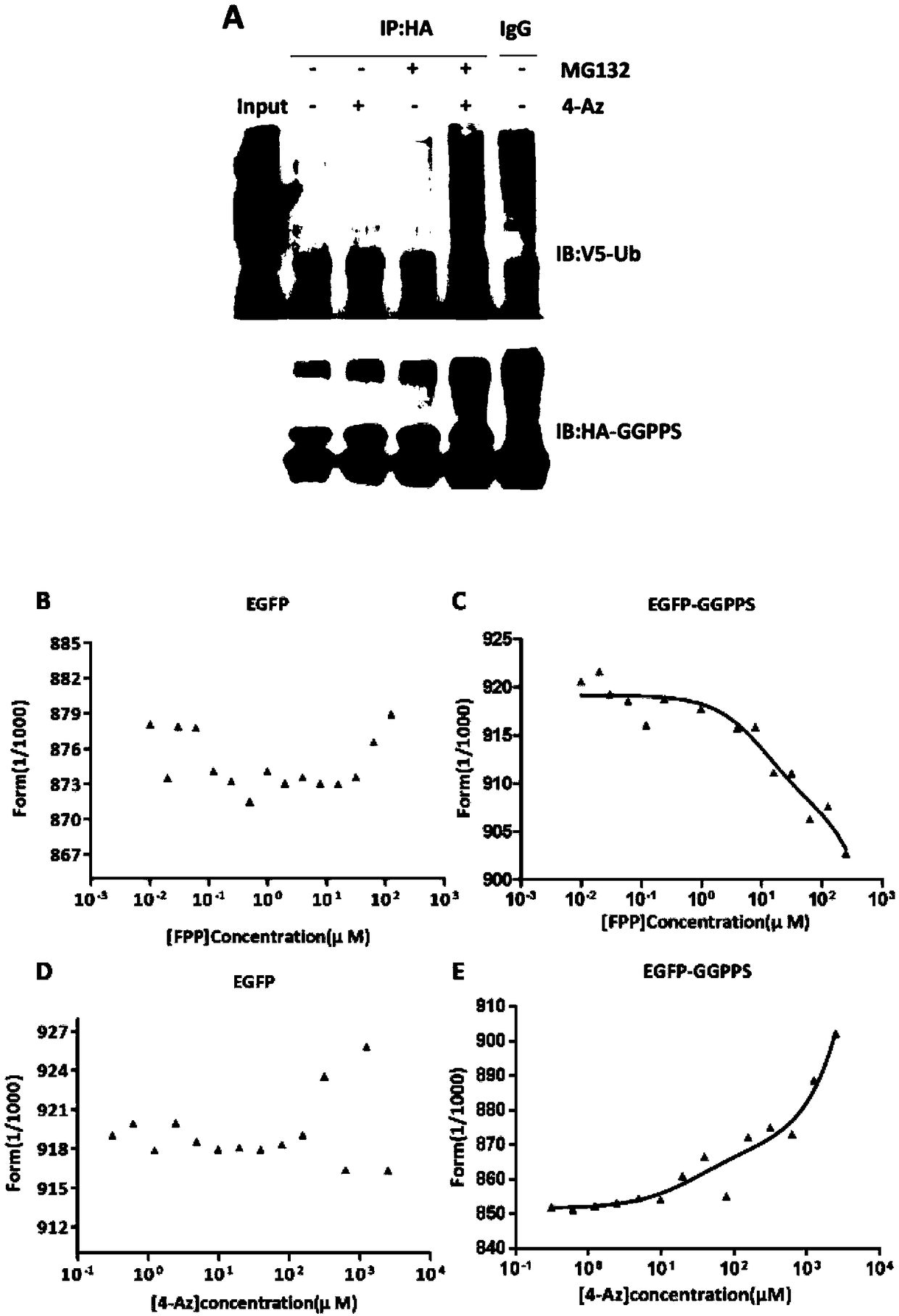
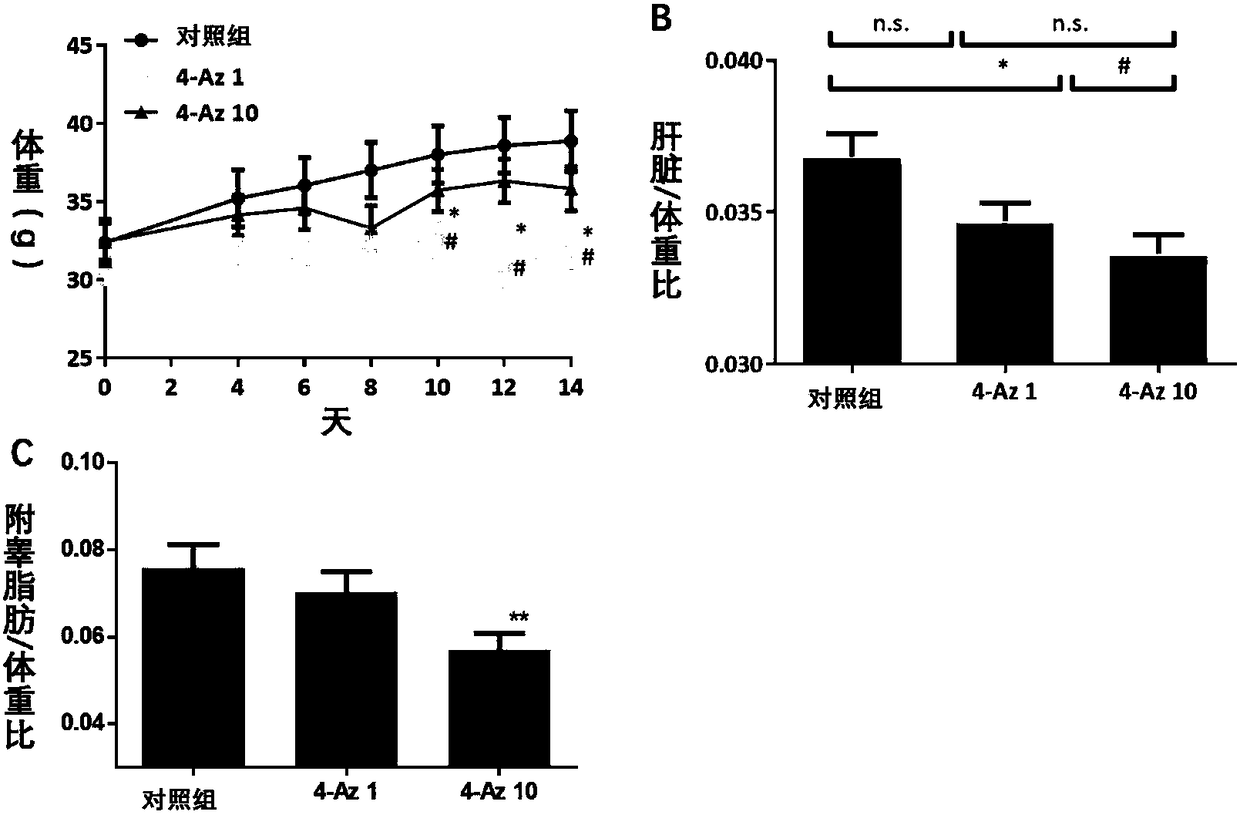
The invention discloses use of nitrine phlorizin (4-Az) as a key branching enzyme GGPPS inhibitor in an MVA pathway (mevalonate pathway), especially use in preparing a drug for treating non-alcoholicfatty liver disease. According to a series of experiments, the 4-Az can cause GGPPS protein to generate ubiquitin-proteasome pathway dependent degradation, has an inhibiting effect on GGPPS protein expression, and can be used as the inhibitor of GGPPS protein expression. More specifically, the nitrine phlorizin can reduce lipid accumulation and fatty degeneration of the livers, can reduce level ofglutamic-pyruvic transaminase and glutamic oxalacetic transaminase in blood, has the activity of protecting the liver function, and can be used for preparing the drug for treating the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
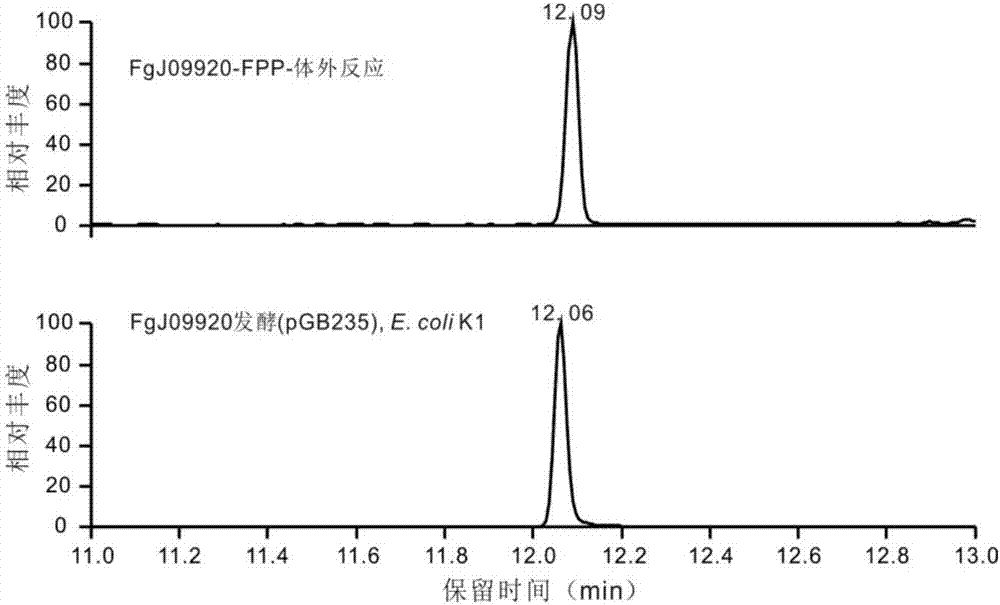
Terpene synthase for producing koraiol and application of terpene synthase
The invention discloses terpene synthase for producing koraiol and an application of the terpene synthase, and belongs to the field of synthetic biology. The terpene synthase FGJ09920 for synthesizing the koraiol is provided, the nucleotide sequence of the terpene synthase is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, the terpene synthase and related genes containing mevalonic acid pathways establish strains for producing the koraiol, atoB genes or idi genes of the mevalonic acid pathways derived from Escherichia coli XL1-blue are over-expressed, a large number of catalytic substrate FPP (farnesyl pyrophosphate) is synthesized, and production of the koraiol can be further facilitated. The terpene synthase has specificity and high efficiency and overcomes the shortcomings that input quantity of raw materials is high, and the yield of the koraiol is low, the yield of the koraiol can be improved, research cost is reduced, and green and environment-friendly production is ensured.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com