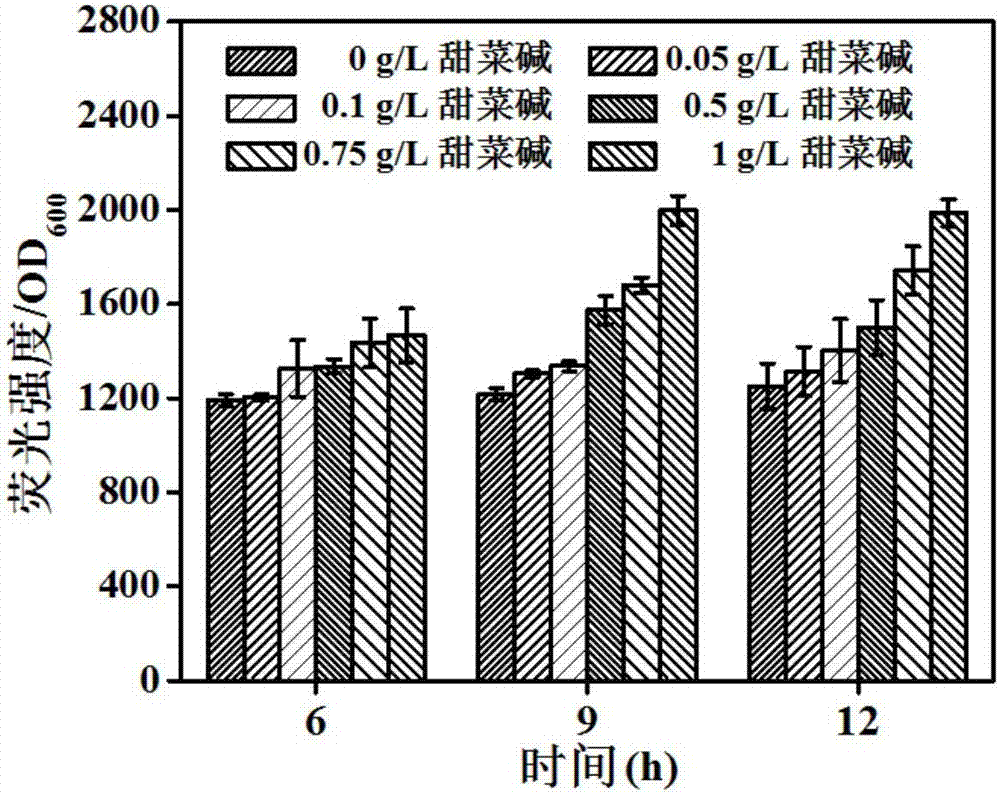
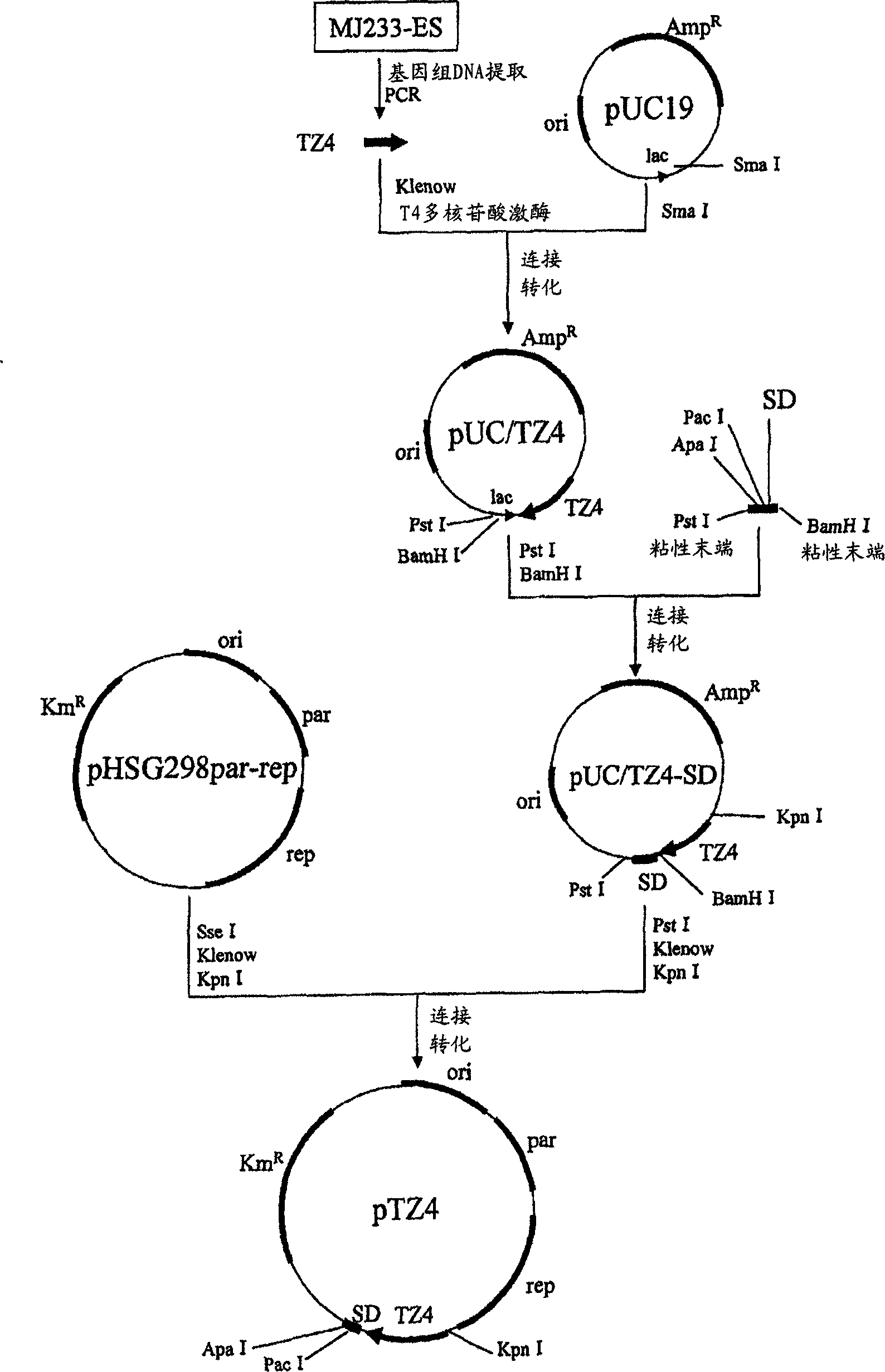
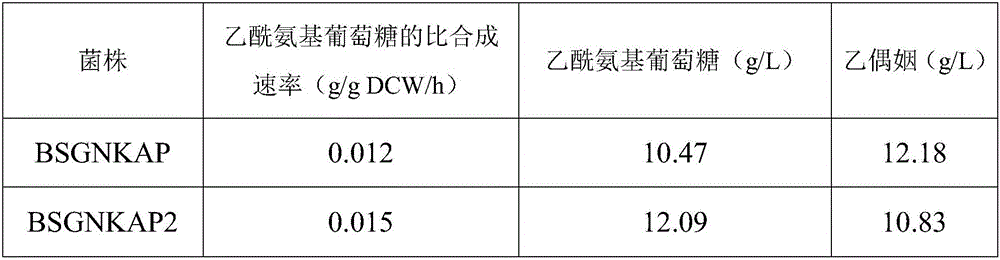
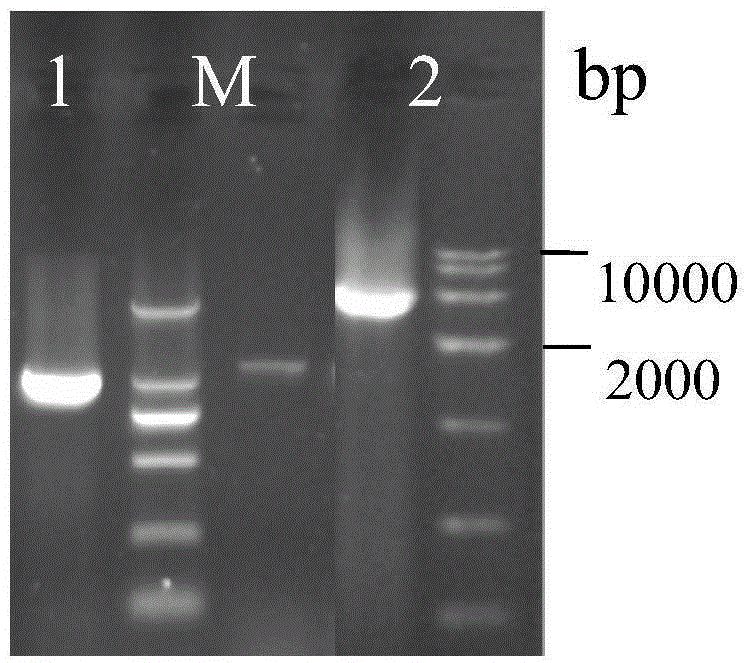
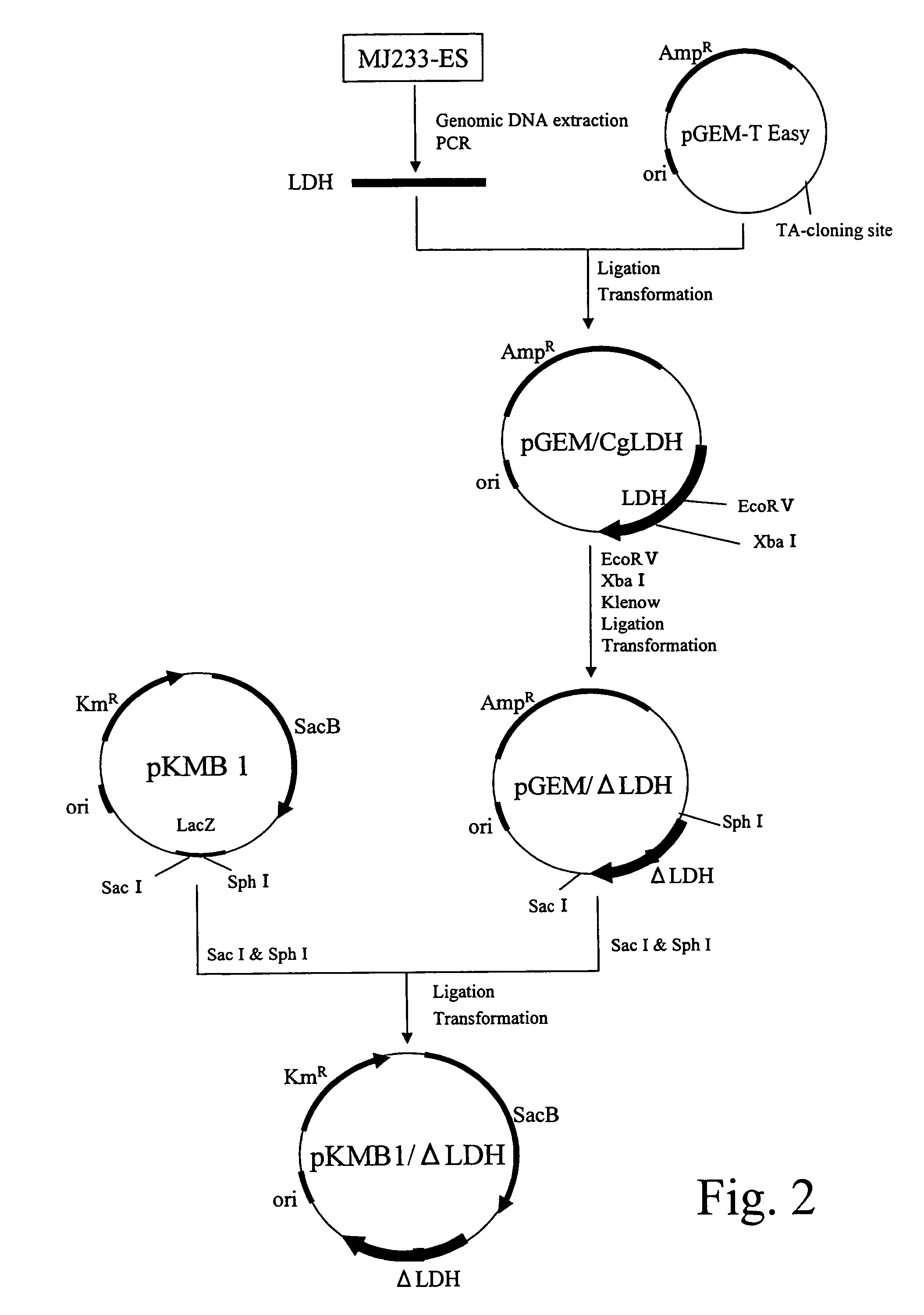
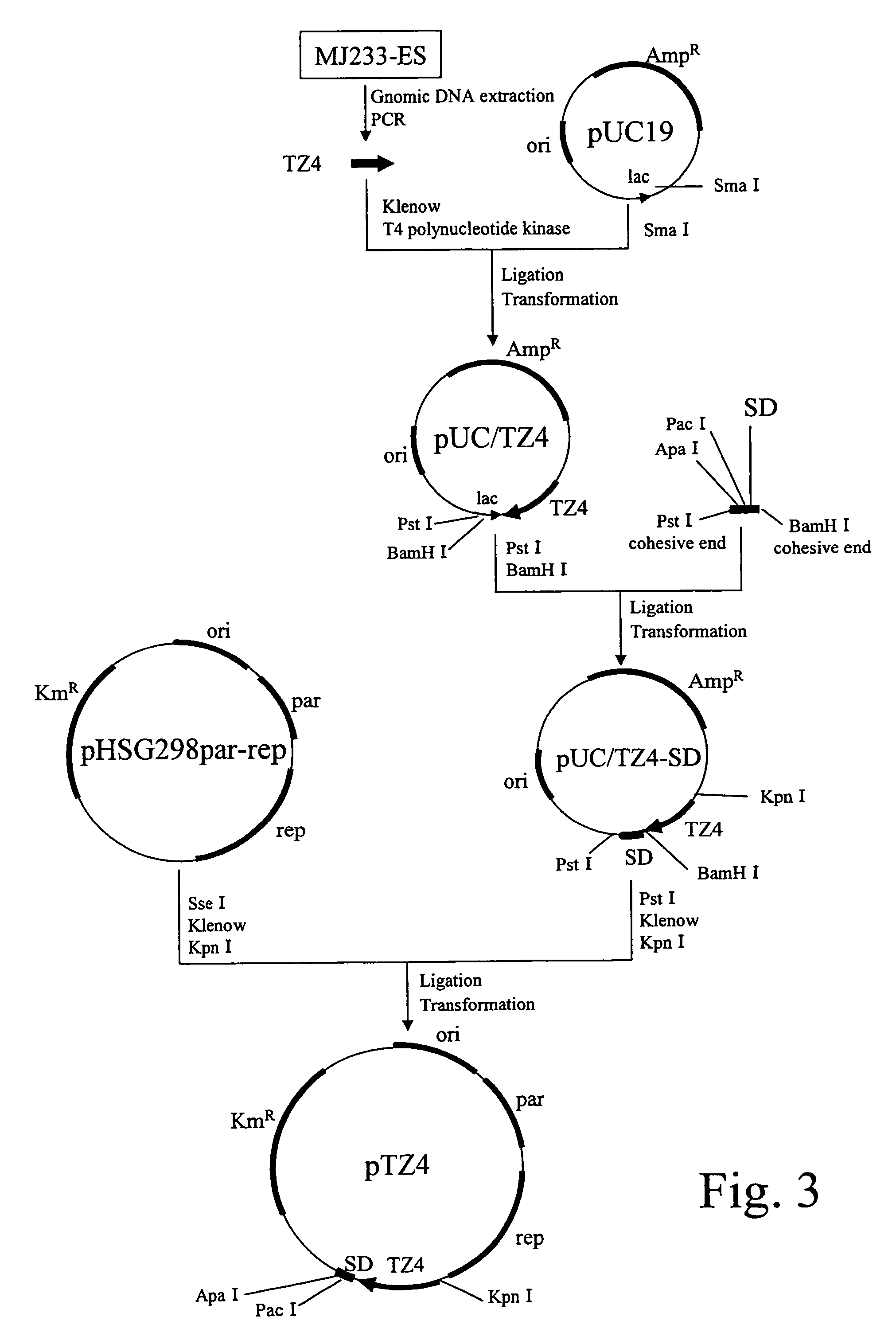
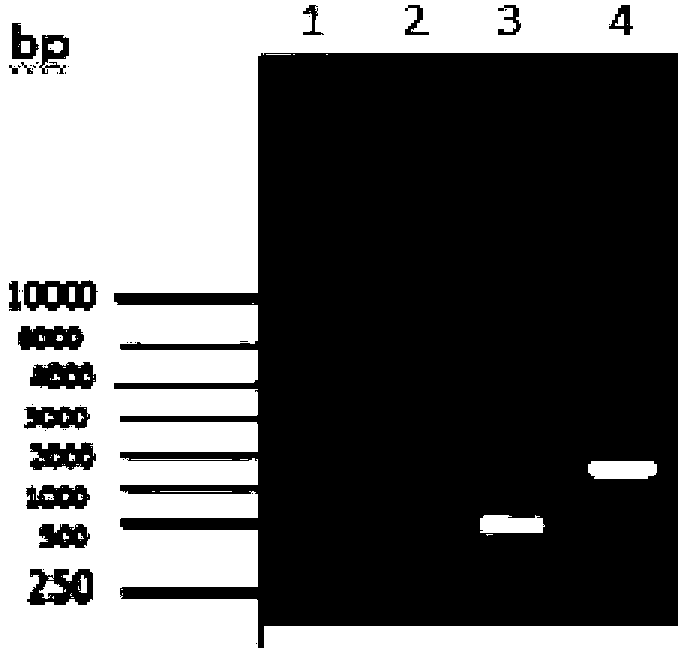
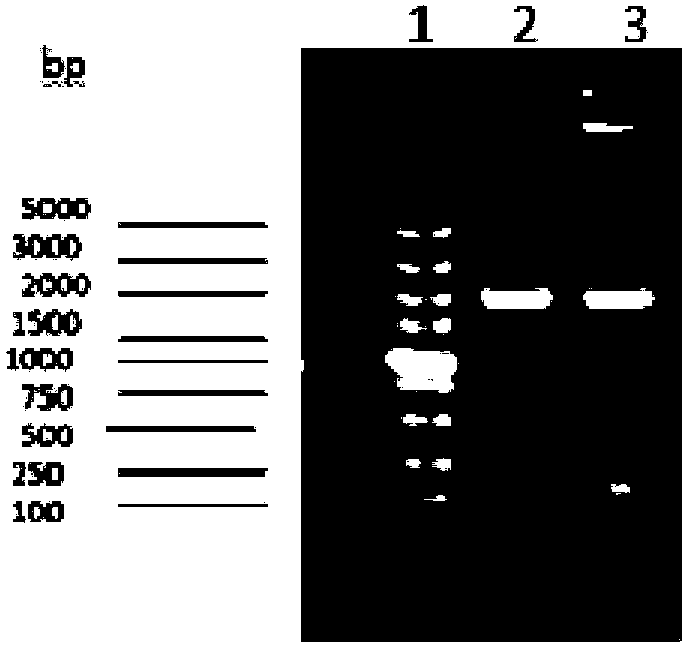
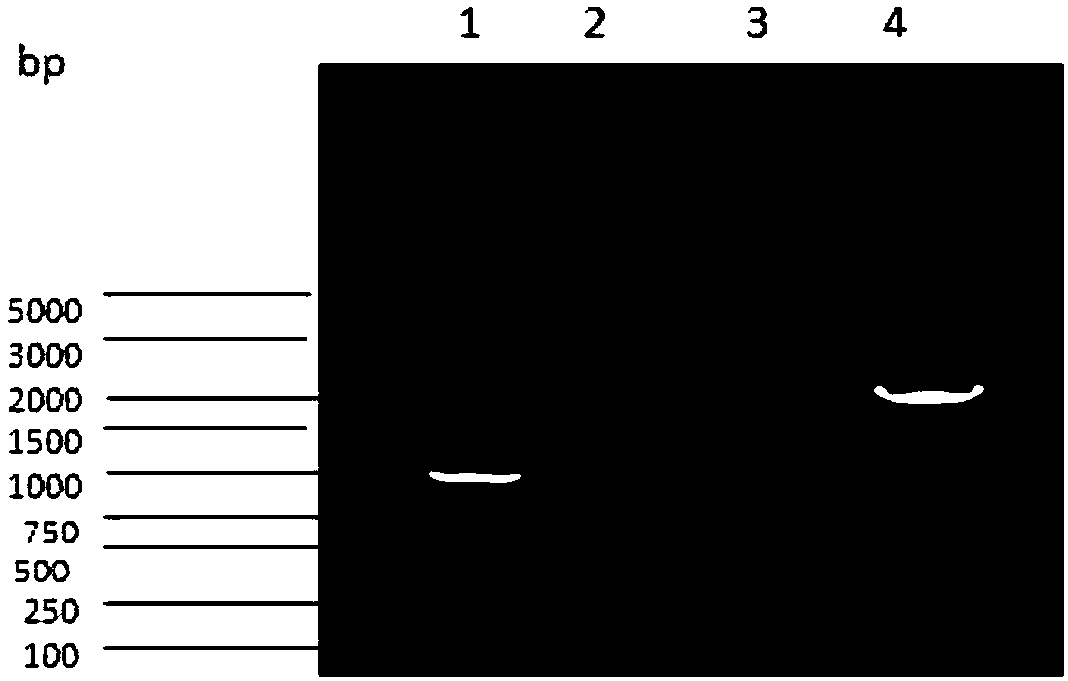
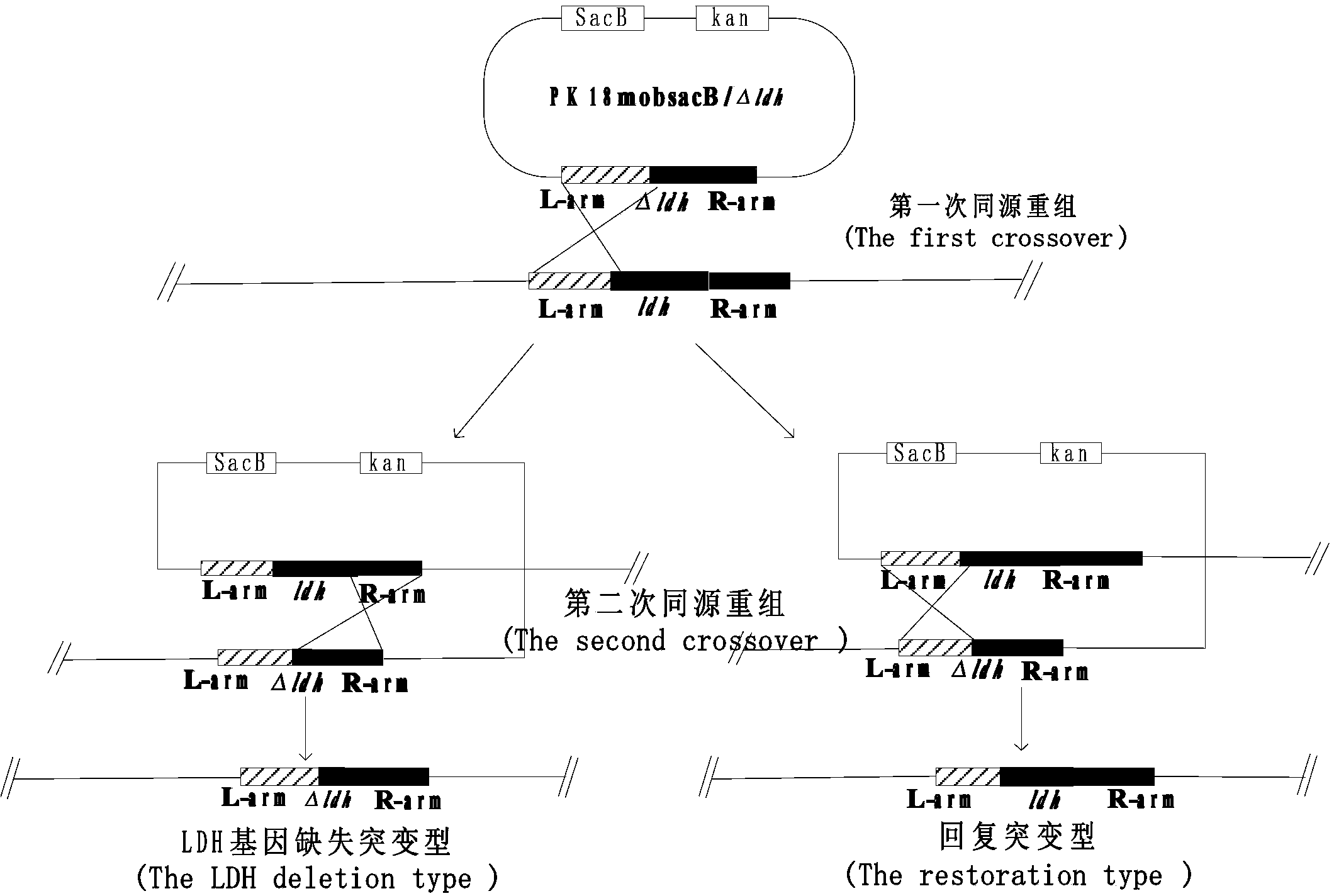
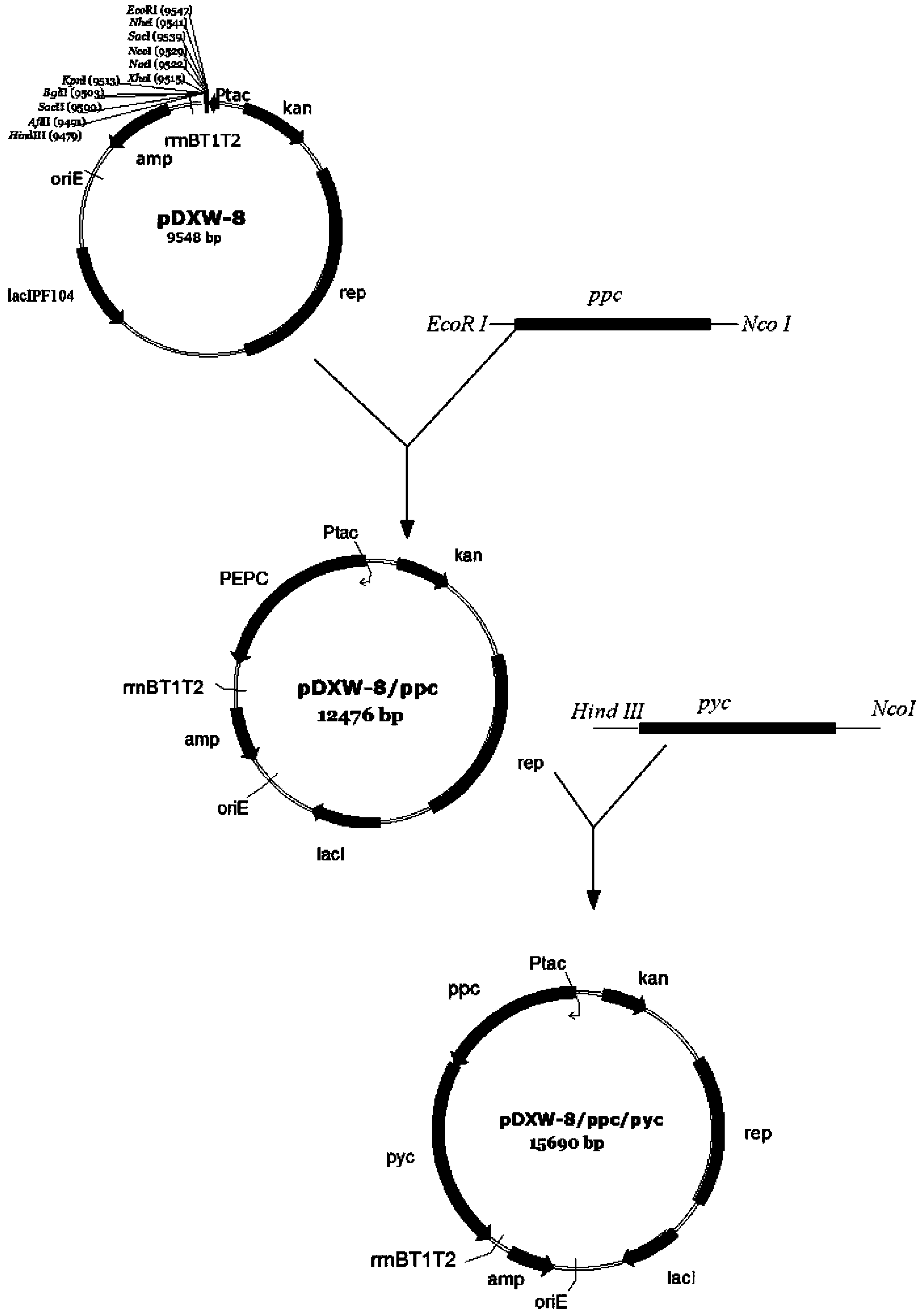
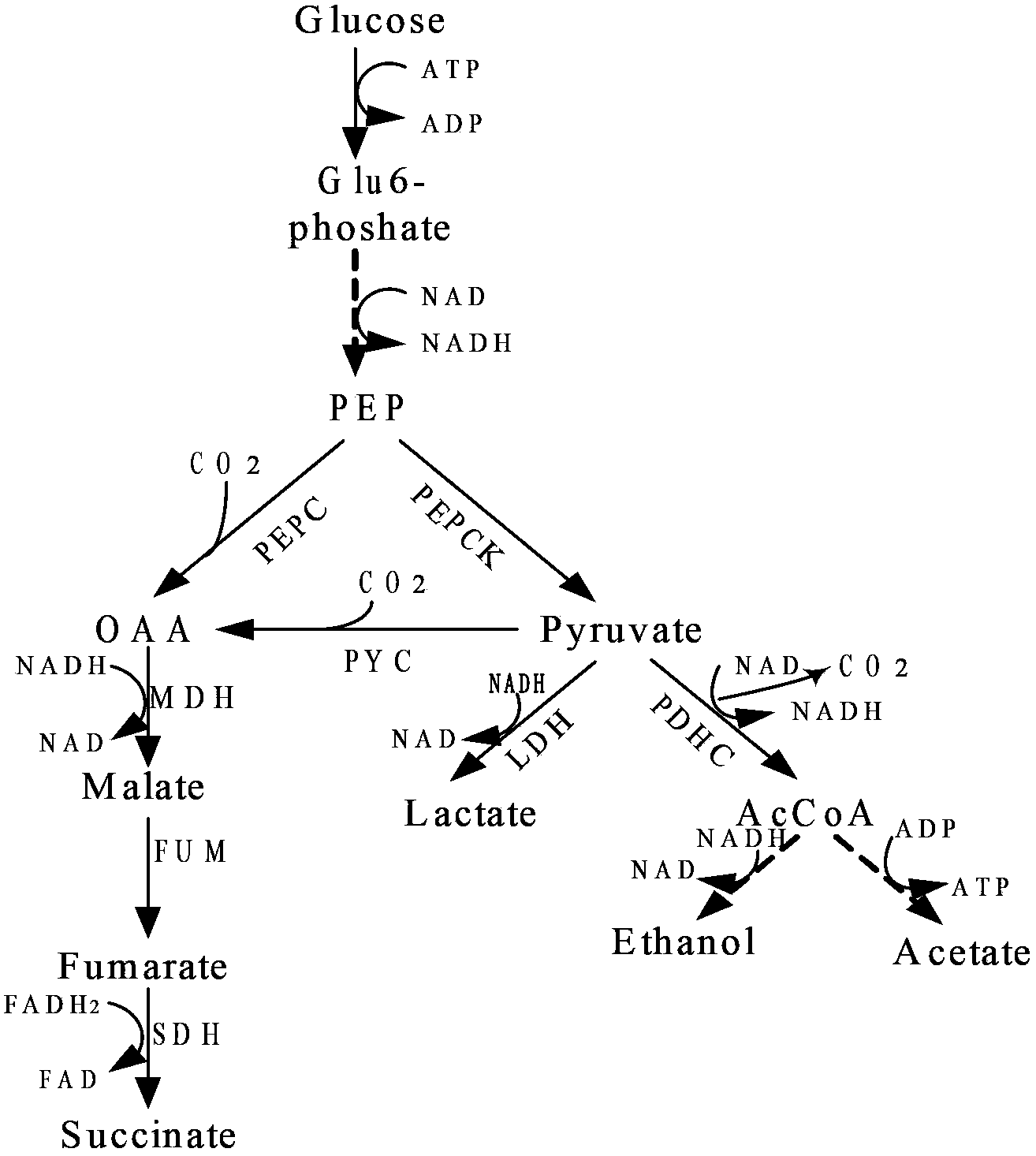
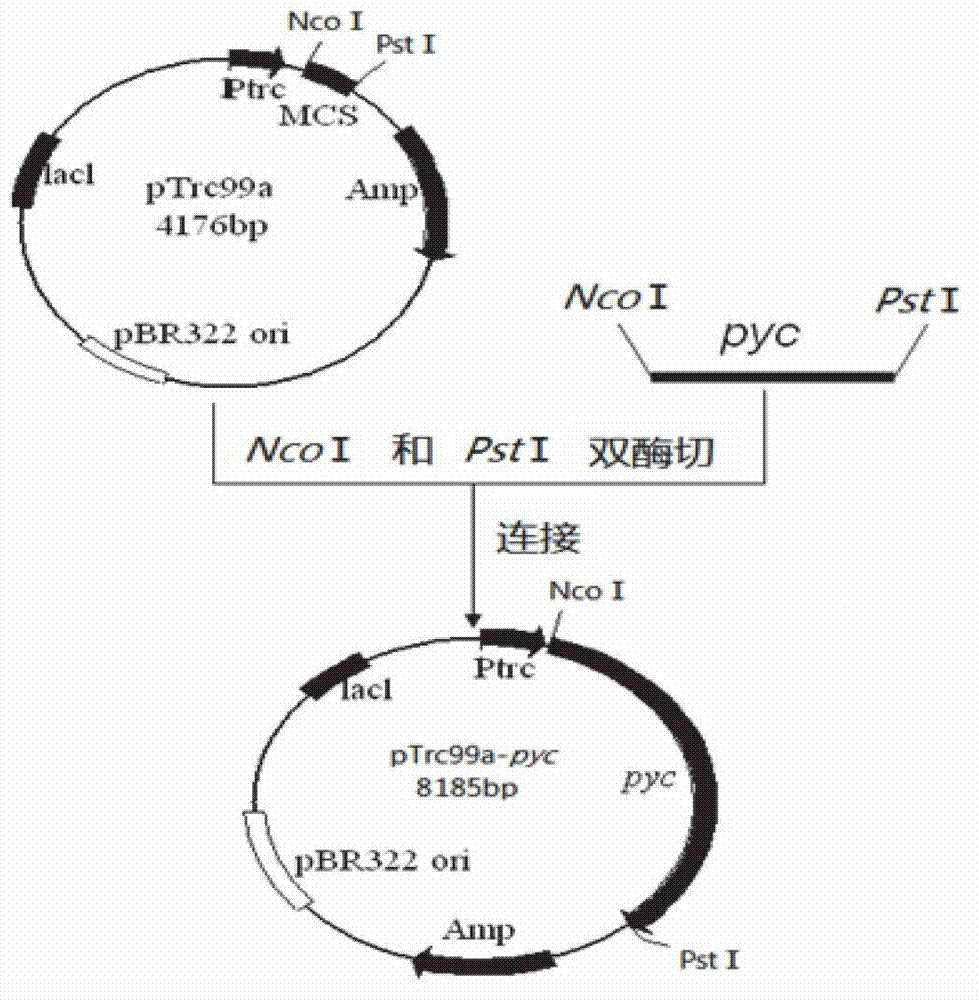
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
204 results about "Pyruvate carboxylase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
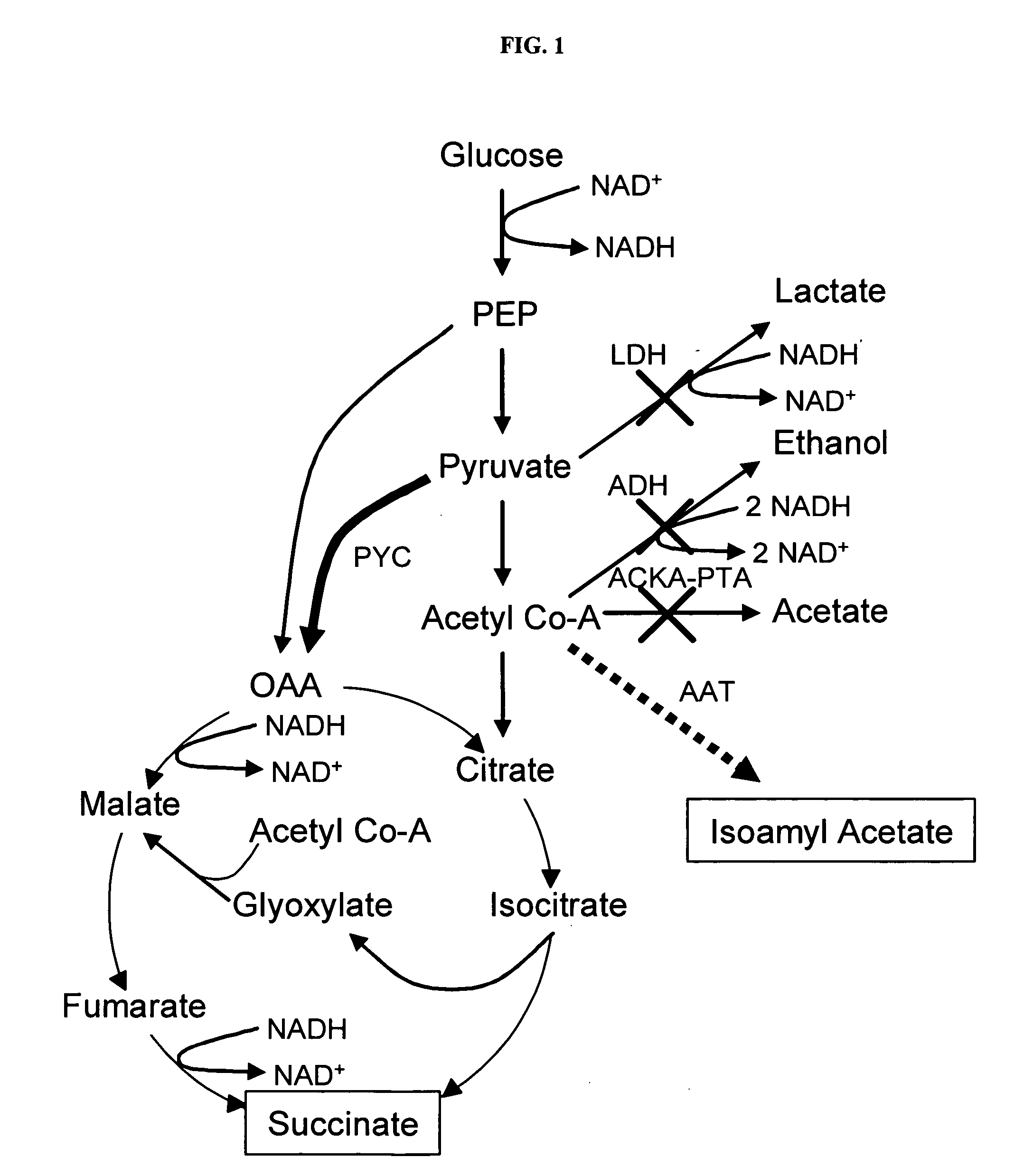
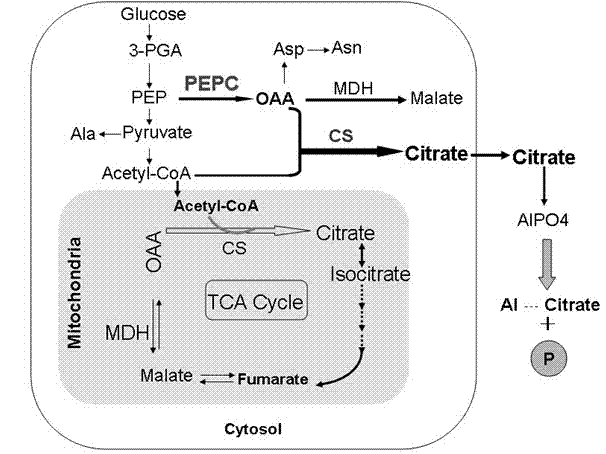
Pyruvate carboxylase (PC) encoded by the gene PC is an enzyme of the ligase class that catalyzes (depending on the species) the physiologically irreversible carboxylation of pyruvate to form oxaloacetate (OAA).
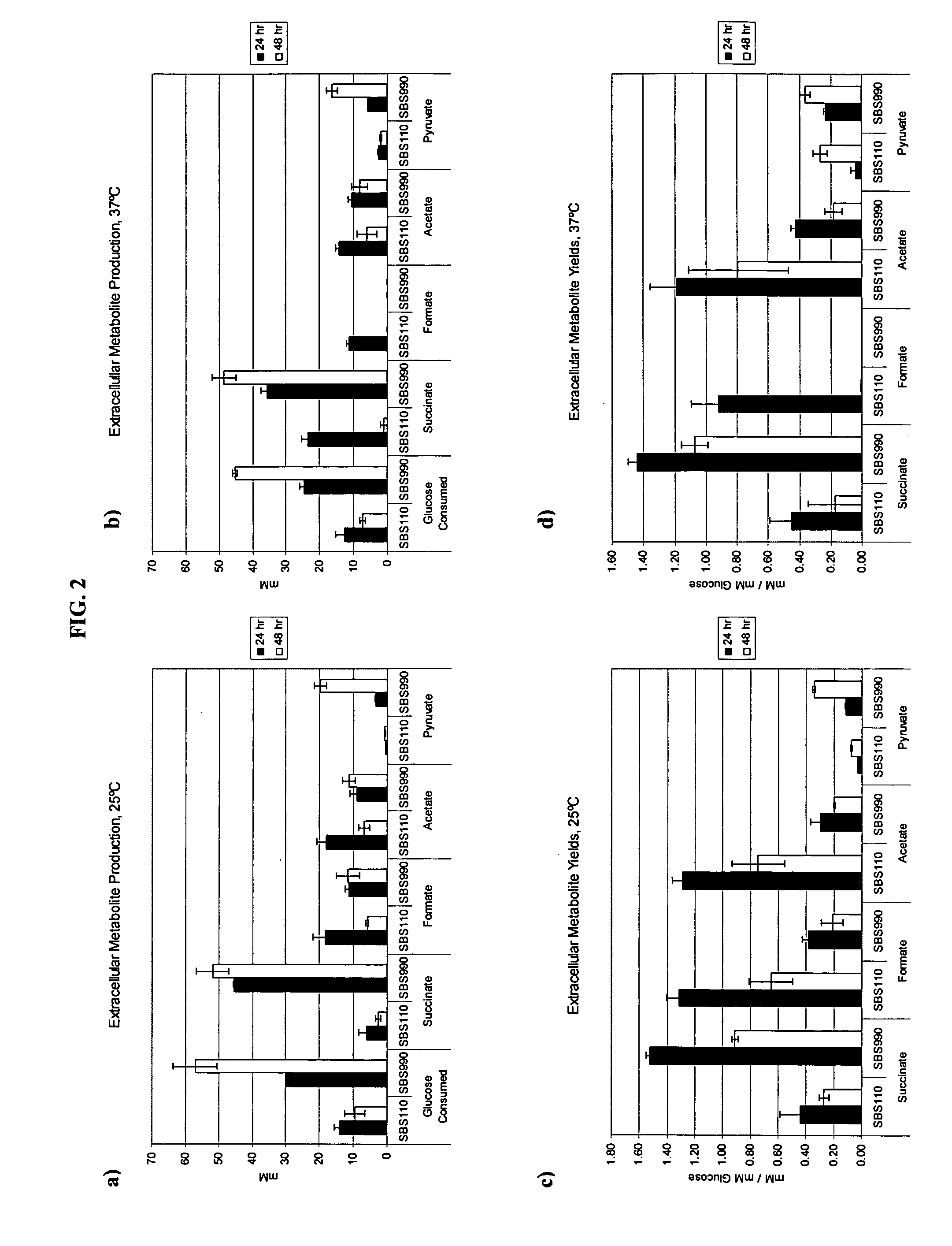
Simultaneous anaerobic production of isoamyl acetate and succinic acid
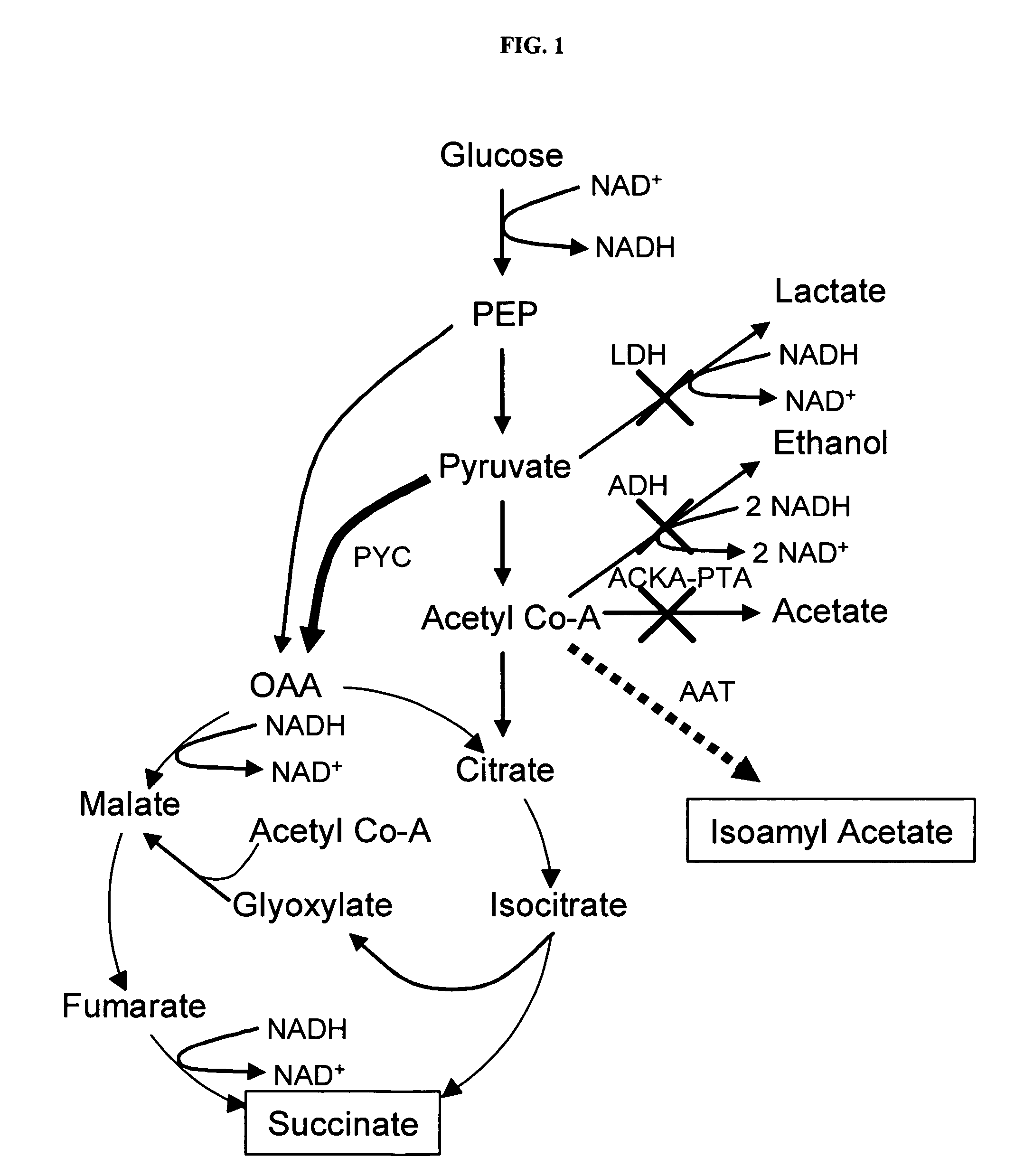
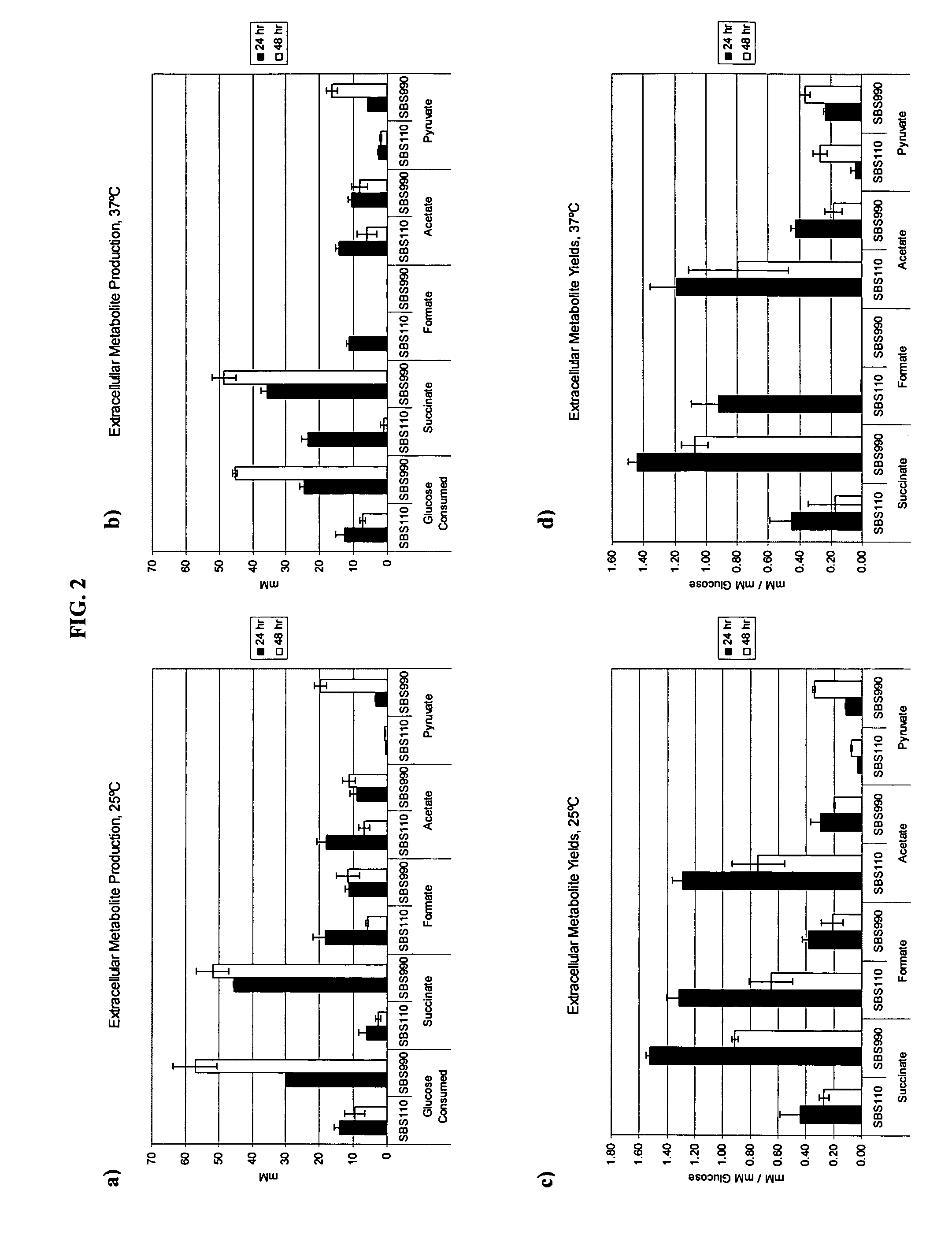
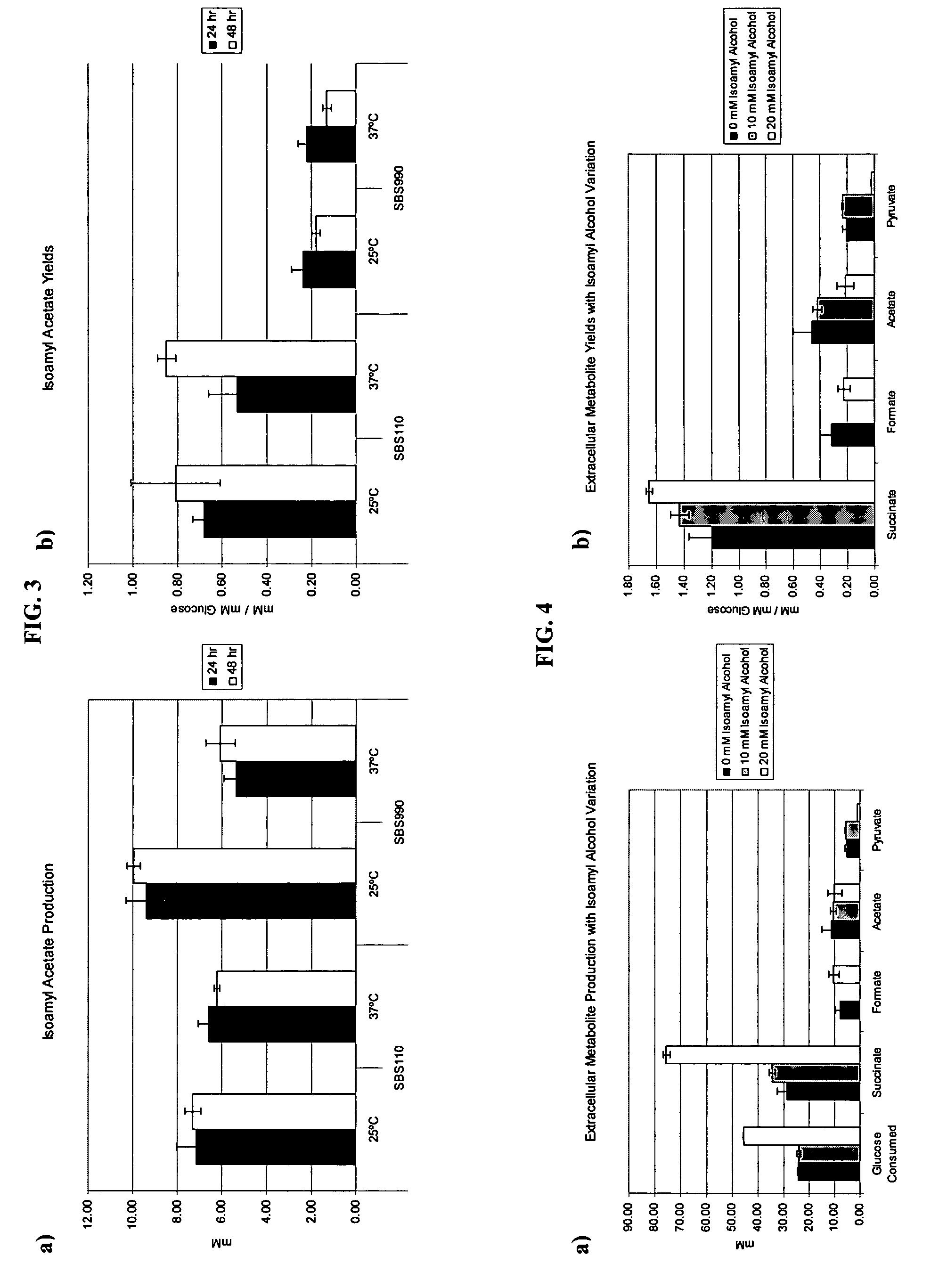
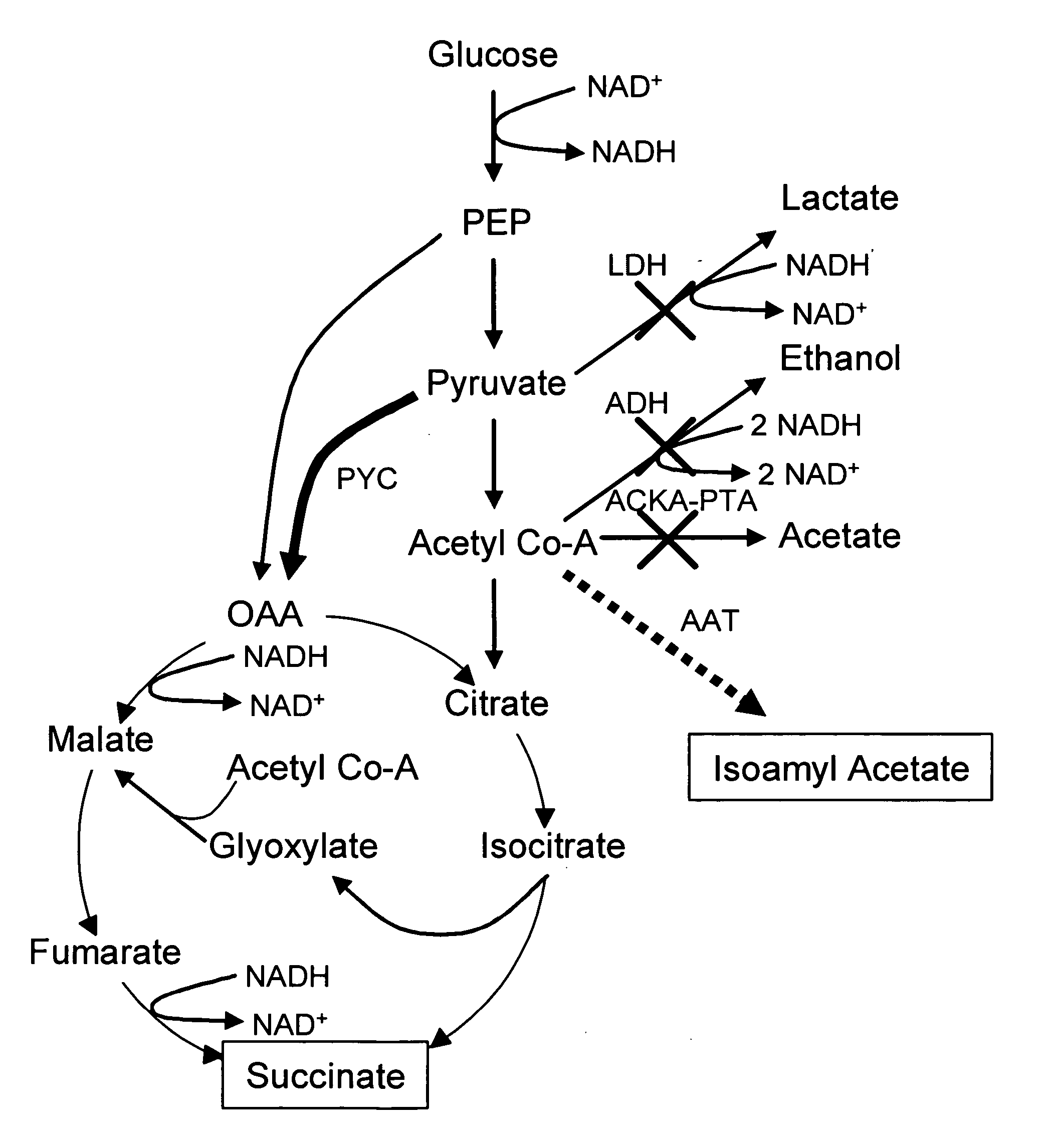
In vivo method of producing esters from acetyle coA, such as isoamyl acetate and succinate, has been developed by producing null mutants in pathways that use acetyl coA and by overexpressing products that use NADH and in order to maintain the proper redox balance between NADH and NAD+. The method is exemplified with null mutations in ldhA, adhE, ackA-pta and overexpression of pyruvate carboxylase and alcohol acetyltransferase. This strain produces higher levels of both isoamyl acetate and succinate.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Simultaneous anaerobic production of isoamyl acetate and succinic acid
InactiveUS20060141594A1Maximizing isoamyl acetate productionEasy to separateBacteriaTransferasesSuccinic acidPyruvate synthesis
In vivo method of producing esters from acetyle coA, such as isoamyl acetate and succinate, has been developed by producing null mutants in pathways that use acetyl coA and by overexpressing products that use NADH and in order to maintain the proper redox balance between NADH and NAD+. The method is exemplified with null mutations in ldhA, adhE, ackA-pta and overexpression of pyruvate carboxylase and alcohol acetyltransferase. This strain produces higher levels of both isoamyl acetate and succinate.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Process for producing succinic acid
ActiveUS20060205048A1Improve productivityProducing succinicBacteriaSugar derivativesPyruvate carboxylaseLactate dehydrogenase
Succinic acid is produced by allowing a bacterium modified to enhance fumarate reductase activity or cell preparation thereof to react with an organic raw material in a reaction solution containing one of a carbonate ion, a bicarbonate ion, and carbon dioxide gas to generate succinic acid. More preferably, succinic acid is produced by allowing a bacterium modified to enhance activities of fumarate reductase and pyruvate carboxylase and decrease lactate dehydrogenase activity or cell preparation thereof to react with an organic raw material in a reaction solution containing one of a carbonate ion, a bicarbonate ion, and carbon dioxide gas to generate succinic acid. Succinic acid is obtained by collecting the produced succinic acid.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Bioengineering cotton fiber properties
InactiveUS7060874B2Increase heightTransferasesFermentationPyruvate carboxylasePhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
The present invention provides plant fiber expansion (FE) genes that encode FE polypeptides, such as phosphoenol pyruvate carboxylase (PEPcase), expansin, endoglucanase, xyloglucan endoglycosyltransferase (XET), and pectin methyl esterase (PME). The invention further provides fiber-specific promoters. Still further, the invention provides molecular strategies for modulating fiber quality and yield in fiber producing plants by modulating expression of FE genes or mutant forms of FE genes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
High-yield fumaric acid Rhizopus delemar engineering bacterium and application thereof
InactiveCN103013843AExcess accumulation promotesOveraccumulation RealizedFungiMicroorganism based processesPyruvate synthesisBacterial strain
The invention discloses a high-yield fumaric acid Rhizopus delemar engineering bacterium and application thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. An encoded gene ScPYC1 of pyruvate carboxylase, which originates from saccharomyces cerevisiae, is overexpressed in a bacterial strain Rhizopus delemar NRRL1526 for producing the fumaric acid through a fermentation method, so that a recombinant bacterial strain R. delemar-pRS303H-PC, of which the activity of the pyruvate carboxylase is improved, is obtained, and the activity of the pyruvate carboxylase of the recombinant bacterial strain R. delemar-pRS303H-PC is improved by 5.4 times (reaches 4.59 U / mg protein); and glucose serves as the only carbon source, the output of the fumaric acid reaches 55.92 g / L and is 1.19 times of that of an original strain after the glucose is fermented for 72h, and the high-yield fumaric acid Rhizopus delemar engineering bacterium has a broad application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
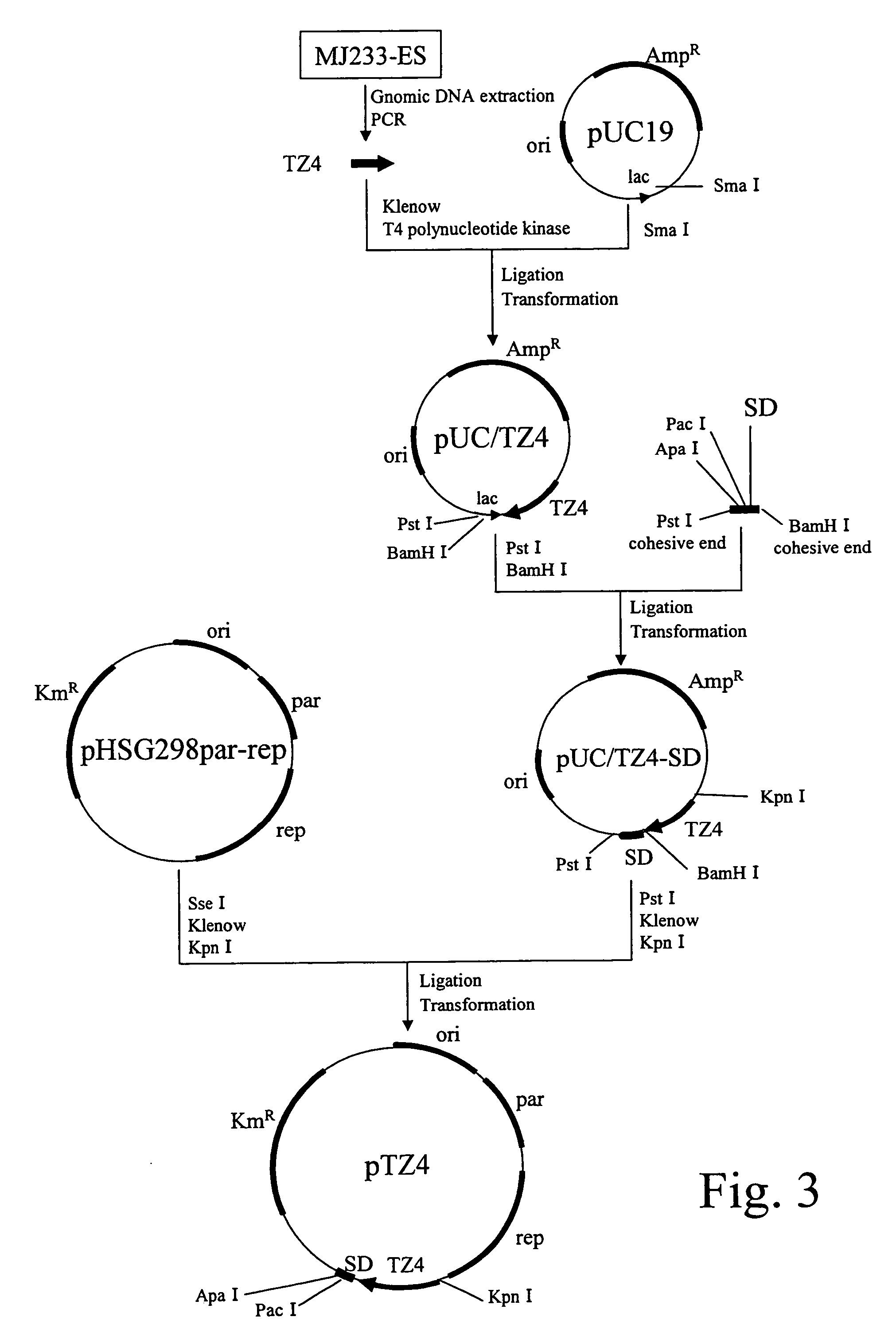
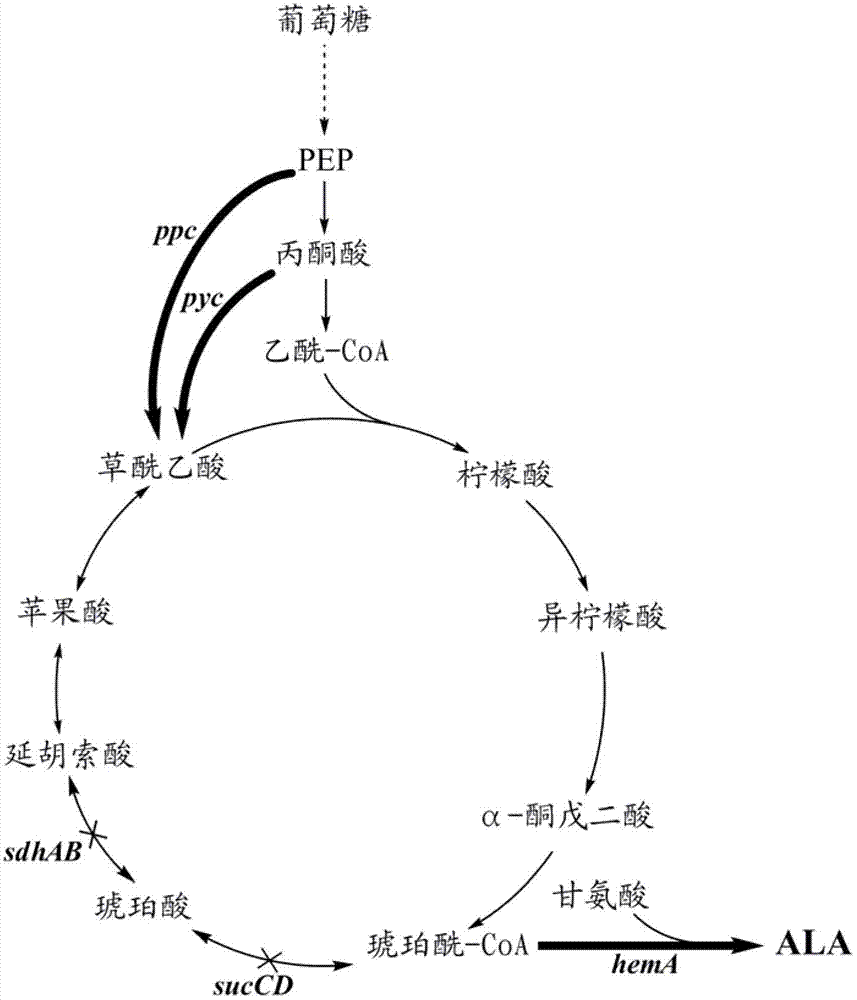
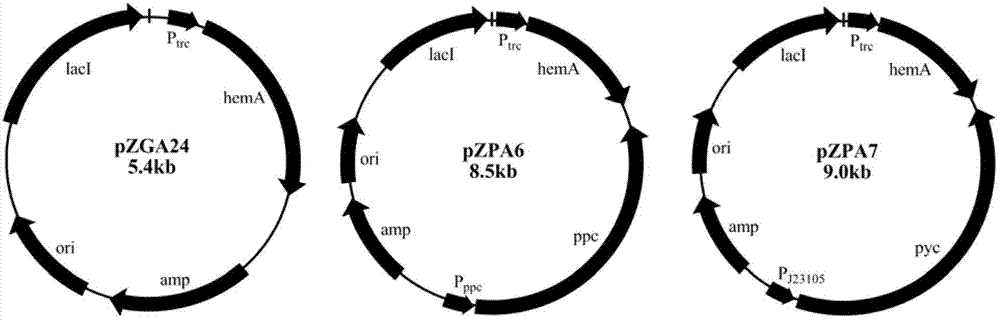
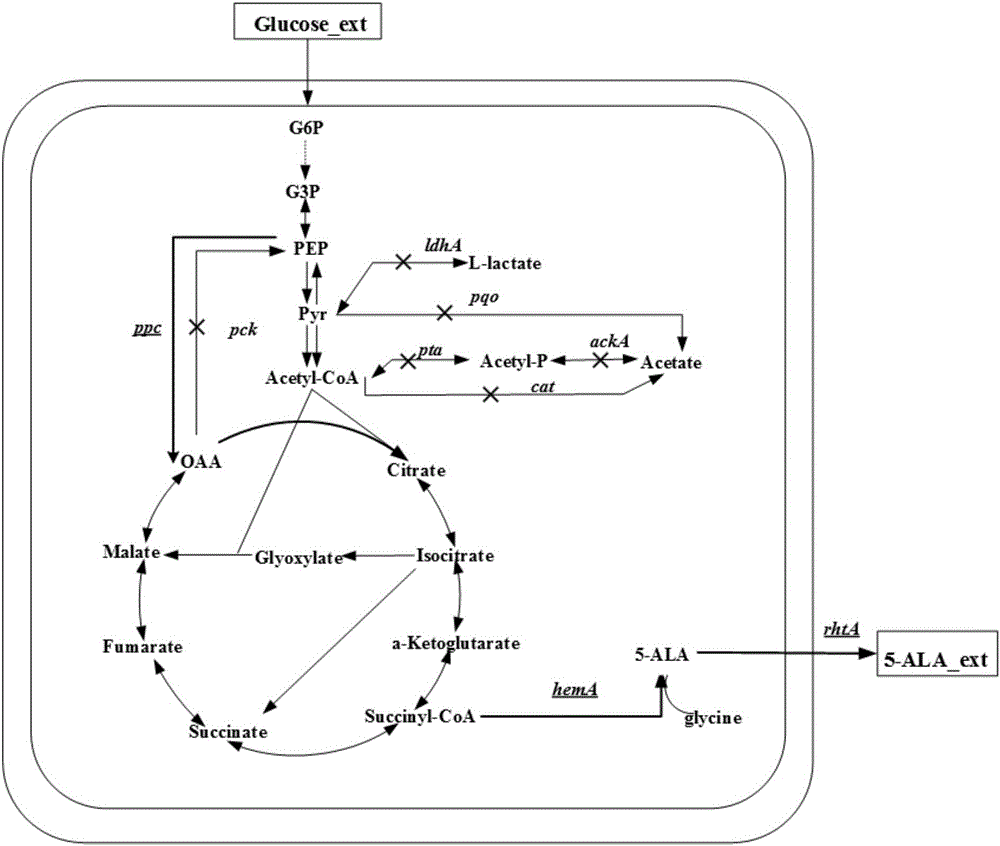
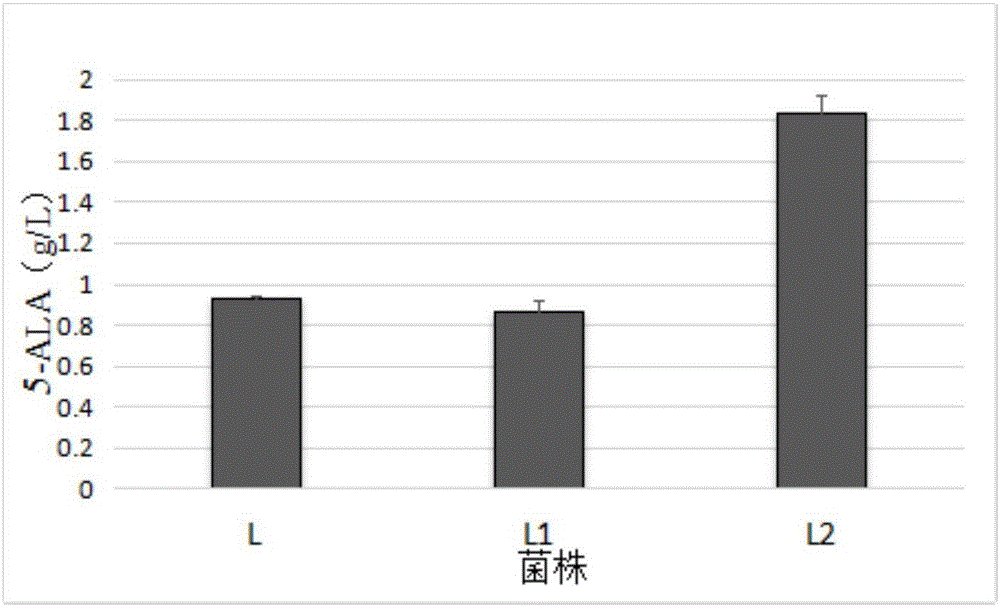
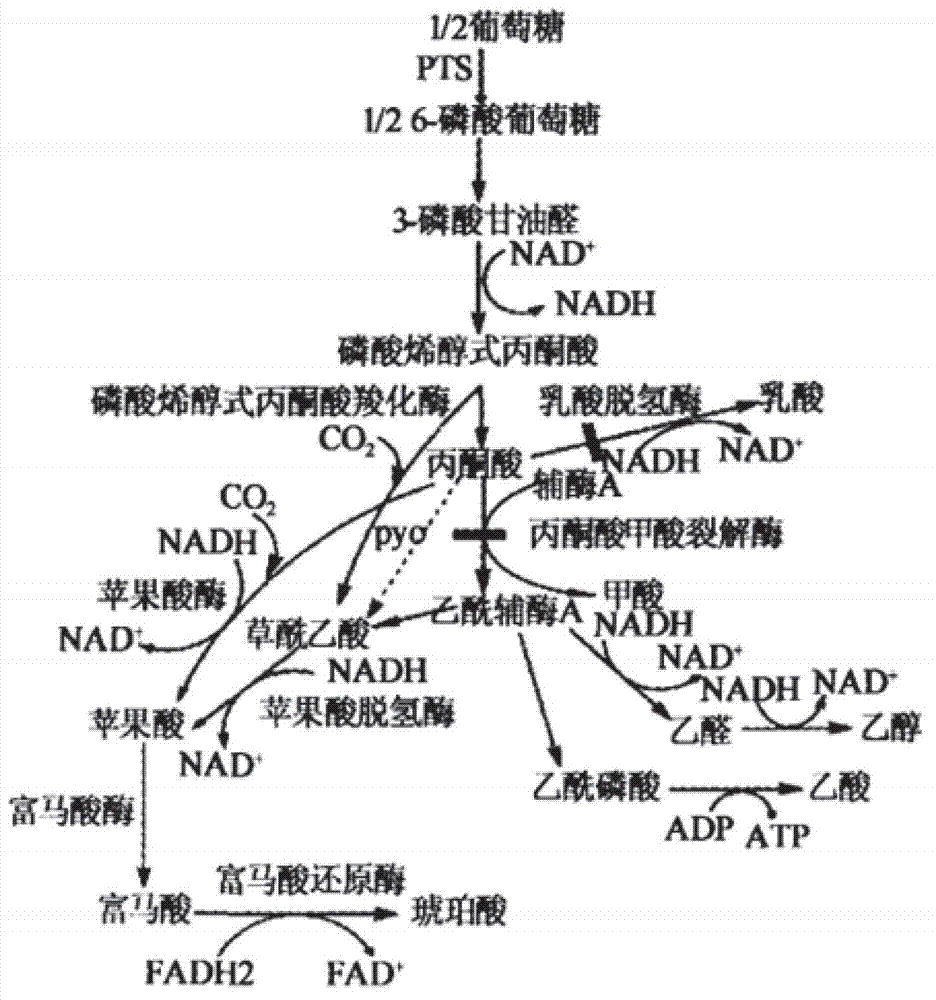
High-yield 5-aminolevulinic acid strain and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN103981203BImprove conversion rateIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphatePhosphoric acid
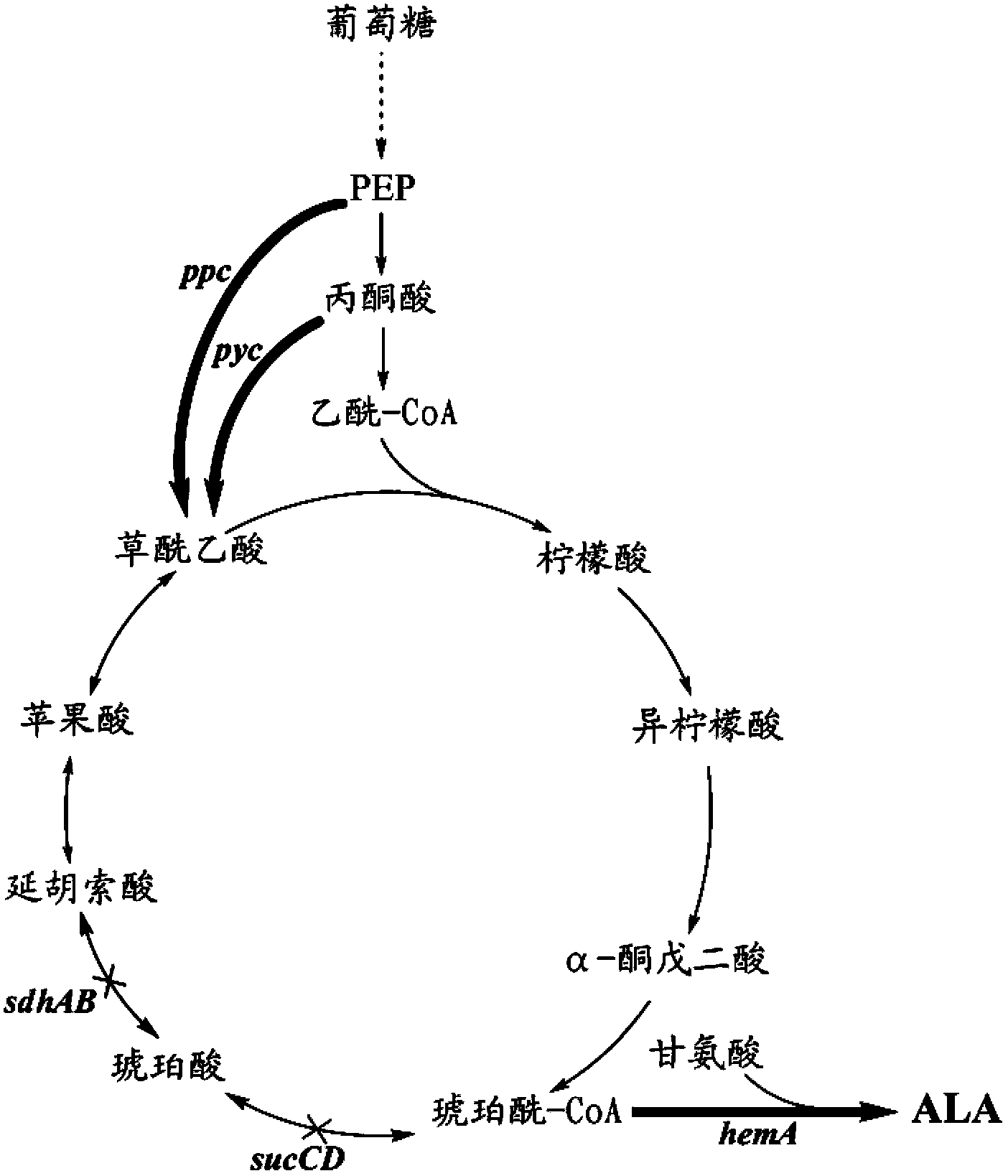
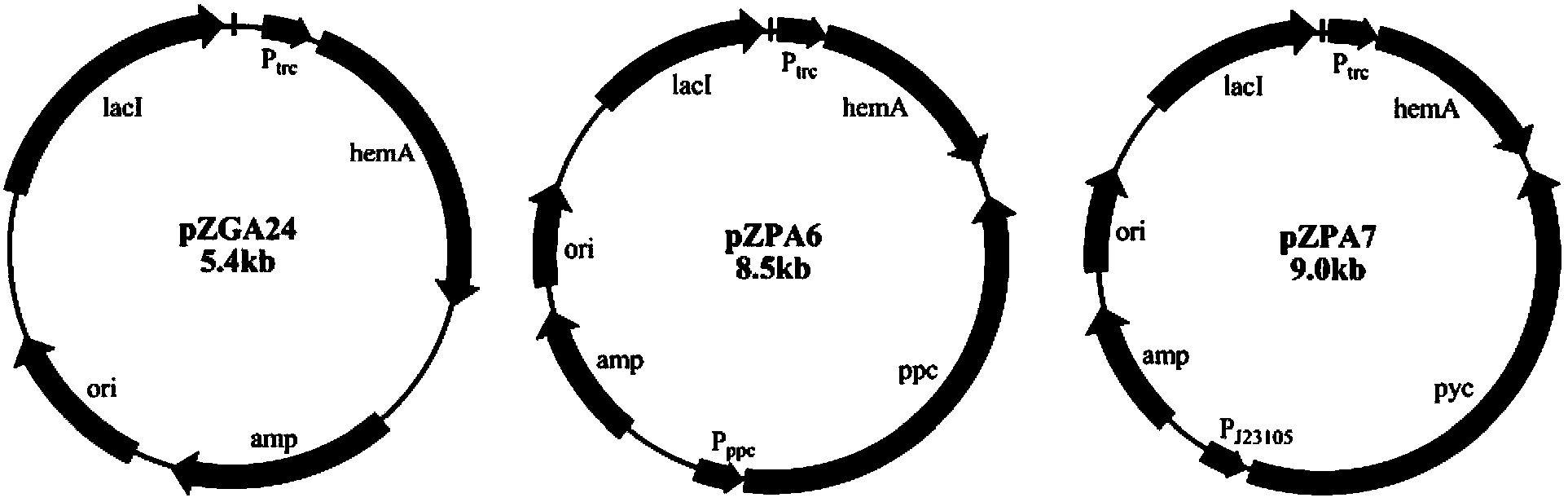
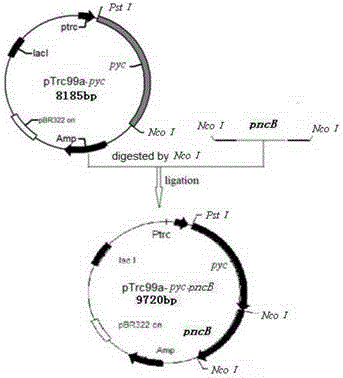
The invention discloses a method for constructing an ALA production strain, that is, enhancing the activity of related enzymes promoting the synthesis of oxaloacetate in the 5-aminolevulinic acid production strain or introducing exogenous related enzymes promoting the synthesis of oxaloacetate , such as phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase or pyruvate carboxylase, and / or weaken the succinyl-CoA downstream metabolic pathway-related enzymes in the strain, such as succinyl-CoA synthetase or succinate dehydrogenase active. The invention also discloses an ALA high-yield strain constructed by the method and a method for preparing ALA by using the strain. The bacterial strain of the invention can produce ALA efficiently, at low cost and with low pollution without adding exogenous succinic acid.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Malic Acid Production in Recombinant Yeast
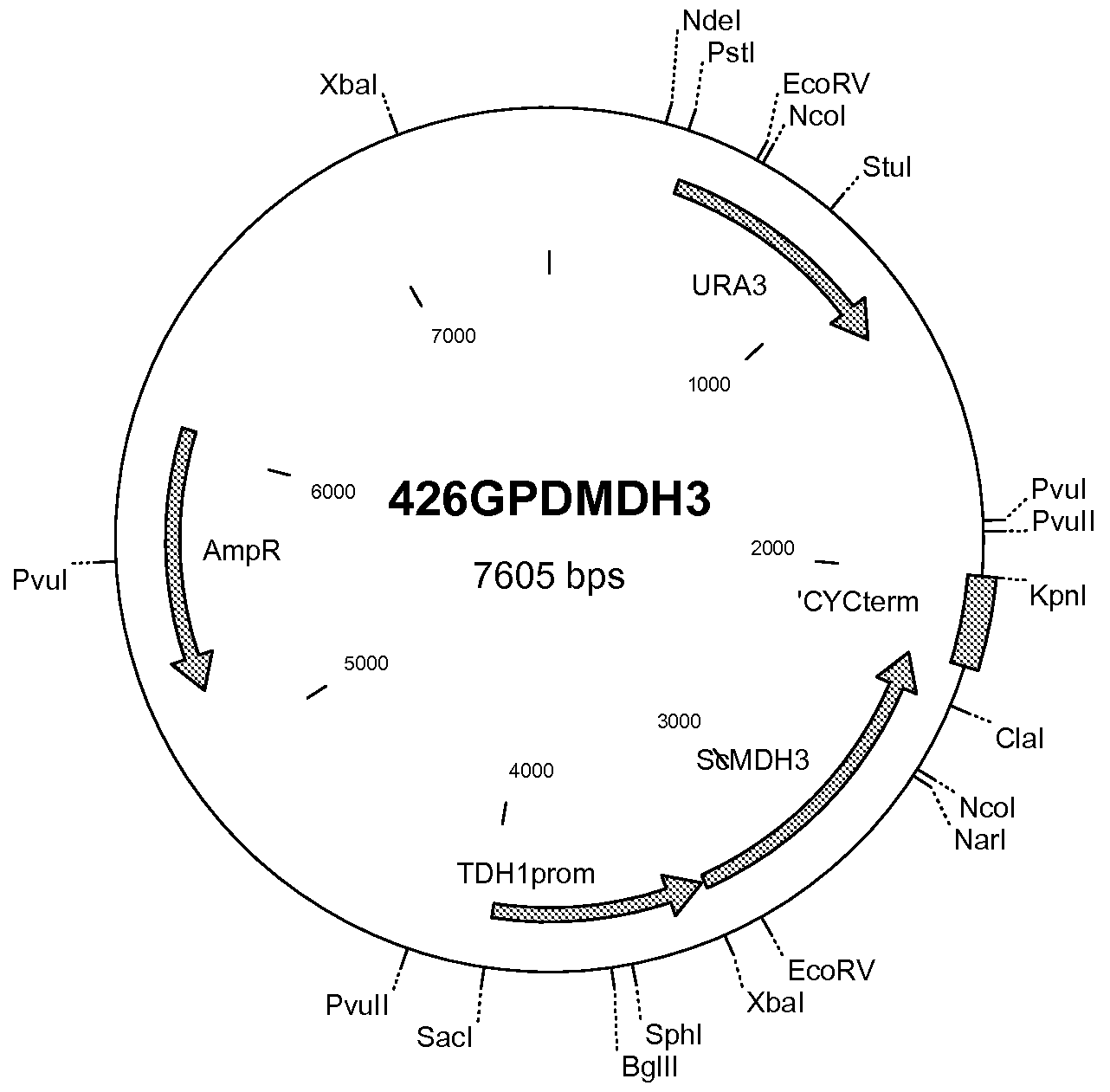
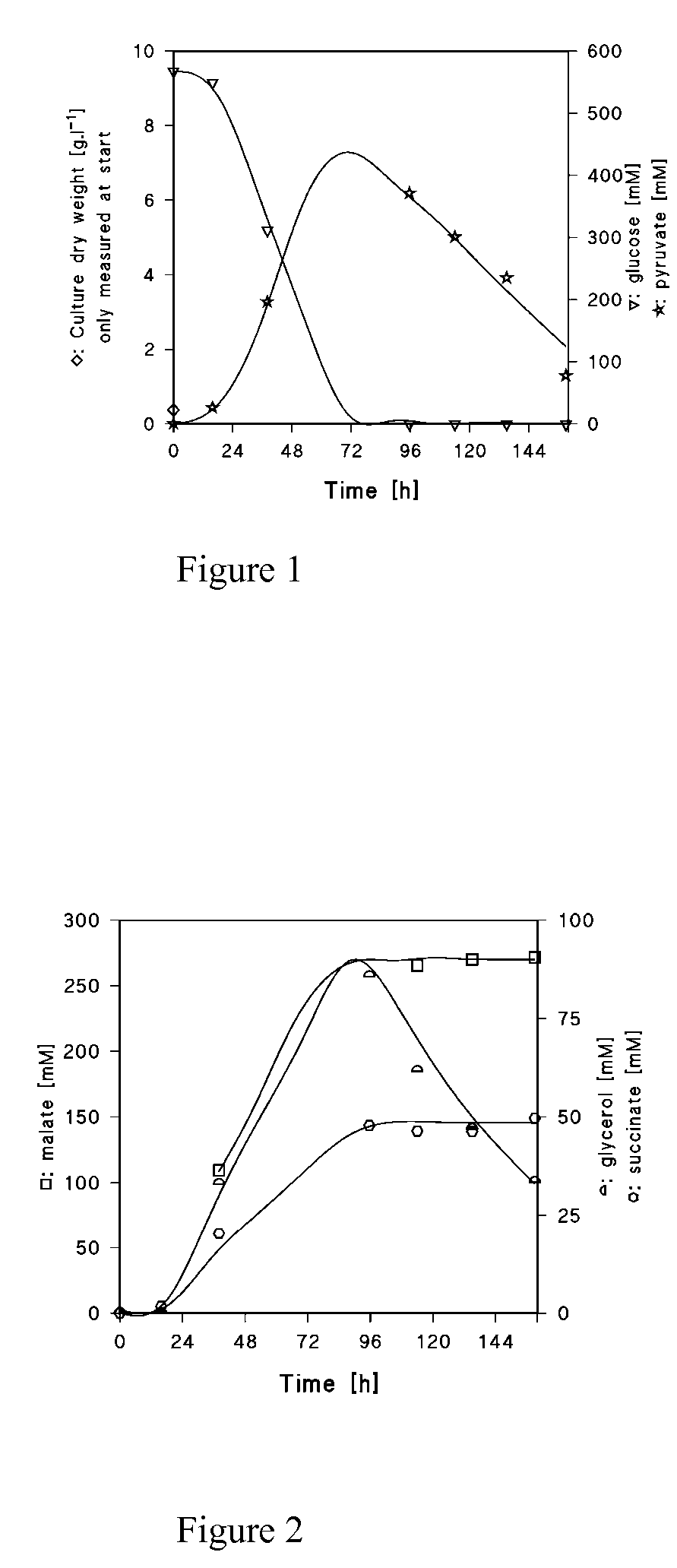
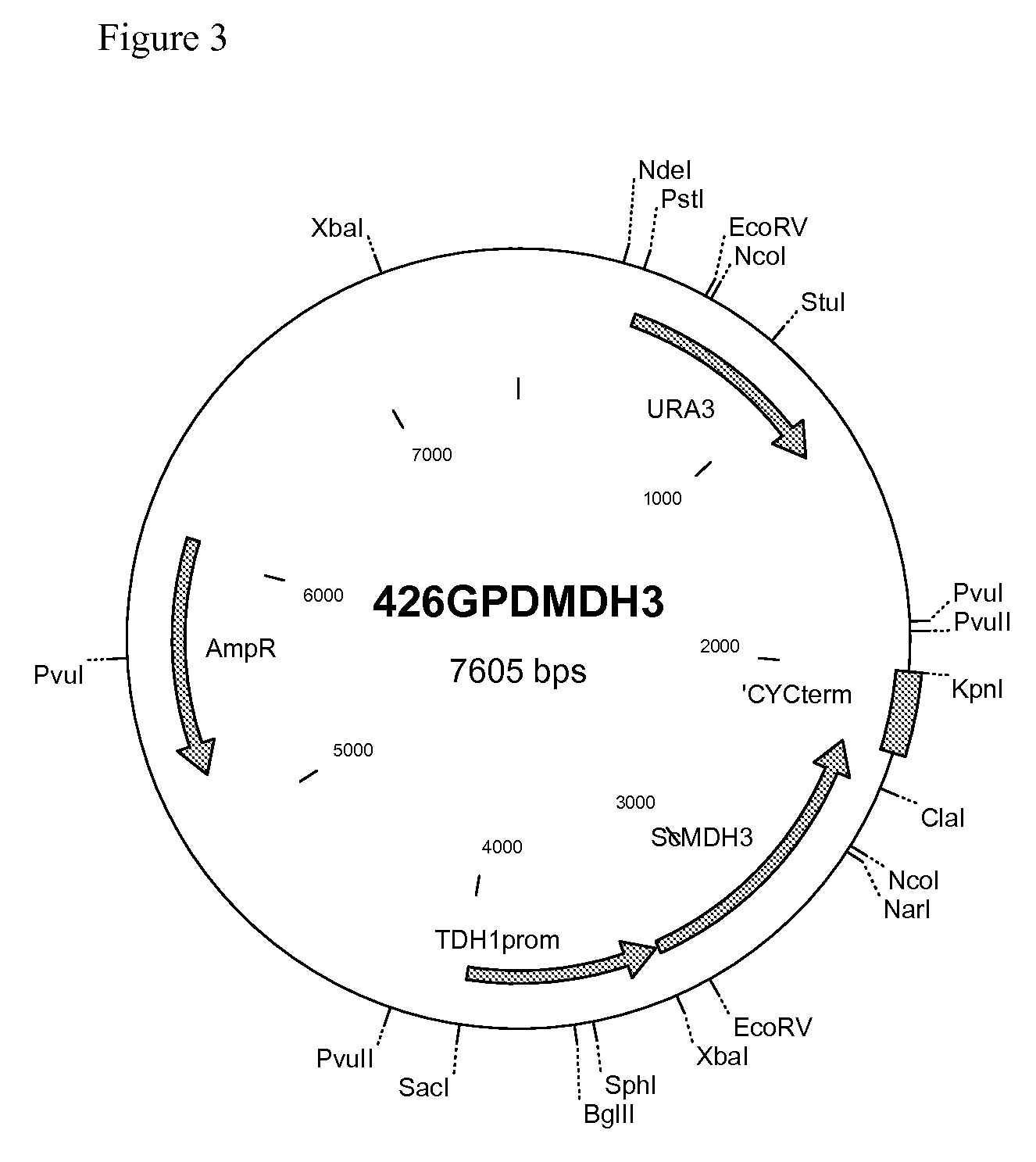
We disclose a recombinant yeast, wherein the yeast is pyruvate decarboxylase enzyme (PDC) activity negative (PDC-negative) and is functionally transformed with a coding region encoding a pyruvate carboxylase enzyme (PYC) wherein the PYC is active in the cytosol, a coding region encoding a malate dehydrogenase enzyme (MDH) wherein the MDH is active in the cytosol and is not inactivated in the presence of glucose, and a coding region encoding a malic acid transporter protein (MAE). We also disclose a method of producing malic acid by culturing such a yeast in a medium comprising a carbon source and a carbon dioxide source and isolating malic acid from the medium.
Owner:TATE & LYLE INGREDIENTS AMERICAS INC
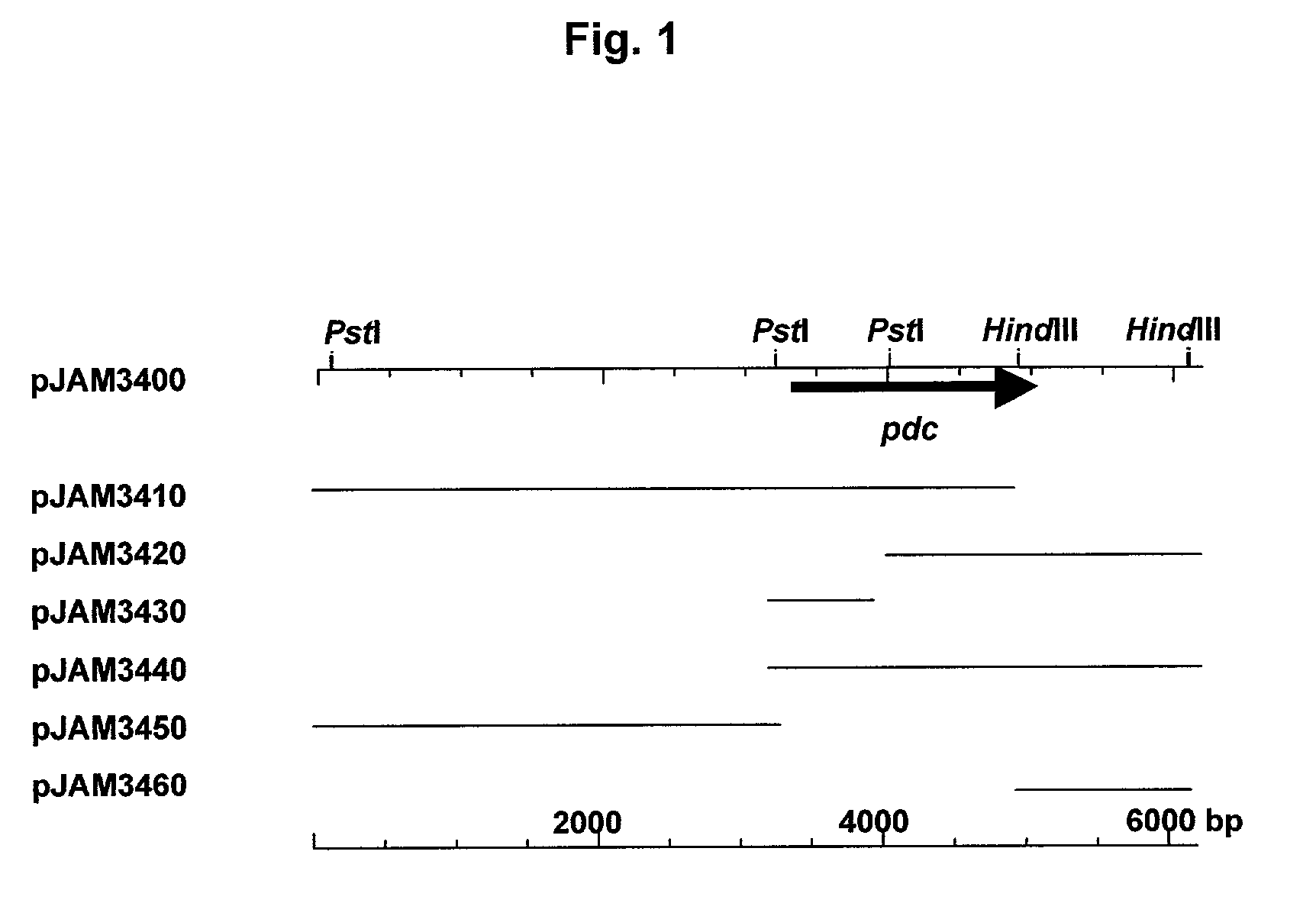
Cloning and sequencing of pyruvate decarboxylase (PDC) genes from bacteria and uses therefor
InactiveUS7326551B2Improve efficiencyImprove filtering effectFungiBacteriaBacteroidesPyruvate carboxylase
The invention provides isolated nucleic acids molecules which encode pyruvate decarboxylase enzymes having improved decarboxylase activity, substrate affinity, thermostability, and activity at different pH. The nucleic acids of the invention also have a codon usage which allows for high expression in a variety of host cells. Accordingly, the invention provides recombinant expression vectors containing such nucleic acid molecules, recombinant host cells comprising the expression vectors, host cells further comprising other ethanologenic enzymes, and methods for producing useful substances, e.g., acetaldehyde and ethanol, using such host cells.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Methods for improving malic acid production in filamentous fungi
InactiveUS20110053233A1Reduce mitochondrial importImprove the level ofFungiPeptidesHeterologousNucleotide
The present invention relates to methods of producing a C4 dicarboxylic acid, comprising: (a) cultivating a filamentous fungal host cell comprising a polynucleotide selected from the group consisting of a heterologous first polynucleotide encoding a C4 dicarboxylic acid transporter, a heterologous second polynucleotide encoding a malate dehydrogenase, and a heterologous third polynucleotide encoding a pyruvate carboxylase; wherein the filamentous fungal host cell is capable of secreting increased levels of the C4 dicarboxylic acid compared to the filamentous fungal host cell without the heterologous polynucleotide when cultivated under the same conditions; and (b) recovering the C4 dicarboxylic acid. The present invention also relates to methods for increasing C4 dicarboxylic acid production, filamentous fungal host cells and malate dehydrogenase variants.
Owner:NOVOZYMES INC
5-amino levulinic acid (ALA) high-yield strain and preparation method and application thereof
A method for constructing an ALA production bacterial strain, the method enhances the activity of related enzymes promoting the synthesis of oxaloacetate and in the 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) production bacterial strain, or introducing exogenous related enzymes promoting the synthesis of oxaloacetate, such as phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase or pyruvate carboxylase, and / or reducing the activity of related enzymes in the downstream metabolic pathway of succinyl coenzyme A in the bacterial strain, such as succinyl coenzyme A synthetase or succinate dehydrogenase, and / or reducing the activity of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylated kinase and / or malic enzyme. An ALA high-yield bacterial strain constructed by utilizing the method, and method for utilizing the bacterial strain to prepare ALA.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Malic acid-production gene engineering bacteria and its construction and use
InactiveCN104046577AThe fermentation method is simpleGood effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFumaraseFermentation
The invention provides malic acid-production gene engineering bacteria Escherichiacoli BA043. The malic acid-production gene engineering bacteria is named as BA043 (Escherichiacoli BA043) and has a preservation registration number CCTCC NO: M2014034. The invention also provides a construction method of the malic acid-production gene engineering bacteria and a method for fermentation production of malic acid. Through knockout or inactivation of fumarase and fumarate reductase and through over coexpression of exogenous pyruvate carboxylase and nicotinic acid phosphoribosyl transferase, recombinant escherichia coli can reduce by-product pyruvic acid generation by glucose metabolism growth so that a malic acid yield and production intensity are greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
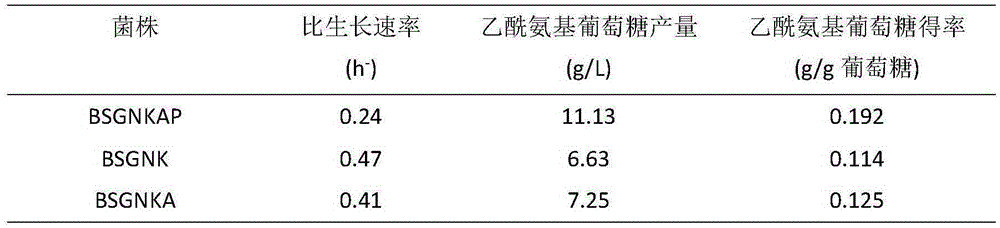
Recombinant bacillus subtilis for efficiently synthesizing acetylglucosamine
ActiveCN105255803AHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPyruvate carboxylaseGlucose polymers
The invention discloses recombinant bacillus subtilis for efficiently synthesizing acetylglucosamine and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. According to the recombinant bacillus subtilis, based on bacillus subtilis BSGNK, the enol phosphate type pyruvate carboxylase encoding gene pckA and pyruvate kinase encoding gene pyk (NCBI upper Gene ID: 938206) are knocked out, the BSGNK regards B.subtilis168delta nagP delta gamP delta gamA delta nag A delta nag B delta ldh delta pta::lox <72> as the host, promoters PxylA and P43 are utilized for controlling recombinant ecpression of glmS and GNAl, and accordingly the glucose kinase encoding gene glcK is knocked out. According to the recombinant bacillus, glucose can be effectively utilized for synthesizing acetylglucosamine, the shake flask fermentation yield can reach 11.13 g / L, the yield is increased by 67.8% compared with a strain before knocking out, and a basis is provided for further improvement of bacillus subtilis for producing glucosamine of metabolic engineering.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Glutamic acid corynebacterium and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN106635944AWith production capacityPromote accumulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPyruvate carboxylaseMicroorganism
The invention belongs to the field of microorganisms, and particularly relates to a glutamic acid corynebacterium and a construction method and application of the glutamic acid corynebacterium. The glutamic acid corynebacterium has the capability of producing L-lysine, and the activities of pyruvic carboxylase exportin and pyruvic carboxylase in a cell are both strengthened. The glutamic acid corynebacterium strengthens the activity of the pyruvic carboxylase exportin, so that the accumulation of the L-lysine is promoted, the yield of the L-lysine is increased, the activity of pyruvic carboxylase is strengthened at the same time, more precursors are provided for the synthesis of the L-lysine, the accumulation capability of the L-lysine is further improved, the amount of the L-lysine in a culture medium is increased, and the capability of production of the L-lysine through the fermentation of the strain is further improved. The experiment shows that the glutamic acid corynebacterium is a strain with high yield of L-lysine, the L-lysine is effectively accumulated, the yield of the L-lysine is improved, and a foundation is laid for the industrialized production of the L-lysine.
Owner:MEIHUA BIOTECH LANGFANG CO LTD
Escherichia coli gene engineering bacterium and method for producing L-threonine by using escherichia coli gene engineering bacterium
ActiveCN106867952AIncrease productionImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseEscherichia coli
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, and particularly relates to an escherichia coli gene engineering bacterium and a method for producing L-threonine by using the escherichia coli gene engineering bacterium. The gene engineering bacterium is characterized in that a promoter P<ppc> of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene (ppc) of an initial strain is replaced into a promoter P<zwf> of 6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene (zwf), so that the goal of regulating the L-threonine production capacity by glycine betaine is achieved. In the fermentation process, the glycine betaine is added, so that the L-threonine yield through shaking flask fermentation can reach 50 to 55g / L; the 5L fermentation tank yield reaches 120 to 150g / L; the saccharic acid conversion rate reaches 59 to 61 percent.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Corynebacterium glutamicum strain for production of 5-aminolevulinic acid and construction and application of corynebacterium glutamicum strain
InactiveCN106047916AIncrease productionHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylasePhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a corynebacterium glutamicum strain for production of 5-aminolevulinic acid and construction and application of corynebacterium glutamicum strain. A construction method includes: (1) deleting a lactic dehydrogenase coding gene 1dhA and acetic acid generation genes pta-ackA, pqo and cat in corynebacterium glutamicum to obtain a strain named CB4; inserting a strong sod promoter in front of a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase coding gene ppc in the strain CB4 to obtain a strain CB5; deleting a gene pck in the strain CB5 to obtain a strain CB6; (2) transferring plasmid pXA and plasmid pEP2<tuf>-rhtA into the strain CB6. The strain constructed according to the method is capable of generating 2.78g / L 5-aminolevulinic acid in a culture medium with 10g / L glucose serving as a carbon source, which lays a foundation for subsequent continuous feeding of a fermentation tank to increase yield of the 5-aminolevulinic acid.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Cloning and sequencing of pyruvate decarboxylase (PDC) genes from bacteria and uses therefor
InactiveUS20080009609A1Improve efficiencyImprove filtering effectFungiBacteriaBacteroidesPyruvate carboxylase
The invention provides isolated nucleic acids molecules which encode pyruvate decarboxylase enzymes having improved decarboxylase activity, substrate affinity, thermostability, and activity at different pH. The nucleic acids of the invention also have a codon usage which allows for high expression in a variety of host cells. Accordingly, the invention provides recombinant expression vectors containing such nucleic acid molecules, recombinant host cells comprising the expression vectors, host cells further comprising other ethanologenic enzymes, and methods for producing useful substances, e.g., acetaldehyde and ethanol, using such host cells.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Coryneform bacterium transformant and process for producing dicarboxylic acids using the same
ActiveUS7368268B2Improve productivityHigh expressionBacteriaSugar derivativesPyruvate synthesisGenetic engineering
The present invention provides an aerobic coryneform bacterium transformant in which a lactate dehydrogenase gene is disrupted, and a pyruvate carboxylase gene is recombined so as to be highly expressed by a genetic engineering method. The aerobic coryneform bacterium transformant of the present invention can produce dicarboxylic acids from saccharides at a high production rate.
Owner:RES INST OF INNOVATIVE TECH FOR THE EARTH
Genetic engineering bacterium for L-theanine production and construction and application thereof
ActiveCN109777763AIncrease enzyme activityGene expression is stableBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliCitrate synthase
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and particularly relates to novel high-efficiency gamma-glutamyl methylamine synthetase and a plasmid-free genetic engineering bacterium for L-theanine production and construction and application thereof. The plasmid-free genetic engineering bacterium which performs denovo synthesis on L-theanine efficiently by taking cheap carbon sources such as glucose as a substrate is provided, escherichia coli serves as a host, and gamma-glutamyl methylamine synthase genes gmas-Mu copied three times are integrated on a genome of the escherichia coli; a glutamate dehydrogenase gene Cgl2079 is copied once; a pyruvate carboxylase gene Cgl0689 is copied once; a citrate synthase gene gltA is copied once, and the genetic engineering bacterium is obtained. After metabolic transformation of a system, the engineering bacterium can perform denovo synthesis on the L-theanine by taking the glucose as the raw material, the fermentation yieldand sugar-acid conversion rate are the highest values reported so far, in fermentation of a 5 L fermentor, the maximum production of the L-theanine can reach 60 g / L, and the sugar-acid conversion ratecan reach 40%.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Carrier for enhancing aluminum-tolerance of plant, and method for establishing the same
InactiveCN102199620ALarge amount of synthesisPromote growthVector-based foreign material introductionPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseNicotiana tabacum
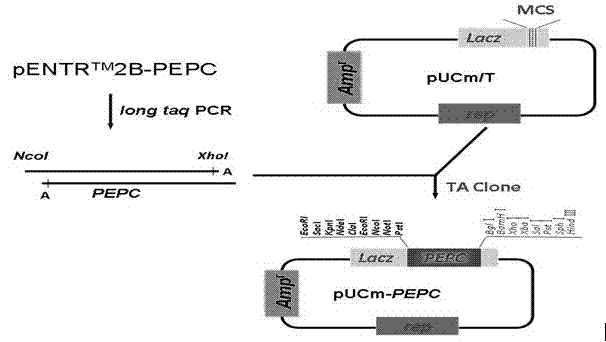
The invention provides a carrier for enhancing aluminum-tolerance of a plant, and a method for establishing the same. The carrier is a plant expression vector having photoinduction promoters and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC) genes. The method for establishing the carrier comprises the following steps: searching for the sequence of the full length gene of Synechococcus vulcanus PEPC in GenBank and designing a pair of primers with sequences as described in the specification; recovering and purifying PEPC full length gene segments and connecting the segments to a pUCm-T vector; establishing an entry vector pENTER*-PrbcS-PEPC; establishing a plant expression vector pH2-35S-PrbcS-PEPC. In the invention, the activity of citrate synthase of tabacoo with transgenic PEPC and CS genes is 2.4 to 2.6 times that of wild tobacco, and the activity of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase of such tabacco is 2.2 to 2.4 times that of wild tobacco. The special-purpose carrier provided in the invention can exert great influence on the improvement of aluminum-tolerance of a plant, and particularly, can significantly promote aluminum-tolerance of plants grown in acid red soil in southern China, thereby providing a novel approach for variety improvement of plants.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Construction and applications of corynebacterium glutamicum mutant strain for producing L-homoserine
The invention discloses construction and applications of a corynebacterium glutamicum mutant strain for producing L-homoserine, and belongs to the technical field of fermentation engineering. Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032 is taken as a starting strain to knock out regulatory protein McbR, homoserine kinase, transport protein MetD, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase; the expression of isocitrate dehydrogenase is down regulated; transport protein BrnFE, aspartic semialdehyde dehydrogenase and homoserine dehydrogenase are overexpressed; and the expression of aspartate kinase, pyruvate carboxylase and the aspartate kinase I derived from escherichia coli are enhanced. Shake flask culture can be performed on the mutant strain for 48 h, and the yield of L-homoserine can reach 8.8 g / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for producing succinic acid
InactiveCN1875108AIncrease consumption rateIncrease spawn rateBacteriaRecombinant DNA-technologyLactate dehydrogenasePyruvate carboxylase
Succinic acid is produced by allowing a bacterium modified to enhance fumarate reductase activity or cell preparation thereof to react with an organic raw material in a reaction solution containing one of a carbonate ion, a bicarbonate ion, and carbon dioxide gas to generate succinic acid. More preferably, succinic acid is produced by allowing a bacterium modified to enhance activities of fumarate reductase and pyruvate carboxylase and decrease lactate dehydrogenase activity or cell preparation thereof to react with an organic raw material in a reaction solution containing one of a carbonate ion, a bicarbonate ion, and carbon dioxide gas to generate succinic acid. Succinic acid is obtained by collecting the produced succinic acid.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP +1
Recombinant bacillus subtilis capable of improving yield of acetylglucosamine, and constructing method thereof
ActiveCN106148261AIncrease productionIncrease concentrationBacteriaStable introduction of DNAPyruvate carboxylaseStart codon
The invention relates to a recombinant bacillus subtilis capable of improving the yield of acetylglucosamine. The recombinant bacillus subtilis is obtained by strengthening the expression of pyruvic carboxylase encoding gene pycA of the acetylglucosamine. The invention also provides a constructing method for the recombinant bacillus subtilis. The constructing method comprises the following steps: constructing a replacing frame of a promoter and an initiation codon of the pyruvic carboxylase encoding gene pycA; replacing an original promoter of the pyruvic carboxylase encoding gene pycA in a bacillus subtilis genome by a P43 strong constitutive promoter in the replacing frame through homologous recombination; meanwhile, replacing an initiation codon GTG of the pycA with ATG. Compared with a starting strain, the yield of the acetylglucosamine of the recombinant bacillus subtilis provided by the invention is greatly improved; the constructing method for the recombinant bacillus subtilis is simple and has an industrial value.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Establishment and application of brewing yeast engineering bacterium strain for producing L-malic acid
ActiveCN105400711ARealize accumulationFungiMicroorganism based processesPyruvate carboxylaseTrimeresurus flavoviridis
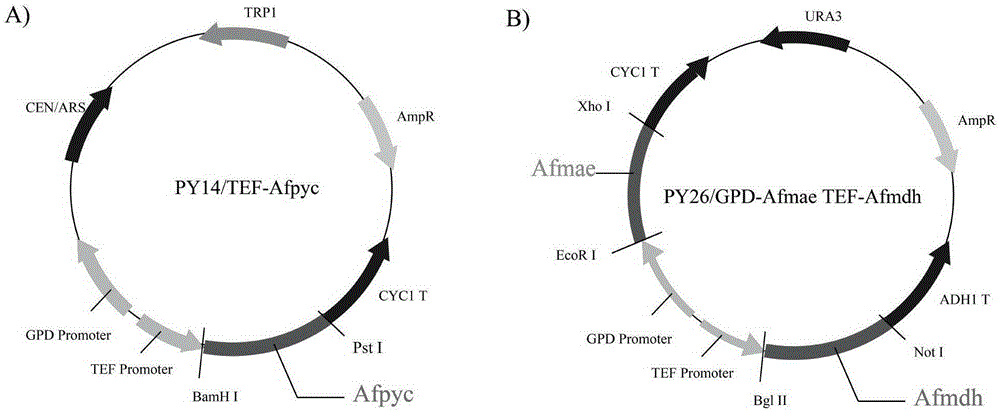
The invention discloses establishment and application of a brewing yeast engineering bacterium strain for producing L-malic acid, and belongs to the field of fermentation engineering. Genes of pyruvic carboxylase (Afpyc), malic dehydrogenase (Afmdh) and malic acid transport protein (Afmae) coming from Aspergillus flavus ATCC13697 are excessively and dissociatively expressed in the bacterium strain S.cerevisiae tTAM(delta)ura3(delta)trpl high in pyruvic acid yield, the malic acid accumulation path is established, and the bacterium W1101 is obtained. The bacterium strain is used for producing L-malic acid through fermentation; after fermentation is conducted for 84 h, the malic acid yield is 27.3 g / L; an original starting bacterium strain does not accumulate malic acid, the metabolism path of aspergillus flavus of the high-yield L-malic acid bacterium strain is successfully applied to brewing yeast, and a new strategy is provided for establishing the high-yield L-malic acid bacterium strain.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing L-aspartic acid through fermentation
ActiveCN106434510AGet Rid of Reliance on Petroleum-Based Fumaric AcidCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaEscherichia coliDry weight
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for directly producing L-aspartic acid through fermentation. The classification naming of the genetically engineered bacterium is Escherichia coli CM-AS-115, and the preservation number of the genetically engineered bacterium is CCTCC NO: M 2016457. The bacterial strain relates to inactivation of multiple genes, evolution, metabolism and domestication are simultaneously carried out on the bacterial strain which knockouts the multiple genes, and a mutant strain, namely, CM-AS-105, which has a lower respiratory quotient under the aerobic condition and of which the highest dry cell weight is 60-70% of dry weight of an original strain W1485 is obtained; meanwhile, the bacterial strain further relates to over expressions of two genes, wherein the two genes comprise an enol phosphate type pyruvate carboxylase encoding gene (ppc) and an aspartase encoding gene (aspA), and the obtained bacterial strain is CM-AS-115. The genetically engineered bacterium for directly producing L-aspartic acid through fermentation achieves a way of completely adopting renewable biomass resources such as starch and cellulose as raw materials to ferment and prepare the L-aspartic acid, and the way is green and environmentally friendly.
Owner:CHANGMAO BIOCHEMICAL ENG CO LTD
Method of producing succinic acid with bacterium comprising a modified fumarate reductase gene or a modified succinate dehydrogenase gene
ActiveUS7763447B2Improve productivityProducing succinicSugar derivativesBacteriaLactate dehydrogenasePyruvate carboxylase
Succinic acid is produced by allowing a bacterium modified to enhance fumarate reductase activity or cell preparation thereof to react with an organic raw material in a reaction solution containing one of a carbonate ion, a bicarbonate ion, and carbon dioxide gas to generate succinic acid. More preferably, succinic acid is produced by allowing a bacterium modified to enhance activities of fumarate reductase and pyruvate carboxylase and decrease lactate dehydrogenase activity or cell preparation thereof to react with an organic raw material in a reaction solution containing one of a carbonate ion, a bicarbonate ion, and carbon dioxide gas to generate succinic acid. Succinic acid is obtained by collecting the produced succinic acid.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
L-threonine high-yield genetic engineering strain and application thereof
InactiveCN107699525AReduce generationIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPyruvate carboxylaseBiotechnology
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and particularly relates to an L-threonine high-yield genetic engineering strain and application thereof. The engineering strain isbuilt by using escherichia coli as host cells through knocking out pka genes of coding lysine acetyltransferase and TCA cyclical transcription regulatory factor arcA gene and simultaneously overpressing phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase coding gene ppc. After the engineering strain is used for fermenting and producing L-threonine; the yield can be improved by 8.97 percent.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Corynebacterium glutamicum engineering bacterium for highly producing succinic acid and building method thereof
InactiveCN103509747AIncrease productionReduce generationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSaccharic acidPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
The invention discloses a corynebacterium glutamicum engineering bacterium for anaerobic conversion to produce succinic acid, and a building method and application thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. A pyruvate carboxylase gene of the corynebacterium glutamicum and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from escherichia coli are cloned to corynebacterium glutamicum (ATCC13032); a lactate dehydrogenase gene of the corynebacterium glutamicum is knocked out in a homologous recombination manner. By adopting the lactic dehydrogenase-defective corynebacterium glutamicum for coexpression of a carboxylase gene, anaerobic production of succinic acid is carried out in a cell reutilization manner, so that the yield of succinic acid can be greatly improved; the yield can be up to 75g / L; the conversion rate of saccharic acid is 75%; the corynebacterium glutamicum engineering bacterium has a good application prospect; a fermentation model, especially a fermentation model for cell reutilization is built according to the optimum condition for biological transformation of succinic acid; the acid-production performance in repeated batch transformation process of cells can be basically kept stable.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Corynebacterium glutamicum recombinant strain for producing 5-aminolevulinic acid
InactiveCN106434513AEasy to transportIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseAminolevulinic acid synthase
The invention discloses a corynebacterium glutamicum recombinant strain for producing 5-aminolevulinic acid. An establishing method comprises steps as follows: (1) a lactic dehydrogenase encoding gene ldhA and acetic acid producing genes pta-ackA, pqo and cat are knocked out from corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 1303, and a strain CG4 is obtained; an sod promoter is inserted in front of a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase encoding gene in the CG4, and a strain CG5 is obtained; a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase encoding gene pck is knocked out from the CG5, and a strain CG6 is obtained; (2) plasmids of an overexpressed 5-aminolevulinic acid synthase gene are transferred into the CG6, and a recombinant strain L is obtained; (3) 5-aminolevulinic acid transport protein plasmids are transferred into the L. The recombinant strain can promote 5-aminolevulinic acid to be transported outside corynebacterium glutamicum cells, and the yield of 5-aminolevulinic acid is 112.3% higher than that of a contrast strain.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Genetic engineering bacterium for producing succinic acid, and construction and application thereof
ActiveCN102864116AEasy to buildThe fermentation method is simpleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliButanedioic acid
The invention provides a genetic engineering bacterium strain for producing succinic acid. The genetic engineering bacterium strain is named as Escherichia coli BA016, the preserving number registration number CCTCC NO is M 2012350. The invention further provides a construction method of the strain and a method for producing succinic acid by fermentation, recombinant escherichia coli can grow by glucose metabolism through joint excessive expression of exogenous pyruvic carboxylase and nicotinic acid ribose phosphate transferase, generation of by-product pyruvic acid is reduced, and accordingly the yield and production intensity of succinic acid are greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Gene engineering bacterium for producing succinic acid, and method for producing succinic acid by fermentation by using same
InactiveCN102643775AIncrease productionIncrease production capacityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliButanedioic acid
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological engineering, and relates to a gene engineering bacterium strain for producing succinic acid, and a method for producing succinic acid by fermentation by using the same. The classification designation of the gene engineering bacterium strain for producing succinic acid is Escherichia coli BA305, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO:M2012102. The construction process mainly comprises the following steps: inactivating or knocking out phosphoenolpyruvic acid carboxylase gene and ptsG gene in a phosphate translocation system; and overexpressing the phosphoenolpyruvic acid carboxylase so that the recombinant colibacillus can efficiently utilize glucose, xylose, arabinose, levulose and other monosaccharides and efficiently utilize mixed saccharides in various proportions and cellulose hydrolysate, thereby greatly enhancing the synthesis efficiency of the succinic acid. The fermentation method adopts a two-stage fermentation mode: the aerobic stage can enhance the biomass, and the anaerobic stage is used for fermentation to produce the acid.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com