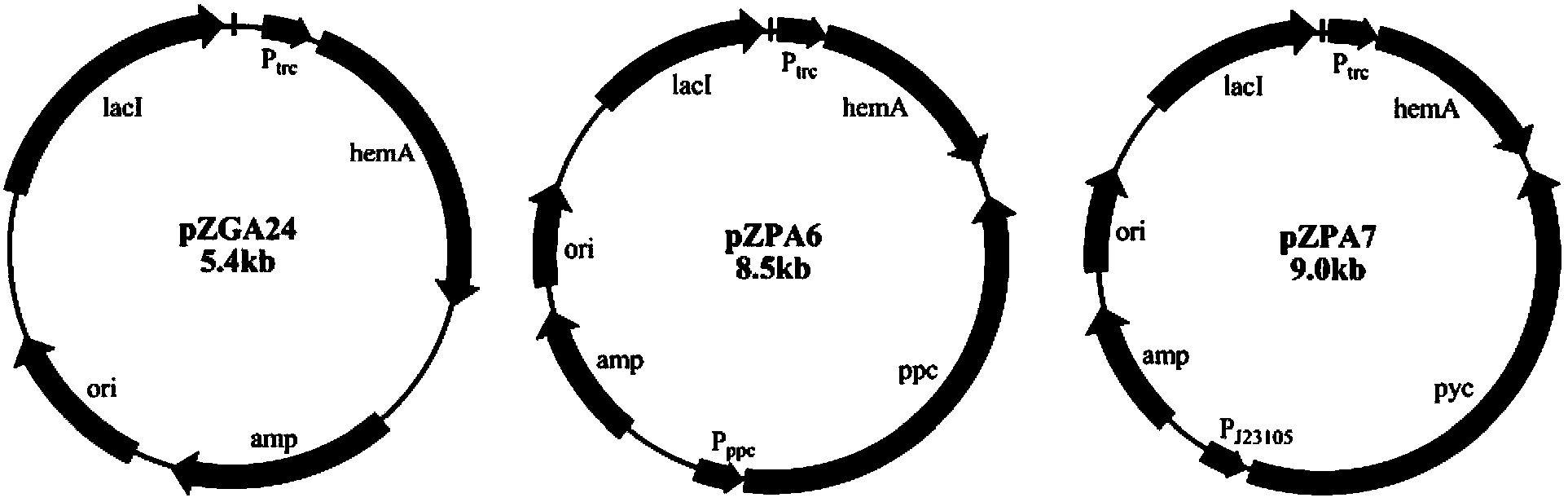
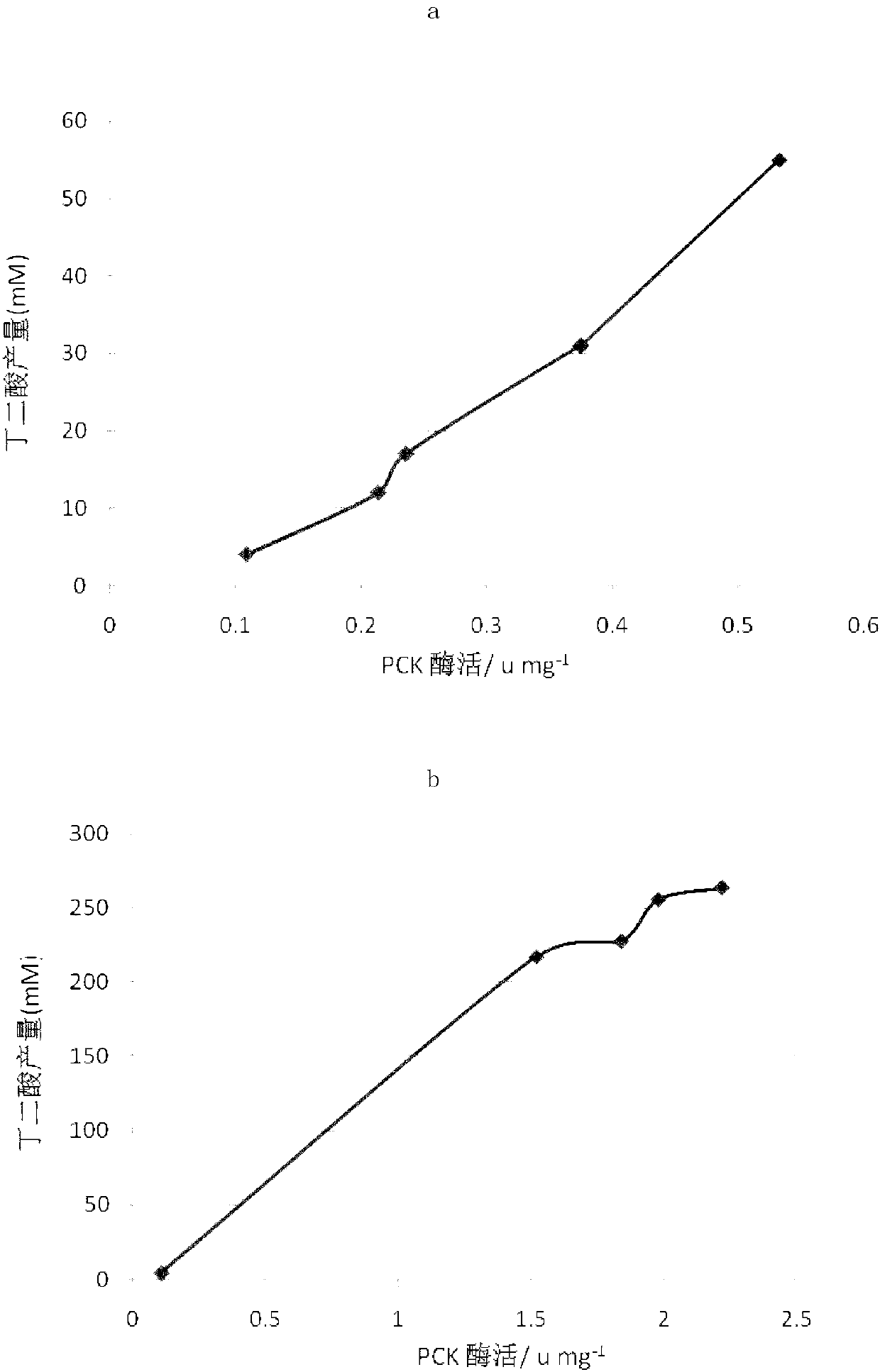
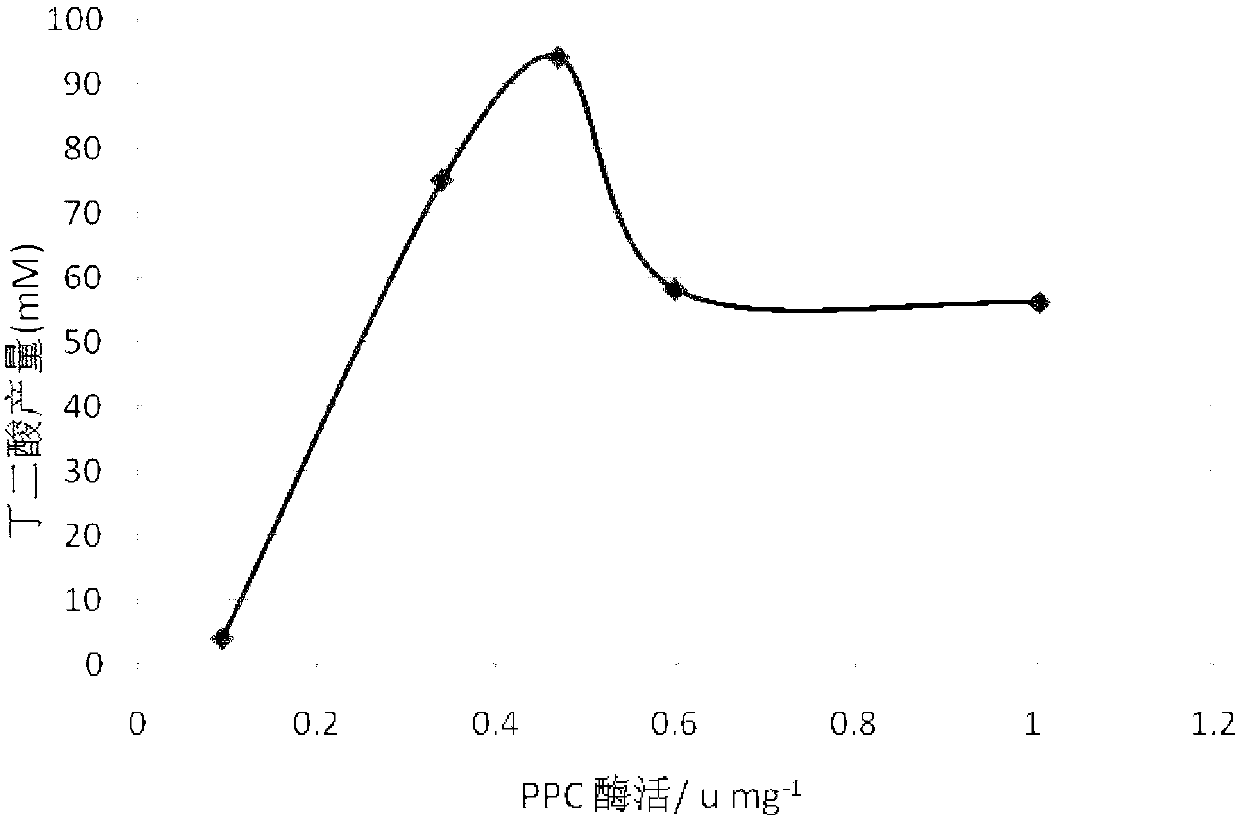
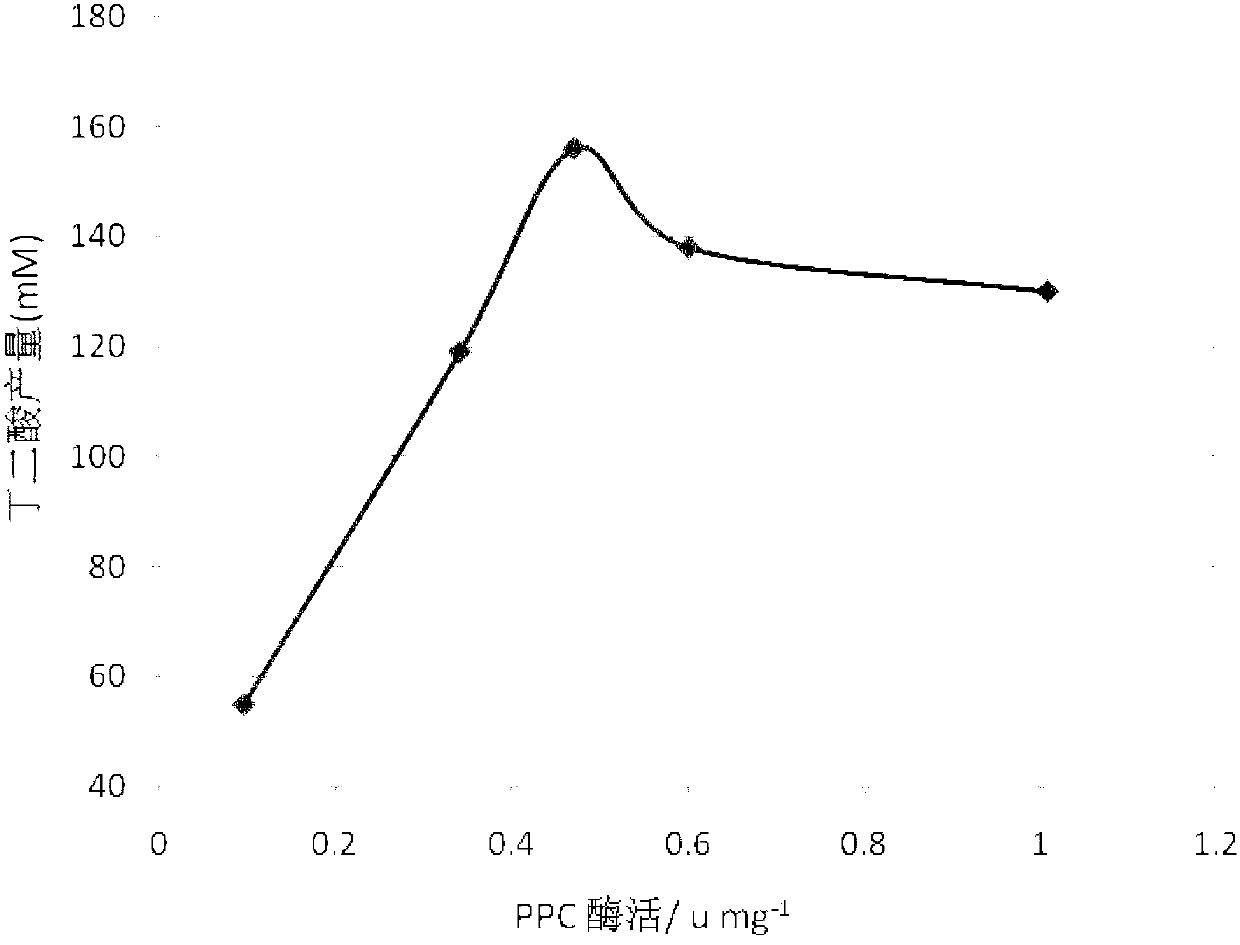
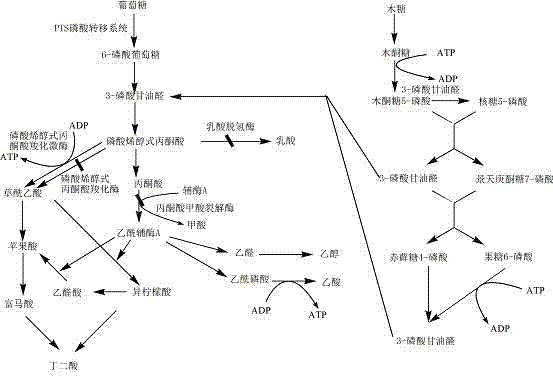
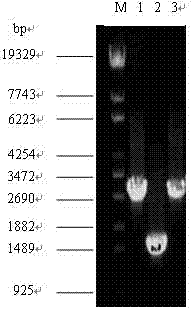
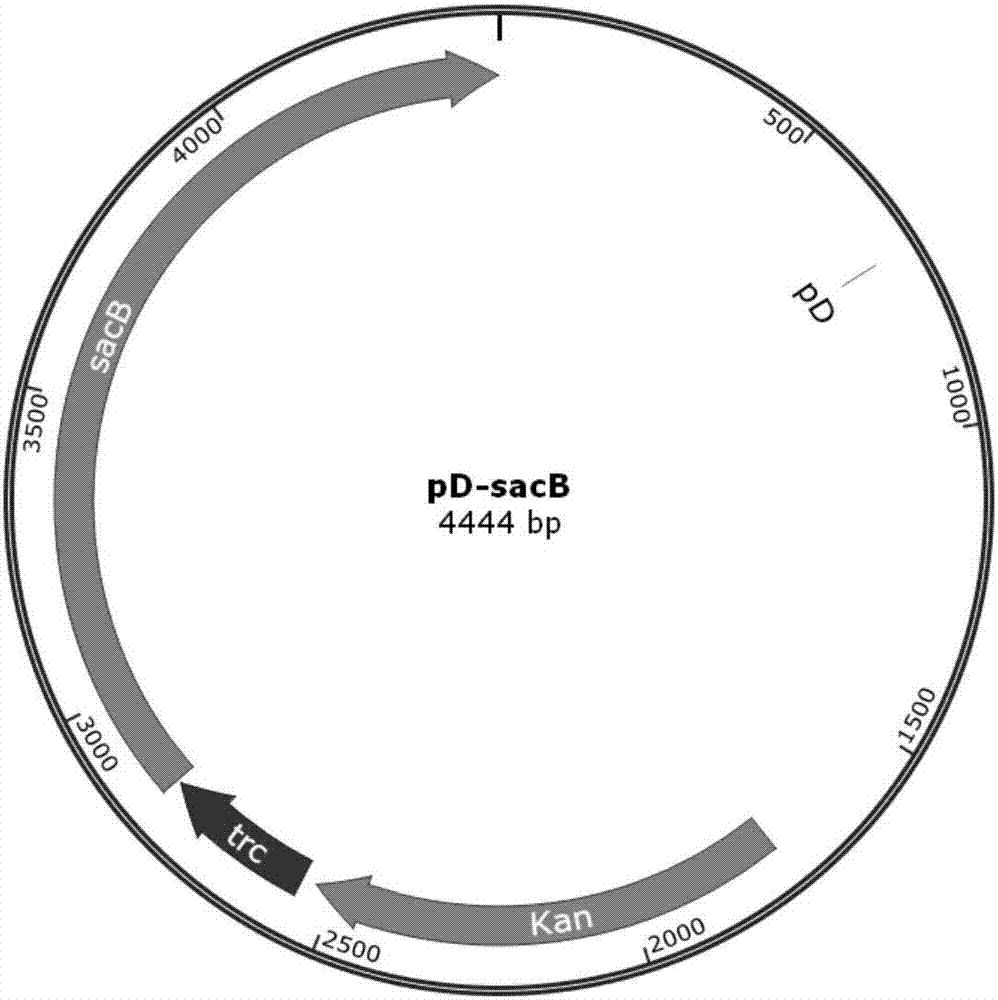
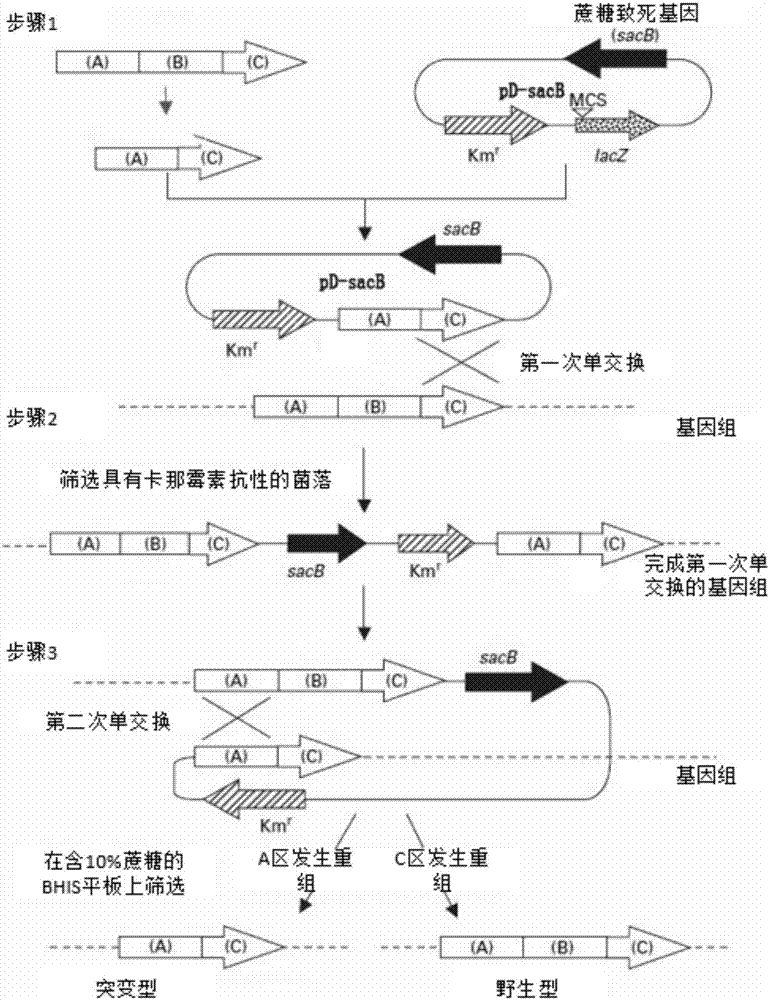
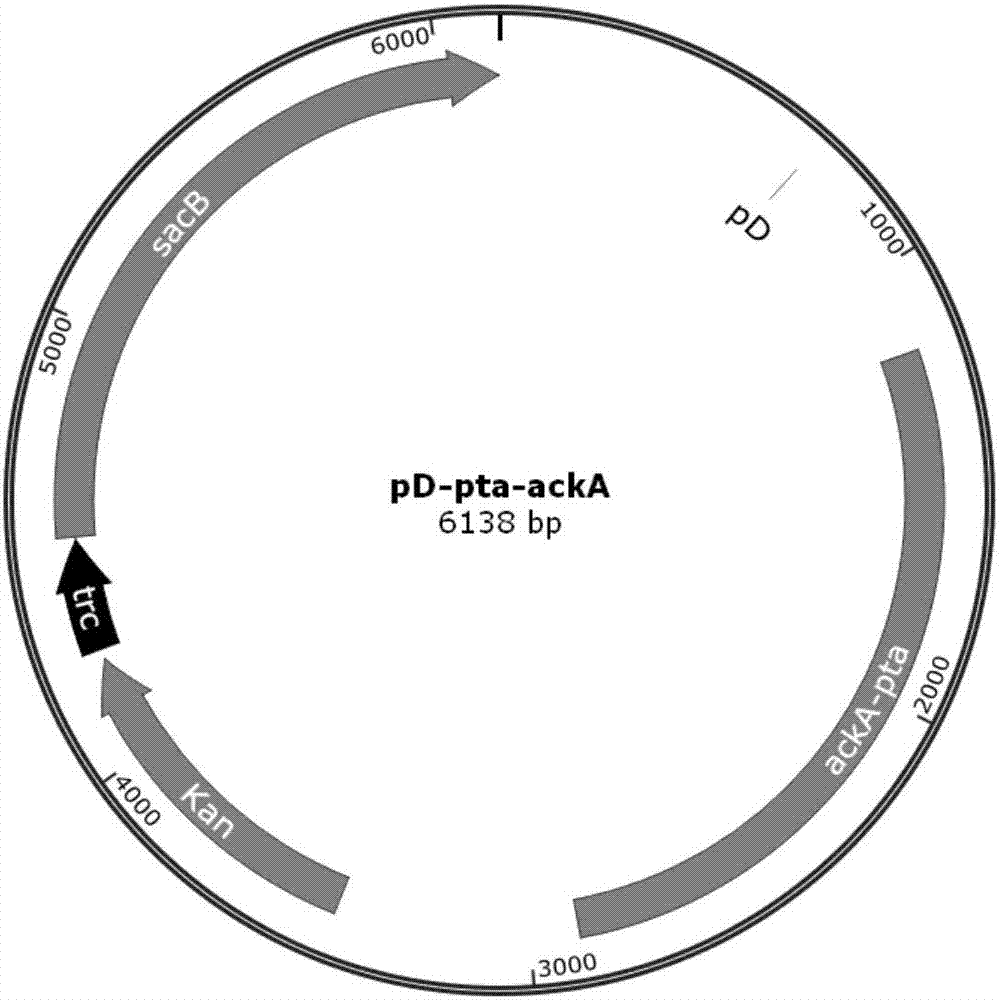
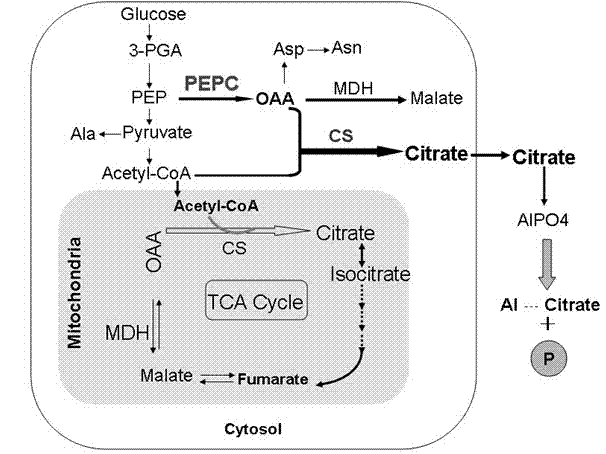
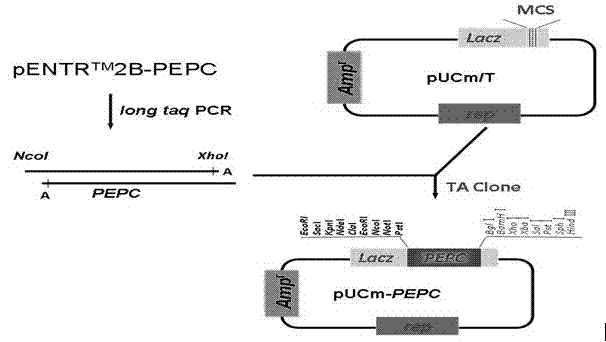
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
117 results about "Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
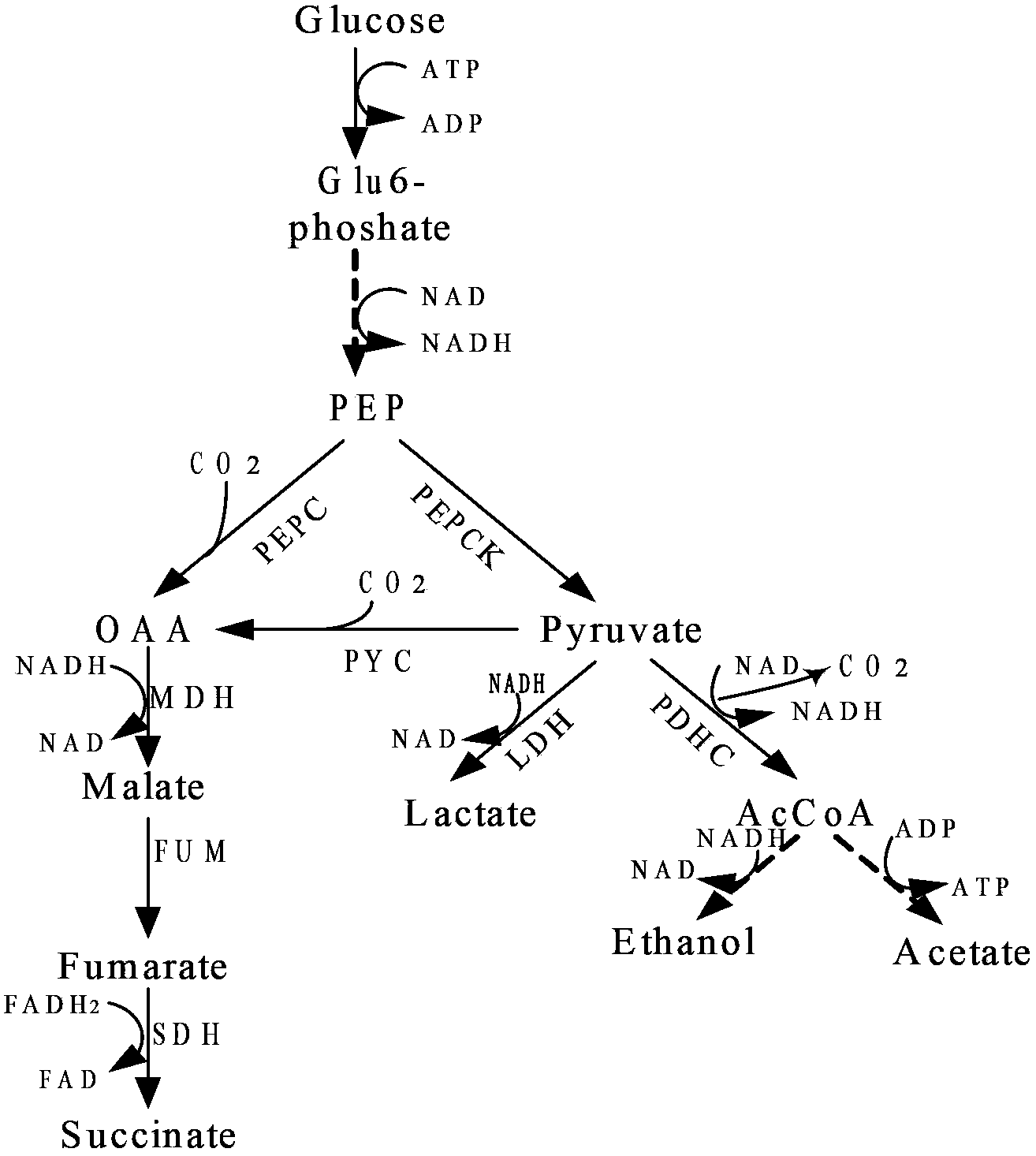
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (also known as PEP carboxylase, PEPCase, or PEPC; EC 4.1.1.31, PDB ID: 3ZGE) is an enzyme in the family of carboxy-lyases found in plants and some bacteria that catalyzes the addition of bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻) to phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to form the four-carbon compound oxaloacetate and inorganic phosphate...
Bioengineering cotton fiber properties
InactiveUS7060874B2Increase heightTransferasesFermentationPyruvate carboxylasePhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
The present invention provides plant fiber expansion (FE) genes that encode FE polypeptides, such as phosphoenol pyruvate carboxylase (PEPcase), expansin, endoglucanase, xyloglucan endoglycosyltransferase (XET), and pectin methyl esterase (PME). The invention further provides fiber-specific promoters. Still further, the invention provides molecular strategies for modulating fiber quality and yield in fiber producing plants by modulating expression of FE genes or mutant forms of FE genes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Novel rumen bacteria variants and process for preparing succinic acid employing the same
ActiveUS20070054387A1High yieldBacteriaSugar derivativesHigh concentrationPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
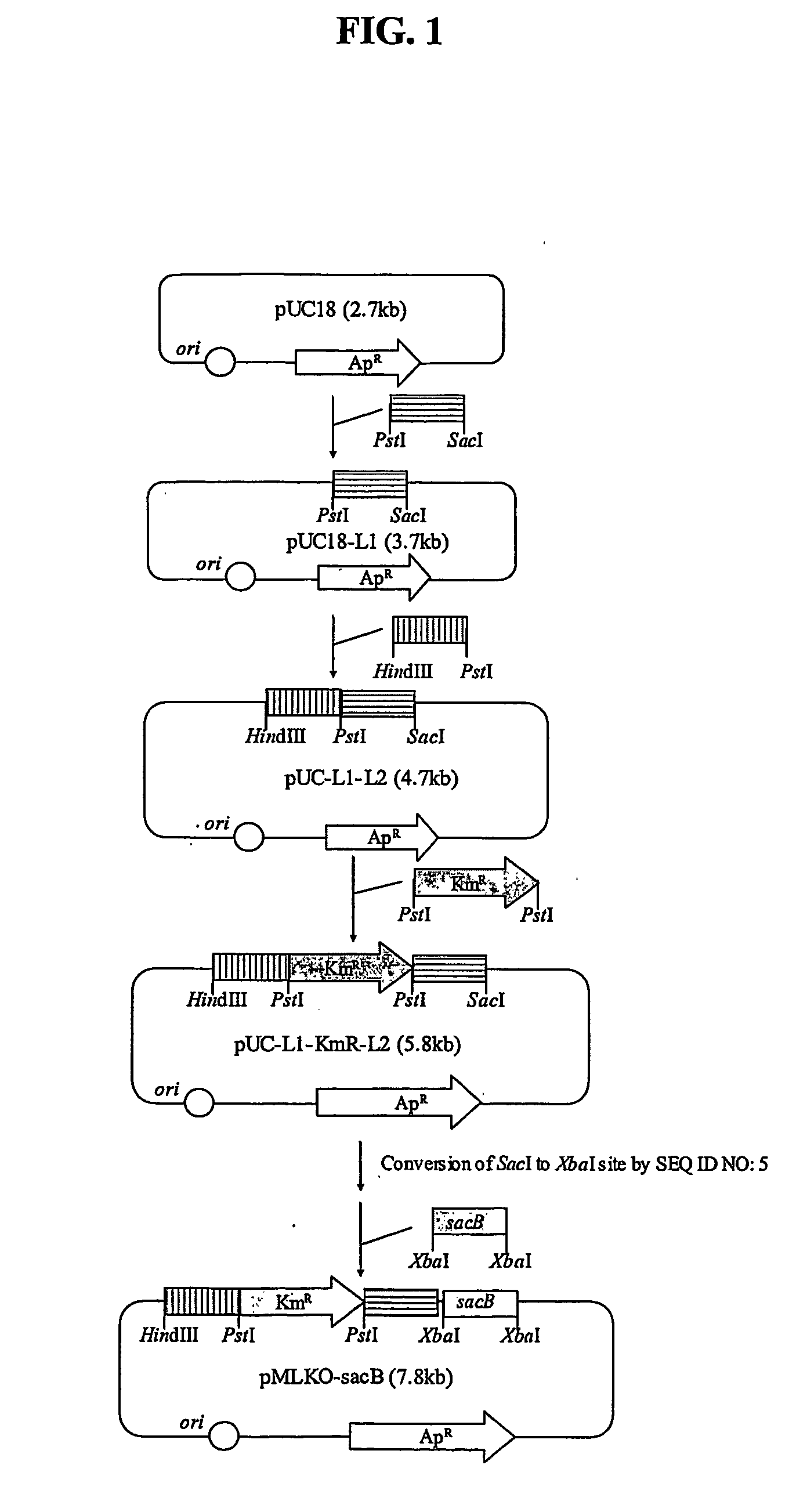
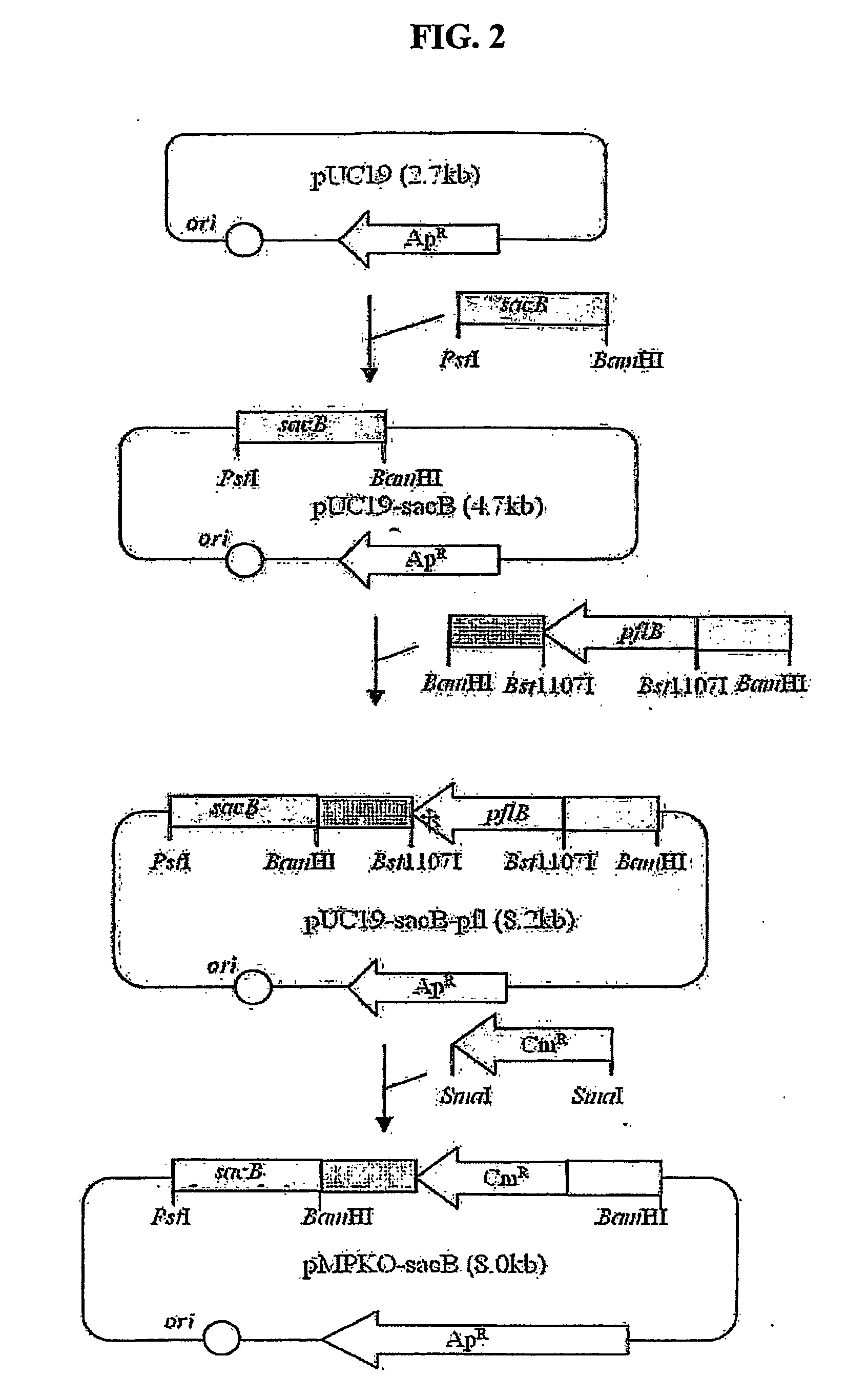
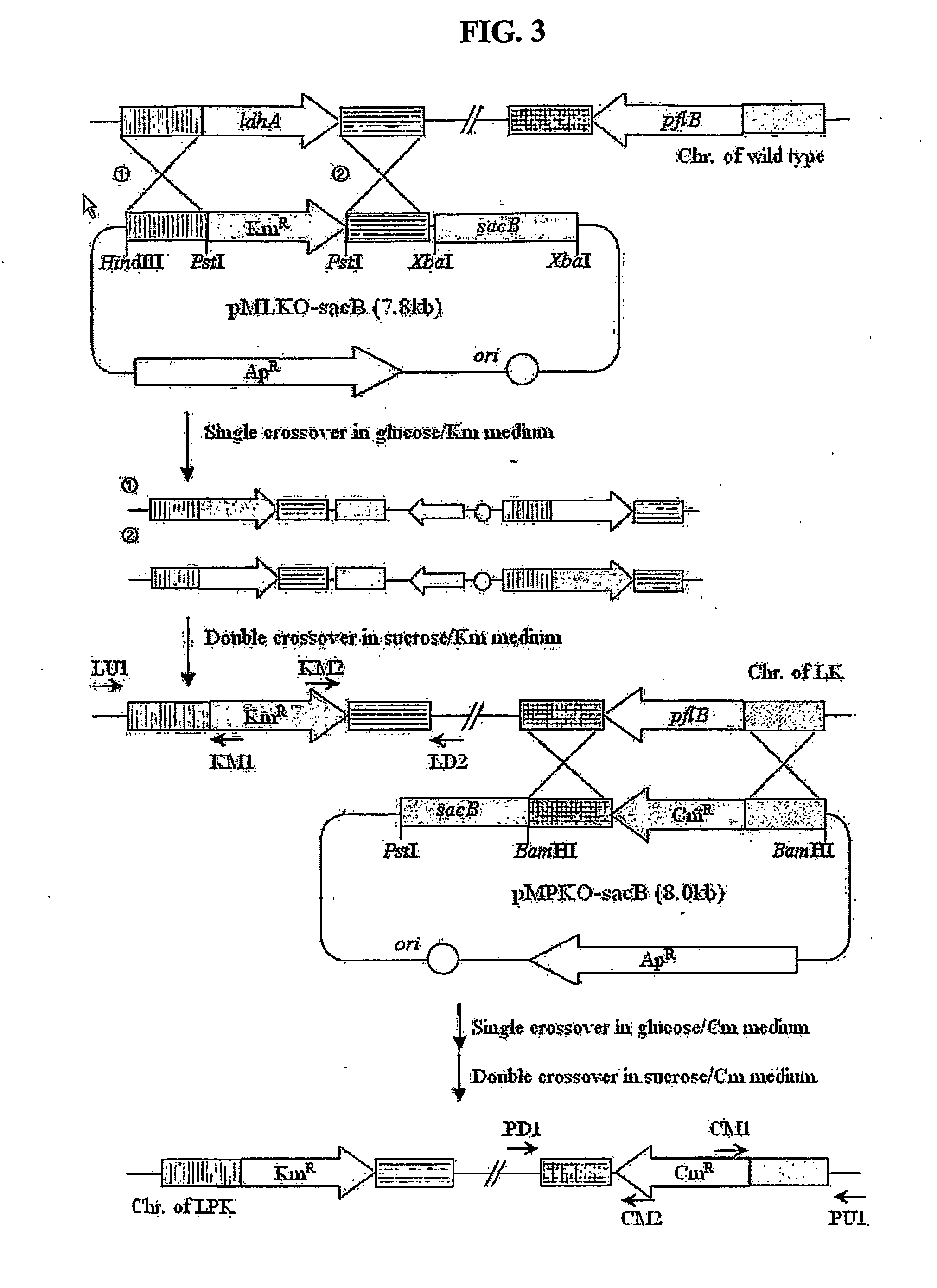
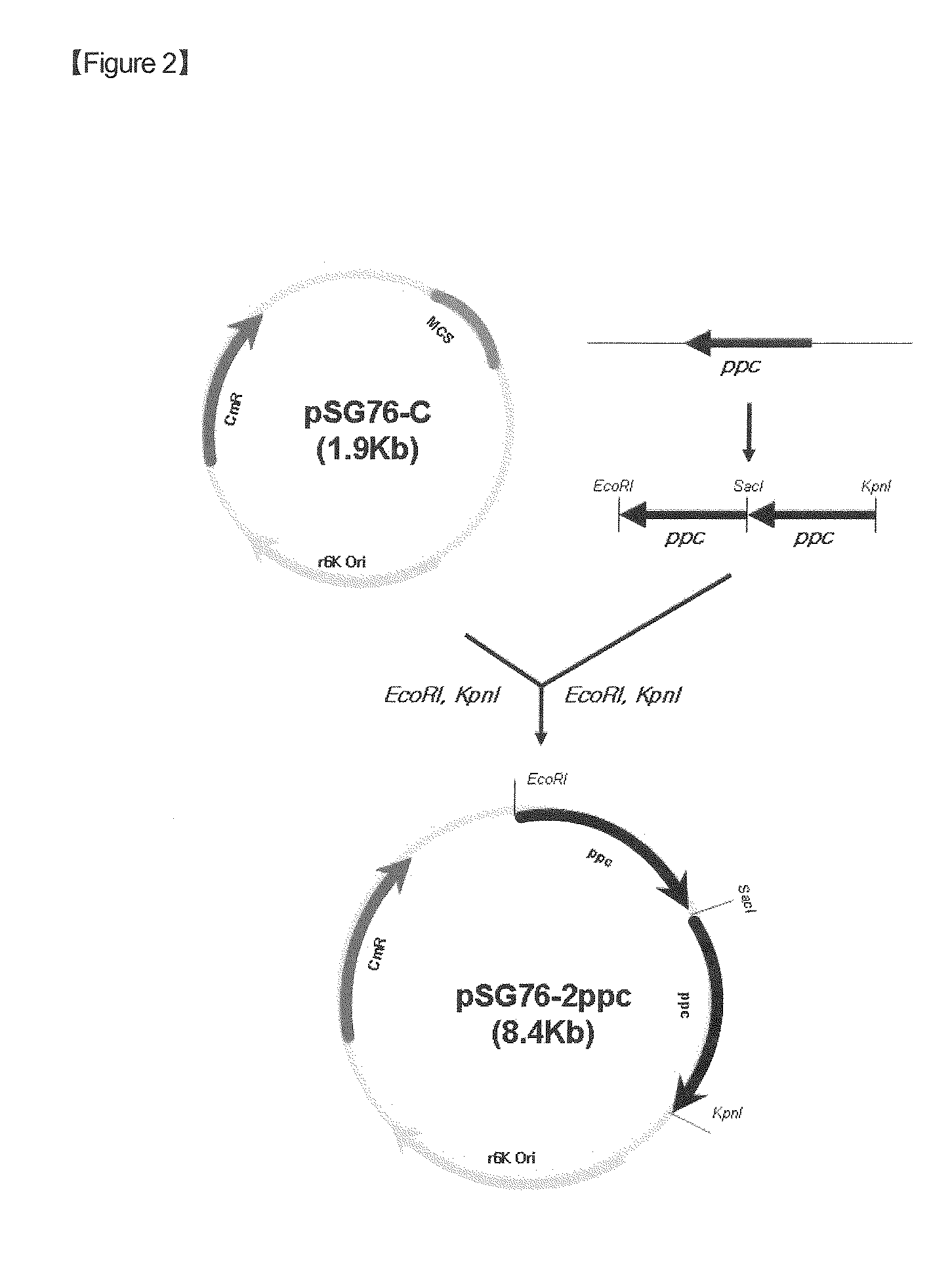
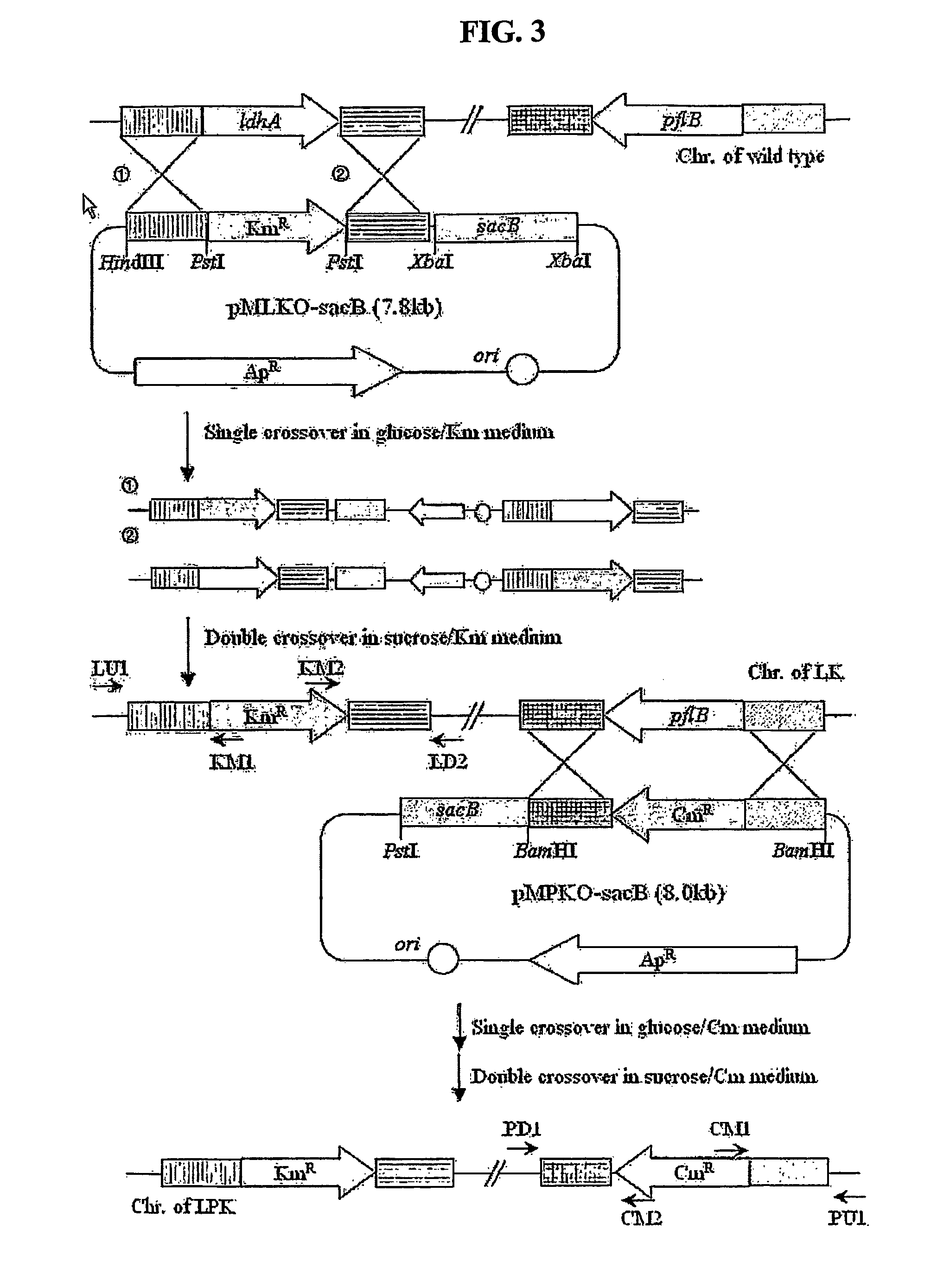
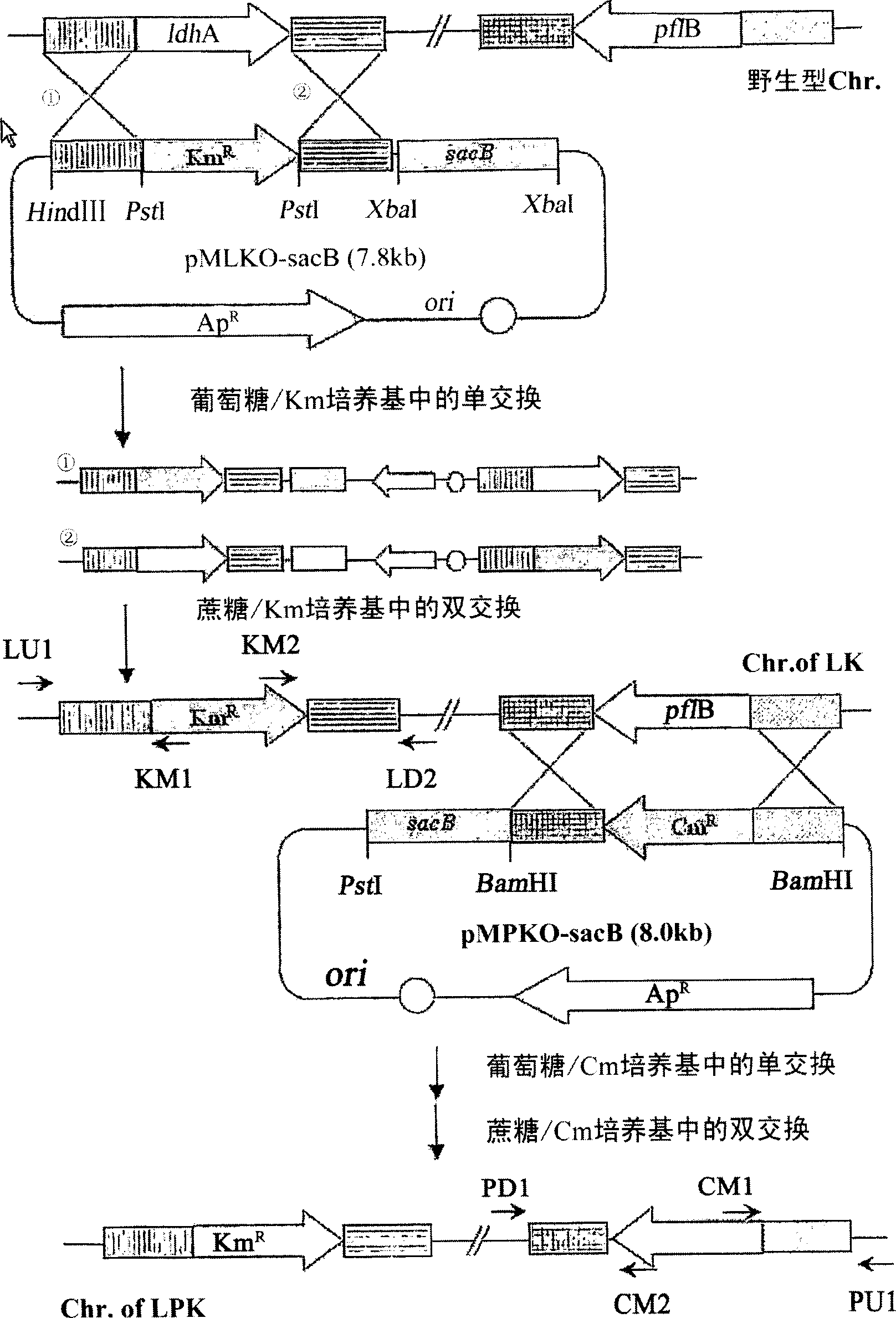
The present invention relates to novel rumen bacterial mutants resulted from the disruption of a lactate dehydrogenase gene (ldhA) and a pyruvate formate-lyase gene (pfl) (which are involved in the production of lactic acid, formic acid and acetic acid) from rumen bacteria; a novel bacterial mutant (Mannheimia sp. LPK7) having disruptions of a lactate dehydrogenase gene (ldhA), a pyruvate formate-lyase gene (pfl), a phosphotransacetylase gene (pta), and a acetate kinase gene (ackA); a novel bacterial mutant (Mannheimia sp. LPK4) having disruptions of a lactate dehydrogenase gene (ldhA), a pyruvate formate-lyase gene (pfl) and a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene (ppc) involved in the immobilization of CO2 in a metabolic pathway of producing succinic acid; and a method for producing succinic acid, which is characterized by the culture of the above mutants in anaerobic conditions. The inventive bacterial mutants have the property of producing succinic acid at high concentration while producing little or no organic acids, as compared to the prior wild-type strains of producing various organic acids. Thus, the inventive bacterial mutants are useful as strains for the industrial production of succinic acid.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
5-amino levulinic acid (ALA) high-yield strain and preparation method and application thereof
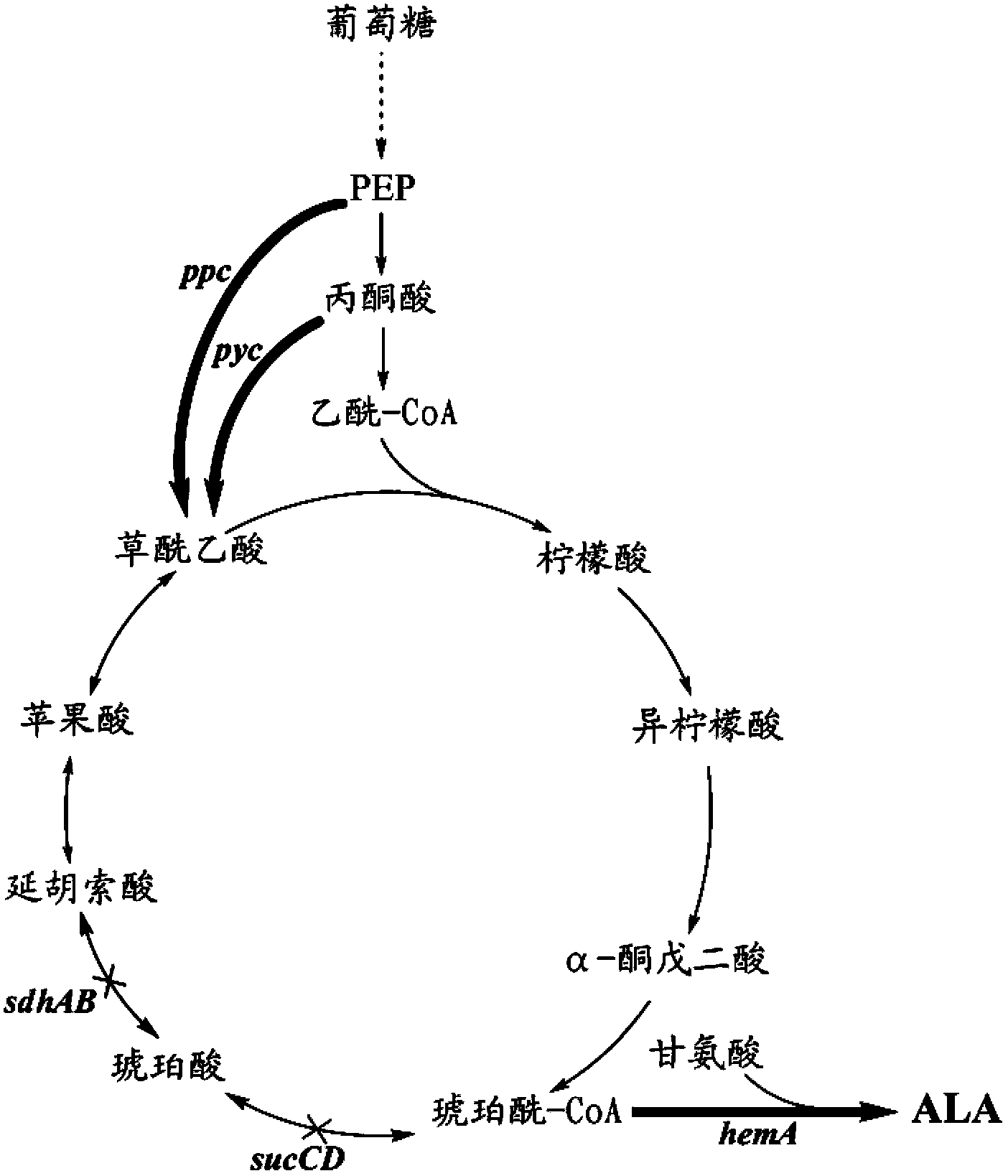
A method for constructing an ALA production bacterial strain, the method enhances the activity of related enzymes promoting the synthesis of oxaloacetate and in the 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) production bacterial strain, or introducing exogenous related enzymes promoting the synthesis of oxaloacetate, such as phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase or pyruvate carboxylase, and / or reducing the activity of related enzymes in the downstream metabolic pathway of succinyl coenzyme A in the bacterial strain, such as succinyl coenzyme A synthetase or succinate dehydrogenase, and / or reducing the activity of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylated kinase and / or malic enzyme. An ALA high-yield bacterial strain constructed by utilizing the method, and method for utilizing the bacterial strain to prepare ALA.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Genes for enhancing drought and heat tolerance in plants and methods of use
ActiveUS20180371487A1Improve drought toleranceImprove heat tolerancePlant peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseBiotechnology
The present disclosure provides methods for increasing drought resistance and heat resistance of a plant. The methods encompass expression of at least one heat shock protein (HSP) from the group consisting of HSP40, HSP60 or HSP70 together with a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC) comprising an aspartic acid (D) at a position that corresponds to the position 509 of SEQ ID NO: 4, in the plant. In comparison to a plant not manipulated in this manner, the disclosed, genetically-modified, plants display improved drought resistance and heat resistance. Also provided are plants that can be obtained by the method according to the invention, and nucleic acid vectors to be used in the described methods.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
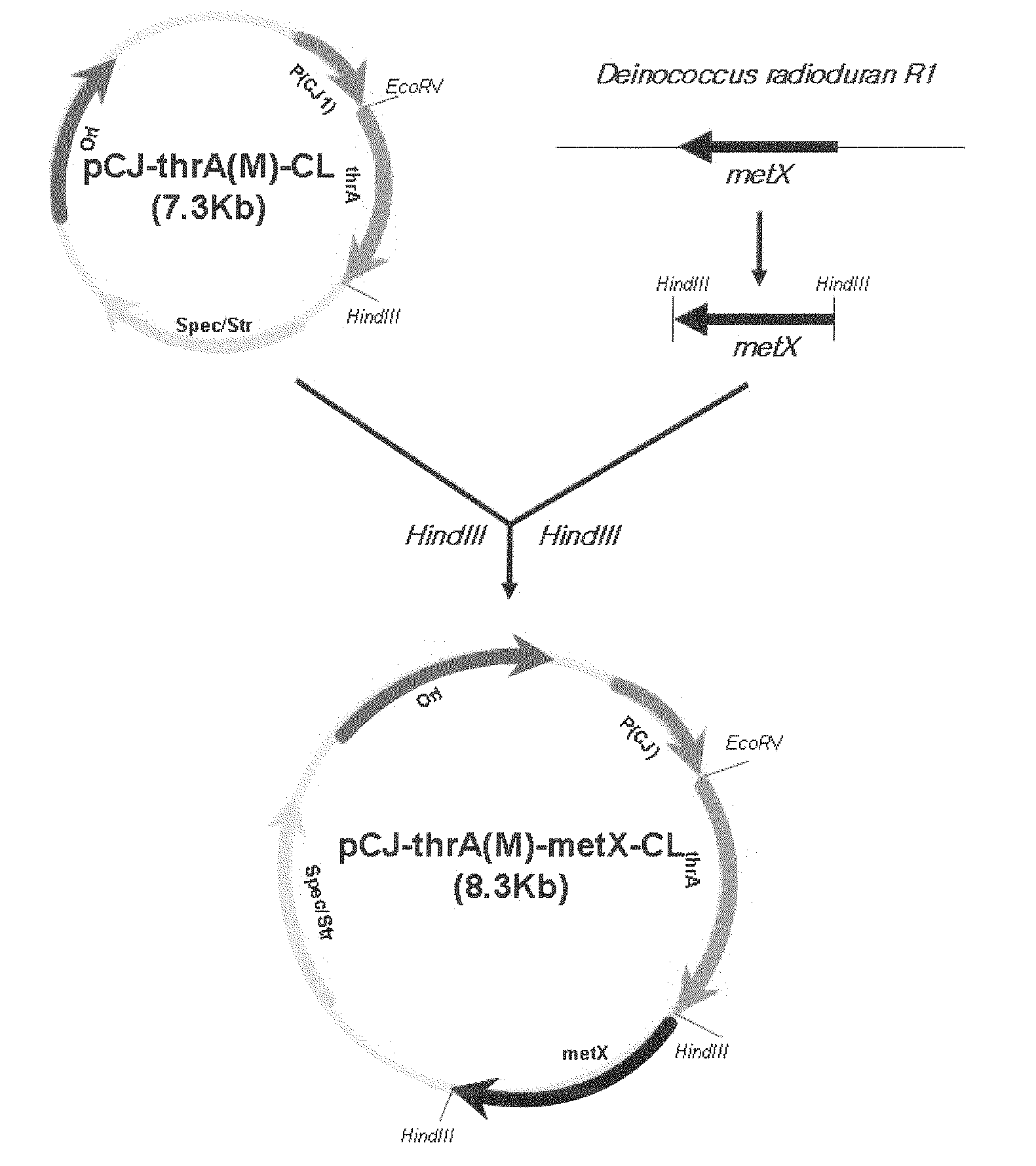
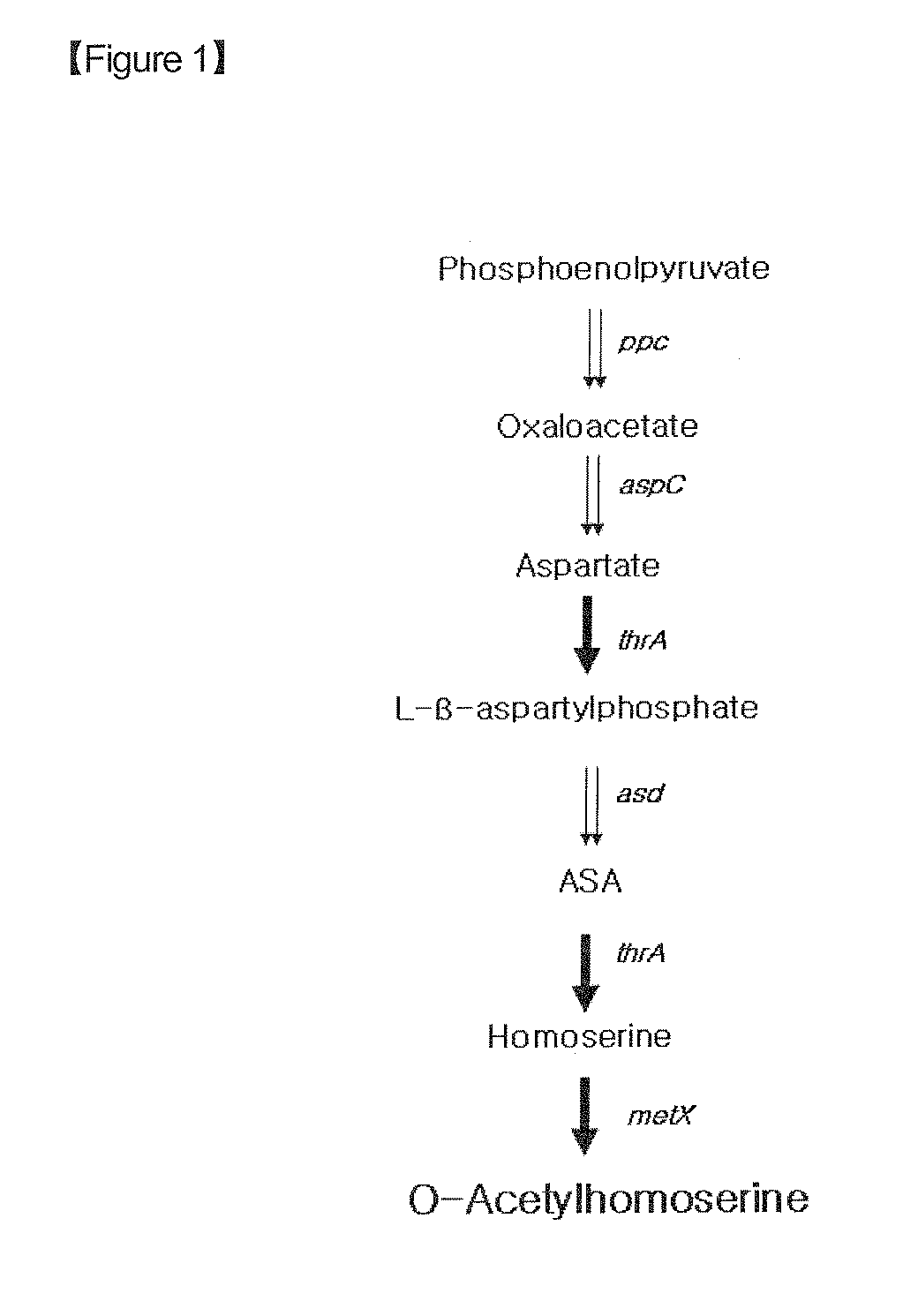
Microorganism producing o-acetyl-homoserine and the method of producing o-acetyl-homoserine using the microorganism
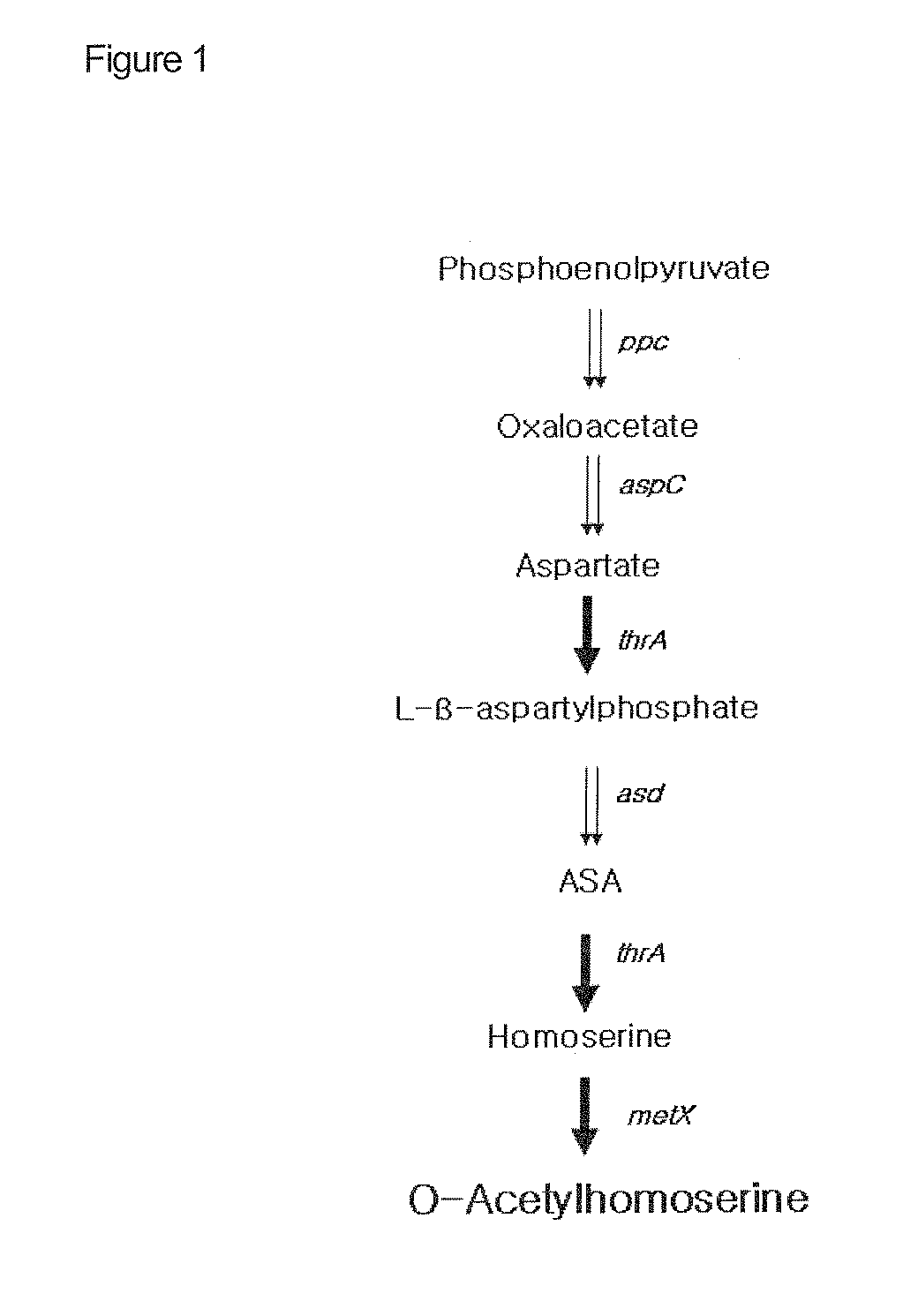
Disclosed is a strain of Escherichia sp., capable of producing O-acetyl homoserine in high yield, with the introduction and enhancement therein of the activity of: homoserine acetyl transferase, aspartokinase and homoserine dehydrogenase; and at least one enzyme selected from a group consisting of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, aspartate aminotransferase and aspartate semi-aldehyde dehydrogenase. Also, a method of producing O-acetyl homoserine using the strain is provided.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
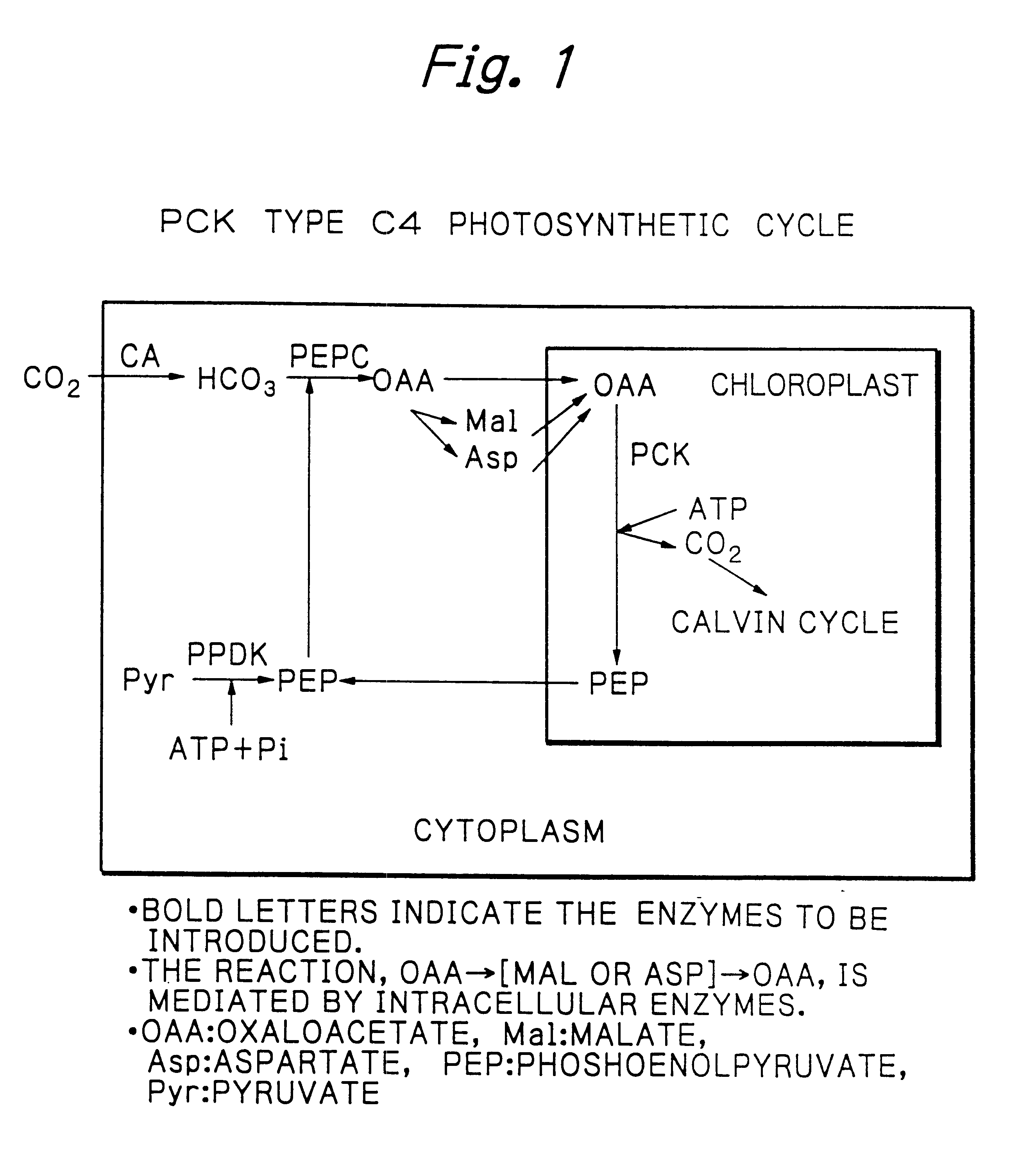
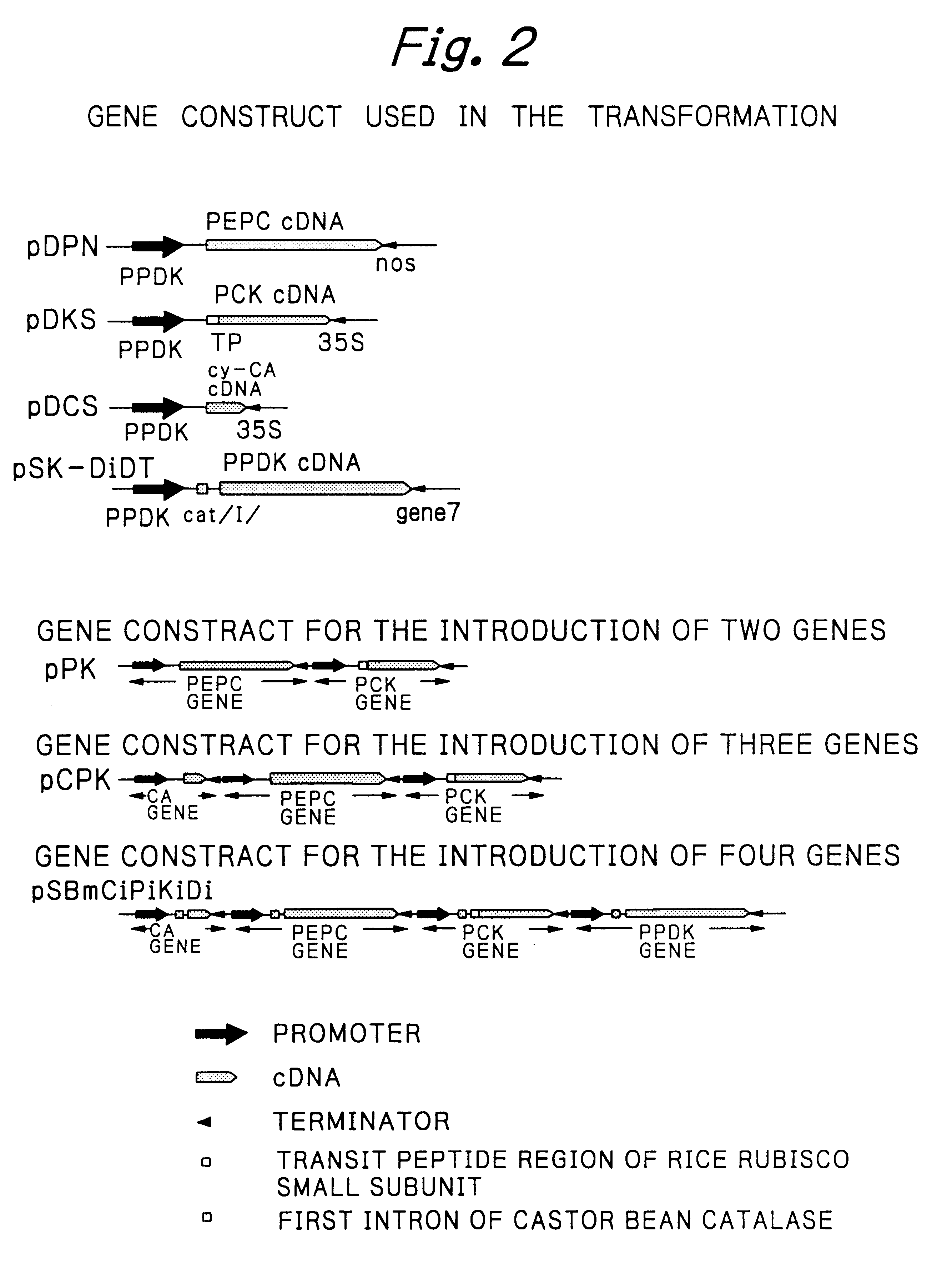
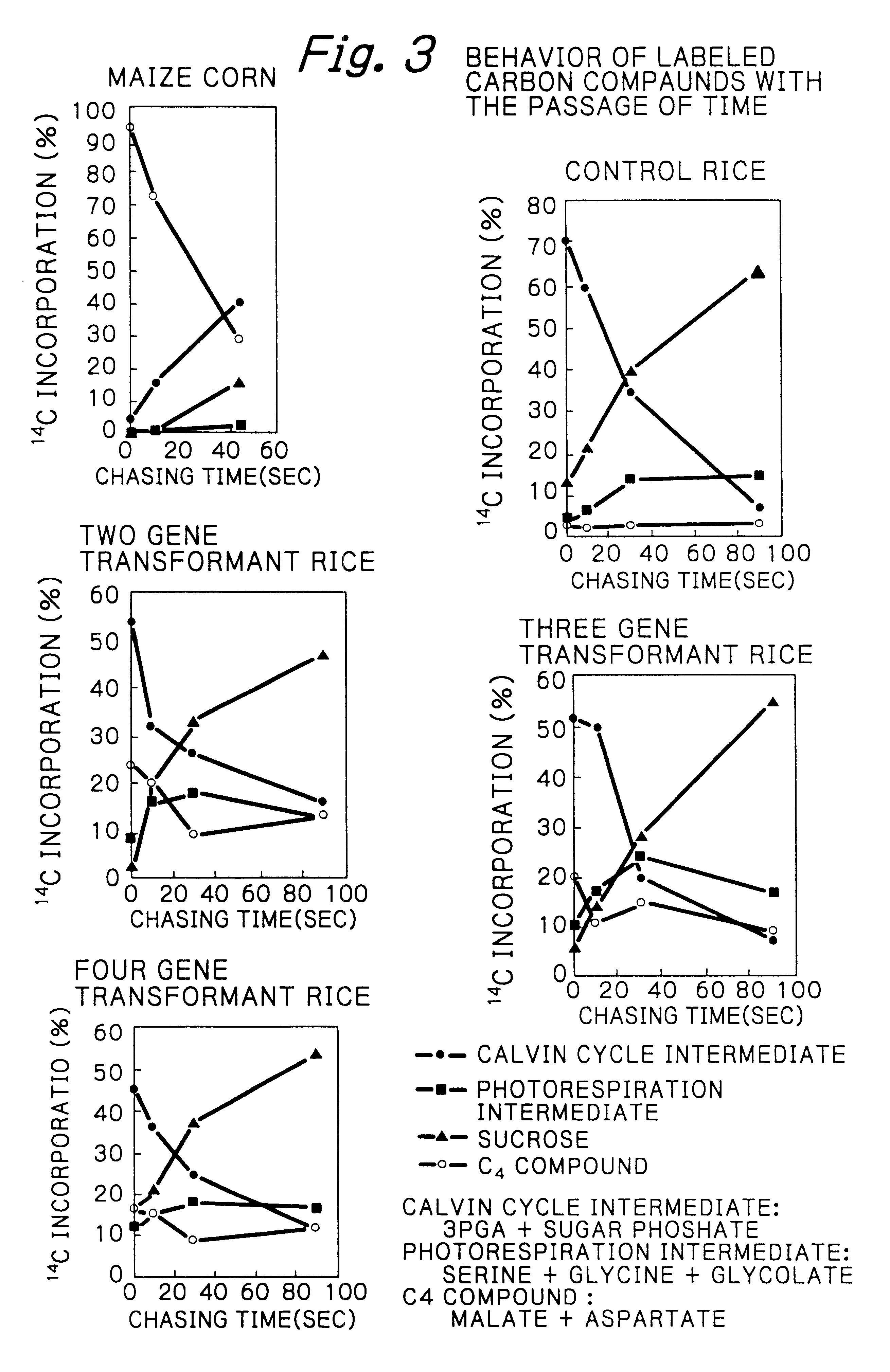
Rice plants transformed to provide a PCK-type C4 cycle and methods of making
The present invention relates a method for transforming a rice plant to provide it with a C4 photosynthetic pathway by way of the introduction of some genes participating in a C4 photosynthetic pathway. To this end, the method of the invention comprises introducing a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC) and a gene coding for a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PCK) which has been connected with a DNA fragment coding for a transit peptide into a rice plant.
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC
Rumen bacteria variants and process for preparing succinic acid employing the same
ActiveUS7470530B2High yieldSugar derivativesBacteriaHigh concentrationPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
Provided are novel rumen bacterial mutants resulted from the disruption of a lactate dehydrogenase gene (ldhA) and a pyruvate formate-lyase gene (pfl) from rumen bacteria; a novel bacterial mutant (Mannheimia sp. LPK7) having disruptions of a ldhA, a pfl,a phosphotransacetylase gene (pta), and a acetate kinase gene (ackA); a novel bacterial mutant (Mannheimia sp. LPK4) having disruptions of a ldhA, a pfl, and a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene (ppc) involved in the immobilization of CO2 in a metabolic pathway of producing succinic acid; and a method for producing succinic acid, characterized by culture of the above mutants in anaerobic conditions. The bacterial mutants have the property of producing succinic acid at high concentration while producing little or no organic acids, as compared to the prior wild-type strains of producing various organic acids. Thus, the bacterial mutants are useful as strains for the industrial production of succinic acid.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Microorganism producing O-acetyl-homoserine and the method of producing O-acetyl-homoserine using the microorganism
Disclosed is a strain of Escherichia sp., capable of producing O-acetyl homoserine in high yield, with the introduction and enhancement therein of the activity of: homoserine acetyl transferase, aspartokinase and homoserine dehydrogenase; and at least one enzyme selected from a group consisting of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, aspartate aminotransferase and aspartate semi-aldehyde dehydrogenase. Also, a method of producing O-acetyl homoserine using the strain is provided.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Escherichia coli gene engineering bacterium and method for producing L-threonine by using escherichia coli gene engineering bacterium
ActiveCN106867952AIncrease productionImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseEscherichia coli
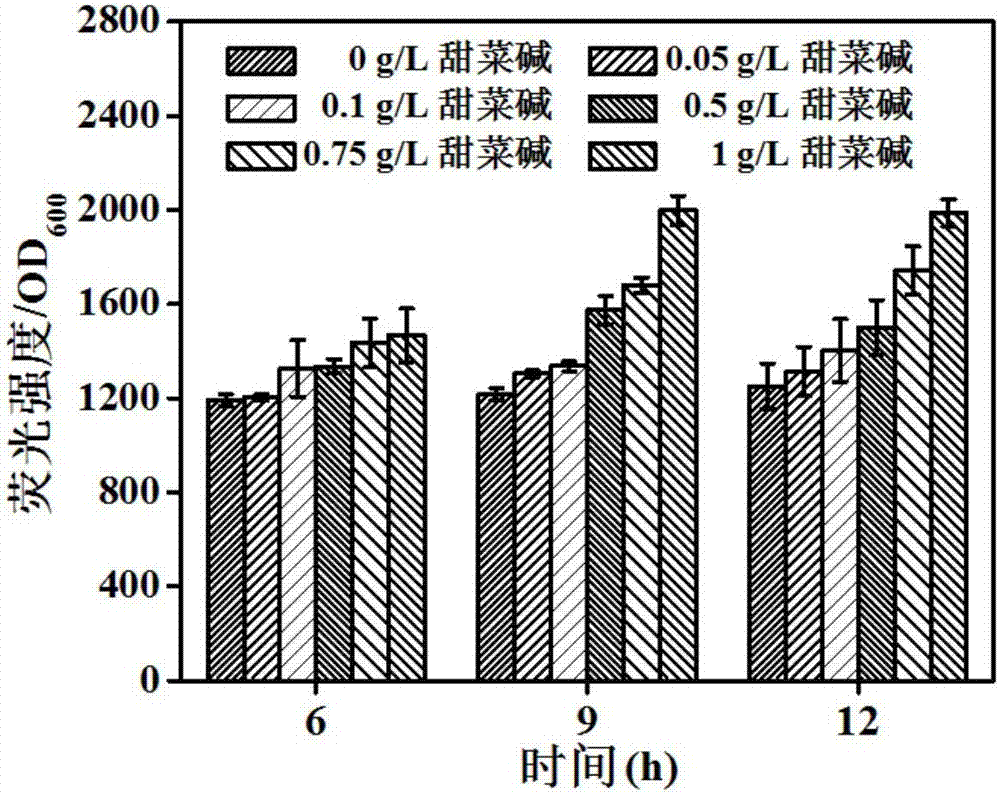
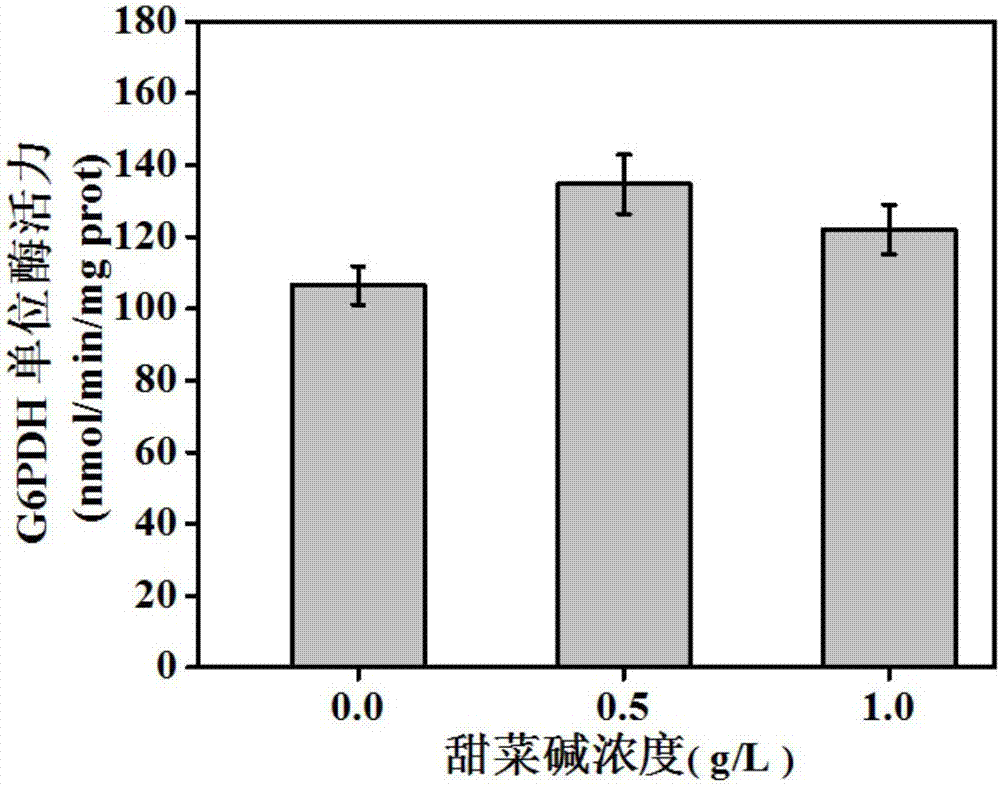
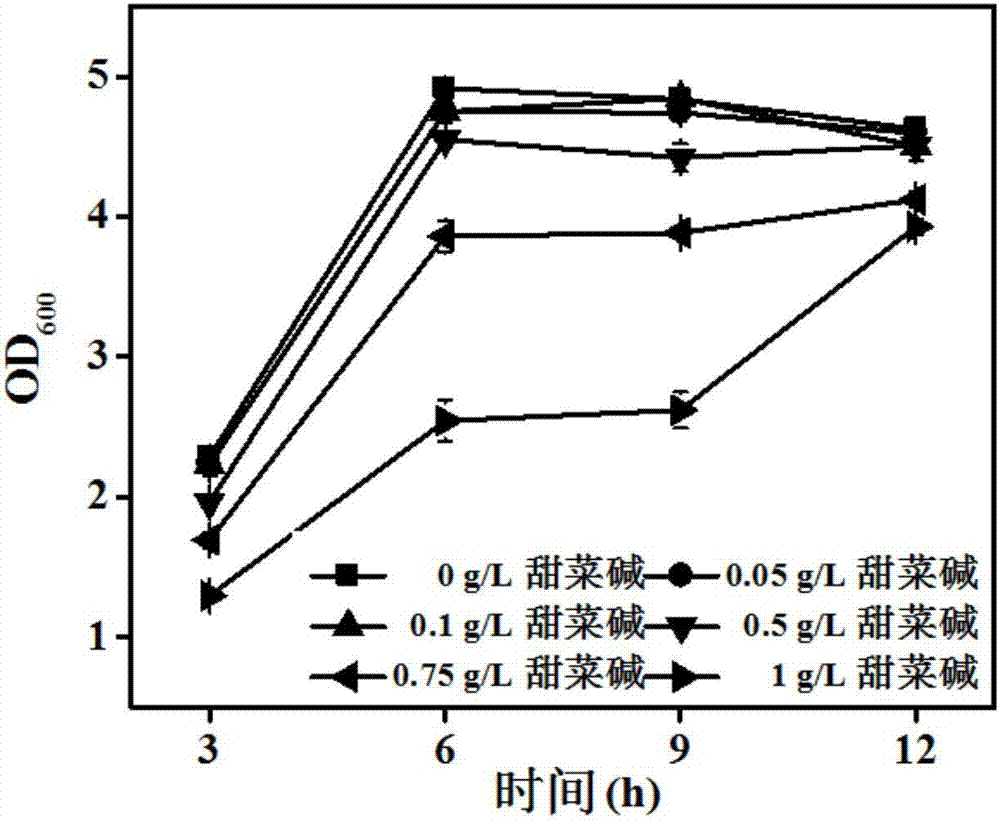
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, and particularly relates to an escherichia coli gene engineering bacterium and a method for producing L-threonine by using the escherichia coli gene engineering bacterium. The gene engineering bacterium is characterized in that a promoter P<ppc> of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene (ppc) of an initial strain is replaced into a promoter P<zwf> of 6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene (zwf), so that the goal of regulating the L-threonine production capacity by glycine betaine is achieved. In the fermentation process, the glycine betaine is added, so that the L-threonine yield through shaking flask fermentation can reach 50 to 55g / L; the 5L fermentation tank yield reaches 120 to 150g / L; the saccharic acid conversion rate reaches 59 to 61 percent.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Corynebacterium glutamicum strain for production of 5-aminolevulinic acid and construction and application of corynebacterium glutamicum strain
InactiveCN106047916AIncrease productionHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylasePhosphoric acid
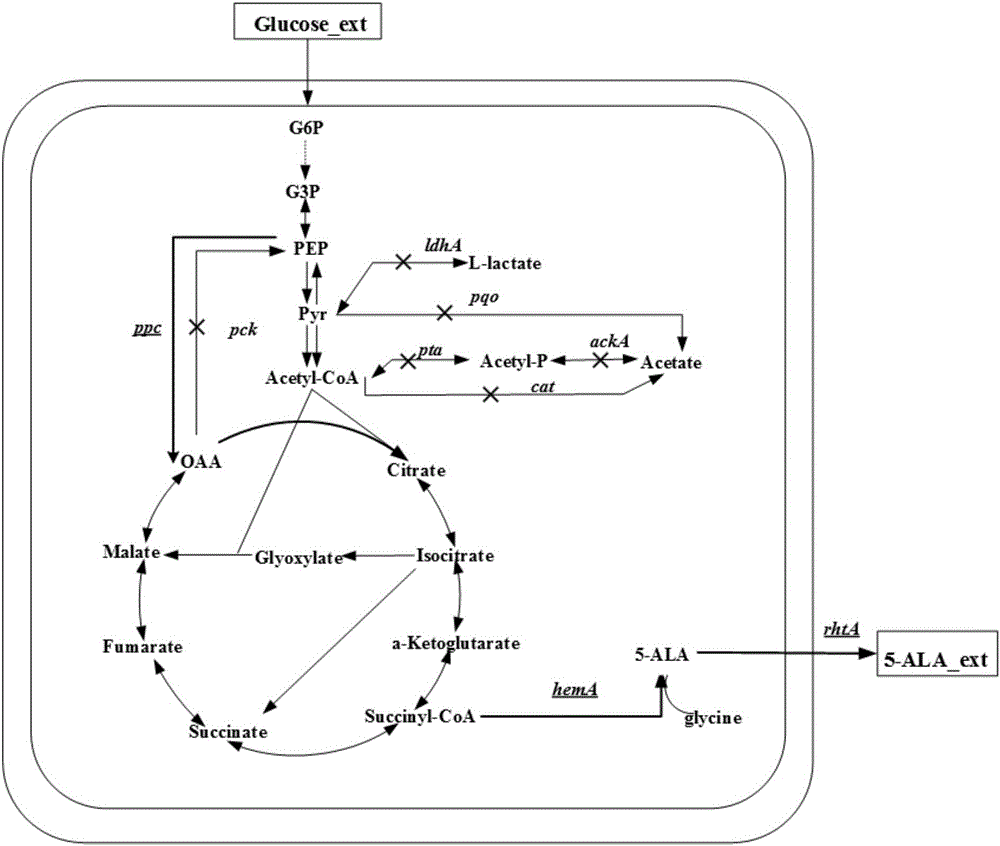
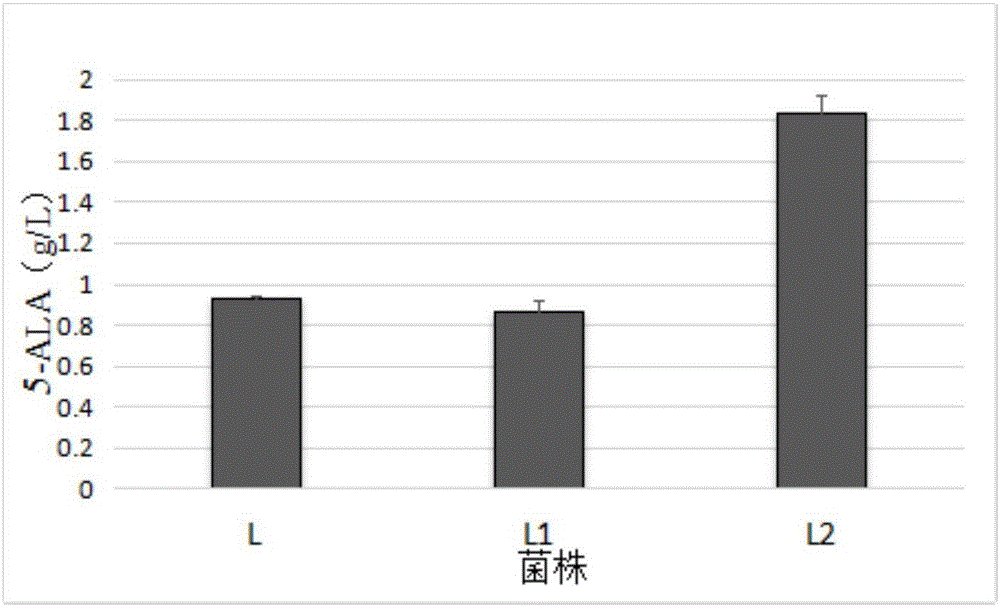
The invention discloses a corynebacterium glutamicum strain for production of 5-aminolevulinic acid and construction and application of corynebacterium glutamicum strain. A construction method includes: (1) deleting a lactic dehydrogenase coding gene 1dhA and acetic acid generation genes pta-ackA, pqo and cat in corynebacterium glutamicum to obtain a strain named CB4; inserting a strong sod promoter in front of a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase coding gene ppc in the strain CB4 to obtain a strain CB5; deleting a gene pck in the strain CB5 to obtain a strain CB6; (2) transferring plasmid pXA and plasmid pEP2<tuf>-rhtA into the strain CB6. The strain constructed according to the method is capable of generating 2.78g / L 5-aminolevulinic acid in a culture medium with 10g / L glucose serving as a carbon source, which lays a foundation for subsequent continuous feeding of a fermentation tank to increase yield of the 5-aminolevulinic acid.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Recombinant bacteria for increasing yield of succinic acid and construction method thereof
ActiveCN103131663AIncrease productionImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseEscherichia coli
The invention discloses recombinant bacteria for increasing the yield of succinic acid and a construction method thereof. The recombinant bacteria disclosed by the invention are obtained so as to increase the enzyme activities of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PPC) and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PCK) in escherichia coli or mutant strains of the escherichia coli. Experiments prove that the expressions of ppc and pck genes of the E.coli are respectively regulated and controlled by using constitutive controlling elements with different expression intensity, and the law between the enzyme activities of the PPC and the PCK and the succinic acid production is explored; and on the basis, the PPC and PCK catalyzing enzymes are simultaneously used for giving play to respective catalyzing advantages through coordinated regulation of the ppc and pck genes of the E.coli, so that the yield and the conversion rate of the E.coli succinic acid are obviously increased.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Genetic engineering bacterium for producing succinic acid and method for producing succinic acid by fermentation of genetic engineering bacteria
InactiveCN102399738AImprove biosynthetic abilityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseEscherichia coli
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and relates to a genetic engineering bacterium for producing succinic acid and a method for producing the succinic acid by fermentation, in particular to a recombinant strain which is grown by utilizing xylose efficiently and is used for producing the succinic acid and a method for producing the succinic acid by utilizing the fermentation of the strain. The genetic engineering strain for producing the succinic acid belongs to the class of Escherichia coli BA204, and the conservation register number is CCTCC No:M2011207. A construction process comprises the steps of: inactivating or removing phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, and over-expressing phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylation kinase, so that the recombinant Escherichia coli can be grown by utilizing xylose metabolism to improve the synthetic efficiency of the succinic acid is improved substantially. In the fermentation method, a two-stage fermentation mode is adopted, wherein in an aerobic stage, biomass is improved; and in an anaerobic stage, acid is produced by the fermentation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Corynebacterium glutamicum for producing high-yield succinic acid by utilizing straw hydrolysate, and construction and applicaitons
InactiveCN107012161AHigh final concentrationHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesTransketolasePhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
The invention discloses a corynebacterium glutamicum for producing high-yield succinic acid by utilizing straw hydrolysate, and a construction and applications. The method comprises the following steps: (1) knocking out side products acetic acid and lactic acid formation pathway related genes from corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032, and introducing anaplerotic pathway phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase and pyruvate carboxylase and phosphopentose pathway transketoaldehydase and transketolase on a strong promoter overexpression chromosome; and introducing xylose transport gene on the chromosome; and (2) expressing pyruvate carboxylase, succinic acid export protein and citrate synthase as well as xylose isomerase and xylulokinase on the corynebacterium glutamicum obtained in the step (1). 98.6gL<-1> of succinic acid can be anaerobically produced after 22.5h by utilizing mixed glucose and xylose in straw hydrolysate, with the yield of 0.98g succinic acid / g total sugar. The final concentration, yield and productivity of succinic acid achieve higher level, and the corynebacterium glutamicum has good industrial potential.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Carrier for enhancing aluminum-tolerance of plant, and method for establishing the same
InactiveCN102199620ALarge amount of synthesisPromote growthVector-based foreign material introductionPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseNicotiana tabacum
The invention provides a carrier for enhancing aluminum-tolerance of a plant, and a method for establishing the same. The carrier is a plant expression vector having photoinduction promoters and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC) genes. The method for establishing the carrier comprises the following steps: searching for the sequence of the full length gene of Synechococcus vulcanus PEPC in GenBank and designing a pair of primers with sequences as described in the specification; recovering and purifying PEPC full length gene segments and connecting the segments to a pUCm-T vector; establishing an entry vector pENTER*-PrbcS-PEPC; establishing a plant expression vector pH2-35S-PrbcS-PEPC. In the invention, the activity of citrate synthase of tabacoo with transgenic PEPC and CS genes is 2.4 to 2.6 times that of wild tobacco, and the activity of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase of such tabacco is 2.2 to 2.4 times that of wild tobacco. The special-purpose carrier provided in the invention can exert great influence on the improvement of aluminum-tolerance of a plant, and particularly, can significantly promote aluminum-tolerance of plants grown in acid red soil in southern China, thereby providing a novel approach for variety improvement of plants.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Method for knocking out pckA to promote synthesis of acetylglucosamine through bacillus subtilis
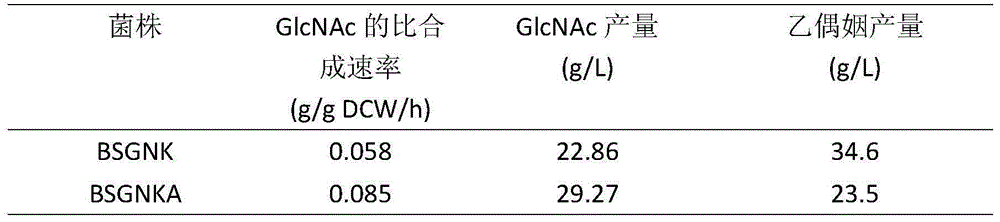
ActiveCN105238724AEasy to buildEasy to useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseTricarboxylic acid
The invention discloses a method for knocking out pckA to promote synthesis of acetylglucosamine through bacillus subtilis and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. The method comprises the steps that BSGNK-PxylA-glmS-P43-GNA1 serves as original strains, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (pckA) genes are knocked out through homologous recombination, the reaction that enolphosphopyruvate is converted into oxaloacetic acid in host bacterium cells is blocked, the carbon flux flowing to a tricarboxylic acid cycle is reduced, and accumulation of acetylglucosamine is promoted. In the process that a composite culture medium is used for fermentation, the acetylglucosamine yield of recombination bacillus subtilis with pckA knocked out reaches 29.27 g / L and is increased by 28.1% compared with that of control strains. The method lays a foundation for transforming bacillus subtilis to produce acetylglucosamine in metabolic engineering.
Owner:JIANGSU HEVI BIOTECH CO LTD
Novel rumen bacteria variants and process for preparing succinic acid employing the same
The present invention relates to novel rumen bacterial mutants resulted from the disruption of a lactate dehydrogenase gene (ldhA) and a pyruvate formate-lyase gene (pfl) (which are involved in the production of lactic acid, formic acid and acetic acid) from rumen bacteria; a novel bacterial mutant (Mannheimia sp. LPK7) having disruptions of a lactate dehydrogenase gene (ldhA), a pyruvate formate-lyase gene (pfl), a phosphotransacetylase gene (pta), and a acetate kinase gene (ackA); a novel bacterial mutant (Mannheimia sp. LPK4) having disruptions of a lactate dehydrogenase gene (ldhA), a pyruvate formate-lyase gene (pfl) and a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene (ppc) involved in the immobilization of CO2 in a metabolic pathway of producing succinic acid; and a method for producing succinic acid, which is characterized by the culture of the above mutants in anaerobic conditions. The inventive bacterial mutants have the property of producing succinic acid at high concentration while producing little or no organic acids, as compared to the prior wild-type strains of producing various organic acids. Thus, the inventive bacterial mutants are useful as strains for the industrial production of succinic acid.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
L-threonine high-yield genetic engineering strain and application thereof
InactiveCN107699525AReduce generationIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPyruvate carboxylaseBiotechnology
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and particularly relates to an L-threonine high-yield genetic engineering strain and application thereof. The engineering strain isbuilt by using escherichia coli as host cells through knocking out pka genes of coding lysine acetyltransferase and TCA cyclical transcription regulatory factor arcA gene and simultaneously overpressing phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase coding gene ppc. After the engineering strain is used for fermenting and producing L-threonine; the yield can be improved by 8.97 percent.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Corynebacterium glutamicum engineering bacterium for highly producing succinic acid and building method thereof
InactiveCN103509747AIncrease productionReduce generationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSaccharic acidPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
The invention discloses a corynebacterium glutamicum engineering bacterium for anaerobic conversion to produce succinic acid, and a building method and application thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. A pyruvate carboxylase gene of the corynebacterium glutamicum and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from escherichia coli are cloned to corynebacterium glutamicum (ATCC13032); a lactate dehydrogenase gene of the corynebacterium glutamicum is knocked out in a homologous recombination manner. By adopting the lactic dehydrogenase-defective corynebacterium glutamicum for coexpression of a carboxylase gene, anaerobic production of succinic acid is carried out in a cell reutilization manner, so that the yield of succinic acid can be greatly improved; the yield can be up to 75g / L; the conversion rate of saccharic acid is 75%; the corynebacterium glutamicum engineering bacterium has a good application prospect; a fermentation model, especially a fermentation model for cell reutilization is built according to the optimum condition for biological transformation of succinic acid; the acid-production performance in repeated batch transformation process of cells can be basically kept stable.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Corynebacterium glutamicum recombinant strain for producing 5-aminolevulinic acid
InactiveCN106434513AEasy to transportIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseAminolevulinic acid synthase
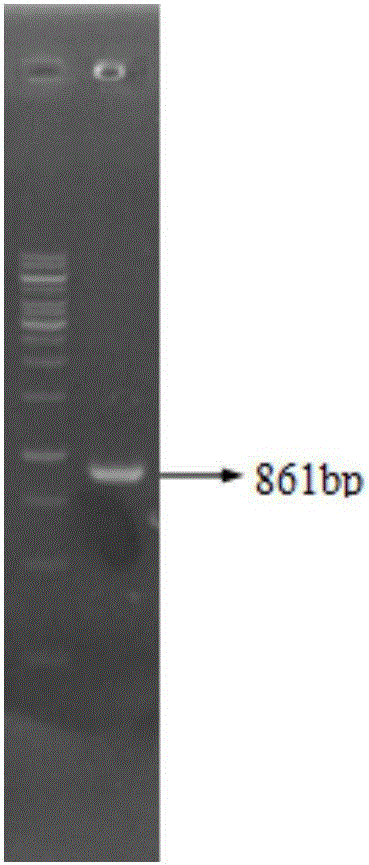
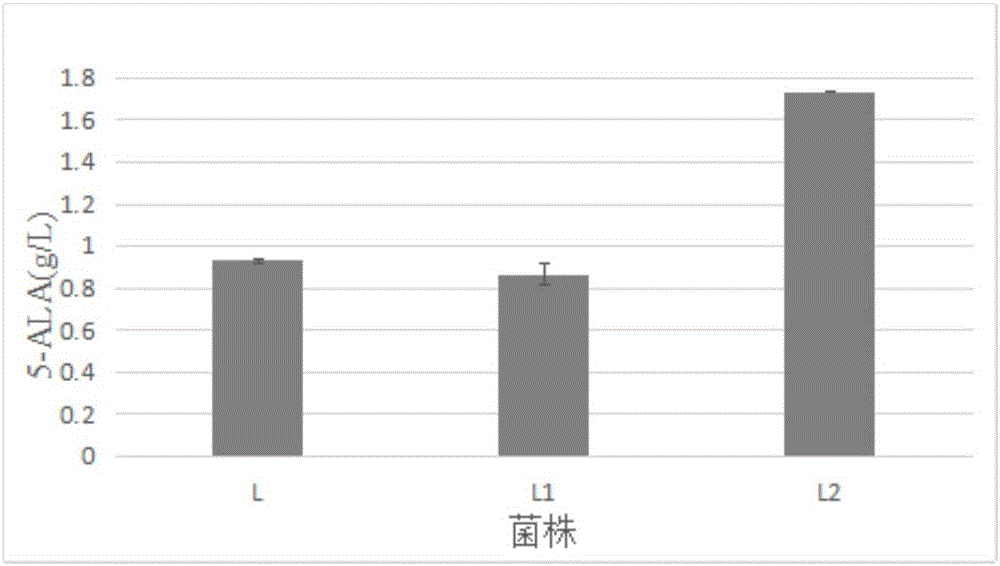
The invention discloses a corynebacterium glutamicum recombinant strain for producing 5-aminolevulinic acid. An establishing method comprises steps as follows: (1) a lactic dehydrogenase encoding gene ldhA and acetic acid producing genes pta-ackA, pqo and cat are knocked out from corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 1303, and a strain CG4 is obtained; an sod promoter is inserted in front of a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase encoding gene in the CG4, and a strain CG5 is obtained; a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase encoding gene pck is knocked out from the CG5, and a strain CG6 is obtained; (2) plasmids of an overexpressed 5-aminolevulinic acid synthase gene are transferred into the CG6, and a recombinant strain L is obtained; (3) 5-aminolevulinic acid transport protein plasmids are transferred into the L. The recombinant strain can promote 5-aminolevulinic acid to be transported outside corynebacterium glutamicum cells, and the yield of 5-aminolevulinic acid is 112.3% higher than that of a contrast strain.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for L-threonine production
InactiveUS7011961B2High expressionEliminate the problemSugar derivativesBacteriaPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseMicroorganism
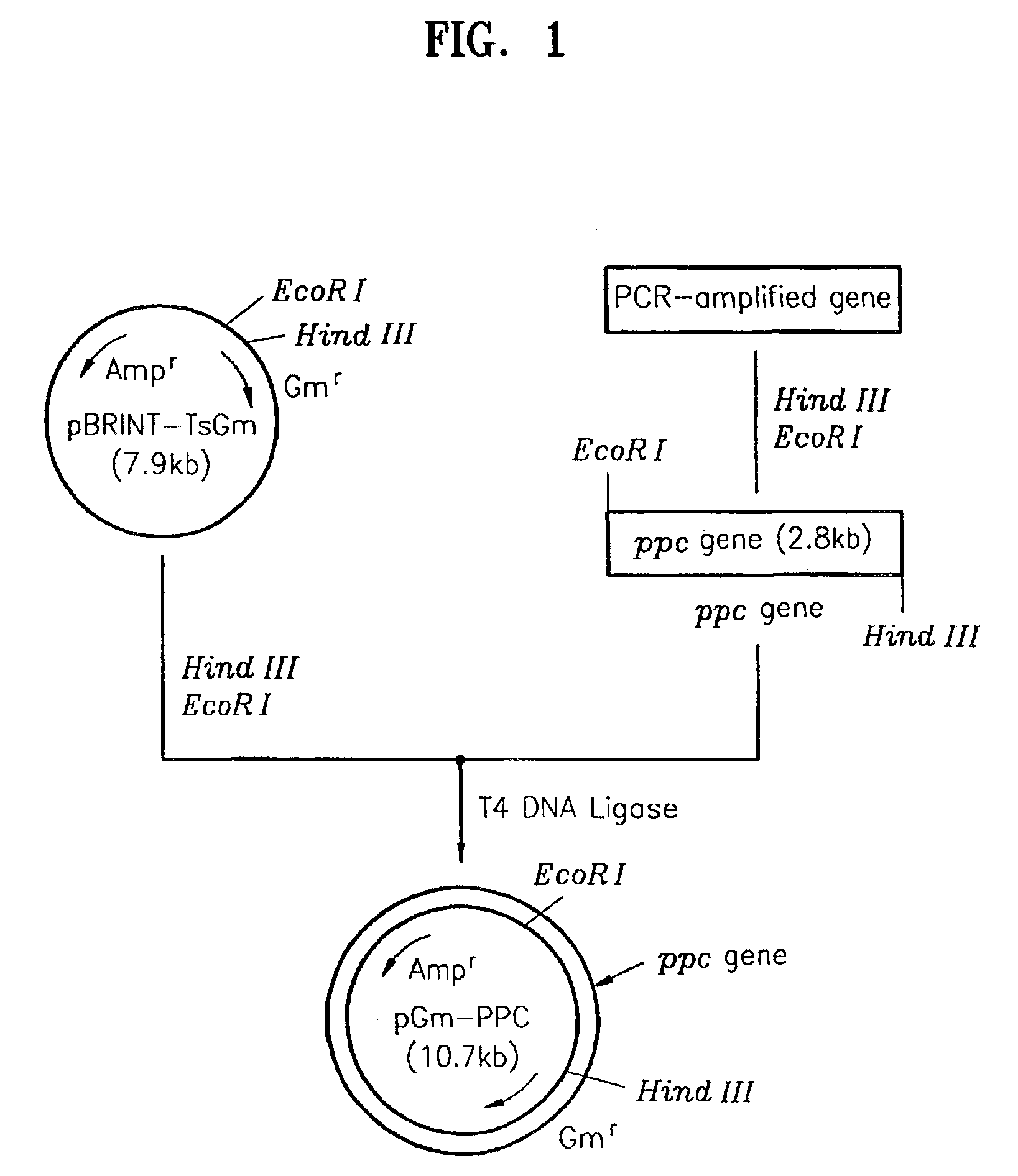
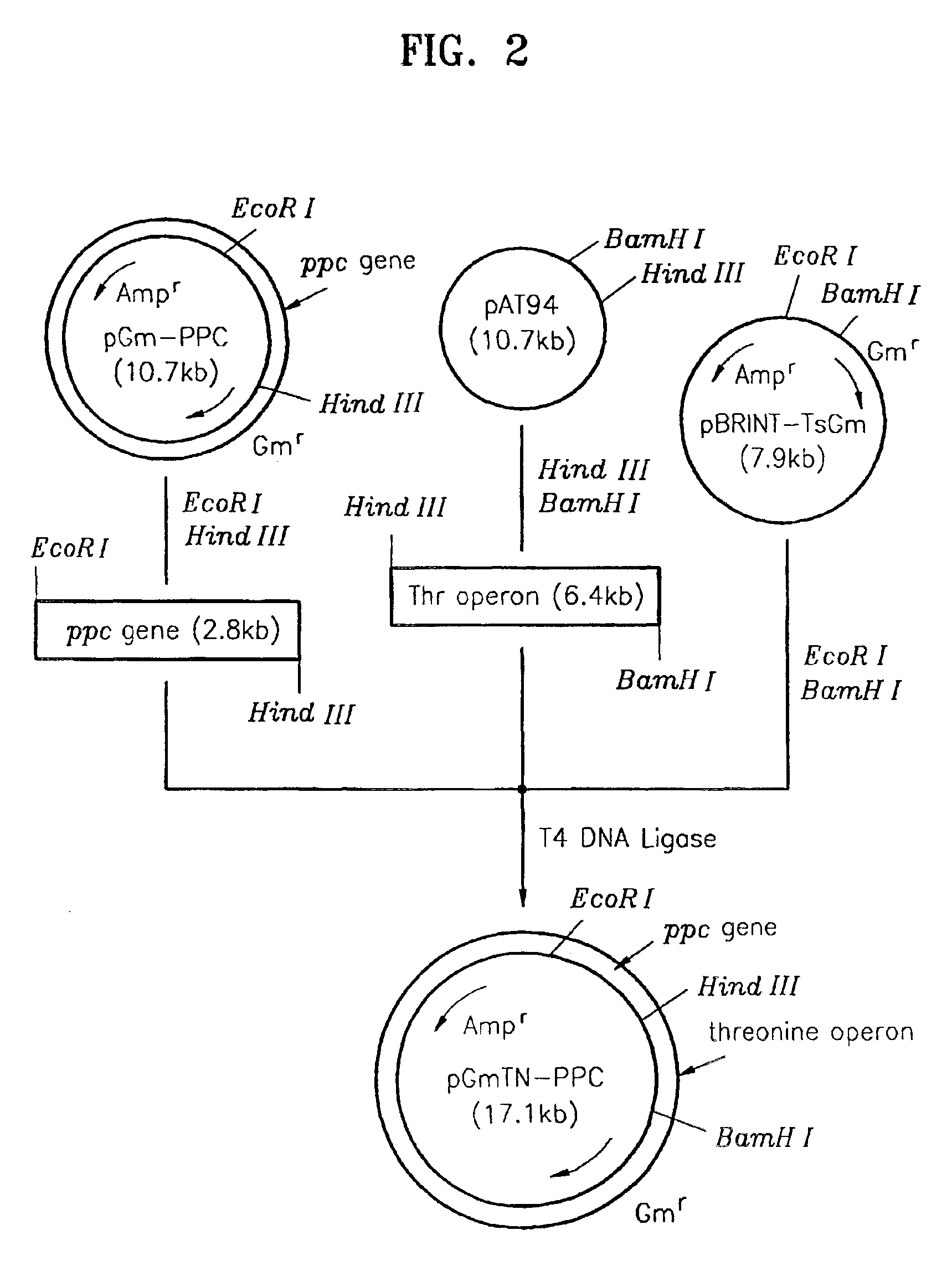
A method of producing L-threonine using a microorganism is provided, one or more copies of each of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene and the threonine operon are additionally intedgrated into a particular site of the chromosomal DNA of the microorganism, whiel its inherent phophoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene and threonine operon remain.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Genetic engineering strain for producing succinic acid by utilizing glucose and acidogenic fermentation method thereof
InactiveCN102533626AOvercomes the inability to utilize glucoseBacteriaRecombinant DNA-technologyPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseEscherichia coli
The invention belongs to the field of biology engineering technology, and relates to a genetic engineering strain for producing succinic acid by utilizing glucose and an acidogenic fermentation method of the genetic engineering strain. The genetic engineering strain for producing succinic acid by utilizing glucose is named as Escherichia coli BA205 and the preservation number is registered as CCTCC No.M2011447. In the construction process, Escherichia coli which is short of lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) gene and Pyruvate formate-lyase (PFL) gene activity is mainly used as an original strain; phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PPC) gene is removed by utilizing a homologous recombination technology; and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase and nicotinic acid phosphoribosyl transferase are excessively co-expressed; therefore the synthesis efficiency of succinic acid is greatly increased. In the fermentation method, a two-stage fermentation manner is adopted, the biomass is improved in an aerobic stage and the acidogenic fermentation is carried out in an anaerobic stage.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
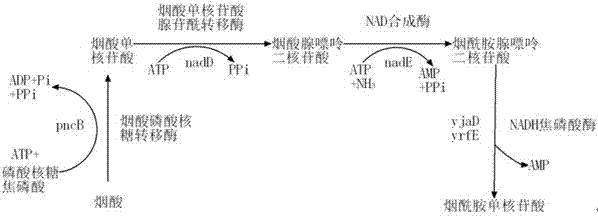
Process for the production of beta-lysine
InactiveCN101400799AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseTransketolase
Process for the production of -lysine by constructing a recombinant microorganism which has a deregulated lysine 2,3-aminomutase gene and at least one deregulated gene selected from the group (i) which consists of aspartokinase, aspartatesemialdehyde dehydrogenase, dihydrodipicolinate synthase, dihydrodipicolinate reductase, tetrahydrodipicolinate succinylase, succinyl-amino-ketopimelate transaminase, succinyl-diamino-pimelate desuccinylase, diaminopimelate epimerase, diaminopimelate dehydrogenase, arginyl-tRNA synthetase, diaminopimelate decarboxylase, pyruvate carboxylase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, transketolase, transaldolase, 6-phosphogluconolactonase, fructose 1,6-biphosphatase, homoserine dehydrogenase, phophoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, succinyl-CoA synthetase, methylmalonyl-CoA mutase, provided that if aspartokinase is deregulated as gene (i) at least a second gene (i) other than aspartokinase has to be deregulated, and cultivating said microorganism.
Owner:BASF SE
Process for prodn. of L-Thr
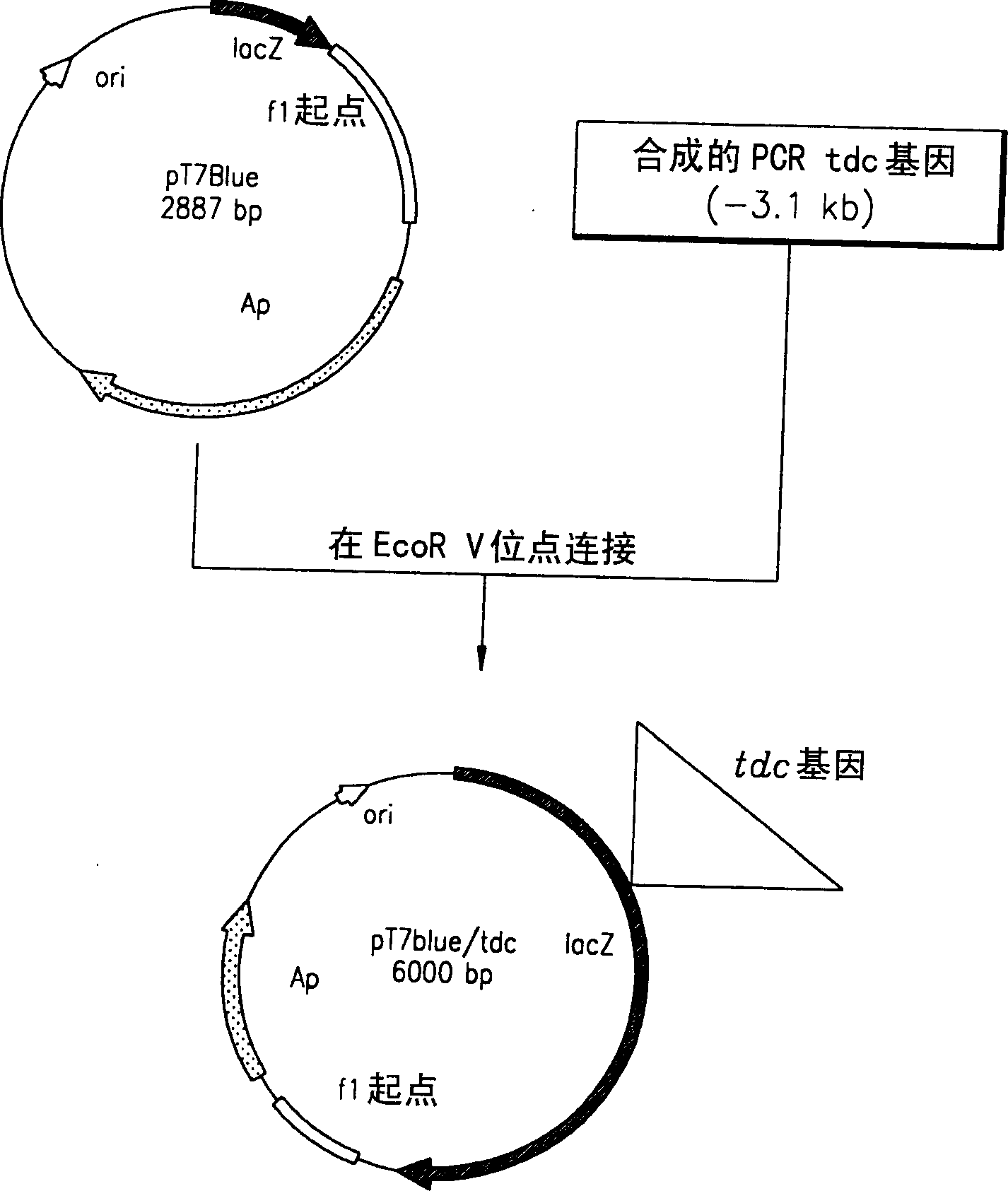
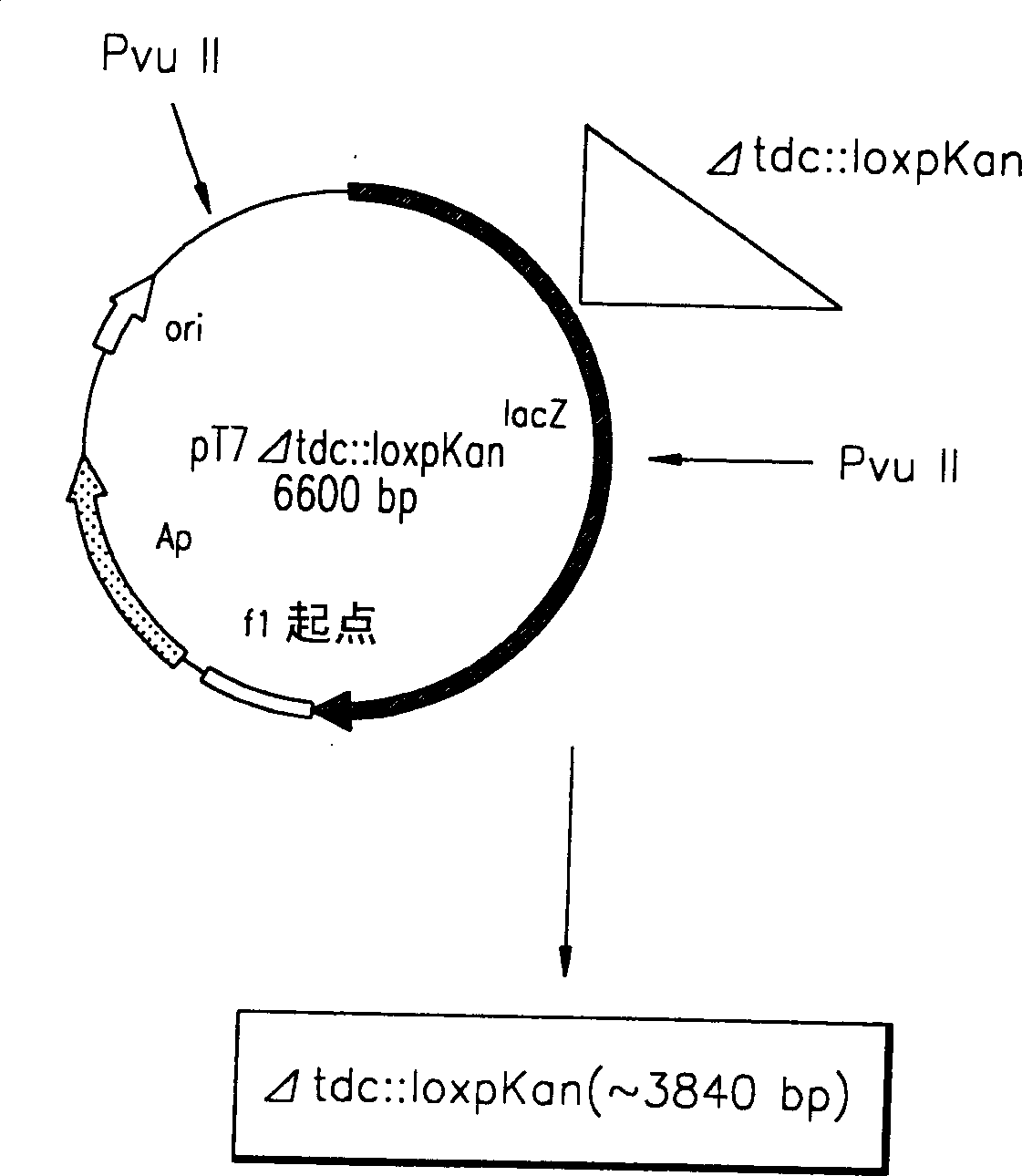
A method for producing L-threonine using a microorganism is provided. In the method, the threonine dehydratase (tdc) gene existing in the genomic DNA of the microorganism is partially deactivated using a recombination technique. For a microorganism strain with enhanced activity of threonine operon-containing enzymes and the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (ppc) gene, the tdc gene engaged in one of the four threonine metabolic pathways is specifically deactivated, thereby markedly increasing the yield of L-threonine.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Carbon dioxide measurement kit
InactiveCN103558370AEasy to useEasy to operateBiological testingFlavin adenine dinucleotidePhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
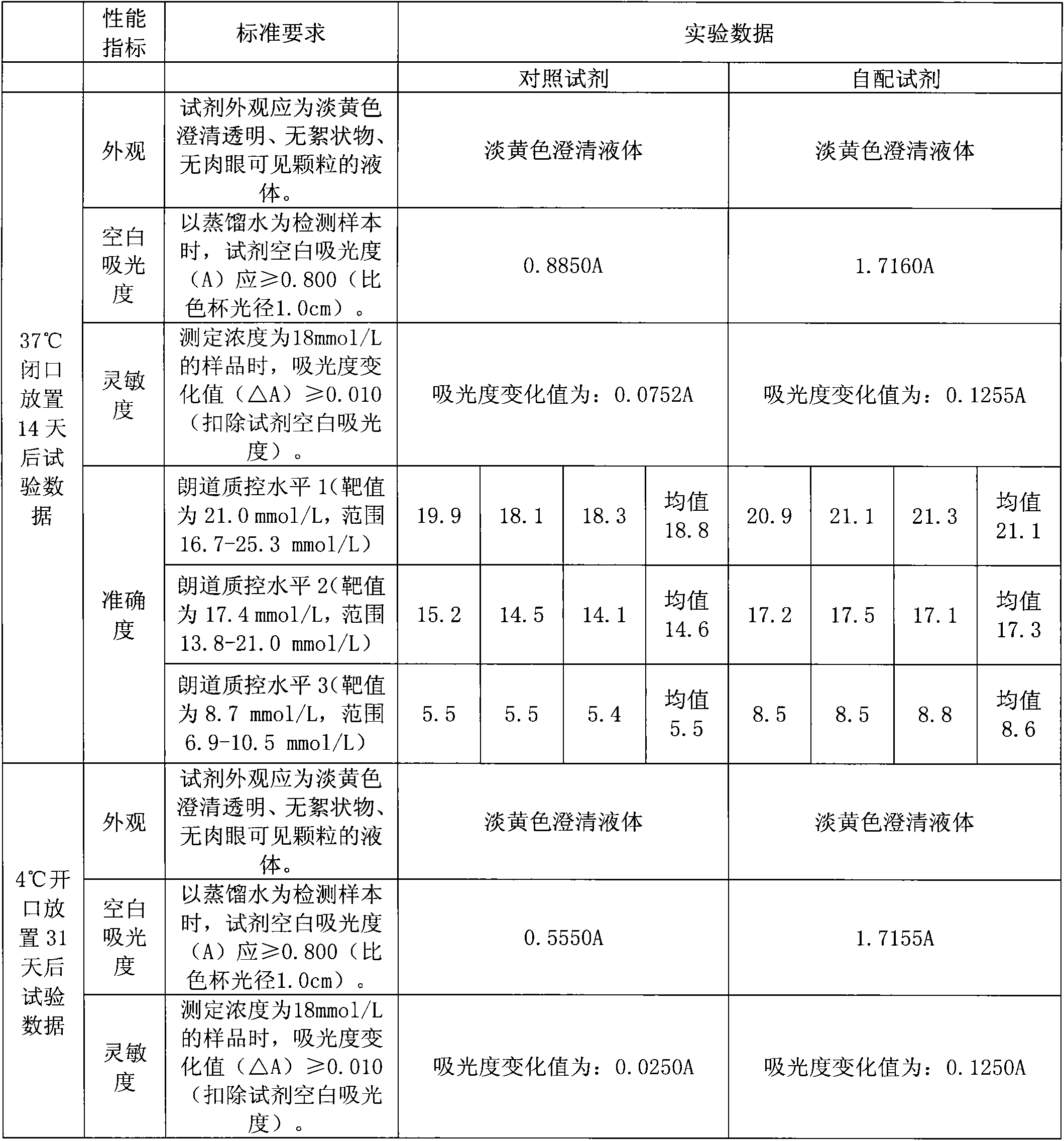
The invention provides a carbon dioxide measurement kit. The carbon dioxide measurement kit mainly comprises the following components: 50 to 200mM of a buffer solution, 10 to 50% of a stabilizer, 0.1 to 5% of a surface active agent, 0.1 to 5g / L of a preservative, 1 to 20mM of a reaction accelerator, 2 to 10mM of 3-acetylpyridine adenine dinucleotide (reduction type), 5 to 50g / L of phosphoenolpyruvic acid, 50 to 500U / L of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, and 1 to 3KU / L of malate dehydrogenase; a recycling system of 3-acetylpyridine adenine dinucleotide (reduction type) comprises (1) 2 to 20g / L of glucose substrate, (2) 100 to 2,000U / L of corresponding glucose dehydrogenase, and (3) 1 to 5mM of 3-acetylpyridine adenine dinucleotide. The carbon dioxide measurement kit is convenient to use and simple to operate; the components participating in coupling reaction are extra added, so that no pollution caused by endogenous and allogenic substances are introduced; the rate of the recycling system is below the main reaction rate, thus the main reaction cannot be interfered; the carbon dioxide measurement kit is high in stability and can be used for a long time.
Owner:QINGDAO JINYANG BIOTECH
Process for the production of beta-lysine
InactiveUS20090029425A1FermentationVector-based foreign material introductionPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseTransketolase
Process for the production of -lysine by constructing a recombinant microorganism which has a deregulated lysine 2,3-aminomutase gene and at least one deregulated gene selected from the group (i) which consists of aspartokinase, aspartatesemialdehyde dehydrogenase, dihydrodipicolinate synthase, dihydrodipicolinate reductase, tetrahydrodipicolinate succinylase, succinyl-amino-ketopimelate transaminase, succinyl-diamino-pimelate desuccinylase, diaminopimelate epimerase, diamino-pimelate dehydrogenase, arginyl-tRNA synthetase, diaminopimelate decarboxylase, pyruvate carboxylase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, transketolase, transaldolase, 6-phosphogluconolactonase, fructose 1,6-biphosphatase, homoserine dehydrogenase, phophoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, succinyl-CoA synthetase, methylmalonyl-CoA mutase, provided that if aspartokinase is deregulated as gene (i) at least a second gene (i) other than aspartokinase has to be deregulated, and cultivating said microorganism.
Owner:BASF AG
Genes for enhancing salt and drought tolerance in plants and methods of use
ActiveUS20200239901A1Improve efficiencyIncrease productionClimate change adaptationVector-based foreign material introductionPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseCarboxysome
The present disclosure provides methods for increasing drought resistance, salt resistance, photosynthetic rate, biomass production and water-use efficiency of a plant. The methods encompass expression of CAM-specific a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC) in the plant. In comparison to a plant not manipulated in this manner, the disclosed, genetically-modified, plants display improved drought resistance and salt resistance. Also provided are plants that can be obtained by the method according to the invention, and nucleic acid vectors to be used in the described methods.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum, construction method thereof and method for producing tetrahydropyrimidine by same
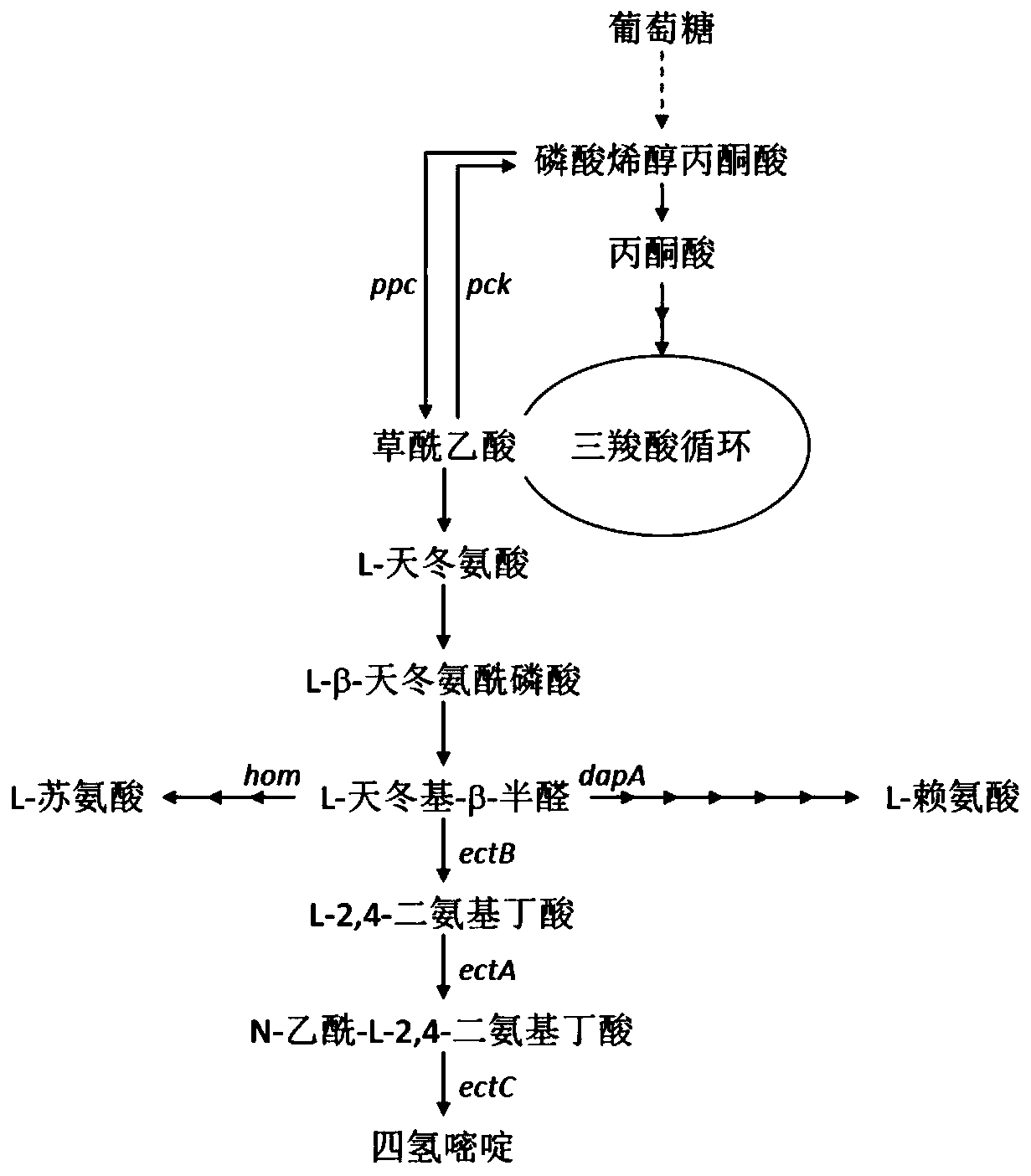
ActiveCN111394288AAvoid Biosecurity ConcernsReduce cumbersome stepsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseSerine dehydrogenase
The invention relates to recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum, a method for constructing the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum and a method for producing tetrahydropyrimidine by using the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum. Compared with wild corynebacterium glutamicum, the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum has phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, homoserine dehydrogenase and dihydropyrimidinedicarboxylate synthetase with reduced expression level, and also has a gene expression cassette for expressing phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase and a gene expression cassette for expressing ectA enzyme, ectB enzyme and ectC enzyme, so that tetrahydropyrimidine can be efficiently produced. The tetrahydropyrimidine produced by using the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum has high yield, the safety of tetrahydropyrimidine products is improved, the production cost is greatly reduced, and the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum has good market application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING BIOINNO BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
C4 type phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC) gene of corn and application thereof in wheat
InactiveCN103805618AImprove photosynthetic efficiencyIncreased breeding yield levelsFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionPyruvate carboxylasePhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
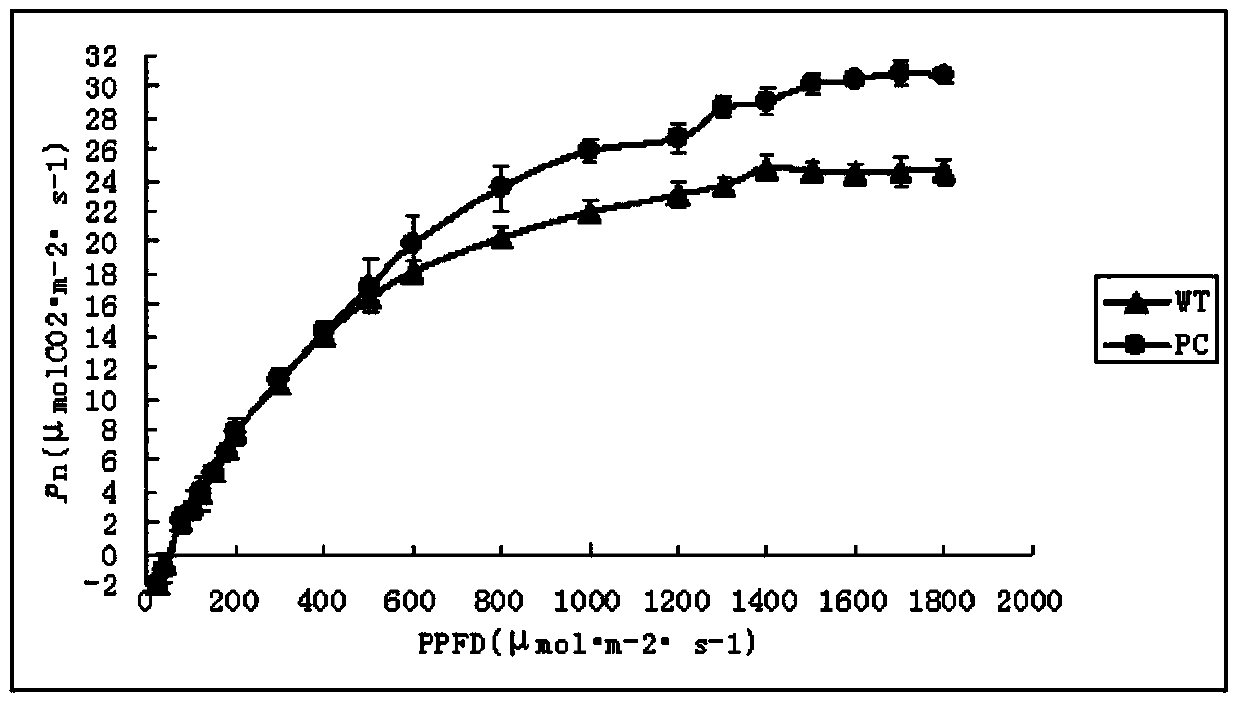
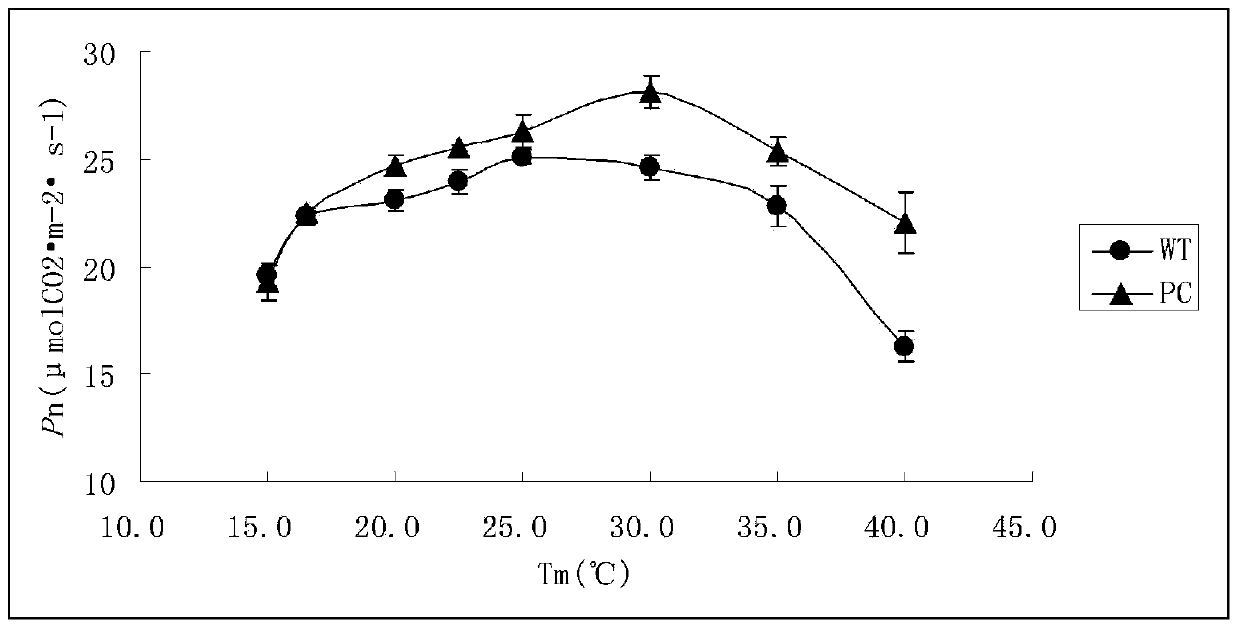
The invention discloses a C4 type phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC) gene of corn and an application thereof in wheat. The novel PEPC gene provided by the invention can be stably expressed and inherited in wheat, and the photosynthetic efficiency is remarkably improved compared with that of an acceptor material, thereby providing an important gene source and parent material support for improving the photosynthetic efficiency of C3 crop by means of a C4 type high photosynthetic efficiency gene and breeding high photosynthetic efficiency transgenetic wheat variety with the level of output greatly improved.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI XIAOMAI INST
CO2 content determination method and CO2 diagnosis kit
InactiveCN1763221AFree from pollutionThe test result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseCO2 content
The present invention relates to one CO2 (bicarbonate) content determining method and CO2 (bicarbonate) diagnosis kit, and belongs to the field of medical detection technology. The kit includes buffering solution, phosphoenolpyruvic acid, inosine, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, nucleoside phosphorylase, xanthine oxidase, peroxidase, urease and stabilizer. Through mixing the sample and reagent in certain volume ratio to generate enzyme coupling reaction, detecting the main wavelength absorbance variation of the reaction product under biochemical analyzer and calculation, CO2 (bicarbonate) content is obtained. The present invention has the advantages of high sensitivity, high precision and no contamination of inner and outer matters.
Owner:王尔中
Corynebacterium glutamicum engineering strain for producing 5-aminolevulinic acid
InactiveCN106434514AEasy to transportIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylasePyruvate carboxylase
The invention discloses a corynebacterium glutamicum engineering strain for producing 5-aminolevulinic acid. A construction method comprises steps as follows: (1) a lactate dehydrogenase coding gene ldhA and acetic acid generation genes pta-ackA, pqo and cat are knocked out from corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032, and a strain CG4 is obtained; an sod promoter is inserted in front of a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase coding gene ppc in the strain CG4, and a strain CG5 is obtained; a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase coding gene pck is knocked out from the strain CG5, and a strain CG6 is obtained; (2) plasmids over-expressing 5-aminolevulinic acid synthase genes are transferred in the CG6, and an engineering strain L is obtained; (3) transport protein plasmids over-expressing 5-aminolevulinic acid are transferred to the L. The engineering strain can promote 5-aminolevulinic acid to be transported outside the corynebacterium glutamicum, and the yield of 5-aminolevulinic acid is 100.4% higher than that of a contrast strain.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com