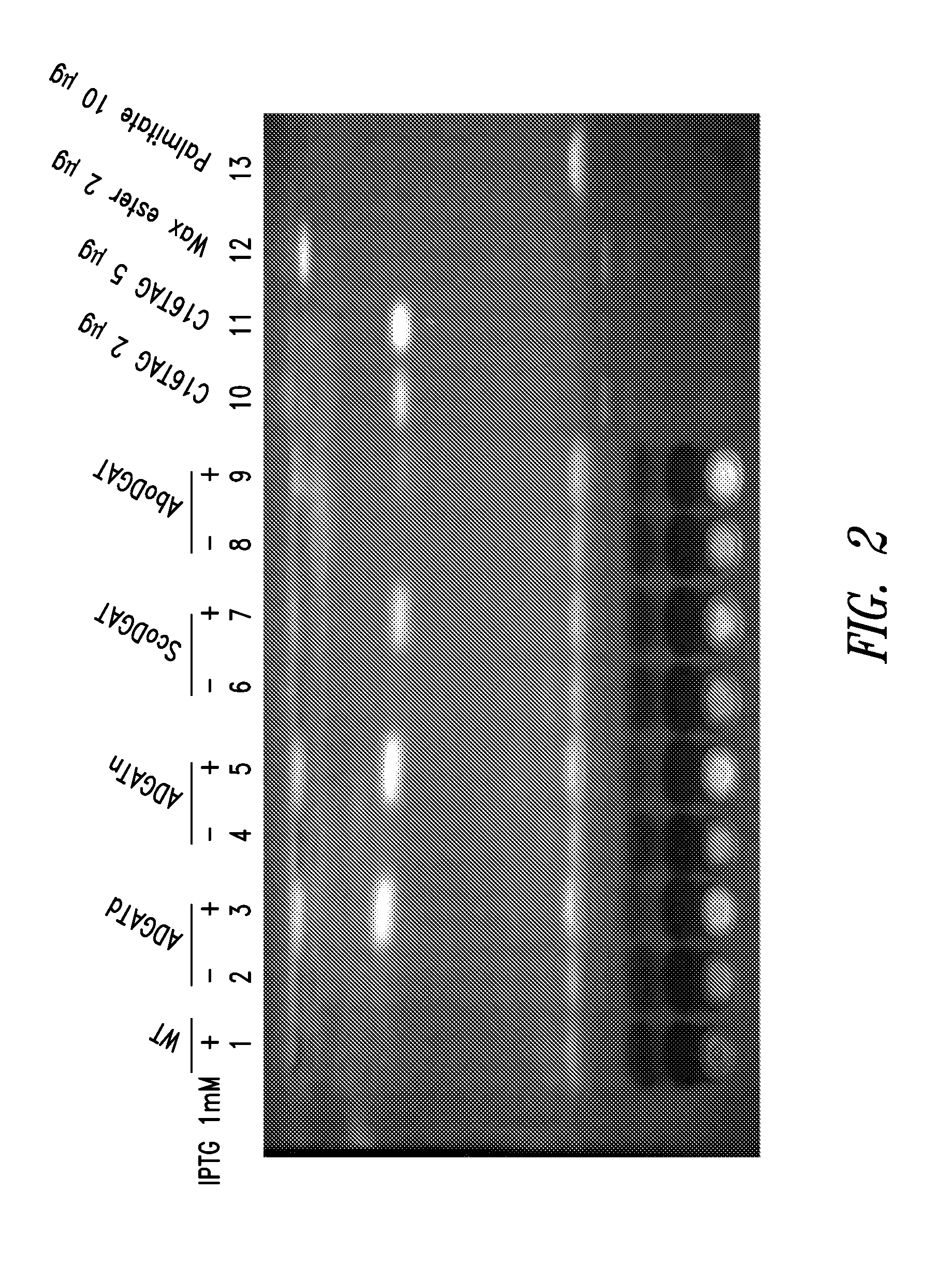
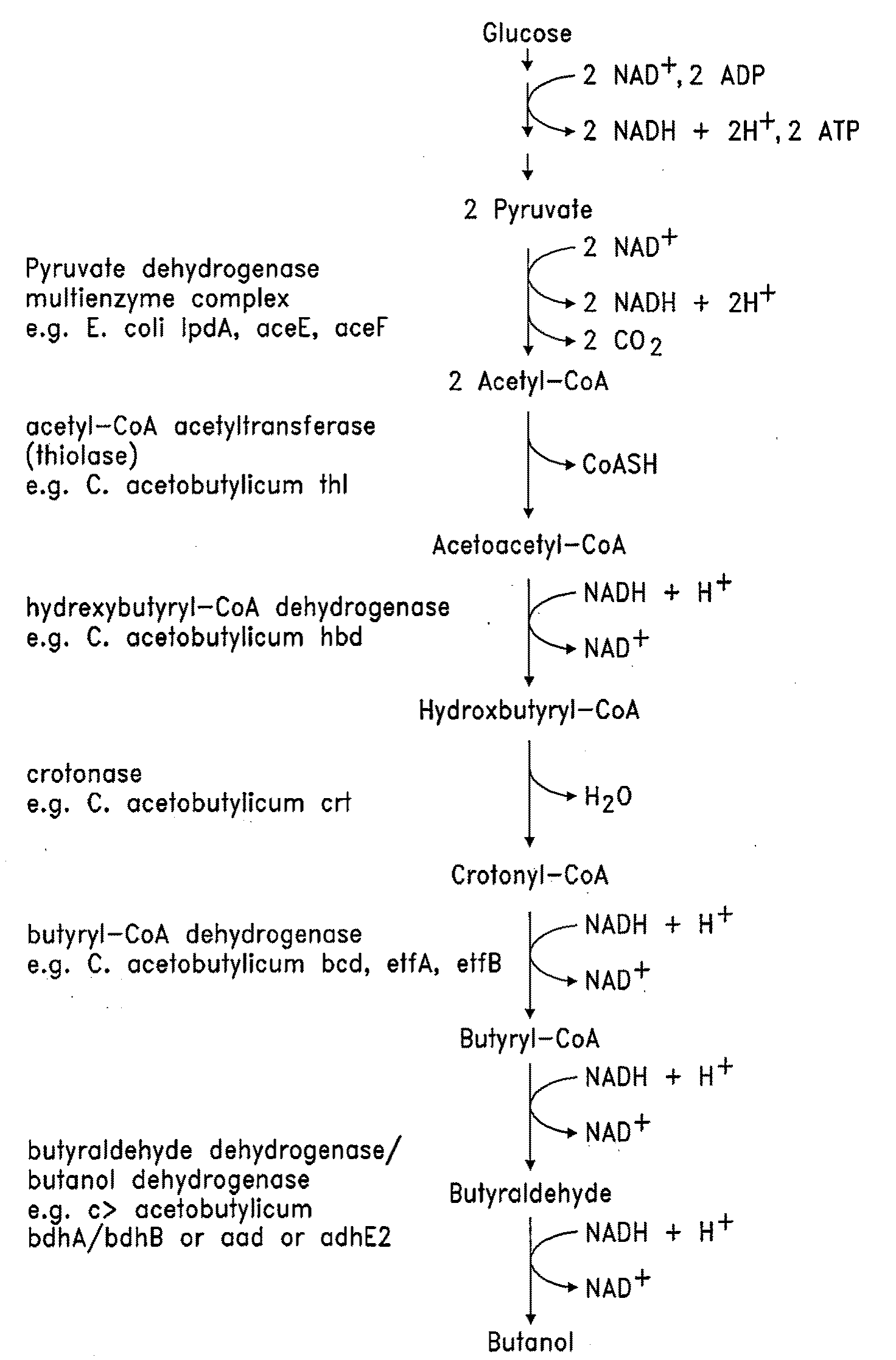
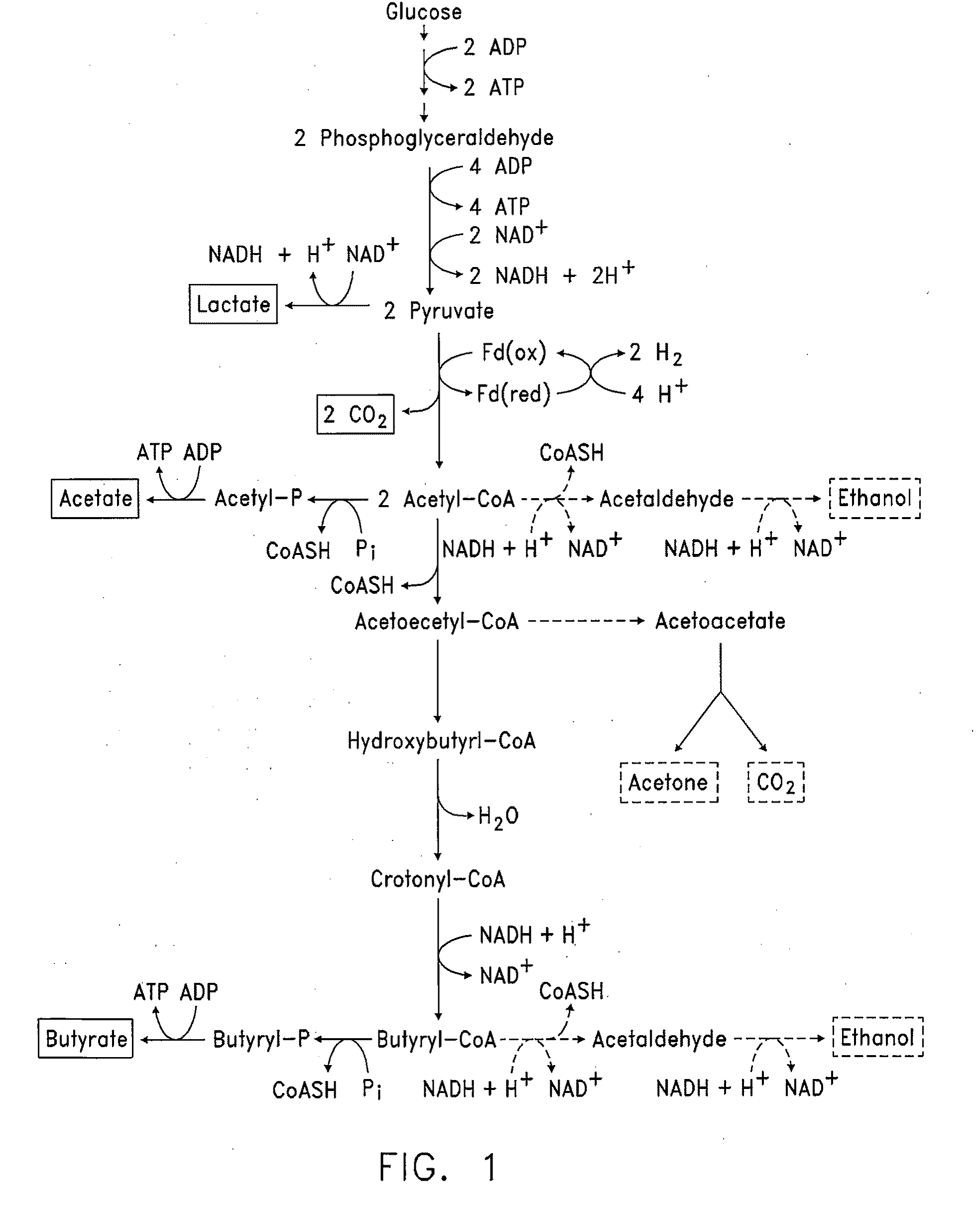
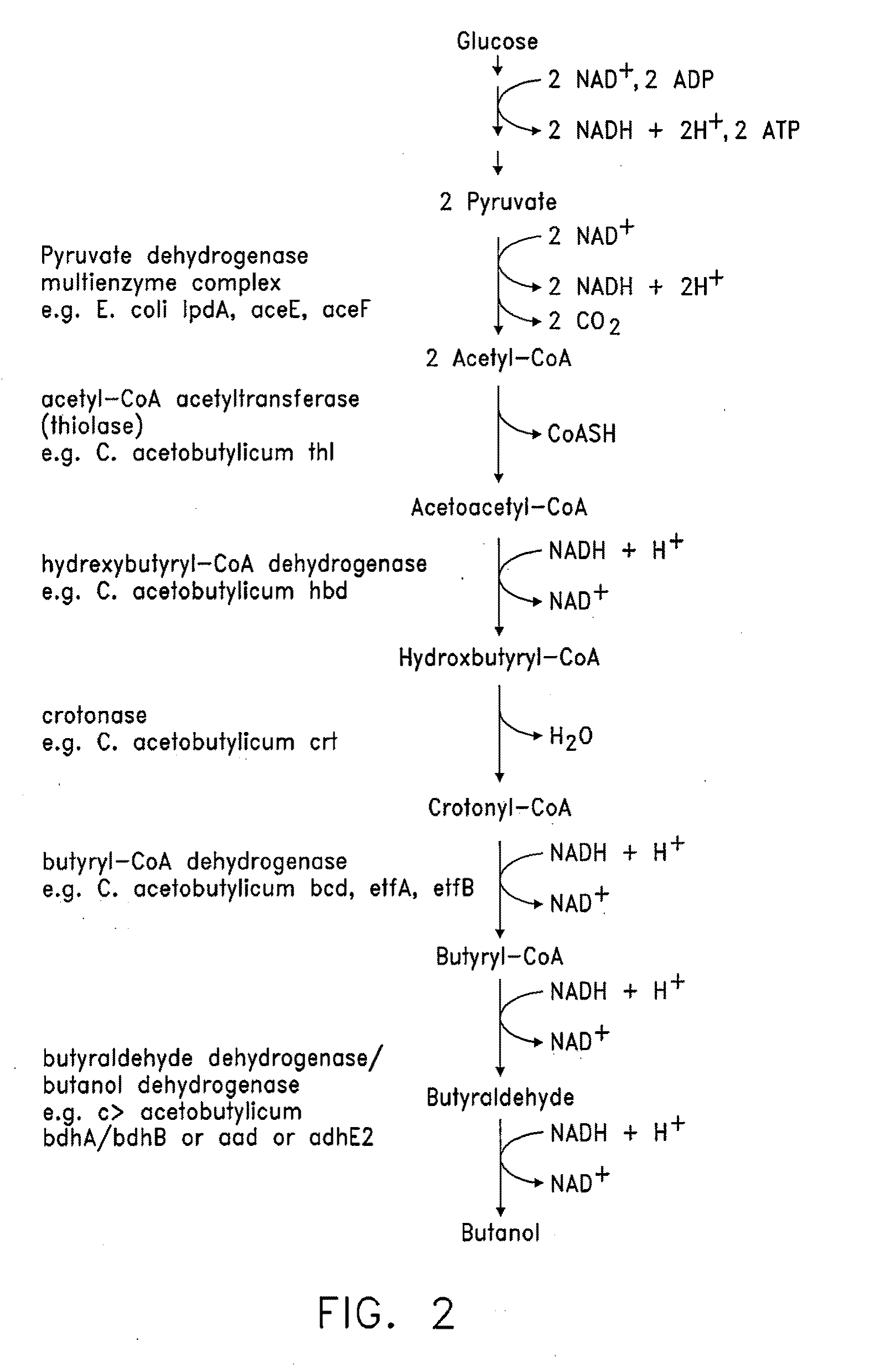
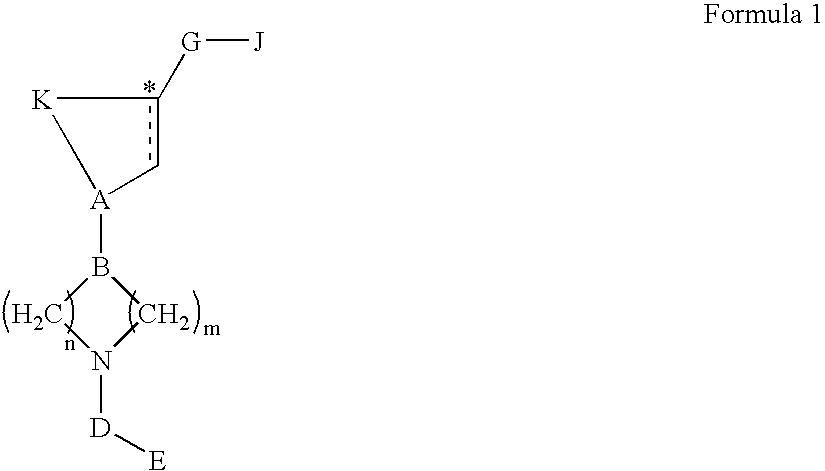Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
348 results about "Acetyl coenzyme" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
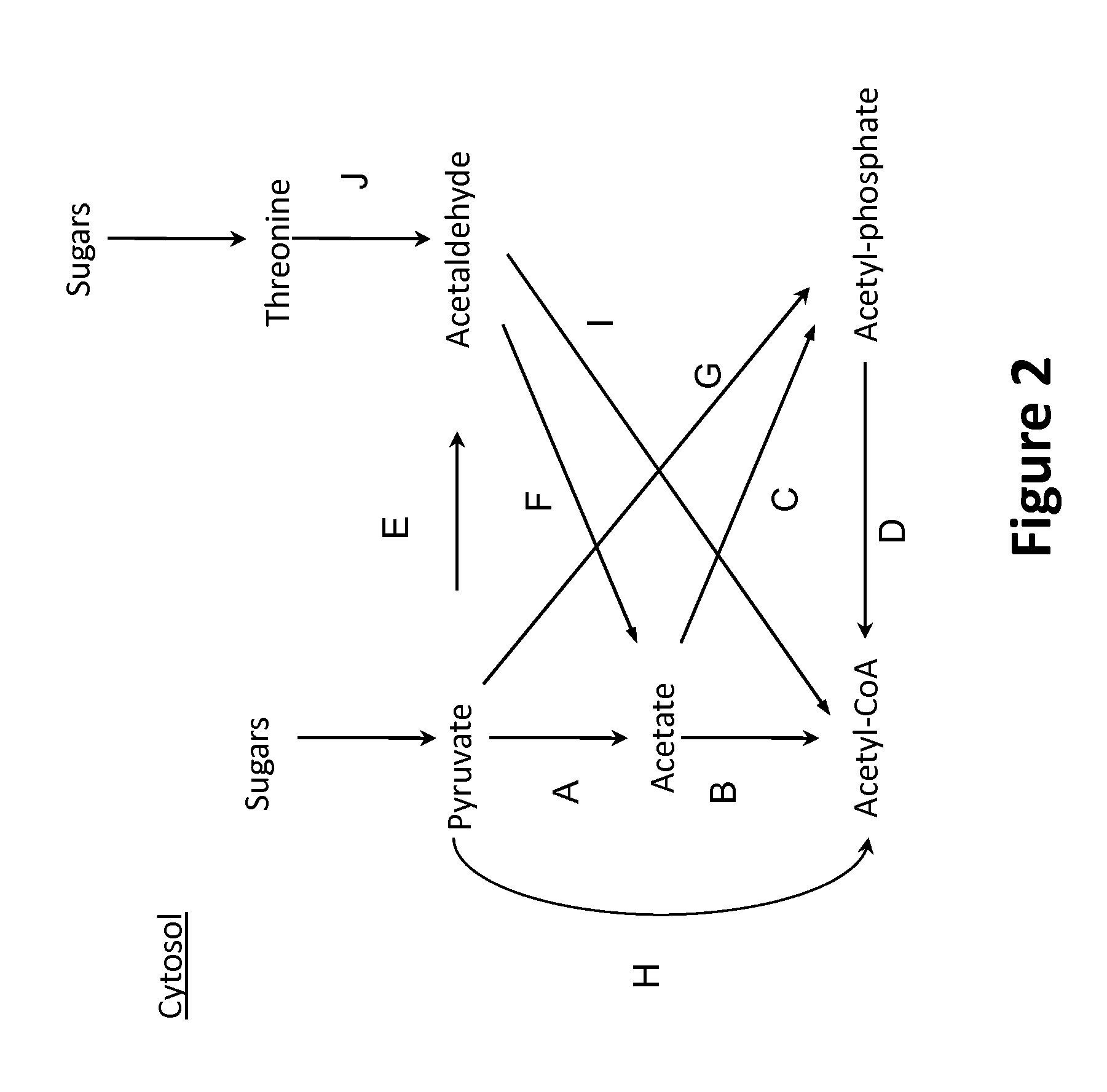
Acetyl Coenzyme A. Acetyl coenzyme a. coenzyme a (coa, CoASH, or HSCoA) is a coenzyme, notable for its role in the synthesis and oxidization of fatty acids, and the oxidation of pyruvate in the citric Acid Cycle. It is adapted from β-mercaptoethylamine, panthothenate and adenosine Triphosphate.
Recombinant microorganism having butanol production capacity and butanol production method
This invention relates to a recombinant microorganism having improved butanol production capacity and butanol production with the use of such recombinant microorganism with good efficiency. In this invention, the acetoacetyl-CoA synthase gene encoding an enzyme capable of synthesizing acetoacetyl-CoA from malonyl-CoA and acetyl-CoA and a group of genes involved in butanol biosynthesis that enables synthesis of butanol from acetoacetyl-CoA are introduced into a host microorganism.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Plant Genes Associated With Seed Oil Content And Methods Of Their Use
InactiveUS20110191904A1High oil contentRaise the ratioOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologyReticulum cell
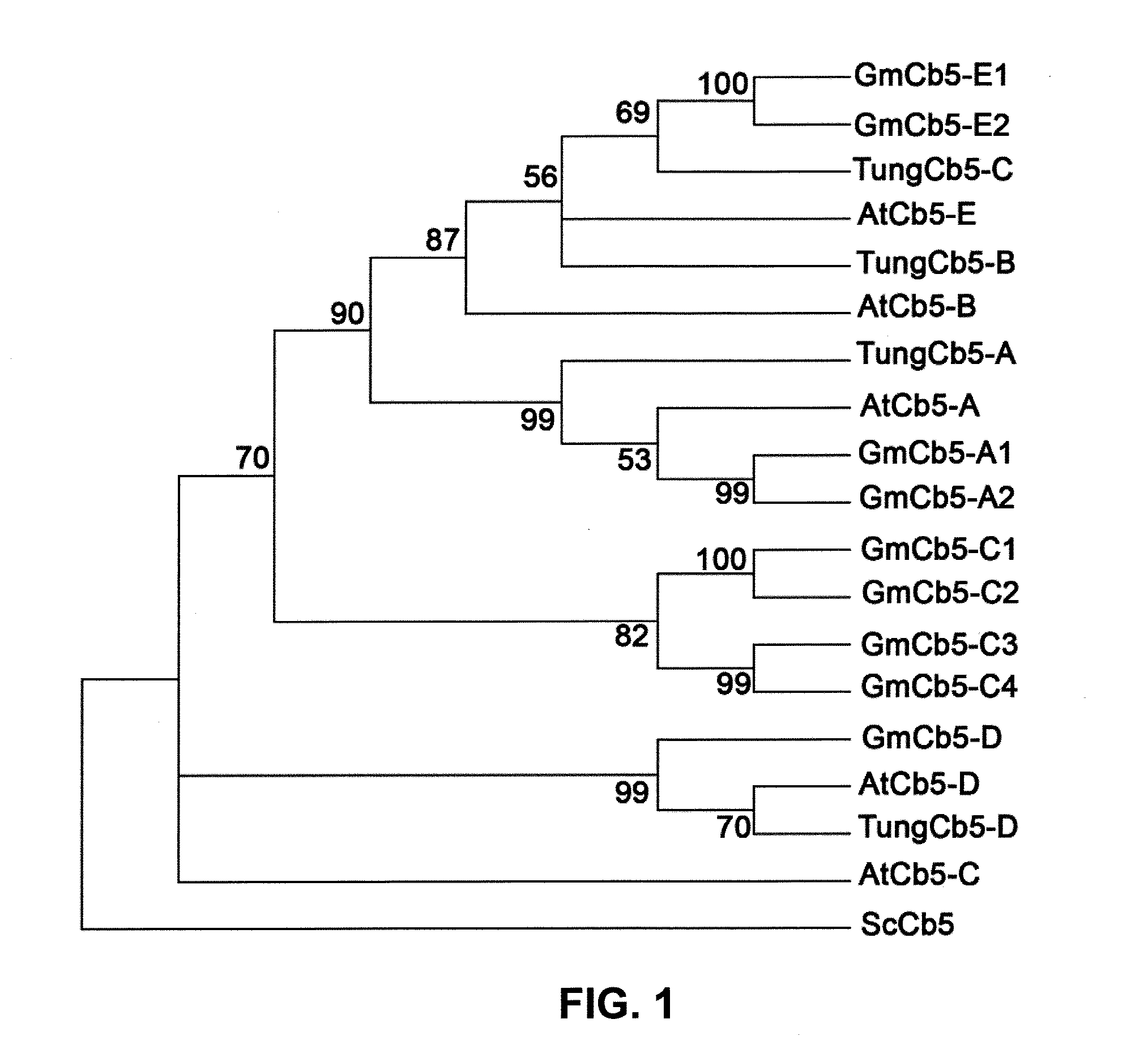
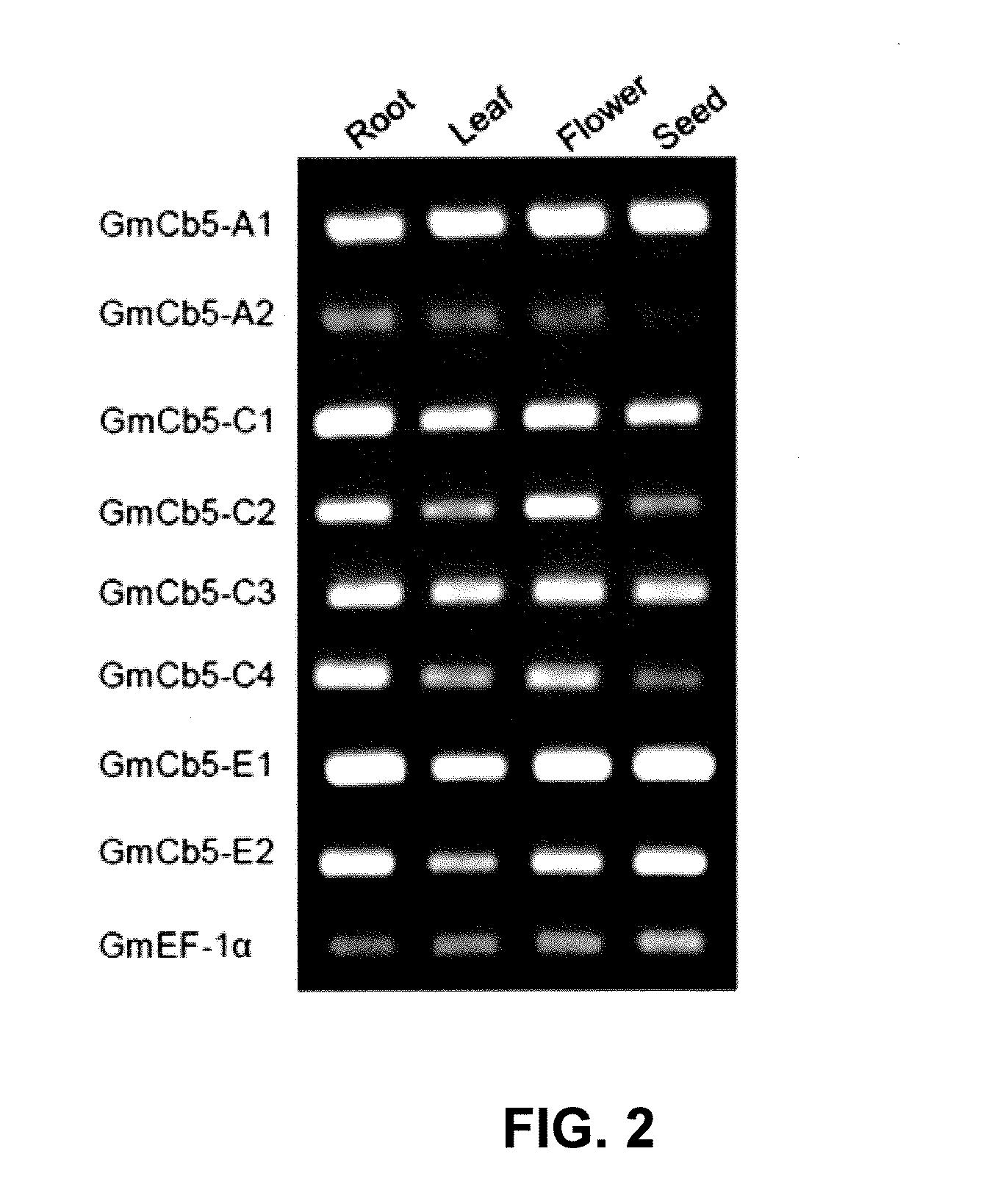
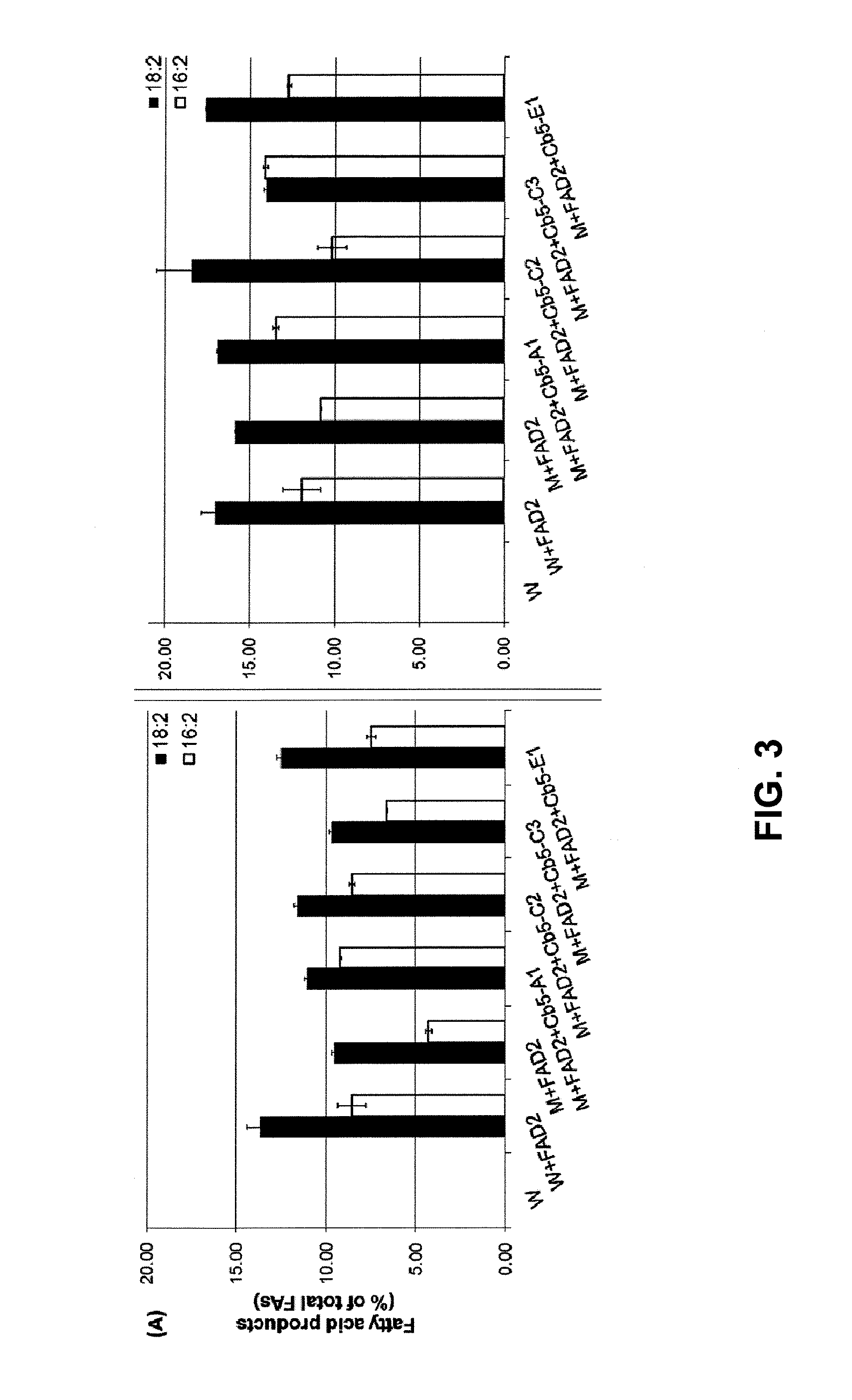
Cytochrome b5 (Cb5) is a haem-binding protein located in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the outer mitochondrial membranes of higher eukaryotes. In higher plants, animals, and fungi, the ER resident Cb5 has been shown to play a role in desaturation of acyl CoA fatty acids. Higher plants Cb5 isoforms from plants such as soybean or Arabidopsis are capable of modulating omega-3 desaturation. Co-expression of certain Cb5 isoforms with FAD3 in a host plant results in increased production of seed oil content as well as altered ratio between different fatty acids. It is also disclosed here that overexpression of Yarrowia ACL enzymes in the plastids of a host plant helps boost the synthesis of acetyl CoA, which in turn, may lead to increased synthesis of fatty acids and enhanced oil accumulation in the seeds.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Use of phosphoketolase for producing useful metabolites
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
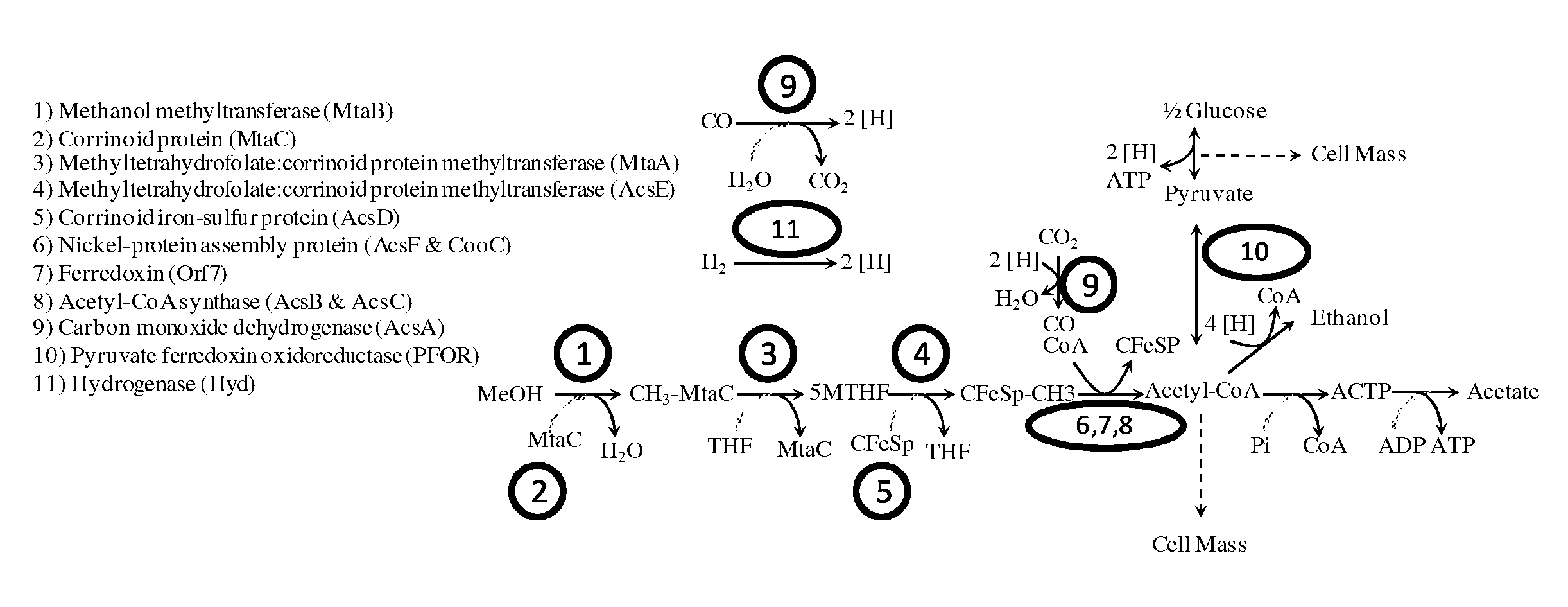
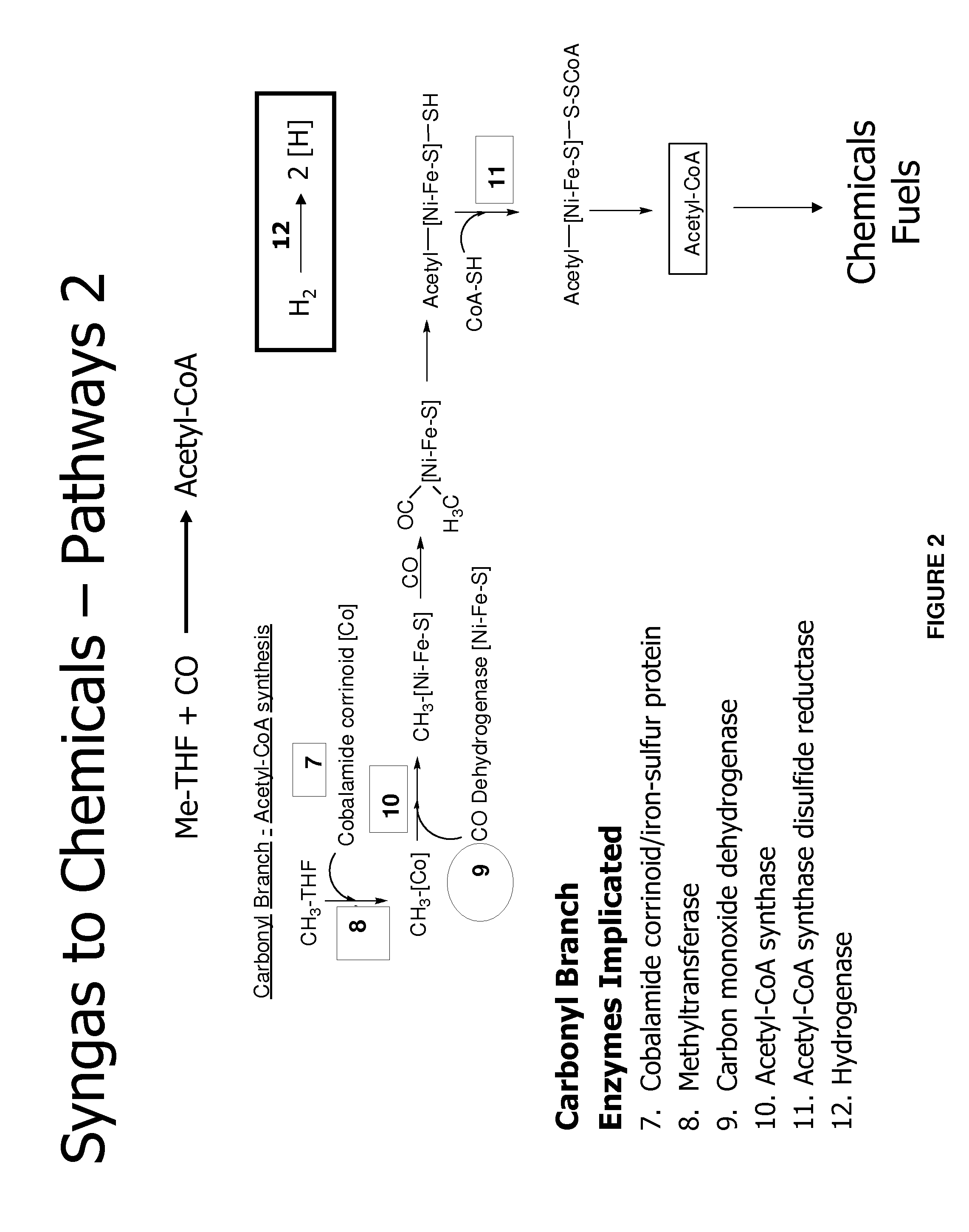
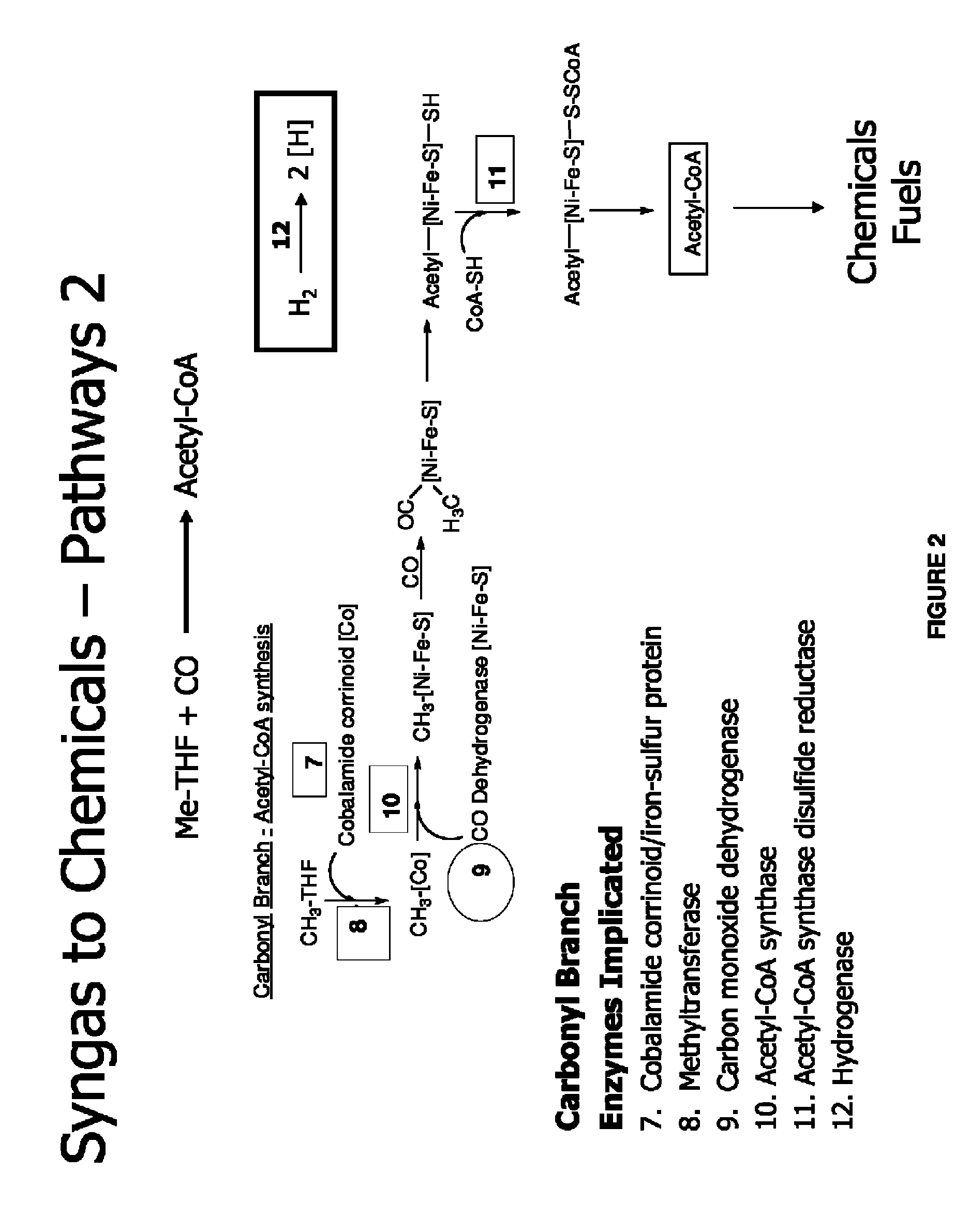
Methods and organisms for utilizing synthesis gas or other gaseous carbon sources and methanol
The invention provides a non-naturally occurring microbial organism having an acetyl-CoA pathway and the capability of utilizing syngas or syngas and methanol. In one embodiment, the invention provides a non-naturally occurring microorganism, comprising one or more exogenous proteins conferring to the microorganism a pathway to convert CO, CO2 and / or H2 to acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA), methyl tetrahydrofolate (methyl-THF) or other desired products, wherein the microorganism lacks the ability to convert CO or CO2 and H2 to acetyl-CoA or methyl-THF in the absence of the one or more exogenous proteins. For example, the microbial organism can contain at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding an enzyme or protein in an acetyl-CoA pathway. The microbial organism is capable of utilizing synthesis gases comprising CO, CO2 and / or H2, alone or in combination with methanol, to produce acetyl-CoA. The invention additionally provides a method for producing acetyl-CoA, for example, by culturing an acetyl-CoA producing microbial organism, where the microbial organism expresses at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding an acetyl-CoA pathway enzyme or protein in a sufficient amount to produce acetyl-CoA, under conditions and for a sufficient period of time to produce acetyl-CoA.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitors
Acetyl Coenzyme A Carboxylase inhibitors, pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds and the use of such compounds to treat for example, Metabolic Syndrome including atherosclerosis, diabetes and obesity.
Owner:PFIZER INC +1
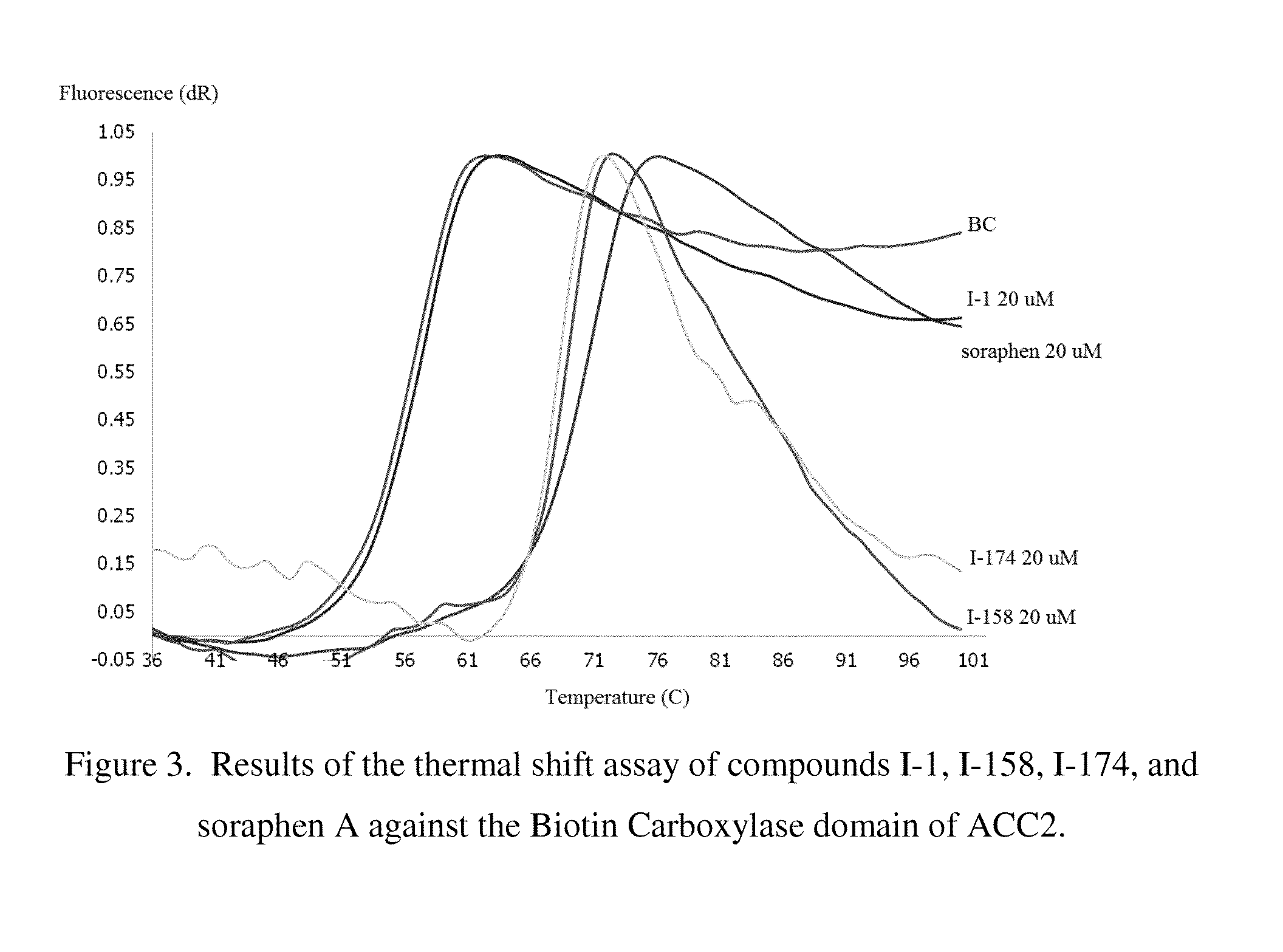
Acc inhibitors and uses thereof
The present invention provides compounds useful as inhibitors of Acetyl CoA Carboxylase (ACC), compositions thereof, and methods of using the same.
Owner:NIMBUS DISCOVERY INC +1
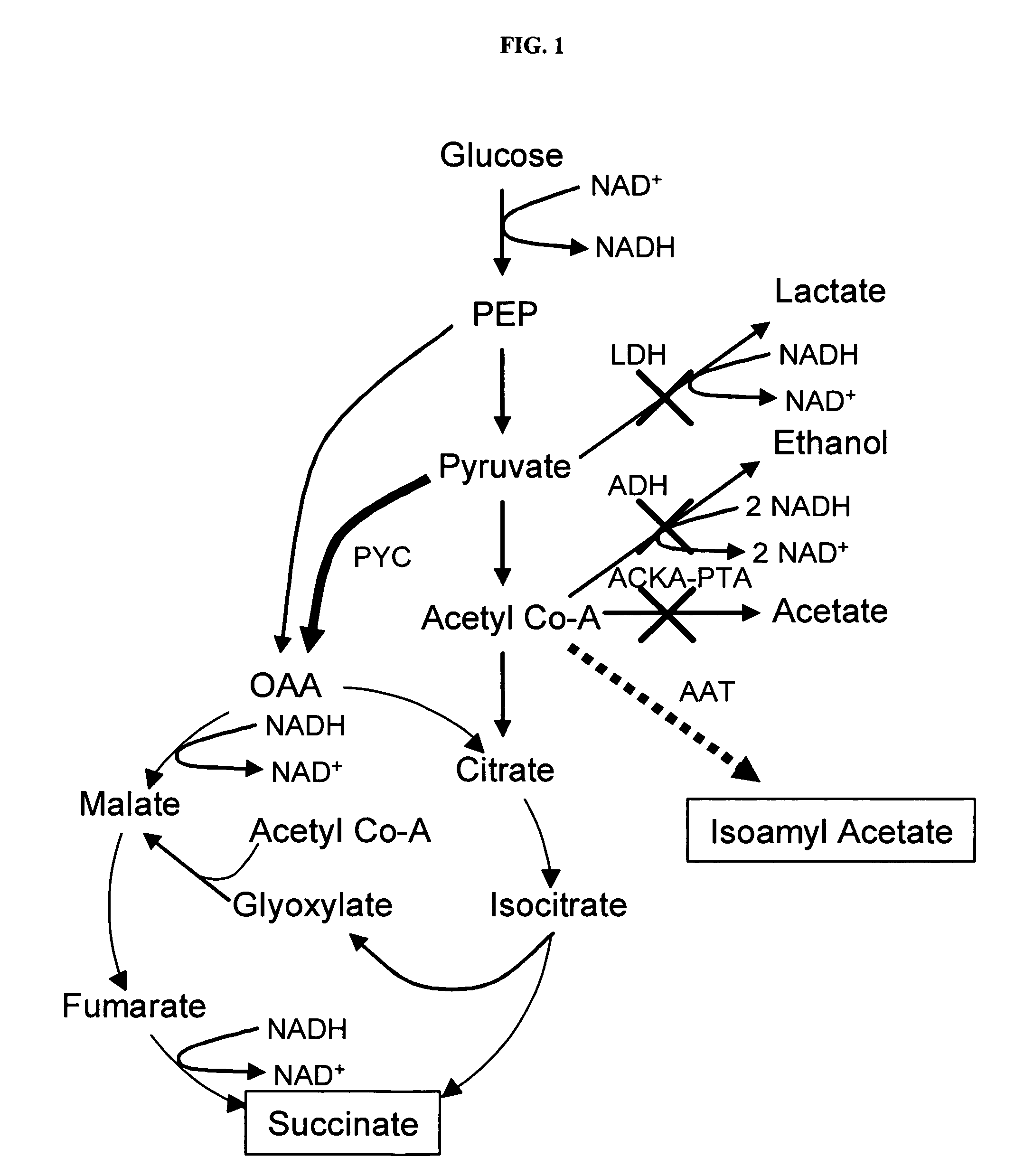
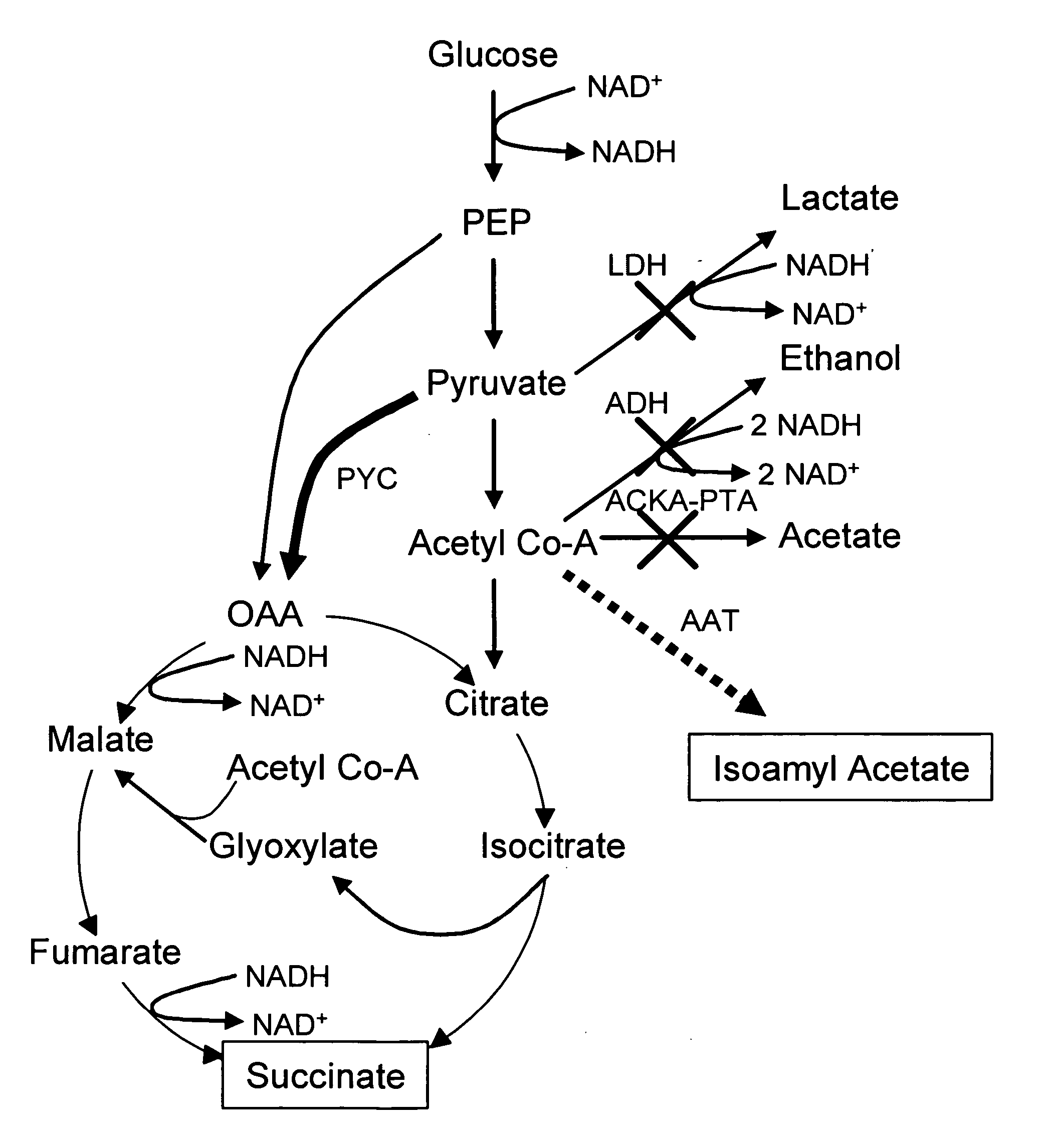
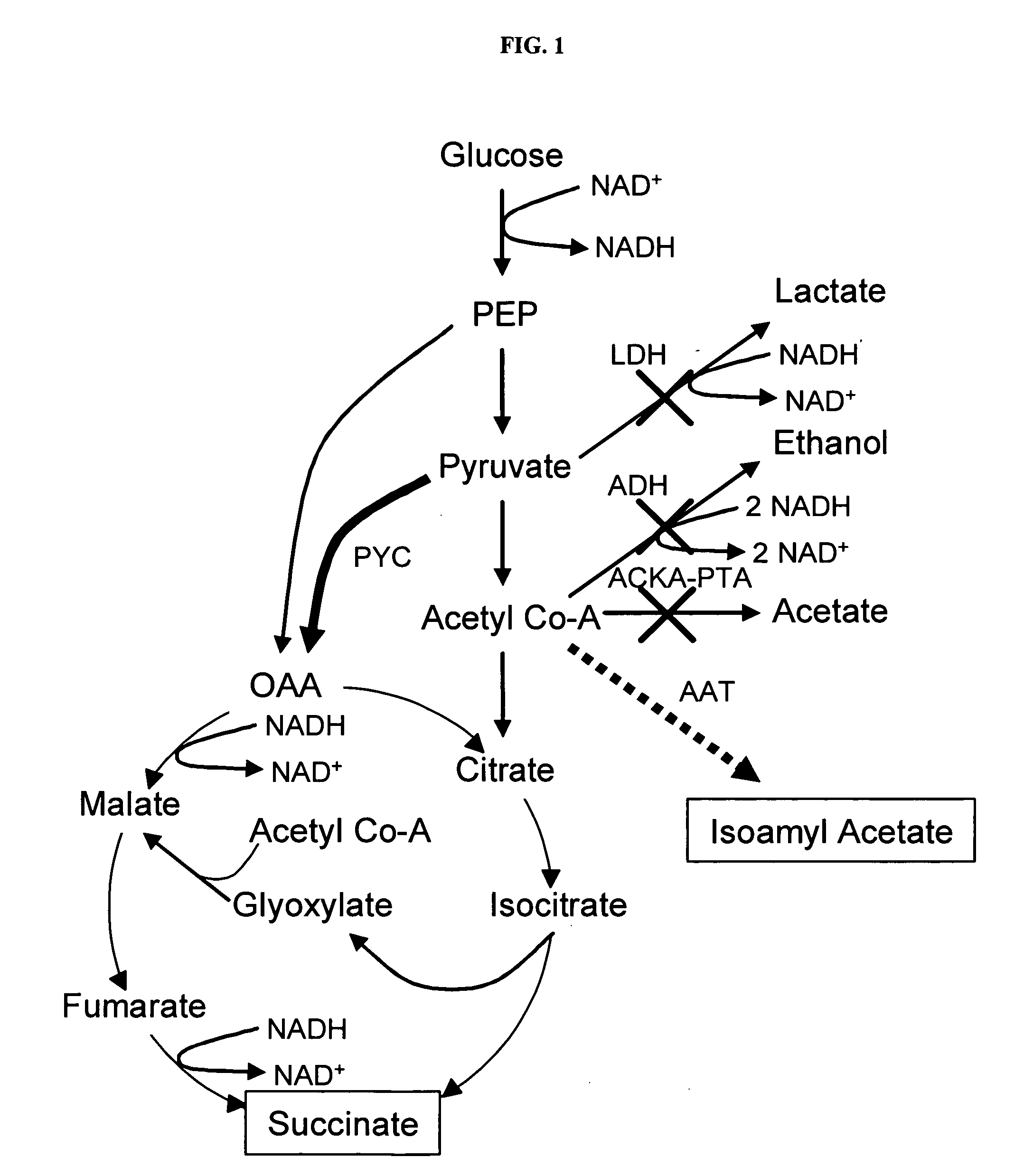
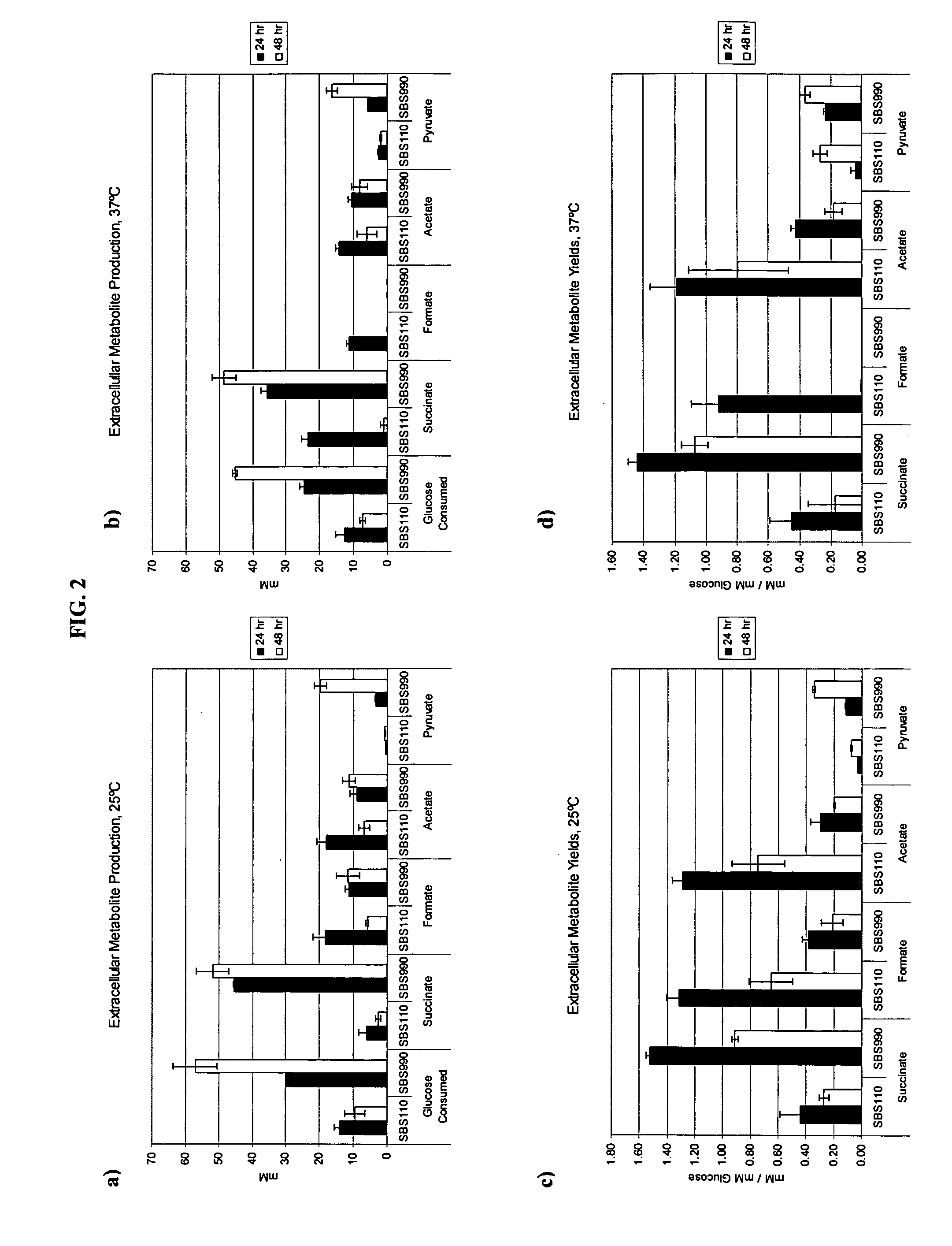
Simultaneous anaerobic production of isoamyl acetate and succinic acid
In vivo method of producing esters from acetyle coA, such as isoamyl acetate and succinate, has been developed by producing null mutants in pathways that use acetyl coA and by overexpressing products that use NADH and in order to maintain the proper redox balance between NADH and NAD+. The method is exemplified with null mutations in ldhA, adhE, ackA-pta and overexpression of pyruvate carboxylase and alcohol acetyltransferase. This strain produces higher levels of both isoamyl acetate and succinate.
Owner:RICE UNIV
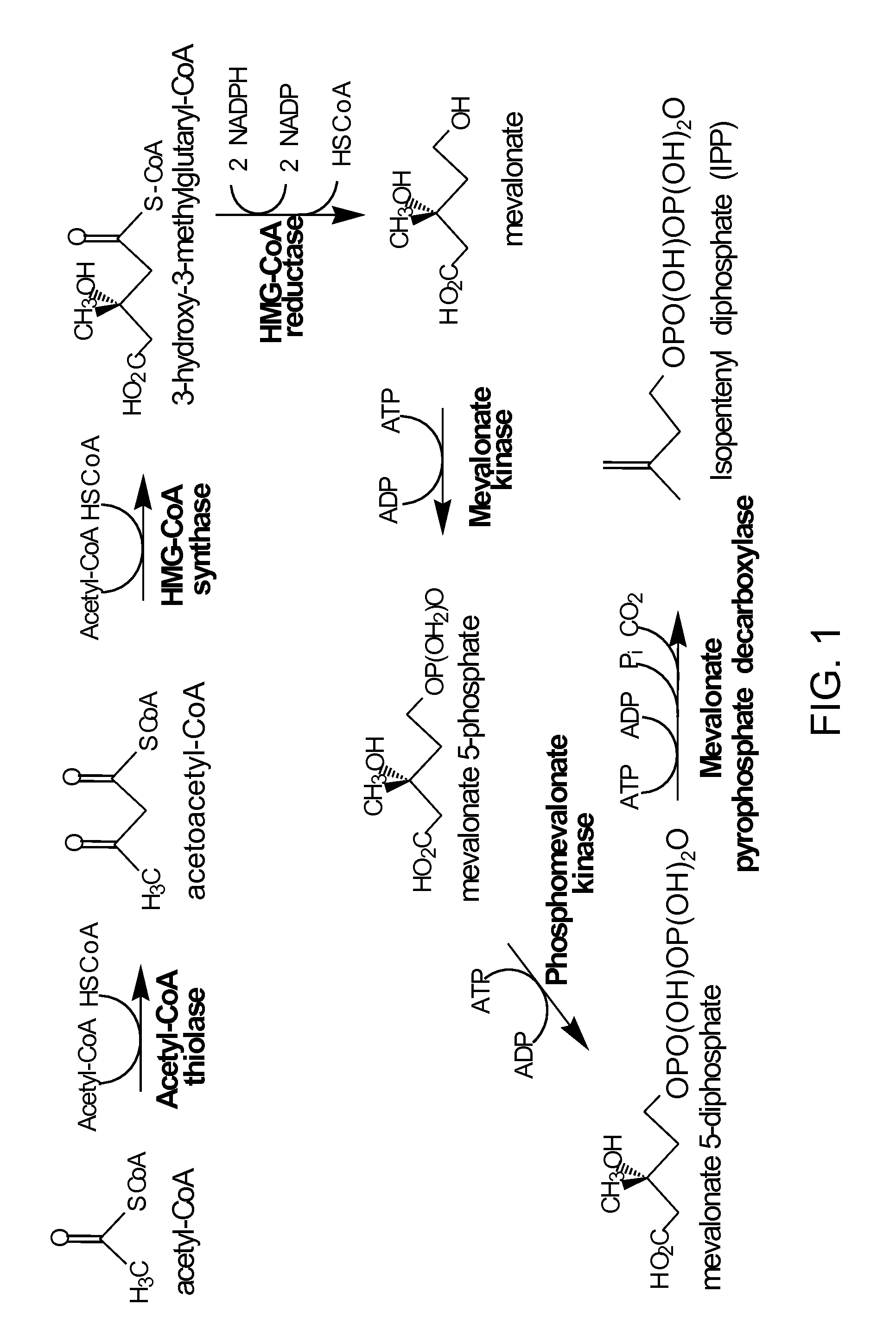
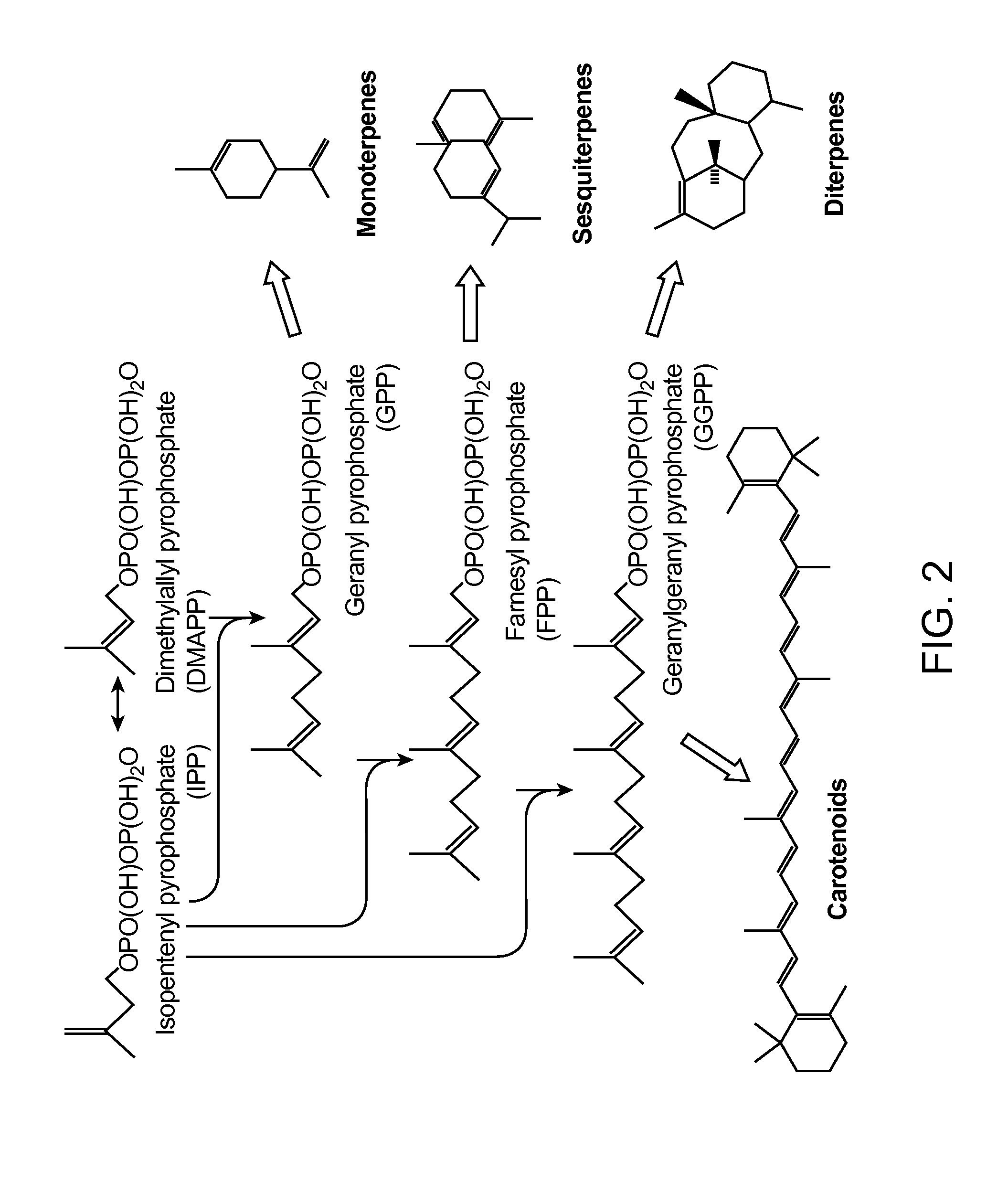
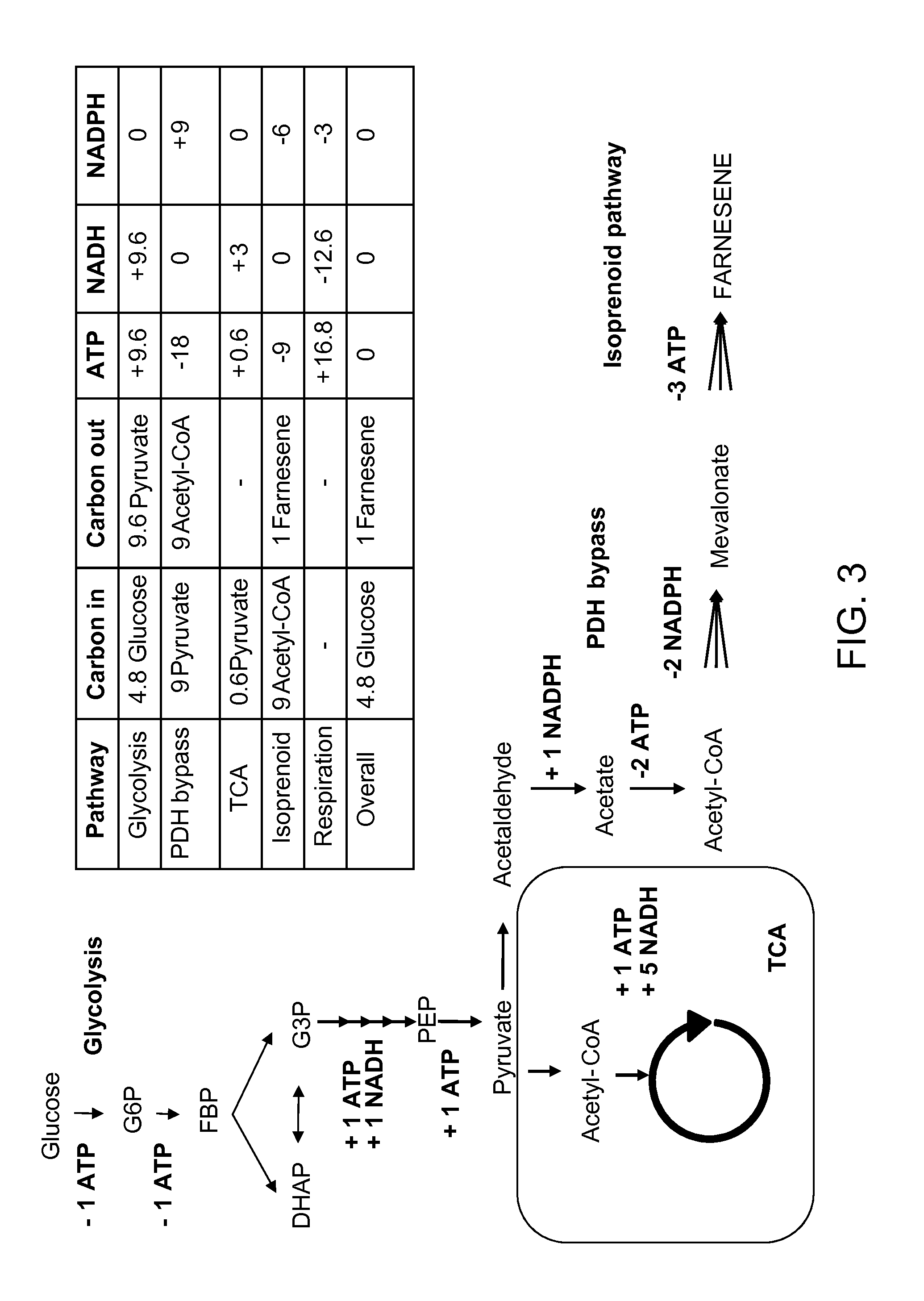
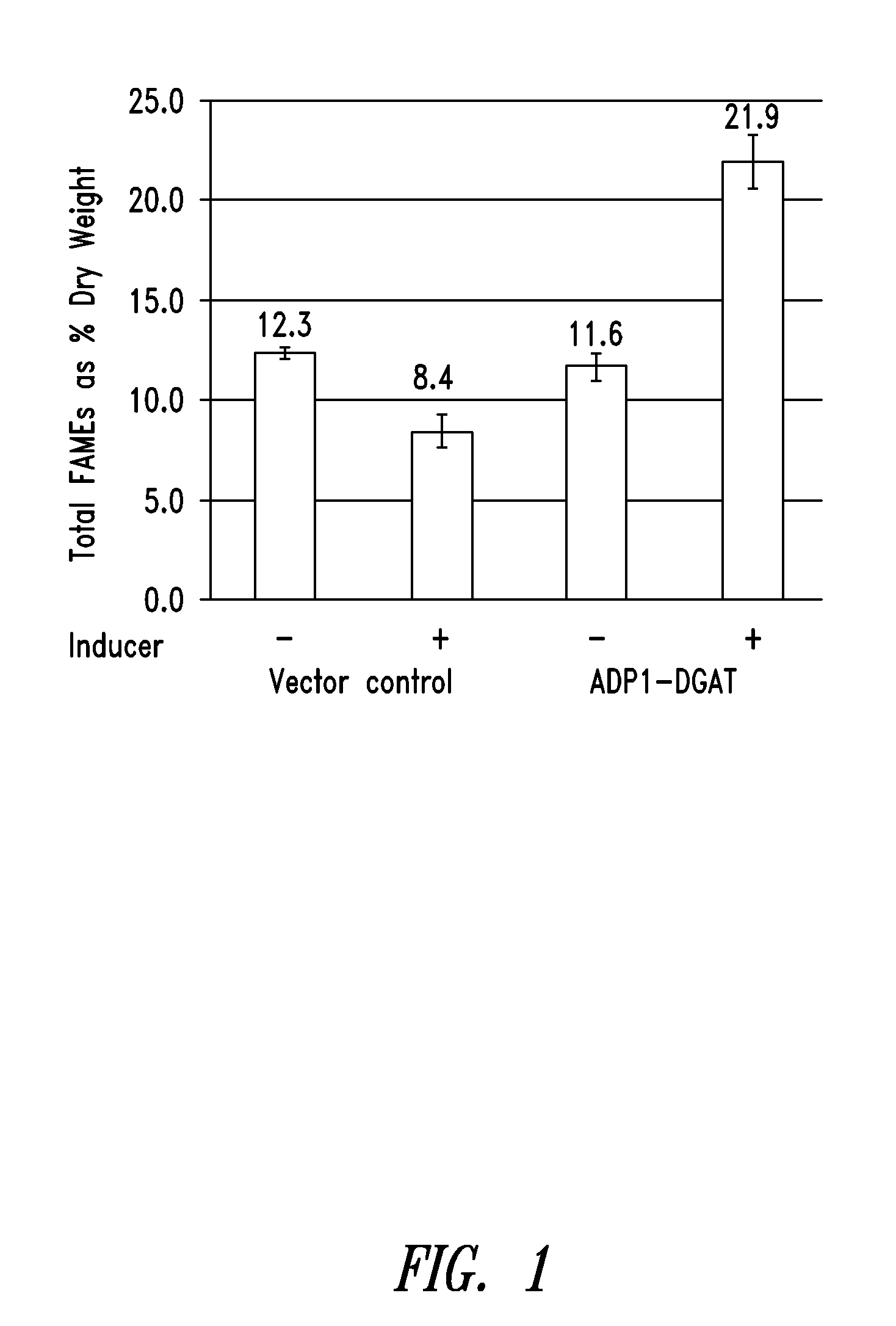
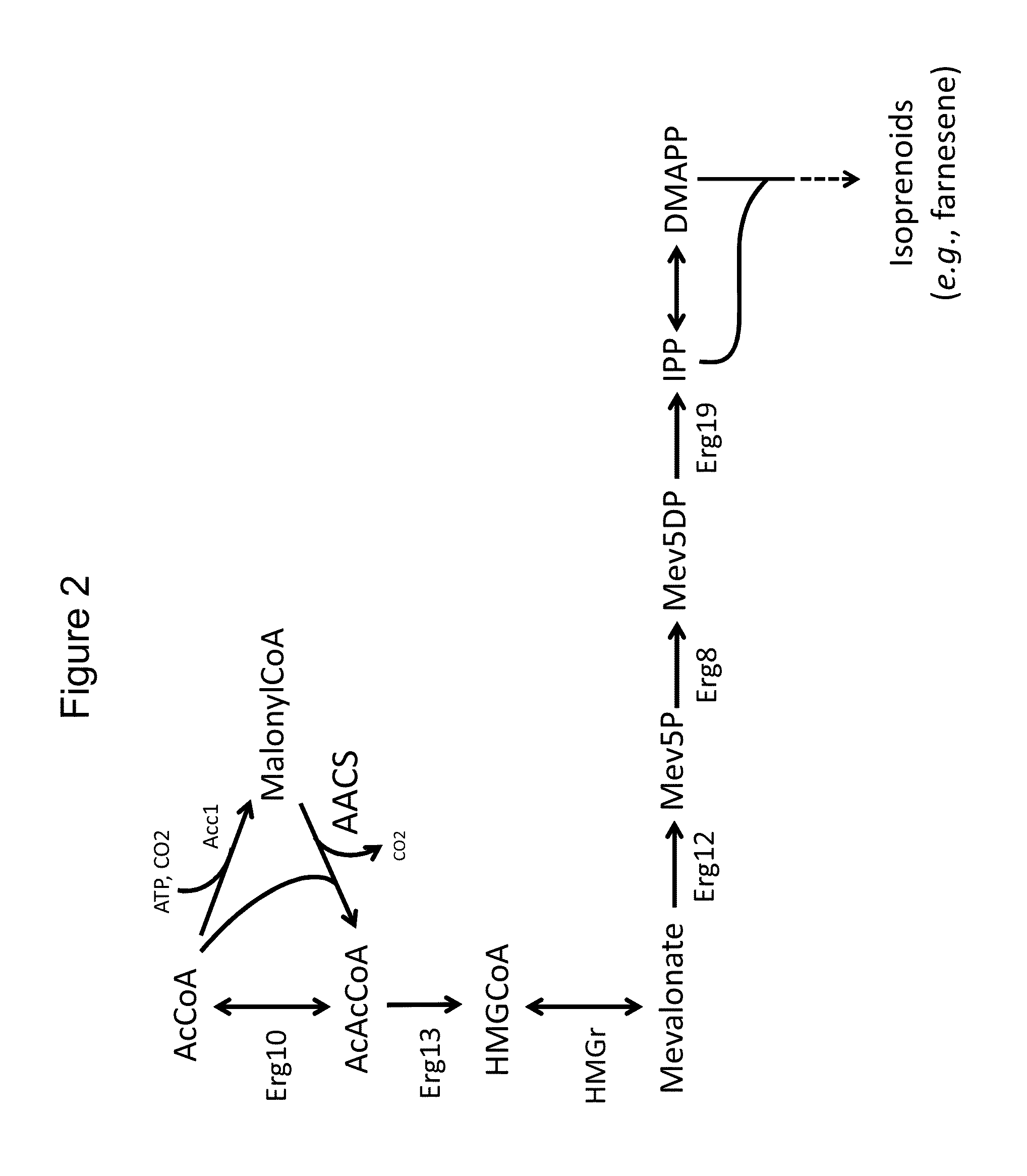
Production of acetyl-coenzyme a derived isoprenoids
ActiveUS8415136B1Avoid high forceThermodynamically favorableFungiTransferasesHeterologousHMG-CoA reductase
Provided herein are compositions and methods for the heterologous production of acetyl-CoA-derived isoprenoids in a host cell. In some embodiments, the host cell is genetically modified to comprise a heterologous nucleotide sequence encoding an acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, acetylating (ADA, E.C. 1.2.1.10) and an MEV pathway comprising an NADH-using HMG-CoA reductase. In some embodiments, the host cell is genetically modified to comprise a heterologous nucleotide sequence encoding an ADA and an MEV pathway comprising an acetoacetyl-CoA synthase. In some embodiments, the genetically modified host cell further comprises one or more heterologous nucleotide sequences encoding a phosphoketolase and a phosphotransacetylase. In some embodiments, the genetically modified host cell further comprises a functional disruption of the native PDH-bypass. The compositions and methods described herein provide an energy-efficient yet redox balanced route for the heterologous production of acetyl-CoA-derived isoprenoids.
Owner:AMYRIS INC
Simultaneous anaerobic production of isoamyl acetate and succinic acid
InactiveUS20060141594A1Maximizing isoamyl acetate productionEasy to separateBacteriaTransferasesSuccinic acidPyruvate synthesis
In vivo method of producing esters from acetyle coA, such as isoamyl acetate and succinate, has been developed by producing null mutants in pathways that use acetyl coA and by overexpressing products that use NADH and in order to maintain the proper redox balance between NADH and NAD+. The method is exemplified with null mutations in ldhA, adhE, ackA-pta and overexpression of pyruvate carboxylase and alcohol acetyltransferase. This strain produces higher levels of both isoamyl acetate and succinate.
Owner:RICE UNIV
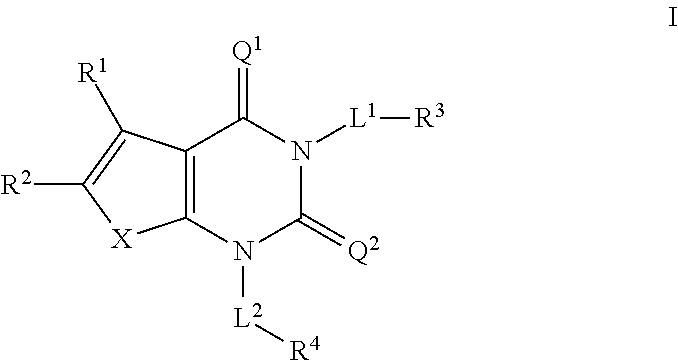
N1-pyrazolospiroketone acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitors
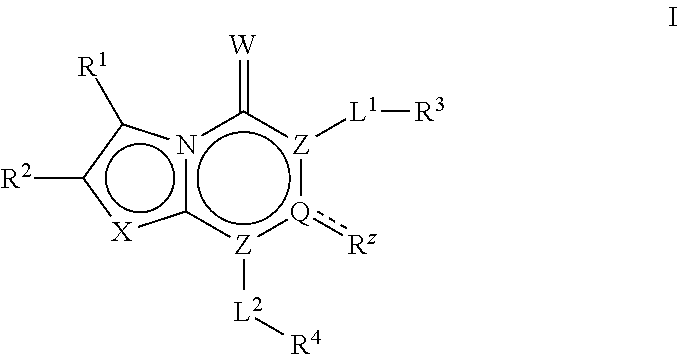
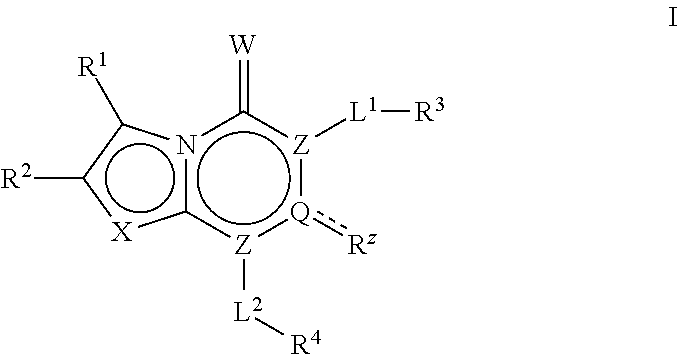
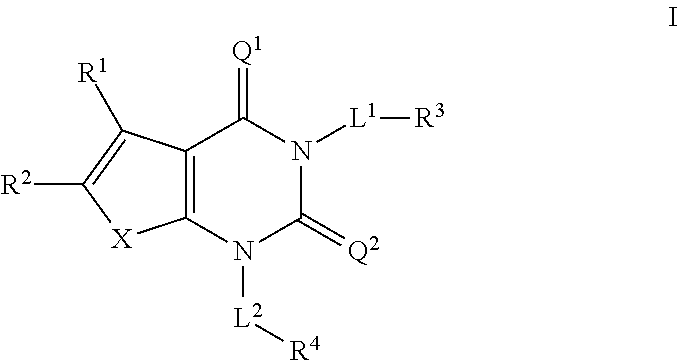
The invention provides a compound of Formula (I) Z N N O N O A1R2 R1 R3R 3 L A2 (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of the compound, wherein R1, R2, R3,Z, A1, L and A 5 2 are as described herein; pharmaceutical compositions thereof; and the use thereof in treating diseases, conditions or disorders modulated by the inhibition of an acetyl-CoA carboxylase enzyme(s) in an animal.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Nucleic acid segments encoding wheat acetyl-CoA carboxylase
InactiveUS6306636B1Reduce the amount requiredAlter fatty acid biosynthesisSugar derivativesBacteriaCarboxysomePolynucleotide
The present invention provides isolated and purified polynucleotides that encode plant polypeptides that participate in the carboxylation of acetyl-CoA. Also provided are methods for identifying such nucleic acid segments and polypeptides. Processes for altering acetyl-CoA carboxylation, increasing herbicide resistance of plants and identifying herbicide resistant variants of acetyl-CoA carboxylase are also provided.
Owner:ARCH DEVMENT
Modified photosynthetic microorganisms for producing triglycerides
This disclosure describes genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms, including Cyanobacteria, that contain one or more exogenous genes encoding a diacylglycerol acyltransferase, a phosphatidate phosphatase, and / or an acetyl-CoA carboxylase, and which are capable of producing increased amounts of fatty acids and / or synthesizing triglycerides.
Owner:LUMEN BIOSCI INC
Butanol production by metabolically engineered yeast
InactiveUS20100062505A1Improve metabolic activityIncreased amount of acetyl-CoAFungiBiofuelsHeterologousYeast
There are disclosed metabolically-engineered yeast and methods of producing n-butanol. In an embodiment, metabolically-engineered yeast is capable of metabolizing a carbon source to produce n-butanol, at least one pathway produces increased cytosolic acetyl-CoA relative to cytosolic acetyl-CoA produced by a wild-type yeast, and at least one heterologous gene encodes and expresses at least one enzyme for a metabolic pathway capable of utilizing NADH to convert acetyl-CoA to n-butanol. In another embodiment, a method of producing n-butanol includes (a) providing metabolically-engineered yeast capable of metabolizing a carbon source to produce n-butanol, at least one pathway produces increased cytosolic acetyl-CoA relative to cytosolic acetyl-CoA produced by a wild-type yeast, and at least one heterologous gene encodes and expresses at least one enzyme for a metabolic pathway utilizing NADH to convert acetyl-CoA to n-butanol; and (b) culturing the yeast to produce n-butanol. Other embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:GEVO INC
Fermentative production of acetone from renewable resources by means of novel metabolic pathway
ActiveUS20100261237A1YieldHigh yieldSugar derivativesHydrolasesAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesAcyl-CoA synthetase
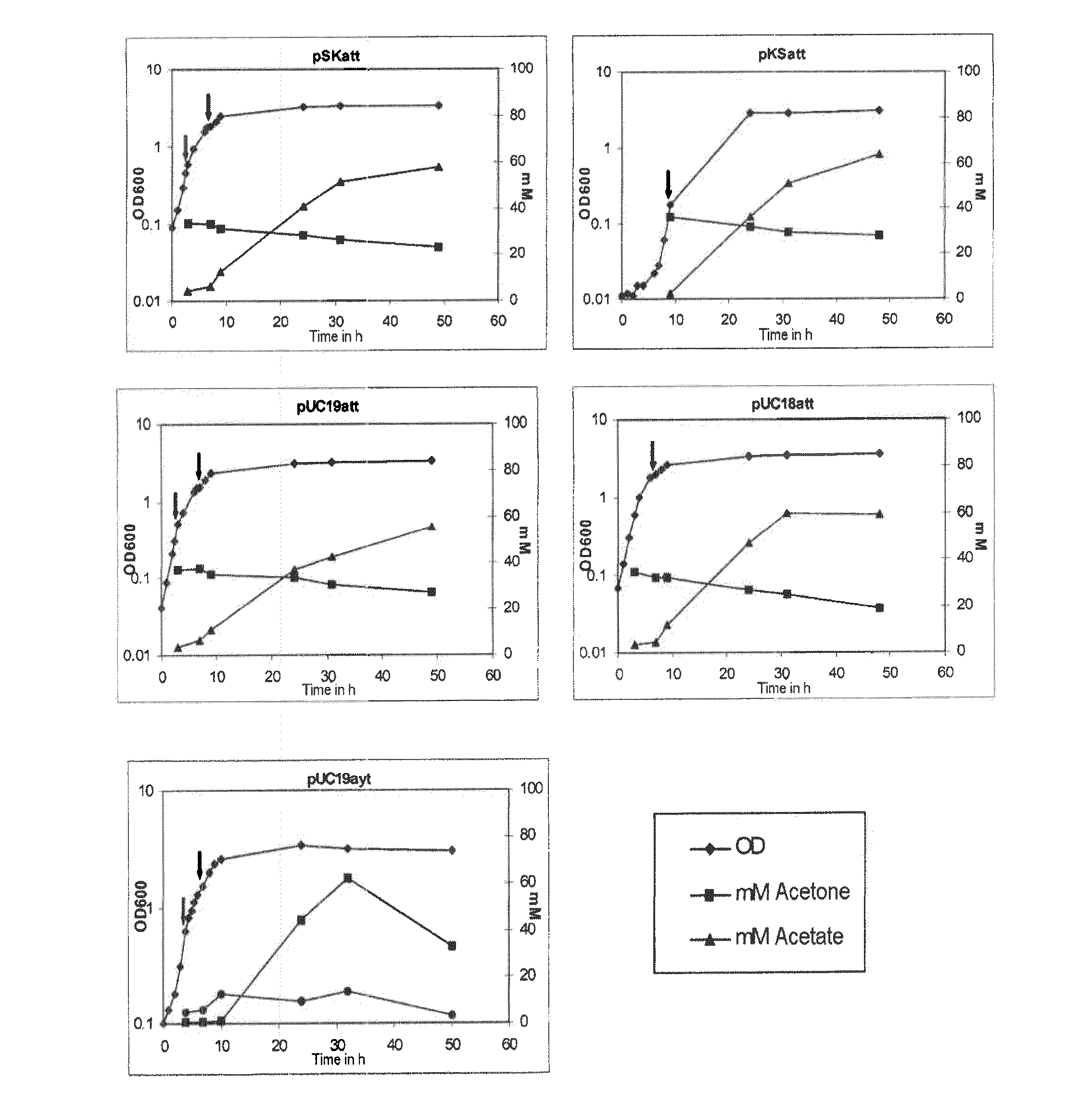
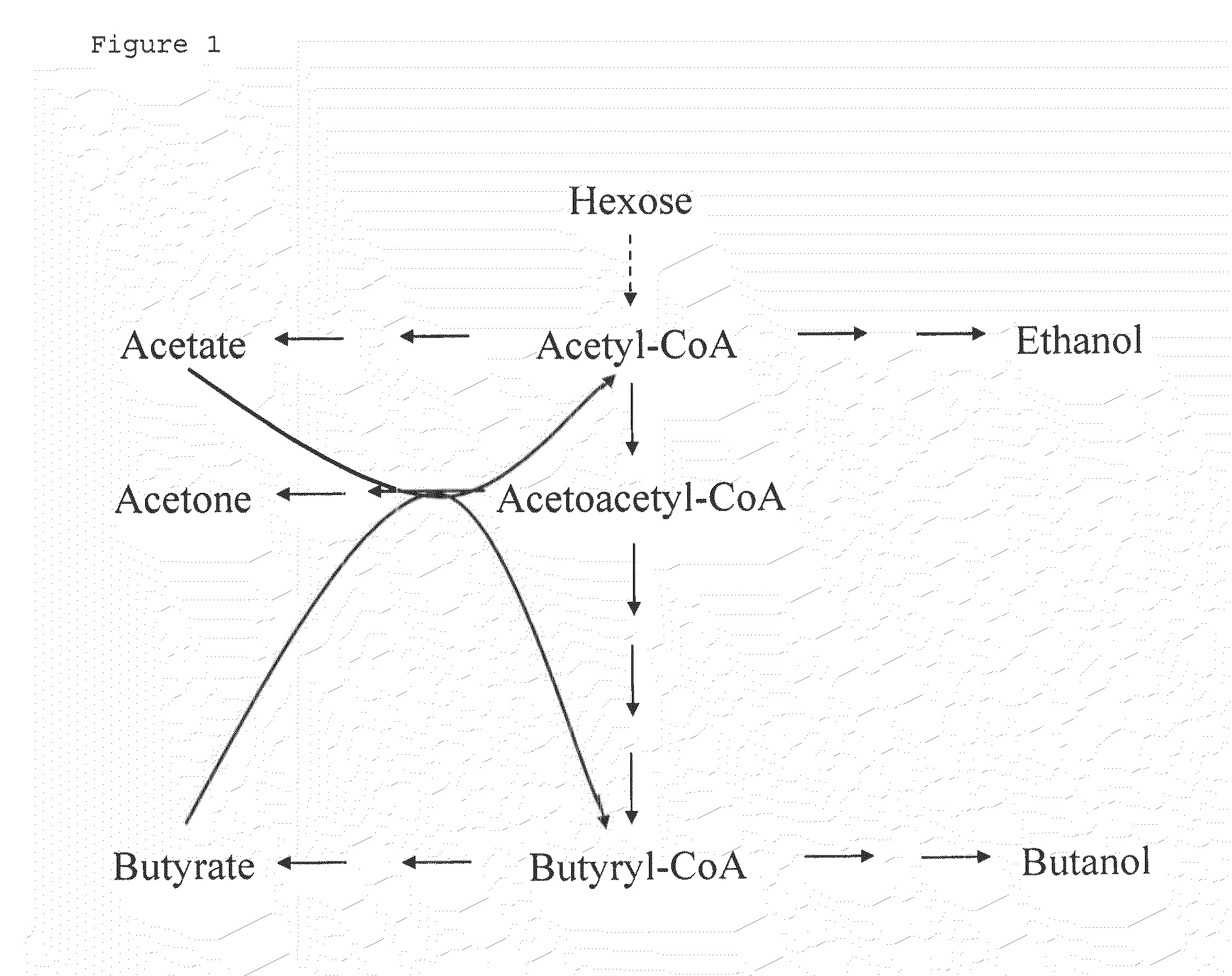
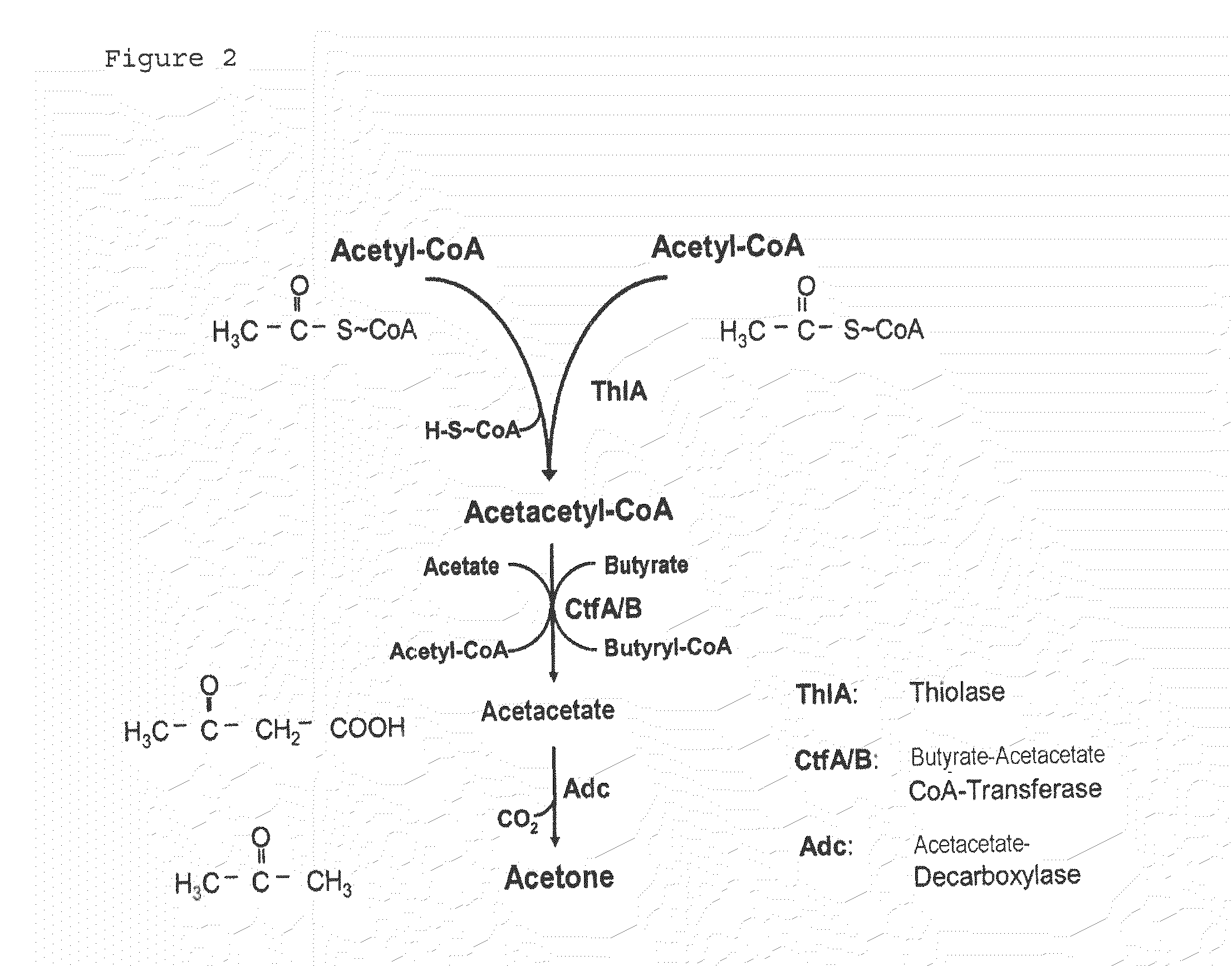
The invention describes a process for preparing acetone starting from acetyl-coenzyme A comprising process steps A. enzymatic conversion of acetyl-CoA into acetoacetyl-CoA B. enzymatic conversion of acetoacetyl-CoA into acetoacetate and CoA and C. decarboxylation of acetoacetate to acetone and CO2, which is characterized in that the coenzyme A is not transferred in process step B to an acceptor molecule. In addition, process step B is surprisingly catalysed by enzymes of the classes of acyl-CoA thioesterase, acyl-CoA synthetase or acyl-CoA thiokinase.A completely novel metabolic pathway is concerned, because the enzymatic hydrolysis of acetoacetyl-CoA without simultaneous transfer of CoA to a receptor molecule has never previously been described for any microbial enzyme.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Methods and organisms for utilizing synthesis gas or other gaseous carbon sources and methanol
The invention provides a non-naturally occurring microbial organism having an acetyl-CoA pathway and the capability of utilizing syngas or syngas and methanol. In one embodiment, the invention provides a non-naturally occurring microorganism, comprising one or more exogenous proteins conferring to the microorganism a pathway to convert CO, CO2 and / or H2 to acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA), methyl tetrahydrofolate (methyl-THF) or other desired products, wherein the microorganism lacks the ability to convert CO or CO2 and H2 to acetyl-CoA or methyl-THF in the absence of the one or more exogenous proteins. For example, the microbial organism can contain at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding an enzyme or protein in an acetyl-CoA pathway. The microbial organism is capable of utilizing synthesis gases comprising CO, CO2 and / or H2, alone or in combination with methanol, to produce acetyl-CoA. The invention additionally provides a method for producing acetyl-CoA, for example, by culturing an acetyl-CoA producing microbial organism, where the microbial organism expresses at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding an acetyl-CoA pathway enzyme or protein in a sufficient amount to produce acetyl-CoA, under conditions and for a sufficient period of time to produce acetyl-CoA.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitors for use as pesticides
InactiveUS20060039943A1Reduce frequencyReduce the populationBiocideAnimal repellantsInsect pestExcipient
The present invention relates to the use of inhibitors of the action of eukaryotic-type Acetyl-CoA carboxylase for controlling insect pests. The inhibitors are selected from arylphenoxypropionates and cyclohexanedione oximes, or their mixtures which may be used together with suitable additives, excipients and carriers. The invention further relates to an insecticidal composition comprising inhibitors of eukaryotic-type Acetyl-CoA carboxylase and further to a method for controlling undesired insect pests by applying an effective amount of eukaryotic-type Acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitors.
Owner:THE STATE OF ISRAEL MINIST OF AGRI & RURAL DEV AGRI RES ORG ARO VOLCANI CENT +1
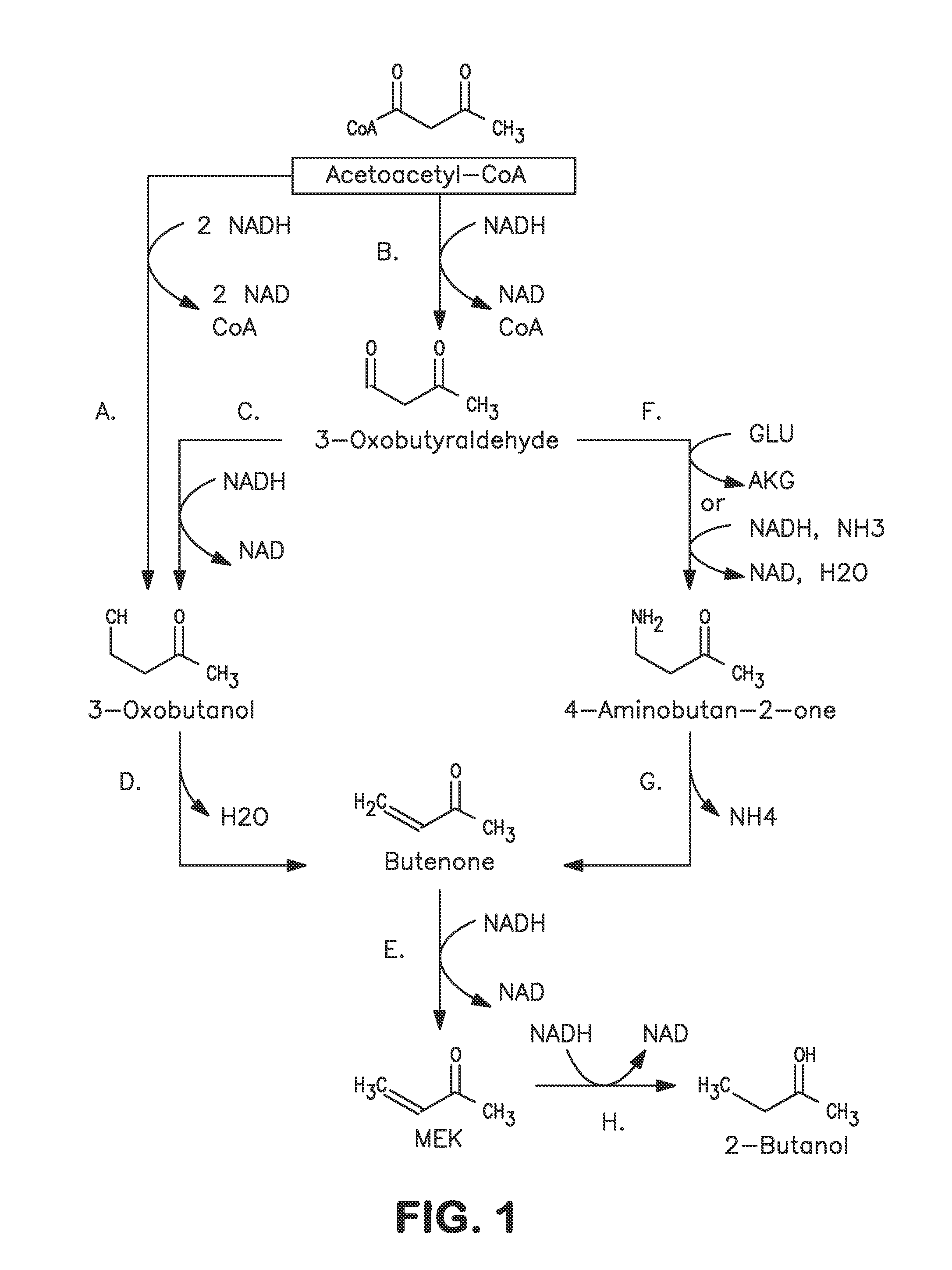
Microorganisms and methods for carbon-efficient biosynthesis of MEK and 2-butanol
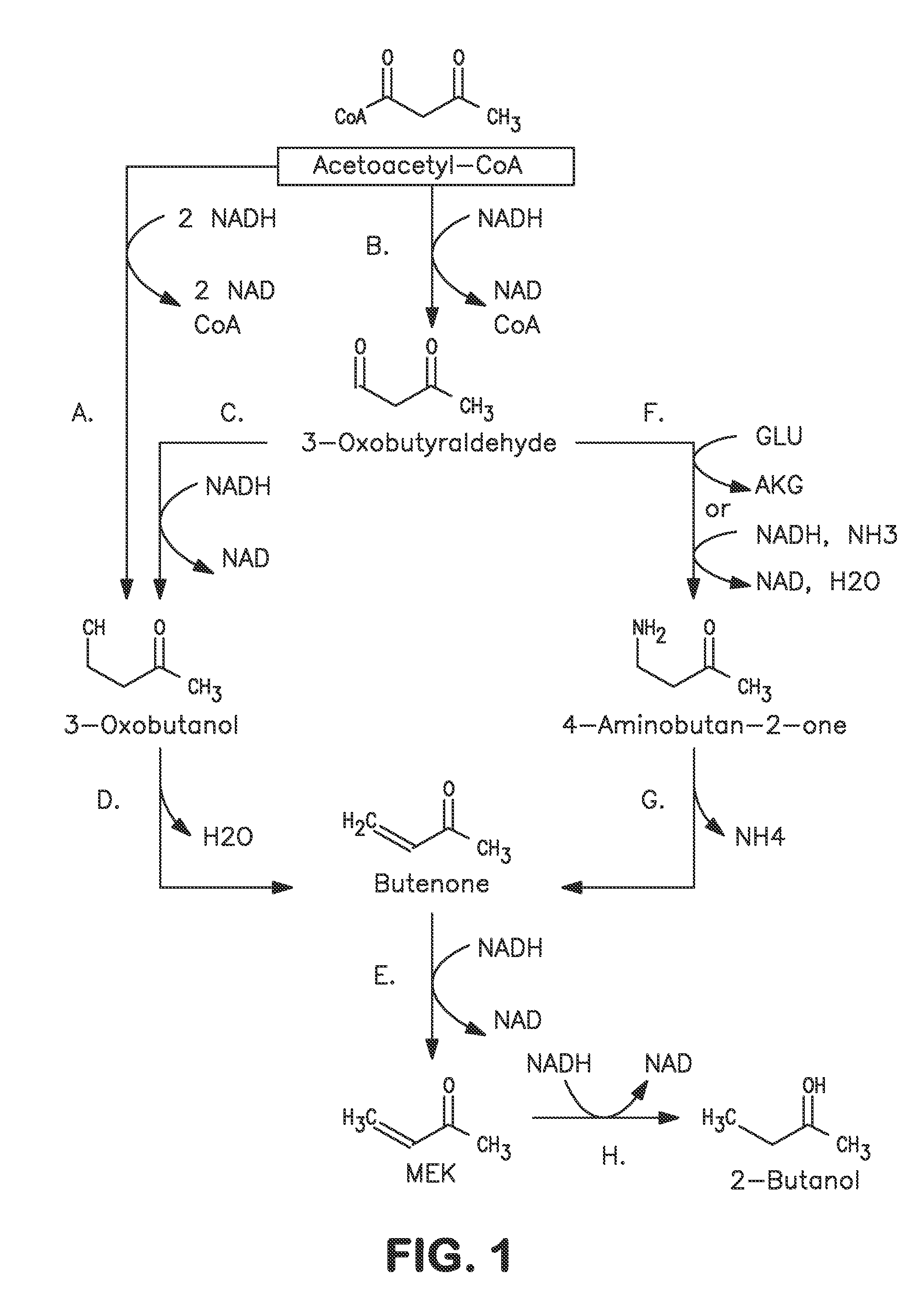
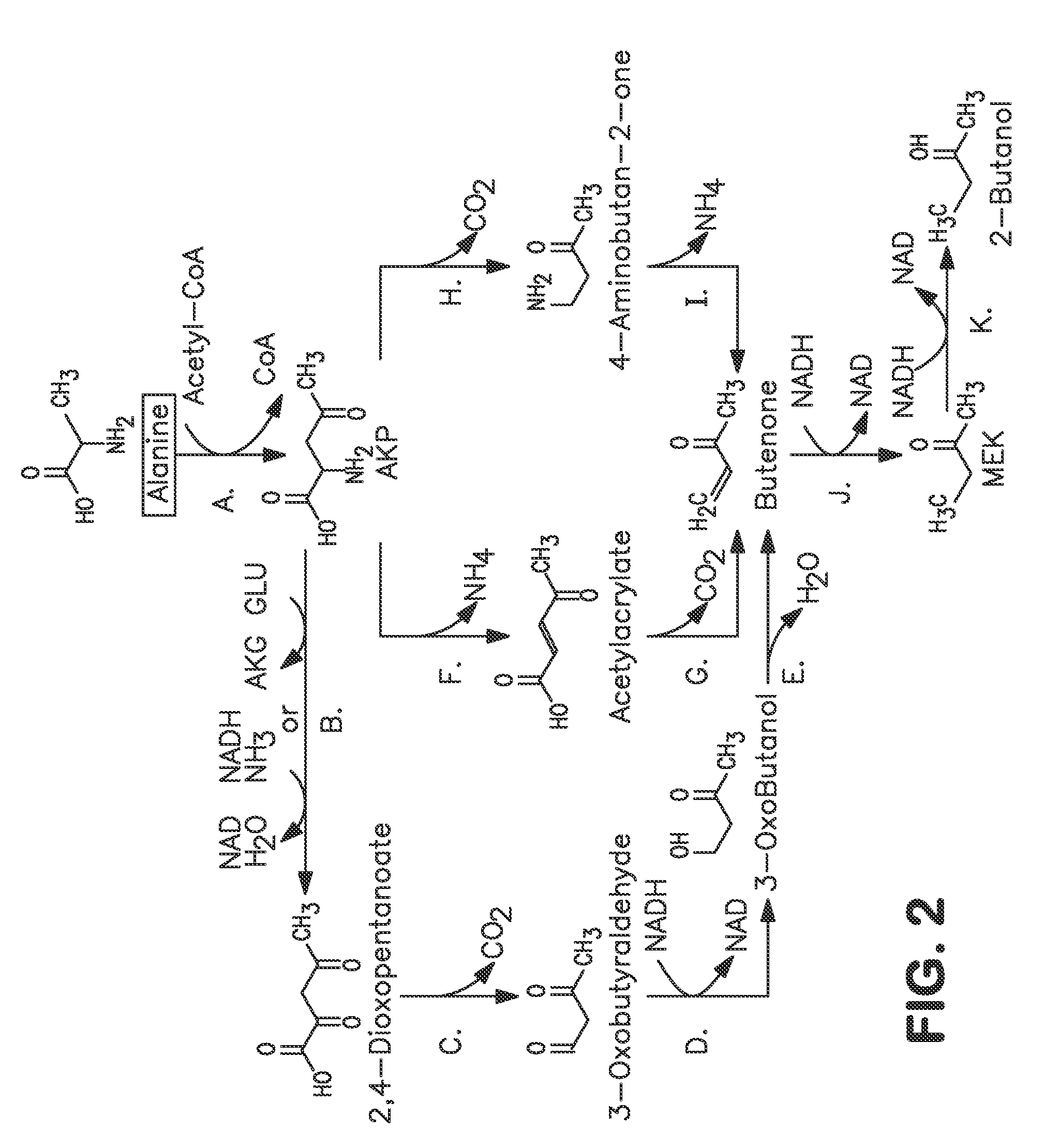
A non-naturally occurring microbial organism has at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding a MEK pathway enzyme expressed in a sufficient amount to produce MEK. The MEK pathway includes an enzyme selected from an acetoacetyl-CoA dehydrogenase (bifunctional), an acetoacetyl-CoA aldehyde dehydrogenase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde reductase, a 3-oxobutanol dehydratase, an MEK oxidoreductase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde aminotransferase, a 4-aminobutan-2-one deaminase, a 2-amino-4-ketopentanoate (AKP) thiolase, an AKP aminotransferase, a 2,4-dioxopentanoate decarboxylase, an AKP deaminase, an acetylacrylate decarboxylase, an AKP decarboxylase, a glutamate dehydrogenase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde oxidoreductase (aminating) and an AKP oxidoreductase (aminating). A 2-butanol pathway further includes an MEK reductase. A method for producing MEK or 2-butanol includes culturing these organisms under conditions and for a sufficient period of time to produce MEK or 2-butanol.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Use of phosphoketolase and phosphotransacetylase for production of acetyl-coenzyme a derived compounds
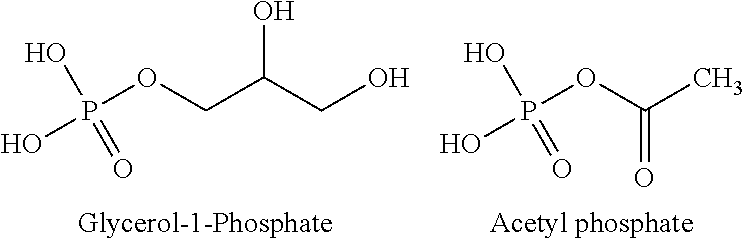
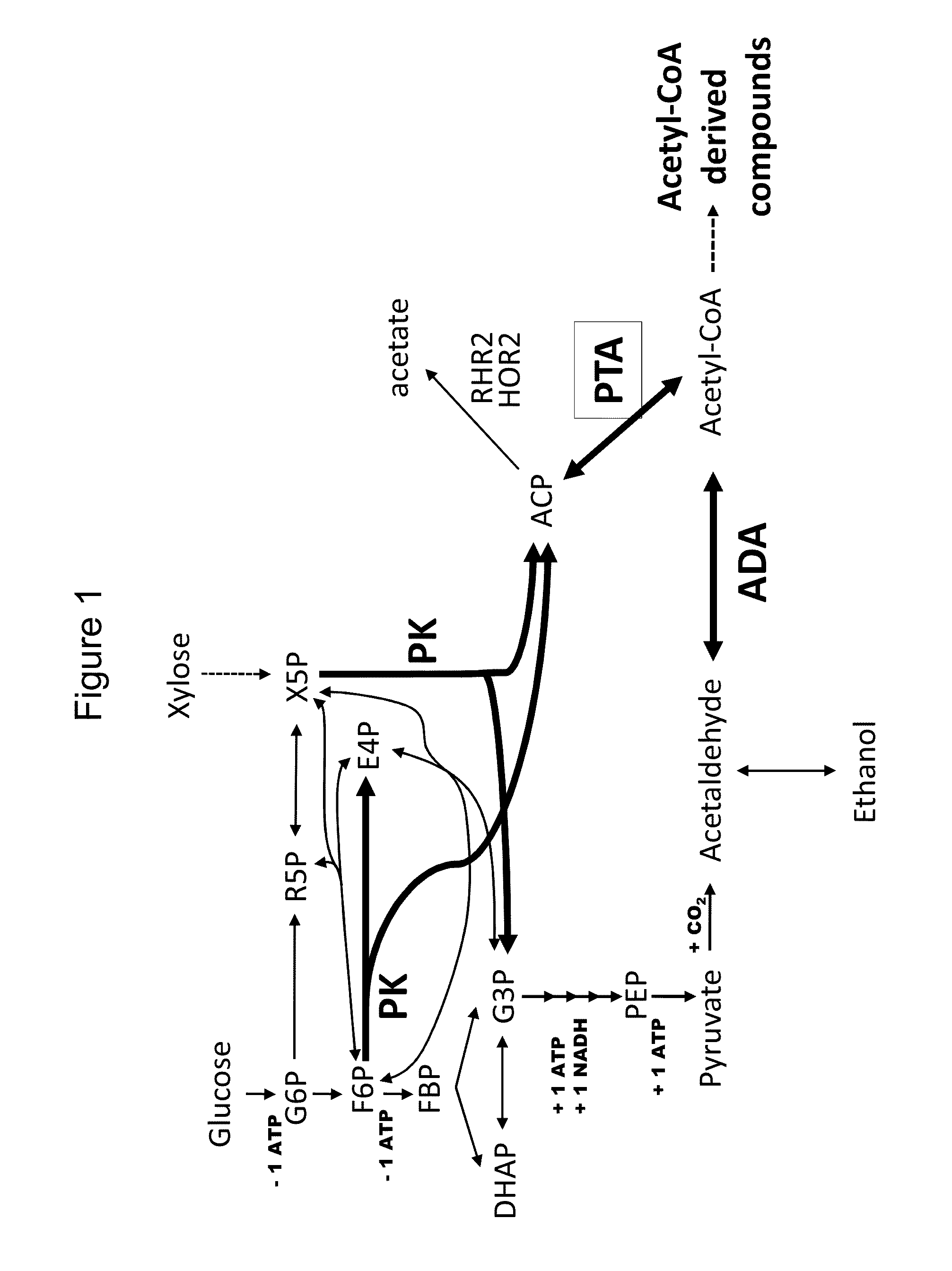
Provided herein are compositions and methods for improved production of acetyl-CoA and acetyl-CoA derived compounds in a host cell. In some embodiments, the host cell is genetically modified to comprise a heterologous nucleotide sequence encoding a phosphoketolase (PK), and a functional disruption of an endogenous enzyme that converts acetyl phosphate to acetate. In some embodiments, the host cell further comprises a heterologous nucleotide sequence encoding a phosphotransacetylase (PTA). In some embodiments, the enzyme that converts acetyl phosphate to acetate is a glycerol-1-phosphatase. In some embodiments, the glycerol-1-phosphatase is GPP1 / RHR2. In some embodiments, the glycerol-1-phosphatase is GPP2 / HOR2. The compositions and methods described herein provide an efficient route for the heterologous production of acetyl-CoA-derived compounds, including but not limited to, isoprenoids, polyketides, and fatty acids.
Owner:TOTALENERGIES ONETECH +1
Methods for stabilizing production of acetyl-coenzyme a derived compounds
ActiveUS20160177341A1Increase probabilityLonger sustained non-catabolic compound productionFungiBacteriaMicroorganismHeterologous
The present disclosure relates to the use of a switch for the production of heterologous non-catabolic compounds in microbial host cells. In one aspect, provided herein are genetically modified microorganisms that produce non-catabolic compounds more stably when serially cultured under aerobic conditions followed by microaerobic conditions, and methods of producing non-catabolic compounds by culturing the genetically modified microbes under such culture conditions. In another aspect, provided herein are genetically modified microorganisms that produce non-catabolic compounds more stably when serially cultured in the presence of maltose followed by the reduction or absence of maltose, and methods of producing non-catabolic compounds by culturing the genetically modified microbes under such culture conditions.
Owner:AMYRIS INC +1
L-Amino Acid-Producing Bacterium and a Method for Producing L-Amino Acid
ActiveUS20070254345A1Improved ability to produce L-amino acidsEfficient productionBacteriaFermentationArginineL-Glutamin
Coryneform bacteria are described that have an ability to produce L-amino acids and are modified so that acetyl-CoA hydrolase activity is decreased. The bacteria are used to produce L-amino acids generated by a biosynthetic pathway in which pyruvic acid is an intermediate, such as L-glutamic acid, L-arginine, L-glutamine, L-proline, L-alanine, L-valine, and L-lysine.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Alpha-ketoglutarate producing yeast engineering strain and construction method thereof
The invention discloses an alpha-ketoglutarate producing yeast engineering strain and a construction method thereof, which belong to the field of genetic engineering. In the method, a molecular approach is adopted, and the yeast engineering strain Y.lipolytica ACL with improved ATP-citrate lyase activity is obtained by over-expressing an ATP-ATP-citrate lyase ACL coding gene from a mouse into a strain Yarrowia lipolytica WSH-Z06 for producing alpha-ketoglutarate by a fermentation method. Compared with a parent strain, the genetic engineering strain provided by the invention can intracellularly accumulate acetyl coenzyme A with the dry cell weight (DCW) of 0.89 mM / g by adopting glycerol as the unique carbon source so as to achieve the ACL activity of 3.56 U / mg protein improved by 7.5 times, achieve the alpha-ketoglutarat yield of 45.3 g / L which is 1.29 times that of parent protein and reduce the pyruvic acid yield to 17.2 g / L which is 68.8 percent of that of the parent strain, and has vast application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
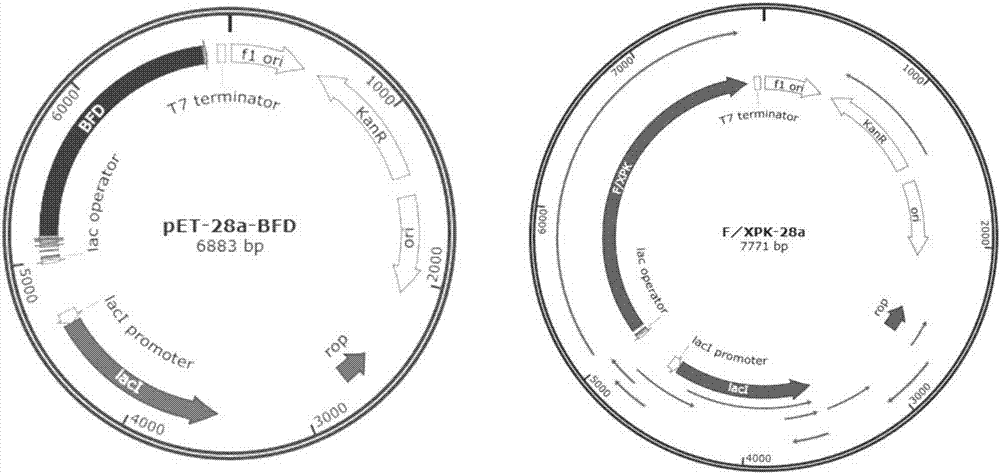
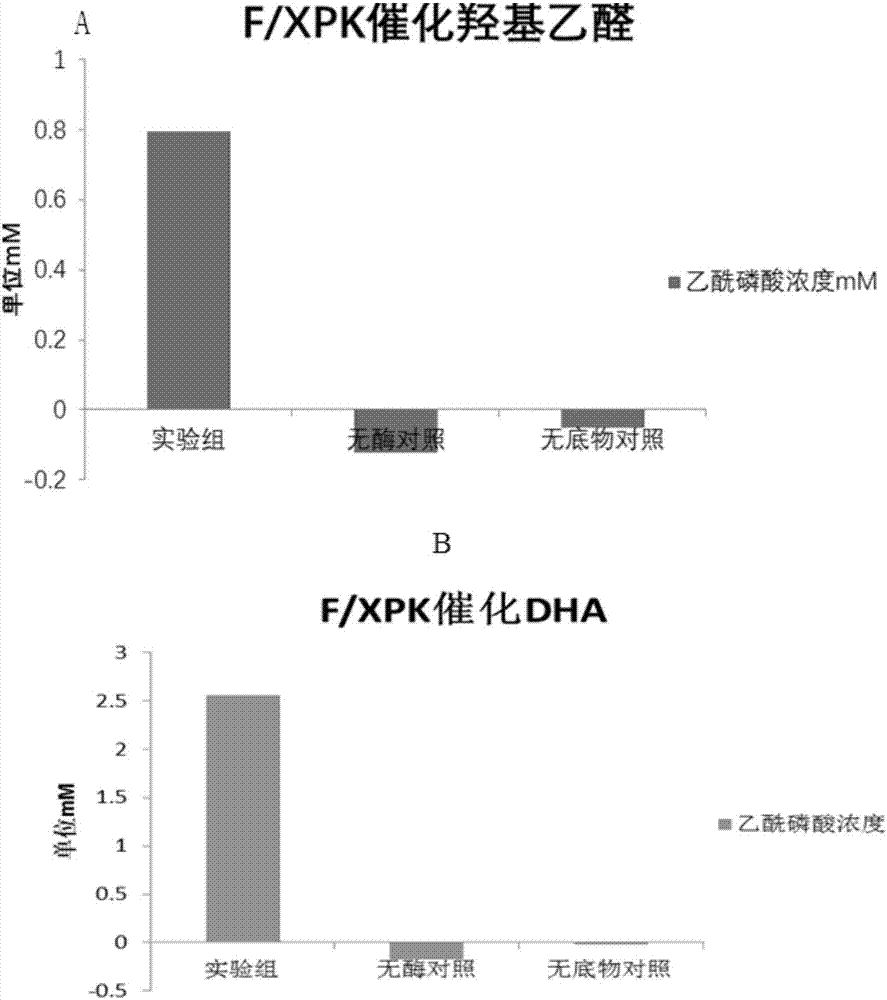
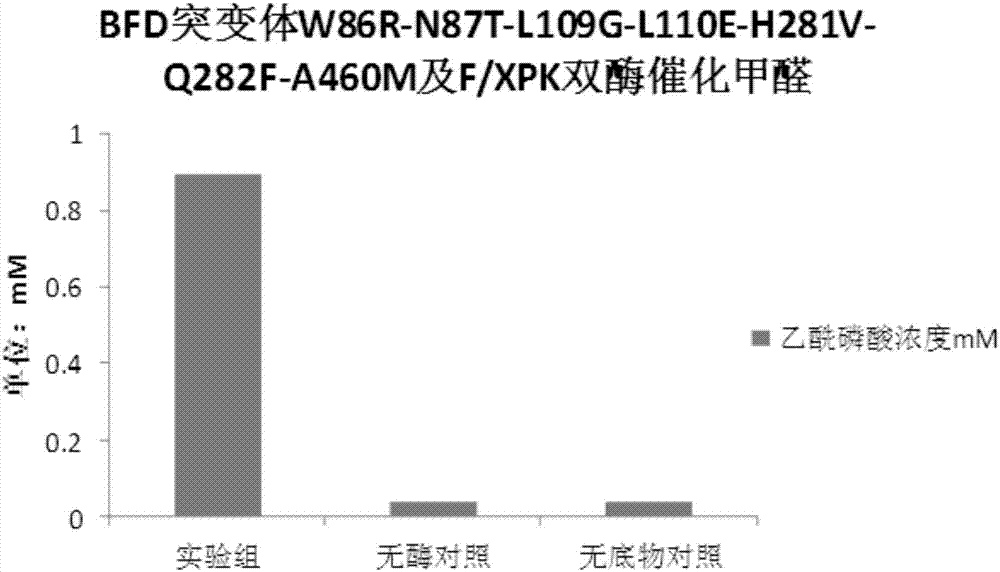
Enzyme for catalyzing formaldehyde to synthesize hydroxyl acetaldehyde and application thereof
ActiveCN106916794AEfficient aggregationNo inputFermentationCarbon-carbon lyasesPhosphate acetyltransferasePhosphoric acid
The invention discloses an enzyme for catalyzing formaldehyde to synthesize hydroxyl acetaldehyde and an application thereof. In the invention, through site-directed mutation of BFD, a mutant of the enzyme is found; and by means of the mutant of the enzyme, high-effect polymerization of the formaldehyde is achieved; meanwhile, through F / XPK, generation of acetyl phosphoric acid from the hydroxyl acetaldehyde or 1,3-dihydroxyacetone is achieved; with combination of phosphotransacetylase (Pta), a route from the formaldehyde to acetyl coenzyme A is achieved in three steps with the enzyme, thereby creating a new formaldehyde assimilation route, namely, synthesizing the acetyl coenzyme A from the formaldehyde in three steps. The route is short and is free of carbon loss and ATP input.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Microorganisms and methods for carbon-efficient biosynthesis of mek and 2-butanol
A non-naturally occurring microbial organism has at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding a MEK pathway enzyme expressed in a sufficient amount to produce MEK. The MEK pathway includes an enzyme selected from an acetoacetyl-CoA dehydrogenase (bifunctional), an acetoacetyl-CoA aldehyde dehydrogenase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde reductase, a 3-oxobutanol dehydratase, an MEK oxidoreductase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde aminotransferase, a 4-aminobutan-2-one deaminase, a 2-amino-4-ketopentanoate (AKP) thiolase, an AKP aminotransferase, a 2,4-dioxopentanoate decarboxylase, an AKP deaminase, an acetylacrylate decarboxylase, an AKP decarboxylase, a glutamate dehydrogenase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde oxidoreductase (aminating) and an AKP oxidoreductase (aminating). A 2-butanol pathway further includes an MEK reductase. A method for producing MEK or 2-butanol includes culturing these organisms under conditions and for a sufficient period of time to produce MEK or 2-butanol.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Microorganisms and methods for production of specific length fatty alcohols and related compounds
The invention provides non-naturally occurring microbial organisms containing a fatty alcohol, fatty aldehyde or fatty acid pathway, wherein the microbial organisms selectively produce a fatty alcohol, fatty aldehyde or fatty acid of a specified length. Also provided are non-naturally occurring microbial organisms having a fatty alcohol, fatty aldehyde or fatty acid pathway, wherein the microbial organisms further include an acetyl-CoA pathway. In some aspects, the microbial organisms of the invention have select gene disruptions or enzyme attenuations that increase production of fatty alcohols, fatty aldehydes or fatty acids. The invention additionally provides methods of using the above microbial organisms to produce a fatty alcohol, a fatty aldehyde or a fatty acid.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Acc inhibitors and uses thereof
The present invention provides compounds useful as inhibitors of Acetyl CoA Carboxylase (ACC), compositions thereof, and methods of using the same. Specifically, bicyclic heteroaryl derivatives containing a imidazole, thiazole or oxazole fused to a pyridinone, pyrimidinone or pyrimidindione are provided. These compounds have therapeutic utility toward treating an ACC enzyme mediated disorder such as obesity in a subject, upon administration in an effective amount to said subject.
Owner:NIMBUS DISCOVERY INC
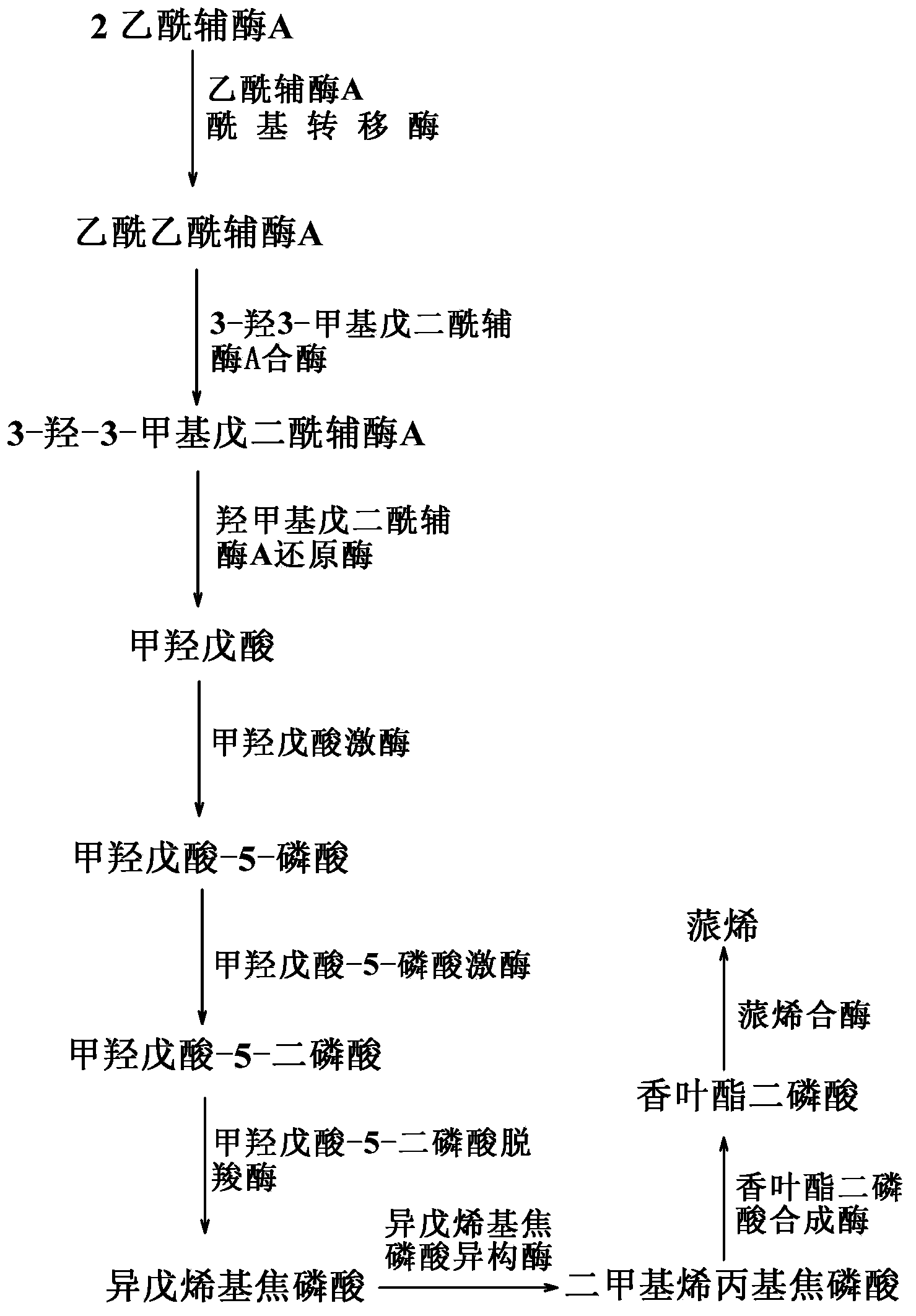
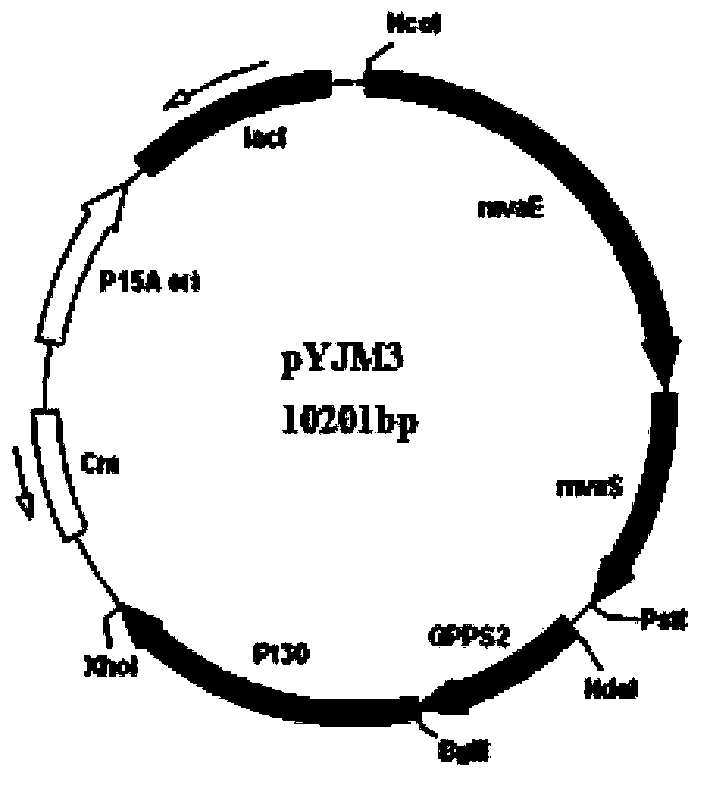
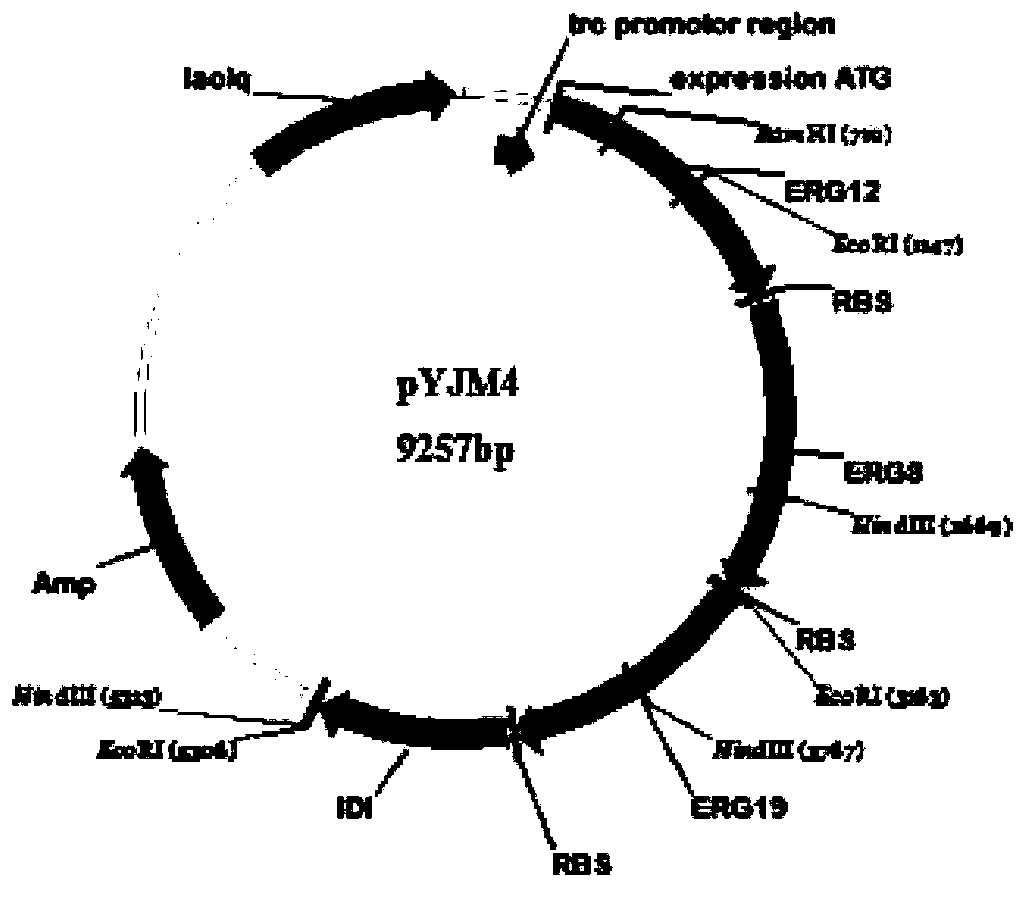
Method for synthesizing alpha-pinene or beta-pinene by adopting biological process
InactiveCN104120148AFast growthShort fermentation cycleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHydroxy methyl glutarylGlutaryl-coenzyme A
The invention provides a biological method for synthesizing alpha-pinene or beta-pinene from acetyl coenzyme A and a reconstitution cell capable of synthesizing the alpha-pinene or beta-pinene, wherein the acetyl coenzyme A is obtained from a simple starting material like glucose. The method for synthesizing the alpha-pinene or beta-pinene by adopting a biological process comprises the following steps: transferring acetyl coenzyme A acyltransferase, 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A synthase, hydroxymethyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase, mevalonic acid kinase, mevalonic acid-5-phosphokinase, mevalonic acid-5-diphosphonic acid decarboxylase, isopentenylpyrophosphate isomerase, geranyldiphosphate synthetase and pinene synthase into an appropriate host cell by adopting metabolic engineering technology, and culturing the obtained reconstitution cell, so that the target product, namely alpha-pinene or beta-pinene can be obtained.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Acc inhibitors and uses thereof
The present invention provides compounds useful as inhibitors of Acetyl CoA Carboxylase (ACC), compositions thereof, and methods of using the same.
Owner:GILEAD APOLLO LLC
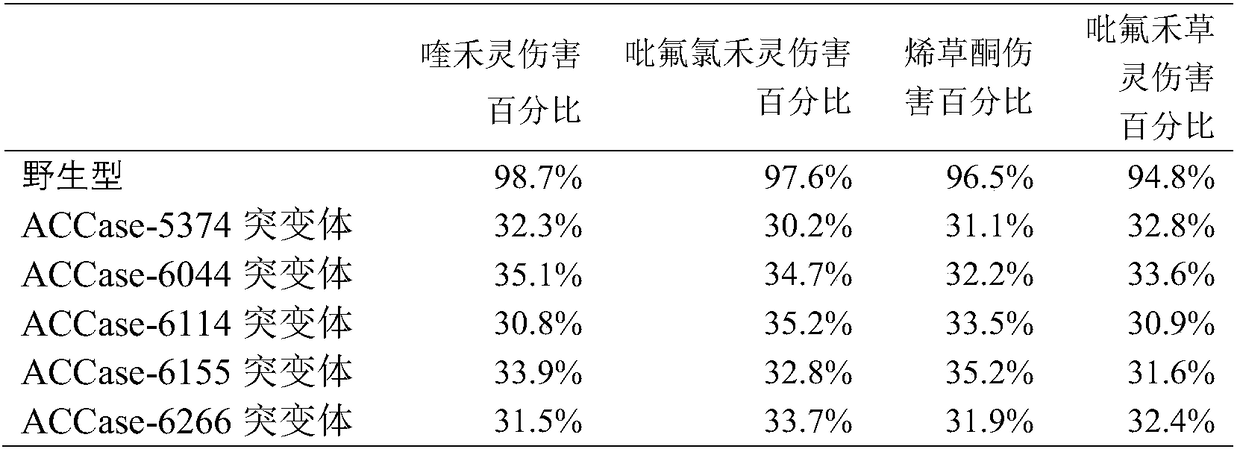
ACCase mutant protein enabling plant to have herbicide resistance, and application thereof
PendingCN108359646AHerbicide resistantMicrobiological testing/measurementLigasesAcetyl-coenzyme A carboxylaseQuizalofop-ethyl
The invention discloses a rice ACCase mutant protein. The amino acid sequence of the ACCase mutant protein has any one or more of mutations in the 1792th position, the 2015th position, the 2038th position, the 2052th position and the 2089th position of the amino acid sequence of the rice ACCase. The invention also discloses a nucleic acid or a gene for encoding the protein. A plant expressing themutant protein has resistance (tolerance) to an acetyl-CoA carboxylase herbicide. After 3 mL quizalofop-ethyl / L water (2 times recommended concentration) is applied to a rice three-leaf seedling of the rice ACCase protein, the plant can still normally grow and seed.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
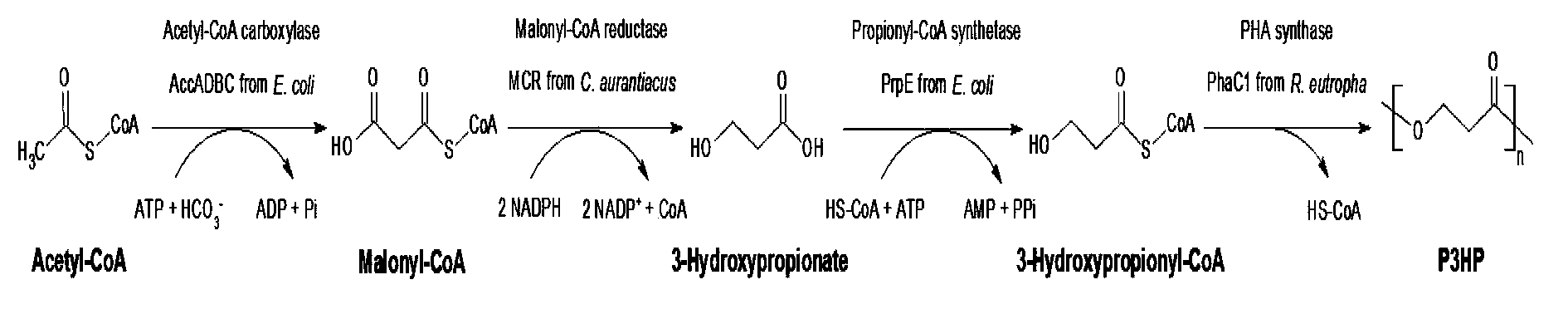
Method for biologically synthesizing poly-3-hydroxypropionic acid
InactiveCN103898034AWide variety of sourcesSimple production processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coli3-Hydroxypropionic acid
The invention provides a recombinant escherichia coli strain, a preparation method of the recombinant escherichia coli strain and a method for biologically synthesizing poly-3-hydroxypropionic acid from acetyl coenzyme A. The method comprises the following steps: with glucose or glycerin and the like as carbon sources, commonly over-expressing endogenous or exogenous acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase genes (acc) and propionyl coenzyme A synthetase genes (prpE) as well as exogenous malony coenzyme A reductase genes (mcr) and polyhydroxyalkanoate synthetase genes (phaC) in proper host cells (such as escherichia coli), and degrading intermediate products by virtue of glucose so as to biologically synthesize the poly-3-hydroxypropionic acid, wherein acetyl coenzyme A is finally obtained from simple starting materials such as the glucose and the like.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
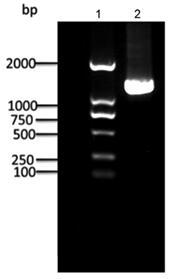
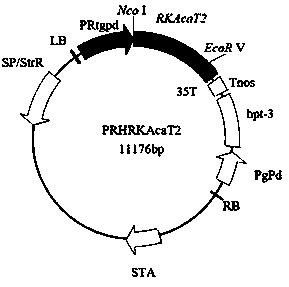
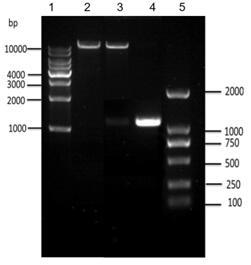
Acetyl coenzyme A acetyltransferase gene RKAcaT2 and application thereof
ActiveCN109666683AIncreased transcript levelsIncrease contentAcyltransferasesGenetic engineeringEnzyme GeneNucleotide
The invention discloses an acetyl coenzyme A acetyltransferase gene RKAcaT2 and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown in SEQ ID NO:1, the amino acid sequence encoded by thegene is shown in SEQ ID NO:2, the gene is a key enzyme gene synthesized by carotenoid in Rhodosporidium kratochvilovae YM25235 and has the functions of the acetyl coenzyme A acetyltransferase, and the carotenoid produced by the Rhodosporidium kratochvilovae YM25235 can be controlled; microorganisms are transformed through the genetic engineering means so as to increase the yield of carotenoid inthe microorganisms, and a foundation is laid for large-scale commercial production of the carotenoid.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com